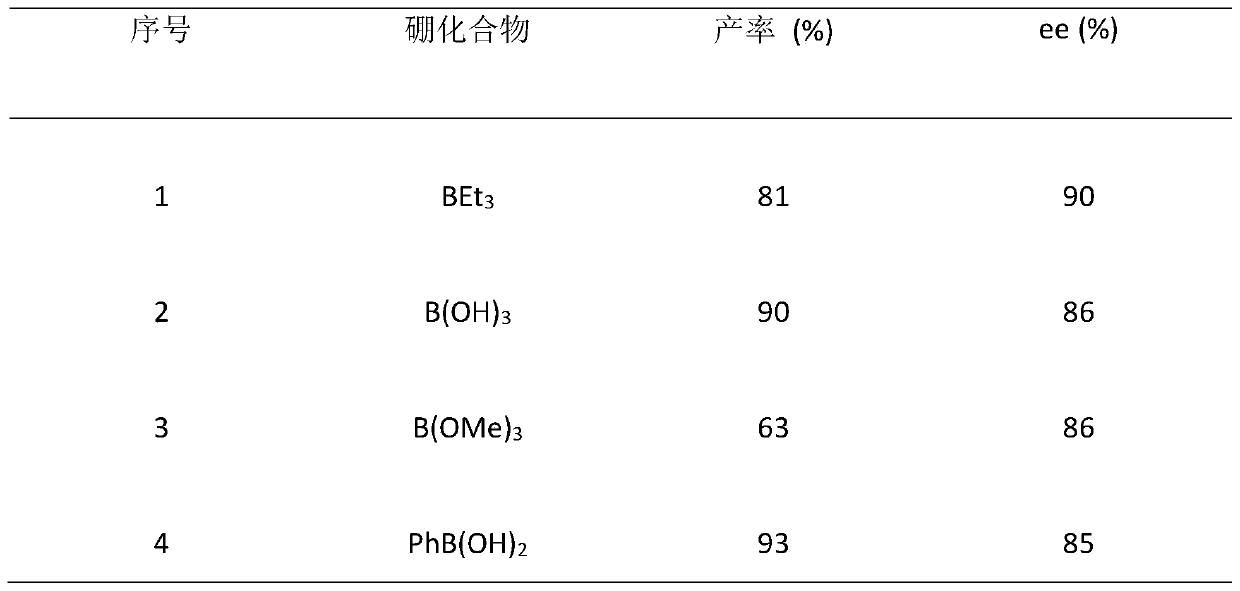
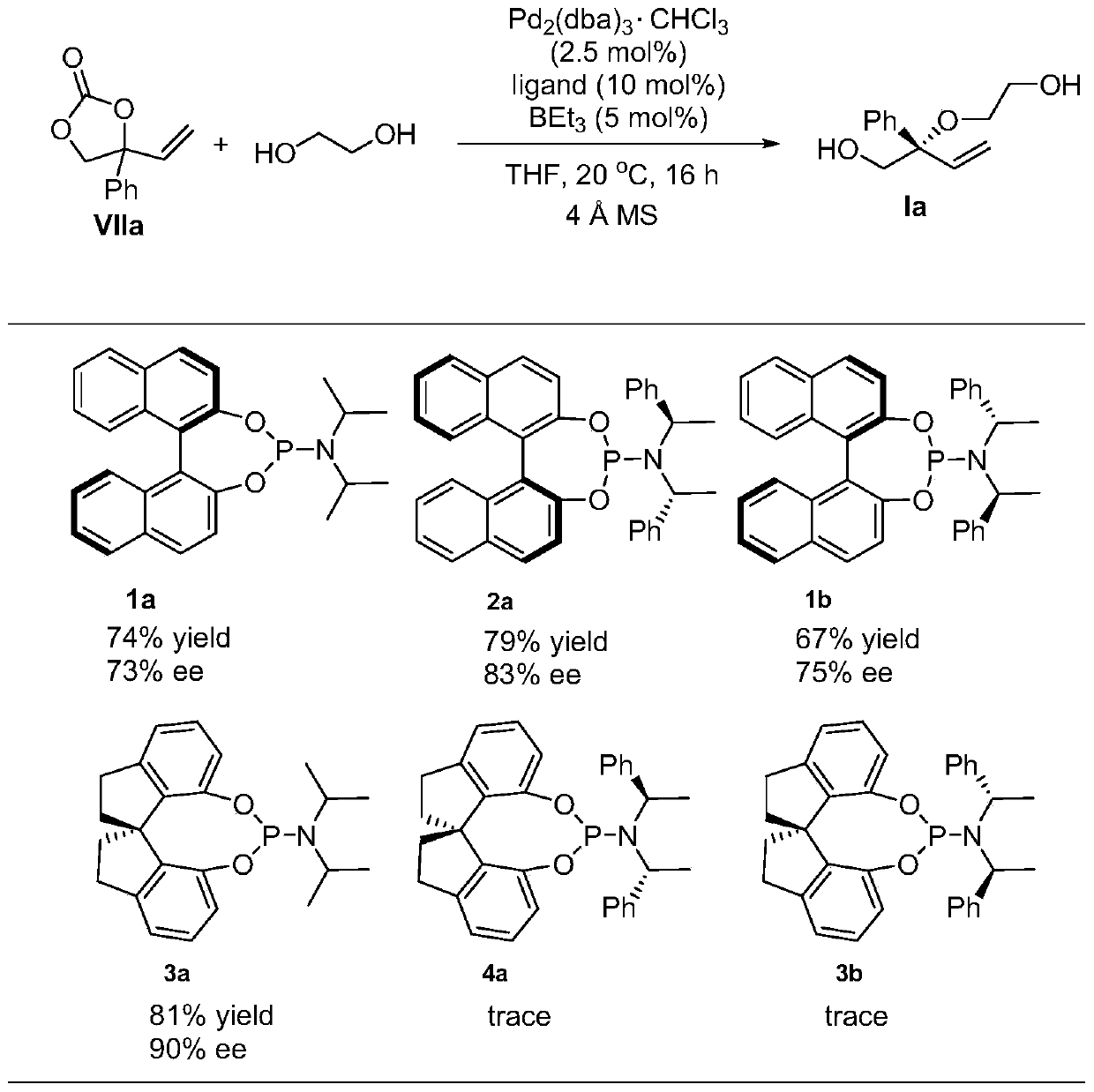
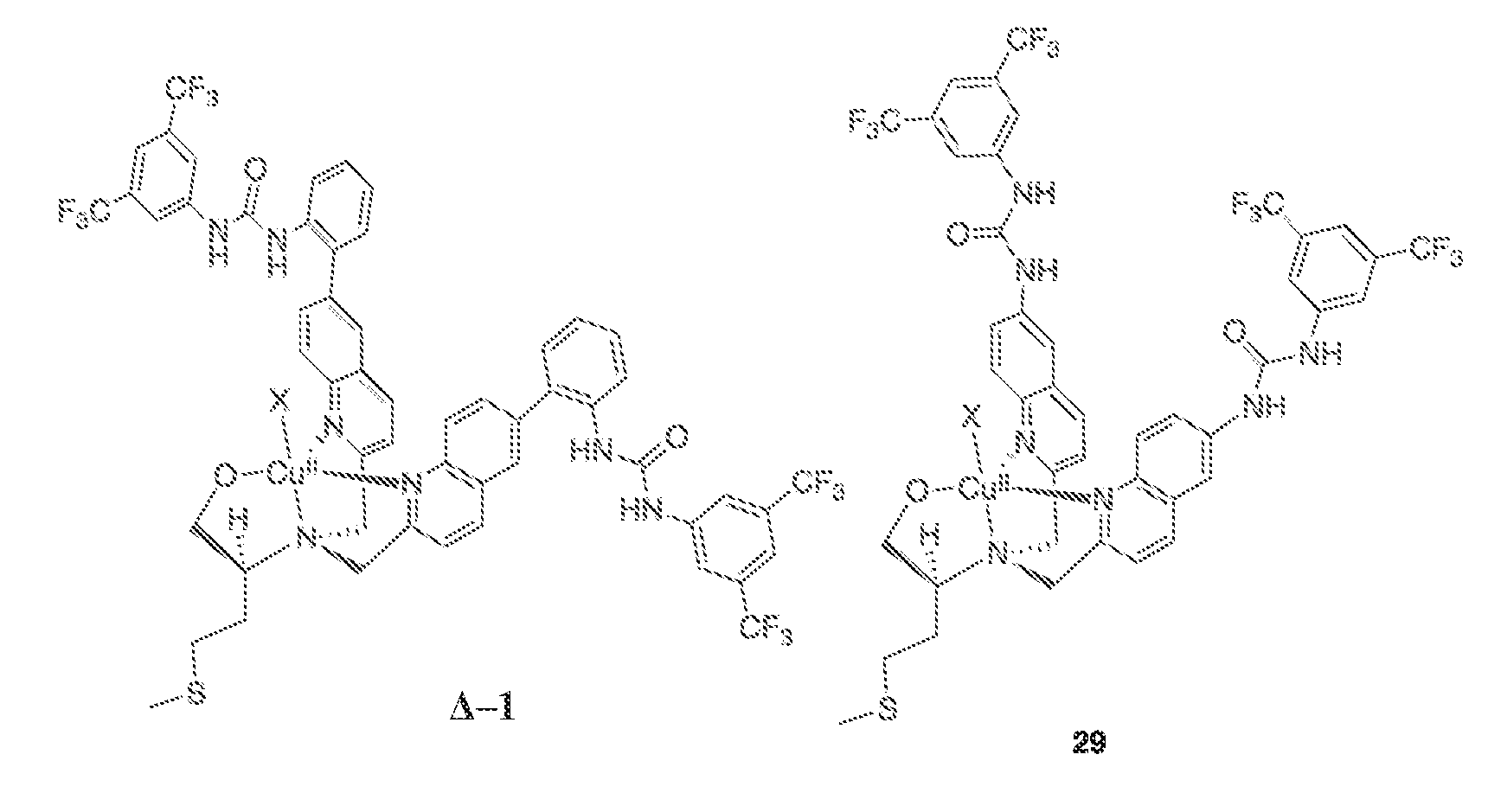
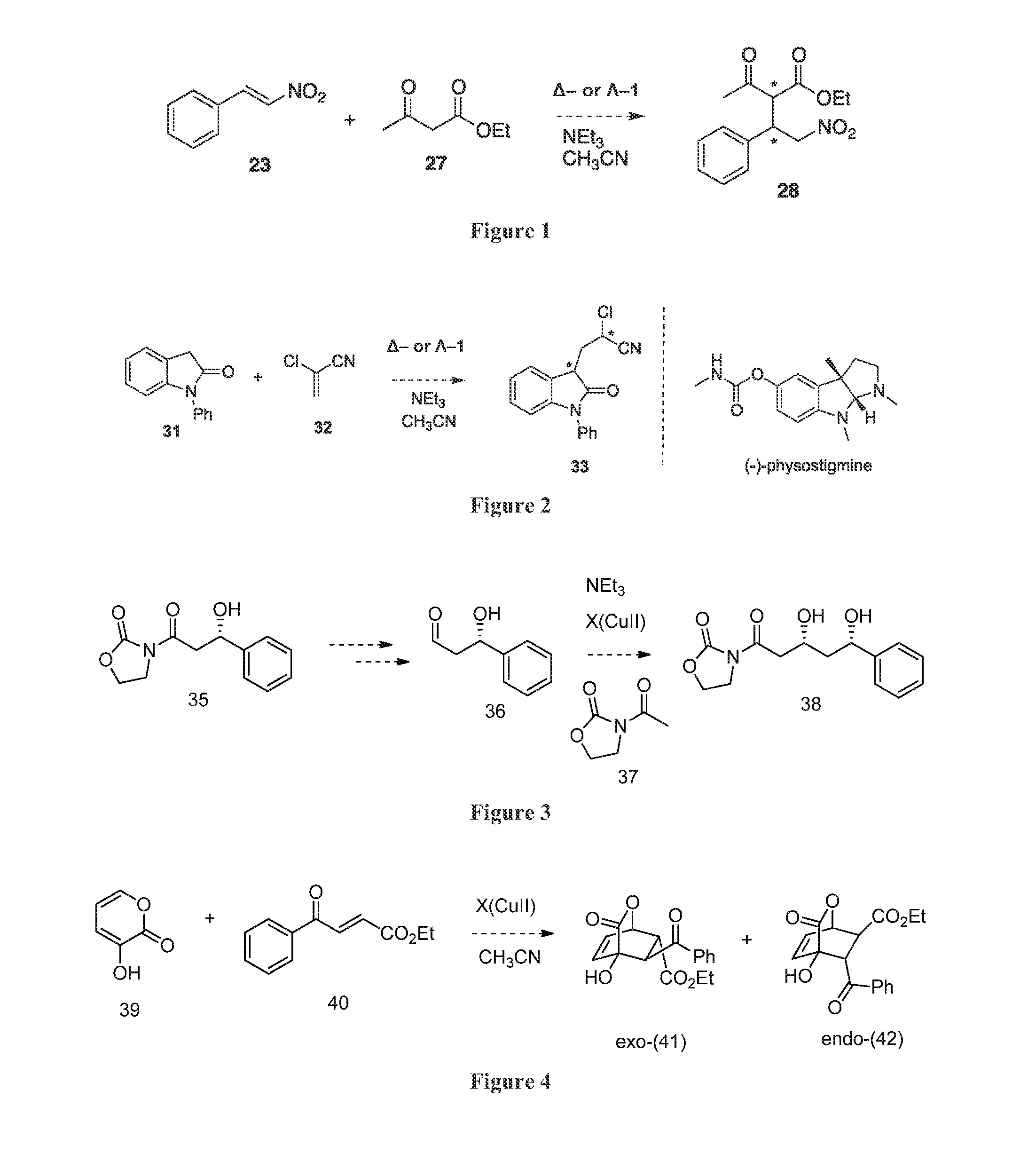
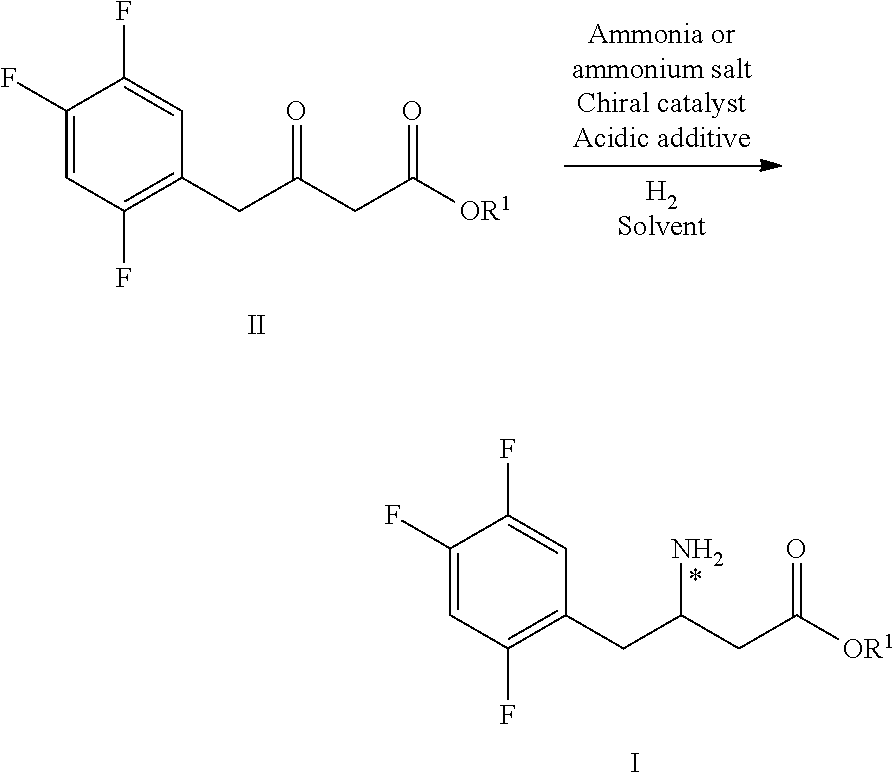
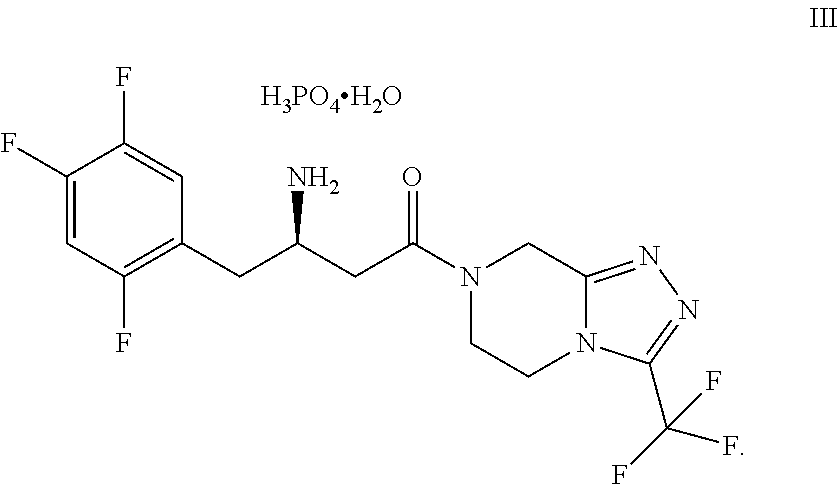
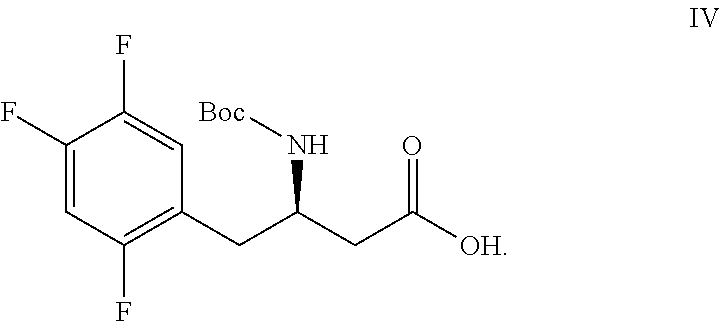
Patents
Literature
36 results about "Stereocenter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In a molecule, a stereocenter is a particular instance of a stereogenic element that is geometrically a point. A stereocenter or stereogenic center is any point in a molecule, though not necessarily an atom, bearing groups, such that an interchanging of any two groups leads to a stereoisomer. The term stereocenter was introduced in 1984 by Kurt Mislow and Jay Siegel. A chirality center is a stereocenter consisting of an atom holding a set of ligands (atoms or groups of atoms) in a spatial arrangement which is not superimposable on its mirror image. The concept of a chirality center generalizes the concept of an asymmetric carbon atom (a carbon atom bonded to four different entities) such that an interchanging of any two groups gives rise to an enantiomer. In organic chemistry, a chirality center usually refers to a carbon, phosphorus, or sulfur atom, though it is also possible for other atoms to be chirality centers, especially in areas of organometallic and inorganic chemistry.
