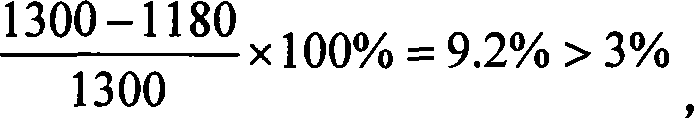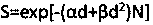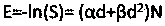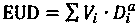Patents
Literature
54 results about "Biological modeling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In the sense of a mathematical model, a biological model can be constructed to gain a deeper understanding of an organism, an ecosystem, a genetic lineage, or a wide variety of other topics in biology. Using mathematics, people can set up and test a model.
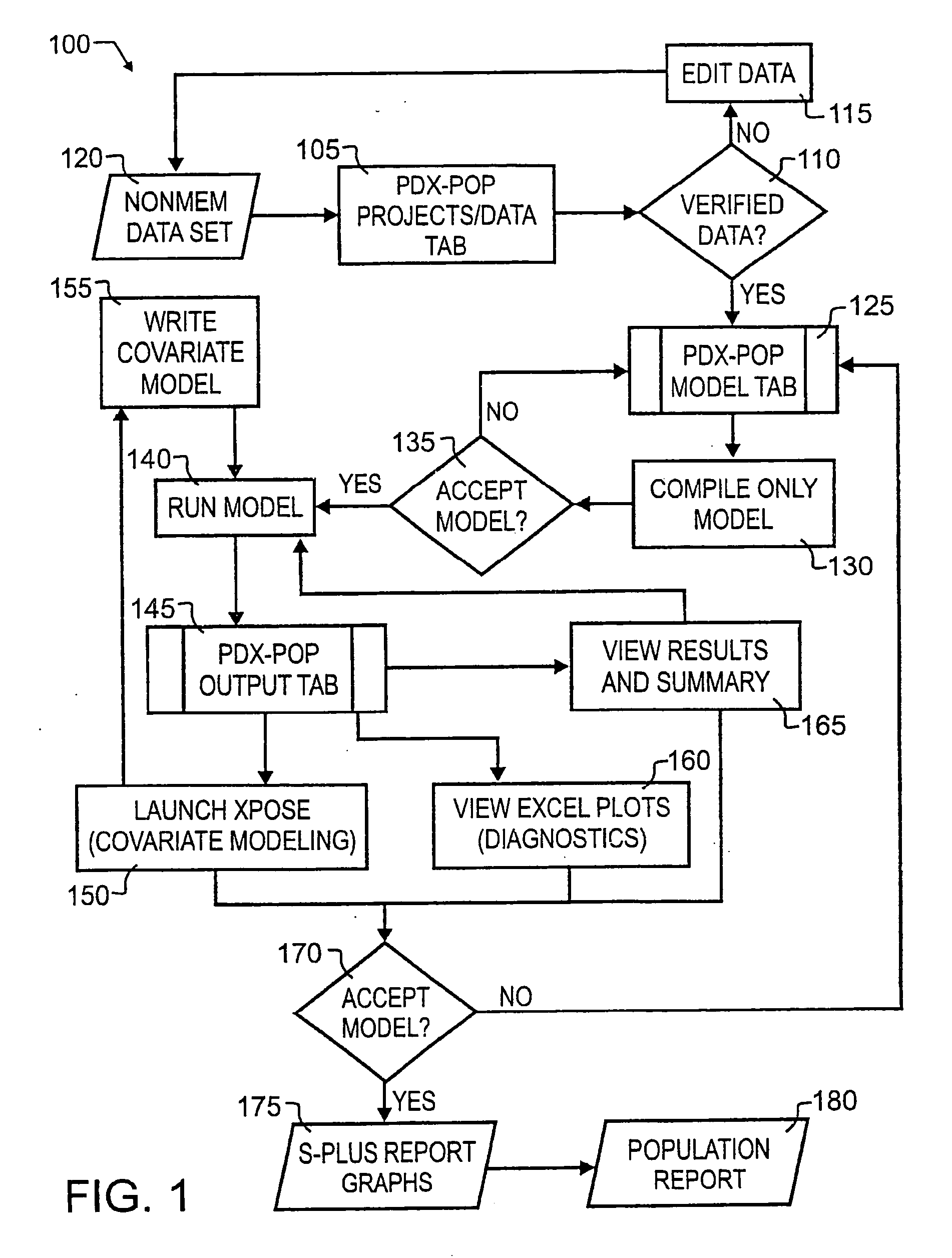
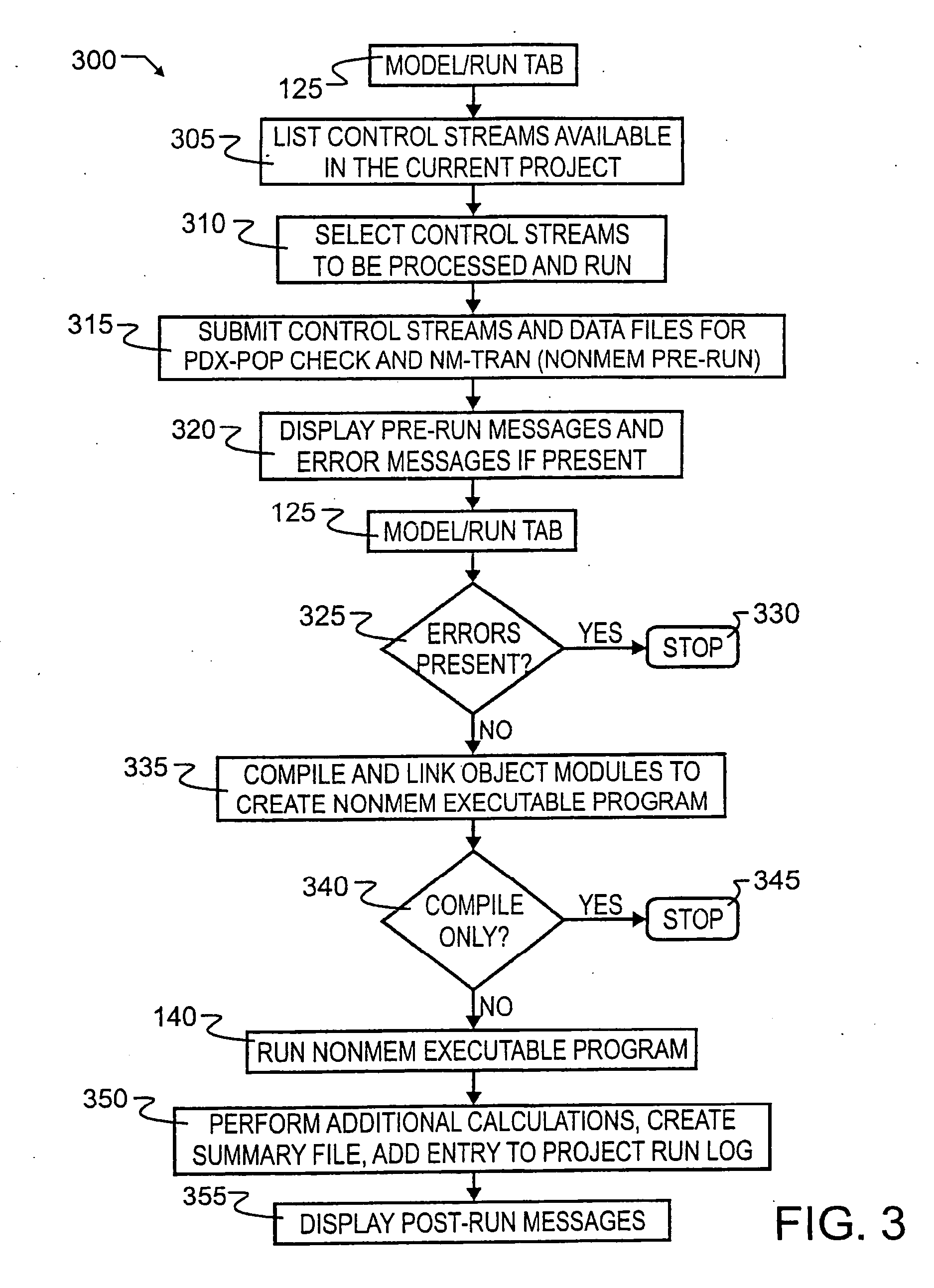
Population pharmacokinetic modeling and analysis (PDX-POP(TM))
InactiveUS20060161408A1Improve experienceUpgrade visualization and reportingChemical property predictionAnalogue computers for chemical processesData setDisplay device
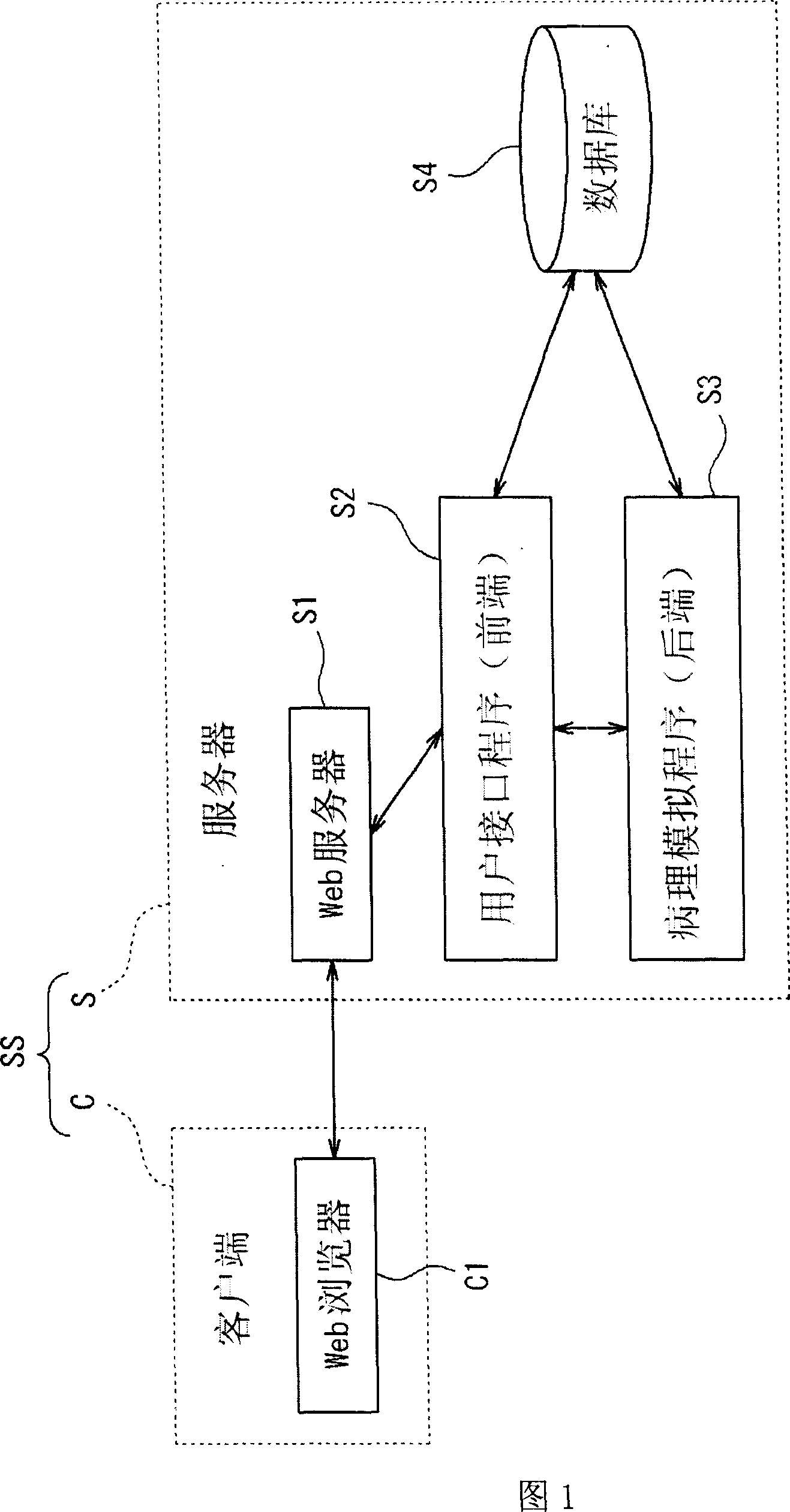
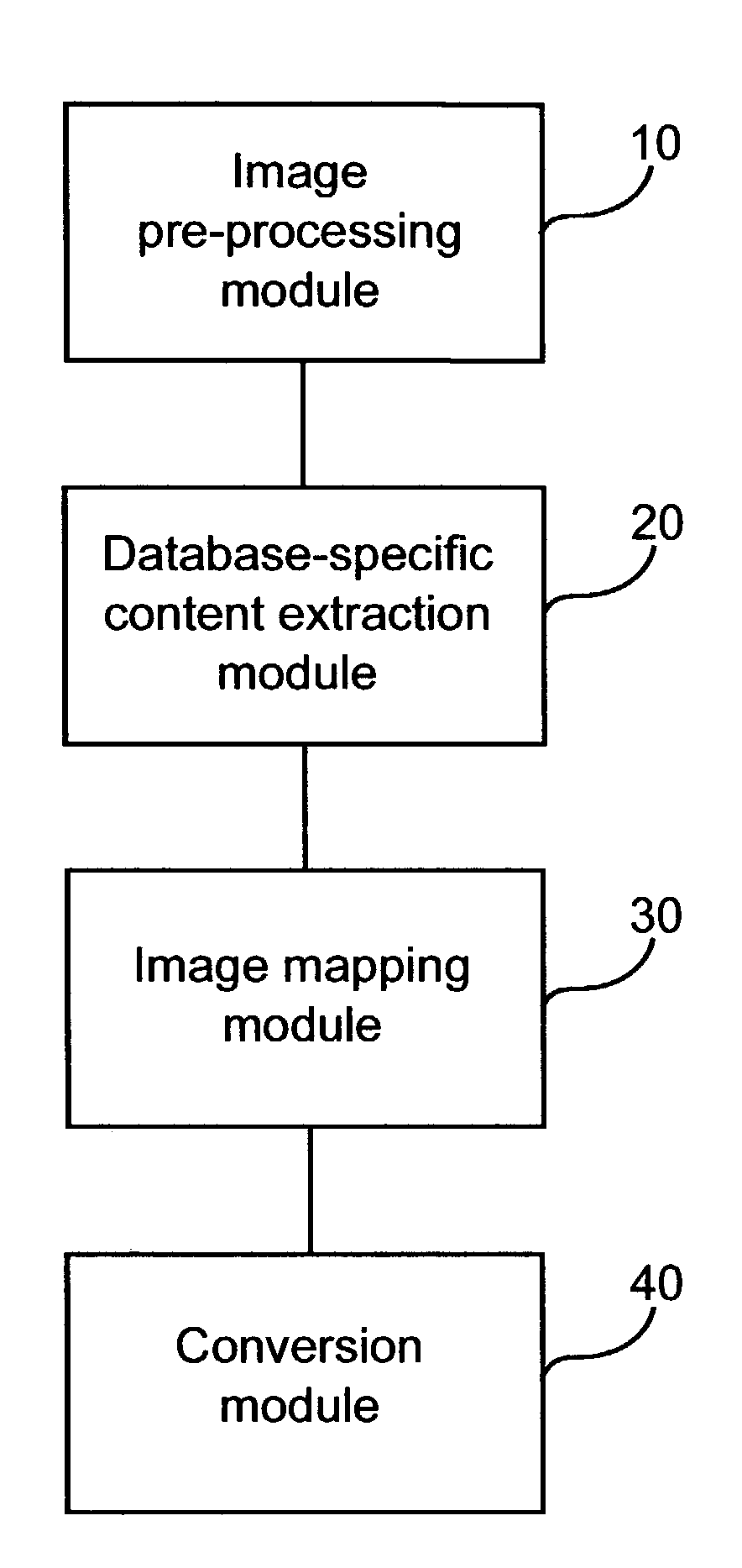
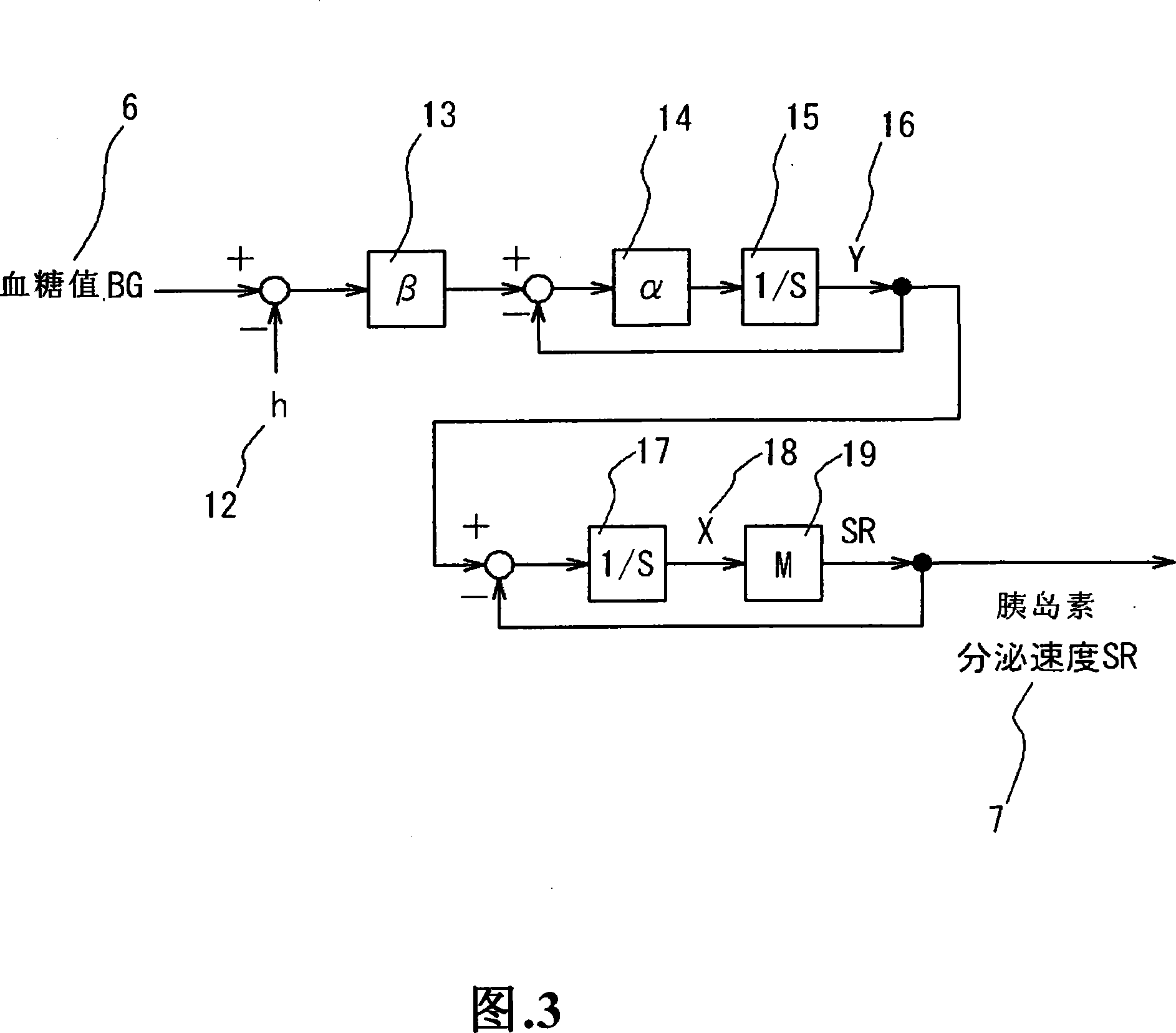
A biological modeling system and method for enhanced computer-aided analysis of biological response data provides information synthesized from multiple sources. An executable model of a biological system is developed from information and structures based on multiple sources. In a preferred embodiment, biological data sets are selected by a user from a first active viewer window on a user computer display. A model is created and then run using integrated pharmacokinetic software. The output is next analyzed using integrated analysis tools. Once analyzed, the model is balanced to ensure that it matches the information and structures. Once the model is created, run, and balanced, it can be used to draw attention to important relations through integrated reporting functions. This program could be run with such programs as NONMEM®.
