Patents
Literature
31 results about "Coulomb repulsion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Written By: Coulomb force, also called electrostatic force or Coulomb interaction, attraction or repulsion of particles or objects because of their electric charge.
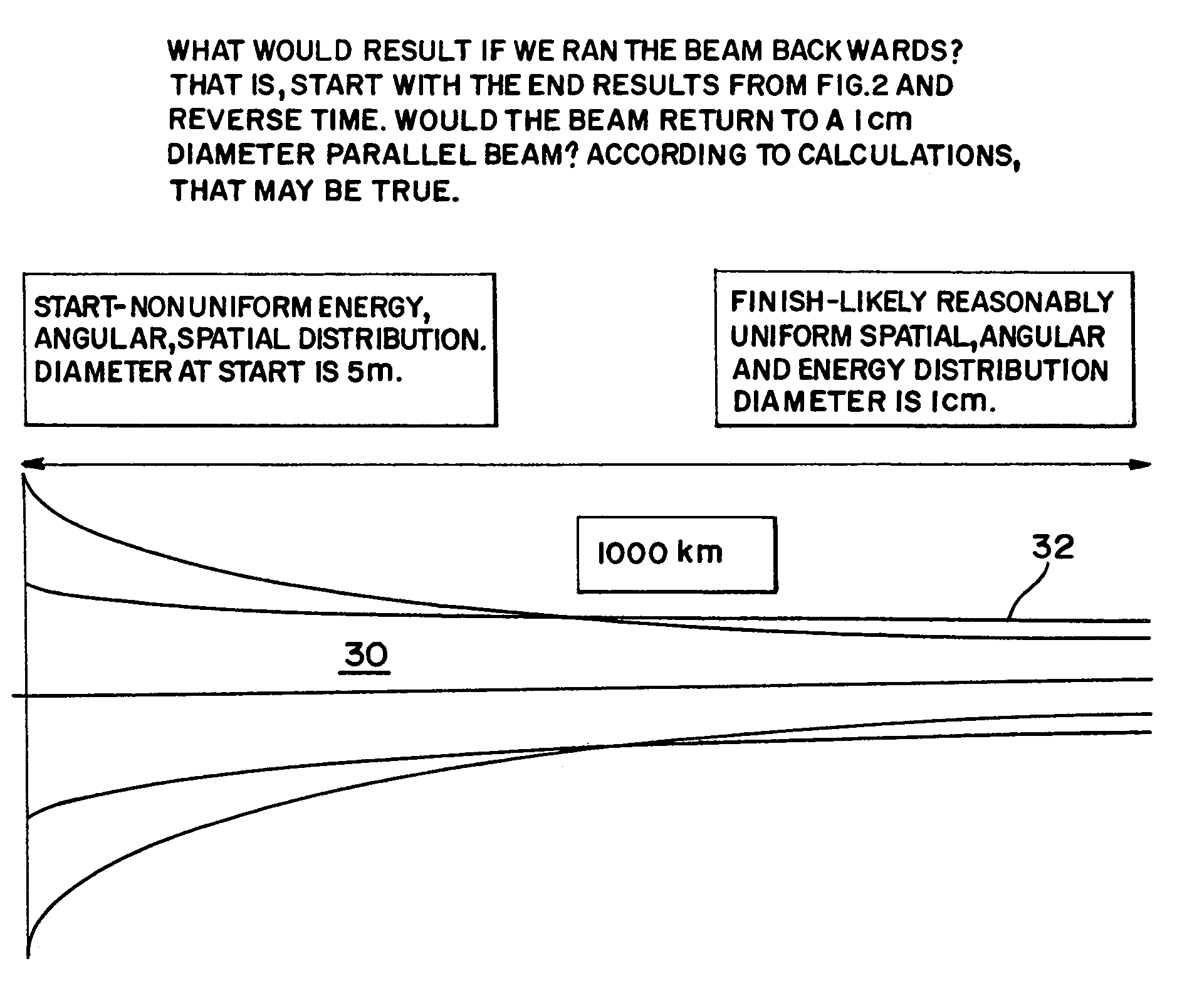
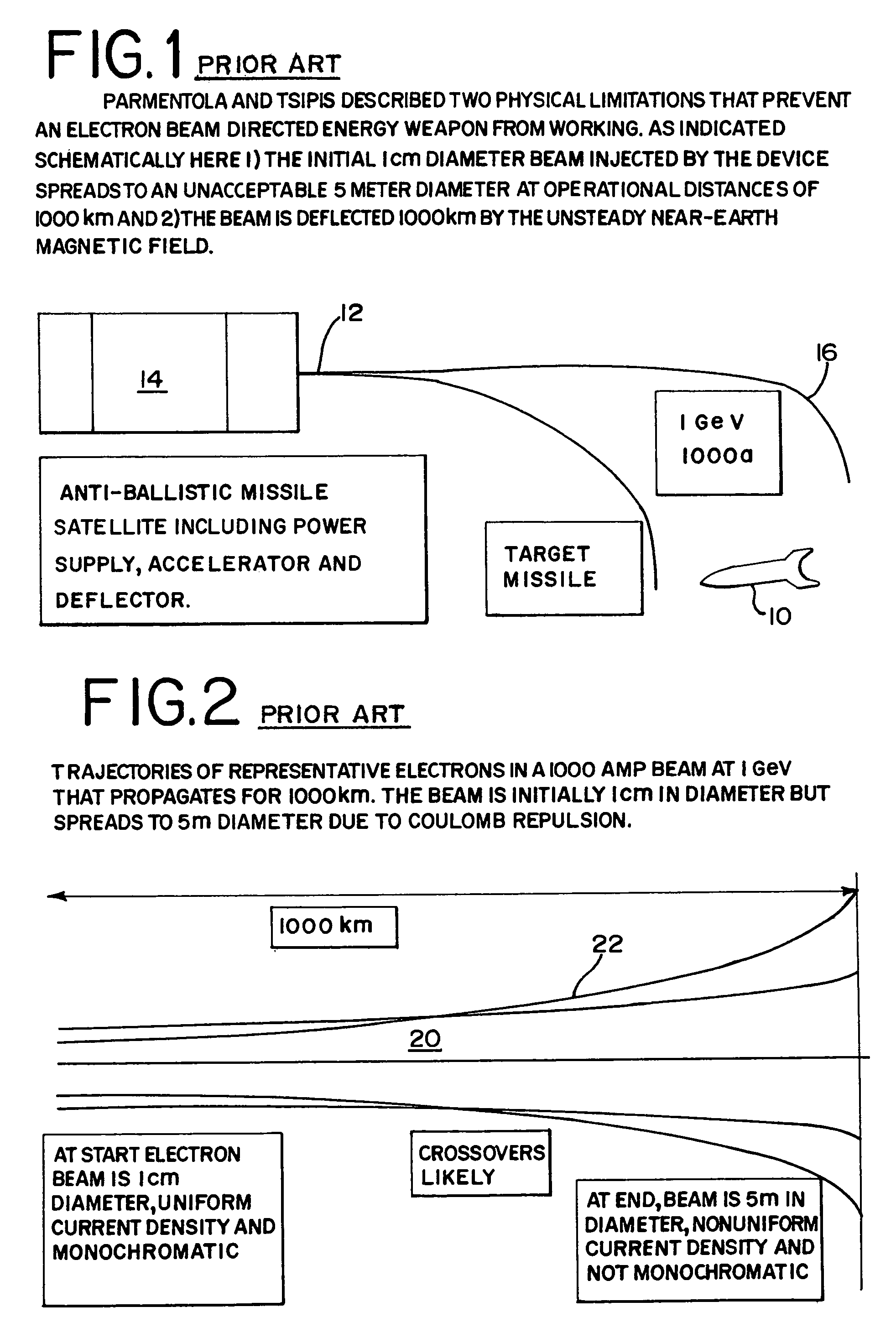
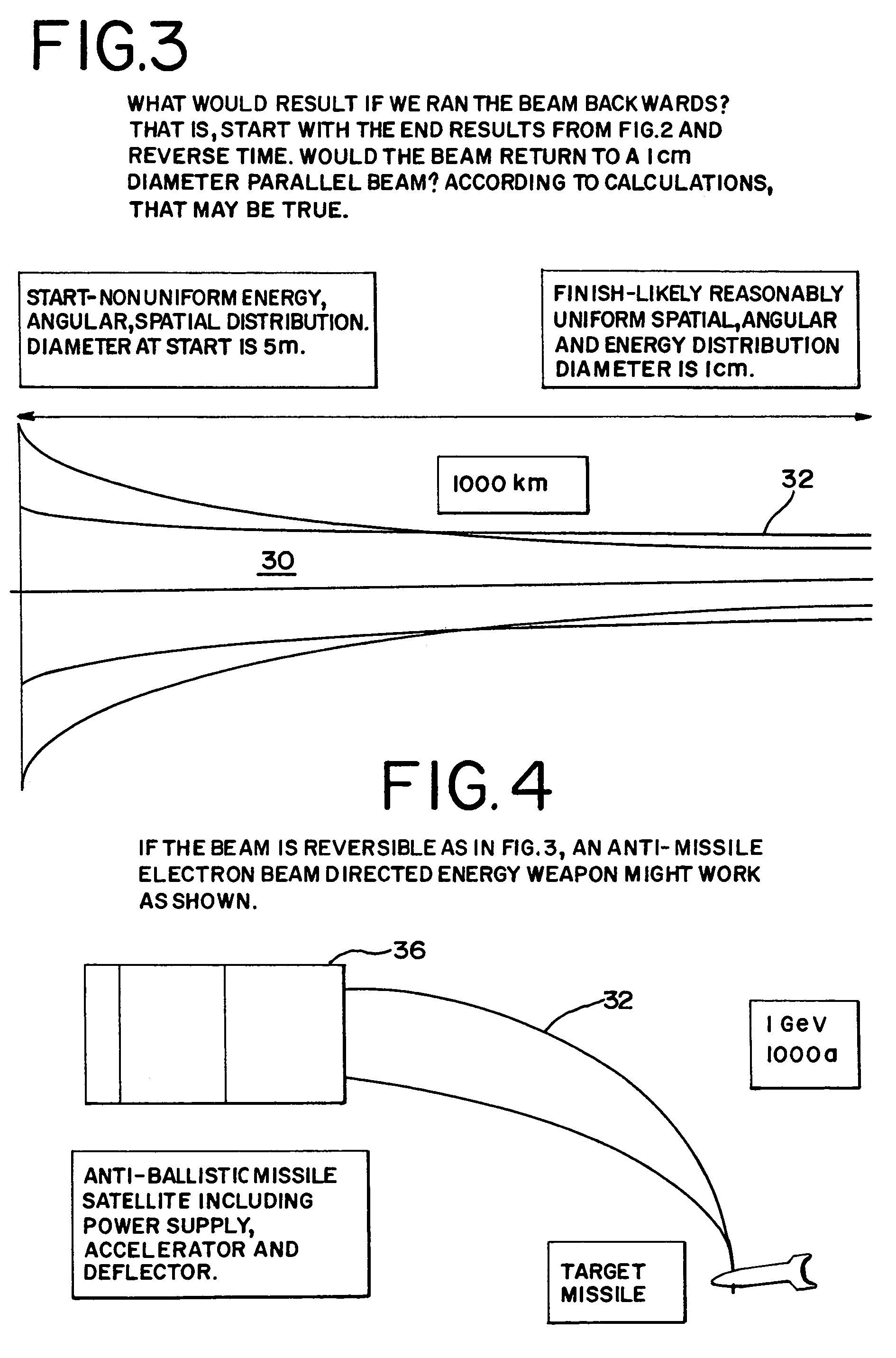
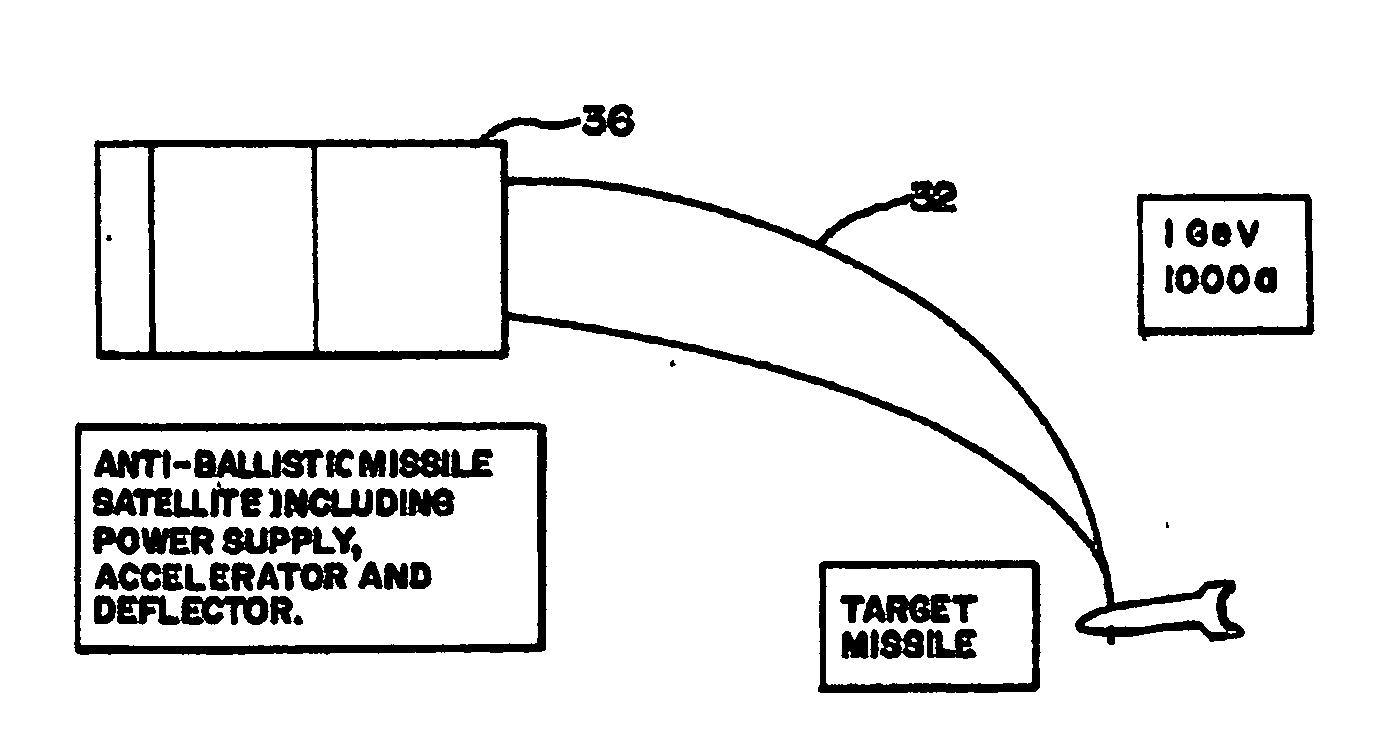
