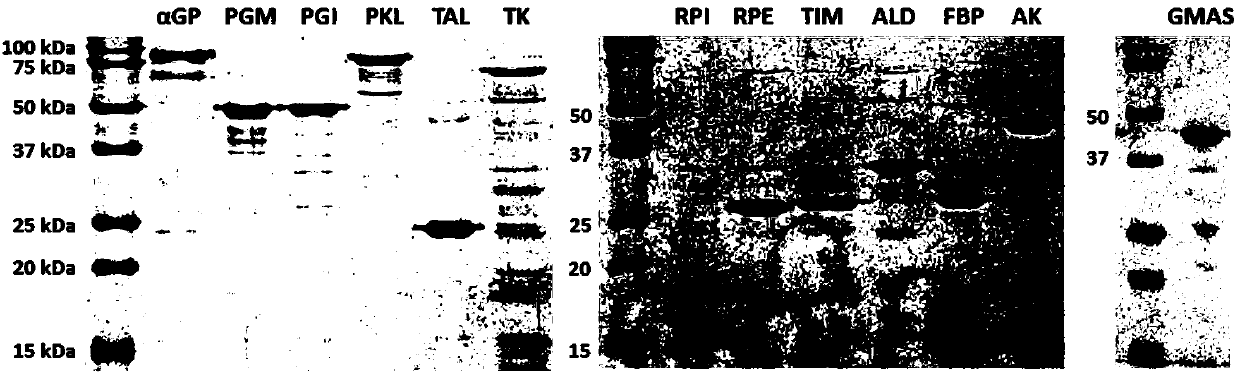
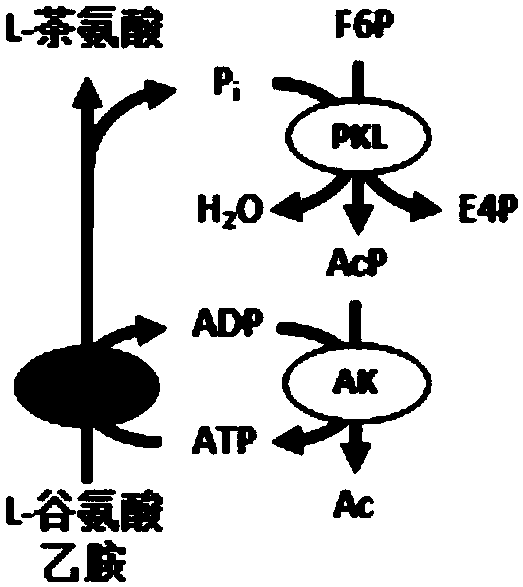
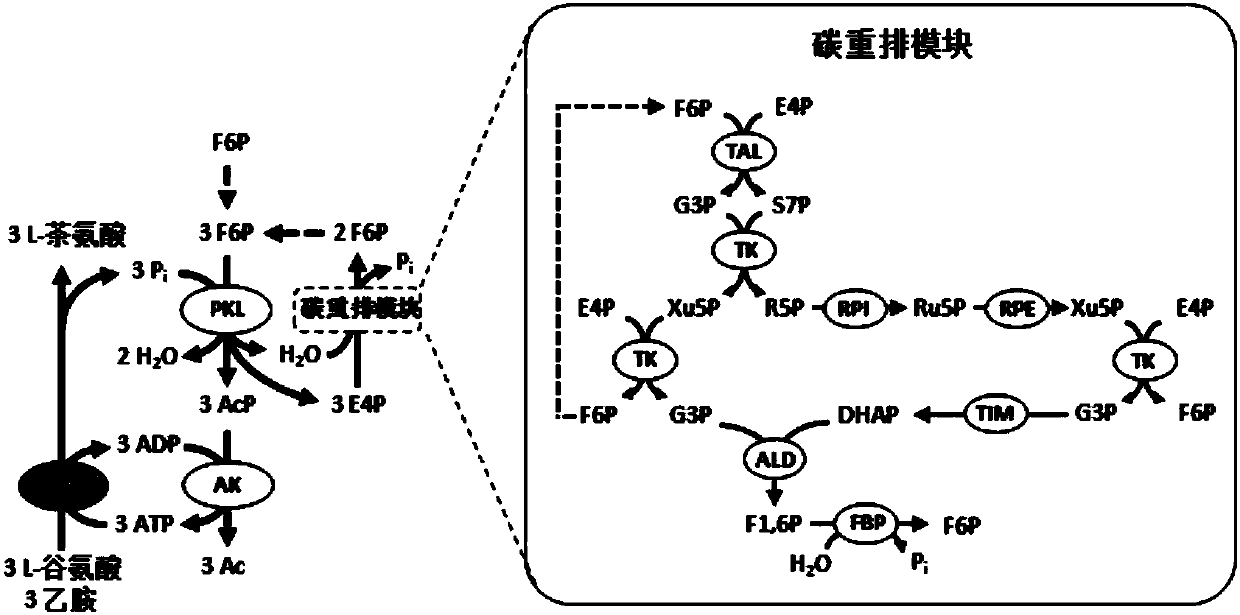
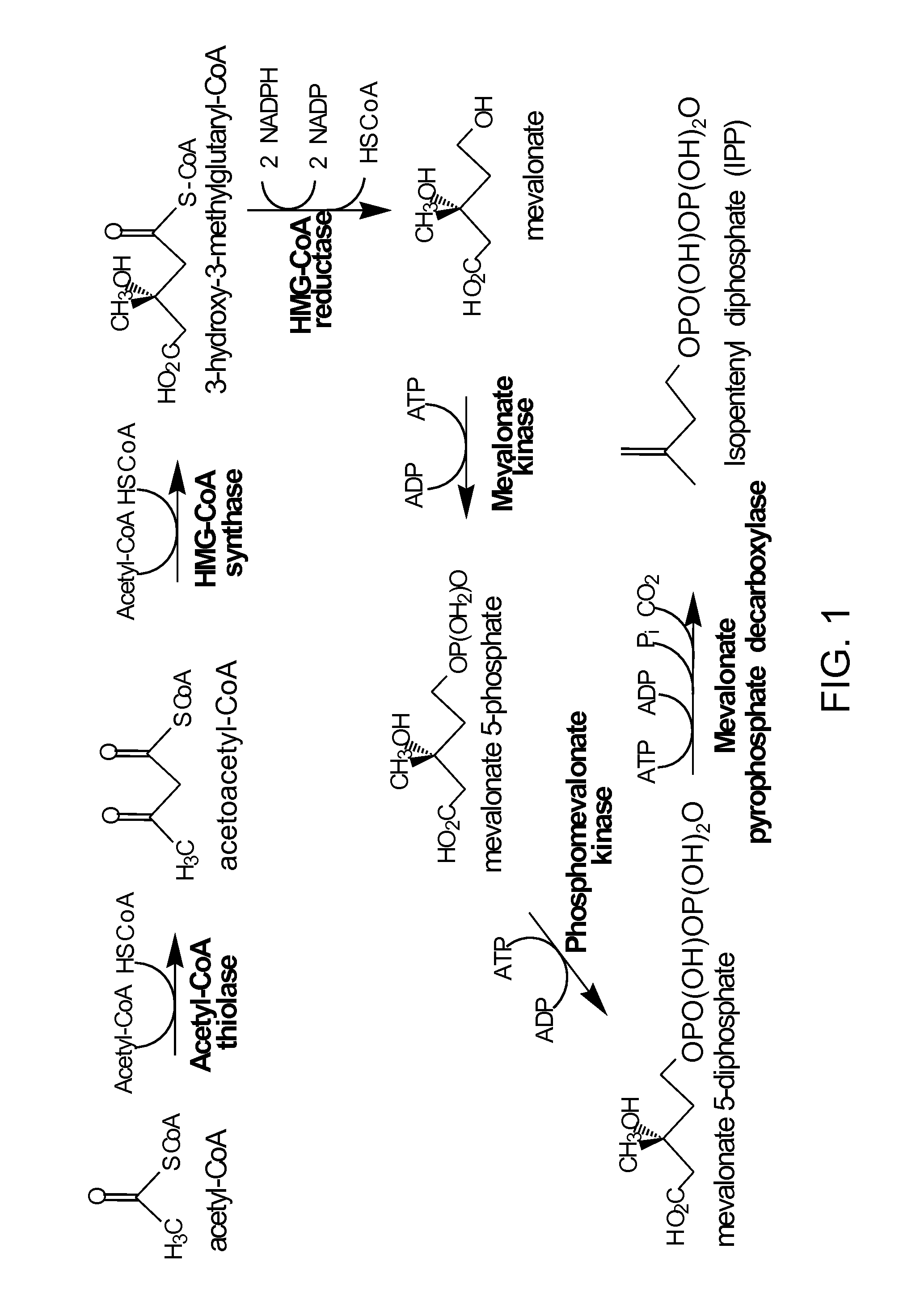
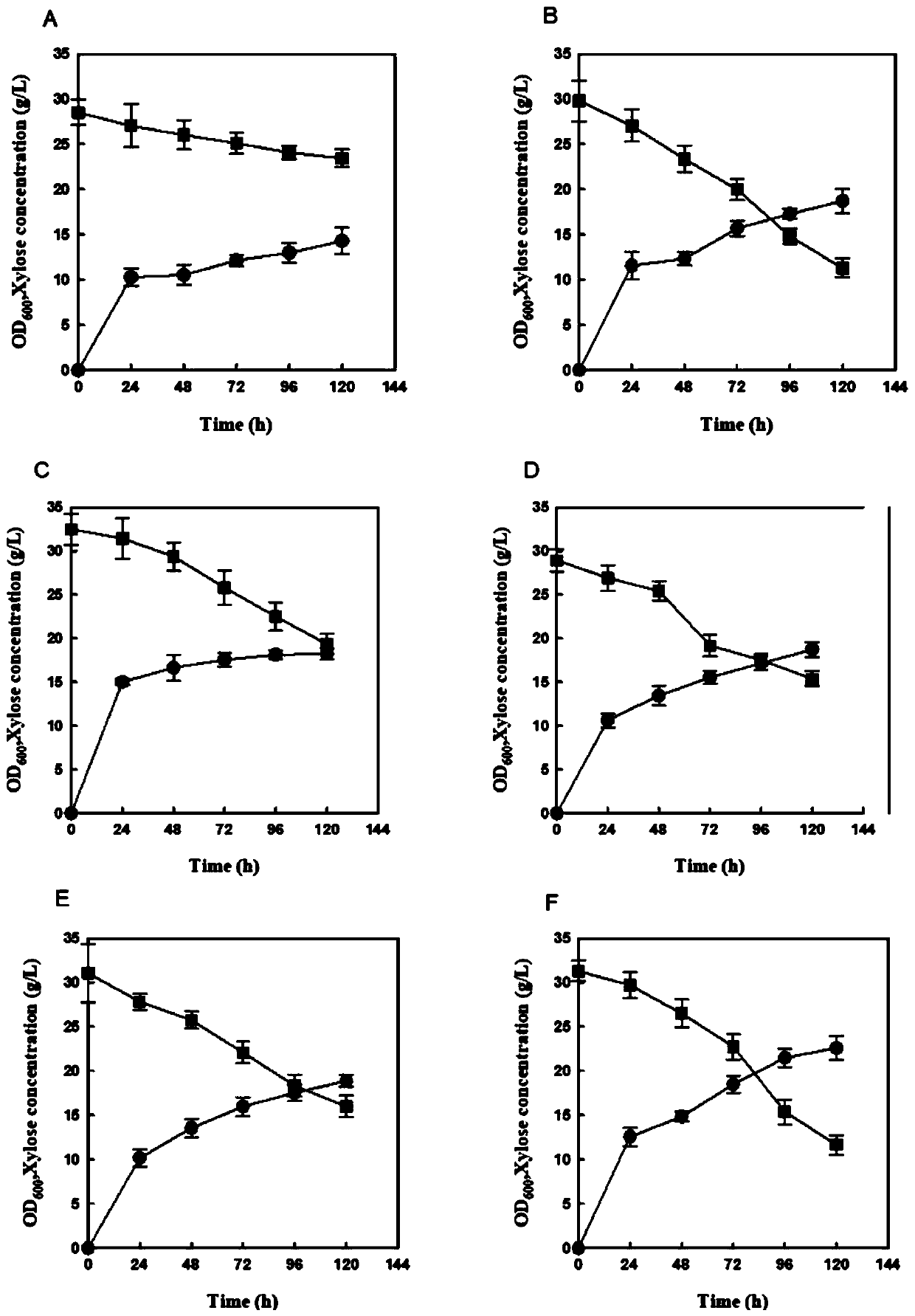
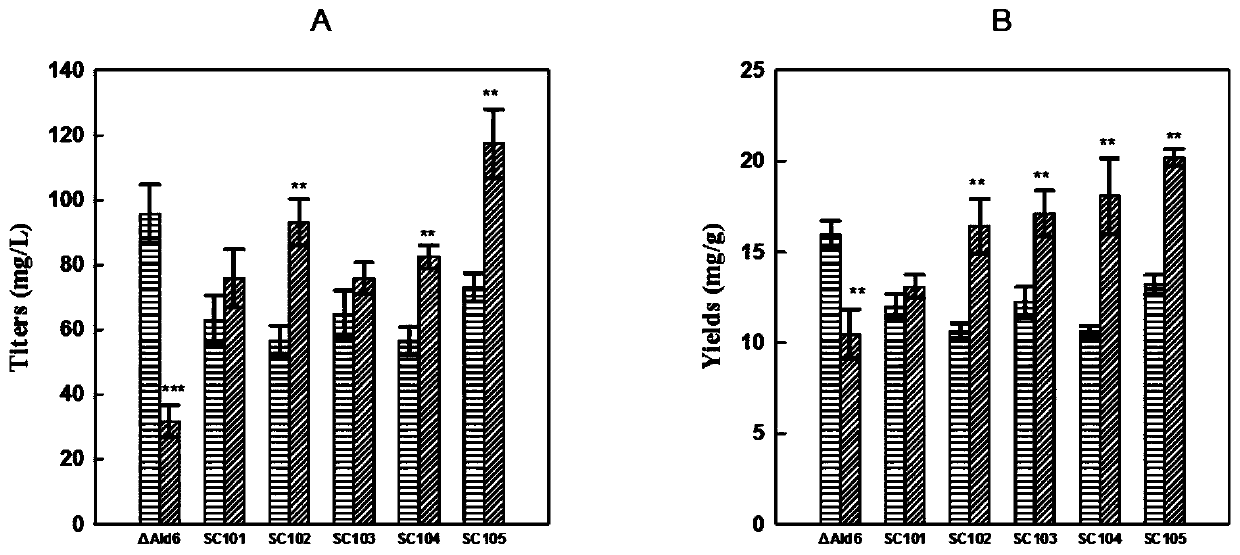
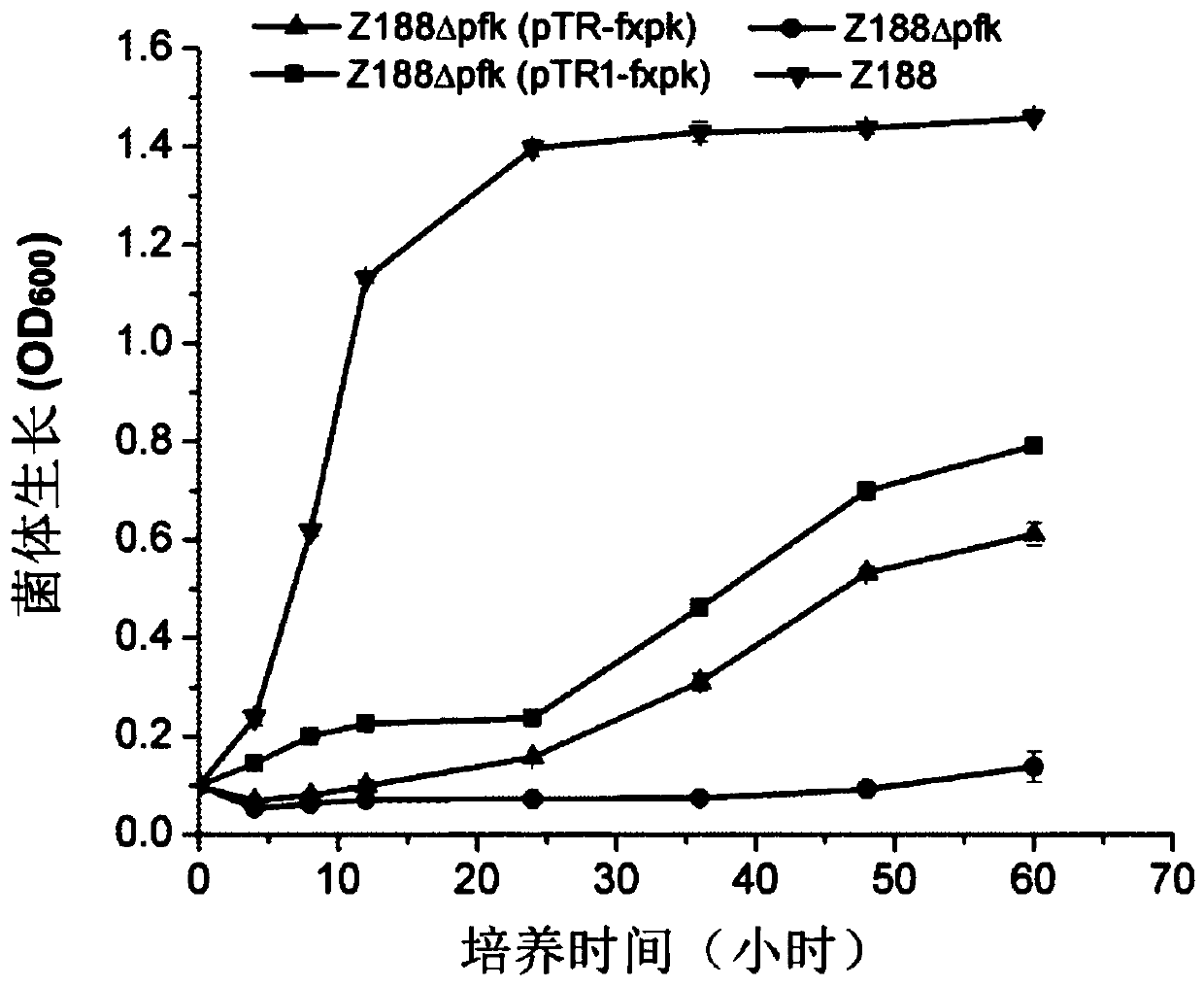
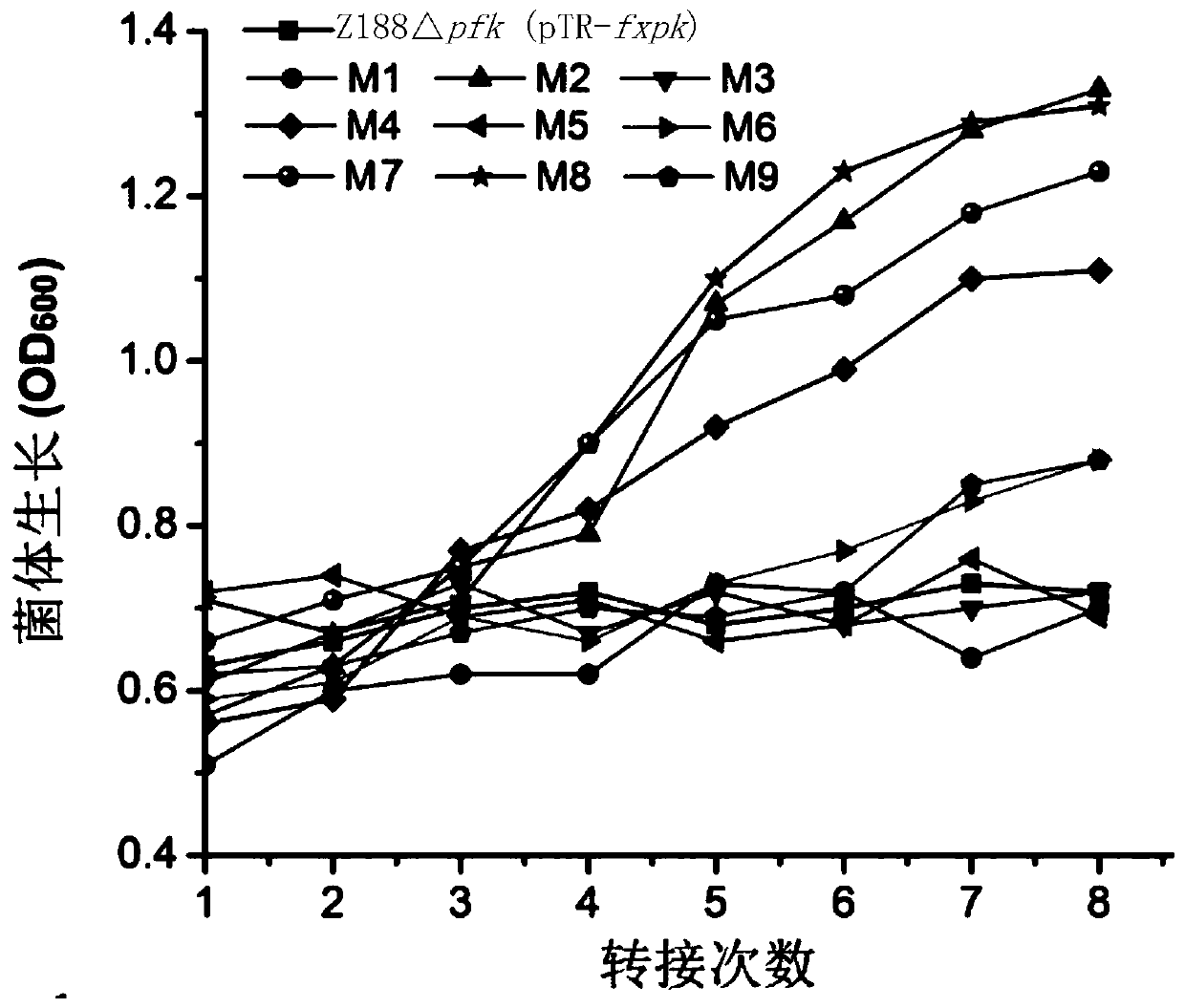
Patents
Literature
30 results about "Phosphoketolase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
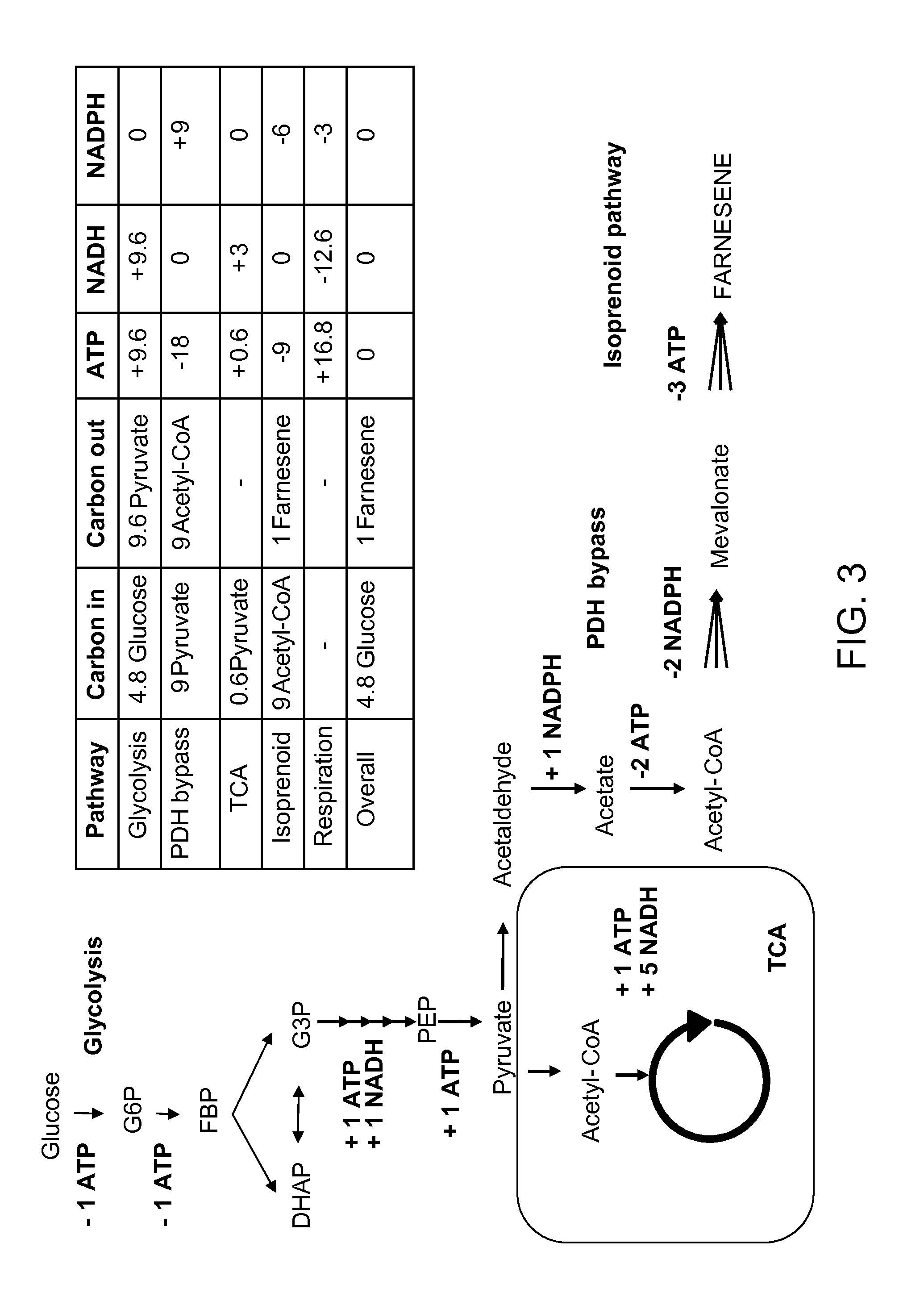
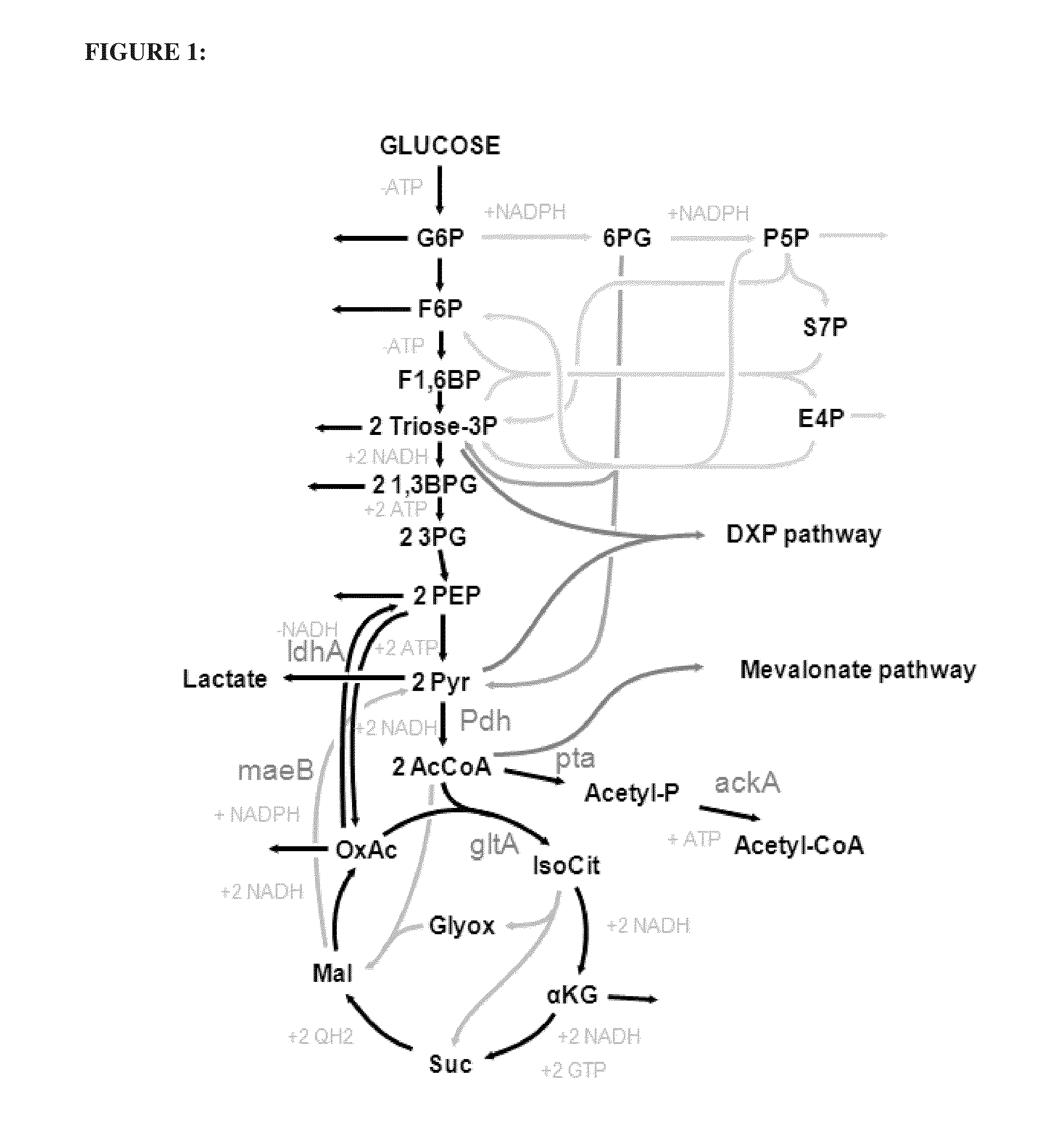