Synthesis of chiral enaminones, their derivatives, and bioactivity studies thereof
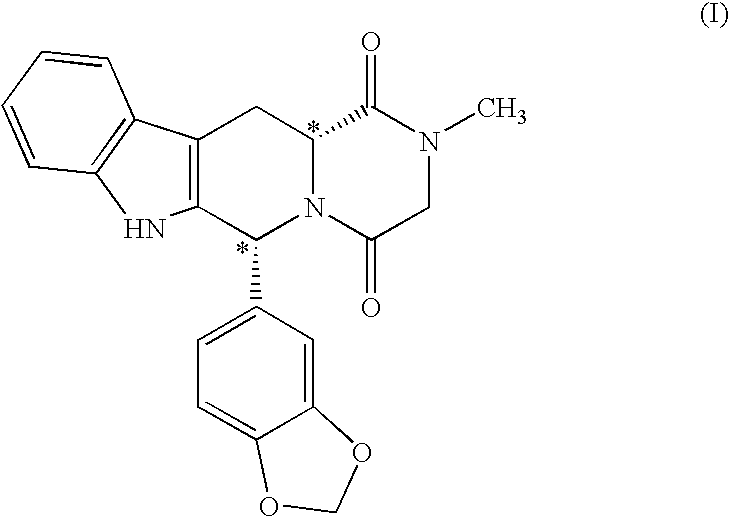
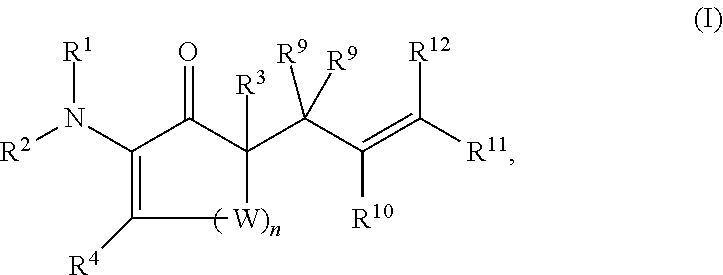
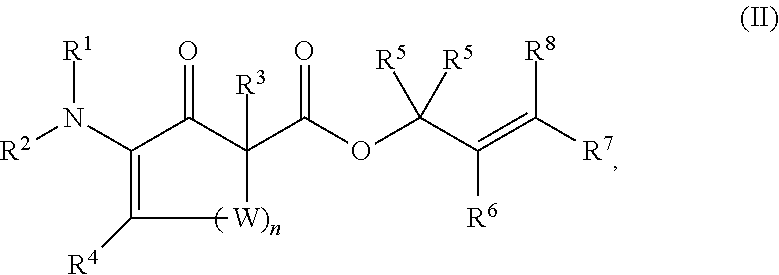
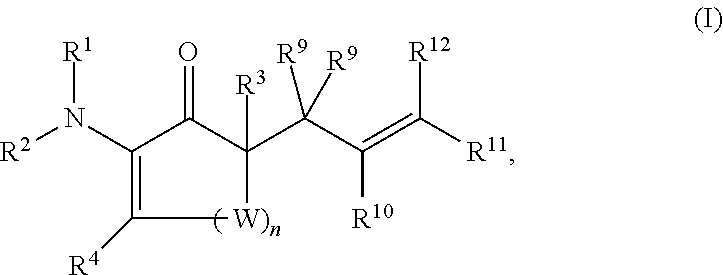
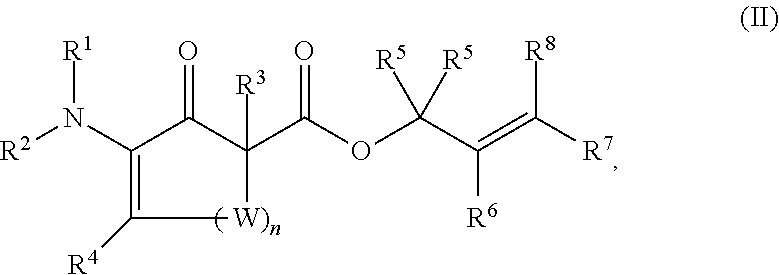
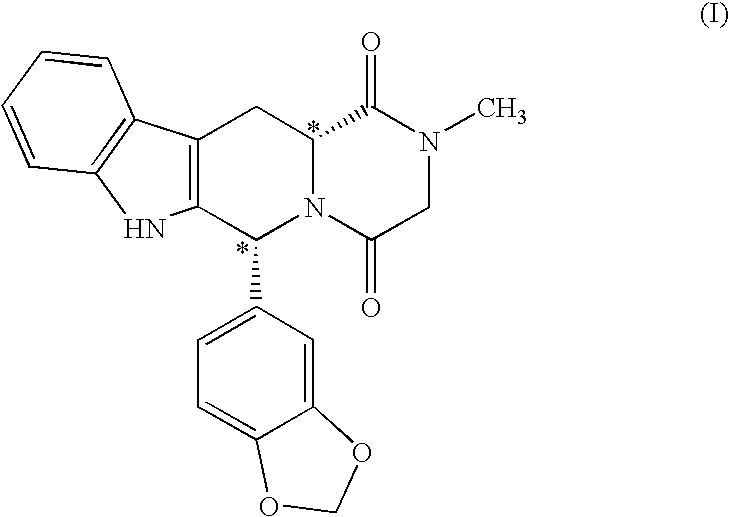
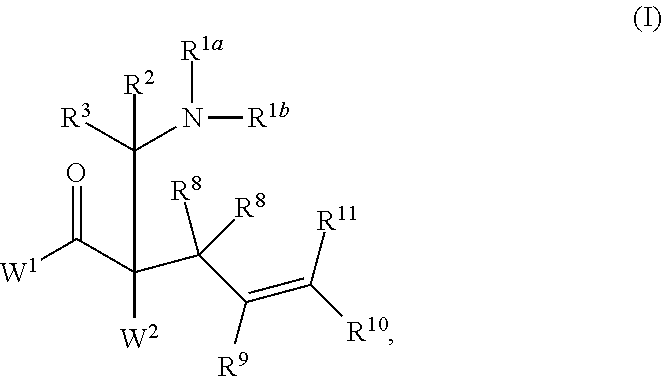
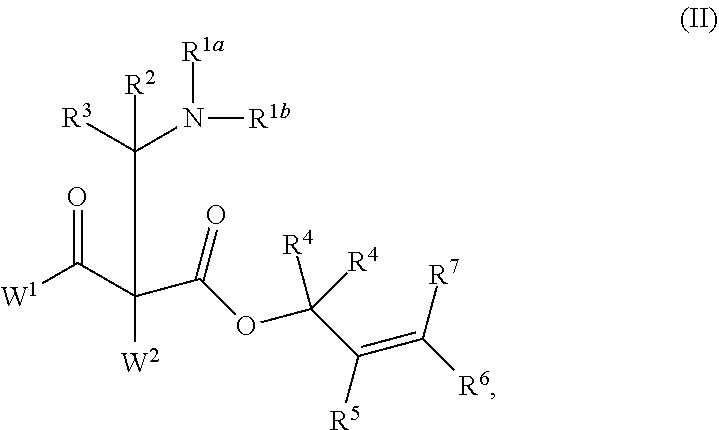
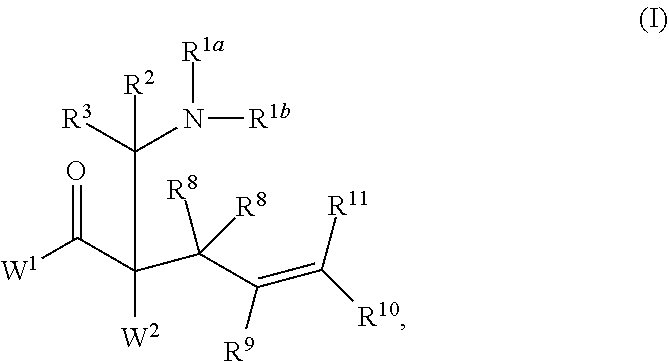
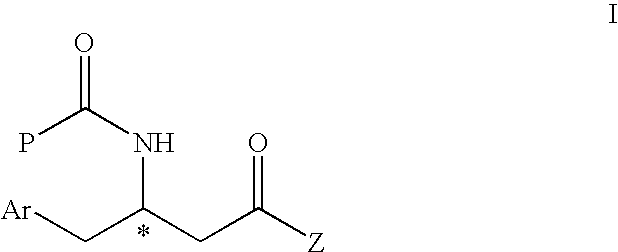
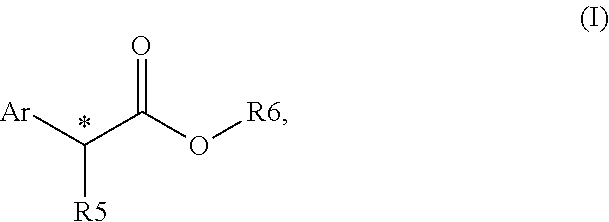
This invention provides enantioenriched heterocyclic enaminone compounds with quaternary stereogenic centers and novel methods of preparing the compounds. Methods include the method for the preparation of a compound of formula (I):comprising treating a compound of formula (II):with a transition metal catalyst under alkylation conditions.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
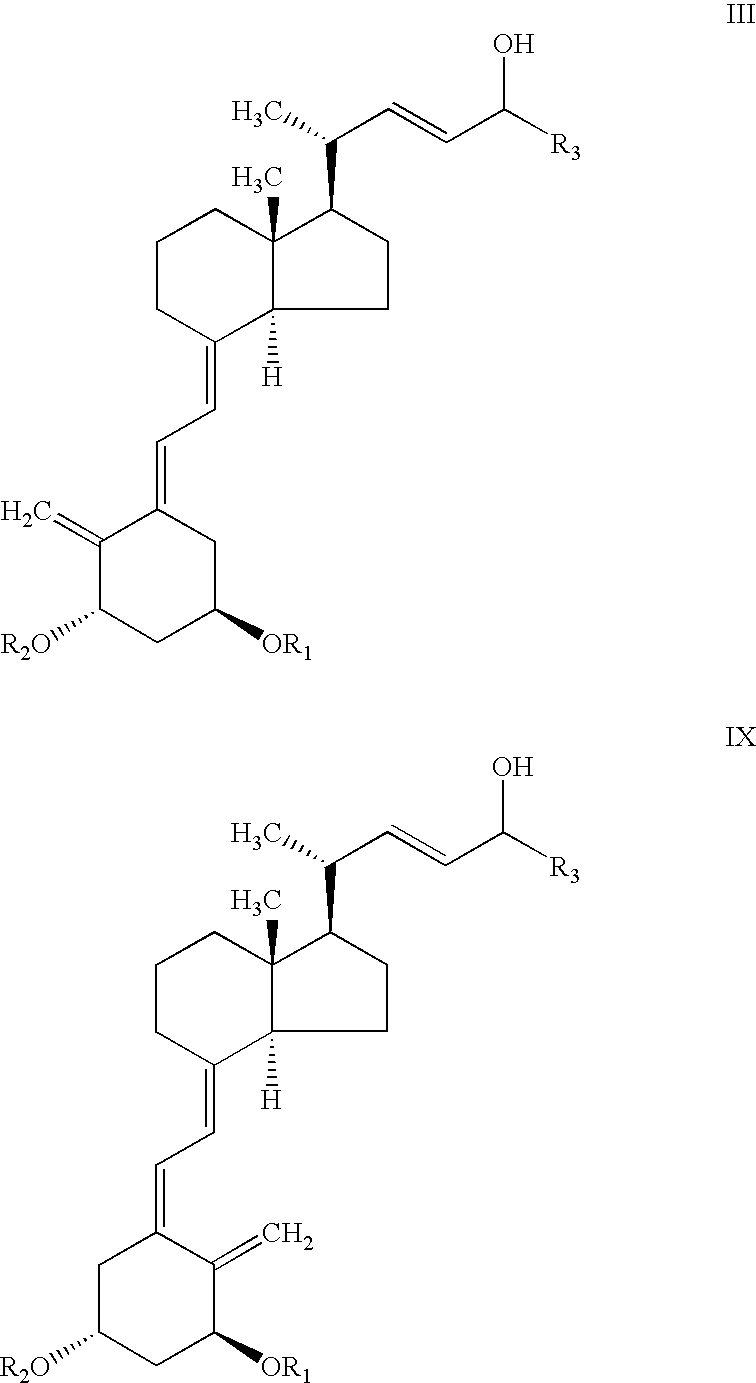
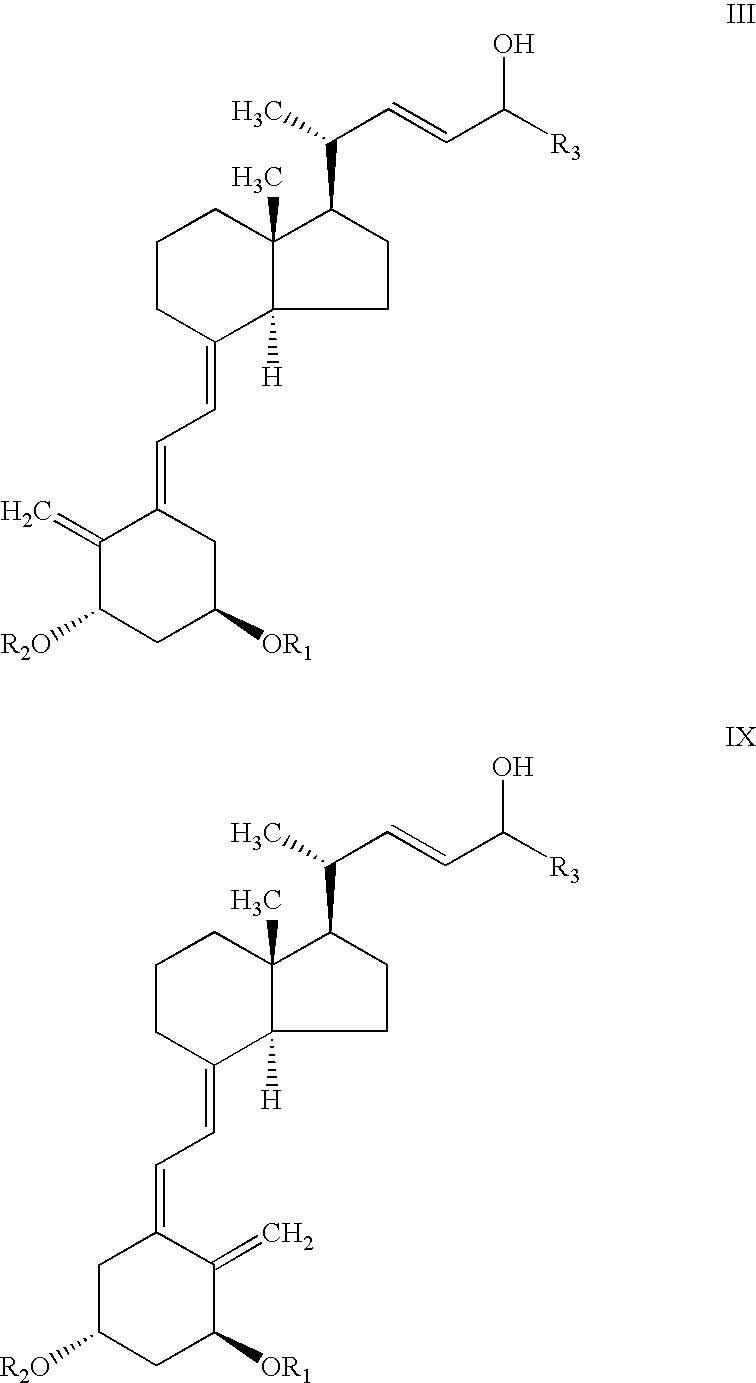
Selective enzymatic esterification and solvolysis of epimeric vitamin D analog and separation of the epimers
Provided is a method of selectively enzymatically esterifying or selectively enzymatically solvolyzing epimers of analogs of vitamin D having a stereogenic center at C-24 that has a free or esterified OH group. The metod can be used, for example, for separating mixed epimers of the vitamin D analog.
Owner:TEVA PHARM USA INC
Synthesis of chiral enaminones, their derivatives, and bioactivity studies thereof
This invention provides enantioenriched heterocyclic enaminone compounds with quaternary stereogenic centers and novel methods of preparing the compounds. Methods include the method for the preparation of a compound of formula (I):comprising treating a compound of formula (II):with a transition metal catalyst under alkylation conditions.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
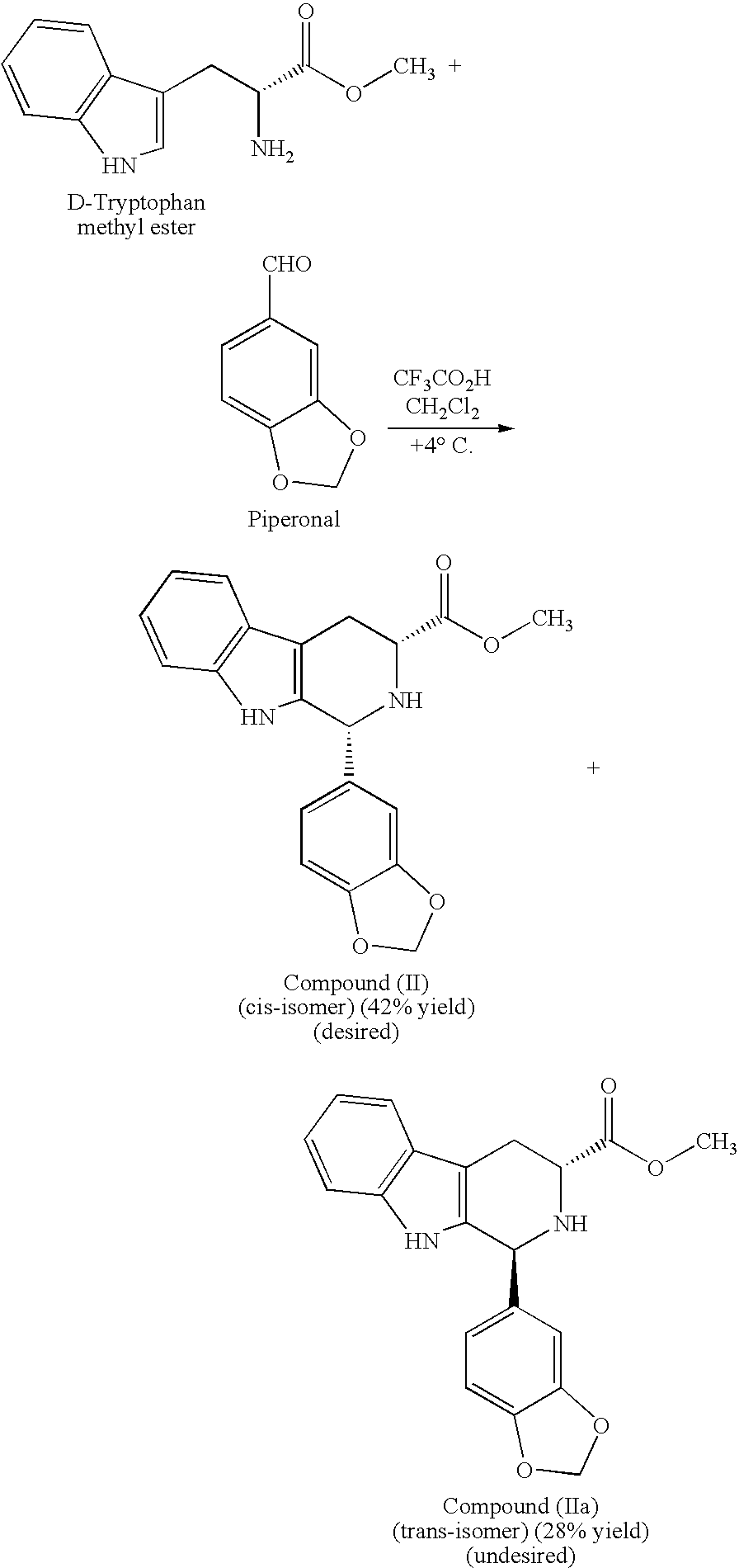
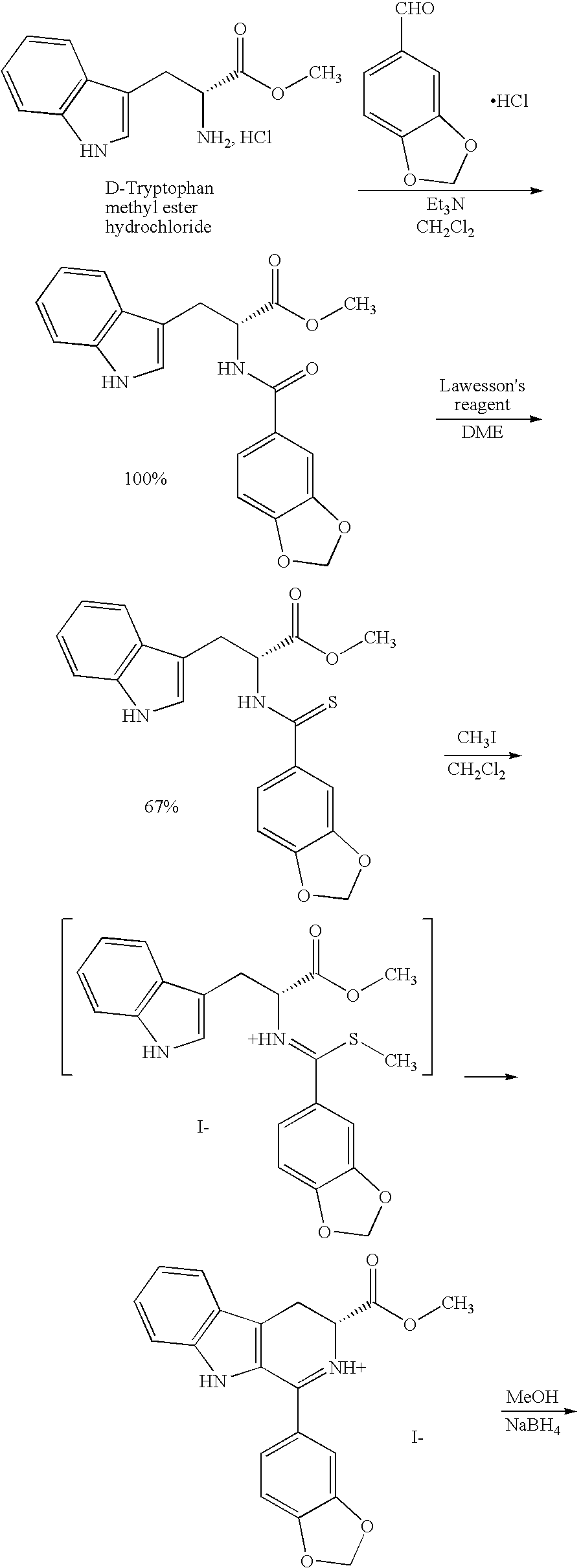
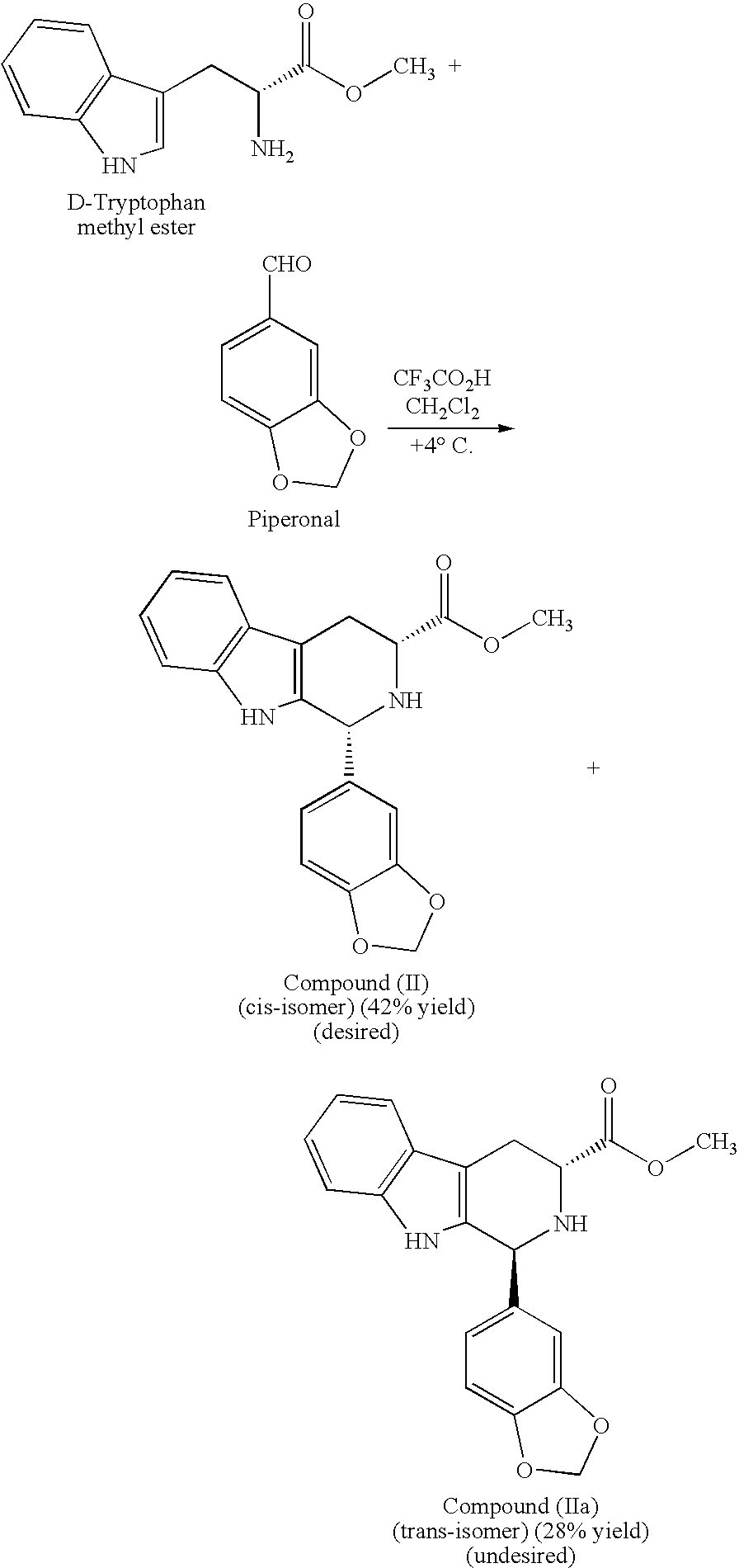
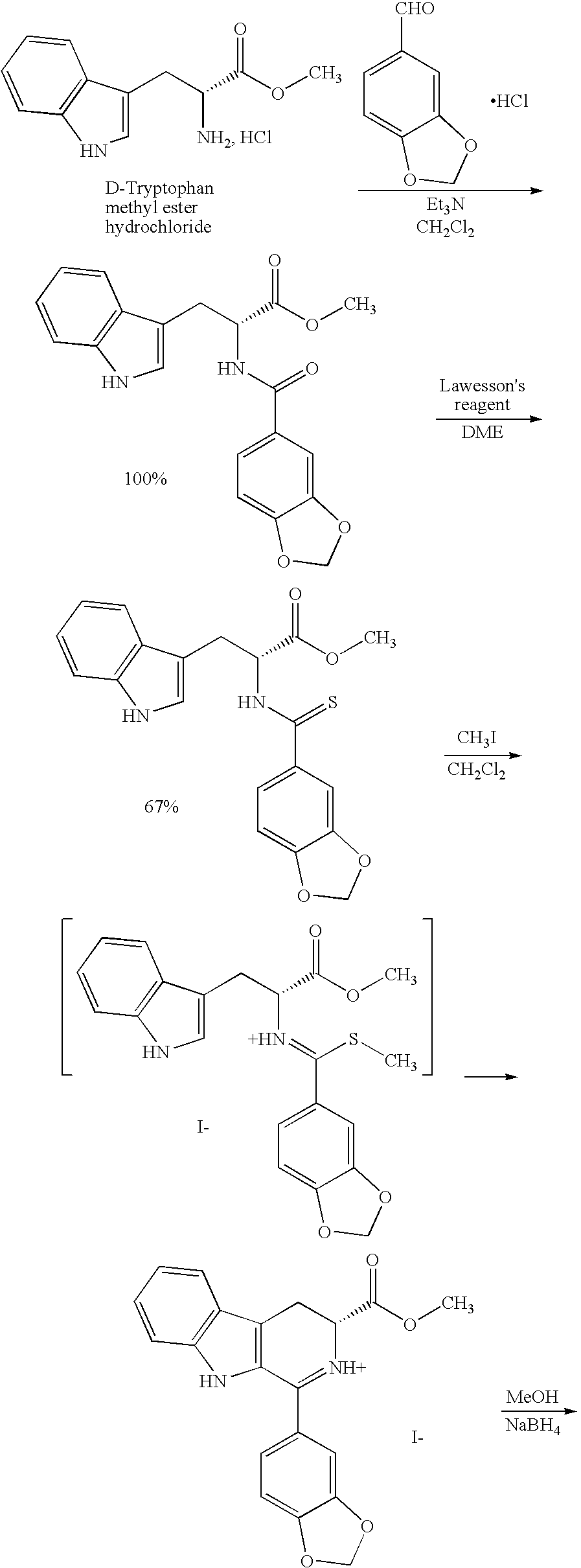
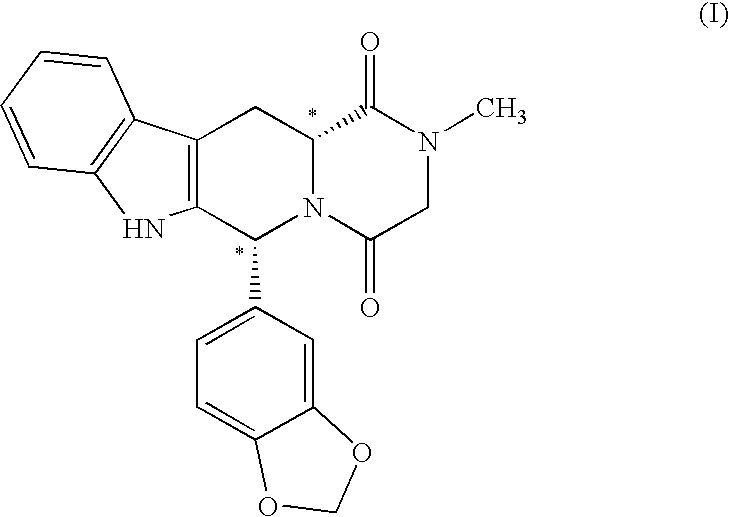
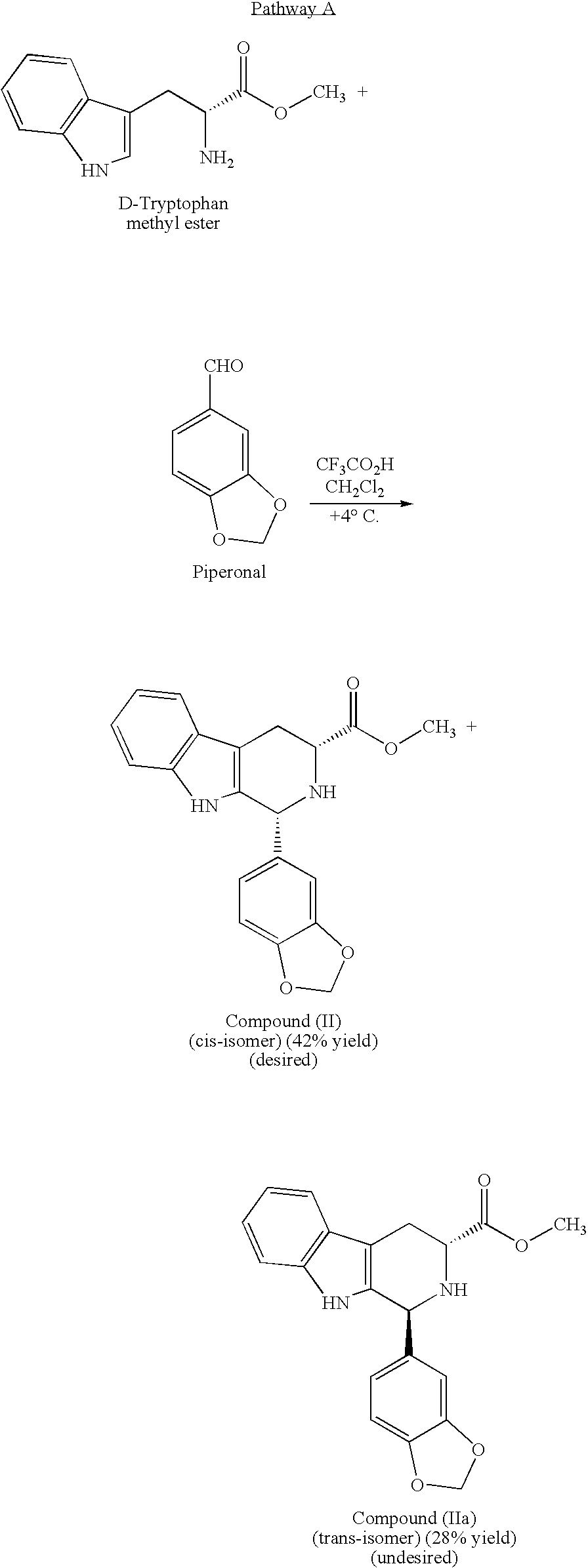
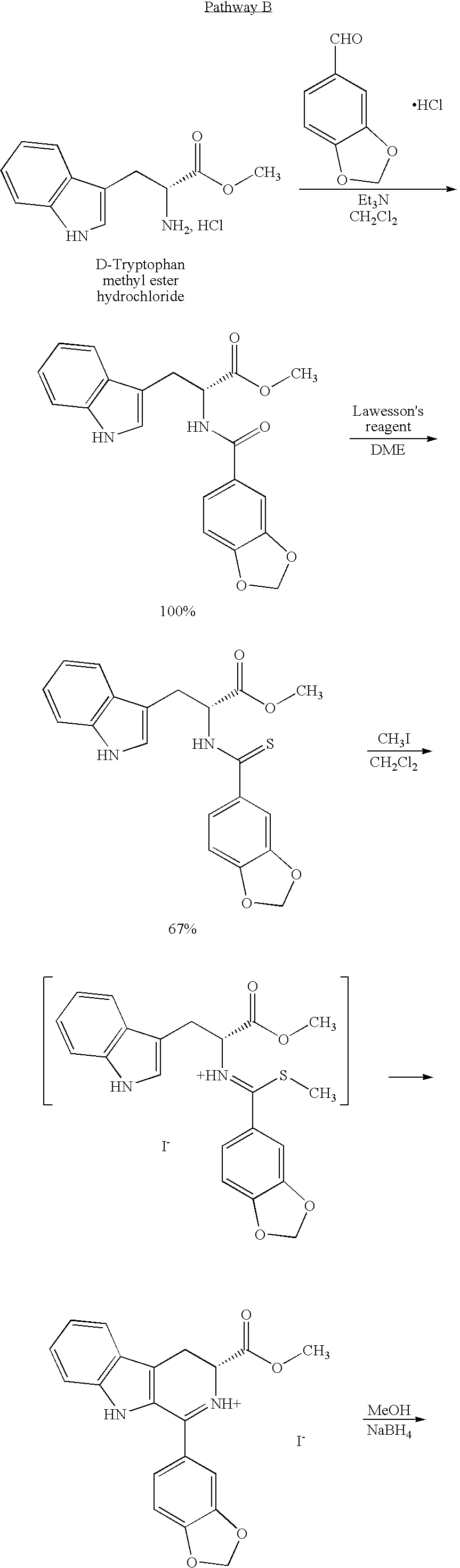
Modified pictet-spengler reaction and products prepared therefrom
ActiveUS20060004203A1High yieldReduce usageBiocideOrganic chemistryPictet–Spengler reactionProcess time
Owner:ICOS CORP
Control and repellency of mosquitoes
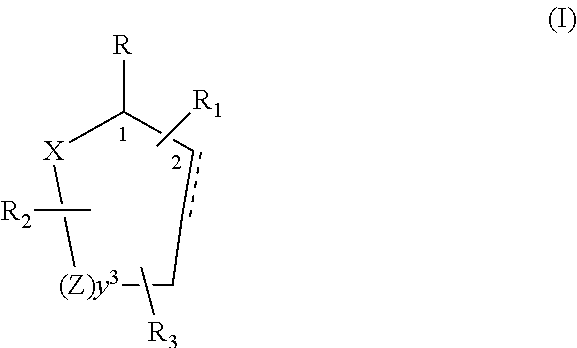
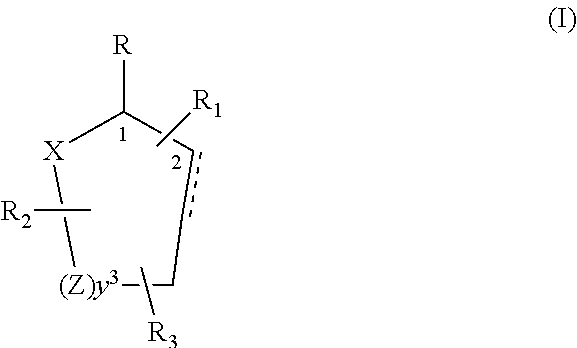
