Patents
Literature
179results about "Dry duplicators" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
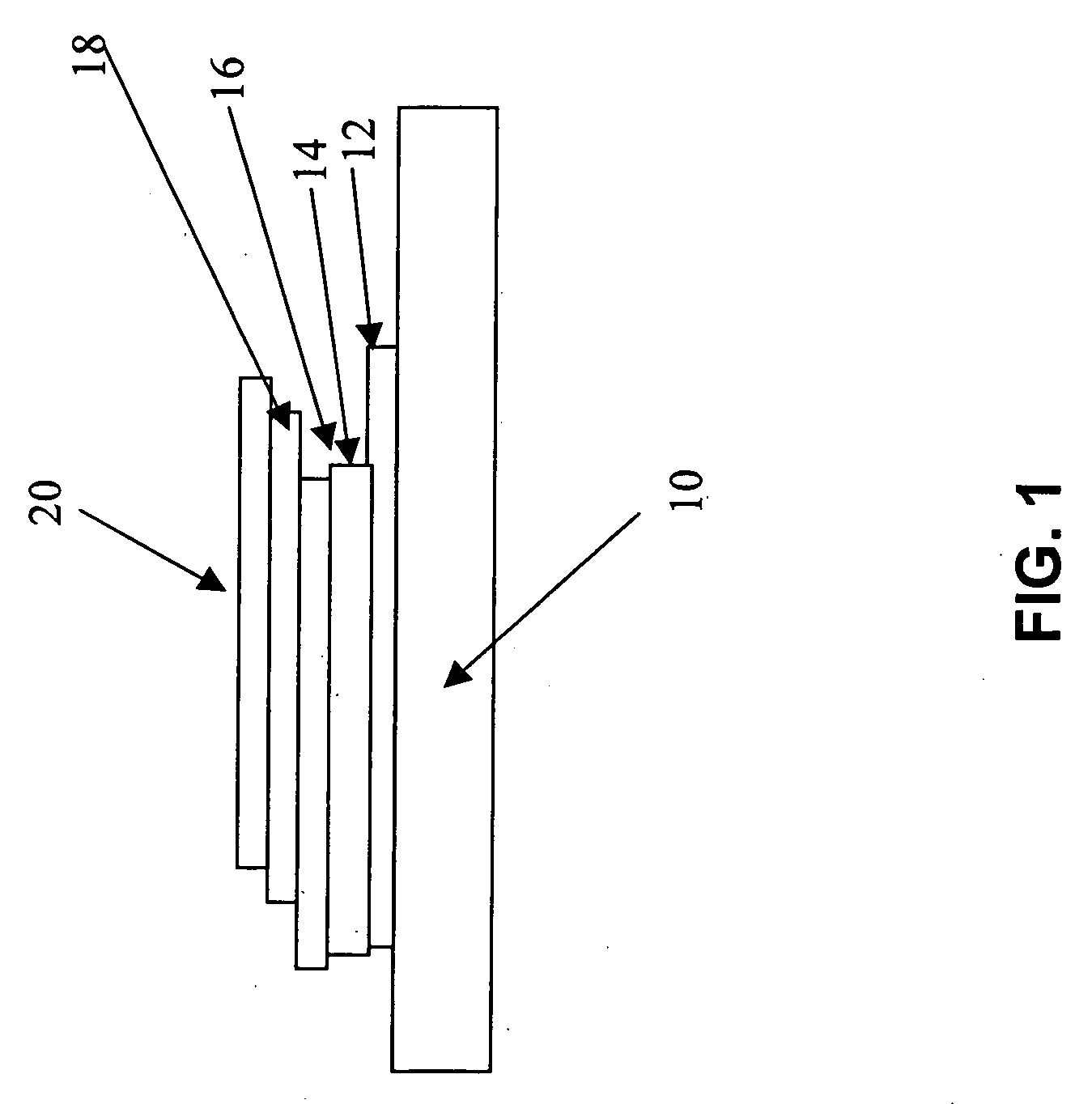
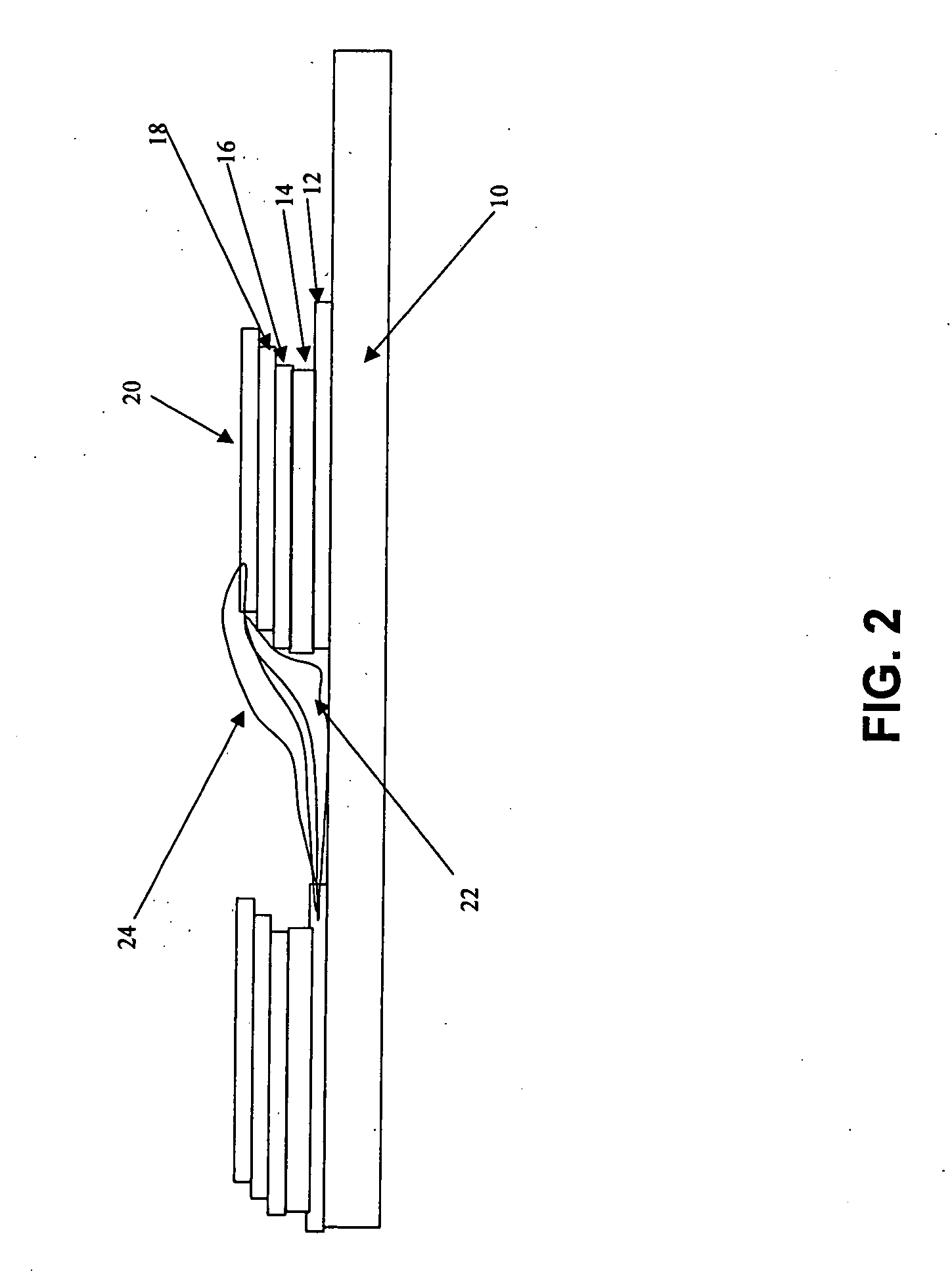
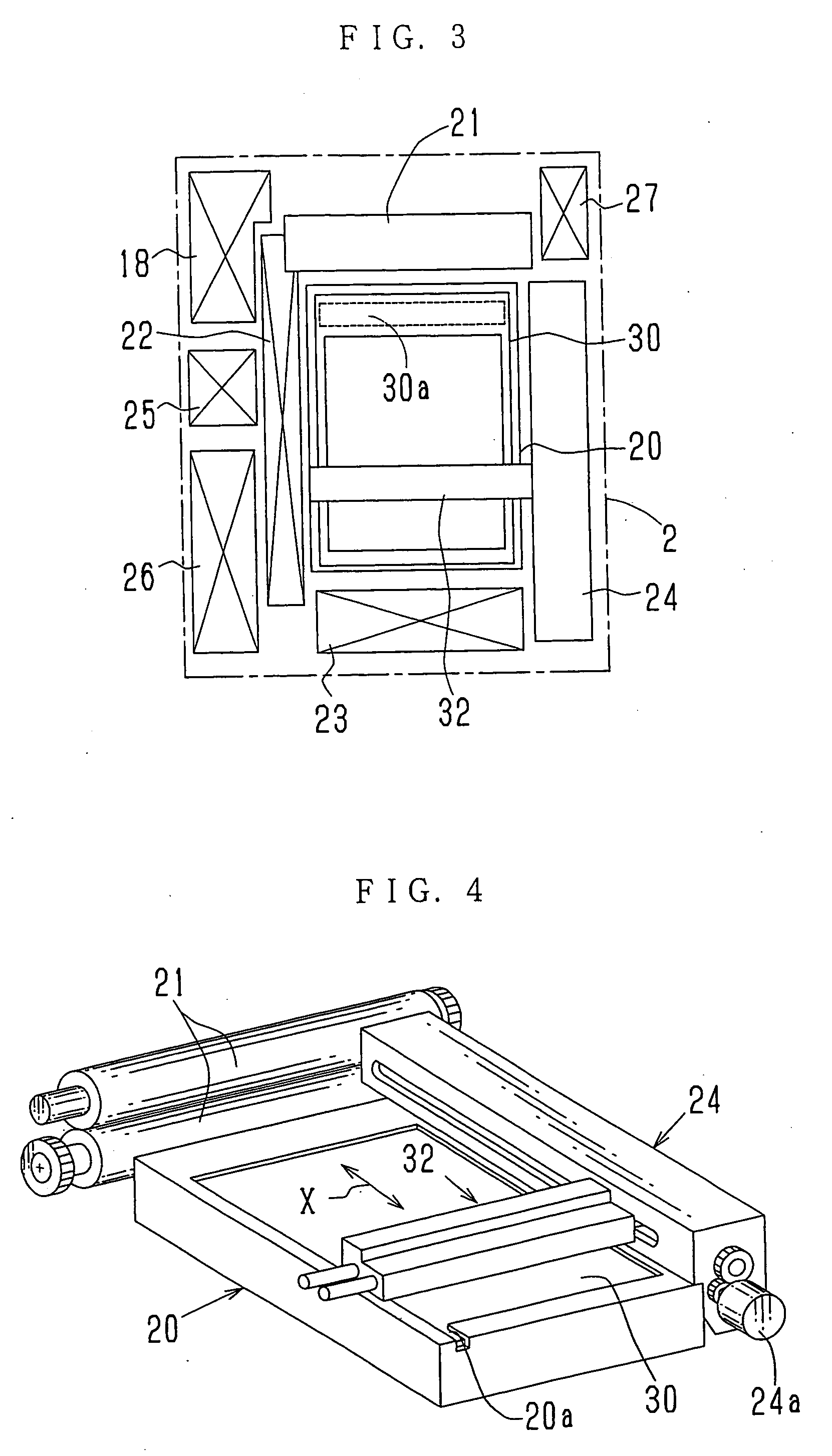
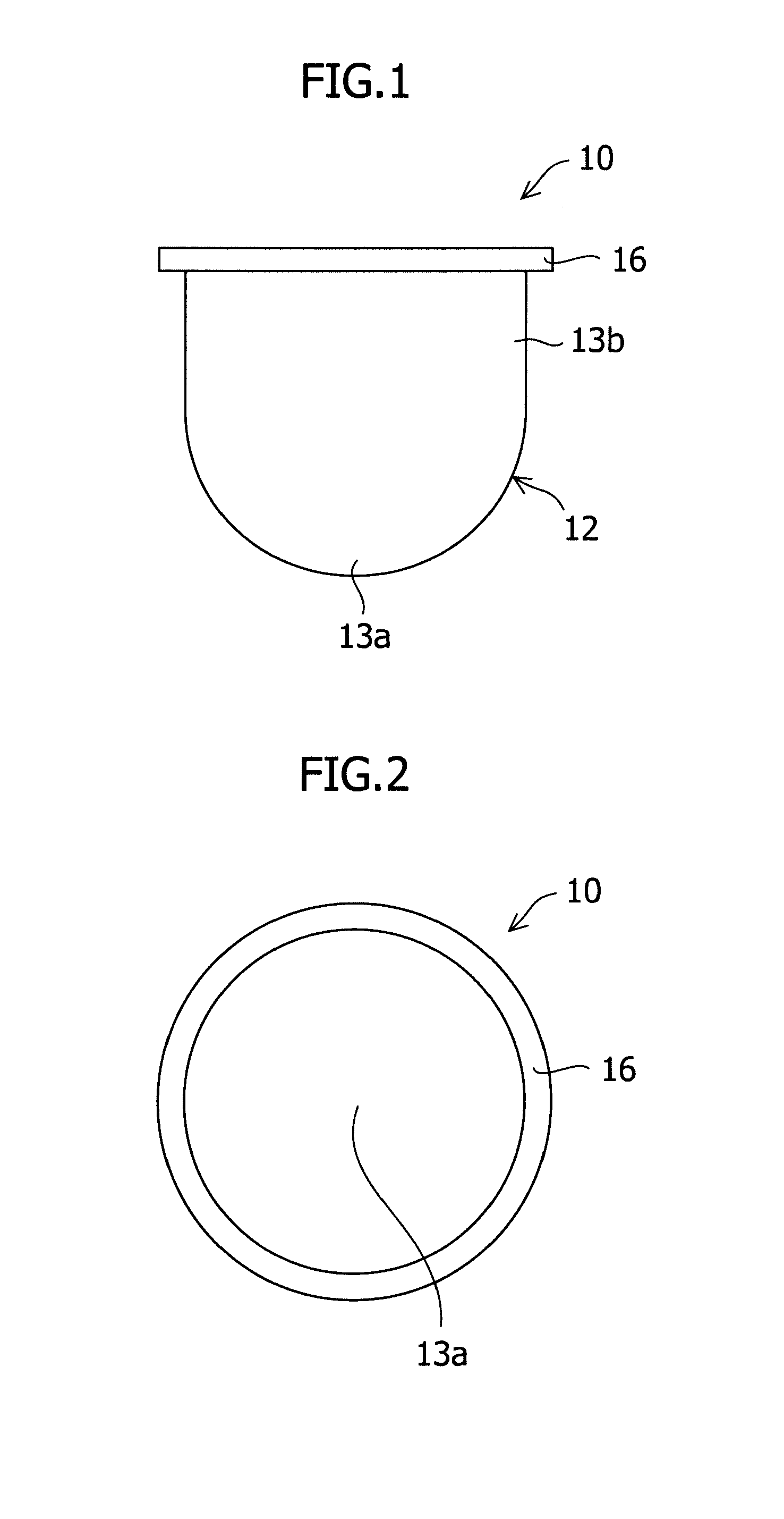
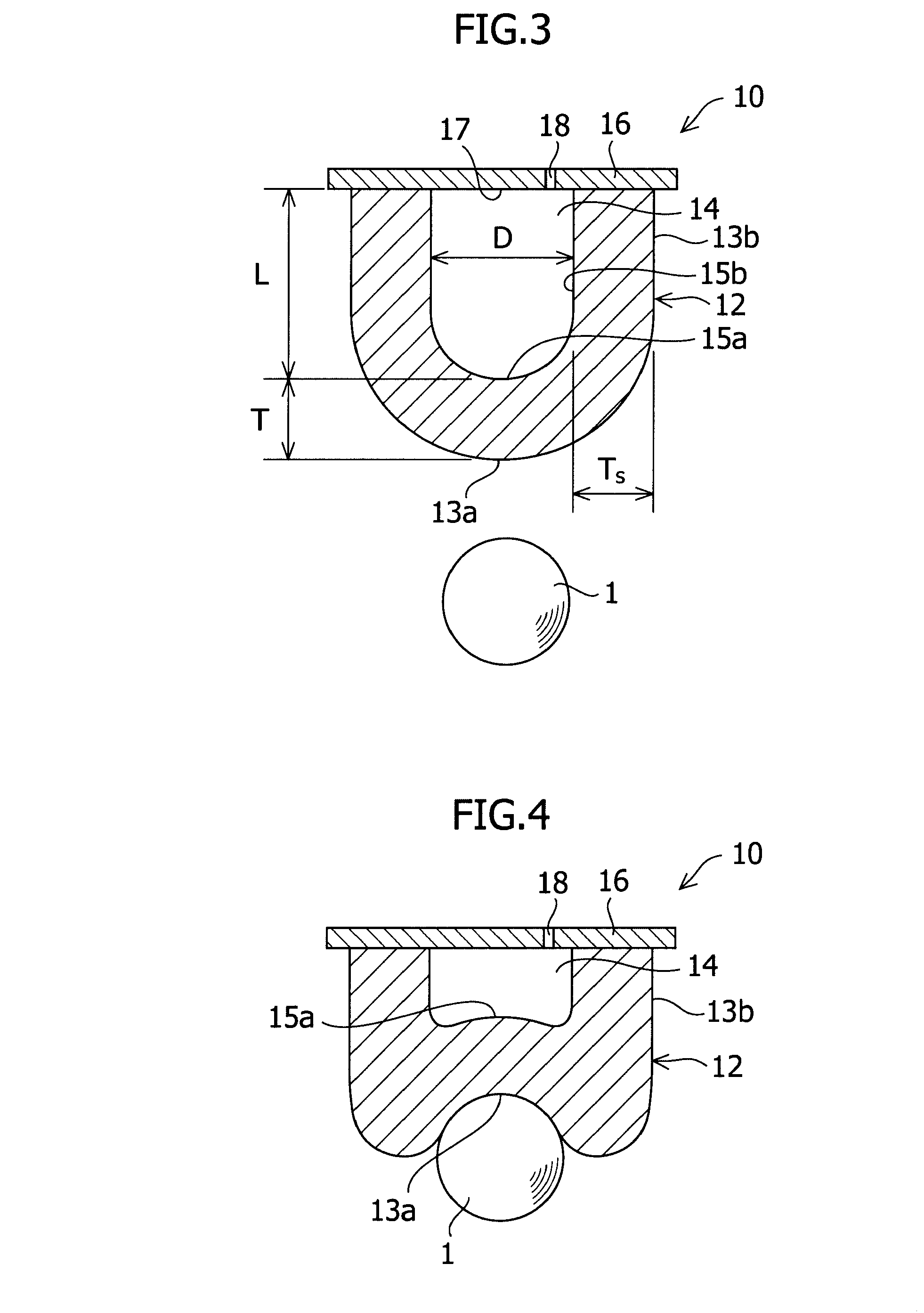
Method to form a pattern of functional material on a substrate by treating a surface of a stamp
InactiveUS20080233280A1Fully removedNanostructure manufactureLayered productsCompound (substance)Electron
The invention provides a method to form a pattern of functional material on a substrate. The method uses an elastomeric stamp having a relief structure with a raised surface and having a modulus of elasticity of at least 10 MegaPascal. At least the raised surface of the stamp is treated by exposing the stamp to heat, radiation, electrons, a stream of charged gas, chemical fluids, chemical vapors, and combinations thereof, to enhance wettability of the surface. A composition of the functional material and a liquid is applied to the relief structure and the liquid is removed to form a film on the raised surface. The elastomeric stamp transfers the functional material from the raised surface to the substrate to form a pattern of the functional material on the substrate. The method is suitable for the fabrication of microcircuitry for electronic devices and components.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
All printed solar cell array
The present invention relates to a method for producing a photovoltaic novelty item. Conductive polymer solutions and semiconductive oxide dispersions are formulated into inks that are laid down on top of one another to produce voltage and current when exposed to light. In addition, these inks may be printed on novelty items, such as magazine advertisements or greeting cards, connecting to printed light emitting graphics.
