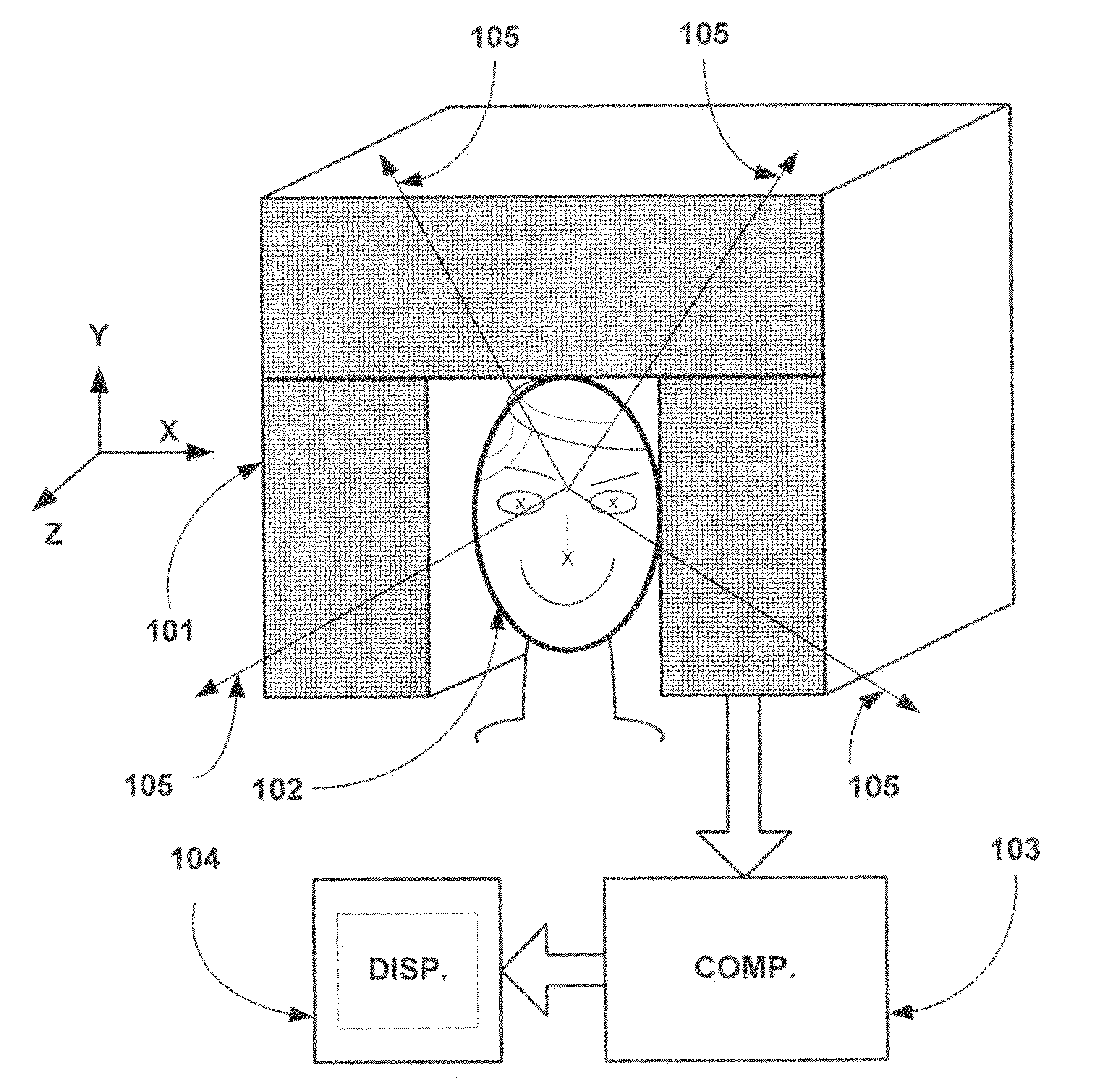
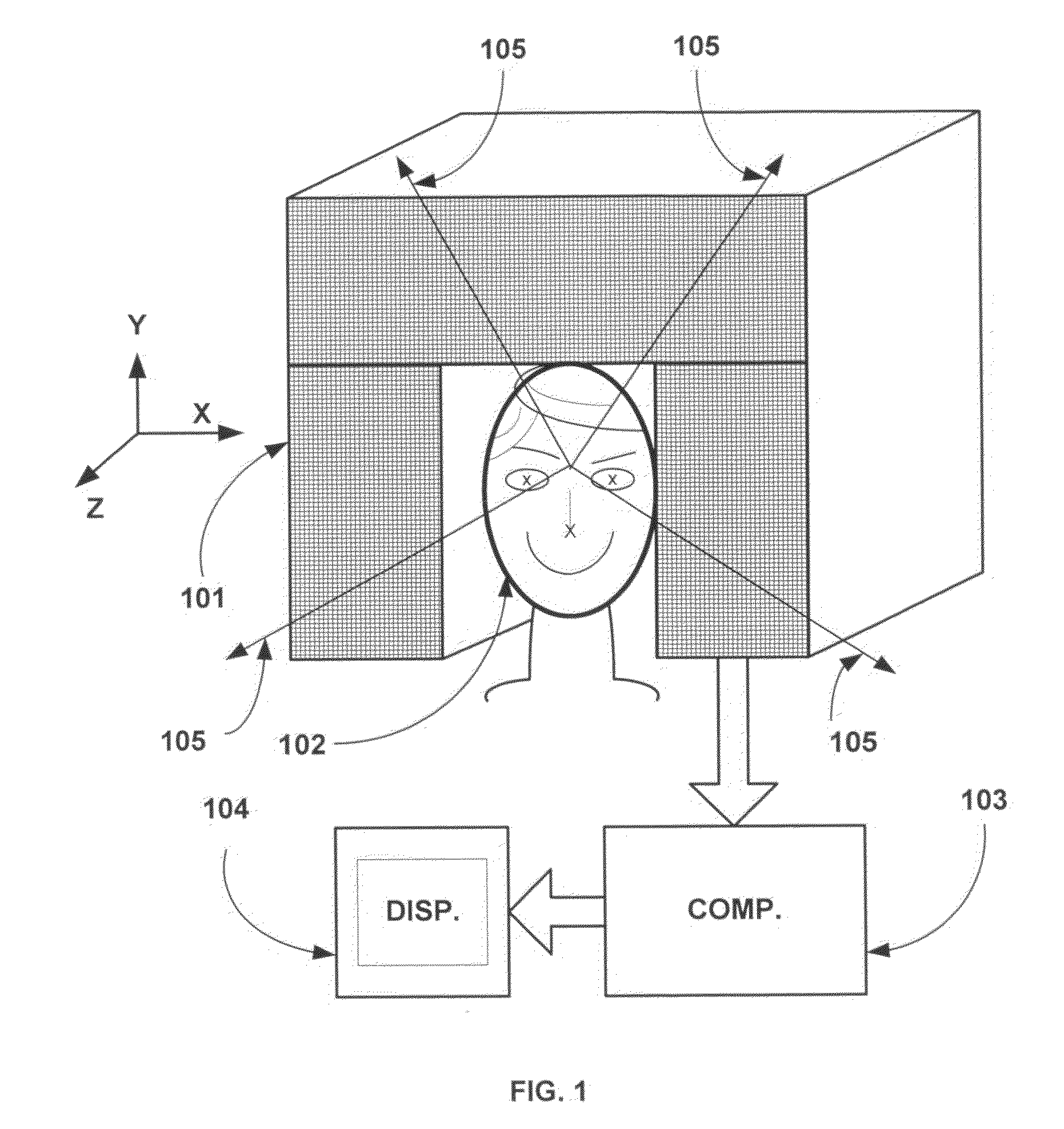
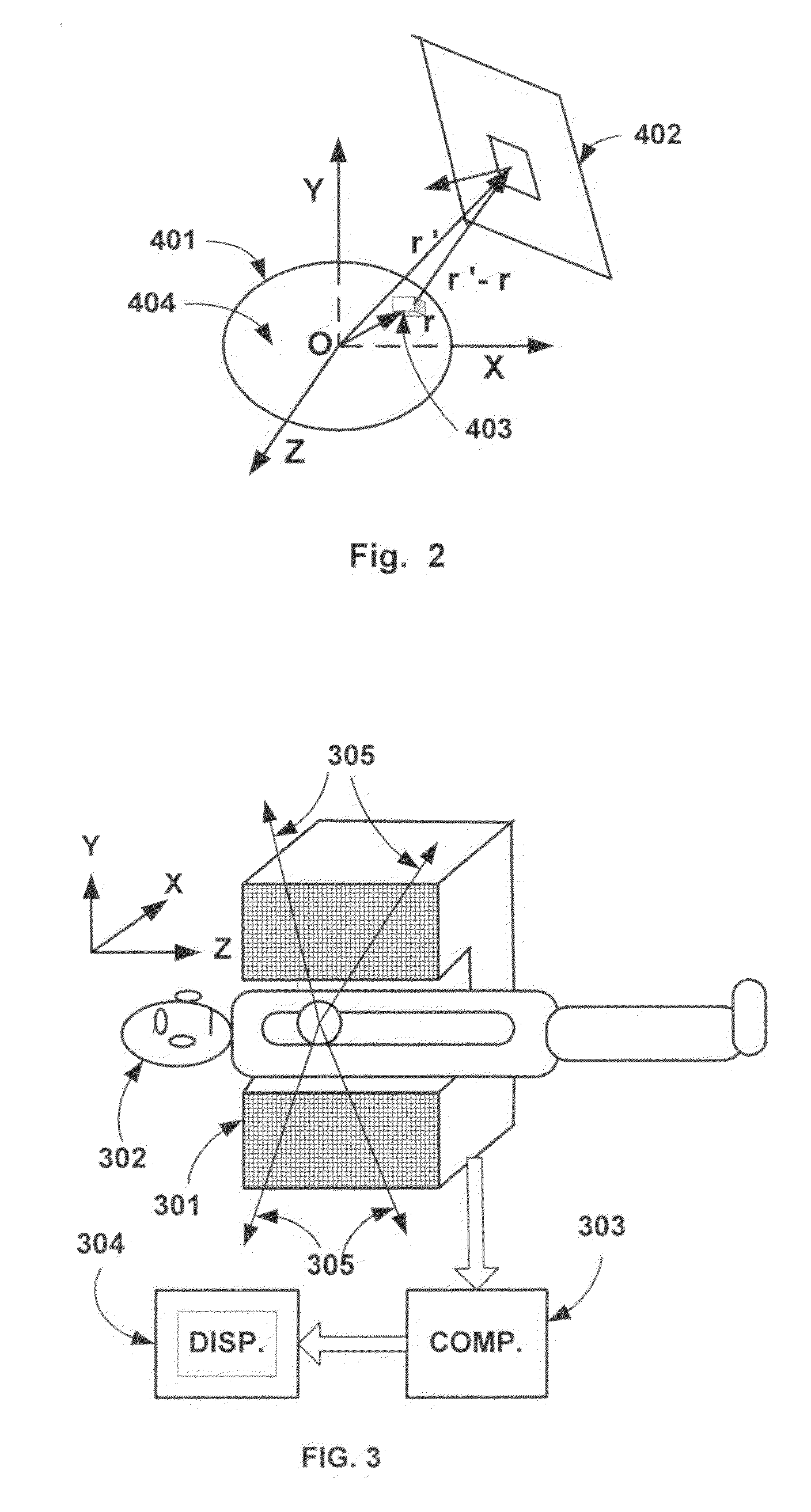
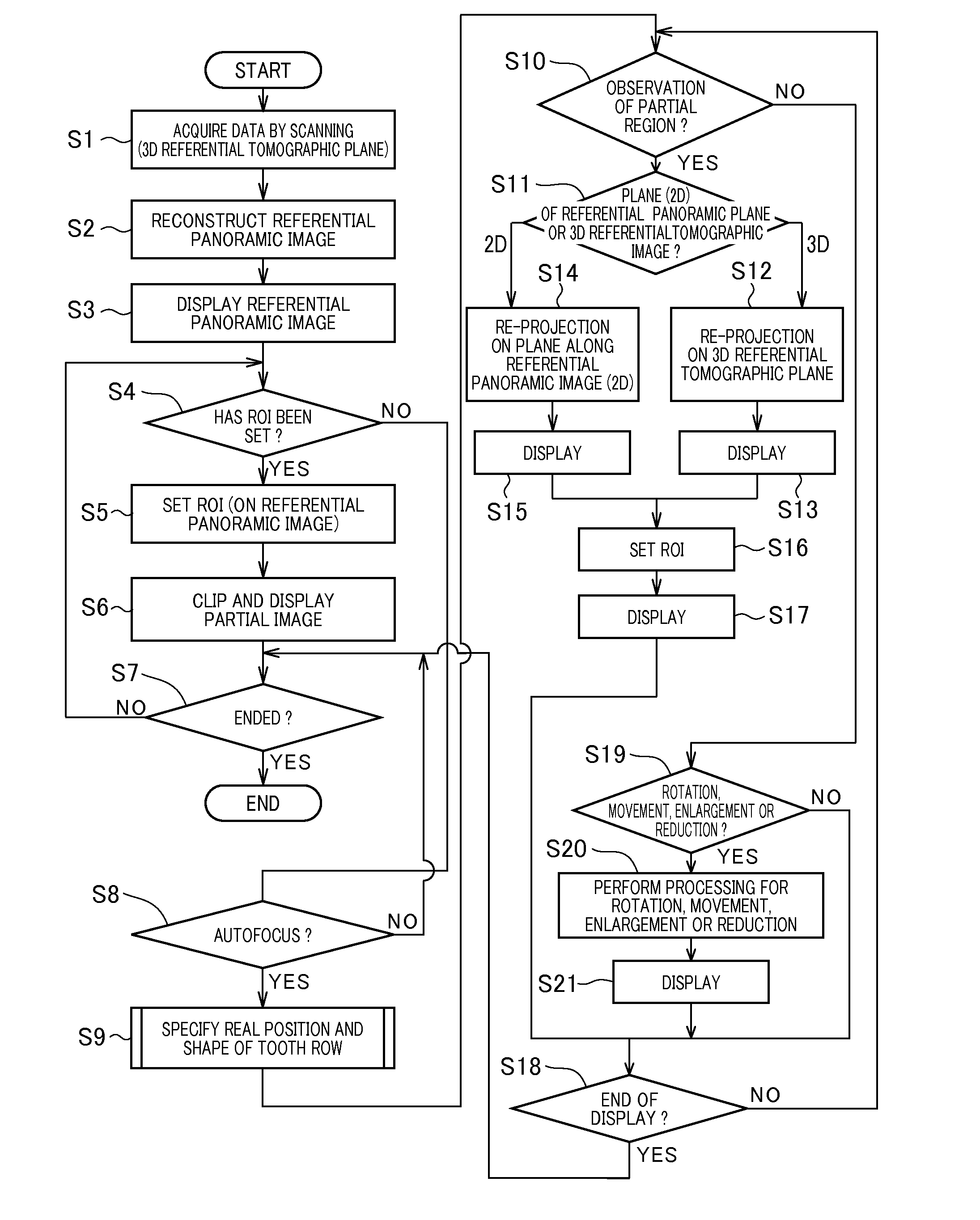
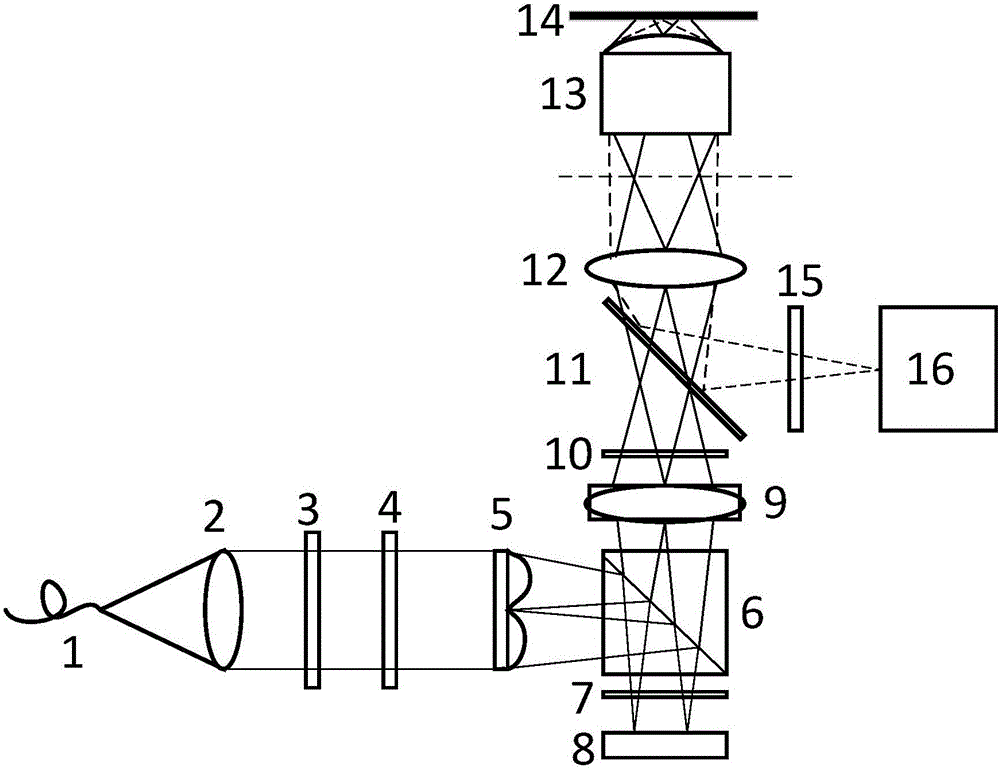
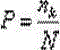Patents
Literature
73 results about "3d image reconstruction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
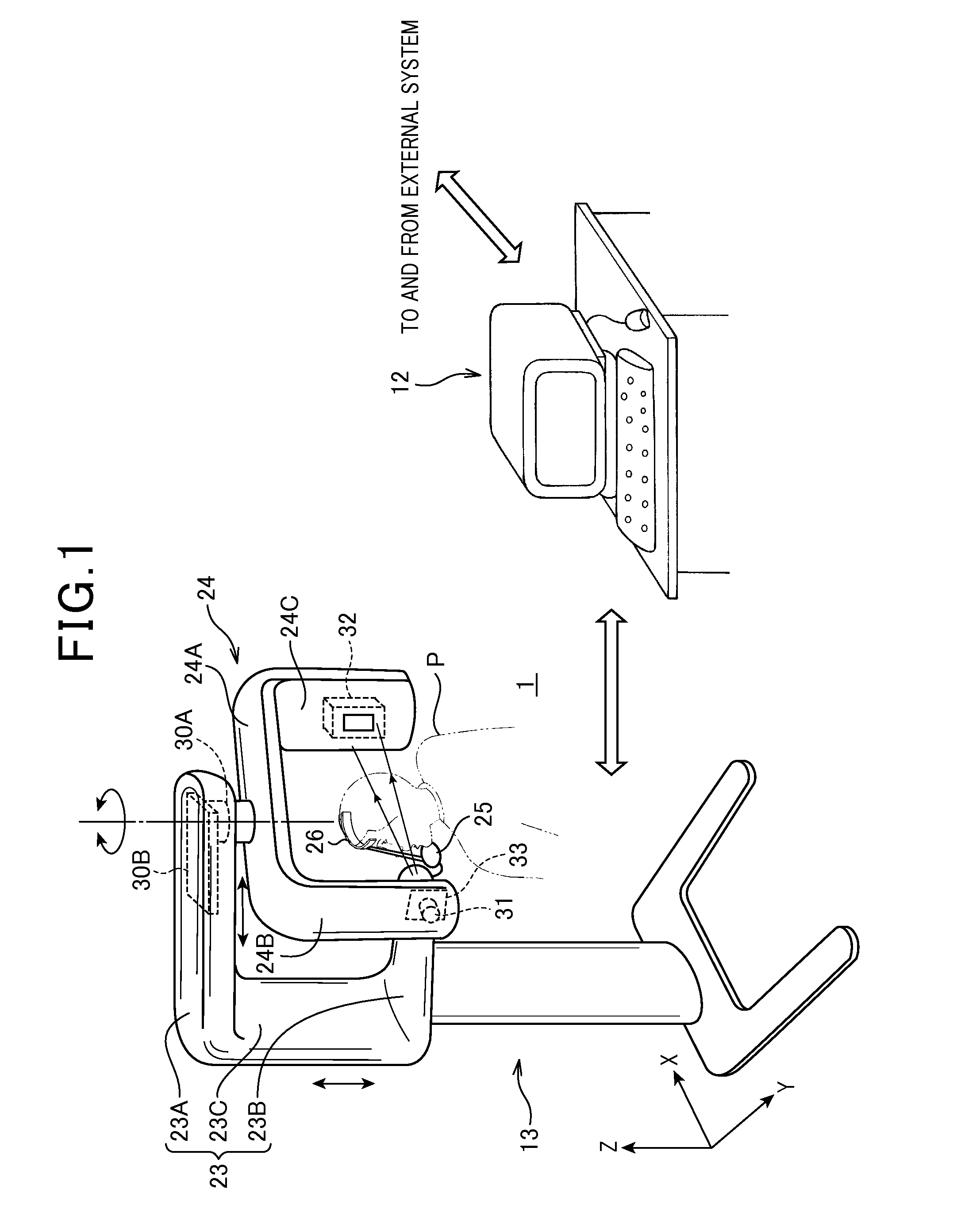
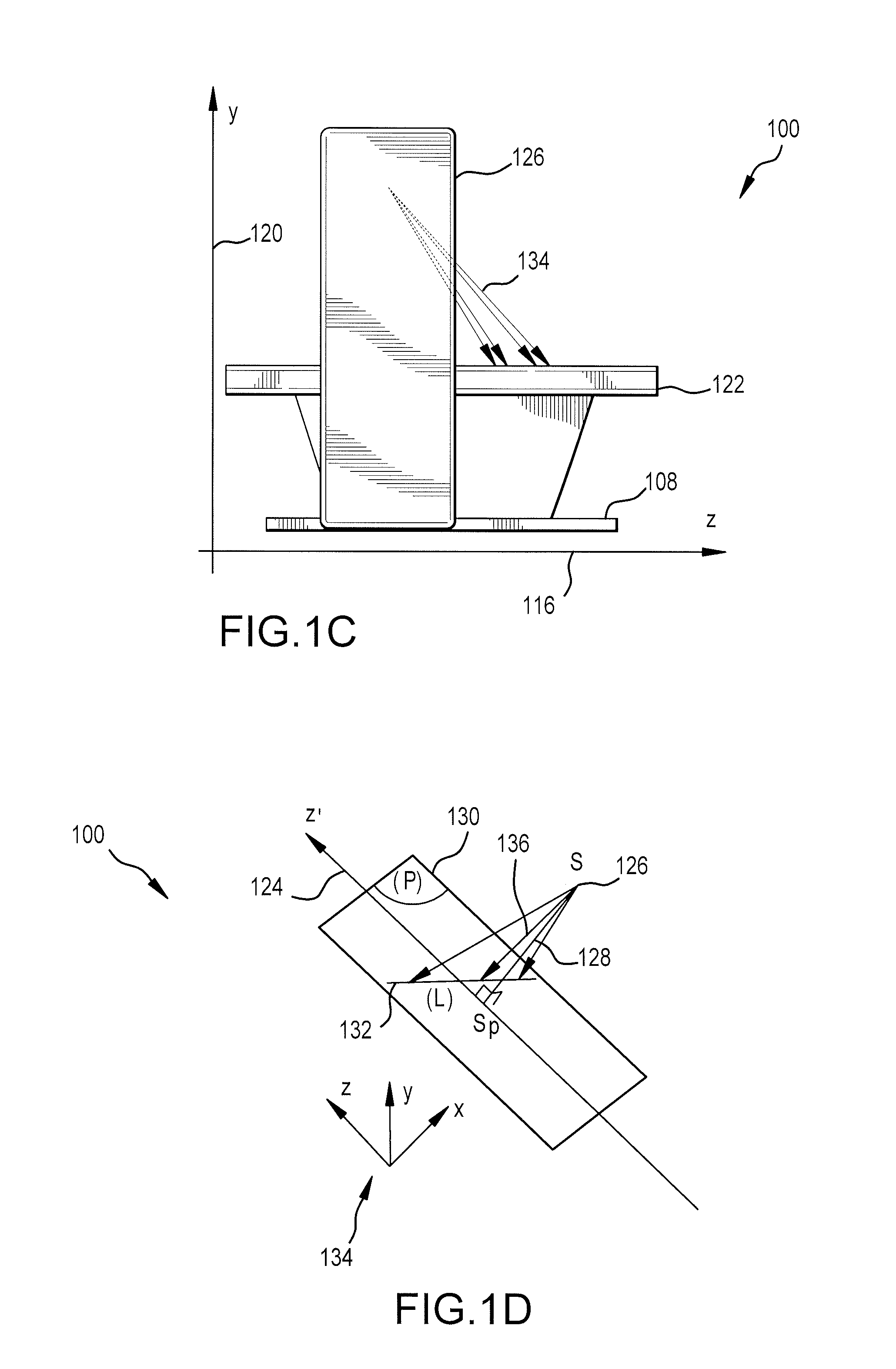
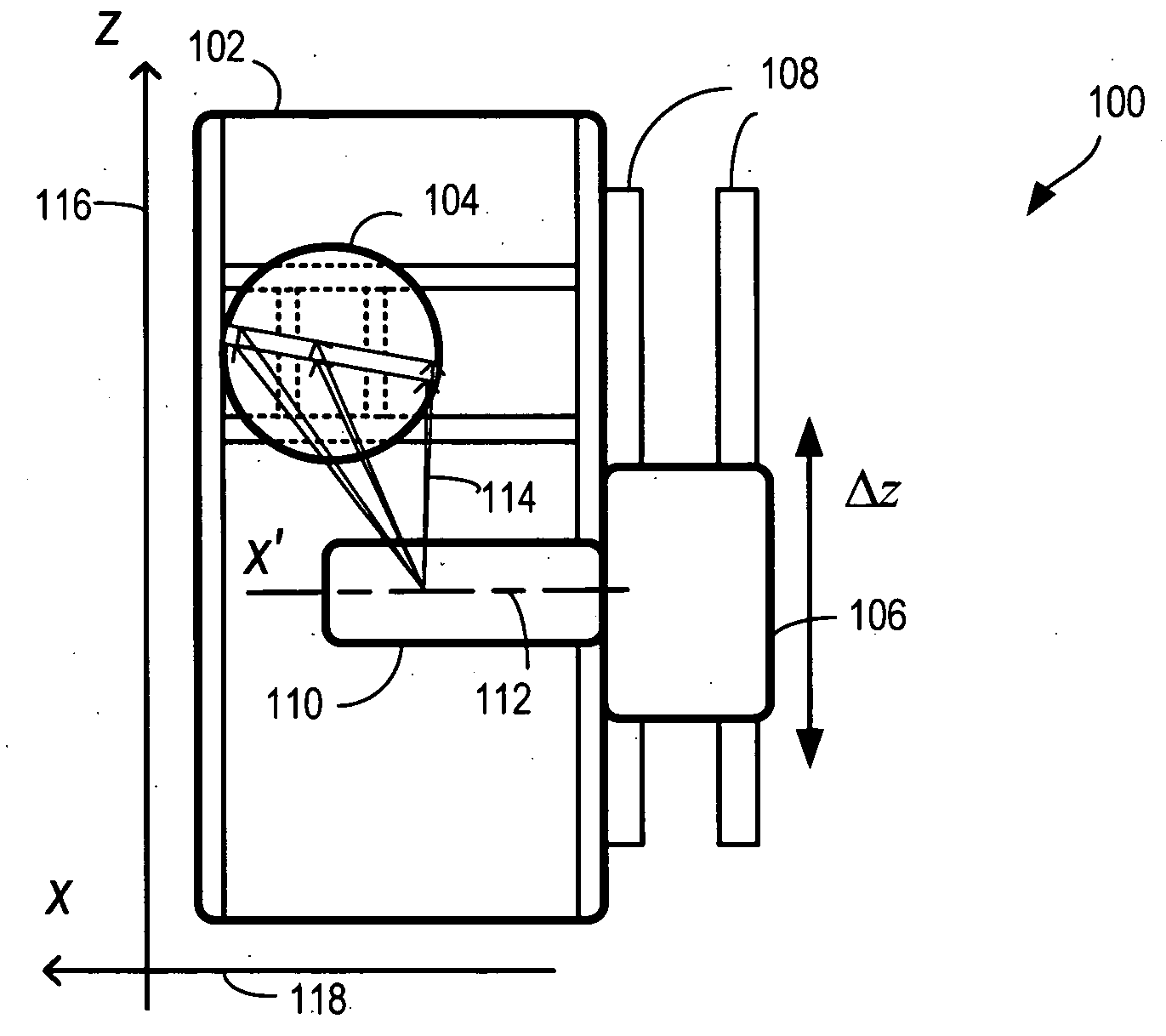
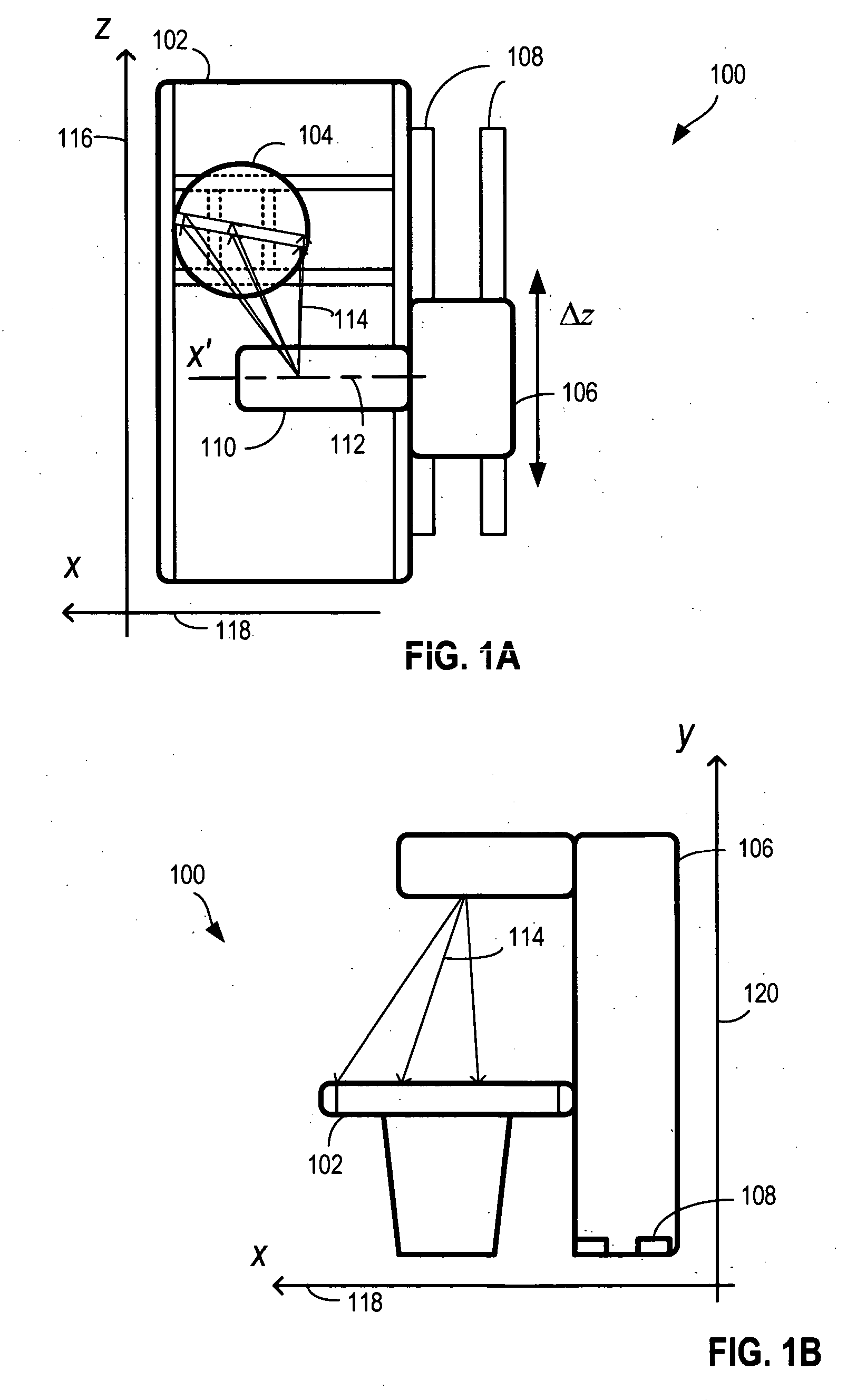
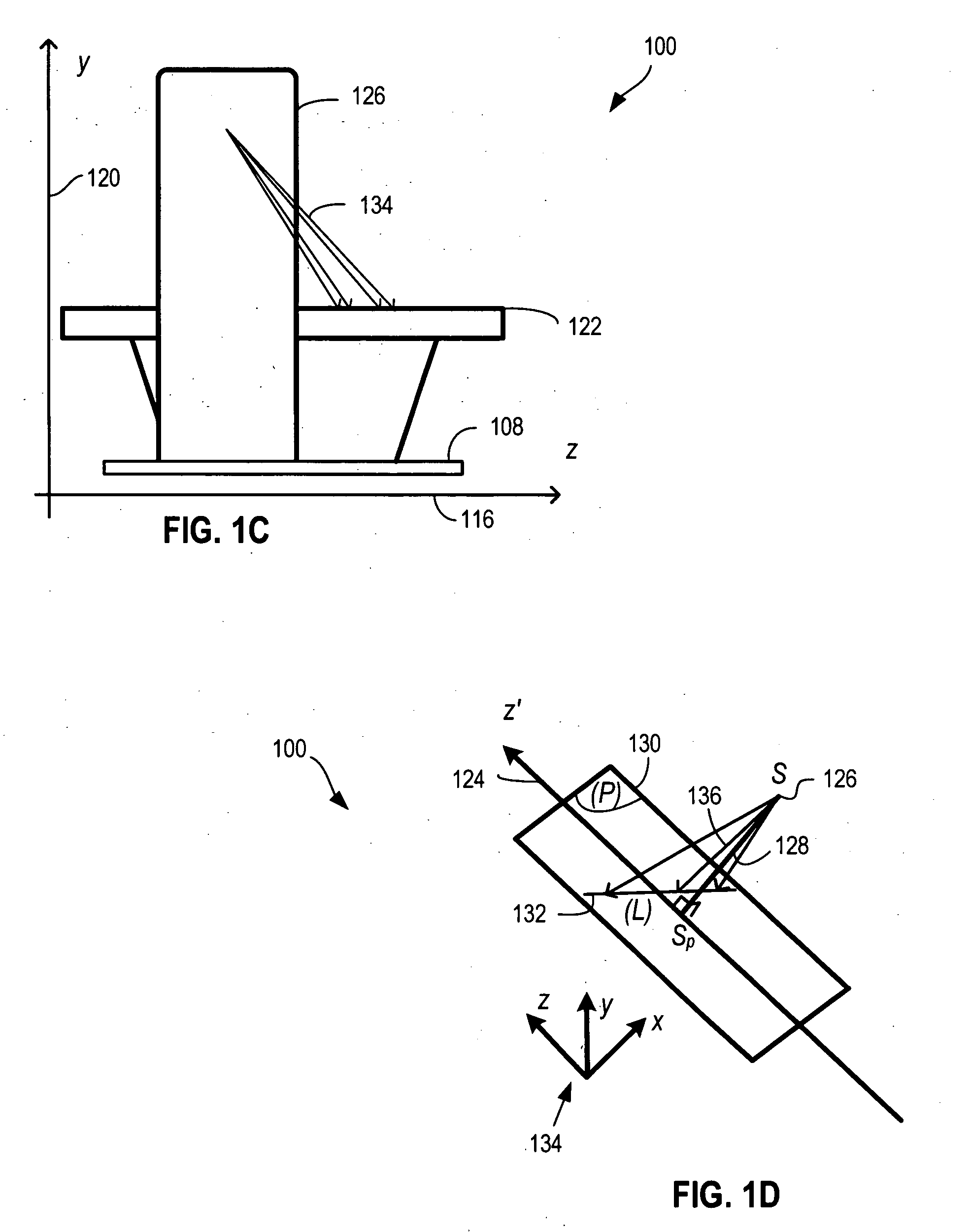
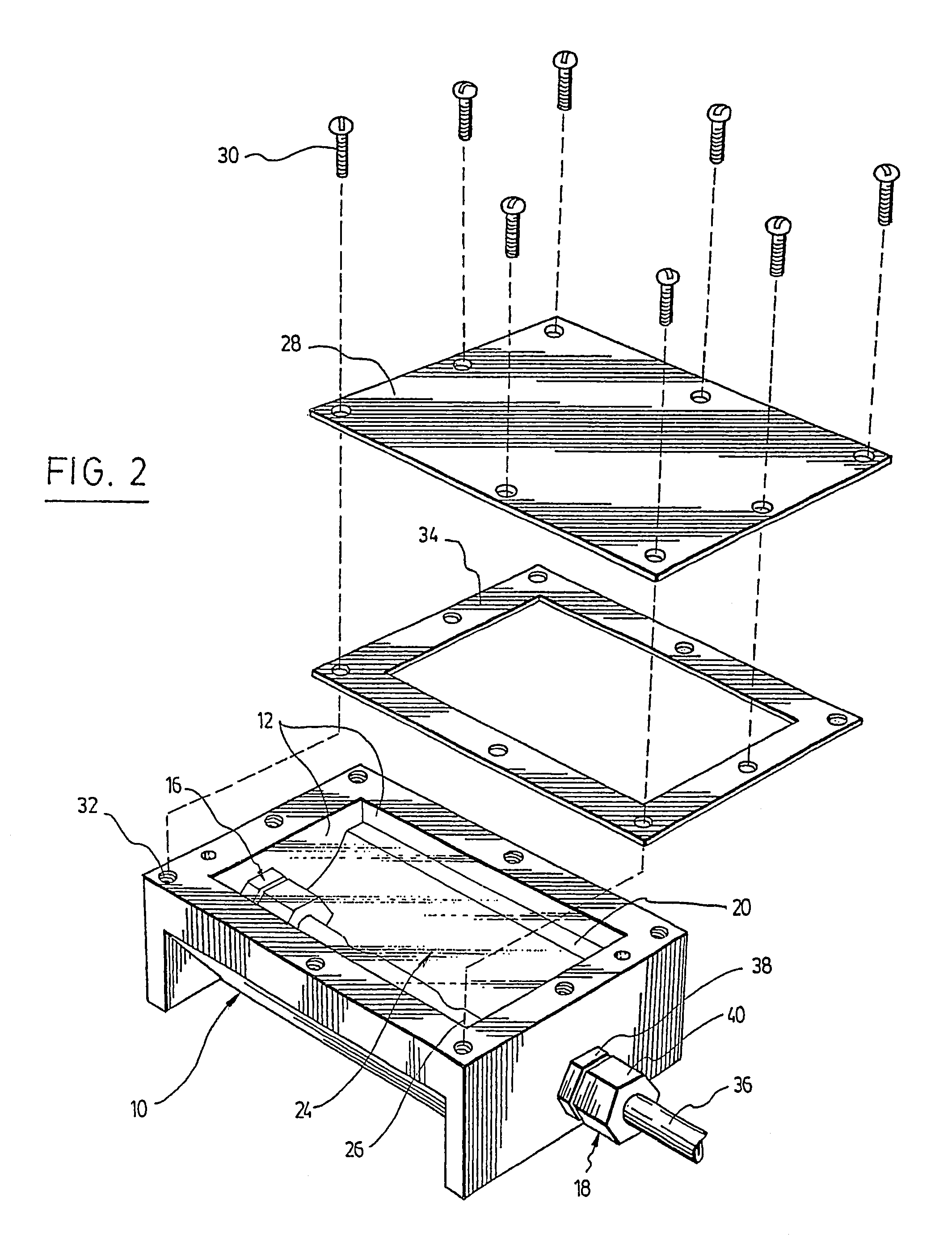
System for multi-dimensional anatomical functional imaging
InactiveUS20100081917A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsReconstruction from projectionAnatomical structuresData set
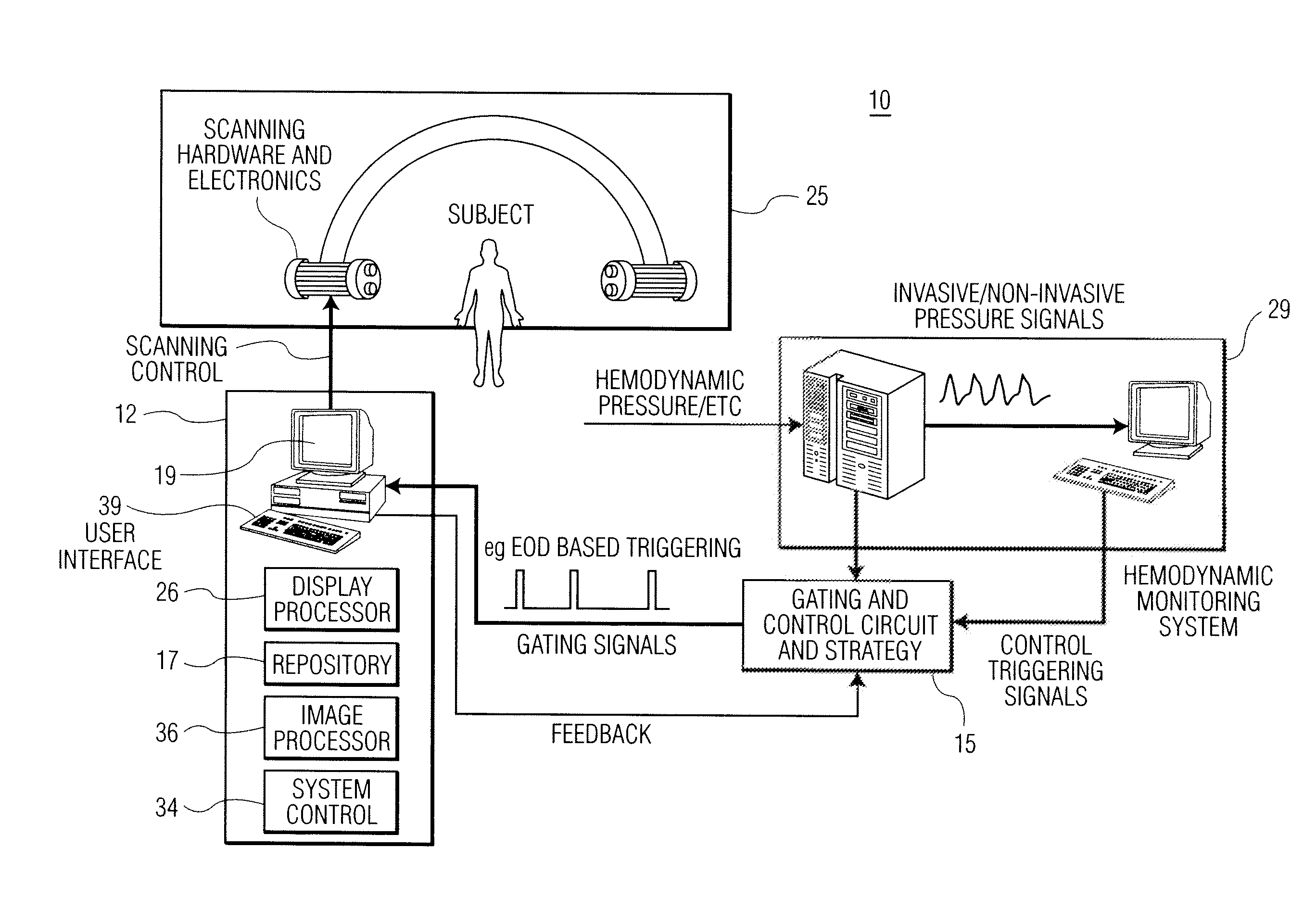
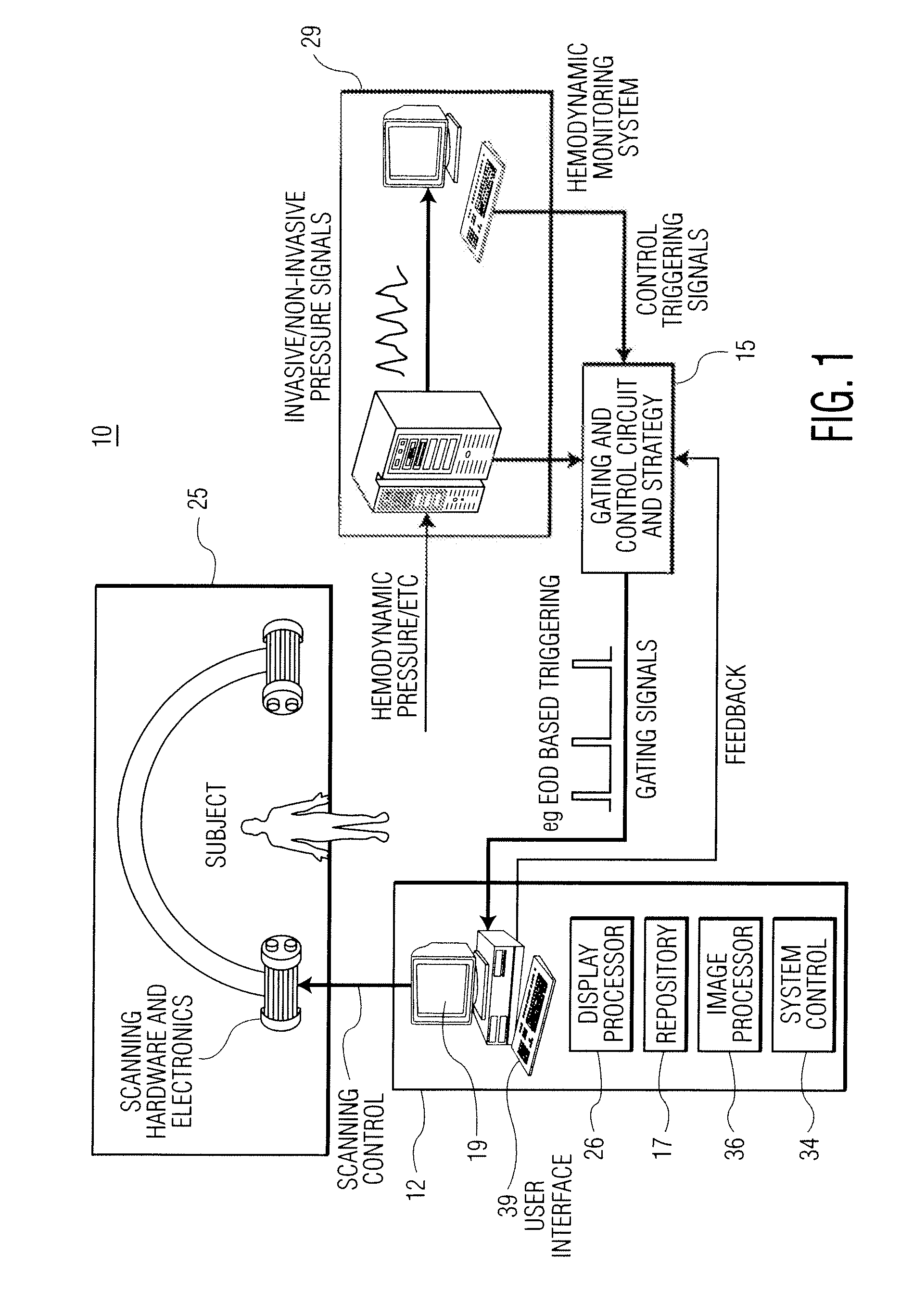
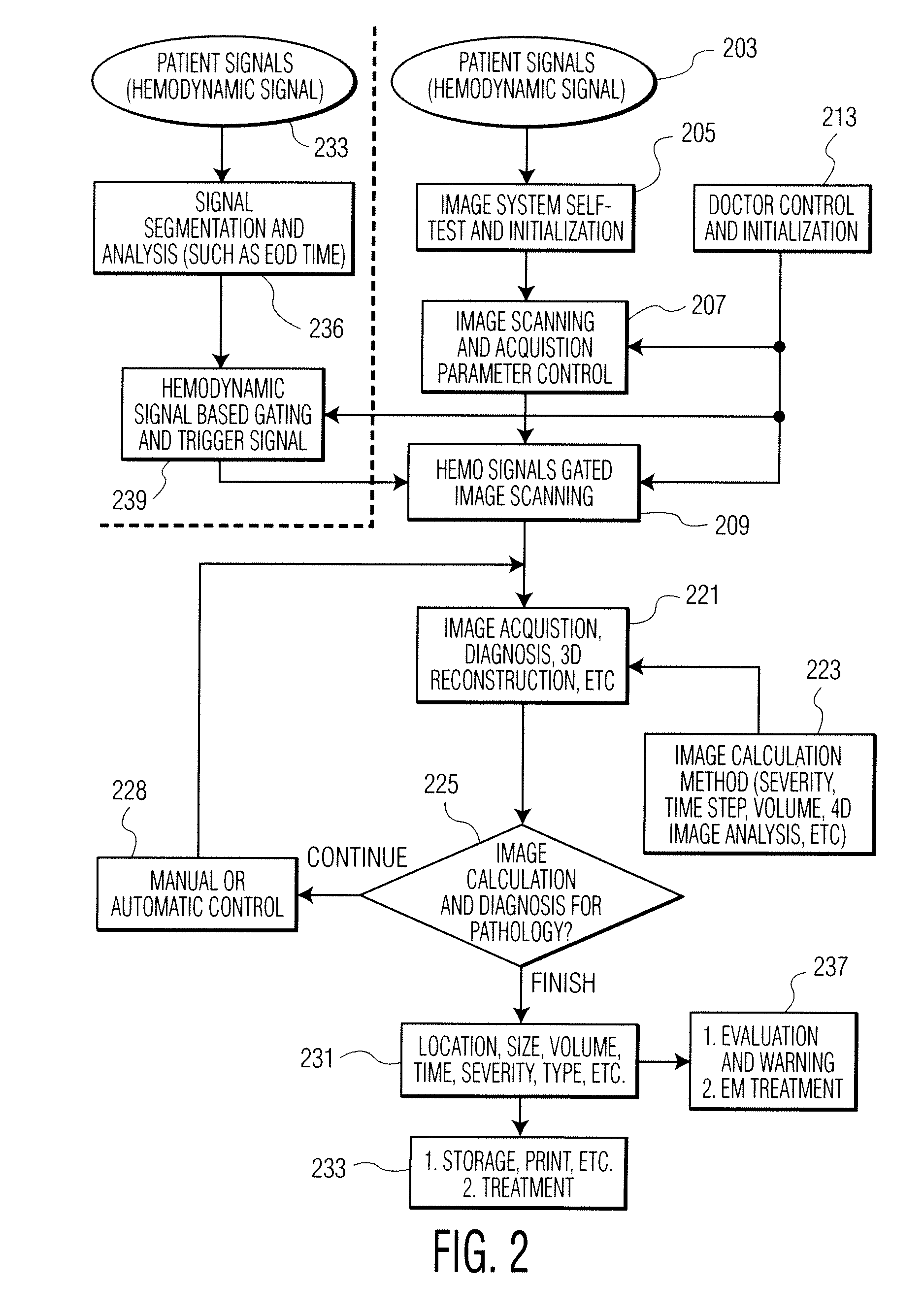
A cardiac functional analysis system reconstructs a 3D anatomical image volume using image frames acquired at predetermined cardiac phases over multiple cardiac cycles in response to a trigger derived from hemodynamic signals. A medical imaging system generates 3D anatomical imaging volume datasets from acquired 2D anatomical images. The system includes an image acquisition device for acquiring 2D anatomical images of a portion of patient anatomy in selectable angularly variable imaging planes in response to a synchronization signal derived from a patient blood flow related parameter. A synchronization processor provides the synchronization signal derived from the patient blood flow related parameter. An image processor processes 2D images acquired by the image acquisition device of the portion of patient anatomy in multiple different imaging planes having relative angular separation, to provide a 3D image reconstruction of the portion of patient anatomy.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
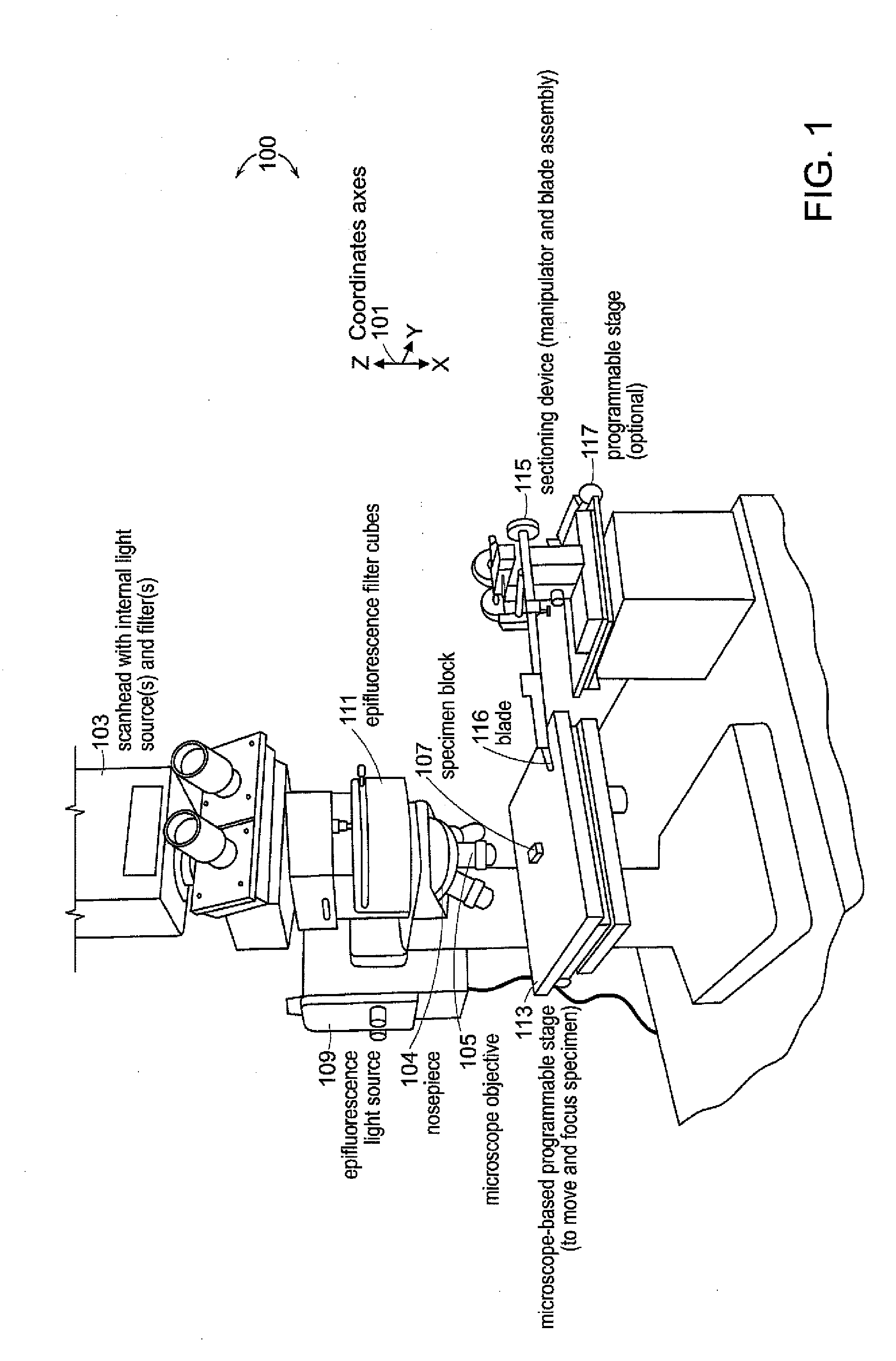
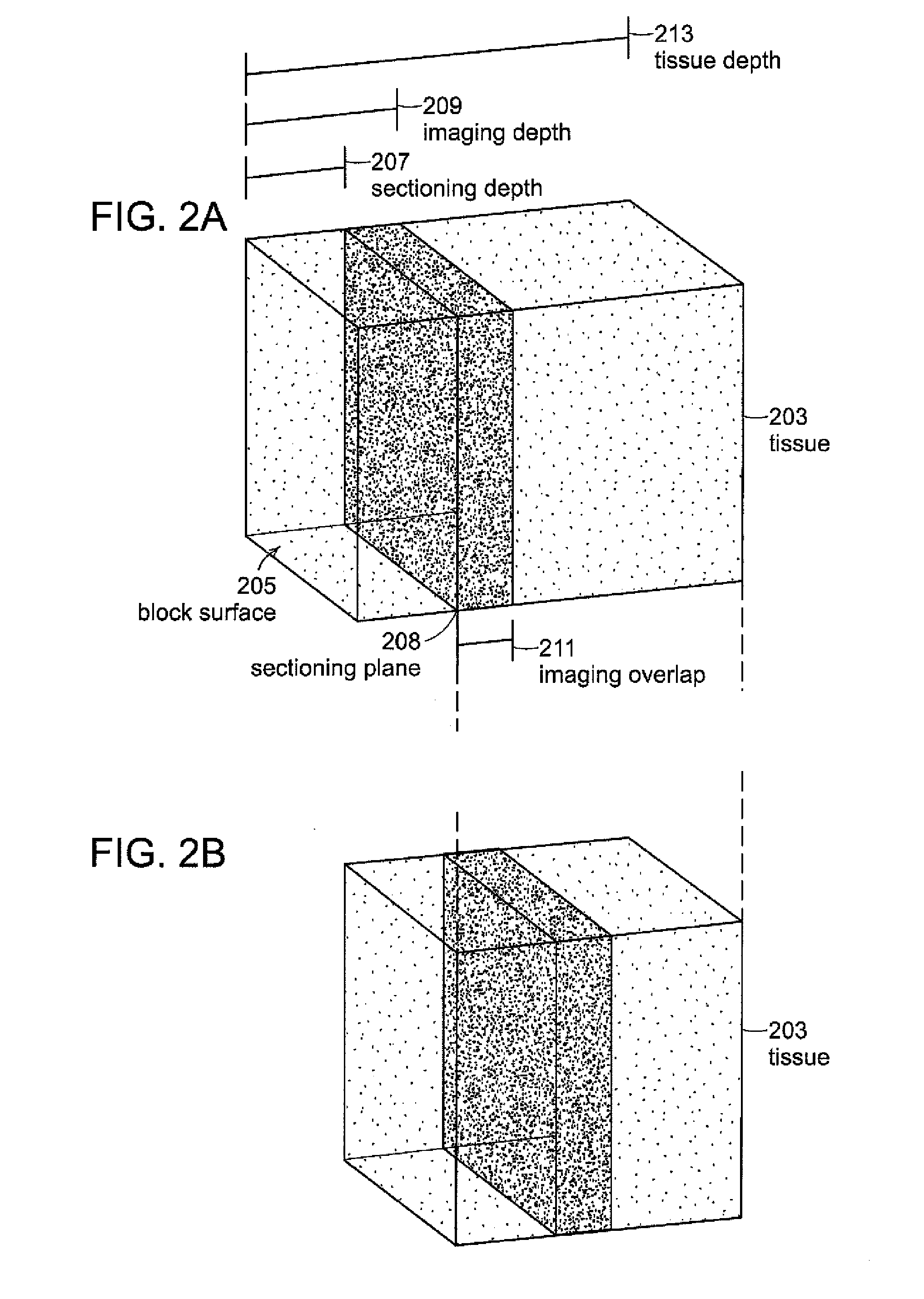
System and methods for thick specimen imaging using a microscope based tissue sectioning device
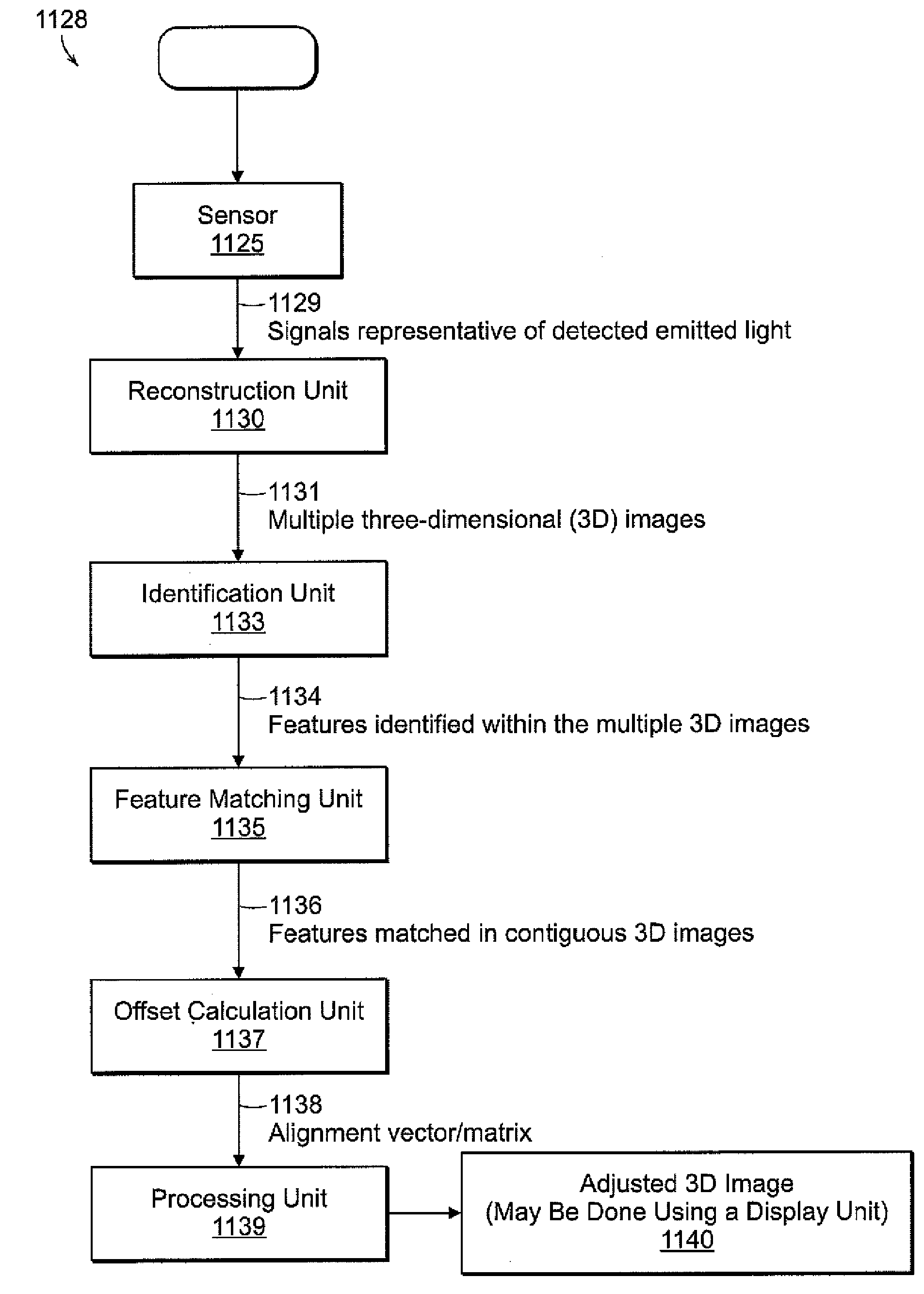
Systems and methods according to embodiments of the present invention facilitate imaging and sectioning of a thick specimen that allow for 3D image reconstruction. An example embodiment employs a laser scanning microscope and sectioning device, where the specimen, and optionally, the sectioning device are affixed to respective programmable stages. The stage normally used for aligning the specimen with the microscope objective is used as an integral component for sectioning the specimen. A specimen is imaged such that the imaging depth is less than the sectioning depth to produce overlap in contiguous sets of images; both acts are repeated until the imaging is completed. A substantially or completely seamless 3D image of the specimen is reconstructed by collecting sets of 2D images and aligning imaged features of structures in overlapping images or portions thereof. Specimen may be from a human, animal, or plant.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