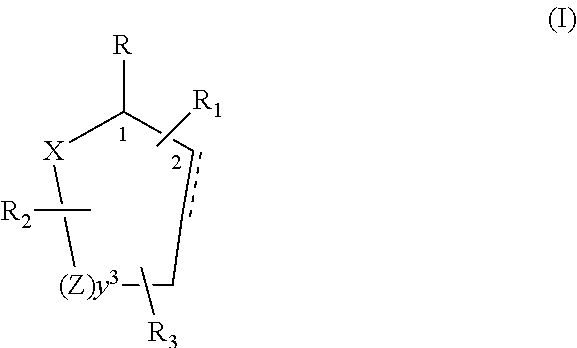
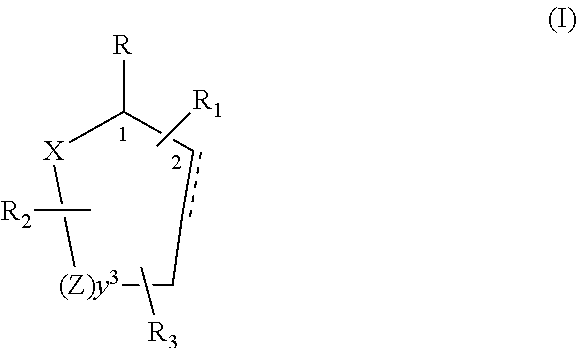
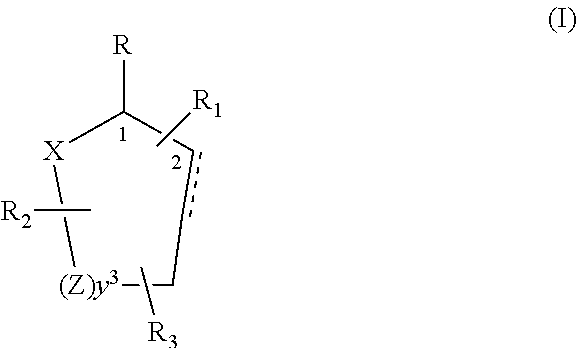
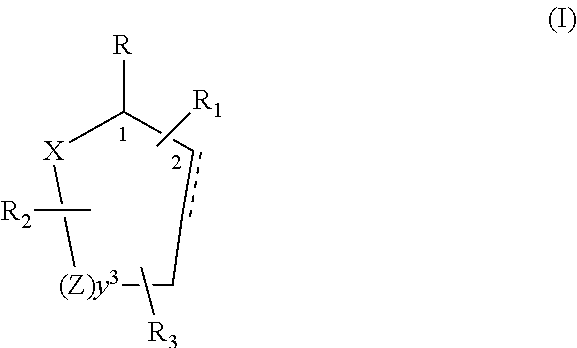
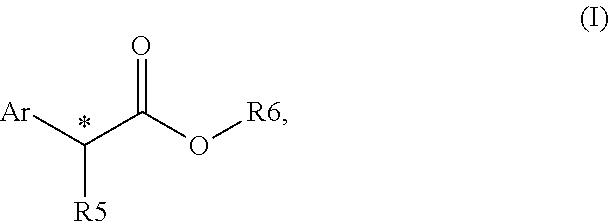
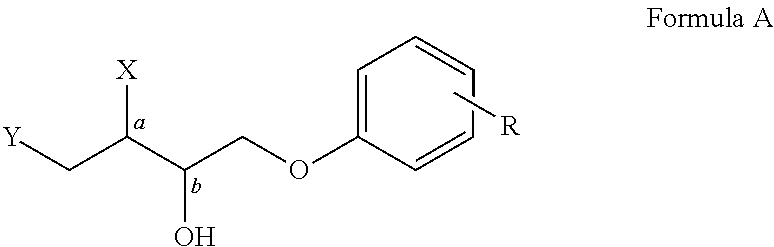
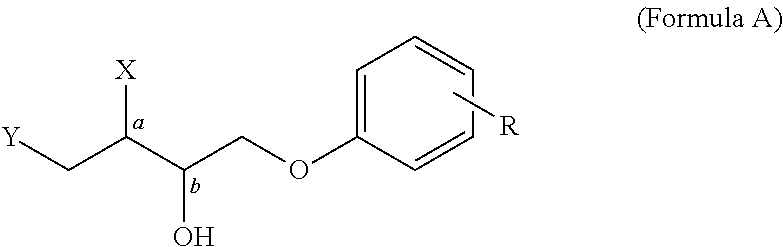
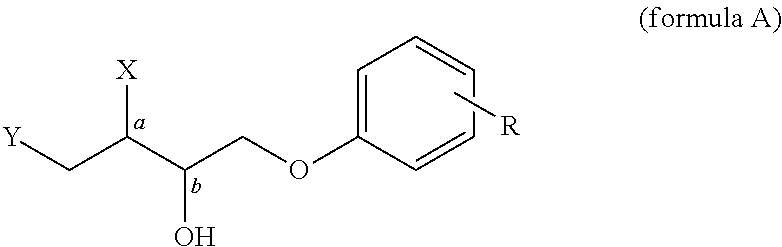
Control or repellency of mosquitoes is accomplished by bringing the insects into contact with at least one of the compounds of the structure (I)whereinR is selected from —OH, ═O, —OC(O)R4, —OR6, —(OR6)2, wherein each R6 is independently selected from an alkyl group containing from 1 to 4 carbon atoms and R4 is a branched or straight chain, saturated or unsaturated hydrocarbyl group with zero to two double bonds and from 1 to 15 carbon atoms;X is O or CH2, with the proviso that when X is O R can only be ═O;each Z is independently selected from (CH) and (CH2);y is a numeral selected from 1 and 2;R1 is selected from H or a branched or straight chain, saturated or unsaturated hydrocarbyl group with zero to two double bonds and from 1 to 15 carbon atoms;R2 is selected from H and a branched or straight chain, saturated or unsaturated hydrocarbyl group with zero to three double bonds and from 1 to 15 carbon atoms;R3 is selected from the group consisting of H and a branched or straight chain, saturated or unsaturated hydrocarbyl group with zero to three double bonds and from 1 to 15 carbon atoms, —(CH2)nOH, —C(O)OR5, —CH2C(O)OR7, —CH2C(O)R8, —C(O)NR9R10, —CH2C(O)NR11R12 where each of R5, R7, R8, R9, R10, R11 and R12 is independently selected from H and a branched or straight chain, saturated or unsaturated hydrocarbyl group with zero to three double bonds and from 1 to 15 carbon atoms and n is an integer of from 1 to 12;the bond between the 2 and 3 positions in the ring structure may be a single or a double bond; andwherein the compounds of structure (I) contain from 11 to 20 total carbon atoms in the compounds, with the proviso that when R is ═O, X is CH2, Z is CH2, y is 1 R2 is H, and R3 is CH2C(O)OR7 then the total number of carbon atoms in the compounds of structure (I) is from 15 to 20 carbon atoms, and when X is O and R is ═O the total number of carbon atoms in the compounds of structure (I) is from 11 to 17 carbon atoms. The invention also includes optical isomers, diastereomers and enantiomers of the named structures. Thus, at all stereocenters where stereochemistry is not explicitly defined, all possible epimers are envisioned.
