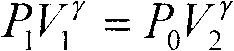Patents
Literature
55results about How to "Rich teaching content" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
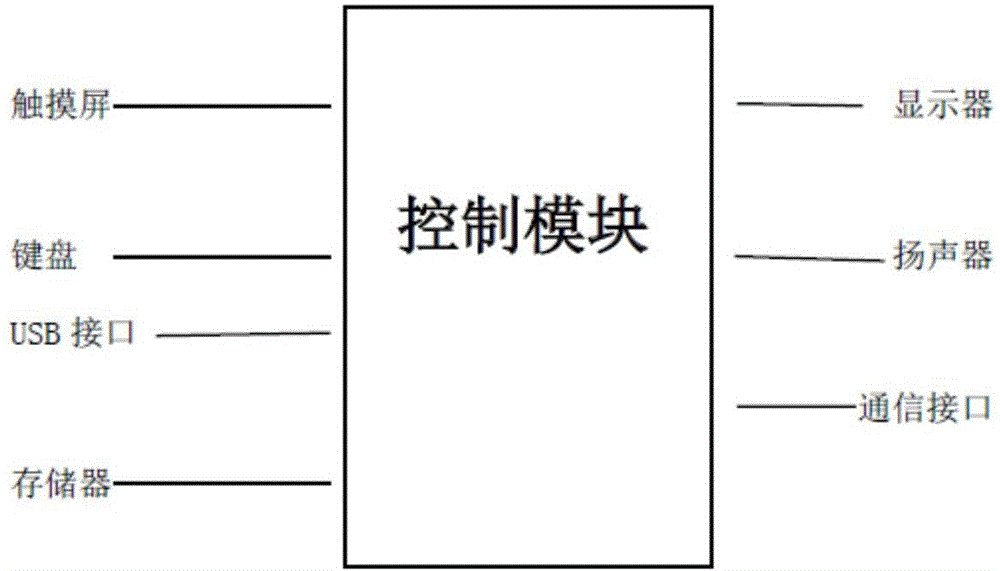
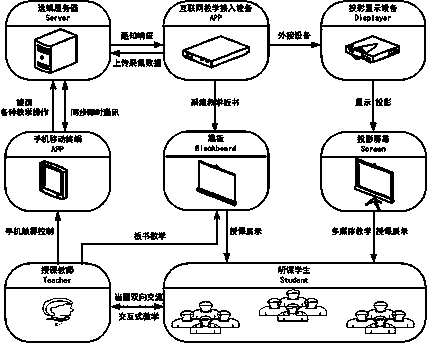
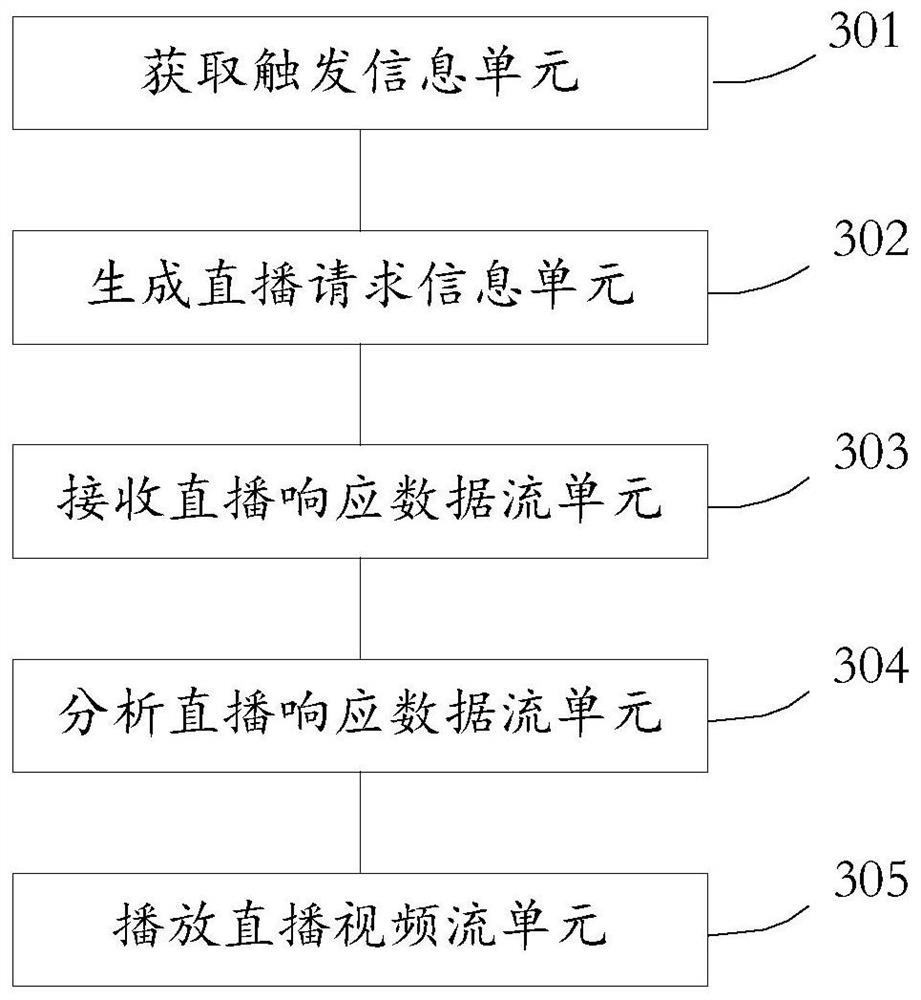
Courseware annotating method and system
InactiveCN104298655AEnhanced interactionEasy to viewElectrical appliancesSpecial data processing applicationsComputer terminalDatabase
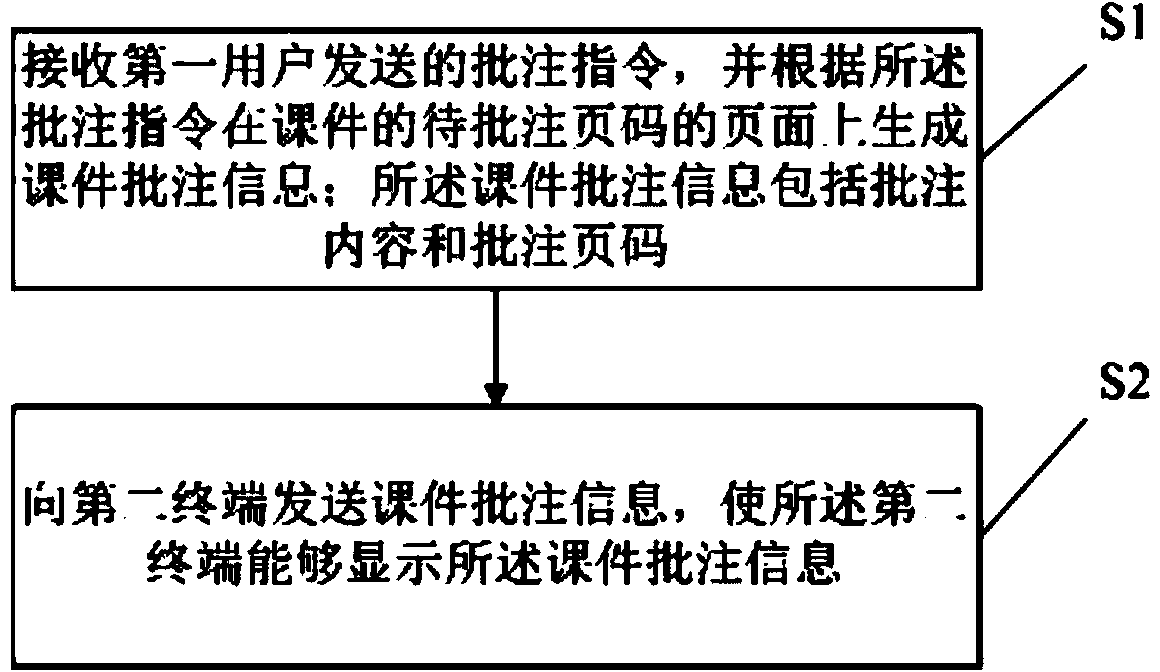
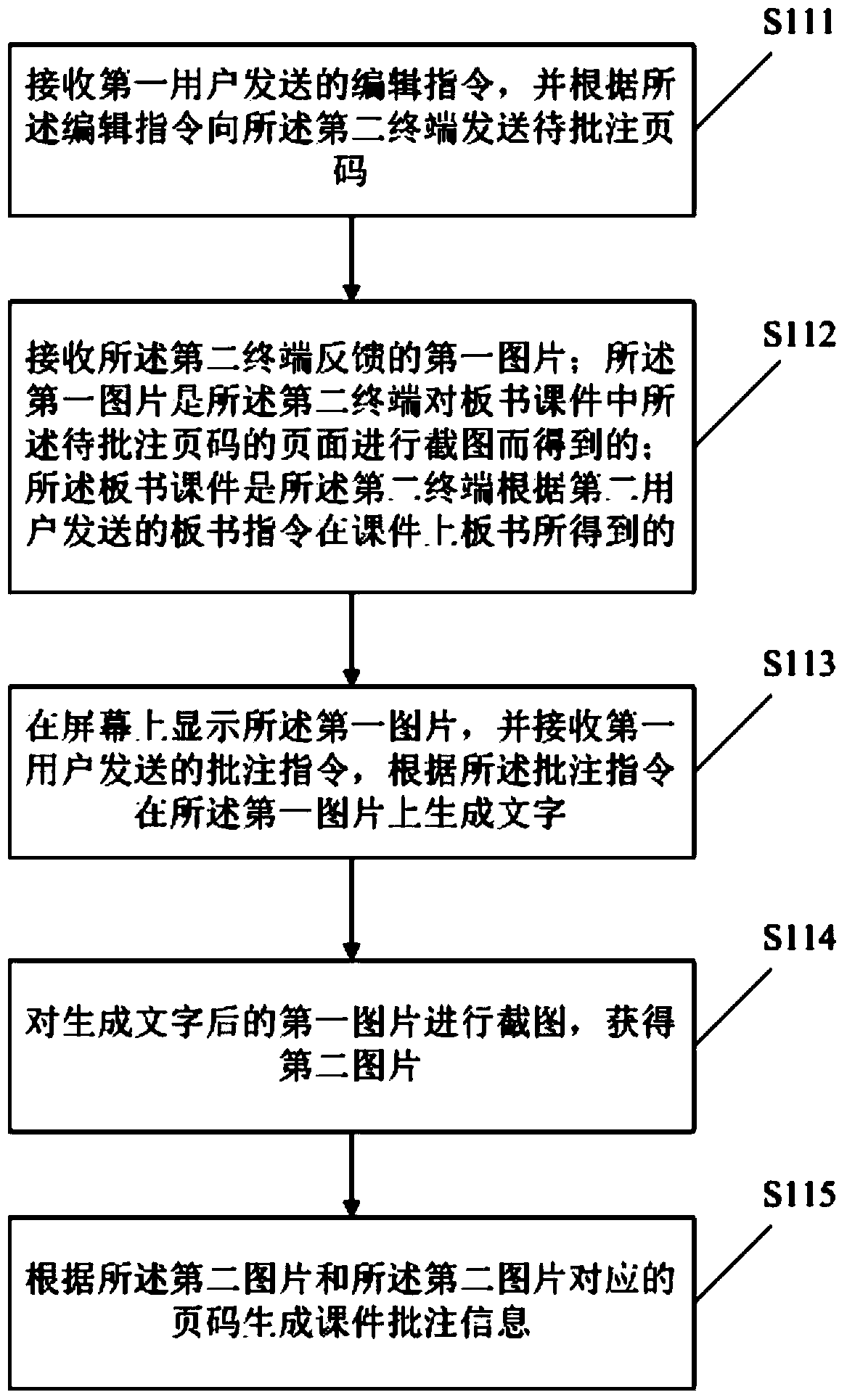
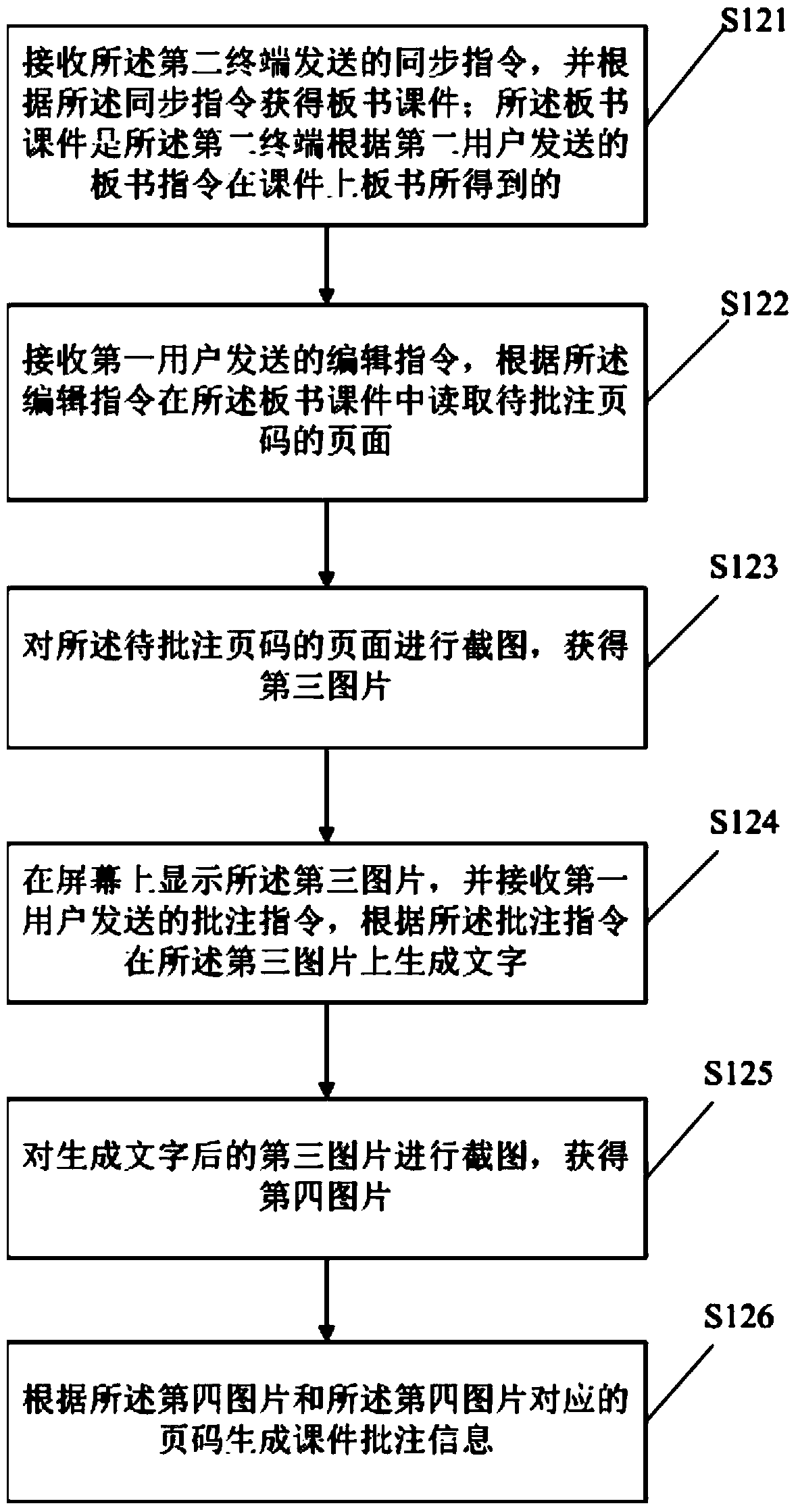
The invention discloses a courseware annotating method. The method comprises the steps that an annotating instruction sent by a first user is received, and courseware annotating information is generated on the page of the to-be-annotated page number of courseware according to the annotating instruction; the courseware annotating information comprises annotating content and annotating page numbers; the courseware annotating information is sent to a second terminal, and the second terminal can display the courseware annotating information. Correspondingly, the invention discloses a courseware annotating system. According to the courseware annotating method and system, the courseware can be annotated on a first terminal, the courseware annotating information can be fed back to the second terminal in time, and the interaction of the first user and a second user is facilitated.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SHIYUAN ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Interactive game teaching system and method
InactiveCN107731038AIncrease interest in learningFoster independent learningElectrical appliancesData centerData memory
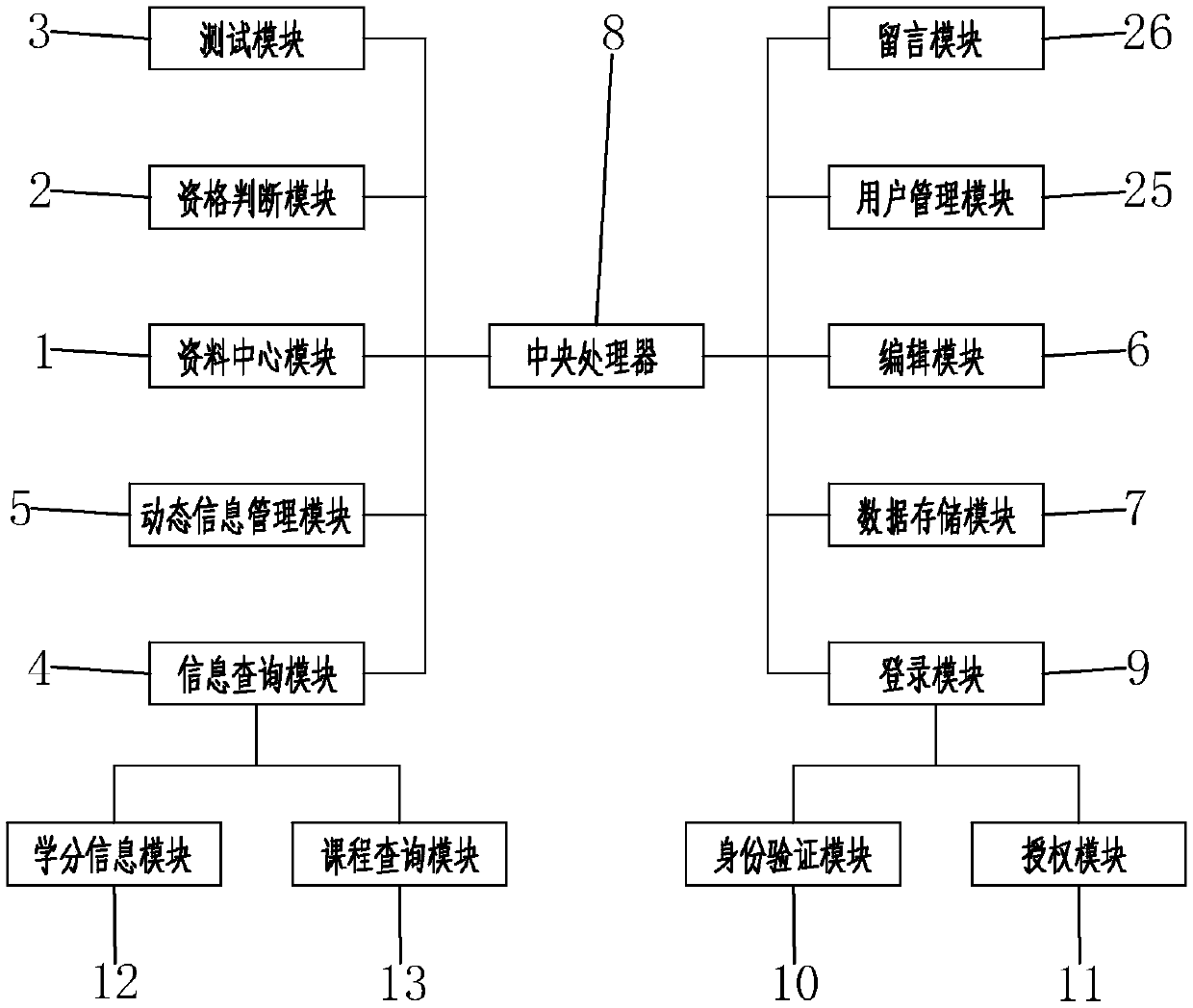
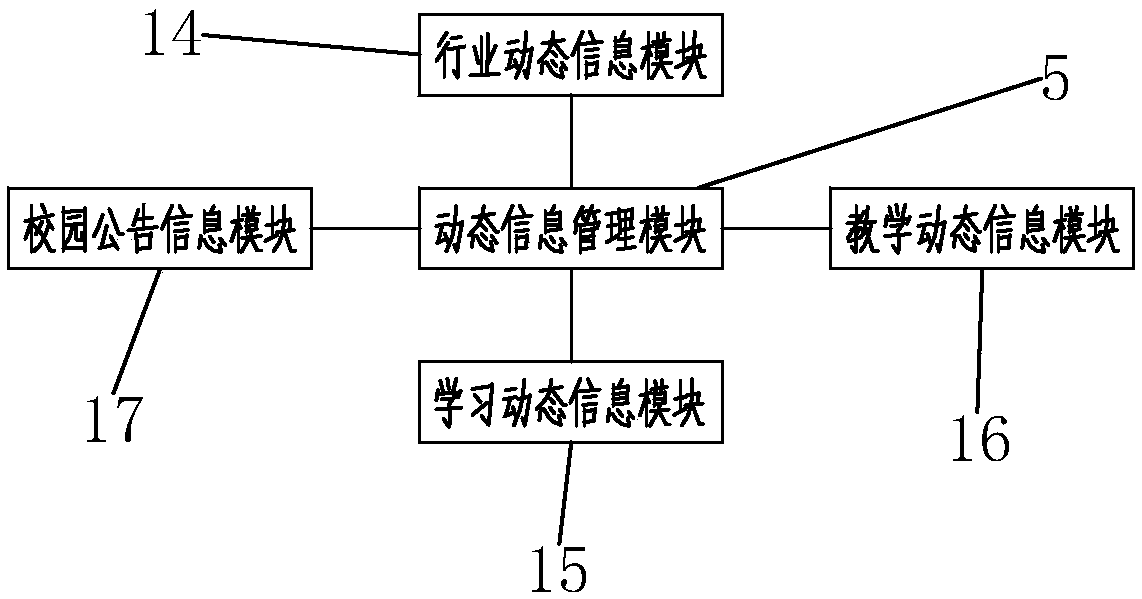
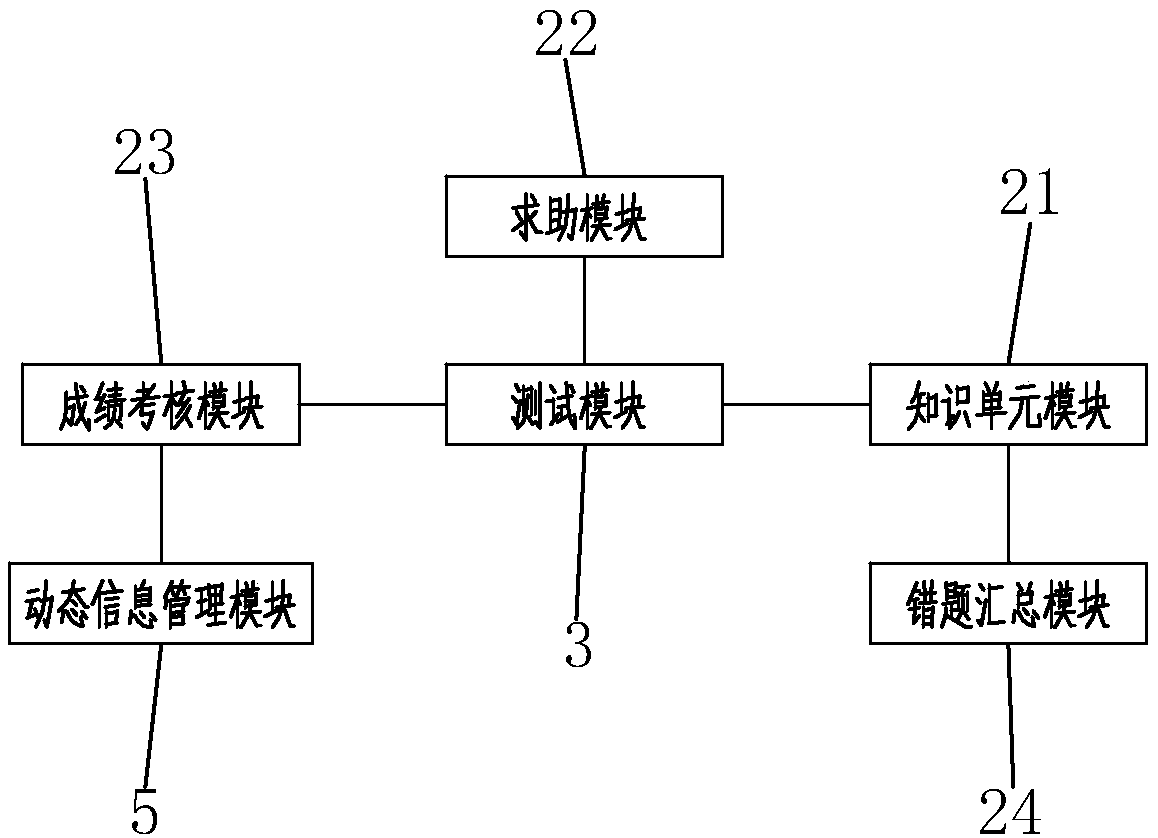
The invention discloses an interactive game teaching system and a teaching method. The teaching system comprises a data center module, a qualification judging module, a test module, an information query module, a dynamic information management module, an editing module, a data memory module, a central processing unit and a login module, wherein the login module, the editing module, the data memorymodule, the data center module, the qualification judging module, the test module, the information query module and the dynamic information management module are connected to the central processing unit; and the teaching method comprises the following steps: (a) conducting logging and browsing; (b) conducting learning simulation; (c) conducting formal testing; (d) seeking for help; and (e) conducting feeding-back. According to the teaching system and the teaching method provided by the invention, learning and game are combined, so that teaching contents are enriched, student's understanding is promoted, impression is strengthened, memory is promoted and student's learning interesting and learning effect are improved; and students, teachers and managers can participate in the interaction of the system, so that an interactive effect of the system is enhanced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG COLLEGE OF CONSTR
