Patents
Literature
181results about "Heat and power cogeneration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
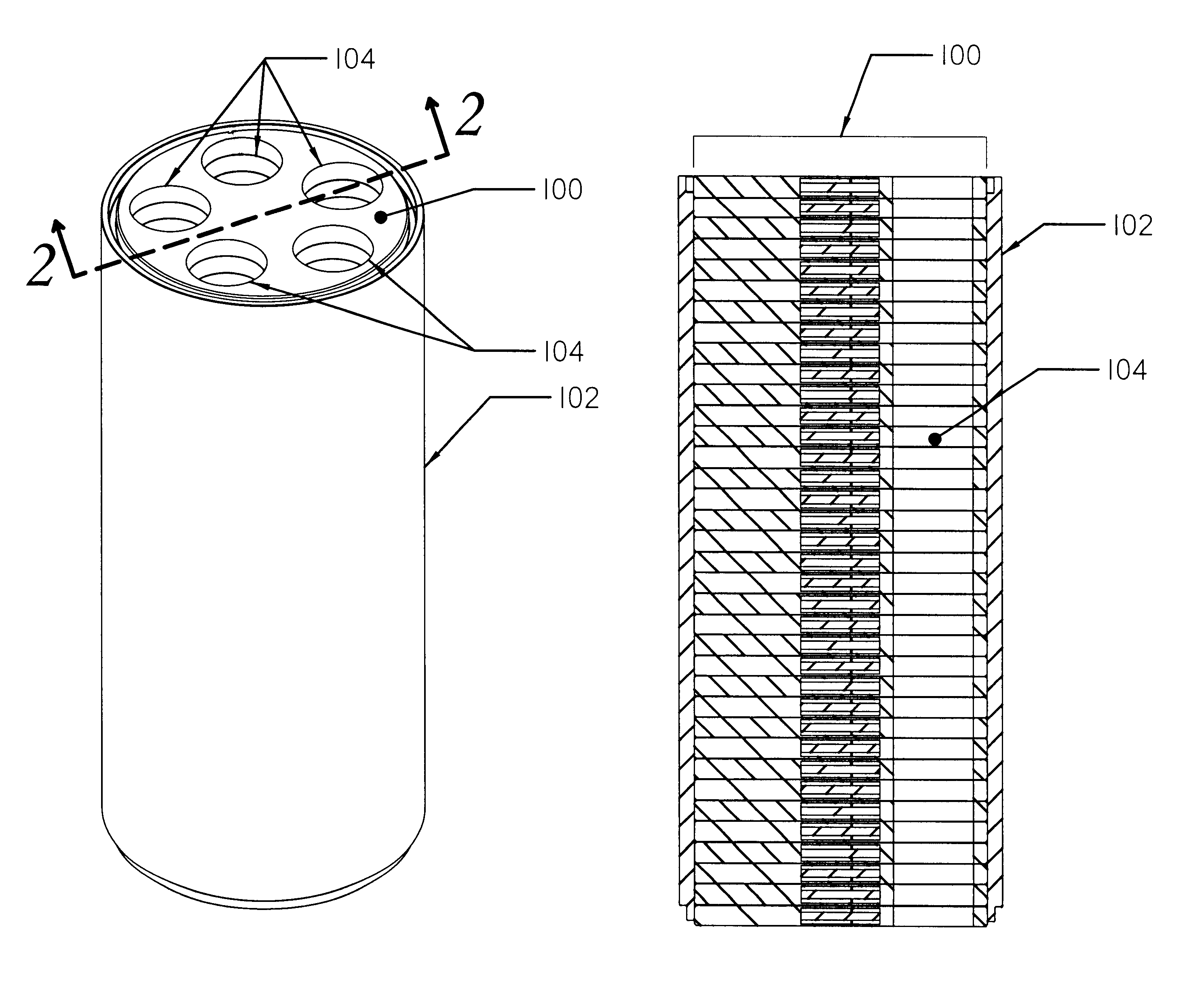
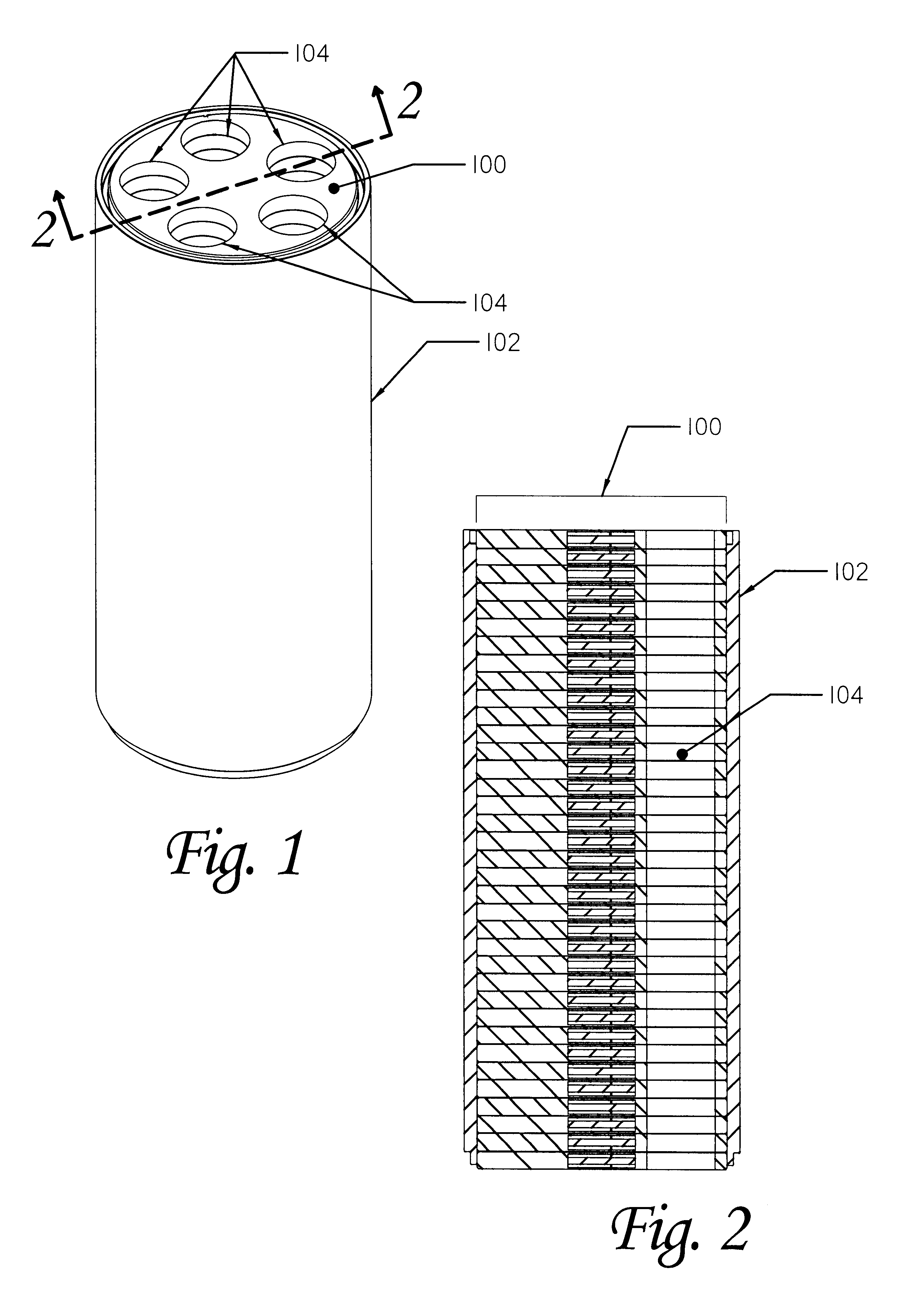
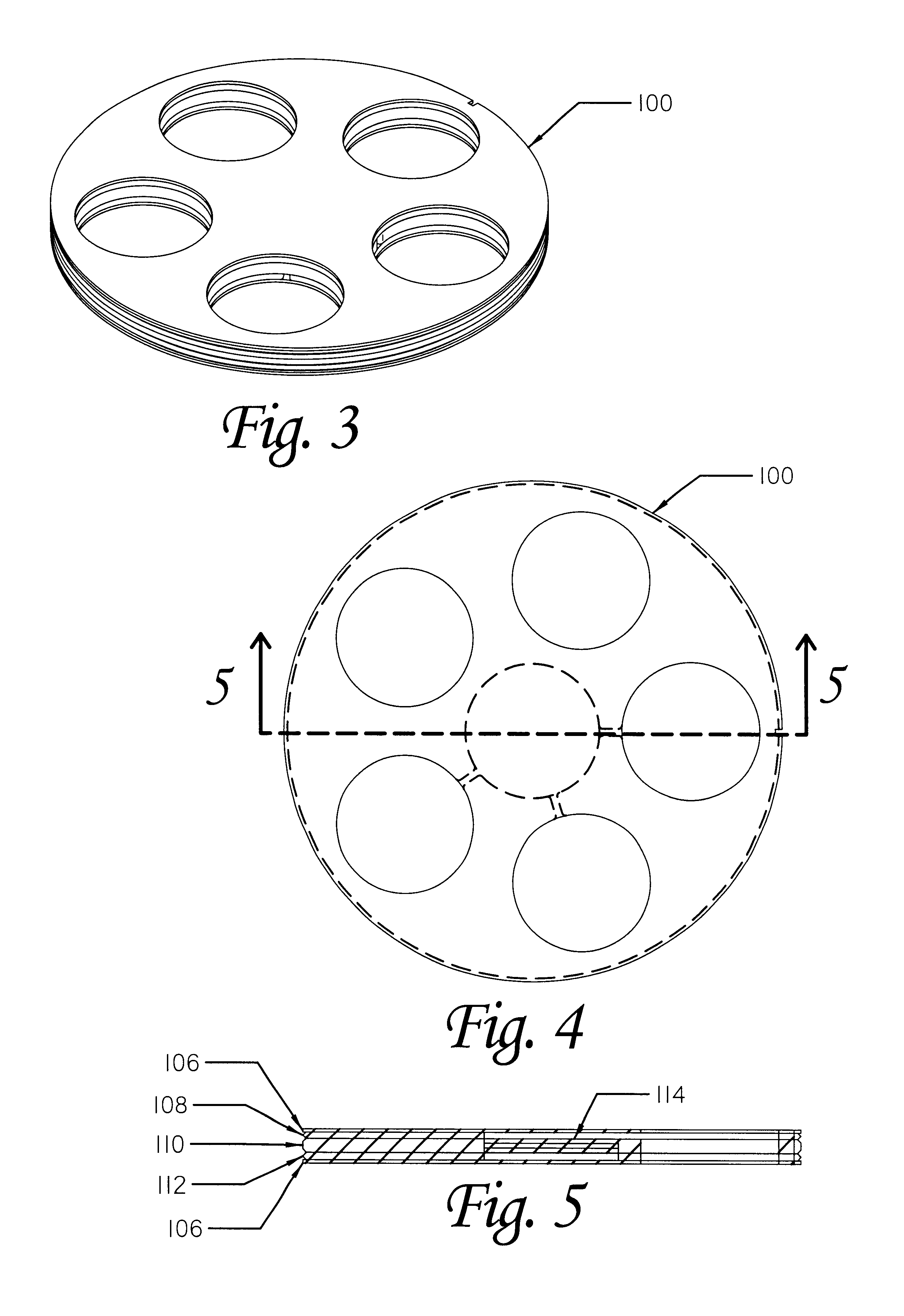
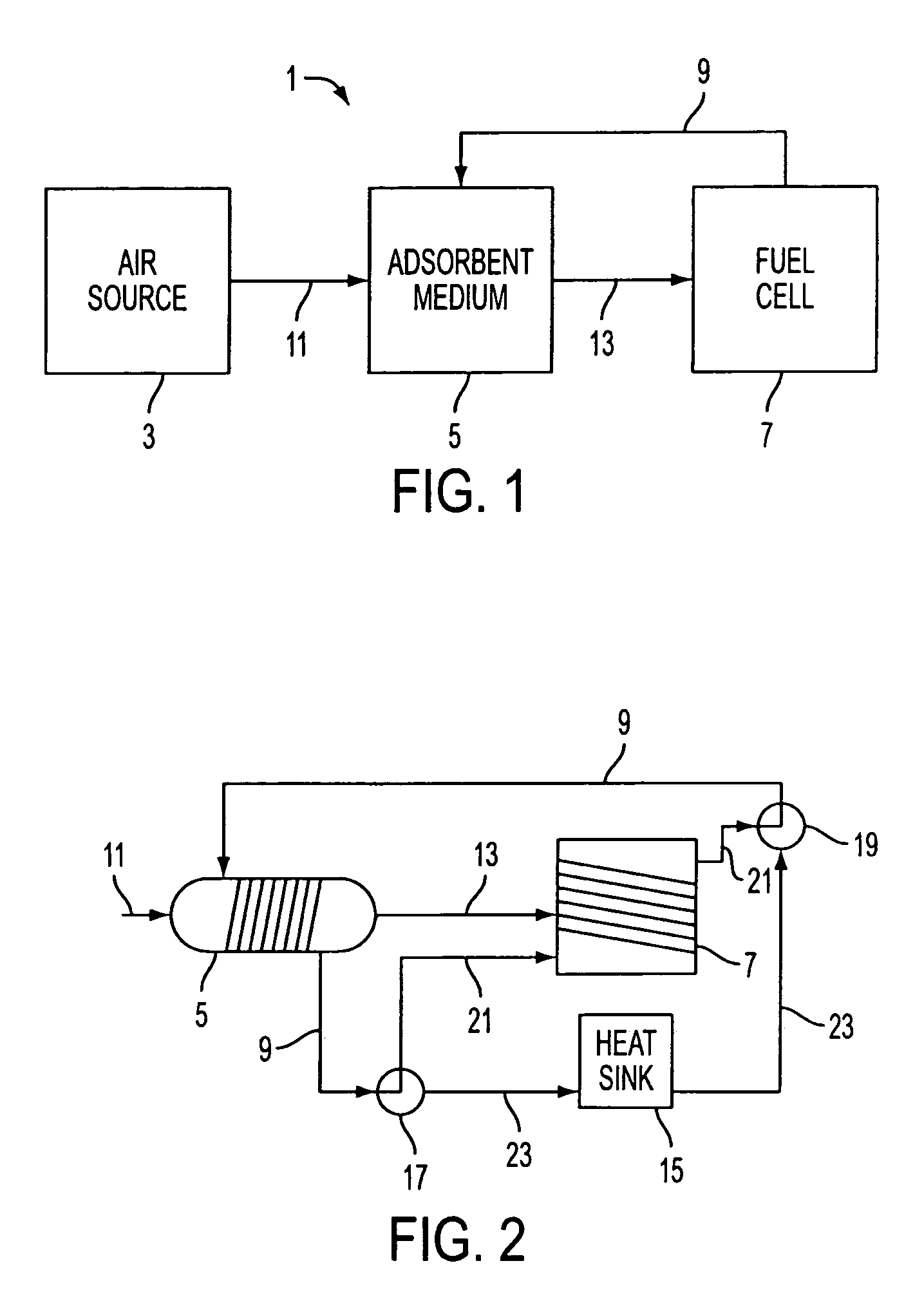
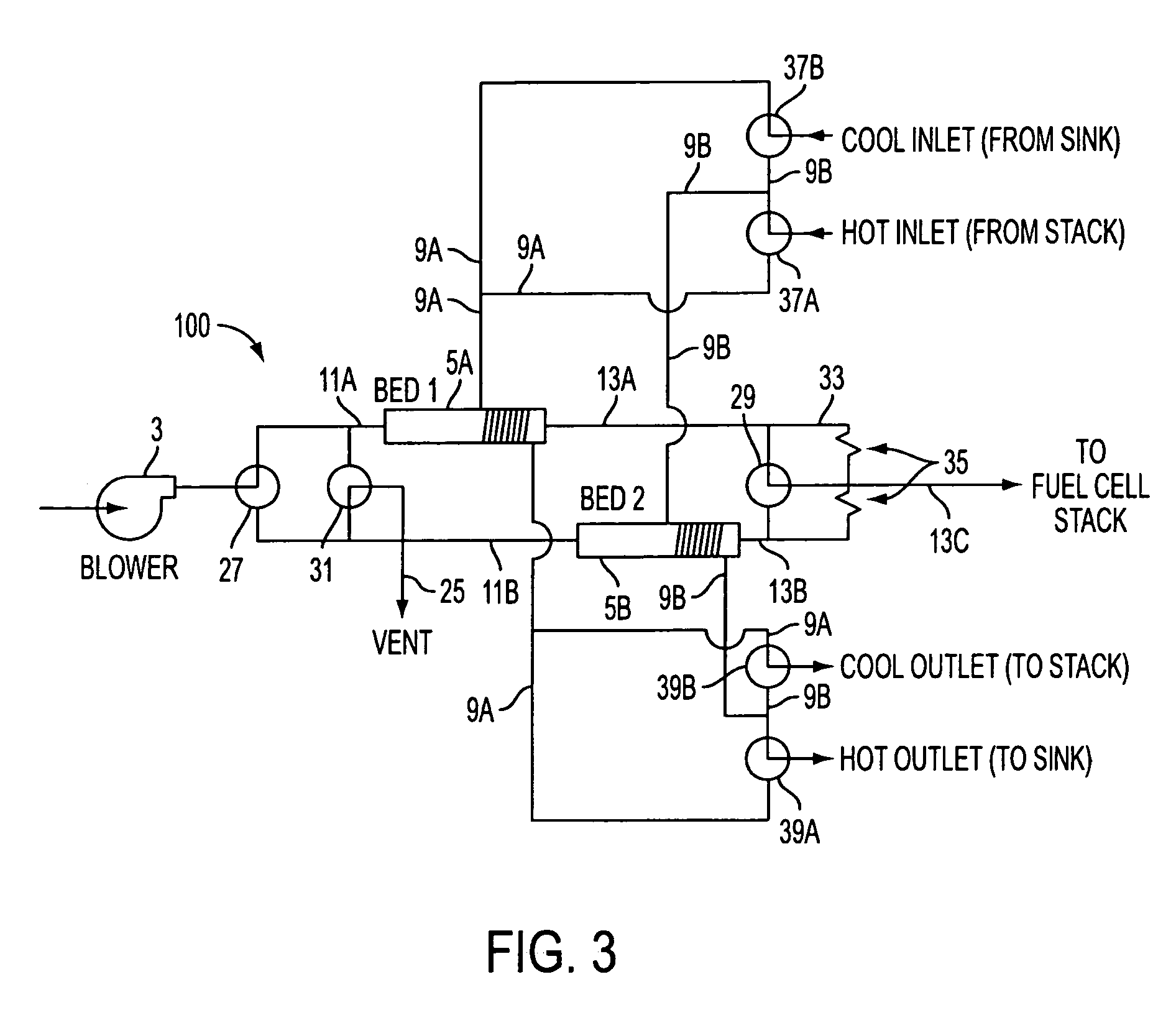
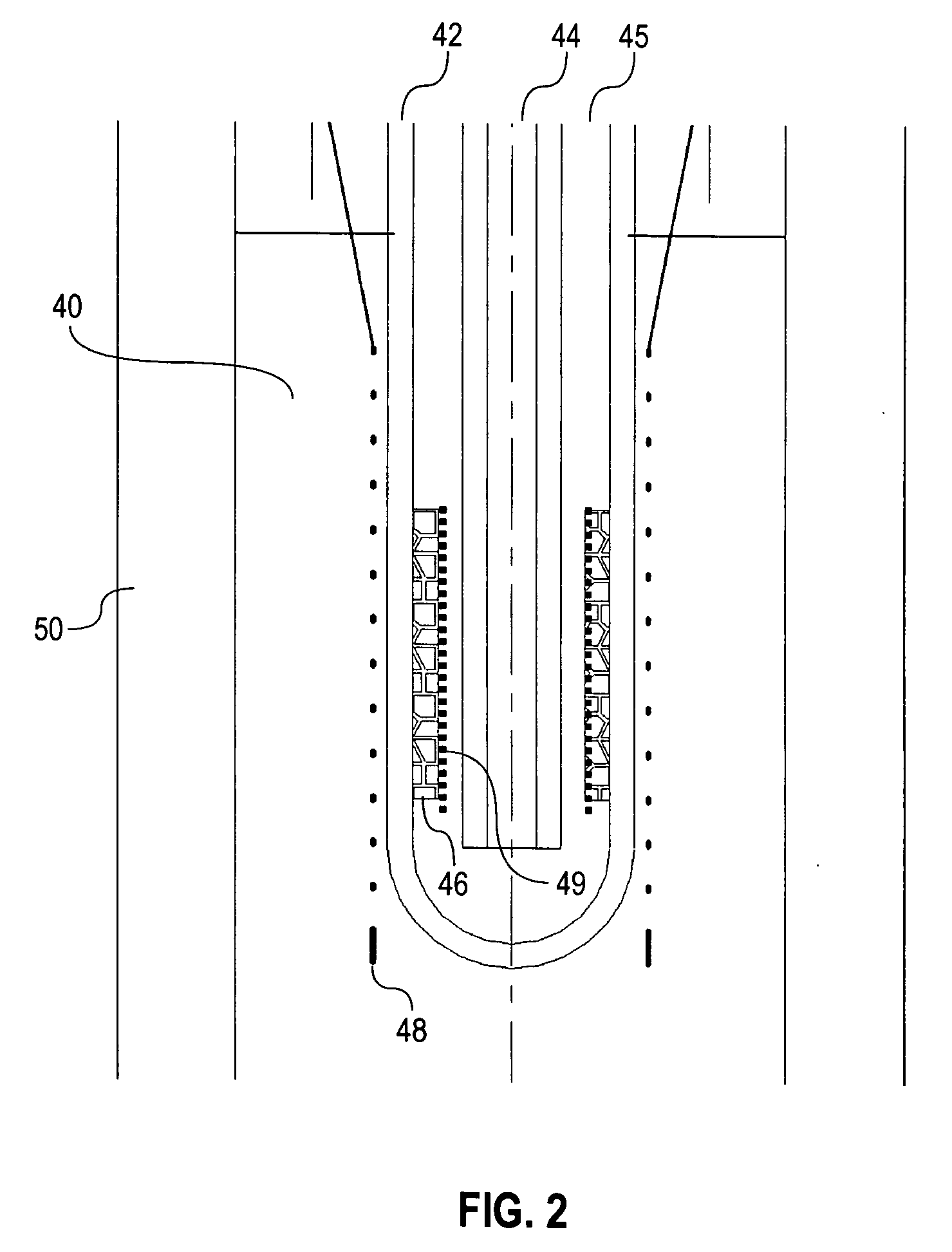
Apparatus and method for heating subterranean formations using fuel cells
InactiveUS6684948B1Eliminate needAvoid inefficiencyFuel cell heat exchangeFuel cells groupingElectricityFuel cells
A fuel cell based subterranean heater for mineral extraction, in situ decontamination, or other applications. The fuel cells are preferably stacked within a casing which is then inserted into a hole bored, or otherwise formed, into the formation to be heated. Conduits within the casing, and preferably formed by adjacent, aligned holes formed through the plates of the individual fuel cells supply fuel and air and extract exhaust gases. An optional manifold is used to span the overburden without applying heat to it directly. The manifold may also function as a heat exchanger between incoming and exhaust gases. Preferably the fuel cell is fueled by gases produced by the formation and also generates electricity which is available for use or export.
Owner:IEP TECH INC
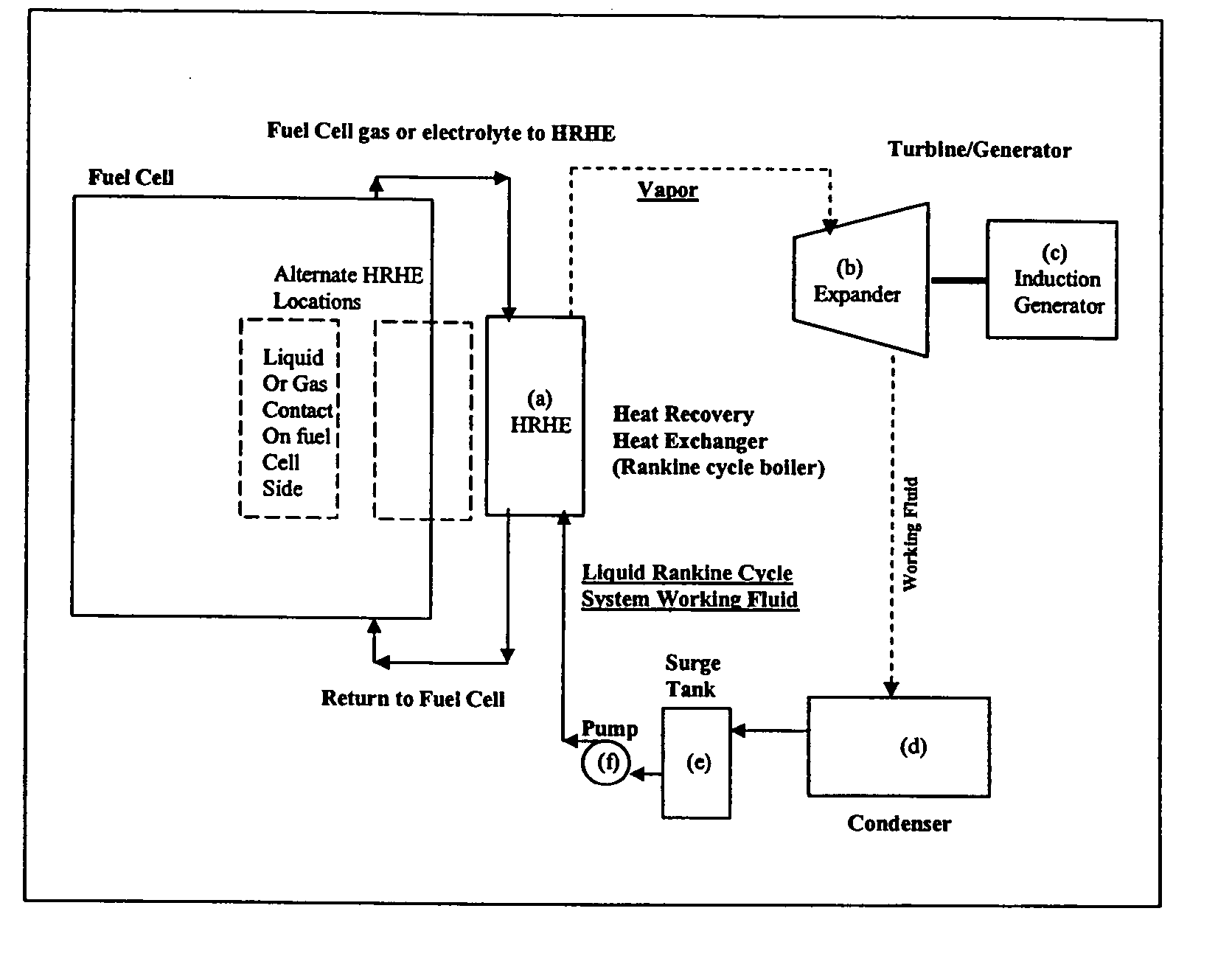
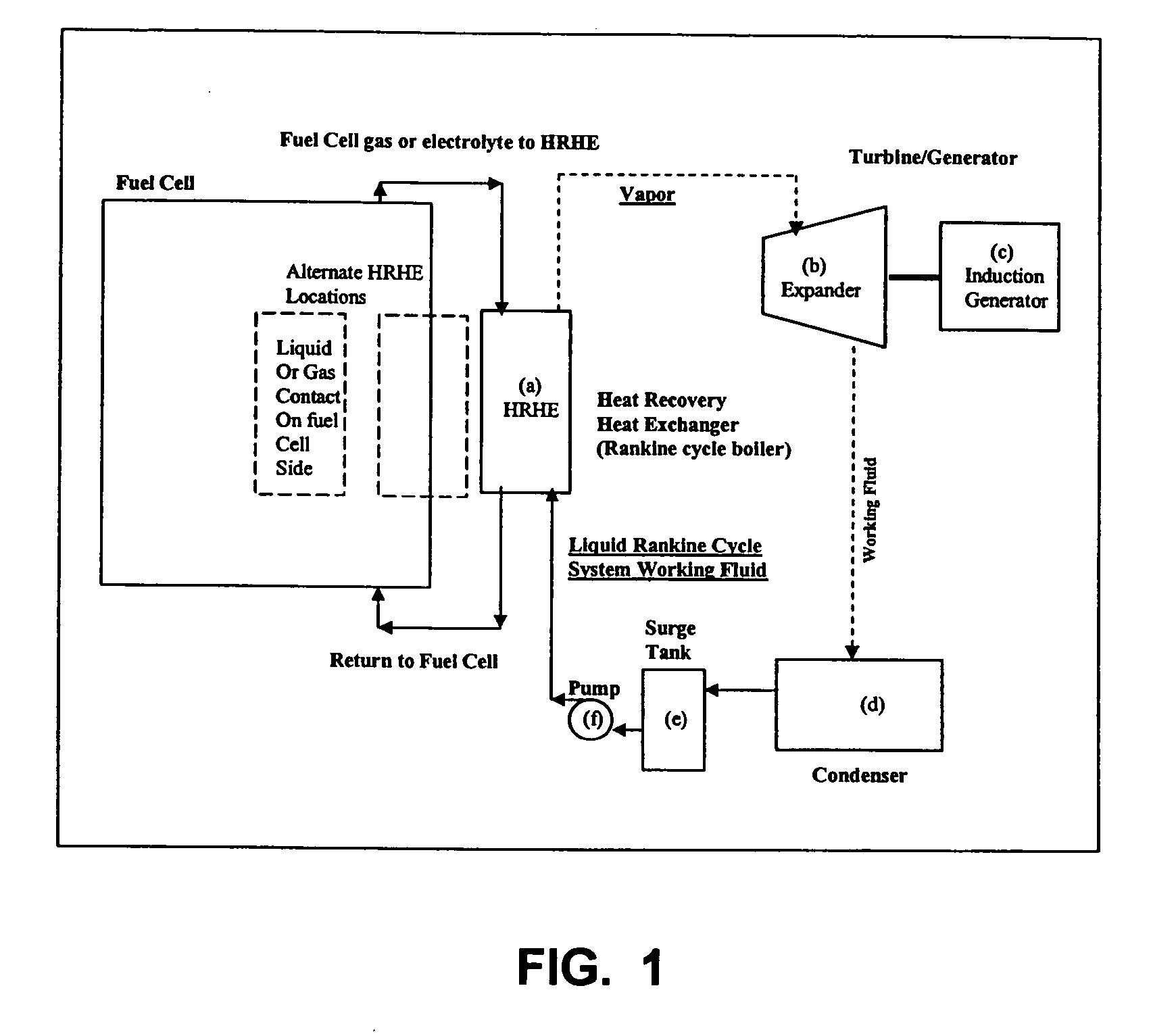
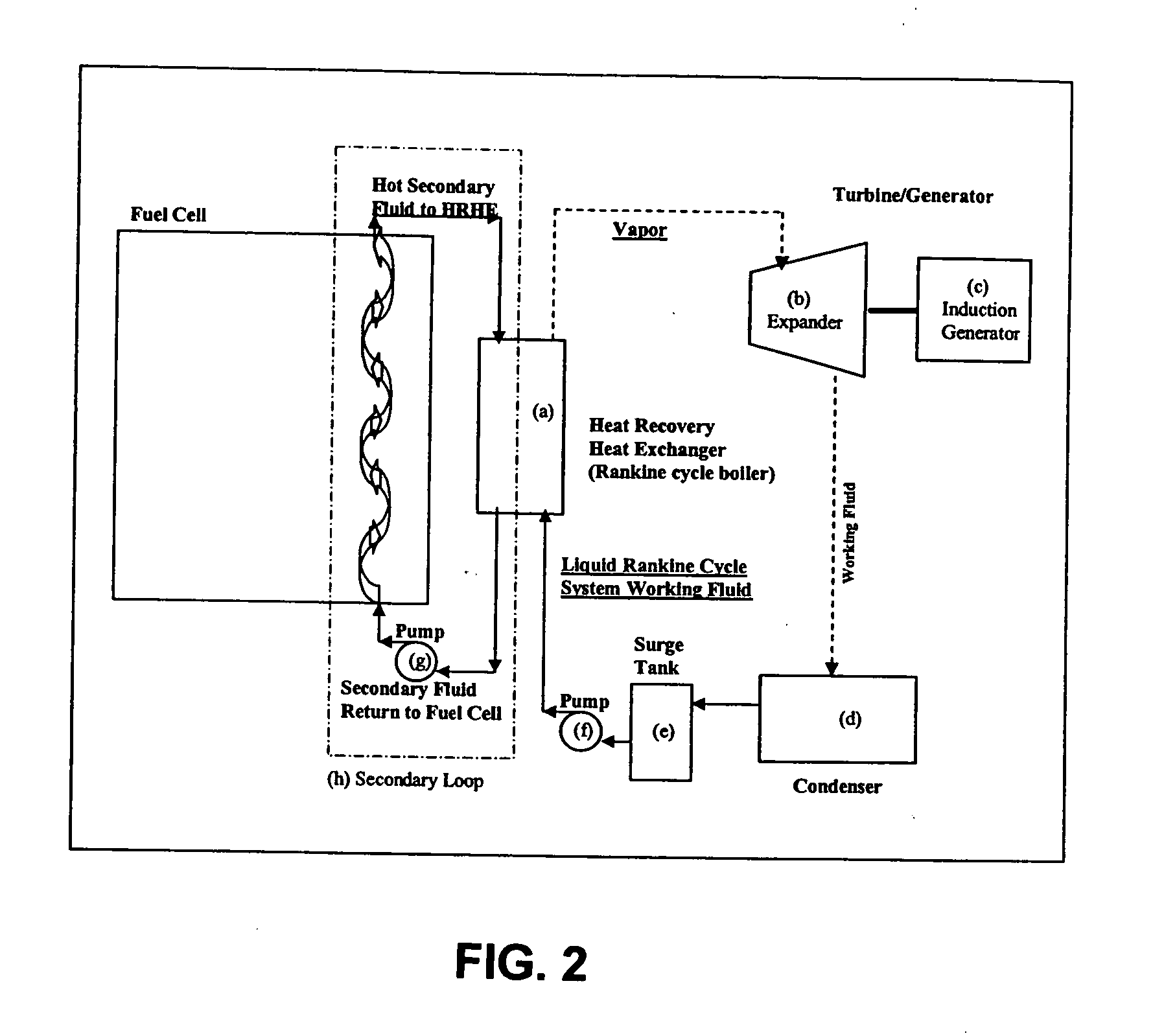
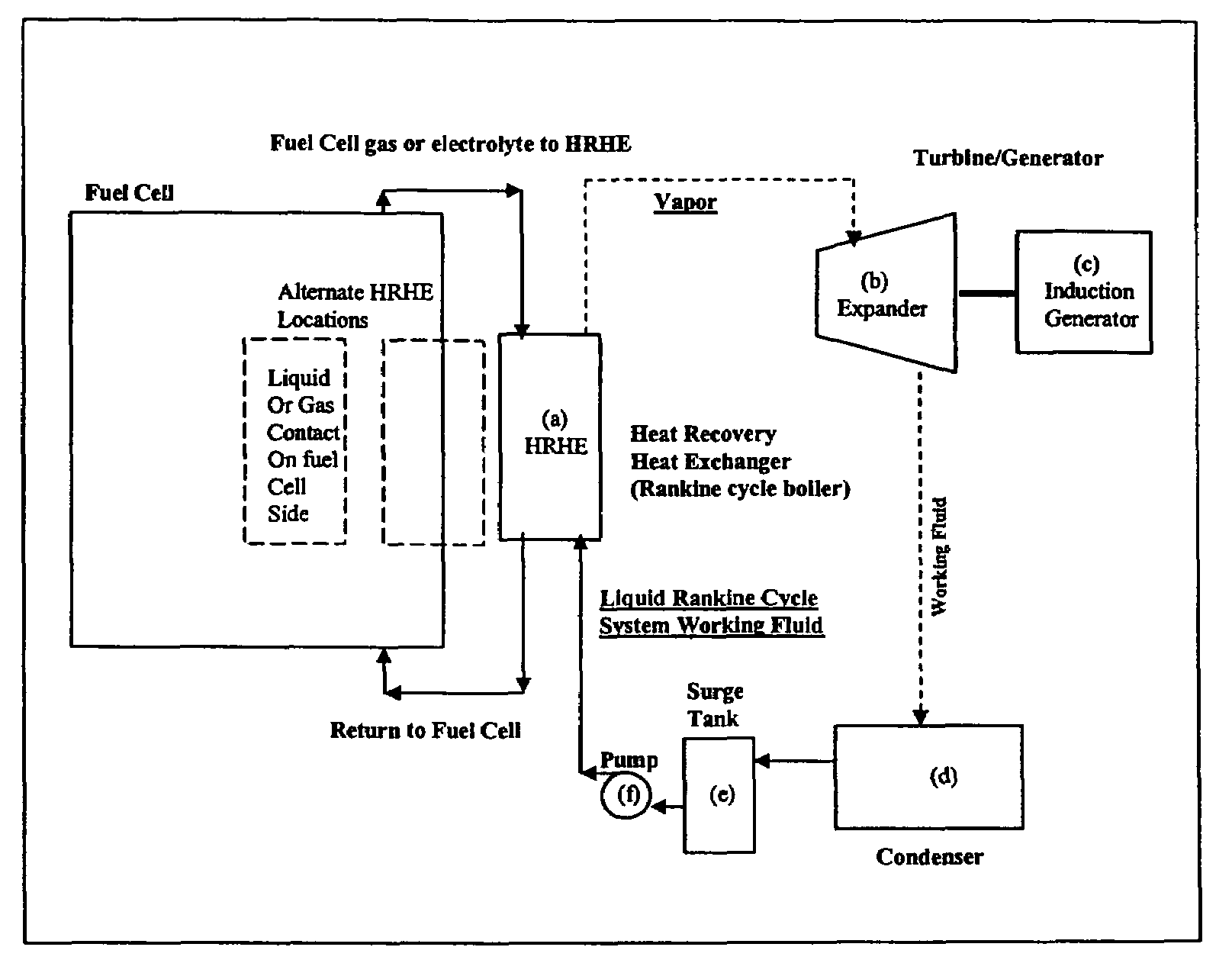
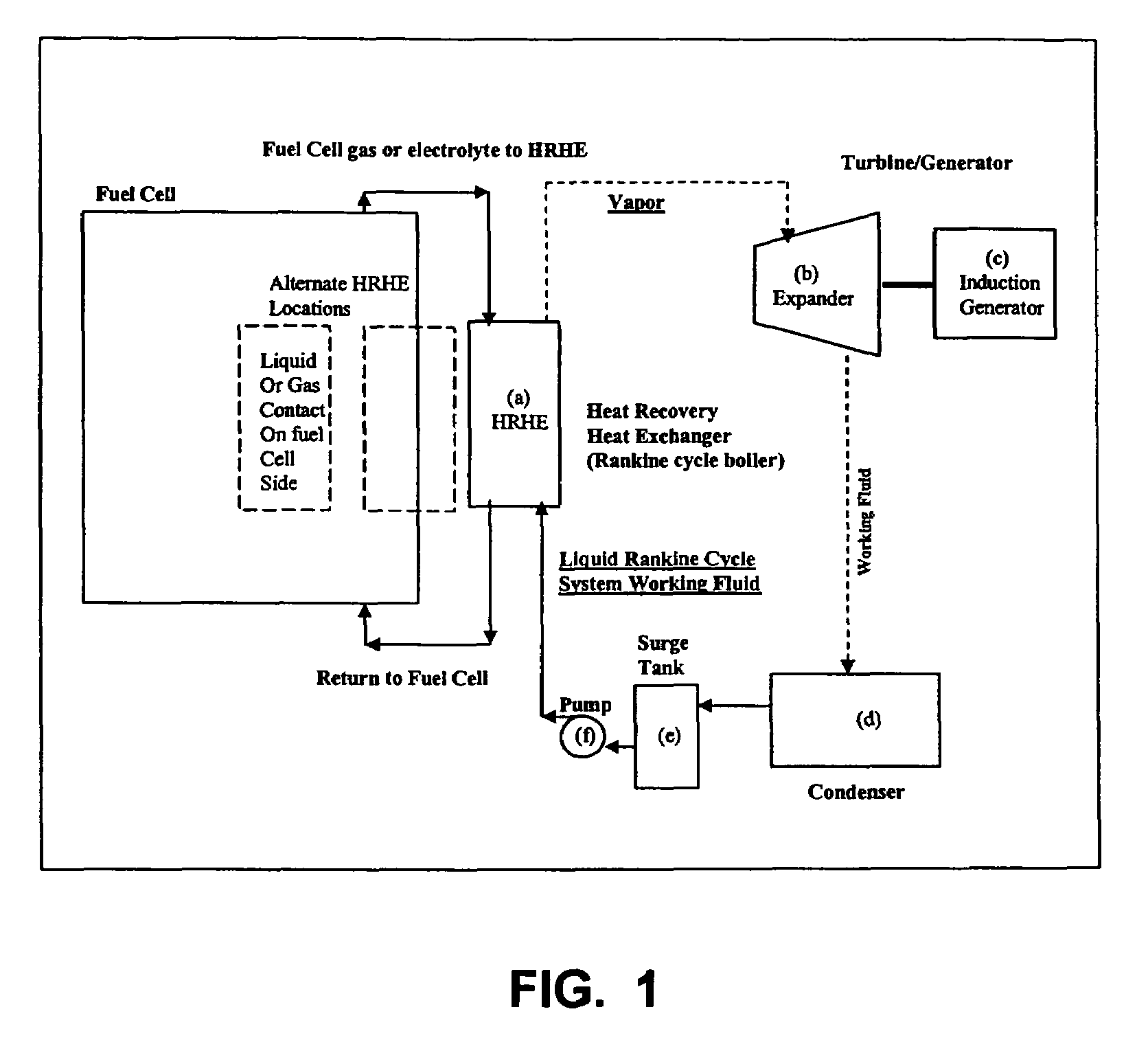
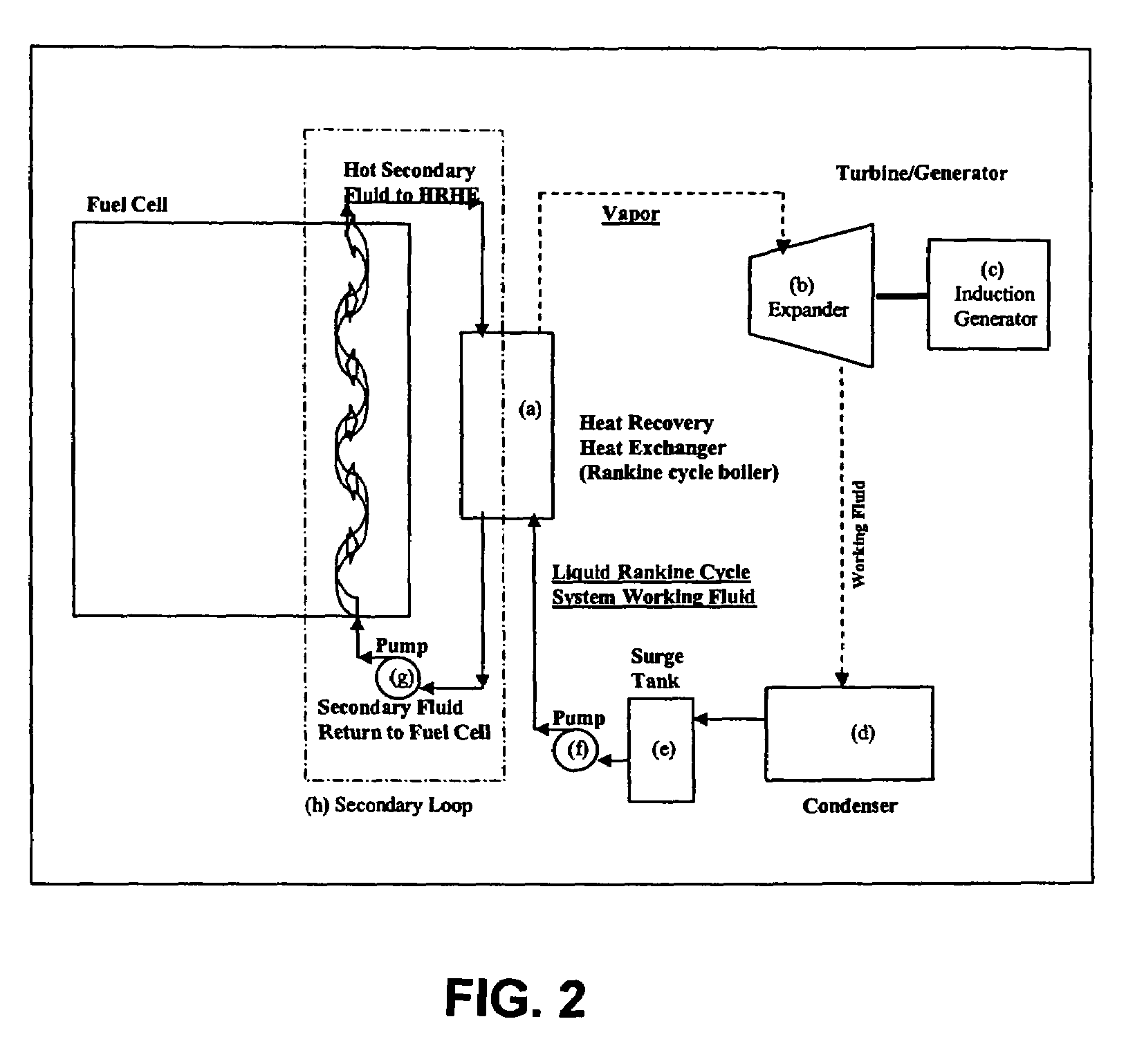
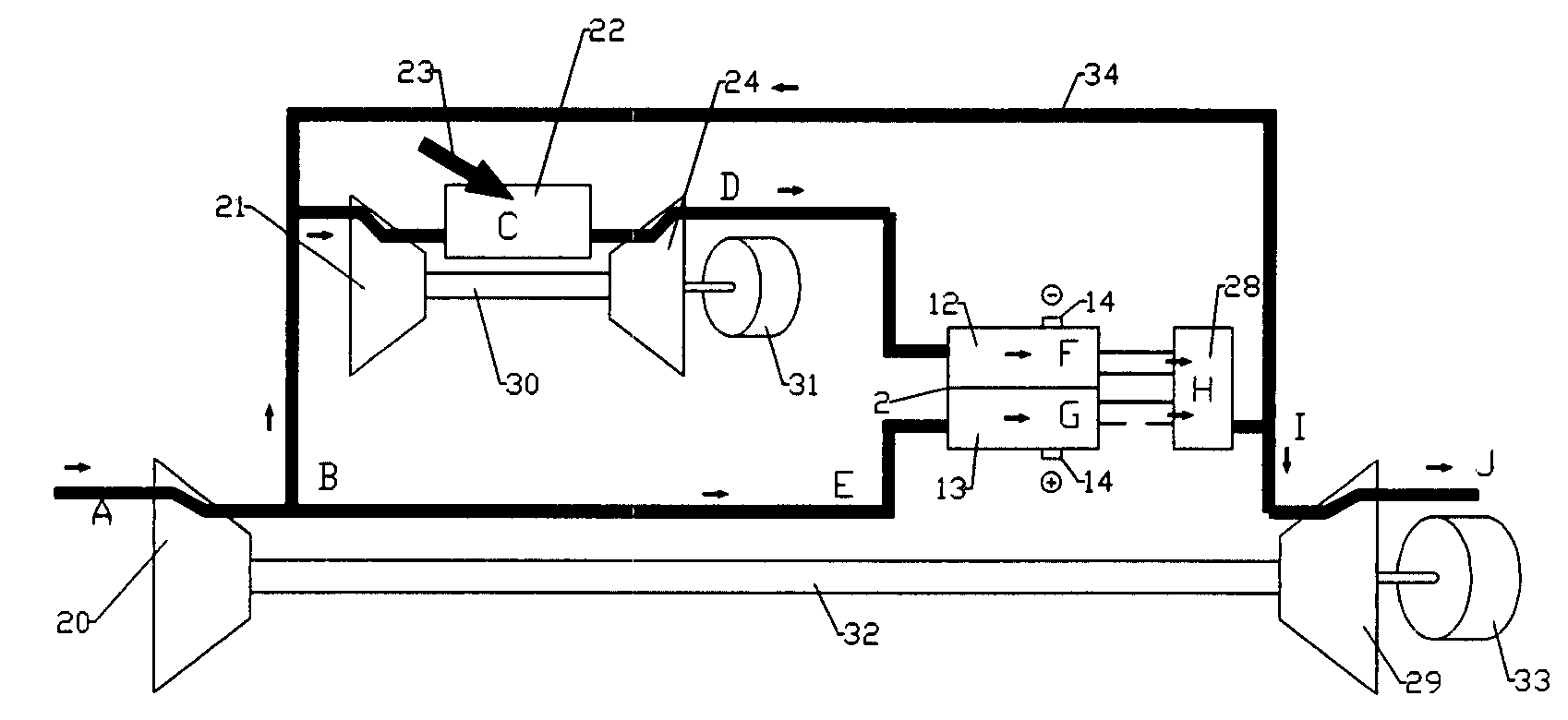
Working fluids for thermal energy conversion of waste heat from fuel cells using rankine cycle systems
A process for recovering waste heat which comprises: (a) passing a liquid phase working fluid through a heat exchanger in communication with a process which produces the waste heat; (b) removing a vapor phase working fluid from the heat exchanger; (c) passing the vapor phase working fluid to an expander, wherein