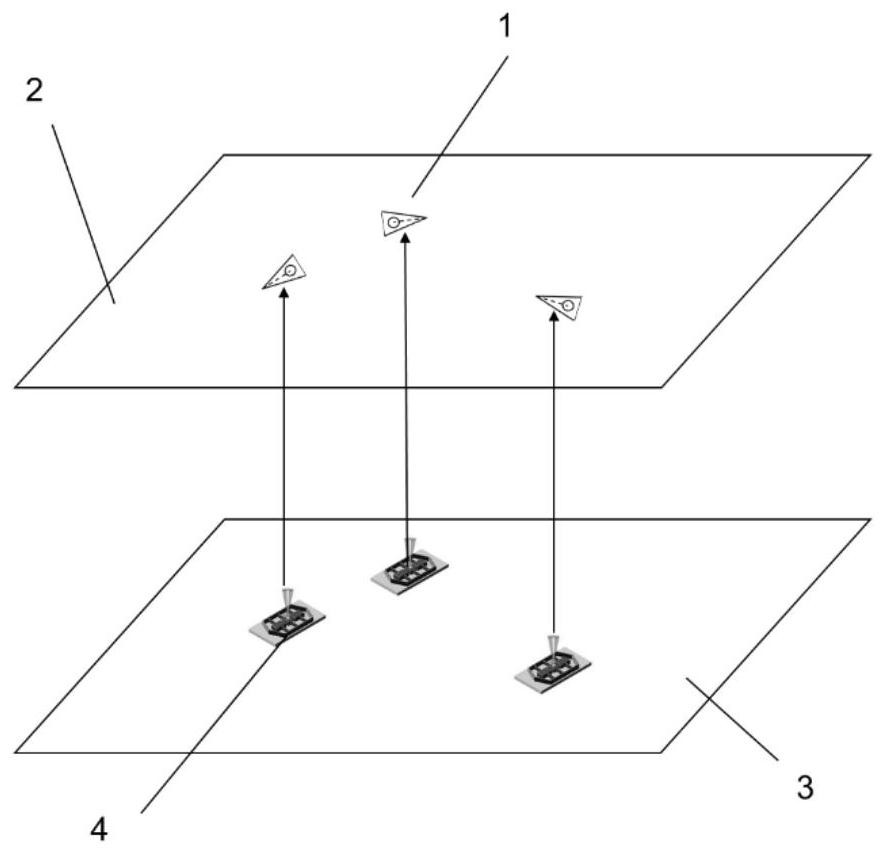
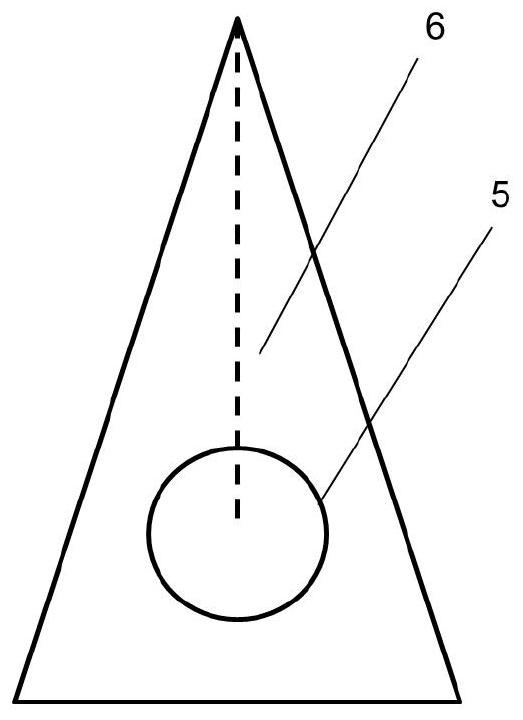
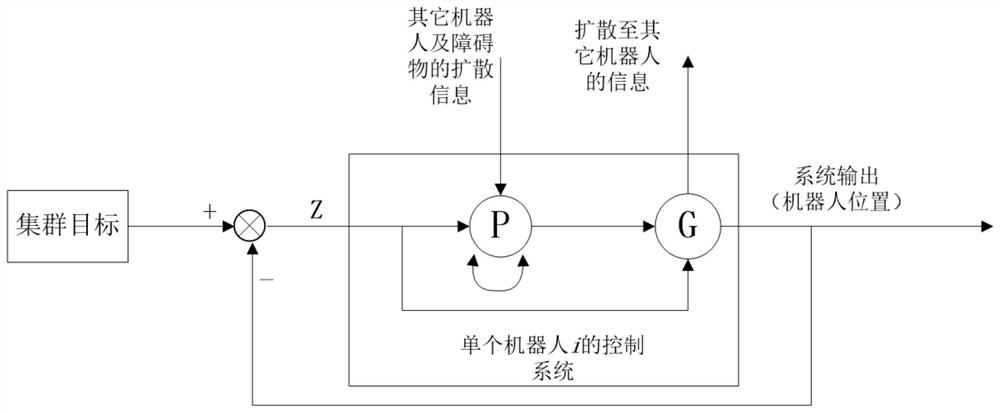
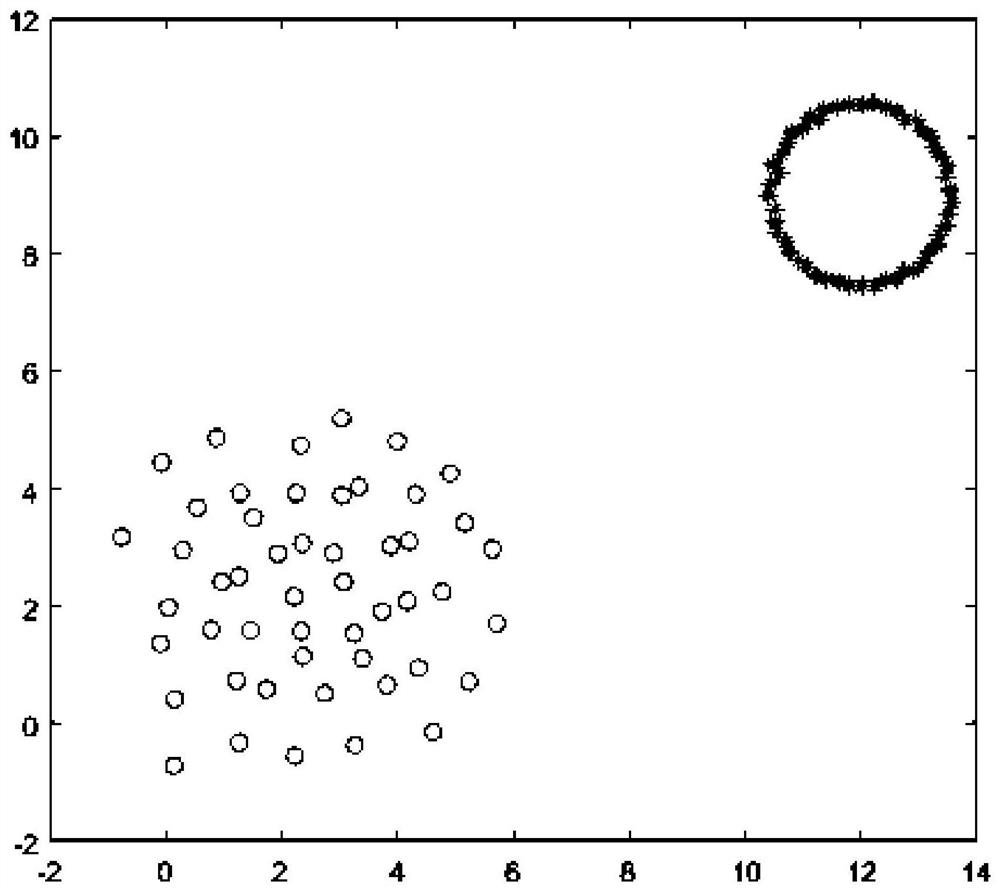
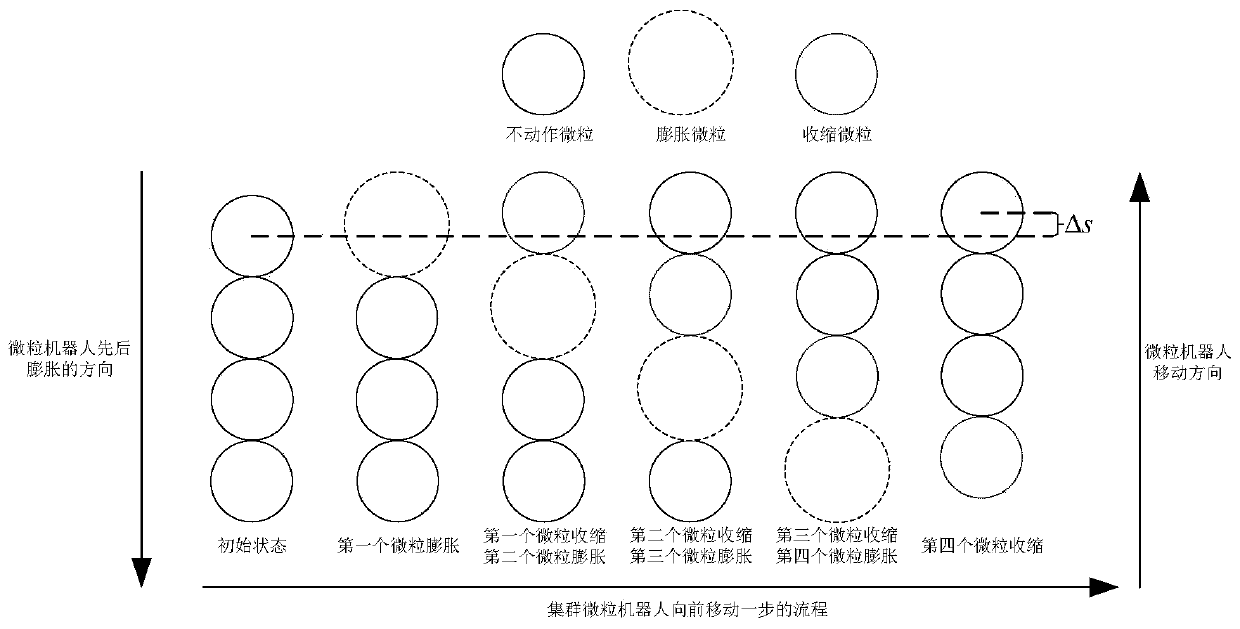
Patents
Literature
63 results about "Swarm robotics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Swarm robotics is an approach to the coordination of multiple robots as a system which consist of large numbers of mostly simple physical robots. It is supposed that a desired collective behavior emerges from the interactions between the robots and interactions of robots with the environment. This approach emerged on the field of artificial swarm intelligence, as well as the biological studies of insects, ants and other fields in nature, where swarm behaviour occurs.
iAnt swarm robotic platform and evolutionary algorithms
ActiveUS9446512B1Performance maximizationFacilitate communicationProgramme-controlled manipulatorAutonomous decision making processMutual correlationRobotic arm
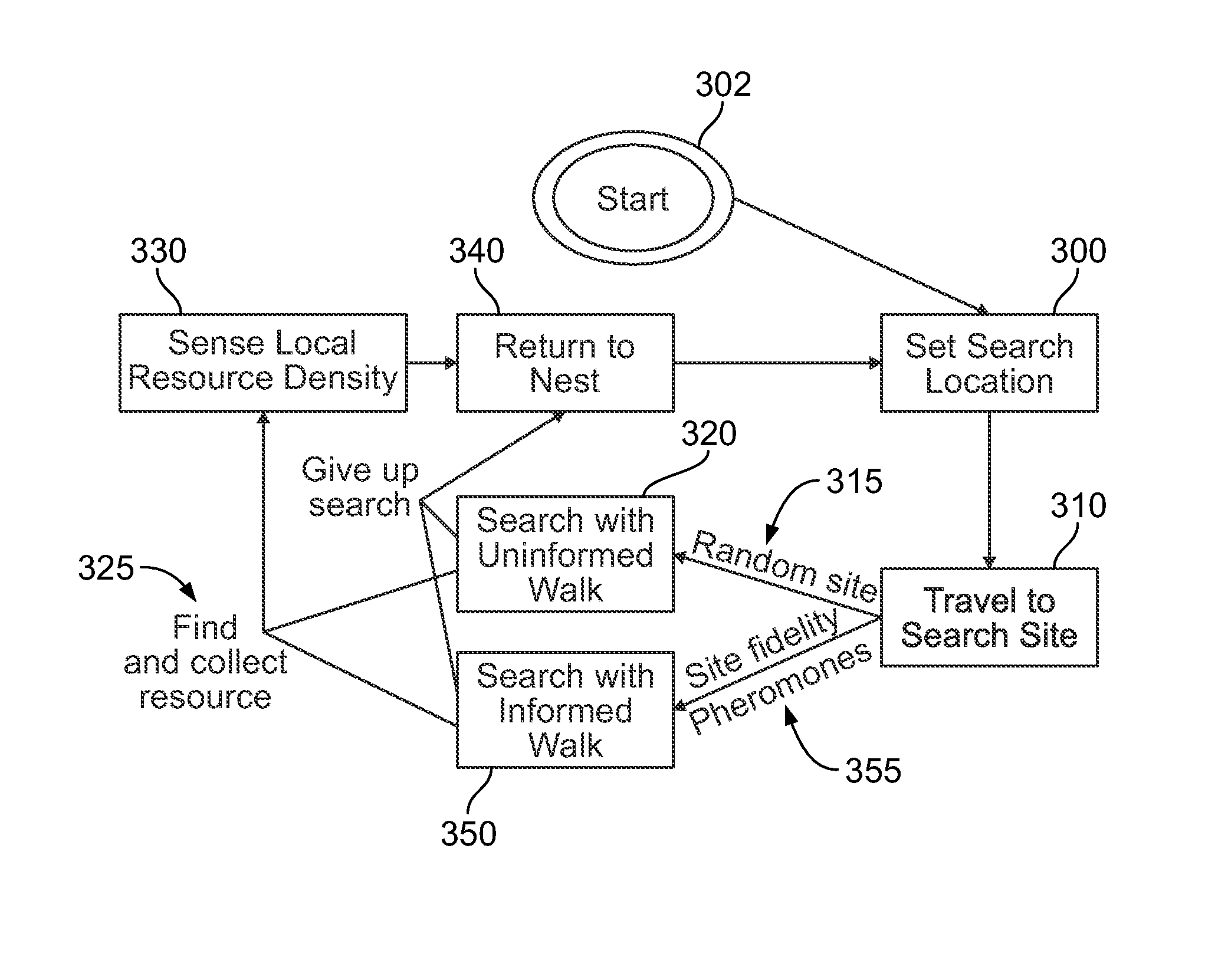
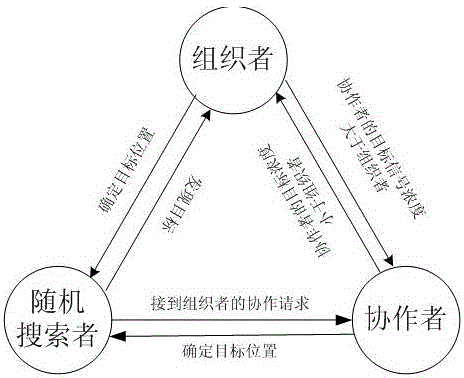
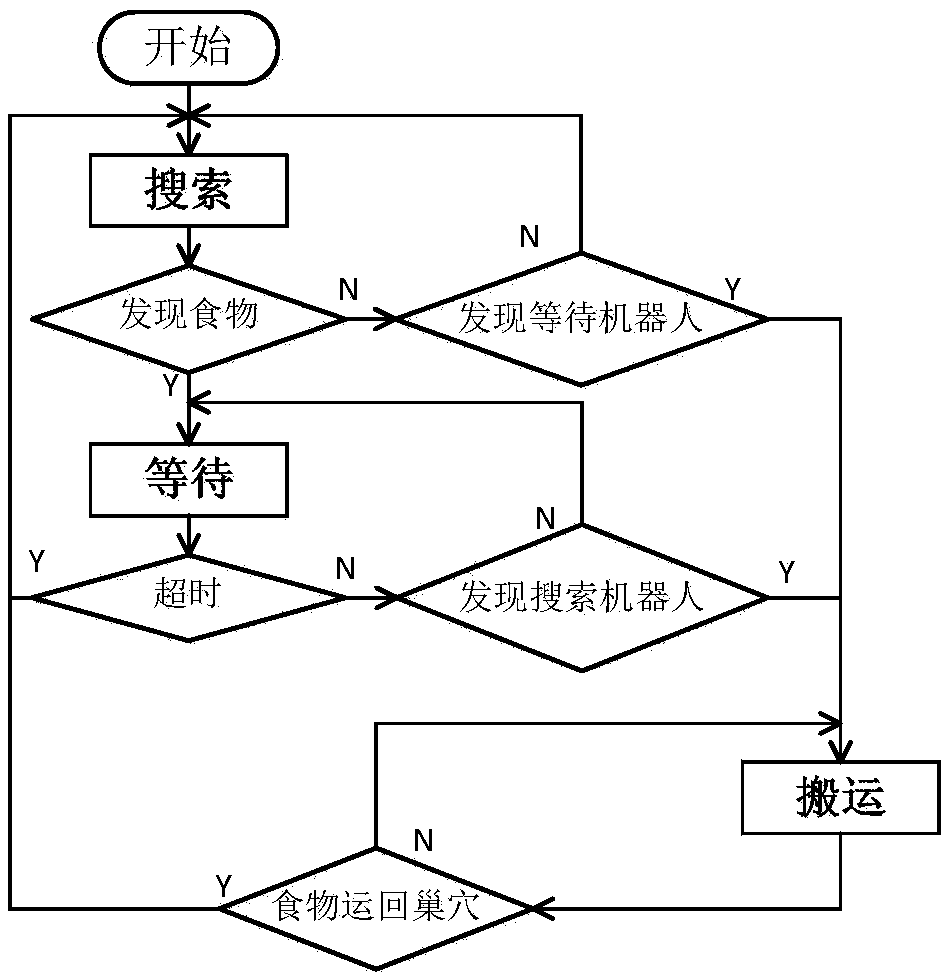
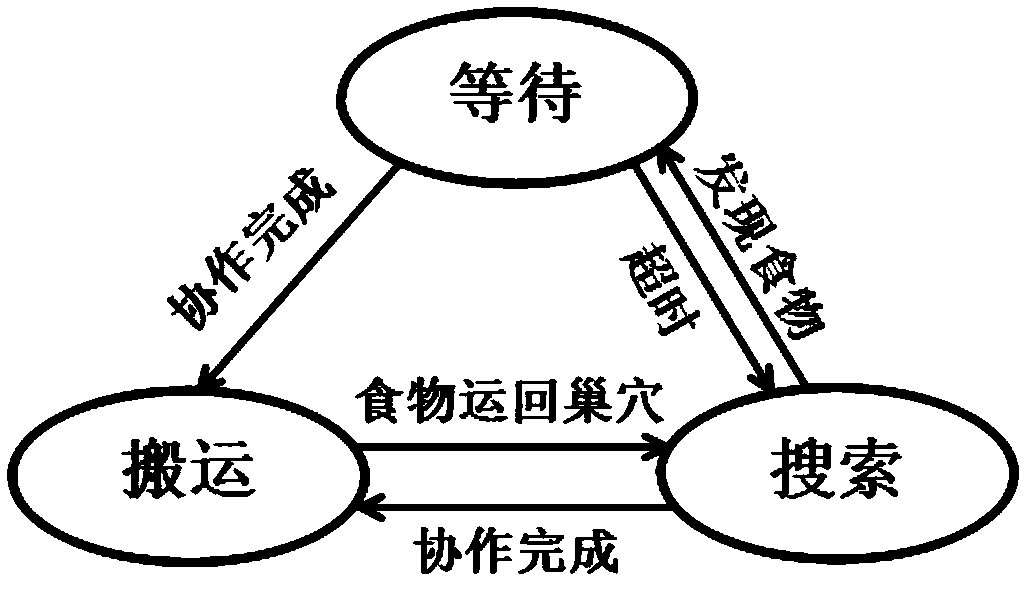
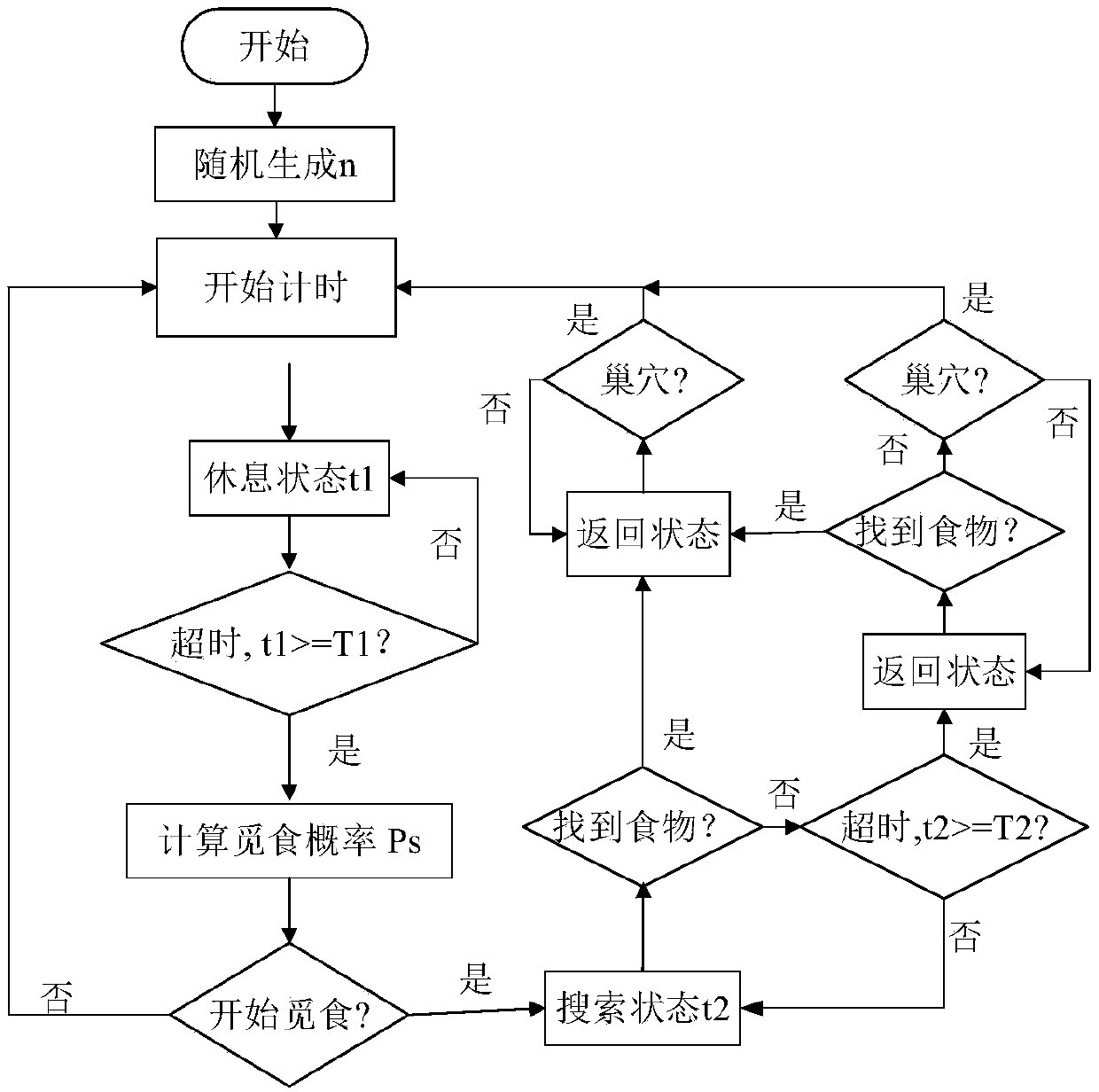
The present invention provides a swarm of robots and a related method of operating the swarm. The robots are programmed to start at a nest and to select a dispersal direction from a uniform random distribution. The robots travel along the dispersal direction until transitioning to a search mode upon reaching a search site, where the robot performs a correlated random walk with fixed step size and direction and using a standard deviation to determine how correlated the direction of the next step of the robot is with the direction of the previous step. If no resource is found within predetermined time t independently determined by each of said robots, the robot returns to the nest and repeats the above steps.