Power supply intelligentized simulation teaching system
InactiveCN101136559AStrong scalabilityFriendly human-computer interfaceCircuit arrangementsEducational modelsCollections dataHuman–machine interface
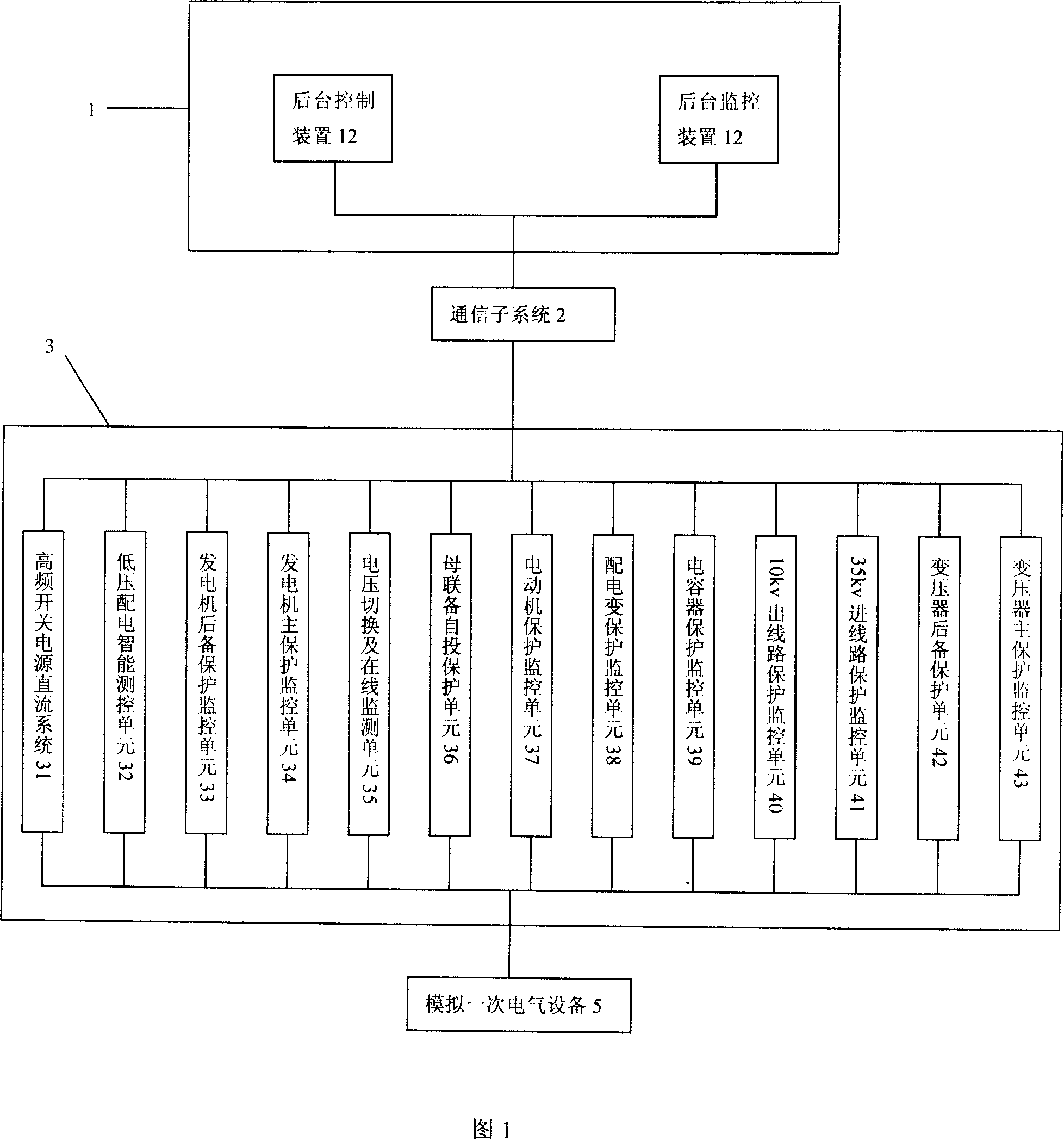
This invention relates to an intelligent simulation teaching system for power supply and distribution including a background control management subsystem, a communication subsystem, a distributed protection and monitor subsystem and a primary analog electric device, in which, the background control subsystem includes a data collection and process module, a monitor and control module, a network communication module and a man-machine interface module, said communication subsystem is a communication net applying Ether net, said distributed protection monitor subsystem includes several units, said background control monitor subsystem is connected with the communication subsystem and the distributed protection monitor subsystem is connected with the communication subsystem and all the units are parallel to the communication subsystem, said analog electric device is connected with the protection monitor subsystem in parallel.
Owner:菱亚能源科技(深圳)股份有限公司
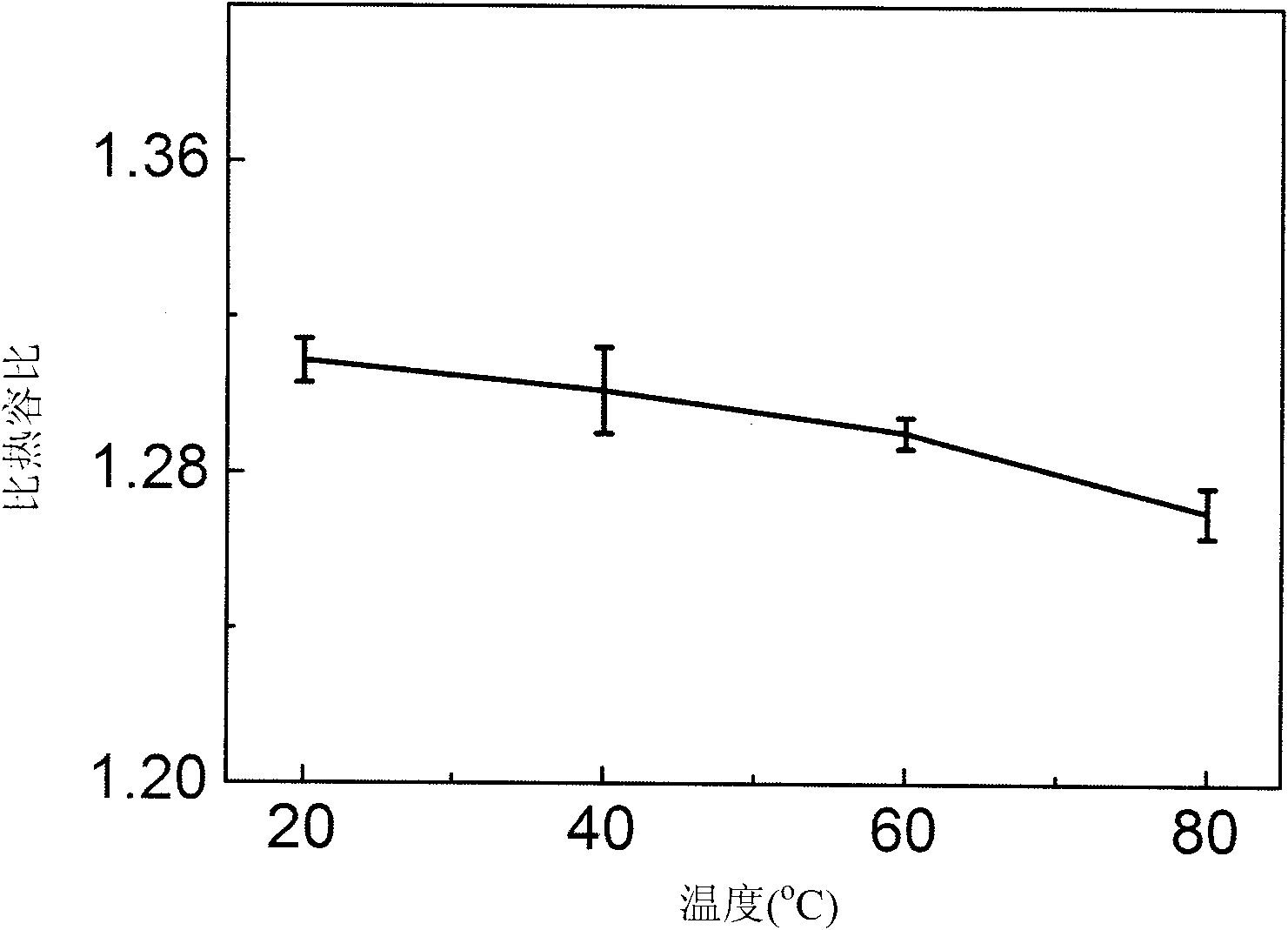
Device and method for measuring specific heat ratio of air under different temperatures
InactiveCN101840650AGuaranteed temperatureAccurate temperatureMaterial heat developmentEducational modelsMicrocontrollerElectricity
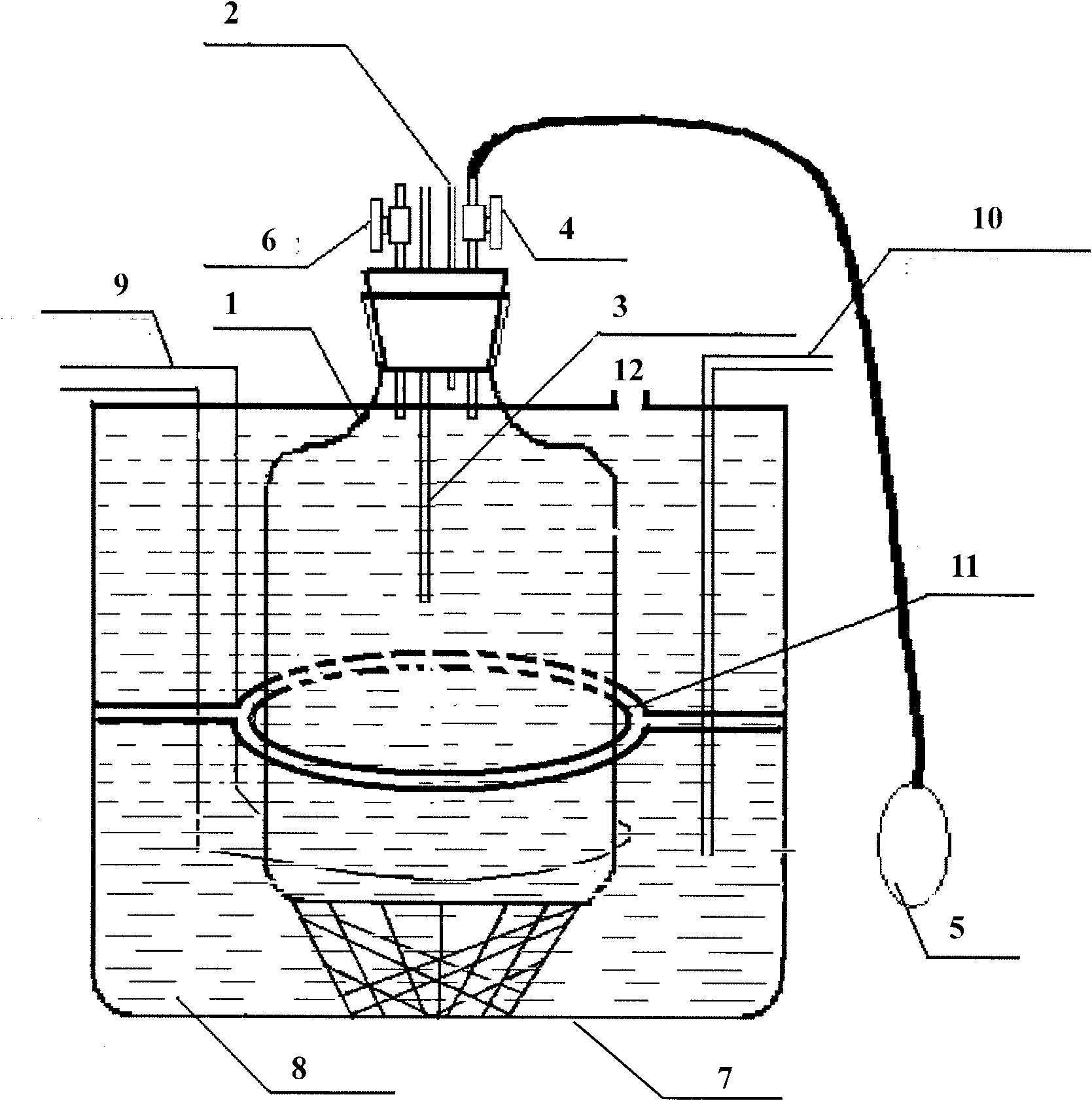
The invention provides a device for measuring specific heat ratio of air under different temperatures, which comprises an air storage bottle, a pressure sensor and an air temperature testing sensor which are arranged in the bottle, wherein an air charge part and an air discharge part are fixed on the air storage bottle. The device is characterized in that the device further comprises a temperature display and control device which is arranged around the air storage bottle. The temperature display and control device comprises a heat bath container, an electric heating part, a bath temperature testing sensor and a microcontroller, wherein the electric heating part and the bath temperature testing sensor are fixedly arranged in the heat bath container and are electrically connected with the microcontroller. The invention further provides a method for measuring the specific heat ratio of the air under different temperatures through above device. The device and the method can ensure that the air temperature can be at a precise range, enriches the experimental teaching contents and improves the learning initiatives of the students.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
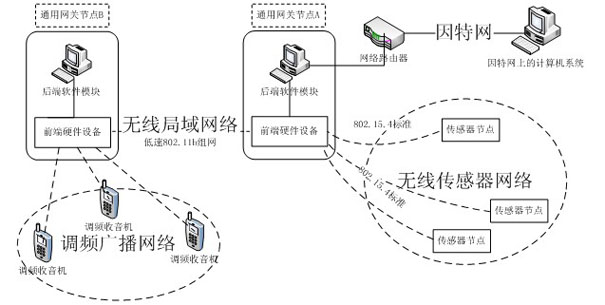
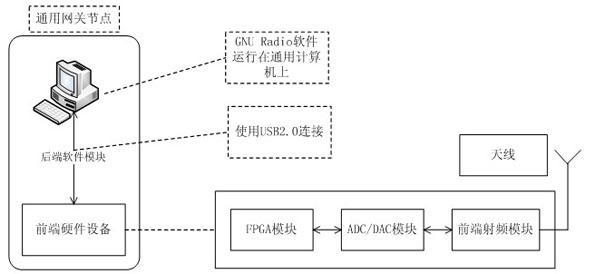
Software wireless technology-based heterogeneous network experimental device
