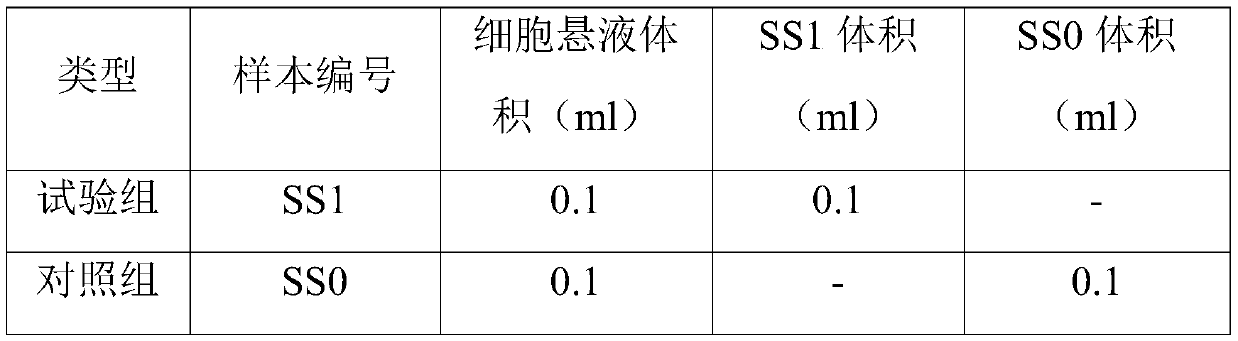
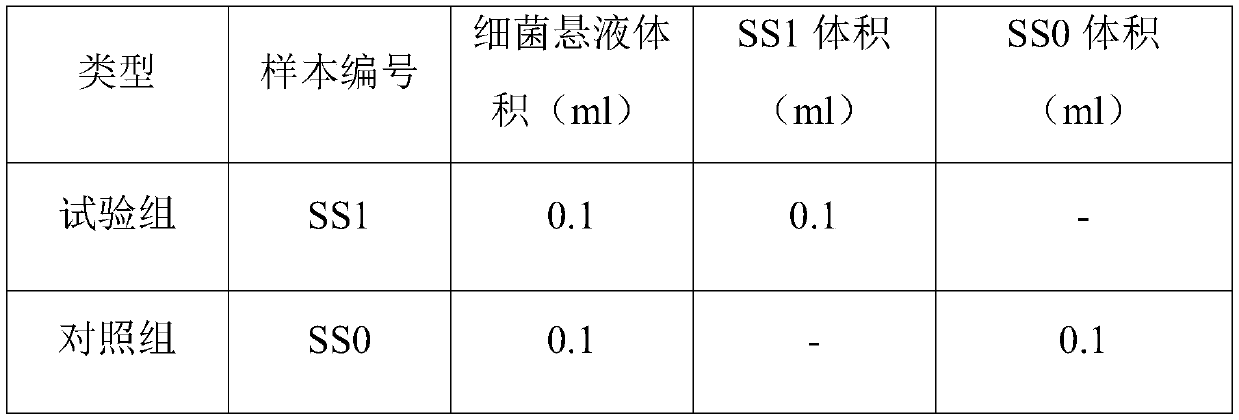
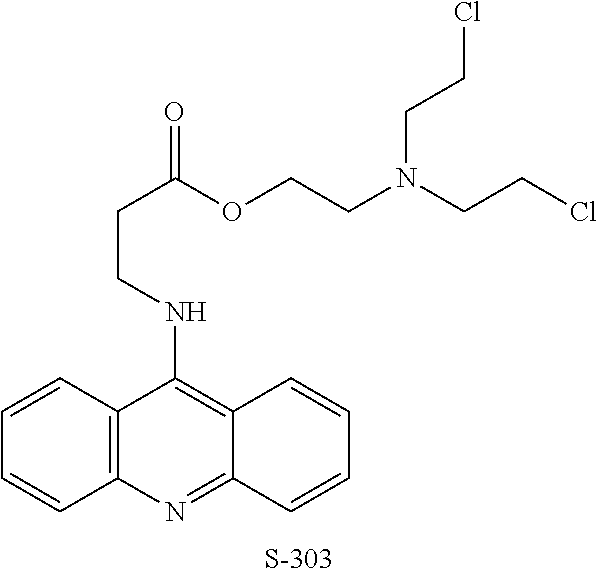
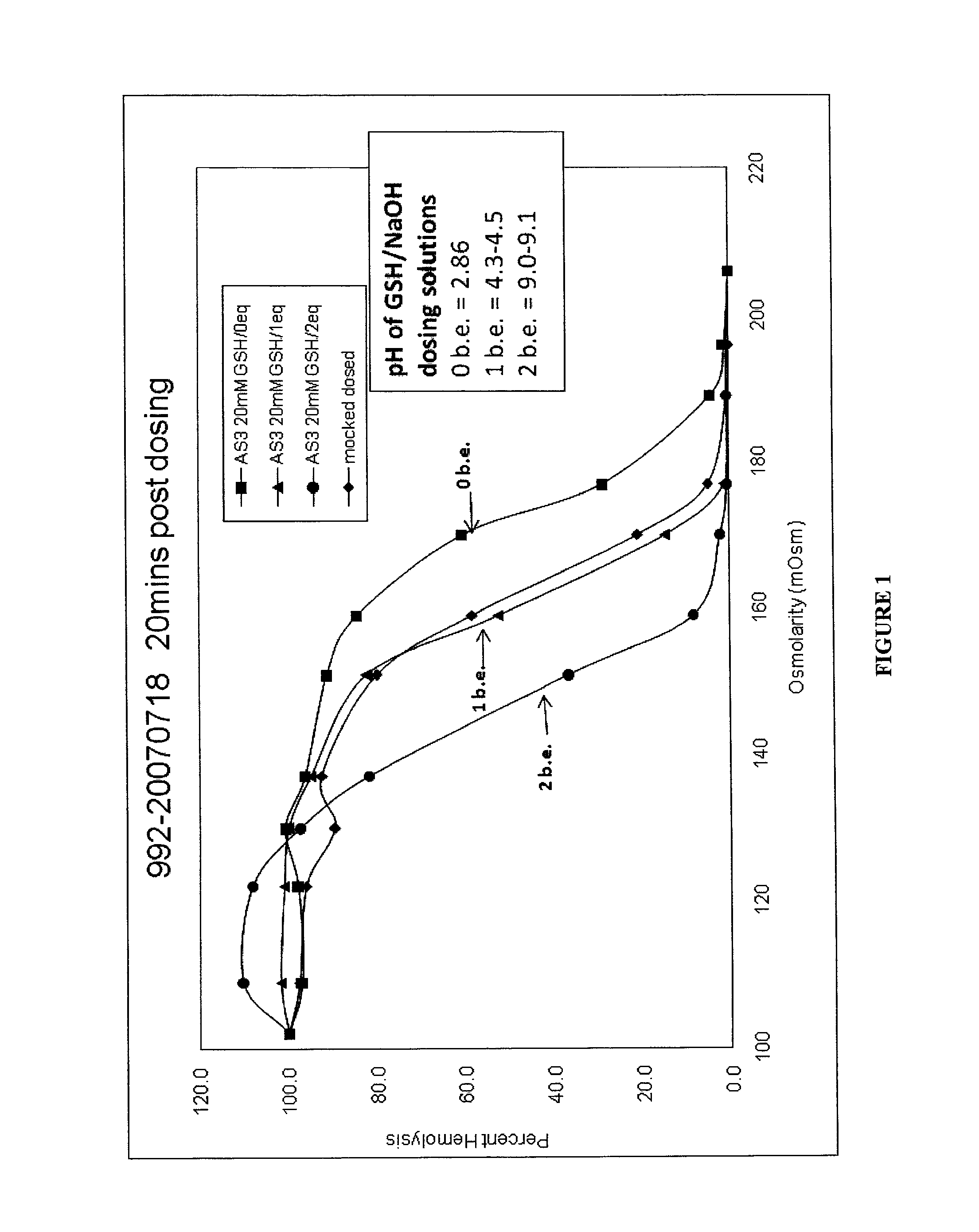
Patents
Literature
83 results about "Pathogen inactivation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
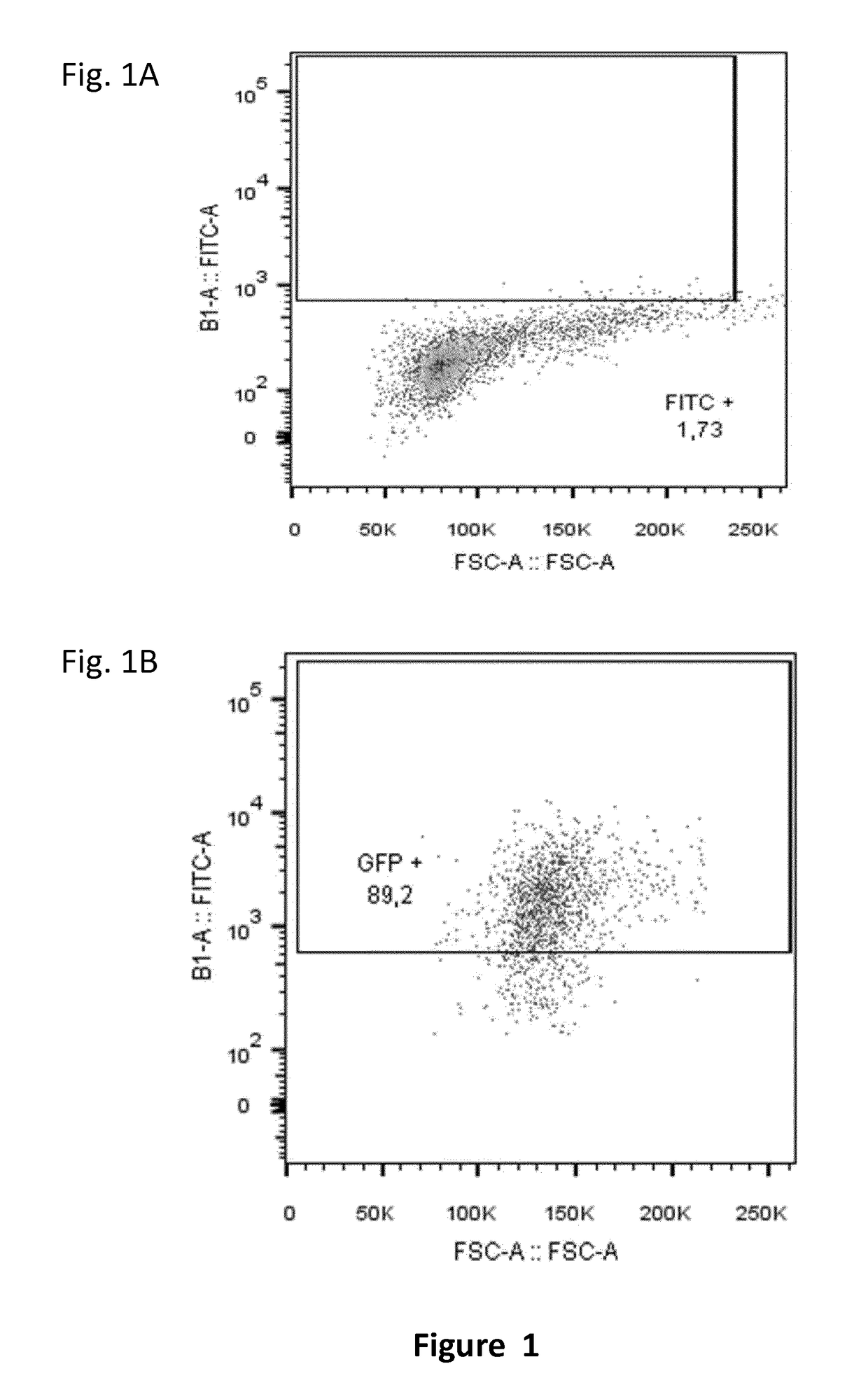
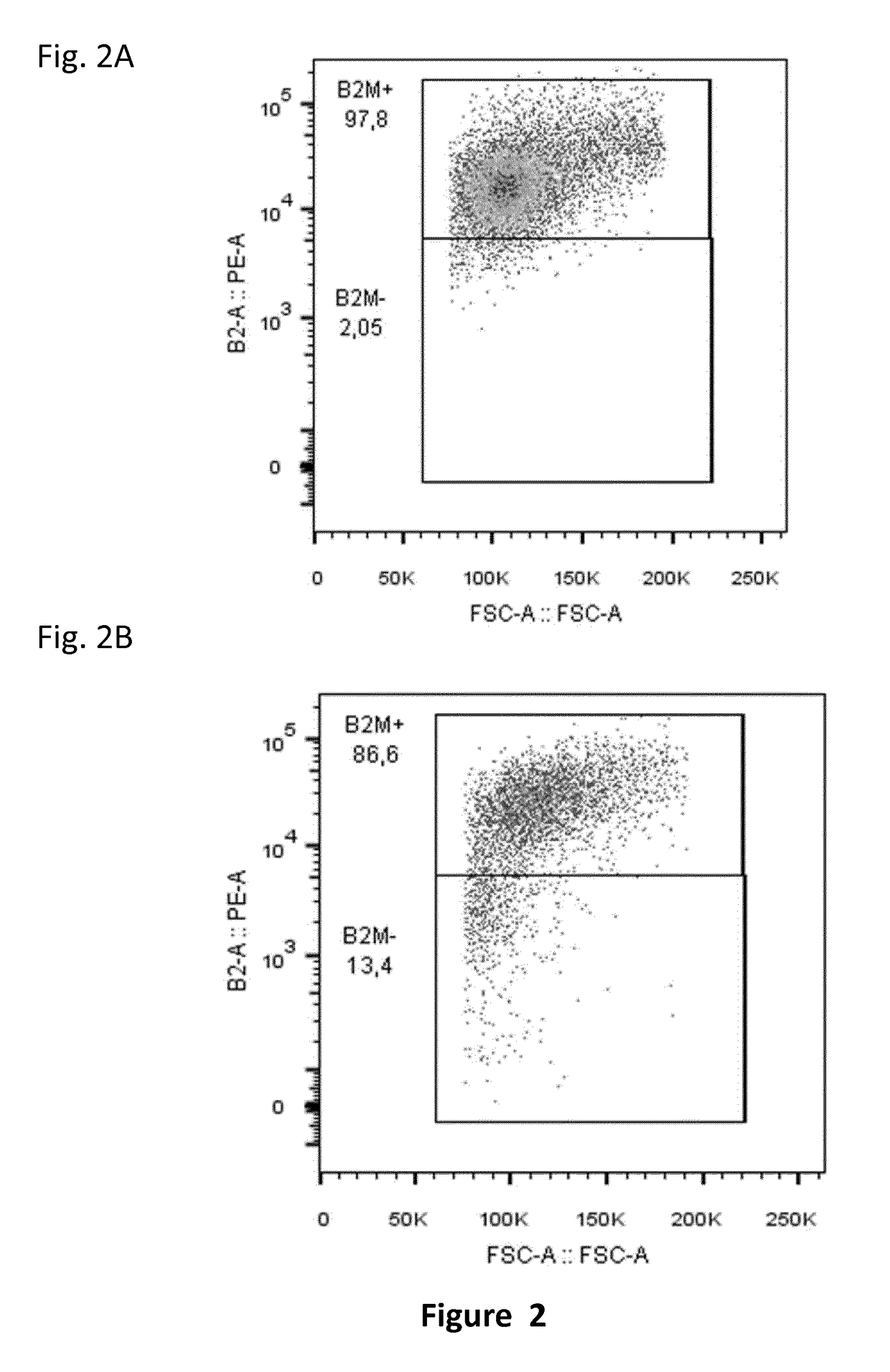
Pathogen inactivation: A process designed to eliminate pathogens from water, air or donated blood. Pathogens include viruses, bacteria, and fungi. Sewage purification systems depend upon pathogen inactivation to purify water to the extent it may be safe enough to drink.
Apparatus and method for bioelectric stimulation, healing acceleration, pain relief, or pathogen devitalization
ActiveUS7117034B2Minimal stressPromote healingElectrotherapyArtificial respirationEngineeringAnimal body
An method and method for generating an electrical signal for use in biomedical applications, including two timing-interval generators, each optionally driving a multistep sequencer; analog, digital or hybrid means for combining the resulting timed signals into a complex electrical signal; optional filtering means for blocking direct current, removing selected frequency components from the resulting signal, and / or providing voltage step-up if needed; and conductive means for coupling the resulting signal to a human or animal body, food, beverage or other liquid, cell or tissue culture, or pharmaceutical material, in order to relieve pain, stimulate healing or growth, enhance the production of specific biochemicals, or devitalize selected types of organisms.
Owner:HEALTHONICS INC
Pathogen inactivating compositions for disinfecting biological fluids
InactiveUS6106773AAvoid bulk processingAvoid capital intensive equipmentBiocideSolvent extractionBlood componentAqueous solution
The present invention is directed to pathogen inactivating compositions that can be used to disinfect various biological fluids, such as blood, blood fractions, and the like. The compositions are suitable for disinfecting biological fluids containing valuable, but labile, components such as proteins without destroying the desired properties of such components. The pathogen inactivating compositions of the present invention are produced by contacting water or an aqueous solution with iodinated matrix material. The compositions can be pre-formulated and stored for subsequent use in disinfecting a wide range of biological fluids.
Owner:AMERICAN NAT RED CROSS
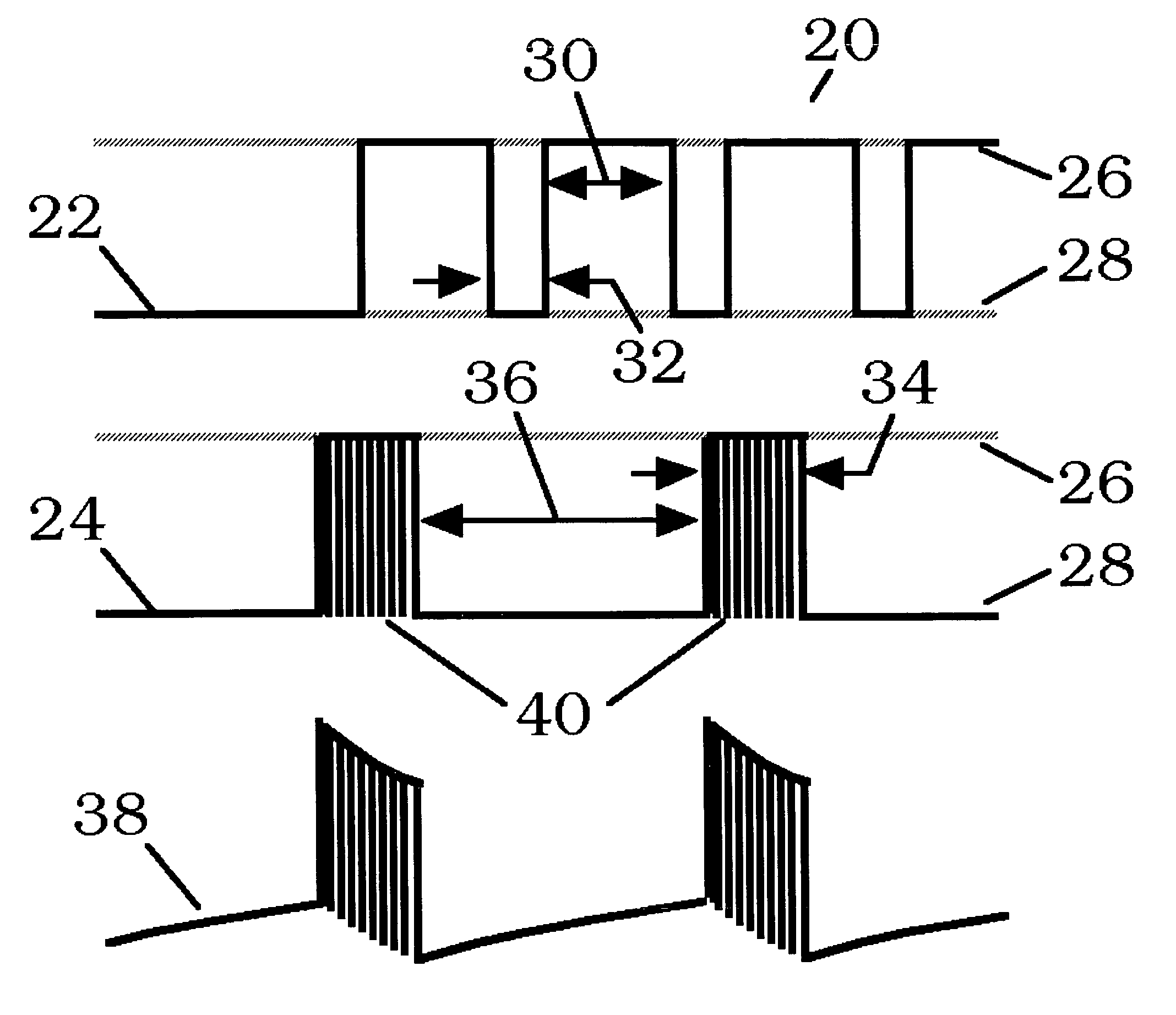
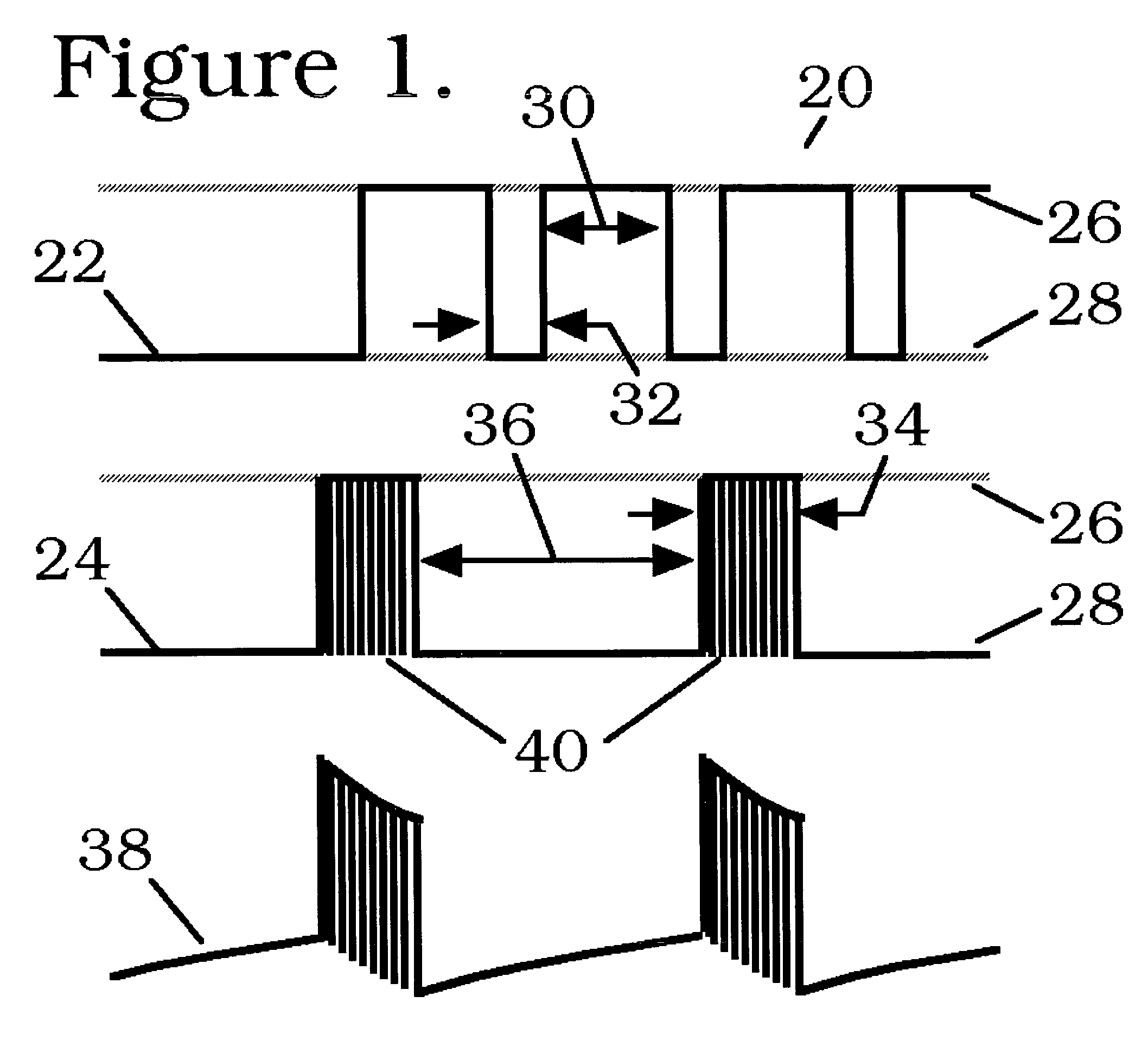
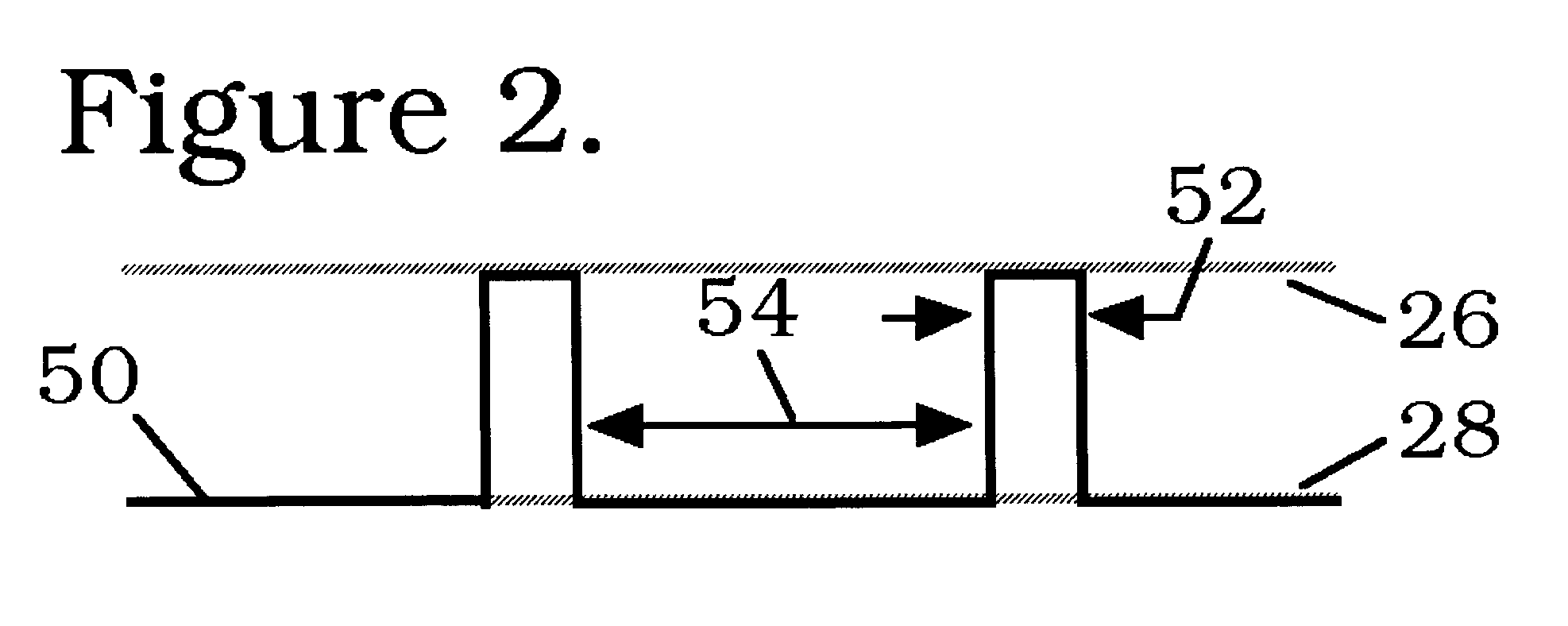
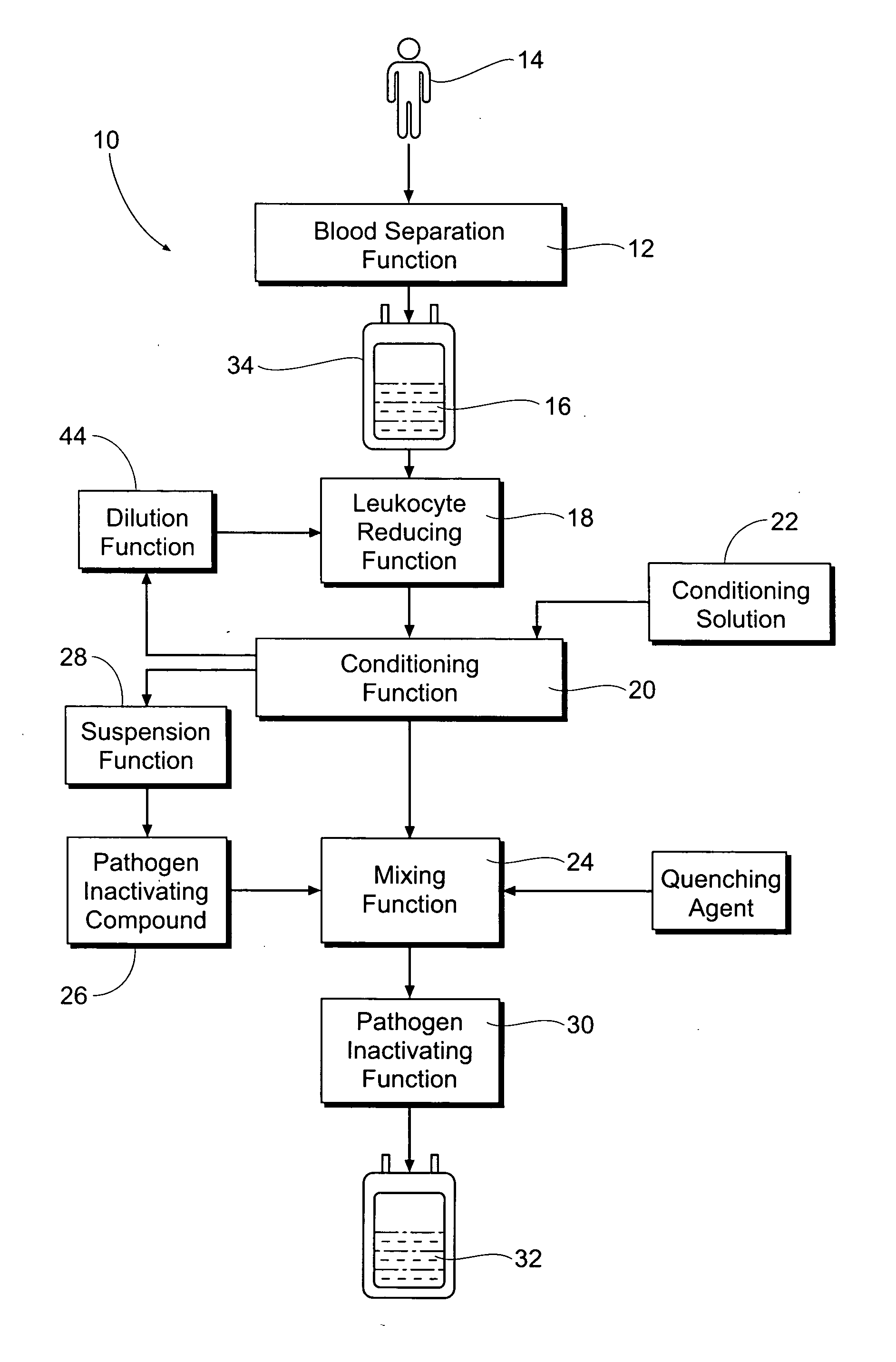
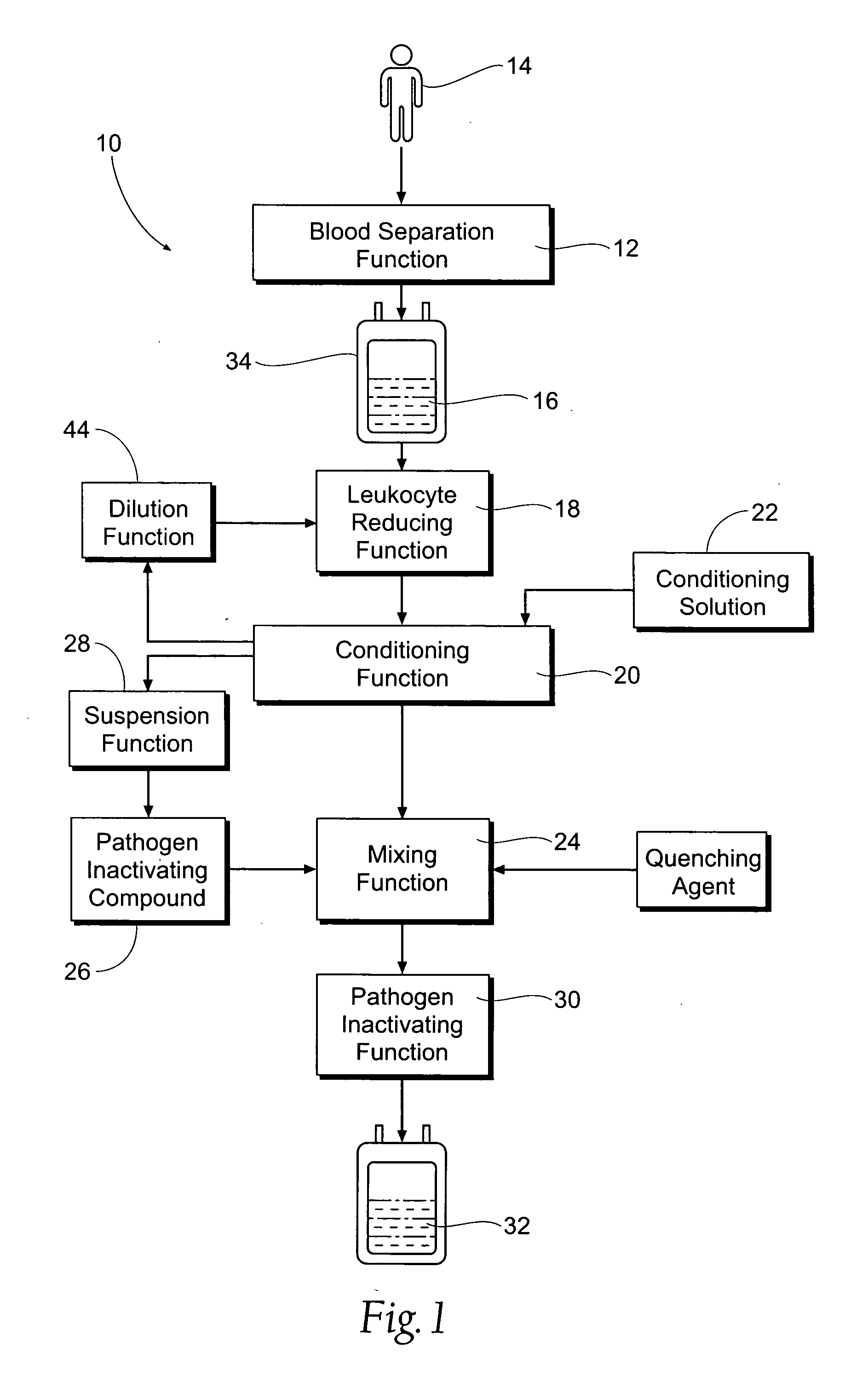
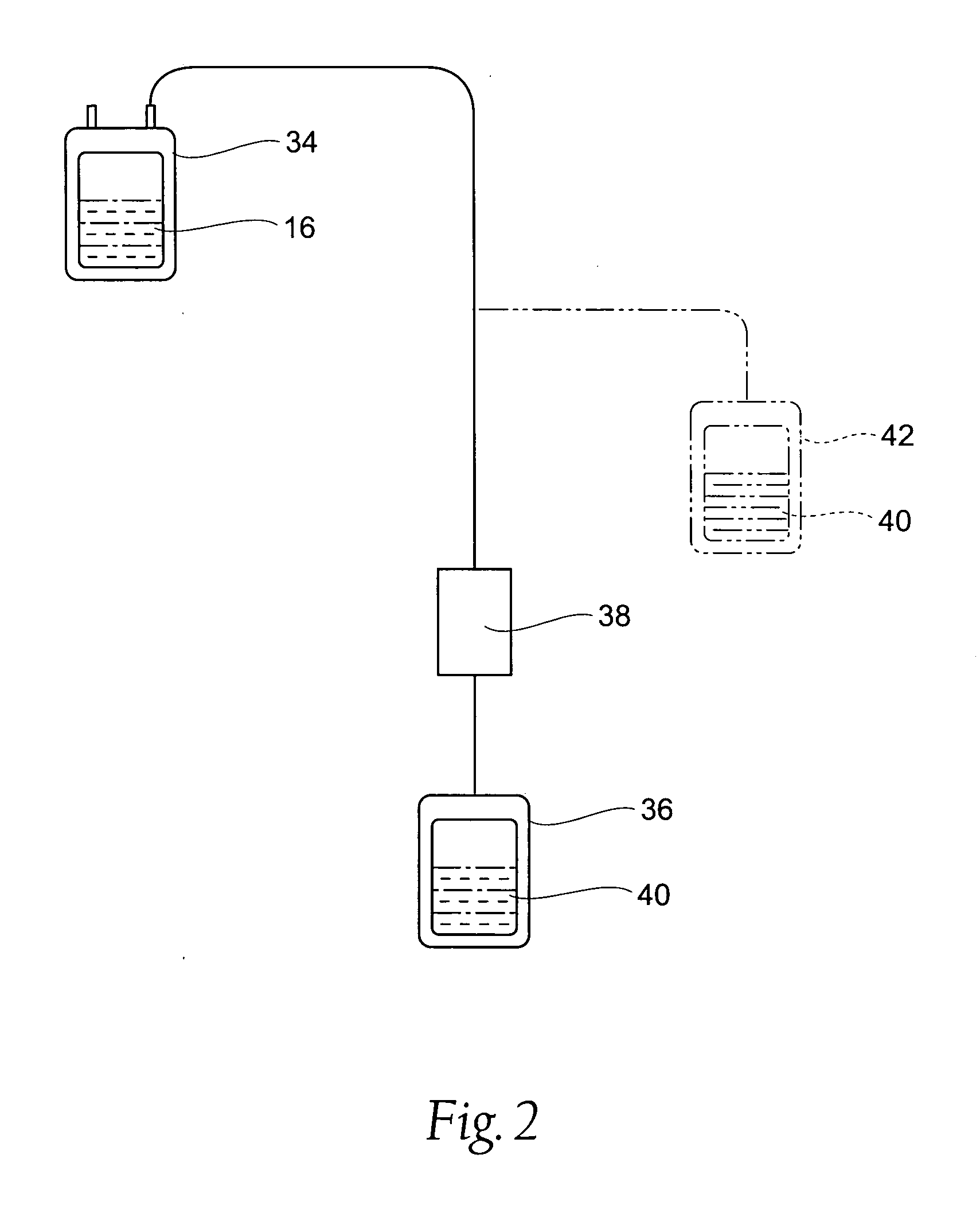
Processing systems and methods for providing leukocyte-reduced blood components conditioned for pathogen inactivation
InactiveUS20050137517A1Reduce exposureReduce exposure timeOther blood circulation devicesMedical devicesPathogen inactivationWhite blood cell
Systems and methods process blood and blood components for subsequent pathogen inactivation processes prior to long term storage and / or transfusion.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC
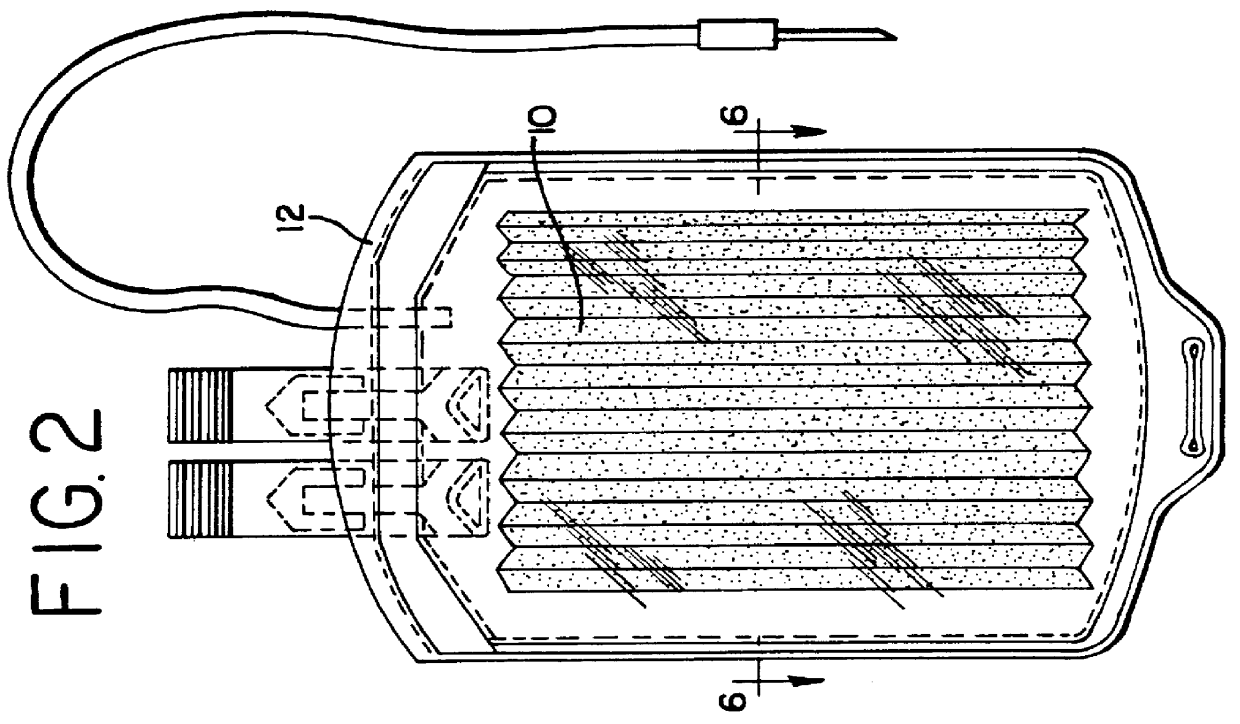
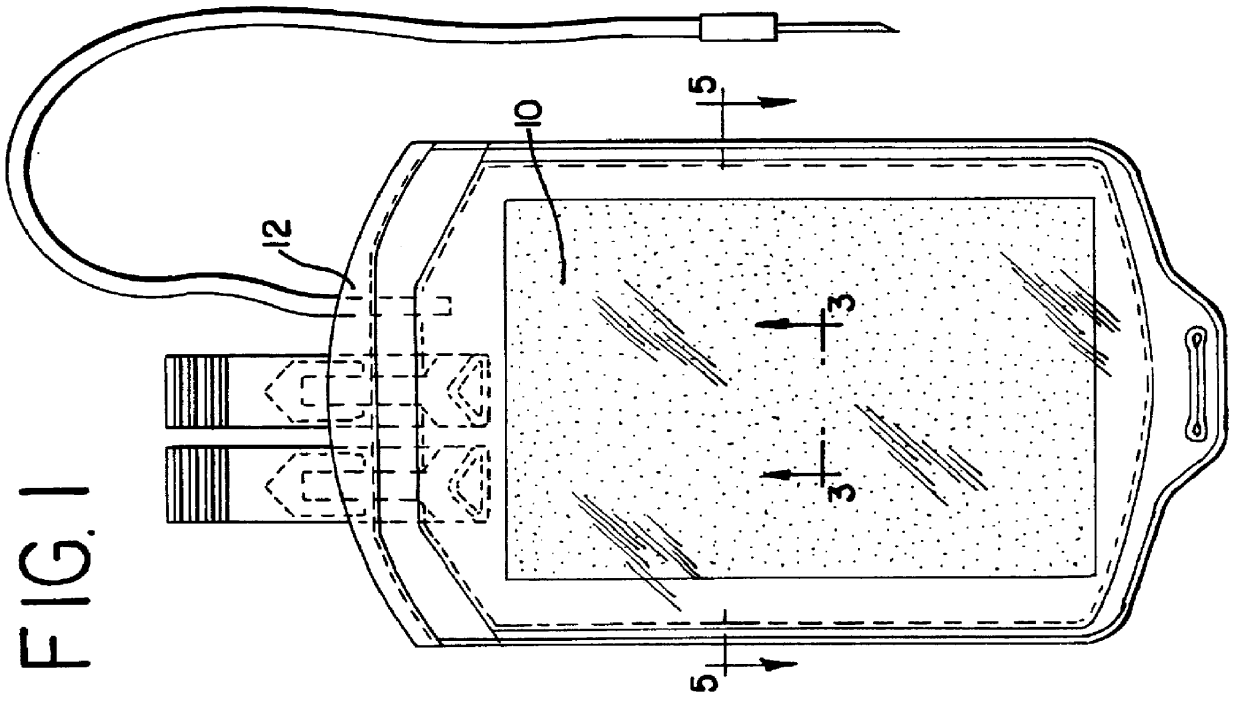
Apparatus, membranes and methods for removing organic compounds from a biological fluid
InactiveUS6099734AReduce concentrationOther blood circulation devicesLoose filtering material filtersChemical compoundBiochemistry
Membranes and methods for making membranes are disclosed. The membranes include a polymeric matrix and a particulate material immobilized within the matrix. The membranes may find particular application in methods and apparatus for removing organic compounds from a biological fluid as part of a pathogen inactivation treatment.
Owner:FENWAL +1
Biological specimen collection and transport system and methods of use
