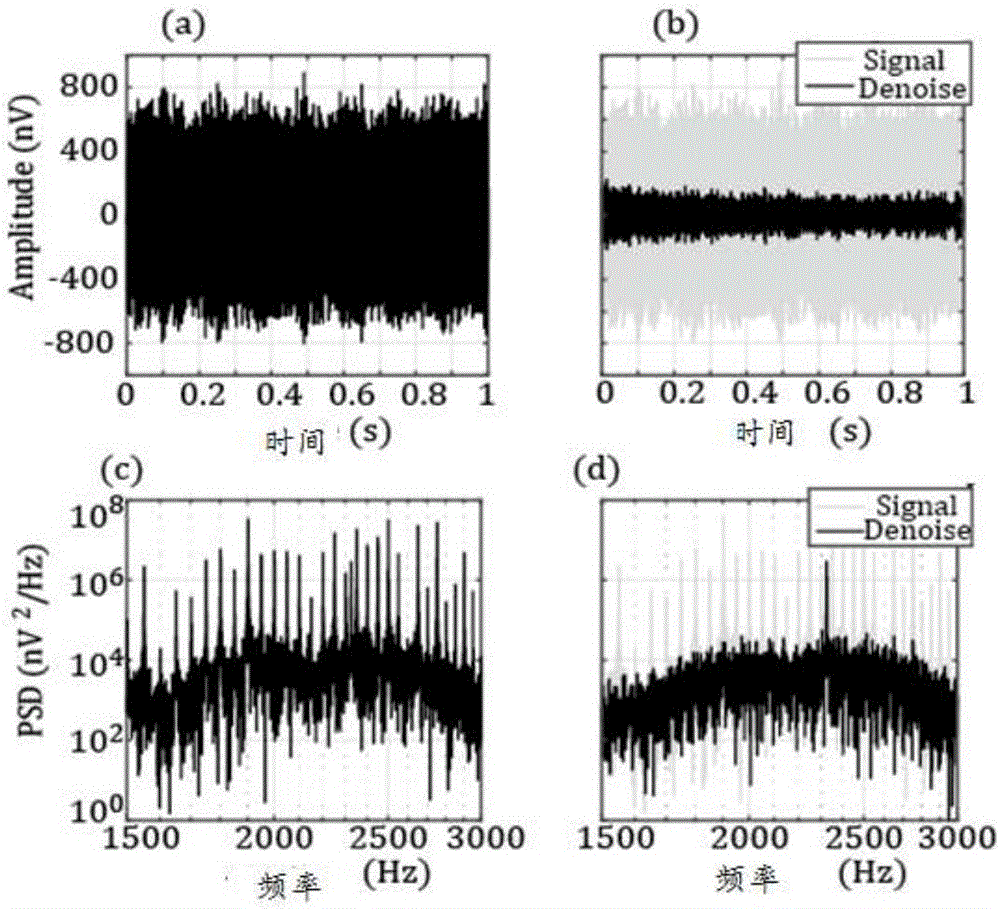
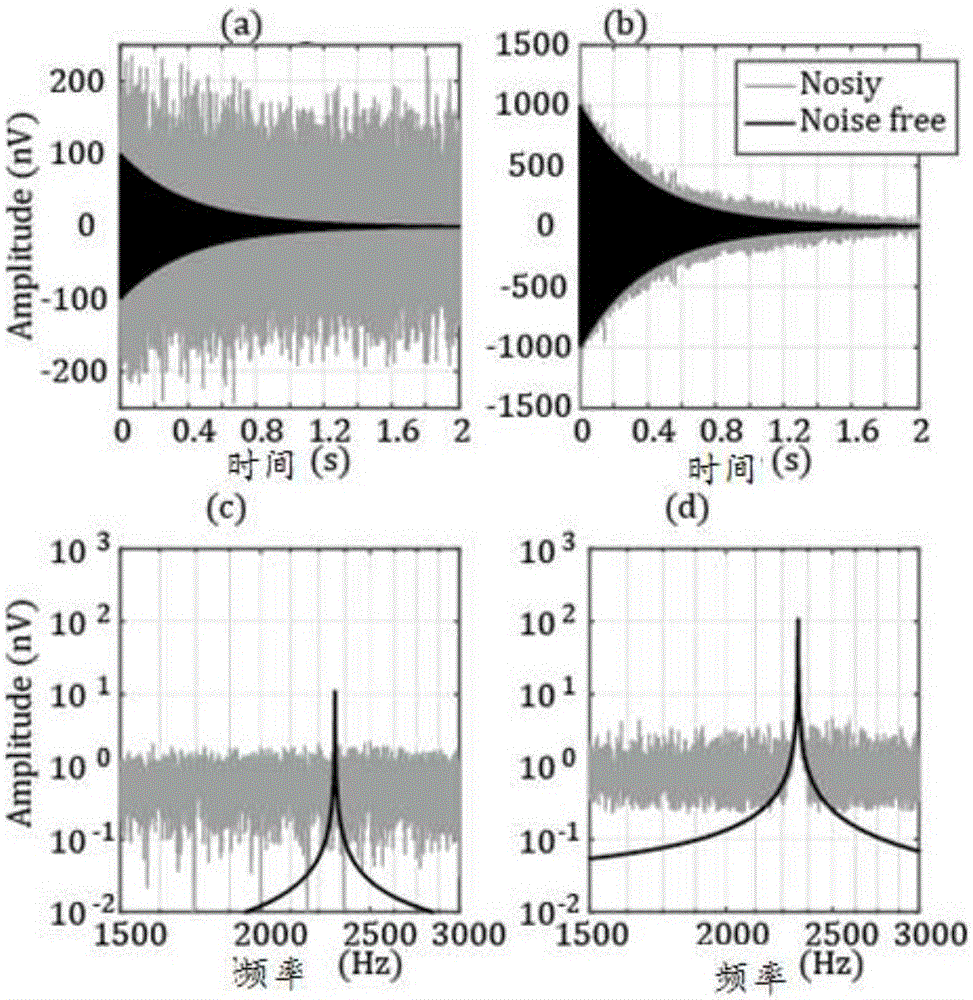
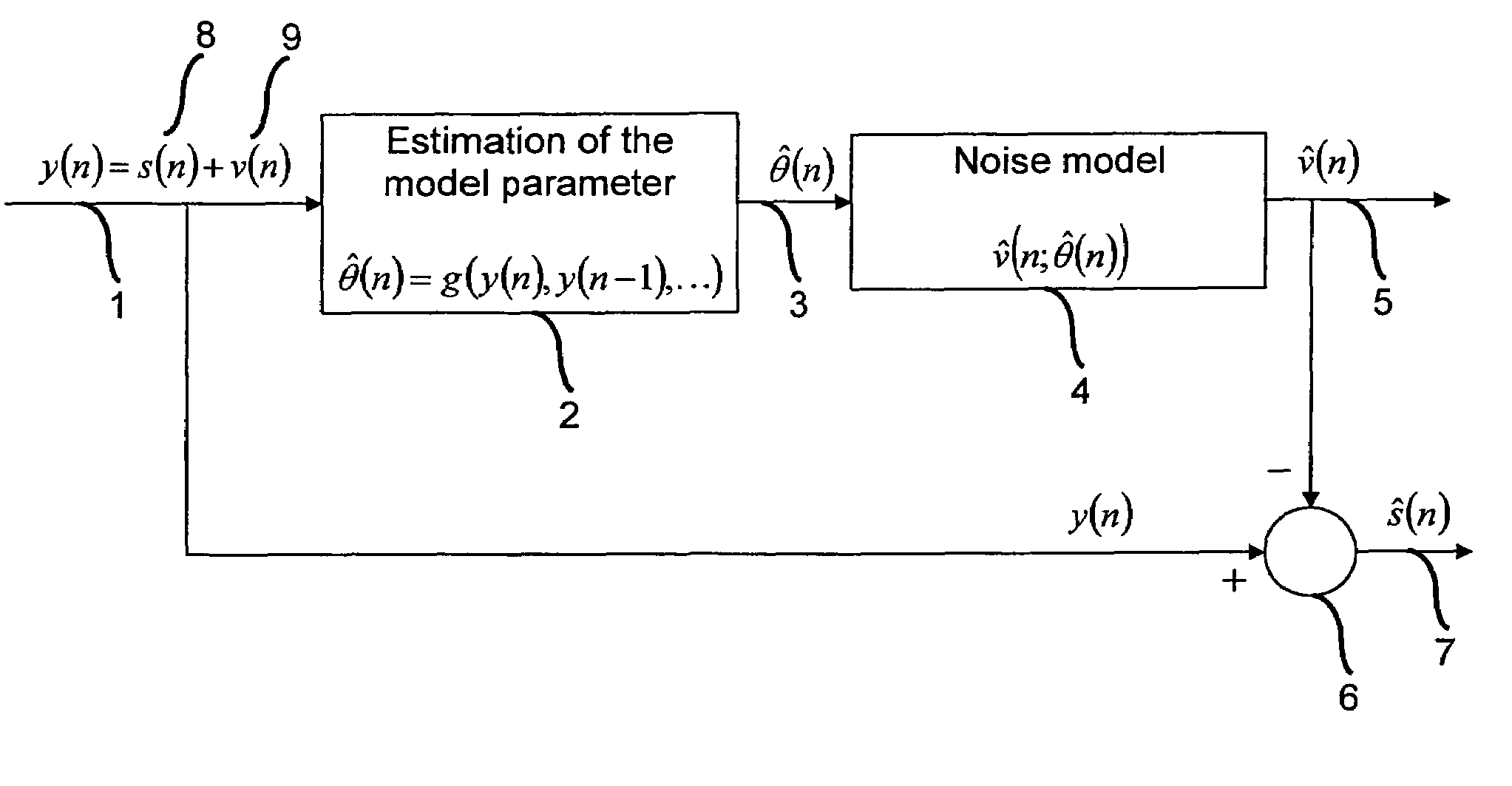
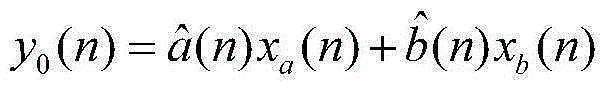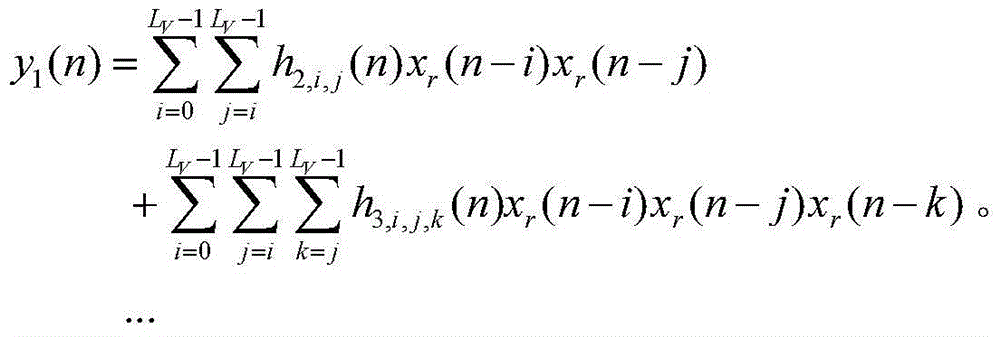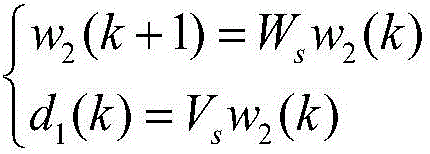Patents
Literature
175 results about "Harmonic noise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
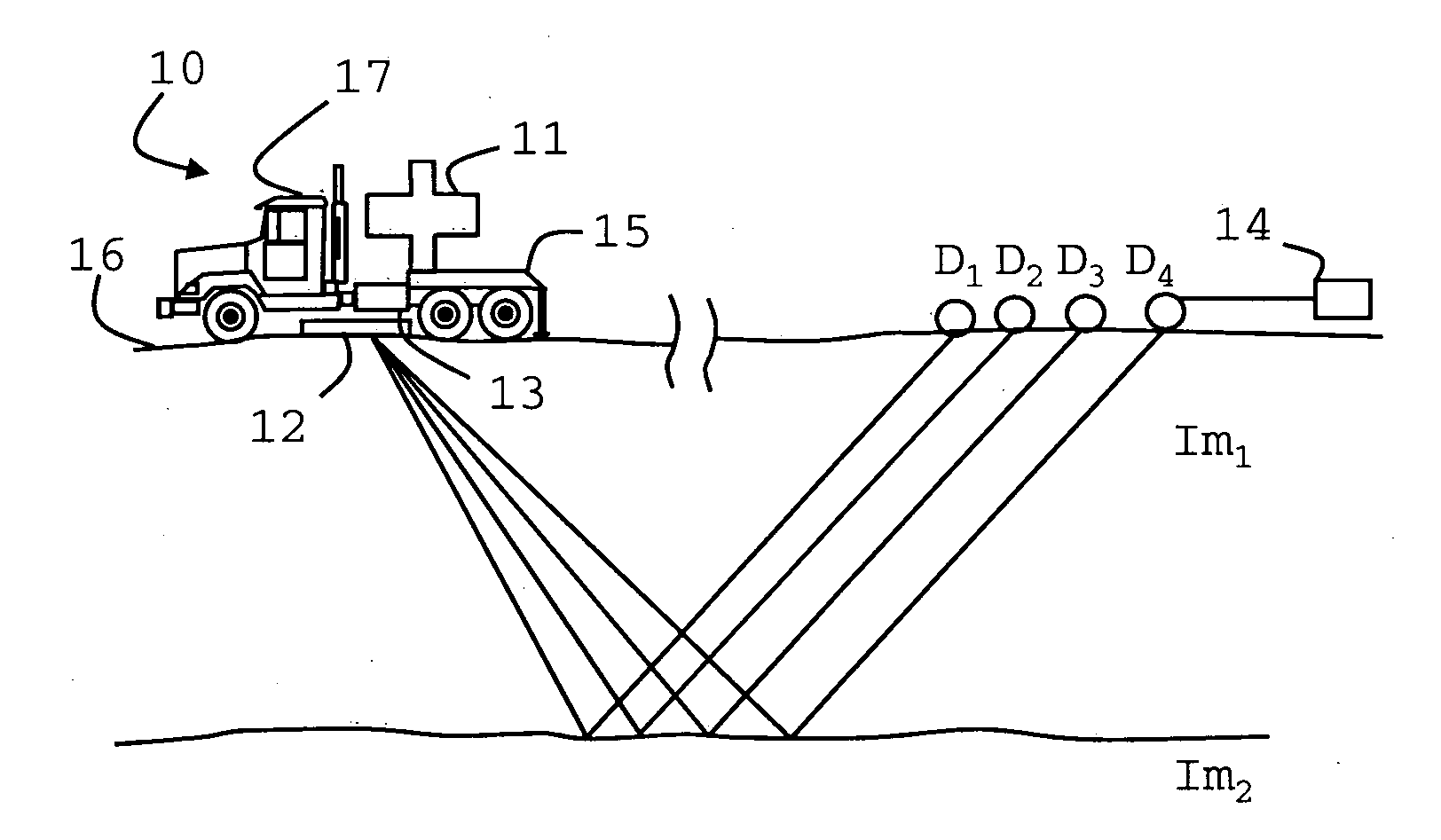
Method of seismic surveying
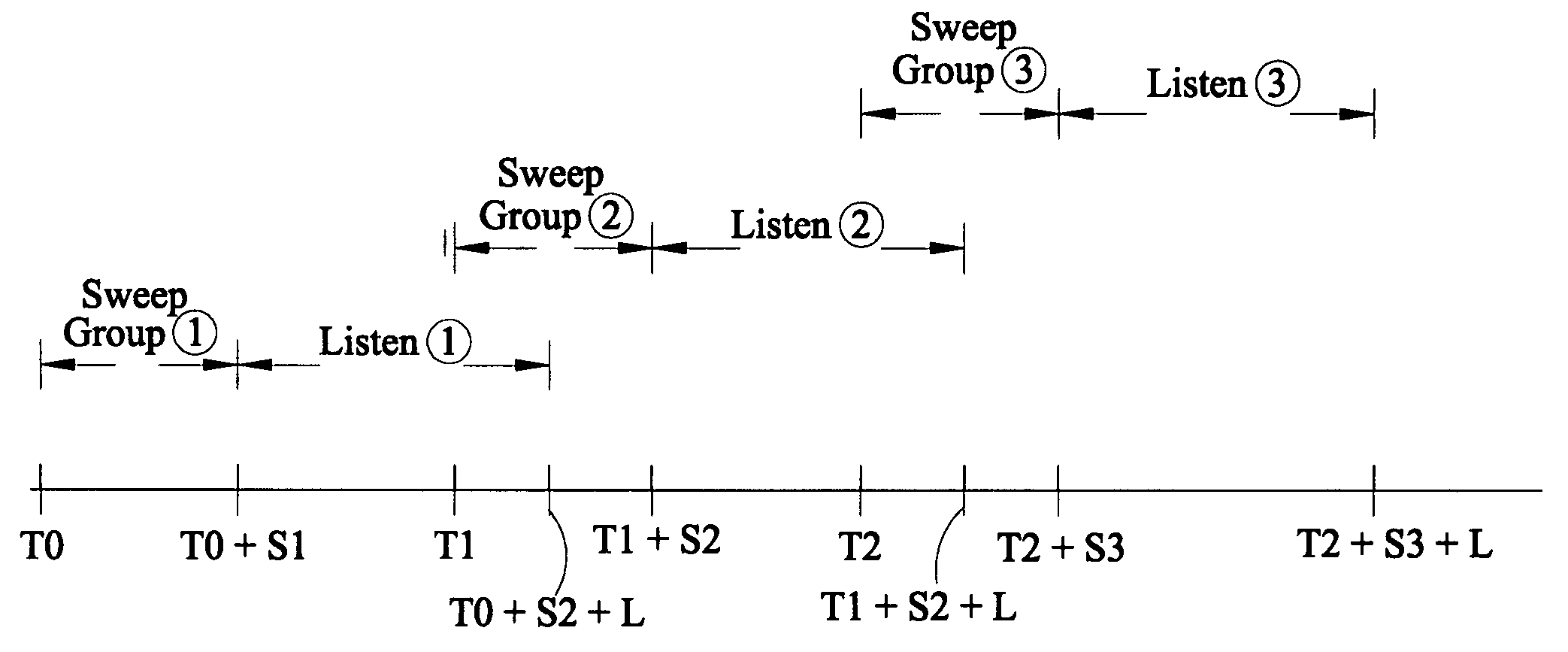
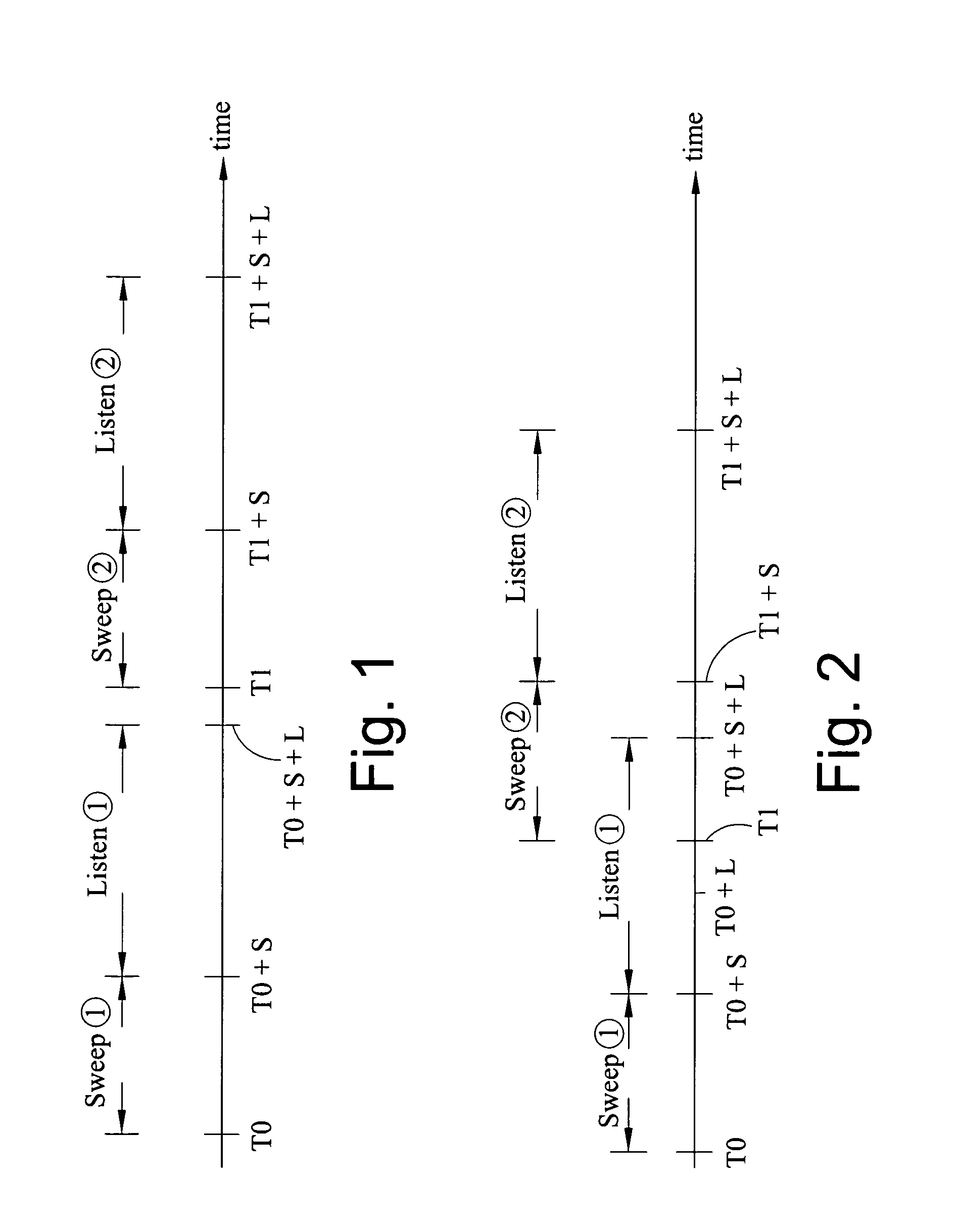
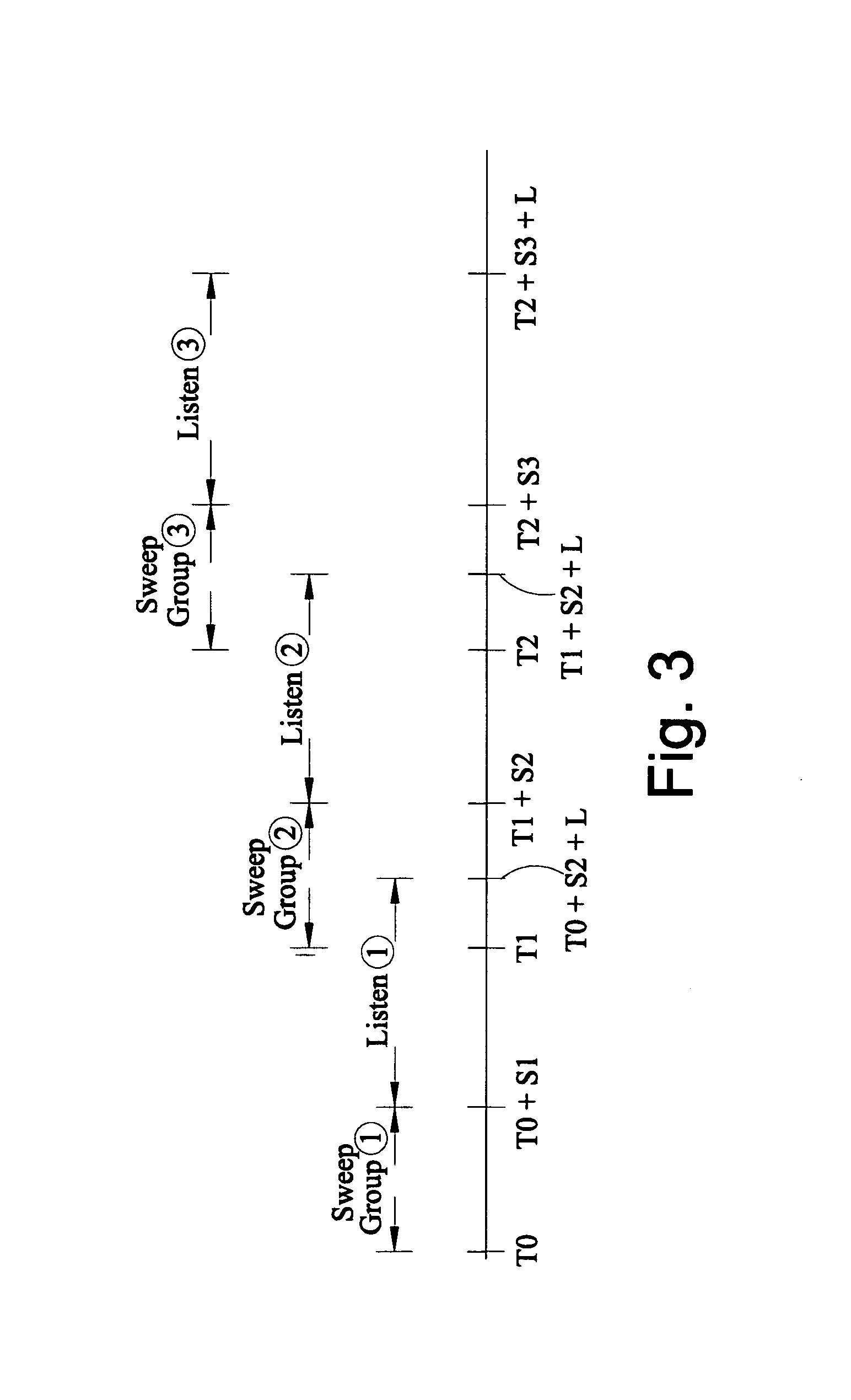
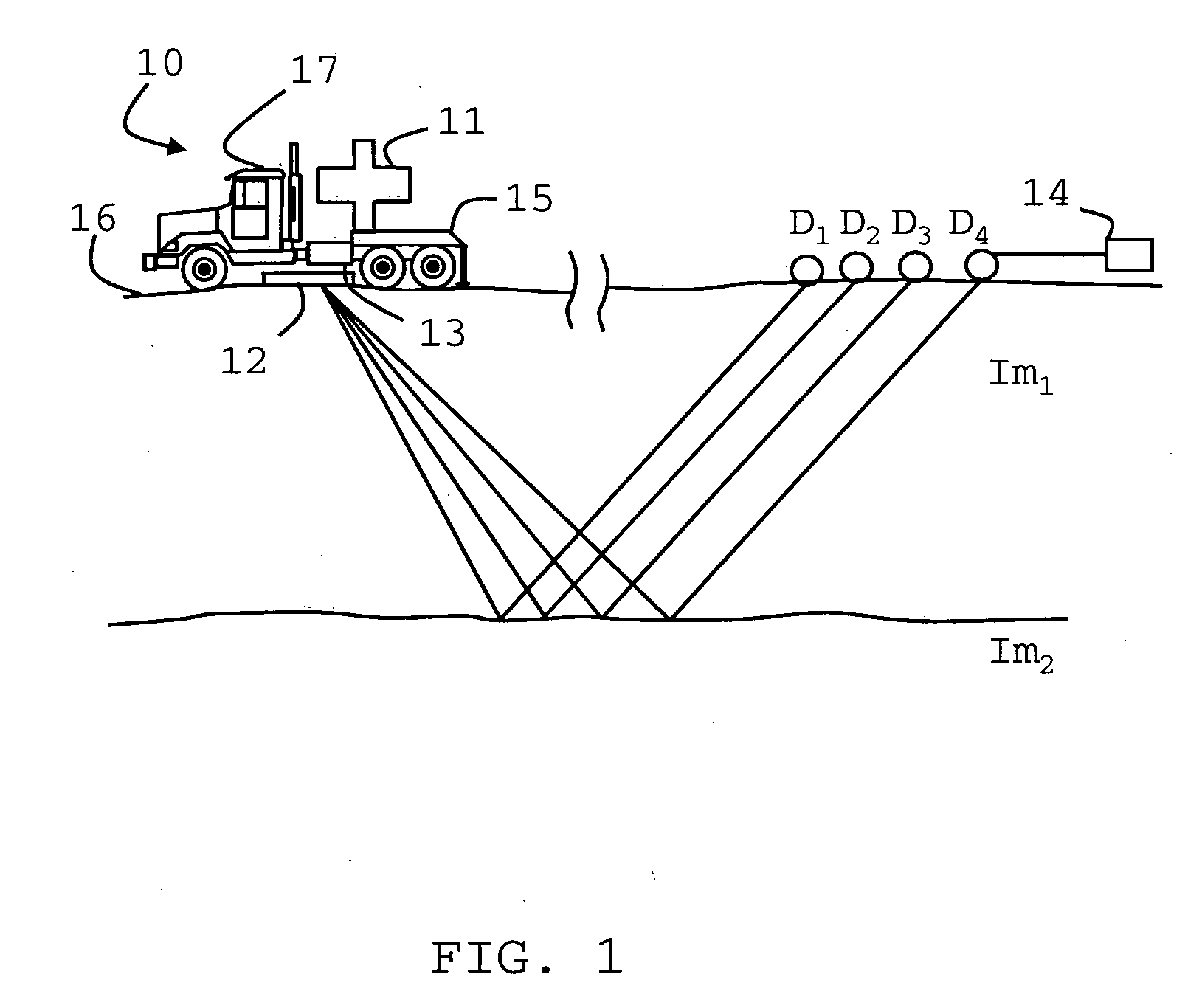
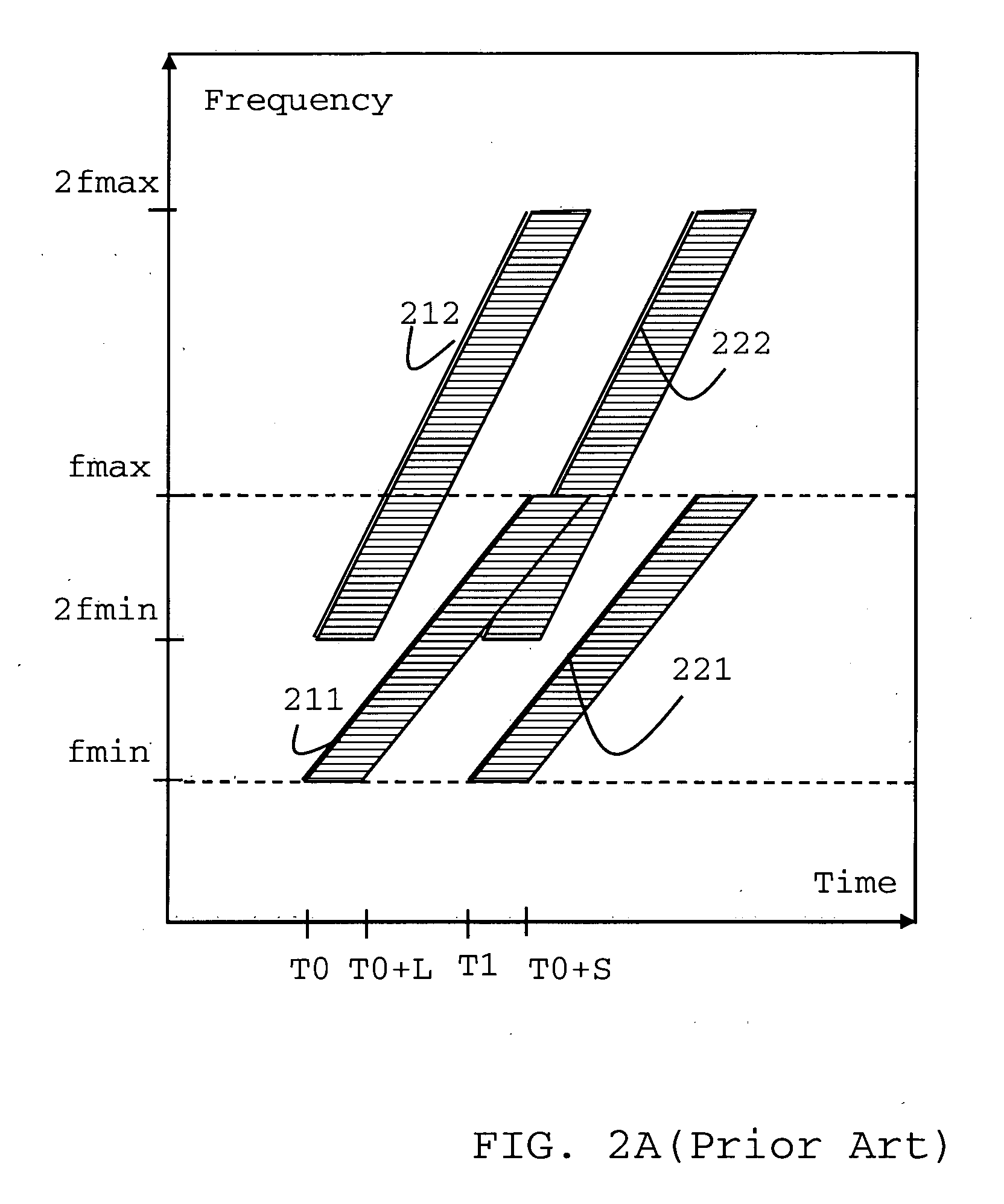
A method of seismic surveying comprising the steps of actuating the or each vibrator in a first vibrator group at time T0, and subsequently actuating the or each vibrator in a second vibrator group at time T1 that satisfies T0<T1<T0+S1+L where S1 is the sweep time of the first vibrator group and L is the listening time. At least one of the first vibrator group and the second vibrator group comprises at least two vibrators. The first group and the second group of vibrators may be the same group, or they may be different groups. This method enables the time required to complete a seismic survey to be reduced compared to the prior art “simultaneous shooting” and “slip-sweep shooting” techniques.In a case where the first group and the second group of vibrators are different, the method may further comprise actuating the or each vibrator in the first vibrator group at time T2, where T1<T2<T1+S2+L and S2 is the sweep time of the first vibrator group, and then actuating the or each vibrator in the second vibrator group at time T3 where T2<T3<T2+S1+L and where T3−T2≠T1−T0. The varying time delay between a shot of the first vibrator group and the corresponding shot of the second vibrator group means that harmonic noise will occur at different times in the shot records so that the noise may be eliminated by appropriately combining the shot records.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