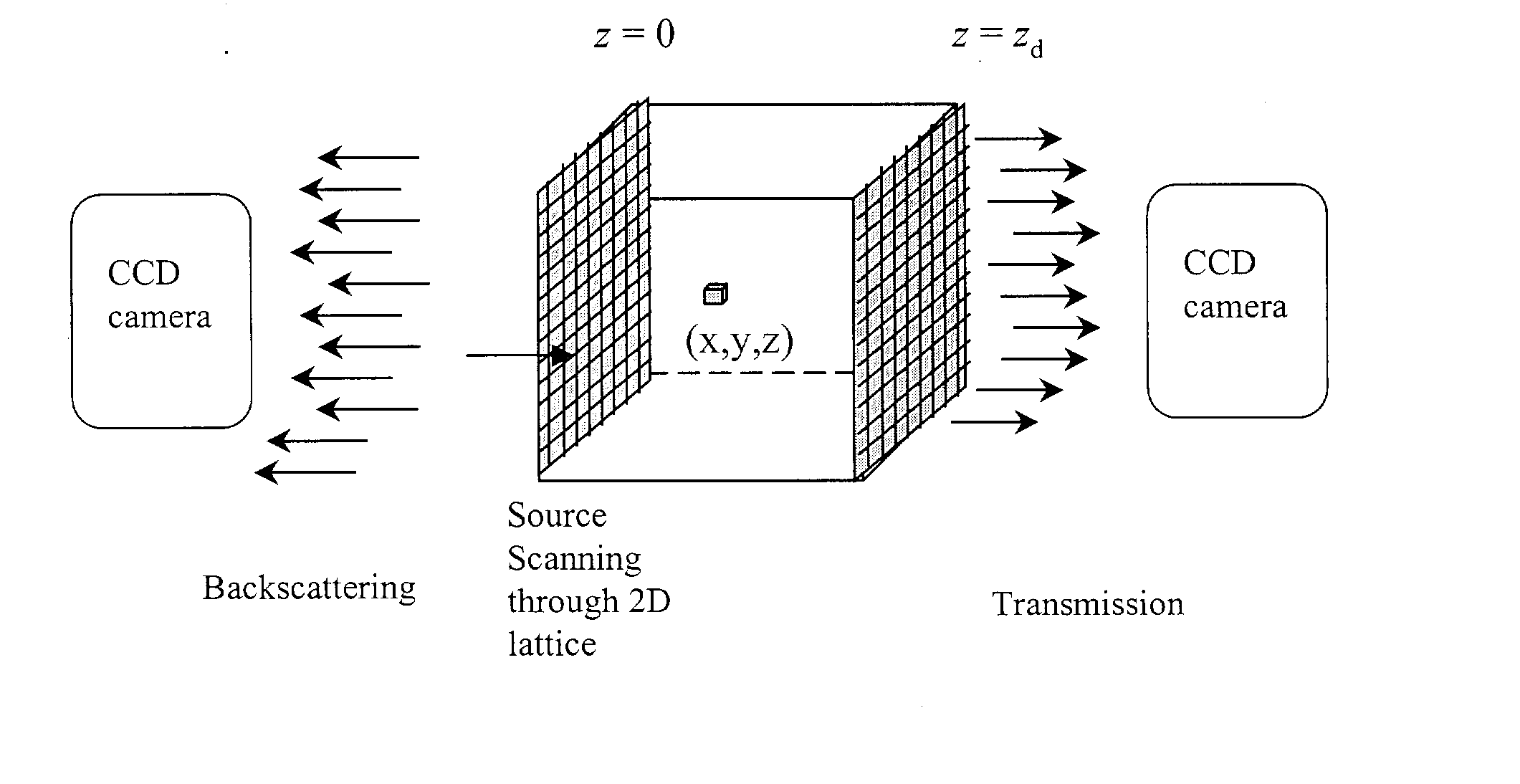
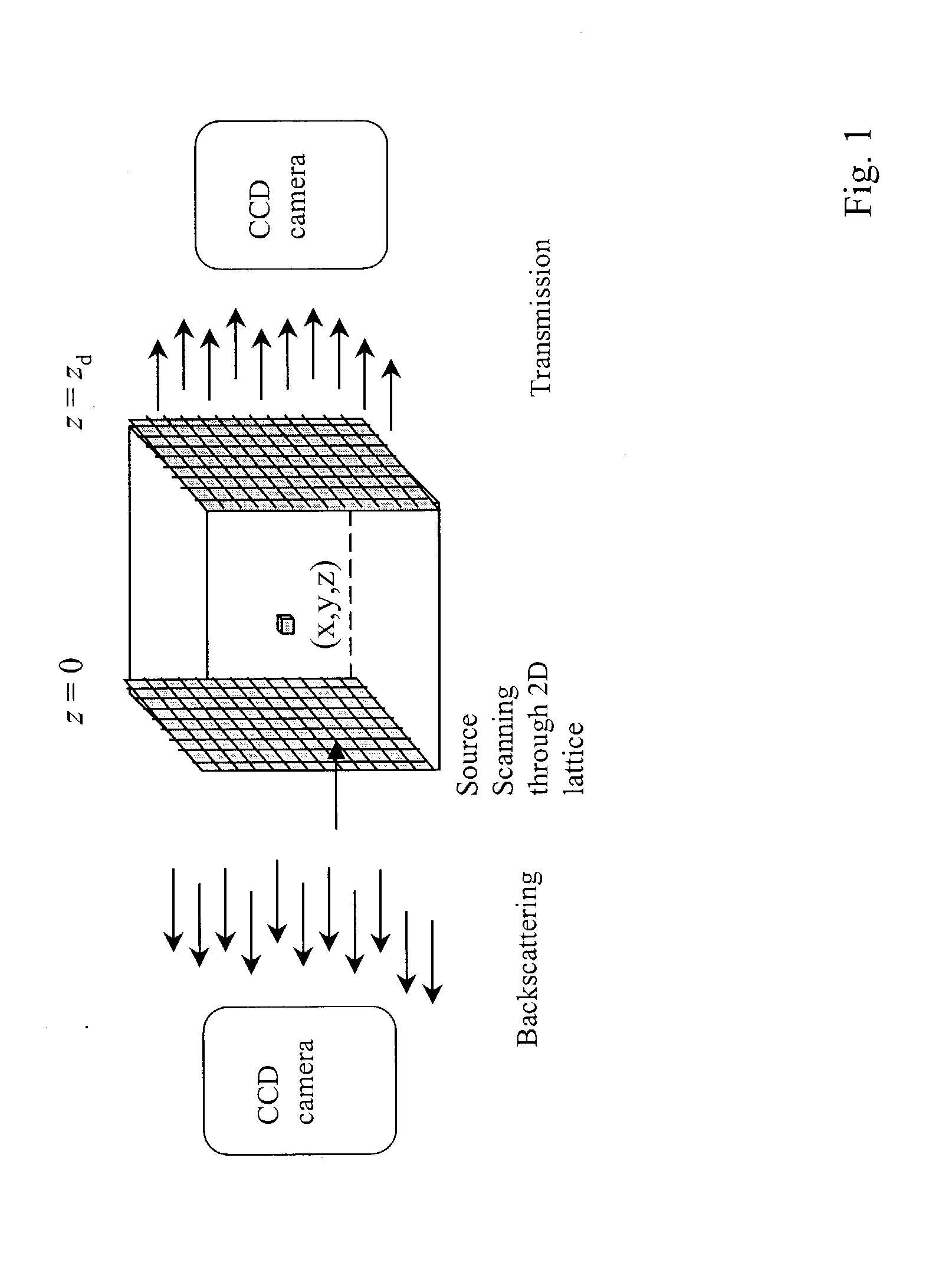
Hybrid-dual-Fourier tomographic algorithm for a fast three-dimensional optical image reconstruction in turbid media
InactiveUS20040030255A1Reconstruction from projectionScattering properties measurementsDiffusionImaging algorithm
A method for imaging objects in a highly scattering turbid medium comprises: using a group of sources and detectors to generate a plurality of emergent energy waves from the medium, determining the intensity data of the emergent energy waves and processing the intensity data by using an image reconstruction algorithm. Arrangement of sources-detectors may be in parallel (transmission and / or backscattering) geometry or in cylinder geometry. The reconstruction algorithm is a novel hybrid dual Fourier tomographic algorithm for a fast 3D image reconstruction. The forward models are the radiative transfer model based on the cumulant solution of the radiative transfer equation or the diffusion model based on the approximate diffusion equation.
Owner:RES FOUND THE CITY UNIV OF NEW YORK
Personal three-dimensional image interactive makeup trial information data processing method and device
InactiveCN102262788APromote the process of e-commerceSolving shopping experience challenges3D-image rendering3D modellingPersonalizationThe Internet
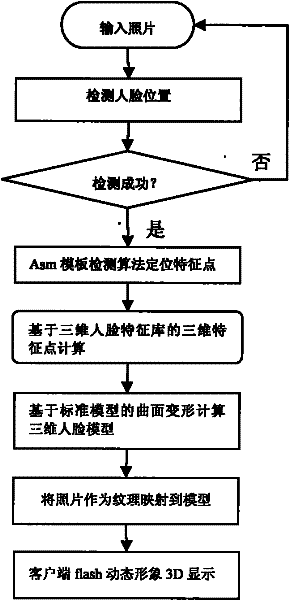
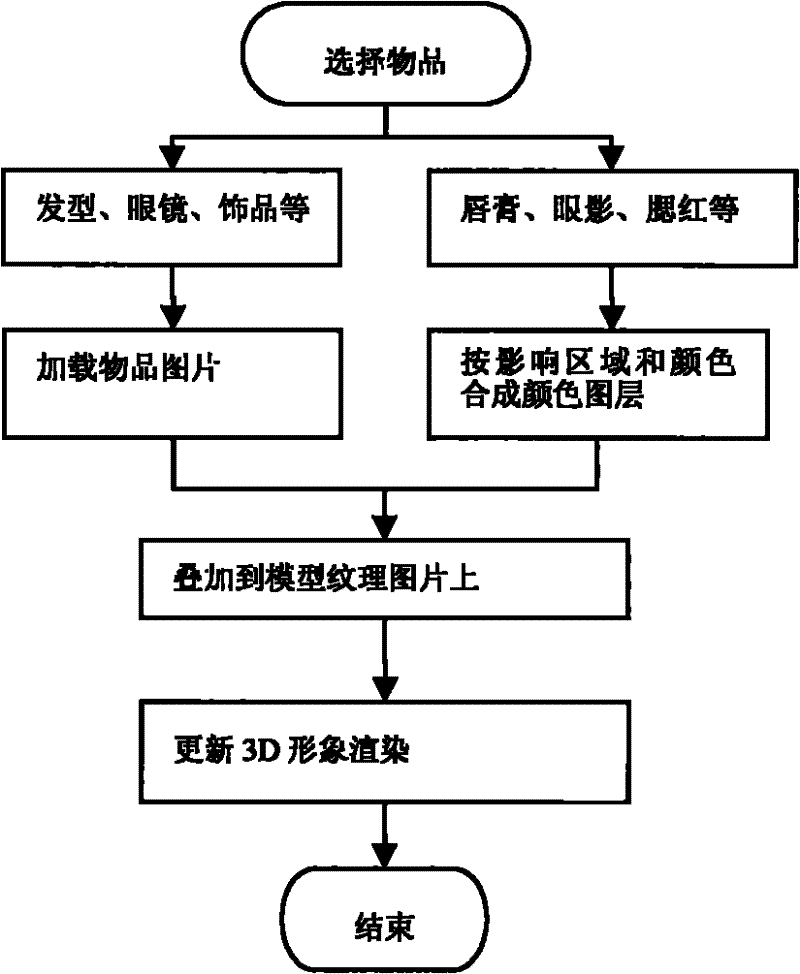
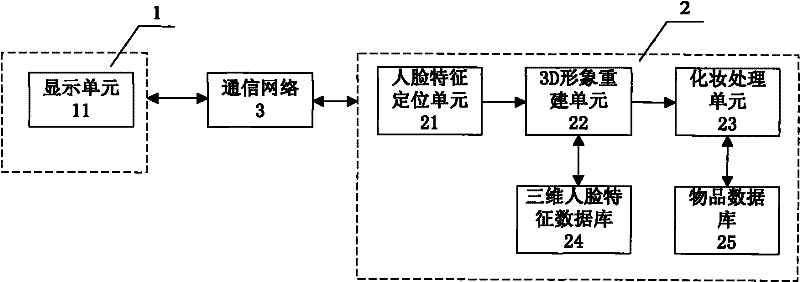
The present invention relates to a personal three-dimensional image interactive makeup test information data processing method and device, including a client, a server, and a communication network. The client includes an Internet terminal, a mobile terminal, and a retail terminal, all of which are equipped with a display unit. The server includes a face feature positioning unit, a 3D image reconstruction unit, a makeup processing unit, a three-dimensional face feature database, and a cosmetic item database. The client is connected to the server through a communication network. The working process of the device includes 1) the client There are 7 steps to obtain user photo information and transmit it to the server. Compared with the prior art, the present invention has the advantages of realizing cross-media application services on the touch screens of Internet terminals, mobile terminals, and retail terminals at the same time, promoting more intelligent development of the industry, wider application service range, more real personalized experience, and time-sensitive , location and terminal conditions and other advantages.
Owner:SHANGHAI YEEGOL INFORMATION TECH
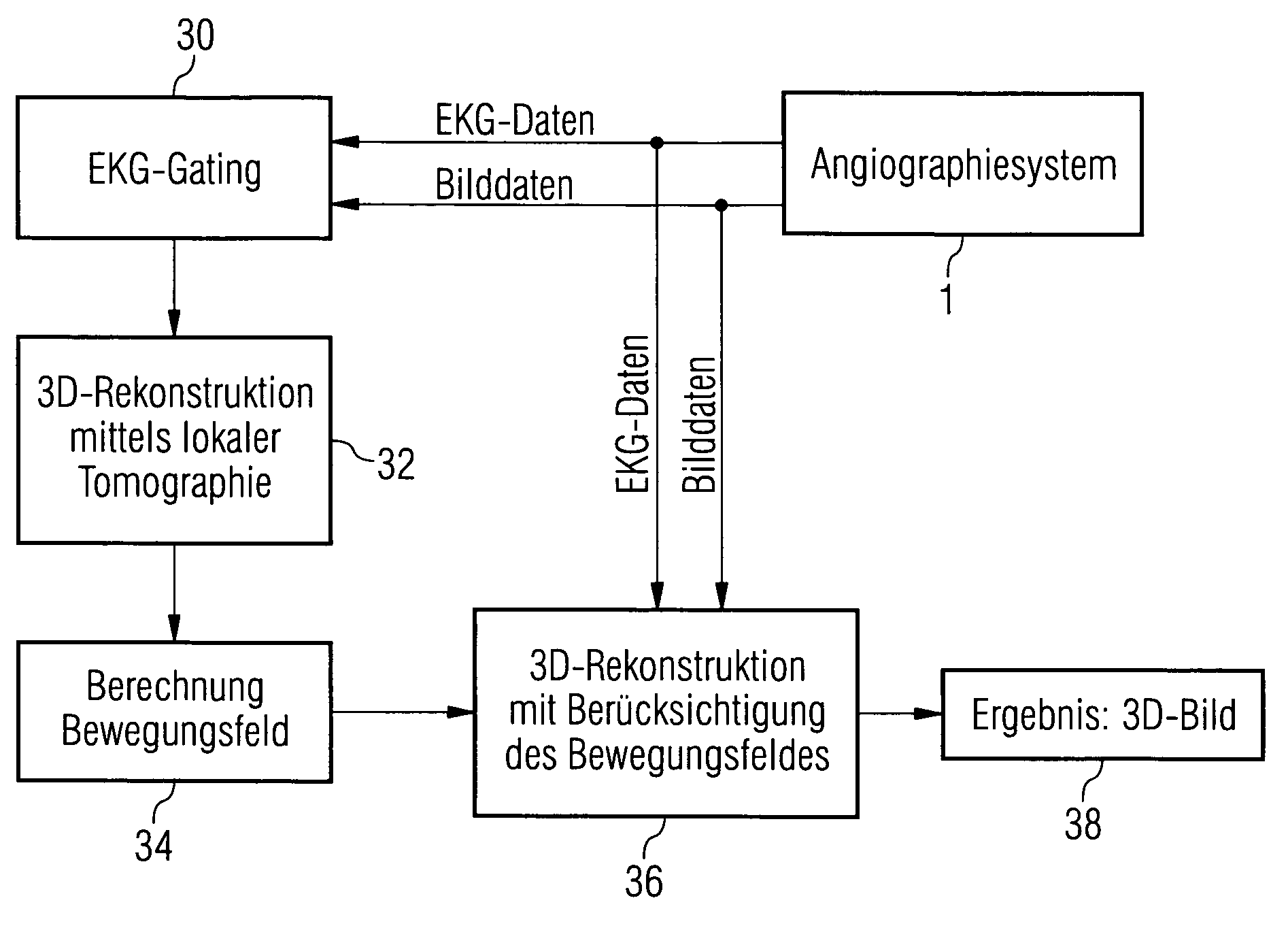
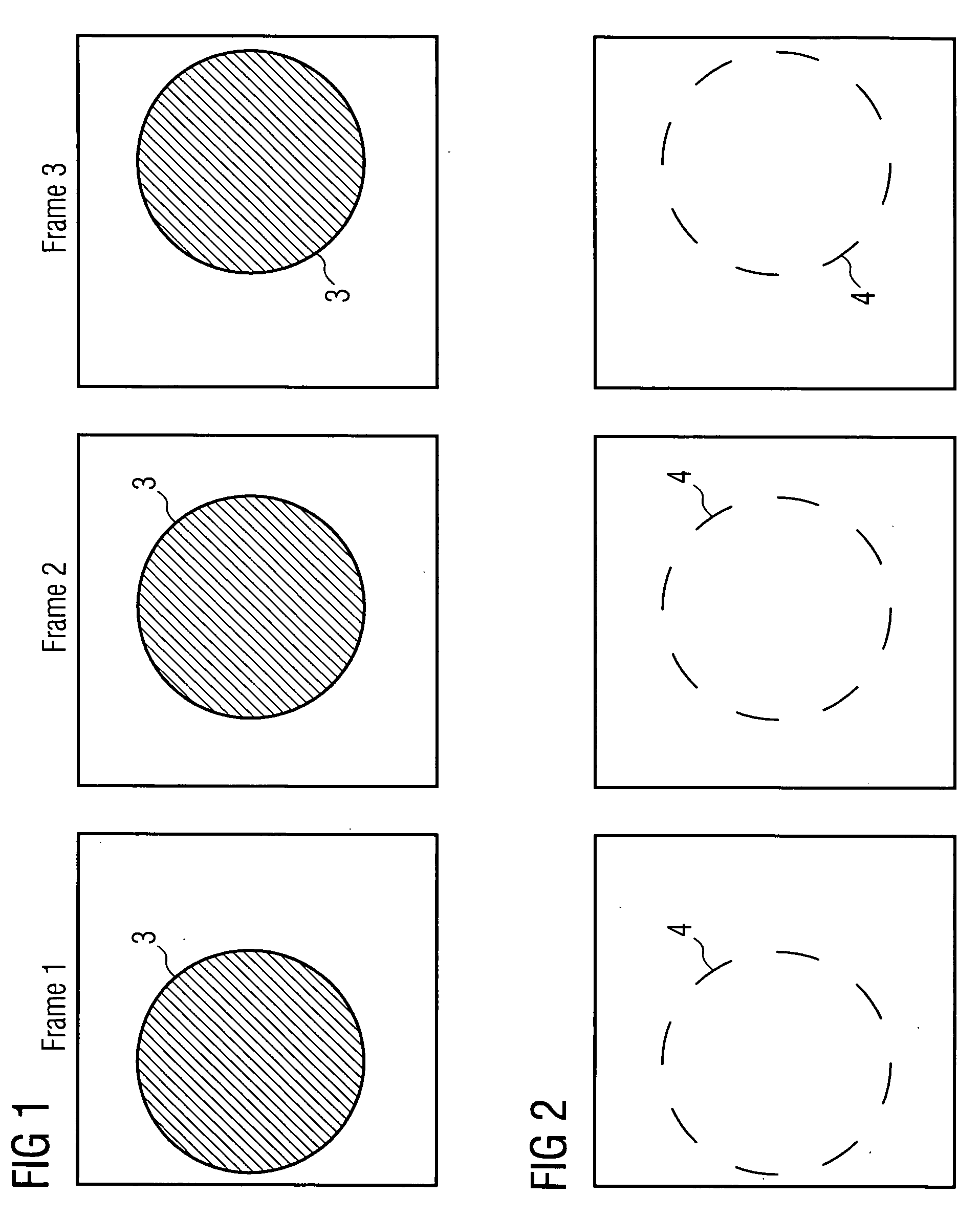
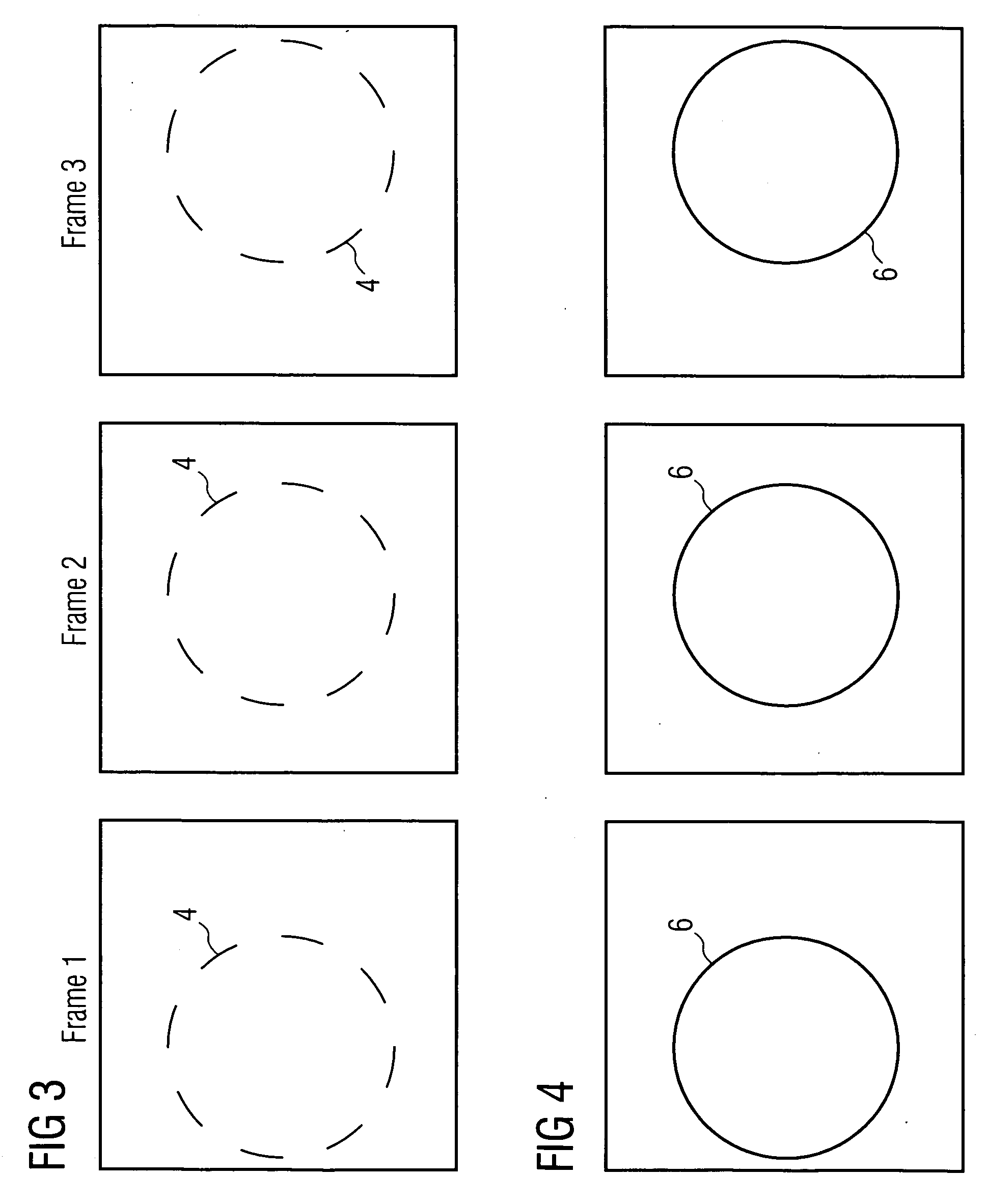
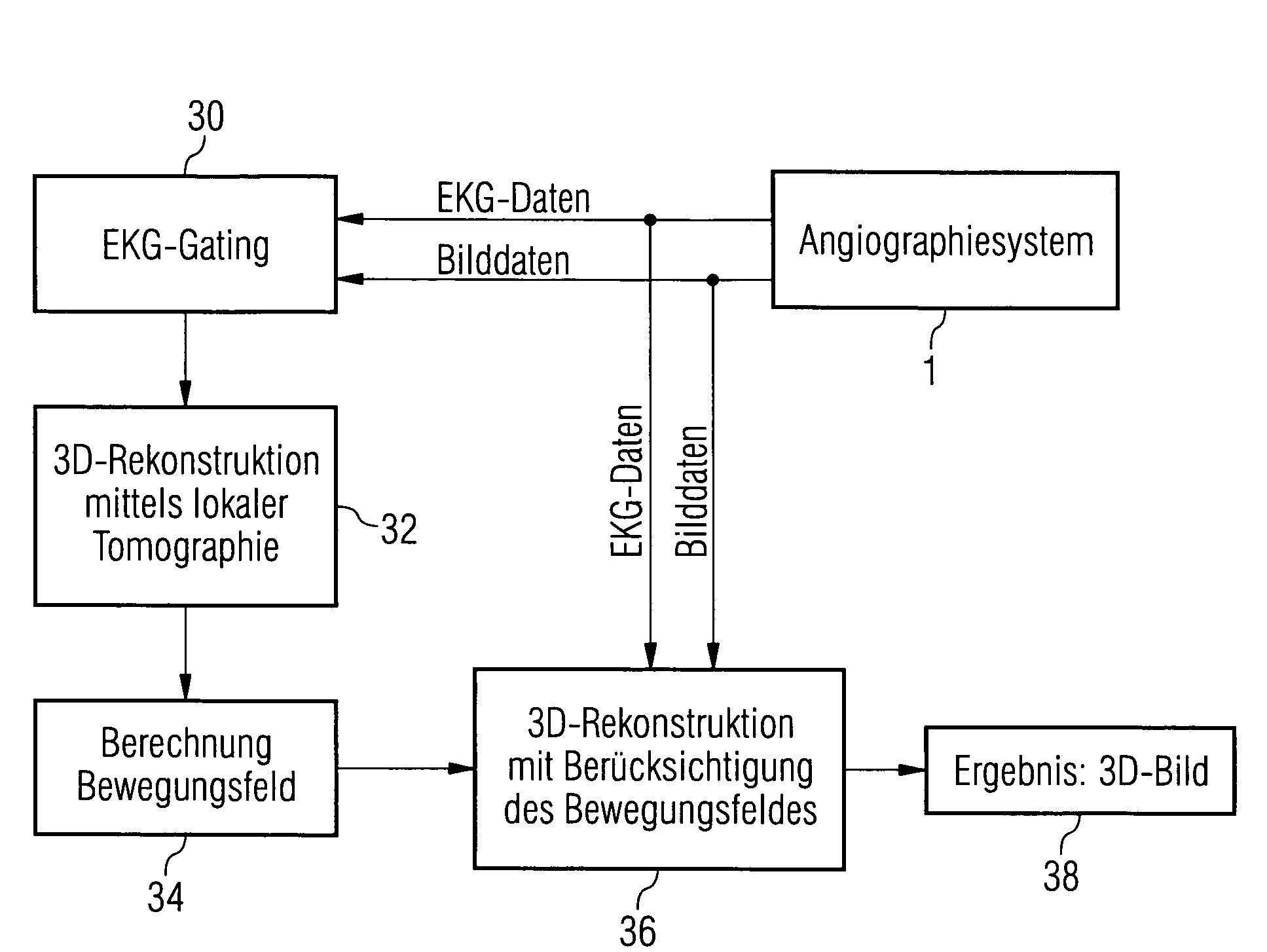
Method and device for reconstructing a 3D image data set of a moving object
InactiveUS20060285632A1High quality imagingReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationEcg gatingMotion field