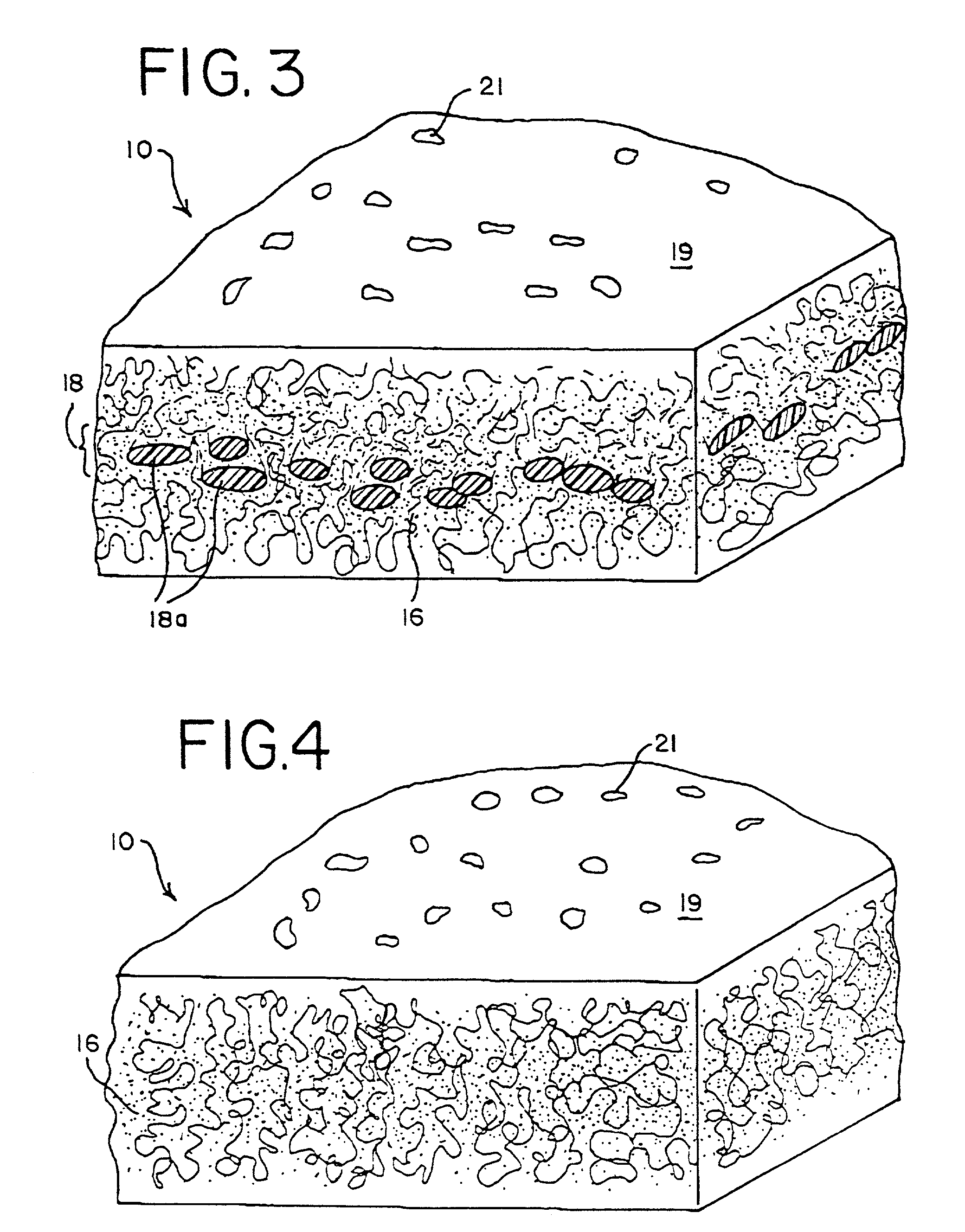
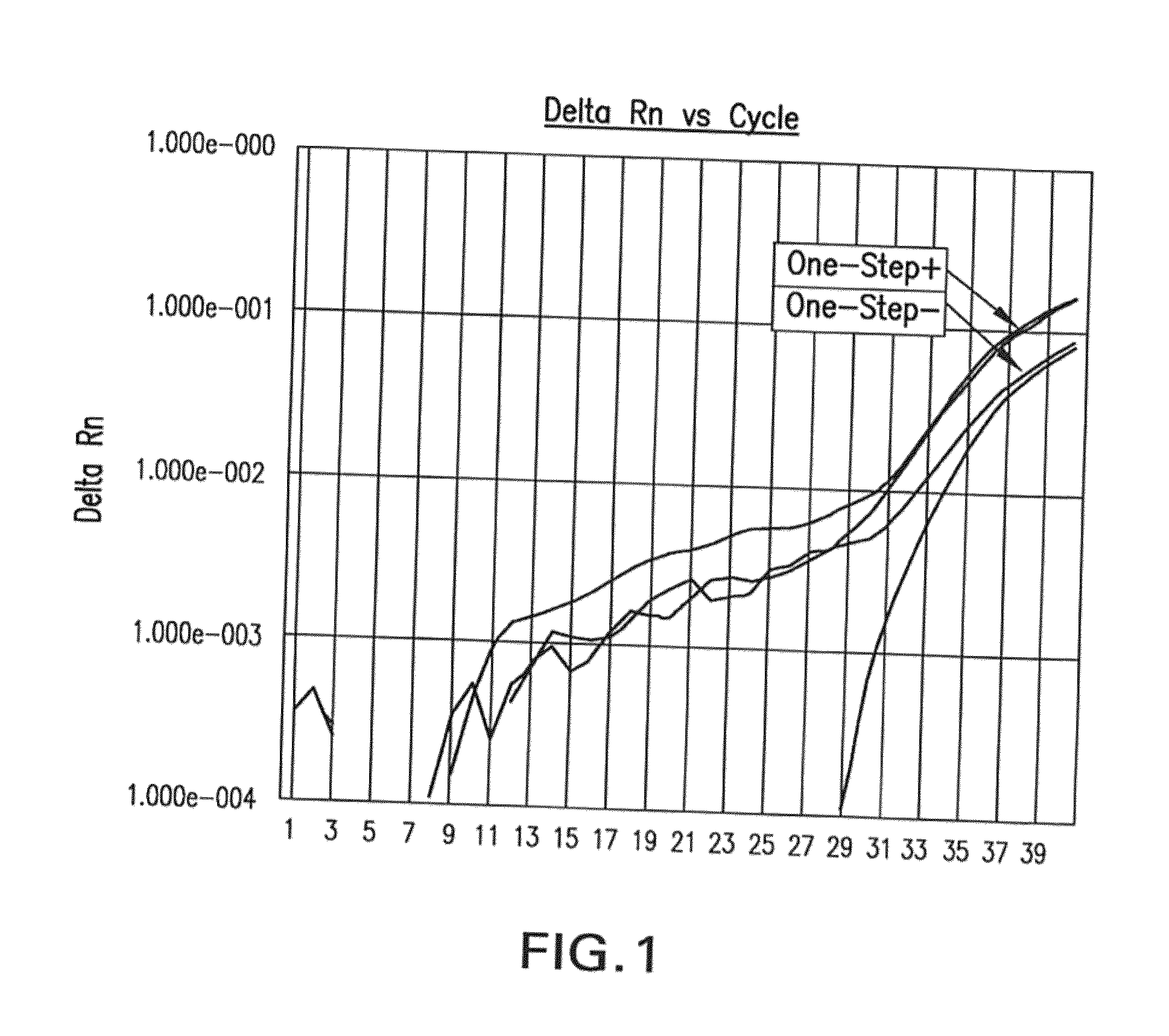
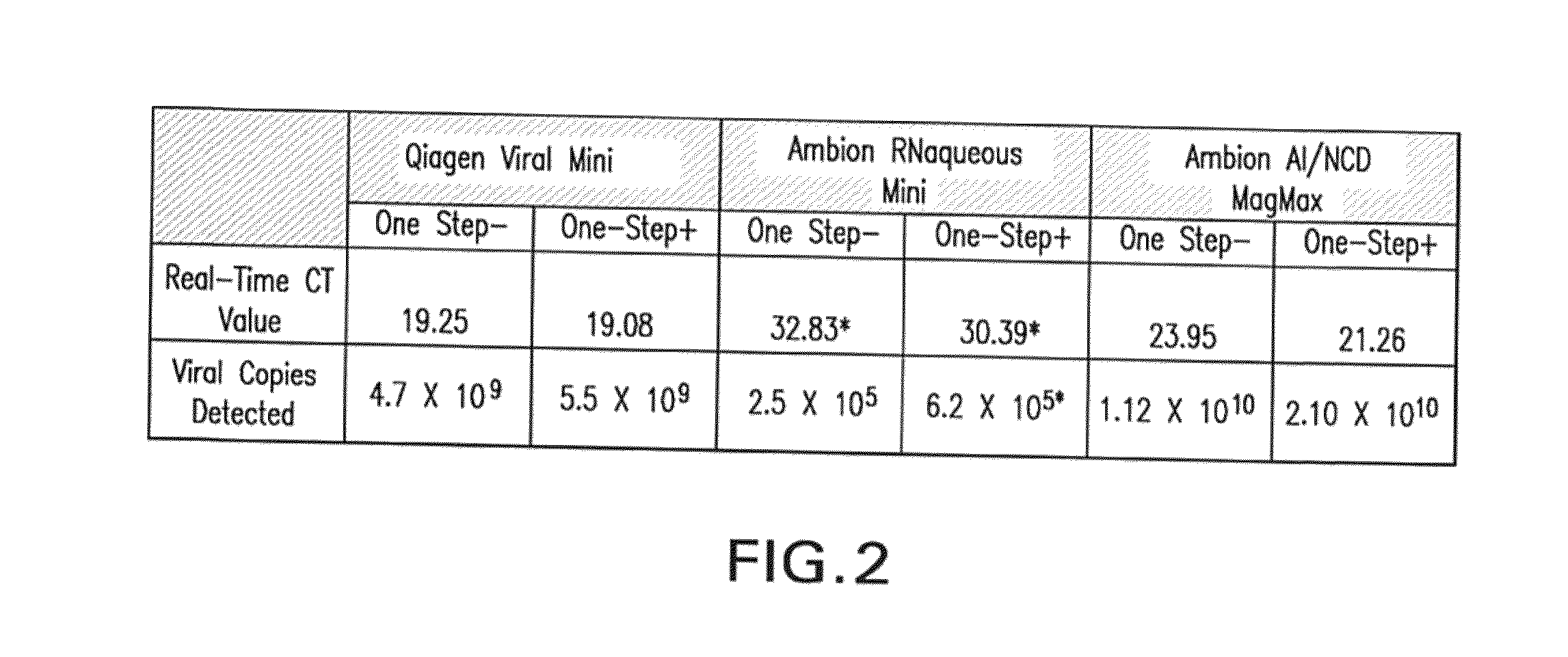
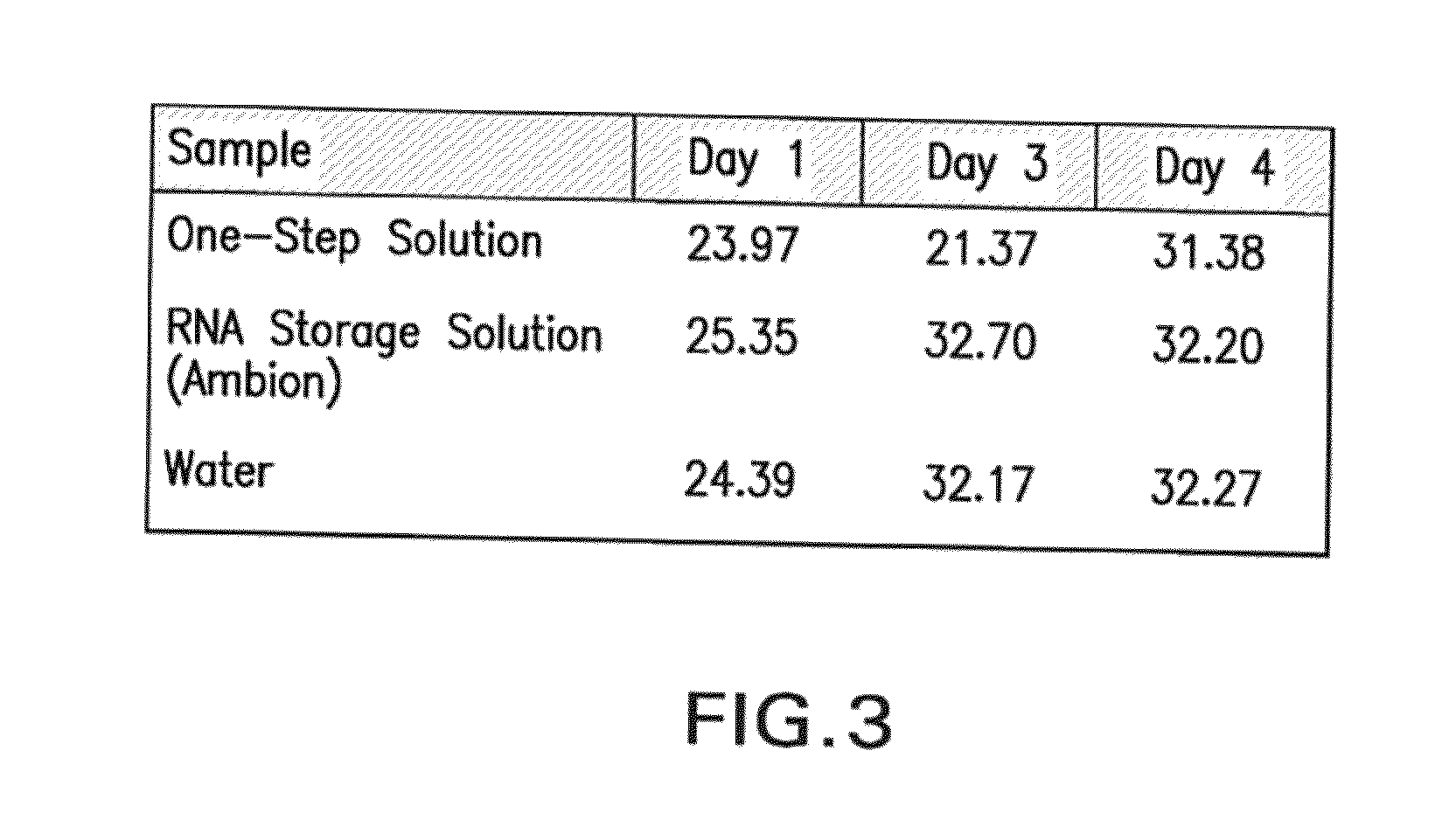
ActiveUS8084443B2Prevent degradationMaintenance of the integrity of the nucleic acidsBiocideBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCellular componentTransport system
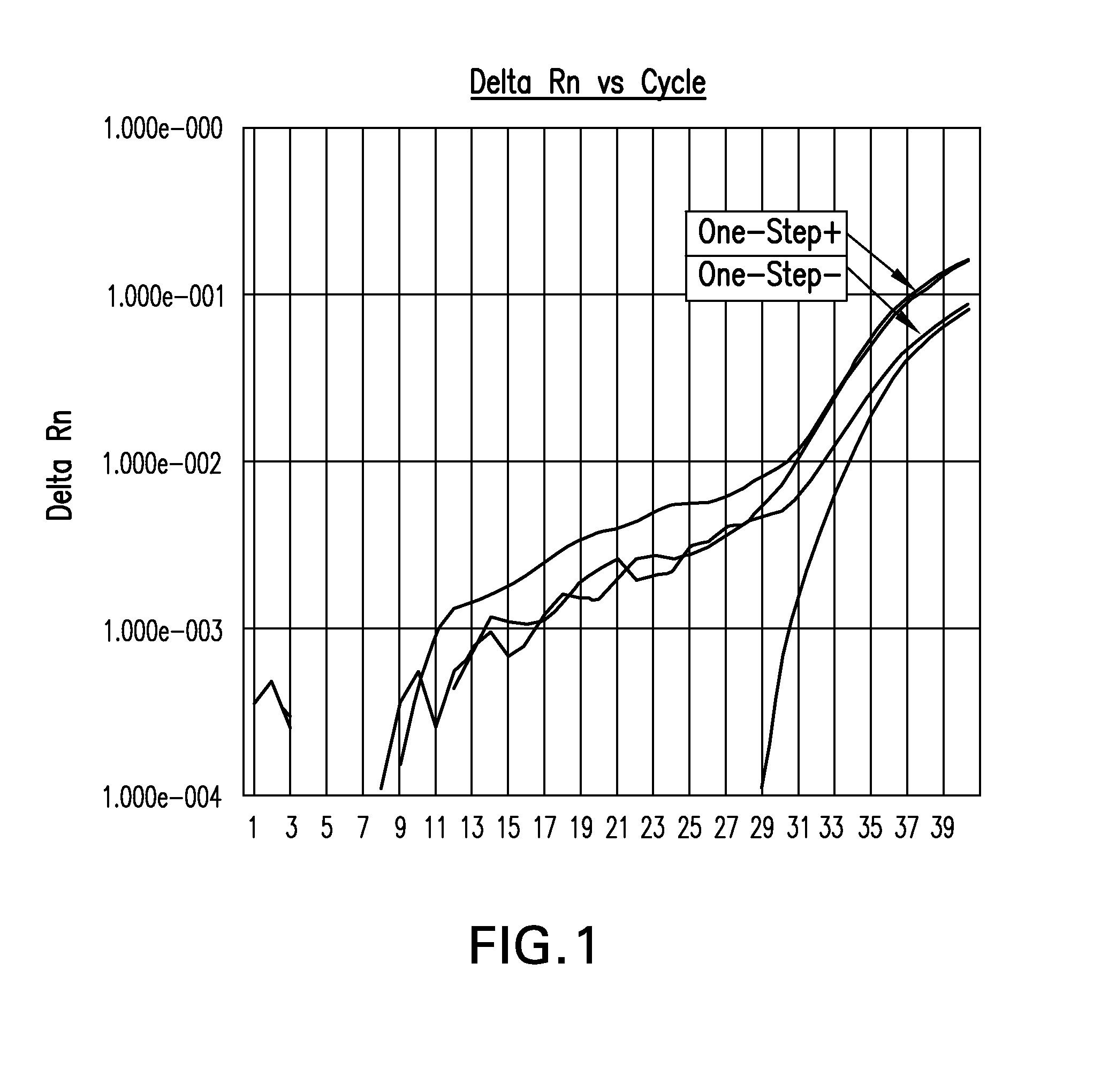
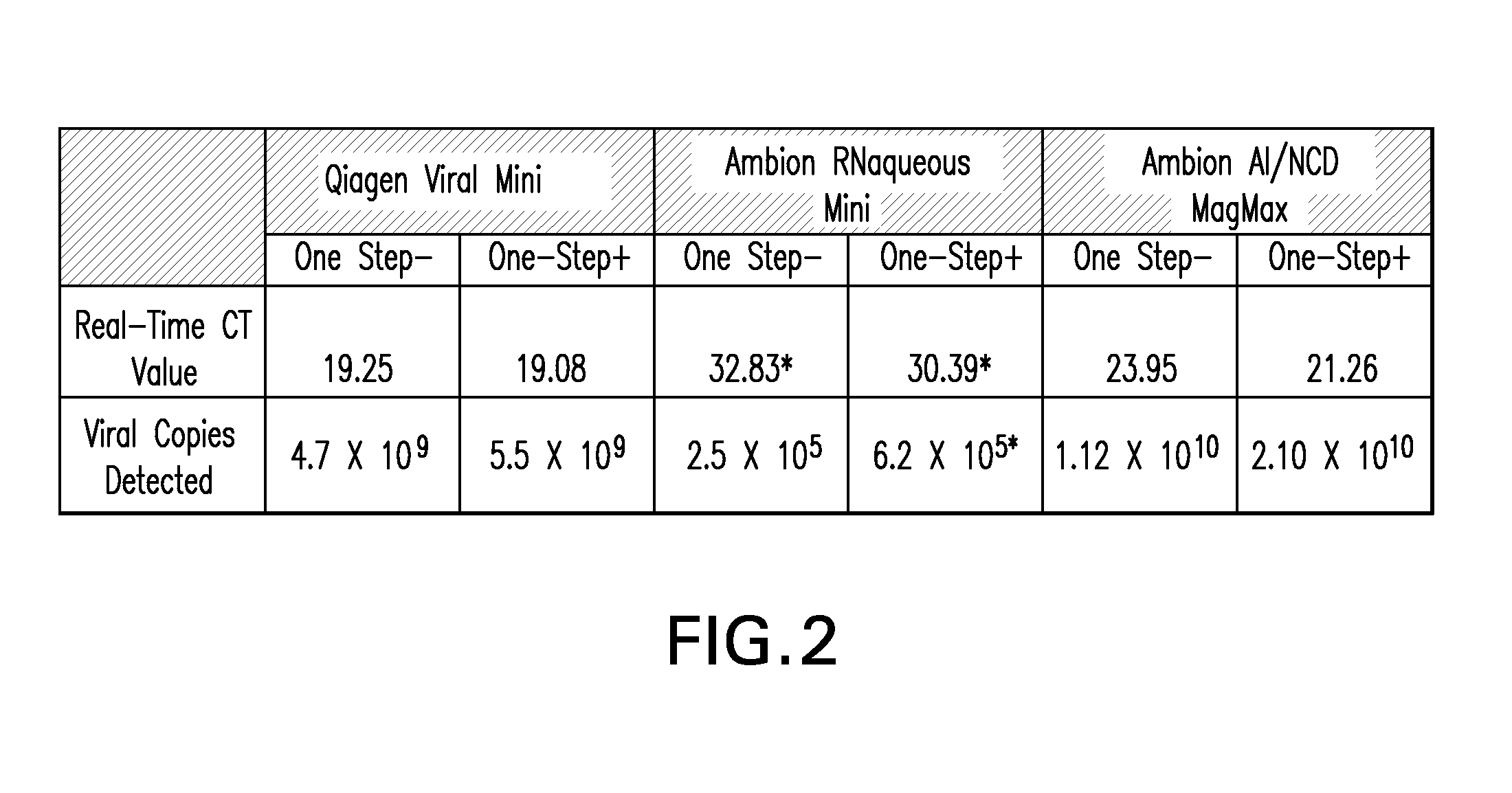
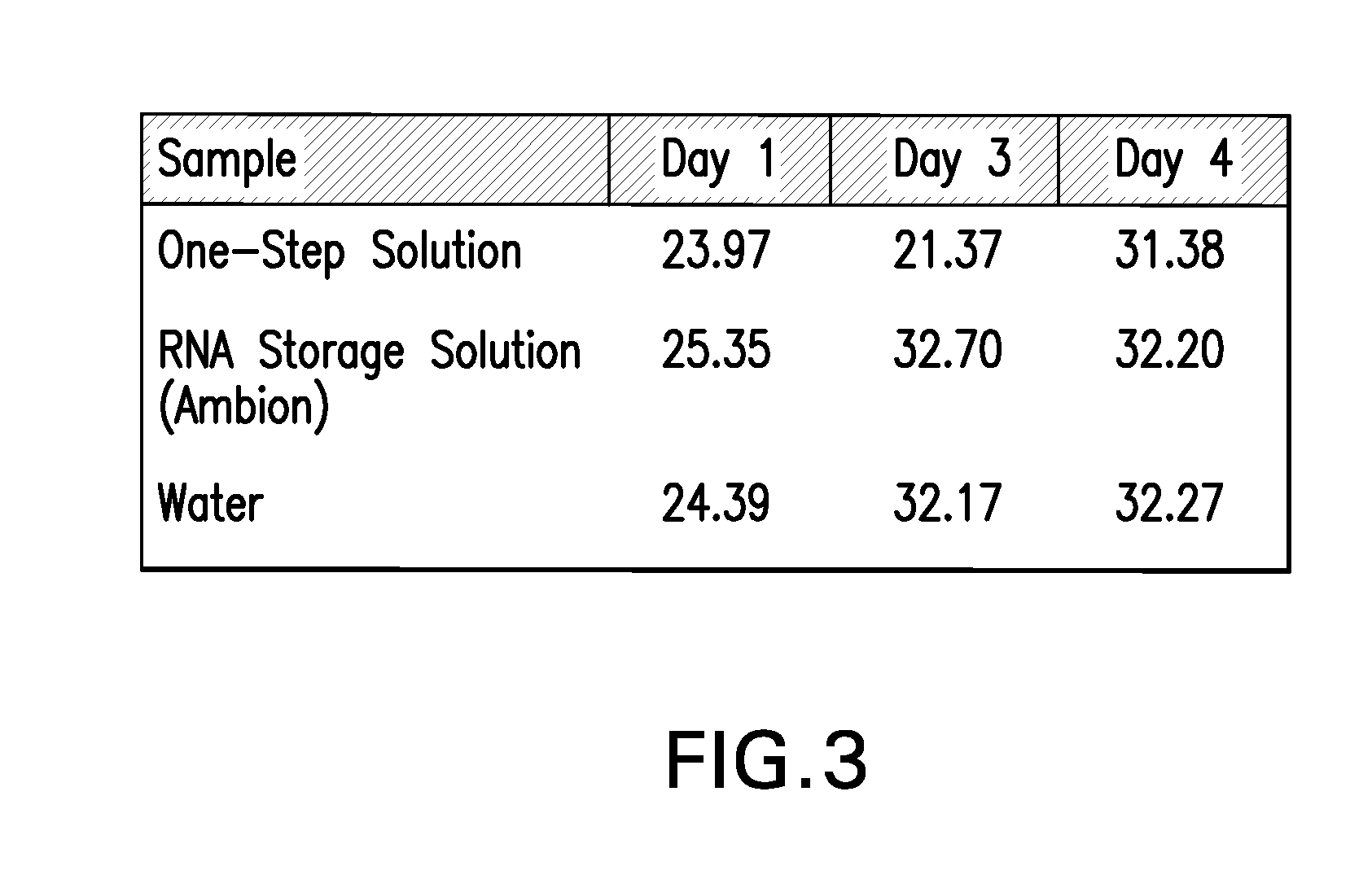
Disclosed are compositions for isolating populations of nucleic acids from biological, forensic, and environmental samples. Also disclosed are methods for using these compositions as one-step formulations for killing pathogens, inactivating nucleases, and releasing polynucleotides from other cellular components within the sample, and stabilizing the nucleic acids prior to further processing or assay. The disclosed compositions safely facilitate rapid sample collection, and provide extended storage and transport of the samples at ambient or elevated temperature without contamination of the sample or degradation of the nucleic acids contained therein. This process particularly facilitates the collection of specimens from remote locations, and under conditions previously considered hostile for preserving the integrity of nucleic acids released from lysed biological samples without the need of refrigeration or freezing prior to molecular analysis.
Owner:LONGHORN VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS LLC
Absorbing pathogen-inactivating compounds with porous particles immobilized in a matrix
InactiveUS6951713B2Reduce risk of leakageReduce decreaseImmobilised enzymesOther blood circulation devicesWhole blood productSorbent
Methods and devices are provided for reducing the concentration of low molecular weight compounds in a biological composition, while substantially maintaining a desired biological activity of the biological composition. The device comprises highly porous adsorbent particles, and the adsorbent particles are immobilized by an inert matrix. The matrix containing the particles is contained in a housing, and the particles range in diameter from about 1 μm to about 200 μm. The matrix can be fibrous, and the particles can have a surface area greater than 750 m2 / g and a pore diameter between about 25 and 800 Å. The device can be used to adsorb and remove a pathogen-inactivating compound that is a nucleic acid-binding compound such as psoralen, an acridine derivative or a dye from a biological composition such as a blood product.
Owner:CERUS CORP
Absorbing pathogen-inactivating compounds with porous particles immobilized in a matrix
InactiveUS20050142542A1Reduce risk of leakageEasy to manufactureImmobilised enzymesOther blood circulation devicesWhole blood productSorbent
Methods and devices are provided for reducing the concentration of low molecular weight compounds in a biological composition, while substantially maintaining a desired biological activity of the biological composition. The device comprises highly porous adsorbent particles, and the adsorbent particles are immobilized by an inert matrix. The matrix containing the particles is contained in a housing, and the particles range in diameter from about 1 μm to about 200 μm. The matrix can be fibrous, and the particles can have a surface area greater than 750 m2 / g and a pore diameter between about 25 and 800 Å. The device can be used to adsorb and remove a pathogen-inactivating compound that is a nucleic acid-binding compound such as psoralen, an acridine derivative or a dye from a biological composition such as a blood product.
Owner:CERUS CORP
Composite membranes and methods for making such membranes
InactiveUS20020066699A1Semi-permeable membranesOther blood circulation devicesBiochemistryOrganic compound