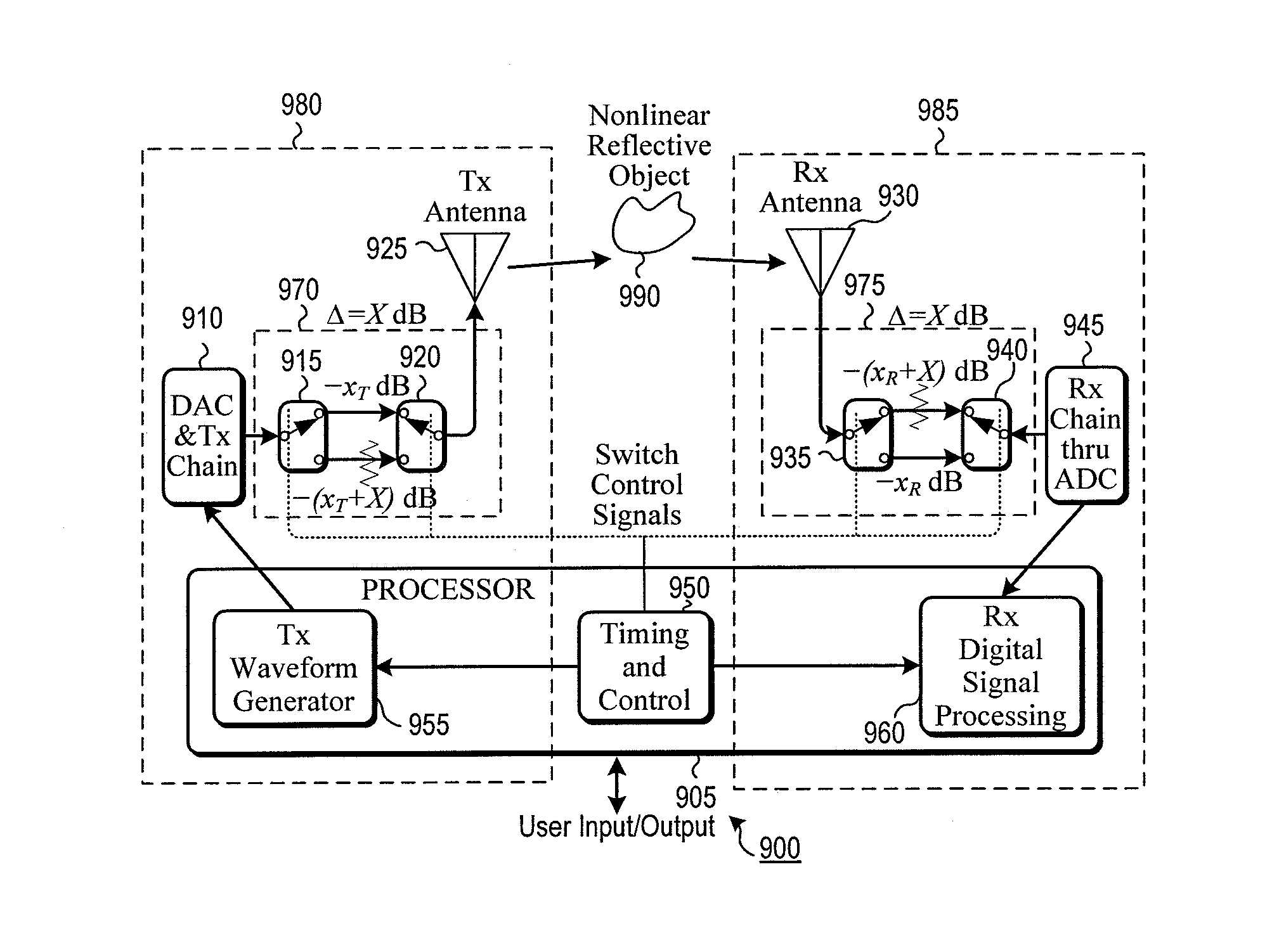
System and method for nonlinear radar
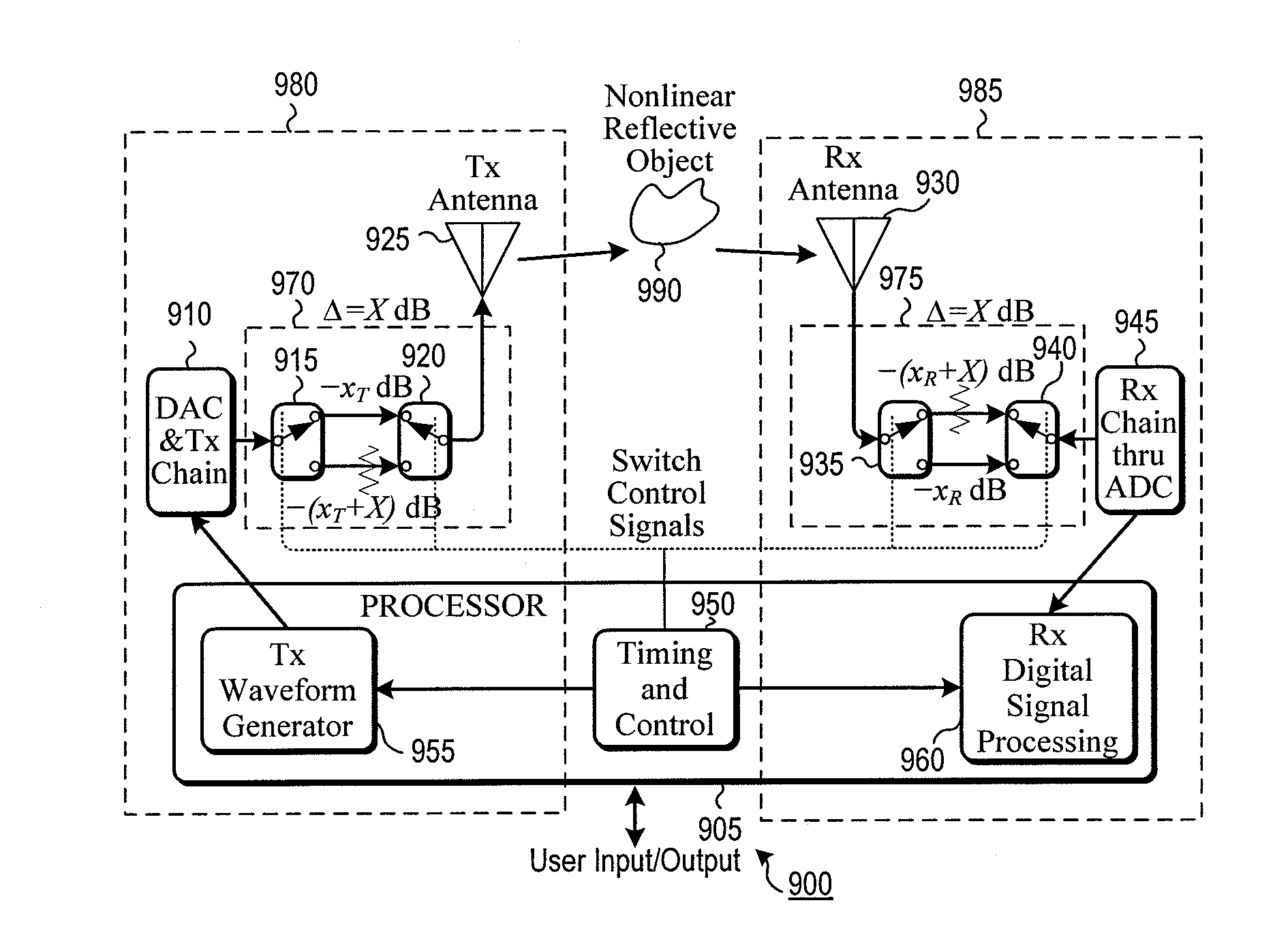
A non-linear radar is disclosed that is able to detect non-linear target responses that are below the harmonic-noise floor of the radar. To accomplish this below-the-noise-floor sensitivity feature the proposal specifically addresses all of the problems commonly faced by non-linear radar such as linearity of the transmitter path, receiver path, and size, weight, and power, and cost (SWaP-C). The radar operates in both standard and nonlinear modes with signal processing that allows display of nonlinear alone, linear alone, or both types of backscatter. Different combinations of six methodologies allow customization to fit different application needs, from low-cost modest performance, to higher cost and extremely high performance.
Owner:APPLIED SIGNALS INTELLIGENCE
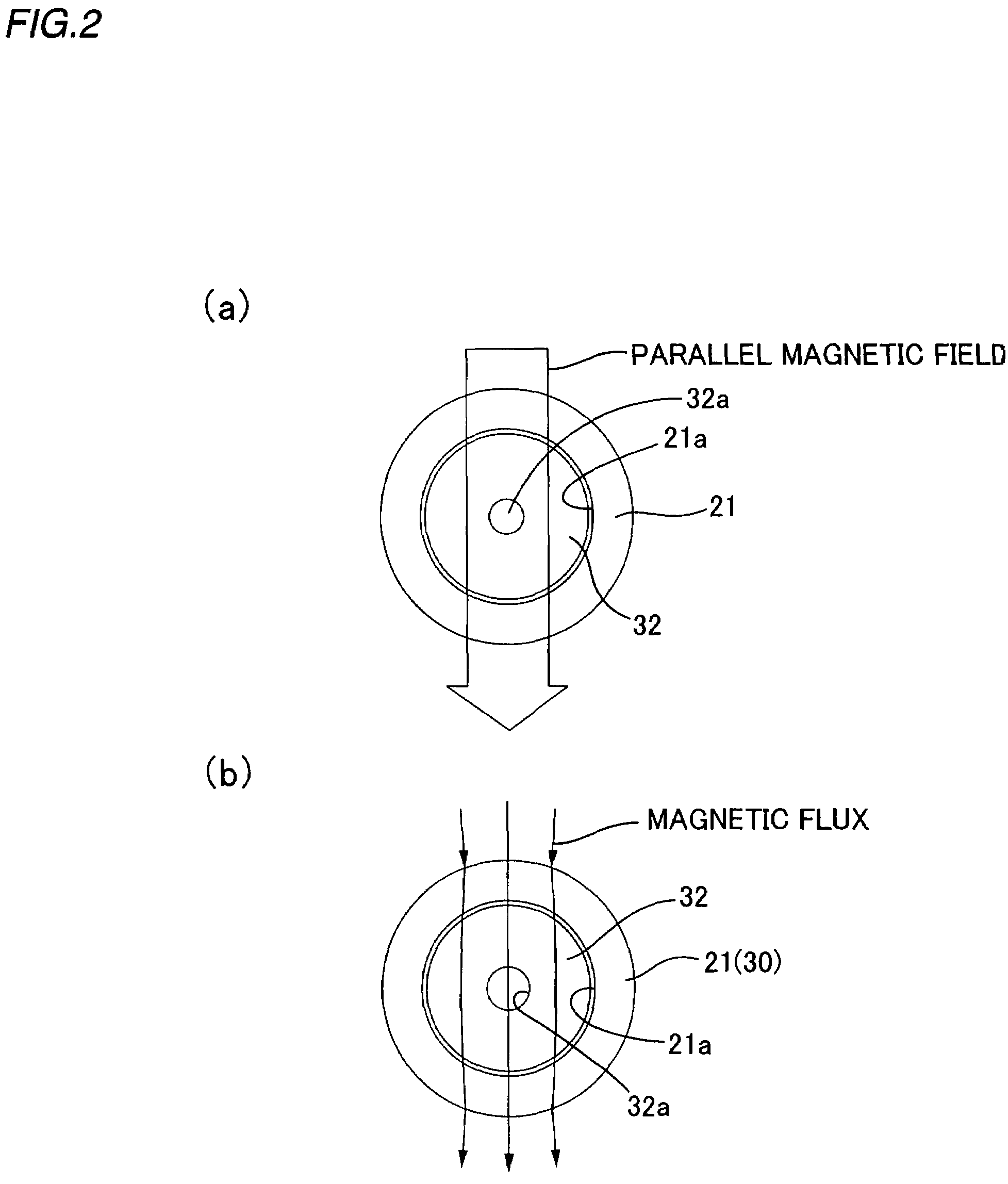
Method for magnetizing ring magnet and magnetic encoder
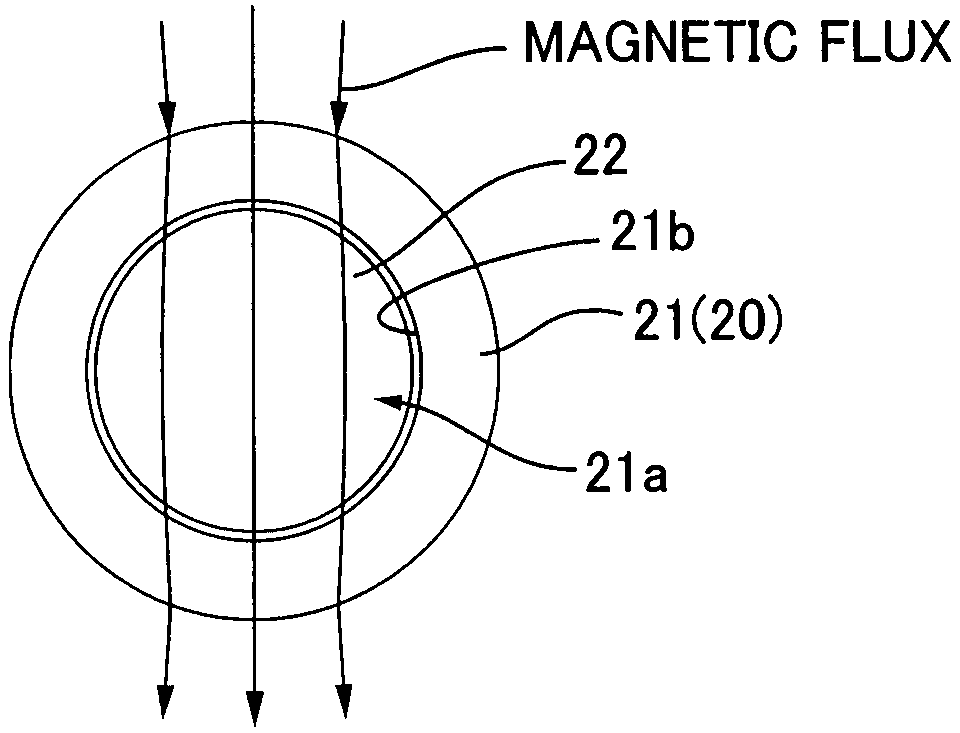
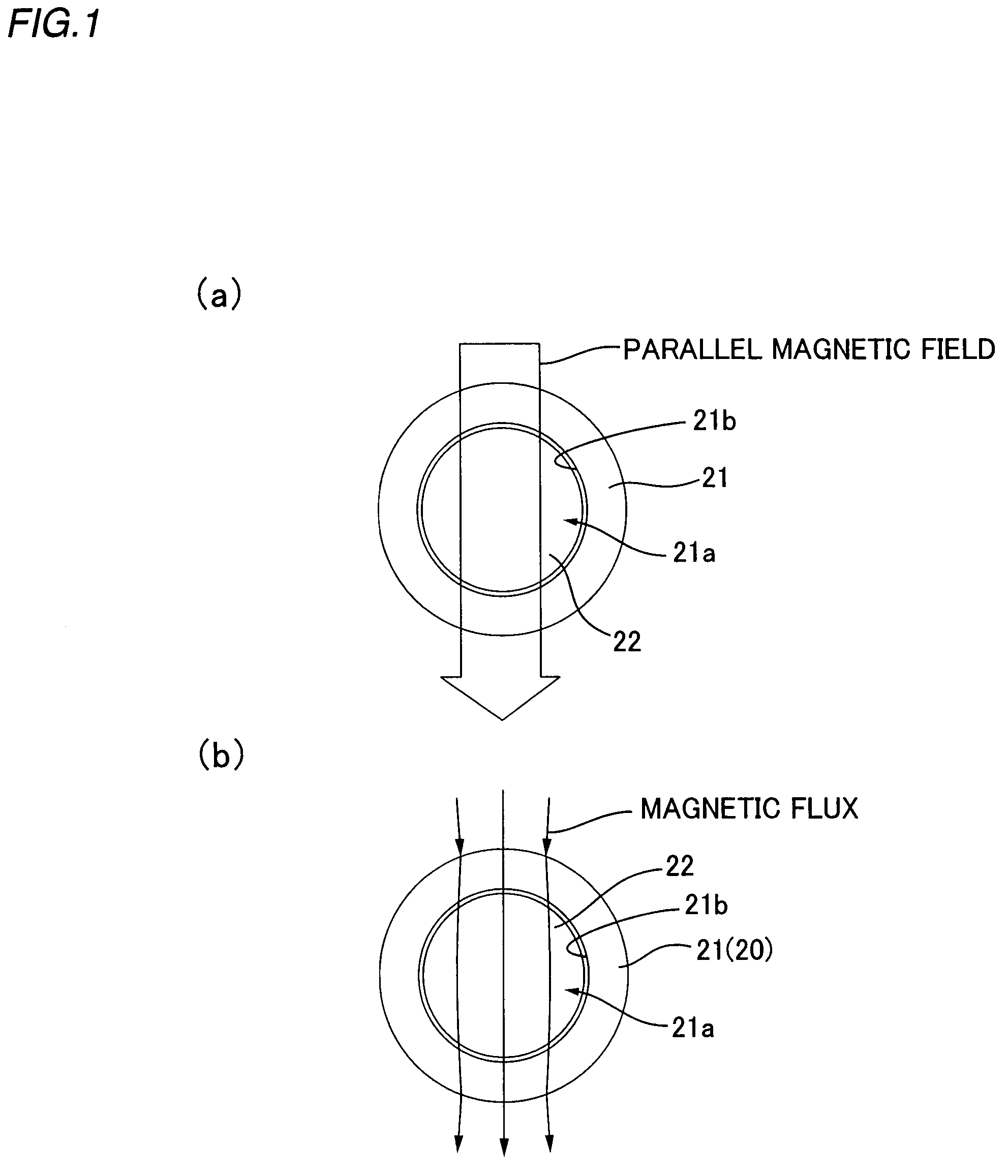
ActiveUS7498914B2Accurate detectionSame magnetic permeabilityElectromagnets without armaturesPermanent magnetsMagnetizationMagnetic flux
Owner:HARMONIC DRIVE SYST IND CO LTD
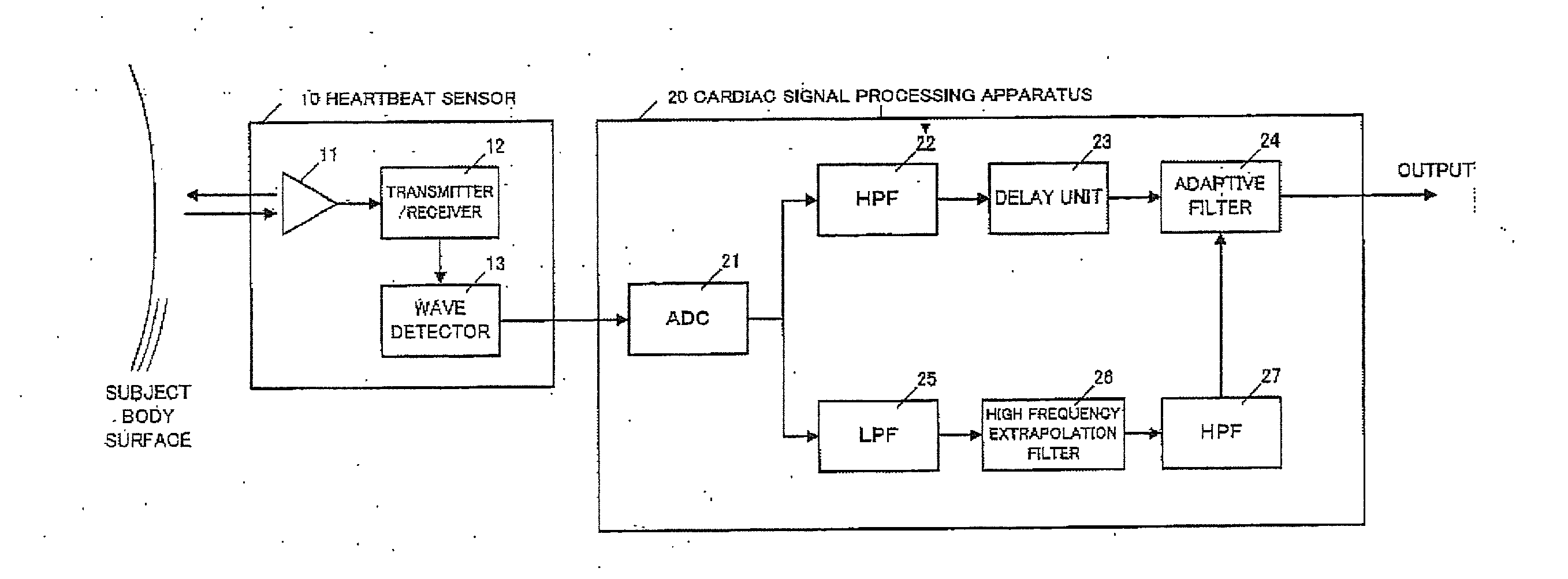
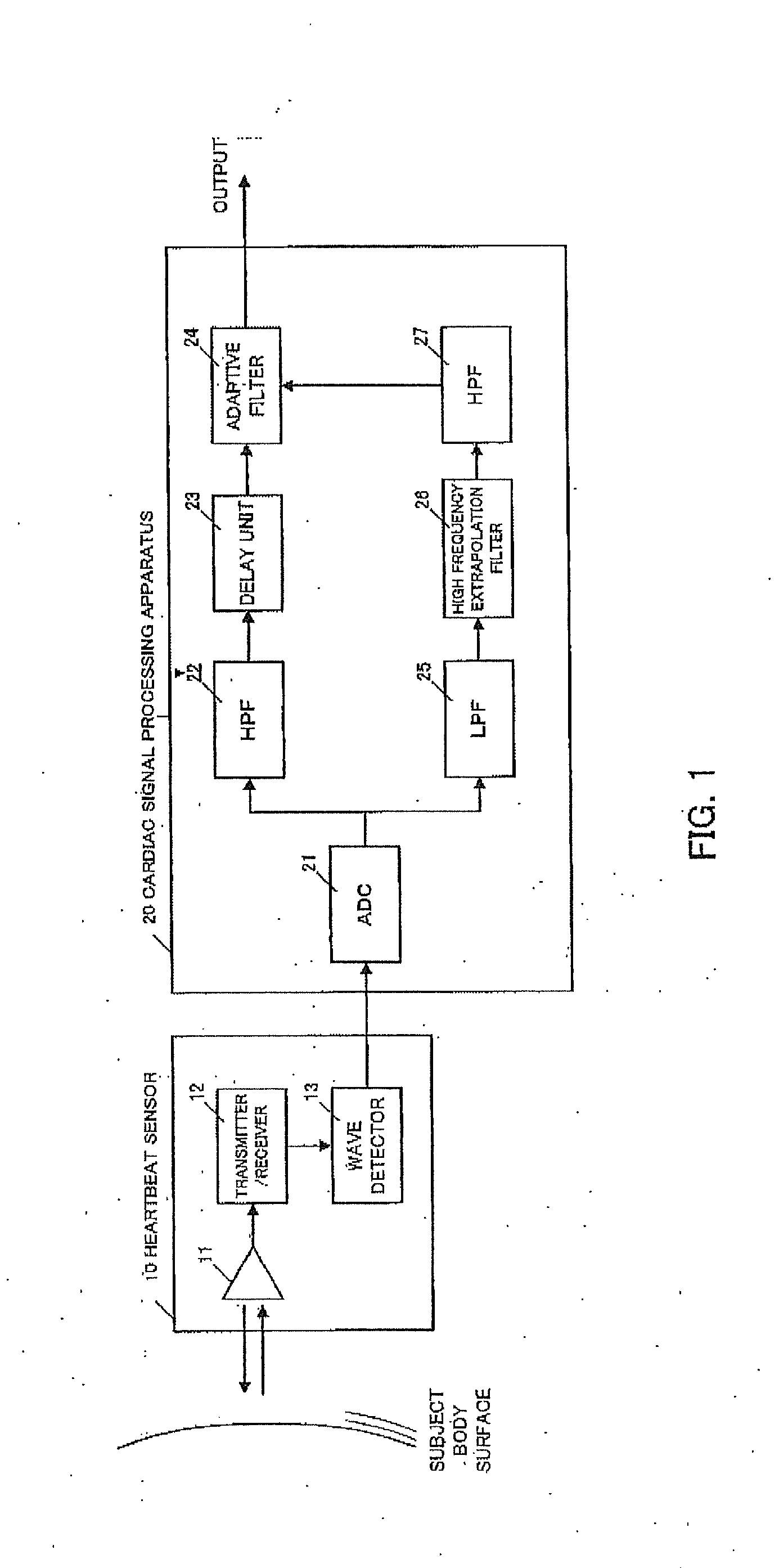
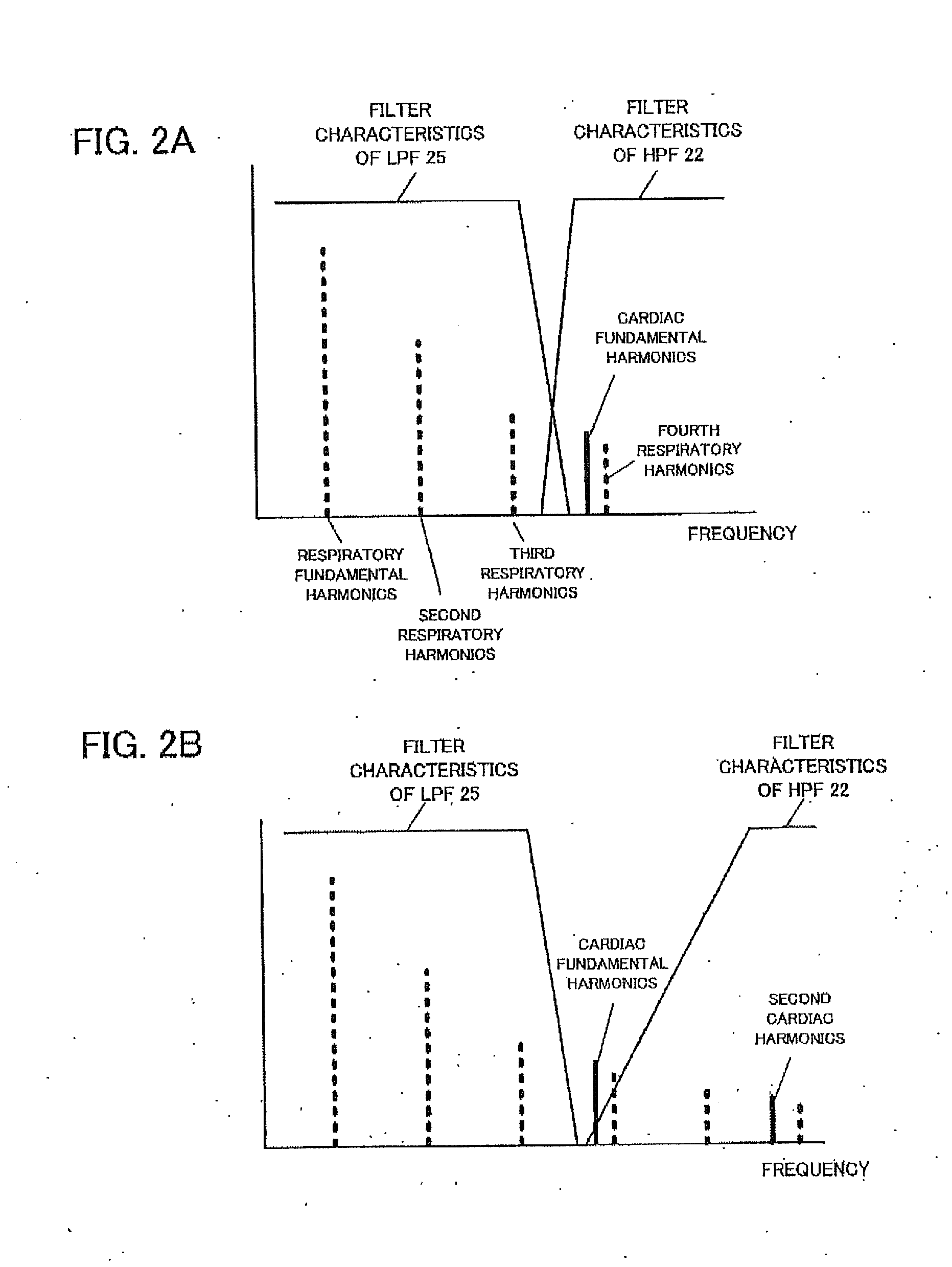
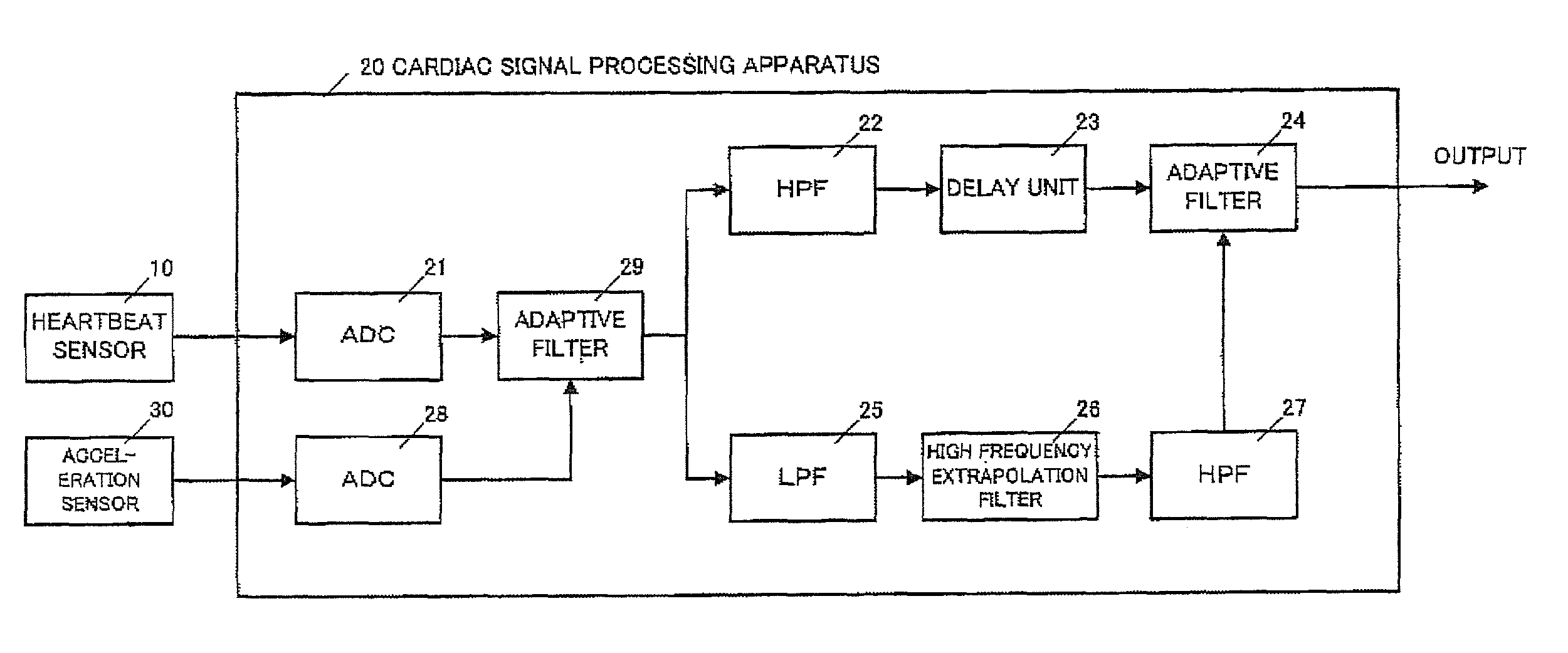
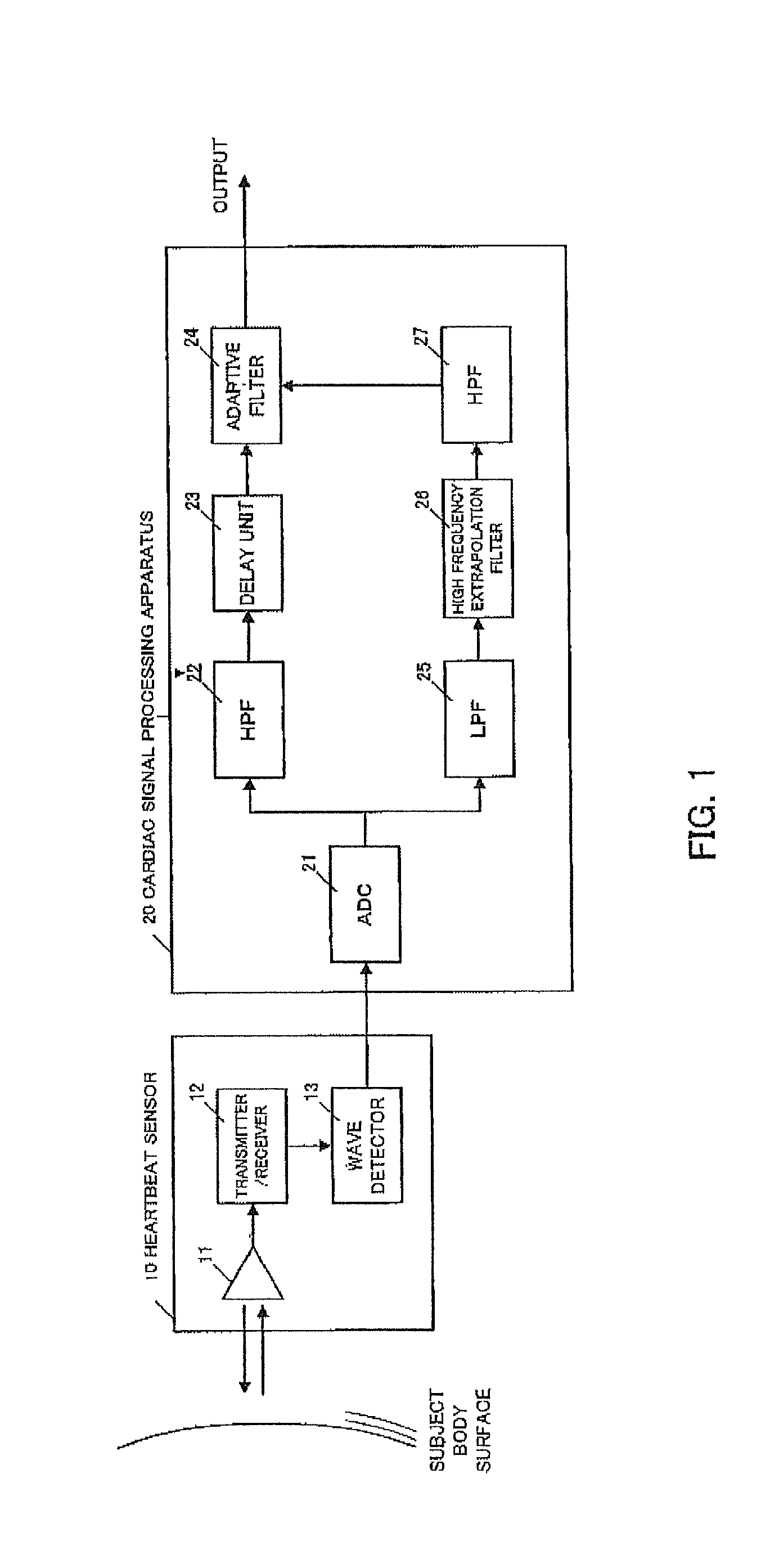
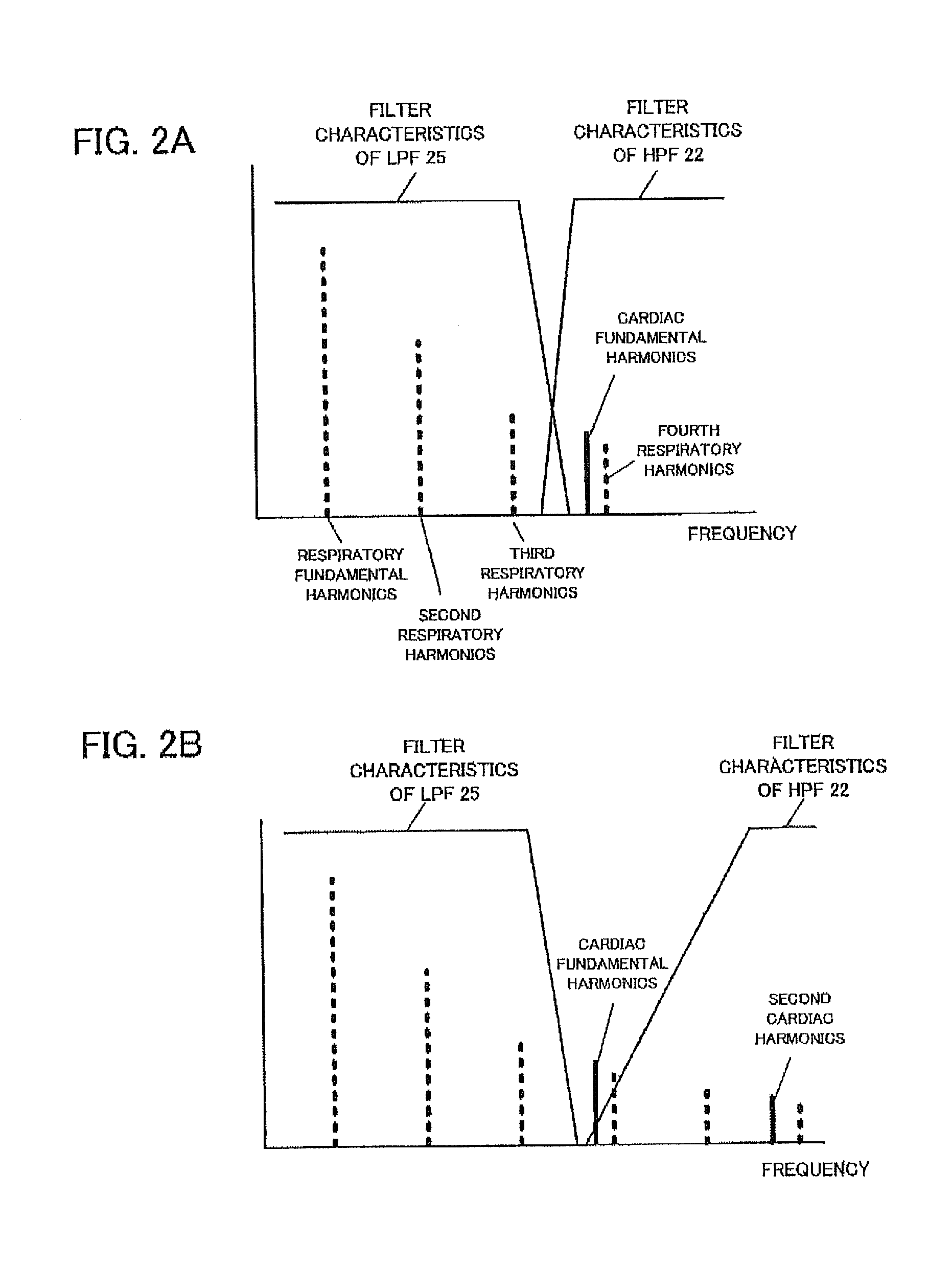
Cardiac signal processing apparatus and cardiac signal processing method
ActiveUS20130197377A1Eliminate distractionsComponent with highCatheterSensorsBand-pass filterEngineering