the waste heat is converted into mechanical energy; and (d) passing the vapor phase working fluid from the expander to a condenser, wherein the vapor phase working fluid is condensed to the liquid phase working fluid. The preferred working fluid is an organic Rankine cycle system working fluid comprising compounds having the following general structure: where x, y, z, and m are each selected from the group consisting of: fluorine, hydrogen, Rf, and R, wherein R and Rf are each an alkyl, aryl, or alkylaryl of 1 to 6 carbon atoms, and wherein Rf is partially or fully fluorinated.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
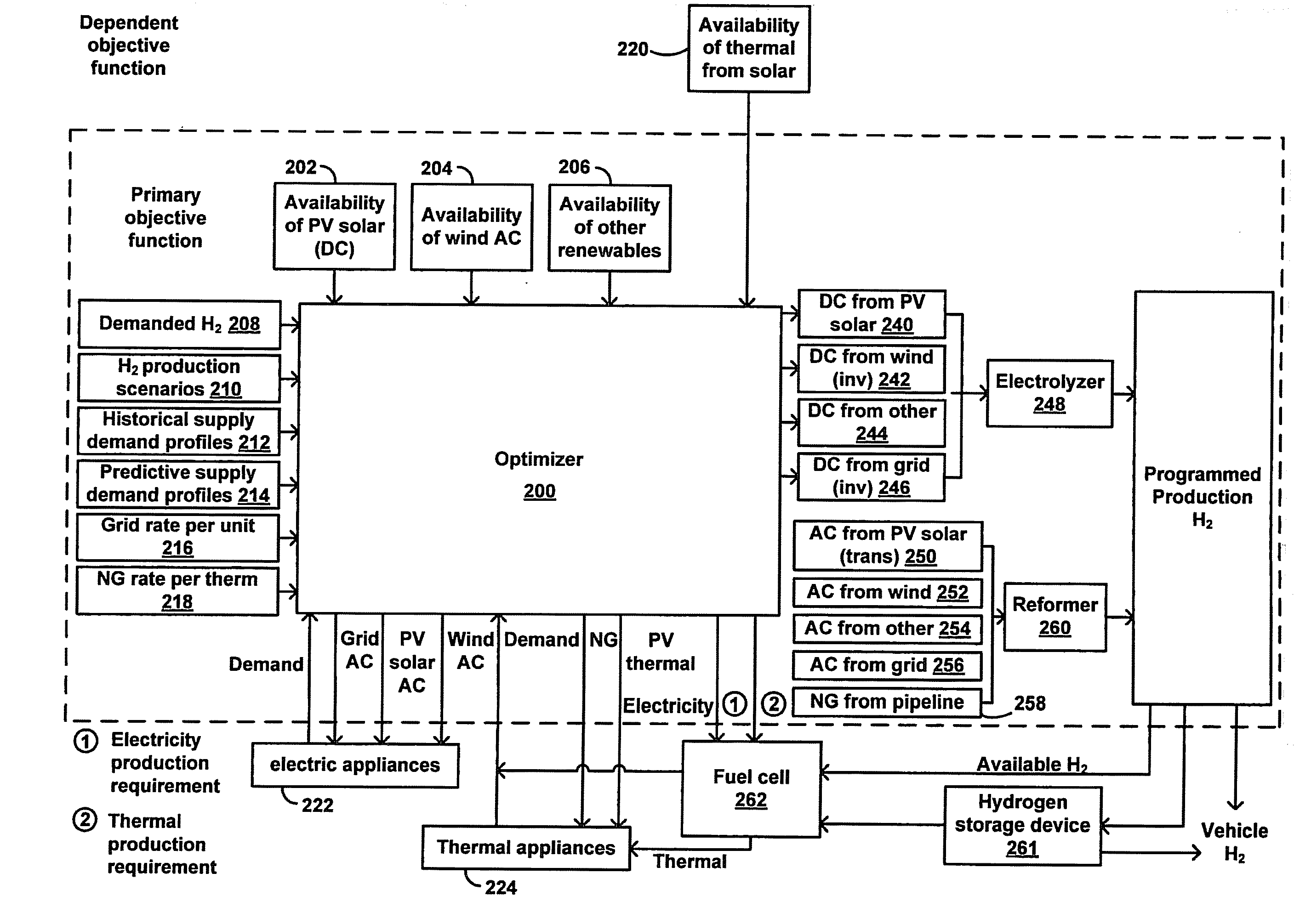
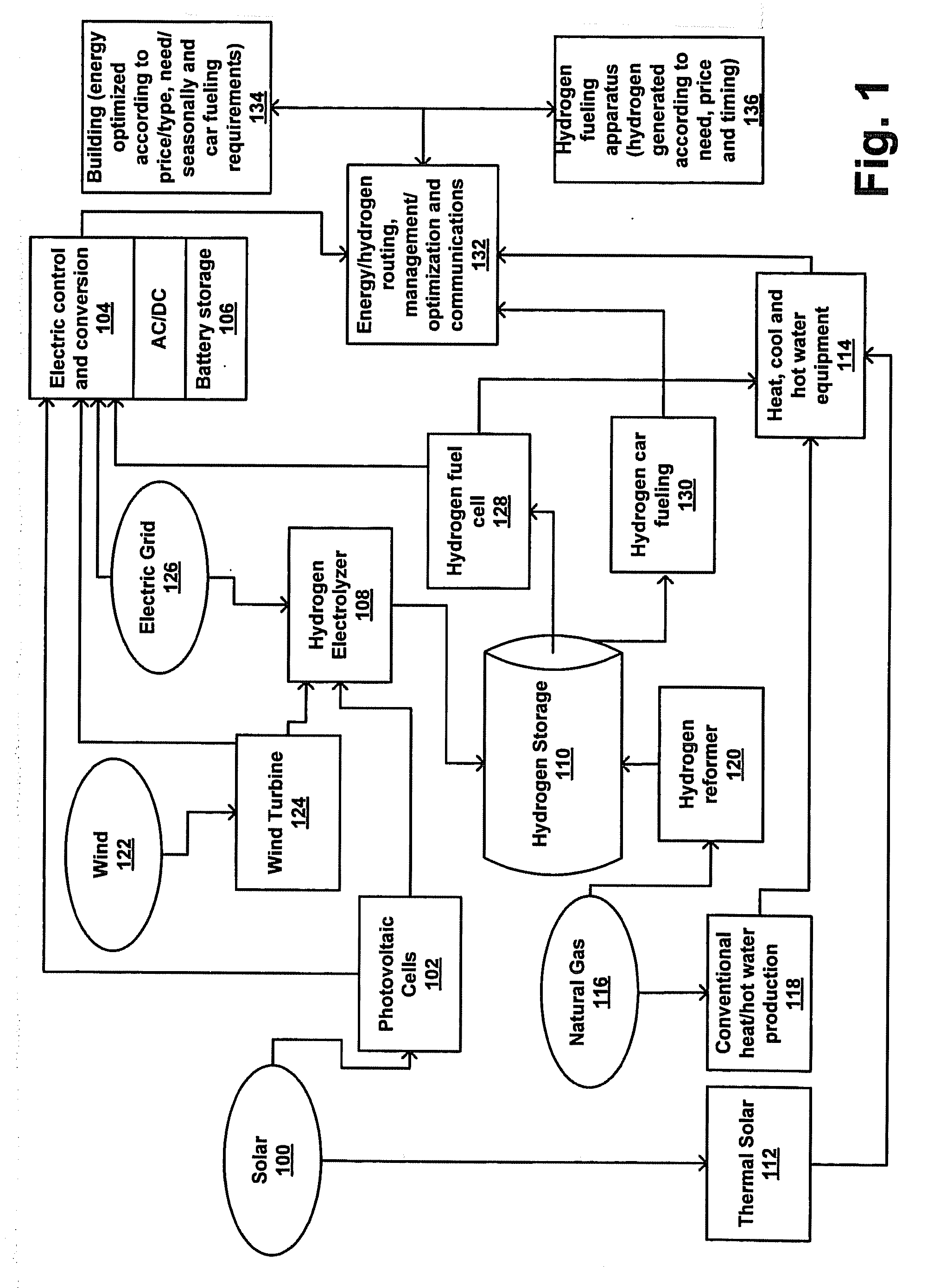
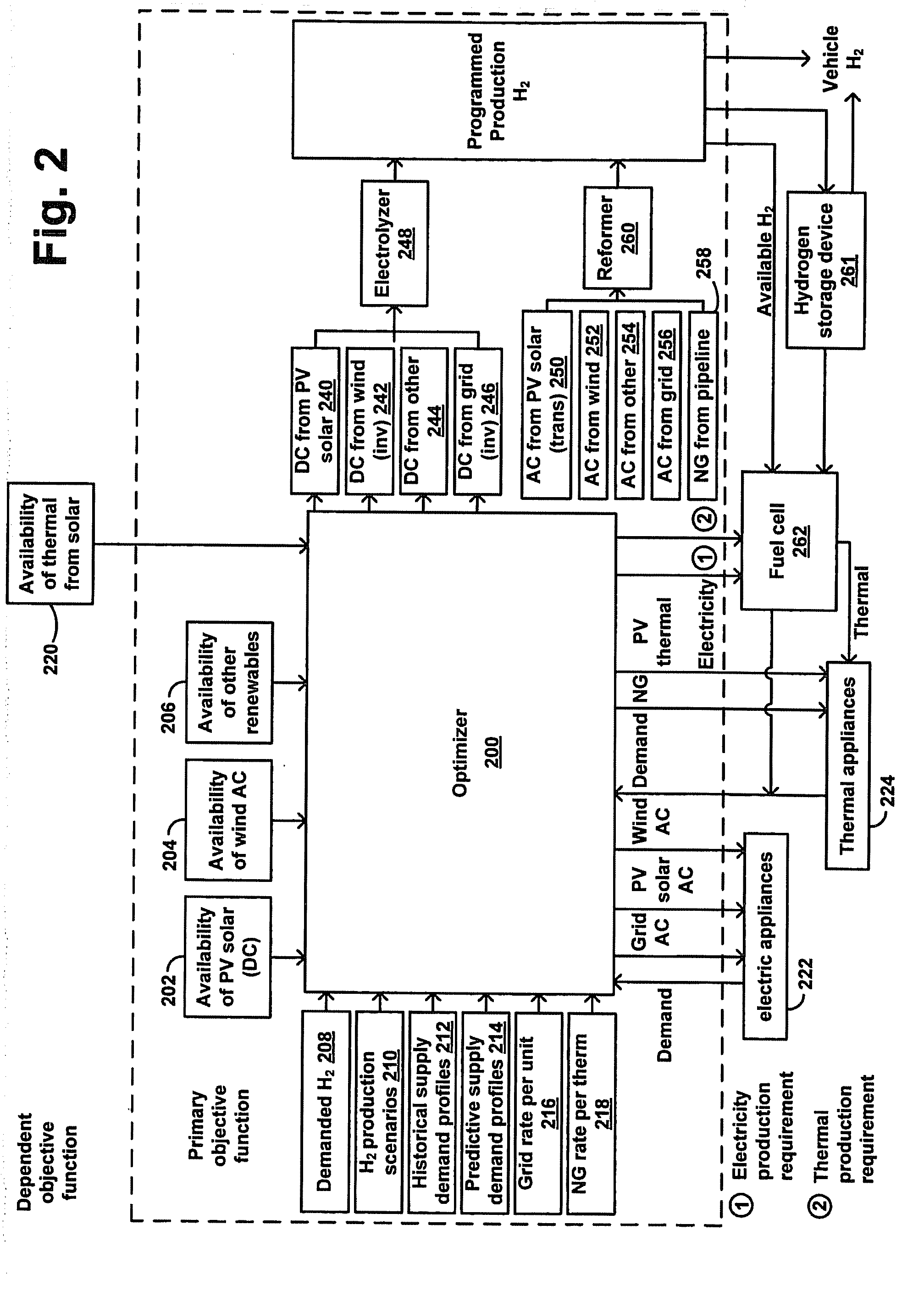
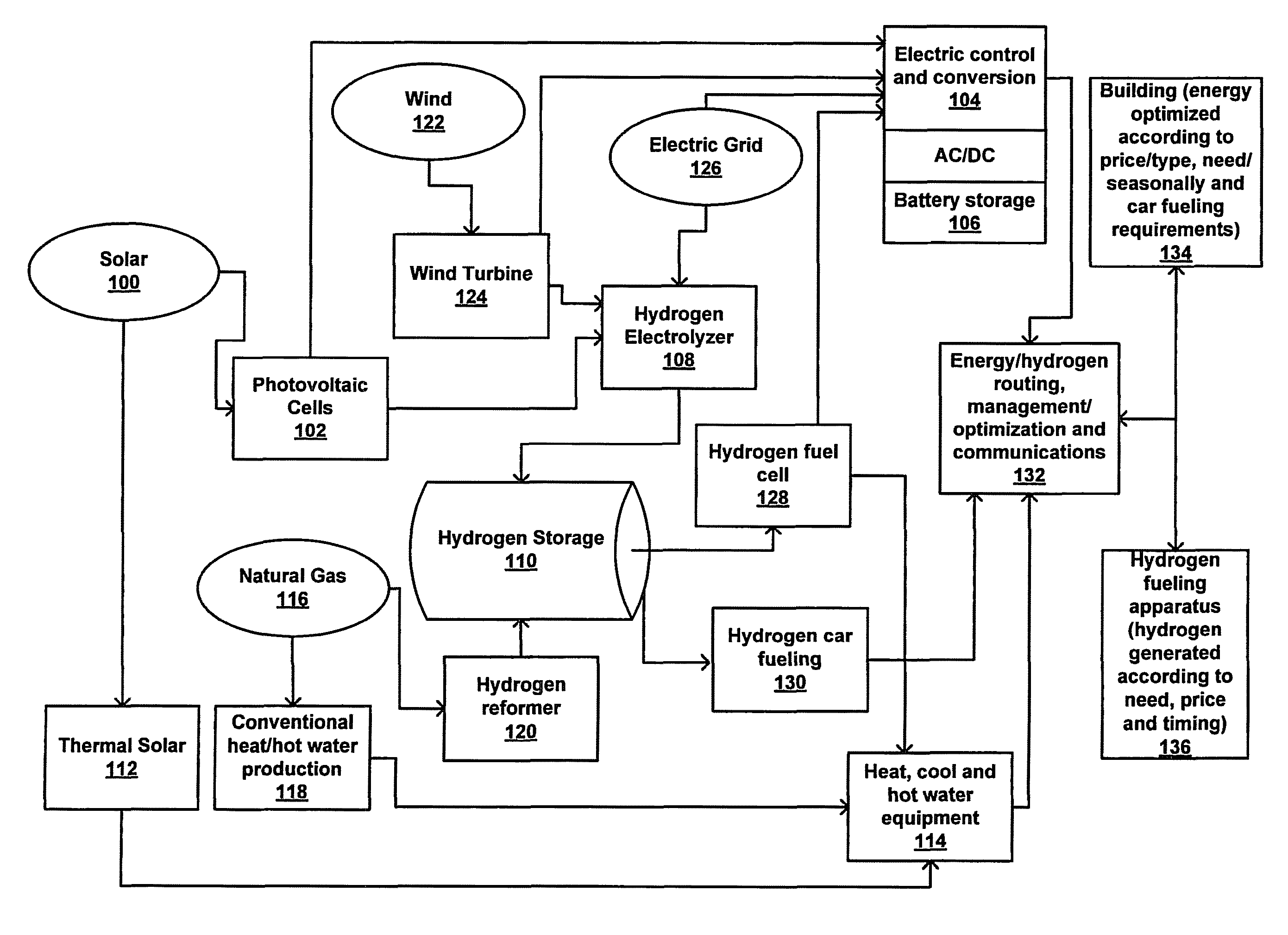
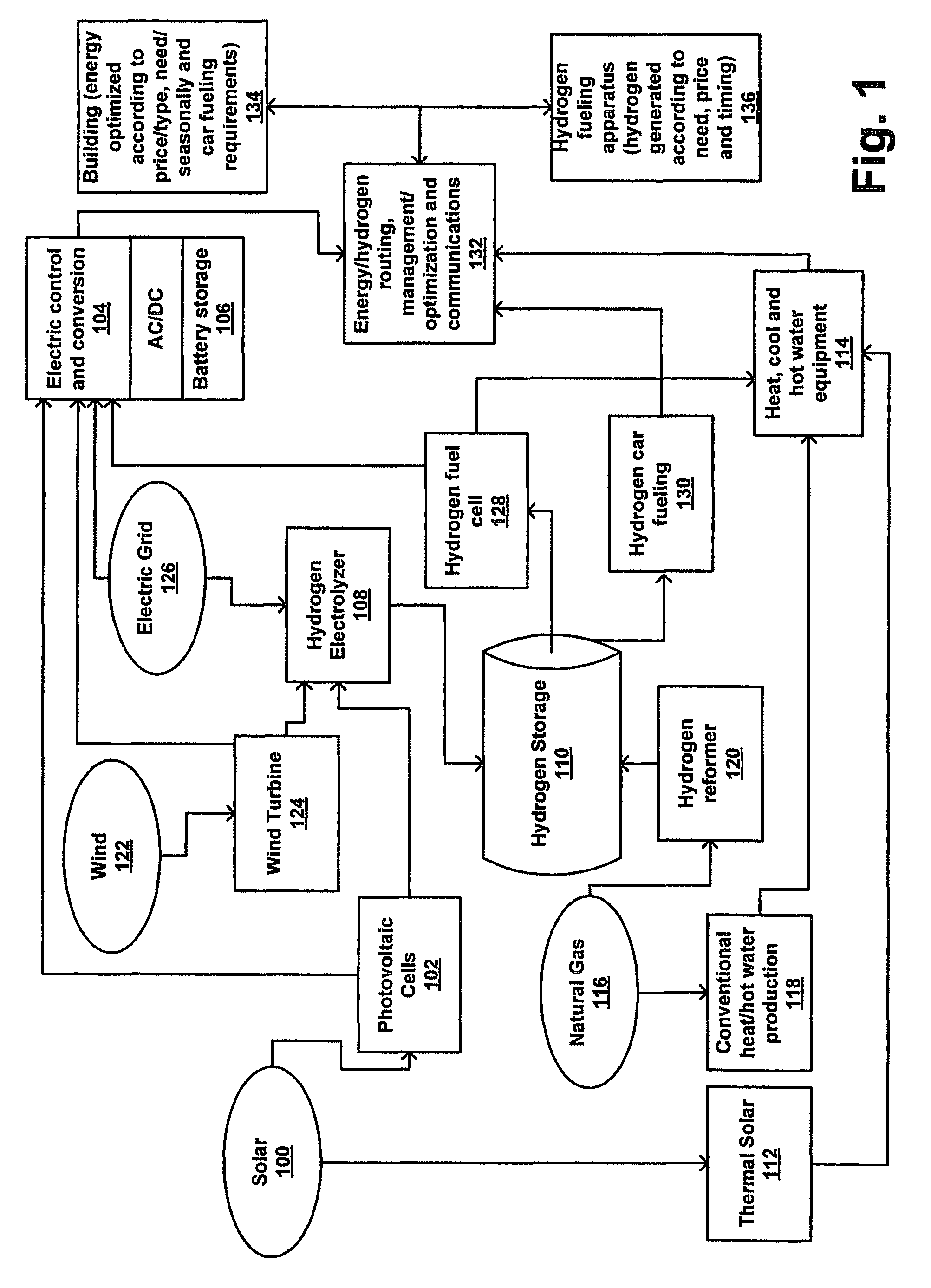
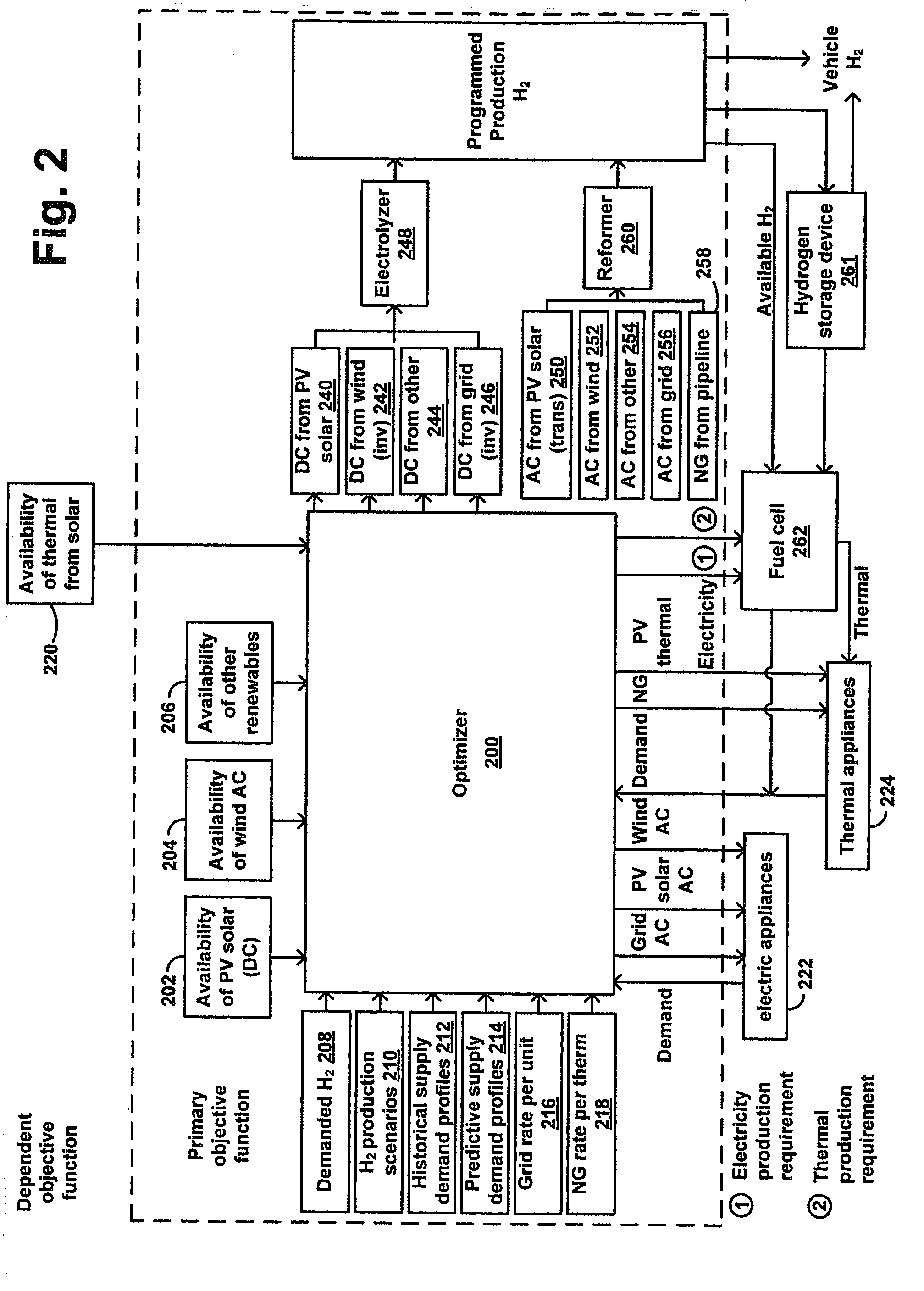
Method and Apparatus for Optimization of Distributed Generation
ActiveUS20090048716A1Low costLower requirementElectrical storage systemBatteries circuit arrangementsThermal energyElectric power
An energy optimization method and control apparatus may be used in a single building or a group of buildings to optimize utility-supplied and renewable sources in order to minimize the total energy cost. Simultaneously, it may also produce and store energy, such as electricity or hydrogen, that can be used to fuel vehicles, provide a means for independent production of household energy needs, or both. Various factors, such as the production of thermal energy and electricity from the renewable sources, the current store of stored energy, the current and expected thermal and electricity requirements of the building (based on a profile), the current and expected electricity loads of the equipment used to process stored energy, the expected thermal and electricity generating capacity of the renewable sources and other factors can be used to determine the mix of renewable-based and utility-based energy that minimizes the total energy cost.
