Patents
Literature
42results about How to "Variation in quality" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nonmagnetic Material Particle Dispersed Ferromagnetic Material Sputtering Target
ActiveUS20090242393A1Good effectFast depositionCellsVacuum evaporation coatingProduction rateSputtering
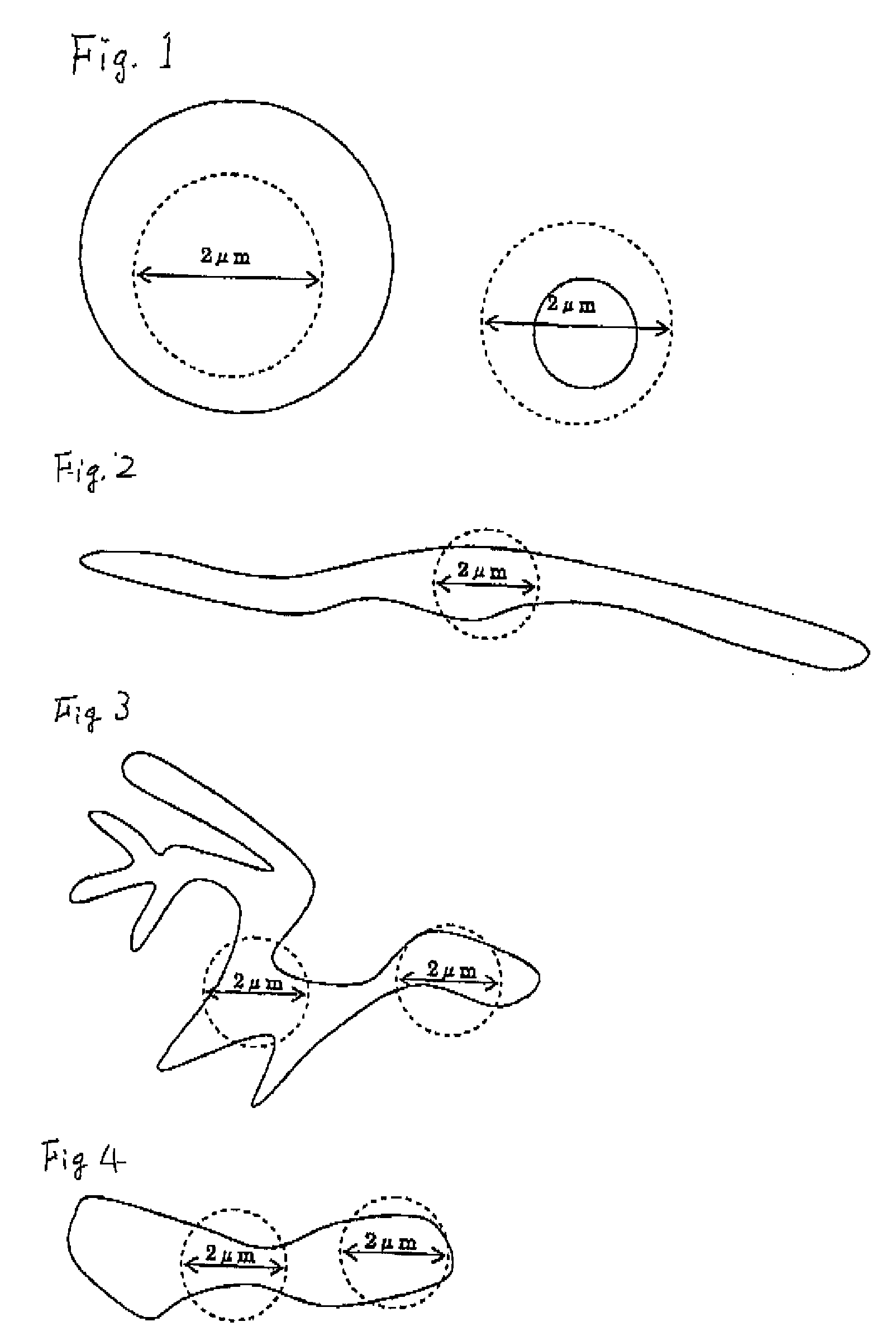
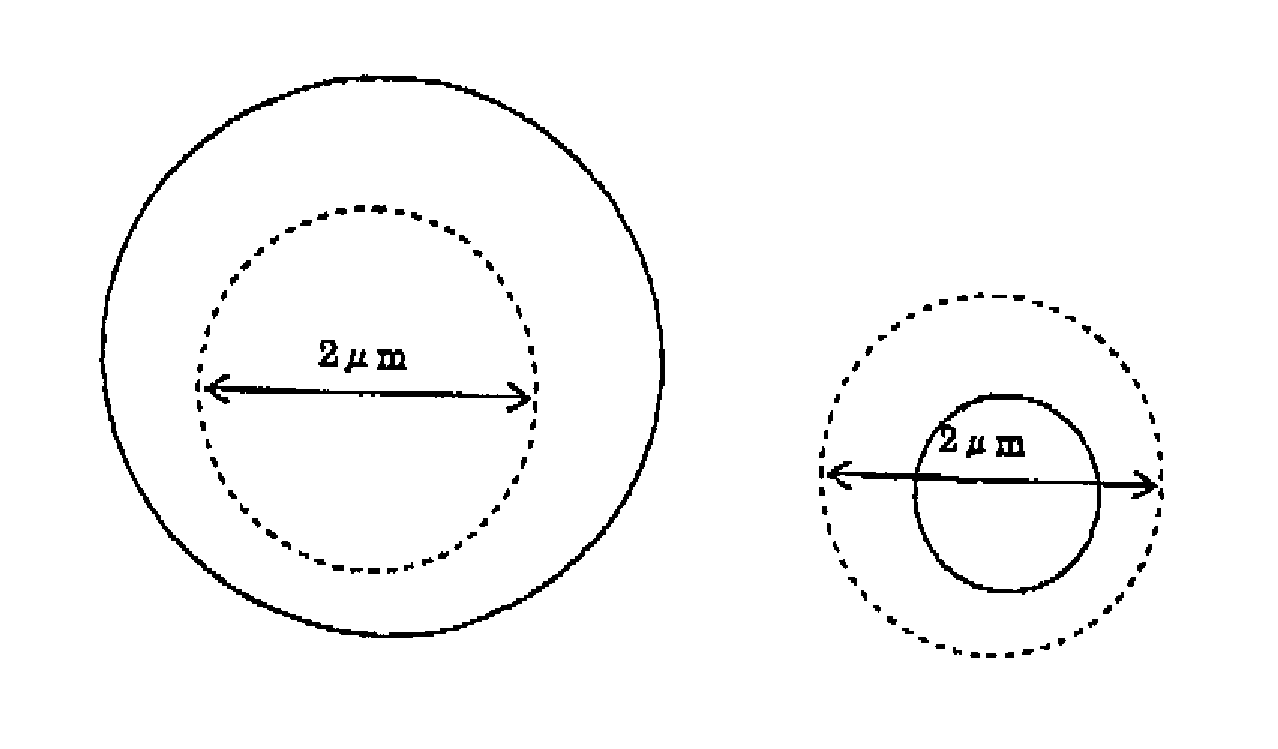
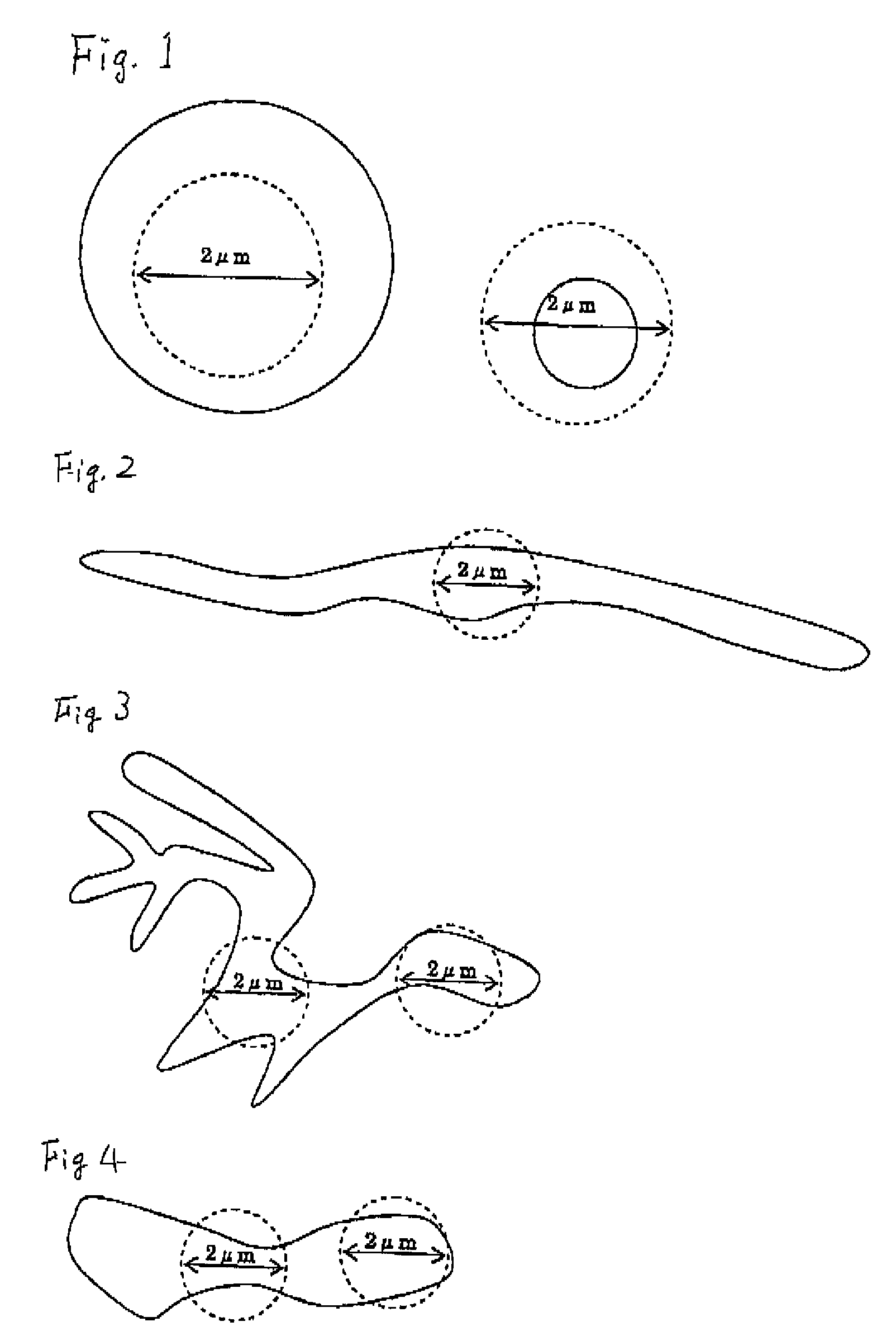
Provided is a nonmagnetic material particle dispersed ferromagnetic material sputtering target comprising a material including nonmagnetic material particles dispersed in a ferromagnetic material. The nonmagnetic material particle dispersed ferromagnetic material sputtering target is characterized in that all particles of the nonmagnetic material with a structure observed on the material in its polished face have a shape and size that are smaller than all imaginary circles having a radius of 2 μm formed around an arbitrary point within the nonmagnetic material particles, or that have at least two contact points or intersection points between the imaginary circles and the interface of the ferromagnetic material and the nonmagnetic material. The nonmagnetic material particle dispersed ferromagnetic material sputtering target is advantageous in that, in the formation of a film by sputtering, the influence of heating or the like on a substrate can be reduced, high-speed deposition by DC sputtering is possible, the film thickness can be regulated to be thin, the generation of particles (dust) or nodules can be reduced during sputtering, the variation in quality can be reduced to improve the mass productivity, fine crystal grains and high density can be realized, and the nonmagnetic material particle dispersed ferromagnetic material sputtering target is particularly best suited for use as a magnetic recording layer.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING& METALS CORP
Gas filled bodies
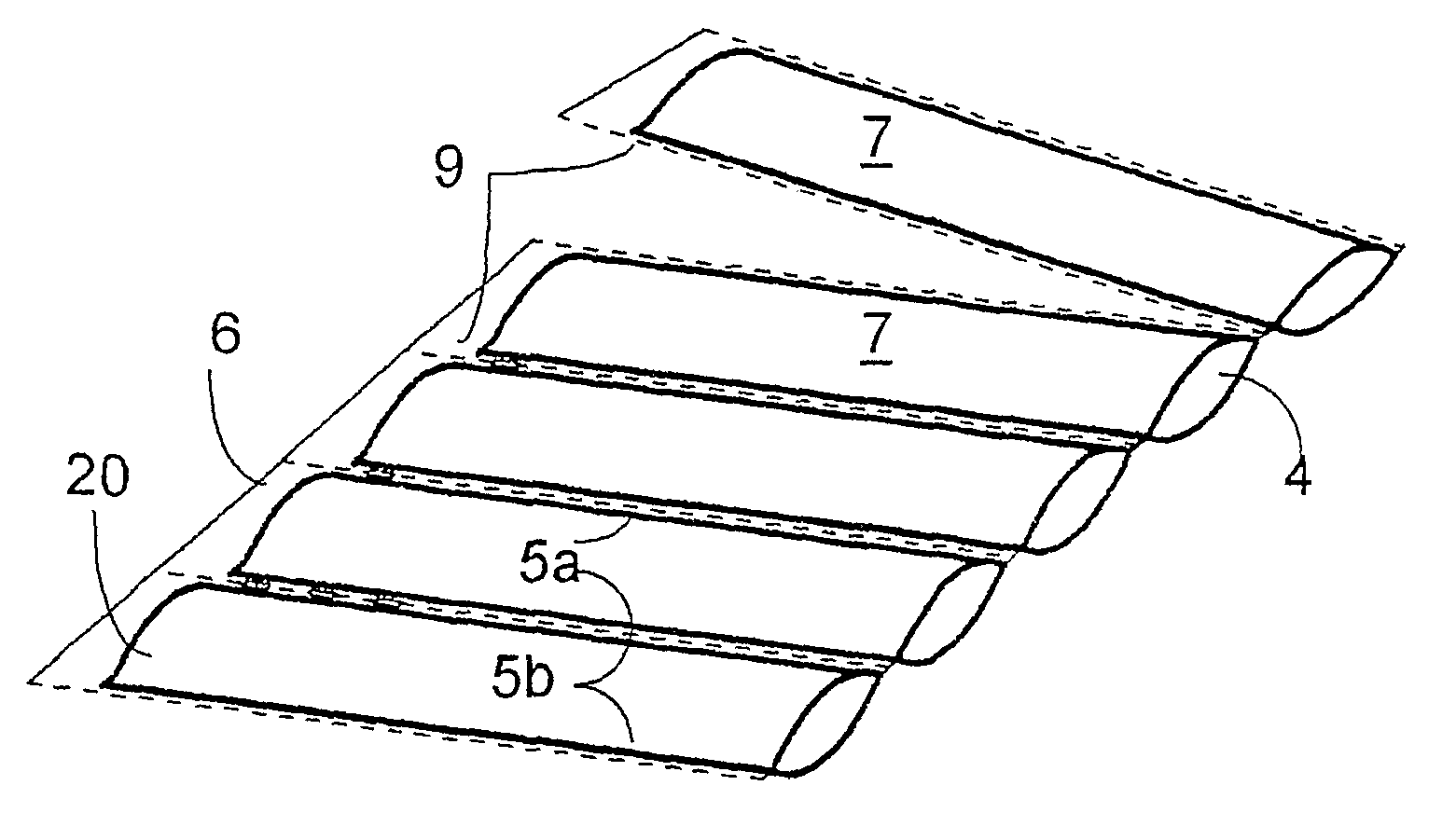
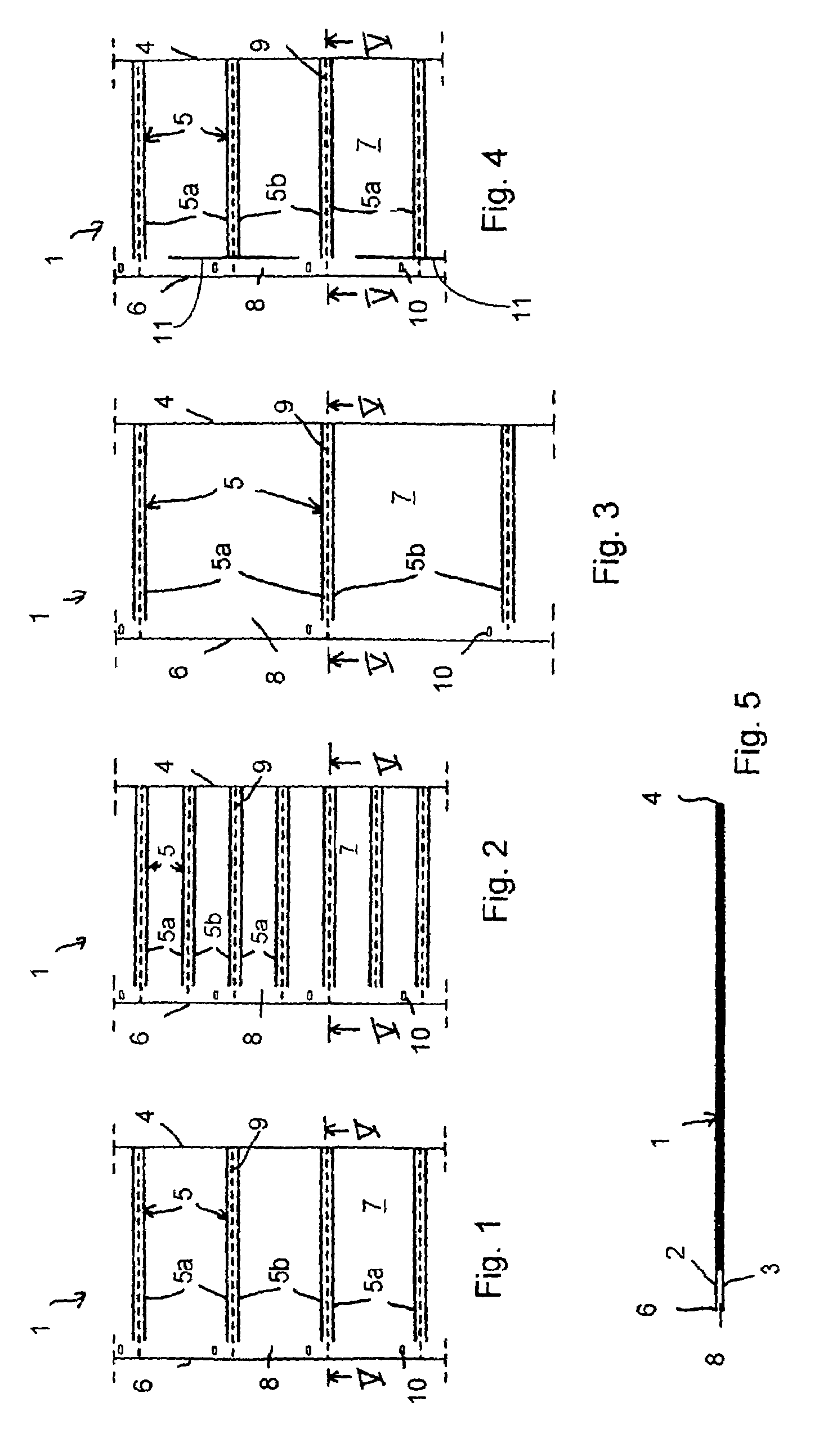
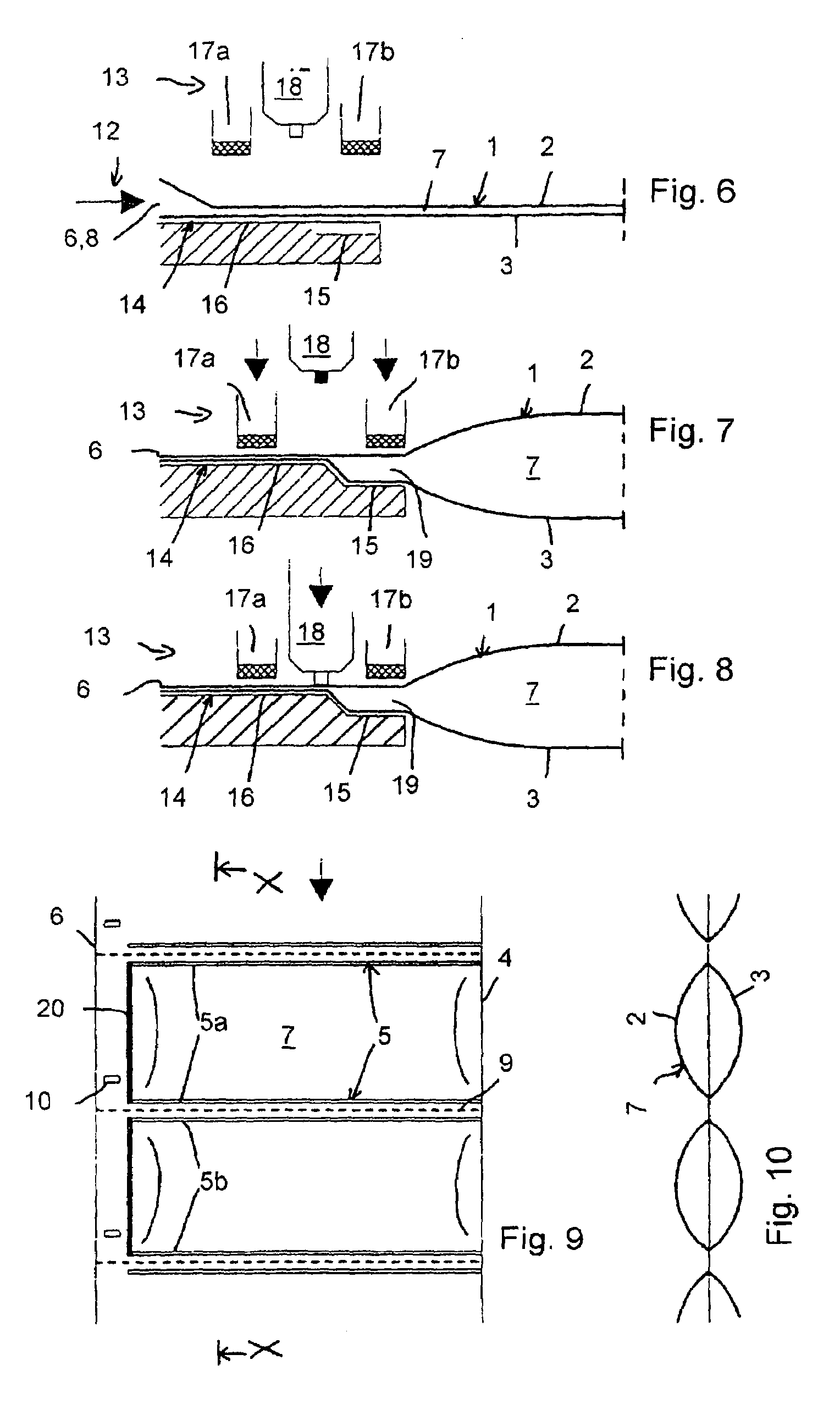
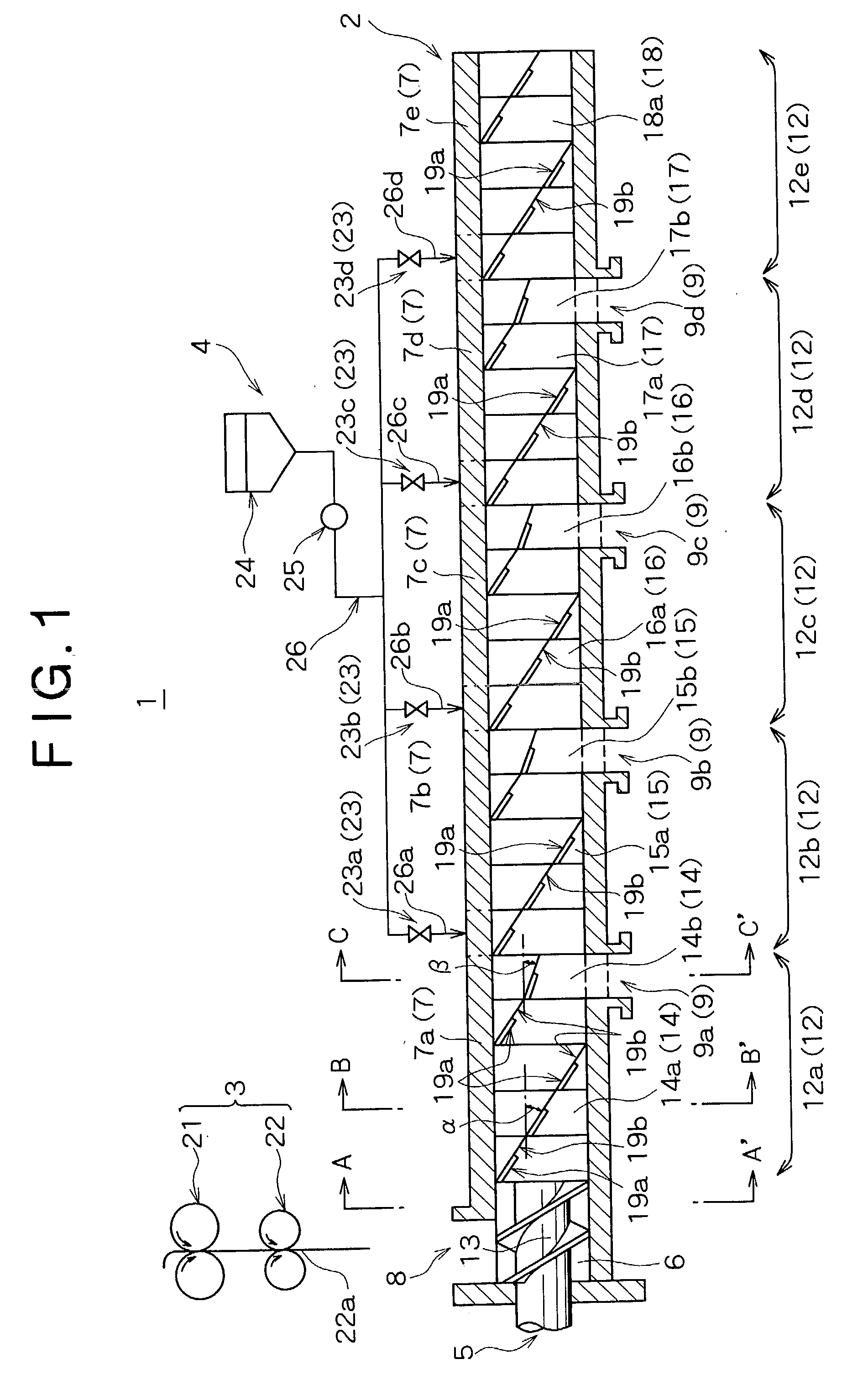
In a plastic tube (1) for the production of gas filled bodies, with two superimposed sheets, connected in a gas tight manner to each other along a first longitudinal edge thereof, the upper sheet (2) and the lower sheet (3) are welded together in the transverse direction along gas tight welded seams (5a,5b), arranged in pairs at a separation from each other, in order to form inflatable pockets (7), which seams extend from the first longitudinal edge (4) to a point at a predetermined separation from the opposing second longitudinal edge (6). The pockets each present, between the upper sheet and the lower sheet, a gas filling opening (8) which is accessible from the second longitudinal edge. Also proposed are a method for the production of gas filled bodies using such plastic tubes and a device for carrying out said method.
