Patents
Literature
136results about How to "Reduce moment of inertia" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Aircraft, preferably unmanned
InactiveCN104364154AExtension of timeExpand the scope ofUnmanned aerial vehiclesEfficient propulsion technologiesFlight vehicleUncrewed vehicle
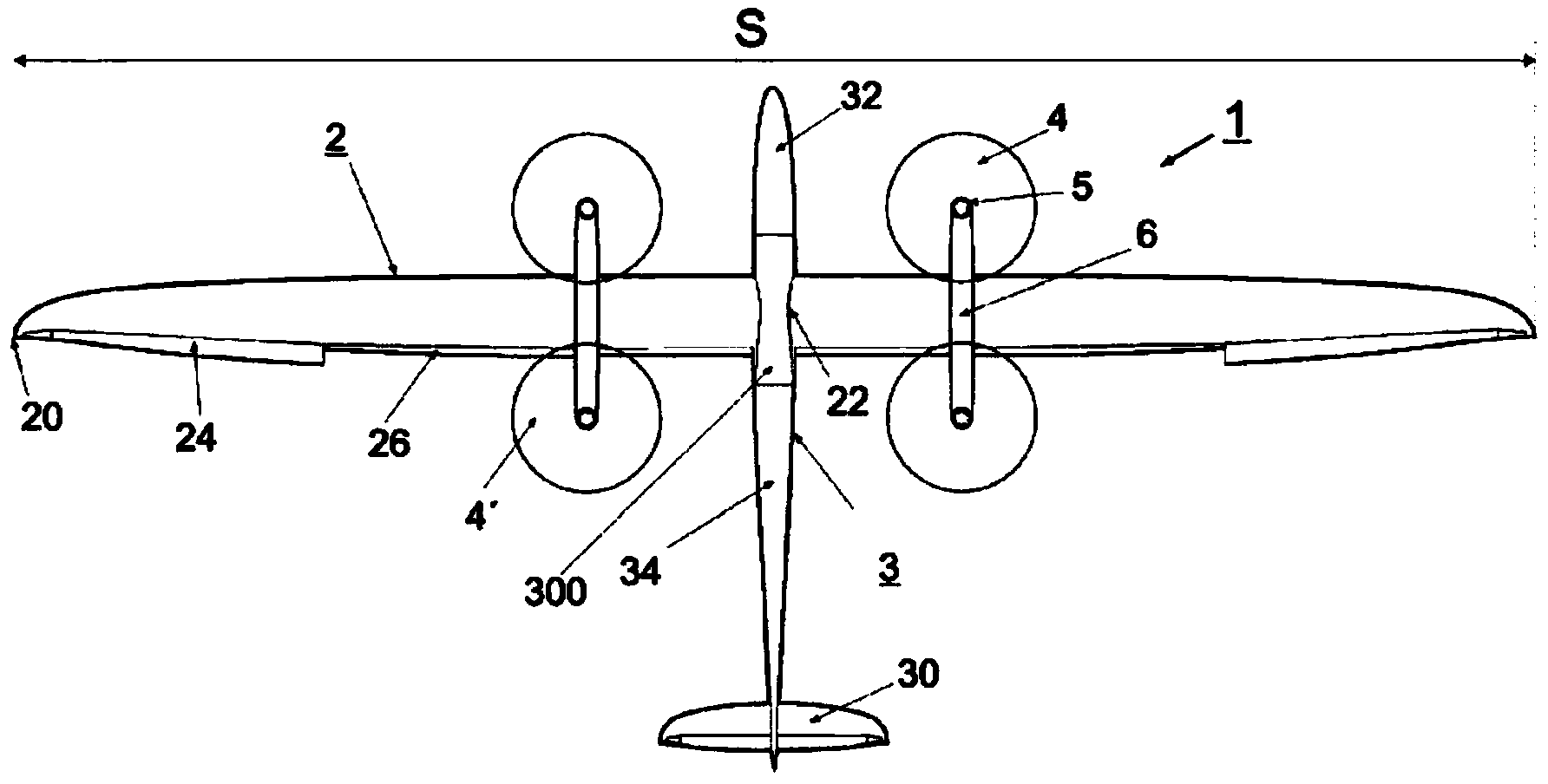
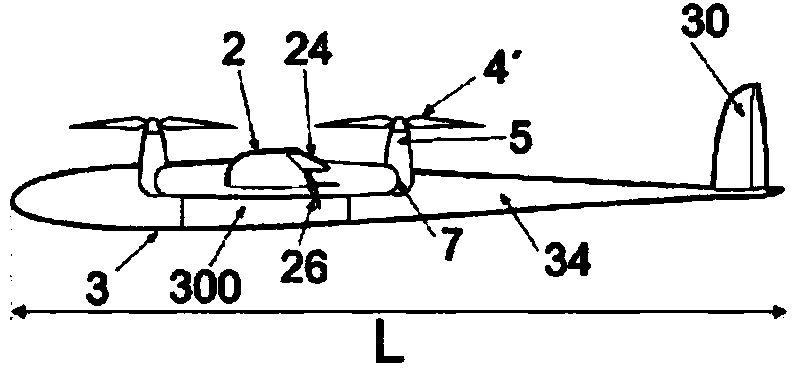
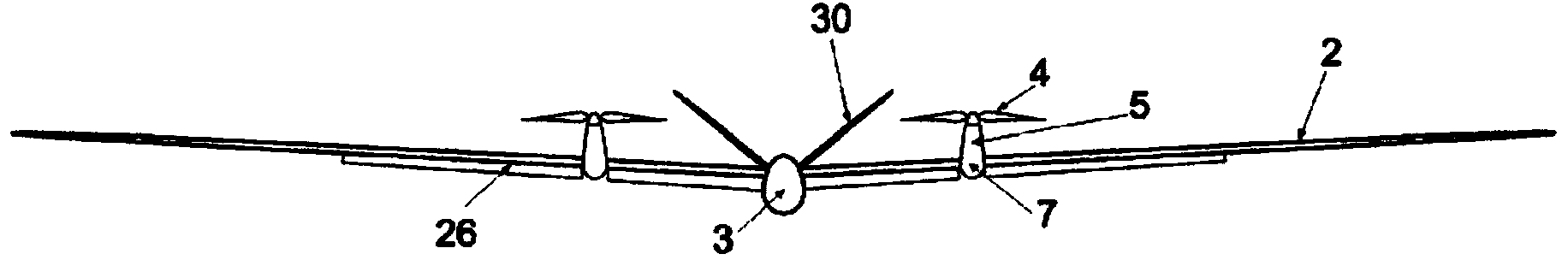
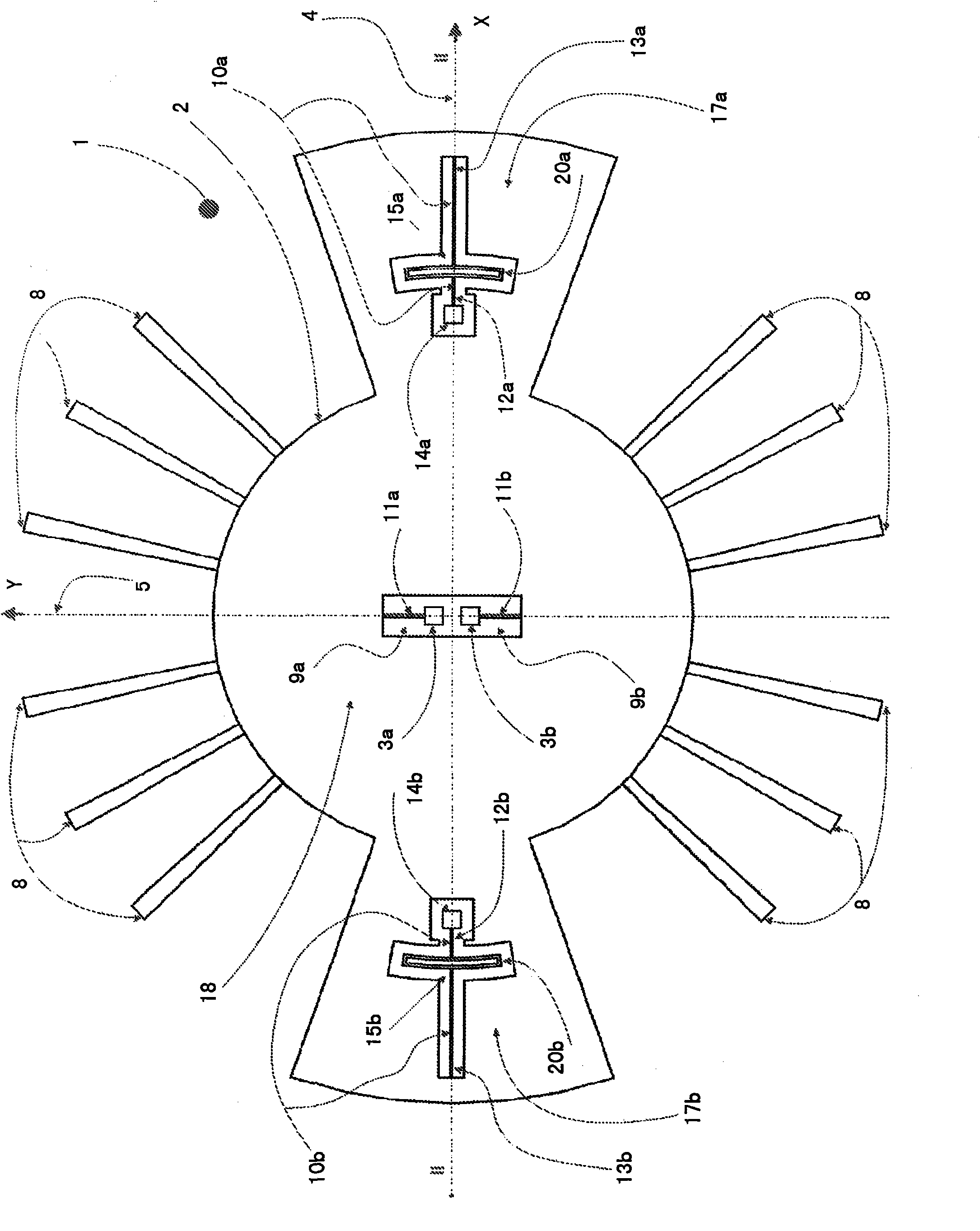
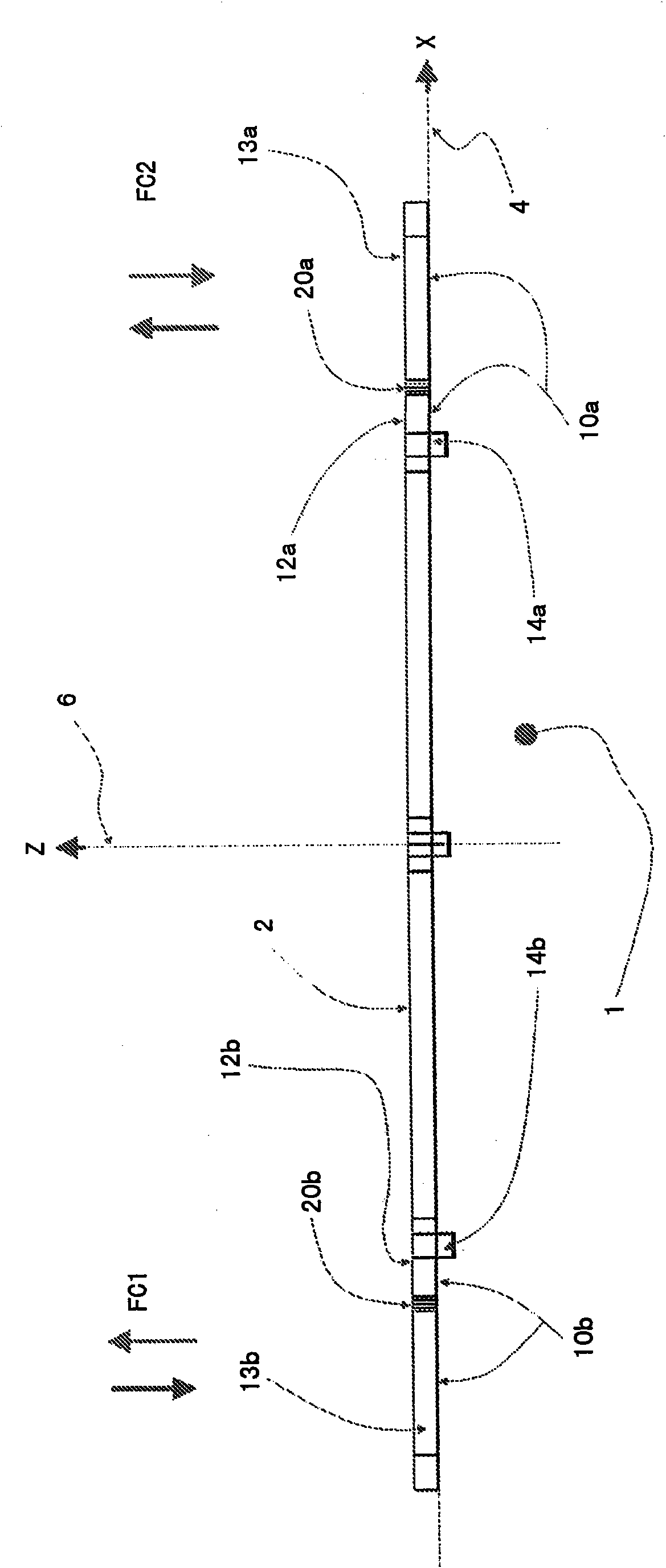
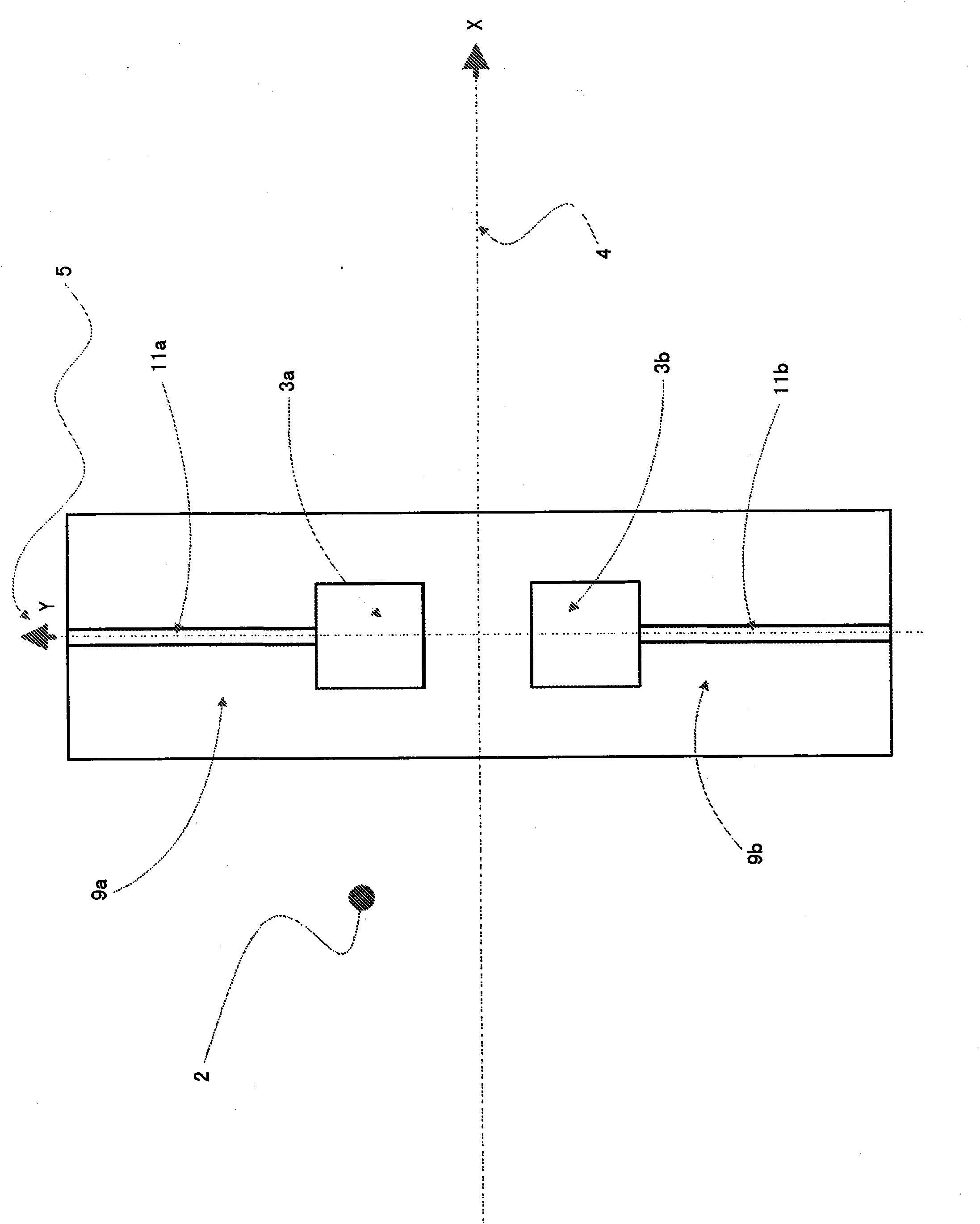
The invention relates to an aircraft (1), preferably an unmanned aircraft (UAV), drone, or unmanned aerial system (UAS), comprising a rigid wing (2), which enables aerodynamic horizontal flight, and at least four rotors (4, 4'), which are driven by means of controllable electric motors (5) and which can be pivoted between a vertical starting position and a horizontal flight position by means of a pivoting mechanism (7), wherein all electric motors (5) and rotors (4) are arranged on the wing (2).