A cardiac signal processing apparatus includes: a unit for acquiring, from a heartbeat sensor, cardiac signals relating to heartbeats of a subject; a low-pass filter for allowing passage of those cardiac signals having a first predetermined frequency or lower, among the cardiac signals; higher harmonic noise acquisition unit for acquiring harmonic signals of low-frequency noise by performing high frequency extrapolation on the signals output from the low-pass filter; a high-pass filter for allowing passage of those cardiac signals having a second predetermined frequency or higher, among the cardiac signals; and higher harmonic noise removal unit for removing the harmonic signals of low-frequency noise from the signals output from the high-pass filter. It is thus made possible to remove noise from the cardiac signals and to obtain desirable heartbeat detection characteristics.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
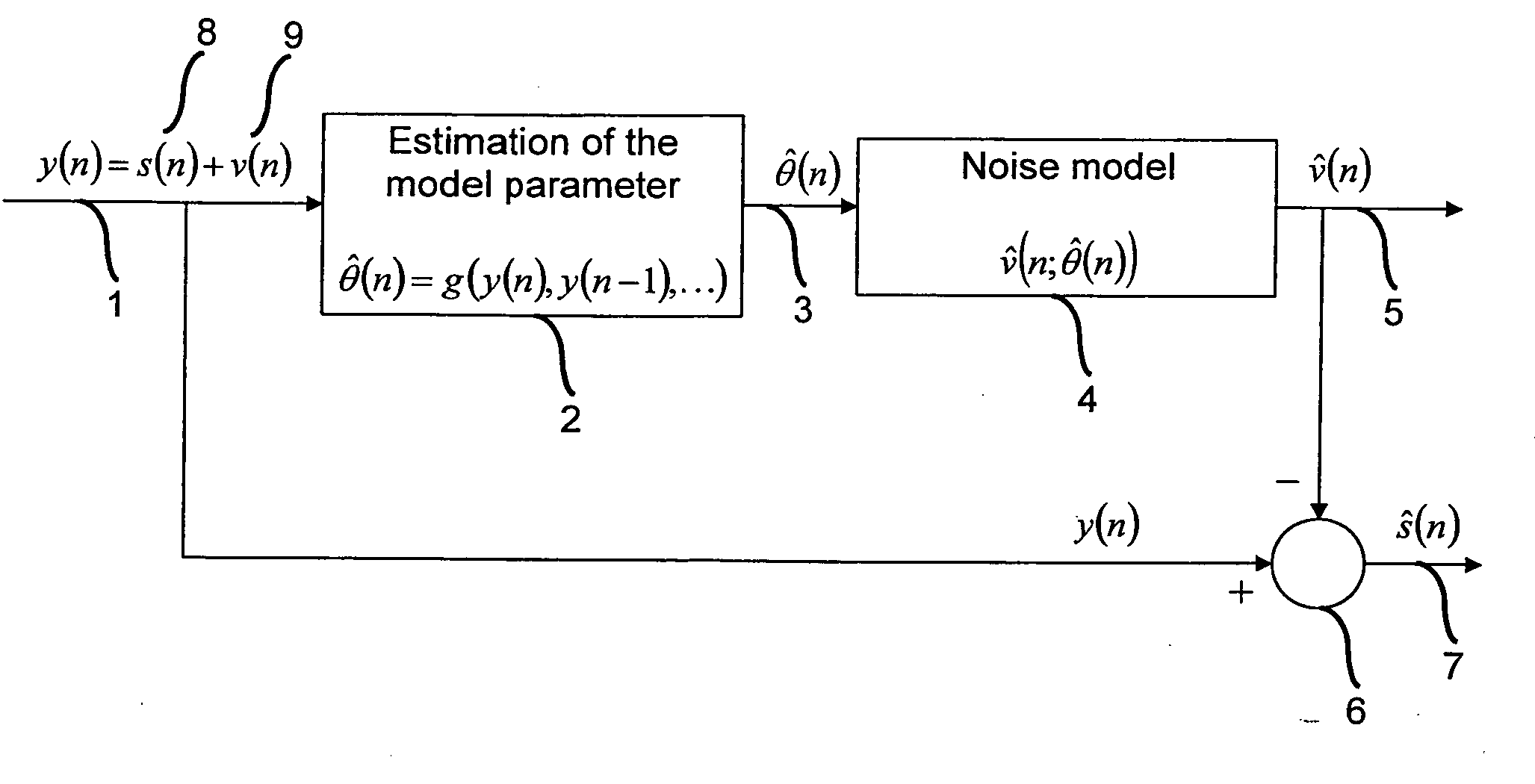
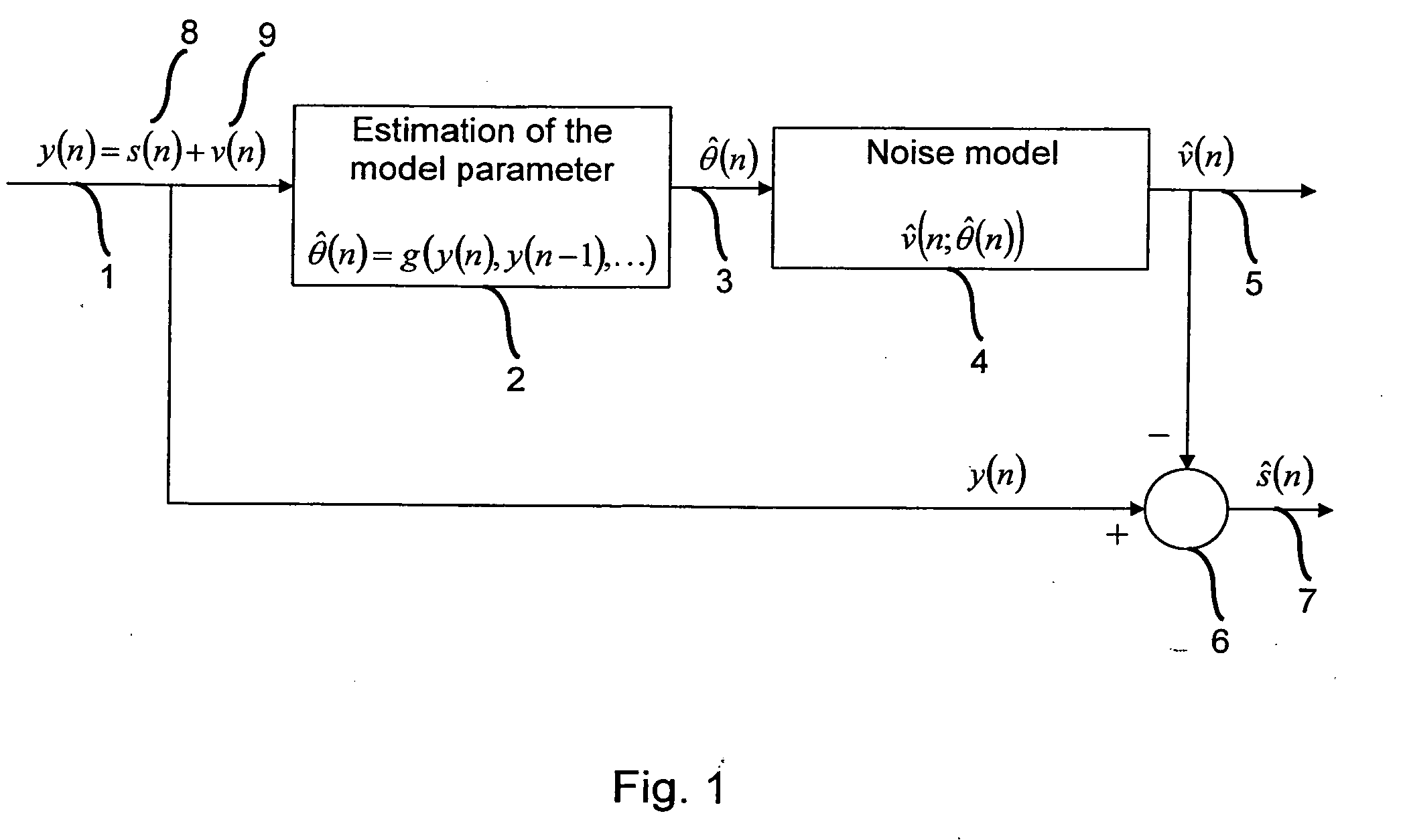
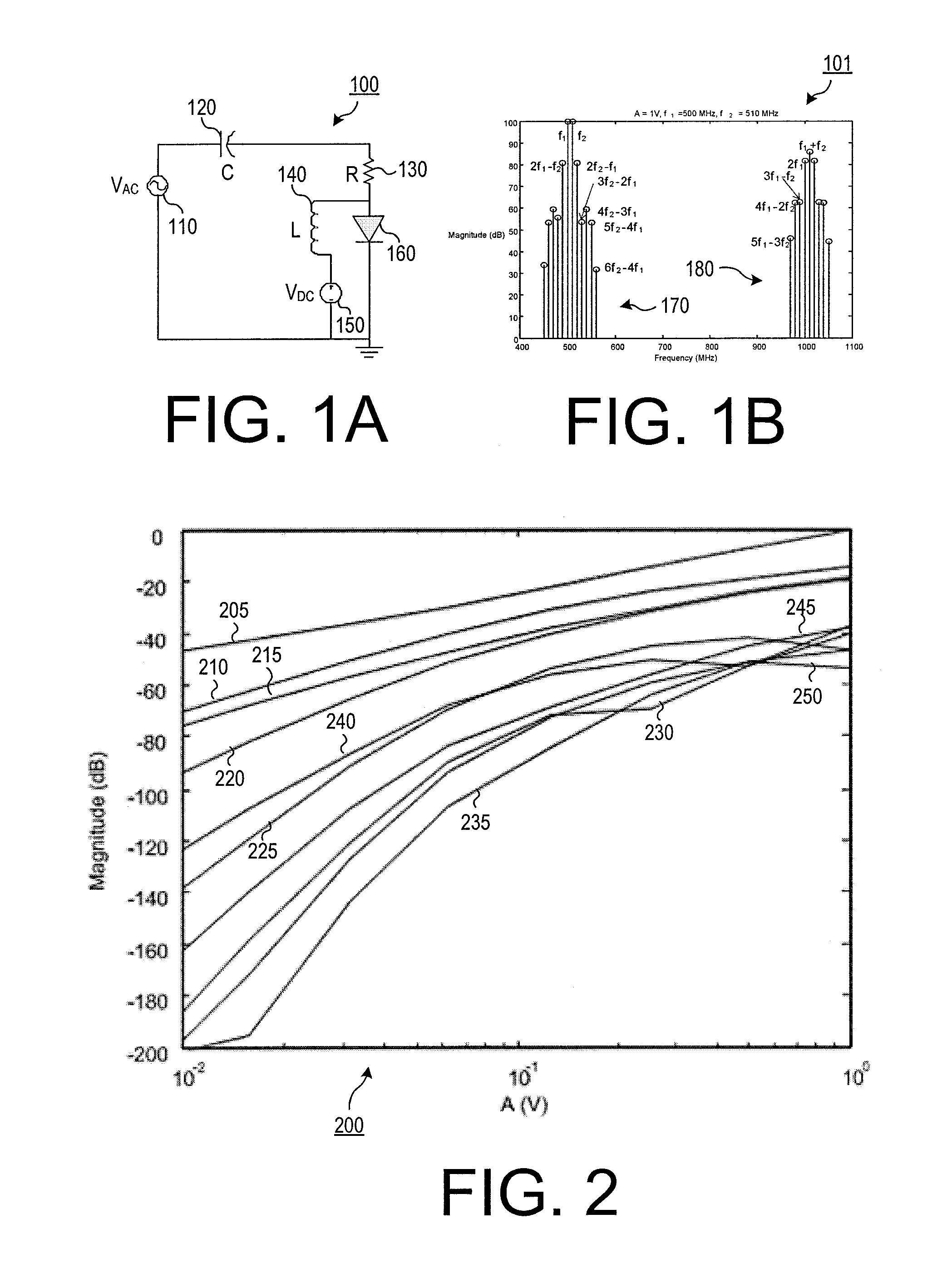
Subtractive cancellation of harmonic noise
InactiveUS20050276363A1Simple technologyImprove accuracyError preventionDigital data processing detailsKaiman filterSignal on
A common problem in audio processing is that a useful signal is disturbed by one or more sinusoidal noises that should be suppressed. One embodiment of the invention provides a method of canceling a sinusoidal disturbance of unknown frequency in a disturbed useful signal. The method comprises the steps of estimating parameters of the sinusoidal disturbance including amplitude, phase and frequency; generating a reference signal on the basis of the estimated parameters; and subtracting the reference signal from the disturbed useful signal. According to one embodiment of the present invention, the estimation is performed by an Extended Kalman filter.