Owner:LORSCH JOHANNES
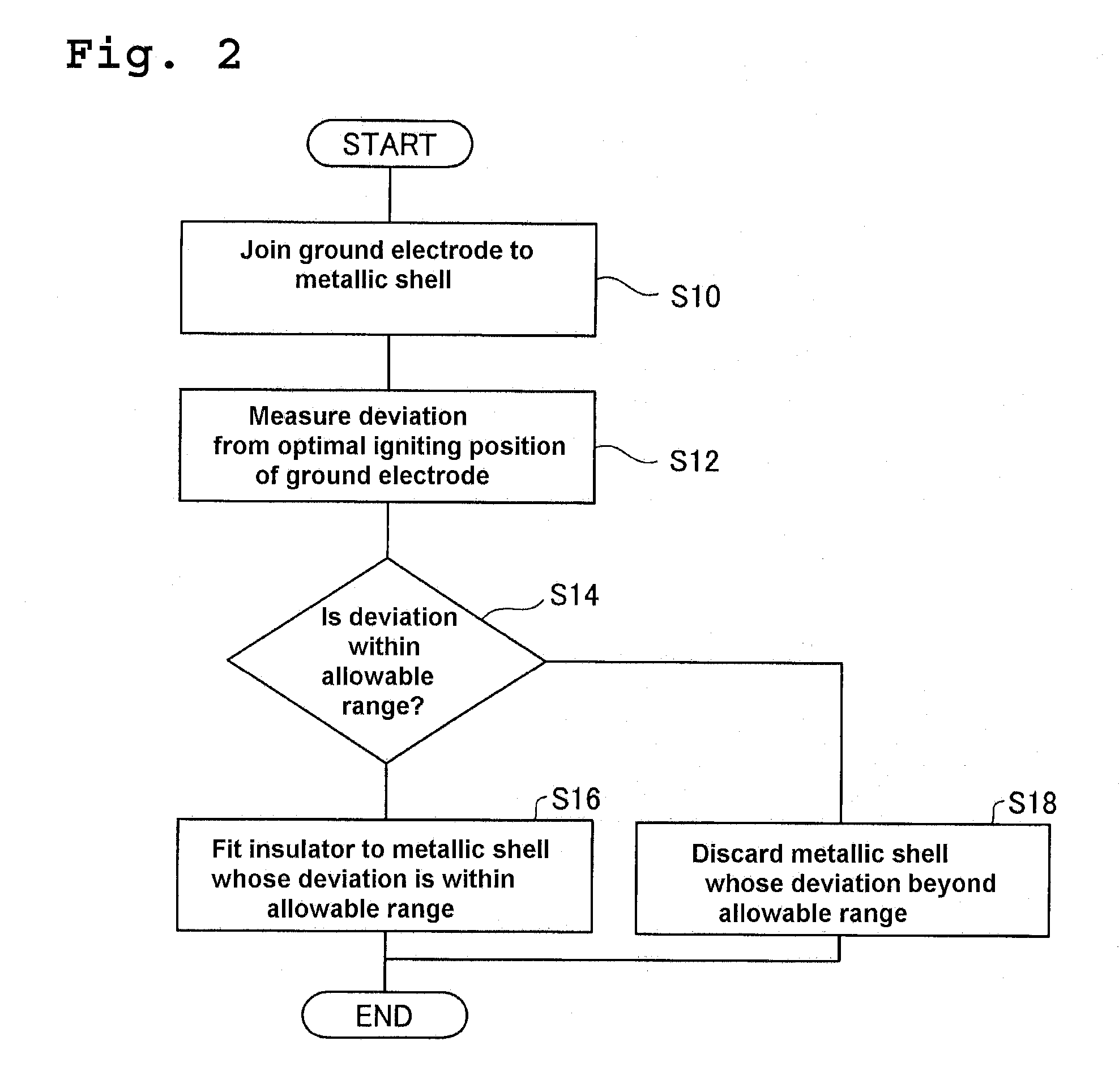
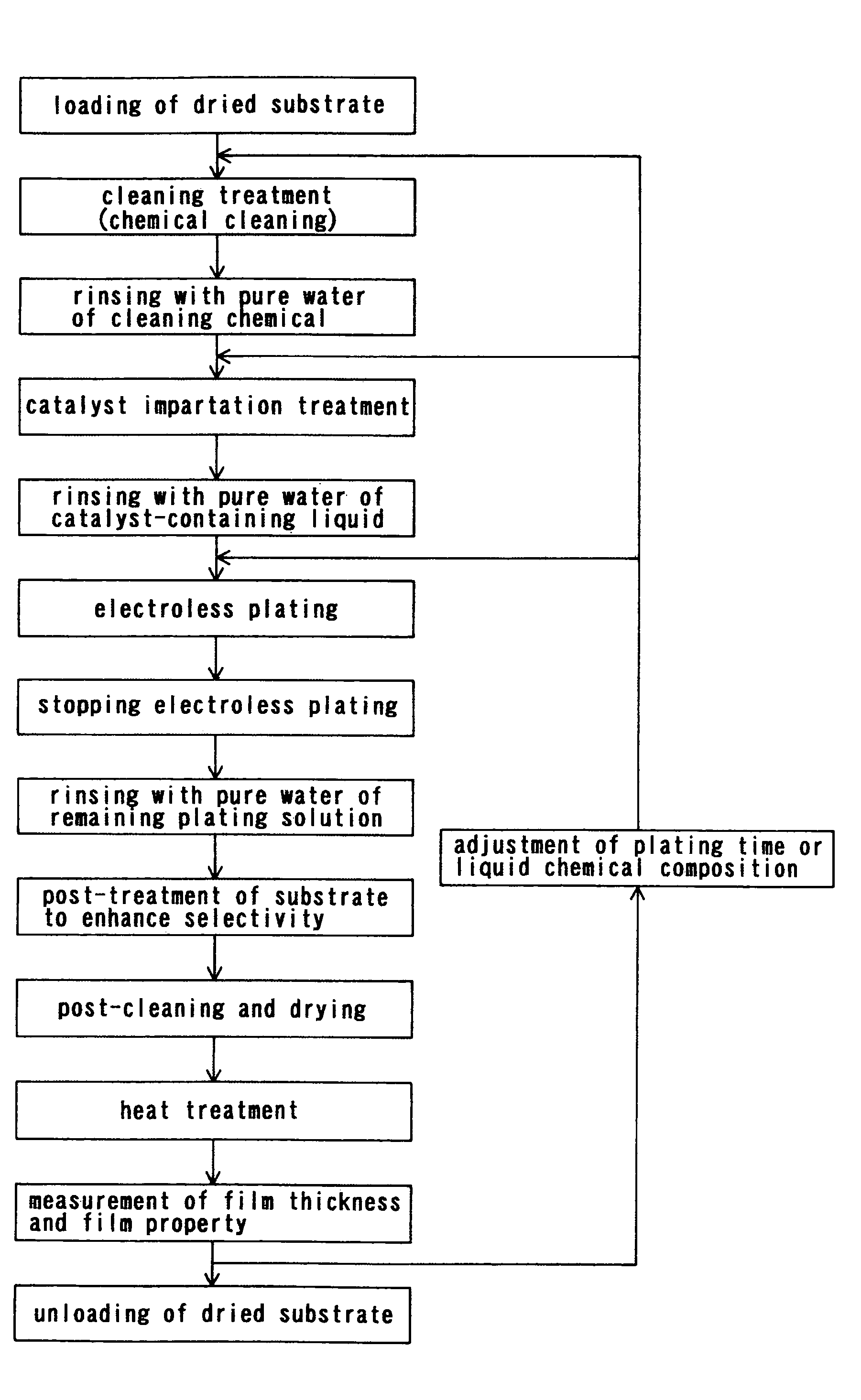
Substrate processing method and apparatus
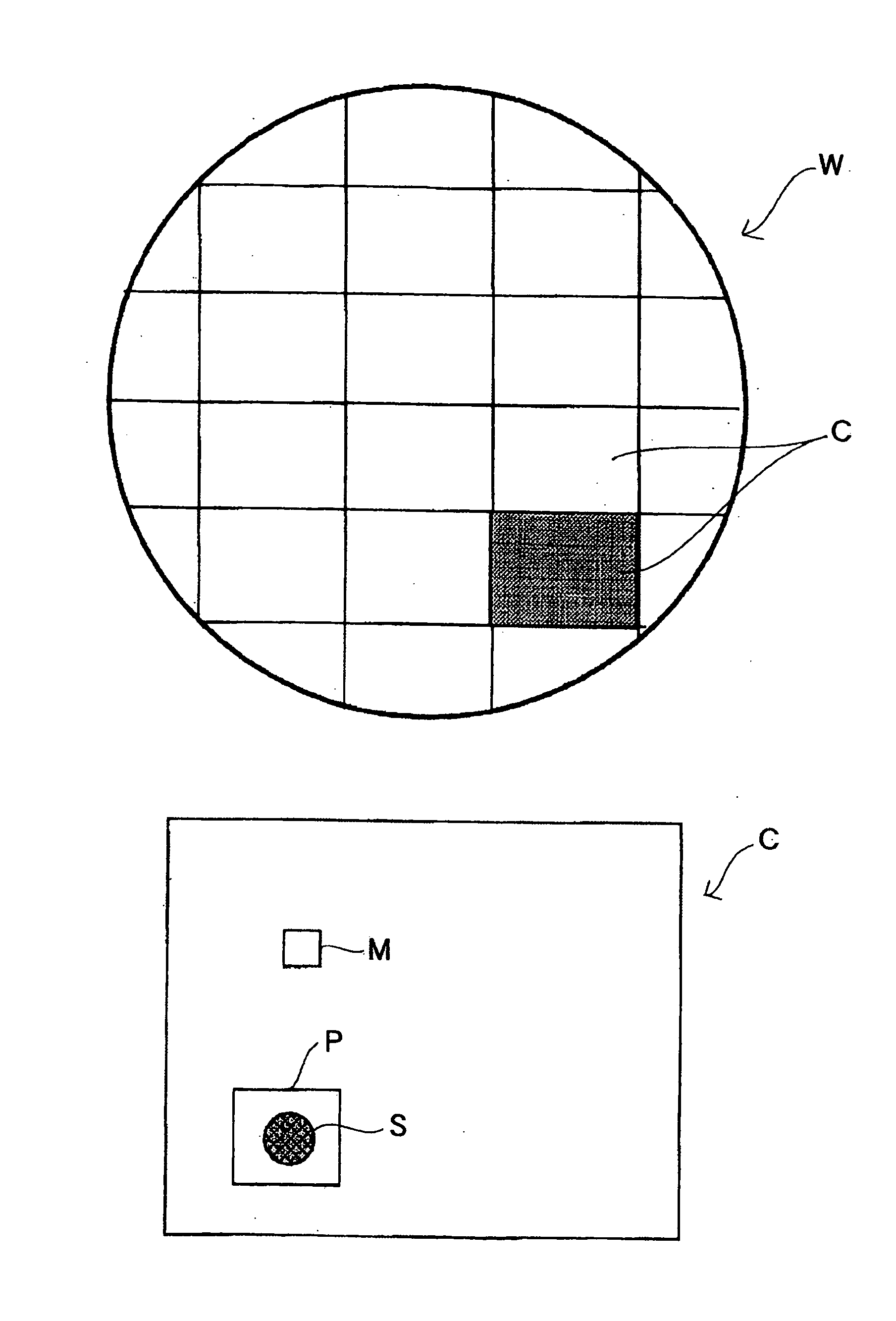
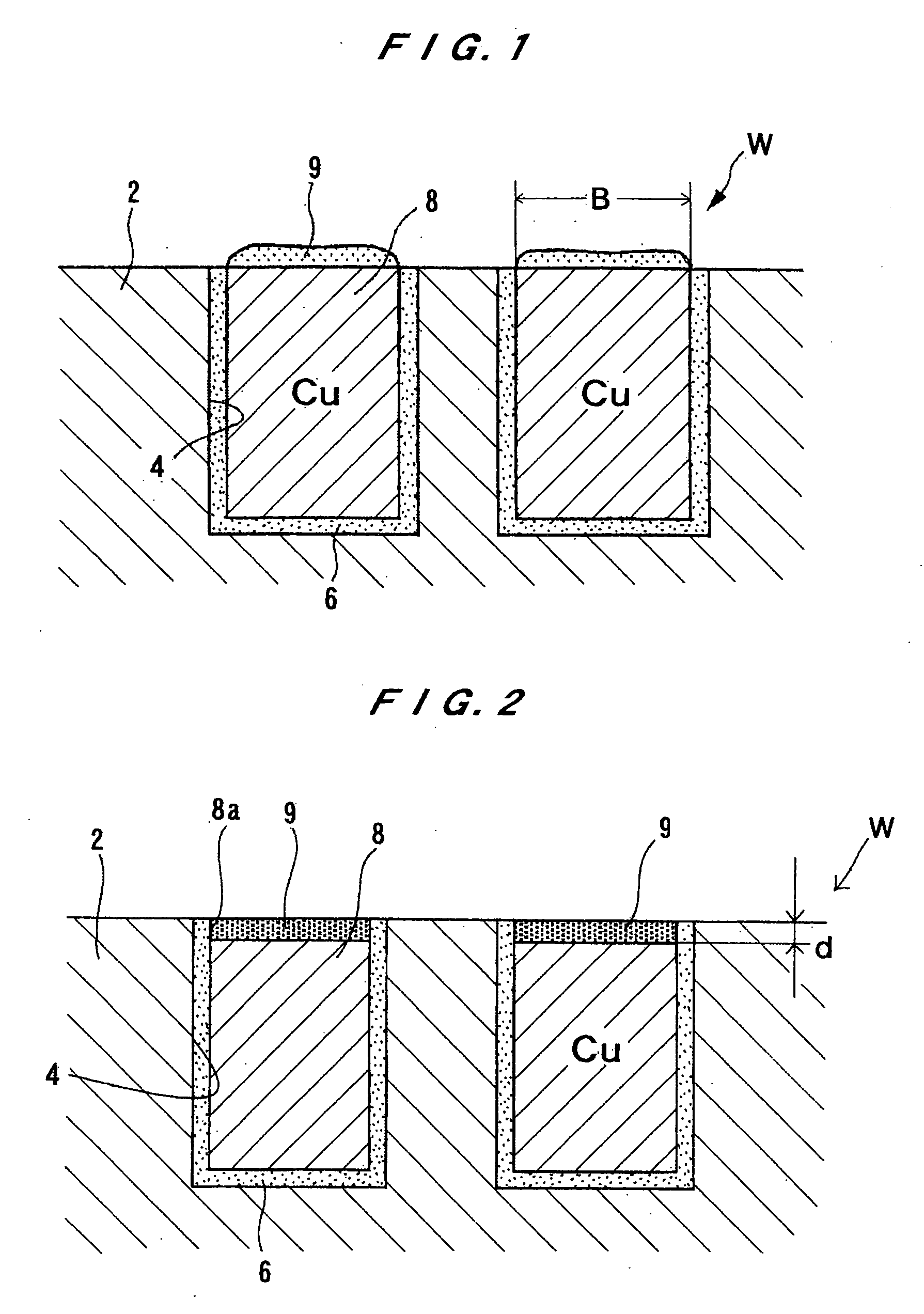
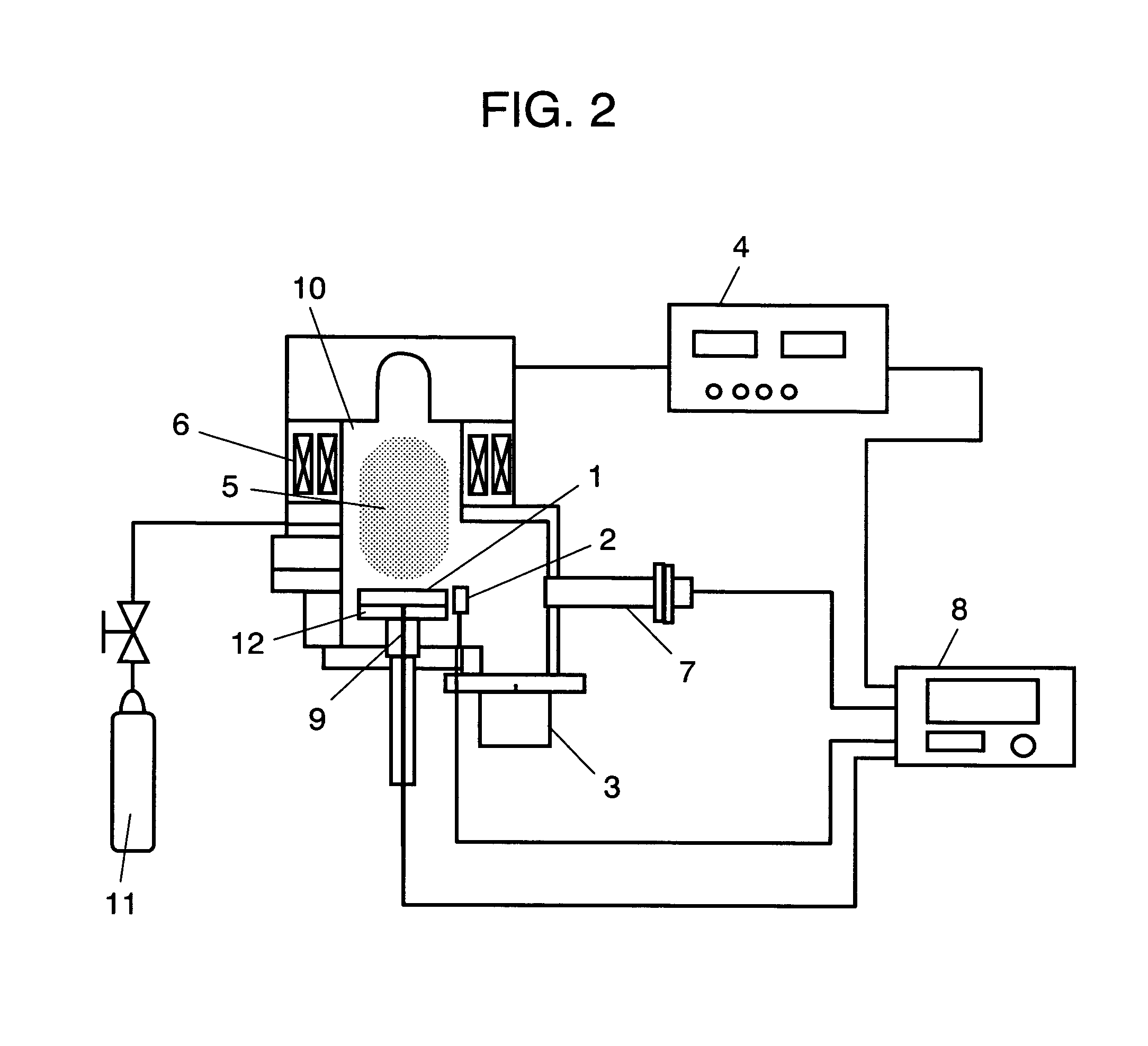
ActiveUS20050009213A1Variation in qualitySuppress mutationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesProcess conditionsMetal
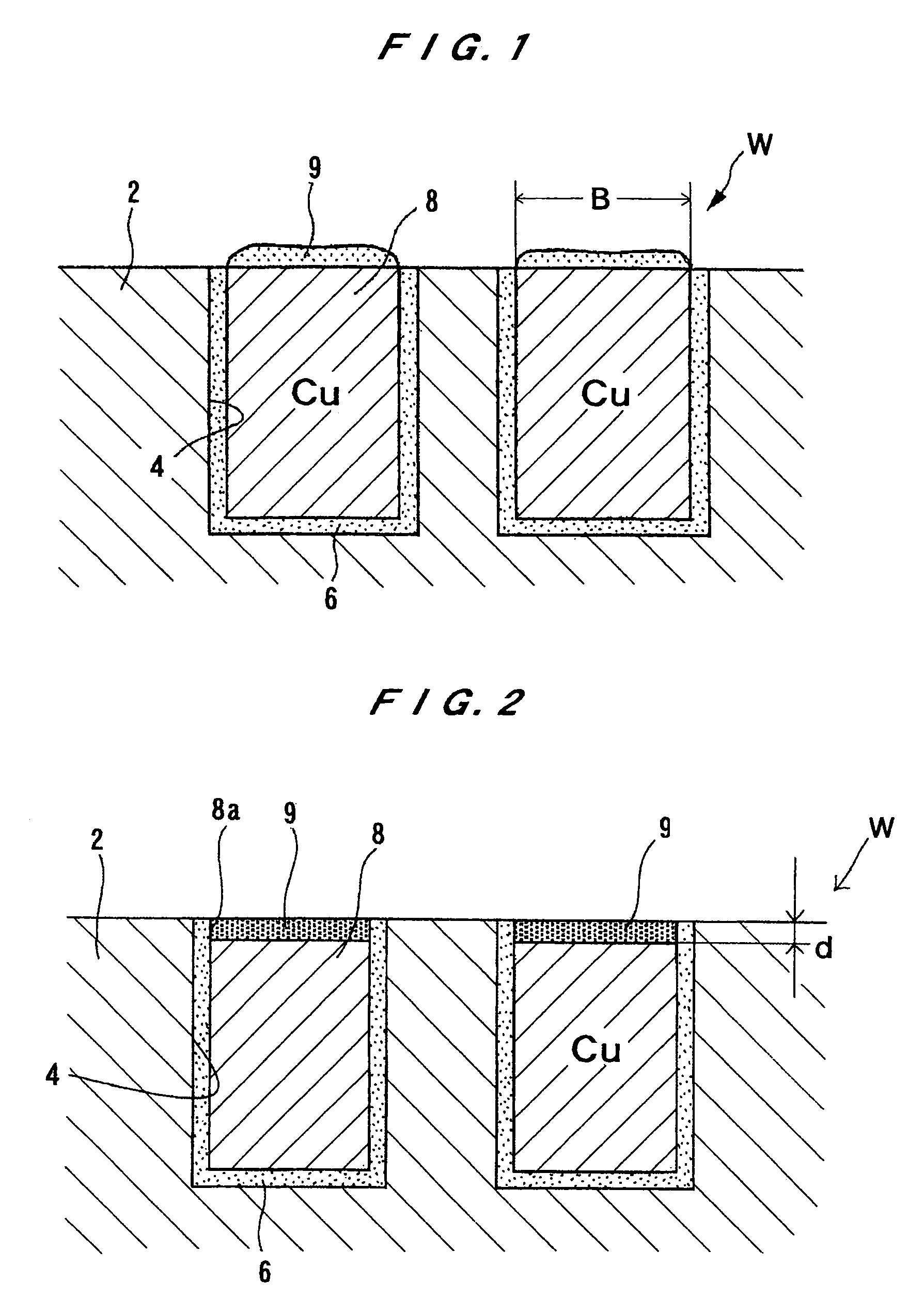
There is provided a substrate processing method and apparatus which can measure and monitor the thickness and / or properties of a film formed on a substrate as needed, and quickly correct a deviation in the process conditions, and which can therefore stably provide a product of constant quality. A substrate processing method for processing a substrate with a metal and an insulating material exposed on its surface in such a manner that the film thickness of the metal portion with the exposed surface of the metal as a reference plane is selectively or preferentially changed, including measuring a change in the film thickness and / or a film property of the metal portion during and / or immediately after processing, and monitoring the processing and adjusting the processing conditions based on the results of measurement.
Owner:EBARA CORP
Method of controlling impurity doping and impurity doping apparatus
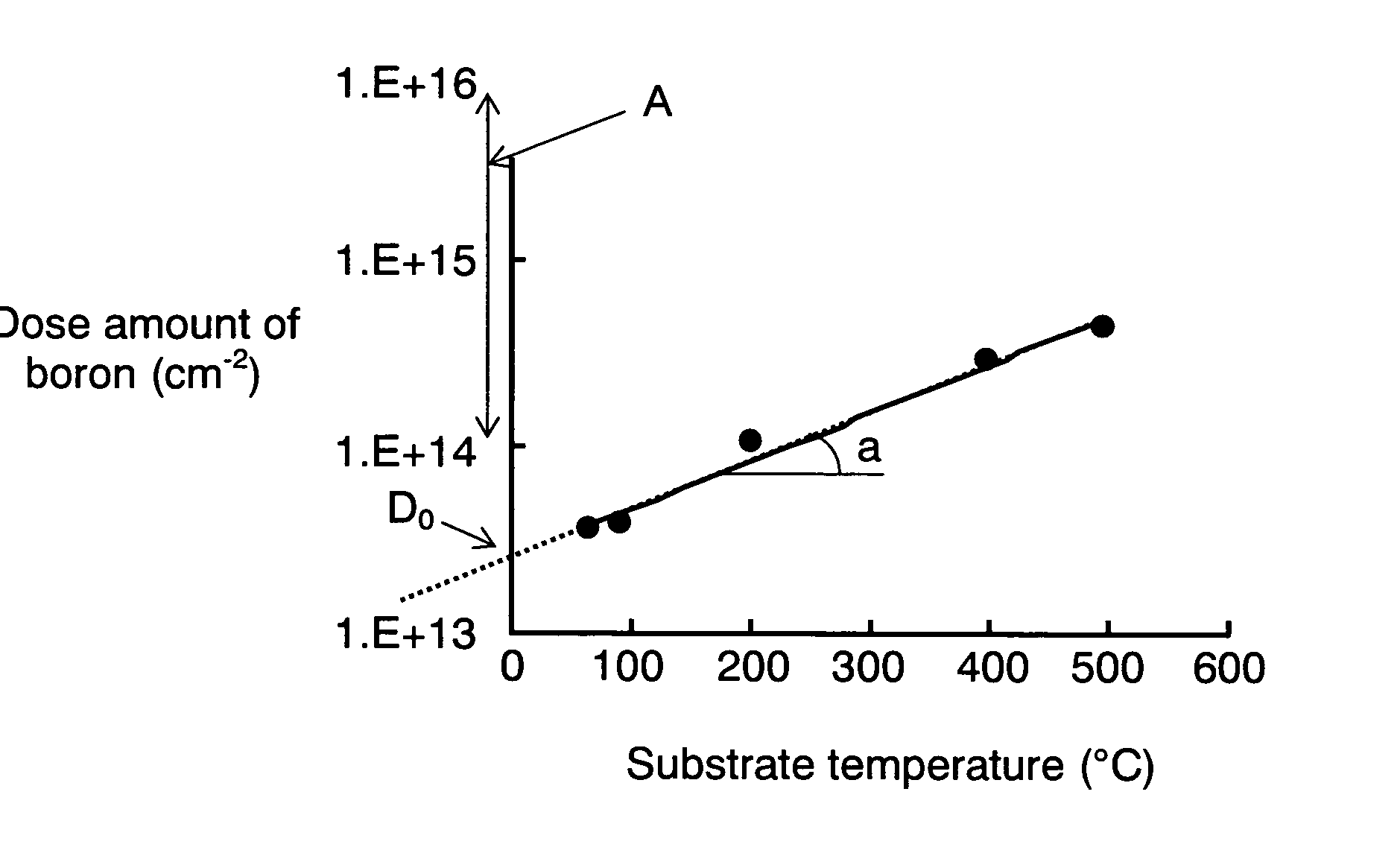
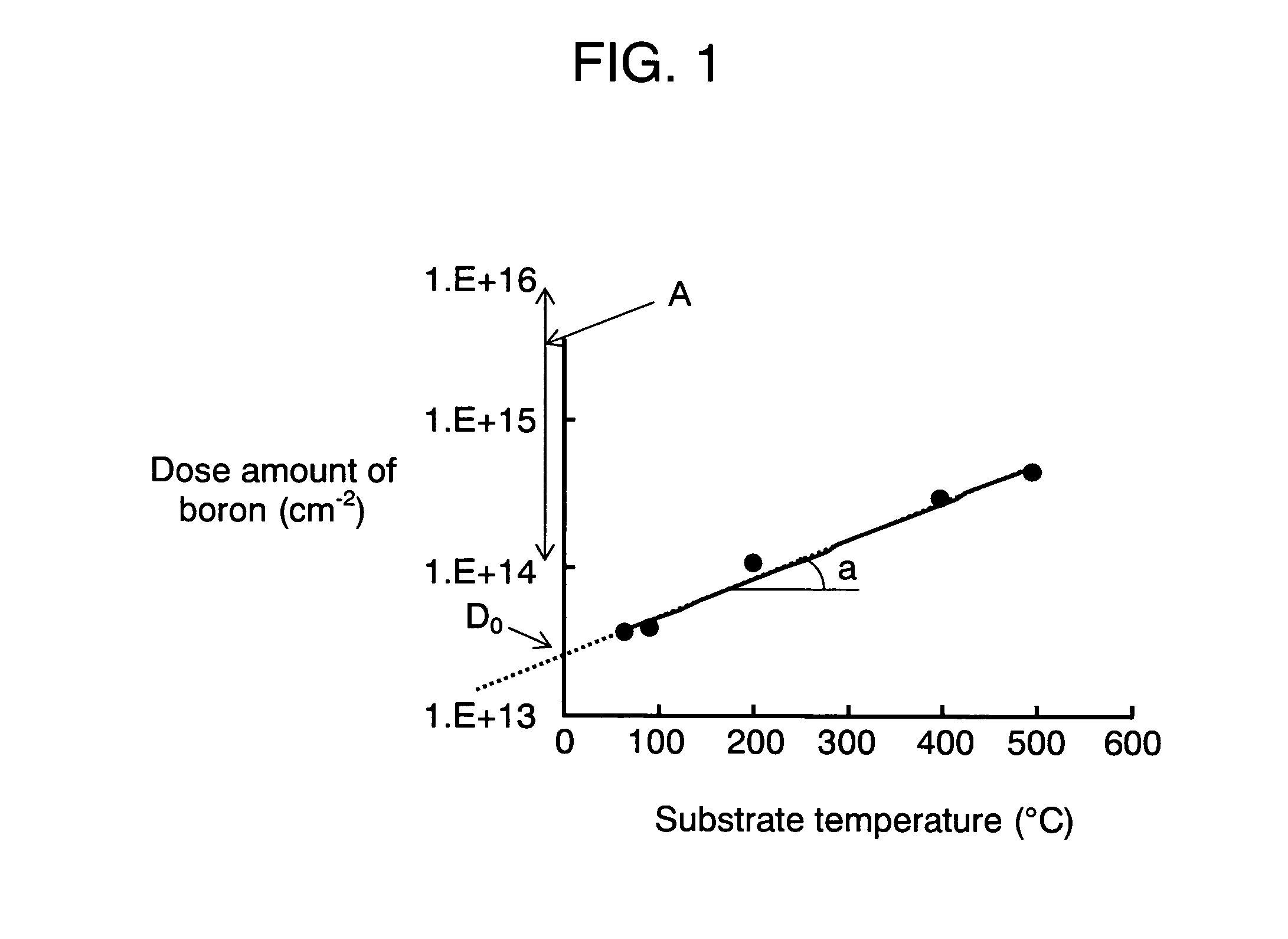
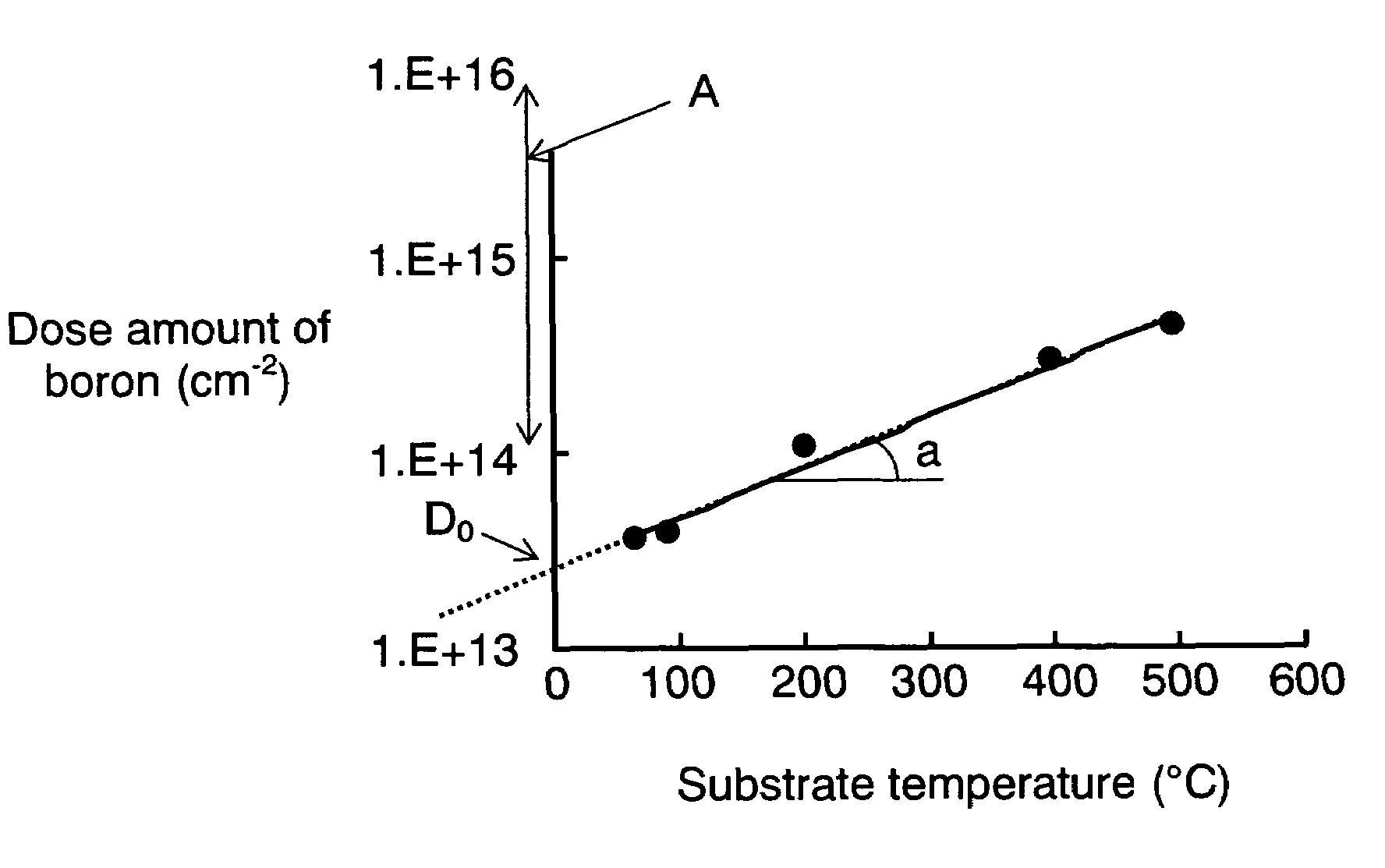
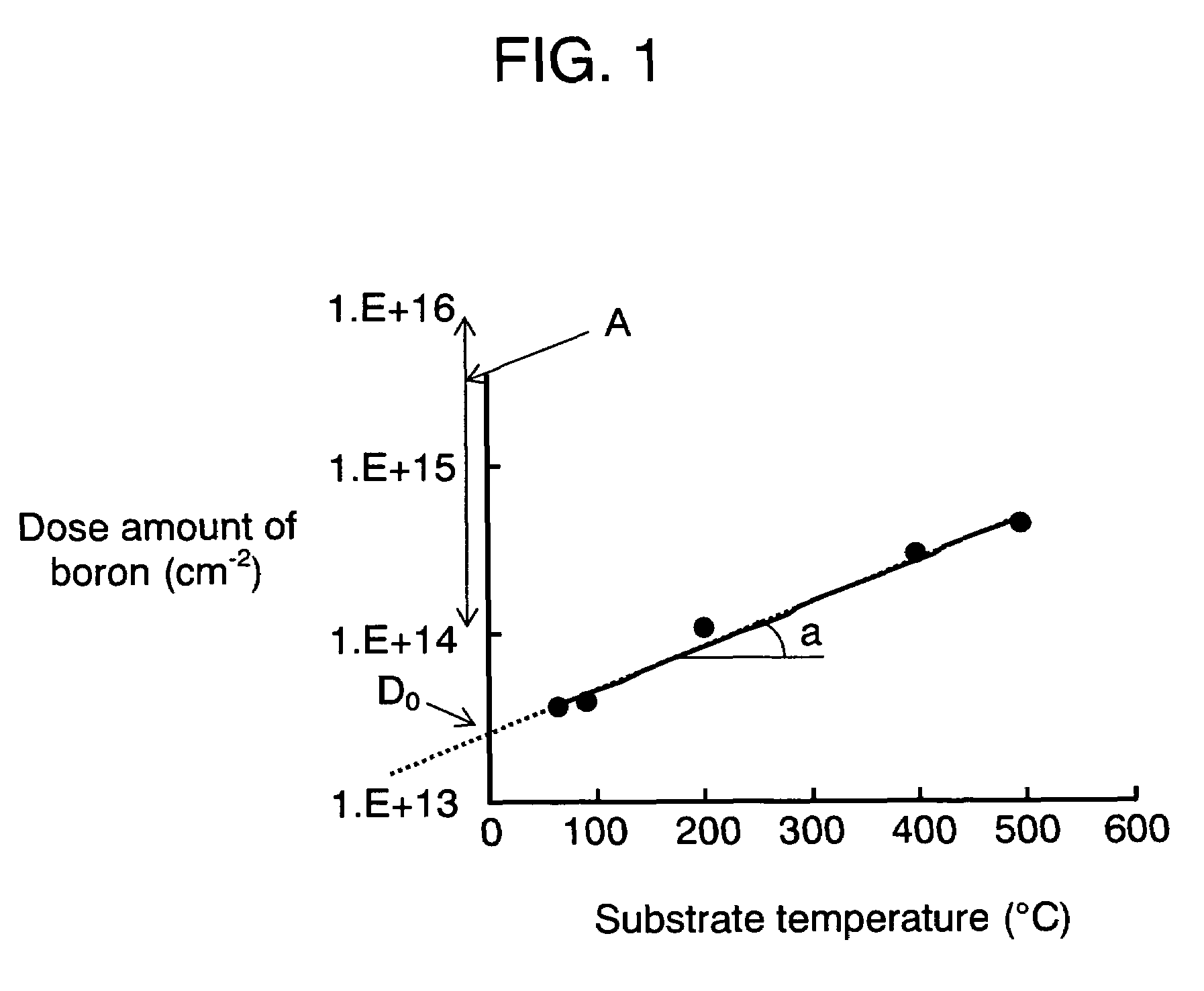
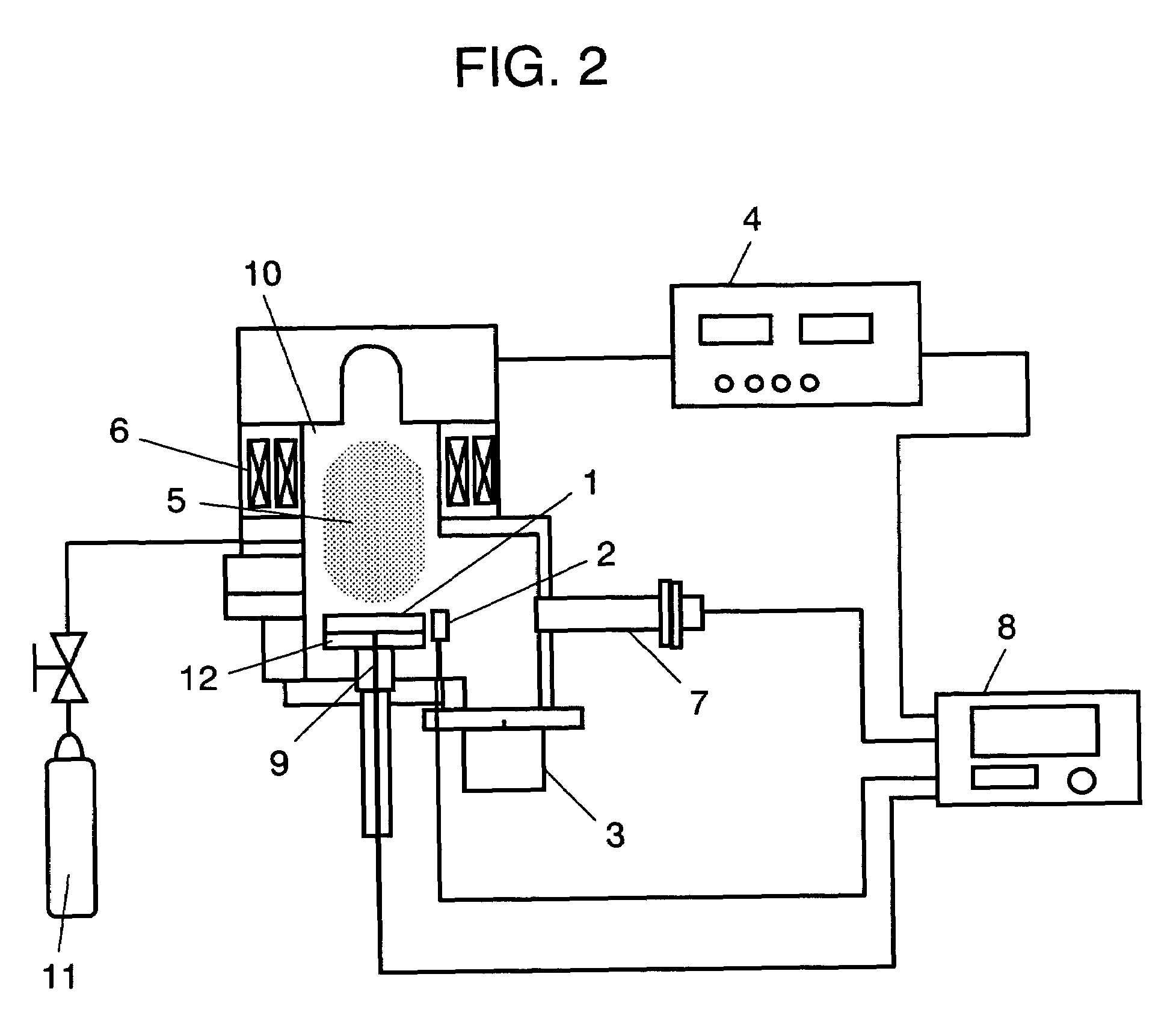
InactiveUS20070059848A1Minimized variation in qualityImprove accuracySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantImpurity doping
Disclosed here is a method of controlling a dose amount of dopant to be doped into object (1) to be processed in plasma doping. According to the method, the doping control is formed of the following processes: determining the temperature of object (1), the amount of ions having dopant in plasma that collide with object (1), and types of gases in plasma during doping; calculating a dose amount by neutral gas according to the temperature of object (1), and a dose amount by ions from the determined amount of ions containing dopant that collide with object (1); and carrying out doping so that the sum of the dose amount by neutral gas and the dose amount by ions equal to a predetermined dose amount.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Gas treatment apparatus
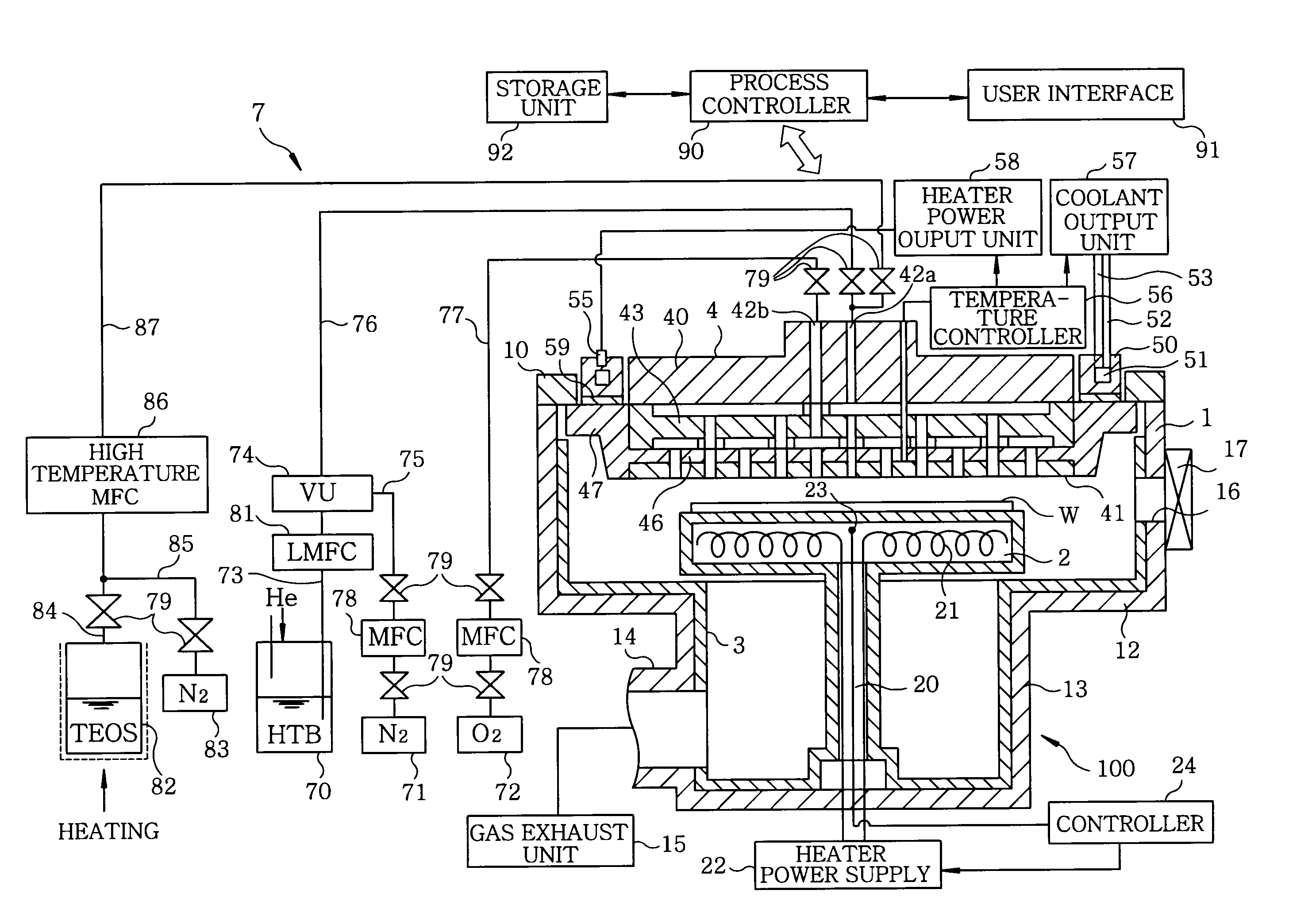
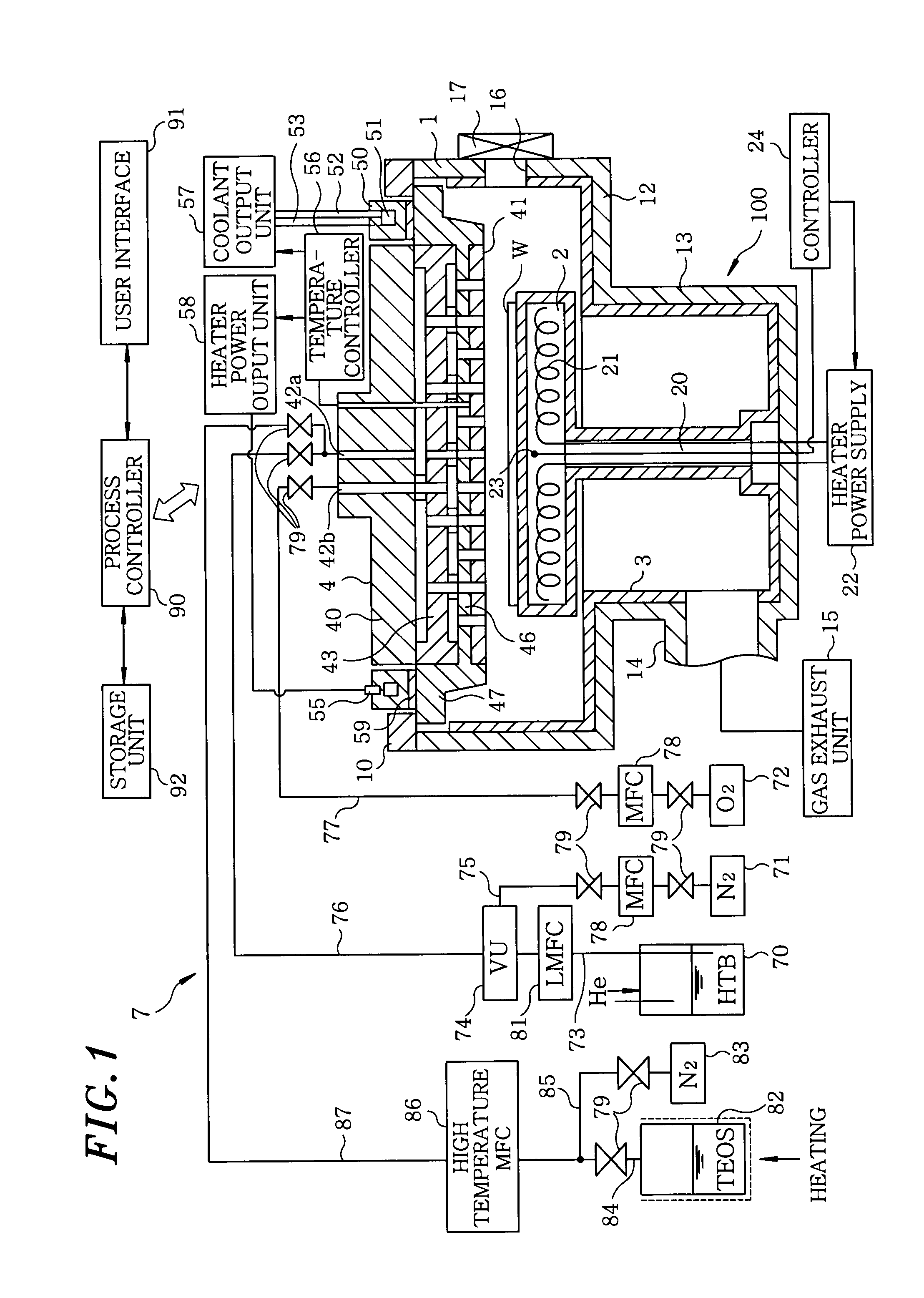
InactiveUS20090250008A1Reducing defect and nonuniformityInhibit temperature riseSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingAtmospheric airProduct gas
A film forming apparatus includes a chamber for accommodating a wafer; a mounting table arranged in the chamber to mount the wafer thereon; a shower head arranged to face the mounting table for injecting a processing gas into the chamber; and a gas exhaust mechanism for evacuating the chamber. The shower head is provided with a center portion in which a plurality of gas injection holes are formed for injecting the processing gas; and an outer peripheral portion disposed at outside of the center portion without having the gas injection holes. The film forming apparatus further includes a heat dissipating mechanism for dissipating heat of the shower head from the entire circumference of the outer peripheral portion to the atmosphere.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