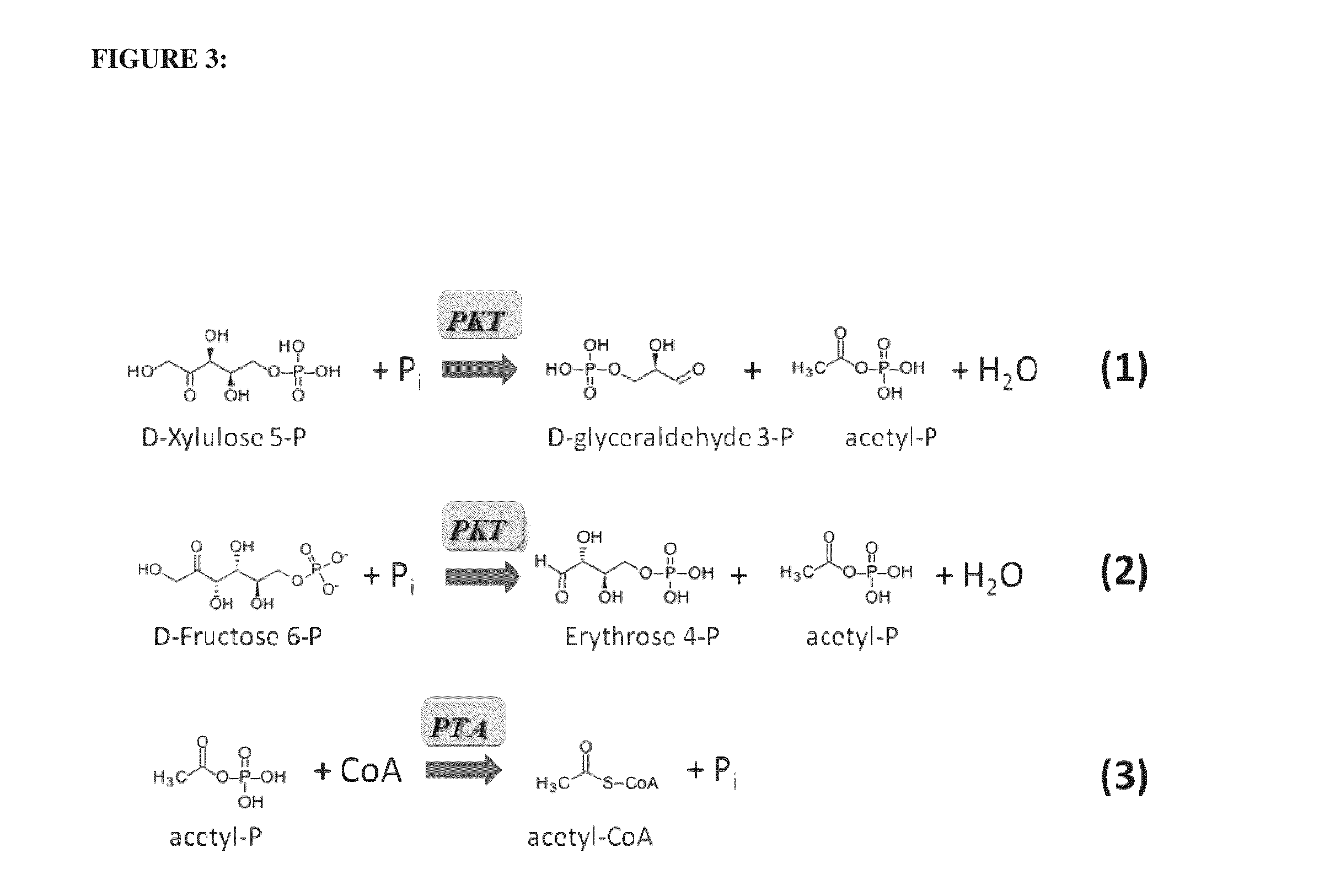
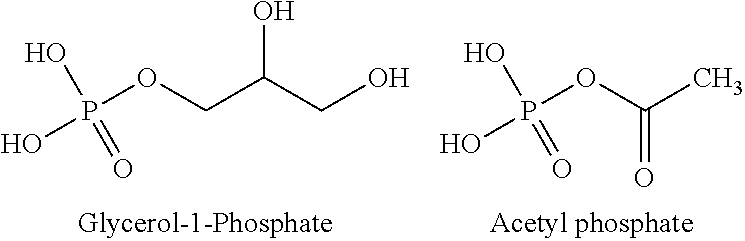
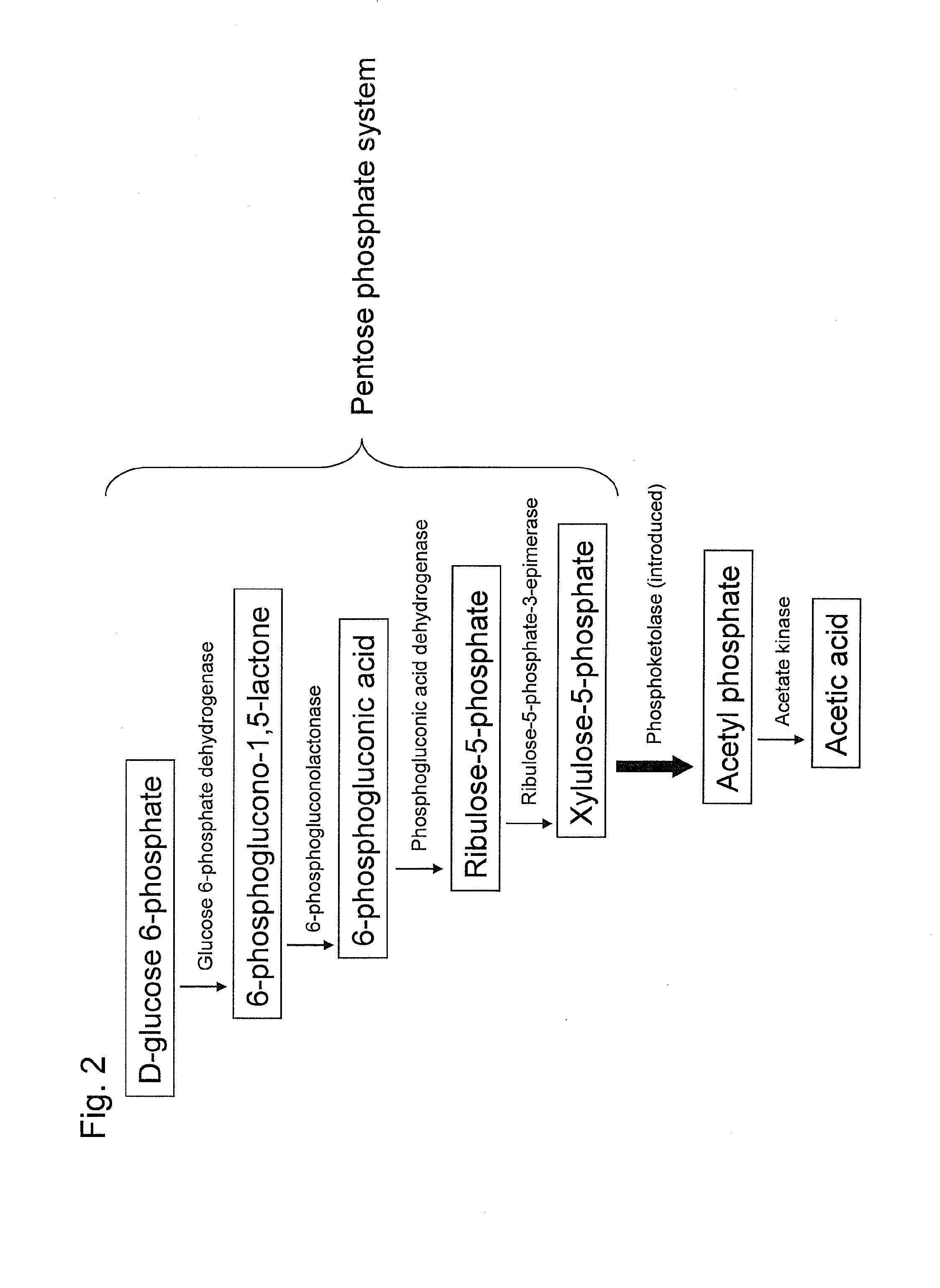
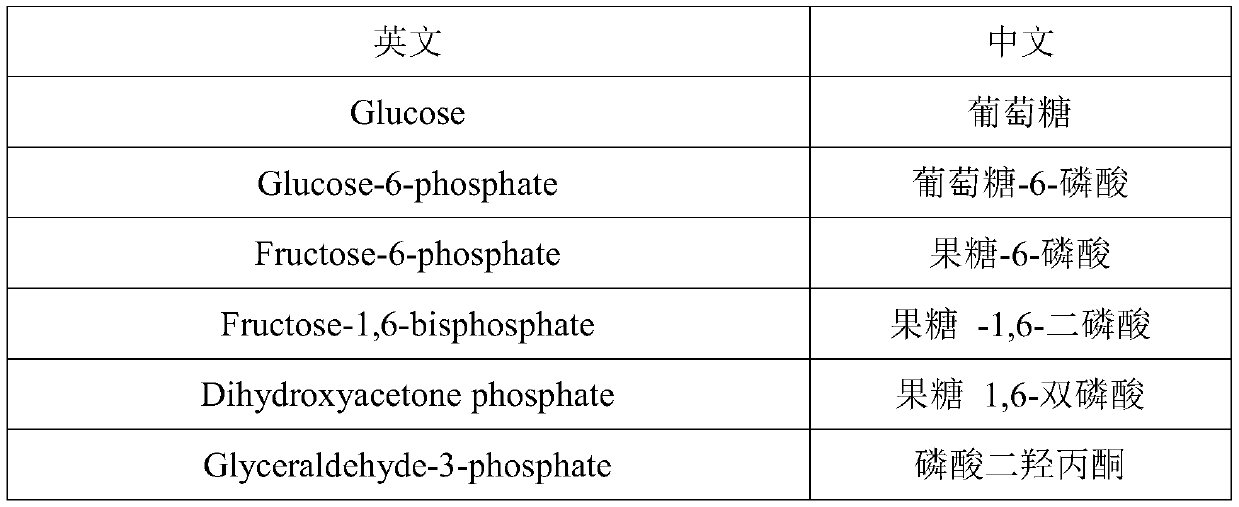
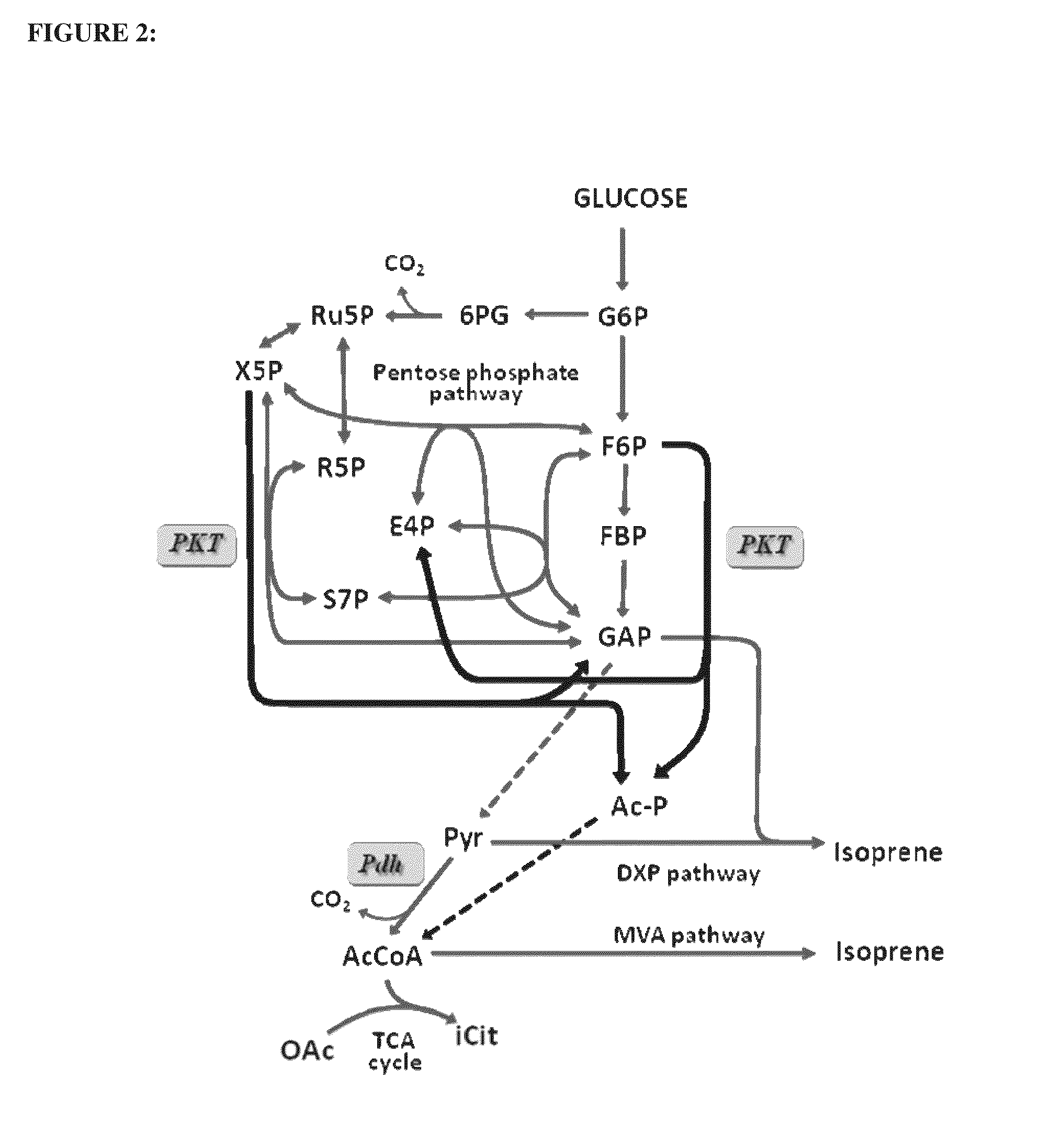
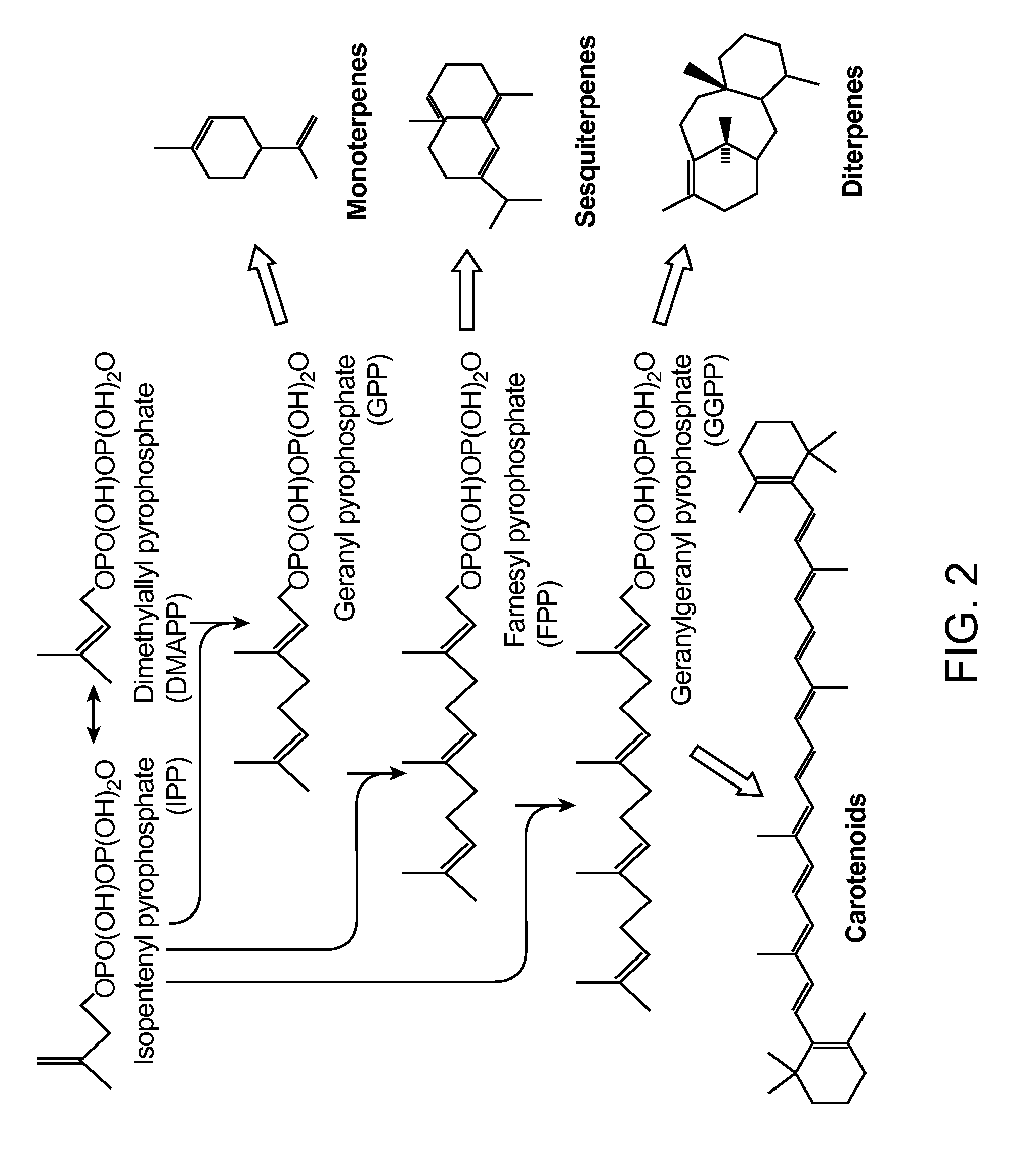
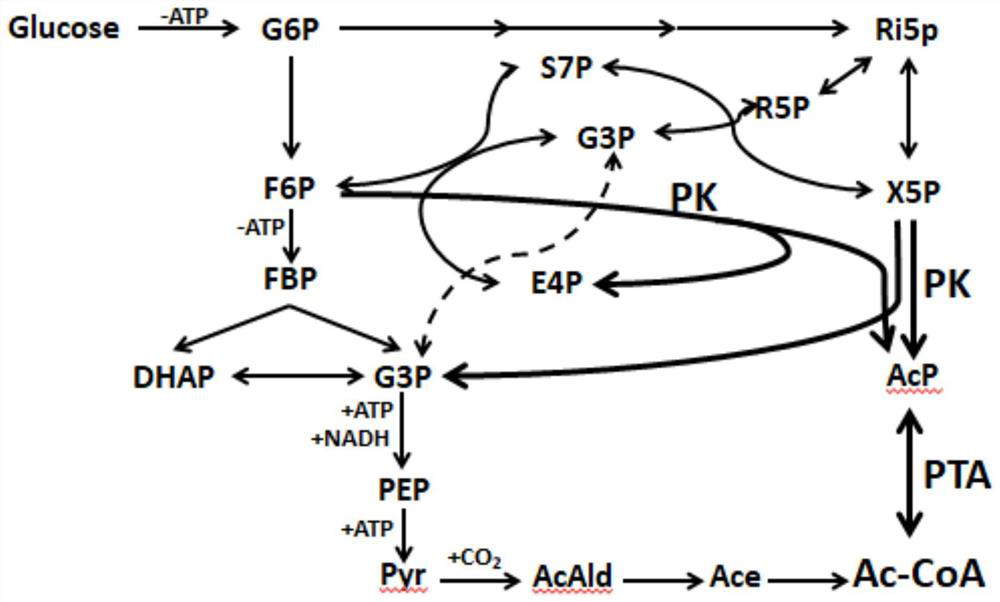
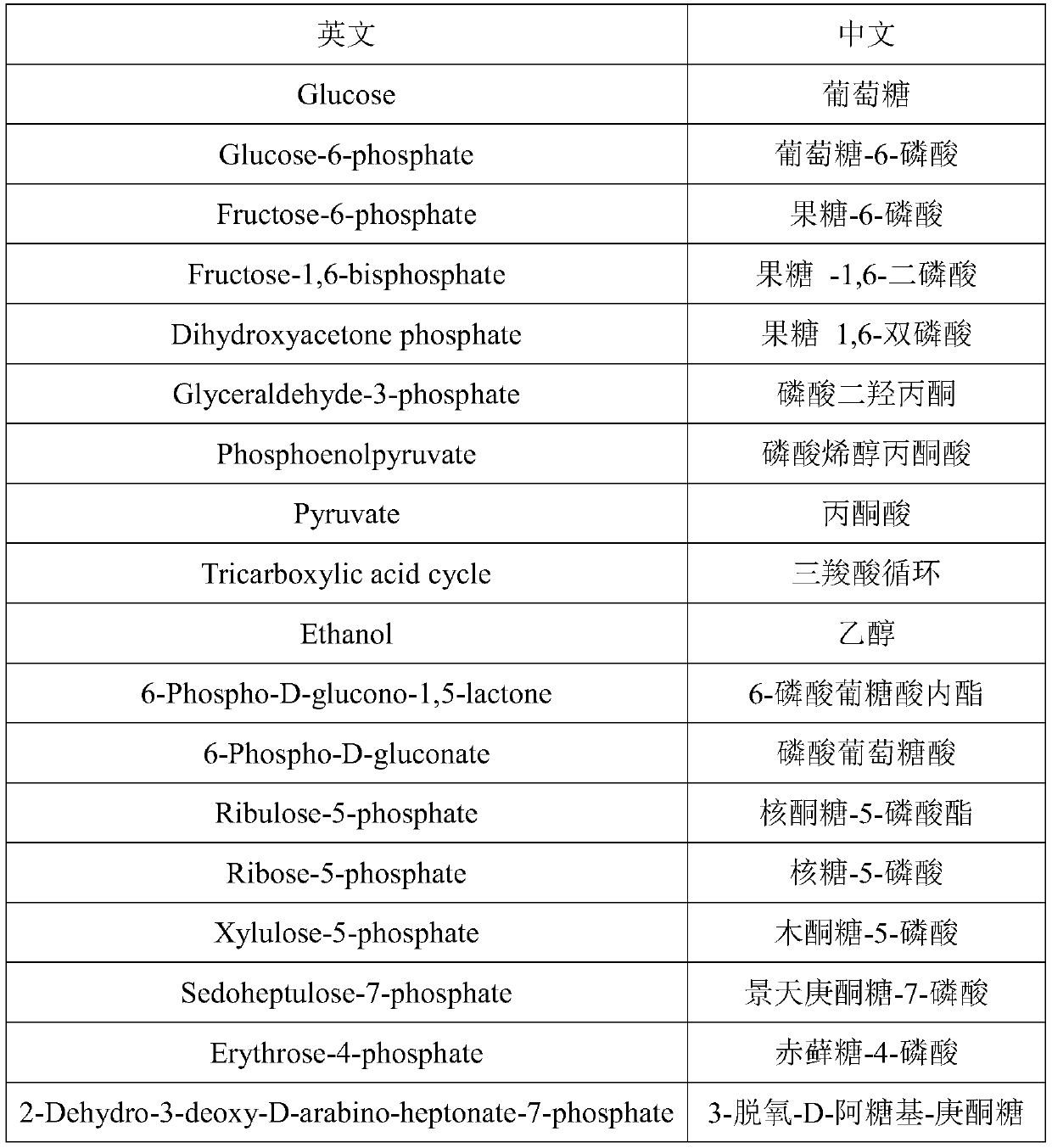
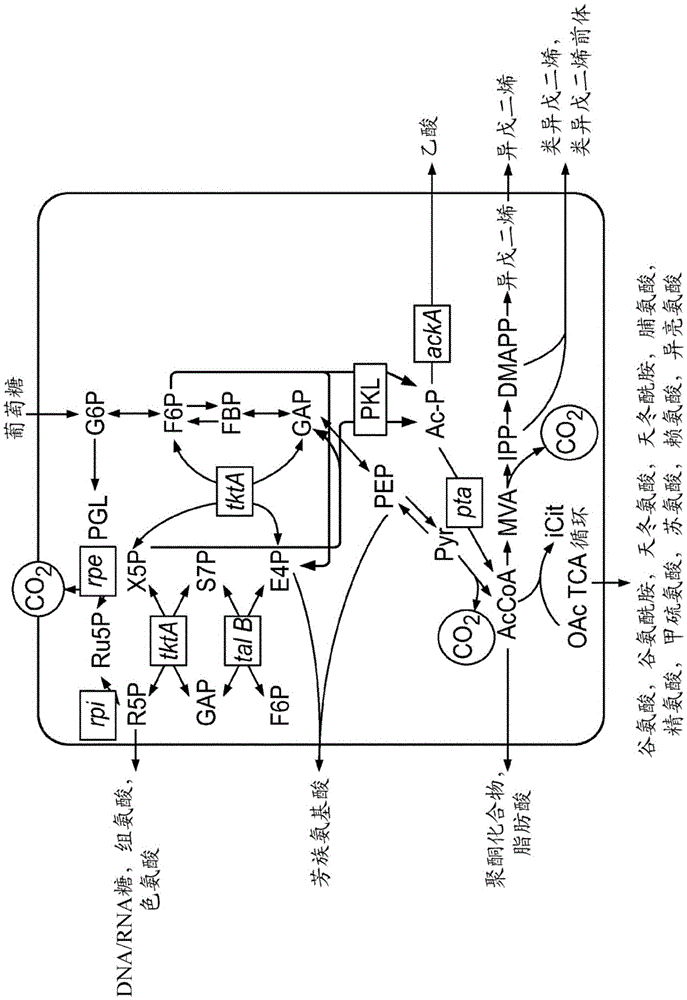
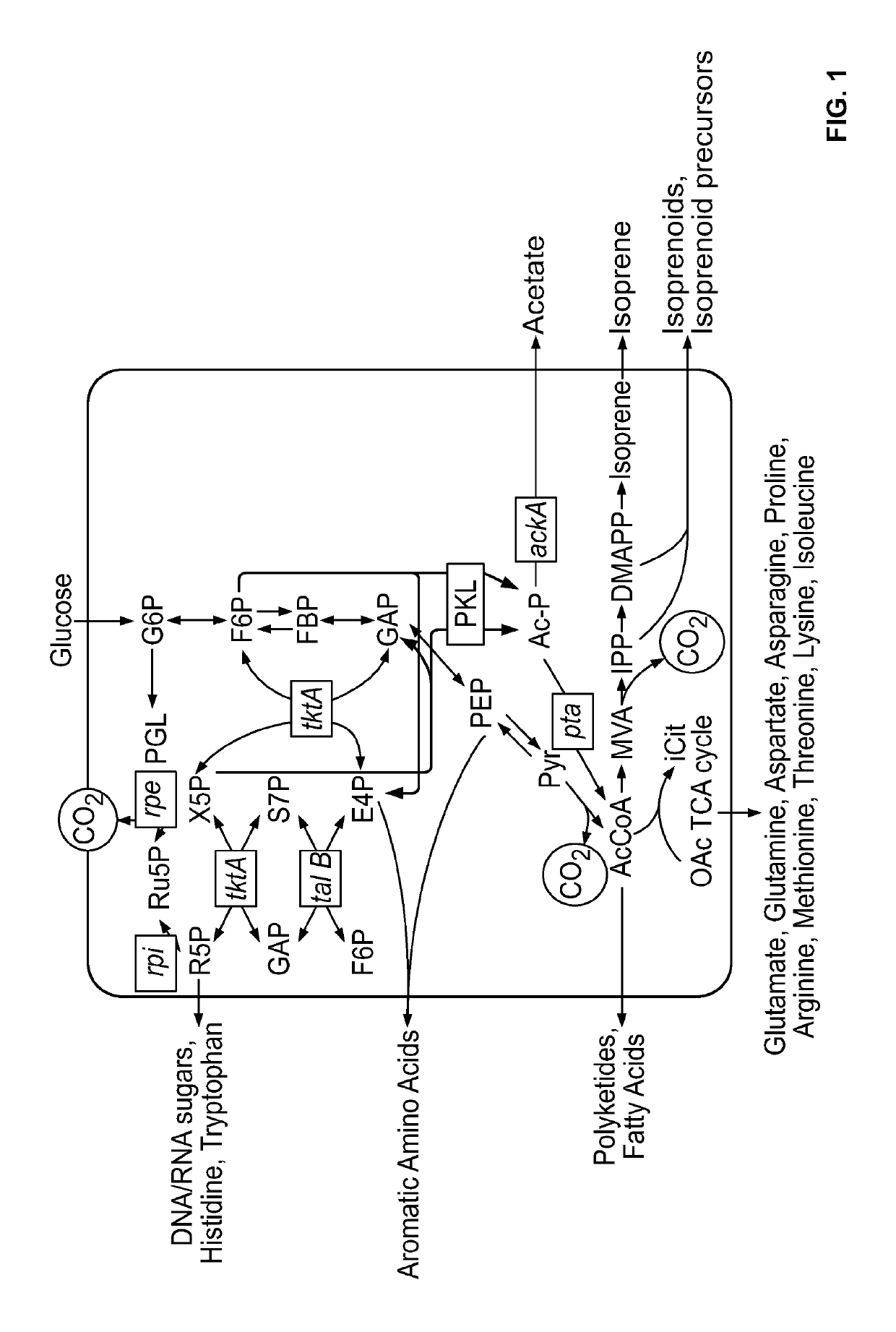
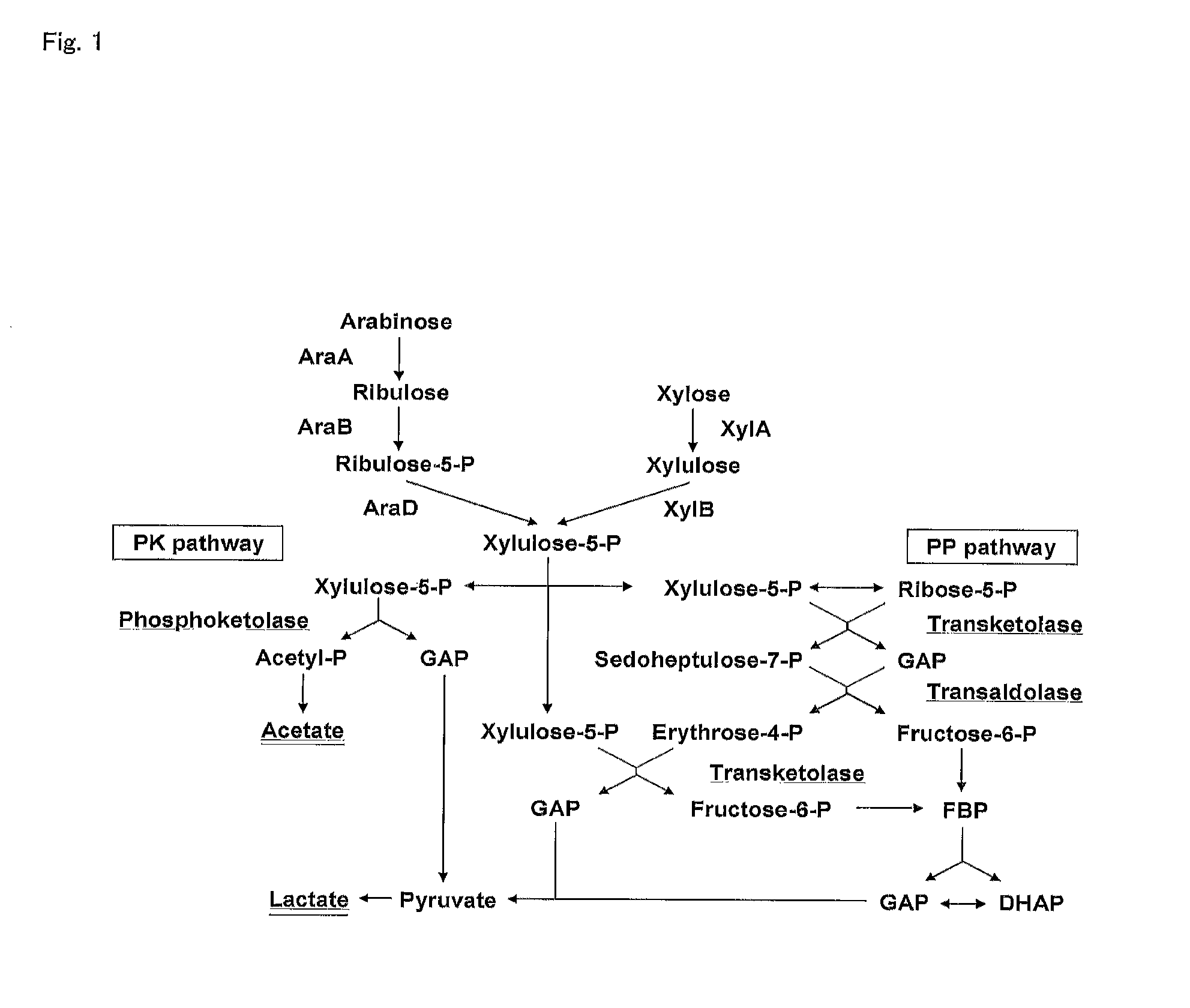
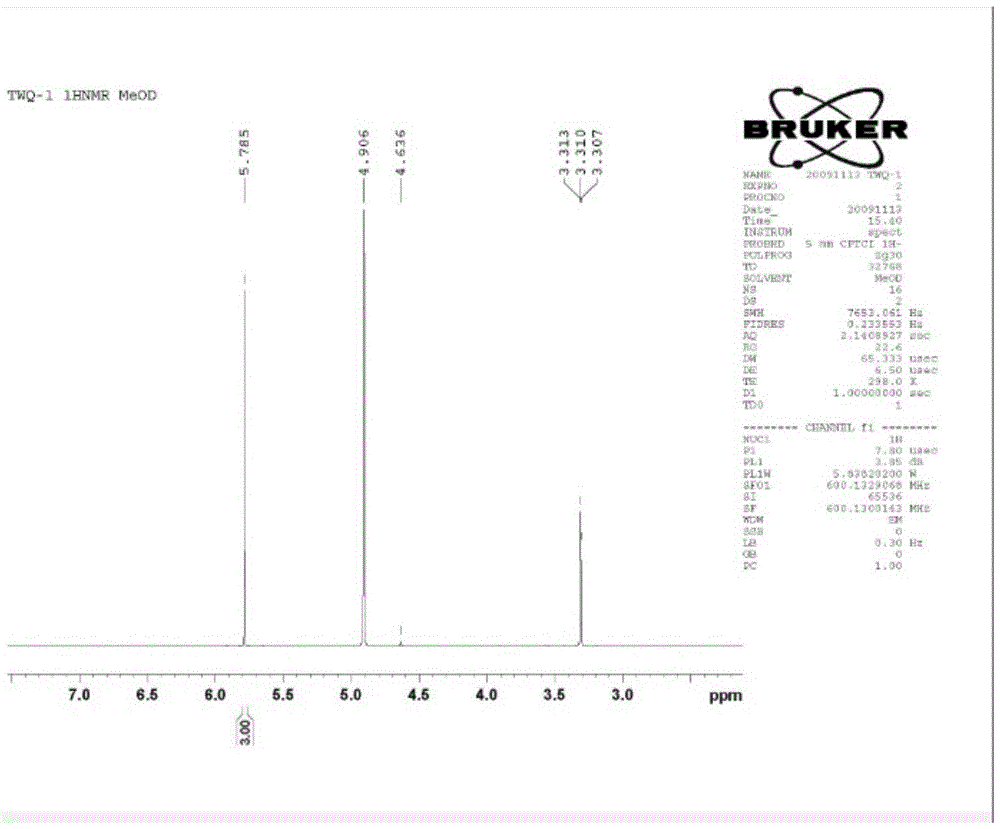
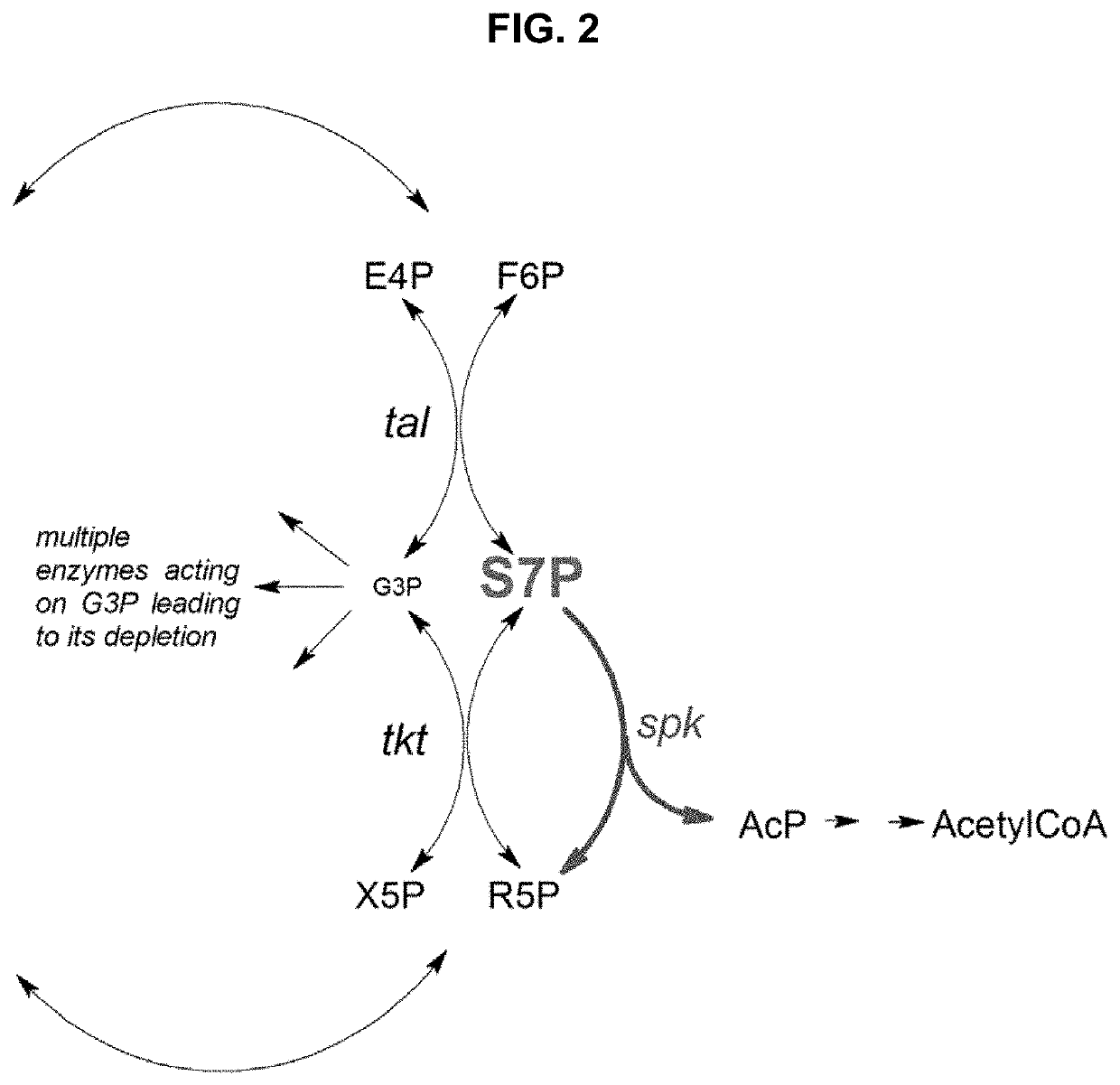
In enzymology, phosphoketolase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reactions D-xylulose 5-phosphate + phosphate ⇌ acetyl phosphate + D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate + H₂O (EC 4.1.2.9) D-fructose 6-phosphate + phosphate ⇌acetyl phosphate + D-erythrose 4-phosphate + H₂O (EC 4.1.2.22) D-sedoheptulose 7-phosphate + phosphate ⇌acetyl phosphate + D-ribose 5-phosphate + H₂O Phosphoketolase is considered a promiscuous enzyme as it was demonstrated to use 3 different sugar phosphates as substrates.
