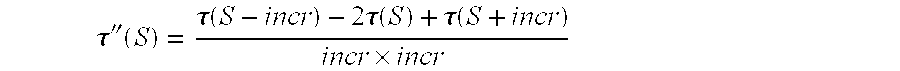Patents
Literature
33results about How to "Simple and accurate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
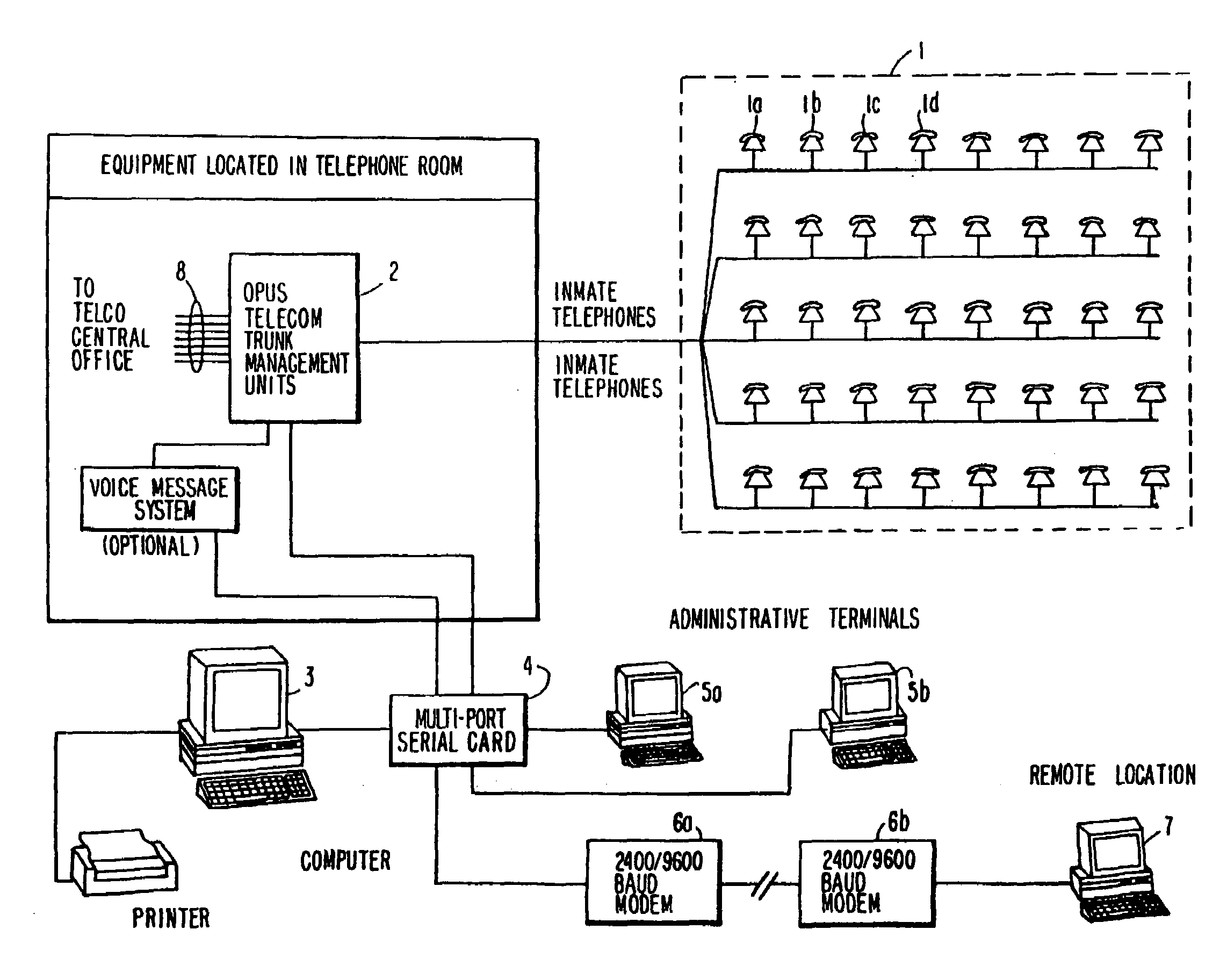
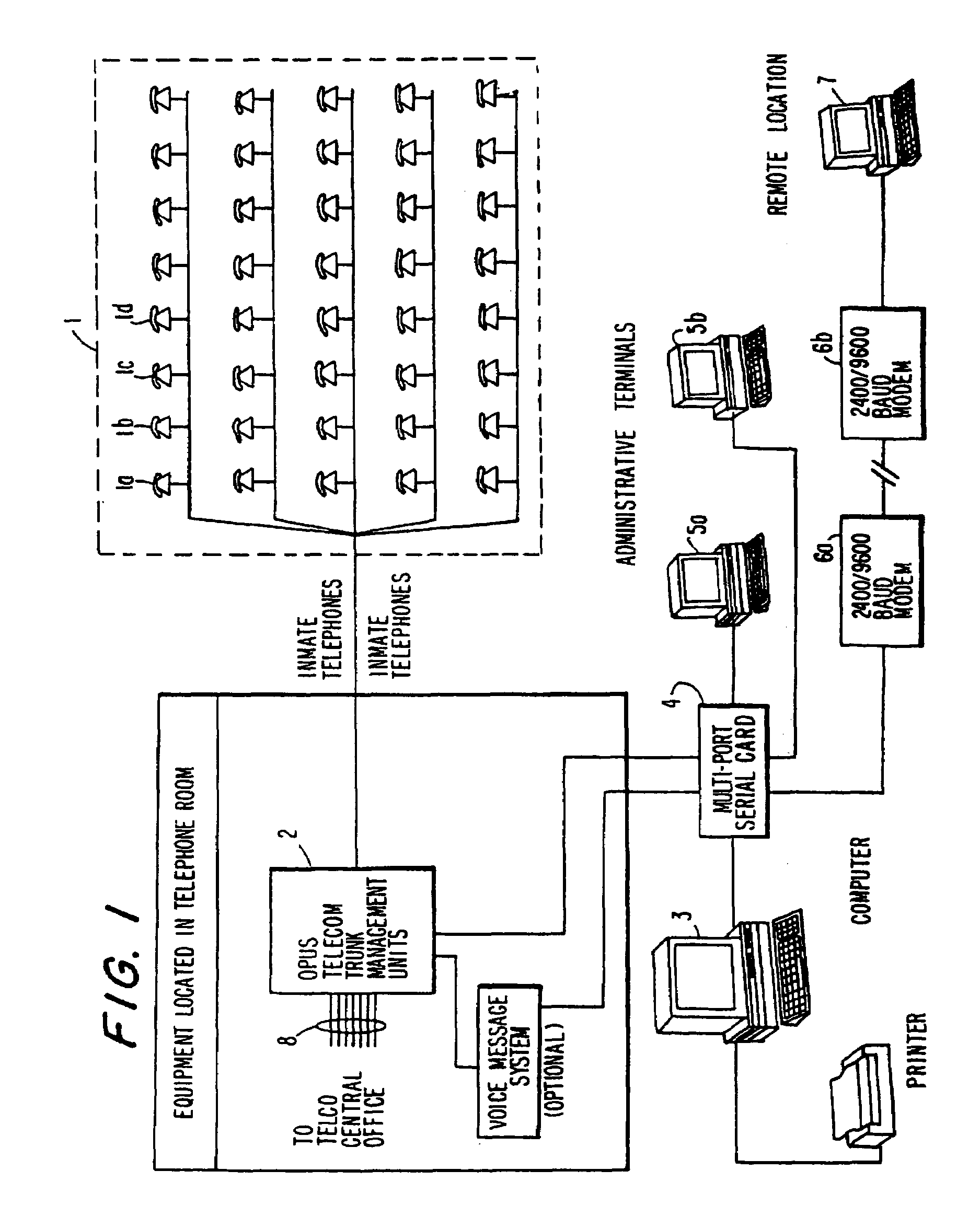
Computer-based method and apparatus for controlling, monitoring, recording and reporting telephone access
InactiveUS7248680B1Less false triggeringSimple and accurateUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionManual exchangesComputer basedTelephone line
A telephone station interface is provided with apparatus for detecting when a called party has or is attempting to patch or bridge one telephone call with another telephone call. The detecting of such bridging or conferencing is accomplished through the detection of tones which are commonly associated with such activities, such as a ring signal, a busy signal, special information tones (SIT tones), dual tone multi-frequency (DTMF) tones or so-called Touch Tones, call progress tones, or other tones that occur when calls are placed. The present invention does not have the capability of sensing clicks, pops, or other audio signals associated with the conferencing of multiple communications circuits. The method and apparatus herein are for managing institutional telephone activity, and utilize a computer control unit to control a trunk management unit, which connects institutional telephones to outside telephone lines.
Owner:SECURUS TECH +1
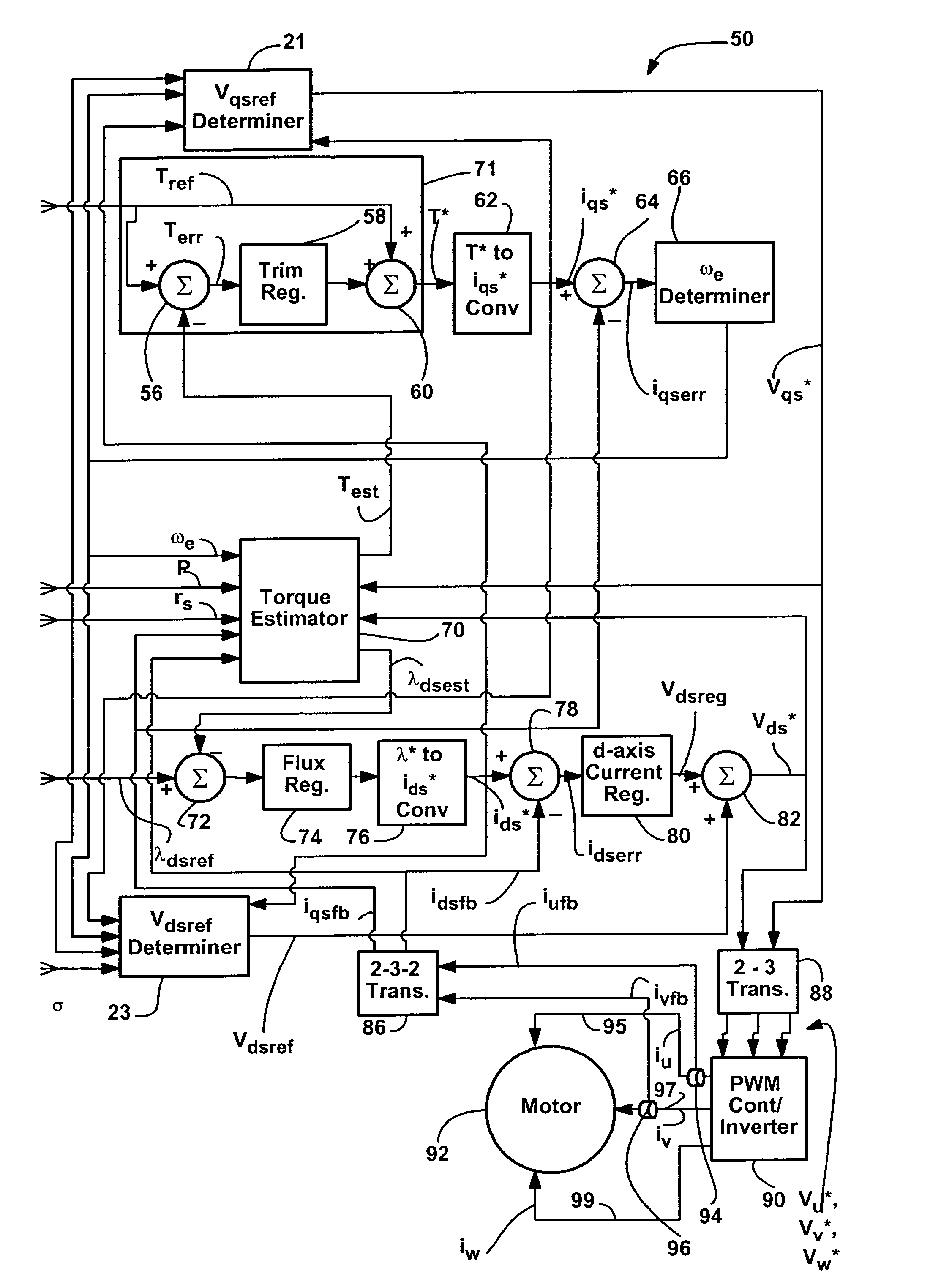
Method and apparatus to regulate loads
ActiveUS20050057208A1Simple and accurateEasy to getSynchronous motors startersAC motor controlEngineeringControl theory
A method and apparatus for use with a controller for controlling a machine wherein a torque reference value is provided, the method for identifying an error representative of the difference between the torque reference value and the torque applied to the machine and using the error value to modify machine operation, the method comprising the steps of obtaining feedback current values corresponding to the currents provided to the machine, mathematically combining the feedback current values to generate an error value, mathematically combining the error value and the torque reference value to generate a torque command value and using the torque command value to control the machine.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
Liver cancer methods and compositions
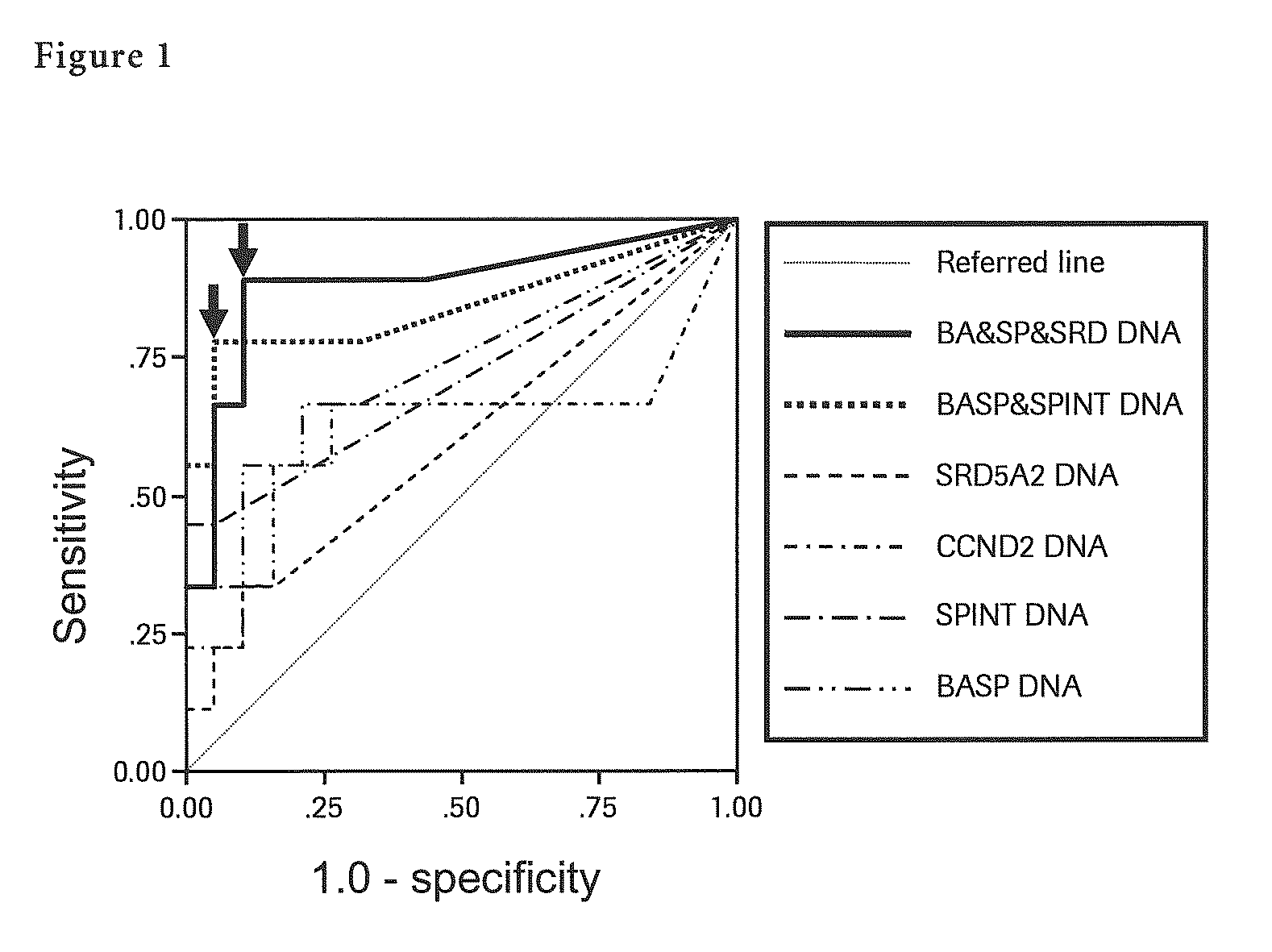
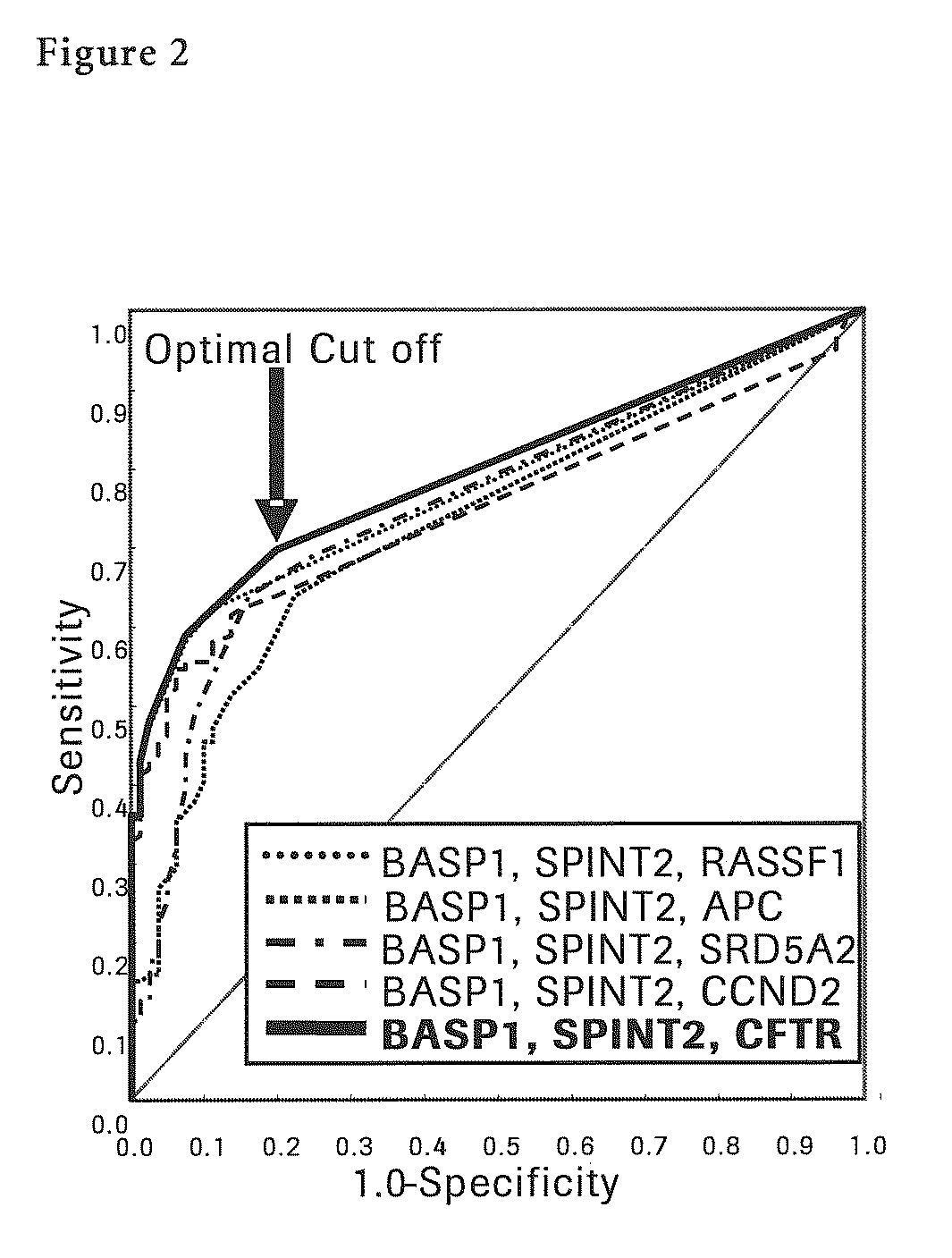
InactiveUS8927209B2Improve automationSimple and accurateSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAfter treatmentOncology
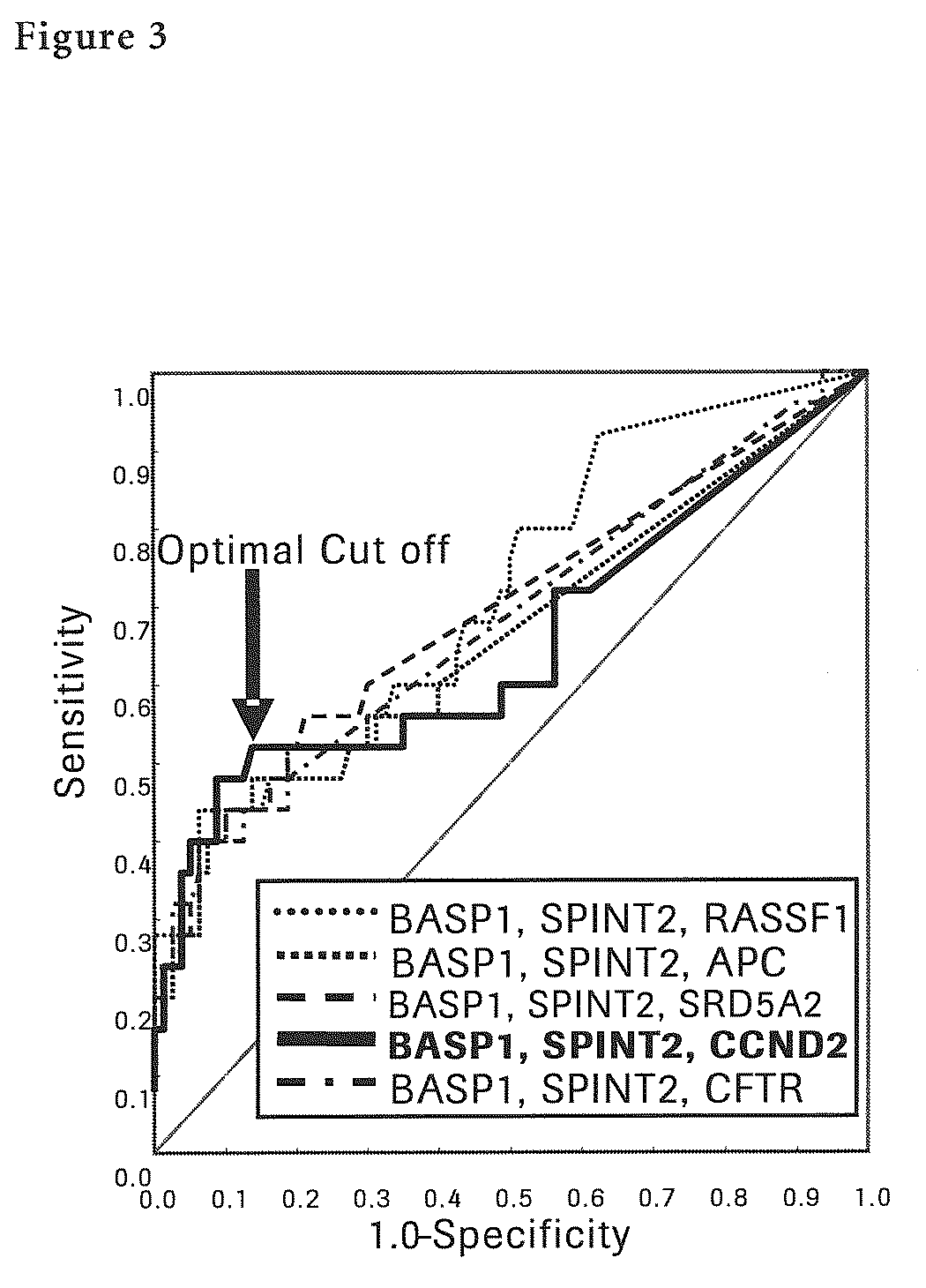
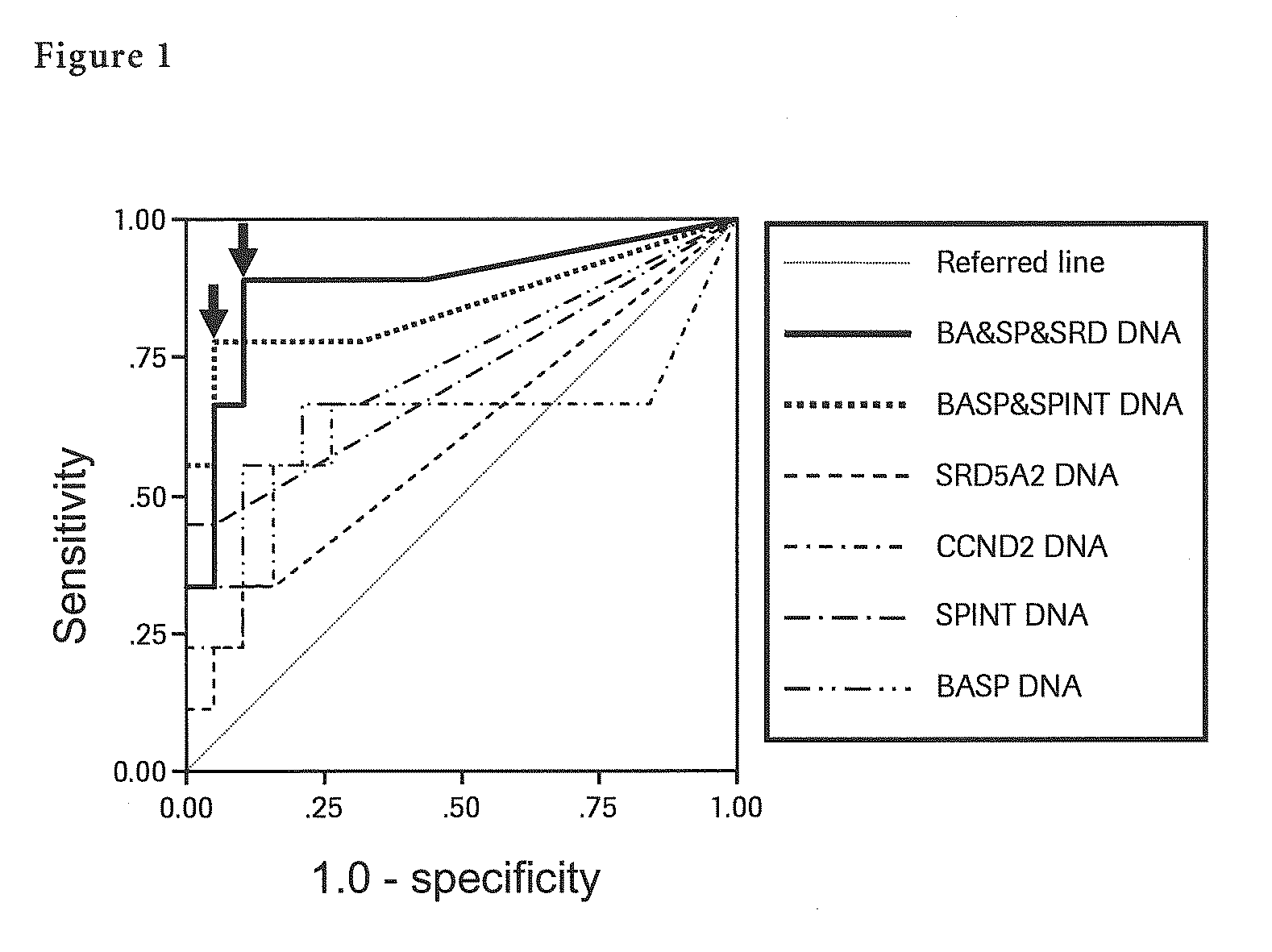
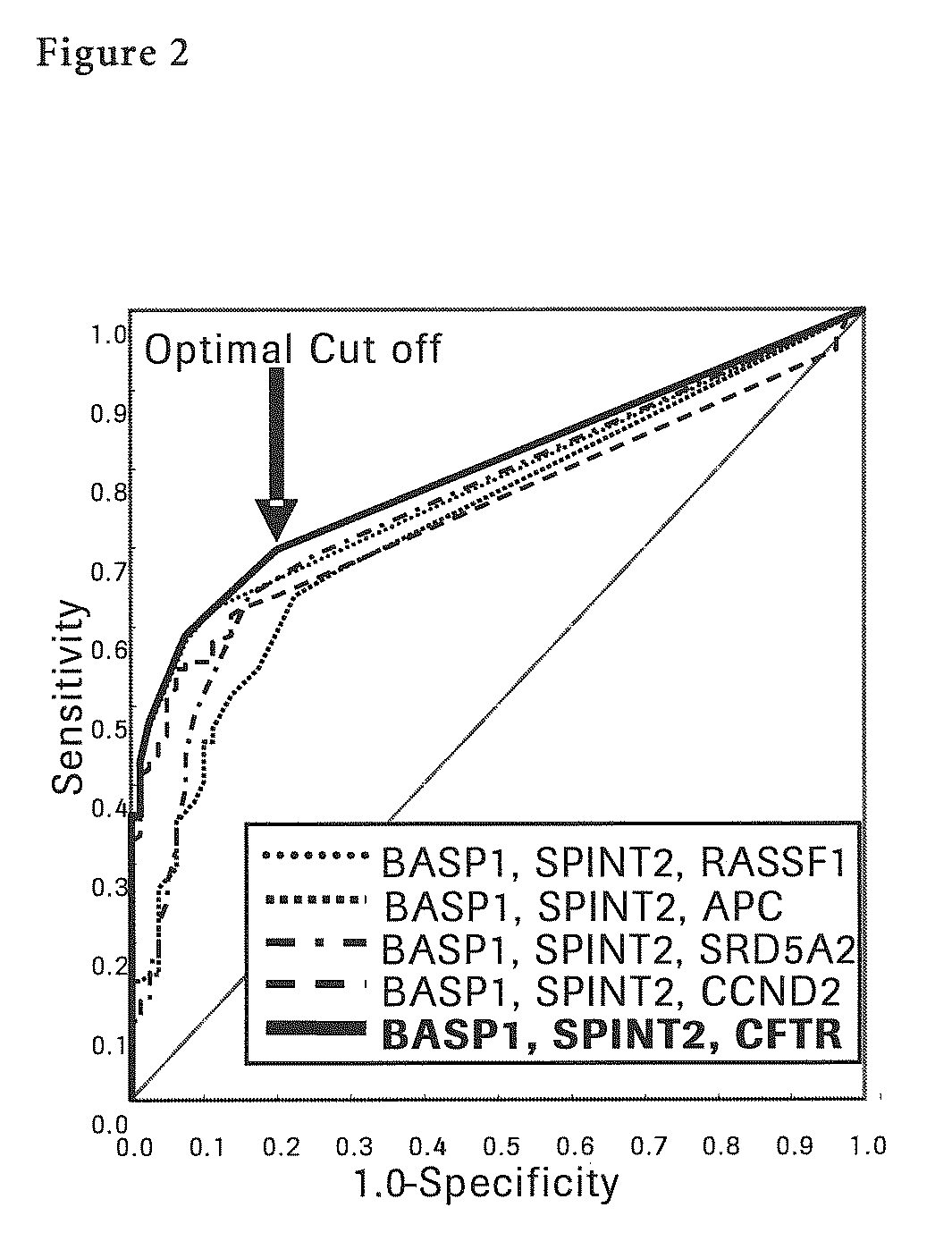
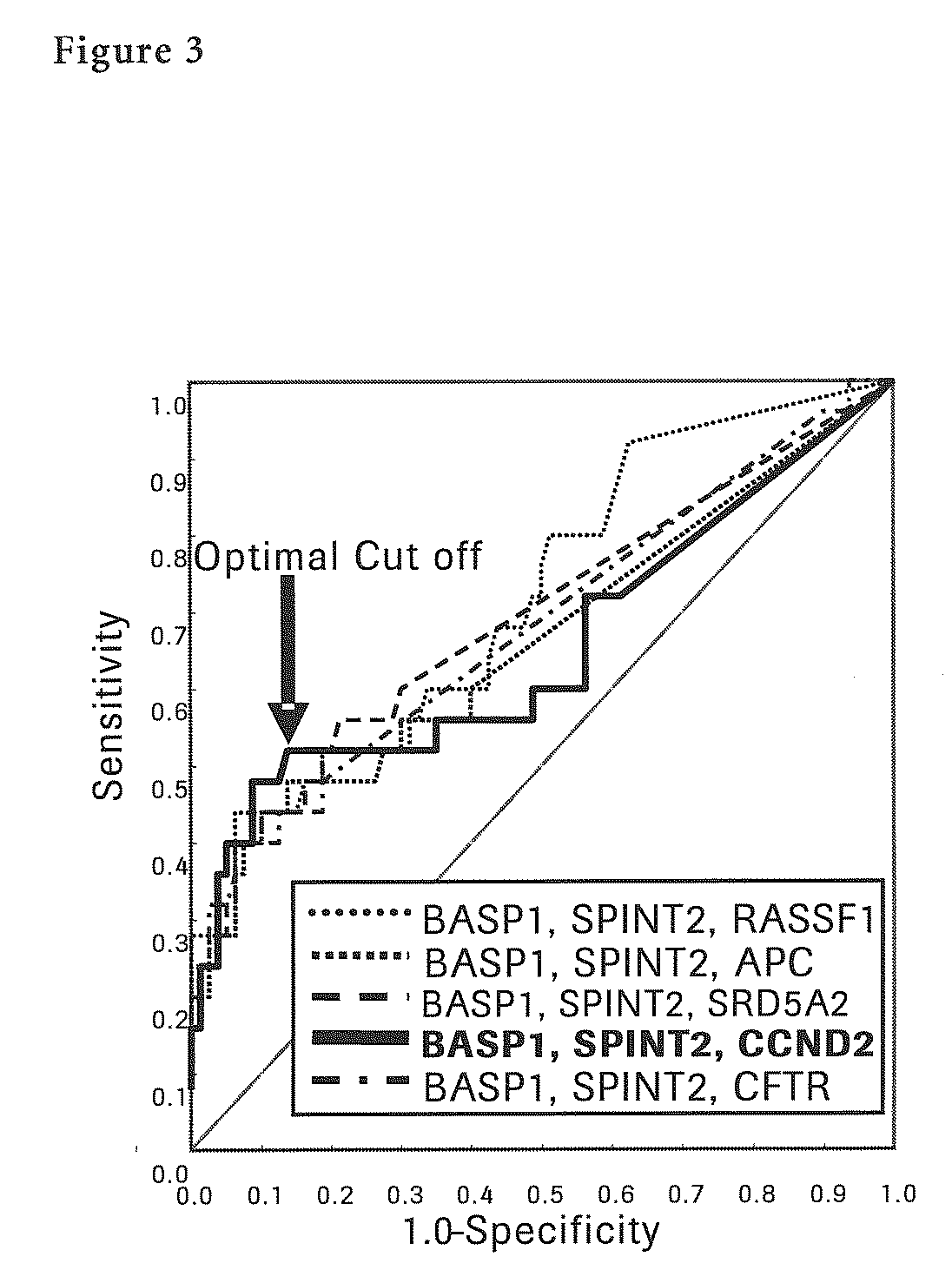
The present invention provides a novel method for detection of liver cancer. This method detects high-sensitively, high-specifically, simply and accurately liver cancer, especially that in early stage by identifying and / or quantifying methylation on particular genes and / or their DNA fragments in clinical specimens, and by combining said methylated DNA values with existing tumor marker values and / or DNA amounts in blood. This invention also detects a precancerous lesion, detects a risk of recurrence after treatment of liver cancer, detects malignancy of liver cancer and monitors progression of liver cancer with time by the same method. As for particular genes, BASP1 gene, SPINT2 gene, APC gene, CCND2 gene, CFTR gene, RASSF1 gene and SRD5A2 gene are mentioned.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Method of clipping signal amplitudes in a modulation system
InactiveUS6879642B2Simple and accurateMaintain directionAngle modulationFrequency-modulated carrier systemsEngineeringLimit value
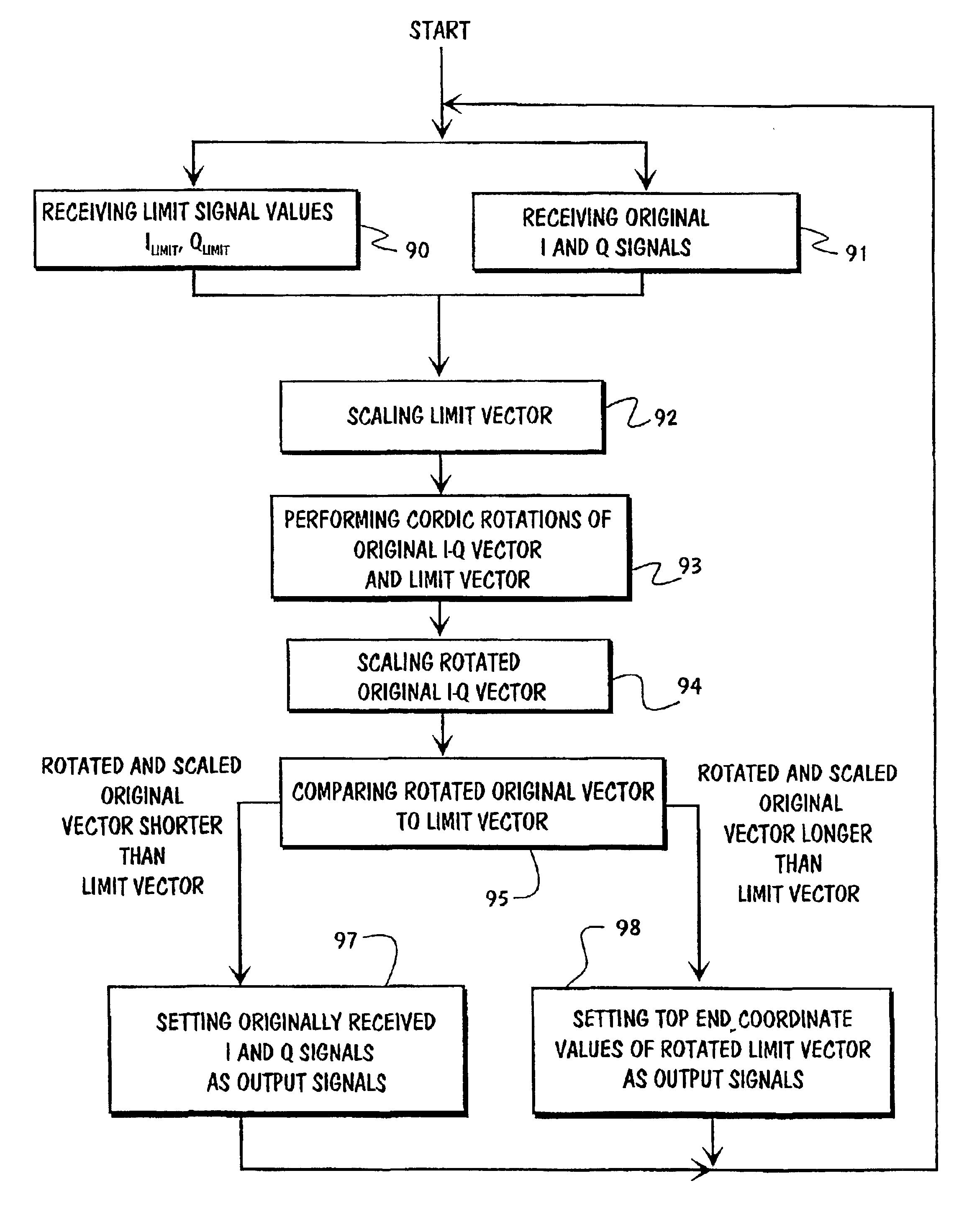
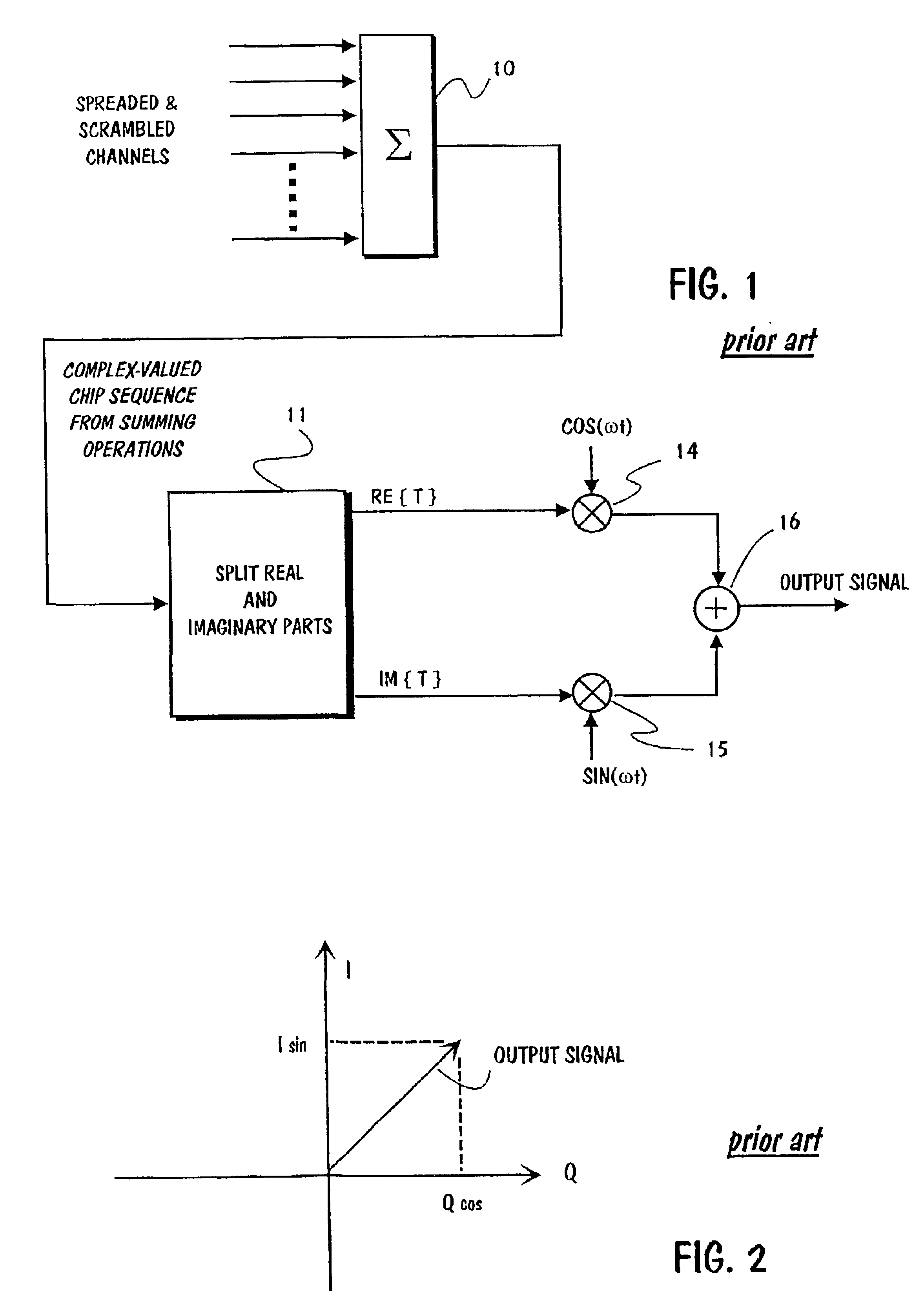
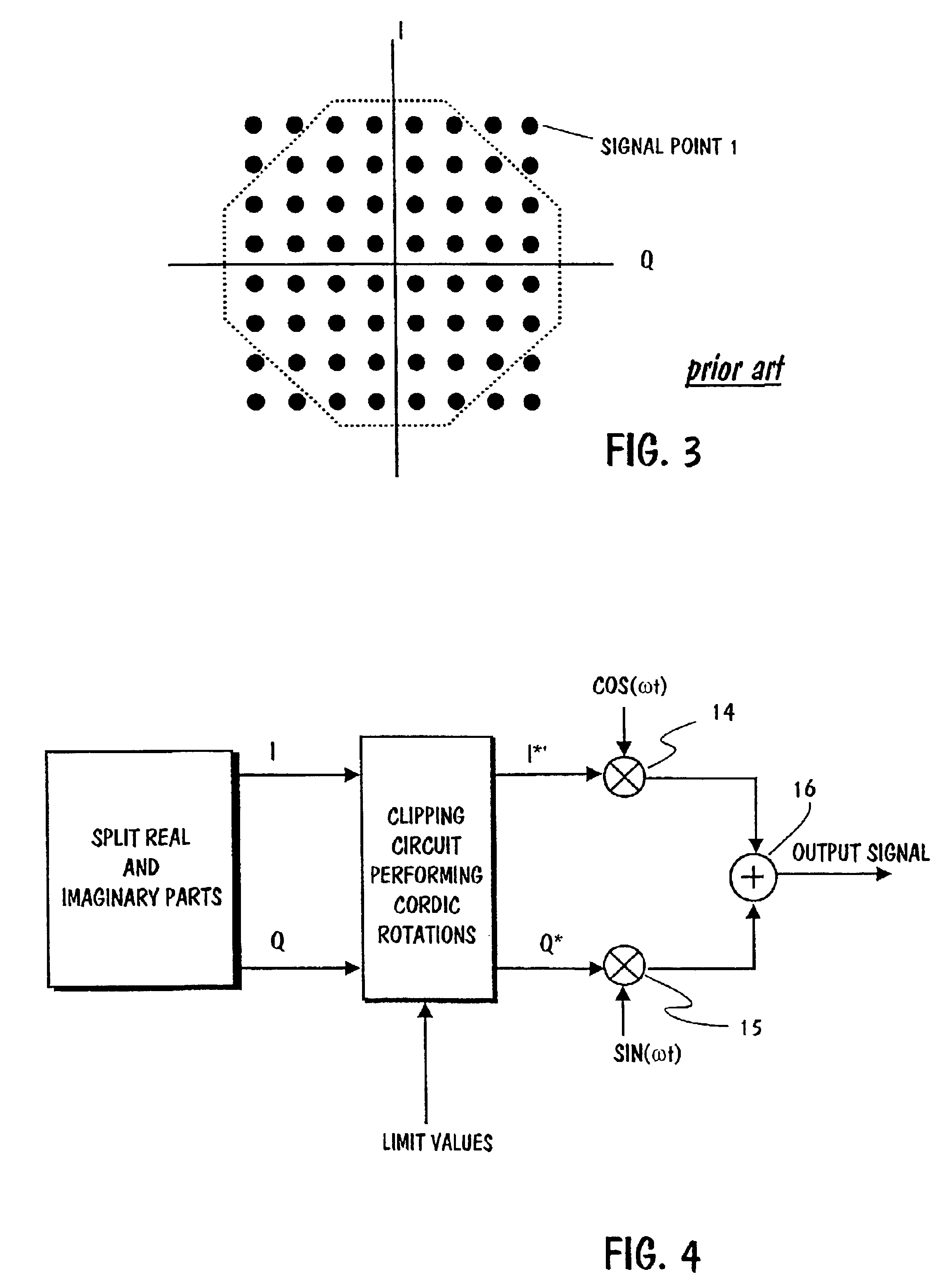
