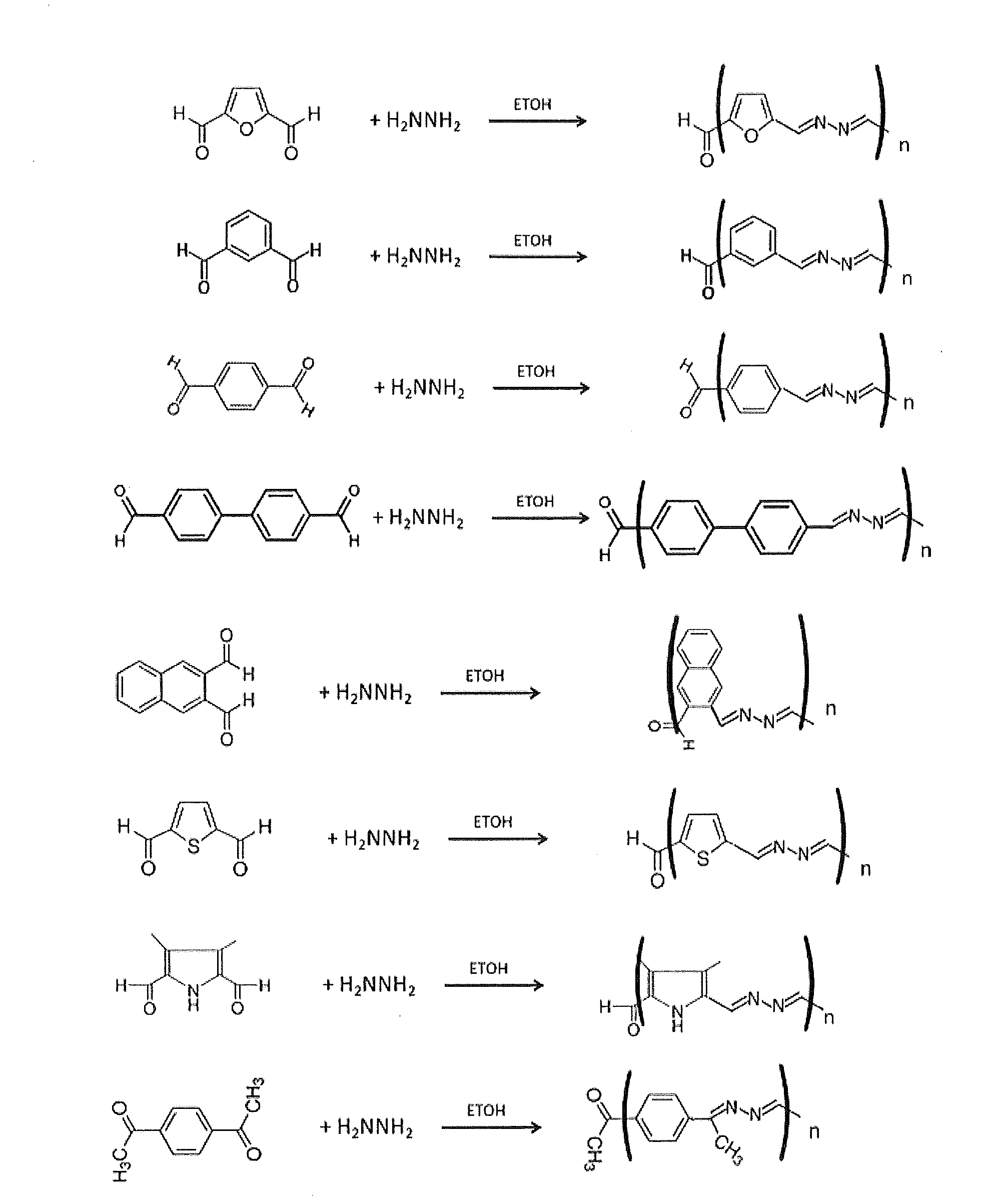
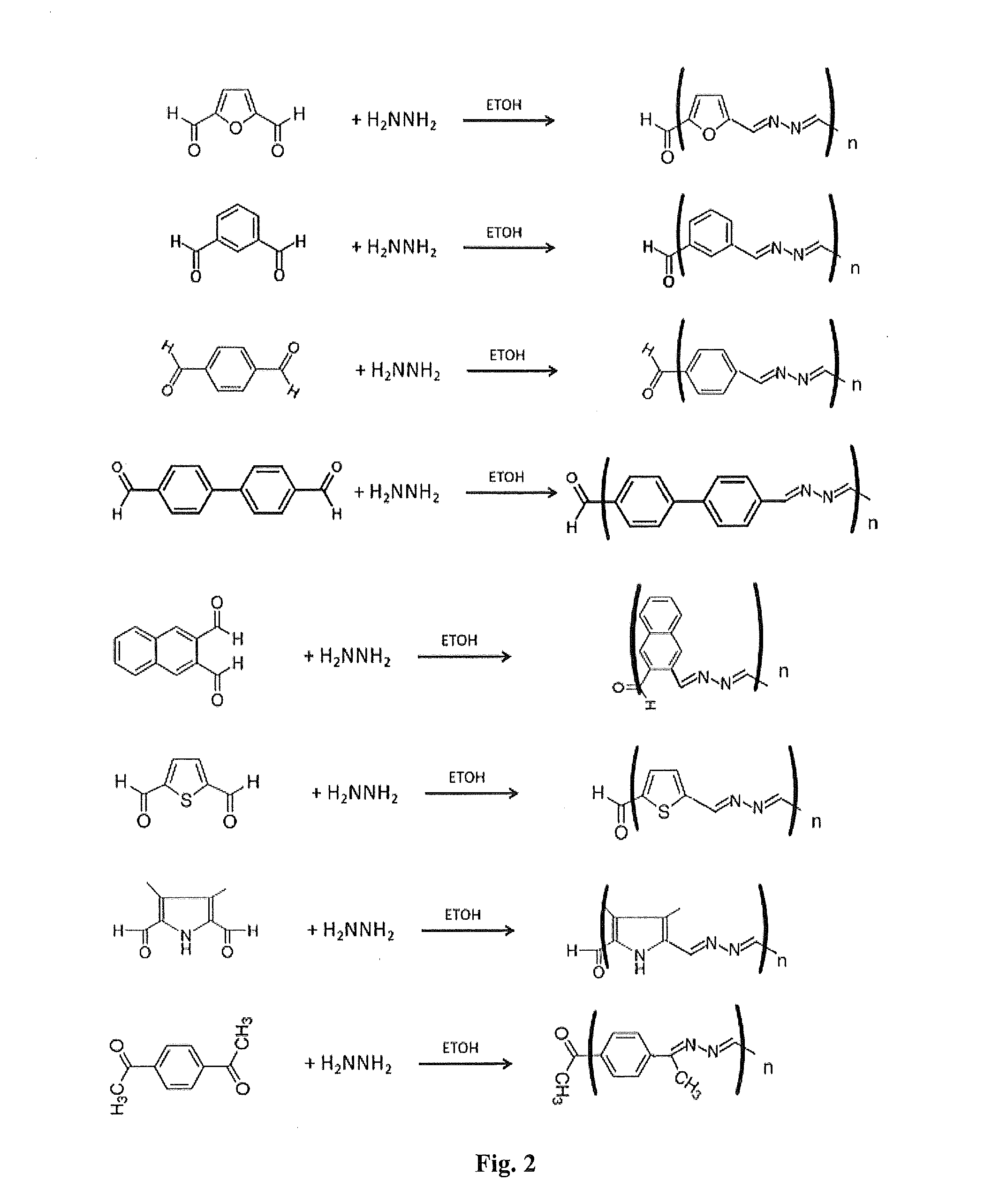
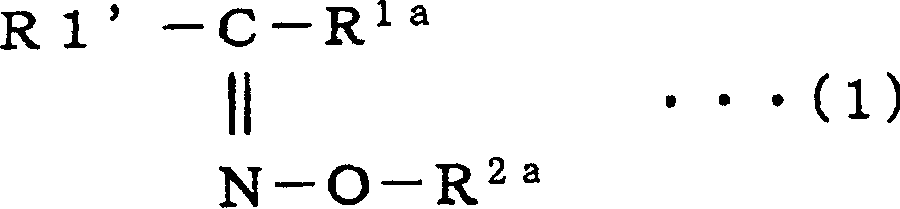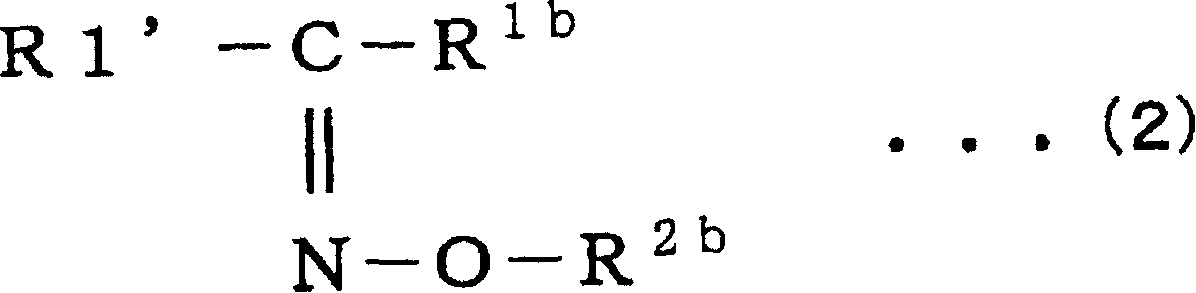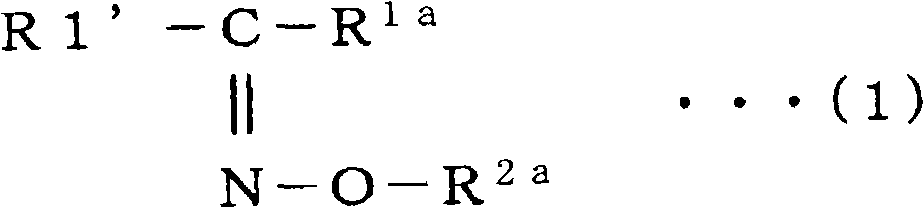Patents
Literature
33results about "Diazomethine dyes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Negative dye-containing curable composition, color filter and method of producing the same
InactiveUS20060051685A1High sensitivityExcellent in heat fastnessOrganic chemistryPhotosensitive materialsArylHydrogen atom
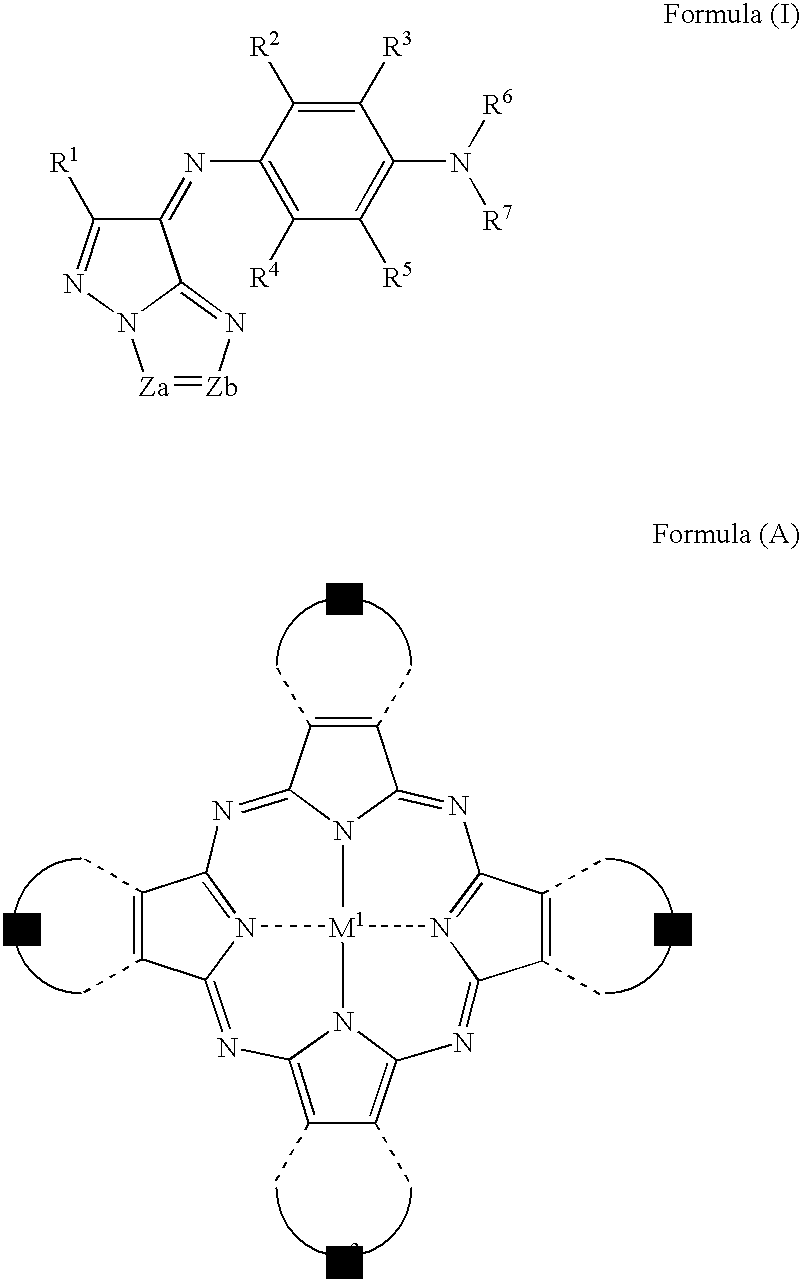
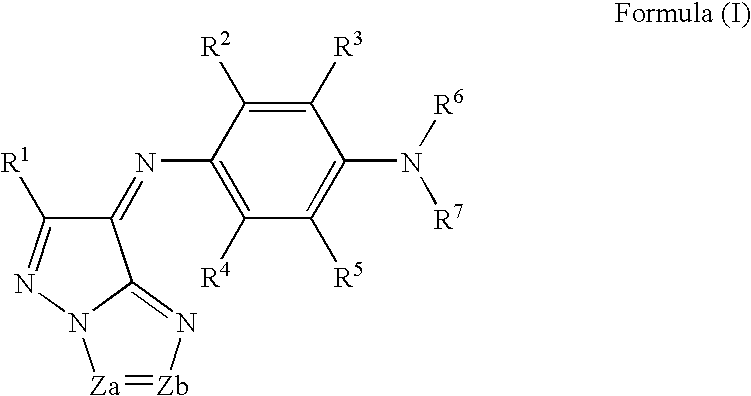
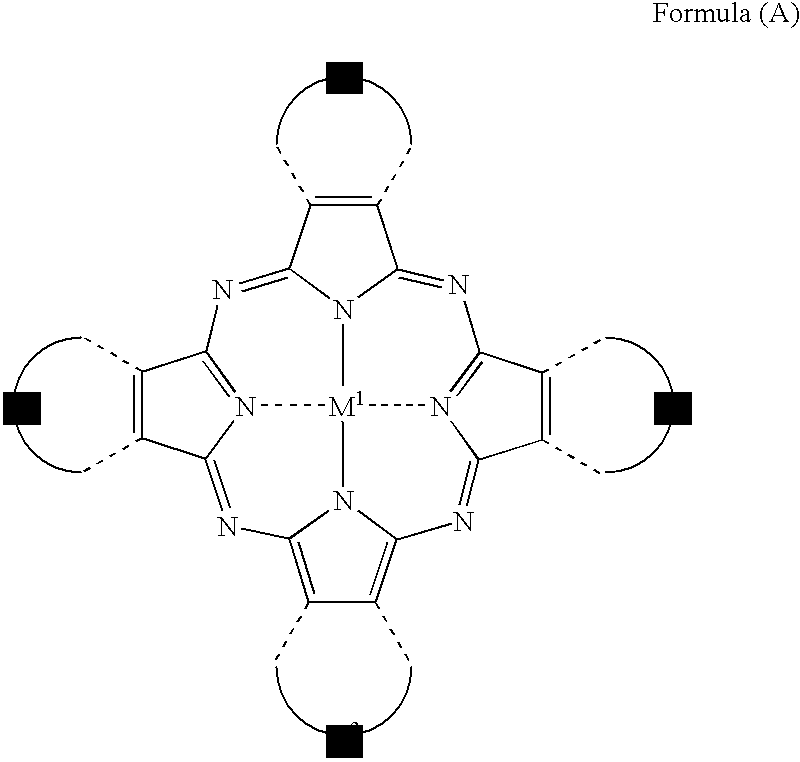
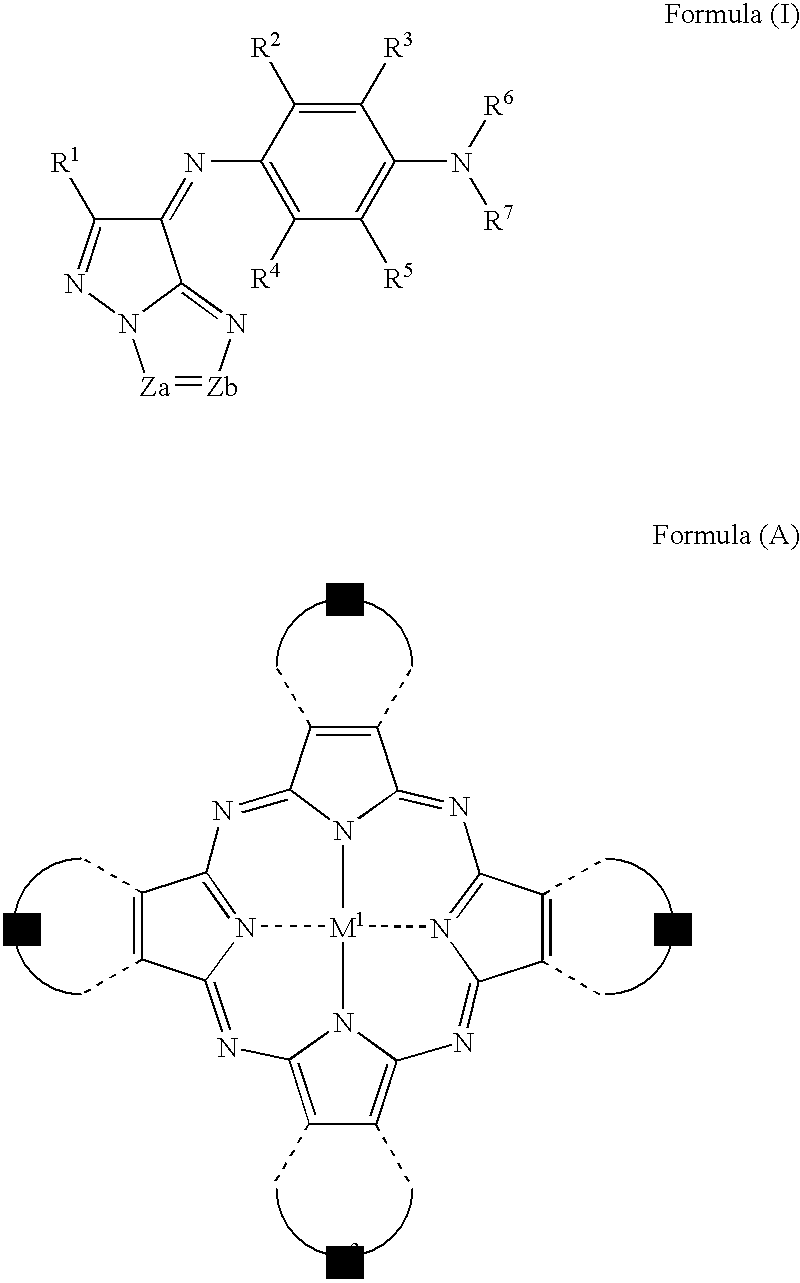
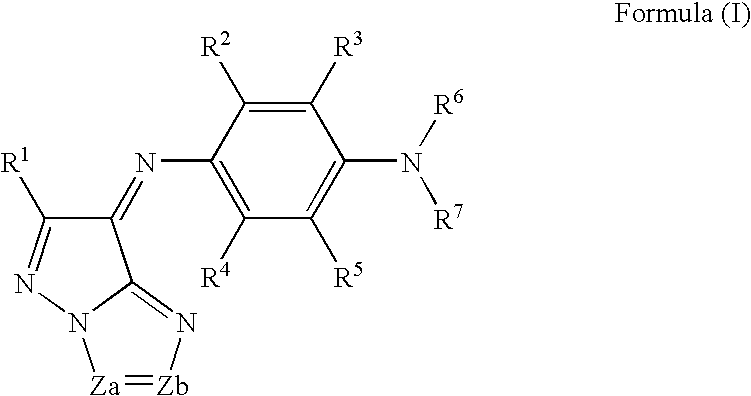
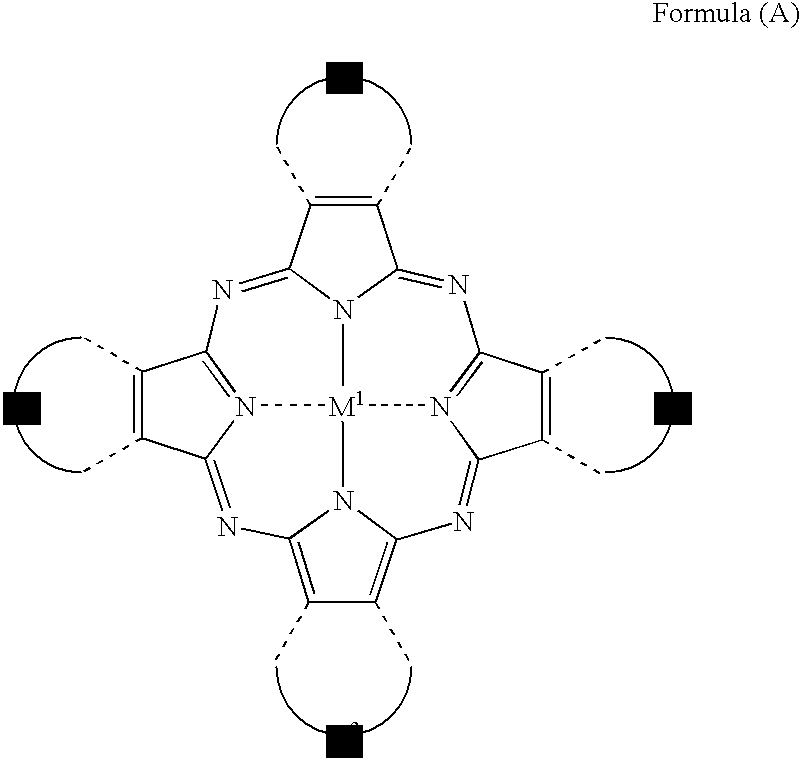
The present invention provides a negative dye-containing curable composition comprising at least (A) an alkali-soluble binder, (B) an organic solvent-soluble dye, (C) a photopolymerization initiator, (D) a radical-polymerizable monomer and (E) an organic solvent, wherein the organic solvent-soluble dye (B) comprises at least one kind of azomethine-type dye represented by the following formula (I) and at least one kind of tetraazaporphyrin-type dye represented by the following formula (A), and the photopolymerization initiator (C) is an oxime-type compound, wherein R1 represents a hydrogen atom or a substituent group; R2 to R5 each represent a hydrogen atom or a substituent group, R6 to R7 each represent an alkyl group, alkenyl group, aryl group or heterocyclic group, Za and Zb each represent —N═ or —C(R8)═; R8 represents a hydrogen atom, alkyl group, aryl group or heterocyclic group; M1 represents a metal, and Z1 to Z4 each represent an atomic group forming a 6-membered ring composed of atoms selected from carbon and nitrogen.