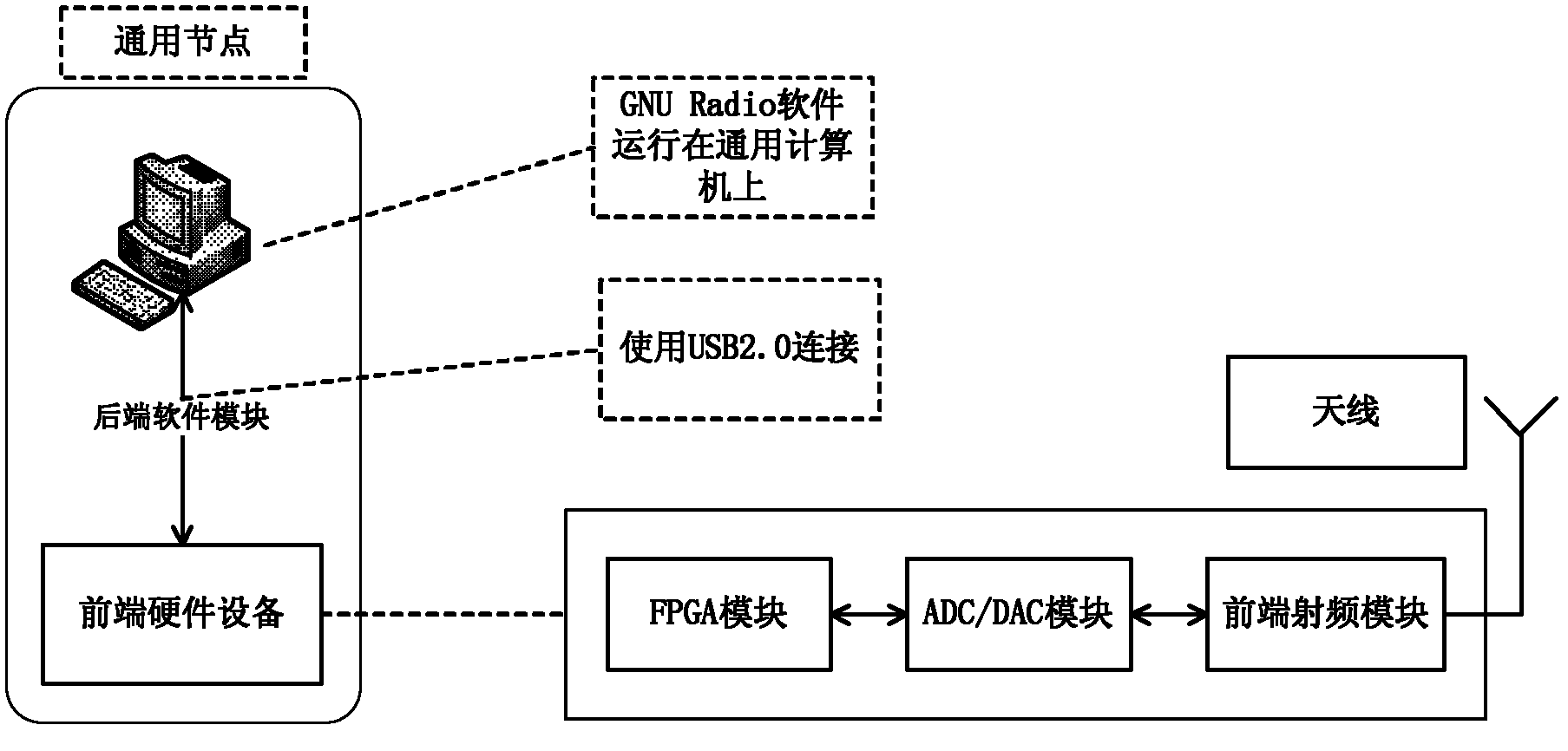
InactiveCN102014036ARich teaching contentCut in any combinationNetworks interconnectionThe InternetGeneral purpose computer
The invention discloses a software wireless technology-based heterogeneous network experimental device. The device faces a wireless sensor network, a wireless local area network, a frequency modulation broadcast network and the Internet. Experimental equipment comprises universal gateway nodes, wireless sensor nodes, a frequency modulation receiver and a host on the Internet. A universal gateway node is structured by software wireless technology and comprises front-end hardware equipment and a rear-end software module, wherein the rear-end software module runs on a universal computer; and the front-end hardware equipment and the rear-end software module are connected through a wire. The universal gateway node can communicate with any experimental equipment and also can realize conversion of various heterogeneous network protocols. The invention designs a heterogeneous network experimental device embodiment and also designs a data transmission experimental embodiment on the basis of the heterogeneous network experimental device embodiment. Compared with the traditional device, the software wireless technology-based heterogeneous network experimental device has rich content of courses and an open experiment environment and it is convenient for students to study and research various heterogeneous networks and more heterogeneous networks.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Intelligent type capacity therapeutic instrument
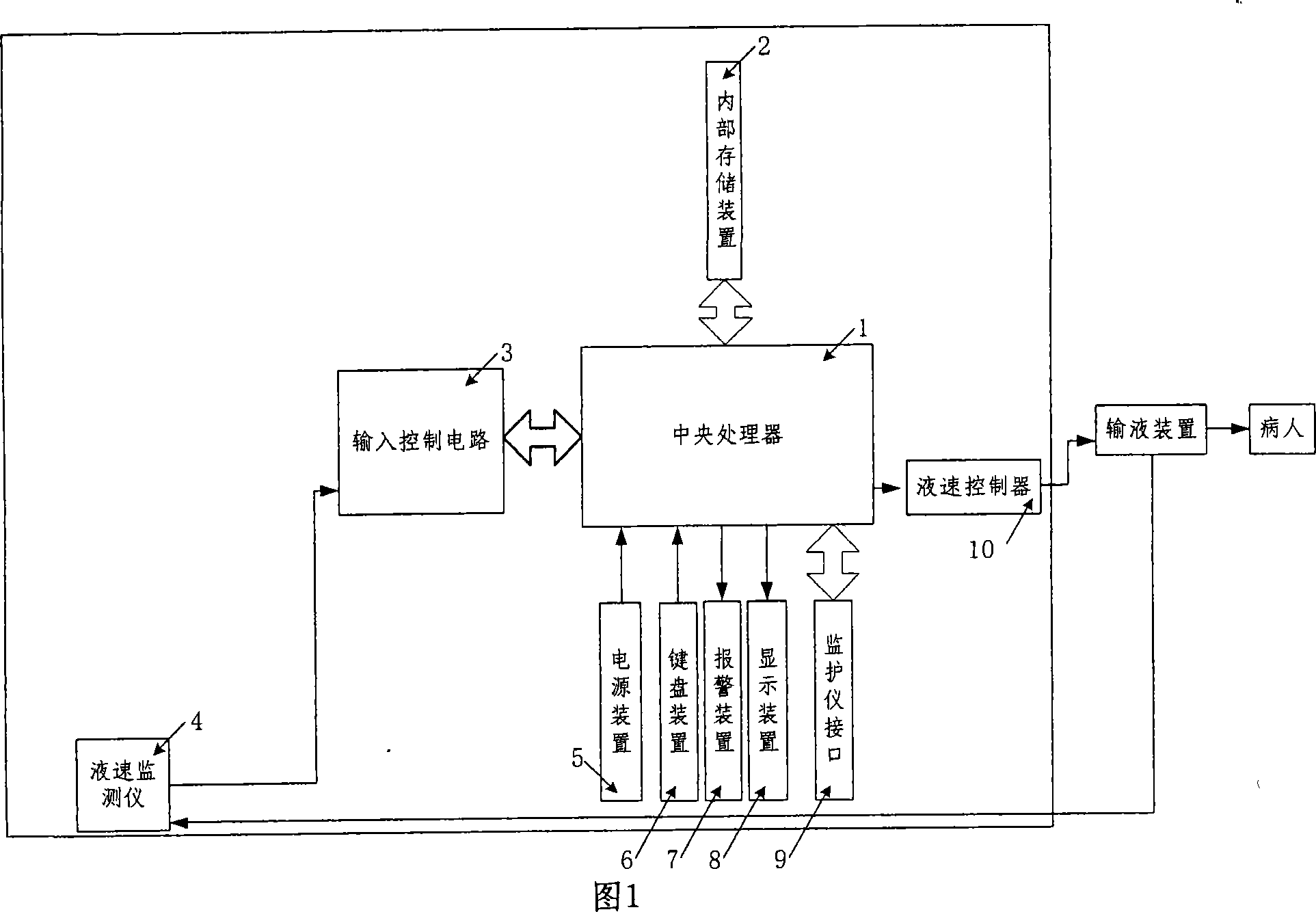
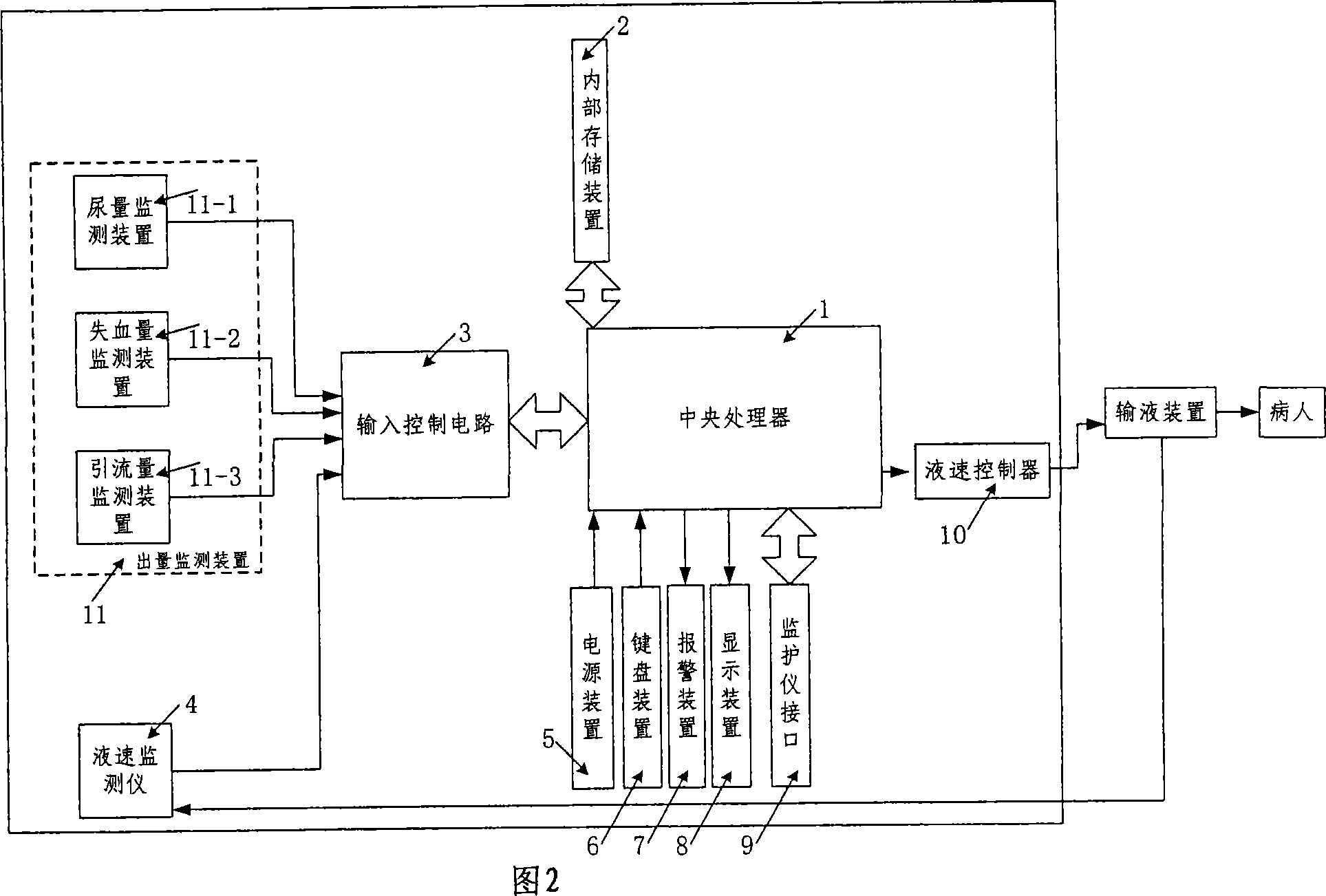
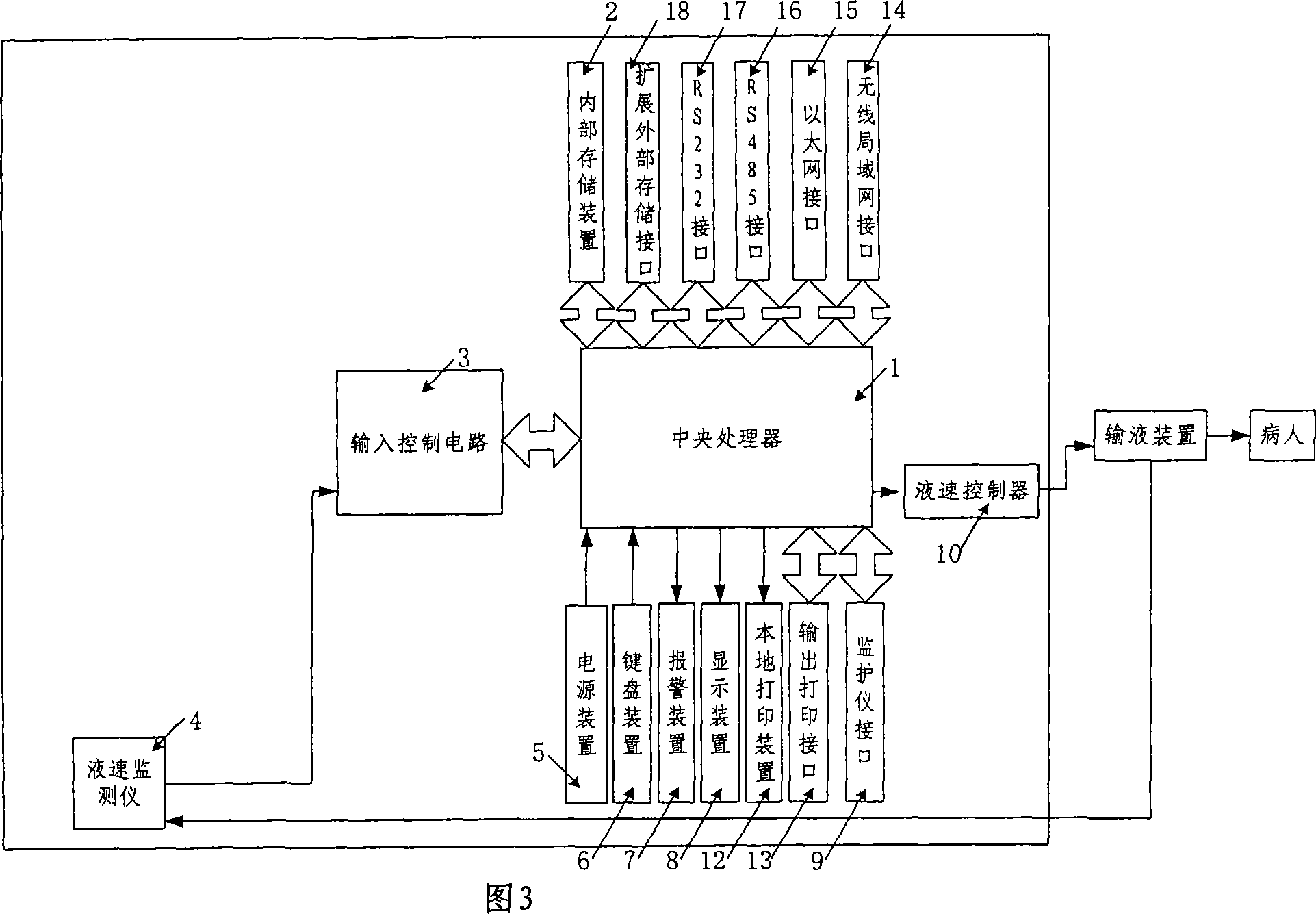
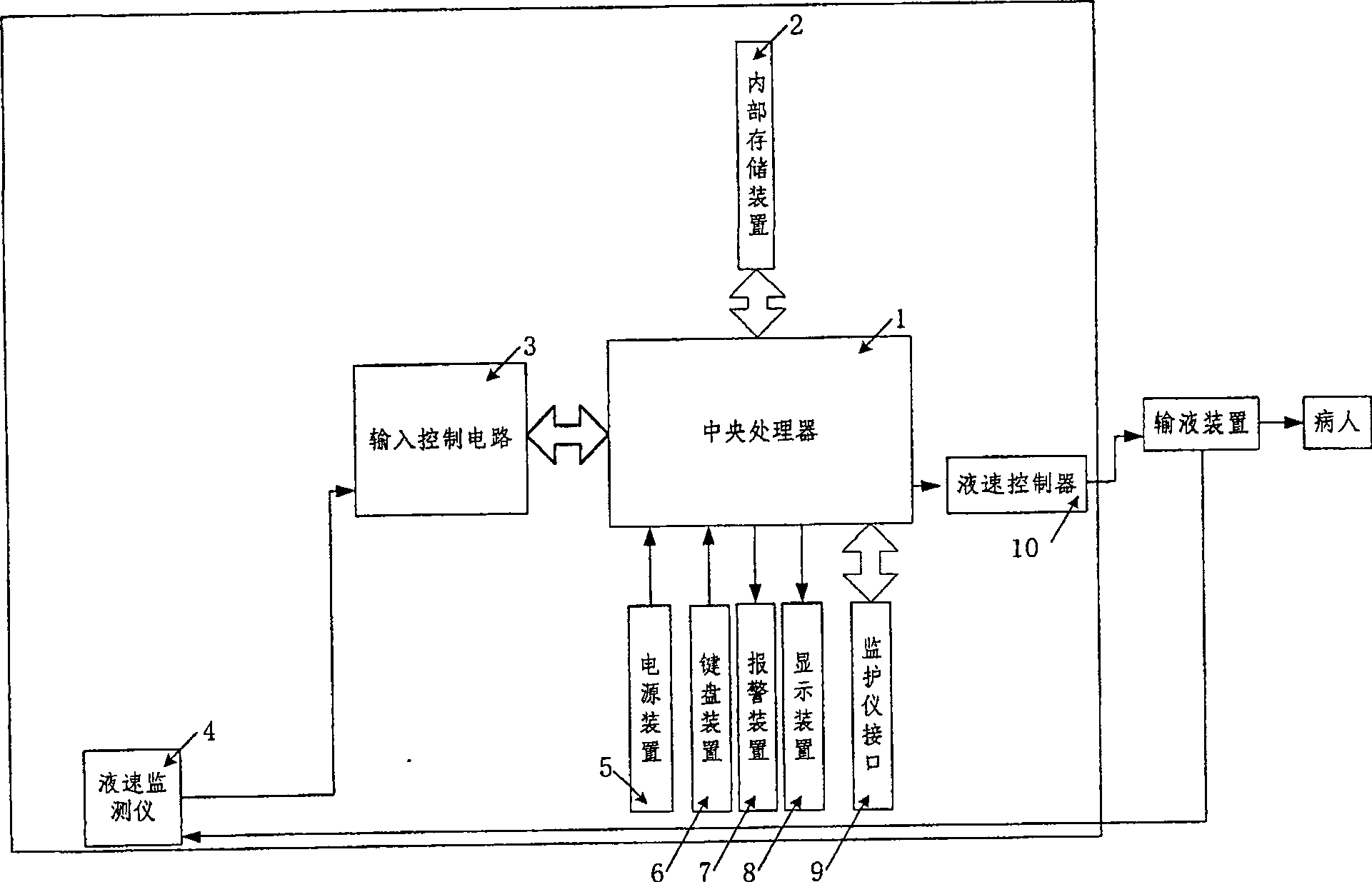
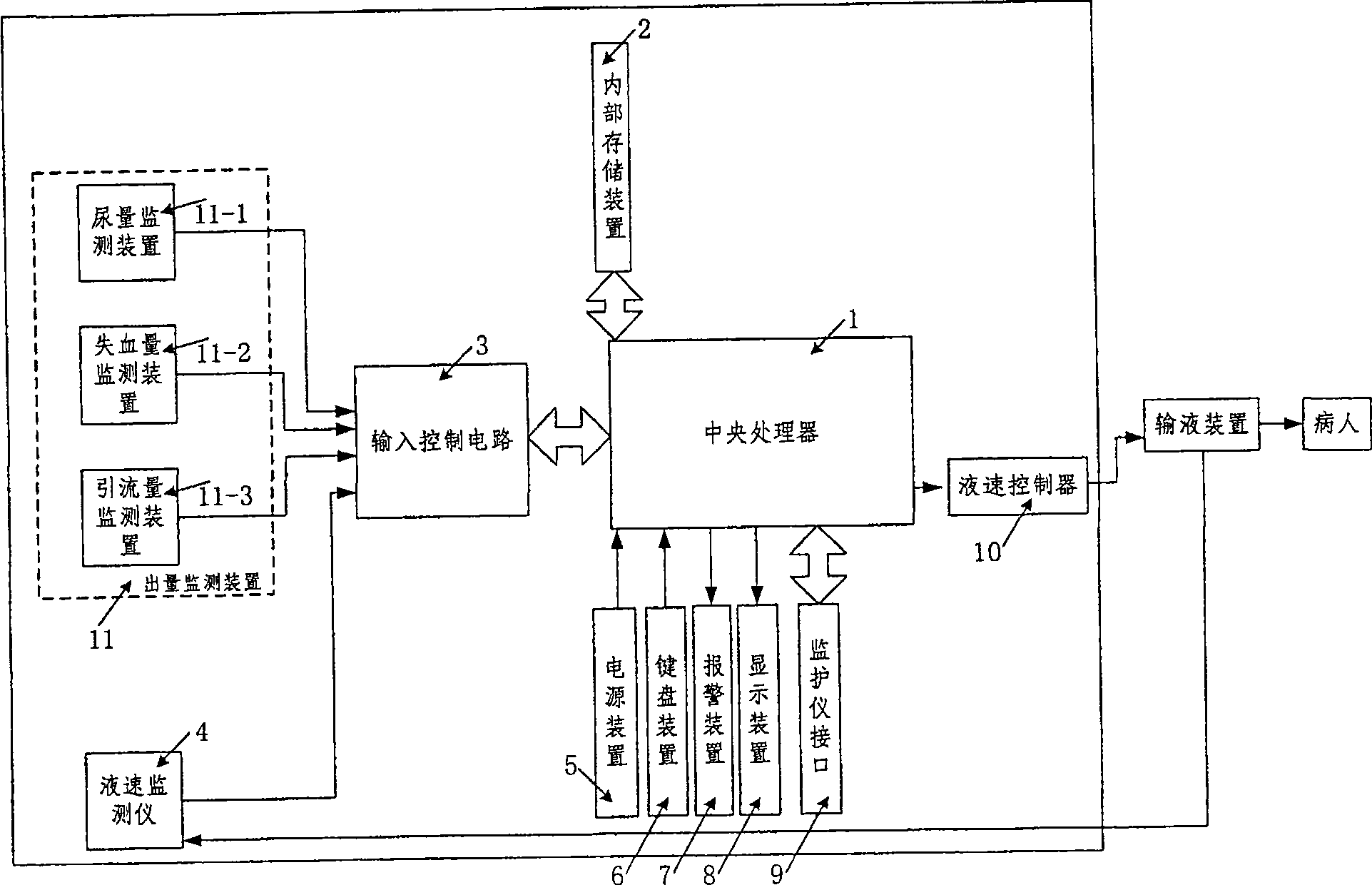
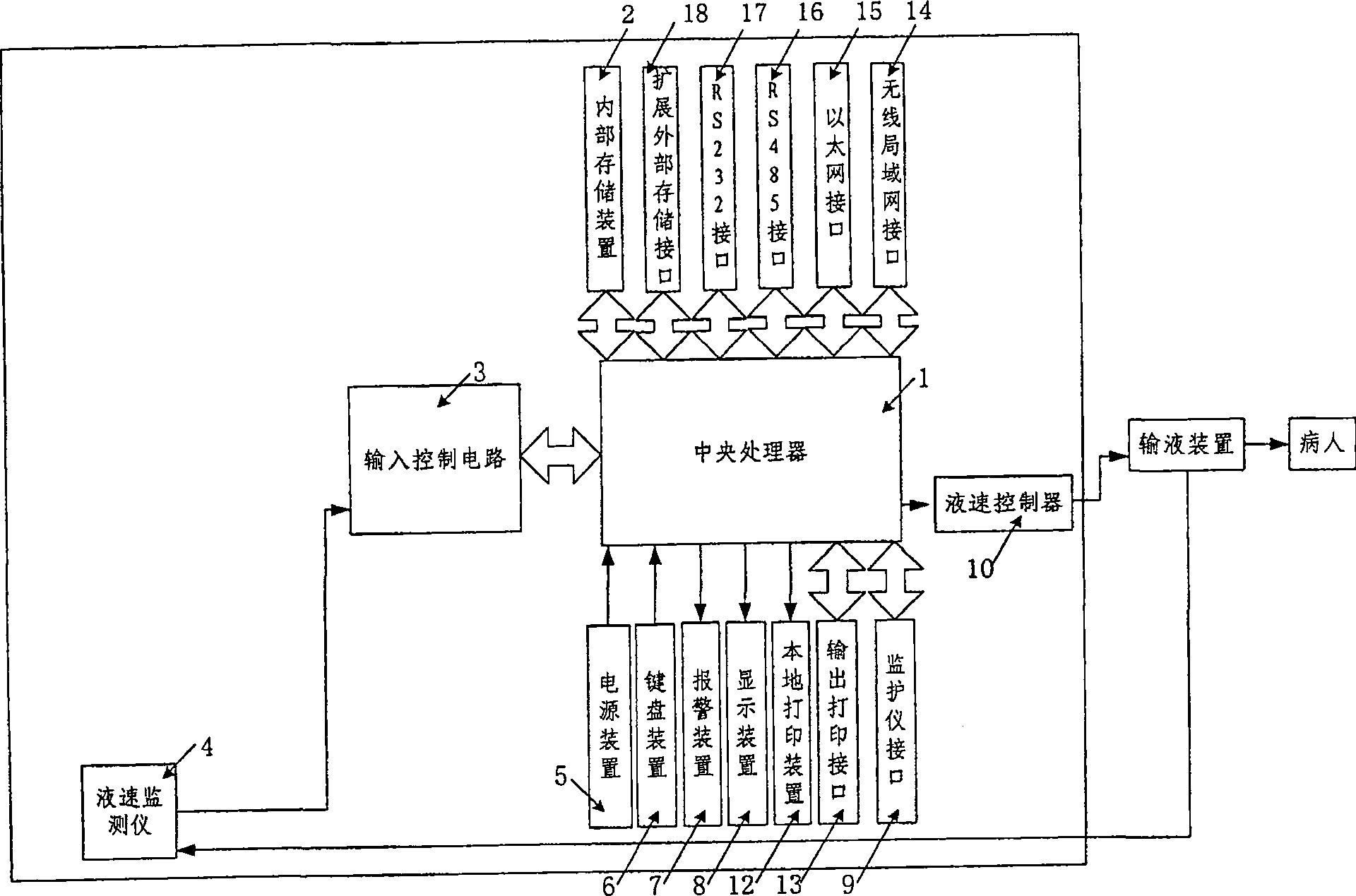
InactiveCN101057981AQuality improvementReduce physical strengthFiltering accessoriesPressure infusionInput controlDisplay device
The invention relates to a kind of intelligent capacity therapeutic equipment, comprising central processor, interior memory, power device, keyboard device, display device, alarm device, input control circuit, monitor interface, liquid speed monitor and liquid speed controller. The interior memory device is used to store program order and operation capacity therapeutic decision program in central processor and the record of patient capacity treatment. The central processor takes relative capacity therapeutic decision program from interior memory device according input patient information from keyboard device, makes patient initial capacity therapeutic program, carries out the capacity therapeutic program according to chosen working mode by doctors, feedbacks and moderates capacity therapeutic program according to sent patient physiological parameter from monitor and stores the capacity treatment record into interior memory device. The central processor also monitors and moderates transfusion speed according to got confirmed transfusion speed.