Amplitudes of signals produced by a digital modulator can be clipped so that instead of processing the output vector of the digital modulator or it's component vectors, processing is applied to the base band I and Q signals prior to modulation. The I- and Q signals are applied to an input of a clipping circuit. Predetermined limit values are also applied to another input of the clipping circuit. The clipping circuit rotates on the I-Q vector towards the limit vector. At the same time the limit vector is rotated towards the I-Q vector. Rotations are performed by using Cordic algorithm. After rotations have been completed, the rotated I-Q vector is aligned with the original limit vector, and the rotated limit is aligned with the original I-Q vector. Then the length of the rotated I-Q vector will be compared with the original limit vector. If the rotated I-Q vector is shorter than the limit vector, then the original I-Q signals are output signals from the clipping circuit. But if the rotated original I-Q vector is longer than the limit vector, then the original I-Q signals will be rejected and substituted by the coordinate values of the rotated limit vector.
Owner:RPX CORP
Method and device to measure the brake force for railroad vehicles
InactiveUS6662641B2Improve consistencyThe process is simple and accurateEngine testingForce measurementRubber membraneBrake shoe
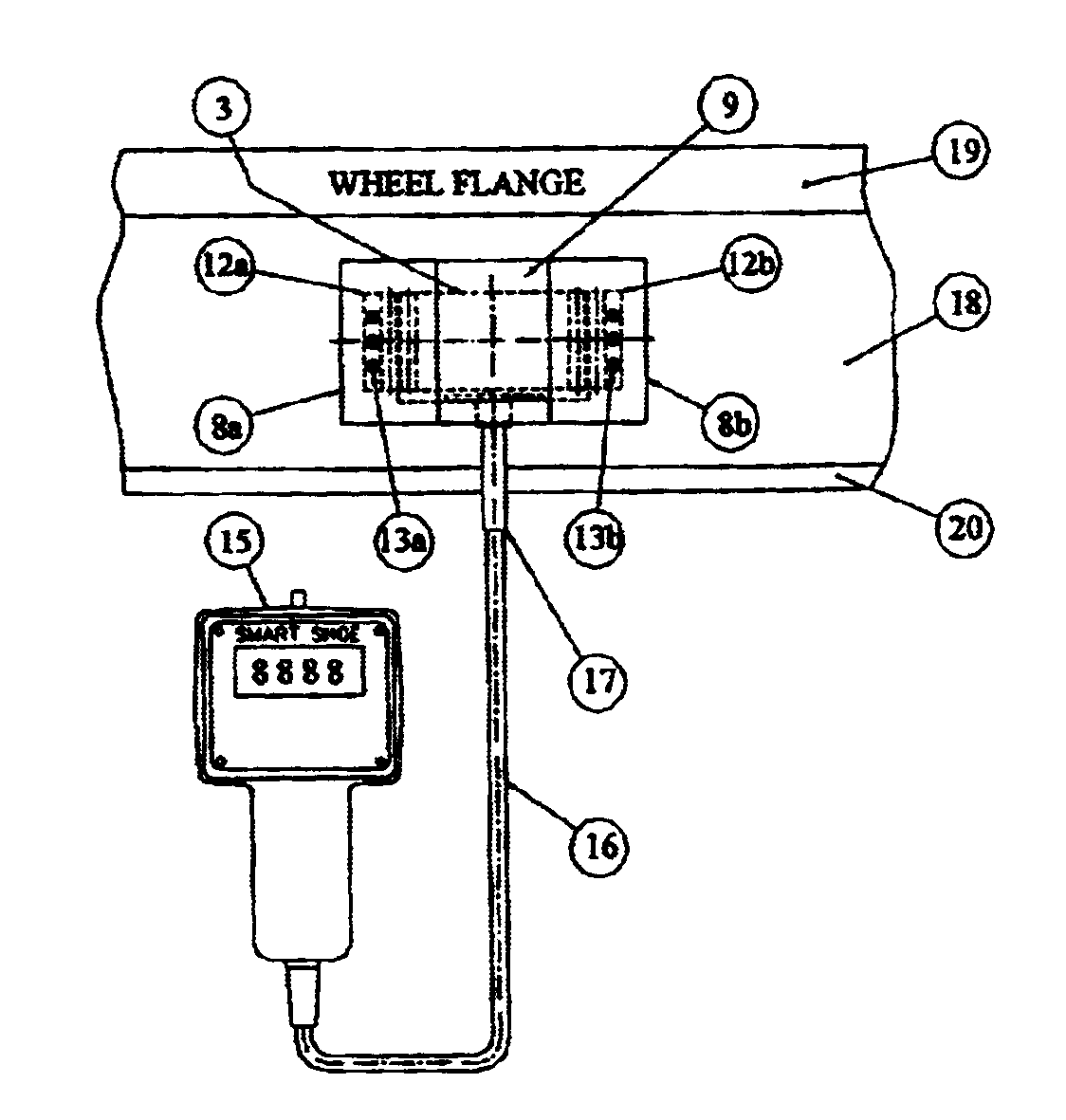
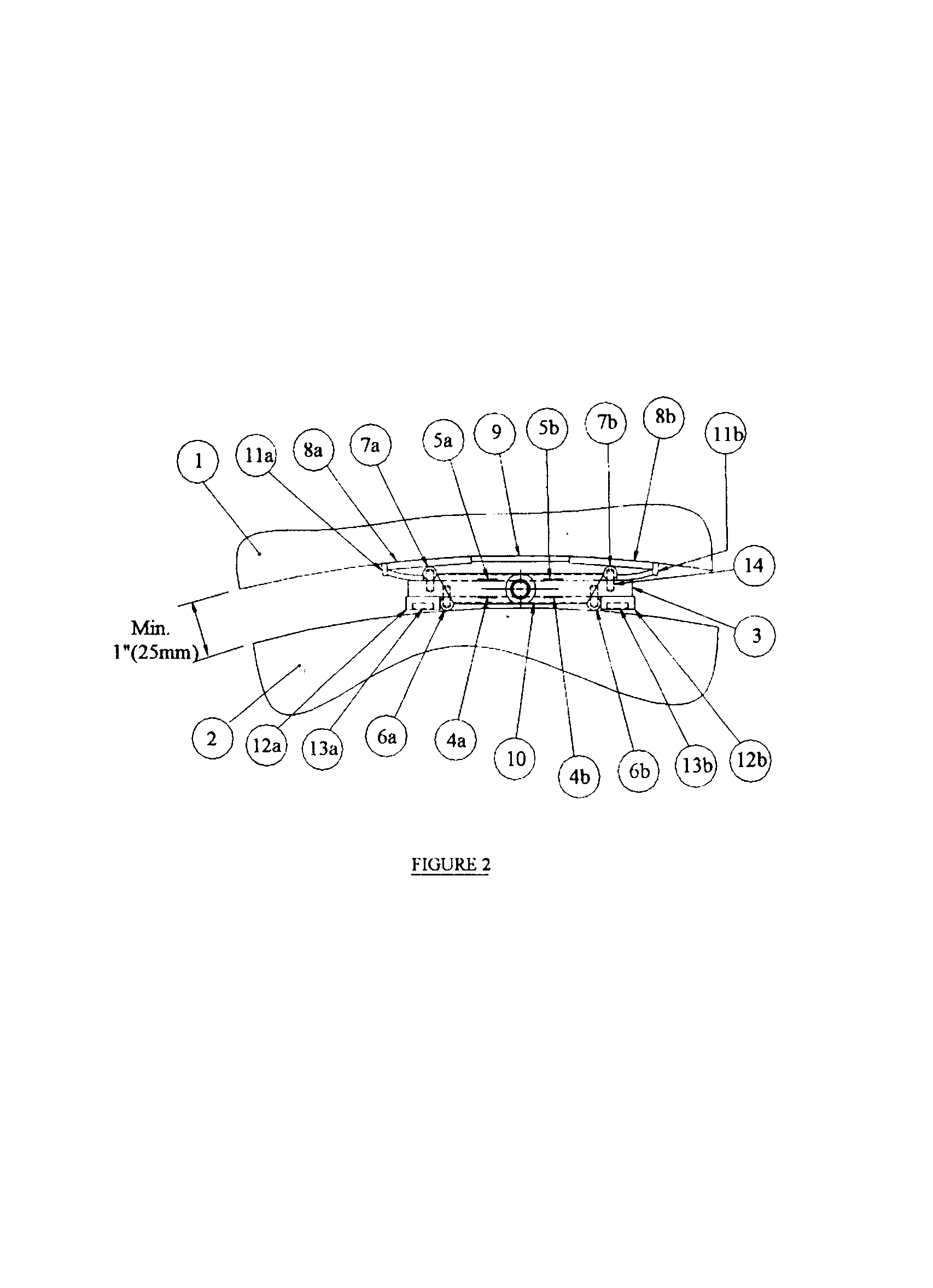
A method to measure the brake force for railroad vehicles without replacing any part of the braking system, comprising the steps of opening a clearance between the braking elements, inserting a special sensor between the braking elements and applying the brake followed by the processing of the signal generated by the sensor and displaying the result in force units. A device to measure the brake force for railroad vehicles, which uses a sensor, the main part of which is a prismatic steel plate (3) with strain gauges (4a, 4b, 5a, 5b,) on both sides. To measure the brake force, the sensor is positioned, depending on the braking system, between the brake shoe (1) and the wheel tread (2) or between the brake pad and the brake disc. When the brake is applied, the sensor comes in contact with the braking surfaces (brake shoe / brake pad and wheel tread / brake disc) through (the intermediary of) four drill rods (6a, 6b, 7a, 7b,) affixed to the sensor body (3), two on each side, in such a way that the mechanical contact between each rod and the sensor body is over a line and the sensor is submitted to a bending moment. To make the device adaptable to any wheel diameter or wear of the brake components and to protect the brake shoe surface, each of the two rods (7a, 7b,) on the brake shoe side (for braking systems using a brake shoe), has a steel wing (8a, 8b,) elastically seated on it. The wings are kept in place by three rubber membranes (9, 11a, 11b,) connecting the wings between them and to the sensor body. The sensor is kept in place during measurements by two sets of magnets (13a, 13b) embedded into two rubber strips (12a, 12b,) bonded on two opposite sides of the sensor body (3).
Owner:SCORTEANU ROMEL +1
Device and method for determining weight, in particular the weight of a container filled with product
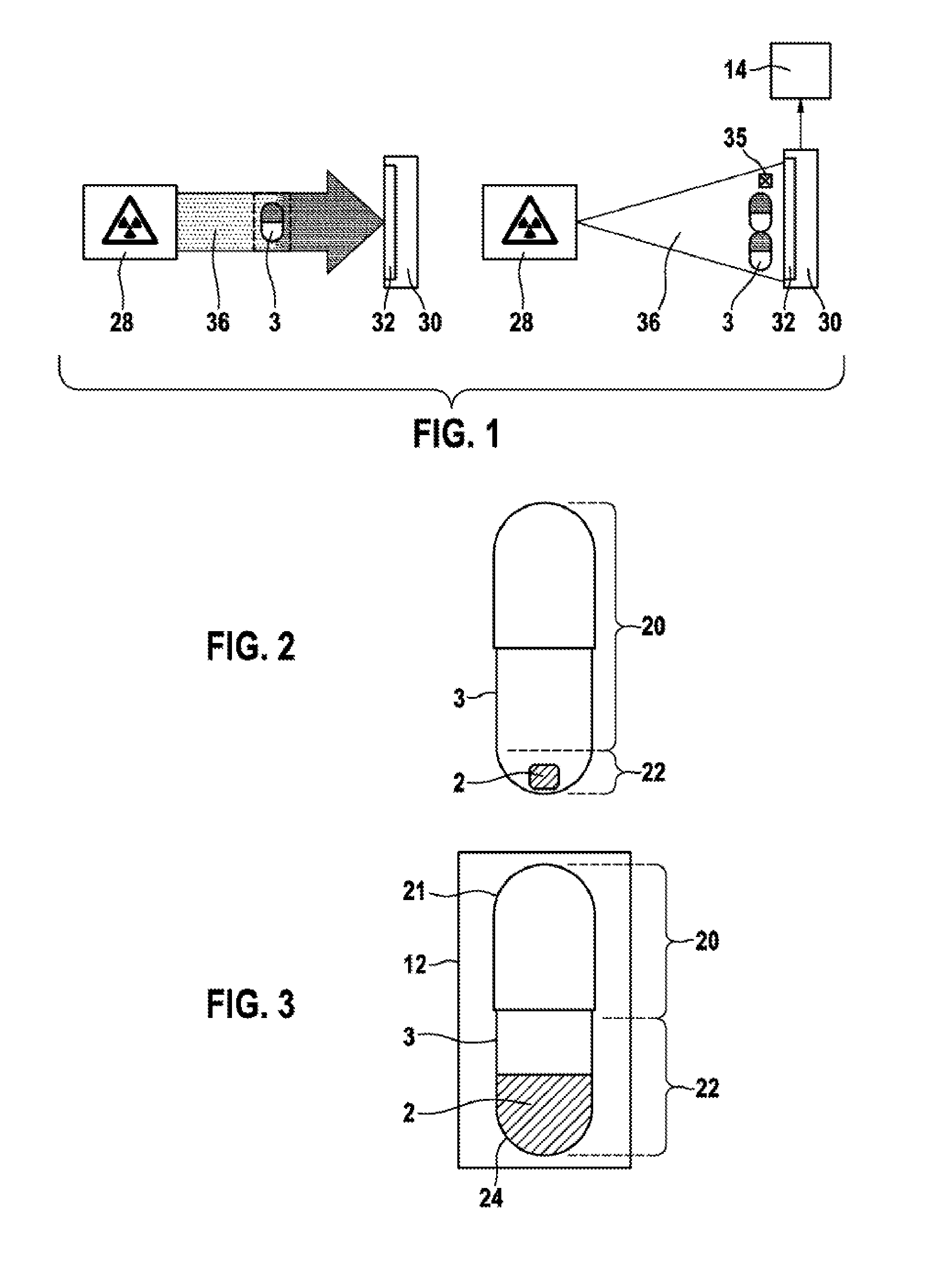
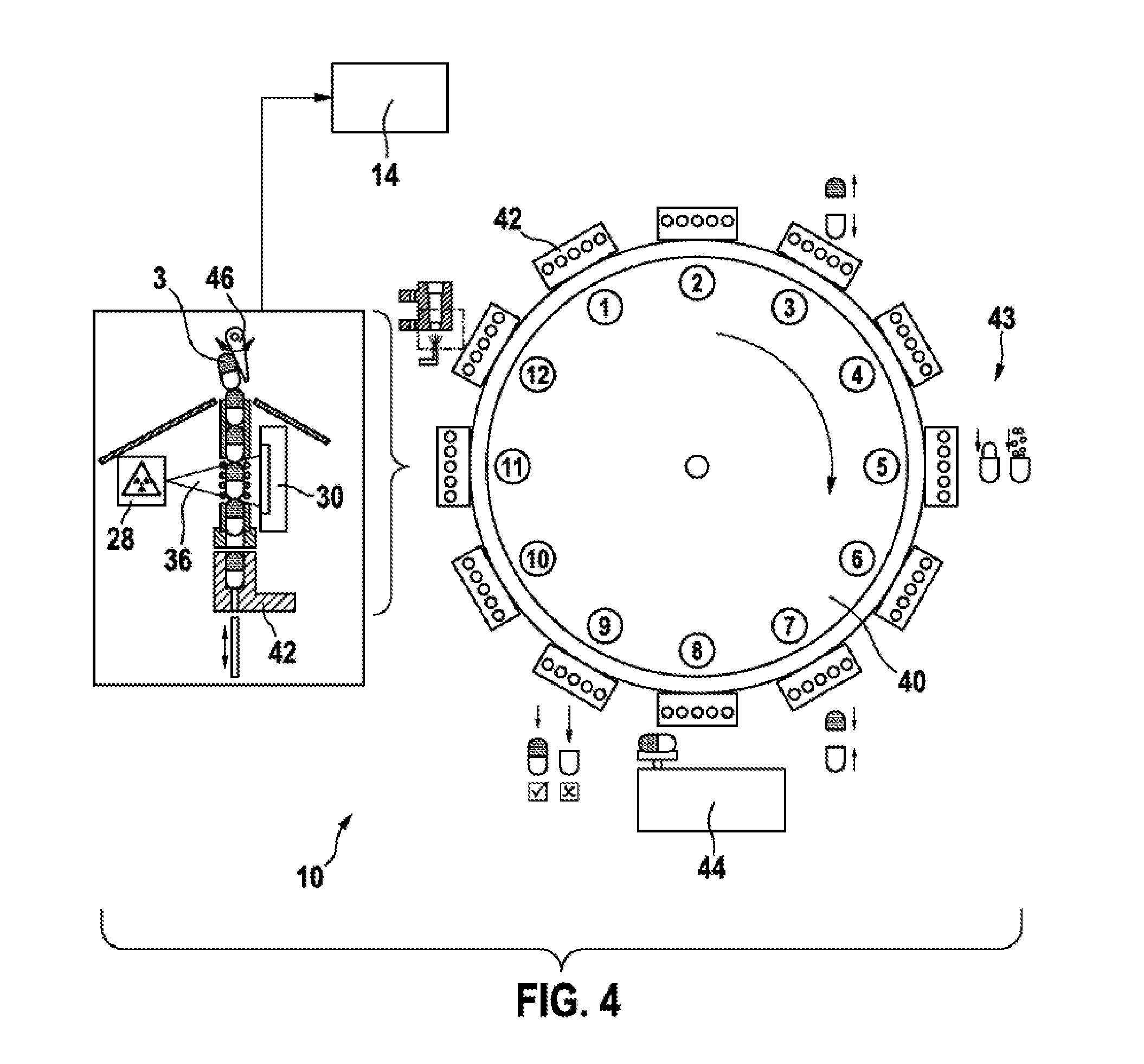
ActiveUS20160140413A1The process is simple and accurateImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisX-rayEngineering
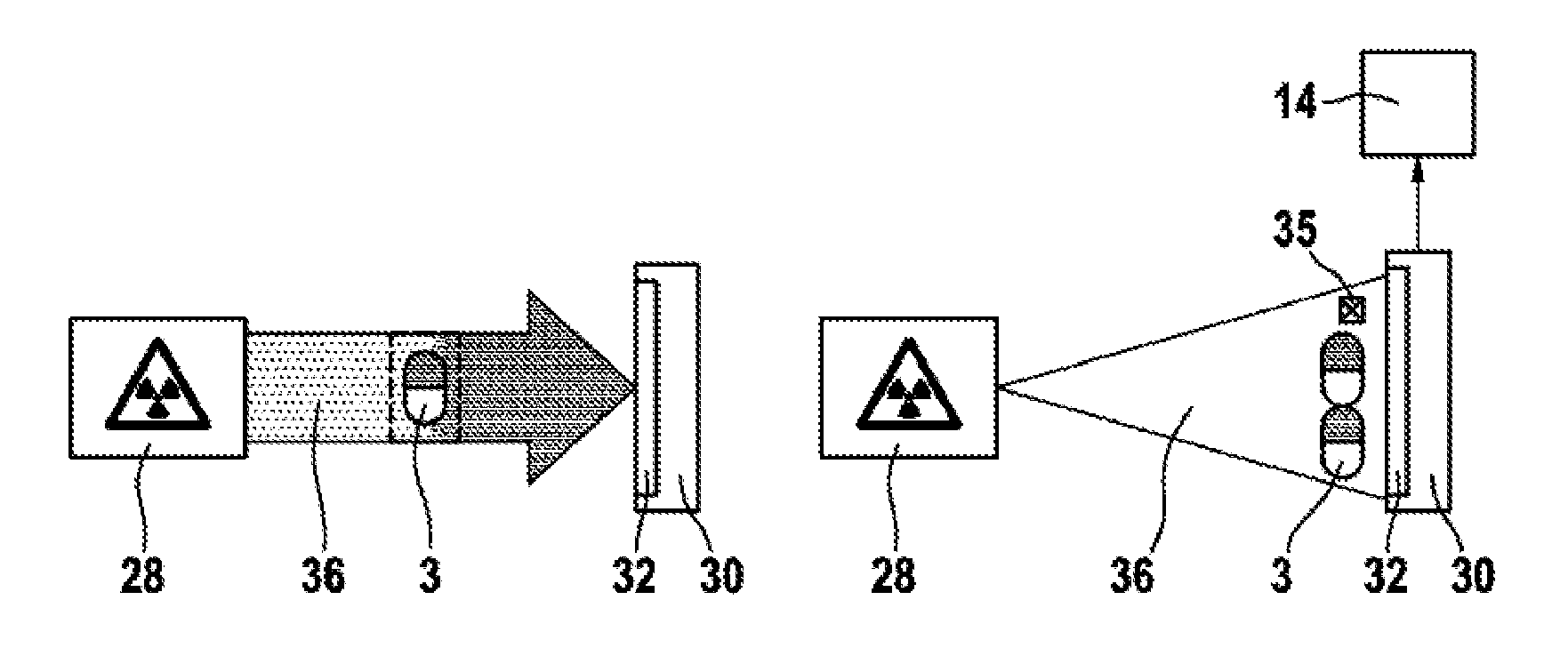
The invention relates to a device and a method for determining the weight of product (2), in particular a pharmaceutical product, which is located in a container (3). The device comprises at least one x-ray source (28), which produces a radiation path (18), for passing radiation through the container (3), and a sensor (14), which detects the radiation of the container (3) through which radiation is passed in the form of an image (12), wherein an evaluating apparatus (14), is provided, which divides the image (12) of the container (3) through which radiation is passed into at least one evaluation region (21) in which there is no product (2).