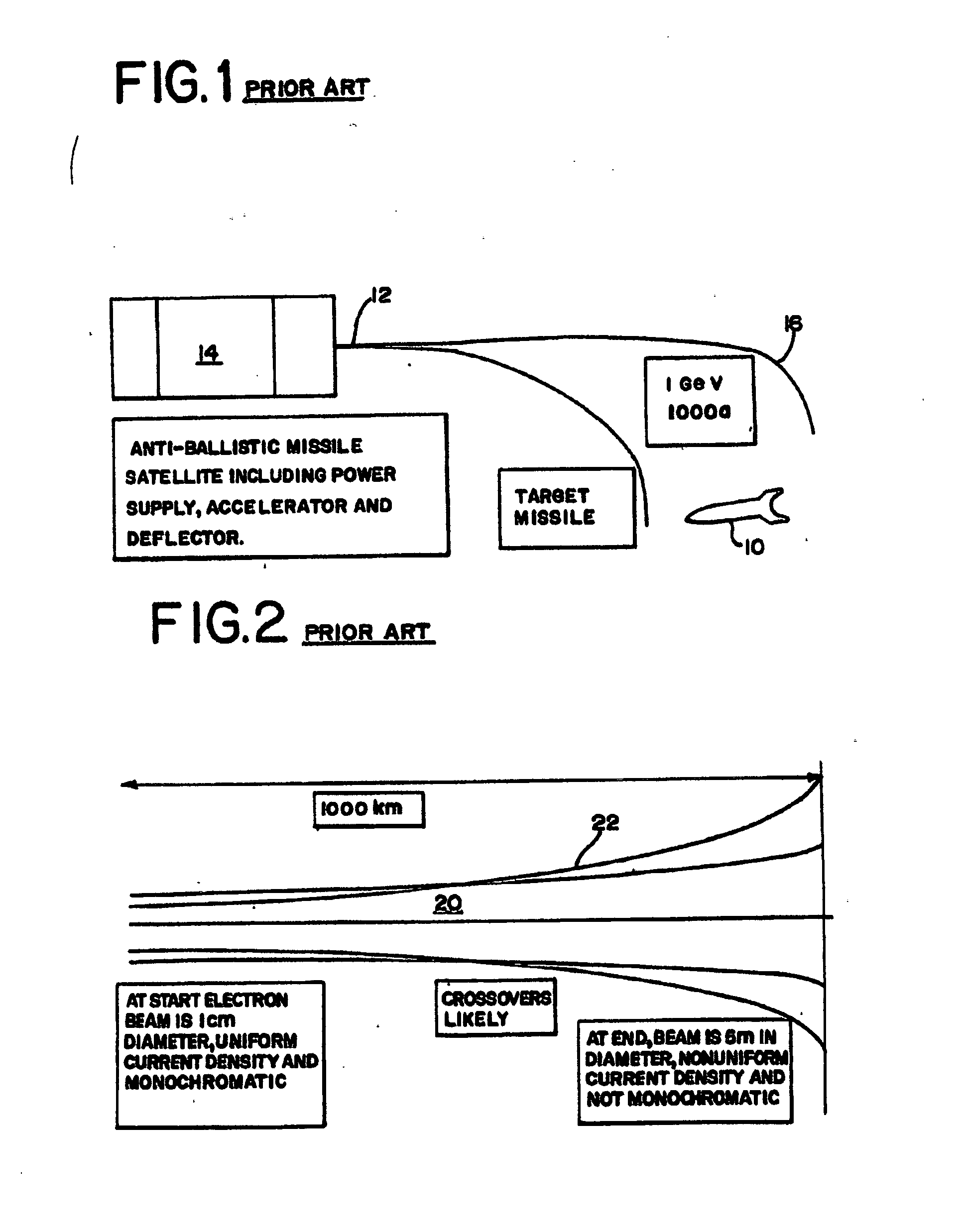
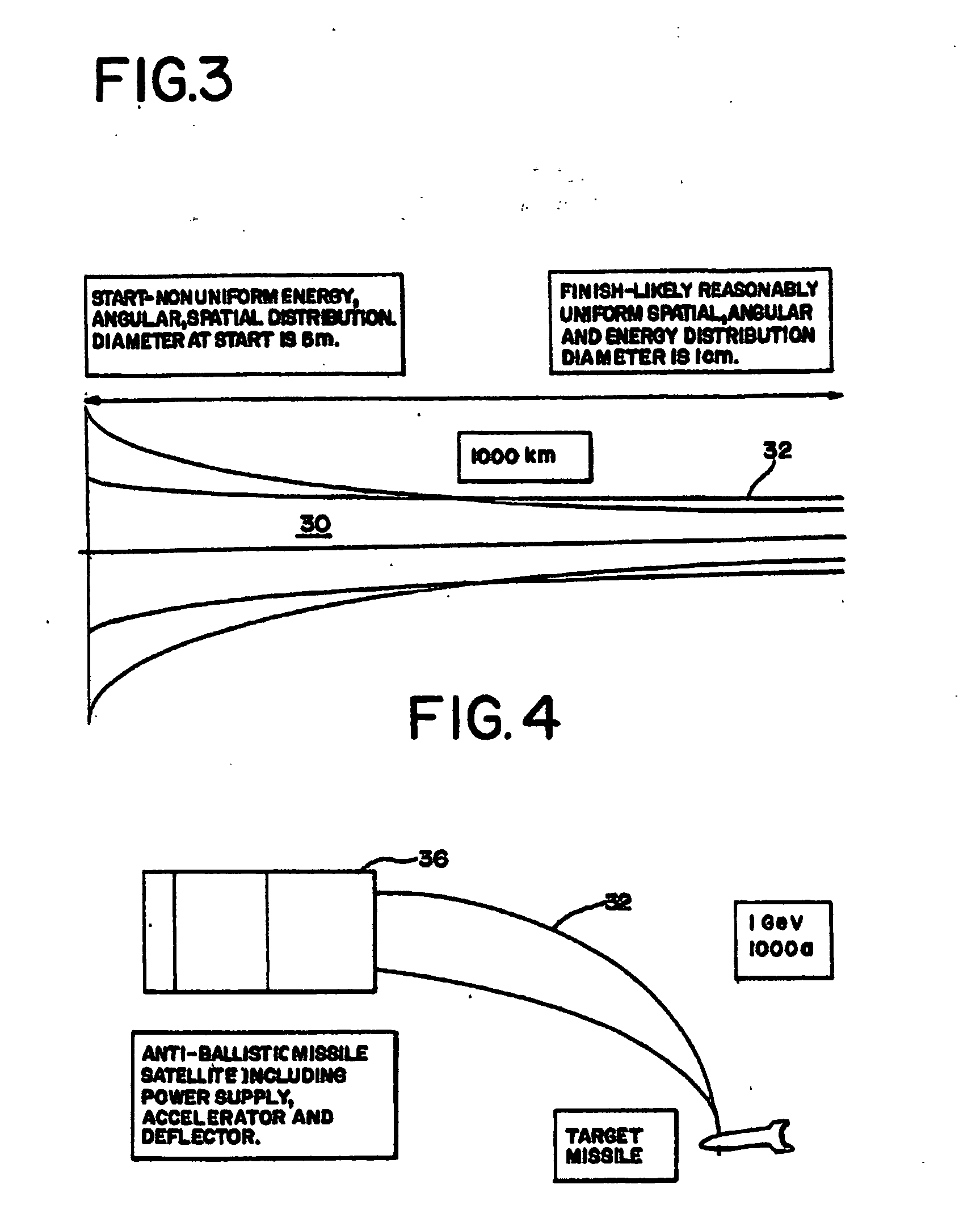
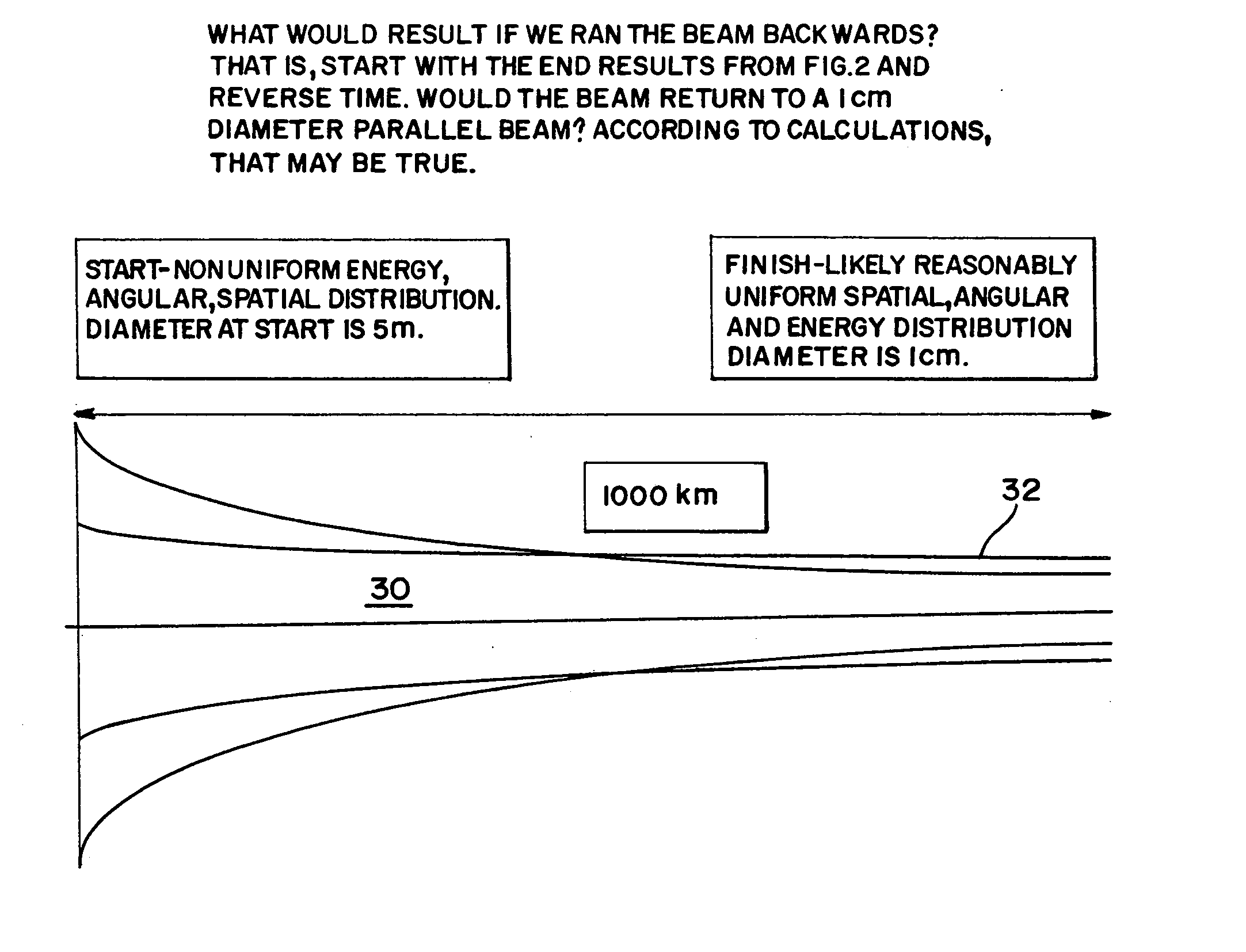
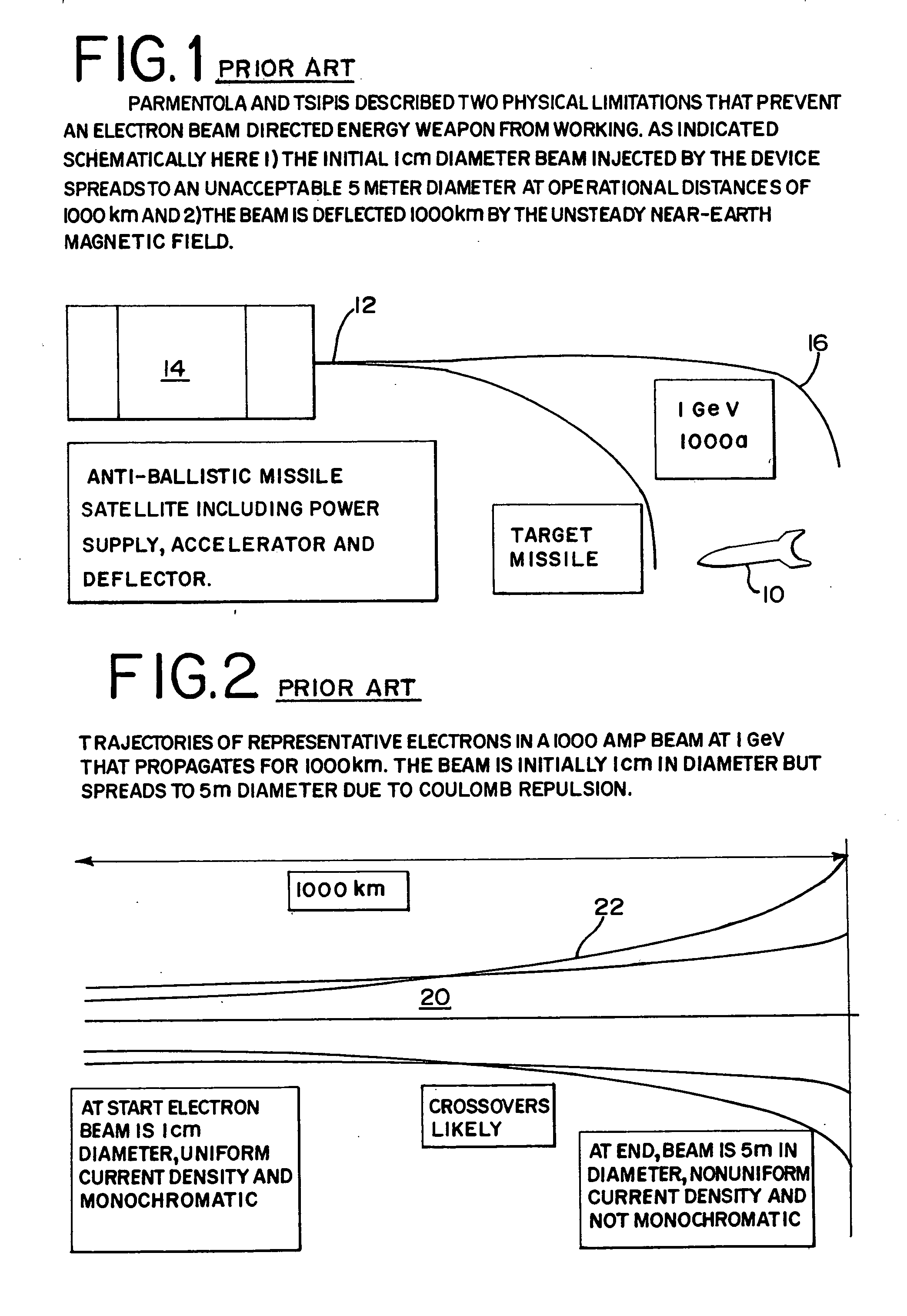
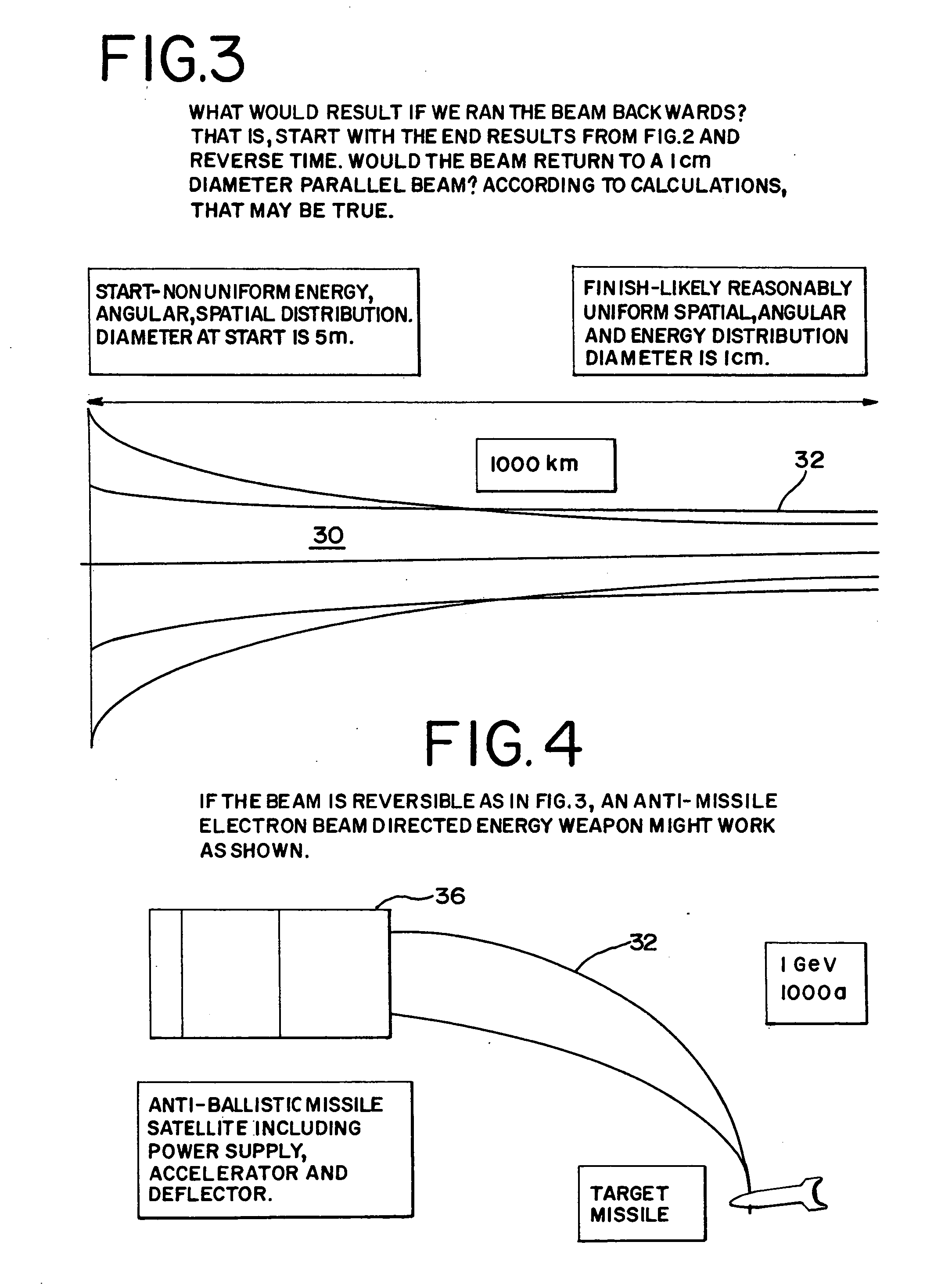
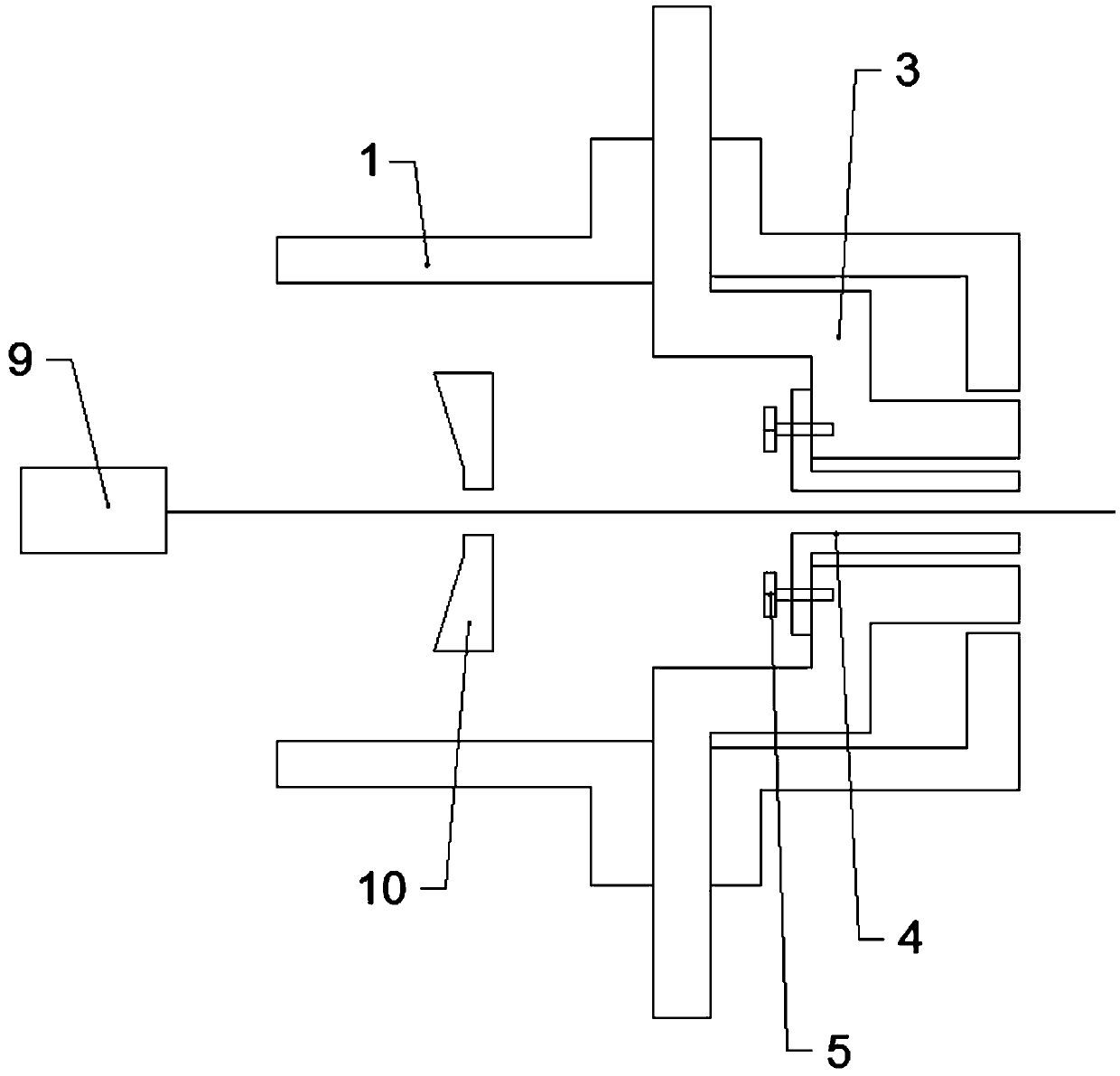
Electron beam directed energy device and methods of using same
InactiveUS7282727B2Avoid excessive distanceLess detectableDefence devicesThermometer detailsX-rayEnergy device
A method and apparatus is disclosed for an electron beam directed energy device. The device consists of an electron gun with one or more electron beams. The device includes one or more accelerating plates with holes aligned for beam passage. The plates may be flat or preferably shaped to direct each electron beam to exit the electron gun at a predetermined orientation. In one preferred application, the device is located in outer space with individual beams that are directed to focus at a distant target to be used to impact and destroy missiles. The aimings of the separate beams are designed to overcome Coulomb repulsion. A method is also presented for directing the beams to a target considering the variable terrestrial magnetic field. In another preferred application, the electron beam is directed into the ground to produce a subsurface x-ray source to locate and / or destroy buried or otherwise hidden objects including explosive devices.