Use of phosphoketolase for producing useful metabolites
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
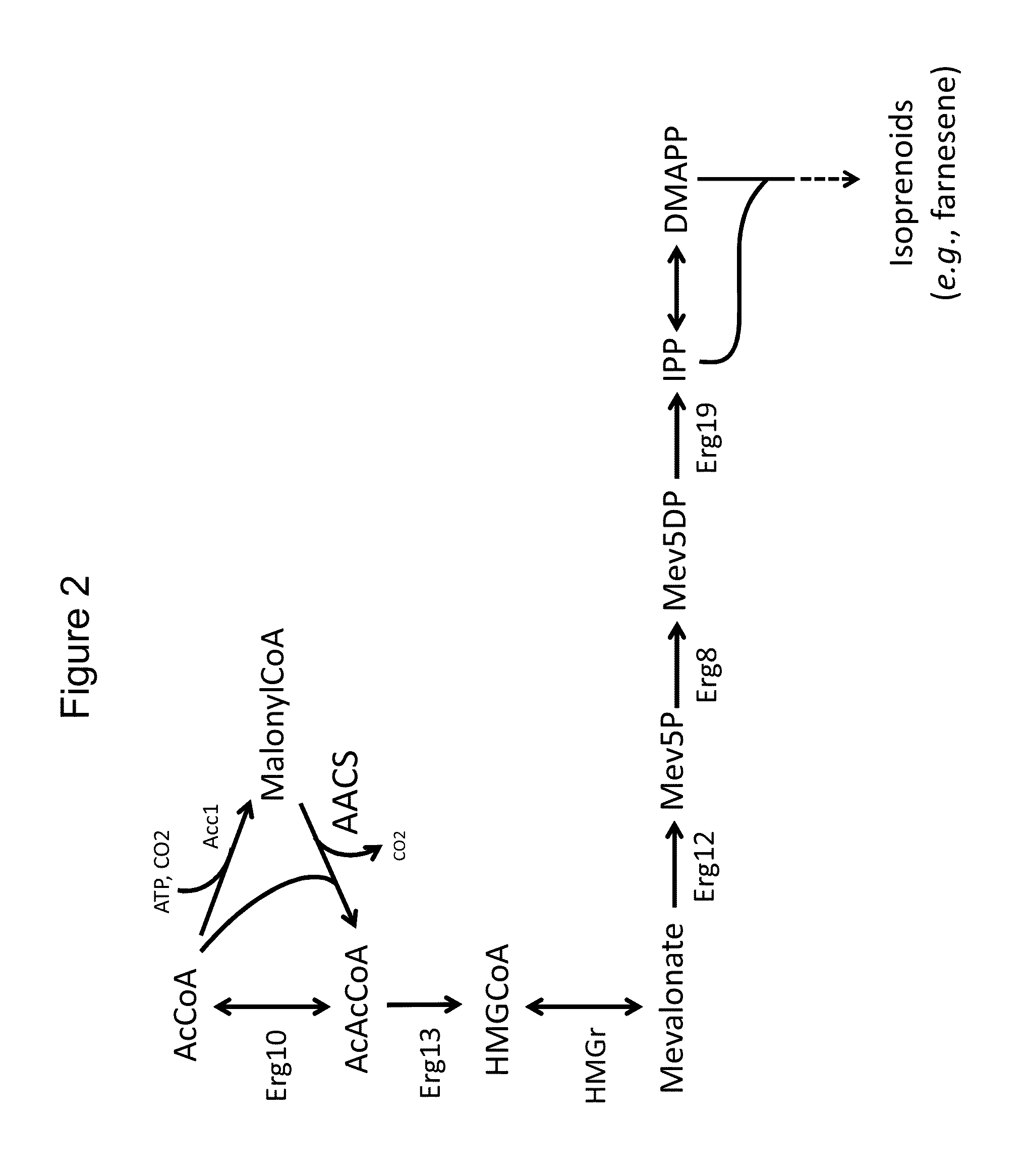
Production of acetyl-coenzyme a derived isoprenoids
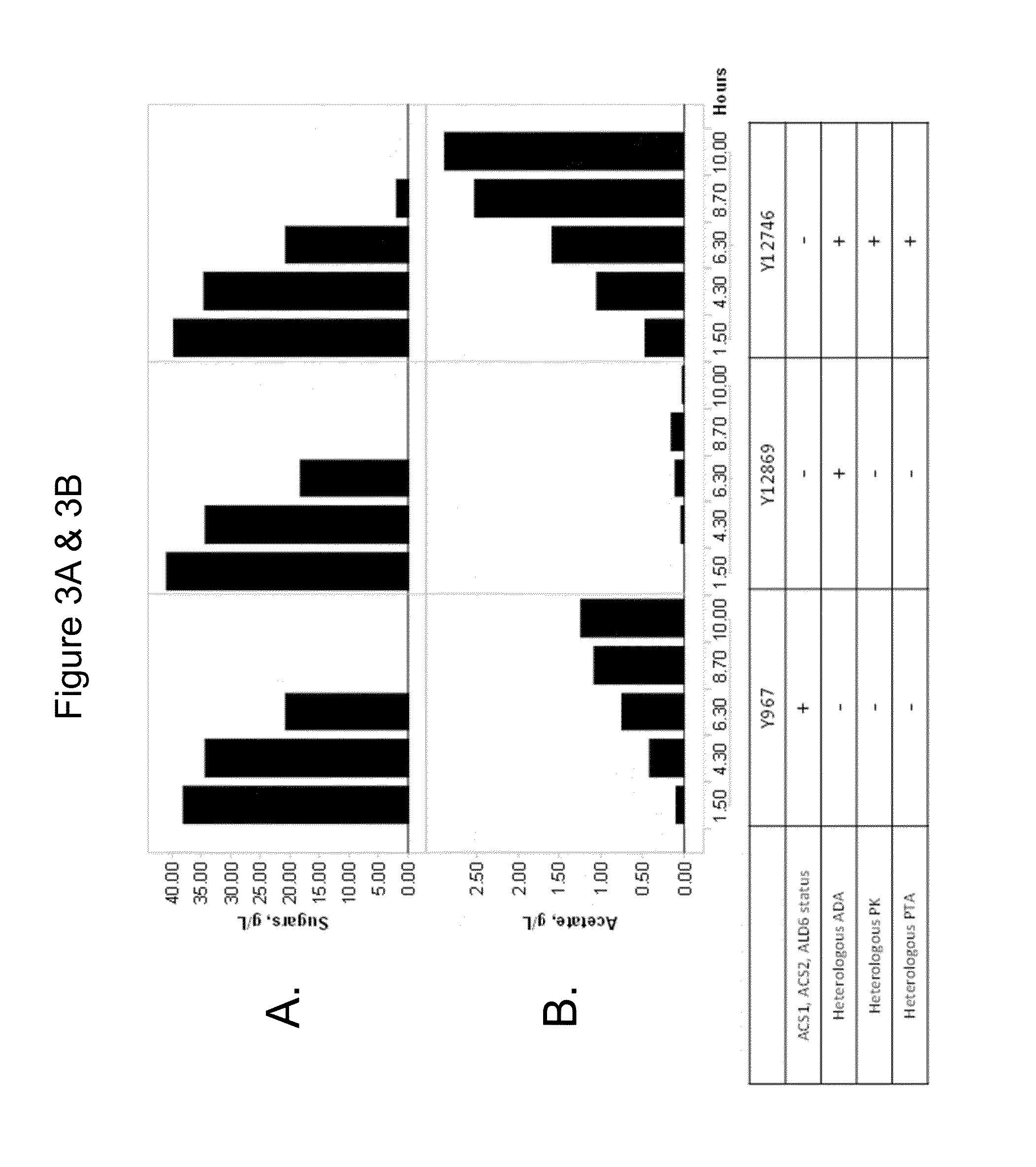
ActiveUS8415136B1Avoid high forceThermodynamically favorableFungiTransferasesHeterologousHMG-CoA reductase
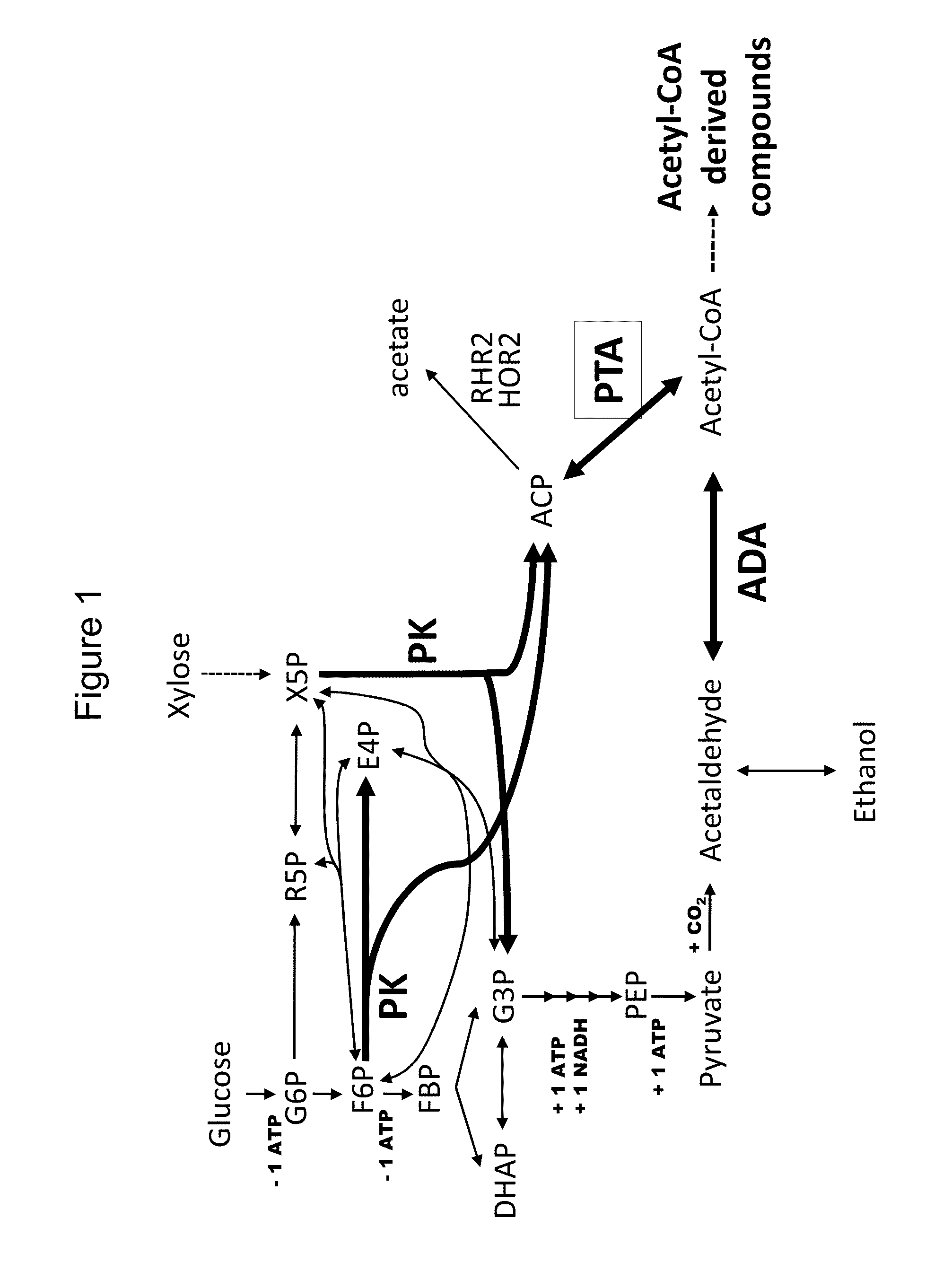
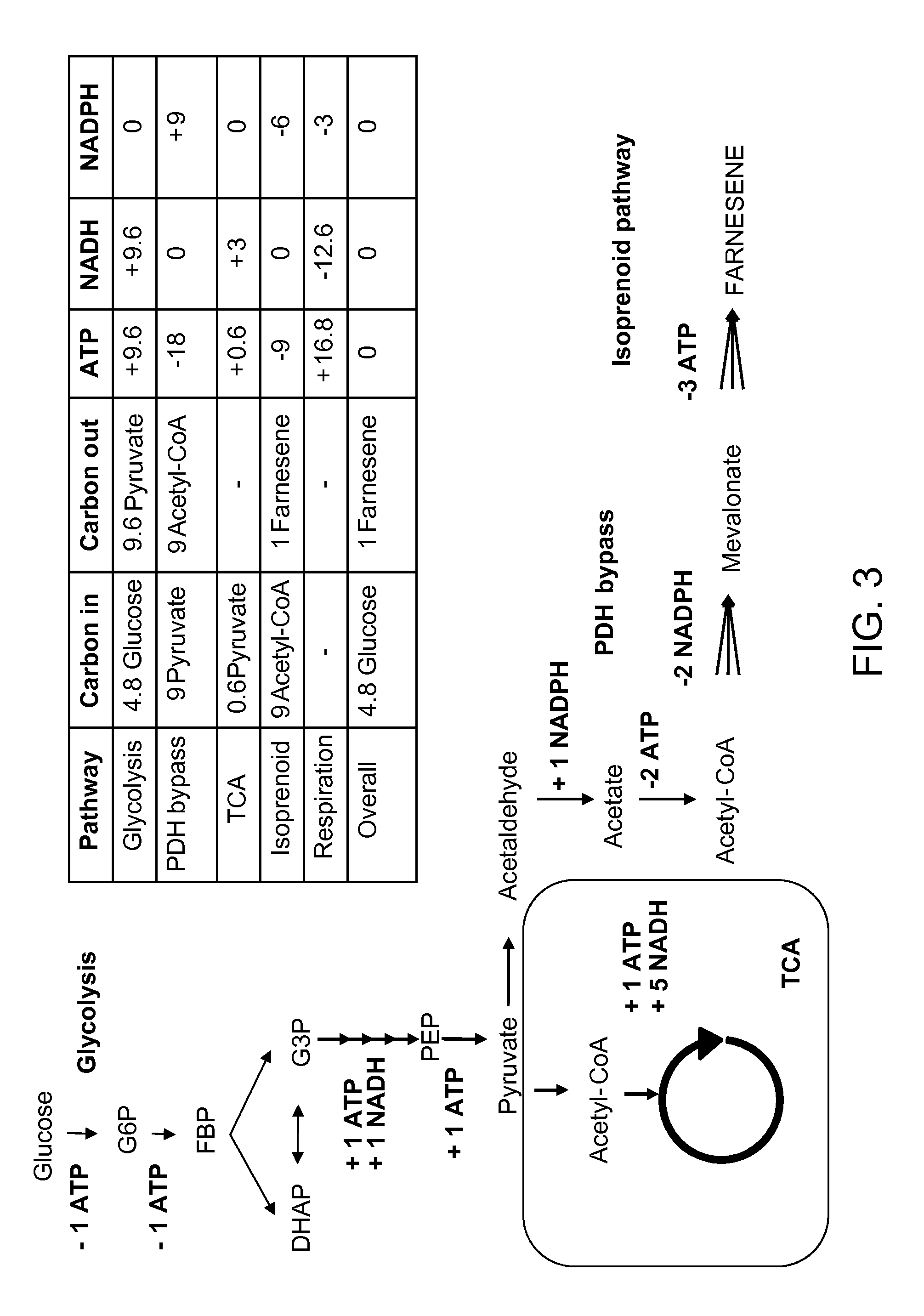
Provided herein are compositions and methods for the heterologous production of acetyl-CoA-derived isoprenoids in a host cell. In some embodiments, the host cell is genetically modified to comprise a heterologous nucleotide sequence encoding an acetaldehyde dehydrogenase, acetylating (ADA, E.C. 1.2.1.10) and an MEV pathway comprising an NADH-using HMG-CoA reductase. In some embodiments, the host cell is genetically modified to comprise a heterologous nucleotide sequence encoding an ADA and an MEV pathway comprising an acetoacetyl-CoA synthase. In some embodiments, the genetically modified host cell further comprises one or more heterologous nucleotide sequences encoding a phosphoketolase and a phosphotransacetylase. In some embodiments, the genetically modified host cell further comprises a functional disruption of the native PDH-bypass. The compositions and methods described herein provide an energy-efficient yet redox balanced route for the heterologous production of acetyl-CoA-derived isoprenoids.
Owner:AMYRIS INC
Utilization of phosphoketolase in the production of mevalonate, isoprenoid precursors, and isoprene
The invention provides for methods for the production of mevalonate, isoprene, isoprenoid precursor molecules, and / or isoprenoids in cells via the heterologous expression of phosphoketolase enzymes.
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
Use of phosphoketolase and phosphotransacetylase for production of acetyl-coenzyme a derived compounds
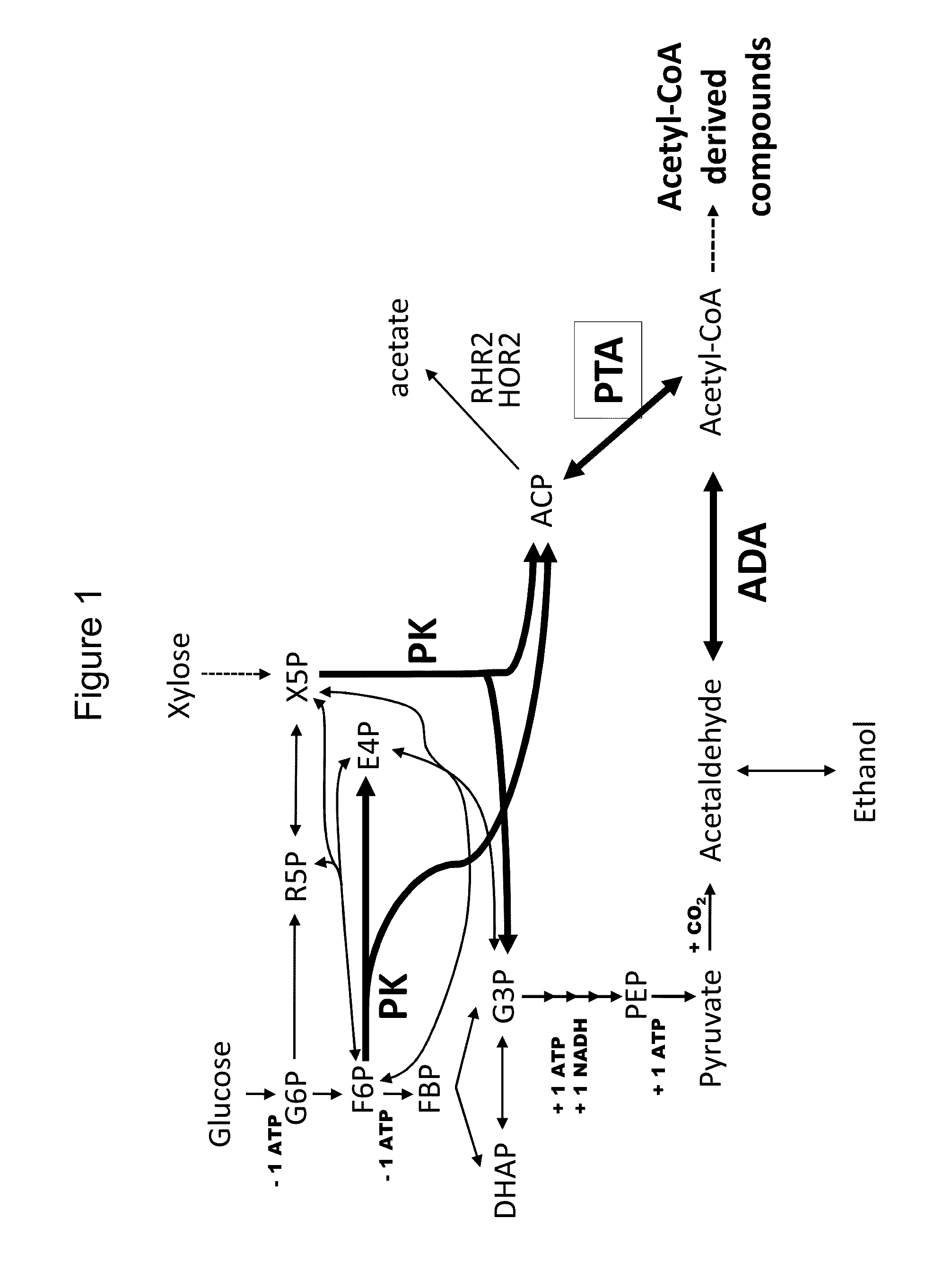
Provided herein are compositions and methods for improved production of acetyl-CoA and acetyl-CoA derived compounds in a host cell. In some embodiments, the host cell is genetically modified to comprise a heterologous nucleotide sequence encoding a phosphoketolase (PK), and a functional disruption of an endogenous enzyme that converts acetyl phosphate to acetate. In some embodiments, the host cell further comprises a heterologous nucleotide sequence encoding a phosphotransacetylase (PTA). In some embodiments, the enzyme that converts acetyl phosphate to acetate is a glycerol-1-phosphatase. In some embodiments, the glycerol-1-phosphatase is GPP1 / RHR2. In some embodiments, the glycerol-1-phosphatase is GPP2 / HOR2. The compositions and methods described herein provide an efficient route for the heterologous production of acetyl-CoA-derived compounds, including but not limited to, isoprenoids, polyketides, and fatty acids.
Owner:TOTALENERGIES ONETECH +1
Recombinant yeast and substance production method using the same
ActiveUS20130295616A1Reduced activityIncrease productivityMicroorganismsTransferasesBiotechnologyAcetic acid
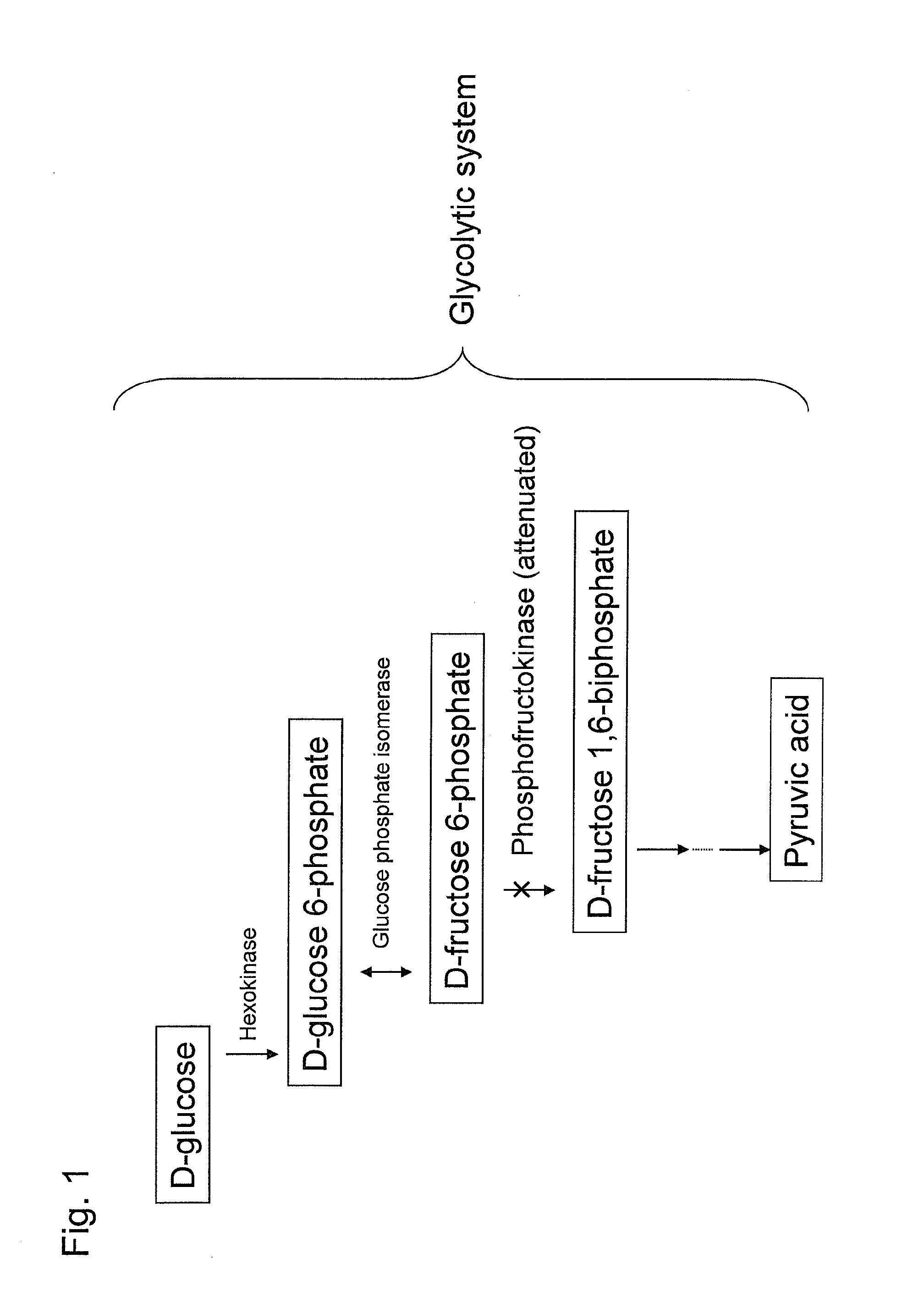
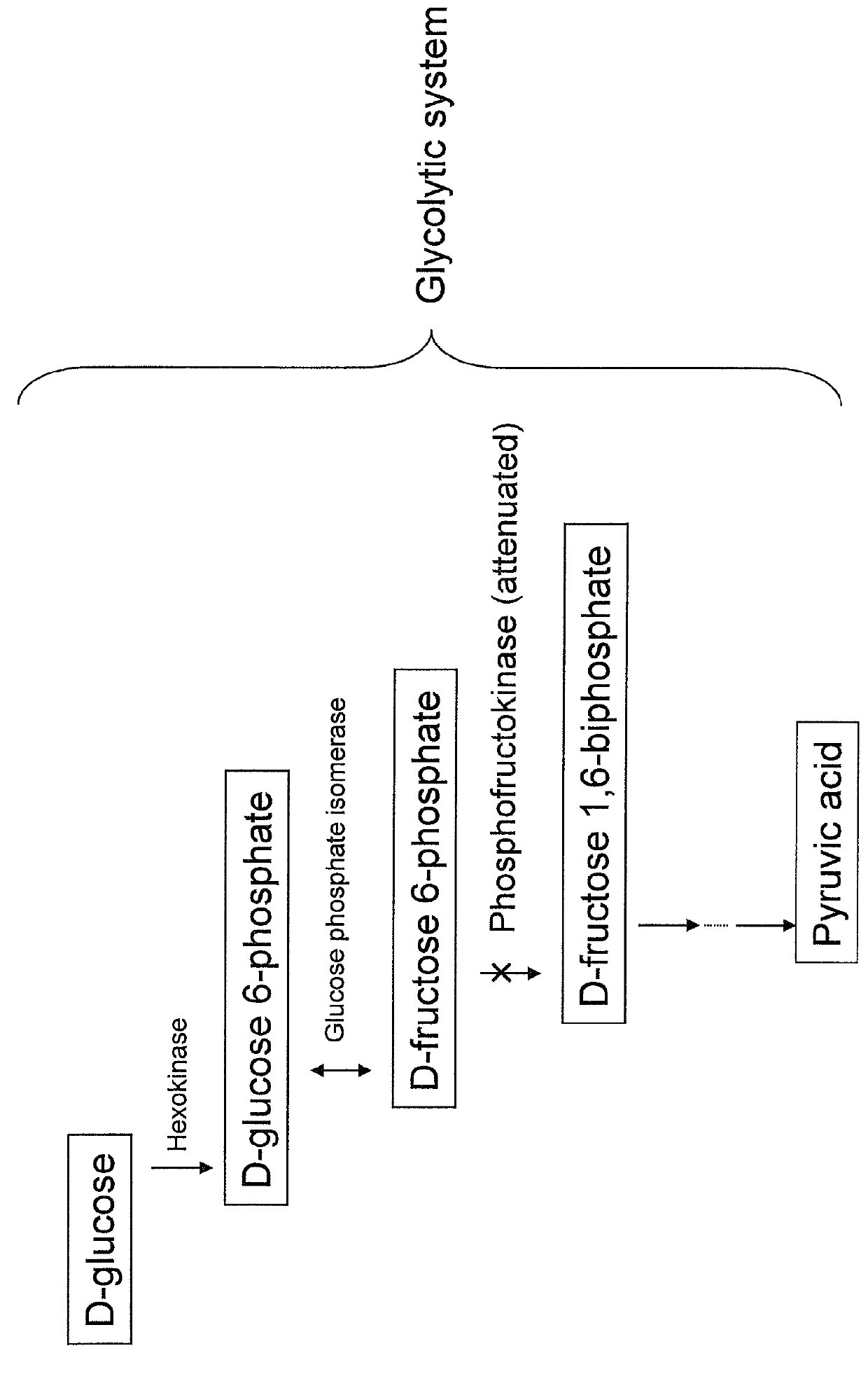
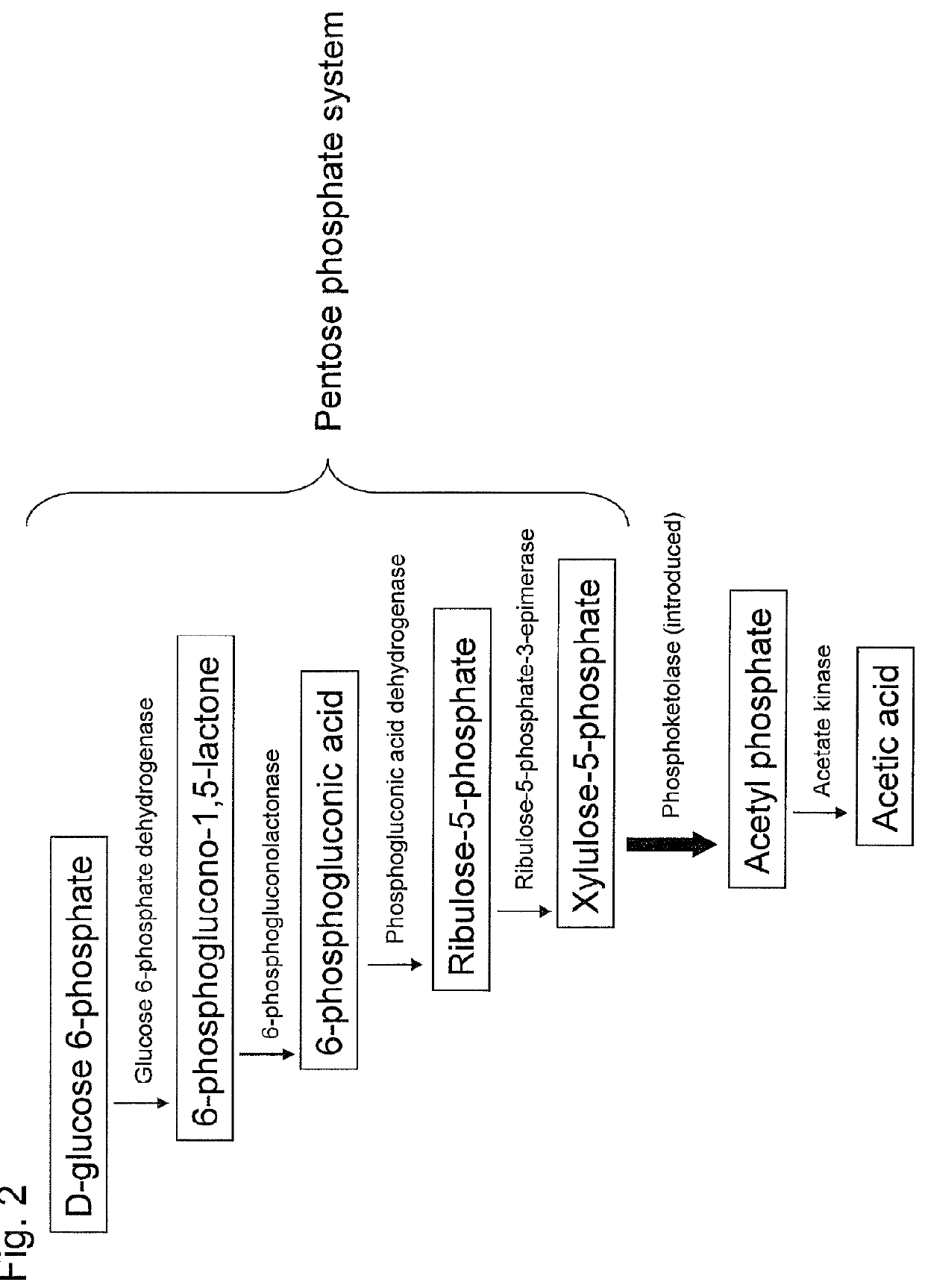
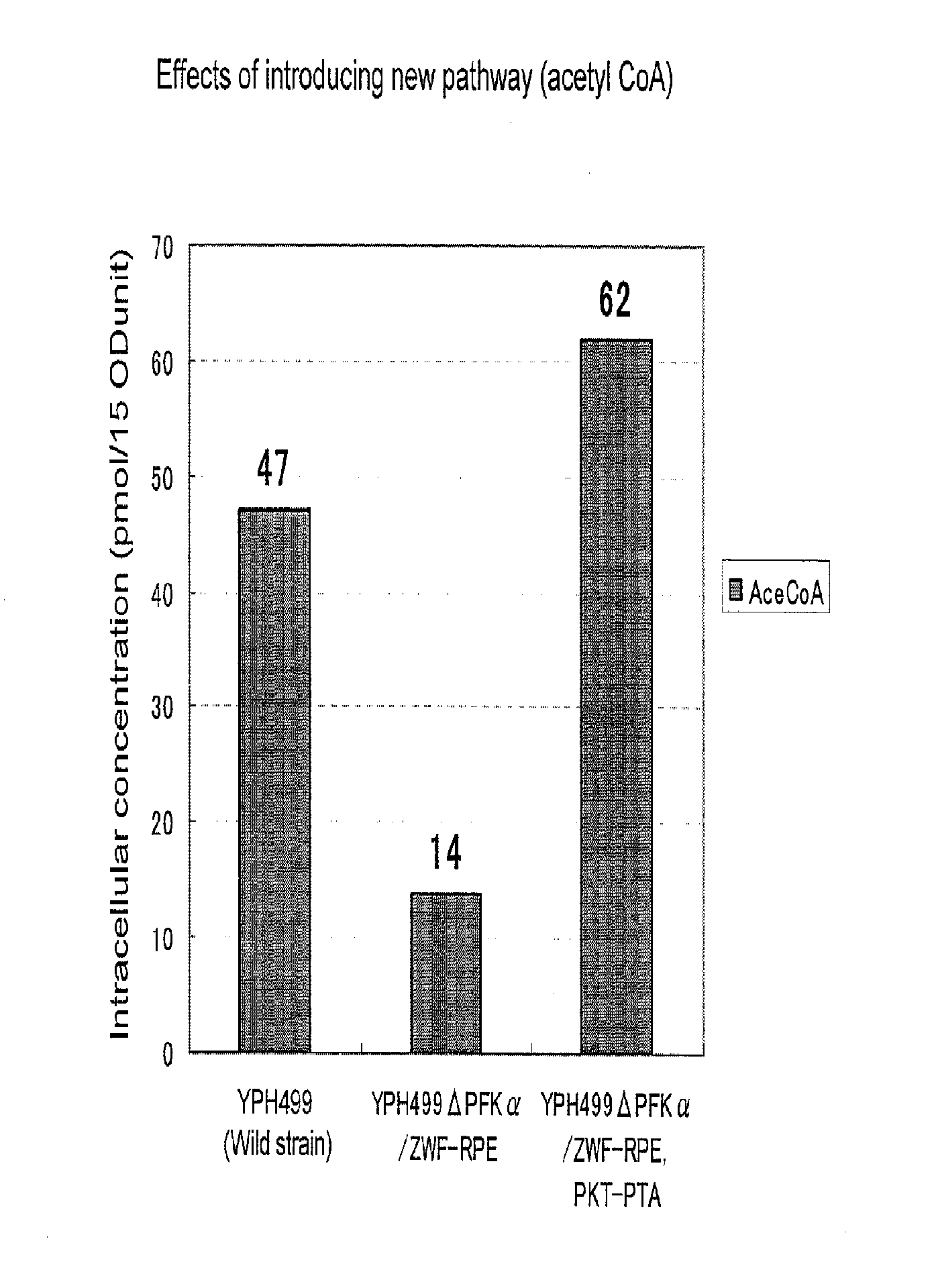
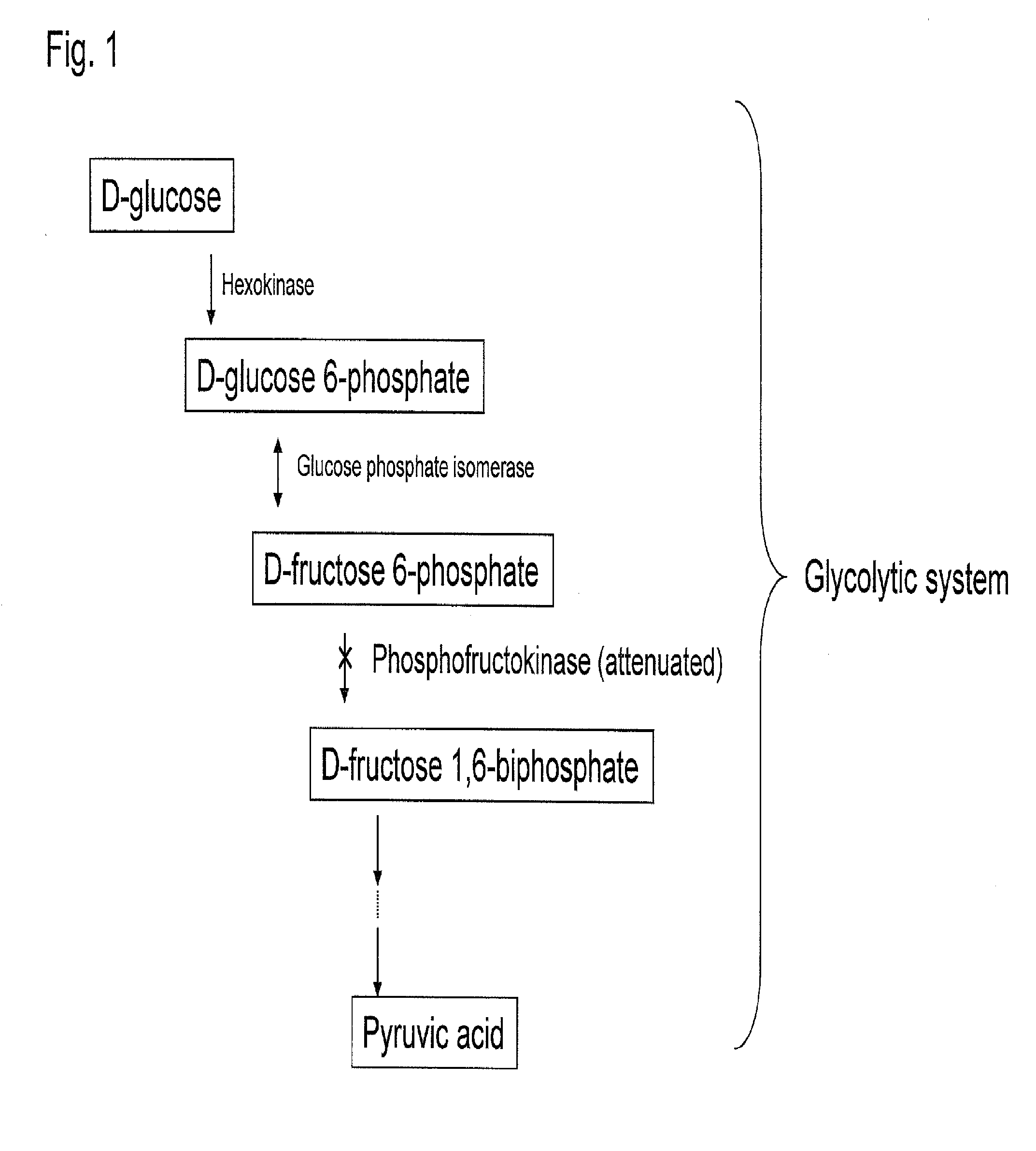
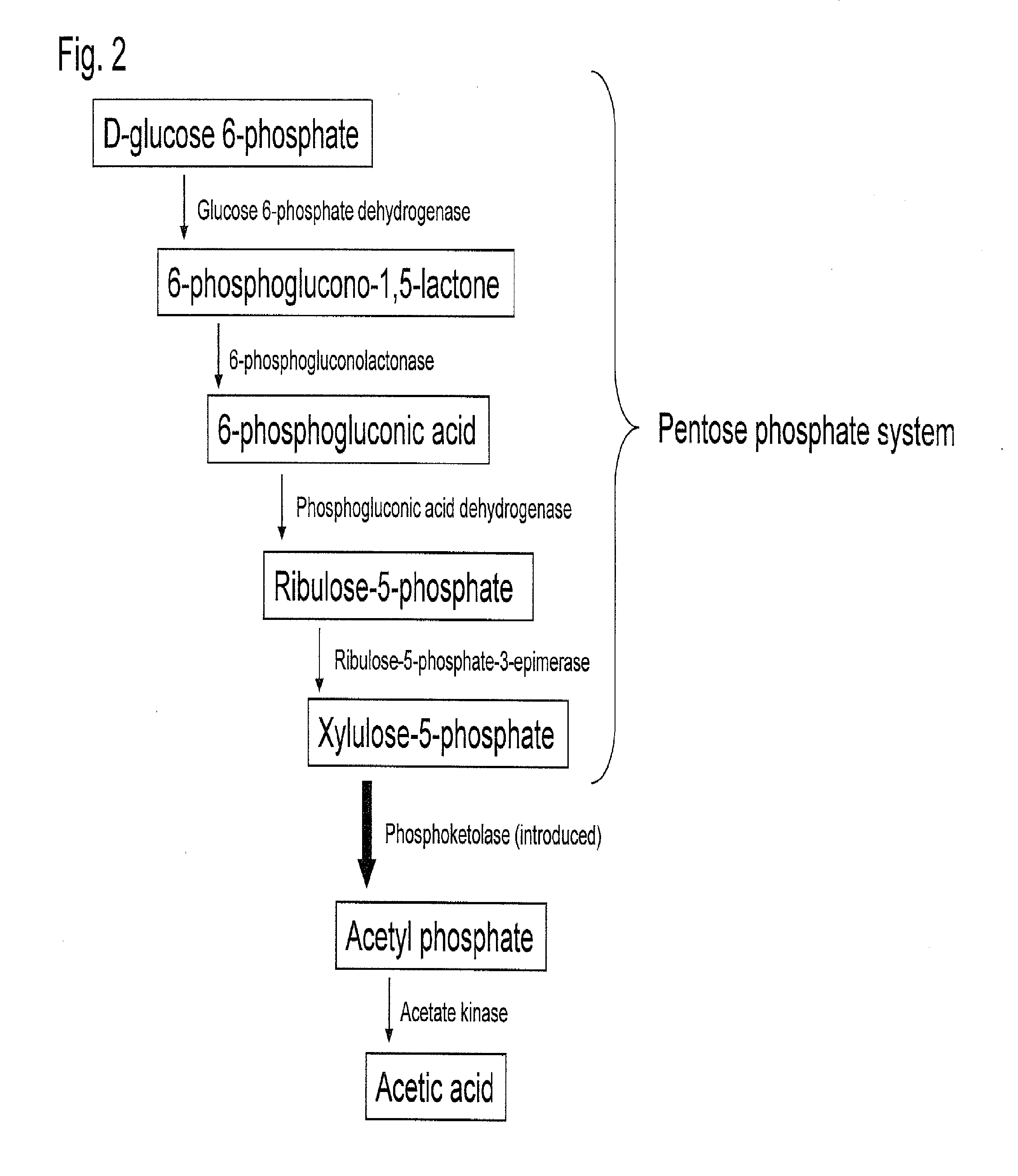
Substance productivity is improved by introducing a metabolic pathway for synthesis of acetyl-CoA or acetic acid from glucose-6-phosphate into yeast. Acetic acid productivity, acetyl-CoA productivity, and productivity of a substance made from acetyl-CoA-derived are improved by attenuating genes involved in the glycolytic system of yeast and introducing a phosphoketolase gene into the yeast.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
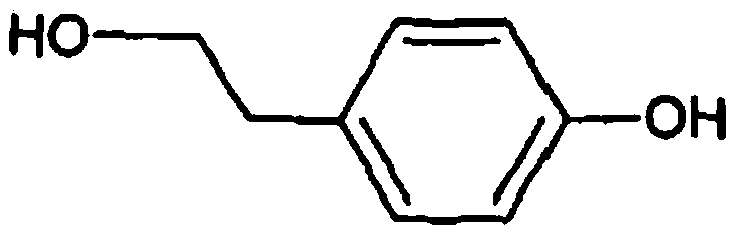
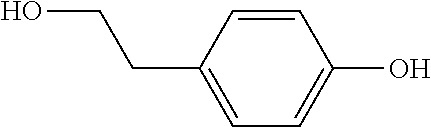
Recombinant yeast, construction method thereof and application thereof for producing tyrosol and derivative