Owner:STC UNM
Group robot cooperation search method based on improved particle swarm algorithm
InactiveCN108958028AImprove convergence efficiencyImprove search efficiencyArtificial lifeAdaptive controlRobotic systemsPotential field
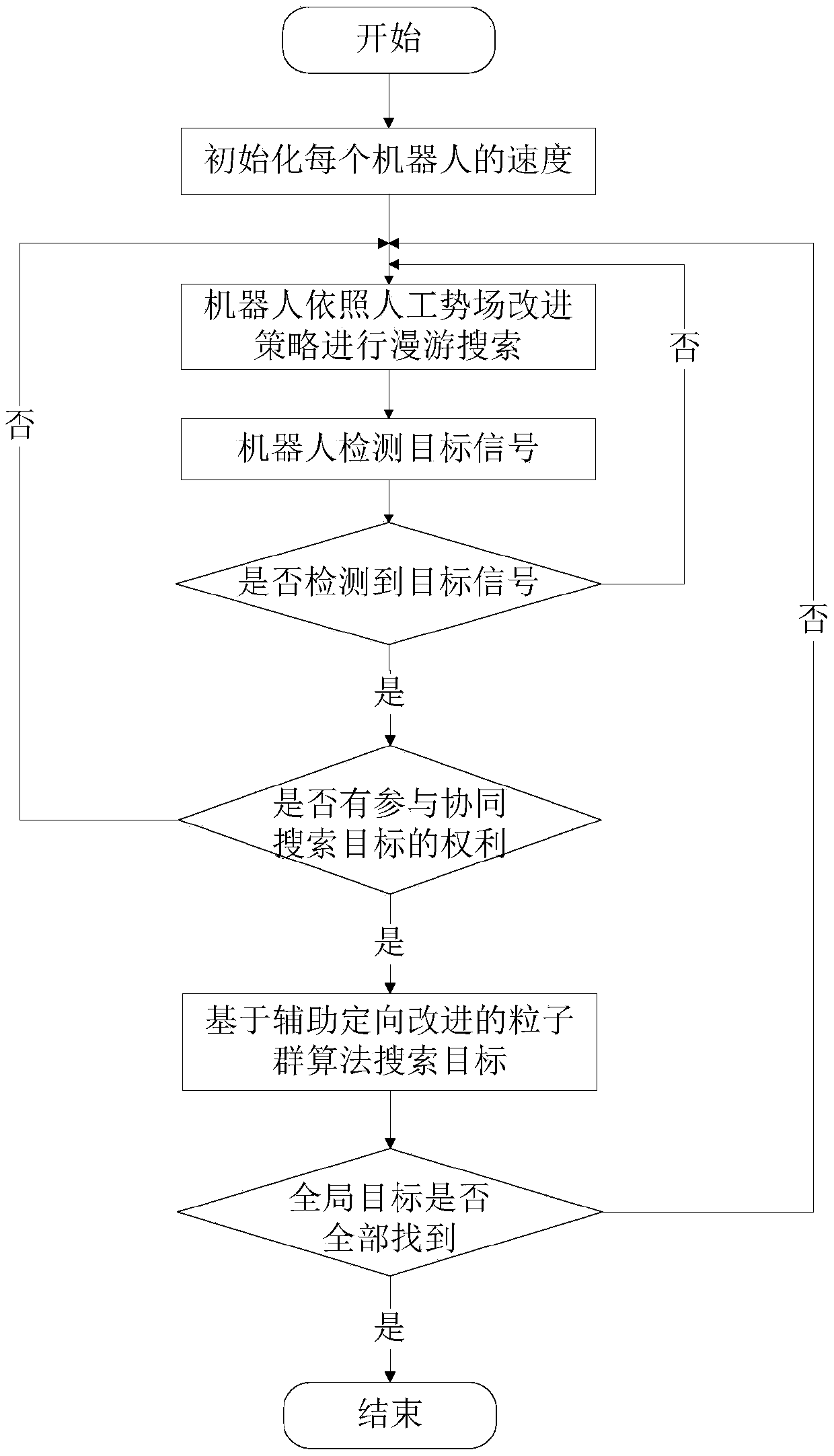
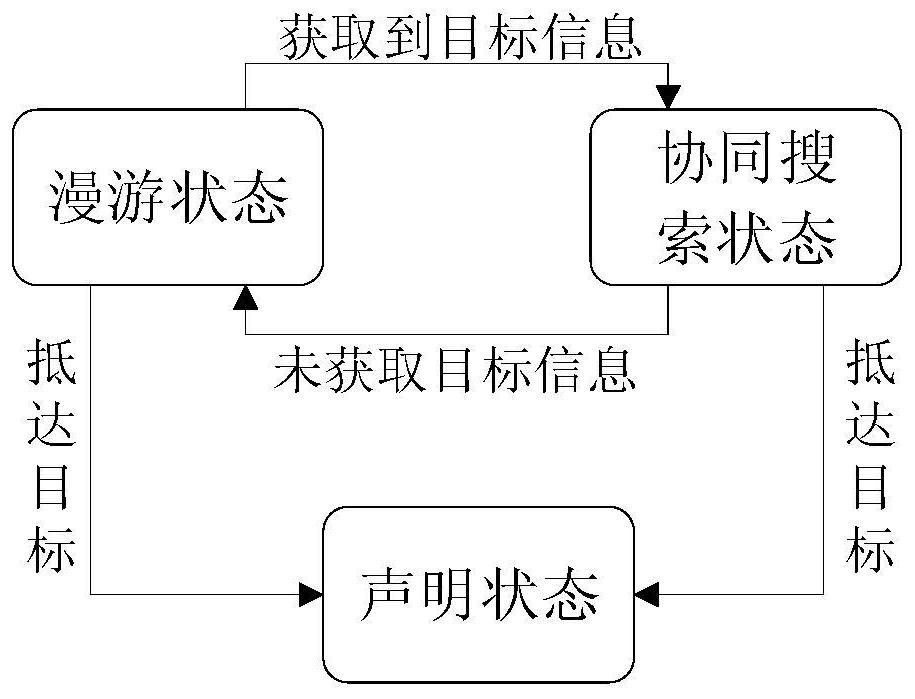
A group robot cooperation search method based on an improved particle swarm algorithm belongs to the group robot technology field and is used to improve problems that an exploration range is too concentrated and a remote area is easy to omit. The method comprises the following steps of (1) initializing a robot system state; (2) using an artificial potential field improvement strategy to carry outroaming search and obtaining the rough position of a target; (3) detecting a target signal by a robot, and then determining whether to obtain a target search right according to a result, and decidingwhether to continue the roaming search or enter a cooperation search phase; (4) adopting the improved particle swarm algorithm by a robot group searching for a same target, carrying out fine search onthe target and improving search efficiency; and (5) discovering all the targets by roaming robots, and carrying out fine positioning through the particle swarm algorithm and ending the task. In the method, the task can be effectively completed during multi-robot cooperation target search; and a PSO algorithm based on an assisted orientation technology can be used to improve the convergence efficiency of the later period of the particle swarm algorithm.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH +1
Swarm robot and sweeping method using swarm robot
ActiveUS20120158176A1Efficient collaborationImprove productivityProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlPattern recognitionEngineering
A swarm robot and a sweeping method using the swarm robot are provided. The swarm robot removes a plurality of objects in a given sweeping area, and at least two swarm robots collaborate to remove the individual object. The swarm robot searches the sweeping area, detects environment information of the sweeping area, locates the swarm robot in the sweeping area, generates a local map and an object map using the environment information and the acquired position, moves to the object according to the local map and the object map, and removes the object.
Owner:KOREA INST OF IND TECH
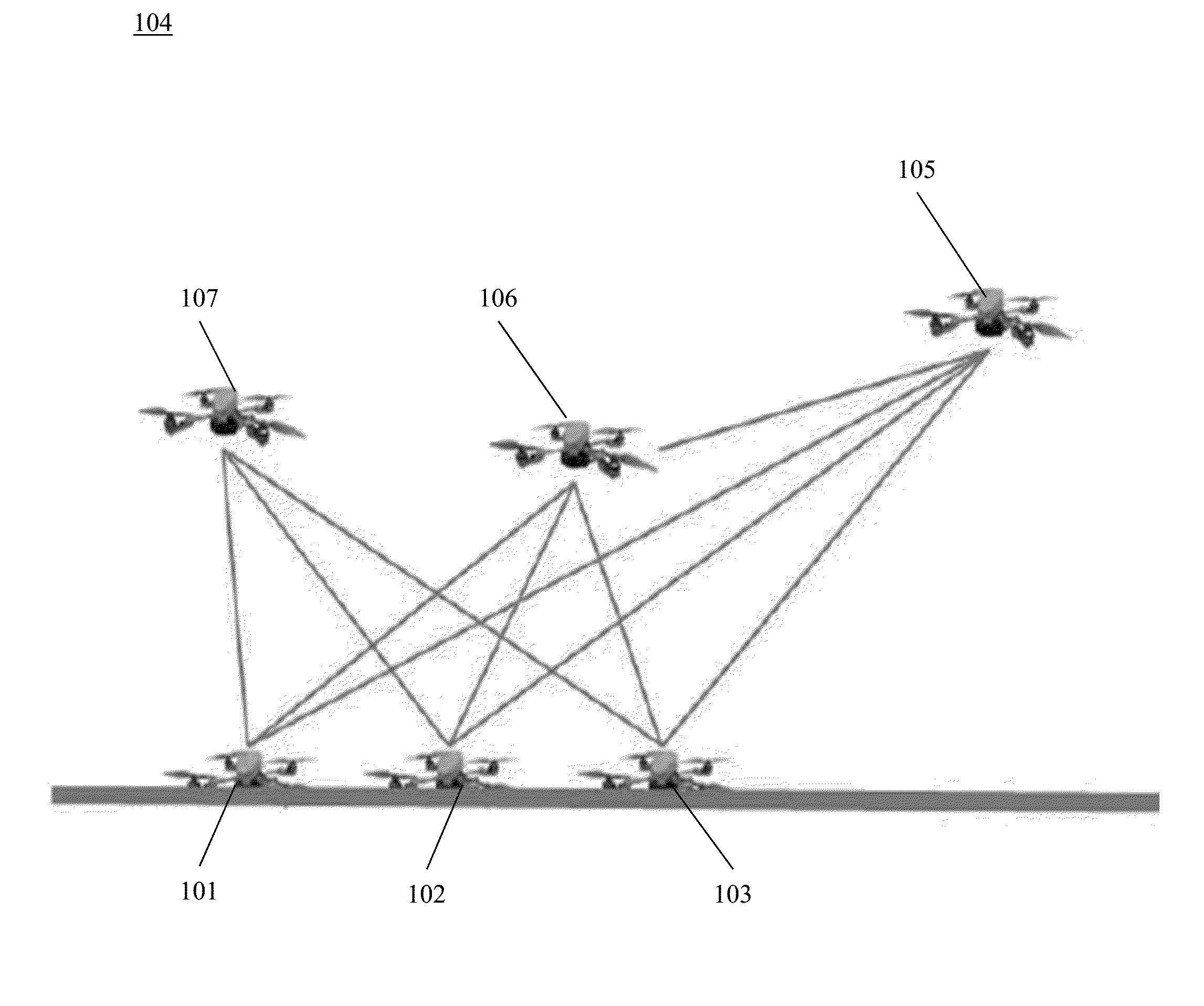
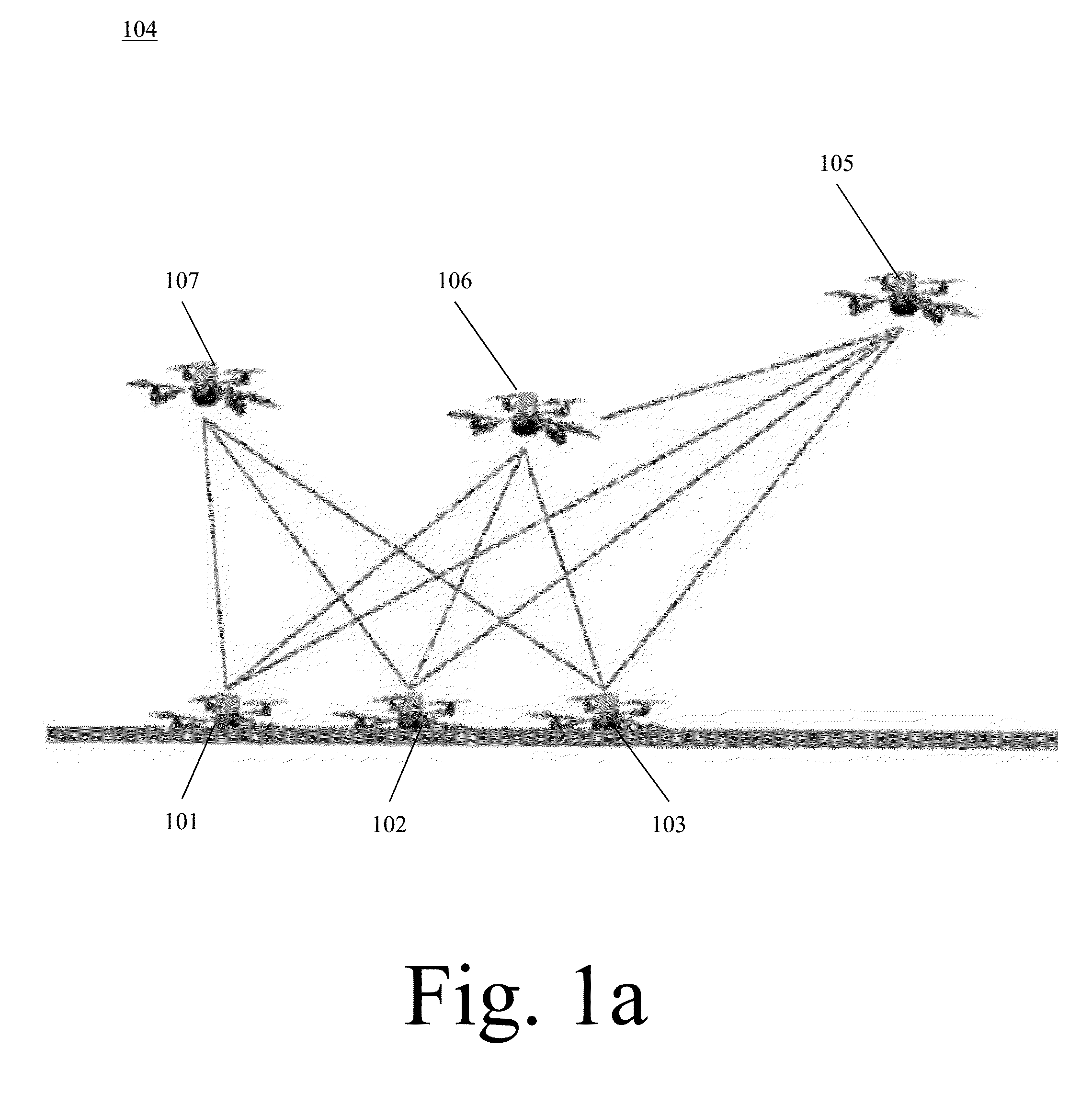
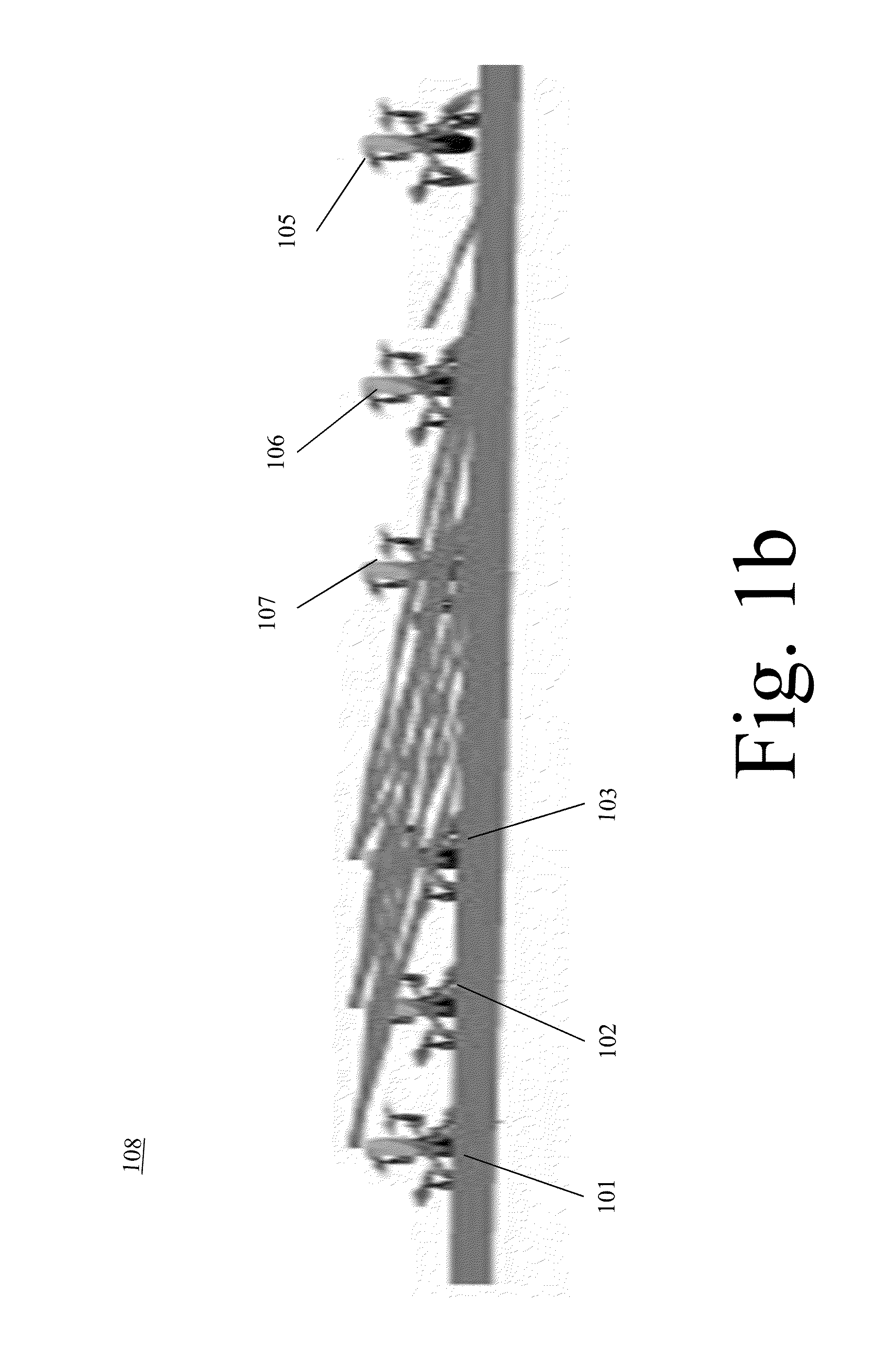
Robotic Swarm Localization Using Ranging Radios
ActiveUS20160114487A1Improve accuracyImprove localizationProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlEngineeringSwarm robotics
Owner:ROBOTIC RES OPCO LLC
Cooperative motion method for robot cluster in obstacle scene
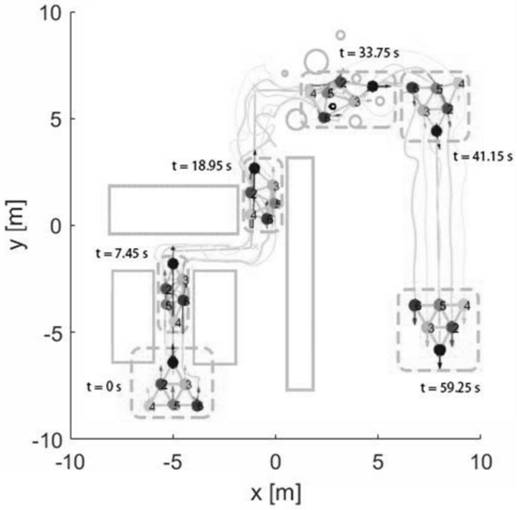
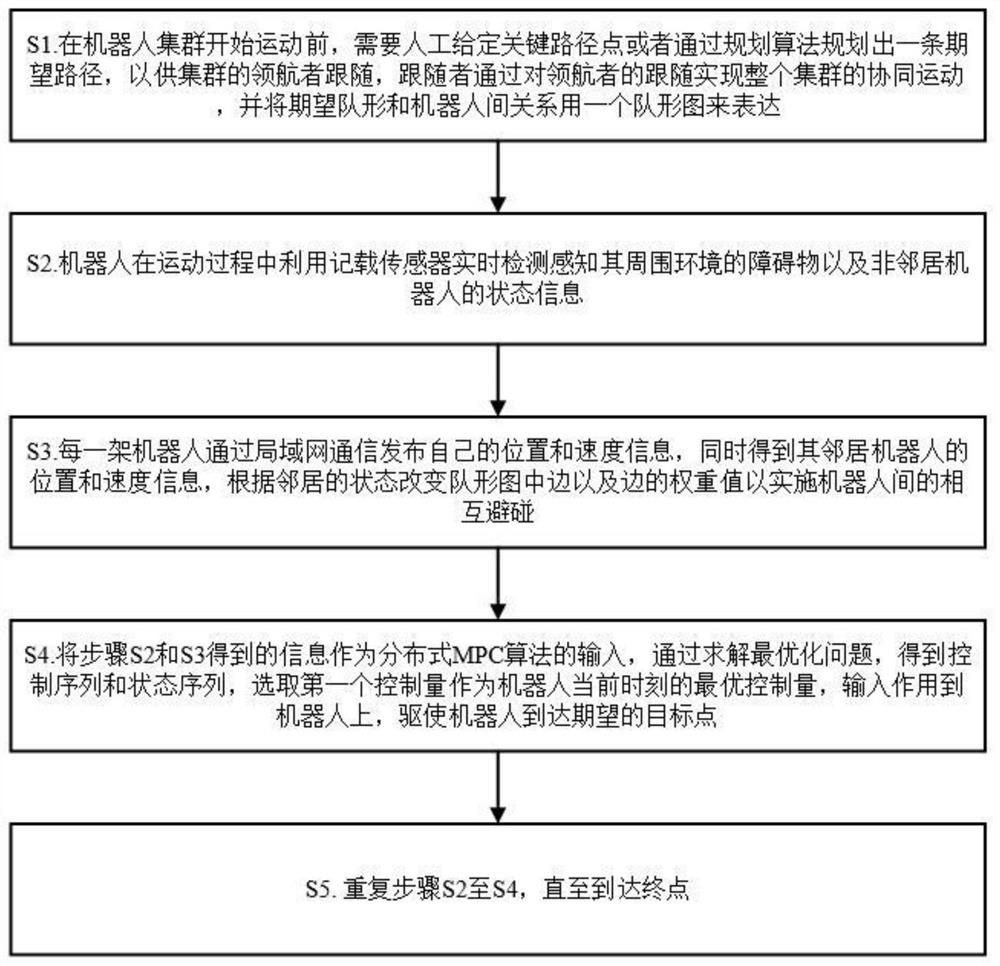
ActiveCN110162035ARealize path planningImplement navigationPosition/course control in two dimensionsCouplingObstacle avoidance
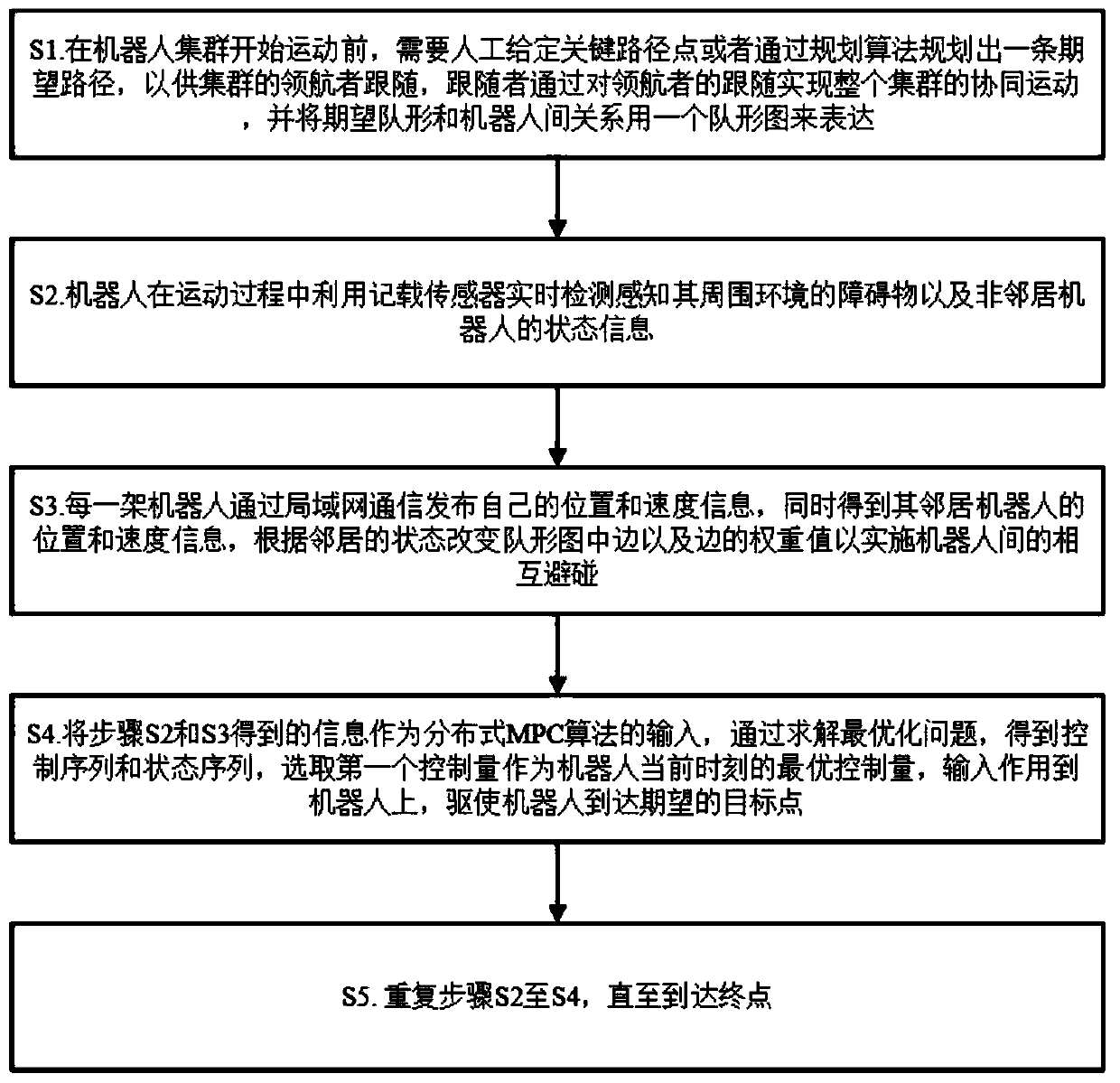
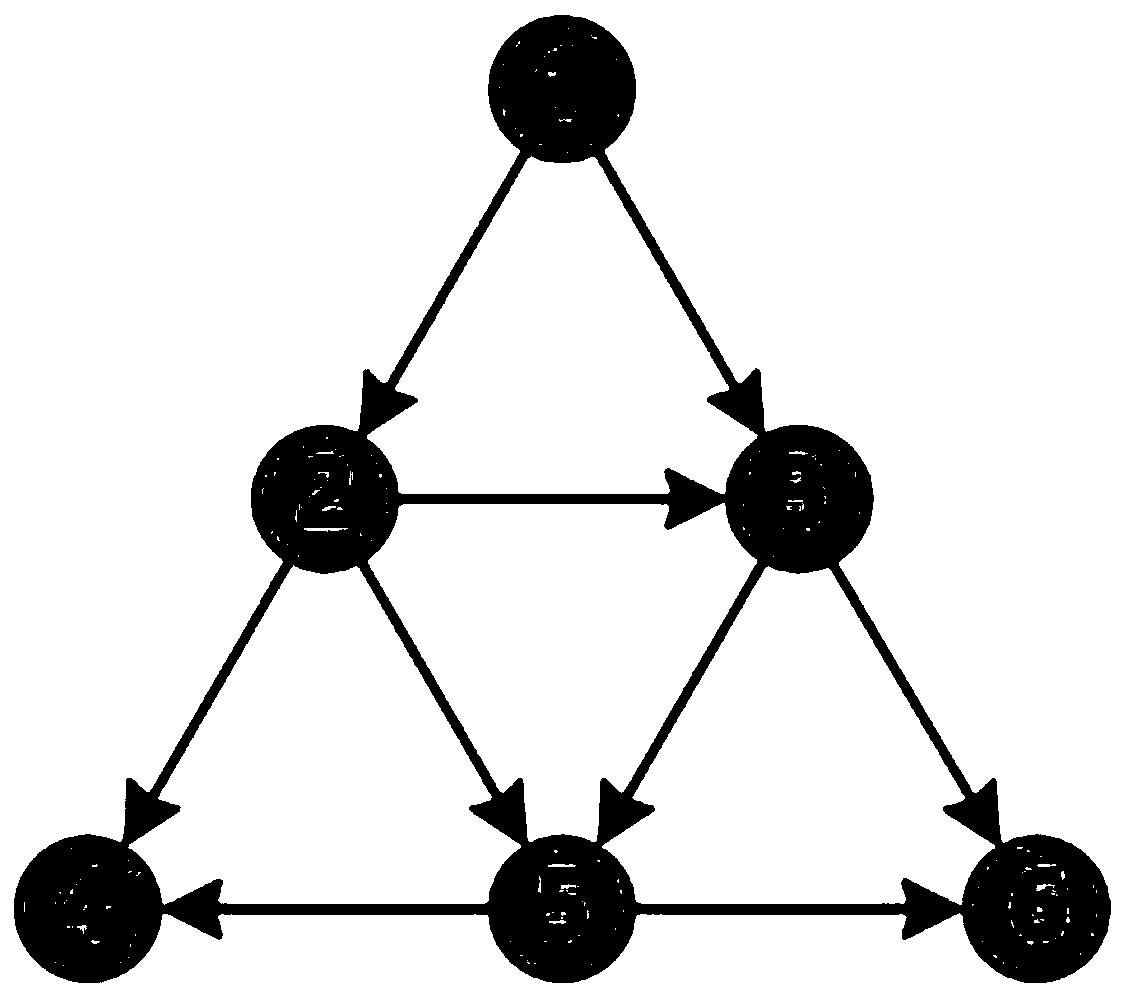
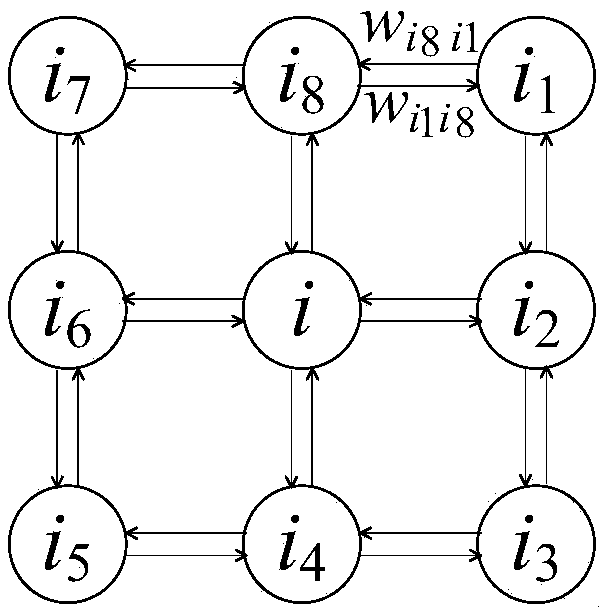
The invention relates to the technical field of robots, more particularly to a cooperative motion method for a robot cluster in an obstacle scene. The method provided by the invention is used for enabling multiple robots to realize formation transformation, dynamic and static obstacle avoidance and cooperative motion in the obstacle scene. The method defines the cooperative control of the robot cluster in a complex environment as a distributed model predictive control problem. Each robot solves an optimization equation independently based on the information of local neighbors, which has betterrobustness and flexibility. At the same time, the method proposes the concept of a formation diagram, and uses a directed diagram to represent the robot formation. Under the premise of ensuring the connectivity of the diagram, local transformation of the desired formation can be realized by changing the edges and weights of the formation, and at the same time, the connectivity and the flexibilityof the cluster can be ensured. Besides, the method provided by the invention has a hierarchical structure. By adopting the hierarchical structure, the coupling between modules can be reduced, and algorithm design and expansion can be facilitated.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
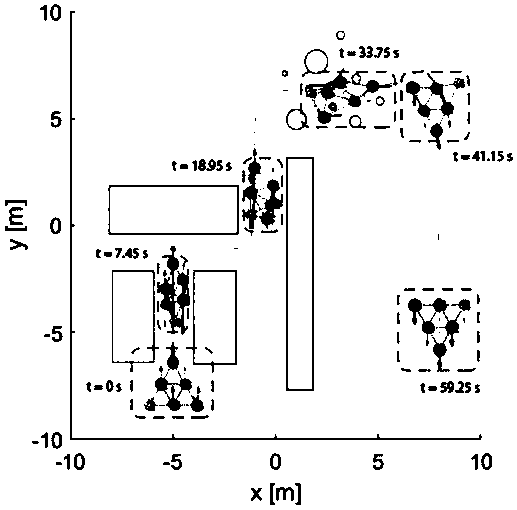
Distributed multi-target tracking method for swarm robots on the basis of PHD (Probability Hypothesis Density) filtering
InactiveCN109298725AAvoiding Measurement-Status Data Correlation ProblemsImprove tracking accuracyNavigational calculation instrumentsTarget-seeking controlVisual field lossHypothesis
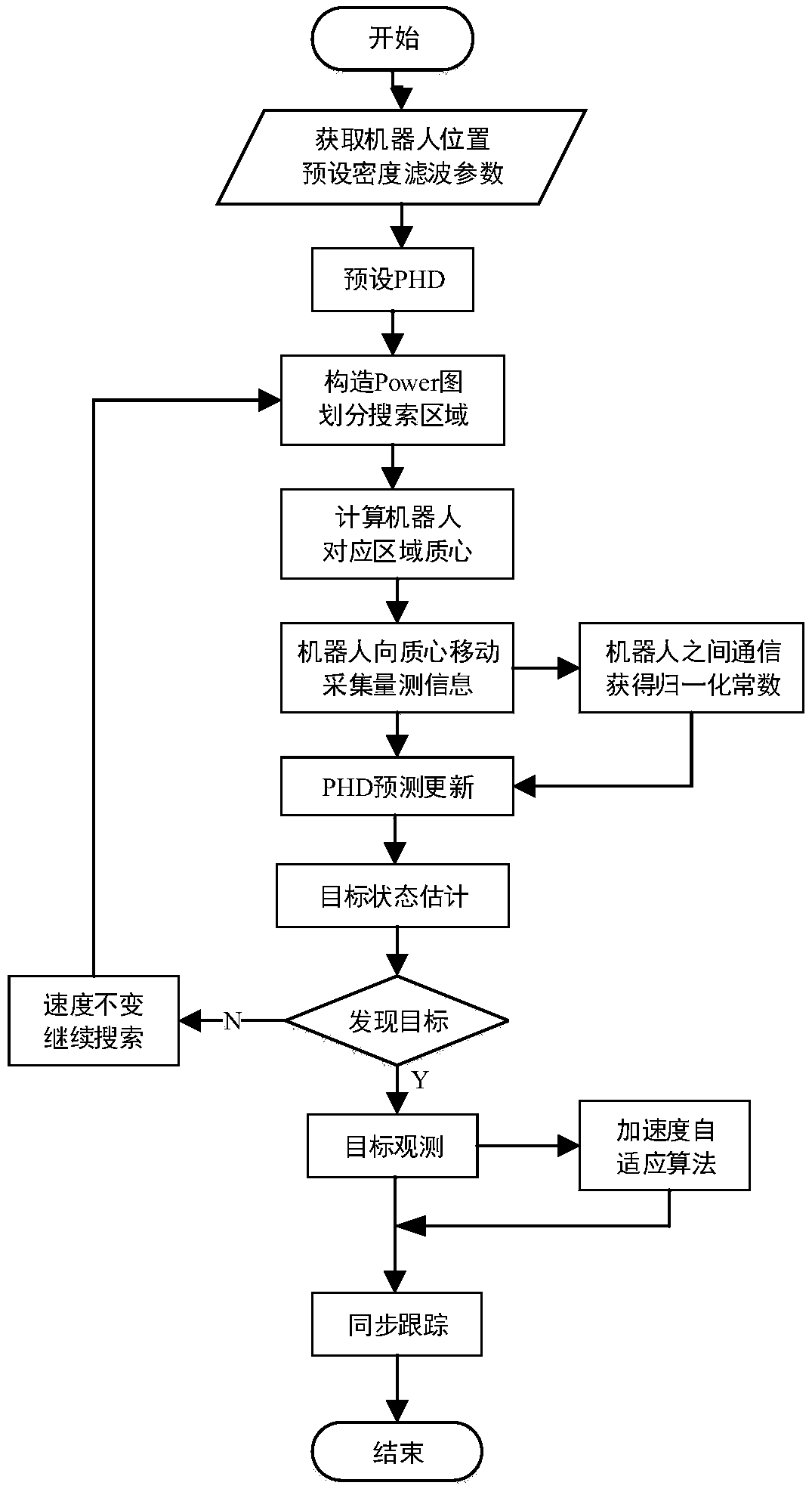