Owner:李崎 +1
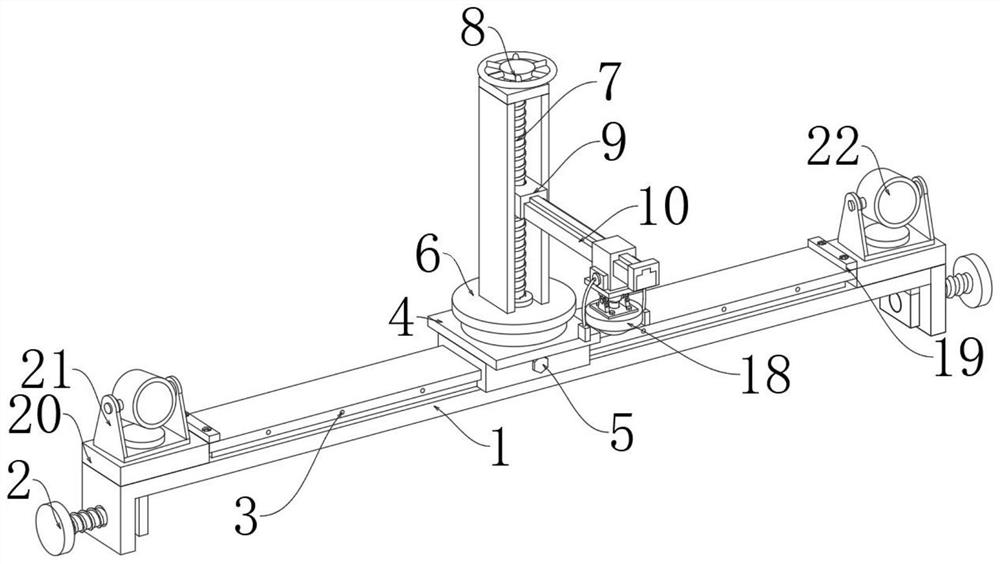
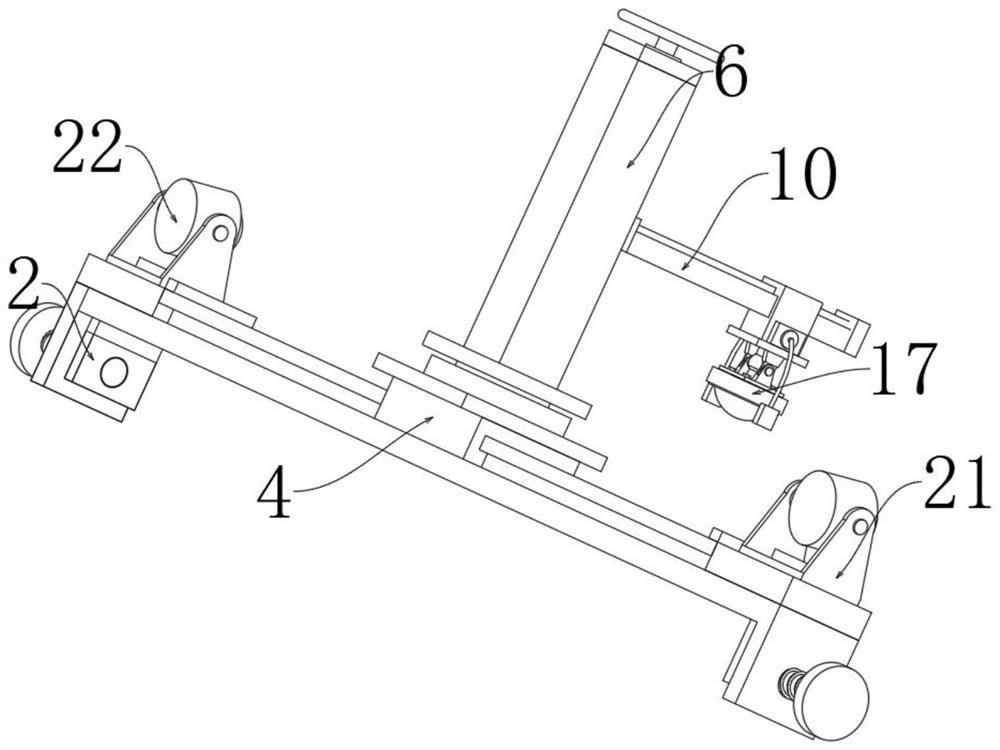
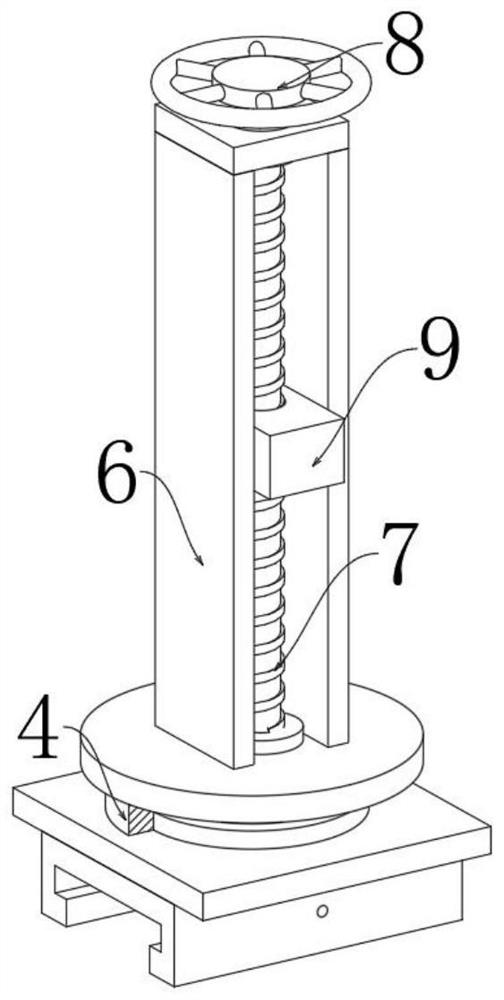
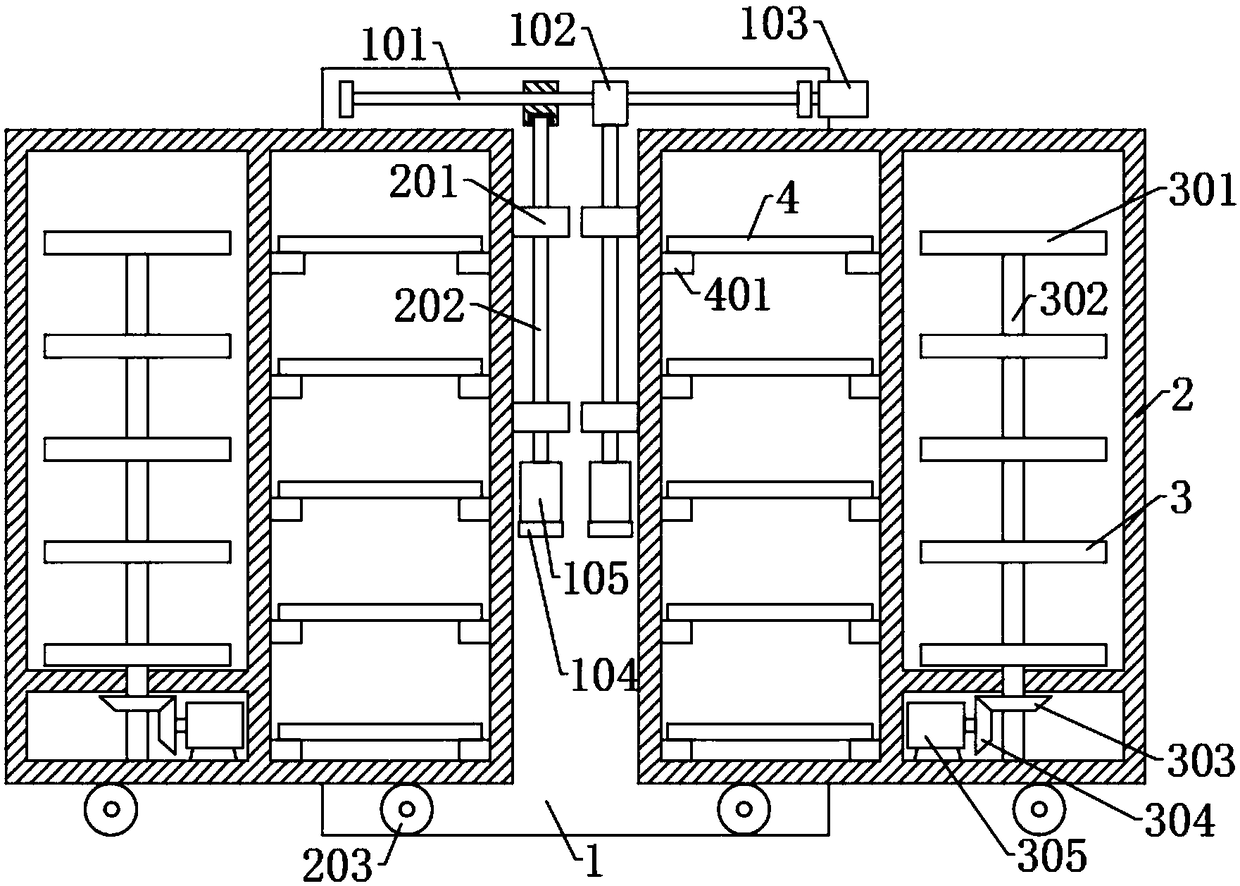
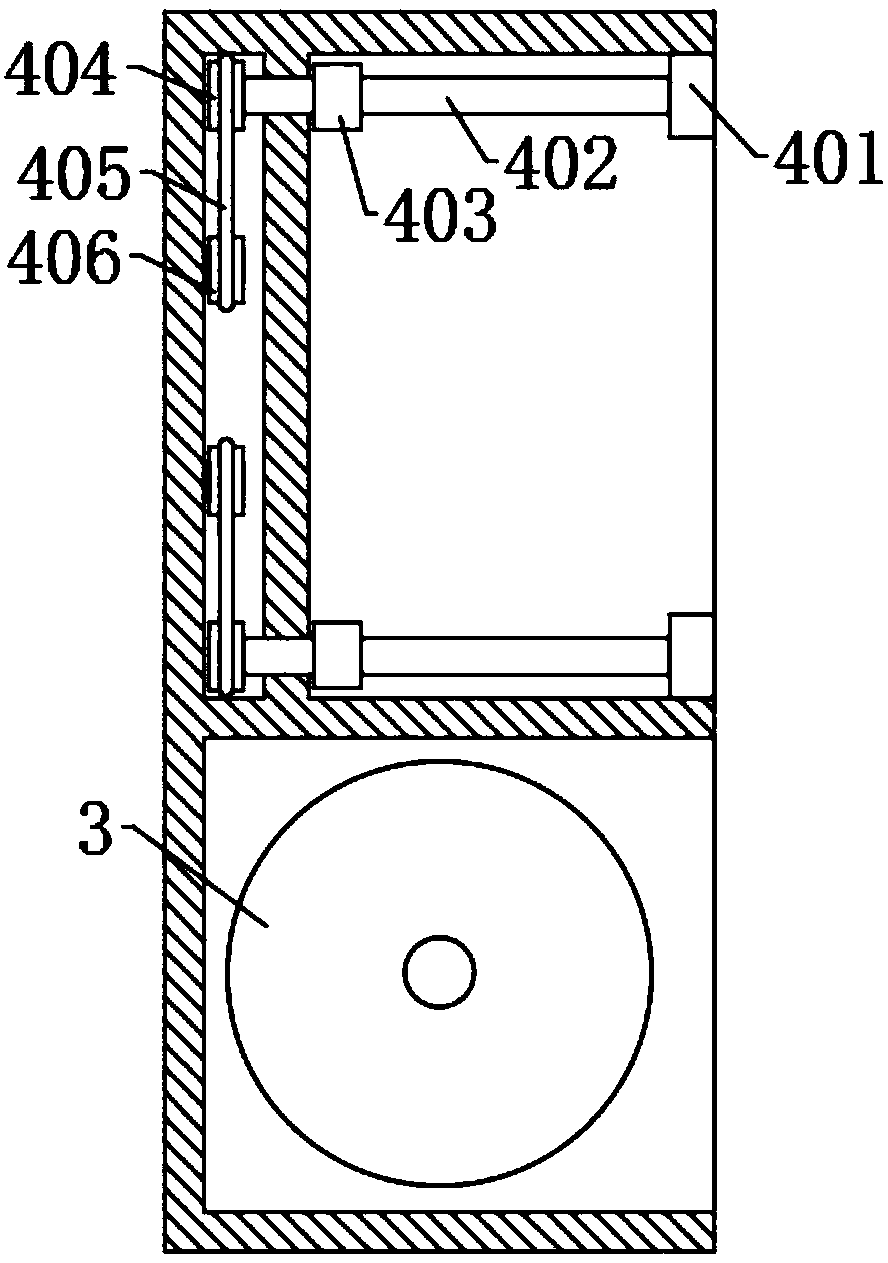
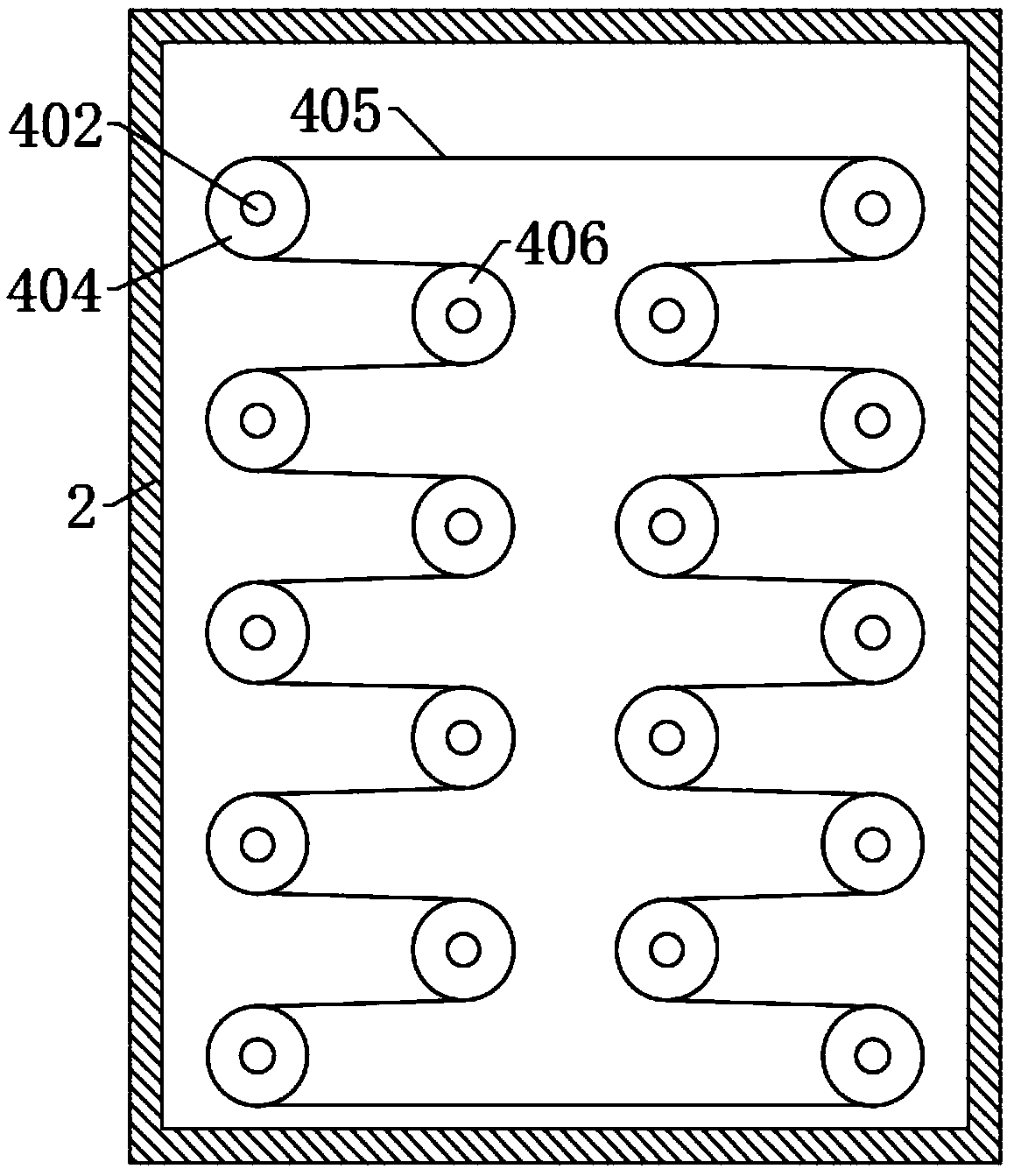
Teaching auxiliary device
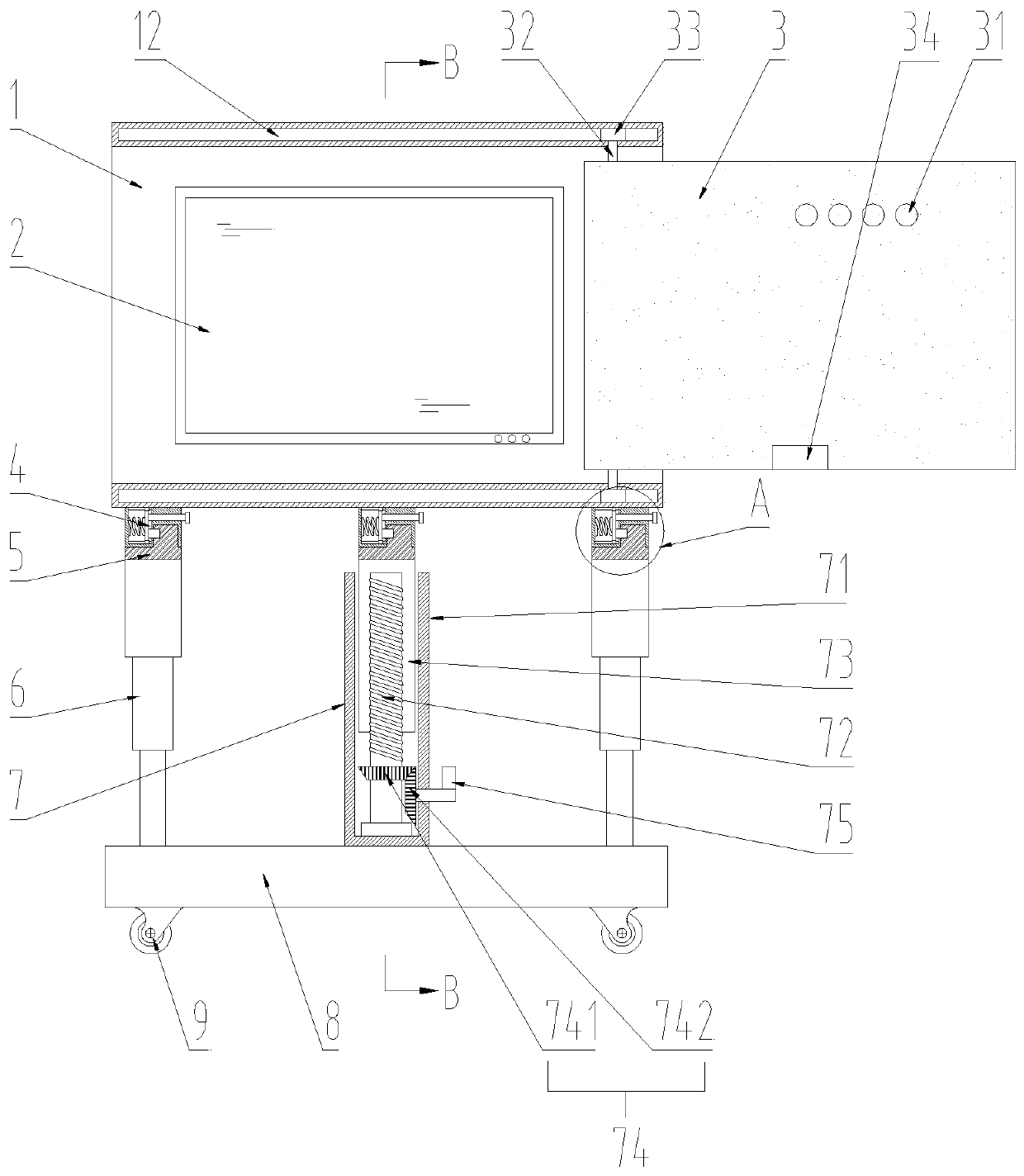
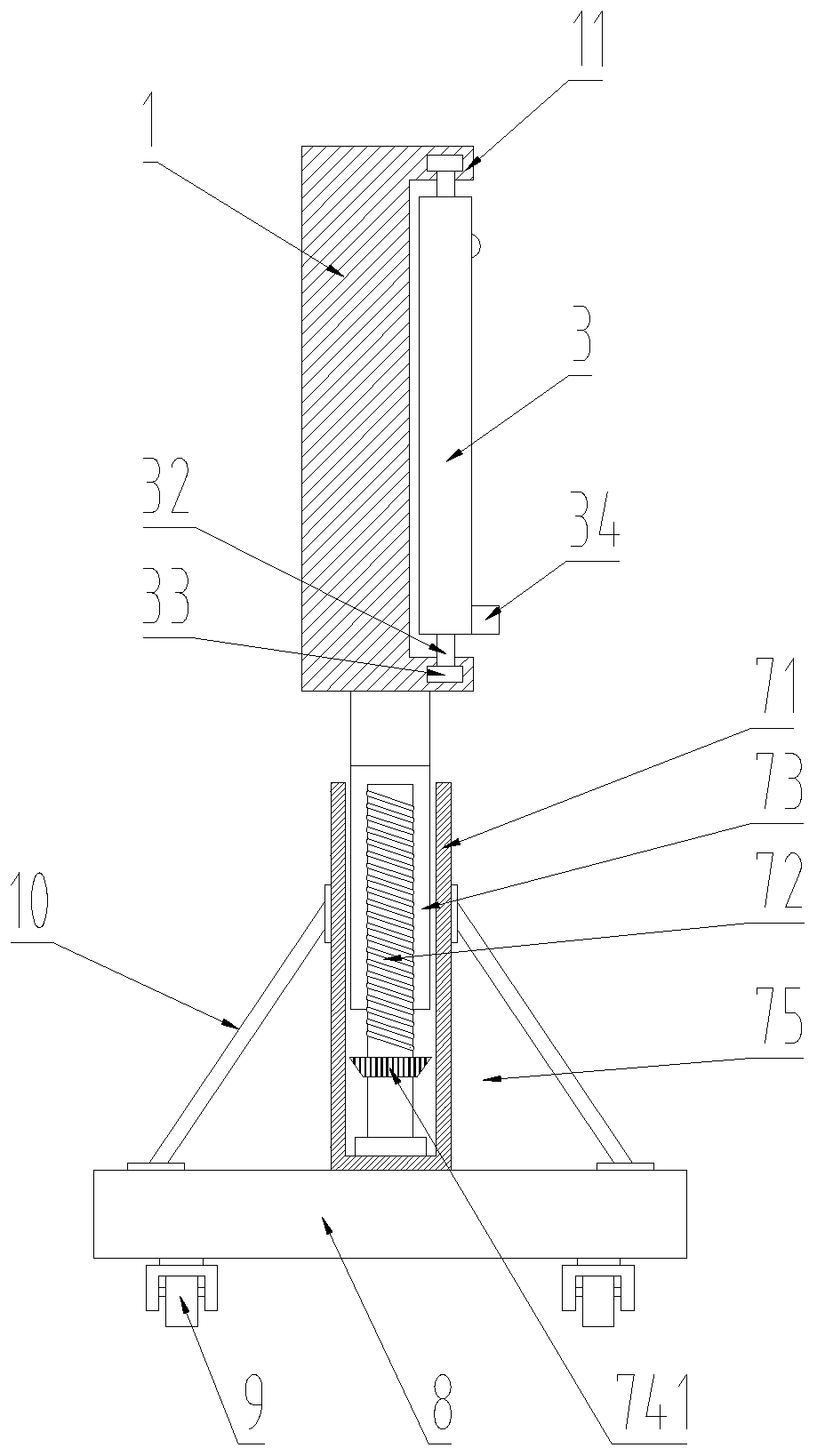
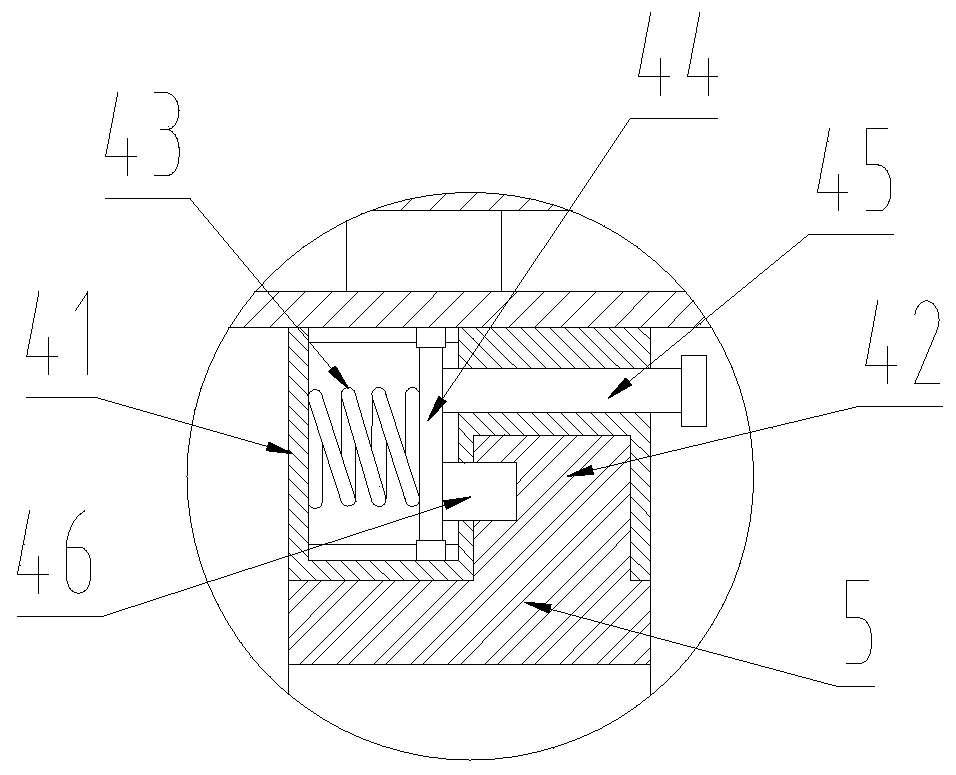
PendingCN110782712ARich teaching contentImprove practicalityFurniture partsStands/trestlesMechanical engineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
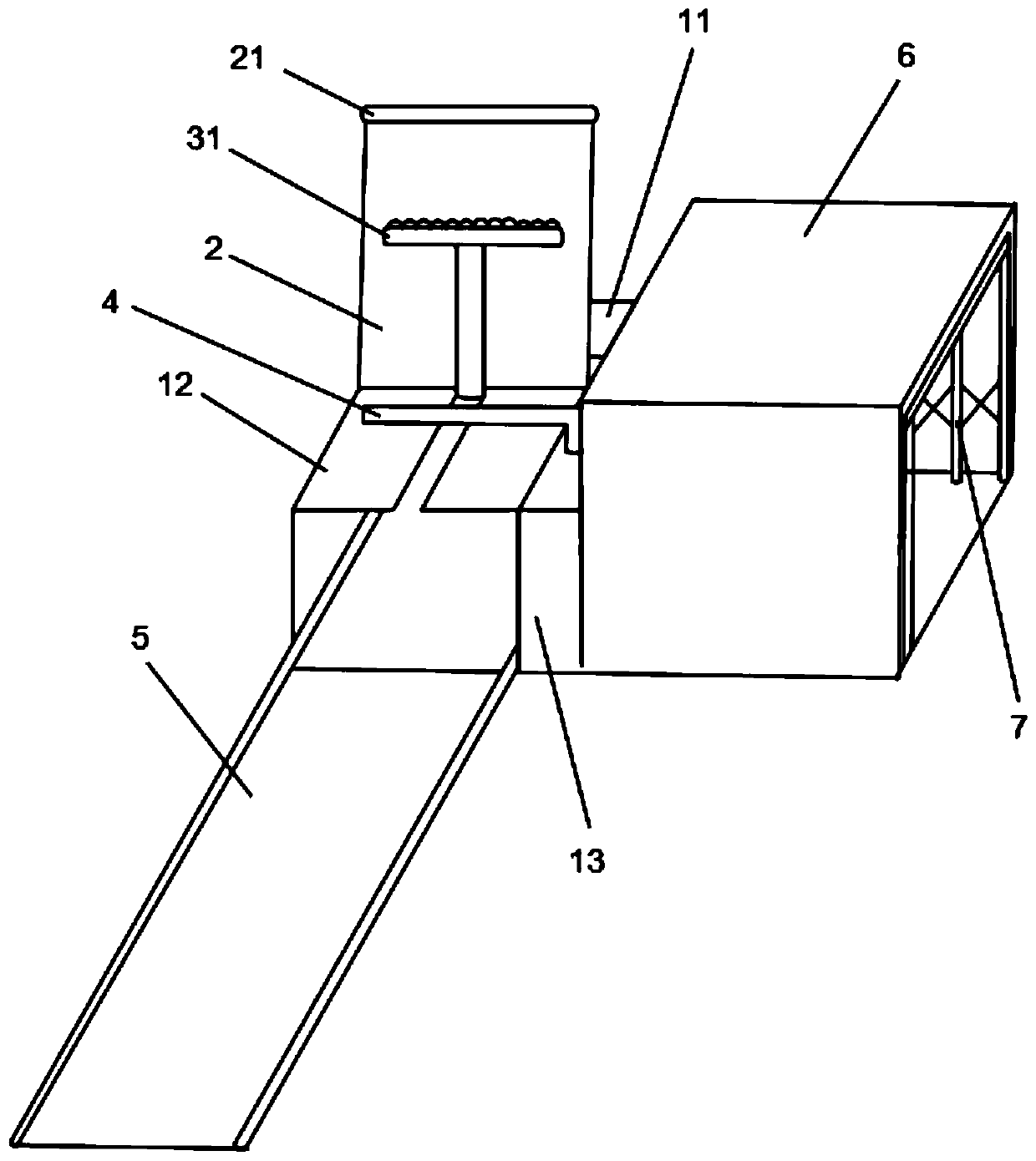
The invention discloses a teaching auxiliary device. The teaching auxiliary device comprises a carrier plate, a base and a moving wheel; the teaching auxiliary device further comprises a magnetic writing pad, a telescopic rod and a height adjusting mechanism; the front surface of the carrier board is slidably connected with the magnetic writing board that can move laterally along the front surfaceof the carrier plate; a magnet is arranged on the front surface of the magnetic writing board; a mounting mechanism is fixedly arranged at the bottom of the carrier plate; the mounting mechanism is detachably connected with a mounting block; the mounting block is arranged at the top of the telescopic rod and the height adjusting mechanism; and the bottoms of the telescopic rod and the height adjusting mechanism are fixed on the base. According to the teaching auxiliary device provided by the invention, video play and material display can be carried out synchronously, the practicability is strong, the installation and disassembly are convenient, carrying is facilitated, the height adjustment is convenient and the operation is simple.
Owner:SICHUAN TECH & BUSINESS UNIV
Cloud-end framework based on teaching plan recording library and pseudo students in online teaching system
PendingCN109816571AImprove learning effectIncrease the number ofData processing applicationsElectrical appliancesInteraction pointObject storage
The invention discloses a cloud-end framework based on a teaching plan recording library and pseudo students in an online teaching system, and the framework comprises a mobile terminal APP which is used for the login of the students, the selection of course operations by the students, the playing of teaching plan videos in a virtual classroom, the acceptance of questions of the students in the interaction process, and the playing of answers and records of interaction points to the students; an object storage server which is used for storing teaching videos, records, questions which can be putforward by a plurality of students and answers corresponding to the questions; a cloud server side which is used for running the course scripts according to course authorities of students, obtaining the corresponding teaching videos and records from the object storage server according to the course scripts and finally sending the obtained teaching video and record to the mobile terminal APP of thestudent for playing, querying the answer of the question in the object storage server according to the question proposed by the student, and then sending the answer of the question to the mobile terminal APP, so that the framework effectively improves the learning effect and the class experiences of the students.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
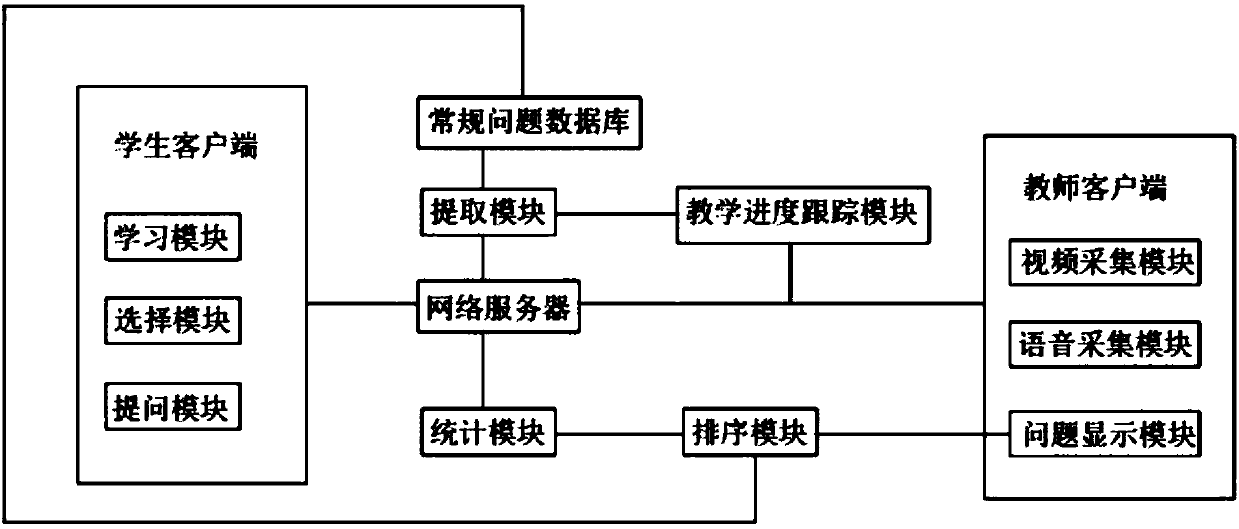
Interactive question answering system based on online class
InactiveCN107742451ARich teaching contentMaintain teaching orderElectrical appliancesThe InternetQuestion answer
The invention discloses an interactive question answering system based on an online class. The system comprises a teacher client end, a teaching progress tracking module, a routine questions database,an extracting module, a plurality of student client ends, a statistic module, an ordering module and a network server, which are interconnected through the Internet. The system is simple in design, during the online class teaching process, routine questions are sent to students for questioning, and the routine questions the students fail to answer and the non-routine questions the students ask are collected, statistic and ordering are conducted, and the questions are answered by the teacher in sequence. Not only are teaching contents of the online class enriched, and question data of the routine questions database expanded, but also the students' learning enthusiasm and learning efficiency are improved, and teaching order of the online class is maintained. The system is high in intellectualization, and good in promotion and advancement effect on education business.