Owner:HONDA RES INST EUROPE
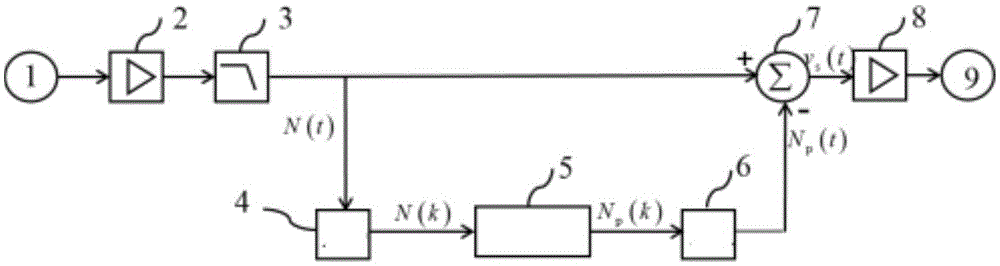
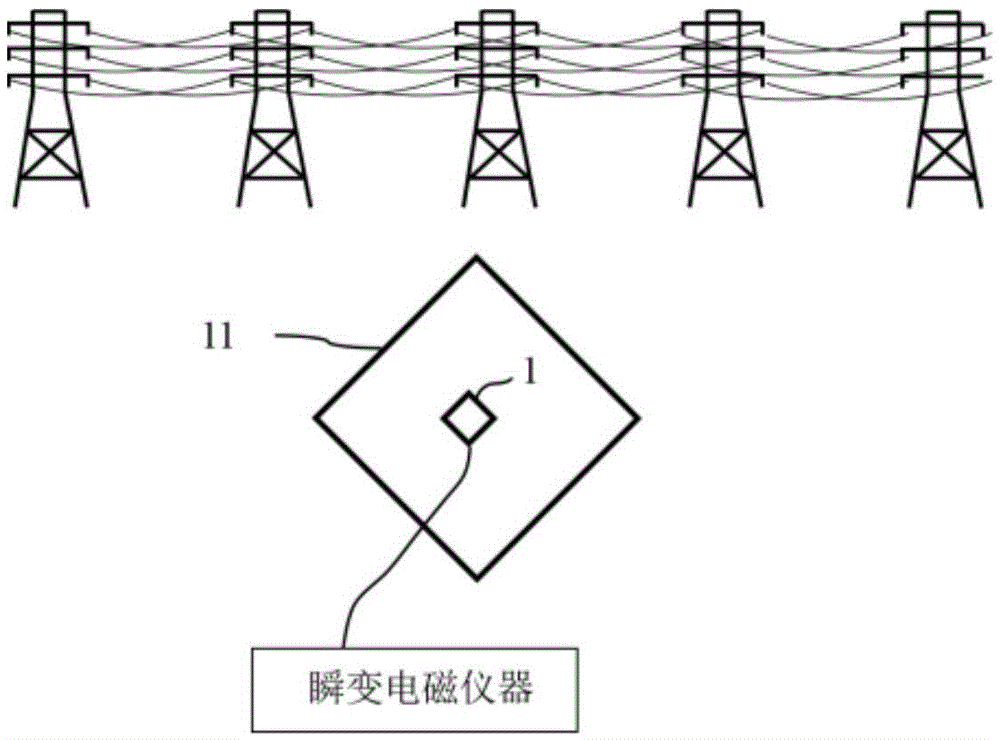
Transient electromagnetic signal power frequency and harmonic interference elimination method and apparatus thereof
InactiveCN105549097AEliminate distractionsEliminate the effects ofElectric/magnetic detectionAcoustic wave reradiationEnvironmental noiseHarmonic interference
The invention belongs to the electromagnetic signal processing and especially discloses a transient electromagnetic signal power frequency and harmonic interference elimination method and an apparatus thereof. The method comprises the following steps of in a first time period, receiving an environmental noise signal N(t), and after amplification, removing a high frequency noise through low-pass filtering; carrying out modeling on power frequency in the signal and a harmonic noise to obtain a power frequency and harmonic interference model; from a second time period, opening an emission machine, receiving a transient electromagnetic induction voltage signal and the environmental noise signal; using the power frequency and harmonic interference model in the first time period to calculate power frequency and harmonic estimation values in the second time period and subsequent time periods; and removing the power frequency and harmonic estimation values from the transient electromagnetic induction voltage signal and the environmental noise signal via a subtractor to acquire a de-noised transient electromagnetic signal. By using the method, the power frequency and harmonic interference with any frequency can be removed.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
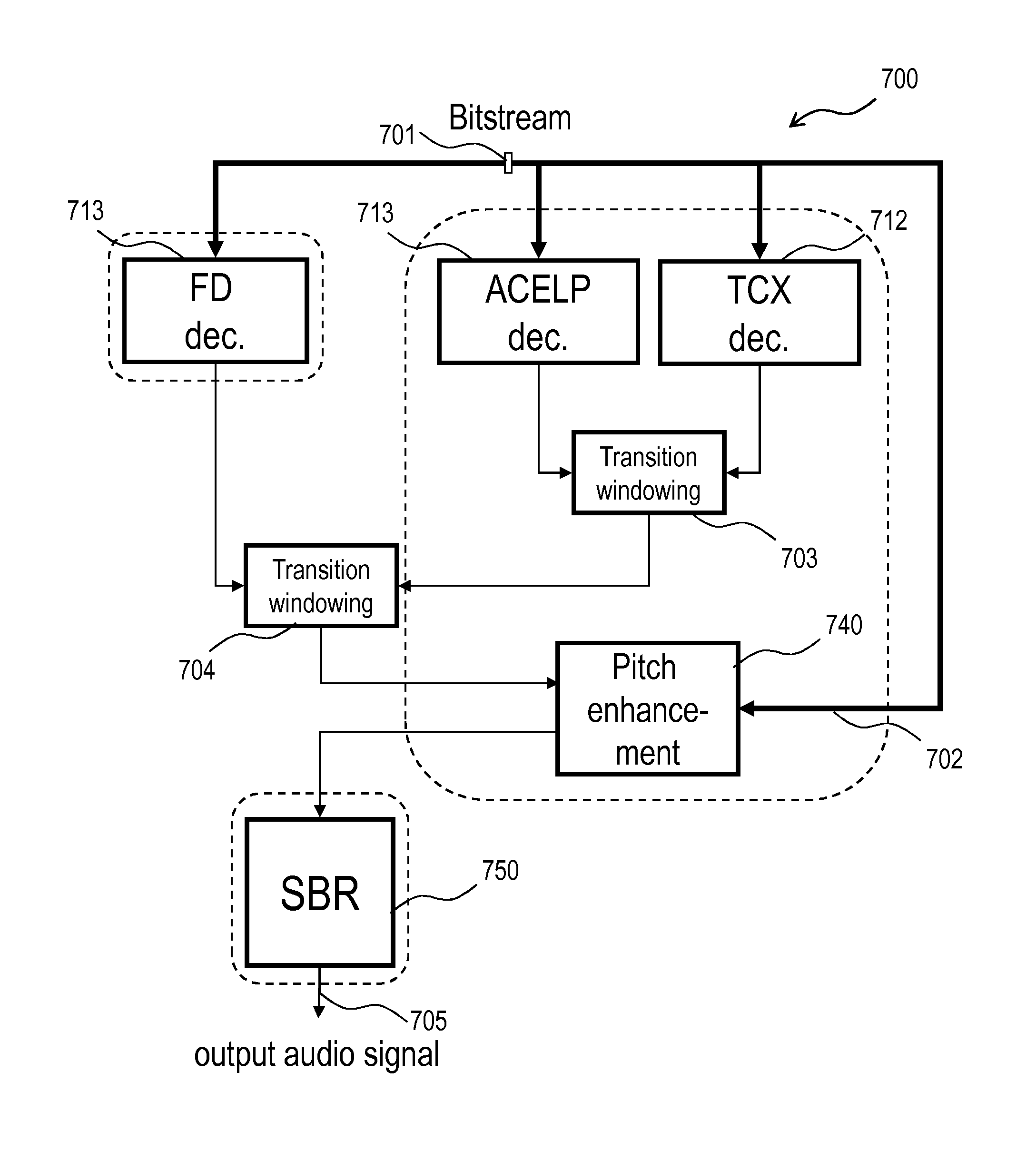
Selective bass post filter
ActiveUS20130096912A1Wider rangeLess benefitSpeech analysisFluid pressure measurementUltrasound attenuationAudio signal
In one aspect, the invention provides an audio encoding method characterized by a decision being made as to whether the device which will decode the resulting bit stream Bitstream should apply post filtering including attenuation of interharmonic noise. Hence, the decision whether to use the post filter, which is encoded in the bit stream, is taken separately from the decision as to the most suitable coding mode. In another aspect, there is provided an audio decoding method with a decoding step followed by a post-filtering step, including interharmonic noise attenuation, and being characterized in a step of disabling the post filter in accordance with post filtering information encoded in the bit stream signal. Such a method is well suited for mixed-origin audio signals by virtue of its capability to deactivate the post filter in dependence of the post filtering information only, hence independently of factors such as the current coding mode.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
Sound processing apparatus and method
ActiveUS20070010997A1Efficiently attenuate and remove noiseAccurate separationEar treatmentSpeech analysisEngineeringNoise suppression
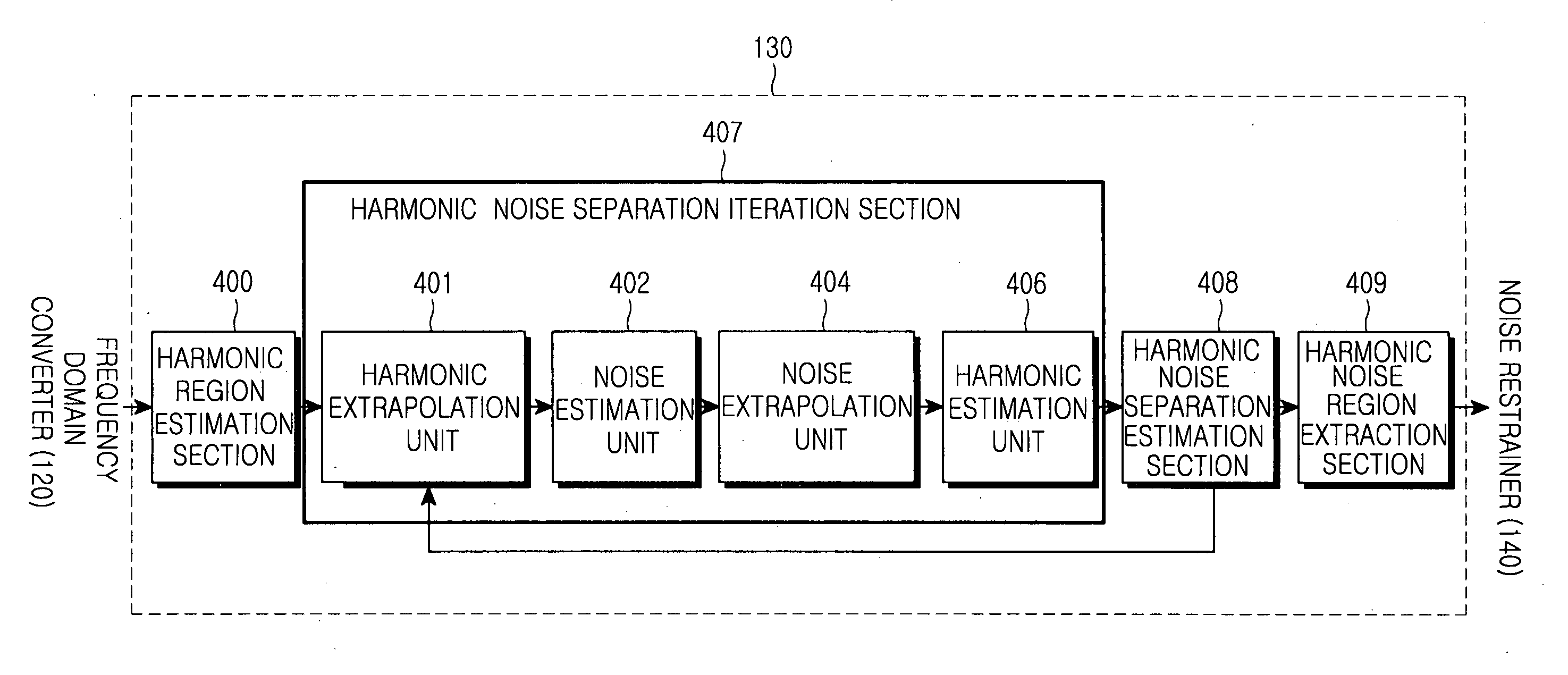
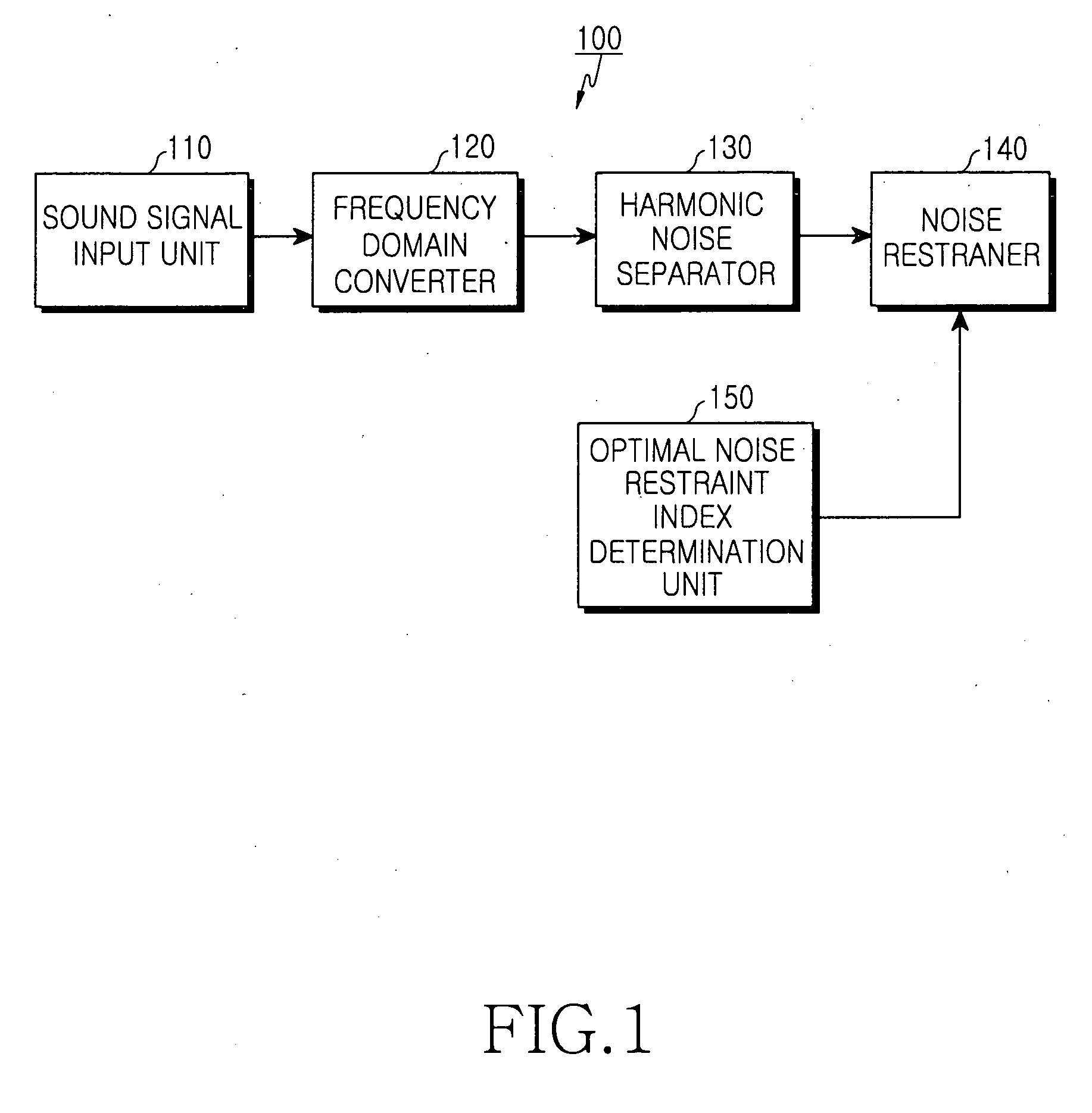
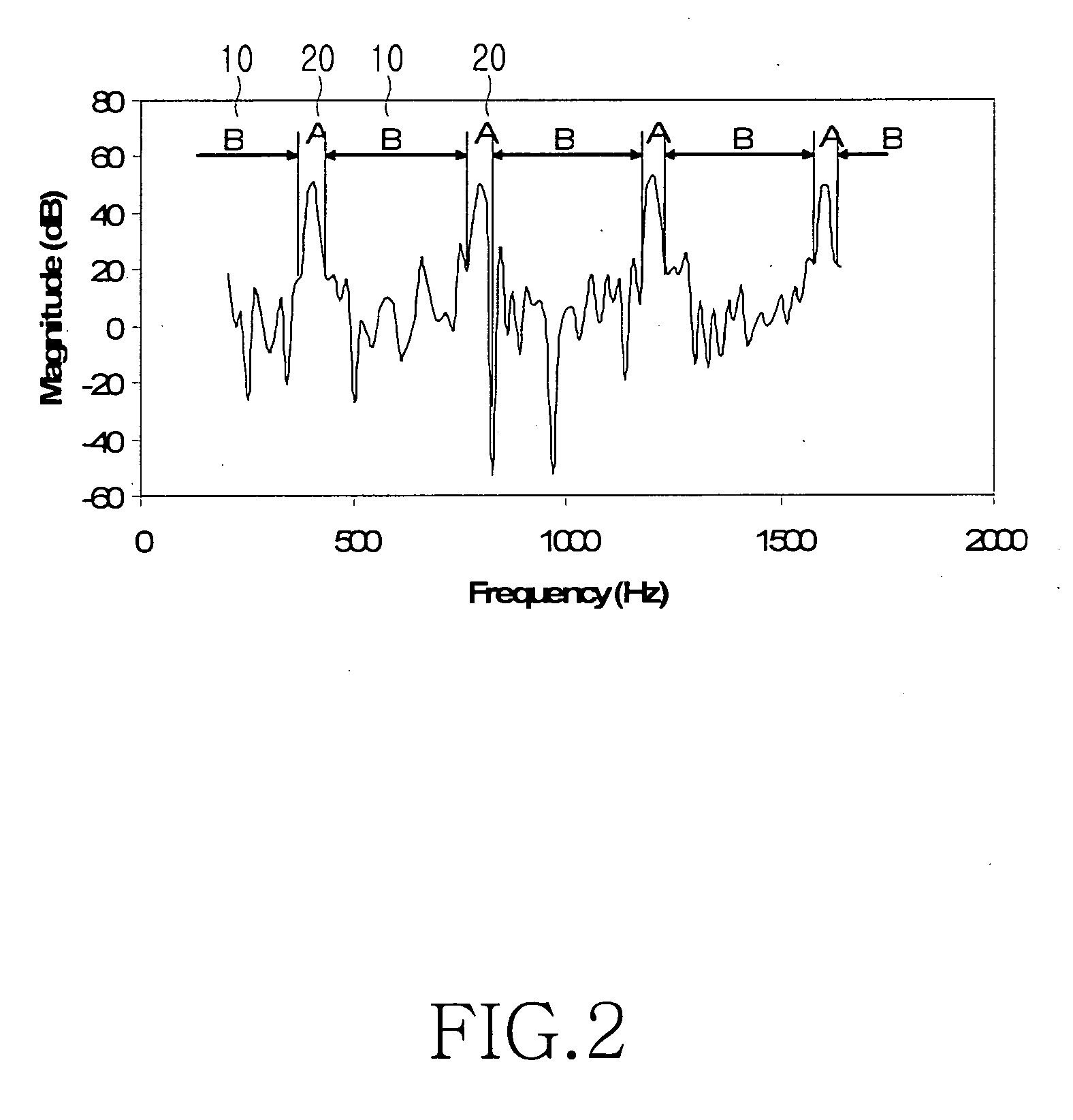
Disclosed is an apparatus and method for processing signals such as sound signals. The sound processing apparatus includes a sound signal input unit for receiving sound signals, a harmonic noise separator for separating a harmonic region and a noise region from the received sound signals, a noise restraint index determination unit for determining an optimal noise restraint index k according to a system and circumstance, and a noise restrainer for restraining the separated noise region depending on the noise restraint index k so as to output noise attenuated signals.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for extracting surface nuclear magnetic resonance signals
ActiveCN106772646ASolving the Difficulty of Efficient ExtractionReduce fit errorWater resource assessmentElectric/magnetic detectionSignal onSelf correlation
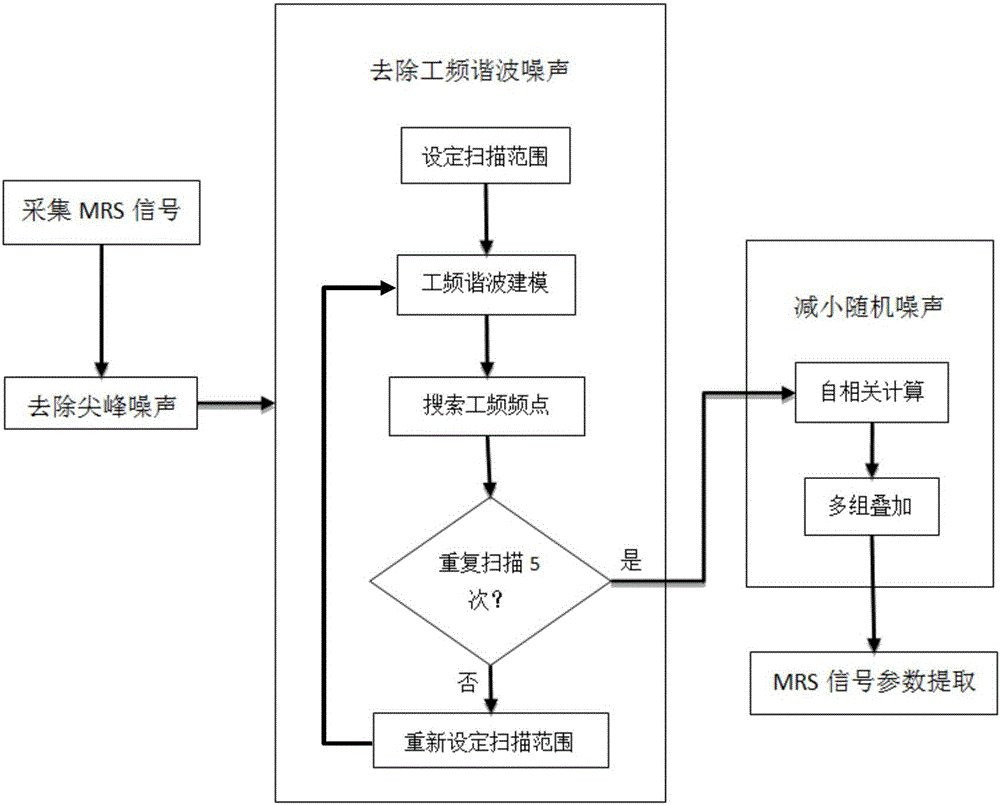
The invention particularly discloses a method for extracting surface nuclear magnetic resonance signals on the basis of power-frequency harmonic modeling and self-correlation. The method includes steps of (1), acquiring a group of MRS (magnetic resonance sounding) noised data by the aid of surface nuclear magnetic resonance groundwater detecting instruments; (2), judging whether spike noise exists or not by the aid of a statistic process, removing the spike noise if the spike noise exists, substituting an interpolation result for the spike noise, and keeping the measurement data unchanged if the spike noise does not exist; (3), using a harmonic modeling process to remove power-frequency harmonic noise from the data after the spike noise is removed from the data; (4), carrying out self-correlation and superposition processing on the result obtained in the step (3) to reduce random noise; (5), extracting MRS signal parameters from the result obtained in the step (4). The method has the advantages that the problem of difficulty in effectively extracting MRS signals due to strong power-frequency harmonic interference and random noise in magnetic resonance depth measuring water exploration work can be solved by the aid of the method, and the fitting errors of the key feature parameters of the acquired MRS signals are small.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Subtractive cancellation of harmonic noise