The invention relates to a distributed multi-target tracking method for swarm robots on the basis of PHD (Probability Hypothesis Density) filtering. The method comprises the following steps that: S1:under an initial state, swarm robots are randomly distributed in a given constrained boundary, a Power graph is constructed according to the position coordinates and the weights of multiple robots, and a search area is divided; S2: the weighted centroid of a Power unit corresponding to each robot is solved; S3: all robots begin to move to corresponding hi(0) from a current position X, relevant measurement information is collected, and a normalization constant is calculated to update the Power graph; S4: according to measurement data, the PHD is updated, new PHD is taken as weight, and S2 is executed to obtain a new centroid position coordinate; S5: S3 and S4 are repeated until a target is in the presence in the visual field of the robot; and S6: after the robot finds the target, the movement state of the target is observed, and a function relationship between current radar measurement information and acceleration is used for estimating an acceleration disturbance quantity in real time,acceleration variance adaption regulation is carried out, and the target is kept at synchronous tracking.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
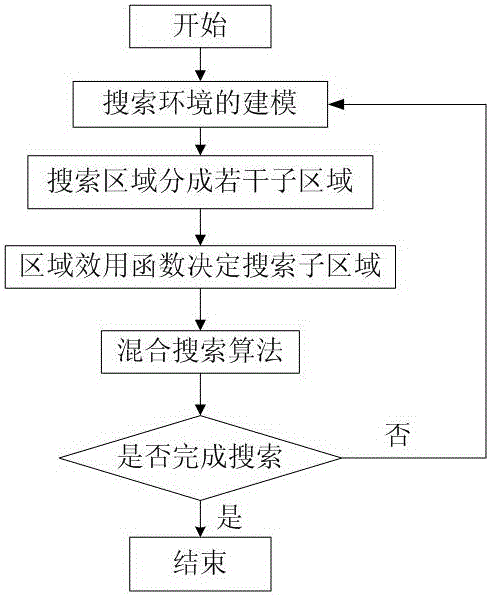
Swarm-robot mixed search method based on biological foraging behavior
The invention provides a swarm-robot mixed search method based on a biological feeding behavior and belongs to the technical field of robots. The invention aims at providing the swarm-robot mixed search method based on the biological feeding behavior, which utilizes swarm robots to search a target and promotes a swarm self-organization principle and cooperative behavior emerging principle. The swarm-robot mixed search method comprises the following steps: modeling a search environment by adopting a grid method; dividing a search region into a plurality of sub-regions and arranging a search sequence of each sub-region; and searching by adopting a mixed search method. According to the swarm-robot mixed search method, the robots are used for replacing people to finish a lot of work, such as searching of survivors of disasters including mine clearance and explosive handling, space detection and earthquakes, and mining accident searching and rescuing and so on.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Neural network-based method for swarm robots to realize cooperative foraging through using pheromone-based communication
ActiveCN109270905AReduce transmissionPromote evolutionTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlNerve networkWorking environment
The invention relates to a neural network-based method for swarm robots to realize cooperative foraging through using pheromone-based communication. The method includes the following steps that: a neural network model is established; a pheromone volatilization model is designed; and a system overall behavior framework model is established. According to the method of the invention, the pheromone volatilization model of swarm robot cooperative foraging behaviors is put forward and is defined as Ii(t), that is, the external input of an i-th neuron at a time t, and in the formula, an attracting pheromone Pa has a large positive value, a repulsion pheromone Po and a repulsion pheromone Pe have small negative values; when a foraging robot finds food and transports the food back to a nest, the foraging robot releases the attracting pheromone Pa; when the robot avoids an obstacle, the robot releases the repulsion pheromone Po; when the robot searches for food randomly in a working environment,the robot releases the repulsion pheromone Pe; the neural network updates output at any time according to the change of the Ii(t); and the evolution of the neural network enables the swarm robots tocommunicate locally, and witness self-organized group behaviors during an interaction process.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
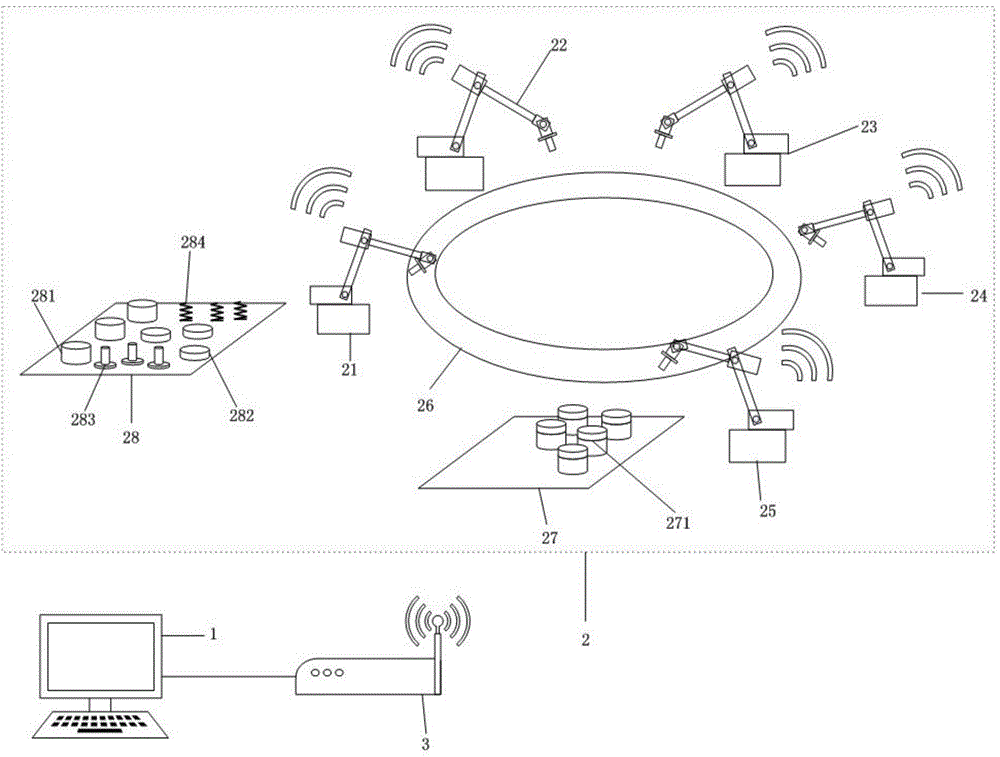
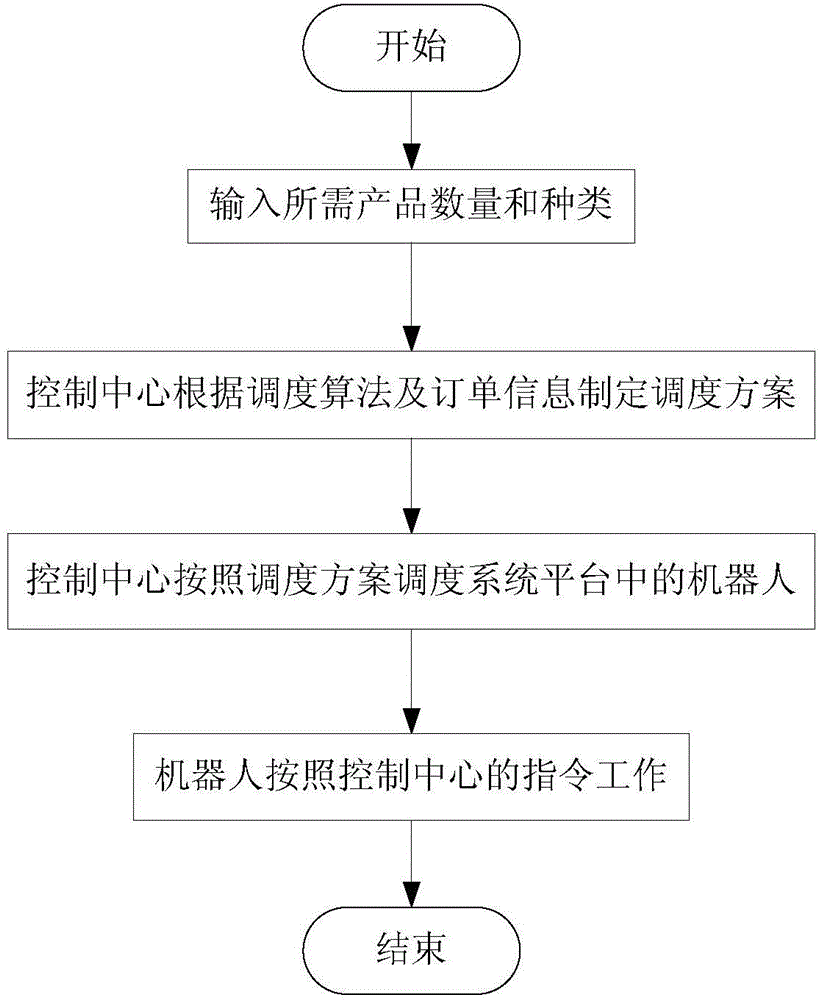
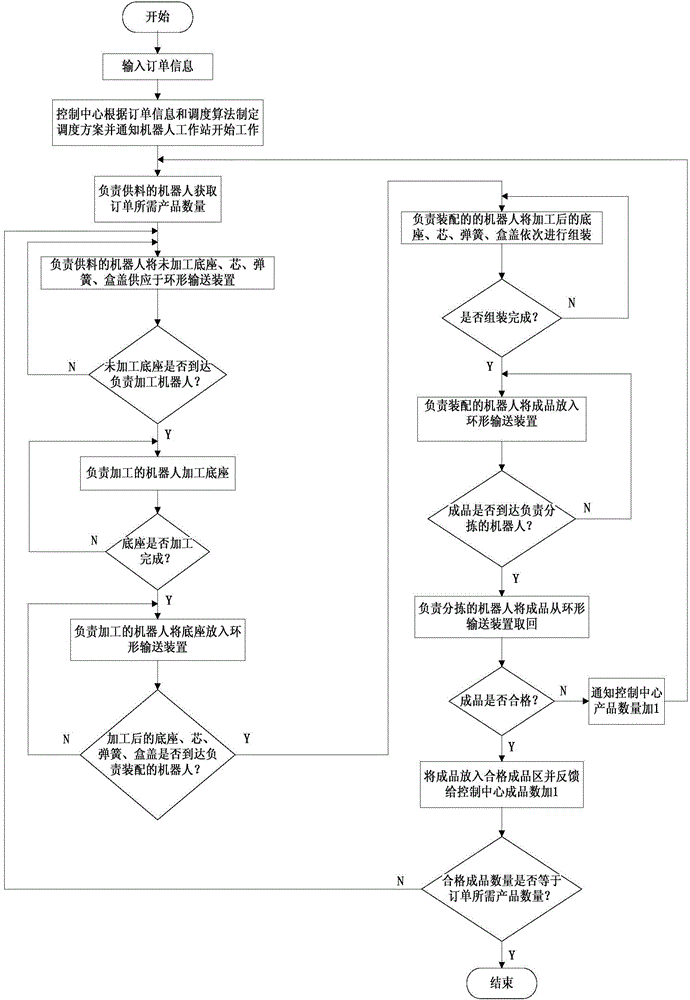
Swarm robot collaborative scheduling measurement and control method and system platform
The invention discloses a swarm robot collaborative scheduling measurement and control method and system platform. The platform comprises a control center, a robot workstation and a wireless module for realizing wireless communication between the control center and the robot workstation, wherein the control center formulates corresponding scheduling plans according to a scheduling algorithm and types and numbers of products in order information, and all intelligent robots are scheduled by the aid of a discrete event queuing theory and WiFi wireless network communication; the swarm robots finish assembly of the products according to the scheduling plans. The number of the intelligent robots and the rotating speed of a circular conveying device can be adjusted according to actual requirements, lines can be changed conveniently at any time, and flexible and elastic production is really realized; besides, the platform adopts a circular conveying mode and is small in occupied space, simple to control, high in practicability, high in cost performance and high in expansibility.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