Owner:BACHMAN WILLIAM J +3
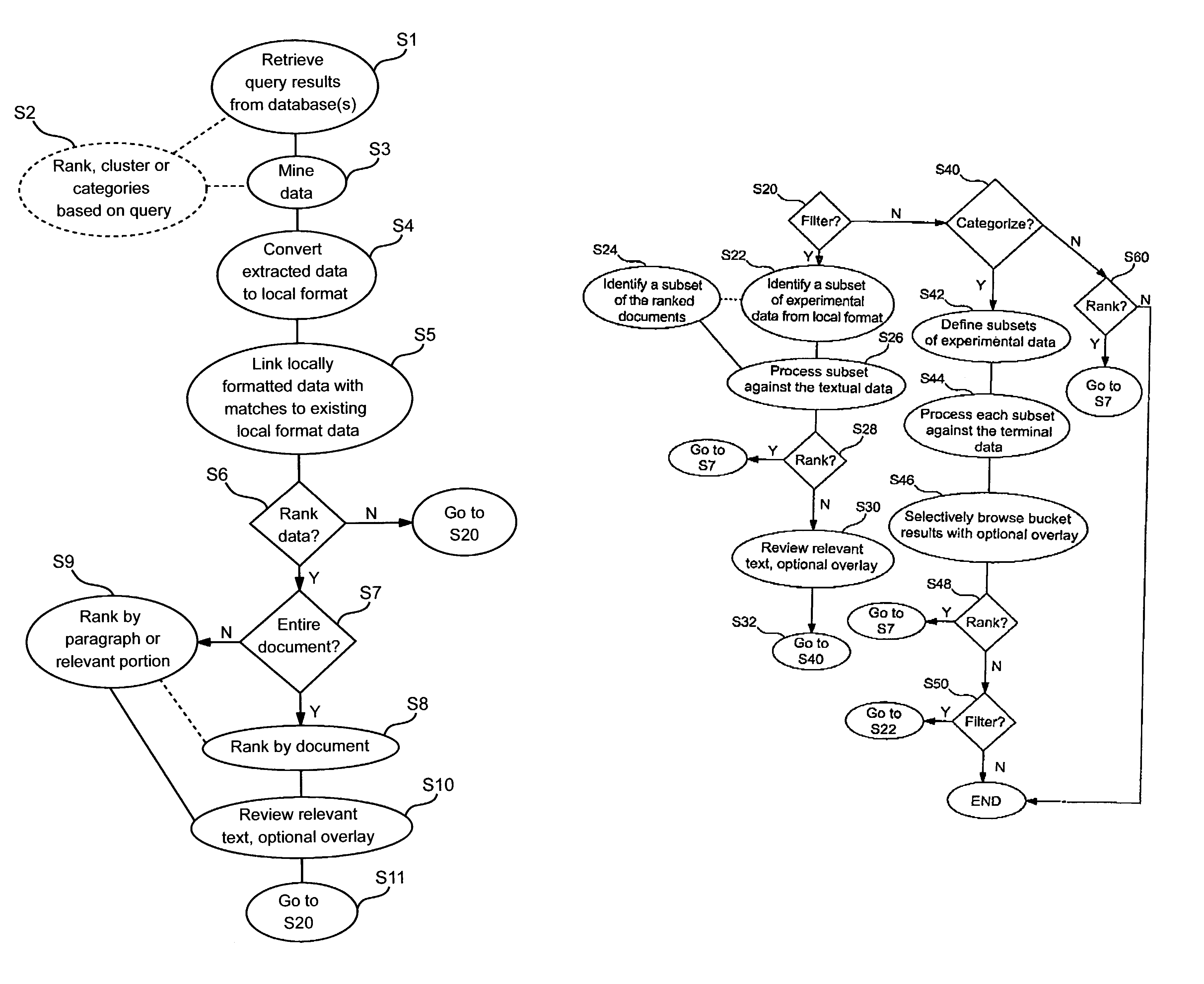
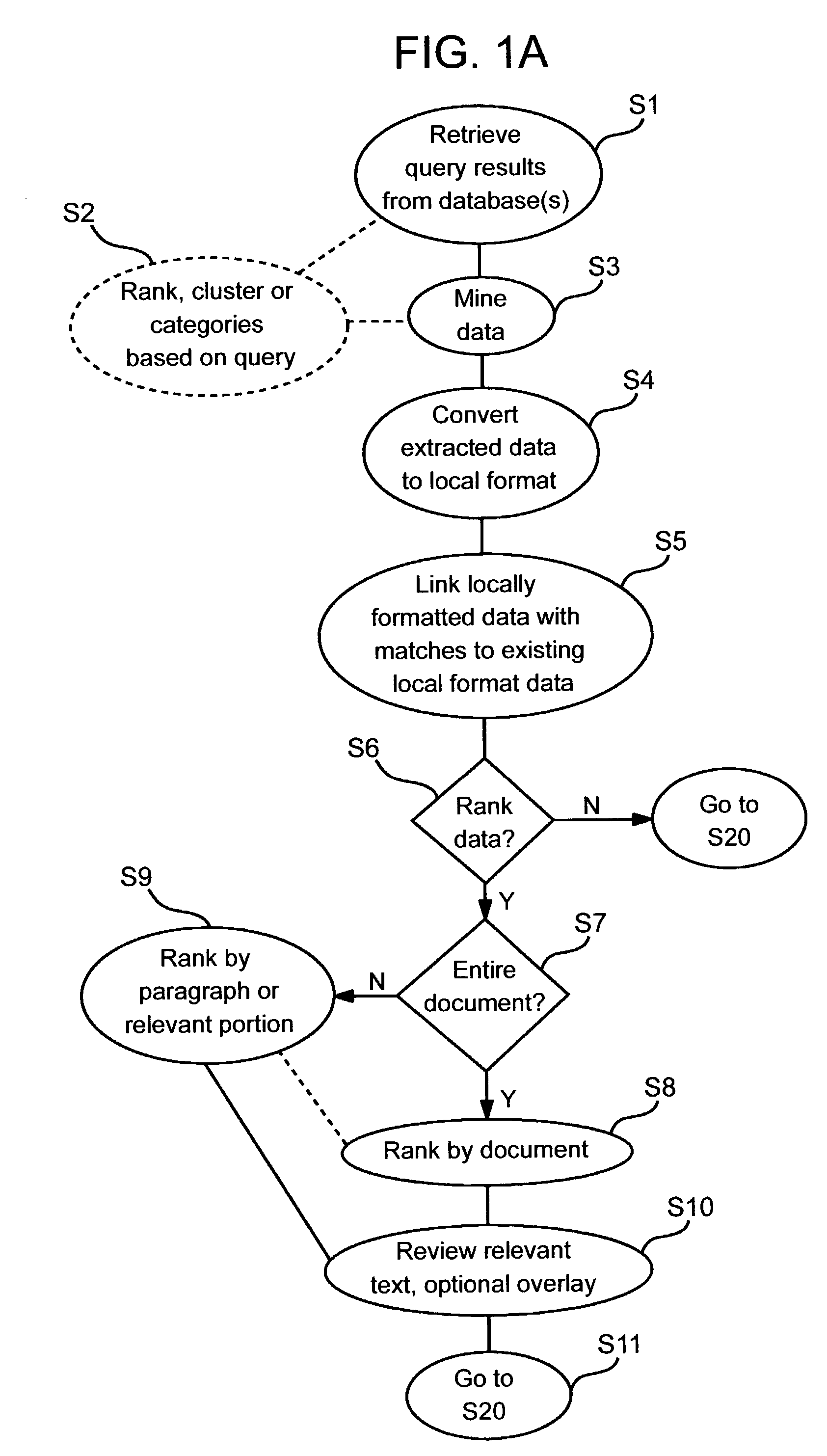
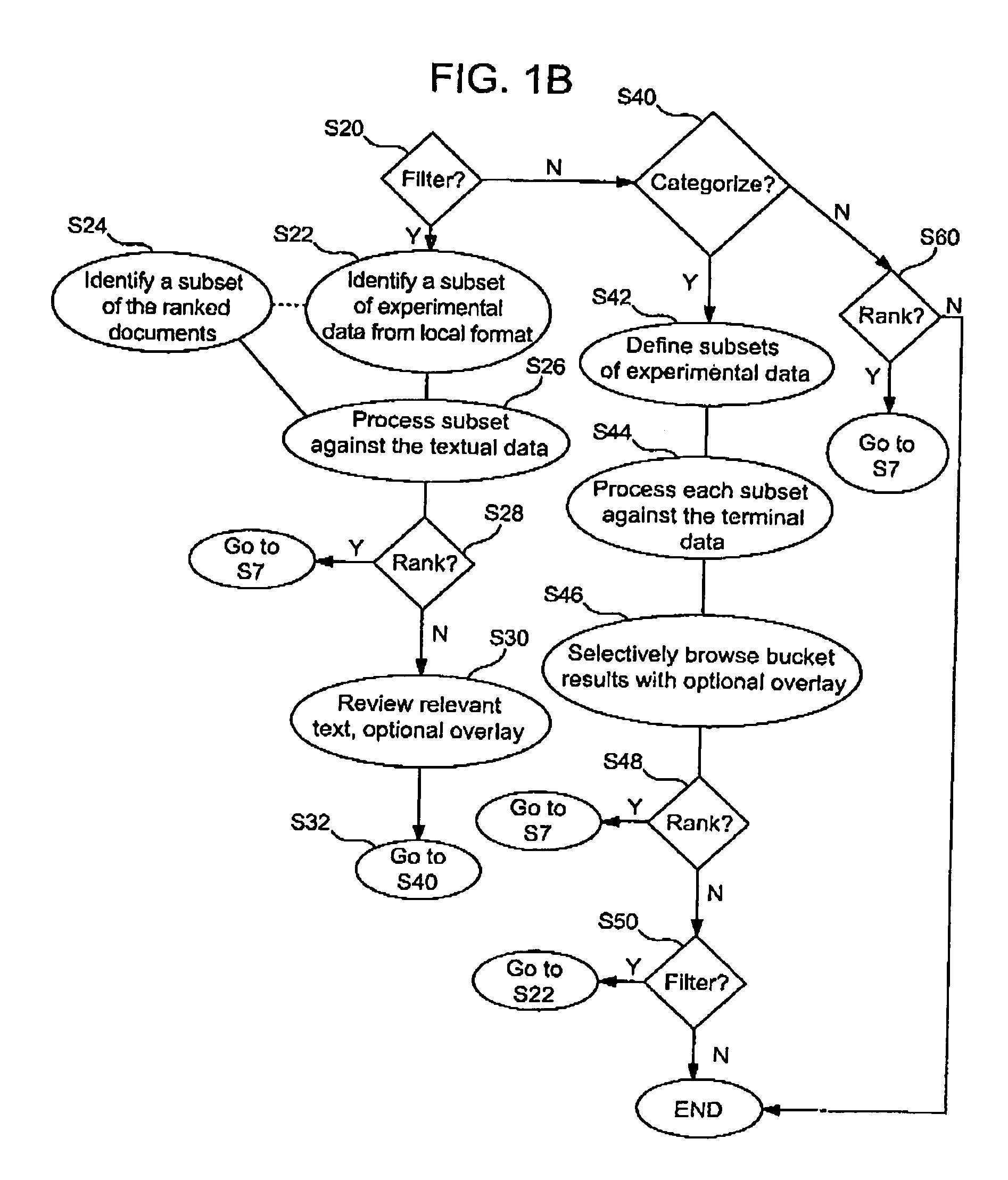
System, tools and methods to facilitate identification and organization of new information based on context of user's existing information
InactiveUS7058643B2Easy to compareData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalBiological modelingData science
A user's context can be captured in terms of experimental results and other locally collected data. The use of extracted links between imported scientific text, biological models or experimental data, and proprietary or public data to provide relevance ranking, filtering, and categorization of imported scientific text or biological models, based upon their linking with the local data is described.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC +1
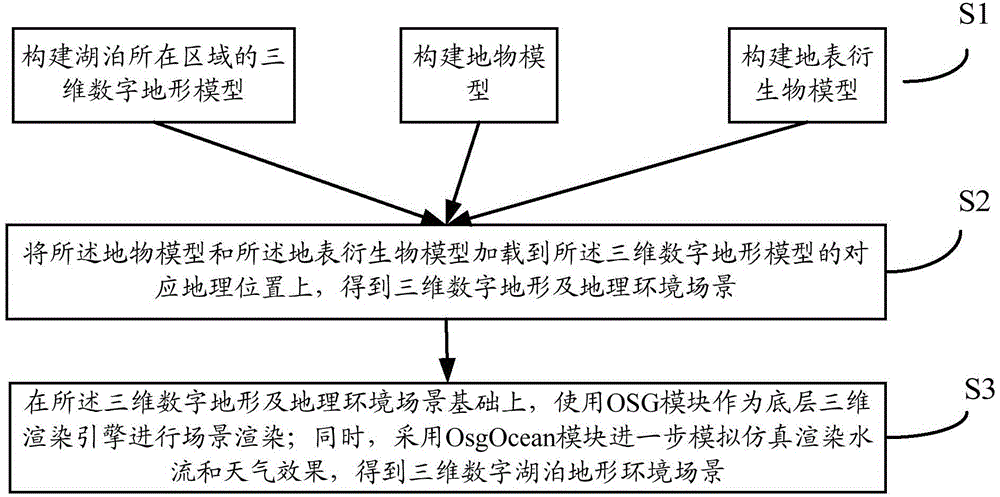
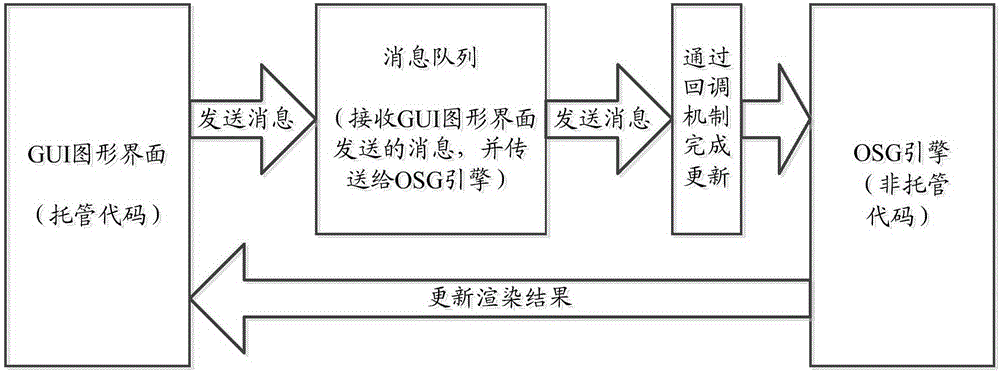
Digital lake three-dimensional visualized simulation method and simulation platform based on OSG
InactiveCN103559739AThe need for realistic simulationMeet the needs of 3D visualization simulationSpecial data processing applicationsICT adaptationTerrainGeographic site
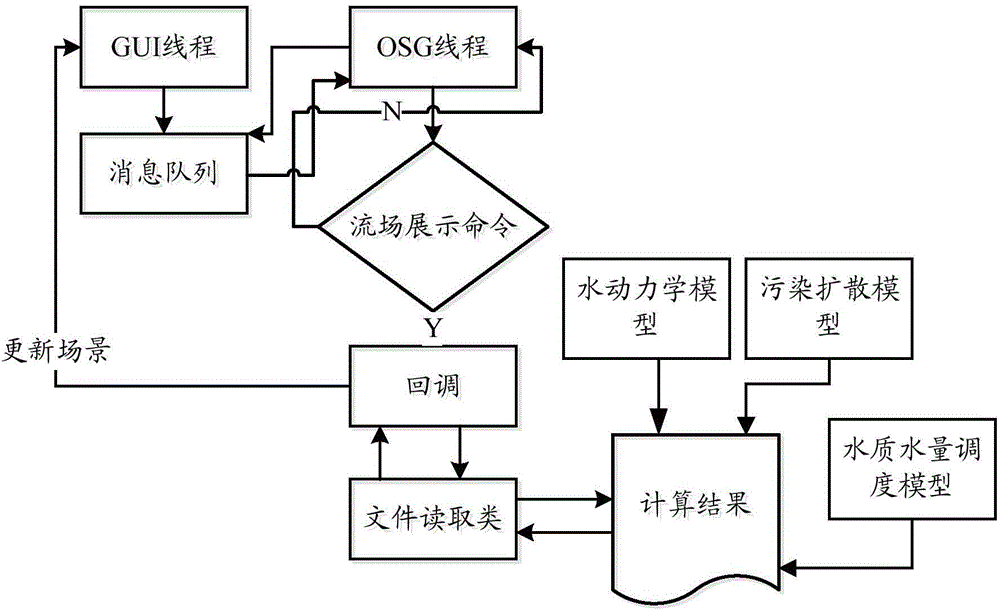
The invention provides a digital lake three-dimensional visualized simulation method and simulation platform based on an OSG. The digital lake three-dimensional visualized simulation method includes the following steps that a three-dimensional digital terrain model, a ground feature model and an earth surface derivative model of the region where a lake is located are built; the ground feature model and the earth surface derivative model are loaded to the corresponding geographical positions of the three-dimensional digital terrain model to obtain a three-dimensional digital terrain and geographical environment scene; based on the three-dimensional digital terrain and geographical environment scene, an OSD module is used as a bottom layer three-dimensional rendering engine for scene rendering; meanwhile, an OsgOcean module is utilized to further simulate a simulation rendering water current and weather effect to obtain a three-dimensional digital lake terrain environment scene; a water current scene and a weather effect scene obtained through simulation are updated under the control of a man-machine interaction mechanism. The digital lake three-dimensional visualized simulation method and simulation platform have the advantages of being convenient to operate, easy to expand, efficient, and capable of achieving real-time performance and meeting the requirement for wide-range terrain and mass spatial data three-dimensional visualized simulation.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
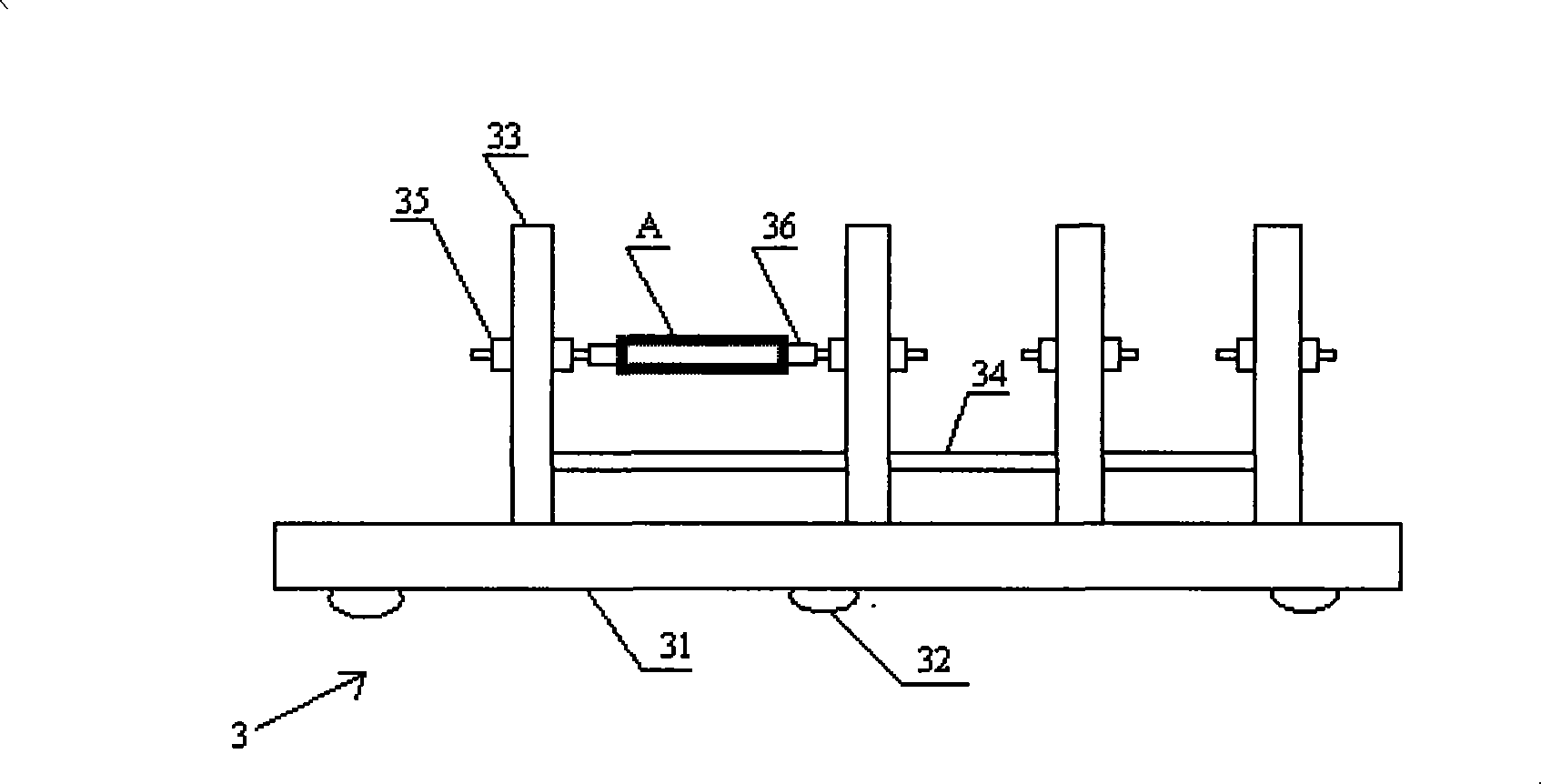
Weave type artificial blood vessel fatigue performance bionic test device and its test method
InactiveCN101105435AAdd test functionSolve the technical problem of lack of full simulationMaterial strength using repeated/pulsating forcesSpecific gravity measurementPeristaltic pumpOutput device
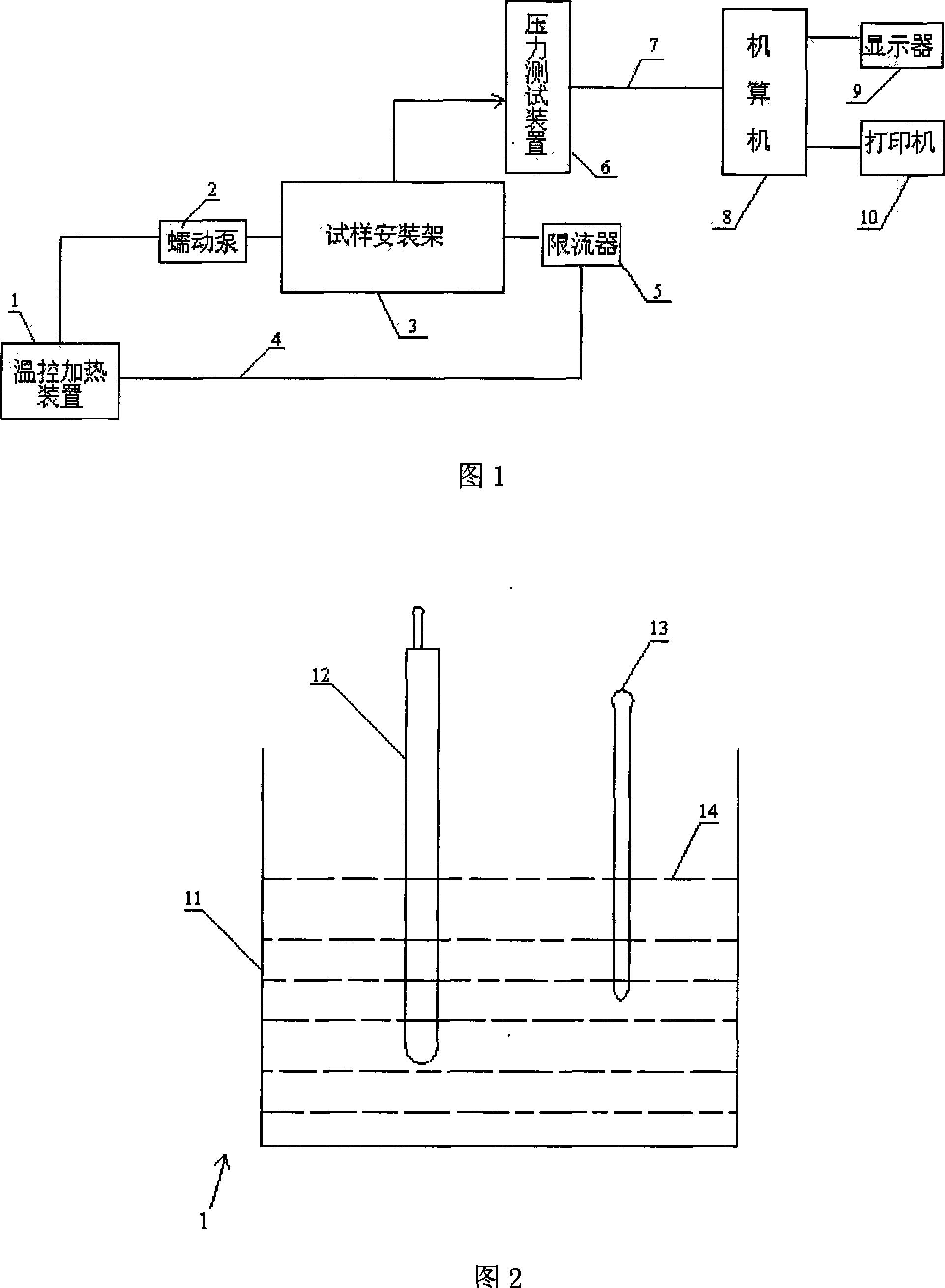
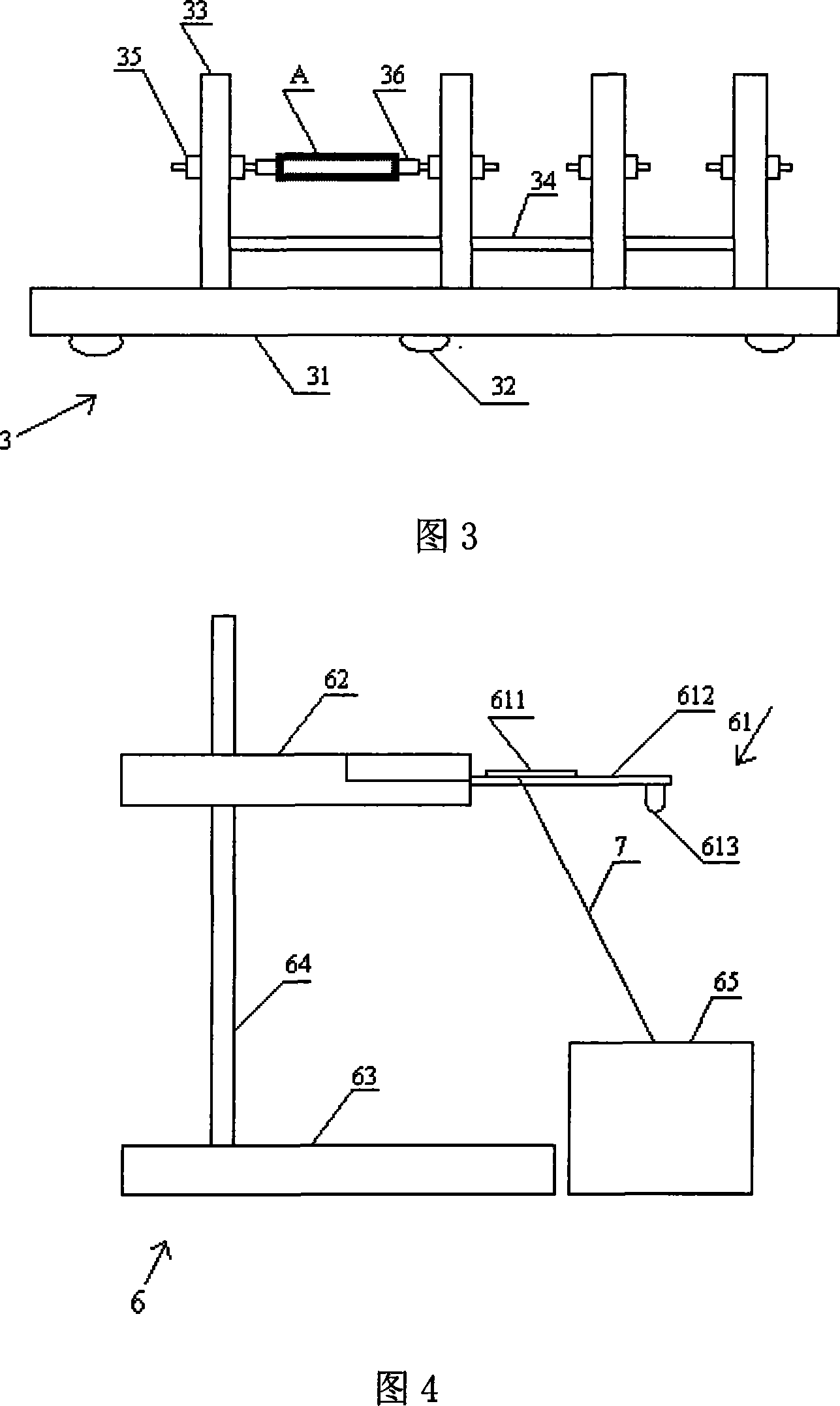
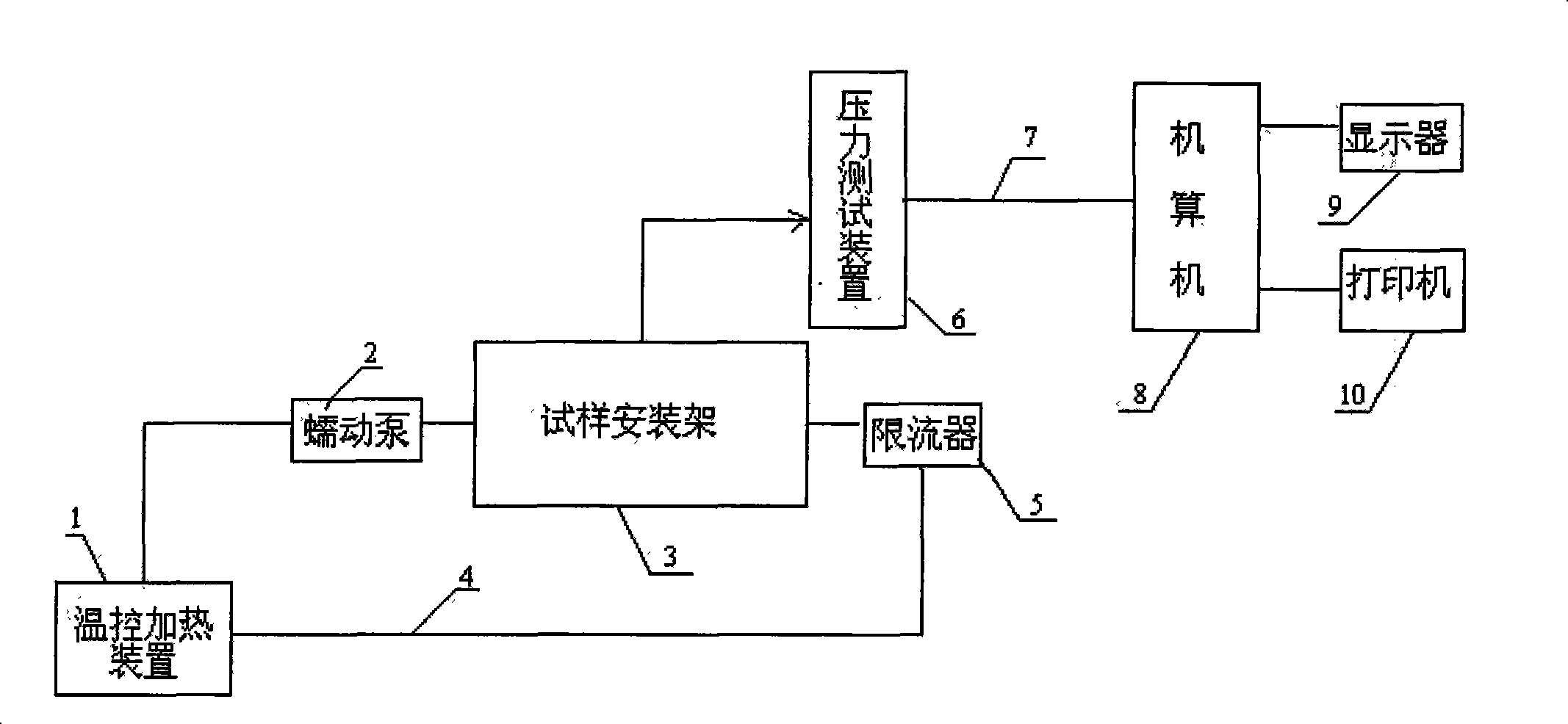
The invention relates to a spinning type artificial blood vessel weary performance biological modeling testing device and the testing method thereof. The invention comprises an electronic peristaltic pump, a fluid restrictor, a computer arranged with signal processing and transforming software and data output equipment. The invention is characterized in that the device also comprises a temperature controlling and heating device, a test sample installation frame and a pressure testing device. The testing steps are: 1. preheat testing machine; 2. test system; 3. choose the specimen of the spinning type artificial blood vessel; 4. adjust the pressure testing device; 5. control water temperature; 6. start the electronic peristaltic pump; 7. test and record; 8. evaluate the weary-resistant performance of the spinning type artificial blood vessel. The weary-resistant performance of the spinning type artificial blood vessel can be scientifically tested and appreciated by the device and the testing method disclosed by the device. And the invention solved the technical problem that the prior testing device and the testing method of the prior device have no safe simulation.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
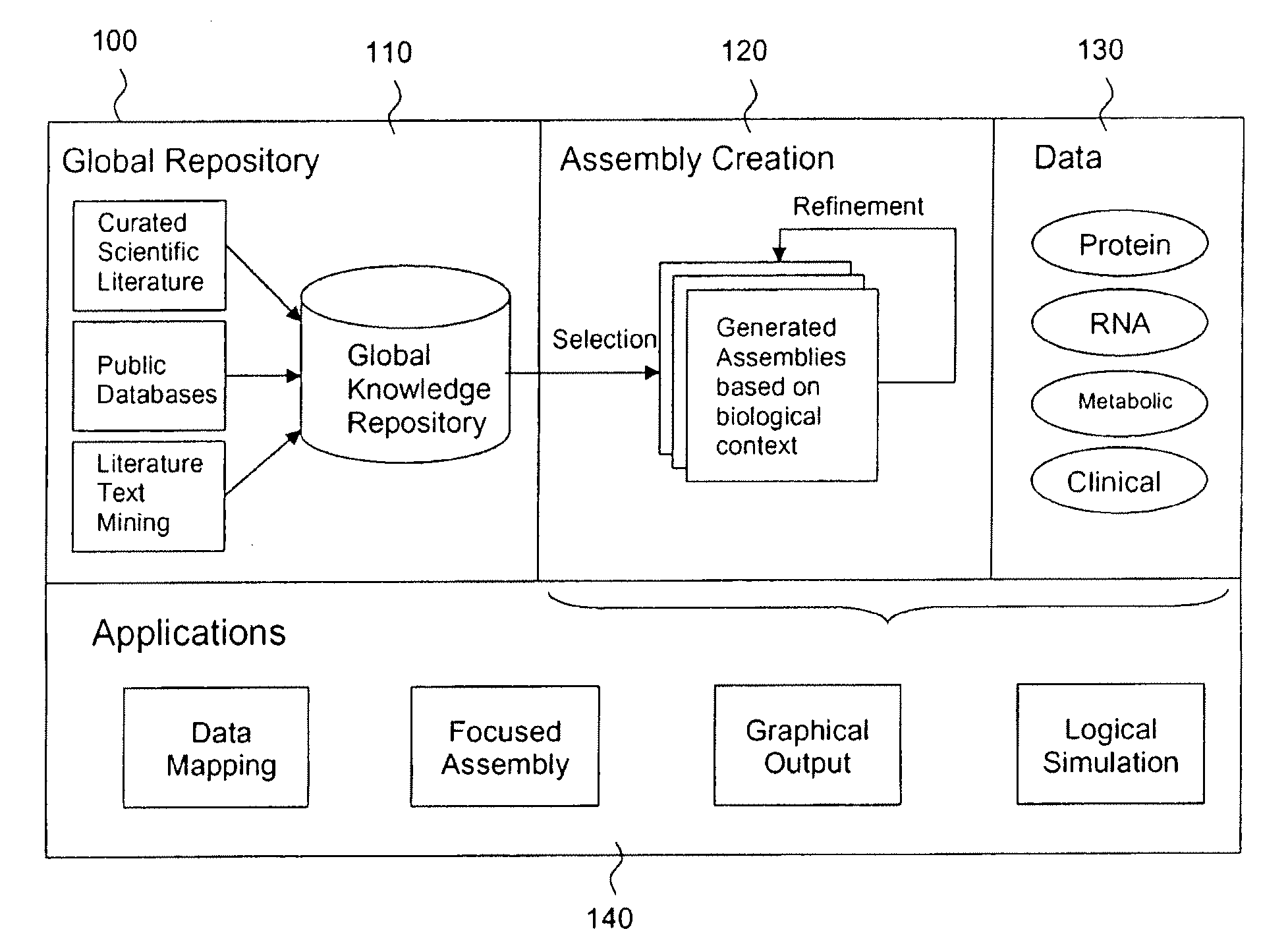
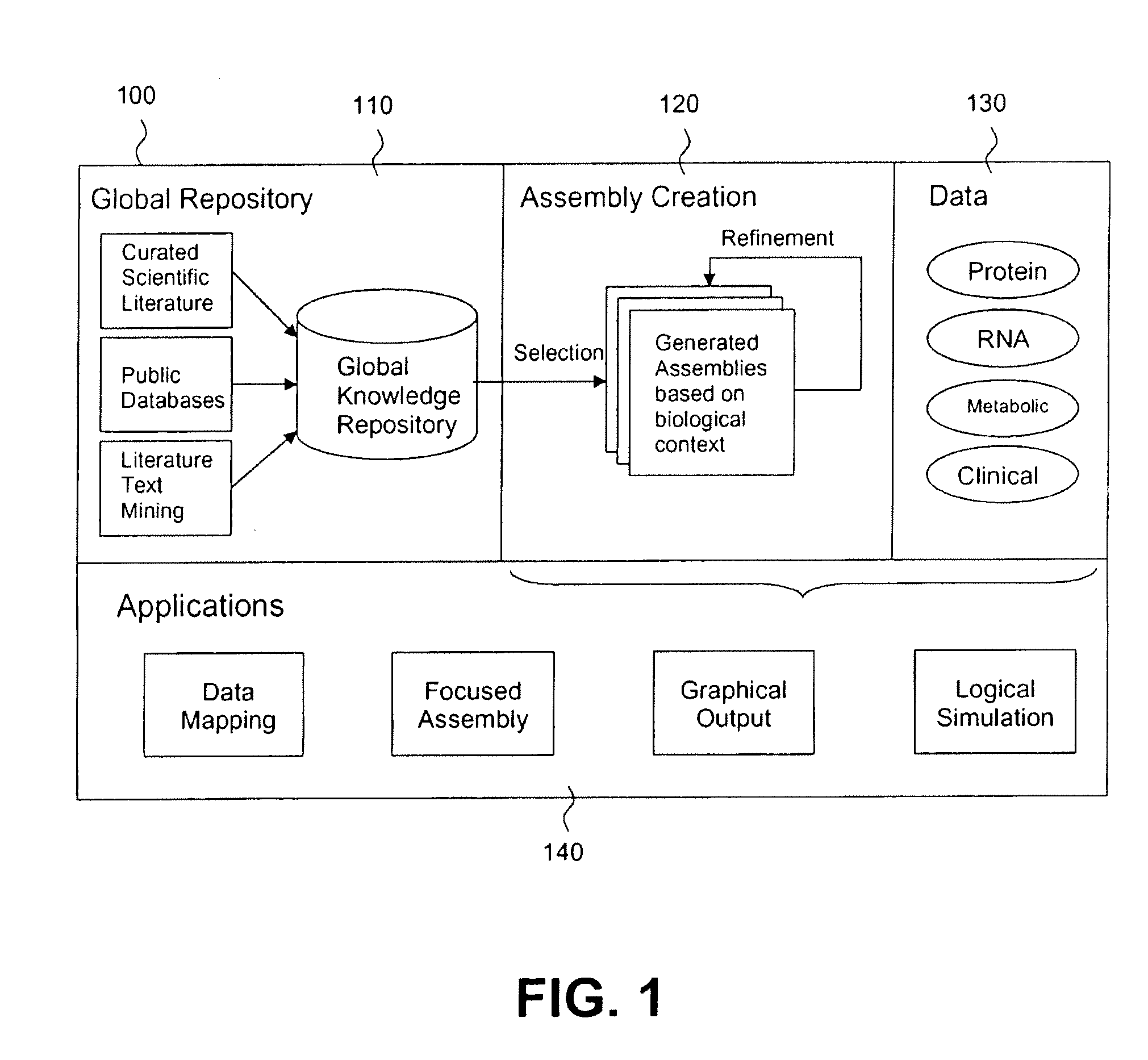
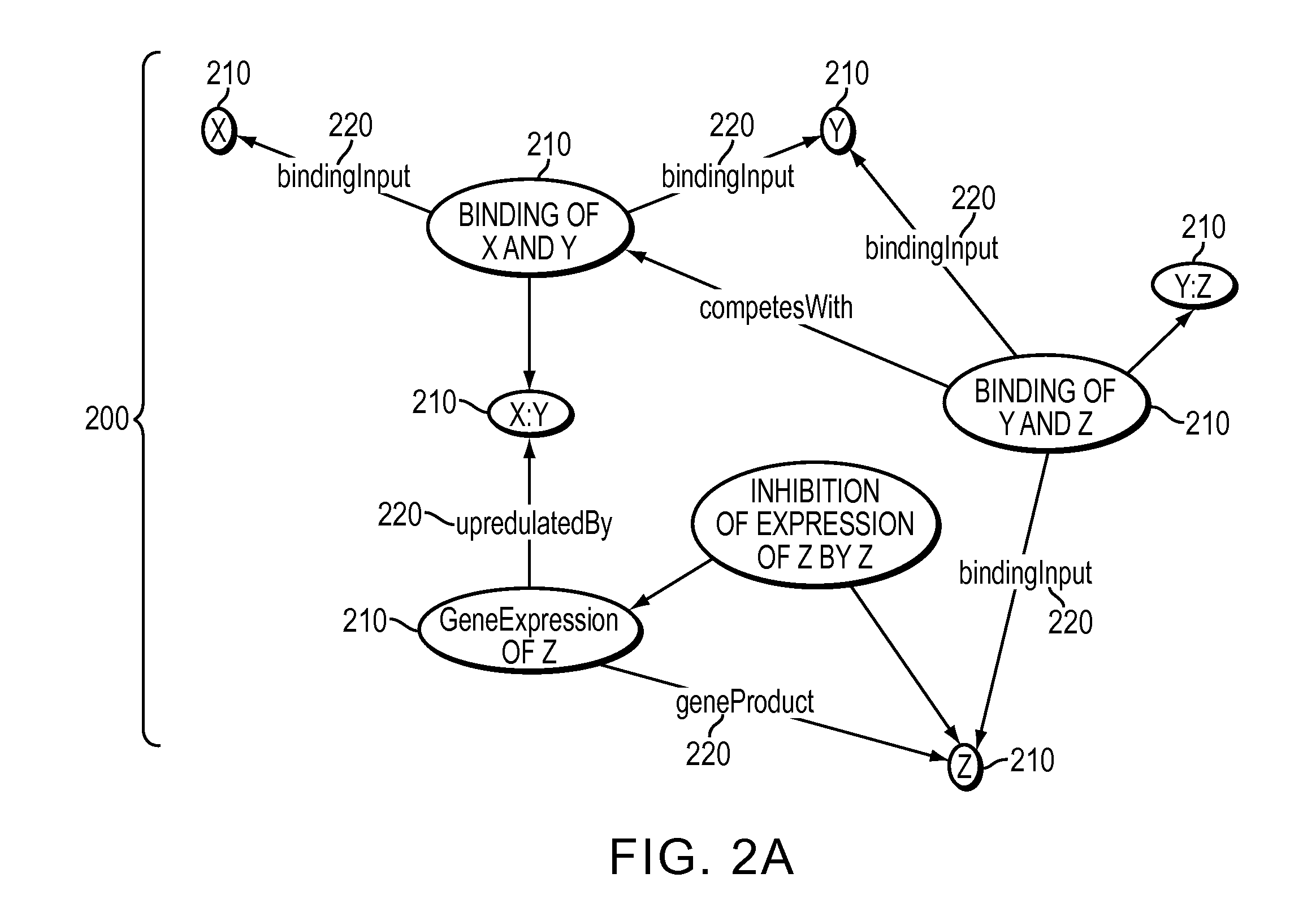
Method, system and apparatus for assembling and using biological knowledge
InactiveUS20090313189A1Efficient modelingFacilitate understanding and revelationDigital computer detailsBiological testingProduction rateBiological modeling
Disclosed are methods, systems and apparatus for constructing assemblies of biological knowledge constituting a biological knowledge base, and for subsetting and transforming life sciences-related data and information into biological models to facilitate computation and electronic reasoning on biological information. A subset of data is extracted from a global knowledge base or repository to reconstruct a more specialized sub-knowledge base or assembly designed specifically for the purpose at hand. Assemblies generated by the invention permit selection and rational organization of seemingly diverse data into a model of any selected biological system, as defined by any desired biological criteria. These assemblies can be mined easily and can be logically reasoned with great productivity and efficiency.