InactiveCN109929883AAltered carbon flux distributionOptimizing Metabolic PathwaysFungiGenetically modified cellsHydroxytyrosolTyrosol
Owner:YANTAI HUAKANG BIOTECH CO LTD
Utilization of phosphoketolase in the production of mevalonate, isoprenoid precursors, and isoprene
The invention provides for methods for the production of mevalonate, isoprene, isoprenoid precursor molecules, and / or isoprenoids in cells via the heterologous expression of phosphoketolase enzymes.
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
Chassis system for ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) regeneration and application
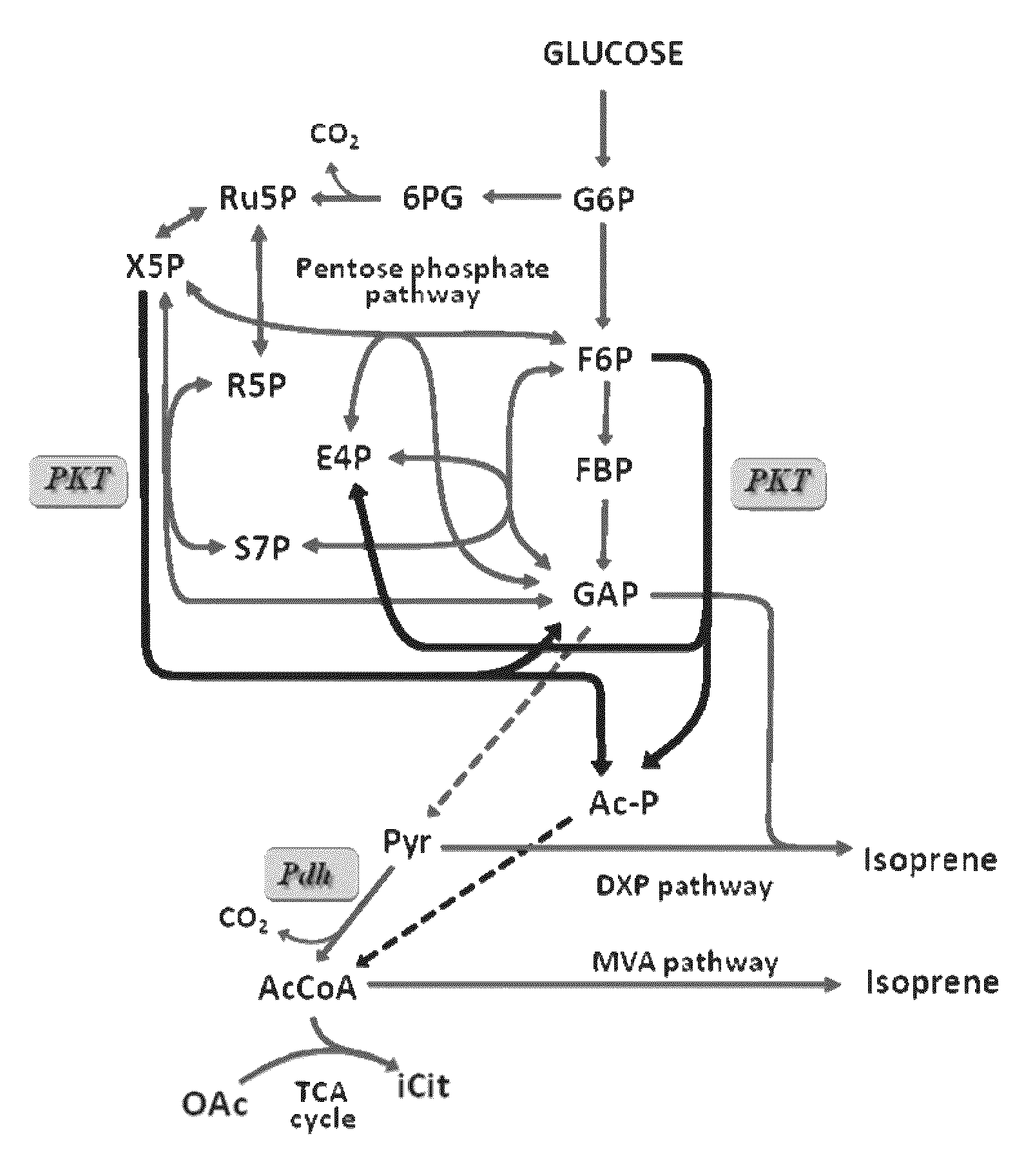
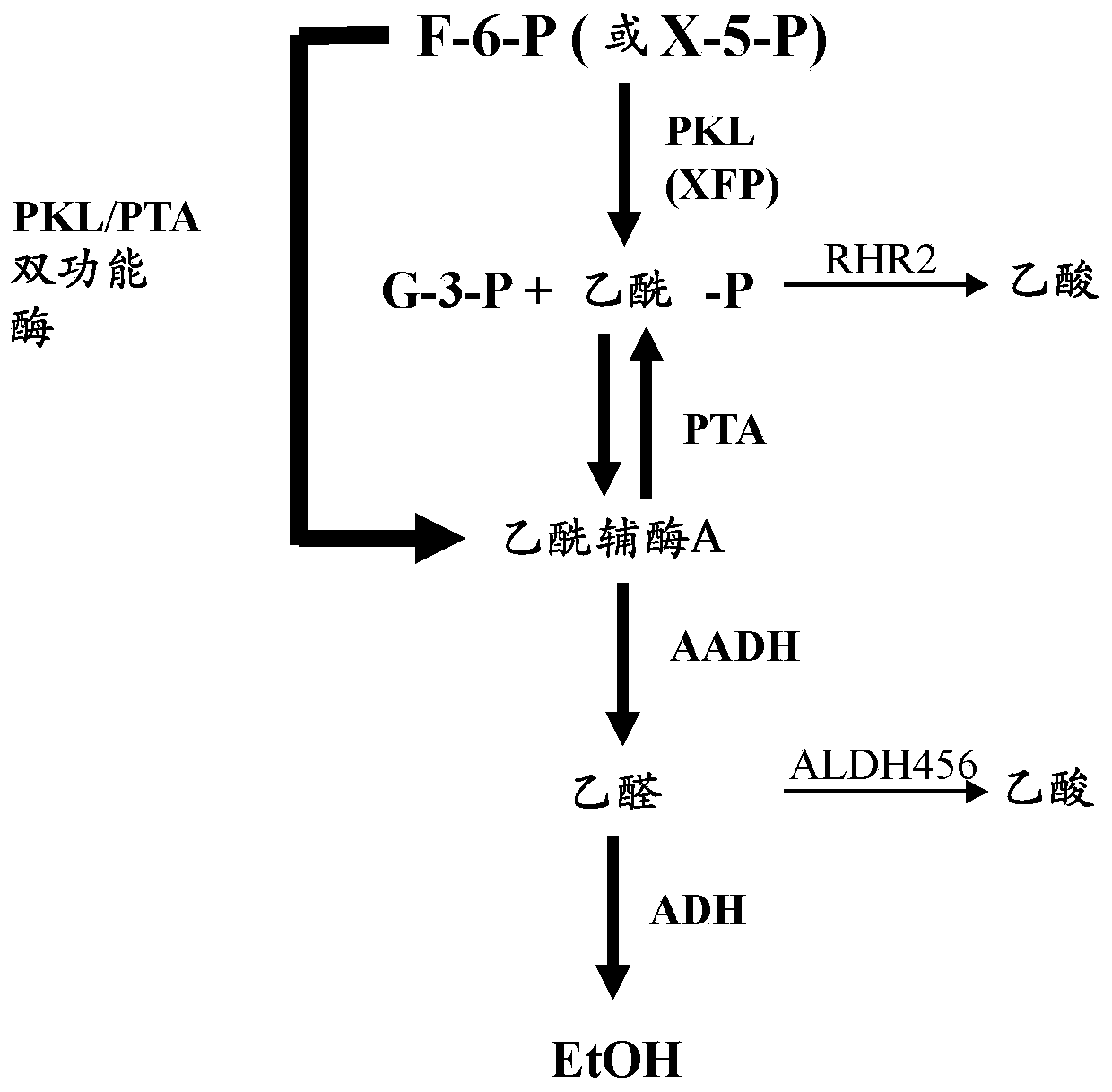
The invention provides a chassis system for ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) regeneration and application. The chassis system for ATP regeneration comprises the following five enzymes: alpha-glucan phosphorylase, glucophosphomutase, phosphoglucose Isomerase, phosphoketolase and acetokinase. In addition, the chassis system can further comprise the following seven enzymes: transaldolase, transketolase,ribose-5-phosphate isomerase, ribulose-3 epimerase, triosephosphate isomerase, fructose-bisphosphate aldolase and fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. The chassis system can be coupled to an enzymic catalyticreaction needing ATP, utilizes starch or maltodextrin as energy, is not added with any coenzyme, can efficiently regenerate the ATP at low cost through a one-pot reaction and is an economical, highlyefficient, stable and sustainable ATP regeneration system.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Production of acetyl-coenzyme a derived isoprenoids
ActiveUS20130236942A1Avoid high forceThermodynamically favorableMicroorganismsTransferasesHMG-CoA reductaseNucleotide
Provided herein are compositions and methods for the heterologous production of acetyl-CoA-derived isoprenoids in a host cell. In some embodiments, the host cell is genetically modified to comprise a heterologous nucleotide sequence encoding an acetaldehyde dehydrogenase, acetylating (ADA, E.C. 1.2.1.10) and an MEV pathway comprising an NADH-using HMG-CoA reductase. In some embodiments, the host cell is genetically modified to comprise a heterologous nucleotide sequence encoding an ADA and an MEV pathway comprising an acetoacetyl-CoA synthase. In some embodiments, the genetically modified host cell further comprises one or more heterologous nucleotide sequences encoding a phosphoketolase and a phosphotransacetylase. In some embodiments, the genetically modified host cell further comprises a functional disruption of the native PDH-bypass. The compositions and methods described herein provide an energy-efficient yet redox balanced route for the heterologous production of acetyl-CoA-derived isoprenoids.
Owner:AMYRIS INC
Use of phosphoketolase and phosphotransacetylase for production of acetyl-coenzyme A derived compounds
Provided herein are compositions and methods for improved production of acetyl-CoA and acetyl-CoA derived compounds in a host cell. In some embodiments, the host cell is genetically modified to comprise a heterologous nucleotide sequence encoding a phosphoketolase (PK), and a functional disruption of an endogenous enzyme that converts acetyl phosphate to acetate. In some embodiments, the host cell further comprises a heterologous nucleotide sequence encoding a phosphotransacetylase (PTA). In some embodiments, the enzyme that converts acetyl phosphate to acetate is a glycerol-1-phosphatase. In some embodiments, the glycerol-1-phosphatase is GPP1 / RHR2. In some embodiments, the glycerol-1-phosphatase is GPP2 / HOR2. The compositions and methods described herein provide an efficient route for the heterologous production of acetyl-CoA-derived compounds, including but not limited to, isoprenoids, polyketides, and fatty acids.