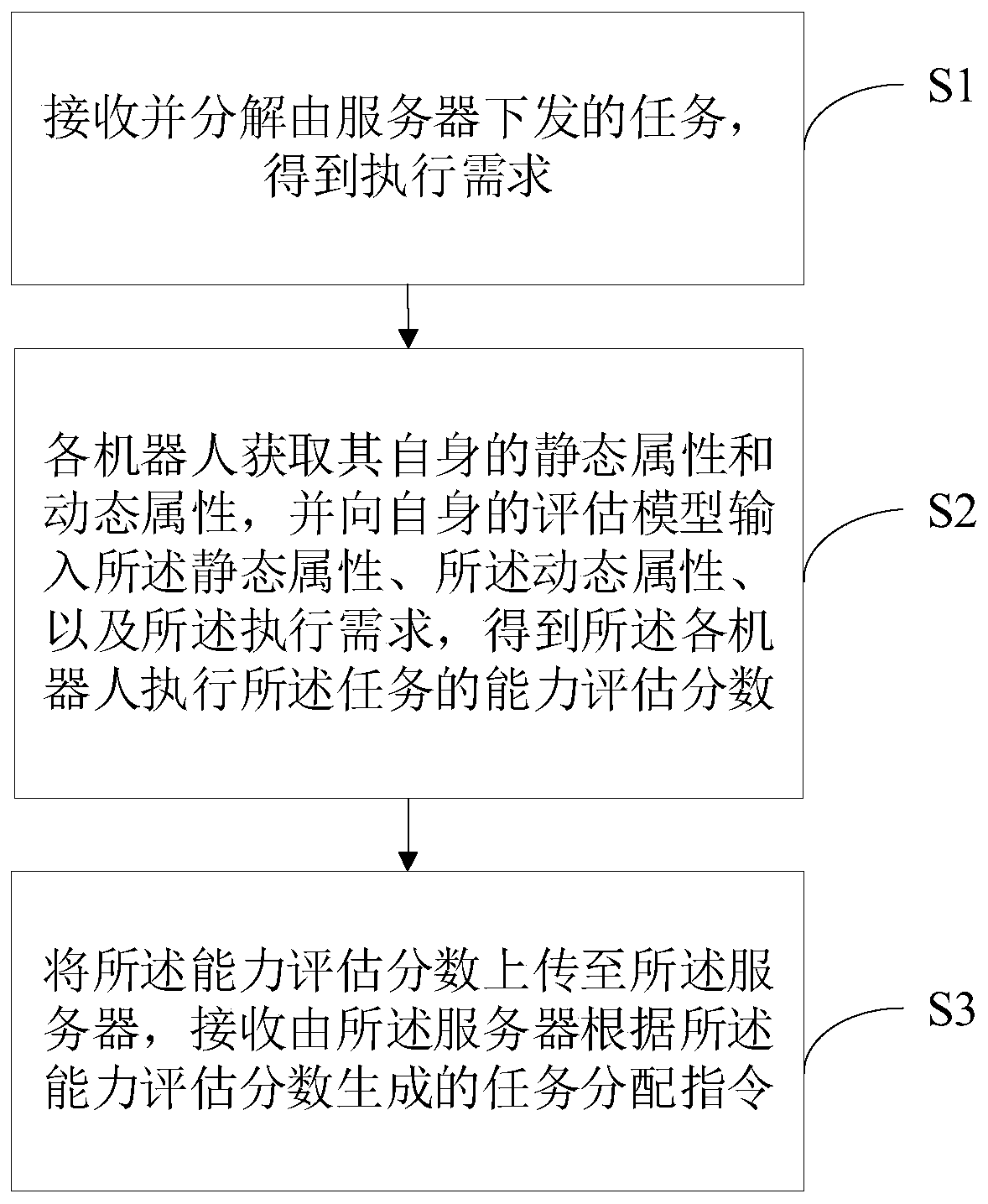
Cluster robot scheduling method, device, system and equipment and computer readable storage medium
ActiveCN111079990AImprove healthImprove timelinessForecastingResourcesSwarm roboticsReal-time computing
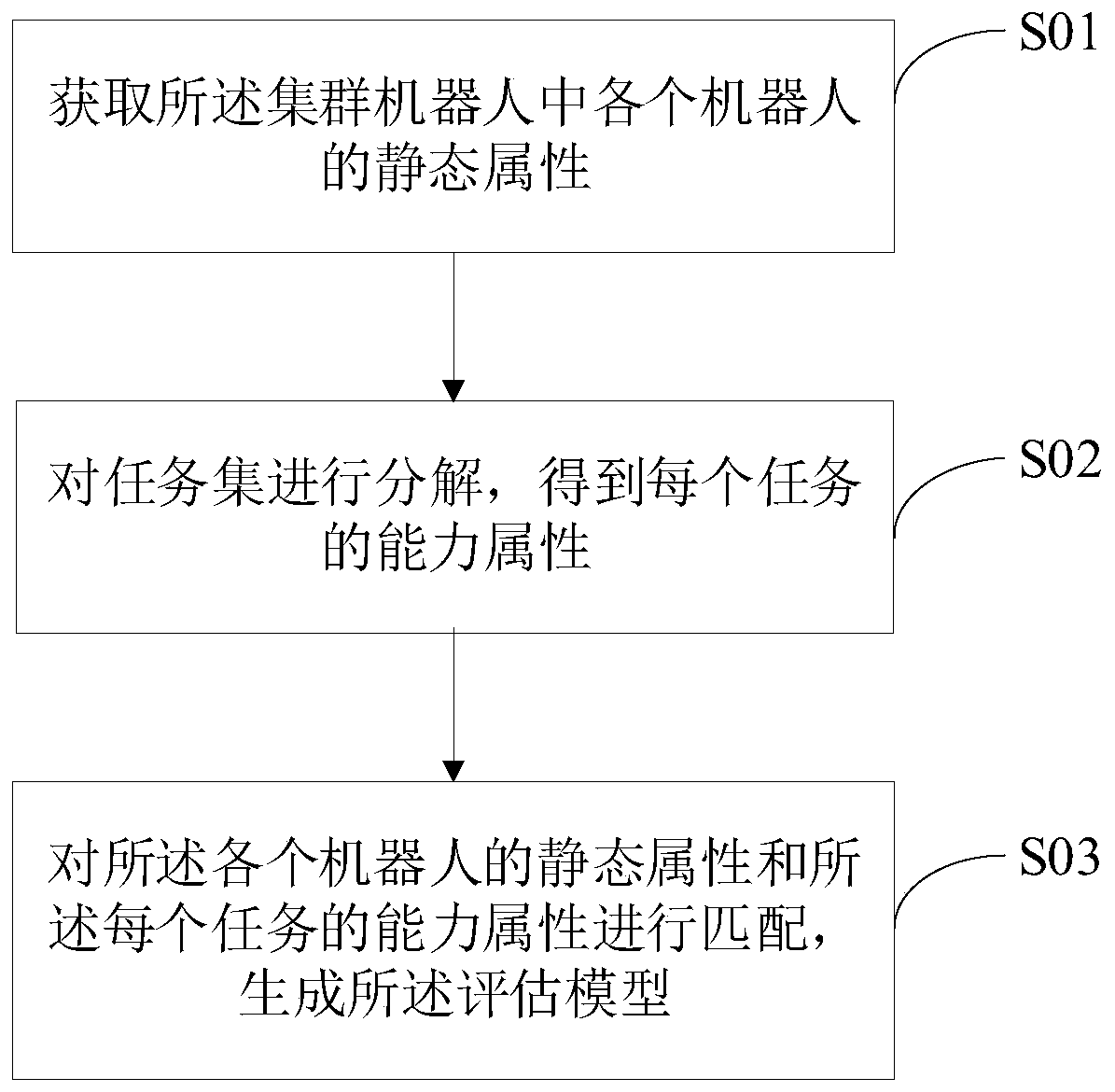
The invention discloses a cluster robot scheduling method, device, system and equipment and a computer readable storage medium. The method comprises the steps: receiving and decomposing a task issuedby a server, and obtaining an execution demand; then, each robot obtains a static attribute and a dynamic attribute of the robot, and inputs the static attribute, the dynamic attribute and the execution demand to an evaluation model of the robot to obtain a capability evaluation score of each robot for executing the task; and uploading the capability evaluation score to the server, and receiving atask allocation instruction generated by the server according to the capability evaluation score. According to the invention, a cluster robot scheduling scheme with high timeliness and accuracy is realized, task scheduling is more reasonable, task execution time is saved, and the overall health degree of the robot is improved.
Owner:JUXING TECH SHENZHEN CO LTD
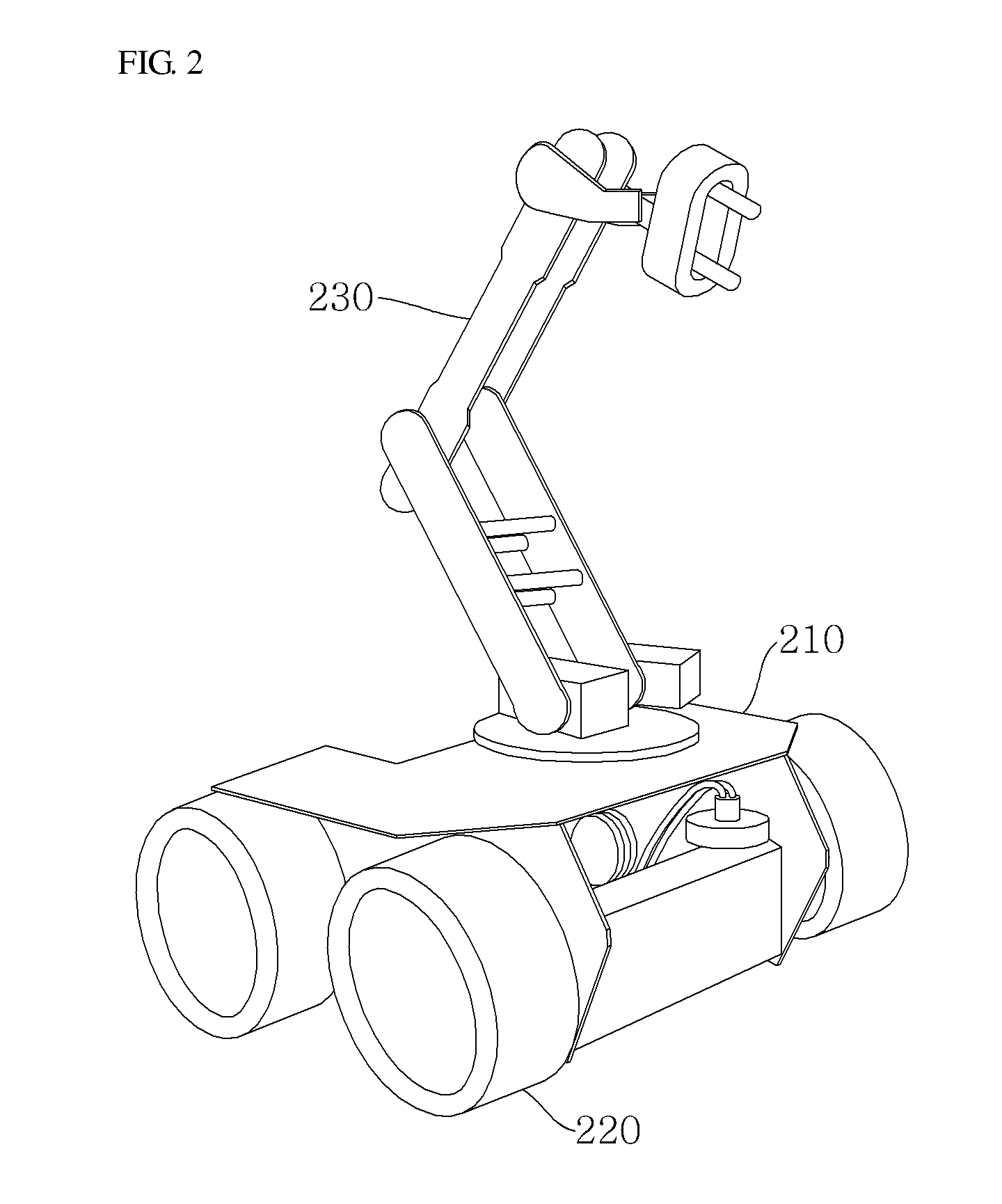
Microrobot and swarm robot system
ActiveCN107175649AStable chargingStable power supplyProgramme-controlled manipulatorMicromanipulatorElectricityCoil array
The invention relates to a microrobot and a swarm robot system comprising multiple microrobots. The swarm robot system comprises multiple microrobot monomers with the same structures, and a test platform for test activities and charging of the multiple microrobot monomers; and the test platform is provided with a platform body, and a wireless charge emitting coil array arranged on the lower surface of the platform body. Each microrobot is provided with a driving part for driving the robot monomers to move; a control part for controlling interaction behaviors of the robot monomers and comprising an upper circuit board, a middle circuit board, two side circuit boards and a lower circuit board arranged in sequence from top to bottom and in mutual circuit connection; and a power supply part for supplying electricity to the driving part and the control part and comprising a battery and a wireless charge coil matched with the wireless charge emitting coil array. The microrobot and the swarm robot system have the characteristics of convenience in movement, delicate structure and stable charge.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
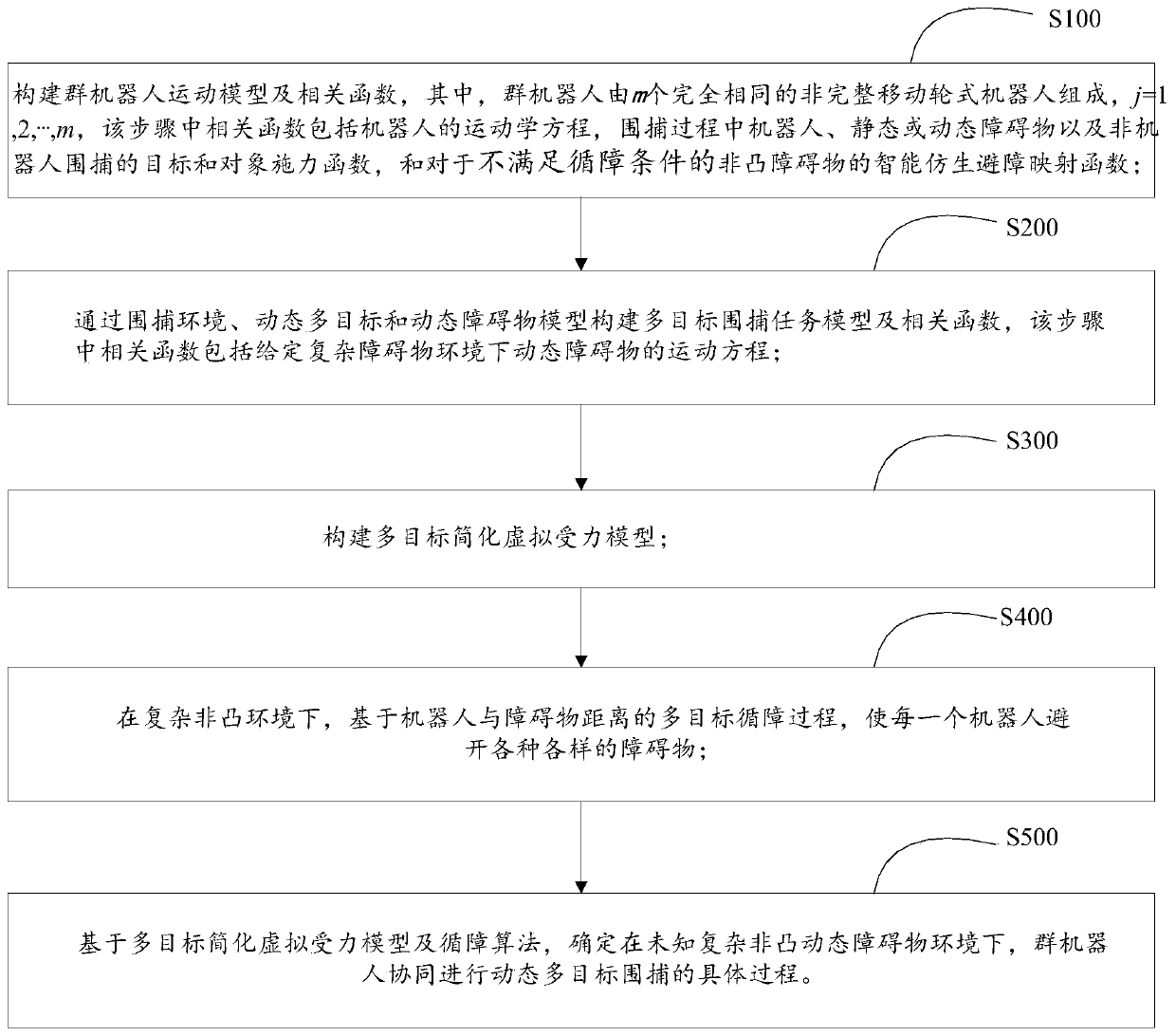
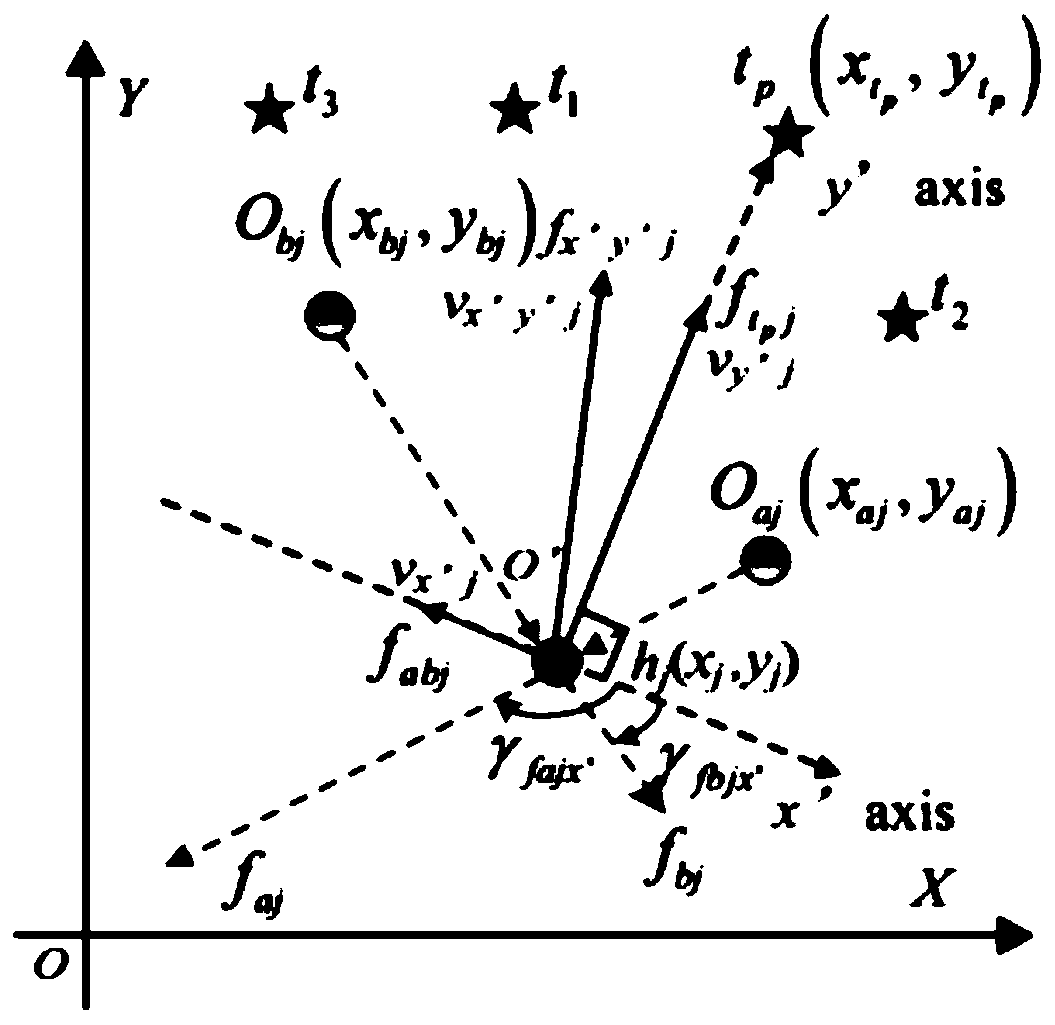
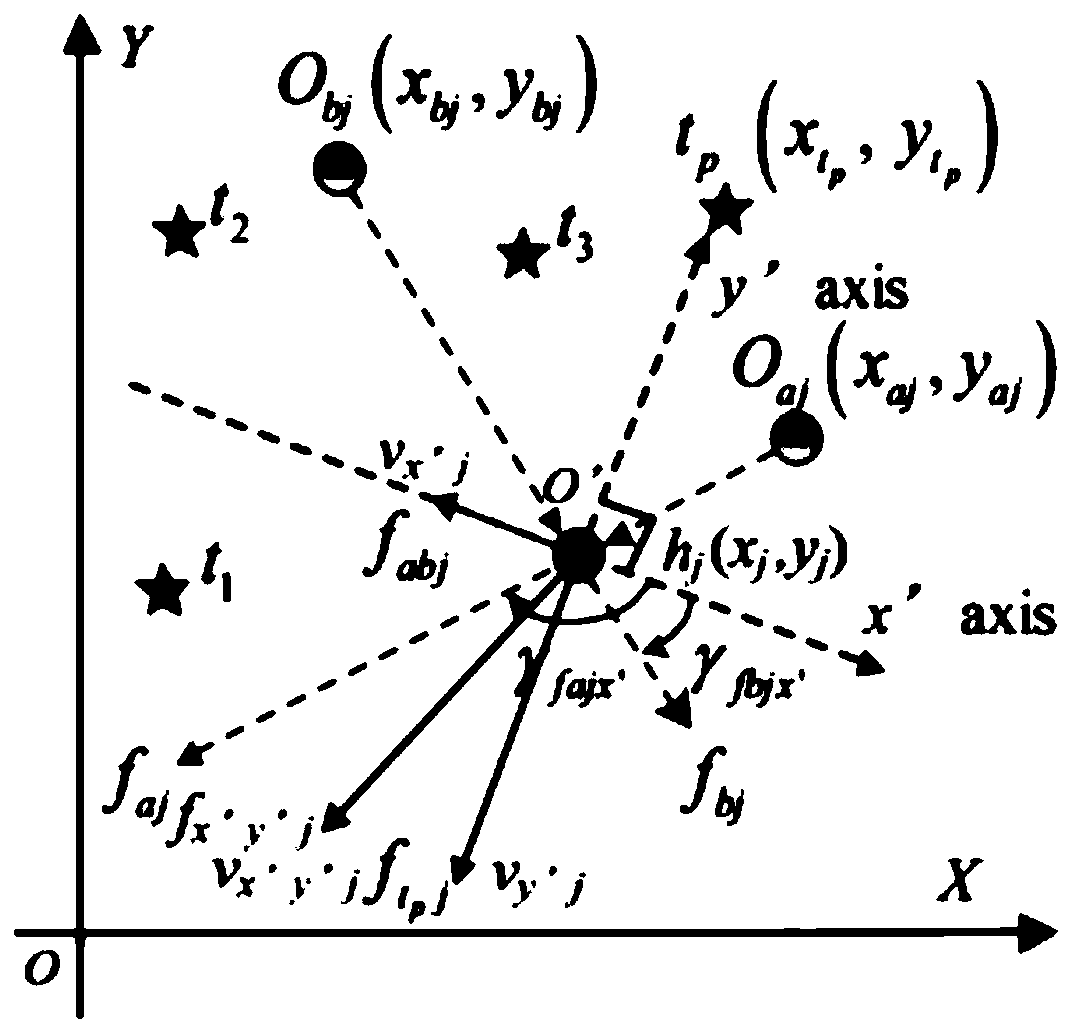
Multi-target capturing method for cooperative operation of swarm robots in complex non-convex environment
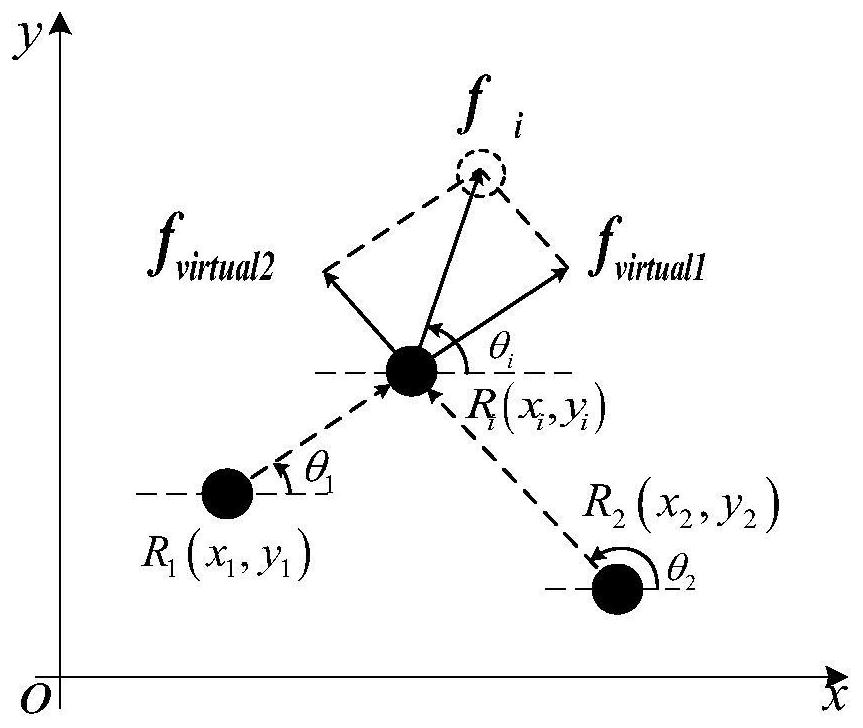
The invention discloses a multi-target capturing method for cooperative operation of swarm robots in a complex non-convex environment. Firstly, a motion model of multiple targets and dynamic obstaclesin a complex non-convex environment is designed; then, the capturing behavior under the complex environment is studied; a multi-target simplified virtual stress model is constructed; based on the stress model, a dynamic multi-target self-organizing task allocation method and a specific process of collaborative self-organizing dynamic multi-target capturing are provided. According to the process multi-target task self-organizing allocation method, one target can be allocated to each robot only based on the two nearest neighbor task information; and then, in a complex non-convex environment, each robot can avoid various obstacles through a multi-target obstacle tracking algorithm based on the distance between the robot and the obstacle, calculation is simple and efficient, implementation iseasy, and the whole method process has good obstacle avoidance performance, robustness, expandability and flexibility.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Swarm robot multi-target searching method in unknown environment
ActiveCN112405547AImprove the efficiency of multi-objective searchShorten the pathProgramme-controlled manipulatorTarget signalObstacle avoidance
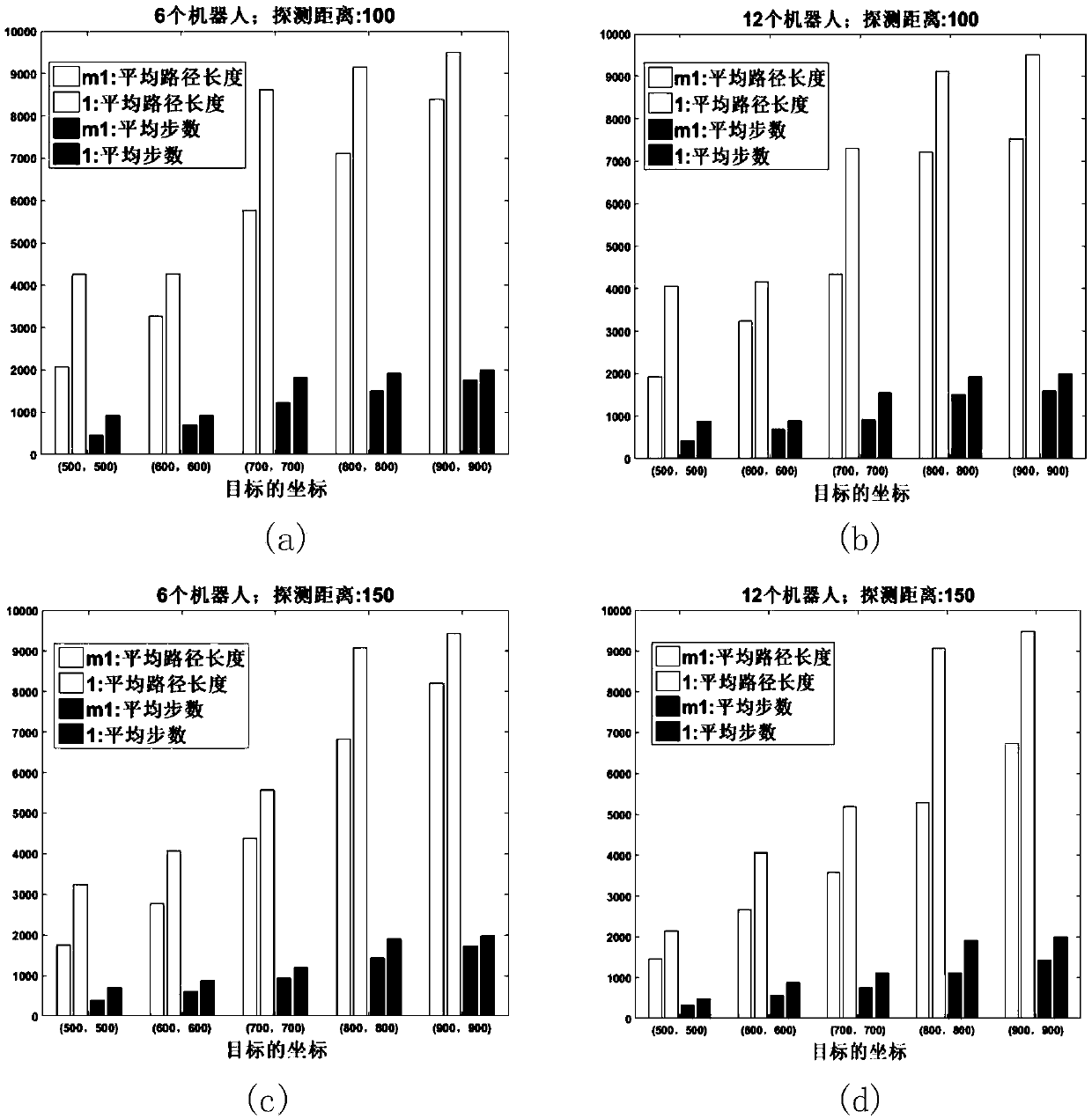
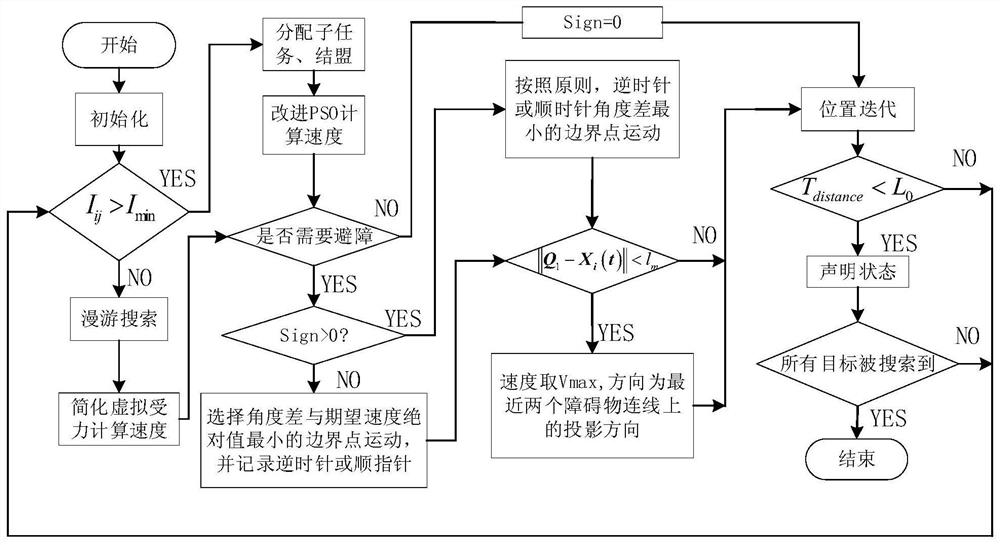
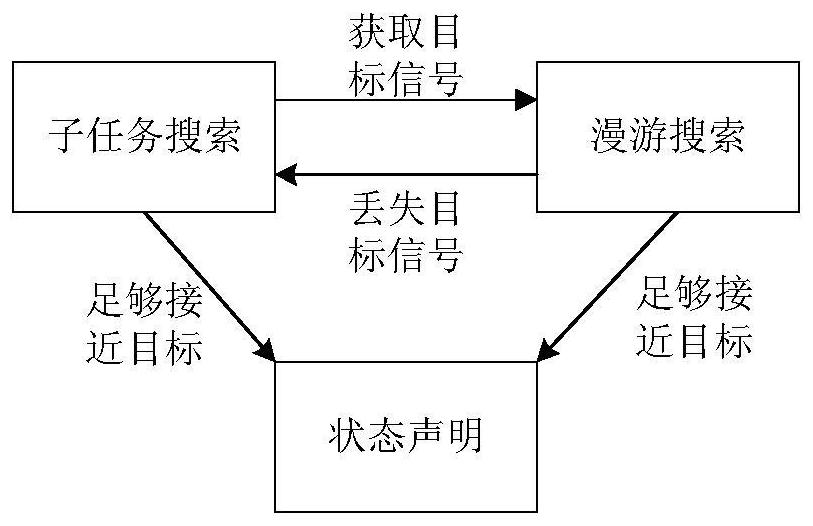
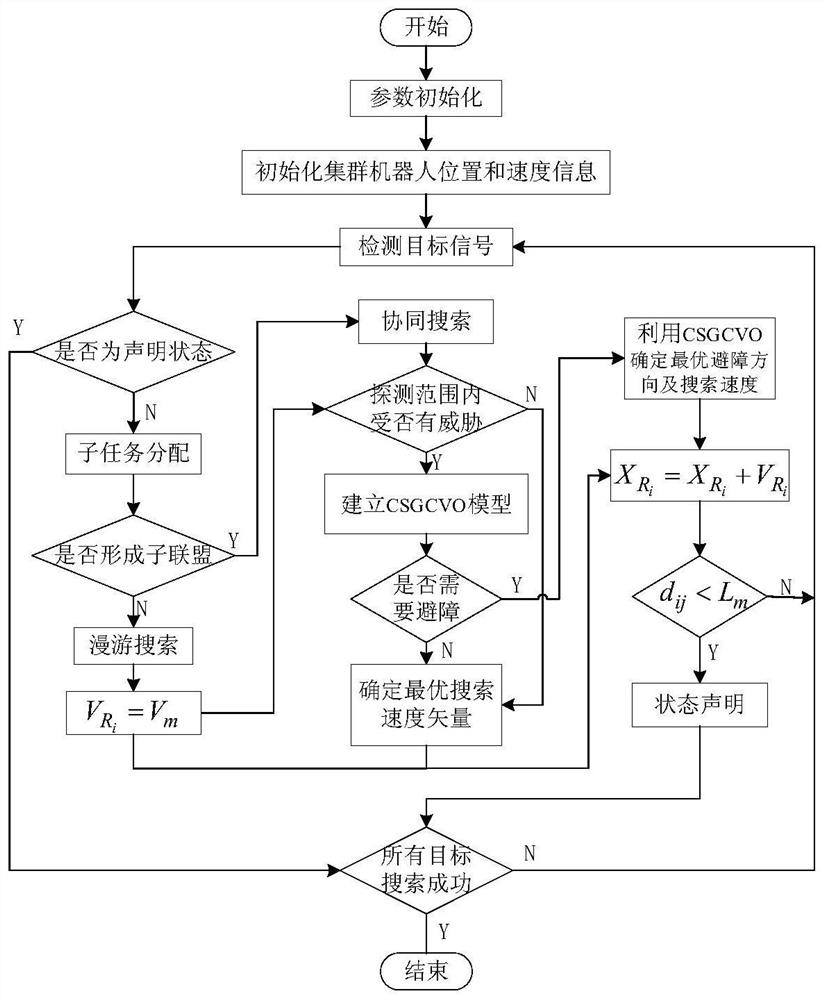