Owner:GENSTRUCT
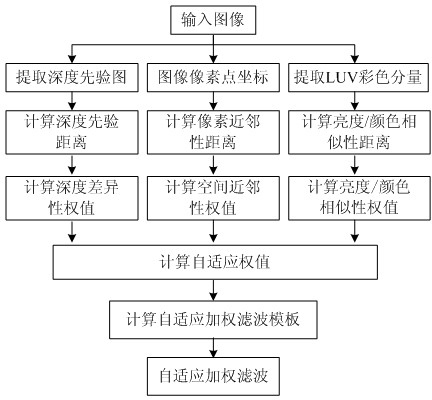
Edge-preserving self-adaptive weighted filtering method for natural scene images
The invention relates to an edge-preserving self-adaptive weighted filtering method for natural scene images. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, calculating a Gaussian template according to the standard deviation of a Gaussian filter, obtaining depth clues in an original image by adopting a dark channel transcendental method, and carrying out normalization to form a depth transcendental image; secondly, calculating a spacial adjacent weight of each coordinate point on the Gaussian template, and calculating the luminance / color similarity weights of two pixels on the original image; calculating the depth difference weight between the two pixels on the original image, and calculating a self-adaptive weighted filtering template of the center of the template corresponding to the pixels; and finally, calculating a self-adaptive weighted filtering result of each pixel in the original image. The method takes into consideration on the characteristic that the sensitivities of eyes to luminance difference and color difference are different during the calculation of the luminance / color similarity weights, so that the method is applicable to biological models.
Owner:SERVICE CENT OF COMMLIZATION OF RES FINDINGS HAIAN COUNTY
Biological model of steroids hormone pollutant in foods and feeds established by utilizing Caenorhadits elegans and method thereof
InactiveCN101982075AIncreased sensitivityObservation is intuitiveAnimal husbandryPollutantBiological modeling
The invention relates to a biological model of steroids hormone pollutant in foods and feeds established by utilizing Caenorhadits elegans and a method thereof, belonging to the field of a safety detection technique of foods and feeds. The biological model of the steroids hormone pollutant in the foods and the feeds is established by utilizing the Caenorhadits elegans. The method of the invention is characterized in that the Caenorhadits elegans is utilized to establish a biological model of steroids hormone pure products; the Caenorhadits elegans is utilized to establish the biological model of steroids hormone in the foods; and the Caenorhadits elegans is utilized to establish a biological model of steroids hormone in the feeds. The invention has the beneficial effects of important significance of the research of the steroids hormone to influence on human health, and short period, high efficiency, conciseness and convenience of the experiment course, less requirements on instruments, low cost and great application value. Moreover, the period of the Caenorhadits elegans from the first stage of larvae to the stage of oviposition and the generation time are detected to identify the precocity phenomenon of organisms under the influence of the steroids hormone by exposing the steroids hormone of the Caenorhadits elegans in the first stage of the larvae.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Biological modeling articulation structure of human phantom and usage
InactiveCN1728195AAngular displacement real-time testEducational modelsHuman bodyBiological modeling
A bionic joint structure of human body model consists of top arm, bottom arm and two rotation parts. It is featured as actively connecting top arm to bottom arm, rotating top arm around axis line of bottom arm, limiting rotary position by spacing screw and positioning notch, regulation frictional force with sliding block and regulation screw, using connection screw to connect down part with up part of bottom arm to let down part rotate relatively to axis line of bottom arm and using pad and anchoring screw to regulate frictional force and rotation.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
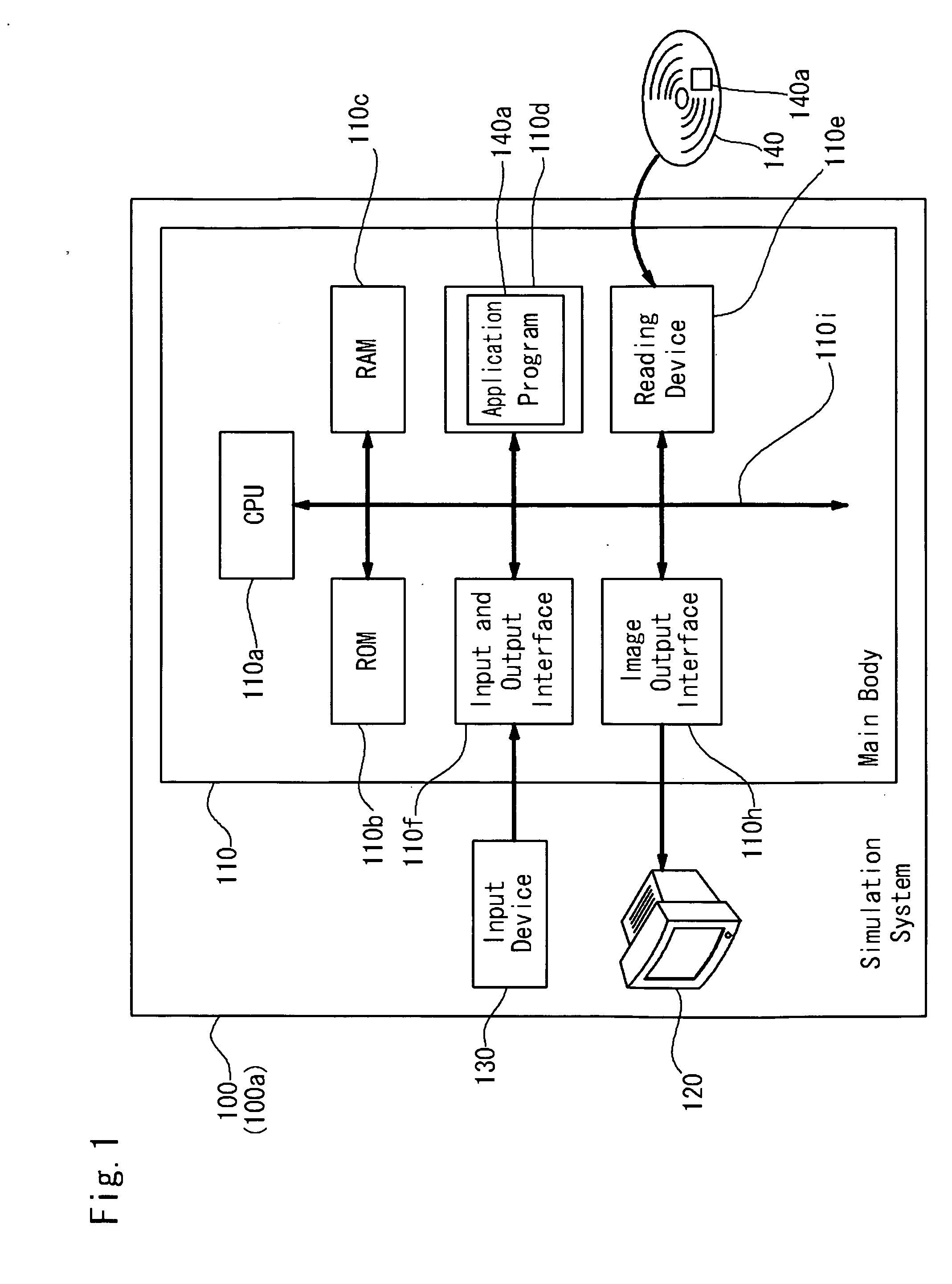
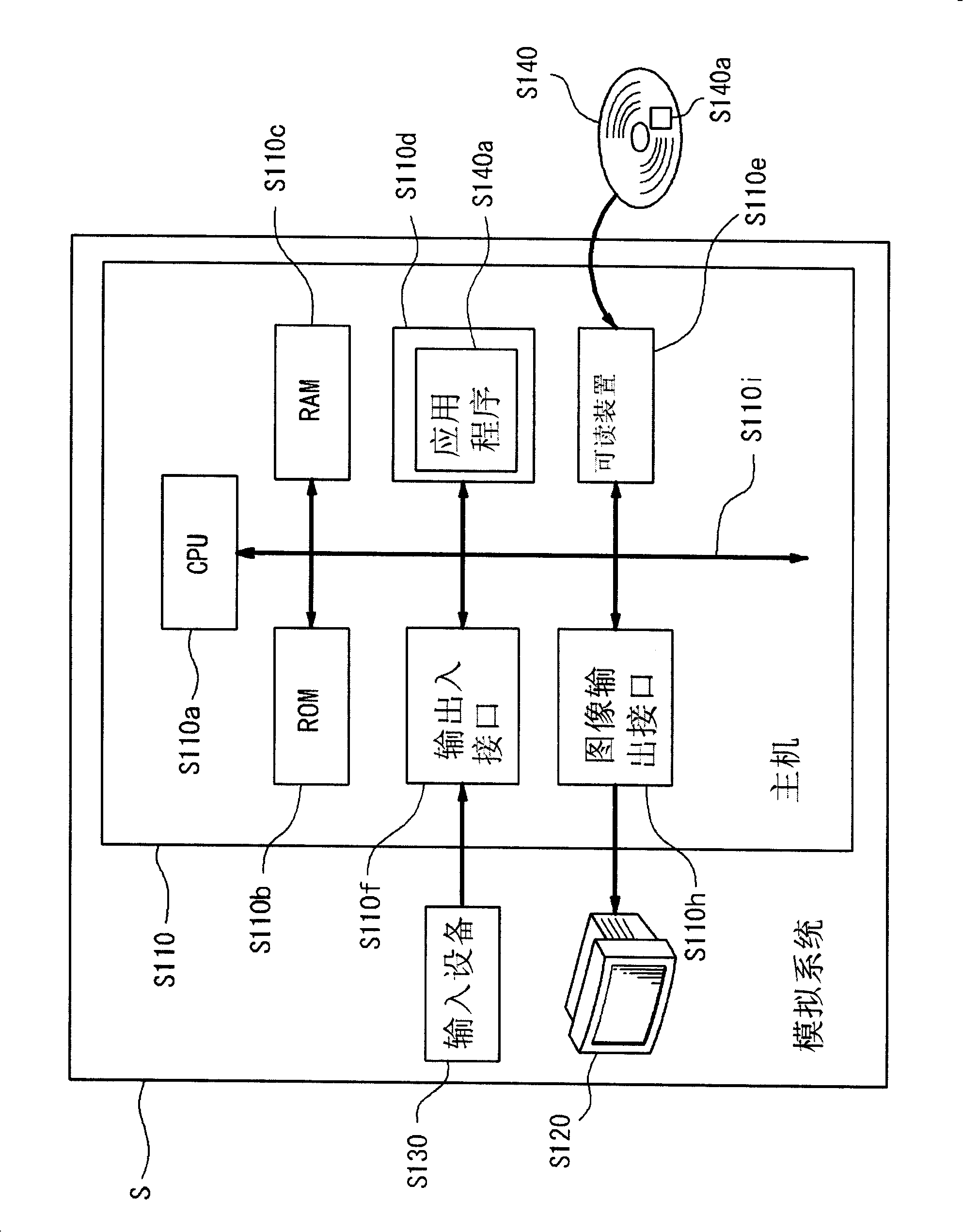
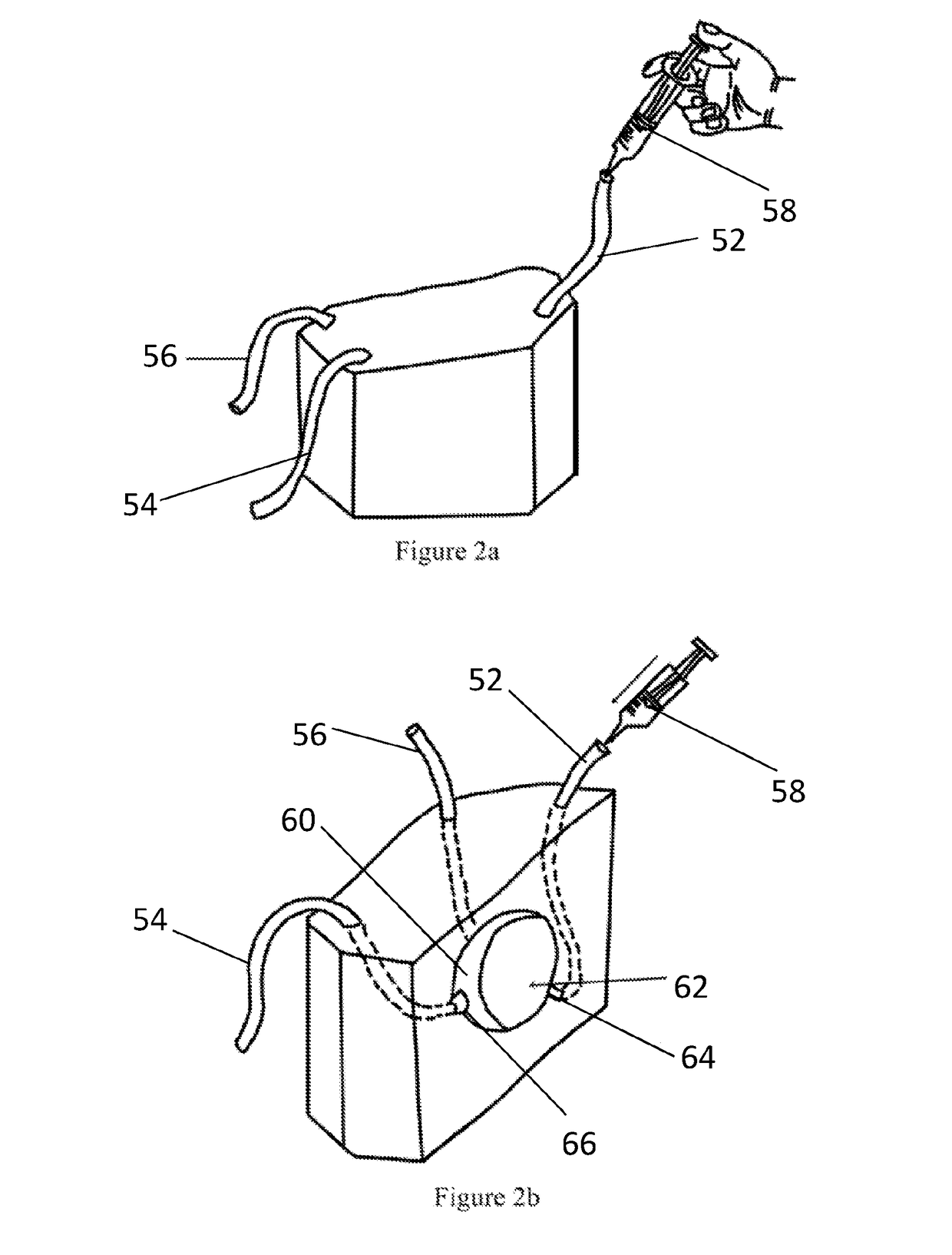
Medical Training Model Device
[Problem] To provide a medical training simulation model having a display enabling training by a simulation model simulating the structure of an organism, and objective and visual recognition of the three-dimensional position of an inserted endoscope, a finger or the like in an organ or tissue.[Means for Solving the Problem] A teaching material model system having a teaching material model for clinical examination inside of an organism has a display screen creating device for creating the internal structure of an organism model formed of a nonmagnetic material by three-dimensional CG on a display screen, a specific signal transmitting device, and a sensor for detecting a signal from the specific signal transmitting device as constituting device, wherein the signal generated by the specific signal transmitting device is detected by the sensor, the signal detected by the sensor is transmitted to create a display screen by the display screen creating device, and the system is provided with a real time display device for displaying the positional situation of the sensor created on the display screen for the internal structure of a teaching material organism model displayed on the display screen by three-dimensional CG.
