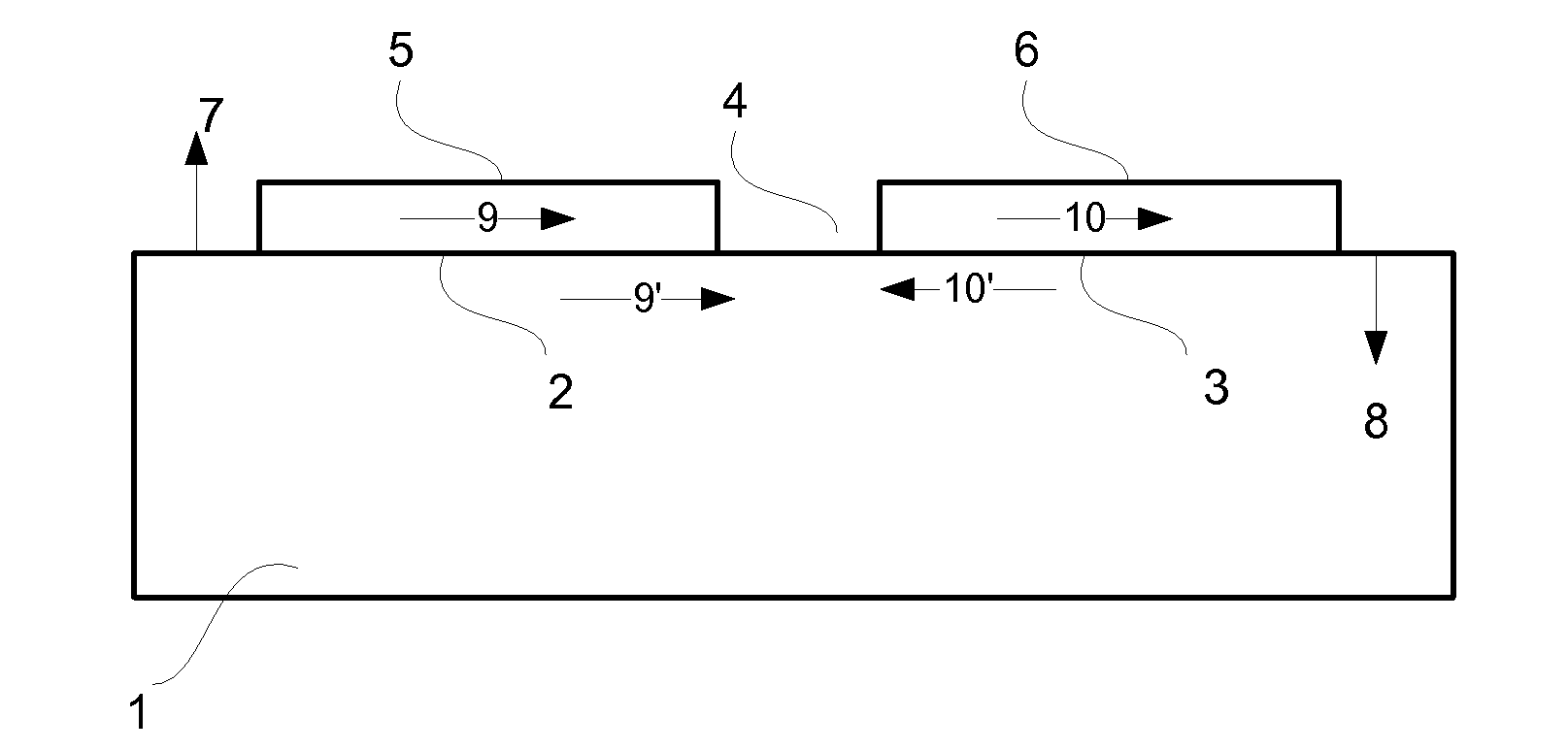
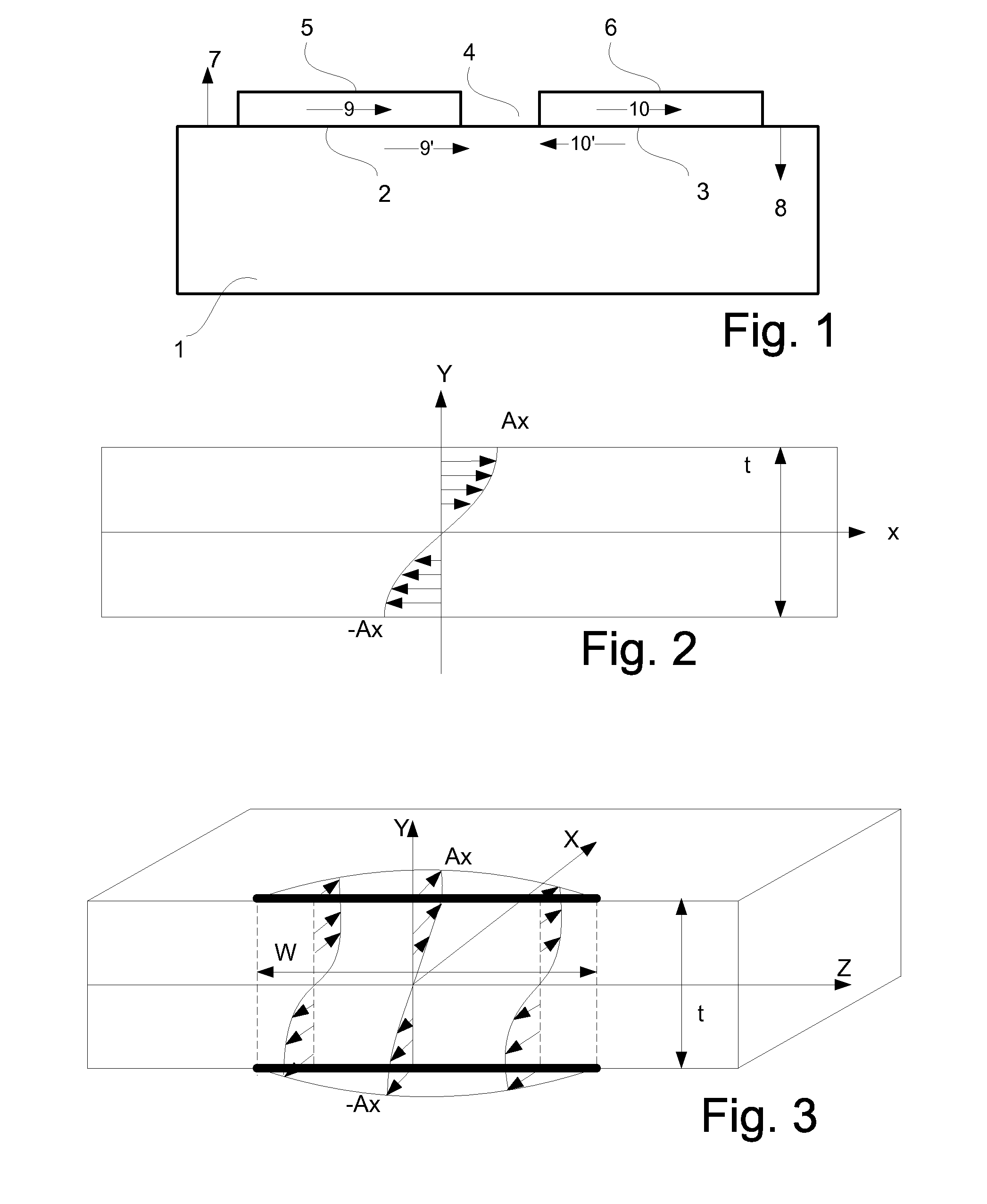
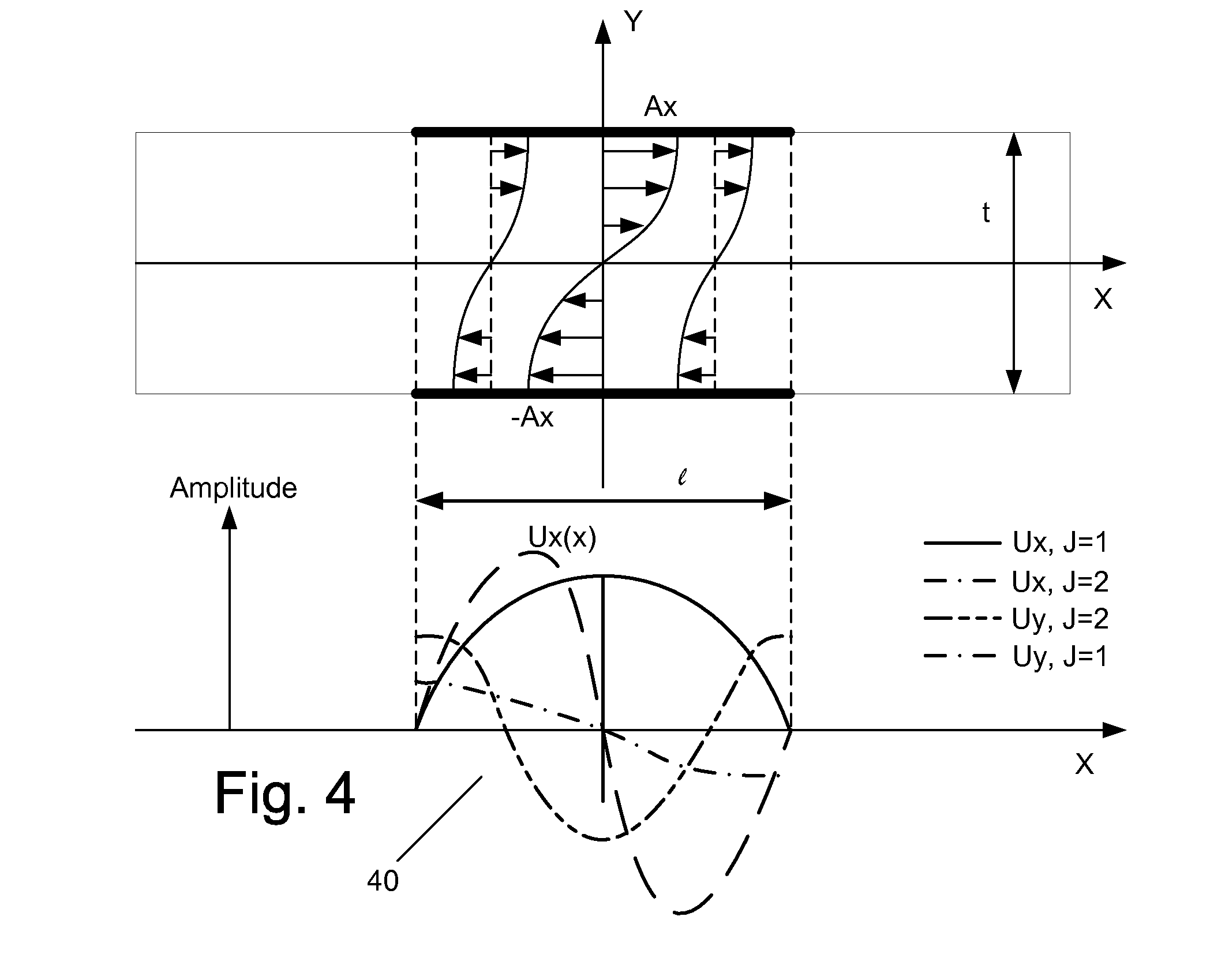
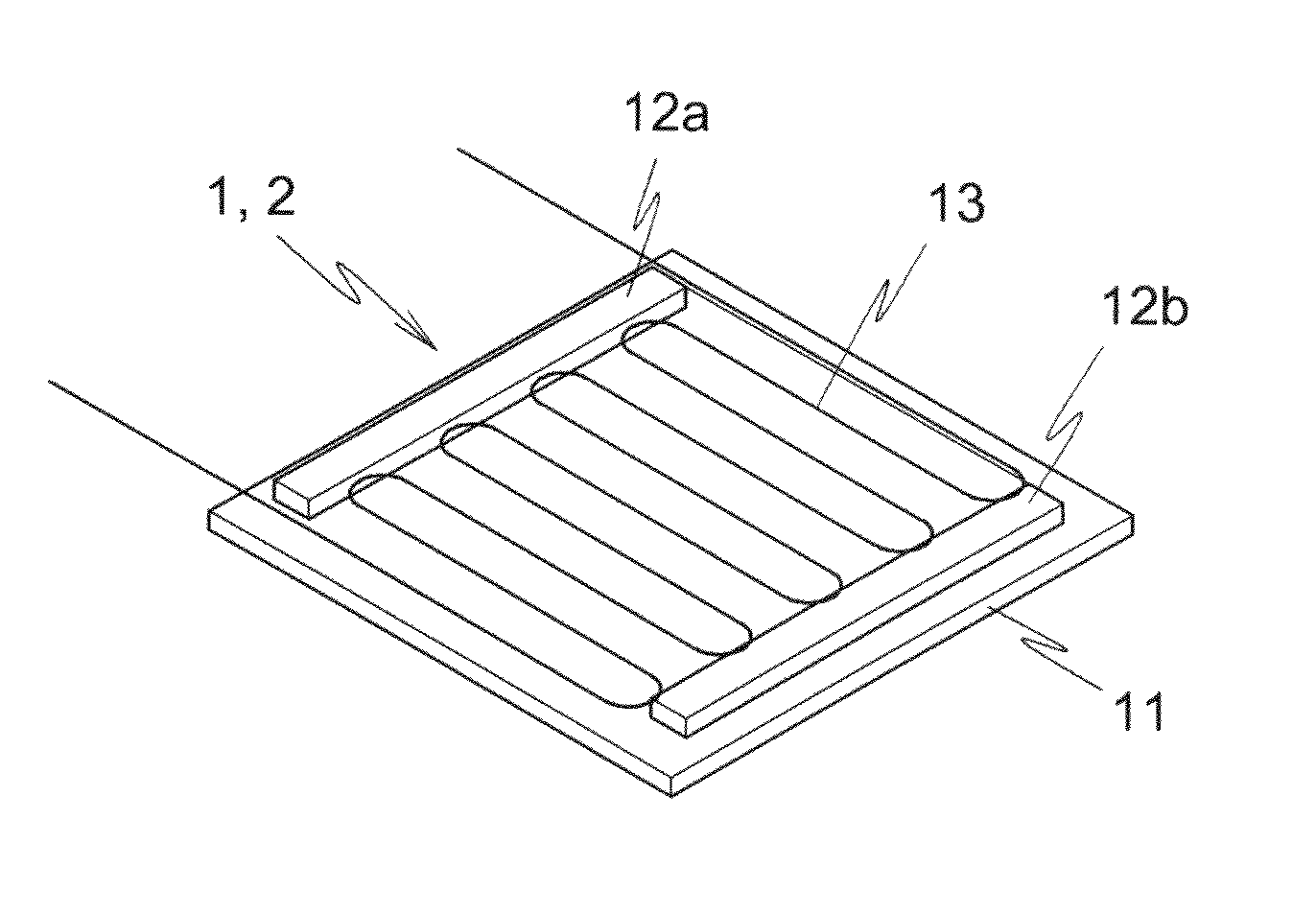
Patents
Literature
77 results about "Shear horizontal" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
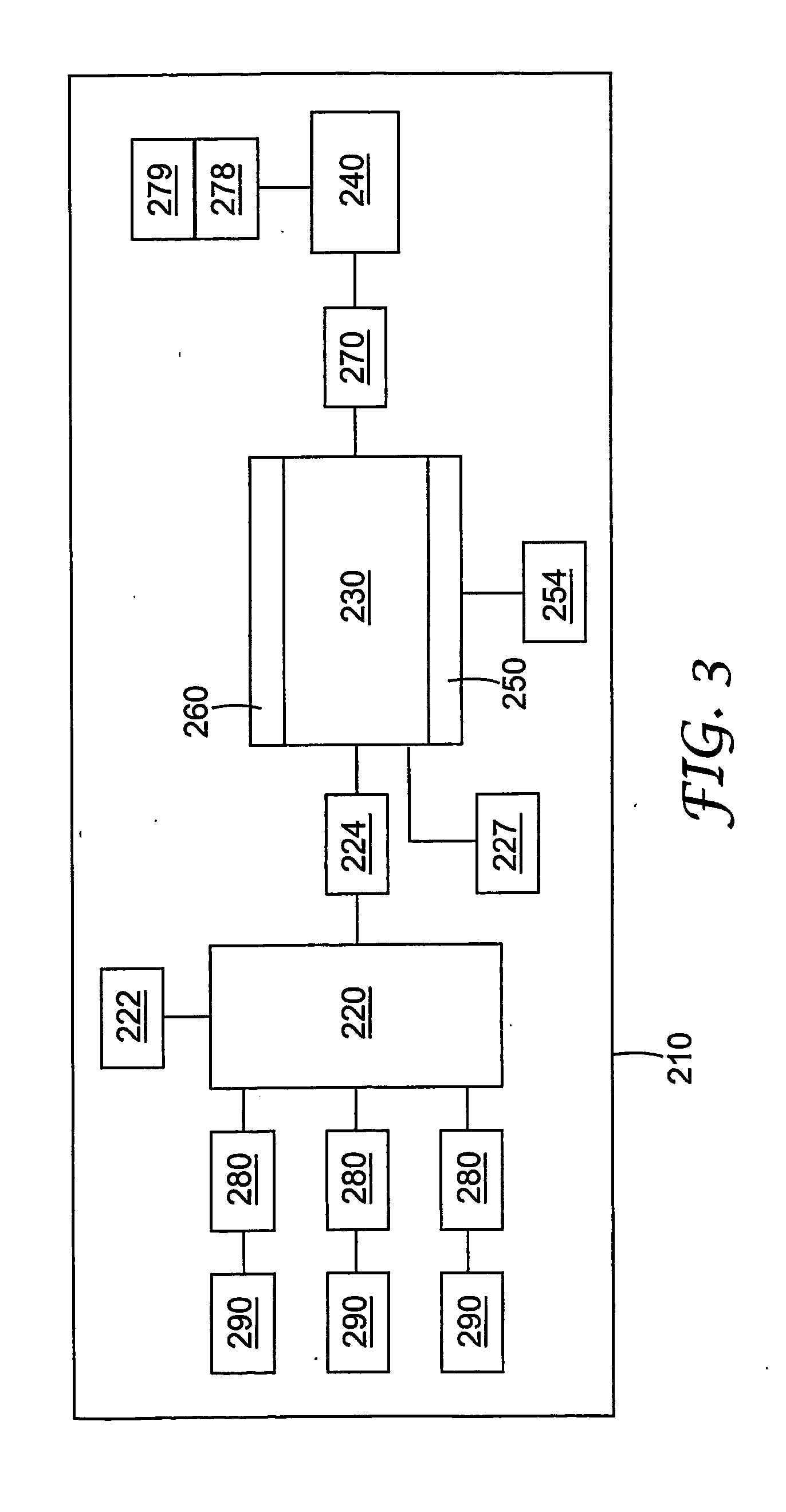
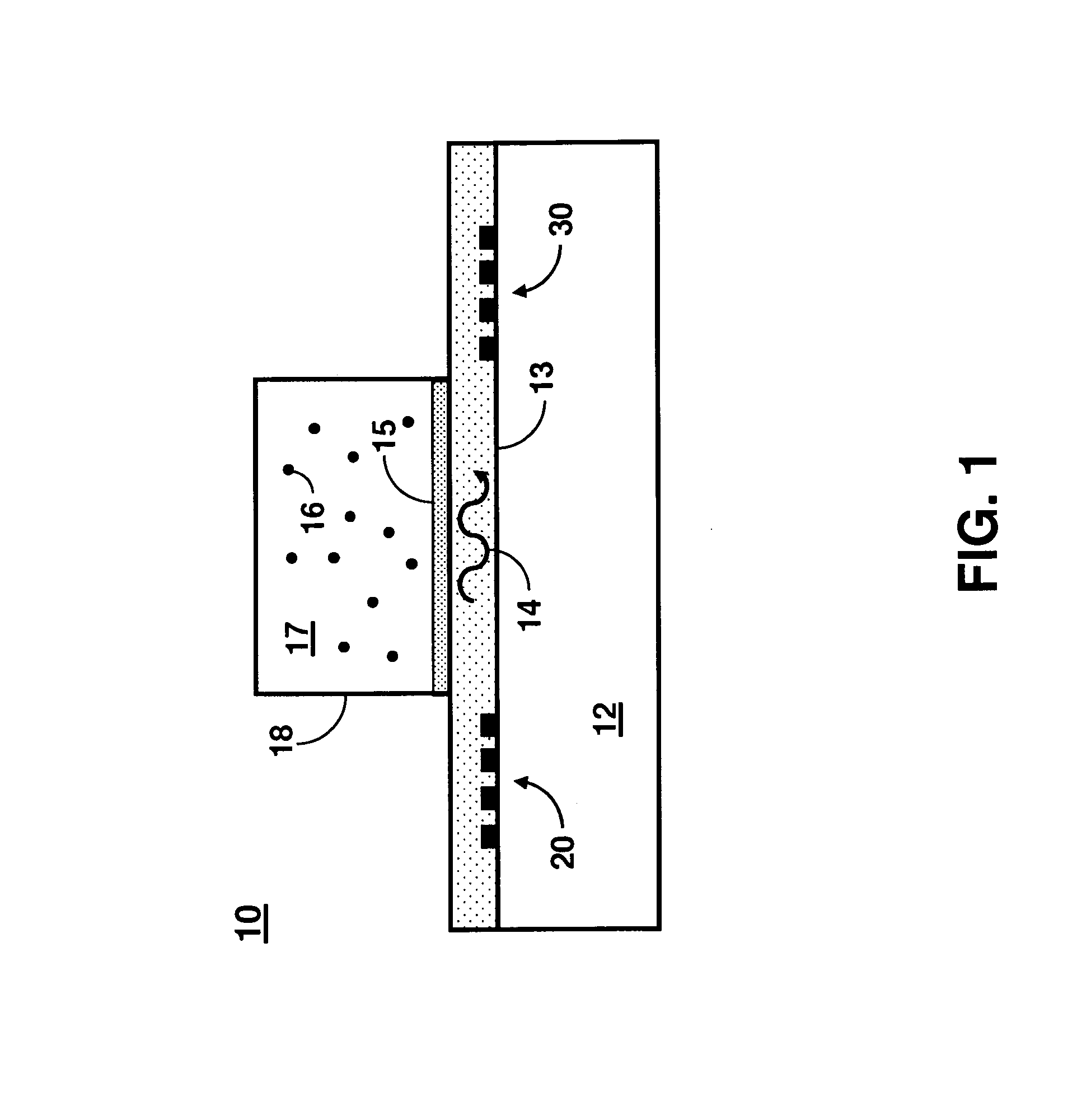
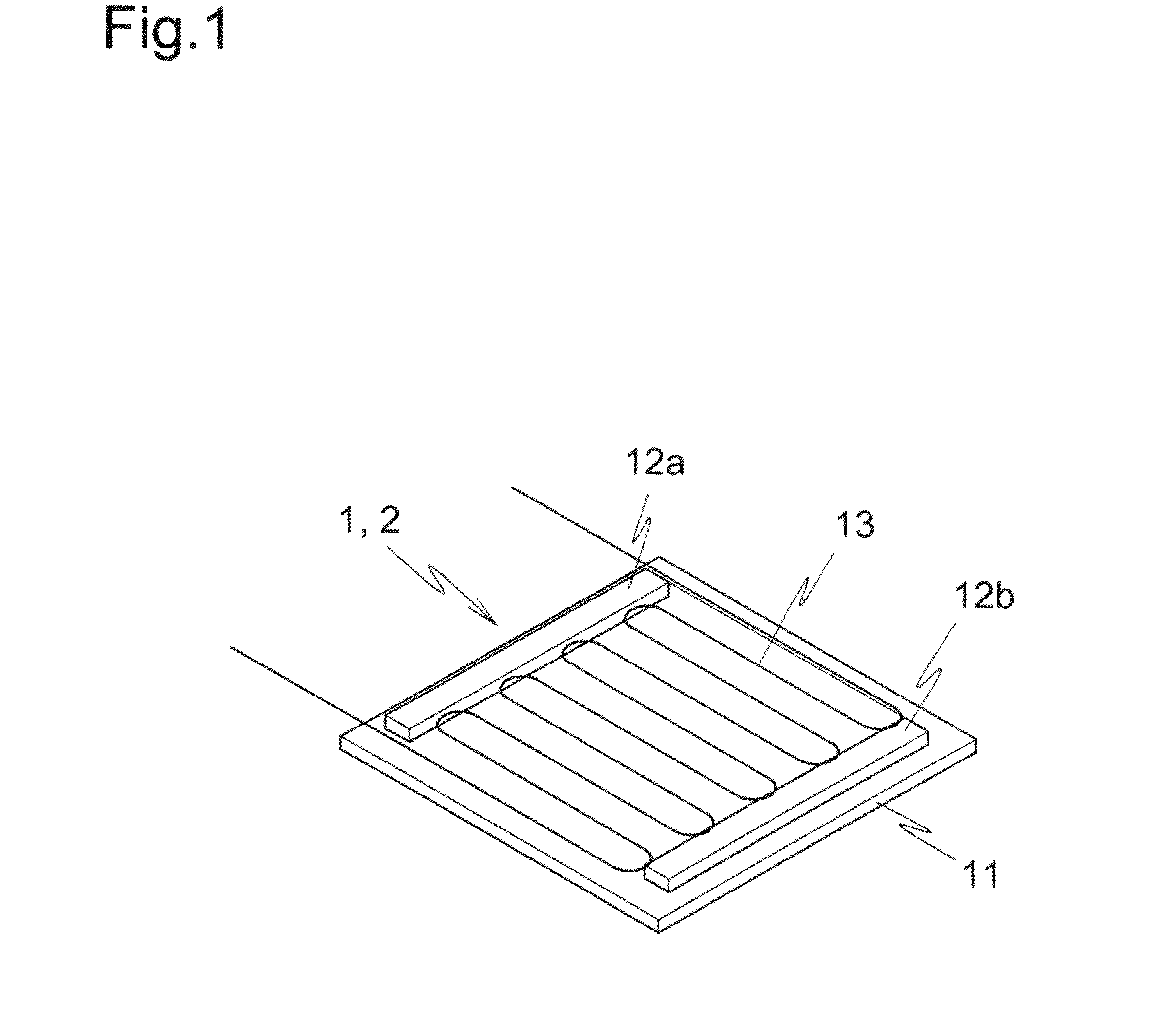
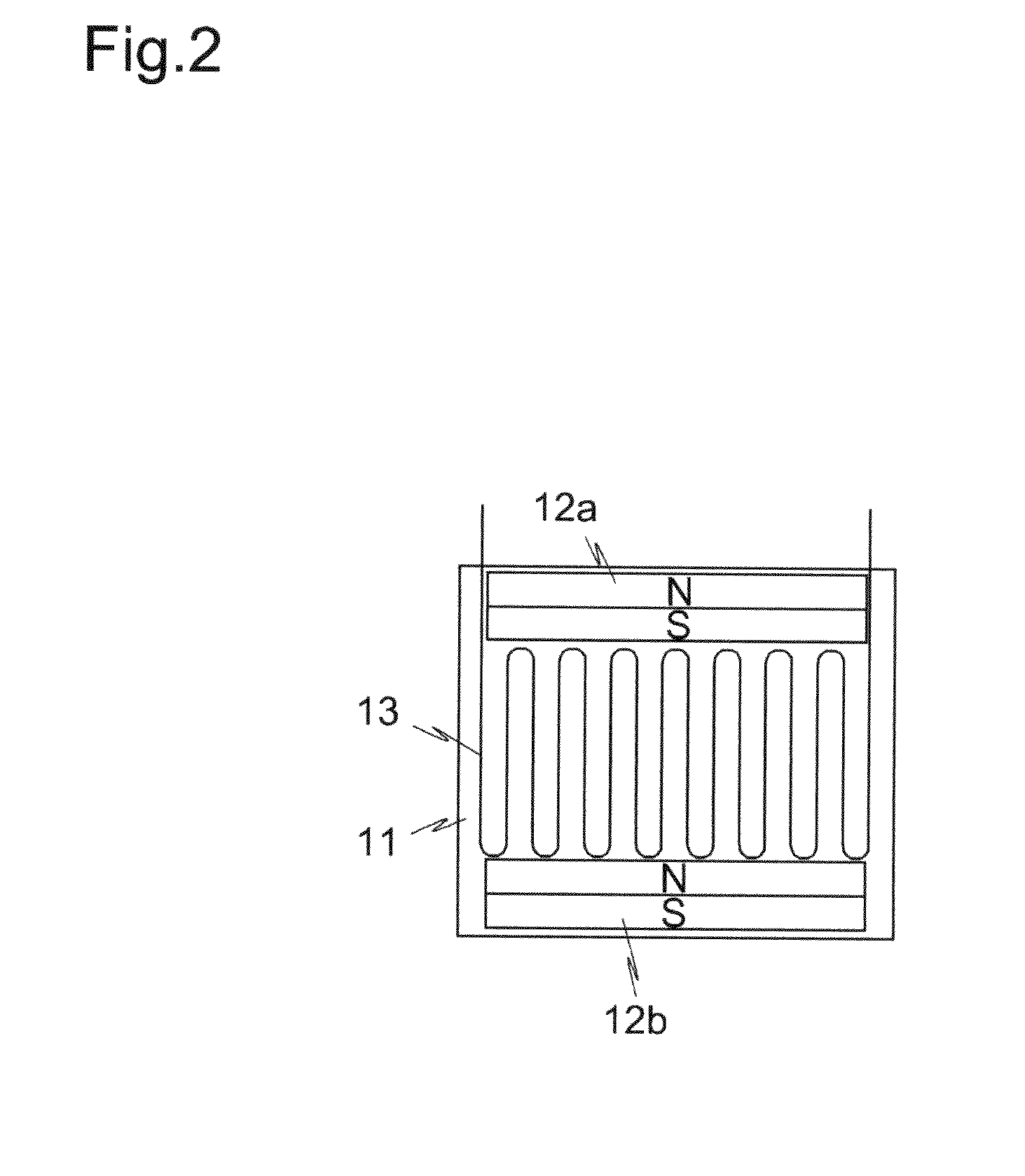
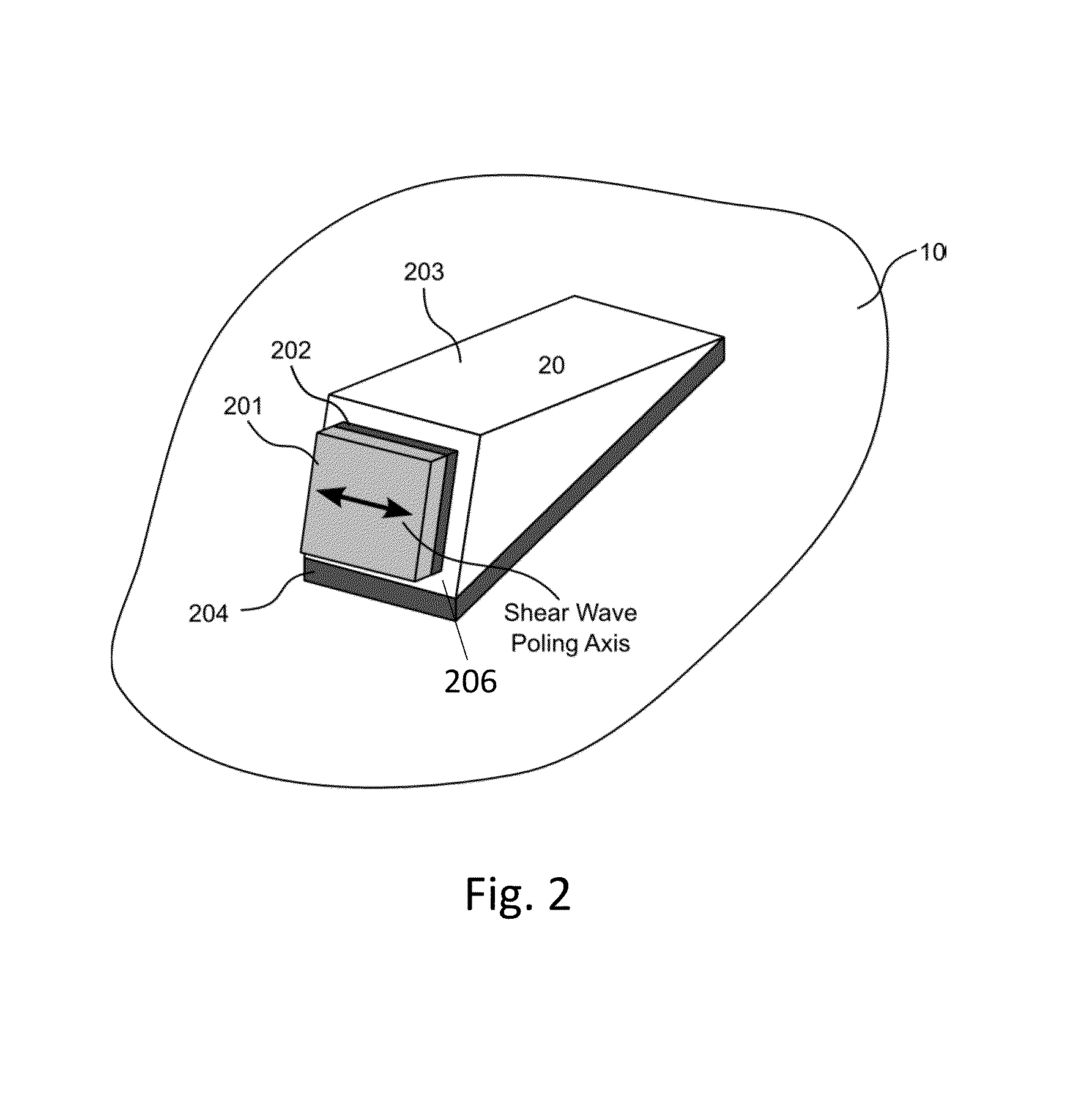
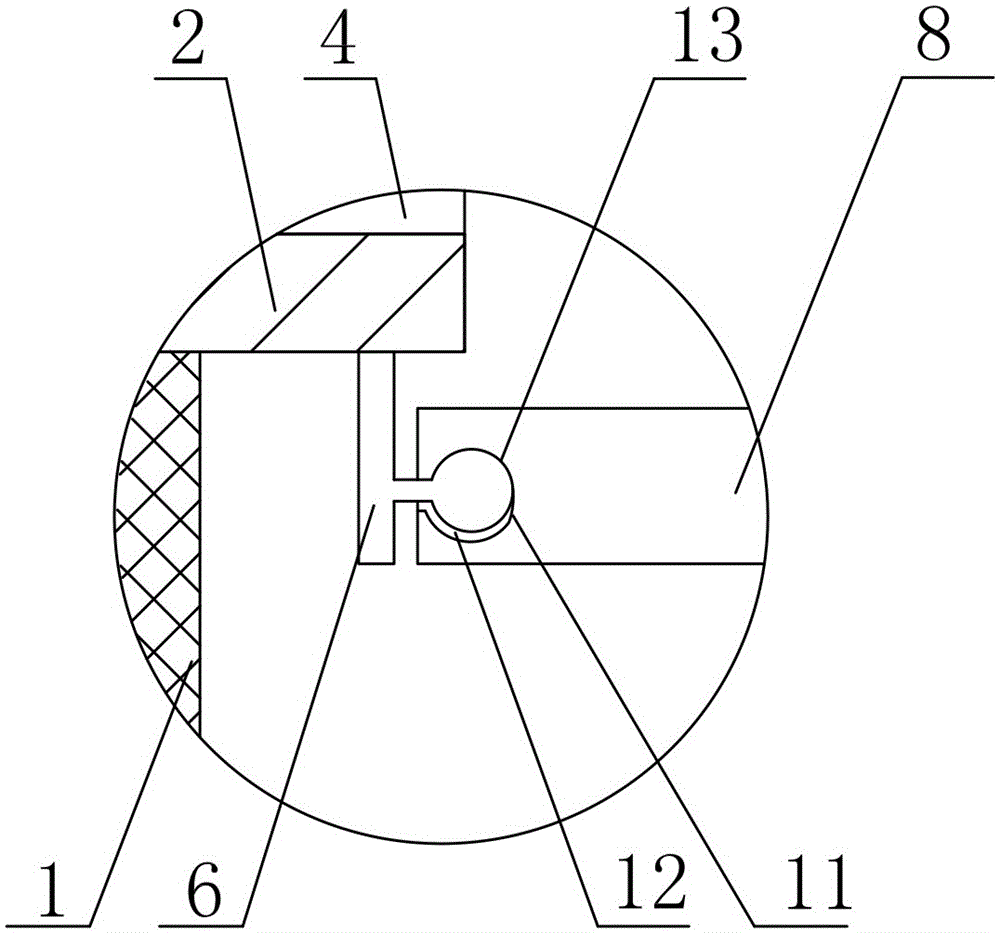
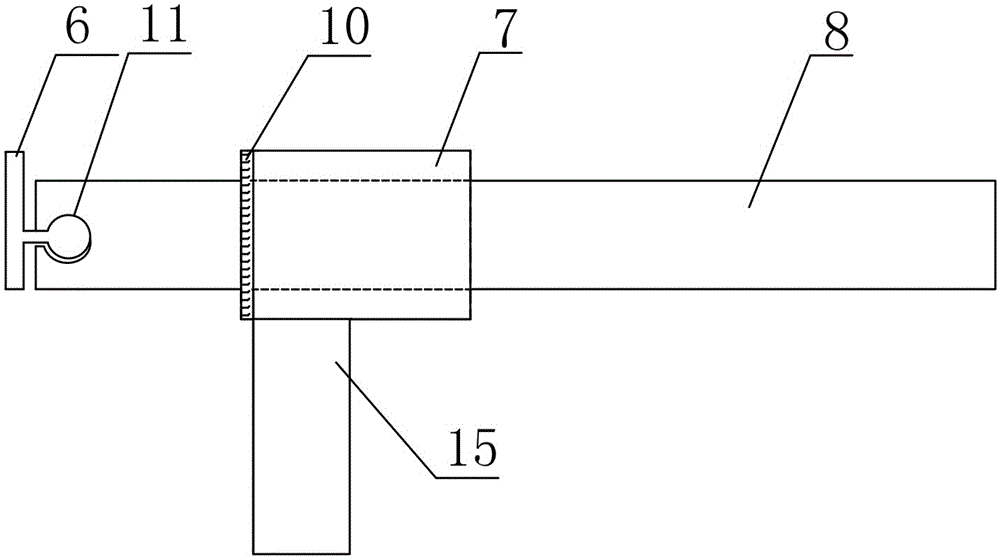
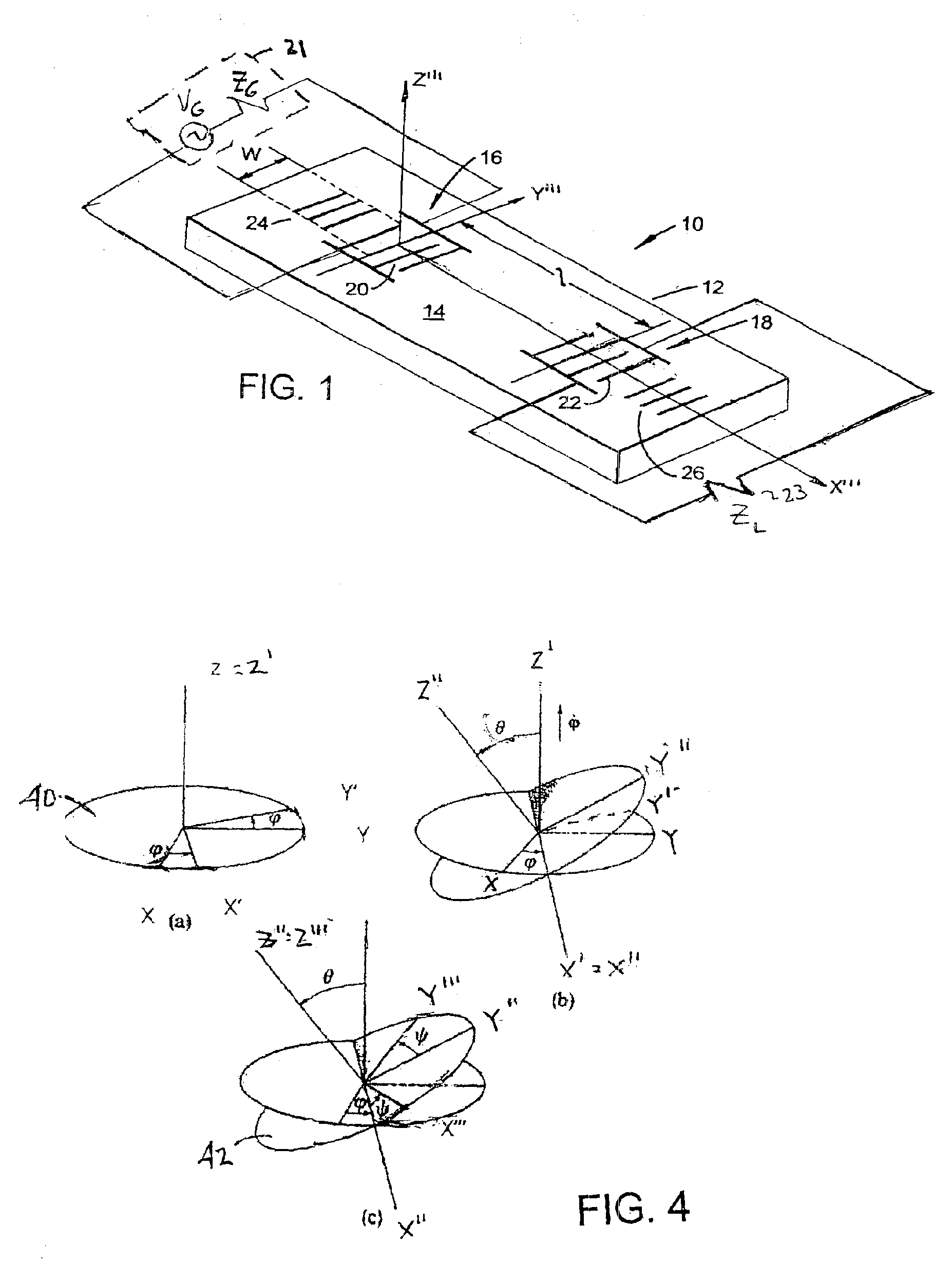
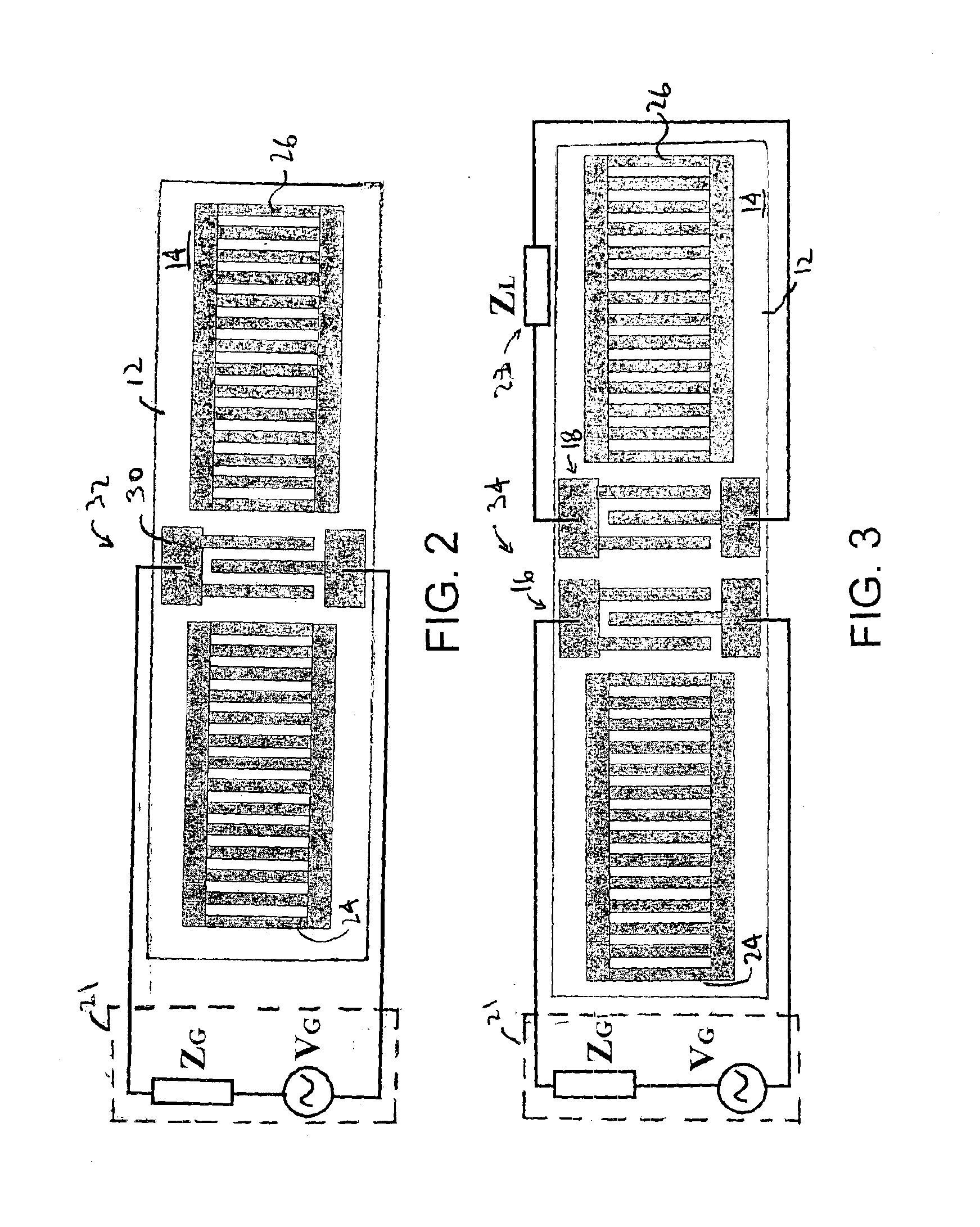
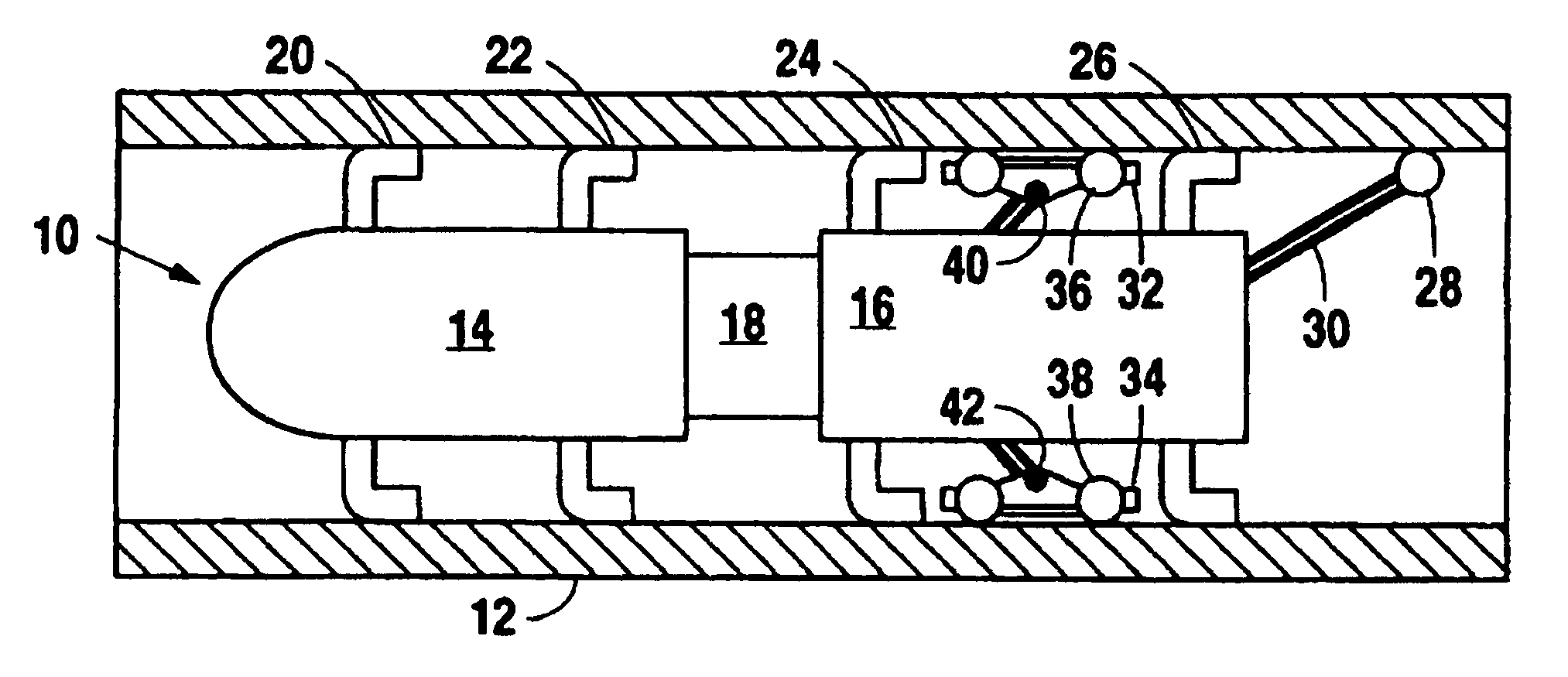
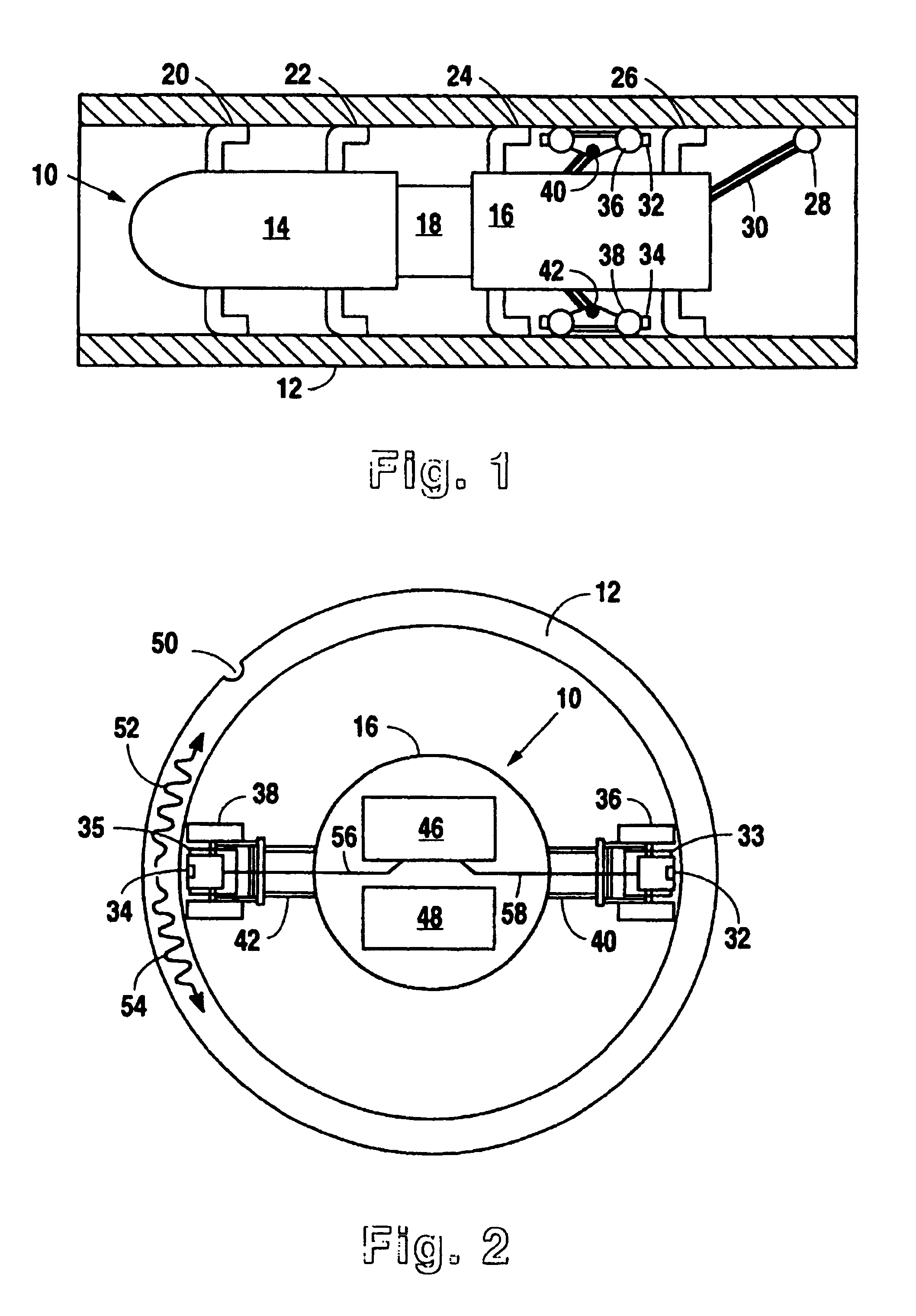
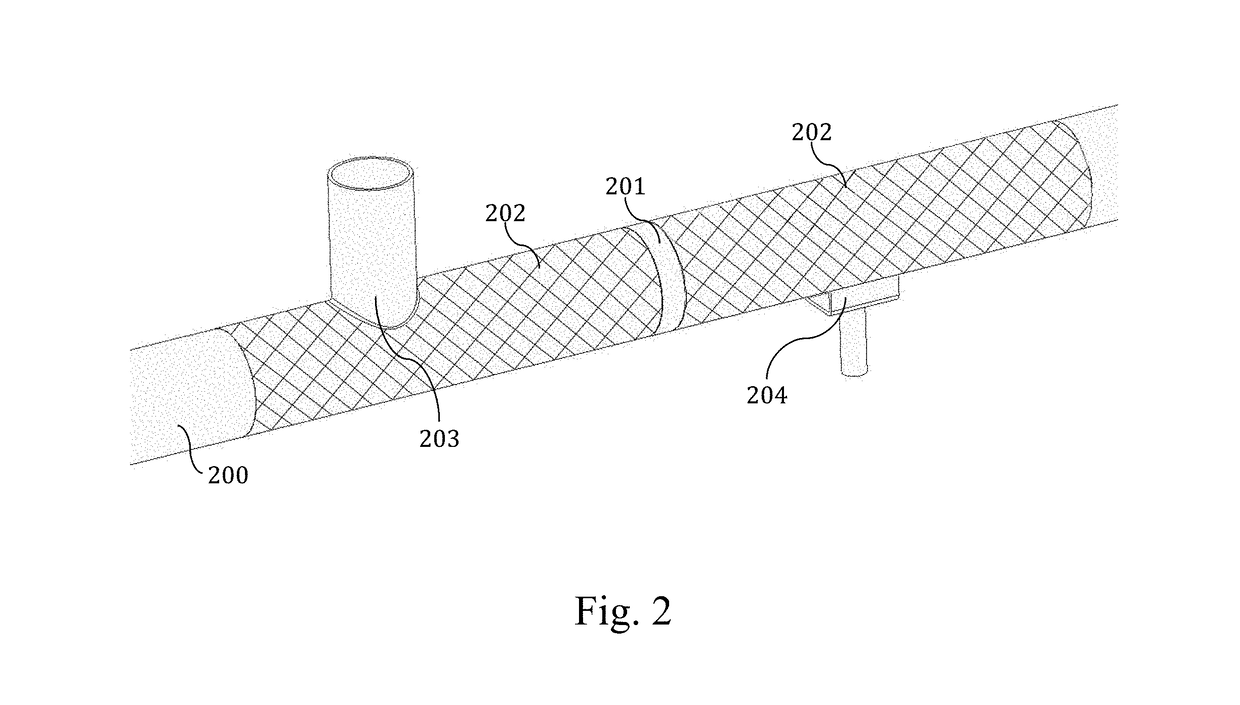
Non-destructive examination apparatus and method for guided waves
InactiveUS20080127732A1Cost-effective and accurateEfficient inspectionAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesVibration measurement in fluidNon destructiveClassical mechanics
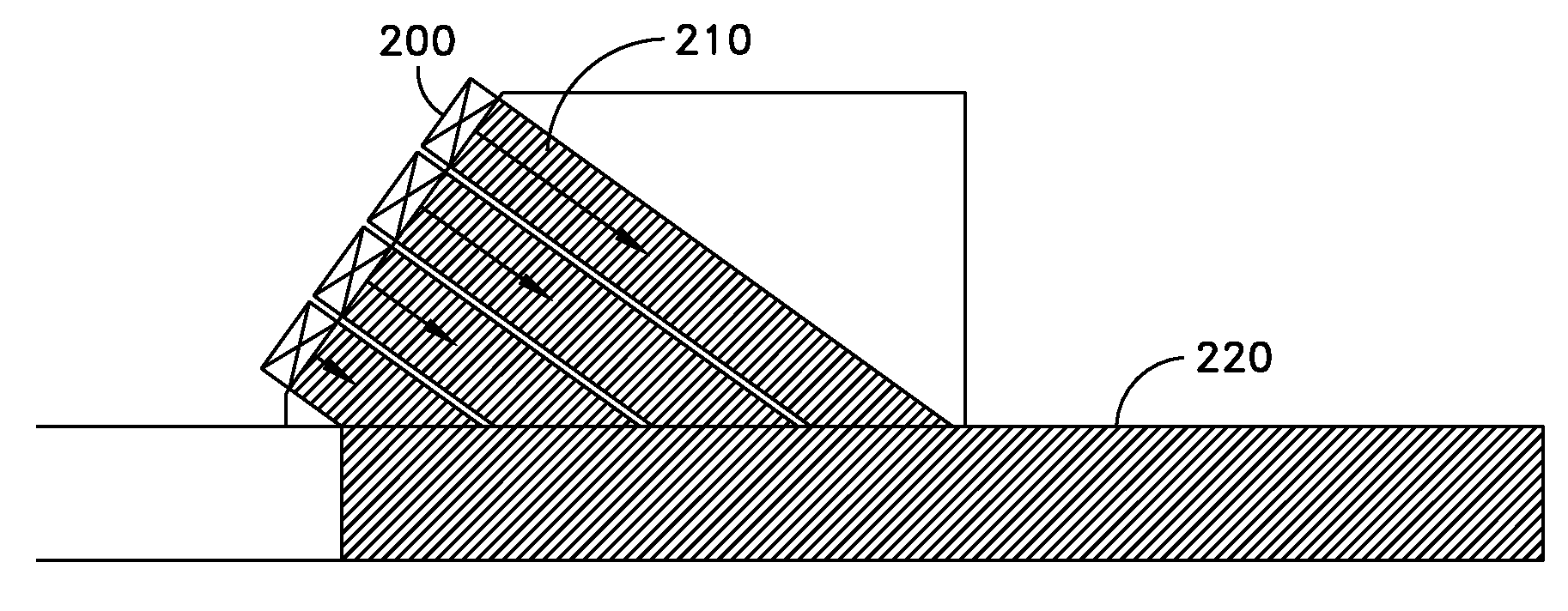