The invention discloses a swarm robot multi-target searching method in an unknown environment. The swarm robot multi-target searching method comprises the following steps that an unknown environment model is constructed; a robot detects a target signal, dynamic division is carried out based on a target response function, and a set where robots completing the same sub-task are located forms a sub-alliance; closed-loop regulation is introduced, resource allocation of each sub-task is evaluated, and a new sub-alliance is formed; robots which do not form the sub-alliance perform roaming search; and the robots forming the sub-alliance search a target based on a particle swarm algorithm of position estimation and an obstacle avoidance strategy of boundary scanning. By means of the swarm robot multi-target searching method in the unknown environment, according to the obstacle avoidance strategy of boundary scanning, the distance and angle relation between the nearest two points and the boundary points and the robots is used for obstacle avoidance; and according to the particle swarm algorithm of position estimation, the approximate position of the target point can be deduced by using theavailable target signal, the particle swarm algorithm is matched, the target position is quickly reached, so that the path and the searching time during target searching are reduced.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
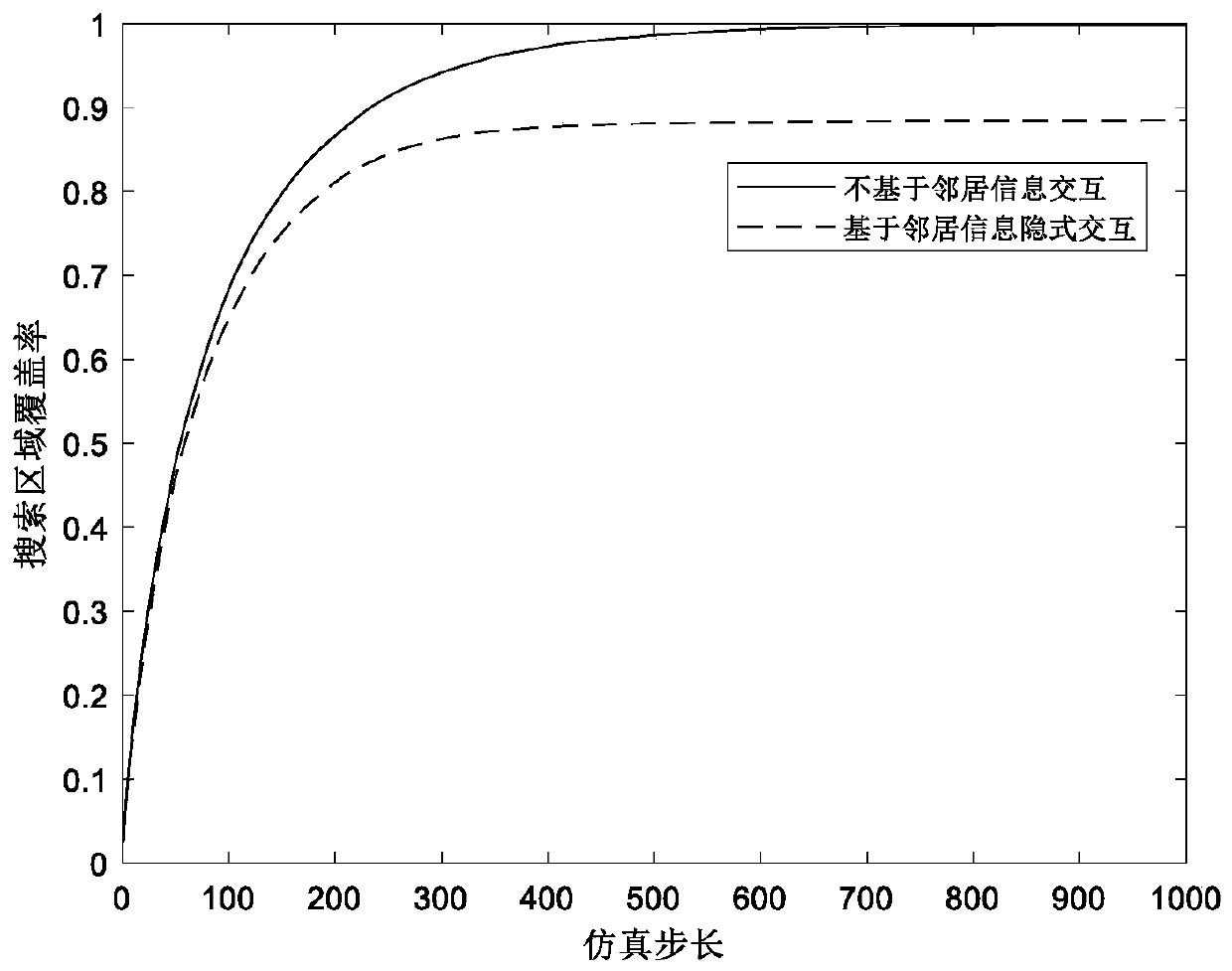
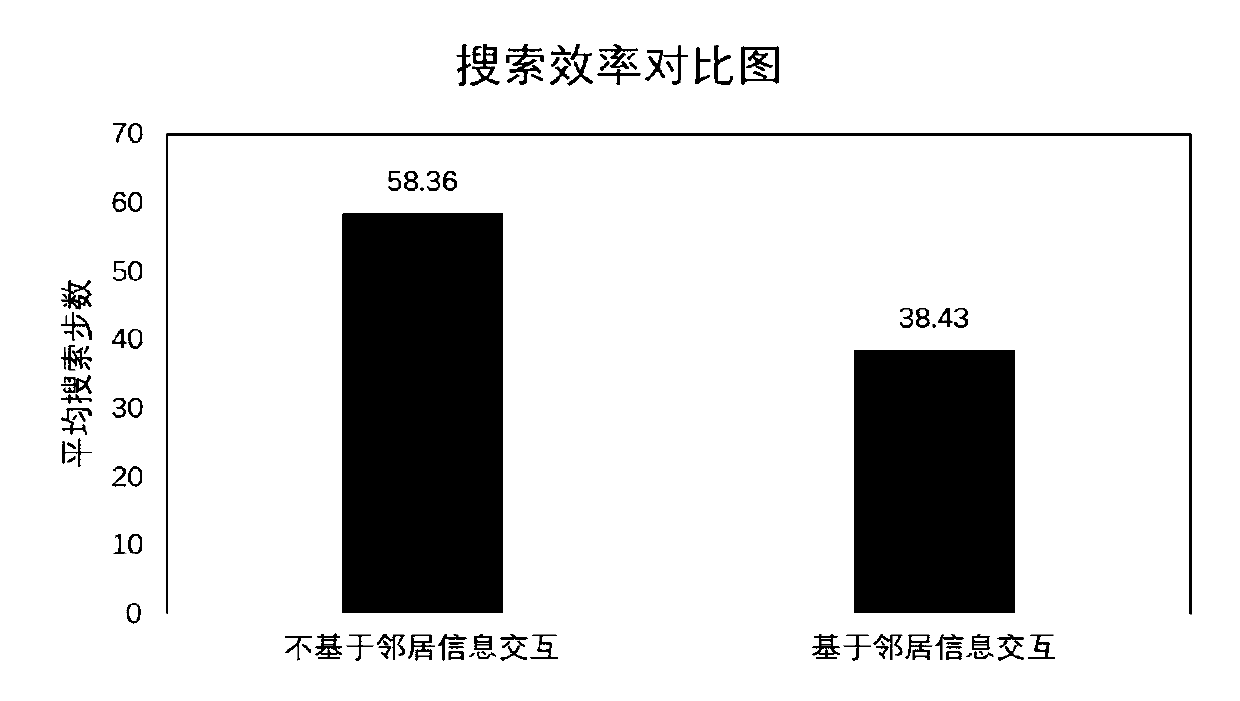
Swarm robot target searching method based on implicit information interaction mode
ActiveCN110381442AOvercoming Interaction BarriersDatabase updatingGeographical information databasesSimulationA* search algorithm
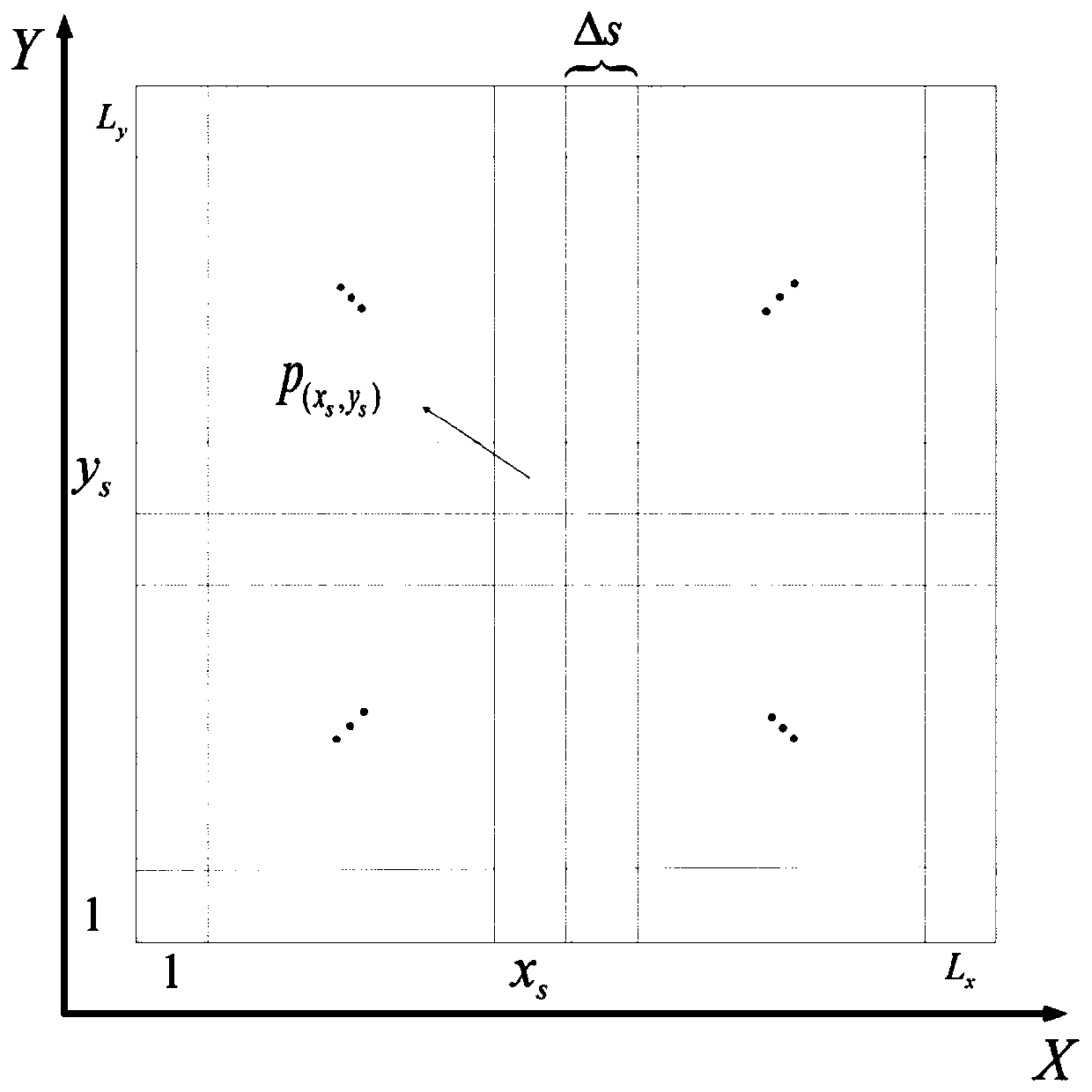
The invention provides a swarm robot target search method based on an implicit information interaction mode, which comprises the following steps: rasterizing a search area into a plurality of square discrete units according to fixed intervals, and establishing a search map of each robot; secondly, for each robot, updating the probability that a target exists in each grid in the search map according to a self detection result; introducing individuals into a search algorithm to actively detect the states of neighbor robots, and information interaction obstacles among different individuals when broadcast communication cannot be performed are overcome, so that multiple robots cooperate with one another to complete a search task under the condition that the target distribution condition is unknown. According to the method, the dependence on an explicit information interaction mode is eliminated, information fusion is carried out only according to the observation of an individual on the neighbor state, and the problem of multi-robot target search under limited communication is solved by adopting an implicit communication mode according to the observation information.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
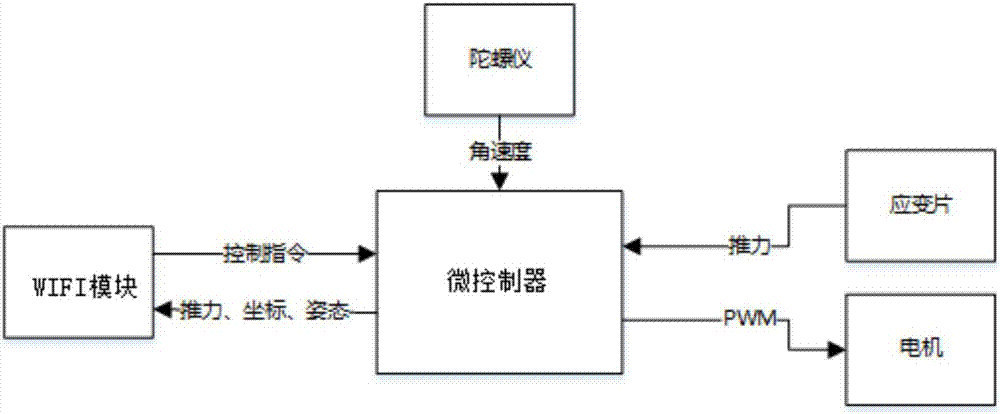
Cluster intelligent control system
InactiveCN107422637AHigh control precisionImprove real-time performanceAdaptive controlMotor speedMicrocontroller
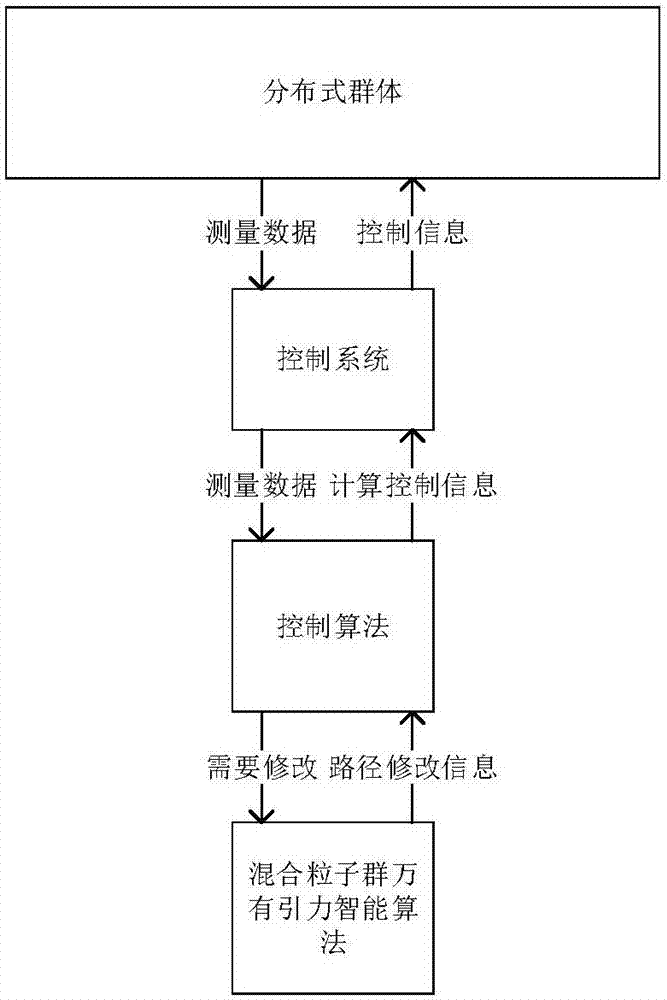
The invention belongs to the robot field and discloses a cluster intelligent control system, which comprises a host computer, a WIFI module, a microcontroller, a strain gauge, a motor, a gyroscope and spiral fan blades, wherein the strain gauge is used for measuring the thrust force value exerted by each fan on an individual robot and transmits the value to the microcontroller, the microcontroller, based on the comparison between the obtained actual thrust value and the target thrust value, adjusts the motor speed in real time; and at the same time, the microcontroller obtains the current angular velocity of the individual robot through the gyroscope so as to obtain the current attitude of the individual robot and to adjust the rotational speed difference of the motor in real time. In doing so, the individual robot in a cluster of robots can move according to a set track. According to the invention, it is possible to adjust and control the actions of a cluster of robots in real time according to the requirements, and to optimize the motion tracks of the cluster of robots by using the mixed particle swarm gravitation algorithm.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Swarm-robot drawing system
InactiveCN104122856AWith return functionPrevent looseningProgramme total factory controlGraphic systemComputer science
The invention provides a swarm-robot drawing system and belongs to the field of the mechanical and electrical information. The swarm-robot drawing system is capable of performing quick ultra-large automatic drawing operations on large places, building and places that people cannot step into with mobile swarm robots as executive bodies, and has the characteristics of reliability, flexibility and high efficiency of the distributed system; the system has the advantages of low equipment cost, open and diversified drawing modes, and unique artistic effects, and is capable of drawing complex figures including fractal patterns. The working principle of the system is that the mobile swarm robots are controlled by drawing genes to perform group cooperation drawing in a certain mode and in an organized way, and the composition result is the macroscopic overall expression of selection activation of the drawing gene in every individual robot. The inventor designs some basic drawing genes and six drawing variations, and also designs the swarm-robot drawing system of a cluster mode which can be used for higher-level drawing expression.