Owner:合肥亚慕信息科技有限公司
Dynamic collision experiment device
InactiveCN104036674AEnhance perceptual knowledgeImprove practical abilityEducational modelsLiquid mediumEngineering
The invention relates to a dynamic collision experiment device. A punched spring and a pressure bearing plate are fixedly connected onto a vertical plate at the lower end of a slope railroad shoe, a laser sensor is installed behind the vertical plate, a laser beam of the laser sensor penetrates a through hole in the vertical plate of the slope railroad shoe to the center of the pressure bearing plate, a trolley is arranged at the upper end of the slope railroad shoe, a barrel is arranged in the trolley, a front baffle and a rear end cover are fixedly connected at the front end and the rear end of the trolley in a sealing mode, the trolley is filled with a liquid medium, the front baffle and the outer end face of the barrel are fixedly connected in a sealing mode, a punch rod and a movable piston are arranged in the barrel, an inner hole of the movable piston is connected with the punch rod in a matching mode, the barrel is divided into a front cavity and a rear cavity through the movable piston, a leakage flow hole is formed in a tail cover at the rear end of the rear cavity, the front end of the punch rod is connected with the through hole in the front baffle in a matching mode and in a sealing mode, a main spring is installed on the step cylindrical face of the punch rod and the step cylindrical face of the movable piston, a restoring spring is installed on the rear end step of the movable piston and the rear end face of the tail cover, and the tail cover and the barrel are fixedly connected in a sealing mode.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
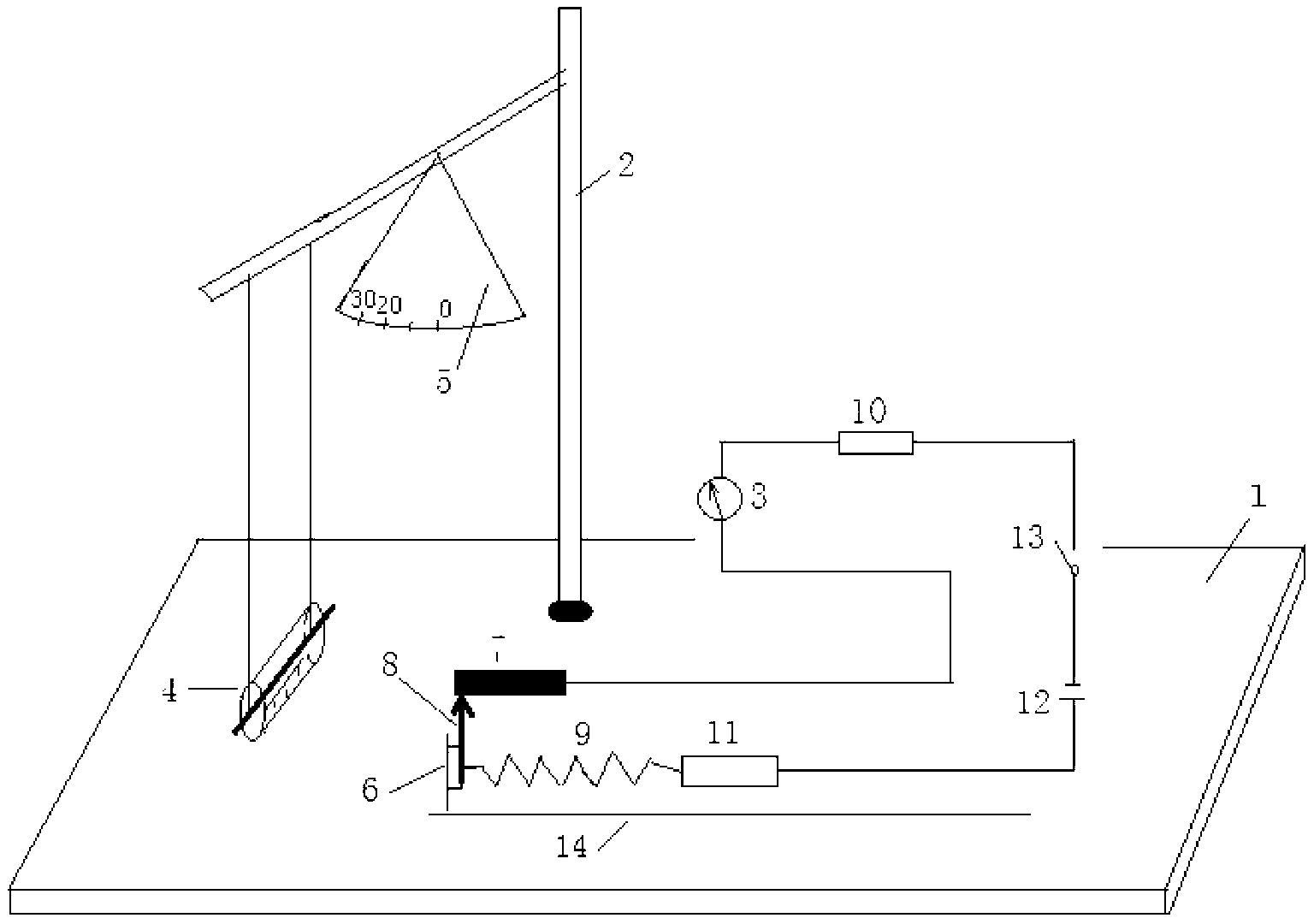
Experimental apparatus for exploring and demonstrating momentum theorem
The invention discloses an experimental apparatus for exploring and demonstrating the momentum theorem. The experimental apparatus comprises a base, a support, a collision weight, a supporting object and an impact force measuring circuit. The support is fixed on the base, the collision weight is hung on the support and can oscillate back and forth, and the impact force measuring circuit can be used for measuring and displaying force born by the supporting object when the collision weight and the supporting object collide. The experimental apparatus is simple in structure, low in cost, simple in operation, obvious in effect, and capable of helping students to visually understand the momentum theorem and enriching teaching content and teaching methods, and materials can be obtained easily.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
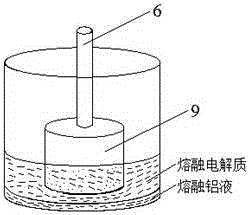
Aluminum electrolytic graphite crucible experimental device and experimental method
ActiveCN105297075ALearn about the variationsRich teaching contentElectrochemical responseFurnace temperature
Provided are an aluminum electrolytic graphite crucible experimental device and experimental method. The device comprises a computer and a heating furnace; a bottom furnace door of the heating furnace is installed at the top end of a lifting mechanism; two silicon carbide rod sets are arranged in the heating furnace, when the device is used, a graphite crucible is located in the heating furnace, an anode conductive rod and a cathode conductive rod are installed, the cathode conductive rod is connected with the graphite crucible, and a graphite anode is installed on the anode conductive rod and located in the graphite crucible. An aluminum ingot is put into the graphite crucible, heating is conducted, after the aluminum ingot and an electrolyte are completely melted, the furnace temperature is kept constant, the heights of melting aluminum and the electrolyte are measured, and data of electric currents changing along with changes of the distance between the anode conductive rod and the bottom face of the graphite crucible are recorded; changes of the electric currents and voltages are observed when an anode effect occurs. The experimental device can simulate an electrochemical reaction in an industrial field device, a good teaching effect is achieved through an early theoretical calculation and arrangement and late experimental phenomenon observation, and meanwhile experimental data can provide guidance and reference data for a production field.