Owner:KOKEN CO LTD
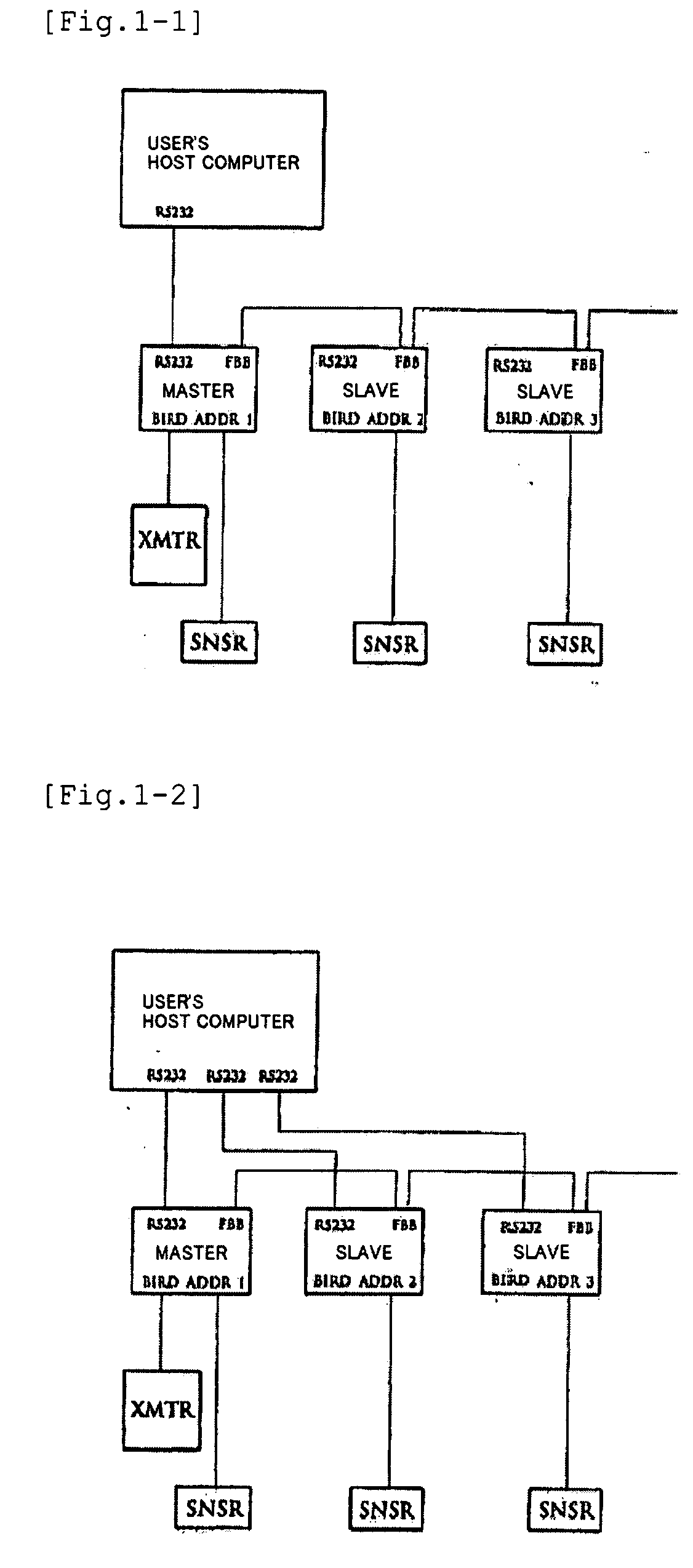
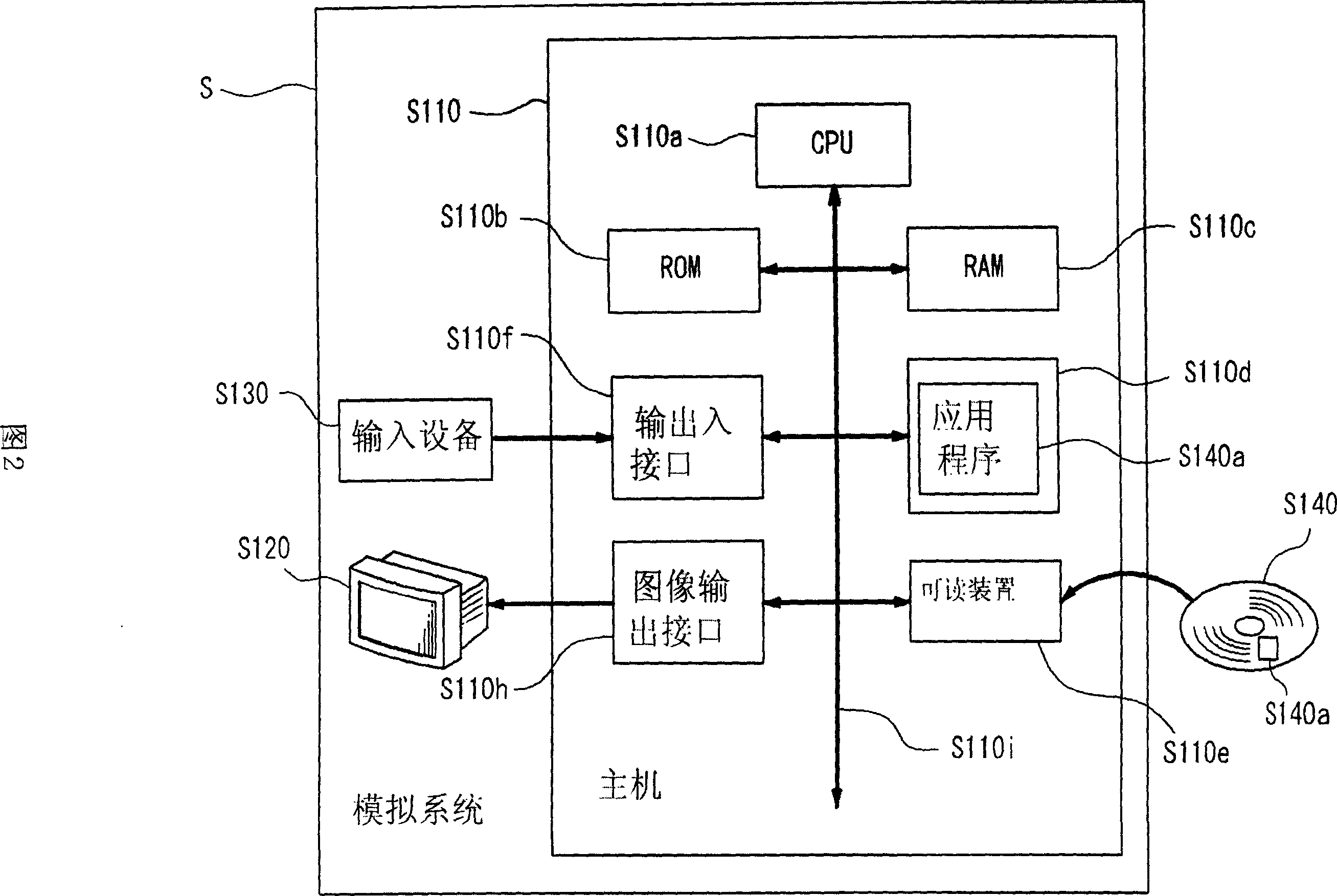
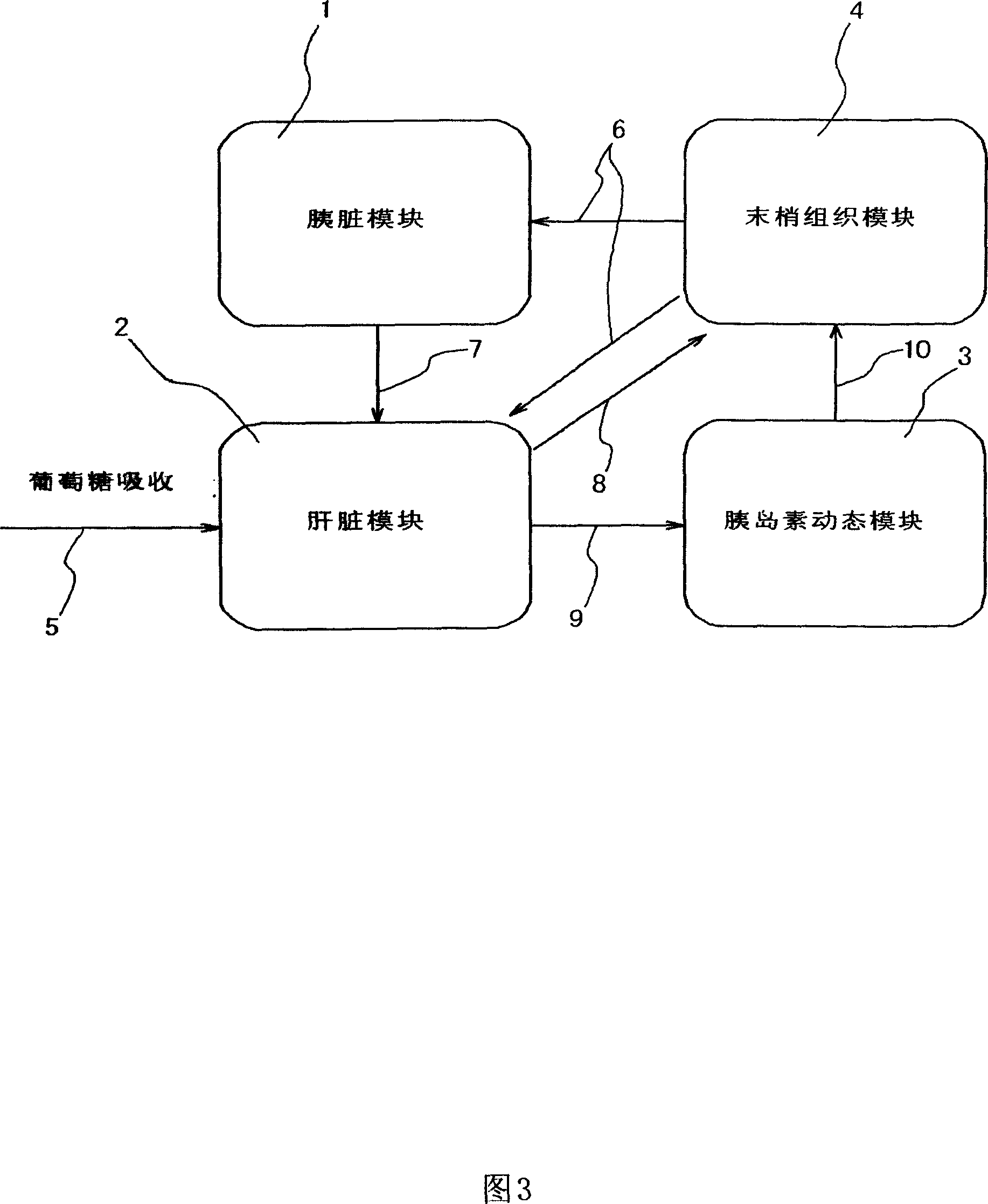
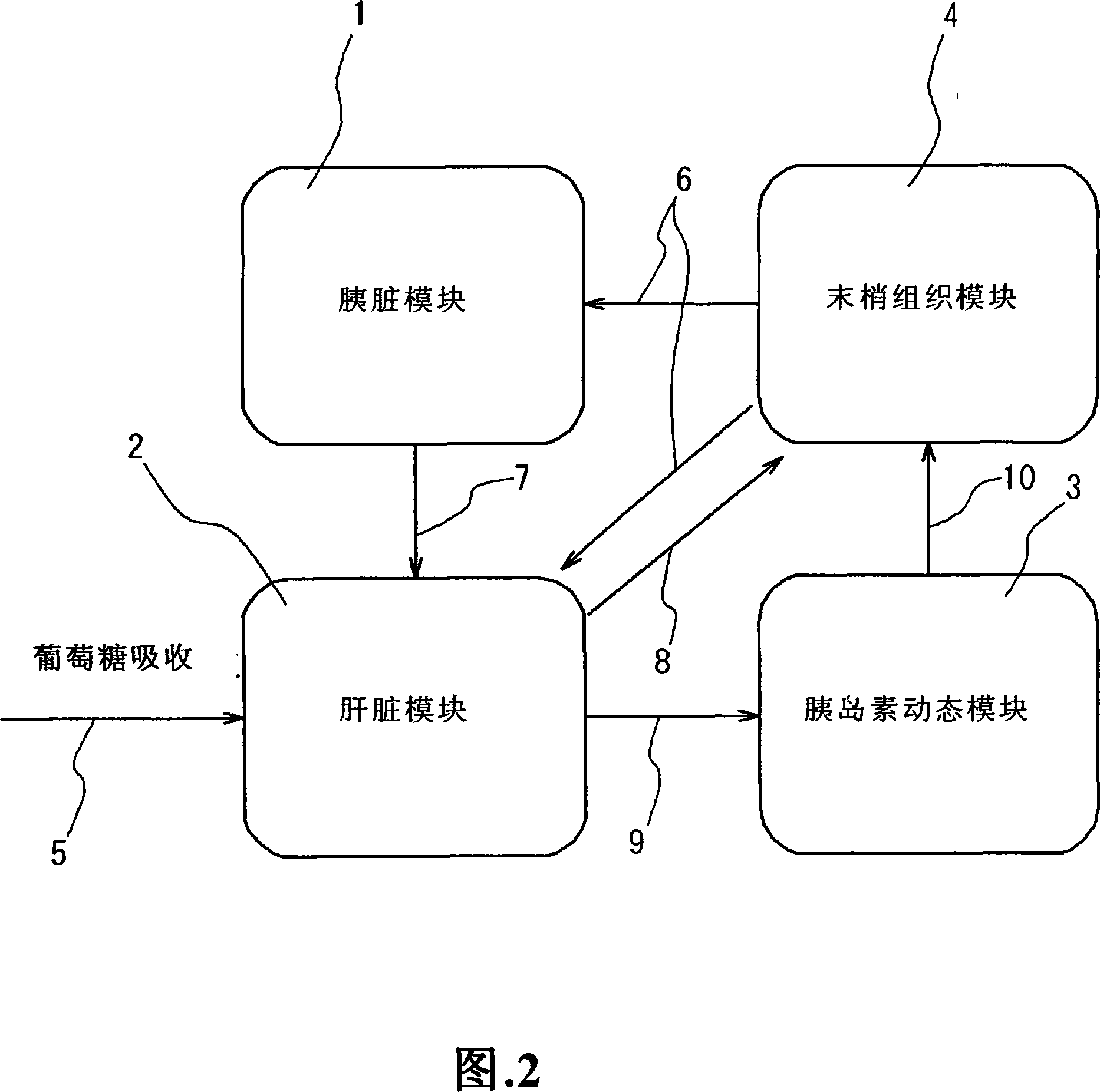
Simulation system for functions of biological organs and recording medium in which program therefor is recorded
InactiveUS20060277015A1Medical simulationAnalogue computers for chemical processesMathematical modelOrgan function
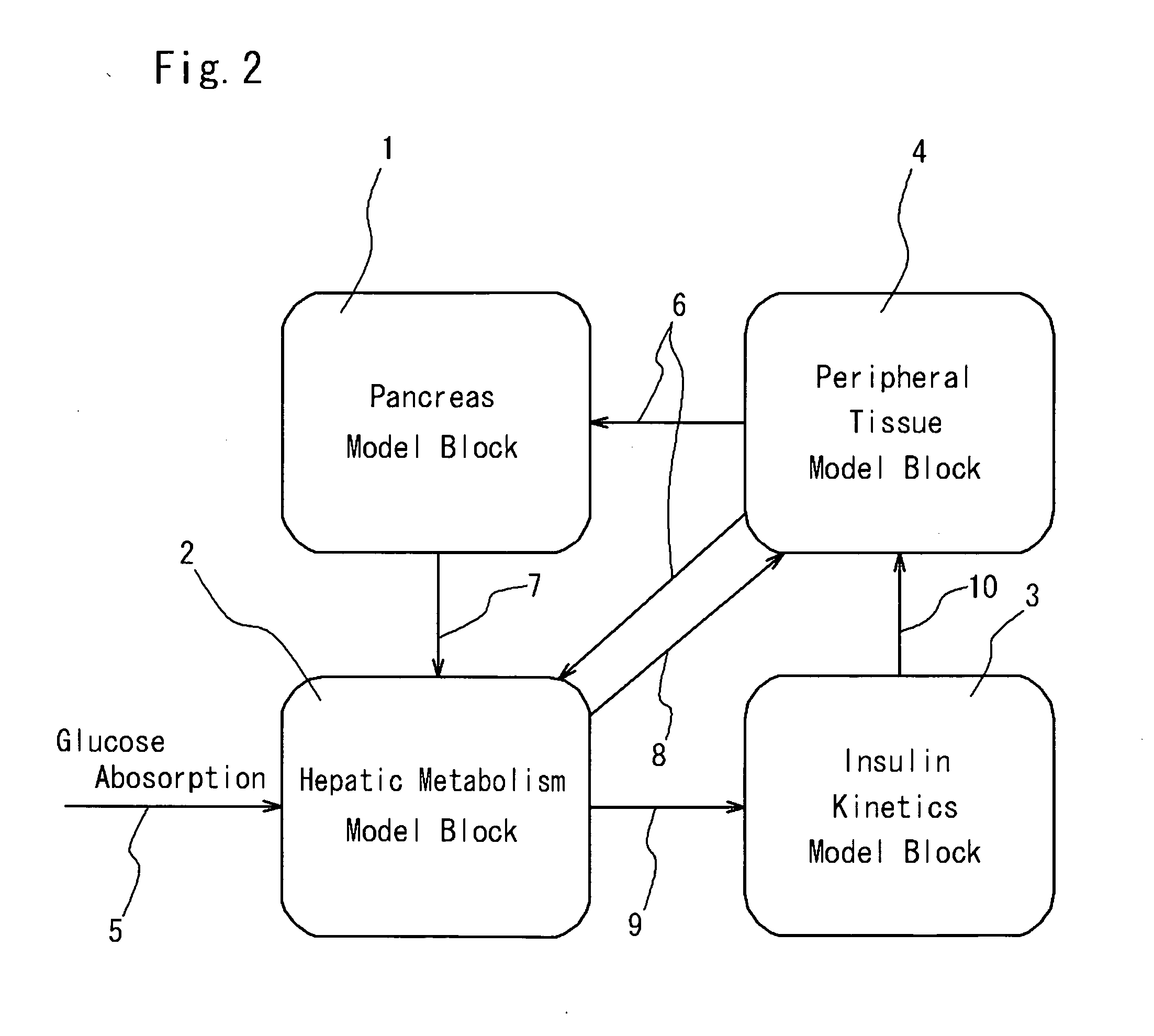
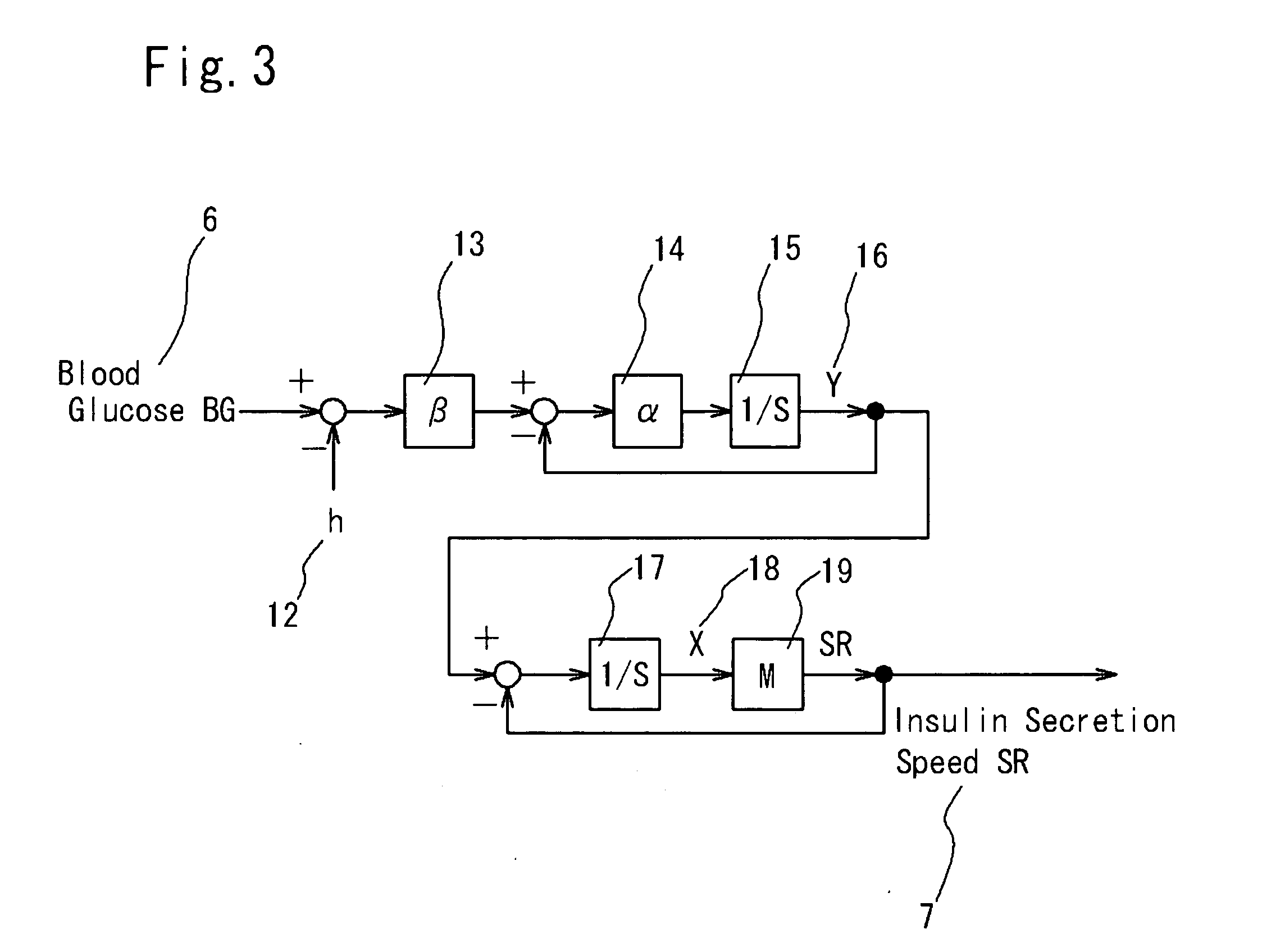
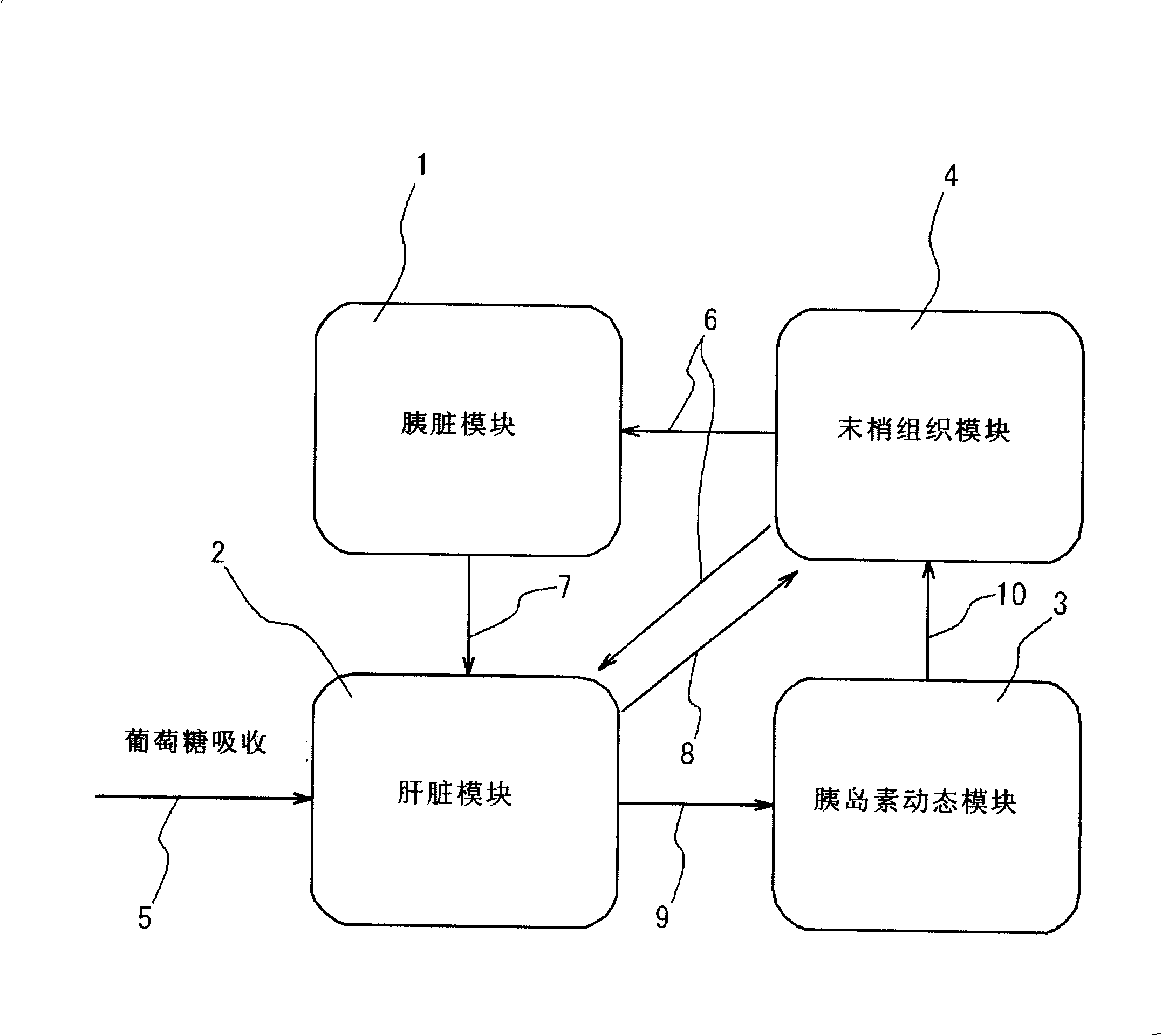
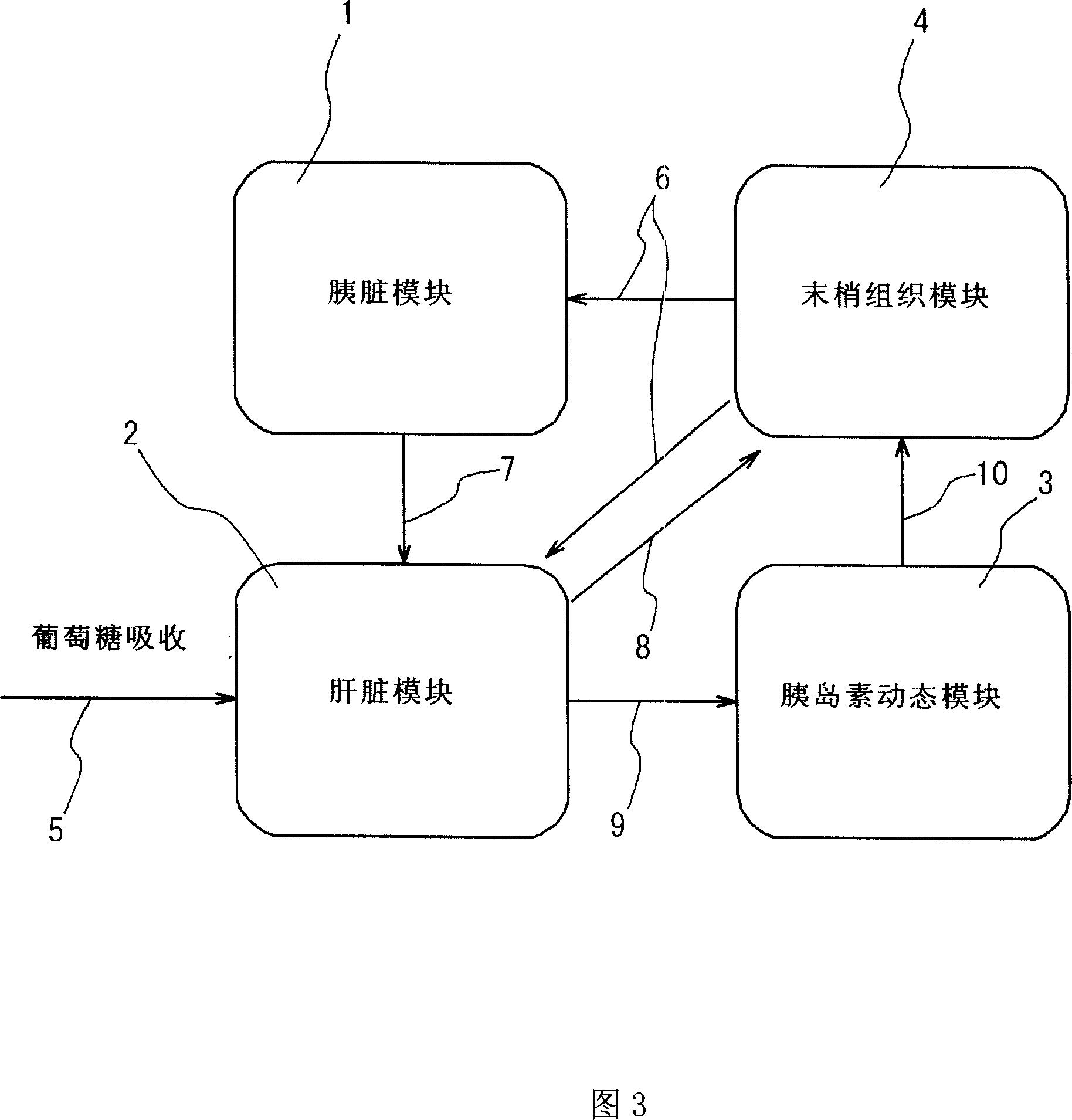
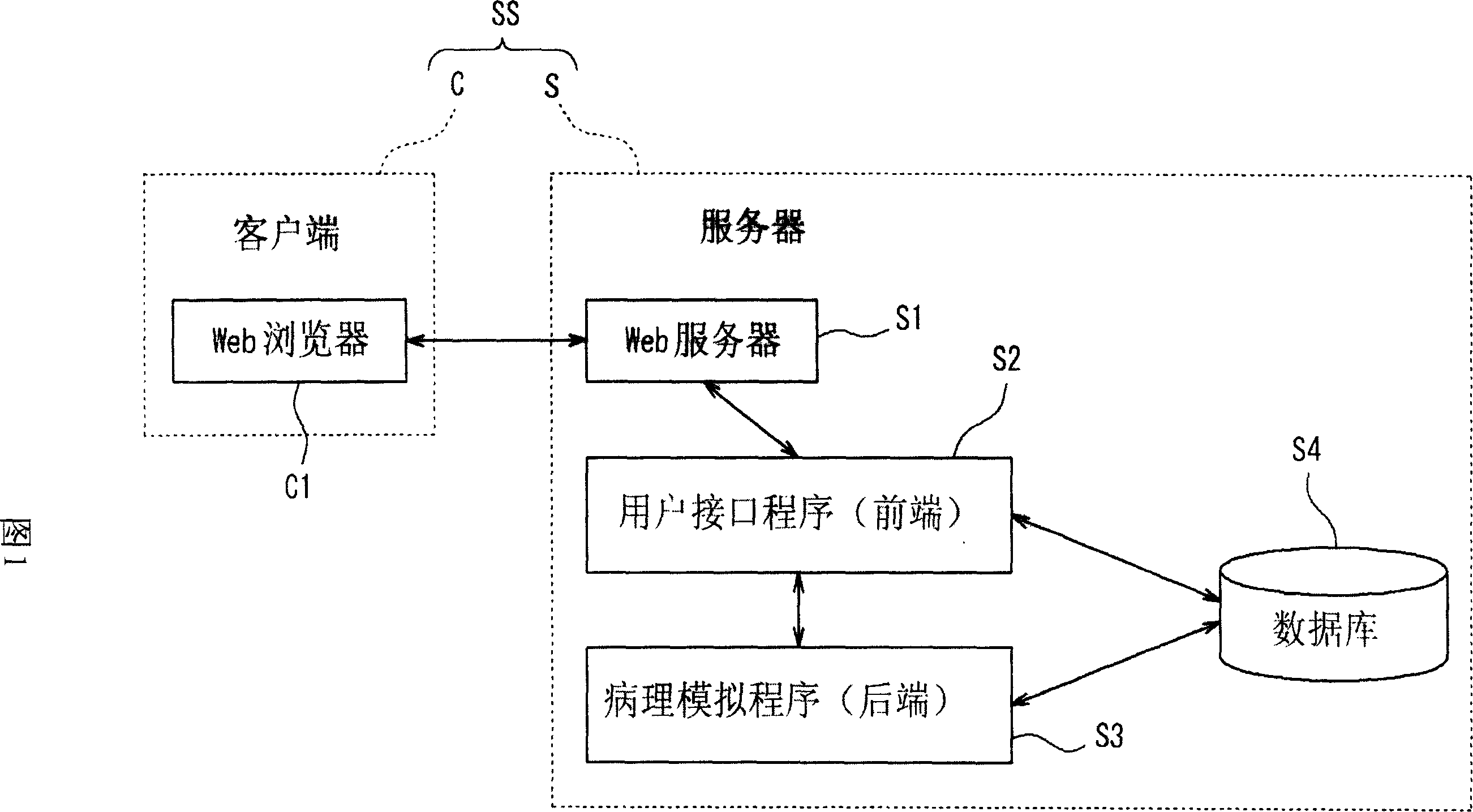
A simulation system for simulating functions of biological organs, comprising a biological model in which the functions of the biological organs are expressed by mathematical models. The biological model comprises a hepatic metabolism model block having specified input and output relating to hepatic function for simulating the hepatic function. The system further comprises arithmetic means for calculating an output value by using measurable status variables of a liver based on input value to the hepatic metabolism model block.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
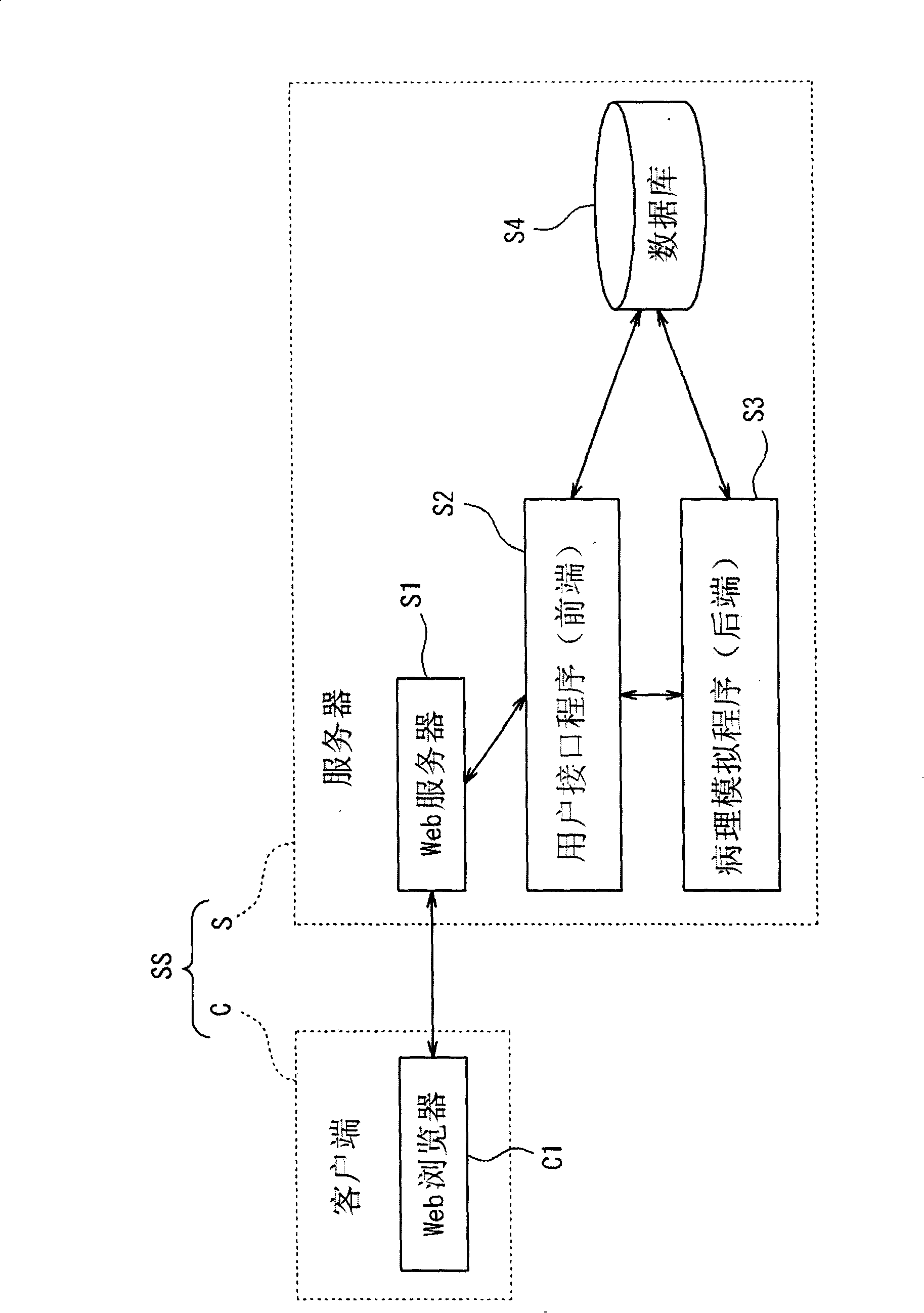
Medical analog system and control system thereof
The invention provides a medical simulation system, which comprises a biological response input part, a biological model generator, a pathological feature acquisition part and an output part, wherein, the biological response input part receives the input of biological response information which reflects a biological actual biological response, the biological model generator produces a biological model to reconstruct an approximate response which simulates the actual biological response, the pathological feature acquisition part obtains pathological feature information which reflects the bio-pathological feature according to the generated biological model, and the output part can output the biological response information and the pathological feature information at the same time.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
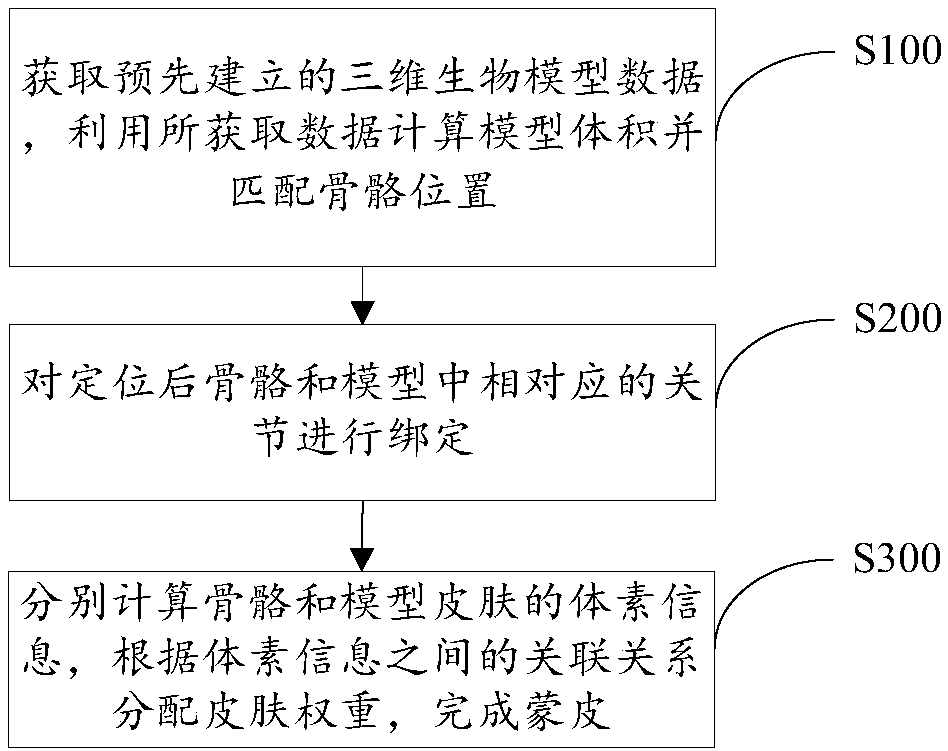
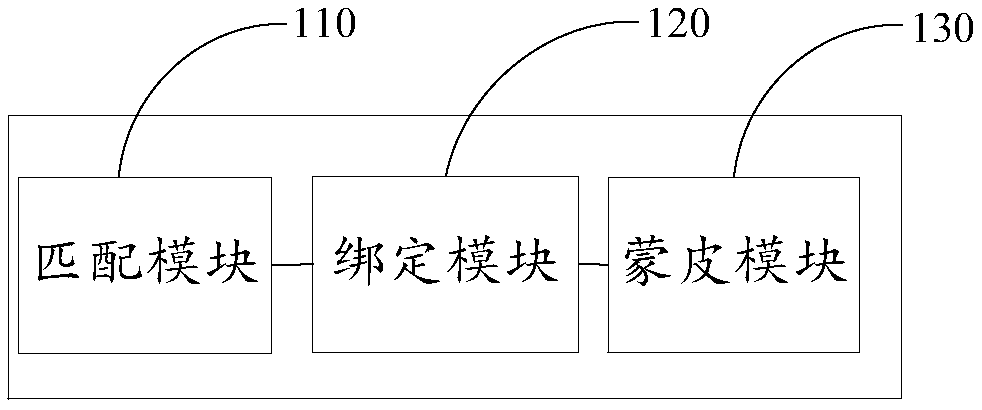
Three-dimensional bio-model skeleton automatic binding system, method and device, and computer program product
InactiveCN108597015AEfficient bindingShorten binding timeImage memory management3D modellingVoxelAnimation
Embodiments of the invention disclose a three-dimensional bio-model skeleton automatic binding system, method and device, and a computer program product. The method comprises the steps of obtaining data of a pre-built three-dimensional bio-model, and calculating the volume of the model by utilizing the obtained data and matching the positions of skeletons; binding the located skeletons and corresponding joints in the model; and calculating voxel information of the skeletons and model skin, and according to an association relationship between the voxel information, allocating skin weights, thereby finishing skin. For the problem of consumption of a large amount of time for binding a large amount of bio-models due to an existing technology for manually binding the skeletons and the joints ofthe three-dimensional bio-model, it is proposed that automatic locating of the skeletons is realized based on the volume of the model and a topological structure, automatic joint binding is realized,and the bound bio-model has basic animation K frame demands, so that the skeleton binding time of the bio-model is greatly shortened and efficient skeleton and joint binding can be performed for thelarge amount of the bio-models.
Owner:江苏辰锐网络科技有限公司
Medical simulation system and its computer program
A medical simulation system includes a biological response inputting section that receives input of biological response information indicating an actual biological response of biological body, a biological model generating section that generates a biological model for reproduction of simulated response simulating the actual biological response, a pathologic condition characteristics acquiring section that acquires pathologic condition characteristics information indicating characteristics of pathologic condition of the biological body based on the generated biological model, and an outputting section that outputs the biological response information and the pathologic condition characteristics information.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