Owner:QUANTUM SYST GMBH
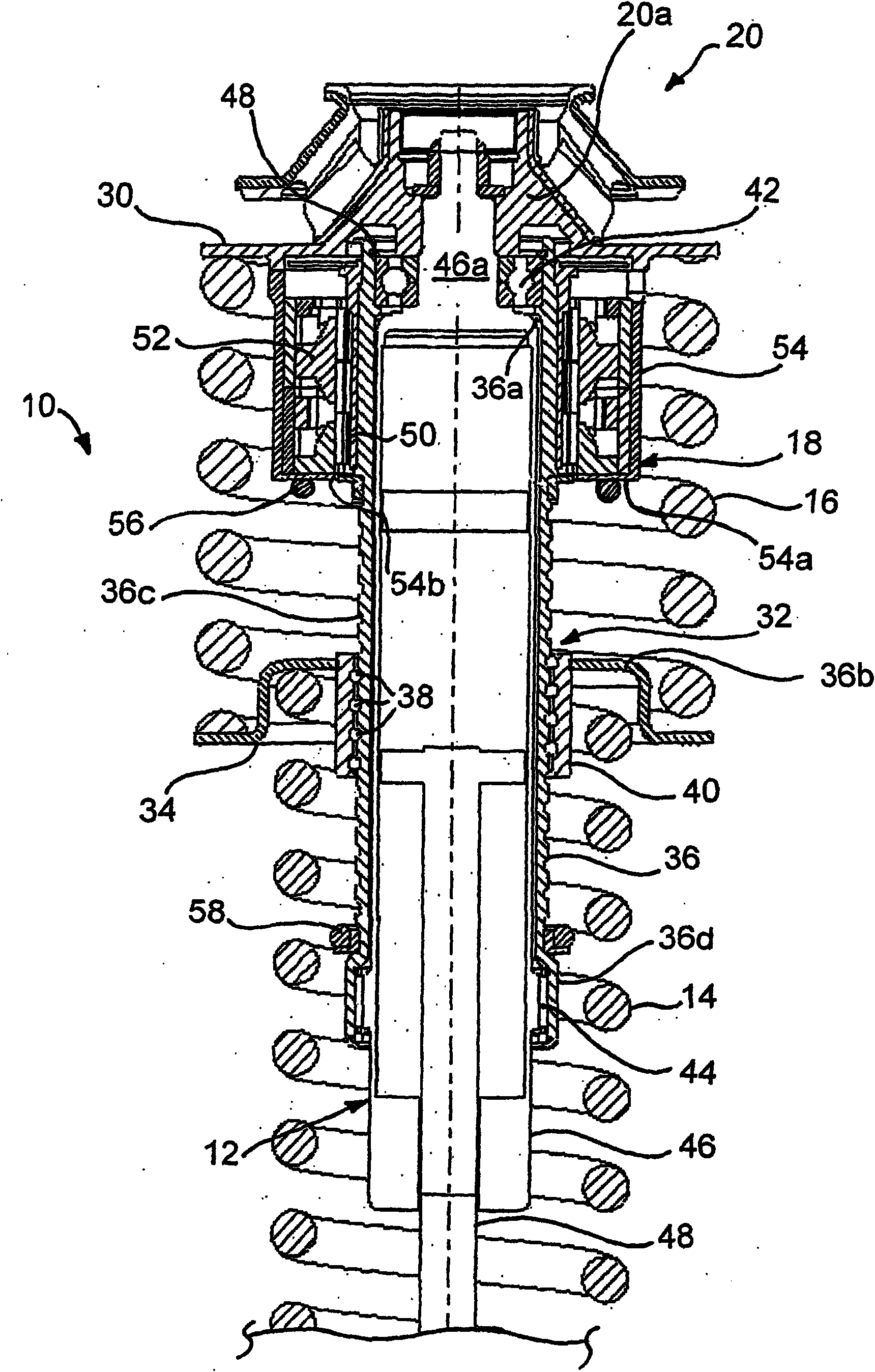
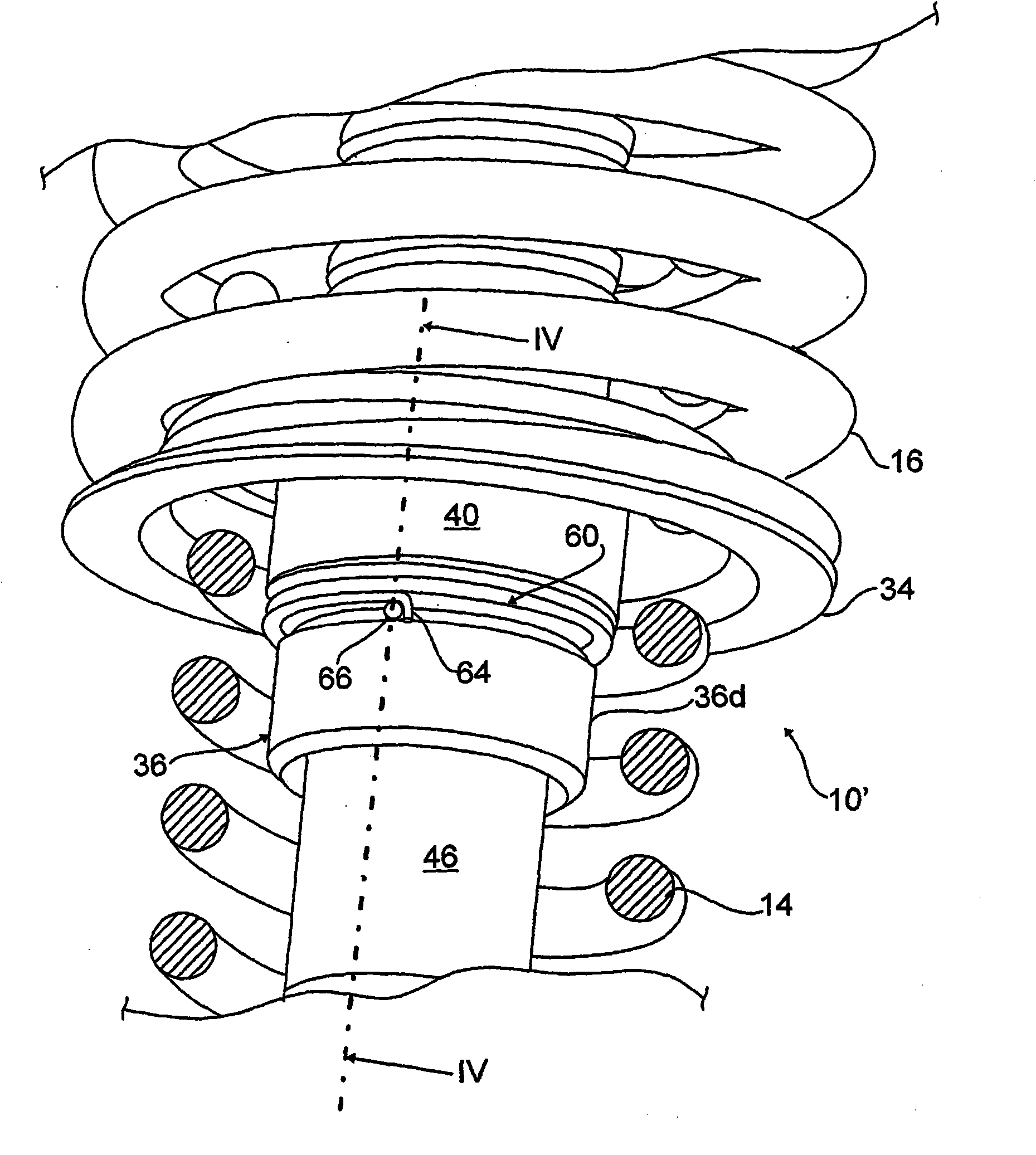
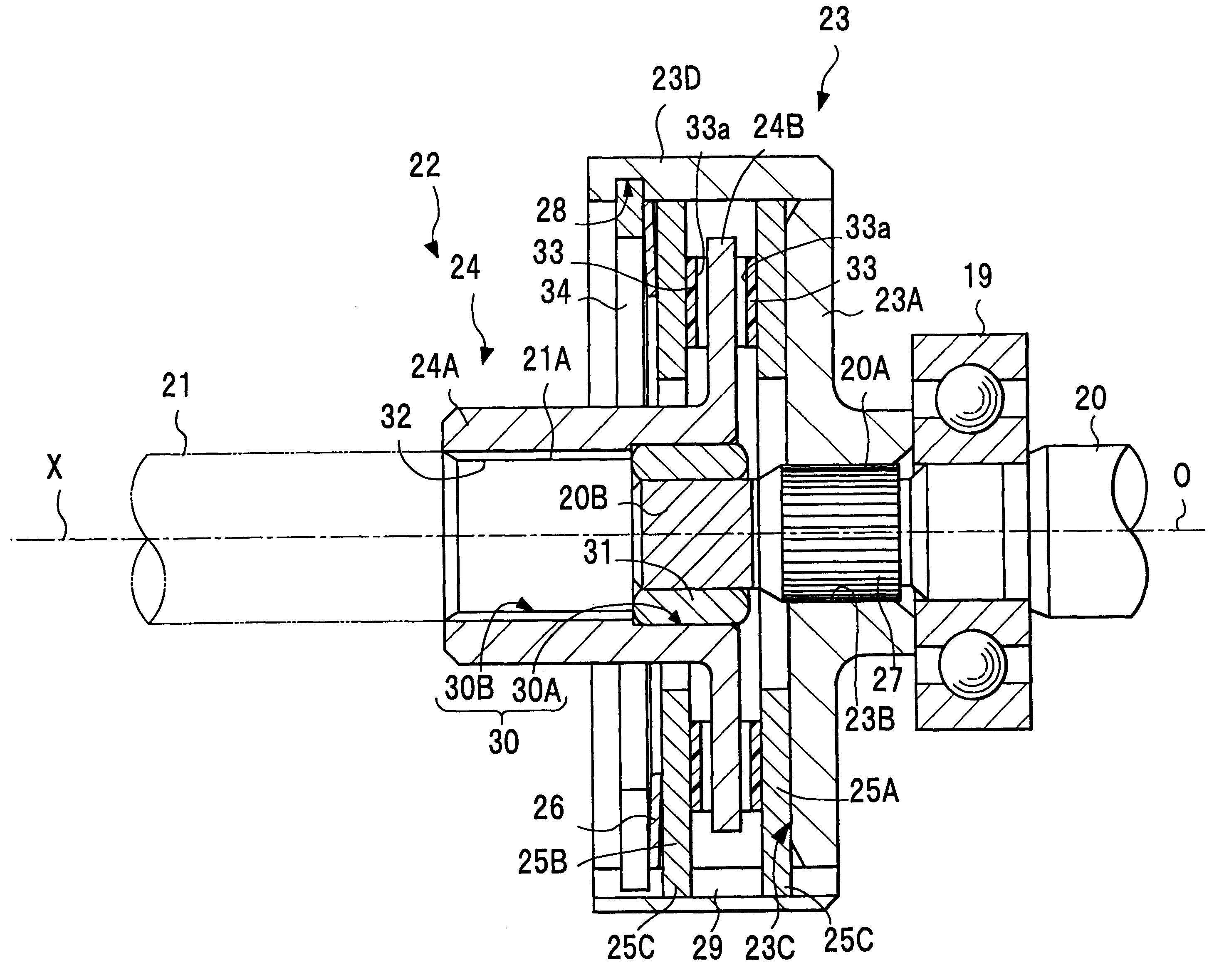
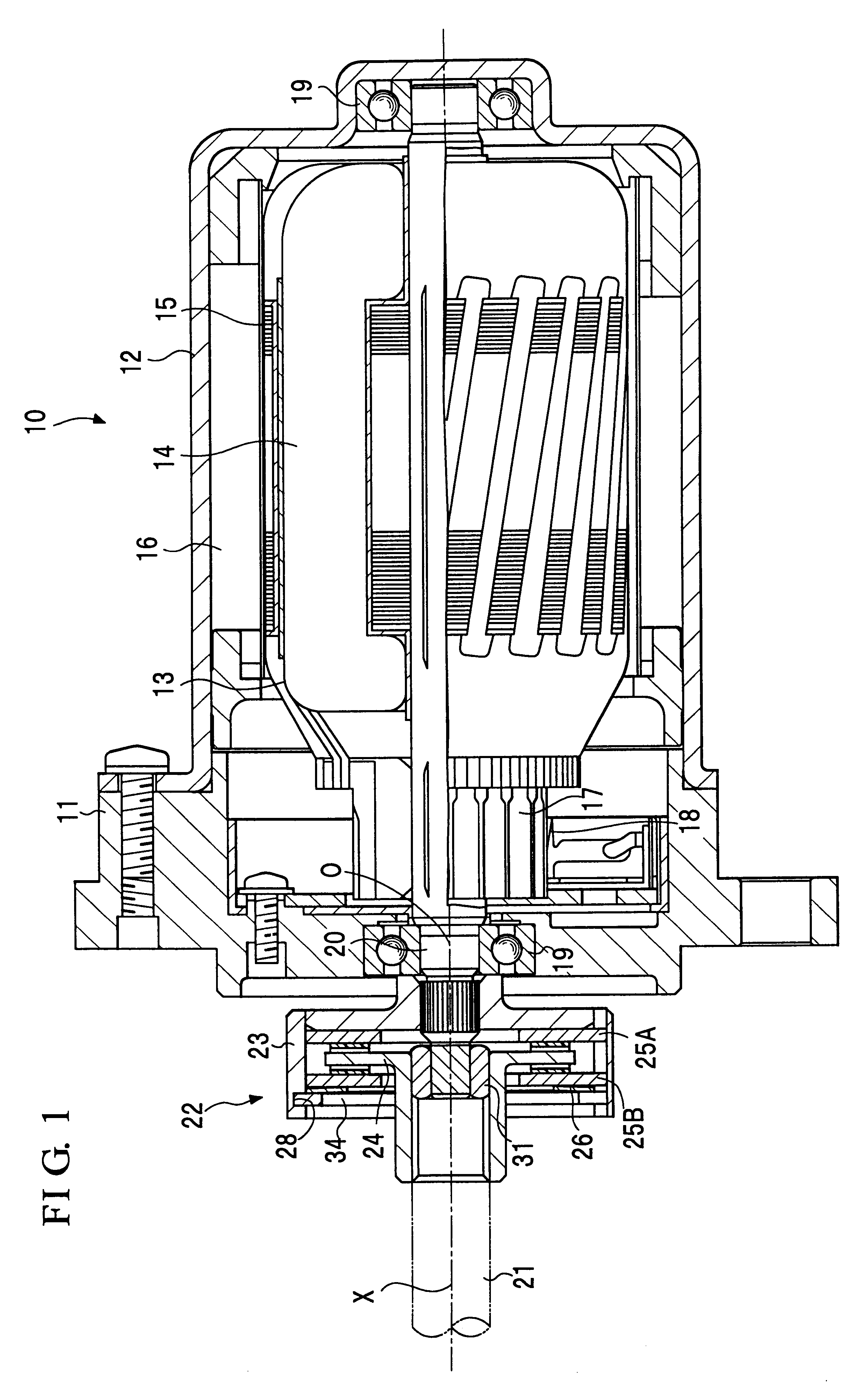
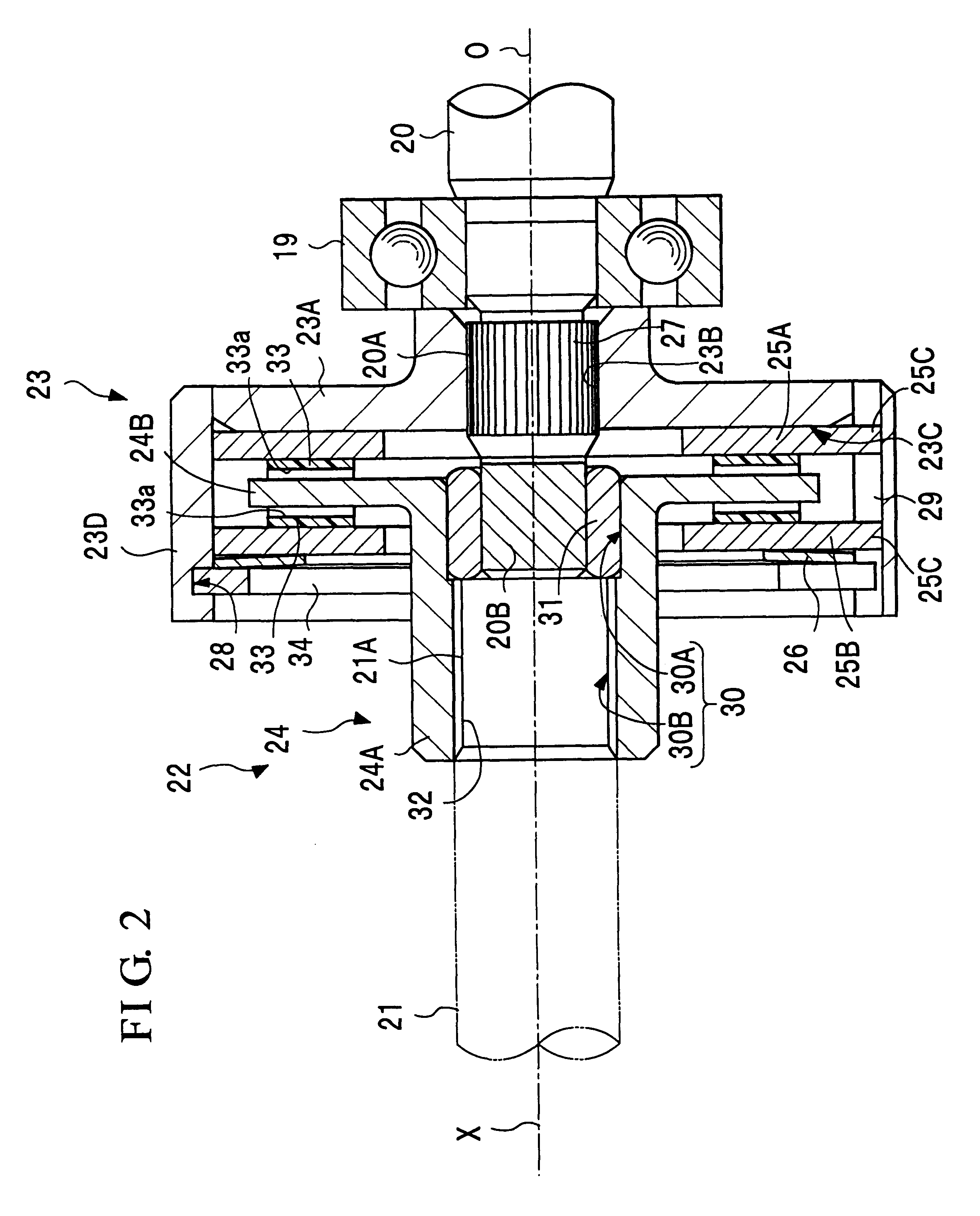
Spring strut arrangement for wheel suspensions of motor vehicles
InactiveCN101896369AWeight advantageReduce reaction forceResilient suspensionsVehicle springsHelical coilShock absorber
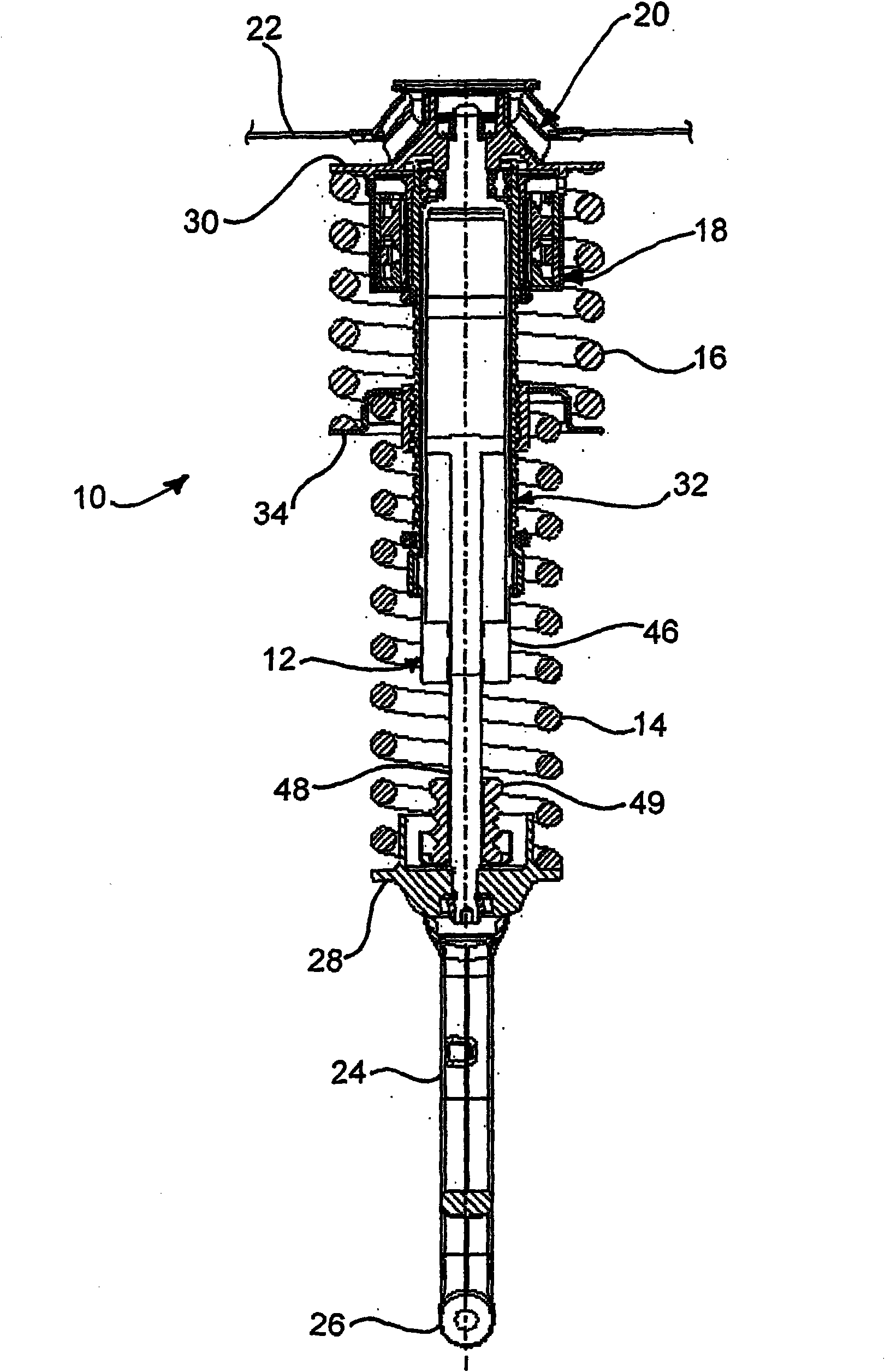
The invention relates to a spring strut arrangement for wheel suspensions of motor vehicles formed of a telescoping shock absorber (12), a suspension spring element (14) preferably designed as a helical compression spring, and a storage spring element (16) preferably designed as a helical coil spring, wherein the spring elements (14, 16) are supported by spring caps (28, 30) on the body (22) of the motor vehicle and on a wheel suspension element (24), and third spring cap (34) located therebetween is displaceably guided relative to the body (22) along the longitudinal axis of the shock absorber by means of an electrically driven positioning drive (32) disposed within the spring elements (14, 16), wherein the positioning drive (32) comprises a positioning spindle (36) rotatably supported about the shock absorber and a positioning nut (40) connected to the displaceable spring cap (34). According to the invention, the shock absorber (12) is disposed on the body (22) of the motor vehicle with the damping tube (46) upward, and the positioning spindle (36) is rotatably supported on the damping tube (46).