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Unsymmetrical cyanine dimer compounds and their application
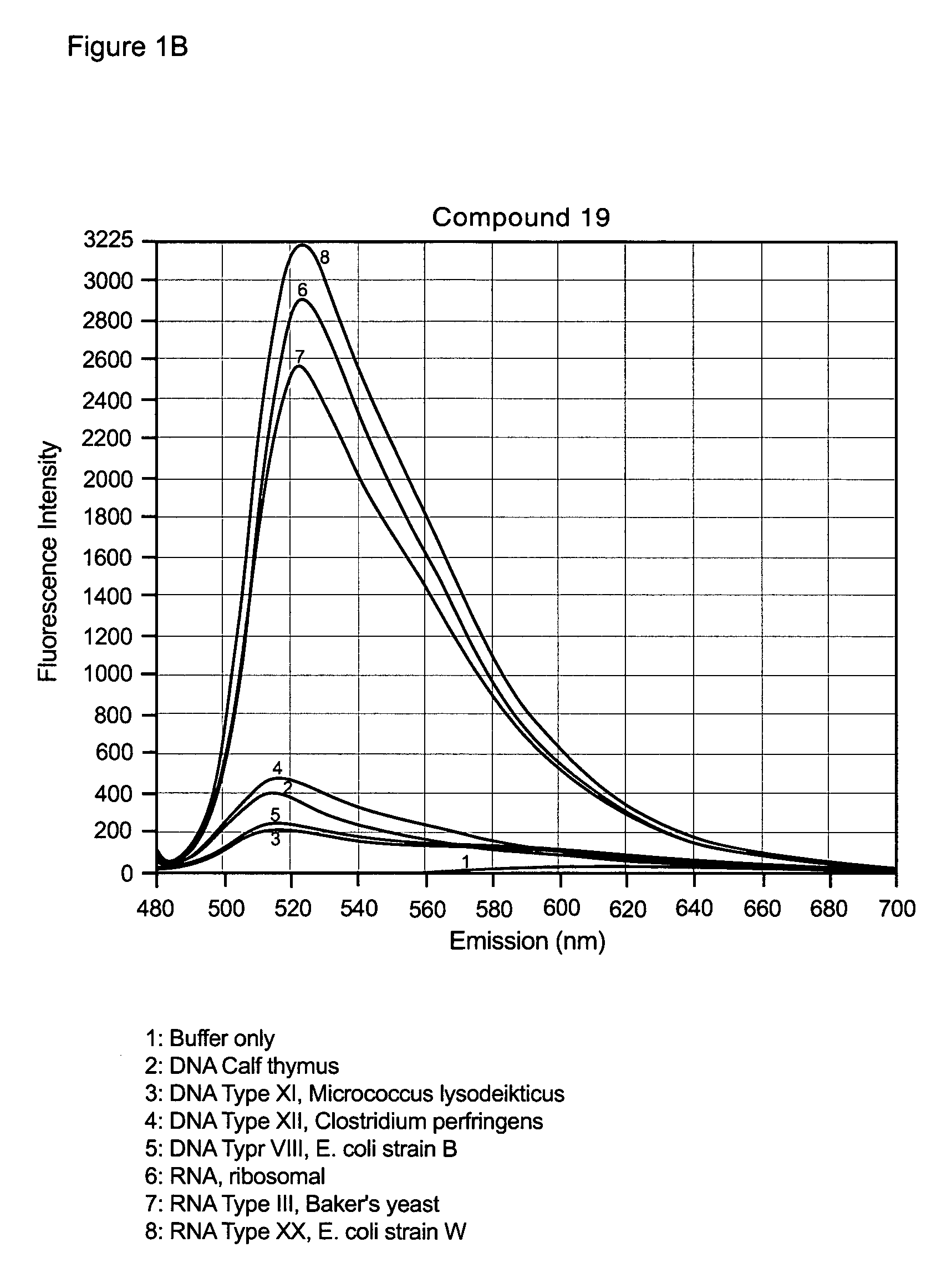
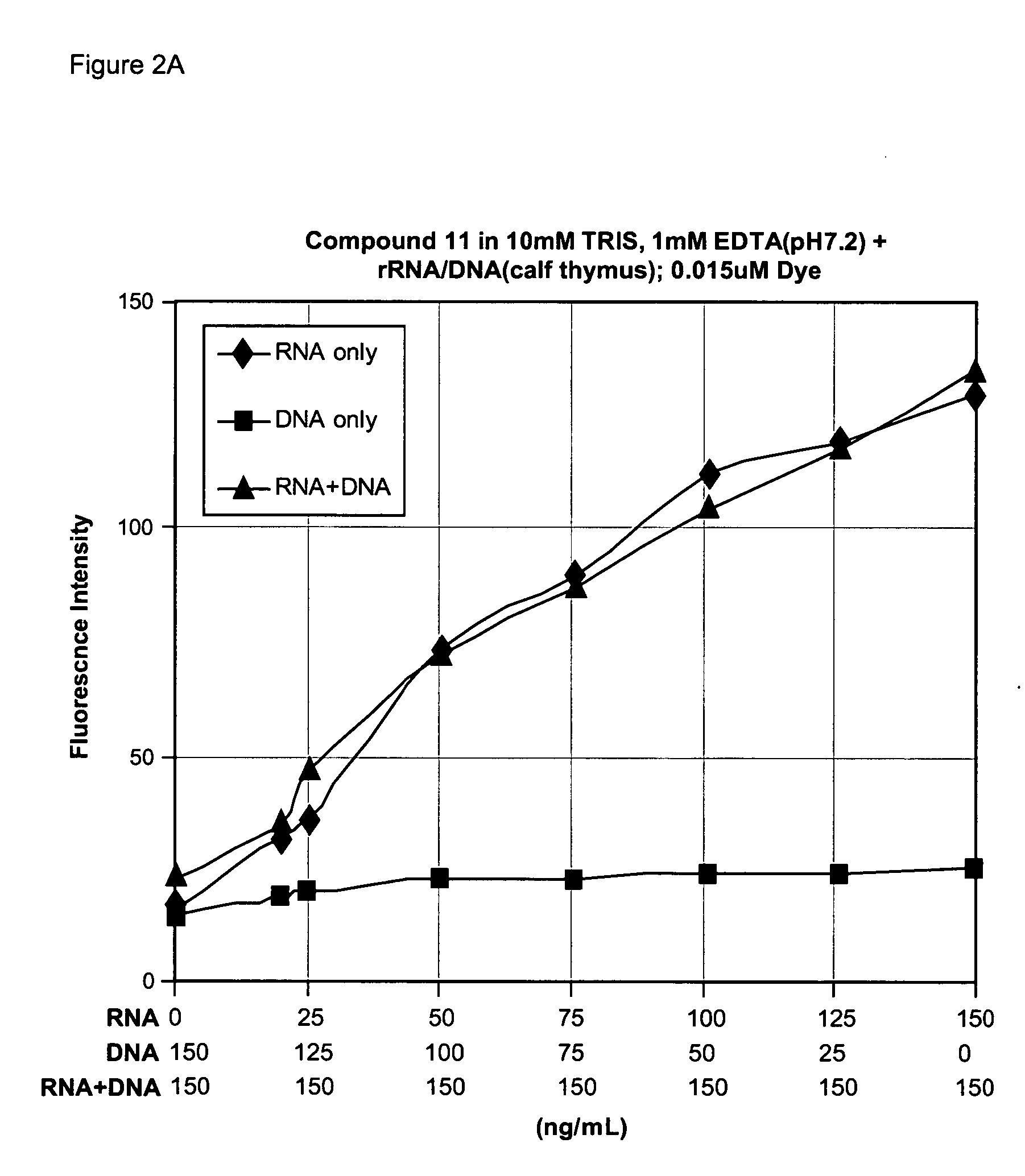
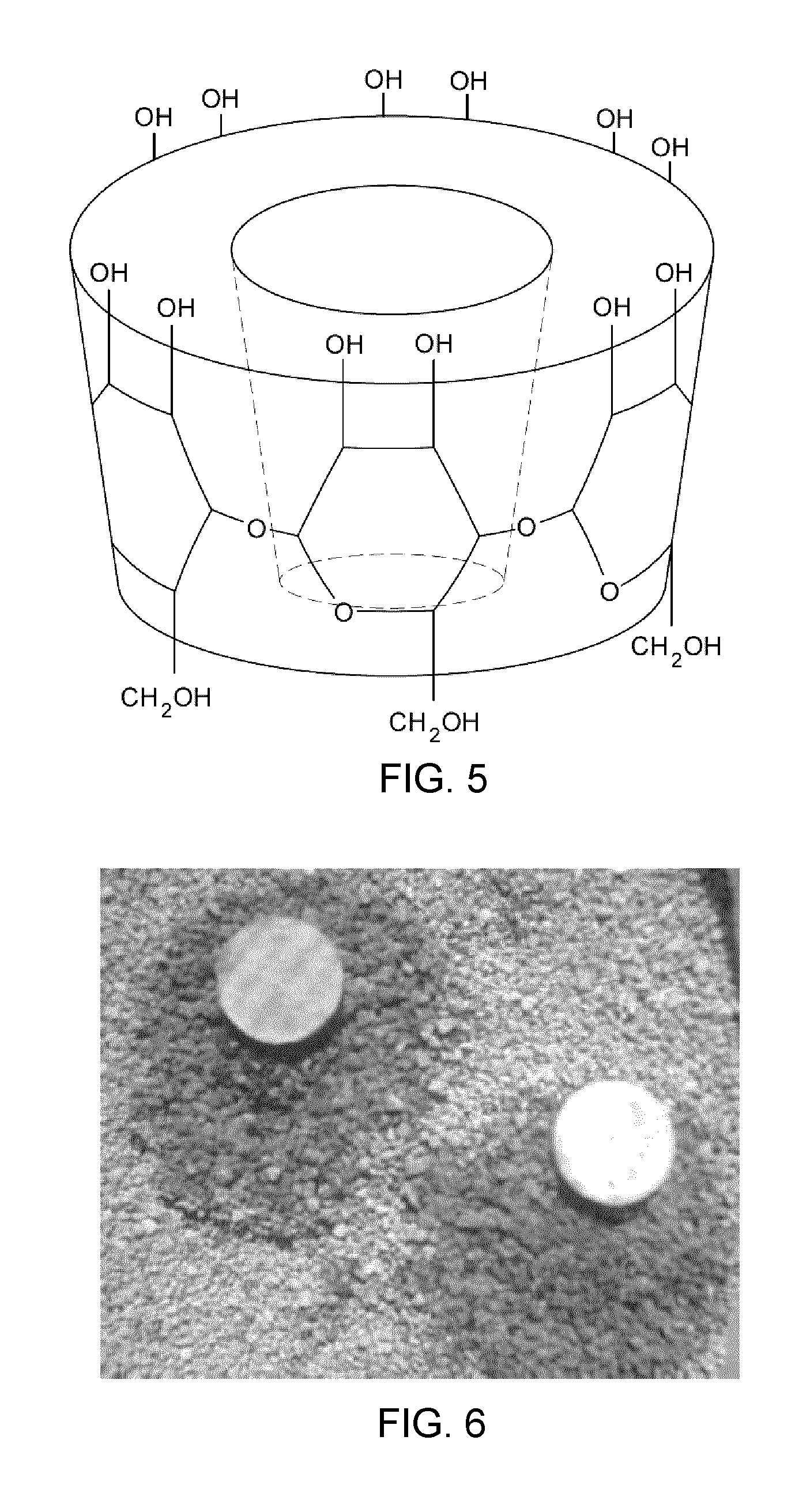
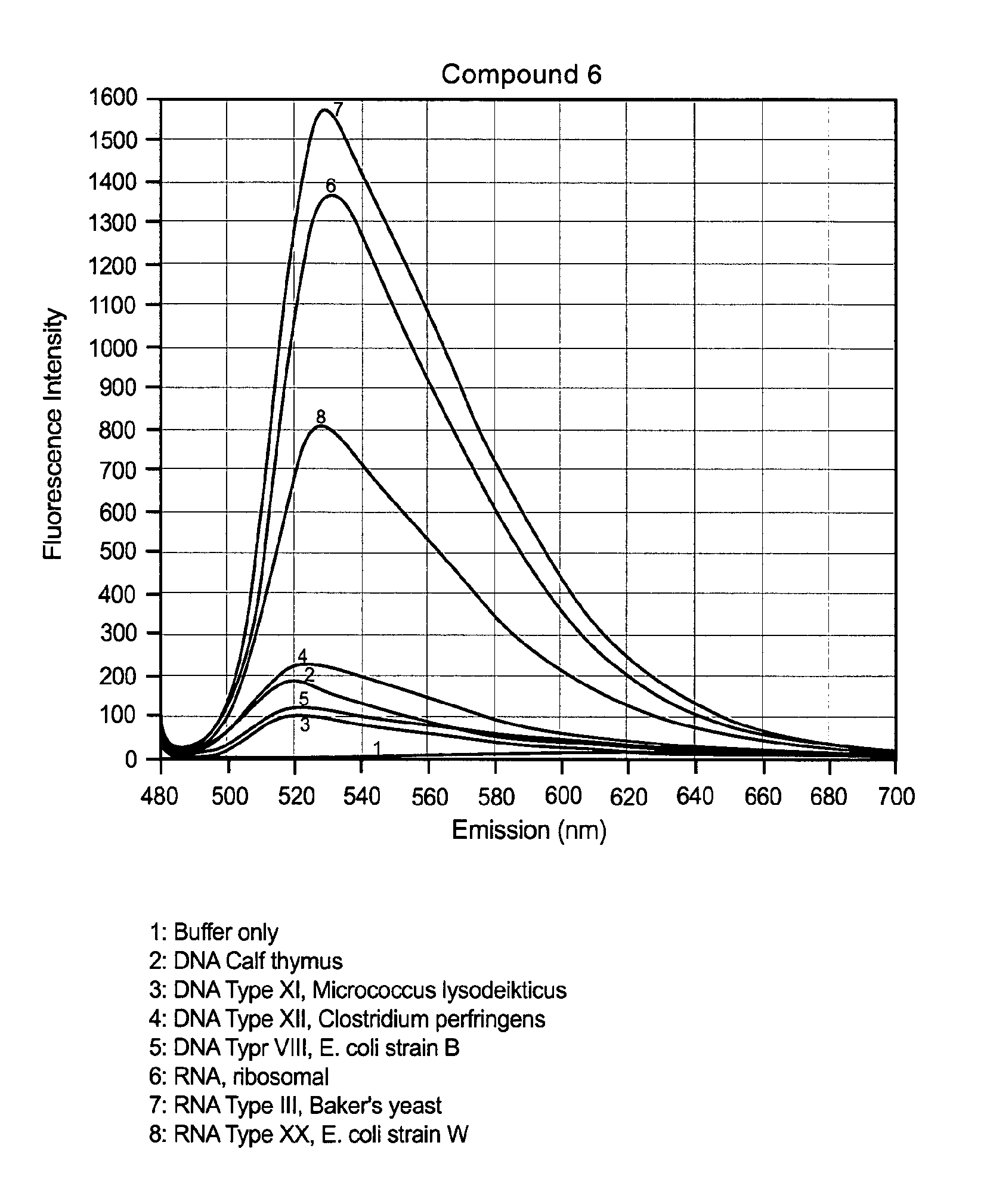
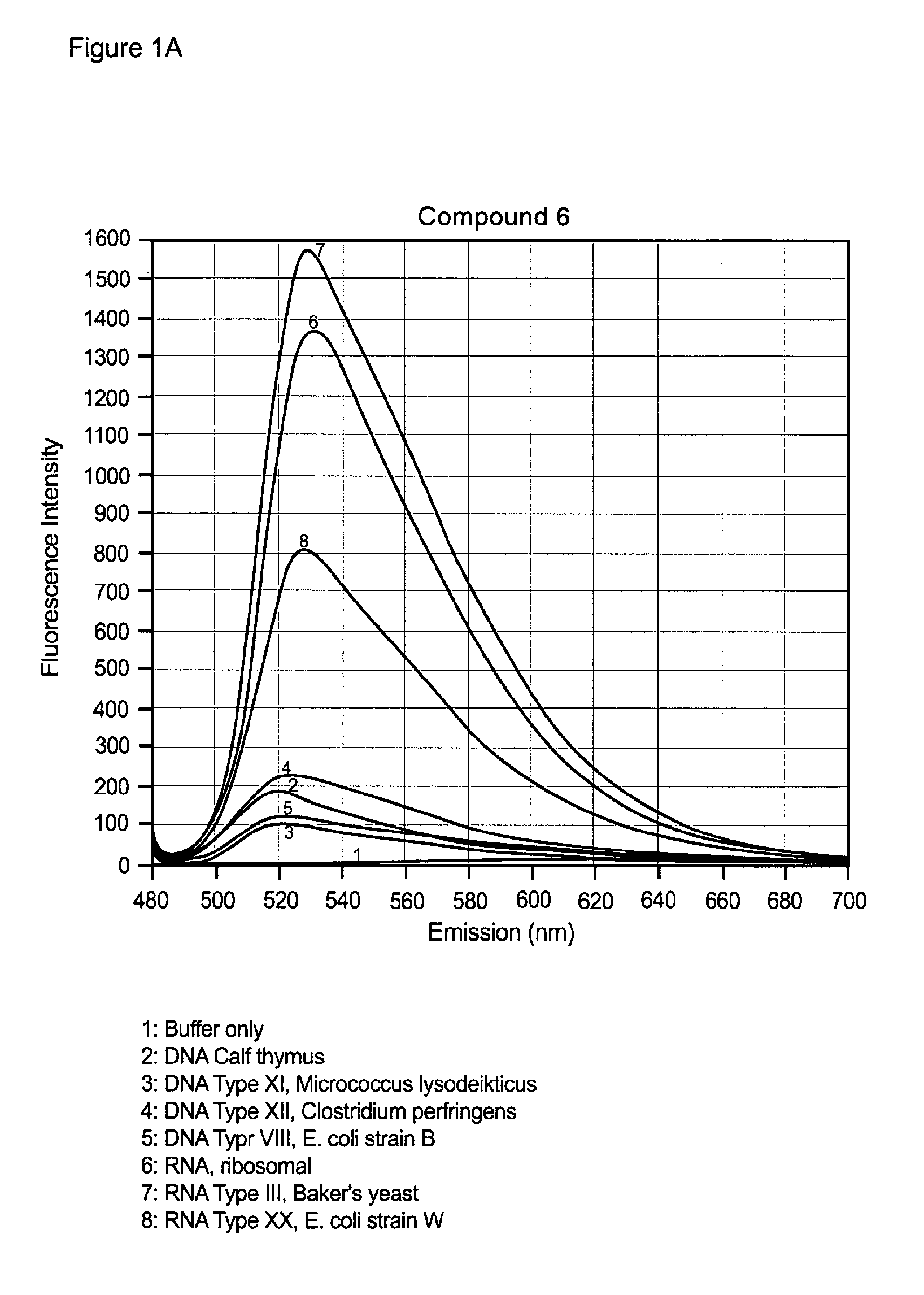
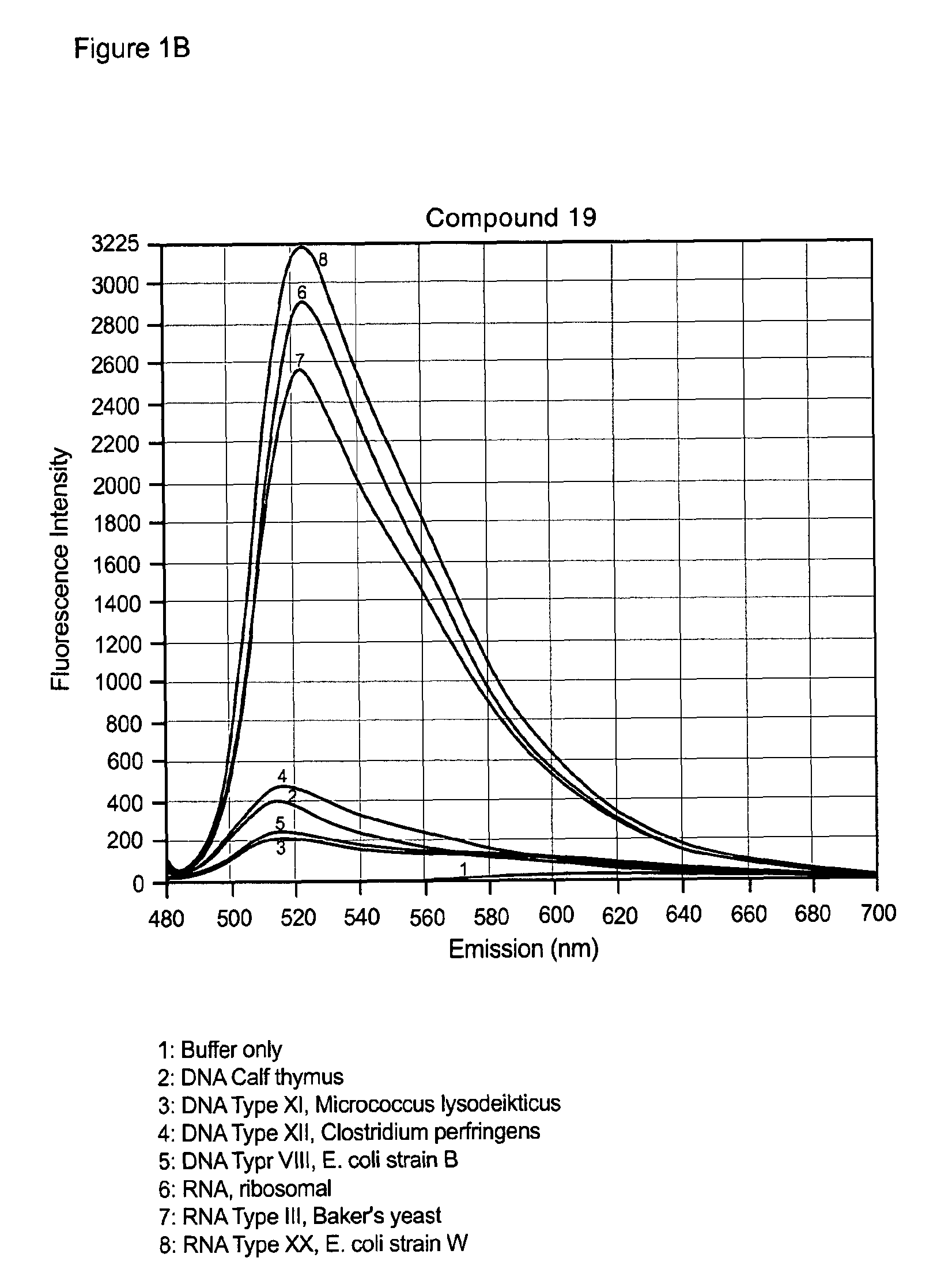
Embodiments of the present invention provide methods and nucleic acid reporter molecules for the detection of nucleic acid in a sample. The nucleic acid reporter molecule comprises two unsymmetrical cyanine monomer moieties, which may be the same or different, that are covalently attached by a linker comprising at least one aromatic, heteroaromatic, cyclic or heterocyclic moiety comprising 3-20 non-hydrogen atoms selected from the group consisting of O, N, S, P and C. The linker may be rigid, relatively flexible or some degree thereof. The unsymmetrical cyanine monomer moieties comprise a substituted or unsubstituted benzazolium moiety and a substituted or unsubstituted pyridinium or quinolinium moiety that is connected by a methine bridge that is monomethine, trimethine or pentamethine. The linkers form the cyanine dimer compounds by attaching to the pyridinium or quinolinium moiety of the monomer moieties. The present nucleic acid reporter molecules find utility in forming a nucleic acid-reporter molecule complex and detecting the nucleic acid. In particular, present nucleic acid reporter molecules with a rigid linker and monomer moieties with a monomethine bridge find utility in detecting RNA in the presence of DNA.
Owner:MOLECULAR PROBES
Oxime ester compound, photopolymerizable composition and color filter utilizing the same
ActiveCN1922142AImprove qualityImprove flatnessOrganic chemistryOptical filtersImage resolutionHazardous substance
An oxime ester compound of specified structure. In particular, in a photopolymerizable composition comprising (a) black color material, (b) organic binder and (c) photopolymerization initiator, the oxime ester compound constitutes the component (c). The oxime ester compound can be used as a highly sensitive photopolymerization initiator. The photopolymerizable composition containing the oxime ester compound in the form of a thin film excels in sensitivity and resolving power while exhibiting high light shielding capability, so that it is capable of forming a resin black matrix (BM) of low cost but high quality. The color filter utilizing this resin BM excels in precision, flatness and durability, so that it is capable of enhancing the display quality of liquid crystal device. Moreover, the production process and color filter per se do not involve any hazardous substances, so that the danger to human body can be reduced and environmental safety can be enhanced. Application thereof can be made to usages in which no color material is used, such as photospacer and rib (liquid crystal divided-alignment protrusion).