Owner:INTELLIGENT GENERATION
Thermally effcient micromachined device
InactiveUS20030027022A1Reduce system sizeImprove performanceFlow mixersFixed microstructural devicesFuel cellsCompound (substance)
A micromachined device for efficient thermal processing at least one fluid stream includes at least one fluid conducting tube having at least a region with wall thickness of less than 50 mum. The device optionally includes one or more thermally conductive structures in thermal communication with first and second thermally insulating portions of the fluid conducting tube. The device also may include a thermally conductive region, and at least a portion of the fluid conducting tube is disposed within the region. A plurality of structures may be provided projecting from a wall of the fluid conducting tube into an inner volume of the tube. The structures enhance thermal conduction between a fluid within the tube and a wall of the tube. A method for fabricating, from a substrate, a micromachined device for processing a fluid stream allows the selective removal of portions of the substrate to provide desired structures integrated within the device. As an example, the micromachined device may be adapted to efficiently react fluid reactants to produce fuel for a fuel cell associated with the device, resulting in a system capable of conversion of chemical to electrical energy.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Working fluids for thermal energy conversion of waste heat from fuel cells using Rankine cycle systems
A process for recovering waste heat which comprises: (a) passing a liquid phase working fluid through a heat exchanger in communication with a process which produces the waste heat; (b) removing a vapor phase working fluid from the heat exchanger; (c) passing the vapor phase working fluid to an expander, wherein the waste heat is converted into mechanical energy; and (d) passing the vapor phase working fluid from the expander to a condenser, wherein the vapor phase working fluid is condensed to the liquid phase working fluid. The preferred working fluid is an organic Rankine cycle system working fluid comprising compounds having the following general structure:where x, y, z, and m are each selected from the group consisting of: fluorine, hydrogen, Rf, and R, wherein R and Rf are each an alkyl, aryl, or alkylaryl of 1 to 6 carbon atoms, and wherein Rf is partially or fully fluorinated.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
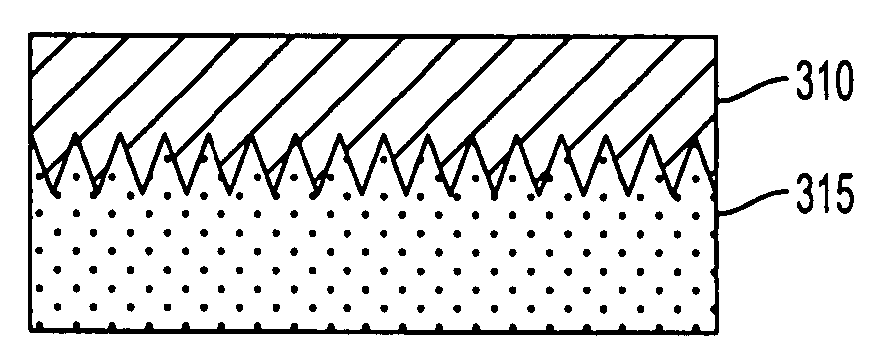
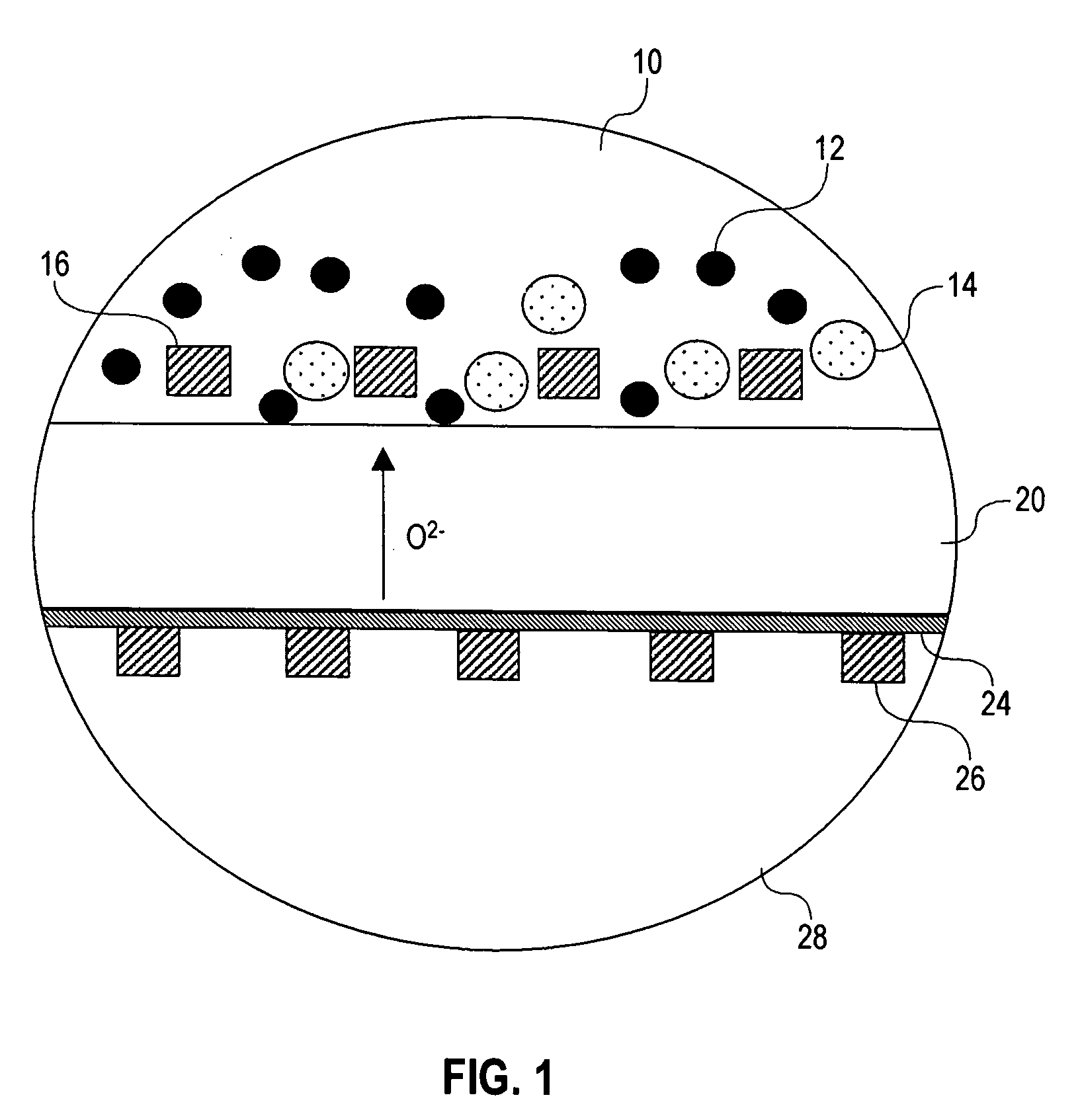
Textured electrolyte for a solid oxide fuel cell
ActiveUS7045237B2Decreases cost per wattImprove adhesionFuel cell heat exchangeFuel cells groupingFuel cellsMaterials science
A ceramic electrolyte for a solid oxide fuel cell includes at least one non-uniform surface portion. Preferably, the electrolyte surface is textured.
Owner:BLOOM ENERGY CORP
Method and apparatus for optimization of distributed generation
ActiveUS8019445B2Lower requirementLow rateElectrical storage systemBatteries circuit arrangementsThermal energyStored energy
An energy optimization method and control apparatus may be used in a single building or a group of buildings to optimize utility-supplied and renewable sources in order to minimize the total energy cost. Simultaneously, it may also produce and store energy, such as electricity or hydrogen, that can be used to fuel vehicles, provide a means for independent production of household energy needs, or both. Various factors, such as the production of thermal energy and electricity from the renewable sources, the current store of stored energy, the current and expected thermal and electricity requirements of the building (based on a profile), the current and expected electricity loads of the equipment used to process stored energy, the expected thermal and electricity generating capacity of the renewable sources and other factors can be used to determine the mix of renewable-based and utility-based energy that minimizes the total energy cost.
Owner:INTELLIGENT GENERATION
Textured electrolyte for a solid oxide fuel cell
ActiveUS20050074650A1Decreases cost per wattImprove adhesionFuel cell heat exchangeFuel cells groupingFuel cellsMaterials science
A ceramic electrolyte for a solid oxide fuel cell includes at least one non-uniform surface portion. Preferably, the electrolyte surface is textured.
Owner:BLOOM ENERGY CORP
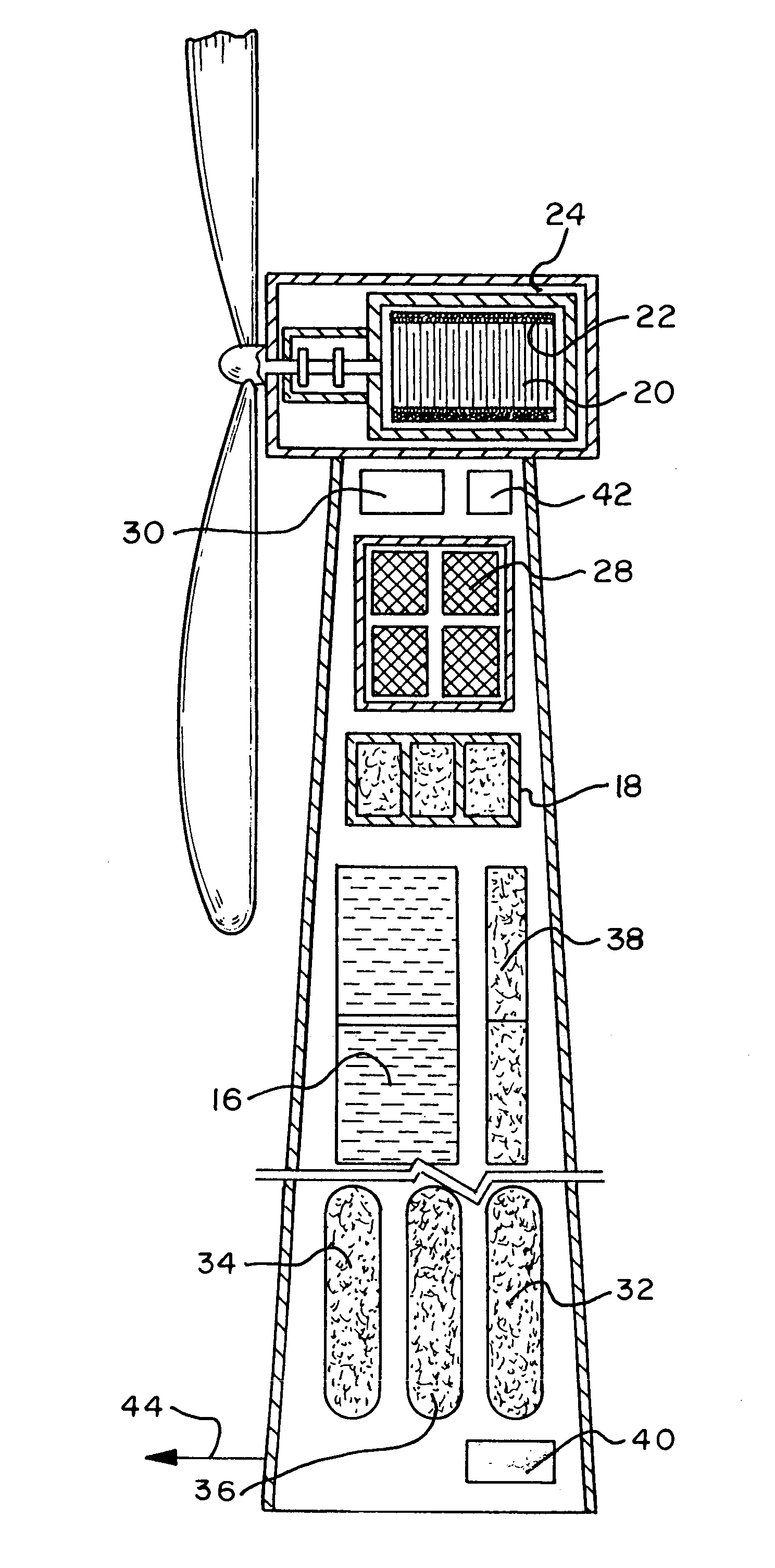
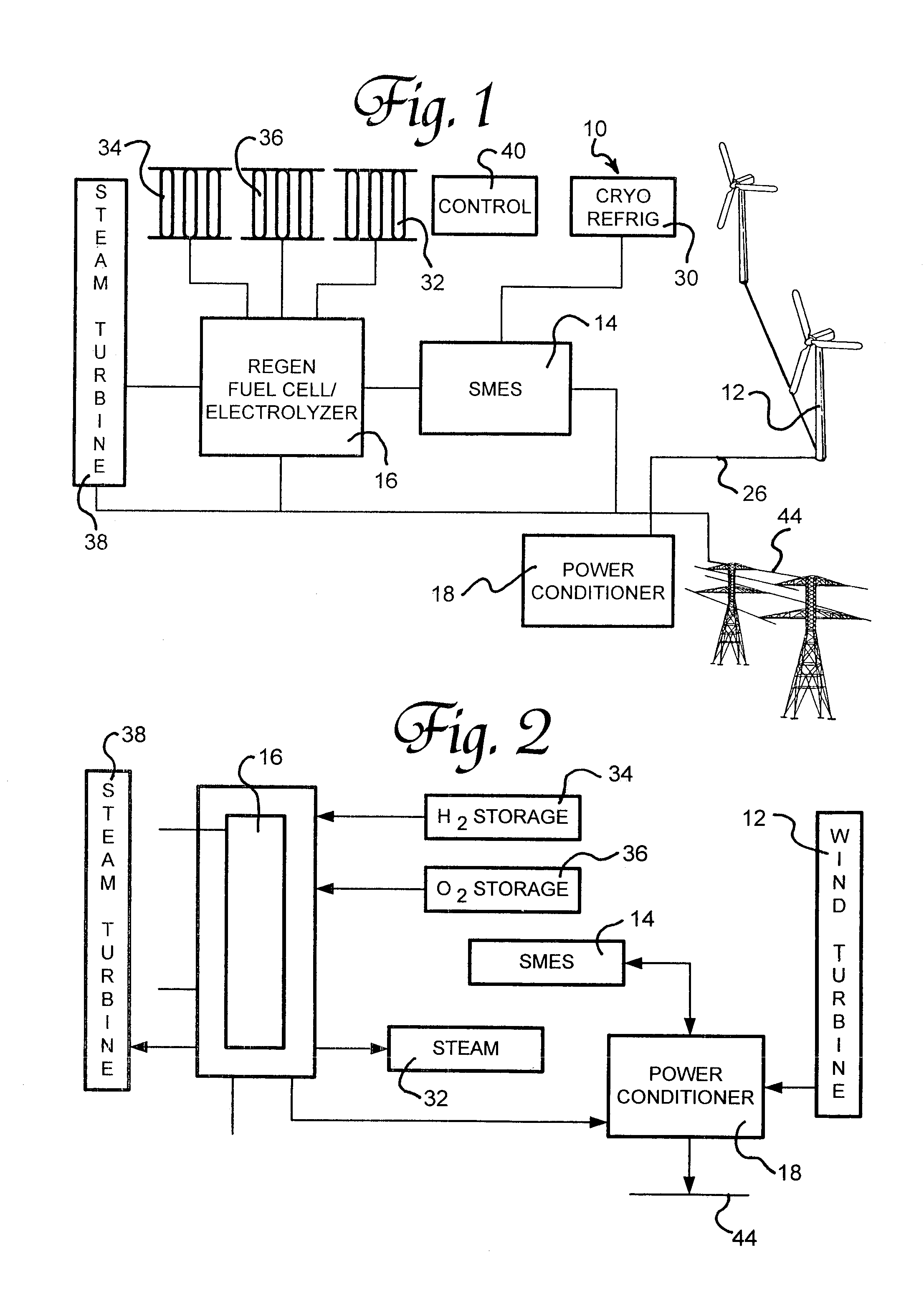
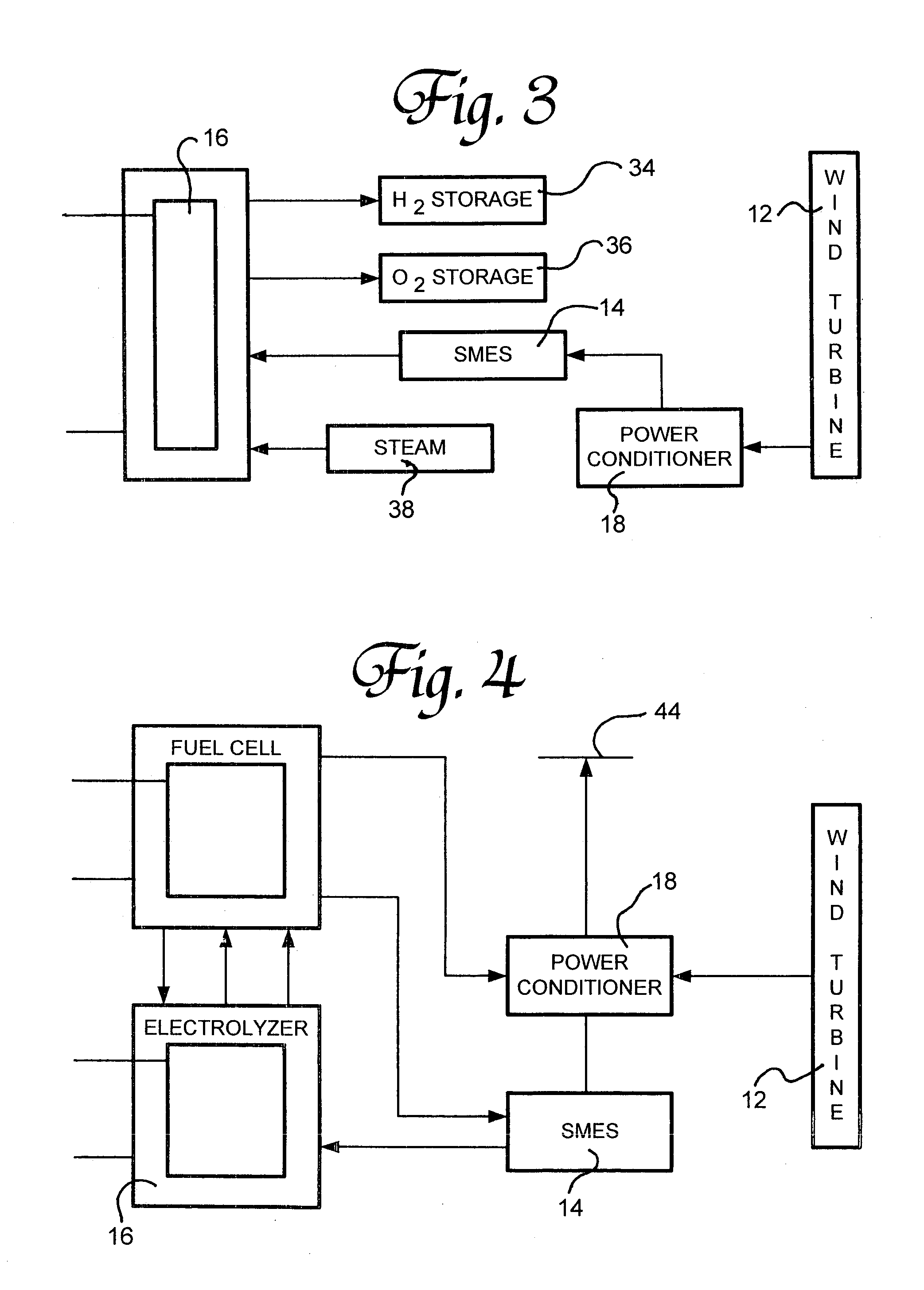
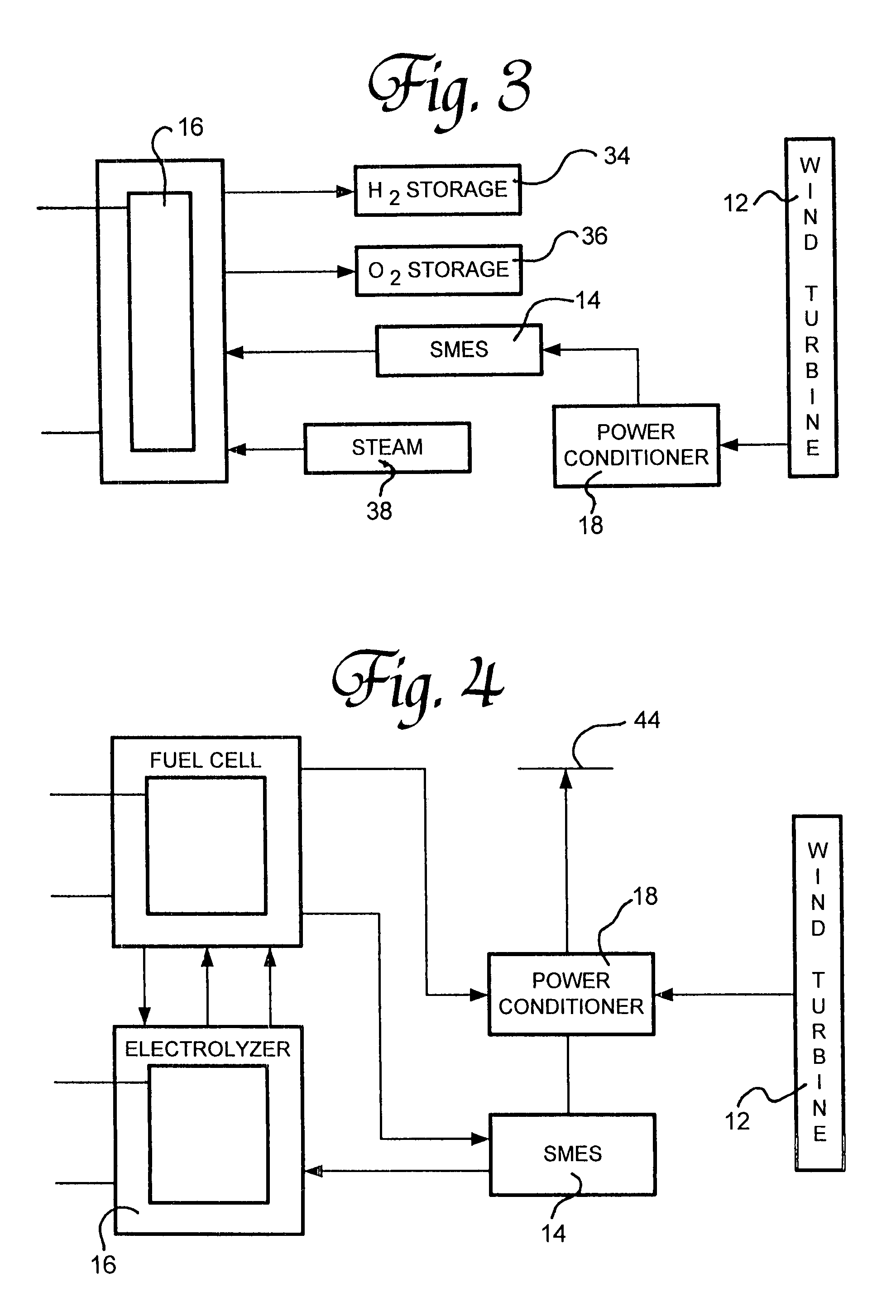
Renewable energy electric power generating system
InactiveUS7233079B1Large capacityEasy to useMachines/enginesWind energy generationElectrolysisMagnetic storage
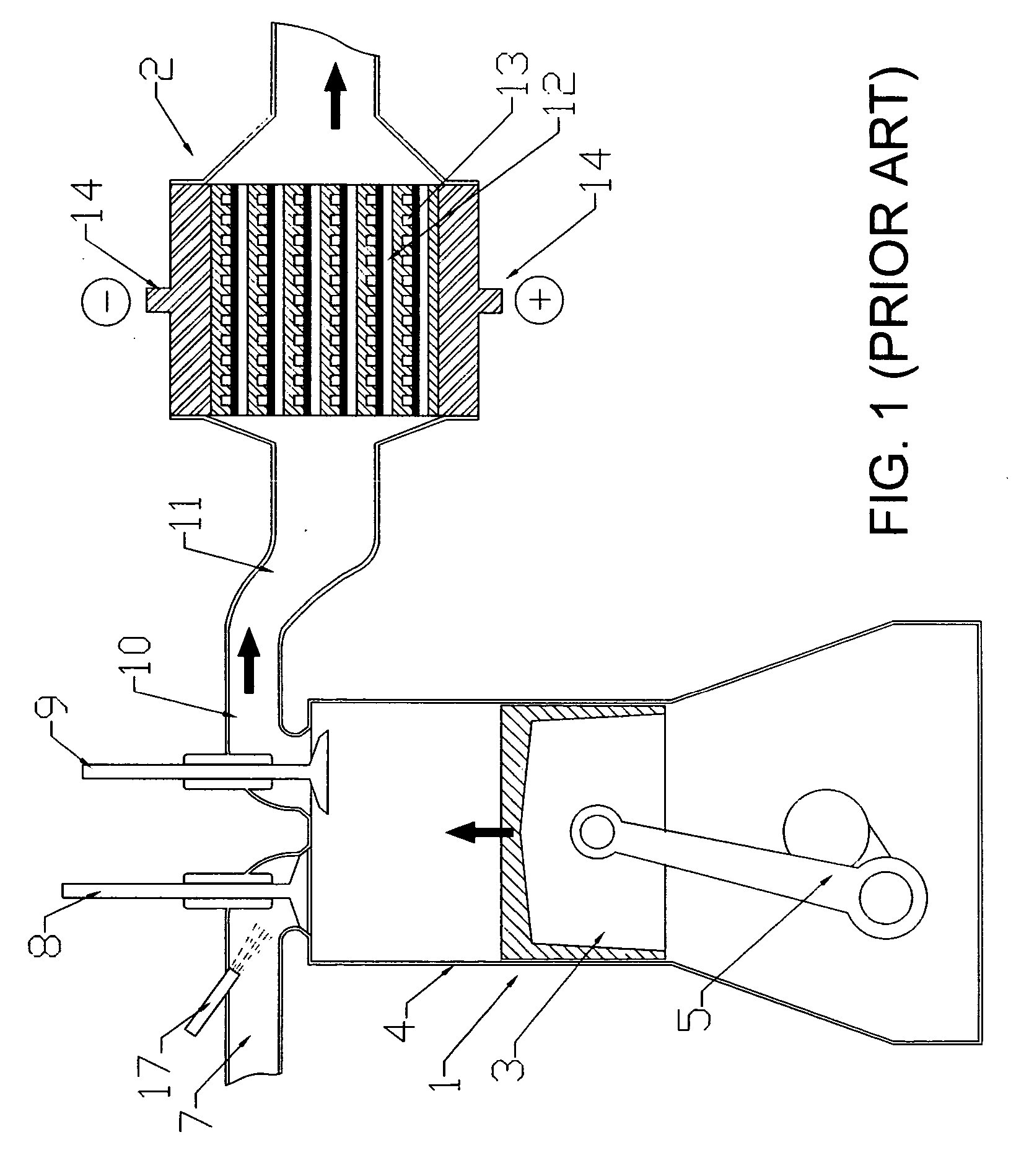
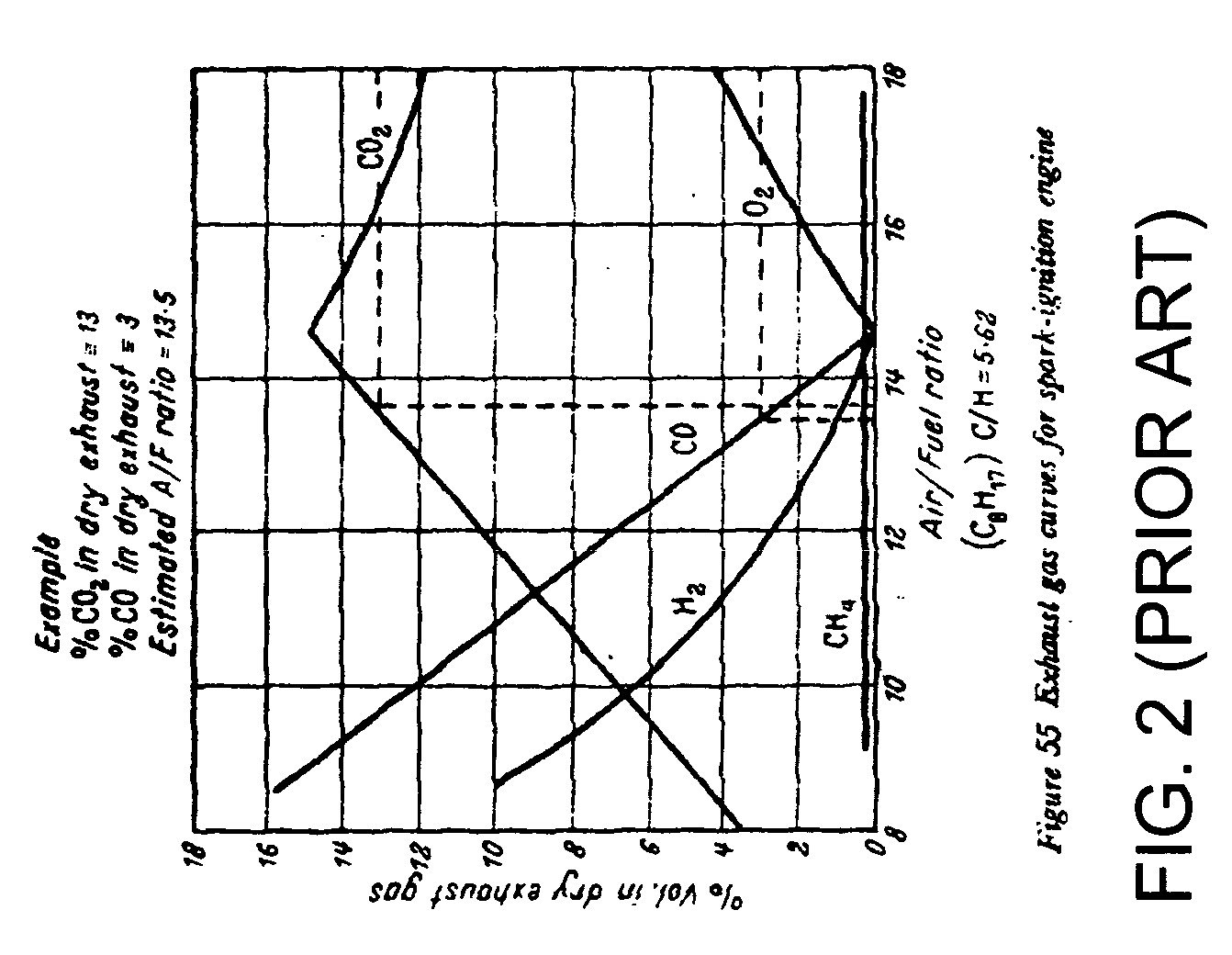
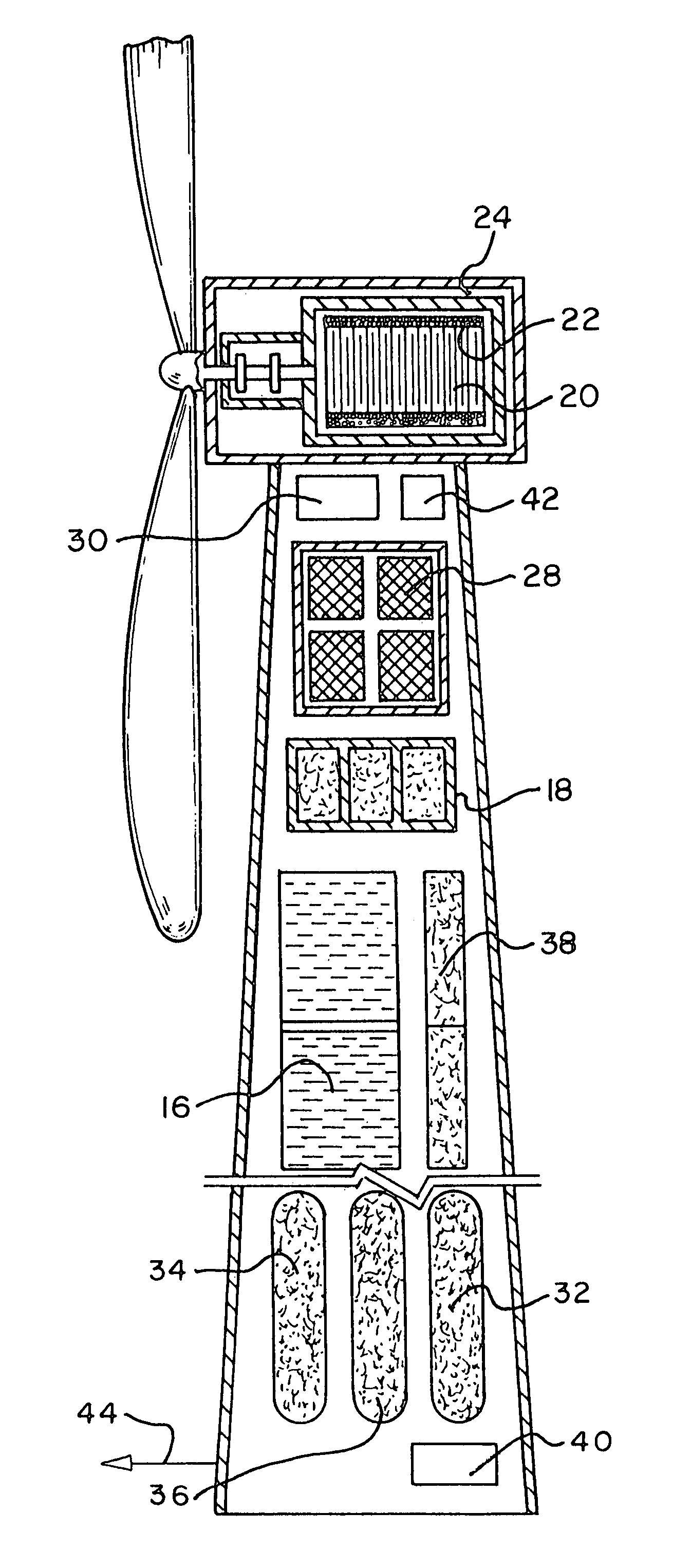
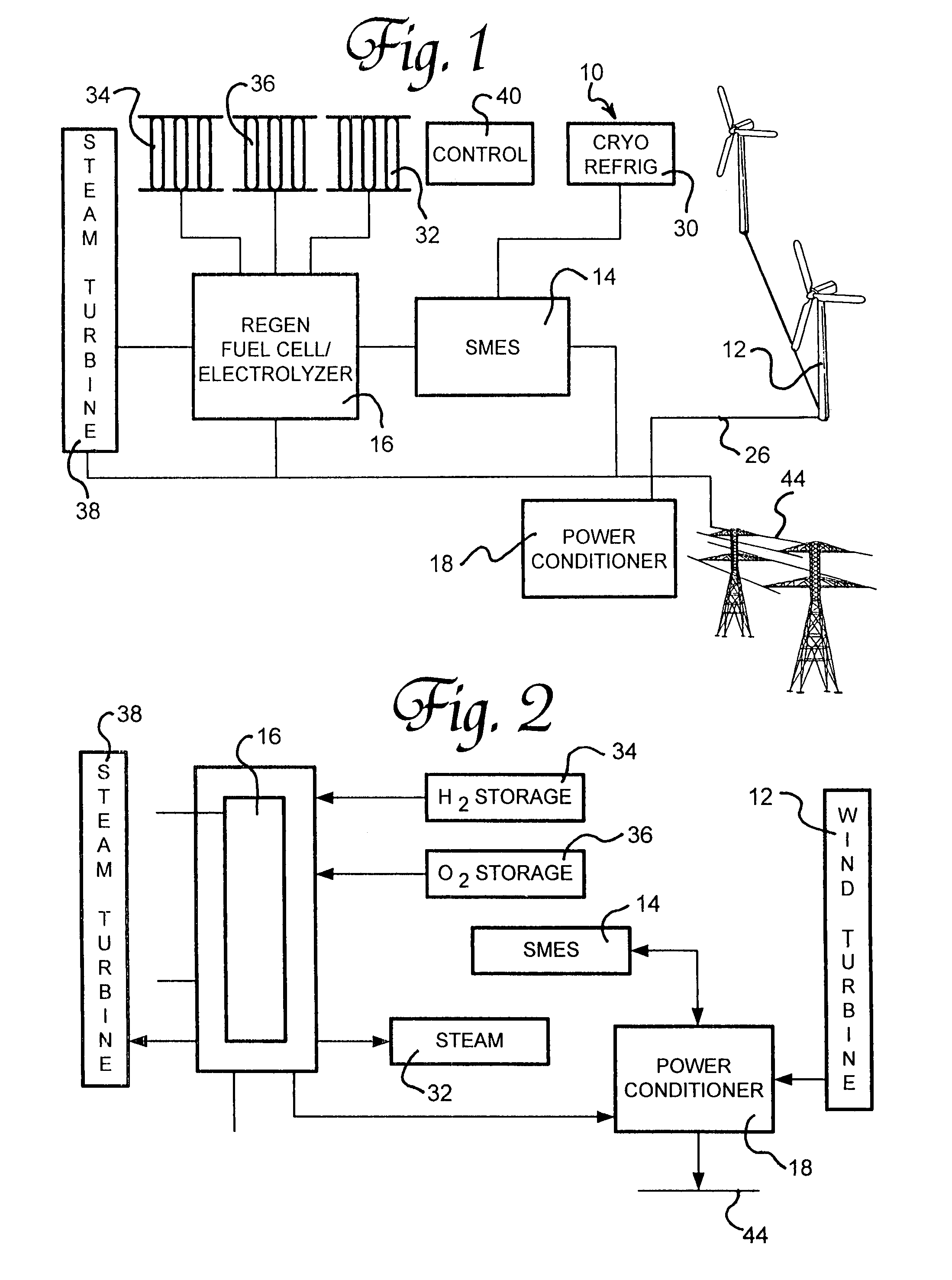
A renewable electric power system includes a high temperature superconducting wind turbine using high temperature superconducting yttrium-barium-copper oxide for the rotor and stator windings as well as a superconducting bearing. Power from the turbine is stored in a high temperature superconducting magnetic storage system that also uses HTS YBCO. Also included is a regenerative solid oxide fuel cell / electrolyzer with steam turbine cogeneration. The system operates on a managed day / night cycle. During daytime, the energy produced by the wind turbines and fuel cells is transmitted to the grid. During nocturnal hours, the wind turbine is used to provide low cost electricity to the reversible fuel cells operating in the electrolysis mode producing hydrogen and oxygen that is stored for later use. Alternatively, the fuel cells can remain in electrolysis mode producing hydrogen and oxygen for the market. A modified interactive system generates power on a continuous twenty-four hour cycle.