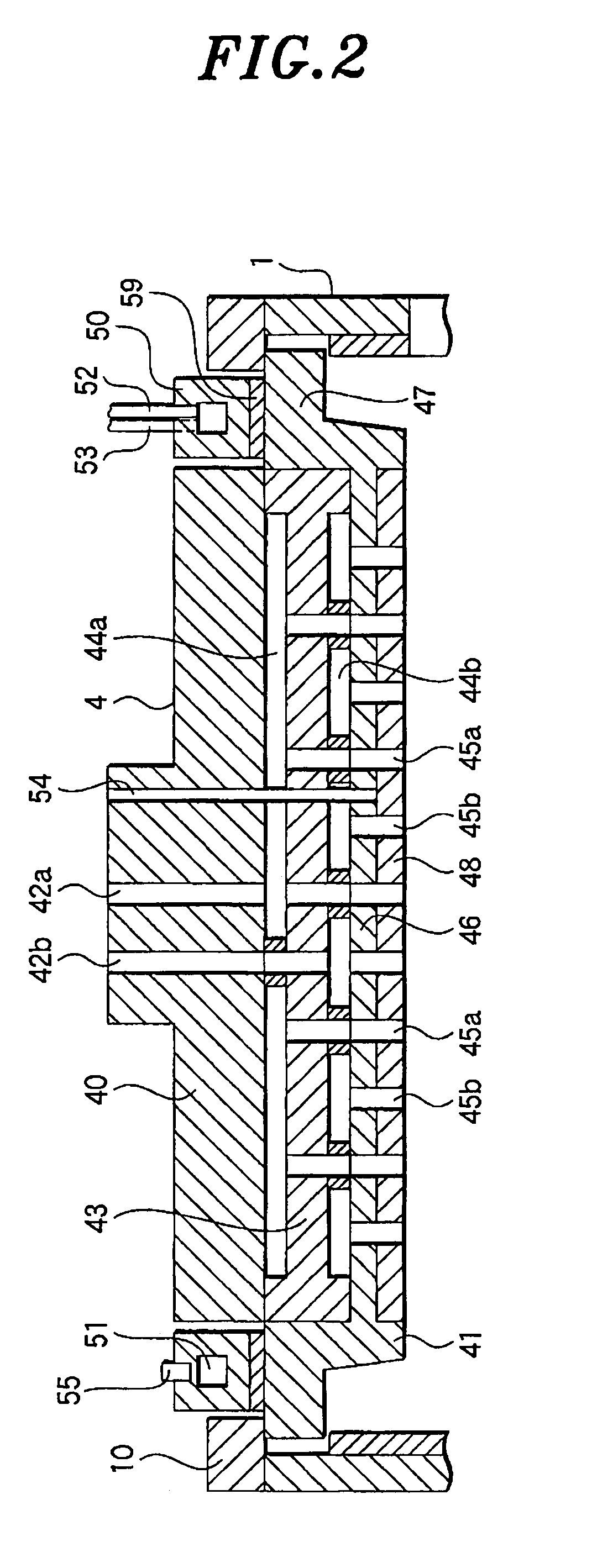
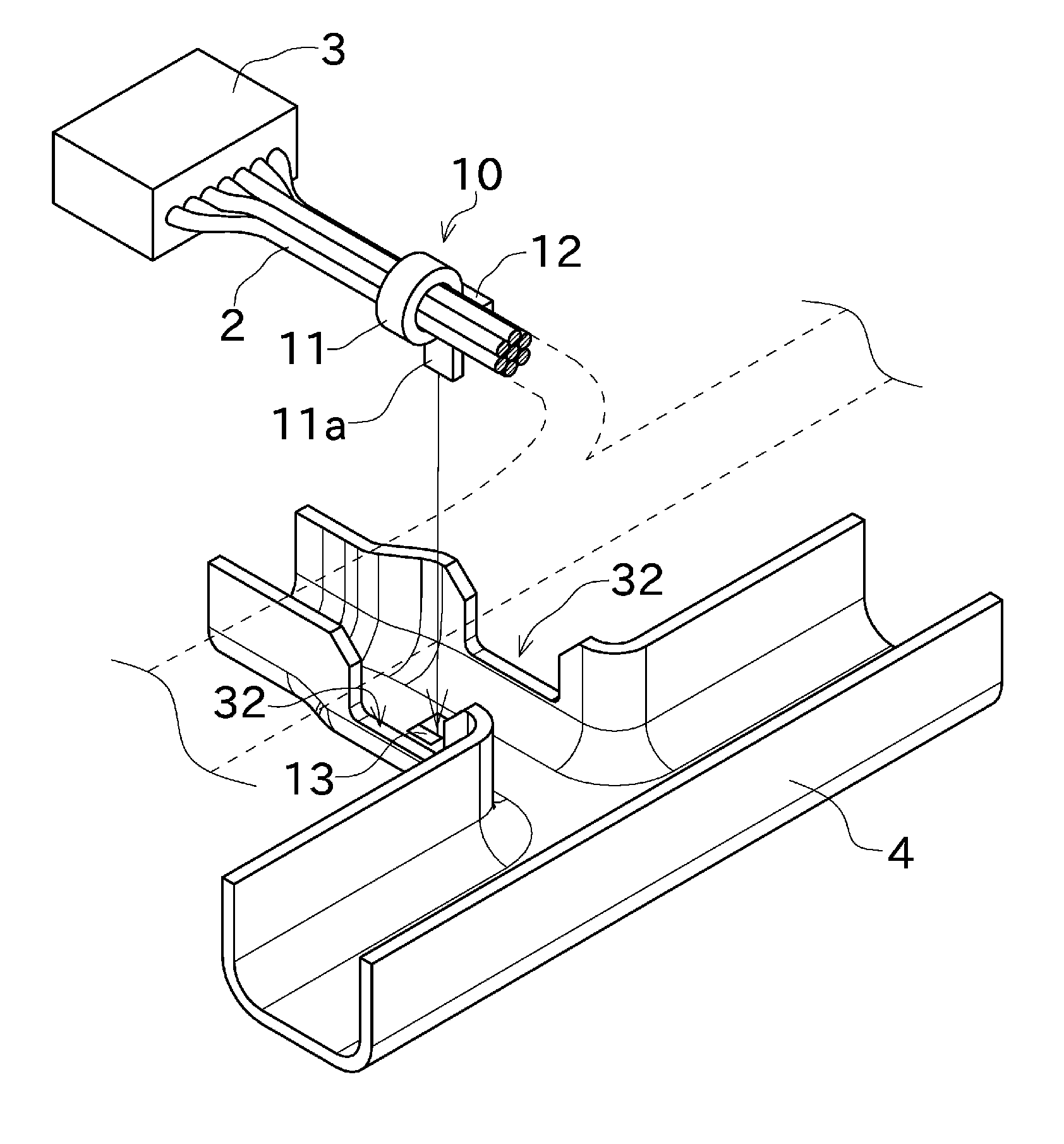
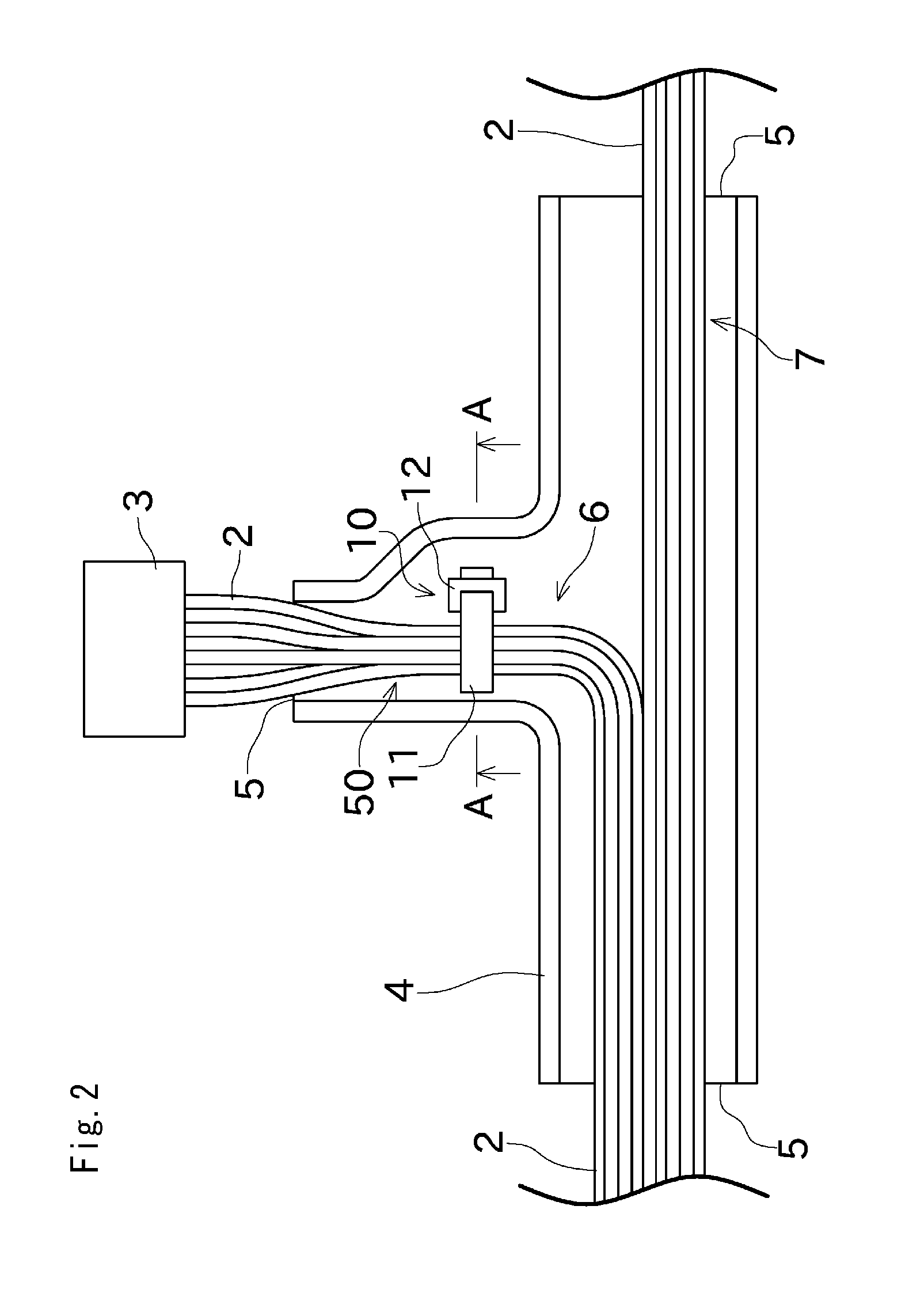
Wire harness and method for manufacturing wire harness
ActiveUS20150294768A1Efficient arrangementSuitable for installationLine/current collector detailsRigid-tube cablesDistal portionElectric wire
The invention of the present application provides a wire harness with an improved accuracy of the dimension, that can be manufactured with an easy operation. A protector (4) defines at least either one of a bending shape and a branching shape of a plurality of electric wires (2). A cable tie (10) is attached to the electric wires (2), and includes a distal portion (11a) to be attached to the protector (4). The protector (4) includes an engaging portion (13) engageable with the distal portion (11a). Positions of the electric wires (2) and the protector (4) relative to each other are settled by engagement of the distal portion (11 a) of the cable tie (10) attached to the electric wires (2) with the engaging portion (13).
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD +1
Method of controlling impurity doping and impurity doping apparatus
InactiveUS7666770B2Improve accuracyVariation in qualitySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantImpurity doping
A method is provided for controlling a dose amount of dopant to be doped into an object to be processed in plasma doping. According to the method, the doping control is formed of the following processes: determining the temperature of the object, the amount of ions having dopant in plasma that collide with the object, and types of gases in plasma during doping; calculating a dose amount by neutral gas according to the temperature of the object, and a dose amount by ions from the determined amount of ions containing dopant that collide with the object; and carrying out doping so that the sum of the dose amount by neutral gas and the dose amount by ions equal to a predetermined dose amount.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
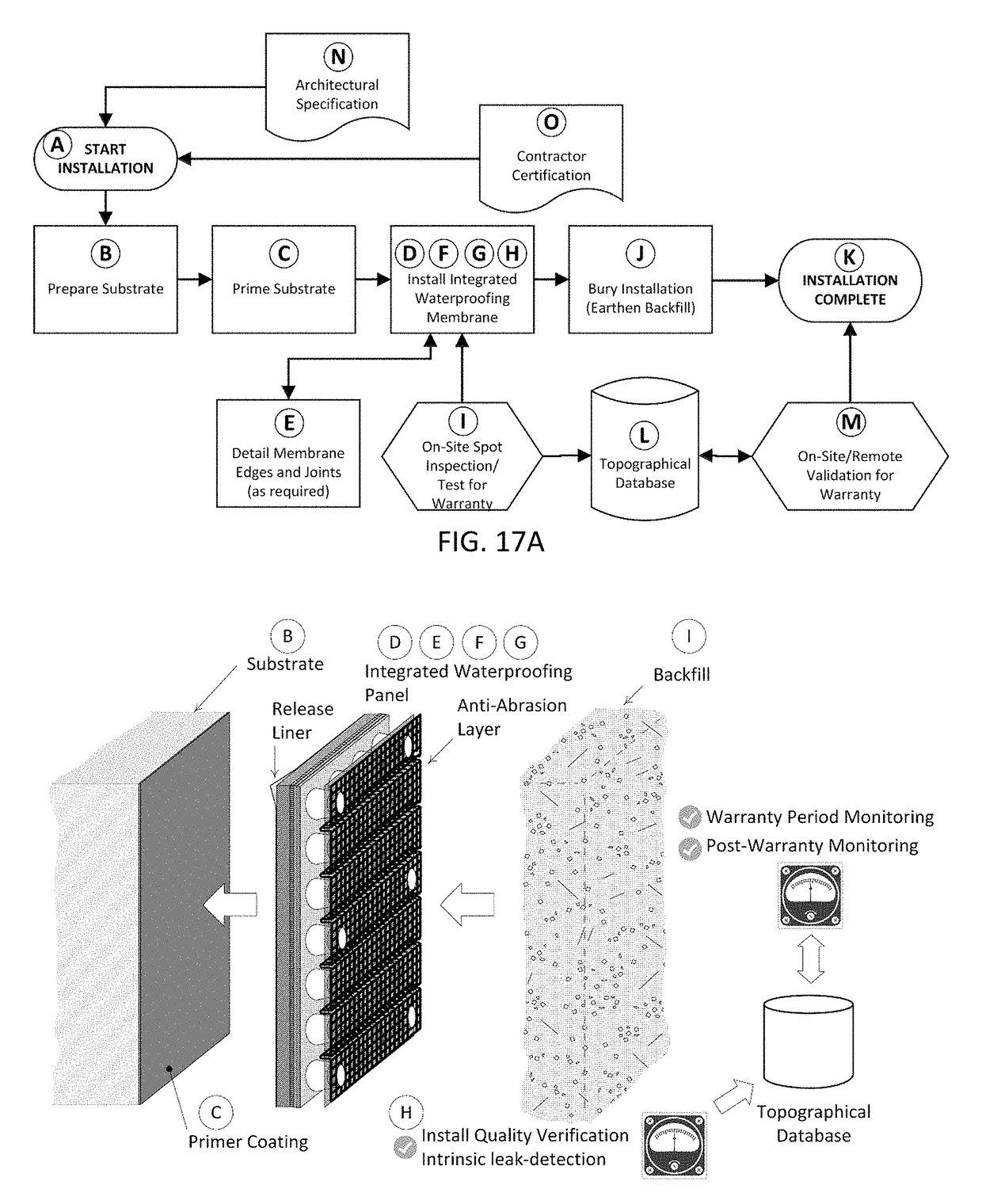
Integrated waterproofing and drainage system with intrinsic leak detection
ActiveUS9771703B1Eliminate variationFacilitate storage and shipmentDetection of fluid at leakage pointConstruction materialEngineeringLeak detection
A complete decreased mistake-proof high-reliability waterproofing system is revealed that integrates the waterproofing membrane, drain panel, and abrasion-protected filter fabric, using a factory-controlled process; furthermore, the system incorporates intrinsic devices for installation verification and leak-detection, and the potential for in situ mapping of the functional topography of the waterproofing installation over time.