Owner:ZEIRA EITAN C
Electrode for secondary battery, manufacturing method thereof and secondary battery employing the same
InactiveUS20090098457A1Improve thickness uniformityIncrease electrode capacityCylinder pressesPlaten pressesElectrical batterySurface roughness
Provided are an electrode for a secondary battery employing an active material layer having improved thickness uniformity by printing low-viscosity ink on the active material layer, a manufacturing method of the electrode, and a secondary battery having improved electrode capacity due to the employing of the electrode. The electrode includes a current collector, and an active material layer formed by printing ink having a viscosity not exceeding 500 mPa·s on the current collector and drying the current collector, wherein the current collector has a surface roughness (Ra) in a range from about 0.025 to 1.0 μm.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Device for printing by transfer onto a cylindrical printing medium
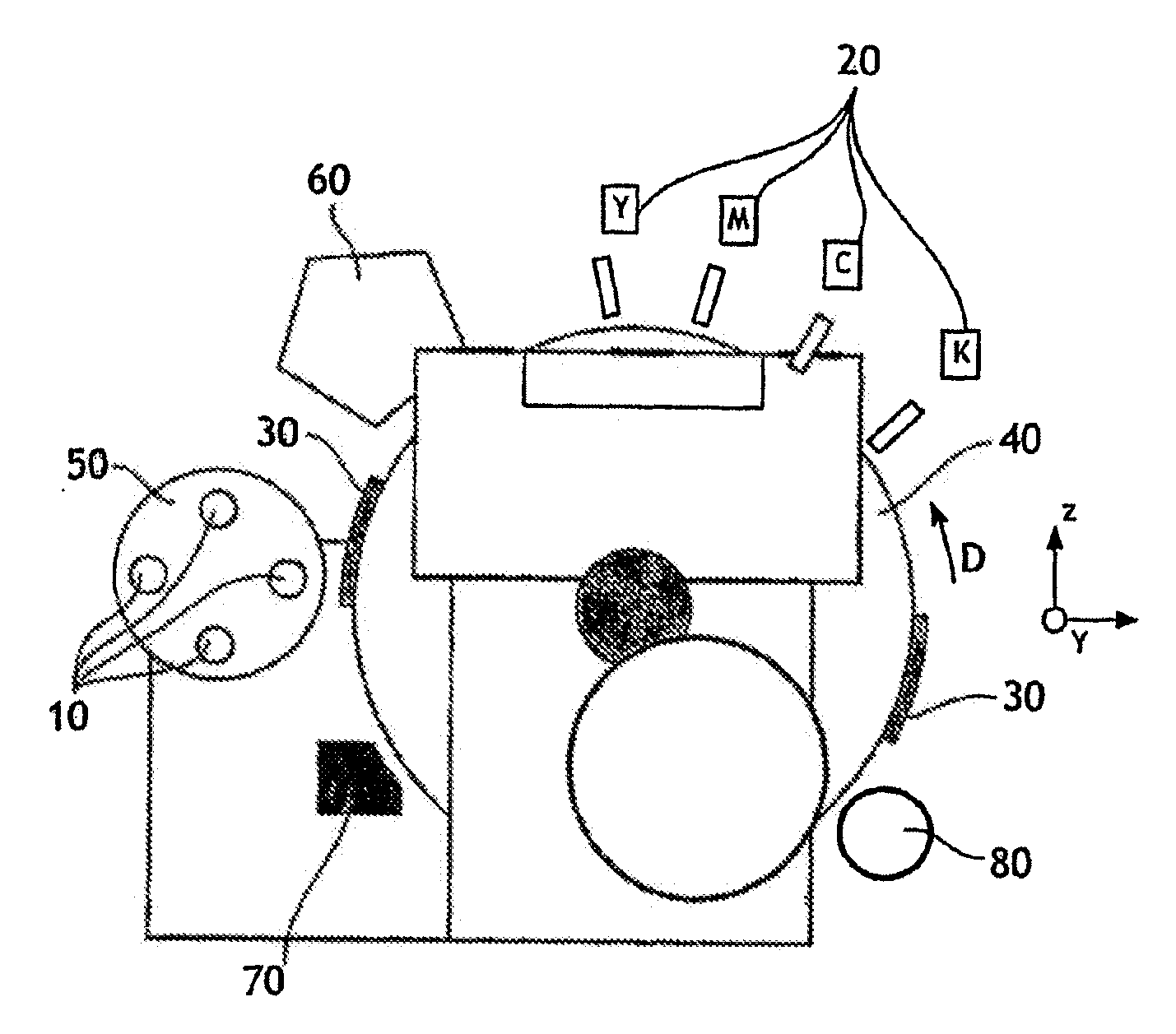
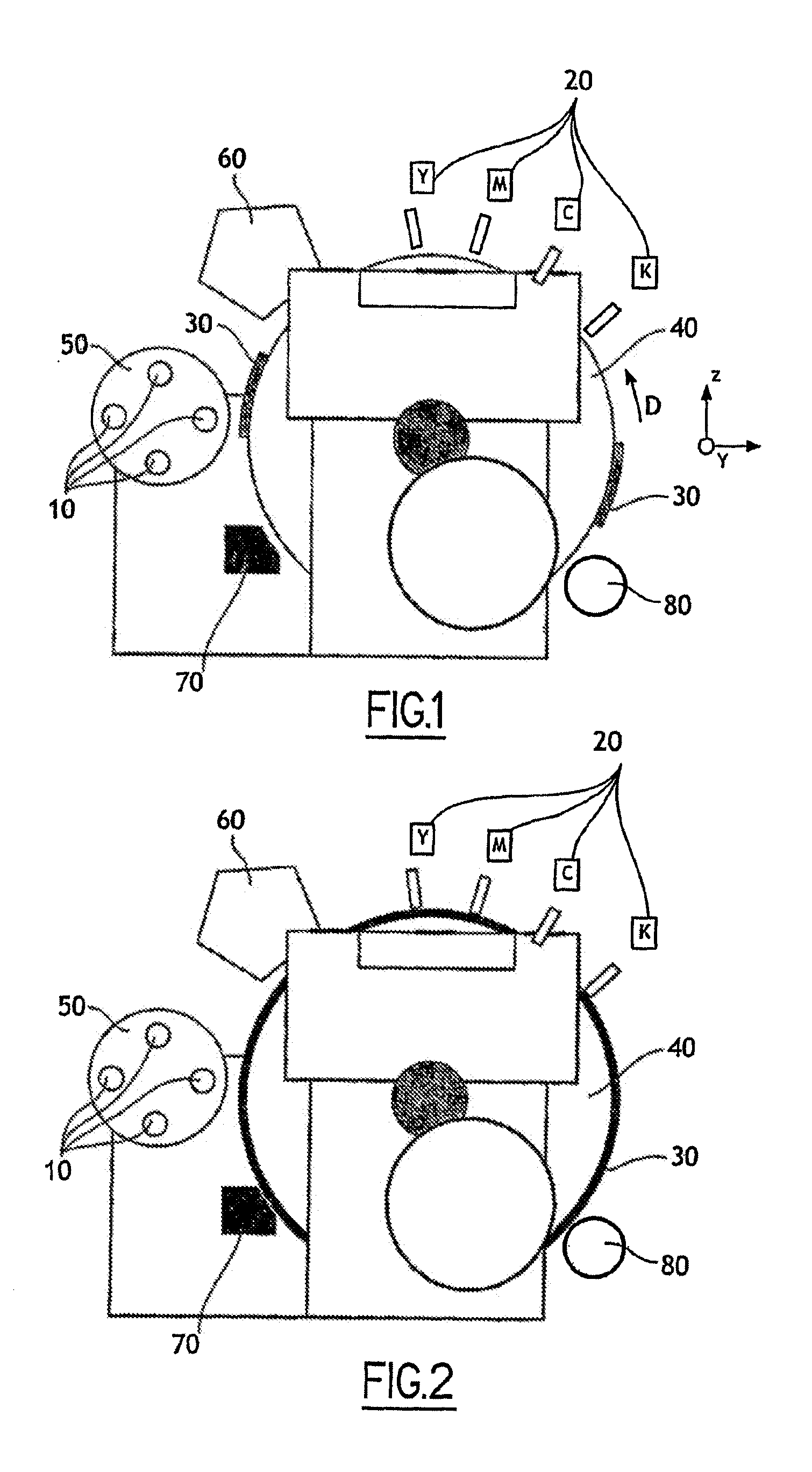
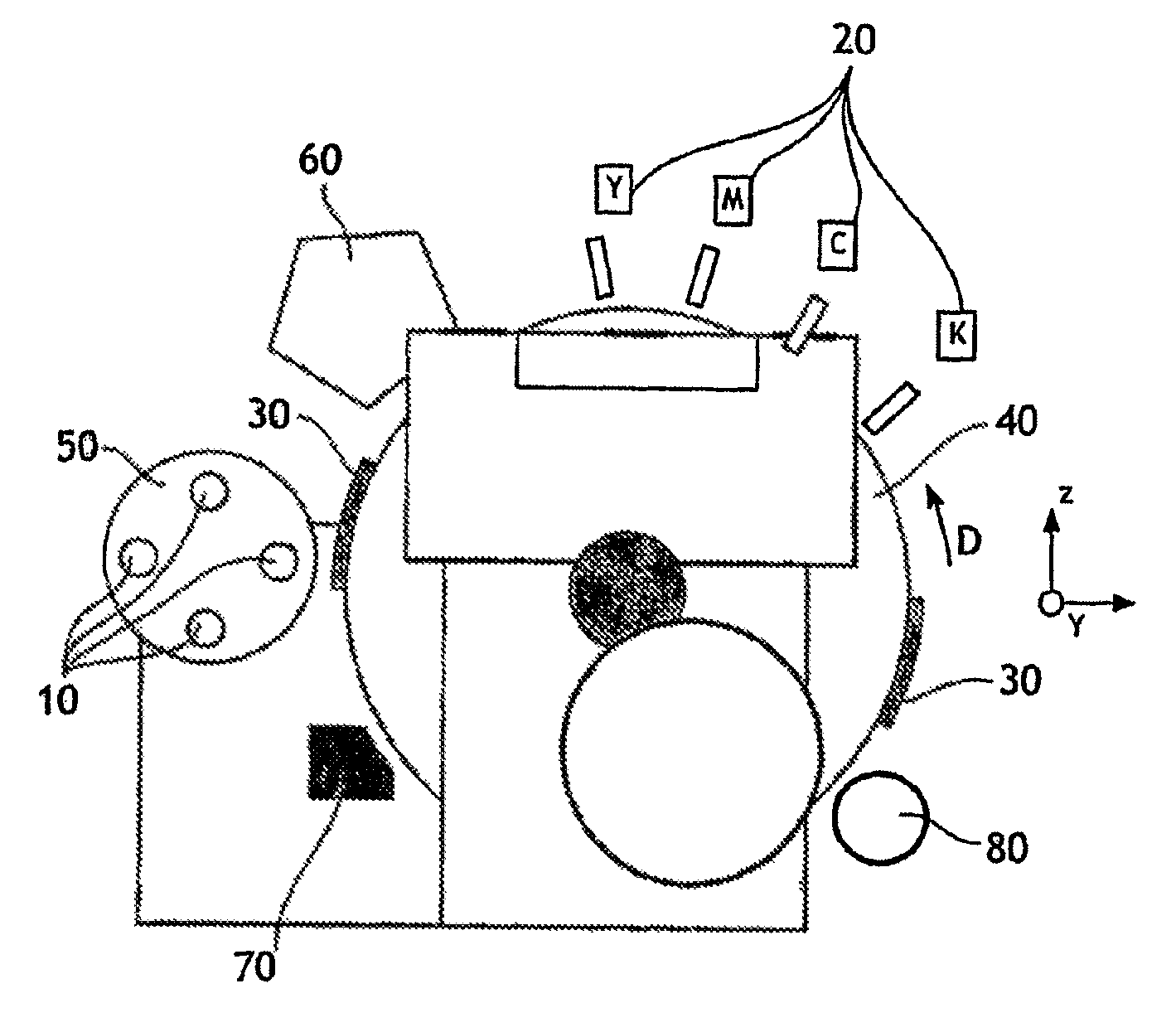
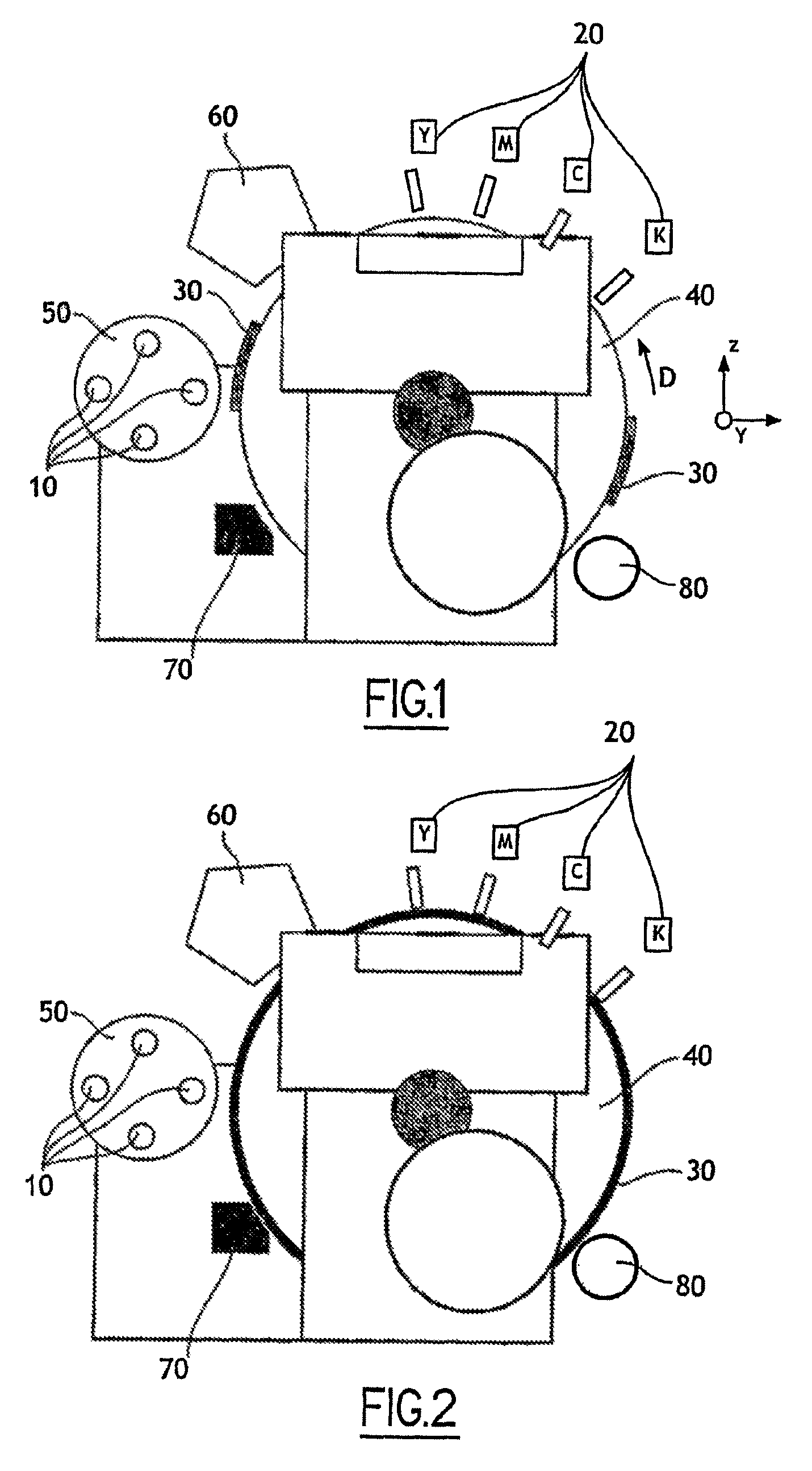
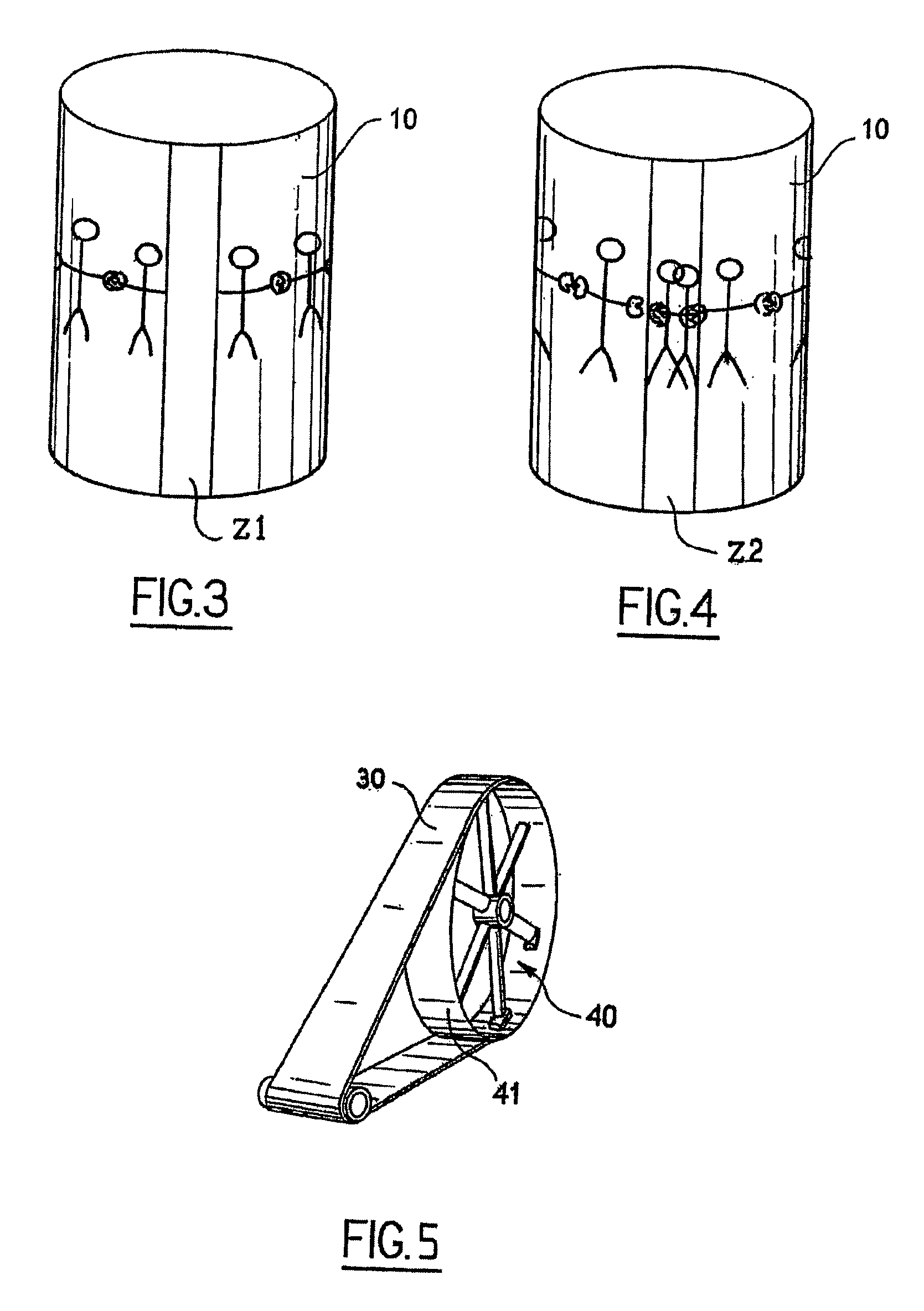
The invention relates to a device for printing by transfer onto a print support (10) comprising at least one blanket (30) driven in a sequential relative movement past a magazine (50) conveying the print supports (10), in which device the blanket (30) has a surface area greater than that of the print support (10), the device further comprising digital printing means (20) which print by spraying ink onto this blanket (30) over a variable area equal to that of the print support (10).
Owner:IMPIKA +1
Intermediate transfer recording medium, method of forming print, and print
InactiveUS6308630B1Quality improvementSimple formatCylinder pressesPlaten pressesComputer scienceRecording media
An intermediate transfer recording medium is comprised by providing a transfer portion having a receptor layer on a substrate film. The transfer portion is printed with the image and thereafter transferred on a surface of a transfer-receiving material. In the first aspect of the intermediate transfer recording medium, the transfer portion is provided with plural hologram patterns 21 with a hologram mark 22 allocated to each the hologram pattern. According to the first aspect of the invention, since an image is formed on the receptor layer through positioning process using the hologram mark and then the transfer portion is transferred to the surface of the transfer-receiving material, no joint of a print plate appears in the hologram pattern and accuracy of transfer is remarkably excellent. On the other hand, In the second aspect of the intermediate transfer recording medium, peeling strength required to peel the transfer portion from the substrate film at the time when transferring the transfer portion to the transfer-receiving material is controlled in the range of 10 to 150 gf / inch. According to the second aspect of the invention, any transfer failure such as tail-extension or chip of the transfer portion is not caused.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
System and methods for data-driven control of manufacturing processes
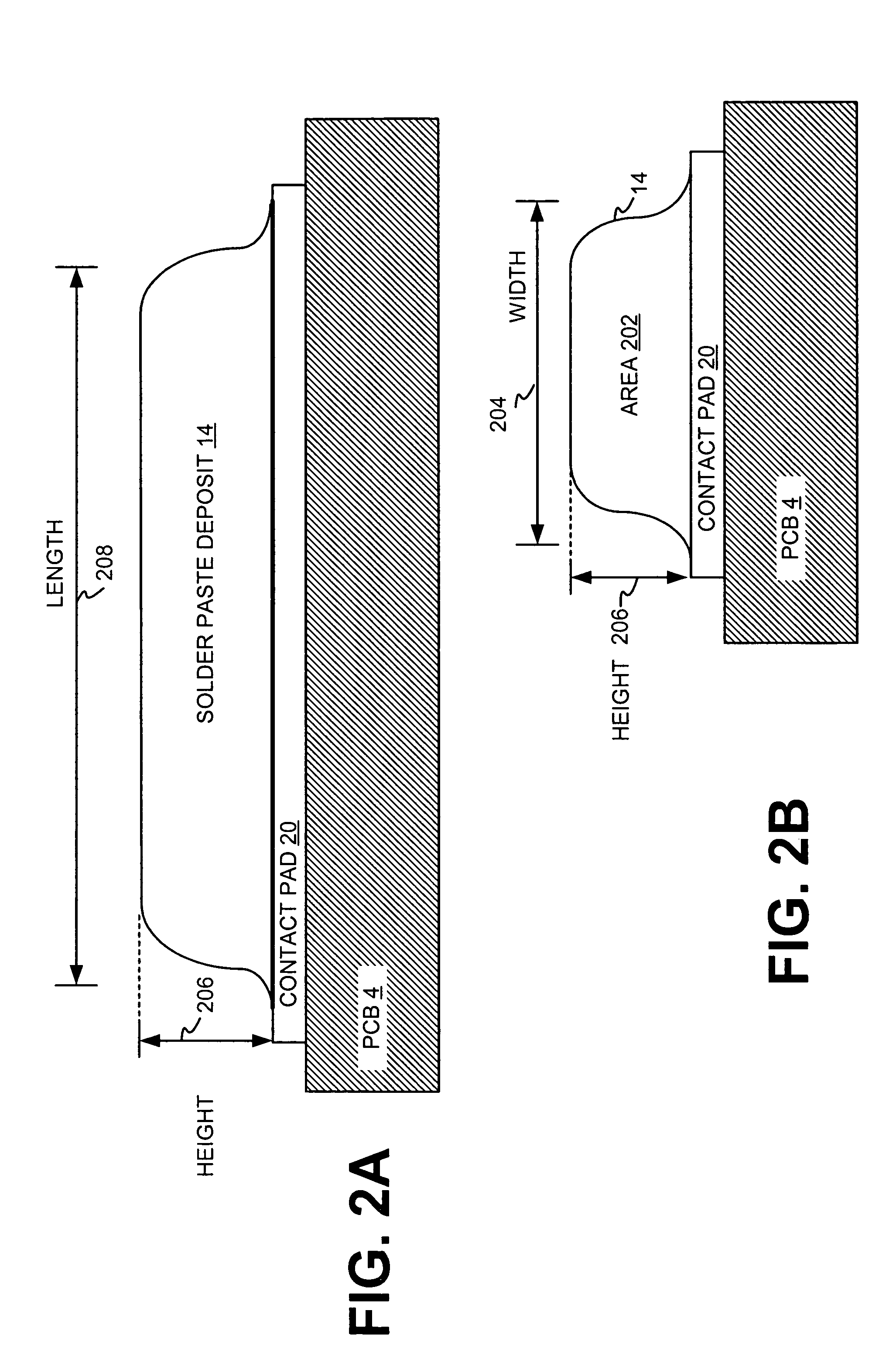
Systems and methods for implementing hybrid, closed-loop control that generates control values for processes defined by a limited number of function evaluations and large amounts of process and measurement noise. The described control system is applied to a stencil printing process for applying solder paste to an electronic medium such as a printed circuit board or semiconductor wafer. The control system is defined by a hybrid approach. A first, coarse algorithm is used to rapidly produce the value of a stencil printer control value resulting in a solder paste deposit having a volume within predetermined acceptable limits. After the coarse algorithm no longer produces solder paste deposits closer to a desired volume, a second, more refined estimator is used to fine tune the process. An additional transitional algorithm may be added between the coarse algorithm and refined estimator. The coarse algorithm may be implemented with a constrained-conjugated gradient search, and the refined search may be a implemented using a least-squares affine estimator or a quadratic estimator. The transitional algorithm may be implemented using a block version of a least-squares affine estimator.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Device and method for printing by transfer onto a cylindrical printing medium
The invention relates to a device for printing by transfer onto a print support (10) comprising at least one blanket (30) driven in a sequential relative movement past a magazine (50) conveying the print supports (10), in which device the blanket (30) has a surface area greater than that of the print support (10), the device further comprising digital printing means (20) which print by spraying ink onto this blanket (30) over a variable area equal to that of the print support (10).
Owner:IMPIKA +1
Radiation-curable polymerizable composition, ink composition, inkjet recording method, printed material, planographic printing plate, and method for forming planographic printing plate
InactiveUS7900558B2Cylinder pressesLiquid surface applicatorsPolymer scienceHindered amine light stabilizers
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Process for producing member having pattern, pattern transfer apparatus, and mold
A pattern transfer apparatus is constituted by a first mold holding portion for holding a first mold for forming a pattern inside a peripheral area of a member and a second mold holding portion for holding a second mold for forming a pattern in the peripheral area of the member.
Owner:CANON KK
Method of producing a high gloss coating on a printed surface
InactiveUS20030113466A1High coatingLow production costCylinder pressesTransfer printingPresent methodPaper sheet
The present invention is directed to a method for producing a high gloss coating on a printed surface. In the present method, an aqueous coating composition is deposited onto a surface to be printed using a blanket roller coating face which is a low energy, non-stick, smooth surface profile. In the present method, simultaneous with the deposition of aqueous coating onto a substrate, or shortly thereafter, pressure either alone or in combination with heat may be applied to the coating in order to create a substantially tack-free surface conforming to the surface of the coating face. By using a highly polished coating face, high gloss coatings may be readily obtained using this methodology in a number of traditional printing techniques including wet trap inline sheet-fed printing, heat-set offset printing, dry trap inline flexographic printing, offset web-fed printing and gravure printing. Coatings which are produced utilizing the present invention have high gloss values heretofore unobtainable using aqueous coating compositions.