Owner:SYNTEGON TECHNOLOGY GMBH
Image comparison method and device, equipment and storage medium
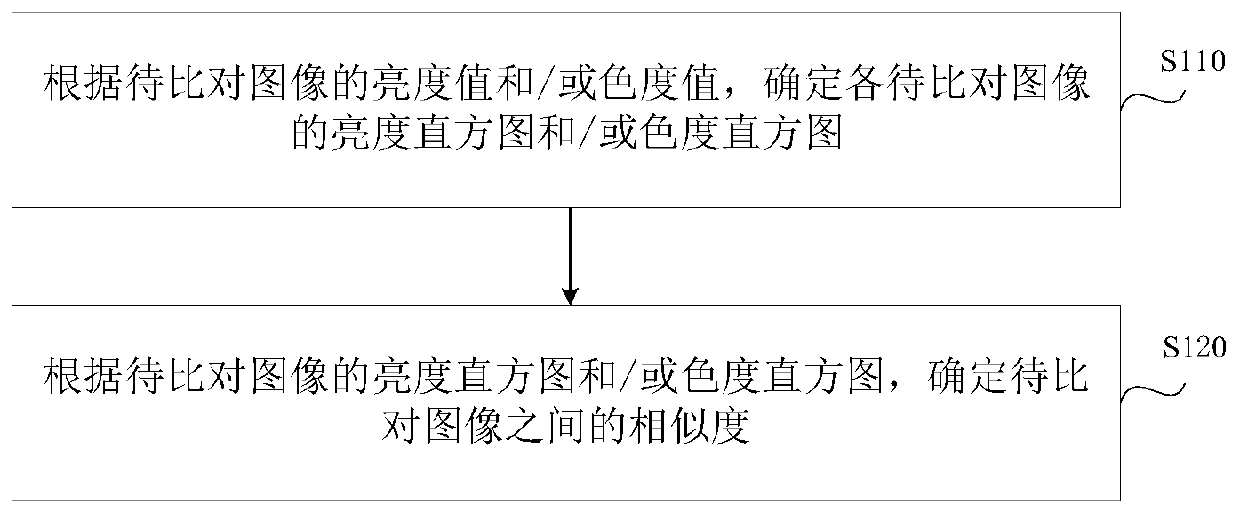
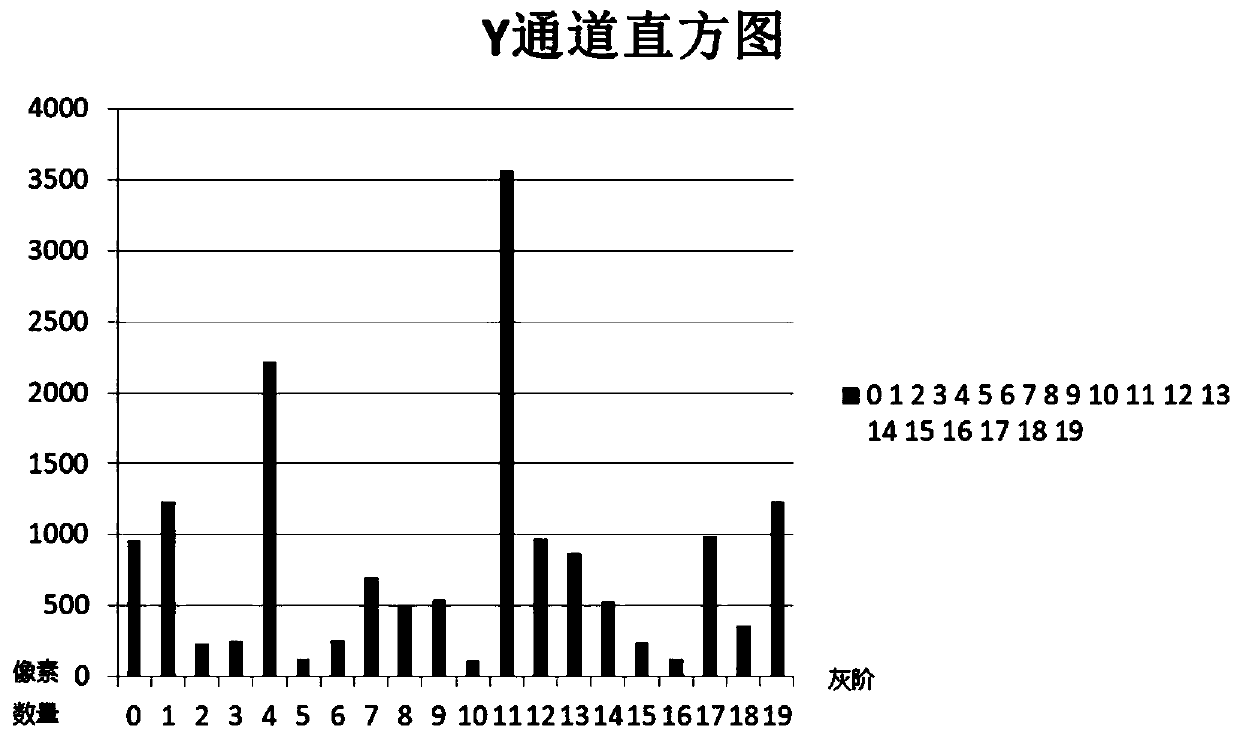
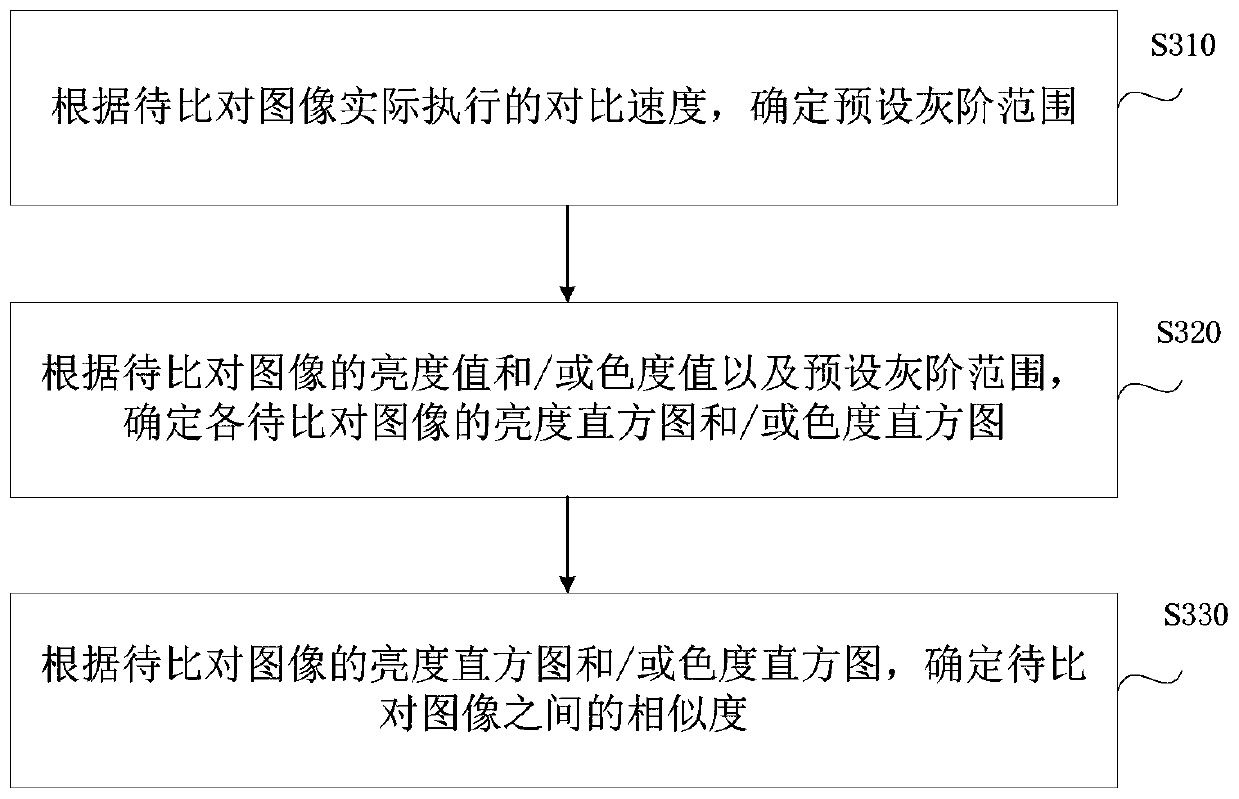
ActiveCN110533117AAccurate comparisonQuick searchCharacter and pattern recognitionBrightness perceptionHistogram
The embodiment of the invention discloses an image comparison method and a device, equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of determining a brightness histogram and / or a chrominance histogram of each to-be-compared image according to brightness values and / or chrominance values of the to-be-compared images; and according to the brightness histogram and / or chrominance histogram of the to-be-compared image, determining the similarity between the to-be-compared images, so that not only can similar images be quickly searched, but also the implementation process is simple andefficient.
Owner:浙江齐聚科技有限公司
Machine learning-based bimodal image omics ground glass nodule classification method
PendingCN112767393AAids in clinical managementImprove predictive performanceImage enhancementImage analysisClassification methodsCt examination
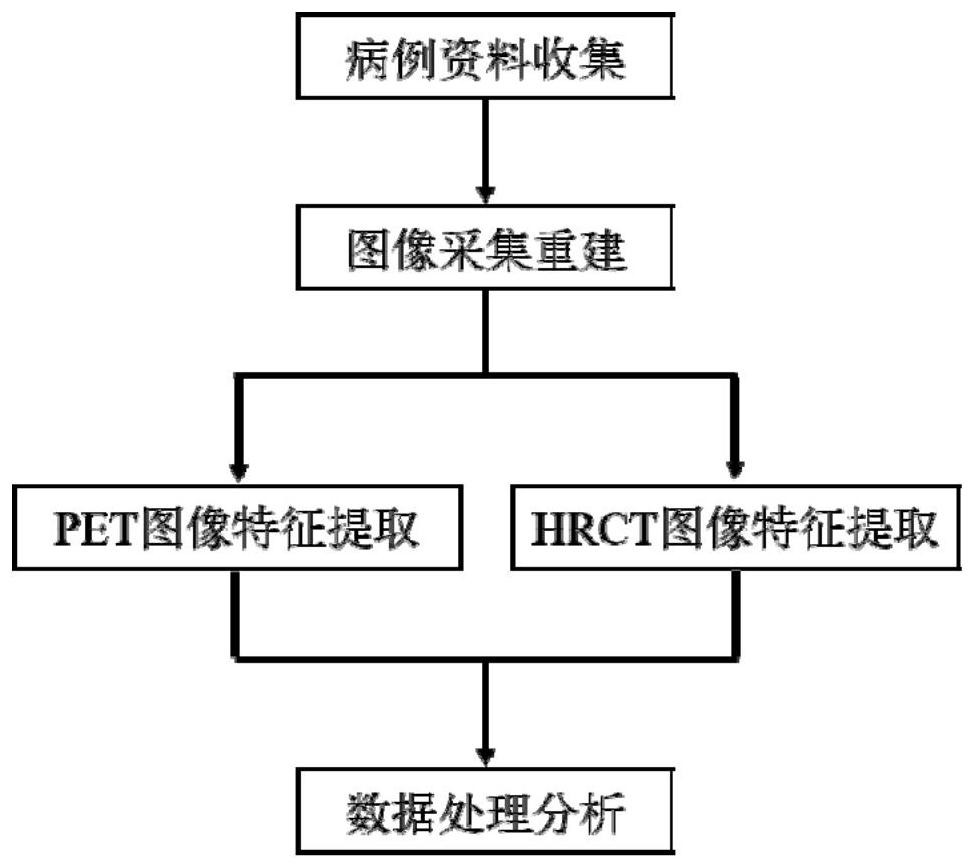
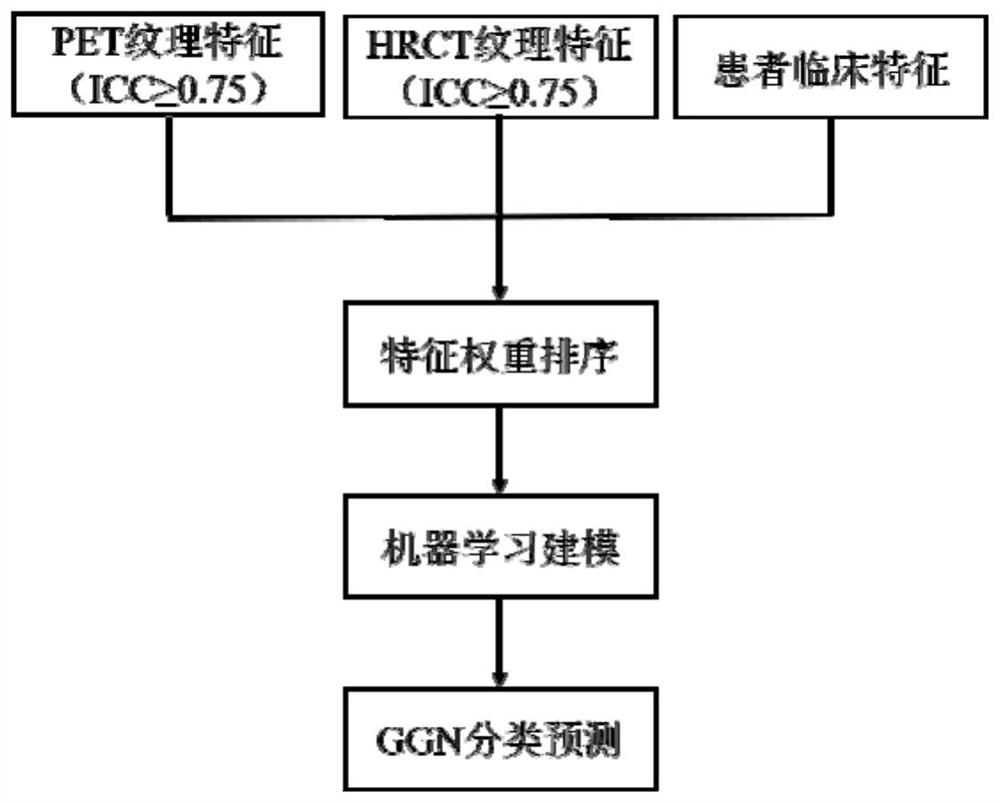
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical treatment, and discloses a machine learning-based bimodal image omics ground glass nodule classification method, which comprises the following steps of: step 1, case data collection: collecting patients who receive 18F-FDG PET / CT examination due to suspicious ground glass nodules (GGN); step 2, image acquisition and reconstruction: performing image acquisition by adopting a PET / CT (positron emission tomography / computed tomography) imaging instrument; step 3, image feature extraction; and step 4, data processing and analysis. According to the method, the image omics model based on the combination of the PET image and the HRCT image is constructed by applying a machine learning method, the GGN is classified, including pre-infiltration lesion, micro-infiltration adenocarcinoma, infiltration adenocarcinoma and benign lesion, verification and testing, the method is good in robustness, high in accuracy, simple and feasible. According to the method, the functional metabolism information and the physical anatomical information of the molecular level of the focus are integrated, the prediction efficiency of traditional CT parameters and single CT radiomics is effectively improved, and clinical management of the GGN is facilitated.
Owner:THE FIRST PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF CHANGZHOU
Liver Cancer Methods and Compositions
InactiveUS20100304372A1Improve automationThe process is simple and accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementMalignancyWilms' tumor
The present invention provides a novel method for detection of liver cancer. This method detects high-sensitively, high-specifically, simply and accurately liver cancer, especially that in early stage by identifying and / or quantifying methylation on particular genes and / or their DNA fragments in clinical specimens, and by combining said methylated DNA values with existing tumor marker values and / or DNA amounts in blood. This invention also detects a precancerous lesion, detects a risk of recurrence after treatment of liver cancer, detects malignancy of liver cancer and monitors progression of liver cancer with time by the same method. As for particular genes, BASP1 gene, SPINT2 gene, APC gene, CCND2 gene, CFTR gene, RASSF1 gene and SRD5A2 gene are mentioned.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
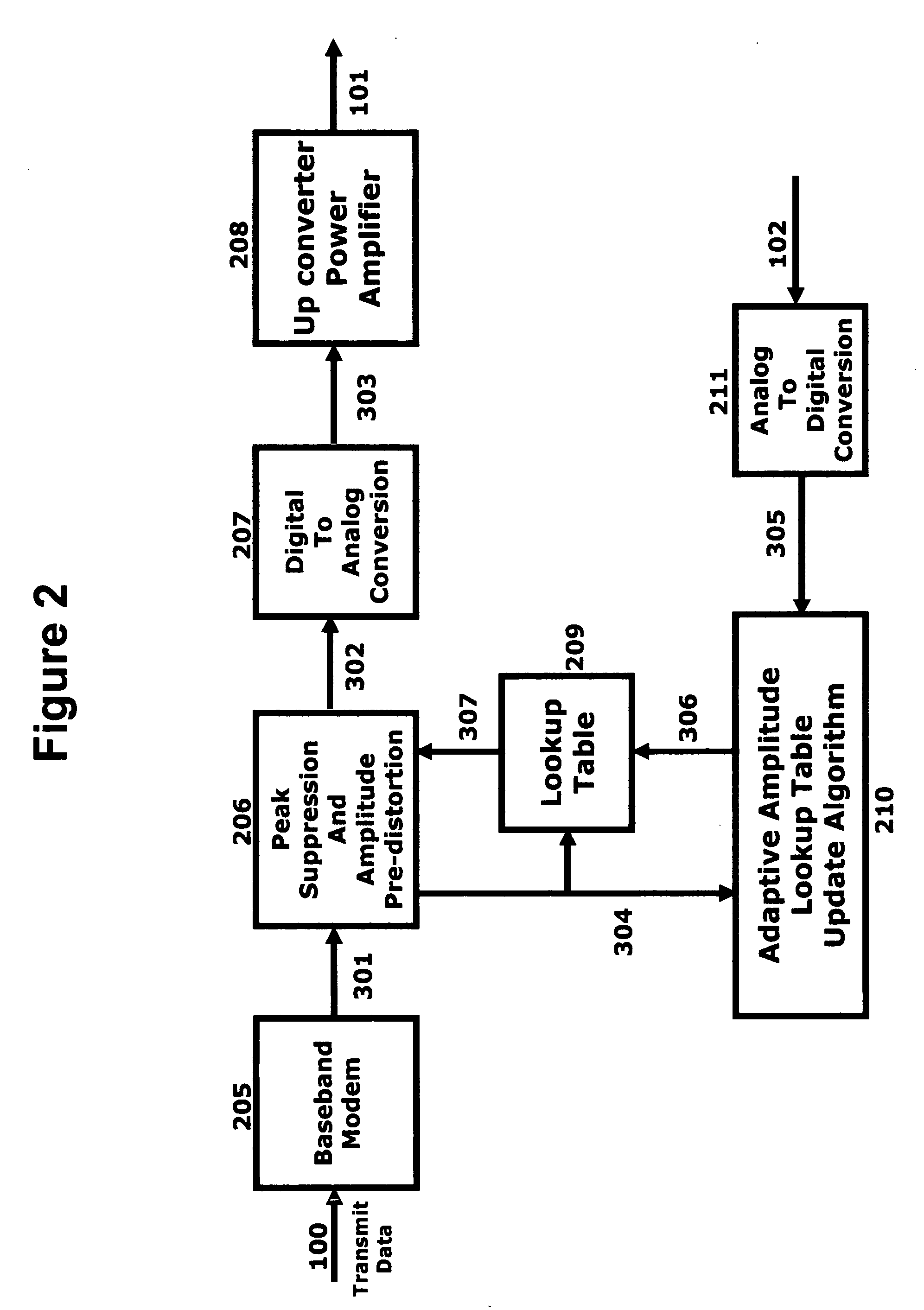
Power booster using peak suppression and pre-distortion for terminal radios
ActiveUS20050141639A1Improve transmission powerSimple and accurateAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyPeak valueEngineering
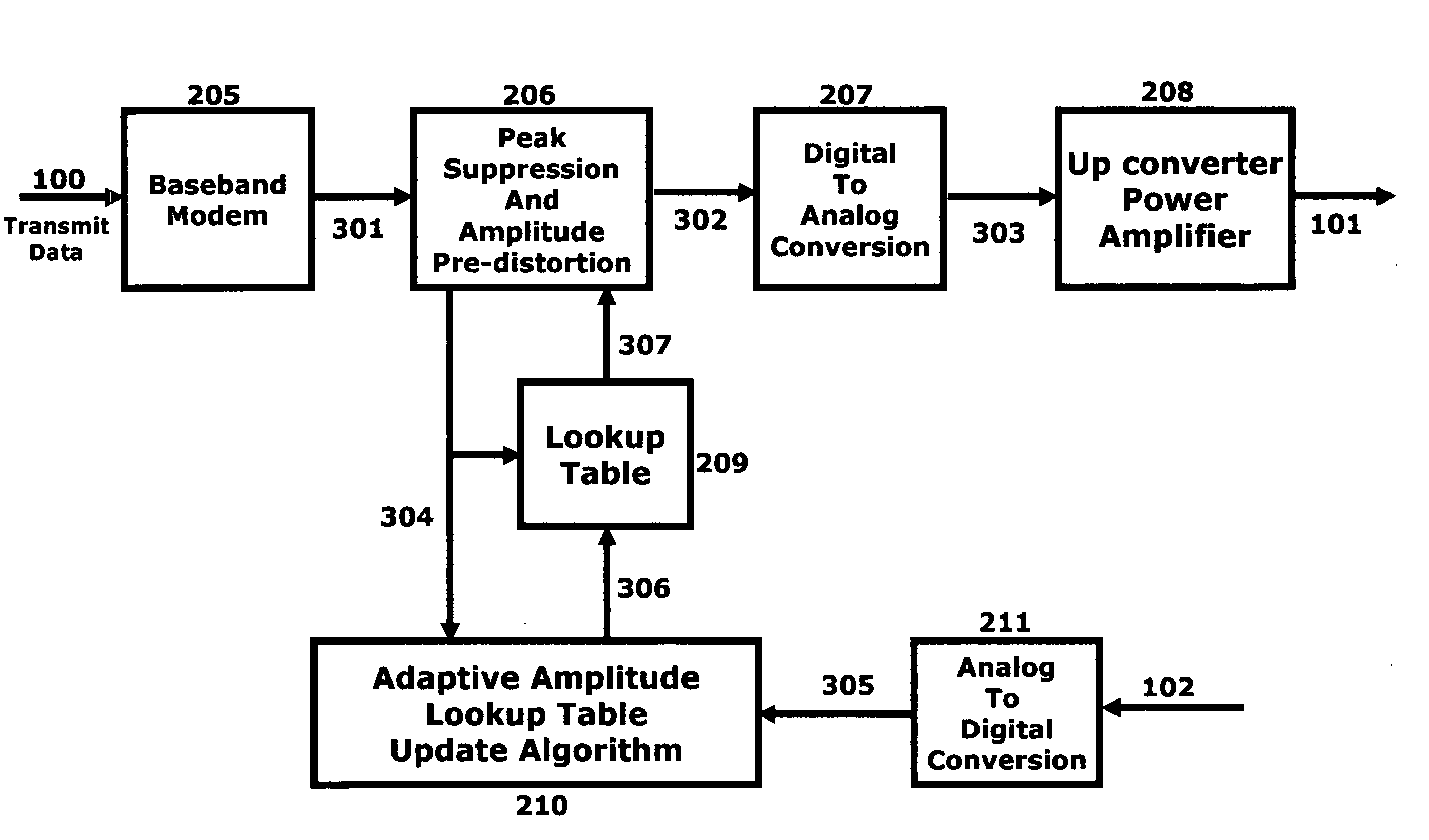
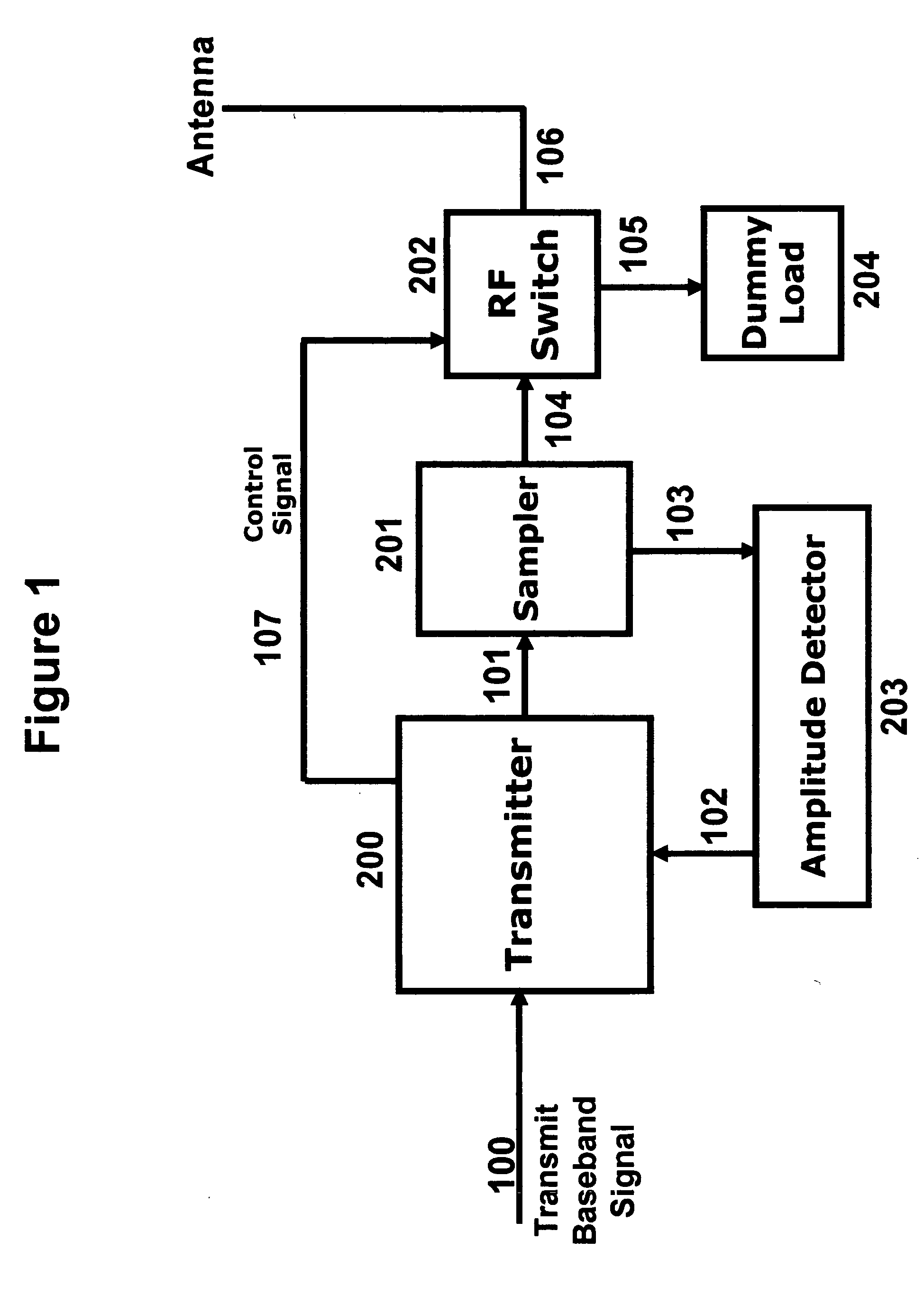