Owner:TOTALENERGIES ONETECH +1
Genetically engineered bacterium for improving yield of beta-carotene and application thereof
ActiveCN113151340AEasy to storeIncrease supplyFungiMicroorganism based processesLipid BodyEngineered genetic
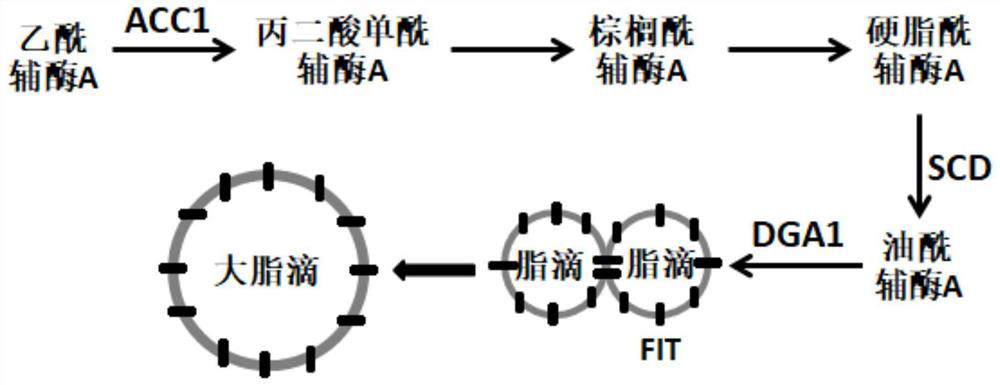
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium capable of increasing the yield of beta-carotene and application thereof, and the genetically engineered bacterium contains a beta-carotene synthetic pathway related gene, a phosphoketolase pathway related gene and a lipid droplet synthetic pathway related gene. A beta-carotene synthetic pathway is covered; a phosphoketolase pathway is increased, the carbon loss is reduced, and more precursor substance acetyl coenzyme A for synthesizing beta-carotene is generated from a carbon source; the supply of a reducing power substance NADPH and an energy substance ATP is increased; and a lipid droplet synthesis pathway is also increased, and the storage of beta-carotene can be increased by increasing the content and volume of intracellular lipid droplets. The highest yield of the beta-carotene of the genetically engineered bacterium reaches 7.8g / L, and the yield of the beta-carotene is remarkably improved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU WISDOM BIO TECH
Recombinant yeast and substance production method using the same
Substance productivity is improved by introducing a metabolic pathway for synthesis of acetyl-CoA or acetic acid from glucose-6-phosphate into yeast. Acetic acid productivity, acetyl-CoA productivity, and productivity of a substance made from acetyl-CoA-derived are improved by attenuating genes involved in the glycolytic system of yeast and introducing a phosphoketolase gene into the yeast.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Method for increasing cell phloroglucinol synthesis yield and application
ActiveCN104357495AReduce generationEmission reductionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyGenetic engineering
The invention discloses a method for increasing the cell phloroglucinol synthesis yield and application, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. According to the method provided by the invention, a recombined cell co-expresses a phosphoketolase fxpk gene, a fructose 1,6-biphosphatase fbp gene and a poly-ketene anhydride synthetase phld gene and also expresses any one or two of a multiple-resistance-factor MarA gene and an acetyl-coenzyme a carboxylase ACCase gene. According to the method provided by the invention, a new phloroglucinol synthesis way is built in the recombined cell, so that the yield of phloroglucinol is greatly increased; as for a contrast group, the phloroglucinol yield is increased by 68.9 percent; meanwhile, by the method, emission of carbon dioxide in a phloroglucinol synthesis process is also reduced; the method has high environmental benefits.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Recombinant yeast and substance production method using the same
ActiveUS20160251633A1Reduced activityIncrease productivityTransferasesOxidoreductasesAcetic acidBiotechnology
Substance productivity is improved by introducing a metabolic pathway for synthesis of acetyl-CoA or acetic acid from glucose-6-phosphate into yeast. Acetic acid productivity, acetyl-CoA productivity, and productivity of a substance made from acetyl-CoA-derived are improved by attenuating genes involved in the glycolytic system of yeast and introducing a phosphoketolase gene into the yeast.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Recombinant yeast, construction method thereof and application of recombinant yeast in preparing tyrosol and derivatives
ActiveCN111139194AAltered carbon flux distributionOptimizing Metabolic PathwaysFungiGenetically modified cellsHydroxytyrosolTyrosol
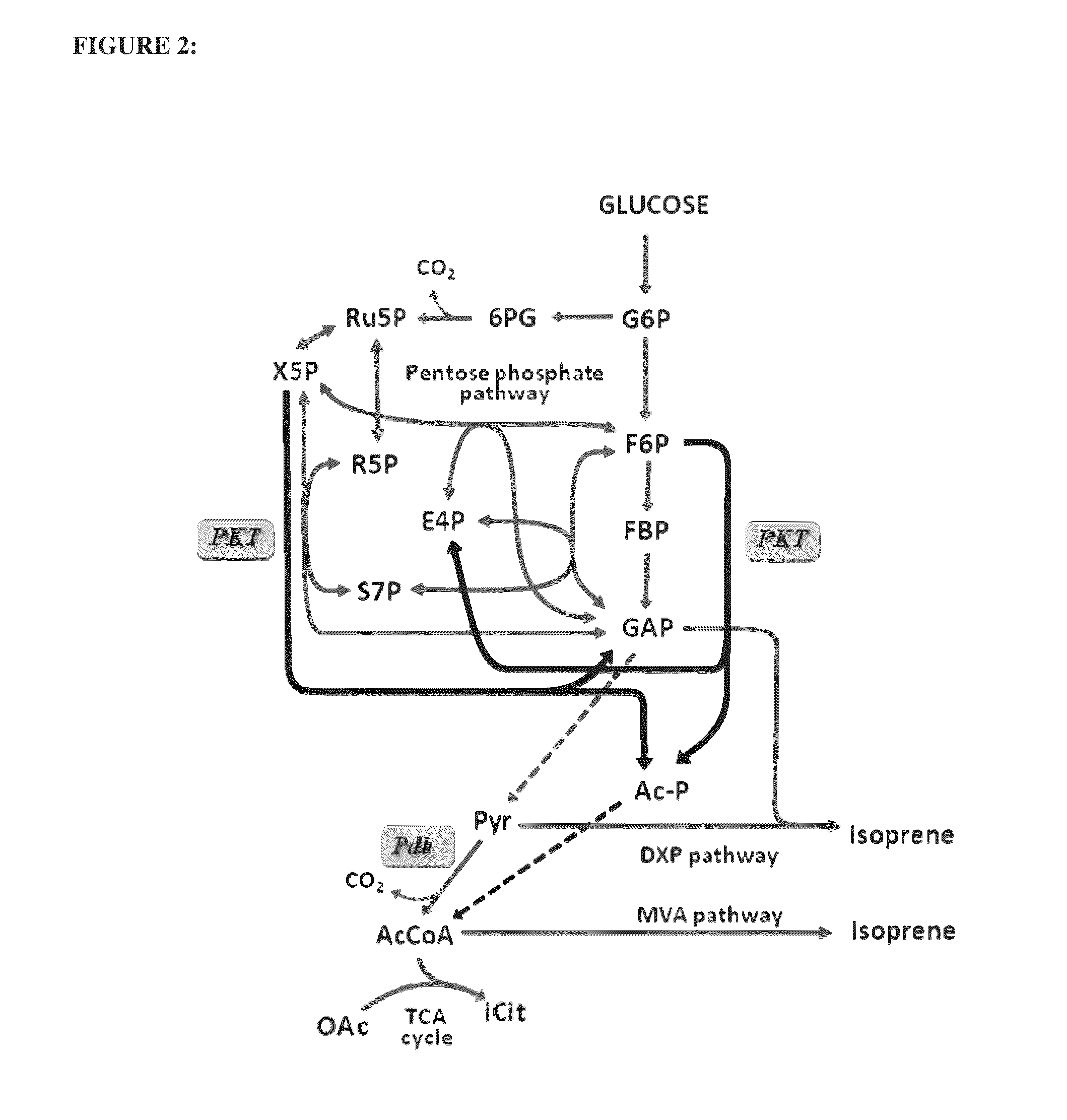
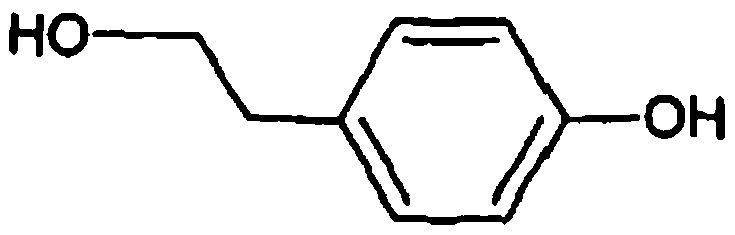
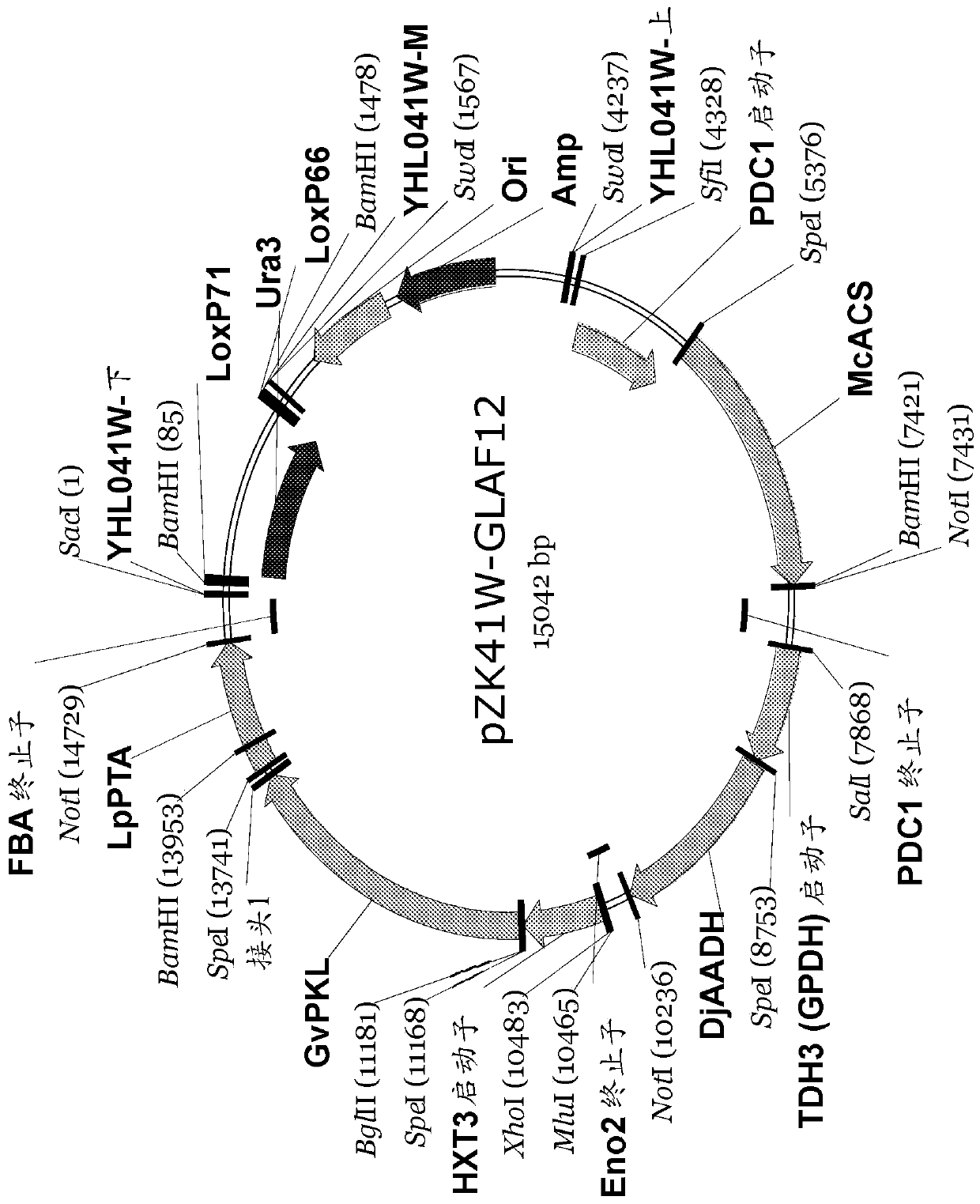
The invention relates to a recombinant yeast, a construction method thereof and an application of the recombinant yeast in preparing tyrosol and derivatives. The recombinant yeast is obtained by introducing an exogenous fructose-6-phosphate phosphoketolase expression gene into a modified yeast cell, and the modified yeast cell is a yeast cell with a metabolic pathway of synthesizing tyrosol through 4-erythrose phosphate and phosphoenolpyruvic acid. The invention first discloses the fact that in a process of expressing fructose-6-phosphate phosphoketolase in yeast, fructose-6-phosphoric acid iscatalyzed into erythrose-4-phosphoric acid and acetyl phosphoric acid while 1,6-fructose diphosphate is synthesized, and xylulose-5-phosphoric acid is catalyzed into glyceraldehyde-3-phosphoric acidand acetyl phosphoric acid, so that distribution of the carbon metabolism flow in yeast is changed, synthesis of an important intermediate substance erythrose-4-phosphoric acid in tyrosol biosynthesisis enhanced, the metabolic pathway for synthesizing tyrosol is optimized, and the yield of tyrosol and derivatives such as hydroxytyrosol and the like is improved.
Owner:SHANDONG HENGLU BIOTECH CO LTD
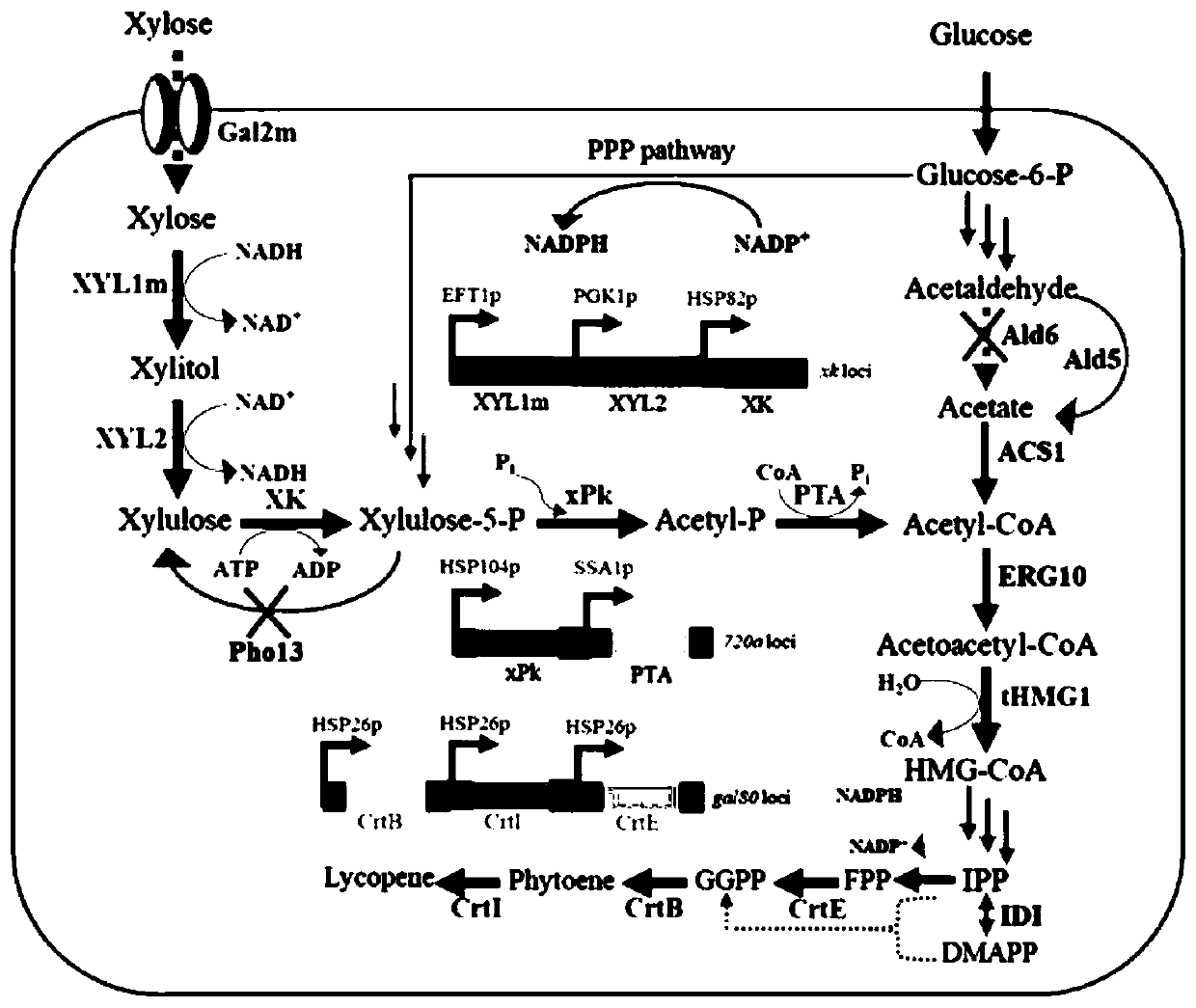
Xylose utilization yeast and application thereof
ActiveCN111235048AReduce manufacturing costReduce wasteFungiMicroorganism based processesEnzyme GenePromoter
The invention discloses xylose utilization yeast and an application thereof. The yeast is integration type engineering bacteria containing an xylose reductase gene XYL1m and an xylitol dehydrogenase gene XLY2 which are mutated, the amino acid sequence of xylose reductase contains one point mutation, K at the 271st-site amino acid is mutated into N, the integration type engineering bacteria also contain a phosphoketolase gene xPK and a phosphotransacetylase gene PTA, the Pho13 gene is knocked out, the integration type engineering bacteria also contain hexose transport protein Gal2 which is mutated, N at the 376th-site amino acid for Gal2 is mutated into F, a promoter at the upper stream of the Gal2 gene is replaced with SSA1, and a promoter of an xylulokinase XK gene is replaced with a strong promoter HSP82. A saccharomyces cerevisia platform for synthetizing carotenoids from xylose is constructed, and important support is provided for preparation of carotenoids by economically utilizing a biological fermentation method.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
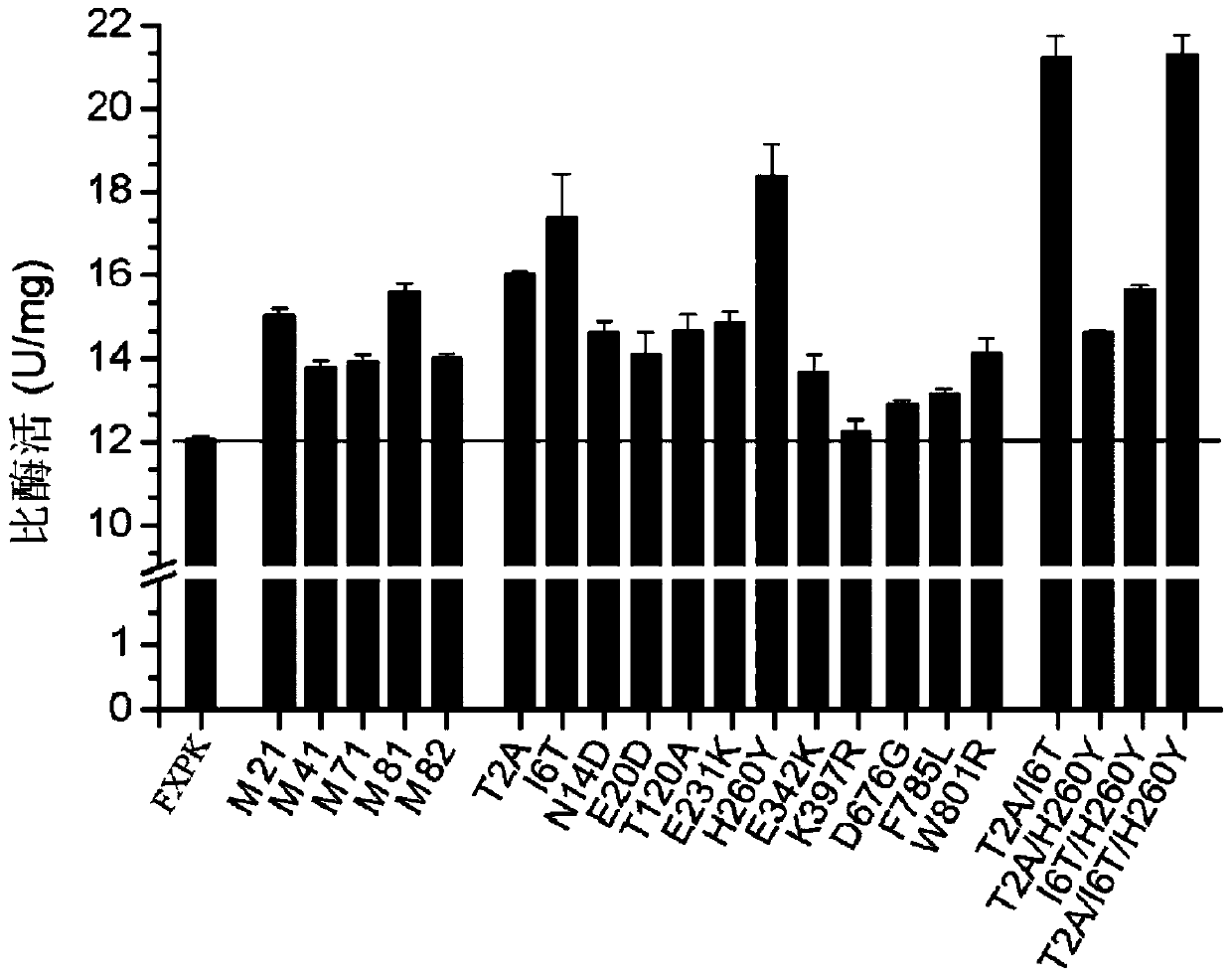
Phosphoketolase with increased activity and application thereof in production of metabolites
ActiveCN110218710AHigh activityIncrease productionAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTransferasesMutated proteinMetabolite
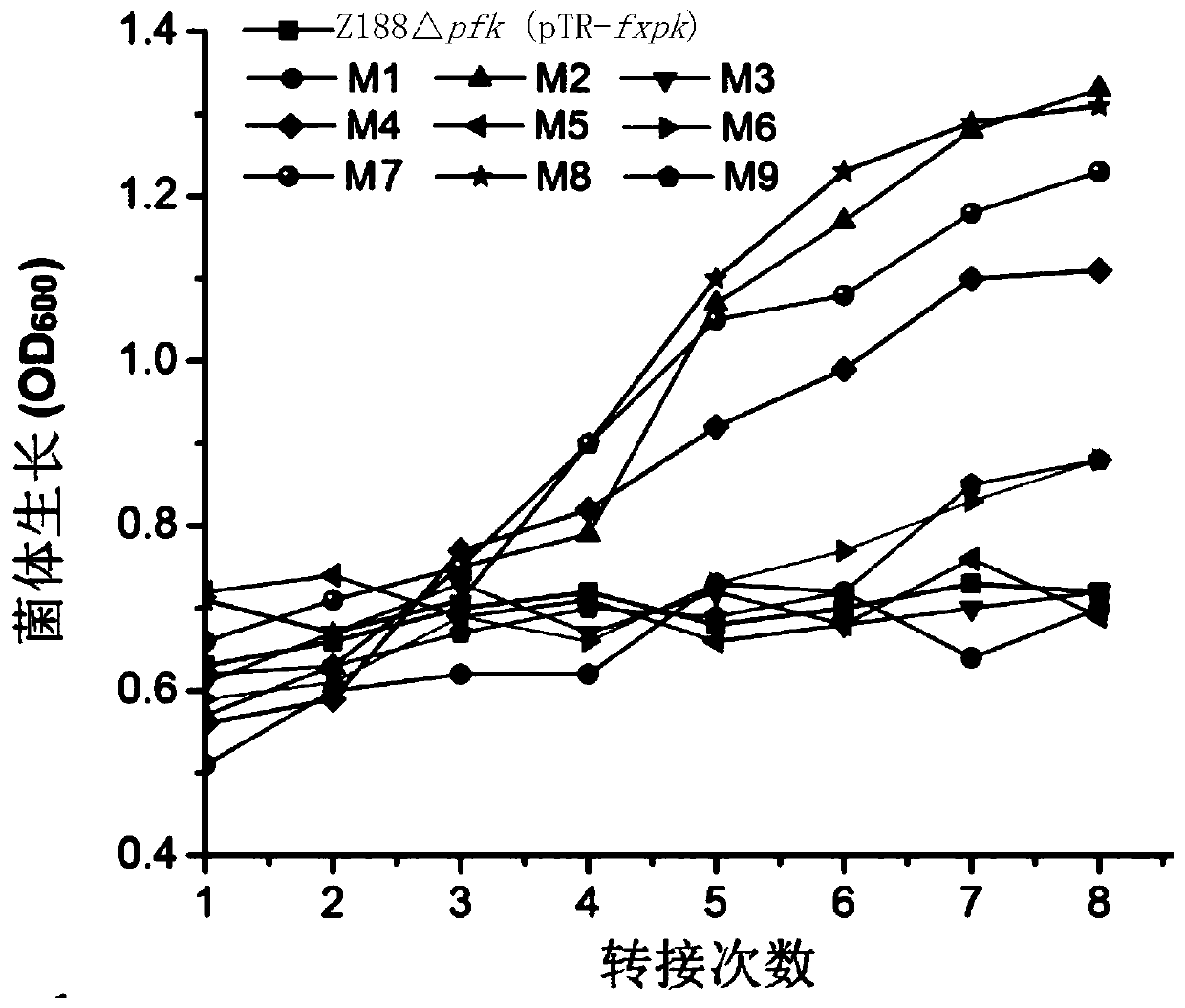
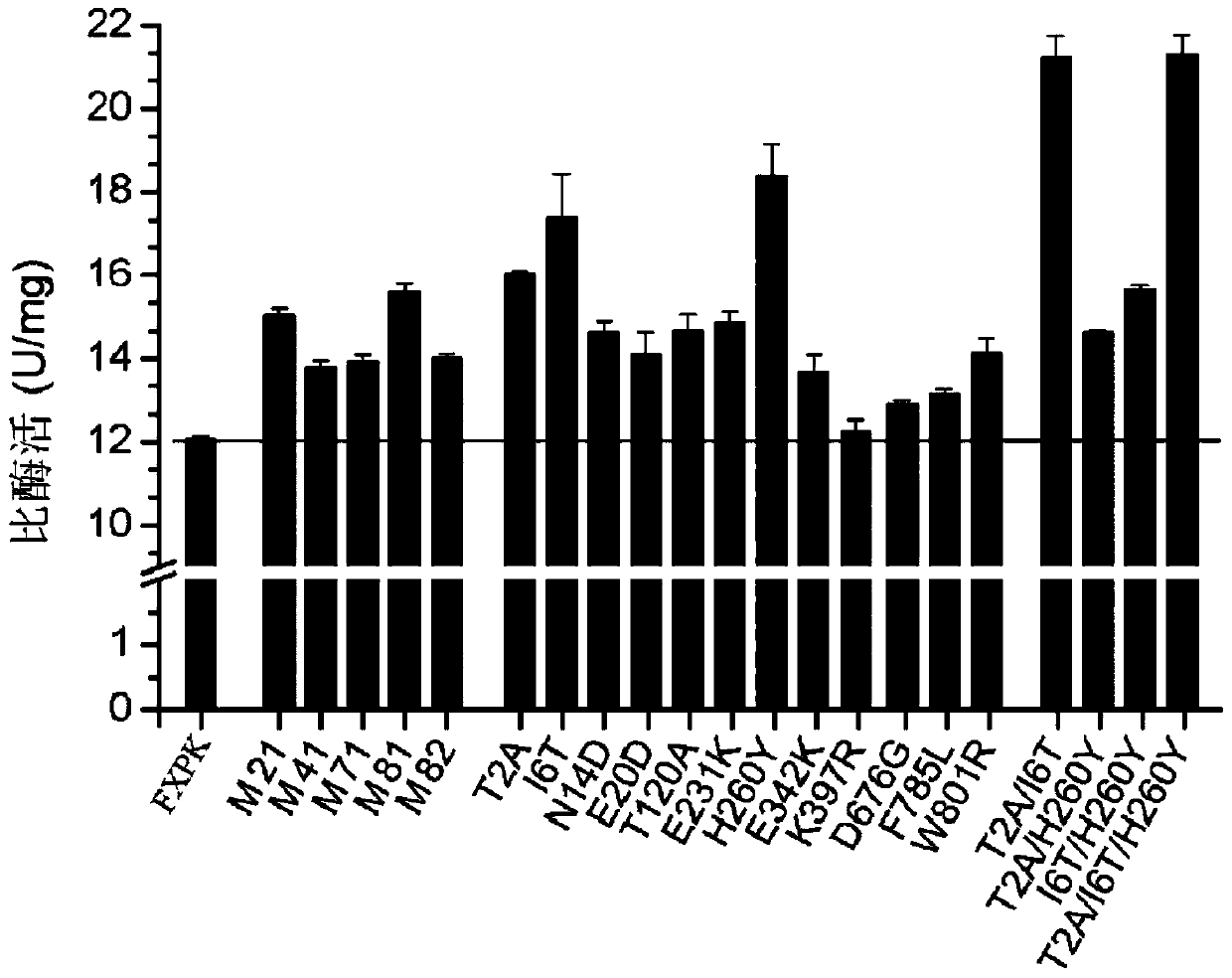
The invention discloses phosphoketolase with increased activity and an application thereof in production of metabolites. Protein provided by the invention is mutant protein, and is the protein obtained by subjecting the phosphoketolase to any one kind or various kinds of the following mutations: a 2nd position is mutated from T to A; a 6th position is mutated from I to T; a 14th position is mutated from N to D; (a 20th position is mutated from E to D; a 120th position is mutated from T to A; a 231st position is mutated from E to K; a 260th position is mutated from H to Y; a 342nd position is mutated from E to K; a 397th position is mutated from K to R; a 676th position is mutated from D to G; a 785th position is mutated from F to L; and a 801th position is mutated from W to R. The invention also protects the application of the mutant protein in preparation of the metabolites. Compared with existing phosphoketolase, enzyme activity of the phosphoketolase of the mutant protein provided by the invention is significantly increased, thereby significantly increasing the yield of target metabolites.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for constructing the recombinant yeasts for preparation of tyrosol and derivatives and its application
PendingUS20220213512A1Increase synthesisIncrease productionFungiGenetically modified cellsHydroxytyrosolTyrosol
A recombinant yeast is constructed by introducing an expressed gene of exogenous Fructose-6-phosphate phosphoketolase into a modified yeast cell, and the modified yeast cell is a yeast cell with a metabolic pathway for synthesizing tyrosol via Erythrose-4-phosphate and phosphoenolpyruvate. The present invention discloses for the first time that in the process of expressing Fructose-6-phosphate phosphoketolase in a yeast, Fructose-6-phosphate is synthesized into beta-D-Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate and also catalyzed into Erythrose-4-phosphate and Acetyl-phosphate, and Xylulose-5-phosphate is catalyzed into Glyceraldehydes-3-phosphate and Acetyl-phosphate, which change the metabolic flux distribution of carbon in the yeast, enhance the synthesis of Erythrose-4-phosphate as an important intermediate for the biosynthesis of tyrosol, optimize the metabolic pathway for synthesizing tyrosol, and increase the yields of tyrosol and its derivatives such as hydroxytyrosol.