Owner:FRAZZITTA JOSEPH +1
Method of Printing Curved Surface and Curved Surface Body Printed by Using Same
InactiveUS20080011177A1Accurate printingCylinder pressesPlaten pressesLetterpress printingEngineering
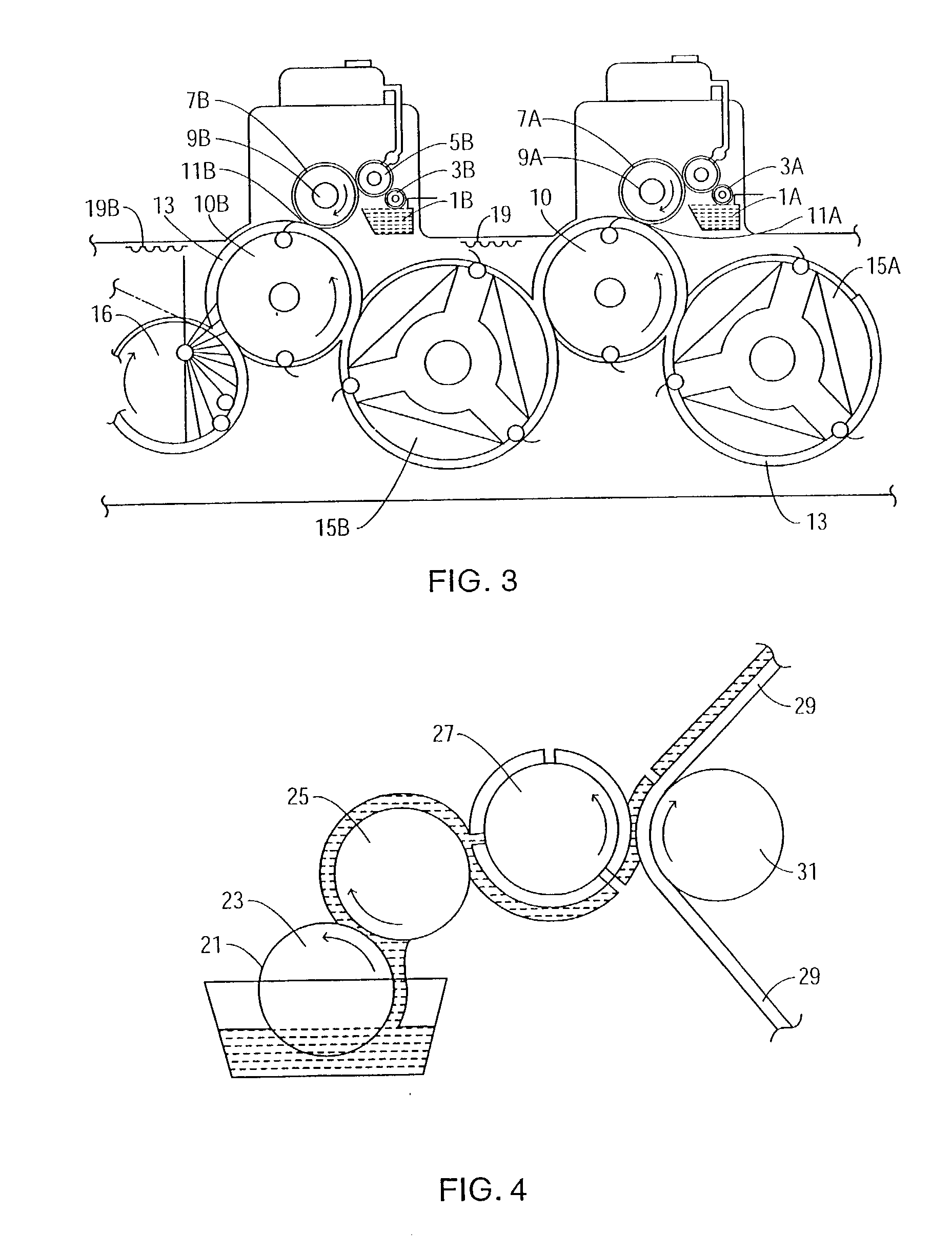
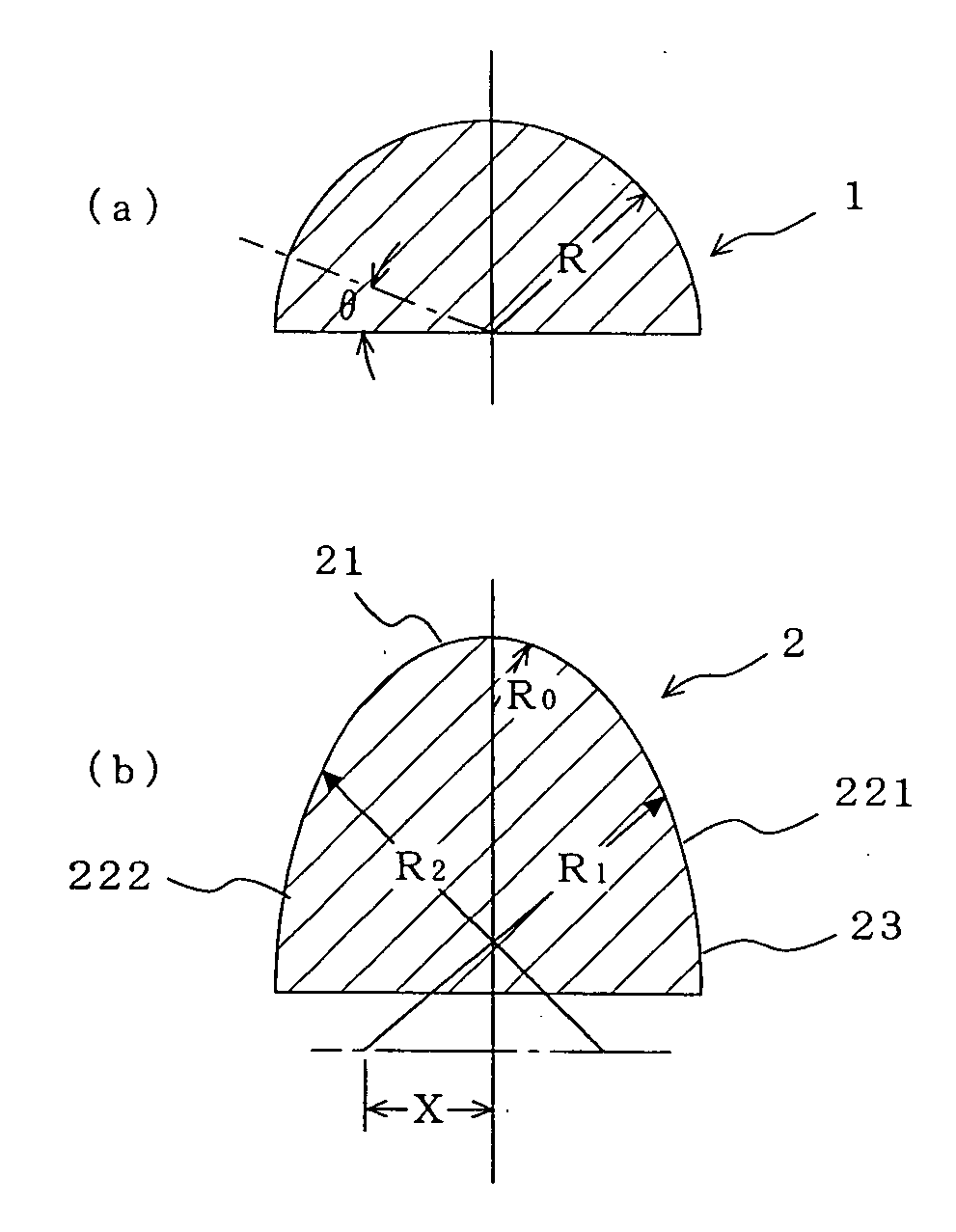
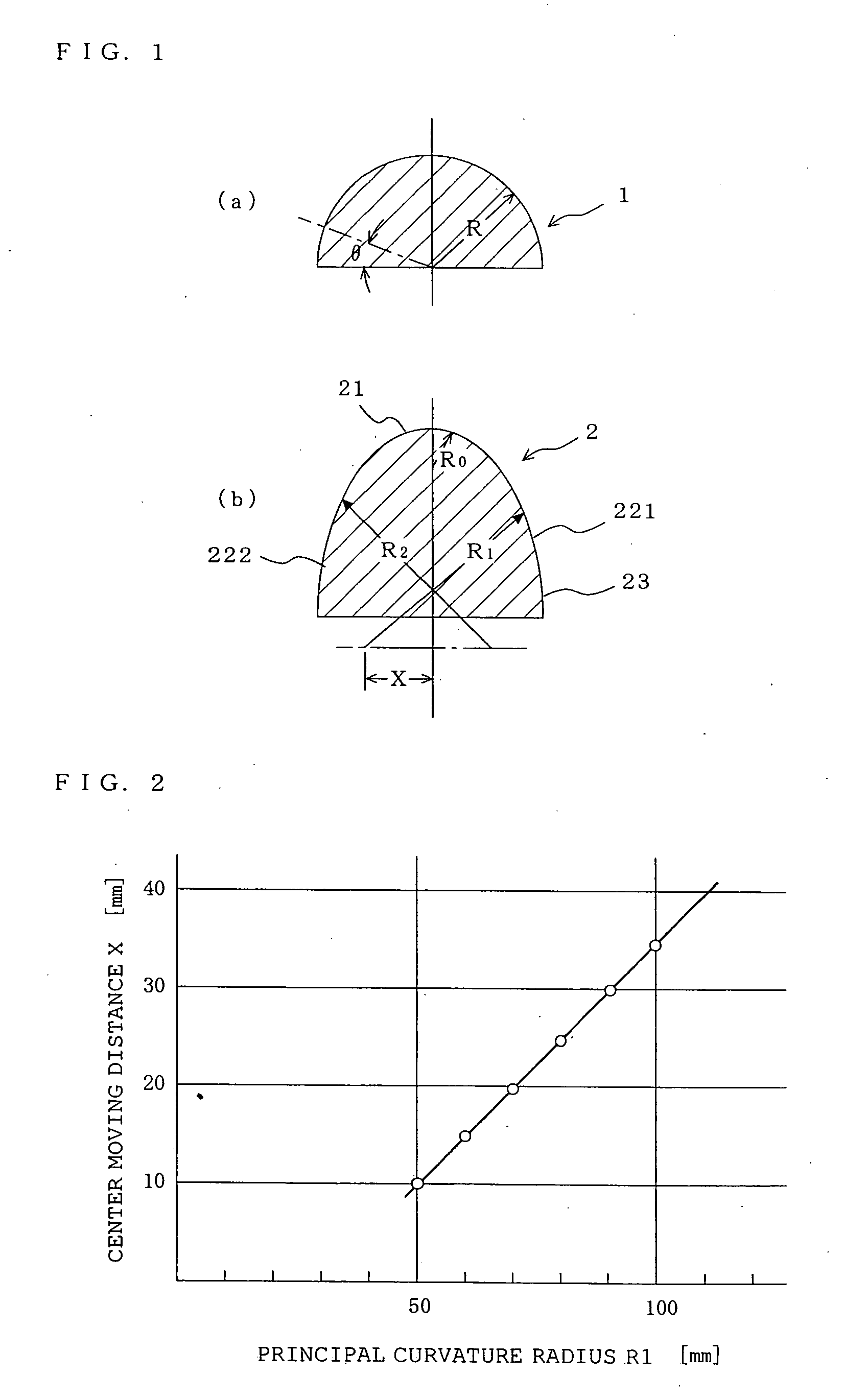
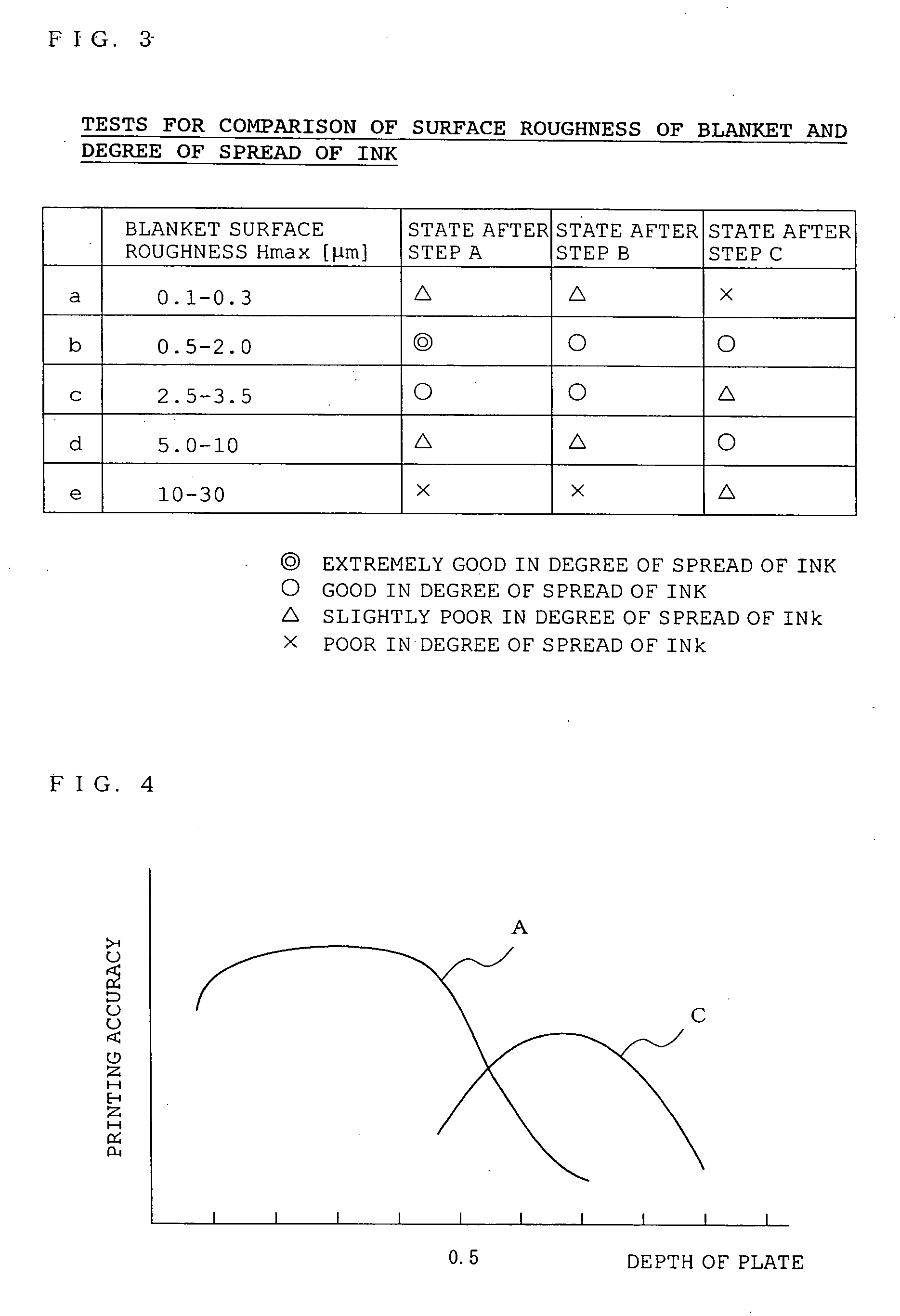
A curved surface printing method comprises a step of applying a printing ink to a raised portion of a letterpress printing original plate which is a planographic plate the raised portion of which is 0.1 to 50 μm high, a step in which an elastic blanket (2) of rubber or rubberish material having a curved surface (221, 222, 21) of a predetermined shape formed on a convex or concave surface of an object (1) to be printed and set in the same polarity direction as that of the convex or concave surface of the object (1) is pressed to the letterpress printing original plate placed in a fixed position and coated with the printing ink, and the printing ink is transferred to the curved surface (221, 222, 21) of the predetermined shape, and a step of moving the elastic blanket (2) to which the printing ink is transferred and which has curved surface (221, 222, 21) of the predetermined shape, bringing the elastic blanket (2) into contact with the curved surface of the object (1), and thus printing the object. A curved surface body printed by this method is also disclosed.
Owner:SHUHOU
Variable cut-off offset press system and method of operation
InactiveUS7066088B2Aid in smooth operation of systemIncrease frictionCylinder pressesTransfer printingImage transferCleaning station
A variable cut-off offset press system and method of operation which utilizes a continuous image transfer belt is provided. The offset printing system comprises at least two plate cylinders adapted to have thereon respective printing sleeves. Each of the printing sleeves is adapted to receive colored ink from a respective ink source. An optional coating source may be provided to fully or partially coat the image transfer belt before inking. The system further comprises at least a impression cylinder, wherein the image transfer belt is positioned to contact each of the printing sleeves at respective nips formed between respective ones of the plate cylinders and the at least one impression cylinder. An image belt cleaning station adapted to remove residual ink or coating from the surface of the image transfer belt after image transfer of a multicolored image from the image transfer belt to a substrate is also provided.
Owner:DAY INT
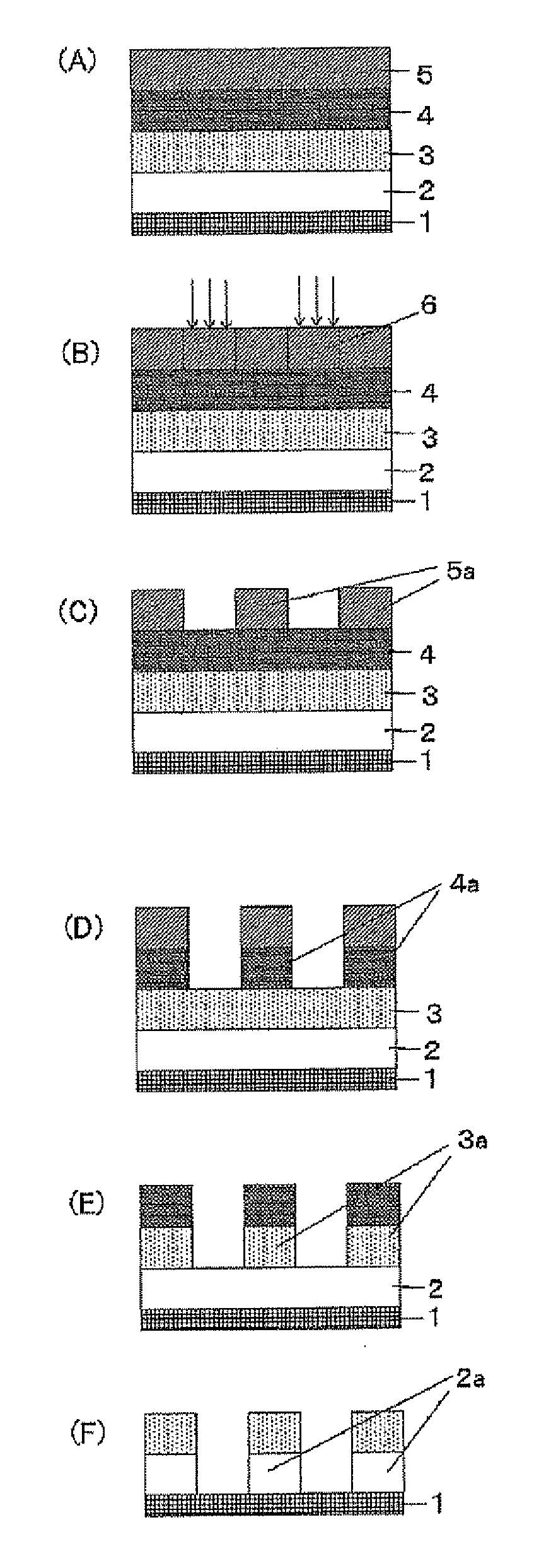
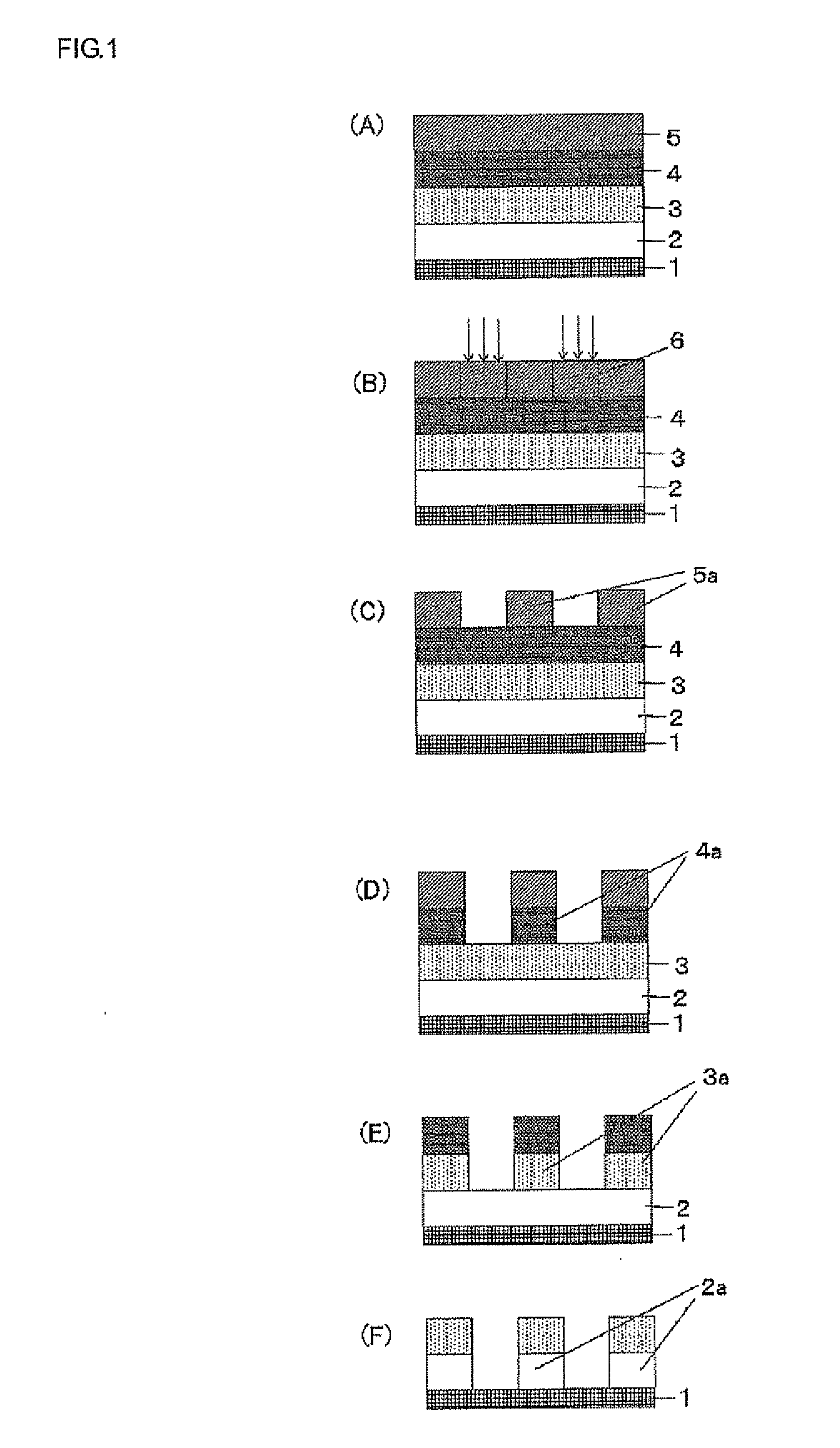
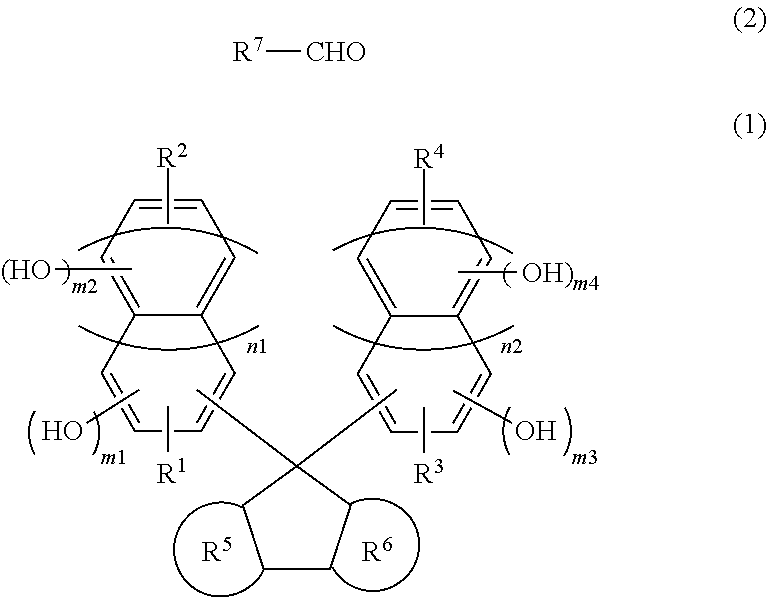
Resist underlayer film-forming composition, process for forming resist underlayer film and patterning process
ActiveUS20110177459A1Excellent etch resistanceImprove featuresMaterial nanotechnologyPhotosensitive materialsResistOrganic solvent
There is disclosed a resist underlayer film-forming composition comprising, at least: a resin (A) obtained by condensing a compound represented by the following general formula (1) with a compound represented by the following general formula (2) by the aid of an acid catalyst; a compound (B) represented by the general formula (1); a fullerene compound (C); and an organic solvent. There can be a resist underlayer film composition in a multi-layer resist film to be used in lithography, which underlayer film is excellent in property for filling up a height difference of a substrate, possesses a solvent resistance, and is not only capable of preventing occurrence of twisting during etching of a substrate, but also capable of providing an excellently decreased pattern roughness; a process for forming a resist underlayer film by using the composition; and a patterning process.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Method for marking a gaming disk by pad printing
A method for marking a side of a straight-sided chip with a decoration by pad printing. The method comprises providing an ink plate with an image defined by radially deformed representation of the decoration of the straight side of the chip in a ring-shaped zone, moving a pad coaxially into contact with the ink plate such that the image transfers to the pad, and moving the pad coaxially into contact with the chip such that the image transfers to the side of the chip.