A technique to boost the output power of portable radio terminals without increasing the power dissipation is described. The input to the terminal transmit amplifier is modified by a peak-to-average reduction and amplitude pre-distortion circuit, prior to being applied to the amplifier. The peak-to-average reduction and pre-distortion circuit clips the baseband samples before applying any amplitude pre-distortion if they exceed a predefined value The peak-to-average reduction and pre-distortion circuit uses a lookup table to pre-distort the peak-to-average reduced signal. The amplitude pre-distortion lookup table is being updated at power up or power down of the terminal radio, during idle time, just before origination of a call, before termination of a call, or while the call is active. During the updating of the lookup table the radio could be in its normal transmit mode, or transmit into a dummy load using an analog transmit switch controlled from the peak-to-average reduction and pre-distortion circuit.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
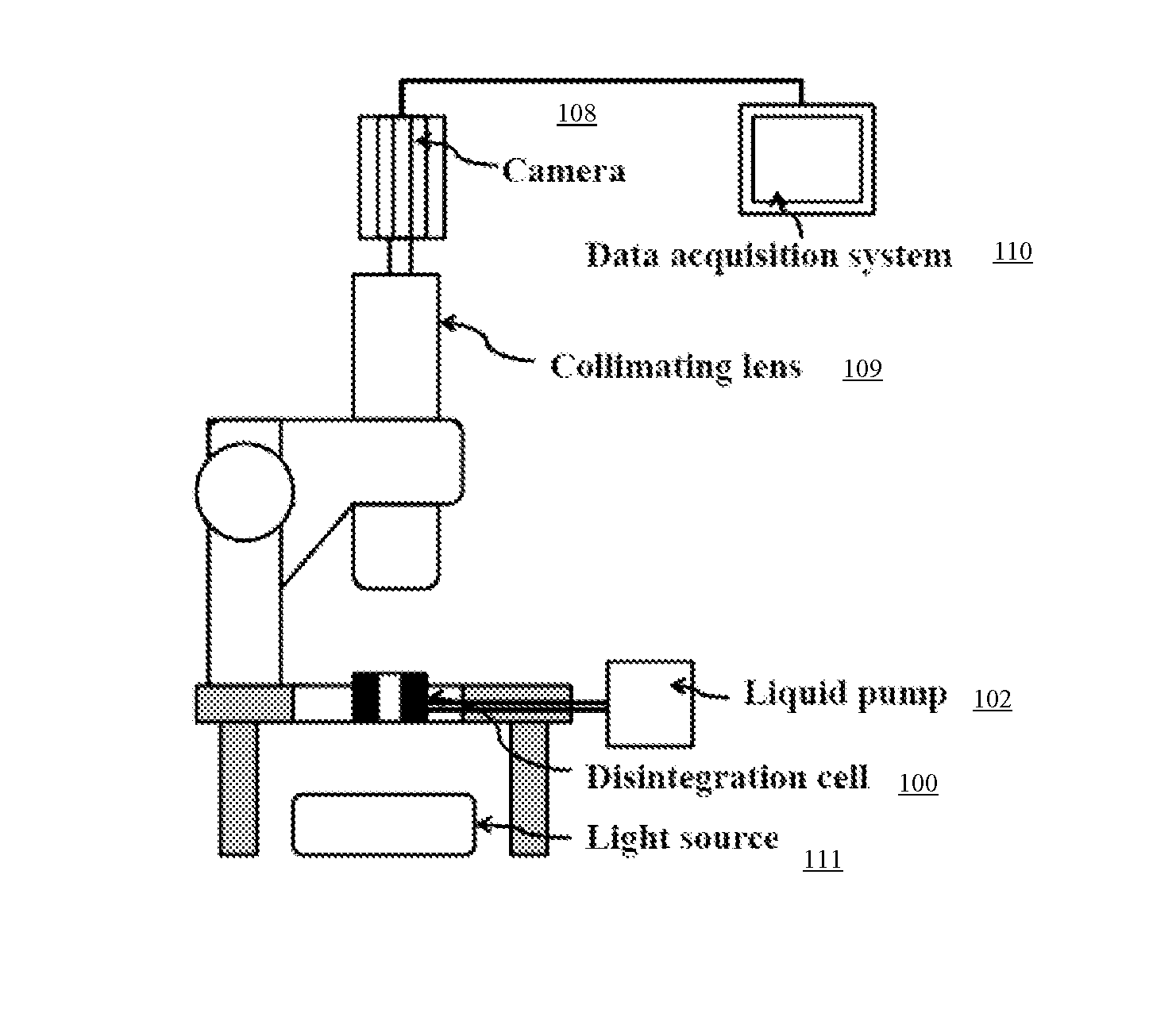
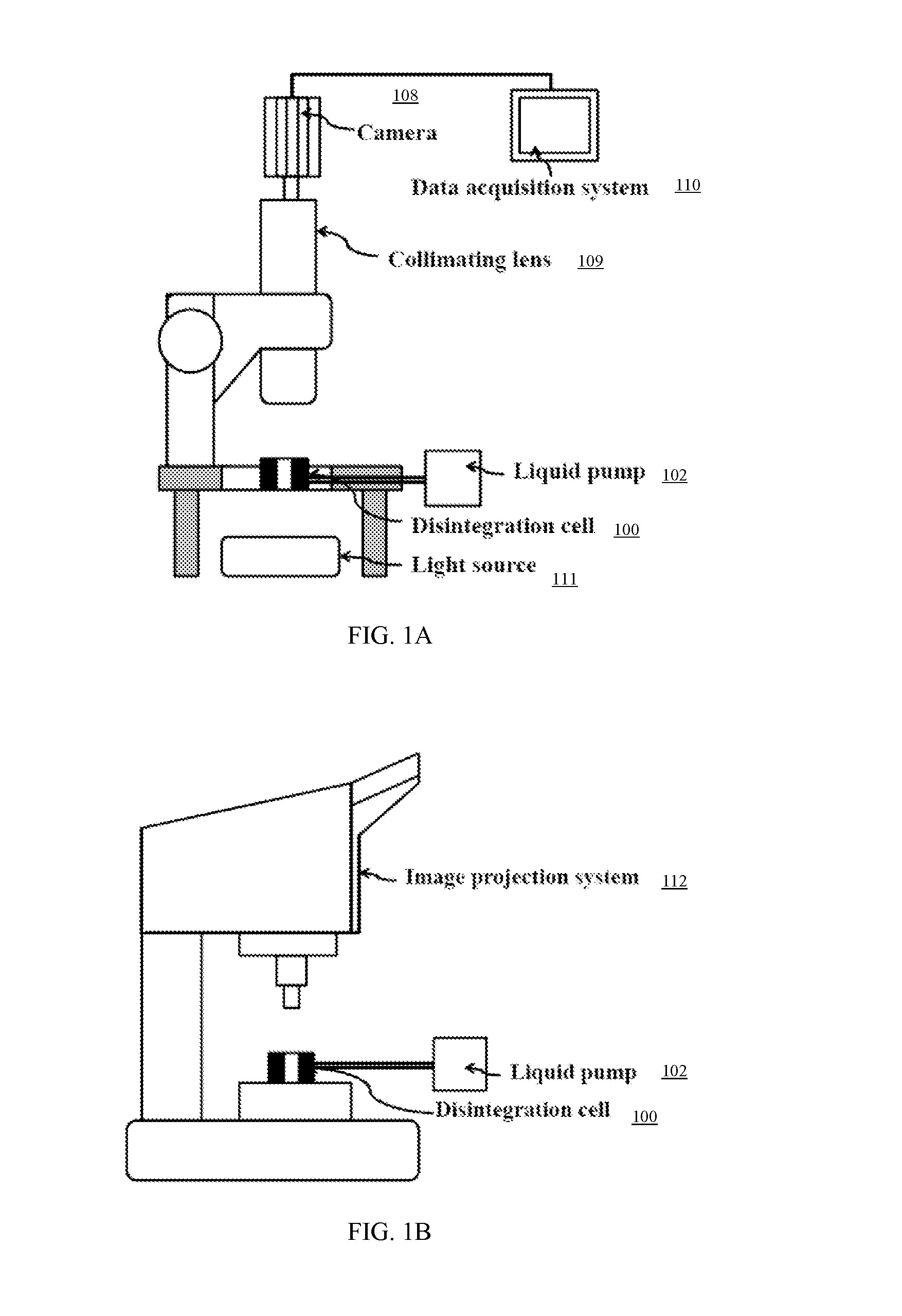
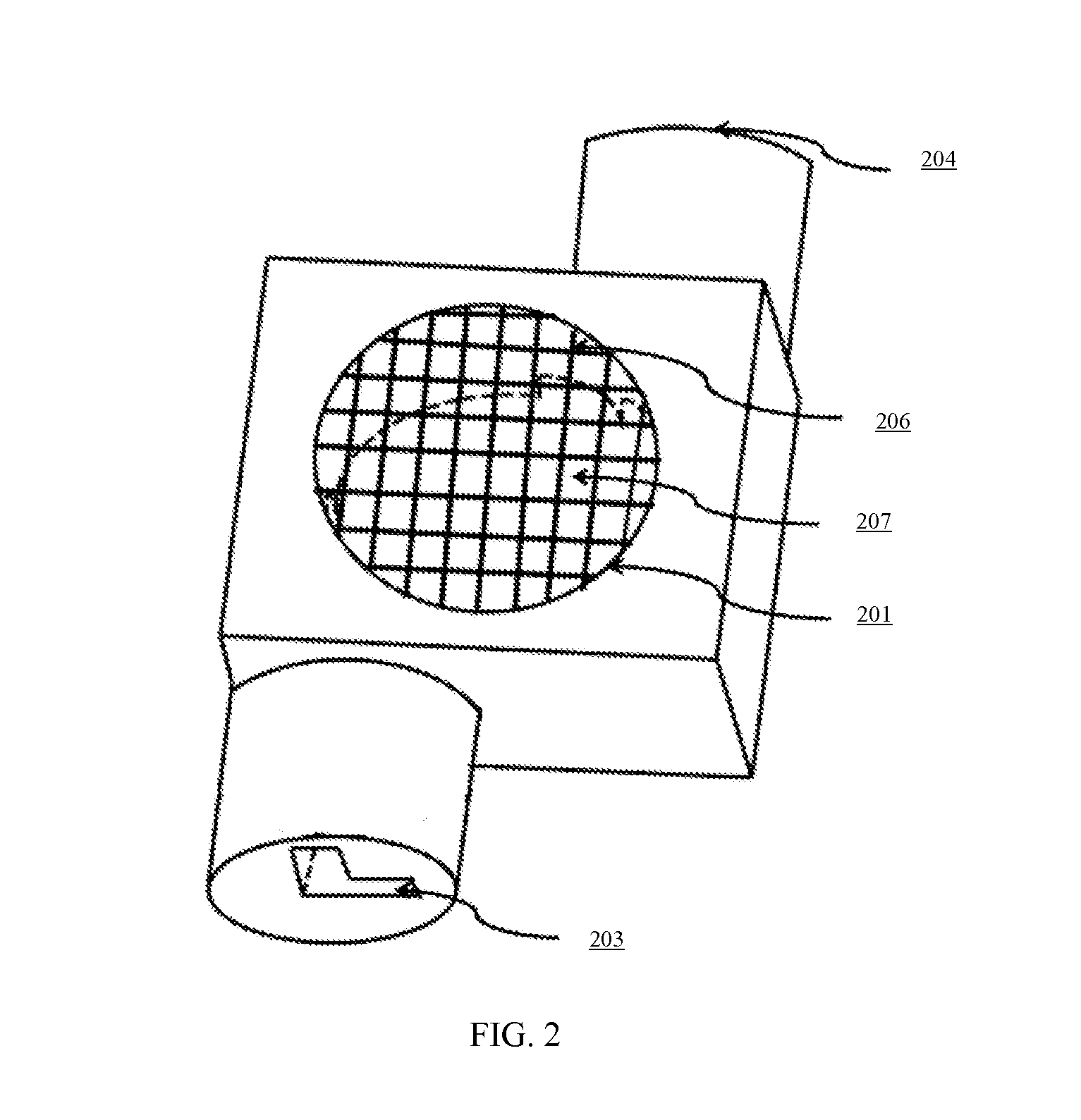
Apparatus and method for visiometric disintegration
InactiveUS20140305225A1Simple and accurateThe process is simple and accurateSurface/boundary effectMaterial strength using steady shearing forcesLight sourceImage capture
In one version of the invention, an apparatus intended for determining the disintegration time of rapidly disintegrating tablets is designed with a disintegration cell having two liquid inlets and outflow from the top. Visualization of tablet inside the disintegration cell is conducted using a camera aided by a base light source and images captured using a computer or any other recording system. Disintegration medium is introduced into the disintegration cell through both inlets to produce a swirling motion and images of the tablet disintegration process are captured. The captured images are analyzed in real-time or off-line, to determine the tablet disintegration time. A visual non-recording method using projected image may also be used.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Torque sensor assembly for a power-assisted bicycle
ActiveUS20130086996A1Simple and accurateQuick responseCycle equipmentsWork measurementTorque sensorEngineering
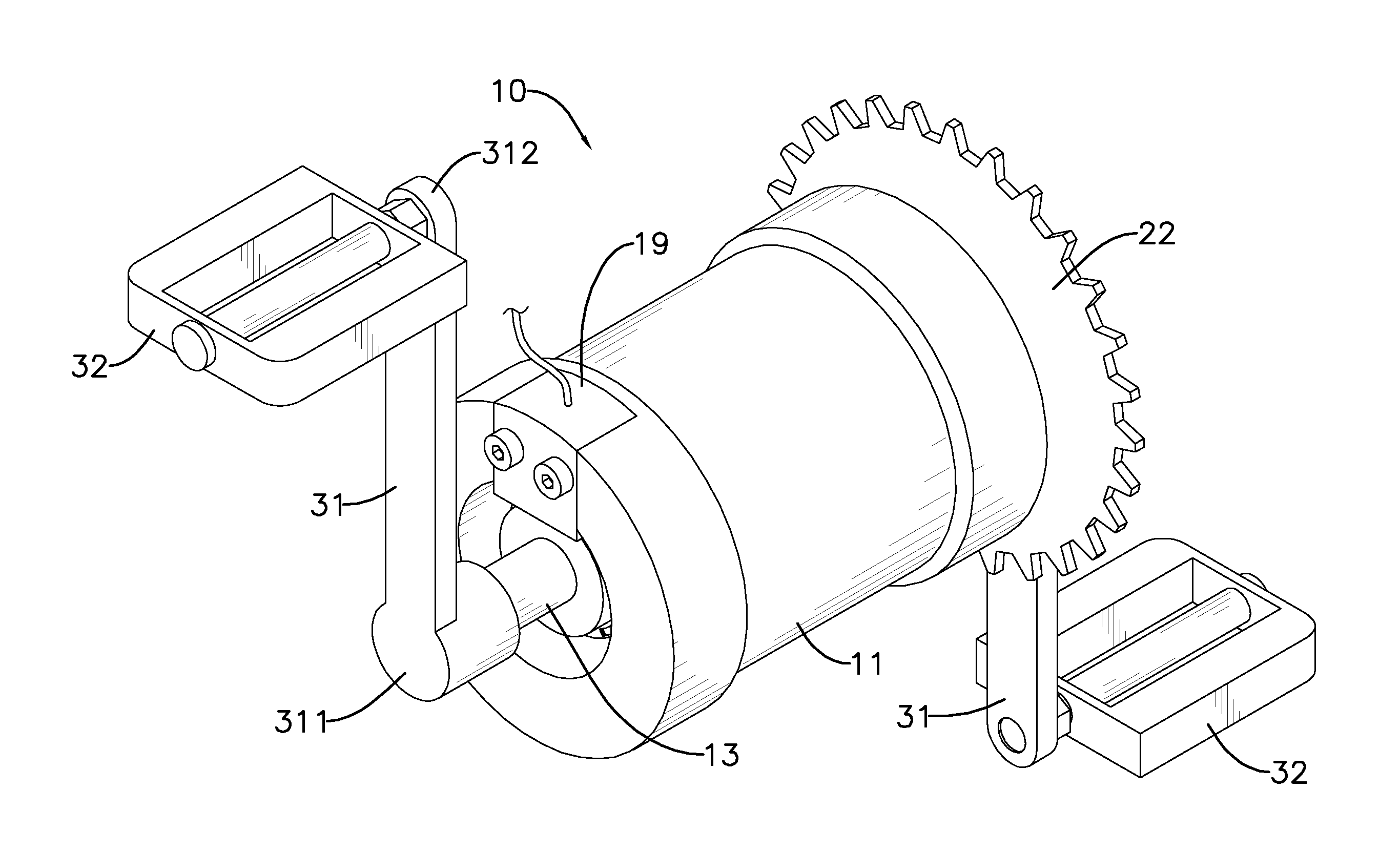
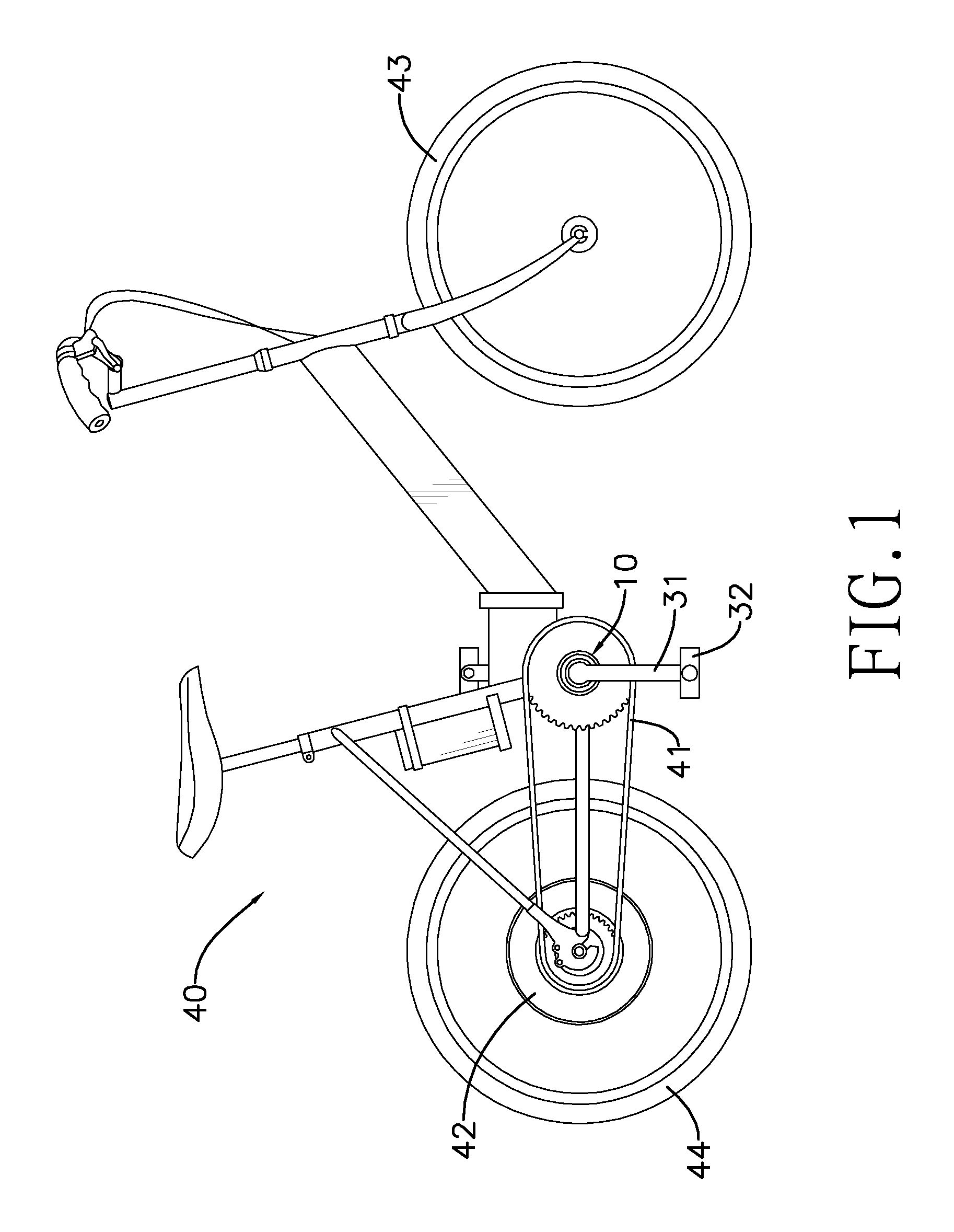
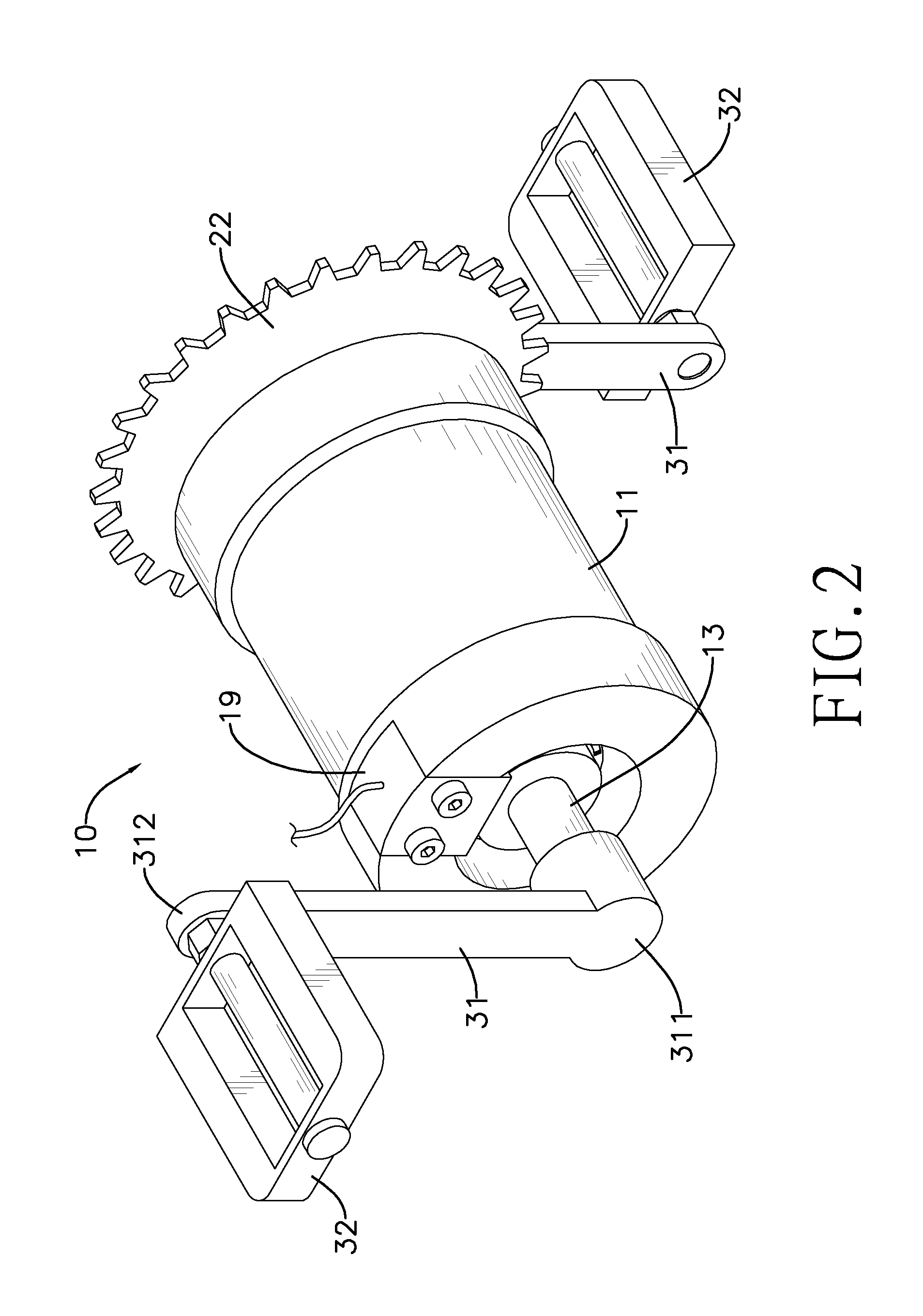
A torque sensor assembly for a power-assisted bicycle has a torque sensor, a one-way bearing, a chainwheel, two cranks and two pedals. The torque sensor has an envelope tube, a middle tube, a transmission axle, a resilient element connected to the middle tube and the transmission axle, a first disc and a second disc respectively attached to the transmission axle and the middle tube, and a detection unit detecting displacement angles of the second disc and the first disc to calculate torques applied to the transmission axle and to drive the power-assisted bicycle according to the torque. The torque sensor assembly has a simple structure, fast, sensitive and accurate torque sensing ability, and can easily be assembled to all kinds of power-assisted bicycles.
Owner:YAO LI HO
Device and method for optical center detection
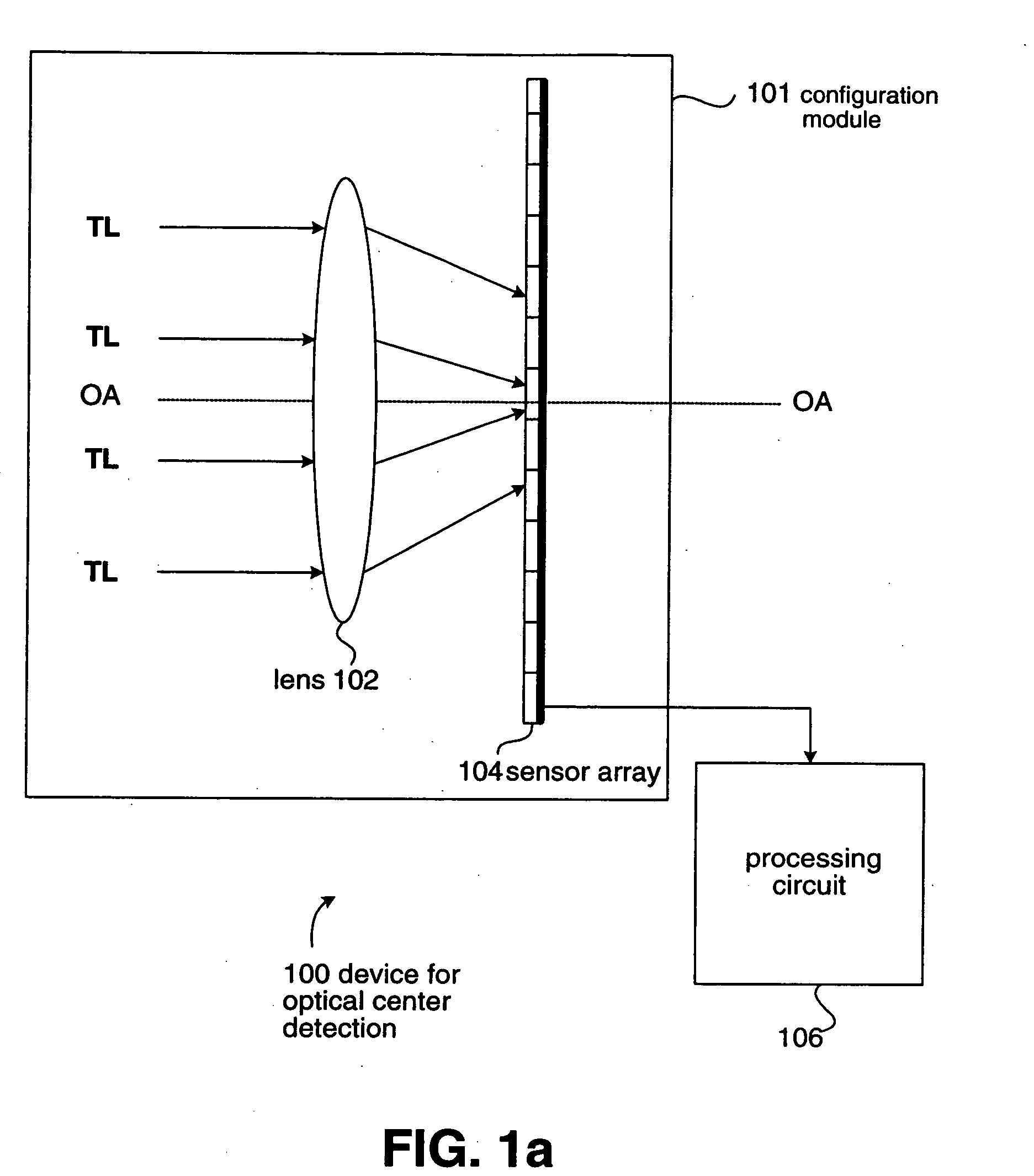
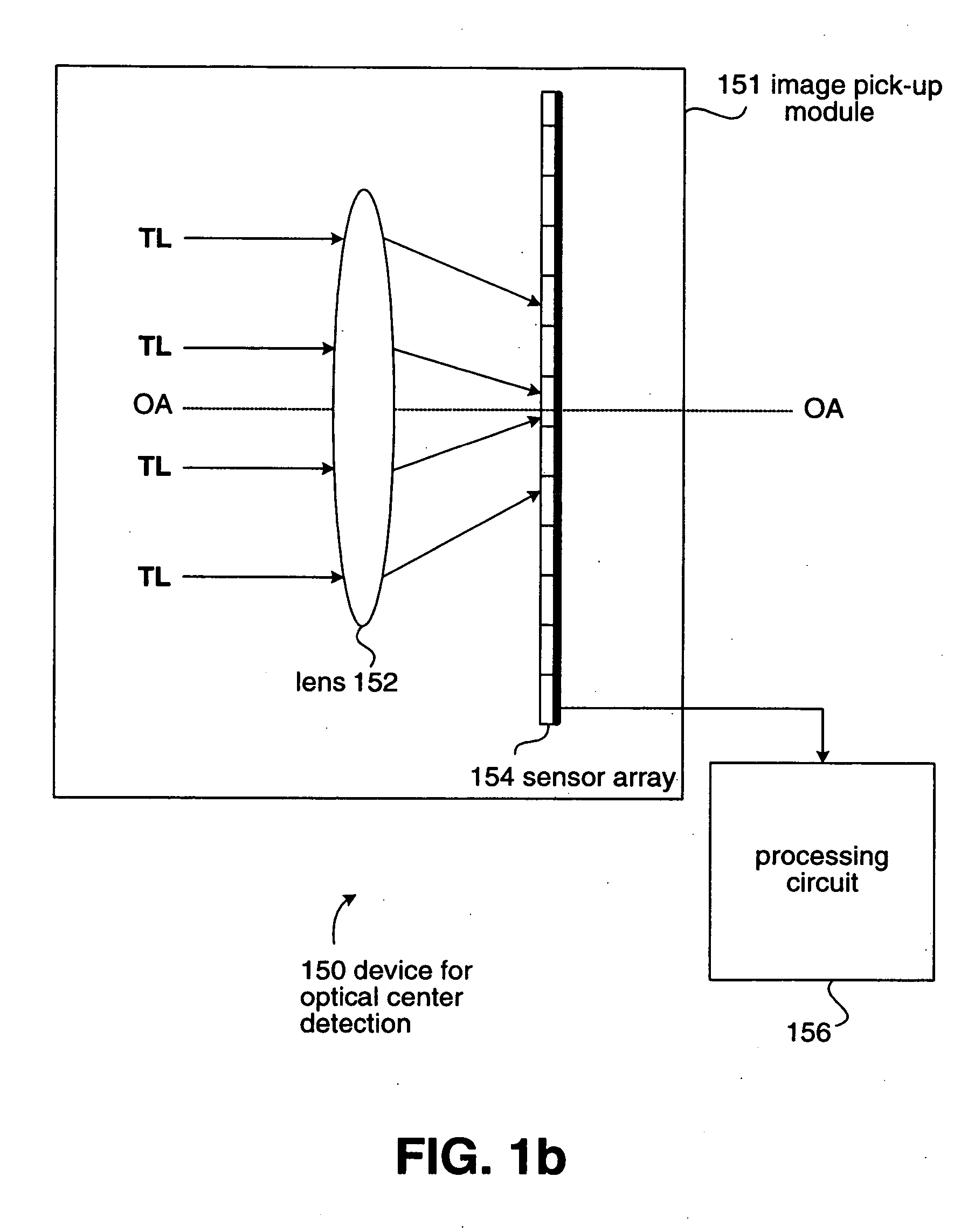
InactiveUS20060007428A1Easily determineSimple and accurateTelevision system detailsPhase-affecting property measurementsPhysicsLight Testing
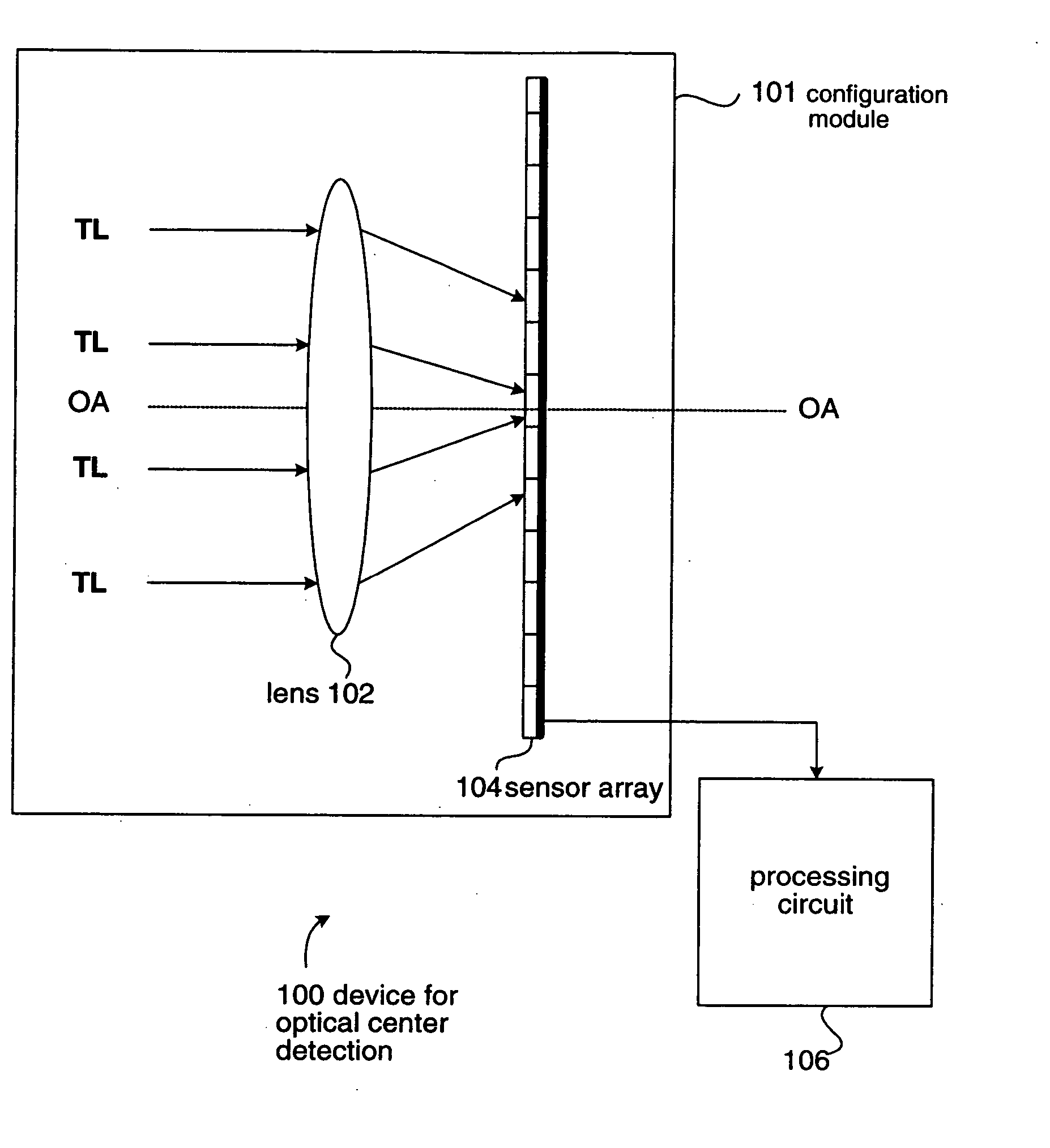
A device is presented for computing an optical center of a sensor array relative to a lens. The sensor array includes a plurality of sensor units, and each sensor unit has a position on the sensor array. The lens defines an optical axis. The device includes a configuration module and a processing circuit. The configuration module is provided for positioning the lens and the sensor array thereon. When test light is parallel to the optical axis and is incident to the lens, the sensor array receives the test light transmitted by the lens so that each sensor unit outputs a value. The processing circuit is linked to the sensor array for receiving values outputted from the sensor units and selecting positions of sensor units outputting a specific value among the values, for computing the optical center of the sensor array.