Owner:LANZHOU RESOURCES & ENVIRONMENT VOC TECH COLLEGE +1
Self-assembled experimental device for measuring flow resistance and flow of fluid and using method of experimental device
ActiveCN106935125AEasy to assembleRich teaching contentEducational modelsStraight tubeDifferential pressure
The invention relates to a self-assembled experimental device for measuring the flow resistance and flow of a fluid and a using method of the experimental device. Water is injected into a water tank, first, second, third and fourth outlet regulating valves are closed, first, second and third transfer valves and a fifth outlet regulating valve are opened, a power supply is switched on, a centrifugal pump is started, after that the centrifugal pump rotates stably, and the first, second, third and fourth outlet regulating valves are opened to the largest degree to exhaust a pipeline; and then, the first, second and third transfer valves are closed, the first, second, third and fourth outlet regulating valves are closed, a differential pressure gauge of an inverted U-shaped tube is zeroed, the resistance loss of part of a straight tube and the resistance loss of the straight tube are tested, and a flowmeter correction experiment is carried out. The experimental device and the using method thereof have the advantages that the resistance loss of part of the straight tube and the resistance loss of the straight tube can be tested, and the flowmeter correction experiment can be carried out, assembling is convenient, and teaching content is enriched.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Experimental device for heterogeneous wireless network having strong bandwidth difference characteristic
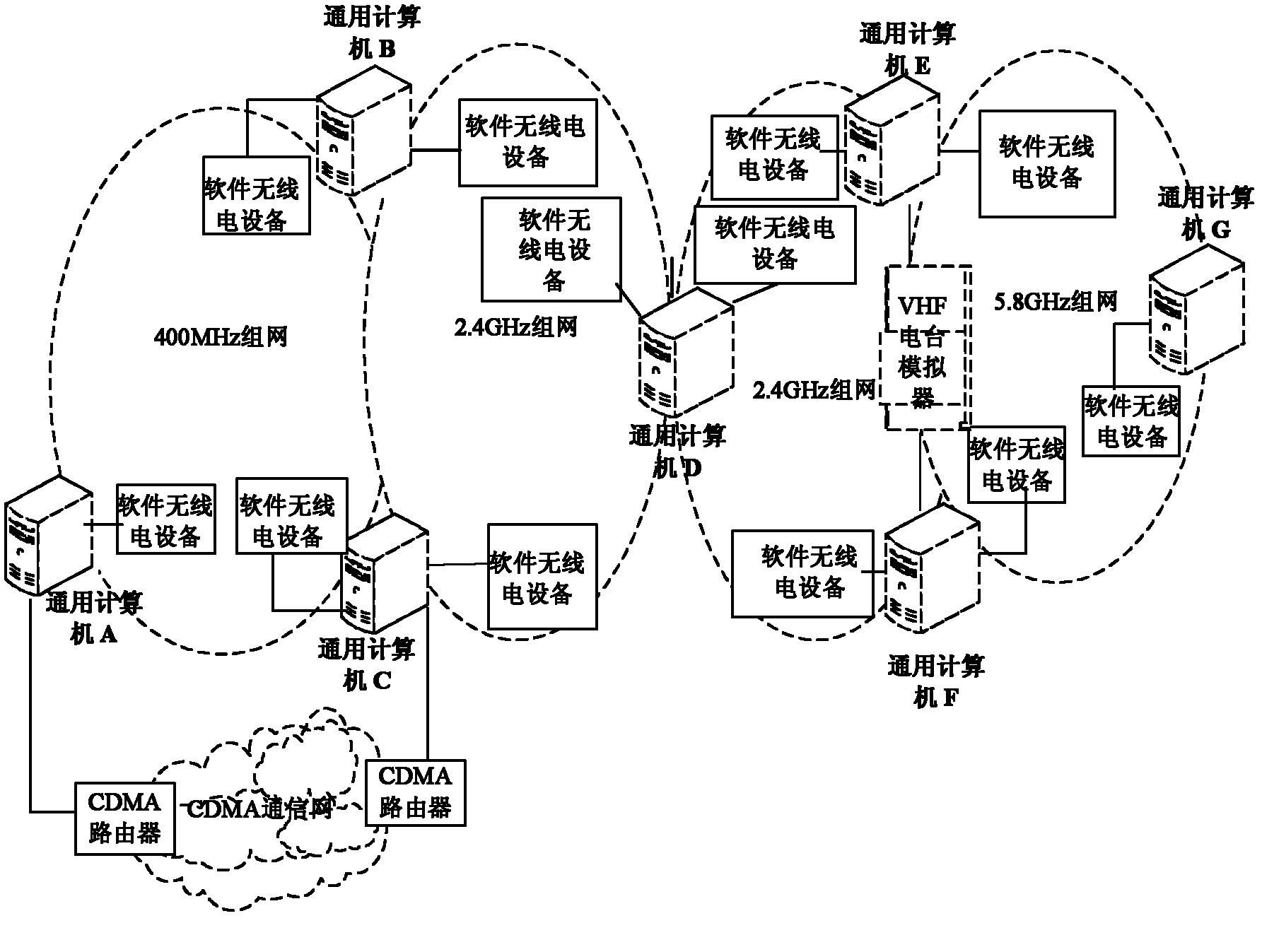
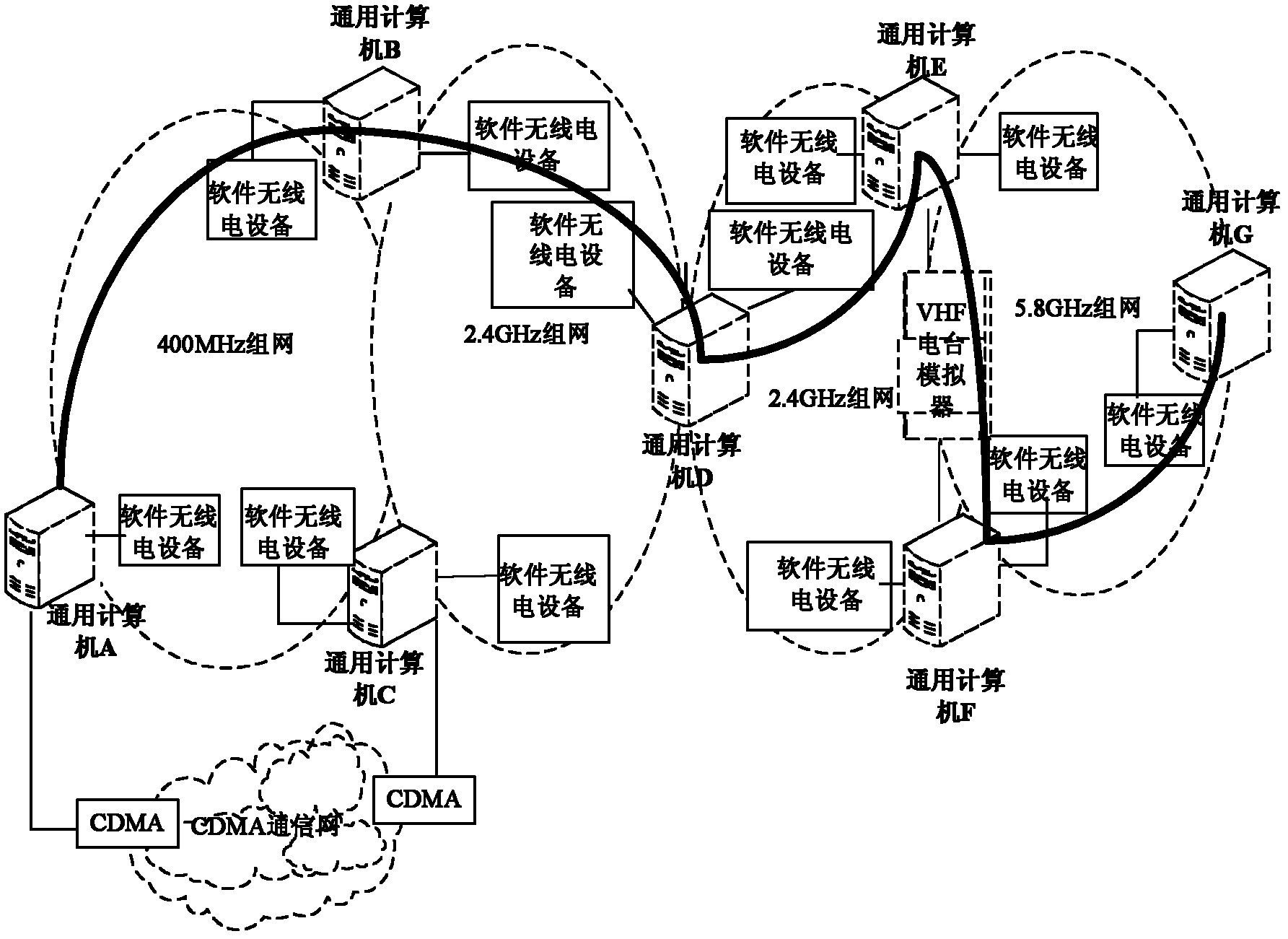
InactiveCN102209342ARich teaching contentCut in any combinationElectrical appliancesWireless communicationRadio equipmentWireless mesh network
The invention discloses an experimental device for a heterogeneous wireless network having a strong bandwidth difference characteristic. The experimental device is applicable to a 2.4GHz wireless network, a 400MHz wireless network, a 5.8GHz wireless network, a code division multiple access (CDMA) network and a very high frequency (VHF) range wireless network. The experimental device comprises a general computer, software radio equipment, a CDMA router and a VHF radio station simulator. The general computer is connected with the software radio equipment for establishing the 2.4GHz wireless network, the 400MHz wireless network and the 5.8GHz wireless network, the software radio equipment comprises front-end hardware equipment and a rear-end software module, the rear-end software module runsin the general computer, the front-end hardware equipment is connected with the rear-end software module by an universal serial bus 2.0 (USB2.0) technology. The general computer is connected with theCDMA network router for establishing the CDMA network. The general computer is connected with the VHF radio station simulator for establishing the VHF range wireless network. The experimental device ensures rich teaching contents and open experimental environment, and provides convenience for students to study and research various heterogeneous networks.
Owner:PLA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Recording and broadcasting device and method for higher vocational chemistry online teaching
InactiveCN114023156AQuality assuranceEasy to operateTelevision system detailsColor television detailsSteering angleEngineering
The invention discloses a recording and broadcasting device and method for higher vocational chemistry online teaching, and the device comprises a mounting plate, the left and right sides of the mounting plate are provided with limiting assemblies, the front side of the top of the mounting plate is provided with positioning holes, the exterior of the top of the mounting plate is connected with a sliding seat, and the outer wall of the front side of the sliding seat is connected with a limiting screw. The top of the sliding seat is connected with a stand column. The position of a first camera assembly in the X direction is adjusted through the sliding seat and the positioning holes formed at equal intervals under the cooperation of limiting screws, the first camera assembly is adjusted in the Z direction through the arrangement of the stand column and a height adjusting lead screw under the cooperation of an adjusting block, and through the cooperation of a sliding block and a cross beam, the position of the first camera assembly in the Y direction is adjusted through the first camera assembly, and the steering angle of the first camera assembly is adjusted through the cooperation of a connecting sleeve, a connector and an auxiliary steering assembly, so that the whole process of a chemical experiment can be clearly recorded, and the recording and broadcasting quality is ensured.
Owner:HUNAN POLYTECHNIC OF ENVIRONMENT & BIOLOGY
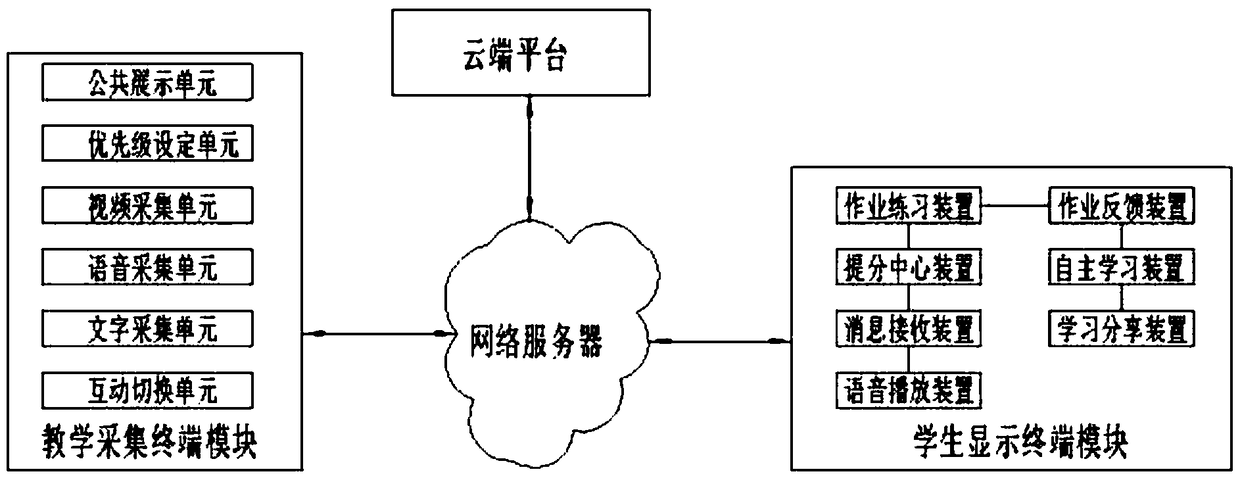
Mobile live broadcast teaching interaction system
InactiveCN108768945ARich teaching contentLecture content and livelyData processing applicationsTransmissionData transmissionShared service
The invention discloses a mobile live broadcast teaching interaction system. The mobile live broadcast teaching interaction system comprises a network server, a cloud platform, a teaching acquisitionterminal module and a student display terminal module; the network server comprises a server data transceiving unit and a data transmission module; the cloud platform is a cloud security storage or sharing server; the teaching acquisition terminal module comprises a public display unit, a priority setting unit, a video acquisition unit, a speech acquisition unit, a text acquisition unit and an interaction switching unit; and the student display terminal module comprises a branch center device, a message receiving device and a speech broadcast device. According to the mobile live broadcast teaching interaction system, a teacher can teach more conveniently and flexibly, the learning interest of a student is increased, and the memory of the student is enhanced; by means of the student displayterminal module, the completion condition, the accuracy rate and the various answer ratios of homework of the student can be viewed and counted; and the teacher truly and efficiently knows the homework completion condition and the teaching content mastering condition of the student through a homework publishing module.
Owner:安徽展航信息科技发展有限公司
One-chip microcomputer based simulation test box for railway four-display of automatic occlusion and the method thereof
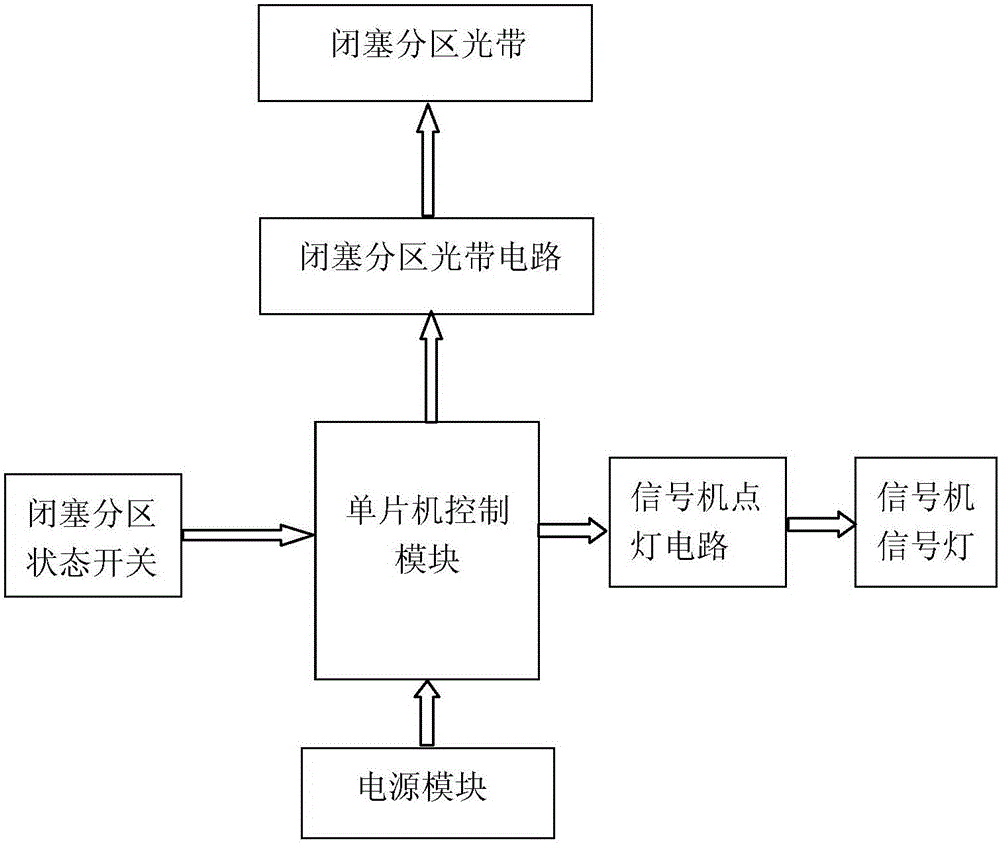
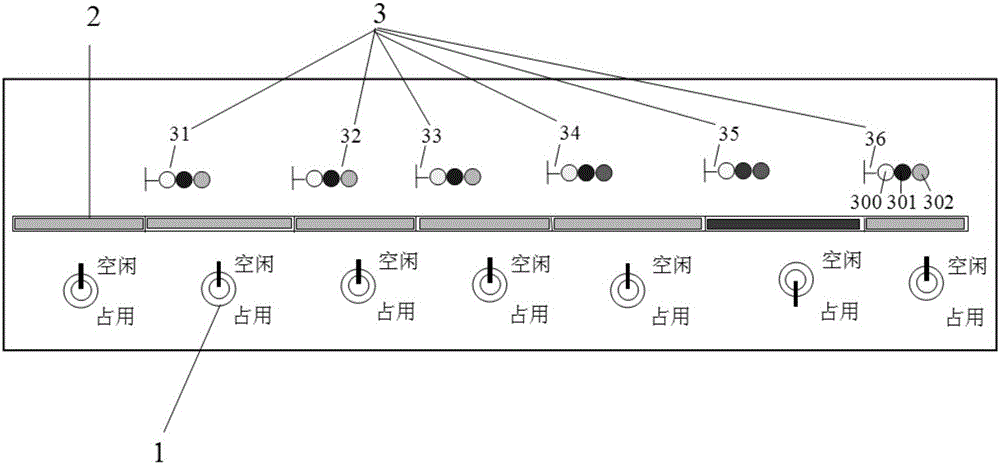
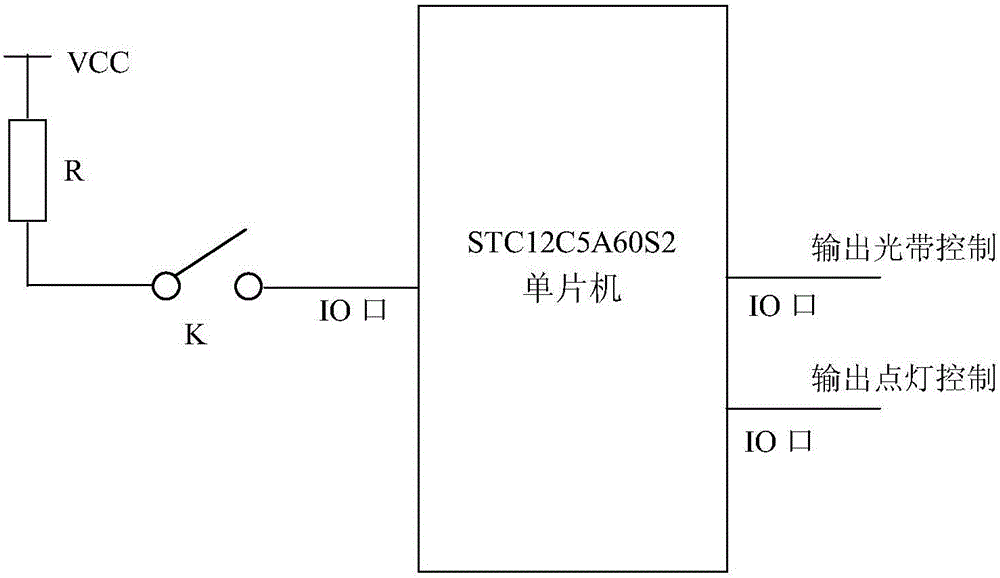
InactiveCN106023707AImprove teaching efficiencyRich teaching contentCosmonautic condition simulationsSimulatorsMachine controlSurface plate
The invention provides a one-chip microcomputer based simulation test box for railway four-display of automatic occlusion and the method thereof. The test box comprises a box body, a panel, a power supply module in the box body, a single-chip machine control module, an occlusion partition state detection circuit, an occlusion partition light strip control circuit, and a signaling machine lighting circuit. The panel is provided respectively with an occlusion partition state switch, an occlusion partition light strip and signaling machine signal lights. The method is performed through the following steps: inputting an occupied state or an idle state for the electric circuit of a simulated track through the dial of the occlusion partition state switch; receiving through the one-chip microcomputer the state information inputted by the occlusion partition state switch; controlling respectively the occlusion partition light strip control circuit and the signaling machine lighting circuit to output corresponding control signals so as to control the occlusion partition light strip and the signaling machine signal lights to display accordingly. With what is provided in the invention, it is possible to demonstrate the working principles of automatic occlusion in concentration and to improve teaching efficiency; small in size and stable and reliable in performance, the test box and the method are rather practical for future wider applications.