Owner:COOPER WILLARD
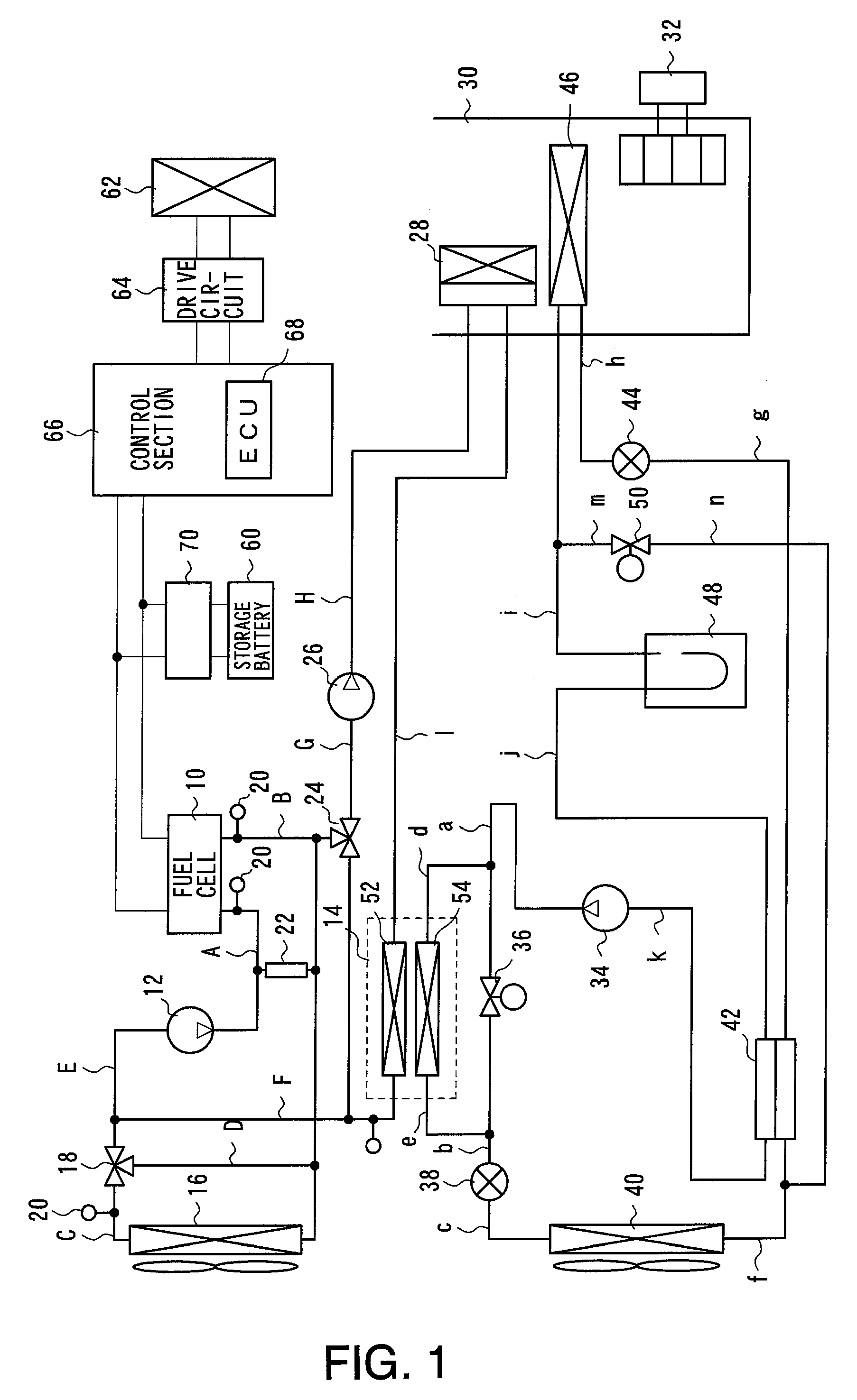
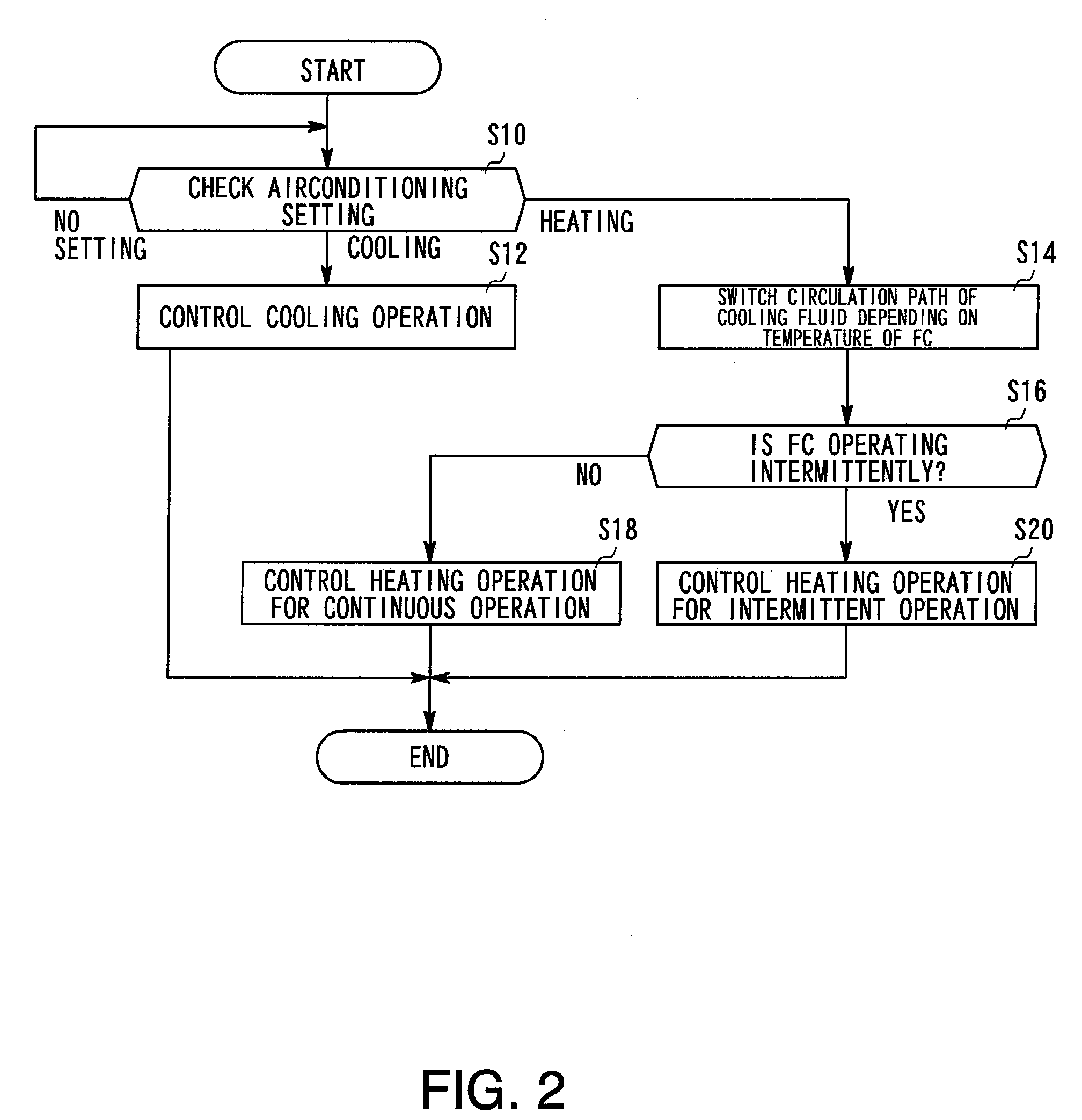
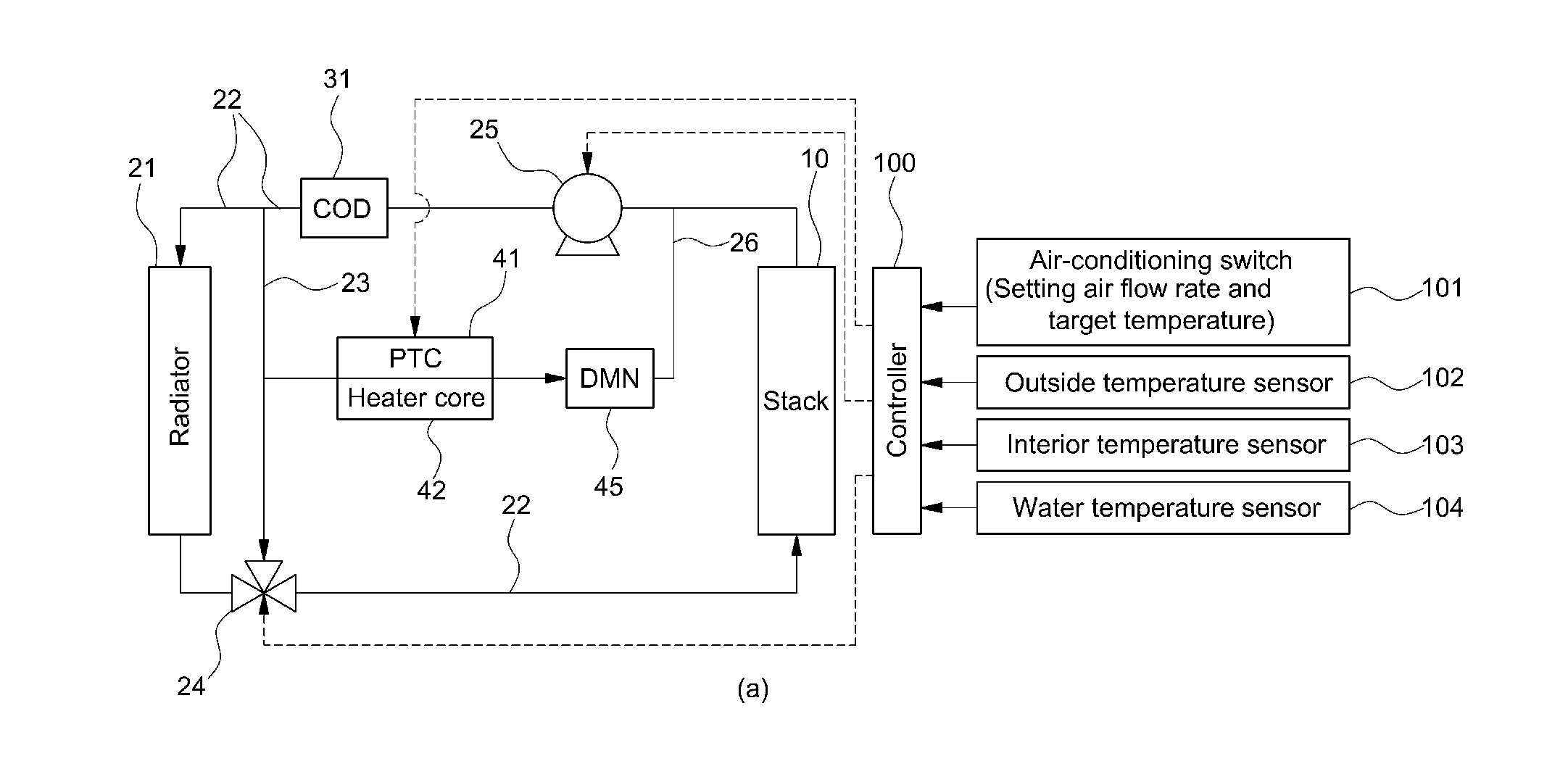
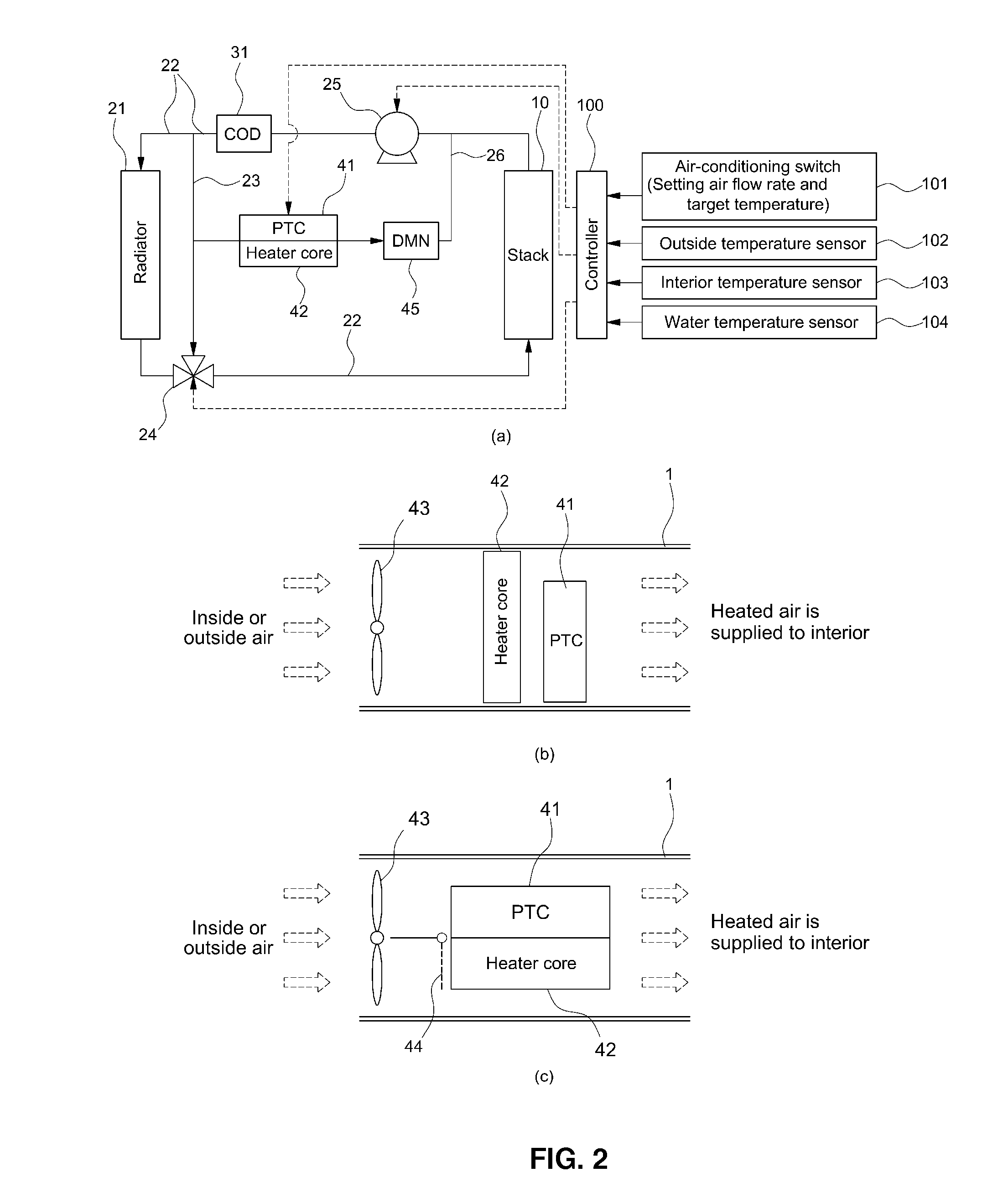
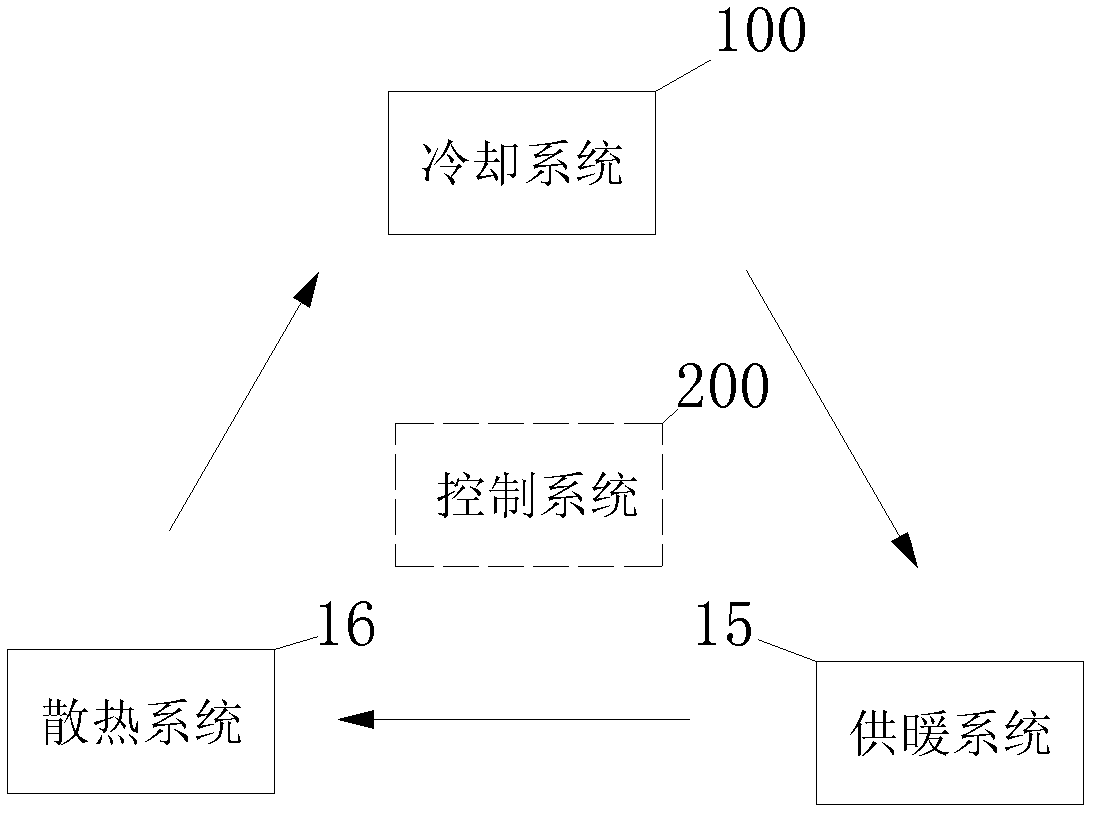
Air conditioning control system
An air conditioning control system having a cooling device for cooling a fuel cell by circulating a liquid coolant through the fuel cell using a main circulation pump while also providing an air conditioning control device for controlling air conditioning in a vehicle interior, wherein heat exchange between the cooling device and the air conditioning control device is possible. When the fuel cell is operated intermittently in the air conditioning control system, the main circulation pump is continuously operated.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Thermally efficient micromachined device
InactiveUS6939632B2Less energyFlow mixersFixed microstructural devicesFuel cellsCompound (substance)
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
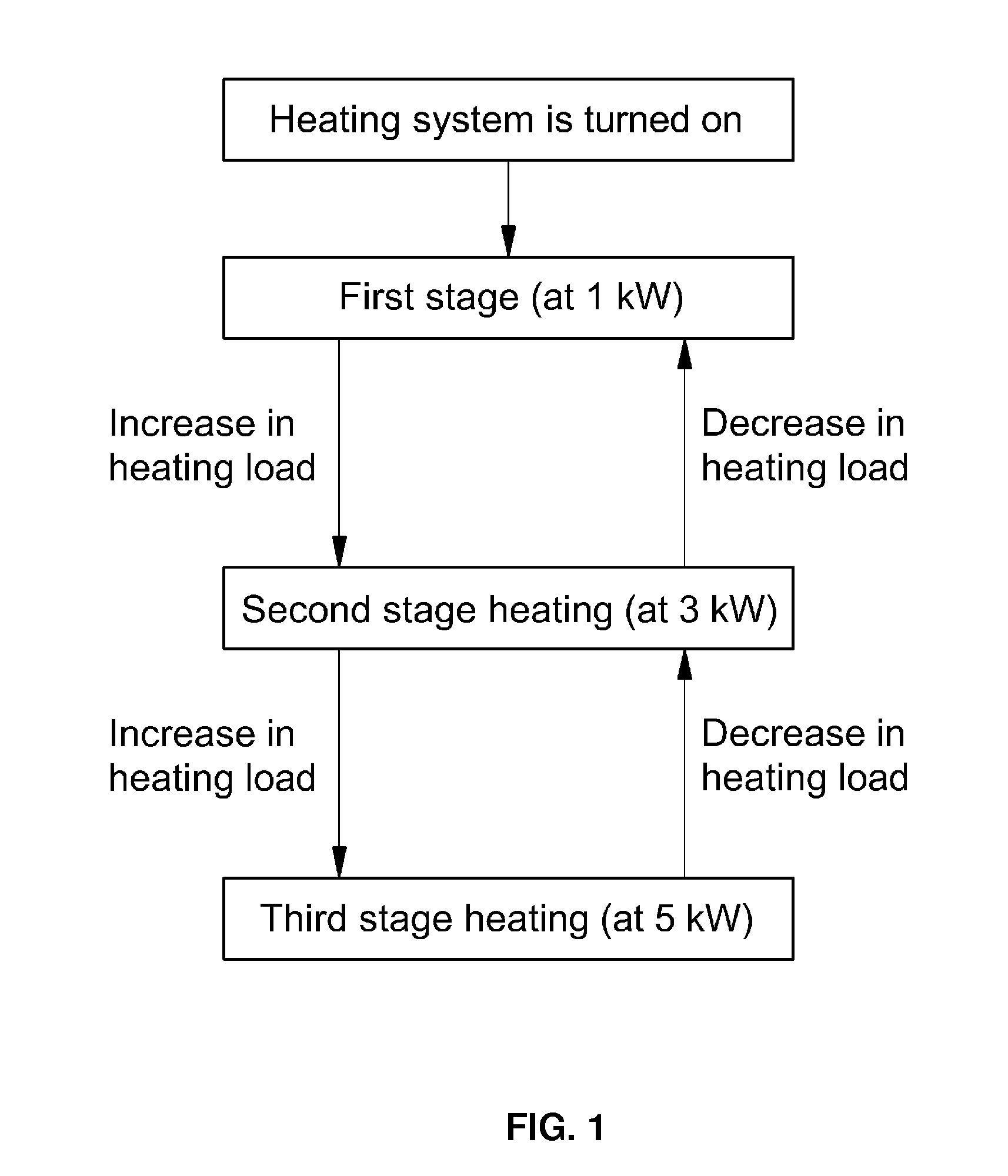
Heating control method for fuel cell vehicle
ActiveUS20120122000A1Reduce power consumptionImprove fuel efficiencyAir-treating devicesFuel cell auxillariesLower limitFuel cells
The present invention provides a heating control method for a fuel cell vehicle, in which an additional heating source is used together with a typical electric heater to reduce power consumption and increase fuel efficiency as compared to the sole use of the electric heater. For this purpose, the present invention provides a heating control method for a fuel cell vehicle which comprises an electric heater for heating air supplied to the interior of the vehicle, and a heater core provided in a coolant line for cooling a fuel cell stack and heating the air supplied to the interior of the vehicle by heat exchange with the coolant discharged from the fuel cell stack. The method comprises: detecting a state of charge (SOC) of a battery when the interior temperature is lower than a predetermined temperature set by a driver and, if the SOC of the battery is above a predetermined lower limit, heating the interior of the vehicle by operating the electric heater by the power of a battery; heating the interior of the vehicle by operating the electric heater by the power generated by the fuel cell stack, if the SOC of the battery is below the lower limit; heating the interior of the vehicle using both the heater core and the electric heater, if the temperature of the coolant is above a predetermined temperature at which the fuel cell stack does not reach a normal operating temperature; and heating the interior of the vehicle using only the heater core while turning off the electric heater, if the temperature of the coolant is increased above a normal operating temperature of the fuel cell stack.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
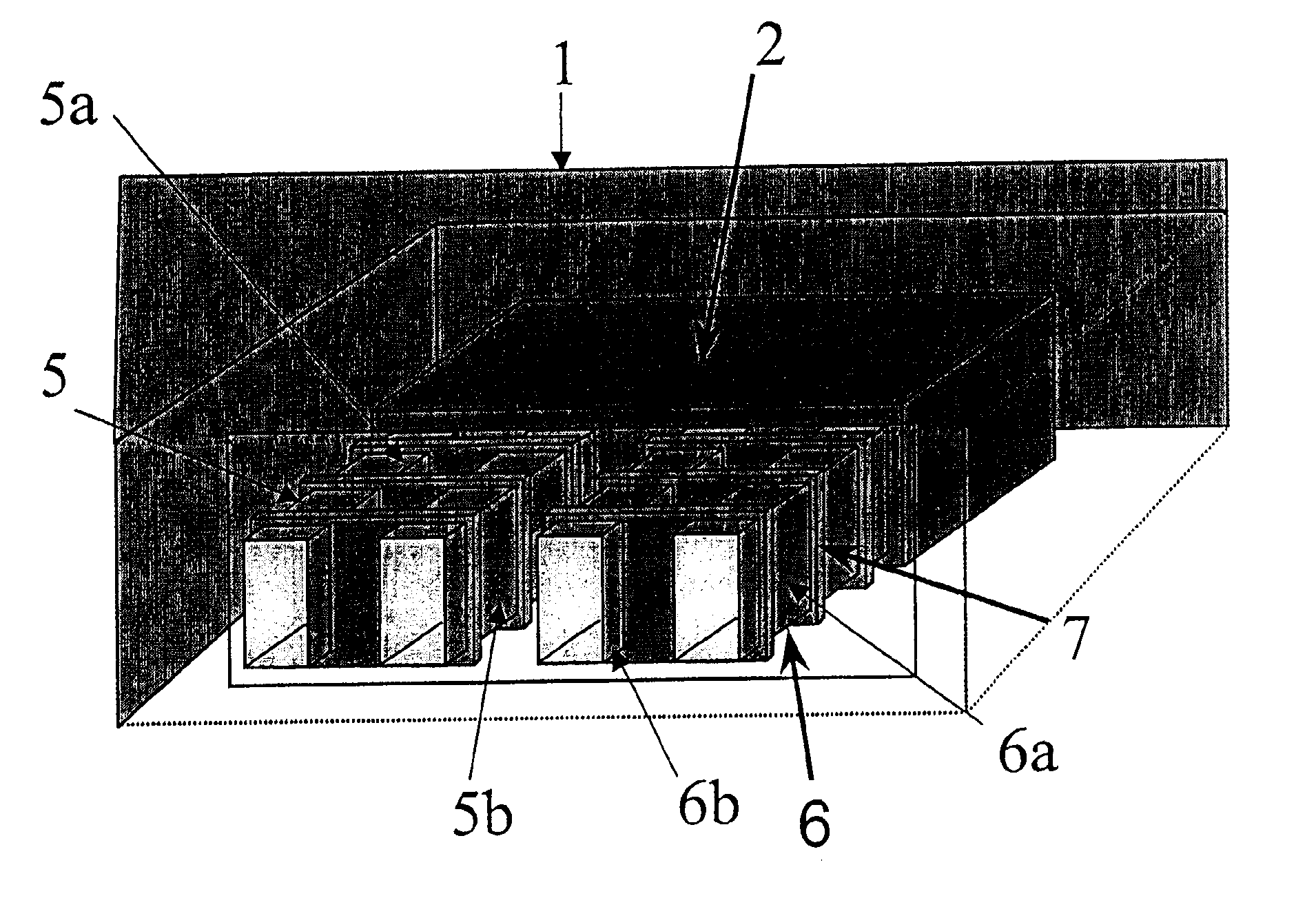
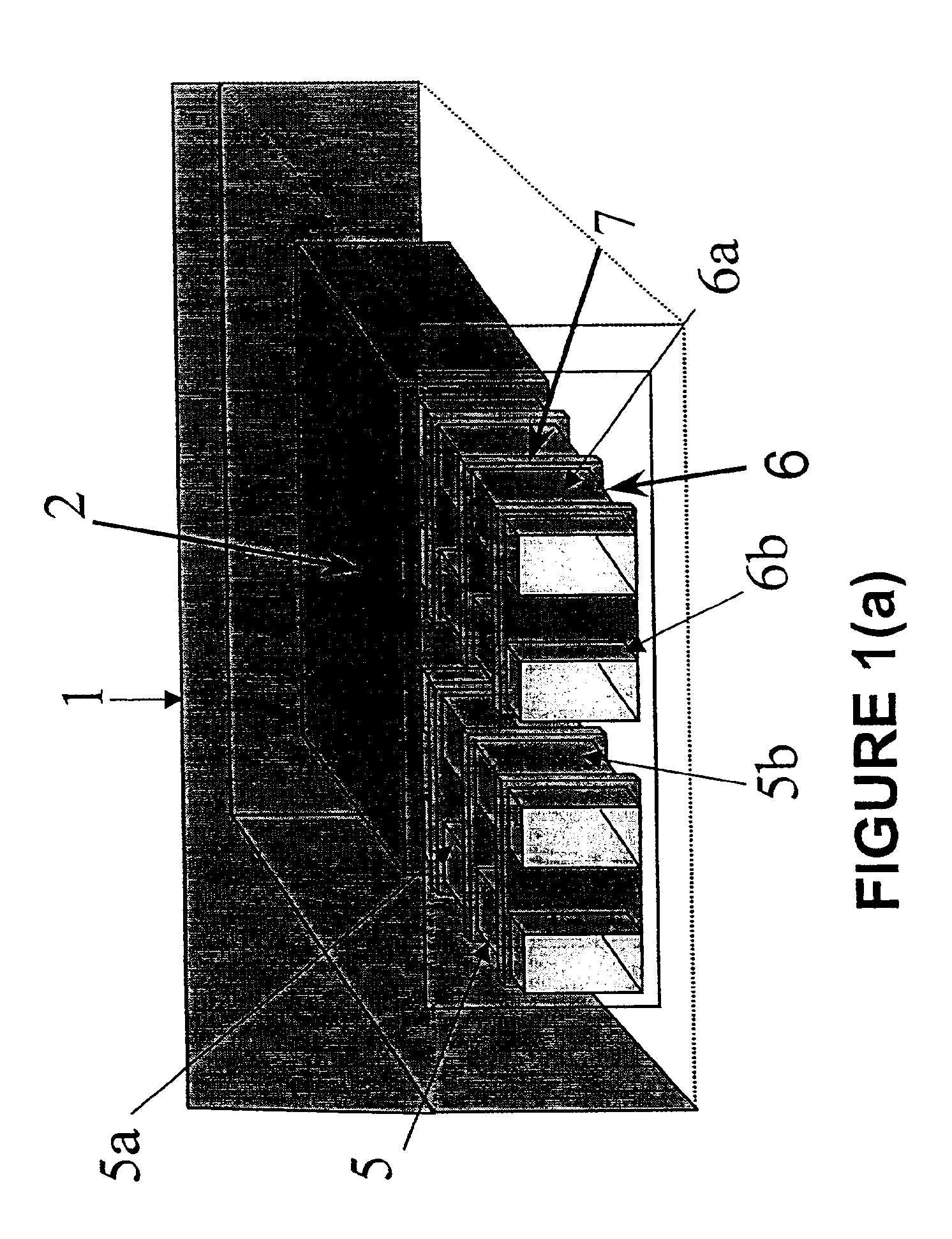
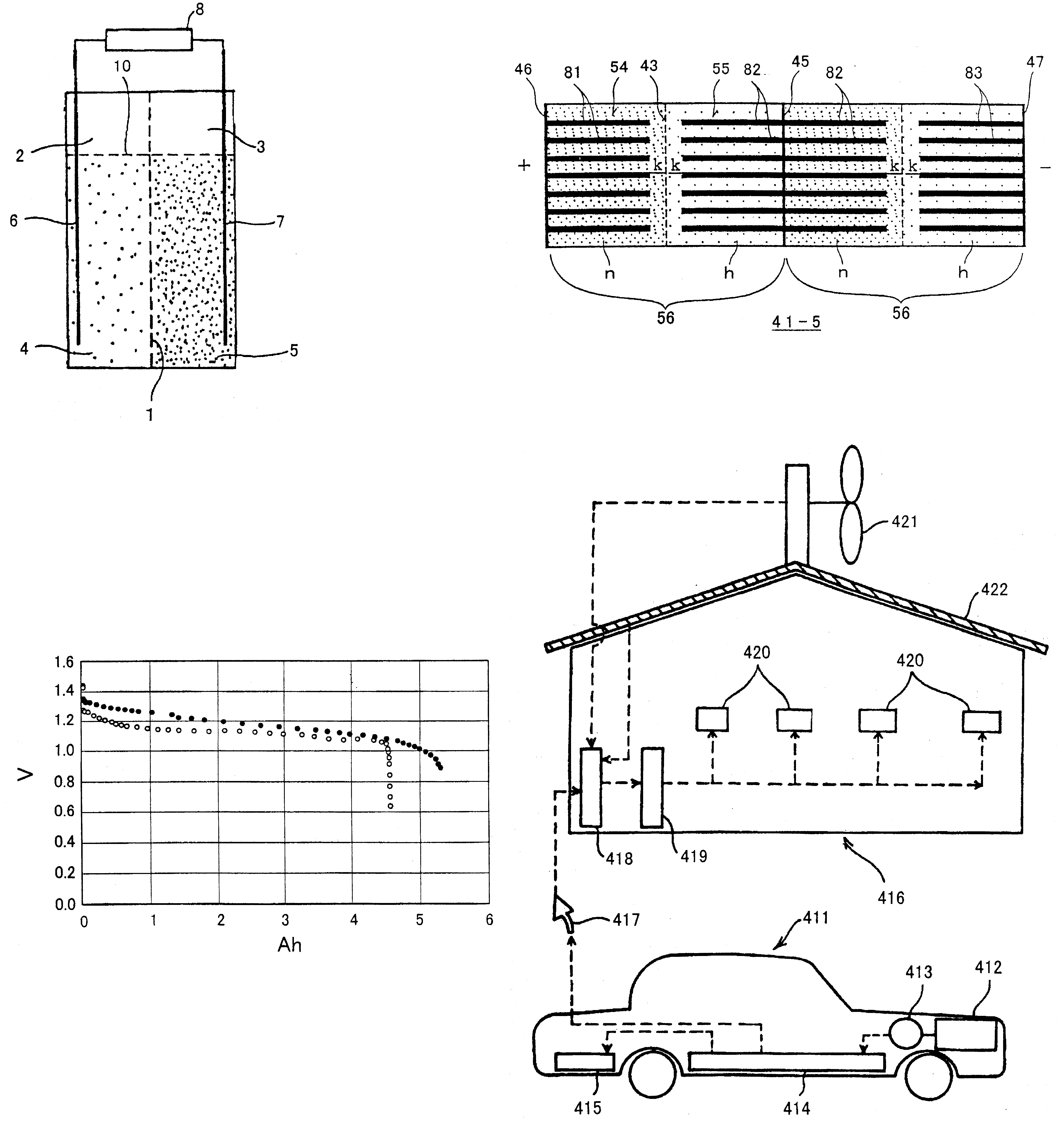
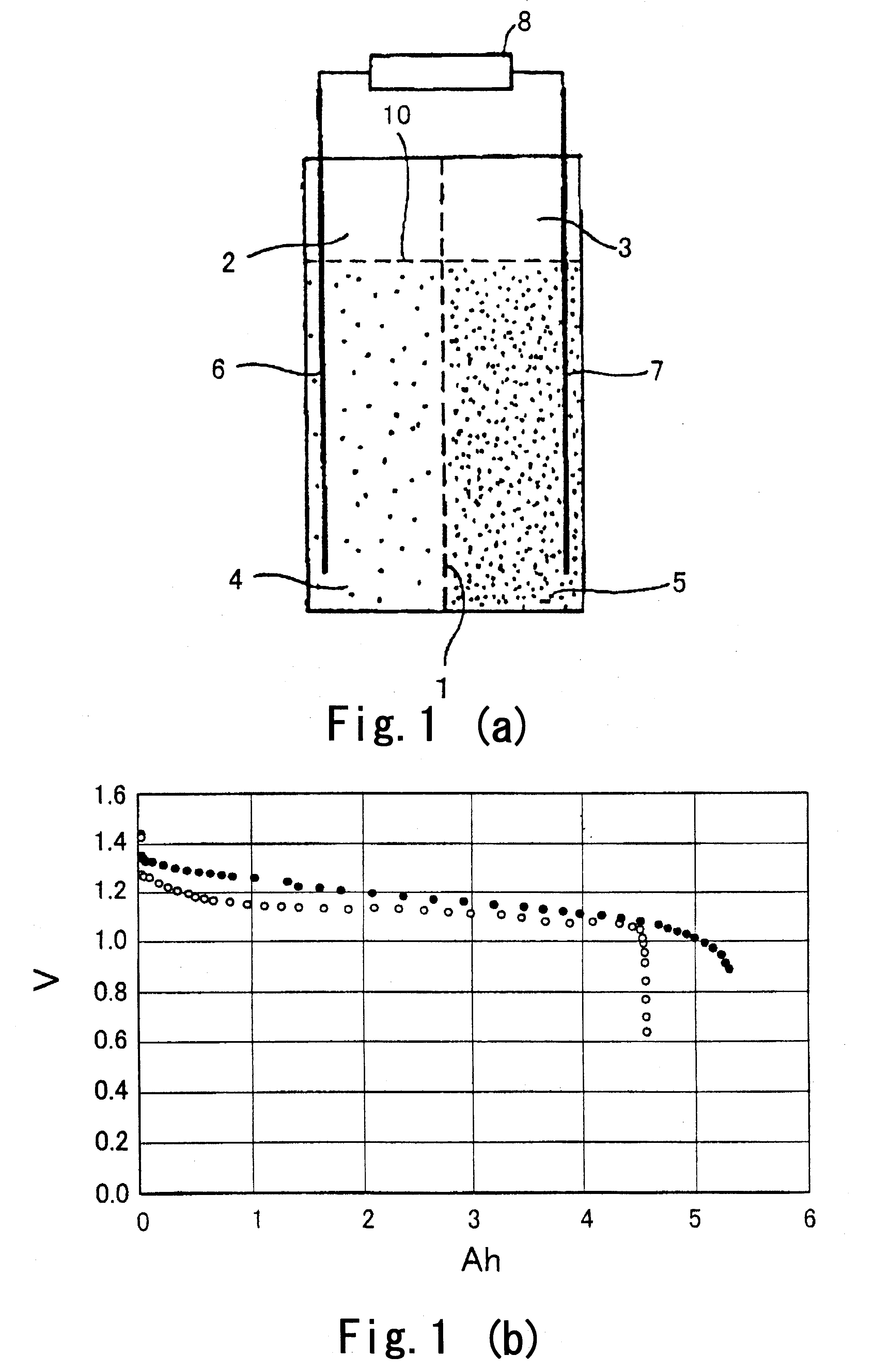
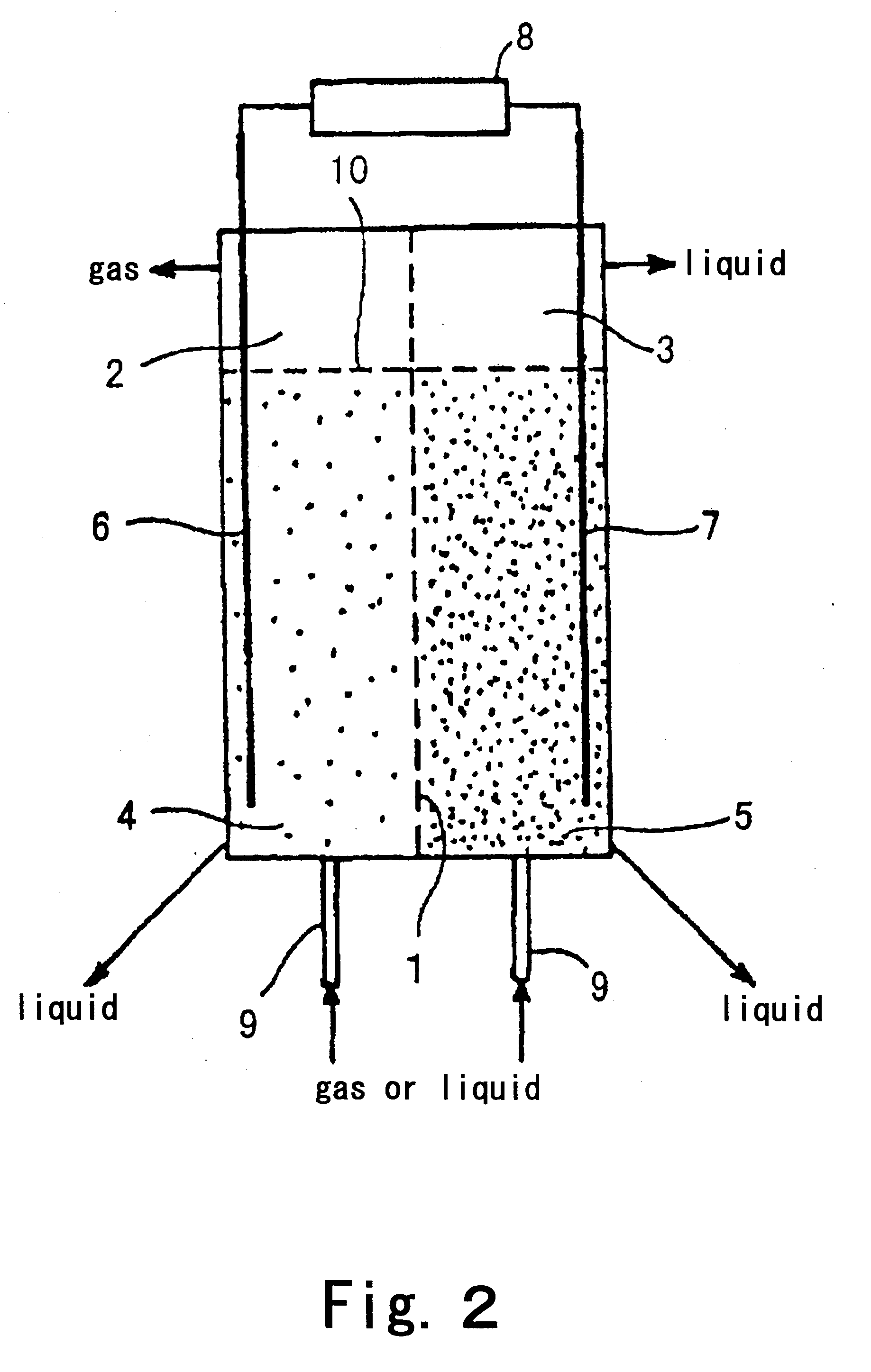
Battery and equipment or device having the battery as part of structure and locally distributed power generation method and power generation device therefor
A battery comprising powdered active materials and capable of storing a large power, and equipment or device having the battery as parts of its structure, wherein an anode cell (2) of two vessels connected via an ion-passing separator (1) is filled with an anode powdered active material and an electrolytic solution (4), a cathode cell (3) is filled with a cathode powdered active material and an electrolytic solution (5) and conductive current collectors (6, 7) in contact with the powdered active materials are provided in the two vessels.
Owner:KAWASAKI HEAVY IND LTD
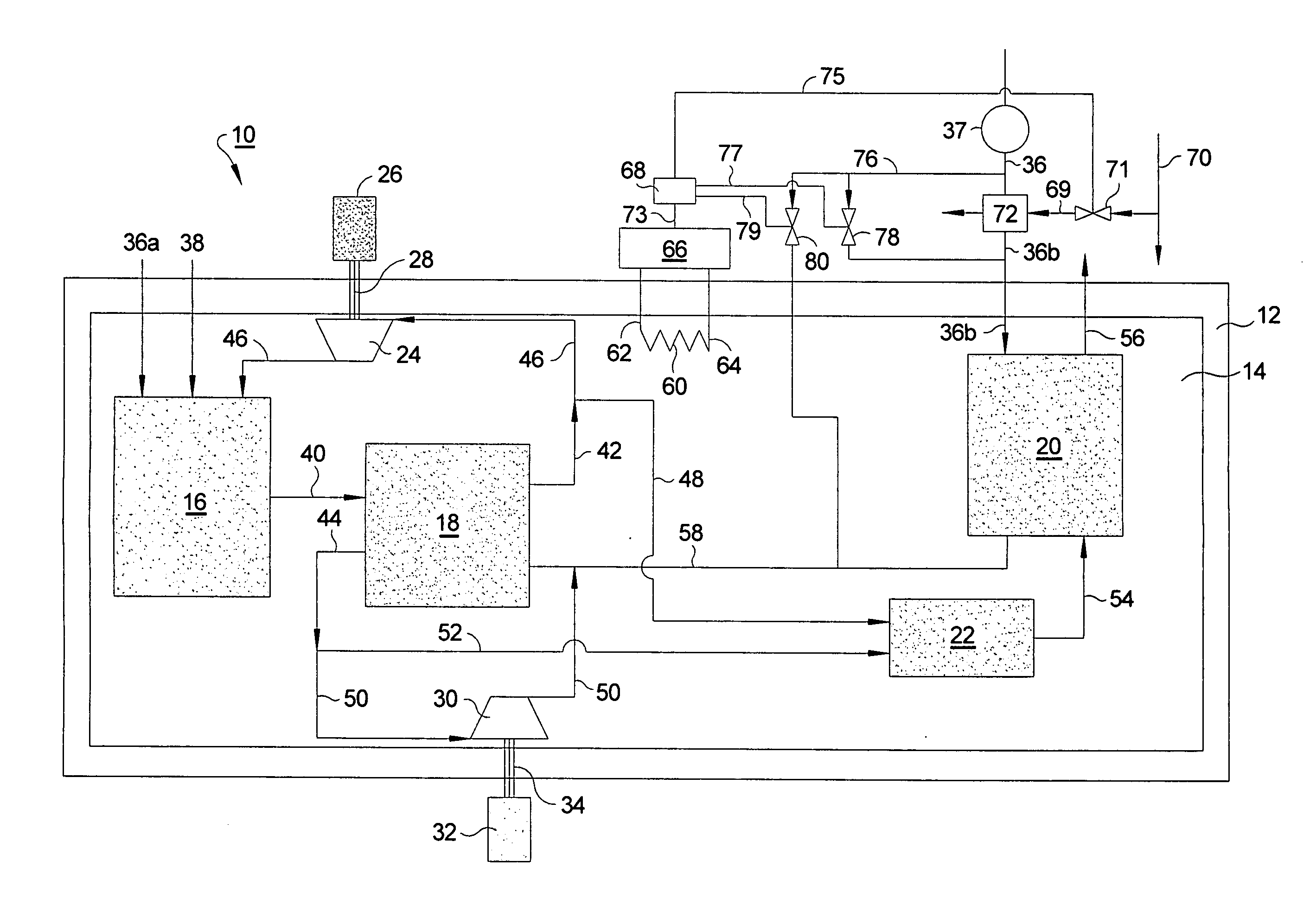