Owner:GAMING PARTNERS INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION +1
Method for thermally processing photosensitive printing sleeves
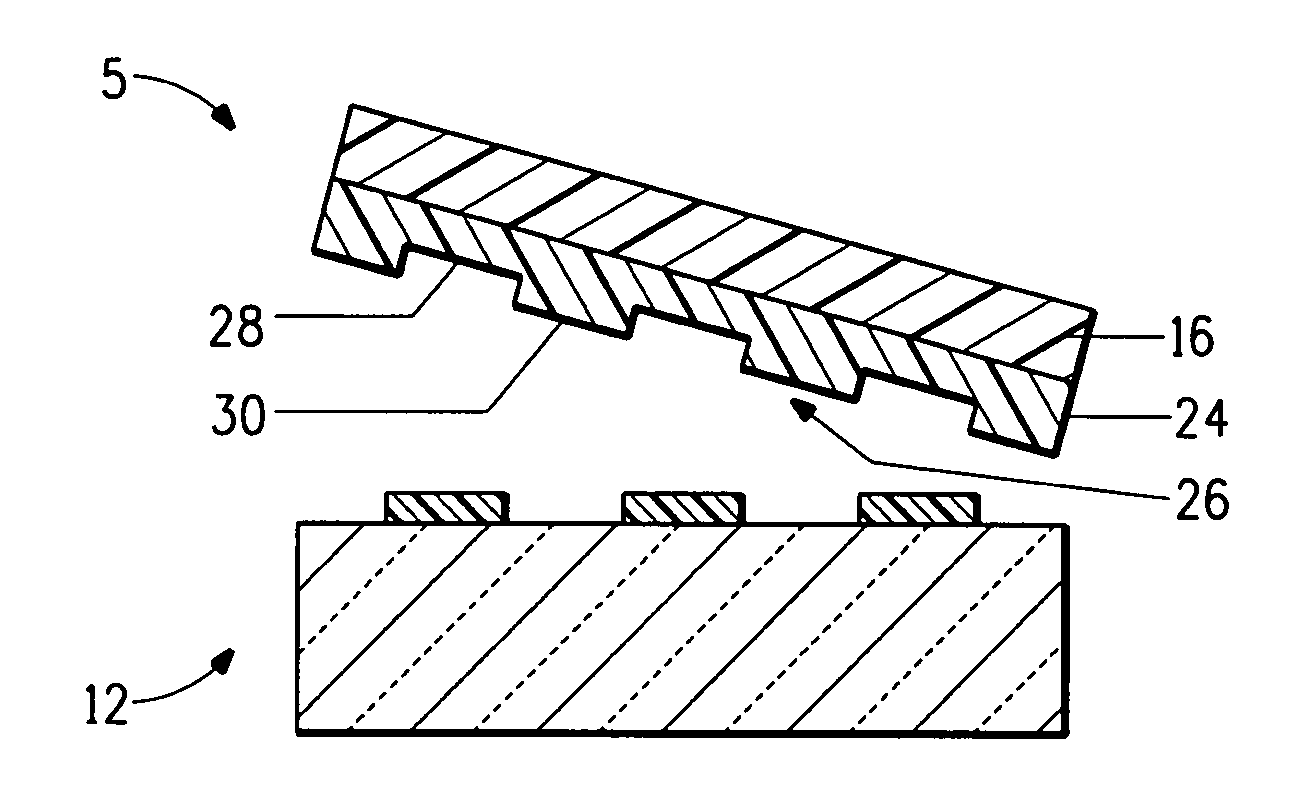
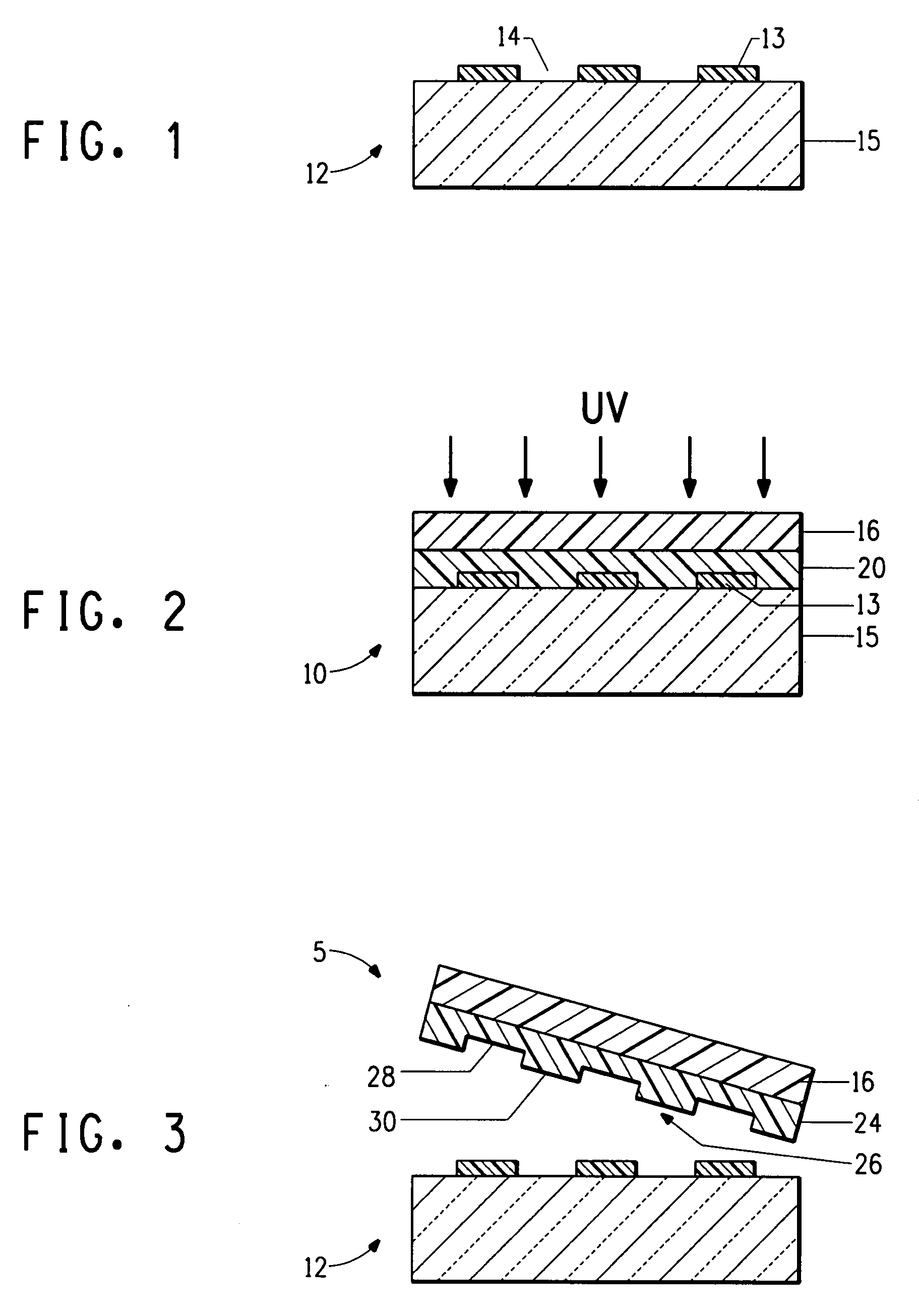
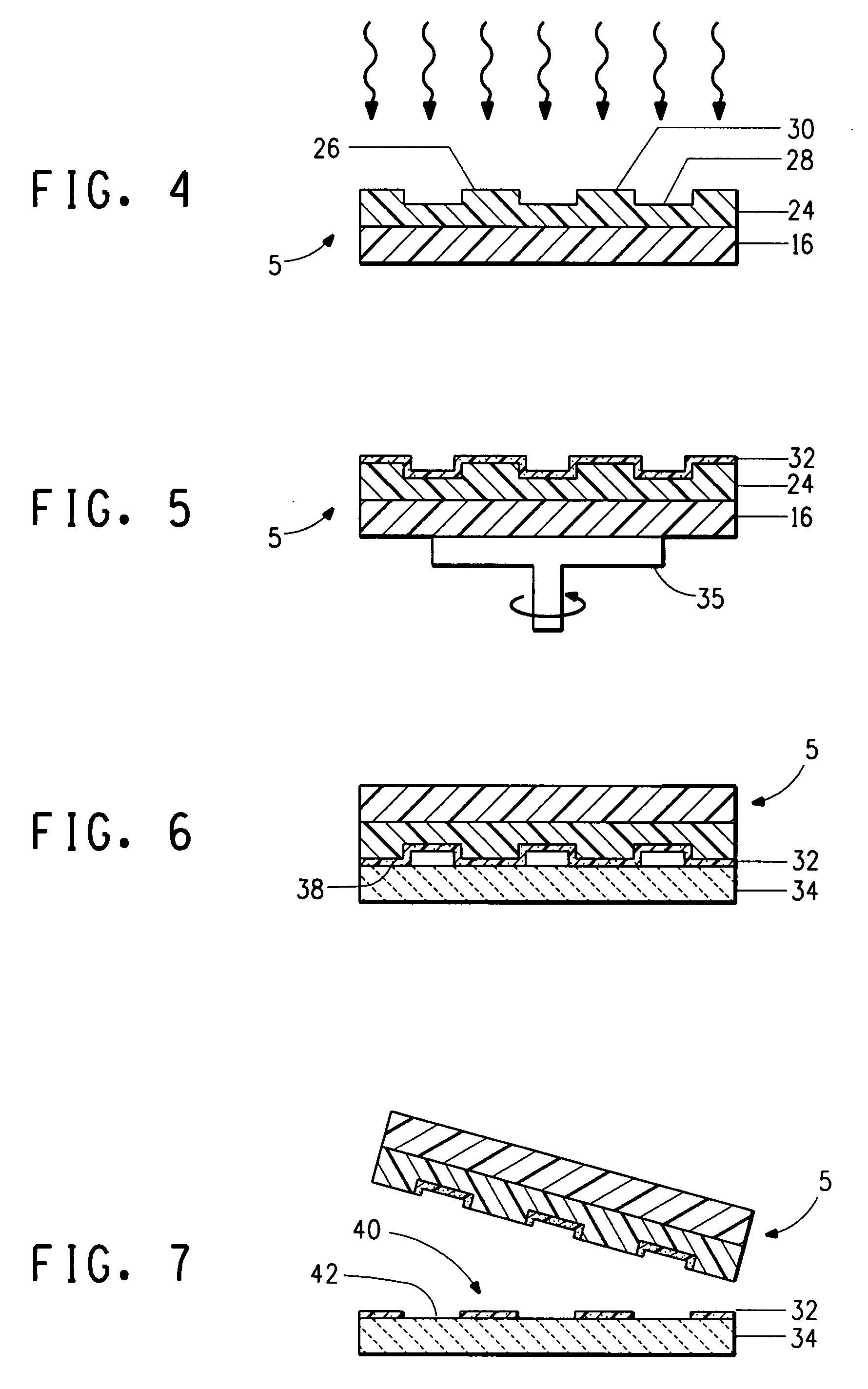
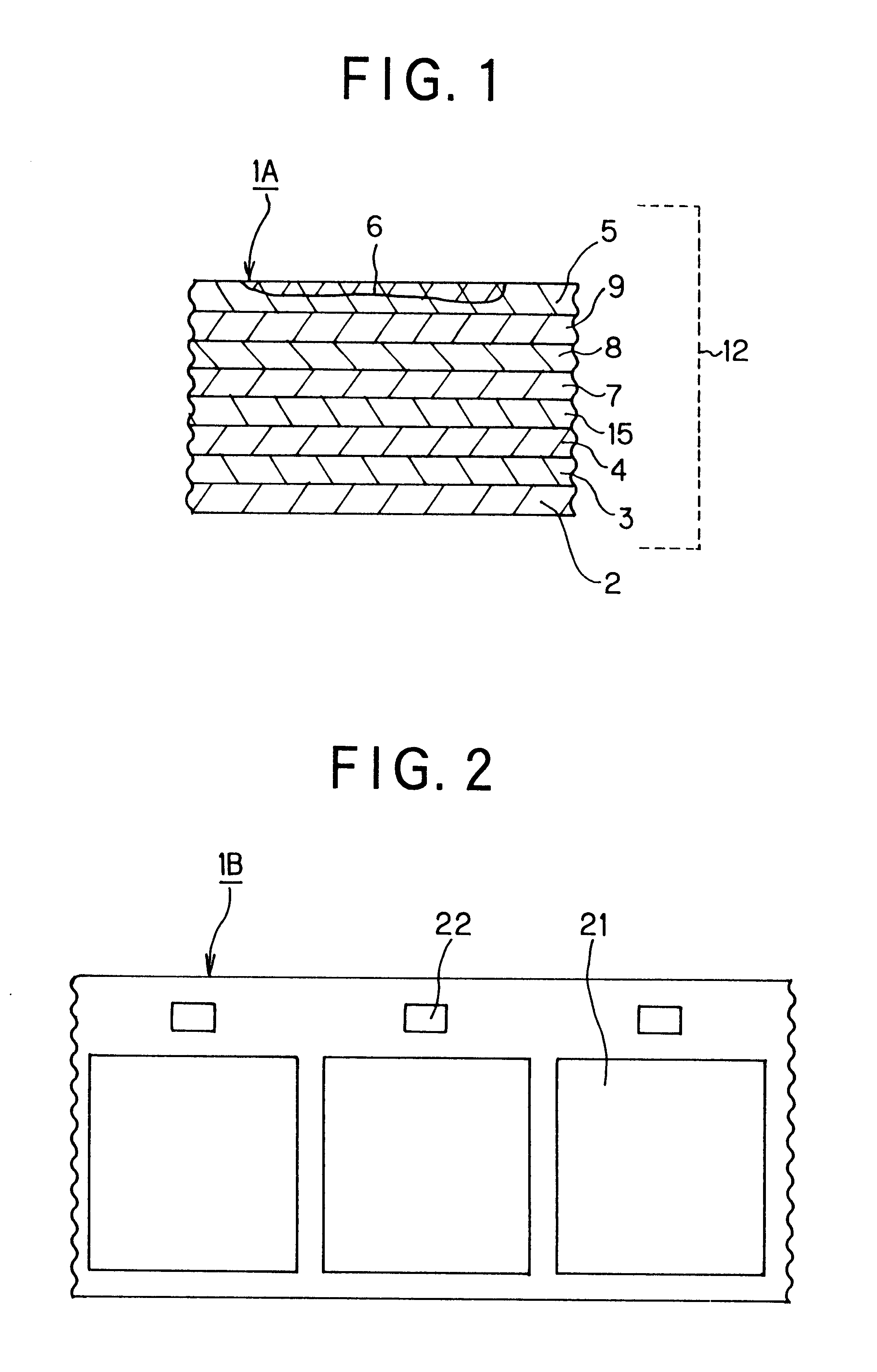
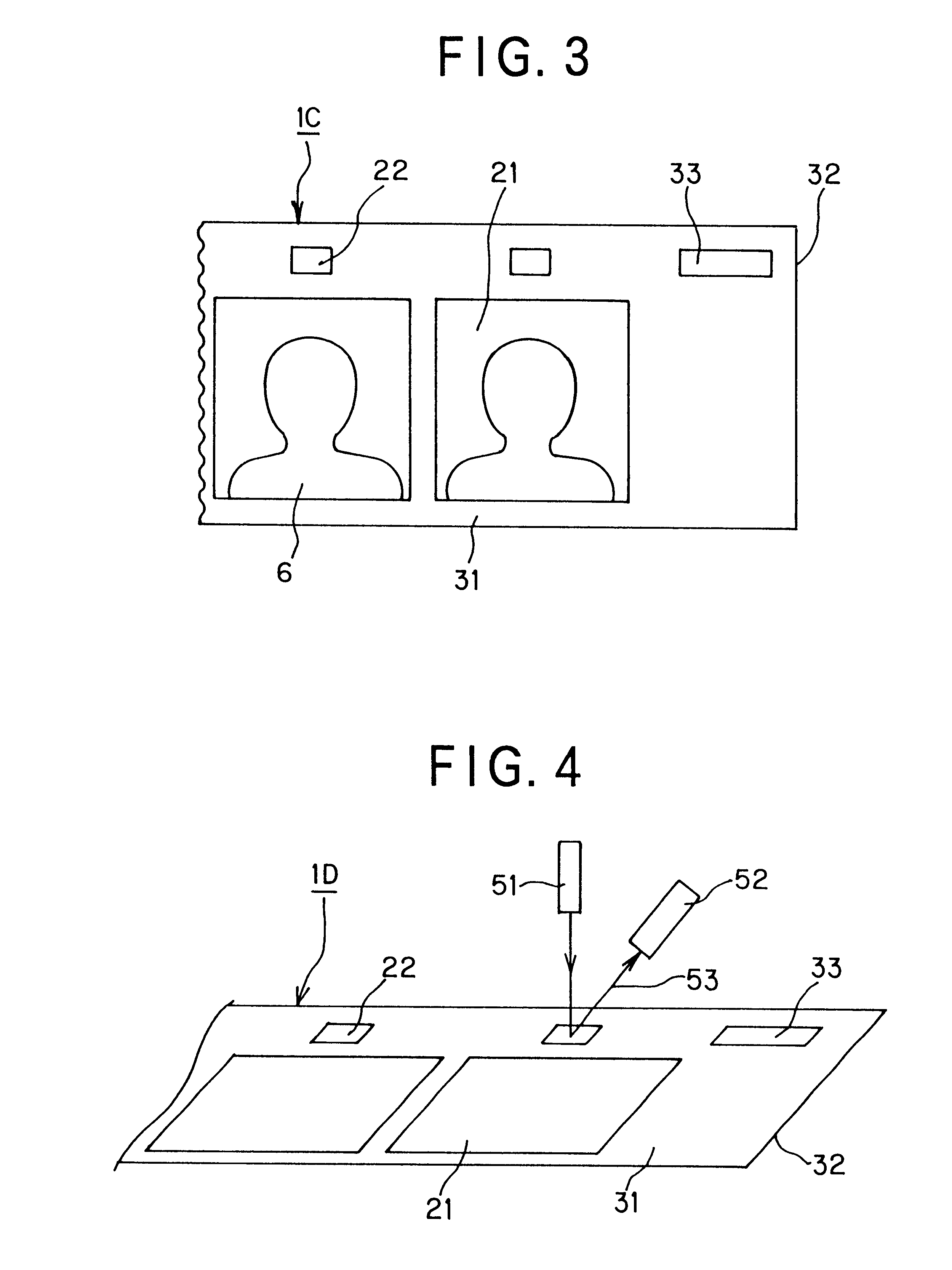
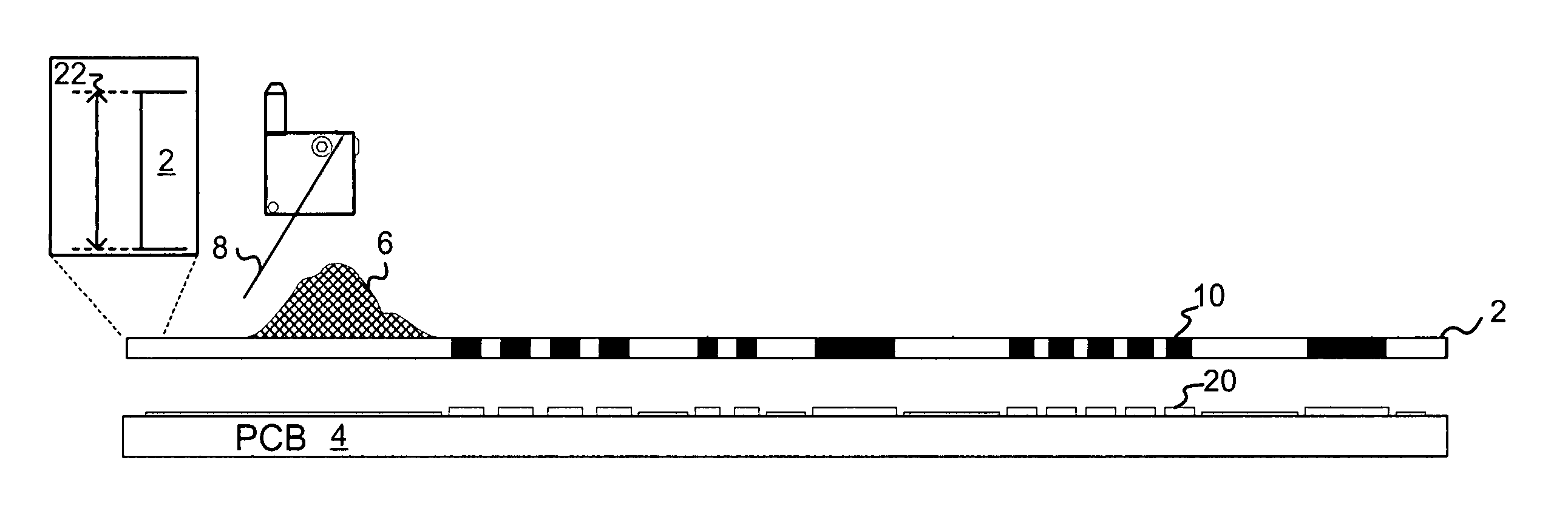
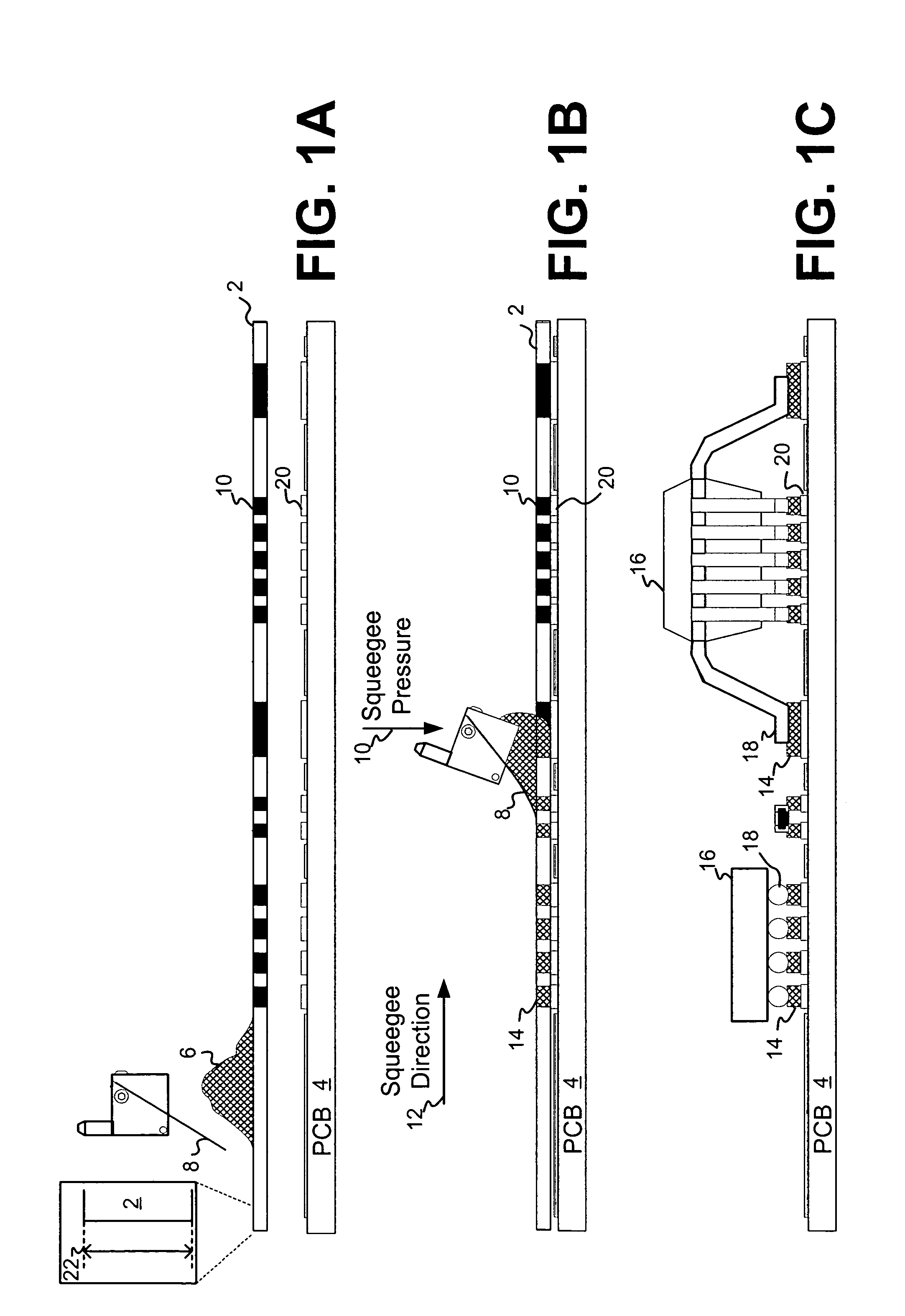
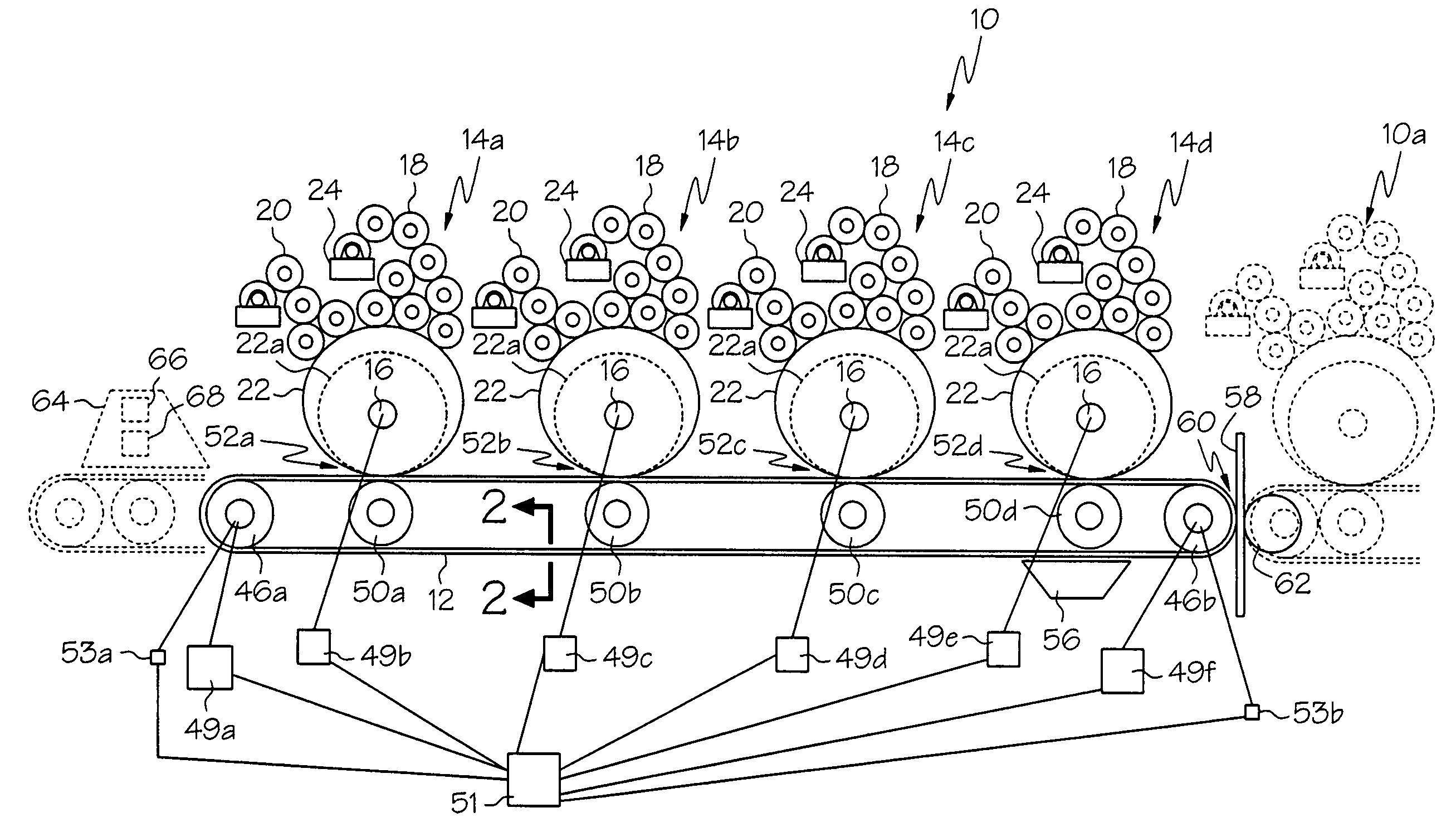
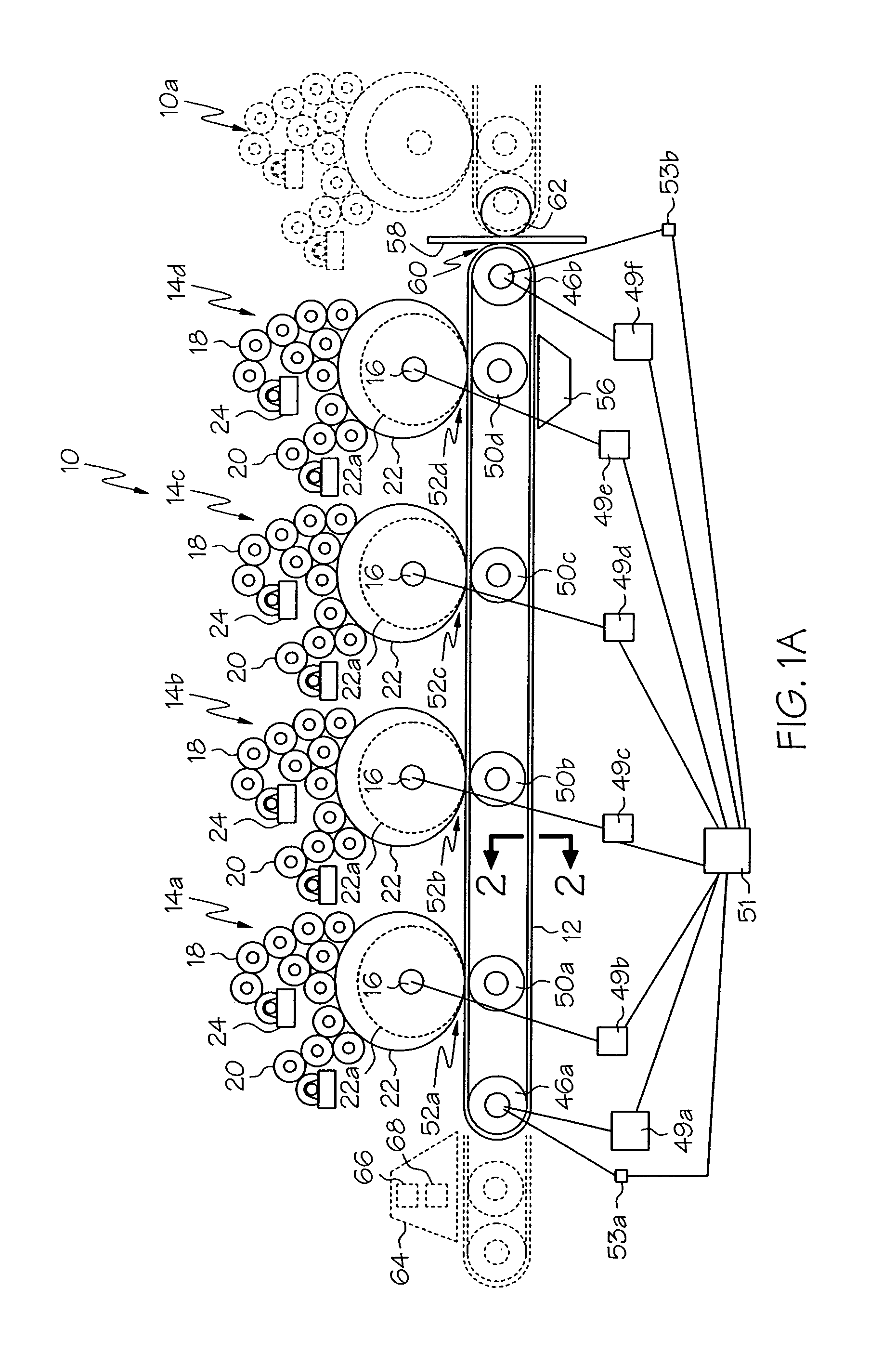
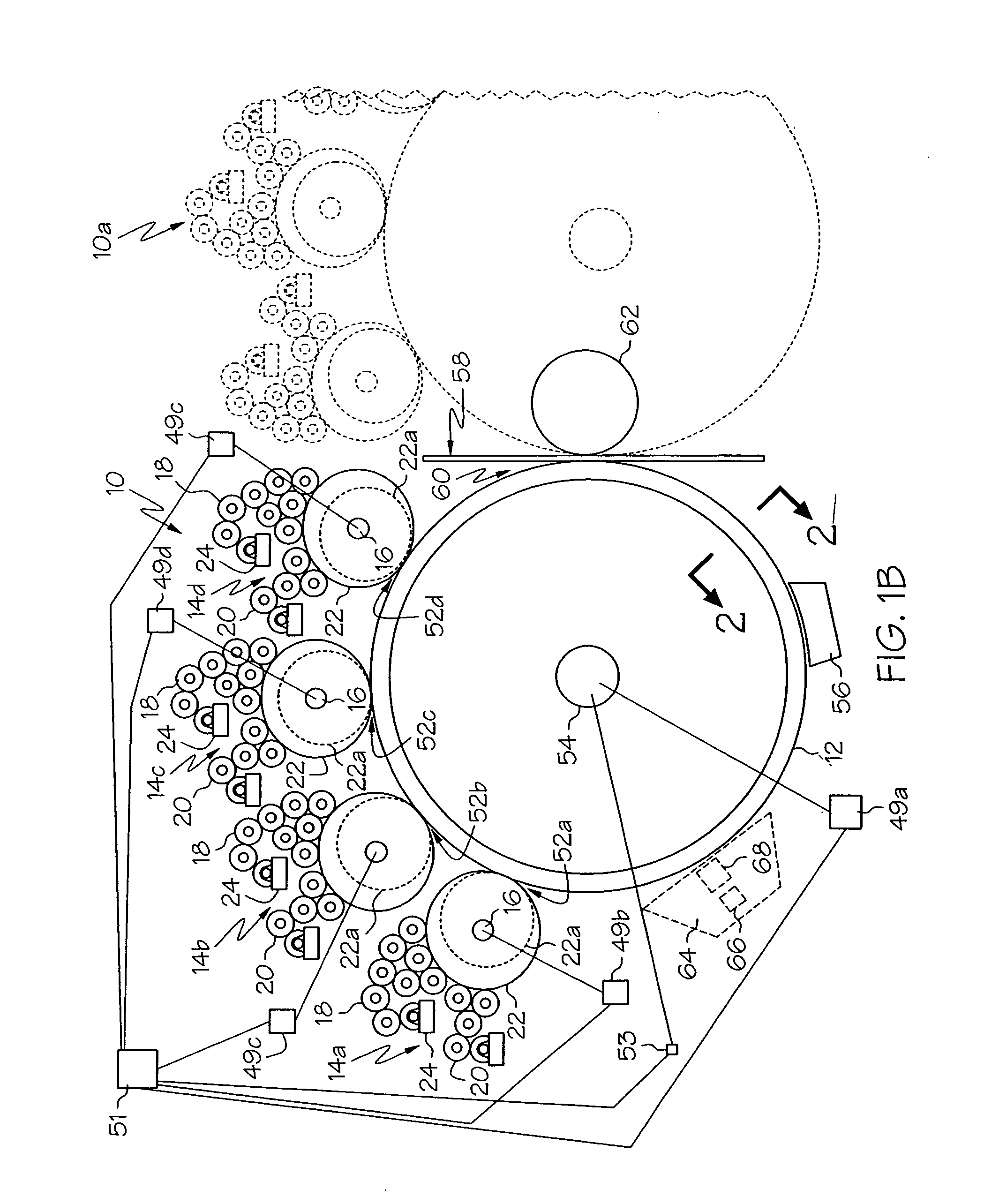
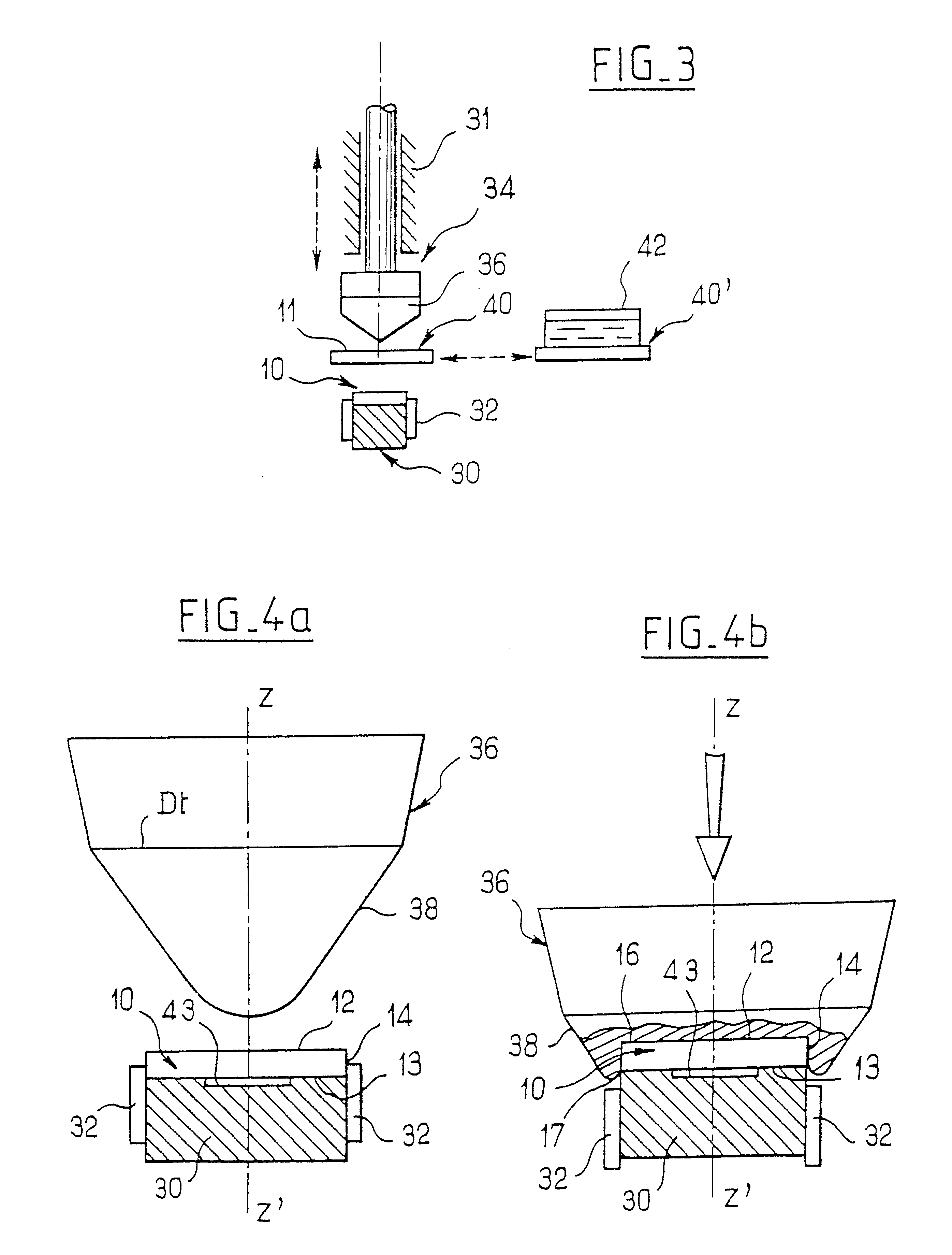
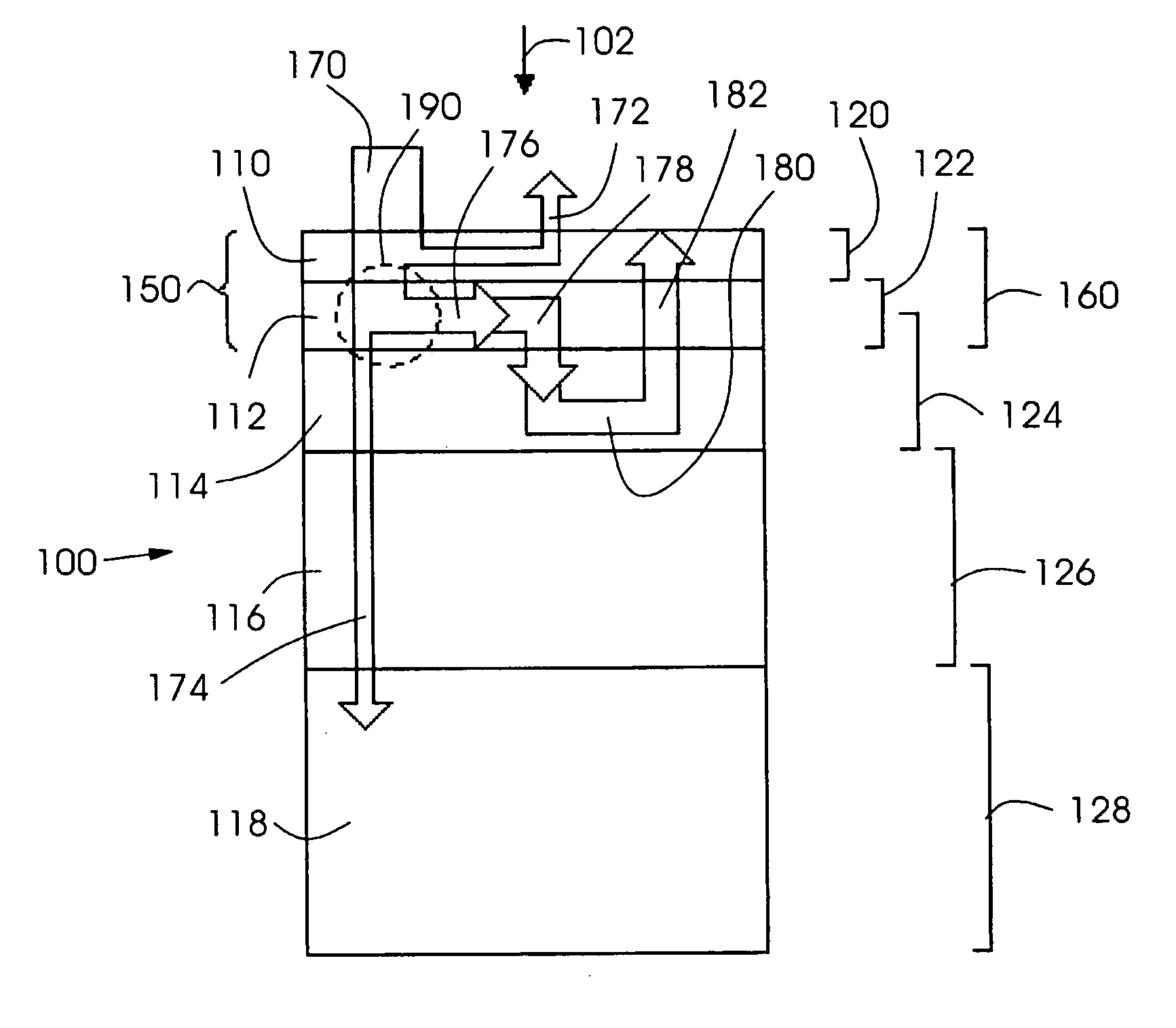
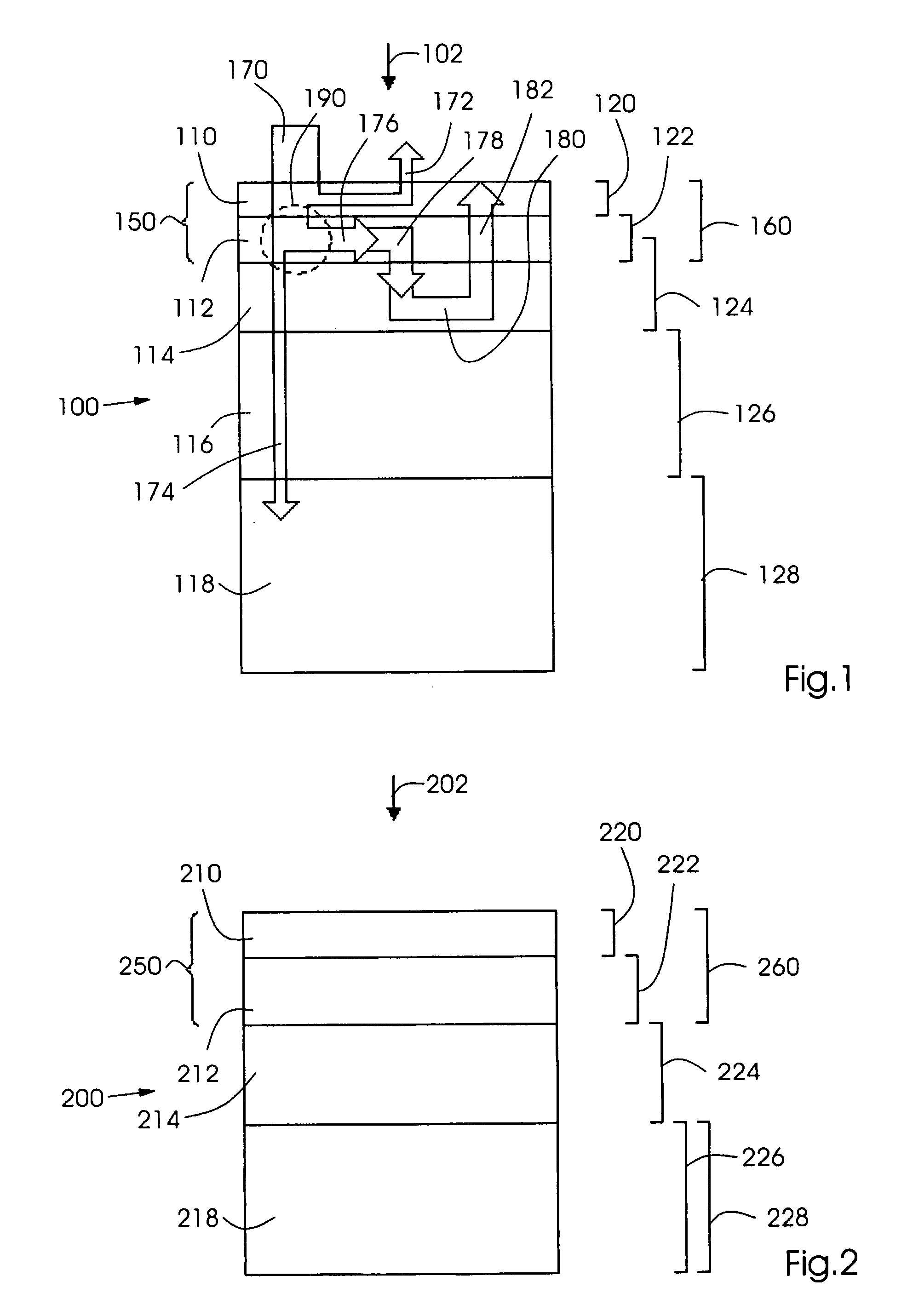
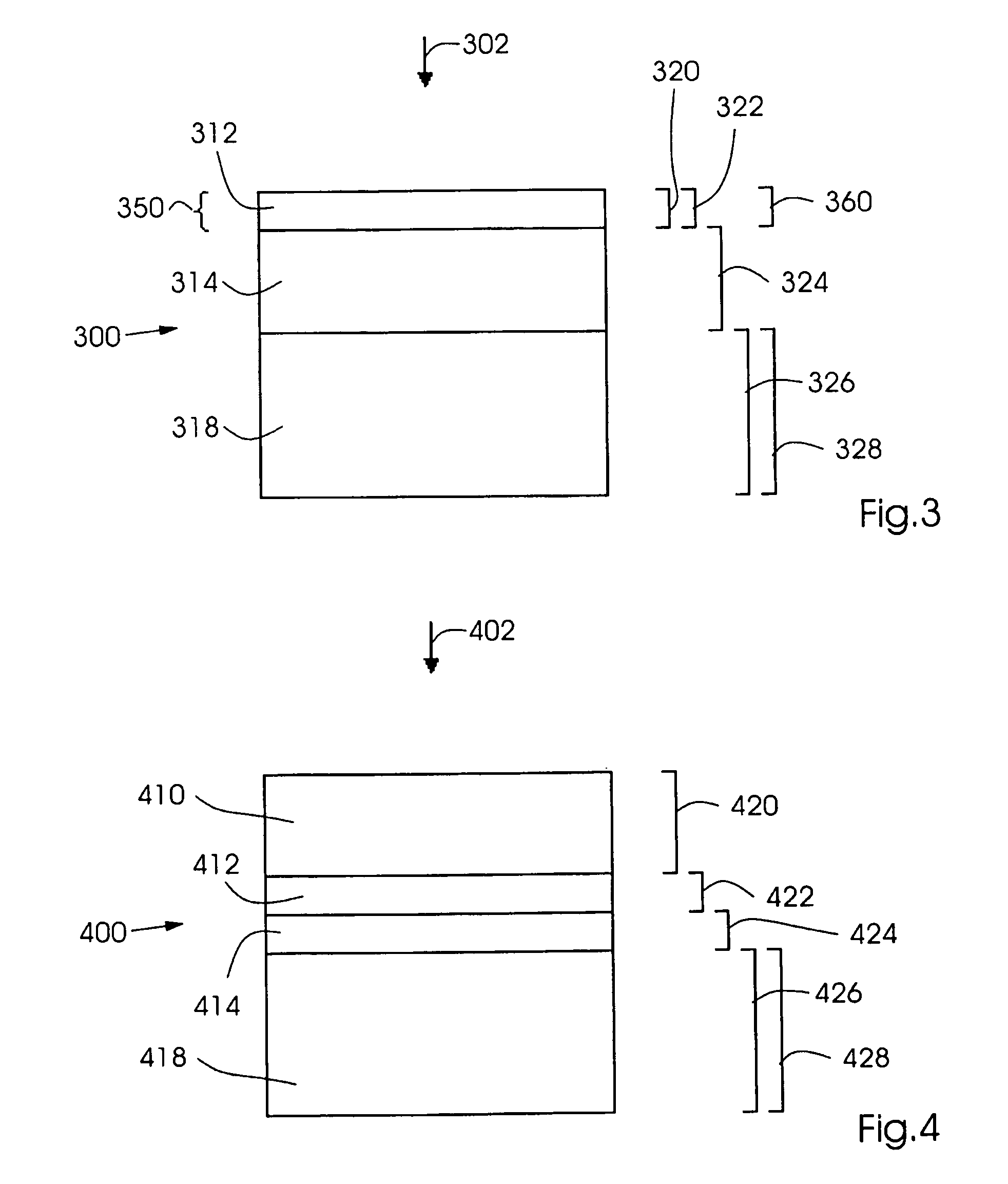
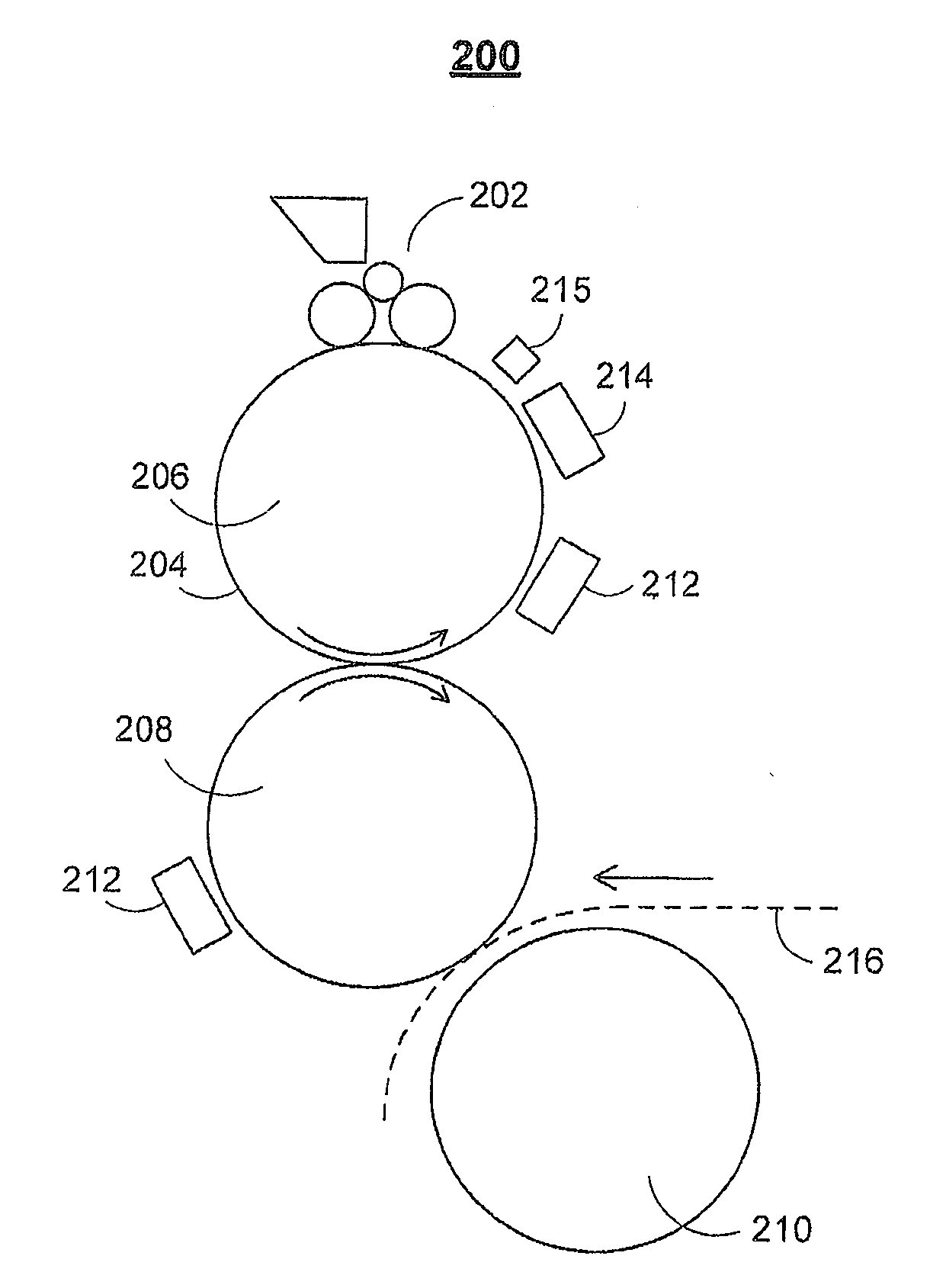
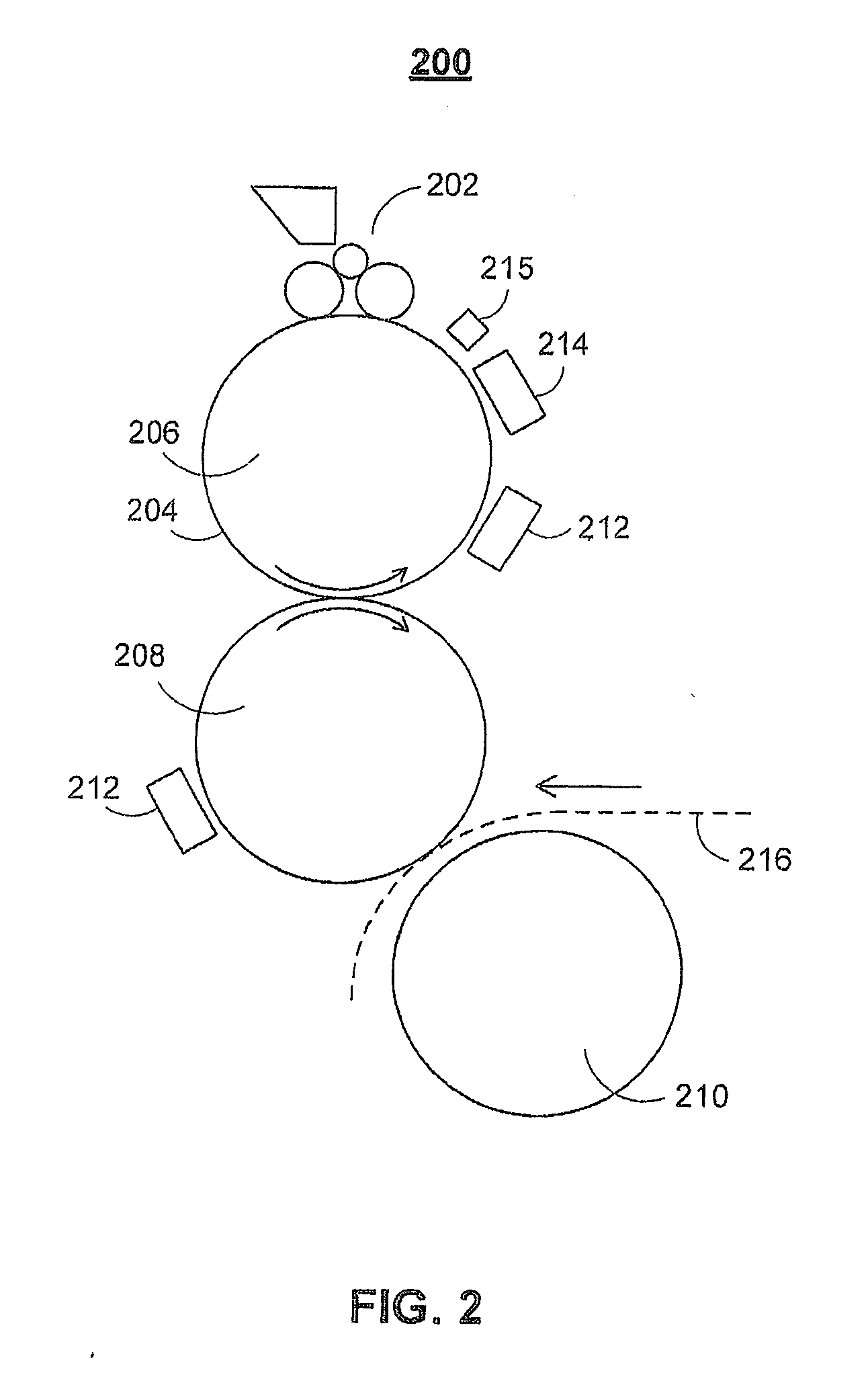
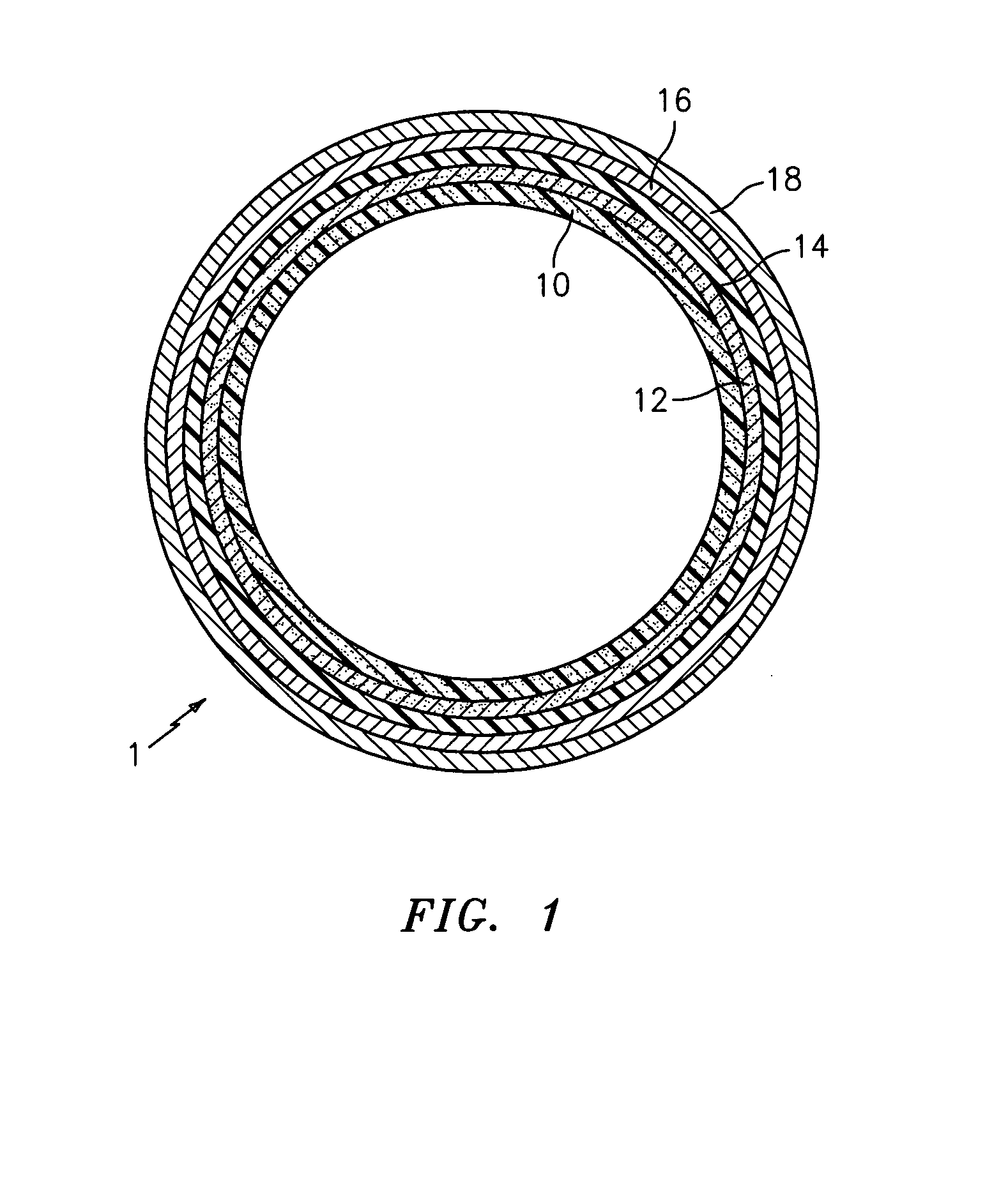
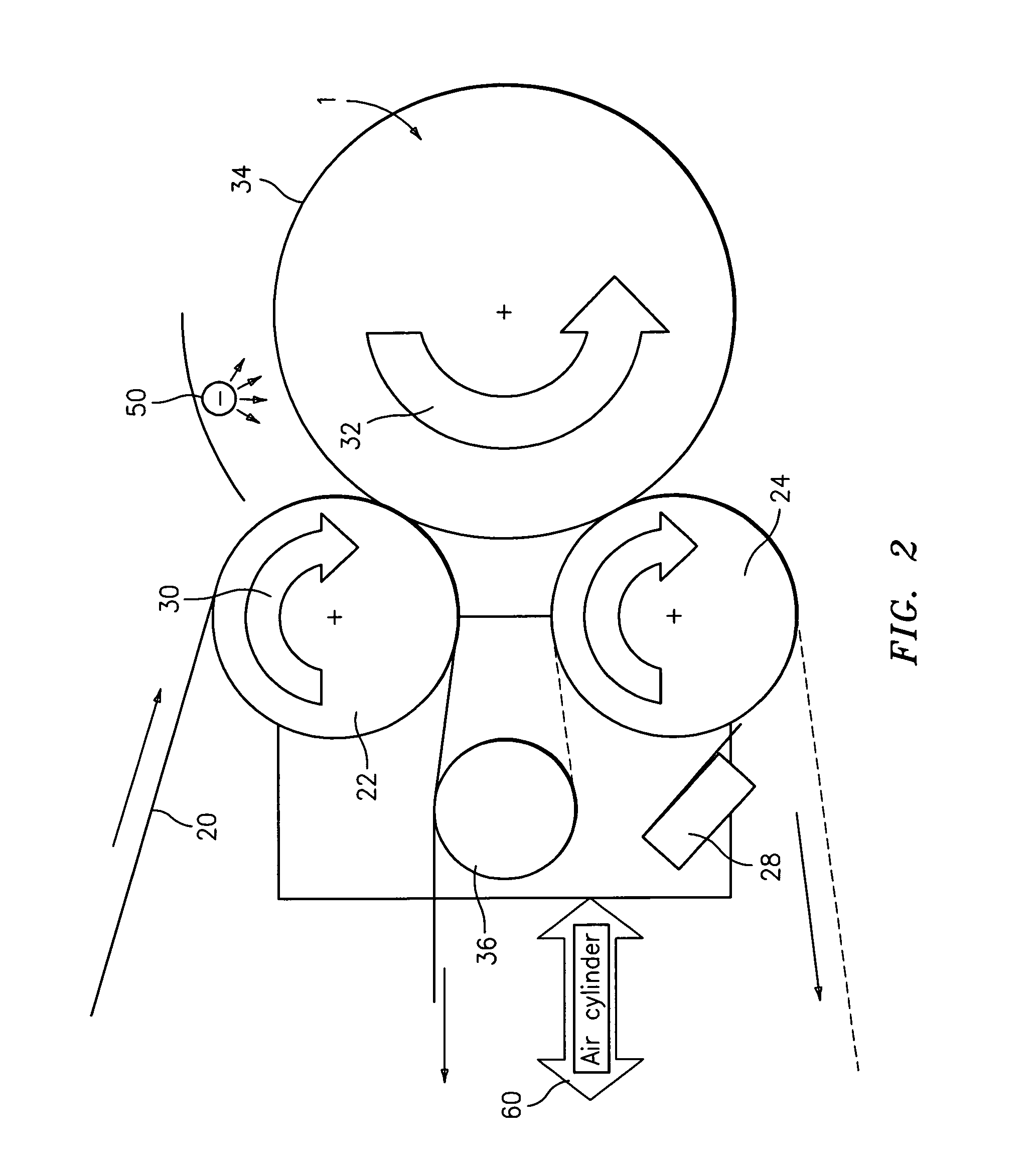
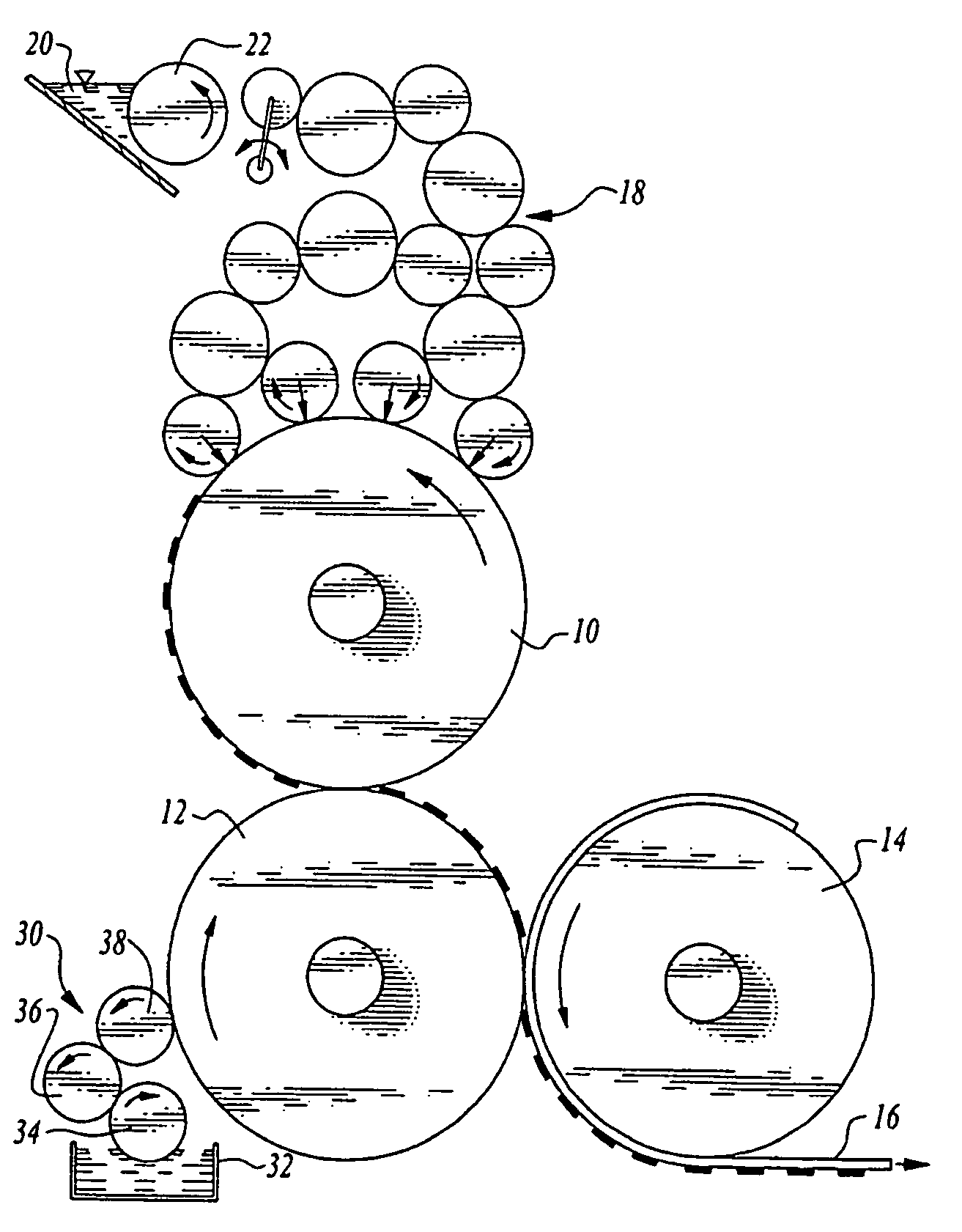
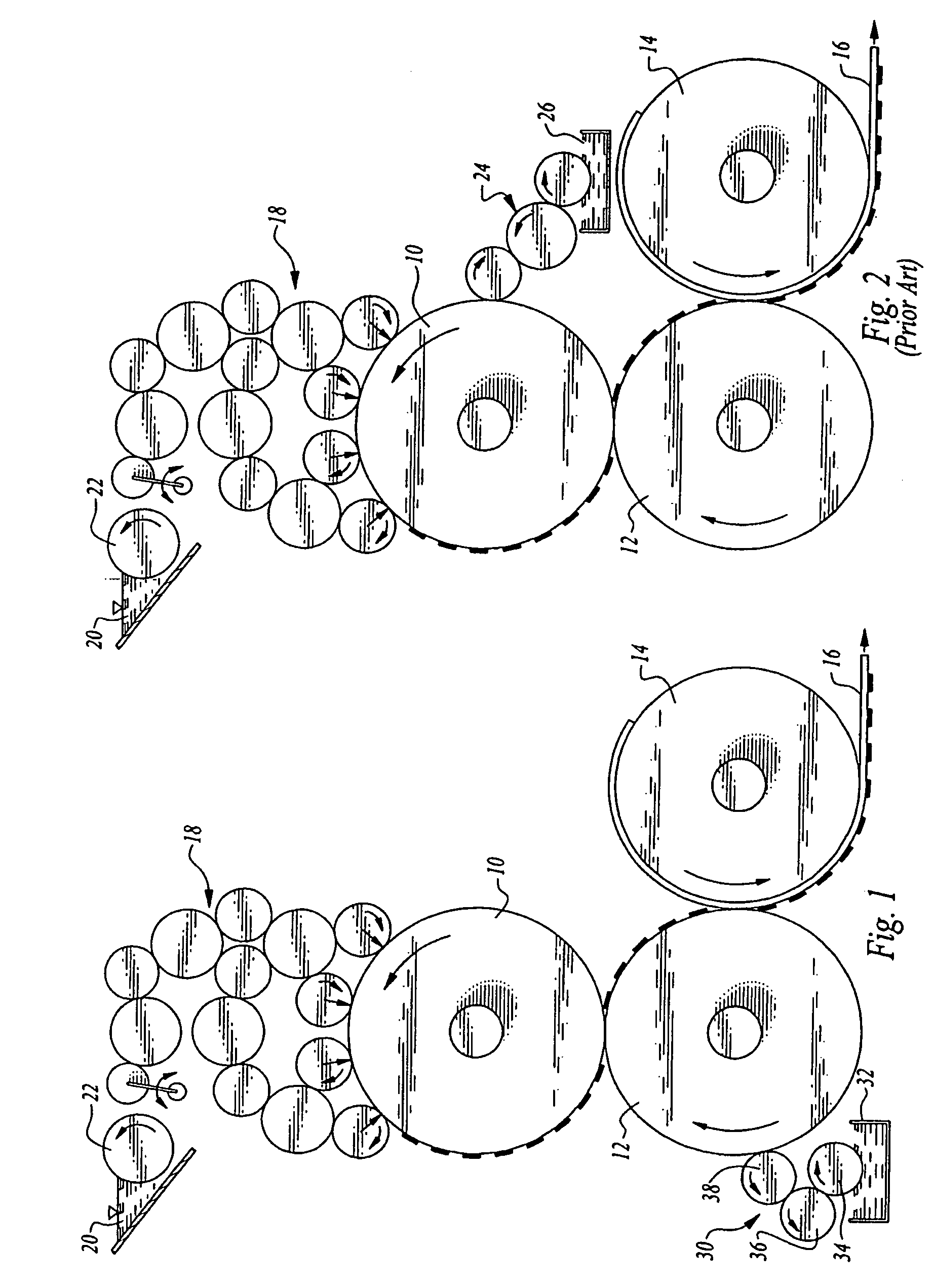
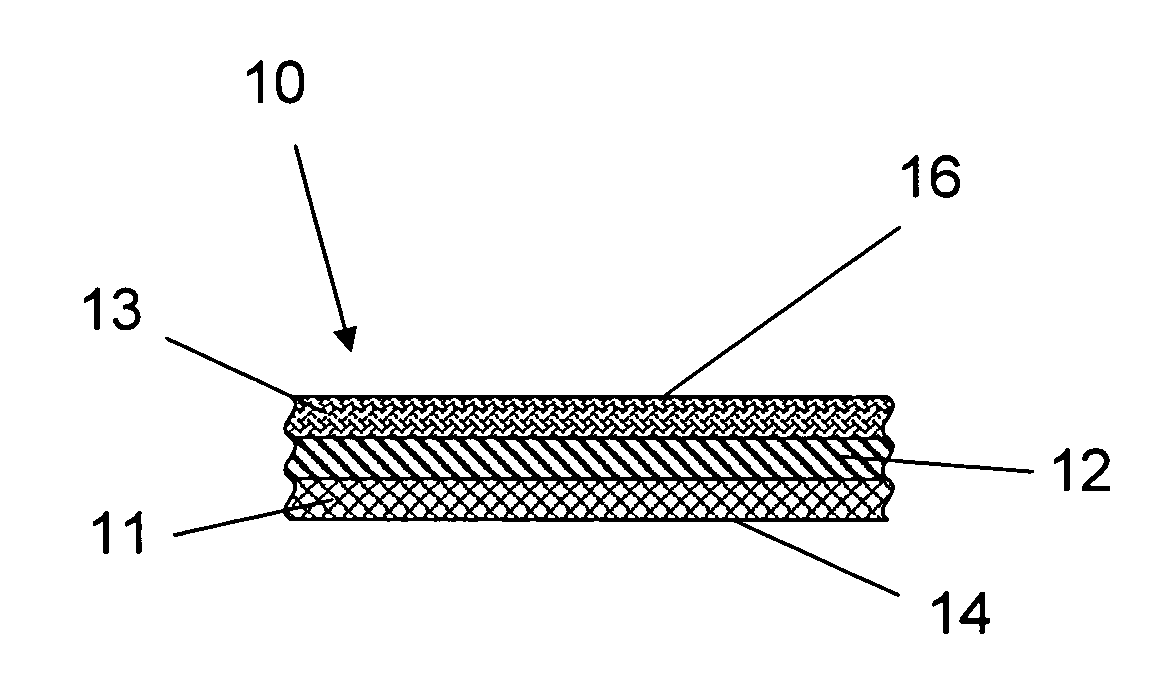
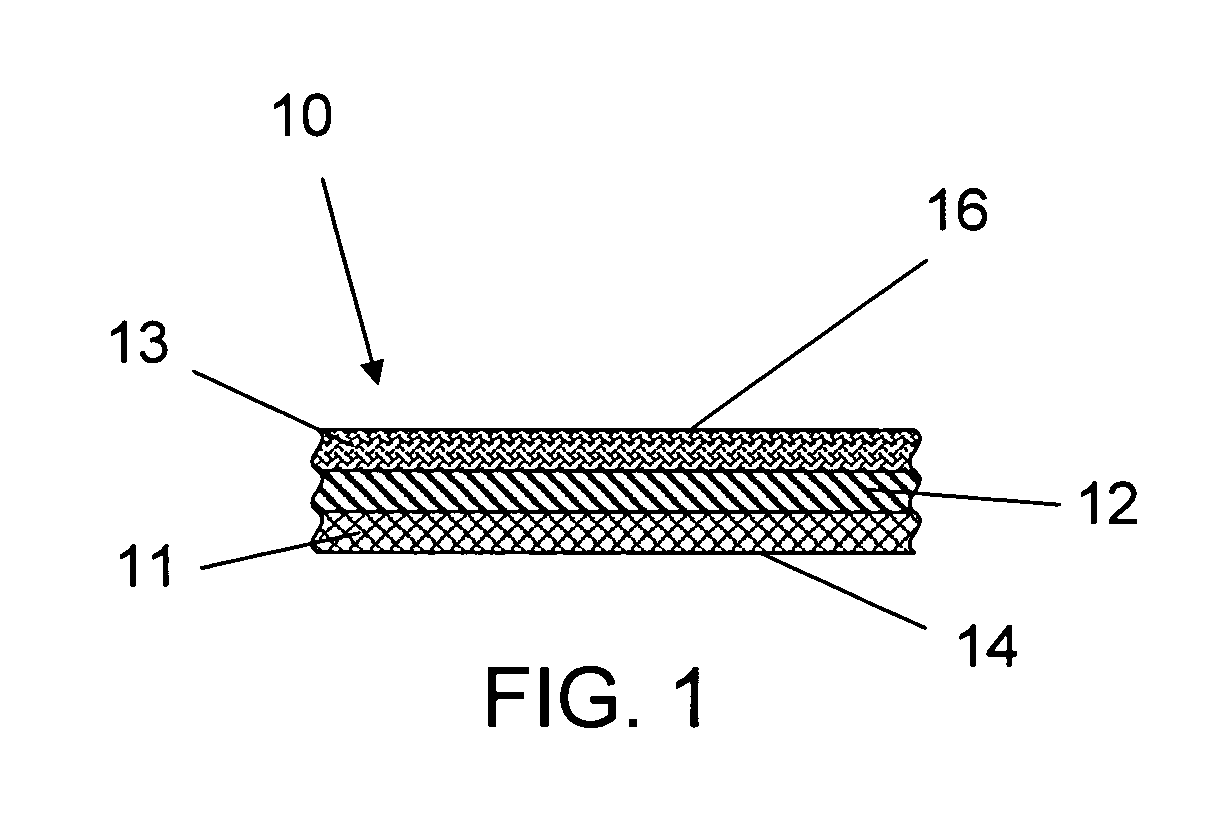
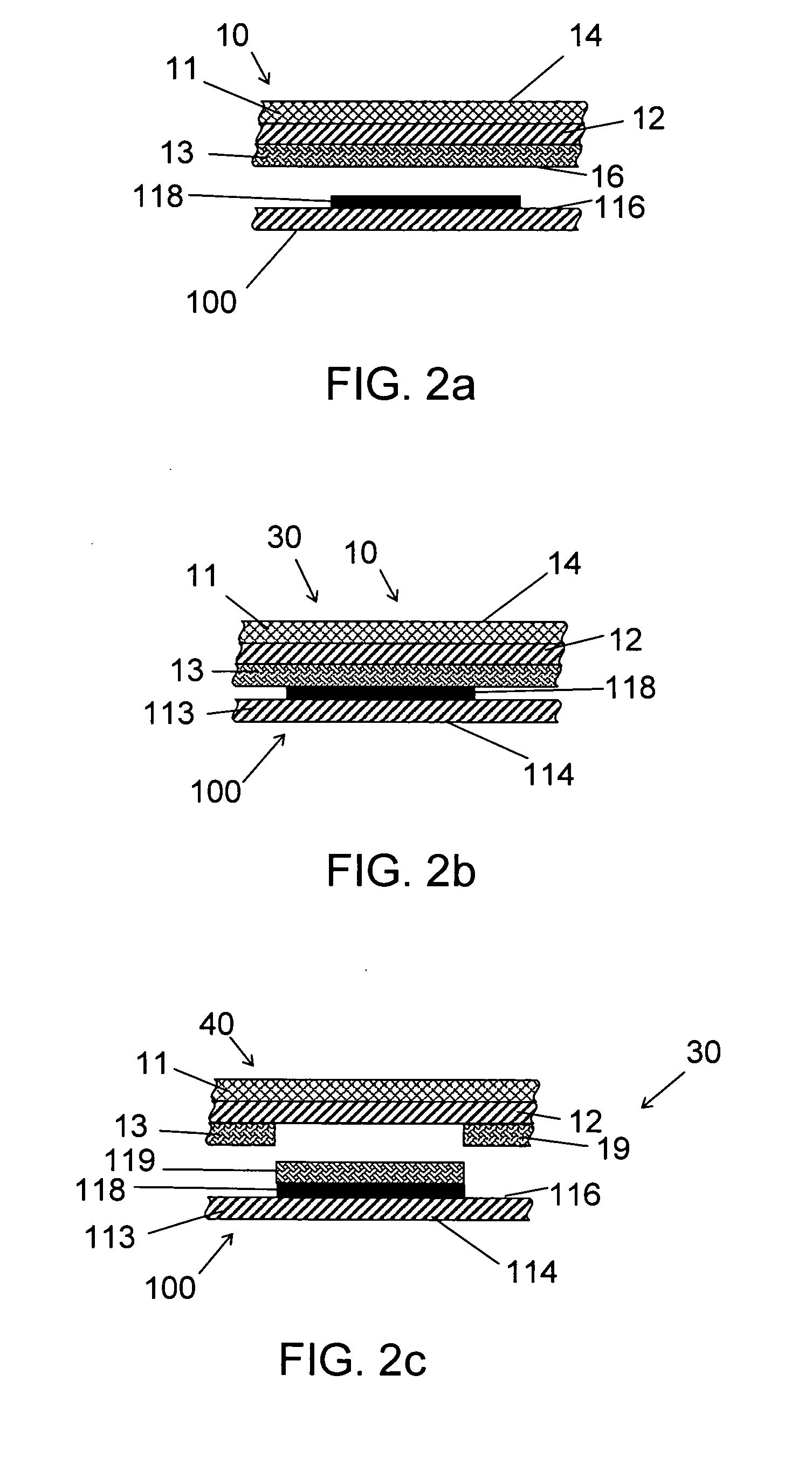
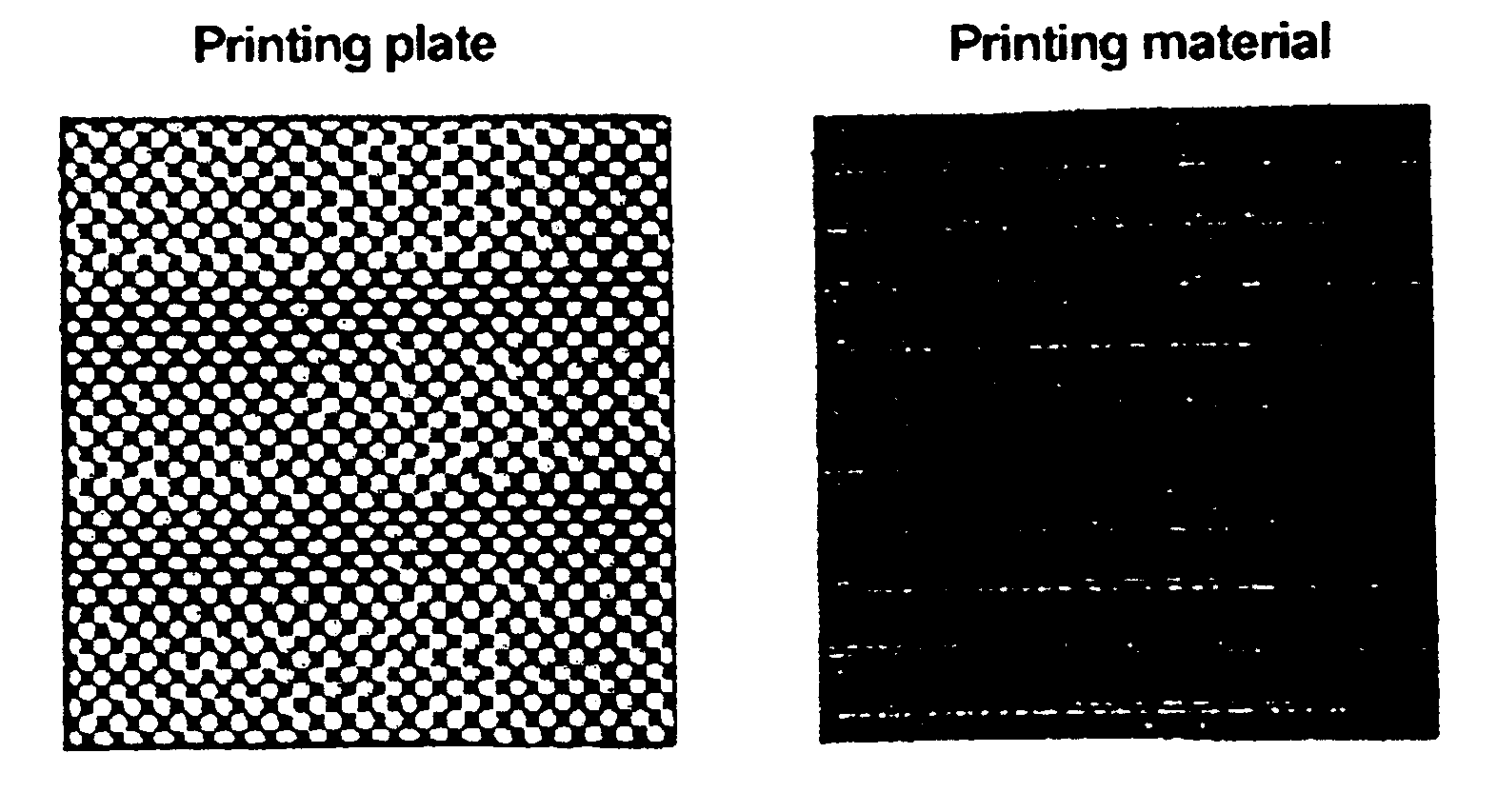
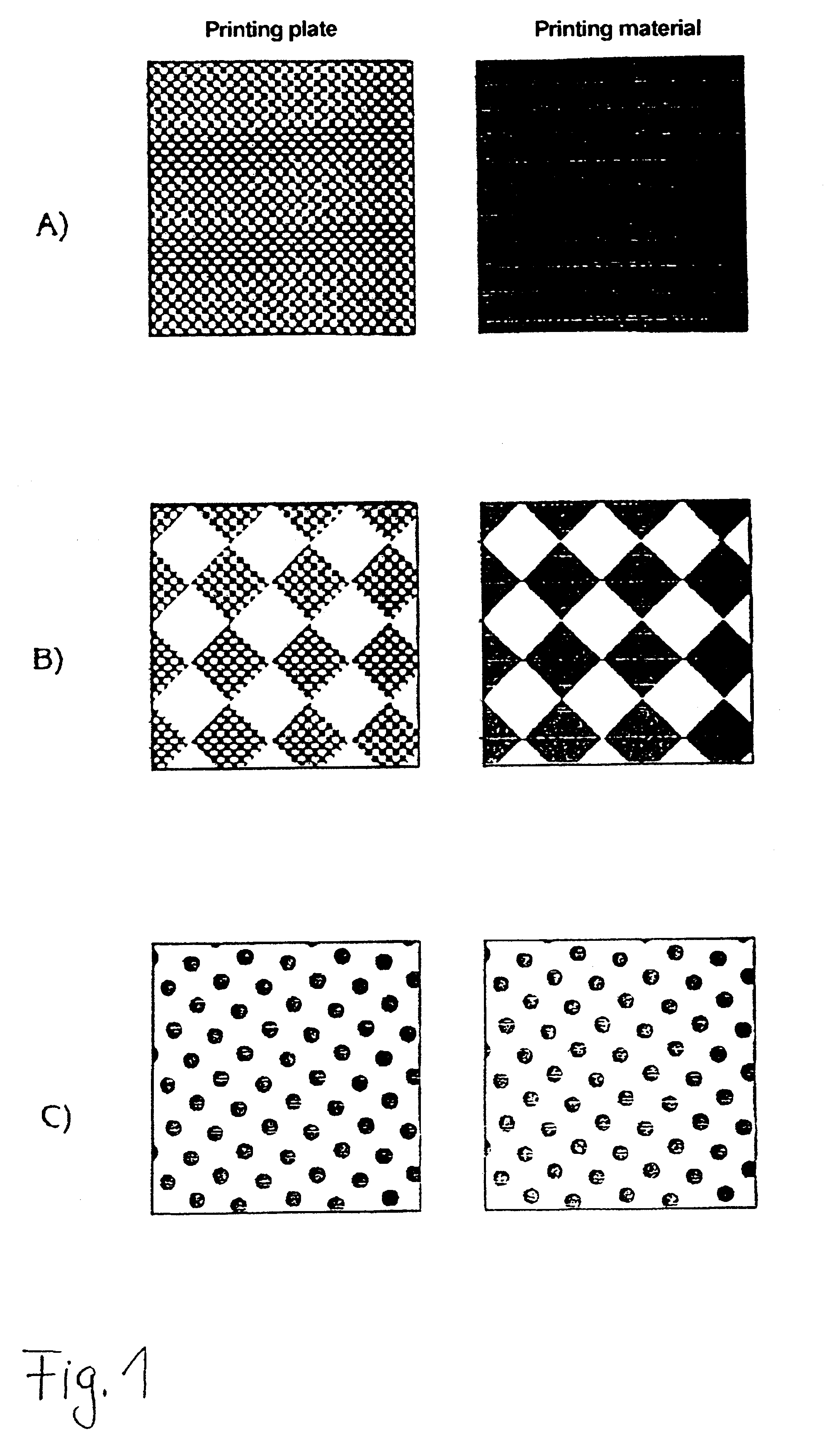
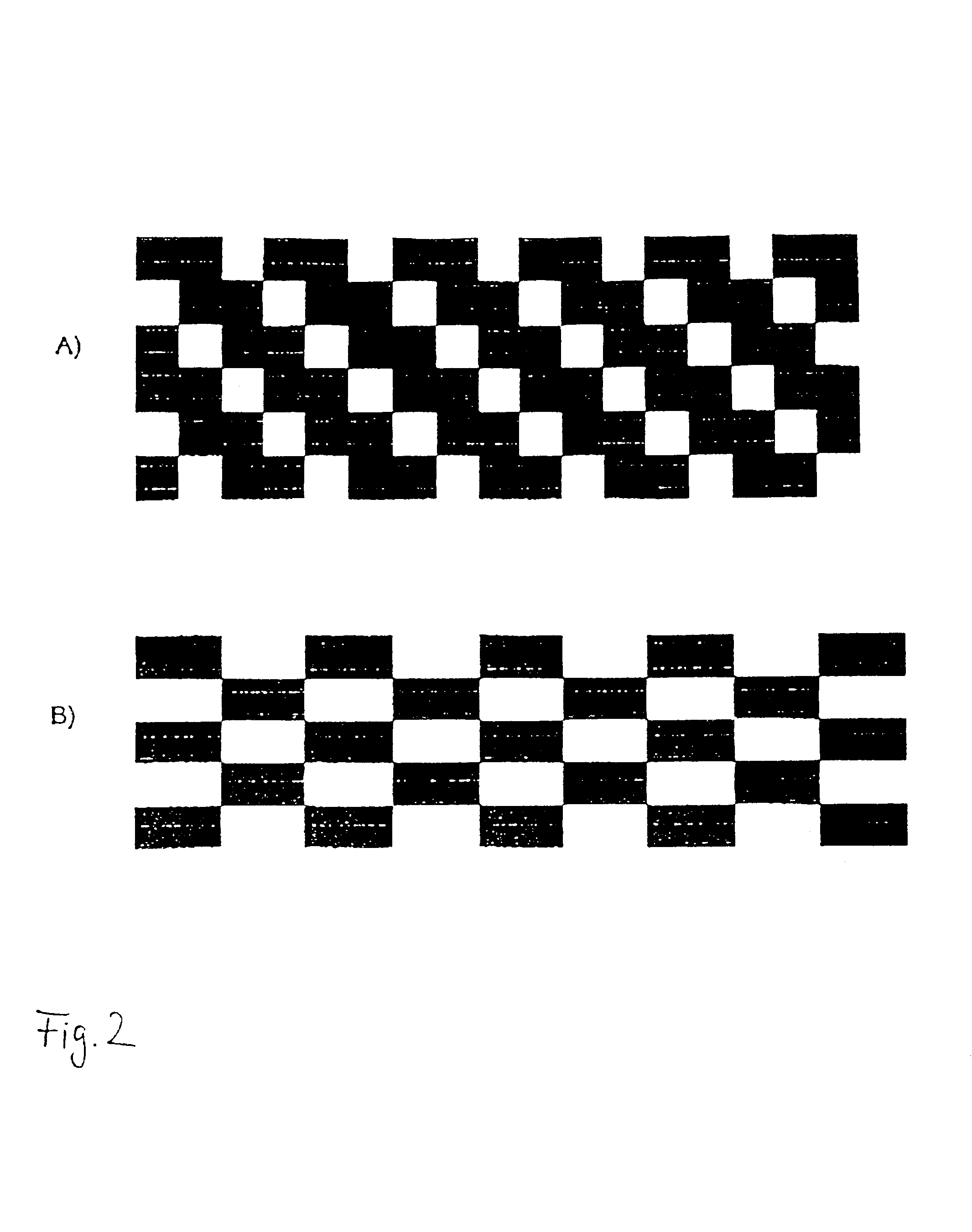
ActiveUS20060105268A1Minimize relief variationHigh image fidelityRadiation applicationsDry duplicatorsPhotopolymerHeat sensitive