Owner:BUILDTECH SOLUTIONS LLC
Crystallization method for semiconductor film, manufacturing method for semiconductor device, and laser irradiation apparatus
InactiveUS20070178631A1Variation in qualityControl generationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIrradiationLaser beams
A semiconductor film formed over a substrate is irradiated by a first laser beam which is incident on a bottom surface of the substrate at an angle and by a second laser beam which is incident on the bottom surface of the substrate at an angle opposite that of the first laser beam and oscillated by an oscillator differing from that of the first laser beam; whereby, part of the semiconductor film is melted, and a portion of the semiconductor film being melted is moved while the positions of irradiation of the first and the second laser beams and are being scanned approximately along the direction of slant for the first laser beam or the second laser beam.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Sputtering target containing zinc sulfide as major component, optical recording medium on which phase change optical disk protective film containing zinc sulfide as major component is formed by using the target, and method for manufacturing the sputtering target
ActiveUS7279211B2Reduce the impact of heatIncrease speedPigmenting treatmentCellsTectorial membraneRefractive index
Provided is a sputtering target and an optical recording medium having formed thereon a phase change optical disc protective film having zinc sulfide as its principal component employing such a target, as well as the manufacturing method thereof, characterized in that the sputtering target has zinc sulfide as its principal component, and is capable of adjusting the refractive index of a film containing conductive oxide in the range of 2.0 to 2.6. This sputtering target, and an optical recording medium having formed thereon a phase change optical disc protective film having zinc sulfide as its principal component employing such a target, is capable of reducing particles (dust emission) and nodules that arise during sputtering, has minimal variation in quality and is capable of improving mass productiveness, and in which the crystal grain is fine and has a high density of 90% or more.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING & METALS CORP
Sputtering Target, Thin Film for Optical Information Recording Medium and Process for Producing the Same
InactiveUS20080299415A1Reducing the affect of heating the substrateIncrease speedVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSputteringProduction rate
A sputtering target is provided that has a relative density of 80% or more and contains a compound having as its principal component zinc oxide satisfying AXBYO(KaX+KbY) / 2(ZnO)m, 1<m, X≦m, 0<Y≦0.9, X+Y=2, where A and B are respectively different positive elements of trivalence or more, and the valencies thereof are respectively Ka and Kb. A ZnO based sputtering target is obtained which does not contain ZnS and SiO2, and, upon forming a film via sputtering, is capable of reducing the affect of heating the substrate, of performing high speed deposition, of adjusting the film thickness to be thin, of reducing the generation of particles (dust) and nodules during sputtering, of improving the productivity with small variation in quality, and which has fine crystal grains and a high density of 80% or more, particularly 90% or more.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING & METALS CORP
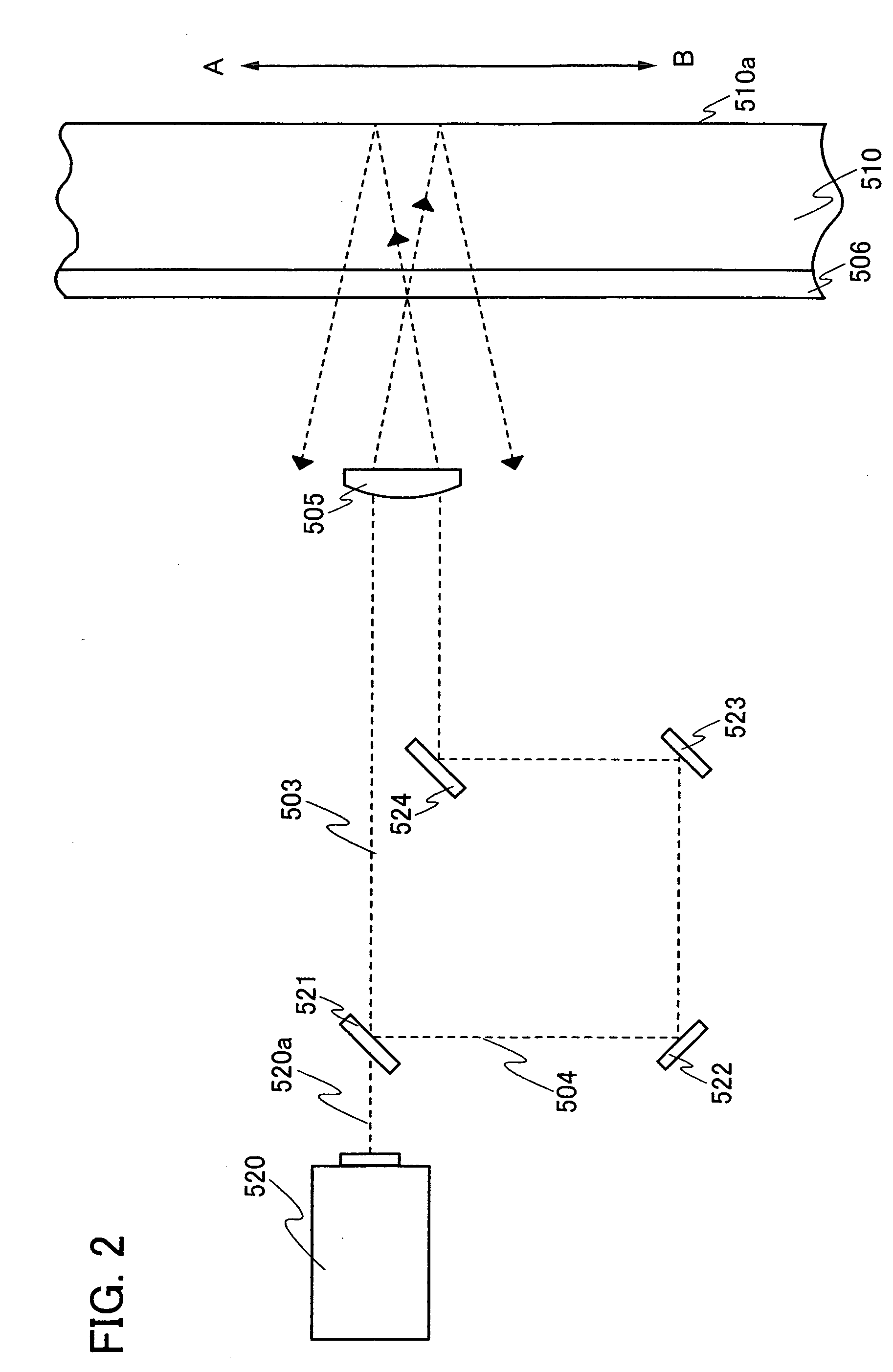
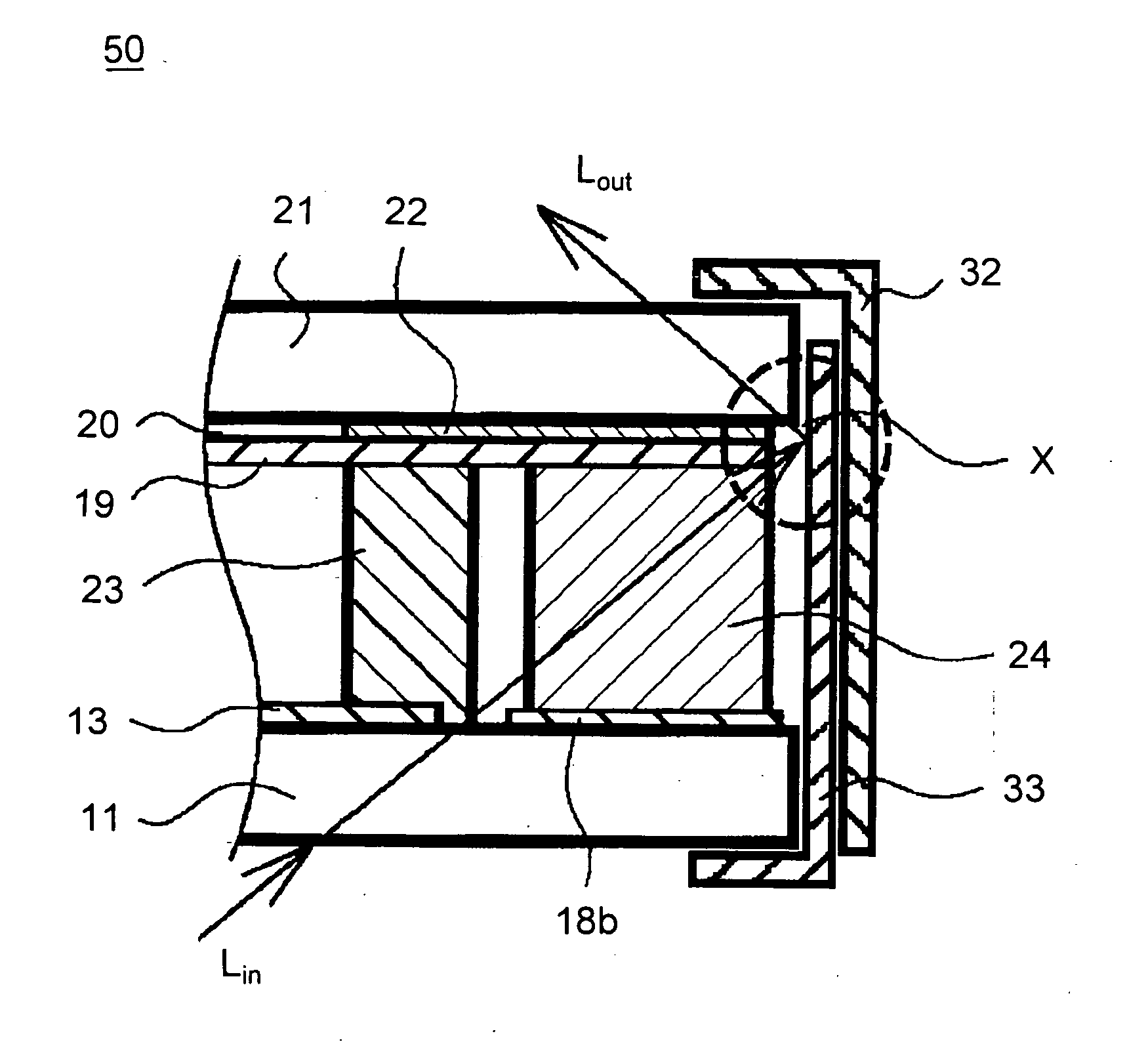
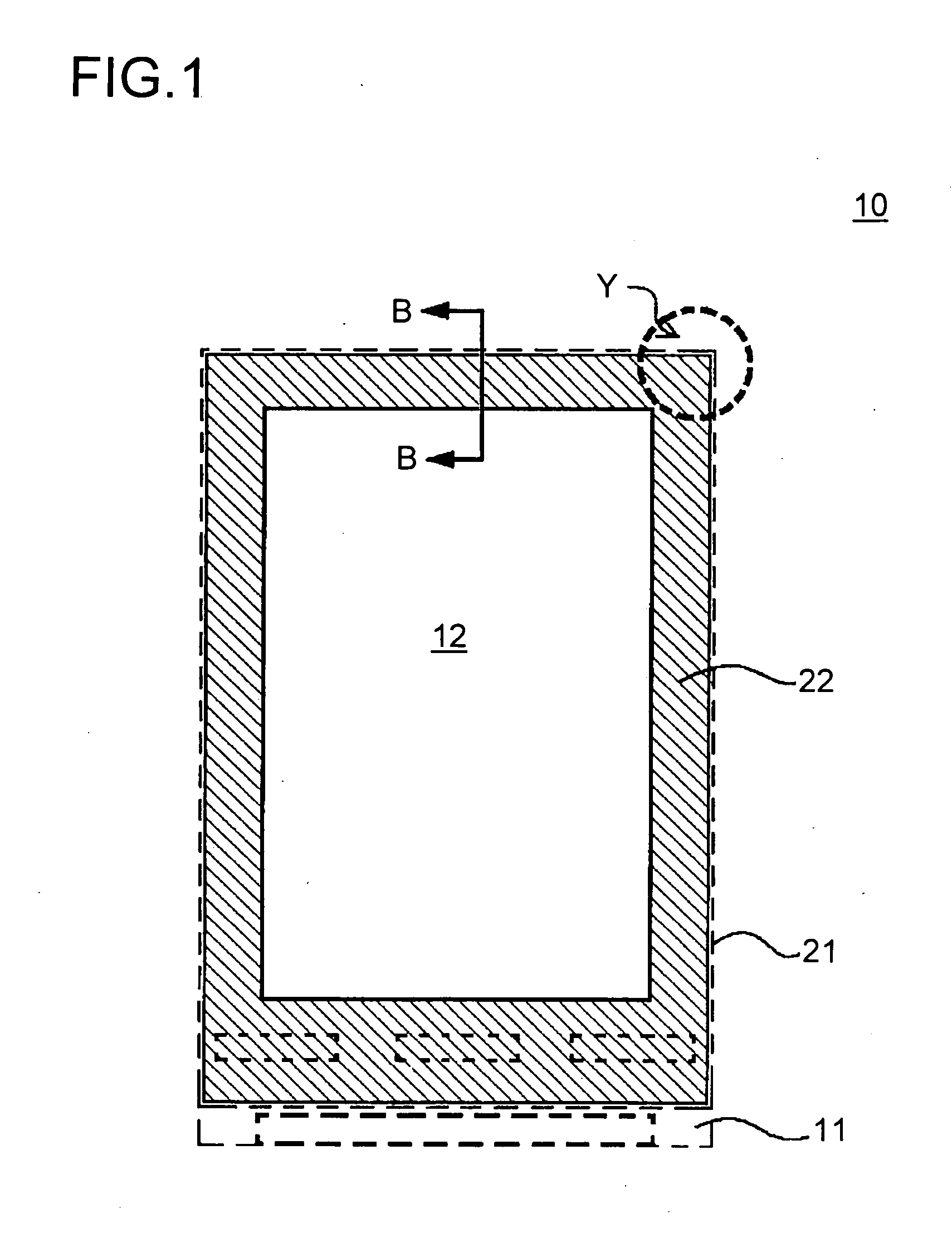
Liquid crystal display apparatus
InactiveUS20060114367A1Improve display qualityEliminate quality differencesNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
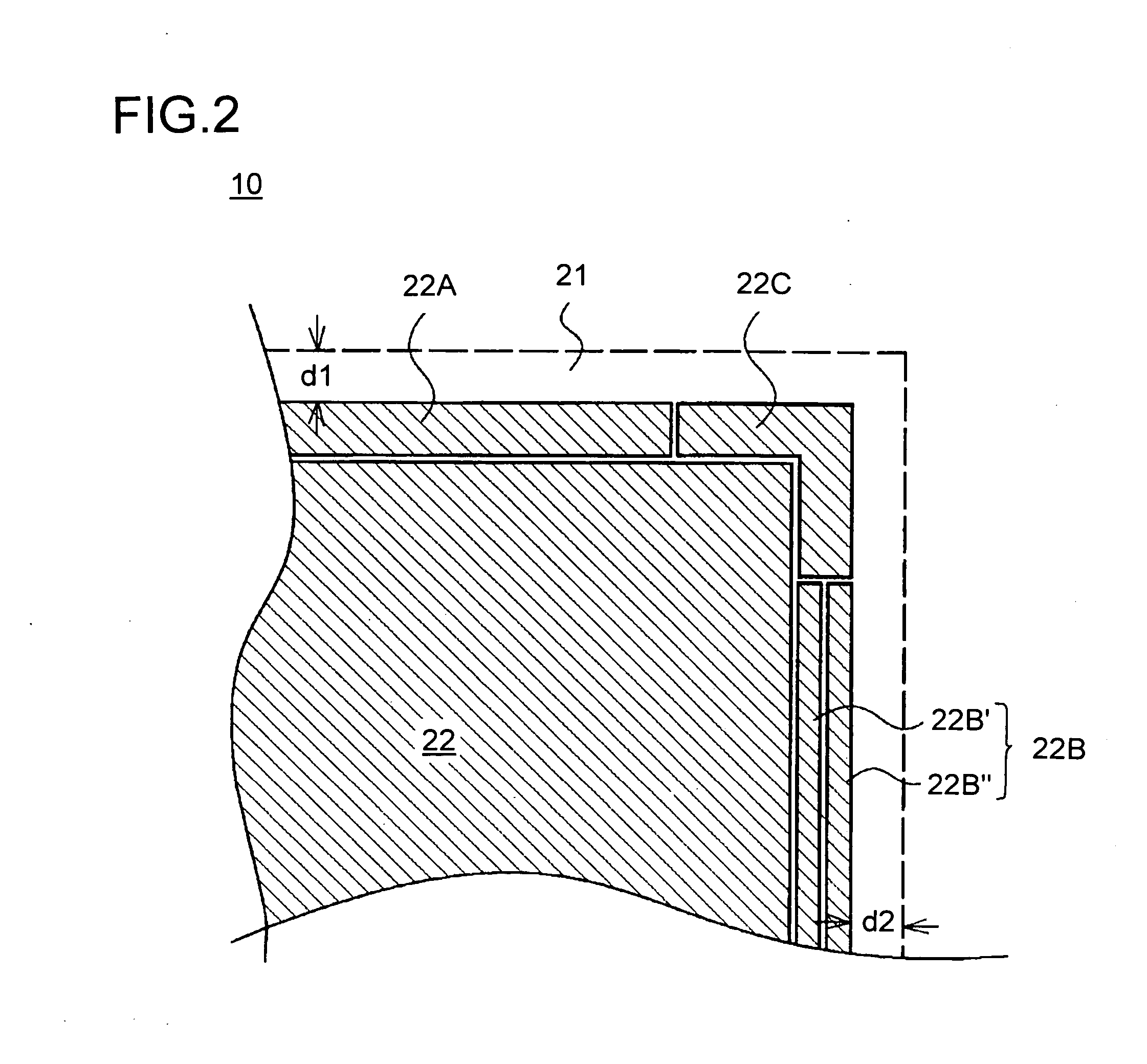
In a liquid crystal display apparatus having a backlight disposed behind a liquid crystal display panel 10, the liquid crystal display panel 10 has first and second substrates 11 and 21 disposed to face each other. The second substrate 21 has a common electrode 20 laid in a display area 12 thereon. The second substrate 21 further has a light-shielding inner black matrix 22 laid around the display area 12 and a light-shielding electrically insulated black matrix 22A, 22B, and 22C laid outside the inner black matrix 22 and electrically separated from the inner black matrix 22 and the common electrode 19. The liquid crystal display panel 10 is held, at the periphery thereof, by metal support frames 32 and 33.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD +1
Integrated waterproofing and drainage system with intrinsic leak detection for building structures and methods of use