System and methods for extracting semantics from images
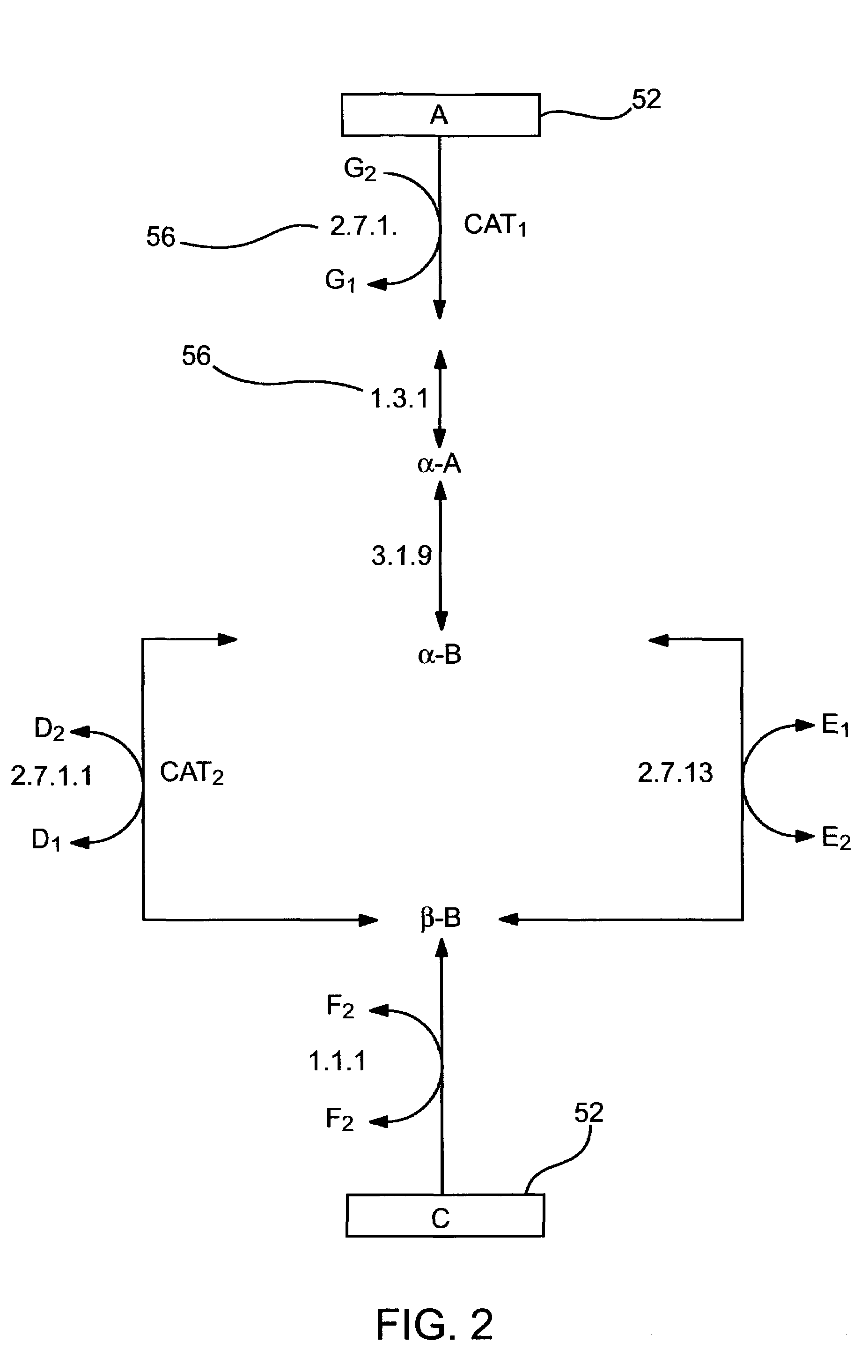
System, tools and methods for extracting the contents from a graphical image, such as the representation of a biological process, and converting the contents into a standardized, machine readable format. The standard format can be used to create editable graphical representations of images, such as biological models.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Medical simulation system, control system and bio dummy experiment system and control system
InactiveCN101008965ACosmonautic condition simulationsData processing applicationsControl systemBiological modeling
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
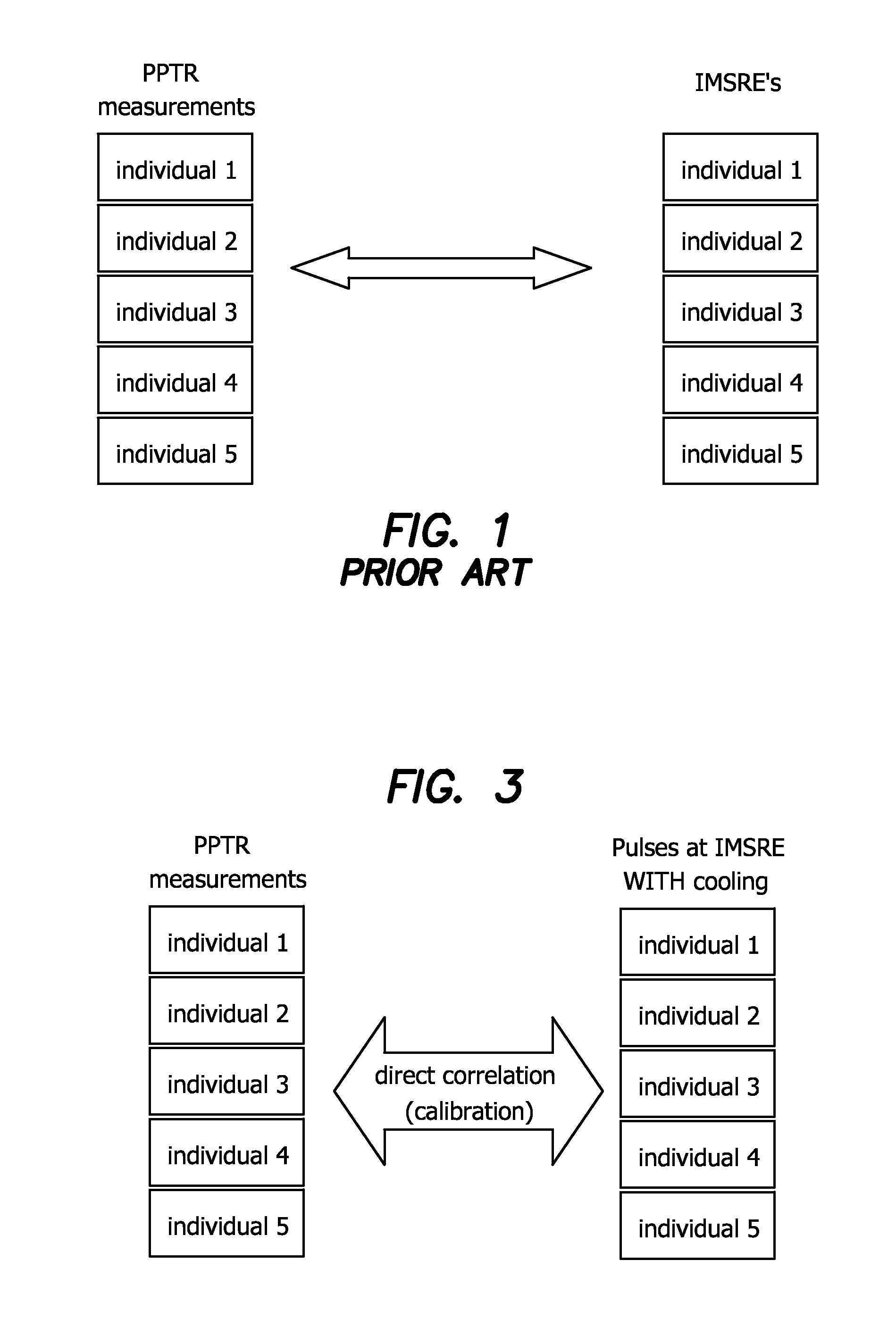
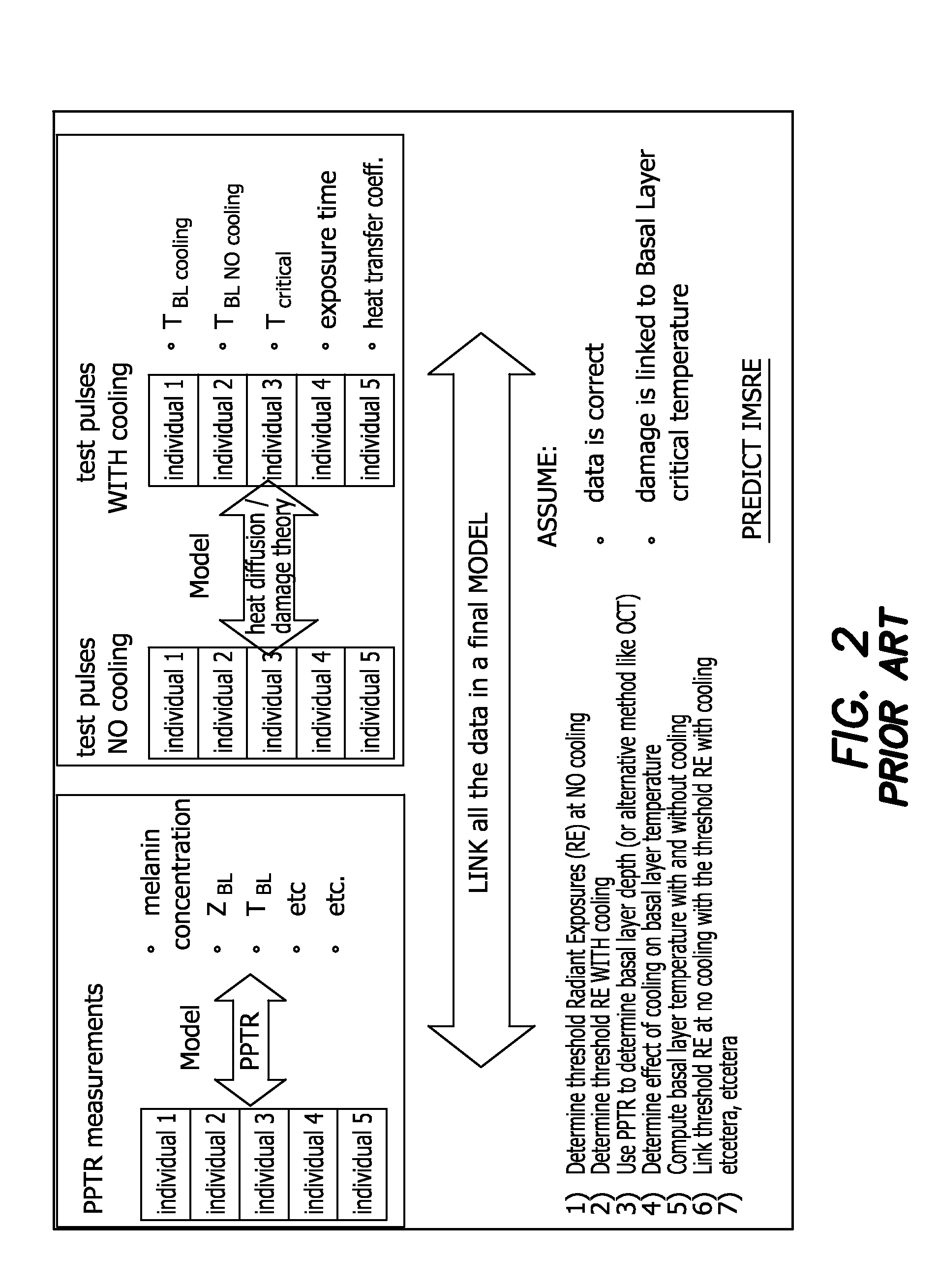
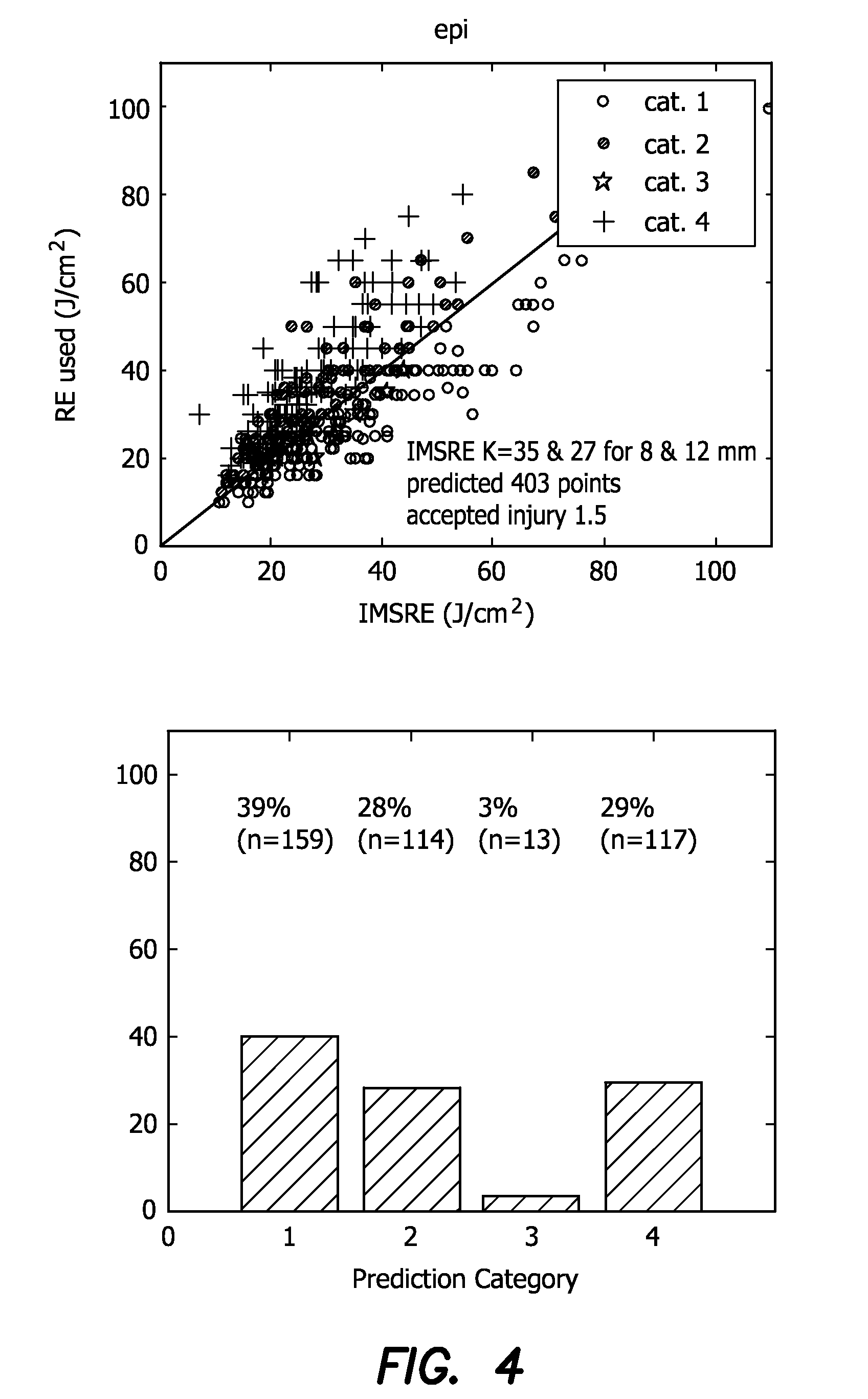
Apparatus and Method to Predict Individual Maximum Safe Radiant Exposure (IMSRE) Based on Measurement of Temporal Temperature Increase Induced by a Sub-Therapeutic Laser Pulse
A method for making pulsed photothermal radiometric measurements to determine individual maximum safe radiant exposure (IMSRE) of biological subjects corresponding to radiant energy exposure (RE) without any use of a biological model includes a calibration procedure, including the steps of applying a statistical regression to an empirical data set of IMSRE and temporal REs applied to a sample population of the subjects to determine a IMSRE corresponding to each temporal RE. The IMSRE is set so that using the statistical regression separation of the data set into an acceptable injury grouping and an unacceptable injury grouping is obtained with a predetermined limitation of the proportion of subjects having unacceptable injury at a temporal RE below the corresponding IMSRE. The separation of the data set is thus used to predict an IMSRE for a corresponding temporal RE to a biological subject not included in the sample population.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Simulation system of function of biological organ
InactiveCN101077307AMedical simulationCosmonautic condition simulationsMathematical modelOrgan function
A simulation system for simulating a function of a biological organ using a biological model in which the function of the biological organ are represented by a mathematical model with a computer is provided. The present system receives input of time-series actual measurement data representing the biological response of a subject, estimates the biological response of the subject at a time point at which the measurement is not performed by using the input time-series actual measurement data, and generates time-series reference data representing the biological response of the subject. The present system further generates a virtual biological organ virtually constructed in a computer system using the times-series reference data. The virtual biological organ corresponds to the function of a biological organ of the subject.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
Method, system, and apparatus for biological model symmetry
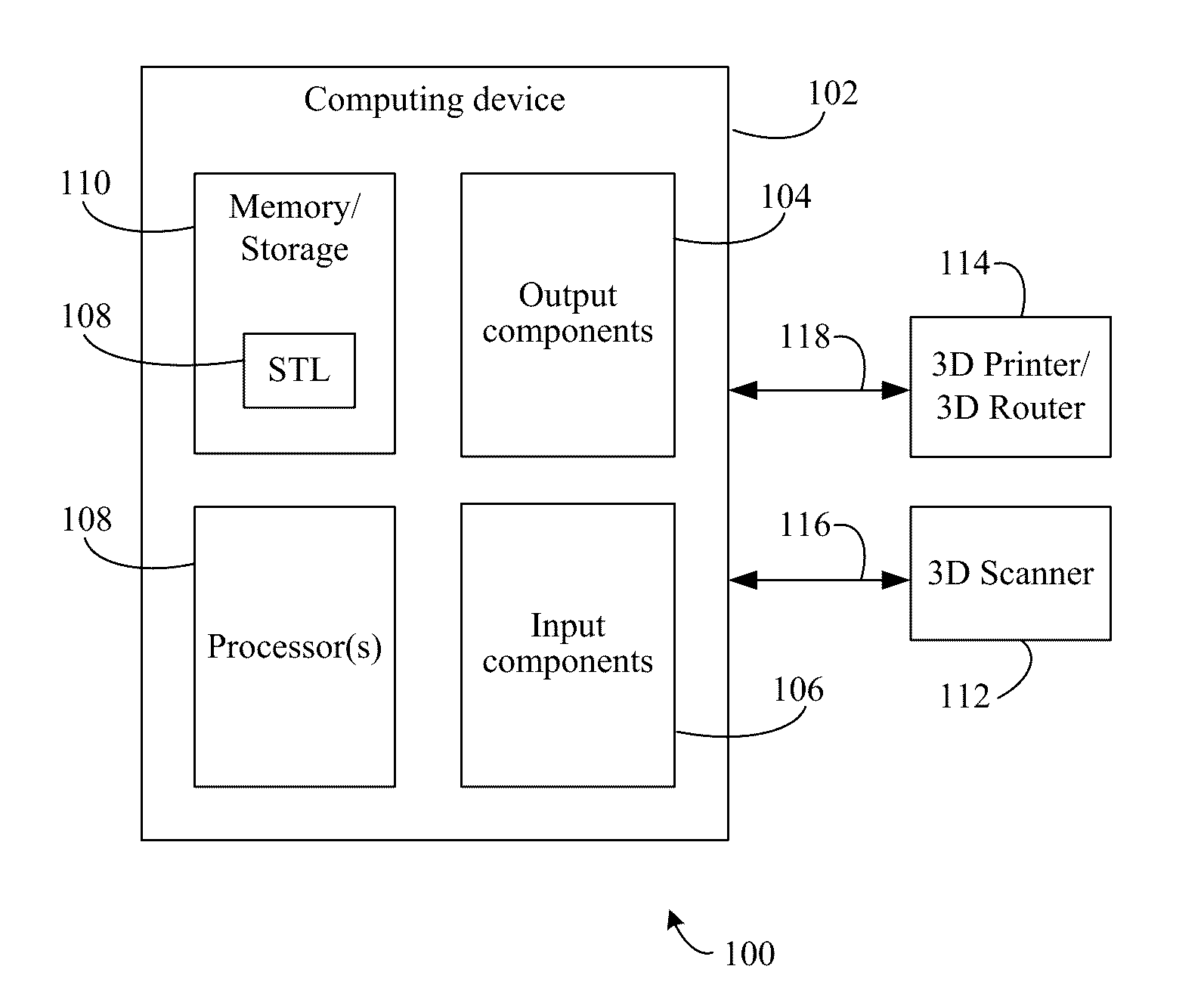
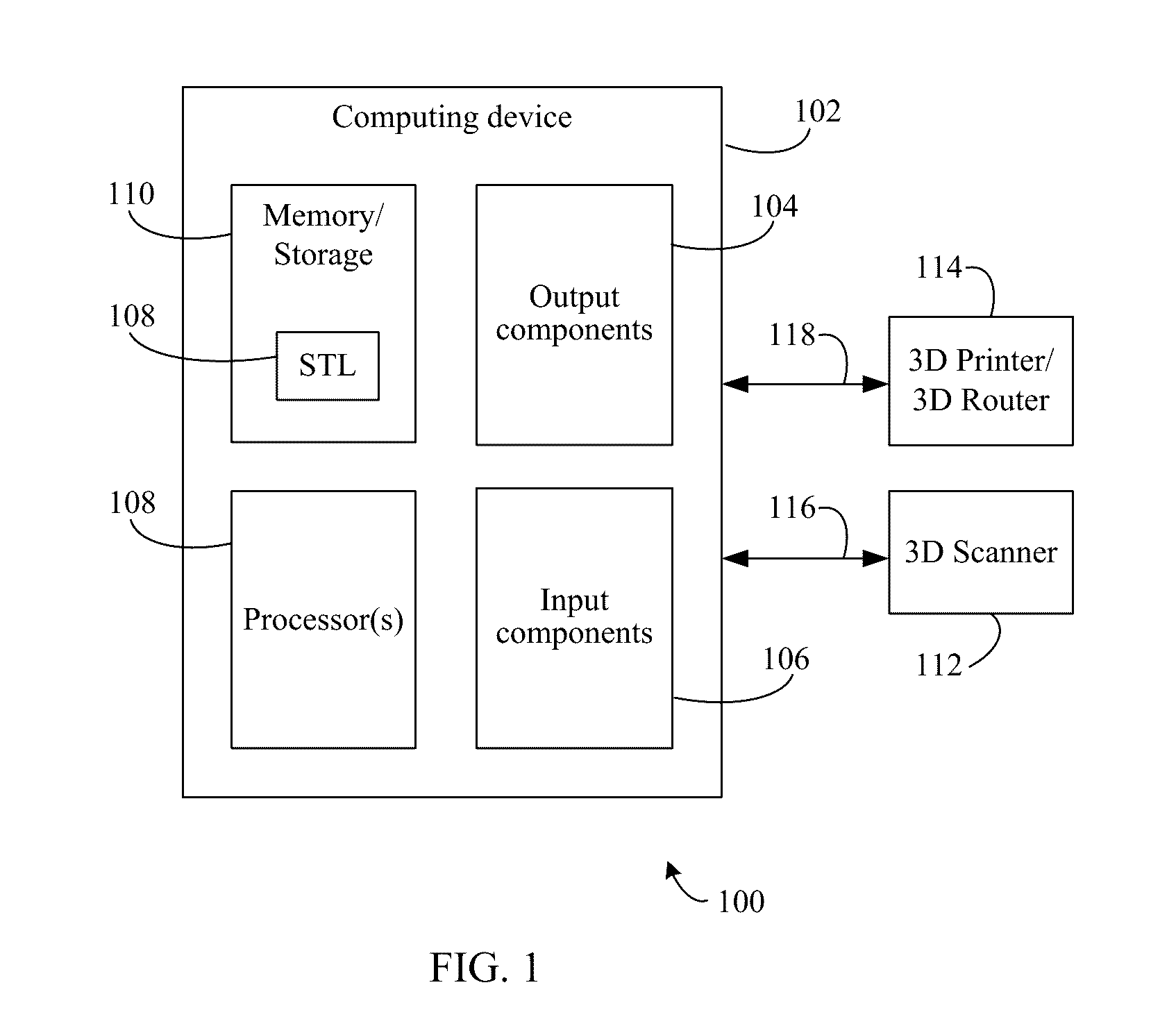
Methods, systems, and apparatuses are described for biological model symmetry. Model data relating to a biological specimen may be generated and / or stored in a memory of a computing system. The model data may be generated using a 3D scanner, or the like, of the biological specimen. The computing system may receive an indication of a selection from a user interface specifying a first portion of the model data that was selected. A mirrored representation of the first portion may be generated by the computing system using a processor(s). A second portion of the model data that is different from the first portion may be replaced with the mirrored representation to generate symmetric biological model data. The symmetric biological model data may then be used to generate a physical symmetric model of the biological specimen. The physical model may be generated using a 3D printer, a 3D router, or the like.