Owner:MITSUBISHI RAYON CO LTD
Acylhydrazone zinc protoporphyrin, and synthesis and application of complex thereof
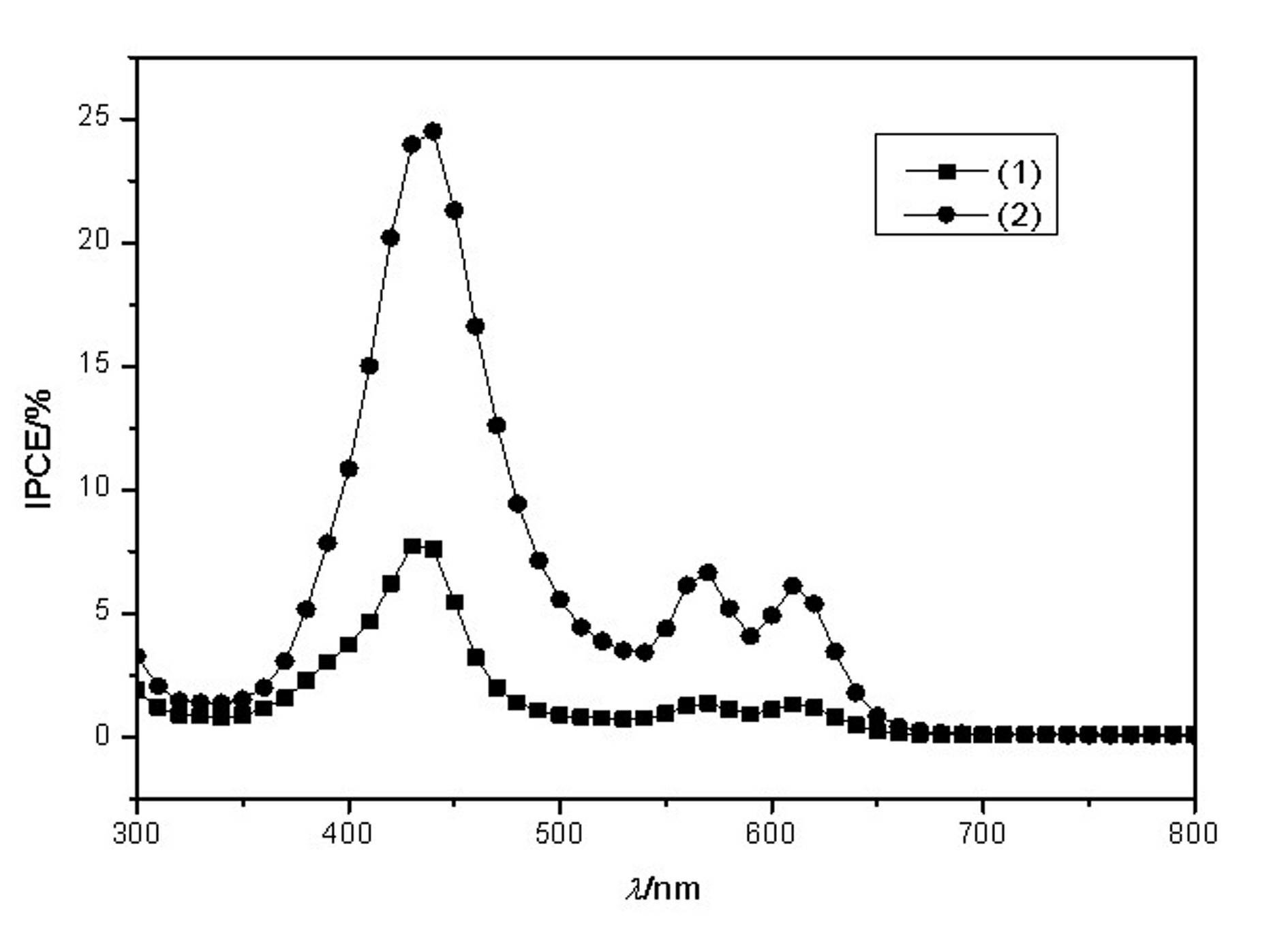
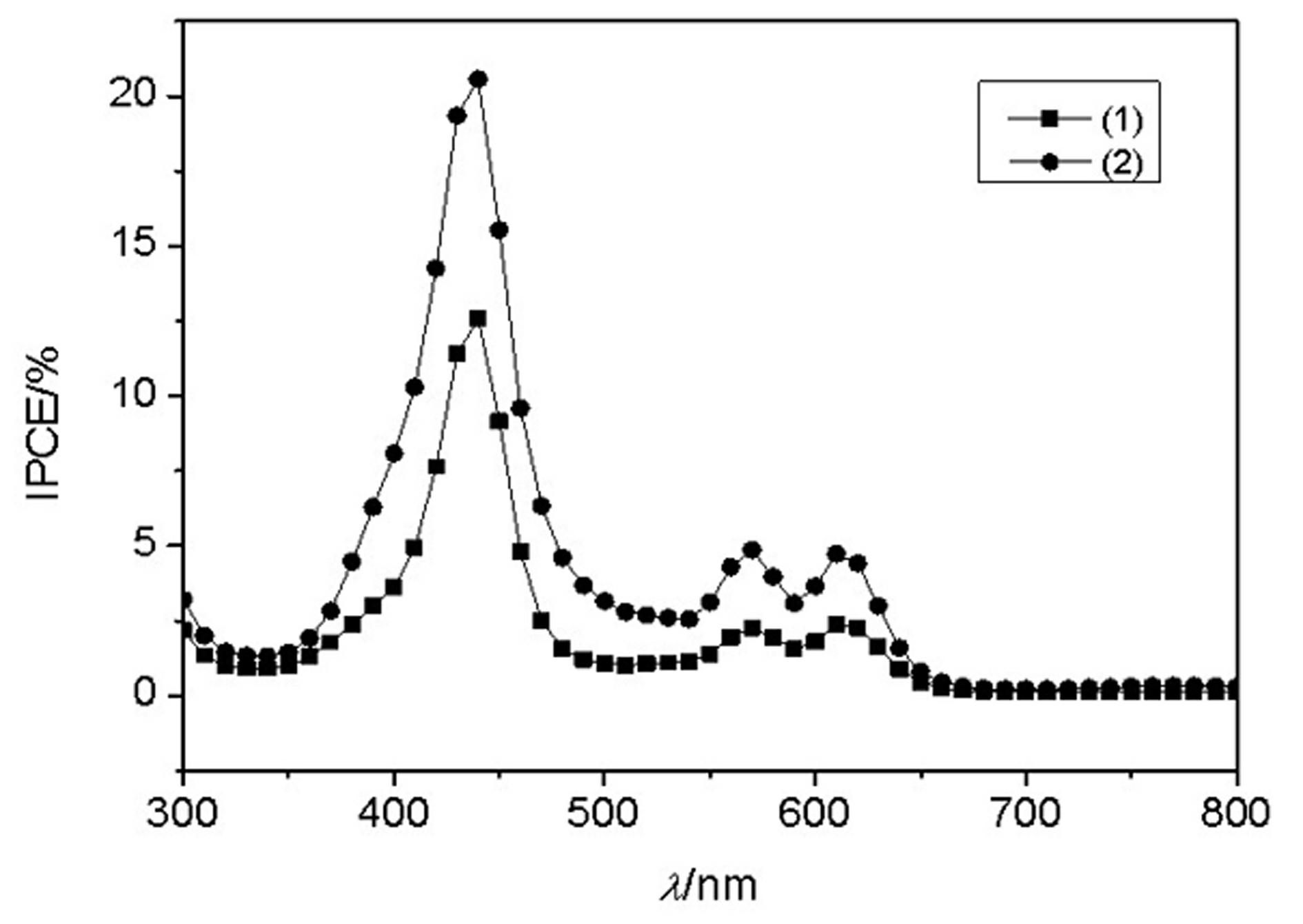
The invention discloses an acylhydrazone zinc protoporphyrin and a zinc and cobalt complex thereof, belonging to the field of chemical synthesis. In the acylhydrazone zinc protoporphyrin, an acylhydrazone structure and a porphyrin structure form a large conjugated system which can absorb a wider range of sunlight as compared with most of porphyrin dyes; and in the zinc and cobalt complex of the acylhydrazone zinc protoporphyrin, acylhydrazone zinc protoporphyrin molecules are connected to form a chain structure or high-dimensional structure, thereby improving the electron transfer efficiency and consequently improving the photoelectric conversion efficiency. Thus, the zinc and cobalt complex can be used as a dye sensitizer for the preparation of fuel-sensitive solar cells. Photoelectric property test results show that the fuel-sensitive solar cells prepared by the invention are capable of outputting a certain current to an external load and have different degrees of photoelectric conversion efficiency under the irradiation of standard light; and for the photocell using the zinc complex of the zinc protoporphyrin acylhydrazone as the dye, the maximum IPCE (Incident Photon to Current Efficiency) value is 13.4%.
Owner:NORTHWEST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Conjugated Schiff base Zn (zinc) porphyrin as well as preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN102417510AGreat absorptionReduce pollutionLight-sensitive devicesOrganic chemistryChemical synthesisPorphyrin
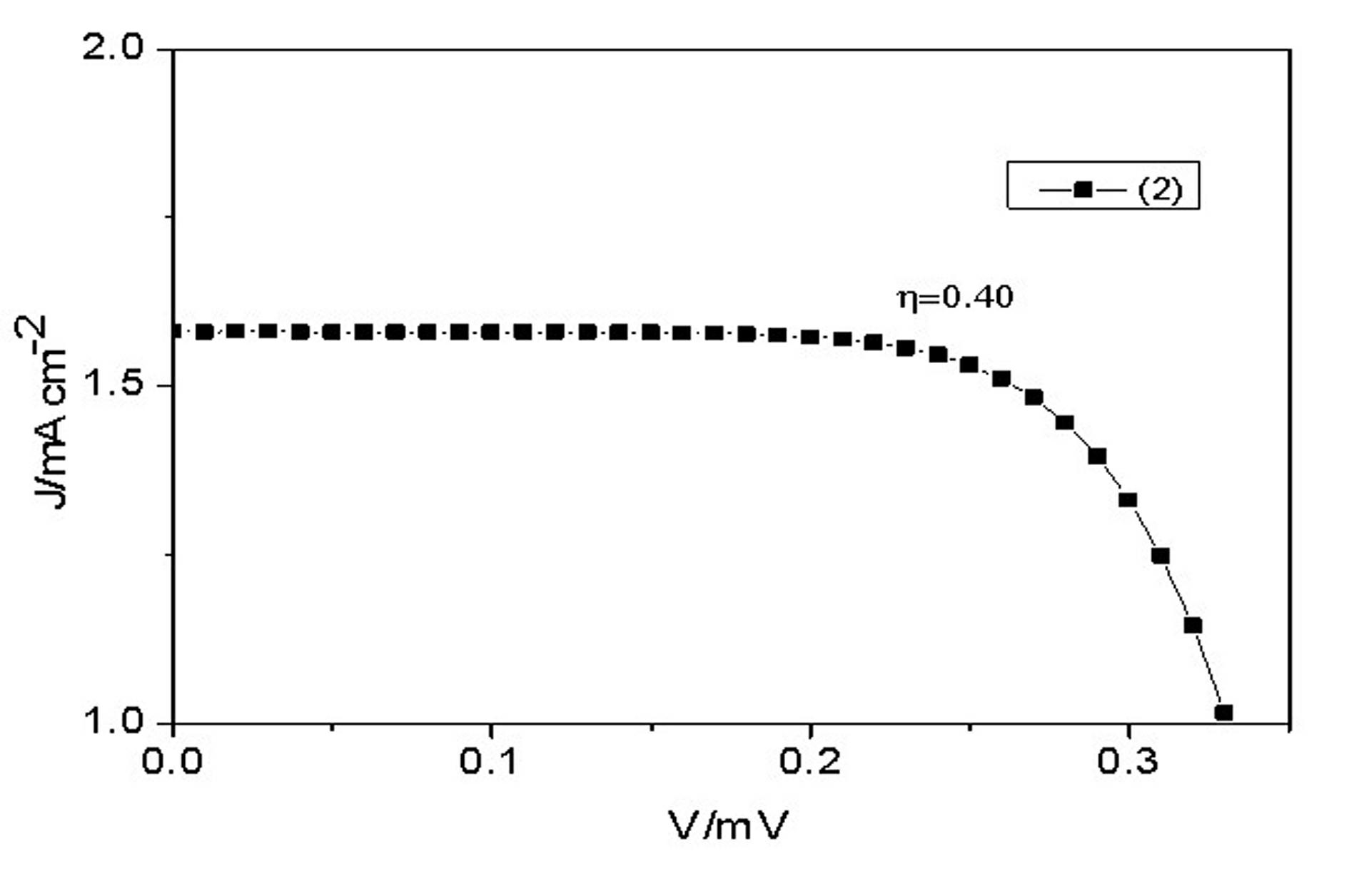
The invention provides a conjugated Schiff base Zn (zinc) porphyrin compound, and belongs to the technical field of chemical synthesis. In the preparation method, porphyrin compound is made from nitrobenzaldehyde and pyrrole by four reaction steps of condensation, reduction, coordination and substitution. Because of a large conjugated system of Schiff base and porphyrin, the sunlight absorptivity of the porphyrin compound is improved, the maximum IPCE (incident photon-to-electron conversion efficiency) value can reach 25%, and the photoelectric conversion efficiency Eta also reaches 0.40, thus the conjugated Schiff base Zn porphyrin compound has good application prospect in preparation of a dye sensitized solar cell. Compared with the traditional ruthenium dye, the obtained conjugated Schiff base Zn porphyrin compound has the advantages that raw materials are cheap and obtained easily, synthetic process is simple, reaction condition is mild, no expensive metal raw material is used, and the effects of low cost, high yield and less environmental pollution are achieved.