Owner:BEDOUKIAN RES
Synthesis of combinatorial libraries of compounds reminiscent of natural products
InactiveUS7109377B2High densityIncrease diversitySequential/parallel process reactionsOrganic compound preparationNatural productHigh density
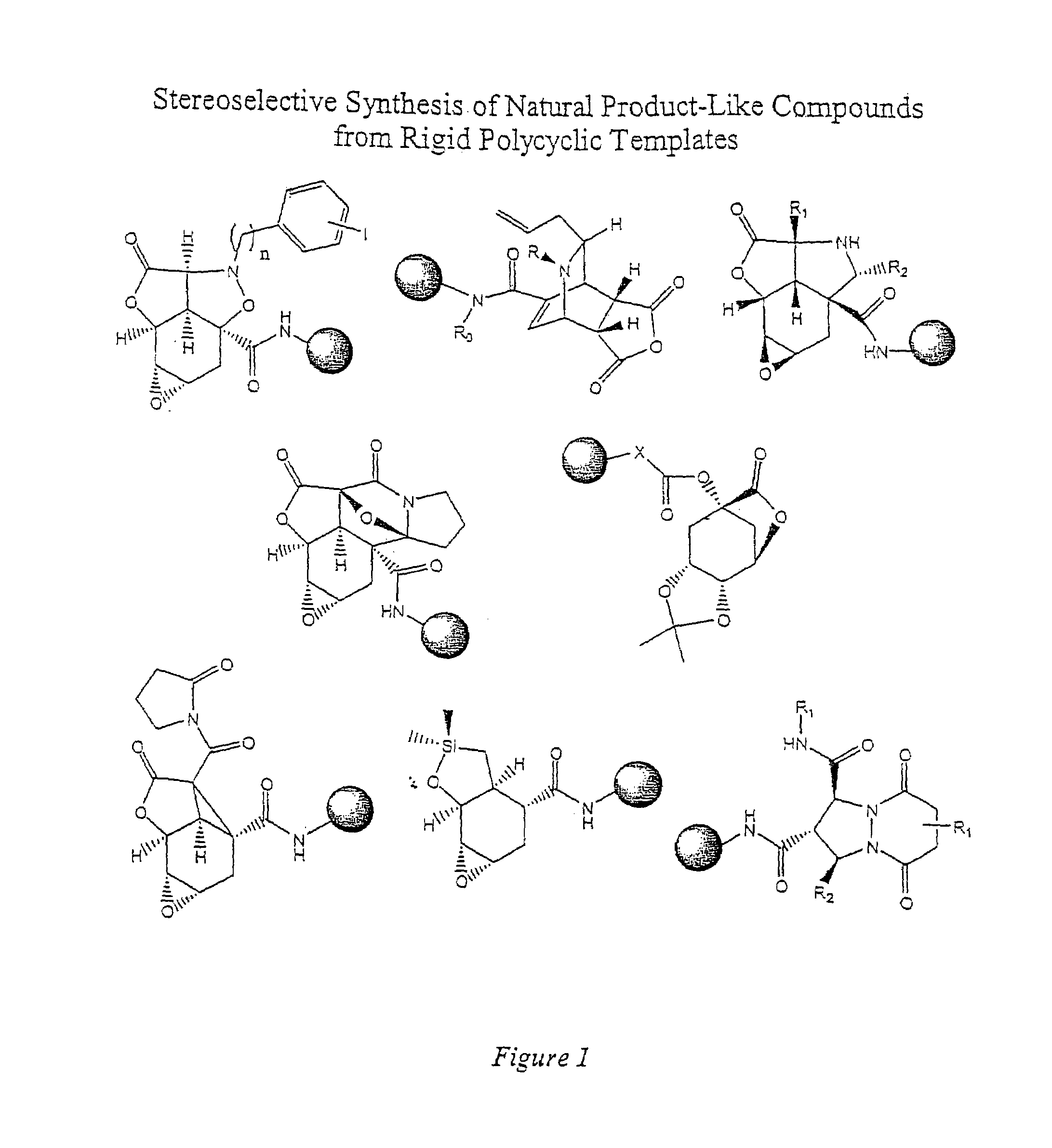
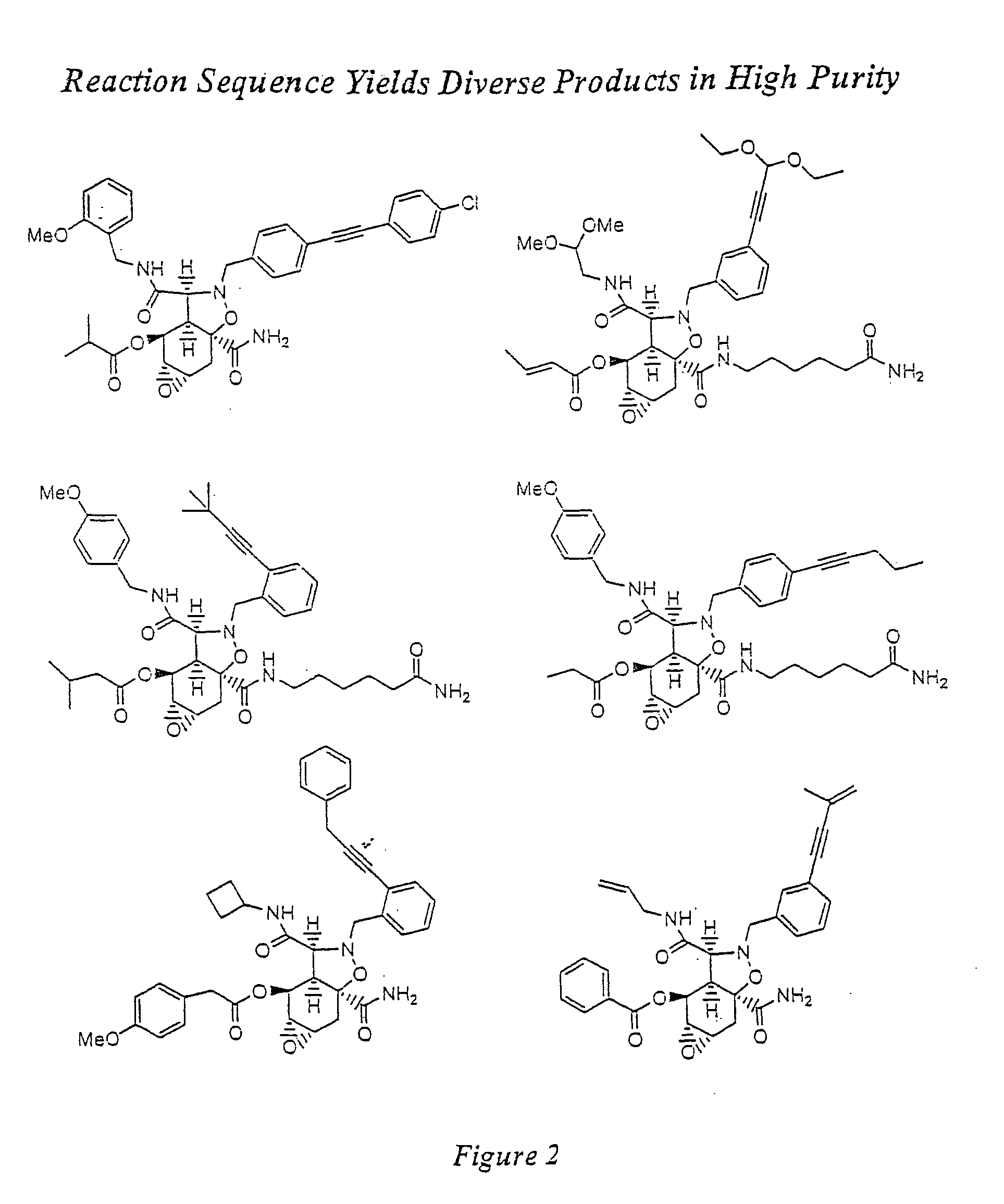
The present invention provides complex compounds reminiscent of natural products and libraries thereof, as well as methods for their production. The inventive compounds and libraries of compounds are reminiscent of natural products in that they contain one or more stereocenters, and a high density and diversity of functionality. In general, the inventive libraries are synthesized from diversifiable scaffold structures, which are synthesized from readily available or easily synthesizable template structures. In certain embodiments, the inventive compounds and libraries are generated from diversifiable scaffolds synthesized from a shikimic acid based epoxyol template. In other embodiments, the inventive compounds and libraries are generated from diversifiable scaffolds synthesized from the pyridine-based template isonicotinamide. The present invention also provides a novel ortho-nitrobenzyl photolinker and a method for its synthesis. Furthermore, the present invention provides methods and kits for determining one or more biological activities of members of the inventive libraries. Additionally, the present invention provides pharmaceutical compositions containing one or more library members.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Enantioselective synthesis of alpha-quaternary mannich adducts by palladium-catalyzed allylic alkylation
This invention provides enantioenriched Mannich adducts with quaternary stereogenic centers and novel methods of preparing the compounds. Methods include the method for the preparation of a compound of formula (I):comprising treating a compound of formula (II):with a transition metal catalyst under alkylation conditions.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Method for chiral spirophosphonate catalyzed synthesis of optically active 2H-1,4-benzoxazine-2-one derivative
InactiveCN105017238AMild reaction conditionsReaction conditions do not need to be harshOrganic chemistryKetonePyrrole
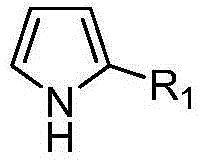
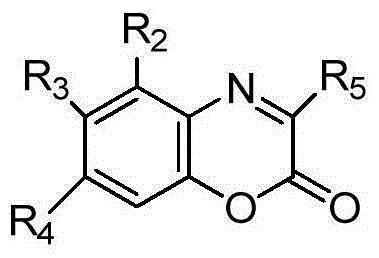
The invention discloses a method for chiral spirophosphonate catalyzed synthesis of an optically active 2H-1,4-benzoxazine-2-one derivative. The method is characterized in that the 2H-1,4-benzoxazine-2-one derivative is prepared through a complete reaction of a benzoxazinone compound and a pyrrole compound as raw materials in an organic catalyst with chiral spirophosphonate as a catalyst. The method using an asymmetric catalysis aza Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction technology to synthesize the optically active 2H-1,4-benzoxazine-2-one derivative containing a trifluoromethyl quaternary stereo center has the advantages of mild reaction conditions, simple process and convenient operation, and the above obtained product has potential good bioactivity and is of great significance to screen new drugs, and obtained chiral compounds can be used as a drug synthesis intermediate.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Process and intermediates for the preparation of N-acylated-4-aryl beta-amino acid derivatives
ActiveUS8278486B2Carbamic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationPtru catalystPhenyl group
Owner:CHIRAL QUEST