Owner:CROMEENS BENJAMIN M
Model method for calculating equivalent uniform dosage of radiotherapy
PendingCN109712714ASolve the problem of large deviation in survival rate predictionAvoid difficultiesMedical simulationHigh cellOriginal data
The invention discloses a model method for calculating an equivalent uniform dosage of radiotherapy, wherein an LQ model is not fundamentally changed and a cell survival condition in a single large dose can be well reflected. Effectiveness of original clinical experience is ensured, and the method can be used for effect evaluation of large dose irradiation after slight correction of the original data. Based on the equivalent uniform dose of a segmented secondary function model, by means of a formula, a treatment planning system can quickly acquire the equivalent uniform doses of a tumor and anormal organization, thereby facilitating comparative evaluation of treatment plans with different dose segmentation modes and different dose distribution patterns. The segmented secondary function model is used for settling a problem of high cell survival rate prediction deviation after performing large-dose irradiation by a traditional linear secondary model. The equivalent uniform dosage modelbased on the model realizes comparison of the treatment effects in different dose distributions. After introducing latent doubling time, the advantages of single large-dose irradiation at an aspect ofovercoming cell proliferation is presented, and a difficulty in clinical application of a radiation biological model is basically solved.
Owner:戴立言 +1
Computer-implemented method for designing a biological model
ActiveUS20150178443A1Data visualisationAnalogue computers for chemical processesBiological modelingComputer science
Owner:DASSAULT SYSTEMES
Bio-model comprising a fluid system and method of manufacturing a bio-model comprising a fluid system
InactiveUS20180322809A1Low costAccurate representationAdditive manufacturing apparatusEducational modelsAnatomical structuresBiological modeling
A bio-model for simulating a surgical procedure comprises a synthetic anatomical structure which has a cavity. A fluid system is coupled to the cavity. In one embodiment the fluid system allows fluid to be pressurized. In one embodiment, the fluid system allows fluid to flow through the cavity. The bio-model may be manufactured based on medical image data using three-dimensional printing.
Owner:UNIVERSITI MALAYA
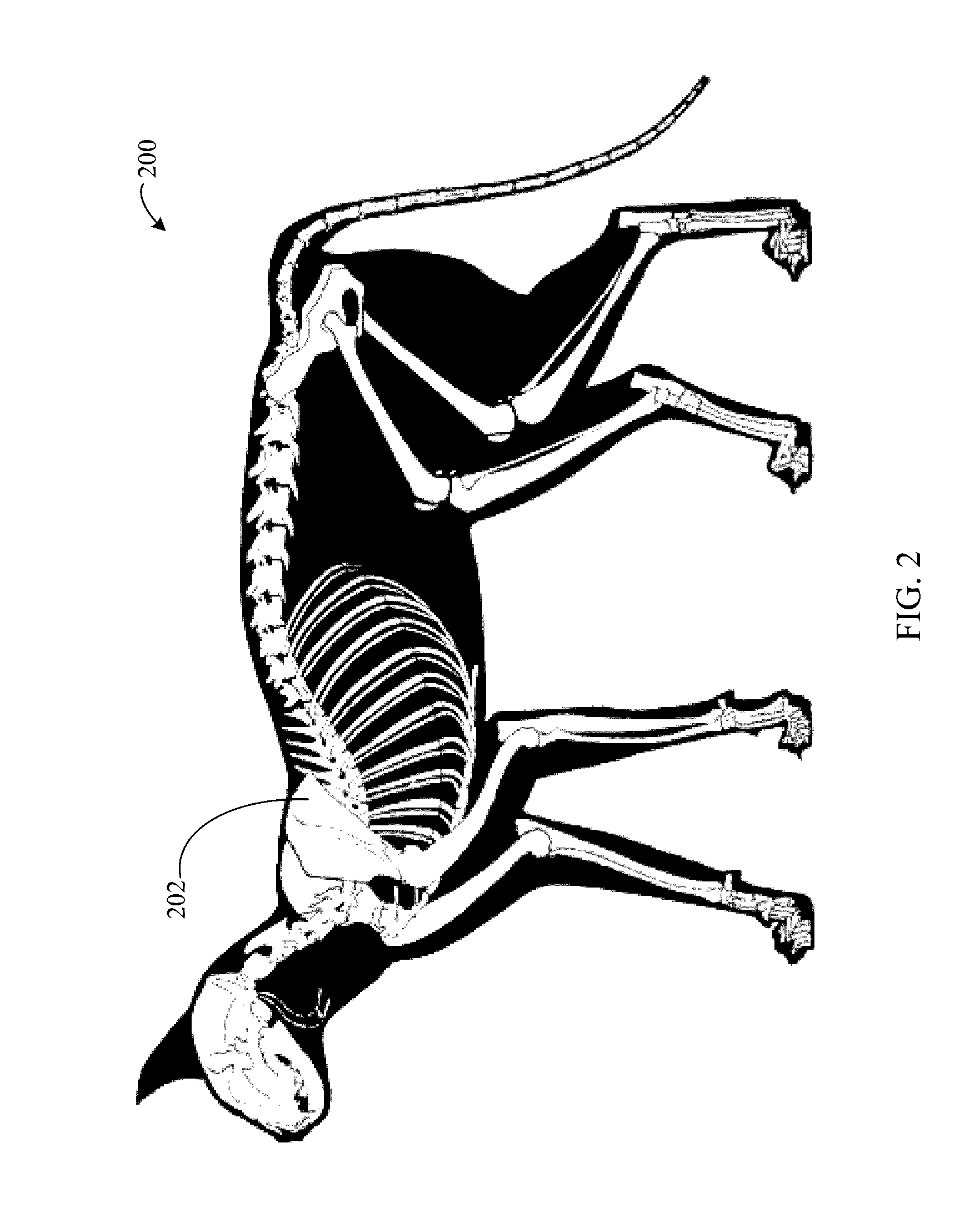
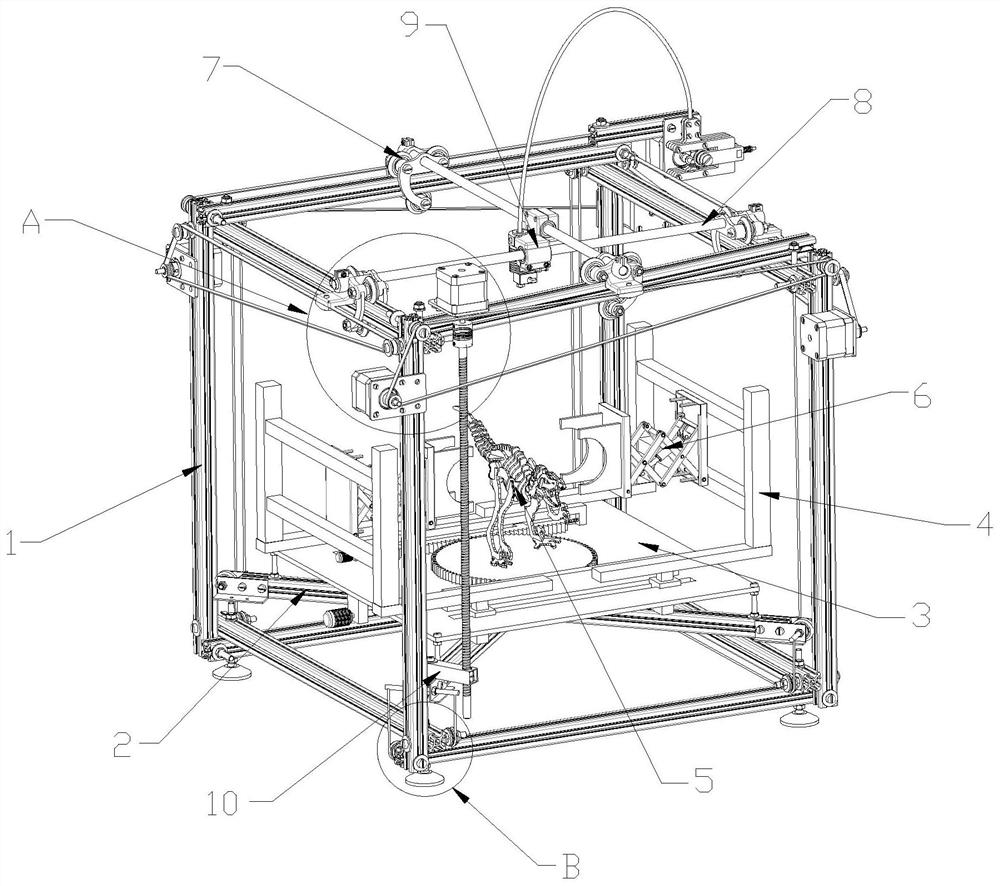
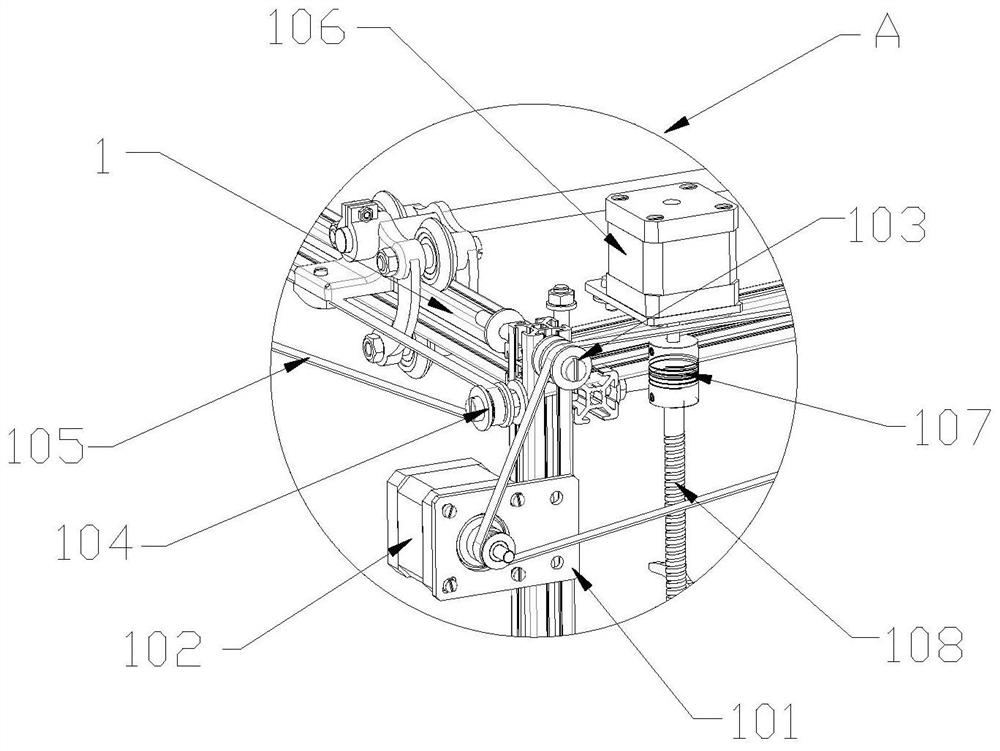
Ancient biological fossil three-dimensional model reconstruction auxiliary device
InactiveCN112721156AEnsure stabilityAvoid a rollover situationManufacturing platforms/substrates3D object support structuresModel reconstructionEnvironmental engineering
The invention discloses an ancient biological fossil three-dimensional model reconstruction auxiliary device which comprises a supporting frame, a cross, a supporting module, a connecting module, a telescopic clamping module, a sliding rope, a displacement rod and a modeling module. According to the ancient biological fossil three-dimensional model reconstruction auxiliary device, ancient organism model modeling of any form can be achieved, the stability of a model can be guaranteed in the modeling process, and the situation that the model turns on one side and topples over in the modeling process is avoided. The ancient biological fossil three-dimensional model reconstruction auxiliary device is wide in application range and high in practicability, can be suitable for three-dimensional modeling of various ancient organisms in any form, and can also be suitable for three-dimensional modeling work of any other object. The problem that in the prior art, in the modeling process of large ancient organisms or objects with the upper gravity centers, the situation that due to the fact that the modeling process is performed from bottom to top, a model is prone to side turning and toppling due to the fact that the gravity centers gradually deviate upwards or deviate from the center is solved.