Owner:AUDI AG
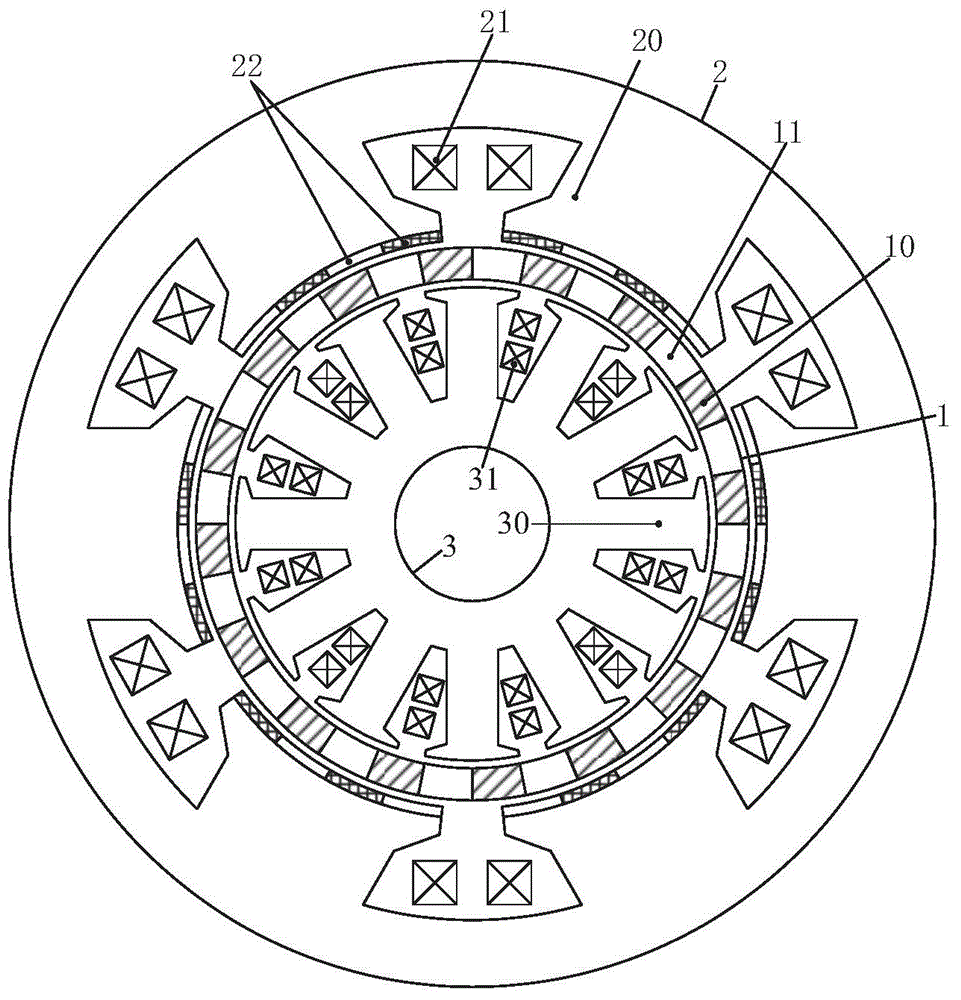
Double-stator magnetic field modulation permanent magnet motor
ActiveCN104883016AImprove power densityImprove power efficiencyMagnetic circuit rotating partsElectric machinesPower factorPermanent magnet motor
The invention discloses a double-stator magnetic field modulation permanent magnet motor comprising an inner stator, an outer stator, and a rotor. Air gaps are formed between the rotor and the inner and outer stators. The rotor is formed by magnetic conductors and non-magnetic conductors which are arranged alternately. The outer stator is formed by outer stator teeth, radial magnetizing permanent magnets, and an armature winding. The radial magnetizing permanent magnets adhere to the inner surfaces of the outer stator teeth. Adjacent permanent magnets on the same outer stator tooth have opposite magnetizing directions. The inner stator is just formed by inner stator teeth equipped with grooves along the circumferential direction and an armature winding in the grooves while not being provided with any permanent magnet. According to the double-stator magnetic field modulation permanent magnet motor, the two armature windings are used while the amount of the permanent magnets is not increased. Thus, an armature magnetic field is fully utilized and a power factor and the power density are increased. Compared with a product in the prior art, the double-stator magnetic field modulation permanent magnet motor is not provided with a rotor magnetic conductive yoke portion, decreased in rotor size and iron loss, and increased in the power density and efficiency, and can be used in power systems such as electric automobile, wind power generation or the like.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Bionic mechanical eyeball based on spherical ultrasonic motor
InactiveCN102922526AMeet the image information requirements required for target trackingReduce quality problemsManipulatorCMOSElastomer
The invention relates to a bionic mechanical eyeball based on a spherical ultrasonic motor. The bionic mechanical eyeball consists of an eyeball, three stator mechanisms and a base plate, wherein a mini-sized CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) camera and an attitude sensor are loaded in the eyeball, each stator mechanism consists of a tooth-shaped annular elastomer and a compressing mechanism, and a piezoelectric ceramic piece is attached to the tooth-shaped annular elastomer and the compressing mechanism is used for generating a pressing force; the eyeball is contacted with internal tooth circles of the tooth-shaped annular elastomers of the three stator mechanisms respectively in a tangential manner and is subjected to compressing and centering by each compressing mechanism; and meanwhile, the three stator mechanisms are vertically fixed on the base plate and symmetrically distributed by rotating around a center shaft for 120 degrees, and an included angle between the plane where the eyeball and a contact circle of each stator mechanism are located and the base plate surface is 65 degrees. According to the bionic mechanical eyeball based on the spherical ultrasonic motor, the structure is simple and compact, the response speed is quick, the control precision is high, and the visual angle of the mechanical eyeball reaches 50 degrees; and the bionic mechanical eyeball based on the spherical ultrasonic motor can be applied to various complex visual systems.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Robot
InactiveCN102407524ACompact structureSmall footprintProgramme-controlled manipulatorMechanical apparatusEngineeringActuator
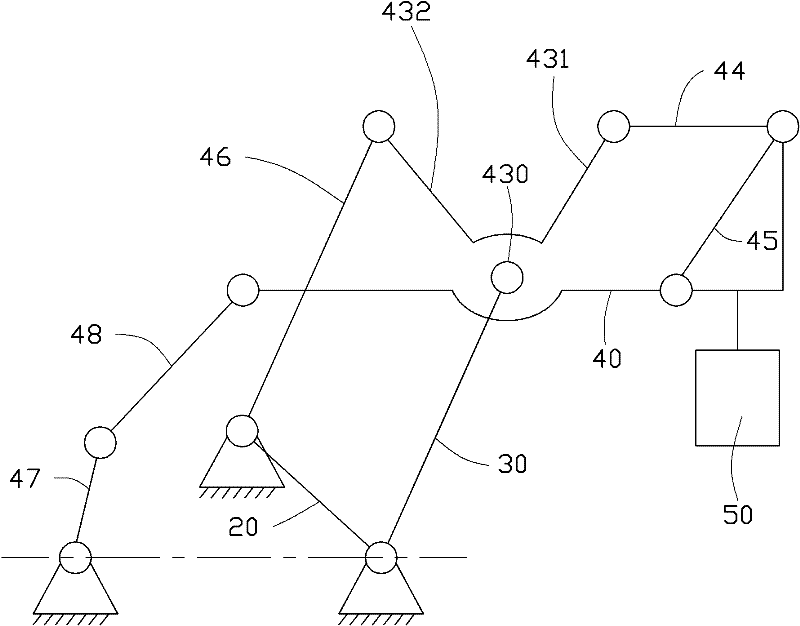
The invention relates to a robot. The robot comprises a frame, a large arm, a small arm, a tail end actuator, a connecting piece connected with the small arm in a rotating mode, a first connecting rod and a second connecting rod which are connected between the connecting piece and the small arm in turn, a third connecting rod connected with the frame and the connecting piece in the rotating mode, a driving connecting rod connected with the frame in the rotating mode, a driven connecting rod connected with the driving connecting rod and the small arm, a first driving component for driving the large arm, and a second driving component for driving the driving connecting rod, wherein the connecting piece, the first connecting rod, the second connecting rod and the small arm form a first parallelogram structure; the connecting piece, the large arm, the third connecting rod and the frame form a second parallelogram structure; the driving connecting rod, the driven connecting rod, the small arm, the large arm and the frame form a pentagonal structure; the tail end actuator is arranged on the second connecting rod; and the first driving component and the second driving component are arranged on the frame. The robot has the advantages that: the robot has a compact structure and is convenient to control.
Owner:HONG FU JIN PRECISION IND (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
Micromechanical rate-of-rotation sensor
InactiveCN101855516AReduce moment of inertiaCompact and robust implementationTurn-sensitive devicesClassical mechanicsRotation sensor
The present invention relates to a micromechanical Coriolis rate-of-rotation sensor for detecting a rate of rotation about a measurement axis which is denoted the X axis below, having a substrate, an oscillation structure and means for generating a rotational oscillation about an excitation axis (Z axis) which is orthogonal to the measurement axis, wherein the oscillation structure is rotatably connected to the substrate by means of first, inner suspension means or by means of a central suspension means, with the result that it can carry out rotational oscillations about a fulcrum relative to the substrate, wherein at least one pair of second suspension means also connects the oscillation structure to the substrate and is arranged on opposite sides of the fulcrum, wherein the at least one pair of second suspension means is arranged at a greater radial distance from the fulcrum than the first, inner suspension means or the central suspension means in order to provide a micromechanical Coriolis rate-of-rotation sensor with a response behaviour which can be designed in a manner specific to the axis of rotation and with sufficient sensitivity to rates of rotation in one or more directions of rotation, which sensor simultaneously has sufficient robustness with respect to the effect of external shock or vibration in the measuring direction or directions (about a detection axis) in order to meet the requirements for electronic signal processing as far as possible and, in particular, to counteract the risk of the oscillation structure sticking on the substrate.
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD GMBH
Smart quadruped robot with flexible waist
The invention discloses a smart quadruped robot with a flexible waist. The smart quadruped robot with the flexible waist comprises a front body, a rear body, a waist mechanism, crotch mechanisms and leg mechanisms. The front body and the rear body are connected through a split Hooke joint, so that relative deflection and pitching of the front body and the rear body are realized. The front body and the rear body are respectively provided with two crotch mechanisms, wherein output shafts of the crotch mechanisms are made to face the outer side of the bodies so that the leg mechanisms can be installed; the output shafts are meshed with bevel gears between transmission shafts for transmission, so that the output shafts are driven through rotation. A fixed shaft is fixed to each crotch mechanism, and the fixed shafts are driven to rotate to rotate a gearbox; in this way, the leg mechanisms can swing front and back as well as up and down. Each leg mechanism comprises a thigh part and a calf part, wherein each thigh part and each calf part are connected through a knee joint; transmission of the knee joints is realized through two bevel gears, so that the calf part made to swing front and back relative to the thigh part. The smart quadruped robot with the flexible waist has the advantages that the capability of passing through a mountain environment of the robot can be improved, the turning radius in the advancing process is reduced, rotational inertia of legs of the robot is reduced, and the energy utilization rate is increased.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Leg configuration for rotatably driven three-dimensional walking robot