Lignan natural product as well as intermediate and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112110933AHigh catalytic activityHigh stereoselectivityOrganic chemistryAntipyreticPtru catalystLignan
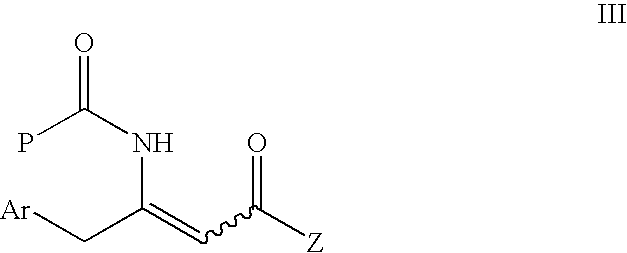
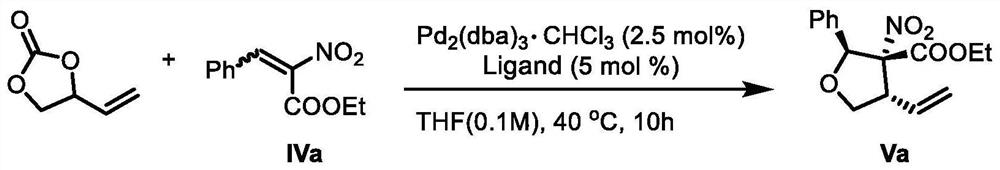
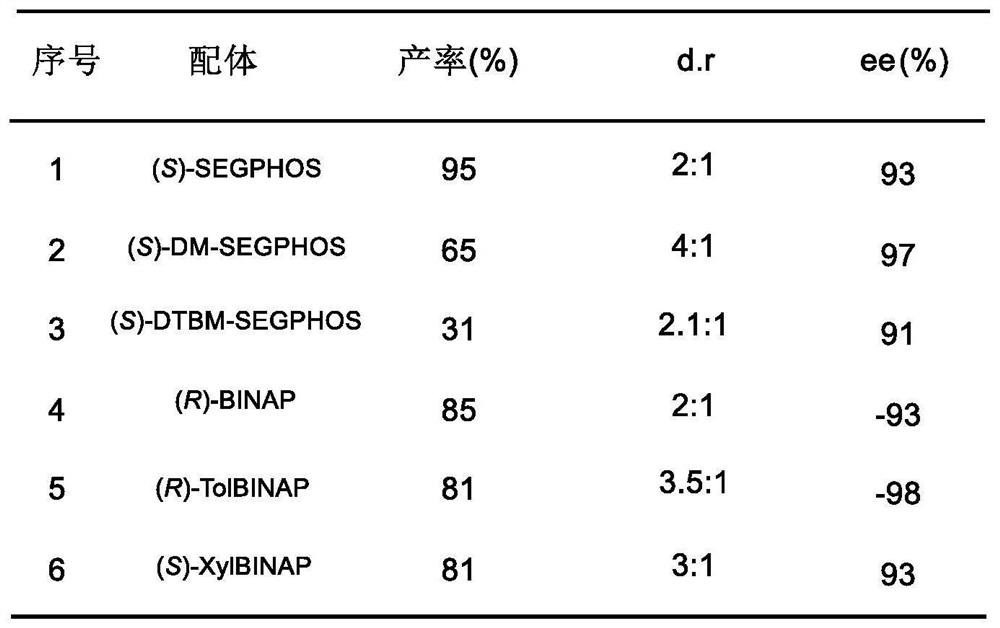
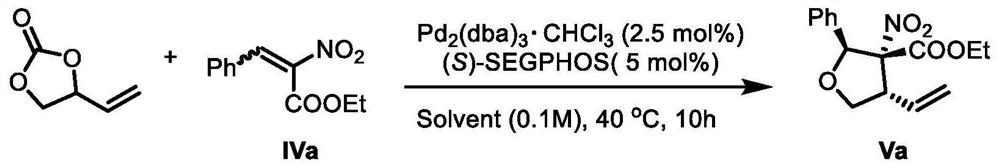
The invention provides a lignan natural product as well as an intermediate and a preparation method thereof. The intermediate is a chiral tetrahydrofuran ring compound V or X containing three three-dimensional centers. The preparation method comprises the following steps: by taking a palladium complex generated by coordination of a palladium source and a chiral ligand as a catalyst, reacting 4-vinyl-1,3-dioxolan-2-one with a compound IV in a solvent under the action of the catalyst to obtain the chiral tetrahydrofuran ring compound V or X containing three three-dimensional centers. According to the preparation method of the lignan natural product, a chiral tetrahydrofuran ring compound V or X is adopted as a reactant for preparation, and then reduction, olefin oxidation, intramolecular cyclization and the like are conducted to finally obtain the lignan natural product with optical purity, so that compared with an existing asymmetric total synthesis method, the method is shortened in reaction steps, and has the advantages that the reaction raw materials are convenient and easy to obtain, the operation is simple, the reaction conditions are mild, and the yield, diastereoselectivity and enantioselectivity of the reaction product are high.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
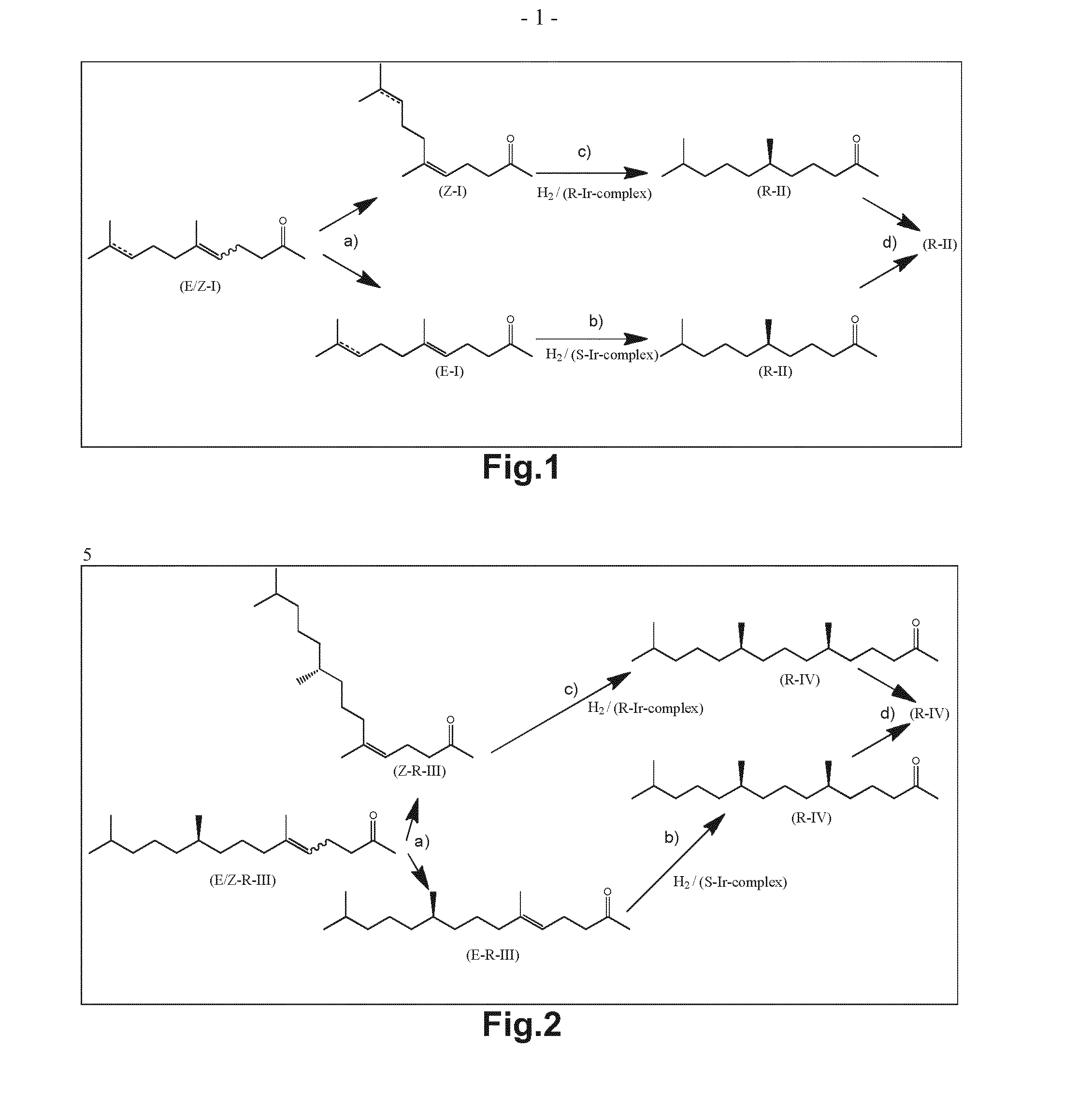
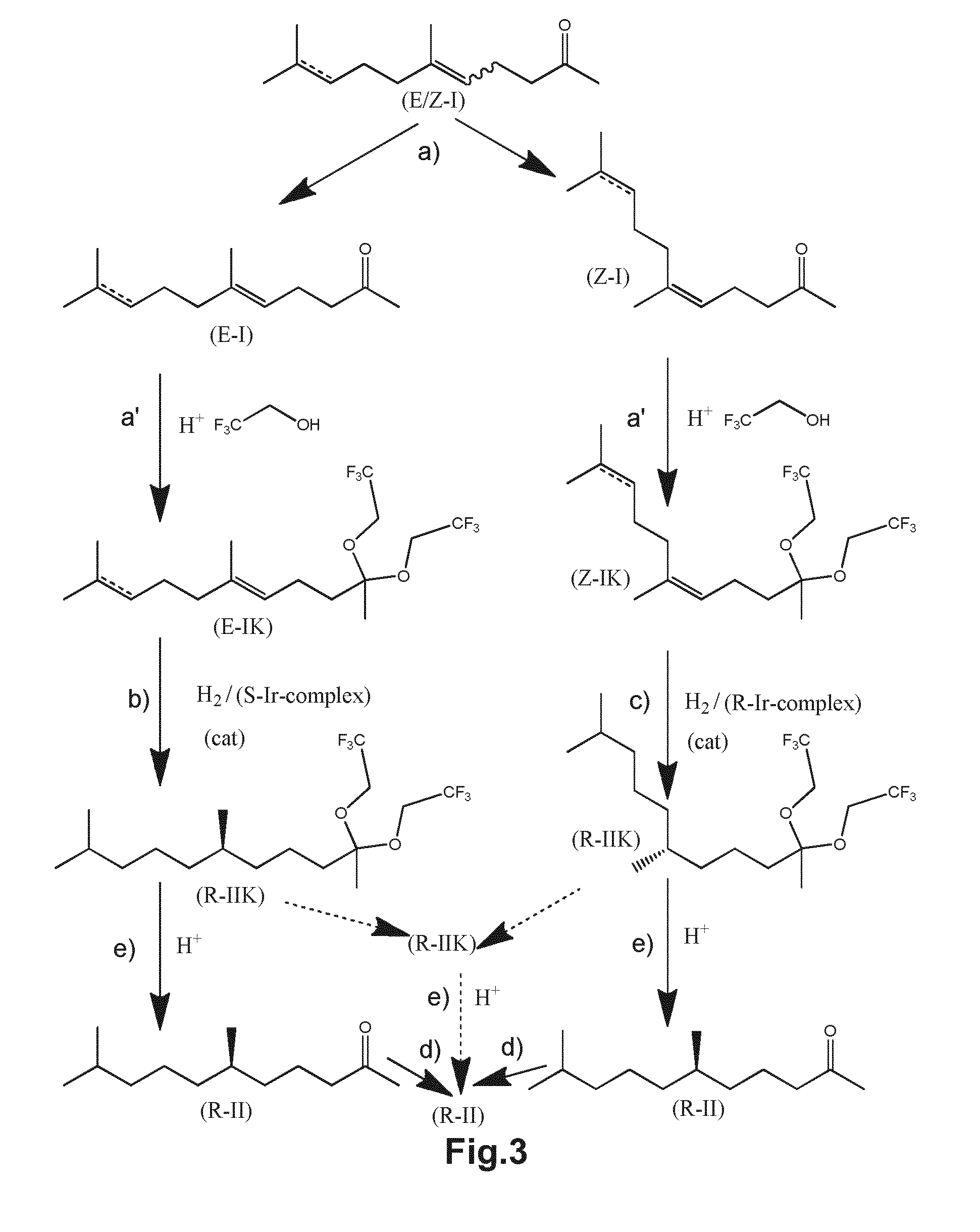
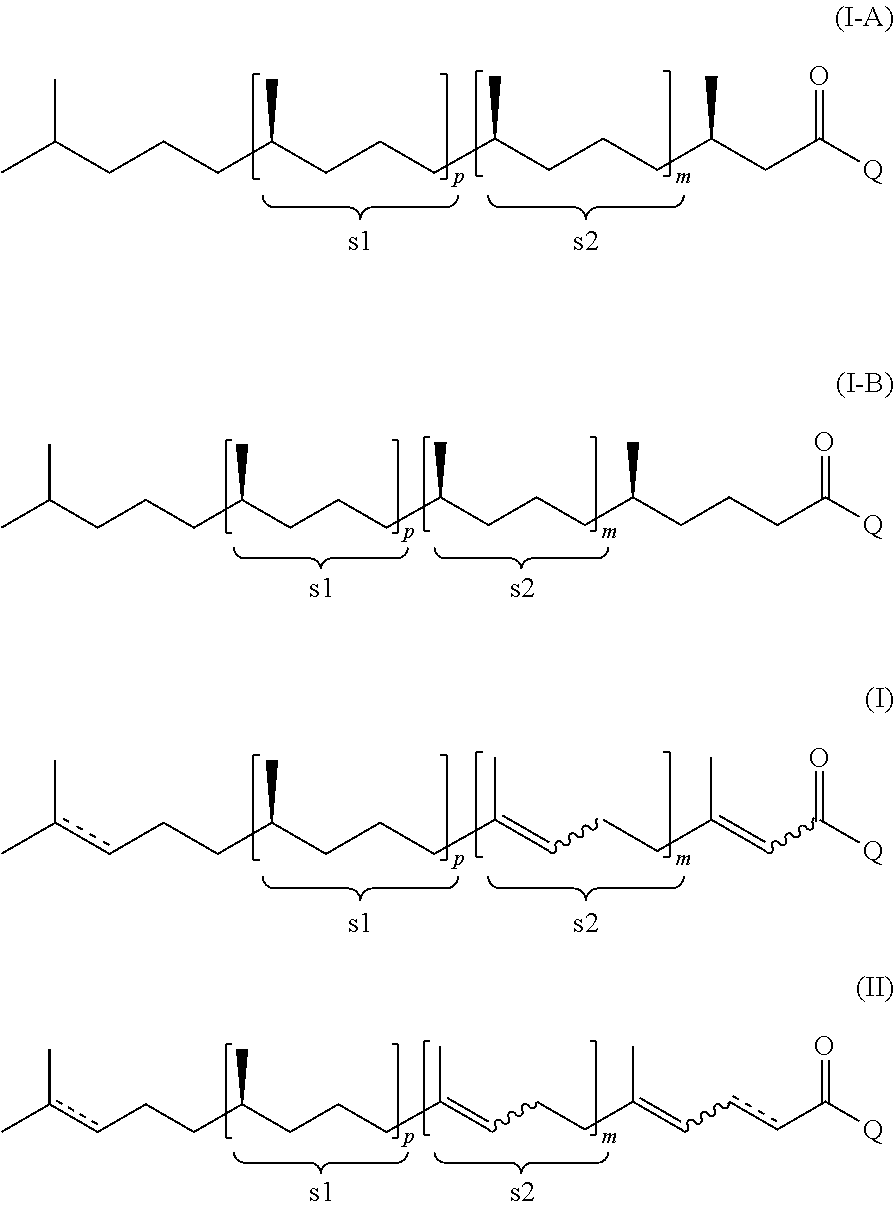
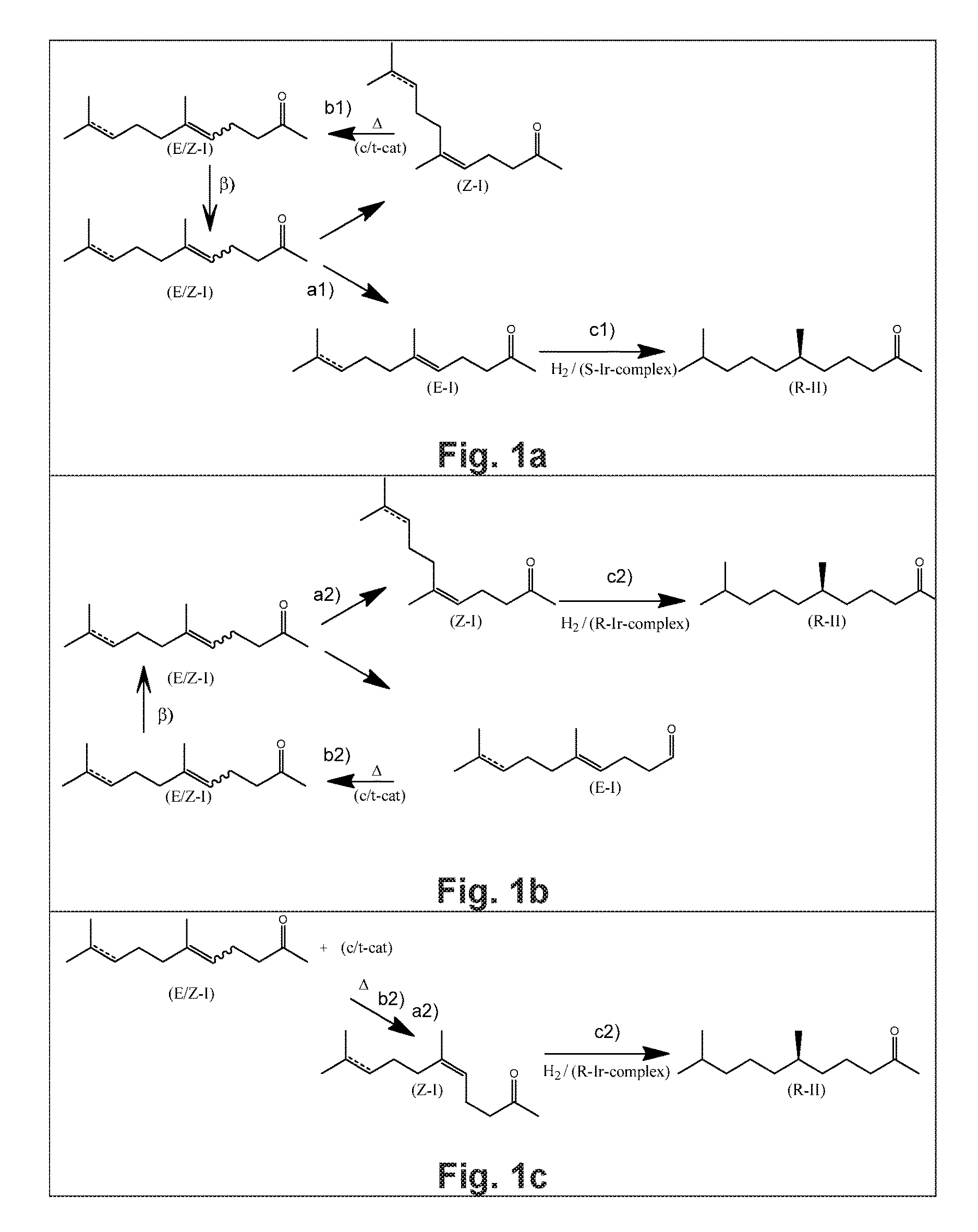
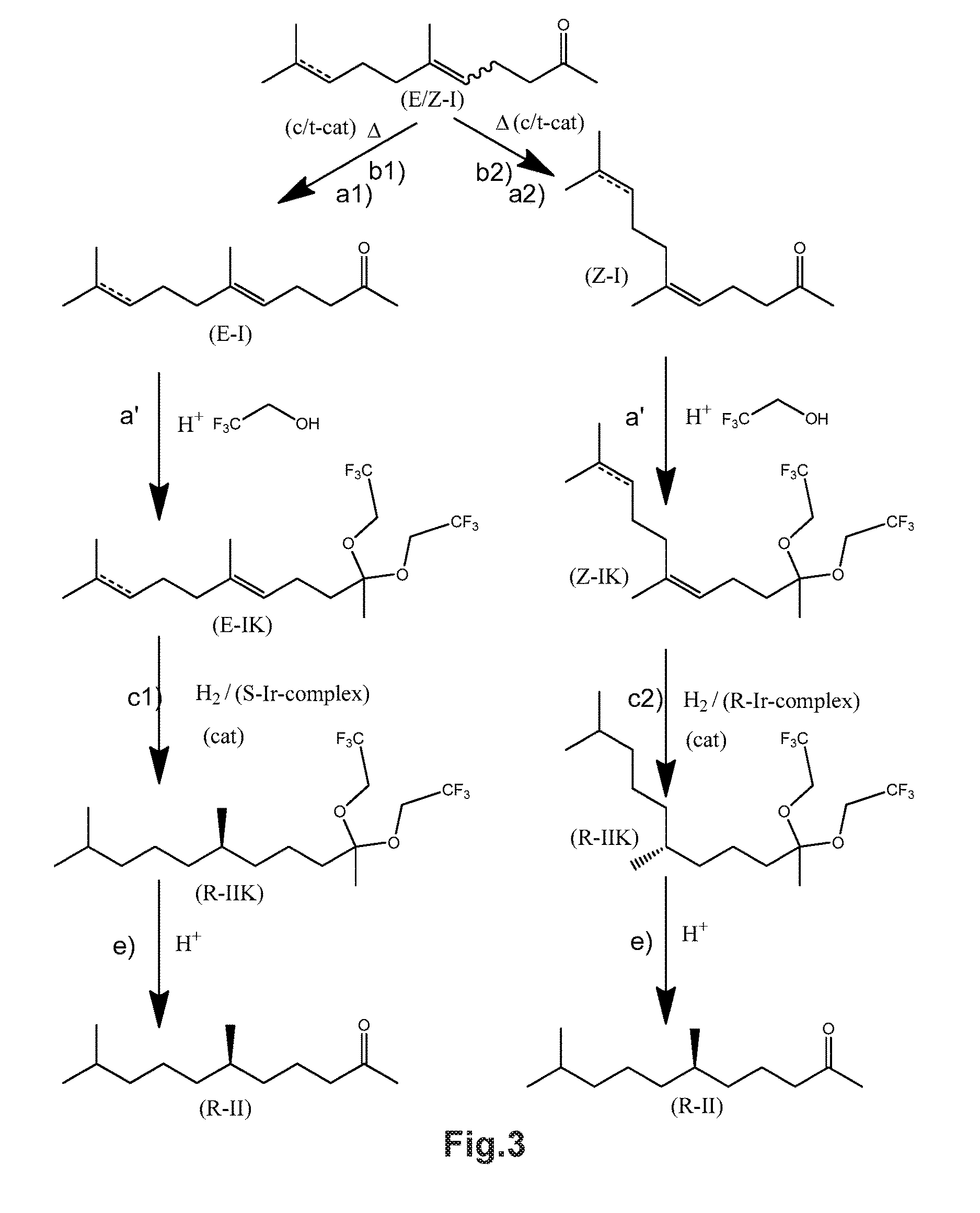
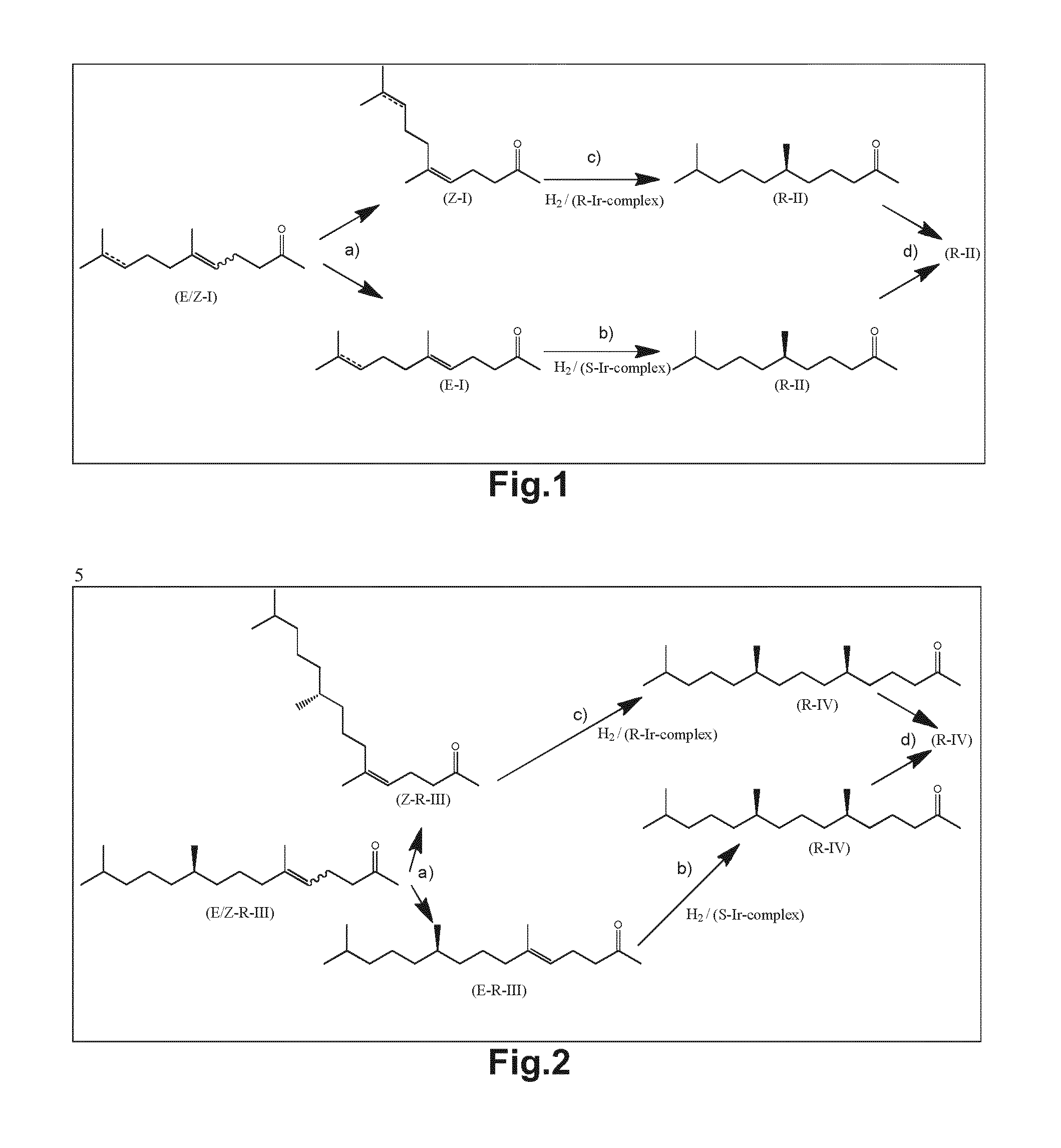
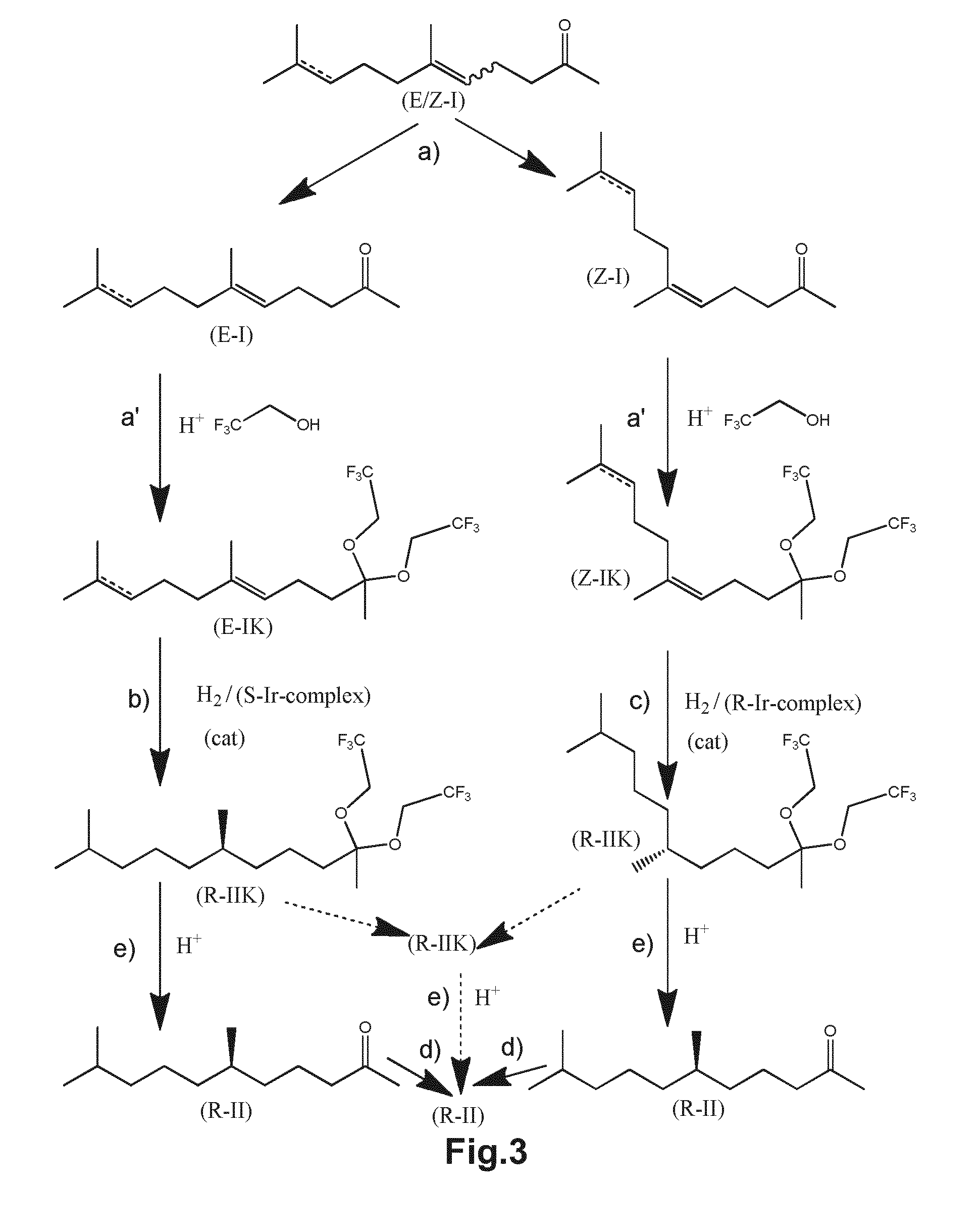
Using mixtures of e/z isomers to obtain quantitatively specific products by combined asymmetric hydrogenations
ActiveUS20150321986A1Improve efficiencyEffectively hydrogenatedOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsAsymmetric hydrogenationDouble bond
The present invention relates to a process of manufacturing compound having stereogenic centres from a mixture of E / Z isomers of unsaturated compounds having prochiral double bonds. The hydrogenation product has a specific desired configuration at the stereogenic centres. The process involves two asymmetric hydrogenation steps. The process is very advantageous in that it forms the desired chiral product from a mixture of stereoisomers of the starting product in an efficient way.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
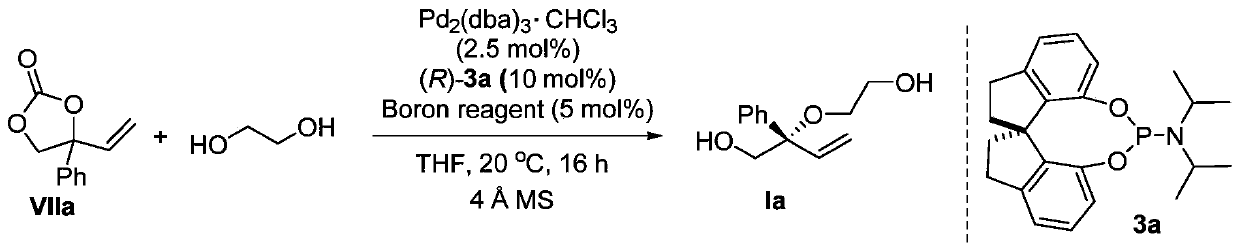
Chiral diol compound, chiral crown ether compound and preparation methods thereof
ActiveCN111056925ANovel structureHigh regional selectivityOrganic chemistry methodsSulfonic acid amide preparationPtru catalystSeparation technology
The invention discloses a chiral diol compound, a chiral crown ether compound and preparation methods thereof. The chiral diol compound and the chiral crown ether compound have tetra-substituted three-dimensional centers, can be widely applied to chiral recognition and chiral separation technologies, and can be used as chiral catalysts and applied to asymmetric catalytic reactions to prepare chiral compounds. According to the preparation method of the compound provided by the invention, racemic 4-substituted-4-vinyl-1,3-dioxolane-2-ketone compounds are used as raw materials and react with diolunder the catalytic action of a palladium complex generated by coordination between a palladium source and a chiral ligand and a boron compound, which are used as catalysts to prepare the chiral diolcompound. The preparation method provided by the invention is a palladium and boron co-catalyzed asymmetric etherification reaction, and has the advantages of high catalytic activity, high regioselectivity, diastereoselectivity and enantioselectivity, mild reaction conditions, and convenient and easily available reaction raw materials.