Owner:LIUZHOU RAILWAY VOCATIONAL TECHN COLLEGE
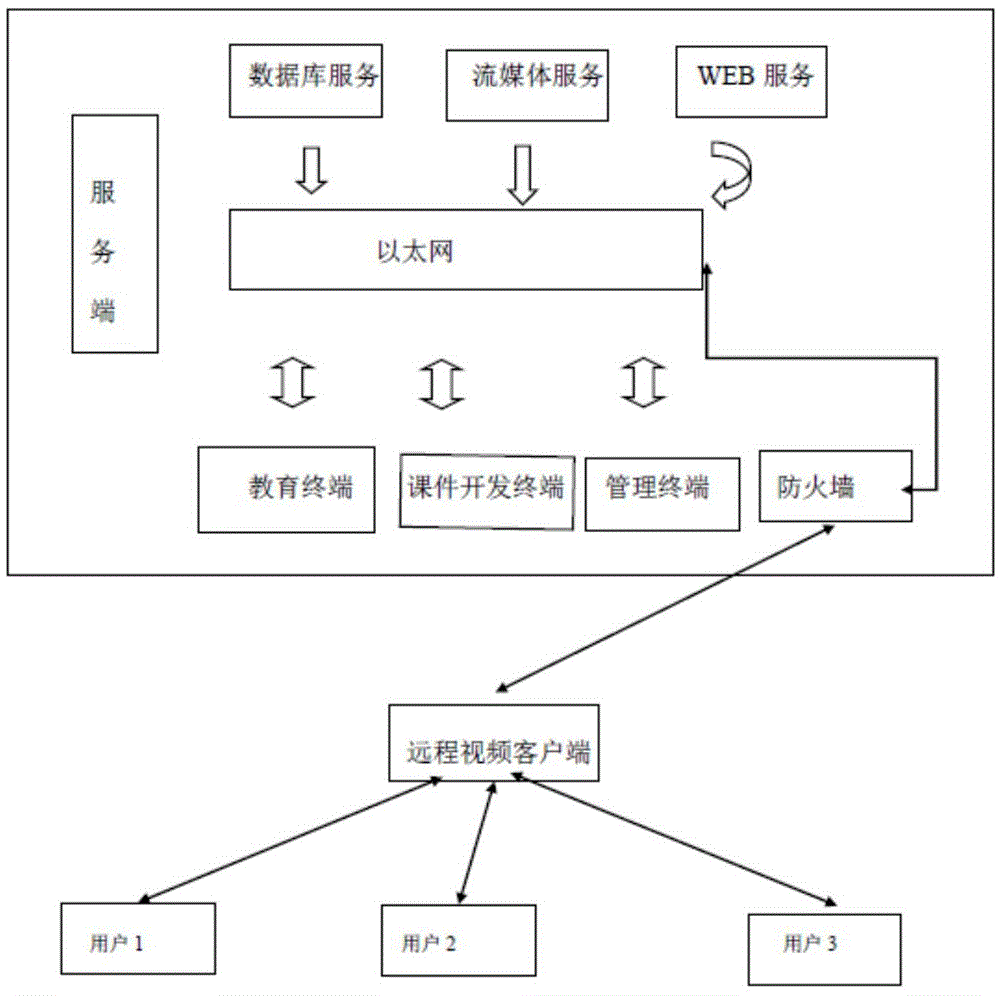
Real-time interaction remote video teaching system
InactiveCN104464415AThe teaching mode is no longer singleEnhanced interactionElectrical appliancesNon real timeTele education
The invention discloses a real-time interaction remote video teaching system suitable for a remote education system. The real-time interaction remote video teaching system comprises server modules, provides user online examination management, and is characterized in that college students or learners can learn indoors through the system. The real-time interaction remote video teaching system comprises various real-time and non-real-time teaching interaction modules; through cooperation of the modules, the system can realize real-time interaction between teachers and students, and between colleges and students, pay attention to student learning situations in real time and improve student learning efficiency by video; in addition, the real-time interaction remote video teaching system provides a plurality of types of real-time and non-real-time communication modes, further reduces communication gaps between teachers and students, and solves the problems that teaching methods are single, and education learning appliances are not advanced.
Owner:NANJING DAWU EDUCATION TECH
Double-sided sounding wall chart, implementation method, and double-sided button implementation circuit and method
InactiveCN104240589BEasy to controlSimple structureMaps/plans/chartsElectrical appliancesSound productionEngineering
The invention discloses a double-faced sound production wall map, an implementation method thereof and a double-faced button implementation circuit and method. The double-faced button implementation circuit comprises a first printed circuit, a second printed circuit and an insulation layer. The first printed circuit is provided with N first contacts, a first switch contact and a second switch negative electrode contact; the second printed circuit is provided with N second contacts, a second switch contact and a first switch negative electrode contact. The first contacts are arranged on X first guide lines, and the second contacts are arranged on Y second guide lines. The insulation layer is clamped between the first printed circuit and the second printed circuit. Through holes are formed in the positions opposite to all the contacts. The first switch contact and the second switch contact are pressed to generate a first selection signal and a second selection signal respectively. The first contact and the second contact are pressed to generate a first using signal and a second using signal respectively. A control unit recognizes the states of the corresponding first contacts and the states of the corresponding second contacts through the first selection signal, the second selection signal, the first using signal and the second using signal. The double-faced sound production function of the wall map is achieved, the voiced teaching contents are enriched, and the space utilization rate of products is improved.
Owner:黄显挺
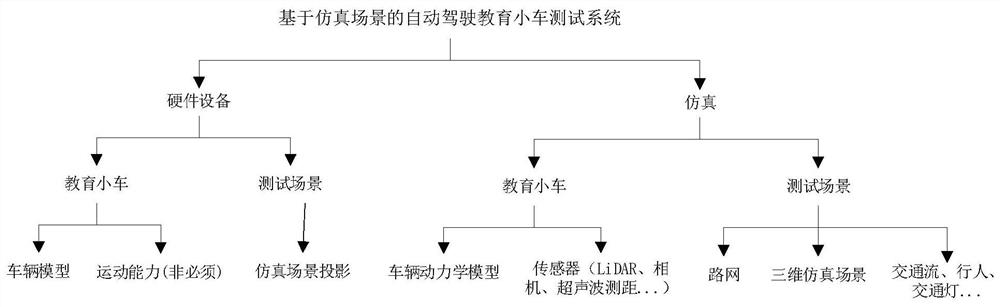
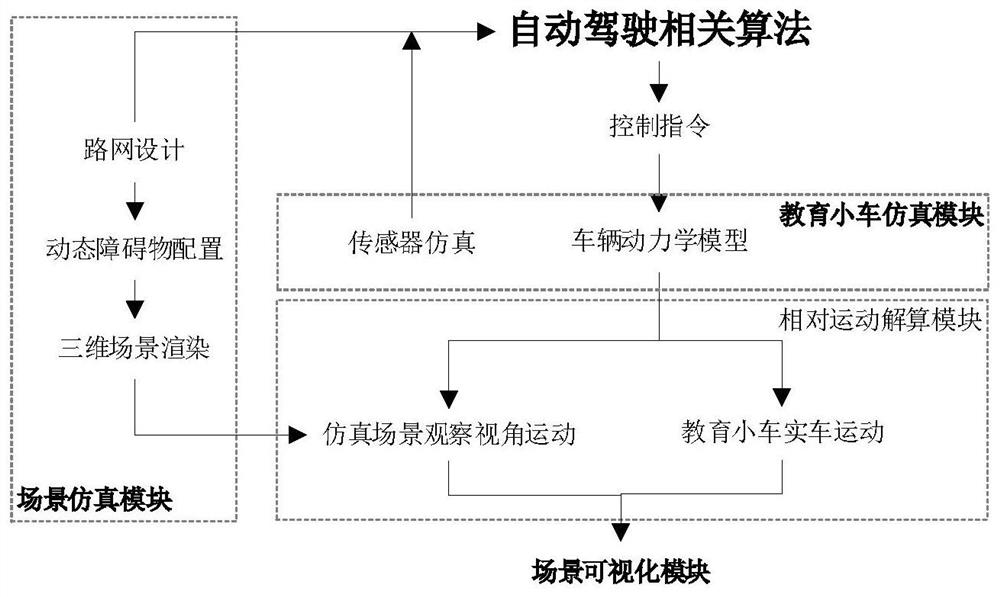
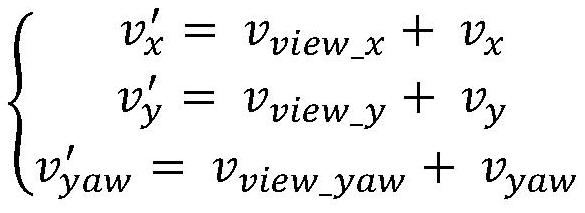
Automatic driving education trolley testing method and system based on simulation scene
PendingCN113705000ALow costImprove securityCharacter and pattern recognitionDesign optimisation/simulationSimulationRoad networks
The invention discloses an automatic driving education trolley testing method and system based on a simulation scene, and the method specifically comprises the steps: building a simulation scene based on a high-precision semantic map, and configuring a simulation education trolley and a dynamic obstacle in the simulation scene; setting up hardware equipment, wherein the hardware equipment comprises visual equipment and a real education trolley, and the real education trolley can run on the visual equipment; enabling the hardware equipment to interact with simulation scene information so that a real education trolley and a simulation education trolley run synchronously, absolutely accurate position, obstacle and sensor information in simulation is provided for an automatic driving algorithm, and the problem of experiment difficulty caused by off-site interference is avoided; a user can design a test scene (road network, traffic flow, traffic light and the like) by himself / herself, the teaching content is richer and more flexible, and the cost of platform building is reduced; and finally, in the method, the real education trolley only moves in a small range, so that the safety of practical teaching is greatly improved.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +1
Electric teaching platform and using method thereof
InactiveCN109637243ASimple and fast fixedSimple and fast mobilityCosmonautic condition simulationsSimulatorsElectricityComputer module
The invention relates to the technical field of teaching appliances, particularly relates to an electric teaching platform which comprises an operating platform and is characterized in that an operating surface cabinet is fixed on the operating platform, the operating surface cabinet comprises a frame and an operation panel, the operation panel is hinged to connect one side of the frame, the corresponding other side is provided with a mechanical lock; the operation panel comprises a mounting frame used for mounting a plurality of module plates, the mounting frame is matched with module platesin a clamping way, each module plate is provided with a plurality of strip-shaped through holes used for fixing a plurality of electronic components, electronic components are detachably connected with the operation panel through strip-shaped through holes and threaded fasteners, and electronic components are electrically connected through leads; each module plate is also provided with a pluralityof experimental wiring terminals for electrical connection. The teaching platform can carry out function modularization arrangement circuits and assemble module plates according to requirements, so that simultaneous teaching and operation on a plurality of people and a plurality of subjects can be achieved, and can carry out function combination among modules, so that the teaching efficiency is improved.
Owner:宁夏大有电气集团有限公司
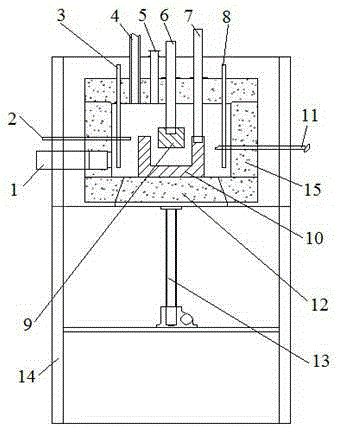
Teaching experiment table for critical state observation and p-v-T relationship determination
ActiveCN106847000AImprove pressure resistanceImprove securityEducational modelsTemperature controlThick wall
The invention discloses a teaching experiment table for critical state observation and p-v-T relationship determination. The teaching experiment table comprises a bottom cavity, wherein a metal cup is arranged in the bottom cavity; a gap is formed between the metal cup and the inner wall of the bottom cavity; the metal cup is filled with mercury; the part between the upper part of a mercury surface in the metal cup and the inner wall of the bottom cavity is filled with hydraulic oil; a metal gas compression cavity extending into the mercury is arranged in the metal cup; a conduit extending into the mercury is arranged at the bottom of the metal gas compression cavity; a quartz glass tube is arranged at the top of the metal gas compression cavity; the metal gas compression cavity and the quartz glass tube are filled with a fluid working medium; an experiment temperature control part for controlling the experiment temperature is arranged at the outer side of the quartz glass tube. A glass compression cavity is replaced with the metal compression cavity, a common glass tube is replaced with the thick-wall quartz glass tube, and a gourd-shaped glass cavity used for conventional gas compression is changed into the metal cavity through a sealed design, so that the pressure resistance and the security of the experiment table are greatly improved.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Intelligent teaching system
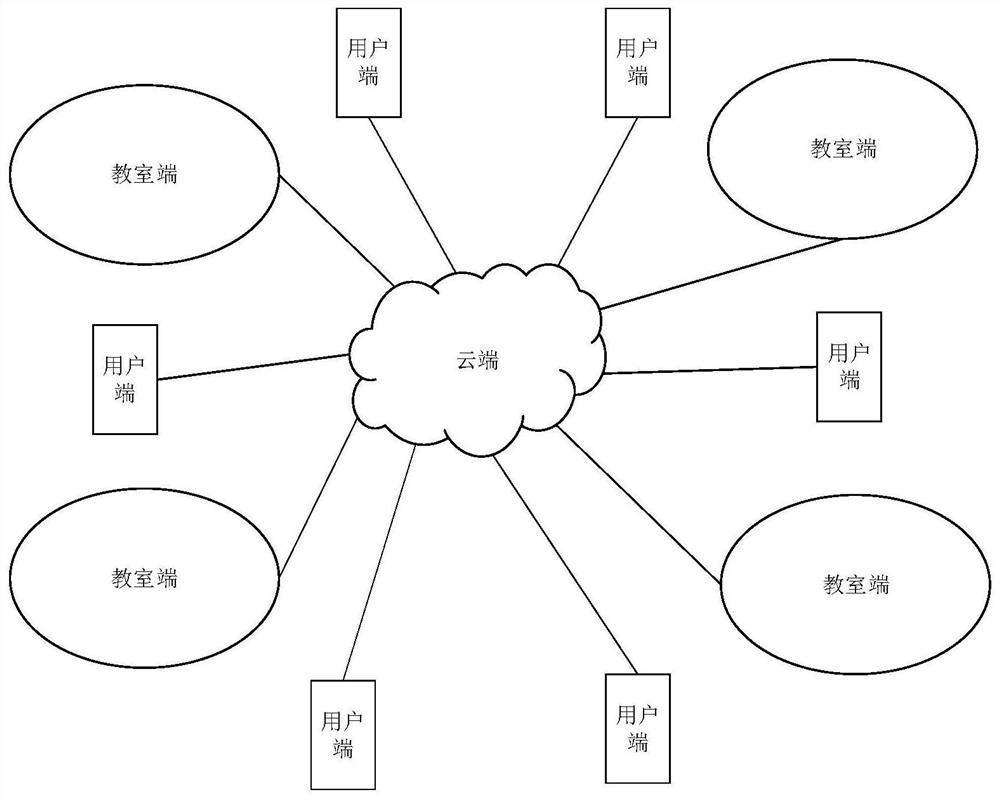
ActiveCN111968425AEase of learning onlineComprehensive and rich teaching contentElectrical appliancesEngineeringData science
The invention discloses an intelligent teaching system, which relates to the field of intelligent education and comprises a cloud end, a plurality of classroom ends and a plurality of user ends, the cloud is used for storing the teaching video collected by the classroom end and allowing a user to register in the cloud and log in the cloud to watch the teaching video; the user ends are used for logging in the cloud and playing the teaching video stored in the cloud; and each classroom end comprises an intelligent blackboard, a teaching video acquisition unit, a plurality of teaching video watching units and a server. According to the system, a traditional teaching mode is improved, the traditional teaching mode is combined with online education, and the teaching quality and the learning effect are guaranteed.
Owner:深圳市中科思达科技有限公司
Teaching training access method
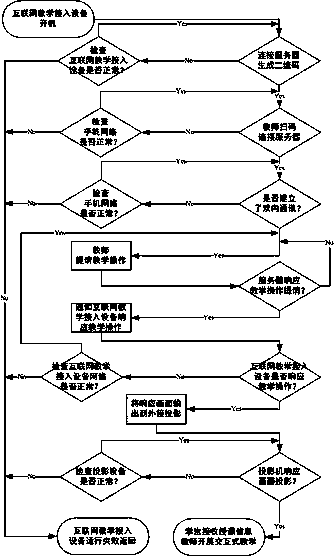
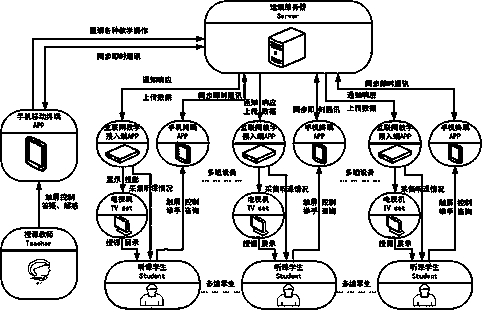
The invention relates to a teaching training method, and belongs to the technical field of modern teaching equipment. The teaching training access method mainly comprises a method for realizing the teaching training by the matched use of teaching access equipment, a mobile terminal and a remote end server. A teacher user uses the mobile terminal equipment, provides various teaching operations forthe remote end server by Internet and notifies the teaching access equipment to respond; various teaching operations are displayed at an externally connected terminal display device; meanwhile, teaching voice is synchronously collected and is transmitted to the teaching access equipment through the remote end server to be played in real time, so that the teaching training process is realized. Themobile terminal, the terminal display equipment and the teaching access equipment are used; by using the Internet and the remote end server, on the promise that a personnel computer is not needed in amultimedia classroom, the Internet interaction teaching can be effectively realized; the effects of cost reduction, operation simplification, flexible movement, convenience and practicability are achieved.