Combined heat and power system
InactiveUS20060199051A1Improve robustnessImprove reliabilityFuel cell heat exchangeFuel cells groupingHydrocotyle bowlesioidesCogeneration
There is described a combined heat and power, or cogeneration, system combining a fuel cell for generating electrical power with a thermal power source, the system comprising: a fuel processor for converting a hydrocarbon fuel into hydrogen in an output stream, the hydrogen rich output stream containing a low content of carbon monoxide; a high temperature hydrogen fuel cell system tolerant to low content of carbon monoxide of up to 5% receiving the output stream and an oxidant fluid stream; and a heat exchange system having a first module associated with the fuel processor and a second module associated with the fuel cell system connected at least in part in series to provide a thermal output.
Owner:HYTEON
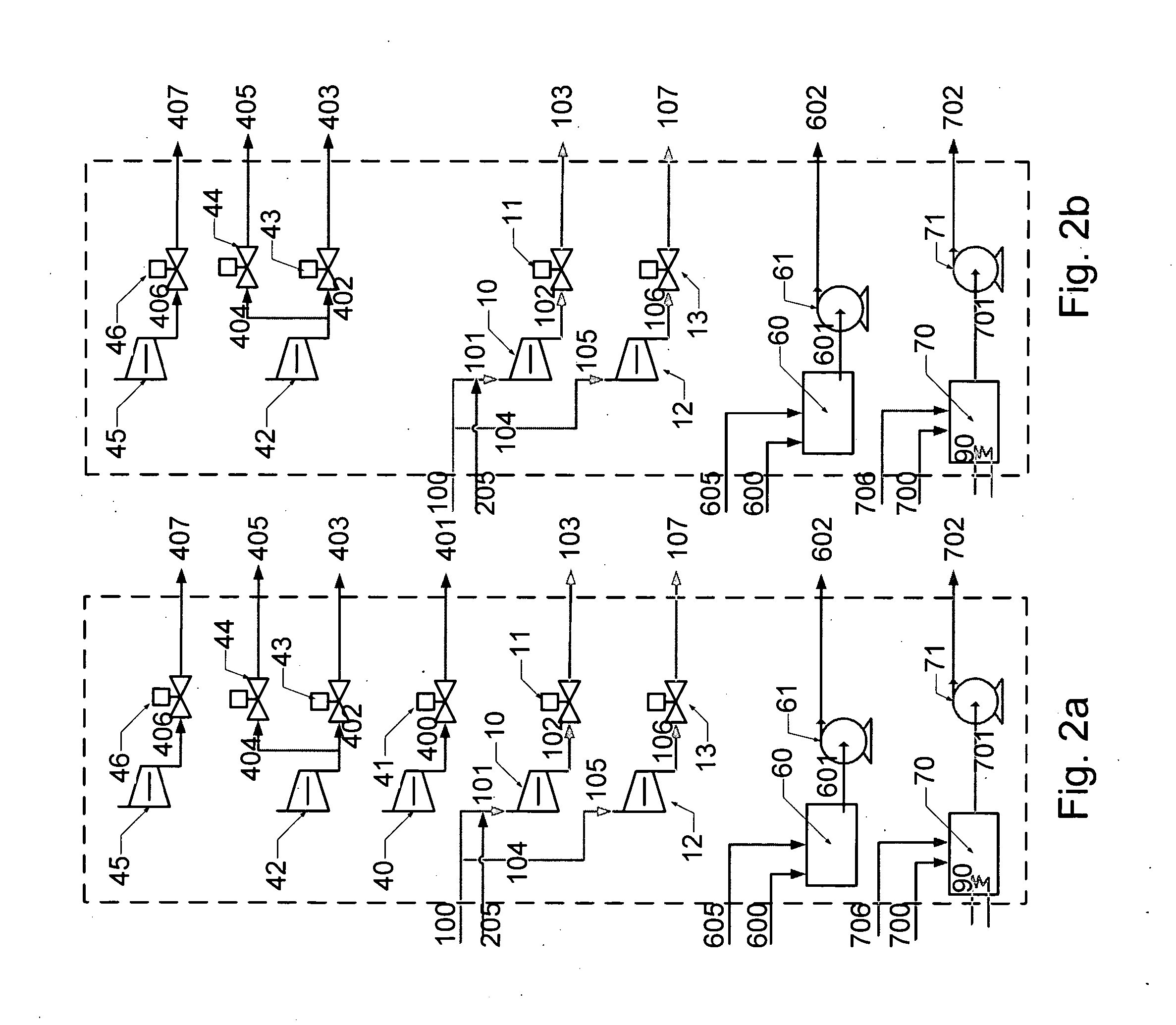
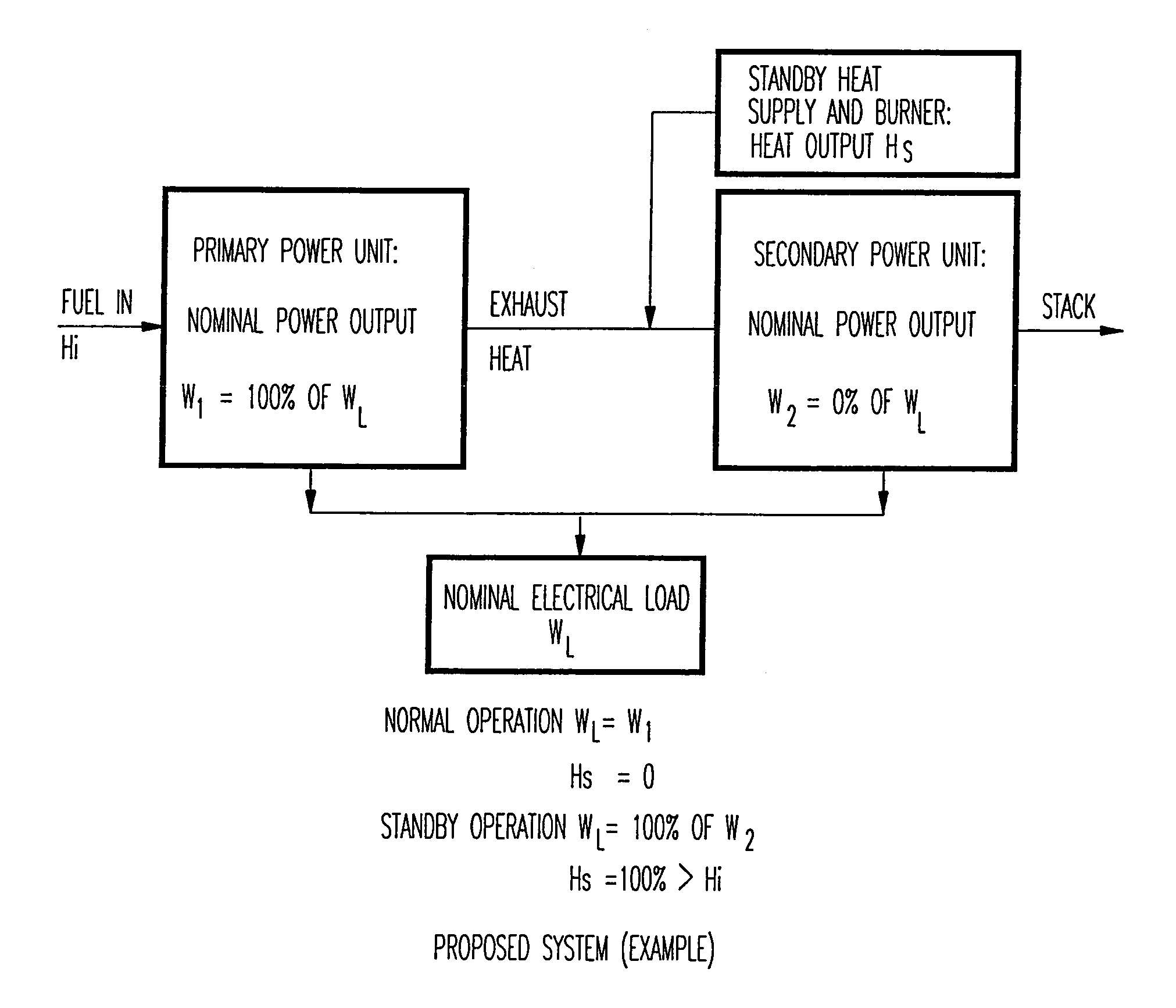
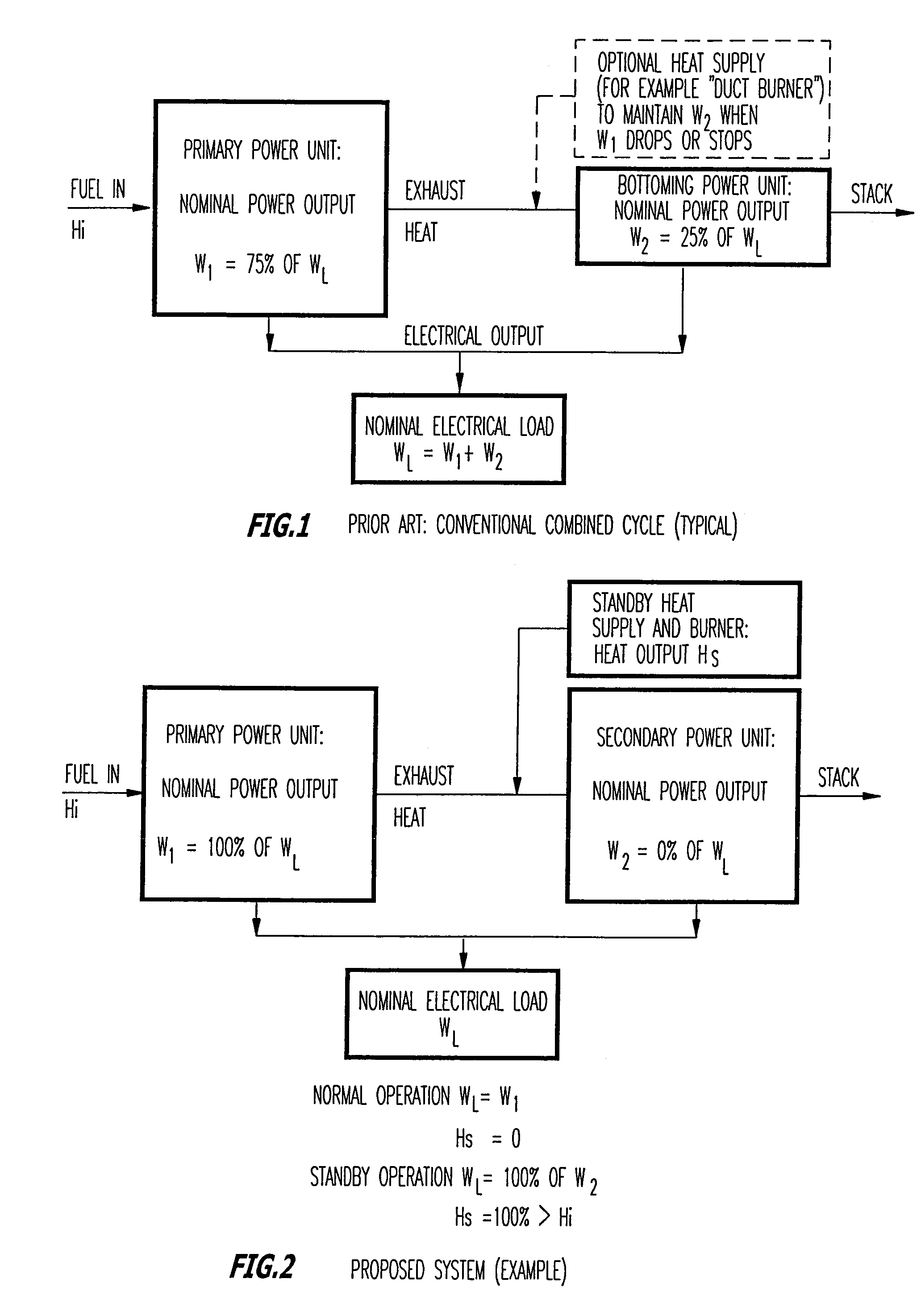
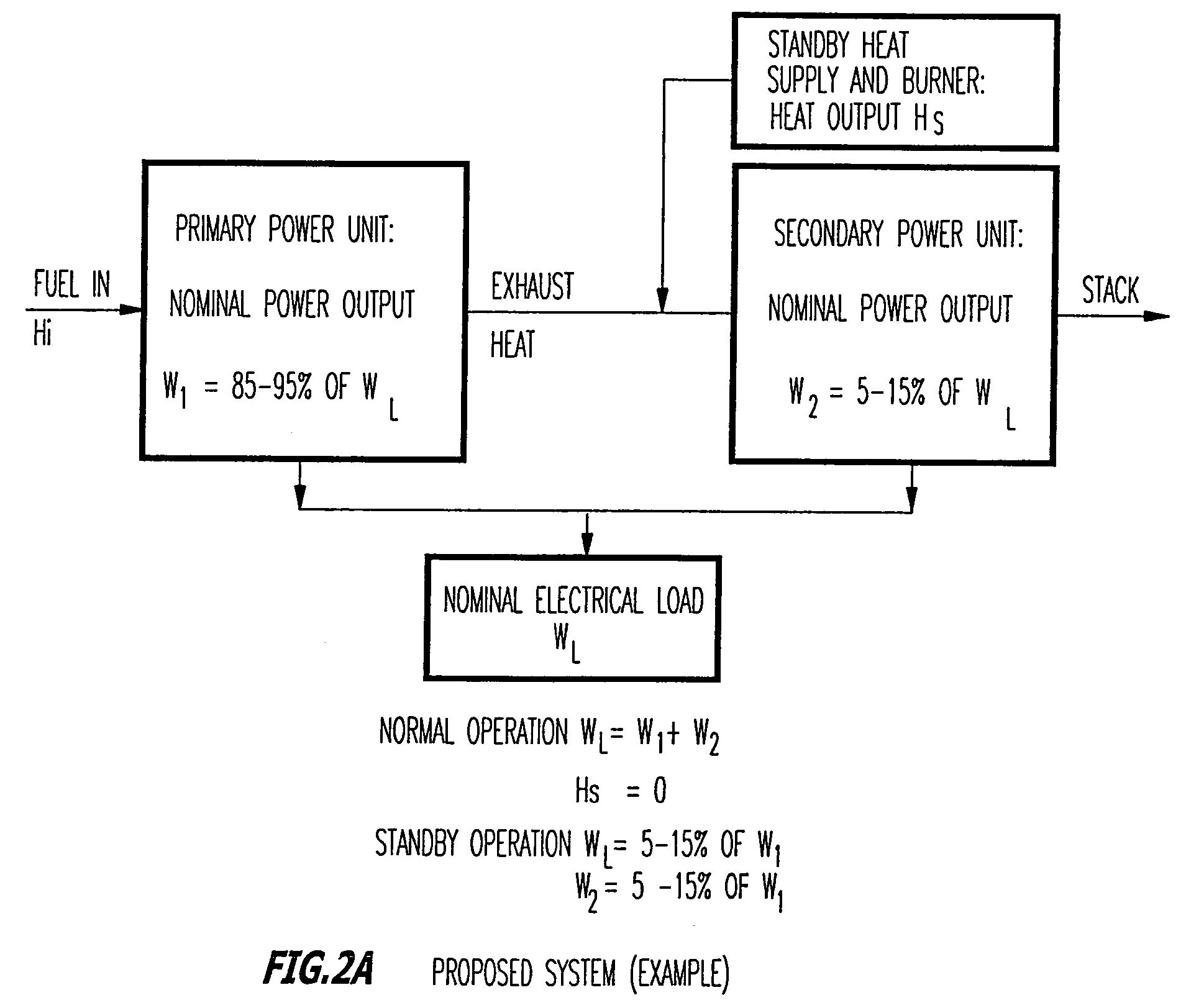
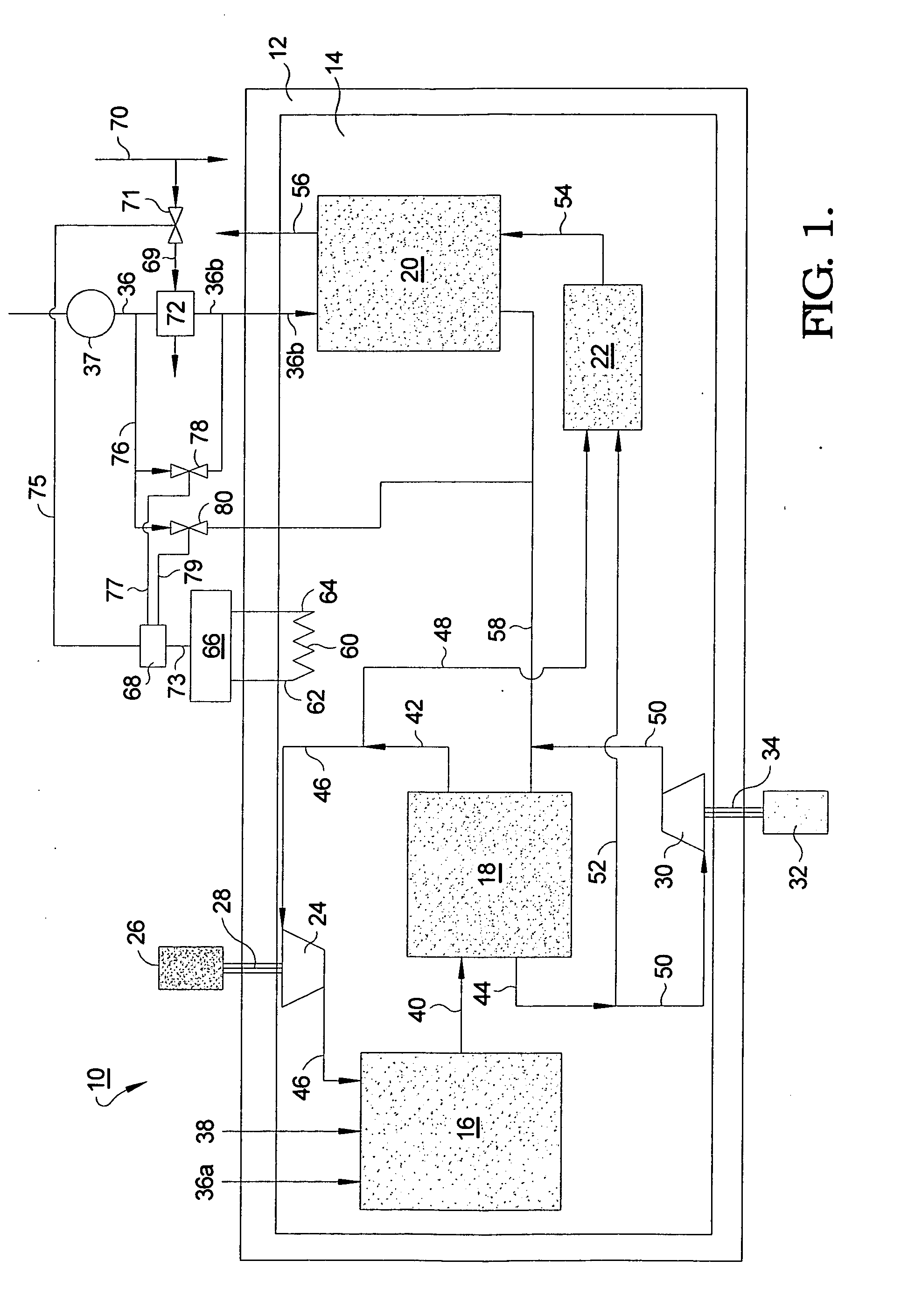
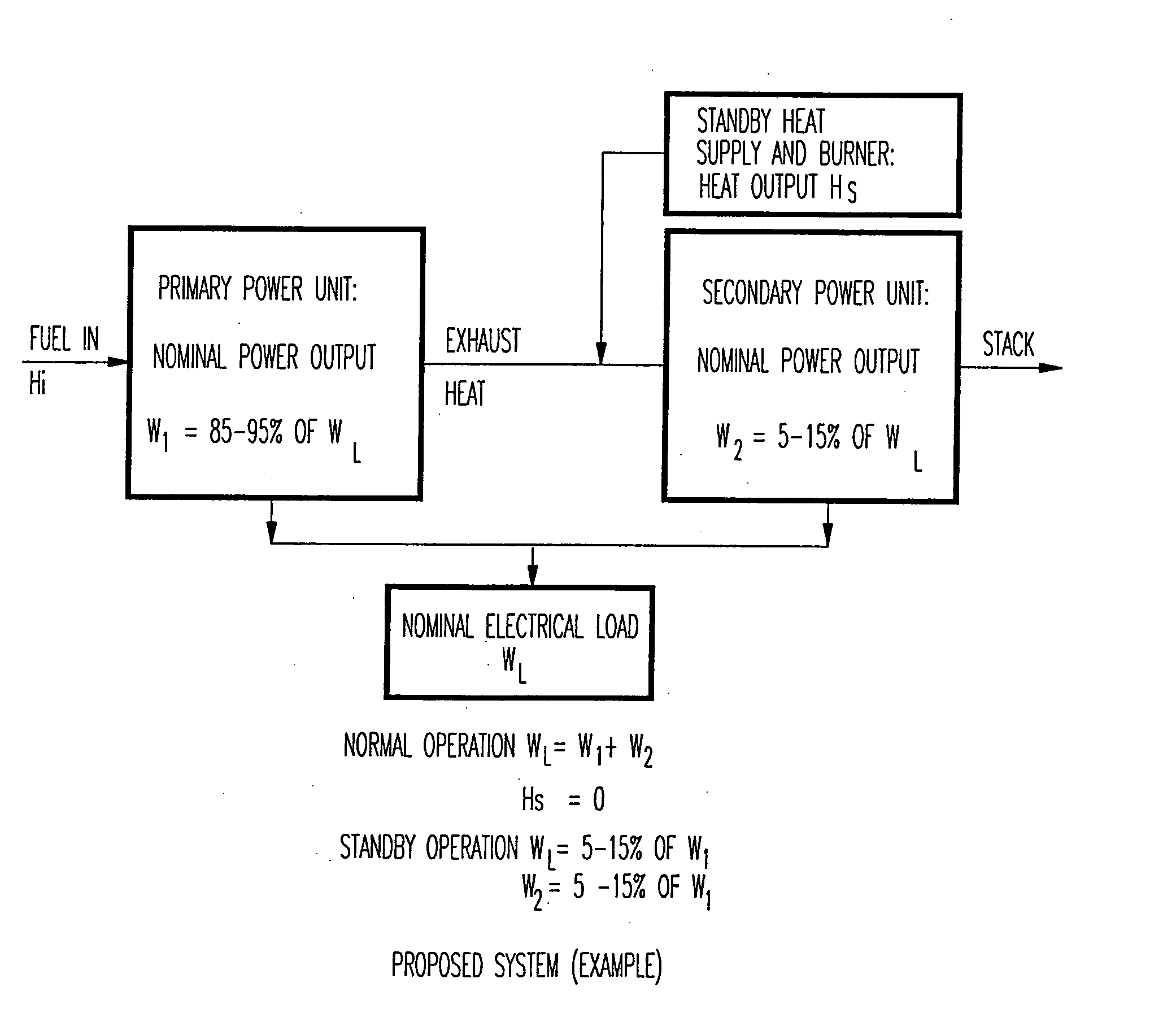
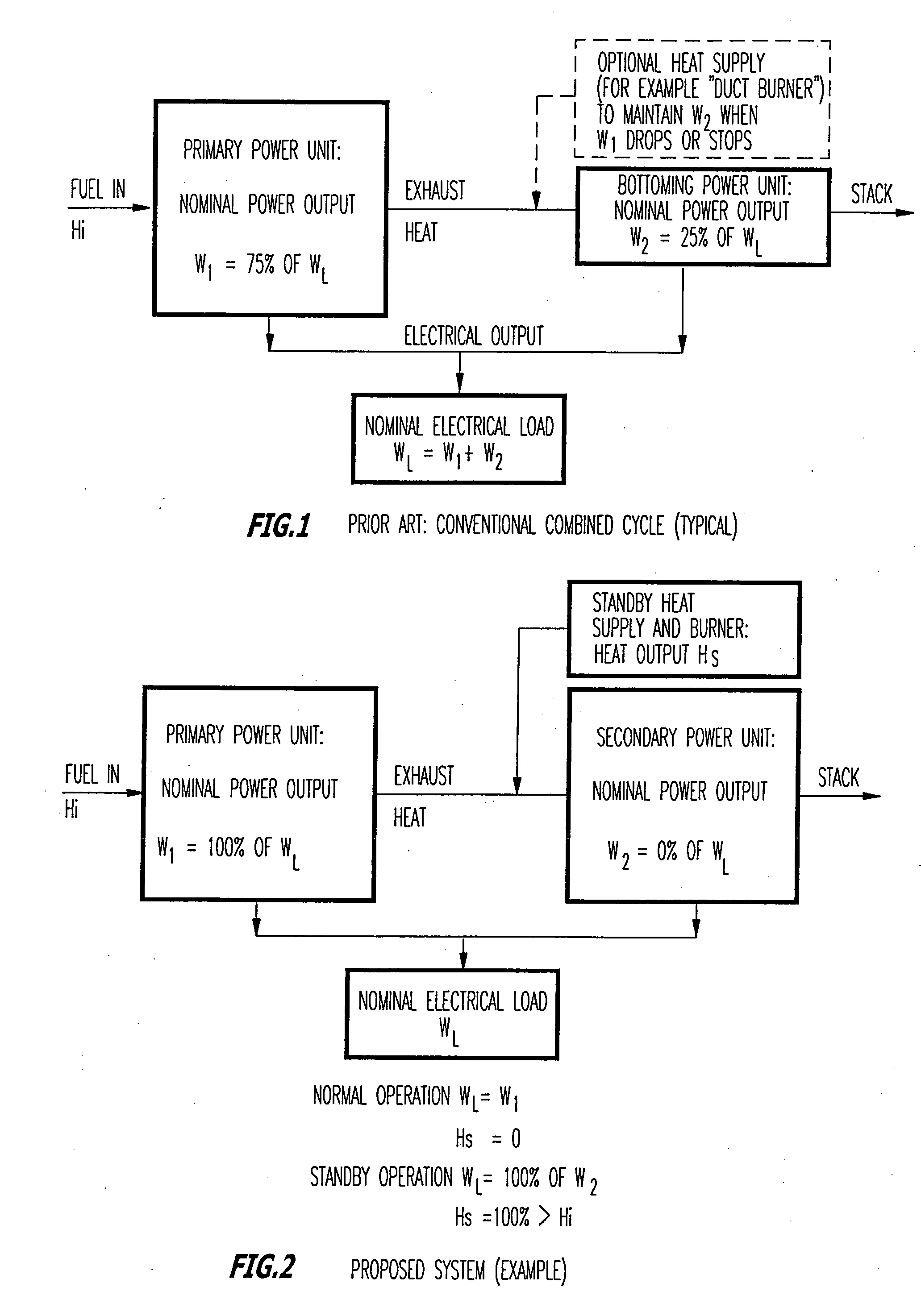
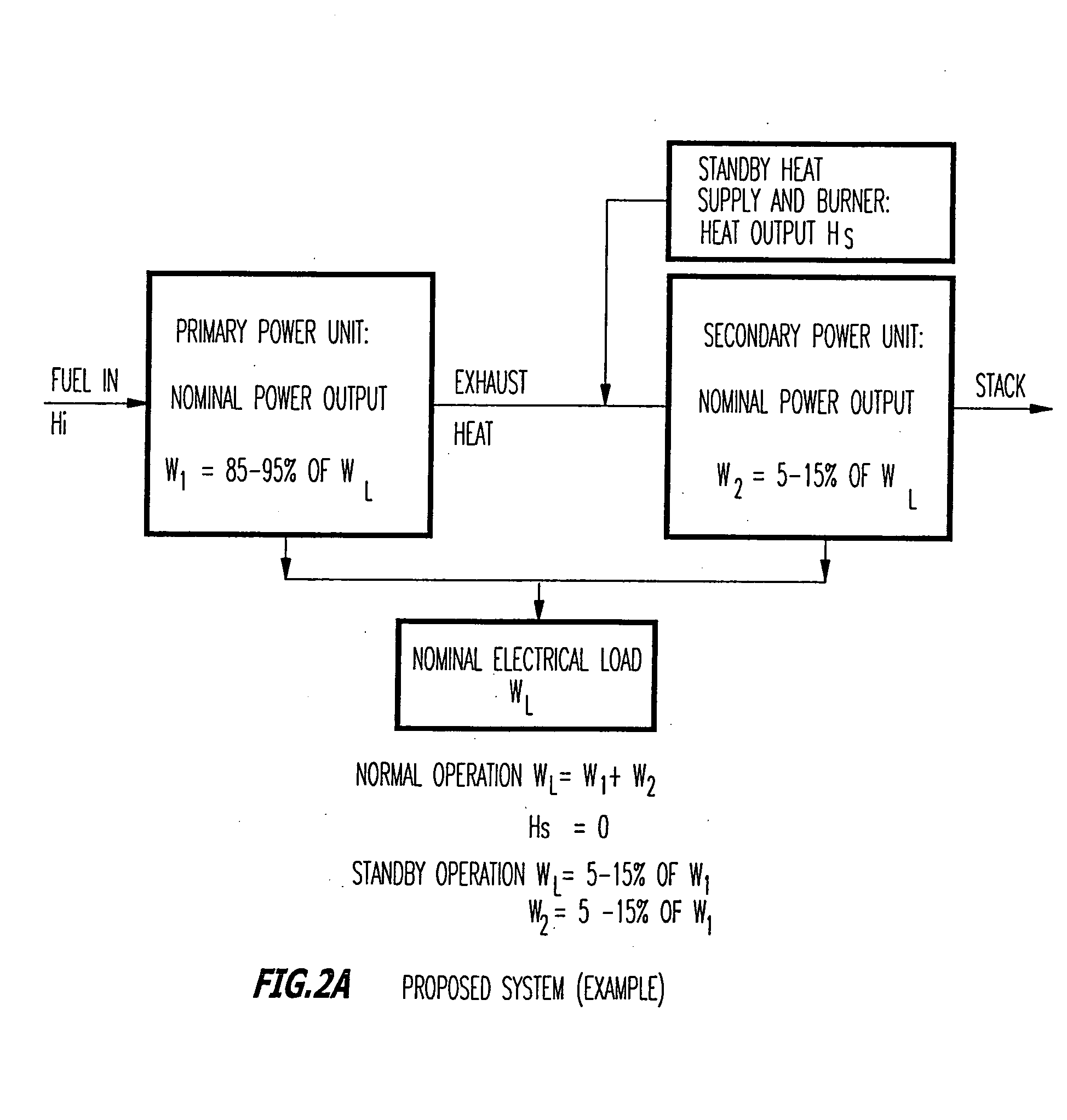
Hybrid power system for continuous reliable power at locations including remote locations
The present inventive subject matter is drawn to a hybrid ultra reliable power generating system for supplying continuous reliable power at remote locations comprising: a primary power unit producing electric power that is supplied to a load. Also a secondary power unit is included in the form of a closed cycle vapor turbine (CCVT) system that is capable of producing 100% of the electric power that is produced by the primary power unit and which is heated in hot standby by rejected heat of the primary power unit, wherein the vaporizer of the CCVT is maintained during hot standby at a temperature above its nominal operating temperature and the vapor turbine of the CCVT is preferable maintained at idle during hot standby at a rotating speed. Furthermore, the present inventive subject matter is drawn to an apparatus that combines a fuel efficient primary power generation unit system such as a high temperature fuel cell with a secondary power unit that is a very high reliability closed cycle vapor turbine (CCVT) which operates according to a Rankine cycle using organic working fluid that is capable of producing approximately 5-15% of the electric power that is produced by the primary power unit and which is heated by rejected heat of the primary power unit, wherein working fluid in the vaporizer of the CCVT is heated by the heat rejected by the primary power unit.
Owner:ORMAT TECH INC
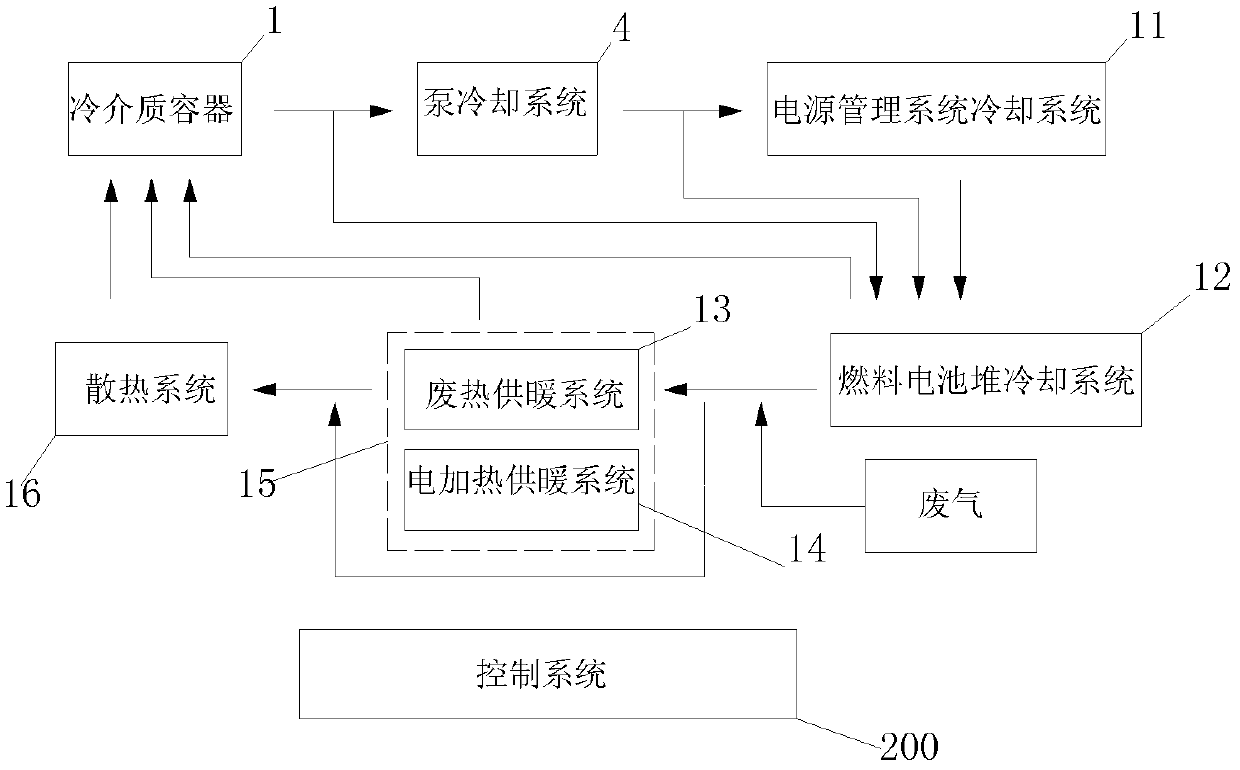
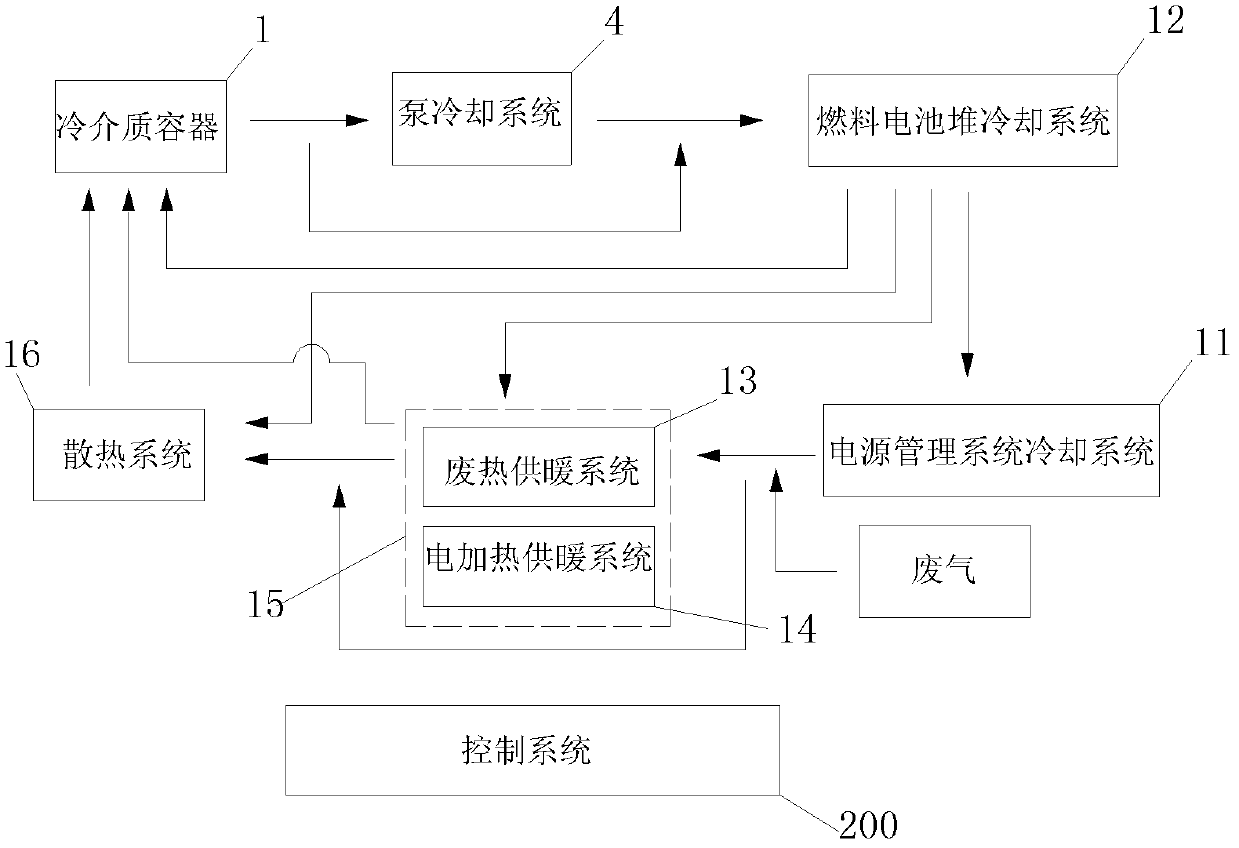
Thermal management system of fuel cell, fuel cell system, and vehicle with the fuel cell system
ActiveCN102610838ALow running costEfficient use ofRailway vehiclesFuel cell auxillariesFuel cellsThermal management system
Owner:DONGFANG ELECTRIC (CHENGDU) HYDROGEN FUEL CELL TECH CO LTD
Hybrid fuel cell system with internal combustion reforming
InactiveUS20050048345A1Increased power plant efficiencyStart fastHydrogenFuel cell auxillariesPartial oxidationAlcohol fuel
The present invention is a hybrid system for generating power from hydrocarbon and alcohol fuels using a two-stage process to achieve high overall energy conversion efficiency. The first stage is a reformer and fuel cell subsystem that uses an internal combustion engine operated at an air / fuel ratio richer than stoichiometric as a partial oxidation reformer for commonly available liquid or gaseous hydrocarbon or alcohol fuels. The engine produces shaft power and a product gas mixture containing hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and traces of light hydrocarbons that is used as fuel in fuel cells to generate electric power. The second stage is a heat engine subsystem that captures heat from the reformer and fuel cell subsystem, and produces additional shaft power. In addition to efficiency, advantages include adaptability to a variety of fuels, quick system startup with immediate shaft power availability, and low emission of pollutantants.