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Asymmetric catalysts
ActiveUS20150112066A1High enantioselectivityEasy accessOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsRedoxStereochemistry
The present invention relates to asymmetric catalysts, including redox-reconfigurable asymmetric catalysts. Methods of producing compounds having one or more stereocenters using the asymmetric catalysts of the present invention are also disclosed.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
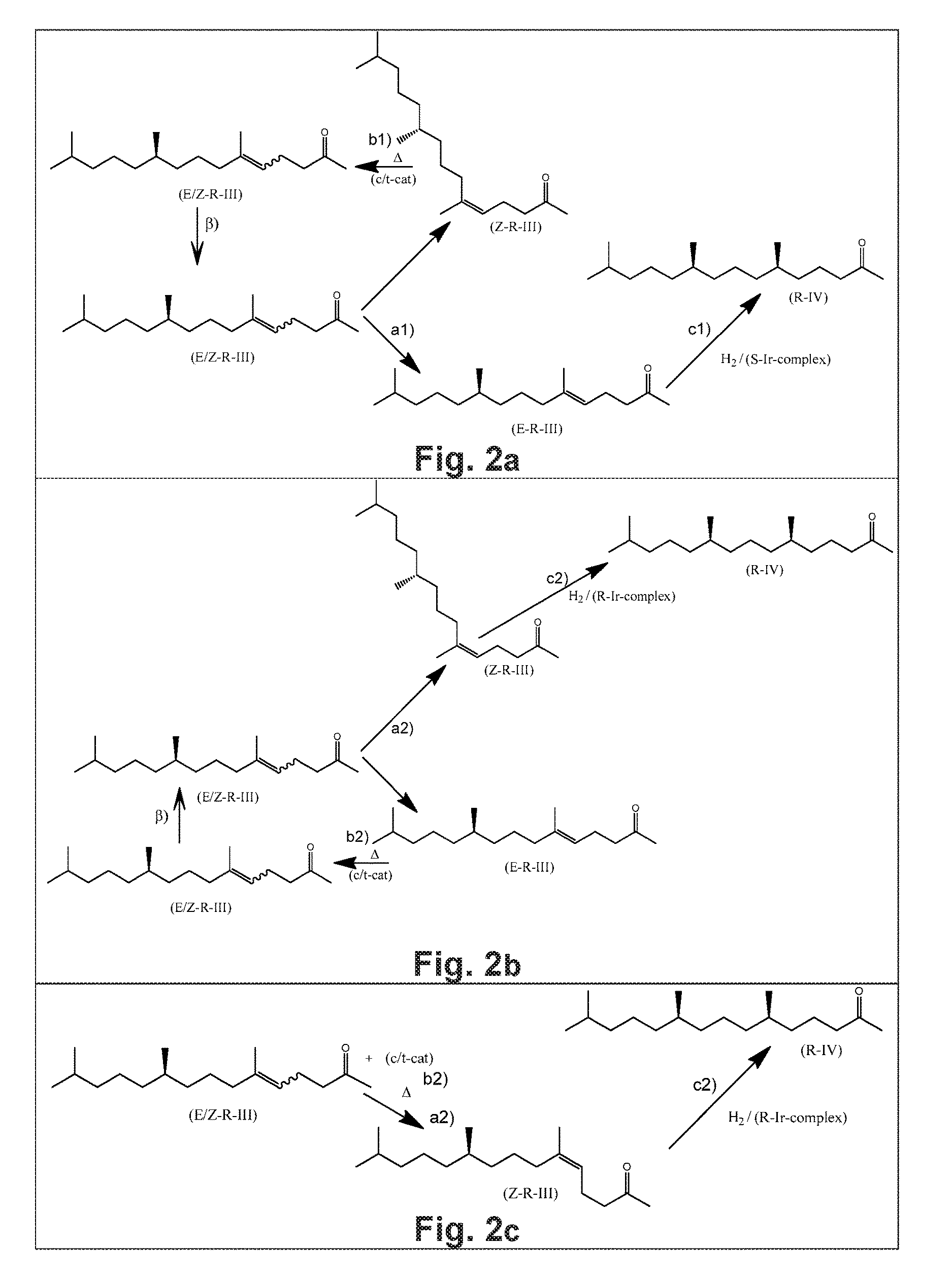
Using mixtures of E/Z isomers to obtain quantitatively specific products by combining asymmetric hydrogenation and isomerization
ActiveUS9573872B2Organic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsIsomerizationChemical compound
The present invention relates to a process of manufacturing compound having stereogenic centers from a mixture of E / Z isomers of unsaturated compounds having prochiral double bonds. The hydrogenation product has a specific desired configuration at the stereogenic centers. The process involves an asymmetric hydrogenation and an isomerization step. The process is very advantageous in that it forms the desired chiral product from a mixture of stereoisomers of the starting product in an efficient way.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Method for preparing sitagliptin intermediate via asymmetrical reduction method
ActiveUS20170305822A1Atom utilization is highShort stepsCarbamic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationPtru catalystPhosphine
Owner:ZHEJIANG HUAHAI PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD +1
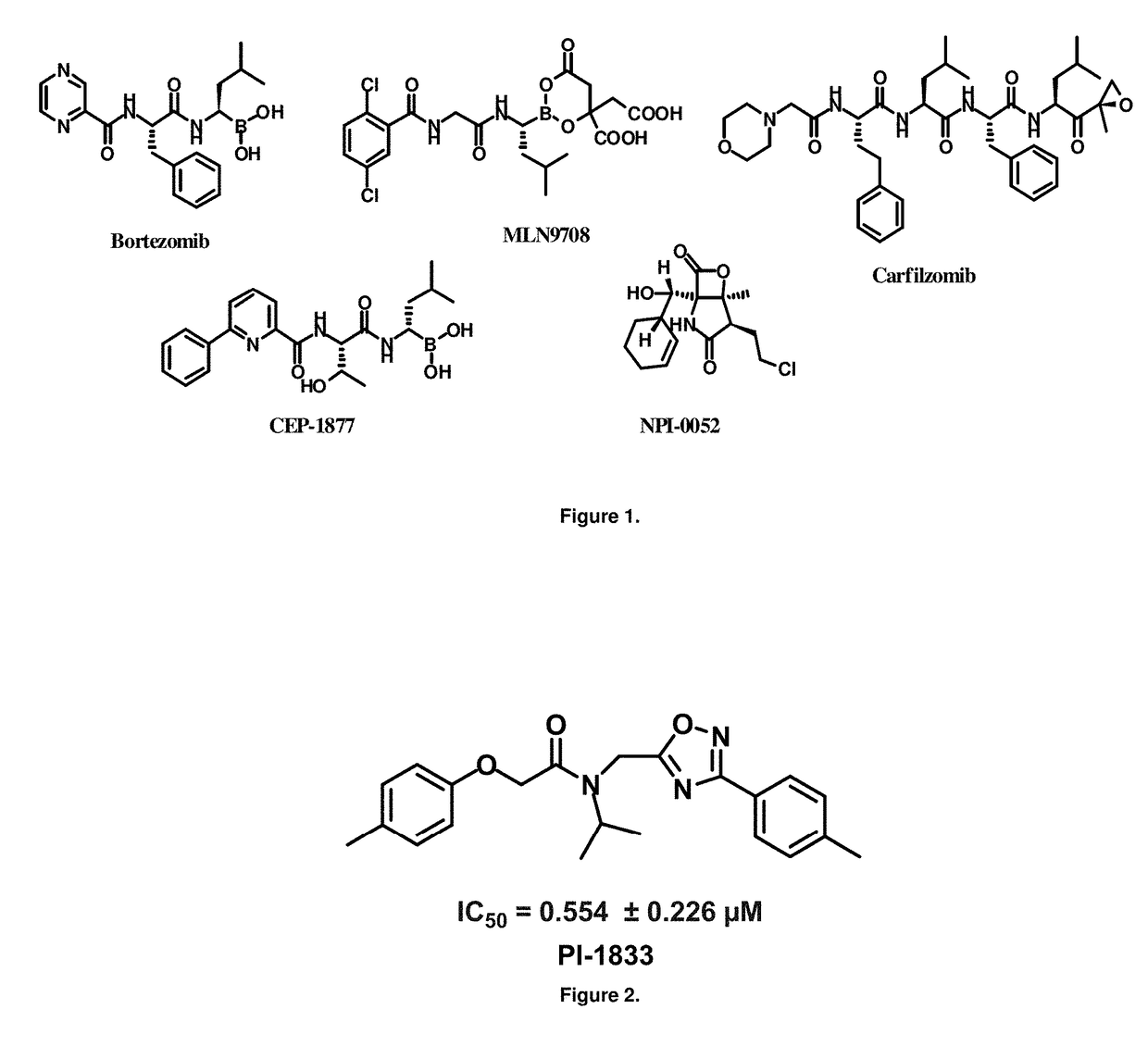
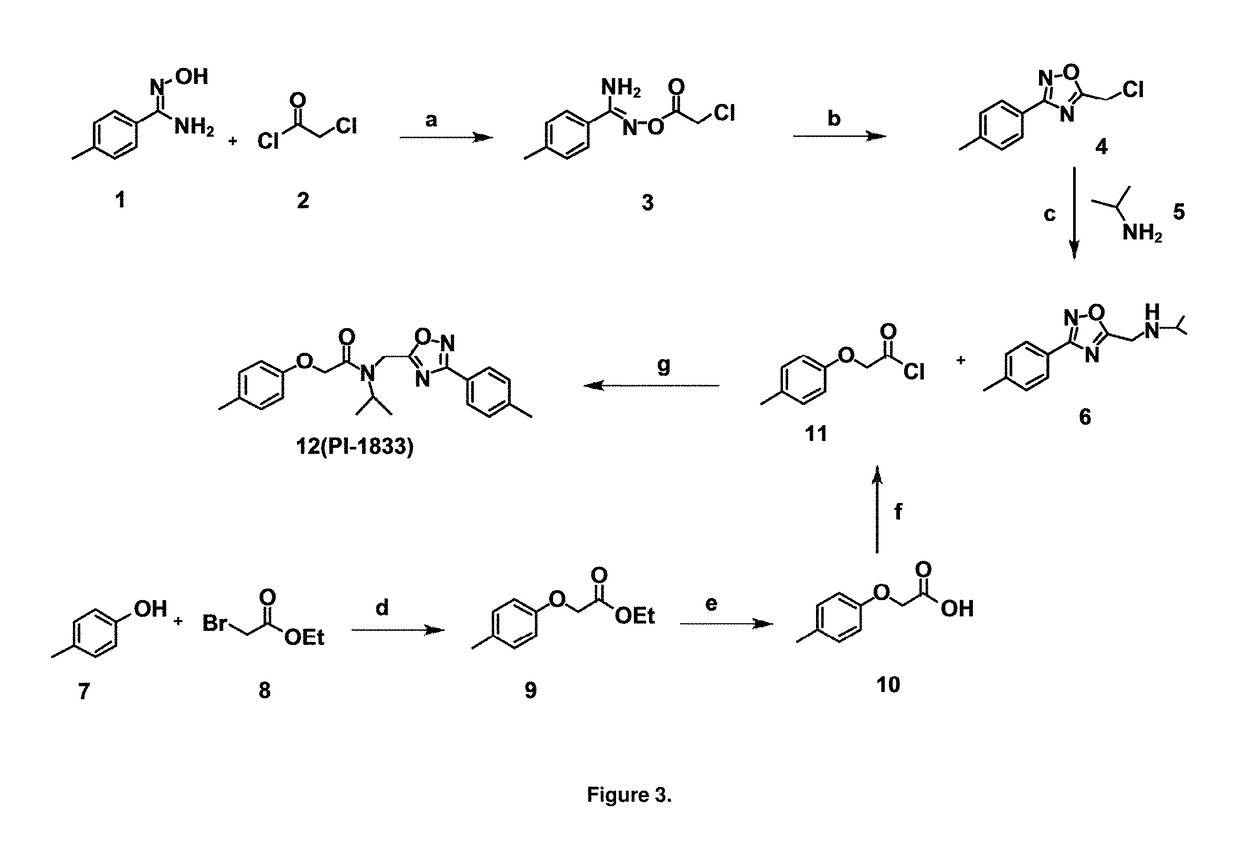
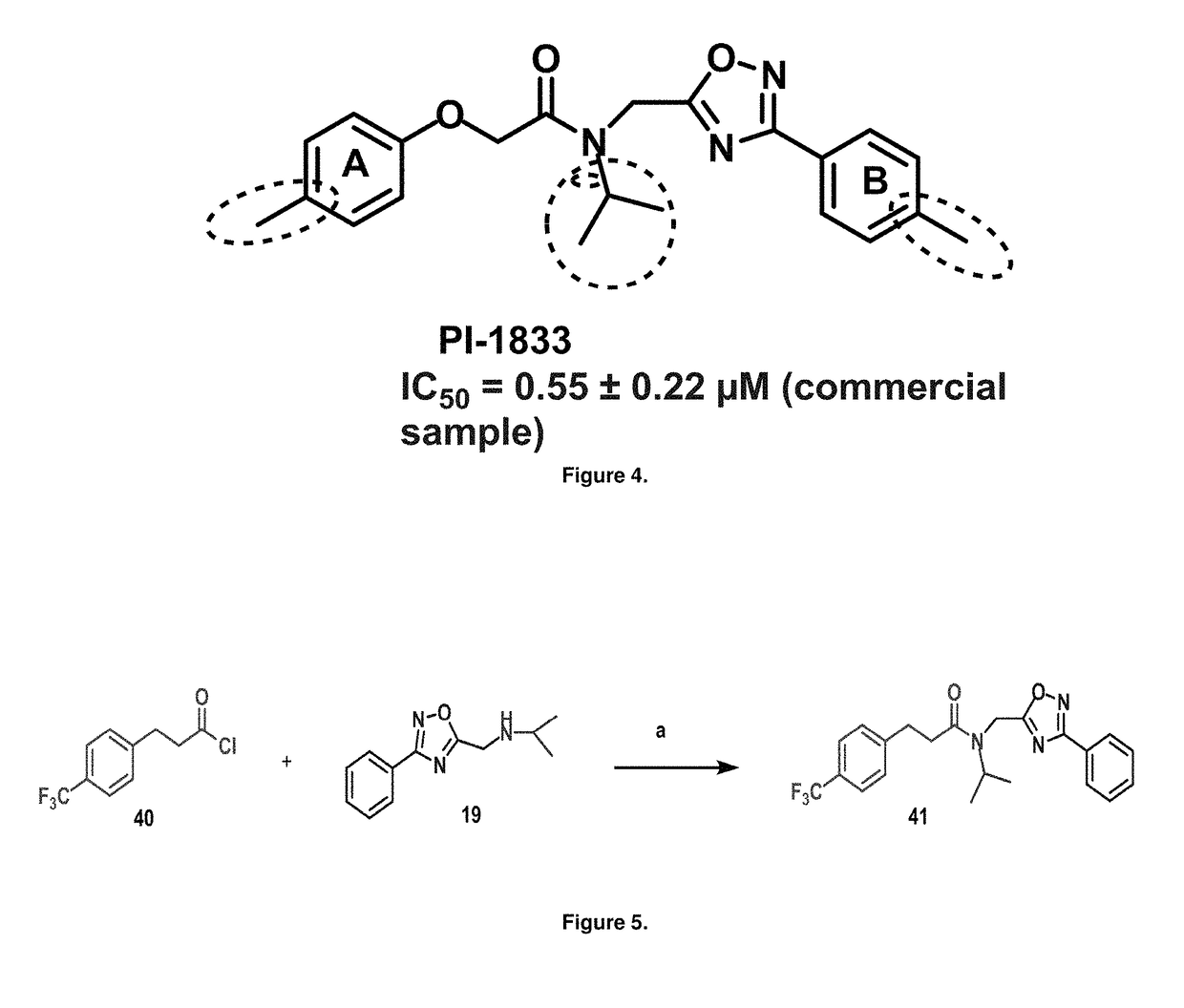
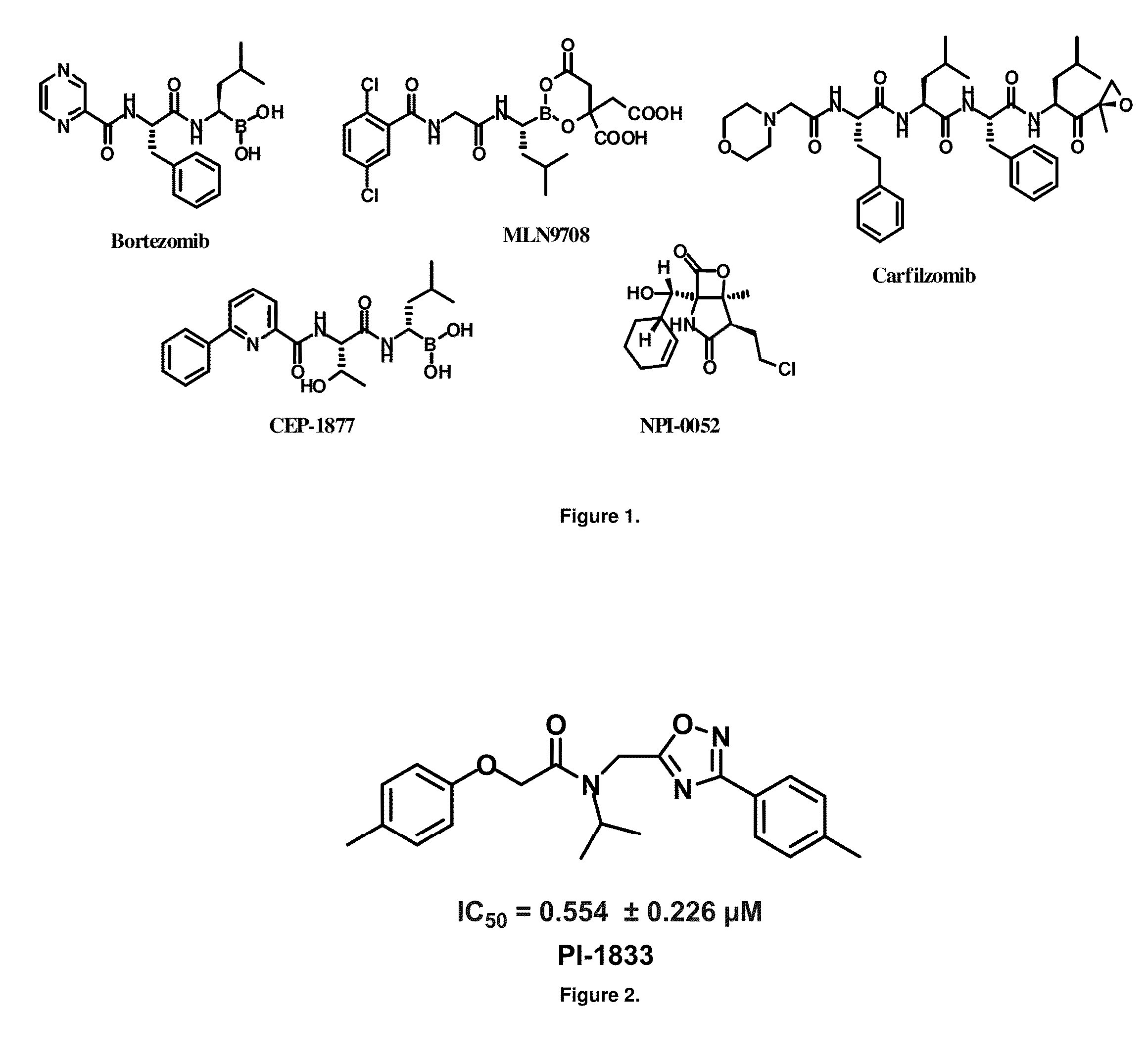
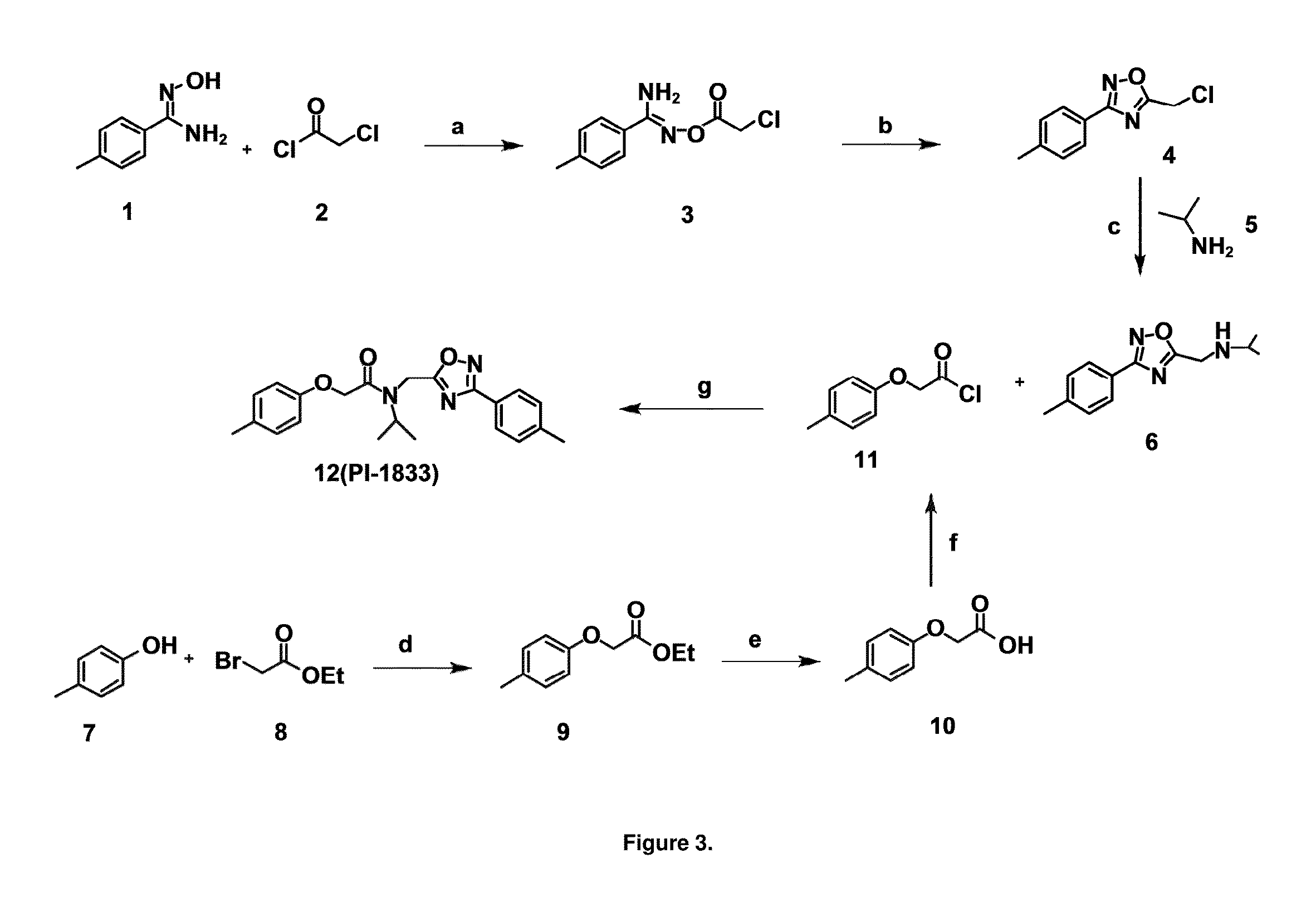
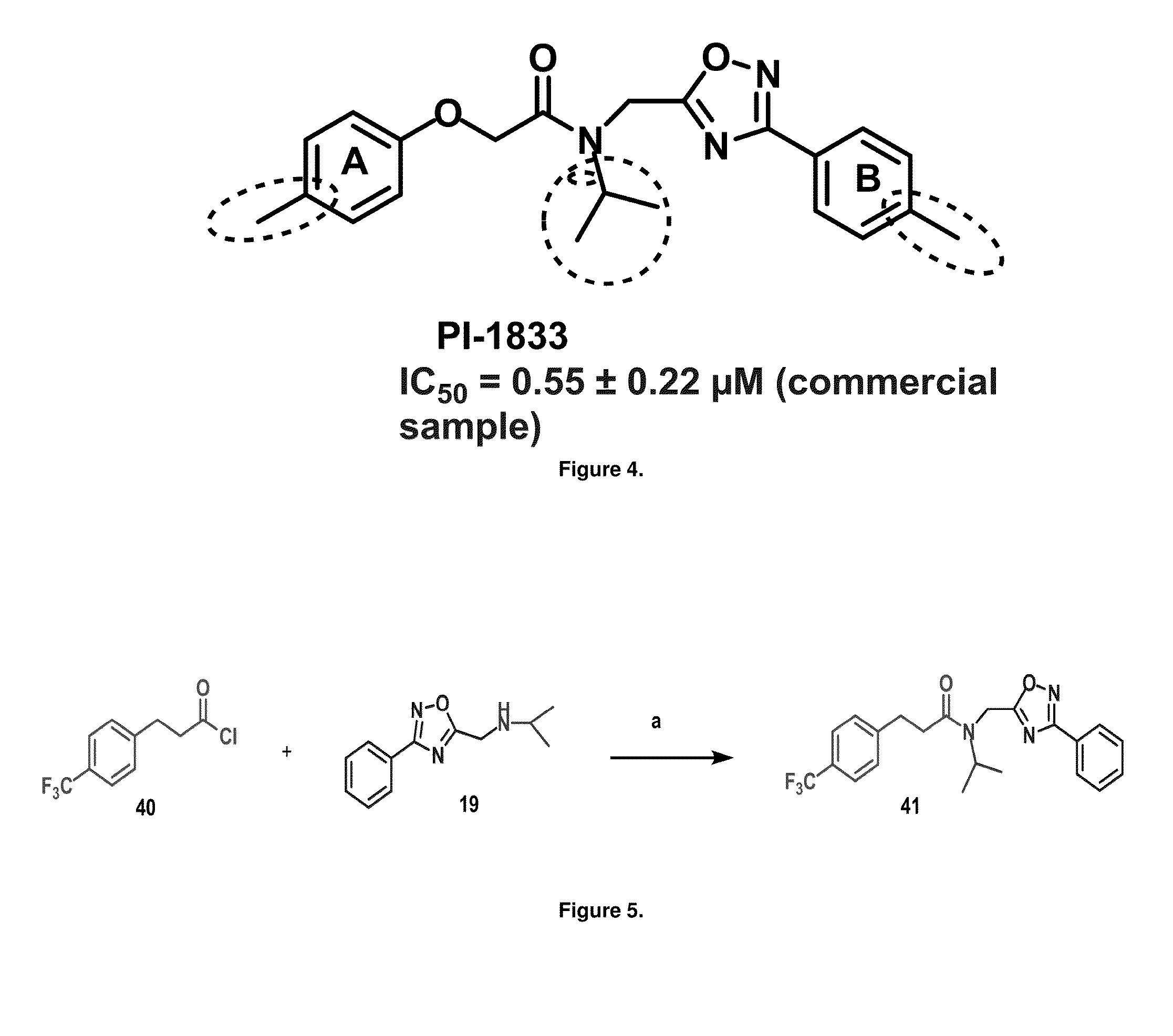
Proteasome chymotrypsin-like inhibition using PI-1833 analogs
Focused library synthesis and medicinal chemistry on an oxadiazole-isopropylamide core proteasome inhibitor provided the lead compound that strongly inhibits CT-L activity. Structure activity relationship studies indicate the amide moiety and two phenyl rings are sensitive toward synthetic modifications. Only para-substitution in the A-ring was important to maintain potent CT-L inhibitory activity. Hydrophobic residues in the A-ring's para-position and meta-pyridyl group at the B-ring significantly improved inhibition. The meta-pyridyl moiety improved cell permeability. The length of the aliphatic chain at the para position of the A-ring is critical with propyl yielding the most potent inhibitor, whereas shorter (i.e. ethyl, methyl or hydrogen) or longer (i.e. butyl, propyl and hexyl) chains demonstrating progressively less potency. Introduction of a stereogenic center next to the ether moiety (i.e. substitution of one of the hydrogens by methyl) demonstrated chiral discrimination in proteasome CT-L activity inhibition (the S-enantiomer was 35-40 fold more potent than the R-enantiomer).