Owner:NORTHWEST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
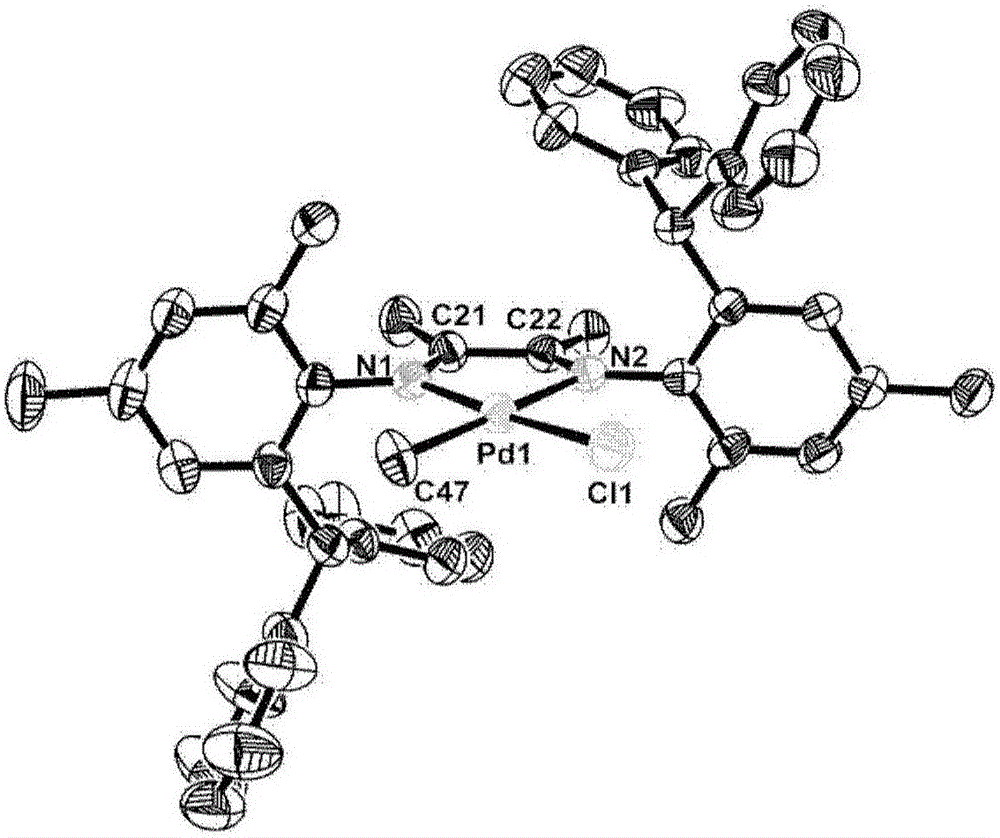
Asymmetric diimine palladium catalyst and ligand, preparation method and application thereof
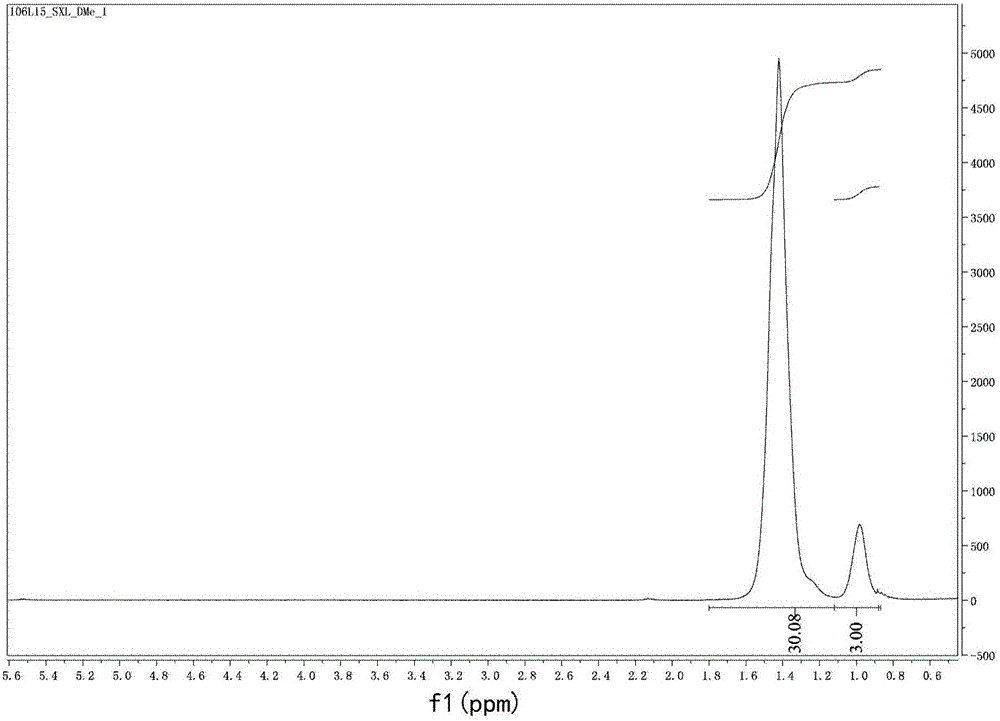
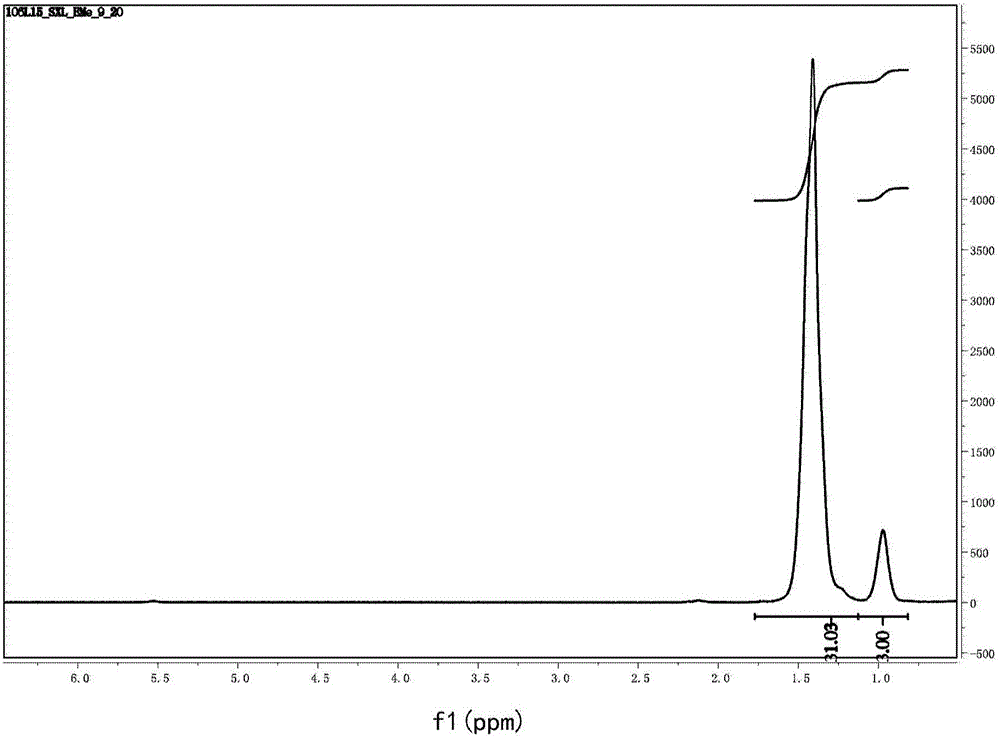
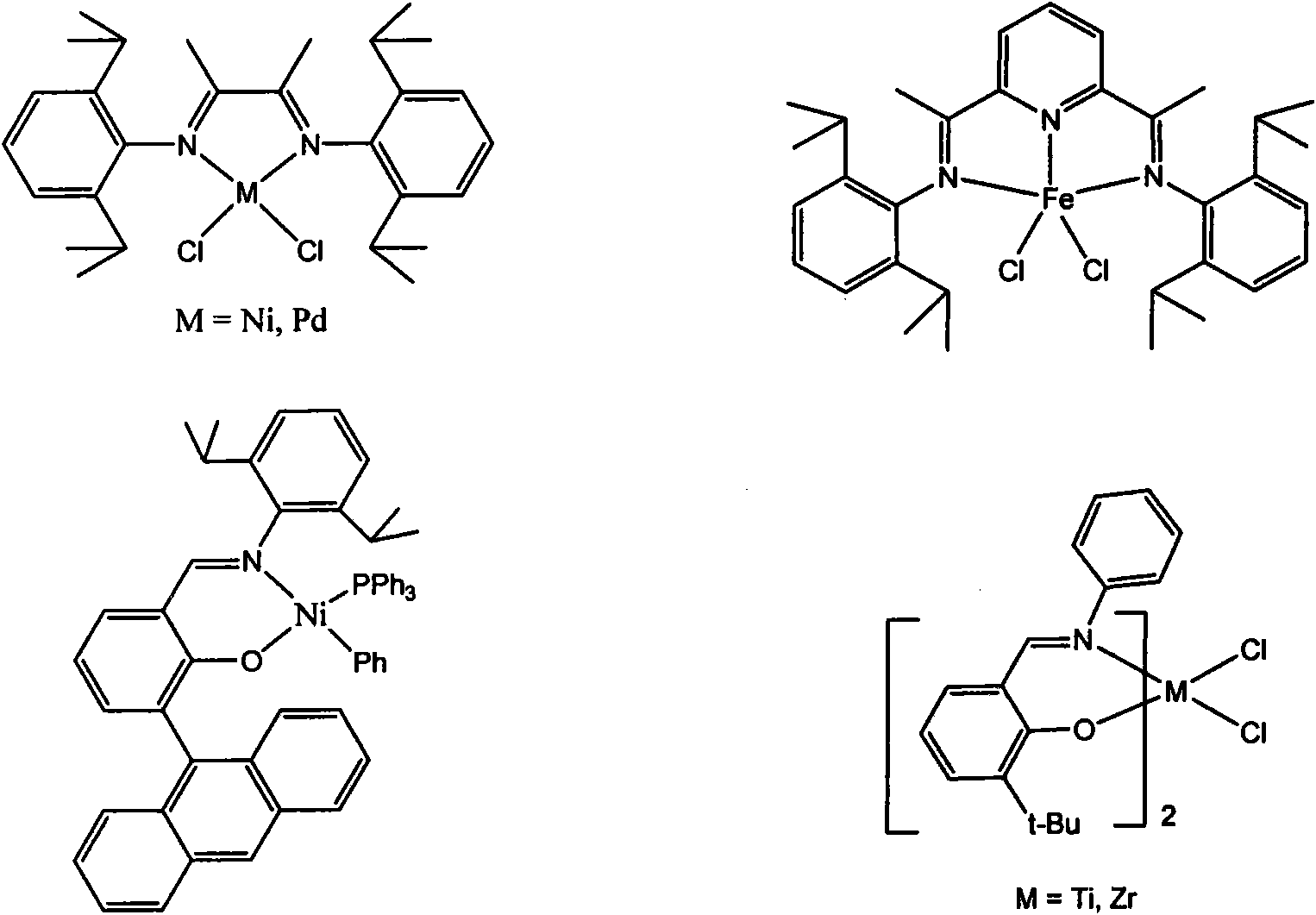
ActiveCN105968027AHigh activityHigh molecular weightPalladium organic compoundsDiazomethine dyesDiiminePolymer science
The invention relates to an asymmetric diimine palladium catalyst as shown in the following formula and a ligand, preparation method and application thereof, wherein R1-R6 and X are defined according to the description. The palladium catalyst has high heat stability and activity on ethylene polymerization, and polyethylene which has an appropriate branching degree and high molecular weight is generated; in addition, the catalyst can be used for copolymerization of ethylene and methyl acrylate. Please see the formula in the description.
Owner:合肥中科科乐新材料有限责任公司
Unsymmetrical cyanine dimer compounds and their application
Embodiments of the present invention provide methods and nucleic acid reporter molecules for the detection of nucleic acid in a sample. The nucleic acid reporter molecule comprises two unsymmetrical cyanine monomer moieties, which may be the same or different, that are covalently attached by a linker comprising at least one aromatic, heteroaromatic, cyclic or heterocyclic moiety comprising 3-20 non-hydrogen atoms selected from the group consisting of O, N, S, P and C. The linker may be rigid, relatively flexible or some degree thereof. The unsymmetrical cyanine monomer moieties comprise a substituted or unsubstituted benzazolium moiety and a substituted or unsubstituted pyridinium or quinolinium moiety that is connected by a methine bridge that is monomethine, trimethine or pentamethine. The linkers form the cyanine dimer compounds by attaching to the pyridinium or quinolinium moiety of the monomer moieties. The present nucleic acid reporter molecules find utility in forming a nucleic acid-reporter molecule complex and detecting the nucleic acid. In particular, present nucleic acid reporter molecules with a rigid linker and monomer moieties with a monomethine bridge find utility in detecting RNA in the presence of DNA.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
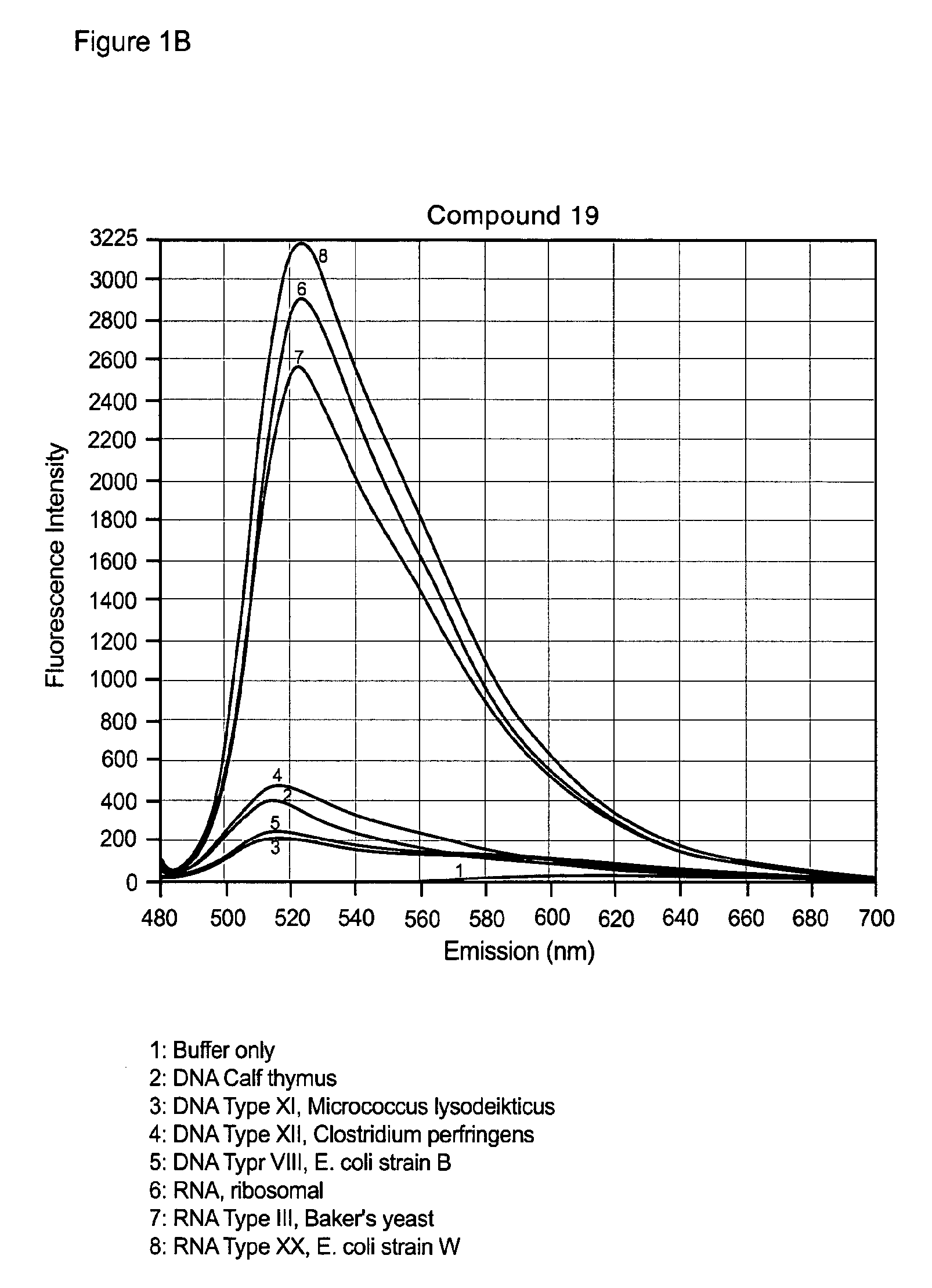
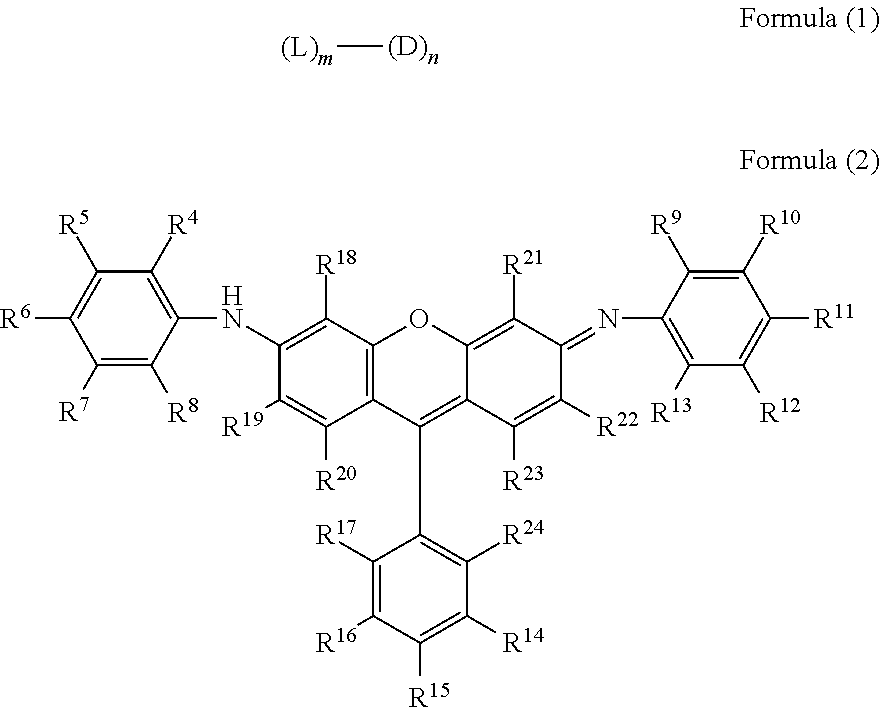
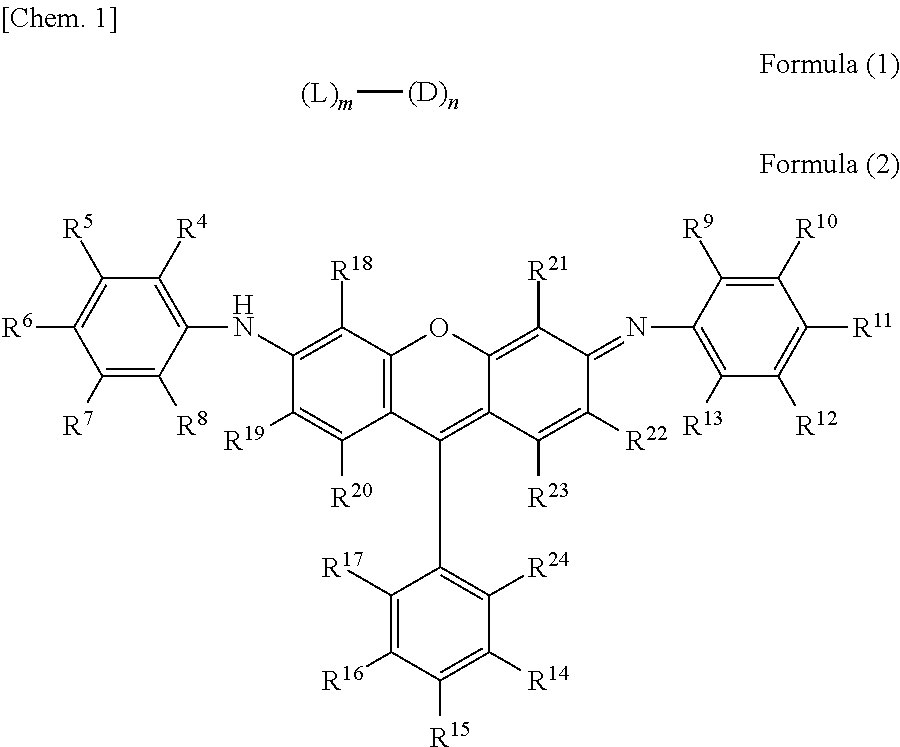
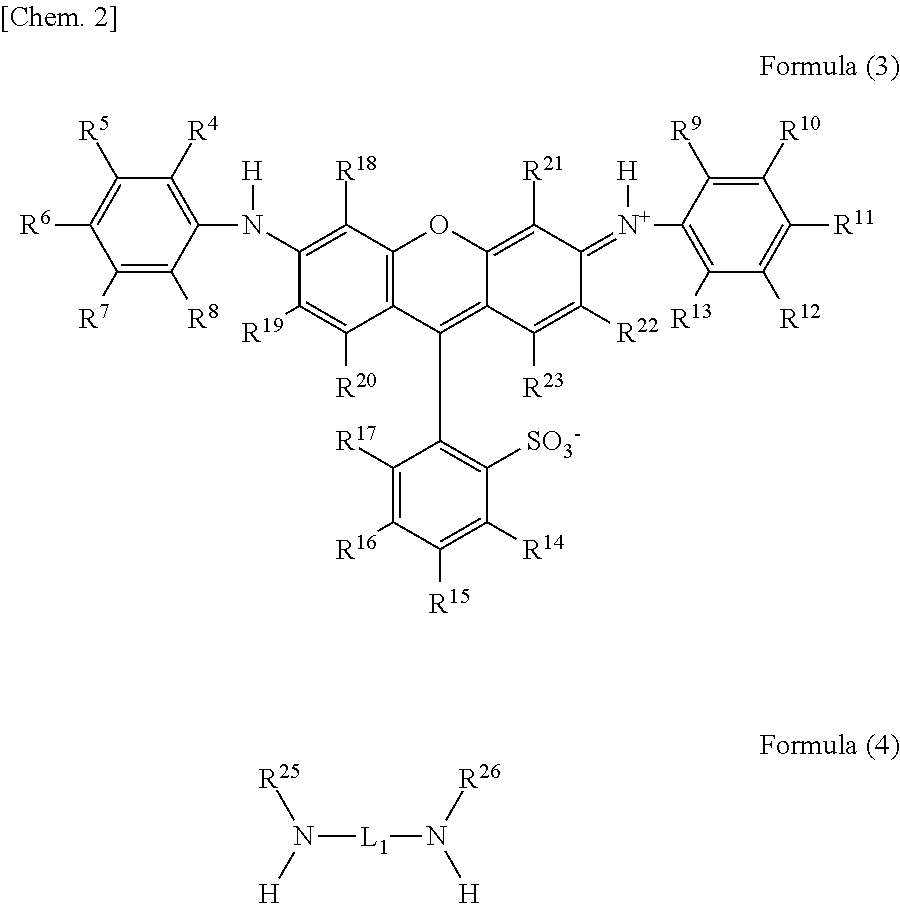
Novel compound having multimer structure of xanthene derivative, coloring composition, ink for inkjet recording, method of inkjet recording, color filter, and color toner
InactiveUS20140176653A1Improve performanceOrganic chemistryMethine/polymethine dyesHydrogenHydrogen atom
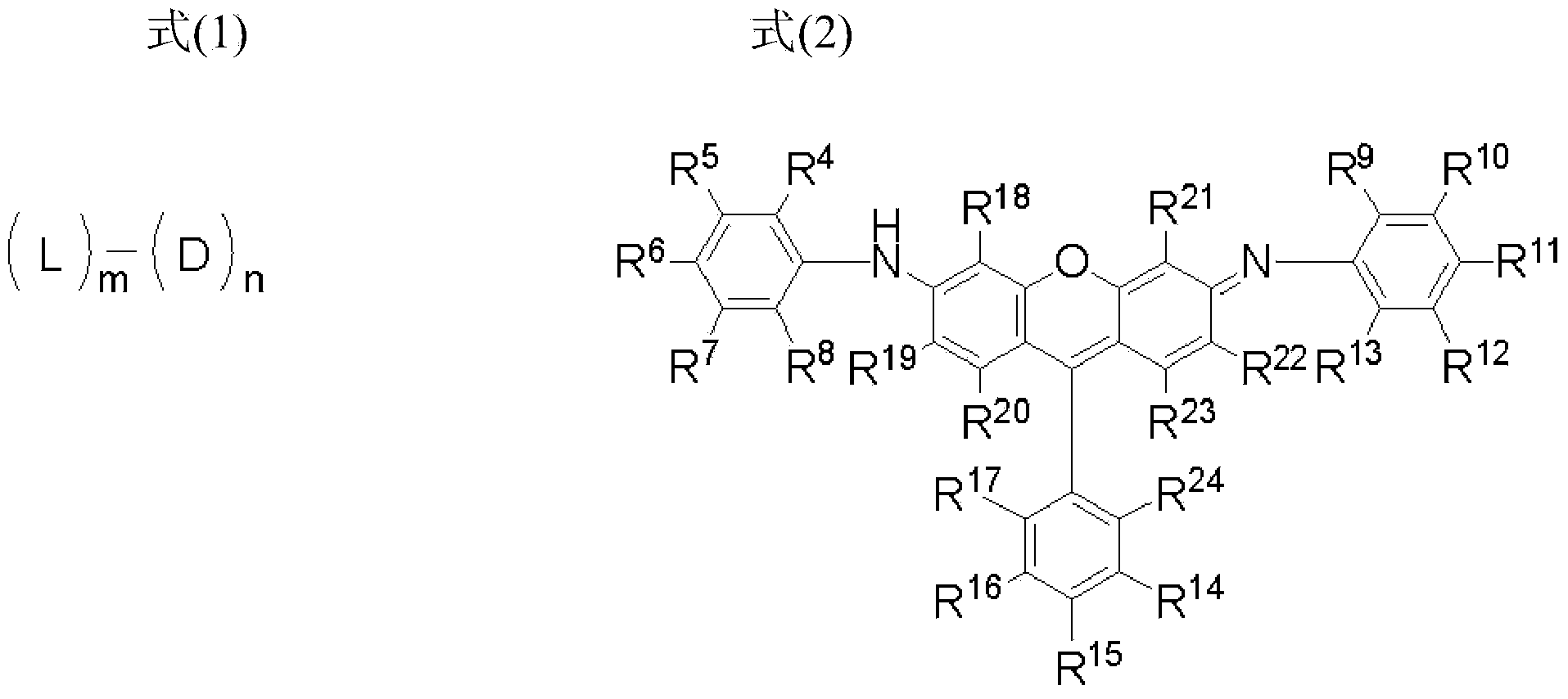
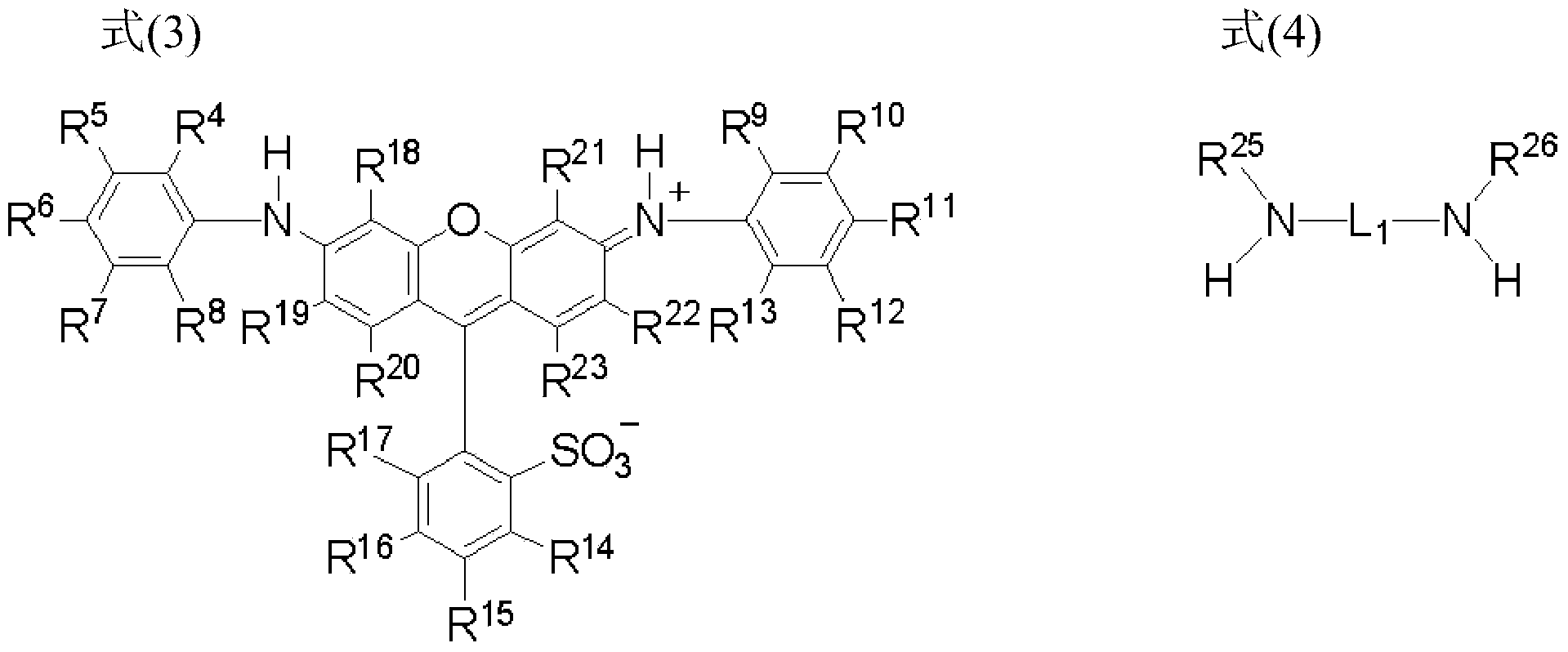
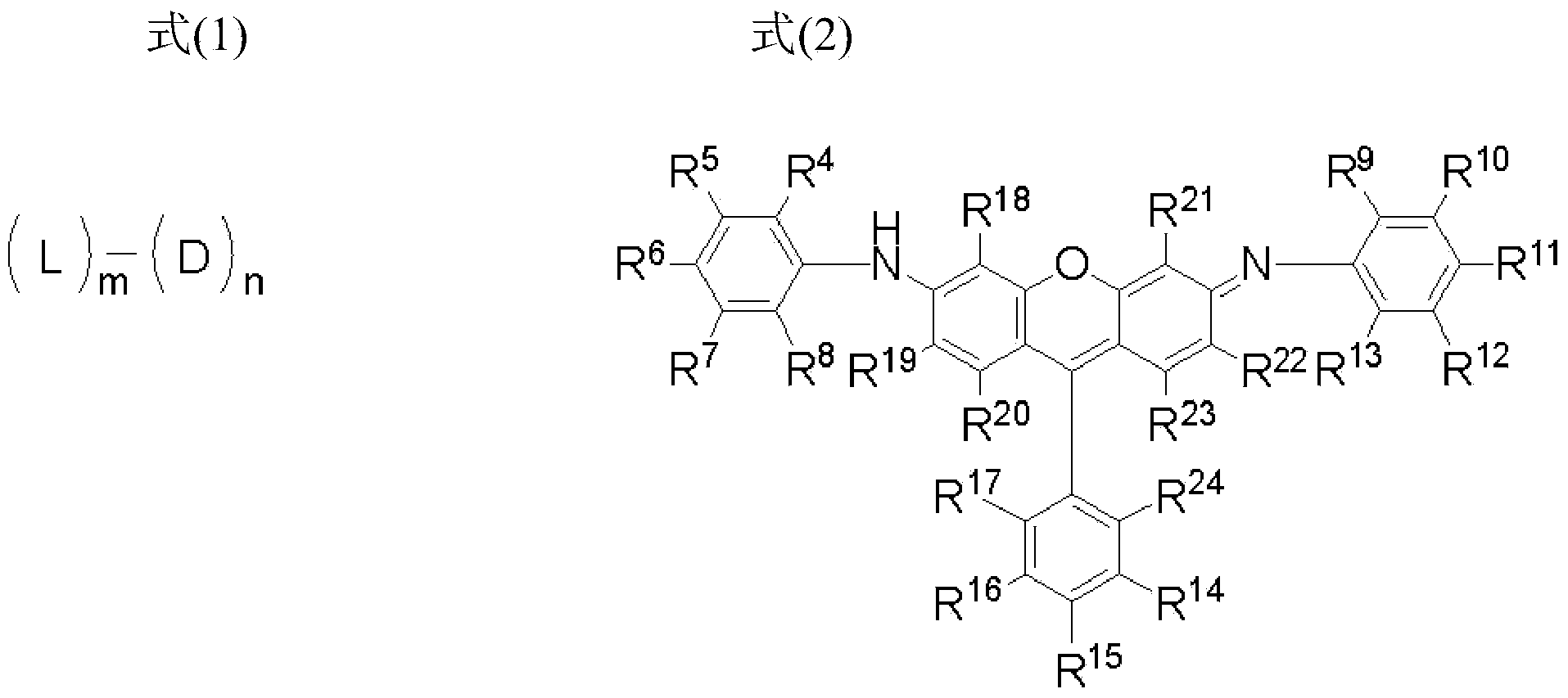
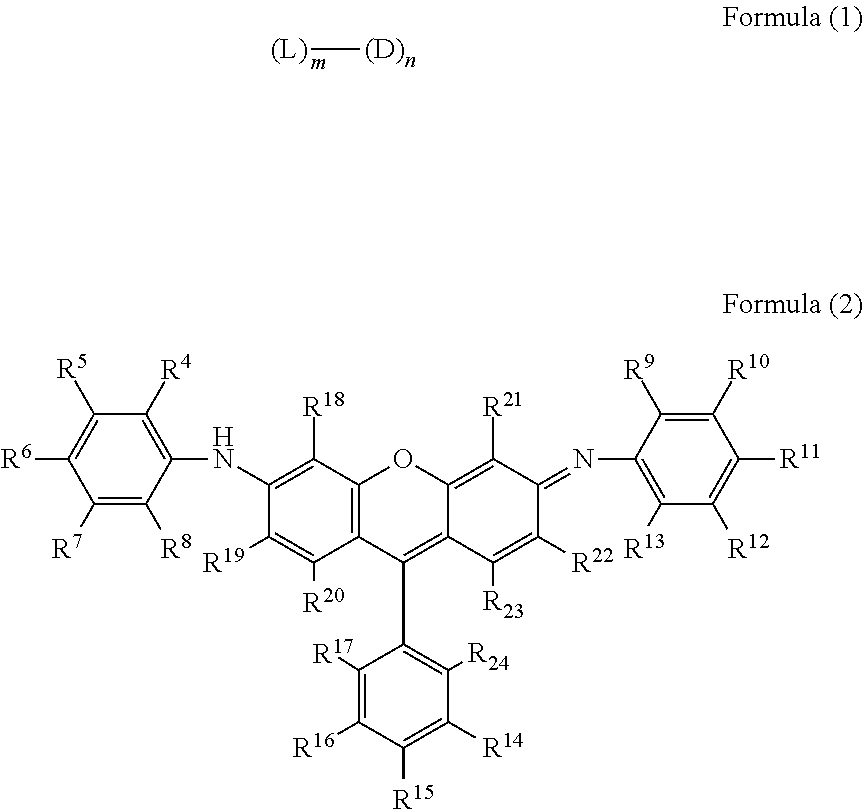
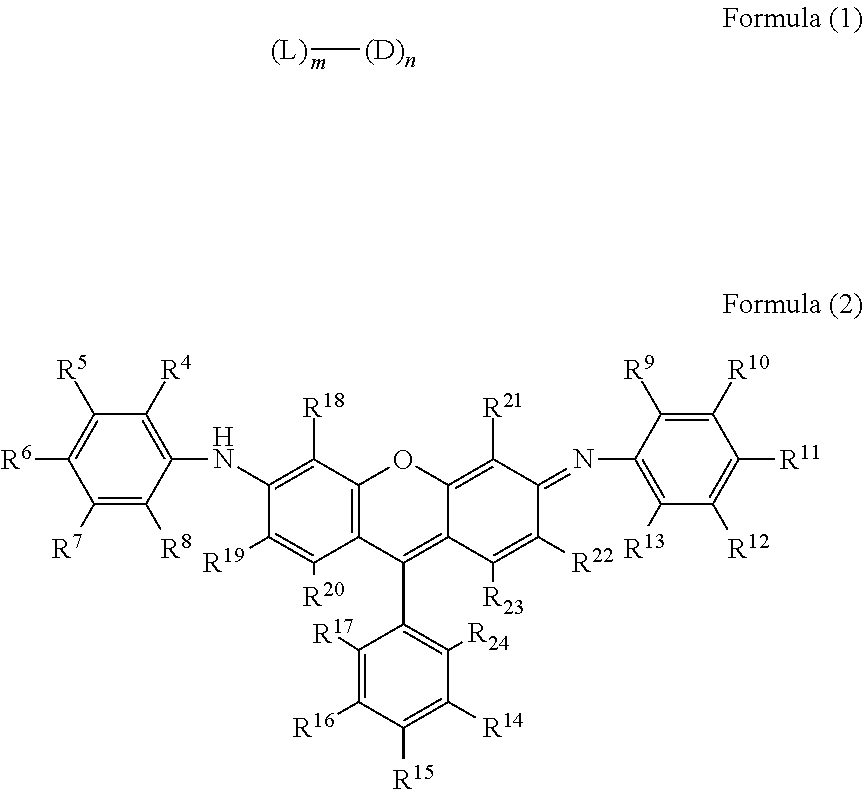
There is provided a compound represented by formula (1):in formula (1), L represents a divalent to tetravalent linking group; D represents a residue obtained by removing 1 to 5 hydrogen atoms from a compound represented by formula (2); m represents an integer of 1 to 10, however, each L may be the same with or different from every other L; n represents an integer of 2 to 10, however, each D may be the same with or different from every other D; and in formula (2), each of R4 to R24 independently represents a hydrogen atom or a substituent, provided that formula (2) has at least one or more ionic hydrophilic groups.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Dichroic dye for polarization film, composition comprising the same for polarization film, method for forming polarization plate and polarization plate prepared thereby
ActiveUS20090290214A1Excellent heat resistance and durability against high-temperatureRaise the ratioLiquid crystal compositionsPerinonesCrystallographyHeat resistance
Disclosed are a new dichroic dye having liquid crystal properties and dichroic properties and capable of being used for forming a polarization film with excellent heat resistance, durability, and polarizing properties, a composition including the same for a polarization film, a method for forming a polarization plate with excellent durability using the composition, and a polarization plate prepared thereby. The new dichroic dye has a structure of R1-L1-(M,L,D) (where, D is a dichroic structure, M is a structure with liquid crystal properties, R1 is a reactive end functional group, and L and L1 are linking structures). The composition for a polarization film includes the dichroic dye. In the method for forming the polarization plate, the composition for a polarization film is applied to a substrate and cured to prepare the polarization plate. The polarization plate has excellent dichroic ratio, heat resistance, durability, and polarizing properties.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