Owner:ANHUI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Biological models capable of exhibiting secondary disease manifestations and useful for developing therapeutic drugs, diagnostic products and therapeutic or diagnostic procedures, methods of using same, and cells, tissues and organs derived therefrom
This invention provides novel animal models for a human pathogen that is capable of exhibiting analogous secondary disease manifestation. Other animal models for a human pathogen are provided by this invention which are capable of exhibiting analogous secondary disease manifestations and are also capable of responding to therapeutic or preventive measures to such secondary disease manifestations. Other animal models for human retrovirus infections are provided including lower primates and primate excluding any members of the order Anthropoidea. Compositions, drugs, products and procedures for therapeutic and diagnostic applications derived from the animal models of this invention are also described and provided.
Owner:ENZO THERAPEUTICS
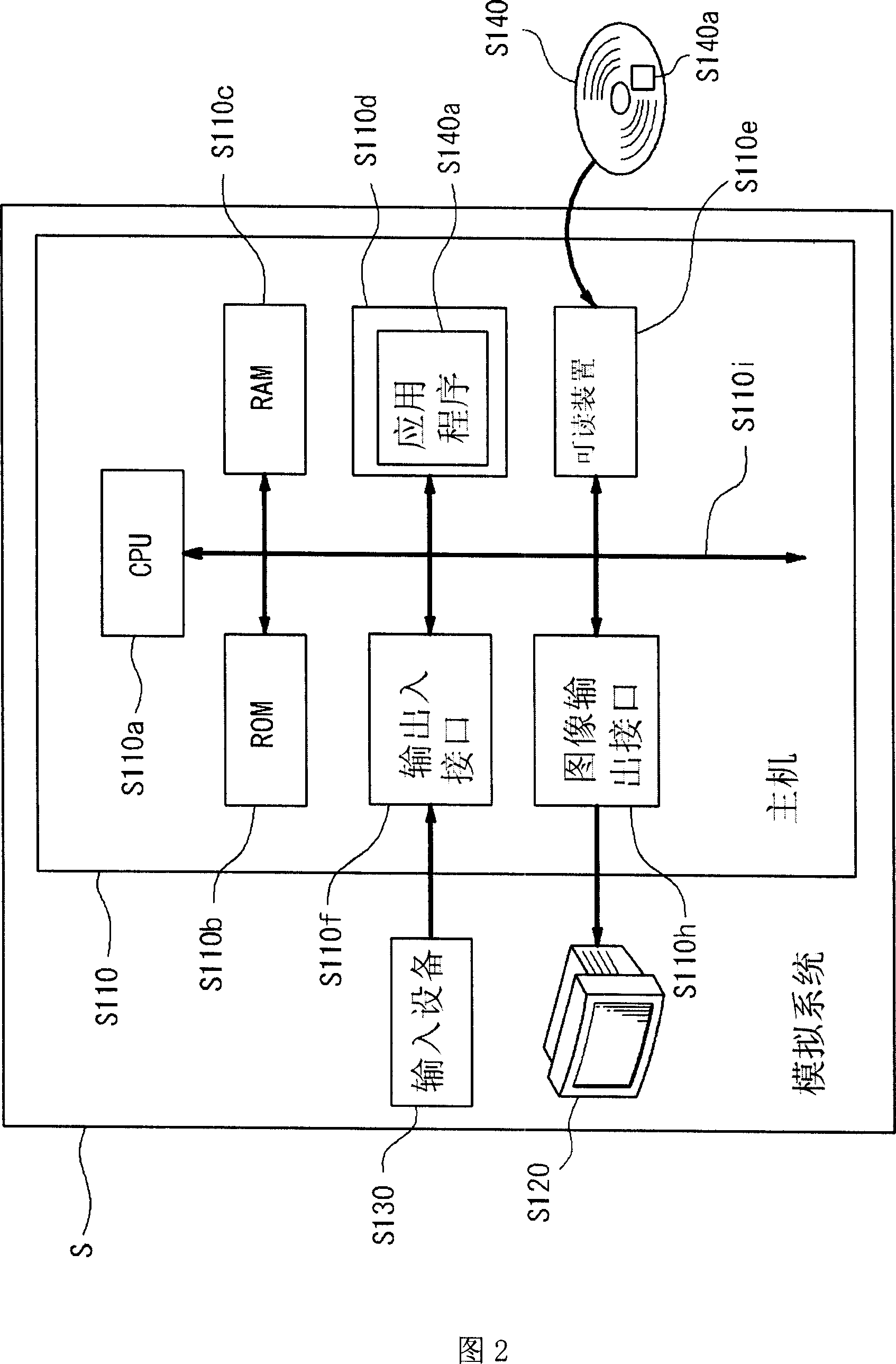
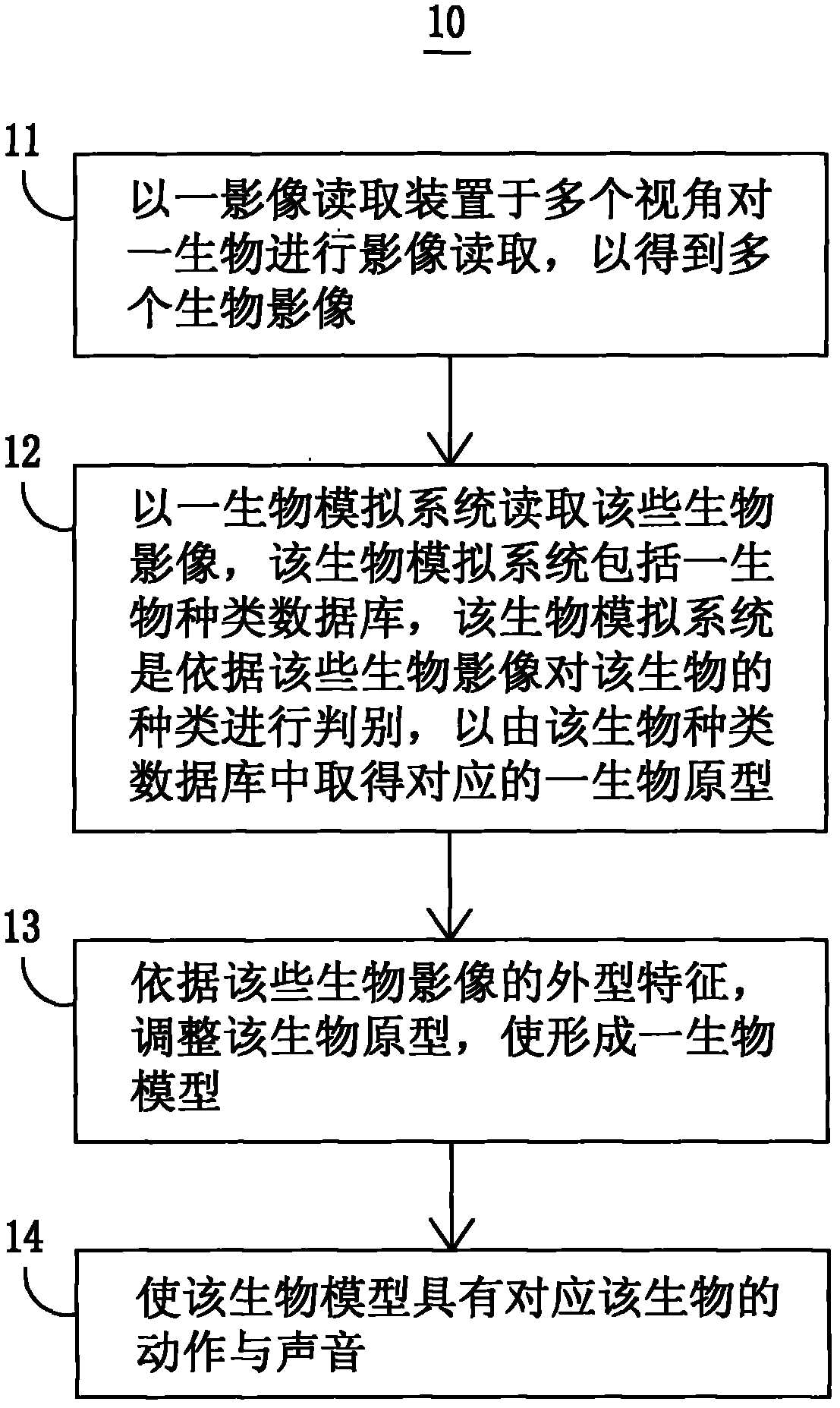
Creature dynamic simulation method and electronic device applying same
The invention discloses a biological dynamic simulation method and an electronic device applying the creature dynamic simulation method. The creature dynamic simulation method is characterized by comprising the following steps of reading images of a creature in multiple viewing angles by an image reading device, and obtaining multiple creature images; reading the multiple creature images by a creature simulation system, wherein the creature simulation system comprises a creature variety data base and is used for judging the creature variety according to the multiple creature images and obtaining a corresponding creature protomodel from the creature variety data base; regulating the creature protomodel according appearance characteristics of the multiple creature images, and forming a creature model; and enabling the creature model to be provided with actions and sounds corresponding to the creature.
Owner:江西联速科技有限公司 +1
Preparation method for three-dimensionally printing biological ceramic scaffold by using a biological ceramic ink
InactiveCN107432953AGood biocompatibilityAvoid Structural DistortionTissue regenerationProsthesisBiological propertyBiological modeling
The invention belongs to the technical field of three-dimensional printing, and specifically discloses a preparation method for three-dimensionally printing a biological ceramic scaffold by using a biological ceramic ink. According to the present invention, hydroxyapatite is prepared by using egg shell as a calcium source, and the excellent mechanical property and the excellent biological characteristics of the silk fibroin are supplemented to obtain the three-dimensional scaffold with characteristics of controlled internal components and controlled shape structure, such that the problem that the biological model ceramic bone repair body cannot be precisely customized in a personalized manber in the clinic can be solved.
Owner:苏州拜博机电科技有限公司
Weave type artificial blood vessel fatigue performance bionic test device and its test method
InactiveCN101105435BAdd test functionSolve the technical problem of lack of full simulationMaterial strength using repeated/pulsating forcesSpecific gravity measurementPeristaltic pumpOutput device
The invention relates to a spinning type artificial blood vessel weary performance biological modeling testing device and the testing method thereof. The invention comprises an electronic peristaltic pump, a fluid restrictor, a computer arranged with signal processing and transforming software and data output equipment. The invention is characterized in that the device also comprises a temperature controlling and heating device, a test sample installation frame and a pressure testing device. The testing steps are: 1. preheat testing machine; 2. test system; 3. choose the specimen of the spinning type artificial blood vessel; 4. adjust the pressure testing device; 5. control water temperature; 6. start the electronic peristaltic pump; 7. test and record; 8. evaluate the weary-resistant performance of the spinning type artificial blood vessel. The weary-resistant performance of the spinning type artificial blood vessel can be scientifically tested and appreciated by the device and the testing method disclosed by the device. And the invention solved the technical problem that the prior testing device and the testing method of the prior device have no safe simulation.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
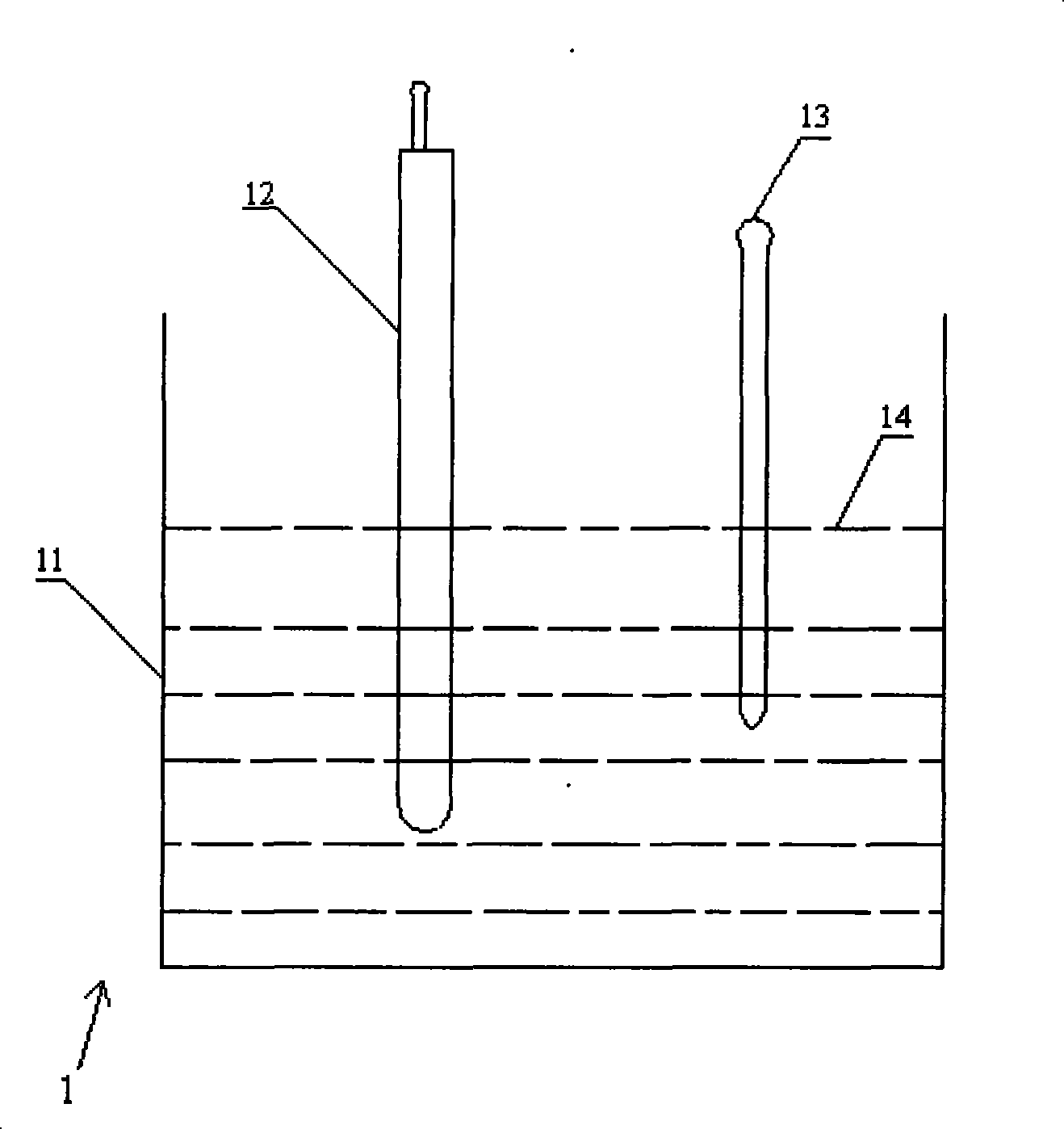
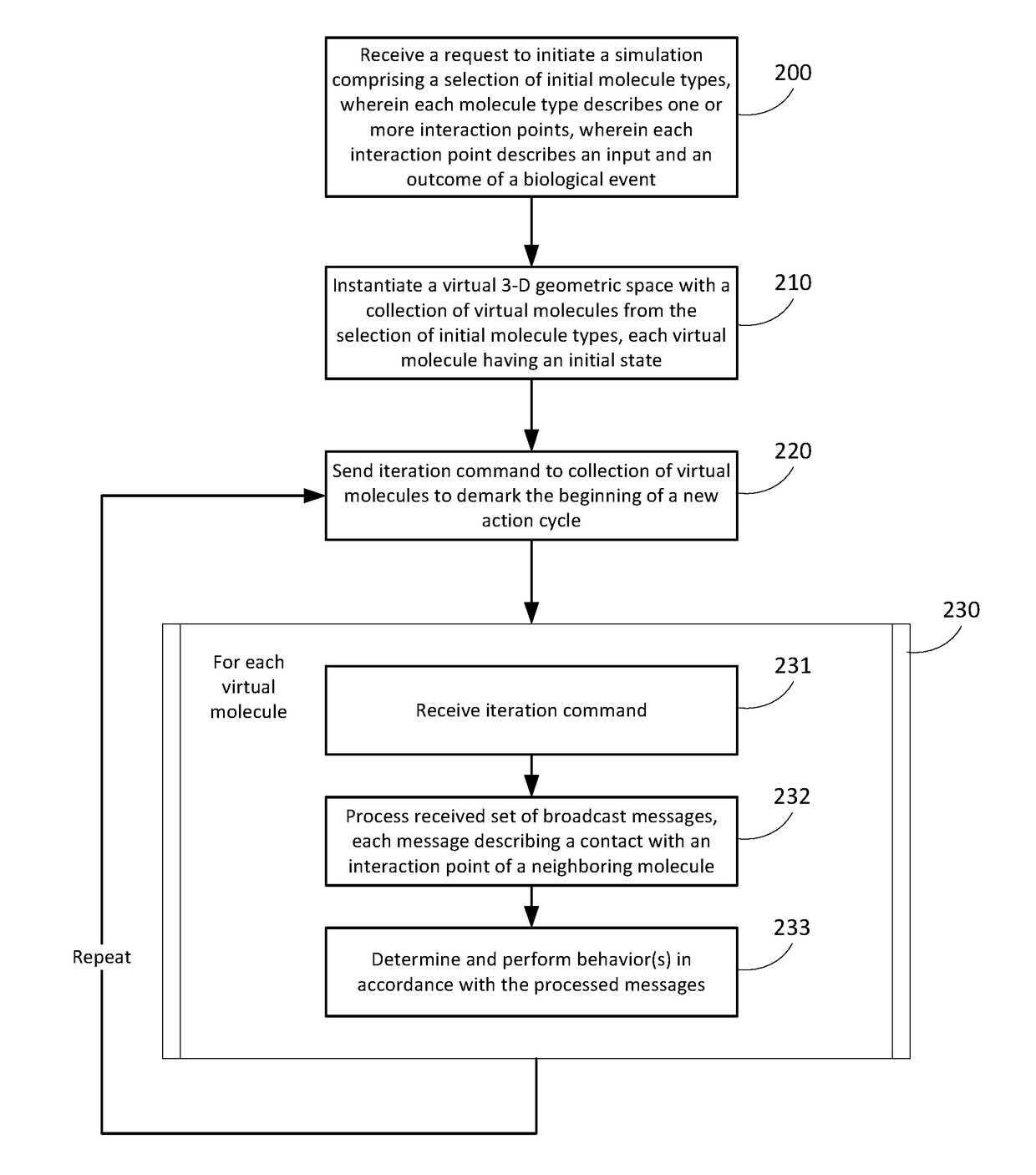
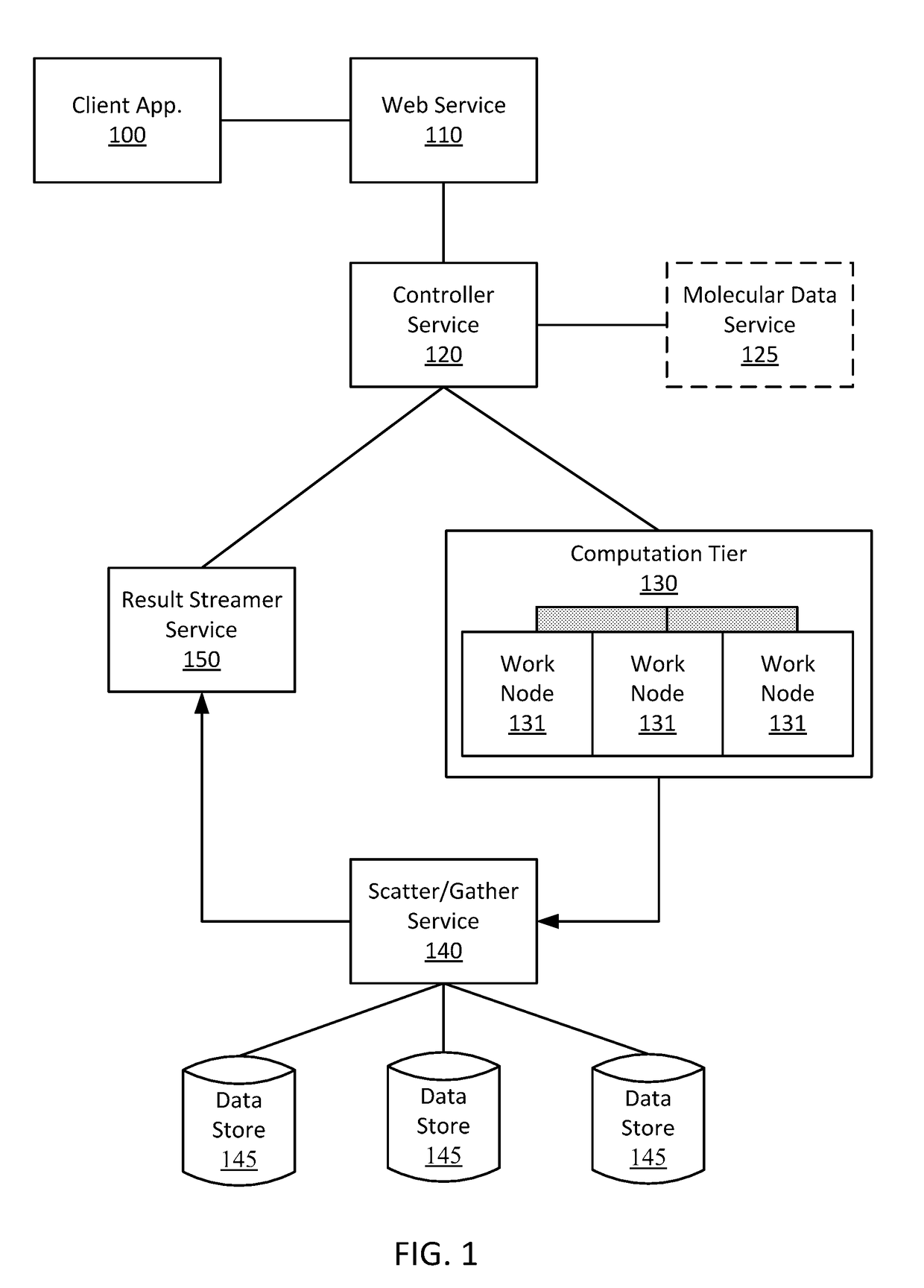
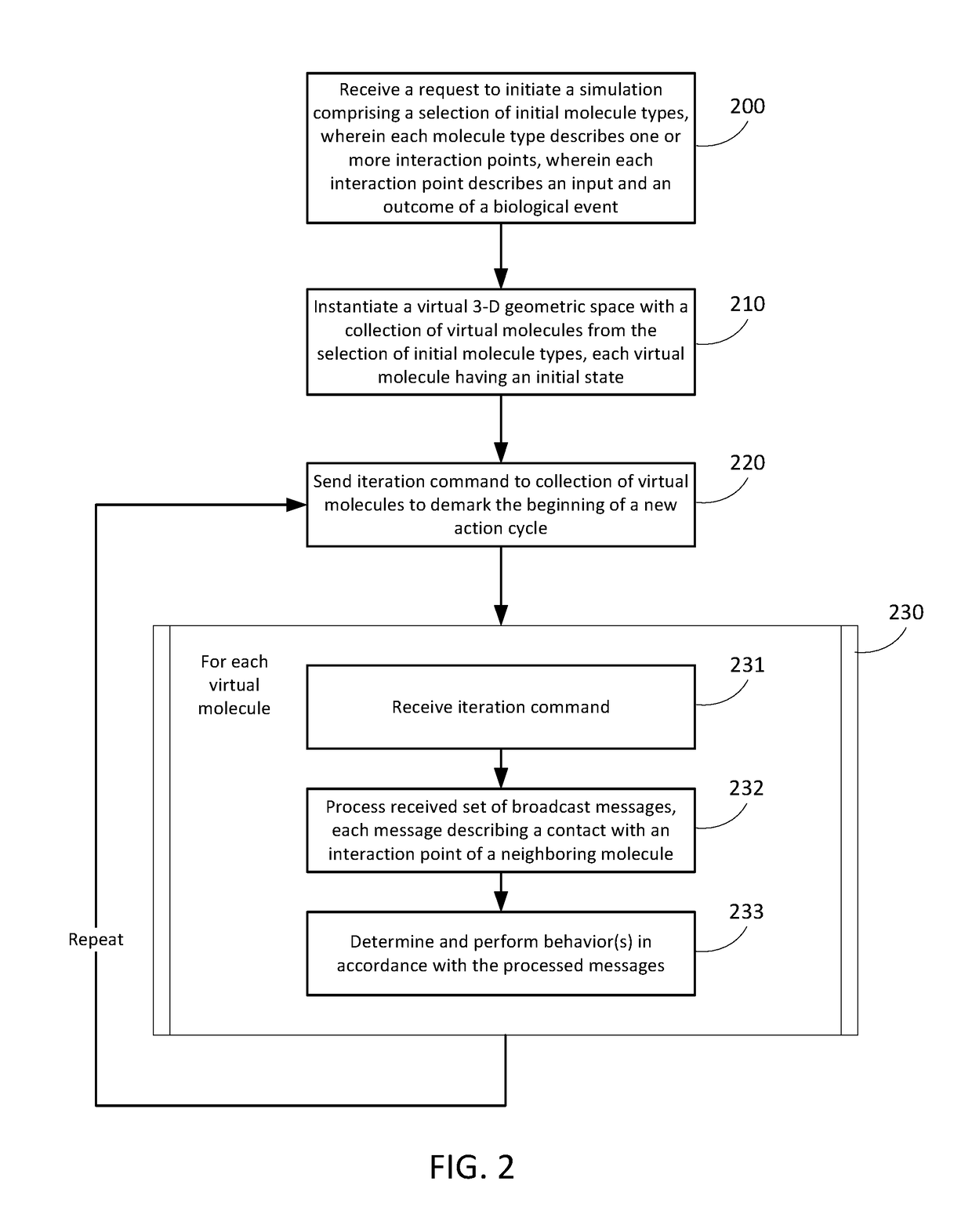
Simulation environment for experimental design
Techniques and systems are disclosed for enabling a simulation environment for experimental design. The interactions of a configuration of molecules inside a biological structure or system, such as a cell (e.g., a neuron) or virtual test tube, are modeled using message-based techniques to communicate between molecules proximal to one another in a virtual 3-D geometric space. Some techniques and systems allow distributed processing of the individual molecular interactions across a plurality of work nodes. Some techniques and systems allow the storage of detailed information about the current state of the simulation of the biological model for each discrete time slice. This enables the ability for a 4-D playback / review of any particular spatial or temporal focus area of the simulation.