InactiveUS7453963B2Simple technologyImprove accuracyError preventionDigital data processing detailsKaiman filterSignal on
A common problem in audio processing is that a useful signal is disturbed by one or more sinusoidal noises that should be suppressed. One embodiment of the invention provides a method of canceling a sinusoidal disturbance of unknown frequency in a disturbed useful signal. The method comprises the steps of estimating parameters of the sinusoidal disturbance including amplitude, phase and frequency; generating a reference signal on the basis of the estimated parameters; and subtracting the reference signal from the disturbed useful signal. According to one embodiment of the present invention, the estimation is performed by an Extended Kalman filter.
Owner:HONDA RES INST EUROPE
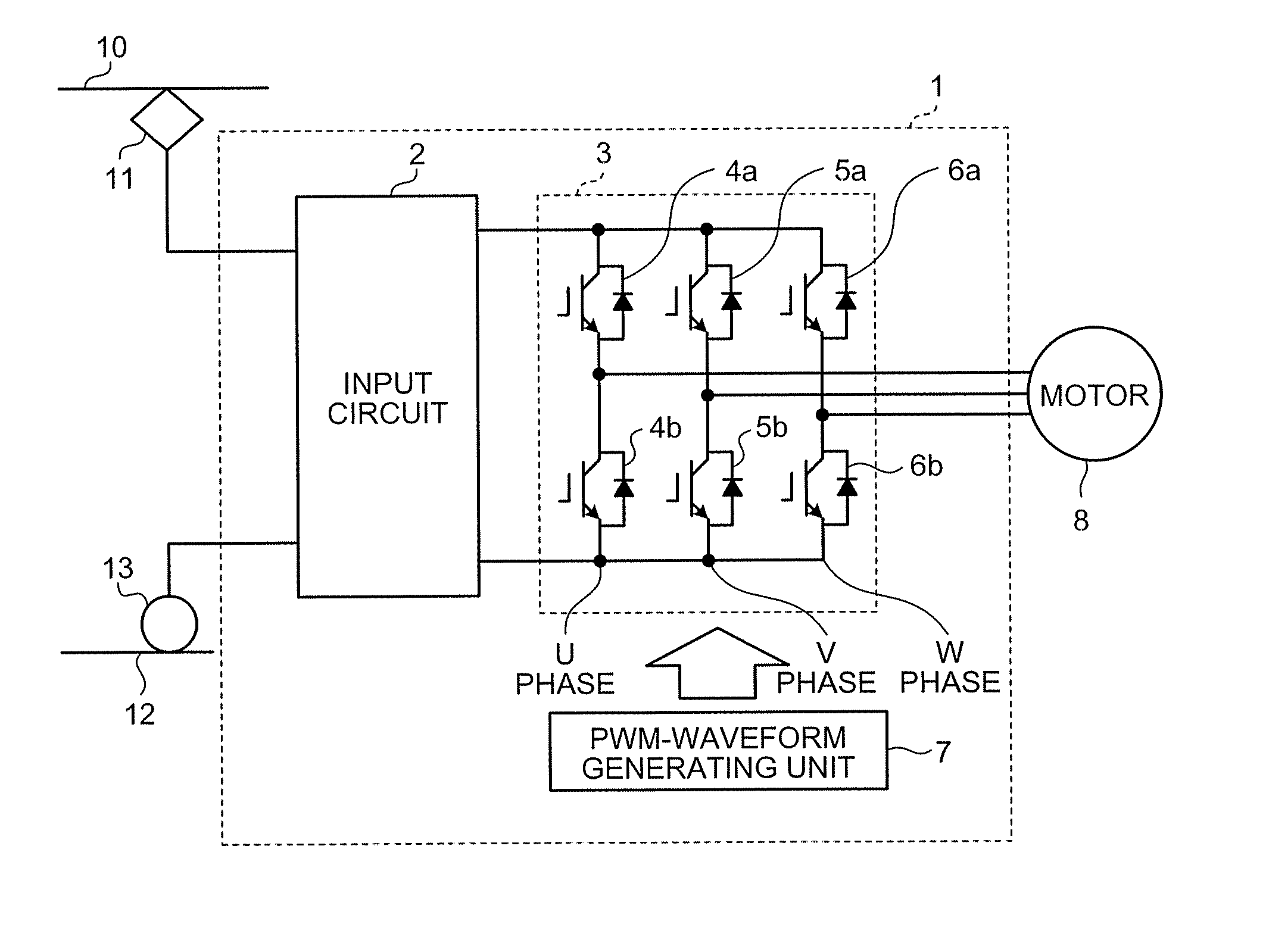
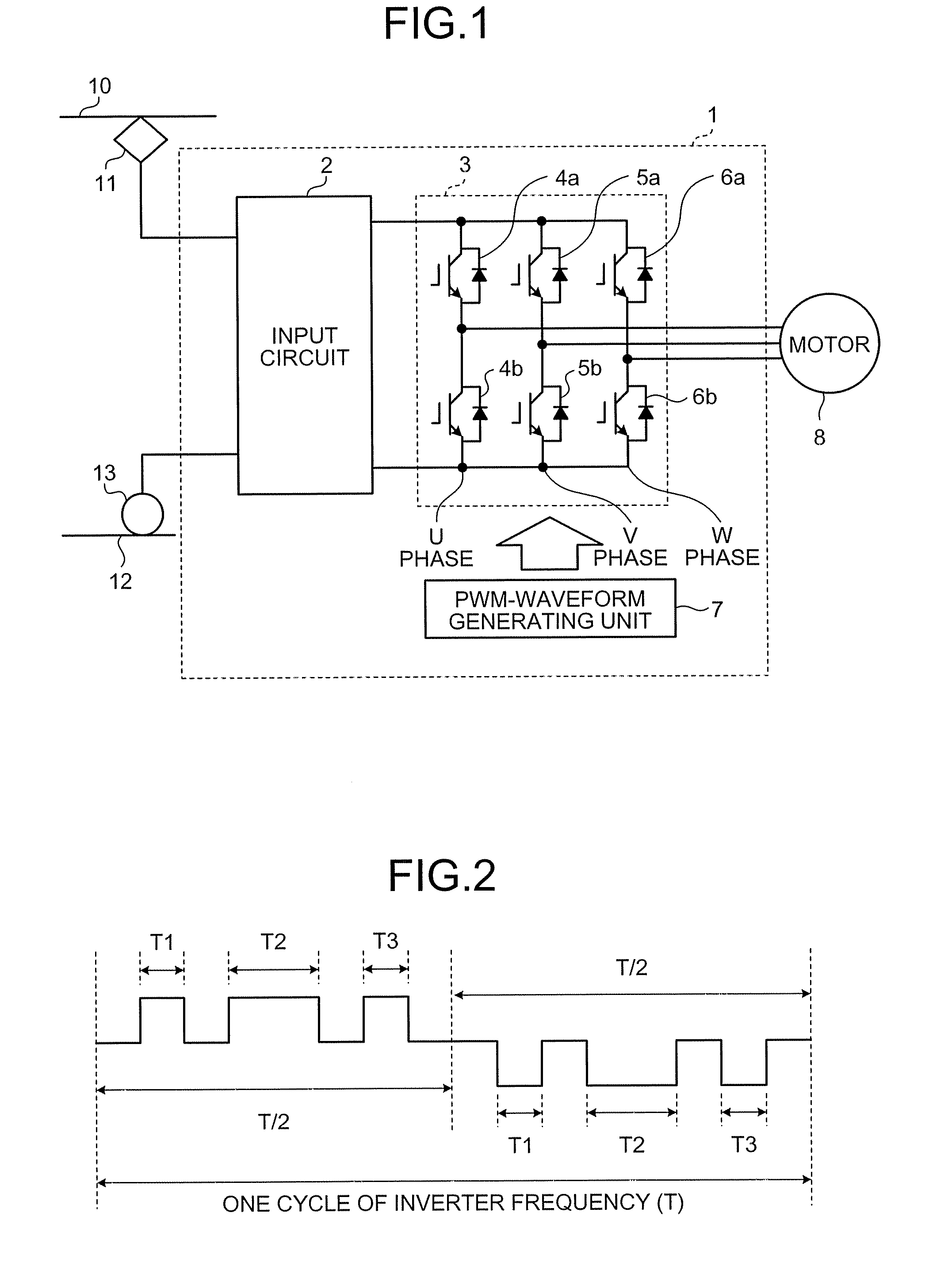
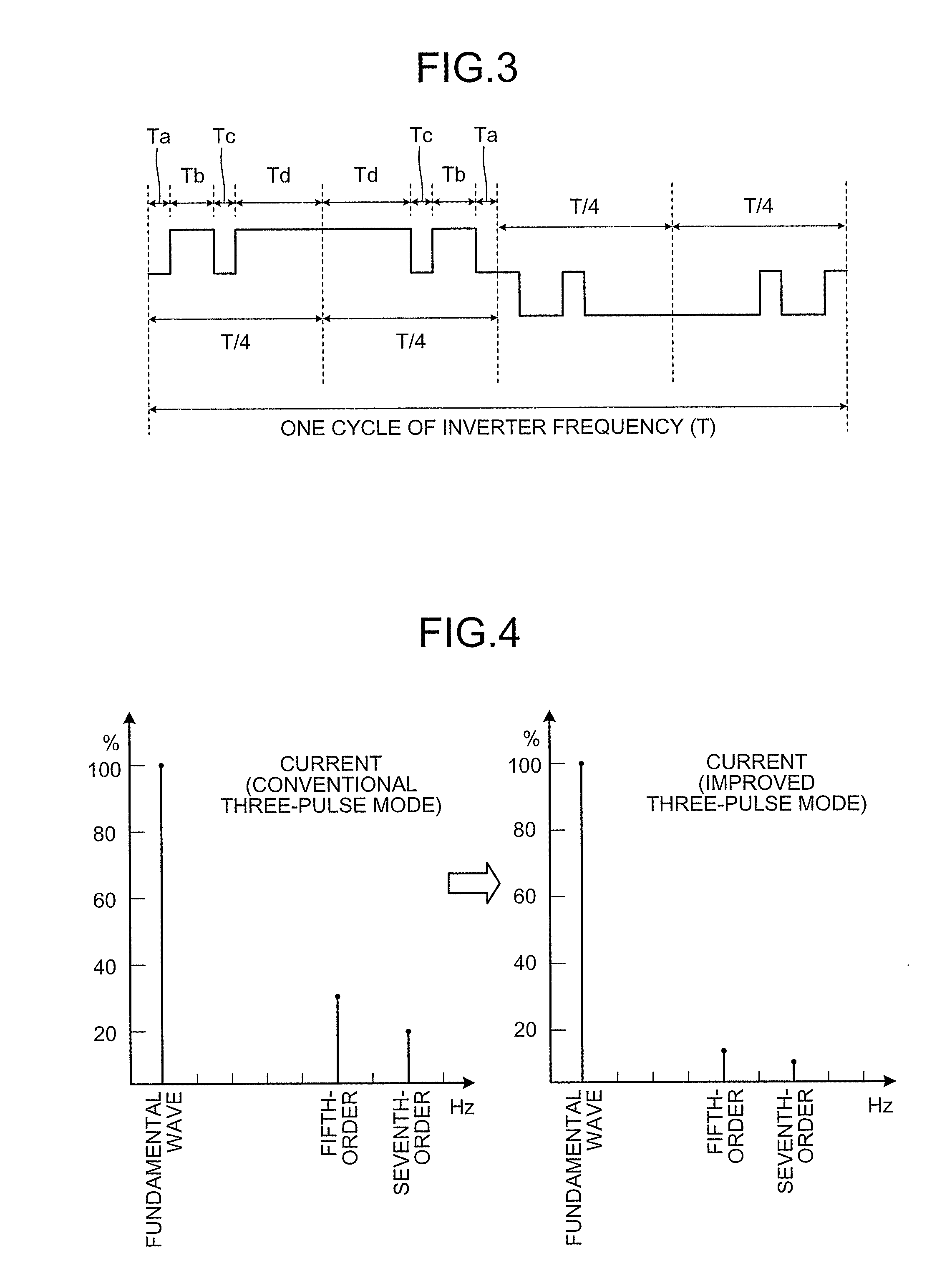
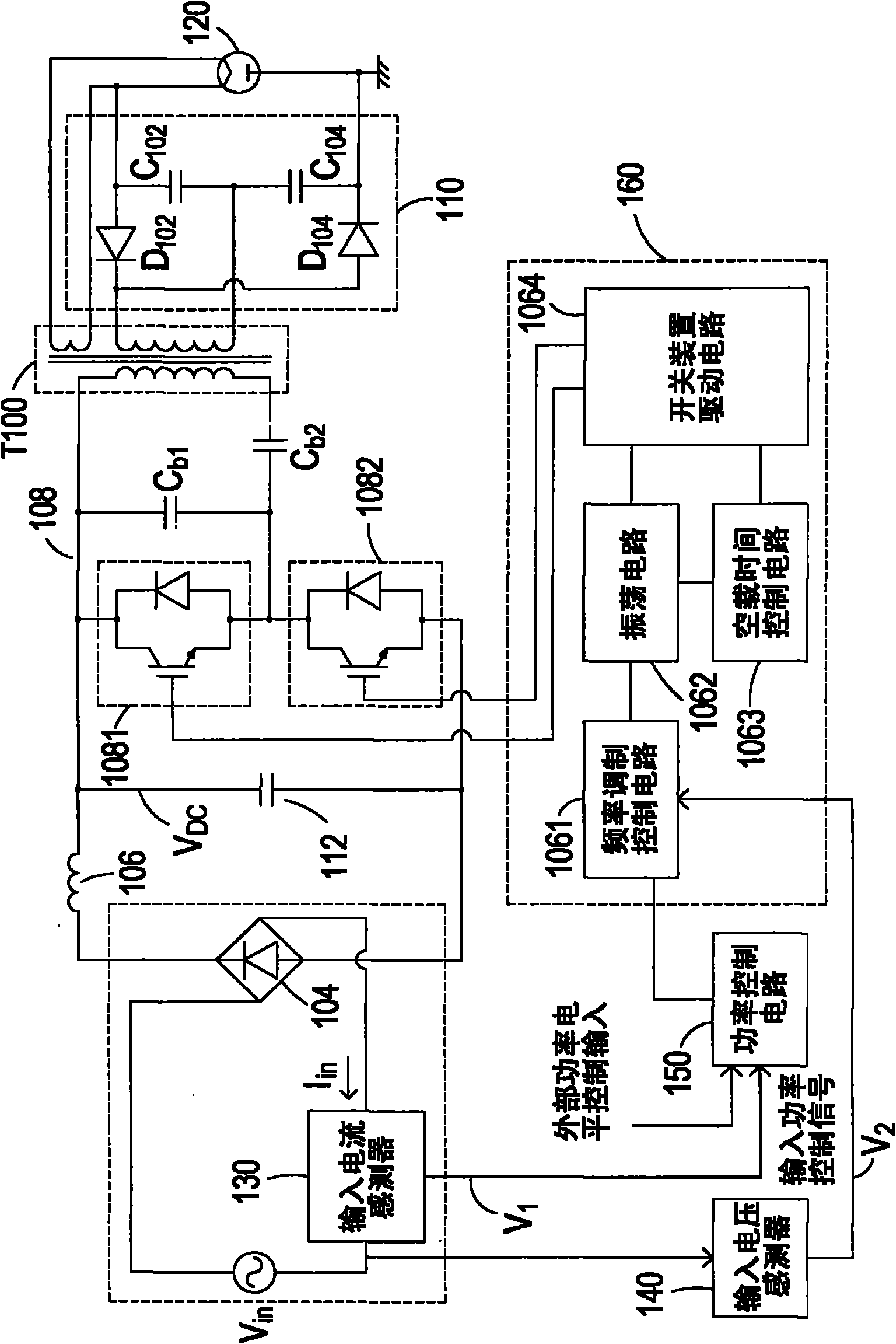
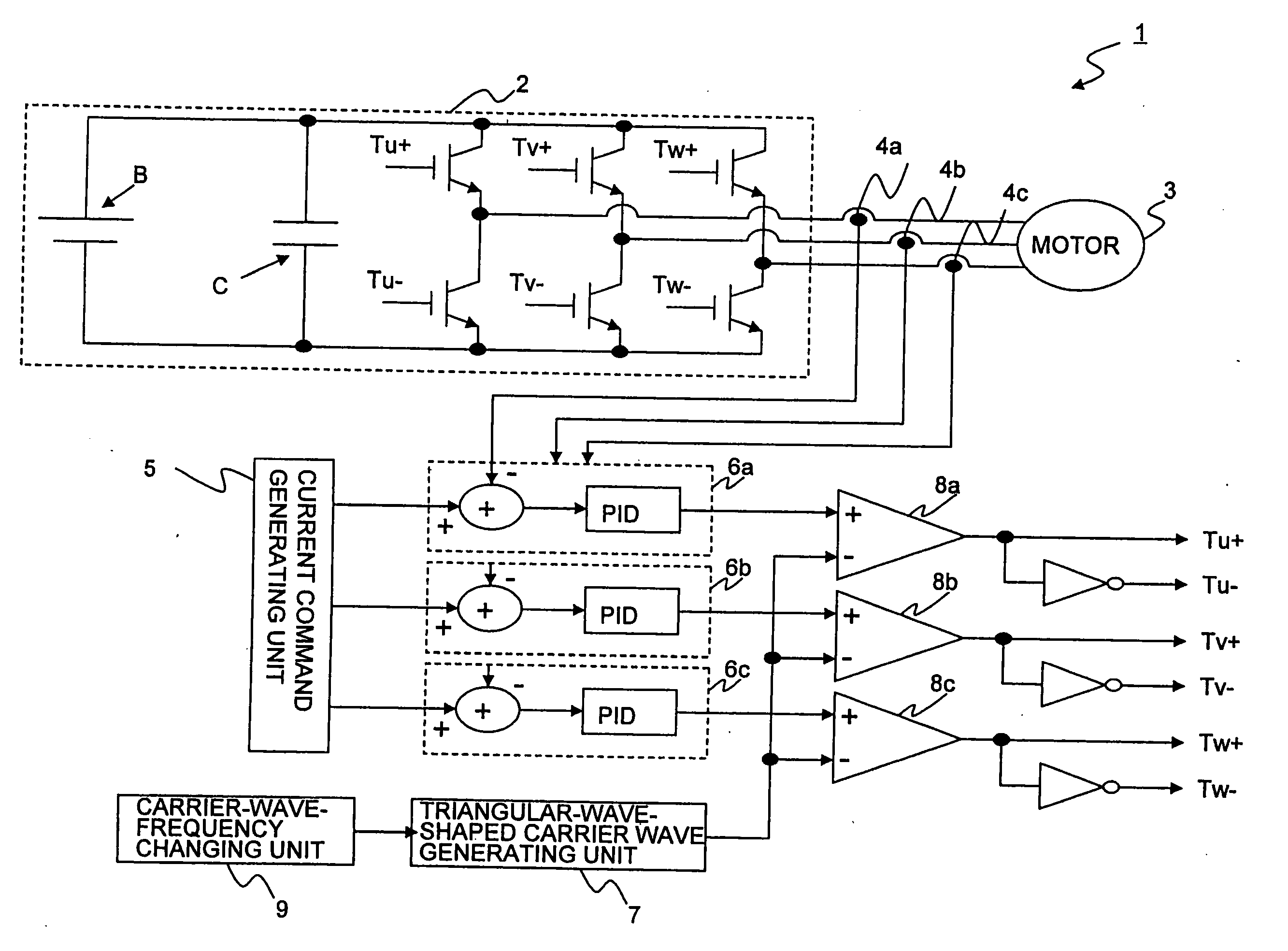
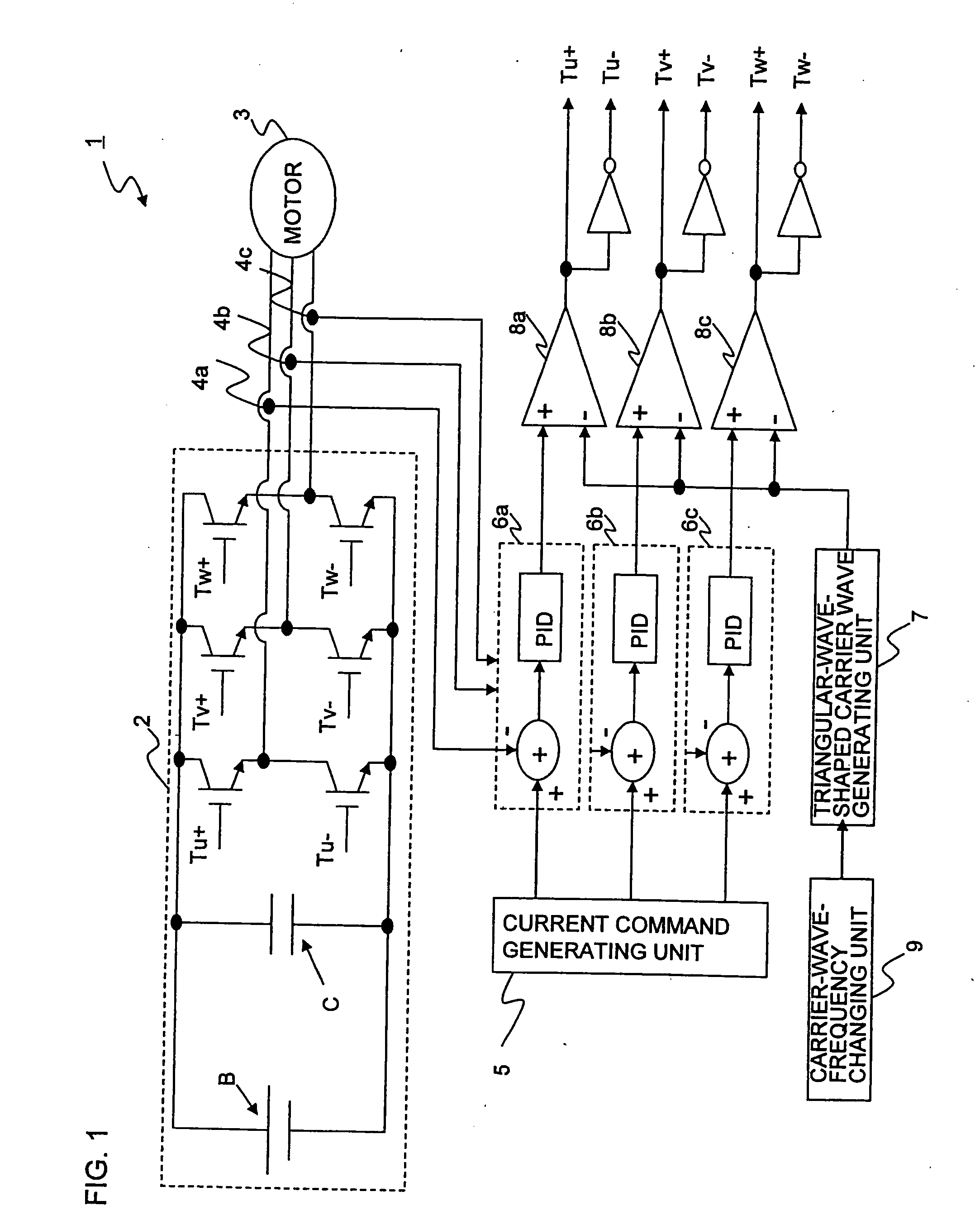
Power Converting Apparatus
InactiveUS20100164418A1Reduce noiseSynchronous motors startersDC motor speed/torque controlWave shapeFull width at half maximum
To reduce, in a power converting apparatus for an electric locomotive, a sixth-order harmonic noise induced by a torque ripple component equivalent to a sixth-order frequency of an inverter frequency. When a motor is driven in a three-pulse mode to drive the electric locomotive, three pulses included within a ½ cycle of the inverter frequency in a PWM waveform, which is used for controlling a switching element of an inverter unit that drives the motor, are set to satisfy Tq≧T / 8, Tp≦Tq / 2, and Tr≦Tq / 2 where, assuming that the three pulses include a first pulse, a second pulse, and a third pulse from an order of generation, Tp is a pulse width of the first pulse, Tq is ½ of a pulse width (full width at half maximum of a pulse) of the second pulse, Tr is a pulse width of the third pulse, and T is a cycle of the inverter frequency.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
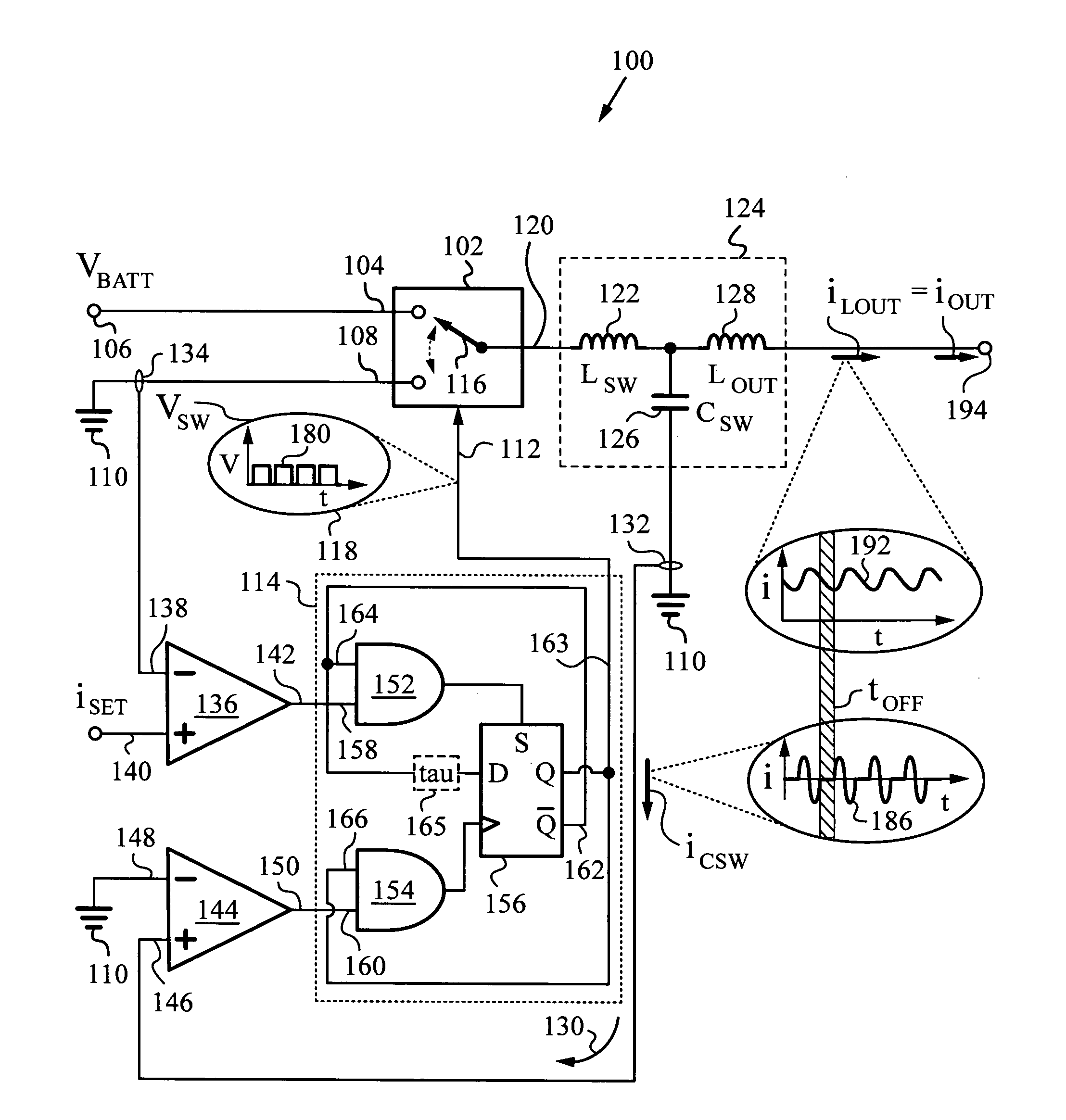
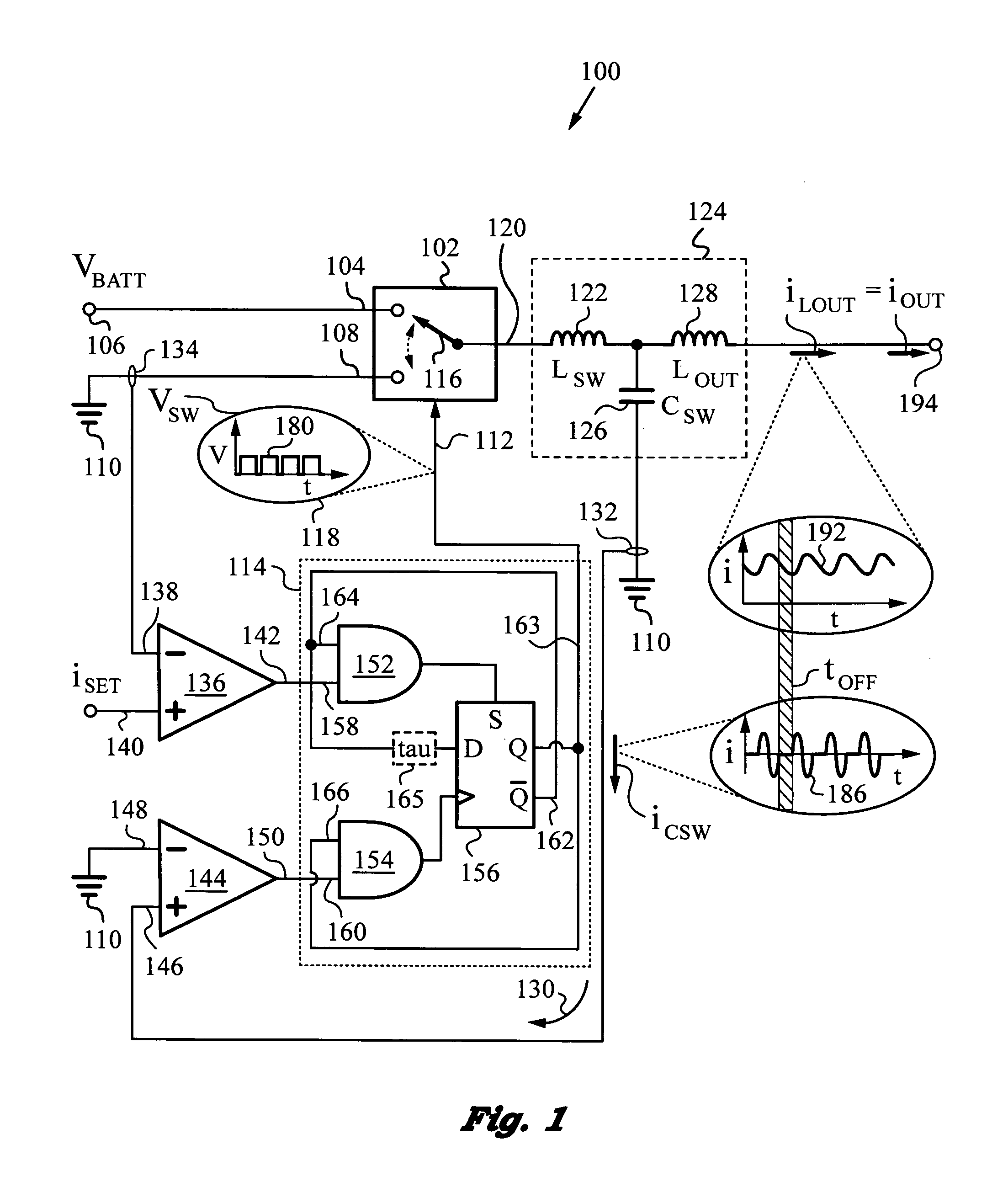
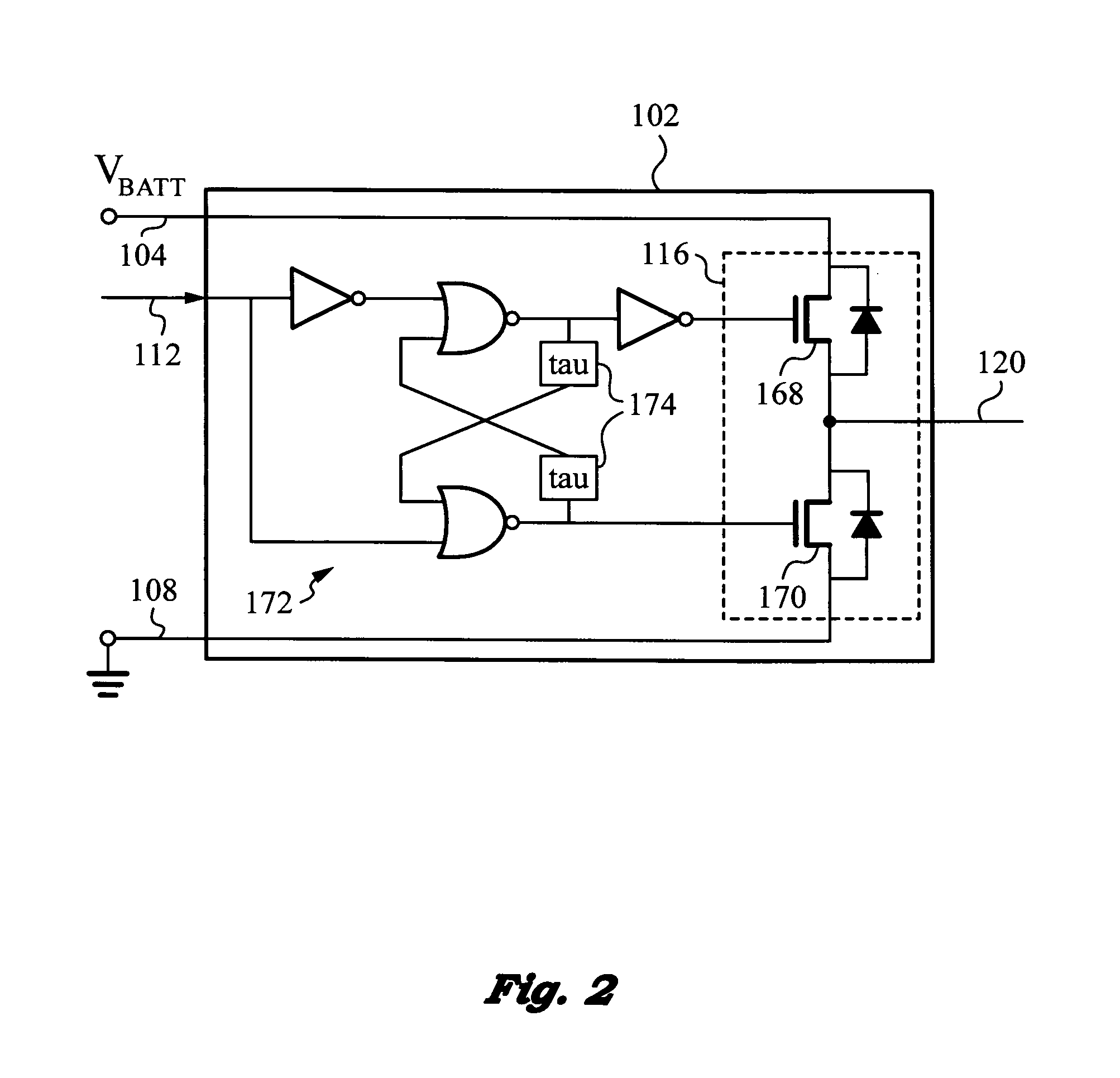
Low-noise, high bandwidth quasi-resonant mode switching power supply
ActiveUS20130214752A1Easy Feedback ControlEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionLow noiseCurrent sensor
High bandwidth, low noise switching power supply operating in quasi-resonant mode for filtering switching harmonic noise, while providing a fast control bandwidth and power at high efficiency. The power supply has an LCL tank defining a resonance period Ttank, and a switching circuit regulation loop for turning on its switching circuit for on-time tON commencing at a time based on a state of regulation of the power supply. A switching capacitor current sensor triggers the switching circuit to turn off at the end of the resonance period Ttank, whereupon the switching and output inductors enter a discharging phase for a period not related to resonance period Ttank. “Quasi-resonant” operation, where the power supply is in resonant mode during on time tON and not in resonant mode during off time tOFF ensures that the output inductor filters the switching harmonic noise of the switching circuit.
Owner:QUANTANCE
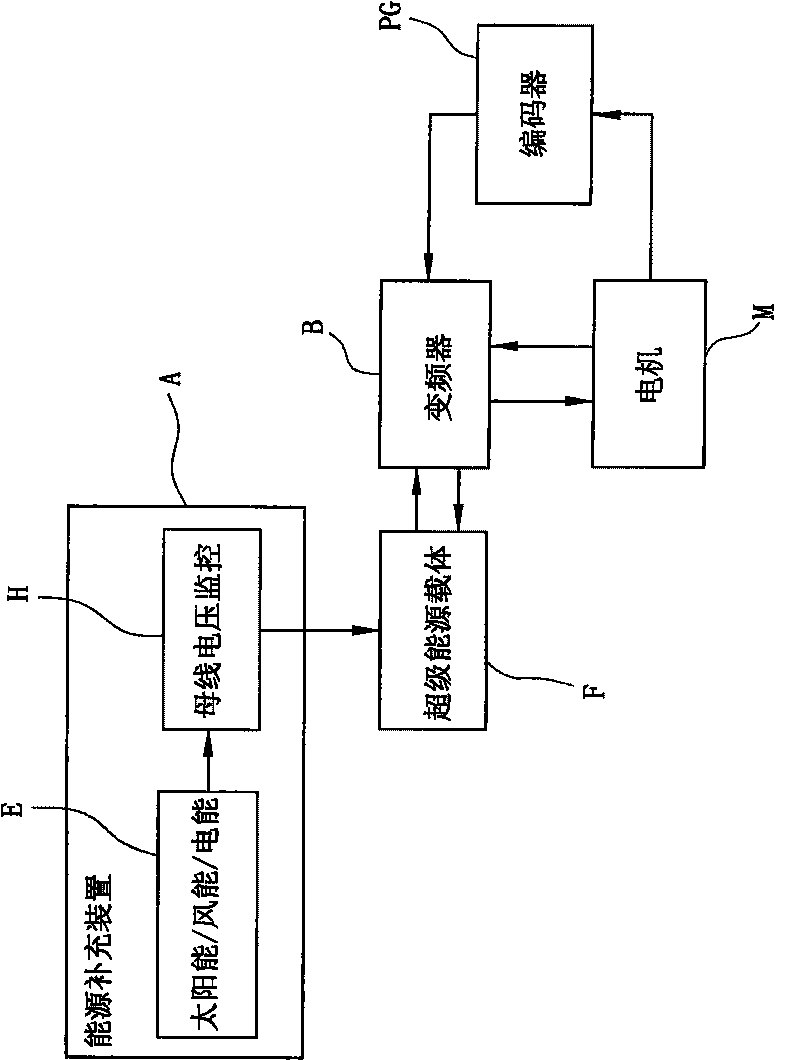
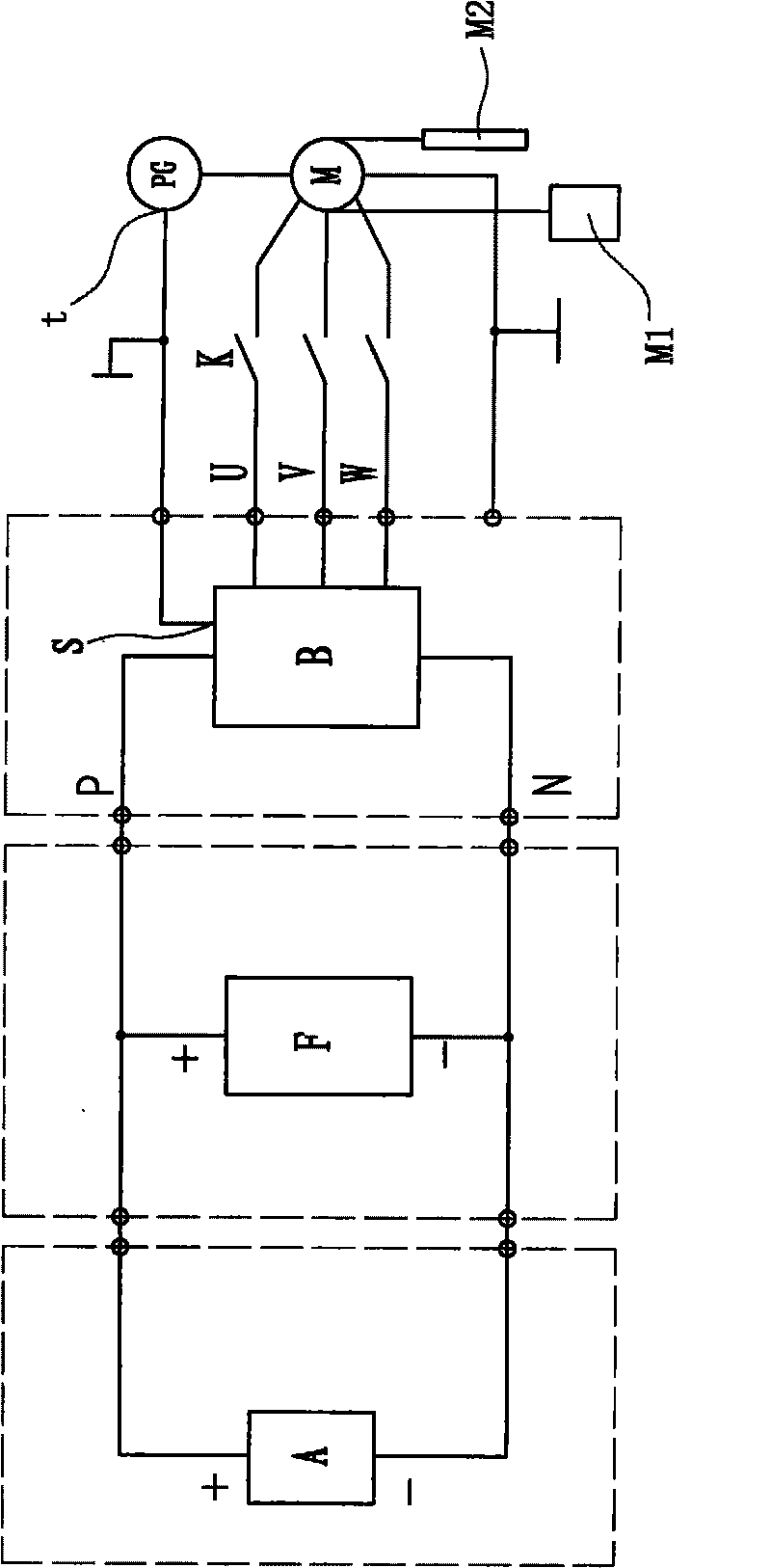
Micro power consumption elevator
InactiveCN101697429ALow costAvoid heat pollutionElectrical storage systemMotor/generator/converter stoppersFrequency changerElectrical battery
The invention relates to a micro power consumption elevator, which comprises a motor, a frequency converter and an encoder. The micro power consumption elevator is characterized by further comprising a super-capacitor component, wherein an positive electrode of the super-capacitor component is connected with a positive electrode input end of the frequency converter; an negative electrode of the super-capacitor component is connected with a positive electrode input end of the frequency converter; in a motor power generation state, the super-capacitor component stores the electric energy generated by the motor, and in a motor electro-motion state, the super-capacitor component supplies power to the motor for running; and an energy supplement device charges the super-capacitor component when the working voltage of the super-capacitor component is lower than a designed voltage lower limit value. The micro power consumption elevator has the advantages that the super-capacitor component is used as a main power supply carrier for continuously supplying power to the elevator and the super-capacitor component not only serves as an energy storage element but also serves as a battery and makes full use of the electric energy generated in the running process of the elevator so that a brake unit (or a brake resistor) is unnecessary to be arranged in the elevator, an inverter is also unnecessary to be arranged in the elevator, not only the equipment cost is saved, but also thermal pollutions and harmonic noise pollutions are avoided, and the micro power consumption elevator is more energy-saving and environment-friendly.