Membranes and methods for making membranes are disclosed. The membranes include a polymeric matrix and a particulate material immobilized within the matrix. The membranes may find particular application in methods and apparatus for removing organic compounds from a biological fluid as part of a pathogen inactivation treatment.
Owner:FENWAL
Biological Specimen Collection and Transport System
ActiveUS20160108463A1Prevent degradationStabilizes and preserves integrityMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningCellular componentMolecular analysis
Disclosed are compositions for isolating populations of nucleic acids from biological, forensic, and environmental samples. Also disclosed are methods for using these compositions as one-step formulations for killing pathogens, inactivating nucleases, and releasing polynucleotides from other cellular components within the sample, and stabilizing the nucleic acids prior to further processing or assay. The disclosed compositions safely facilitate rapid sample collection, and provide extended storage and transport of the samples at ambient or elevated temperature without contamination of the sample or degradation of the nucleic acids contained therein. This process particularly facilitates the collection of specimens from remote locations, and under conditions previously considered hostile for preserving the integrity of nucleic acids released from lysed biological samples without the need of refrigeration or freezing prior to molecular analysis.
Owner:LONGHORN VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS LLC
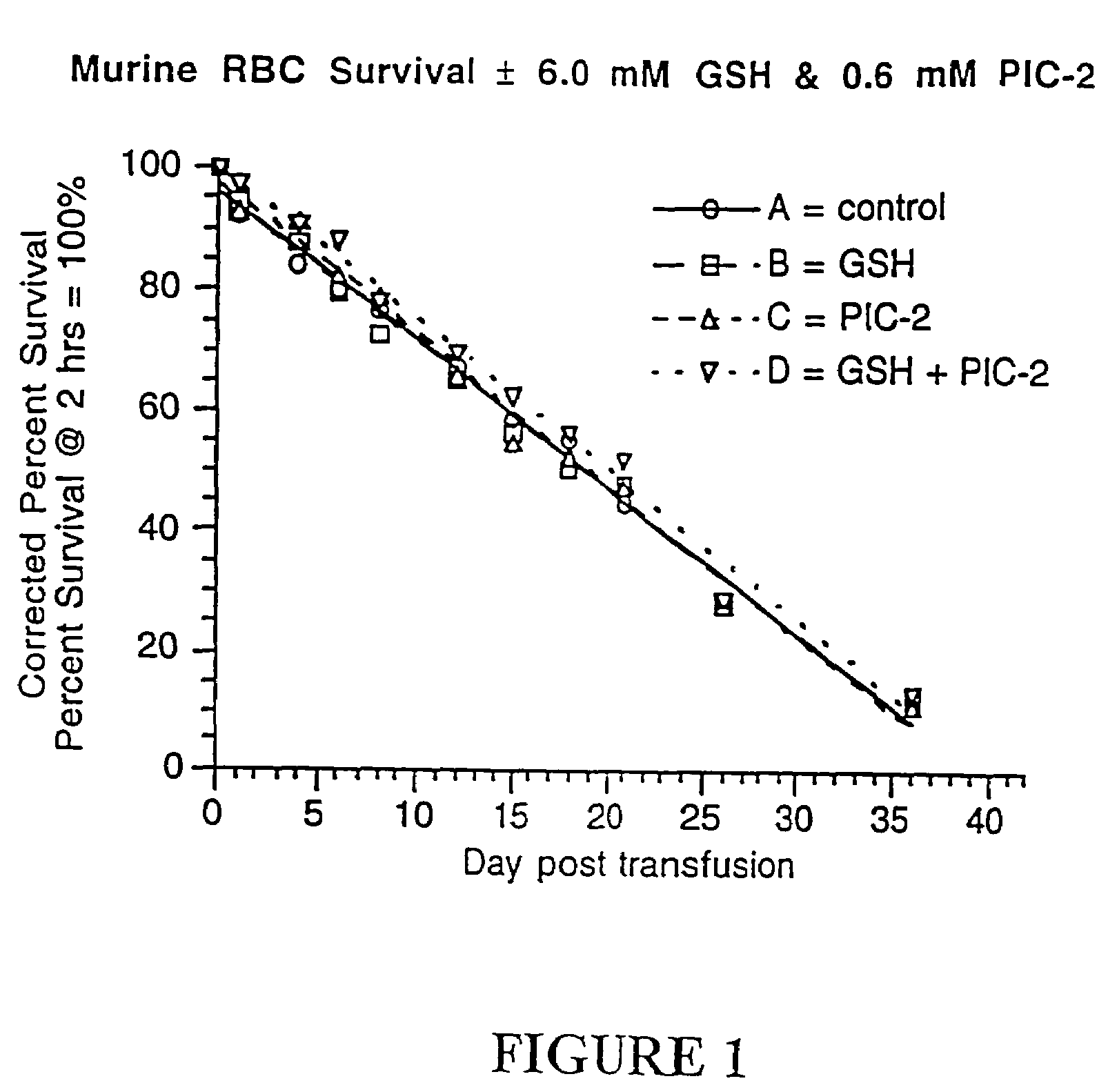
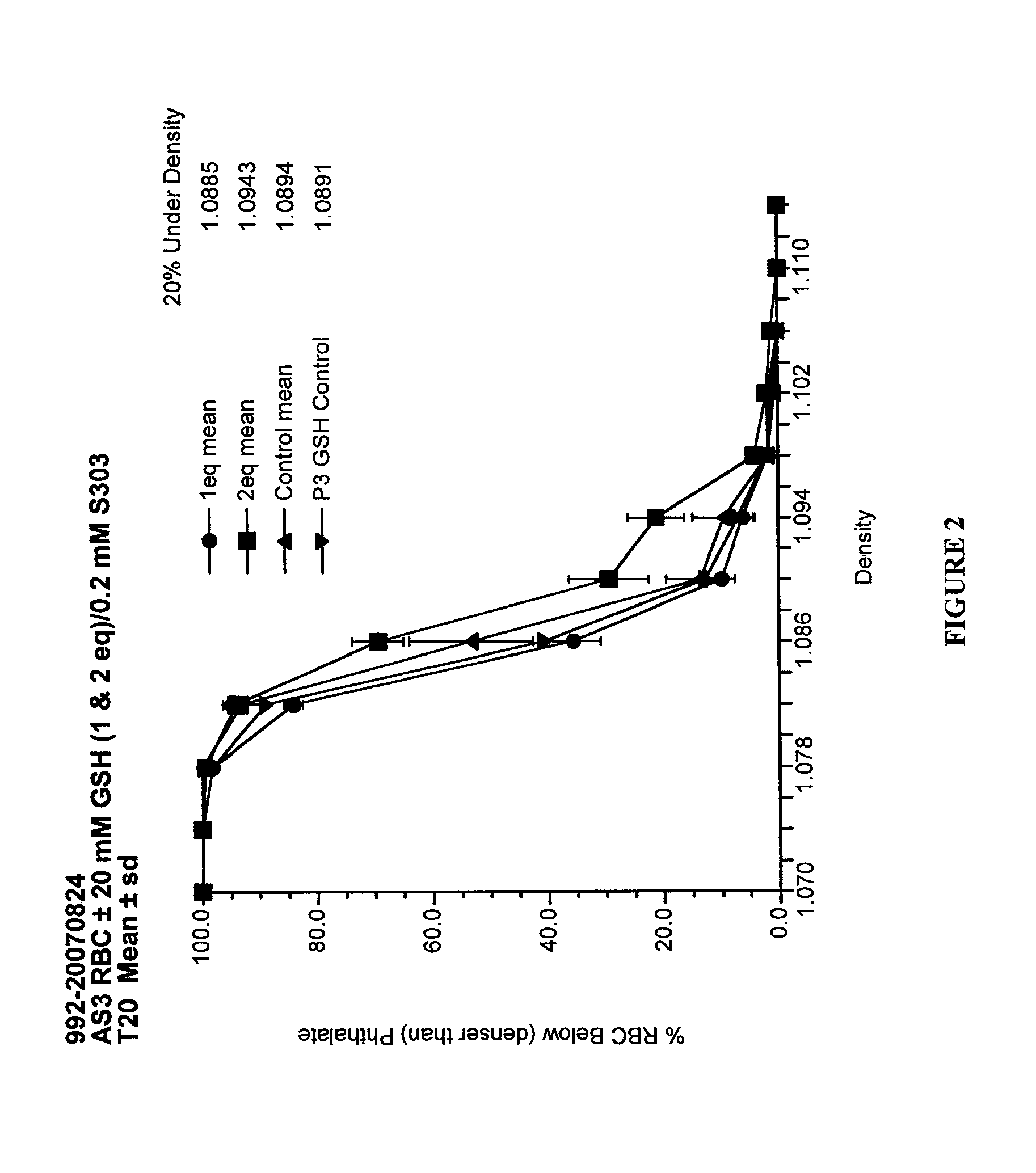
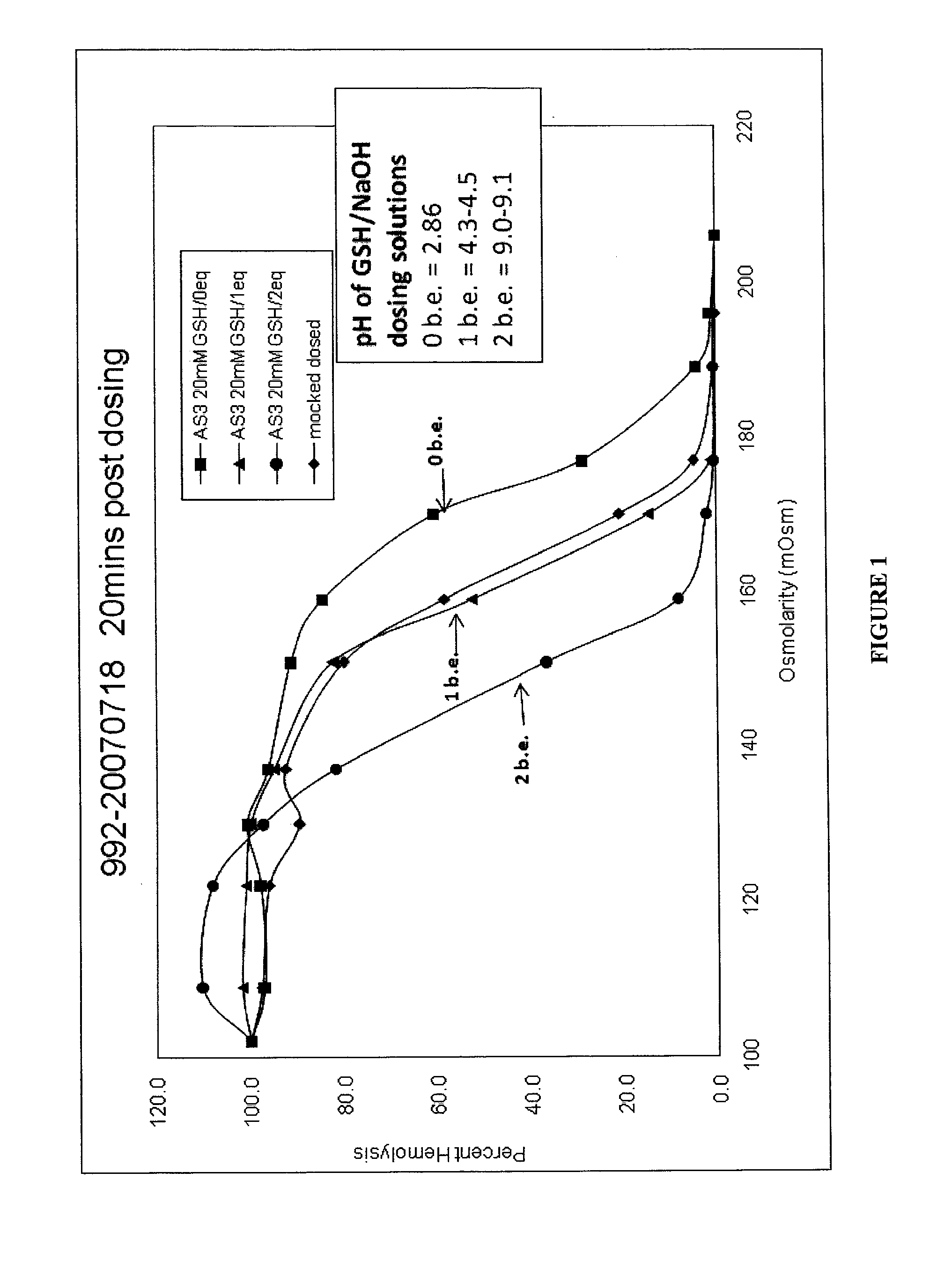
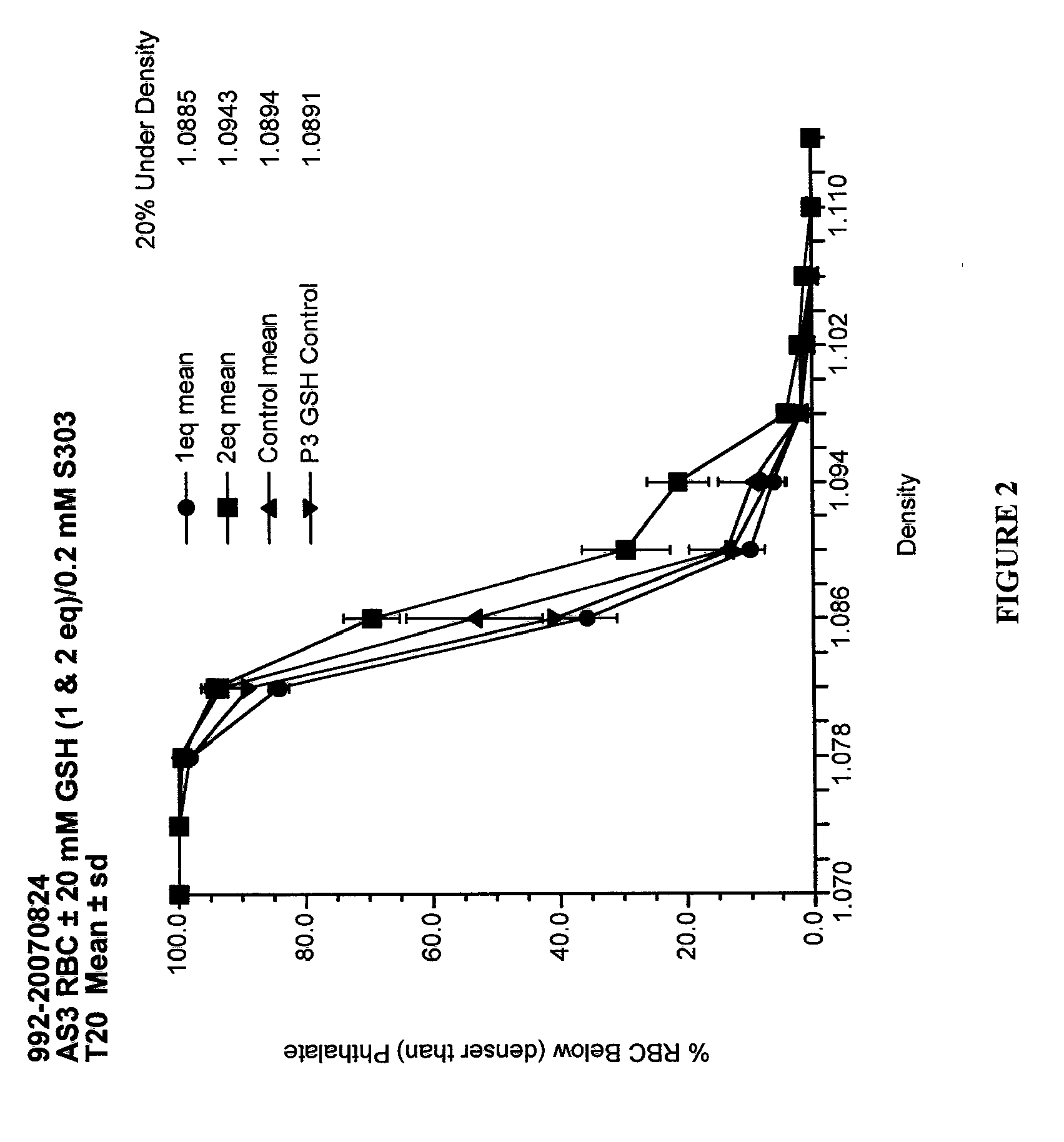
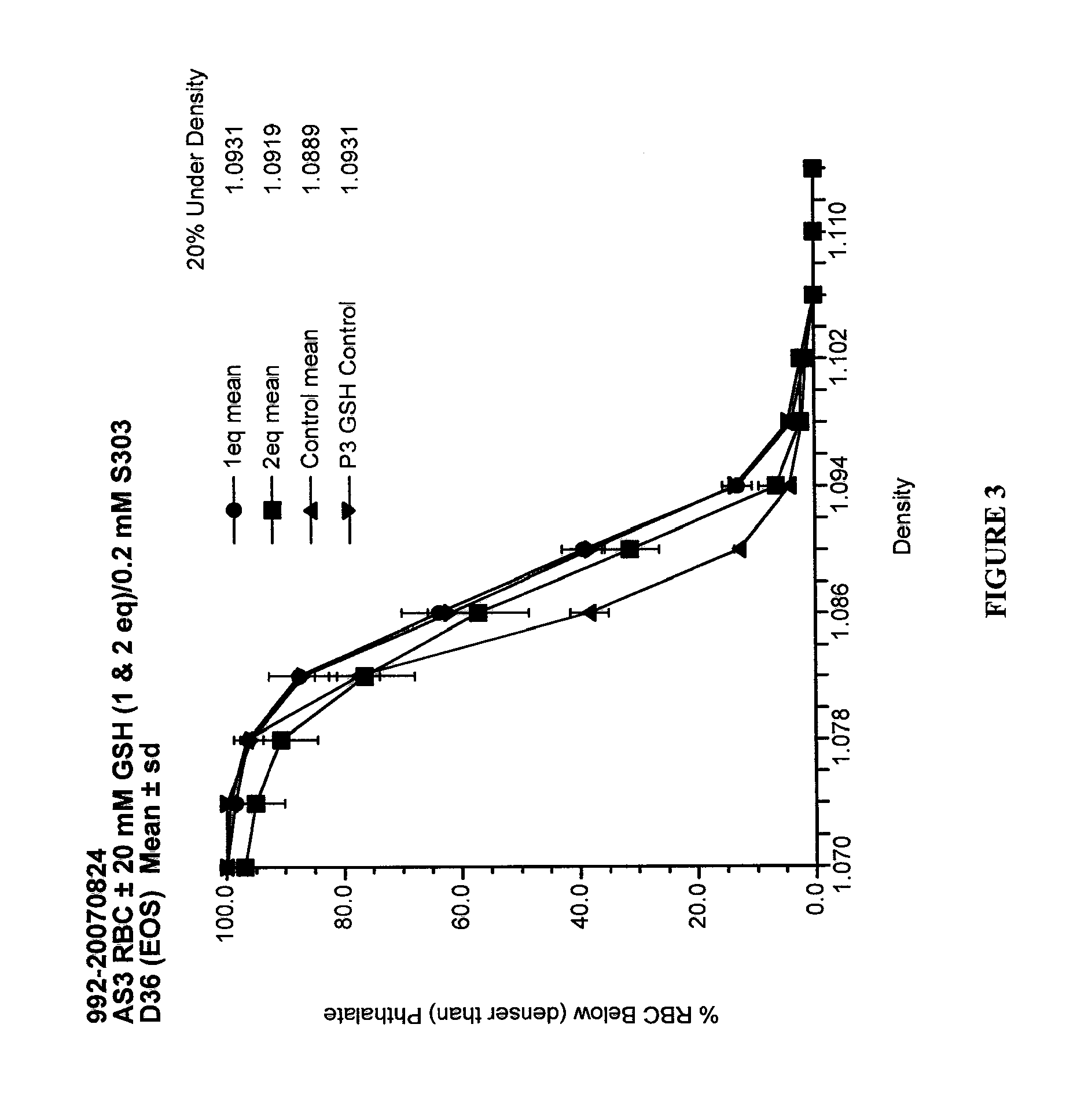
Quenching methods for red blood cell inactivation process
ActiveUS7655392B2Quenching is improvedImprove the situationBiocideOrganic active ingredientsHigh concentrationThiol
Methods are provided for improved quenching of undesired side reactions upon treating a red blood cell composition with a pathogen inactivating compound comprising a nucleic acid binding ligand and a functional group which is, or which is capable of forming, an electrophilic group. In some embodiments, the improved methods use a suitably high concentration of quencher that comprises a nucleophilic functional group that is capable of covalently reacting with the electrophilic group, wherein the treatment occurs within a desired pH range to provide sufficient quenching. Preferred quenchers for use in some of the methods include thiols, such as glutathione, which have been suitably neutralized such that addition to a red blood cell composition results in the desired concentration of quencher at a desirable pH range of 6.8 to 8.5.
Owner:CERUS CORP
Method and device to detect and treat diseases such as tumor or virus infection
InactiveCN103732271AEnhanced couplingOther blood circulation devicesHaemofiltrationExtracorporeal circulationCellular component
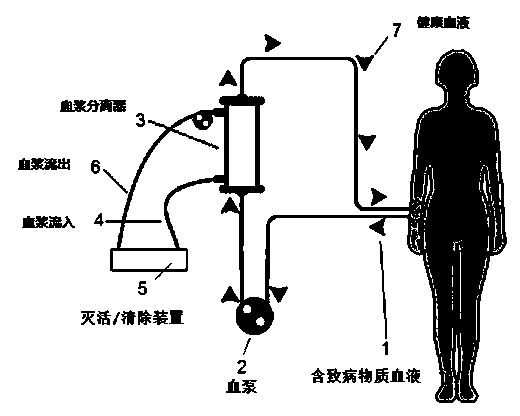
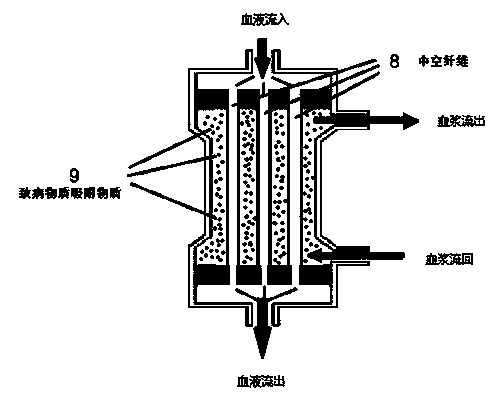
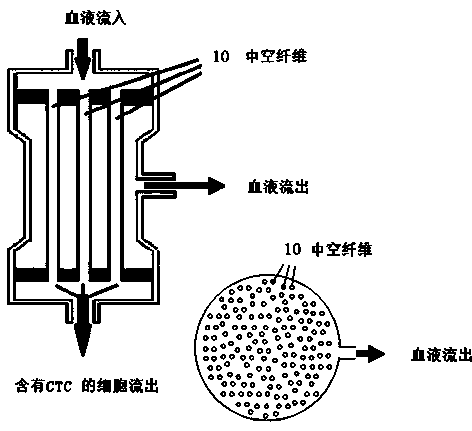
The invention provides a method to reduce the rate of tumor metastasis and tumor recurrence after surgery and chemotherapy and radiotherapy by removing circulating tumor cells (CTC) in the blood after surgery and chemotherapy and radiotherapy by means of specificity, thereby improving the survival rate of cancer patients. The invention provides a method and a system for removing tumor cells. Patients ' blood is guided out to pass through a container, an antibody or a ligand capable of combining with the specificity of the tumor cells is fixed on a solid-phase carrier in the container, whne the patients ' blood passes through the container, the tumor cells can be absorbed by the specificity to be unable to flow back to patients ' blood, and then the tumor cells are removed from the blood to reduce the recidivation of tumor patients and to prolong their survival rate. The removed tumor cells