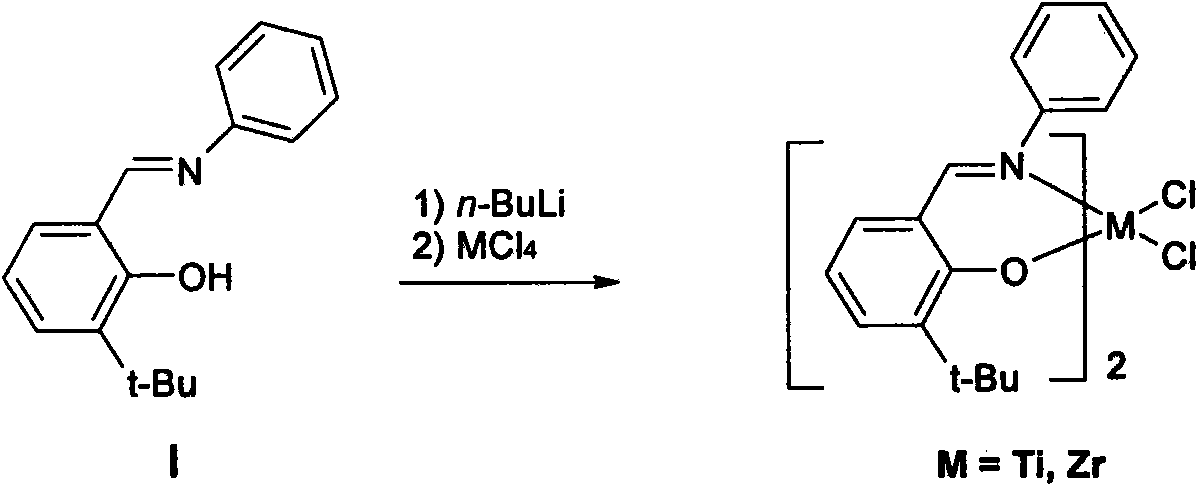
Self-assembled olefin polymerization catalyst
The present invention relates to a self-assembled olefin polymerization catalyst comprising a transition metal compound according to formula (I) LqMmXnwherein M is a transition metal selected from the group consisting of Group 3-11 of the periodic table; X is independently selected from the group consisting of H, halogen, CN, optionally substituted N(Ra)2, OH, optionally substituted C1-C20 alkyl, optionally substituted C1-C20 alkoxy, wherein Ra is independently selected from the group consisting of optionally substituted C1-C20 alkyl, optionally substituted C6-C20 aryl and halogen; q is an integer of at least 2; m is an integer of at least 2; n is an integer making (I) electrically neutral; L is independently a ligand which has at least two linked coordination units, wherein each coordination unit binds to a different transition metal.- The present invention also relates to a process for the polymerization of olefins using the transition metal compound of the invention and to the polyolefins obtained from this polymerization process. Finally, the invention also relates to new ligands L present in the transition metal compound and to methods of making the ligand L.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Chromogenic absorbent material for animal litter and related chromogenic solution
A chromogenic absorbent material and related chromogenic solution, use, process and application for an animal litter. The chromogenic absorbent material includes an absorptive material for absorbing an animal excretion; an oxidizing agent responsive to peroxidatic / pseudoperoxidatic activity in the animal excretion to provide oxidizing activity; and an inclusion complex including a host compound and a guest compound, the guest compound being a chromogenic indicator associated with the host compound and being chromogenically responsive to the oxidizing activity of the oxidizing agent. The chromogenic absorbent material may be prepared from the chromogenic solution including the oxidizing agent and the inclusion complex. The chromogenic absorbent material may be used as particles combined with animal litter for detection of peroxidatic / pseudoperoxidatic activity in the animal excretion. The chromogenic material or solution may include a buffering agent, a colour enhancer, a stabilizer or a metal-scavenger agent or a combination thereof.
Owner:7905122 CANADA
Unsymmetrical cyanine dimer compounds and their application
Embodiments of the present invention provide methods and nucleic acid reporter molecules for the detection of nucleic acid in a sample. The nucleic acid reporter molecule comprises two unsymmetrical cyanine monomer moieties, which may be the same or different, that are covalently attached by a linker comprising at least one aromatic, heteroaromatic, cyclic or heterocyclic moiety comprising 3-20 non-hydrogen atoms selected from the group consisting of O, N, S, P and C. The linker may be rigid, relatively flexible or some degree thereof. The unsymmetrical cyanine monomer moieties comprise a substituted or unsubstituted benzazolium moiety and a substituted or unsubstituted pyridinium or quinolinium moiety that is connected by a methine bridge that is monomethine, trimethine or pentamethine. The linkers form the cyanine dimer compounds by attaching to the pyridinium or quinolinium moiety of the monomer moieties. The present nucleic acid reporter molecules find utility in forming a nucleic acid-reporter molecule complex and detecting the nucleic acid. In particular, present nucleic acid reporter molecules with a rigid linker and monomer moieties with a monomethine bridge find utility in detecting RNA in the presence of DNA.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Novel compound having xanthene derivative multimeric structure, colored composition, ink for inkjet recording, inkjet recording method, color filter, and color toner
InactiveCN103764767AExcellent ozone resistanceGood light fastnessOrganic chemistryMethine/polymethine dyesHydrogen atomHydrogen
The purpose of the present invention is to provide a novel compound having a specific xanthene derivative multimeric structure, and that provides a printed item having greater ozone resistance, light resistance, and other image durability characteristics than conventional printed items. The compound is indicated by general formula (1). (In general formula (1), L indicates a divalent to tetravalent linking group. D indicates a residue having 1-5 hydrogen atoms removed from a compound indicated by general formula (2). m indicates an integer between 1 and 10. However the plurality of L can each be the same or different. n indicates an integer between 2 and 10. However, the plurality of D can each be the same or different. In general formula (2), R4-R24 each independently indicate a hydrogen atom or a substituent group, but same have at least one ionic hydrophilic group.)