Owner:H LEE MOFFITT CANCER CENT & RES INST INC
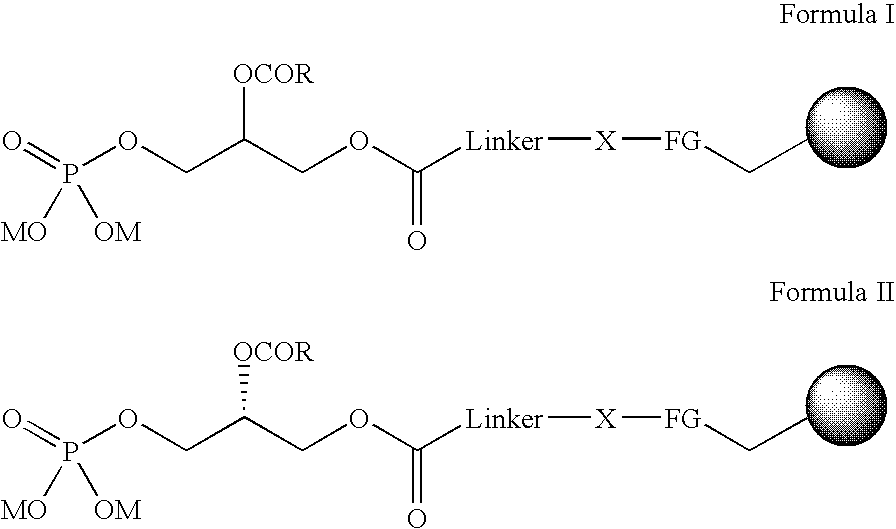
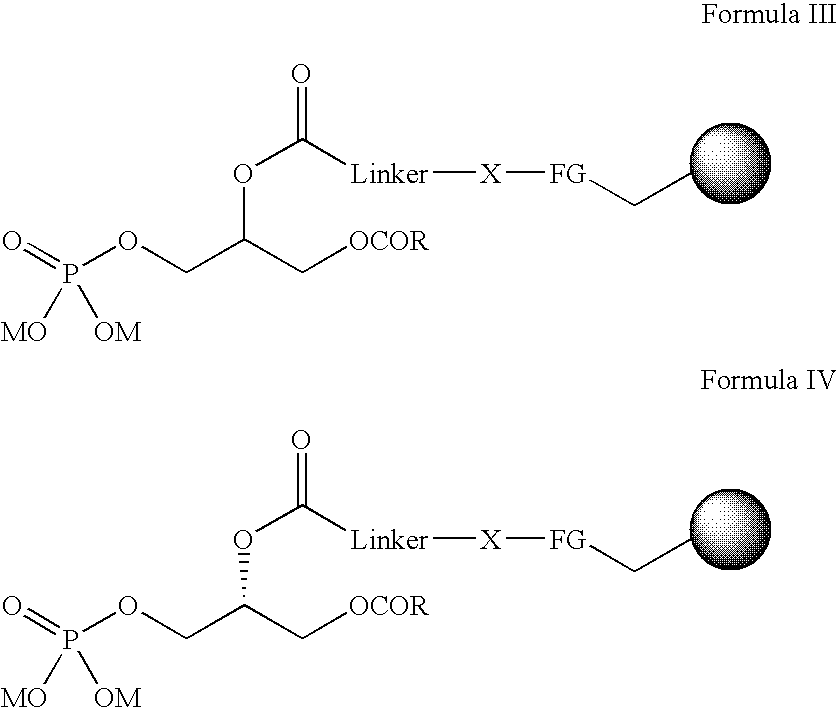
Immobilised phosphatidic acid probe
Probes comprising an immobilised Phosphatidic Acid attached onto a solid support are described, for example, as shown in formula I and V: (a) the linker consists of aryl, heteroaryl, alkyl with possible heteroatoms and / or unsaturations, preferably chains of (CH2)n, with n=8-20, most preferably n=11; (b) the heteroatom X maybe O, S, or most preferably NH; (c) the functional group (FG) is a carbonyl from a carboxylate (thiolo)ester, or, most preferably an amide; (d) the R-substituent carries an aryl, alkyl group, or a combination, preferably R=CmH2m+1, m=8-20, m=16 optimal; (e) the ion M represents any cation, preferably Na+, NH4+; (f) unsaturations are allowed, such as in an arachidonyl side chain and (g) =solid support with attachment to functional group, where: R=aryl, alkyl group, or a combination, preferably R=CmH2m+1, m=8-20, m=16 is optimal. R3 is P(O) (OM)2; R5=H(PI(3)P); R3=H; R4=P(O)(OM)2; R5=H(PI(4)P); R3=H; R4=H; R5=P(O)(OM)2(PI(5)P); R3=P(O)(OM)2; R4=P(O)(OM)2; R5=H(PI(3,4)P2); R3=P(O)(OM)2; R4=H; R5=P(O)(OM)2(PI(3,5)P2); R3=H; R4=P(O)(OM)2; R5P=P(O)(OM)2(PI(4,5)P2); or R3=P(O)(OM)2; R4=P(O)(OM)2; R5=H(O)(OM)2(PI(3,4,5)P3). M=any cation, preferably Na+, NH4+ *Denotes a stereogenic center. More preferably a stereogenic centre with an R absolute configuration. Linker=aryl, heteroaryl, alkyl with possible heteroatoms and / or unsaturations. Preferably chains of (CH2)n with n=8-20, most preferably n=11. X=O, S, or, most preferably NH. FG=Carbonyl from a carboxylate, thiolo(ester), or, most preferably an amide. Unsaturations are allowed, such as in an arachidonyl side chain.=solid support with attachment to functional group. Use of the probes to identify Phosphatidic Acid binding protein or phosphoinositide binding proteins is also described.
Owner:HOLMES ANDREW BRUCE +2
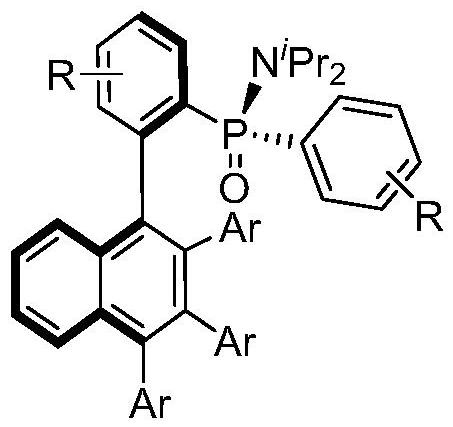
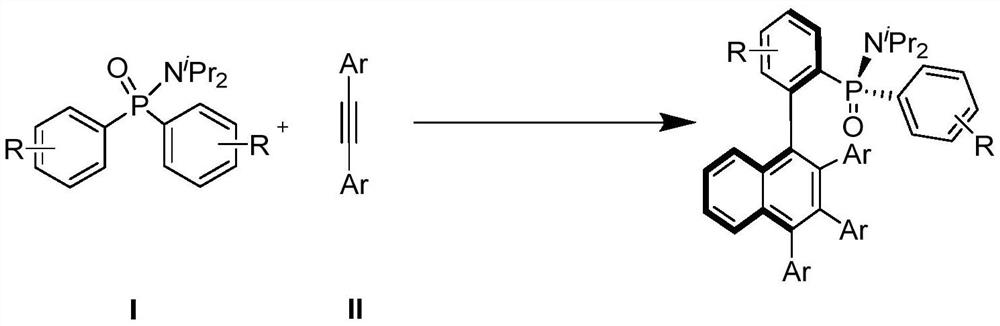
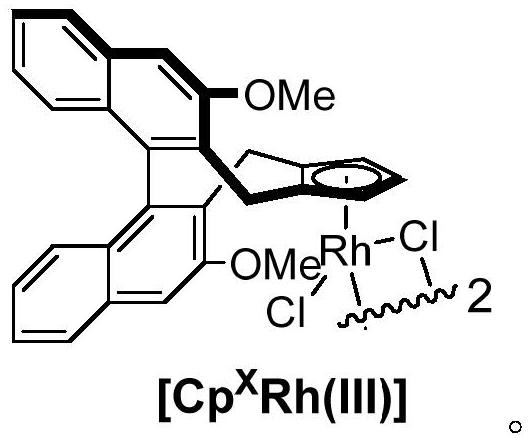
Axially chiral biaryl compound with P-stereo center and synthesis method and application thereof
InactiveCN113292598AEasy to manufactureHigh catalytic activityOrganic compound preparationGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsBoronic acidEthylic acid
The invention discloses an axially chiral biaryl compound with a P-stereo center and a synthesis method and application thereof. The structural formula of the compound is shown in the specification, chiral trivalent rhodium [CpXRh(III)] is used as a catalyst, diaryl phosphonamide and diaryl acetylene are used as raw materials, and enantioselective coupling is conducted under the assistance of silver trifluoromethanesulfonate or silver hexafluoroantimonate and silver acetate to obtain the compound. Diarylacetylene is taken as an initial raw material, the compound is stable in property and easy to prepare, but the compound is seldom applied to arylation reaction. In the prior art, aryl arylation is mainly carried out by using brominated aromatic hydrocarbon, arylboronic acid and the like. The simple diarylacetylene is adopted as an arylation reagent, the axially chiral biaryl and the P-center chiral compound are stereoscopically and specifically synthesized through double activation of C-H bonds in the aryl phosphonamide and the diarylacetylene, and the method has the advantages of being mild in reaction condition, high in enantioselectivity, good in diastereoselectivity and the like.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
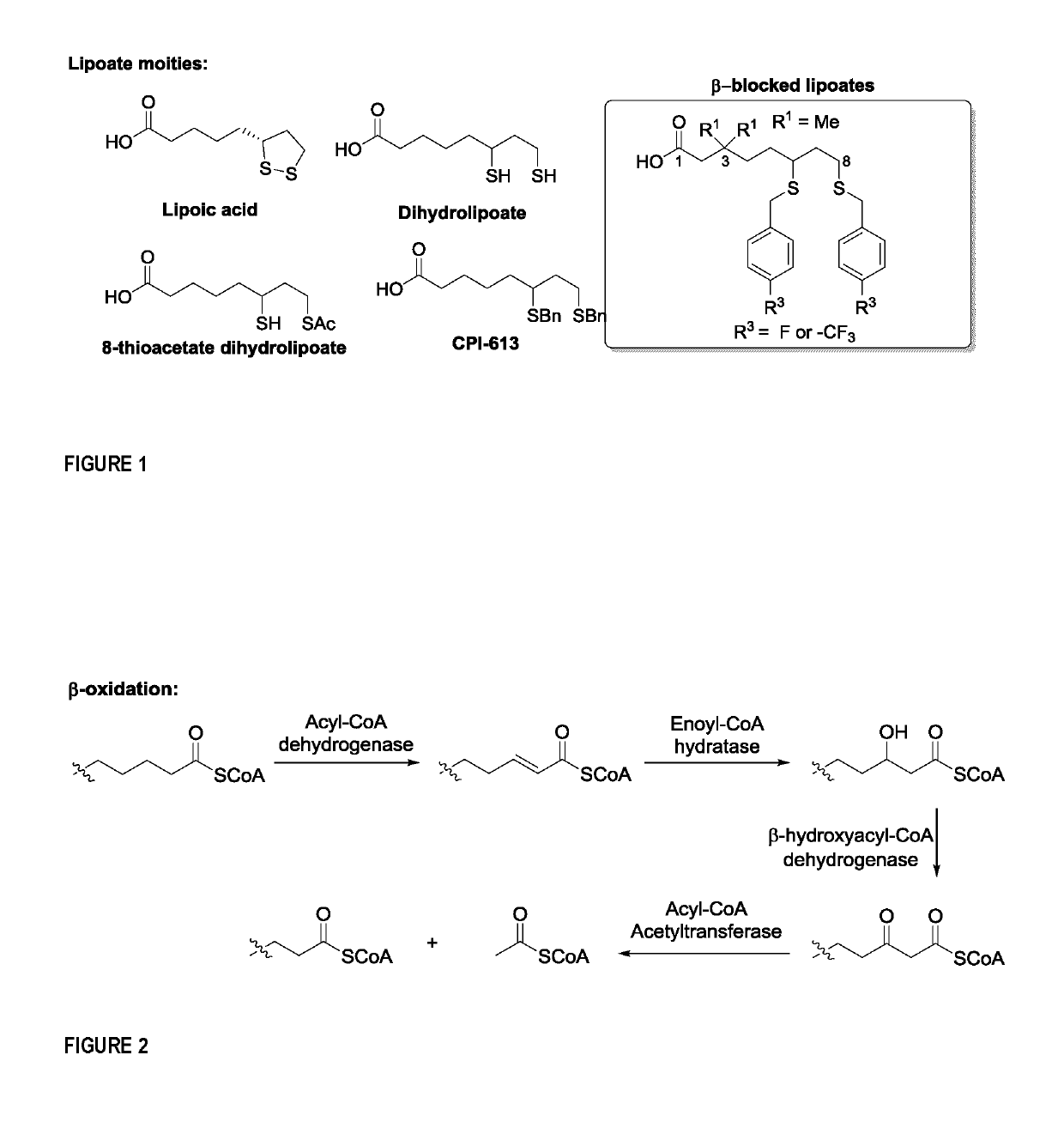
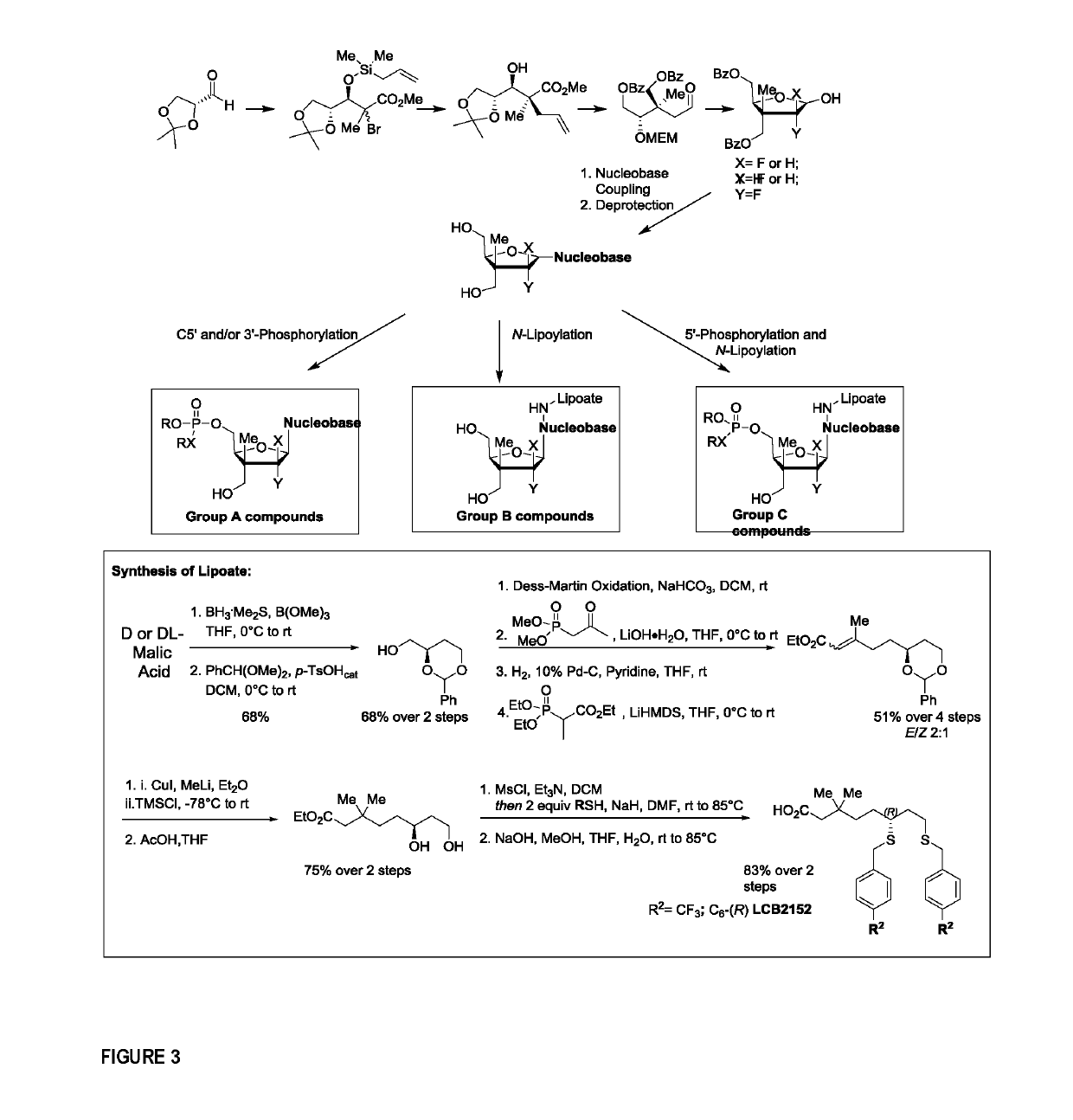
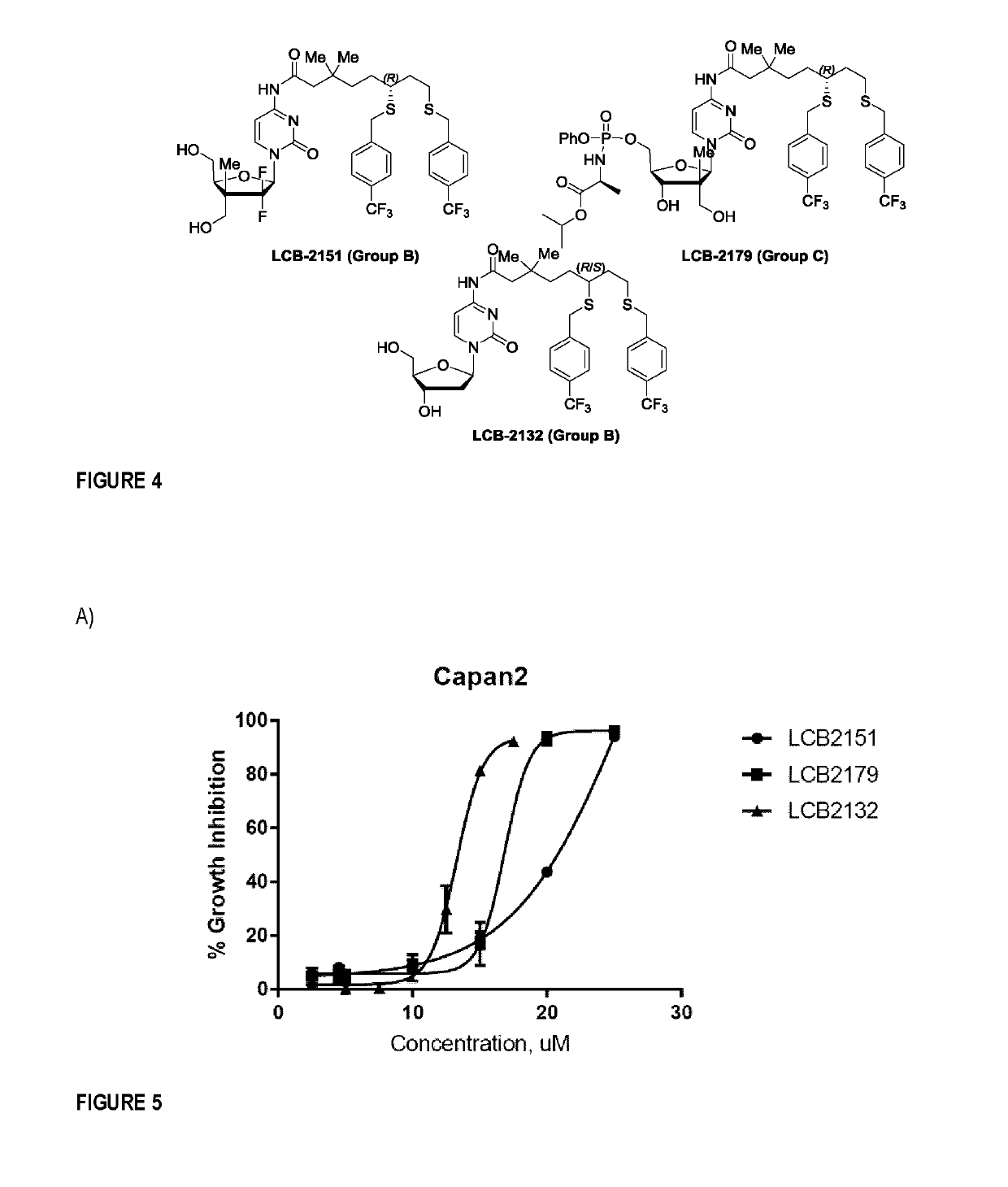
Nucleoside analogues and methods of use thereof
Nucleoside analogues that can be used as anticancer or antiviral agents are presented. These compounds are nucleoside and / or nucleotide prodrugs. In particular, the subject matter relates to nucleoside analogues comprising a tetrahydrofuranyl, or tetrahydrothienyl moiety which: have a quaternary stereogenic all-carbon center at the 3′ position and bear a phosphoryl group at either one of, or both of positions C5′ and / or C3′; have a quaternary stereogenic all-carbon center at one of the 3′ position, 2′ position, or no quaternary stereogenic center at all, and bear a β-blocked lipoate derivative attached through an amide bond to the primary amine of the nucleobase; or have a quaternary stereogenic all-carbon center at the 2′ position and bear a phosphorylated prodrug at the C5′-position and a β-blocked lipoate derivative attached through an amide bond to the primary amine of the nucleobase.