can be washed out from the solid-phase carrier for counting. The invention further provides a method to remove pathogen from blood. Blood is withdrawn from a patient and its plasma and cellular components are separated by means of a plasma separator under the effect of a blood pump, the plasma portion inactivates the pathogen in the blood via a pathogen inactivating device, flows back to extracorporeal circulation passage to merge with the cellular components and then is returned to the patient. The method adopts a physical means, so that side effects can be reduced. The device is simple in structure and can be connected with other blood purification devices.
Owner:王天欣 +1
UV air cleaning and disinfecting system
InactiveUS6855295B2Increase exposureEffective radiationCombination devicesMechanical apparatusUV Radiation ExposureAir filter
A UV air cleaning and disinfecting system has an enclosed chassis with an inlet / outlet surface panel on one planar side thereof, and the chassis is mounted in the space behind a drop ceiling with its surface panel coplanar with the ceiling surface and facing into the room space. The surface panel has a pair of inlet vent arrays on opposite longitudinal sides of the surface panel from each other, and a pair of outlet vent arrays on opposite latitudinal sides of the surface panel from each other. Arranged in the chassis are an air blower unit and an array of UV lamps. The positioning of the inlet and outlet vent arrays establish four mutually circulating air streams in a four-leaf-clover pattern in the room space, which obtains a high-efficiency throughput of air handled by the system. The UV lamp array is arranged longitudinally across the chassis between the inlet ventsat a lower elevational position of the chassis. A pair of air filters is arranged at intake chambers separated by UV-blocking baffles at opposite longitudinal sides of the main chamber housing the air blower in the center of the chassis at an upper elevational position from the array of UV lamps. The upward and downward movement of the air through the filters and over the UV lamps toward the center causes swirling movements which enhance the exposure of pathogens in the air to UV radiation exposure. The surface panel is formed with a series of cascading door sections to allow wide access across the center of the chassis for maintenance of the UV lamps, with a first door section connected to an interlock switch for cutting off electrical power to the UV lamps and fan when the first door section is opened. The UV-blocking baffles have an angled shape and slits at an upper flange thereof covered with fused silica shields. The system's chassis is dimensioned to fit on ceiling rails spaced at standard 4 foot length and 2 foot width intervals. The system can provide 99% or higher inactivation of pathogens in the air with 2 to 7 or more air changes per hour for standard sized rooms.
Owner:KULP JOHN C
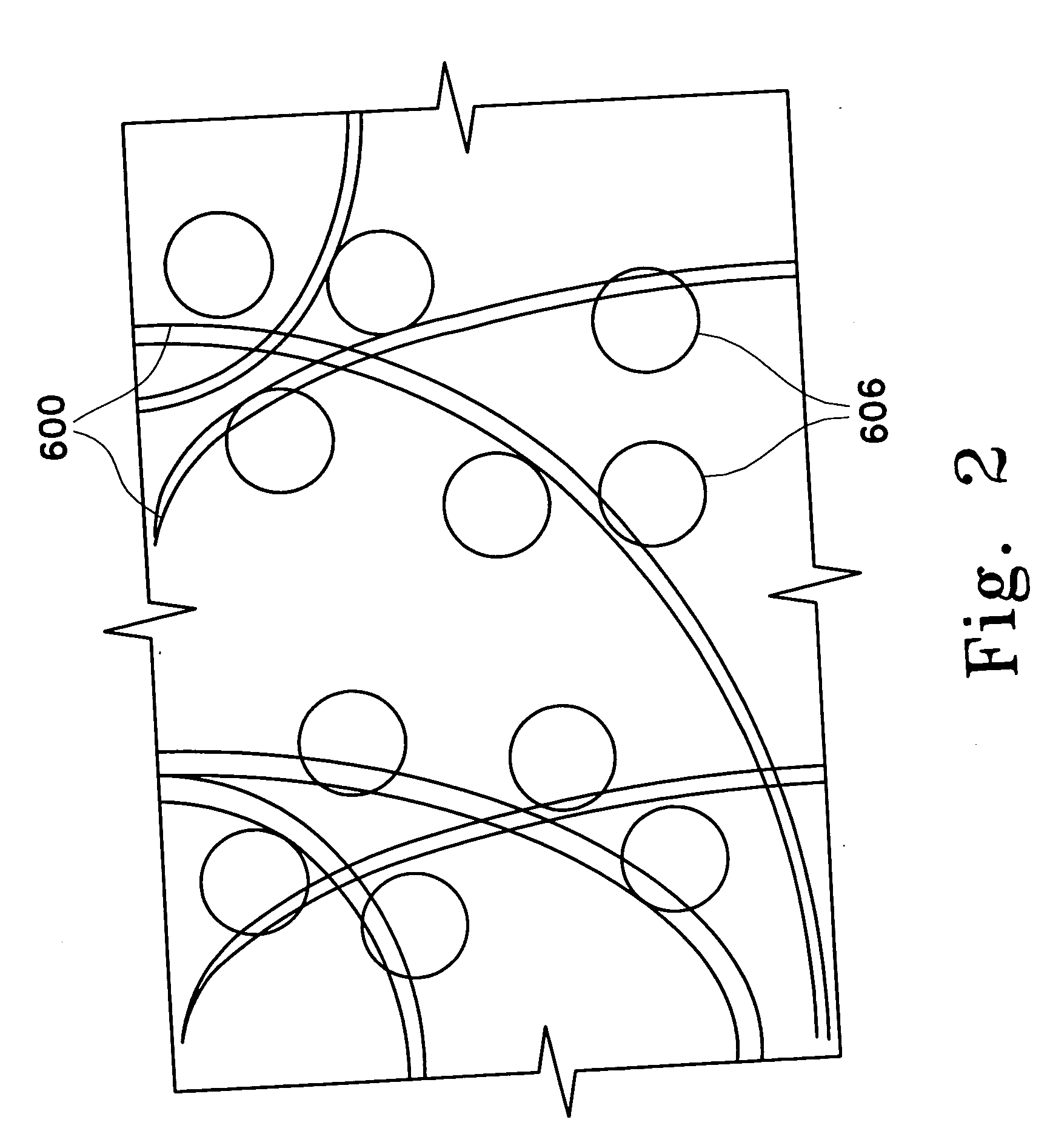
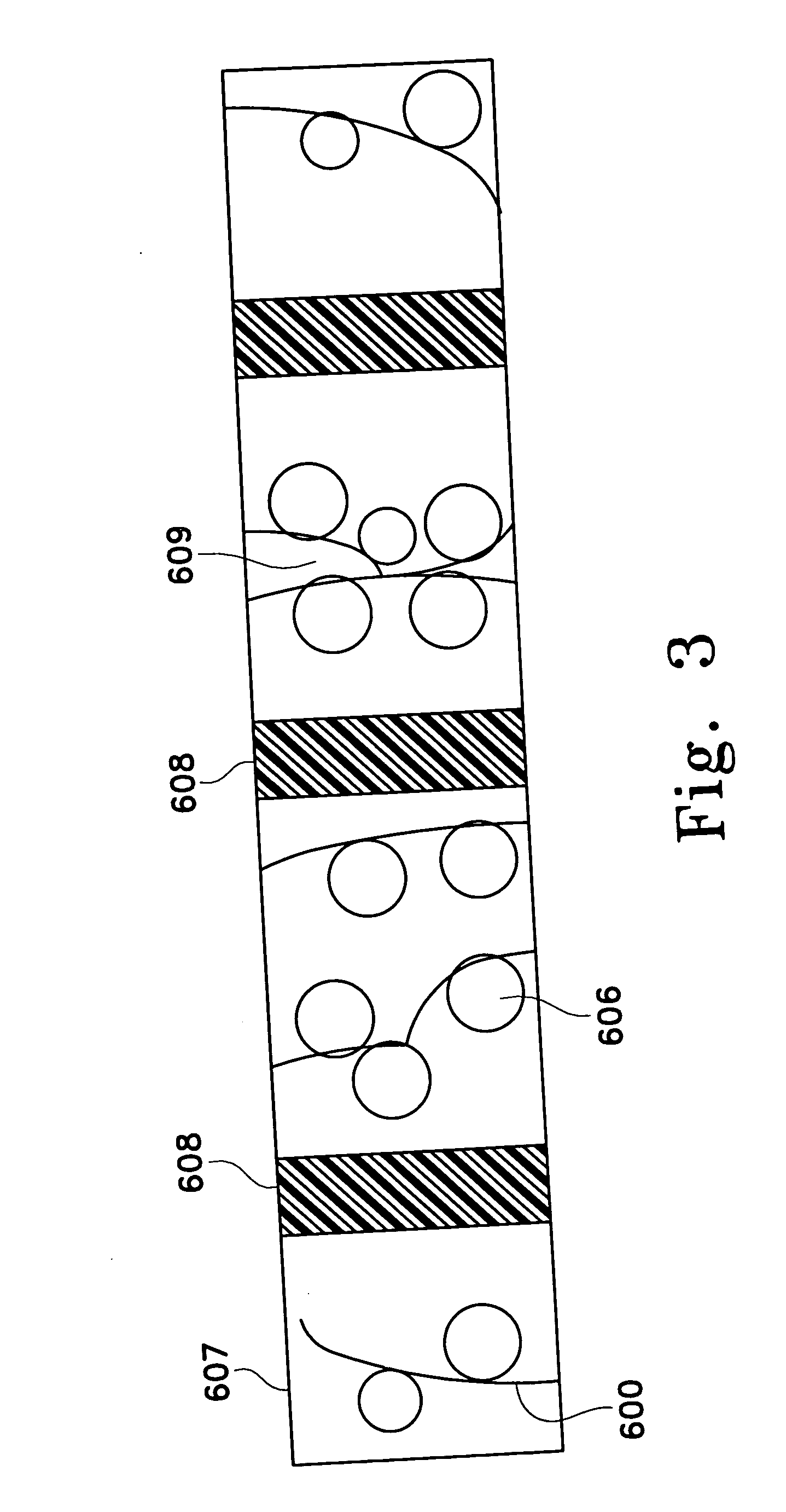
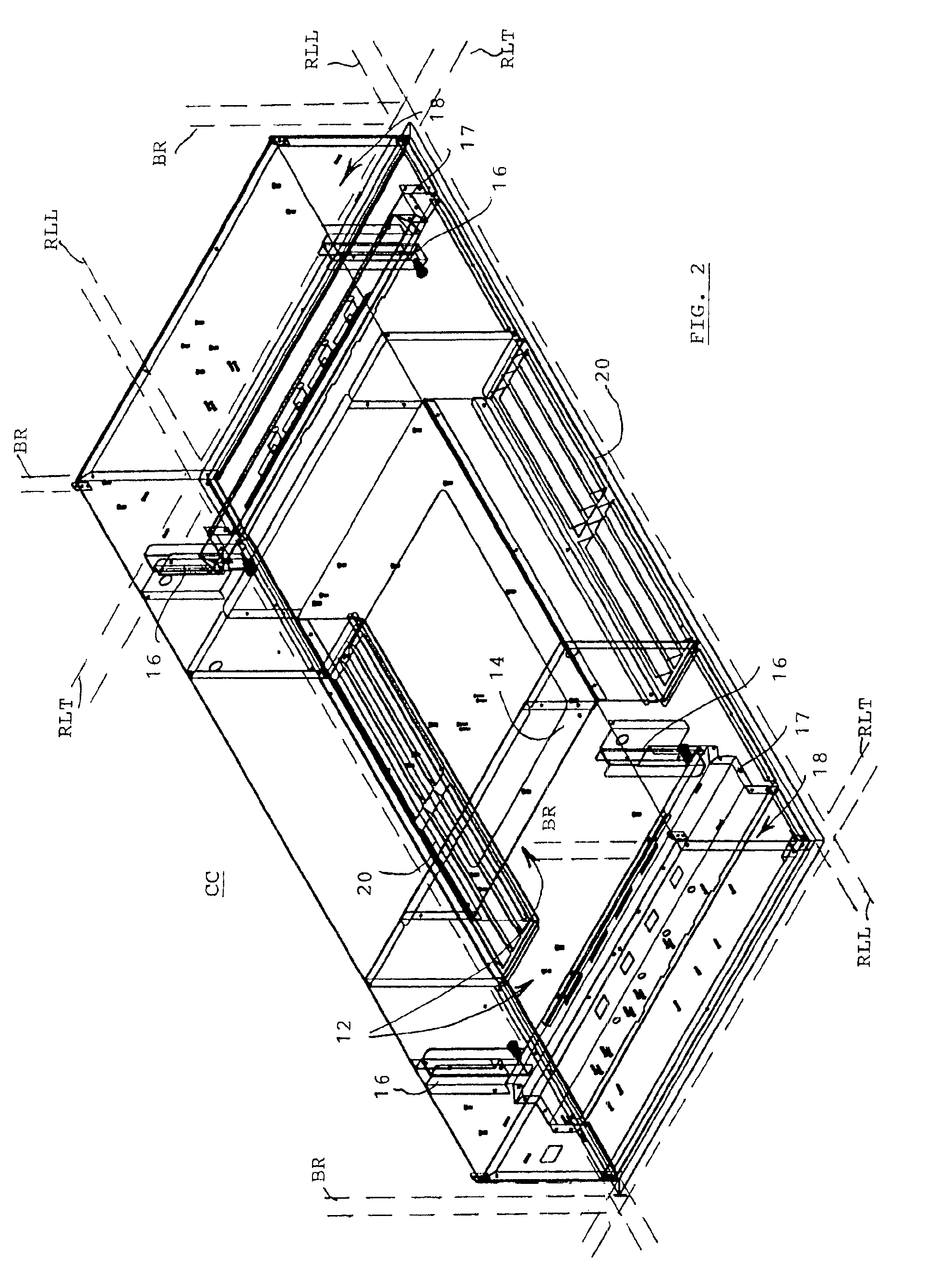
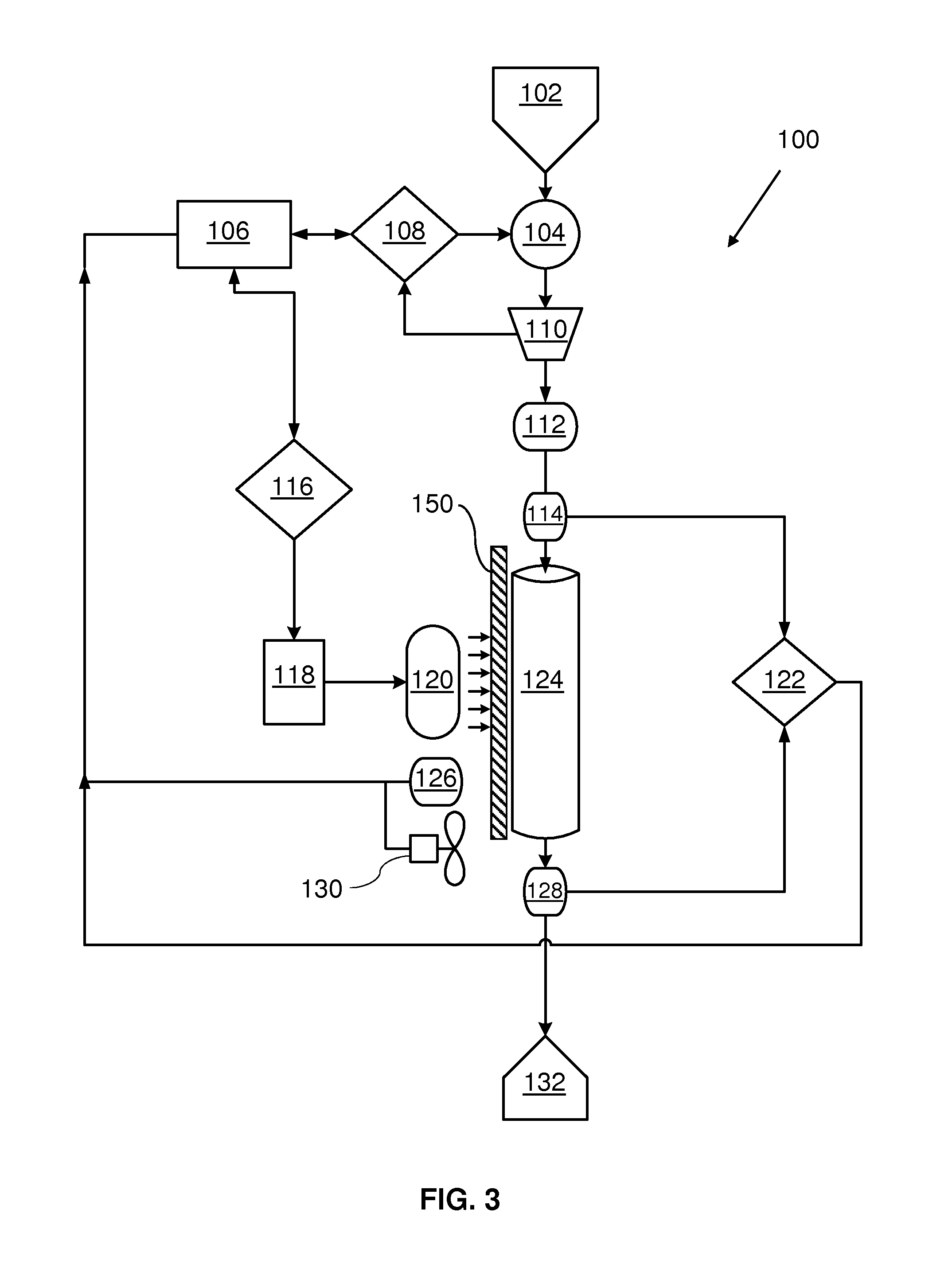
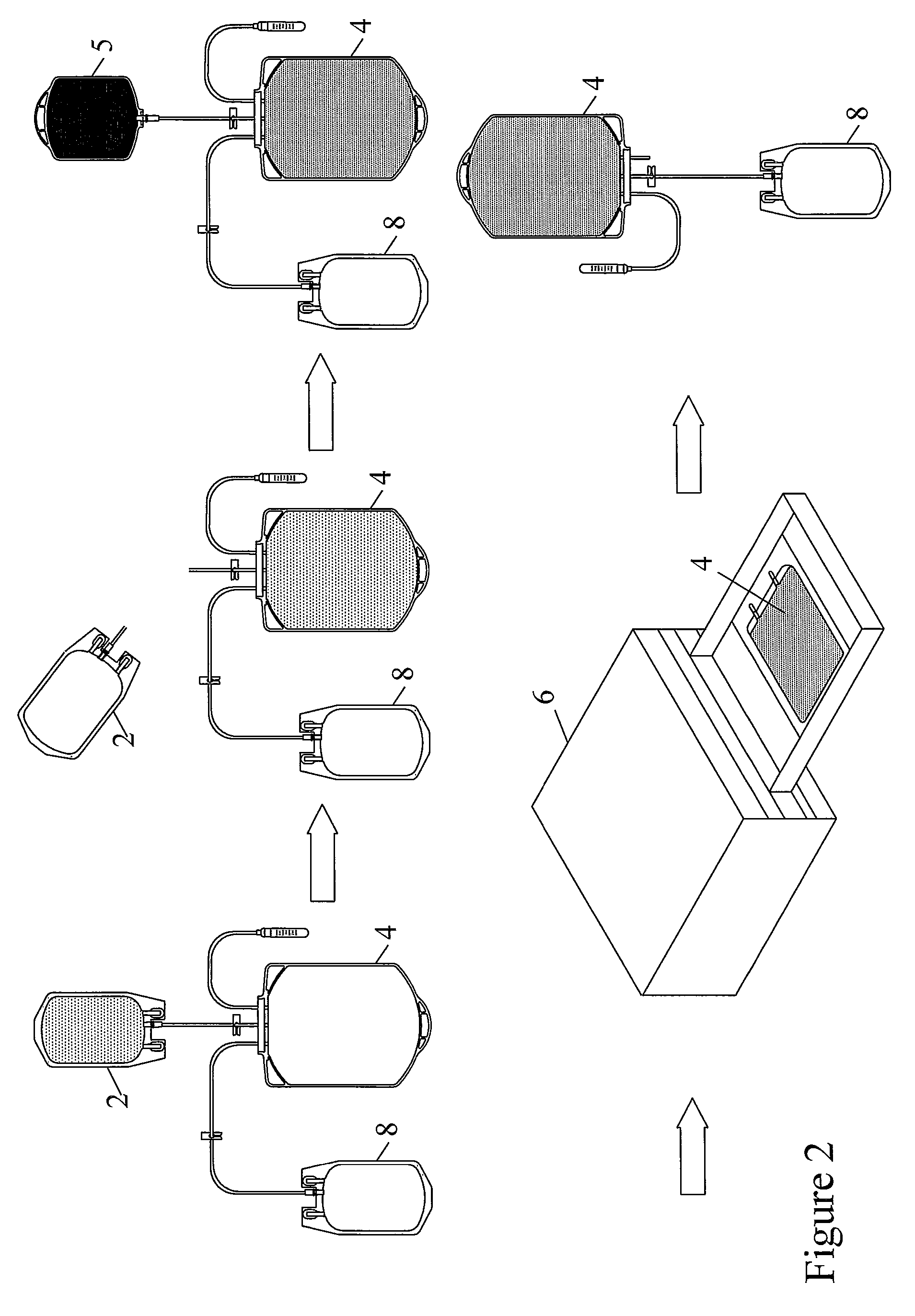
Systems and methods for pathogen inactivation in blood using UV irradiation while minimizing heat transfer thereto
InactiveUS9265876B1Reducing and preventing heat transferReduce pathogensRadiation pyrometryEnergy modified materialsMedicineEnergy absorption
The systems and methods for pathogen reduction in donor blood operates by exposure of blood to UVC irradiation. Unwanted wavelengths of light, mostly in the infrared spectra, may be precluded from reaching blood by providing a layer of IR-absorbing fluid positioned between blood and the source of UV irradiation, whereby minimizing energy absorption and heating of blood. Some embodiments further disclose a system configured to utilize the same IR-absorbing fluid to actively cool blood by flowing along the flow path thereof.