InactiveUS20180010329A1Improve and eliminate variation in installation qualityLow costDetection of fluid at leakage pointSynthetic resin layered productsEngineeringLeak detection
The inventive disclosures are directed to a factory-controlled process for making improved, risk-optimized commercial-building waterproofing systems. The improved waterproofing-panel systems also include improved intrinsic leak-detection capabilities.
Owner:BUILDTECH SOLUTIONS LLC
Impedance matching device
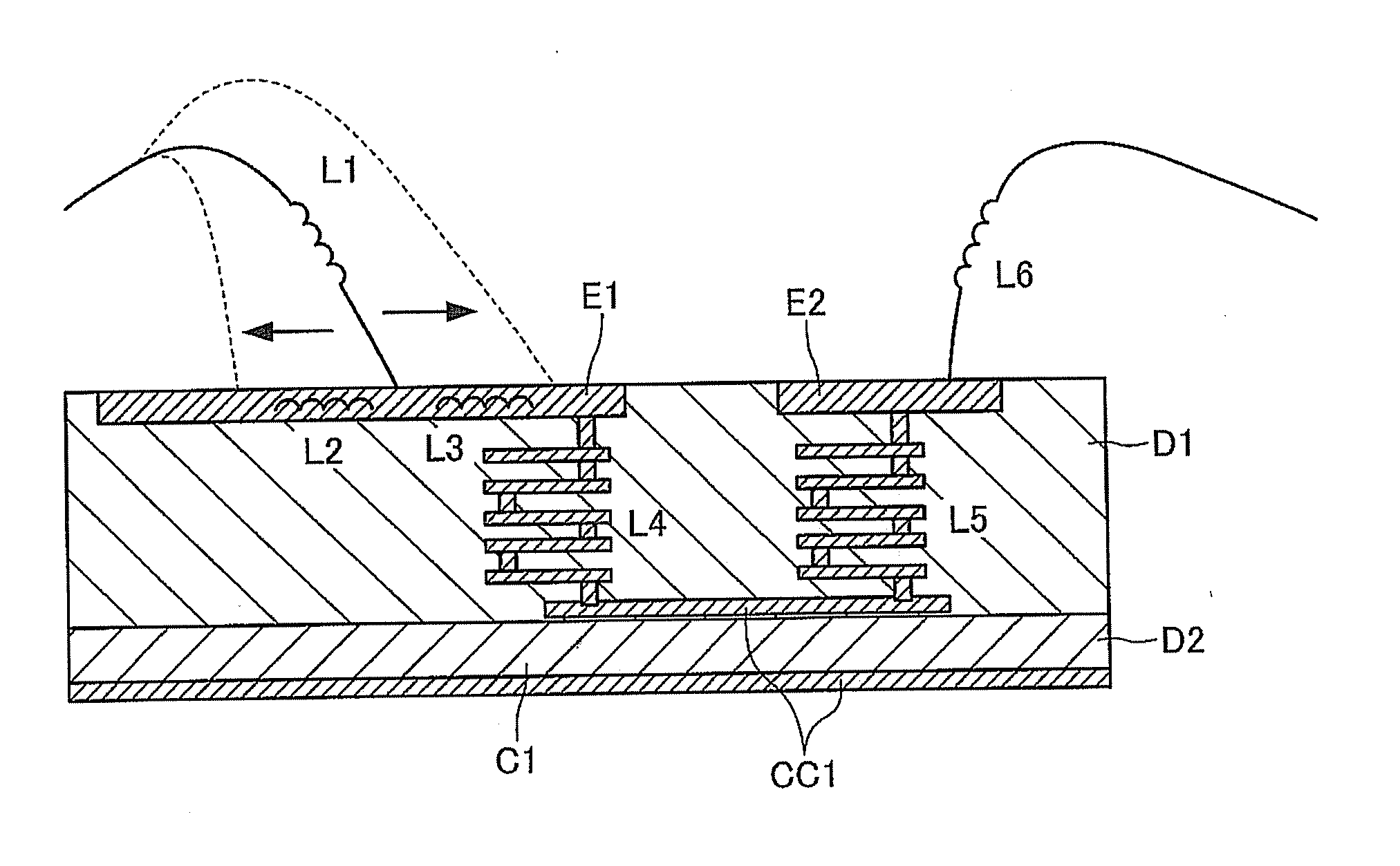
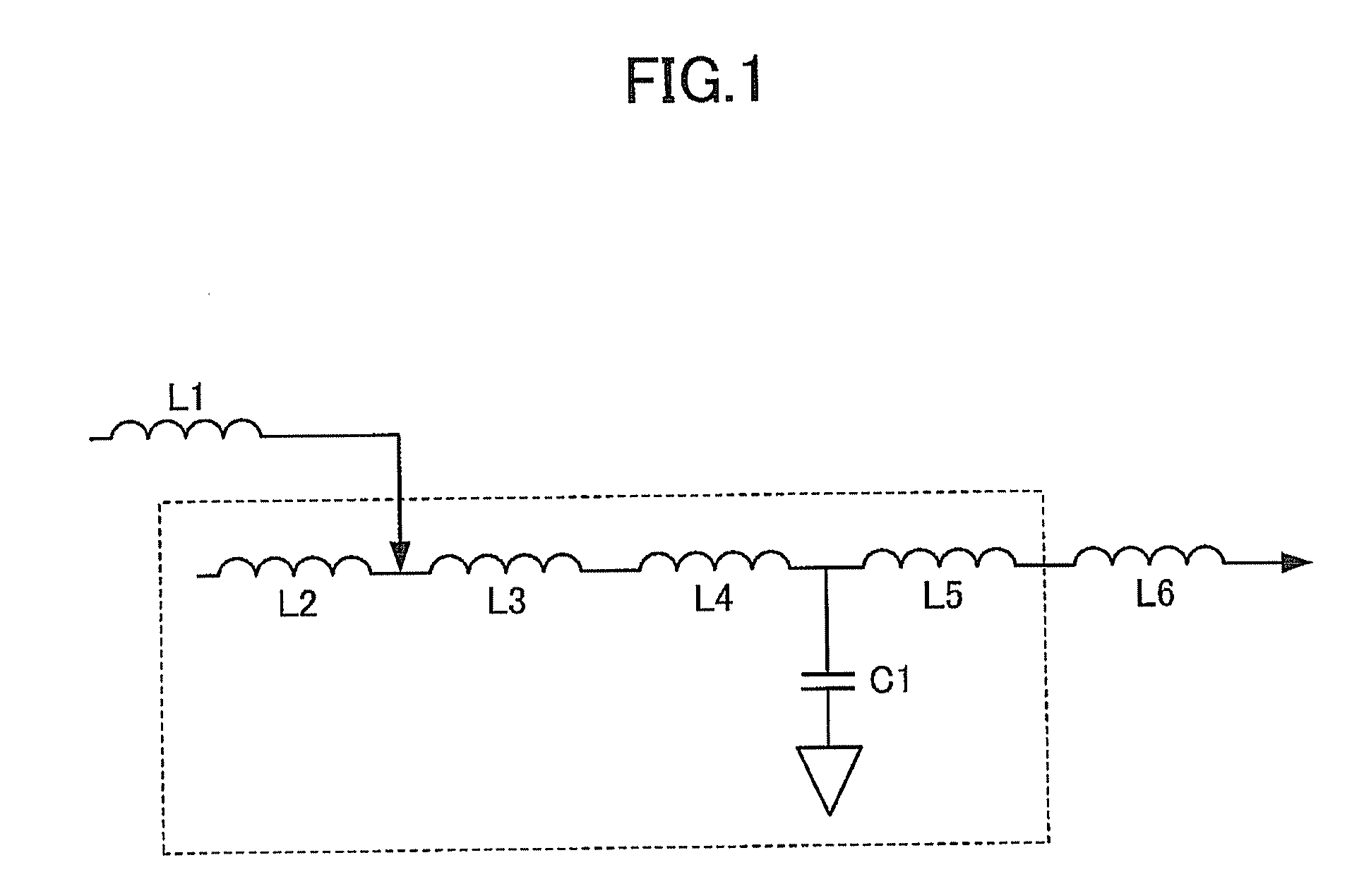
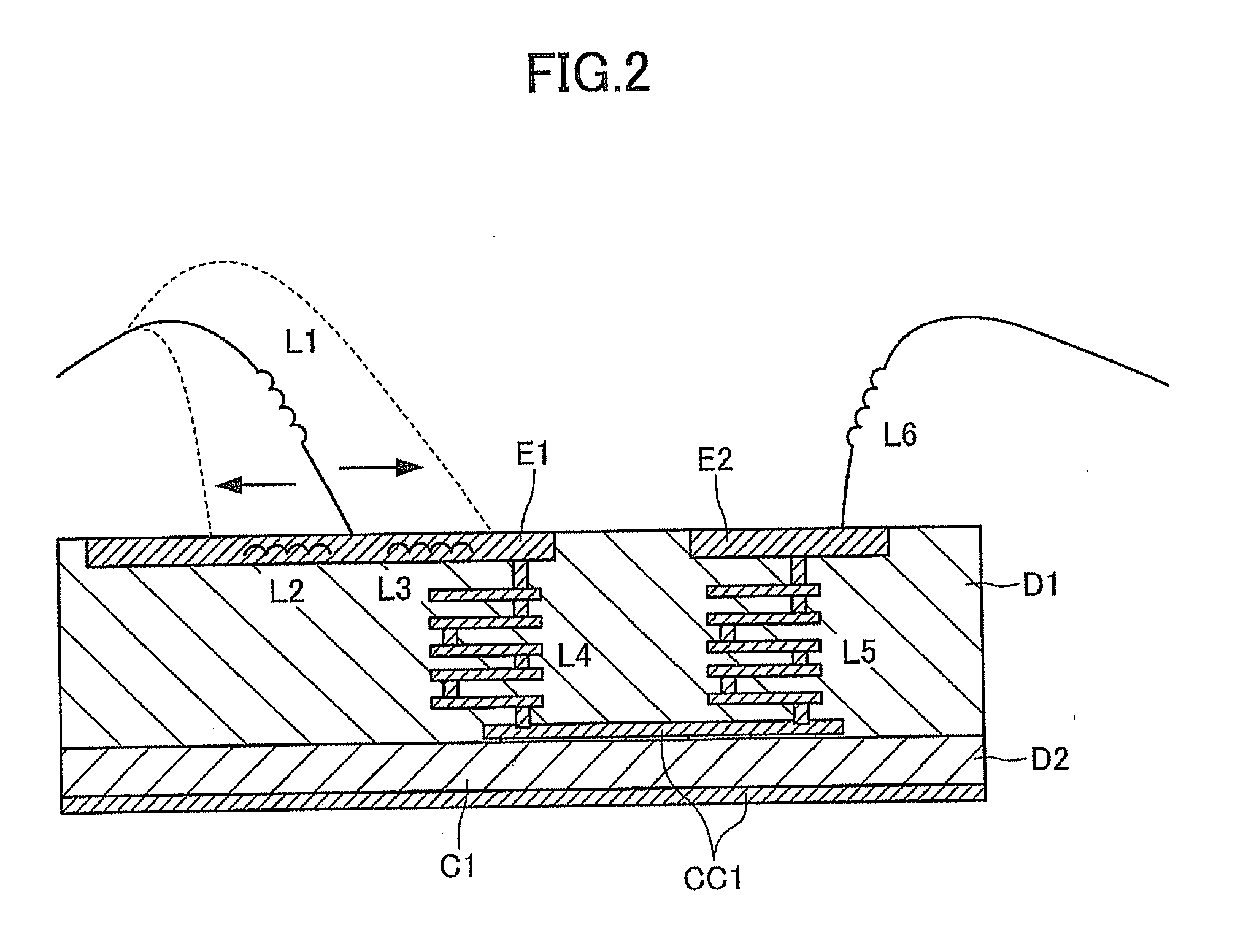
InactiveUS20120019334A1Large-current toleranceVariation in qualityMultiple-port networksSignal inductance without magnetic coreElectricityElectrical conductor
The present invention intends to provide a small-sized impedance matching device with a small variation in quality and large-current tolerance. The above described intention of the present invention is achieved by an impedance matching device, which comprises a wiring portion comprising a conductor pattern for wiring, embedded inside or formed on the surface of first dielectric material, and either one or both of an inductor portion comprising a conductor pattern for inductor, embedded inside or formed on the surface of the first dielectric material, or a capacitor portion comprising at least one pair of conductor patterns for capacitor and second dielectric material with a dielectric constant larger than that of the first dielectric material, existing between the pair of conductor patterns for capacitor wherein the thicknesses of the conductor pattern for wiring and the conductor pattern for inductor are 20 μm or more.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Kneading apparatus and method for kneading rubber or rubber composition
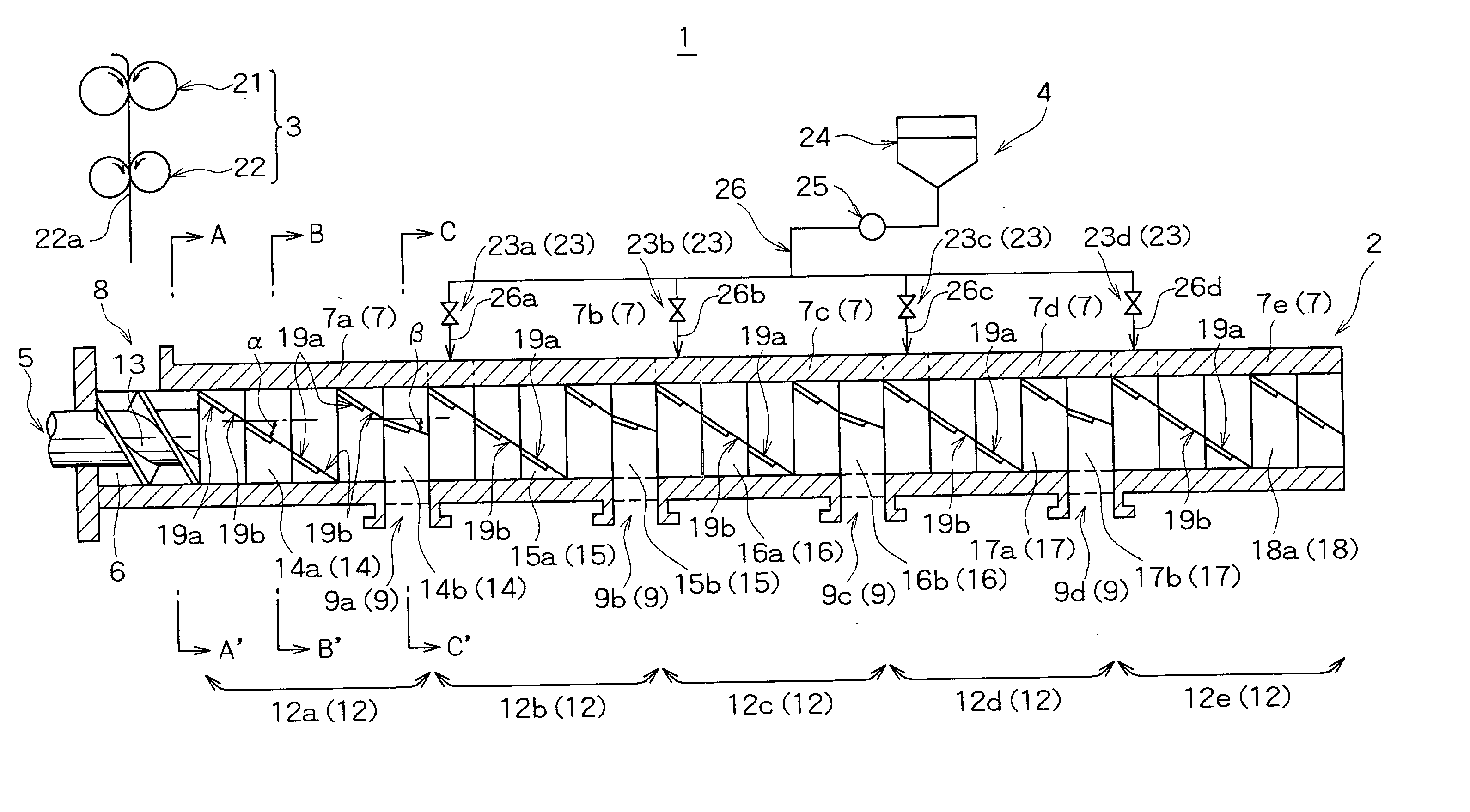
InactiveUS20030090955A1Dispersion be controlledLow viscosityDischarging apparatusRotary stirring mixersEngineeringMaterial supply
A continuous kneading apparatus and method are provided wherein discharge ports are provided at a plurality of positions of the barrel to discharge a kneaded product, and one of the plurality of the discharge ports is selected according to a desired kneading condition so as to discharge the kneaded product from only the selected discharge port. Another continuous kneading apparatus and method are provided wherein a plurality of charging ports are provided at a plurality of positions of the barrel to supply a material to be kneaded into the chamber, and one of the plurality of charging ports is selected according to a desired kneading condition. The kneading apparatuses and methods permit adjustment and control of a viscosity and a dispersion degree of a compounding agent over a wide range, and continuous kneading to achieve significant rationalization of a process for producing a kneaded product.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
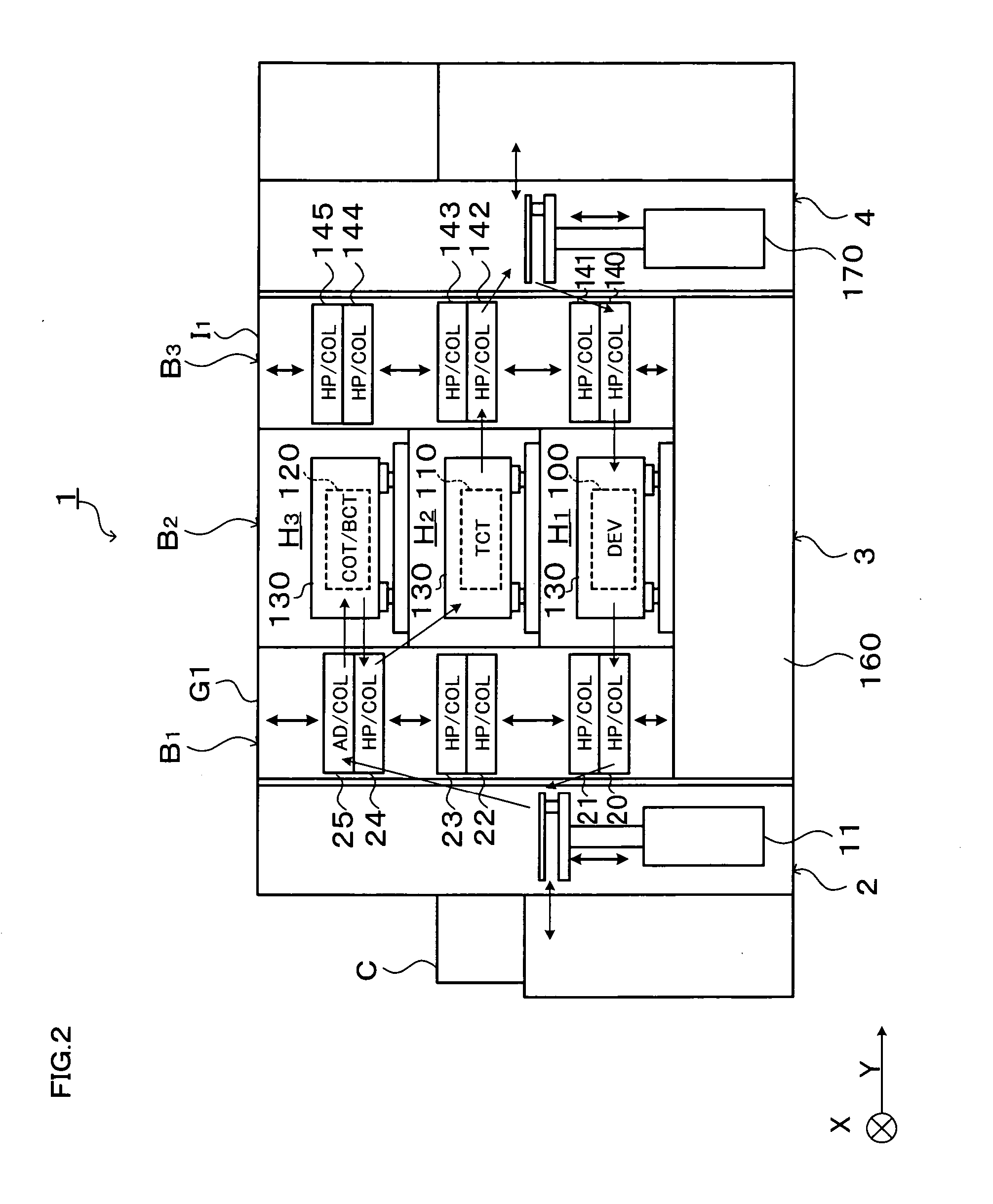
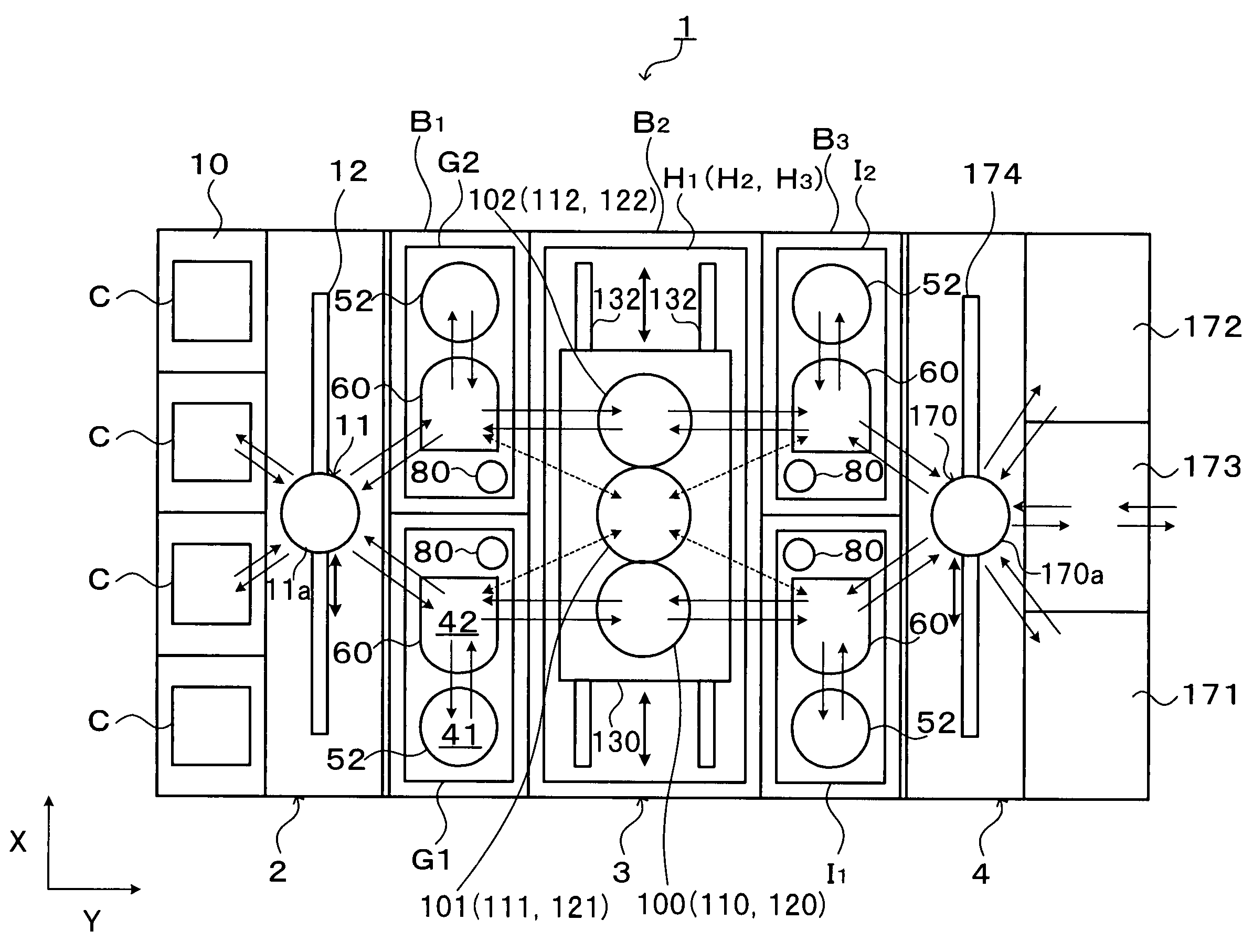
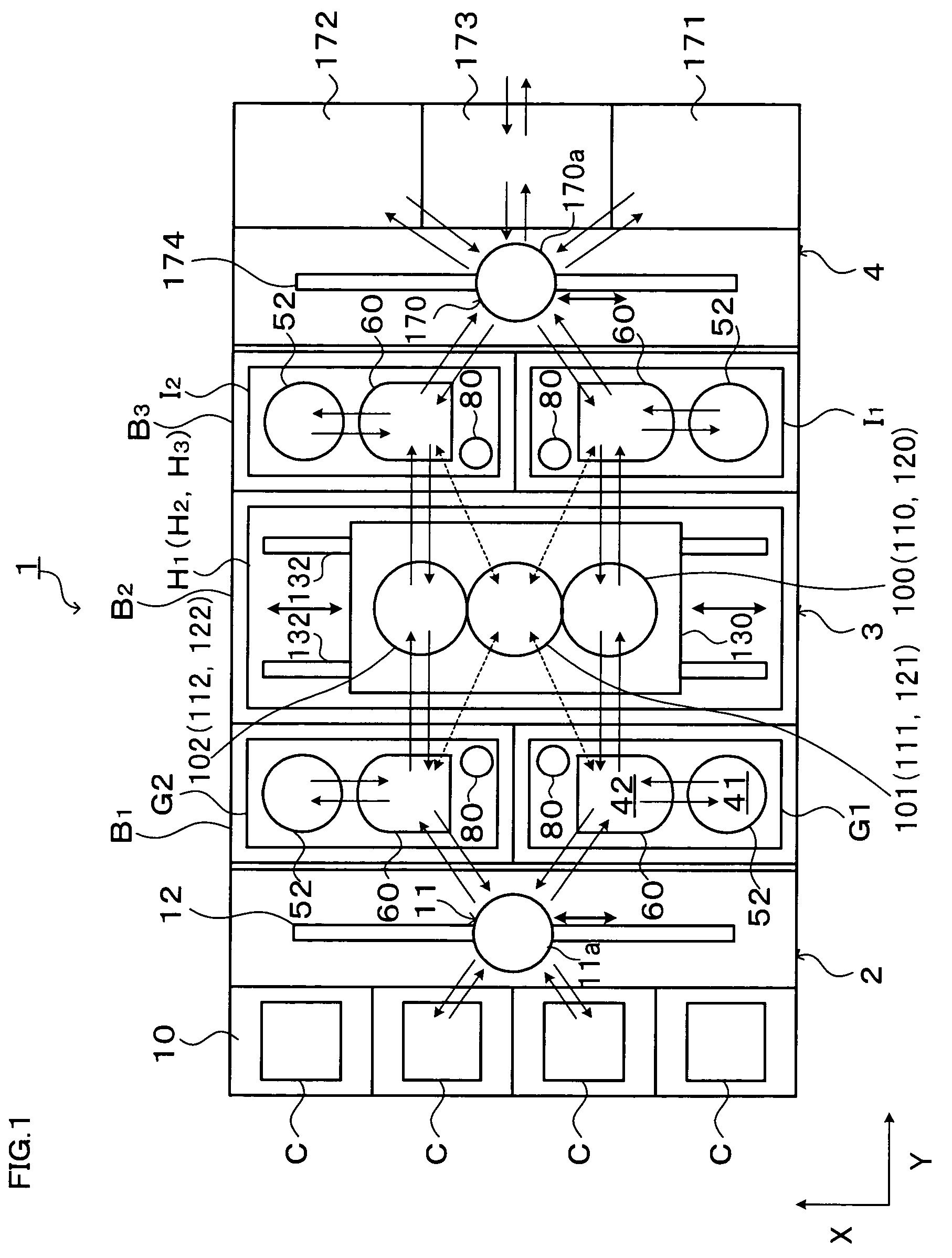
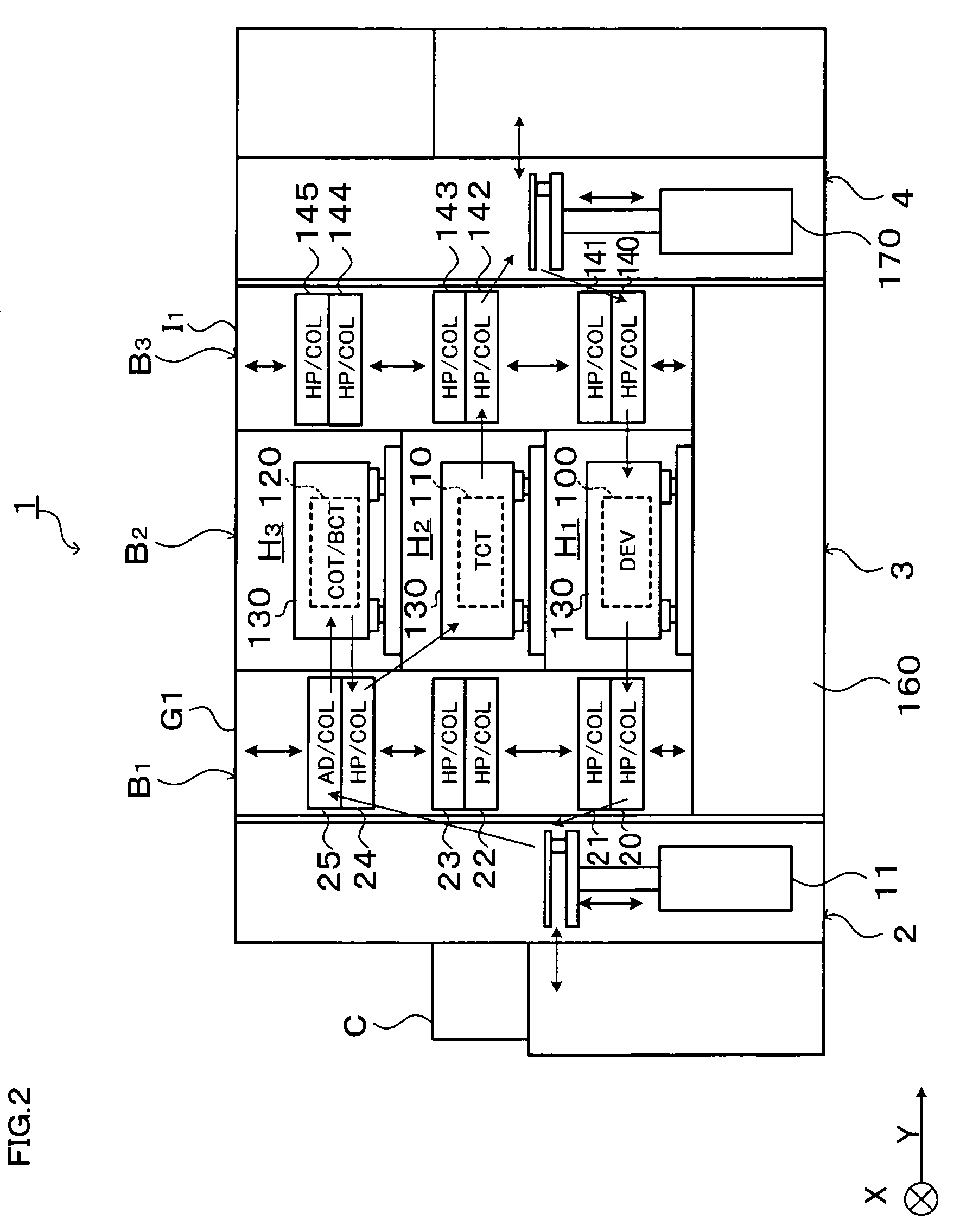
Substrate processing system
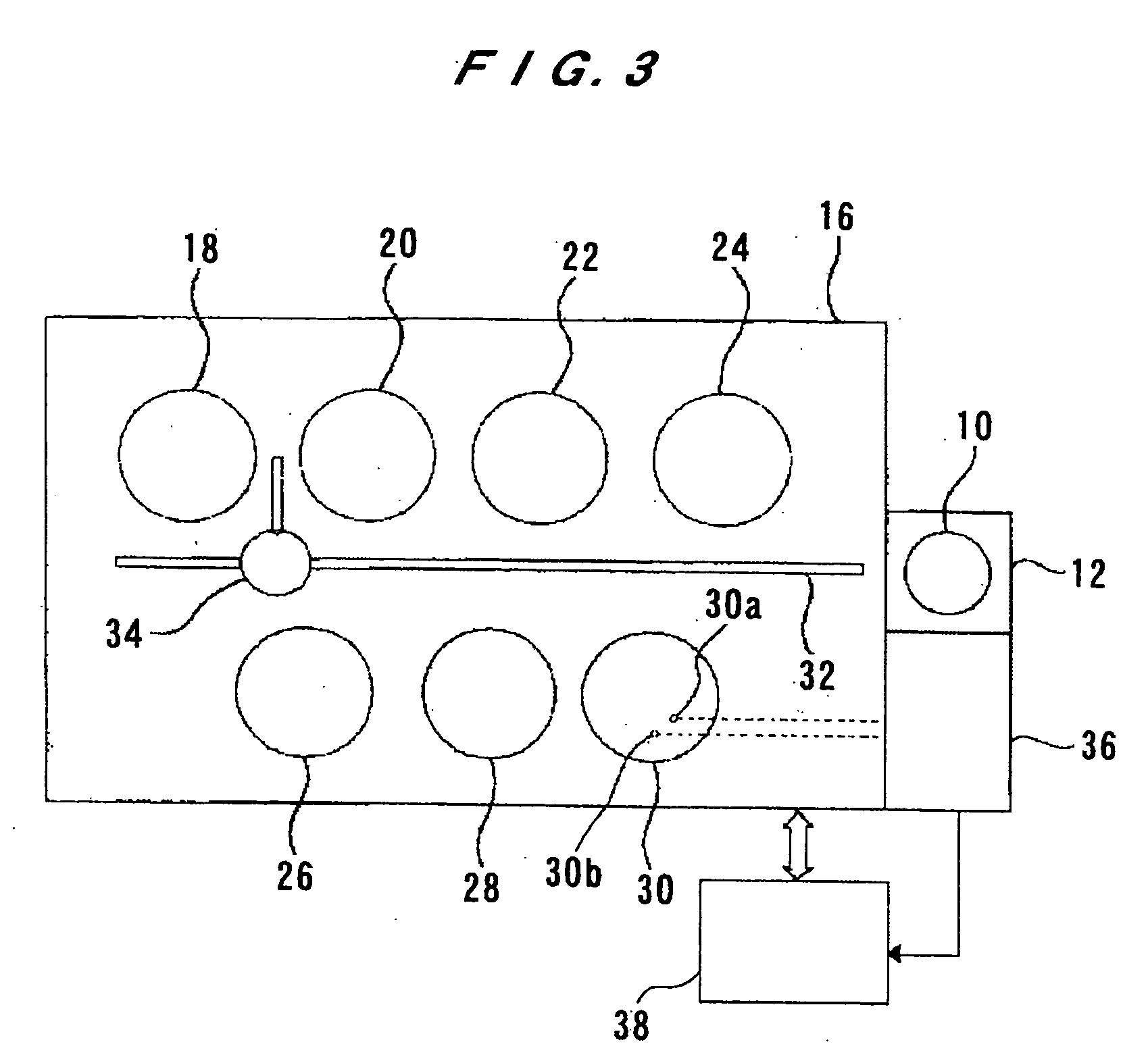
InactiveUS20060266290A1Reduce time differenceFlexible responseConveyorsLiquid processingEngineeringTime difference
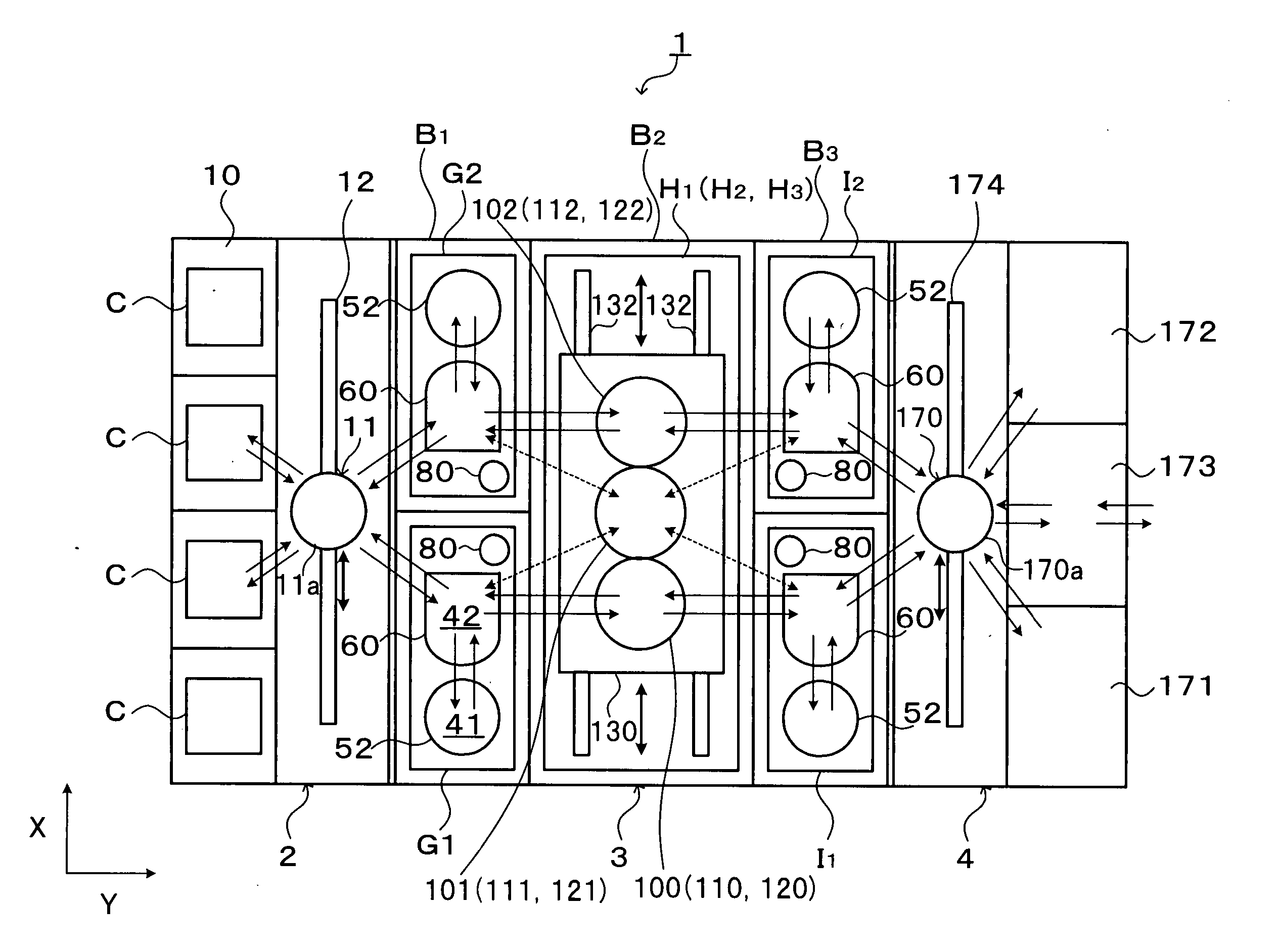
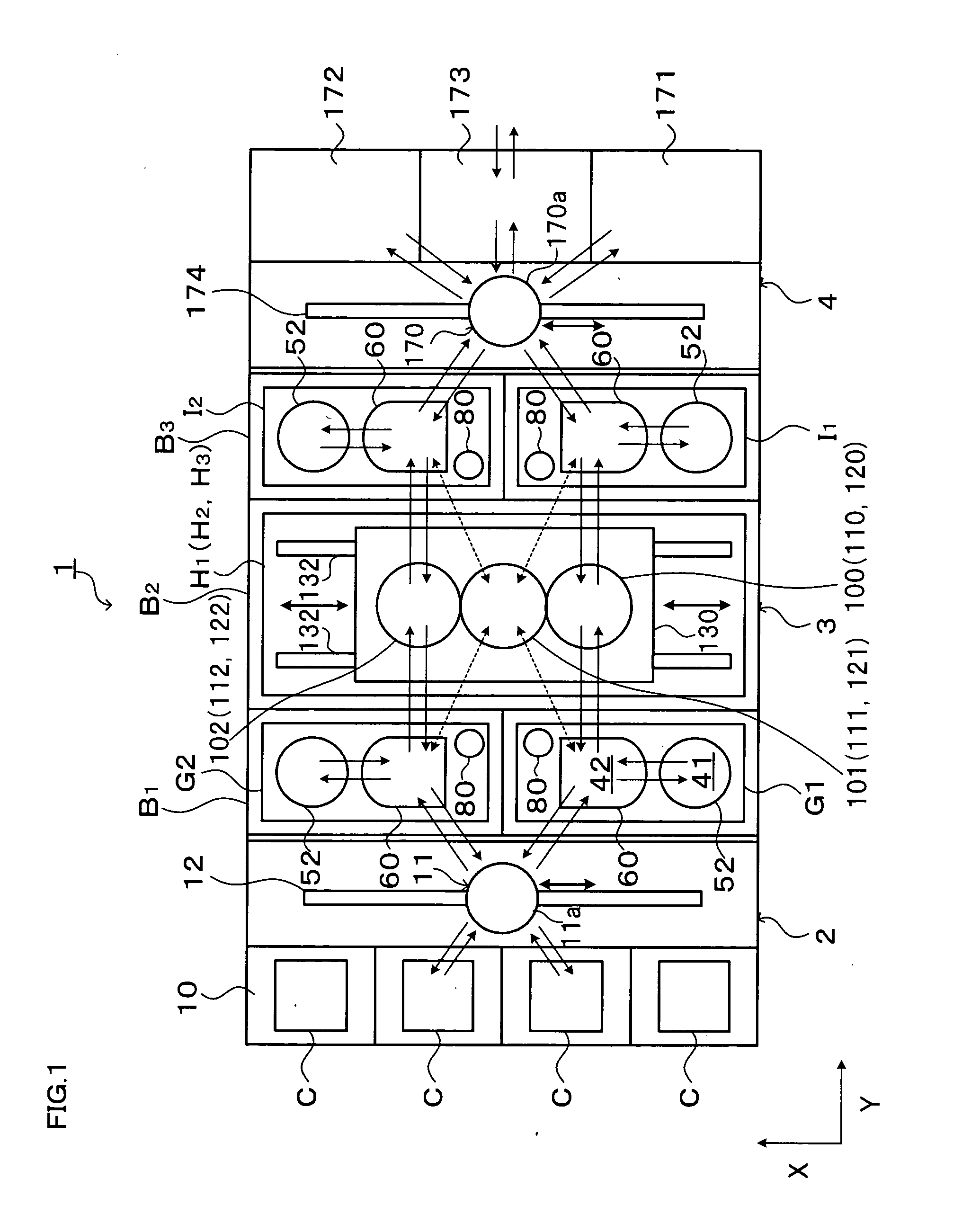
In the present invention, a plurality of first units capable of accommodating the substrate and a second unit are provided, in which a substrate is carried between the first unit and the second unit. The first units and the second unit are arranged side by side in a plan view, and at least one of the plurality of the first units is a processing unit for performing processing for the substrate. The plurality of first units are arranged in a line in the horizontal direction, and at least two first units adjacent to each other in the horizontal direction of the plurality of first units are movable in the horizontal direction to be able to transfer the substrate to / from the second unit. According to the present invention, the substrate processing system including a plurality of units flexibly deals with various substrate processing recipes and reduces the processing time difference among substrates and the carriage waiting time of the substrate.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
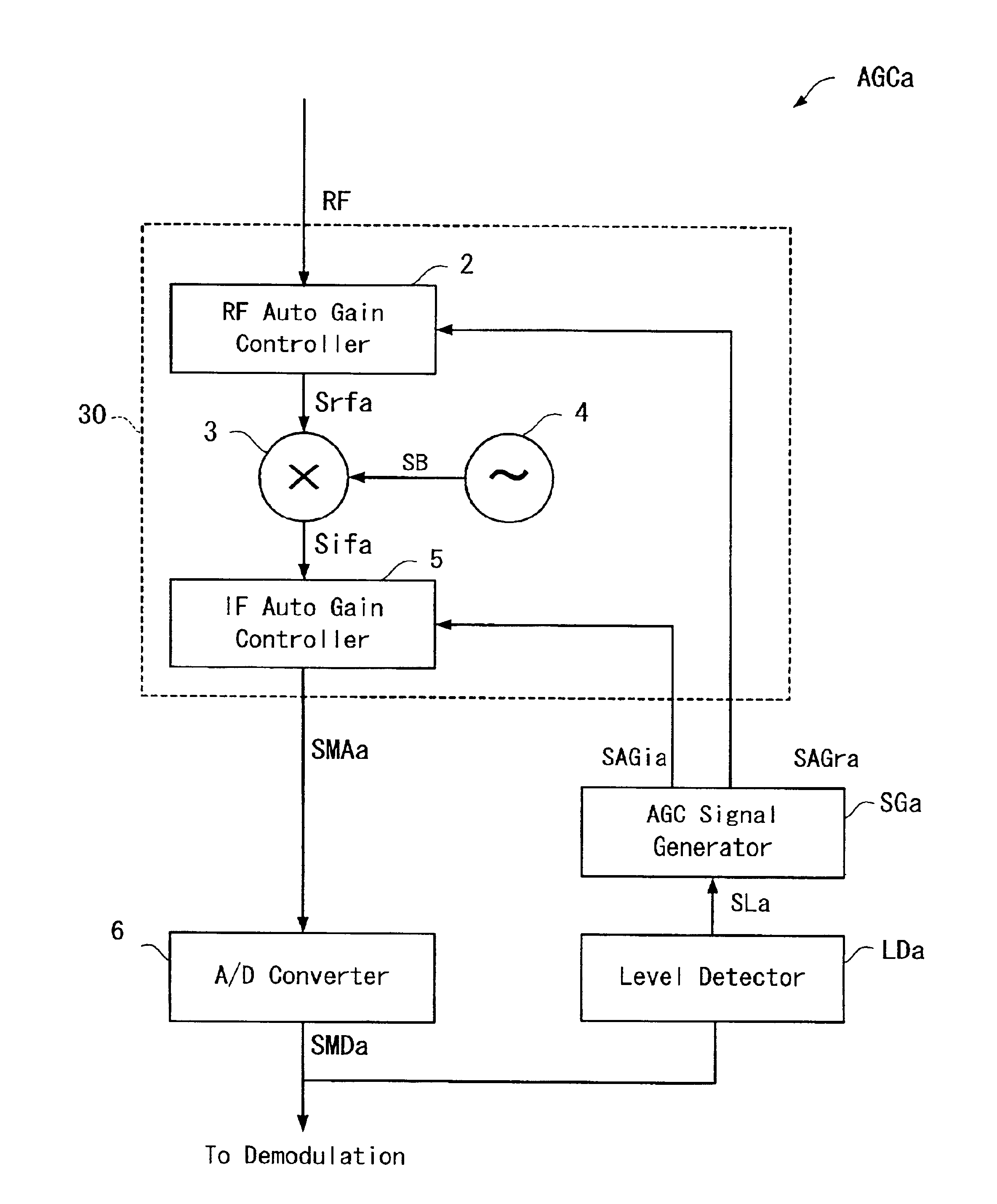
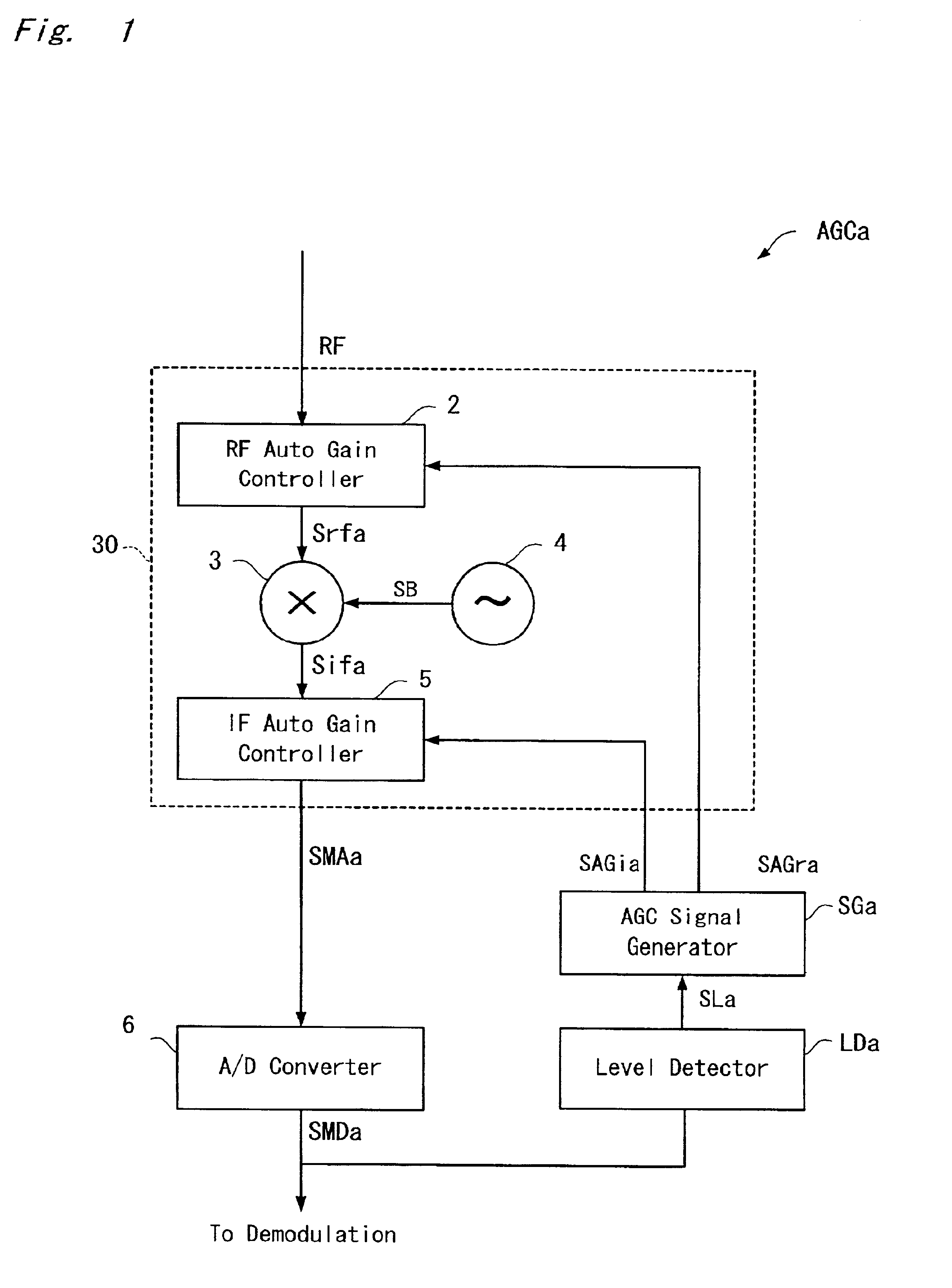
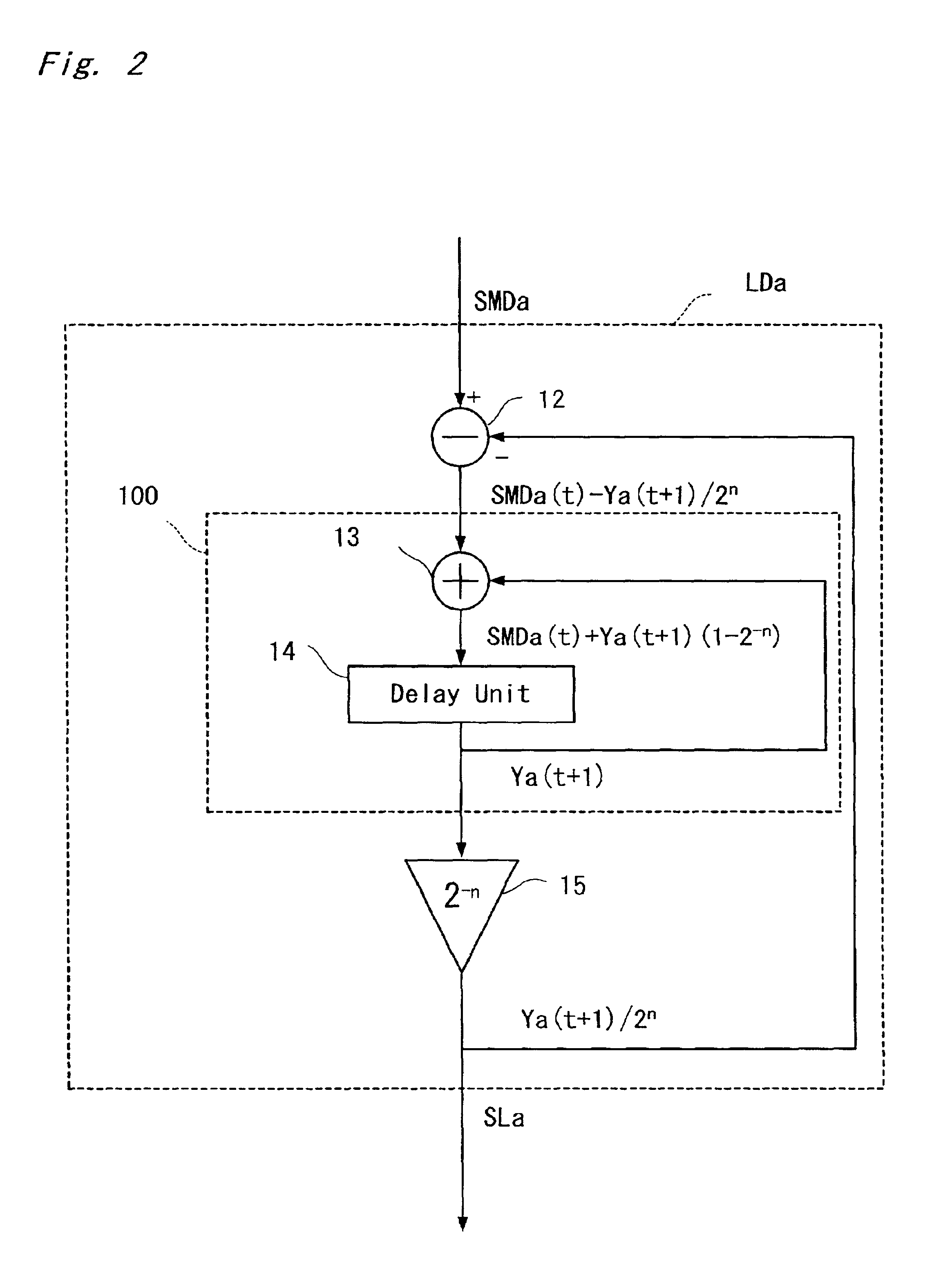
Automatic gain control apparatus
InactiveUS6934522B2Wide dynamic rangeEnhanced inhibitory effectGain controlRadio transmissionIntermediate frequencyAutomatic gain controller