The invention provides a leg configuration for a rotatably driven three-dimensional walking robot. The leg configuration comprises a rack, a leg telescoping mechanism, a parallel drive mechanism, and a rotatably driven mechanism. The rotatably driven mechanism is connected with the parallel drive mechanism in a driving manner. The parallel drive mechanism is connected with the leg telescoping mechanism in a driving manner. The leg telescoping mechanism is connected with the rack. The leg configuration for a rotatably driven three-dimensional walking robot has special dead point postures, and under the postures, ground impact force stressed by toes cannot be transmitted to a driver, so the robot has very good impact resistance and load resistance capability. The leg configuration solves problems of impact resistance for a robot to work in complex terrain and poor environment operating conditions.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Injection molding machine driving device, injection device and mold clamping device
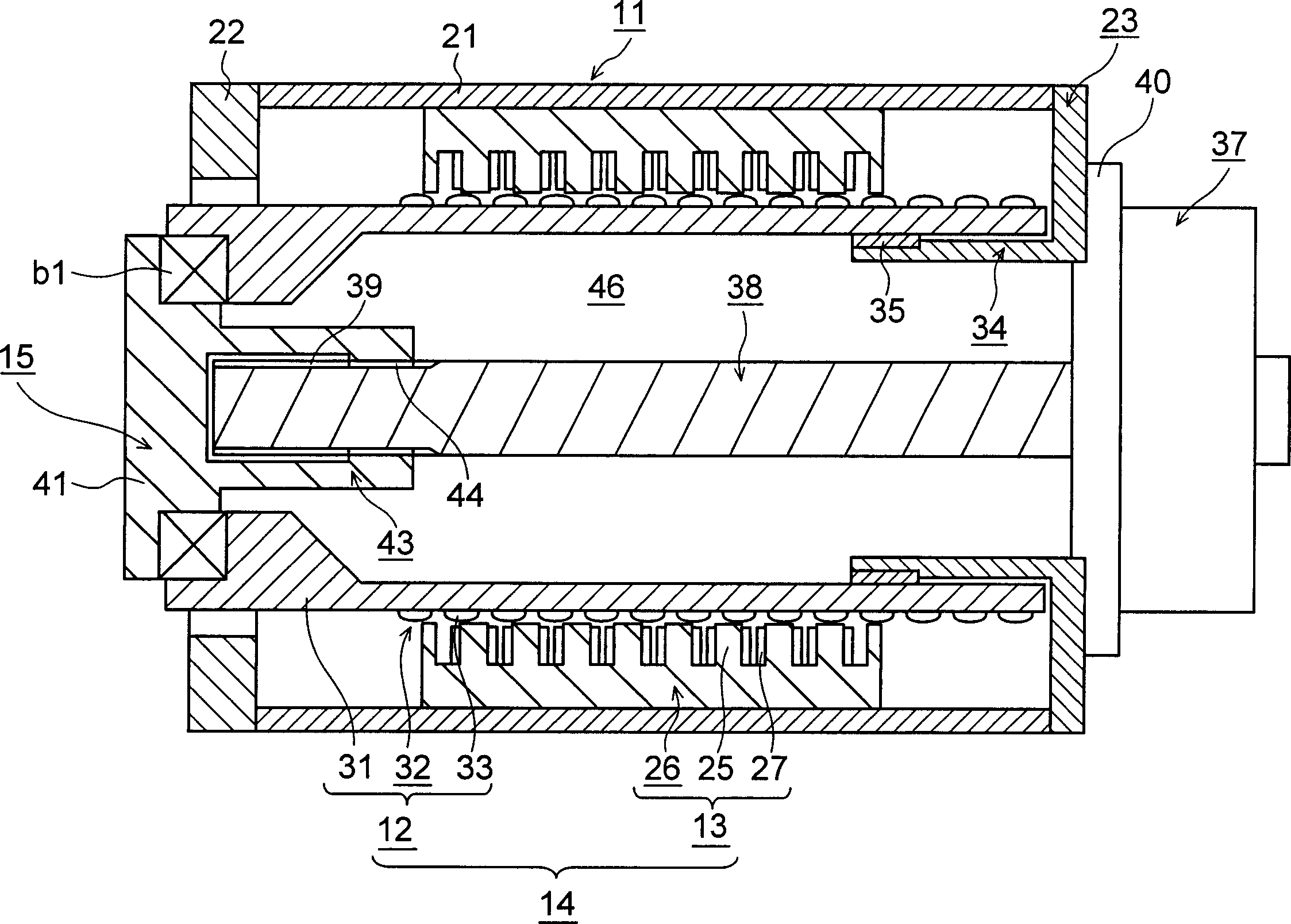
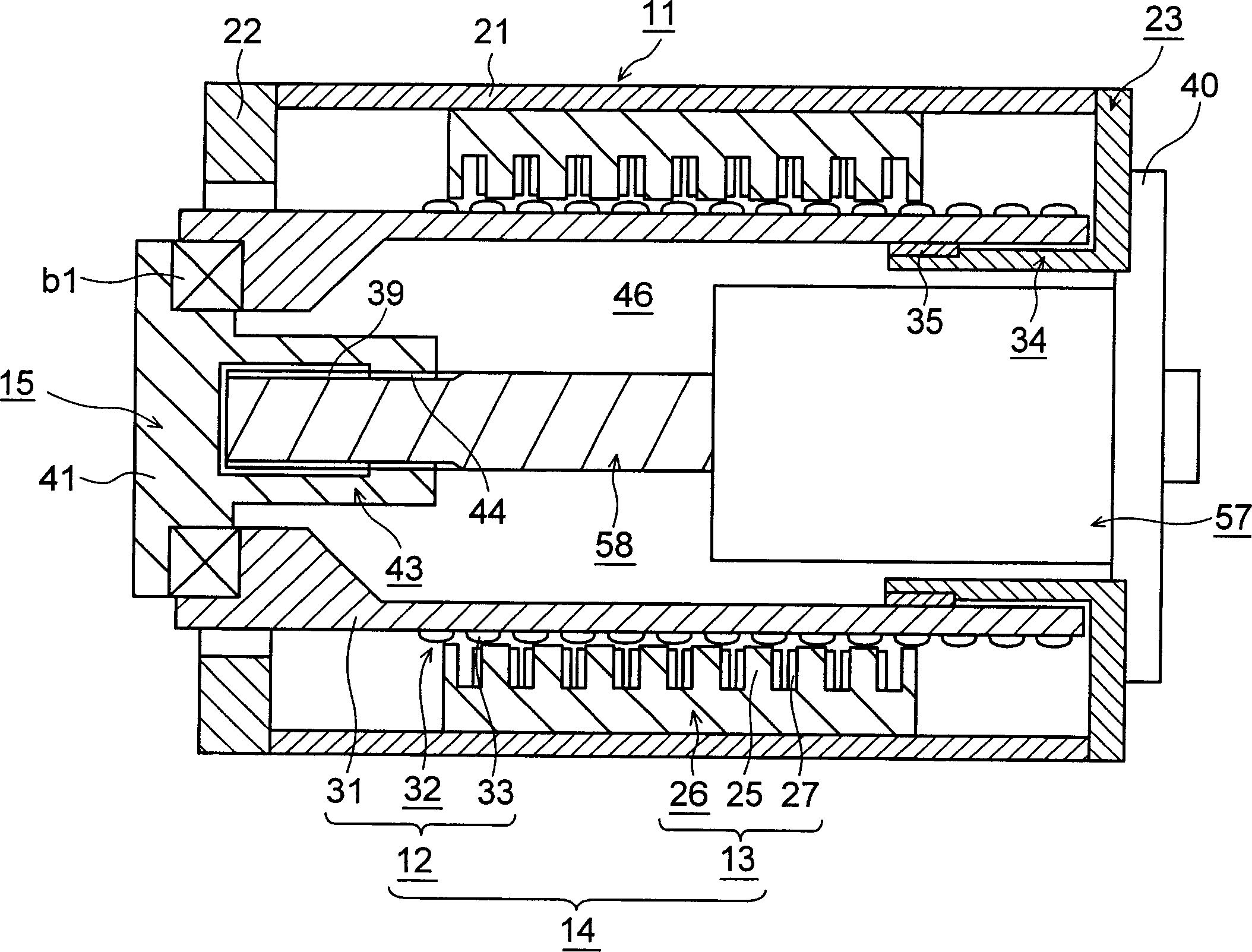
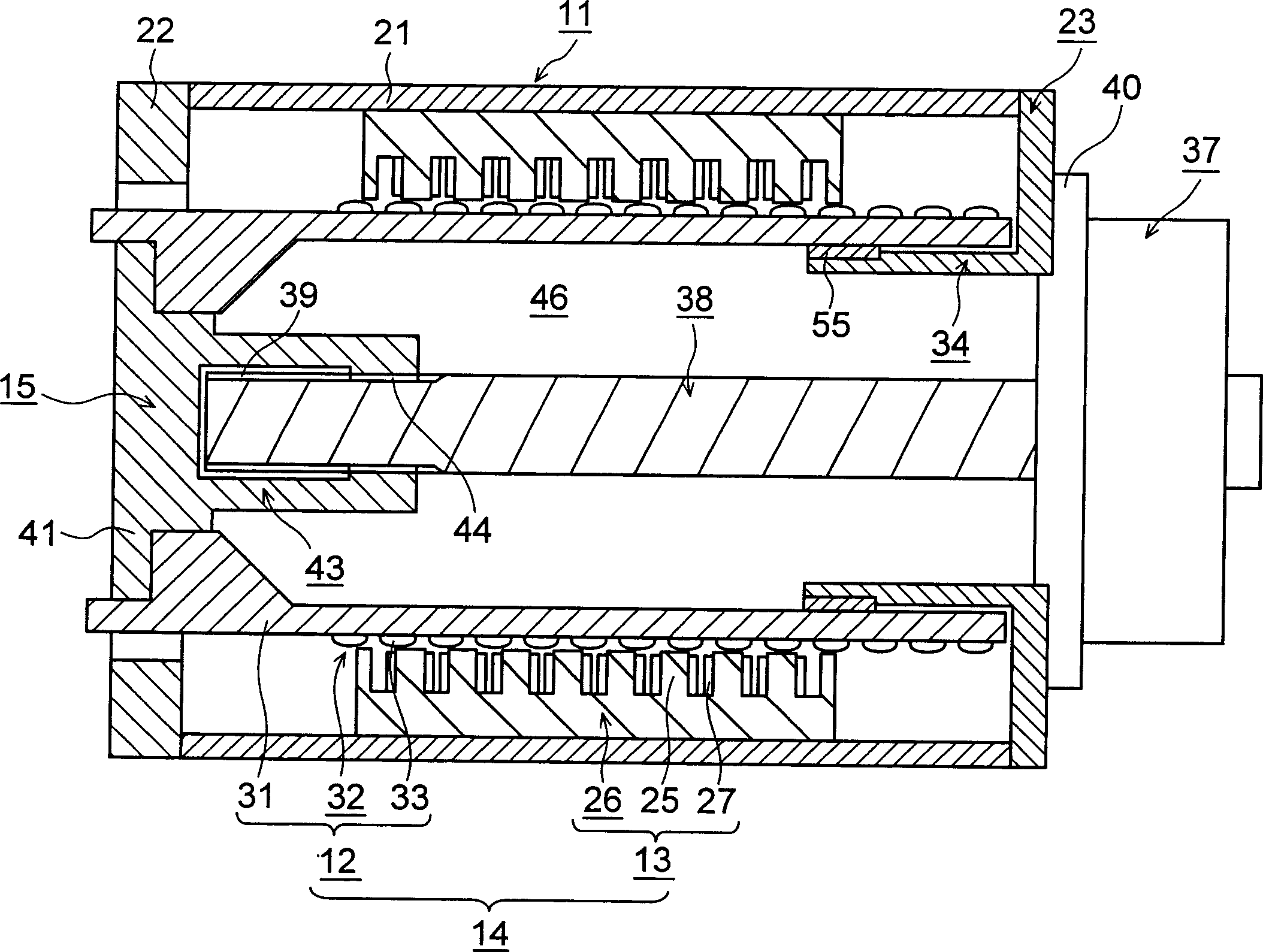
The object is to provide an injection molding machine driving device capable of generating a large thrust and of continuous drive with a short cycle. It comprises a casing body (11), a cylindrical linear motor (14) provided with a mover (12) disposed in the casing body (11) for advance and retraction and a stator (13) attached to the casing body (11), the linear motor (14) constituting a first drive section, a driven body (15) advanced and retracted together with the mover (12), and a second drive section attached to the casing body (11) and disposed so as to axially overlap the linear motor (14) at least partially. A slight axial increase in the radial dimension makes it possible to sufficiently increase the area of a permanent magnet (23) for the mover (12), thus increasing the capacity of the linear motor (14).
Owner:SUMITOMO HEAVY IND LTD
Cantilever mechanism for piezoelectric power generation
InactiveCN103888023AImprove energy conversion performanceRaise the natural frequencyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSplit linesElastic substrate
The invention relates to a cantilever mechanism for piezoelectric power generation. The cantilever mechanism comprises a base (1), an elastic substrate (2), a piezoelectric material thin sheet (3), mass blocks (4) and a wire, wherein one end of the elastic substrate (2) is connected with the base (1), the piezoelectric material thin sheet (3) is laminated with the elastic substrate (2), the mass blocks (4) are arranged at one end, far away from the base (1), of the elastic substrate (2), an electrode (31) and an electrode (32) are arranged on the surface of the piezoelectric material thin sheet (3), an electrode cutting line (33) is arranged between the electrode (31) and the electrode (32), the electrode cutting line (33) is formed in an area in a middle line in the direction from the base (1) to the mass blocks (4), wherein the electrodes are not arranged in the area. The mass blocks (4) are symmetrically distributed and arranged relative to the electrode cutting line (33), and the cantilever mechanism for piezoelectric power generation has multi-mode characteristics and broadband characteristics.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Wet clutch
ActiveCN103174767AReduced Weight DisadvantagesReduce moment of inertiaFluid actuated clutchesFriction clutchesEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention relates to a wet clutch, comprising a first sub-clutch, a second sub-clutch and a clutch cover. The first sub-clutch and the second sub-clutch are respectively provided with an inner sheet bearing member and an outer sheet bearing member, the inner sheet bearing member is connected with a rotor without relative rotation, the outer sheet bearing member is respectively connected with a second transmission input shaft, the axial exterior of the first outer sheet bearing member of the first sub-clutch is enclosed by the seond outer sheet bearing member of the second sub-clutch, the outer sheets are respectively connected with the corresponding outer sheet bearing members without relative rotation and in an axial movable manner, the outer sheet bearing members are respectively provided with tooth areas, thereby the outer radius of the second outer sheet bearing member is larger than the inner radius of the first outer sheet bearing member.
Owner:SCHAEFFLER TECH AG & CO KG
Multi-legged walking robot capable of flexibly steering and advancing
InactiveCN108382484ARealize the walking propulsion functionFlexible steeringVehiclesMotor driveEngineering
The invention belongs to the field of robots, and discloses a multi-legged walking robot capable of flexibly steering and advancing. The multi-legged walking robot comprises a torso unit and a plurality of walking leg units. Each walking leg unit comprise a first support frame, a first motor driving module, a second support frame, a passive foot module and two leg propulsion modules, and each legpropulsion module comprises a second motor driving module, a thigh and a shank; and the passive foot module comprises a passive support foot and a passive rotating joint, the passive support foot is fixedly mounted on the passive rotating joint, and the passive rotating joint is rotatably mounted at the lower end of one of the shanks. The first motor driving modules of the robot can drive the walking leg units to rotate integrally, to change the propulsion plane, in-situ 360-degree flexible steering of the robot can be realized by combining the passive rotating joints and the support feet, therequired torque for steering is extremely small and only joint friction needs to be overcome, and the leg propulsion modules can fulfill the walking propulsion function of the robot.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Centrifuge used in multi-parameter complex test environment
InactiveCN101915653ARestricted degrees of freedomReduce quality problemsWeather/light/corrosion resistanceStatic/dynamic balance measurementBall bearingDynamic balance
The invention discloses a centrifuge used in a multi-parameter complex test environment. The centrifuge comprises a stand, a driving motor, an arm, a transmission mechanism and a dynamic balance executing mechanism, wherein the arm is provided with a web plate; the transmission mechanism comprises a belt transmission mechanism and a gear mechanism; the gear mechanism comprises a pinion which is coaxial with a driven pulley and a bull gear which is fixedly connected with the arm; the upper surface of the bull gear is contacted with the bottom surface of the arm; the lower surface of the bull gear is provided with an annular groove for accommodating a thrust ball bearing capable of providing axial support for the bull gear; the bull gear is connected with the stand through the thrust ball bearing; a gap is reserved between the lower surface of the bull gear and the stand; the bull gear is provided with a through hole; the bottom of the through hole is extended inwards to form a step for arranging an angular contact ball bearing; a cover plate which is fixedly connected with the stand to compress the angular contact ball bearing is arranged above the angular contact ball bearing; and the driving motor and the transmission mechanism are arranged in the stand. The centrifuge has the advantages of small space occupied by the body, high capacity of the arm and capability of carrying various environmental chambers and realizing adaptive dynamic balance of the arm.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Wind power plant for generating energy
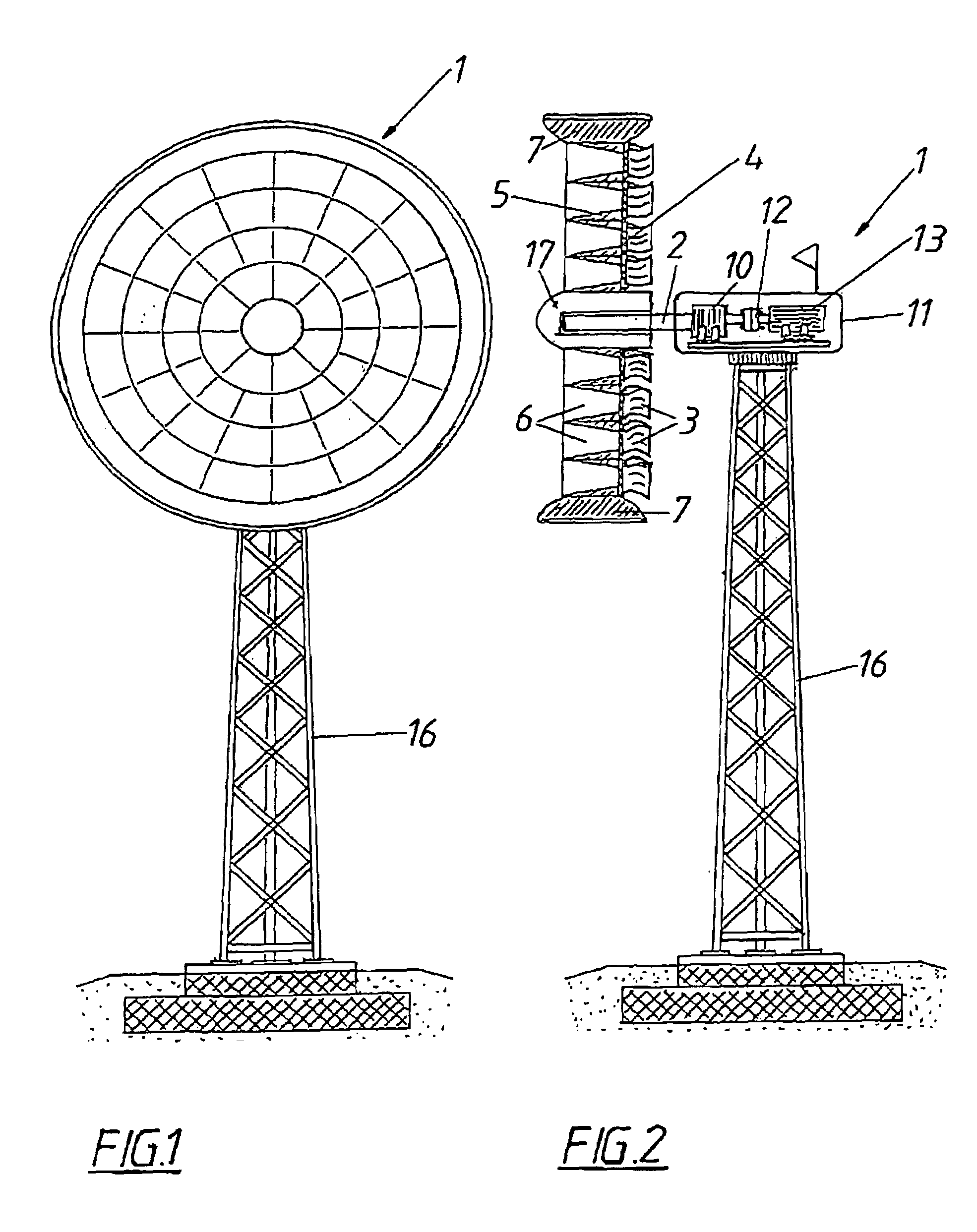
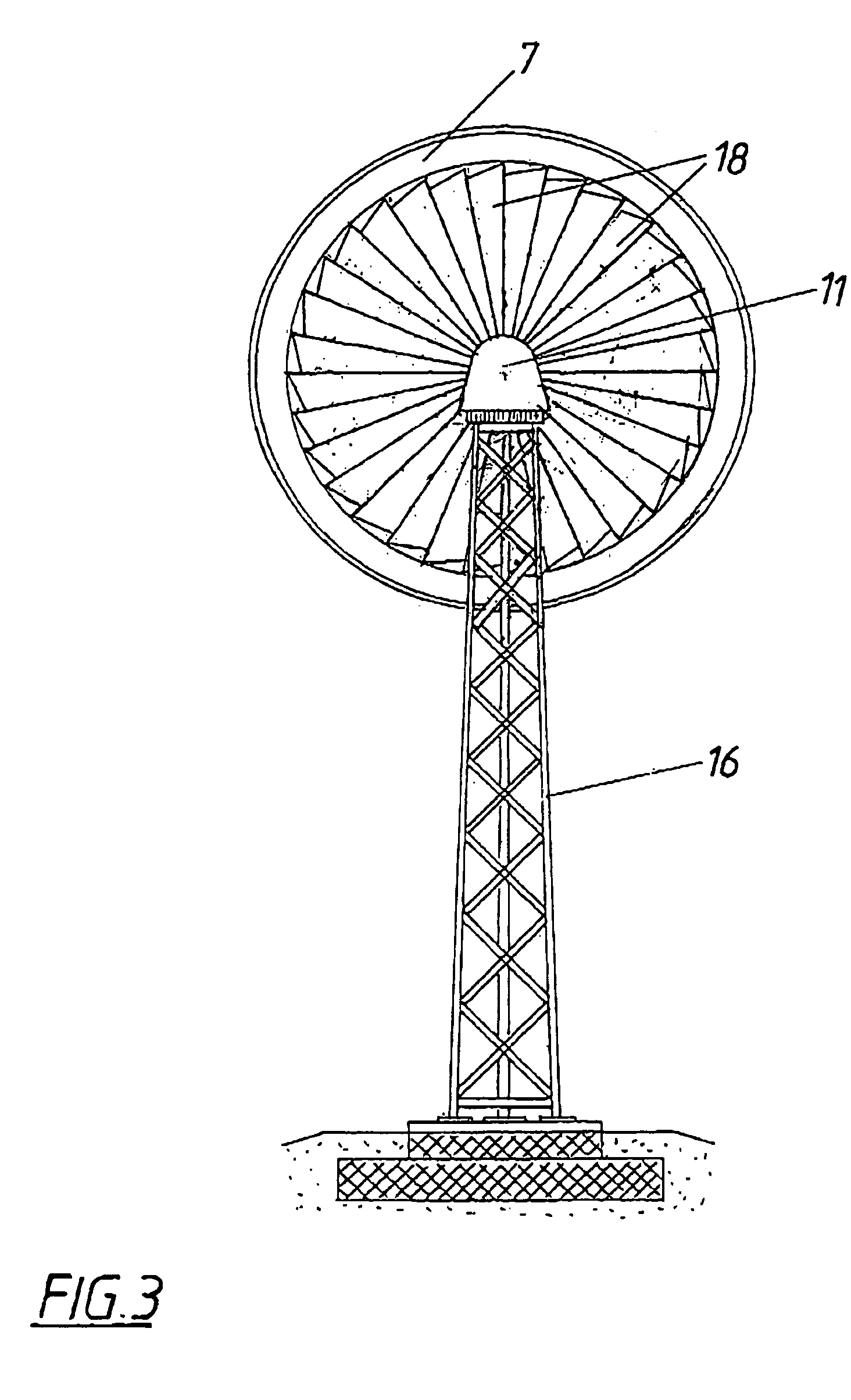
InactiveUS7118344B2Improve efficiencyIncrease airflowPropellersWind motor controlPeaking power plantPower station
A wind power system (1) for generating power is proposed, comprising a rotor which is axially flowed through, is rotatably held on a shaft (2) and is provided with blades (3), as well as a guide device (5) which accelerates the air flow through the rotor (4). In order to provide advantageous conditions for generating power it is proposed that the guide device (5) consists of several flow conduits (6) tapering in the direction of flow, which conduits are arranged on the rotor (4) in a distributed way in the manner of a rim around the shaft (2), that the blades (3) are associated with one flow conduit (6) each and that the rotor (4) comprises an outside jacket (7) enclosing the same.