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
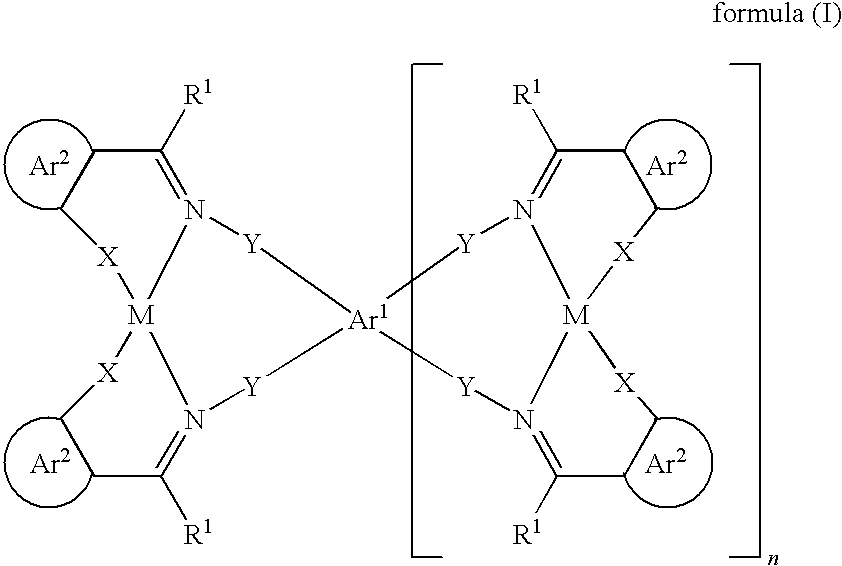
Organic electroluminescent devices comprising azomethine-metal complexes
InactiveUS8487300B2High glass transition temperatureImprove thermal stabilityElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesHost materialOrganic electroluminescence
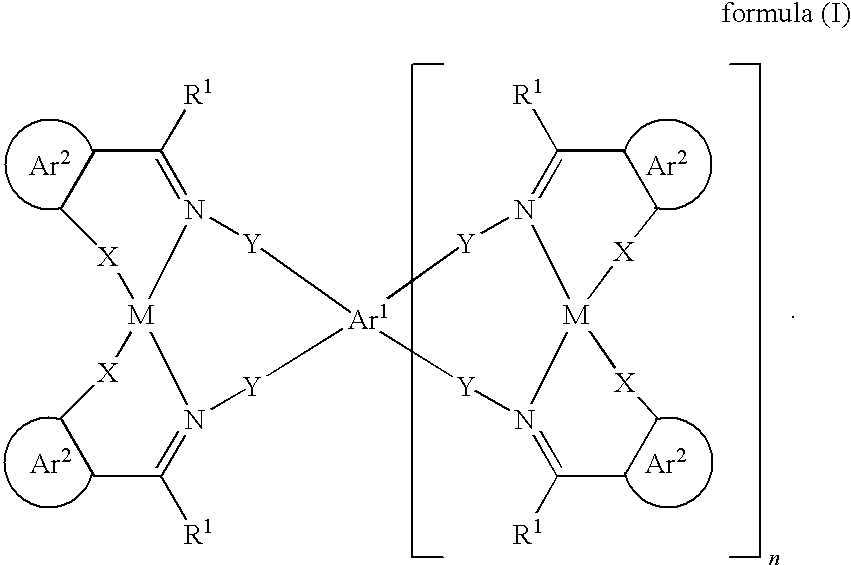
The present invention relates to phosphorescent organic electroluminescent devices which contain as a matrix material of emitting layer, metal complexes of the formula (I)
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Dichroic dye for polarization film, composition comprising the same for polarization film, method for forming polarization plate and polarization plate prepared thereby
ActiveUS8197708B2Excellent heat resistance and durability against high-temperatureRaise the ratioLiquid crystal compositionsPerinonesCrystallographyHeat resistance
Disclosed are a new dichroic dye having liquid crystal properties and dichroic properties and capable of being used for forming a polarization film with excellent heat resistance, durability, and polarizing properties, a composition including the same for a polarization film, a method for forming a polarization plate with excellent durability using the composition, and a polarization plate prepared thereby. The new dichroic dye has a structure of R1-L1-(M,L,D) (where, D is a dichroic structure, M is a structure with liquid crystal properties, R1 is a reactive end functional group, and L and L1 are linking structures). The composition for a polarization film includes the dichroic dye. In the method for forming the polarization plate, the composition for a polarization film is applied to a substrate and cured to prepare the polarization plate. The polarization plate has excellent dichroic ratio, heat resistance, durability, and polarizing properties.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Negative dye-containing curable composition, color filter and method of producing the same
The present invention provides a negative dye-containing curable composition comprising at least (A) an alkali-soluble binder, (B) an organic solvent-soluble dye, (C) a photopolymerization initiator, (D) a radical-polymerizable monomer and (E) an organic solvent, wherein the organic solvent-soluble dye (B) comprises at least one kind of azomethine-type dye represented by the following formula (I) and at least one kind of tetraazaporphyrin-type dye represented by the following formula (A), and the photopolymerization initiator (C) is an oxime-type compound,wherein R1 represents a hydrogen atom or a substituent group; R2 to R5 each represent a hydrogen atom or a substituent group, R6 to R7 each represent an alkyl group, alkenyl group, aryl group or heterocyclic group, Za and Zb each represent —N═ or —C(R8)═; R8 represents a hydrogen atom, alkyl group, aryl group or heterocyclic group; M1 represents a metal, and Z1 to Z4 each represent an atomic group forming a 6-membered ring composed of atoms selected from carbon and nitrogen.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Metal organic liquid crystal dyes
InactiveCN107406770ALiquid crystal compositionsMethine/polymethine dyesMetallomesogenCrystallography
Owner:GAUZY
Compound having multimer structure of xanthene derivative, coloring composition, ink for inkjet recording, method of inkjet recording, color filter, and color toner
InactiveUS8845760B2Improve performanceMethine/polymethine dyesOrganic chemistryHydrogenHydrogen atom
There is provided a compound represented by formula (1):in formula (1), L represents a divalent to tetravalent linking group; D represents a residue obtained by removing 1 to 5 hydrogen atoms from a compound represented by formula (2); m represents an integer of 1 to 10, however, each L may be the same with or different from every other L; n represents an integer of 2 to 10, however, each D may be the same with or different from every other D; and in formula (2), each of R4 to R24 independently represents a hydrogen atom or a substituent, provided that formula (2) has at least one or more ionic hydrophilic groups.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Oxime ester compound, photopolymerizable composition and color filter using the same
InactiveCN101805282AGood shading effectImprove qualityOrganic chemistryOptical filtersPolymer scienceHazardous substance
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Metal organic liquid crystal dyes
ActiveUS20170355908A1Liquid crystal compositionsMethine/polymethine dyesMetallomesogenCrystallography
A dye composition dissolvable within a liquid crystal host device (including: polymer dispersed liquid crystal, polymer network liquid crystal, polymer stabilized liquid crystal, liquid crystal displays and similar devices), comprising eutectic mixtures of dichroic metallomesogen molecules. The aforesaid metallomesogen molecules comprise chromophore groups synthesized by physical and chemical mixing methods.