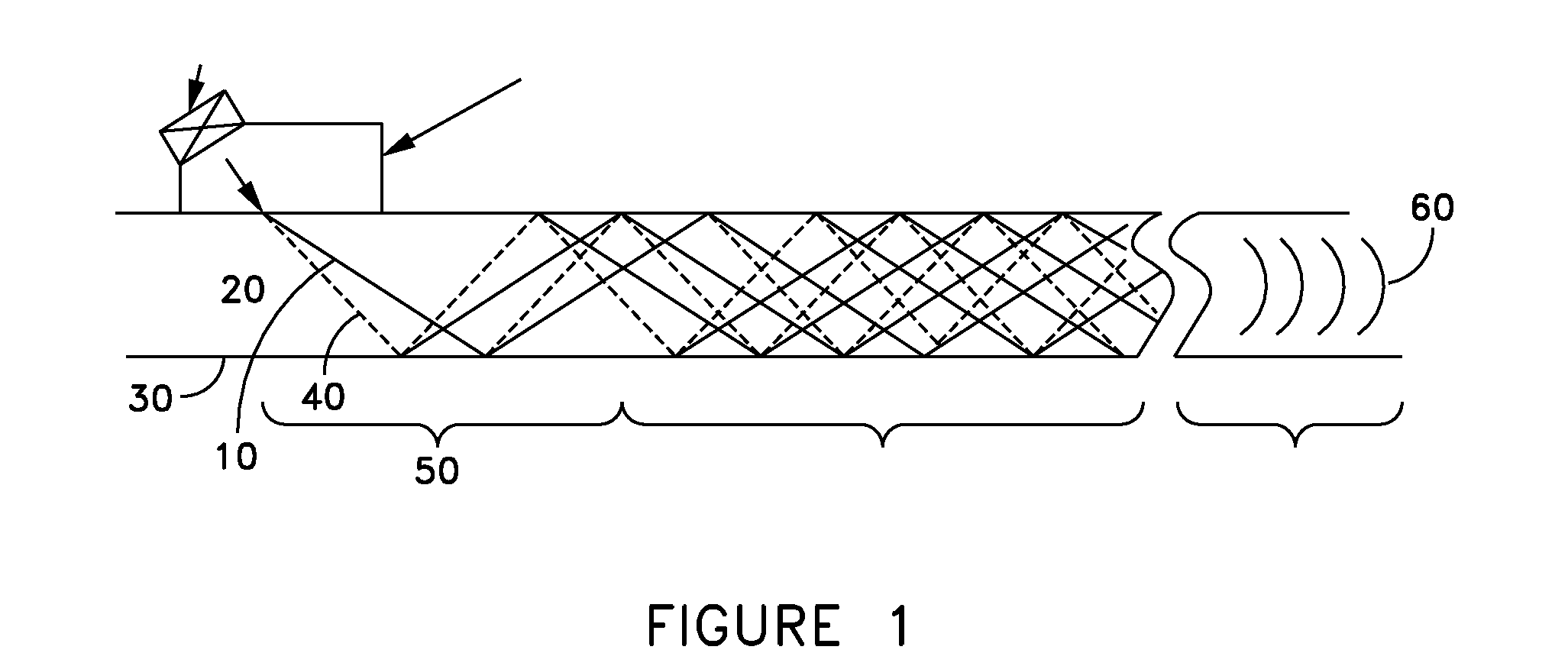
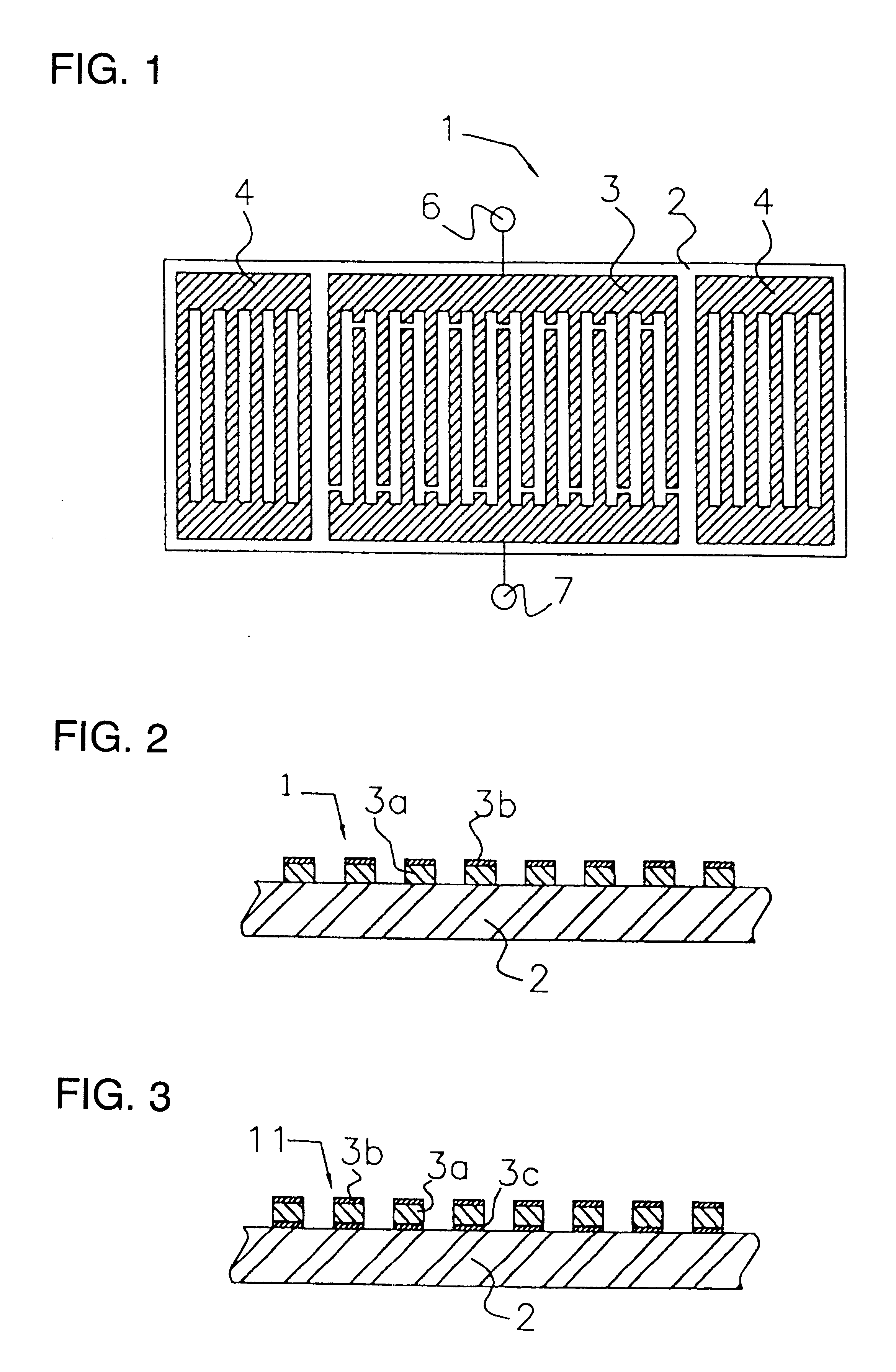
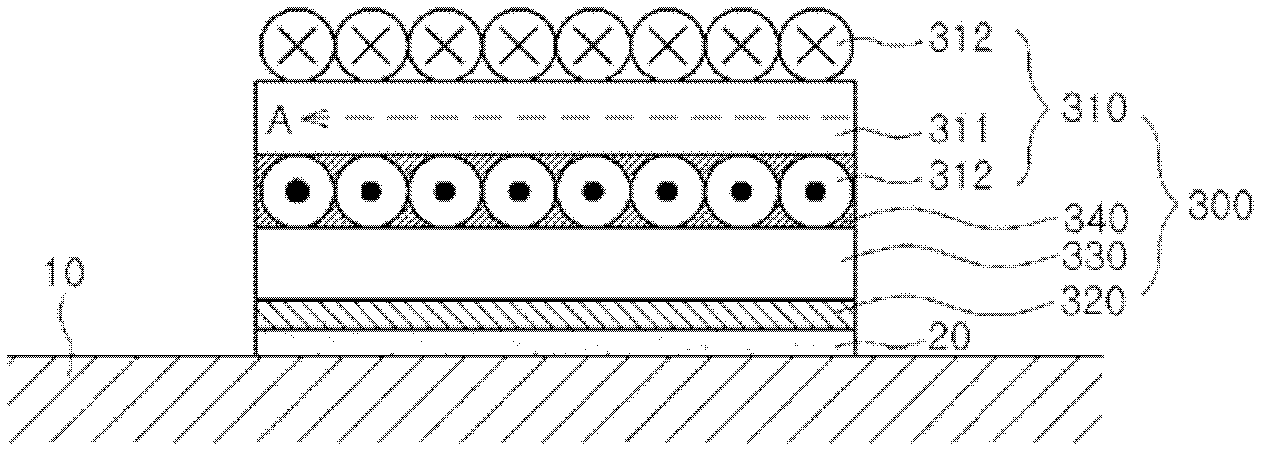
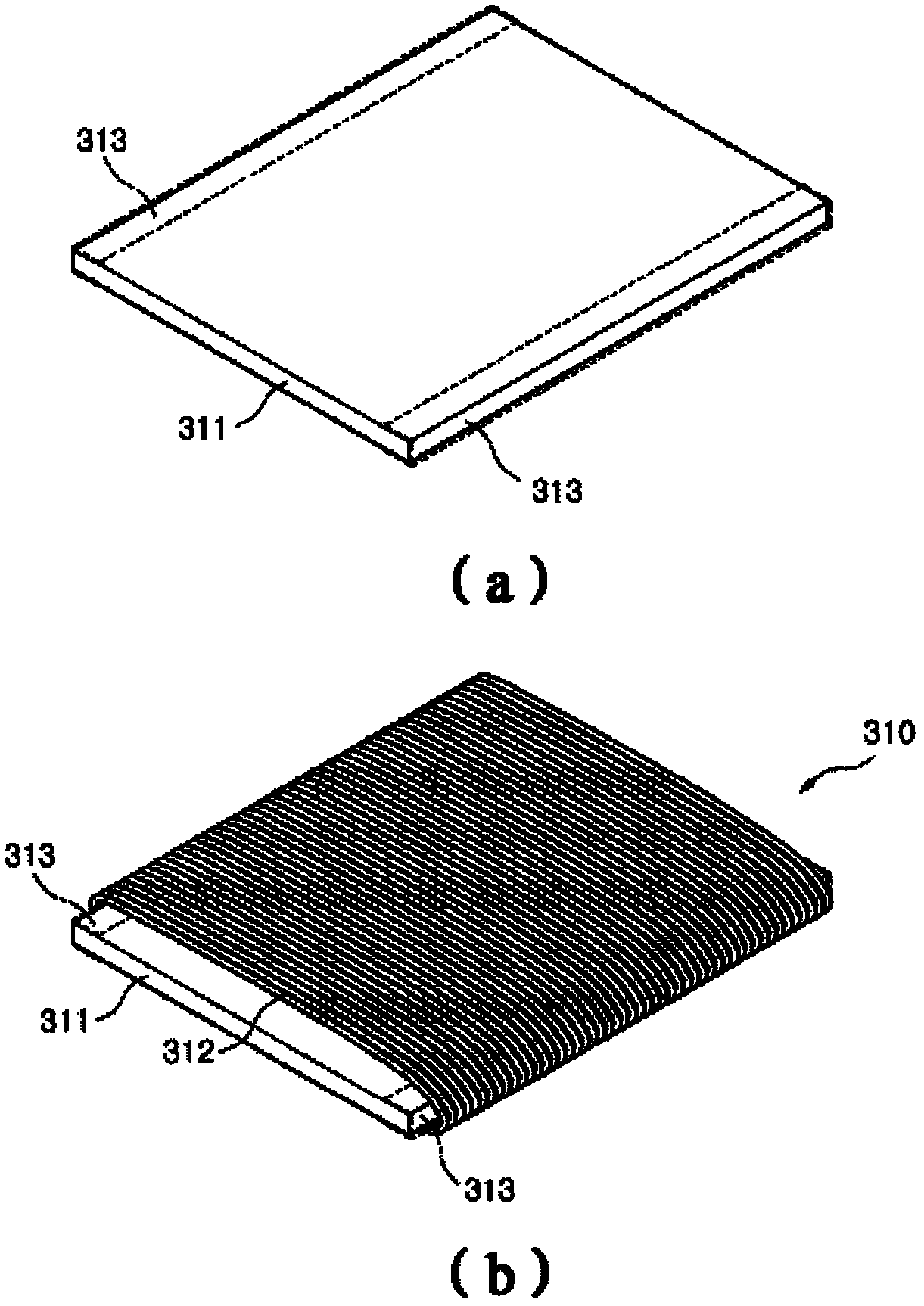
A method of performing a non-destructive examination of a piece of material, having the steps of providing an angle beam wedge and at least two transducers placed upon the wedge, wherein the transducers are placed in a phased array, placing the wedge upon the piece of material to be examined, producing a guided wave into the piece of material to be examined, wherein the guided wave is placed into the material through a synthetically changed incident angle, receiving the guided wave from the piece of material, and determining one of a presence of defects and lack of defects in the piece of material from the received guided wave. Transducers used may include 360 degree guided wave, radial polarized units, parallel shear units for shear horizontal activation and guided wave wheel probes.
Owner:FUKUOKA BROADCASTING CORPORATION
Integrated microchip sensor system for detection of infectious agents