Owner:GUDRUN WIESER
Force feedback main manipulator for minimally invasive surgery
ActiveCN110811843AReduce moment of inertiaMinus moment of inertiaDiagnosticsSurgical manipulatorsLess invasive surgeryEngineering
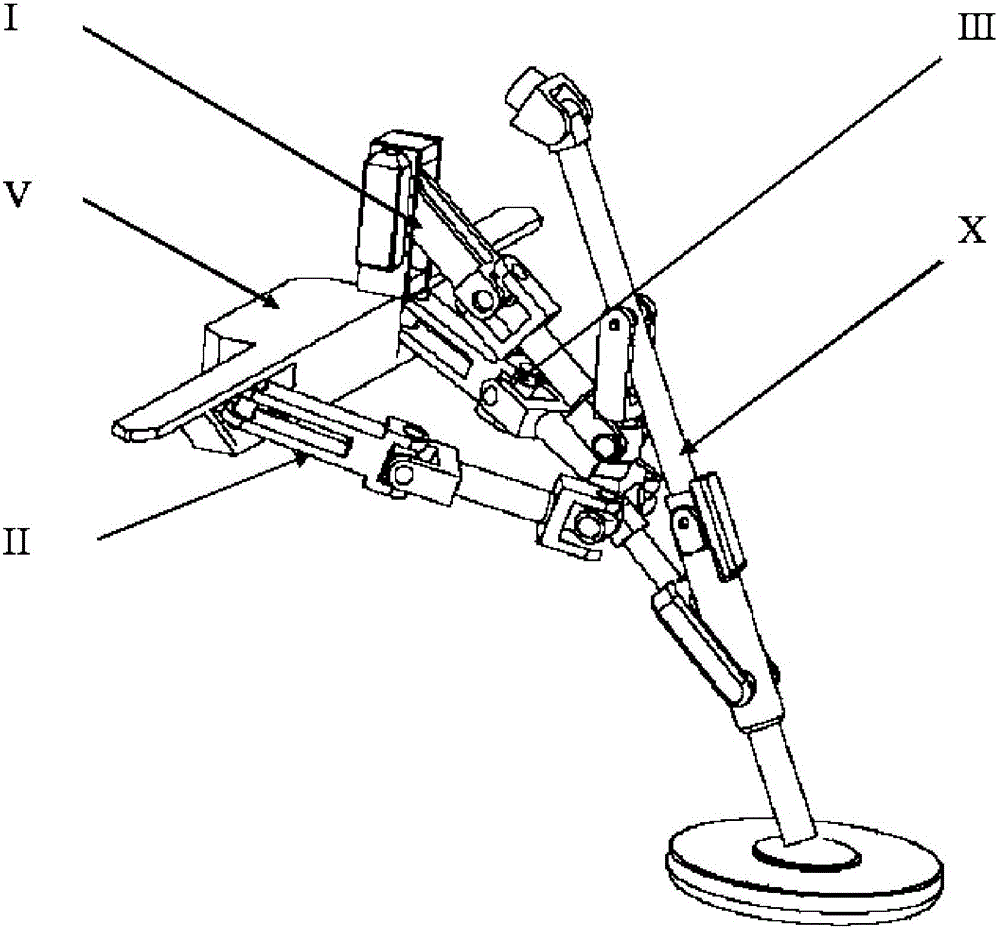
The invention discloses a force feedback main manipulator for minimally invasive surgery. The force feedback main manipulator comprises a first parallelogram structure, a second parallelogram structure, an attitude adjusting mechanism and a clamping mechanism; the first parallelogram structure and the second parallelogram structure are both formed by a plurality of rod pieces which are sequentially hinged end to end; a first hinging point of the first parallelogram structure is coaxial with a first hinging point of the second parallelogram structure; a second hinging point of the first parallelogram structure is connected with a second hinging point of the second parallelogram structure through a connecting rod; the tail end of the second parallelogram structure is a wrist part, wherein the wrist part can be keep horizontal under connection of the first parallelogram structure and the second parallelogram structure; the wrist part is hinged with the attitude adjusting mechanism; and the attitude adjusting mechanism is hinged with the clamping mechanism. The force feedback main manipulator provided by the invention can meet the requirements of minimally invasive surgery, conforms toergonomics, has a force feedback function and is low in cost.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Direct molding process for hot-extruded hollow axle
ActiveCN104043769AIncrease torqueEasy to useMetal-working apparatusEngine componentsUltimate tensile strengthProcess design
The invention discloses a direct molding process for a hot-extruded hollow axle. The process comprises pipe inspection and processing, gradient heating treatment, mold loading, horizontal and radial loading, integral heating after demolding, mold reloading and reloading, wherein direct variable-diameter hot extrusion forming of the hollow axle is effectively finished after repeating the steps are repeated and the inspection treatment is performed. The direct molding process has the advantages of reasonable process design, simple mold structure, high upsetting speed, high yield, good use effect and low cost, and is particularly suitable for large-scale industrial production of high-speed train axles. The weight of the axle is reduced greatly, and the strength and torque force of the hollow axle are effectively enhanced and ensured.
Owner:雷中坤
Method for producing beveled cage rotor and beveled cage rotor
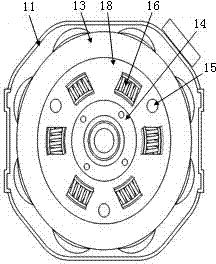
ActiveCN102474163AGuaranteed uptimeSimple structureAsynchronous induction motorsStatorsEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention relates to a method for producing a beveled cage rotor (1) for an asynchronous machine (2) and to a cage rotor (1) that can be produced by means of such a method. In order to improve the efficiency of the asynchronous machine (2), the cage rotor (1) comprises a laminated rotor core (5) having grooves (4), short-circuit rings (6) made of a first material and case onto the end face of the laminated rotor core (5), and short-circuit bars (3; 11; 12) made of a second material having a higher specific electrical conductivity than the first material and disposed in the grooves (4), wherein the laminated rotor core (5) and the short-circuit bars (3; 11; 12) comprise a bevel and nearly completely fill in an inner groove region (7) as seen in the radial direction of the laminated rotor core (5).
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Light detection machine foreign matter detection device and method
ActiveCN102384916AReduce radius of gyrationReduce moment of inertiaOptically investigating flaws/contaminationLow noiseForeign matter
The invention discloses a light detection machine foreign matter detection device, which comprises a light detection plate for holding bottle bodies, wherein the light detection plate is provided with more than one detection station; each detection station is provided with more than two groups of light detection camera groups near the bottle bodies on the light detection plate; and each light detection camera group respectively corresponds to one group of bottle bodies arranged at intervals. The invention also discloses a light detection machine foreign matter detection method, which comprises the following steps: dividing a plurality of detection stations along the light detection plate; on each detection station, shooting and detecting all bottle bodies which pass through the detection station once; arranging more than two groups of light detection camera groups near the bottle bodies on each detection station; and respectively shooting and detecting one group of bottle bodies distributed at intervals by each light detection camera group. The light detection machine foreign matter detection device has the advantages of simple and compact structure, long service life, low noise and the like.
Owner:TRUKING TECH LTD
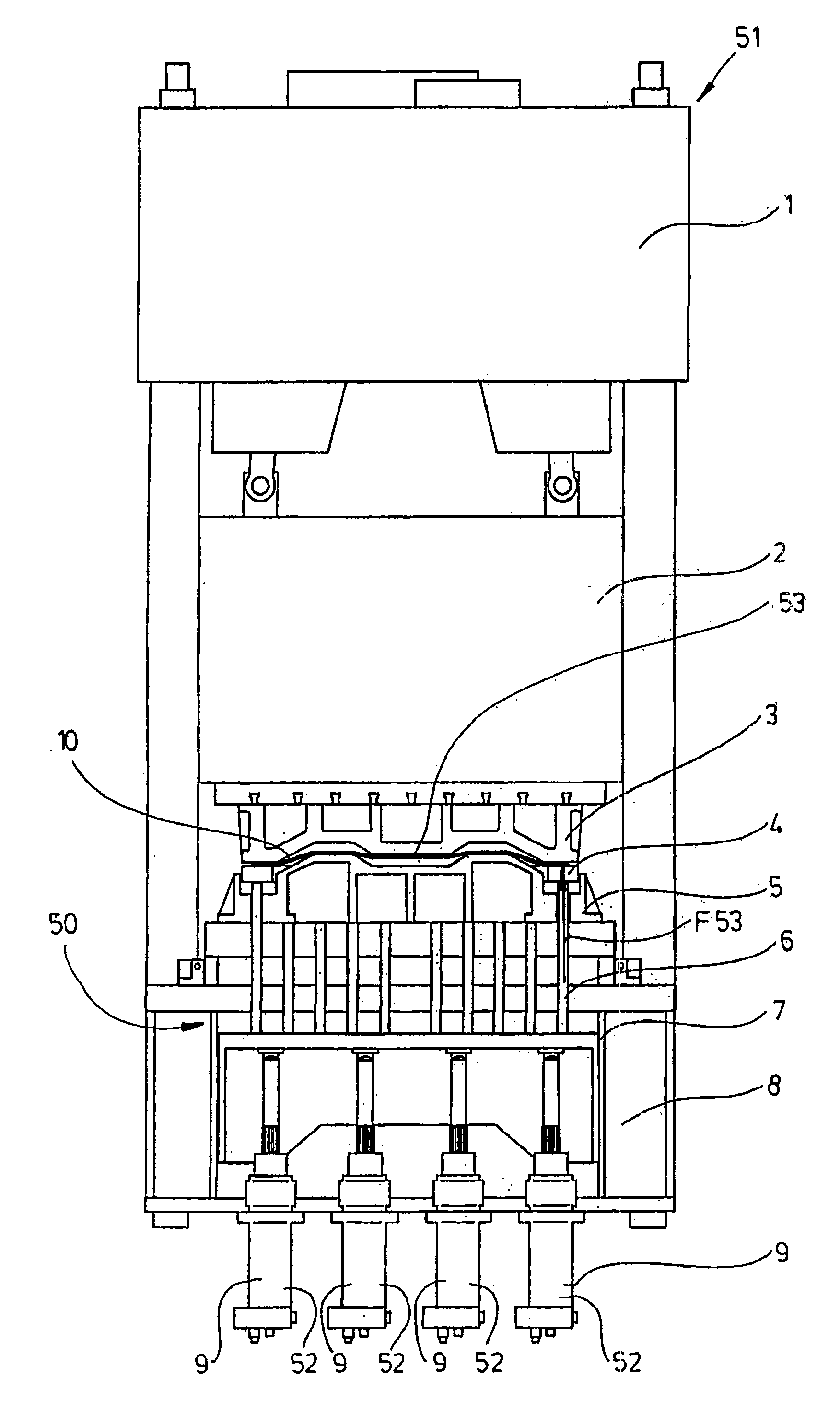
Die cushion device comprising a hybrid drive unit
The invention relates to a die cushion device (50) for a forming press (51) for generating a blank retaining force (F53) between a bottom die (5) and a top die (3). Said die cushion device (50) comprises at least one hybrid drive unit (52) which acts upon at least one blank holder (4) of the bottom die (5) and is formed by at least one first drive unit and at least one second drive unit. The first drive unit and the second drive unit form a die cushion module (9) that encompasses a part, by means of which the blank holder (4) can be moved upward and downward by at least one of the drive units. A downward pressure that can be transmitted from the top die (3) to said part and causes a descending movement can be blocked or decelerated only by the first drive unit in order to prevent the second drive unit from being overloaded, the part being disconnectable from the second drive unit during the descending movement.