Owner:RETSKY MICHAEL W
Coulomb force neutralized fusion reactor
A fusion reactor that has a multiple of fuel rings per second that spin in a spiral form. The fusion reactor produces a sustainable, controlled fusion reaction that produces more energy than it uses. The reactor employs a system of resonant magnetic fields that control the direction of the fuel particles' momentum and polarity, and neutralizes the interactive forces of the fuel particles linear Coulomb repulsions. The rotating ring has a geometric rate of radius reduction for ring stability and efficient fusion reaction. Preferably, a stream of lithium nuclei are utilized as fuel. In merging lithium nuclei within the controlled spiral of a resonant magnetic field, positive alpha charges are produced. These high-energy alpha charges are then directed into a generator for the purpose of pumping electrons to produce electricity.
Owner:FRANZ DENNIS L
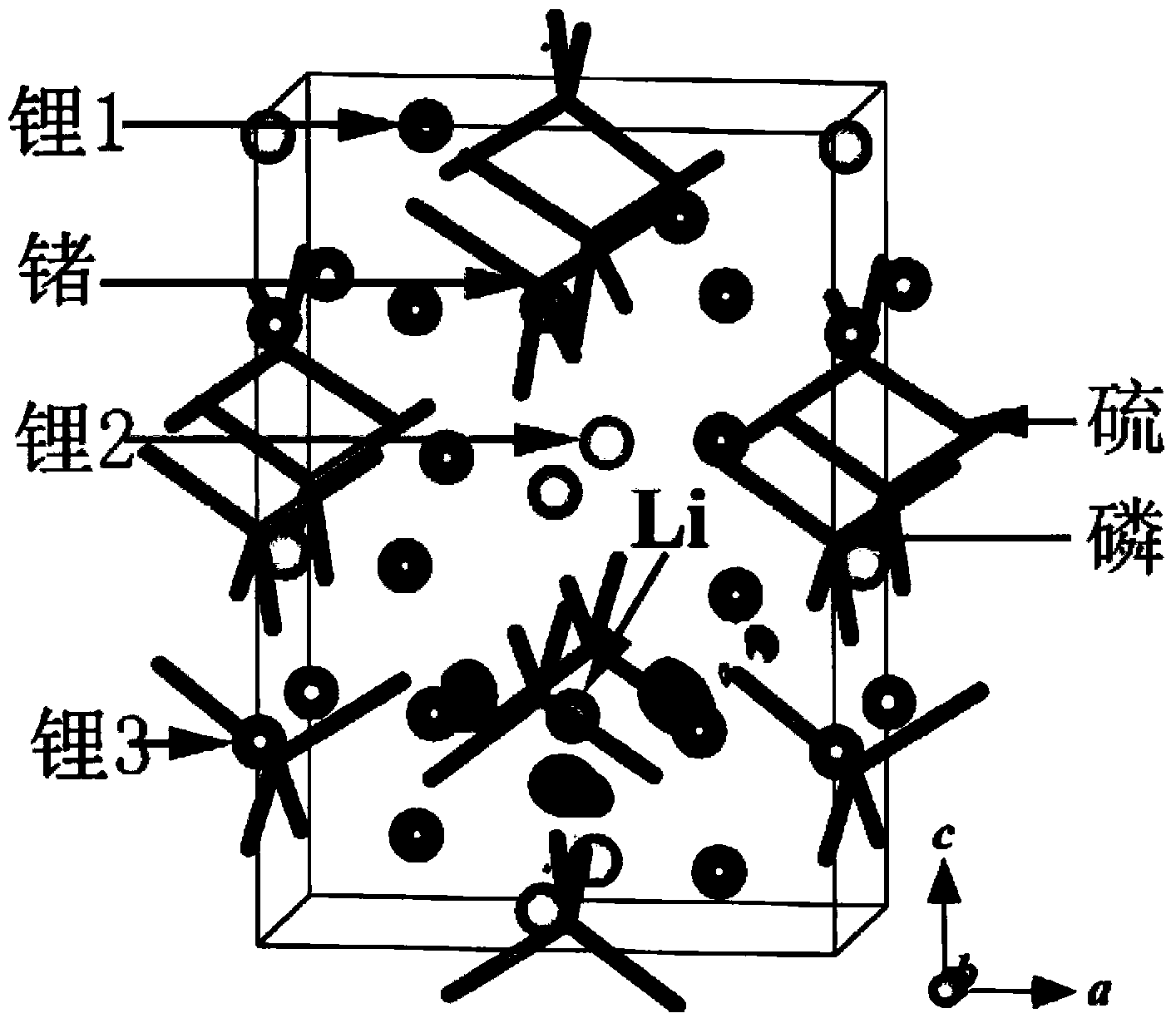
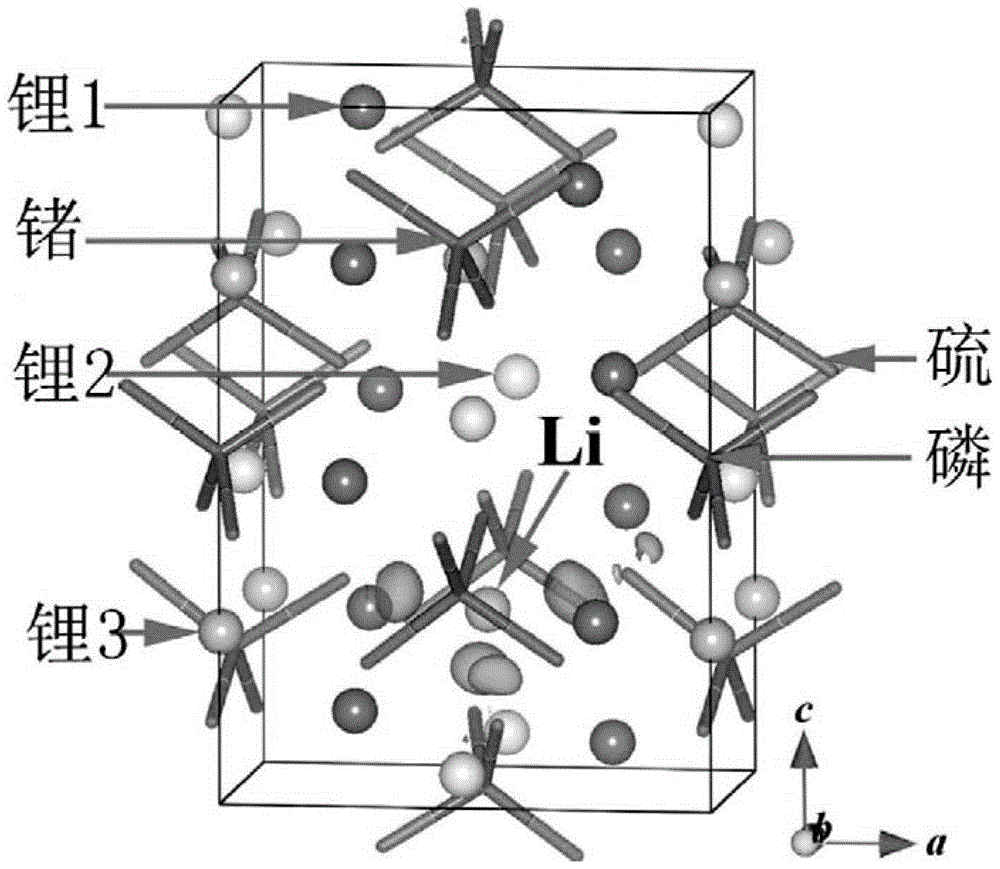