InactiveUS20110136262A1Rapid direct early detectionHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesComponent separationSingle crystalMicrofluidic channel
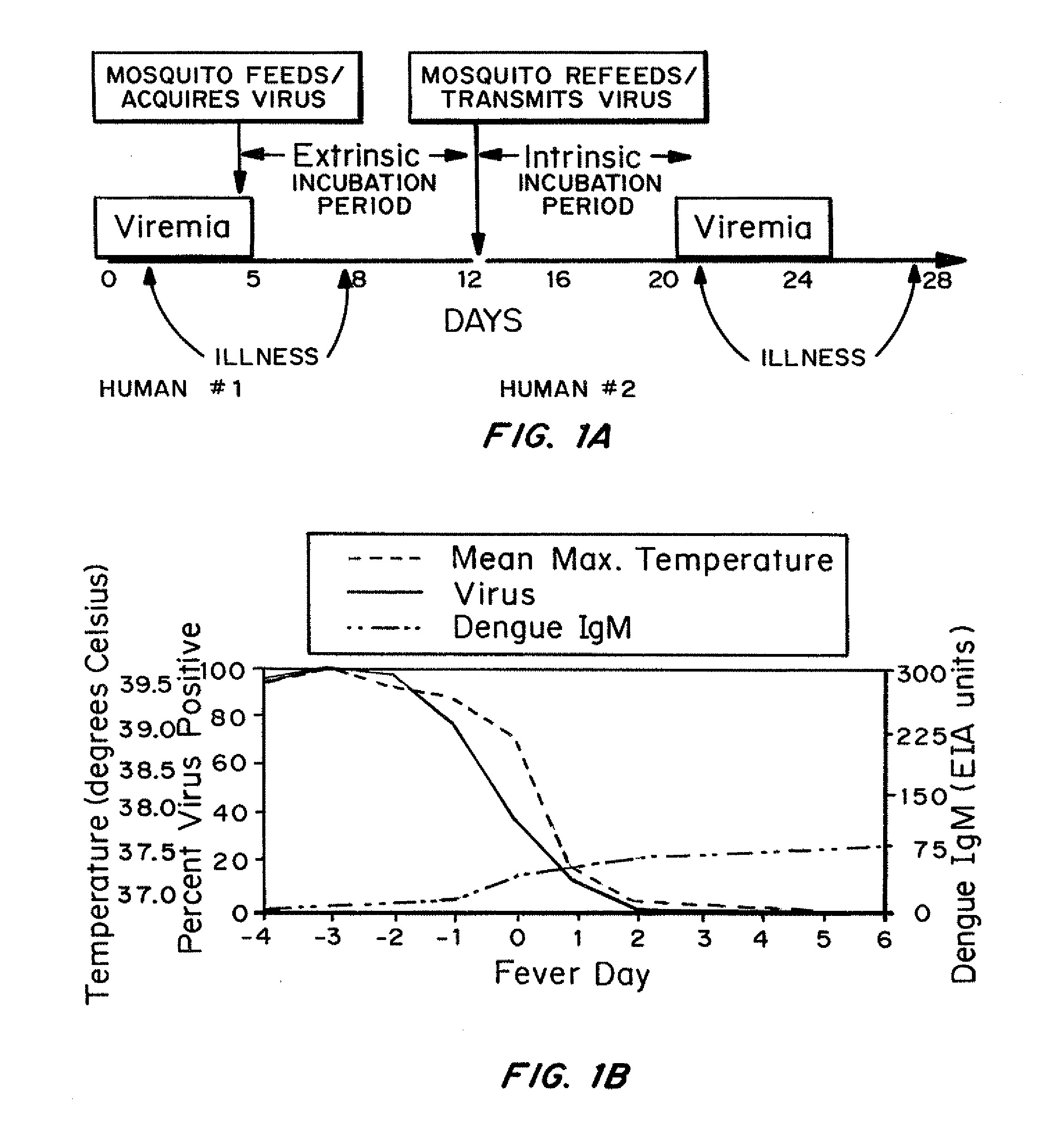
An integrated multiplexed acoustic wave biosensor chip system with enhanced sensitivity has been developed. The biosensor system incorporates one or more microfluidic channels, coated with target-specific binding films enabling rapid and early detection of viral, bacterial or parasitic targets such as Dengue virus and sexually transmitted diseases in specimens from potentially infected patients. The biosensors are used in portable analytical systems that are suitable for real-time point of care (POC) clinical diagnosis in cost sensitive and / or resource limited settings. The highly sensitive biosensors utilize thinned single crystal piezoelectric substrates that propagate layer guided shear horizontal acoustic plate mode (LG-SH-APM) waves in sensing regions bearing immobilized binders that provide simultaneous and direct detection of mass changes due to multiple bound target pathogens or molecules.