Owner:MASCHFAB MULLER WEINGARTEN AG
Drive train for a motor vehicle
ActiveCN103702851ALow costSave construction spaceClutchesGas pressure propulsion mountingElectric machineDrivetrain
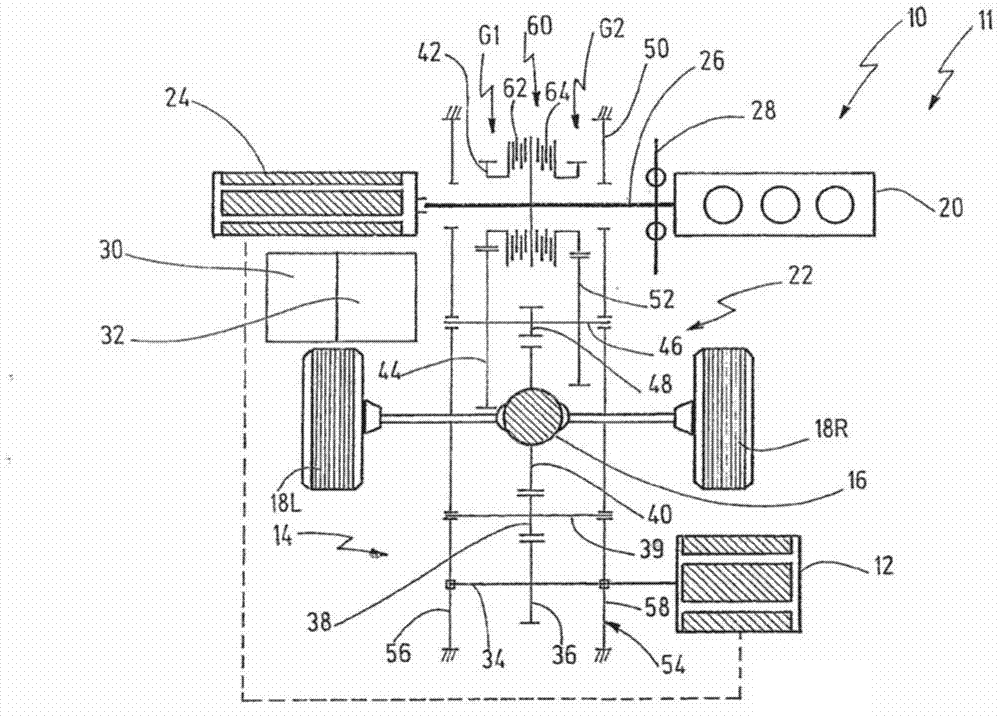
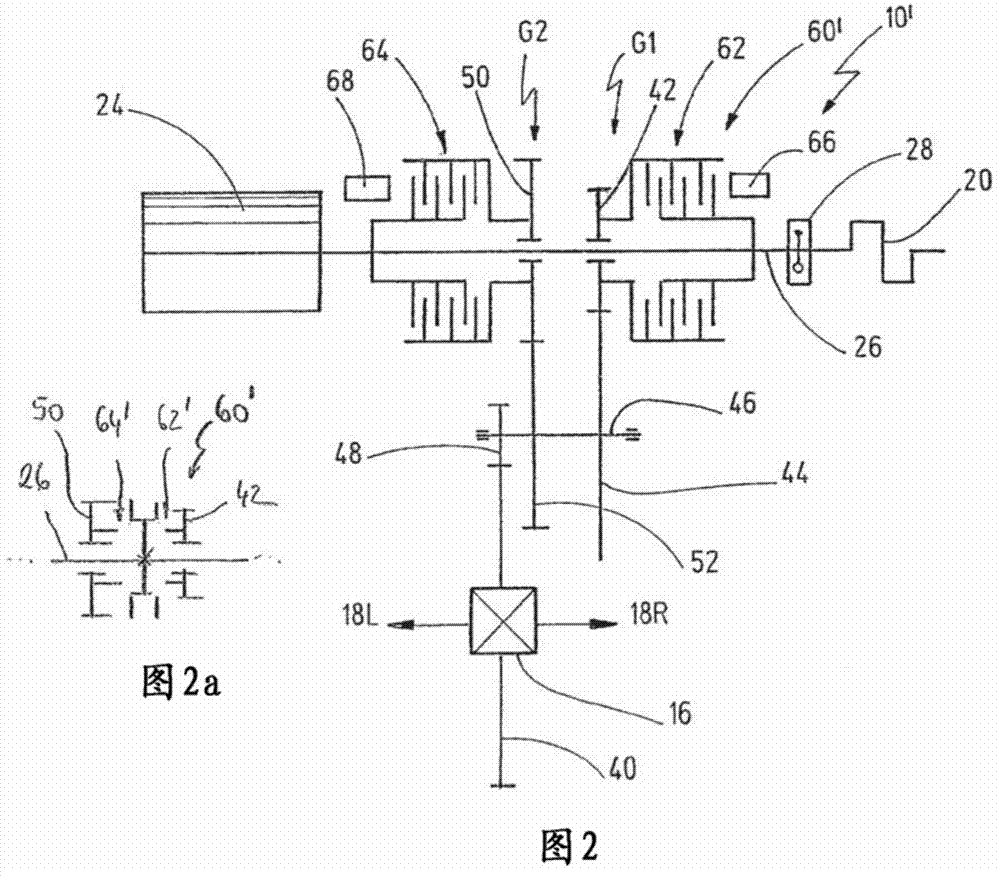
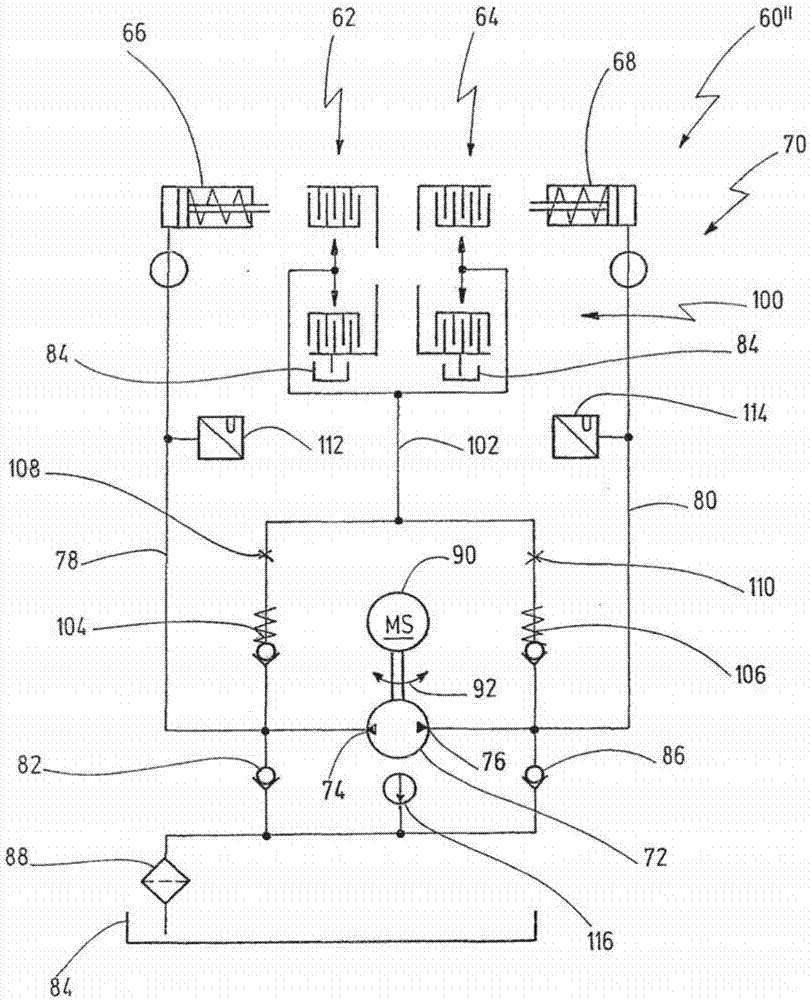
A drive train (10) for a motor vehicle (11), with a first electric machine (12) for providing driving power, wherein the first electric machine (12) is connected to an electric power accumulator (32); a differential (16) which can distribute driving power to two driven wheels (18L, 18R) or axles of the motor vehicle (11); a first transmission arrangement (14) which connects the first electric machine (12) to the differential (16); an internal combustion engine (20); a second electric machine (24) which is coupled to the internal combustion engine (20) in order to charge the electric power accumulator (32) in a generator mode; and a second transmission arrangement (22) which connects the internal combustion engine (20) to the differential (16); wherein the second transmission arrangement (22) has a first gear stage (G1) and a second gear stage (G2) which are alternatively switchable by means of a clutch arrangement (60) for transmitting driving power from the internal combustion engine (20) to the differential (16).
Owner:GETRAG GETRIEBE & ZAHNRADFABRIK HERMANN HAGENMEYER GMBH & CO KG
Eddy current retarder with torsional vibration reduction function
ActiveCN103692918AEasy to set upReduce moment of inertiaElectric devicesElectrodynamic brake systemsDrive shaftEngineering
The invention relates to an automobile braking device, in particular to an eddy current retarder with a torsional vibration reduction function. The eddy current retarder with the torsional vibration reduction function comprises a stator, an upstream rotor and a downstream rotor, wherein the upstream rotor is used for being connected with an automobile gear box, the downstream rotor is used for being connected with a transmission shaft on the front end of a rear axle, and a vibration reduction buffering device used for being connected with the transmission shaft on the front end of the rear axle is arranged on the downstream rotor. During operation, a torsional countermoment which is instantaneously generated acts on the vibration reduction buffering device, so as to reduce torque impact which is instantaneously generated through the buffering and damping effects of the vibration reduction buffering device, thereby achieving the purpose of reducing impact and vibration; in addition, when the retarder is not braked, the vibration reduction buffering device is connected into a transmission system in series, so as to be favorable for reducing torque fluctuation which is generated by an engine and a shafting space angle and improving the NVH (Noise, Vibration and Harshness) performance of the transmission system. In conclusion, by using the eddy current retarder, vibration and noise caused by the retarder to an automobile can be reduced.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU YUTONG BUS CO LTD
Heatable housing, device for producing steam and cooking appliance
InactiveCN101160492AReduce moment of inertiaLower energy requirementsSteam generation heating methodsInterior space
The invention relates to a heatable housing for a device for producing steam, with at least one wall that delimits an interior space, which is enclosed by the housing at least in areas and which serves to hold a liquid to be vaporized. The wall has at least one recess for accommodating at least one heating device. The invention also relates to a device comprising an inventive housing, and to a cooking appliance for producing steam with such a device.
Owner:RATIONAL AG
Walk assistance device
InactiveCN101460118AReduce moment of inertiaReduce loadProgramme-controlled manipulatorWalking aidsEngineeringMoment of inertia
A walk assistance device capable of transmitting a force generated by a leg link to a user's trunk via a load transfer portion, wherein the leg link includes an upper first link portion connected to the load transfer portion via a first joint portion, a lower second link portion connected to a foot attachment portion via a second joint portion, a middle third joint portion connecting the first link portion to the second link portion such that a distance between the first joint portion and the second joint portion is variable, and a driving source that drives the third joint portion. The moment of inertia around the first joint portion of the leg link is reduced to decrease a load on the user's leg in walking. The driving source is disposed above the third joint portion of the first link portion so that the center-of-gravity of the entire leg link is located above the third joint portion. In the case where the driving source includes an electric motor and a reduction gear, the electric motor is disposed above the reduction gear.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
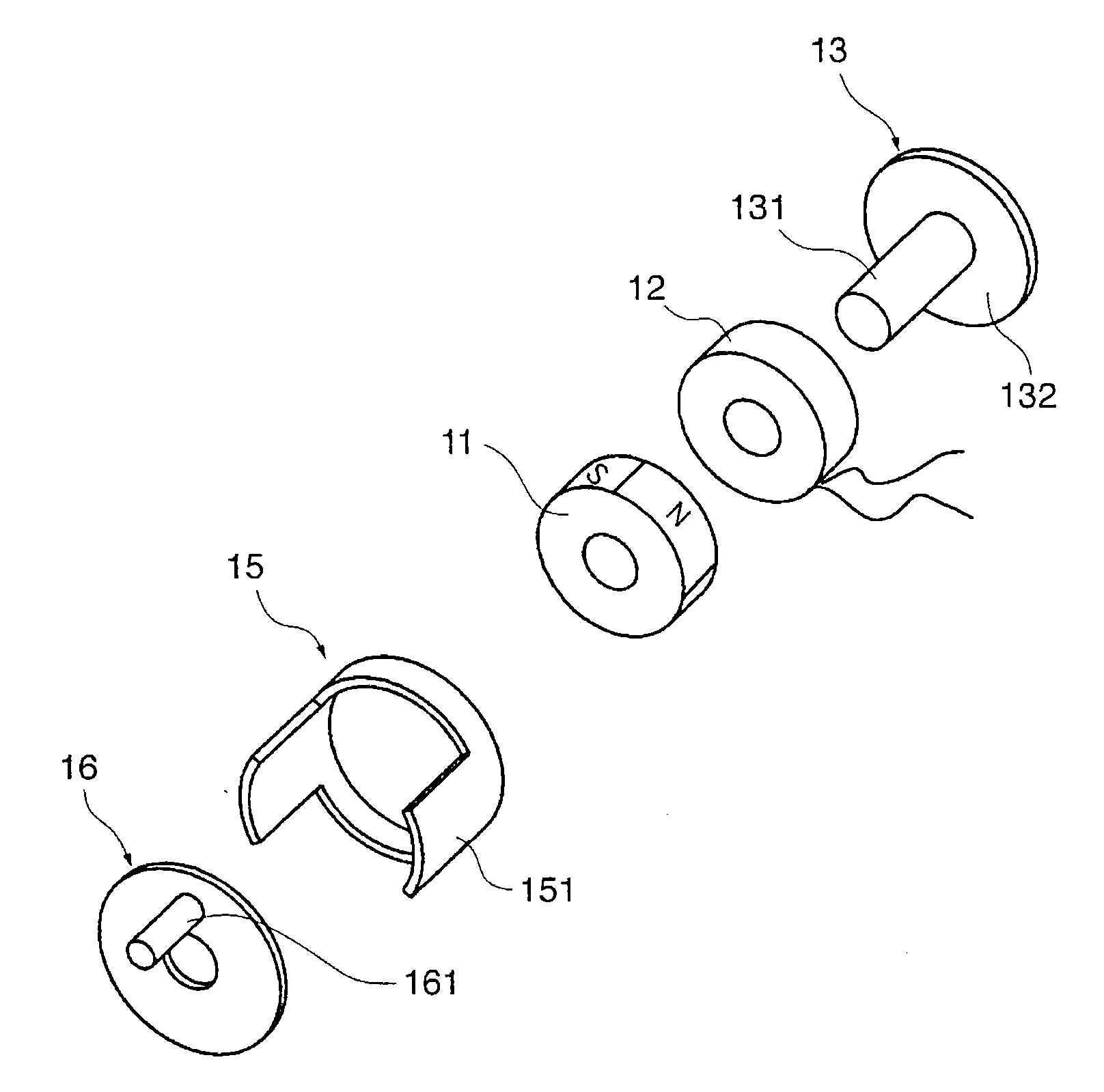
Driving device and light amount controller
InactiveUS20070063591A1Reduce moment of inertiaIncrease torqueTelevision system detailsColor television detailsMagnetic polesMoment of inertia
A driving device which makes it possible to reduce the moment of inertia of a rotor and increase torque. A magnet is formed to have a hollow cylindrical shape and has magnetized sections which are magnetized to have alternately different poles in a circumferential direction thereof. A coil is wound coaxially with the magnet and is disposed in axially side-by-side relation to the magnet. A stator yoke is formed of a soft magnetic material and fixes the magnet and the coil. A rotor yoke is formed of a soft magnetic material, and has magnetic pole portions formed in opposed relation to the magnetized sections, for being magnetized by the coil. The rotor yoke is supported in a manner rotatable with respect to the stator yoke. An rotation restricting part limits a range of rotation of the rotor yoke within a predetermined angle.