Owner:SHANDONG HENGLU BIOTECH CO LTD
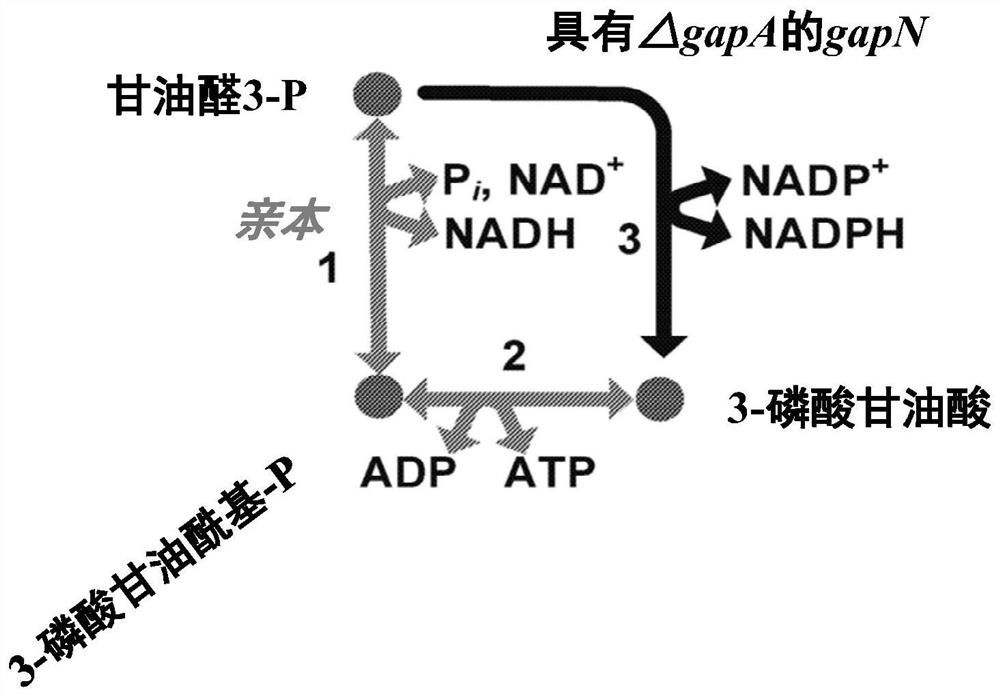
Engineered microorganisms with g3p---> 3pg enzyme and/or fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase including those having synthetic or enhanced methylotrophy
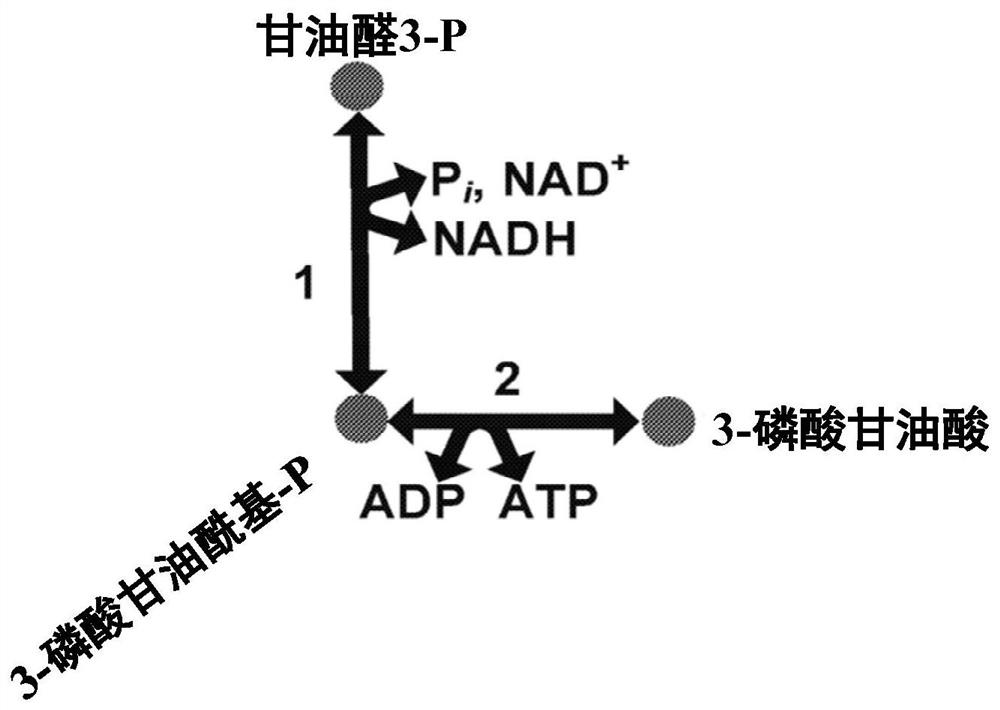
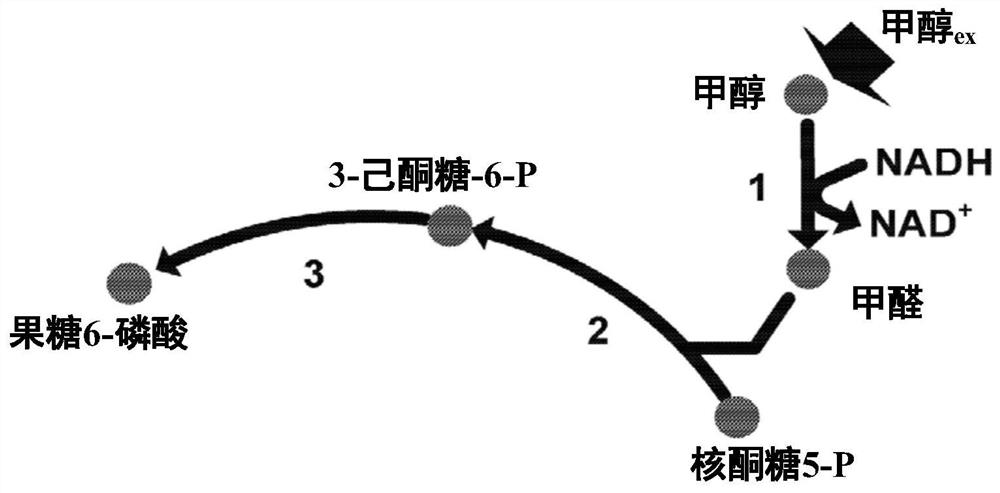
Described herein are engineered cells including ones having synthetic methylotrophy which include an NADH-dependent enzyme capable of converting G3P to 3PG (e.g.,6. methanolicus gapN) and / or fructose-1, 6-bisphosphatase, along with hexulose-6-phosphate synthase, 6-phospho-3-hexuloisomerase, a phosphoketolase, or a combination thereof. Engineered cells of the disclosure beneficially maintain adequate pool sizes of phosphorylated C3 and / or C4 compounds, and / or provide increased levels of NADPH. As such, the modifications allow for the generation of C6 compounds from Cl (e.g. a methanol feedstod) and C5 compounds, the regeneration of C5 compounds from C6 compounds by carbon rearrangement, and an improved balance between regeneration of C5 compounds and lower glycolysis.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
Homolactic Fermentation from Pentose
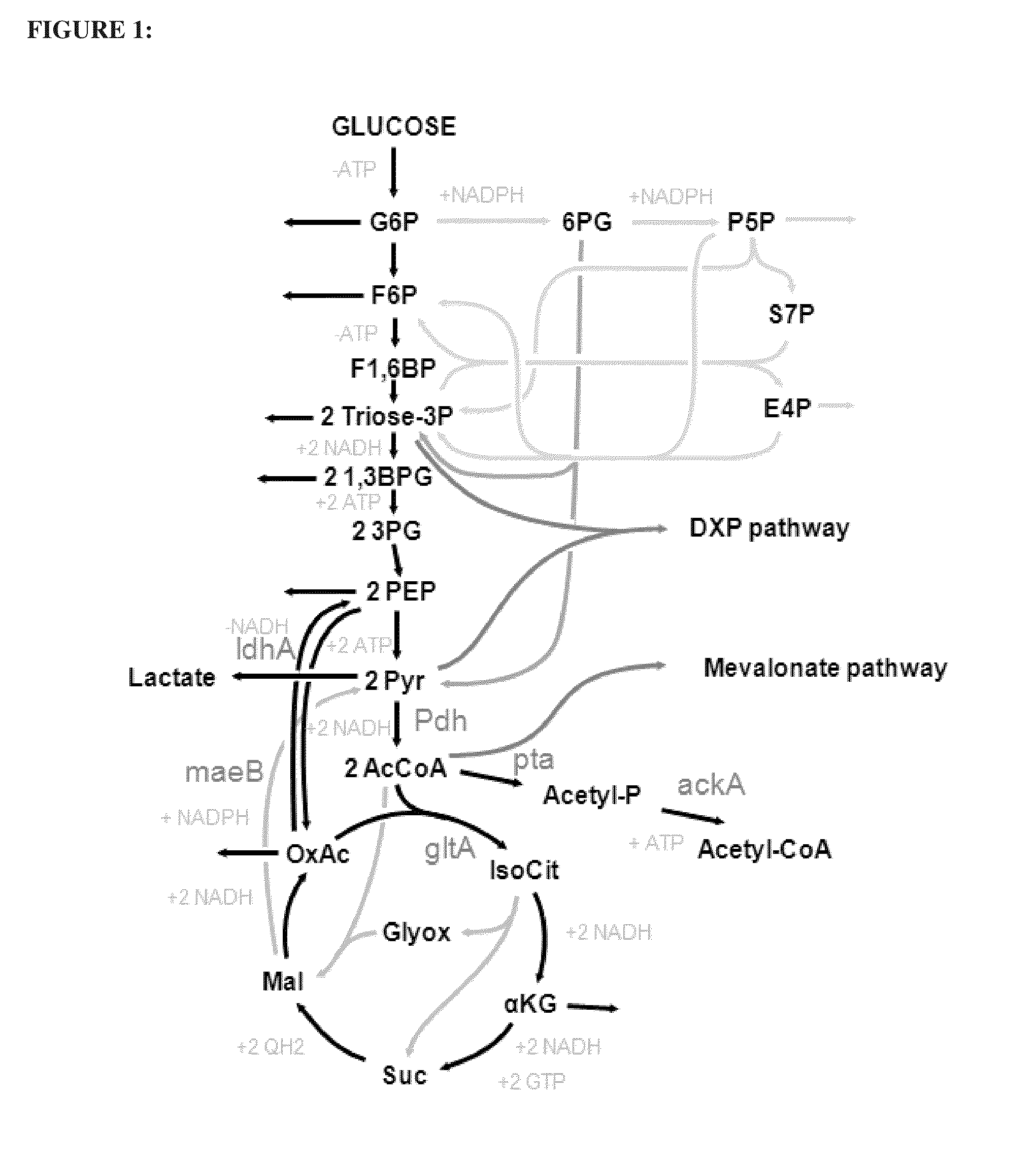
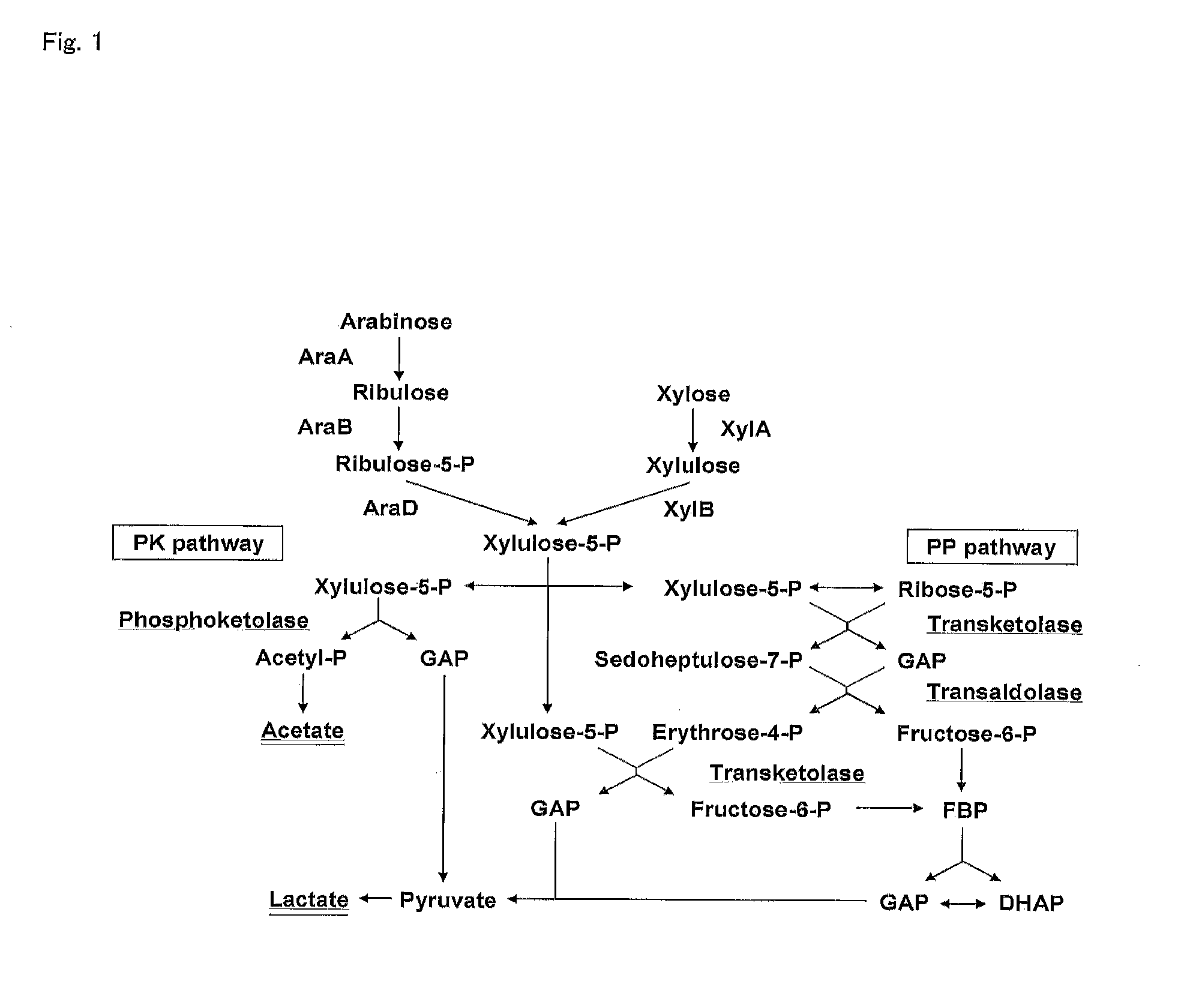
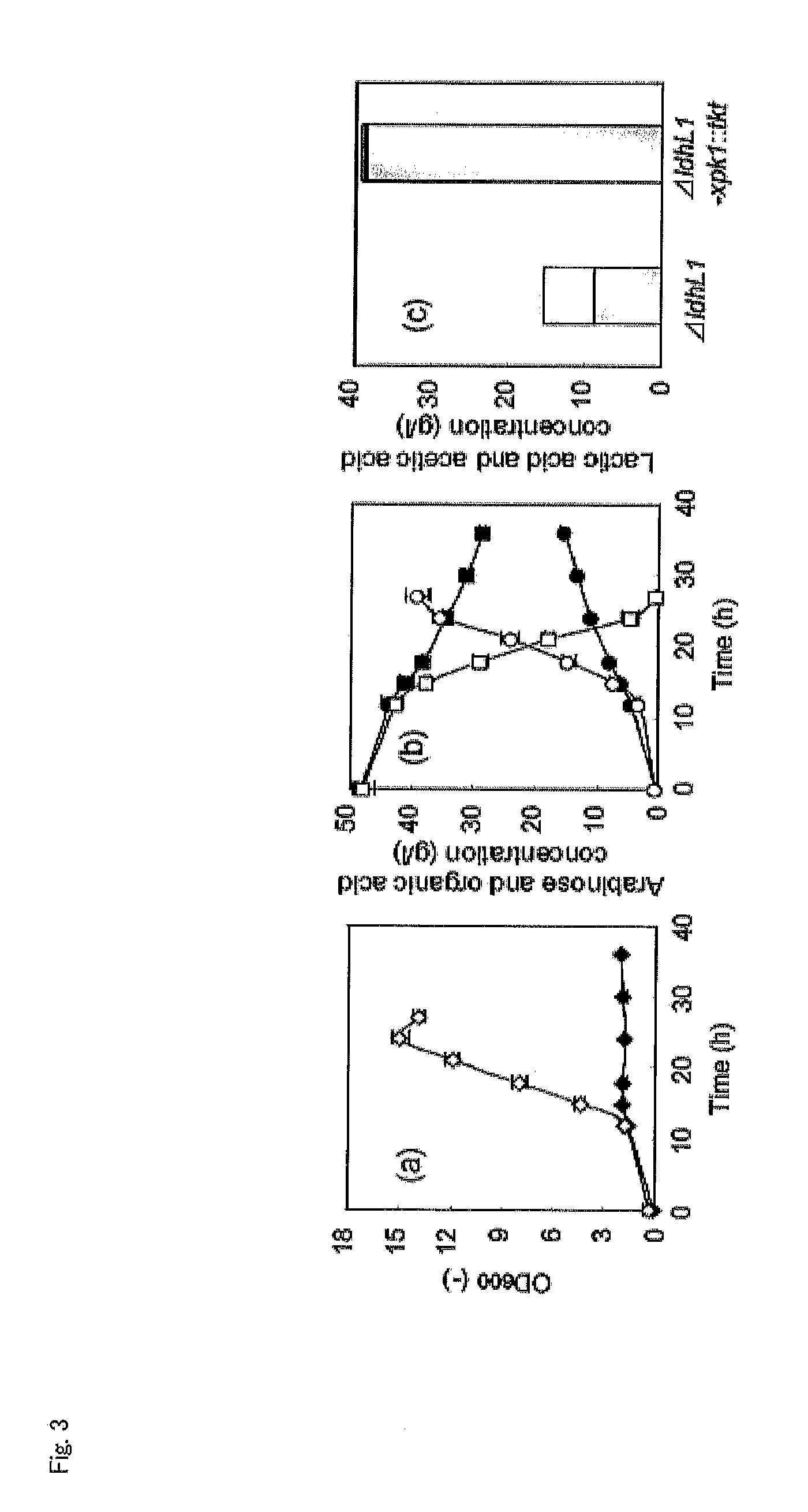
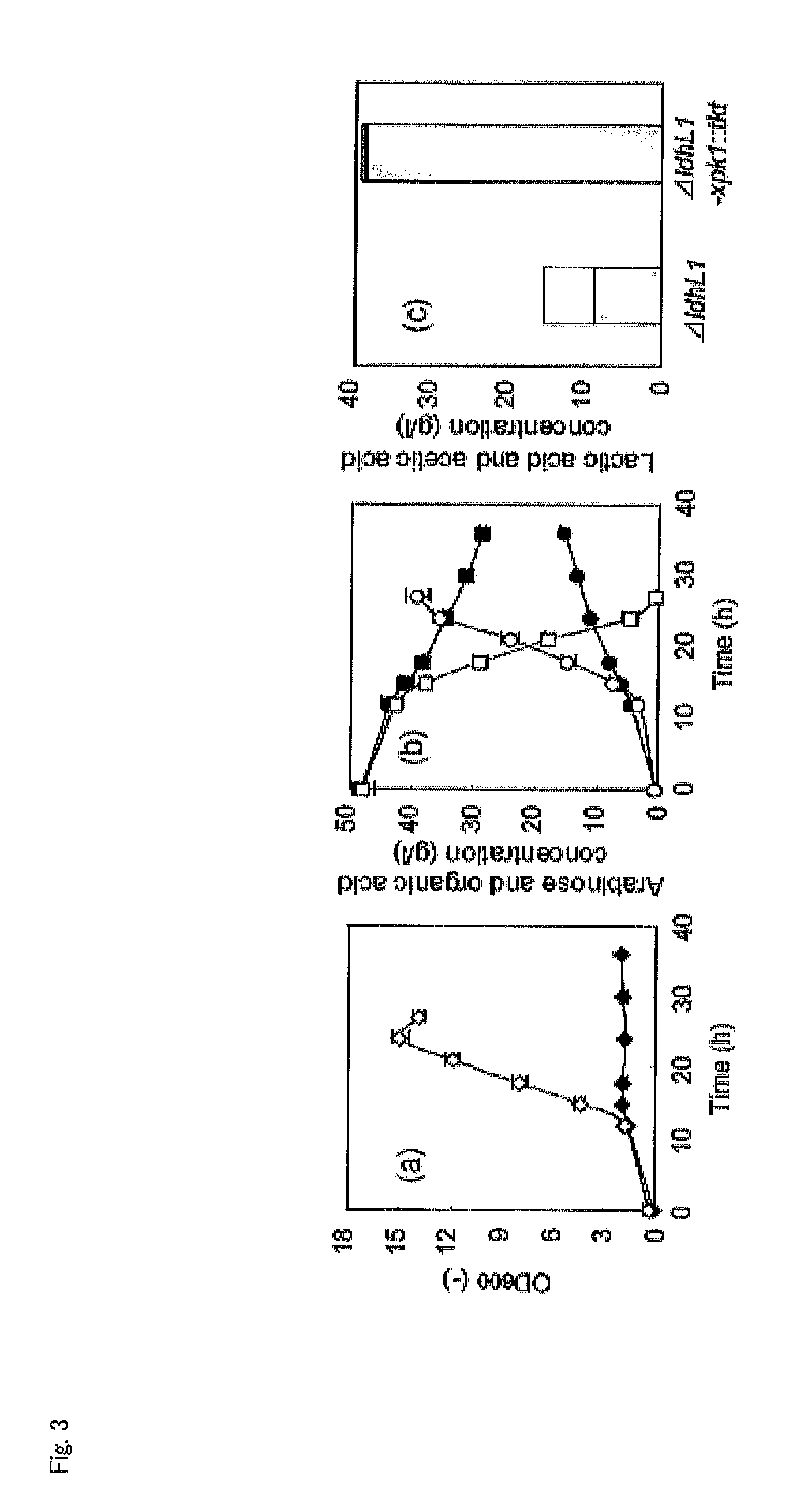
InactiveUS20120058528A1Efficient productionBacteriaUnicellular algaeLactobacillusPentose phosphate pathway
Provided is a lactic acid bacterium capable of homolactic fermentation using a pentose as a substrate, the lactic acid bacterium utilizing a pentose, and in which a phosphoketolase pathway is blocked and a pentose phosphate pathway is activated. Also provided is a method for producing lactic acid from a pentose using the lactic acid bacterium and a method for preparing the lactic acid bacterium.