Owner:DBL TECH LLC
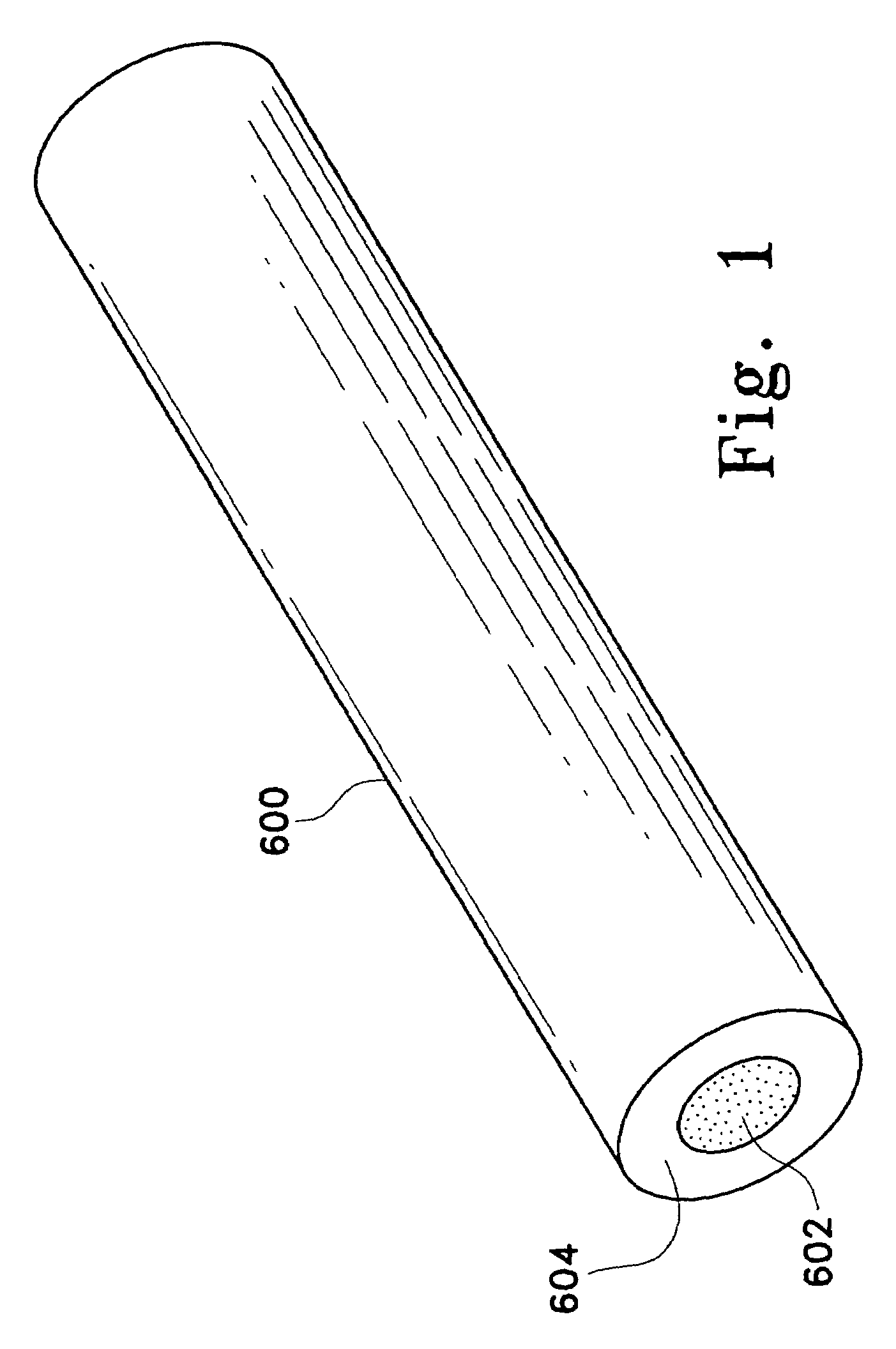
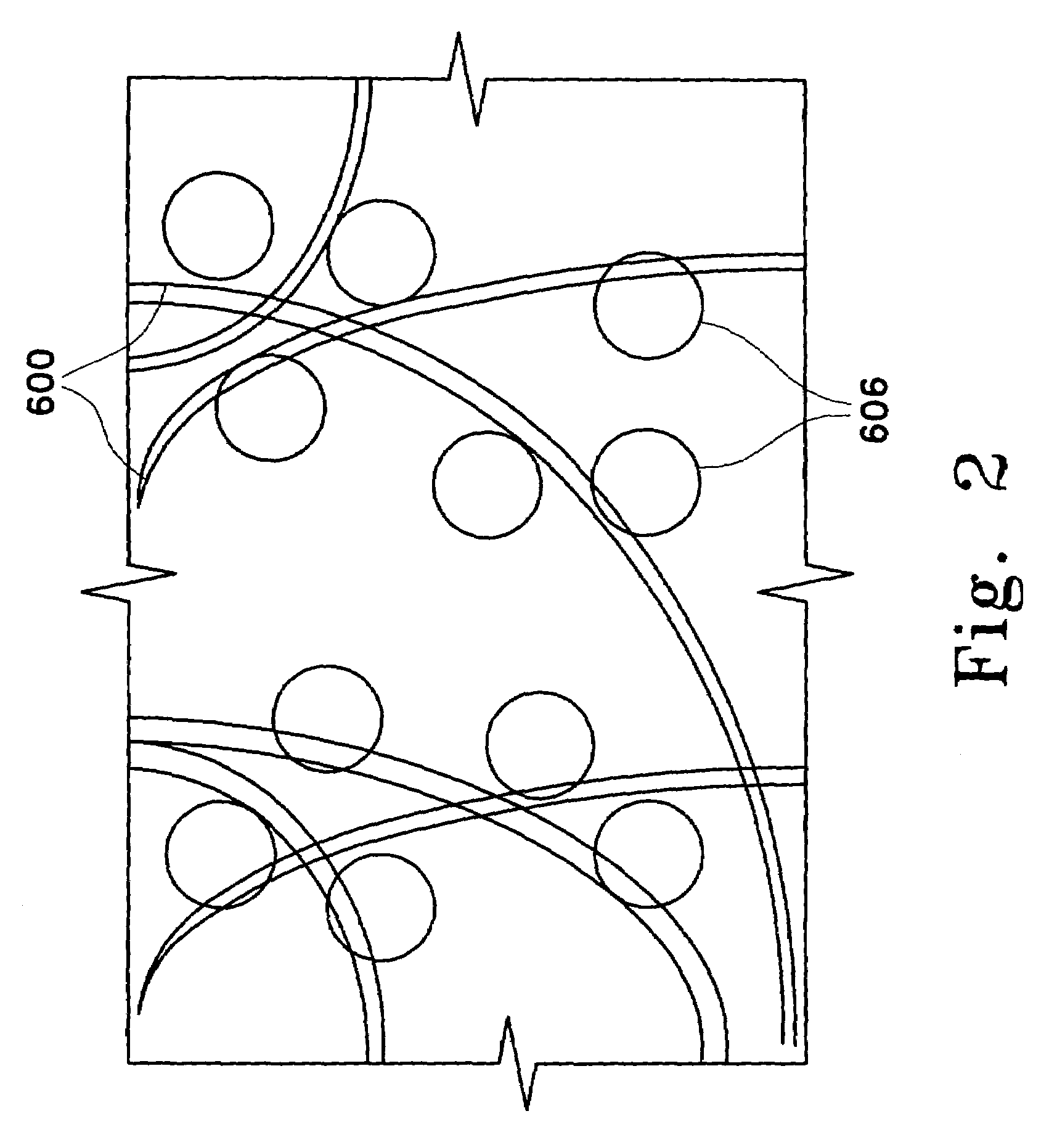
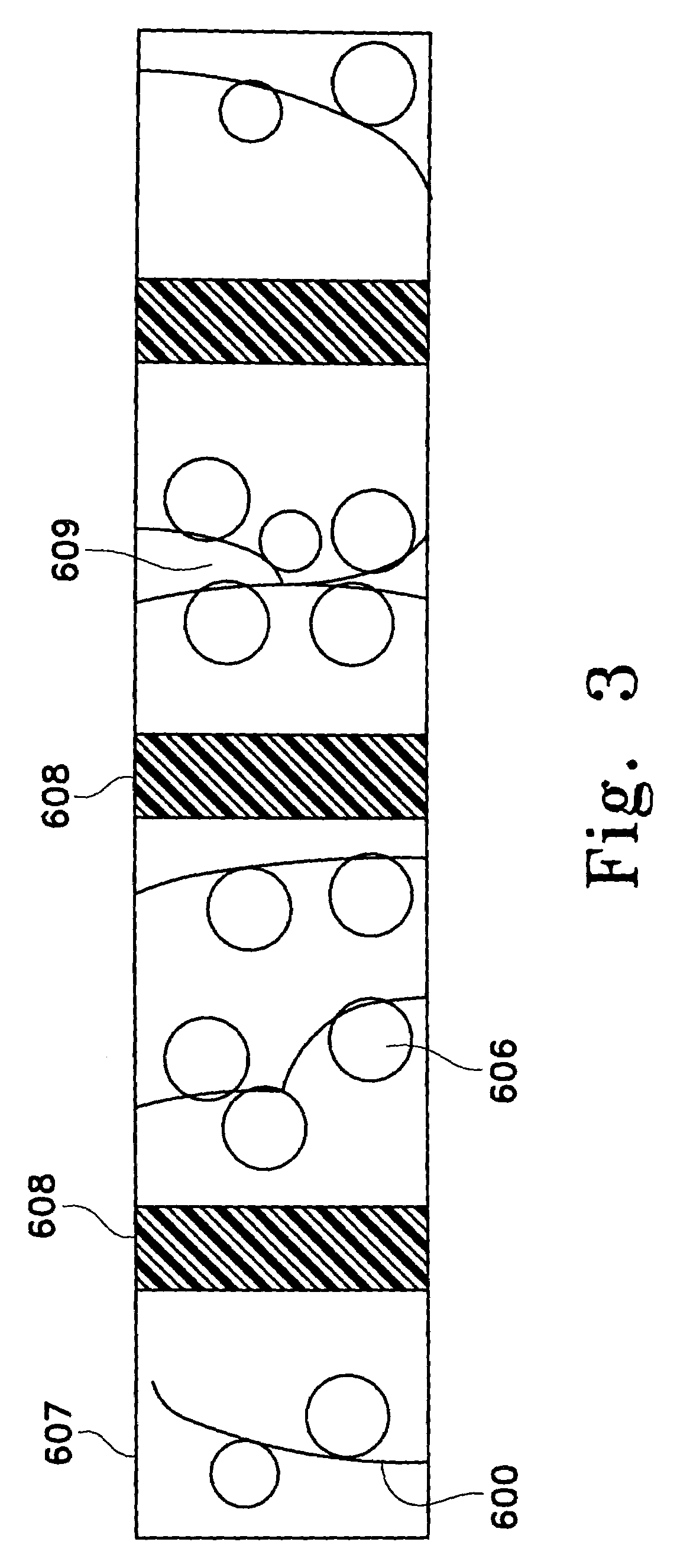
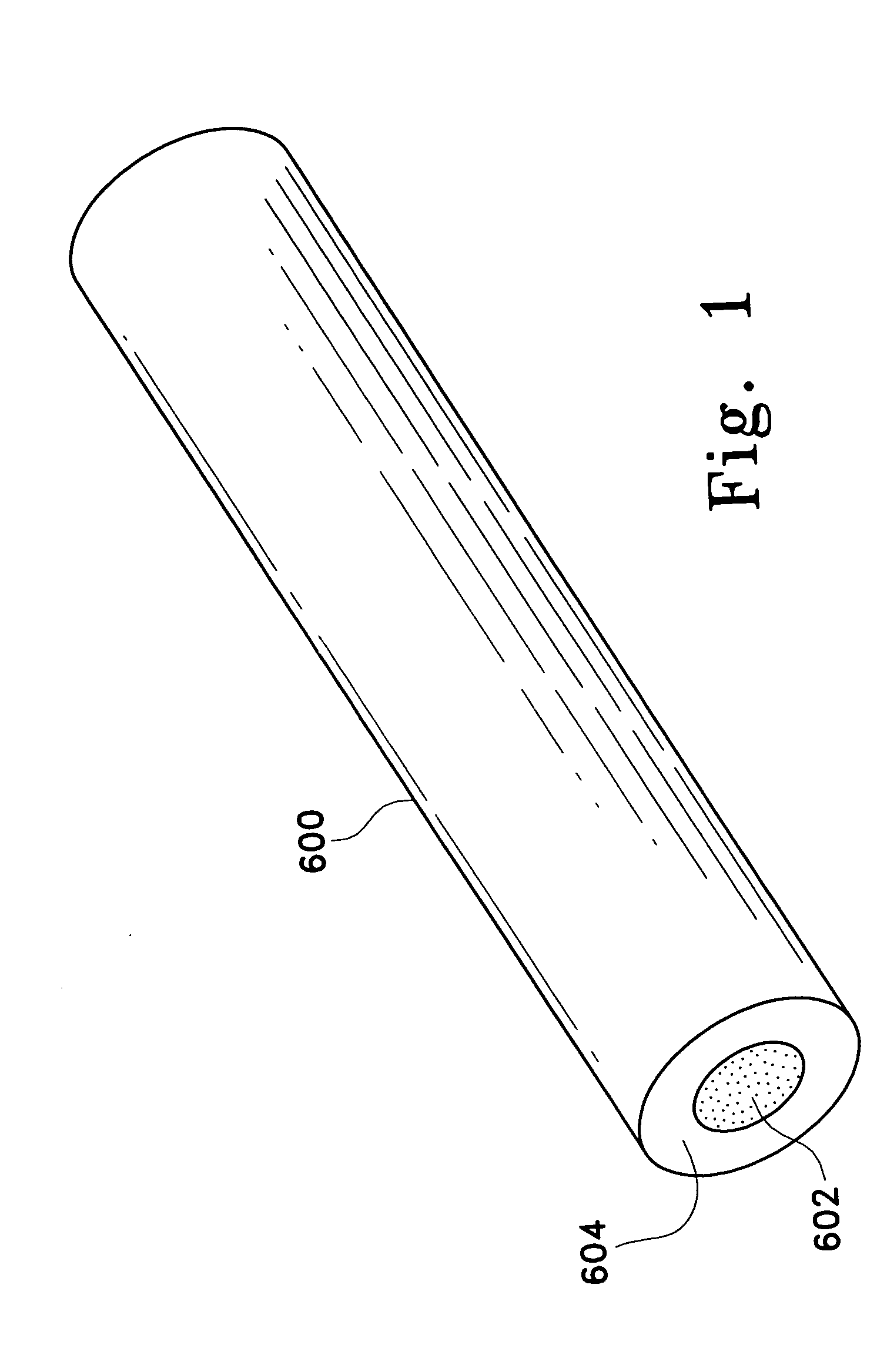
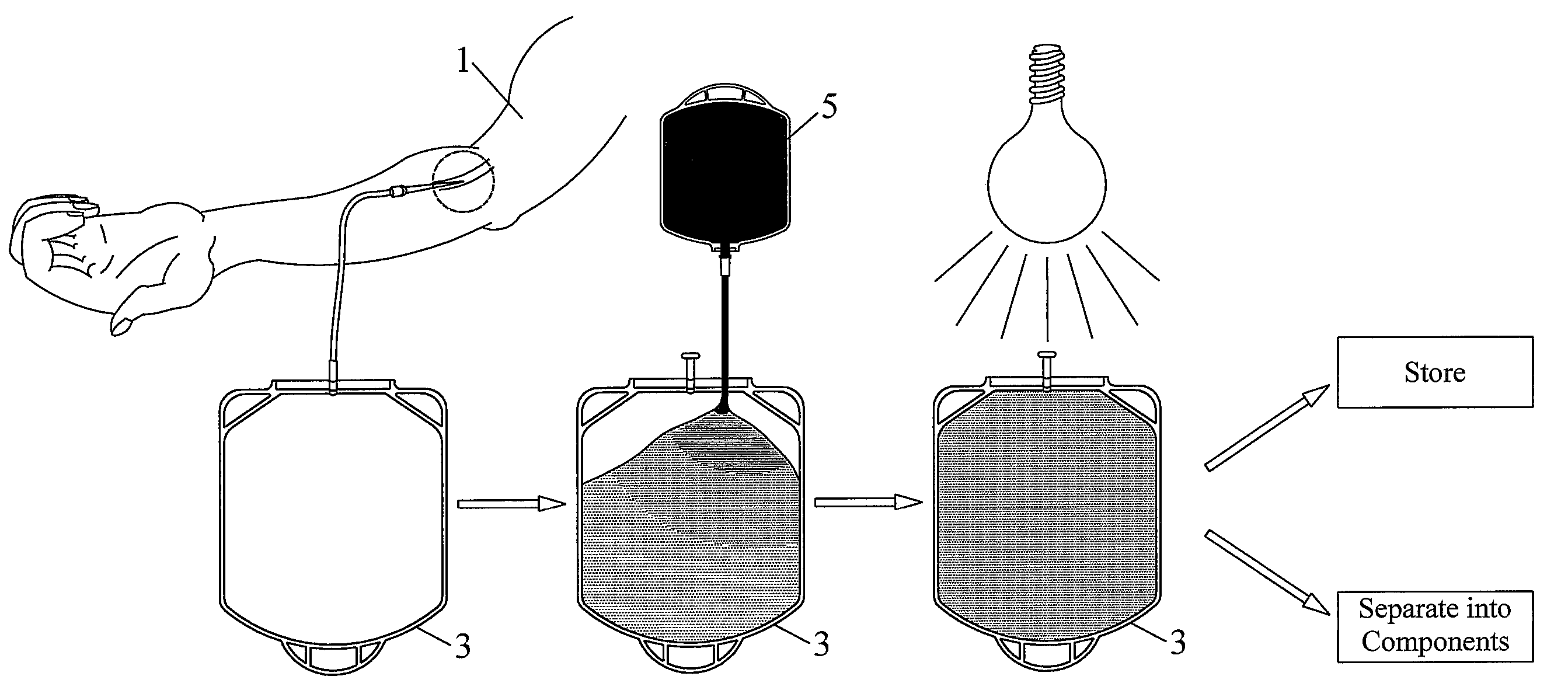
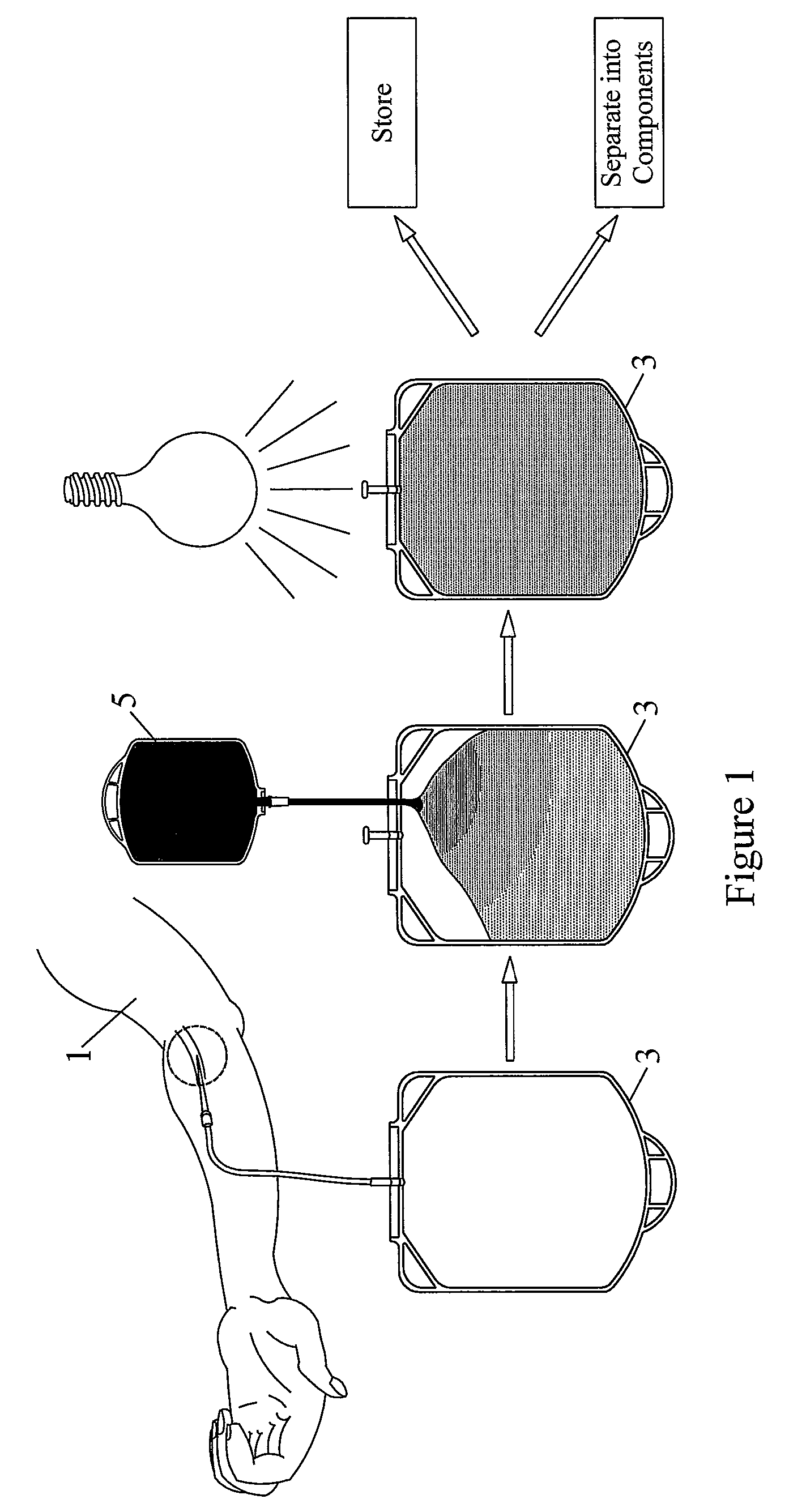
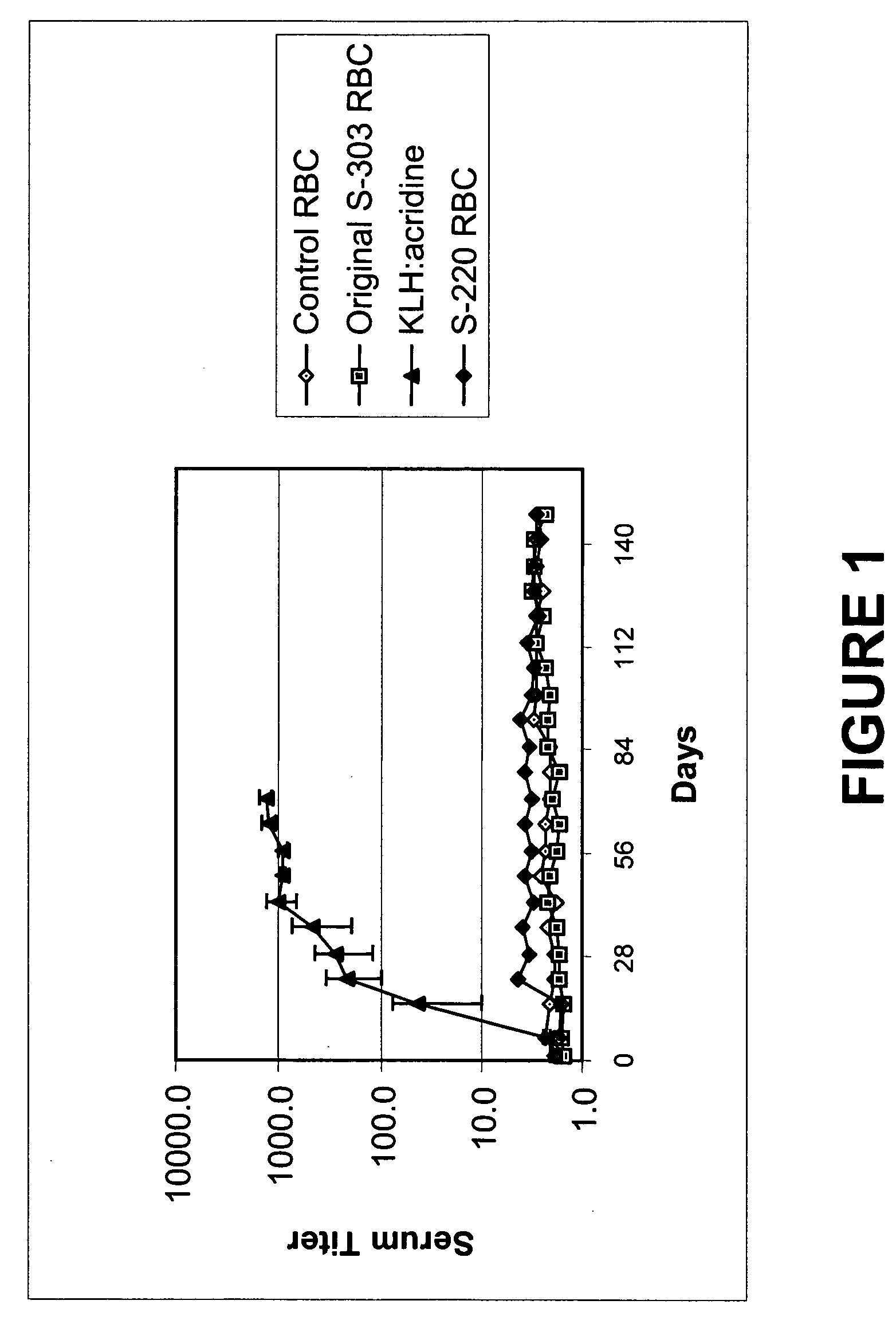
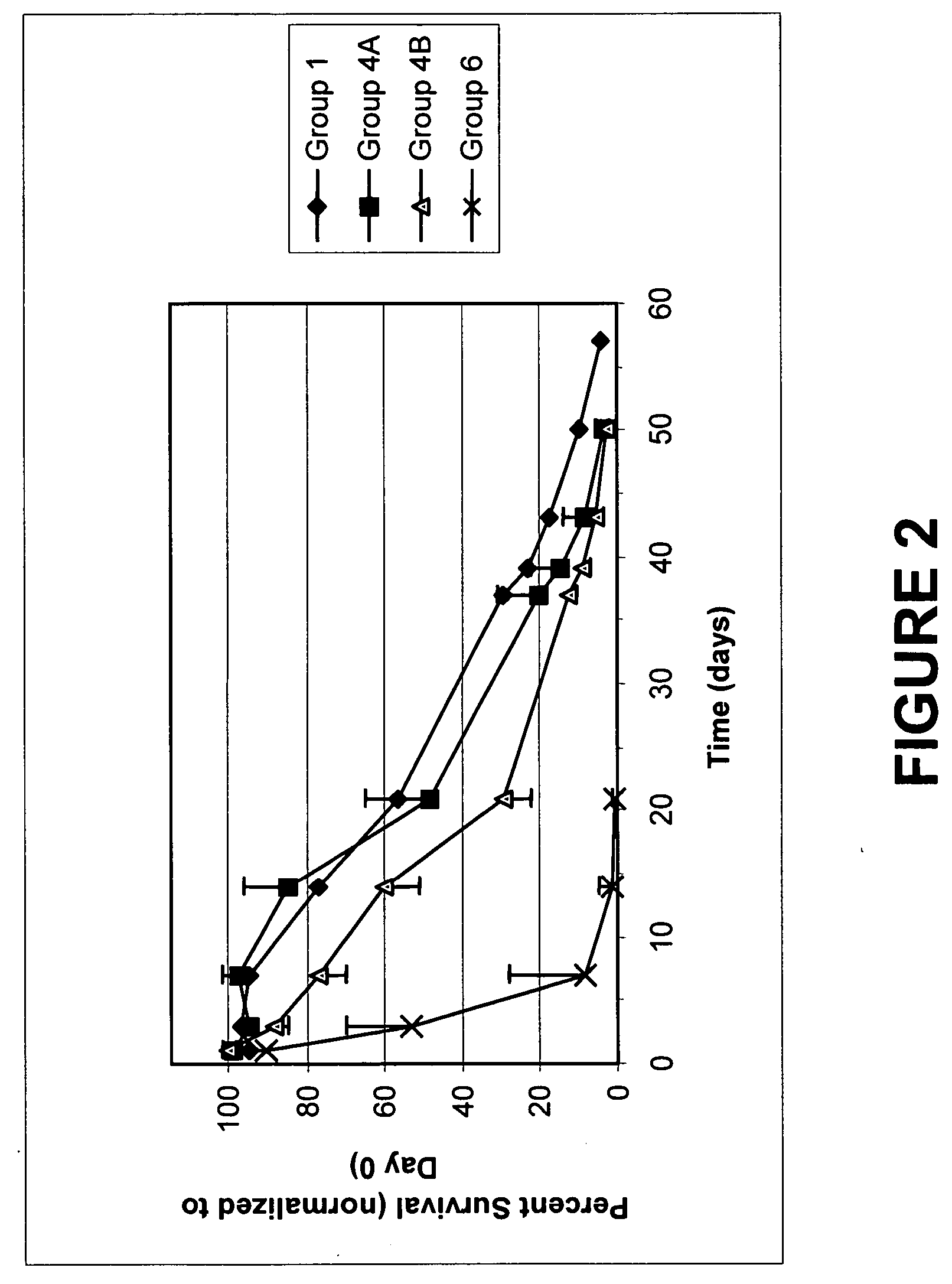
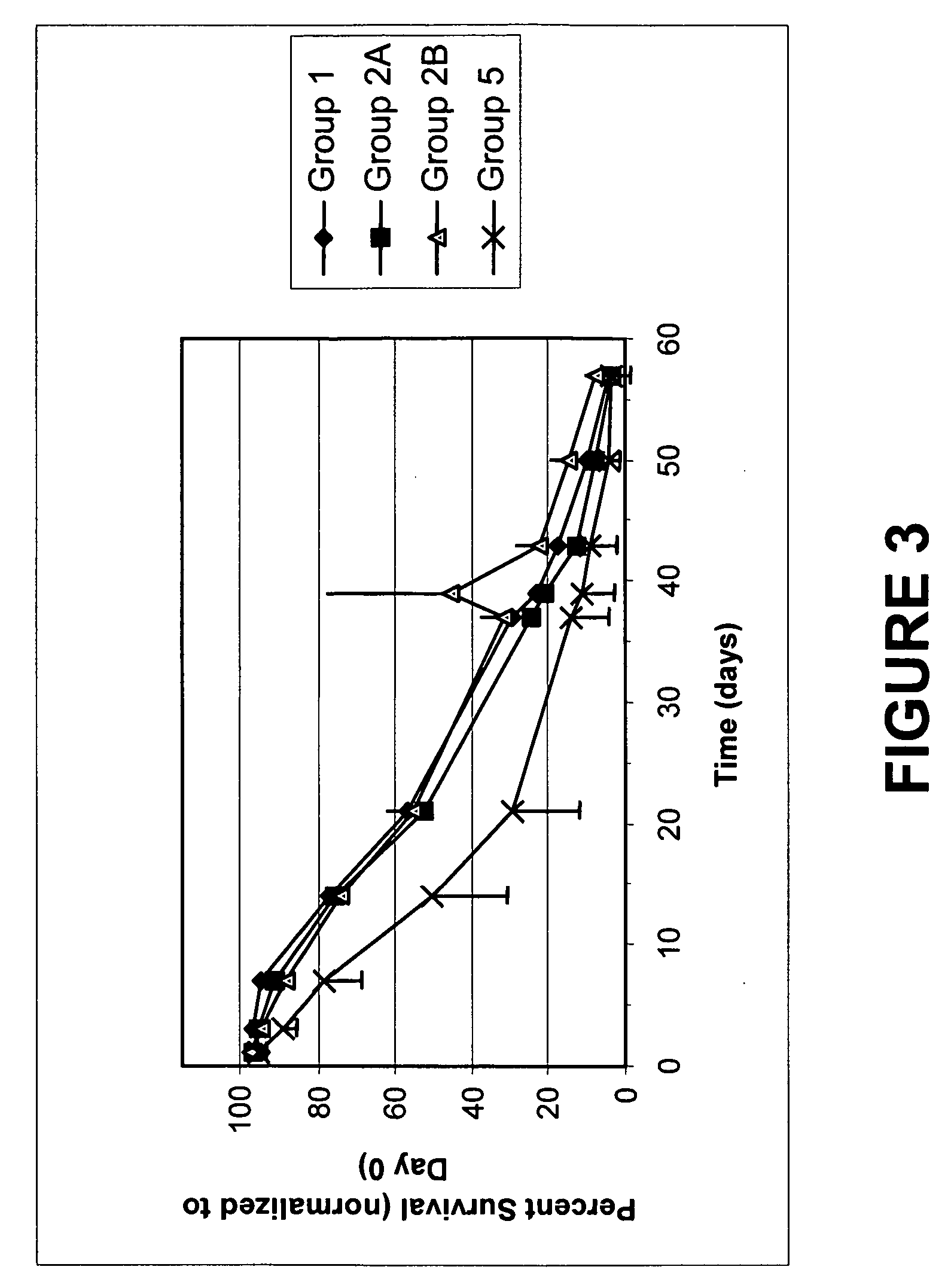
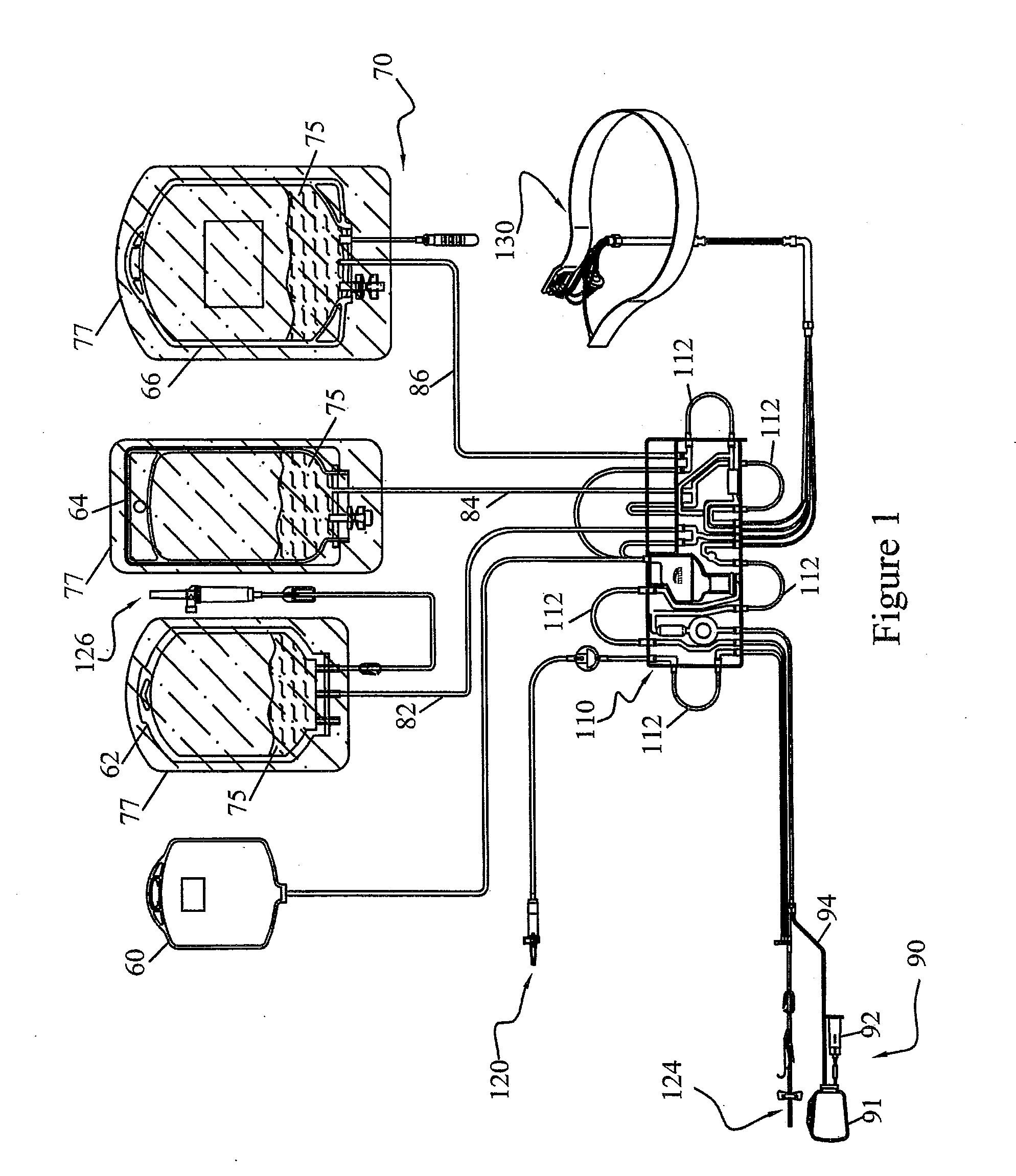
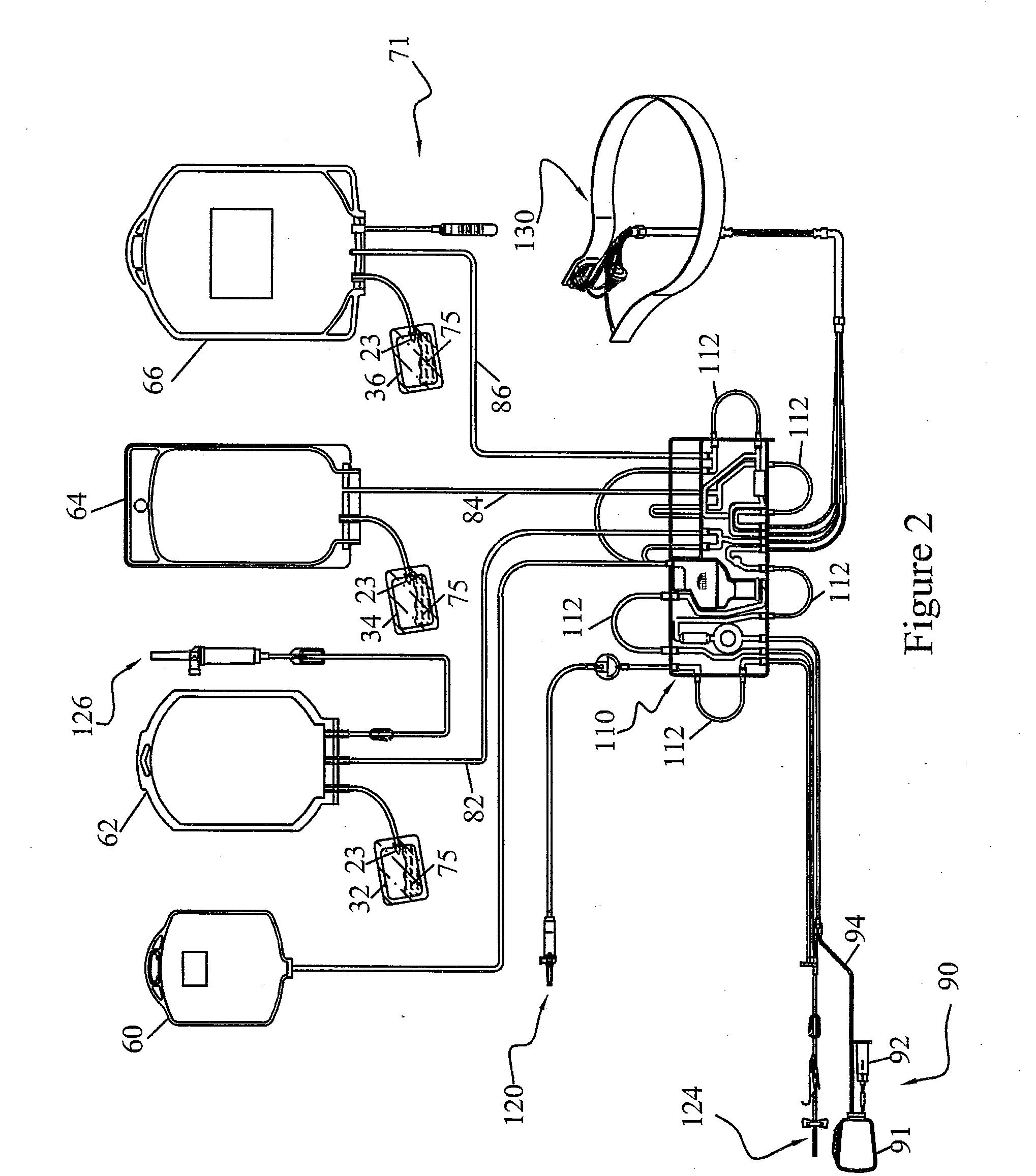
Pathogen Inactivation of Whole Blood
This invention is directed toward a method of pathogen inactivating whole blood. The steps include collecting whole blood from a donor into a bag; illuminating the whole blood with light at a sufficient energy so that an alloxazine photosensitizer present in the whole blood may be photolyzed to inactivate any pathogens which may be present in the whole blood; and storing the pathogen inactivated whole blood. The invention also includes a method of separating the pathogen inactivated whole blood into components.
Owner:TERUMO BCT BIOTECH
Adsorbing pathogen-inactivating compounds with porous particles immobilized in a matrix
InactiveUS7611831B2Reduce risk of leakageReduce decreaseBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsWhole blood productMatrix method
Owner:CERUS CORP
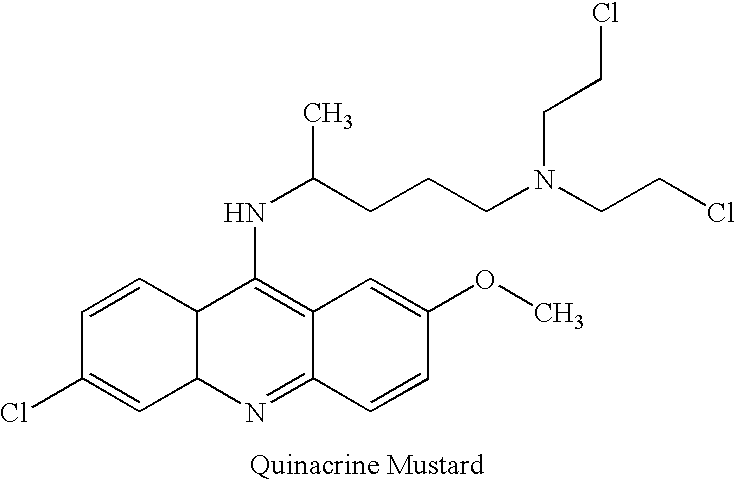
Methods for quenching pathogen inactivators in biological materials
InactiveUS7293985B2Reduces unwanted side reactionReducing unwanted side reactionBiocideOther blood circulation devicesThiolChemical compound
Methods are provided for quenching undesired side reactions of pathogen inactivating compounds in biological materials comprising red blood cells. In a particular embodiment, methods are provided for quenching undesired side reactions of a pathogen inactivating compound that includes a functional group which is, or which is capable of forming, an electrophilic group. In this embodiment, the material is treated with the pathogen inactivating compound and a quencher, wherein the quencher comprises a nucleophilic functional group that is capable of covalently reacting with the electrophilic group. The electrophilic group on the pathogen inactivating compound is preferably a non-radical cationic group. In one embodiment, the pathogen inactivating compound includes a nucleic acid binding ligand and a mustard group, wherein the mustard group is capable of reacting in situ to form the electrophilic group. Preferred quenchers are thiols, such as glutathione. The methods permit inhibition of the modification of red blood cells in red blood cell containing materials during pathogen inactivation.