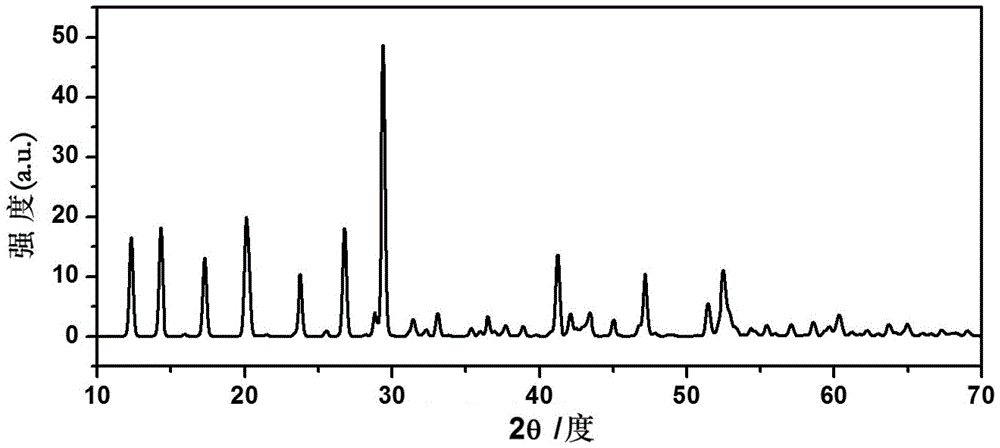
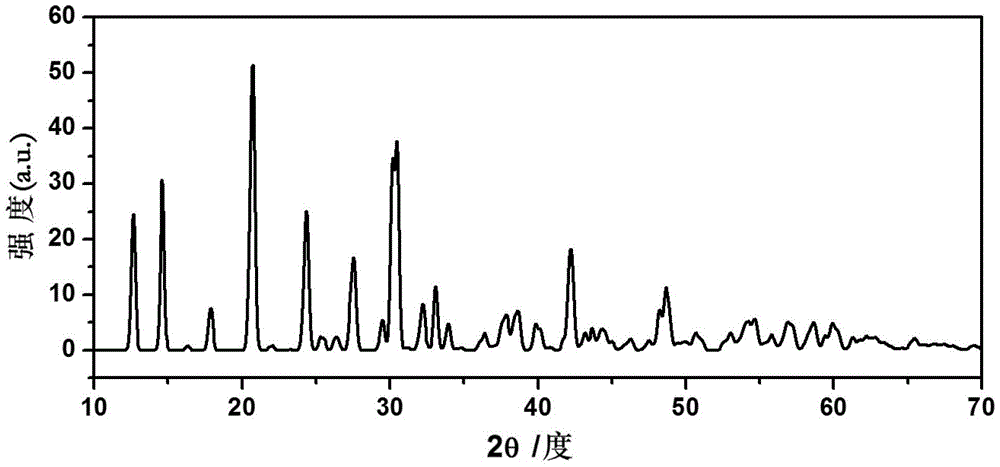
Solid-state electrolyte material of lithium ion battery
ActiveCN103401018AImprove structural stabilityIncrease attractivenessSecondary cellsSolid state electrolyteSpace group
The invention provides a solid-state electrolyte material of a lithium ion battery. The general formula of the solid-state electrolyte material is (LimZn)MP2X12, and the solid-state electrolyte belongs to a triclinic crystal system and a P1 space group, wherein Z is a high-valence metal element, the cationic valence is more than +1 valence and less than or equal to +3 valence, and the high-valence metal element Z is at least one of Mg, Al, Ca, Ti, Cu, Zn, Ga, In, Sr, Ru, Rh, Pd, Ag, Cd, Ba, Os, Ir, Pt or Hg; M is at least one of Ge, Si, Sn, Al or P; and X is at least one of O, S or Se. The research on the micro structure characteristics of the solid-state electrolyte material (LimZn)MP2X12 indicates that the micro interaction mechanisms such as Coulomb force, Van der Waals