Owner:MEACHAM G B KIRBY
Renewable energy electric power generating system
A renewable electric power system includes a high temperature superconducting wind turbine using high temperature superconducting yttrium-barium-copper oxide for the rotor and stator windings as well as a superconducting bearing. Power from the turbine is stored in a high temperature superconducting magnetic storage system that also uses HTS YBCO. Also included is a regenerative solid oxide fuel cell / electrolyzer with steam turbine cogeneration. The system operates on a managed day / night cycle. During daytime, the energy produced by the wind turbines and fuel cells is transmitted to the grid. During nocturnal hours, the wind turbine is used to provide low cost electricity to the reversible fuel cells operating in the electrolysis mode producing hydrogen and oxygen that is stored for later use. Alternatively, the fuel cells can remain in electrolysis mode producing hydrogen and oxygen for the market. A modified interactive system generates power on a continuous twenty-four hour cycle.
Owner:COOPER WILLARD
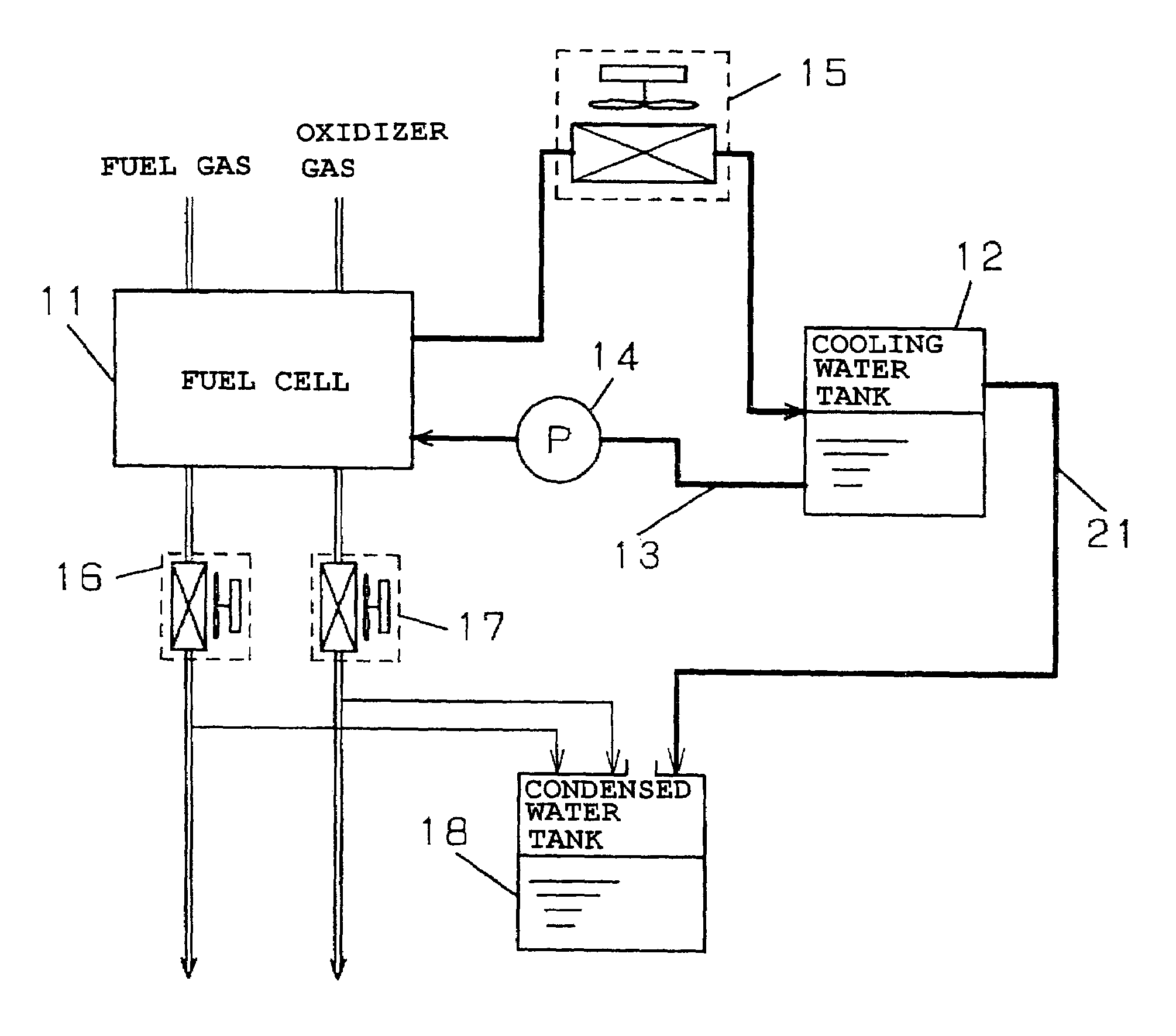
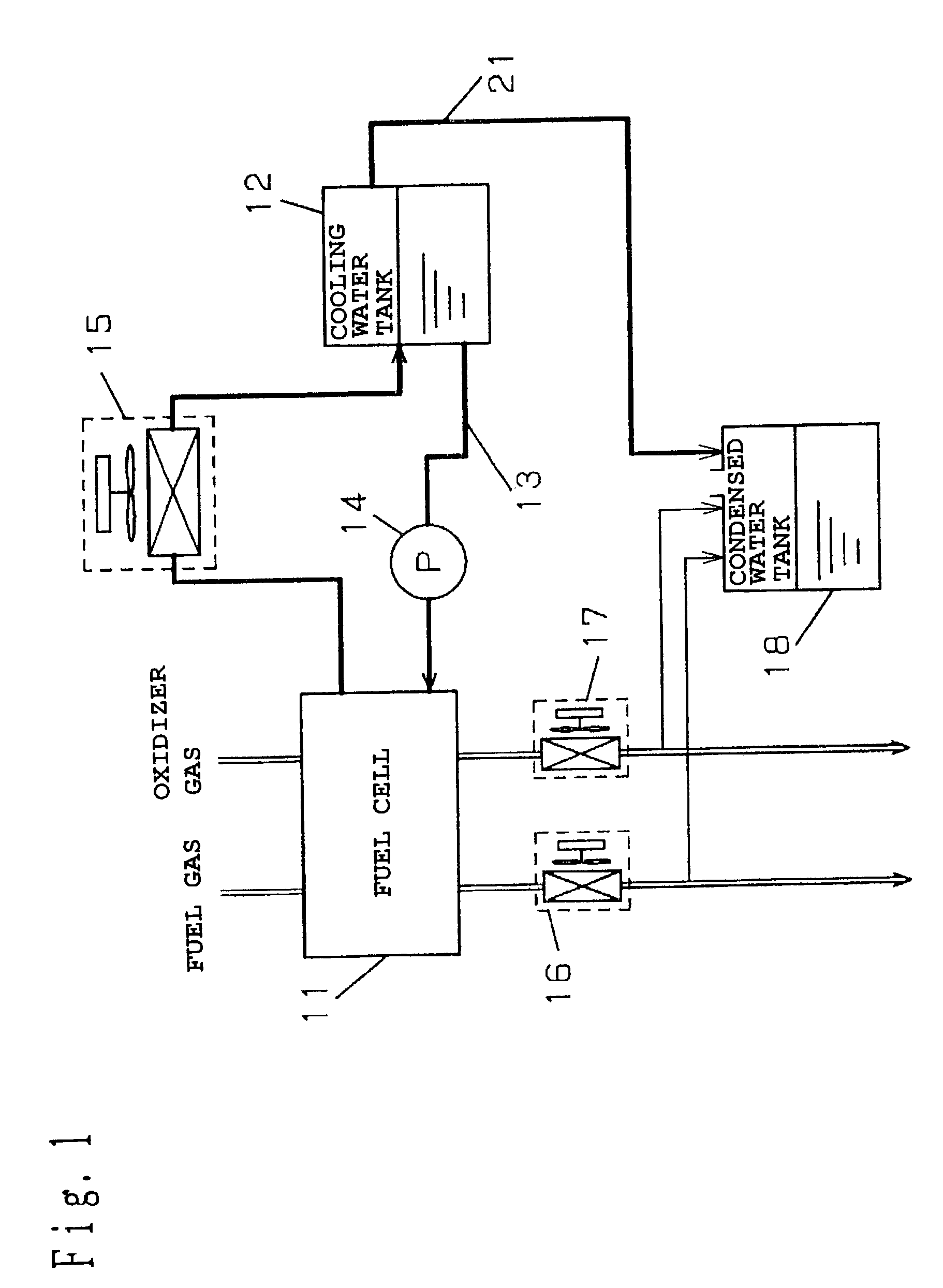
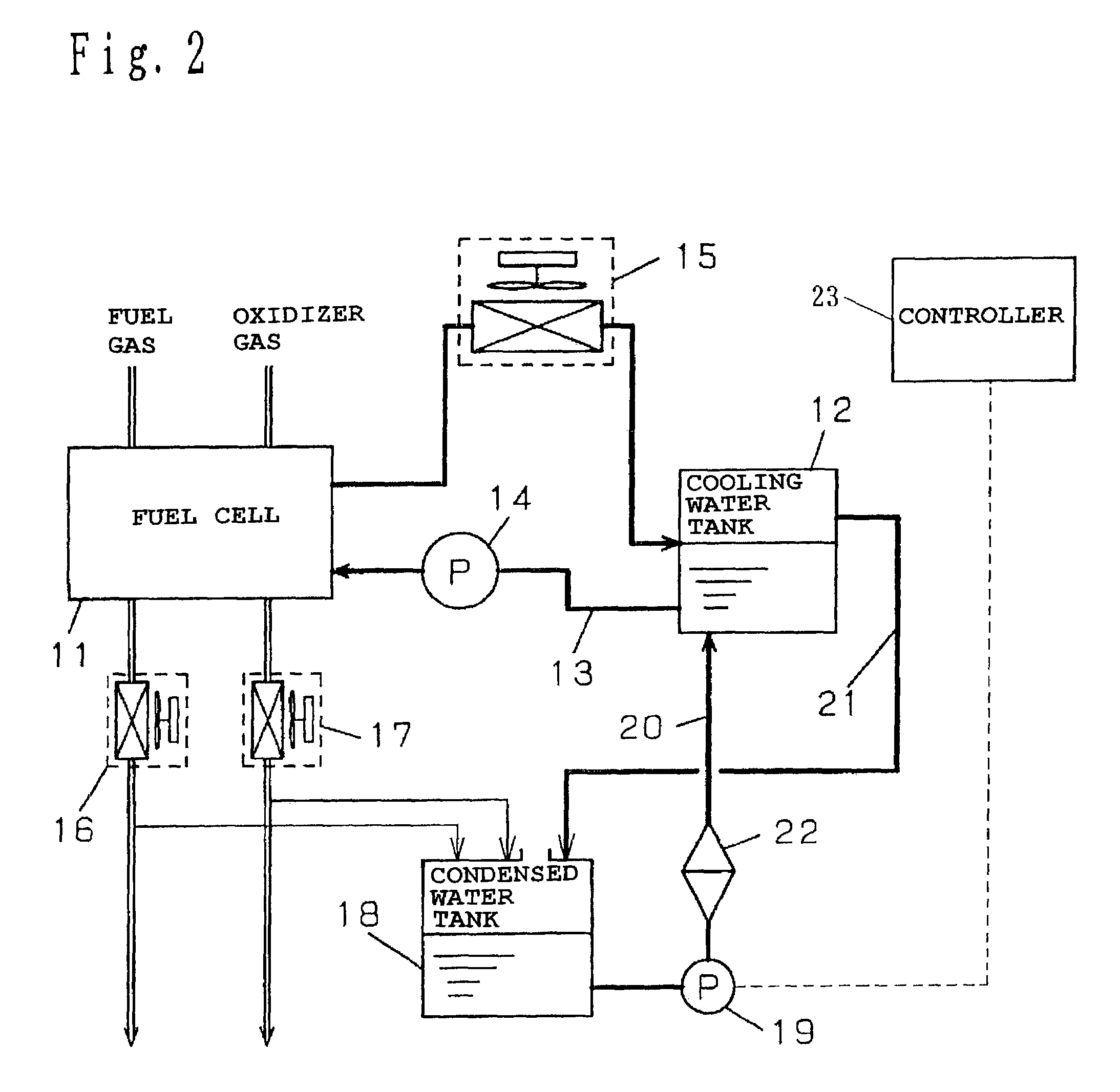
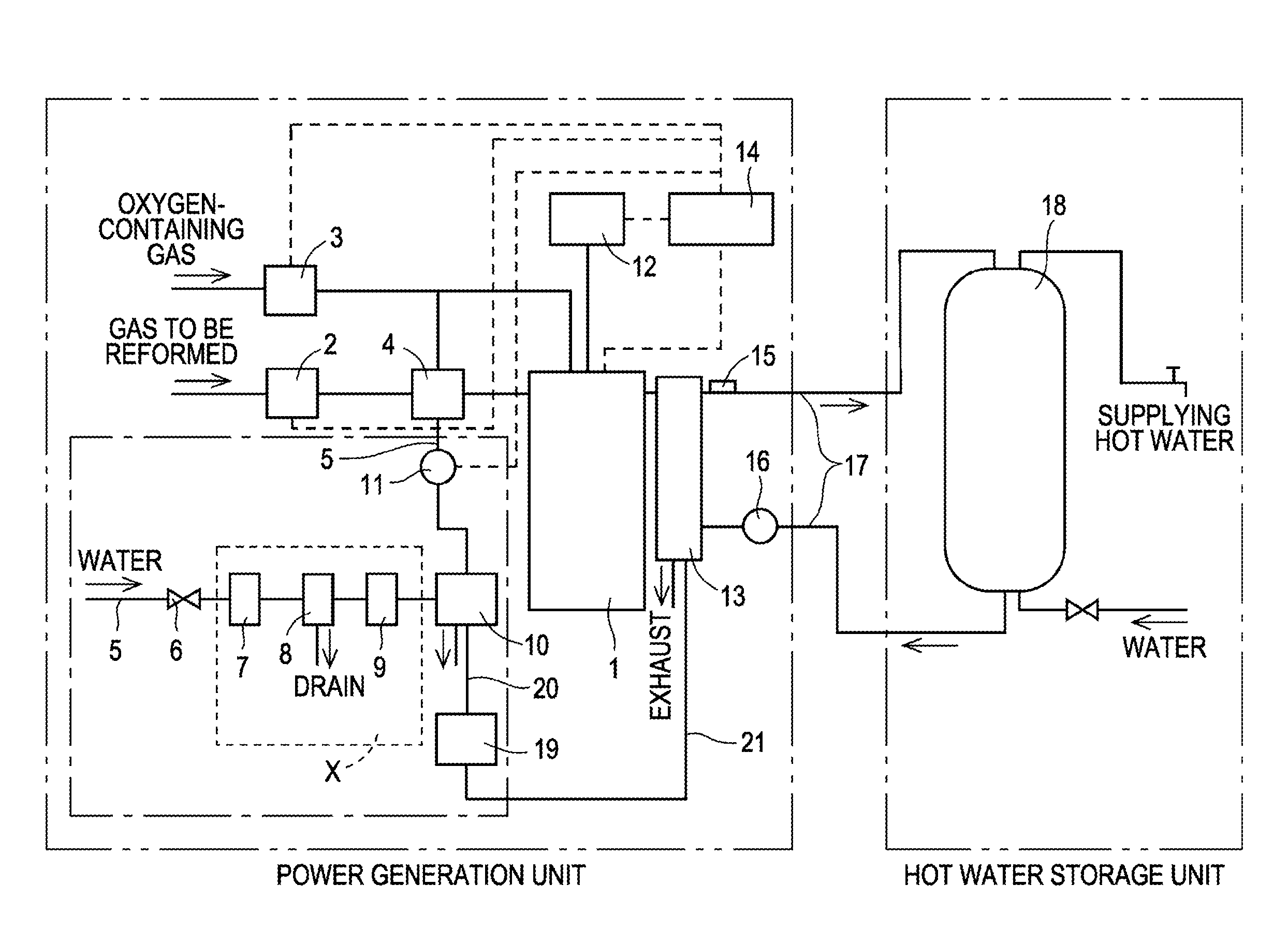
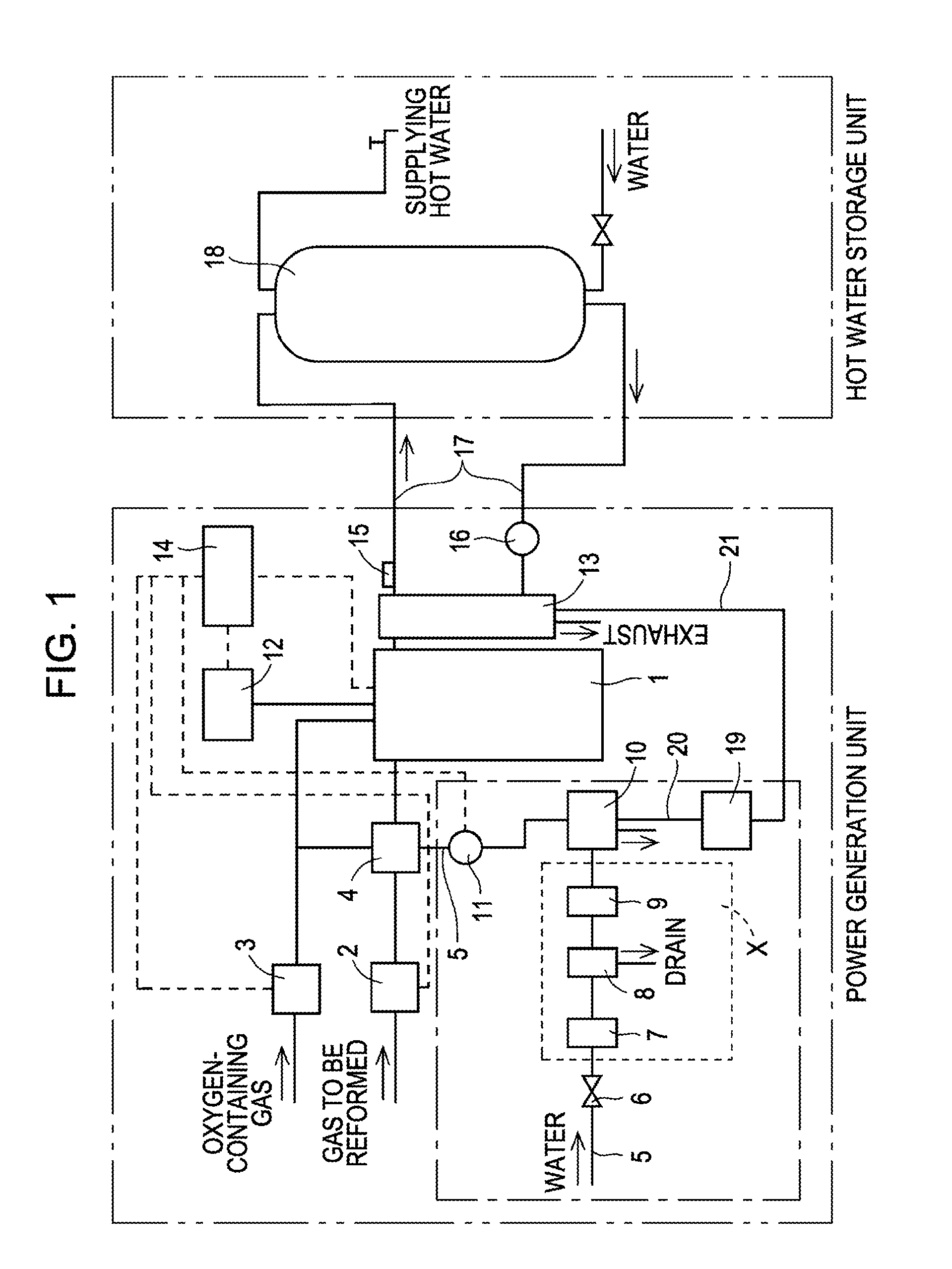
Fuel cell system and operation method having a condensed water tank open to atmosphere
InactiveUS7052790B2Easy constructionLow costFuel cell auxillariesFuel cell applicationsAtmospheric airWater vapor
To avoid pressure variation in a cooling water channel, extend a life of an ion exchange resin used to maintain quality of cooling water and reduce power consumption by auxiliary machinery at low cost. There is provided a polymer electrolyte fuel cell, a cooling water tank, a cooling water channel, a cooling water pump, a heat exchanger, a fuel-side condenser and an oxidizer-side condenser that cool exhaust fuel gas and exhaust oxidizer gas discharged from the fuel cell to condense content water vapor, a condensed water tank that stores the water condensed in the fuel-side condenser and the oxidizer-side condenser, a water supply channel having a water supply pump for feeding the condensed water to the cooling water tank, and a water discharge channel for the cooling water tank.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Fuel cell combined heat and power generation
InactiveUS20090004516A1Low utilization efficiencyAvoid overall overheatingHydrogenElectricity cogenerationThermal energyElectric force
A cogeneration system having flexible and controllable cogeneration loops. There is a first cogeneration loop to recover heat from a fuel cell power module, thereby producing a heat to electricity ratio between 0 and approximately 1.0. There is a second cogeneration loop to produce supplemental thermal energy for hot water generation and / or space heating. This loop can be connected or disconnected via switching valves depending on the thermal demands of hot water and / or space heating. This loop can also be useful to control the fuel processor temperature to prevent it from being overheated in cases when the fuel cell has low fuel utilization efficiency. With this second loop, it becomes possible to adjust the heat to electricity ratio at any desirable levels such as more than 2. It is also possible to produce the hot water at a higher temperature or superheated steam, which would have been difficult if only the first loop is used.