The invention relates to a method and device for reconstructing a 3D image data set of a moving object from a set of projection images, which were recorded at least partially one after the other from different projection directions. The projection images are hereby assigned by ECG gating to a motion phase of the object in each instance and an incomplete 3D image of the object is computed in this motion phase from these few projection images using local tomography. Motion fields are determined from these 3D images and are used during the final 3D image reconstruction for motion corrections.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
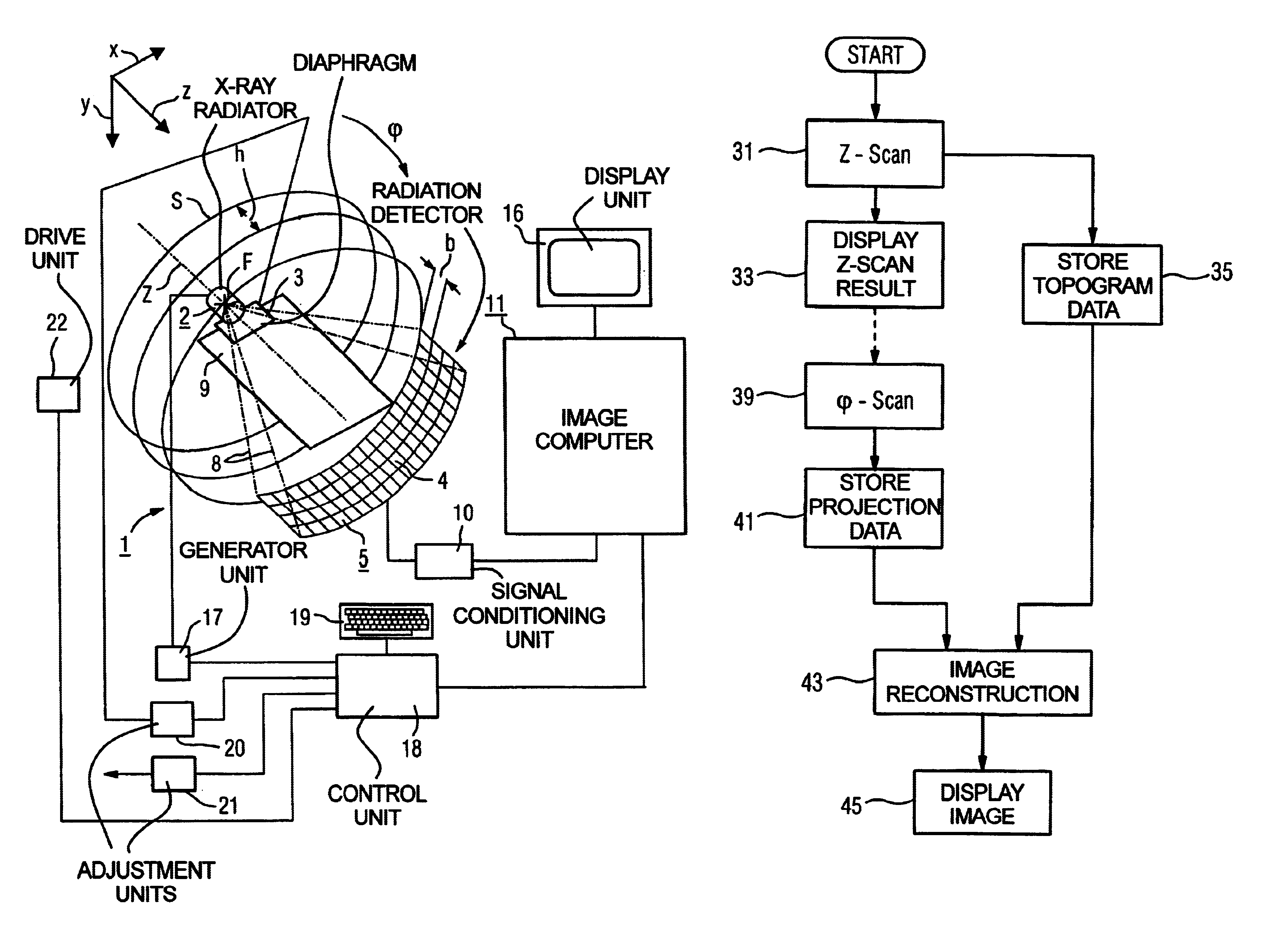
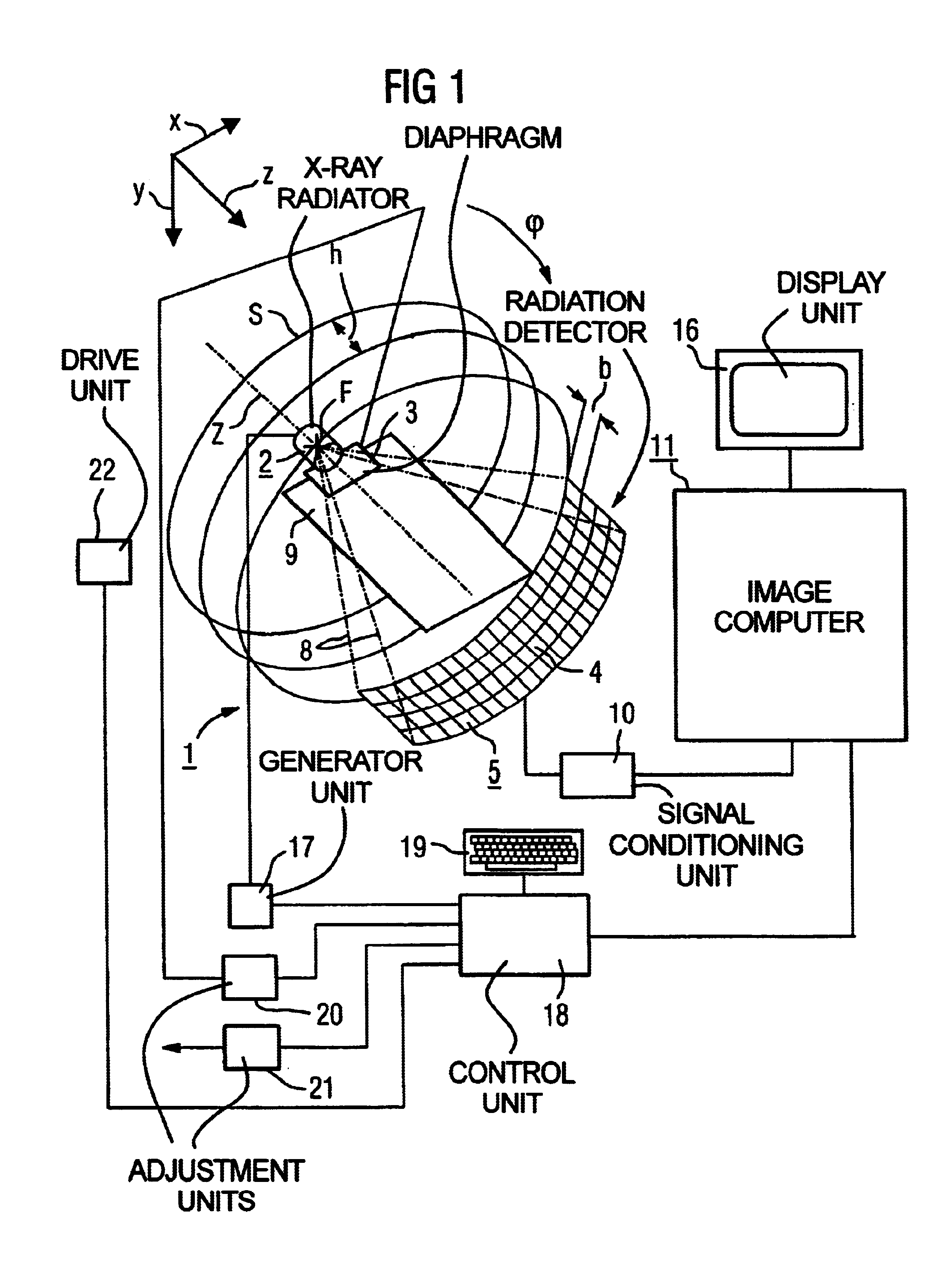
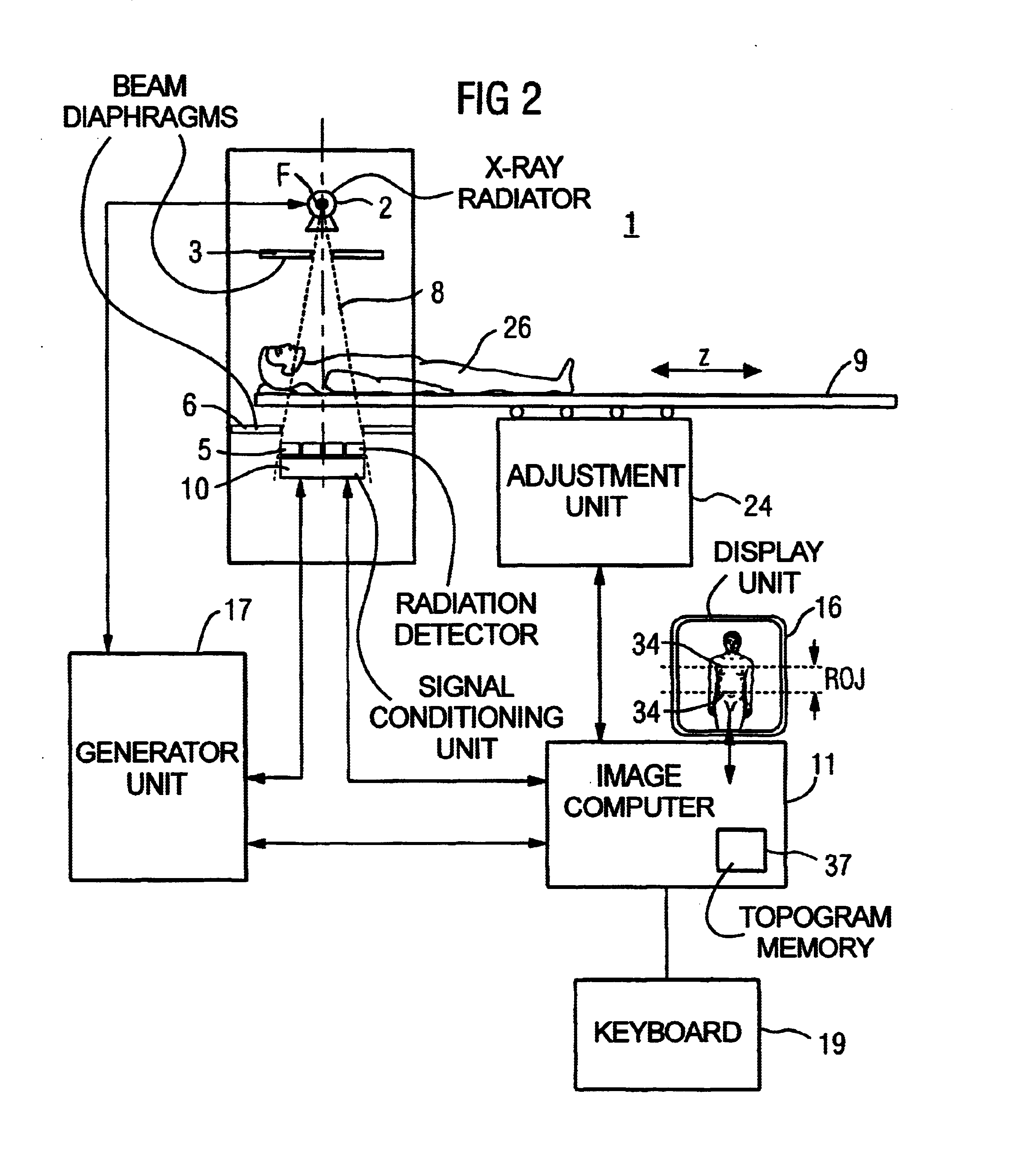
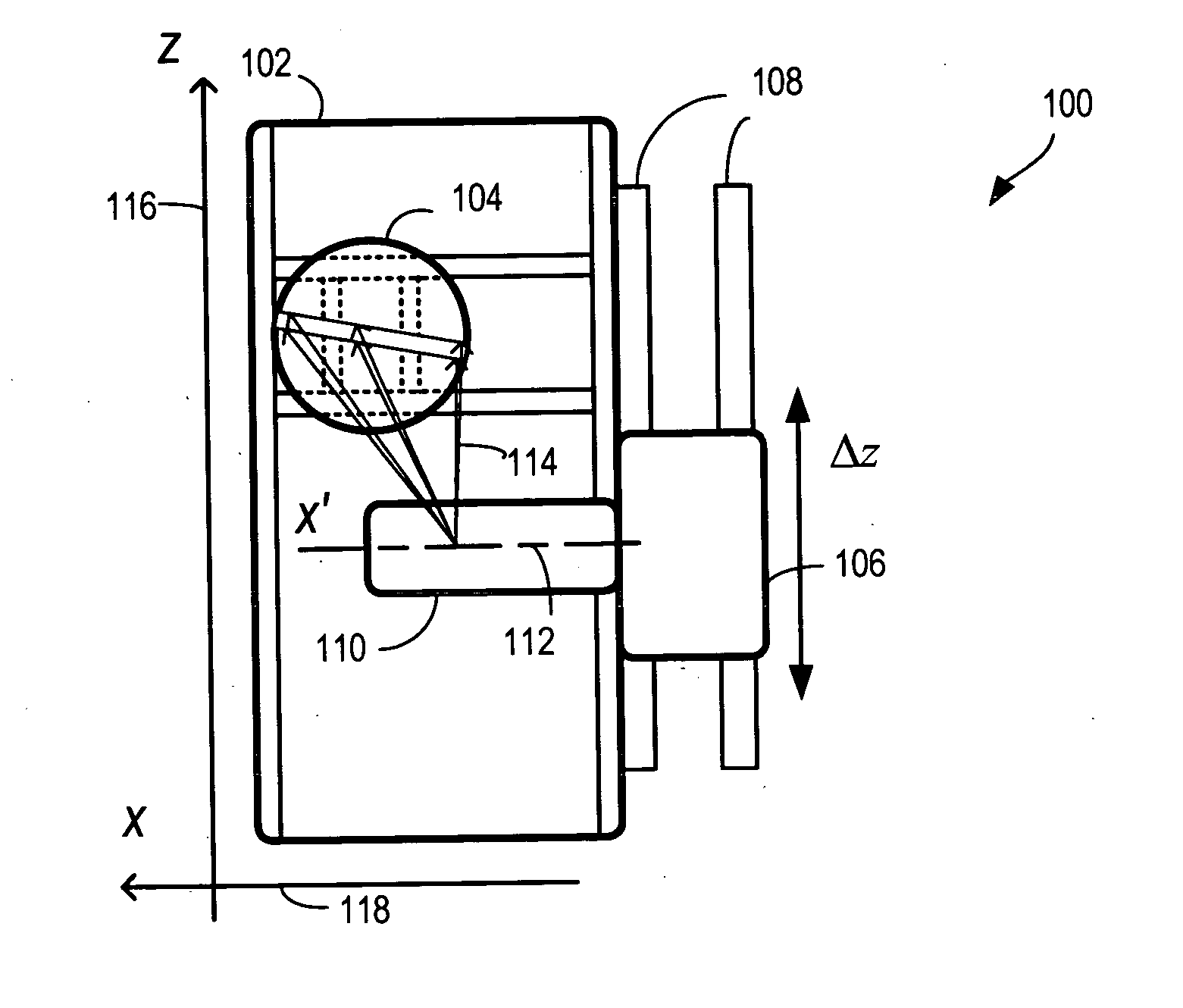
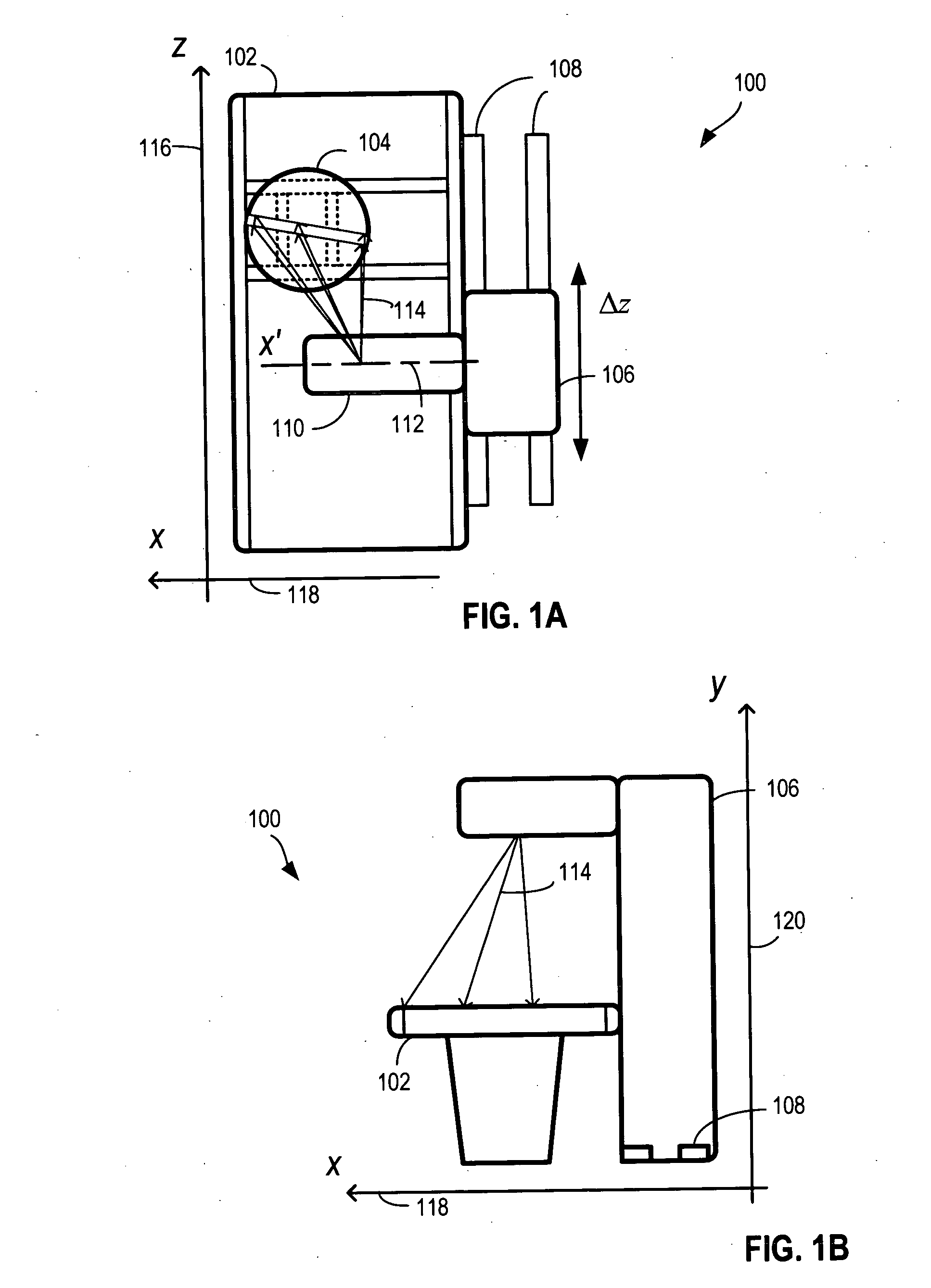
Method for generating an image by means of a tomography capable X-ray device with multi-row X-ray detector array
InactiveUS6928137B2Short timeRapid image reconstructionReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationComputed tomographyX-ray
In a method for generating an image of an examination subject with a tomography-capable X-ray device, particularly a computed tomography device, having a multi-row X-ray detector array, an X-ray radiator that rotates about a system axis and emits a conical x-ray beam, and a positioning device by means of which the subject is positionable relative to the X-ray radiator in different z-positions in a direction parallel to the system axis, the image is reconstructed from the raw data that are generated from the X-ray radiator. Raw data are generated from both a rotation scan and a linear scan. In the linear scan, all transmission values for the image reconstruction are acquired in one continuous linear scanning movement, so that the rotation scan can be picked up while the X-ray radiator is in continuous rotation. A topogram that is executed prior to the actual rotation scan for the purpose of selecting a region of interest of the subject for the subsequent rotation scan can be utilized as a linear measurement dataset. A particularly rapid acquisition of initial data for the subsequent 3D image reconstruction occurs.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
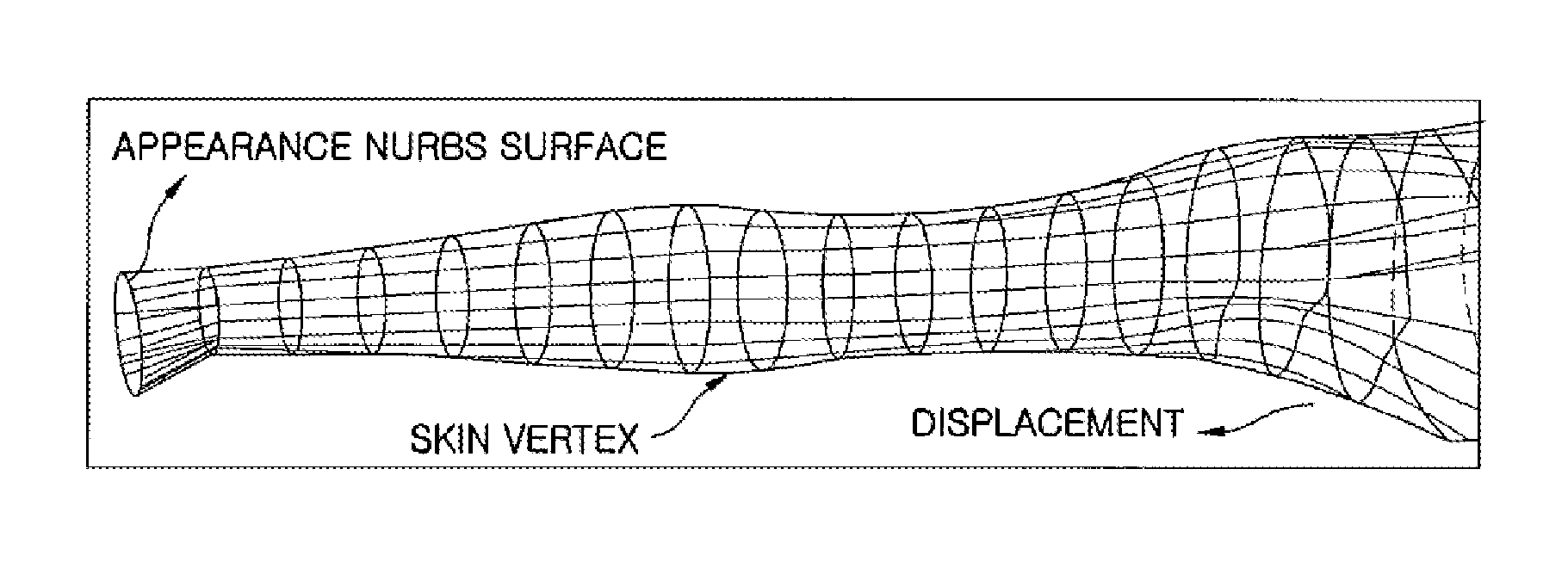
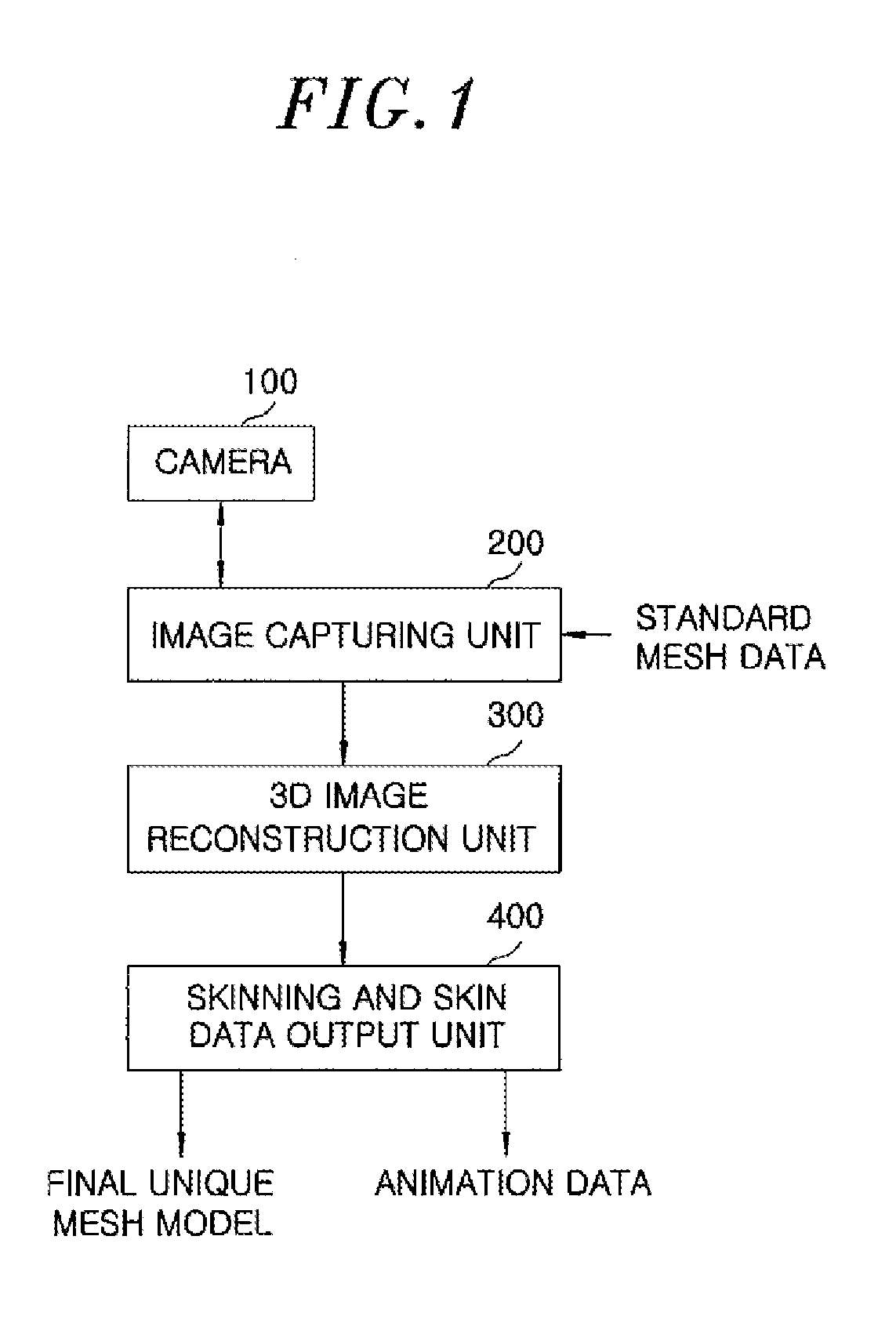
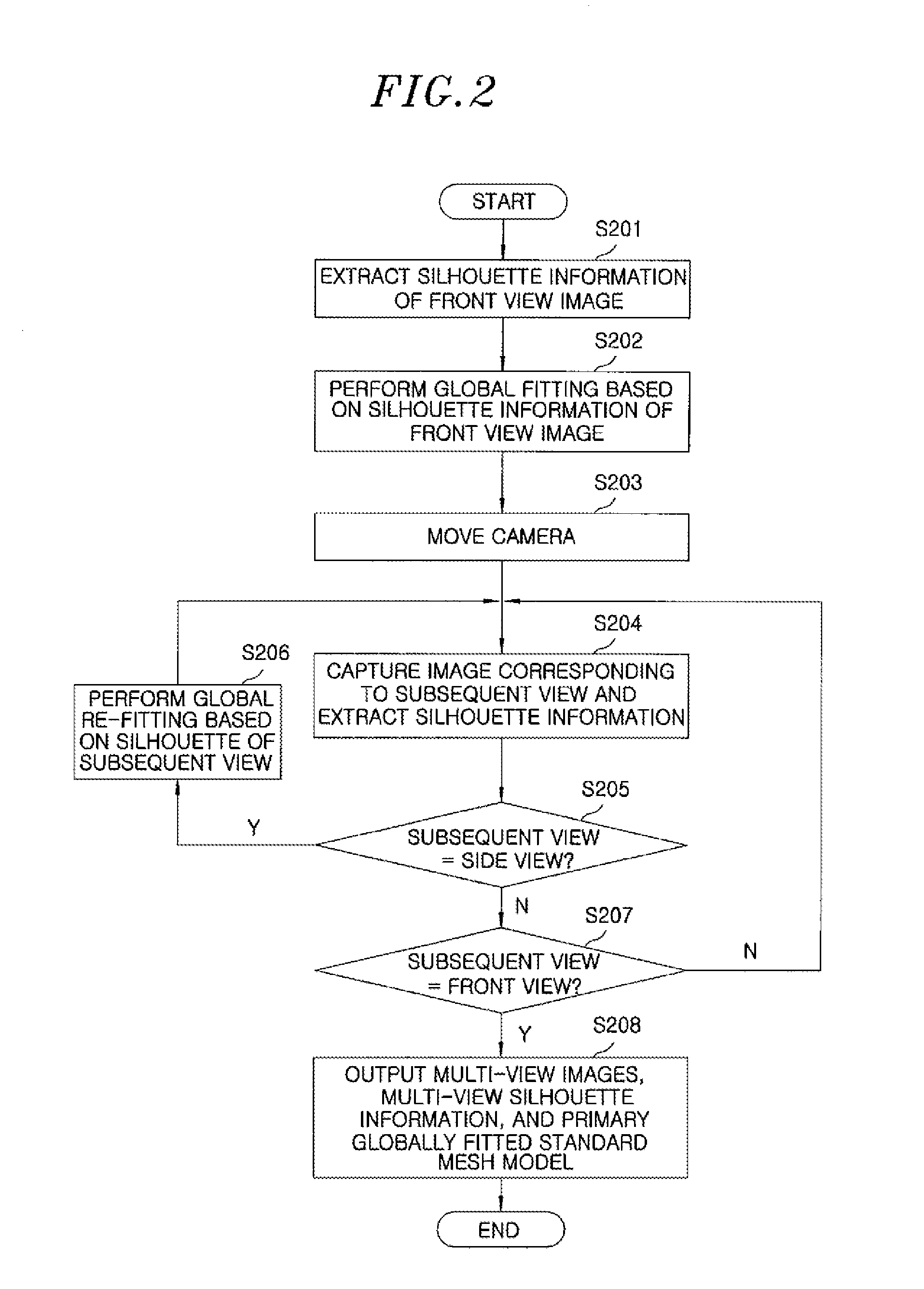
Apparatus and method for reconstructing outward appearance of dynamic object and automatically skinning dynamic object
InactiveUS20130107003A1Guaranteed CompatibilityFree and realistic shapeDetails involving processing stepsAnimationAnimationMesh model