Owner:王海
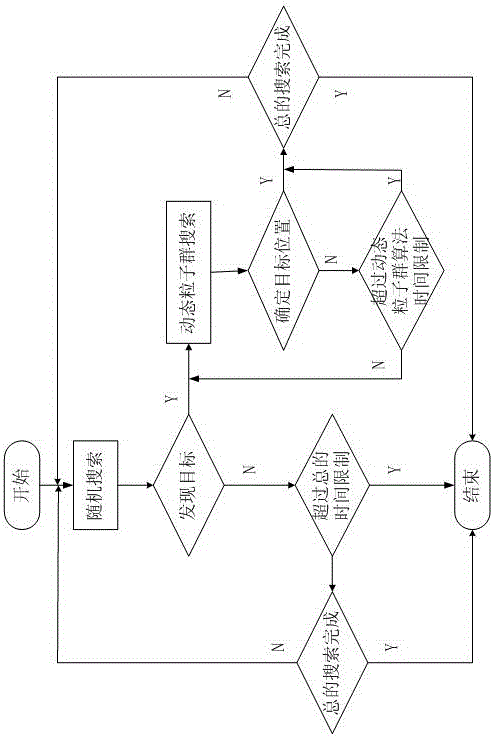
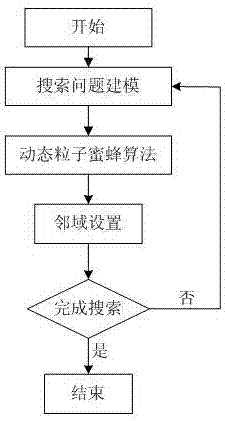
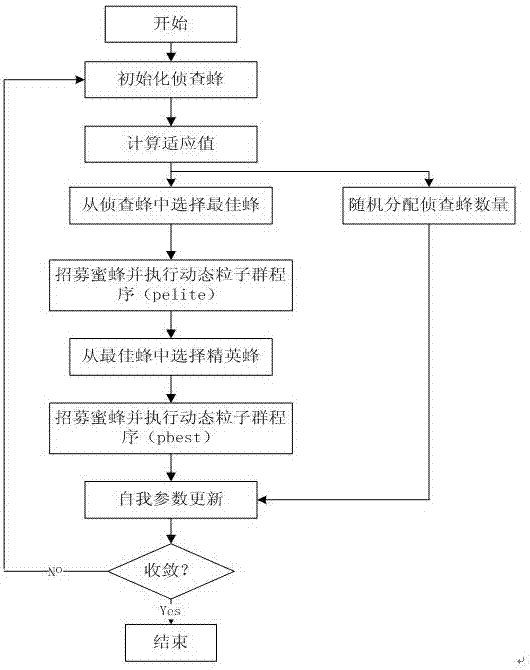
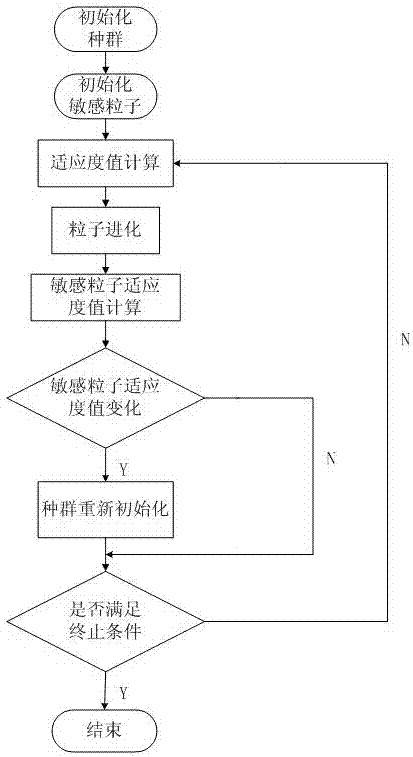
Swarm robot search method based on dynamic particle bee algorithm
ActiveCN107103356AImprove accuracyImprove the speed of global searchArtificial lifePattern recognitionSearch problem
The invention discloses a swarm robot search method based on a dynamic particle bee algorithm. The method comprises the following steps of using a combined auction method to carry out modeling on a search problem; setting a search field and search time T; and using the dynamic particle bee algorithm to search till that a whole search area is searched or the set search time arrives, and then ending the search. In the invention, based on a dynamic particle algorithm and a bee algorithm, the method is applied to a swarm robot work process so that swarm robots can rapidly search an object in short time, and search efficiency and accuracy of a search result are greatly increased.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
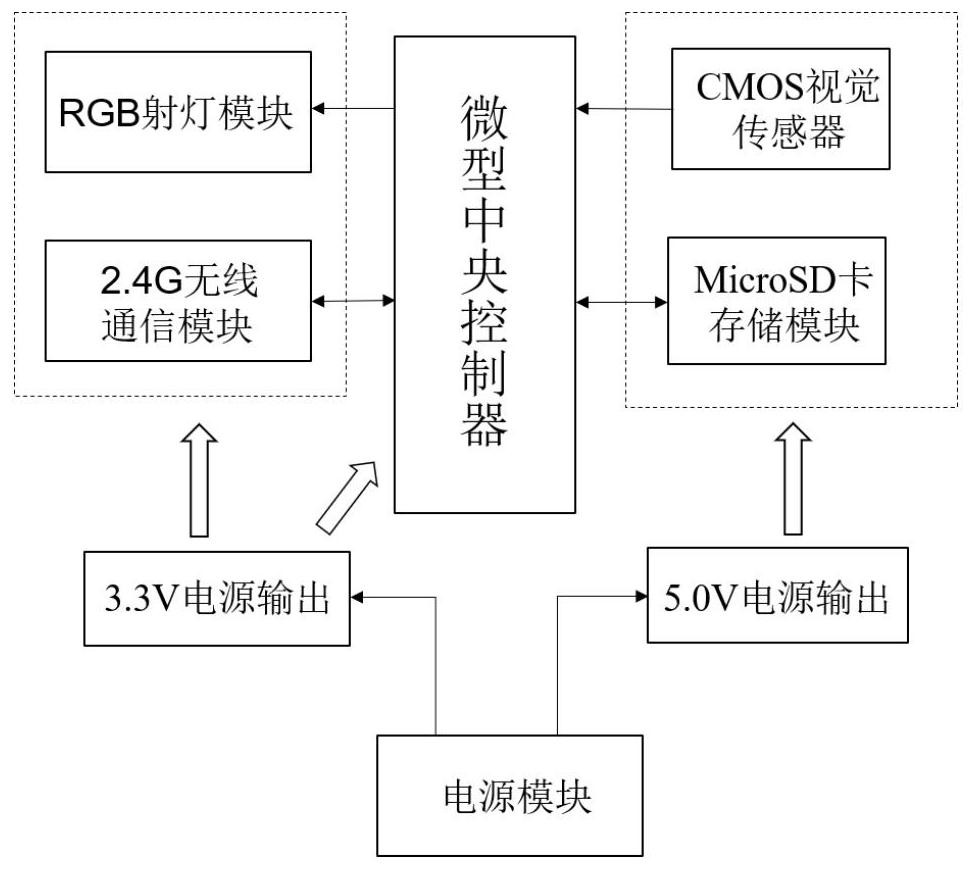
Active shared projection plane sensing system and method for desktop cluster robots
ActiveCN112601060AImprove portabilityImage enhancementImage analysisLaser transmitterComputer graphics (images)
The invention discloses an active sharing projection plane sensing system and method for desktop cluster robots. The system comprises a CMOS visual sensor module, an RGB spotlight module, a micro processing unit, a MicroSD card storage module, a 2.4 g wireless communication module and a power supply module. The system is based on a visual sensing technology, and a robot individual firstly emits RGB spotlight marks to a top projection surface, captures top image information by utilizing a visual sensor, recognizes positions and pointed directions of all marks on the image information, calculates relative positions and relative heading directions of neighbors relative to the robot individual, and stores the relative positions and the relative heading directions into a memory. According to the invention, the robot only needs to carry the cheap camera module and the laser emitter, the state information of the robot and the motion state information of the surrounding neighbors can be actively shared, and the mobility of a clustering algorithm to a machine cluster can be improved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
A Distributed Swarm Robot Collaborative Swarm Algorithm Based on Improved Gene Regulation Network
ActiveCN108415425BOptimizing Model ParametersSmall communication rangeGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationCluster algorithmComputation complexity
The invention provides a distributed group robot cooperative clustering algorithm based on an improved gene regulation network. Through embedding a diamond mesh distribution equation and a trajectoryfollowing equation in a gene regulation network model based on the Turing reaction diffusion mechanism, the moving vector speed of each robot is controlled, thus each robot whose initial state is in random distribution always gathers at a preset cluster trajectory position at a time t, the robots are arranged in a self-organized way to be in a diamond mesh distribution and can avoid obstacles in adynamic environment and repair formation by themselves. Parameter values in the improved gene regulation network are given by an NSGA II optimization algorithm. The distributed group robot cooperative clustering algorithm has the advantages of low computational complexity and good expansibility, for any robot, only the collection of the location information of a neighboring robot is needed, so arequired communication range is small, and the communication burden is effectively reduced. In addition, if some robots fail in operation, a system can still work normally, and the algorithm has goodrobustness and a great application prospect.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
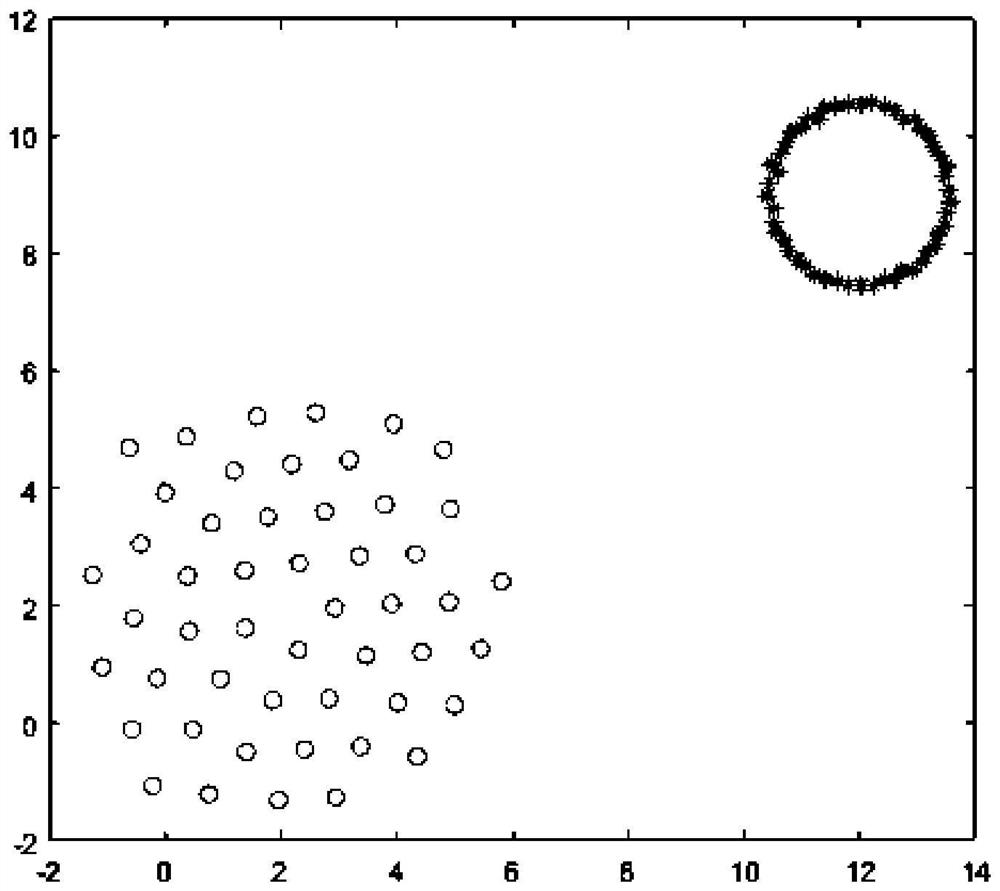
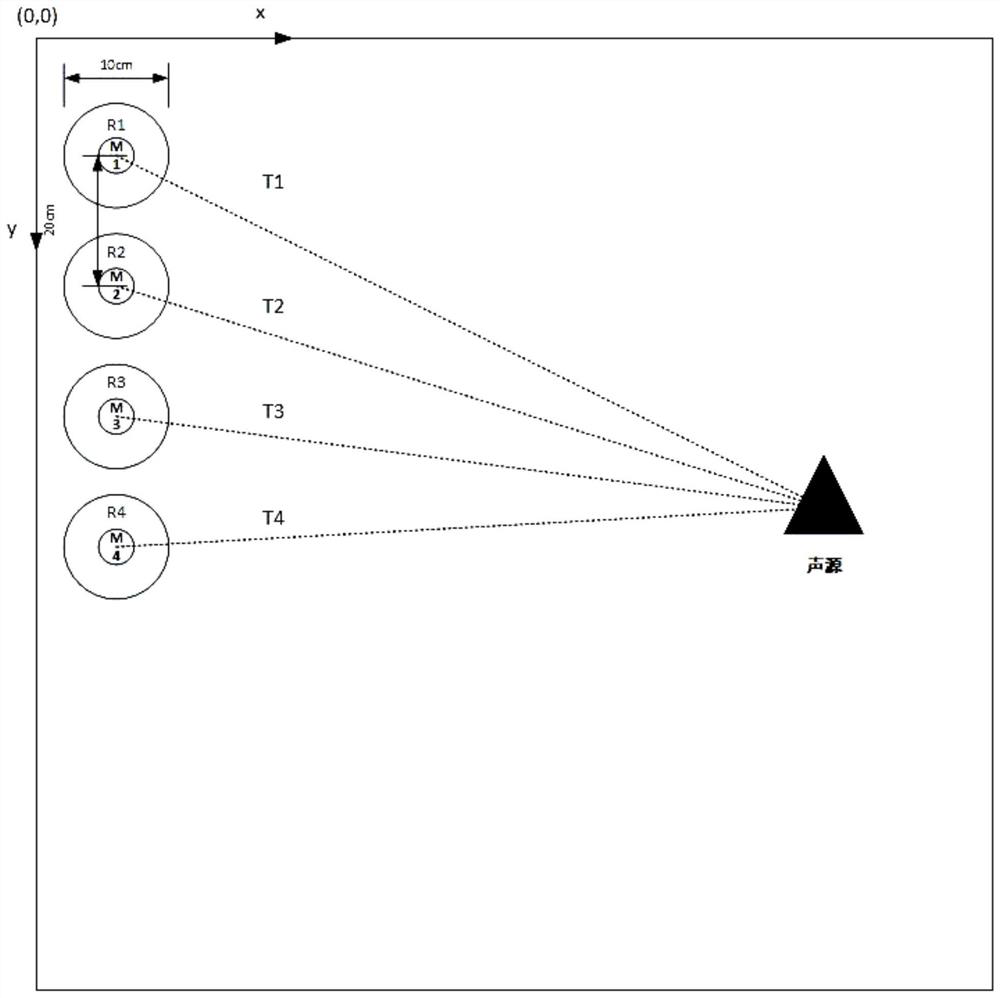
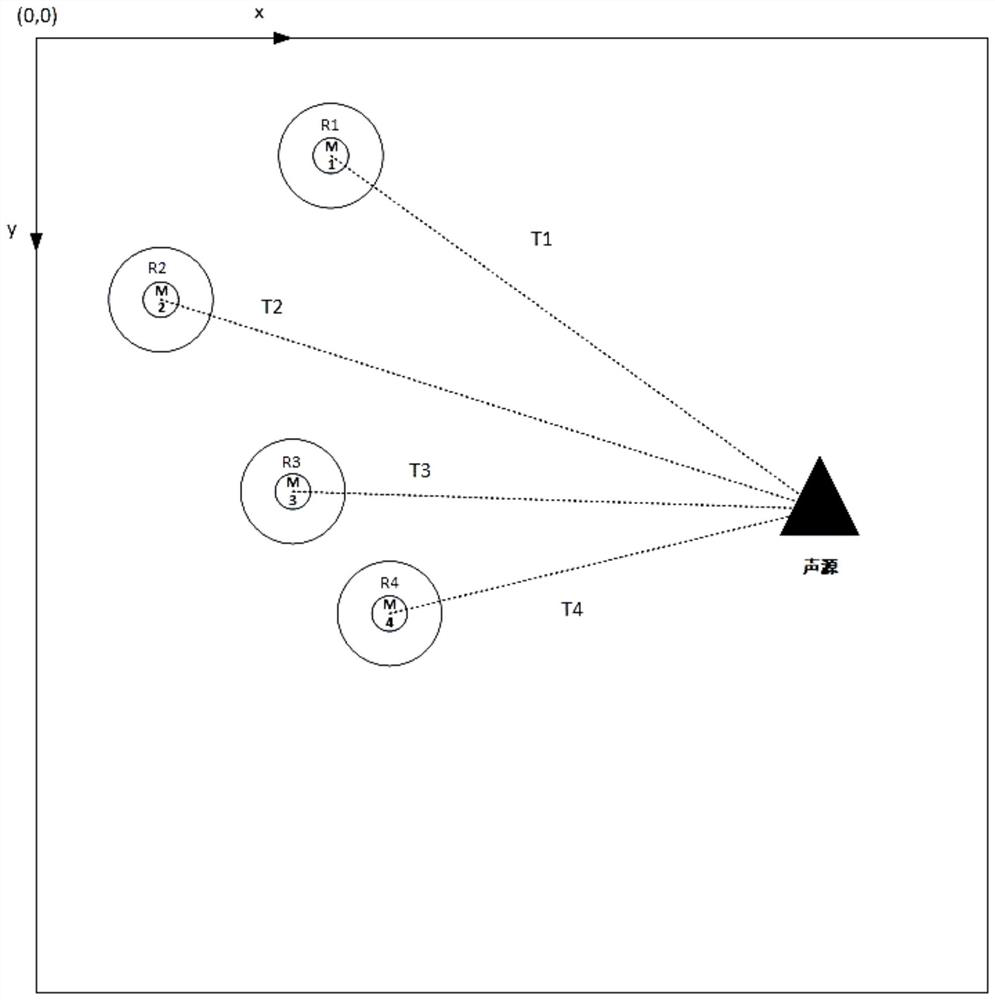
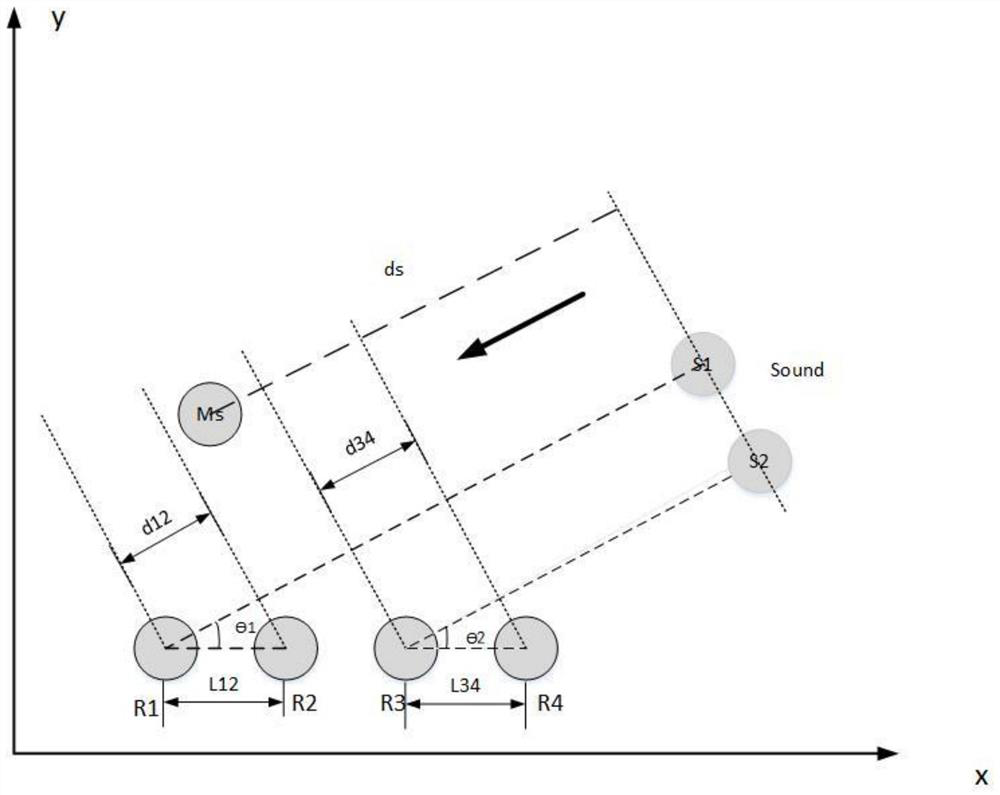
Indoor static sound source positioning method based on swarm robots
ActiveCN112098940ASimple structureImprove fault toleranceSustainable transportationPosition fixationSound source locationSound sources