Owner:林肯电梯(中国)有限公司
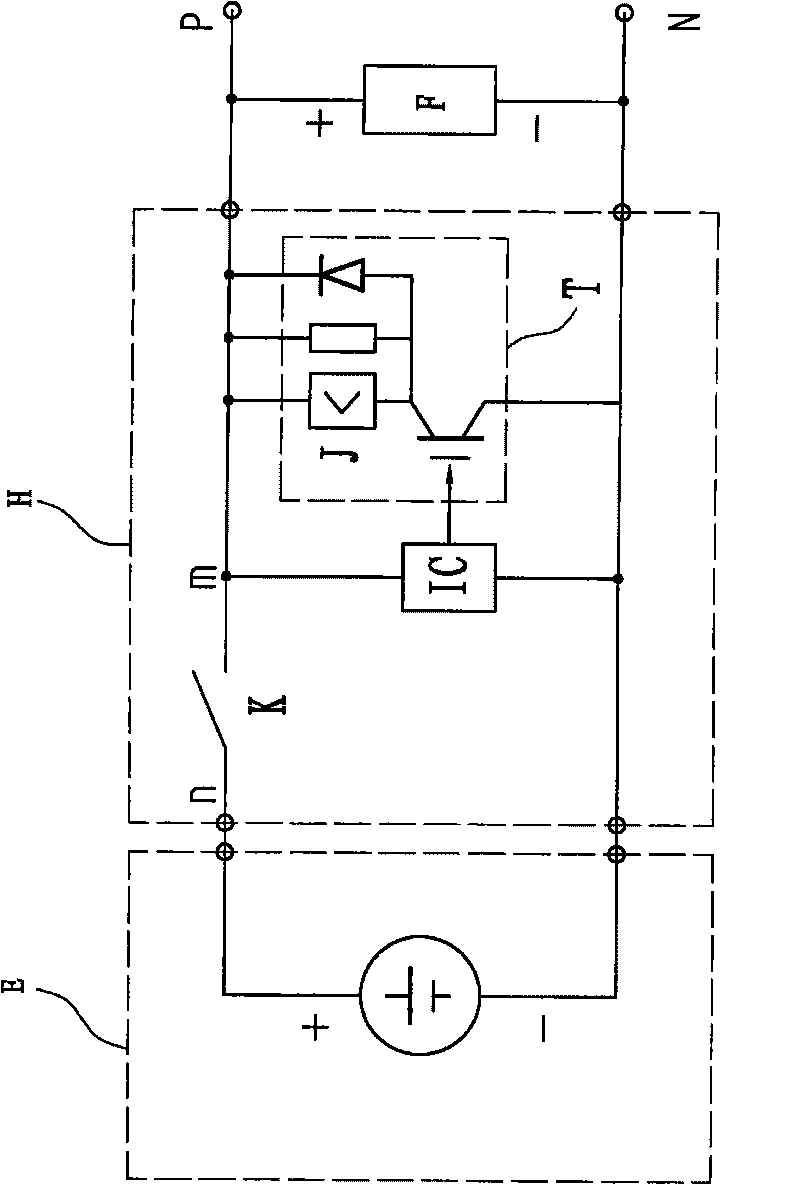
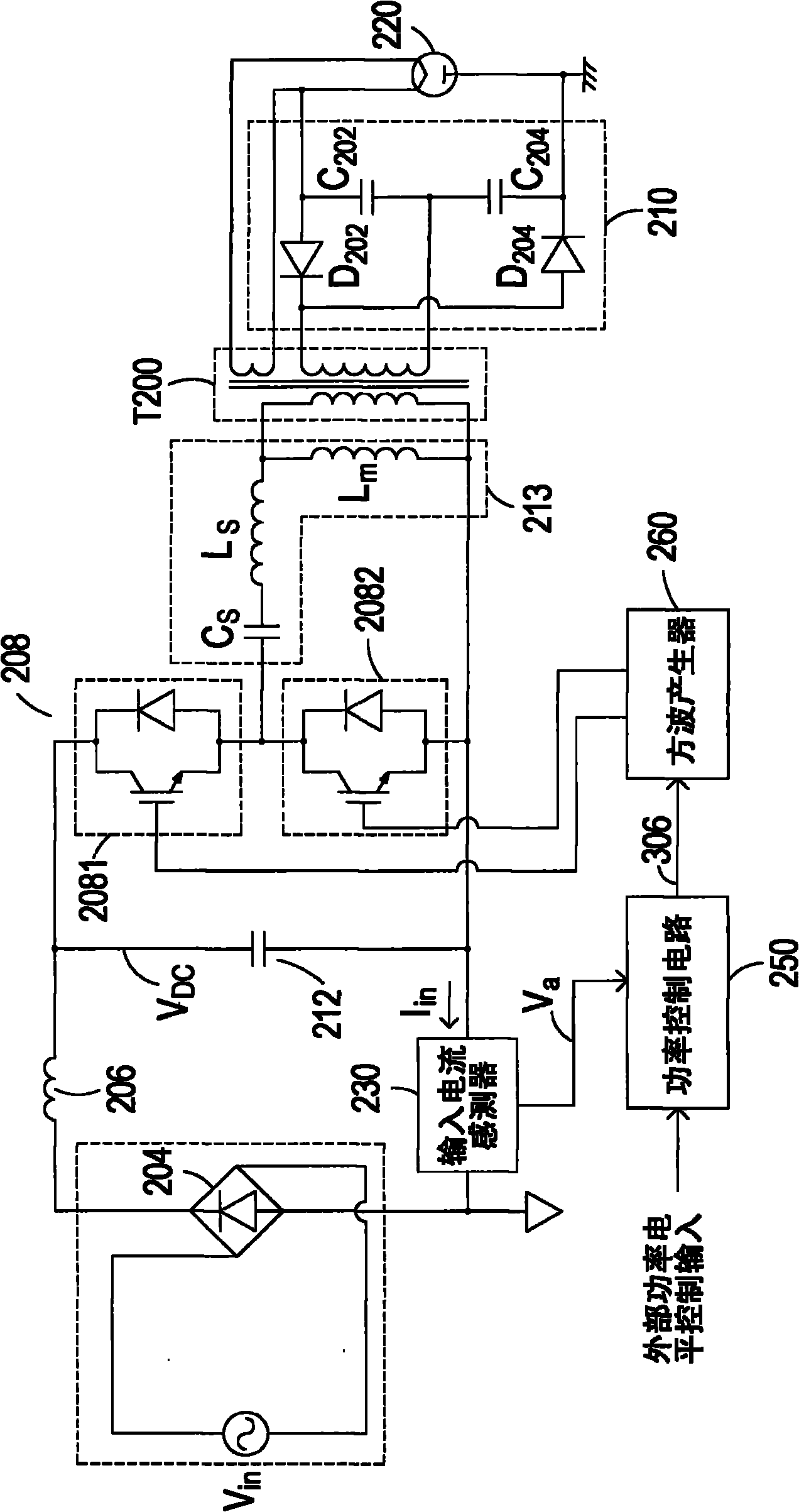
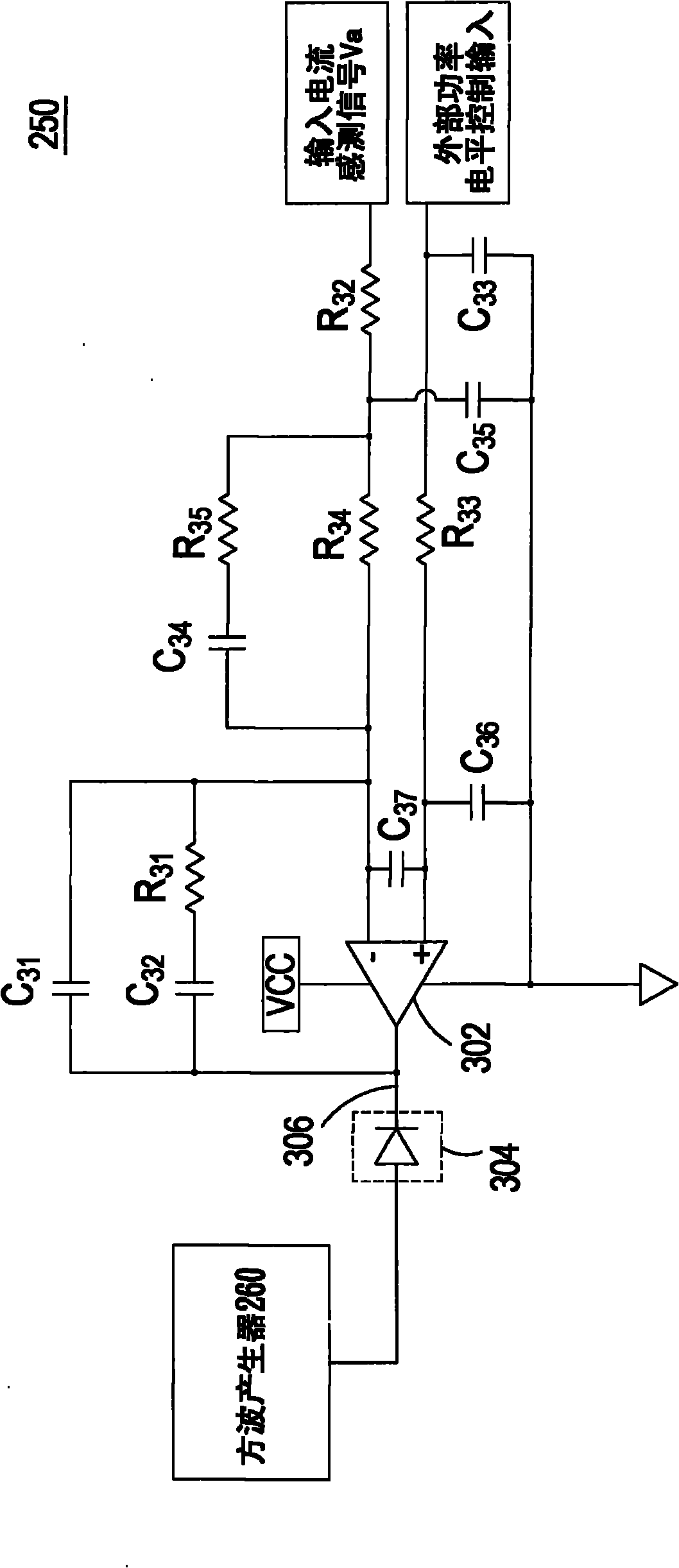
Alternating-current to direct-current converter and control circuit thereof
ActiveCN102340251AEliminate Harmonic NoiseOutput power adjustmentAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionControl signalHarmonic control
The invention provides an alternating-current to direct-current converter and a control circuit thereof. The control circuit comprises a power control circuit and a square wave generator, wherein the power control circuit is used for comparing an input current sensing signal generated by one input current of the alternating-current to direct-current converter with a frequency modulation control signal generated by a power level control input, and the frequency modulation control signal is also used for the output power control of the alternating-current to direct-current converter and the harmonic control of the input current; and the square wave generator is connected to the power control circuit and generates a driving signal for driving the switching circuit of the alternating-current to direct-current converter according to the frequency modulation control signal, the frequency of the driving signal changes with the frequency modulation control signal, therefore the harmonic noise of the input current of the alternating-current to direct-current converter is eliminated, the switching frequency of a switch is adjusted and the output power of the alternating-current to direct-current converter is adjusted at the same time.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
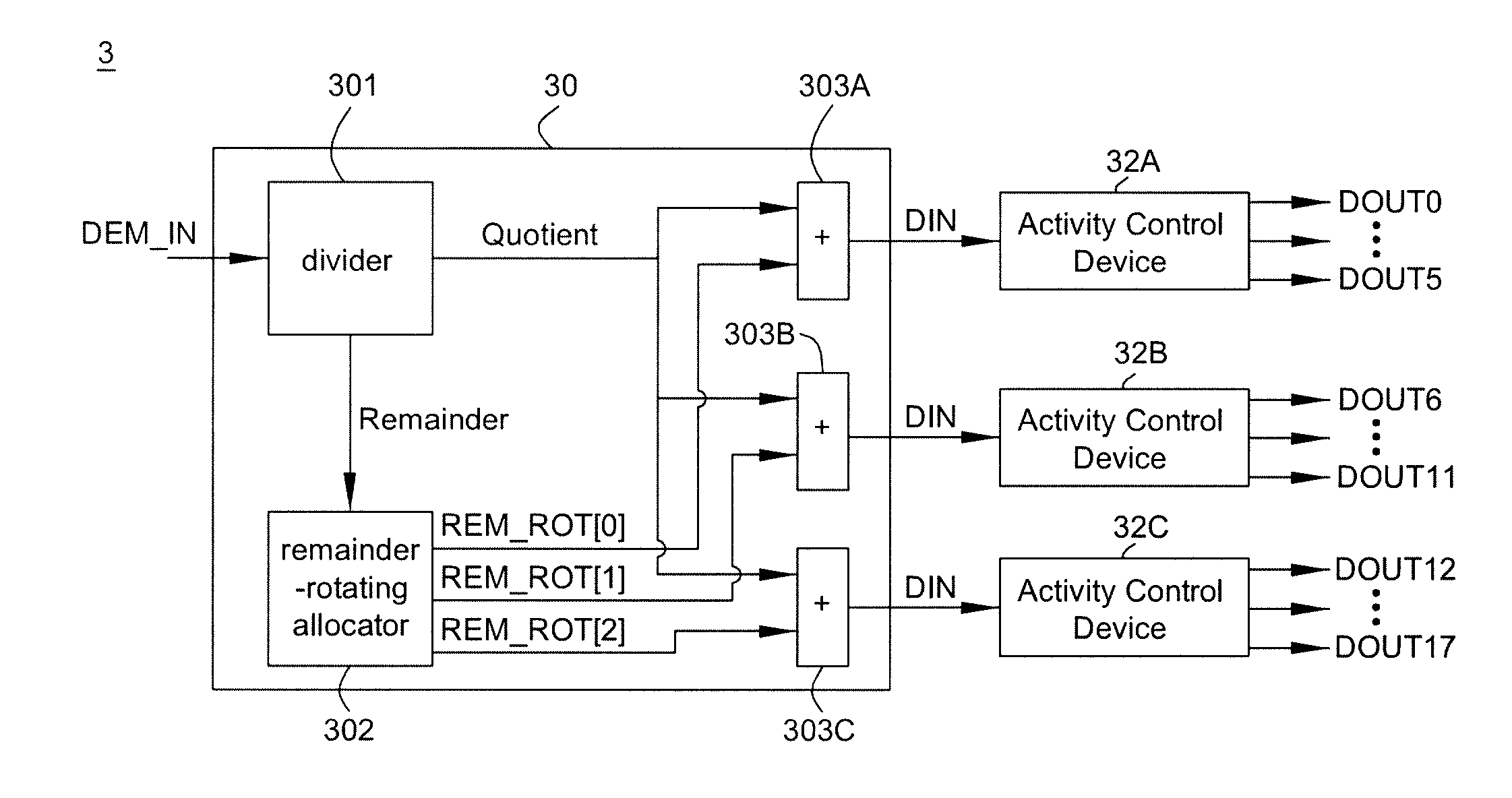
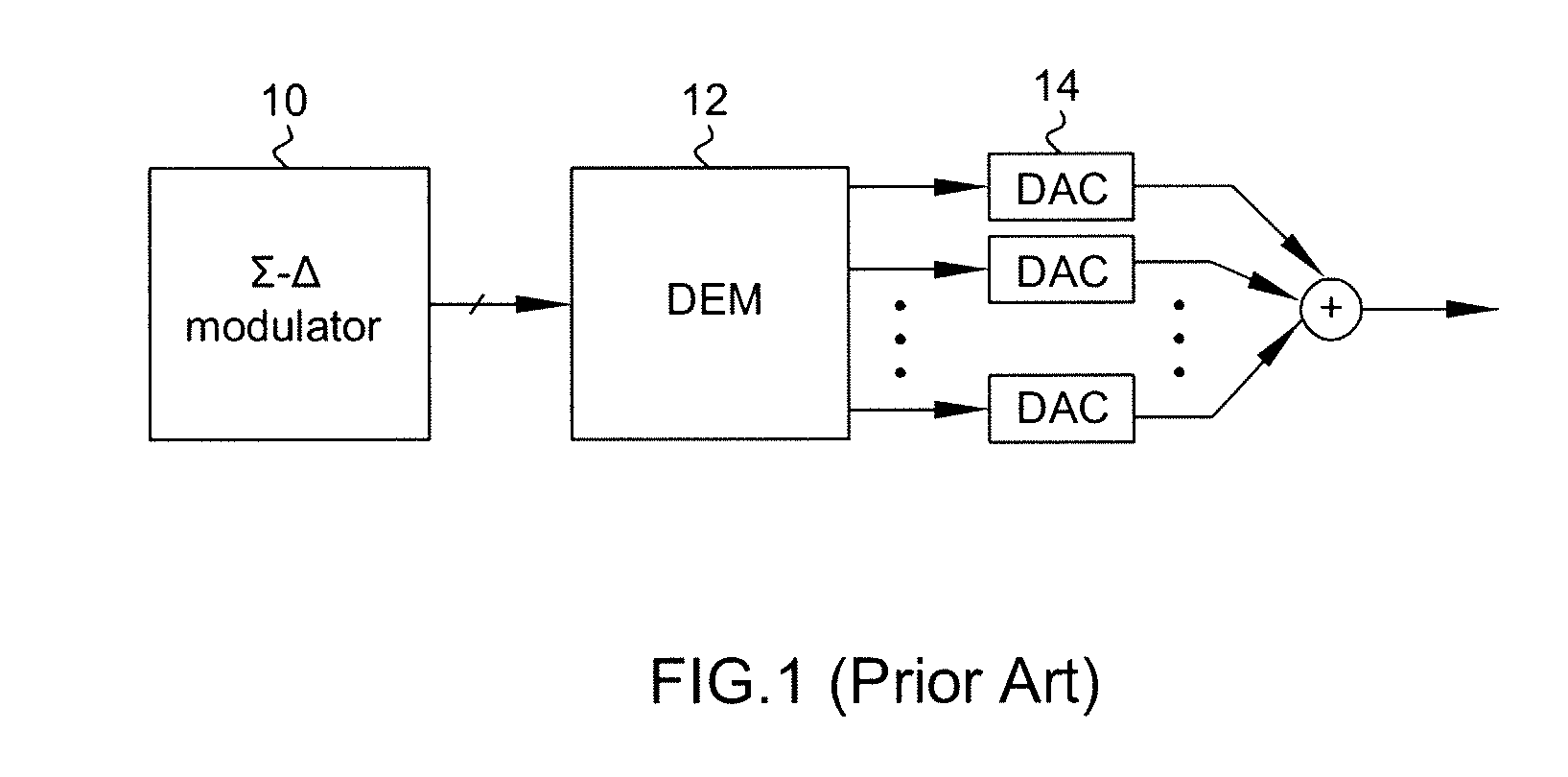
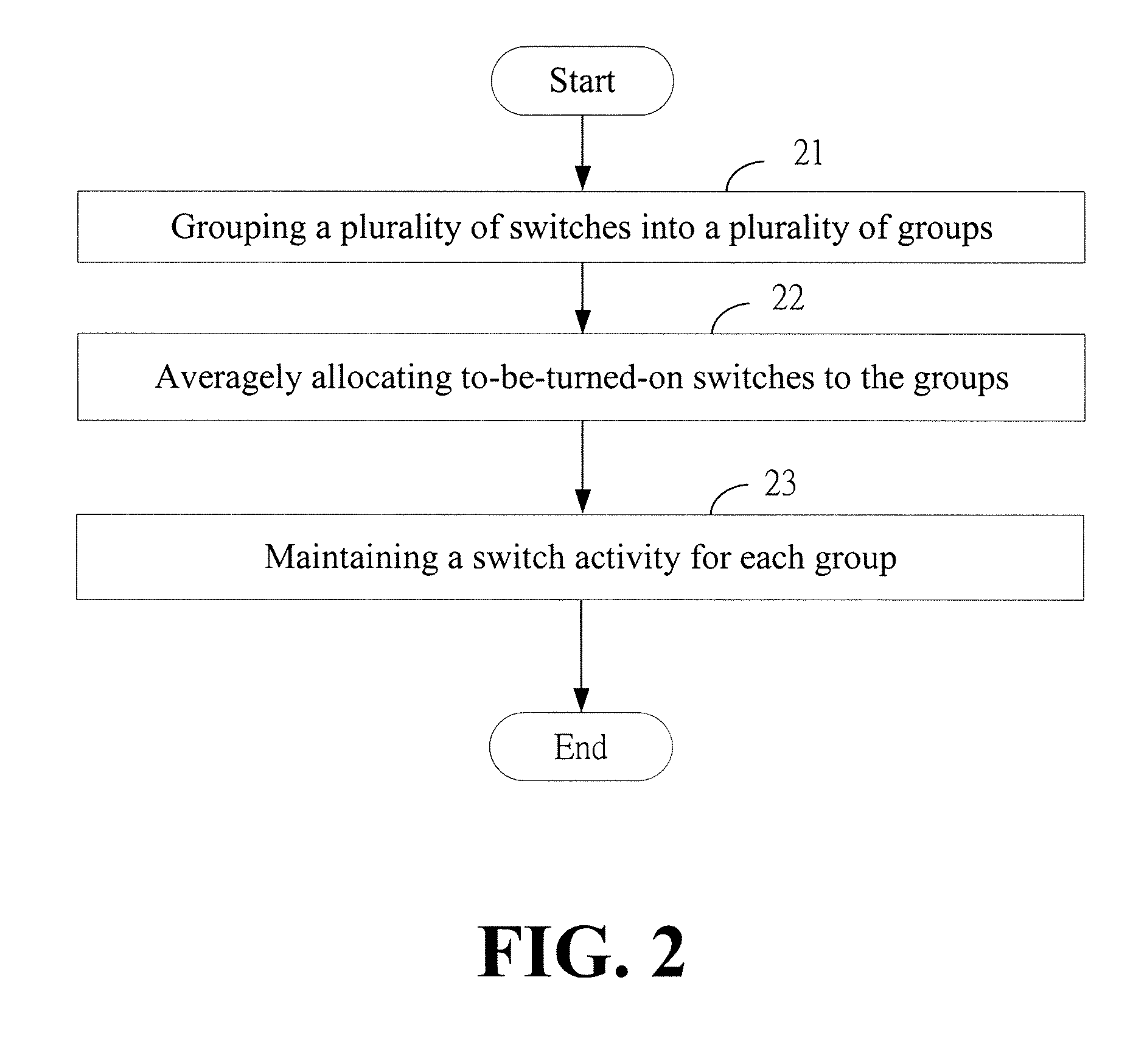
Dynamic Element Matching Method and System Thereof
ActiveUS20110227629A1Reduce noiseElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionMatching methodsHarmonic noise
A dynamic element matching method and system thereof is provided. The method includes grouping a plurality of switches into a plurality of groups; allocating a plurality of to-be-turned-on switches of the switches for an input signal to the groups; and maintaining a switch activity of each of the groups at a predetermined value. Accordingly, mismatch noise and harmonic noise are effectively reduced.
Owner:XUESHAN TECH INC
Vibroseis acquisition method
ActiveUS20100142320A1Enhance fundamentalSeismic data acquisitionSeismic signal processingHarmonic noiseFrequency interval
A method of performing a Vibroseis survey is described including the step of obtaining signals generated by activating vibratory sources at times T0 and T1, respectively, for a sweep period S and a listening time L such that T1<T0,S+L, wherein harmonic noise within the signals are attenuated using a first method to estimate the harmonics in a time-frequency interval in which harmonics of the sweep T1 overlap with the response to the fundamental of sweep T1 and using a second method for estimating the harmonics in a time-frequency with no overlap.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
System and method for nonlinear radar
A non-linear radar is disclosed that is able to detect non-linear target responses that are below the harmonic-noise floor of the radar. To accomplish this below-the-noise-floor sensitivity feature the proposal specifically addresses all of the problems commonly faced by non-linear radar such as linearity of the transmitter path, receiver path, and size, weight, and power, and cost (SWaP-C). The radar operates in both standard and nonlinear modes with signal processing that allows display of nonlinear alone, linear alone, or both types of backscatter. Different combinations of six methodologies allow customization to fit different application needs, from low-cost modest performance, to higher cost and extremely high performance.
Owner:APPLIED SIGNALS INTELLIGENCE
Methods of manufacture for a low control voltage switch
ActiveUS7129767B2Low control voltageImprove linearity and harmonic noise rejection characteristicTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringField-effect transistor
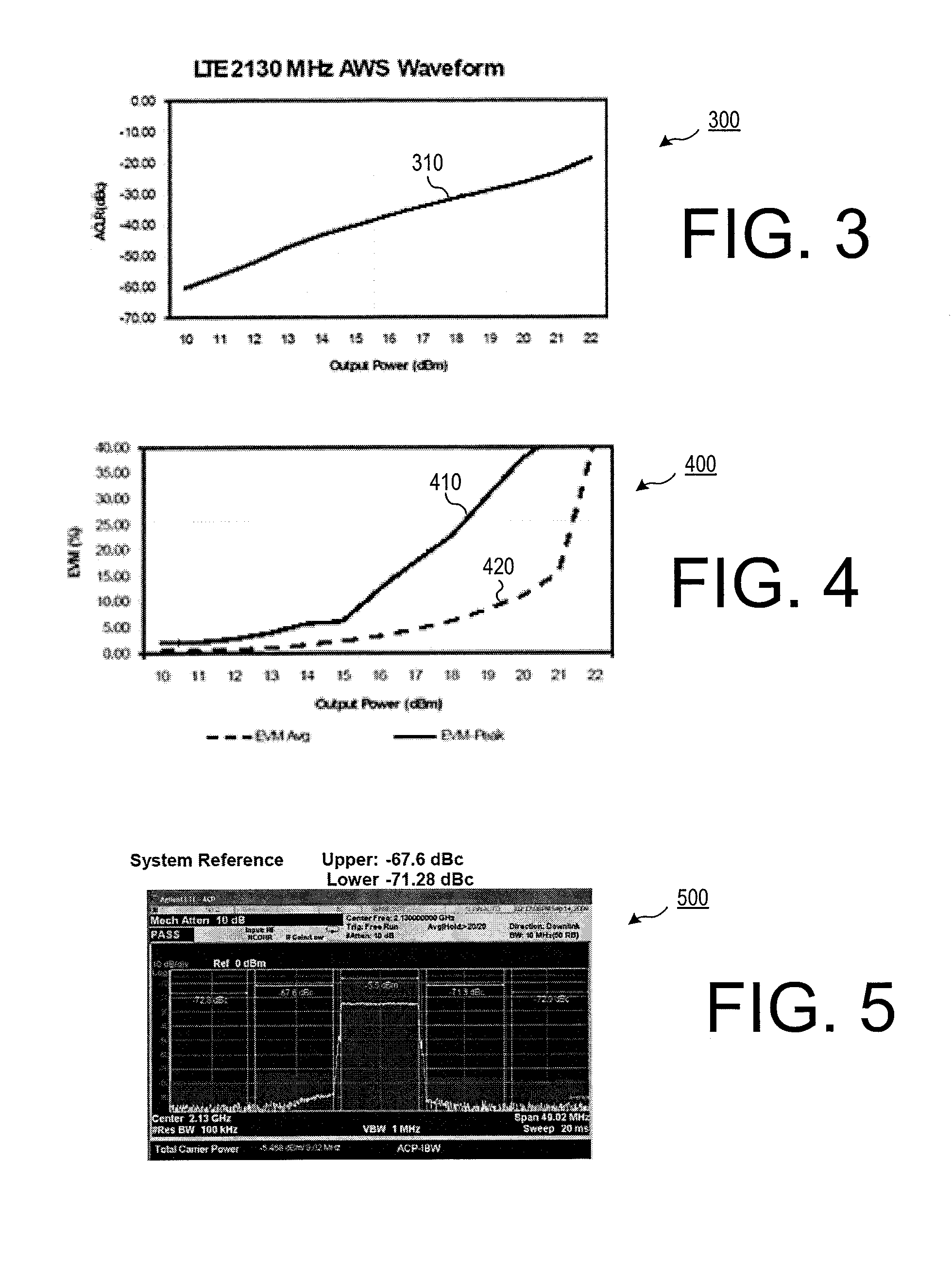
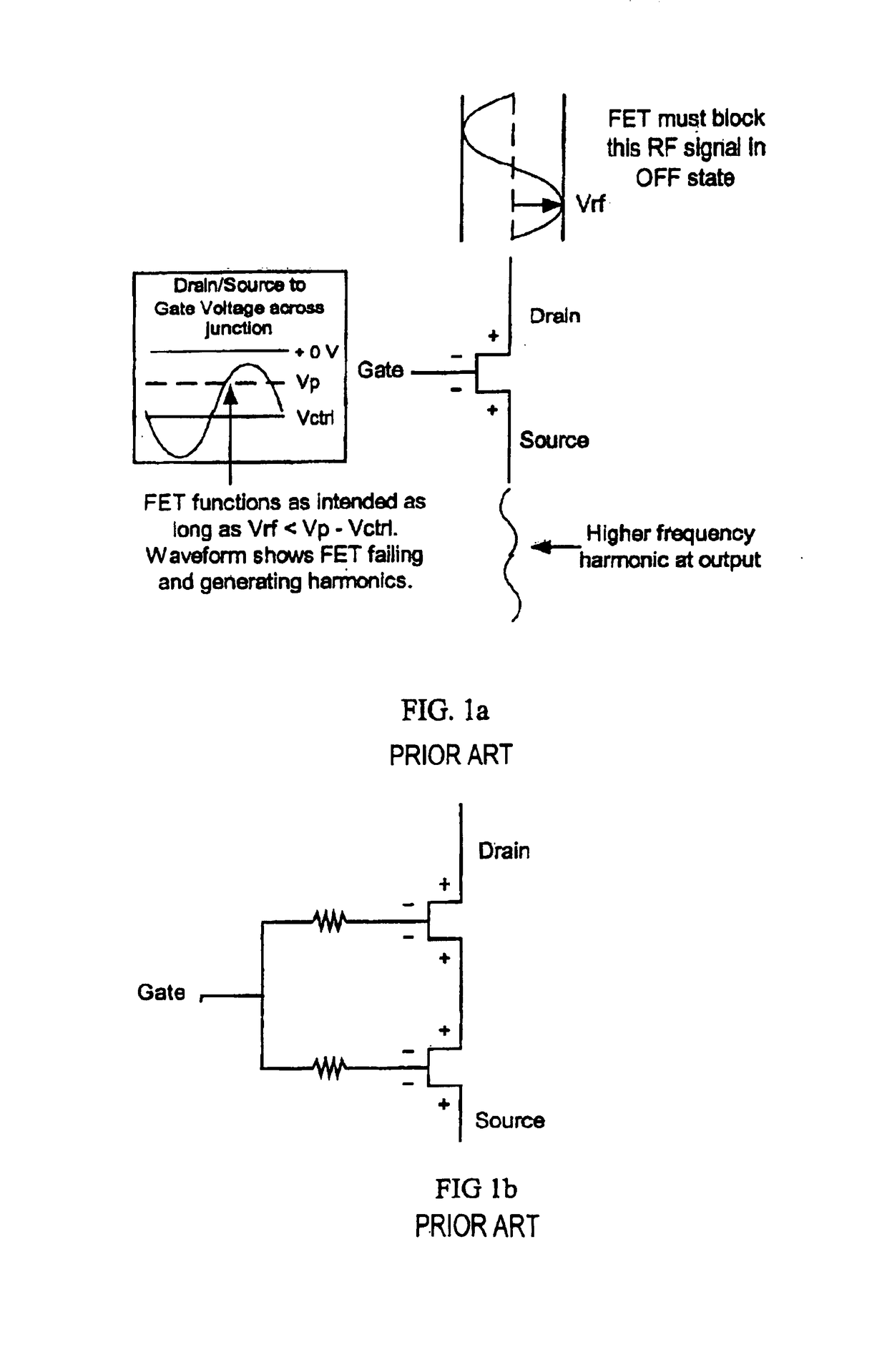
A low control voltage switch utilizing a plurality of field effect transistors (FETs) having a total of six gates to allow the switch to operate at a low control voltage without the need to increase device periphery or die size. Feed-forward capacitors connected between the gate and source of an uppermost FET and the gate and drain of a lowermost FET are used to reduce signal distortion and improve the linearity and harmonic noise rejection characteristics of the FETs within the switch and thus lower the harmonics of the switch.