Owner:HYTEON
Liquid anode electrochemical cell
InactiveUS20060019132A1High voltageIncrease powerFuel cells groupingCell electrodesFuel cellsLiquid cathode
An electrochemical cell is provided which has a liquid anode. Preferably the liquid anode comprises molten salt and a fuel, which preferably has a significant elemental carbon content. The supply of fuel is preferably continuously replenished in the anode. Where the fuel contains or pyrolizes to elemental carbon, the reaction C+2O2−→CO2+4e− may occur at the anode. The electrochemical cell preferably has a solid electrolyte, which may be yttrium stabilized zirconia (YSZ). The electrolyte is connected to a solid or liquid cathode, which is given a supply of an oxidizer such as air. An ion such as O2− passes through the electrolyte. If O2− passes through the electrolyte from the anode to the cathode, a possible reaction at the cathode may be O2+4e−→2O2−. The electrochemical cell of the invention is preferably operated as a fuel cell, consuming fuel and producing electrical current.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Aeroplane drink dispenser
InactiveUS7592084B2Easy to produceEasy to useFuel cell heat exchangeReactant parameters controlThermal energyFuel cells
A drink dispenser which is particularly suitable for use on board a passenger plane, comprises a drink preparation unit and a supply unit. The supply unit has a fuel cell system with a fuel cell and is configured to supply the drink preparation unit with water, electric energy, and thermal energy produced by the fuel cell.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
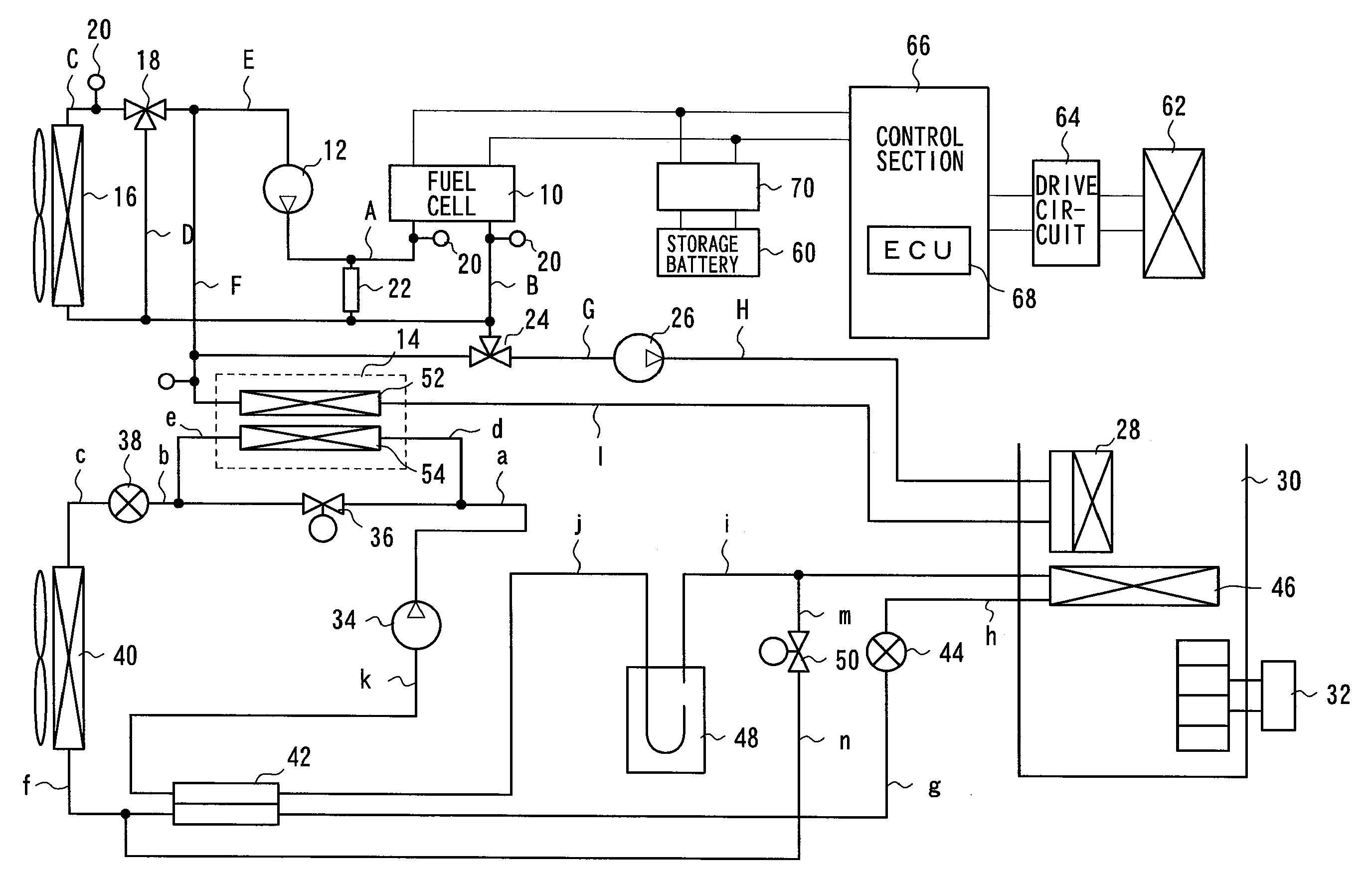
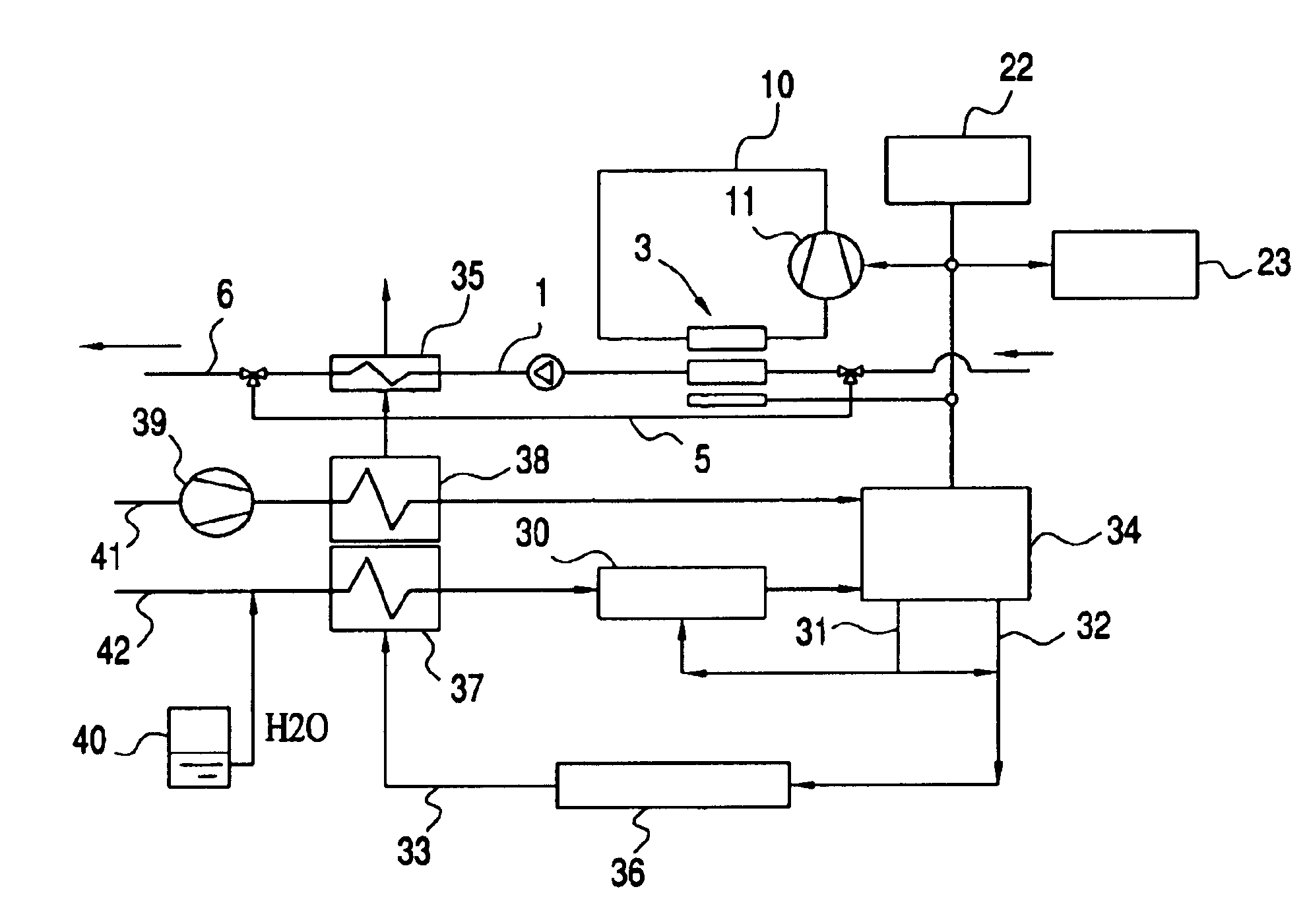
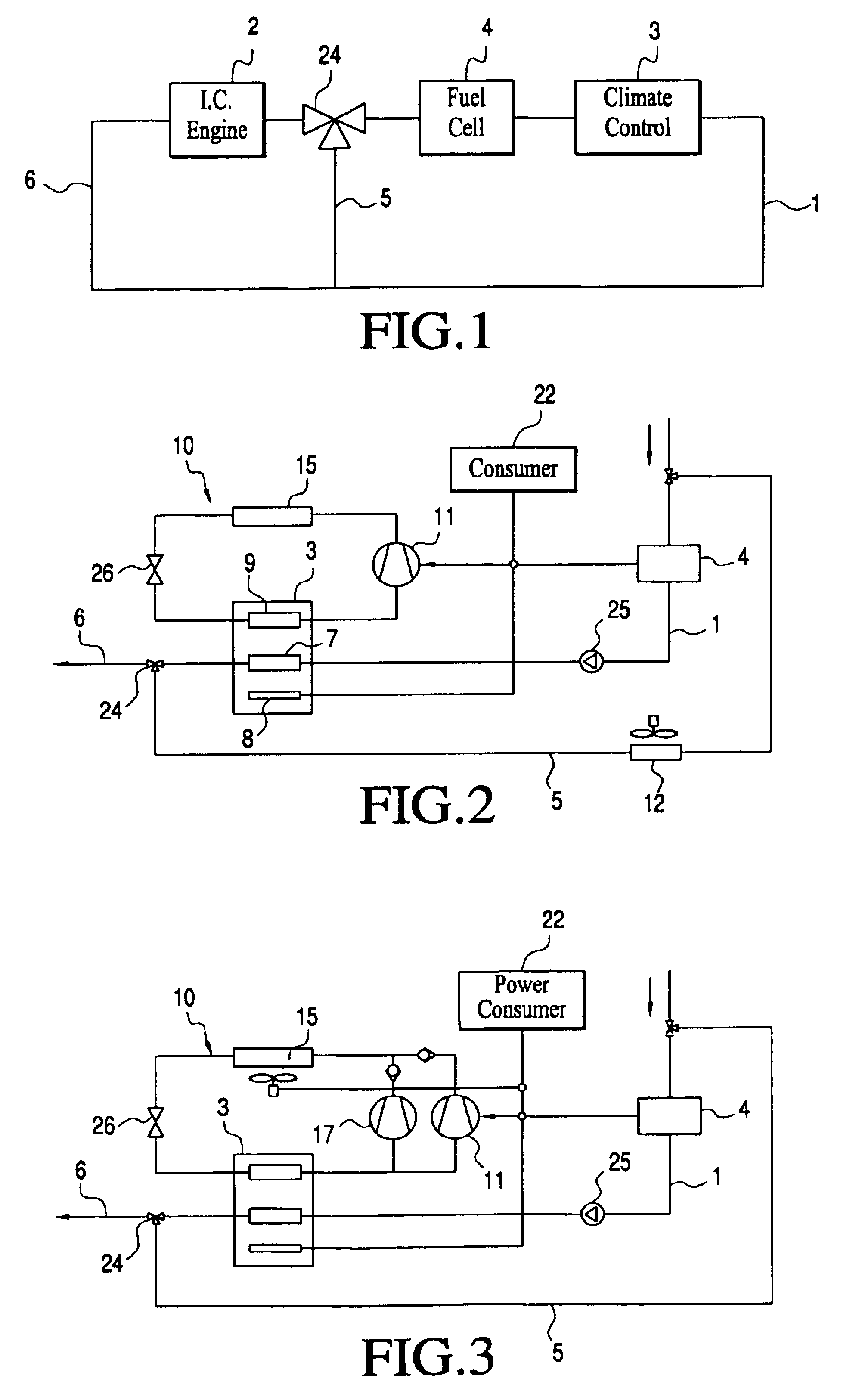
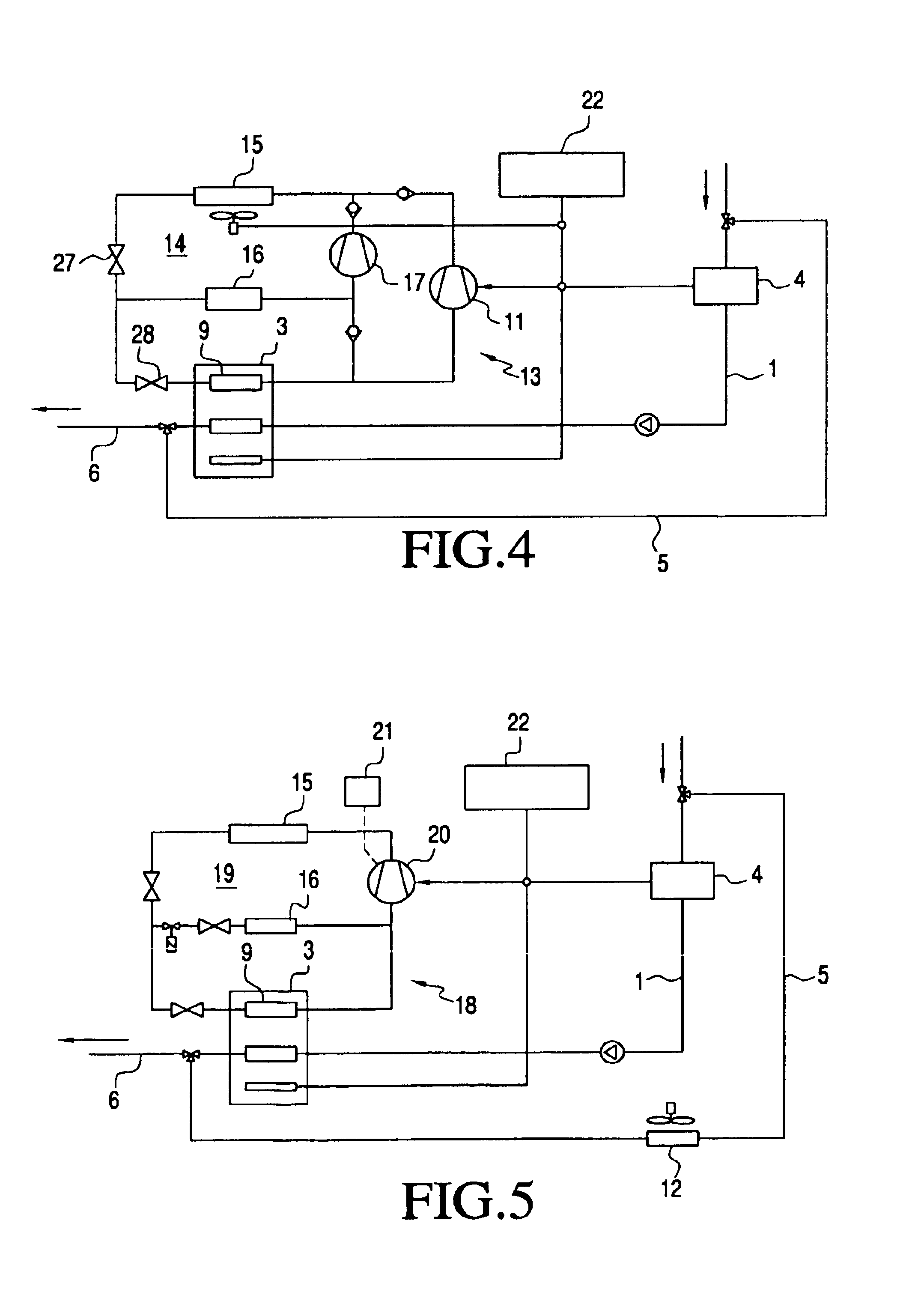
System with an internal combustion engine, a fuel cell and a climate control unit for heating and/or cooling the interior of a motor vehicle and process for the operation thereof
InactiveUS6865901B2Improve controlEasy to useAir-treating devicesFuel cell heat exchangeFuel cellsExternal combustion engine
A system with an internal combustion engine which has a heat transfer circuit, a fuel cell and a climate control unit which is accommodated in the heat transfer circuit of the internal combustion engine. The system has a heat transfer arrangement for transferring the exhaust heat of the fuel cell to the heat transfer circuit and a bypass for bridging a segment of the heat transfer circuit which runs through the internal combustion engine so that, in the bypassed operating state, an isolated circuit is formed. In stationary operation, this enables an optimized operating mode since the internal combustion engine is no longer heated and the exhaust heat of the fuel cell is fully available for heating purposes. The climate control unit can have a fuel cell and an arrangement for transferring the heat produced by the fuel cell to the vehicle interior has a fan unit by which an air flow can be produced for cooling the fuel cell and a heating unit which is powered by the fuel cell and by which the air flow for heating the vehicle interior can be additionally heated. For cooling or heating the interior of a motor vehicle, the system can have a cooling circuit with a compressor, a condenser, an expansion element, and a first evaporator and an APU or a fuel cell to electrically power the compressor, and a second cooling circuit a second evaporator, the second cooling circuit being connected to the first cooling circuit.
Owner:WEBASTO THERMOSYST INT
Fuel cell system using external heat sources for maintaining internal temperature
ActiveUS20070119638A1Batteries circuit arrangementsElectricity cogenerationEngineeringInternal temperature
A solid oxide fuel cell system including electric resistance elements for heating of space and components within the “hot zone” enclosure of the system, preferably in combination with means for using “waste” heat from other sources, to assist in warm-up from a cold start and / or to maintain a stand-by temperature of reformer and fuel cell elements within the system and / or to maintain optimum operating temperatures within the system during periods of very low electrical demand on the system. A method is included for using off-peak grid electricity, battery-stored onboard electricity, or vehicle-generated electricity to energize the resistance heaters, as well as utilizing gaseous waste heat sources such as vehicle exhaust gas to complement the resistance heating.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
Hybrid power system for continuous reliable power at locations including remote locations
The present inventive subject matter is drawn to a hybrid ultra reliable power generating system for supplying continuous reliable power at remote locations comprising: a primary power unit producing electric power that is supplied to a load. Also a secondary power unit is included in the form of a closed cycle vapor turbine (CCVT) system that is capable of producing 100% of the electric power that is produced by the primary power unit and which is heated in hot standby by rejected heat of the primary power unit, wherein the vaporizer of the CCVT is maintained during hot standby at a temperature above its nominal operating temperature and the vapor turbine of the CCVT is preferable maintained at idle during hot standby at a rotating speed. Furthermore, the present inventive subject matter is drawn to an apparatus that combines a fuel efficient primary power generation unit system such as a high temperature fuel cell with a secondary power unit that is a very high reliability closed cycle vapor turbine (CCVT) which operates according to a Rankine cycle using organic working fluid that is capable of producing approximately 5-15% of the electric power that is produced by the primary power unit and which is heated by rejected heat of the primary power unit, wherein working fluid in the vaporizer of the CCVT is heated by the heat rejected by the primary power unit.