The invention discloses an indoor static sound source positioning method based on swarm robots, and the method employs a plurality of robots for the indoor sound source positioning, each robot carriesa single microphone, is simple in structure, and improves the error-tolerant rate in a positioning process. In the positioning process, multiple times of sound source position calculation are carriedout, and higher positioning precision is obtained by continuously approaching a sound source. In each sound source position calculation, grouping positioning is carried out according to the number ofrobots, finally, weights are allocated according to the difference value of the positioning result of each group and the average value of the positioning results of all groups, and the final sound source position judgment at a certain moment is obtained after each group of results are multiplied by the weights and accumulatively added. The optimal sound source position is obtained by assigning weights to multiple groups of sound source position estimation values at different moments. The reference microphone is arranged to simplify the calculation amount of the swarm robot in the positioningprocess, and the positioning precision is improved through cooperation and multiple times of movement of multiple robots.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
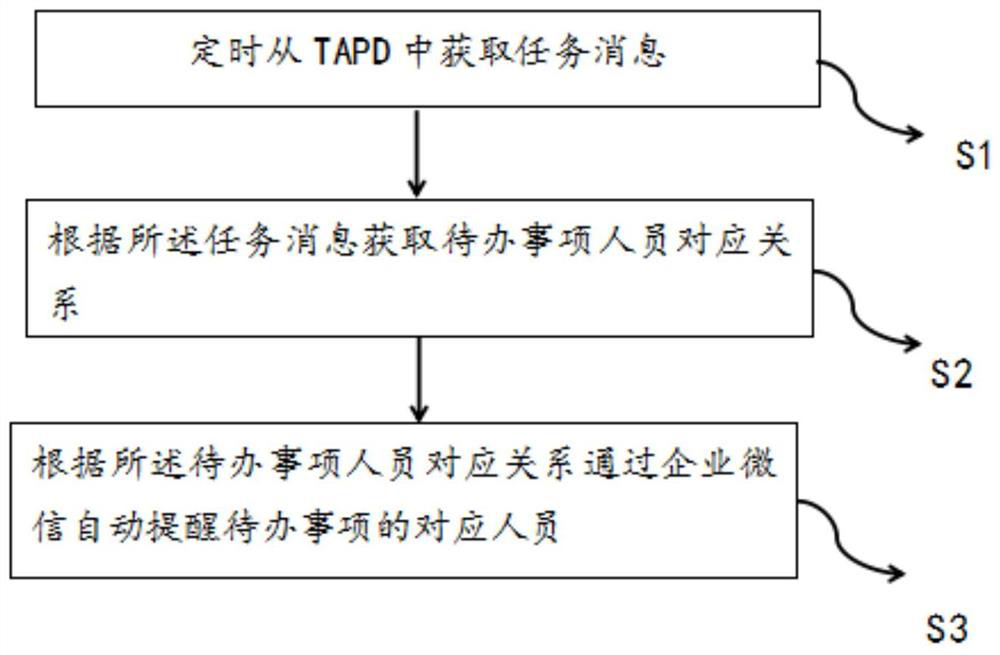
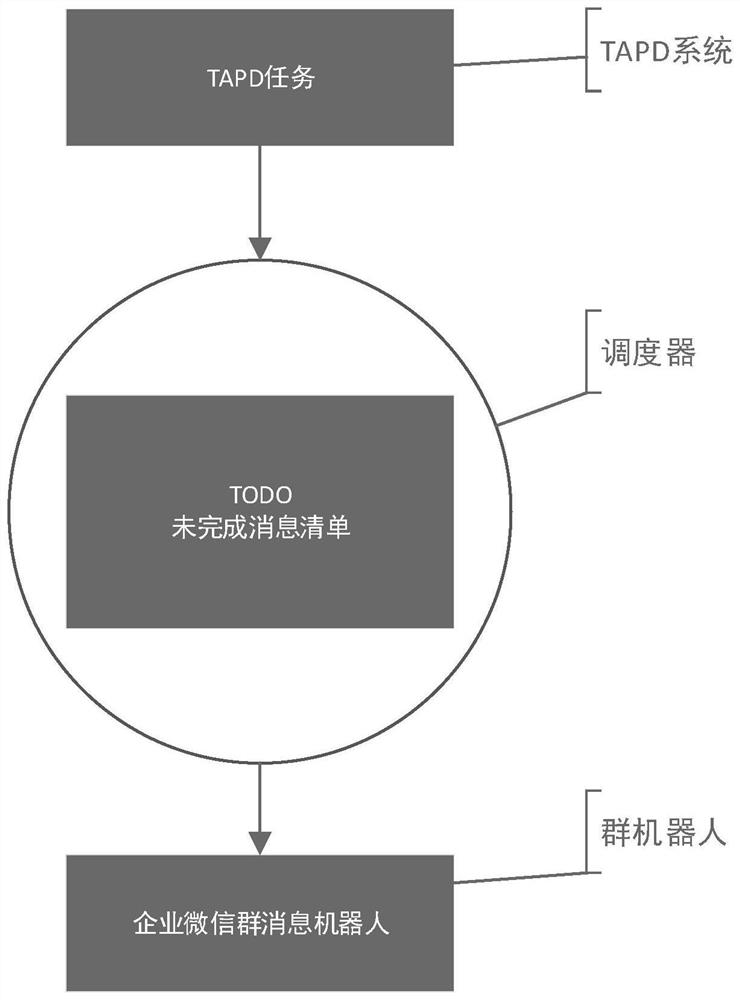
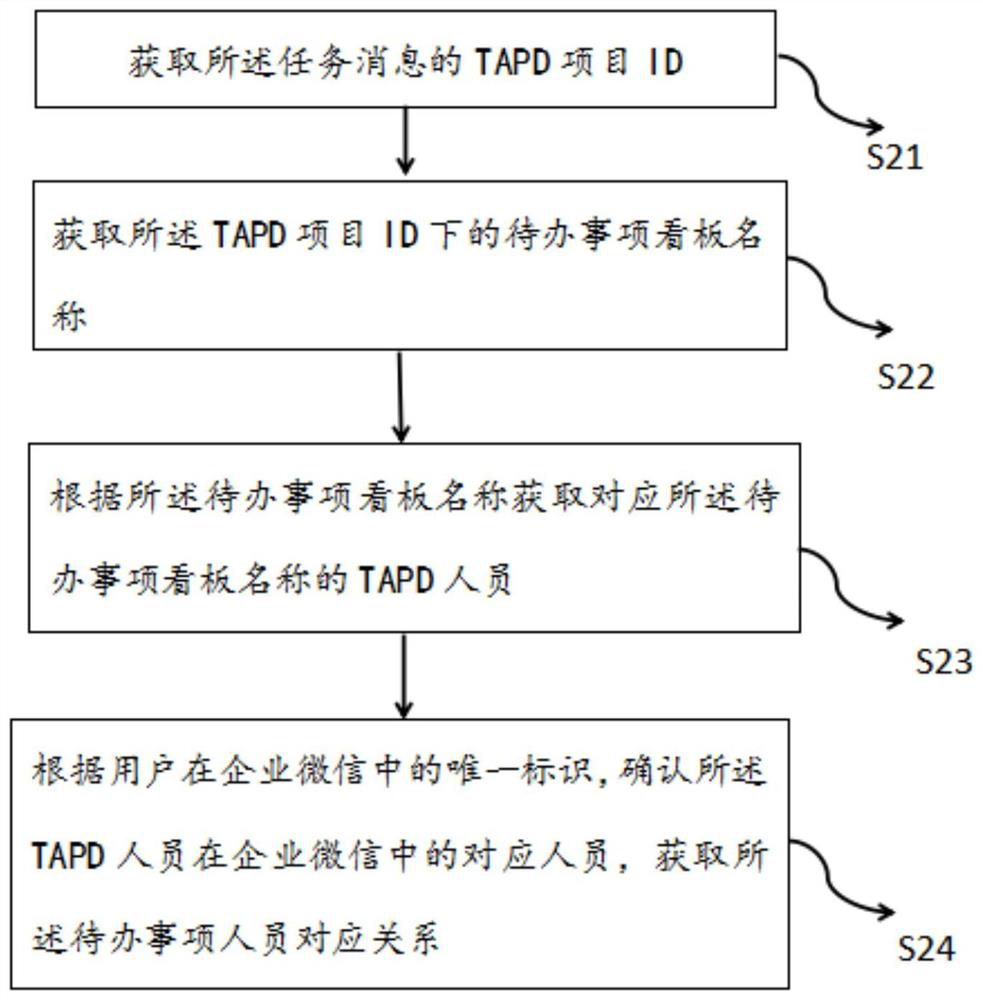
TODO automatic reminding method and system, electronic equipment and readable storage medium
PendingCN112365238AImprove human efficiencyFlexible Scheduling ConfigurationOffice automationData switching networksBusiness enterpriseSoftware engineering
The invention discloses a TODO automatic reminding method and system, electronic equipment and a readable storage medium. The method comprises the steps: obtaining task messages from a TAPD regularly;according to the task message, obtaining a corresponding relationship of personnel of a to-do list; and automatically reminding the corresponding personnel of the to-do list through enterprise WeChataccording to the corresponding relationship of the personnel of the to-do list. Through the application, the TAPD task can be fed back to the enterprise WeChat group through the enterprise WeChat group robot, and the corresponding employee is reminded regularly, so that the human efficiency is improved.
Owner:BEIJING MININGLAMP SOFTWARE SYST CO LTD
Self-organizing task allocation method based on a dynamic response threshold value in group robot foraging
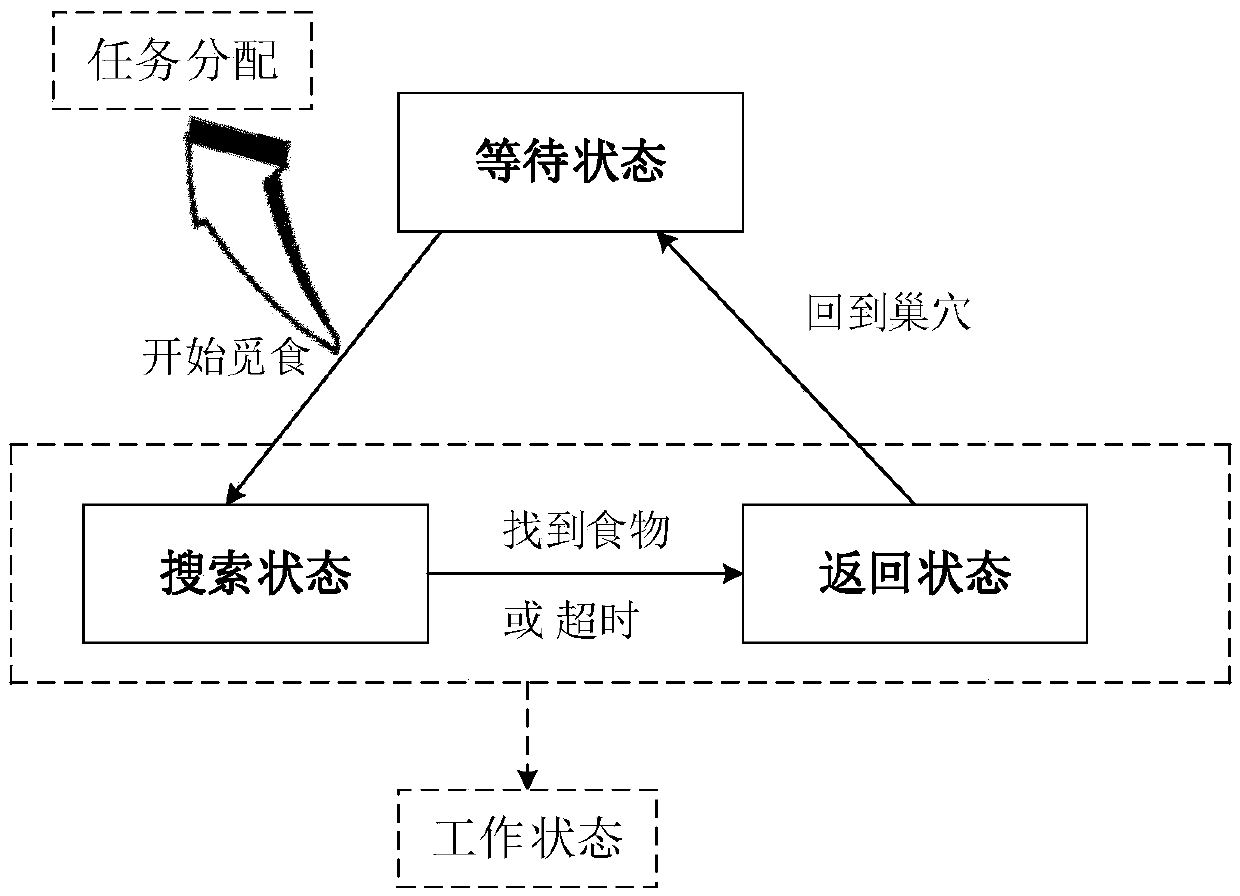
ActiveCN109615057AReduce physical interactionImprove foraging efficiencyArtificial lifeResourcesSimulationTraffic flow
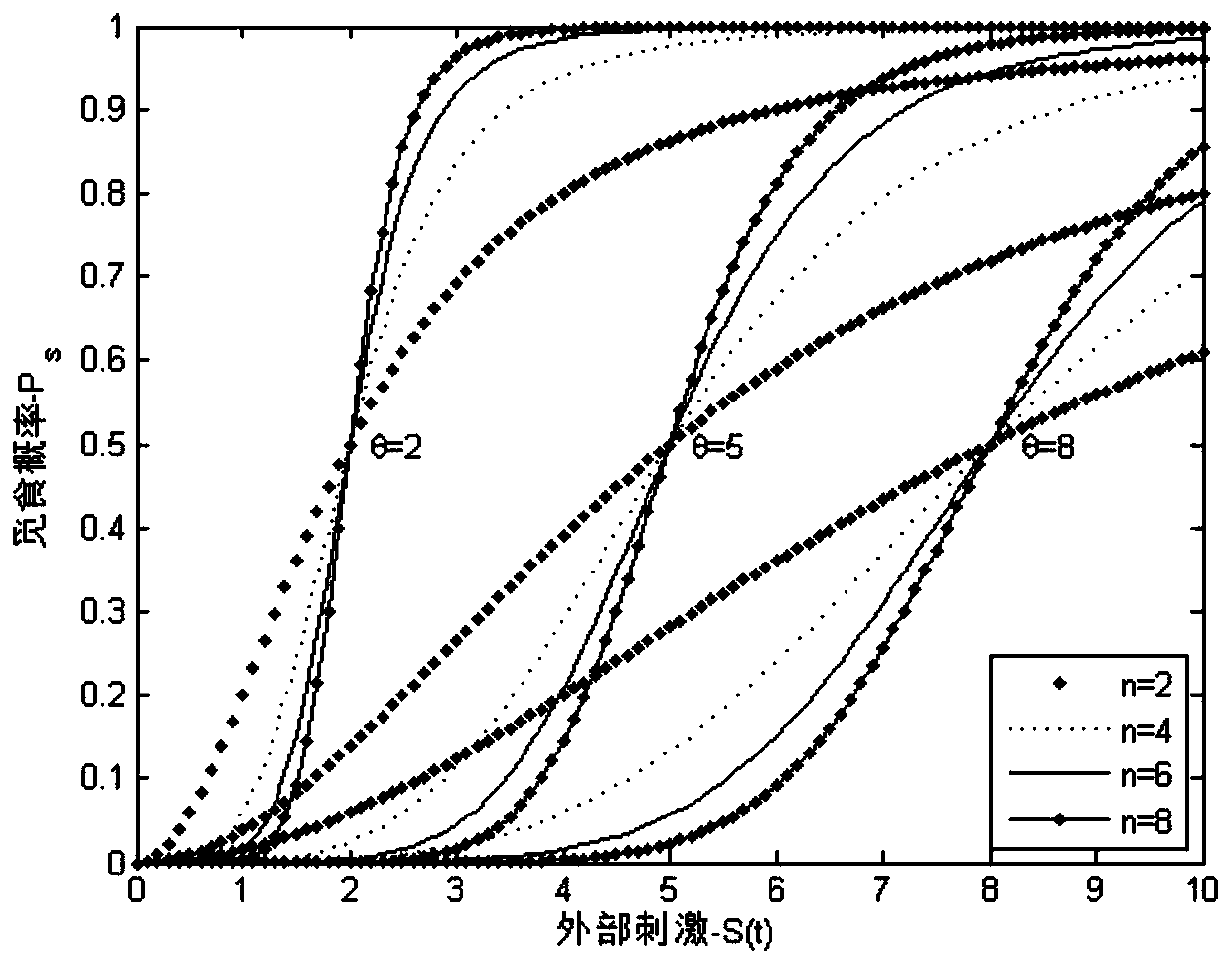
The invention discloses a self-organizing task allocation method based on a dynamic response threshold value in group robot foraging. The method comprises the steps that when a foraging task starts, all robots are gathered in a nest to be in a waiting state, when the waiting time exceeds given time, a dynamic response threshold model is used for calculating the foraging probability, and based on the foraging probability, the robots decide whether to start foraging or not, namely, the robots are switched from the waiting state to a searching state; wherein in the dynamic response threshold model, the traffic flow density, namely the average obstacle avoidance frequency of the robot and the density of the foraging robot within a period of time, is used as a dynamic change threshold to measure the traffic condition of movement of the robot in the environment, and the swarm robot makes an appropriate response to the change of the environment to generate self-organizing task distribution. Adynamic response threshold model based on the traffic flow density is constructed, so that the group robot system can generate self-organized task distribution, physical interaction between robots isreduced, and the foraging efficiency of the group robot is improved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Swarm robot lunar surface intelligent building system and method, robot and using method
PendingCN112666953AReduce energy consumptionSolve the problem of energy consumptionBuilding material handlingPosition/course control in two dimensionsControl engineeringControl theory
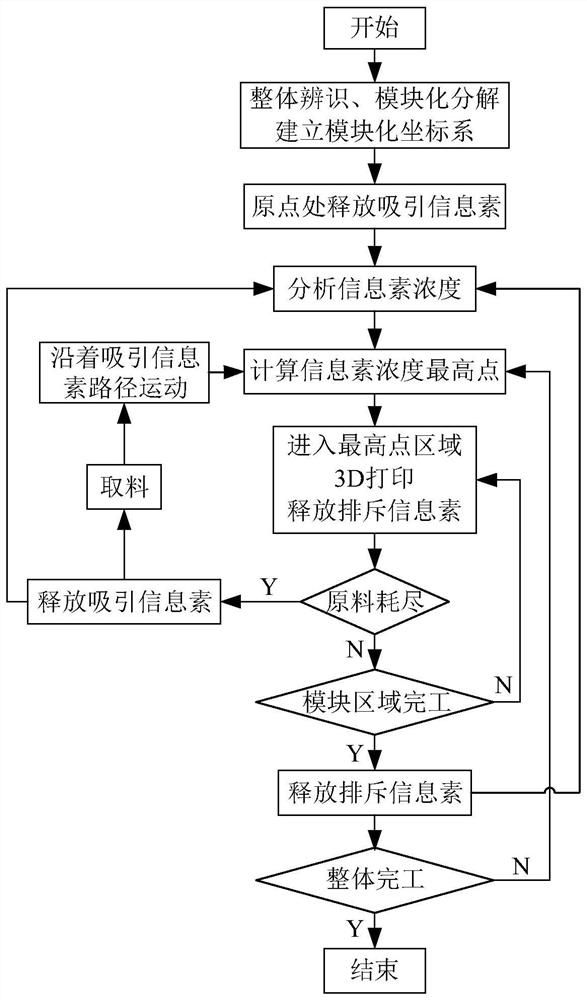
The invention discloses a swarm robot lunar surface intelligent building system and method, a robot and a using method, and the system comprises three modules: a region dividing module, a coordinate building module and a pheromone releasing module.According to the system, firstly, the overall structure is identified, analyzed and modularly decomposed; each module coordinate system is estabished on the basis of the global coordinate system; then, pheromones are released to attract all the robots to carry out corresponding construction on all the target areas. According to the system, the problems that the single-point construction efficiency of a single robot is low, and the energy consumption is high and the system is unstable due to global communication of a plurality of robots are solved, and it is ensured that the swarm robot efficiently, stably and quickly implements a building task. According to the system, the principles of modular decomposition and simultaneous startup of multiple modules are utilized, so that the working efficiency is greatly improved; according to the system, simple individual behaviors are connected in series through pheromones, control over the overall behaviors is achieved, and energy consumption caused by global communication and instability of the system are avoided.