Owner:AVIANA MOLECULAR TECH
Acousto-Mechanical Detection Systems and Methods of Use
InactiveUS20070281369A1Improve sensor sensitivityRapid and accurate resultMultiple-port networksAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAnalyteCoupling
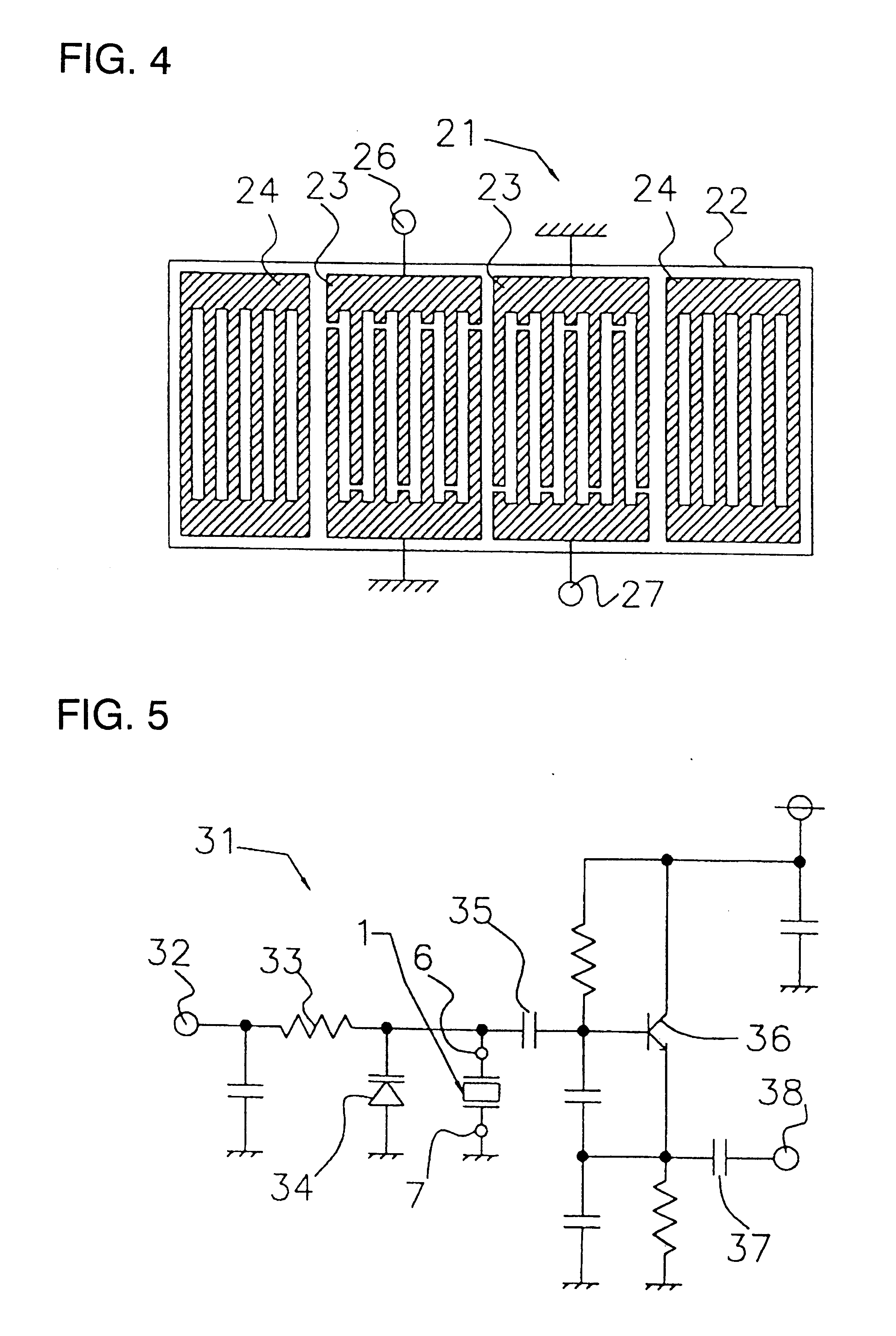
Detection systems and methods for detecting target biological analytes within sample material using acousto-mechanical energy generated by a sensor are disclosed. The acousto-mechanical energy may be provided using an acousto-mechanical sensor, e.g., a surface acoustic wave sensor such as, e.g., a shear horizontal surface acoustic wave sensor (e.g., a LSH-SAW sensor). A variety of techniques for modifying the effective mass of the target biological analytes in sample material are disclosed, including fractionating or disassembling the target biological analytes in the sample material (e.g., lysing the target biological analyte), adding a detectable mass to the target biological analyte or enhancing coupling of the target biological analyte (e.g., through the use of magnetic particles), exposing the sample material to a reagent that causes a change in at least detectable physical property in the sample material if the target biological analyte is present (e.g., a change in viscous, elastic, and / or viscoelastic properties), etc.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
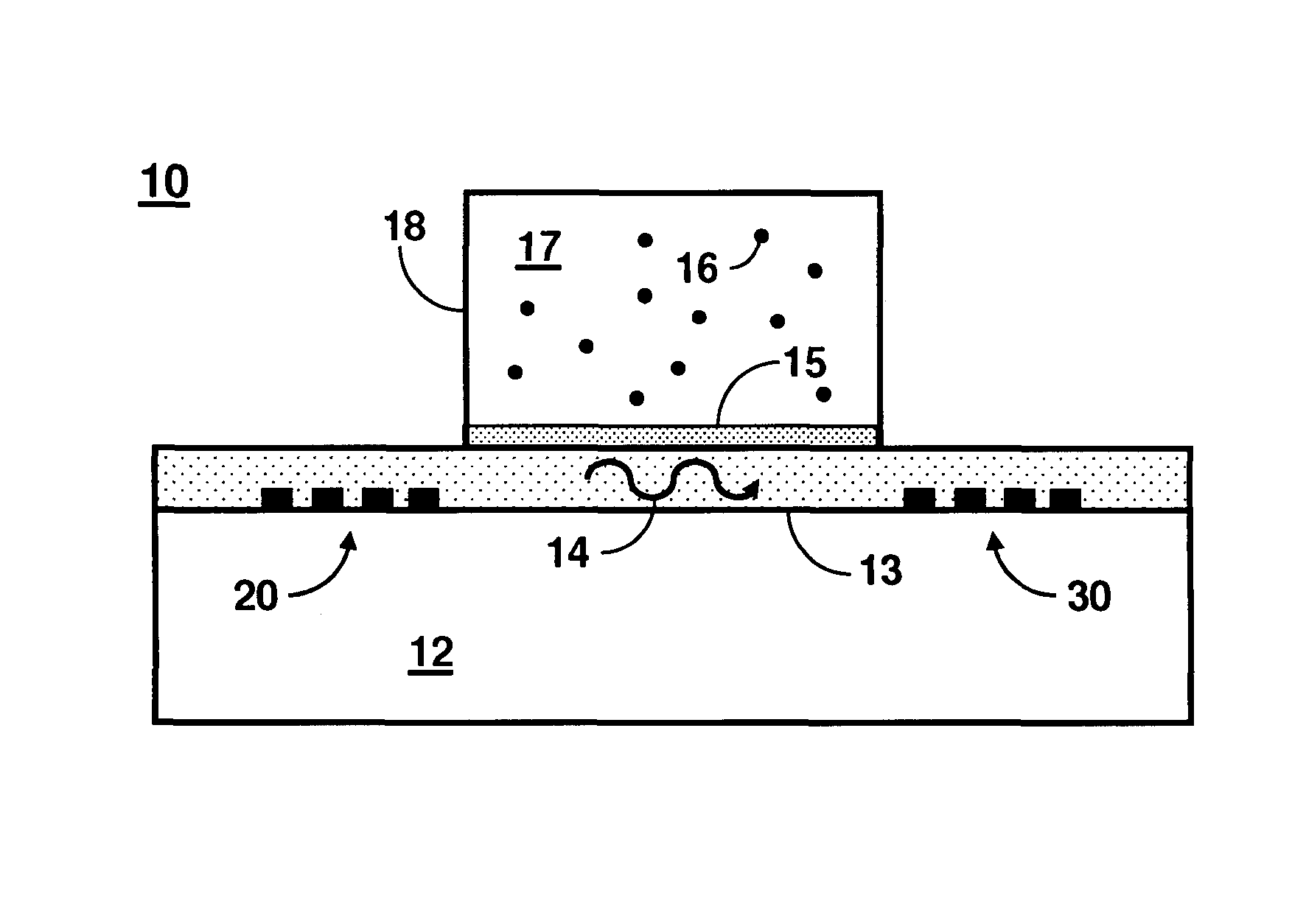
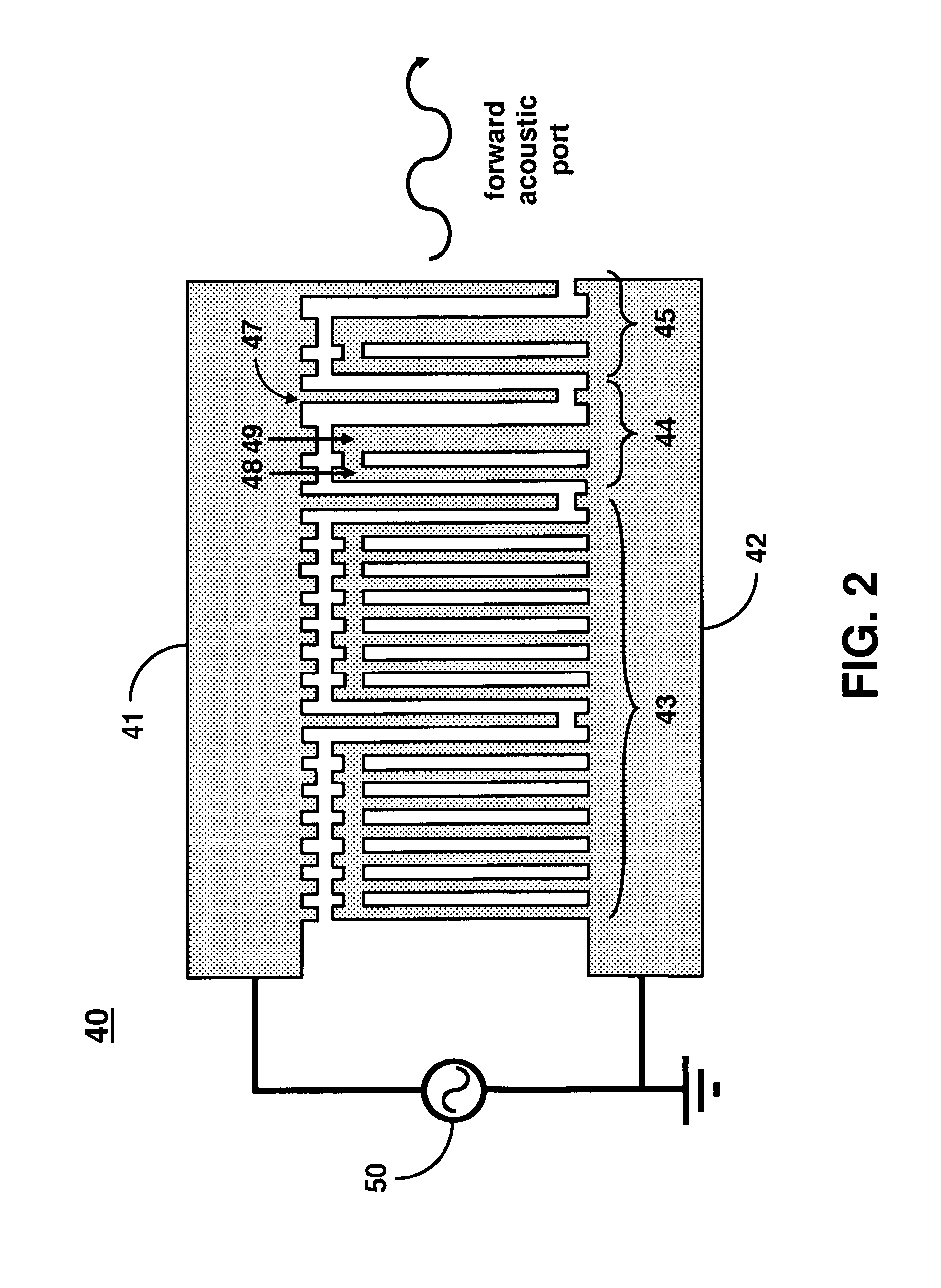
High-frequency shear-horizontal surface acoustic wave sensor
ActiveUS8436509B1Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMulti analyteImpedance matching
A Love wave sensor uses a single-phase unidirectional interdigital transducer (IDT) on a piezoelectric substrate for leaky surface acoustic wave generation. The IDT design minimizes propagation losses, bulk wave interferences, provides a highly linear phase response, and eliminates the need for impedance matching. As an example, a high frequency (˜300-400 MHz) surface acoustic wave (SAW) transducer enables efficient excitation of shear-horizontal waves on 36° Y-cut lithium tantalate (LTO) giving a highly linear phase response (2.8° P-P). The sensor has the ability to detect at the pg / mm2 level and can perform multi-analyte detection in real-time. The sensor can be used for rapid autonomous detection of pathogenic microorganisms and bioagents by field deployable platforms.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
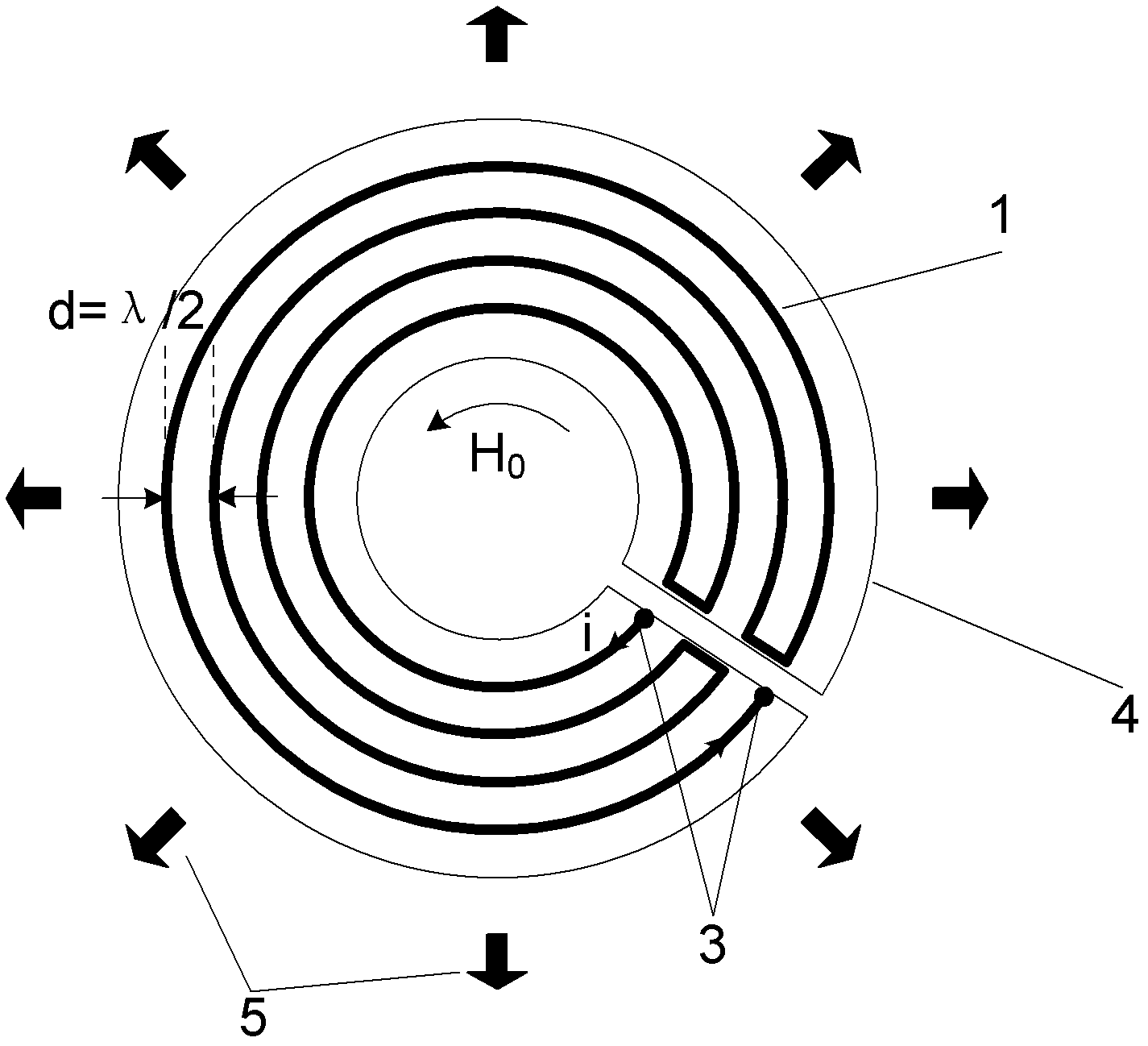
Omni-directional shear horizontal (SH) guided wave electromagnetic ultrasonic transducer
ActiveCN102662003AMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUltrasonic sensorConductive materials
An omni-directional shear horizontal (SH) guided wave electromagnetic ultrasonic transducer comprises an annular ferronickel belt with an opening, wherein the ferronickel belt is pre-magnetized through a permanent magnet or electromagnet, a meandered line coil is adhered to one surface of the ferronickel belt, and the end portion of the meandered line coil is located at the position of the opening of the ferronickel belt. Each lead wire in the meandered line coil is a single-turn lead wire or a 2-4-split split type lead wire. The radial distance between centers of adjacent lead wires in the meandered line coil is d, and d=lambada / 2, wherein lambada is the wavelength of the SH guided wave mode which is used at the current frequency f. The omni-directional SH guided wave electromagnetic ultrasonic transducer is applicable to defect detecting and health monitoring of various uniform and isotropic elastic plate structures including conducting materials and non-conducting materials.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Surface acoustic wave resonator, filter, duplexer and communication apparatus
InactiveUS6218763B1Avoid damageAvoid etchingImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSurface acoustic wave resonatorsDuplexer
A surface acoustic wave resonator includes a piezoelectric substrate and an interdigital transducer disposed thereon. The surface acoustic wave resonator operates using a shear horizontal wave, and the interdigital transducer includes an electrode film made of a metal containing W or Ta as its main component and a thin film made of Al.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Methods of detection using acousto-mechanical detection systems
InactiveUS20100075347A1Easy to detectImprove detection limitMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansTarget analysisAnalyte
Methods for detecting target biological analytes within sample material using acousto-mechanical energy generated by a sensor are disclosed. The acousto-mechanical energy may be provided using an acousto-mechanical sensor, e.g., a surface acoustic wave sensor such as, e.g., a shear horizontal surface acoustic wave sensor (e.g., a LSH-SAW sensor). The detection of the target biological analytes in sample material are enhanced by coupling of the target biological analyte (e.g., through the use of magnetic particles), application of a magnetic field to draw the target analyte to the sensor surface, and subsequent removal of the magnetic field before measuring detection.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Non-destructive examination apparatus and method for guided waves
InactiveUS7938008B2Cost-effective and accurateEfficient inspectionAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesVibration measurement in fluidNon destructiveClassical mechanics
A method of performing a non-destructive examination of a piece of material, having the steps of providing an angle beam wedge and at least two transducers placed upon the wedge, wherein the transducers are placed in a phased array, placing the wedge upon the piece of material to be examined, producing a guided wave into the piece of material to be examined, wherein the guided wave is placed into the material through a synthetically changed incident angle, receiving the guided wave from the piece of material, and determining one of a presence of defects and lack of defects in the piece of material from the received guided wave. Transducers used may include 360 degree guided wave, radial polarized units, parallel shear units for shear horizontal activation and guided wave wheel probes.
Owner:FUKUOKA BROADCASTING CORPORATION
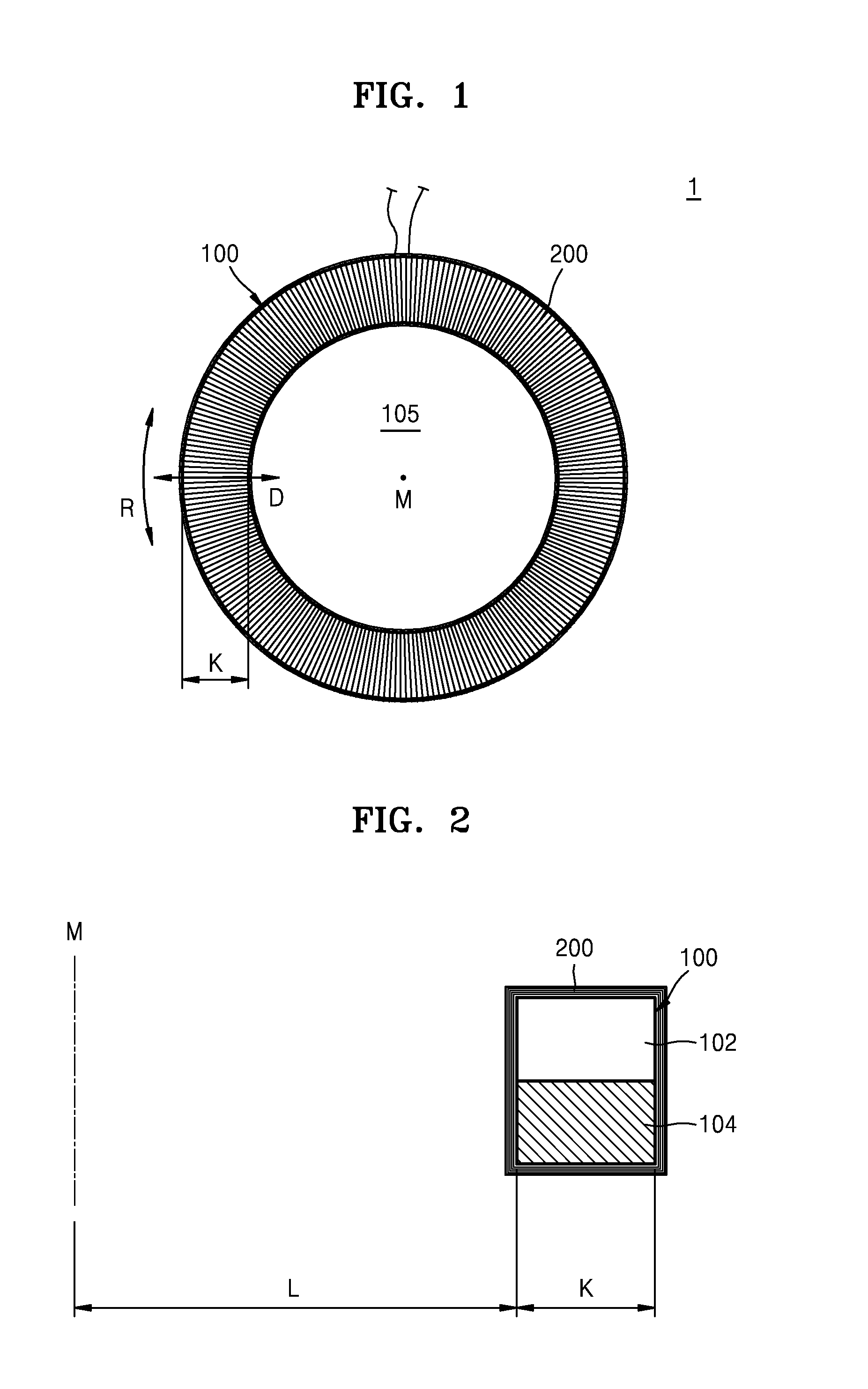
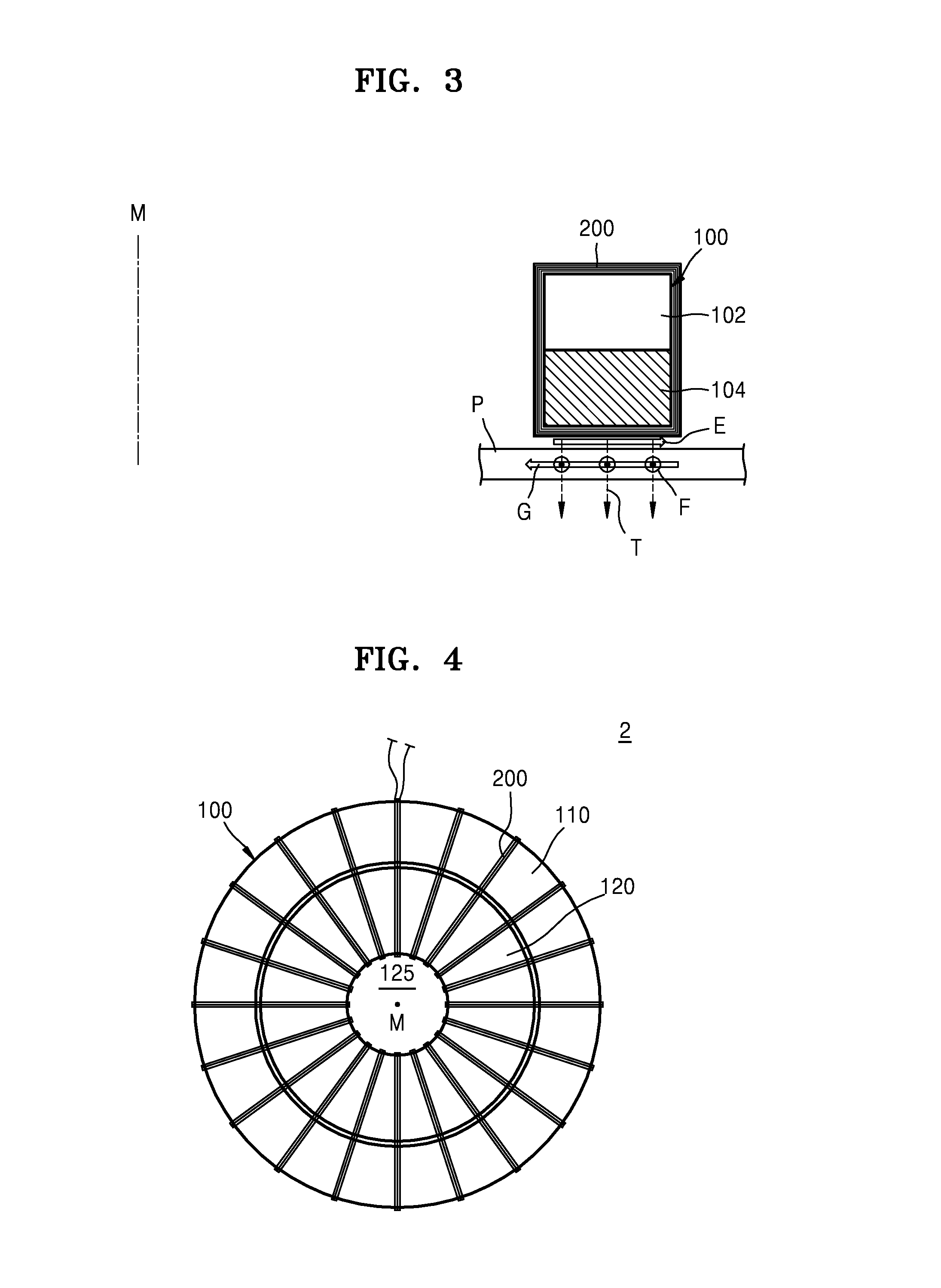
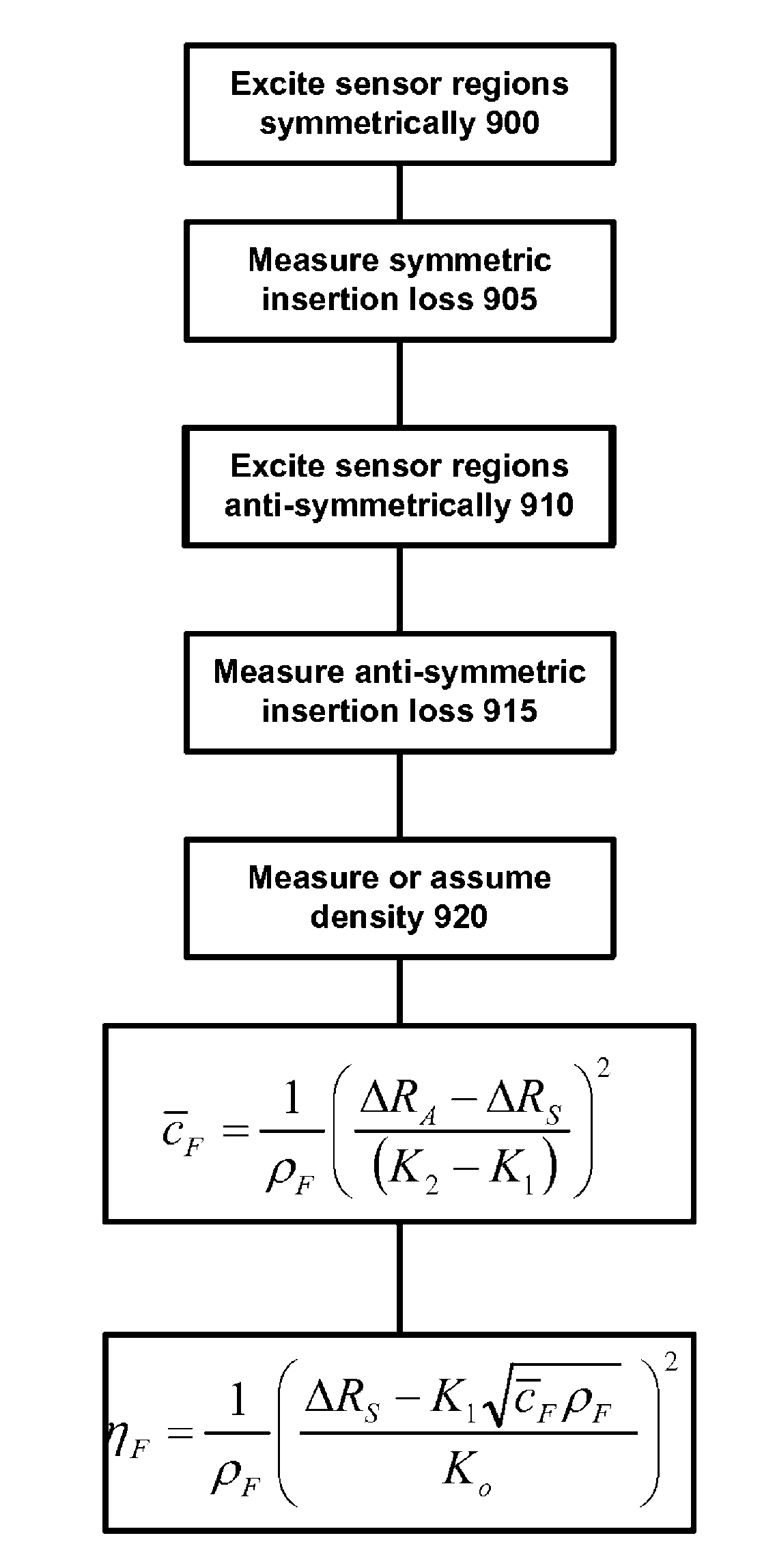
Sensor, system, and method, for measuring fluid properties using Multi-Mode Quasi-Shear-Horizontal Resonator
InactiveUS20090216467A1High degree of symmetryMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesFlow propertiesResonator filterDual mode
A system and a method for providing information on two of the three variables, density (ρ), viscosity (η), and elastic modulus (c) of a fluid, such that independent knowledge of one variable allows the remaining two variables to be measured by a single sensor. The present invention relies on the interaction of a predominantly shear horizontal acoustic wave device (“quasi-shear-horizontal”) with the fluid, so as to measure subtle differences in the interaction of two or more acoustic resonance states or waveguide modes of a multi-mode resonator or waveguide, and to derive the desired fluid characteristics therefrom. The most preferred embodiment is a dual-mode coupled resonator filter geometry with one resonant mode having a high degree of symmetry and the other having a high degree of anti-symmetry. By combining the additional information of multi-moded operation with the inherent ability of a horizontally-polarized quasi-shear-horizontal acoustic wave device (AWD) to operate in fluid environments, one obtains a multi-mode quasi-shear-horizontal (MMQSH) resonator.