Owner:ORMAT TECH INC
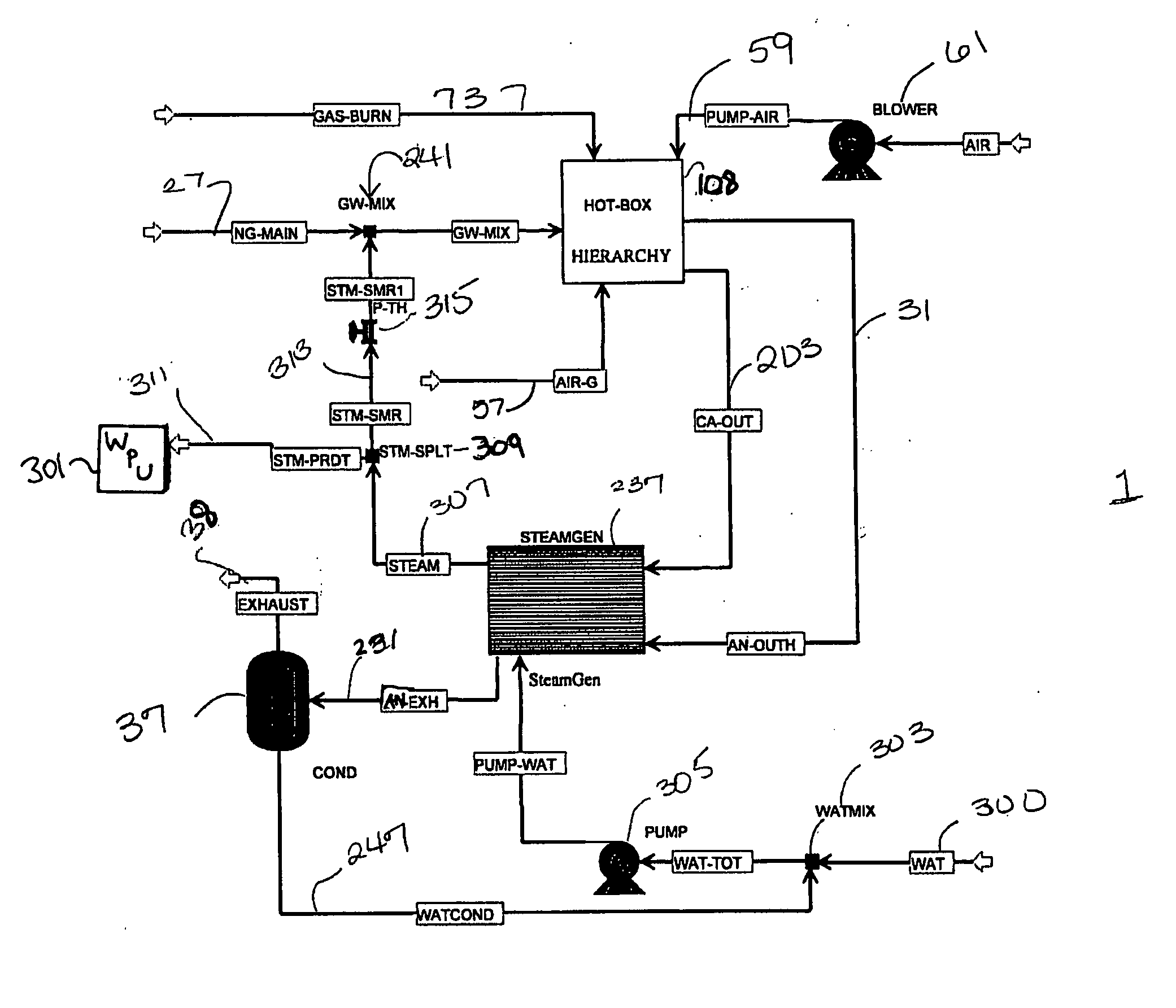
Fuel cell system
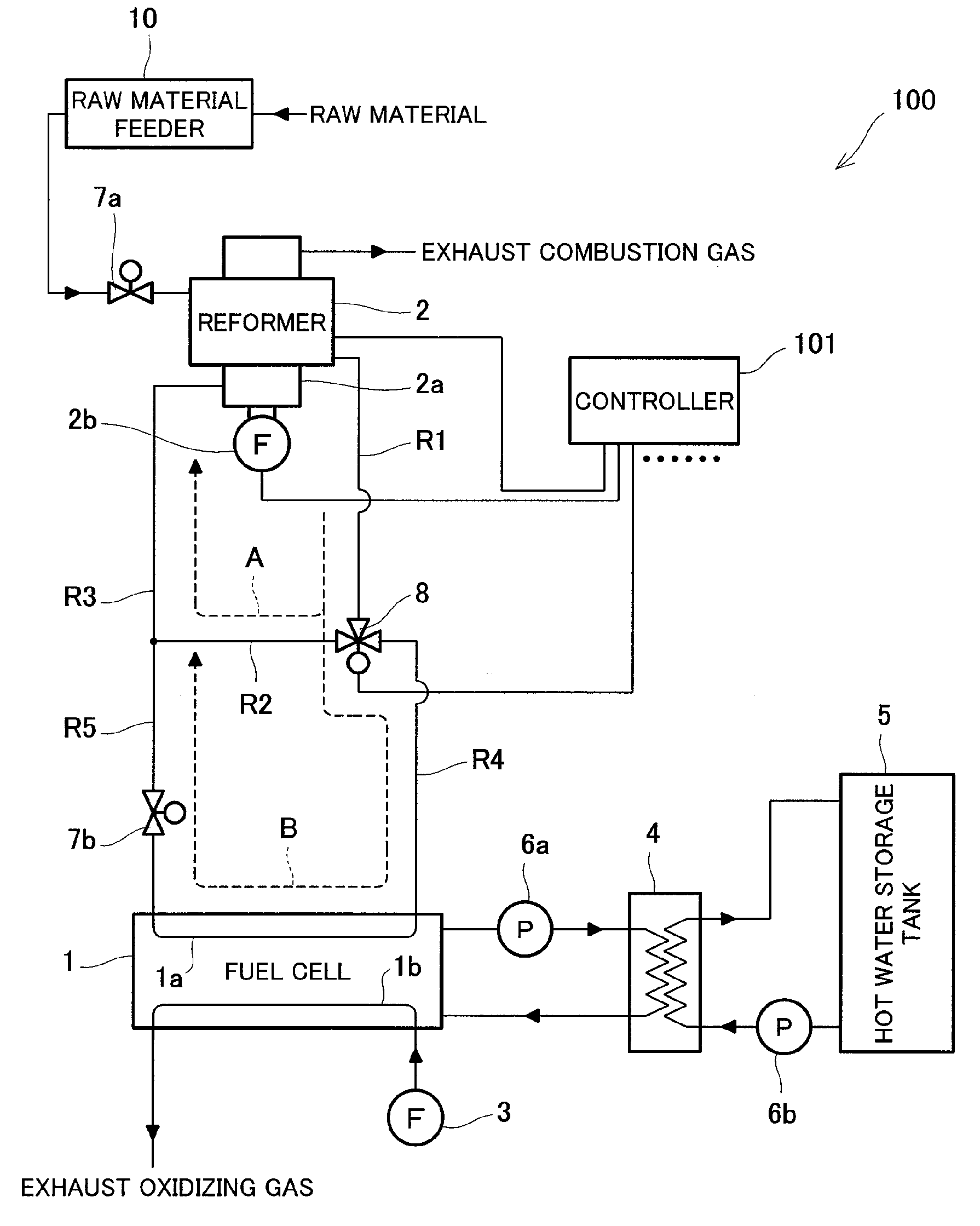
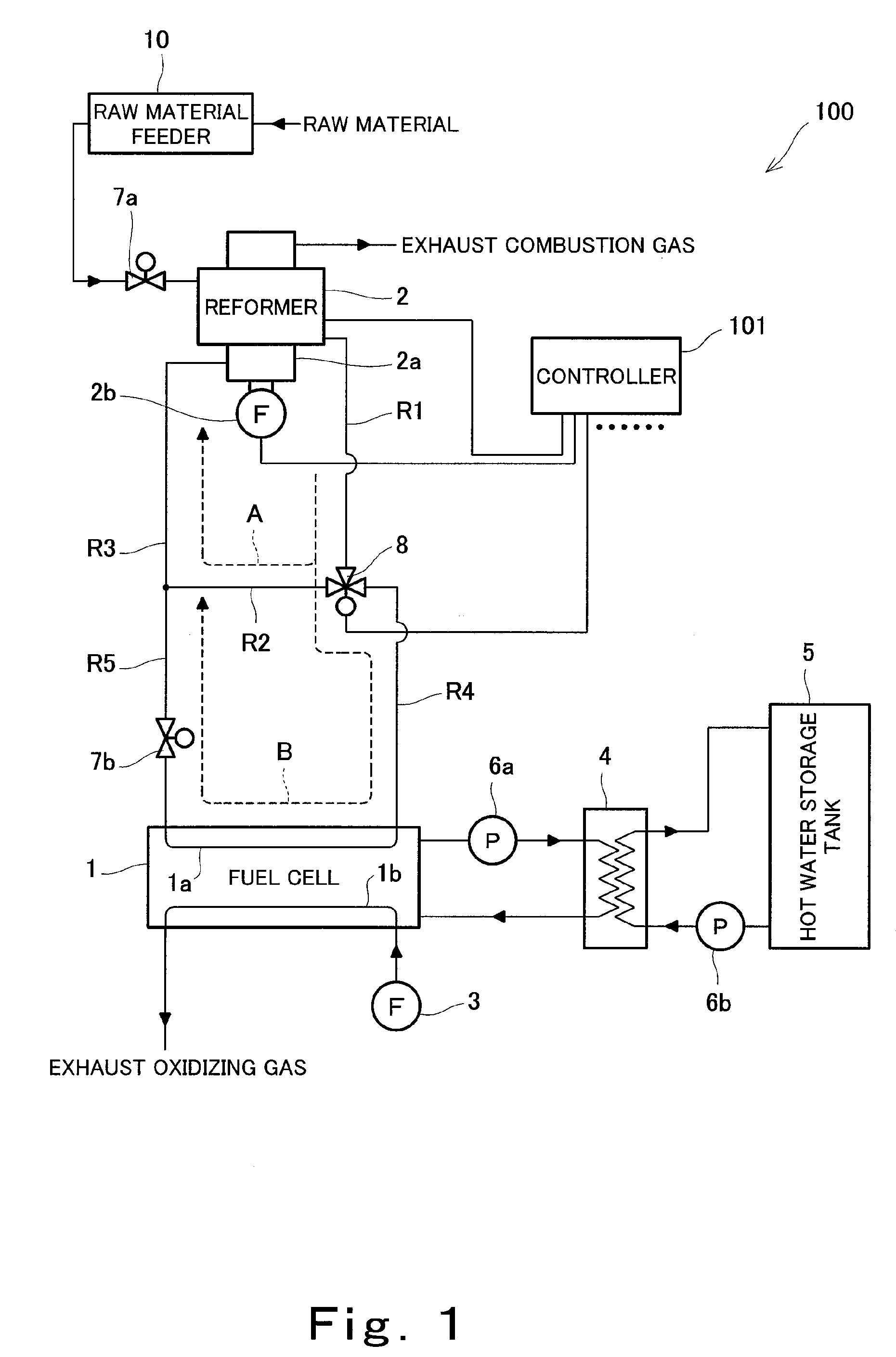
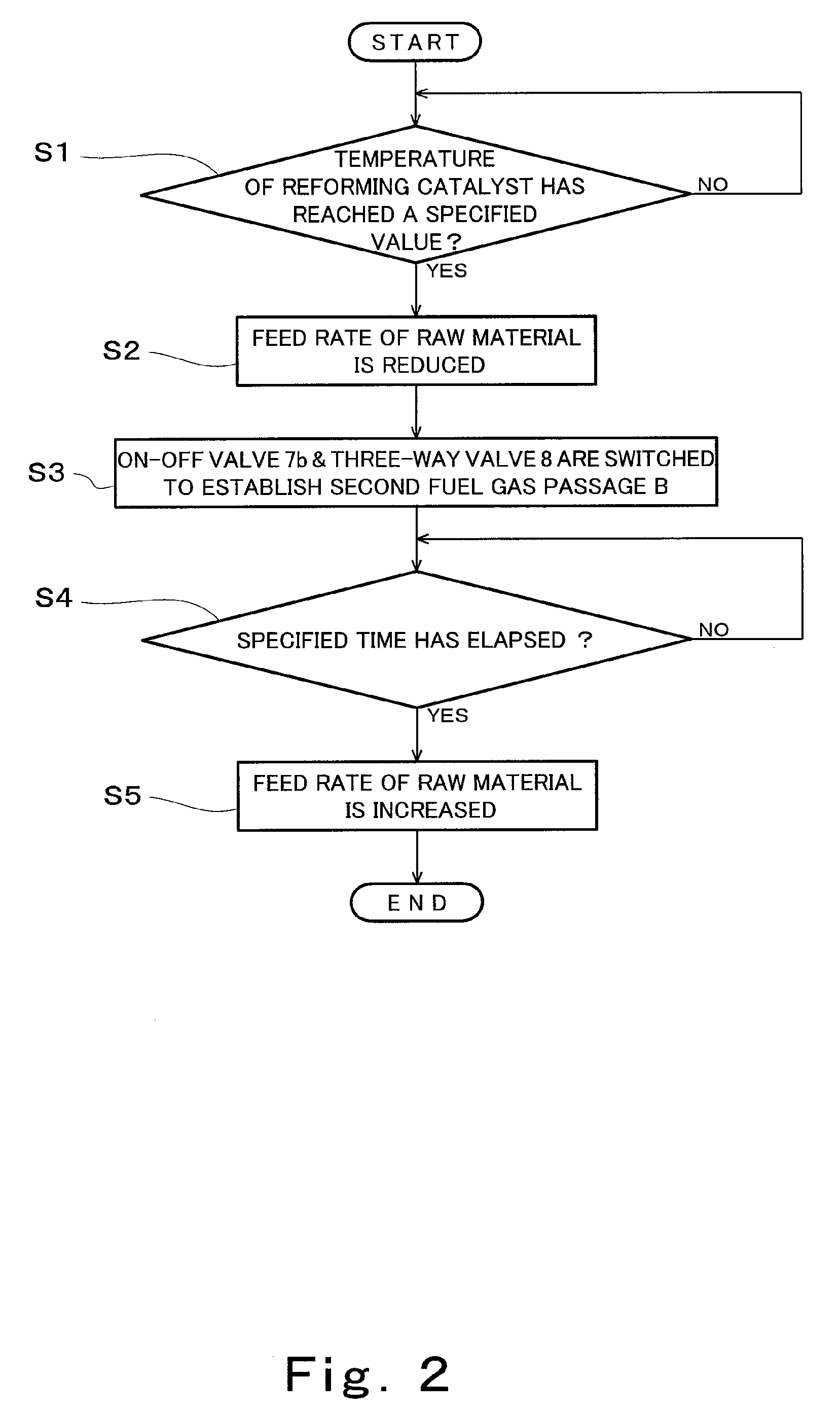
InactiveUS20090092883A1Reduce adverse effectsInhibition is effectiveHydrogenChemical industryCombustorFuel cells
A fuel cell system is provided, the system comprising: a fuel cell (1) configured to generate electric power by use of a fuel gas; a reformer (2) configured to generate the fuel gas by reforming a raw material; a combustion burner (2a) configured to supply heat for reforming; a raw material feeder (10) configured to control the feed rate of combustion fuel to the combustion burner; a combustion fan (2b) configured to supply air to the combustion burner; a fuel gas passage (R1, R4); an off gas passage (R3, R5); a bypass passage (R2); a switching valve (8); and a controller (101), wherein the inside of the fuel cell is filled with the raw material before the fuel gas is supplied, and wherein the controller controls the raw material feeder so as to reduce the feed rate of the combustion fuel to the combustion burner when controlling the switching valve so as to shut off the bypass passage to supply the fuel gas generated in the reformer to the fuel cell. This fuel cell system is environmentally-friendly and capable of suppressing the emission of carbon monoxide at the start of a power generating operation to mitigate the adverse effect upon the ecosystem.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Heat pump with heat recovery
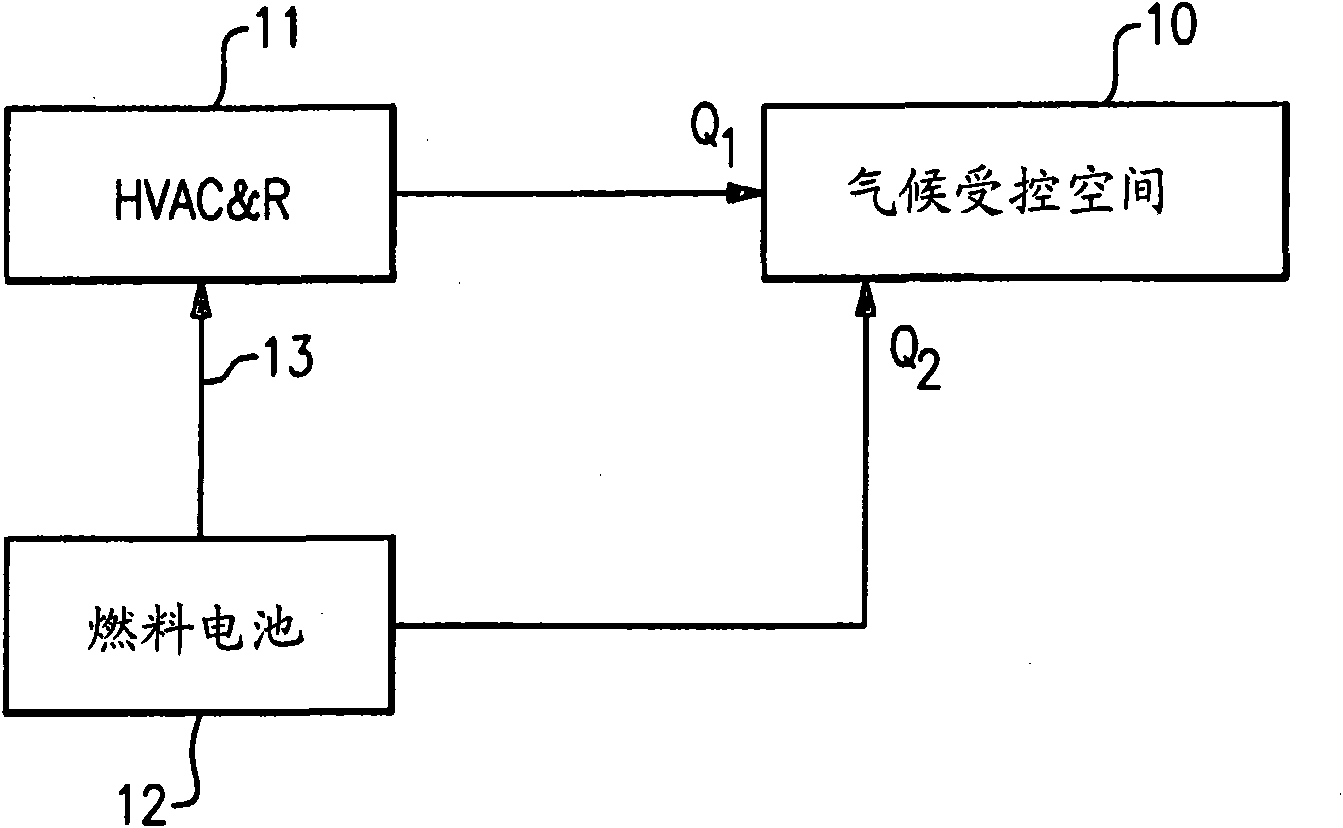
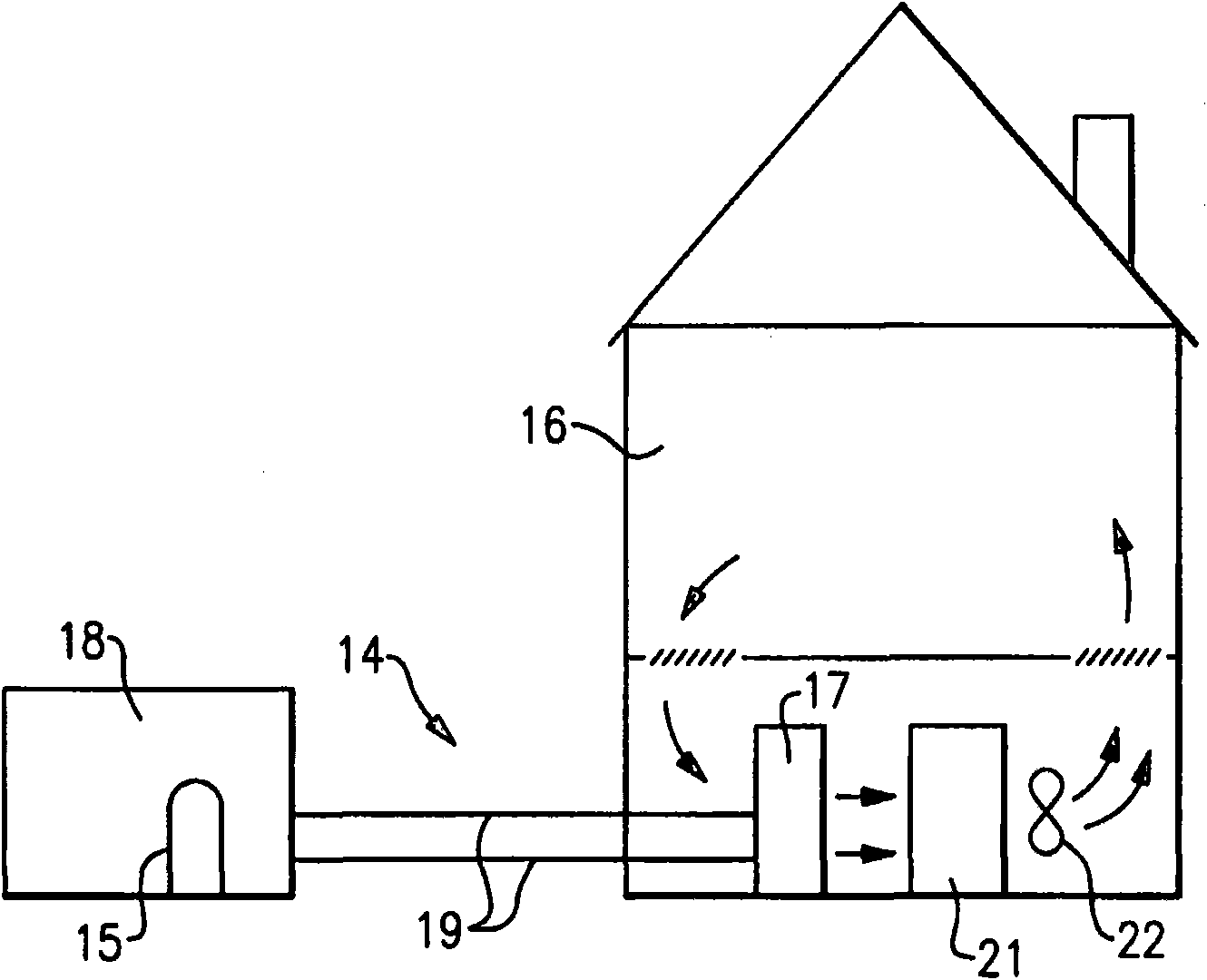
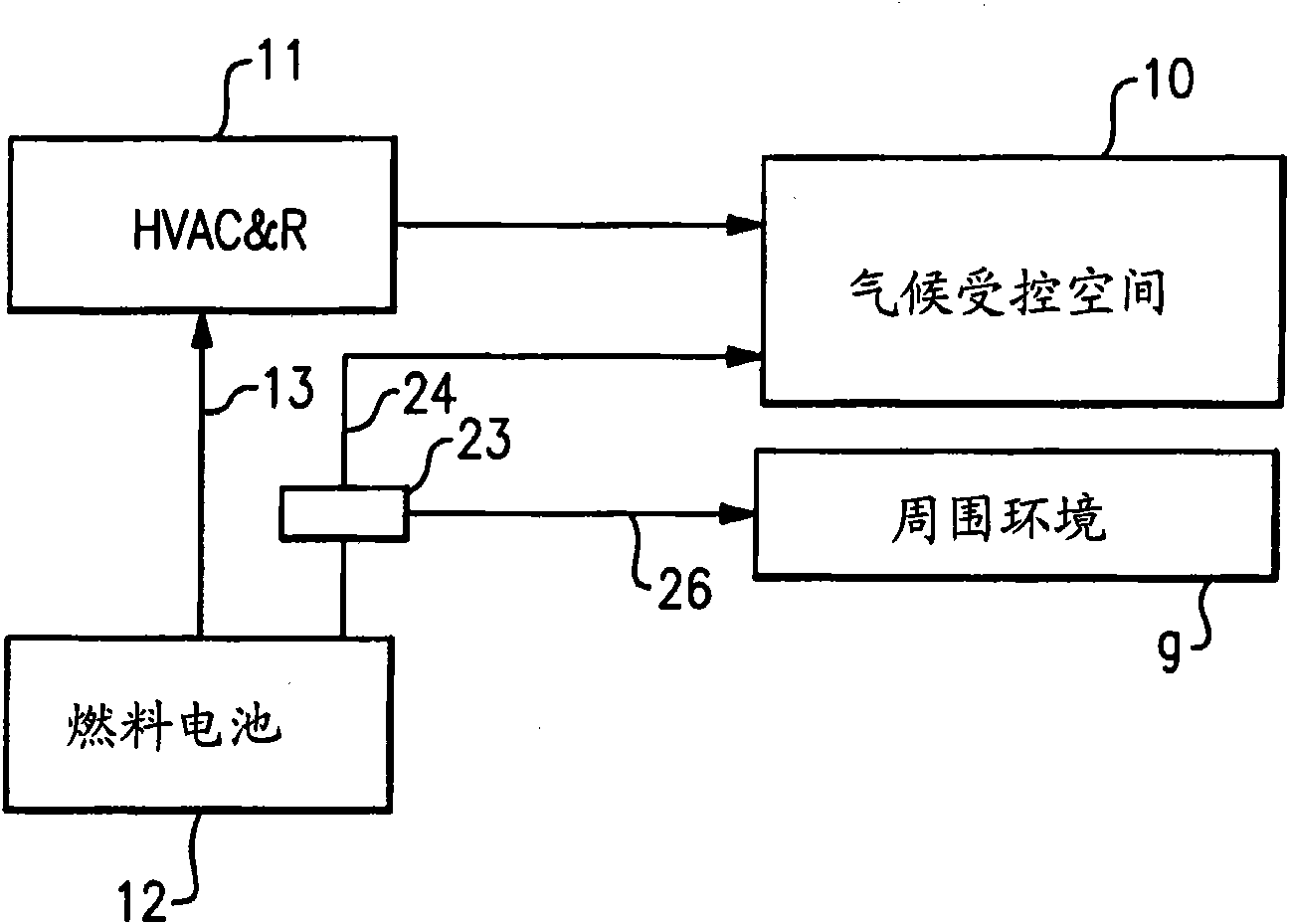
A fuel cell is provided to furnish electrical power to an HVAC&R system, and the waste heat from the fuel cell is transferred to a secondary fluid directed to flow to the climate-controlled space of a building during periods of time in which heating is required. The heat rejected by the fuel cell may be a supplemental or primary source of heat as well used for precise temperature control within the climate-controlled space of the building. A channeling assembly is used to selectively direct the fuel cell heat either to and / or away from the climate-controlled space served by the HVAC&R system. Higher energy efficiencies of the HVAC&R equipment are achieved, and the 'cold blow' phenomenon is reduced or eliminated.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
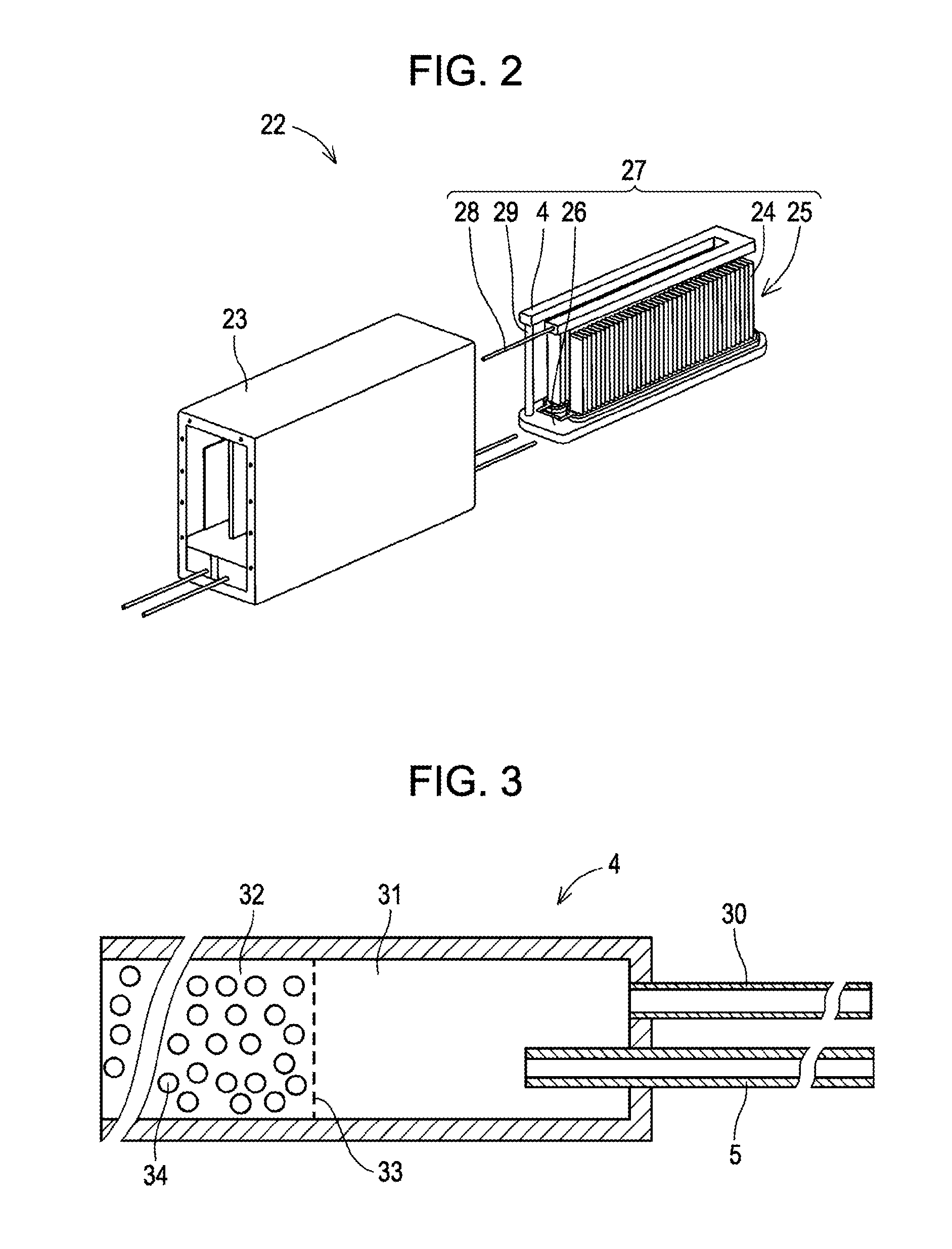
Fuel Cell Apparatus
InactiveUS20110053017A1Efficient startHydrogenFuel cell applicationsSteam reformingPartial oxidation
A fuel cell apparatus comprises a cell stack, a reforming portion (reforming catalyst), a vaporizing portion, a reforming target gas supply, an oxygen-containing gas supply, a water supply, and a controller. The cell stack comprises a plurality of fuel cells electrically connected in series in a housing case. The reforming portion is disposed over the cell stack and is to be exposed to a gas produced by burning a fuel gas from the fuel cells. The reforming catalyst can perform partial oxidation reforming, autothermal reforming and steam reforming as a reforming reaction. The vaporizing portion generates steam to be supplied to the reforming portion. The reforming target gas supply supplies a reforming target gas to the reforming portion. The oxygen gas supply supplies an oxygen gas to the reforming portion. The water supply supplies water to the vaporizing portion. The controller controls the reforming reaction in the reforming portion.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
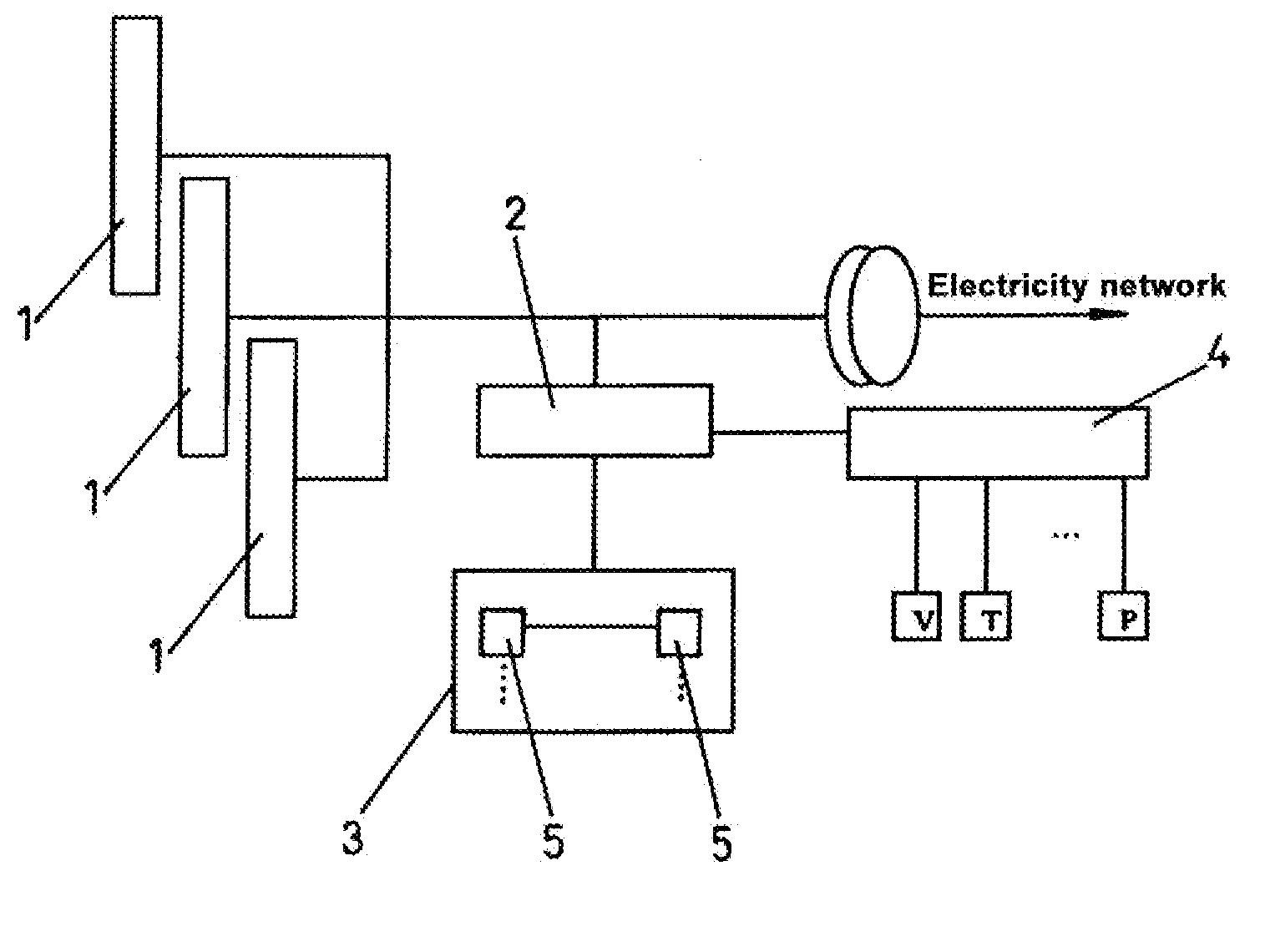
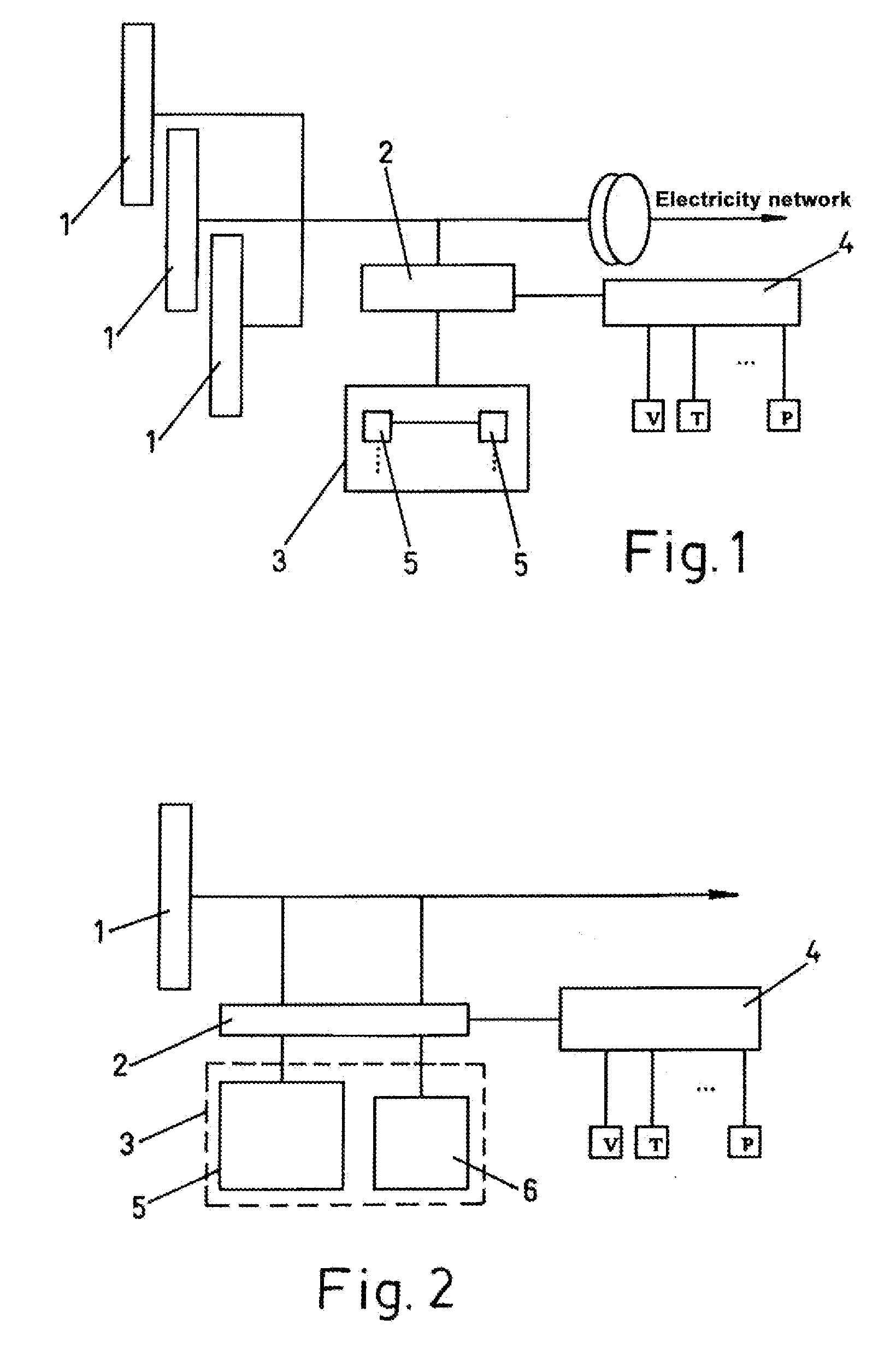
Production system for electric energy and hydrogen
ActiveUS20100259102A1Fast response dynamicSlow response dynamicBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric circuitsElectrolysisTurbine
System for producing electric energy and hydrogen based on renewable energy sources, such as wind energy from one or several wind turbines, and incorporating means for producing hydrogen. The system comprises a hybrid electrolyzer device, which comprises a combination of at least two different electrolysis technologies and at least one control device, which manages the hydrogen production between the two electrolyzers of the different electrolysis technologies; being at least one electrolyzer of a rapid dynamics electrolysis technology type and, at least the second one of a substantially slower dynamics electrolysis technology type.
Owner:ACCIONA ENERGIA SA +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com