In an automatic gain control amplifier, an RF automatic gain controller controls the gain of a radio frequency signal. A frequency converter frequency-converts the radio frequency signal into an intermediate frequency signal. An IF automatic gain controller controls the gain of the intermediate frequency. A level detector detects a signal level of the gain-controlled intermediate frequency signal, and generates a level signal. An automatic gain control signal generator separately controls, based the level signal, the RF automatic gain controller and the IF automatic gain controller.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP +1
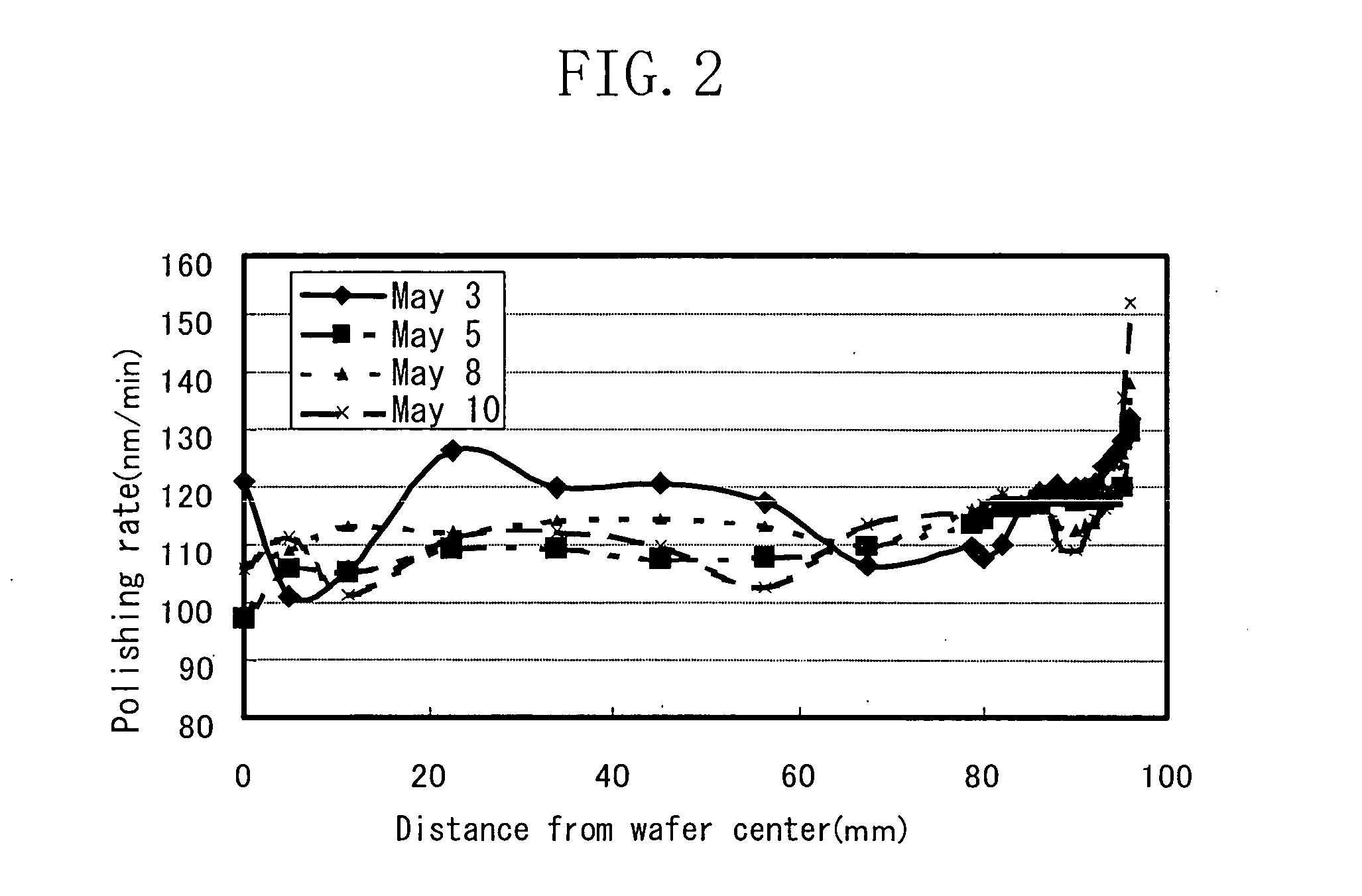
Semiconductor device fabrication method and semiconductor device fabrication system
ActiveUS20050014377A1Reduce variationAllocation is accurateSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringStep height
A polishing-rate distribution of a target film is compared with a desired post-polishing film-thickness distribution of the target film, thereby obtaining a pre-polishing film-thickness distribution of the target film by a reverse calculation, so that film growing conditions can be controlled in advance so as to allow the target film to have, after polishing, a film-thickness distribution that is the same as the desired film-thickness distribution. Therefore, even if there is a possibility that variation in the step height of the wafer surface might be produced by polishing, the finally obtained target film's film-thickness distribution can be the desired film-thickness distribution. Accordingly, semiconductors in which device-to-device variation in characteristic is reduced can be provided.
Owner:PANNOVA SEMIC
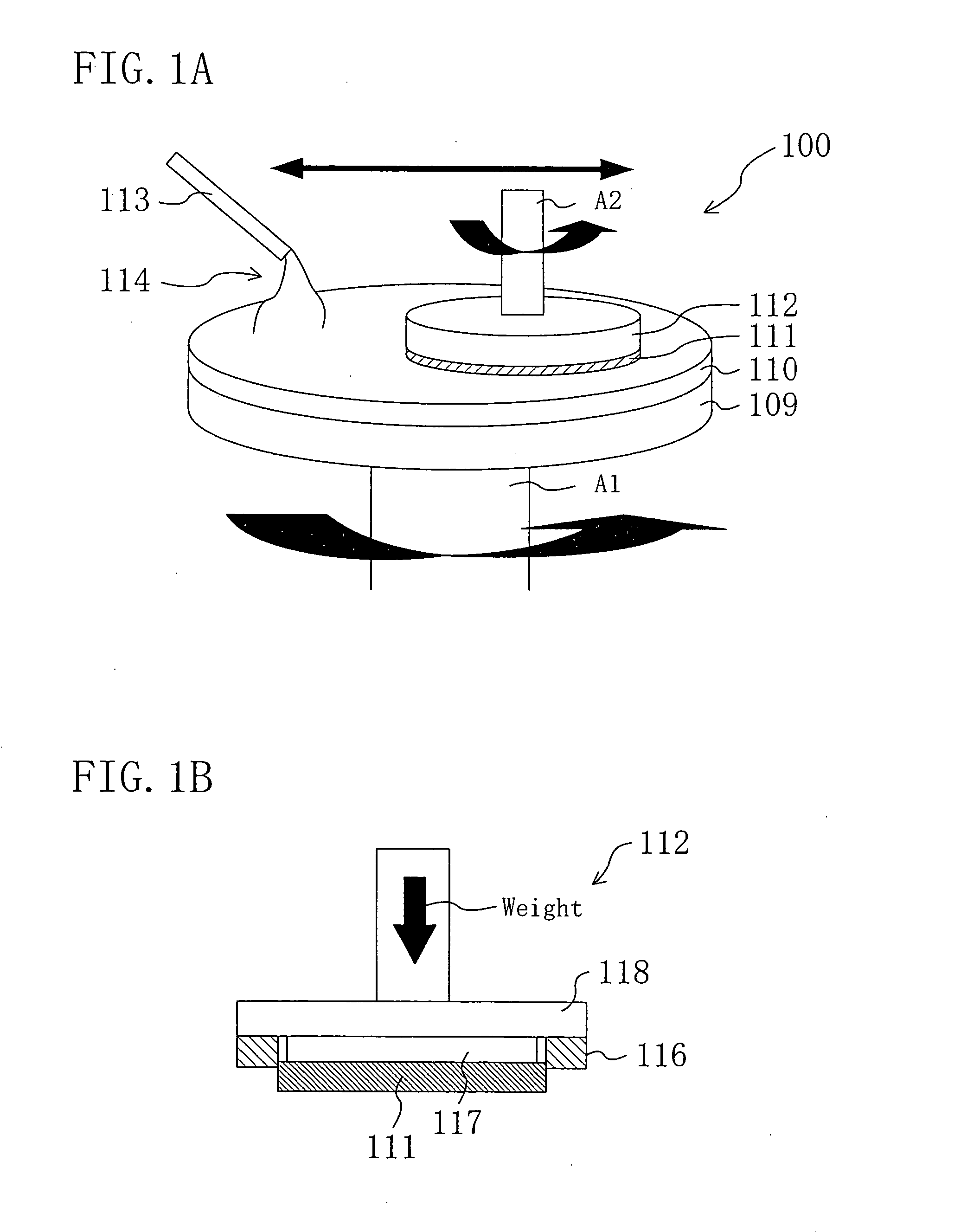
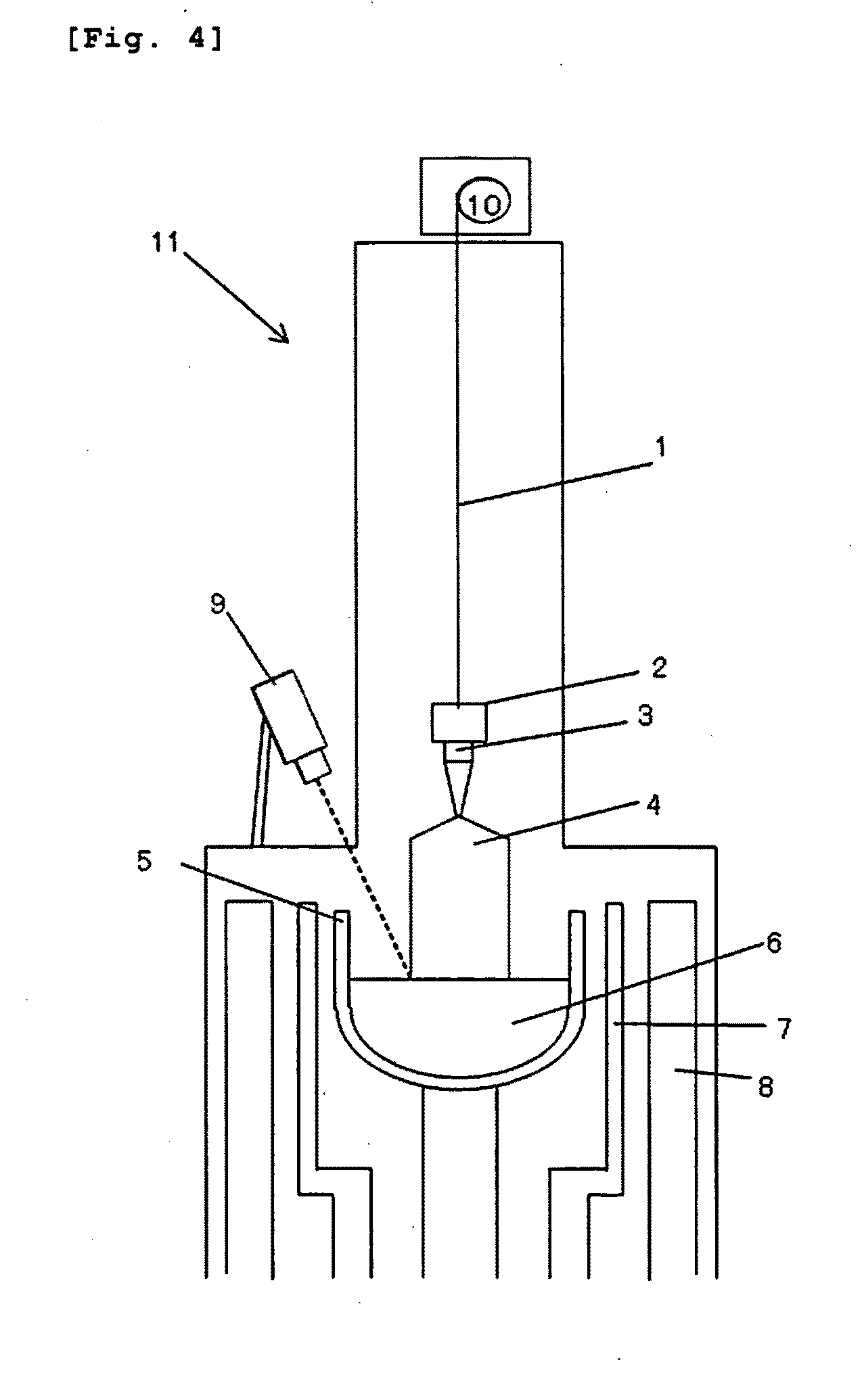
Method for detecting the diameter of a single crystal and single crystal pulling apparatus
ActiveUS20100128253A1Increase productionReduction in variation in qualityBy zone-melting liquidsMaterial analysis by optical meansCzochralski methodSingle crystal
The invention is a method for detecting the diameter of a single crystal grown by the Czochralski method, wherein the diameter of a single crystal is detected by both a camera and a load cell, the diameter detected by the camera is corrected based on a difference between the diameter detected by the camera and the diameter calculated by the load cell and a correction coefficient α obtained in advance according to a growth rate of the single crystal, and a value obtained by the correction is set as the diameter of the single crystal, and a single crystal pulling apparatus including both a camera and a load cell for detecting the diameter of a single crystal to be pulled upwardly. As a result, it is possible to improve the measurement accuracy of the diameter of a large-diameter, heavy crystal and achieve the enhancement of yields and a reduction in variations in quality.
Owner:SHIN-ETSU HANDOTAI CO LTD
Crystallization method for semiconductor film, manufacturing method for semiconductor device, and laser irradiation apparatus
InactiveUS7563661B2Control generationGeneration of in-plane variations in the properties of a crystallized semiconductor film can be suppressedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIrradiationLaser beams
A semiconductor film formed over a substrate is irradiated by a first laser beam which is incident on a bottom surface of the substrate at an angle and by a second laser beam which is incident on the bottom surface of the substrate at an angle opposite that of the first laser beam and oscillated by an oscillator differing from that of the first laser beam; whereby, part of the semiconductor film is melted, and a portion of the semiconductor film being melted is moved while the positions of irradiation of the first and the second laser beams and are being scanned approximately along the direction of slant for the first laser beam or the second laser beam.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Integrated waterproofing and drainage system with intrinsic leak detection for building structures and methods of use
InactiveUS10344470B2Improve and eliminate variation in installation qualityLow costDetection of fluid at leakage pointSynthetic resin layered productsEngineeringFace sheet
Owner:BUILDTECH SOLUTIONS LLC
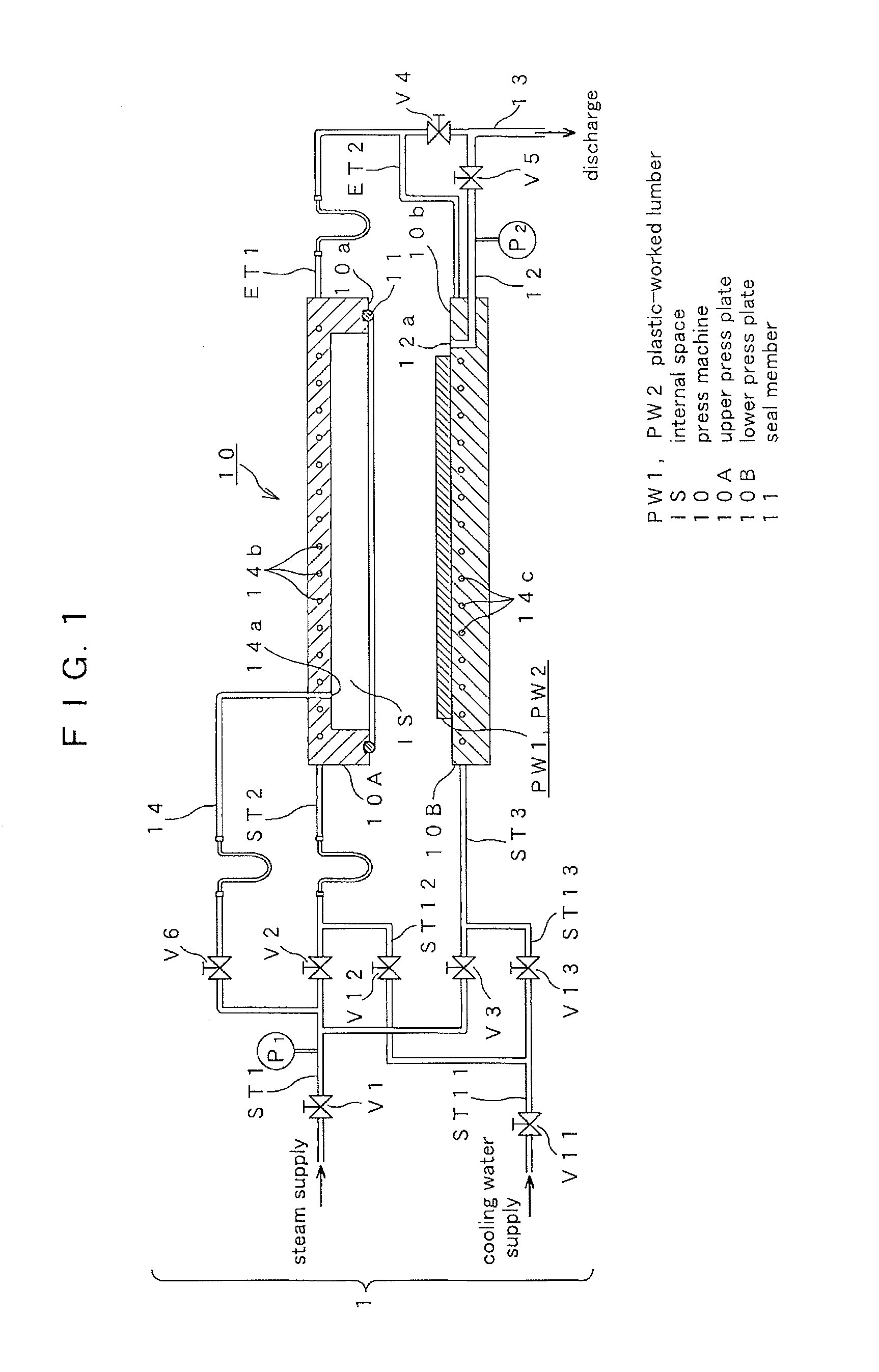
Cooling method for hot press forming and hot press forming apparatus
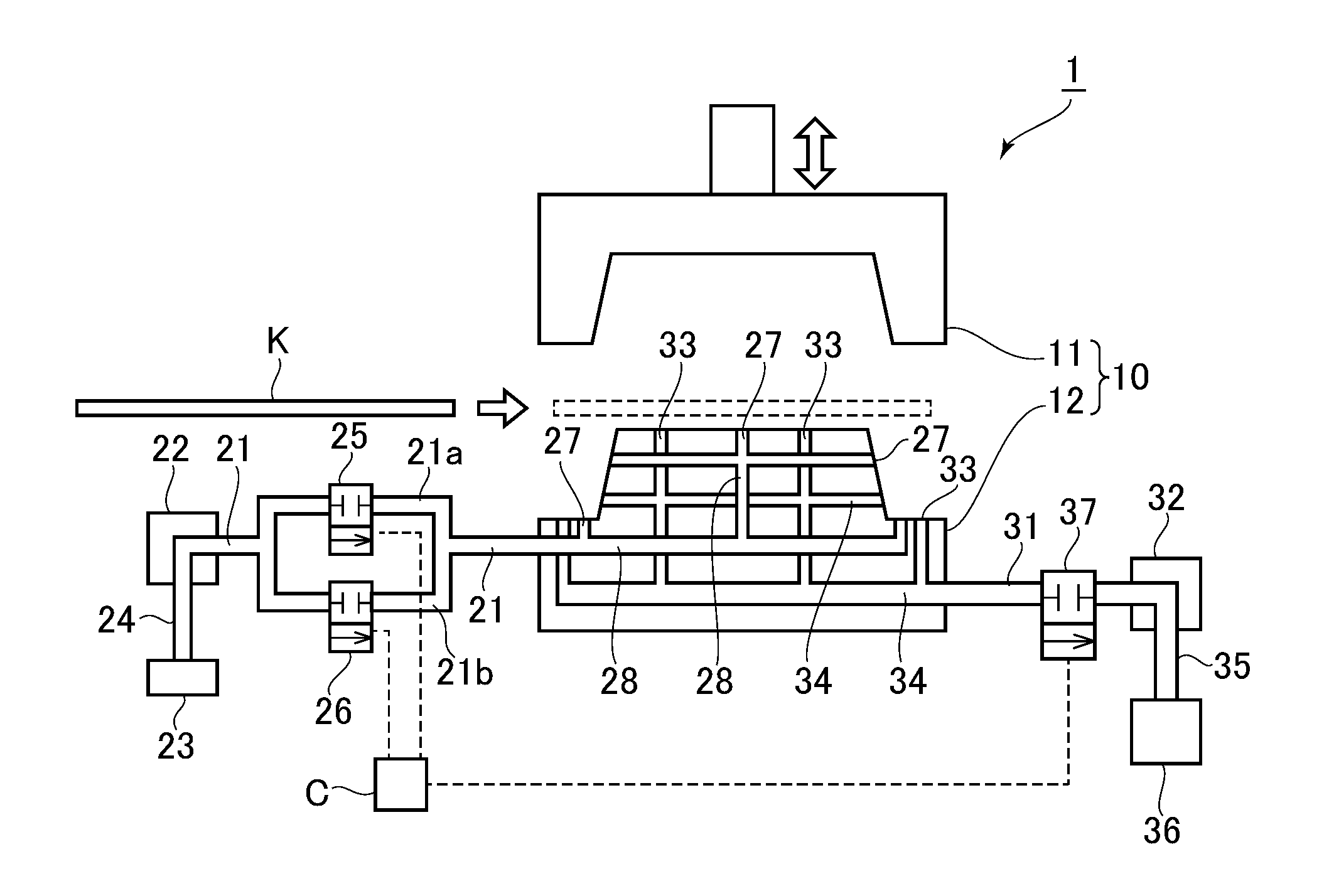
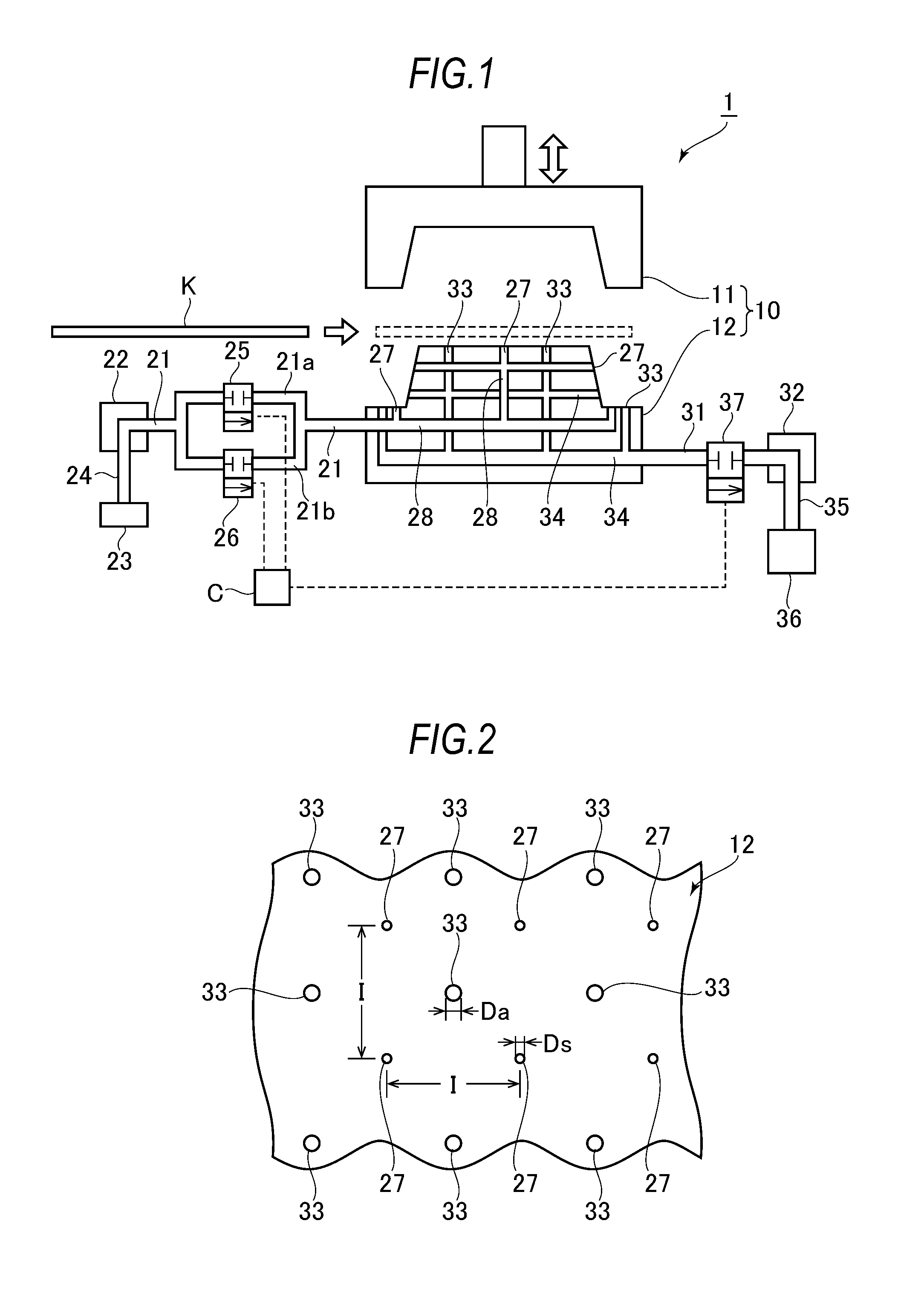
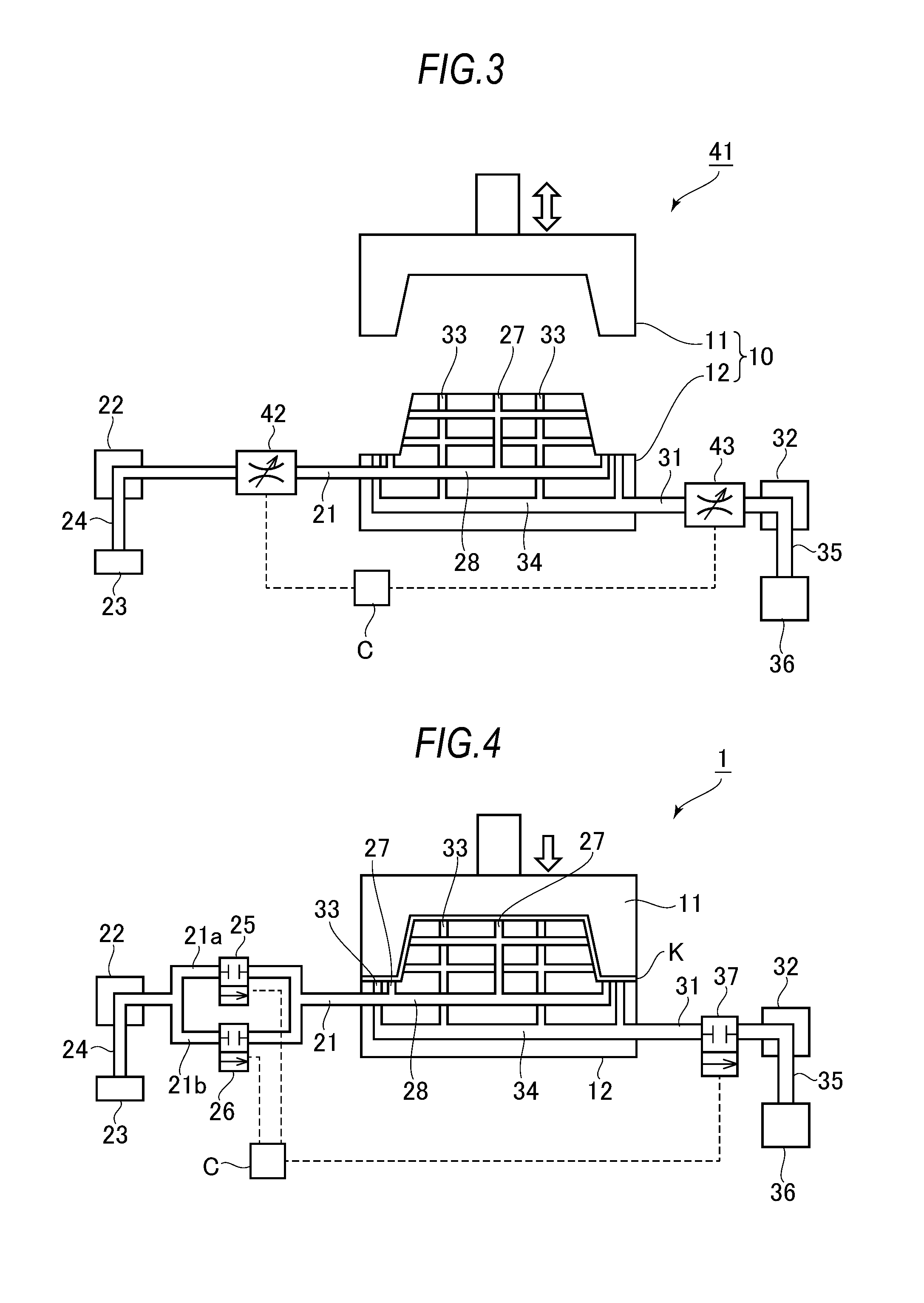
ActiveUS20160167101A1Suppress of variation of qualitySuppress distortion of shapeShaping toolsThermal compressionEngineering