Owner:ASIA OPTICAL CO INC
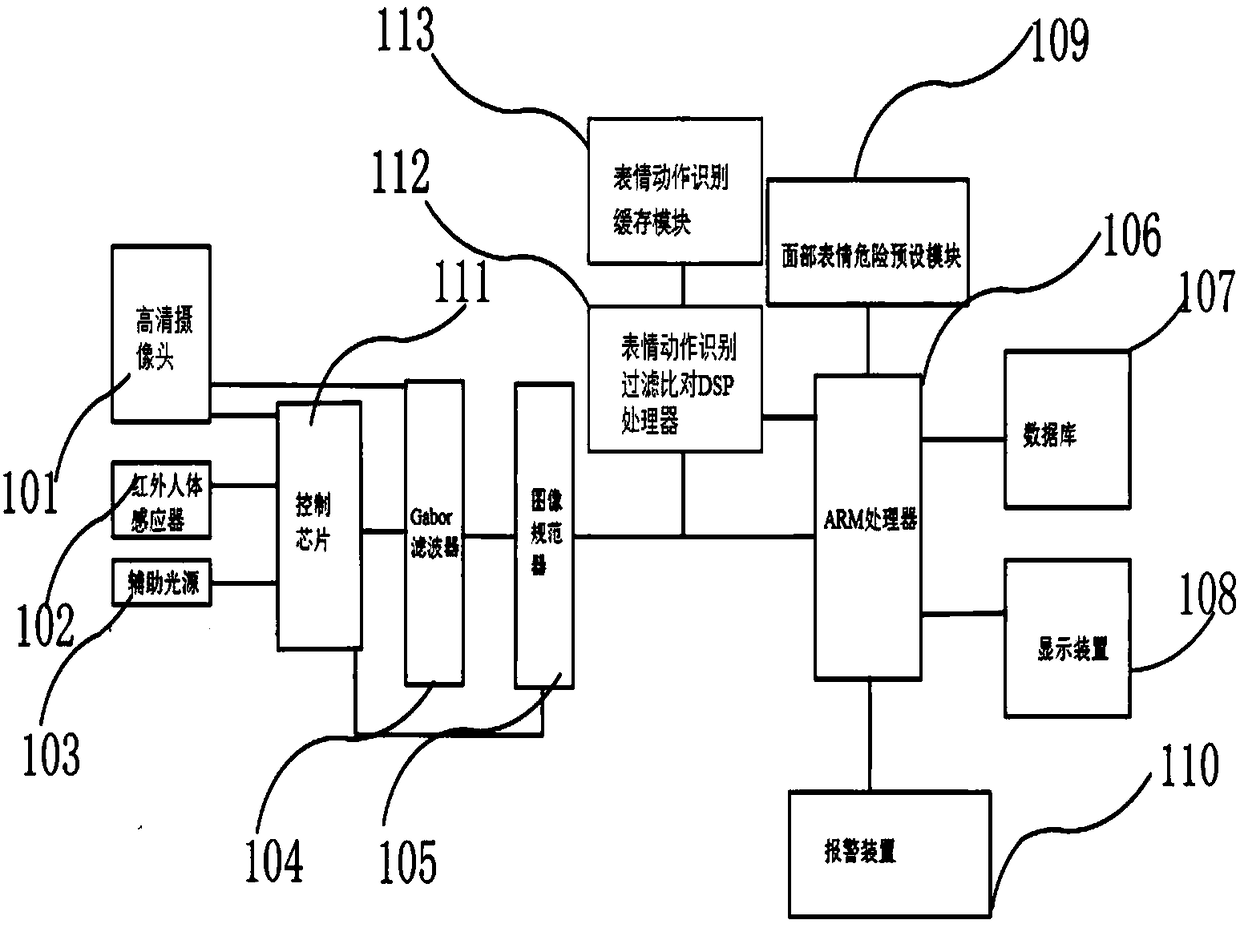
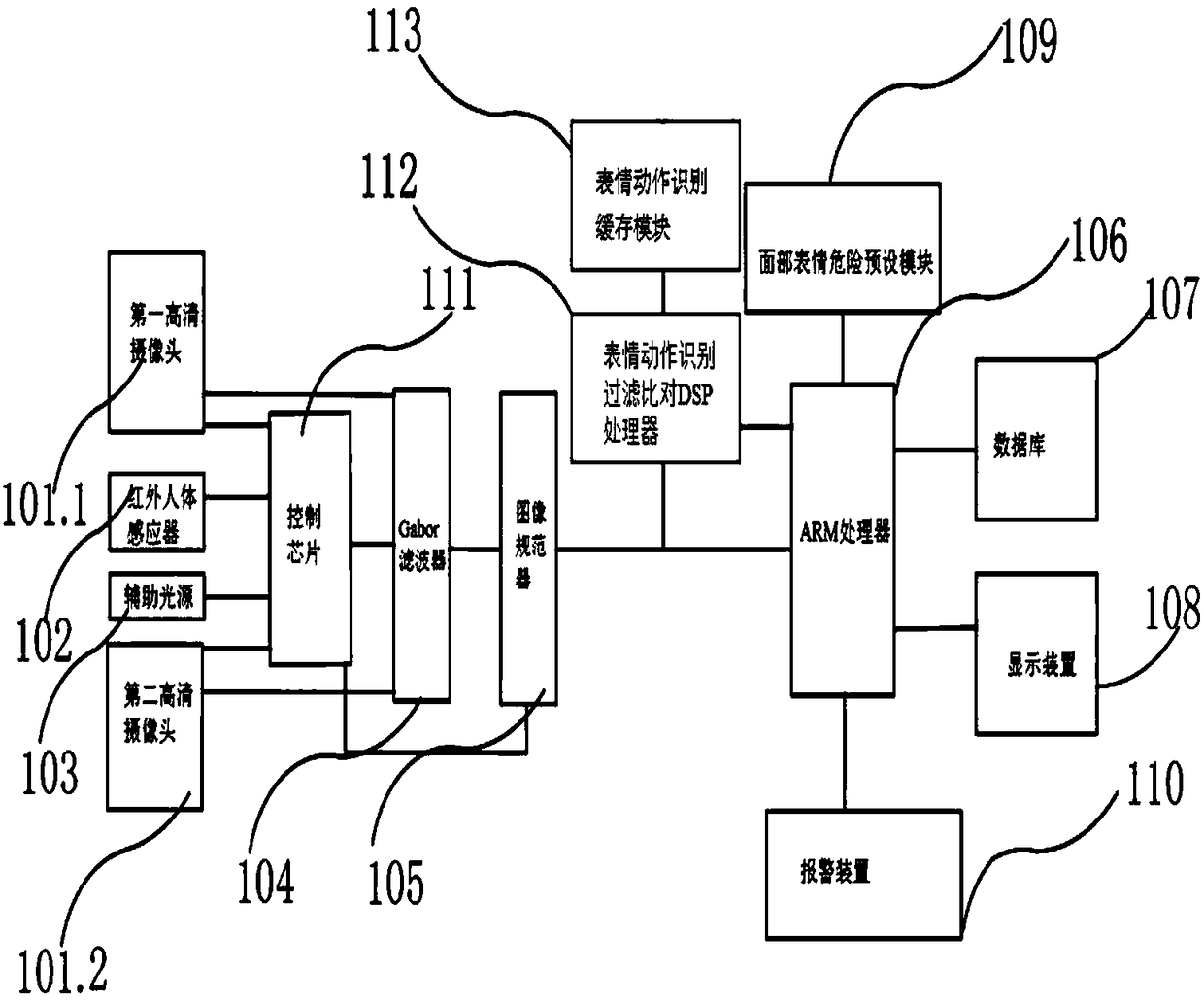
Precise face recognition system
PendingCN108197609APrevent theftEasily solve facial recognition problemsCharacter and pattern recognitionProtocol authorisationPaymentDisplay device
The invention belongs to the technical field of face recognition and especially relates to a novel precise face recognition system. The system includes a high definition camera, an infrared human bodysensor, an auxiliary light source, a control chip, a Gabor filter, an image normalizer, an ARM processor, a database and a display device. An expression action recognition filtering and comparison DSP processor is also connected with an expression action recognition buffer module. Through setting of the expression action recognition filtering and comparison DSP processor and the expression actionrecognition buffer module, a series of expressions or actions for identity verification of a person can be taken as identify verification information, so that credit card fraud when the precision face recognition system is applied to payment can be prevented and a problem of face recognition of twins can be solved easily.
Owner:梁纳星
Ramp speed limit identification method
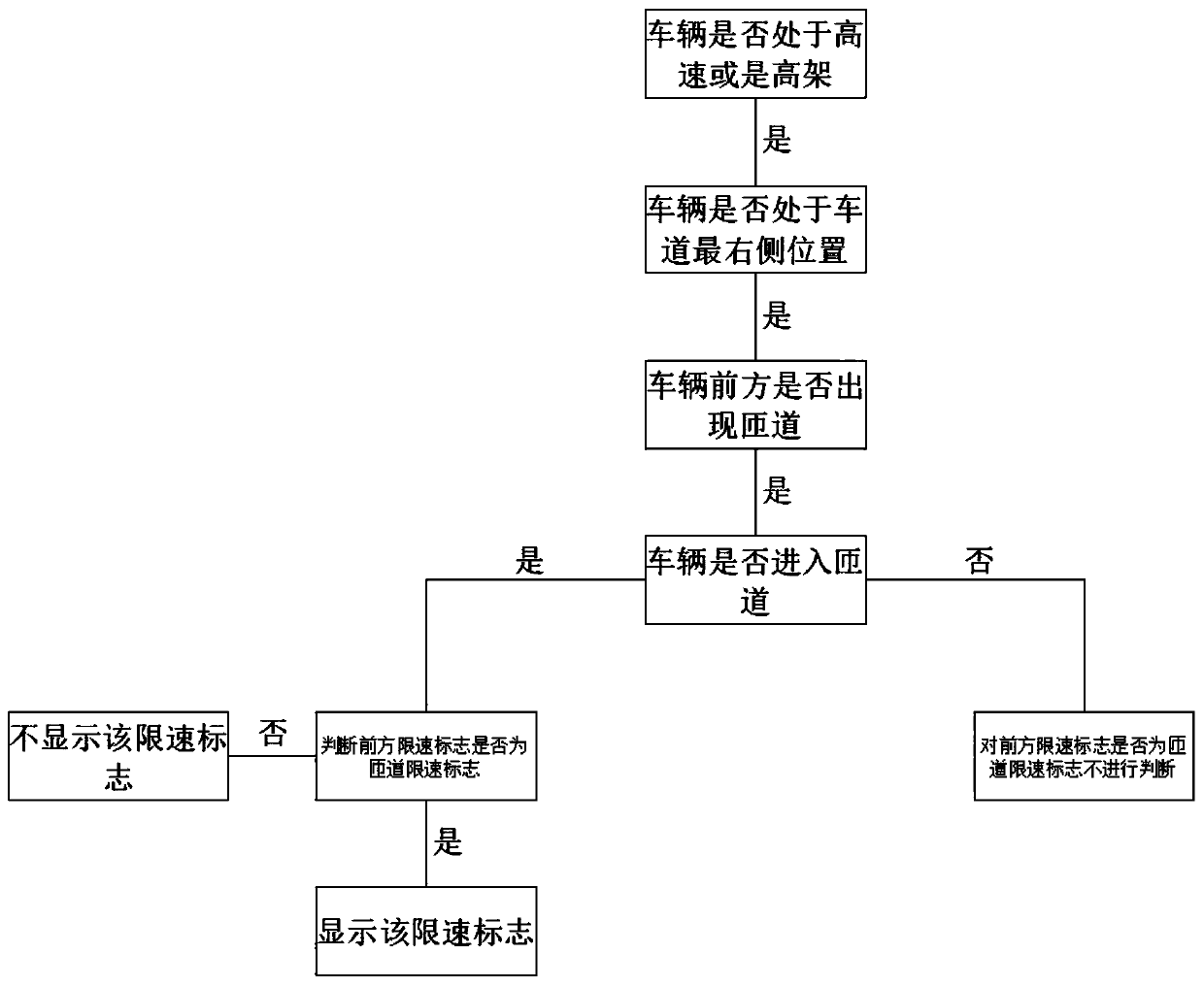
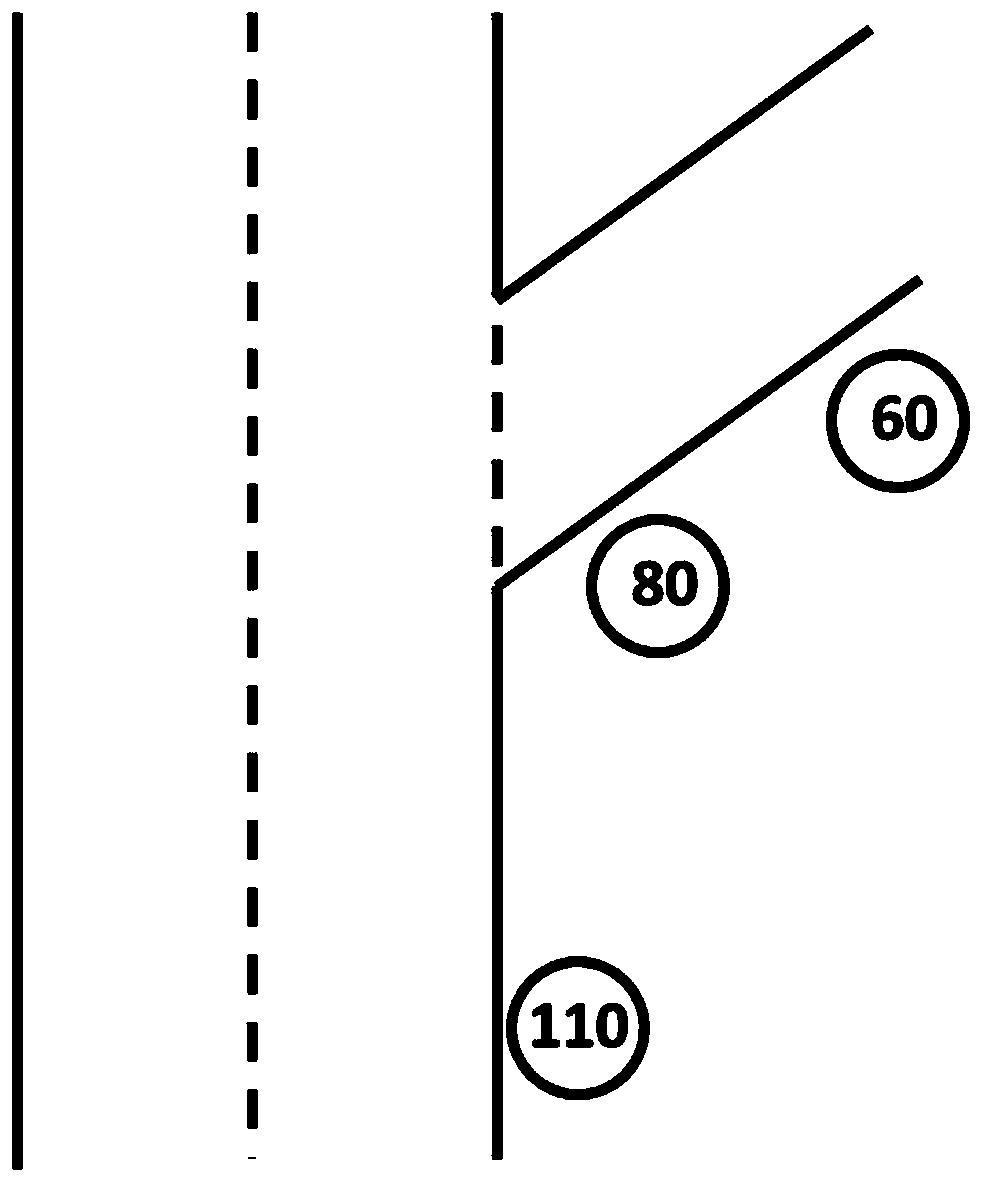
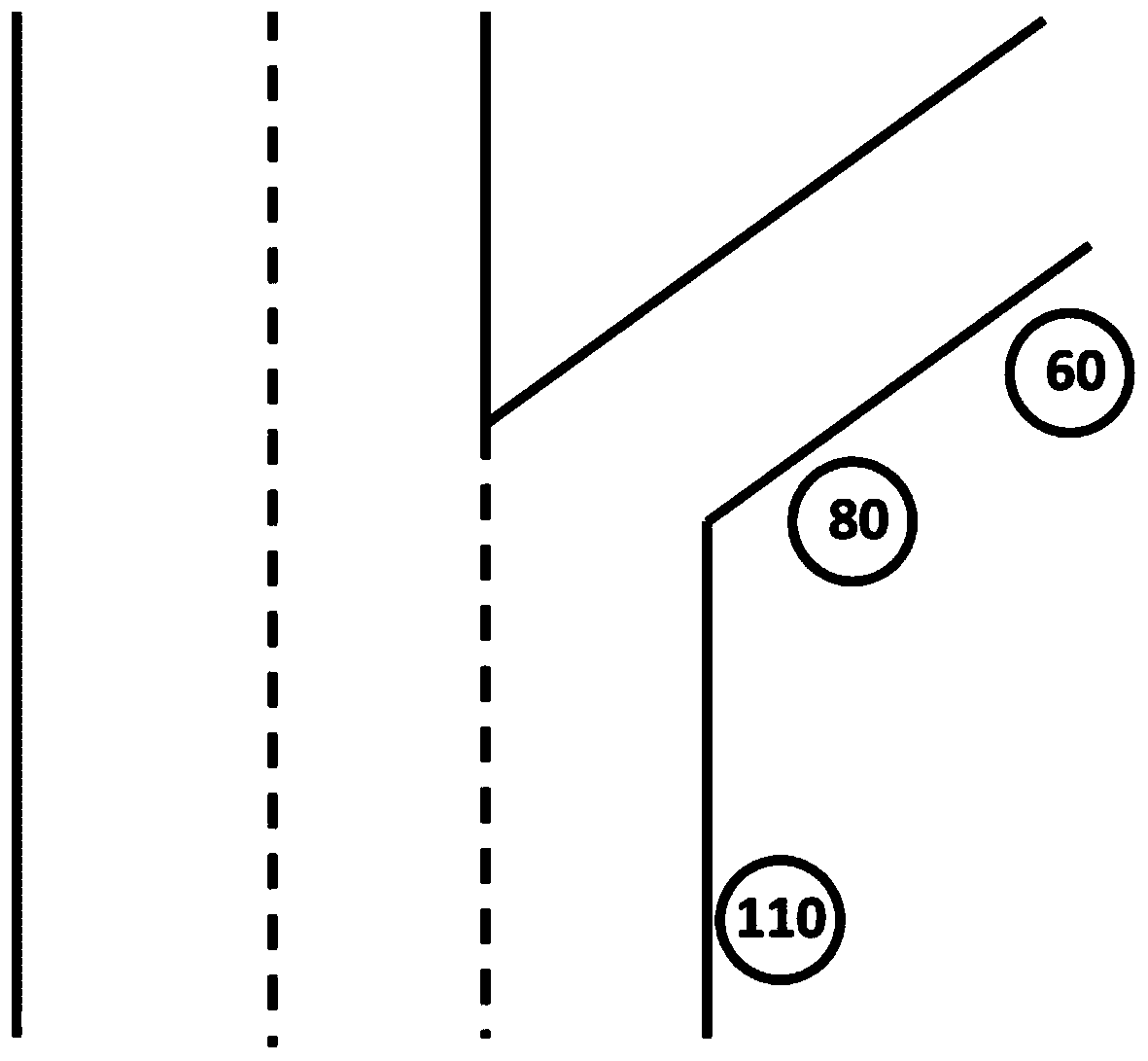
InactiveCN111524351AIncrease the burdenSimple operation logicDetection of traffic movementControl systemSpeed limit
The invention relates to the technical field of automobile control, in particular to a ramp speed limit recognition method. The method comprises steps of judging whether the vehicle runs at a high speed or an elevated road; if yes, the lane position where the vehicle travels is judged; and if the vehicle runs on the rightmost lane, judging whether the currently recognized speed limit sign is a ramp speed limit sign or not according to the change condition of the right lane line of the vehicle, the running condition of the vehicle and the comparison condition of the currently recognized speed limit sign and the previous recognized speed limit sign. The ramp speed limit recognition method is simple and small in logical operation amount, does not cause burden to a control system, can accurately and quickly recognize ramp speed limit, is high in accuracy, and has great popularization value.