An apparatus for reconstructing appearance of a dynamic object and automatically skinning the dynamic object, includes an image capturing unit configured to generate a multi-view image and multi-view silhouette information of a dynamic object and a primary globally fitted standard mesh model; and a 3D image reconstruction unit configured to perform global and local fitting on the primary globally fitted standard mesh model, and then generate a Non Uniform Rational B-Spline (NURBS)-based unique mesh model of the dynamic object. Further, the apparatus includes a data output unit configured to generate and output a final unique mesh model and animation data based on the NURBS-based unique mesh model of the dynamic object and at least two pieces of operation information about the dynamic object.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
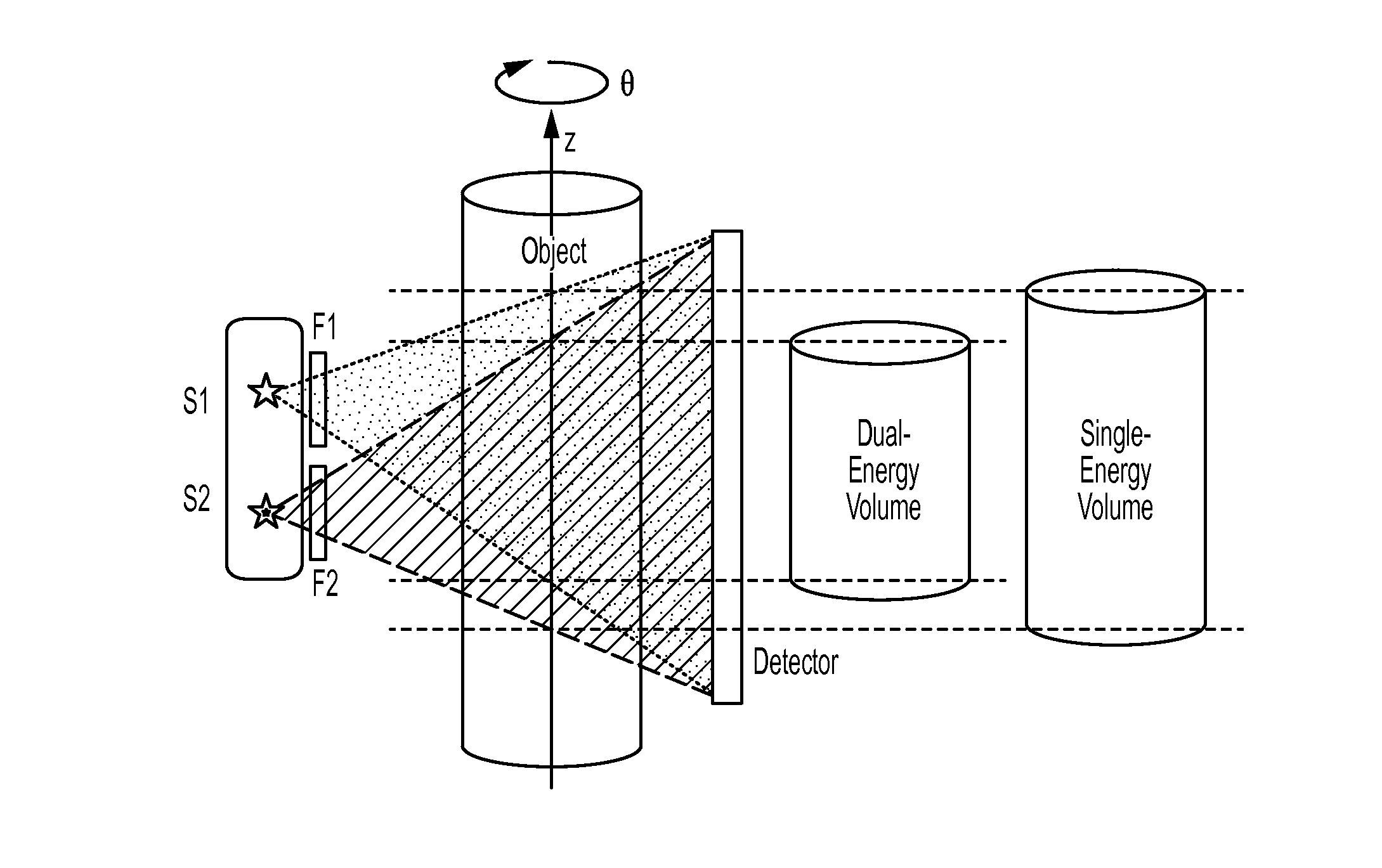
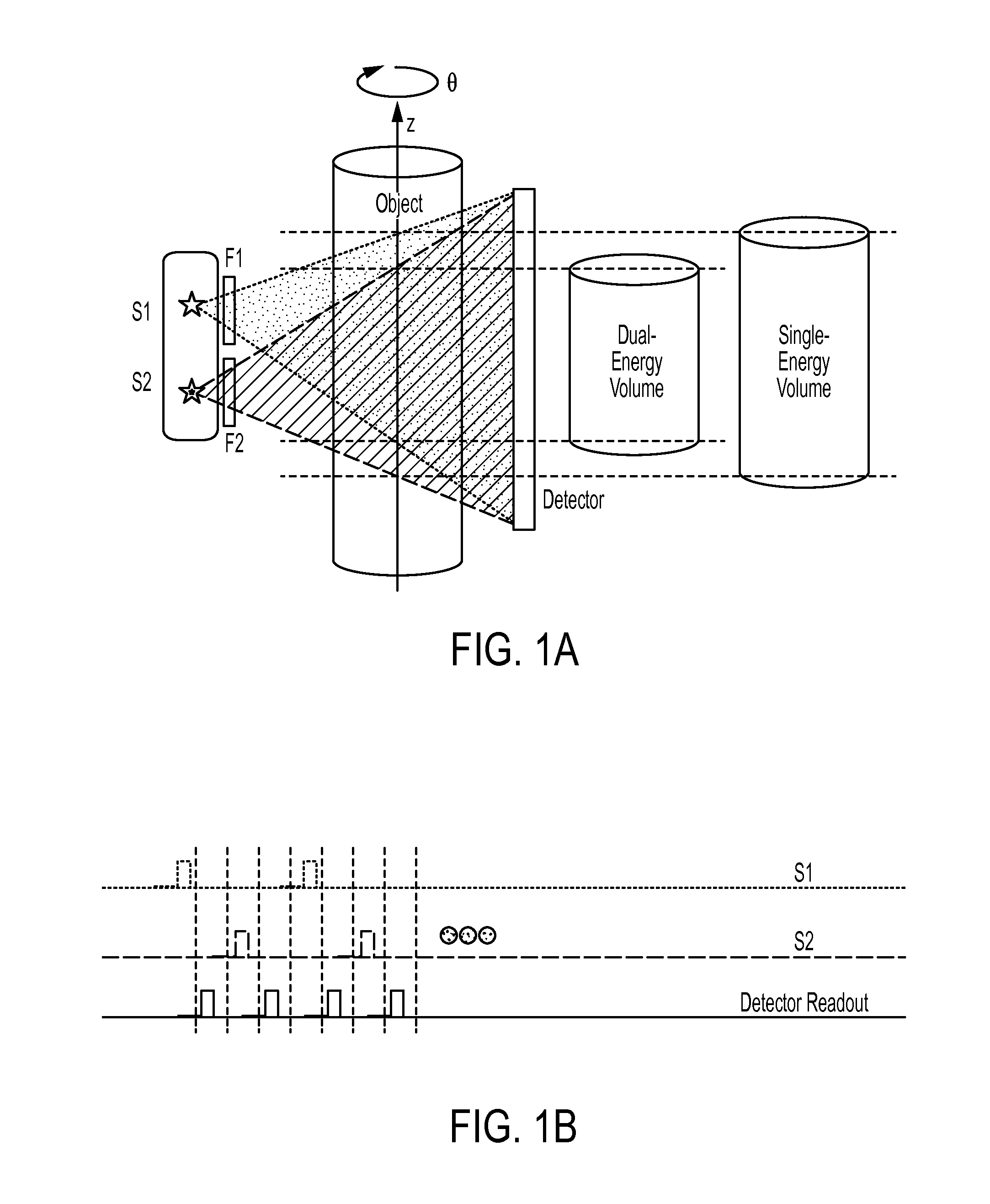
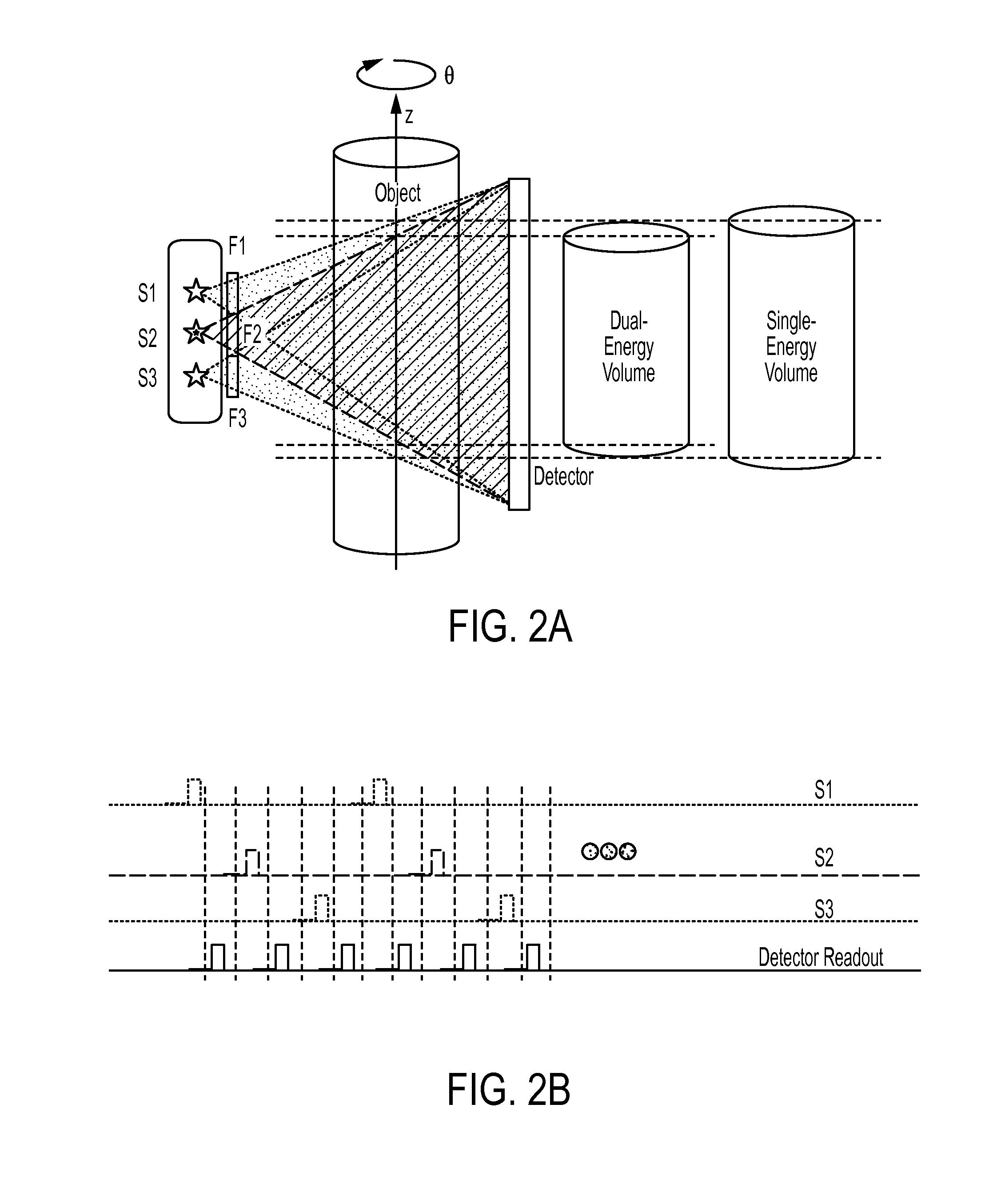
Dual-energy cone-beam computed tomography with a multiple source, single-detector configuration
The present invention is directed to a system and method for dual-energy (DE) or multiple-energy (spectral) cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) using a configuration of multiple x-ray sources and a single detector. The x-ray sources are operated to produce x-ray spectra of different energies (peak kilovoltage (kVp) and / or filtration). Volumetric 3D image reconstruction and dual or triple energy 3D image decomposition can be executed using data from the CBCT scan. The invention allows for a variety of selections in energy and filtration associated with each source and the order of pulsing for each source (“firing pattern”). The motivation for distributing the sources along the z direction in CBCT includes extension of the longitudinal field of view and reduction of cone-beam artifacts.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC +1
Methods and apparatuses for 3D imaging in magnetoencephalography and magnetocardiography
InactiveUS20110313274A1Improve accuracyEffective informationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMagnetocardiographyReconstruction problem
This invention discloses methods and apparatuses for 3D imaging in Magnetoencephalography (MEG), Magnetocardiography (MCG), and electrical activity in any biological tissue such as neural / muscle tissue. This invention is based on Field Paradigm founded on the principle that the field intensity distribution in a 3D volume space uniquely determines the 3D density distribution of the field emission source and vice versa. Electrical neural / muscle activity in any biological tissue results in an electrical current pattern that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is measured in a 3D volume space that extends in all directions including substantially along the radial direction from the center of the object being imaged. Further, magnetic field intensity is measured at each point along three mutually perpendicular directions. This measured data captures all the available information and facilitates a computationally efficient closed-form solution to the 3D image reconstruction problem without the use of heuristic assumptions. This is unlike prior art where measurements are made only on a surface at a nearly constant radial distance from the center of the target object, and along a