Owner:湖南省咕咕嗒科技有限公司
Internet-based folk art teaching demonstration device
ActiveCN110223546AQuality improvementRich teaching contentElectrical appliancesTeaching apparatusDisplay deviceDisplay board
The invention discloses an Internet-based folk art teaching demonstration device. The Internet-based folk art teaching demonstration device comprises a network teaching server and a teaching display device, wherein the network teaching server comprises a folk art material collection module, a teaching courseware making module, a teaching display module and a folk art material library; the teachingdisplay device comprises a front box and a rear box, and a display board is arranged in the middle of the front box and the rear box; a horizontal rod with a connecting ring is arranged at the top ofa push rod of an electric push rod; a leading wire rod is arranged at the top of a fixing piece of the electric push rod, and the free ends of leading wires on leading wire columns are fixed on the front inner side wall of the rear box; the electric push rod is fixed to a conveying device. The Internet-based folk art teaching demonstration device carries out the demonstration teaching of folk artworks through network and real objects, and the network and the real objects are complementary, the teaching quality is improved, and the teaching content of the folk art can be further enriched through the network demonstration teaching; and through the real object demonstration teaching, the folk art works can be freely displayed on the display board, it is ensured that the folk art works cannot be damaged after display, and thus the quality of folk art teaching is improved.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Live broadcast teaching control method and device, medium and electronic equipment
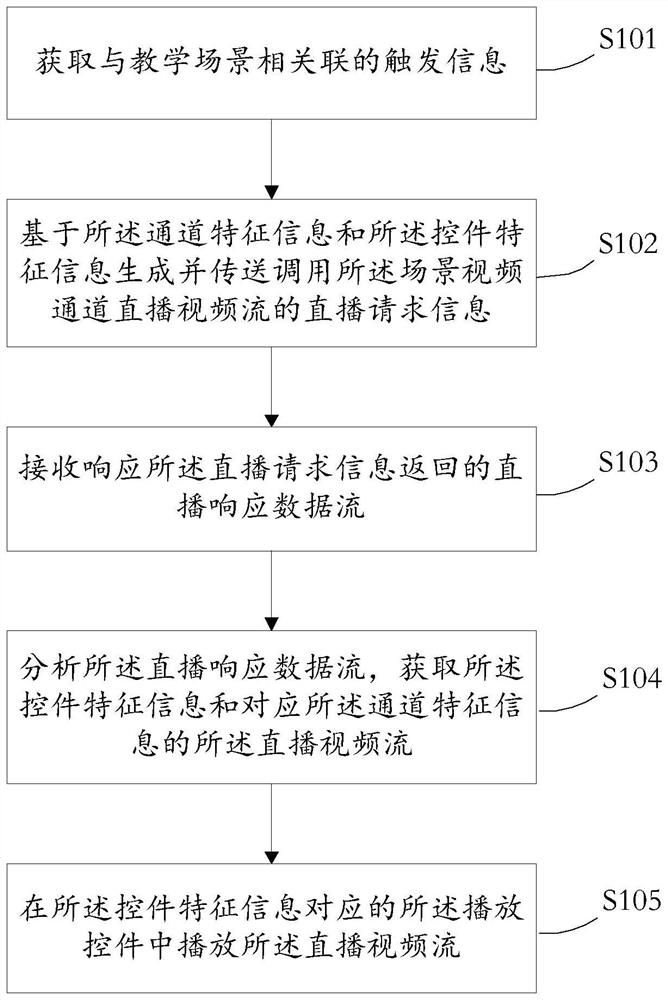
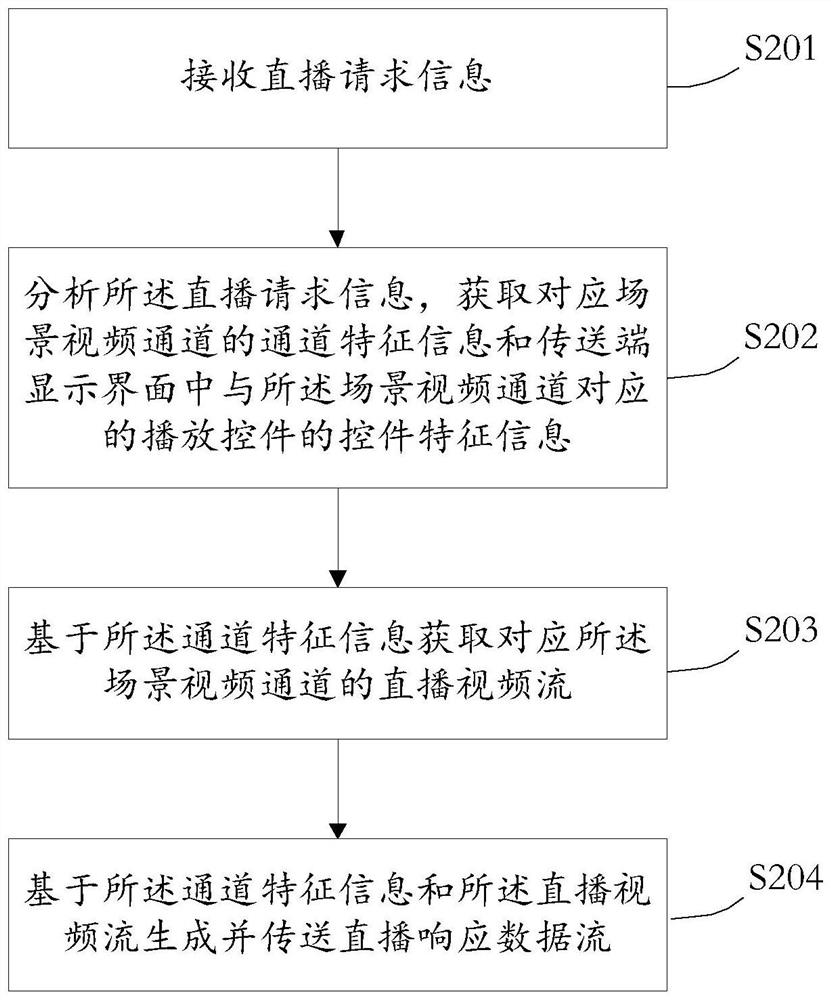
PendingCN112330996ASolve the problem of real-time control of multiple scene video channelsImprove understandingElectrical appliancesEngineeringElectronic equipment
The invention provides a live broadcast teaching control method and device, a medium and electronic equipment. According to the invention, the method comprises the steps: in live broadcast teaching, applying the live broadcast video stream of the scene video channel associated with the real-time working scene by determining the channel unique identification information and the control unique identification information associated with the teaching scene, and displaying the received live broadcast video stream on the playing control corresponding to the control unique identification information.In live broadcast teaching, a plurality of scene video channels in a real-time working scene are controlled in real time through a teaching terminal, and a live broadcast video stream associated withthe teaching scene is played in cooperation with the teaching scene. The problem that a teacher end controls a plurality of scene video channels in real time in live broadcast teaching is solved. Therefore, the teaching process is smoother, the teaching content is richer, the teaching efficiency is improved, and students can quickly understand the teaching content through on-site demonstration.
Owner:BEIJING AMBOW SHENGYING EDUCATION & TECH CO LTD
Showcase for marketing major education
InactiveCN108113344AIncrease storage capacityImprove storage typesShow cabinetsShow shelvesEngineeringVertical path
Owner:SHANDONG POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE
Multifunctional movable platform for robot
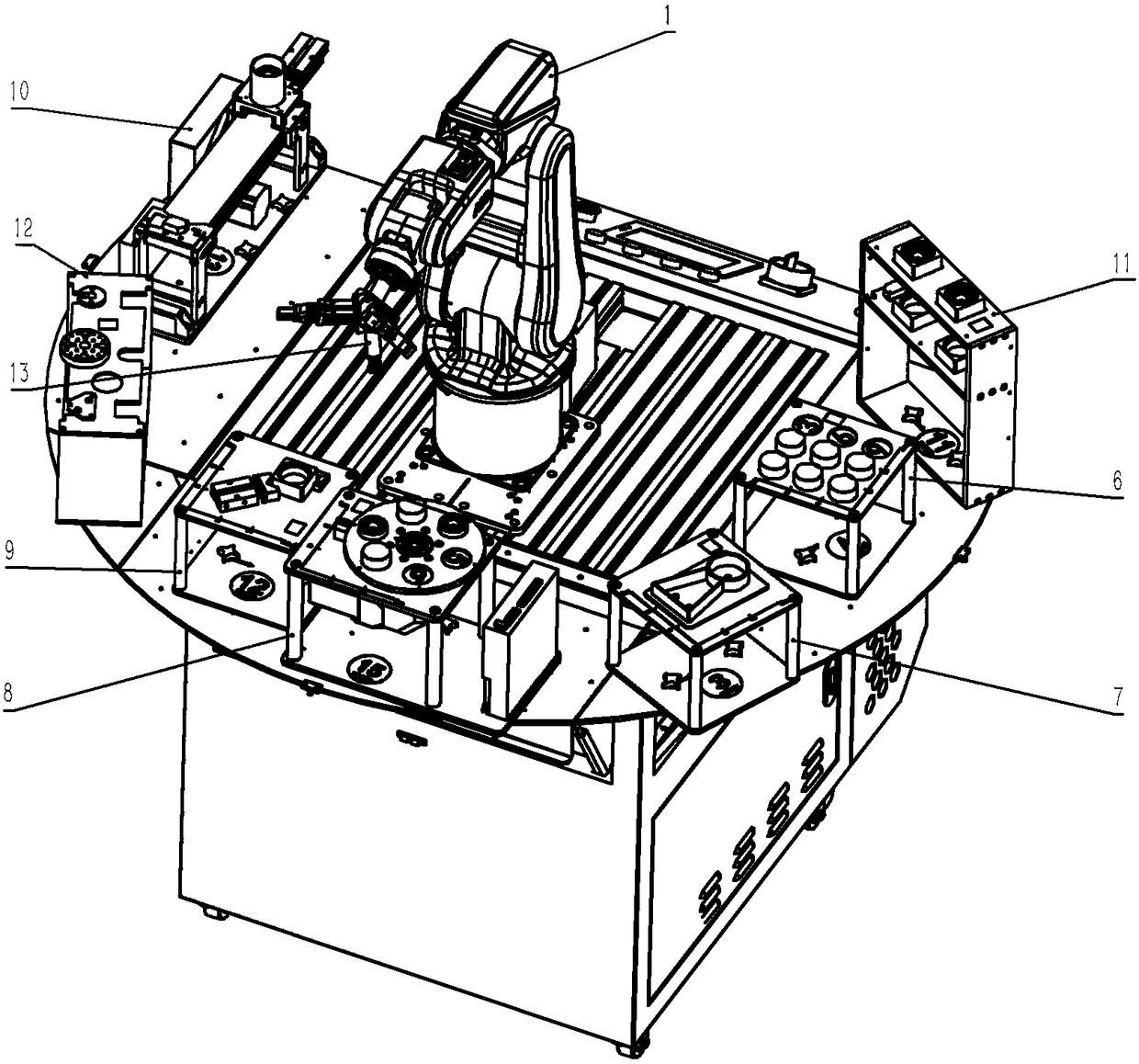
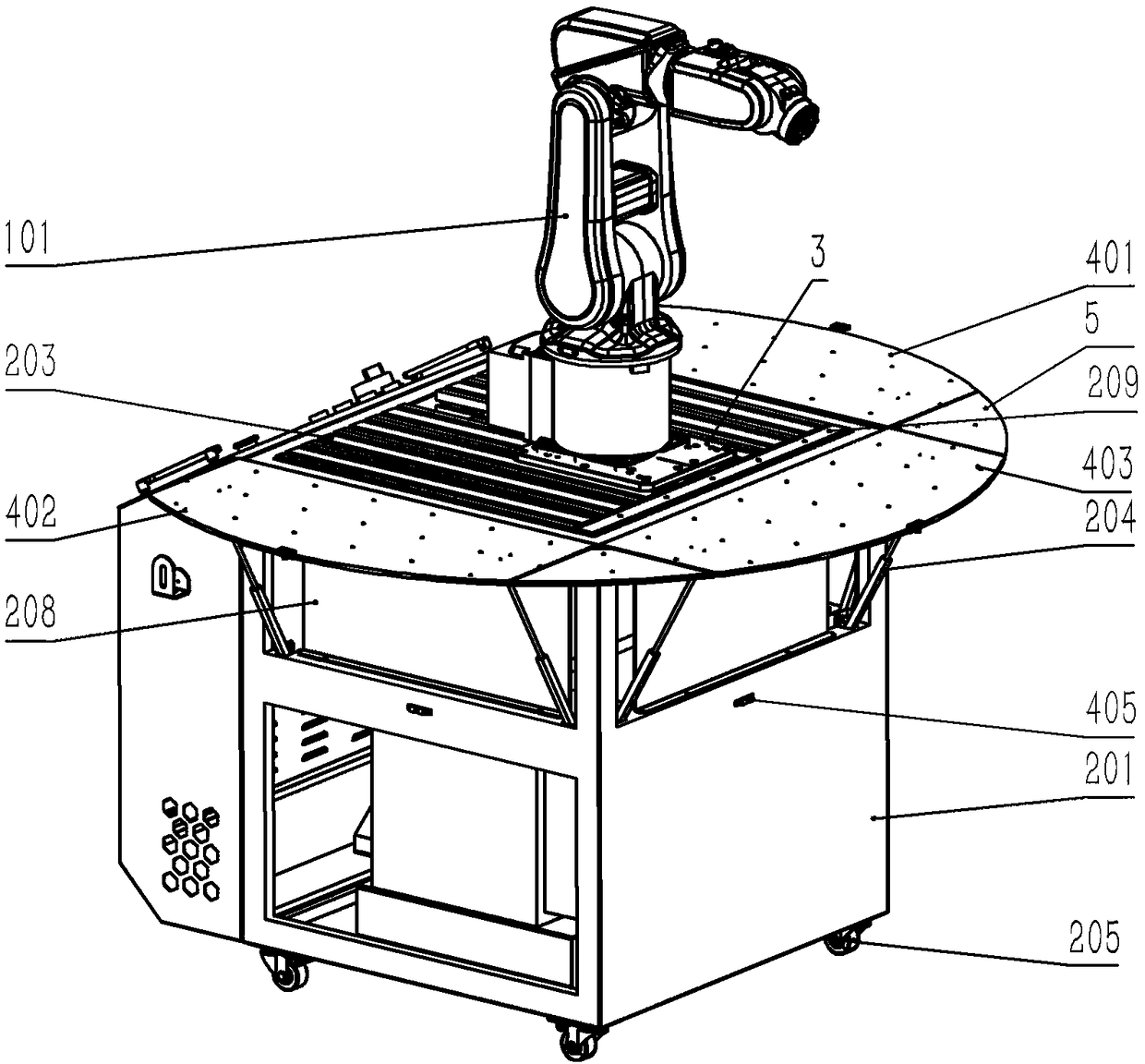
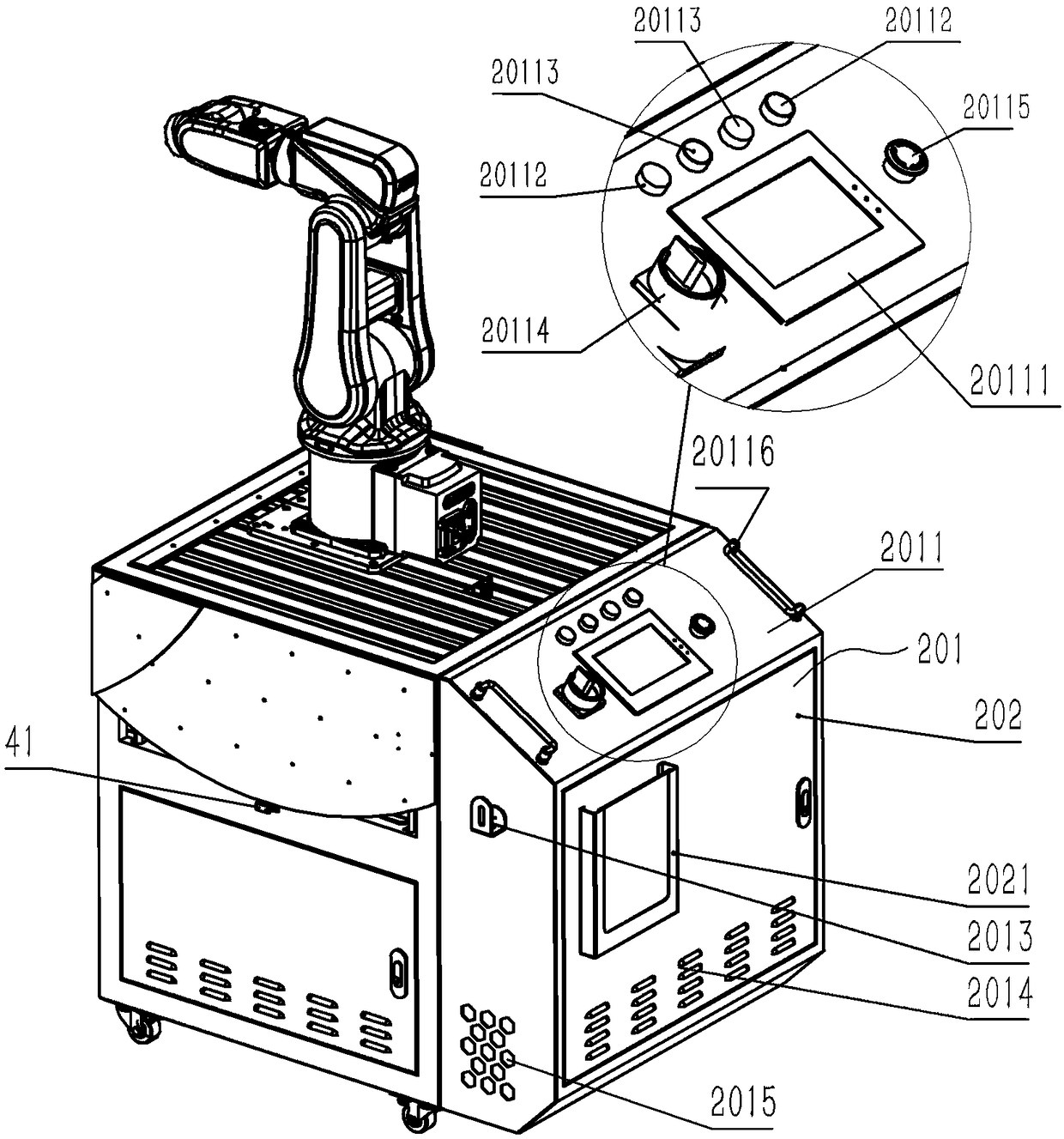
PendingCN108436891ARich teaching contentThe assessment process is simpleProgramme-controlled manipulatorEngineeringMultiple function
The invention provides a multifunctional movable platform for a robot. The multifunctional movable platform for the robot gives consideration to the universality of industrial production and practicalteaching, a modular decomposition design is adopted for teaching contents, and the practical project arrangement of teaching is from the shallowness to the deepness and from easiness to difficulty, so that a practical device is rich in teaching contents, simple in examination links, and relatively low in practical project content relevance. The multifunctional movable platform for the robot comprises a movable table cabinet, the multi-axis robot, a demonstration module, a carrying module, a workpiece welding module, a servo rotary disc module, an assembly location module, a stock bin conveying combination module, a stereoscopic warehouse module, a standby fixture frame and an end fixture, wherein a table surface composed of a sectional material is arranged at the central position of the upper end surface of the movable table cabinet; the bottom of the multi-axis robot is fixedly installed on the table surface through a universal base; a control and display panel structure is arrangedin an outer area at one side of the table surface of the movable table cabinet; and the other sides of the table surface are connected with a reversible platform veneer through hinges or butts.
Owner:合肥海渡工业机器人有限公司
Demonstration method and device for white laser generation principle
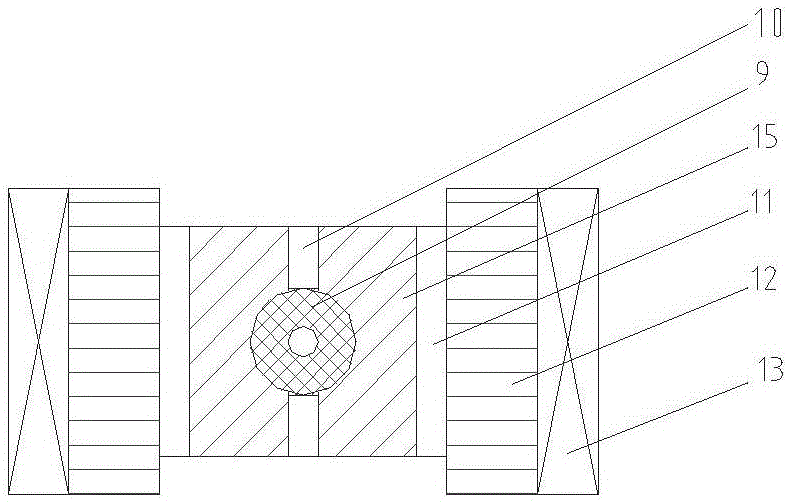
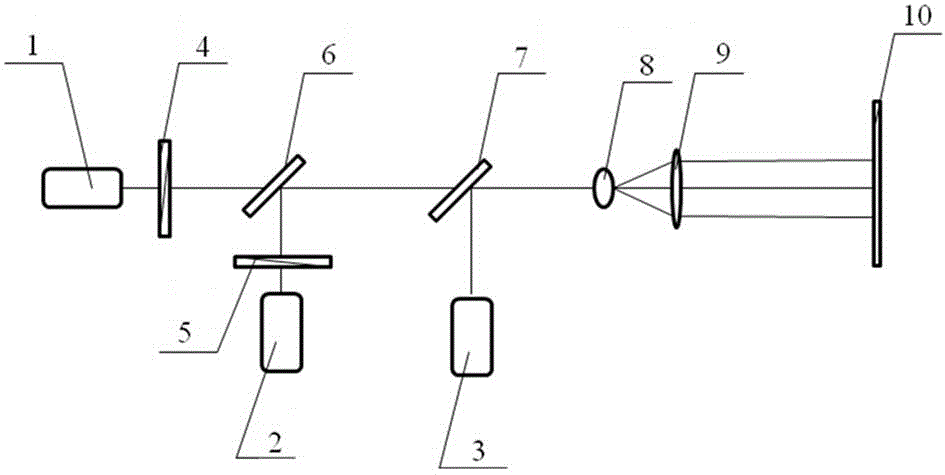
The invention provides a demonstration method and device for the white laser generation principle and belongs to the field of teaching experiment instruments. Red laser and green laser are combined into a path of laser beam through a first dichroscope and the laser beam and blue laser are combined into a path of laser beam through a second dichroscope; white laser is obtained by adjusting the intensity proportions of the red laser, the green laser and the blue laser. The demonstration device has the advantages that the intensity proportions of the red laser, the green laser and the blue laser can be changed by rotating polarizing films and thus the white laser can be obtained. With the device, the forming principle of white laser can be demonstrated intuitively; the experimental phenomenon of colorimetry that different red, green and blue ratios correspond to different colors can be intuitively demonstrated by rotating the polarizing films, so that the effect is remarkable and the teaching content is better enriched.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com