Owner:KNOWLES CAPITAL FORMATION
Method and apparatus for monitoring wall thinning of a pipe using magnetostrictive transducers and variation of dispersion characteristics of broadband multimode shear horizontal (SH) waves
InactiveUS20100244591A1Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMeasuring outputEngineering
Magnetostrictive transducers for monitoring wall thinning in a pipe, and an apparatus and method for monitoring wall thinning in a pipe using magnetostrictive transducers are provided. The magnetostrictive transducers generate broadband multimode shear horizontal (SH) waves, and allow the generated SH waves to travel along the pipe, thus correctly monitoring a status of the wall thinning of the pipe. The apparatus includes a transmitting transducer which is installed outside of a pipe and generates shear horizontal (SH) waves traveling along the pipe, a receiving transducer which is spaced apart from the transmitting transducer and measures the shear horizontal (SH) waves traveling along the pipe, and a controller for monitoring wall thinning of the pipe by exciting and measuring output signals of the transmitting and receiving transducers.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF STANDARDS & SCI
Method and apparatus for acoustic downhole telemetry and power delivery system using transverse or torsional waves
ActiveUS20160265349A1Improve linking efficiencyInterference minimizationSurveySonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionOn-off keyingTransmitted power
Methods and apparatus for transmitting power and data along a metal pipe using wideband acoustic waves. Arrangements use shear-horizontal waves, transmitting narrowband signals for power applications and wideband signals for communications having a bandwidth greater than the coherence bandwidth of the acoustic-electric channel. Chirp wave signals, direct sequence spread signals, and on-off keying are used. Acoustic-electric channels include wedges fixed to a pipe or other substrate, transducers fixed to the wedges, and electronics linked to each transducer for sending and receiving power and signals. Matching networks, rectification circuits, and non-coherent signal reception methods may be used.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
Electromagnetic ultrasonic detection probe
InactiveCN102879478AEnergizing energyImprove receiver sensitivityMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesCapacitanceNon magnetic
The invention discloses an electromagnetic ultrasonic detection probe, which consists of one or more than one pair of permanent magnets, a non-magnetic material spacer, two or more runway-shaped planar coils, a carbon steel sheet, a probe protection layer, a shell, a capacitor and a changeover switch. The electromagnetic ultrasonic detection probe is characterized in that the runway-shaped planar coils are runway-shaped coils which are formed by winding enameled wires or made of printed circuit boards (PCB). The electromagnetic ultrasonic detection probe has the advantages that switching of the transmission / receiving operation of the same electromagnetic ultrasonic probe is realized by using excitation signals on the coils; when the probe serves as a transmitting probe, all runway-shaped coils are connected in parallel to supply high excitation energy; and when the probe serves as a receiving probe, all runway-shaped coils are connected in series to realize high receiving sensitivity. The electromagnetic ultrasonic probe can excite and receive shear horizontal (SH) wave in a metal pipeline or a flat plate, and the pipeline and the flat plate can be subjected to flaw detection by using only one probe.
Owner:NANTONG TIANHUA HERUI TECH VENTURES
Variable-wavelength low-order shear-horizontal-wave electromagnetic acoustic transducer
ActiveCN103831227AAdaptableIncrease flexibilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wave generationMechanical vibrations separationElectrical conductorUltrasonic sensor
The invention relates to a variable-wavelength low-order shear-horizontal-wave electromagnetic acoustic transducer which can be used for ultrasonic flaw inspection for conductor materials, and belongs to the technical field of nondestructive inspection. An array-magnet equidistant change driving system mainly functions in providing a bias magnetic field with variable magnet spacing, namely variable wavelength, to an electrical system of the transducer. The SH (shear horizontal) modal magnet array type EMAT (electromagnetic acoustic transducer) can better meet inspection requirements by changing wavelength and changing excitation frequency at the same time, and the transducer can be adjusted according to actual inspection requirements. Therefore, the EMAT has higher adaptability and flexibility.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Slide bar type tensile limiting-displacement vibration isolation support
ActiveCN105064528AImprove stabilitySimple structureShock proofingEarthquake intensityVibration isolation
The invention discloses a slide bar type tensile limiting-displacement vibration isolation support which comprises a vibration isolation rubber pad, an upper steel sheet and a lower steel sheet. The upper steel sheet and the lower steel sheet are anchored to an upper structure and a lower structure. The slide bar type tensile limiting-displacement vibration isolation support is characterized in that the two sides or the periphery of the bottom of the upper steel plate are / is symmetrically provided with slide bars and tensile limiting-displacement mechanisms composed of pull rods and sleeves, wherein the pull rods are provided with sliding grooves; the slide bars are fixedly connected with the upper steel sheet, the sleeves are anchored to the lower structure through bases, and the slide bars are circular rod pieces arranged on a vertical plate; the sliding grooves are clamp grooves formed in one ends of the pull rods and matched with the slide bars, and the sliding grooves are formed in the slide bars in a sleeving mode and connected with the slide bars in a sliding mode. Compared with the prior art, the slide bar type tensile limiting-displacement vibration isolation support is simple in structure and high in horizontal shearing resistance and vertical tensile deformation resistance, the stability of the support is greatly improved, the problems of toppling and ultralimit of tensile stress of the vibration isolation support possibly generated by vibration isolation of a high-rise building are well solved, and the slide bar type tensile limiting-displacement vibration isolation support is especially suitable for application and popularization of laminated rubber vibration isolation supports of high-rise buildings in earthquake regions of high earthquake intensity.
Owner:ZHONGCHUAN NO 9 DESIGN & RES INST
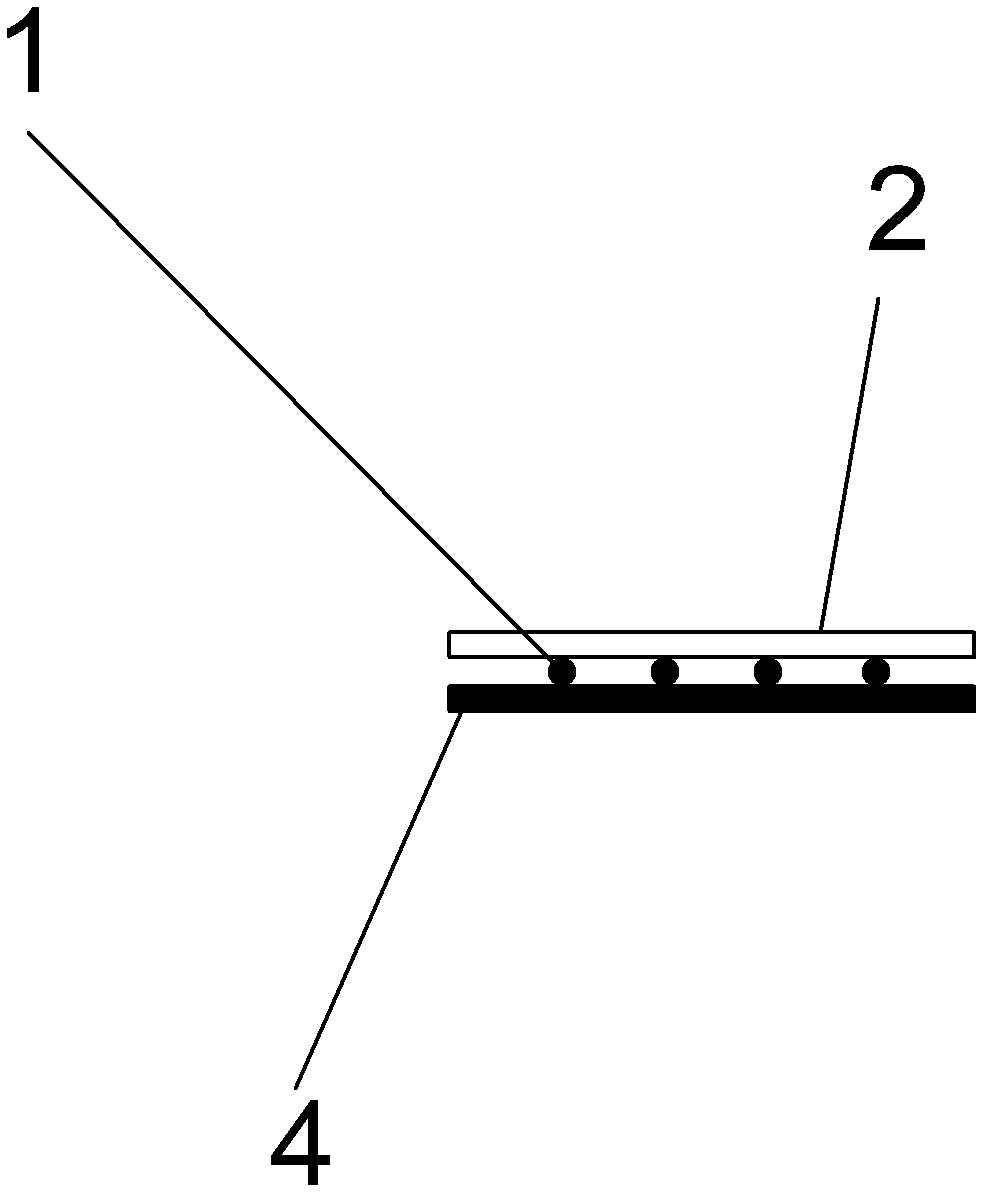
Magnetostrictive phased array transducer for transducing shear horizontal bulkwaves
ActiveUS20130145851A1Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMechanical vibrations separationPower flowMeander
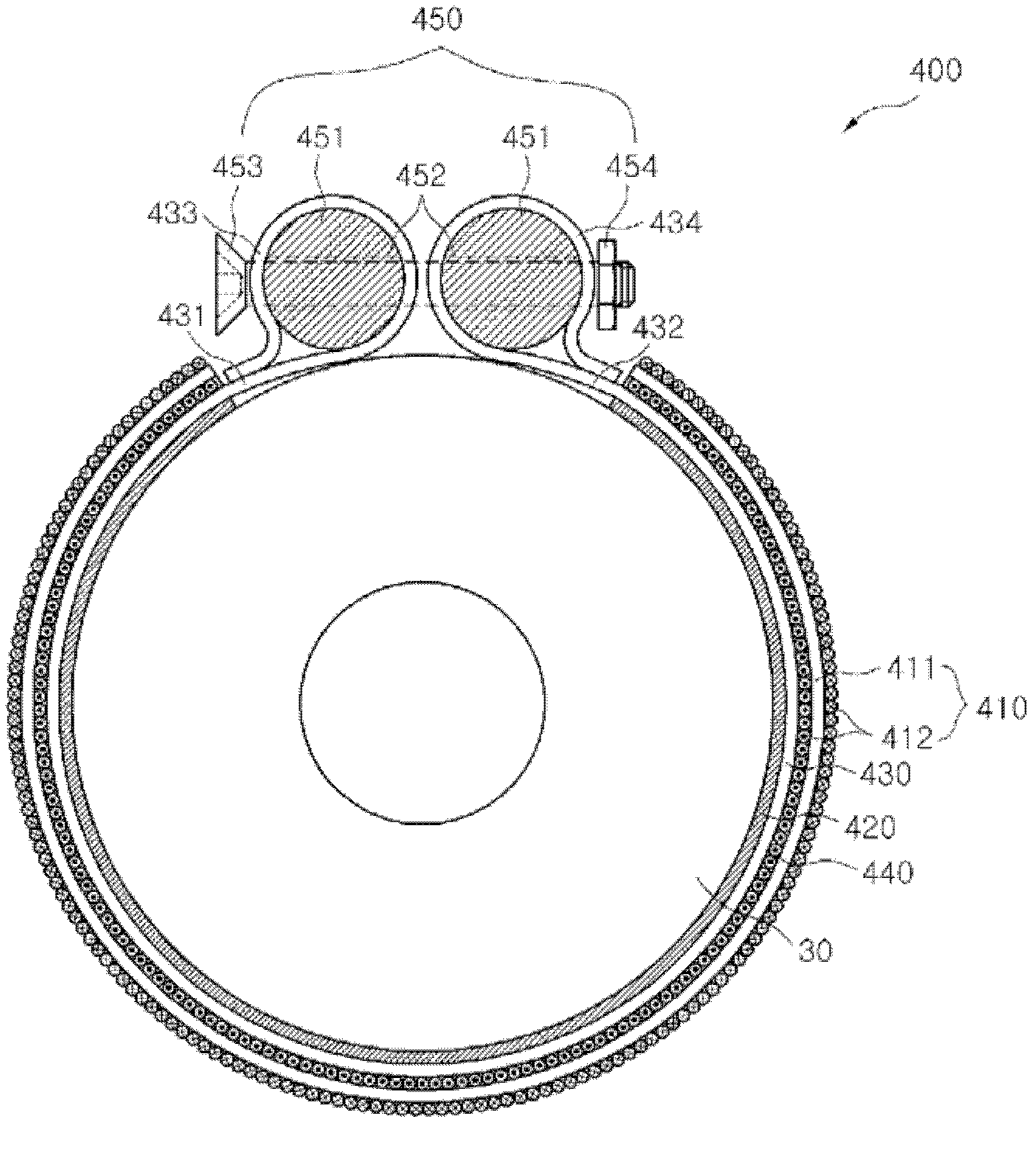
A magnetostrictive phased array transducer for transducing shear horizontal bulkwaves including a plurality of magnetostrictive members each having a bottom surface of a plate-shaped structure made of a ferromagnetic material, which is mounted to be adhered closely to the surface of a mounting place; an insulator disposed on a side surface of each magnetostrictive member; a meander coil having a plurality of coil lines extended in the direction parallel with the bottom surface on each insulator, wherein adjacent coil lines are connected so that current flows in the opposite directions to each other, thereby generating a dynamic magnetic field with respect to each magnetostrictive member; and a magnet mounted to generate a static magnetic field perpendicular to the dynamic magnetic field. When the current is supplied to the meander coil, a plurality of magnetostrictive members generate a plurality of shear horizontal bulkwaves while being deformed by the magnetostriction effect.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF STANDARDS & SCI
High-frequency shear-horizontal surface acoustic wave sensor
ActiveUS8669688B1Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMulti analyteImpedance matching
A Love wave sensor uses a single-phase unidirectional interdigital transducer (IDT) on a piezoelectric substrate for leaky surface acoustic wave generation. The IDT design minimizes propagation losses, bulk wave interferences, provides a highly linear phase response, and eliminates the need for impedance matching. As an example, a high frequency (˜300-400 MHz) surface acoustic wave (SAW) transducer enables efficient excitation of shear-horizontal waves on 36° Y-cut lithium tantalate (LTO) giving a highly linear phase response (2.8° P-P). The sensor has the ability to detect at the pg / mm2 level and can perform multi-analyte detection in real-time. The sensor can be used for rapid autonomous detection of pathogenic microorganisms and bioagents by field deployable platforms.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Contact sh-guided-wave magnetostrictive transducer
InactiveCN102474690AImprove reliabilityUniform Bias Magnetic FieldPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesProcessing detected response signalAcousticsRadio frequency
A contact shear horizontal (SH) mode guided-wave magnetostrictive transducer including: a transduction band which is disposed on a surface of an object to be tested and in which electromagnetic acoustic transduction occurs; and radio frequency (RF) coils disposed on the transduction band, wherein the transduction band includes a plate-shaped solenoid including a magnetostrictive strip in which the electromagnetic acoustic transduction for transmitting or receiving SH mode guided waves occurs, and solenoid coil wound in a spiral form along a circumference of the magnetostrictive strip so as to form a bias magnetic field in a lengthwise direction of the magnetostrictive strip, and the RF coils are used to form a dynamic magnetic field in a widthwise direction of the magnetostrictive strip or to detect a change of magnetic flux in the magnetostrictive strip.
Owner:RES COOPERATION FOUND OF YEUNGNAM UNIV +1
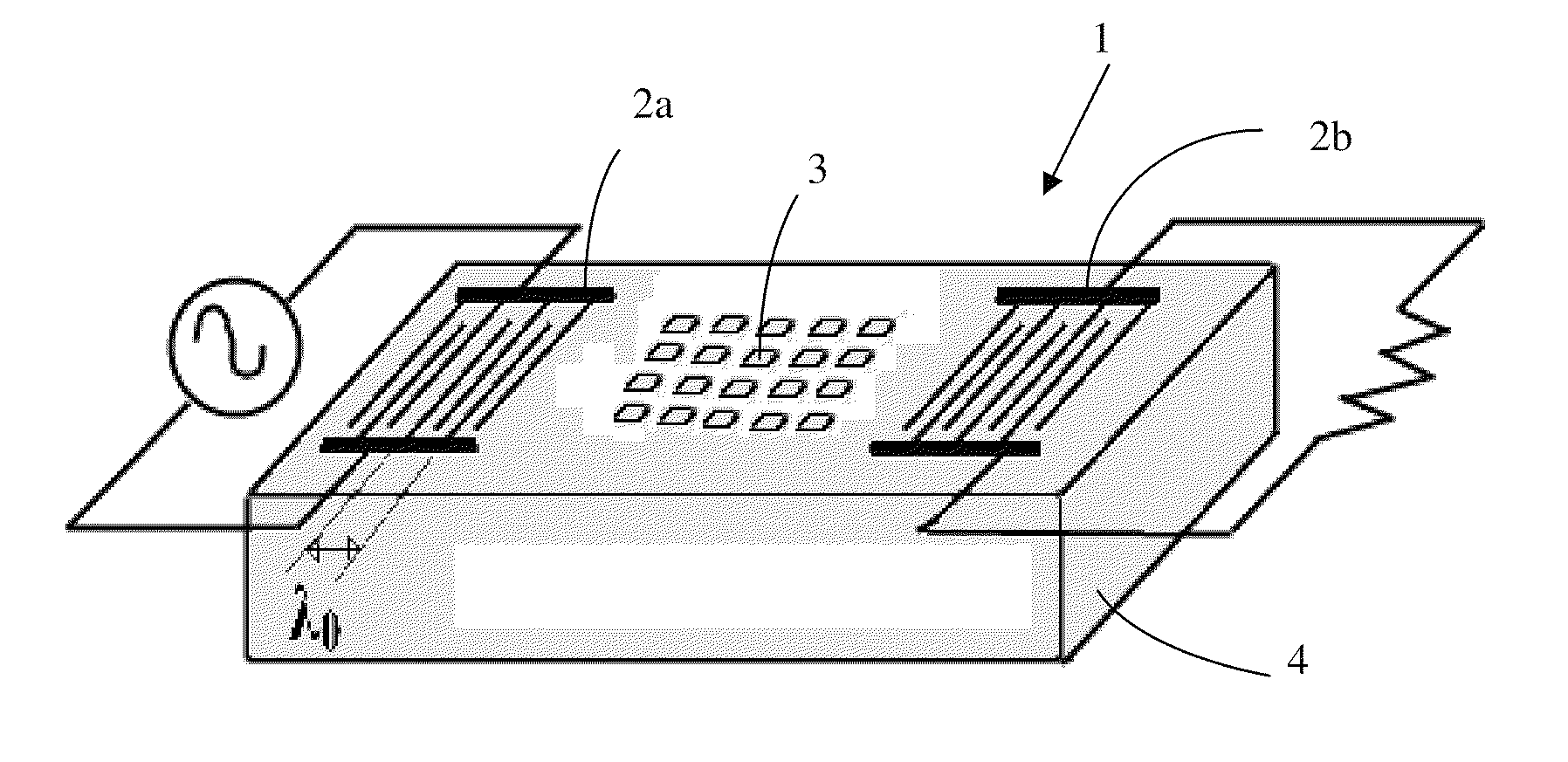
Surface acoustic wave sensor
ActiveUS7053522B1Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSurface acoustic wave sensorBiological agent
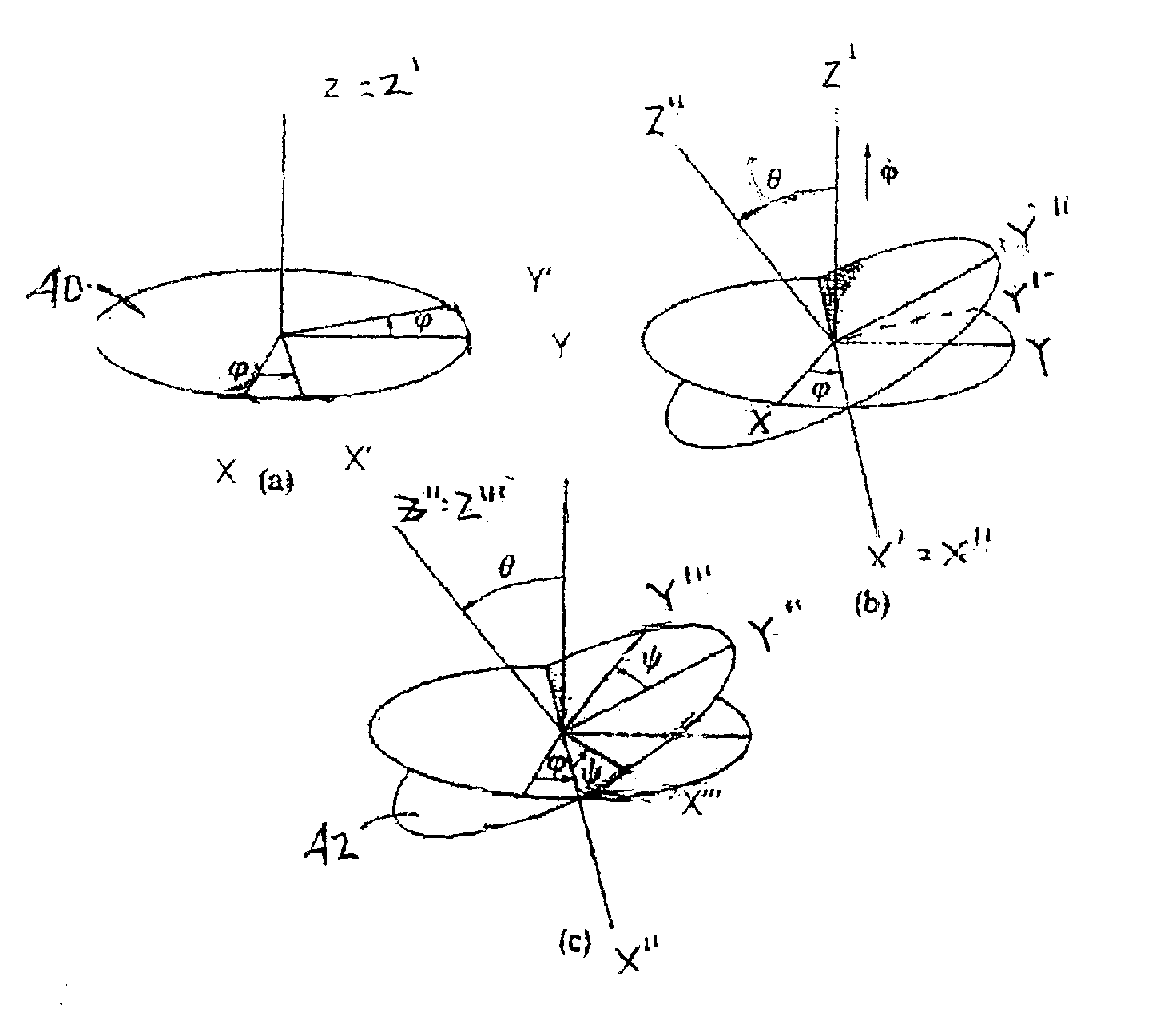
A Surface Acoustic Wave (SAW) Device that includes a substrate formed from a material selected from the LGX family of crystals and having a SAW propagation surface defined by Euler angles relative to the corresponding crystal axes having a range of −5°<φ<+5°, −5°<θ<50° and 80°<ψ<100°. The device being utilized for liquid sensor applications including the detection of chemical or biological agents present in a liquid environment. The device may or may not include the deposition of one or more chemical and / or biological films upon the propagation surface to enhance the sensitivity thereof. At least one interdigital transducer is formed upon the substrate propagation surface and that is operative to launch surface acoustic waves having a shear horizontal mode.