single direction. Therefore necessary, useful, and available data is ignored and not measured in prior art. Consequently, prior art does not provide a closed-form solution to the 3D image reconstruction problem and it uses heuristic assumptions. The methods and apparatuses of the present invention reconstruct a 3D image of the neural / muscle electrical current pattern in MEG, MCG, and related areas, by processing image data in either the original spatial domain or the Fourier domain.
Owner:SUBBARAO MURALIDHARA
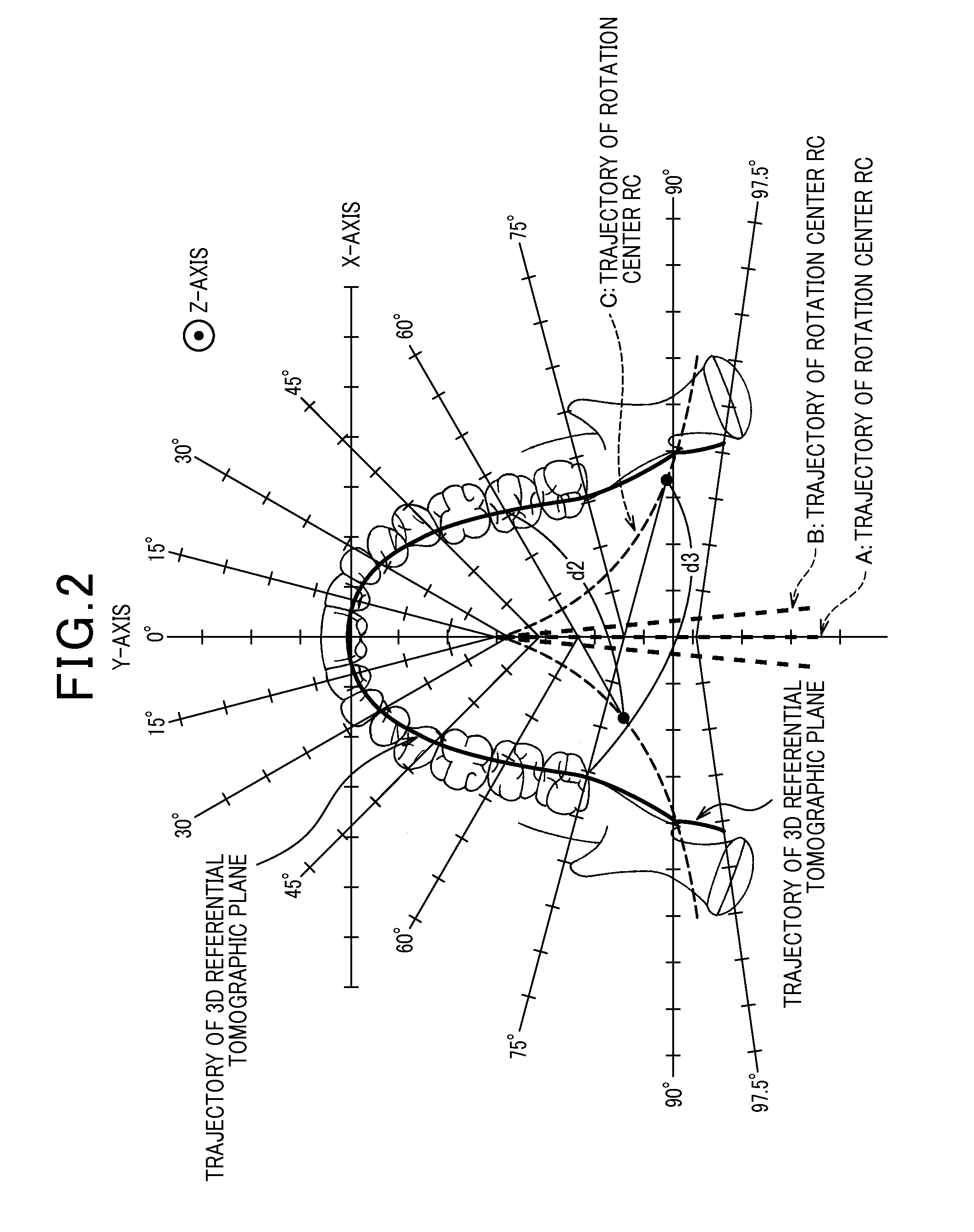
Radiation imaging apparatus and phantom used for the same
InactiveUS20130114799A1Less distortionAccurate checkReconstruction from projectionTomosynthesisX-rayRadiation imaging
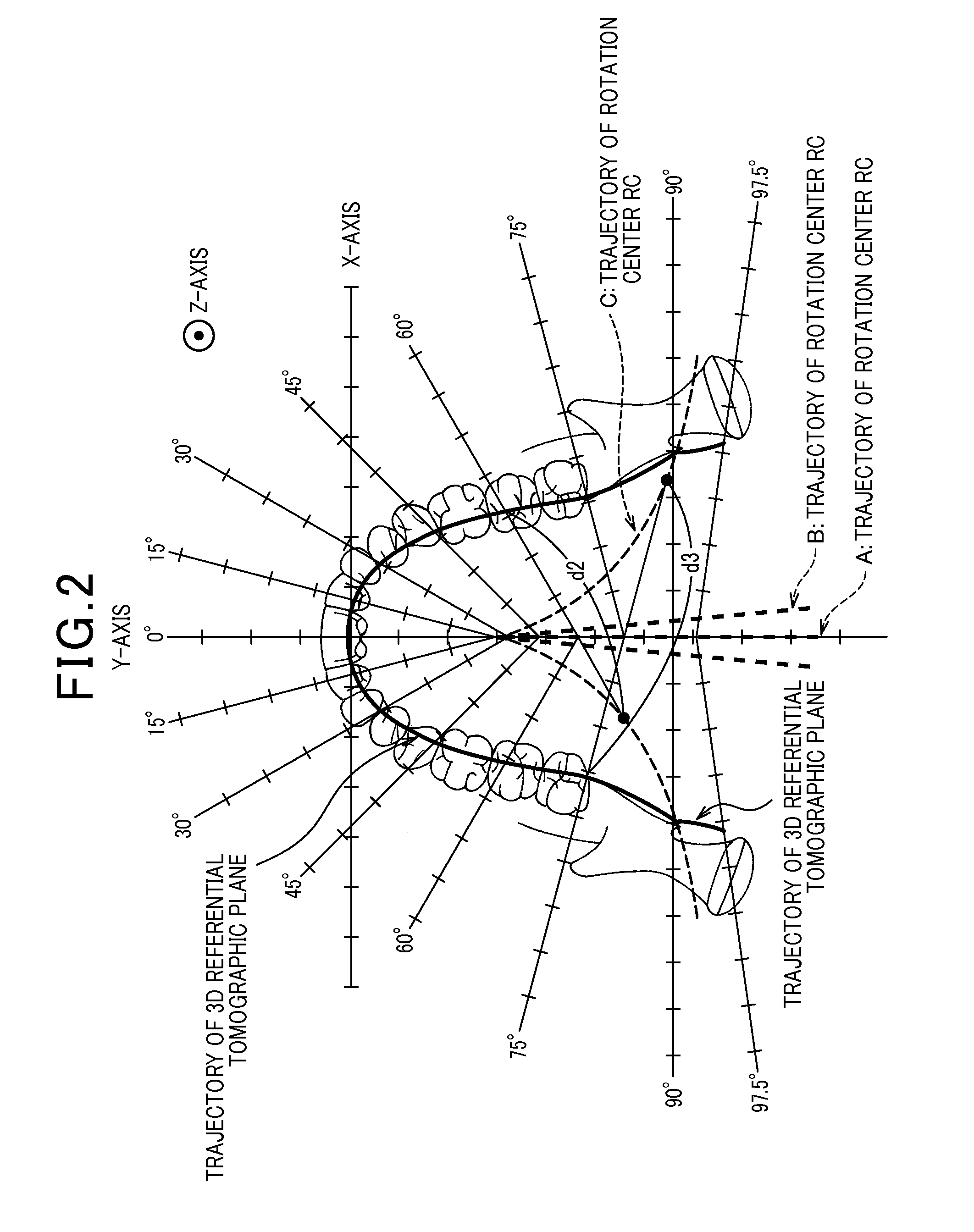
In the imaging space provided by a panoramic imaging apparatus, a phantom is arranged. The phantom is located to a predetermined tomographic plane and includes markers which image known positional information with an X-ray beam. The X-ray beam from an X-ray source is acquired as X-ray transmission data by a detector, and a panoramic image is produced using the data. Based on known positional information of the markers and information of marker positions in the panoramic image, distance information (Rs, Rd) between the X-ray tube and the detector and height information (B1) of the X-ray tube to the detector are calculated. From this calculated results and the acquired data, parameters (Δx / ΔFi, θ, Δθ / ΔFi, D, A, CX, CY) defining positional relationships among the X-ray tube, the detector, and the tomographic plane are calculated such that amounts of changes in the position connecting the X-ray tube and the detector are considered in the parameters. This allows the parameters to be calibrated for 3D image reconstruction.
Owner:TAKARA TELESYST
System for dynamic low dose x-ray imaging
InactiveUS20060182224A1Facilitate real-time tracking and low-dose imagingFacilitate real-time guidanceRadiation diagnosis data transmissionSolid-state devicesTomosynthesisData set
A system for low dose x-ray imaging provides for dynamic generation of an x-ray beam with specific shape, and dynamic tracking of a detector with said beam. The detector is rotatable, and translatable along two orthogonal axes, and may mount with a circular detector tray, the tray rotating around a rotation axis. Specific detector shapes include an elongated rectangular matrix, for example with additional detector cells near the rotation center to provide an increased area of continuous detection. Dynamic low-dose x-ray tomosynthesis or limited-angle tomographic imaging is enabled via simultaneous x-ray tube and detector motions during examination, such as fluoroscopic examination of a human body. Data acquired at multiple projection angles is input to a 3D image reconstruction algorithm that provides a refreshed 3D data set during continuing examination. The system may thus also automatically track a point in three-dimensional space, for example continuously locating the tip of a catheter.