Owner:DONGFENG MOTOR CORP HUBEI
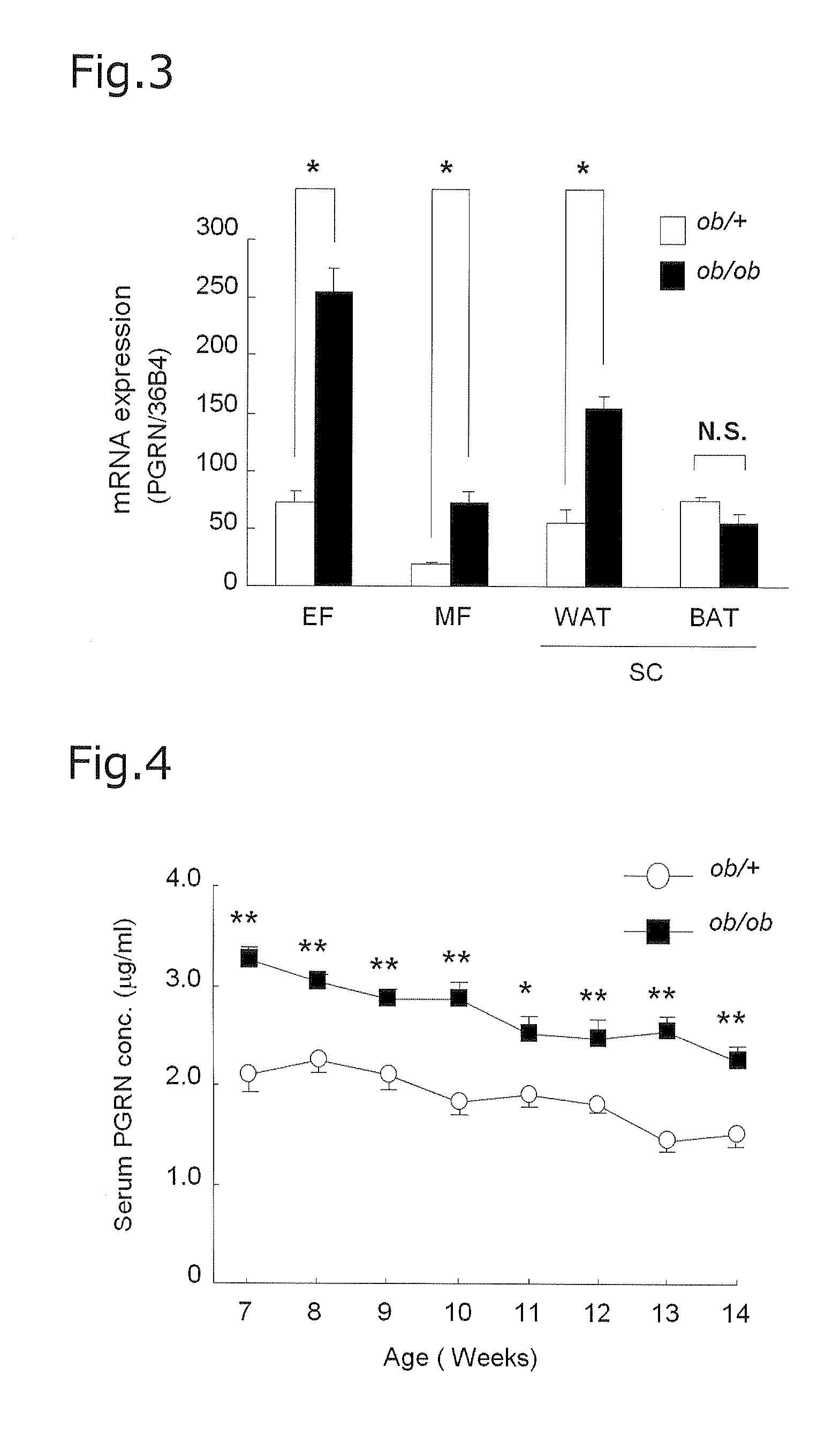
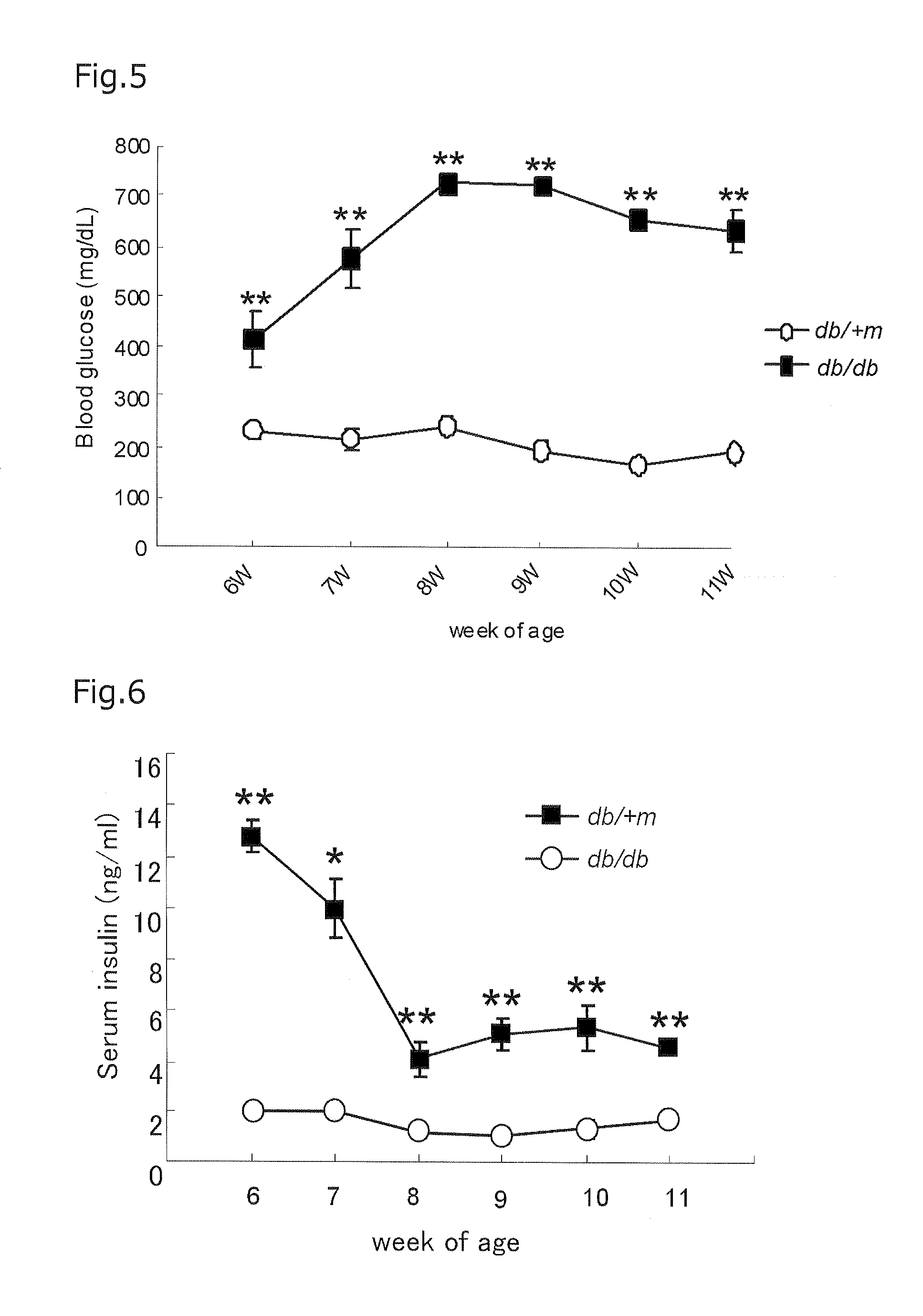
Blood insulin resistance and diabetes marker progranulin, method for analyzing concentration of progranulin in blood sample, and method for screening for substance that improves insulin resistance and improves or suppresses diabetes
InactiveUS20130210039A1Simple and accurateImprove resistanceCompound screeningApoptosis detectionBlood markersAmino acid
The present invention provides a marker capable of detecting insulin resistance and diabetes in a collected blood sample, a method for analyzing said marker, a method for screening a substance improving insulin resistance, and improving or suppressing diabetes. A blood insulin resistance marker and a blood diabetes marker, which comprises a polypeptide comprising at least 15 continuous amino acids in an amino acid sequence constituting progranulin. A method for analyzing a blood marker, which comprises the steps of: measuring a concentration of an insulin resistance marker or a diabetes marker in a collected blood sample; and comparing the measured concentration with a normal blood concentration of the marker. A method for screening a substance improving insulin resistance, and improving or suppressing diabetes, which comprises the steps of: administering a candidate substance to a living body expressing insulin resistance or suffering from diabetes; measuring a blood concentration of a marker in the living body after administration; and comparing the measured concentration of the marker with a blood concentration of the marker not administered with the candidate substance.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP +1
Wooden material grinding force determining method
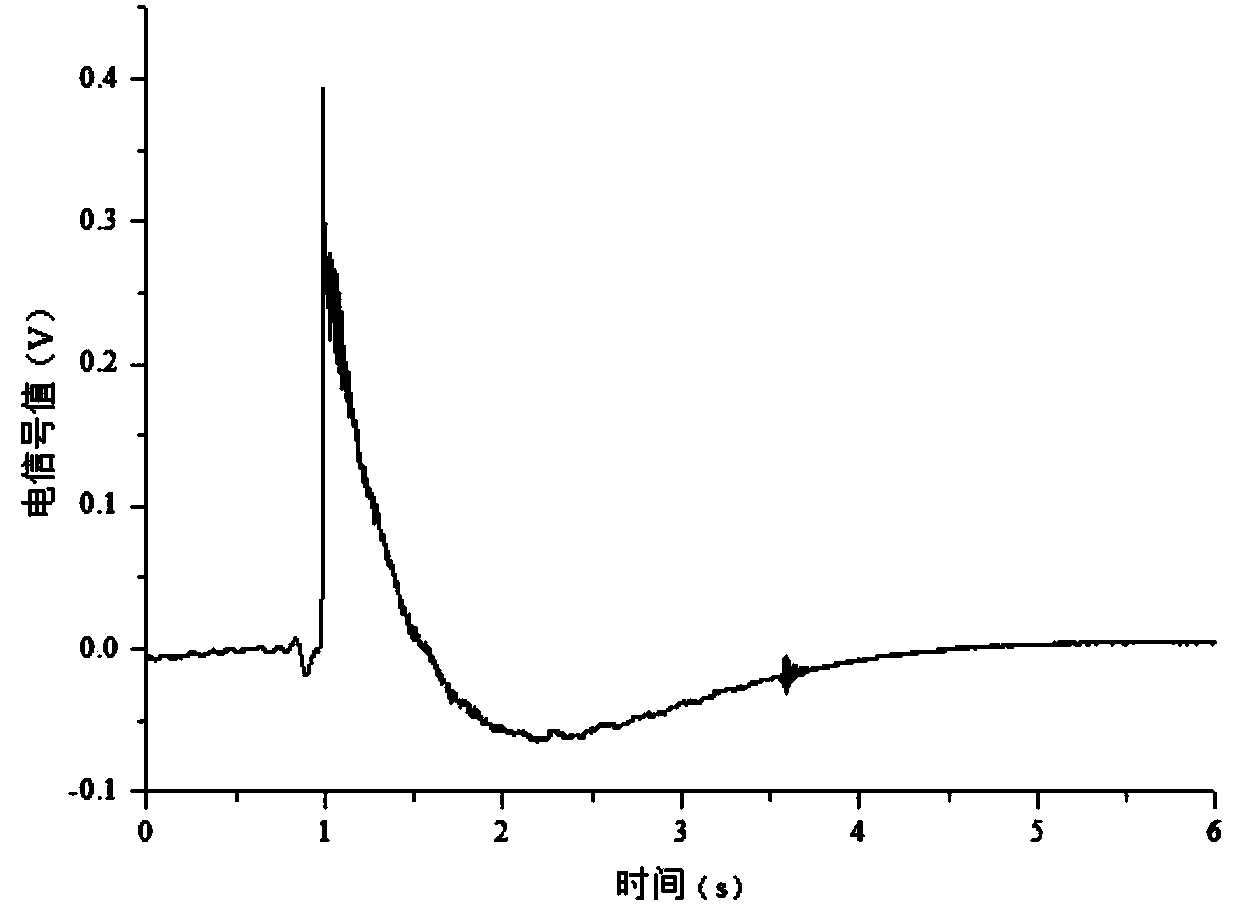
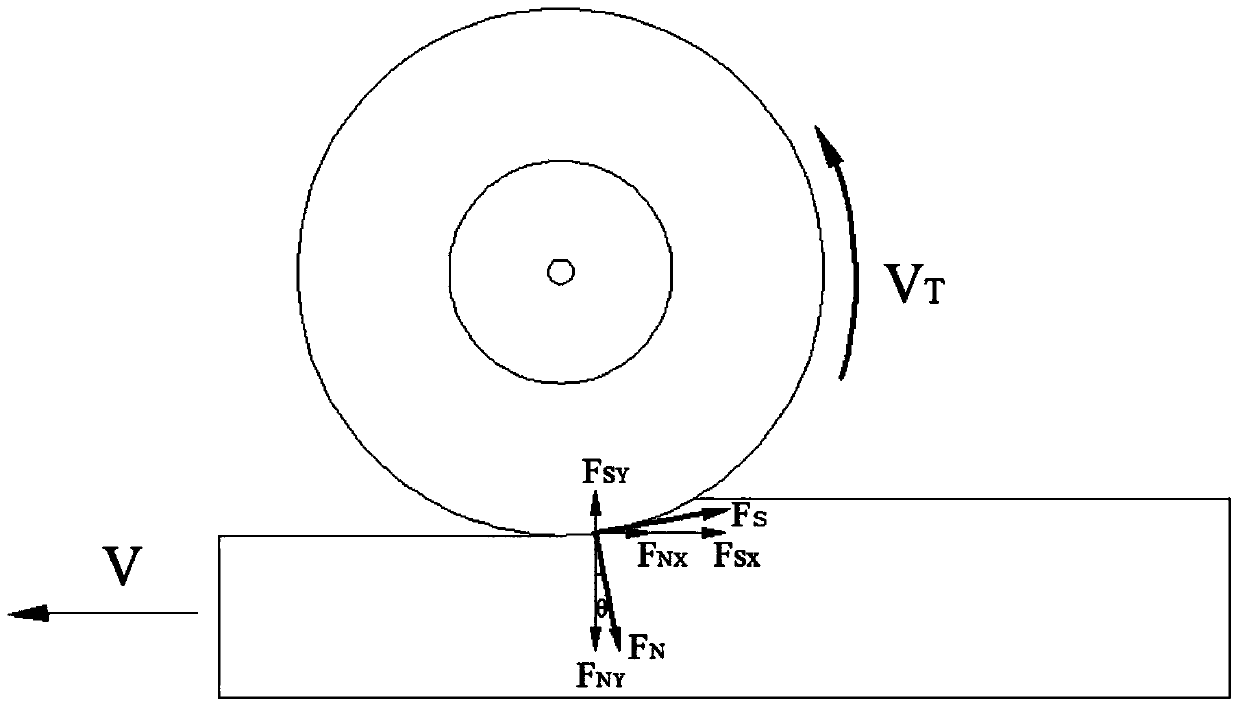
InactiveCN103743515AReal-time and simpleSimple and accurateApparatus for force/torque/work measurementElectricityHorizontal force
The invention provides a wooden material grinding force determining method. The method comprises the following steps of calibrating the relation between a force in the horizontal direction and an electric signal value by utilizing a deweighting method, carrying out linear-regression analysis on the obtained electric signal value and the force in the horizontal direction to obtain a proportional relation of the grinding force and the electric signal value; horizontally placing a wooden material test piece onto a worktable through a tool, arranging a force sensor between the worktable and the tool, connecting the force sensor with a charge amplifier, connecting the charge amplifier with a signal analyzer, and connecting the signal analyzer with a computer; grinding a wooden product, generating a charge value through the variation of the horizontal force on the test piece detected by the force sensor, utilizing the charge amplifier and amplifying and converting the charge value to a voltage signal to be collected by the signal analyzer, fitting the electric signal collected by the signal analyzer to obtain an electric signal value, and converting the electric signal value according to the proportional relation to obtain a maximal value and an average value of the grinding force. The determination method is strong in real-time property, strong in accuracy, simple, high efficient and reliable.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Method and a device for estimating a porosity ratio of a sample of material from at least one gray-scale coded image
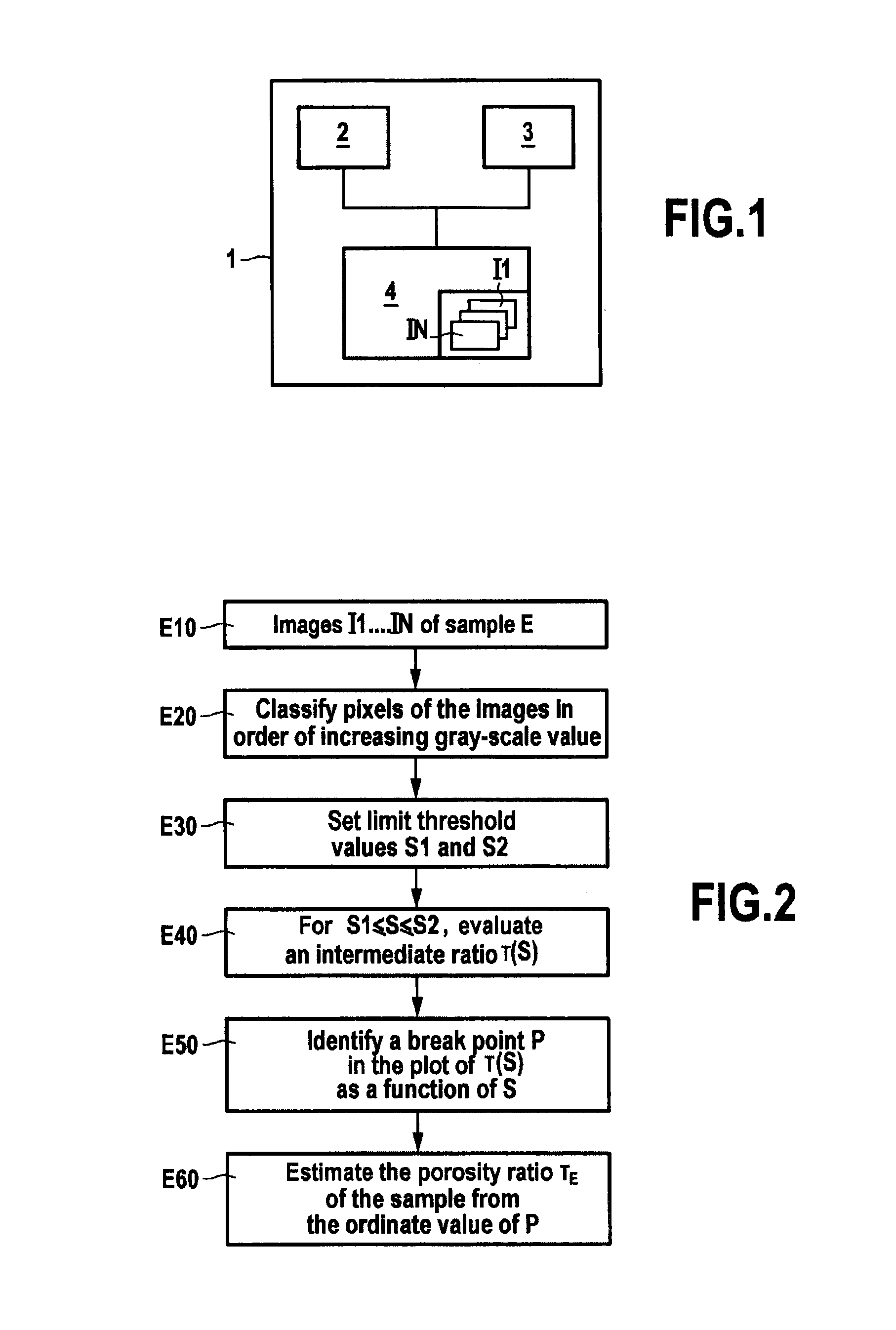
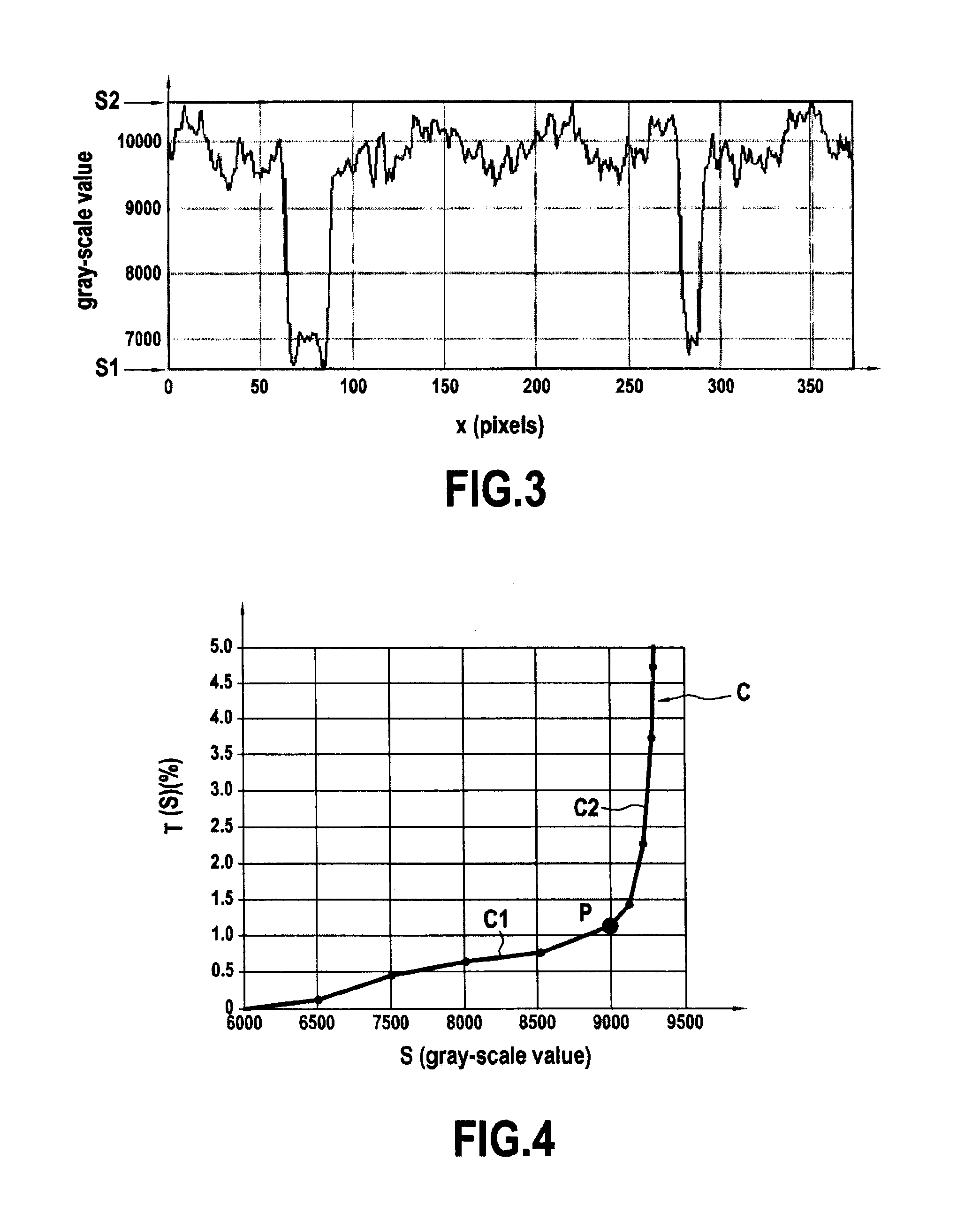
ActiveUS20140286564A1Simple and accurateDifficult to useImage enhancementImage analysisPorosityLimit value
A method and device for estimating a porosity ratio of a sample of material from at least one gray-scale coded image. The method includes: evaluating an intermediate ratio of a sample for each value of a plurality of gray-scale threshold values lying between two determined limit values, the intermediate ratio being equal to a ratio of a number of pixels of the at least one image having a gray-scale value bounded by the threshold value to a total number of pixels of the at least one image; and estimating the porosity ratio of the sample by analyzing variations in the intermediate ratio as a function of the threshold value.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
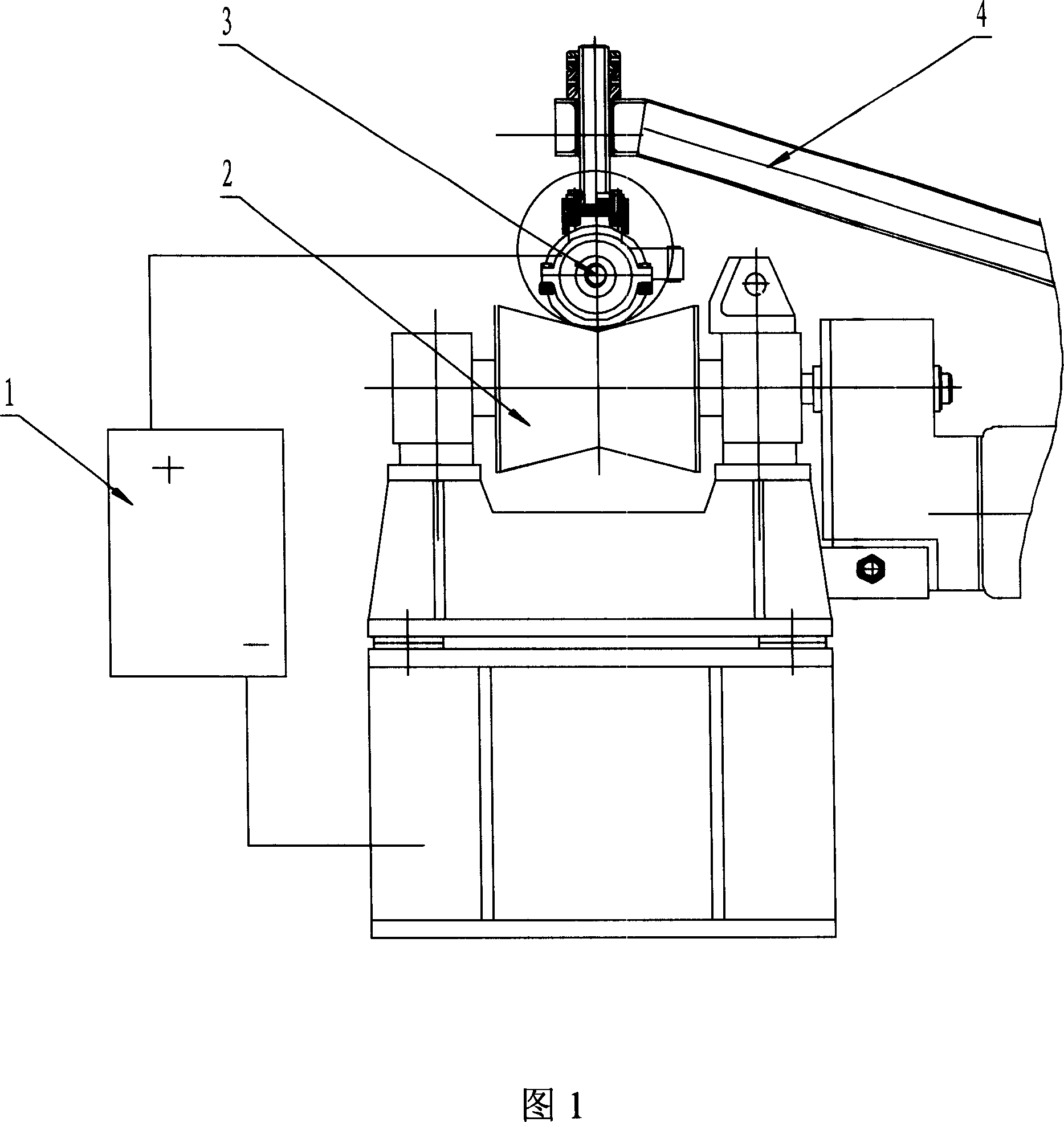
Electric perforating method of seamless tube blank
The invention relates to the electrical drilling for the seamless tube blank. It uses a robot to grip a carbon element made contact head, adjusting the location of the contact head manually or using programmable controller, with the contact aiming to the center of the tube blank, raising the robot, delivering the tube blank till the drilling position, connecting one end of the electric power with the contact head, the other end with the tubular blank, dropping down the robot, aligning the center of the tube with the robot quickly contacting the tube blank end surface smelting the metal through electric arc to get the required holes. Using electrical arc, it is simple in centering, stable and reliable with quick drilling speed, fine quality, low cost, improved pass rate, easy for the realization of automatic production.
Owner:包头市钢威机电有限公司
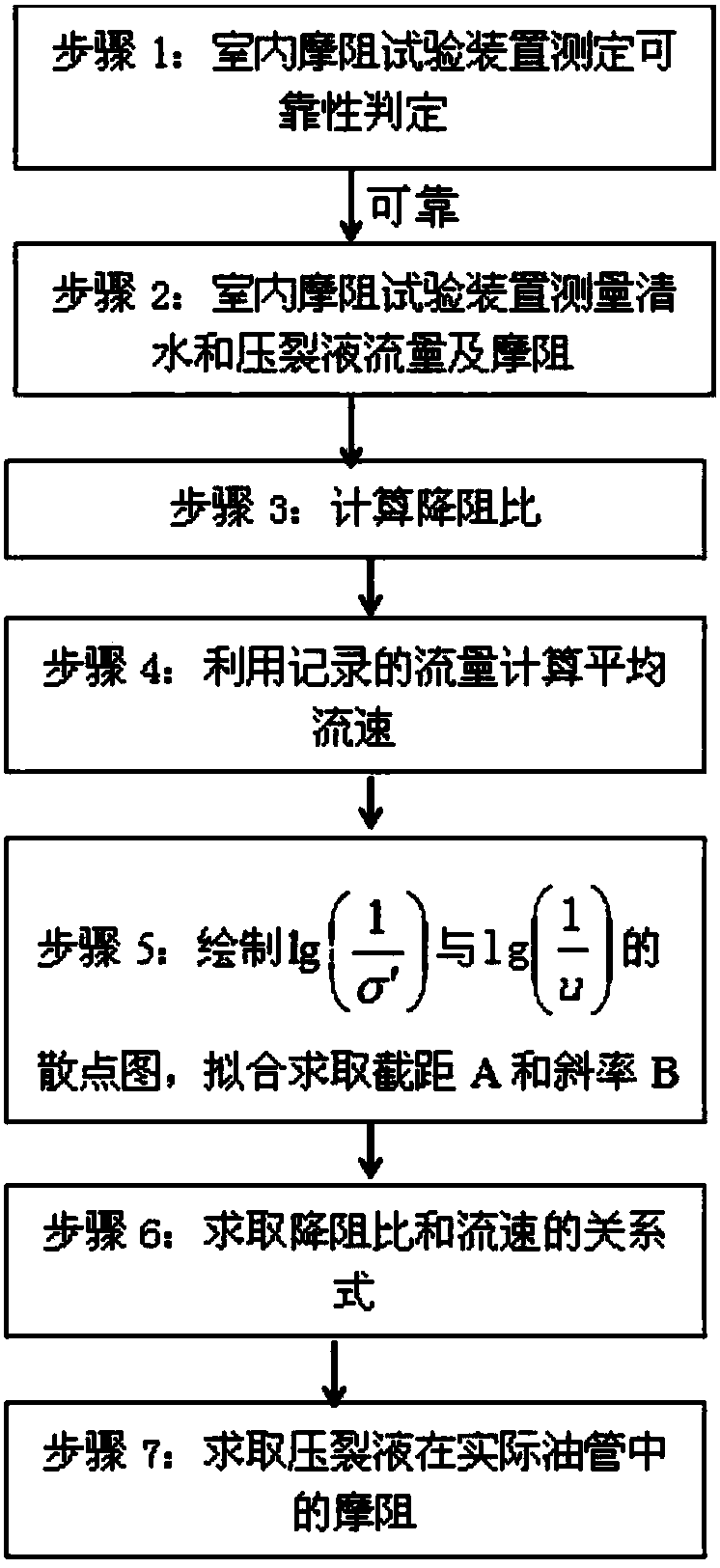
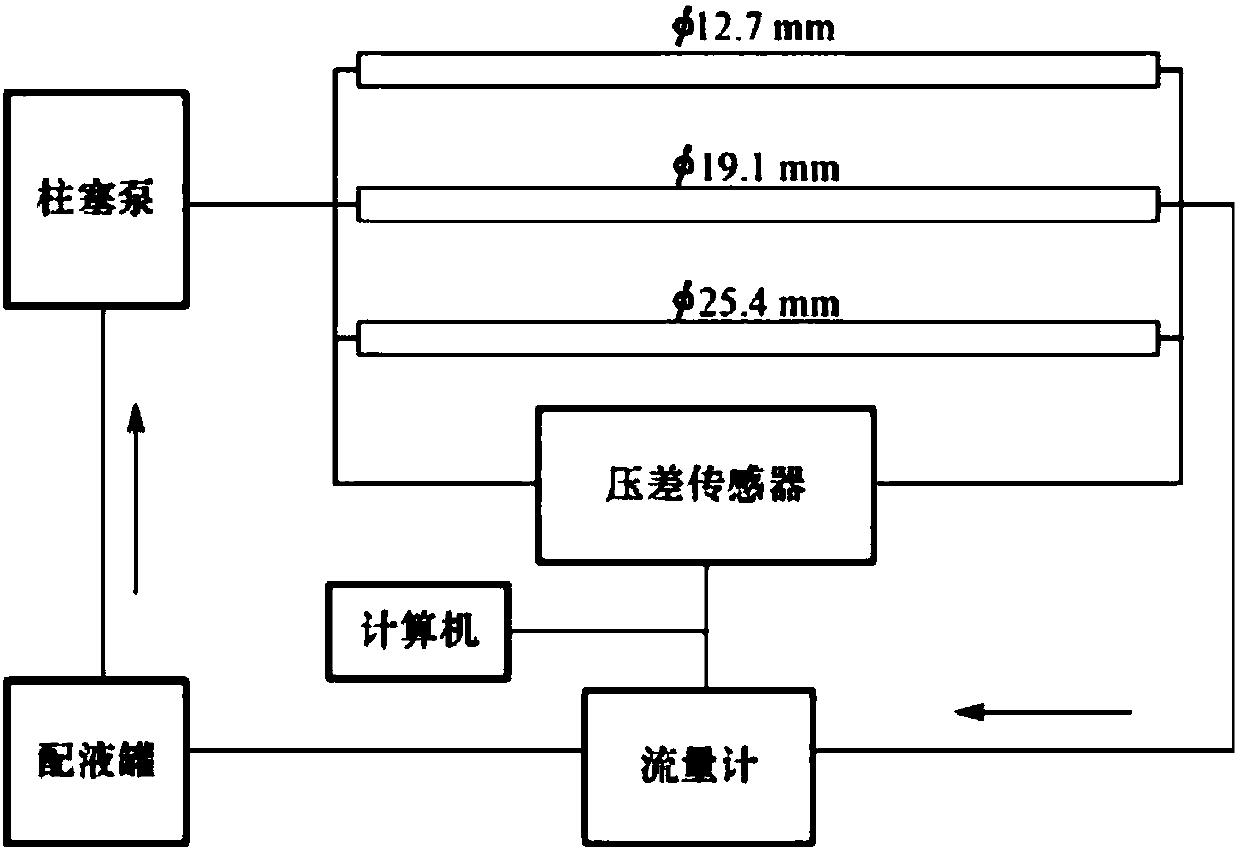
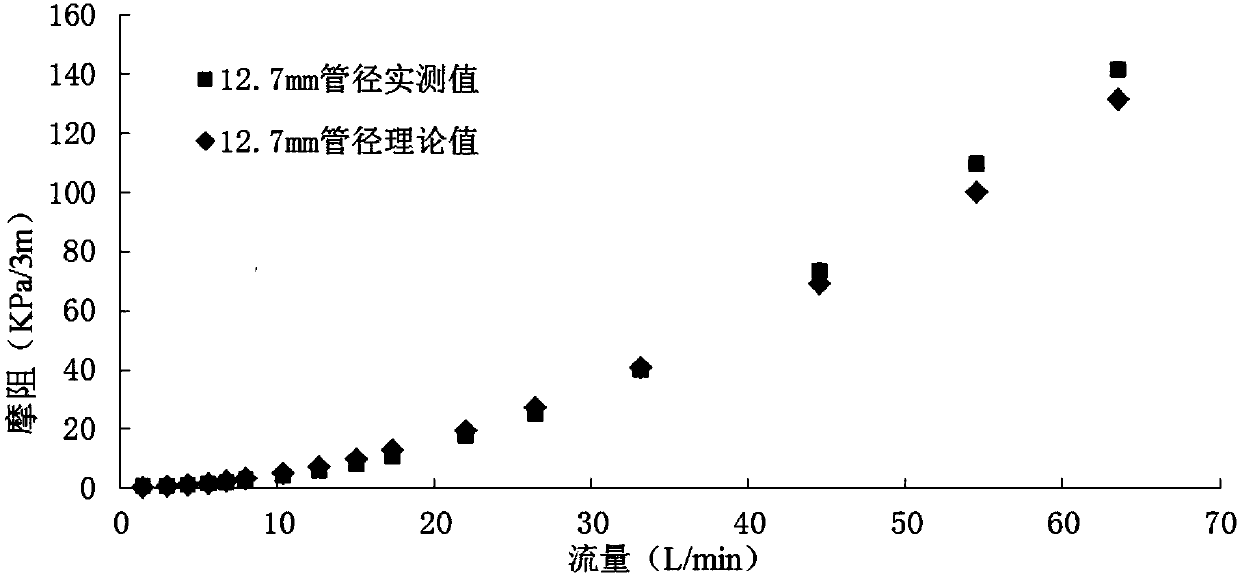
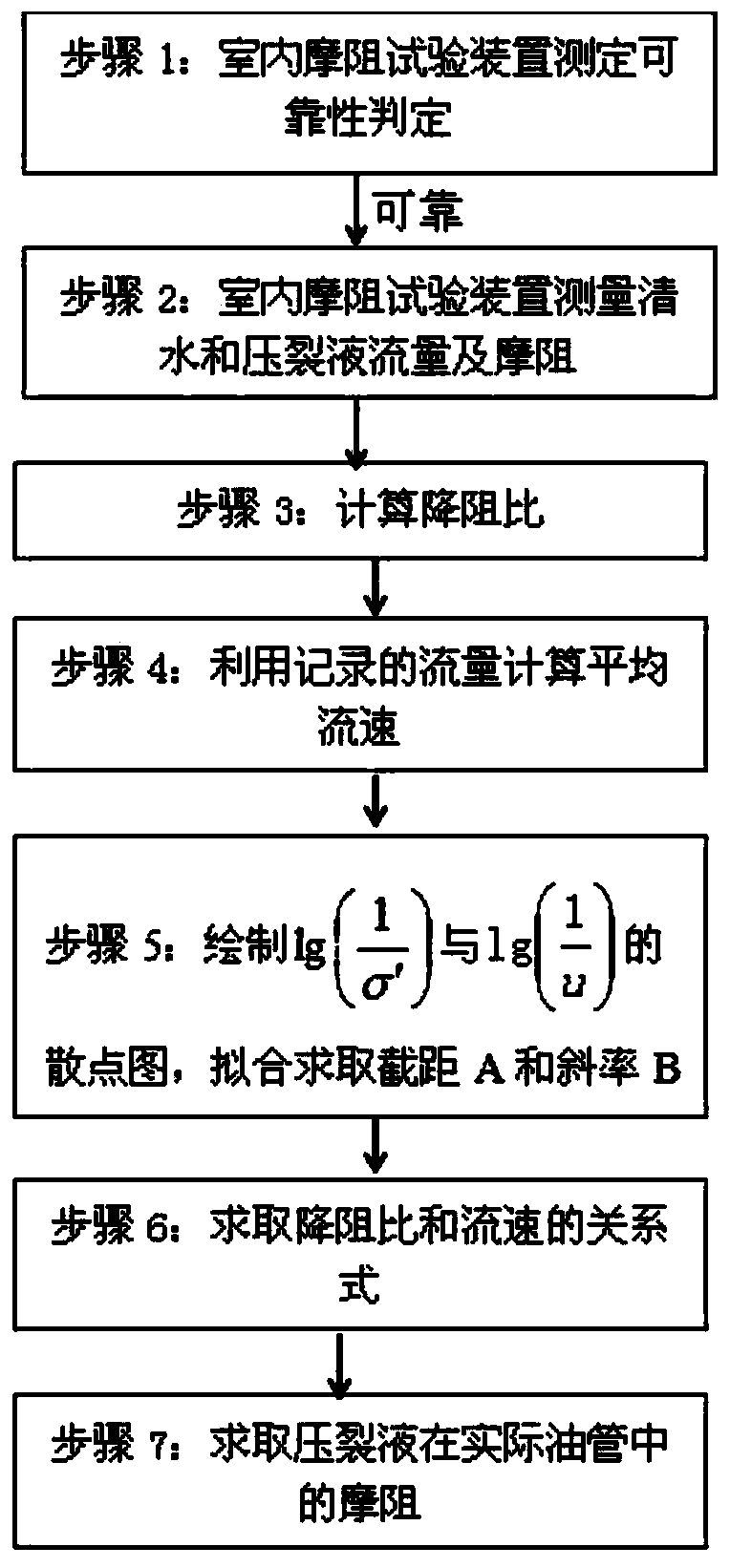
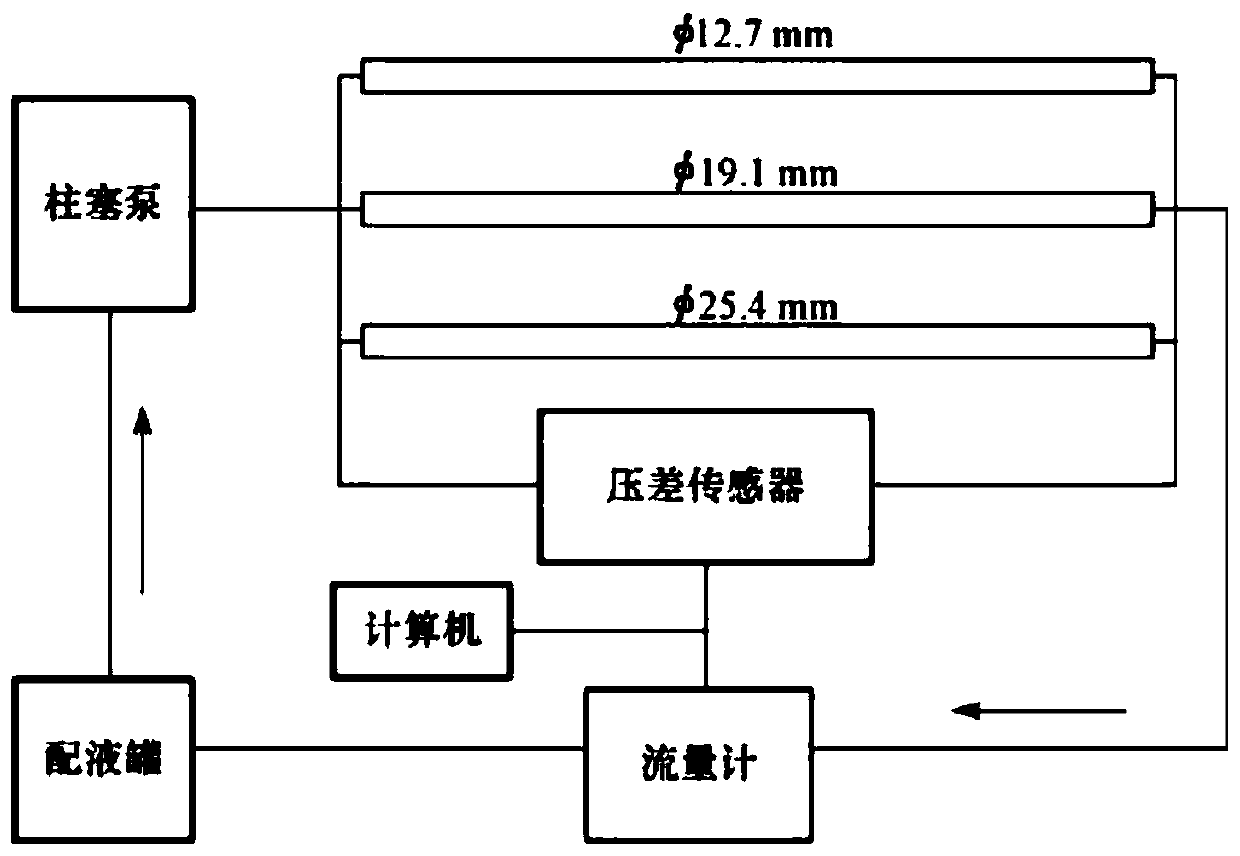
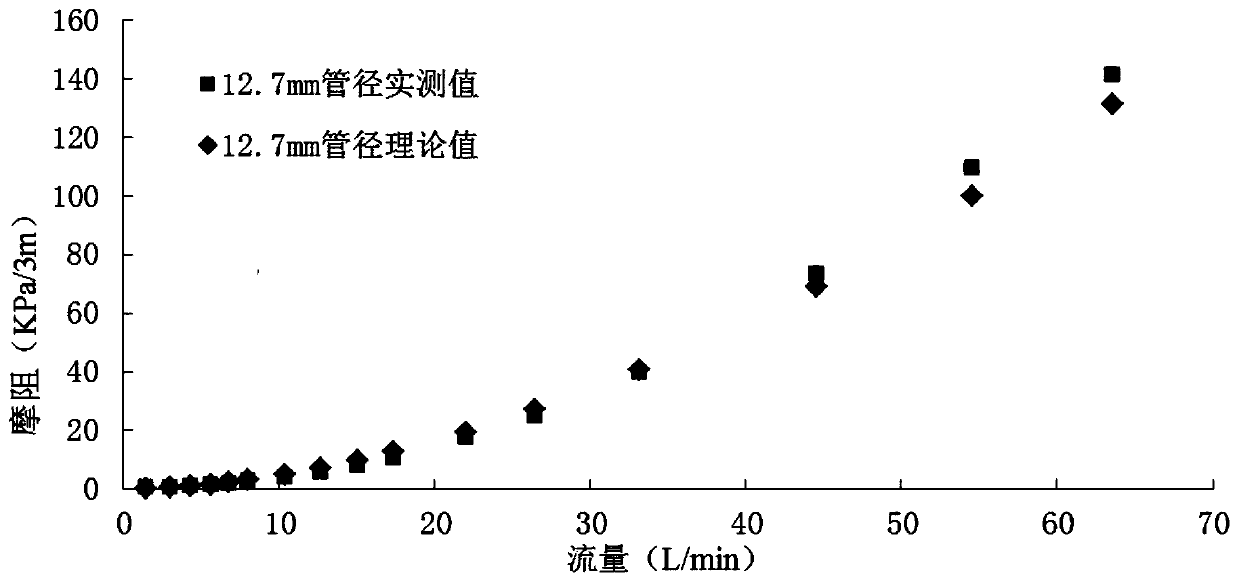
Determining method for fracturing water horsepower
ActiveCN107939367AImprove calculation accuracyReduce consumptionFluid removalComplex mathematical operationsFracturing fluidMaterial consumption
The invention provides a determining method for fracturing water horsepower. By improving the calculation precision of the frictional resistance of a fracturing fluid, frictional resistance calculation is accurate, and obtained construction pressure is accurate, so that the fracturing water horsepower is more accurate, material consumption is reduced, and the cost is saved. By using the method ofcombining the experiment with the theory, through the frictional resistance experiment of indoor small pipe column inner diameter and a guanidine gum liquid, the relationship between flow rate and antifriction ratio is obtained by using a fitting method, and then by using the obtained relationship, the frictional resistance of different pipe column inner diameters and the guanidine gum fracturingliquid under the flow rate is calculated. By means of the method, the problem that the coefficient of empirical formula is difficult to calculate is avoided, calculating of the antifriction ratio is simpler and more accurate, and the calculated frictional resistance of the guanidine gum fracturing liquid is closer to the actual frictional resistance.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