In hot press forming a thin steel sheet K, when cooling the thin steel sheet K by supplying a refrigerant to an ejection hole (27) communicated from a supply path (28) inside a lower mold (12), precooling in which an ejection amount per unit time period of the refrigerant from the ejection hole (27) is suppressed is carried out, and thereafter, main cooling is carried out by increasing the ejection amount per unit time period.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
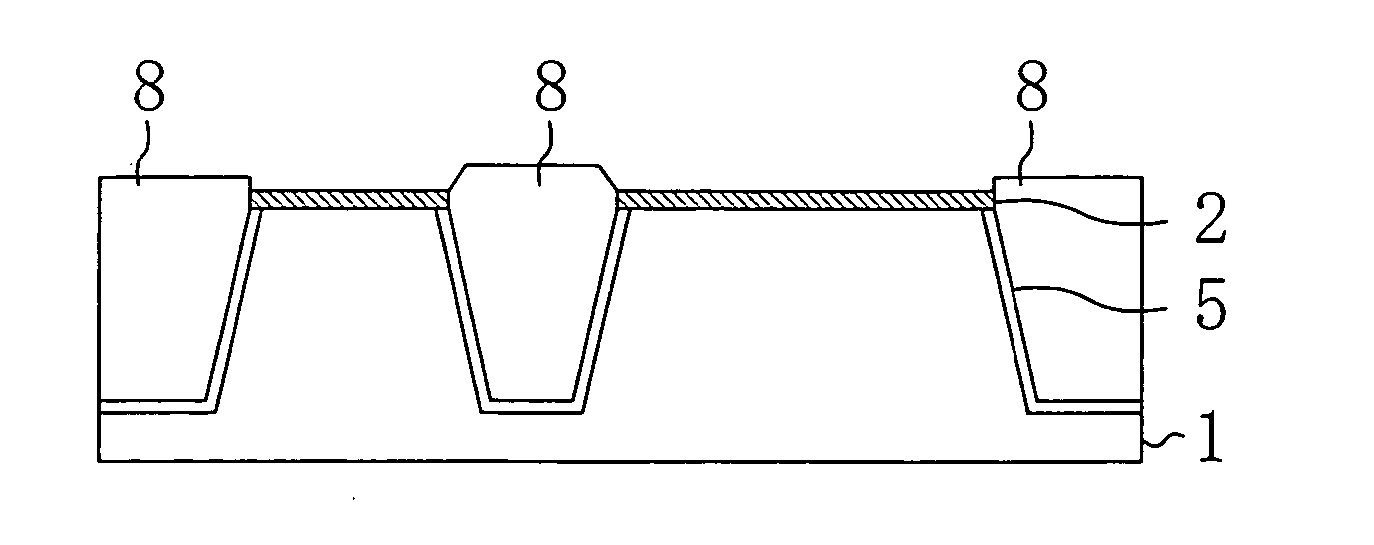
Nonmagnetic material particle dispersed ferromagnetic material sputtering target
ActiveUS9034153B2Reduce particlesVariation in qualityCellsVacuum evaporation coatingProduction rateSputtering
Provided is a nonmagnetic material particle dispersed ferromagnetic material sputtering target comprising a material including nonmagnetic material particles dispersed in a ferromagnetic material. The nonmagnetic material particle dispersed ferromagnetic material sputtering target is characterized in that all particles of the nonmagnetic material with a structure observed on the material in its polished face have a shape and size that are smaller than all imaginary circles having a radius of 2 μm formed around an arbitrary point within the nonmagnetic material particles, or that have at least two contact points or intersection points between the imaginary circles and the interface of the ferromagnetic material and the nonmagnetic material. The nonmagnetic material particle dispersed ferromagnetic material sputtering target is advantageous in that, in the formation of a film by sputtering, the influence of heating or the like on a substrate can be reduced, high-speed deposition by DC sputtering is possible, the film thickness can be regulated to be thin, the generation of particles (dust) or nodules can be reduced during sputtering, the variation in quality can be reduced to improve the mass productivity, fine crystal grains and high density can be realized, and the nonmagnetic material particle dispersed ferromagnetic material sputtering target is particularly best suited for use as a magnetic recording layer.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING & METALS CORP
Fixing Device
ActiveUS20170090367A1Reduce qualityVariation in qualityElectrographic process apparatusEngineeringSheet material
A nip member is disposed inside the endless belt and elongated in a longitudinal direction. A backup member sandwiches the endless belt against the nip member to form a nip portion at which the backup member and the endless belt are in contact with each other and configured to convey a recording sheet in a conveying direction perpendicular to the longitudinal direction. A downstream end of the nip portion in the conveying direction is arced with a longitudinal center portion thereof further upstream than longitudinal end portions thereof. The nip member includes a first portion sandwiching the endless belt against the backup member, and a second portion positioned downstream of the first portion in the conveying direction and bent in a direction away from the backup member. The second portion is arced with a longitudinal center portion thereof further upstream in the conveying direction than longitudinal end portions thereof.
Owner:BROTHER KOGYO KK
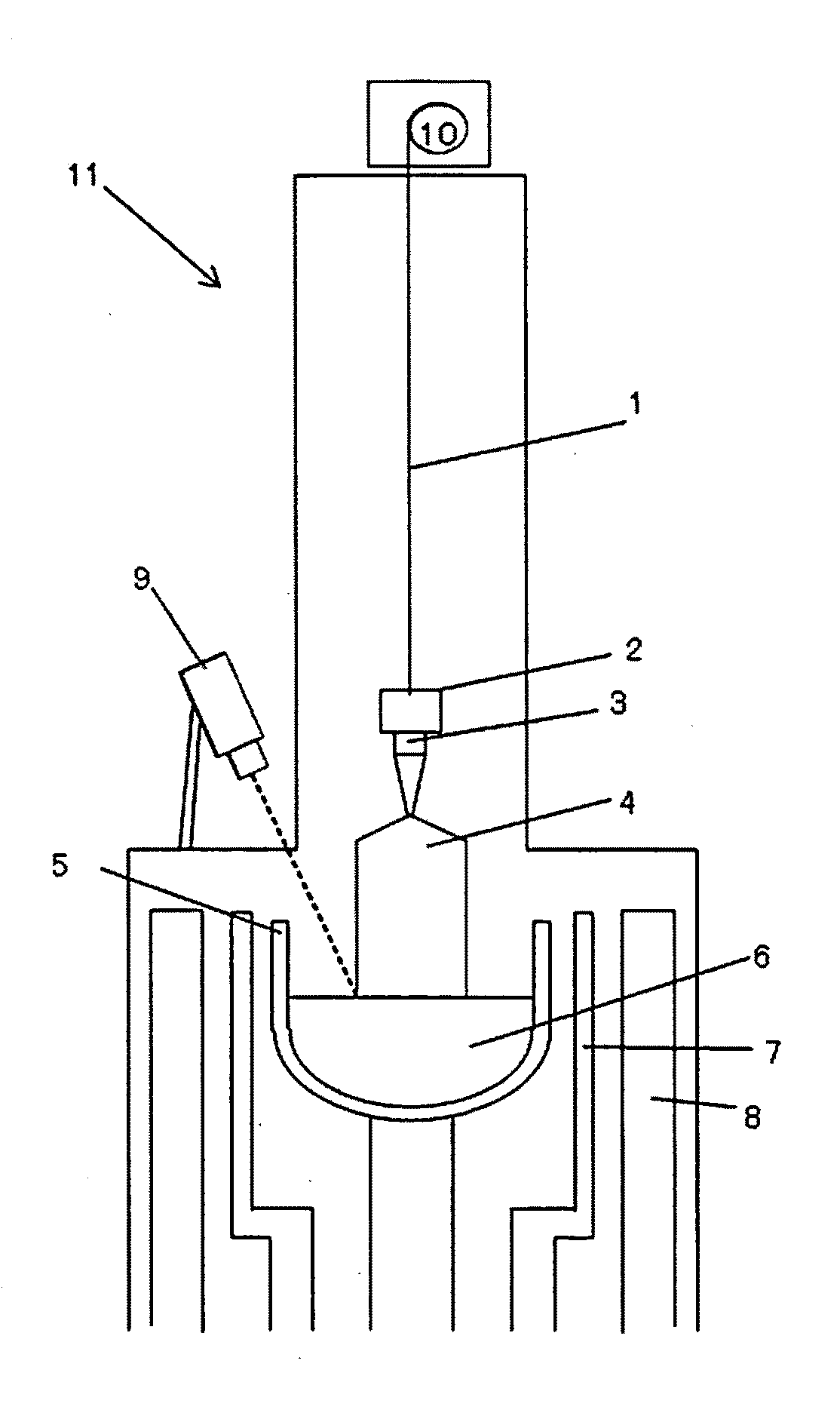
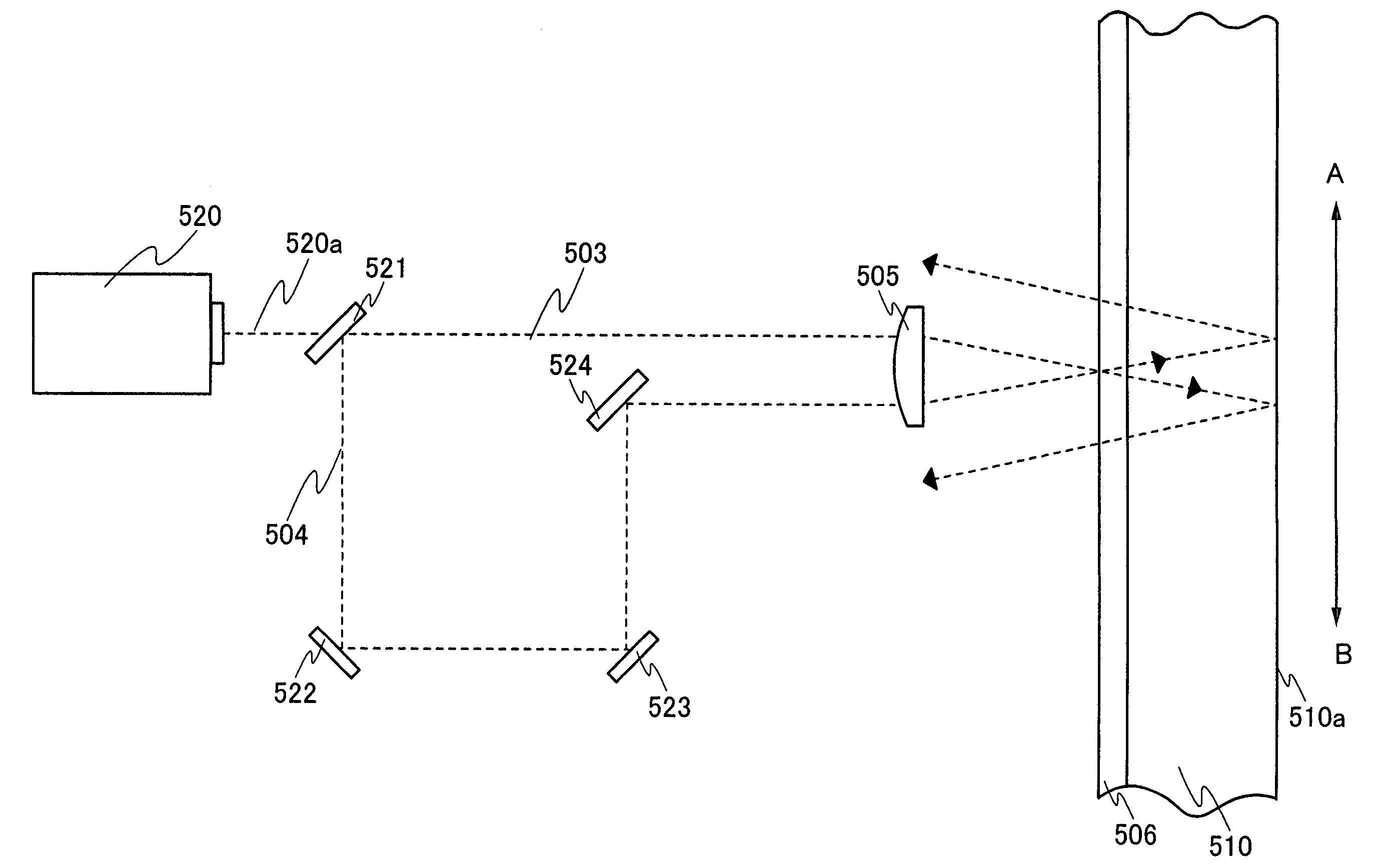
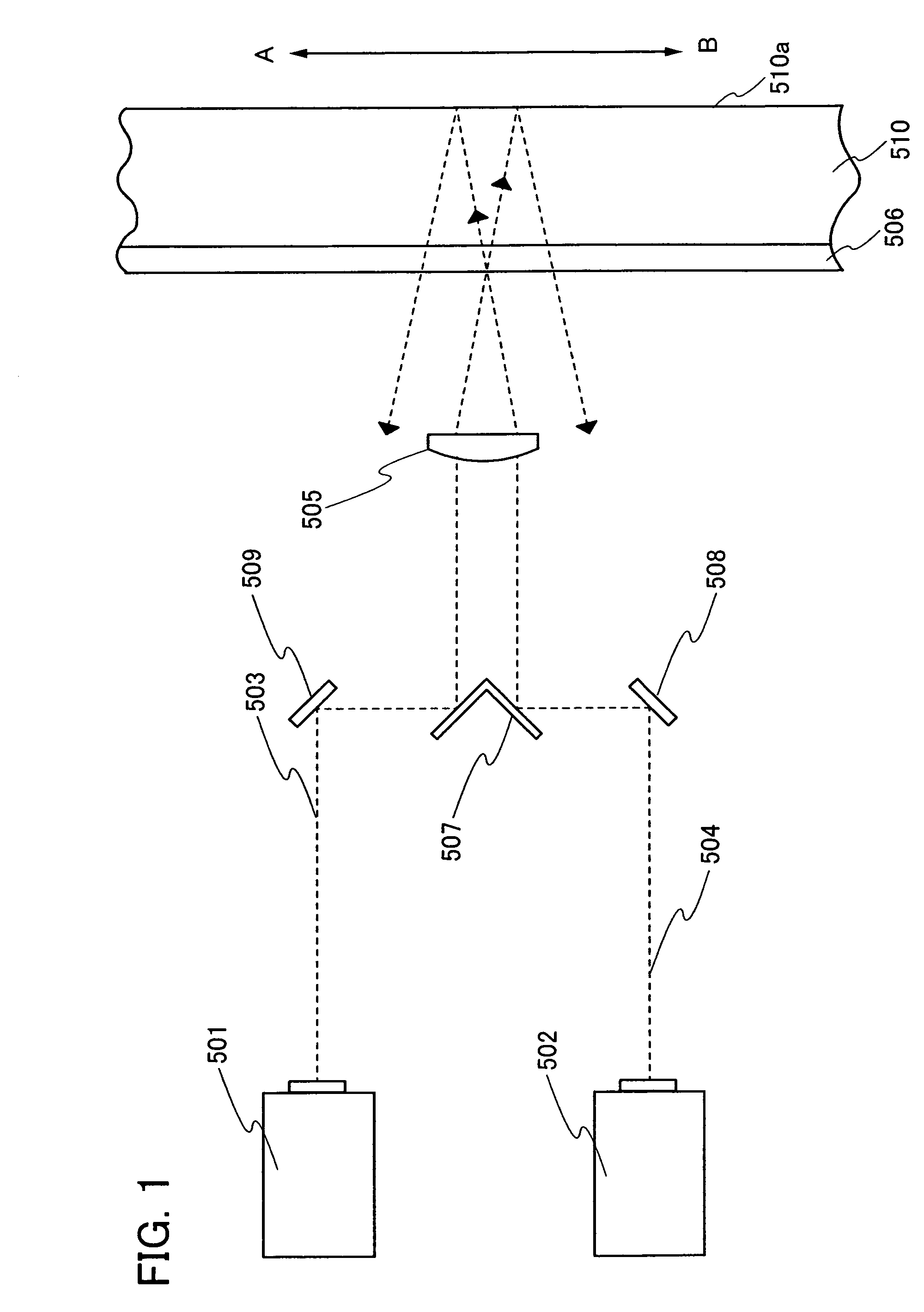
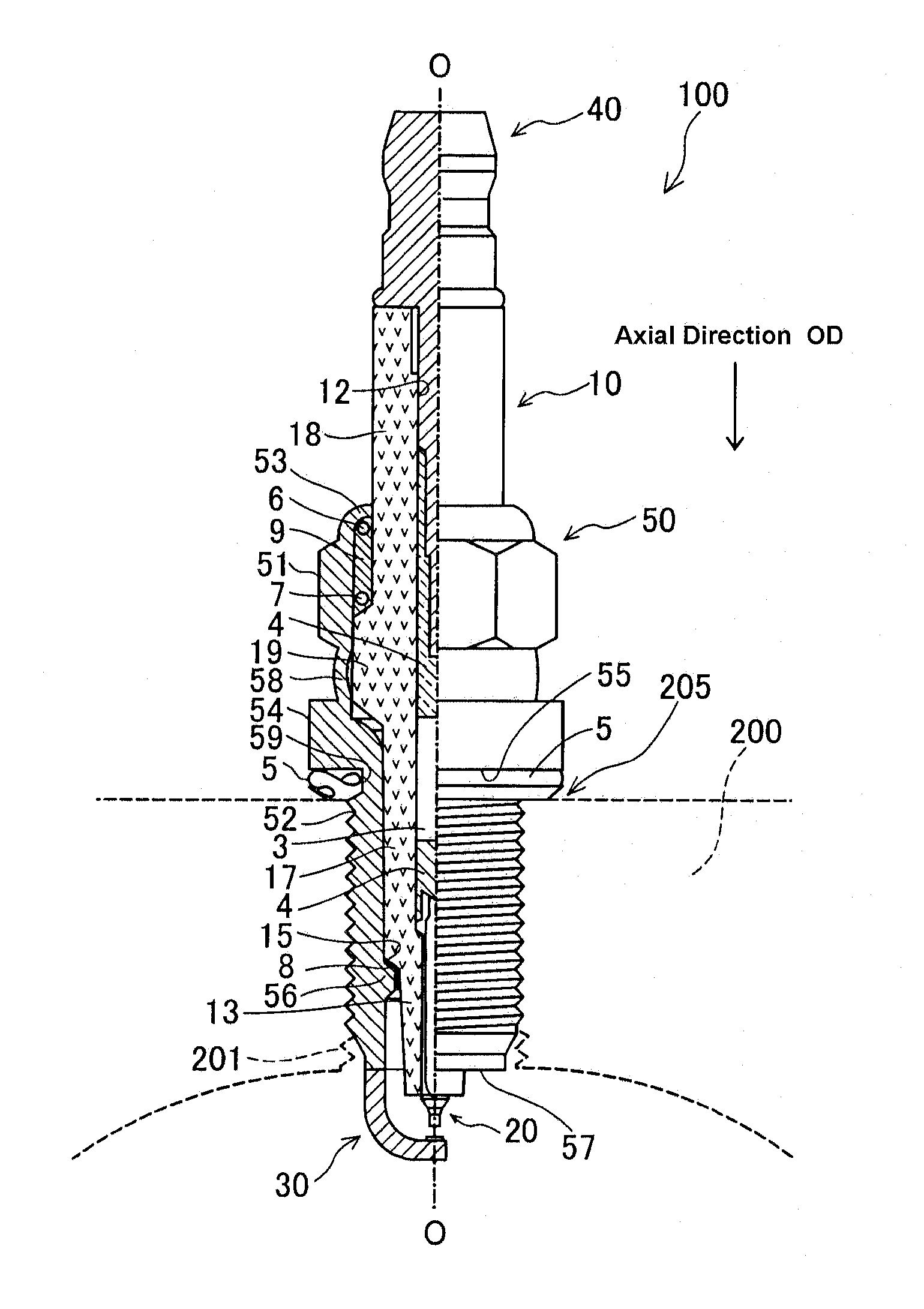
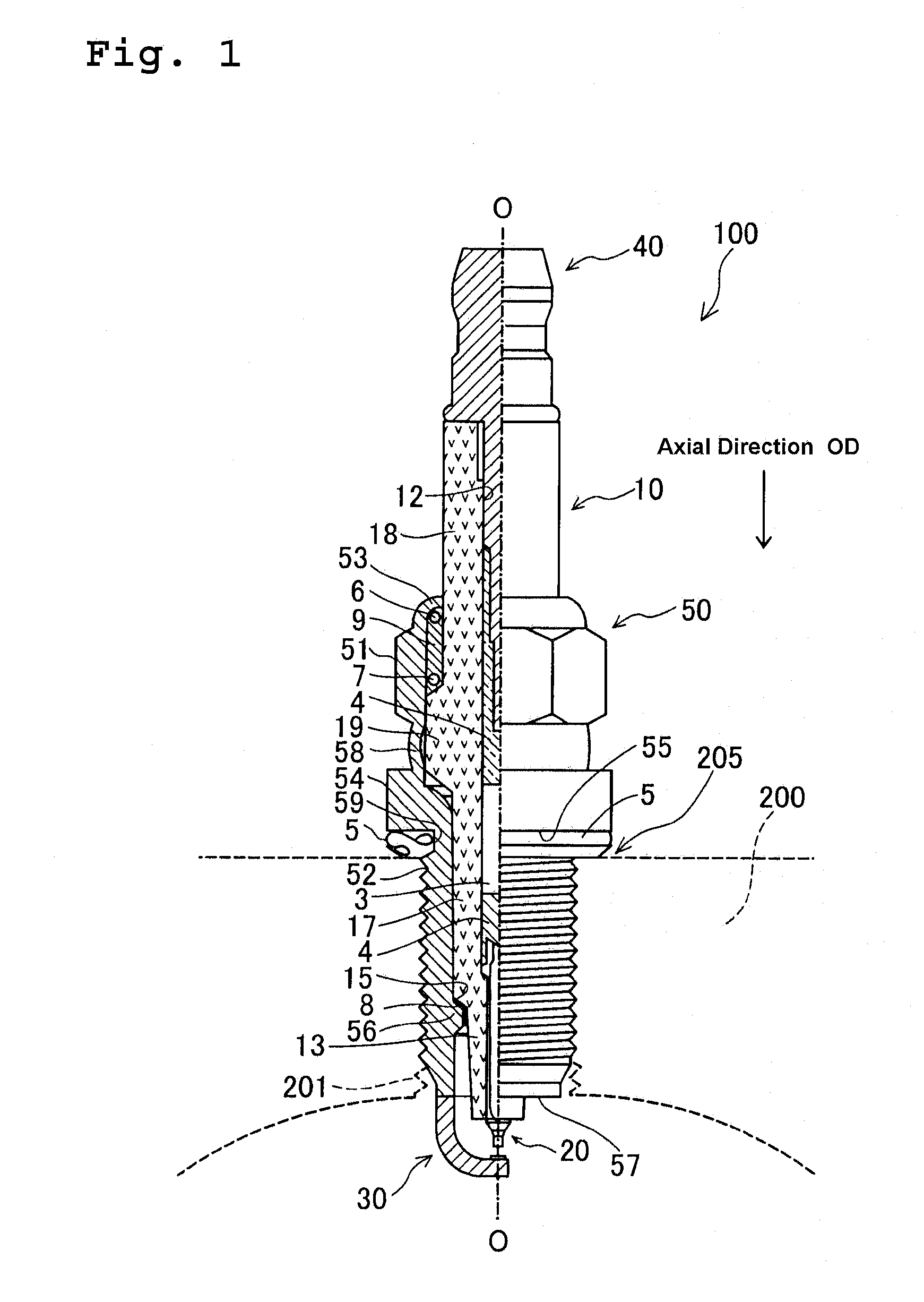
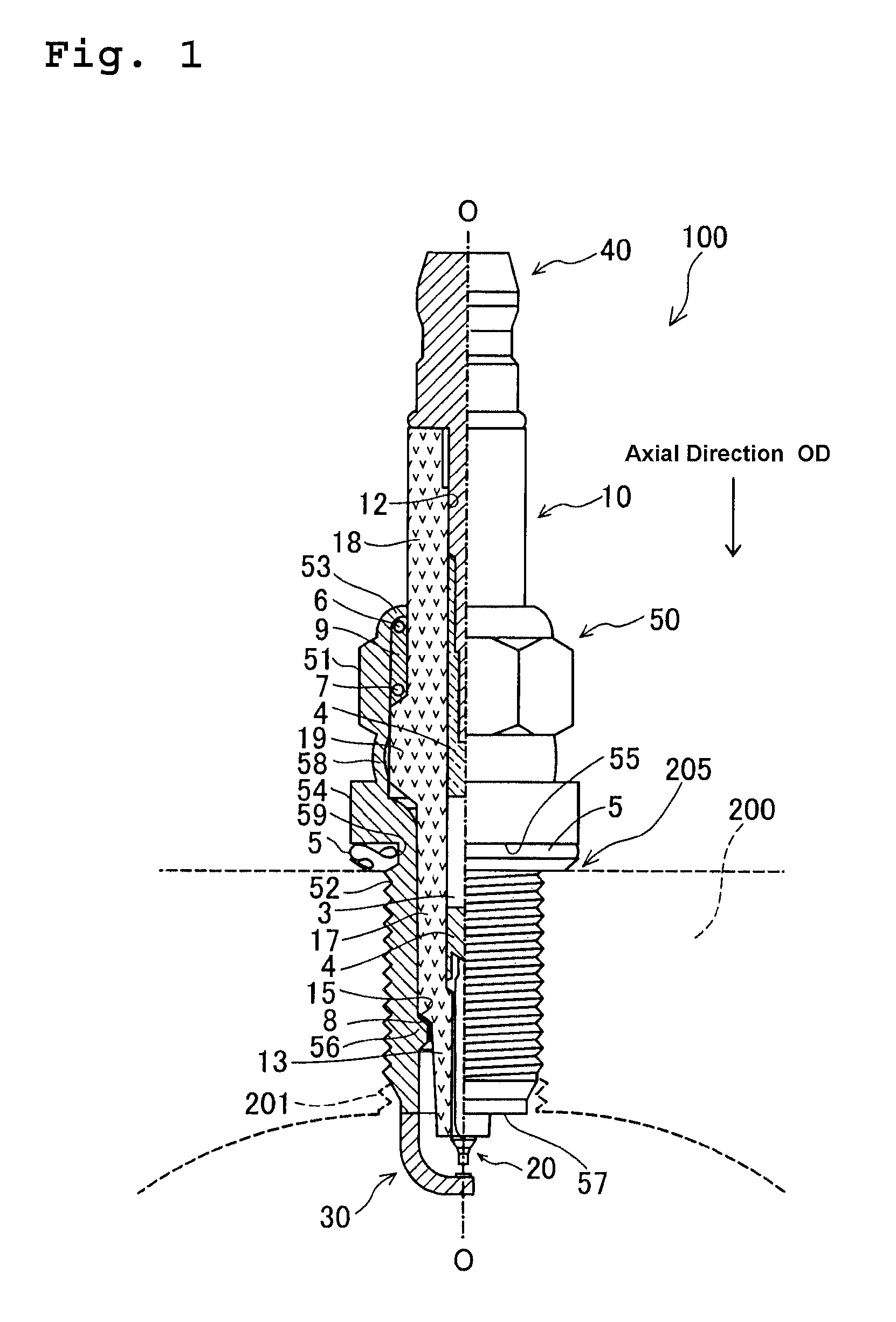
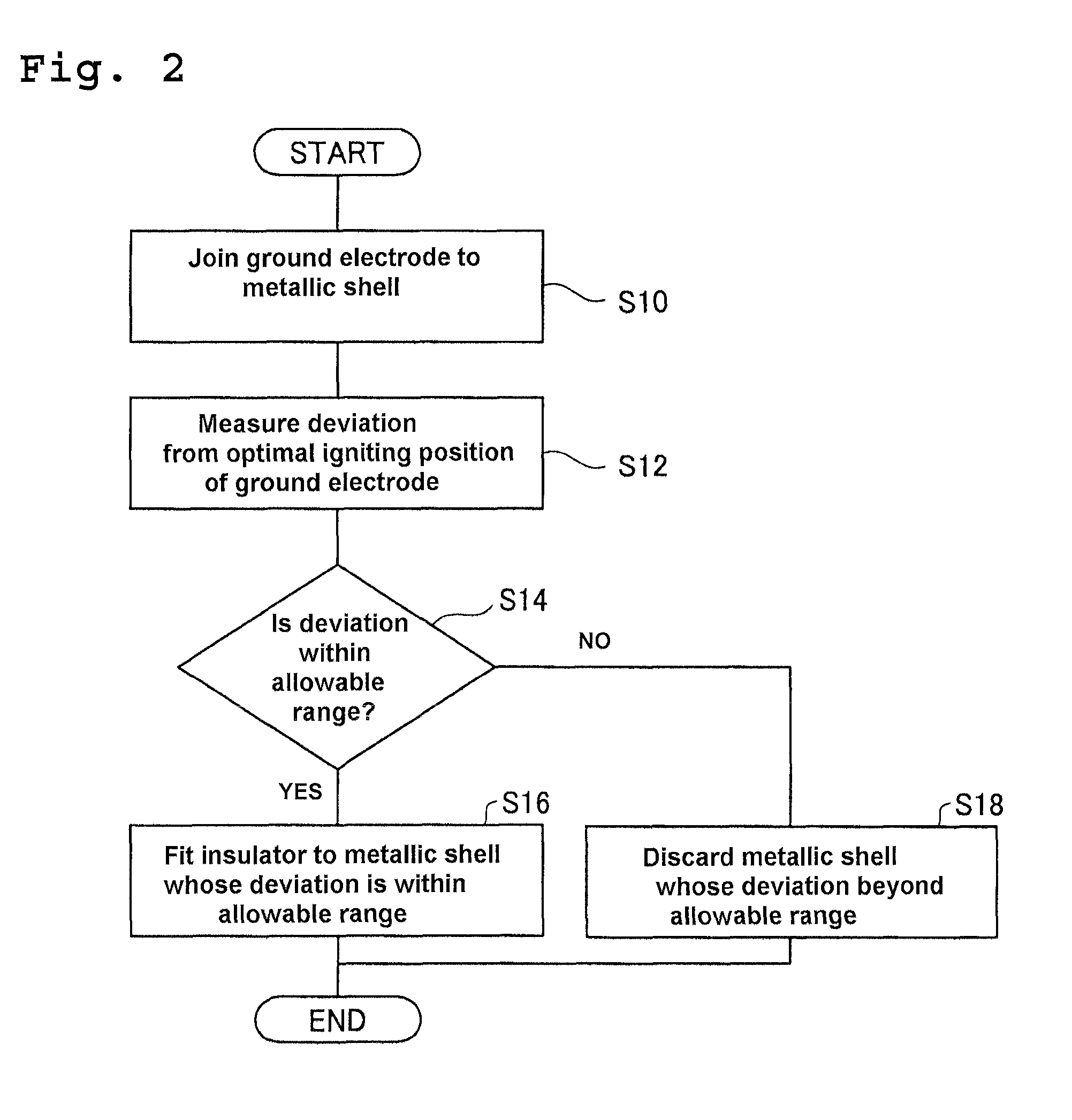
Method for measuring deviation of joint position of member and method for producing spark plug
ActiveUS20110287683A1Suppress mutationVariation in qualityUsing optical meansSpark gaps adjustmentEngineeringSpark plug
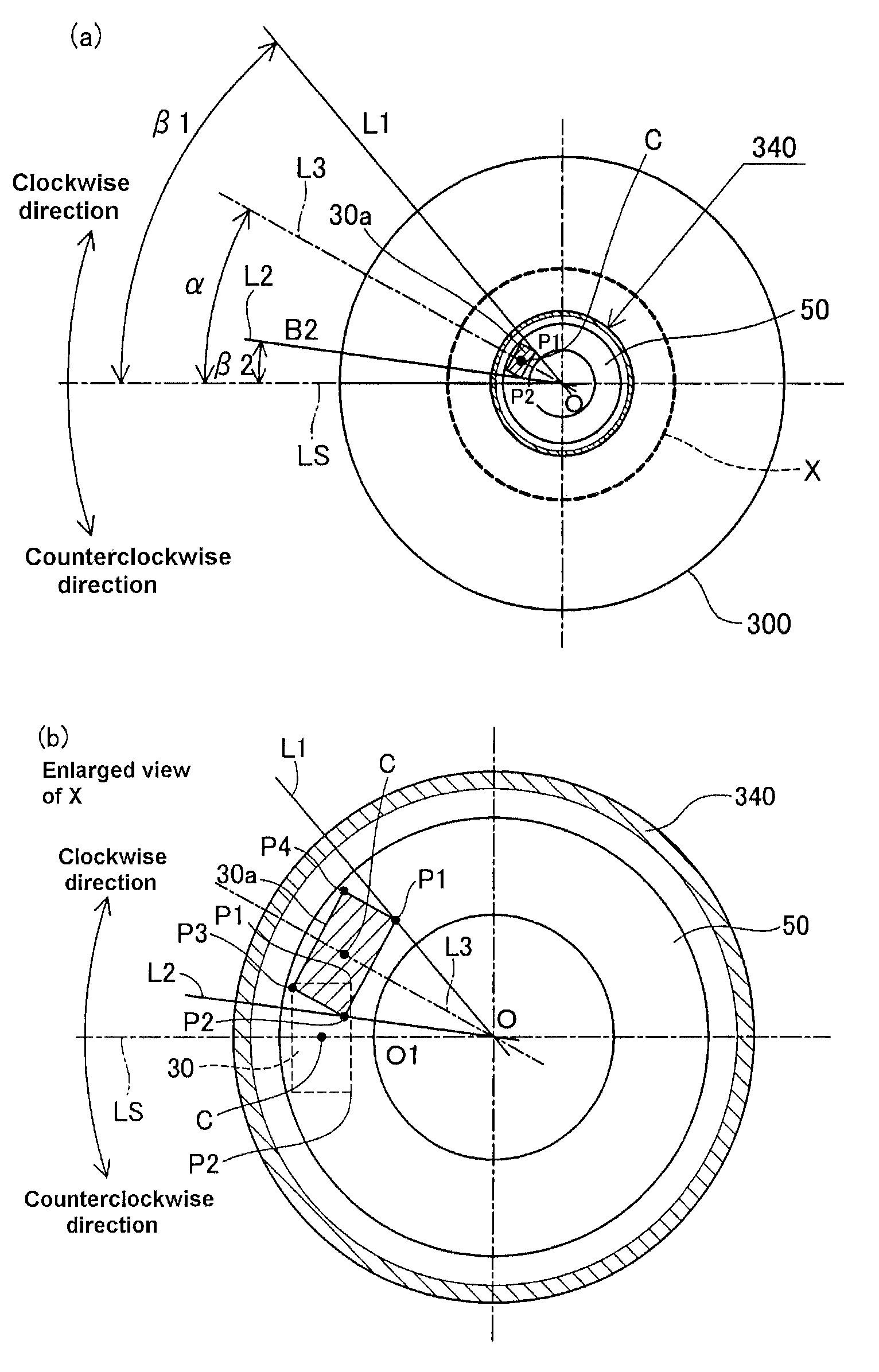
In a method for measuring deviation of a ground electrode from an optimal igniting position, a metallic shell is engaged with a female thread jig. Then the axis O of the metallic shell, a predetermined first measuring point P1 and a predetermined second measuring point P2 on a front end face of the ground electrode are detected. Then, a circumferential angle β1 formed between a reference straight line “LS” connecting O to the optimal igniting position O1, and a first straight line L1 which connects O to P1 is measured, followed by a measurement of a circumferential angle β2 formed between LS and a second straight line L2 connecting O to P2 Thereafter, the deviation of the ground electrode from O1 is measured as a circumferential angle “α” between “LS” and a third straight line L3 connecting the axis O to the center C of the front end face.
Owner:NGK SPARK PLUG CO LTD
Substrate processing method