Owner:FOREVISION IMAGING TECH LLC
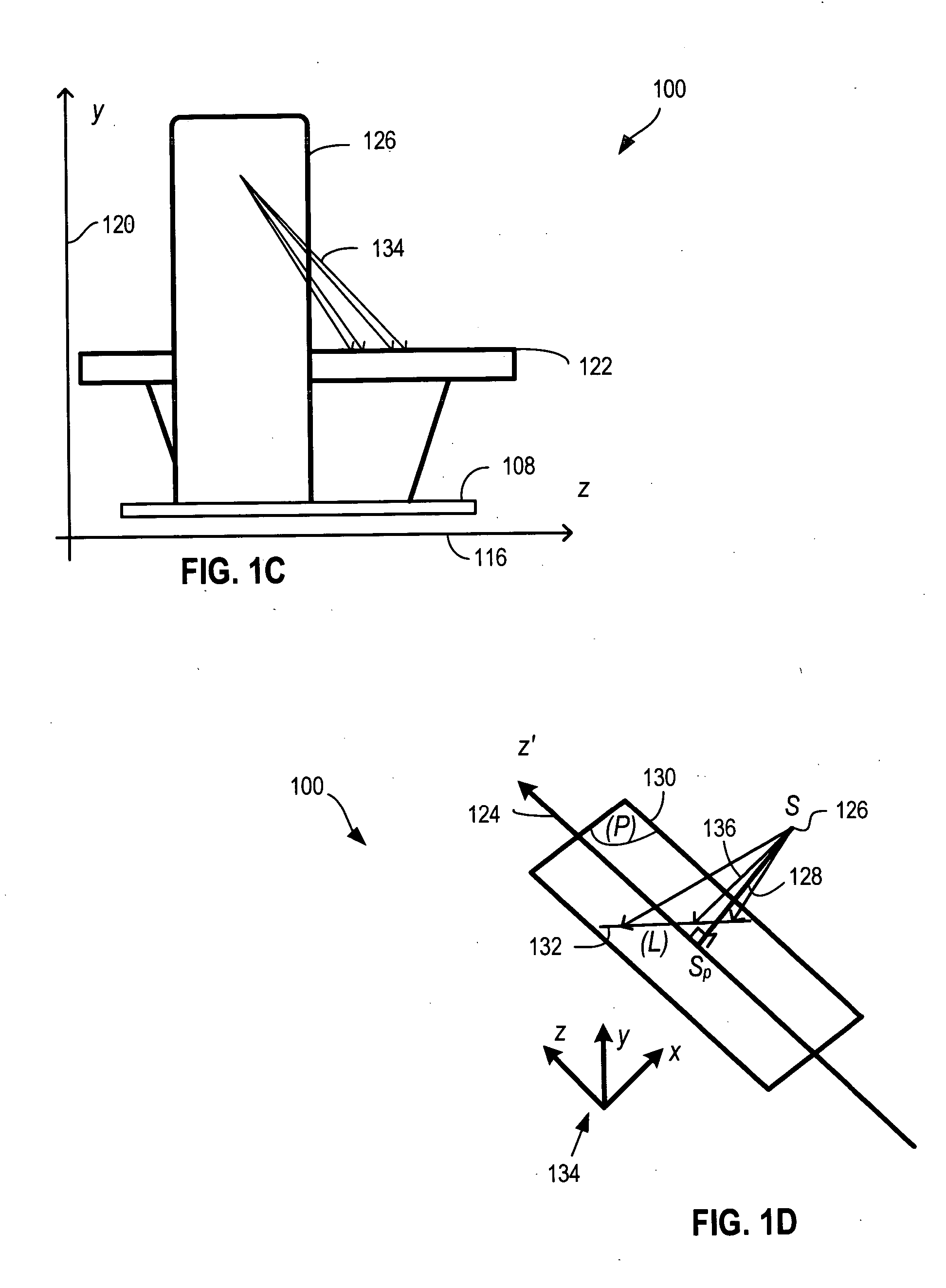
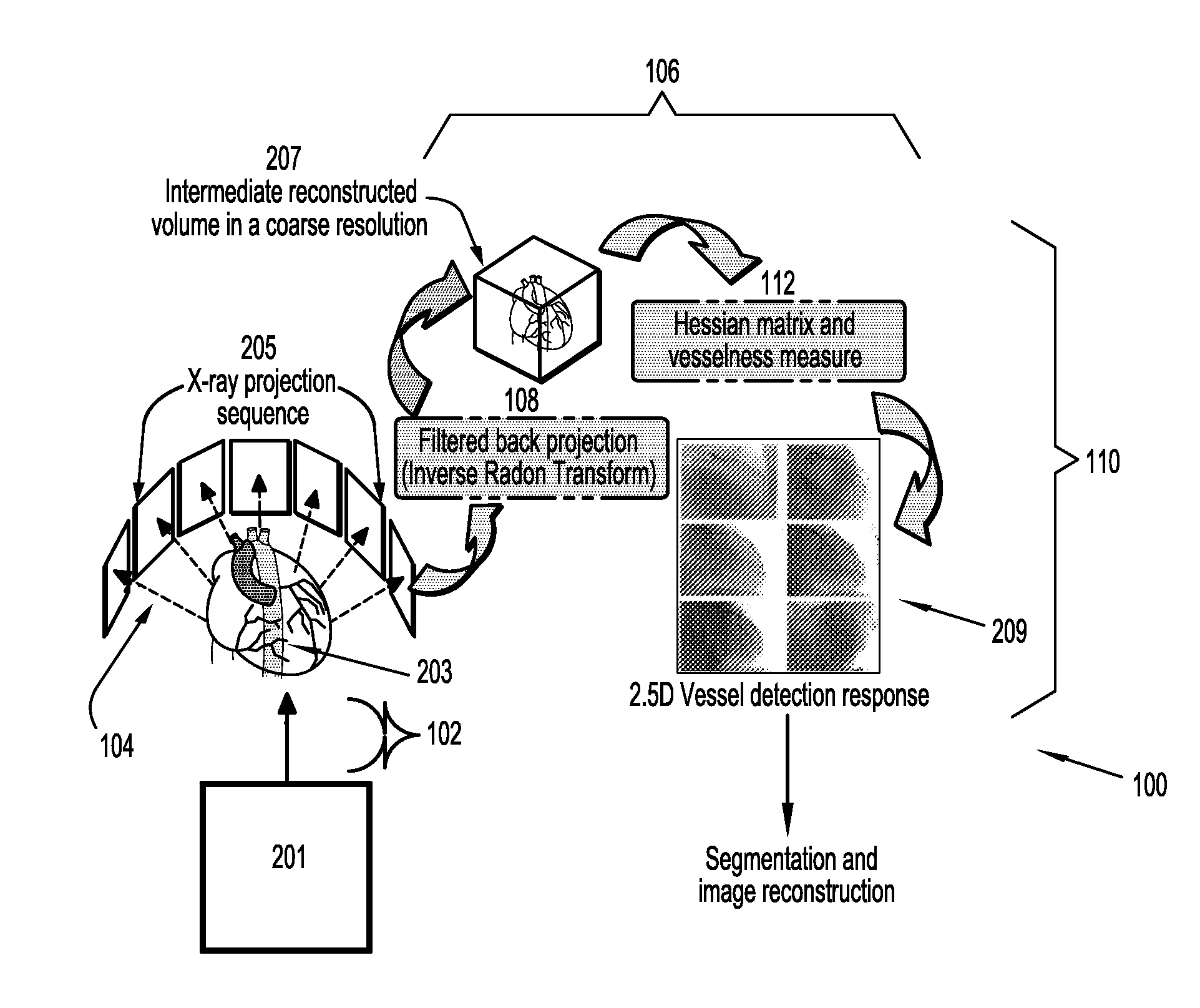
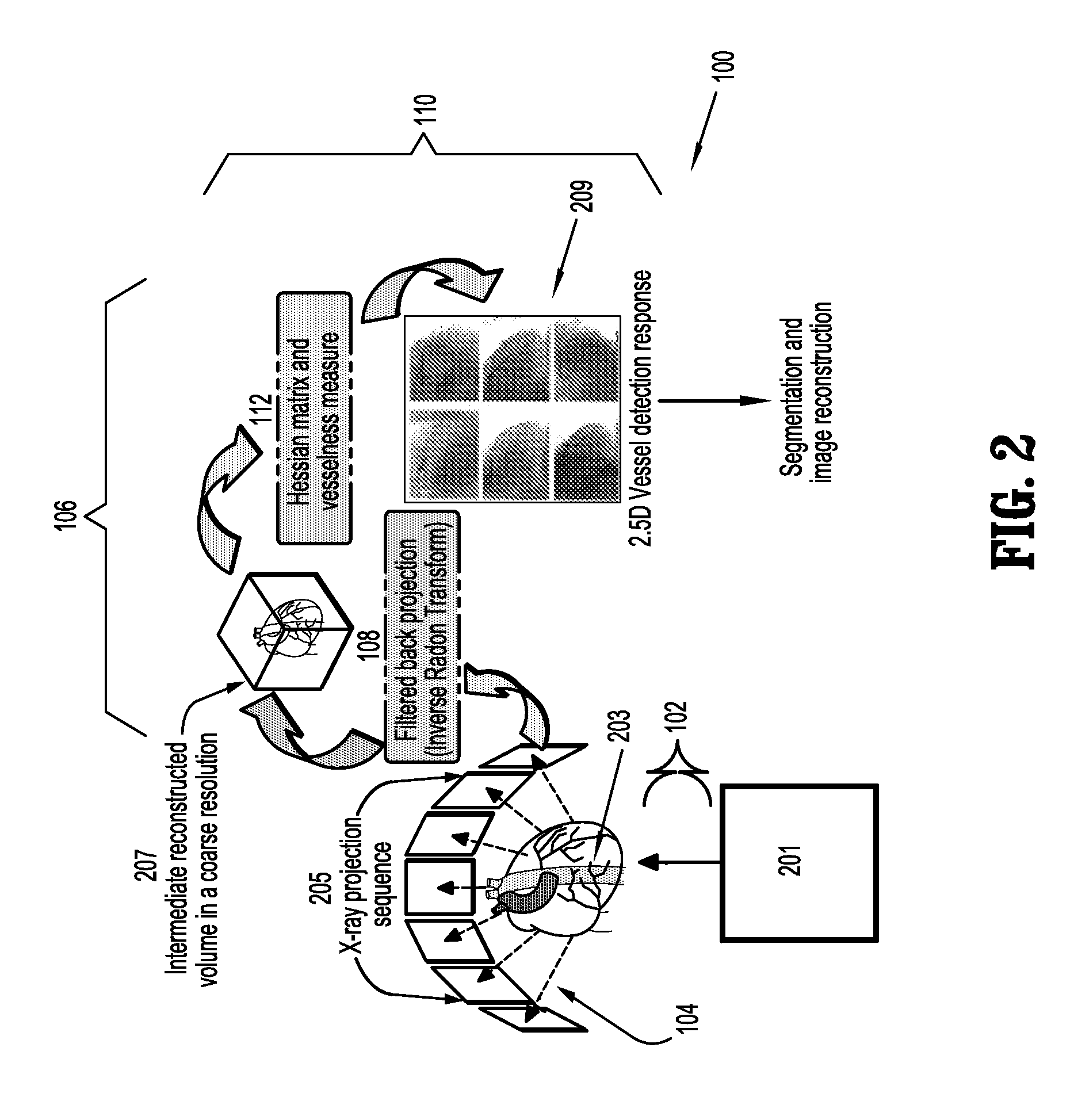
Vessel Extraction Method For Rotational Angiographic X-ray Sequences
A method (100) of blood vessel extraction for rotational angiographic X-ray sequences, comprising obtaining a 2.5D vesselness detection response in 3D (208). The method (100) utilizes the projection matrices to realize the correspondence among different image frames to extract low level image features for subsequent segmentation and 3D image reconstruction.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Cdma-based 3D imaging method for focal plane array lidar
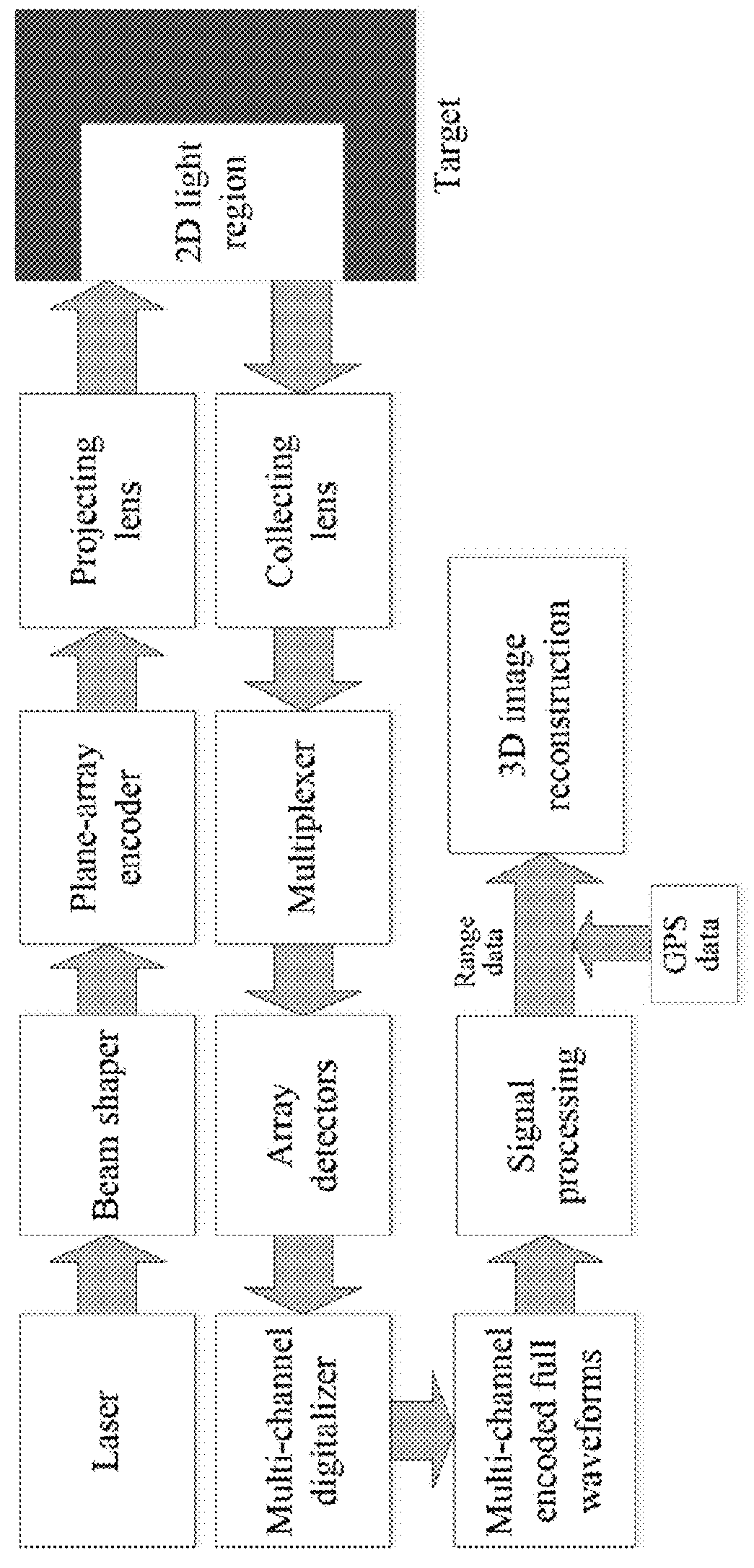
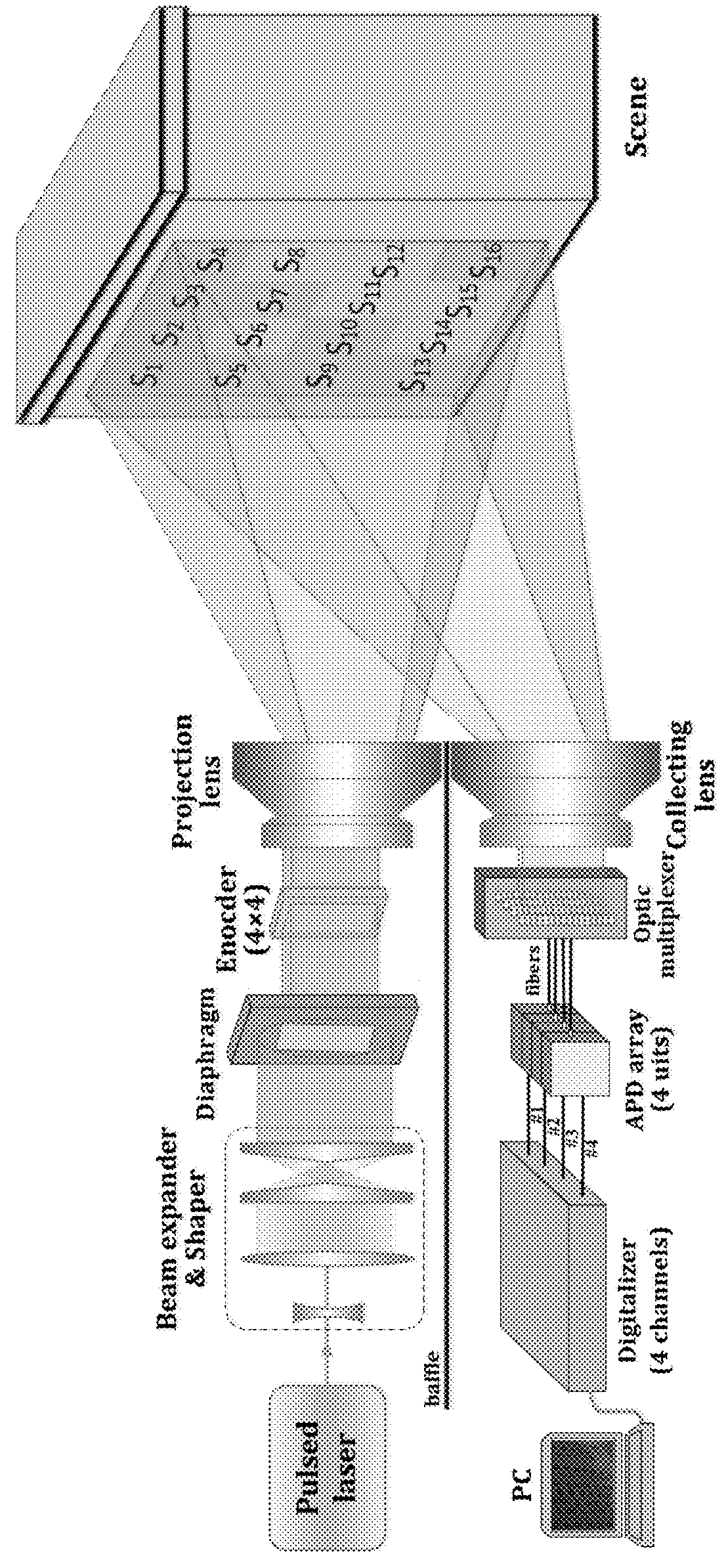
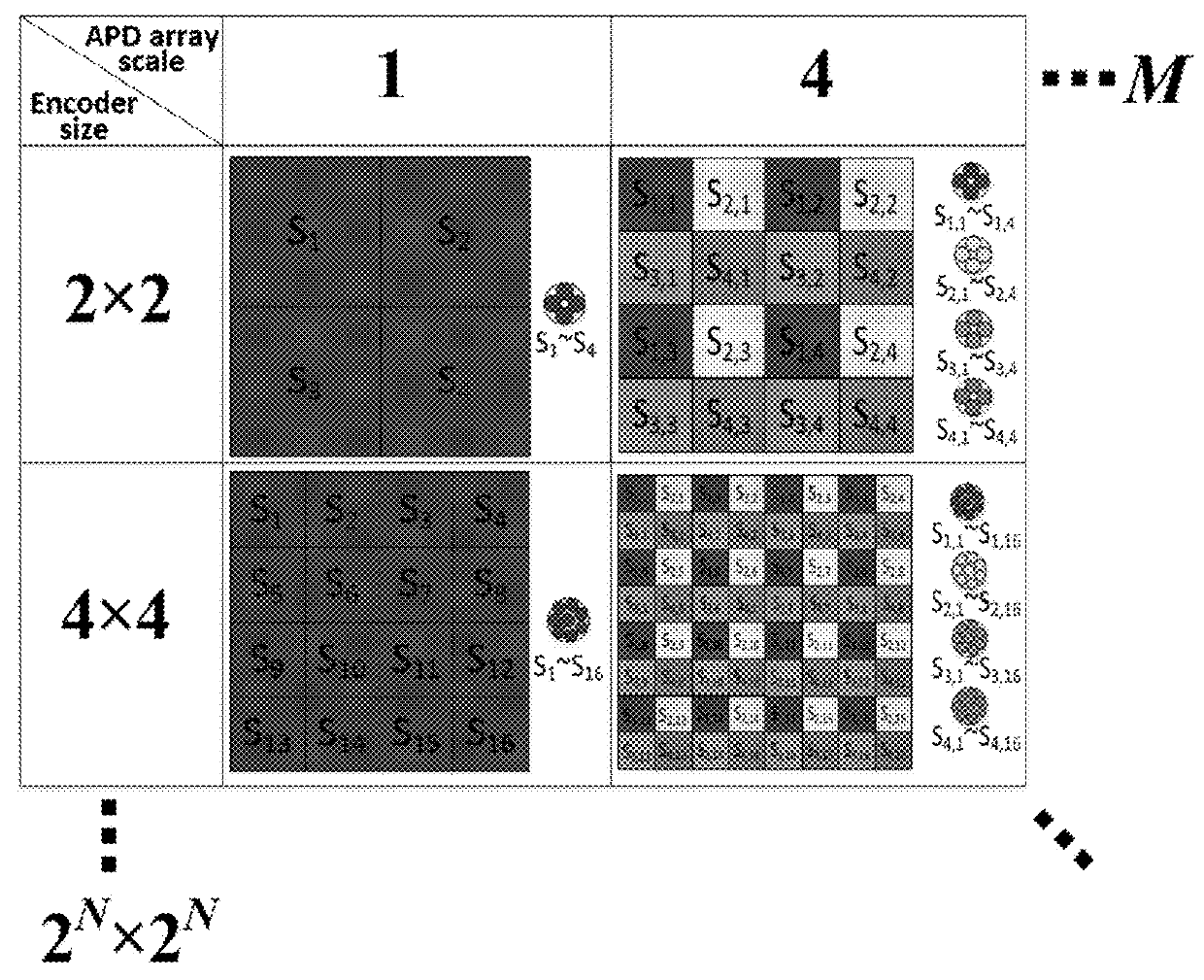
ActiveUS20180267169A1Accurate range demodulationReduce information redundancyElectromagnetic wave reradiationShaped beamCode division multiple access
A focal plane array light detection and ranging 3D imaging method based on a code division multiple access technique is provided. A narrow laser pulse is shaped into a flat-top beam. The shaped beam is space-time encoded by a focal plane array-based optical encoder. The encoded beam is projected onto the target. The echo signals are obtained by a collecting lens. According to the encoding rule, the signals are grouped and multiplexed into several channels; subsequently, the multi-channel multiplexed signals are captured by a focal plane array detector and converted by a multi-channel digitizer. The multi-channel encoded full waveform signals are acquired from the digitizer by a PC terminal. The encoded full waveforms can be demodulated into the flight ranges for all subpixels via signal processing. By orthogonal range correction and pixel splicing and integrating the geographical data of all pixels, the 3D image reconstruction of the target can be accomplished.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Automobile or mobile device 3D image acquisition and naked-eye 3D head-up display system and 3D image processing method
The invention discloses an automobile or mobile device 3D image acquisition and naked-eye 3D head-up display system and a 3D image processing method. The automobile or mobile device 3D image acquisition and naked-eye 3D head-up display system includes a head-up display, a group of naked-eye 3D screens, a group of bionic 3D viewpoints, a 3D intelligent center, an automobile left side and right side bionic 3D viewpoint sight glass and an intra-automobile naked-eye 3D rearview mirror. With the automobile or mobile device 3D image acquisition and naked-eye 3D head-up display system and the 3D image processing method of the invention adopted, when a driver drives an automobile or uses a mobile device, he or she does not need to leave his or her sight from a road ahead to acquire information, and the driver can judge the relative distances of his or her automobile and other automobiles or pedestrians in adjacent lanes or lanes behind the his or her automobile according to 3D images which come from one group of bionic 3D viewpoints, are played by one group of naked-eye 3D screens in the automobile and have been subjected to bionic 3D image reconstruction technological processing; and an automobile naked-eye 3D playing platform can be provided for a 3D navigation map provided by the invention and other 3D navigation maps made by a third party.
Owner:彭波
Radiation imaging apparatus and phantom used for the same
InactiveUS9408579B2Less distortionAccurate checkReconstruction from projectionTomosynthesisX-rayRadiation imaging
In the imaging space provided by a panoramic imaging apparatus, a phantom is arranged. The phantom is located to a predetermined tomographic plane and includes markers which image known positional information with an X-ray beam. The X-ray beam from an X-ray source is acquired as X-ray transmission data by a detector, and a panoramic image is produced using the data. Based on known positional information of the markers and information of marker positions in the panoramic image, distance information (Rs, Rd) between the X-ray tube and the detector and height information (B1) of the X-ray tube to the detector are calculated. From this calculated results and the acquired data, parameters (Δx / ΔFi, θ, Δθ / ΔFi, D, A, CX, CY) defining positional relationships among the X-ray tube, the detector, and the tomographic plane are calculated such that amounts of changes in the position connecting the X-ray tube and the detector are considered in the parameters. This allows the parameters to be calibrated for 3D image reconstruction.
Owner:TAKARA TELESYST
System for dynamic low dose x-ray imaging and tomosynthesis
InactiveUS7340032B2Facilitate real-time tracking and low-dose imagingFacilitate real-time guidanceRadiation diagnosis data transmissionSolid-state devicesTomosynthesisData set
A system for low dose x-ray imaging provides for dynamic generation of an x-ray beam with specific shape, and dynamic tracking of a detector with said beam. The detector is rotatable, and translatable along two orthogonal axes, and may mount with a circular detector tray, the tray rotating around a rotation axis. Specific detector shapes include an elongated rectangular matrix, for example with additional detector cells near the rotation center to provide an increased area of continuous detection. Dynamic low-dose x-ray tomosynthesis or limited-angle tomographic imaging is enabled via simultaneous x-ray tube and detector motions during examination, such as fluoroscopic examination of a human body. Data acquired at multiple projection angles is input to a 3D image reconstruction algorithm that provides a refreshed 3D data set during continuing examination. The system may thus also automatically track a point in three-dimensional space, for example continuously locating the tip of a catheter.
Owner:FOREVISION IMAGING TECH LLC
Total internal reflection microscopy method and device based on free-form surface shaping
The invention discloses a total internal reflection microscopy device based on free-form surface shaping.The device comprises a light source and a line polarized light generating module, a free-form surface focusing module, a digital microscopy refection module, an optical enlargement transmission module and a fluorescence imaging module which are sequentially arranged along a light path, wherein the line polarized light generating module is used for converting light beams emitted by the light source into line polarized light; the free-form surface focusing module is used for converting the line polarized light into annular focused light; the digital microscopy refection module is used for selecting annular focused light reflected in an area; the optical enlargement transmission module is used for achieving total internal reflection illumination of the light beams; the fluorescence imaging module is used for exciting a sample to emit fluorescent light and collecting a fluorescent light signal image.The invention further discloses a total internal reflection microscopy method based on free-form surface shaping.According to the total internal reflection microscopy method and device based on free-form surface shaping, no mechanical vibration module is adopted, scanning is conducted more stably, and noise is lower; the utilization rate of laser energy is higher, and an imaging view field is more uniform; a DMD control controls scanning, the angle is more accurate, and it is helpful to achieve layered scanning and 3D image reconstruction.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
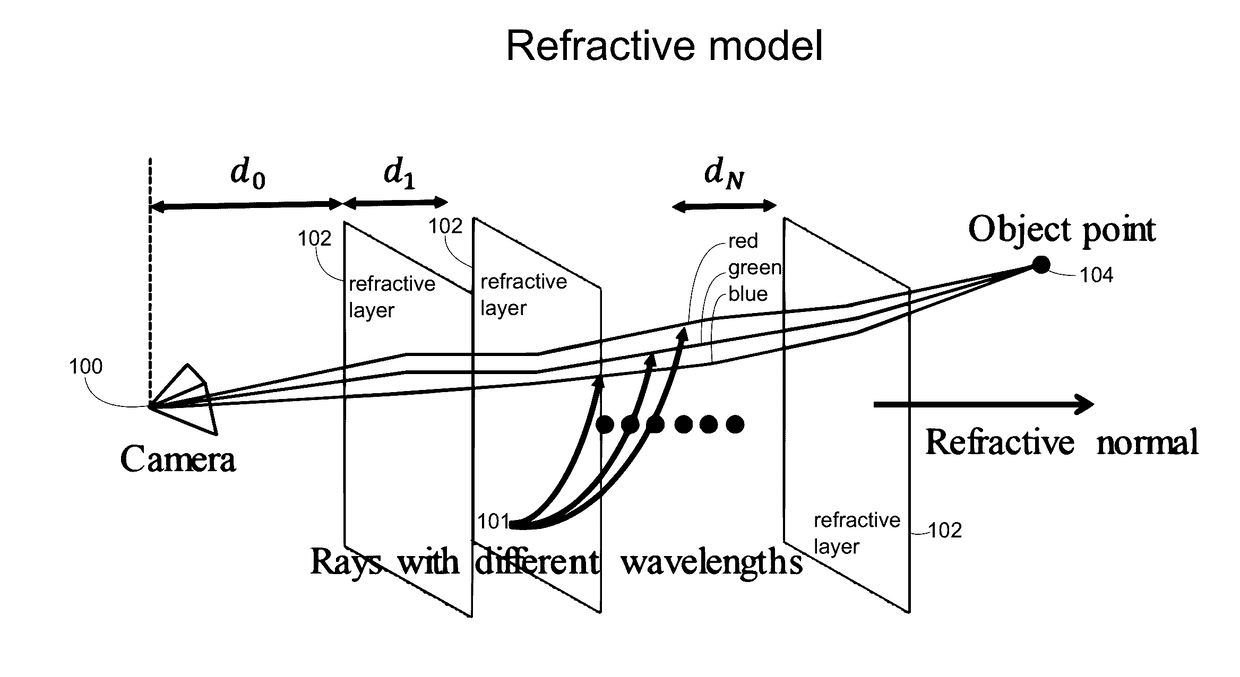
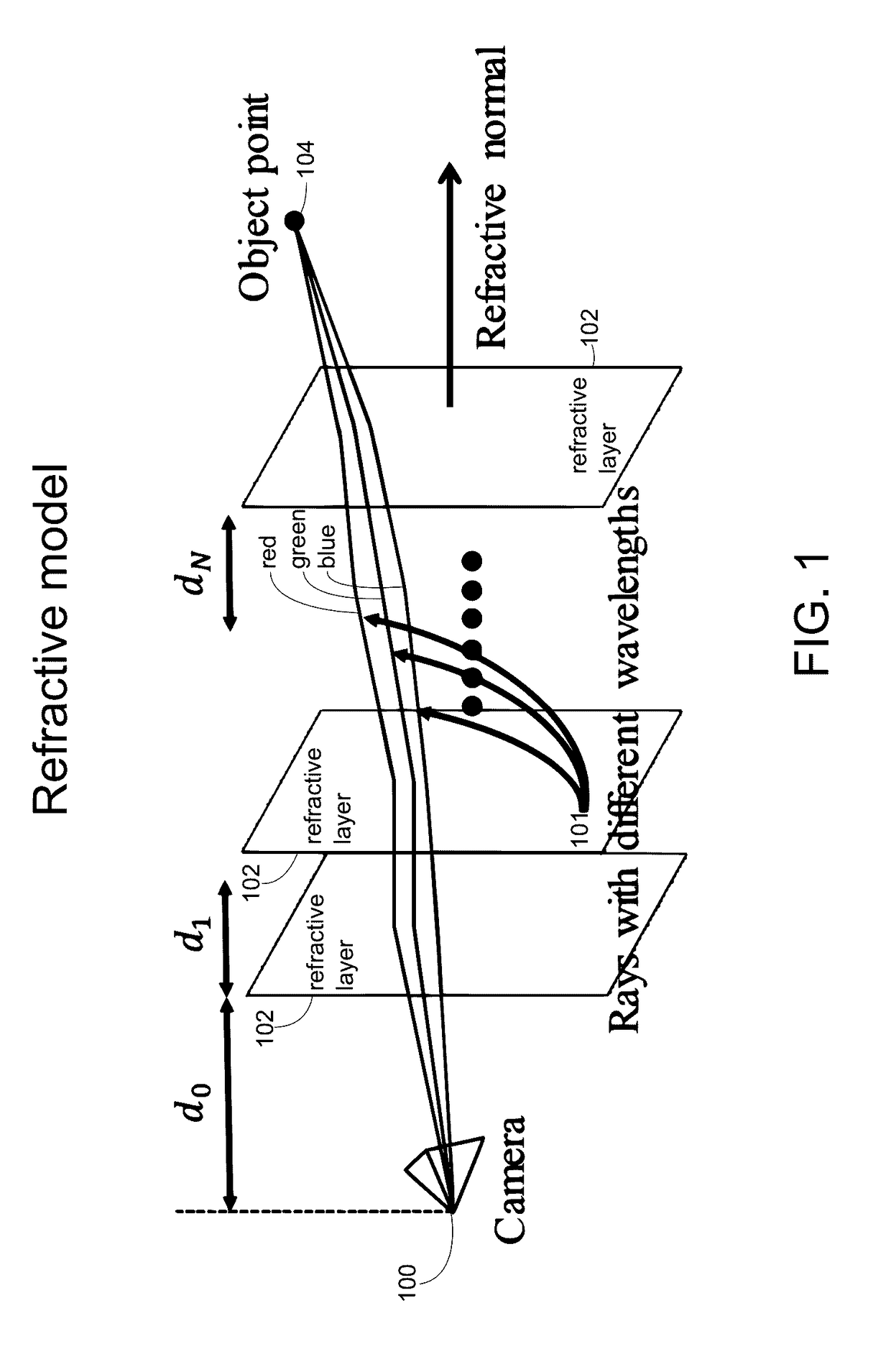
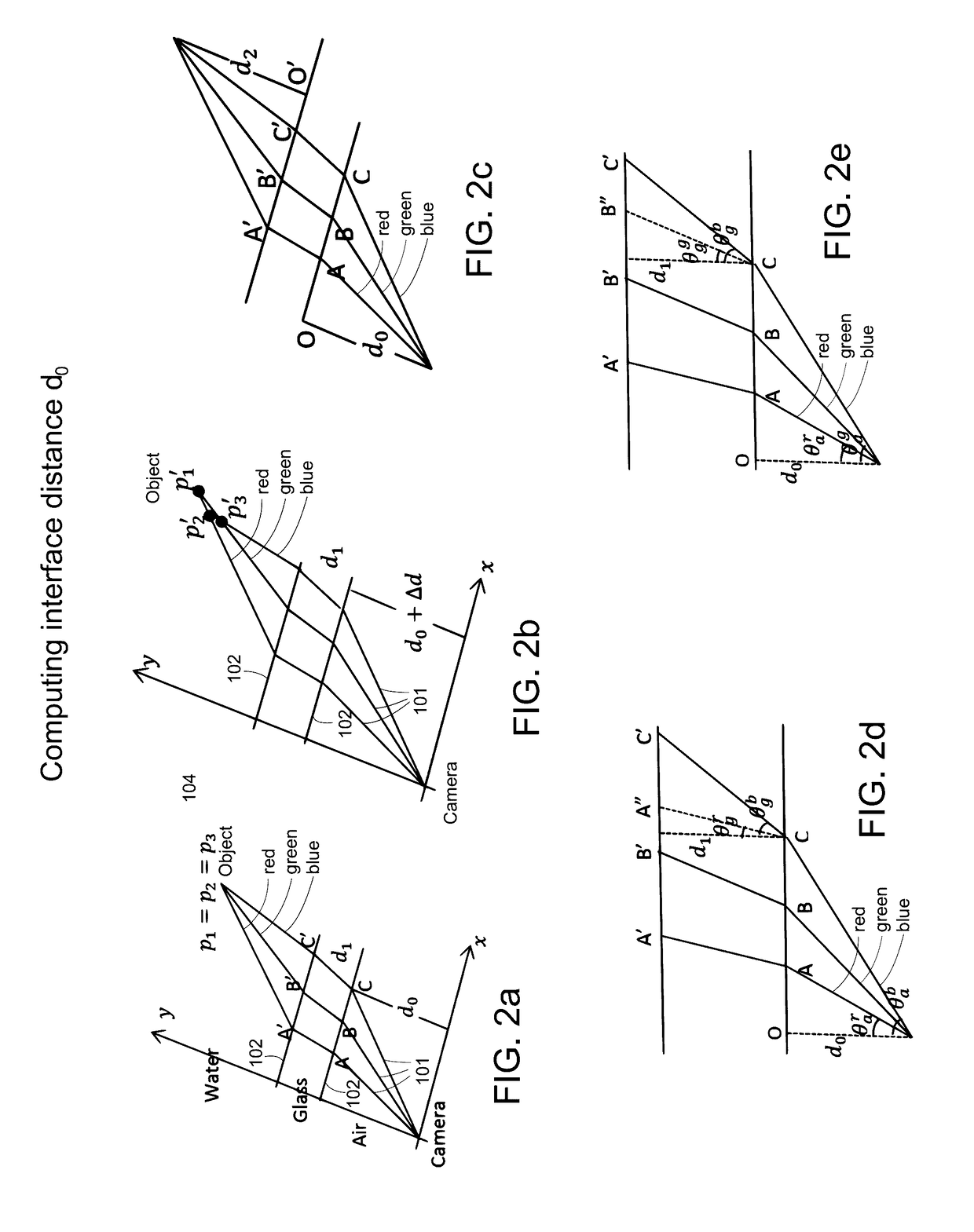
Underwater 3D image reconstruction utilizing triple wavelength dispersion and camera system thereof
An underwater camera system includes a projector operable to project a pattern of electromagnetic radiation toward a target object. The electromagnetic radiation includes at least three different wavelengths. A sensor directed toward the target object receives reflected electromagnetic radiation from the target object and stores corresponding image data received from the sensor. One or more processors process the image data to compute a refractive normal according to a wavelength dispersion represented by differences in the image data, and to compute an interface distance corresponding to a distance from a center point of the sensor to a first refractive interface nearest the sensor according to the refractive normal. The processors generate a 3D representation of the target object by back projecting each pixel of the image data at the first, second, and third wavelengths in order to determine an object point location according to the refractive normal and interface distance.