An improved method of manufacturing a photosensitive printing element that minimizes relief variation and improves image fidelity. The method involves a step of pre-curing the first (floor layer) of photocurable material prior to depositing an additional layer or layers of photocurable material that may be imaged and developed to produce a desired relief image on the surface of the photosensitive printing element. The photosensitive printing element is then thermally developed by contacting the photosensitive printing element with at least one roll that is capable of moving over at least a portion of the imaged surface of the flexographic printing element to remove the softened or melted non-crosslinked photopolymer. Non-crosslinked photopolymer on the imaged and exposed surface of the flexographic printing element can be softened or melted by positioning a heater adjacent to the imaged surface of the flexographic printing element and / or heating the at least one roll that contactable with the imaged surface of the flexographic printing element.
Owner:MACDERMID PRINTING SOLUTIONS
Printing form having a plurality of planar functional zones
InactiveUS20050181187A1Well formedDecorative surface effectsDry duplicatorsAbsorbed energyEngineering
Imageable printing forms are irradiated by radiant energy corresponding to the image information, the energy being absorbed in the printing form. The energy coupled in in this manner is available for patterning the printing form surface. A printing form having a plurality of substantially planar functional zones, which have at least one informational zone that is modifiable in accordance with image information and an absorption zone for absorbing energy from a radiation is distinguished in that a buffer zone is provided which differs at least partially from the absorption zone, receives energy from the absorption zone, and releases energy to the informational zone.
Owner:HEIDELBERGER DRUCKMASCHINEN AG
Security document with raised intaglio printed image
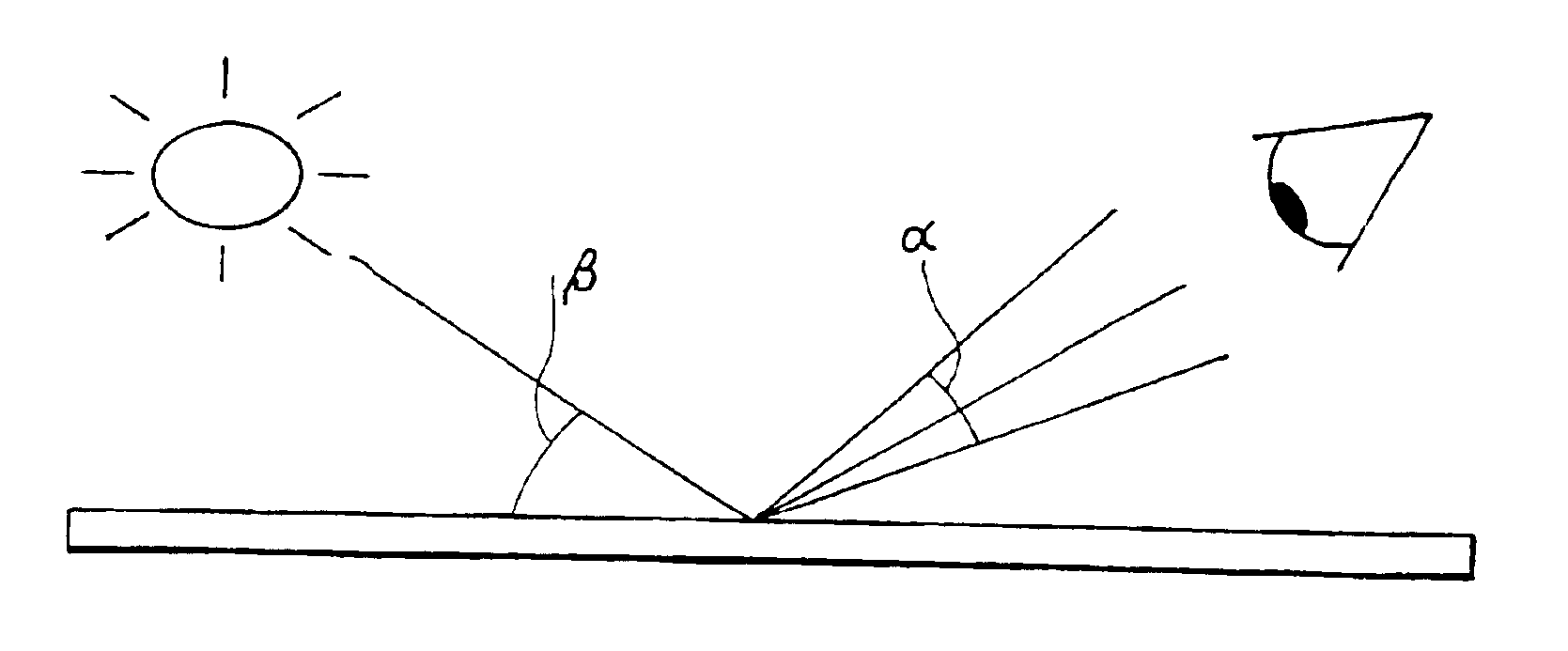
InactiveUS6905755B1Superior tonal effectHigh light transmittanceCylinder pressesDigitally marking record carriersMeasuring instrumentTransmittance
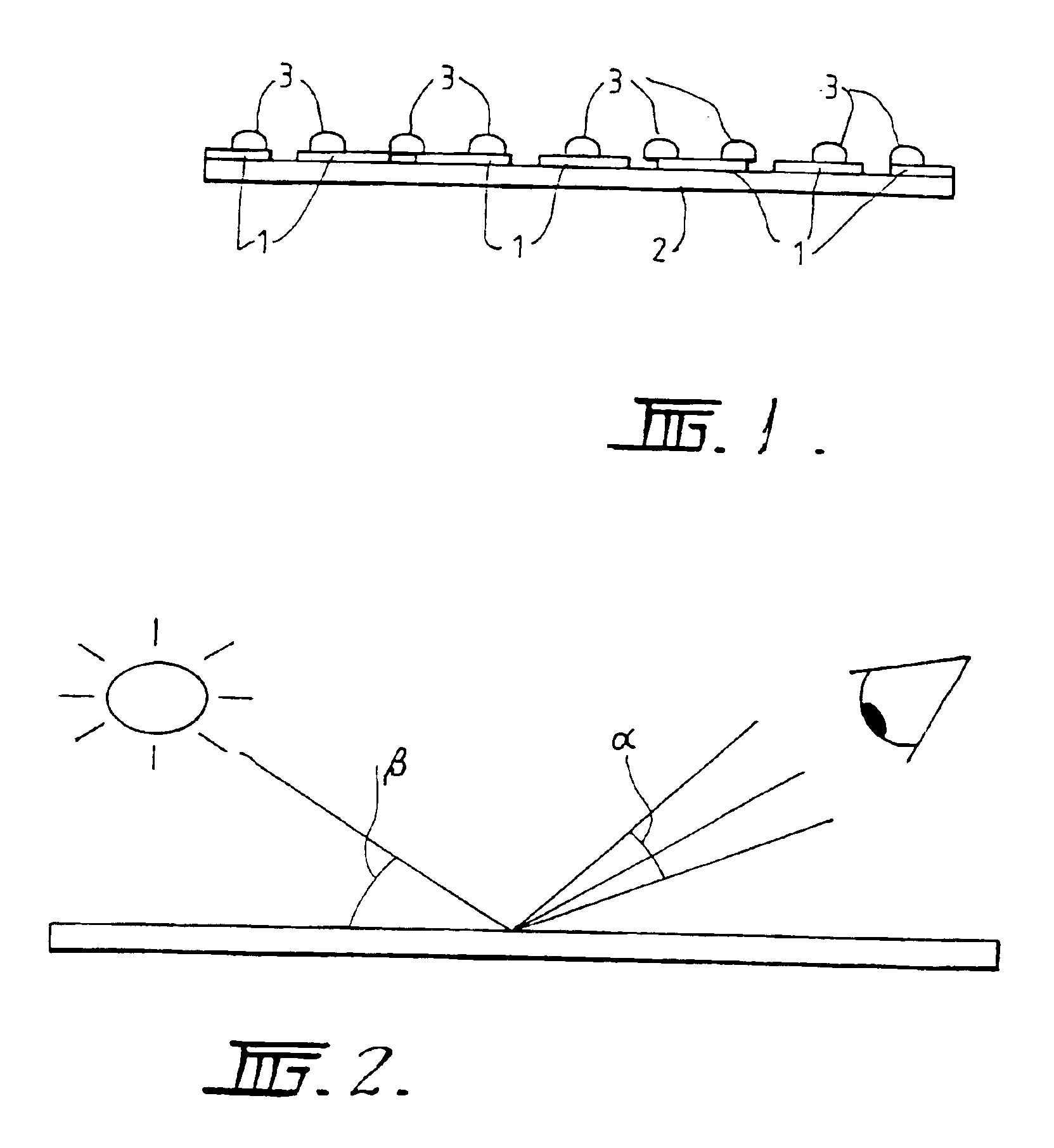
A security document or other device including a substrate (2), a smooth highly reflective layer (1) applied thereto and having a reflectivity of at least 60 gloss units, and a raised printed image (3) applied to said reflective layer by a printing process