Owner:MACOM TECH SOLUTIONS HLDG INC
Active noise control algorithm for transformer
InactiveCN102176668AEasy accessSimple modeling methodAdaptive networkTransformerFundamental frequency
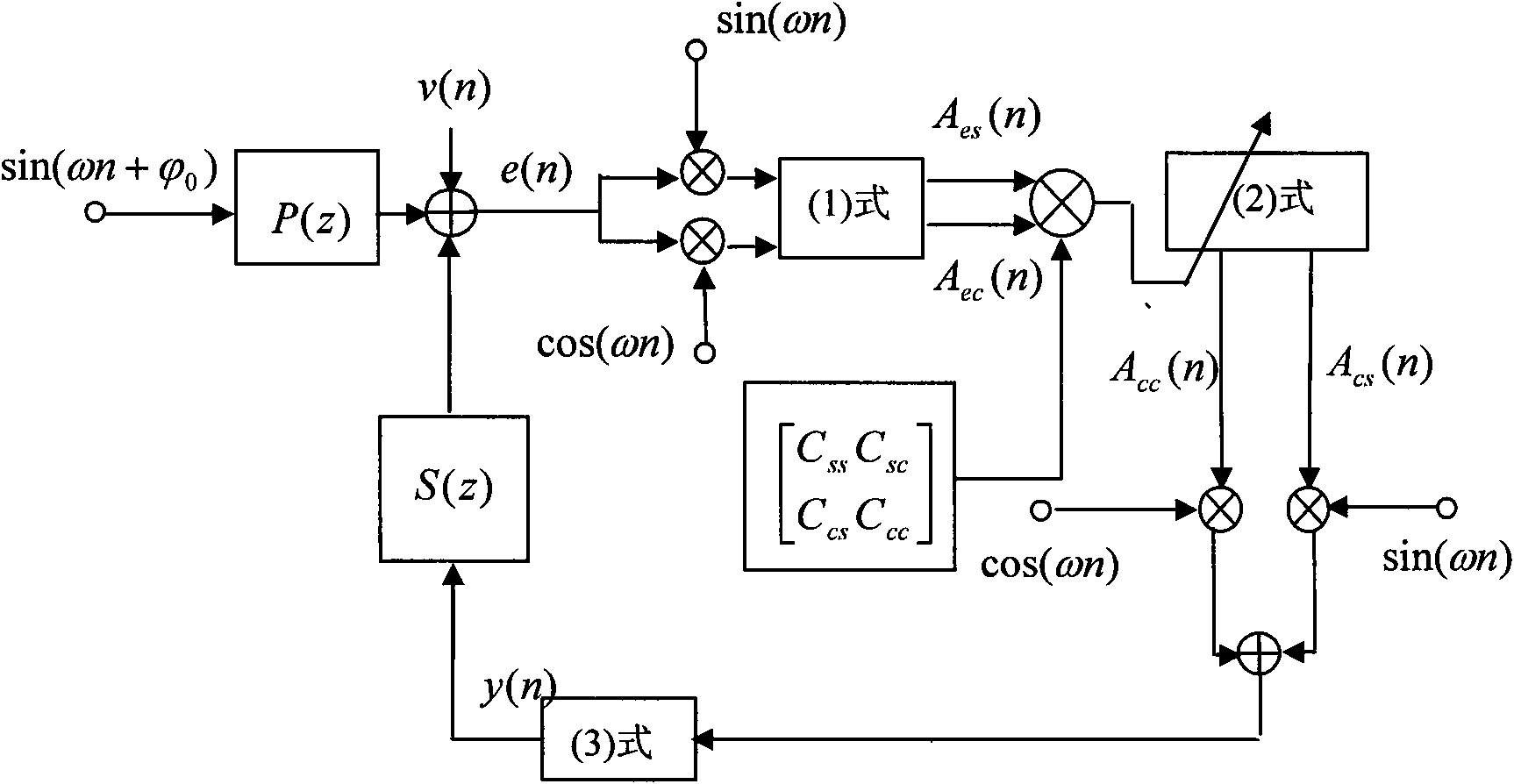
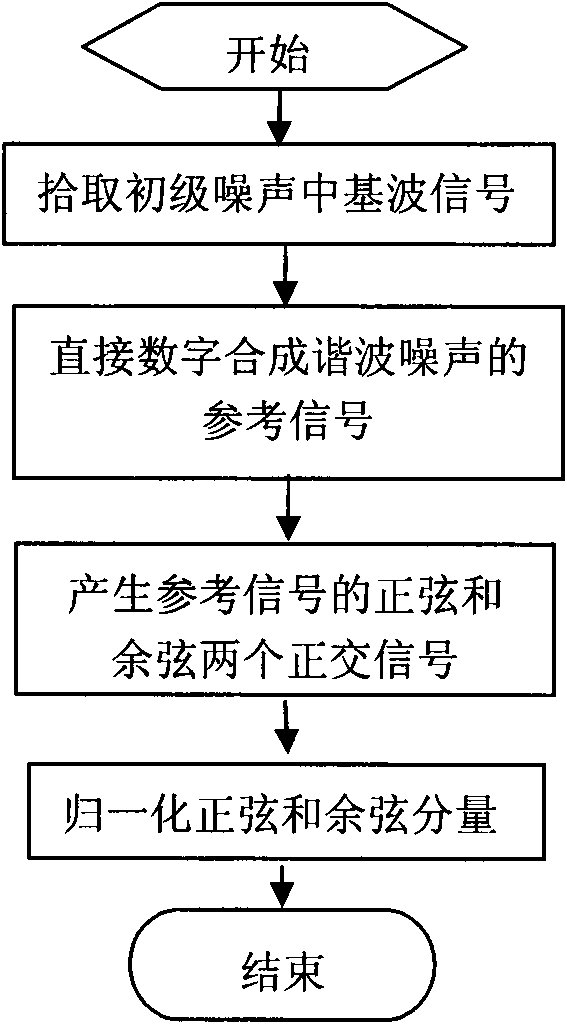
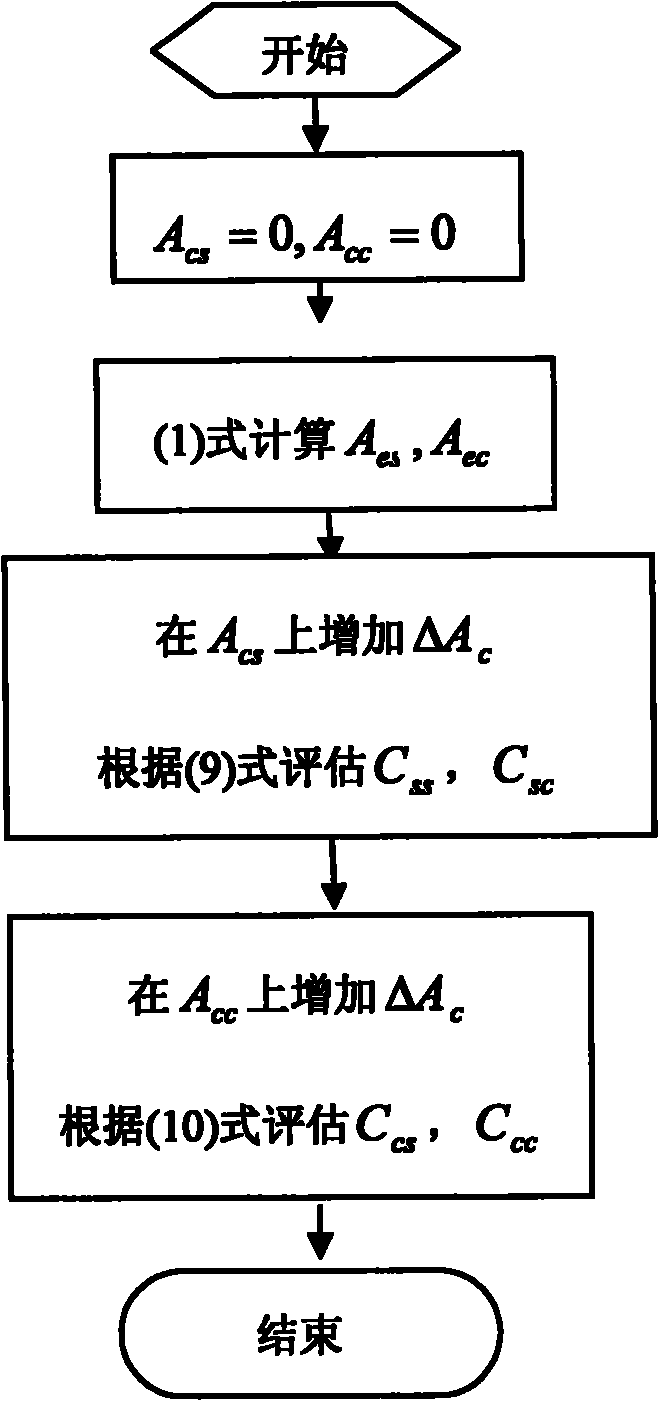
The invention discloses an improved active noise control algorithm for a transformer. The active noise control algorithm has the remarkable advantages that: (1) reference signals are obtained via adopting DDS (direct digital synthesis) by only needing to collect fundamental frequency components in primary noises, thus the reference signals are acquired simply; (2) an simple off-line disturbance modeling method is adopted; and (3) the updating interval of the control weight of the algorithm is a multi-harmonic noise period, thus being low in calculated amount. During modeling, the added disturbance magnitude is over 5 times than variable quantity of primary harmonic noises or over 10% of primary harmonic noise amplitude, thus ensuring to obtain the preferable modeling result of transfer functions of a secondary path. The stability and the noise reduction performance of the algorithm are both considered for the dereferencing of a leakage coefficient (le) in an update formula of the control weight, thus the dereferencing is 0.9999; and the convergence rate and the stability of the algorithm are both considered for the dereferencing of a convergence coefficient (mu), thus the dereferencing is 0.05 when the distance between an error microphone and a control source is 20cm.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Nonlinear narrowband active noise control method based on Volterra filter
InactiveCN104575512AReduce narrowband noiseEasy to implementSpeech analysisNoise controlNonlinear filter
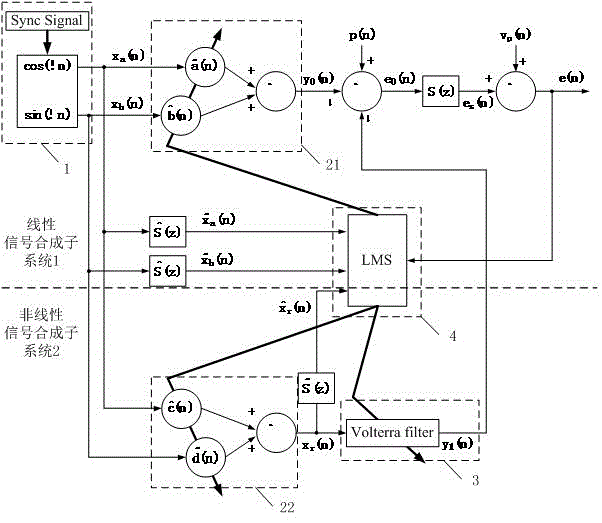
The invention provides a nonlinear narrowband active noise control method based on a Volterra filter and aimed at a situation that higher harmonic noise is generated after a narrowband noise source is distorted nonlinearly. A linear signal synthesis subsystem (1), a nonlinear signal synthesis subsystem (2), a reference signal generation module and a least mean square algorithm module are used in the method; a reference signal in the method is generated by a synchronous signal generator based on a source noise frequency obtained by a non-acoustic sensor; one part of a secondary source is synthesized through a linear combiner, the other part of the secondary source is synthesized through another linear combiner and the nonlinear Volterra filter, and when primary source noise is distorted nonlinearly, a fundamental component and a higher harmonic component are independently inhibited by a linear filter and the nonlinear Volterra filter respectively. According to the nonlinear narrowband active noise control method, the nonlinearly distorted narrowband noise can be effectively inhibited, and the influence of nonlinearity on system performance can be easily analyzed due to an independent working structure.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
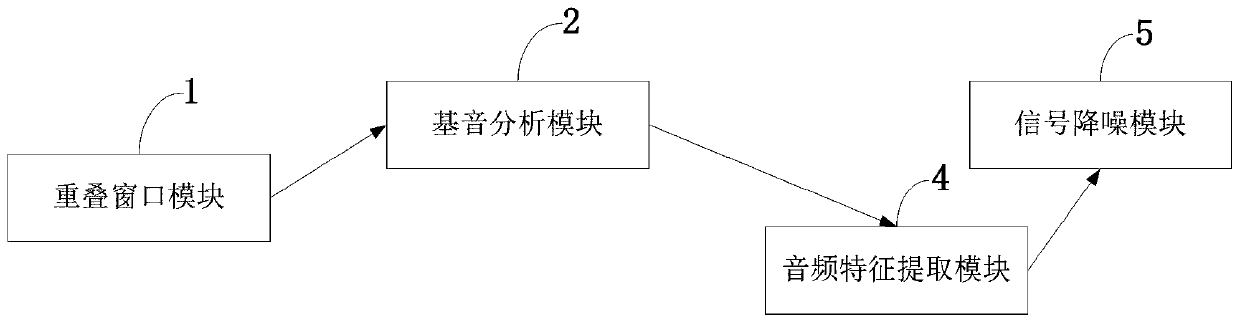
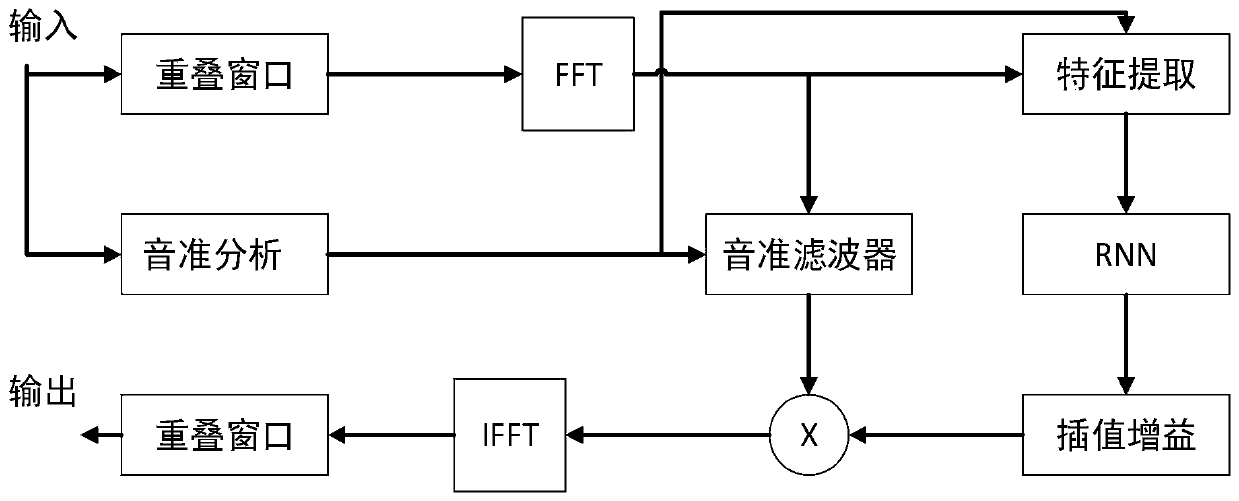
Audio noise reduction system and method based on structure of GRU network
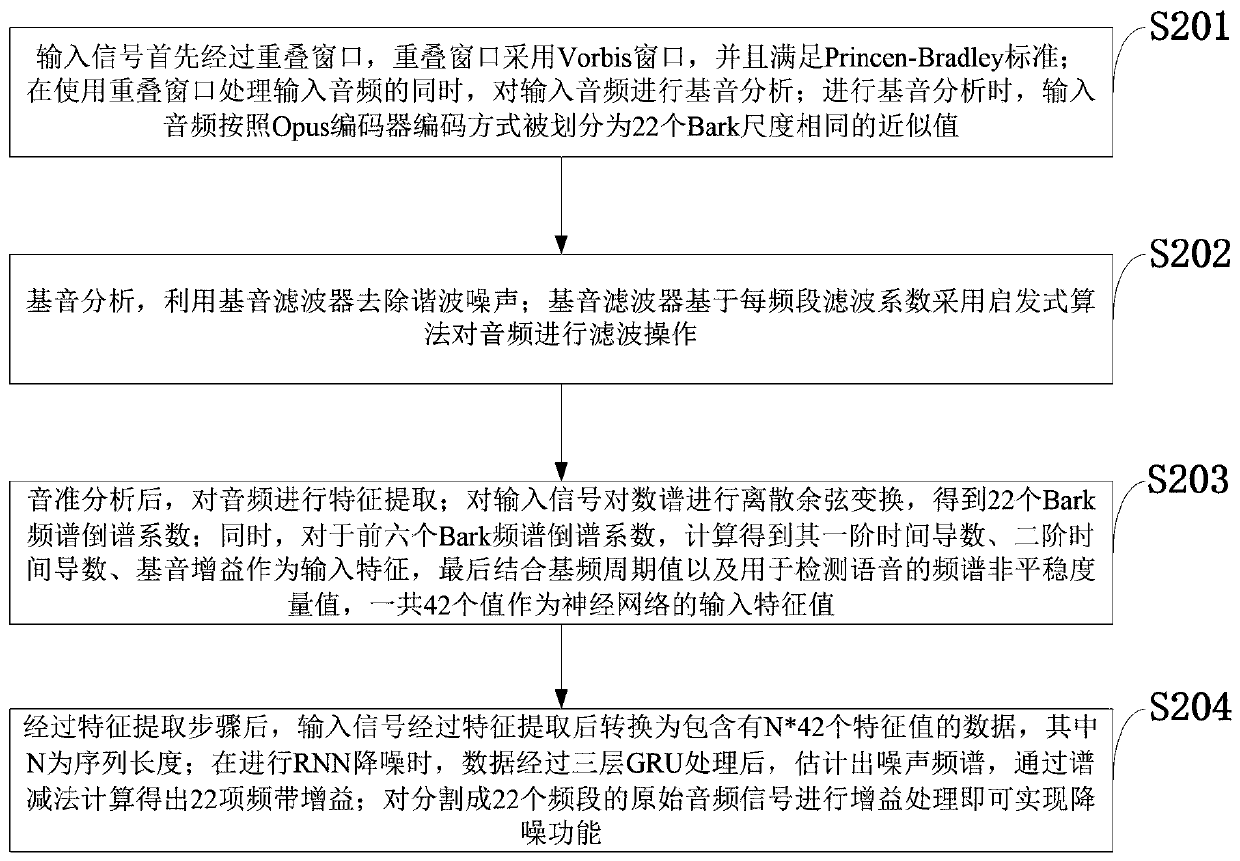
The invention belongs to the technical field of Internet audio processing, and discloses an audio noise reduction system and method based on a structure of a GRU network. The noise reduction method based on the structure of the GRU network comprises the following steps: enabling input signals to pass through an overlapping window at first, wherein the overlapping window is a Vorbis window, and meets the standard of Princen-Bradley; fundamental tone analysis: removing harmonic noises by using a fundamental tone filter; carrying out feature extraction on audio after fundamental tone analysis; after the feature extraction step is carried out, converting the input signals into data containing N* 42 feature values after feature extraction, wherein N is a sequence length; when RNN noise reduction is carried out, after three layers of GRU processing are carried out on the data, estimating a noise frequency spectrum, and calculating to obtain 22 frequency band gains through spectral subtraction; carrying out gain processing on the original audio signals divided into 22 frequency bands so as to fulfill a noise reduction function. Compared with a traditional audio noise reduction scheme suchas Speex, the audio noise reduction system and method realize better properties to a certain extent.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
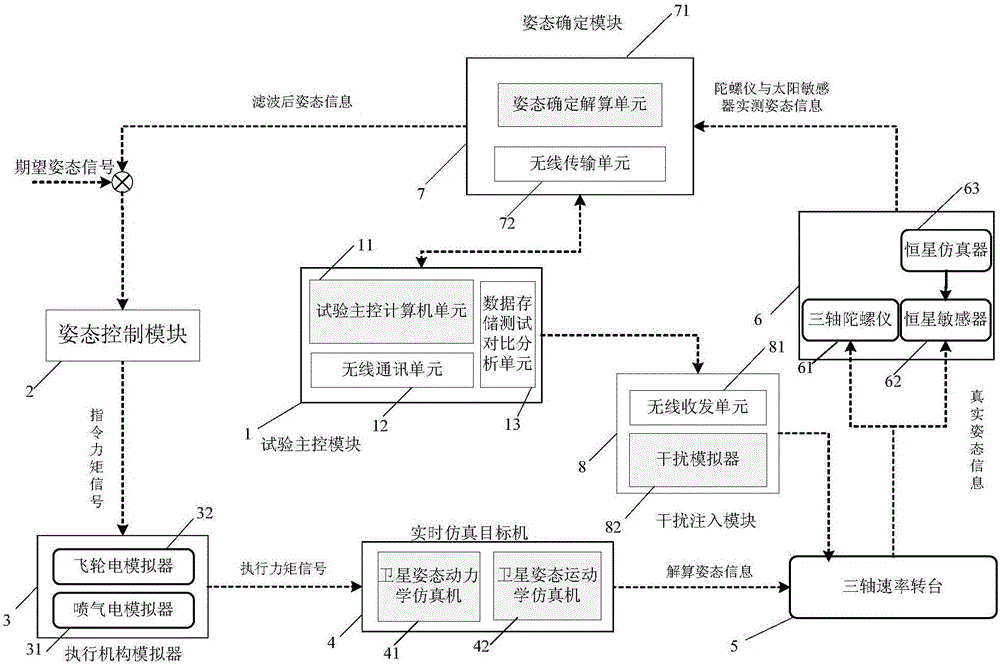
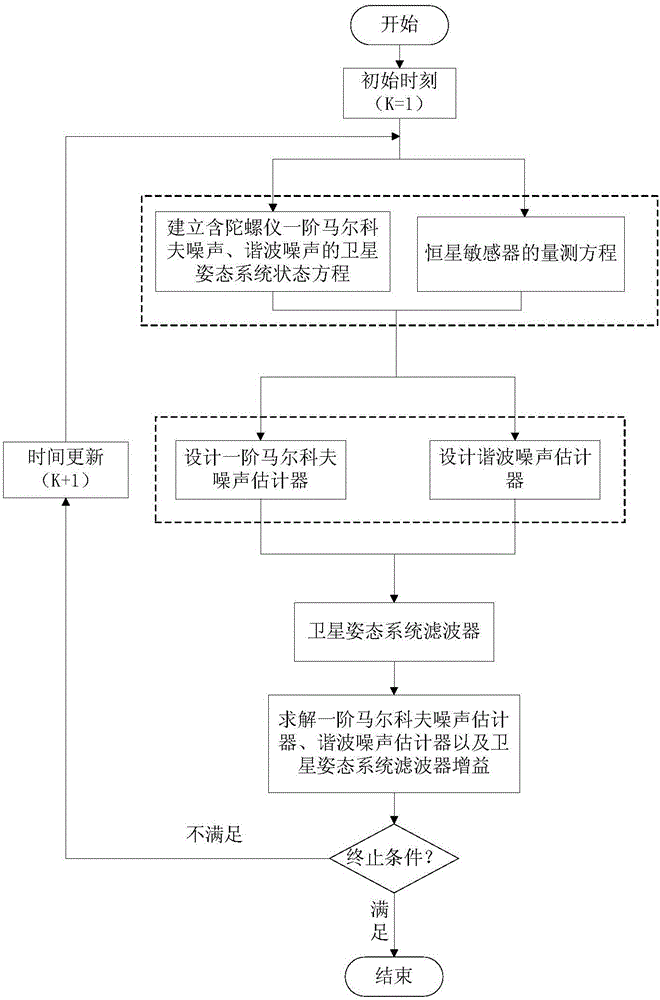
Method for determining anti-interference attitude in multi-source interference environment, and test platform
The invention relates to a method for determining the anti-interference attitude in multi-source interference environment, and a test platform. The platform comprises a test master control module, an attitude control module, an actuating mechanism simulator, a real-time simulation target machine, a triaxial rate turntable, a sensor module, an attitude determination module and an interference injection module; the test plate is a generalized test platform, can complete injection of different types of interference noises through the interference injection module, and can select an attitude determination algorithm class in the attitude determination module to complete comparison analysis of the attitude determination algorithm filtering performances of different types of anti-interference attitudes; and the anti-interference attitude determination method can effectively solve the problem of attitude determination precision decrease caused by gyroscope first-order Markov noises, carrier vibration harmonic noises, Gaussian white noises and other multi-source noises of sensor modules; and the method and the test platform are suitable for ground simulation verification in the aviation and aerospace fields, and can be used in highly precise attitude and position measurement of a spacecraft attitude determination system.