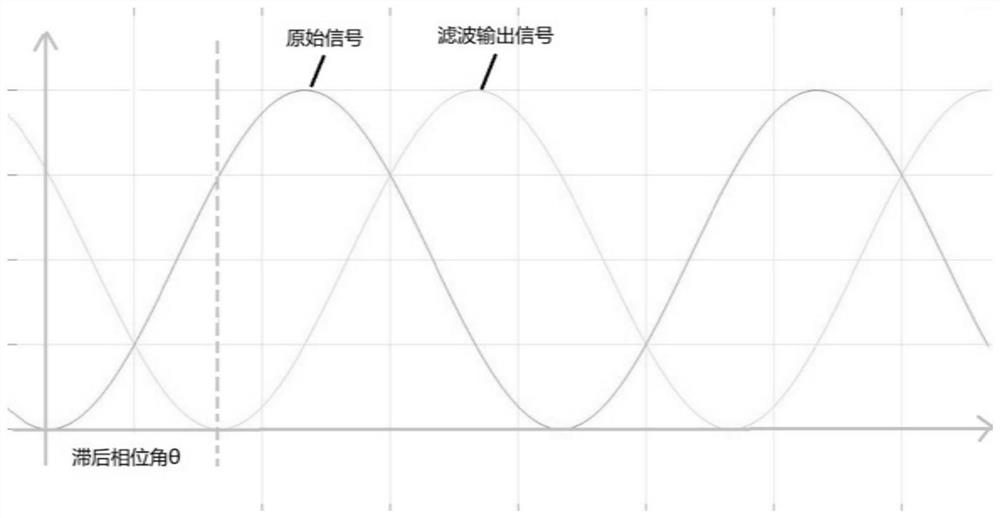
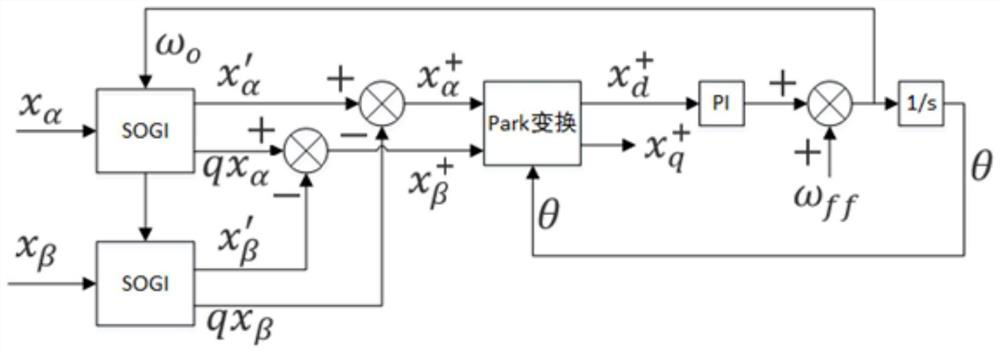
Method for solving phase lag caused by three-phase current sampling and filtering, electronic equipment and computer readable storage medium
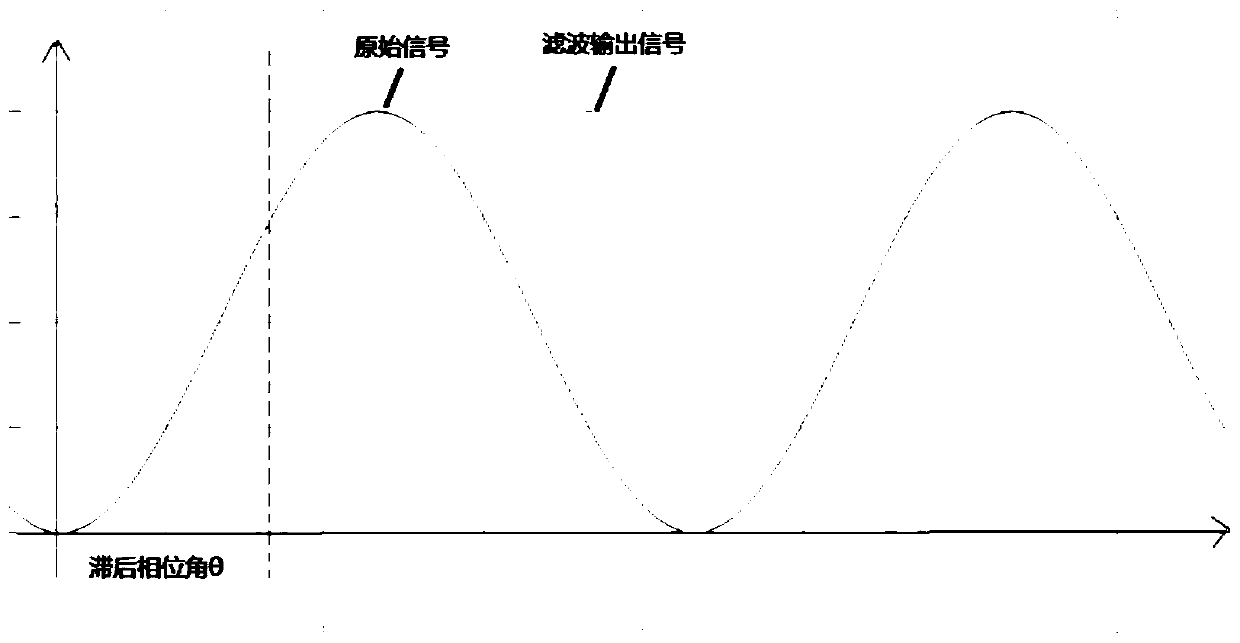
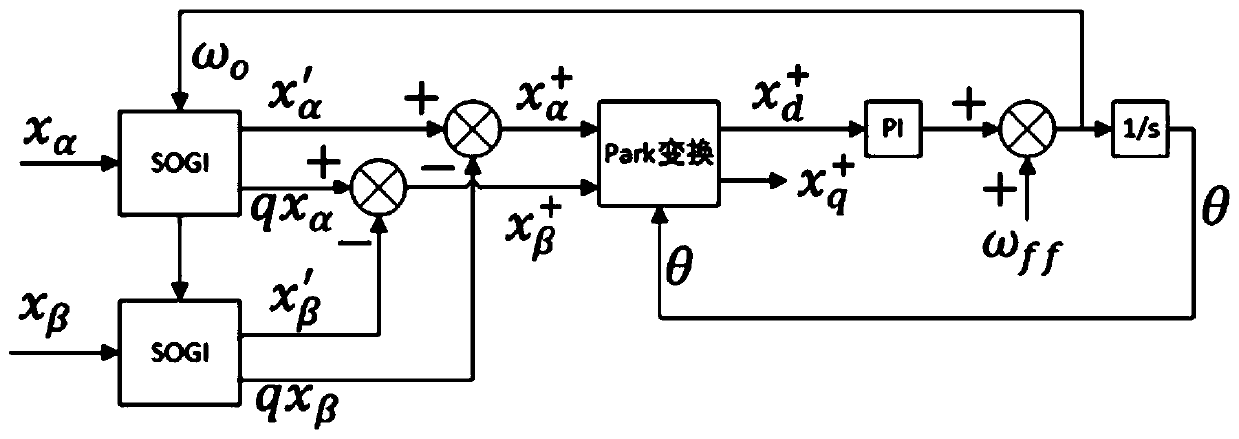
ActiveCN111308173ASolve the problem of phase lagExtend your lifeMeasurement using digital techniquesFrequency changerLow-pass filter
The invention relates to a method for solving phase lag caused by three-phase current sampling and filtering, electronic equipment and a computer readable storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: A, sampling a three-phase alternating current signal of a frequency converter and storing the three-phase alternating current signal as a digital quantity alternating current signal; B, converting the digital quantity alternating-current signal into a digital quantity direct-current signal, and filtering the converted digital quantity direct-current signal through a digital low-pass filter; and C, performing inverse transformation on the filtered digital quantity direct-current signal to recover the filtered digital quantity direct-current signal into a three-phase alternating-current signal. According to the invention, the problem of phase lag when the controller filters the three-phase alternating current signal is solved, signal sampling and filtering are accurate, the service life of the frequency converter is greatly prolonged, the failure rate is greatly reduced, the software filtering algorithm is simple and accurate to realize, and the filtering reliability and effectiveness are greatly enhanced.
Owner:GUANGDONG HIWAVE TECH
Thrust load measuring device for sealed mixing device and calibration method for same
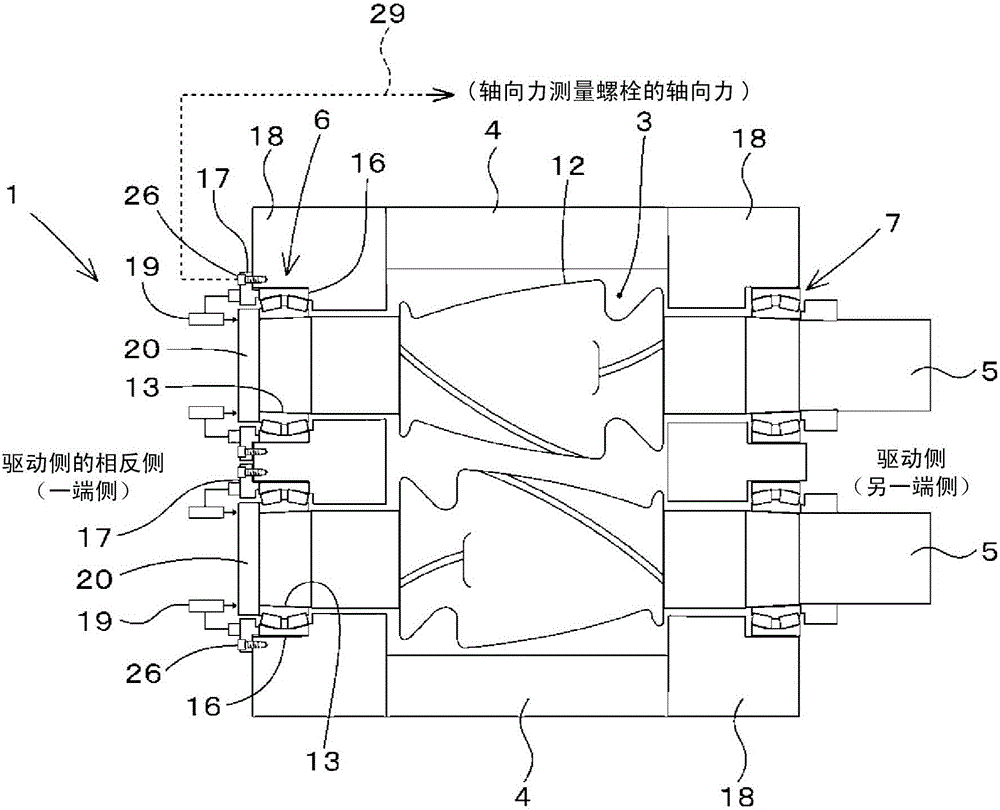
InactiveCN105828925ASimple and accurateRotary stirring mixersTransportation and packagingRelative displacementConversion coefficients
The relative displacement in the axial direction between an outer ring fixing member (17) or casing (18) and an inner ring fixing member (20) or rotor (5) is determined, said outer ring fixing member (17) being a member for affixing an outer ring (16) of a bearing (6) on one side, and said inner ring fixing member (20) being a member for affixing an inner ring (13) of the bearing (6) on the one end side. When calculating a thrust load acting on the rotor (5) by multiplying the determined relative displacement by a conversion coefficient, an axial force measuring bolt (26) is used as a tightening bolt for affixing the bearing (6) on the one end side, said axial force measuring bolt (26) enabling measurement of a load acting in the axial direction. The axial force measured by the axial force measuring bolt (26) and the relative displacement during measurement of the axial force are used to calibrate the conversion coefficient.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Electric perforating method of seamless tube blank
The invention relates to the electrical drilling for the seamless tube blank. It uses a robot to grip a carbon element made contact head, adjusting the location of the contact head manually or using programmable controller, with the contact aiming to the center of the tube blank, raising the robot, delivering the tube blank till the drilling position, connecting one end of the electric power with the contact head, the other end with the tubular blank, dropping down the robot, aligning the center of the tube with the robot quickly contacting the tube blank end surface smelting the metal through electric arc to get the required holes. Using electrical arc, it is simple in centering, stable and reliable with quick drilling speed, fine quality, low cost, improved pass rate, easy for the realization of automatic production.
Owner:包头市钢威机电有限公司
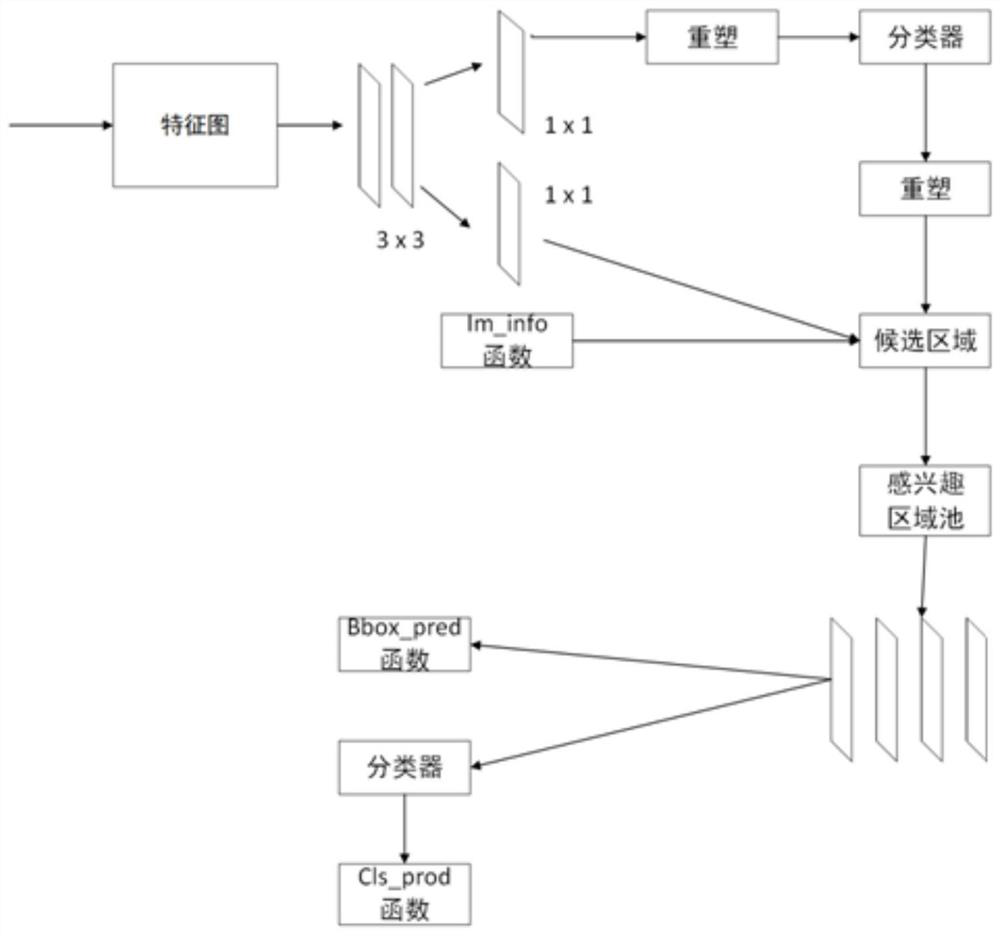
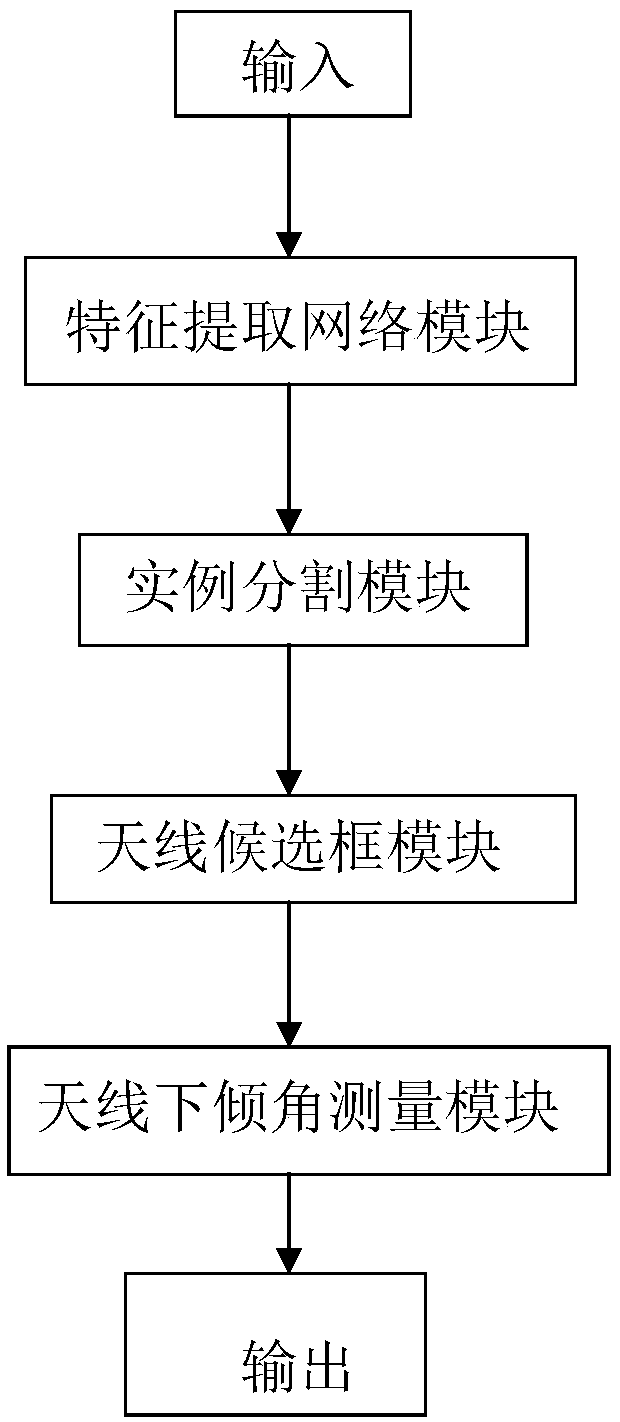
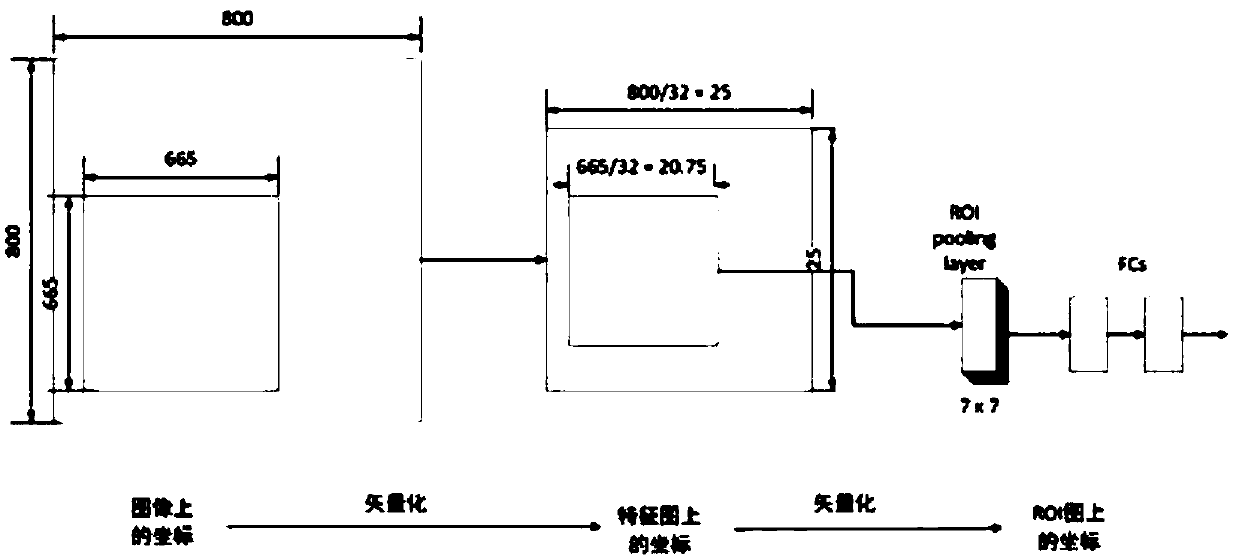
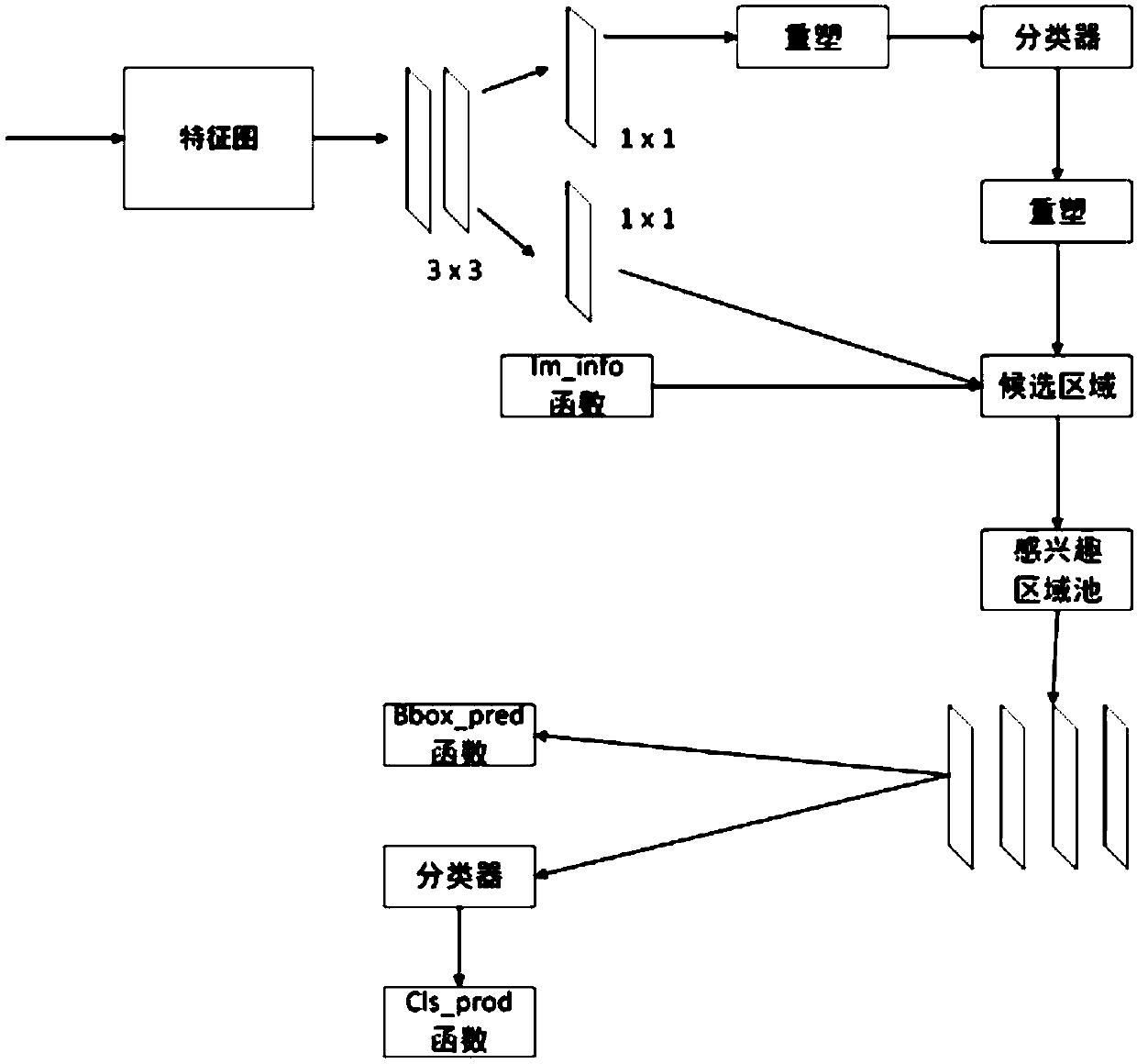
An Antenna Downtilt Measurement Method Based on Deep Instance Segmentation Network
ActiveCN109579774BSimple and accurate measurementAccurate measurementAngle measurementImage enhancementFeature extractionAlgorithm
Owner:WUYI UNIV
Antenna downtilt angle measuring method based on deep instance segmentation network
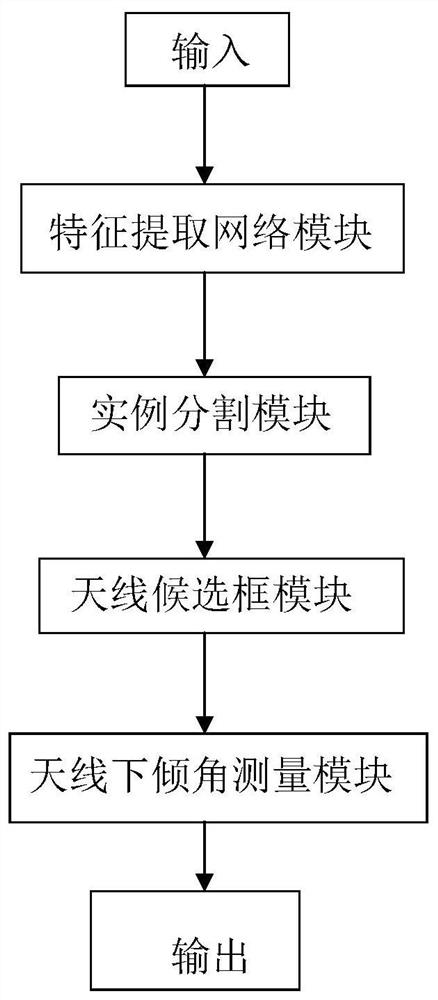
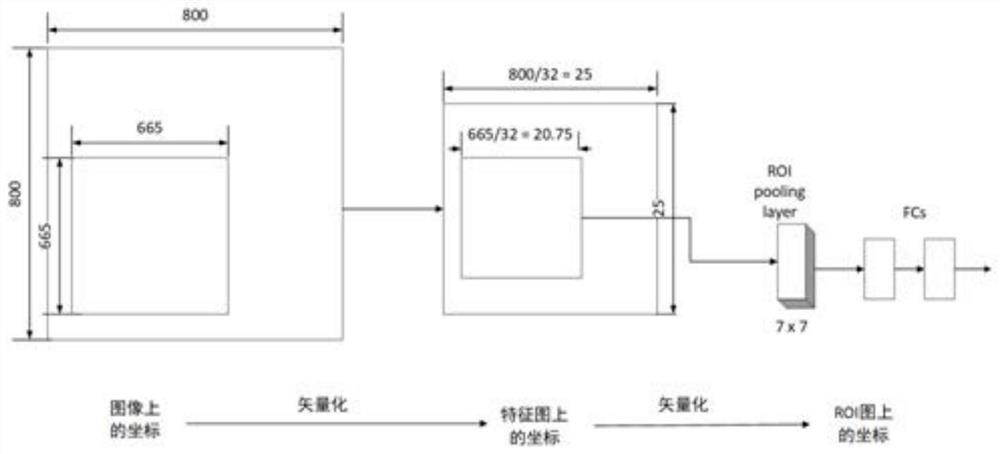
ActiveCN109579774ASimple and accurate measurementAccurate measurementImage enhancementAngle measurementFeature extractionNetwork module
The invention discloses an antenna downtilt angle measuring method based on a deep instance segmentation network. The method comprises the following steps: shooting a full range of antenna video through an unmanned aerial vehicle; transmitting the antenna video to a server in real time, and the server measuring the antenna downtilt angle in real time through a deep learning algorithm. The deep learning algorithm comprises a feature extraction network module configured to acquire an antenna feature image. The instance segmentation module performs the following steps: directly mapping a region of interest to the feature image; dividing a candidate region into k*k units; calculating four fixed coordinate positions for determining a center point of a unit for each unit; calculating values of four fixed coordinate positions by a bilinear interpolation method; and performing a maximum pooling operation and implementing backpropagation. According to the antenna downtilt angle measuring methodbased on the deep instance segmentation network, the antenna downtilt angle is more accurate by distinguishing an antenna pixel and a background pixel of the instance segmentation module, and a convenient, safe, effective and accurate antenna measuring method is established.