Owner:KANSAI CHEM ENG CO LTD +1
Phosphoketolases for improved production of acetyl coenzyme a-derived metabolites, isoprene, isoprenoid precursors, and isoprenoids
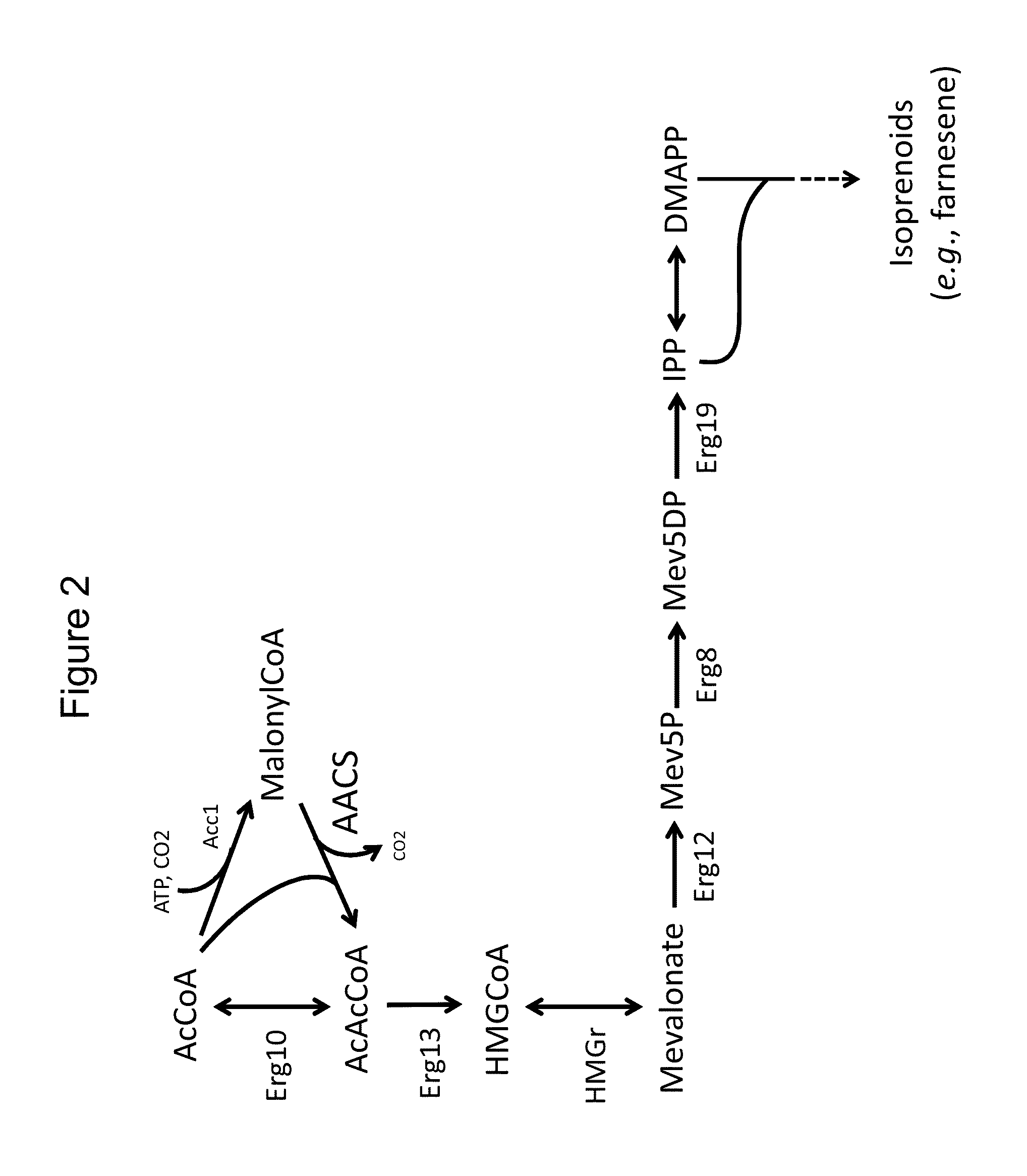
The invention provides phosphoketolases for improved production of acetyl coenzyme a-derived metabolites, isoprene, isoprenoid precursors, and isoprenoids. This present invention relates to cultured recombinant cells comprising a heterologous phosphoketolase (PKL) polypeptide that are capable of increased production of acetyl coenzyme A-derived metabolites, as well as methods for producing and using the same. In some embodiments, the recombinant cells further comprise one or more mevalonate (MVA) pathway polypeptides for the production of isoprenoid precursors, isoprene and isoprenoids.
Owner:DANISCO US INC +1
Phosphoketolases for improved production of acetyl coenzyme A-derived metabolites, isoprene, isoprenoid precursors, and isoprenoids
ActiveUS10246694B2Increase productionMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationMetaboliteIsoprene
This present invention relates to cultured recombinant cells comprising a heterologous phosphoketolase (PKL) polypeptide that are capable of increased production of acetyl coenzyme A-derived metabolites, as well as methods for producing and using the same. In some embodiments, the recombinant cells further comprise one or more mevalonate (MVA) pathway polypeptides for the production of isoprenoid precursors, isoprene and isoprenoids.
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
Phosphotransketolase with increased activity and its application in the production of metabolites
ActiveCN110218710BHigh activityIncrease productionAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTransferasesMutated proteinMetabolite
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Compositions and methods for increasing ethanol production by yeast using gcy1 and dak1
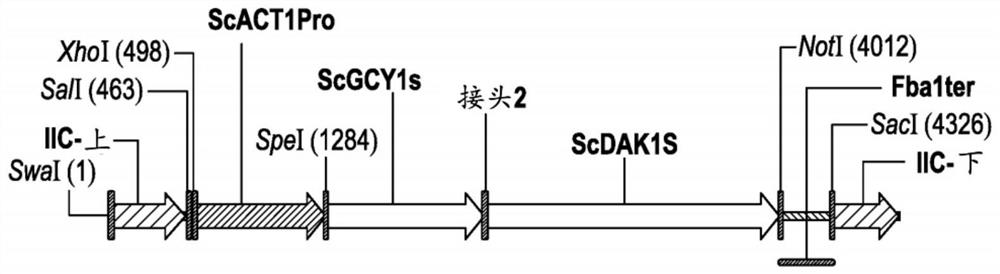
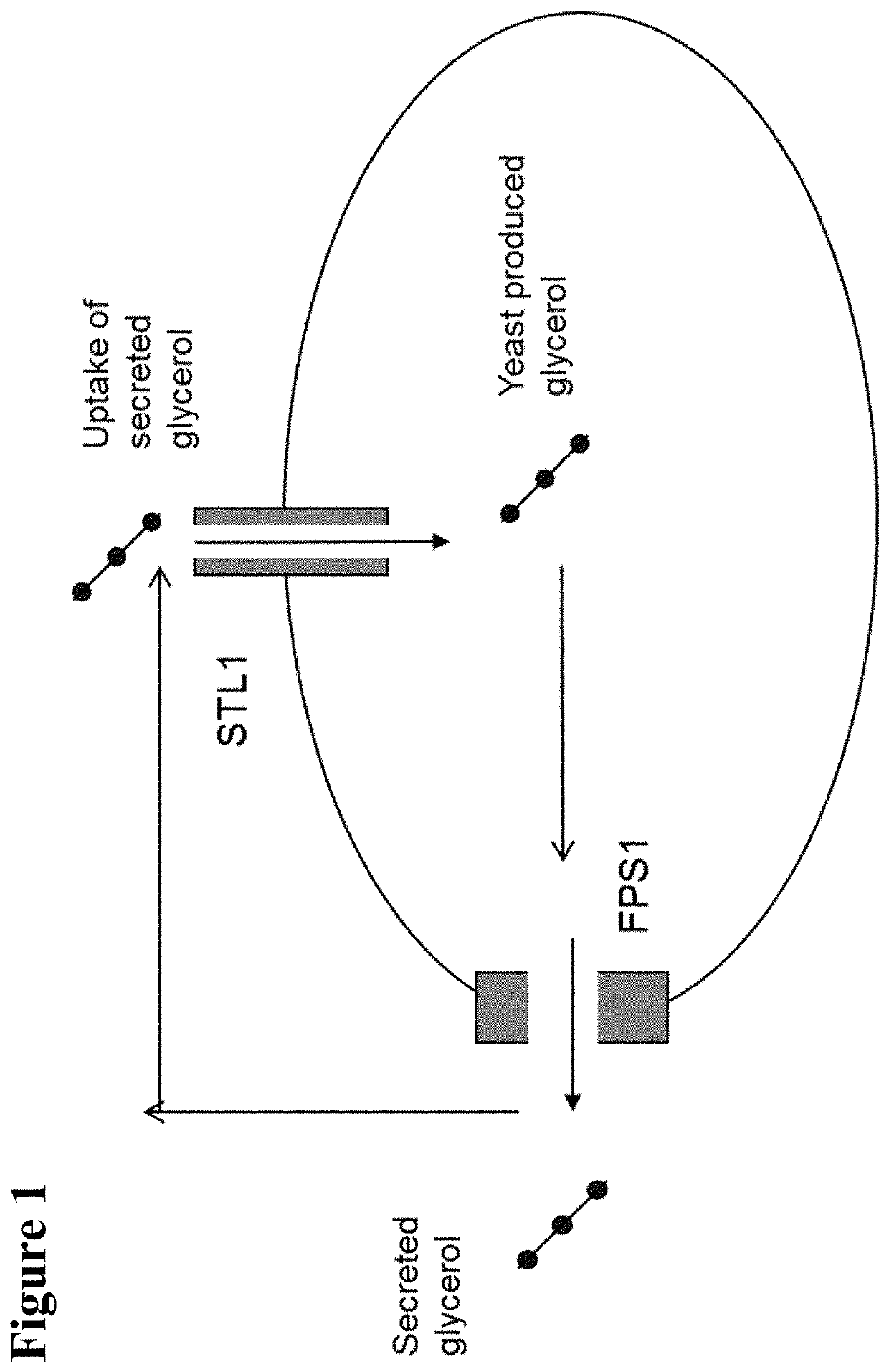
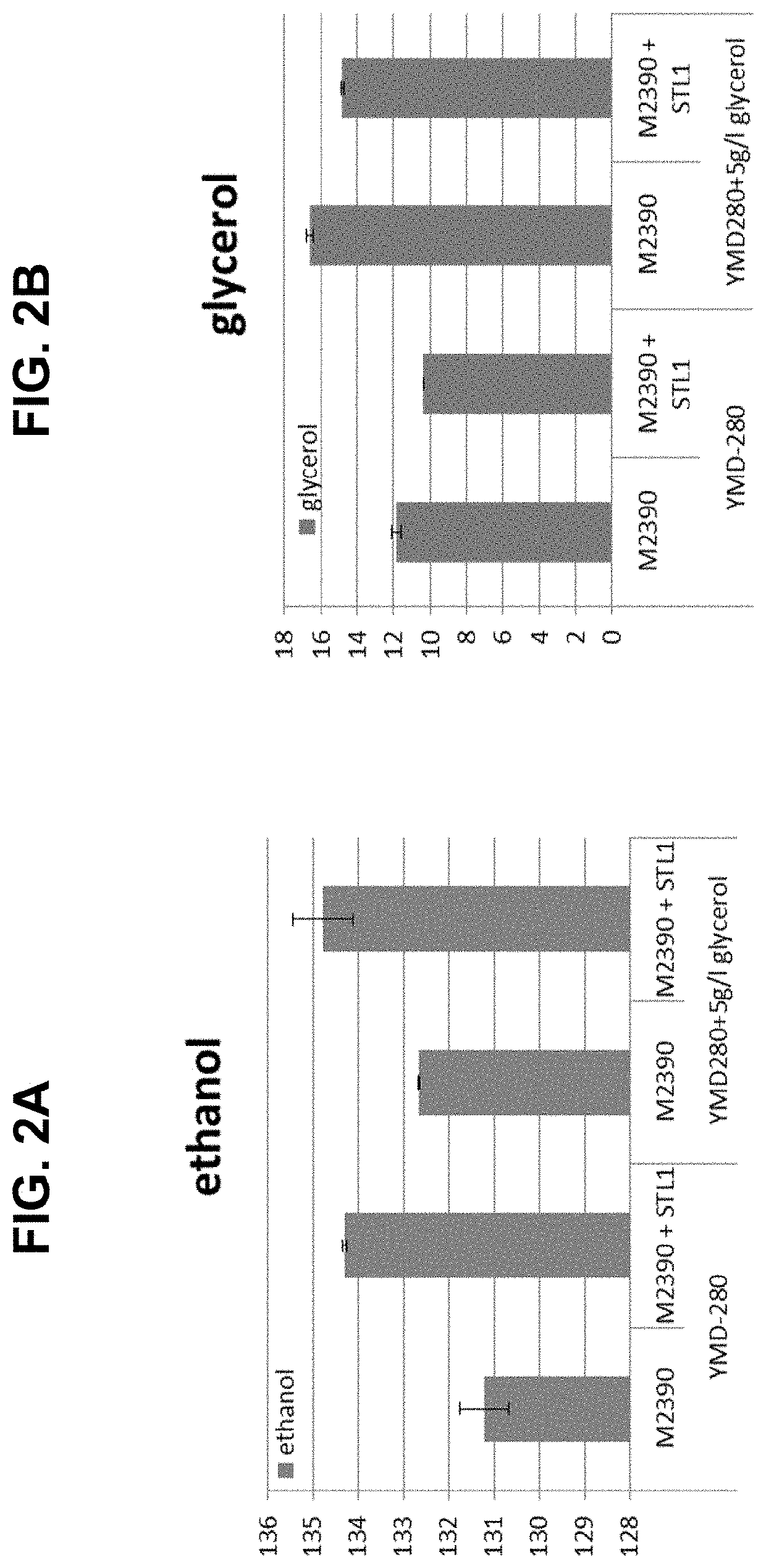
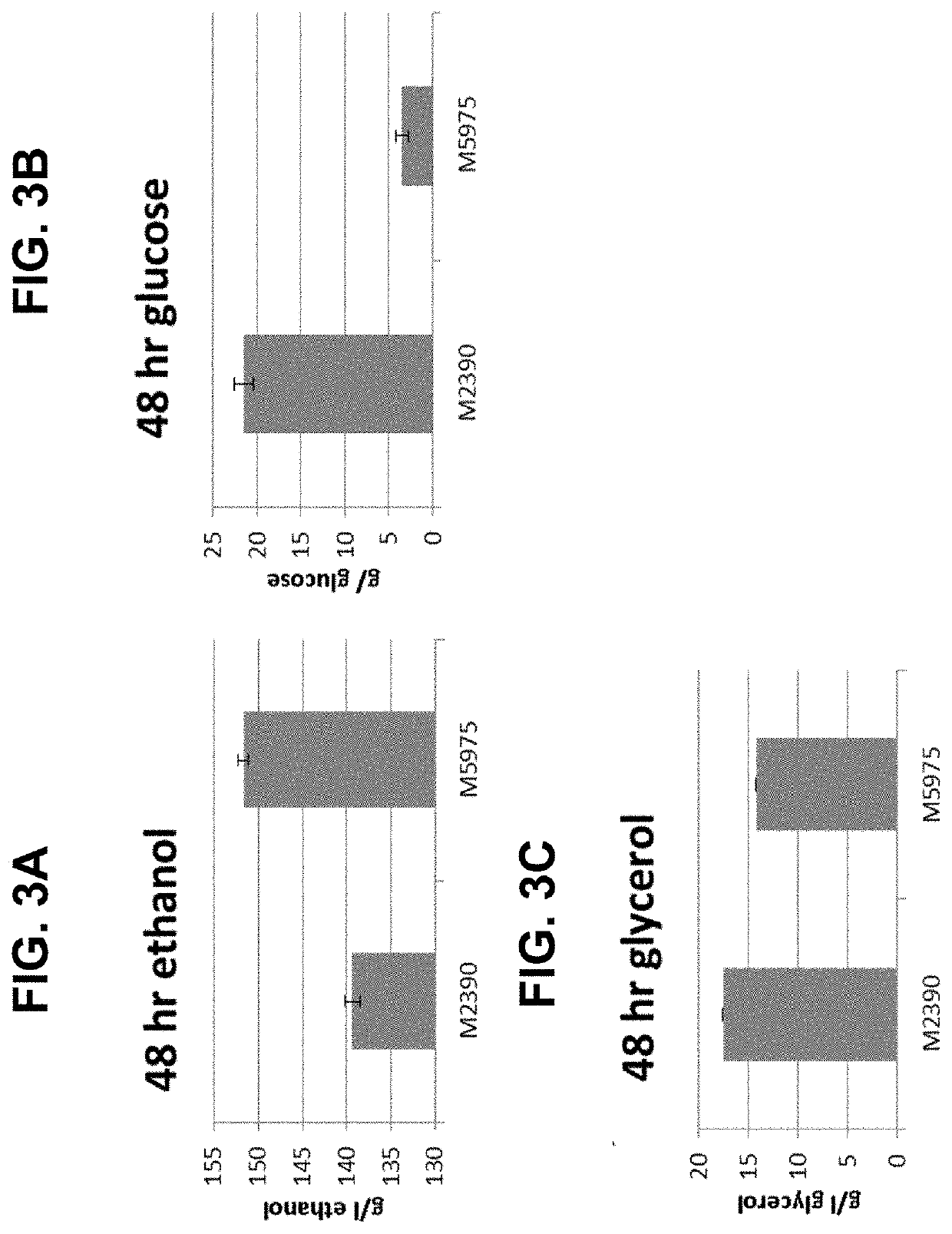
Described are compositions and methods relating to yeast expressing glycerol dehydrogenase and dihydroxyacetone kinase polypeptides in combination with an exogenous phosphoketolase pathway, as well asto bifunctional glycerol dehydrogenase-dihydroxyacetone kinase fusion polypeptides, and their various and combined uses in starch hydrolysis processes for alcohol production.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Methods for producing isopropanol and acetone in a microorganism
PendingUS20220090045A1Reduction and modulation of glycerol productionImprove robustnessMicroorganism based processesDepsipeptidesHeterologousAcetoacetate decarboxylase
The present disclosure provides for novel metabolic pathways to increase acetone and isopropanol formation. More specifically, the present disclosure provides for a recombinant microorganism comprising a plurality of first native and / or heterologous enzymes that function in a first engineered metabolic pathway to convert fructose-6-phosphate to acetyl-CoA and acetate (e.g., phosphoketolase and acetate kinase), wherein the plurality of first native and / or heterologous enzymes is activated, upregulated, or overexpressed. The recombinant microorganism further comprises a plurality of second native and / or heterologous enzymes that function in a second engineered metabolic pathways to convert acetyl-CoA and acetate to isopropanol (e.g., thiolase, CoA transferase and acetoacetate decarboxylase), wherein the plurality of second native and / or heterologous enzymes is activated, upregulated, or overexpressed. Also provided are methods for making isopropanol or acetone using the recombinant microorganisms.
Owner:LALLEMAND HUNGARY LIQUIDITY MANAGEMENT LLC
Homolactic fermentation from pentose
Provided is a lactic acid bacterium capable of homolactic fermentation using a pentose as a substrate, the lactic acid bacterium utilizing a pentose, and in which a phosphoketolase pathway is blocked and a pentose phosphate pathway is activated. Also provided is a method for producing lactic acid from a pentose using the lactic acid bacterium and a method for preparing the lactic acid bacterium.
Owner:KANSAI CHEM ENG CO LTD +1
A kind of method and application of improving cell phloroglucinol synthesis output
ActiveCN104357495BReduce generationEmission reductionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEnzyme GeneCoenzyme A biosynthesis
The invention discloses a method for increasing the cell phloroglucinol synthesis yield and application, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. According to the method provided by the invention, a recombined cell co-expresses a phosphoketolase fxpk gene, a fructose 1,6-biphosphatase fbp gene and a poly-ketene anhydride synthetase phld gene and also expresses any one or two of a multiple-resistance-factor MarA gene and an acetyl-coenzyme a carboxylase ACCase gene. According to the method provided by the invention, a new phloroglucinol synthesis way is built in the recombined cell, so that the yield of phloroglucinol is greatly increased; as for a contrast group, the phloroglucinol yield is increased by 68.9 percent; meanwhile, by the method, emission of carbon dioxide in a phloroglucinol synthesis process is also reduced; the method has high environmental benefits.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Bifunctional phosphoketolase-phosphotransacetylase fusion polypeptides
Described are compositions and methods relating to bifunctional phosphoketolase-phosphotransacetylase fusion polypeptides and the use thereof in starch hydrolysis processes for alcohol production.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
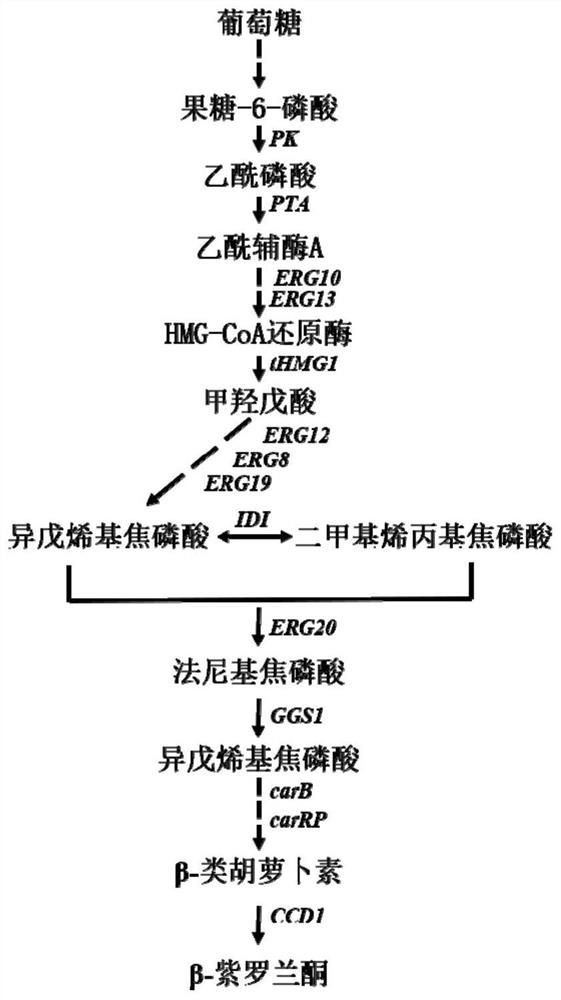
A kind of high-yield β-ionone genetically engineered bacteria and its construction method and application
ActiveCN110628806BIncrease productionEnhance metabolic pathway metabolic strengthFungiHydrolasesEngineeringEngineered genetic
The invention discloses a high-yielding β-ionone genetically engineered bacterium and its construction method and application, belonging to the field of microbial fermentation. The method is to successfully construct high-yield β-ionone genetically engineered bacteria by strengthening the MVA pathway and introducing the phosphoketolase pathway to increase the supply of acetyl-CoA in the cytoplasm and the metabolic flow of the terpenoid synthesis pathway. The genetically engineered bacteria obtained according to the method of the present invention can produce β-ionone under conventional fermentation conditions, the shake flask fermentation output can reach about 358mg / L, and the 3L fermenter output can reach about 0.98g / L, which is close to industrialization Level. The invention can use simple culture medium to ferment and produce spice β-ionone, can realize one-time high-efficiency transformation and integration of multiple genes, can significantly shorten the construction time of engineering bacteria, and the obtained engineering bacteria can use simple carbon sources such as glucose and glycerin to produce spice β-ionone Fermentative production of ionone has good industrial application prospects.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Metabolic Pathways with Increased Carbon Yield
ActiveUS20210189372A1Improve efficiencyEnhance carbon fluxHydrolasesTransferasesBiotechnologyPhosphoric Acid Esters
The present invention relates to the conversion of a carbon source into acetyl phosphate with increased carbon yield. In particular, the invention provides metabolically engineered micro-organisms capable of producing acetyl phosphate from a carbon source with increased carbon yield, which micro-organisms have been transformed with at least one exogenous nucleic acid encoding a phosphoketolase having sedoheptulose-7-phosphate phosphoketolase activity and which are further genetically modified to have eliminated transketolase activity. The invention also provides methods for the production of chemicals using said micro-organisms.
Owner:TOTALENERGIES ONETECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com