Owner:北京七星航宇科技有限公司
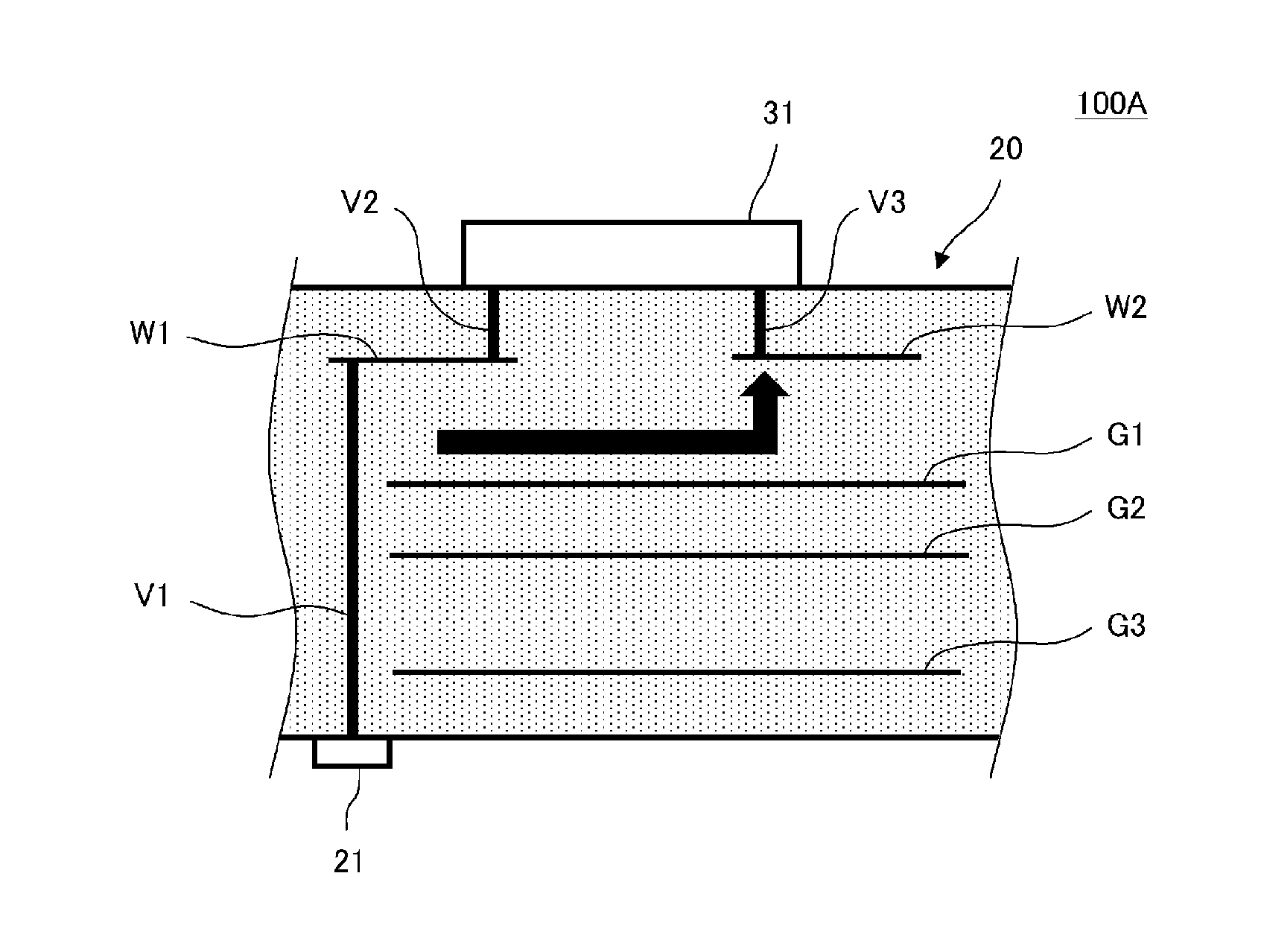
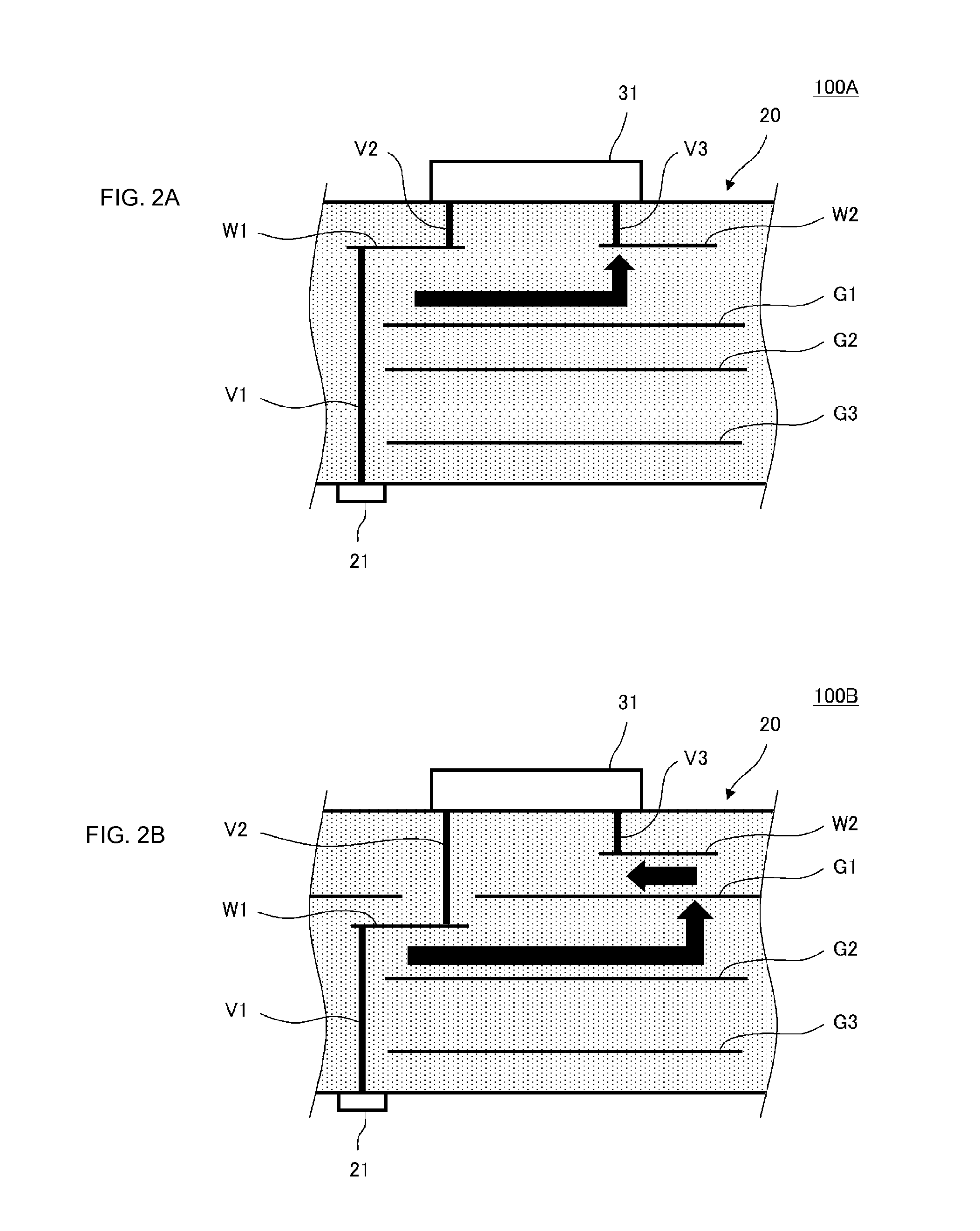
High-frequency module
ActiveUS20140002209A1Reduce the impactDegradationTransmission noise suppressionPrinted inductor incorporationElectricityElectrical conductor
A multilayer substrate includes therein wiring conductors, ground conductors, interlayer connection conductors, and a matching inductor. A control signal input terminal is provided on a second main surface of the multilayer substrate. Electrodes on which a high-frequency switch is mounted are electrically connected to the wiring conductors through the interlayer connection conductors. The control signal wiring conductor is located on a dielectric layer close to the second main surface of the multilayer substrate, and the high-frequency signal wiring conductor is located on a dielectric layer close to a first main surface of the multilayer substrate. The ground conductor, which is superposed with the control signal wiring conductor in plan view is separated from the matching device conduction ground conductor by a separation portion. With this structure, influence of harmonic noise due to input of high-frequency switch control signals is reduced and degradation of the communication characteristics is reduced.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
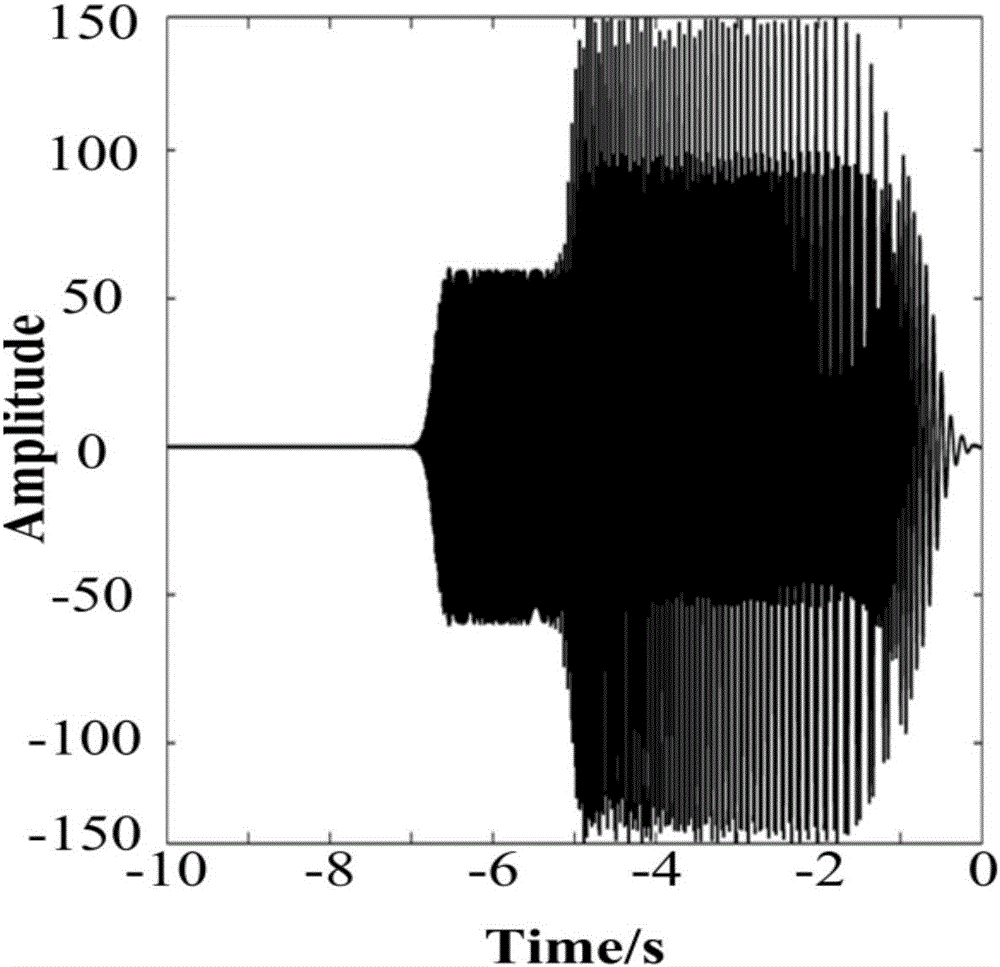
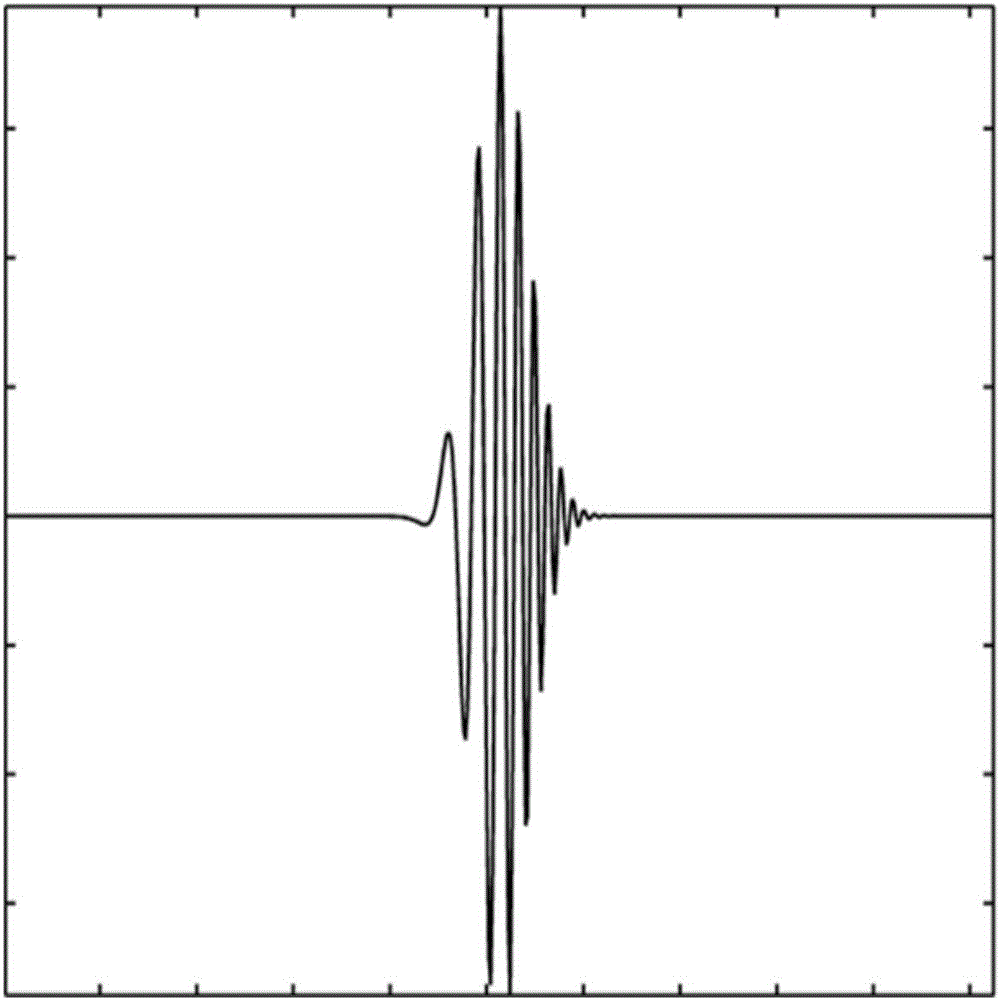
Harmonic noise suppression method based on waveform morphology sparse modeling
ActiveCN106680874AFast implementation of inverse transformationGuaranteed sparsitySeismic signal processingSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Chirplet transform
The invention discloses a harmonic noise suppression method based on waveform morphology sparse modeling. The harmonic noise suppression method includes the steps of 1) constructing Chirplet transform according to waveform morphological characteristics of harmonic noise in seismic records acquired via vibroseis slip sweep, and constituting an over-complete dictionary with continuous wavelet transform; 2) quickly implementing Chirplet positive and inverse transforms; 3) determining Chirplet transform parameters based on time-frequency distribution characteristics of correlated data; and 4) according to the starting frequency of a reference scanning signal, determining the filter cutoff frequency of the harmonic noise to achieve fidelity separation of an effective signal from the harmonic noise. The invention solves the problem of harmonic noise interference in the seismic data acquired via vibroseis slip sweep, and achieves the purpose of improving the signal-to-noise ratio of the seismic data. The method of the invention determines the Chirplet transform according to the time-frequency distribution characteristics of the harmonic noise, and ensures the sparseness; the fast implementation of the Chirplet transform guarantees the efficiency of transform, and the correction coefficient guarantees the accuracy of inverse transform reconstruction; and the Chirplet transform parameters are automatically determined according to the data drive, a strong adaptability is gained and single-channel calculation facilitates parallel processing.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Cardiac signal processing apparatus and cardiac signal processing method
ActiveUS8597196B2Eliminate distractionsComponent with highCatheterSensorsBand-pass filterEngineering
A cardiac signal processing apparatus includes: a unit for acquiring, from a heartbeat sensor, cardiac signals relating to heartbeats of a subject; a low-pass filter for allowing passage of those cardiac signals having a first predetermined frequency or lower, among the cardiac signals; higher harmonic noise acquisition unit for acquiring harmonic signals of low-frequency noise by performing high frequency extrapolation on the signals output from the low-pass filter; a high-pass filter for allowing passage of those cardiac signals having a second predetermined frequency or higher, among the cardiac signals; and higher harmonic noise removal unit for removing the harmonic signals of low-frequency noise from the signals output from the high-pass filter. It is thus made possible to remove noise from the cardiac signals and to obtain desirable heartbeat detection characteristics.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
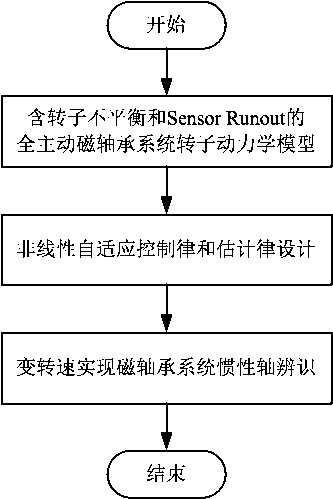
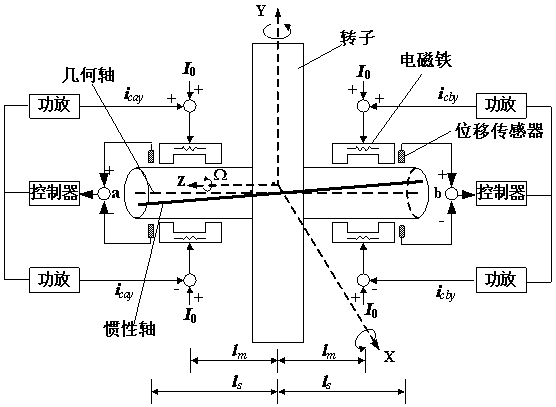
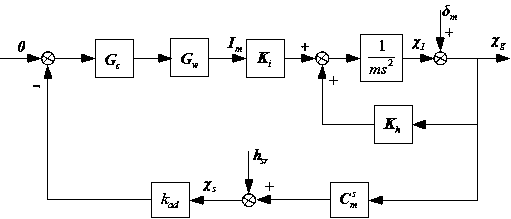
Identifying method for inertia shaft of full-automatic magnetic bearing system based on nonlinear self-adaption control
InactiveCN107727088AOvercome the disadvantage of large identification errorRealize identificationRotary gyroscopesAdaptive controlMagnetic bearingSystem stability
The invention discloses an identifying method for an inertia shaft of a full-automatic magnetic bearing system based on nonlinear self-adaption control. The method comprises the following steps that firstly, a full-automatic magnetic bearing rotor dynamics model with rotor imbalance and displacement sensor harmonic noise is established; secondarily, a nonlinear self-adaption control rule and estimation rule are provided, the system stability and astringency of estimation parameters are proved, it is guaranteed that a magnetic suspension rotor inertia shaft displacement estimation value is convergent to zero, and meanwhile the high-level harmonic component fourier coefficient of displacement sensor harmonic noise is estimated; then, a variable rotation speed strategy is adopted, the same frequency component of displacement sensor harmonic noise and recognizable degree of rotor imbalance are improved, the fourier coefficient values of two same frequency components are solved, and finallyidentifying for the inertia shaft of the full-automatic magnetic bearing system is achieved. According to the identifying method for the inertia shaft of the full-automatic magnetic bearing system based on nonlinear self-adaption control, speed raising or speed reduction for one time is only needed, and identifying of the magnetic bearing inertia shaft can be achieved online, so that a magnetic suspension rotor rotates around the inertia shaft.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
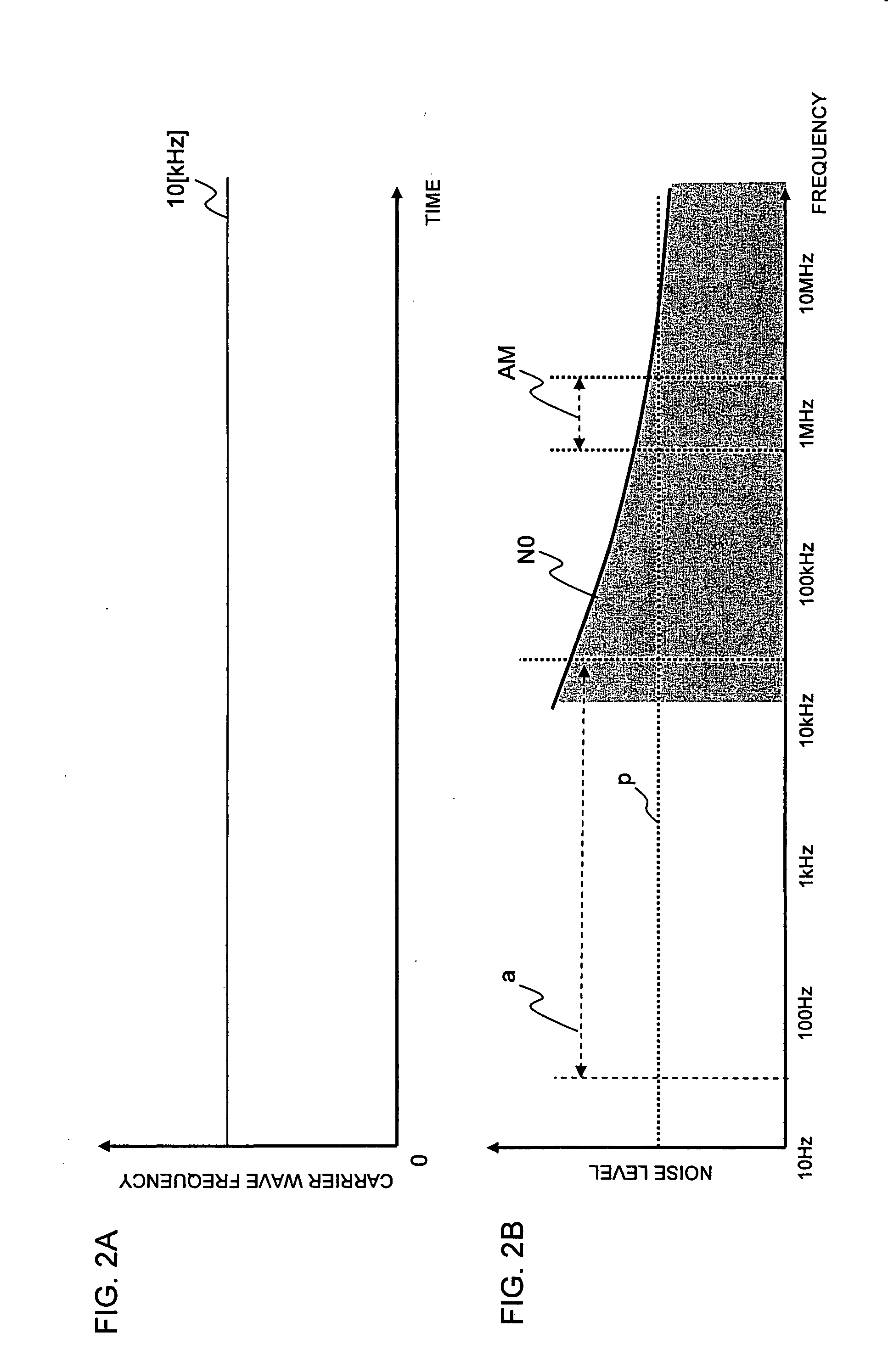
Power control apparatus and method
ActiveUS20070247881A1Ac-dc conversionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsControl signalCarrier signal
A power control apparatus and power control method that reduce harmonic noise produced when modulating a carrier wave frequency over predetermined cycles. A command value signal is generated for obtaining a desired output voltage, and a carrier wave is output. The frequency of the carrier wave is modulated by a desired frequency over predetermined cycles, and the desired frequency also modulates. The carrier wave is compared to a command value signal and a resulting control signal is provided to a switching unit. Harmonic noise caused by the modulation frequency can be spread, and the peak of the harmonic noise caused by the first modulation frequency can be reduced. Therefore, noise caused by a modulation frequency can be reduced.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
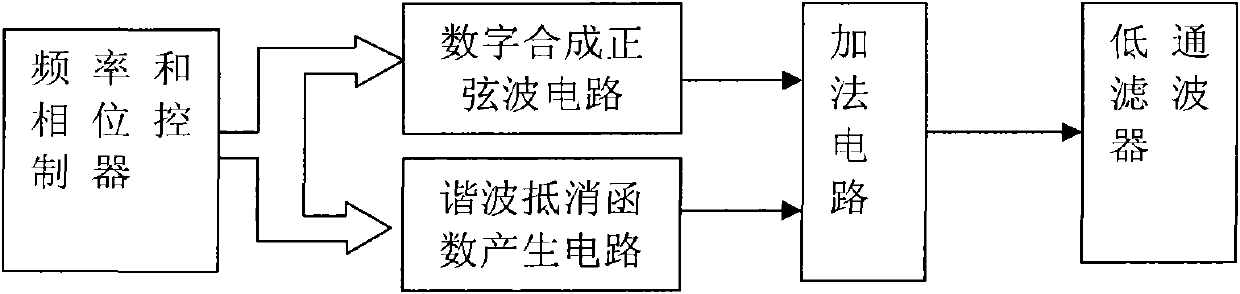
System and method for reducing harmonic noise of digital-synthesis sine waves
ActiveCN101777890ASmall harmonic noisePulse generatorGenerator stabilizationLow-pass filterPhase control
The invention provides a system and a method for reducing the harmonic noise of digital-synthesis sine waves. The system comprises a frequency and phase controller, a digital-synthesis sine wave circuit, a harmonic counteraction function generation circuit, an adder circuit and a low-pass filter, the harmonic counteraction function generation circuit is utilized to control the digital-synthesis sine wave circuit to generate a step sine wave according to a set frequency, meanwhile, the harmonic counteraction function generation circuit is controlled to generate a 'harmonic counteraction function wave' synchronized with the step sine wave, the two signals are superposed by the adder circuit, the fundamental wave signal and the M-1 harmonic component in an output signal are not counteracted, other harmonic components are remarkably reduced, the output signal then passes through the low-pass filter, a cutoff frequency is appropriately selected, so that M-1 and higher subharmonics far from the fundamental wave can be filtered, and thereby a sine wave signal with little harmonic noise can be obtained.
Owner:中国航天科技集团公司第五研究院第五一四研究所
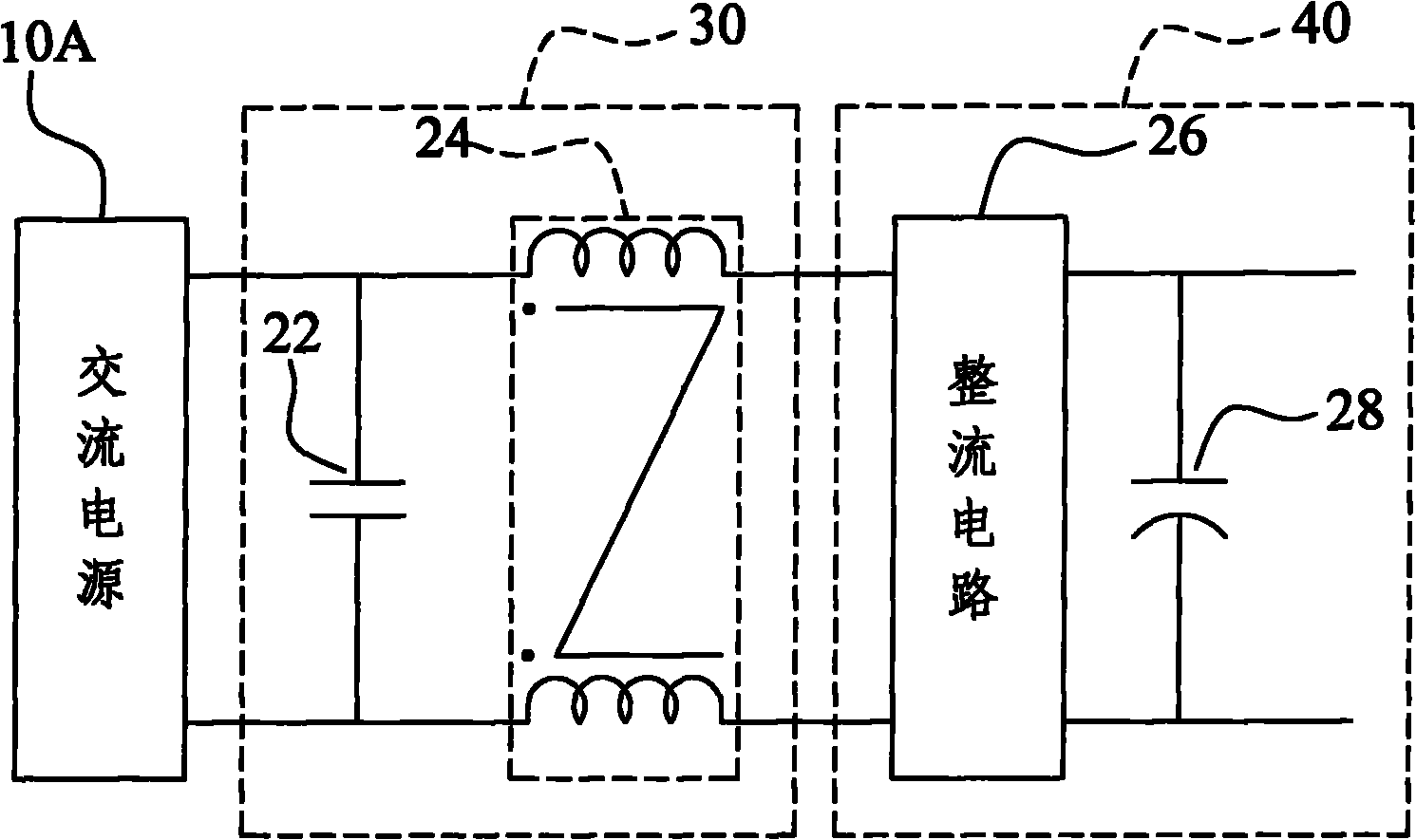
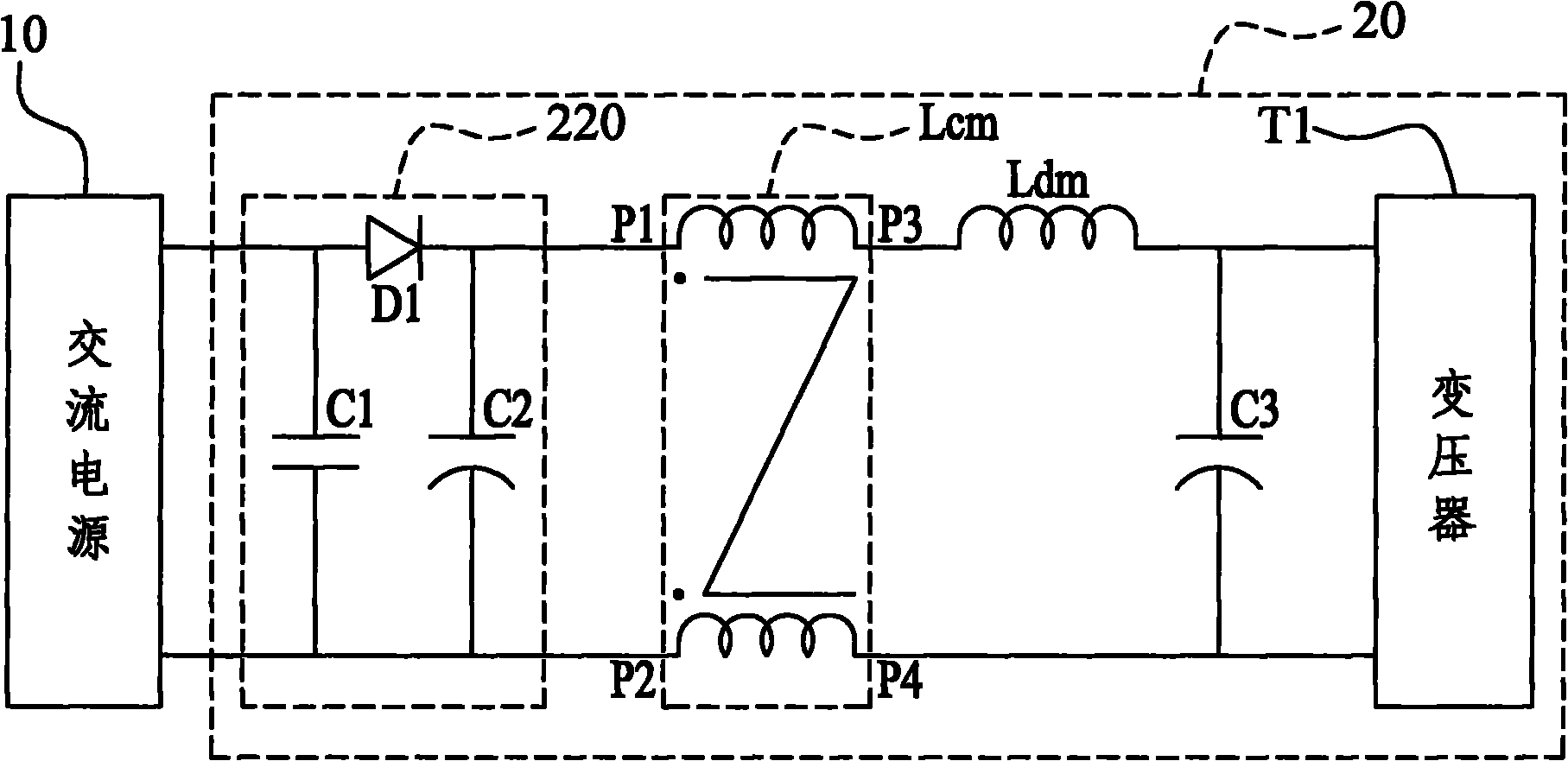
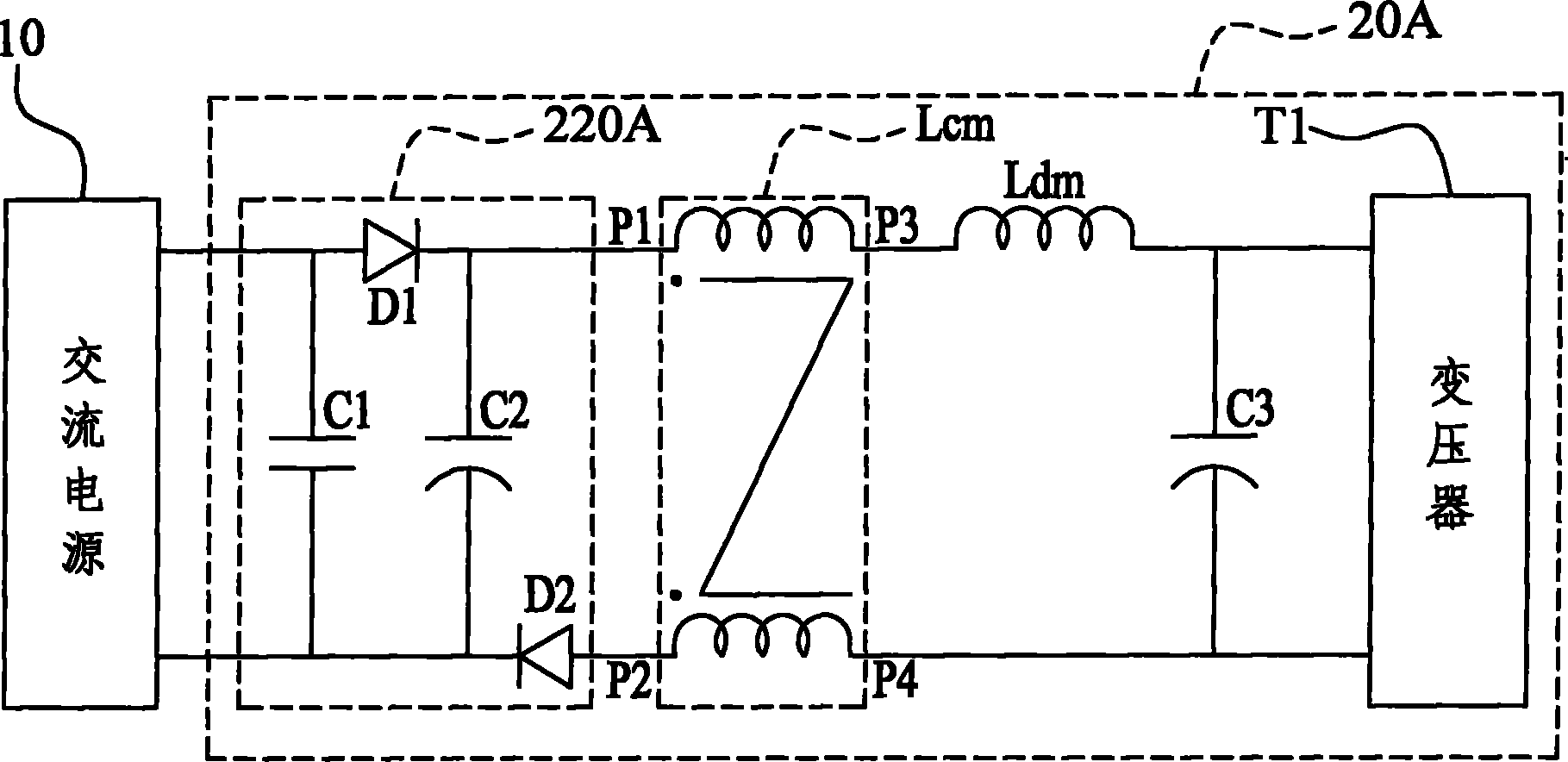
AC-DC conversion device capable of filtering electromagnetic interference
InactiveCN102136805ABest low frequency EMI characteristicsHarmonic noise suppressionAc-dc conversion without reversalCapacitanceElectromagnetic interference
The invention discloses an AC-DC conversion device capable of filtering electromagnetic interference, comprising a half-bridge conversion filtering unit, a common mode inductor, a differential mode inductor and a load end capacitor. The half-bridge conversion filtering unit is connected among an AC power source as well as a first pin and a second pin of the common mode inductor in series. The differential mode inductor is connected between a third pin of the common mode inductor and the load end capacitor in series. The half-bridge conversion filtering unit can inhibit harmonic noise of a power supply during AC-DC conversion, thus the AC-DC conversion device capable of filtering electromagnetic interference has a better low frequency electromagnetic interference characteristic.
Owner:ELEMENTECH INT
Subtractive cancellation of harmonic noise
A common problem in audio processing is that a useful signal is disturbed by one or more sinusoidal noises that should be suppressed. One embodiment of the invention provides a method of canceling a sinusoidal disturbance of unknown frequency in a disturbed useful signal. The method comprises the steps of estimating parameters of the sinusoidal disturbance including amplitude, phase and frequency; generating a reference signal on the basis of the estimated parameters; and subtracting the reference signal from the disturbed useful signal. The estimation is performed by an Extended Kalman filter.
Owner:HONDA RES INST EUROPE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com