Owner:THE GOVERNORS OF THE UNIV OF ALBERTA
Mulitimodality imaging phantom and process for manufacturing said phantom
InactiveUS20050123178A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic Radiology ModalitySonification
A multimodality imaging phantom is disclosed which is useful for calibrating devices for imaging vascular conduits. The phantom is compatible with X-ray, ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging techniques. It allows testing, calibration, and inter-modality comparative study of imaging devices, in static or dynamic flow conditions. It also provides a geometric reference for evaluation of accuracy of imaging devices. The tissue-mimicking material is preferably an agar-based solidified gel. A vessel of known desired geometry runs throughout the gel and is connected to an inlet and outlet at its extremities for generating a flow circulation in the vessel. Said phantom also contains fiducial markers detectable in the above-mentioned modalities. The markers are preferably made of glass and are embedded in a layer of agar gel containing a fat component. The markers are implanted at precise known locations to allow identification and orientation of plane views, and they can be used for calibration, resealing and fusion of 3D images obtained from different modalities, and 3D image reconstruction from angiographic plane views. Also disclosed is a process for manufacturing said phantom.
Owner:LINSTITUT DE RES & DEVS CLINIQUES DE MONTREAL +2
Method and device for reconstructing a 3D image data set of a moving object
InactiveUS7315605B2High quality imagingReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationEcg gatingData set
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
System for Generating Images of Multi-Views
InactiveUS20120128234A1Readily availableHigh acceptanceCharacter and pattern recognitionSteroscopic systemsBody imagesBackground image
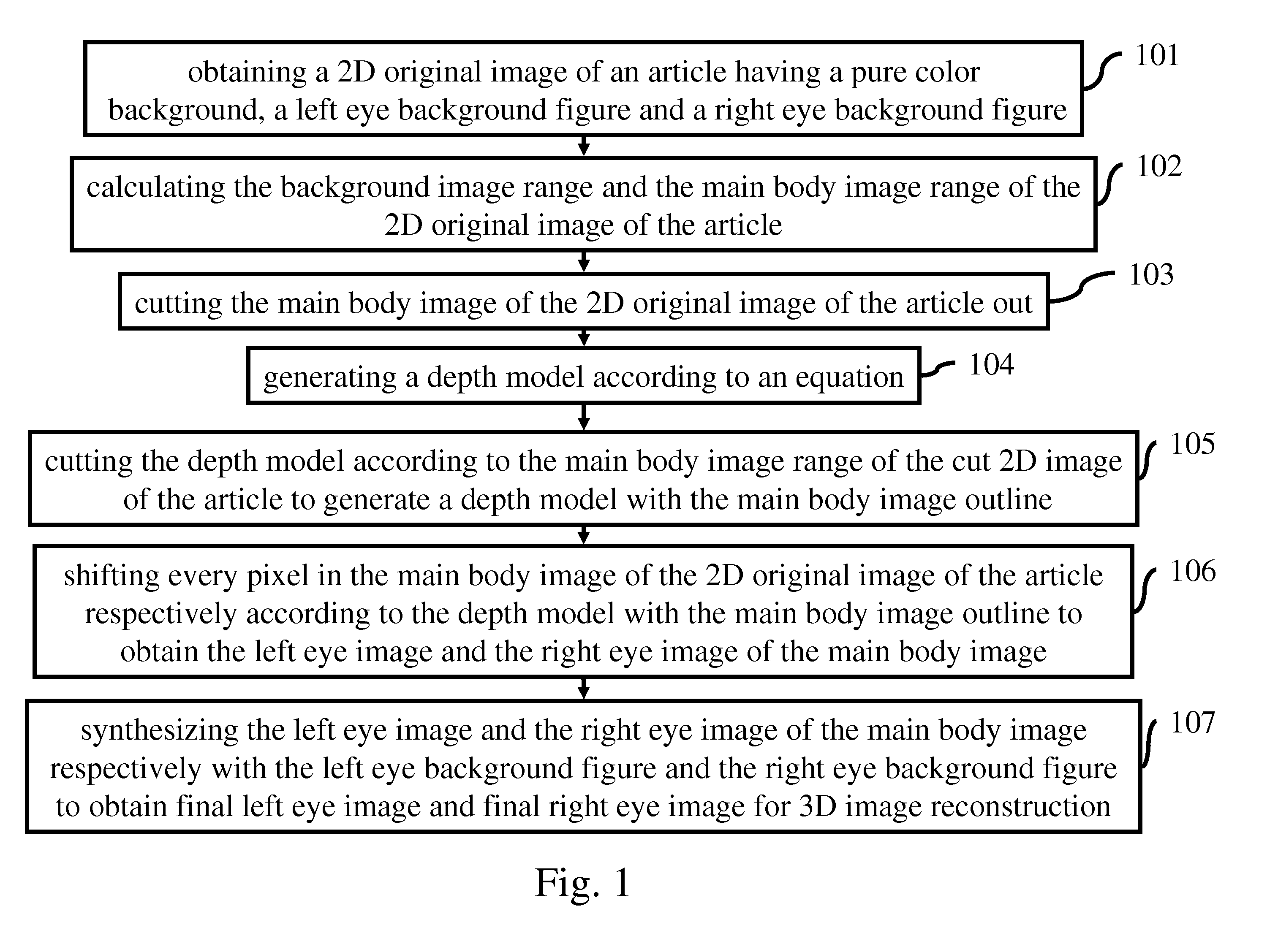
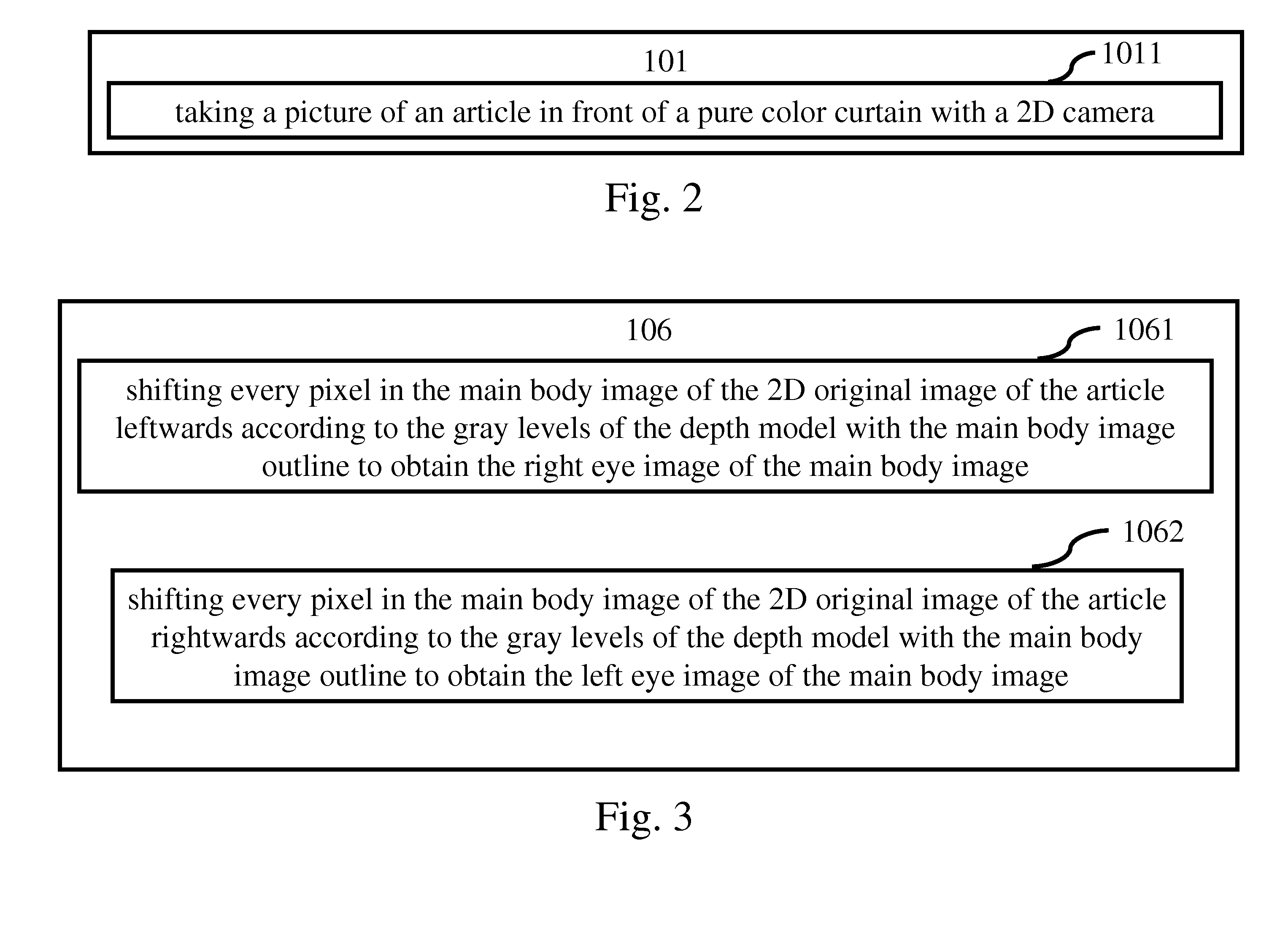
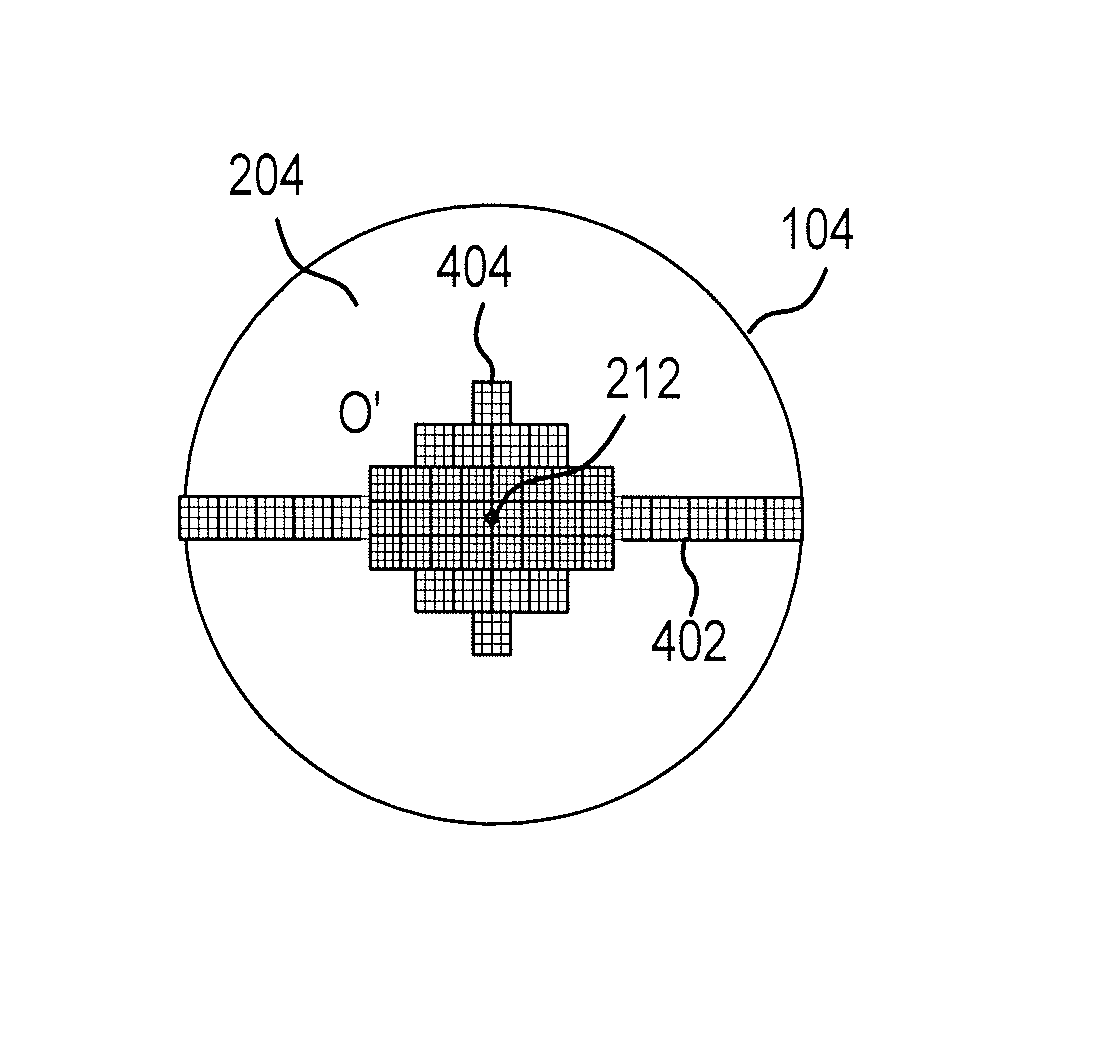
The present invention provides a system for generating images of multi-views. The system includes a processing unit; an image range calculating module coupled to the processing unit to calculate the ranges of a background image and a main body image of a 2D original image of an article; a depth model generating module coupled to the processing unit to generate a depth model according to an equation; an image cutting module coupled to the processing unit to cut the 2D original image of the article or the depth model to generate a cut 2D image of the article or a depth model with a main body image outline; a pixel shifting module coupled to the processing unit to shift every pixel in the main body image of the 2D original image of the article according to the depth model with the main body image outline to obtain shifted main body images of multi-views; and an image synthesizing module coupled to the processing unit to synthesize the shifted main body images of multi-views and background figures of multi-views to obtain final images of multi-views for 3D image reconstruction.
Owner:CHUNGHWA PICTURE TUBES LTD
System for dynamic low dose x-ray imaging
InactiveUS7342993B2Facilitate real-time tracking and low-dose imagingFacilitate real-time guidanceRadiation diagnosis data transmissionSolid-state devicesTomosynthesisData set
A system for low dose x-ray imaging provides for dynamic generation of an x-ray beam with specific shape, and dynamic tracking of a detector with said beam. The detector is rotatable, and translatable along two orthogonal axes, and may mount with a circular detector tray, the tray rotating around a rotation axis. Specific detector shapes include an elongated rectangular matrix, for example with additional detector cells near the rotation center to provide an increased area of continuous detection. Dynamic low-dose x-ray tomosynthesis or limited-angle tomographic imaging is enabled via simultaneous x-ray tube and detector motions during examination, such as fluoroscopic examination of a human body. Data acquired at multiple projection angles is input to a 3D image reconstruction algorithm that provides a refreshed 3D data set during continuing examination. The system may thus also automatically track a point in three-dimensional space, for example continuously locating the tip of a catheter.
Owner:FOREVISION IMAGING TECH LLC
System for dynamic low dose x-ray imaging and tomosynthesis
InactiveUS20060182225A1Facilitate real-time trackingFacilitate low-dose imagingRadiation diagnosis data transmissionSolid-state devicesTomosynthesisData set
A system for low dose x-ray imaging provides for dynamic generation of an x-ray beam with specific shape, and dynamic tracking of a detector with said beam. The detector is rotatable, and translatable along two orthogonal axes, and may mount with a circular detector tray, the tray rotating around a rotation axis. Specific detector shapes include an elongated rectangular matrix, for example with additional detector cells near the rotation center to provide an increased area of continuous detection. Dynamic low-dose x-ray tomosynthesis or limited-angle tomographic imaging is enabled via simultaneous x-ray tube and detector motions during examination, such as fluoroscopic examination of a human body. Data acquired at multiple projection angles is input to a 3D image reconstruction algorithm that provides a refreshed 3D data set during continuing examination. The system may thus also automatically track a point in three-dimensional space, for example continuously locating the tip of a catheter.
Owner:FOREVISION IMAGING TECH LLC
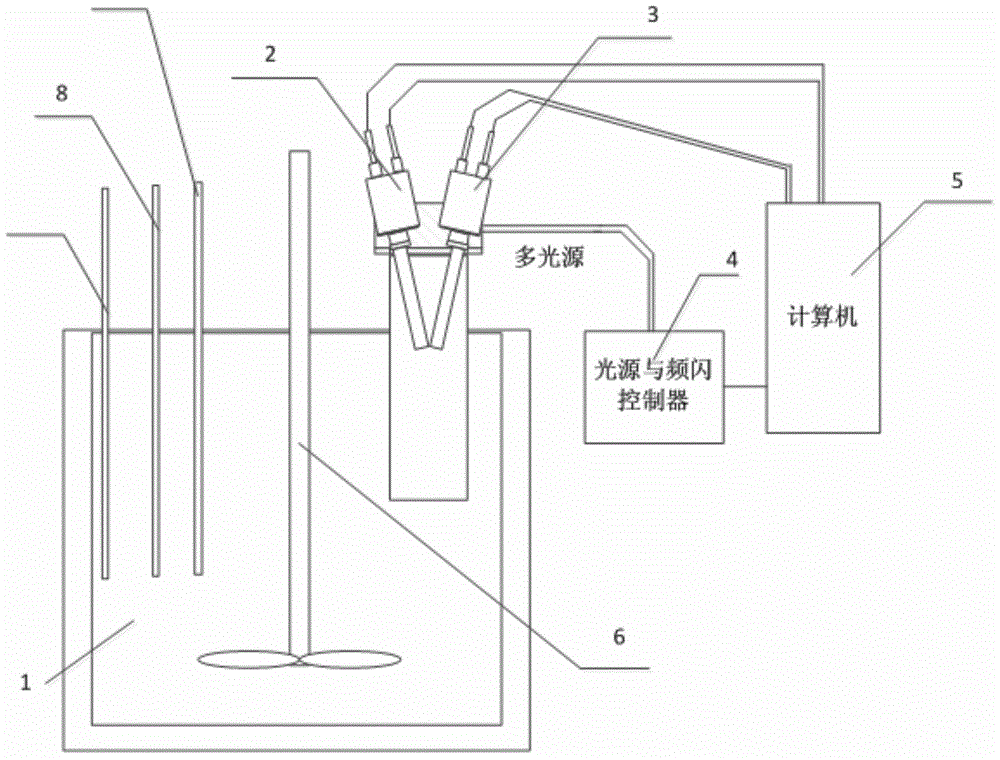
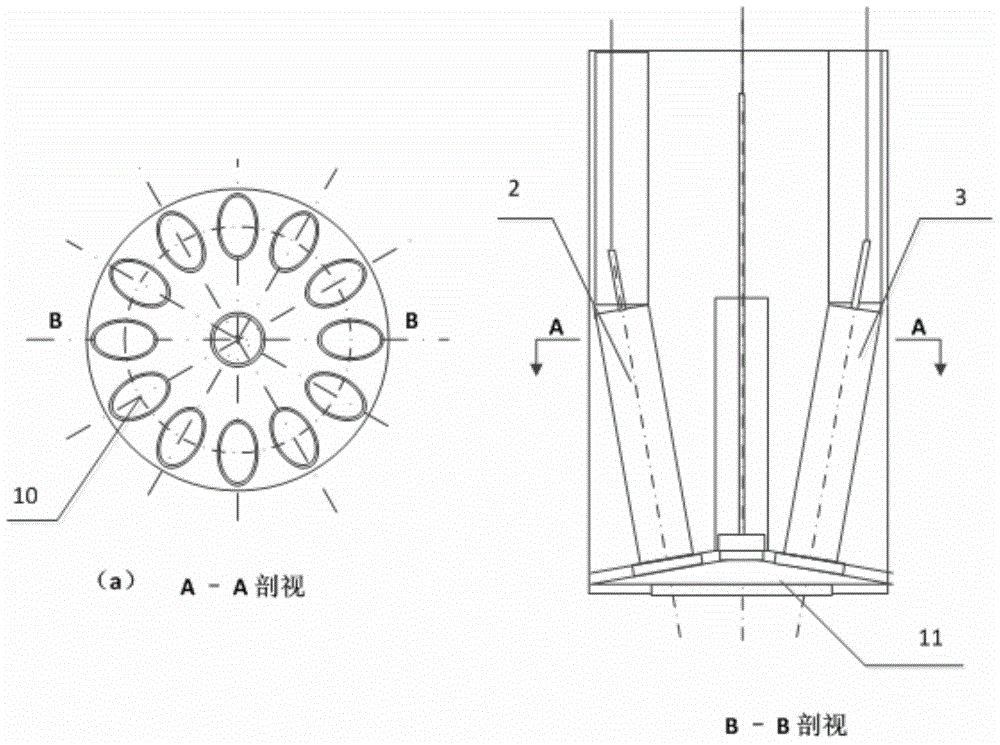
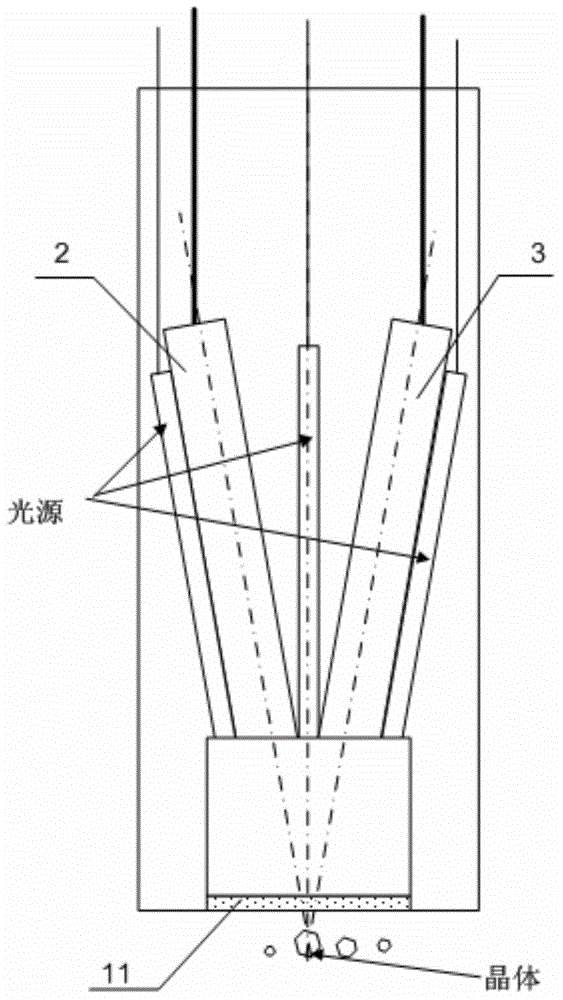
Probe type online three-dimensional imaging detection system and probe type online three-dimensional imaging detection method
ActiveCN103558129APromote crystallizationCrystallization process control and scale-upMaterial analysisProbe typeImaging processing
The invention discloses a probe type online three-dimensional imaging detection system which comprises a crystal growth reactor, a three-dimensional imaging probe, a light source and a strobe controller, a computer for processing an image, and a display, wherein the three-dimensional imaging probe is used for transmitting a 2D image to the computer; the computer is used for firstly deleting a background by using a splitting technology and then identifying corresponding points and lines from the 2D image by using an angle / edge / line detection technology; for few angles / lines which are detected difficultly, indistinct angles / lines are predicted / estimated by using molecule modeling and a crystal shape model on the basis of the obtained angles and lines, 3D image reconstruction is realized by using the determined points and lines, then particle description characteristics of 3D crystals are obtained by combining with solution parameters measured online, and finally, the control and the amplification of a crystallization process in a reactor are realized by using a crystalline form grain number balancing model and computational fluid mechanics. The system and the method provided by the invention are capable of directly acquiring the image from the solution and realizing the reconstruction of the 3D crystalline form, and are high in image processing speed.
Owner:PHARMAVISION QINGDAO INTELLIGENT TECH LTD
Voxel-driven spiral reconstruction for cone-beam computer tomography
InactiveCN1742296AQuality improvementImprove time resolutionReconstruction from projectionRadiation diagnosticsUltrasound attenuationAttenuation coefficient
A method is disclosed for generating computer tomography images using a 3D image reconstruction method. According to the method, to scan an object to be examined using a cone-shaped bundle of rays originating from a focal point and a planar, preferably multi-line detector for detecting the bundle of rays, the focal point is displaced along a spiral trajectory around the object to be examined. The detector delivers output data corresponding to the detected radiation and image voxels from the scanned examined object are reconstructed from the optionally pre-processed output data, the image voxels reflecting the attenuation coefficients of the respective voxel. Each image voxel is reconstructed separately from projection data, which covers a projection angular range of at least 108° and an approximate weighting is carried out for each voxel considered in order to standardize the projection data using the voxel.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Multimodality imaging phantom and process for manufacturing said phantom
InactiveUS7439493B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic Radiology ModalitySonification
A multimodality imaging phantom is disclosed which is useful for calibrating devices for imaging vascular conduits. The phantom is compatible with X-ray, ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging techniques. It allows testing, calibration, and inter-modality comparative study of imaging devices, in static or dynamic flow conditions. It also provides a geometric reference for evaluation of accuracy of imaging devices. The tissue-mimicking material is preferably an agar-based solidified gel. A vessel of known desired geometry runs throughout the gel and is connected to an inlet and outlet at its extremities for generating a flow circulation in the vessel. Said phantom also contains fiducial markers detectable in the above-mentioned modalities. The markers are preferably made of glass and are embedded in a layer of agar gel containing a fat component. The markers are implanted at precise known locations to allow identification and orientation of plane views, and they can be used for calibration, resealing and fusion of 3D images obtained from different modalities, and 3D image reconstruction from angiographic plane views. Also disclosed is a process for manufacturing said phantom.