Owner:CERUS CORP
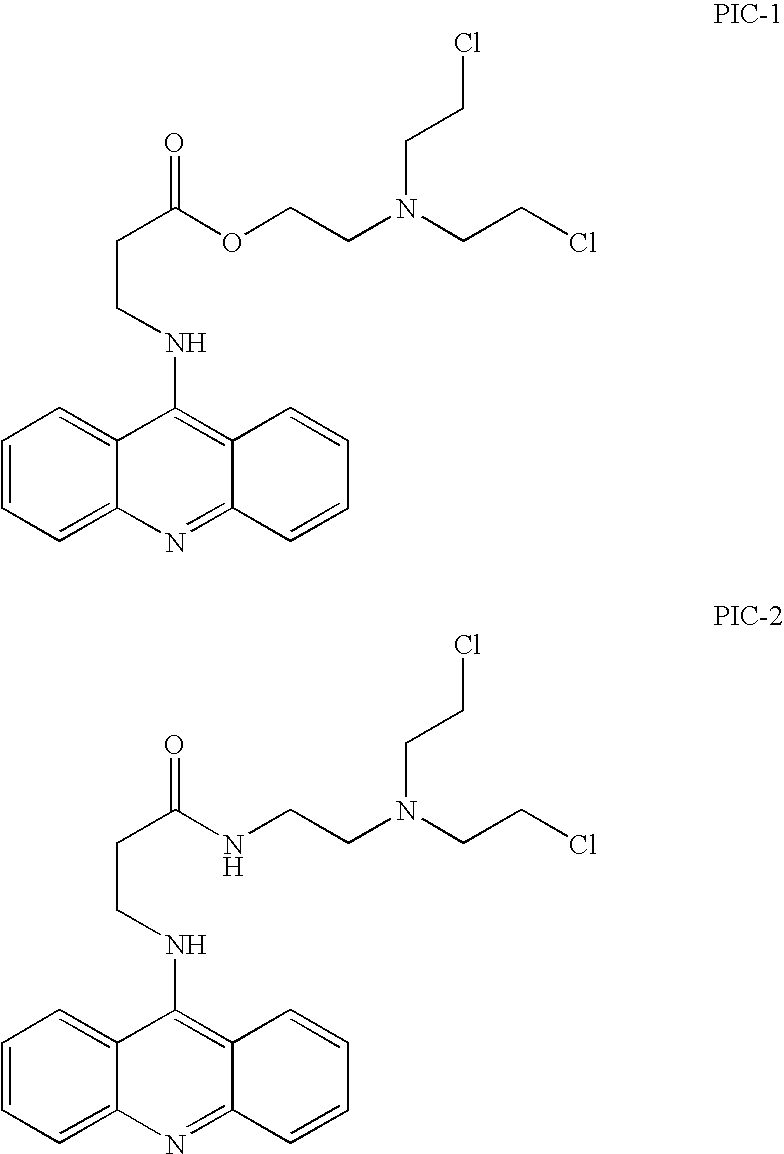
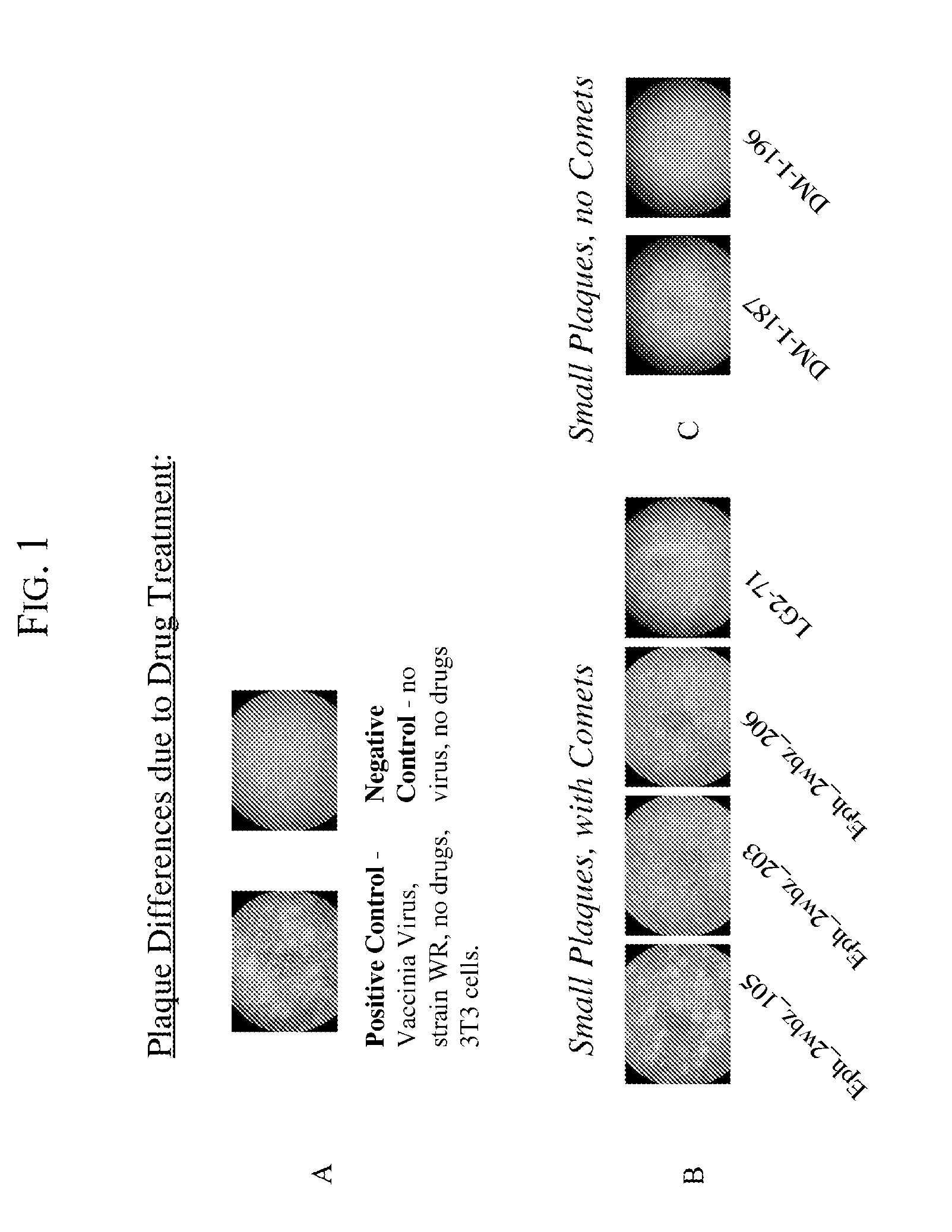
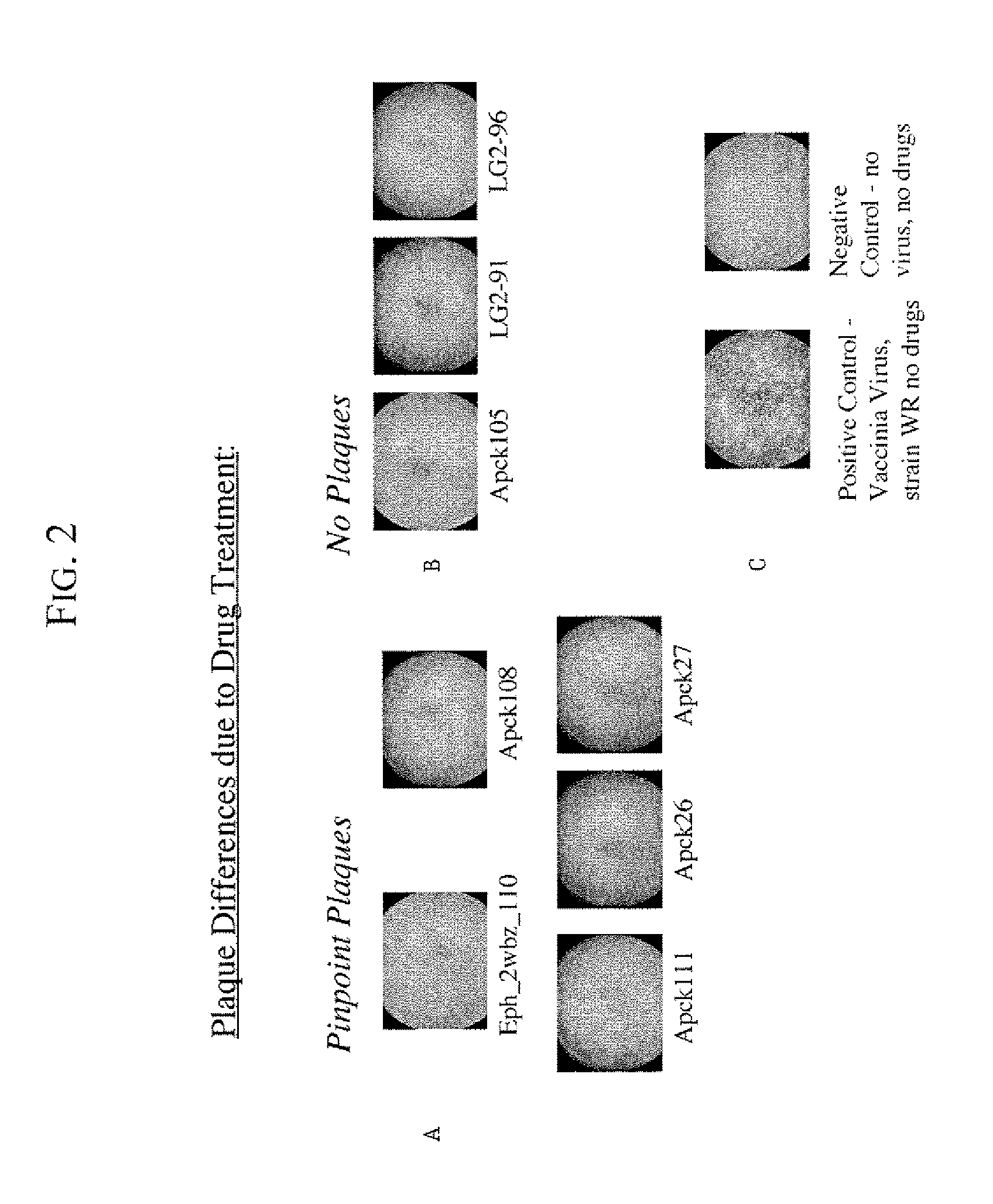
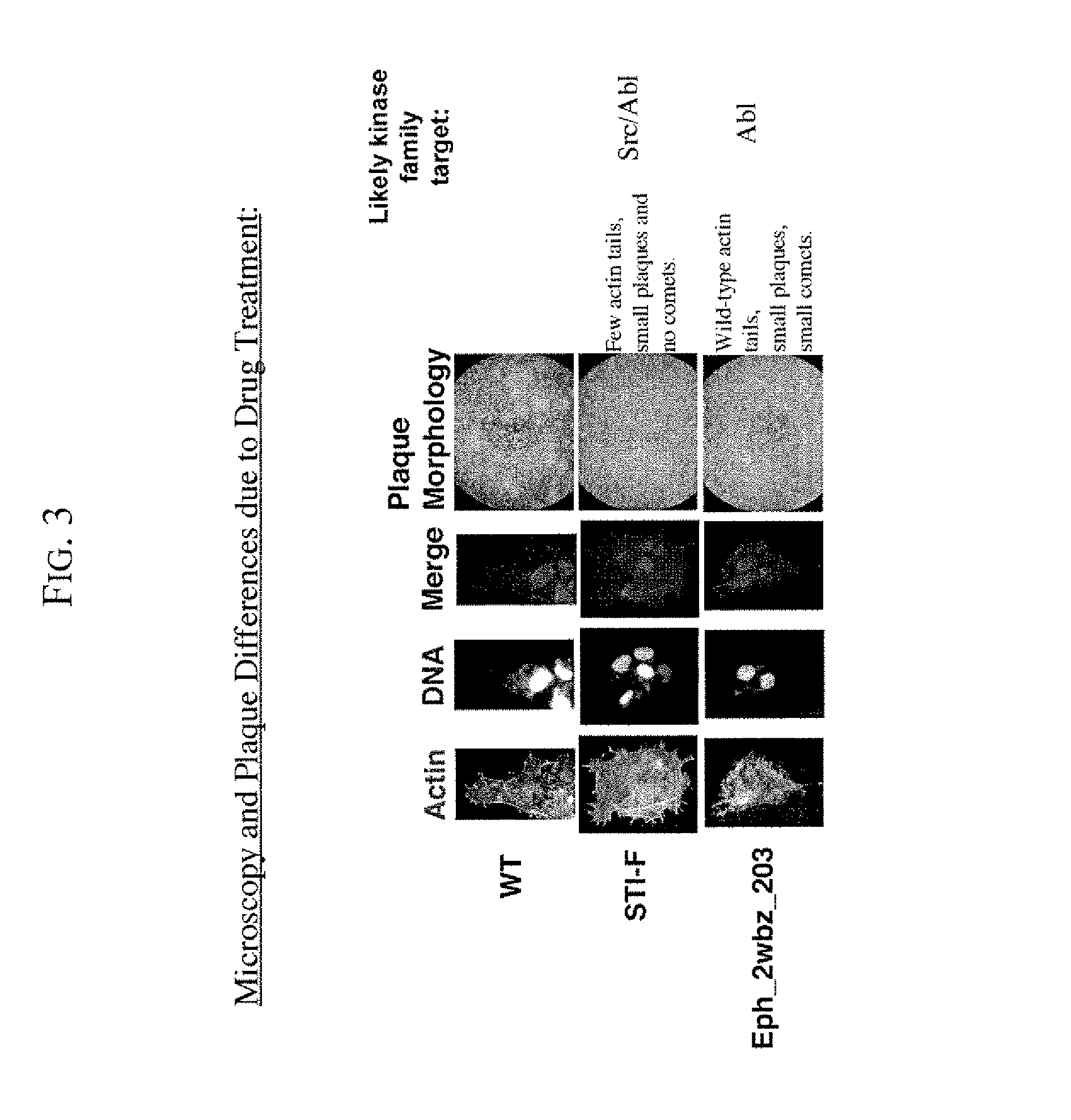
Kinase inhibitors for preventing or treating pathogen infection and method of use thereof
The present invention provides compositions and methods of use thereof to prevent and / or treat pathogenic infection. In particular, the present invention provides the use of kinase inhibitors to inhibit kinases that involve in pathogen-host cell interactions that are associated with or cause pathogenic infections, therefore, to effectively prevent and / or treat pathogenic infections with far less likely to engender resistance as compared to conventional antibiotics and anti-viral drugs. The present invention further provides the use of kinase inhibitors for the treatment of acute pathogenic infections for a short period of time to avoid toxicities that may caused by long term use of these kinase inhibitors.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
Quenching methods for red blood cell inactivation process
ActiveUS20060115466A1Undesired side reactionImprove the situationOrganic active ingredientsBiocideHigh concentrationThiol
Methods are provided for improved quenching of undesired side reactions upon treating a red blood cell composition with a pathogen inactivating compound comprising a nucleic acid binding ligand and a functional group which is, or which is capable of forming, an electrophilic group. In some embodiments, the improved methods use a suitably high concentration of quencher that comprises a nucleophilic functional group that is capable of covalently reacting with the electrophilic group, wherein the treatment occurs within a desired pH range to provide sufficient quenching. Preferred quenchers for use in some of the methods include thiols, such as glutathione, which have been suitably neutralized such that addition to a red blood cell composition results in the desired concentration of quencher at a desirable pH range of 6.8 to 8.5.
Owner:CERUS CORP
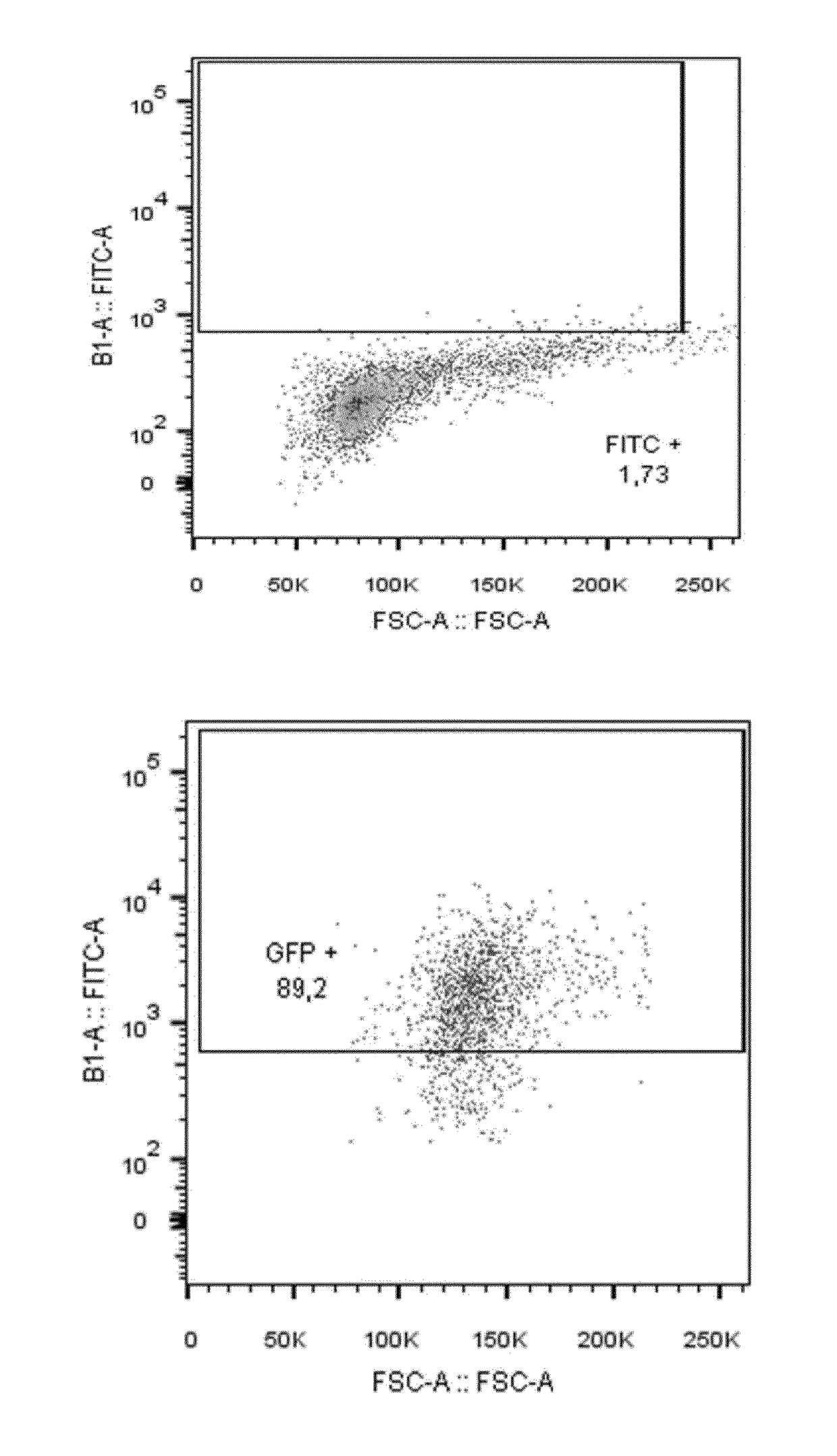
Methods for improving functionality in nk cell by gene inactivation using specific endonuclease
PendingUS20180171298A1Efficient and durable responseFunction increasePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyCytotoxicityNuclease
The present invention relates to methods for improving therapeutic activity of NK cell, such as their cytotoxic / cytolytic activity, to be used in immunotherapy, by gene editing. In particular, these methods comprise a step of reduction or inactivation of gene expression using specific endonuclease such as TAL-nuclease, CRISPR or Argonaute. An additional genetic modification can be performed by (over)expressing at least one gene involved in N K function. The present invention encompasses also engineered NK cell, pharmaceutical composition containing the same.
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
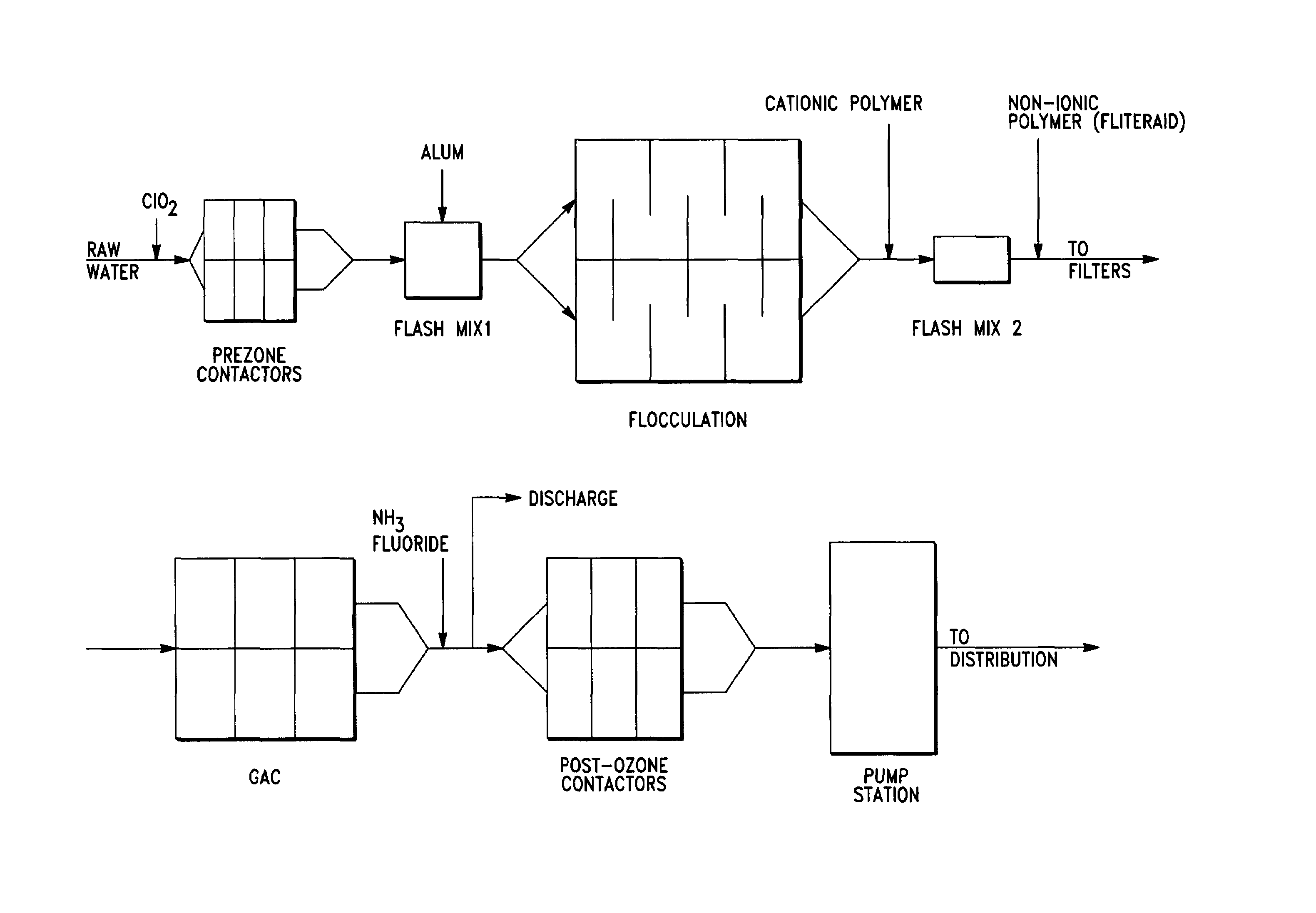
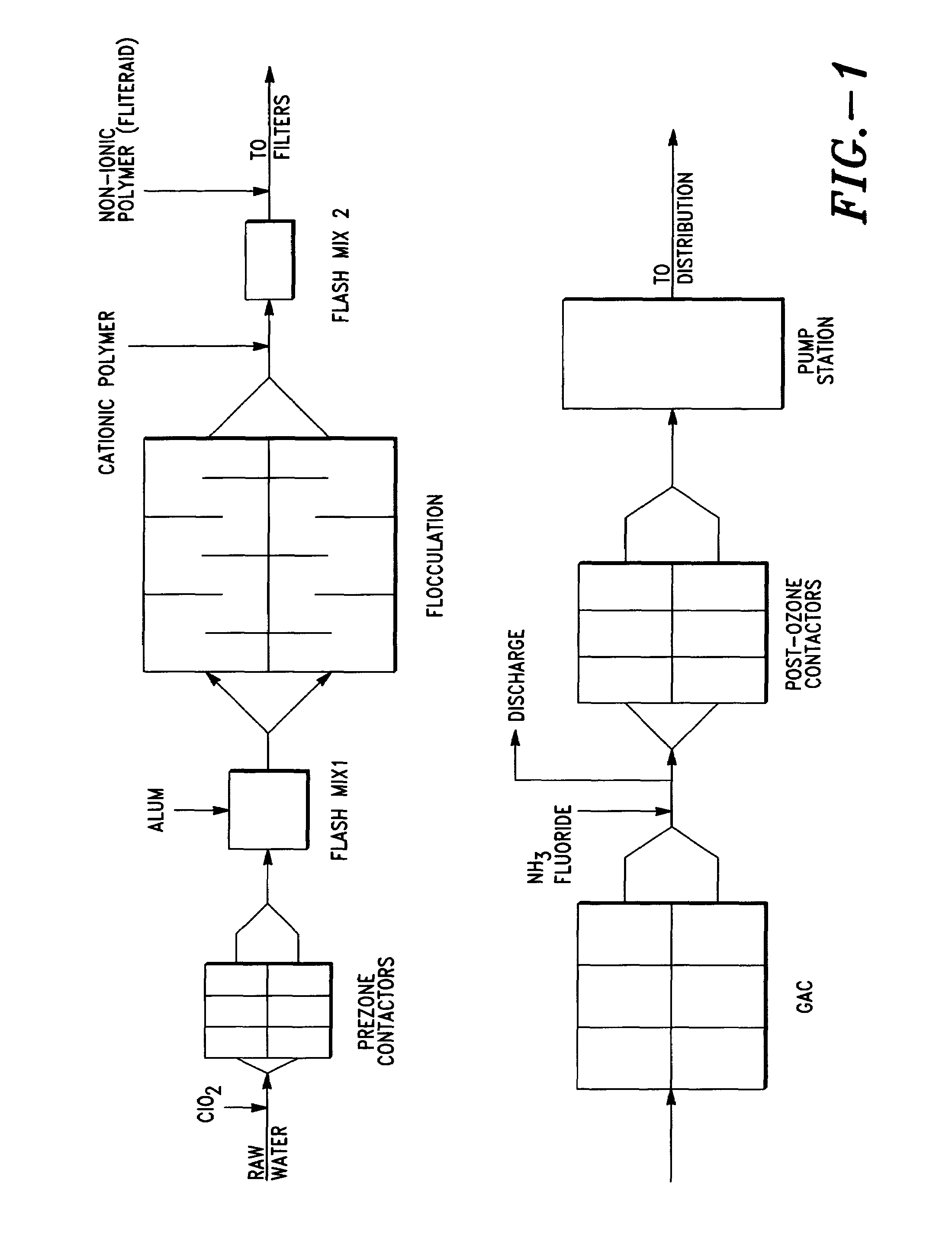
Use of chlorine dioxide and ozone for control of disinfection by-products in water supplies
InactiveUS7008543B2Treatment involving filtrationSolid sorbent liquid separationDisinfection by-productChlorine dioxide
A method of oxidation or pathogen inactivation in water supplies using the combination of treatments of chlorine dioxide and ozone in the sequential steps prior to filtration and distribution. Results indicate that the addition of chlorine dioxide before prezonation reduces the bromate formation and chlorine dioxide can be substituted for preoxidation with ozone, while maintaining the enhanced filtration effects observed from the presence of a preoxidant. A majority of the chlorite formed from reactions of chlorine dioxide with constituents in raw water are converted to chlorate by the following ozonation step.
Owner:CONTRA COSTA COUNTY WATER DISTRICT
Two-dimensional ultrathin nanosheet graphite phase carbon nitride material rich in nanopores, and preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN109850857ASuitable light absorption characteristicsImprove separation efficiencyMaterial nanotechnologyPhysical/chemical process catalystsDecompositionElectron
The invention discloses a two-dimensional ultrathin nanosheet graphite phase carbon nitride material rich in nanopores, and a preparation method and applications thereof, and belongs to the technicalfield of nanometer functional material preparation, solar energy utilization, and environment protection. The two-dimensional ultrathin nanosheet graphite phase carbon nitride material rich in nanopores is prepared through oriented thermal polymerization combined two-step thermal processing technology; more specifically, a liquid phase template agent is adopted to control the thickness of a nanosheet g-C3N4 material, two-step thermal processing technology parameter design is adopted for forming of nanopores on nanosheets; the forming of the nanopores is capable of introducing more active sites, so that the nanosheet g-C3N4 material obtained at last possesses appropriate light absorption characteristic, and relatively high photo-induced electron and cavity separation efficiency, a defect ofblock-shaped g-C3N4 material that photocatalytic efficiency is low is improved, and the two-dimensional ultrathin nanosheet graphite phase carbon nitride material rich in nanopores can be directly used for organic matter decomposition, microbial pathogen inactivation, and photocatalytic reduction CO2 to produce organic matters under sunlight.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preserving fluid for biological sample nucleic acid detection and application thereof
PendingCN111549101ALower storage temperatureReduce storage requirementsMicrobiological testing/measurementNuclease inhibitorBlood plasma
The invention provides a preserving fluid for biological sample nucleic acid detection and an application thereof. The preserving fluid is composed of a nuclease inhibitor, a surfactant, a chelating agent and a buffer solution. The preserving fluid is mixed with a solid sample or a liquid sample to denature proteins, inactivate pathogens, and inactivate DNA and RNA nuclease. The pathogens are inactivated, so the safety of a potential high-infectivity clinical sample is greatly improved, and good protection is formed for surrounding personnel and downstream operating personnel of the sample; the DNA and RNA nuclease is inactivated, so that the content and integrity of DNA and RNA in the sample are kept in a sampling state to the maximum extent, and the strict requirements on the aspects oftemperature, time and the like of clinical sample transportation and storage are reduced. The preserving fluid can be used for clinical high-infectivity nucleic acid detection of biological samples, and the biological samples comprise throat swabs, body fluids, lavage fluids, whole blood, whole blood cells, serum or plasma.
Owner:WUXI SHENRUI BIO PHARMA
Quenching methods for red blood cell pathogen inactivation
ActiveUS8900805B2Reduce concentrationReduce reduction reactionBiocideDead animal preservationRed blood cellMicrobiology
The present invention provides improved methods for treating red blood cell compositions with a pathogen-inactivating compound under conditions which provide suitable pathogen inactivation while maintaining cell vitality. Also provided methods of reducing dehydration in red blood cells, as well as treated red blood cell compositions.
Owner:CERUS CORP
Quenching methods for red blood cell pathogen inactivation
ActiveUS20110286987A1Reduction of unwanted side reactionReducing and minimizing adverse effectBiocideDead animal preservationCellular viabilityRed Cell
The present invention provides improved methods for treating red blood cell compositions with a pathogen-inactivating compound under conditions which provide suitable pathogen inactivation while maintaining cell vitality. Also provided methods of reducing dehydration in red blood cells, as well as treated red blood cell compositions.