Owner:LCB PHARMA
Proteasome chymotrypsin-like inhibition using pi-1833 analogs
Focused library synthesis and medicinal chemistry on an oxadiazole-isopropylamide core proteasome inhibitor provided the lead compound that strongly inhibits CT-L activity. Structure activity relationship studies indicate the amide moiety and two phenyl rings are sensitive toward synthetic modifications. Only para-substitution in the A-ring was important to maintain potent CT-L inhibitory activity. Hydrophobic residues in the A-ring's para-position and meta-pyridyl group at the B-ring significantly improved inhibition. The meta-pyridyl moiety improved cell permeability. The length of the aliphatic chain at the para position of the A-ring is critical with propyl yielding the most potent inhibitor, whereas shorter (i.e. ethyl, methyl or hydrogen) or longer (i.e. butyl, propyl and hexyl) chains demonstrating progressively less potency. Introduction of a stereogenic center next to the ether moiety (i.e. substitution of one of the hydrogens by methyl) demonstrated chiral discrimination in proteasome CT-L activity inhibition (the S-enantiomer was 35-40 fold more potent than the R-enantiomer).
Owner:H LEE MOFFITT CANCER CENT & RES INST INC
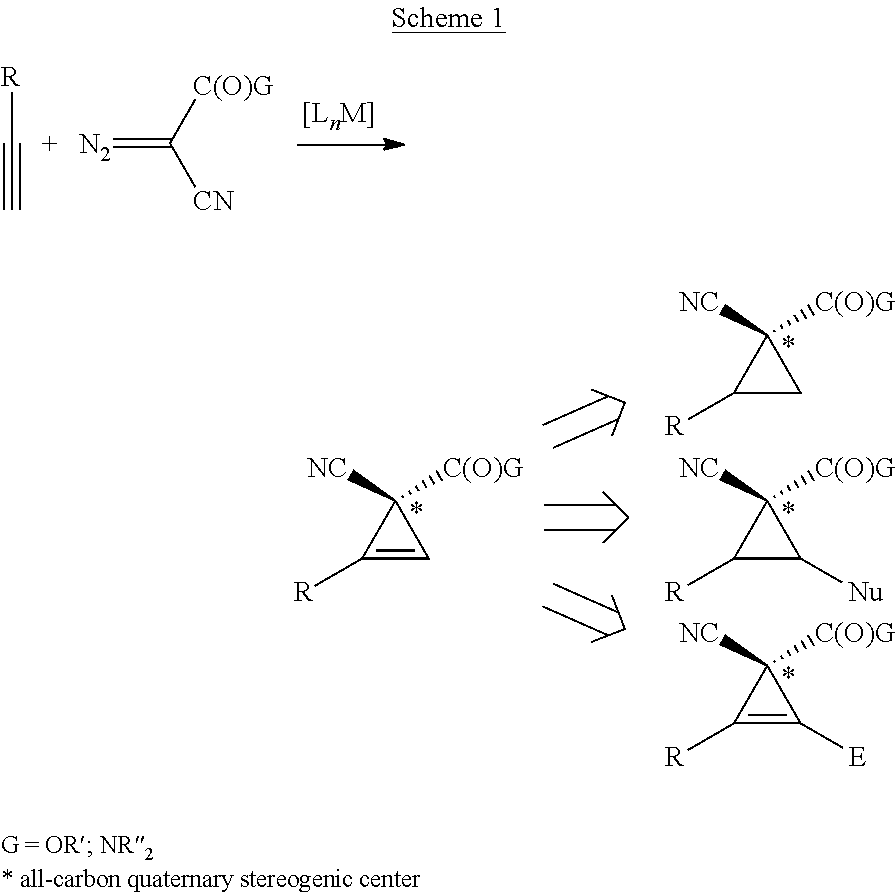
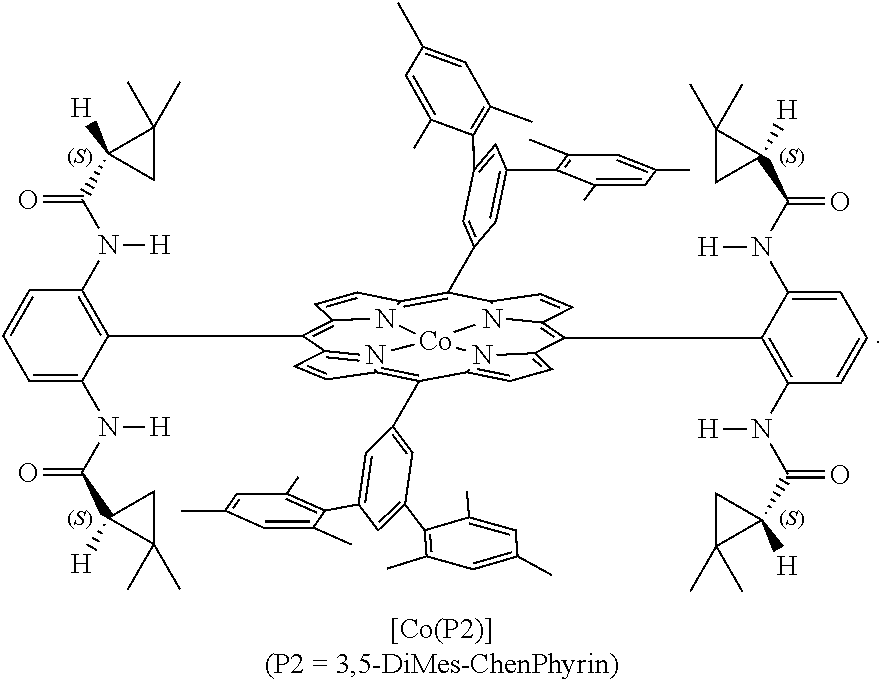
Enantioselective cyclopropenation of alkynes
InactiveUS20130030170A1Improve efficiencyHigh enantioselectivityHydrocarbon by isomerisationCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationPorphyrinAlkyne
The cobalt(II) complex of new D2-symmetric chiral porphyrin 3,5-DiMes-ChenPhyrin, [Co(P2)], has been shown to be a highly effective chiral metalloradical catalyst for enantioselective cyclopropenation of alkynes with acceptor / acceptor-substituted diazo reagents such as α-cyanodiazoacetamides and α-cyanodiazoacetates. The [Co(P2)]-mediated metalloradical cyclopropenation is suitable to a wide range of terminal aromatic and related conjugated alkynes with varied steric and electronic properties, providing the corresponding tri-substituted cyclopropenes in high yields with excellent enantiocontrol of the all-carbon quaternary stereogenic centers. In addition to mild reaction conditions, the Co(II)-based metalloradical catalysis for cyclopropenation features a high degree of functional group tolerance.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Control and repellency of mosquitoes
Control or repellency of mosquitoes is accomplished by bringing the insects into contact with at least one of the compounds of the structure (I)whereinR is selected from —OH, ═O, —OC(O)R4, —OR6, —(OR6)2, wherein each R6 is independently selected from an alkyl group containing from 1 to 4 carbon atoms and R4 is a branched or straight chain, saturated or unsaturated hydrocarbyl group with zero to two double bonds and from 1 to 15 carbon atoms;X is O or CH2, with the proviso that when X is O R can only be ═O;each Z is independently selected from (CH) and (CH2);y is a numeral selected from 1 and 2;R1 is selected from H or a branched or straight chain, saturated or unsaturated hydrocarbyl group with zero to two double bonds and from 1 to 15 carbon atoms;R2 is selected from H and a branched or straight chain, saturated or unsaturated hydrocarbyl group with zero to three double bonds and from 1 to 15 carbon atoms;R3 is selected from the group consisting of H and a branched or straight chain, saturated or unsaturated hydrocarbyl group with zero to three double bonds and from 1 to 15 carbon atoms, —(CH2)nOH, —C(O)OR5, —CH2C(O)OR7, —CH2C(O)R8, —C(O)NR9R10, —CH2C(O)NR11R12 where each of R5, R7, R8, R9, R10, R11 and R12 is independently selected from H and a branched or straight chain, saturated or unsaturated hydrocarbyl group with zero to three double bonds and from 1 to 15 carbon atoms and n is an integer of from 1 to 12;the bond between the 2 and 3 positions in the ring structure may be a single or a double bond; andwherein the compounds of structure (I) contain from 11 to 20 total carbon atoms in the compounds, with the proviso that when R is ═O, X is CH2, Z is CH2, y is 1 R2 is H, and R3 is CH2C(O)OR7 then the total number of carbon atoms in the compounds of structure (I) is from 15 to 20 carbon atoms, and when X is O and R is ═O the total number of carbon atoms in the compounds of structure (I) is from 11 to 17 carbon atoms. The invention also includes optical isomers, diastereomers and enantiomers of the named structures. Thus, at all stereocenters where stereochemistry is not explicitly defined, all possible epimers are envisioned.
Owner:BEDOUKIAN RES
Asymmetric catalysts
ActiveUS9221744B2High enantioselectivityEasy accessOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsRedoxStereochemistry
The present invention relates to asymmetric catalysts, including redox-reconfigurable asymmetric catalysts. Methods of producing compounds having one or more stereocenters using the asymmetric catalysts of the present invention are also disclosed.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
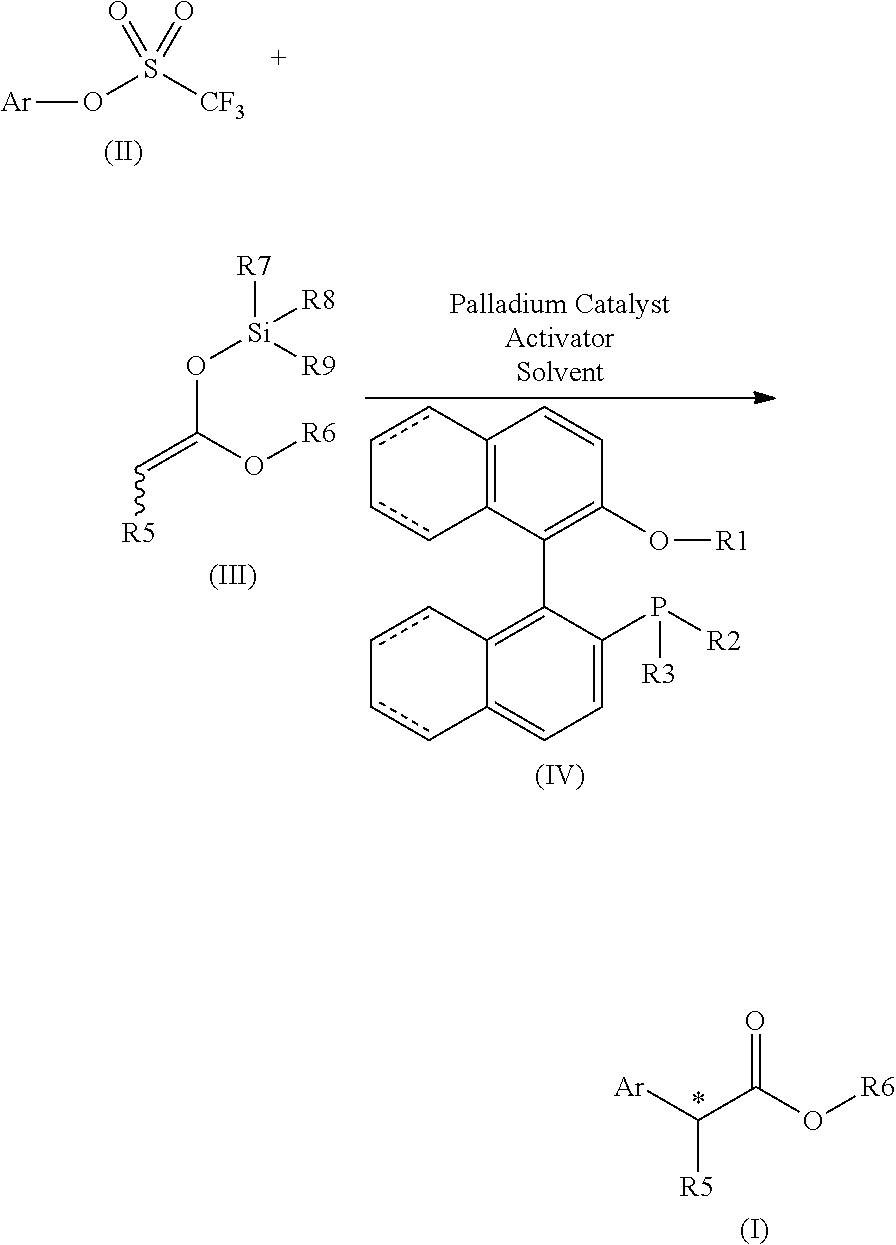
Chiral phosphines for palladium-catalyzed asymmetric alpha-arylation of ester enolates to produce tertiary stereocenters in high enantioselectivity
ActiveUS20150166586A1Excellent enantioselectionAvoid racemizationCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationPresent methodPalladium catalyst
The disclosure provides new and improved methods for the Pd-catalyzed asymmetric α-arylation of ester compounds, which produce the corresponding α-aryl moiety in high enantioselectivity (generally >90% ee). The present methods utilize a palladium catalyst supported by new (R)—H8-BINOL-derived monophosphine ligands. The method is applicable to a wide variety of aryl triflate substrates having variations in both electronic and steric properties. These aryl triflate substrates react with various α-alkyl (Z)- and / or (E)-0-trimethylsilyl ketene acetals in the presence of a Pd catalyst, (R)—H8-BINOL-derived monophosphine ligand, and a mild activator, for example, LiOAC, to provide the asymmetric α-arylation of ester compounds in high ee.
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV
A kind of highly enantioselective C-5 α-stereocenter 4-nitroisoxazole alcohol compound, its preparation method and application
ActiveCN107540623BEfficient preparationImprove efficiencyBiocideOrganic chemistryAlcoholCombinatorial chemistry
Provided are a C-5 alpha-stereocenter 4-nitro isoxazole alcohol compound with high enantioselectivity and a preparation method and application thereof. The structural formula is shown in the description, wherein R1 refers to Me, Et, Ph and thienyl, and R2 refers to Me and normal-butyl. By adopting the new method to synthesize the C-5 alpha-stereocenter 4-nitro isoxazole alcohol compound with the high enantioselectivity, the C-5 alpha-stereocenter 4-nitro isoxazole alcohol compound with the high enantioselectivity serves as an initiator to synthesize a fungicide pyrazol compound (CAS: 1845899-33-3) with a high yield through four synthesis steps, and the specific information is shown in the description. At present, this kind of method is not reported, and the new method has the advantages ofbeing applicable in common use, low in cost, reasonable in reaction path, simple in post-processing and efficient in preparation of the compound with high optical purity.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
Phenolytic Kinetic Resolution of Azido and Alkoxy Epoxides
InactiveUS20140350276A1Silicon organic compoundsCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationAlcoholKinetic resolution
Disclosed herein is a single step catalytic process for the production of enantiomerically pure α-Aryloxy-α′-Azido / Alkoxy alcohols of formula (A). The invention, in particular discloses phenolytic kinetic resolution of racemic anti and syn azido / alkoxy epoxides to generate two stereocentres of high optical purities of formula (A).
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Using mixtures of E/Z isomers to obtain quantitatively specific products by combined asymmetric hydrogenations
ActiveUS9458076B2Improve efficiencyQuality improvementOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsAsymmetric hydrogenationDouble bond
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Modified amino acid derivatives for the treatment of neurological diseases and selected psychiatric disorders
PendingCN113767088AStrong anticonvulsant activityPotent and broad anticonvulsant activityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseIn vivo
2-(2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl)propanamide and 2-(2-oxopyrrolidin-1-yl)propanamide derivatives with R-configuration at the stereogenic center are disclosed, showing broad- spectrum protective activity in animal models of epileptic seizures, pain, depression and anxiety that are simultaneously devoid of undesirable sedative effects. Additionally, the disclosed derivatives have neuroprotective effects in the in vitro and in vivo studies.
Owner:JAGIELLONIAN UNIVERSITY +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com