Owner:NEUROINITIATIVE LLC
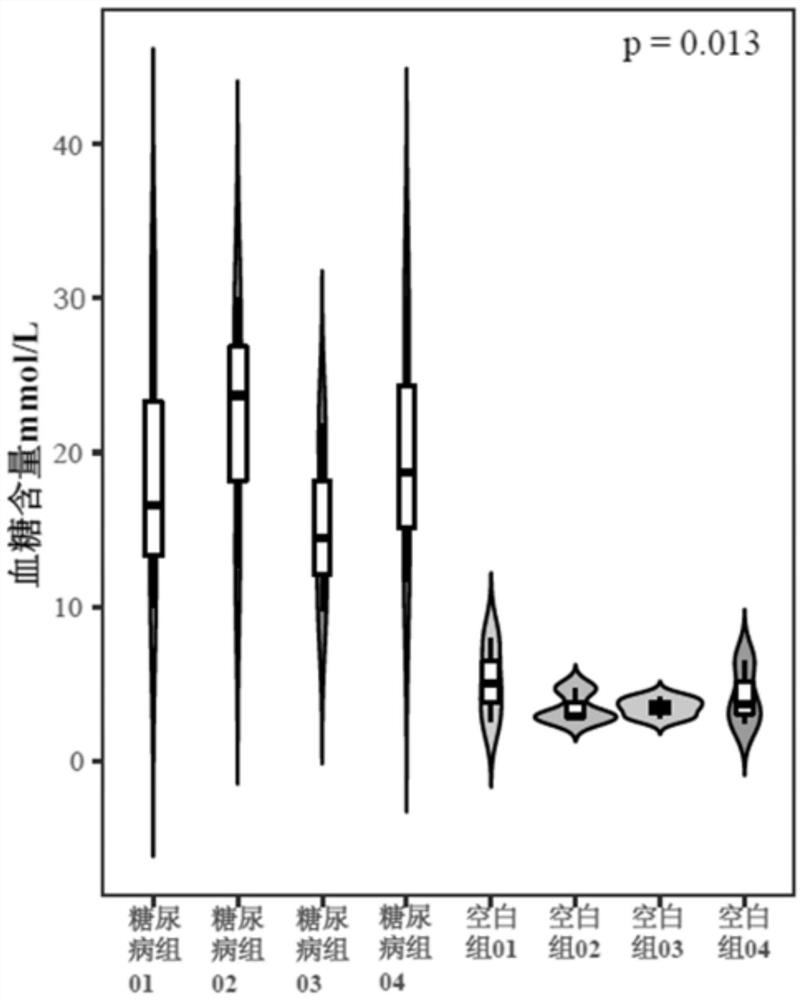
Method for constructing diabetic zebrafish model
ActiveCN113080108ALow costReduce mortalityClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaBiotechnologyDiabetes mellitus
The invention relates to the field of biological modeling, in particular to a method for constructing a diabetic zebrafish model. According to the method, the content of sugar in zebrafish feed is increased to induce the construction of the diabetic zebrafish model, so that the certainty of the administration dosage is realized. The death rate of modeling is low, the modeling time is short, the administration dosage can be controlled, the method is simple and convenient, the cost of consumables needed in the modeling process is low, and the method has good application prospects.
Owner:WENZHOU UNIVERSITY
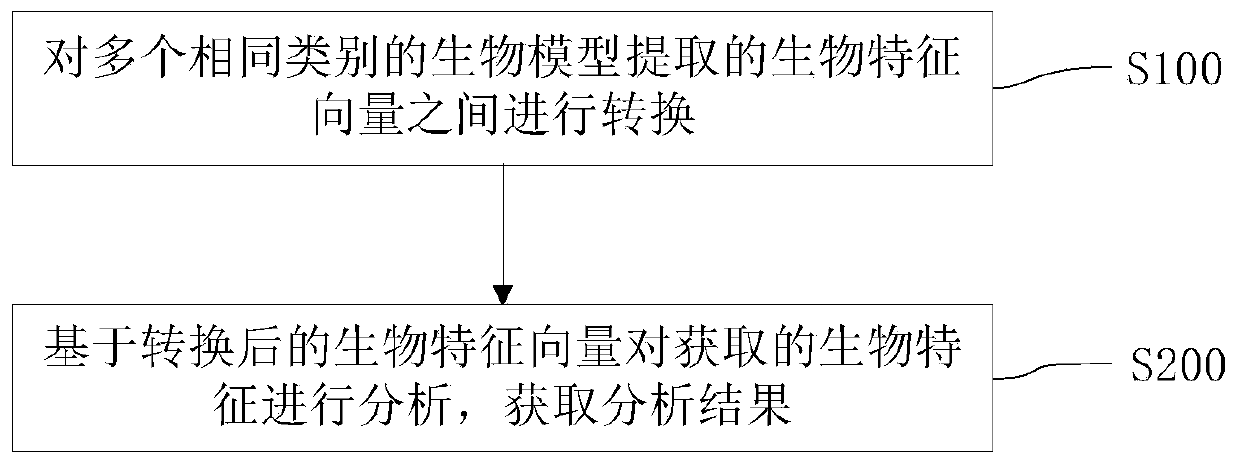
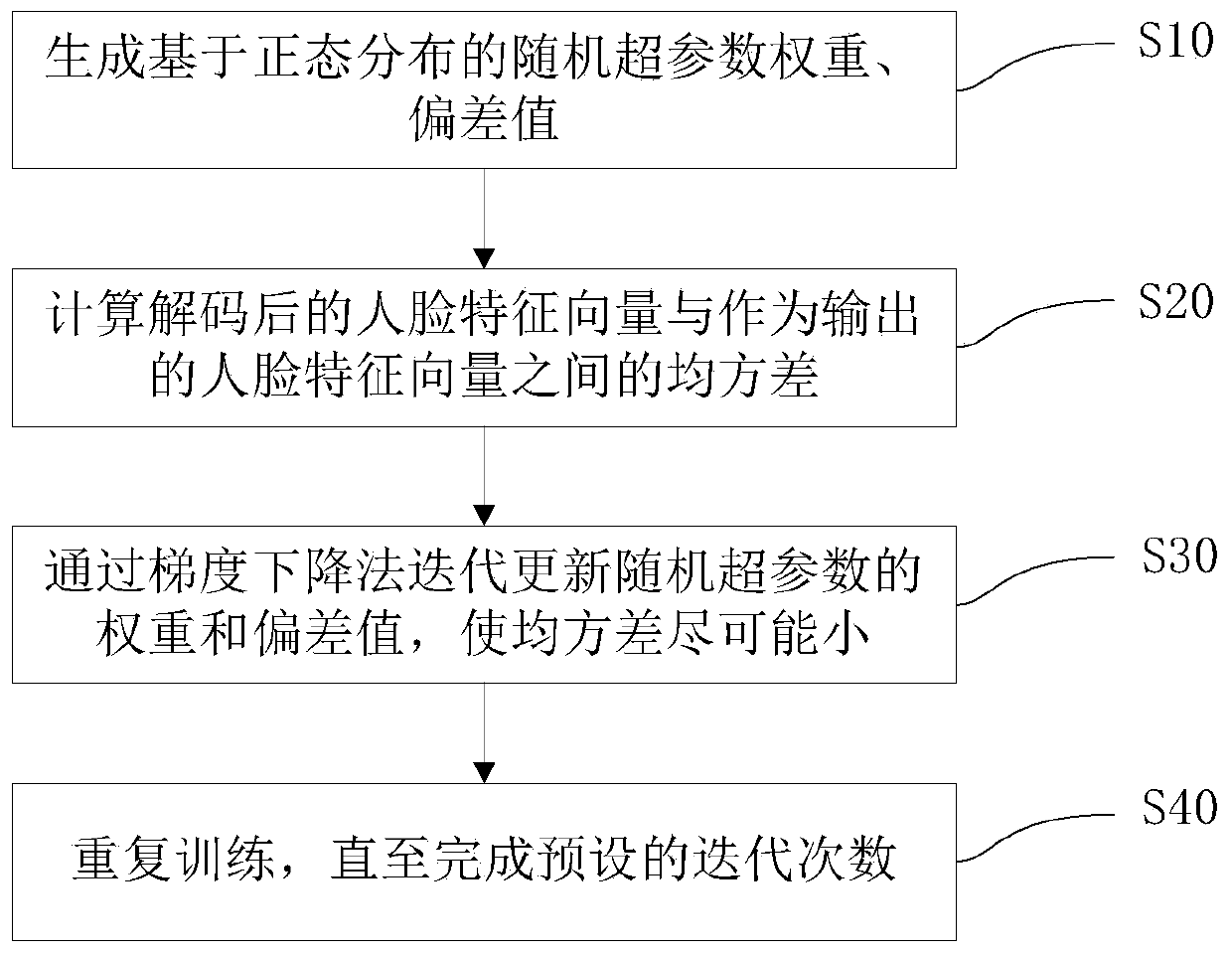
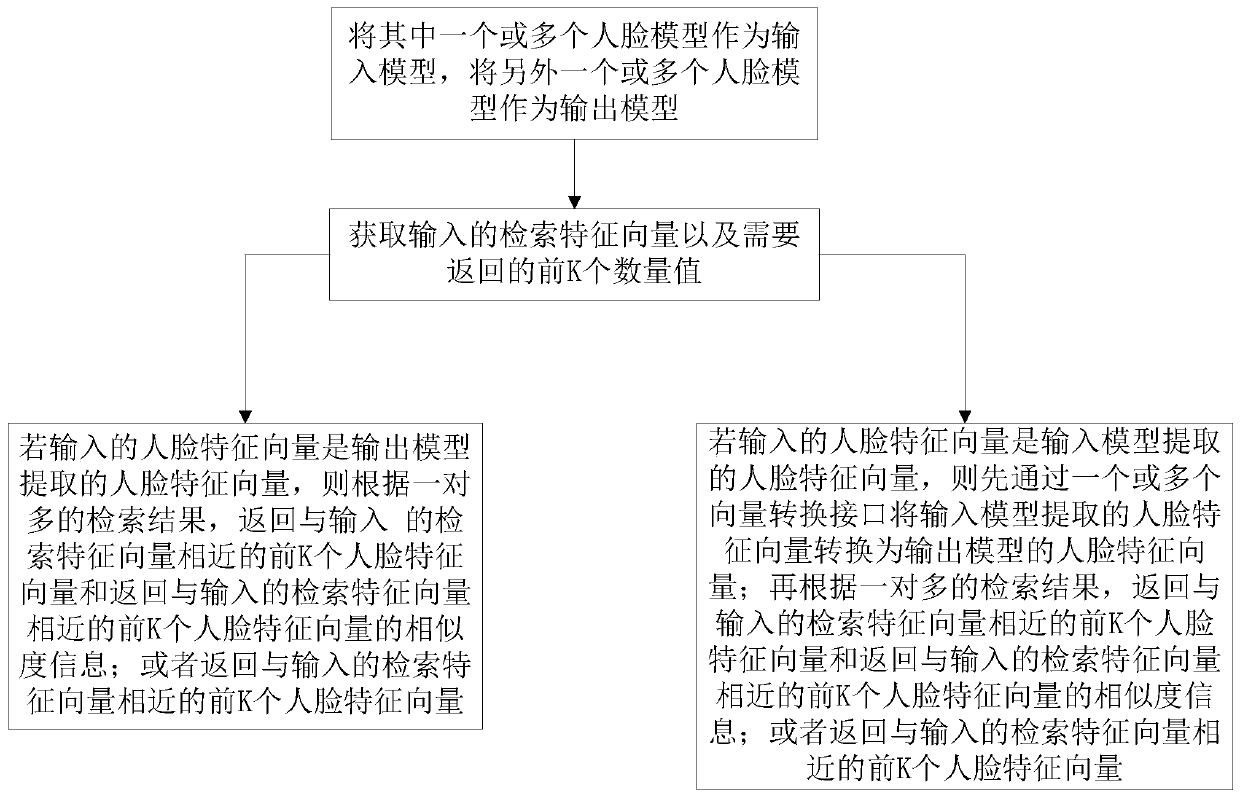
Biological characteristic management method, system and device and medium
ActiveCN111428652AImprove compatibilitySave storage spaceCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionEngineering
The invention provides a biological feature management method, system and device and a medium. The method comprises the following steps: converting biological feature vectors extracted from a plurality of biological models of the same category; and analyzing the obtained biological characteristics based on the converted biological characteristic vector to obtain an analysis result. According to the method, the biological feature vectors are converted, so that the biological models can be compatible during common use, and the compatibility between the biological models is improved; and analyzing the acquired biometric feature vector based on the converted biometric feature vector to obtain an analysis result. According to the method, the biological feature vectors are converted, so that thebiological feature vectors extracted from different biological models can be fused, and some biological models do not need to collect part of the biological feature vectors again, therefore, the storage space required for storing the biological feature vector can be saved, and the time required for re-extracting the biological feature vector can be reduced, so that the biological model can be updated smoothly in real time.
Owner:恒睿(重庆)人工智能技术研究院有限公司
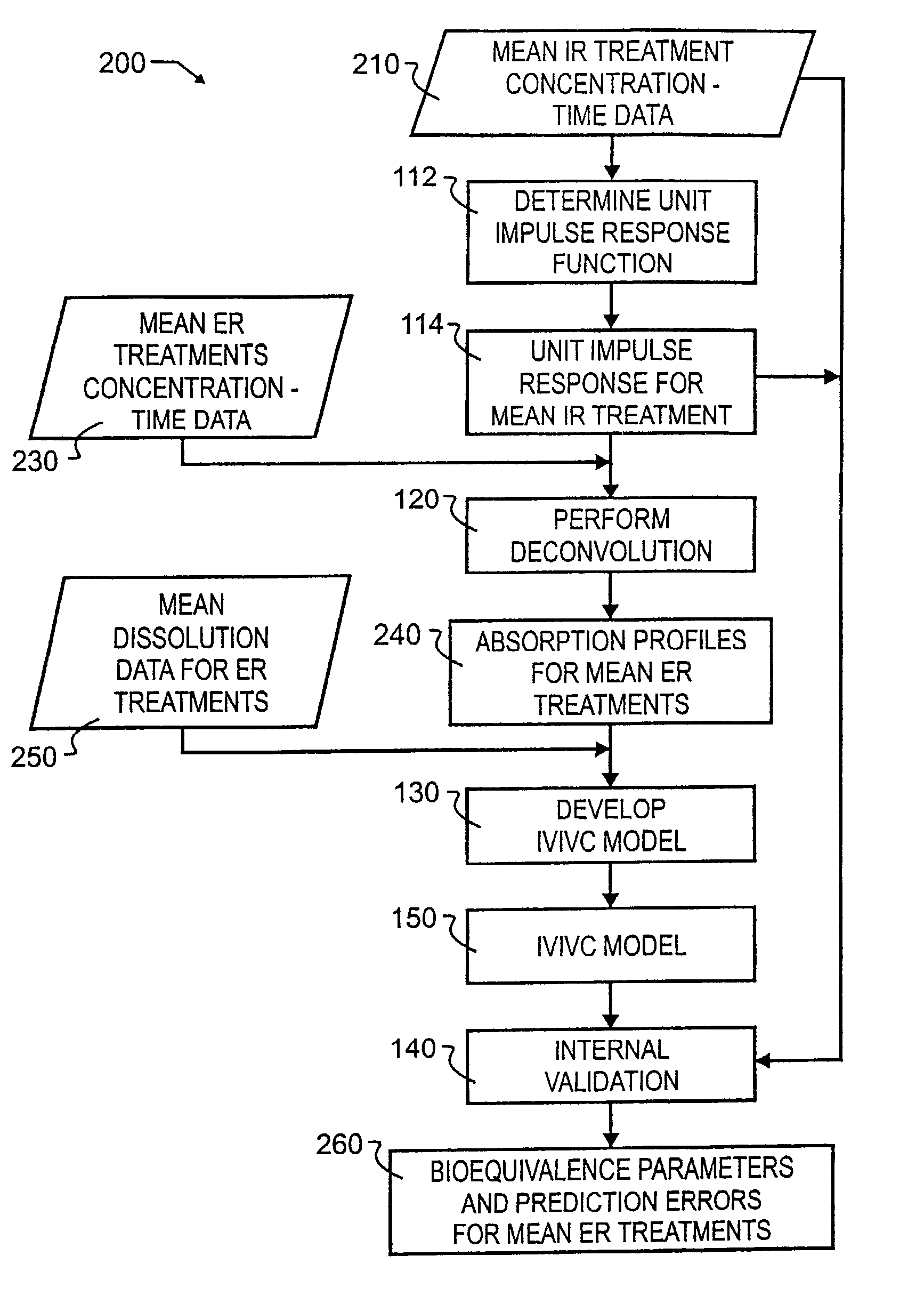
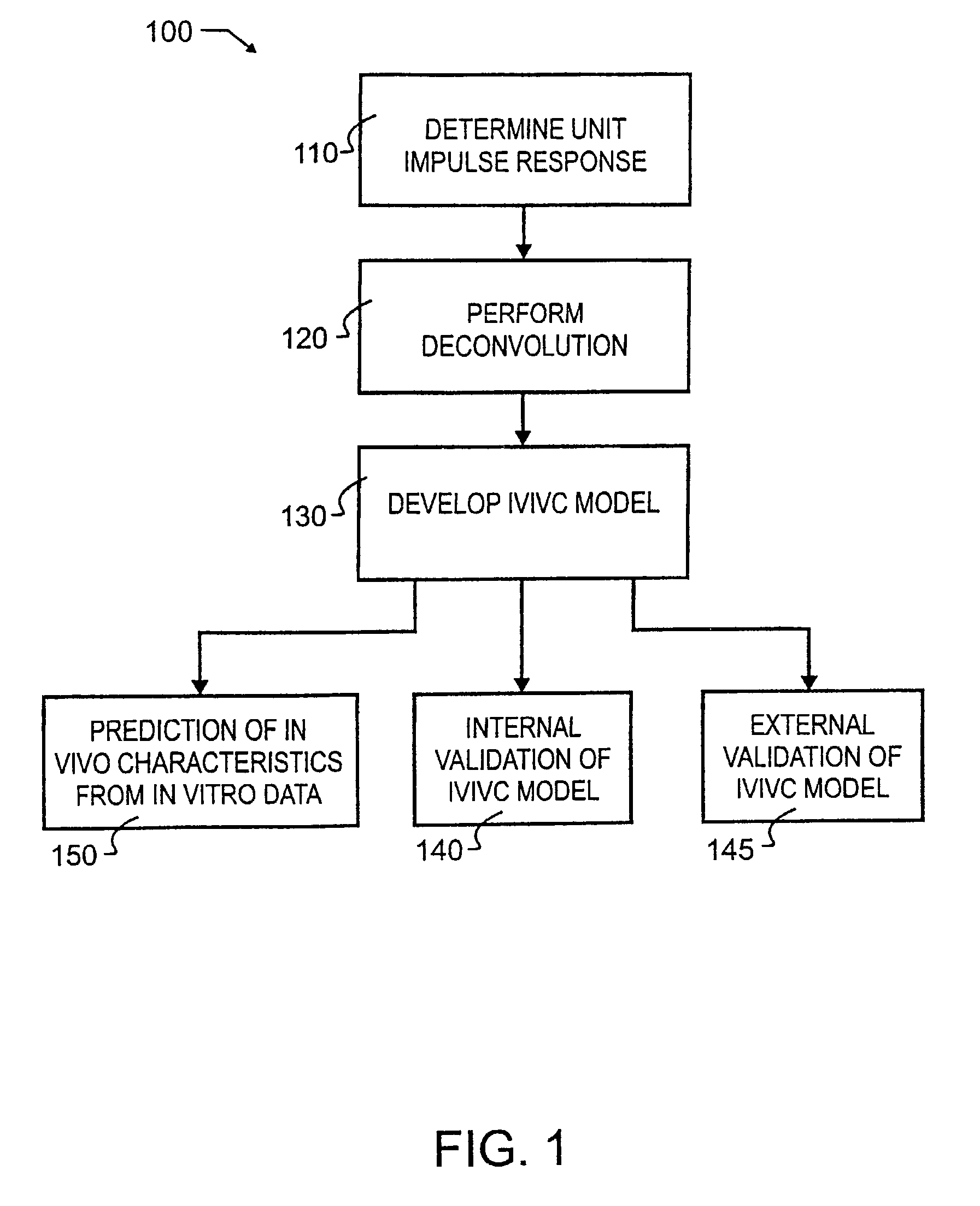
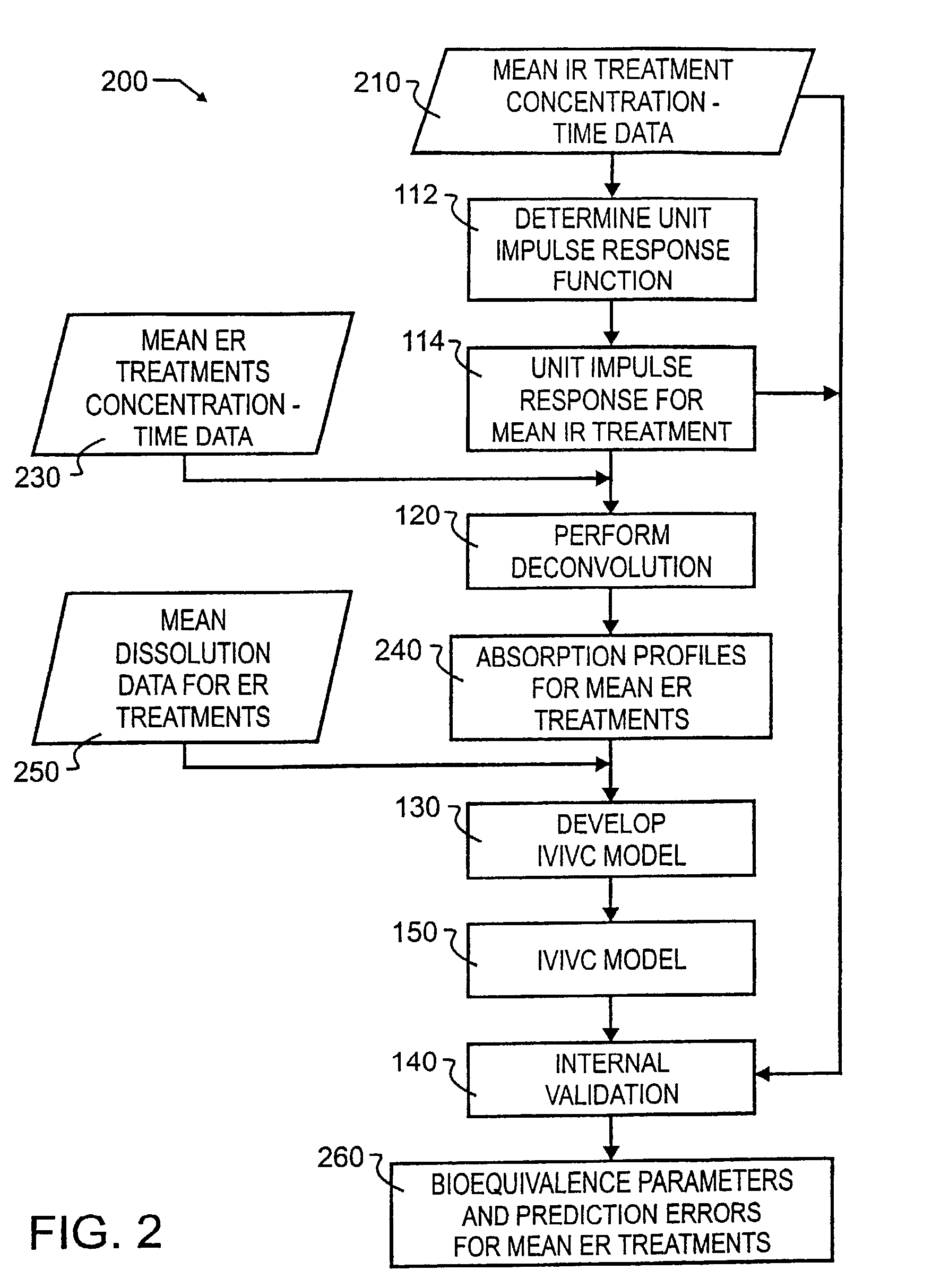
Tool for in vitro-in vivo correlation
InactiveUS7027970B2Accurately reflect observed phenomenonLaborious and time-consumingAnalogue computers for chemical processesBiostatisticsImmediate releaseComputer aid
A biological modeling system and method for enhanced computer-aided analysis of biological response data provides information synthesized from immediate and extended release in vivo data and in vitro data. An executable model of a biological system is developed from information and structures based on the data. In a preferred embodiment, a two stage approach to modeling is used in the development of an IVIVC. The first stage of the procedure is deconvolution, where the percentage of drug absorbed is determined. In the second stage, the in vivo percentage absorbed data is correlated to the in vitro fraction or percentage dissolved data. This correlation then represents a point-to-point relationship between the in vitro dissolution and the in vivo input rate of the drug from the dosage form. In such a correlation, the in vitro dissolution and in vivo absorption profiles are either directly superimposable or may be made to be superimposable by the use of a scaling factor. Prior to the deconvolution stage, a unit impulse response function can be determined from immediate-release concentration-time data. This impulse response function is used in the deconvolution process to determine the in vivo percent absorbed for the extended release formulations. A nonlinear IVIVC model is developed that can incorporate time-scaling and time-shifting into the model if needed. After the two-stage modeling is completed, the predictability of the developed IVIVC model is evaluated by both internal and external validation.
Owner:GLOBOMAX
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com