Owner:WUYI UNIV
A method for determining the horsepower of fracturing water
ActiveCN107939367BImprove calculation accuracyReduce consumptionFluid removalComplex mathematical operationsMaterial consumptionFracturing fluid
The invention provides a determining method for fracturing water horsepower. By improving the calculation precision of the frictional resistance of a fracturing fluid, frictional resistance calculation is accurate, and obtained construction pressure is accurate, so that the fracturing water horsepower is more accurate, material consumption is reduced, and the cost is saved. By using the method ofcombining the experiment with the theory, through the frictional resistance experiment of indoor small pipe column inner diameter and a guanidine gum liquid, the relationship between flow rate and antifriction ratio is obtained by using a fitting method, and then by using the obtained relationship, the frictional resistance of different pipe column inner diameters and the guanidine gum fracturingliquid under the flow rate is calculated. By means of the method, the problem that the coefficient of empirical formula is difficult to calculate is avoided, calculating of the antifriction ratio is simpler and more accurate, and the calculated frictional resistance of the guanidine gum fracturing liquid is closer to the actual frictional resistance.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
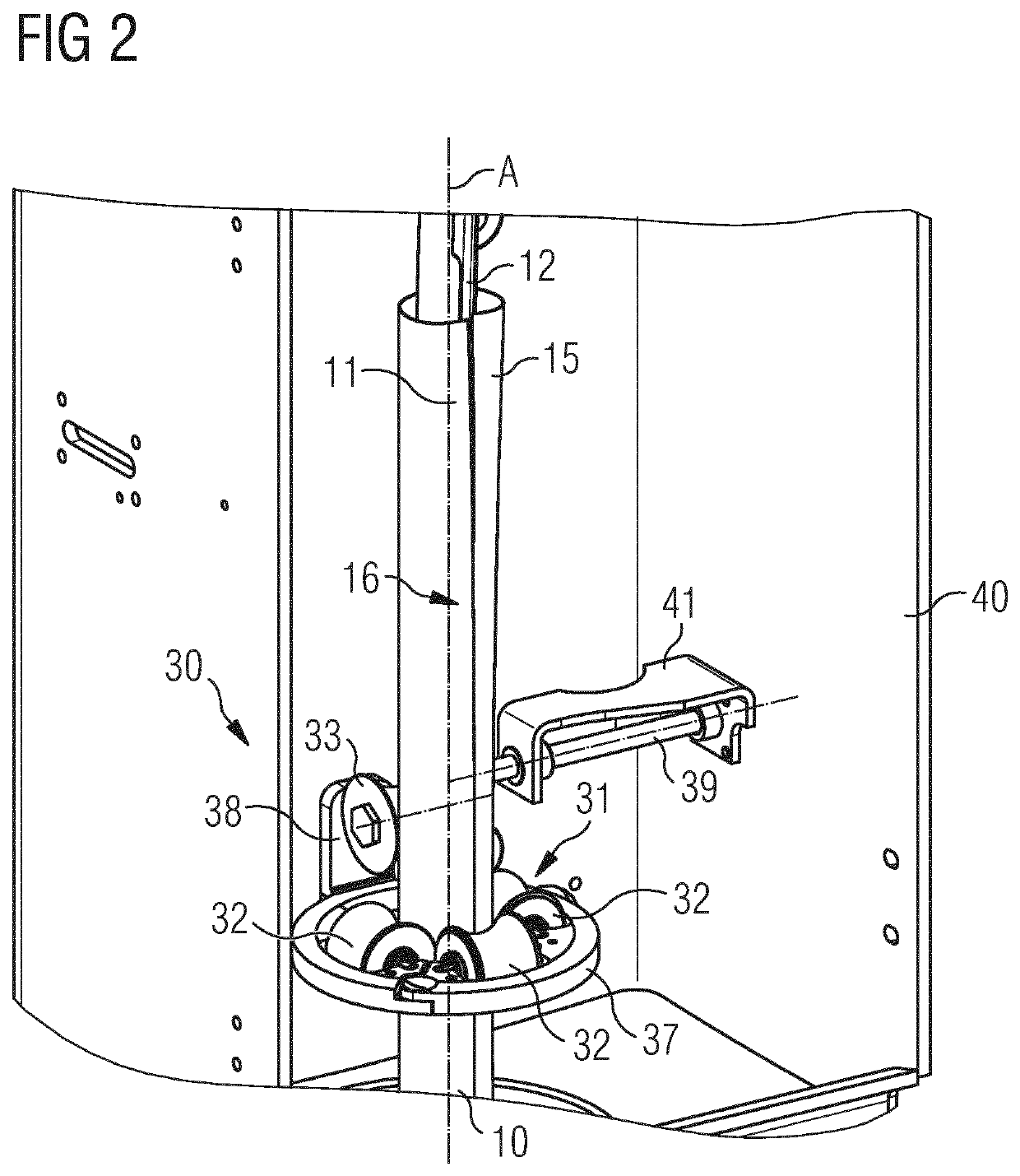
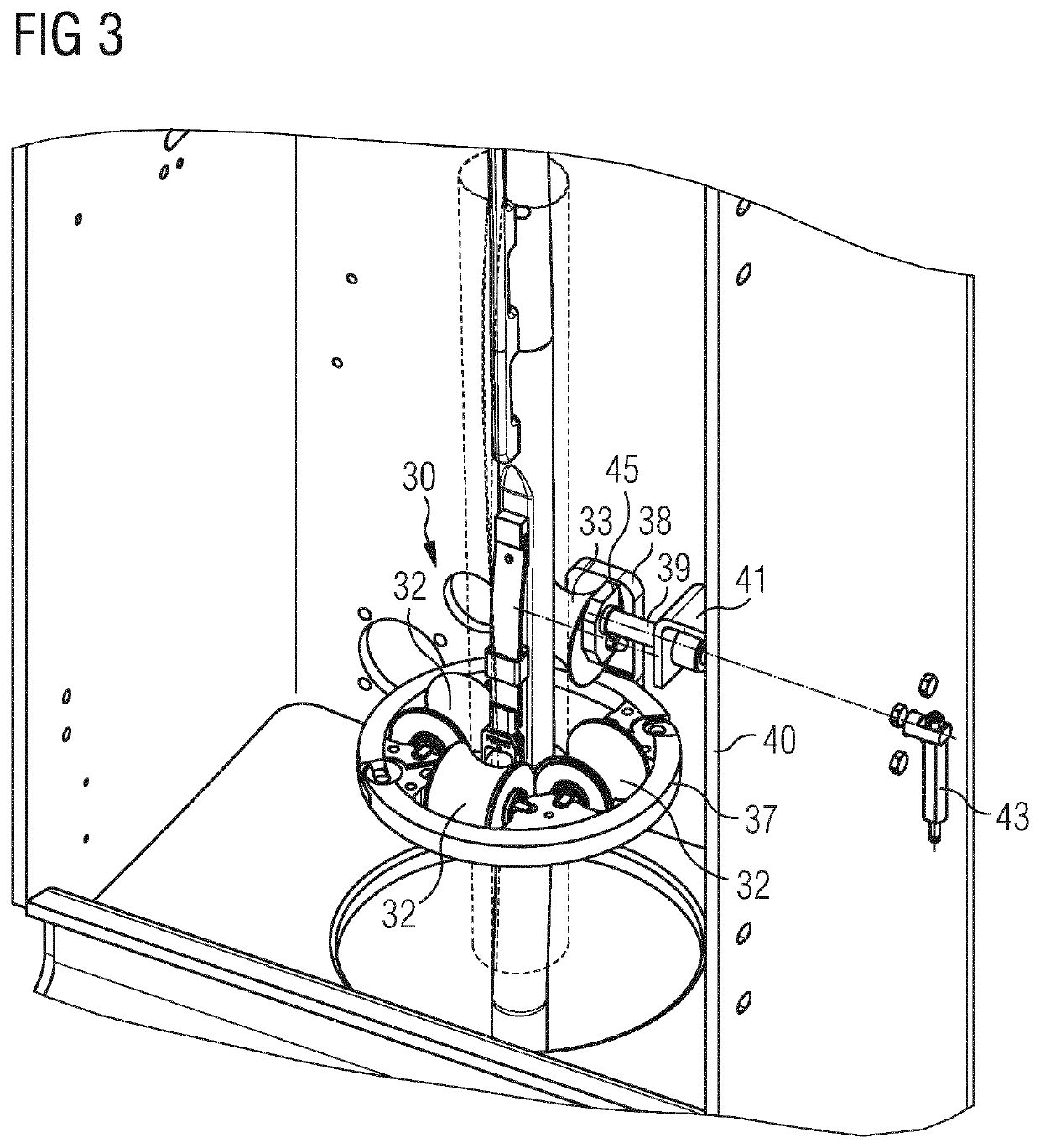
Guiding device
ActiveUS20200001518A1Simple and accurateAccurate and simple wayWrapping material feeding apparatusWrapper twisting/gatheringPhysicsRotational axis
A guiding device for guiding a sheet of packaging material (3) in a packaging machine (1) for producing sealed packages (2), said guiding device comprising a plurality of folding rollers defining a passage (31) for said sheet of packaging material (3) and causing a first longitudinal edge (11) of said sheet of packaging material (3) to superimpose to a second longitudinal edge (15) of said sheet of packaging material (3), opposite said first longitudinal edge (11), to define an overlapping area (16) of said first longitudinal edge (11) and said second longitudinal edge (15), said overlapping area having a certain extension, said passage having a longitudinal axis (A), said plurality of folding rollers comprising a group of first folding rollers (32) rotatable around first rotation axes (C) arranged in a common first plane, said plurality of folding rollers further comprising at least one second folding roller (33) rotatable around a second rotation axis (D) arranged in a second plane, different from said first plane, said guiding device further comprising a driving arrangement (34) for moving said at least one second folding roller (33) towards and away from said longitudinal axis (A) of said passage (31) so as to control the extension of said overlapping area (16).
Owner:TETRA LAVAL HLDG & FINANCE SA
Method for solving phase lag caused by three-phase current sampling and filtering, electronic equipment, and computer-readable storage medium
ActiveCN111308173BSolve the problem of phase lagExtend your lifeMeasurement using digital techniquesLow-pass filterTransverter
Owner:GUANGDONG HIWAVE TECH
Balance Management system
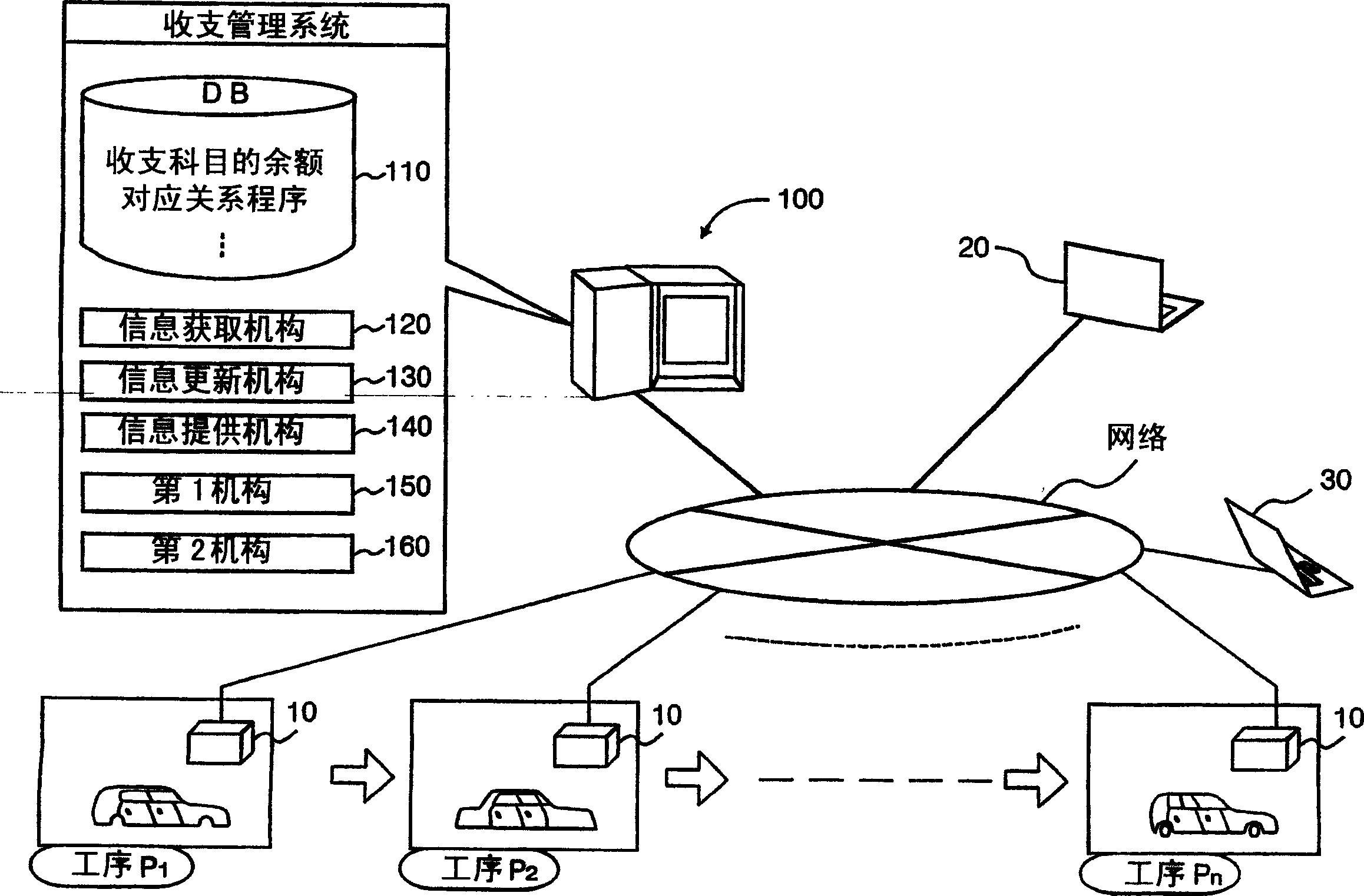
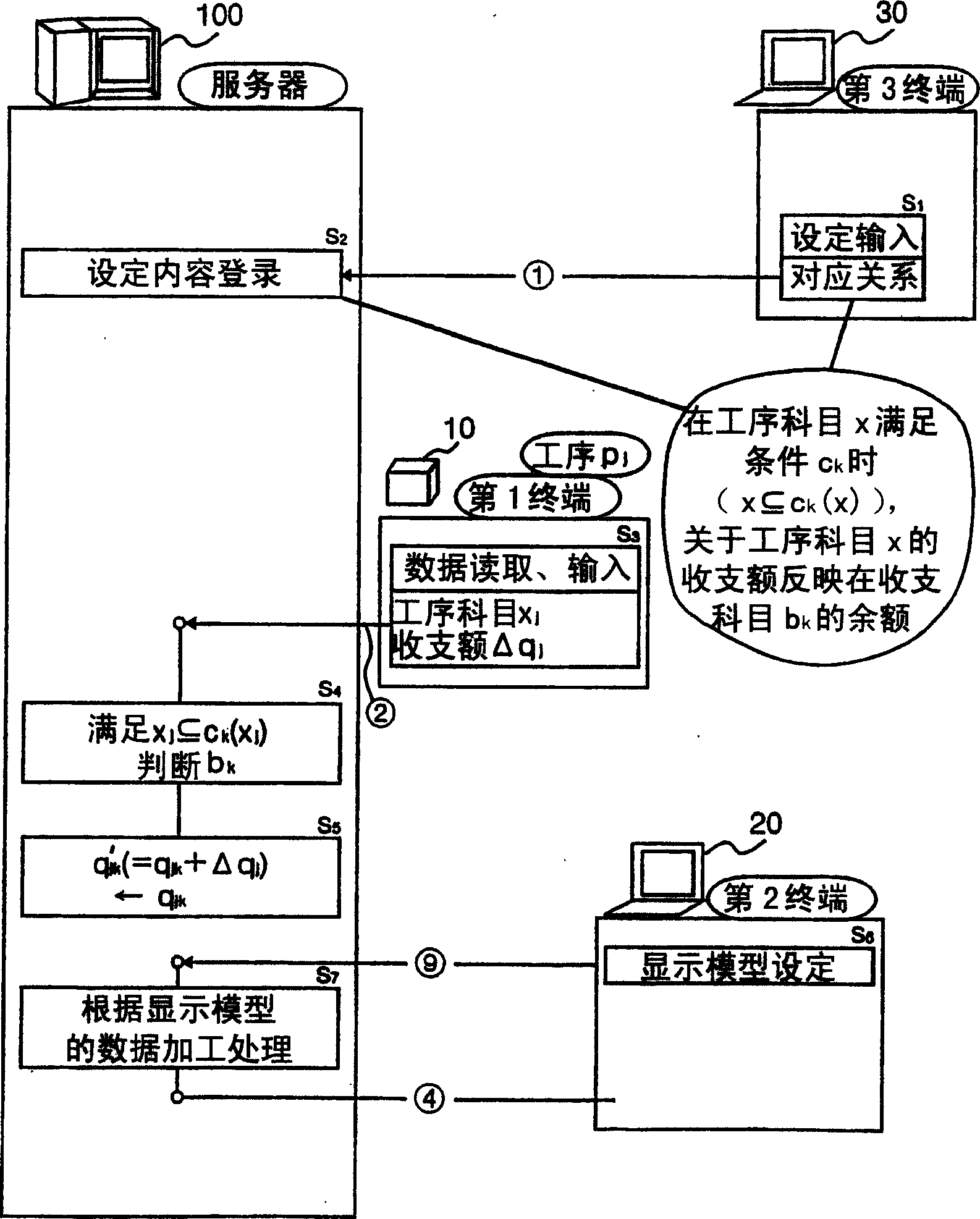
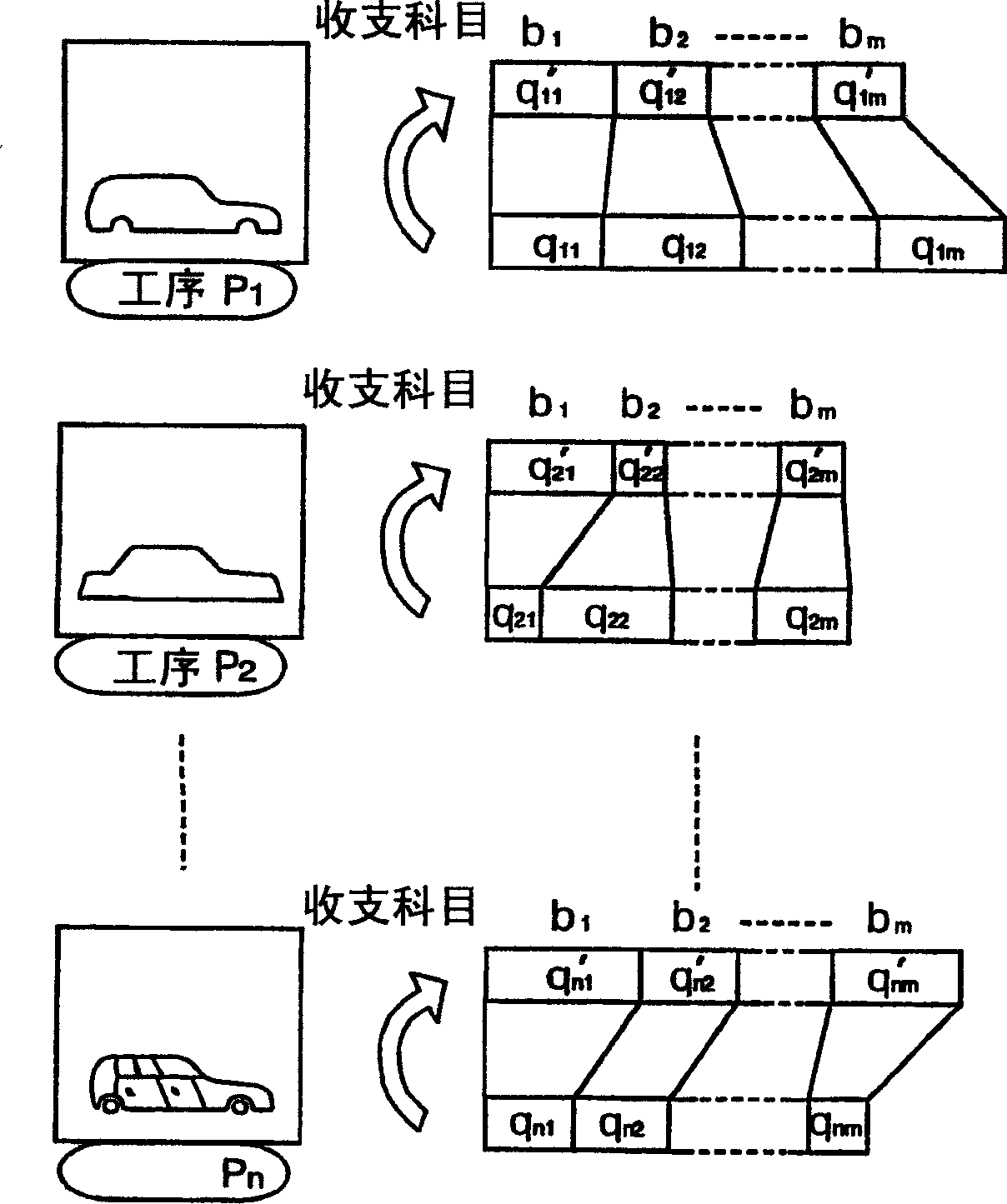
InactiveCN1628309APrevent complications etc.Simple and accurateFinanceResourcesRelevant informationComputer science
A system for a user to simply and precisely grasp various information on the balance occuring at one or more steps. The balance management system is constructed of a server and is provided with a DB (information managing means), information acquiring means information updating means and information providing means. The DB manages information on the balance of a balance item and information on the correspondence for each step that which balance of a balance item reflects the balance of which step item. The information acquiring means acquires information on each step item and the balance corresponding to the step item, from the first terminal corresponding to each step. The information updating means updates the information on the balance of the balance item corresponding to the step item, on the basis of the information on the correspondence managed by the DB and the information on the step item and the balance acquired by the information acquiring means. The information providing means provides a second terminal with the information on the balance item and the balance of one or more steps managed by the DB.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
System for picture packaging and framing
InactiveUS20180155109A1Easy to useThe process is simple and accuratePicture framesDomestic mirrorsFixed frameEngineering
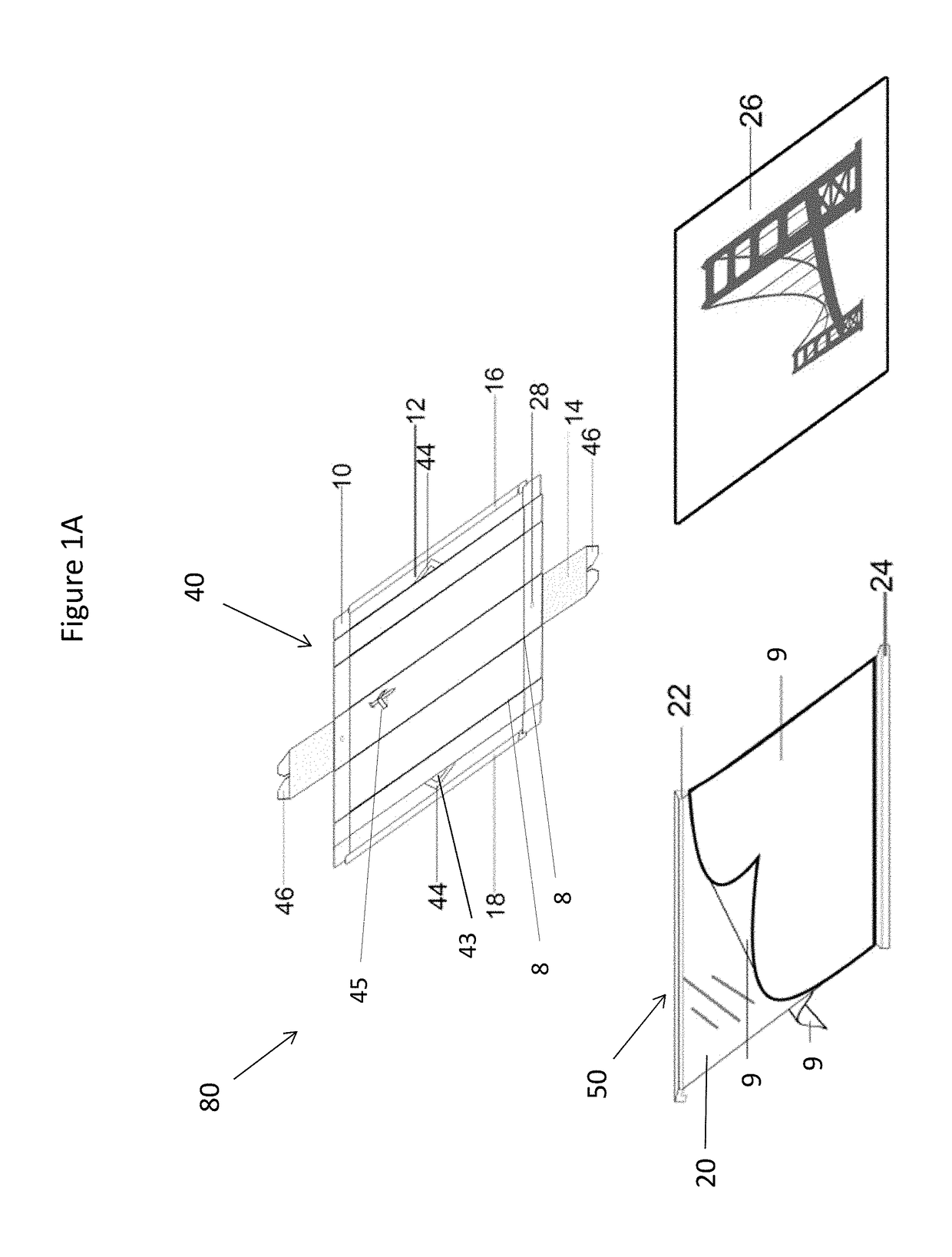
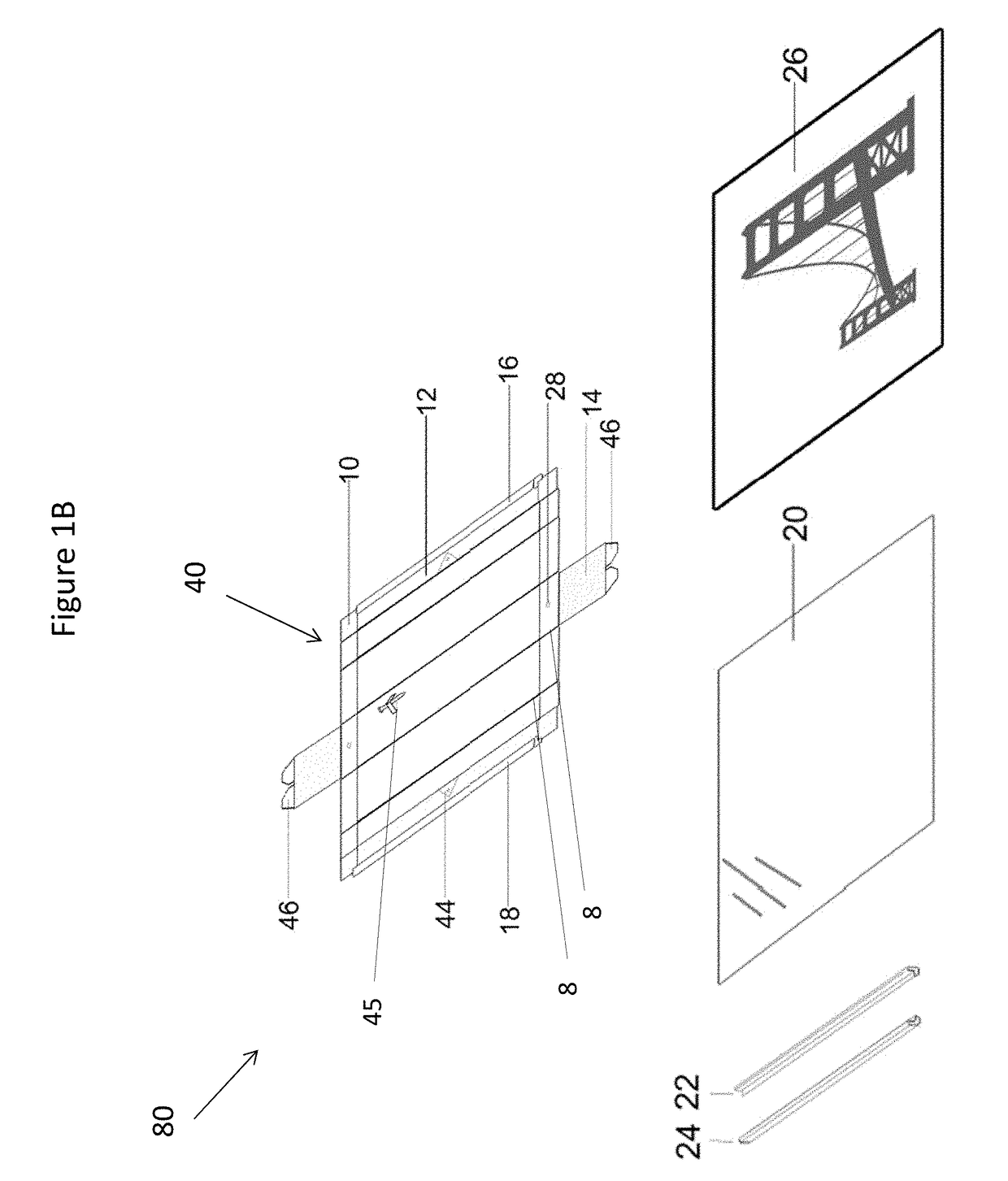
A system and method for packaging and framing a picture comprises a partially assembled frame; wherein the partially assembled frame comprises one of: one fixed frame member is fixedly attached to a backing board adapted for holding the picture; two opposite fixed frame members are fixedly attached to the picture; or two opposite fixed frame members are fixedly attached to a backing board adapted for holding the picture. The system further comprises completion frame members adapted for joining to the fixed frame members to complete a frame for the picture and the partial assembly is adapted for rolling or folding up for packaging the picture.
Owner:FRAME TO GO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com