Owner:GAUZY
Chromogenic Absorbent Material for Animal Litter and Related Chromogenic Solution
A chromogenic absorbent material and related chromogenic solution, use, process and application for an animal litter. The chromogenic absorbent material includes an absorptive material for absorbing an animal excretion; an oxidizing agent responsive to peroxidatic / pseudoperoxidatic activity in the animal excretion to provide oxidizing activity; and an inclusion complex including a host compound and a guest compound, the guest compound being a chromogenic indicator associated with the host compound and being chromogenically responsive to the oxidizing activity of the oxidizing agent. The chromogenic absorbent material may be prepared from the chromogenic solution including the oxidizing agent and the inclusion complex. The chromogenic absorbent material may be used as particles combined with animal litter for detection of peroxidatic / pseudoperoxidatic activity in the animal excretion. The chromogenic material or solution may include a buffering agent, a colour enhancer, a stabilizer or a metal-scavenger agent or a combination thereof.
Owner:7905122 CANADA
Molecular tracers and modified proppants for monitoring underground fluid flows
The present invention relates to modified proppants and methods of using the modified proppants that use metal ligand tracers to characterize subterranean fluid flow. The metal and ligands are best chosen to be a strongly-coordinating, chelating ligand with a functional group for the chosen flow environment.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC +1
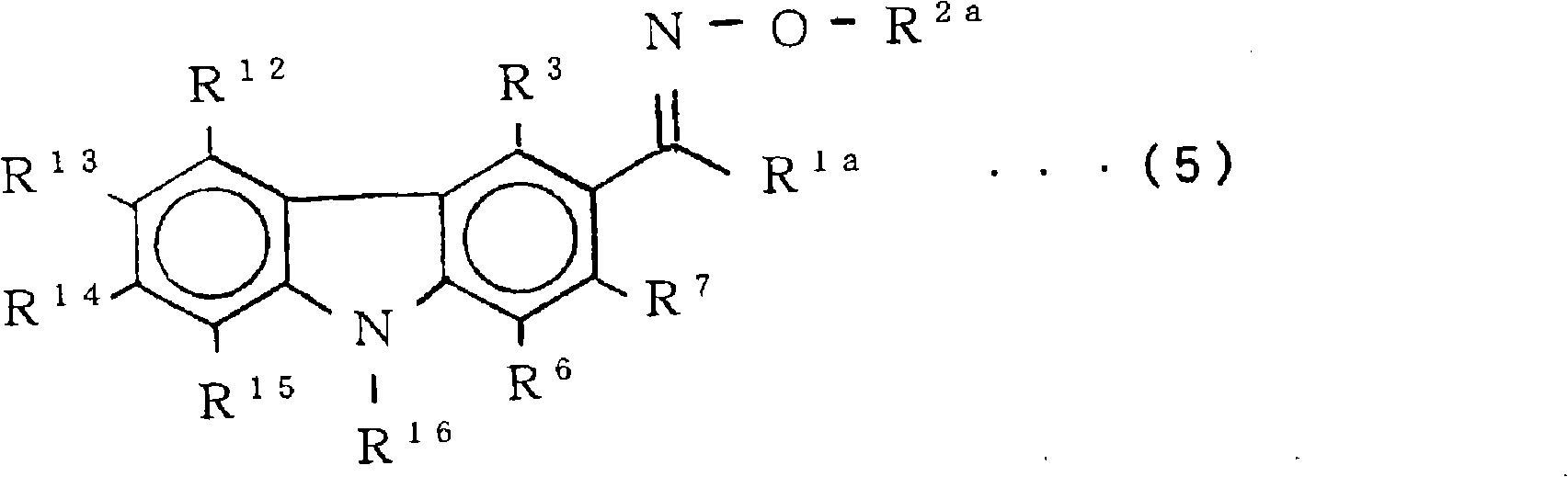
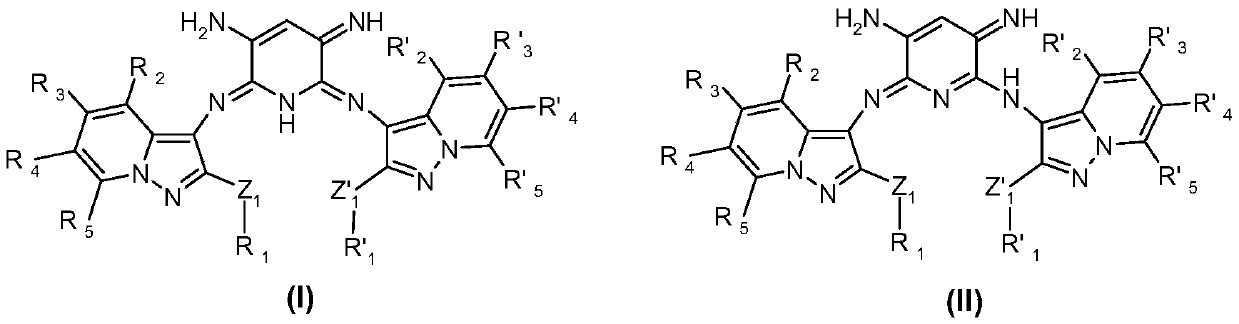
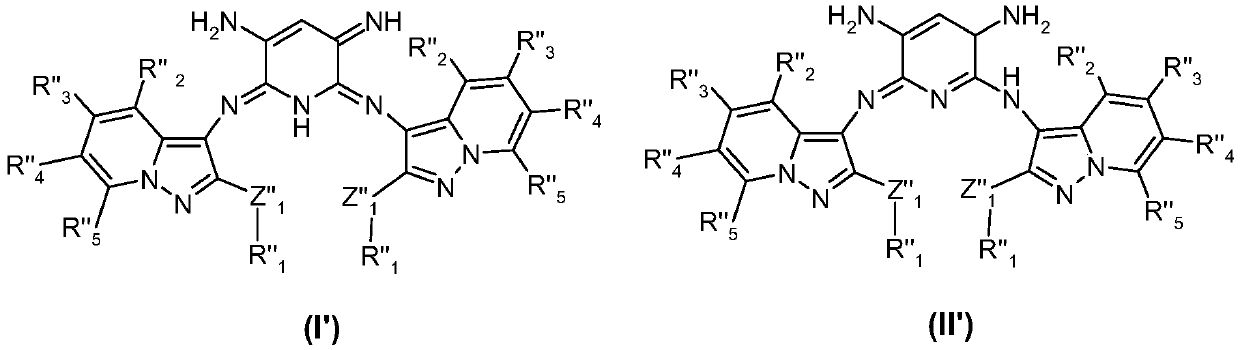
Use of azomethine compounds carrying two pyrazolopyridine units for dyeing keratin fibers
The invention relates to a compound chosen from the compounds of formulae (I) and (II), the leucoforms thereof, the optical and geometrical isomers thereof and the tautomers thereof, and also the addition salts thereof with an acid or a base, and the solvates thereof. The invention also relates to the use of these particular compounds for dyeing keratin fibres.
Owner:LOREAL SA
Fluorescent compound for detection of isocyanate substances and its preparation method and its application as a test paper type detection probe
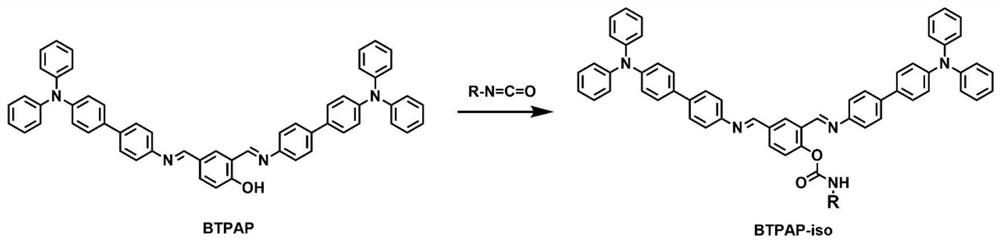
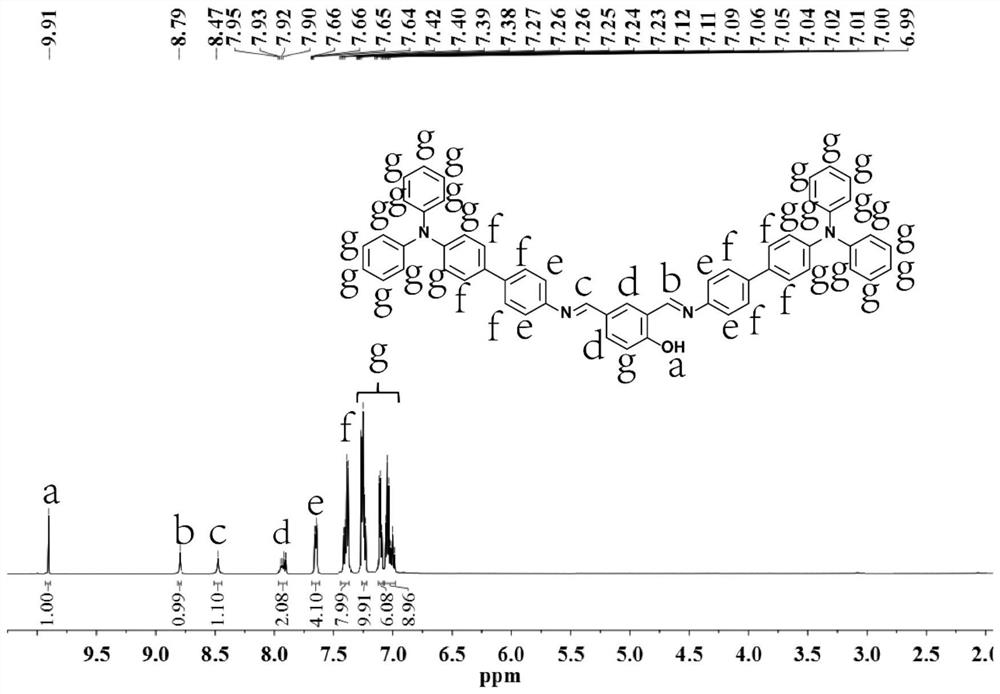
ActiveCN110330444BAchieving Sensitive DetectionBlocking the ESIPT effectAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorFluoProbesQuantum yield
The invention discloses a fluorescent compound used for detecting isocyanate substances, a preparation method and its application as a test paper type detection probe. The fluorescent compound is 2,4-bis(((4'-(diphenylamino)-[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)imino)methyl)phenol. The fluorescent compound is prepared by a one-step method, has simple preparation and high yield, can respond quickly and specifically to isocyanate substances, and its fluorescence intensity will increase with the increase of isocyanate concentration. The fluorescent compound can be made into a portable test paper probe for detecting isocyanate substances in the air, and can realize visual detection of volatile isocyanate gases. The probe has an aggregation-induced luminescence effect, and can have a higher fluorescence quantum yield when a test paper type probe is used for detection. The fluorescent probe prepared by the invention can be used in the detection of solution and gaseous isocyanate substances, and can be used to monitor the isocyanate in the atmosphere, water resources and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor modulators for the treatment of cardiopulmonary disease
The present invention provides compounds effective as sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor modulators for the treatment of cardiopulmonary disorders such as hypertension (including malignant hypertension), angina, myocardial infarction, arrhythmia , congestive heart failure, coronary heart disease, atherosclerosis, angina, dysrhythmia, cardiomyopathy (including hypertensive cardiomyopathy), heart failure, cardiac arrest, bronchitis, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, cystic fibrosis , croup, emphysema, pleurisy, pulmonary fibrosis, pneumonia, pulmonary embolism, pulmonary hypertension, mesothelioma, ventricular conduction abnormalities, complete cardiac obstruction, adult respiratory distress syndrome, sepsis syndrome, idiopathic pulmonary Fibrosis, scleroderma, systemic sclerosis, retroperitoneal fibrosis, prevention of keloid formation, or cirrhosis.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Color material dispersion liquid, coloring resin composition, color filter, liquid crystal display device, and light-emitting display device
ActiveUS20200148885A1Improve heat resistanceAvoid color changesDiaryl/thriaryl methane dyesOptical filtersArylPolymer science
A color material dispersion liquid including a color material, a dispersant and a solvent, wherein the color material contains a compound which is represented by the following general formula (I) and which contains one or more structures selected from the following structures (i) and (ii); wherein (i) “A” is an aliphatic hydrocarbon group containing two or more alicyclic hydrocarbon groups, containing a saturated aliphatic hydrocarbon group at a terminal position directly bound to “N”, and optionally containing O, S, N in a carbon chain, and (ii) at least one of R2 to R5 is a cycloalkyl group optionally containing a substituent group or an aryl group optionally containing a substituent group.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Color material dispersion liquid, color resin composition, color filter, liquid crystal display device, and light-emitting display device
ActiveUS11084934B2Improve heat resistanceAvoid color changesDiaryl/thriaryl methane dyesOptical filtersArylPolymer science
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Unsymmetrical diimine palladium catalyst and its ligand, preparation method and use
The invention relates to an asymmetric diimine palladium catalyst as shown in the following formula and a ligand, preparation method and application thereof, wherein R1-R6 and X are defined according to the description. The palladium catalyst has high heat stability and activity on ethylene polymerization, and polyethylene which has an appropriate branching degree and high molecular weight is generated; in addition, the catalyst can be used for copolymerization of ethylene and methyl acrylate. Please see the formula in the description.
Owner:合肥中科科乐新材料有限责任公司
Popular searches
Monoazomethine dyes Originals for photomechanical treatment Photosensitive materials for photomechanical apparatus Immunoassays Photomechanical apparatus Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing Porphines/azaporphines Photovoltaic energy generation Semiconductor devices Imino compound preparation
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com