Owner:UNIV OF MAINE SYST BOARD TRUSTEES
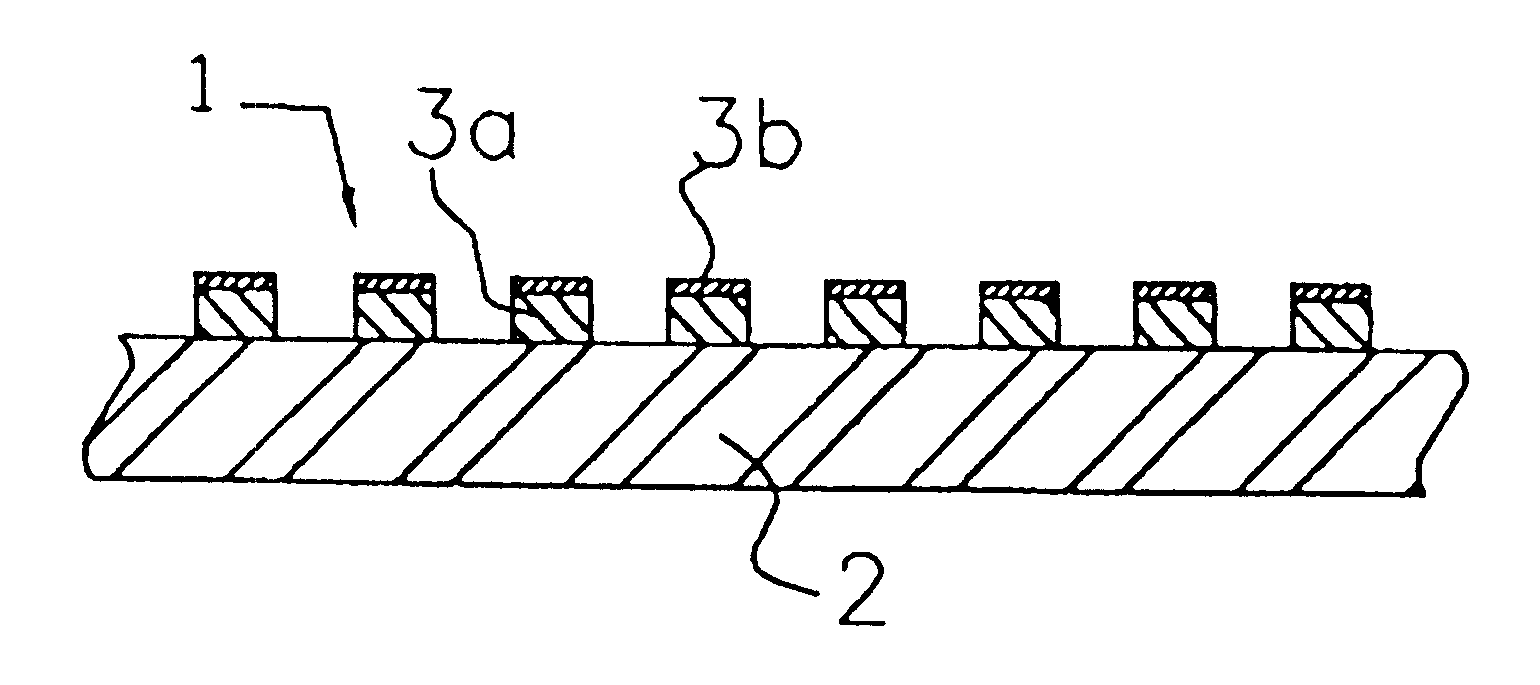
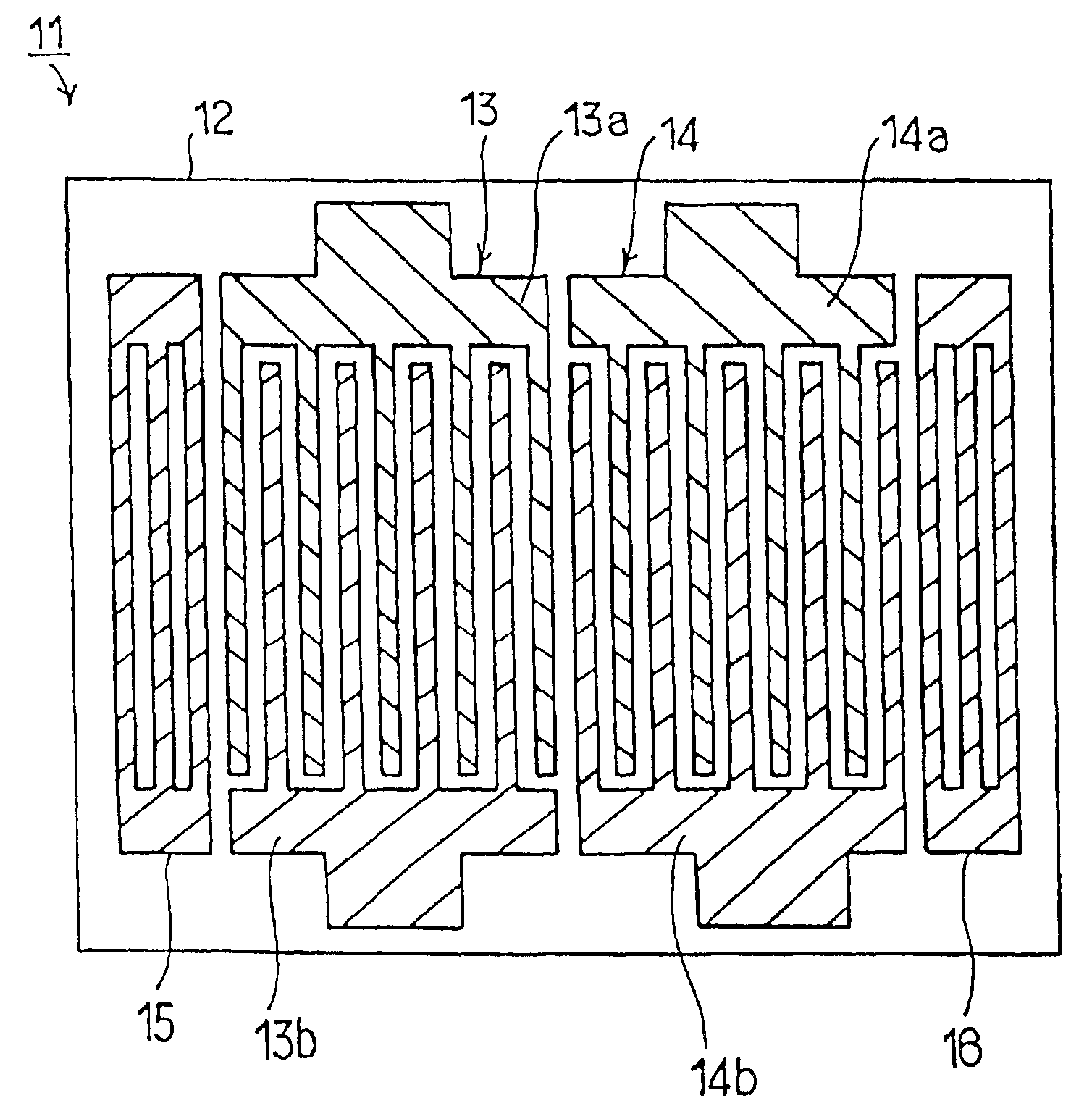
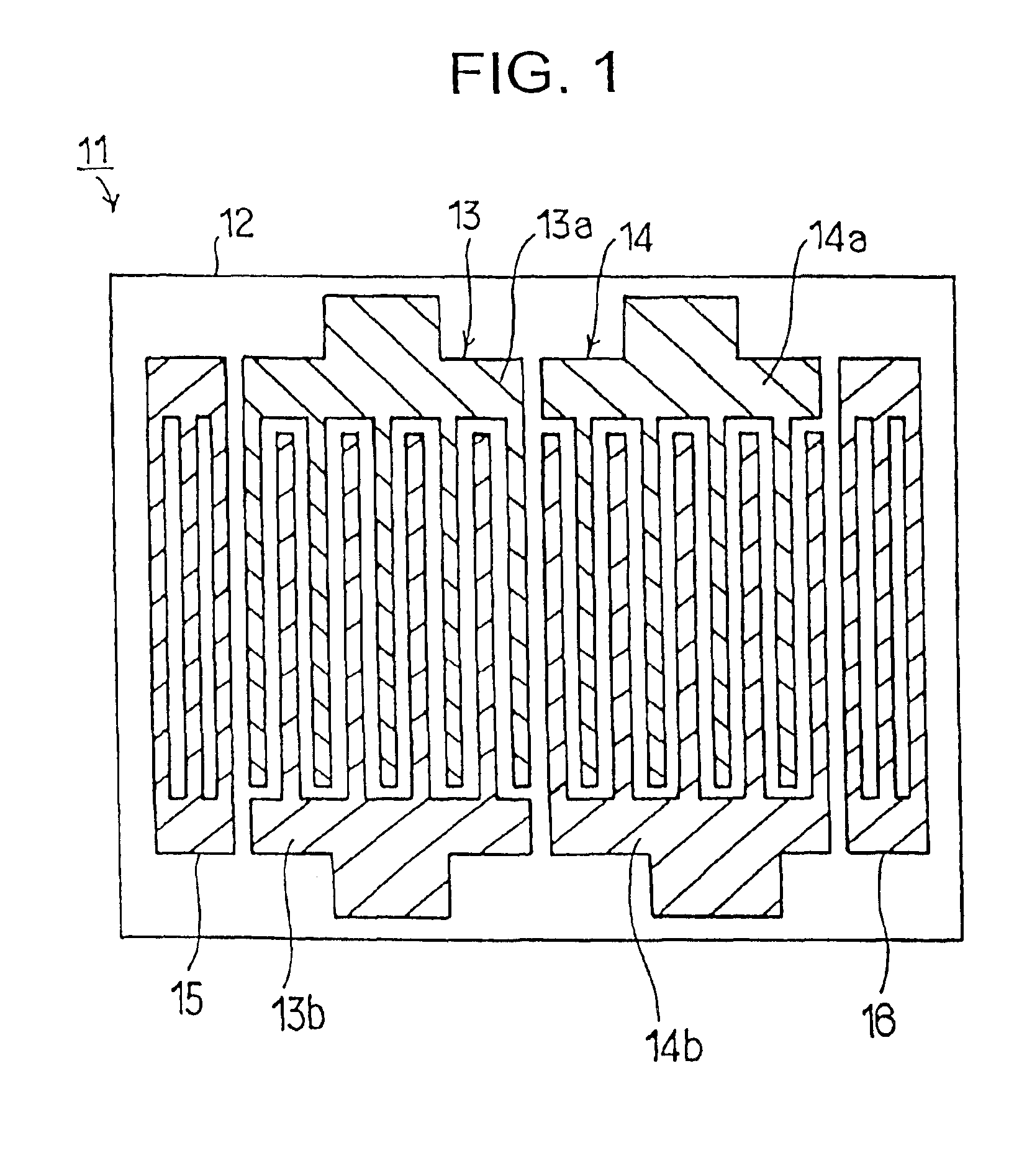
Method for manufacturing a surface acoustic wave device using a shear horizontal type surface acoustic wave
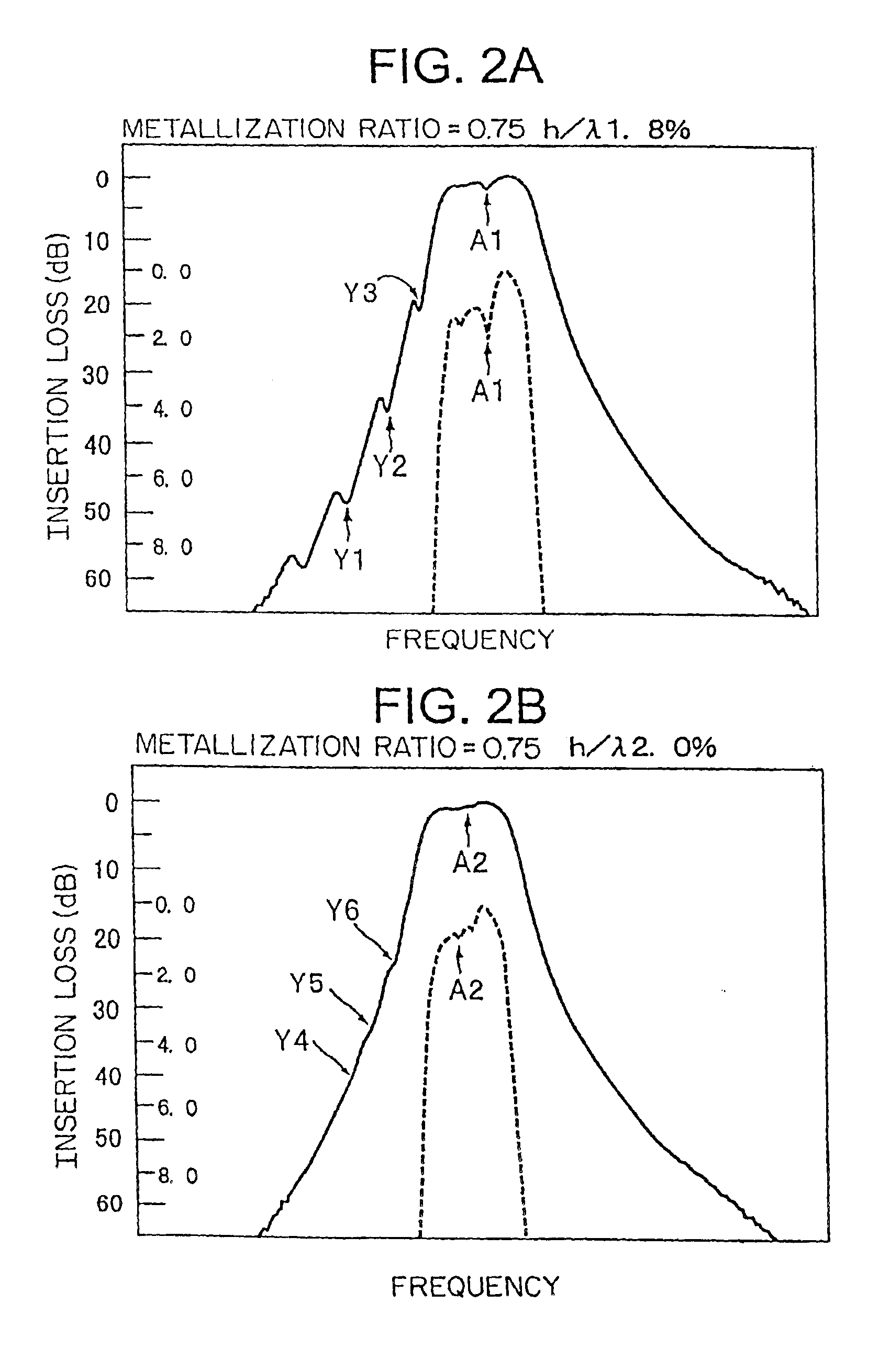
InactiveUS6865786B2Minimizes and eliminates rippleRemarkable effectPrinted circuit assemblingPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyTransverse modeSurface acoustic wave sensor
In a method of manufacturing a surface acoustic wave device using a Shear Horizontal type surface acoustic wave, at least one interdigital transducer (IDT) is made of a material having a larger mass-load effect than that of aluminum. The metallization ratio of the IDT and the normalization film thickness h / λ of the IDT are controlled such that ripple caused by a transversal mode wave is about 1.5 dB or less, where “h” indicates the film thickness of the electrodes and “h” indicates the wavelength of a surface acoustic wave.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Method and apparatus for manipulating particles
InactiveUS20160193613A1Improve conductivityAvoid heatingDielectrophoresisElectrostatic separatorsElectricityAcoustic wave
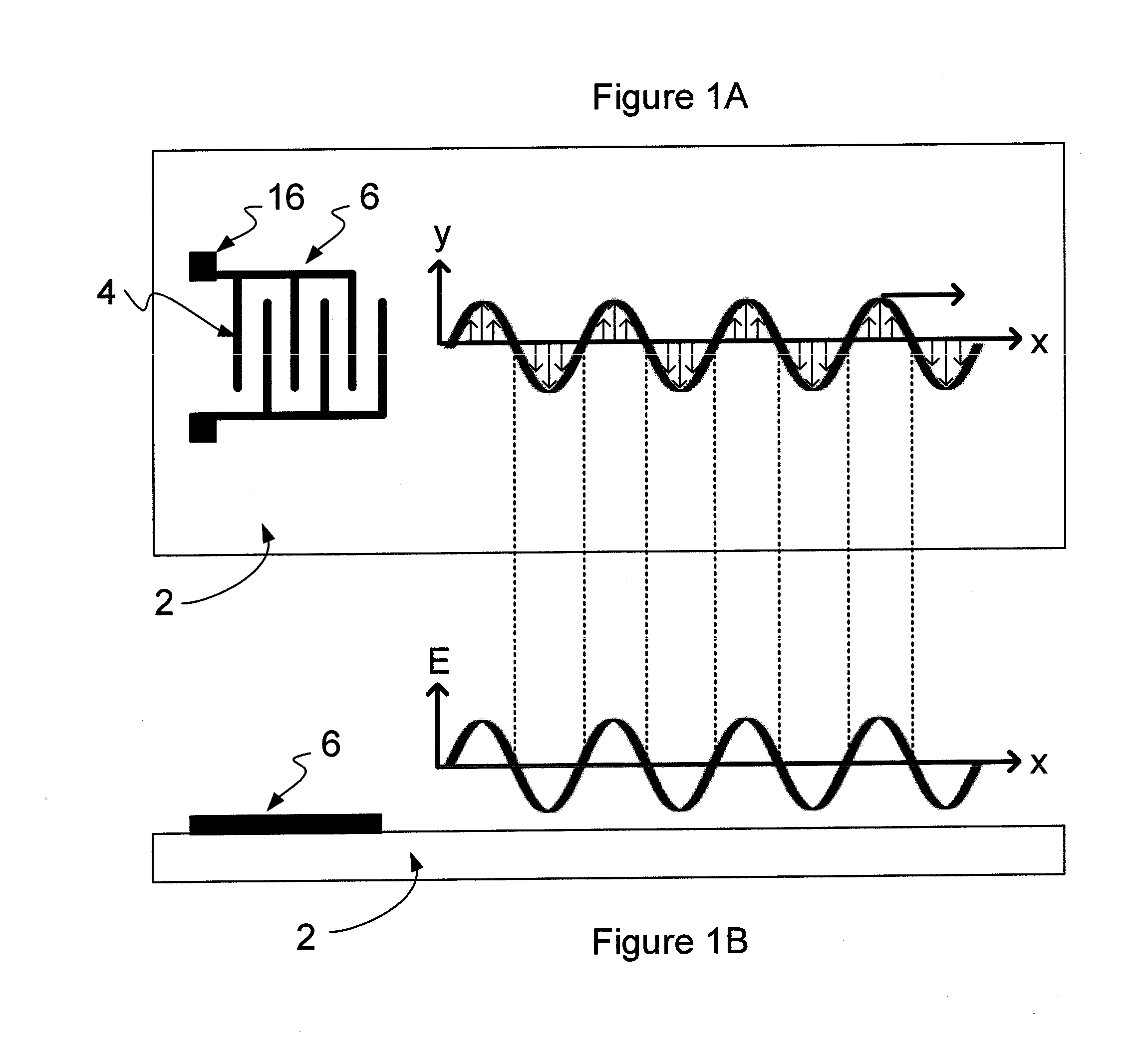
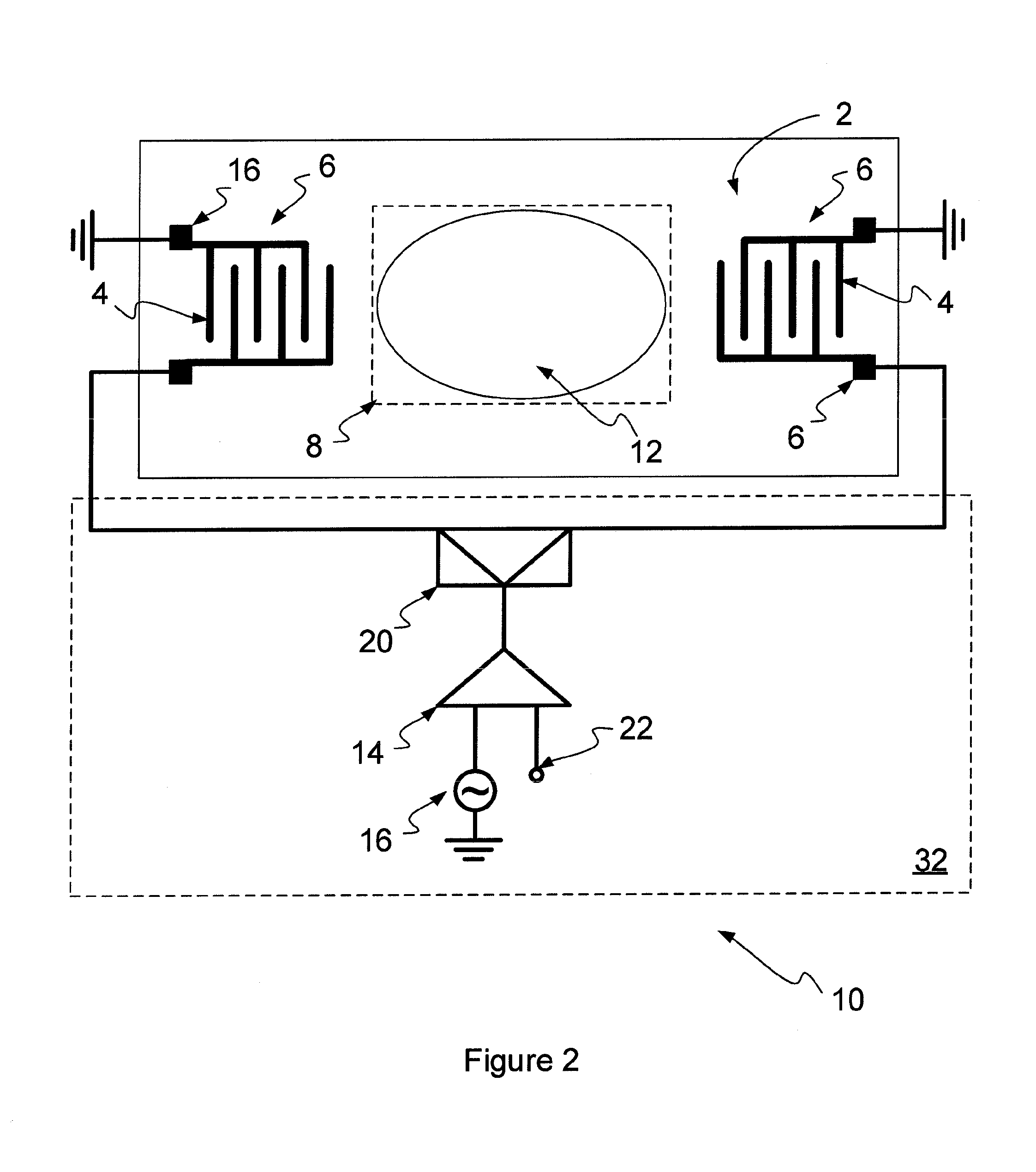
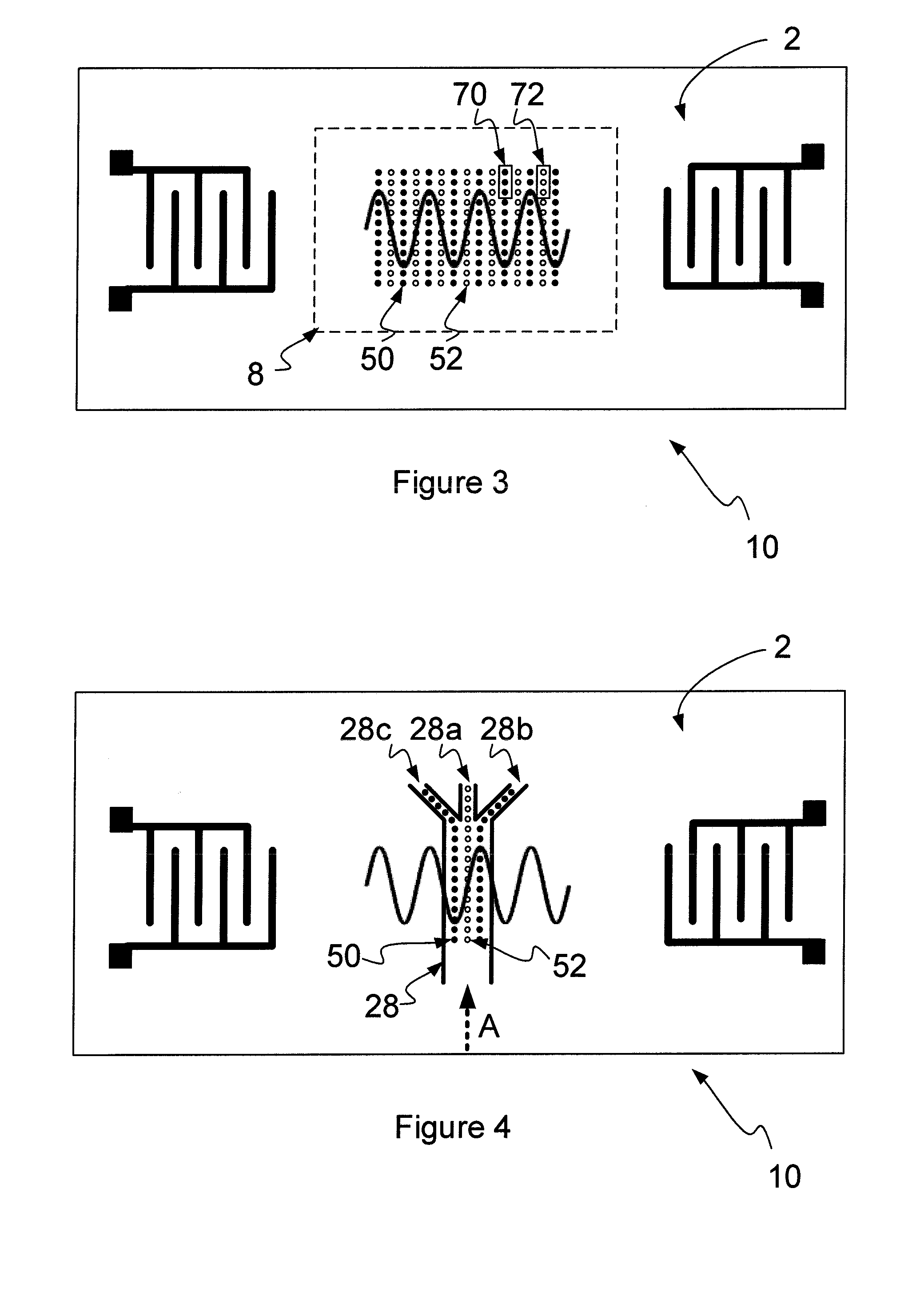
A method and apparatus for manipulating polarizable dielectric particles. The method includes positioning a liquid containing the particles above a surface of a piezoelectric material (2). The method also includes inducing a shear-horizontal surface acoustic wave in the piezoelectric material (2), thereby to form a time-varying non-uniform evanescent electric field extending into the liquid. The method further includes using the time-varying non-uniform evanescent electric field to apply a force to at least some of the particles (50, 52) by dielectrophoresis.