ActiveUS7407821B2Quick correctionQuality improvementSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesProcess conditionsMetal
Owner:EBARA CORP
Plastic-worked lumber and process for manufacturing the same
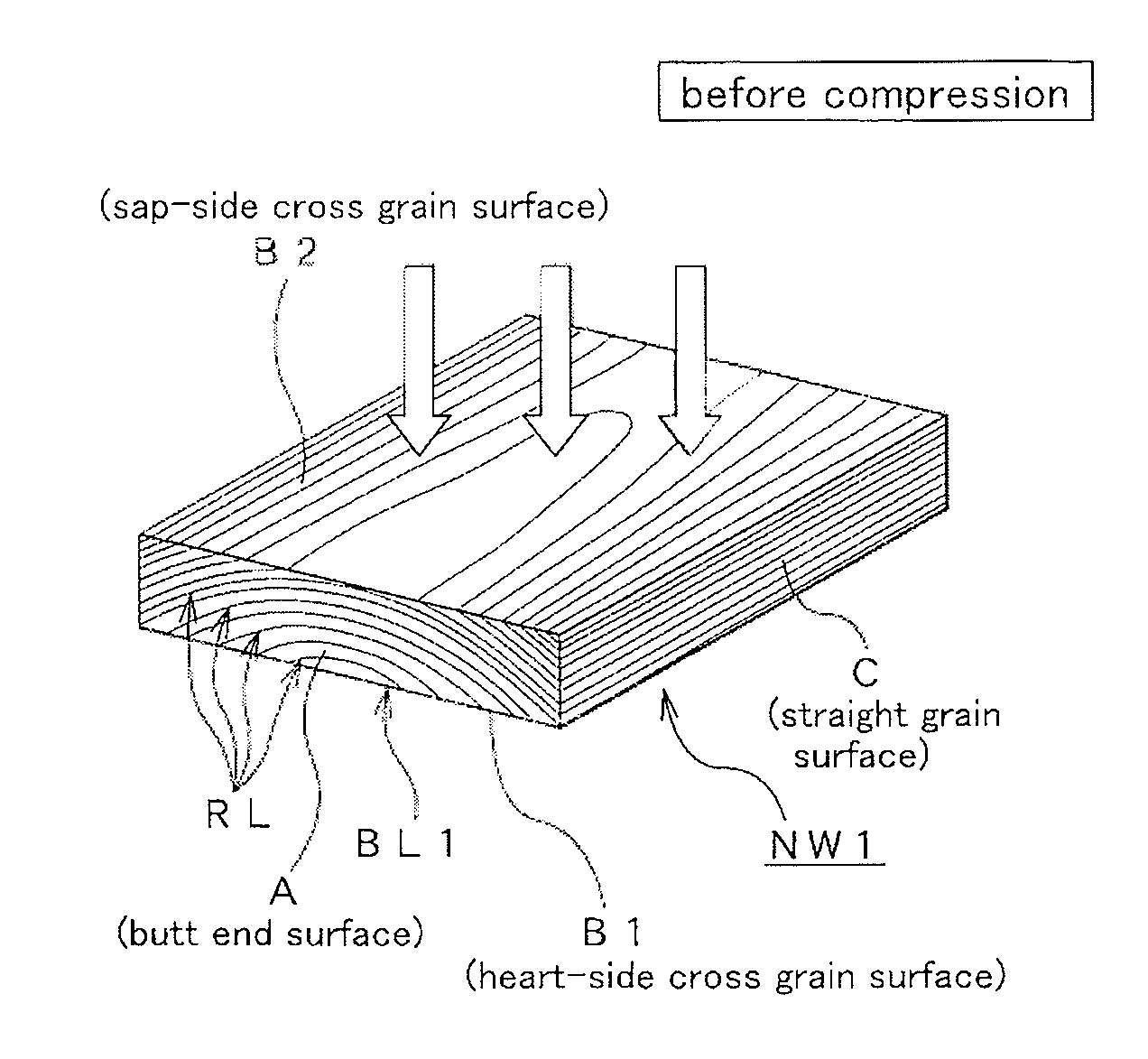
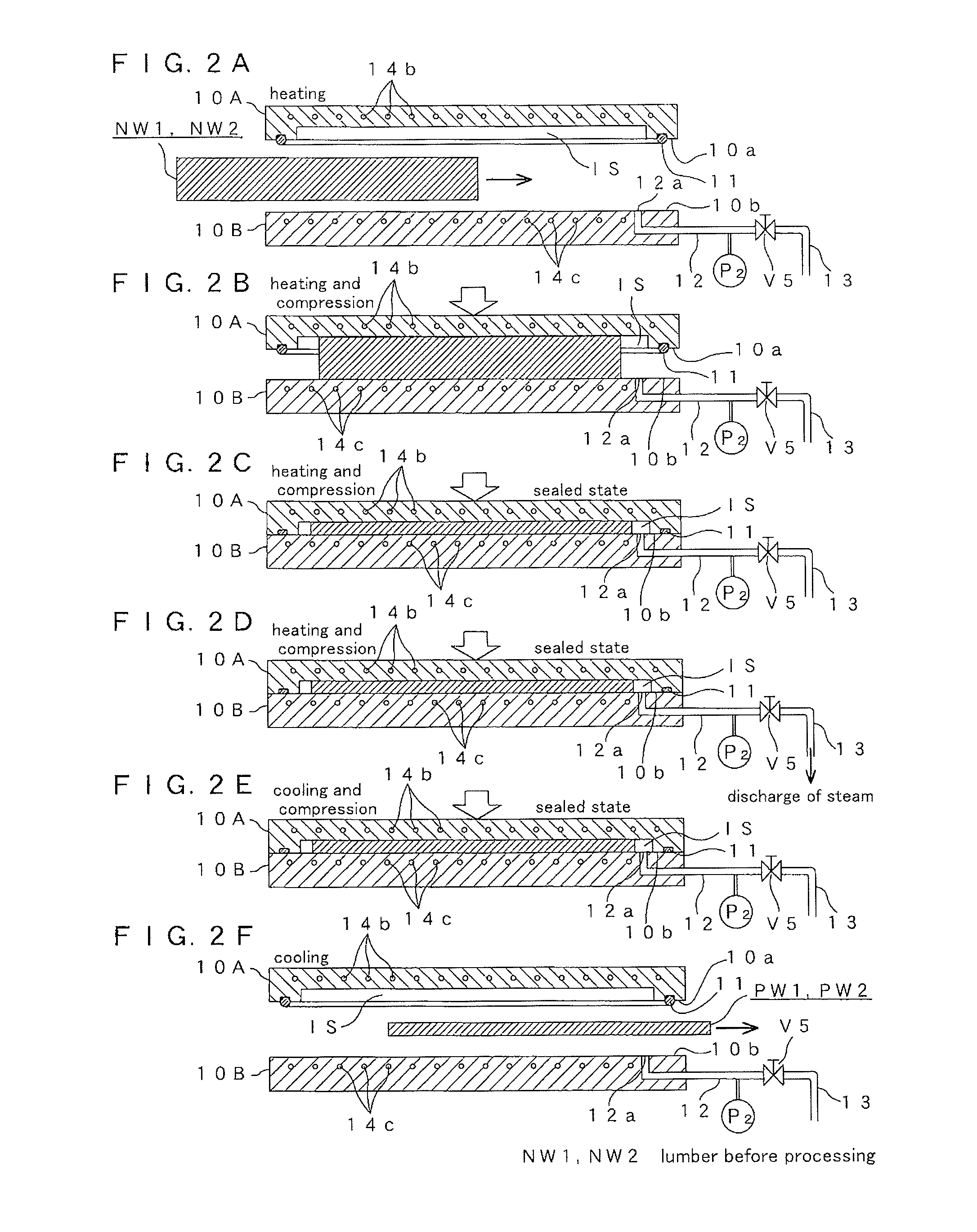
InactiveUS20120021176A1Reduce variationRaise the ratioWood compressionLayered productsPlastic propertySpecific gravity
Plastic-worked lumber. PW1 and PW2 has air-dried specific gravity twice or more than those of lumber before processing NW1 and NW2 and acute crossing angles within a range of 45 degrees or less. The acute crossing angles are formed by all of annual ring lines RL on a butt end surface of the plastic-worked lumber PW1 or PW2 and a heart-side cross grain surface or a pith-side straight grain surface of the plastic-worked lumber PW1 or PW2. The plastic-worked lumber PW1 and PW2 is prepared by heating and compression to lumber NW1 or NW2 so that the lumber NW1 or NW2 is heated and compressed in a thickness direction thereof and plastically worked.
Owner:MYWOOD 2
Method for measuring deviation of joint position of member and method for producing spark plug
ActiveUS8628367B2High measurement accuracySuppress mutationUsing optical meansSpark gaps adjustmentMeasurement pointEngineering
In a method for measuring deviation of a ground electrode from an optimal igniting position, a metallic shell is engaged with a female thread jig. Then the axis O of the metallic shell, a predetermined first measuring point P1 and a predetermined second measuring point P2 on a front end face of the ground electrode are detected. Then, a circumferential angle β1 formed between a reference straight line “LS” connecting O to the optimal igniting position O1, and a first straight line L1 which connects O to P1 is measured, followed by a measurement of a circumferential angle β2 formed between LS and a second straight line L2 connecting O to P2 Thereafter, the deviation of the ground electrode from O1 is measured as a circumferential angle “α” between “LS” and a third straight line L3 connecting the axis O to the center C of the front end face.
Owner:NGK SPARK PLUG CO LTD
Substrate processing system
InactiveUS7503710B2Reduce time differenceSmall sizeLiquid processingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringTime difference
In the present invention, a plurality of first units capable of accommodating the substrate and a second unit are provided, in which a substrate is carried between the first unit and the second unit. The first units and the second unit are arranged side by side in a plan view, and at least one of the plurality of the first units is a processing unit for performing processing for the substrate. The plurality of first units are arranged in a line in the horizontal direction, and at least two first units adjacent to each other in the horizontal direction of the plurality of first units are movable in the horizontal direction to be able to transfer the substrate to / from the second unit. According to the present invention, the substrate processing system including a plurality of units flexibly deals with various substrate processing recipes and reduces the processing time difference among substrates and the carriage waiting time of the substrate.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
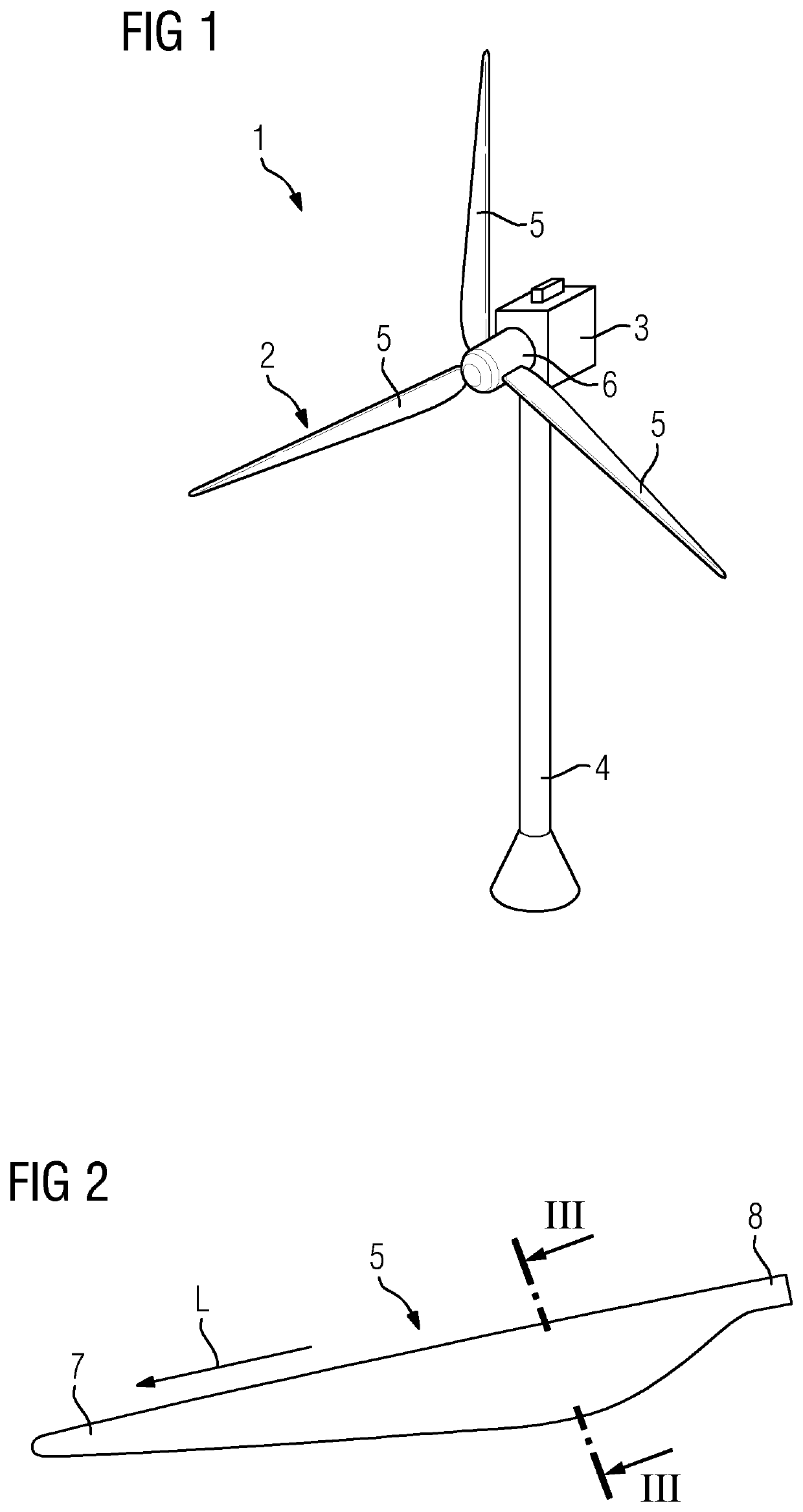
Vacuum assisted resin transfer molding method, a pressure applying device and a mold arrangement
PendingUS20200198264A1Quality of electrical connectionMinimize changesMachines/enginesDomestic articlesFiberElectrical conductor
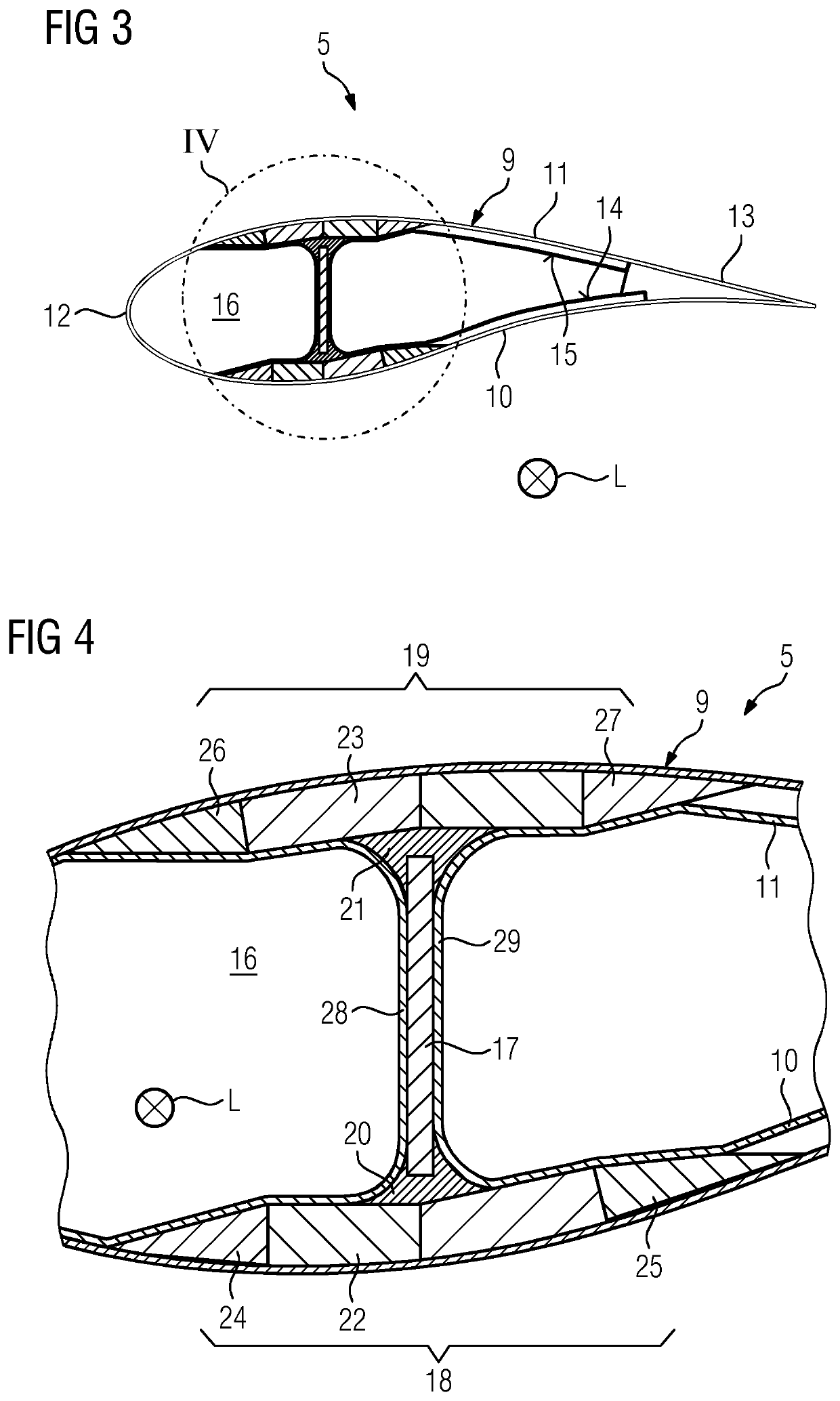
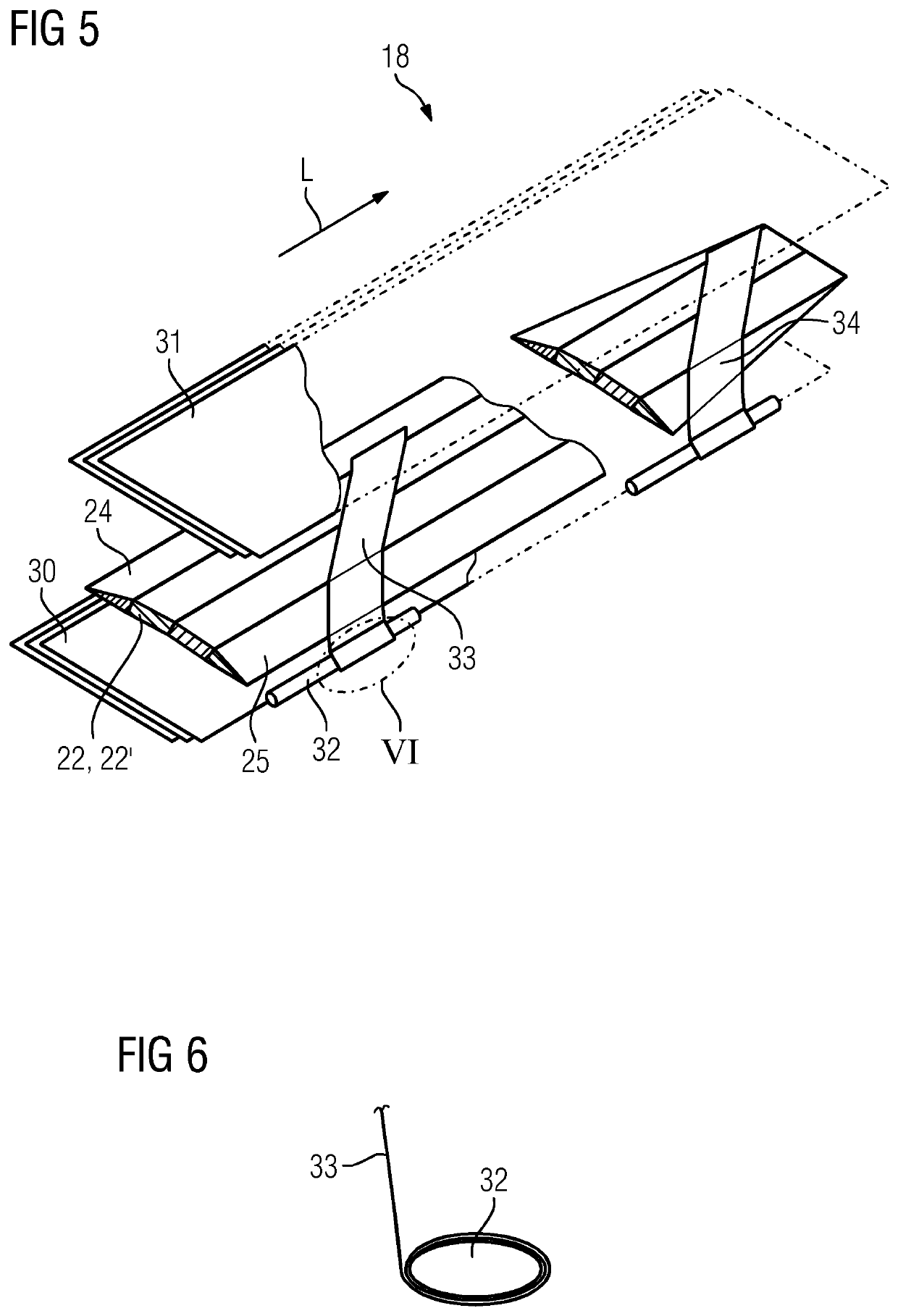
Provided is a vacuum assisted resin transfer molding method for producing a component, in particular a spar cap, of a rotor blade including a lightning protection system, wherein the vacuum assisted resin transfer molding method includes the steps of: a) placing) an electrically conductive beam fiber material of an electrically conductive beam, an electrically conductive fiber mat and an electrical conductor of the component in a mold arrangement electrically connecting the electrically conductive beam fiber material to the electrical conductor by means of the electrically conductive fiber mat, wherein an electrical connection between the electrical conductor and the electrically conductive fiber mat is generated, c) subjecting the mold arrangement to underpressure, d) applying an external pressure on the electrical connection from outside the mold arrangement, e) injecting resin into the underpressurized mold arrangement, and f) applying heat to the mold arrangement for curing the resin.
Owner:SIEMENS GAMESA RENEWABLE ENERGY AS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com