Owner:RES & DEV INST OF NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV IN SHENZHEN +1
Swarm robot multi-target search method based on unknown environment collision conflict prediction
PendingCN114706422AShorten the timeReduce energy consumptionPosition/course control in three dimensionsTarget ResponseTarget signal
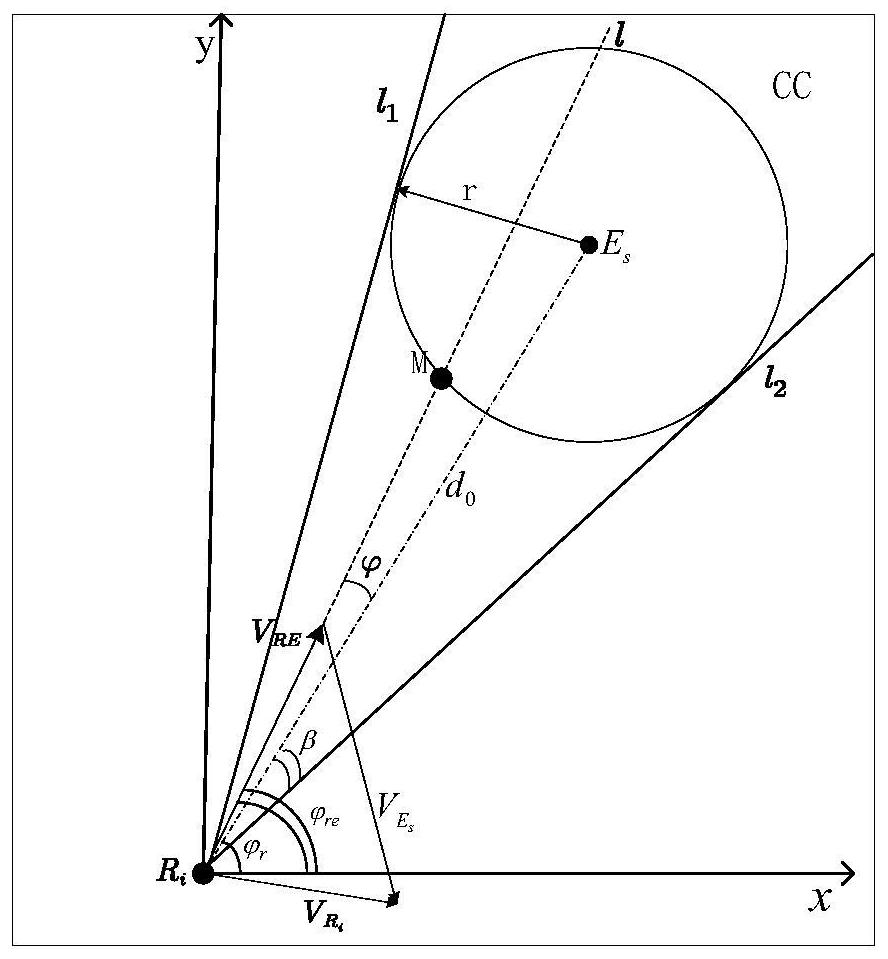
The invention discloses a swarm robot multi-target search method based on unknown environment collision conflict prediction. The method comprises the following steps: constructing an unknown environment model and a target response function; the robot detects a target signal and performs dynamic task division to form a sub-alliance; introducing closed-loop regulation to reform a new sub-alliance; the robots not forming the sub-alliance perform roaming search, and the robots forming the sub-alliance perform coordinated search; in the roaming search and coordination search process, an obstacle avoidance method combining a collision expansion geometric cone and a speed obstacle method is adopted for obstacle avoidance; if the distance between the robot and the target is smaller than the threshold value, target searching is successful, and target searching is stopped; and if all the targets are successfully searched, ending the task, otherwise, continuing to search the targets until all the target search tasks are completed. According to the method, the obstacle avoidance method combining the collision expansion geometric cone and the speed obstacle method is adopted for obstacle avoidance, and the task searching time, the obstacle avoidance frequency and the energy consumption of the swarm robot are reduced.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Scalable cluster particle robot self-organizing cooperative tracking control method
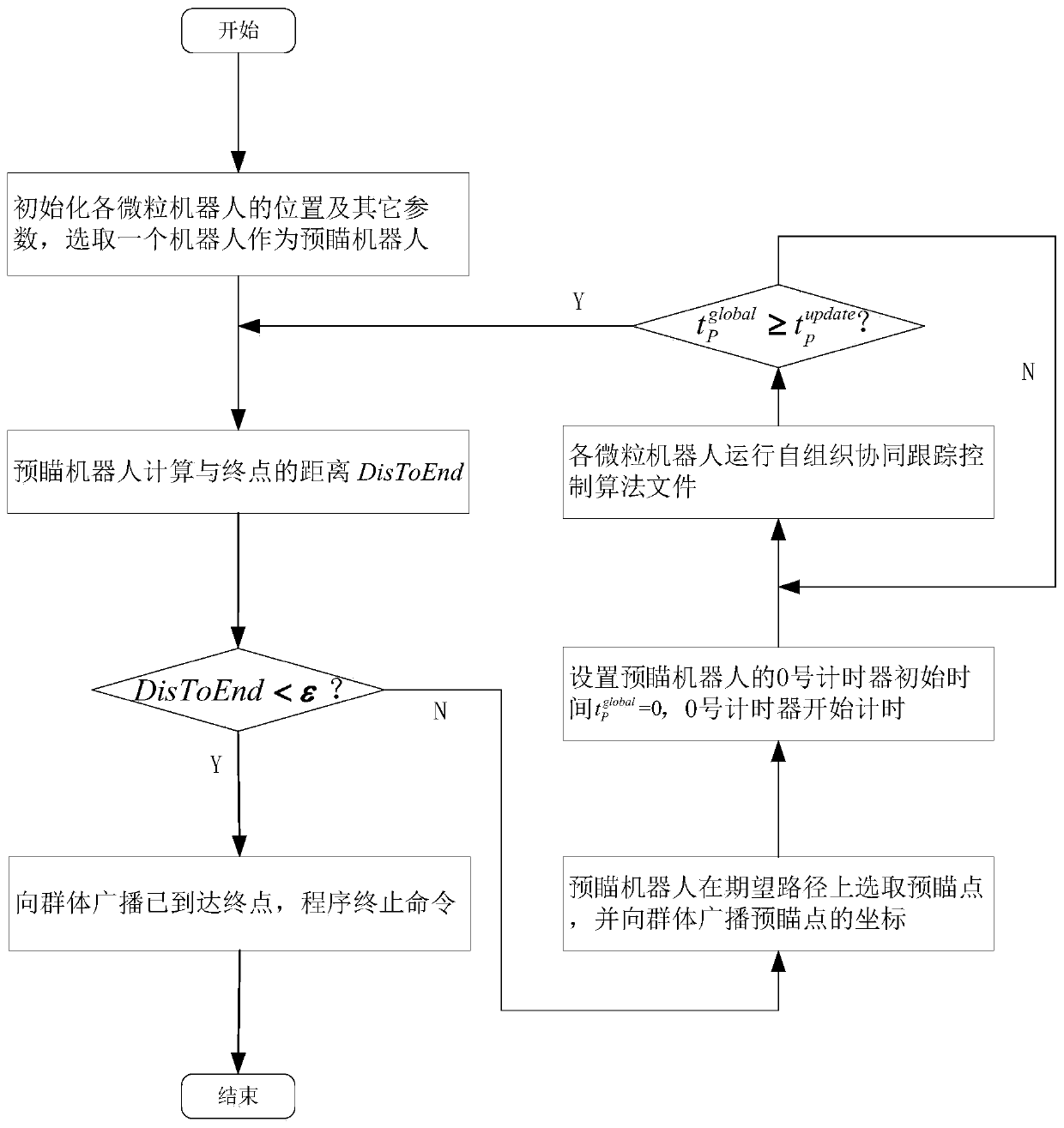
ActiveCN110750093AReduce control difficultySmall amount of calculationPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesSimulationReal-time computing
The invention discloses a scalable cluster particle robot self-organizing cooperative tracking control method. A preview distance and a preview point are calculated based on a single-point preview theory; a cluster particle robot is driven to track a desired path in a self-organizing manner; and when the cluster robot has a lateral displacement deviation, the cluster robot can return to the desired path. According to the scalable cluster particle robot self-organizing cooperative tracking control method provided by the invention, the numbering of each robot in the group is not required, the robot cluster is not required to maintain a fixed formation, and the communication with a specific individual is not required; therefore, other particle robots can be extended to join the cluster in theprocess of cooperative motion.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Robot cluster intelligent data synchronization method and system
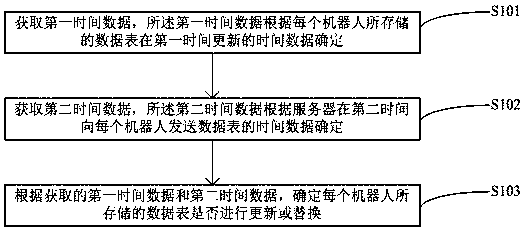
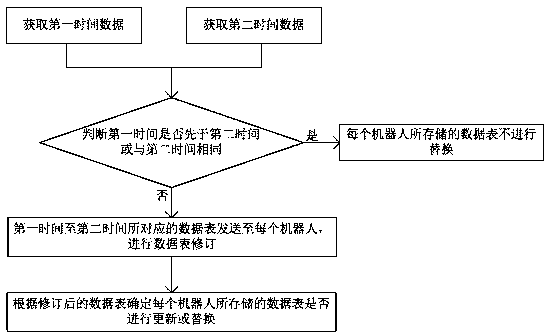
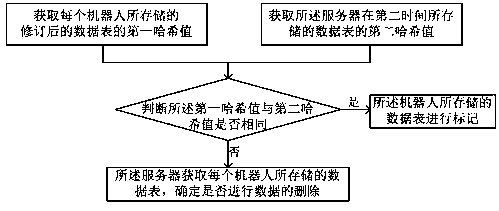
PendingCN111506668AImplement updateEasy to deployDatabase distribution/replicationSpecial data processing applicationsData synchronizationSimulation
The invention belongs to the technical field of intelligent robots, and relates to a robot cluster intelligent data synchronization method and a robot cluster intelligent data synchronization system,which solve the technical problem that a cluster robot is inconsistent with a server data table in a method in the prior art. The robot cluster intelligent data synchronization method comprises the following steps of: acquiring first time data, wherein the first time data is determined according to the updating time of a data table stored in each robot at the first time; acquiring second time data, wherein the second time data is determined according to the time when the server sends the data table to each robot at the second time; and determining whether the data table stored by each robot isupdated or replaced according to the obtained first time data and second time data. The robot cluster intelligent data synchronization method is used for synchronizing data of the robot and the server, and meets the requirement of people for convenient maintenance of the cluster robot.
Owner:XIAN ANCN INTELLIGENT INSTR +1
Cluster robot cooperative positioning system and method
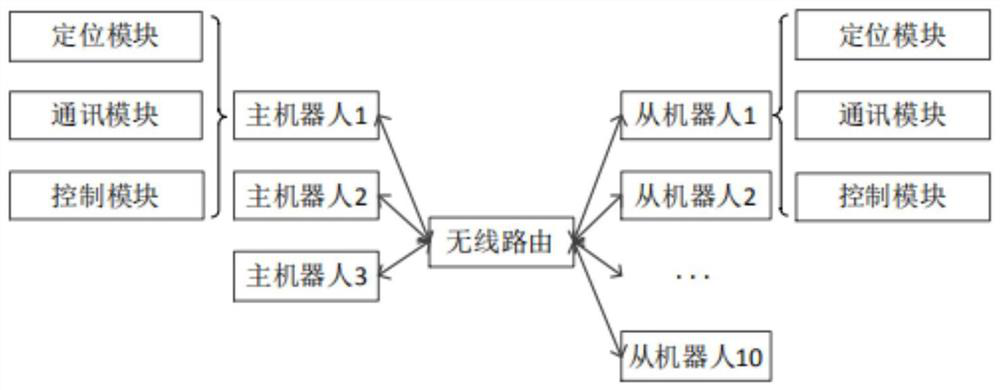
PendingCN112731923AImprove the ability to identify obstaclesReduce high costPosition/course control in two dimensionsEngineeringRobot control
The invention discloses a cluster robot cooperative positioning system and method, and the system comprises: a main robot which is used for the construction of an environment map and navigation positioning; a slave robot which is in communication connection with the main robot and is used for carrying out navigation and positioning based on the map constructed by the main robot and the main robot; and a robot control module which is used for processing the positioning data and the communication data between the master robot and the slave robot and completing the cooperative operation between the cluster robots constructed by the master robot and the slave robot. Through a small number of high-precision laser radars and a small number of reference objects, high-precision positioning the same as that of common laser radars is provided, the high cost problem of the natural navigation robot during cluster robot positioning is effectively reduced, and meanwhile, through local sharing of high-precision radar data, the obstacle recognition capability of the common radars is improved.
Owner:WUHAN WANJI INFORMATION TECH
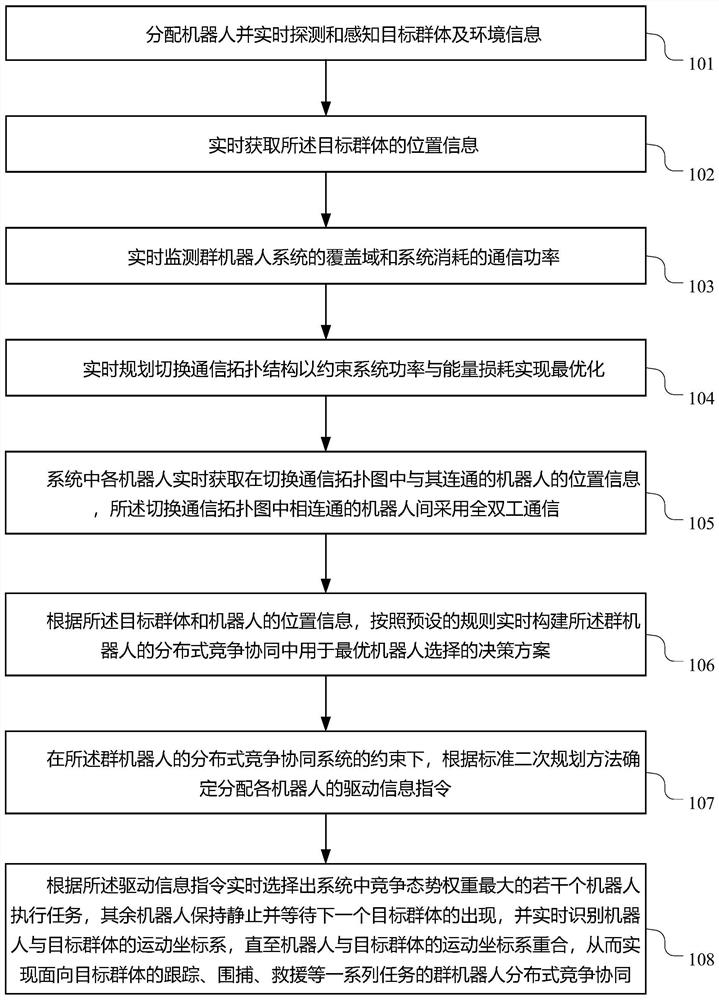
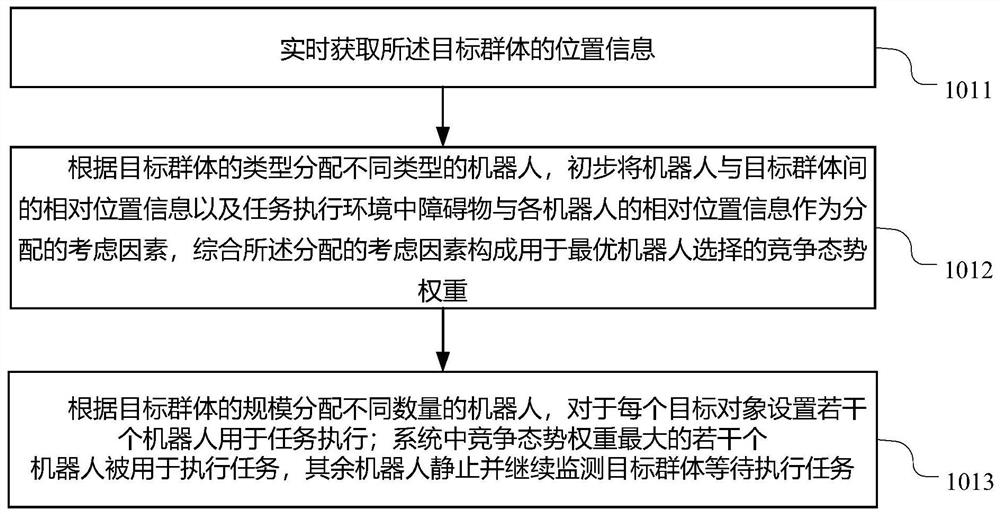
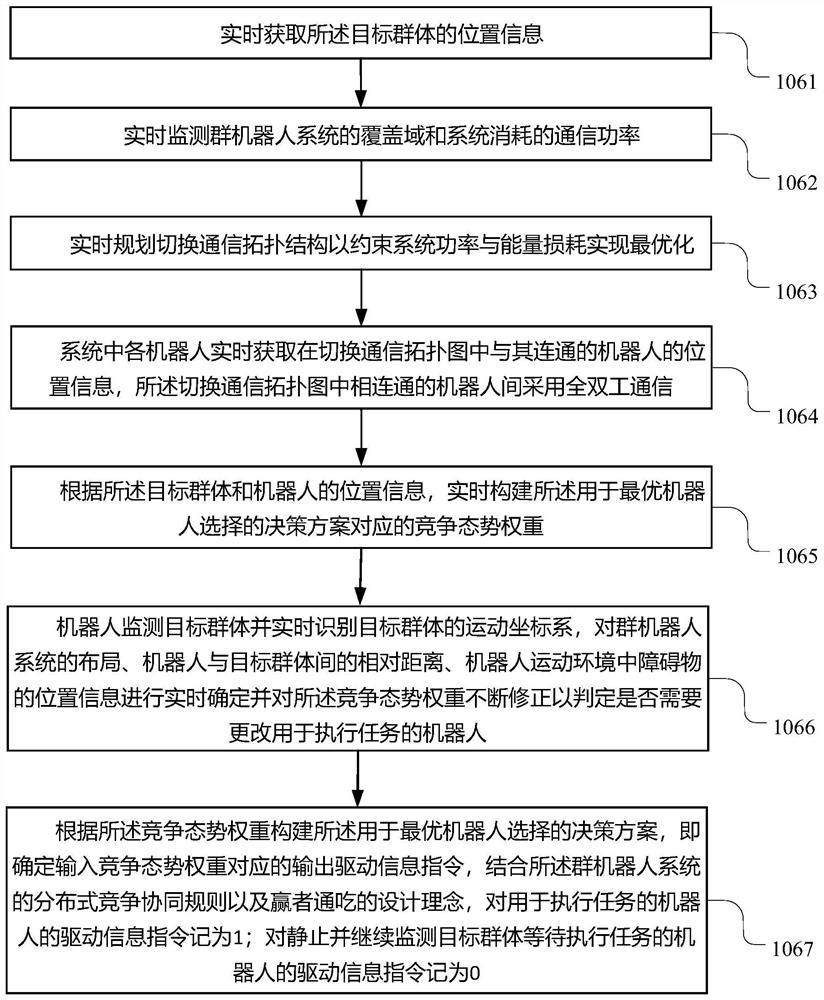
Swarm robot distributed competition cooperation method for multi-target tracking
InactiveCN111830916AReduce communication loadLighten the computational burdenTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlEngineeringComputer science
The invention provides a swarm robot distributed competition cooperation method for multi-target tracking. The swarm robot distributed competition cooperation method comprises the following steps: 1)distributing robots and detecting position information and environment information of a target group, a coverage area of swarm robots, consumed communication power and the like in real time; 2) for each robot, acquiring information mastered by the robot communicated with the robot in a communication topological graph in real time; 3) constructing a decision scheme for optimal robot selection in swarm robot distributed competition cooperation in real time according to the information, and determining a driving information instruction for allocating the robots according to a quadratic programming method; and 4) selecting an optimal robot according to the driving information instruction, and identifying a motion coordinate system of the robot and the target group in real time to realize distributed competition cooperation of the swarm robots for multi-target task execution. According to the method, the application scene of the swarm robot is broadened by constructing a competitive cooperation mechanism, the communication load and loss are reduced through distributed design, and the stability of a swarm robot system is guaranteed.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
A Cooperative Motion Method for Swarm Robots in Scenes with Obstacles
ActiveCN110162035BReduce couplingSimple designPosition/course control in two dimensionsEngineeringComputer vision
The invention relates to the technical field of robots, more particularly to a cooperative motion method for a robot cluster in an obstacle scene. The method provided by the invention is used for enabling multiple robots to realize formation transformation, dynamic and static obstacle avoidance and cooperative motion in the obstacle scene. The method defines the cooperative control of the robot cluster in a complex environment as a distributed model predictive control problem. Each robot solves an optimization equation independently based on the information of local neighbors, which has betterrobustness and flexibility. At the same time, the method proposes the concept of a formation diagram, and uses a directed diagram to represent the robot formation. Under the premise of ensuring the connectivity of the diagram, local transformation of the desired formation can be realized by changing the edges and weights of the formation, and at the same time, the connectivity and the flexibilityof the cluster can be ensured. Besides, the method provided by the invention has a hierarchical structure. By adopting the hierarchical structure, the coupling between modules can be reduced, and algorithm design and expansion can be facilitated.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Navigation escape method for swarm robots under coverage of complex environment area
ActiveCN114237226AEffective coverageImprove stabilityPosition/course control in two dimensionsCellular automationSimulation
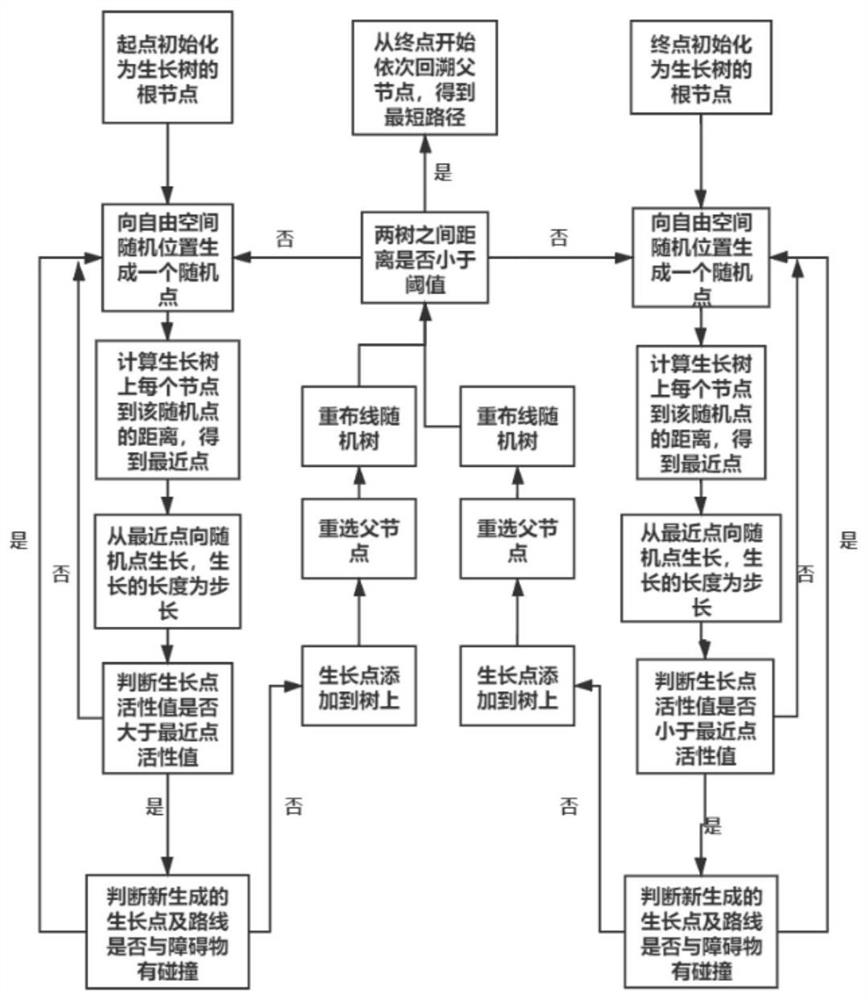
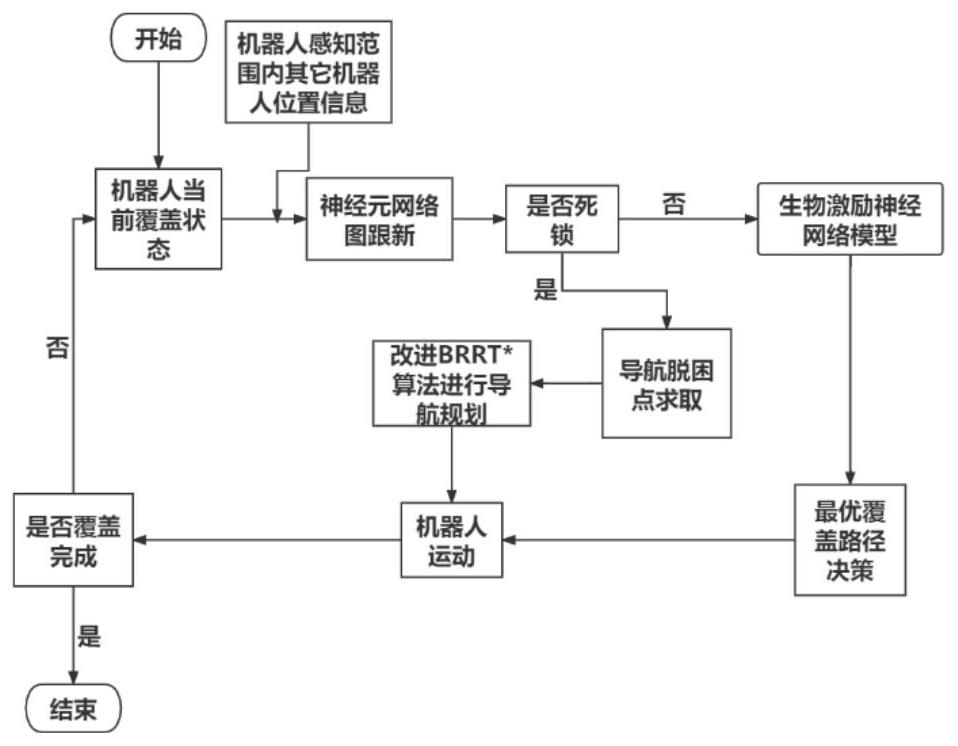
The invention relates to a navigation escape method under complex environment area coverage of a swarm robot, and aims to solve the problem of low coverage efficiency caused by deadlock when the swarm robot executes area coverage in an unknown complex environment under communication limitation. The invention provides a navigation escape mechanism which is suitable for an unknown environment and is smaller in calculated amount, so that the robot escapes from deadlock. When the robot is deadlocked in the area coverage process, an optimal navigation deadlock-out point of the robot is found by introducing a cellular automaton mechanism, and path planning is carried out by improving a BRRT * (bidirectional fast expansion star) navigation algorithm to enable the robot to escape from a dead area, so that efficient coverage of the swarm robot to a complex environment is realized.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com