Owner:UNIV OF LEEDS
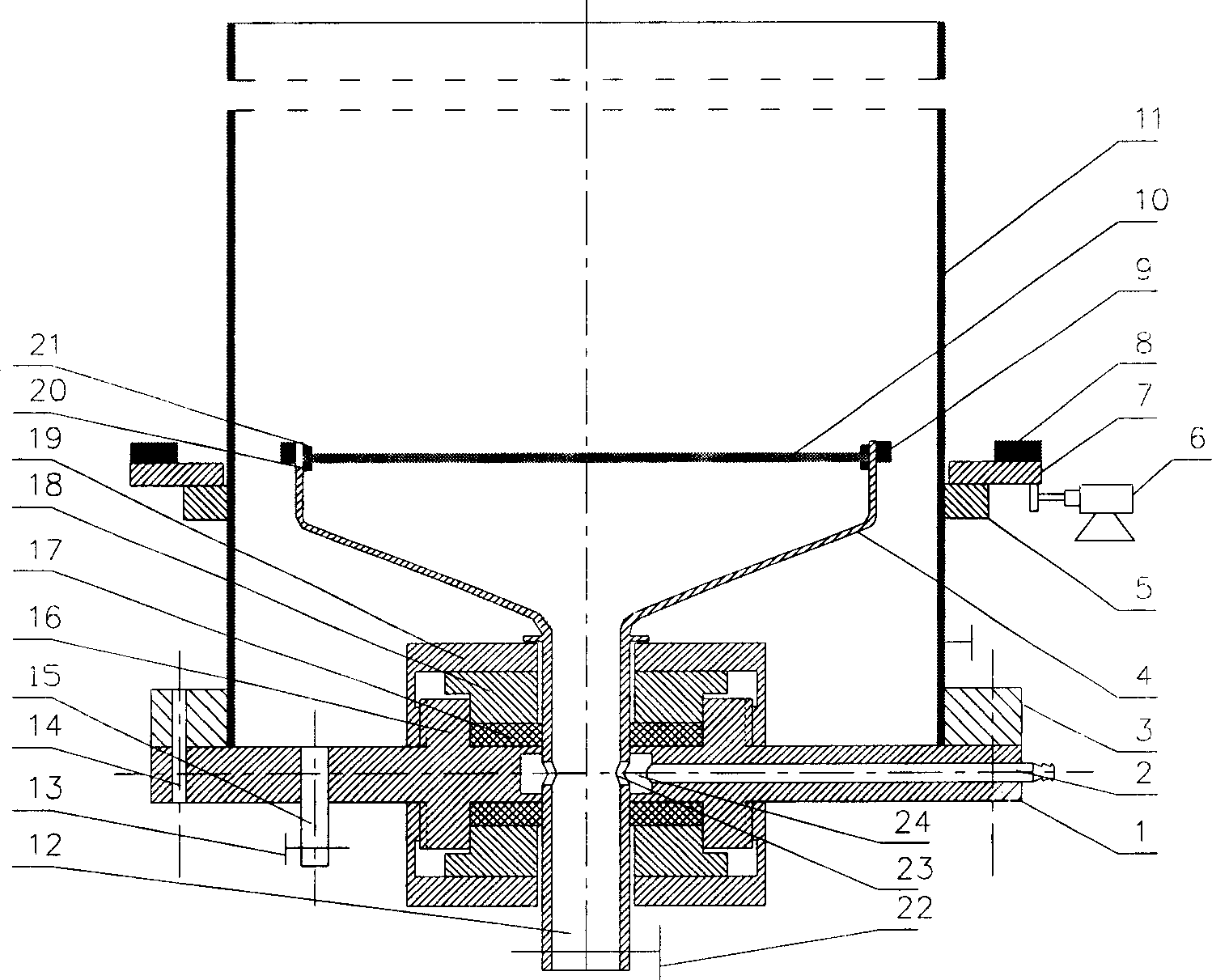
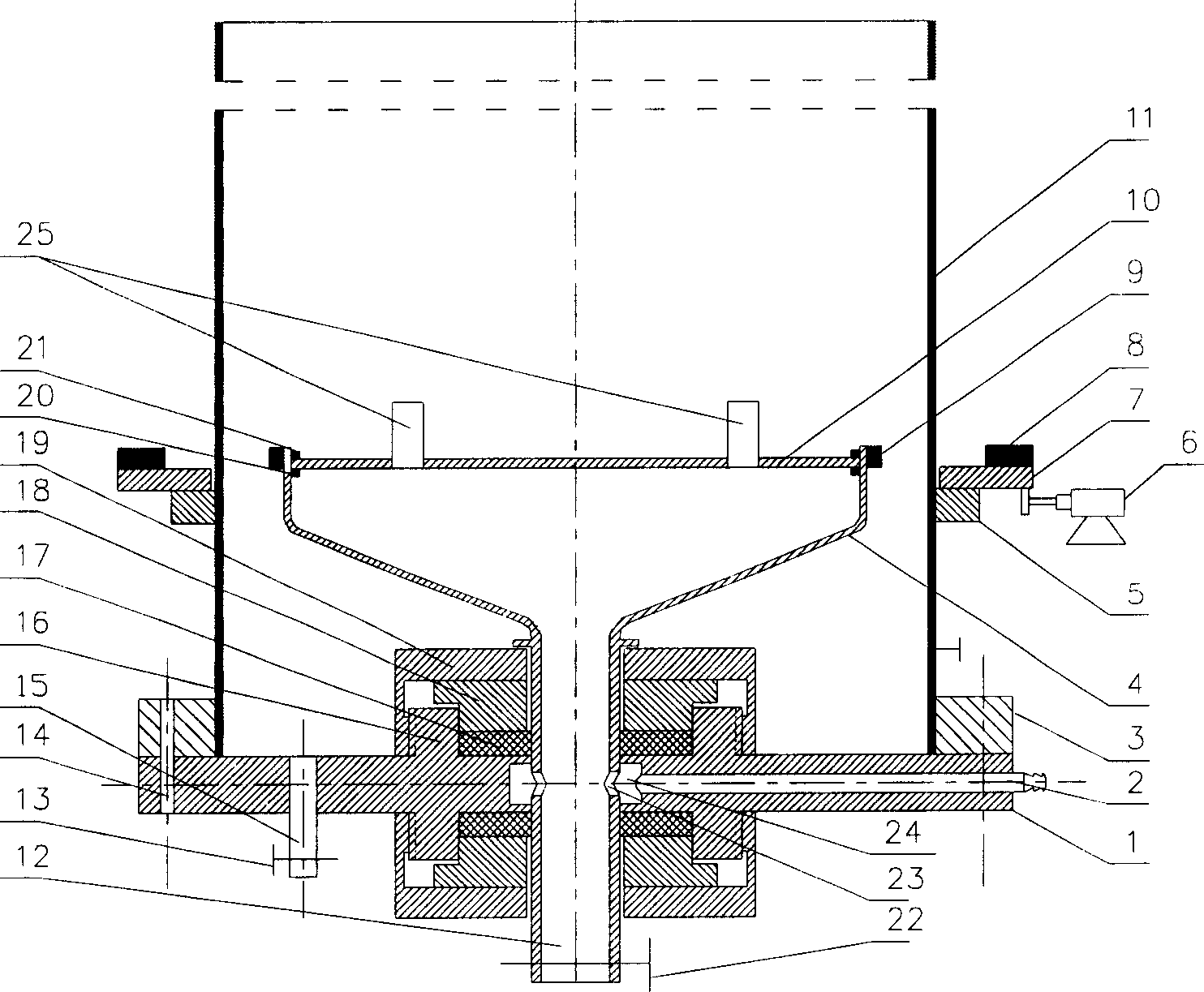
Method and apparatus for inspecting pipelines from an in-line inspection vehicle using magnetostrictive probes
InactiveUSRE40515E1Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial analysis using acoustic emission techniquesNon destructiveEngineering
A method and system for implementing magnetostrictive sensor techniques for the nondestructive evaluation of pipeline structures. The system consists of a magnetostrictive sensor instrument unit, a data storage unit, and a plurality of magnetostrictive sensor probes are positioned on an in-line inspection vehicle. The instrumentation unit includes electronics for transmitting excitation pulses to a transmitting magnetostrictive sensor probe as well as electronics for amplifying and conditioning the signals detected by a receiving magnetostrictive sensor probe. The magnetostrictive sensor probes include both plate magnetostrictive sensors and permanent magnets which provide a DC bias magnetic field necessary for magnetostrictive sensor operation. The transmitting and receiving probes are attached to the in-line inspection vehicle by way of mechanical arms on opposing sides of the vehicle. The mechanical arms are spring loaded and are equipped with rollers which maintain the probes at approximately constant distances from the inside diameter of the pipe wall. The method involves generating pulses of shear horizontal waves of frequencies less than 200 kHz. The transmitting magnetostrictive sensor probe generates a wave that propagates in both directions around the circumference of the pipe wall from a point adjacent to the transmitting probe. Both waves are thereafter received at the receiving probe spaced 180 degrees apart from the transmitting probe. Any defect present in the pipe wall within the circumference being investigated will show up in the received signal.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES INST
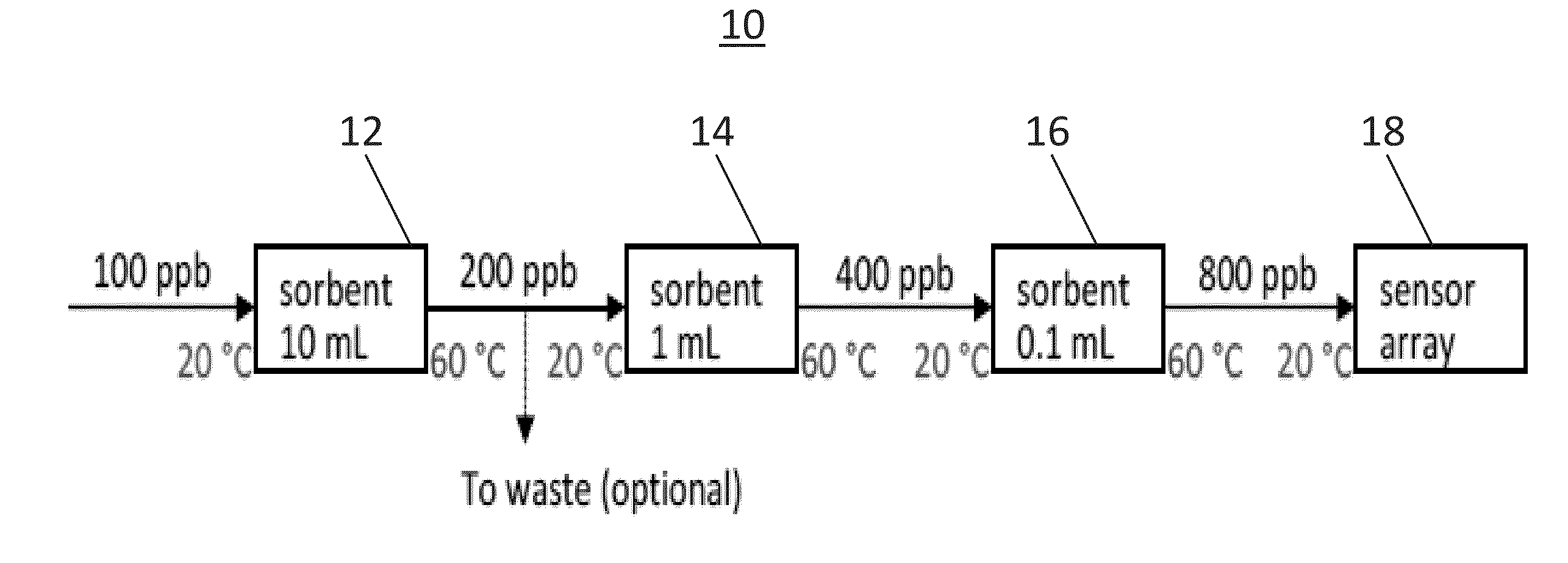
Detection of hydrocarbons in aqueous environments
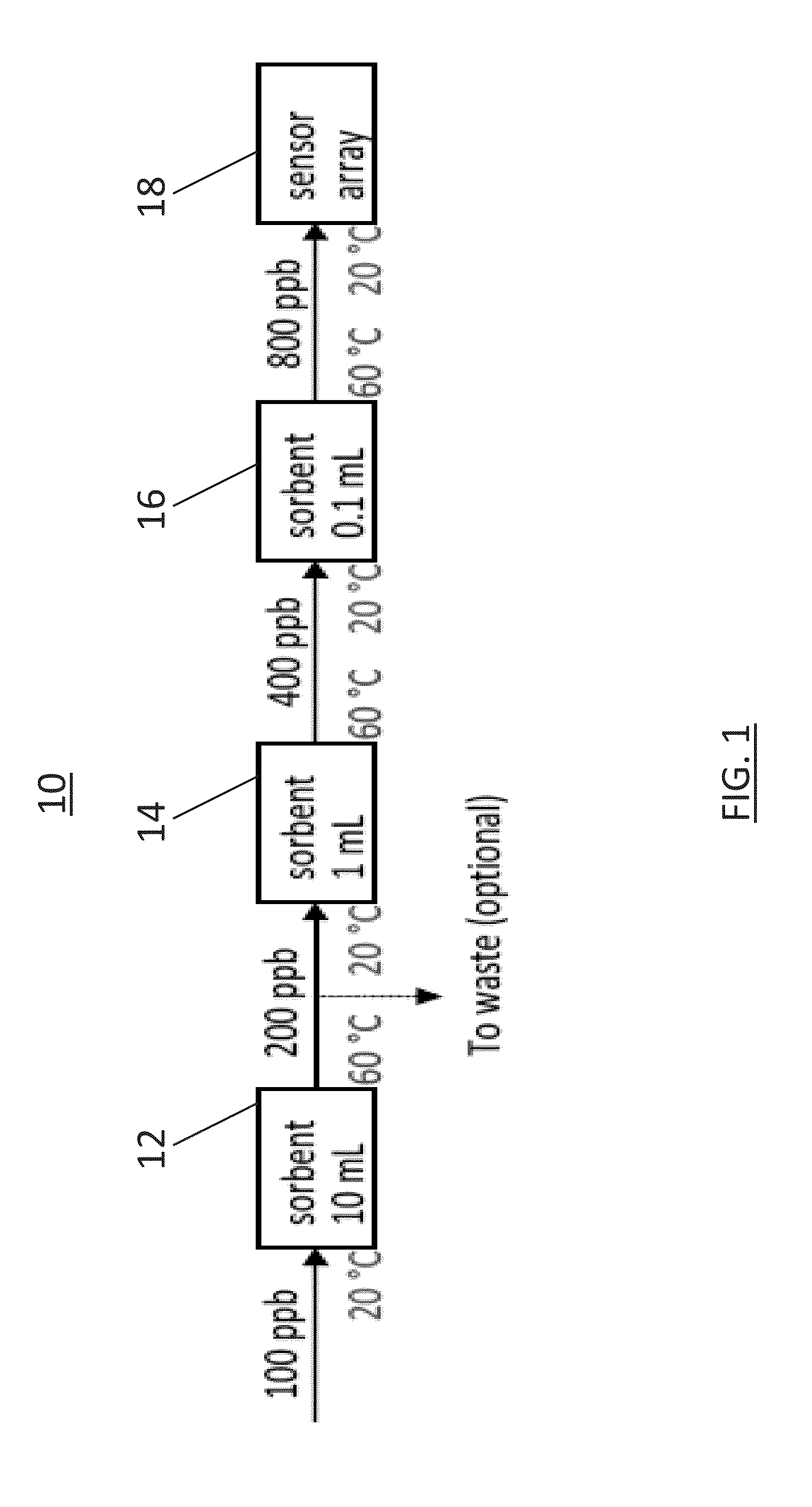
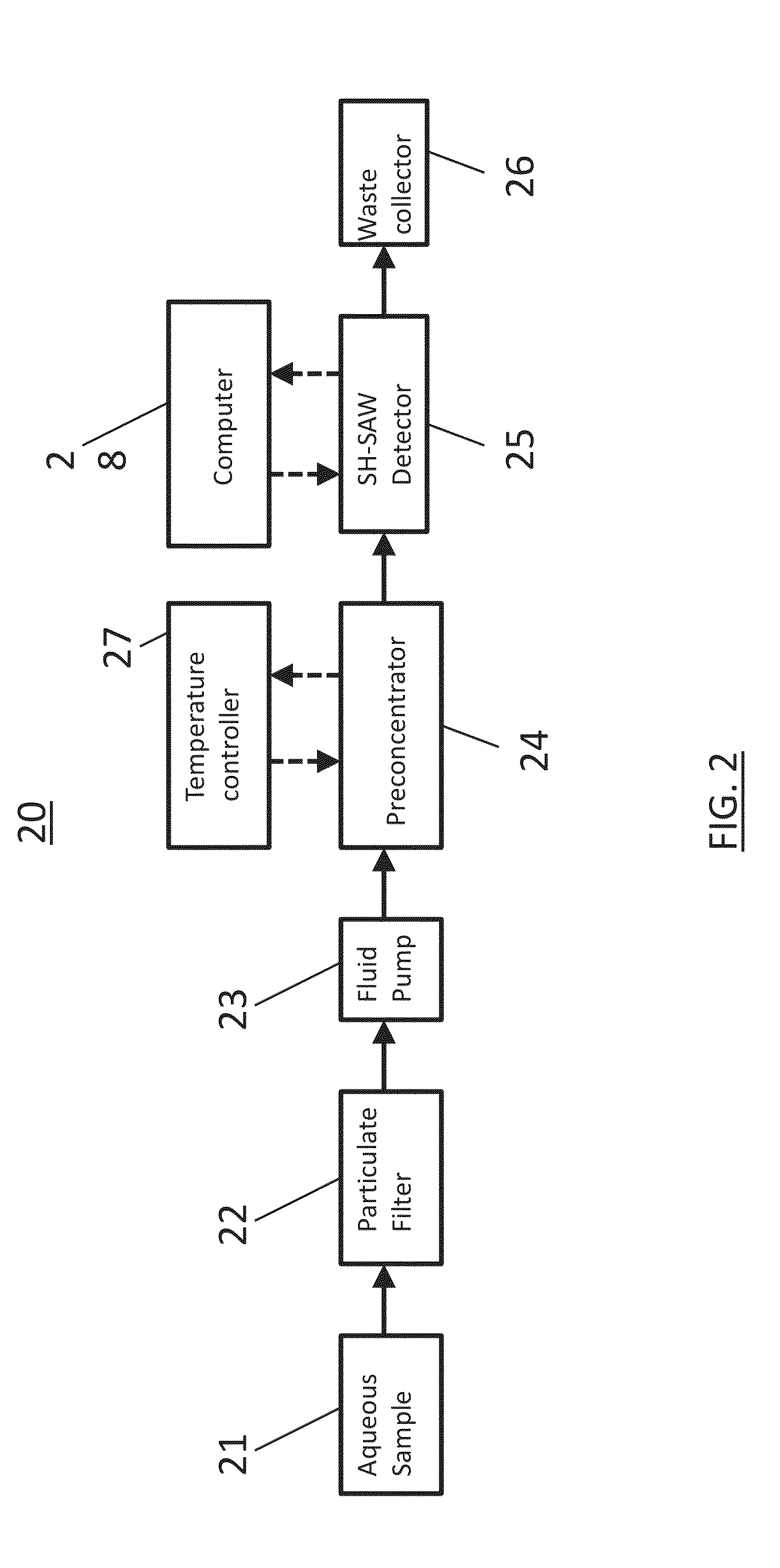
ActiveUS9244051B2Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPreparing sample for investigationContinuous useSorbent
A process for a pre-concentration unit including: a sorbent material coated passage-way having an entrance for receiving a hydrocarbon-containing groundwater sample and for pre-concentrating the hydrocarbons in a hydrocarbon-containing groundwater sample by successive sorption / desorption cycles, and having an exit for discharging the pre-concentrated hydrocarbons; a heating unit for heating the sorbent material coated passage-way; and; an array of shear horizontal-surface acoustic wave sensors with coatings adapted for detecting and quantifying the pre-concentrated hydrocarbons, disposed at the exit of the sorbent material coated passage-way; and a housing for enclosing the pre-concentration unit and the array of shear horizontal-surface acoustic wave sensors, adapted for continuous use at a body of hydrocarbon-containing groundwater, and coupled to mathematical methods for generating concentrations of specific analytes from both transient and steady-state signals.
Owner:MARQUETTE UNIVERSITY
Magnetic driven rotation gas distribution device in gas-fluid etc. heterogeneous system
InactiveCN1795973AChange speedWide distributionMixing methodsChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsEngineeringTower
The invention relates to a magnetic driving rotary gas distributor equipment of gas-liquid multi-phase system. It includes a tower device with magnetic driving device, the rotary-type gas distributor can be directly rotated in the tower bottom to make gas distribution. The gas distributor is driven by rotary permanent magnetic field produced by magnetic driving device and rotated so as to implement goal of rotary gas distribution. In the supporting disk of the gas distributor a gas ingress pipe hole is set, and the ring-shaped gas distribution cavity chamber in the supporting disk and the gas-feeding circular hole on the rotary hollow shaft can be used for making gas distribution, in the bottom end of the rotary hollow shaft a cleaning pollution-discharging valve is mounted.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
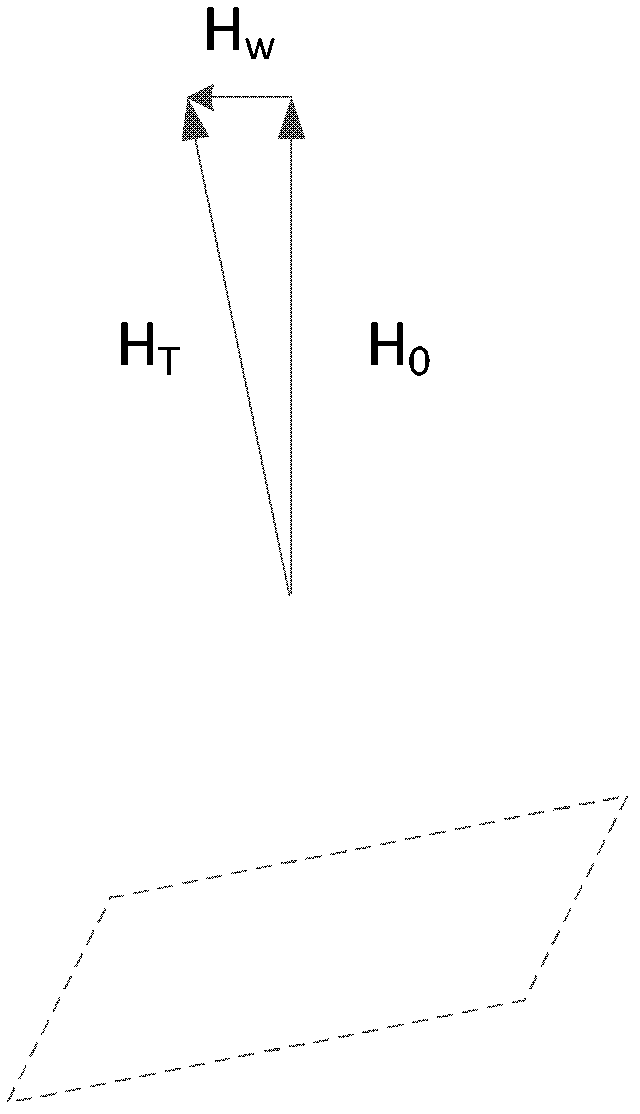
Omni-directional shear-horizontal wave magnetostrictive patch transducer and method of winding coil
ActiveUS20140354388A1Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesTransformersOmni directionalMagnet
Provided is a transducer. The transducer includes a permanent magnet that generates a magnetostatic field, a patch disposed below the permanent magnet and formed of a material that deforms according to a magnetic field, an insulator disposed on a top surface of the patch, and a coil wound around the patch and the insulator in a certain form and allowing a magnetomotive field to be induced on the patch according to an applied current. The wound coil has a form in which directions of the magnetostatic field generated by the permanent magnet and the magnetomotive field generated by winding the coil are orthogonal to each other.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Omni-directional shear-horizontal wave electromagnetic acoustic transducer
ActiveUS20160003779A1Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSpecific gravity measurementMagnetic polesConductive materials
A transducer is provided. The transducer includes: a permanent magnet unit formed in a form of a circular ring having upper and lower surfaces each having a predetermined diametrical direction width while having a circular through-portion in a central portion of the permanent magnet unit, the permanent magnet unit generating a vertical magnetic flux due to opposite magnetic poles that are formed in the upper and lower surfaces; and a coil wound in a diametrical direction across an area between an inner surface formed by the circular through-portion of the permanent magnet and an outer surface formed by an outer circumference of the permanent magnet and also wound in a circumferential direction of the permanent magnet, wherein the coil comprises a conductive material so that a current is applied to the coil, and when an alternating current is applied to the coil, a direction of the alternating current flowing along the coil and a direction of a magnetic field passing through the coil are orthogonal to each other.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Sensor, system, and method, for measuring fluid properties using multi-mode quasi-shear-horizontal resonator
InactiveUS7878044B2Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesFlow propertiesResonator filterDual mode
A system and a method for providing information on two of the three variables, density (ρ), viscosity (η), and elastic modulus (c) of a fluid, such that independent knowledge of one variable allows the remaining two variables to be measured by a single sensor. The present invention relies on the interaction of a predominantly shear horizontal acoustic wave device (“quasi-shear-horizontal”) with the fluid, so as to measure subtle differences in the interaction of two or more acoustic resonance states or waveguide modes of a multi-mode resonator or waveguide, and to derive the desired fluid characteristics therefrom. The most preferred embodiment is a dual-mode coupled resonator filter geometry with one resonant mode having a high degree of symmetry and the other having a high degree of anti-symmetry. By combining the additional information of multi-moded operation with the inherent ability of a horizontally-polarized quasi-shear-horizontal acoustic wave device (AWD) to operate in fluid environments, one obtains a multi-mode quasi-shear-horizontal (MMQSH) resonator.