such as the gravure process, the raised printed image having a height of at least 10 microns and being printed using a translucent ink having a large value of 85 to 95 as measured on an XL 211 Hazegard haze measuring instrument, which render it substantially transparent or translucent while causing scattering of the light reflectance and transmittance in at least a partially specular manner. A method of producing a document is also disclosed.
Owner:NOTE PRINTING AUSTRALIA
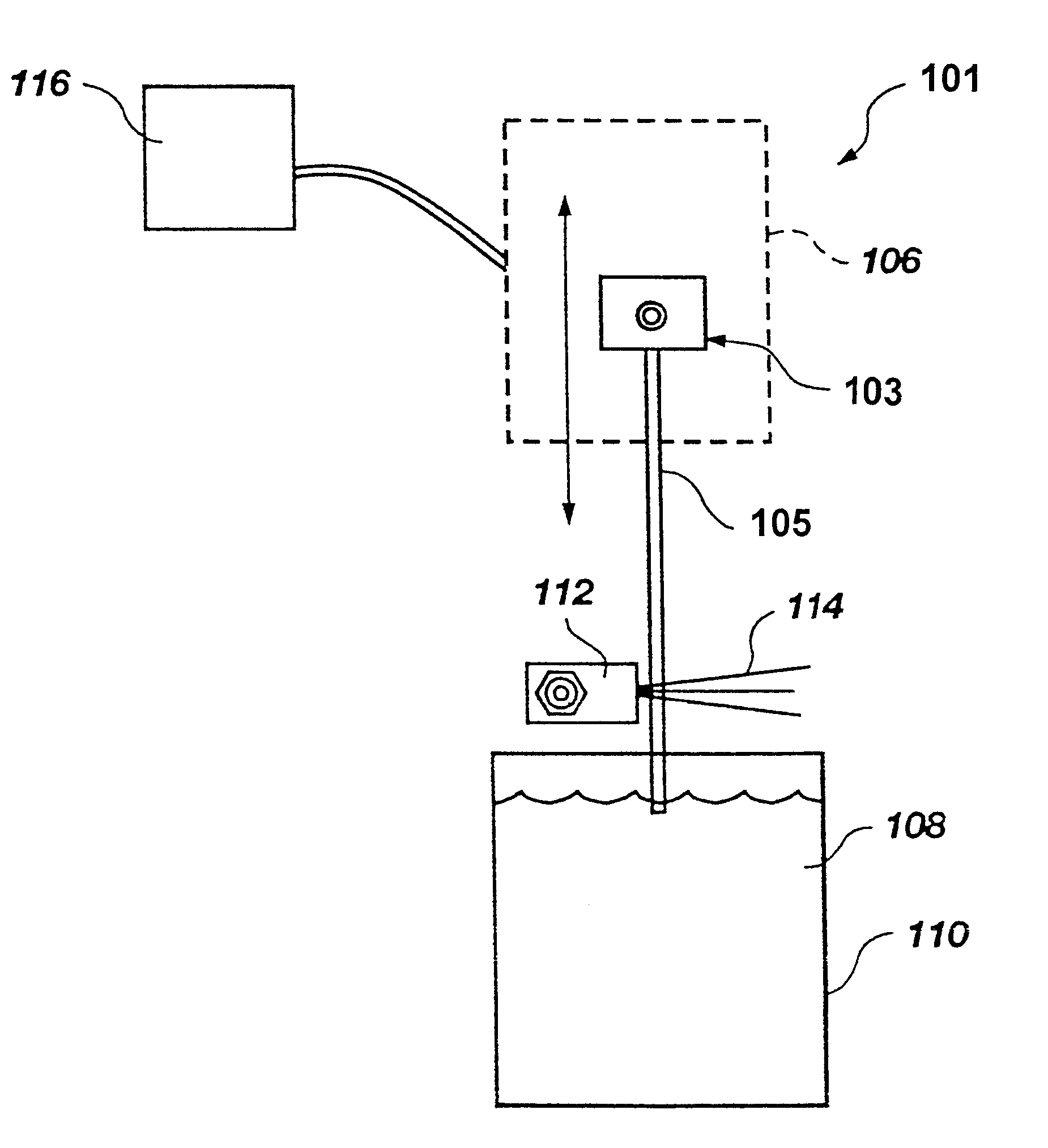
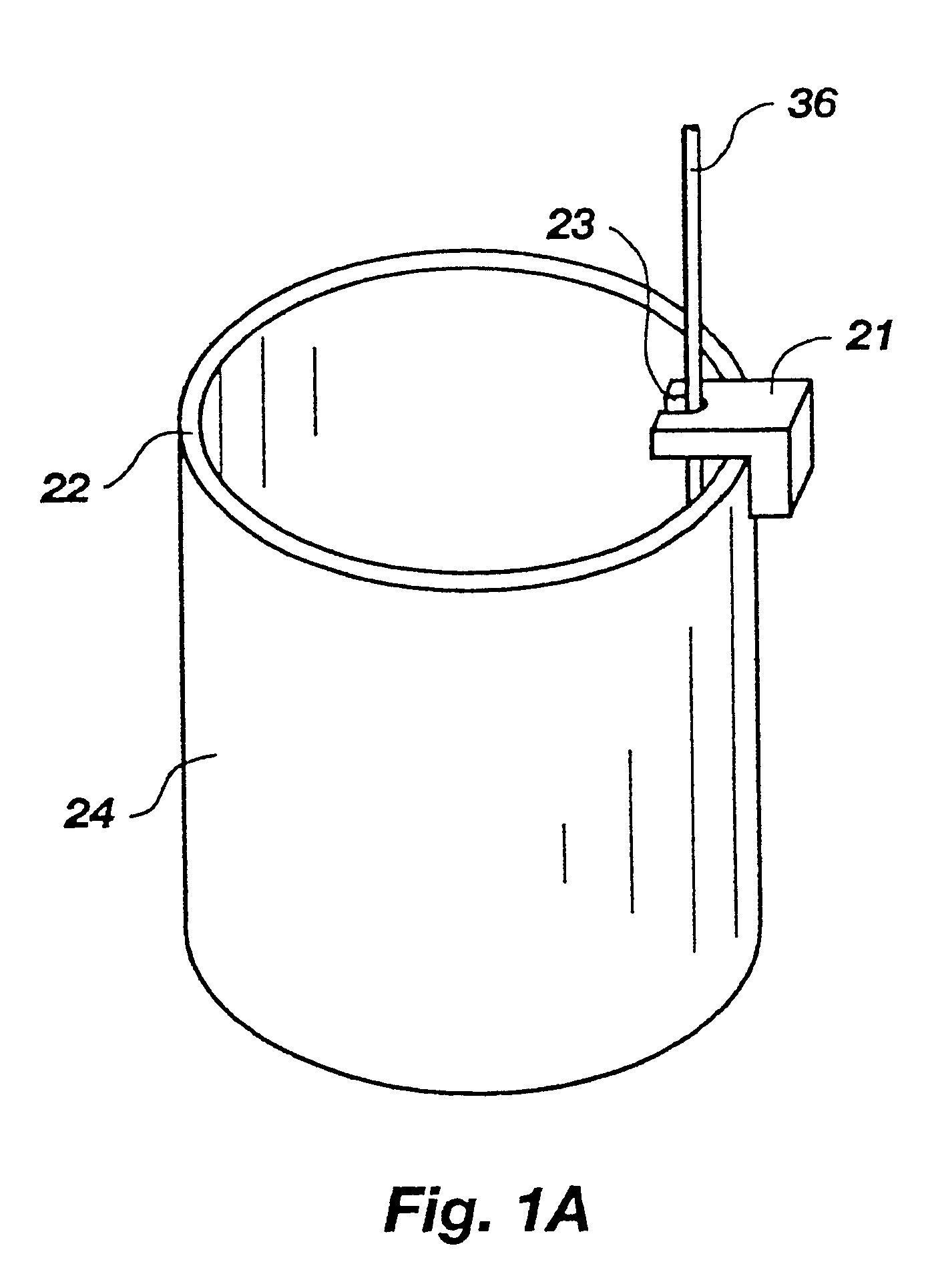
Apparatus and Methods for Controlling Application of a Substance to a Substrate
InactiveUS20110132213A1Dry duplicatorsHectographic duplicationControl substancesBiomedical engineering
Apparatus and methods for controlling application of a substance to a substrate involve the use of a gating agent that blocks the substance from or attracts the substance to the substrate. The apparatus and methods may utilize ink jet technology to apply the gating agent directly to the substrate or to an intermediate surface. The substance may be an ink, an electrically conductive material, a magnetic material, a carrier for a therapeutic, diagnostic, or marking substance other than an ink, or a carrier for any other type of substance.