Owner:CANON KK
A wind turbine blade equipped internally with collection means
ActiveCN101091055AUnchanged structureAvoid blockingEngine fuctionsBlade accessoriesTurbine bladeEngineering
The vane for a wind energy installation is equipped with collecting devices and comprises at least two parts so that a hollow space is formed, in which devices are placed for collection of dust, particles or loose objects. The collecting dvices consist of a container with a funnel-shaped opening, with a valve or adhesive surfaces on the inside. The devices may also be a kind of filter positioned between chambers inside the vane.
Owner:LM GLASSFIBER
Analog electronic timepiece
InactiveCN1307695AReduce moment of inertiaThe value of holding energy decreasesGearworksVisual indicationGear wheelElectric machine
An analog electronic timepiece capable of decelerating the rotation of a rotor (1a) of a step motor (1) through a train wheels before it is transmitted to an hour hand (17) and a minute hand (15), wherein the gravity center of a second shaft rotating body comprising a center wheel gear (9), a center wheel pinion (10), and a second shaft (11) to which the minute hand (15) is installed is displaced by an angle range of less than + / -90 DEG , from the axis of the second shaft (11), in the direction opposite to the direction in which a time indicating part (15a) of the minute hand (15) is extended so as to reduce a moment on the second shaft (11) caused by the minute hand (15) and the second shaft rotating body, whereby a breakage of the hand due to disturbance can be prevented even if the value of the holding energy of the step motor (1) is reduced.
Owner:CITIZEN WATCH CO LTD
Electric straddled vehicle
ActiveCN102448806AImprove versatilityImproved weight balanceMotorised scootersAxle suspensionsAutomotive engineeringEngineering
An electric straddled vehicle which has, despite the fact that the vehicle is a lightweight and inexpensive vehicle using a small-sized, highly versatile motor, the balance of weight in the left-right in the width direction of the vehicle relative to the vehicle body centerline is optimized. An electric motor (250) is disposed within a cantilever swing arm (214) at a position at which, when viewed from a side of the vehicle body, the electric motor is superposed on the region in which a rear wheel (WR) is projected. A motor driver (216) is disposed within the swing arm (214) so as to straddlethe vehicle body centerline (C) at a position in front of the rear wheel (WR) relative to the vehicle body. The motor driver (216) is disposed in such a manner that the position (G2) of the center ofgravity thereof is offset to the side opposite to the side to which the electric motor (250) is offset from the vehicle body centerline (C). The motor driver (216) is provided behind a rocking shaft (215) relative to the vehicle body at a position close to the rocking shaft (215) and is inserted and mounted to a recess (308) open to the upper surface side of the swing arm (214). An FET (316) for conducting and interrupting an electric current to the motor is at least supported on the lower surface of a lid member (264) of the motor driver (216).
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Device and method for producing tooth-like profiled sections on workpieces
ActiveCN1913988AAdjust the rotation positionEasy to adjustGear wheelsRapid processingMechanical engineering
The invention relates to a device for producing cylindrical workpiece having defined profiled sections. The device comprises a workpiece holder that is axially displaceable and intermittently rotates about a longitudinal axis, and shaping tools that periodically act upon the workpiece. The inventive device is characterized by at least one drive for the intermittent rotation of the workpiece holder, which is mechanically separate from the drive for the shaping tools. The drive is linked with an electronic control which controls the intermittent rotational movement depending on the drive of the shaping tools. The invention allows to adjust any intermittent movement relative to the position and angle of the workpiece, thereby contributing to a precise and especially rapid processing of the workpiece.
Owner:ERNST GROB
Driving and brake integration system based on wheel hub motor
ActiveCN104553744AReduce torqueReduce moment of inertiaElectrodynamic brake systemsMotor depositionMotor driveControl system
The invention provides a driving and brake integration system based on a wheel hub motor. The driving and brake integration system based on the wheel hub motor comprises a wheel hub motor driving system, an electromagnetism and friction braking system and a finished automobile control system, wherein the wheel hub motor driving system comprises a car axle, a motor stator, a wheel hub, a motor rotor and a brake disc, the motor stator is coaxially welded with the car axle, and the wheel hub is connected with the motor stator via a bearing; the shell of the motor rotor is fixedly connected with the wheel hub; the motor rotor is fixedly connected with the brake disc. According to the driving and brake integration system, the motor rotor is adopted to directly drive the wheel hub, the driving and brake integration system has the advantages of simple structure and high transmission efficiency, the rotation moment and the rotation inertia of an automobile are reduced, the comfort and the safety of the automobile are improved, meanwhile, since an electromagnetic brake system is increased, the use ratio of car energy is effectively improved, braking action time is shortened, and the brake performance and the traffic safety of the finished automobile are improved.
Owner:北京勇搏科技有限公司
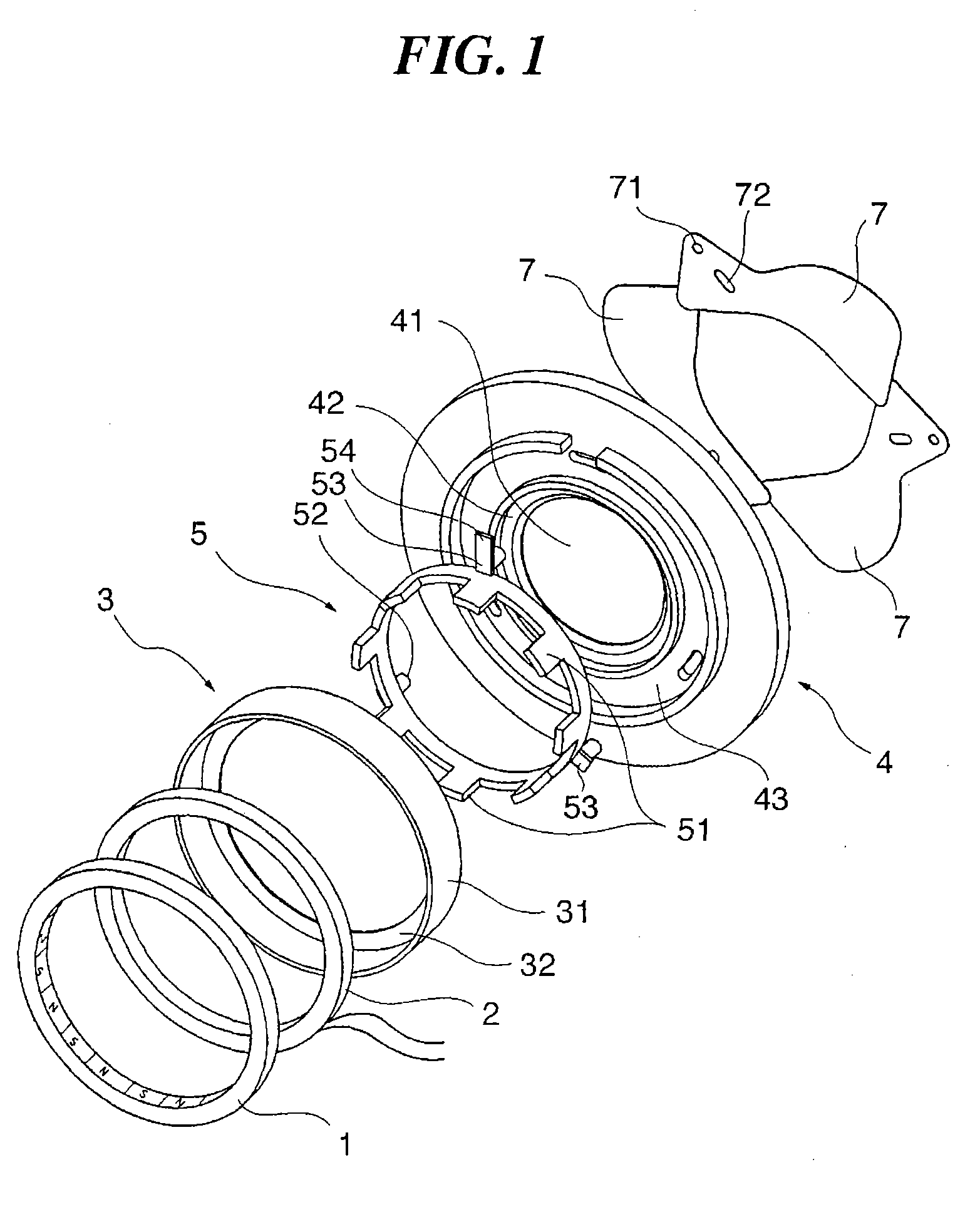
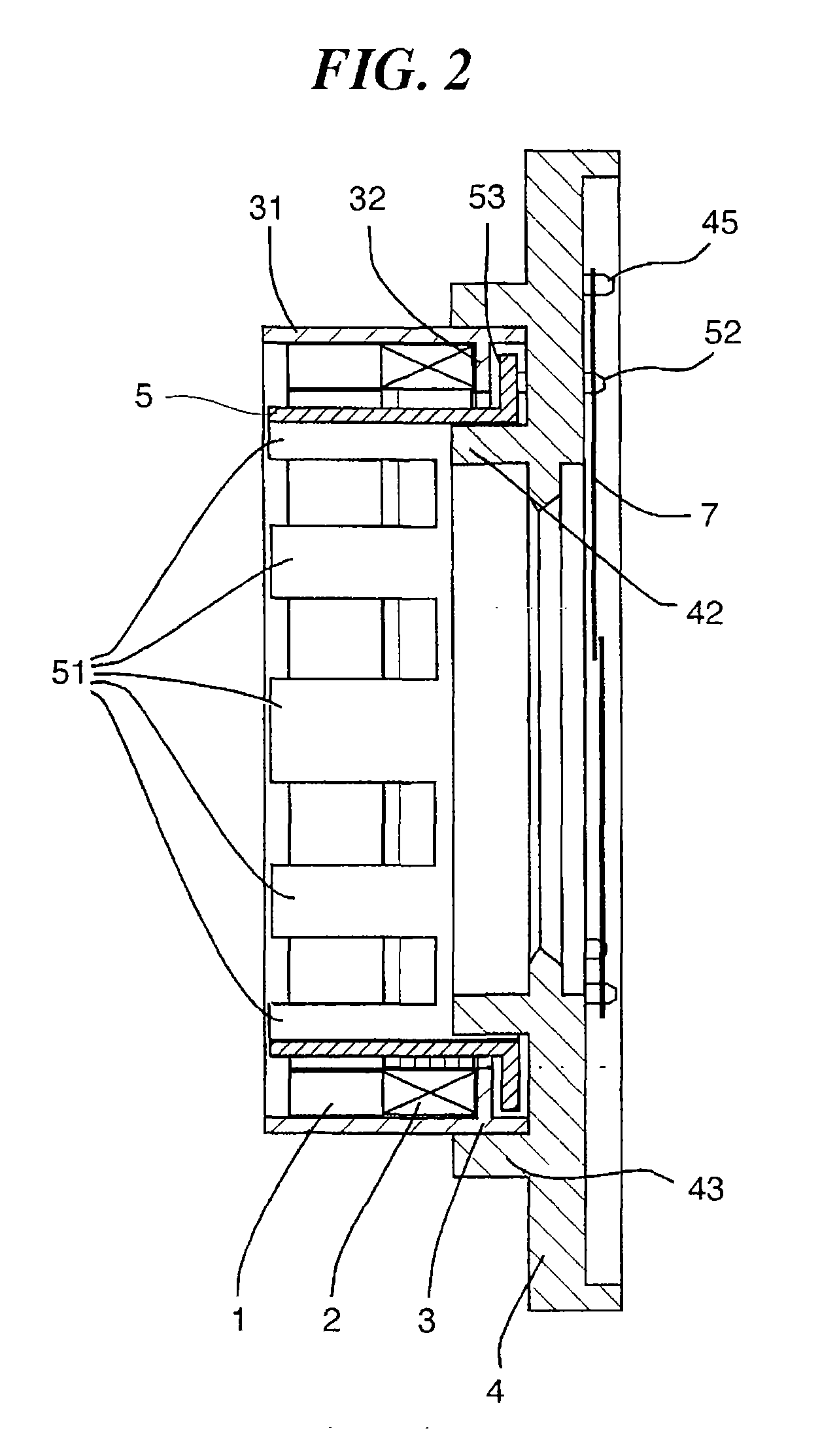
Power steering system
InactiveUS6231448B1Reduce moment of inertiaAccurately determinedSlip couplingElectrical steeringMoment of inertiaEngineering
A power steering system to reduce the moment of inertia of the torque limiter and to accurately determine pressing force by a forcing member is provided. The torque limiter of the system has a basic structure in which a substantially-cylindrical rotating member which is rotatable together with one of the output shaft and the input shaft; and a rotated member which is rotatable together with the other of the output shaft and the input shaft, and which is forced toward the rotating member side by a forcing member supported by the rotating member. Typically, the rotating member is a substantially-cylindrical limiter cover with a bottom, and the rotated member is a limiter plate contained in the limiter cover. The forcing member may be supported by a concave portion formed in an inner-peripheral area of the limiter cover, or may be supported by a projecting portion which is formed by deforming the cylindrical portion of the limiter cover toward the inside. In the above basic structure, the rotated member may separately comprise a cylindrical portion, on the inner-peripheral surface of which plural splines are formed in parallel with its axial direction, these splines being engaged with the splines formed in the outer-peripheral surface of the other of the output shaft and the input shaft; and a flange portion, which is forced toward the rotating member side, by which the flange portion functions as a friction clutch. In this structure, efficiency of forming the limiter plate can be improved.
Owner:MITSUBA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com