Owner:CERUS CORP
Methods and Systems for Preparing Blood Products
InactiveUS20100189597A1Other blood circulation devicesPharmaceutical containersWhole blood productPhotosensitizer
Owner:CARIDIANBCT BIOTECH
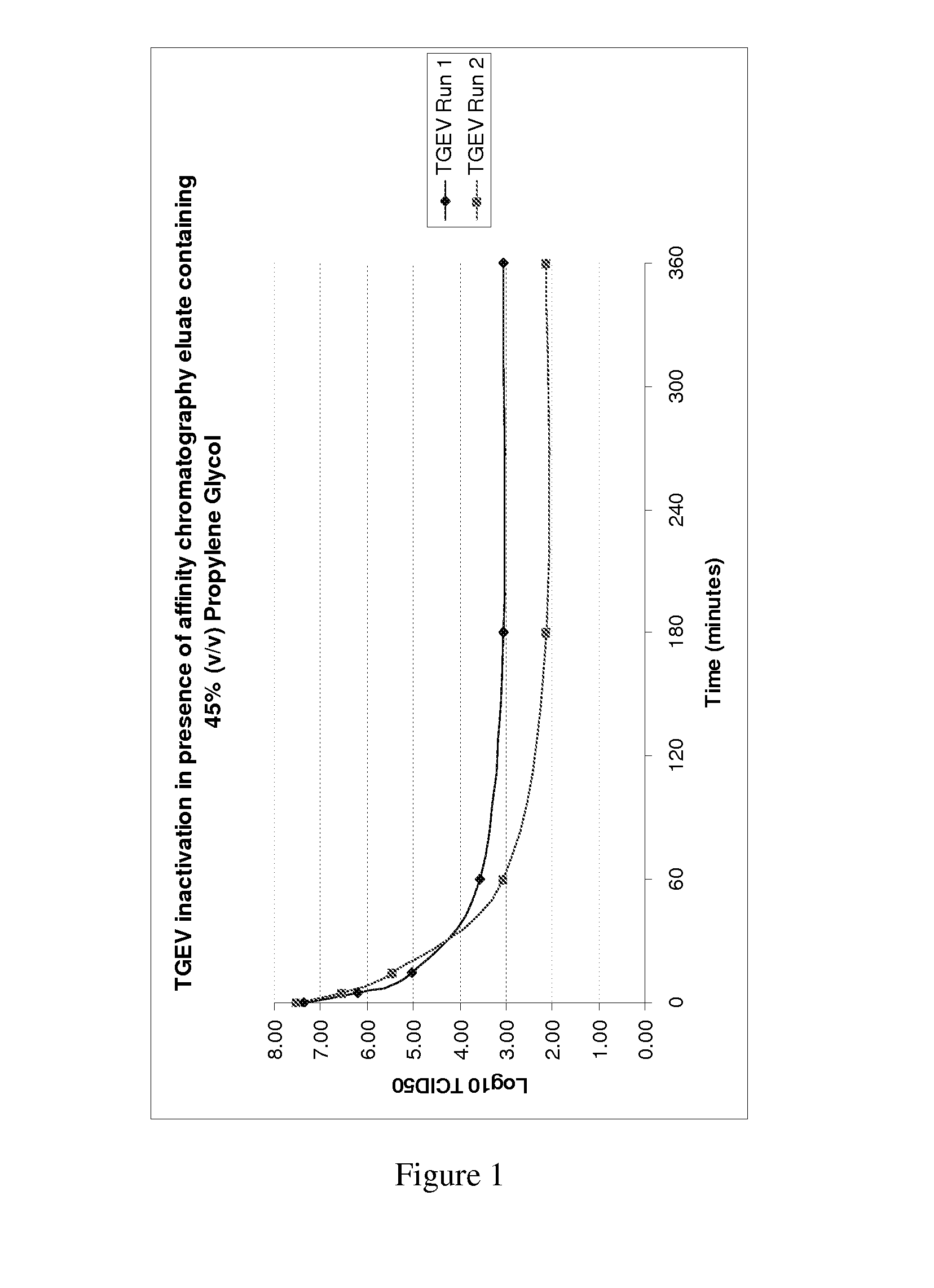
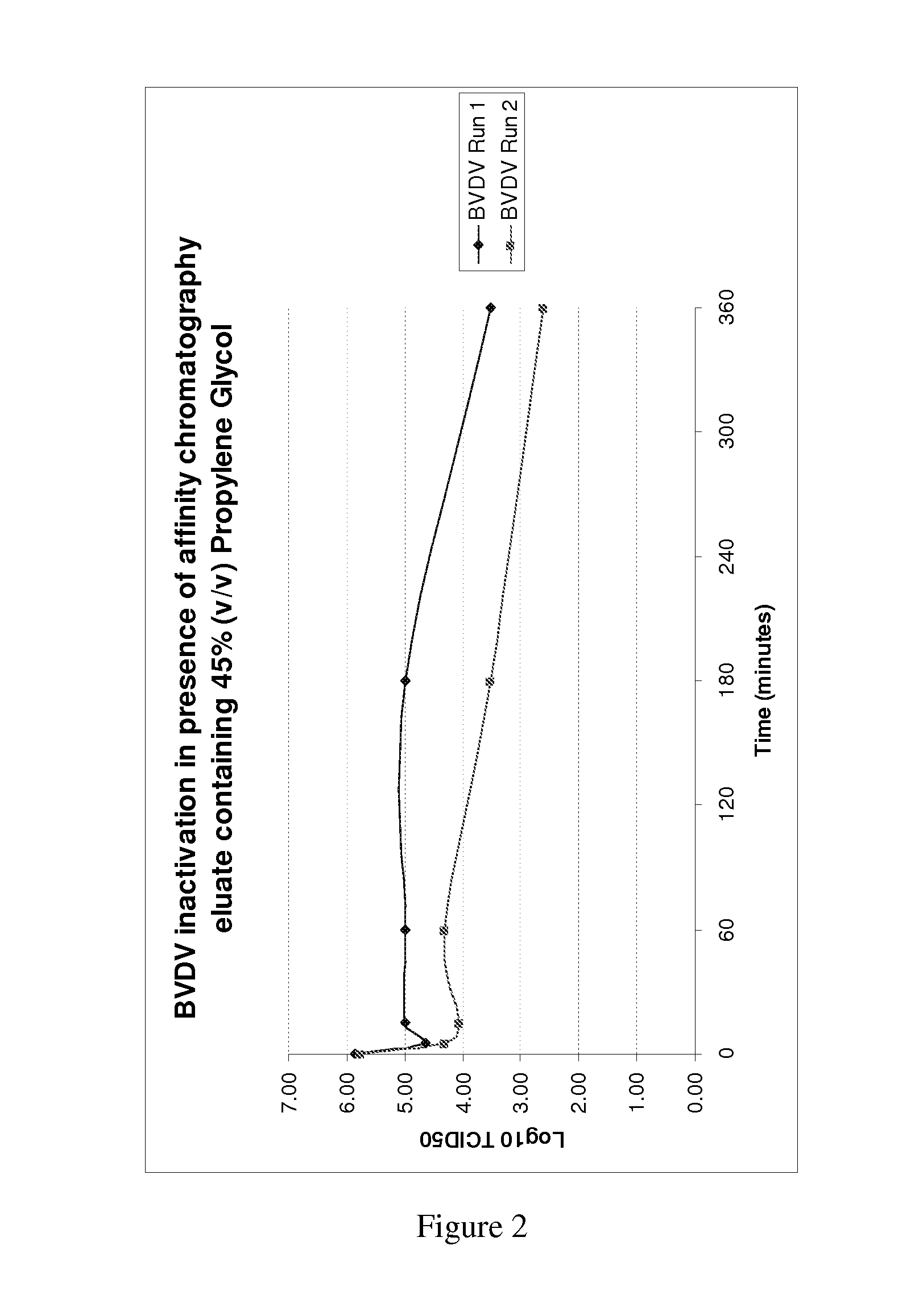
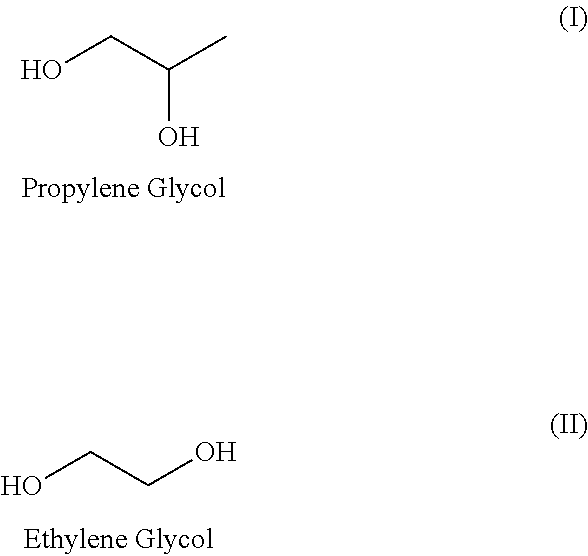
Glycols as pathogen inactivating agents
The disclosure relates to uses, methods and compositions for the inactivation of pathogens in biological compositions, using a glycol as a pathogen inactivating agent.
Owner:LABE FR DU FRACTIONNEMENT & DES BIOTECH SA
Methods for preparing platelet products
ActiveUS20170202882A1Speed up the processEfficient preparationMammal material medical ingredientsBlood/immune system cellsPlatelet productChemistry
Owner:CERUS CORP
Anaerobic Blood Storage and Pathogen Inactivation Method
ActiveUS20190167792A1Reducing microparticle formationReduce formationEnergy modified materialsMammal material medical ingredientsHemolysisMicroparticle
A method for reducing hemolysis and microparticle formation during storage of pathogen reduced blood. Oxygen reduced blood compositions comprising SAGM and riboflavin having reduced hemolysis. Oxygen reduced blood compositions comprising SAGM and riboflavin having reduced microparticles. Oxygen and pathogen reduced blood compositions comprising CPAD and riboflavin having reduced hemolysis. Oxygen and pathogen reduced blood compositions comprising SAGM and riboflavin having reduced microparticles.
Owner:HEMANEXT INC
Compositions and methods for inhibiting pathogen infection
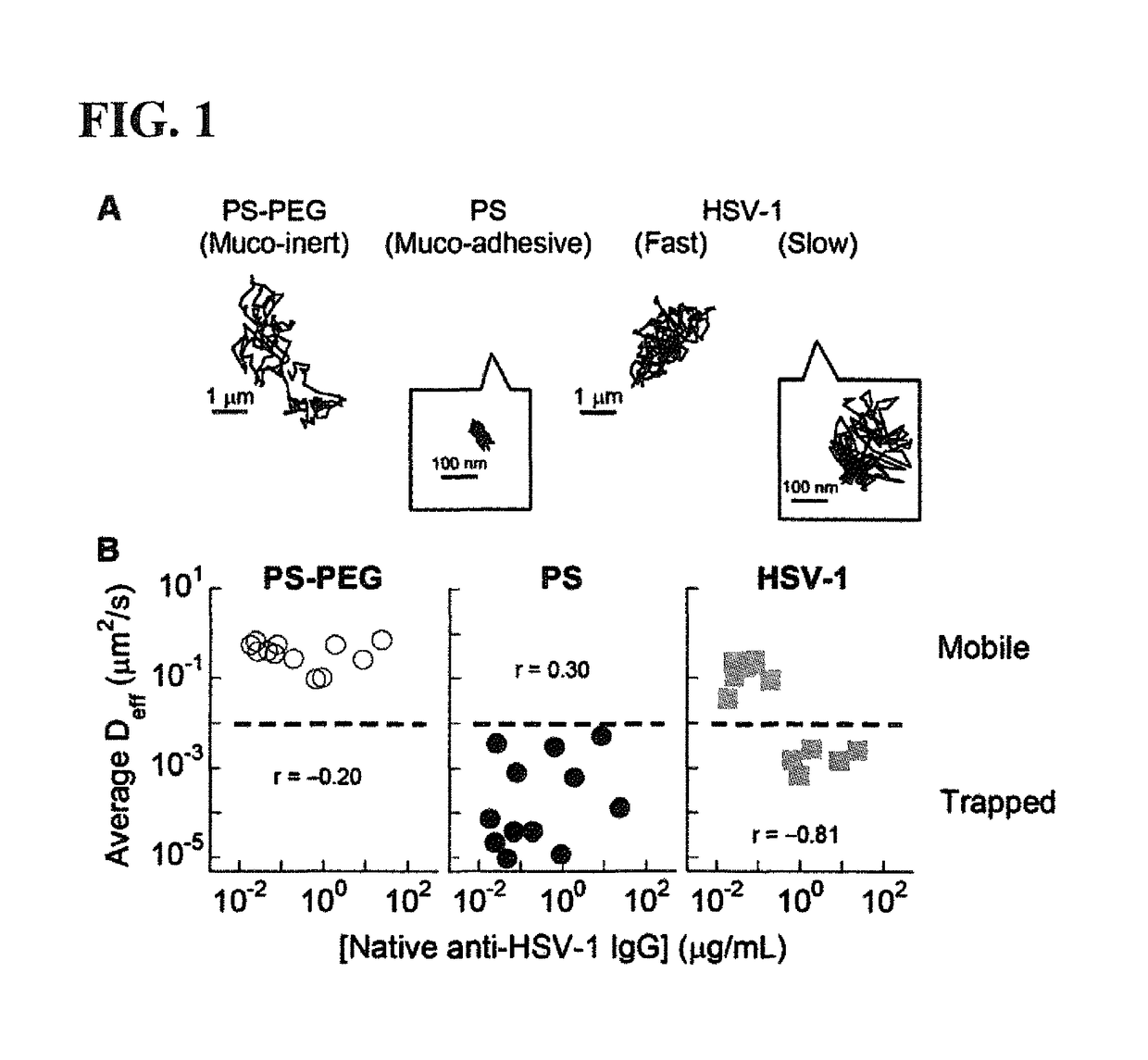
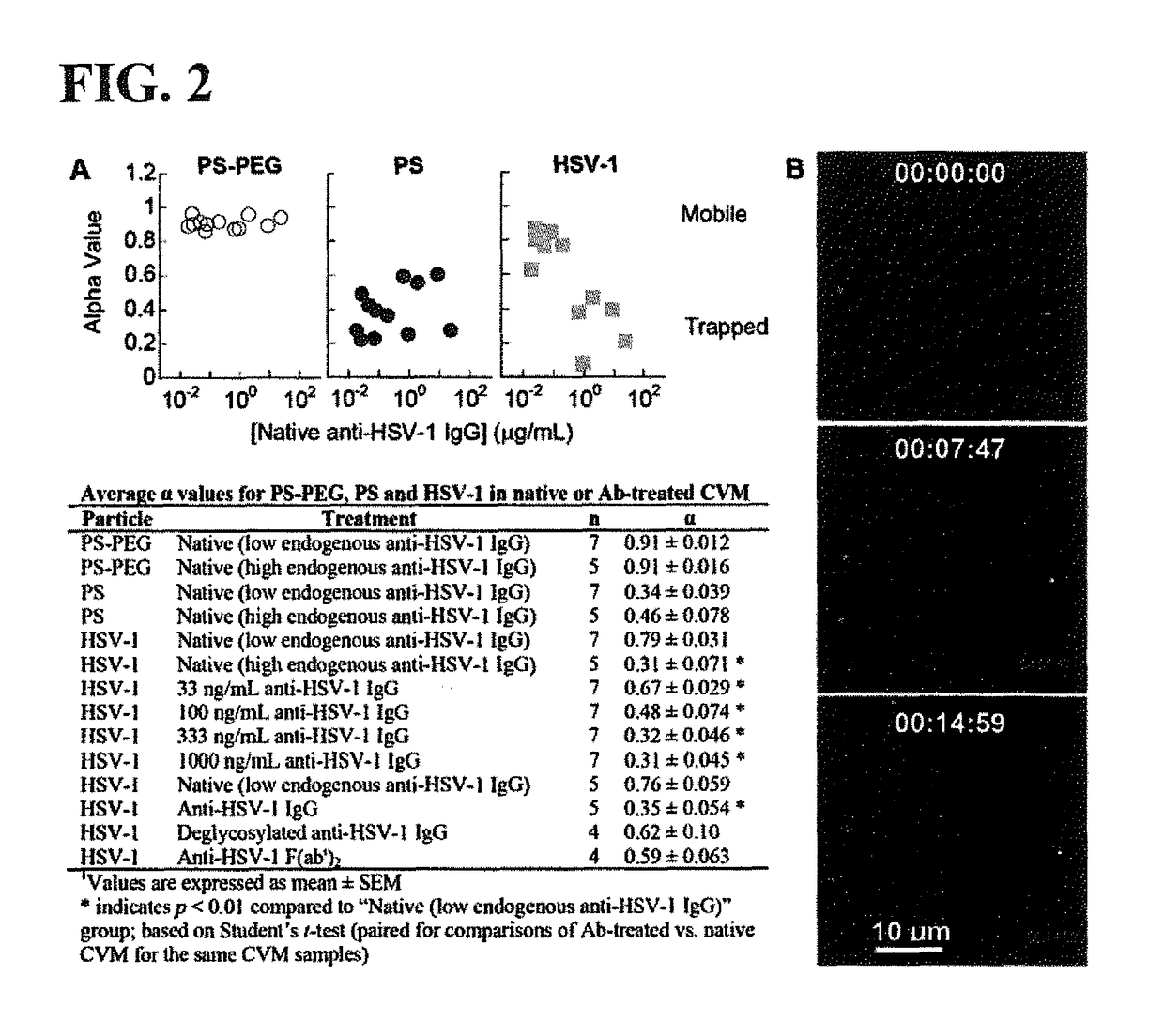
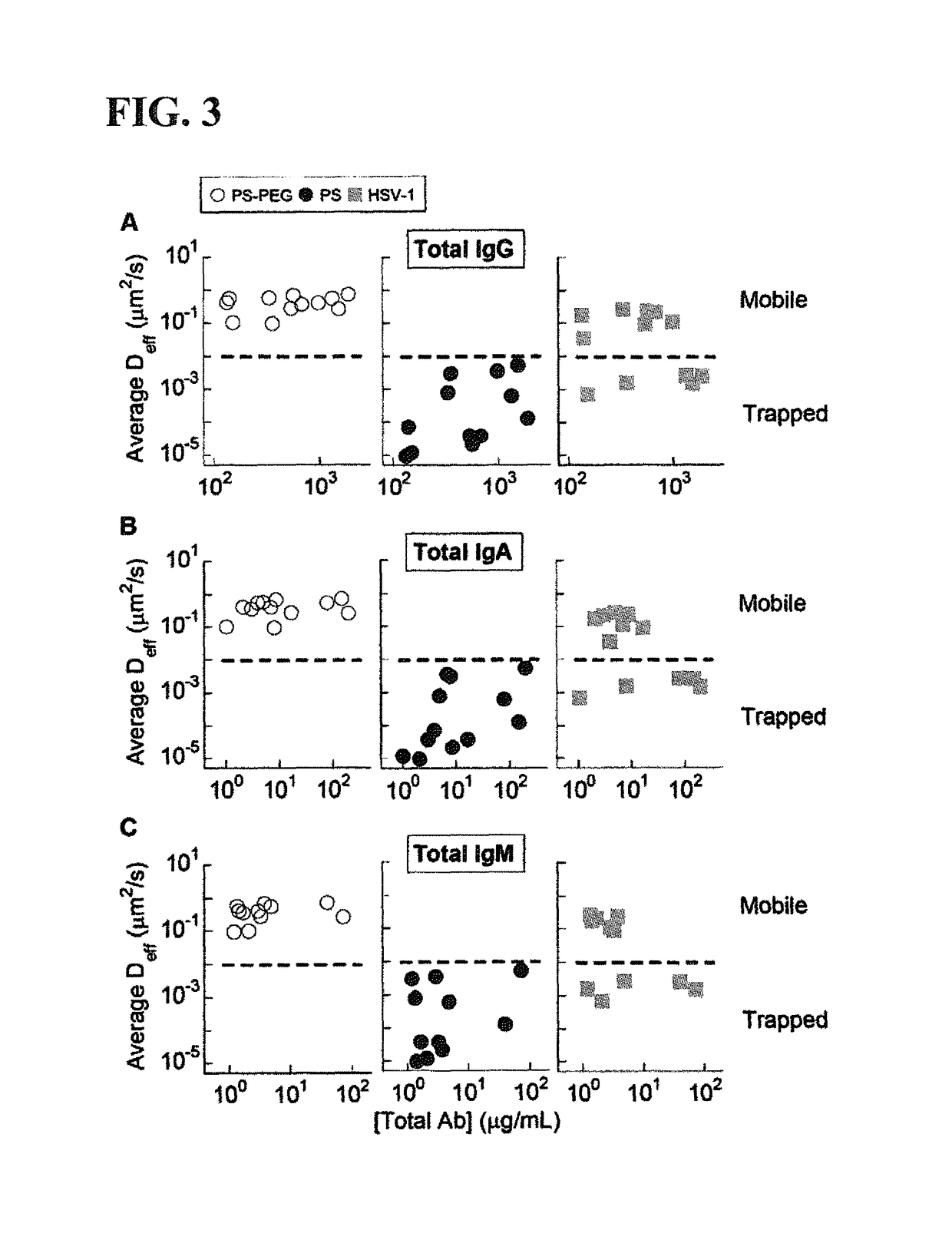
ActiveUS10100102B2Enhances trapping potencyImmunoglobulins against animals/humansImmunoglobulins against bacteriaSubject matterSecretion
The presently-disclosed subject matter relates to antibodies, compositions, and methods for inhibiting and treating pathogen infection and providing contraception. In particular, the presently-disclosed subject matter relates to inhibiting and treating pathogen infection and providing contraception in a subject using compositions and antibodies capable of trapping pathogens or sperm in mucus, thereby inhibiting transport of pathogens or sperm across mucus secretions. The subject matter further relates to methods for monitoring the effectiveness of vaccines by detecting antibodies capable of trapping pathogens in mucus.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
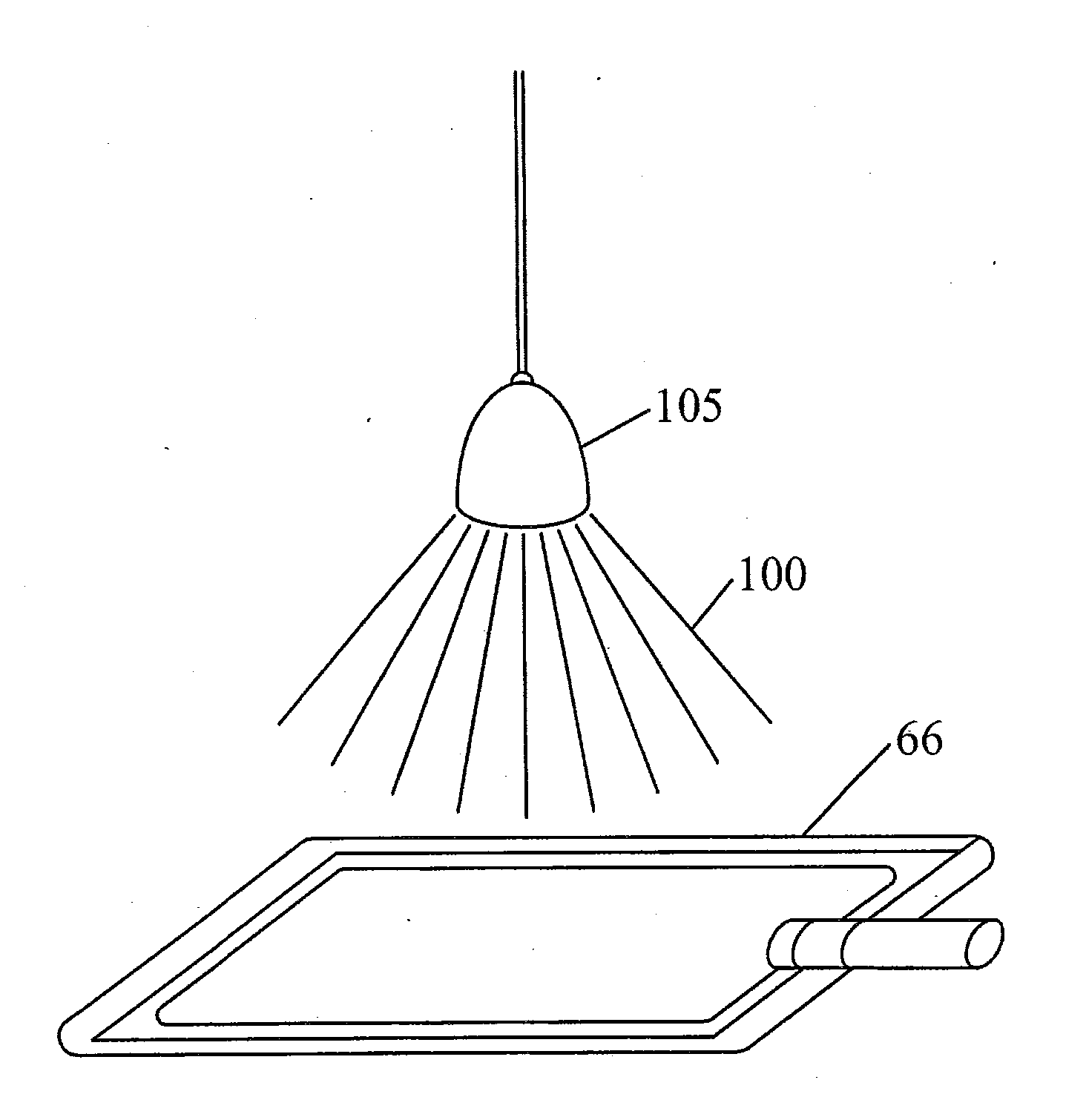
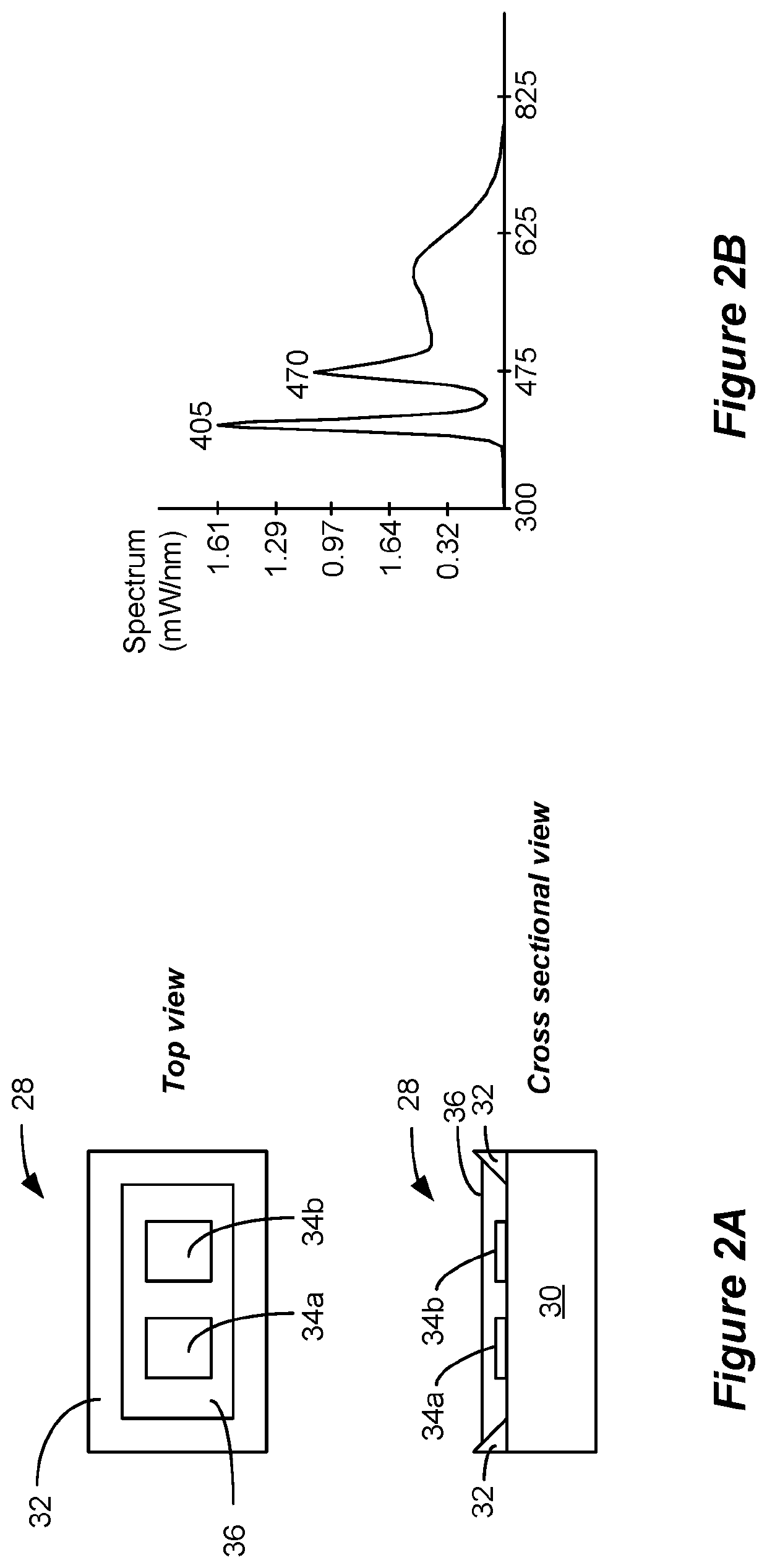
Light Fixture Having a Fan and Ultraviolet Sterilization Functionality
A lighting fixture is disclosed with effective disinfection properties against bacteria, fungi, and viruses. The fixture includes a fan to continuously draw air into the light fixture. The air drawn in is irradiated with UV radiation within the fixture, such as is provided from UV LED chips. The relatively small volume of the light fixture allows the flux or energy density of the UV radiation to be made more intense. After the air is sterilized, it can be put back into the room or building in which the fixture is placed. The white light provided by white light LEDs in the fixture provides illumination, and can further provide significant emission peaks at 405 nm and 470 nm which is also useful to pathogen inactivation.
Owner:CALYXPURE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com