Owner:LINSTITUT DE RES & DEVS CLINIQUES DE MONTREAL +2
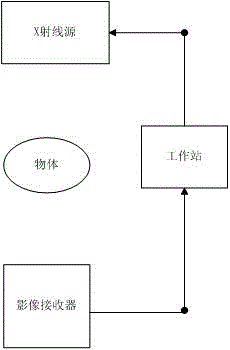
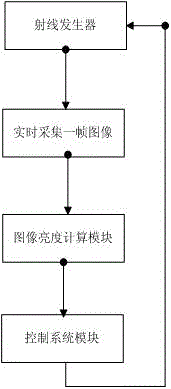
3D C-shaped arm automatic dosage control method
A 3D C-shaped arm automatic dosage control method belongs to the technical field of medical apparatus and instruments and is characterized in that a 3D C-shaped arm can perform 3D image reconstruction of a 2D sequence image; in an acquisition process of the 2D sequence image, accurate guidance can be provided for automatic exposure dosage of the next image according to the brightness value of the previous image. In an acquisition process of 2D sequences, in particular to human body lumbar vertebra, a C-shaped arm has a direct exposure area in a rotation acquisition process due to the geometrical features of the C-shaped arm, and the direct exposure area can directly affect calculation of the brightness value of an image area-of-interest; gray level distribution of an image is calculated through a probability statistics method, recognition and division of the area-of-interest can be achieved, and the brightness mean value of the image is calculated; and the accurate guidance can be provided for the exposure dosage of the next image through the calculation result. The advantage of the invention is that the accuracy of the calculation result can be ensured by calculating the gray level distribution through the probability statistics method.
Owner:NANJING PERLOVE RADIAL VIDEO EQUIP
Image reconstructing methjod using x-ray volume photography
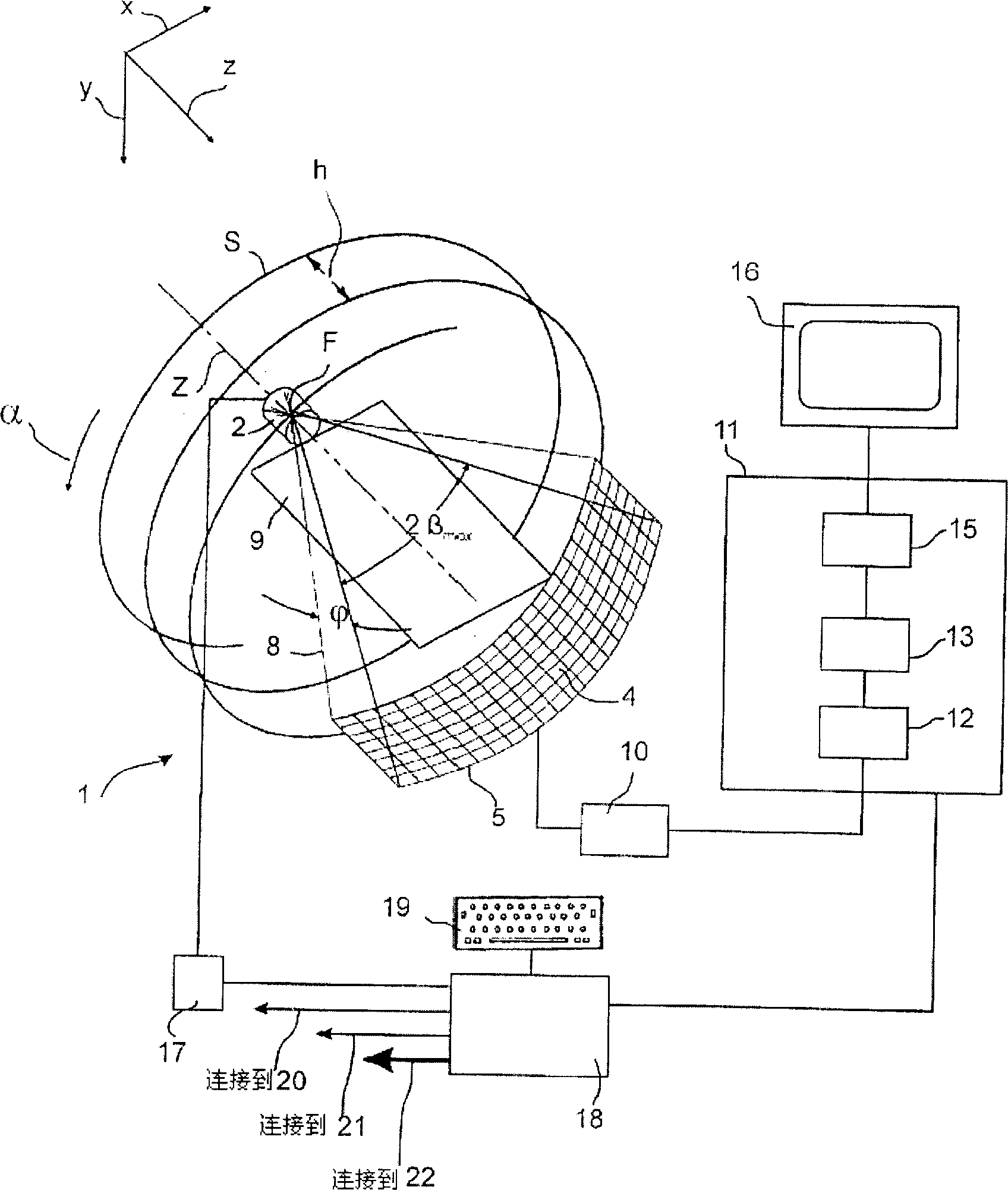
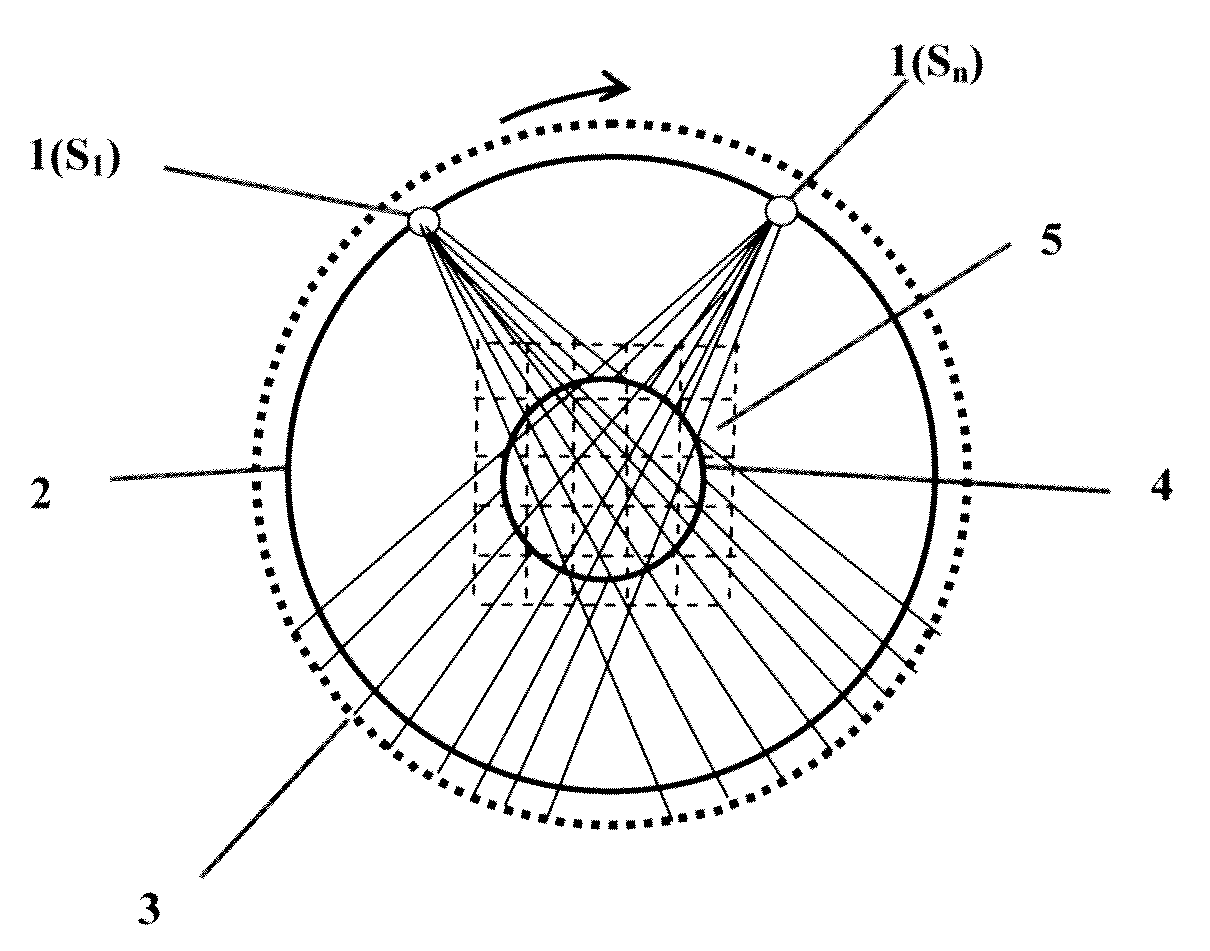
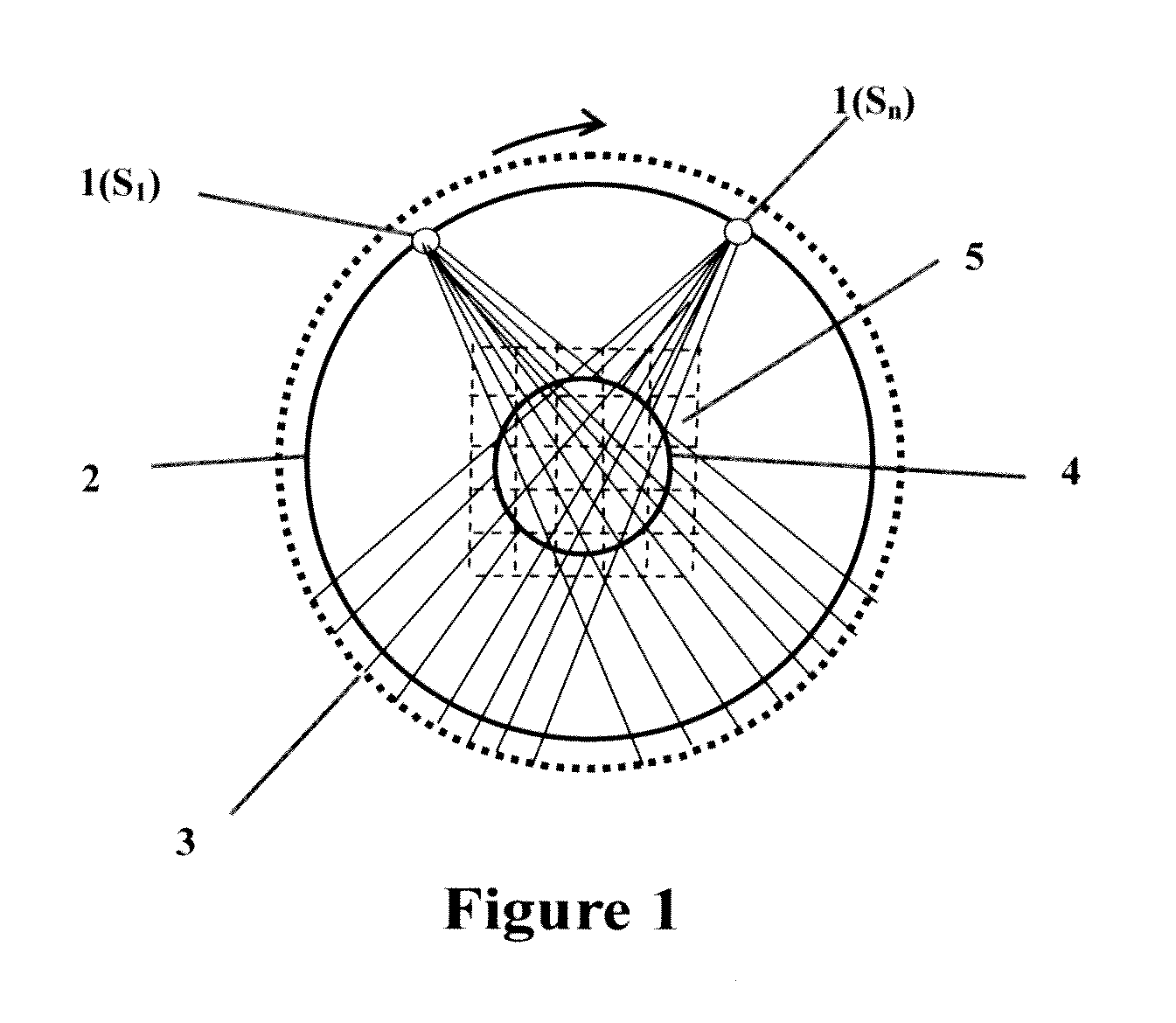
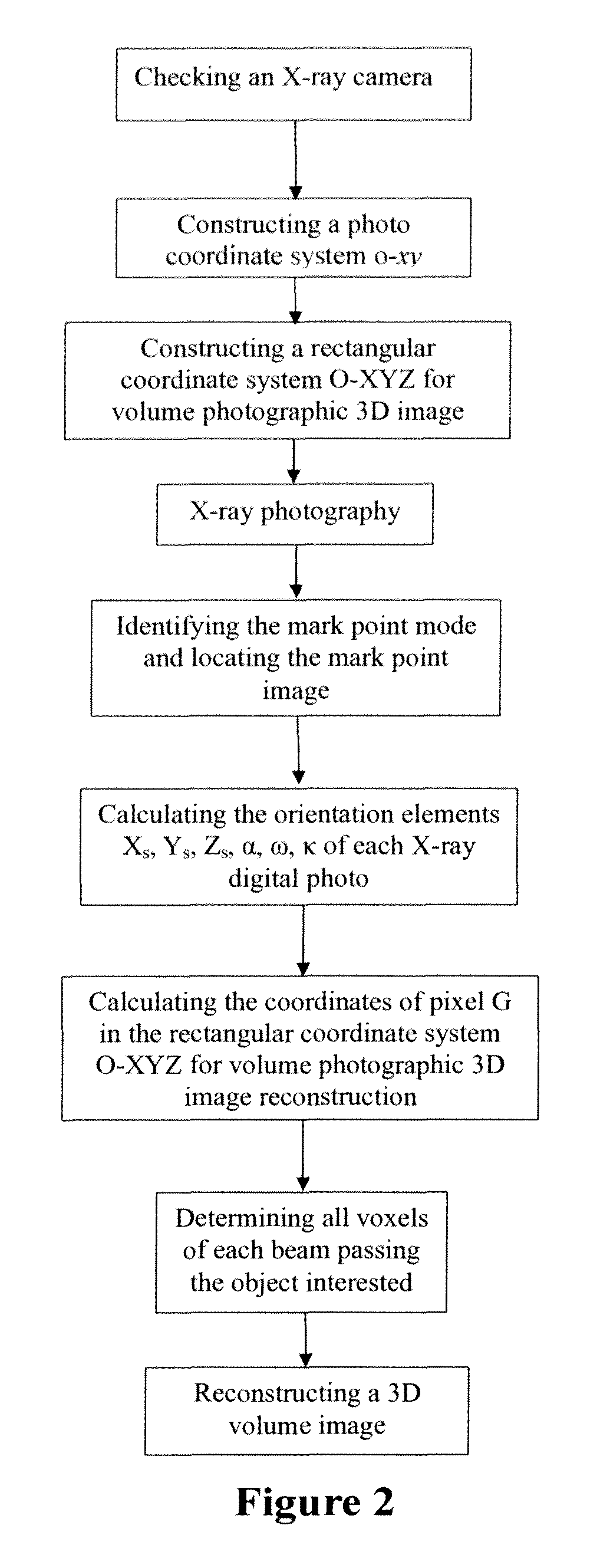
InactiveUS20100195891A1High resolutionSimple structureReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionSoft x rayVoxel
A 3D image reconstructing method using X-ray volume photography acquires a plurality of X-ray area array images of the object interested according to locating principle of the digital photographic measurement. A plurality of mark points of the known 3D positions are simultaneously taken in the X-ray photo, and the method uses the coordinates of the mark points in the rectangular coordinate system for volume photographic 3D image reconstruction and the coordinates of the mark points in the X-ray photo coordinate system to construct a transforming relationship of the two coordinate systems. The method determines the path and the position of each X beam by using the transforming relationship and gets all voxels of each X-ray passing the object interested. The method uses the voxel g and the pixel G of the same X beam path to get Radon set of equations to determine the gray scale value of voxel g, then determines the gray scale values of all voxels g by computer and reconstructs a 3D volume image of the object interested based on the gray scale value of voxel g.
Owner:SHU JIA
Method for repairing incomplete 3D depth image using 2d image information
ActiveUS20200035013A1Easy to understandReduce distortion problemsImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionRadiology
Owner:NAT CENT UNIV
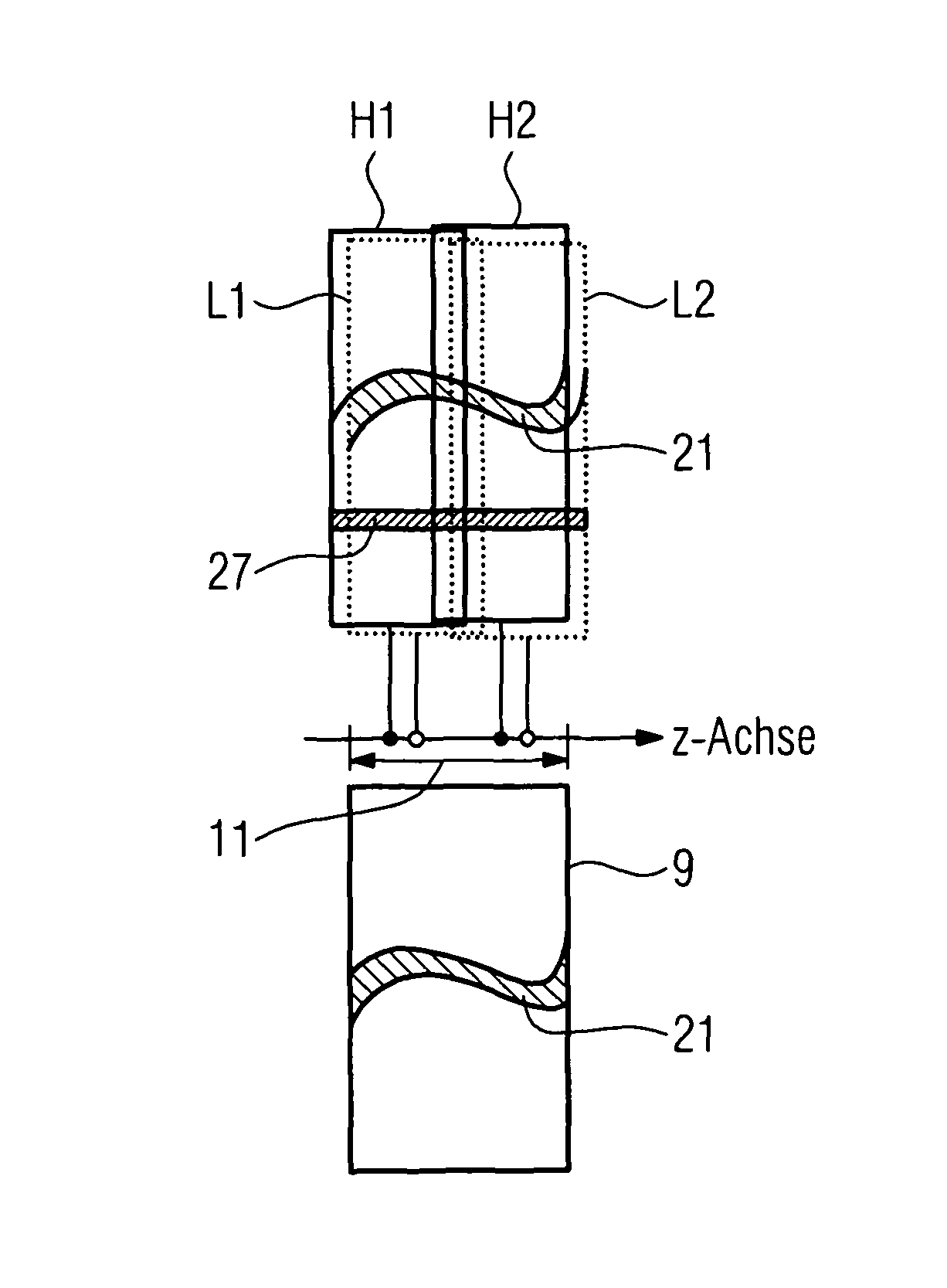
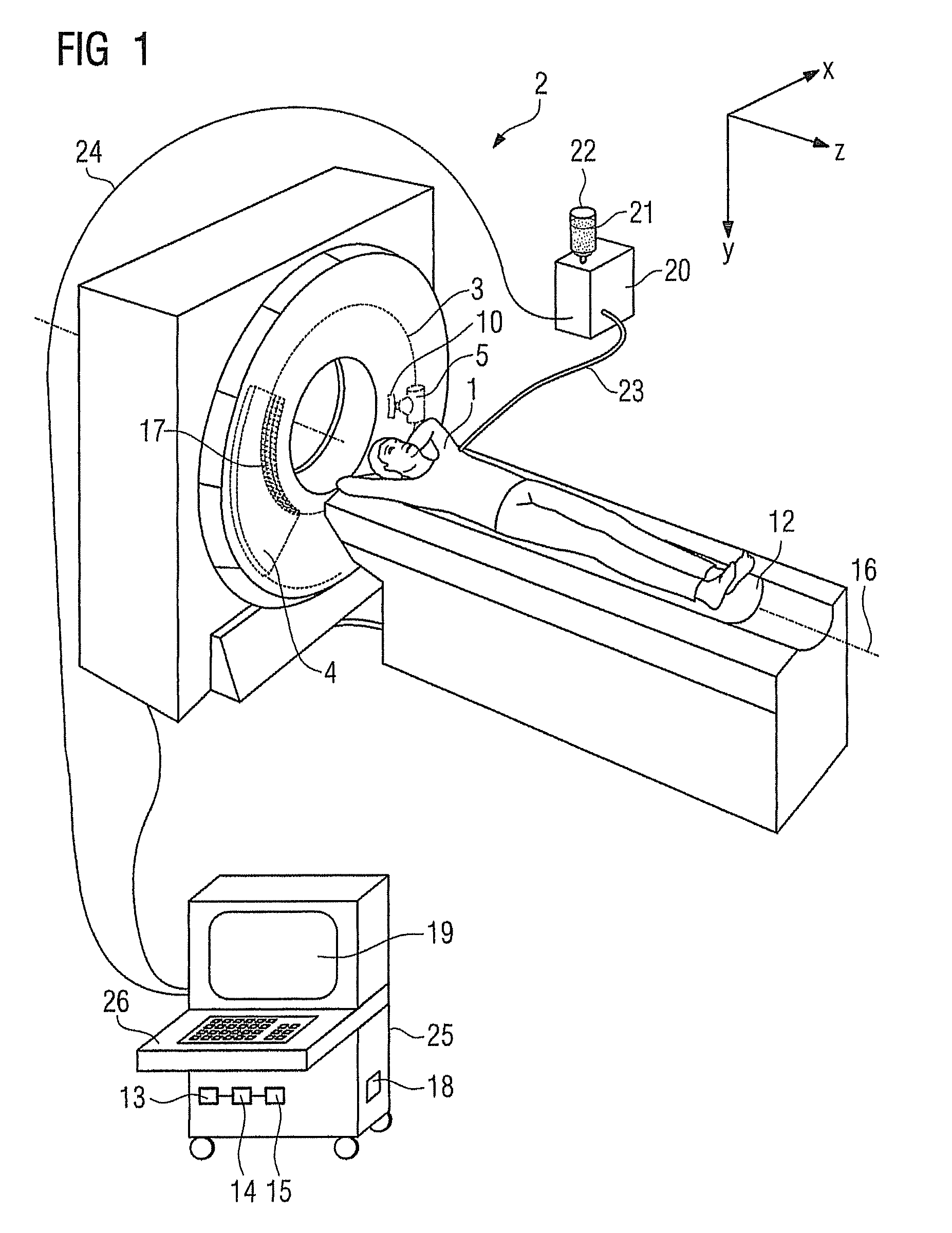
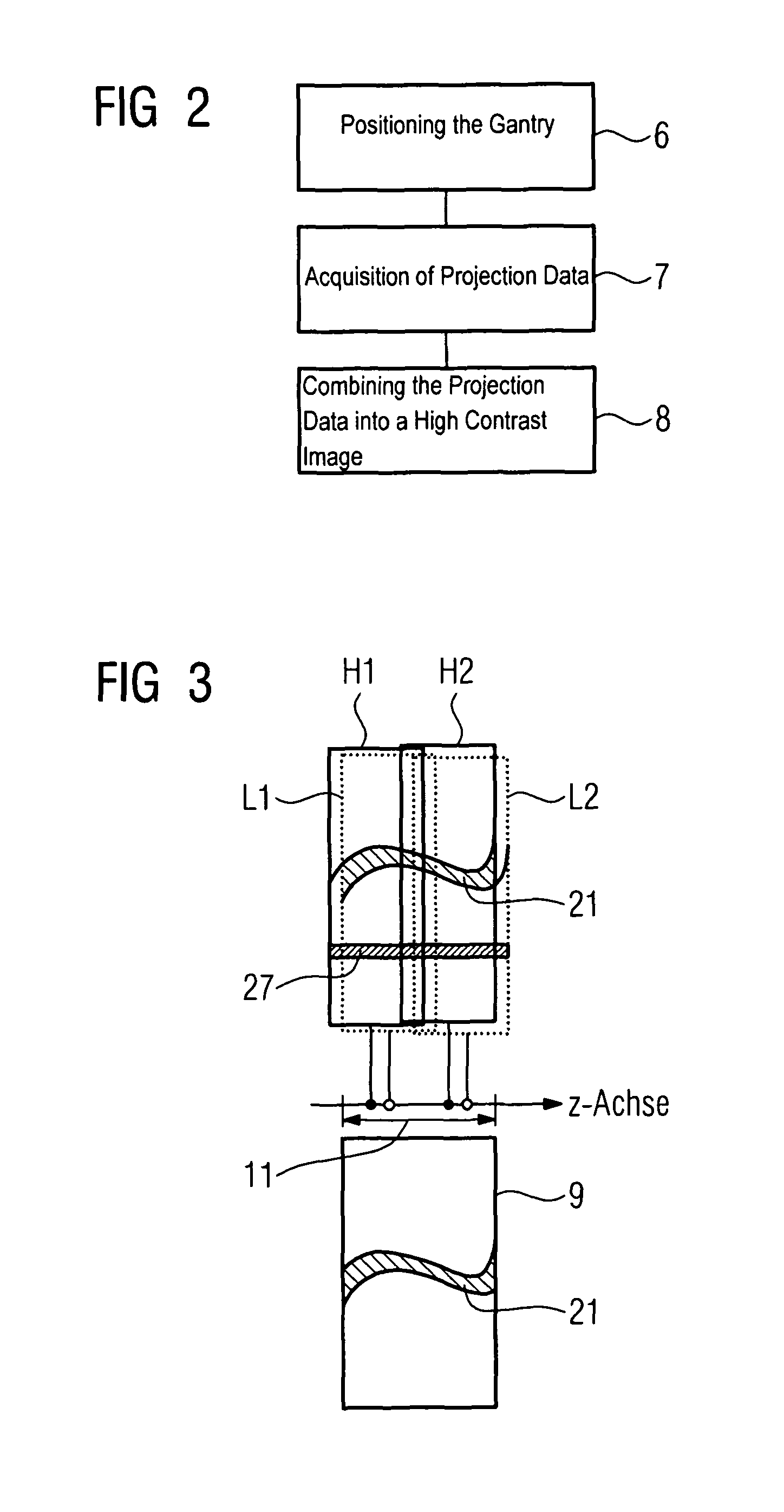
Method and computed tomography scanner for carrying out an angiographic examination
ActiveUS8447009B2Large z-coverageImprove spatial resolutionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingDiagnostic Radiology ModalityX-ray
A method and a computed tomography scanner are disclosed for carrying out an angiographic examination of a patient, wherein the utilized computed tomography scanner includes at least one recording system mounted on a gantry such that it can rotate about a z-axis. Projection data is acquired from at least one prescribed angular position of the gantry for at least two different energies of X-ray radiation. The projection data is subsequently combined to form a resulting projection image by evaluating the projection data corresponding to the respective angular position, in which projection image at least one substance, which should be displayed selectively, is imaged with a high image contrast compared to the respective individual projection data. This procedure extends the field of application of the computed tomography scanner to projection-based angiography examinations, which were previously restricted to C-arm systems. 3D image reconstruction methods and projection methods can be carried out on opposite sides and with great flexibility during an examination, without the need for an additional modality. By using a multispectral technique, it is possible to contrast agent. The projection data at dispense with recording a native projection data record without the different energies are moreover acquired with no or little time offset, and so a computationally expensive and error-prone registration of the data records can be dispensed with.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com