Owner:KNOWLES CAPITAL FORMATION
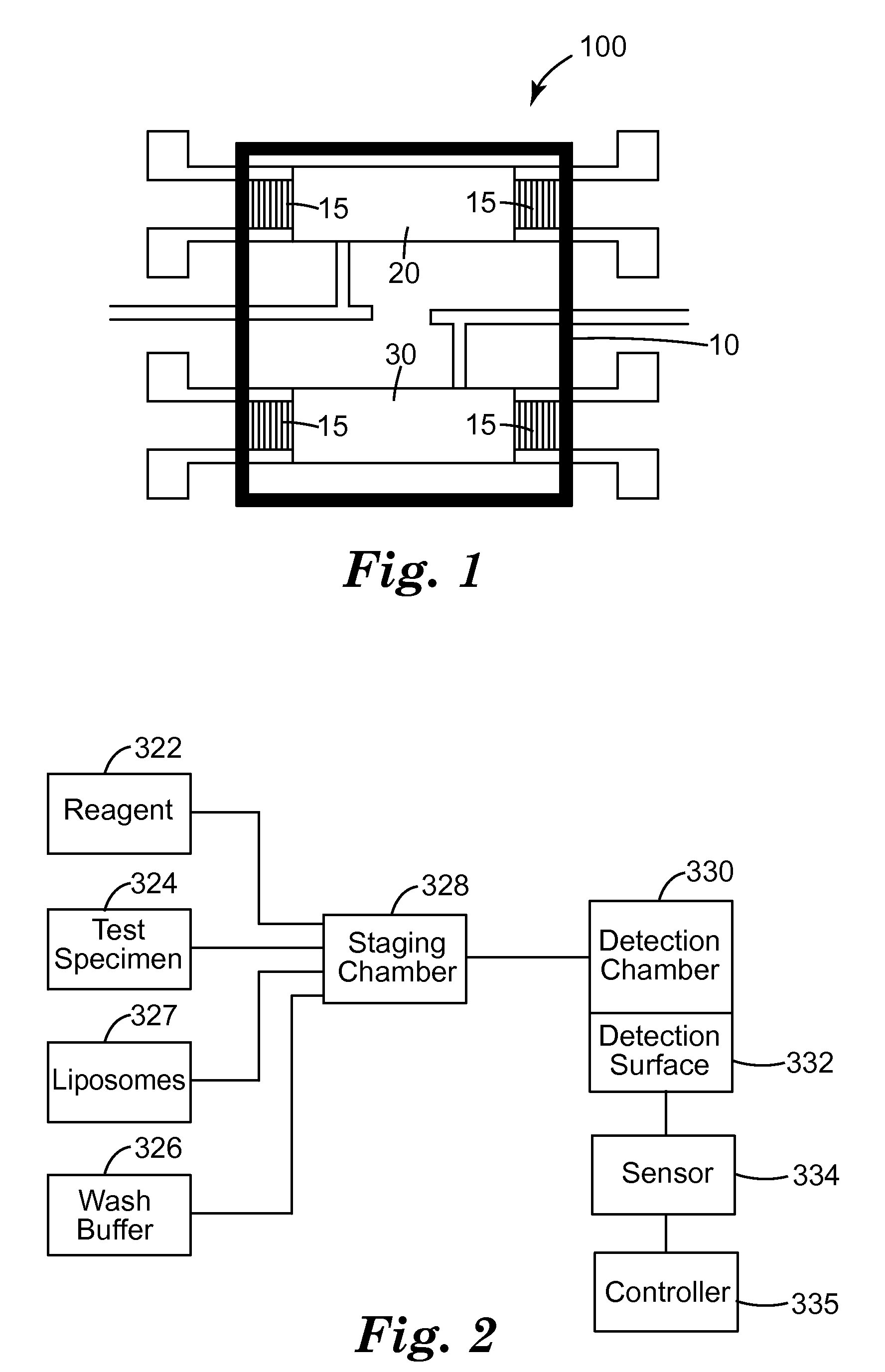
Method of detection of bioanalytes by acousto-mechanical detection systems comprising the addition of liposomes
InactiveUS20100151553A1Easy to detectGood signal responseMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentAnalyteMechanical energy
Methods for detecting target biological analytes within sample material using acousto-mechanical energy generated by a sensor are disclosed. The acousto-mechanical energy may be provided using an acousto-mechanical sensor, e.g., a surface acoustic wave sensor such as, e.g., a shear horizontal surface acoustic wave sensor (e.g., a LSH-SAW sensor). The detection of the target biological analytes in sample material are enhanced by contacting the target biological analyte and / or the sensor surface with liposomes that amplify the sensor sensitivity by (1) modifying the rheological properties of the fluid near the sensor surface; (2) changing the mass attached to the surface; and / or (3) modifying the dielectric properties of the fluid near the sensor surface, the sensor surface itself and / or any intervening layers on the sensor surface.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
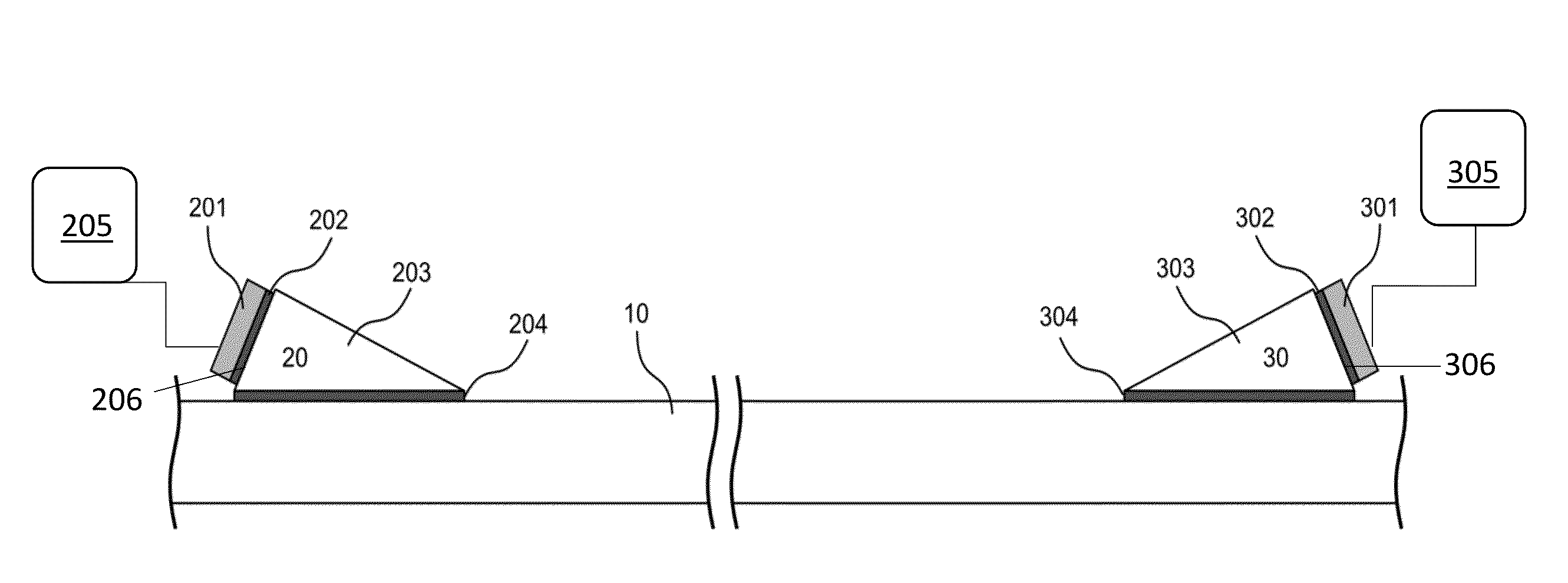
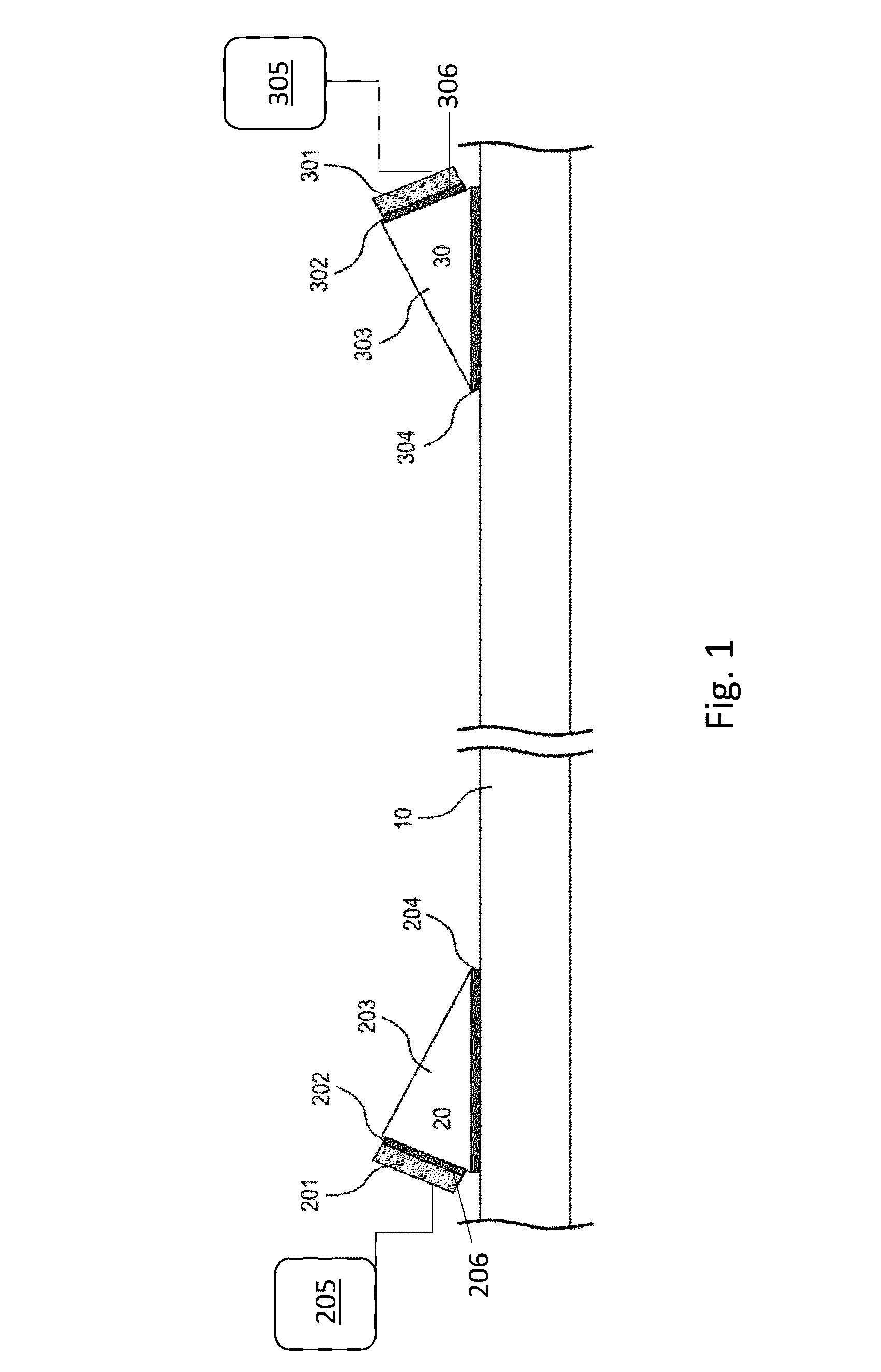
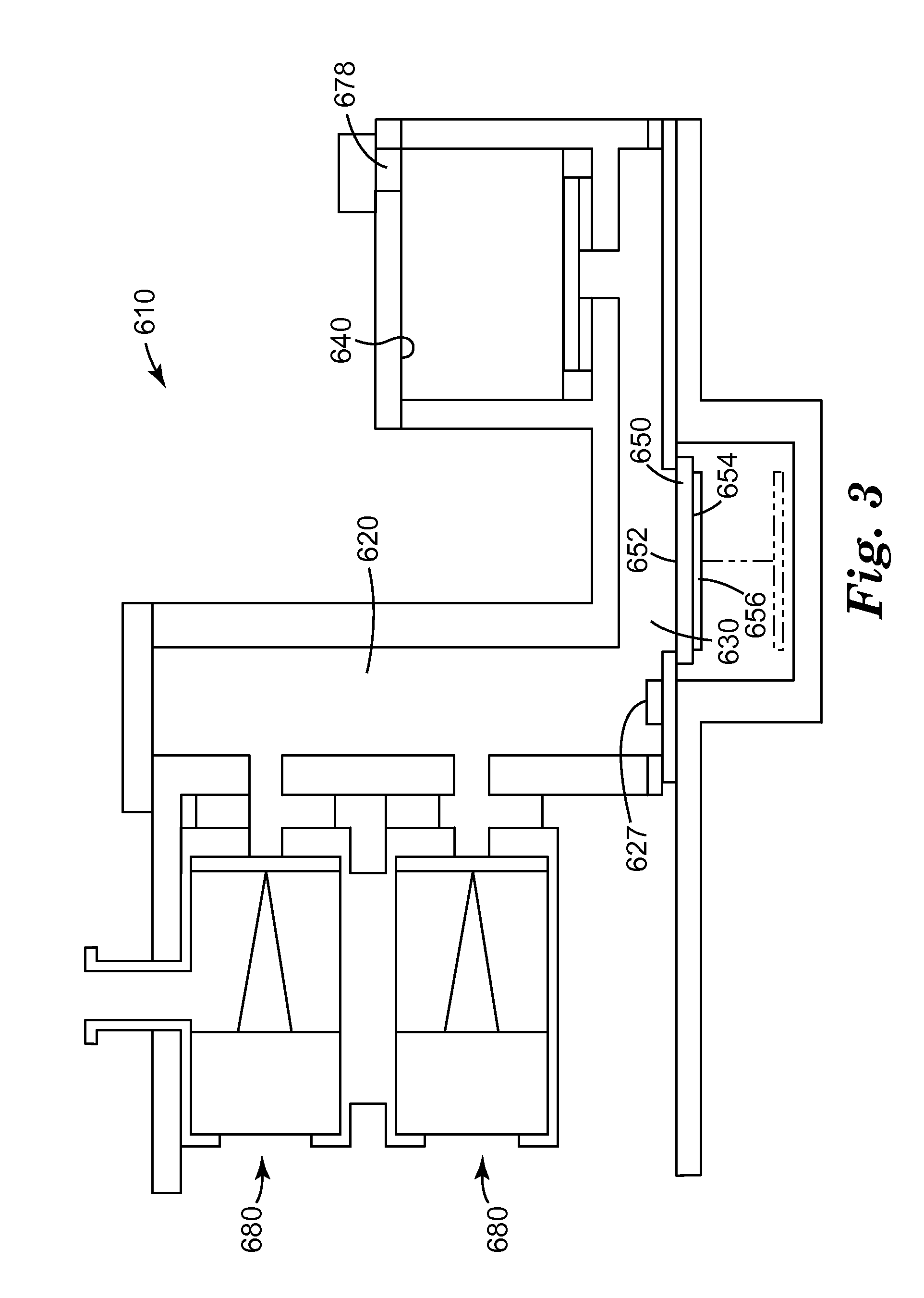
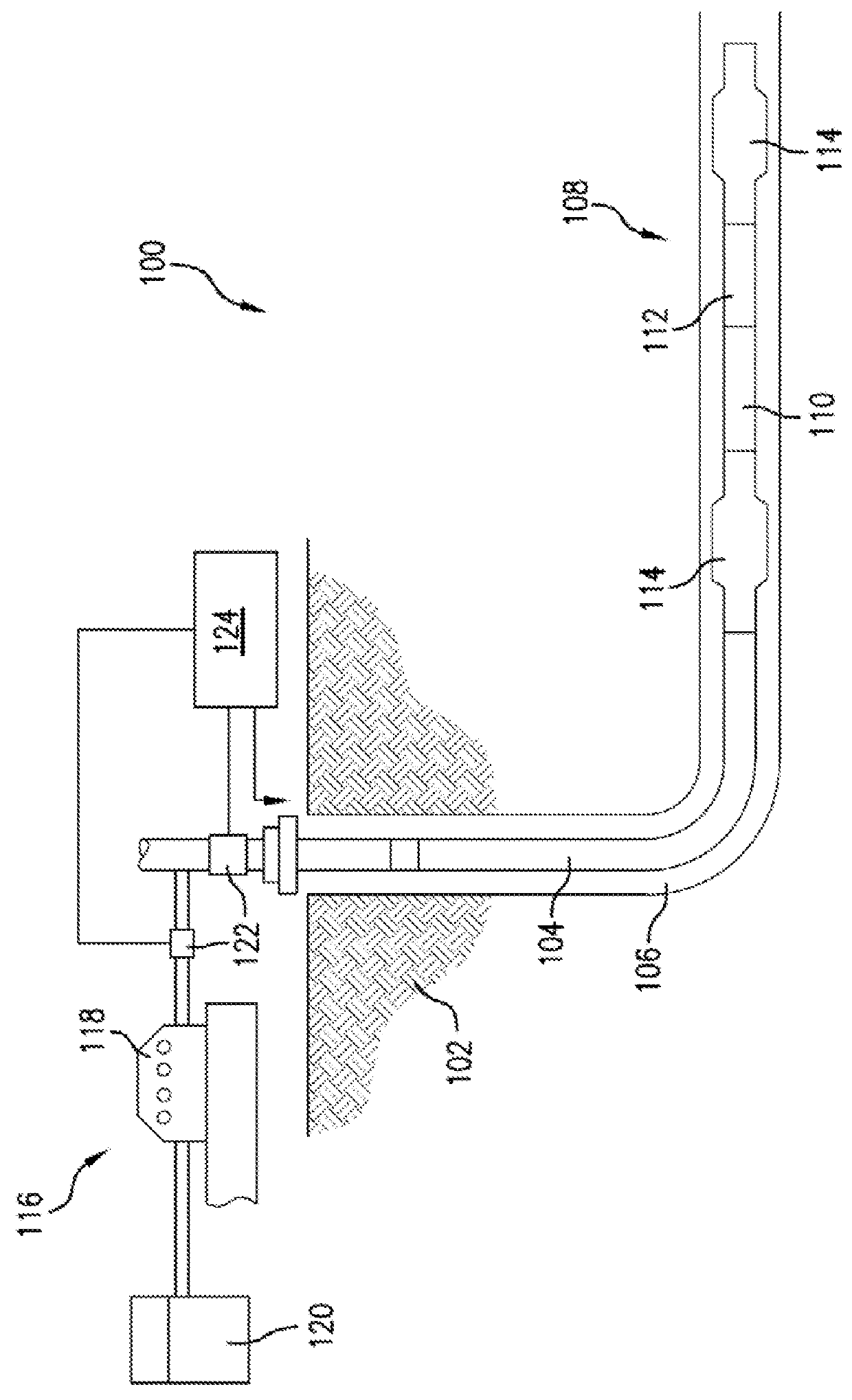
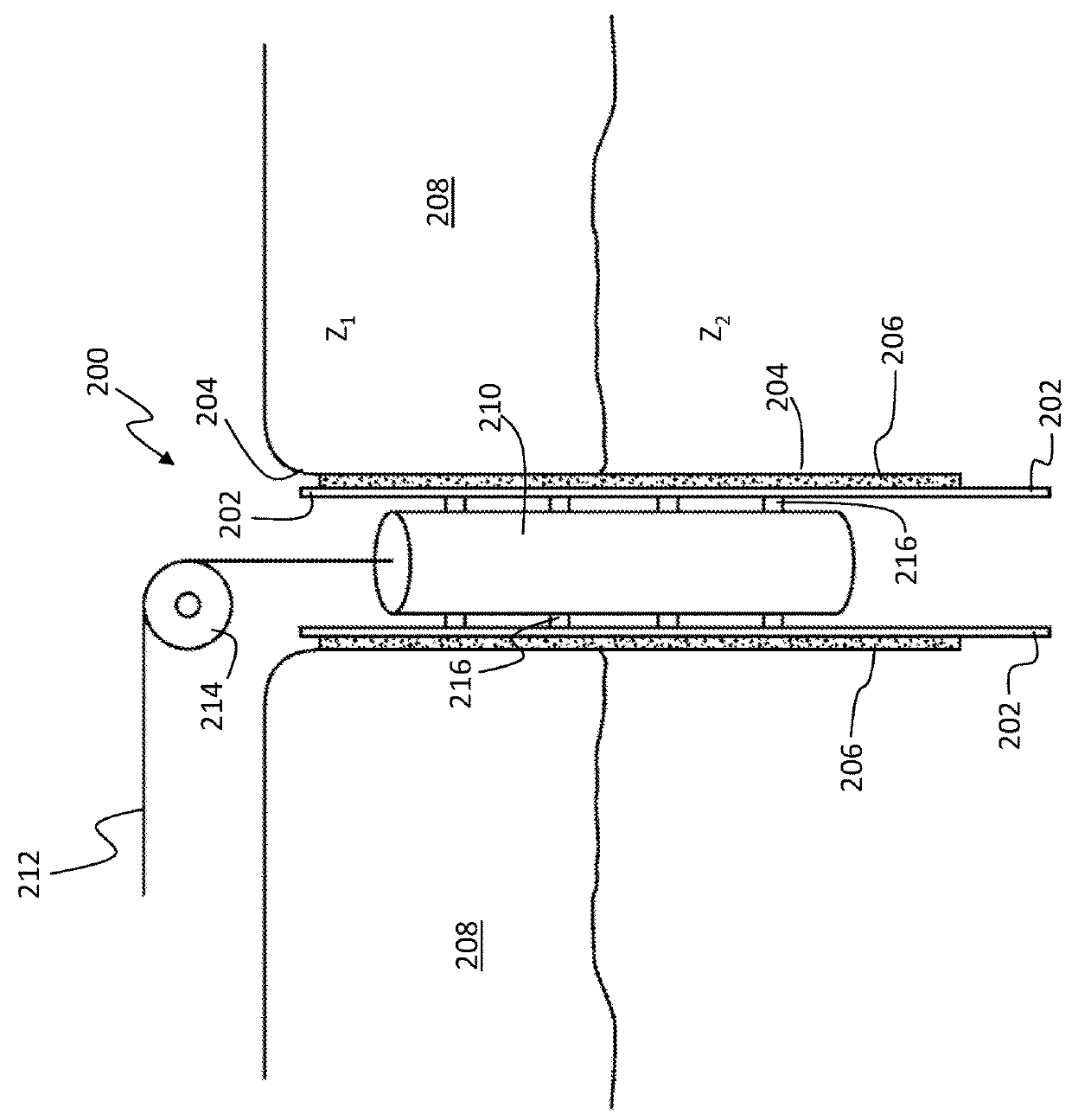
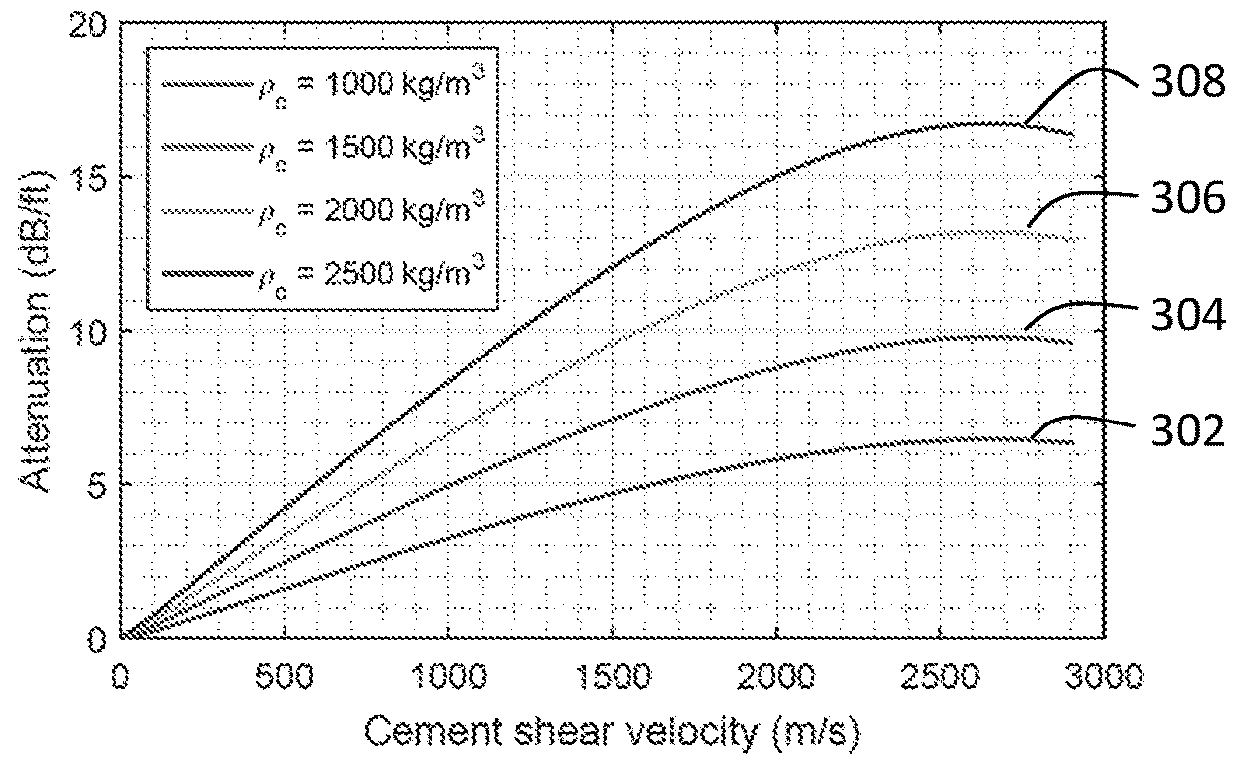
Evaluation of physical properties of a material behind a casing utilizing guided acoustic waves
Systems and methods for determining physical properties of a material in contact with an external surface of a casing disposed in a borehole including inducing, with a transducer, a first shear horizontal (SH) wave in the casing at a first SH order, measuring, with a sensor disposed on the casing, an attenuation of the first SH wave to generate a first measurement, inducing a second SH wave in the casing at a second SH order that is different from the first SH order, measuring an attenuation of the second SH wave to generate a second measurement, and extracting a physical properties of the material in contact with the external surface of the casing from the first and second measurements.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Microcavity enhanced surface acoustic wave devices
ActiveUS8089196B1High sensitivityReduced Power RequirementsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesImpedence networksPolystyreneFinite element method
Shear-horizontal surface acoustic wave sensors with micro-cavities in the delay paths were studied using finite element methods. The microcavity devices are SAW delay path devices that have the delay path etched with square patterns at various wavelength dimensions and varying depths to increase the dispersion and bulk to surface wave conversion. Additionally the microcavities are filed with polystyrene to act as an inhomogeneous waveguide for further entrapment of wave energy near the device surface. The effects of micro-cavities and grooves on SAW propagation show significantly greater energy transmission than the other structures presented traditional sensors.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Medium-range magnetostrictive ultrasonic guided wave scanner systems and methods
ActiveUS10119942B2Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMagnetizationUltrasonic guided wave
An inspection system includes a magnetostrictive scanner probe, a ferromagnetic strip, at least one magnet, and a processor. The magnetostrictive scanner probe includes a probe body for supporting at least one flexible sensor coil and a position encoder. The ferromagnetic strip is configured to be coupled to a structure, and the at least one magnet is configured to apply a biasing magnetization to the ferromagnetic strip. The processor is configured to cause a time-varying current to be generated in the at least one flexible sensor coil to induce a time-varying magnetization in said ferromagnetic strip perpendicular to said biasing magnetization to generate shear horizontal-type guided wave energy into said structure, and process reflected shear horizontal-type guided wave energy received by the at least one flexible sensor coil as the probe is moved relative to said structure to generate at least one two-dimensional image of a region of said structure.
Owner:FUKUOKA BROADCASTING CORPORATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com