Owner:R R DONNELLEY & SONS CO
Coated paper stocks for use in electrostatic imaging applications
InactiveUS6048575AAvoid curlImprove adhesionDry duplicatorsPretreated surfacesVitrificationAntistatic agent
Coated paper stocks for electrostatic imaging comprising a substrate coated on at least one surface with a resin layer comprised of olefinic material and a pin-hole free, continuous coating layer over said resin layer. The continuous layer has a glass transition temperature above 100 DEG C. and is comprised of one or more natural or synthetic film forming polymers and an anti-static agent. As a single layer this continuous coating layer functions as both a heat protective and imaging layer. In an alternate embodiment two separate coating layers are provided with separate heat protective and imaging functionalities.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Process for the offset printing of a catalytic species via a hydrophilic phase
An offset printing process comprising the steps of: applying a hydrophilic phase to a printing plate with or without an oleophilic phase, the hydrophilic phase comprising at least one catalytic species, and applying the hydrophilic phase applied to the printing plate to a receiving medium thereby realizing in a single step a functional pattern of the at least one catalytic species on the receiving medium, wherein, if the hydrophilic phase is applied with the oleophilic phase, the oleophilic and hydrophilic phases are either applied separately from an ink and a fountain medium or are applied together in the form of a single fluid ink, the single fluid ink consisting of a dispersing phase and a dispersed phase, and the hydrophilic phase is exclusive of an ionomer.
Owner:AGFA NV
Electronic still camera, instant printer and instant film
InactiveUS20050263026A1Easy constructionSimple mechanical structureCylinder pressesPlaten pressesLight beamStill camera
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic fluid suitable for high speed and high resolution dot-on-demand inkjet printing and method of making
ActiveUS20120225264A1Increase printing speedImproved resolution characteristicCylinder pressesMaterial nanotechnologyRare earthOxidation state
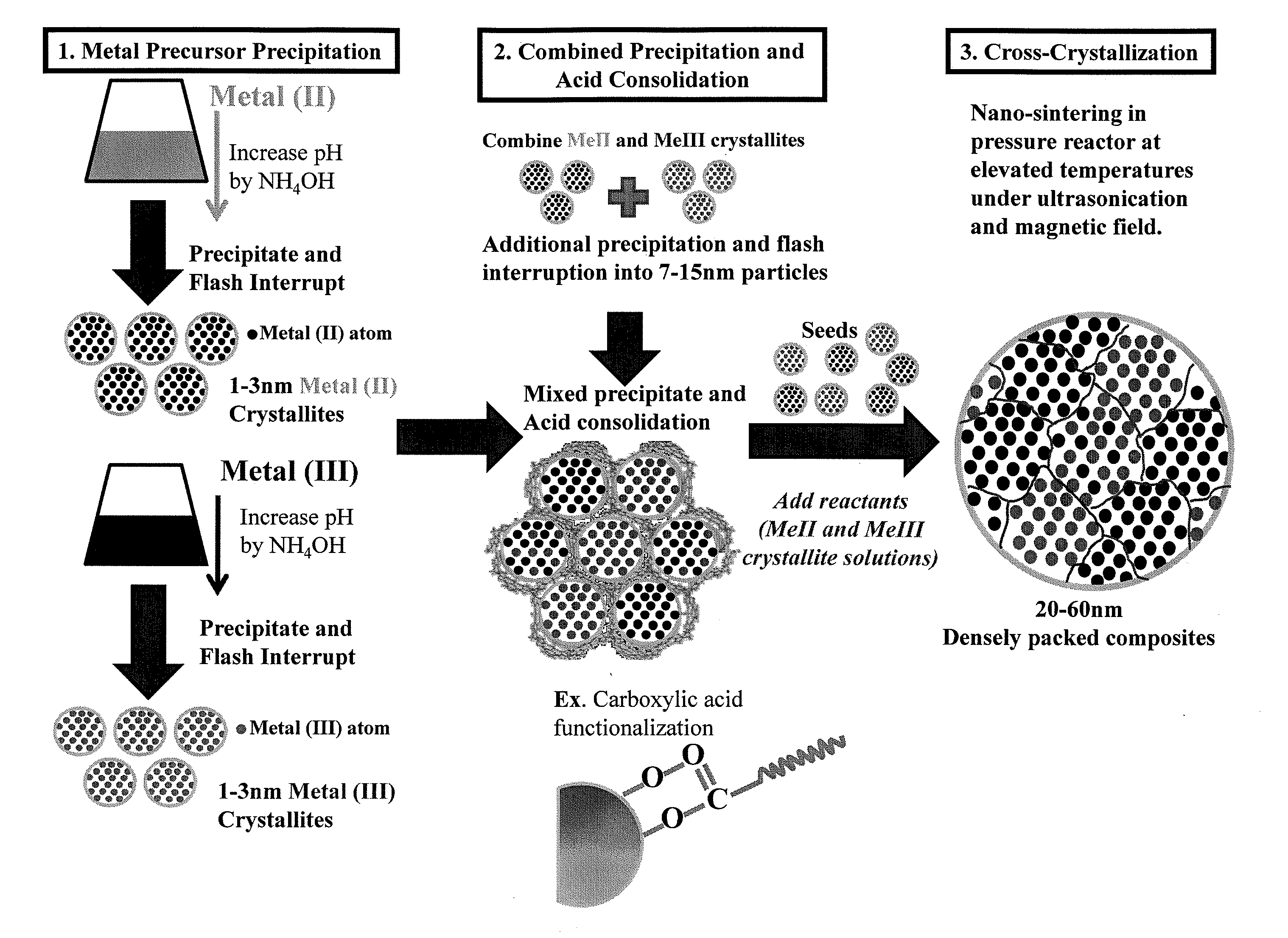
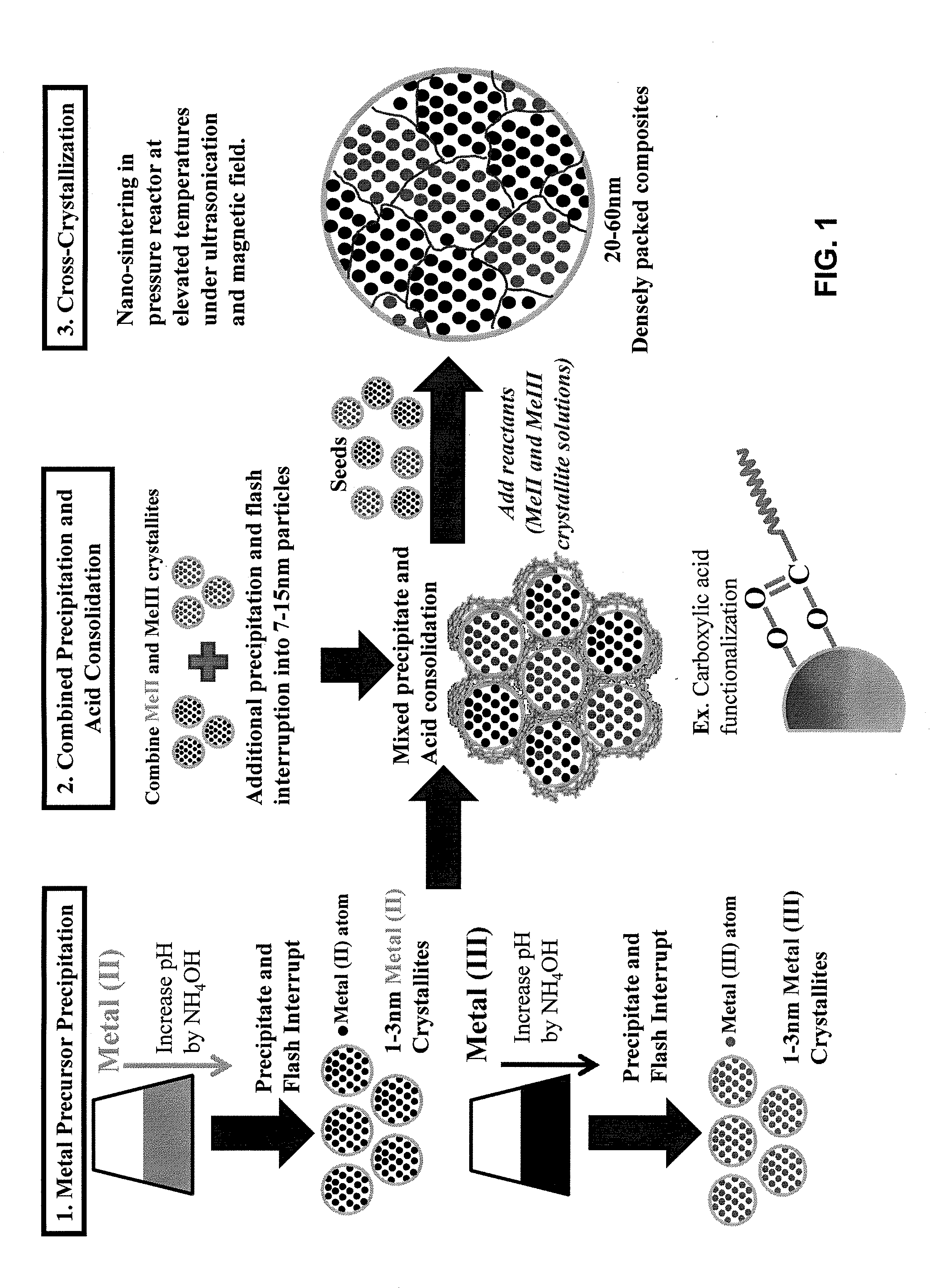
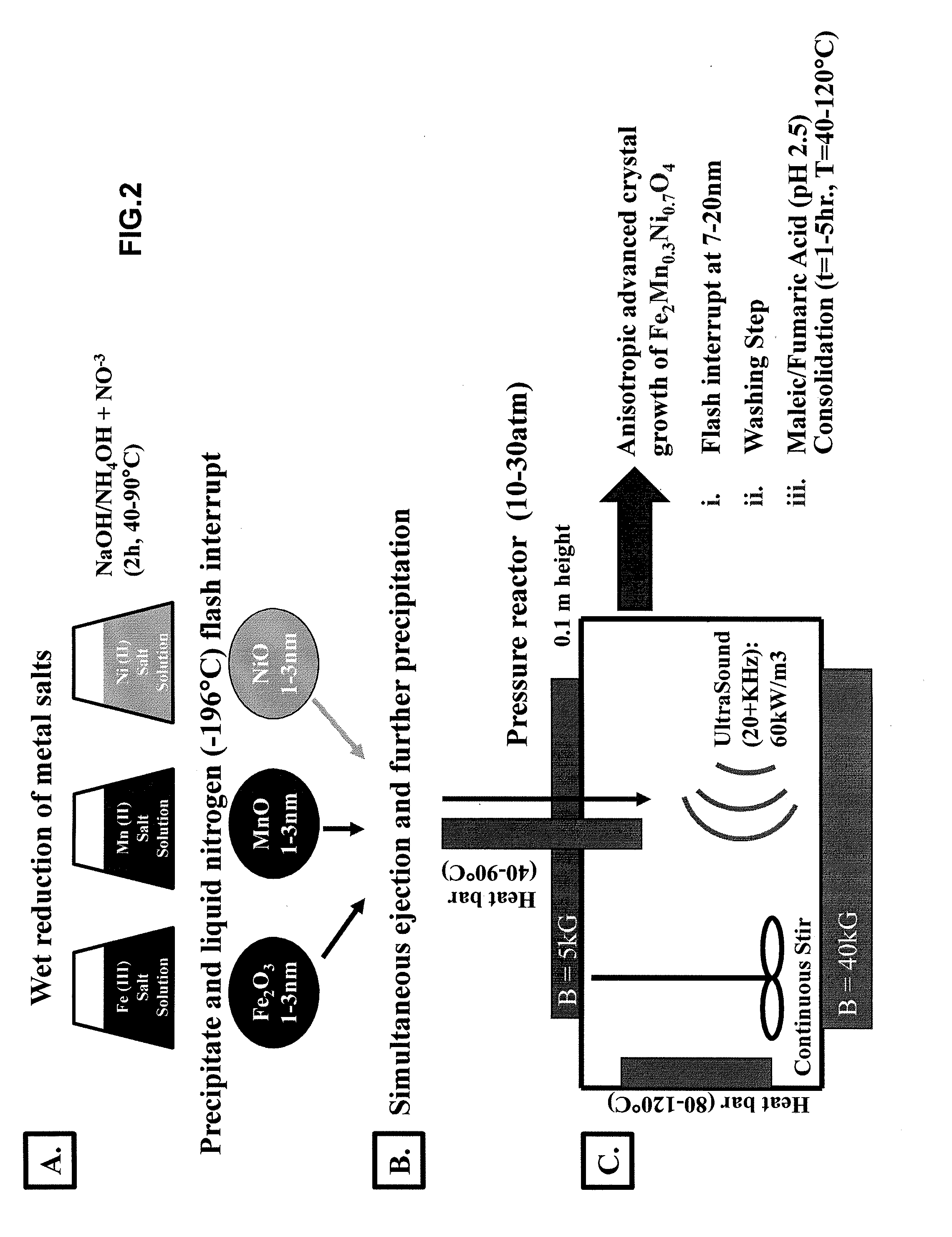
A magnetic fluid composition include a suspension of nano-particles including cross-crystallized multi-metal compounds dispersed in a solvent, the cross-crystallized multi-metal compounds including at least two or more metals having different valencies or oxidation states, the metals selected from the group consisting of a monovalent metal (Me+), a divalent metal (Me2+), a trivalent metal (Me3+), a quadrivalent metal (Me4+) and a rare earth metal. The magnetic fluid having a viscosity and surface tension that permits dispensing from an inkjet printer at a rate of at least 2.5 m / s, at a resolution of at least 600 dpi, supporting jetting pulse frequencies of at least 15 KHz per nozzle (enabling high speed inkjet printing applications of at least 0.6 m / sec per individual nozzle row per print head), and enabling uninterrupted, industrial level print output of magnetic ink character recognition (MICR) code lines suitable for high speed magnetic data scanning per established industry regulations (ANSI X9).
Owner:VILLWOCK THOMAS
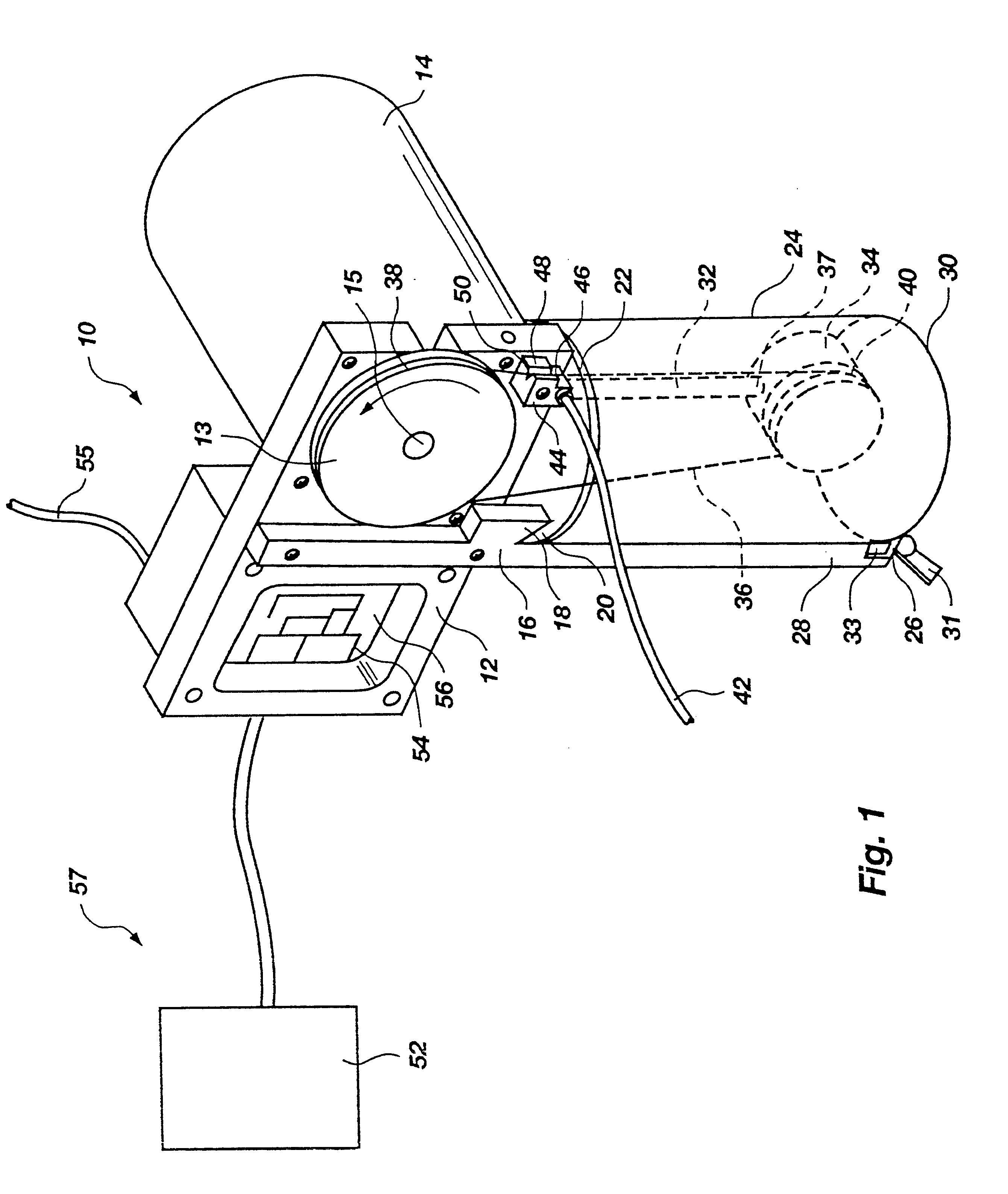
Metering device for paint for digital printing
InactiveUS6319555B1Easy constructionReduce manufacturing costCylinder pressesInking apparatusEngineeringDigital image
A paint injector for digital printing in which paint is deposited in metered amounts on a print medium comprises a wheel rotatable by a shaft of a motor, an idler disposed in a paint reservoir, and an endless cable disposed around the wheel and the idler. The motor is preferably computer controlled such that the rotation of the wheel and thus movement of the cable is selectively controlled. As the wheel is rotated, paint contained within the paint reservoir coats the cable and is thus drawn by the cable in front of an air stream. The air stream pulls the paint from the cable and carries it toward the print medium. By employing a plurality of such paint injectors into a single print head, each containing a different color of paint, and secured to a computer controlled, movable carriage positioned over the print medium, a digital image can be painted by the print head on the print medium.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Method for thermally processing photosensitive printing sleeves
ActiveUS7081331B2Minimize relief variationHigh image fidelityPhotosensitive materialsRadiation applicationsPhotopolymerHeat sensitive
An improved method of manufacturing a photosensitive printing element that minimizes relief variation and improves image fidelity. The method involves a step of pre-curing the first (floor layer) of photocurable material prior to depositing an additional layer or layers of photocurable material that may be imaged and developed to produce a desired relief image on the surface of the photosensitive printing element. The photosensitive printing element is then thermally developed by contacting the photosensitive printing element with at least one roll that is capable of moving over at least a portion of the imaged surface of the flexographic printing element to remove the softened or melted non-crosslinked photopolymer. Non-crosslinked photopolymer on the imaged and exposed surface of the flexographic printing element can be softened or melted by positioning a heater adjacent to the imaged surface of the flexographic printing element and / or heating the at least one roll that contactable with the imaged surface of the flexographic printing element.
Owner:MACDERMID PRINTING SOLUTIONS
Lithographic offset press and lithographic offset press printing method
An offset lithography printing press and method wherein dampening structure applies a thin moisture layer directly to a blanket cylinder to facilitate separation between the blanket cylinder and paper or other printable sheet material when passing through a nip between the blanket cylinder and an impression cylinder.
Owner:DOMOTOR JULIUS
Method for forming images and intermediate transfer recording medium
InactiveUS6994765B2Excellent various fastness propertyStrong filmCylinder pressesPlaten pressesSuperimpositionImage formation
The present invention provides a method for image formation, that can yield thermally transferred images which are excellent in various fastness properties even under severe service conditions, and an intermediate transfer recording medium for use in the method for image formation. The method for image formation comprises the steps of: providing an intermediate transfer recording medium comprising a substrate film and a transfer portion provided separably on the substrate film; forming an image on the intermediate transfer recording medium in its transfer portion; transferring the transfer portion onto an object; and, thereafter, again transferring the intermediate transfer recording medium in its next transfer portion once or more onto the object with the image formed thereon. In this case, in the intermediate transfer recording medium, a hologram image is set every at least second image plane, and an image can be formed on the transfer portion having the hologram image. This can offer an advantage that the transfer portion, with a thermally transferable image formed thereon, can be transferred onto an object followed by the superimposition of a transfer portion, to be served as the outermost surface in the final form onto the transferred portion once or more to provide a strong film for protecting the thermally transferred image. Thus, the problems of the prior art could have been solved.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Heat transfer masking sheet materials and methods of use thereof
In one embodiment, a method of applying an image to a substrate includes the steps of: imaging a printable surface with an image to form an imaged surface having a printed area and a non-printed area; positioning a masking sheet comprising an outer masking layer adjacent the imaged surface such that the outer masking layer is in contact with the imaged surface; transferring a corresponding portion of the outer masking layer to the printed area of the imaged surface, leaving a negative image mask on the masking sheet; transferring the negative image mask to a transfer layer of a heat transfer paper to form a heat transfer paper having a masked portion corresponding to the negative image mask and an unmasked portion; and transferring the unmasked portion corresponding to the printed area to a substrate. Other methods of making and using negative image masks are also disclosed.
Owner:NEENAH PAPER INC
Method for printing on spherical object and pad to be used therefor
ActiveUS20090211476A1Increased bending stiffnessLarge thicknessCylinder pressesPlaten pressesEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:BRIDGESTONE SPORTS
Enhanced halftone screening method for the dry offset printing process
ActiveUS8400681B1Increase in print contrastIncrease in color vibrancyCylinder pressesDigitally marking record carriersContinuous toneScreening method
A method of file preparation, ripping and plate making for high end graphics printed on cylindrical products utilizing Dry Offset printing presses. While utilizing two inverse angle techniques and one fixed angle on the Black, with virtually unlimited color pluralities, encompassing a majority of all open areas of the common printing blanket without any ink overlap. The nesting of the halftone dots at even coarse line screen rulings eliminating a dot rosette pattern and creating a continuous tone appearance. Print contrast is increased to that of offset printing quality and ink contamination over the course of the run length is virtually eliminated. This current invention also increases the ability to print white with colors as opposed to needing white coating done in advanced to transparent plastics and metallic surfaces.
Owner:MORAVCIK GIRARD J
Method of varying the ink density of the full tone in offset printing within a rotary printing machine
A method of varying the ink density of the full tone in printing within a rotary printing machine with an ink application system which can provide a constant quantity of ink which, in spite of constant ink supply from the inking unit, permits control of the full-tone density or adaptation of the raster tonal values in the print. The method includes setting the binary image on a printing plate. A basic raster of raster points, which determines the area coverage of the binary image, is produced on the printing plate for the variable-area image information. The basic raster is then superimposed on a fine microraster in such way that the area coverage of the basic raster is reduced by a percentage which can be set between 0% and 100%.
Owner:MANROLANAD AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com