force and the like have important effect on the structure stability of the solid electrolyte material; and by enhancing the Coulomb attraction effect among ions and enhancing the shielding of the Coulomb repulsion effect among the ions, the total energy of the material system is greatly reduced, thereby enhancing the structure stability of the solid electrolyte material.
Owner:CONTEMPORARY AMPEREX TECH CO
Electron beam directed energy device and methods of using same
InactiveUS20100171446A1Avoid excessive distanceLess detectableElectrode and associated part arrangementsCathode-ray tube indicatorsX-rayEnergy device
A method and apparatus is disclosed for an electron beam directed energy device. The device consists of an electron gun with one or more electron beams. The device includes one or more accelerating plates with holes aligned for beam passage. The plates may be flat or preferably shaped to direct each electron beam to exit the electron gun at a predetermined orientation. In one preferred application, the device is located in outer space with individual beams that are directed to focus at a distant target to be used to impact and destroy missiles. The aimings of the separate beams are designed to overcome Coulomb repulsion. A method is also presented for directing the beams to a target considering the variable terrestrial magnetic field. In another preferred application, the electron beam is directed into the ground to produce a subsurface x-ray source to locate and / or destroy buried or otherwise hidden objects including explosive devices.
Owner:RETSKY MICHAEL WALTER
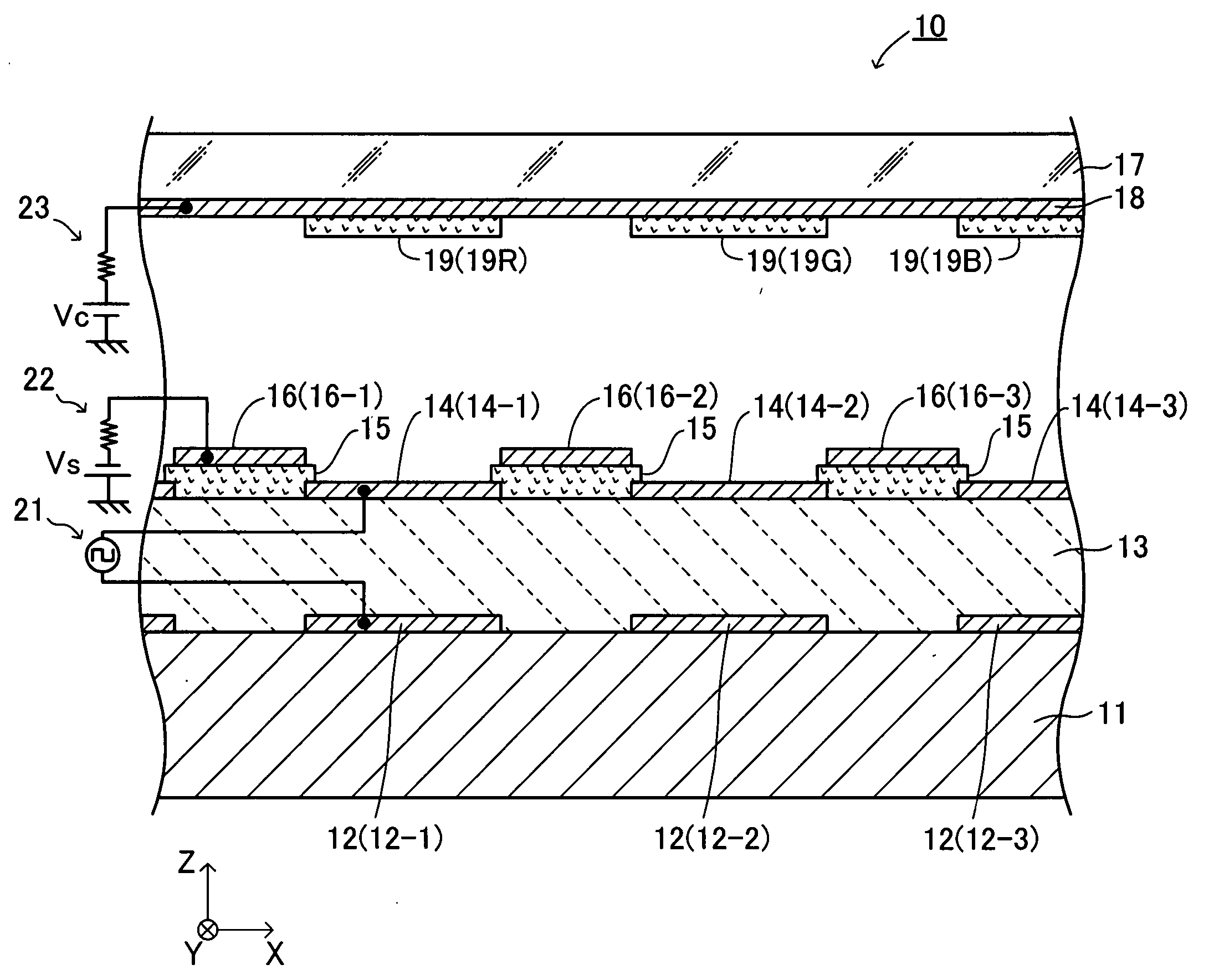
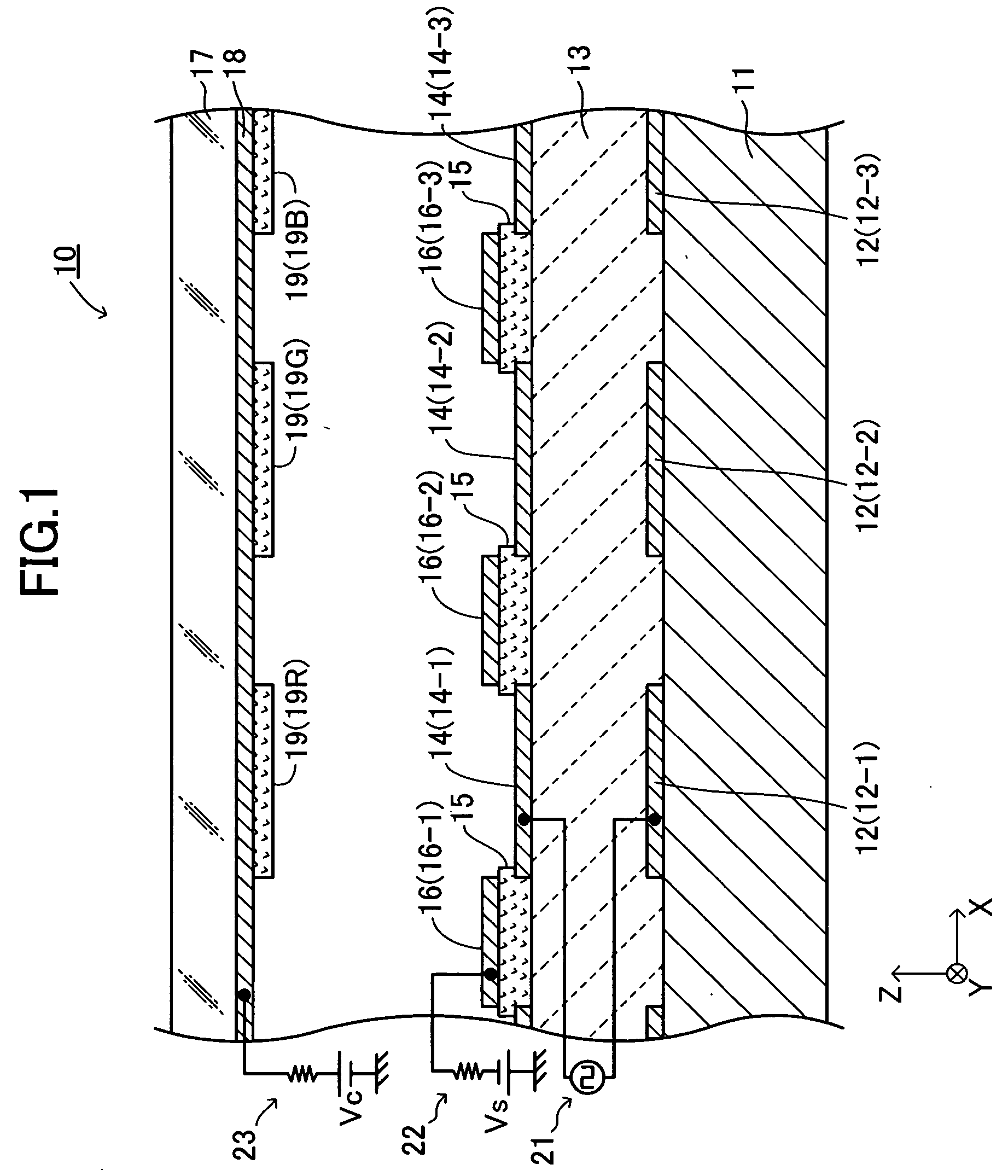
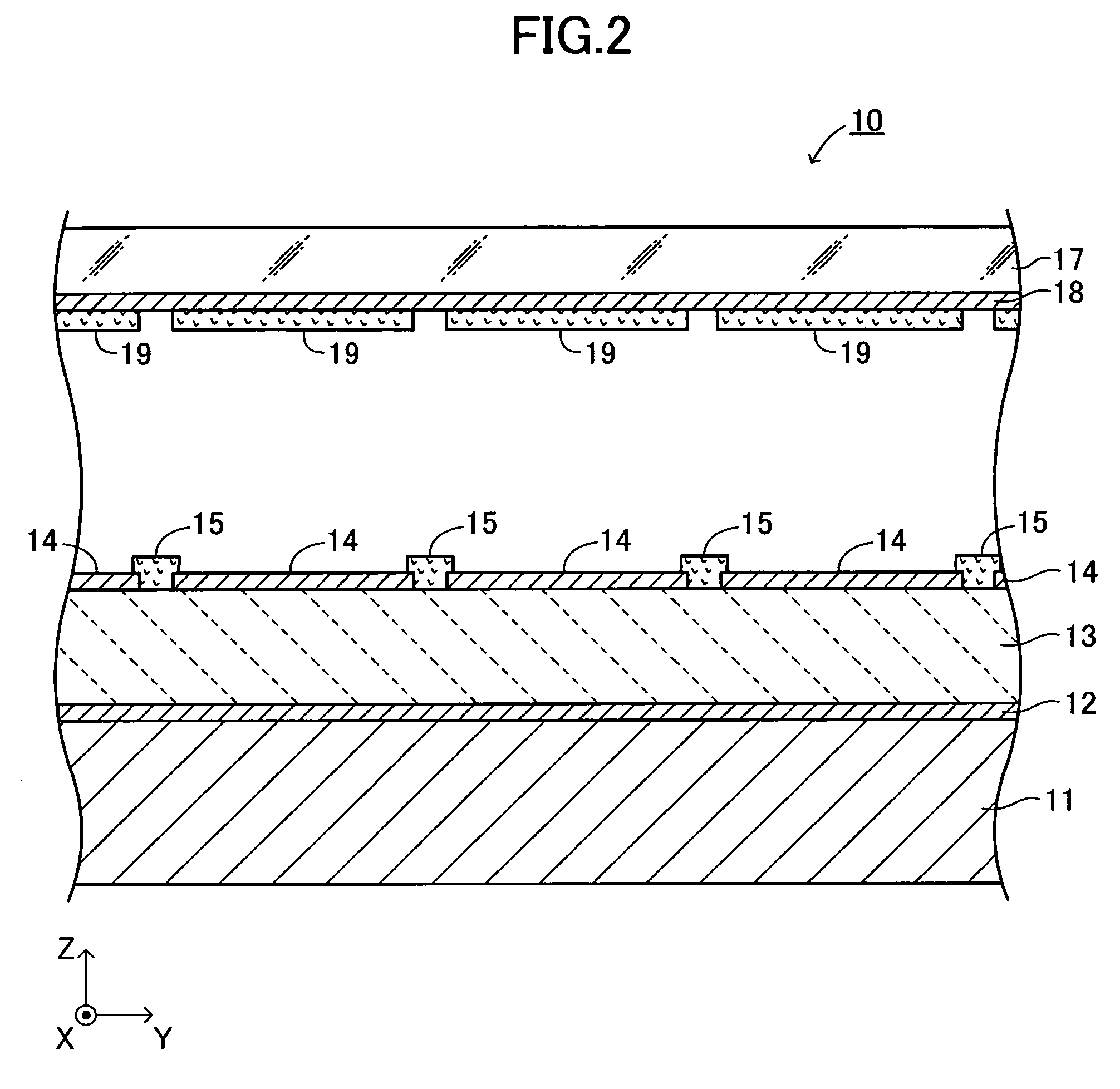
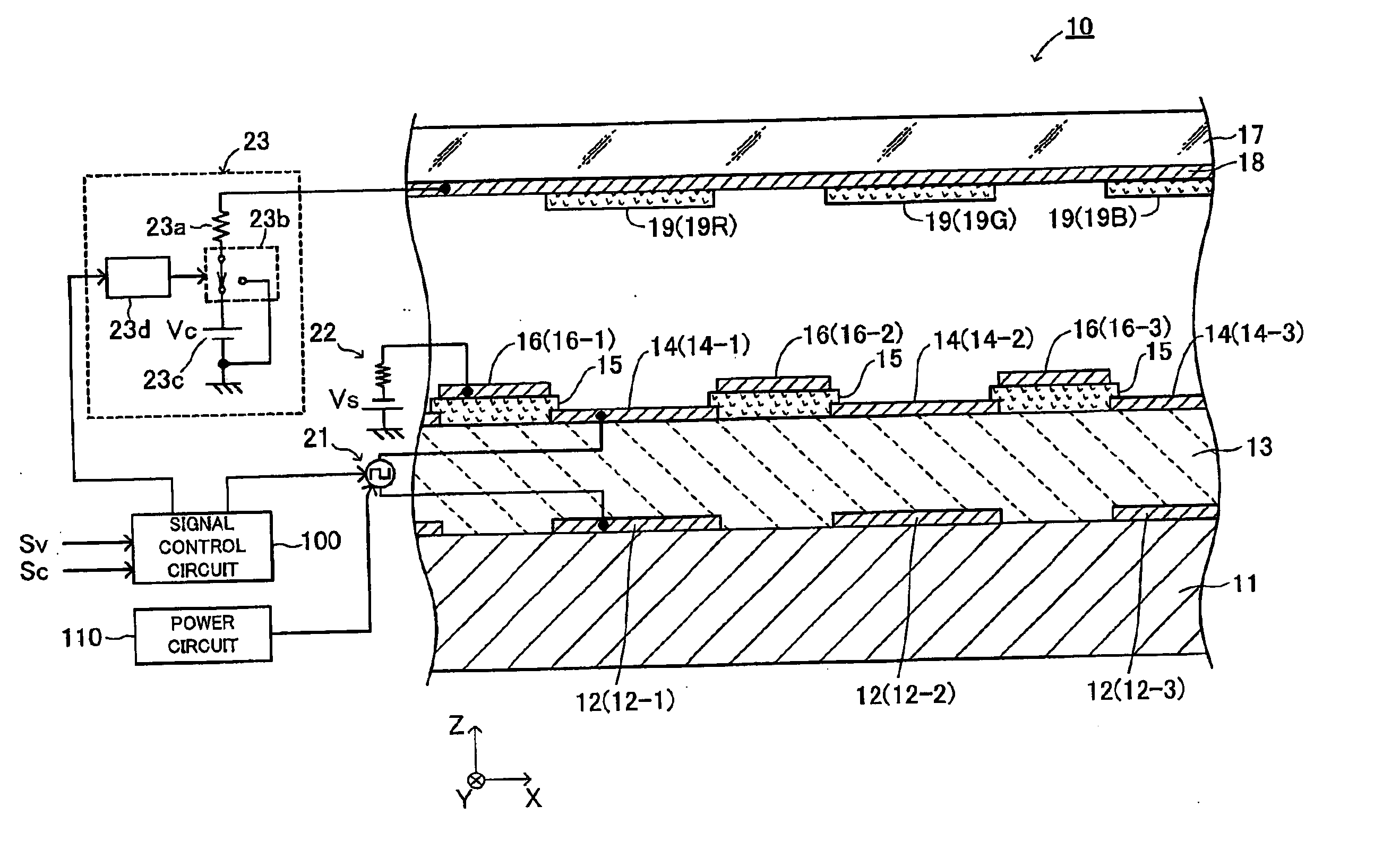
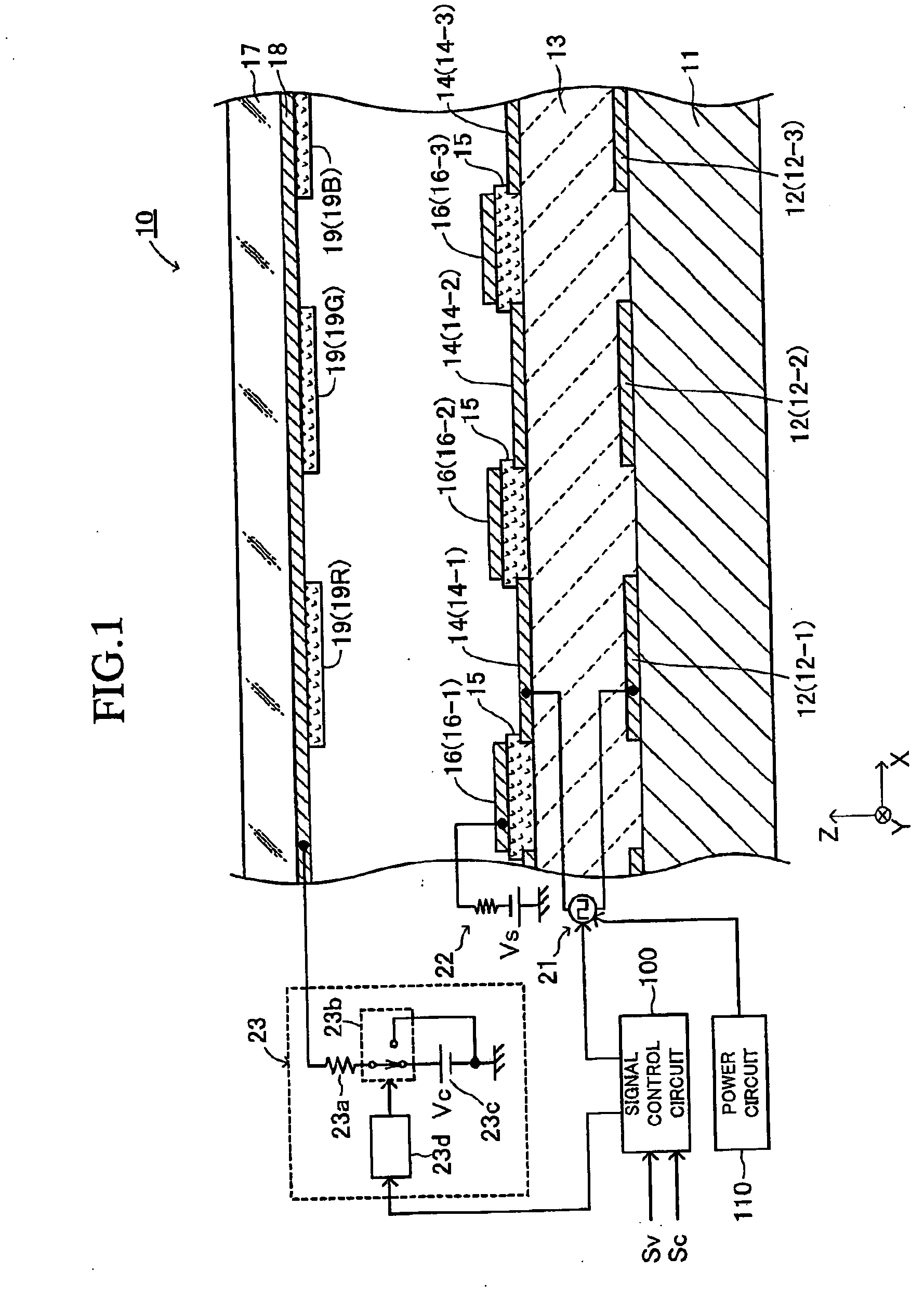
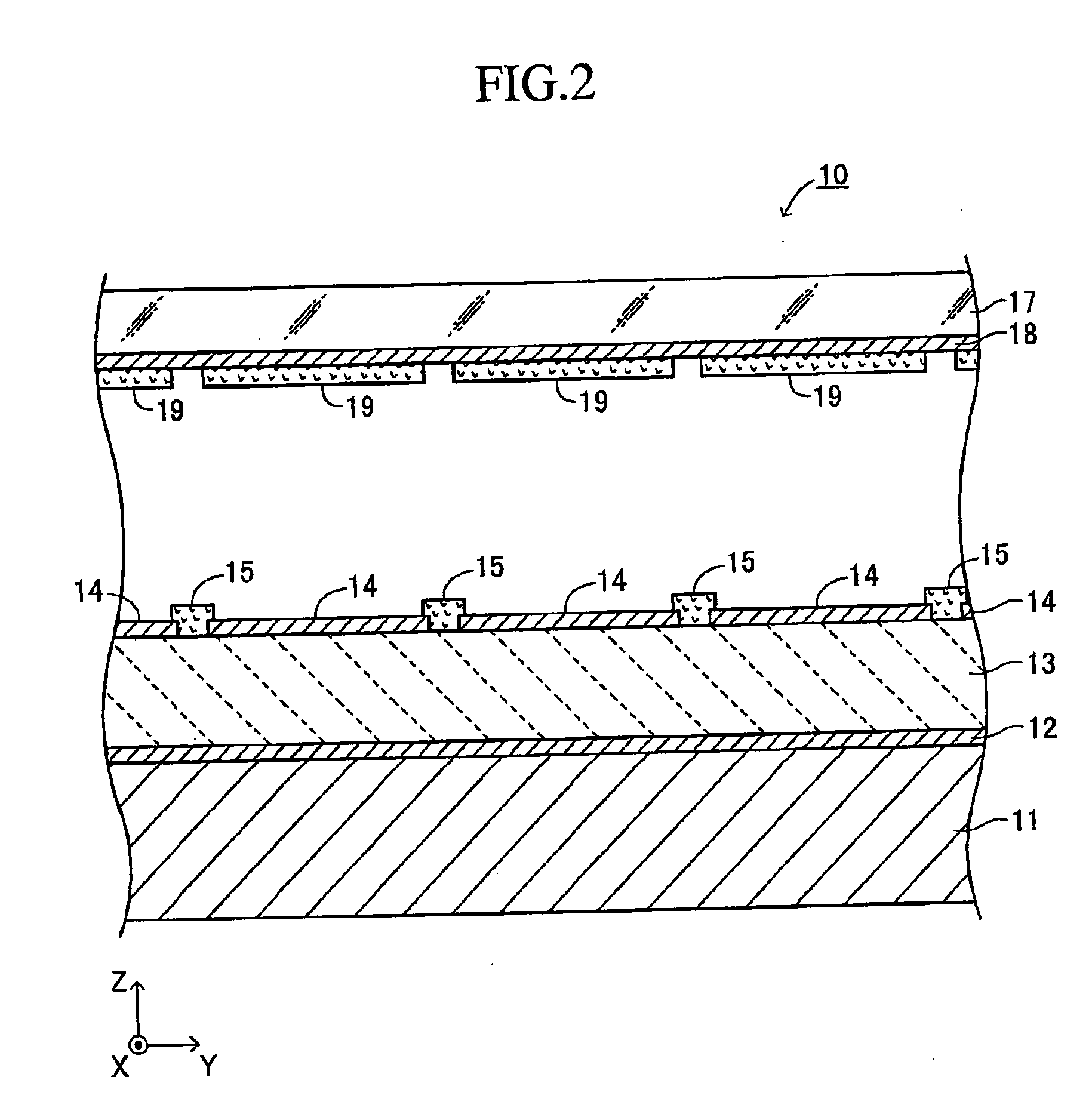
Electron-emitting apparatus
InactiveUS7304440B2Avoid emissionsSuppress emissionDischarge tube luminescnet screensCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesElectricityPotential difference
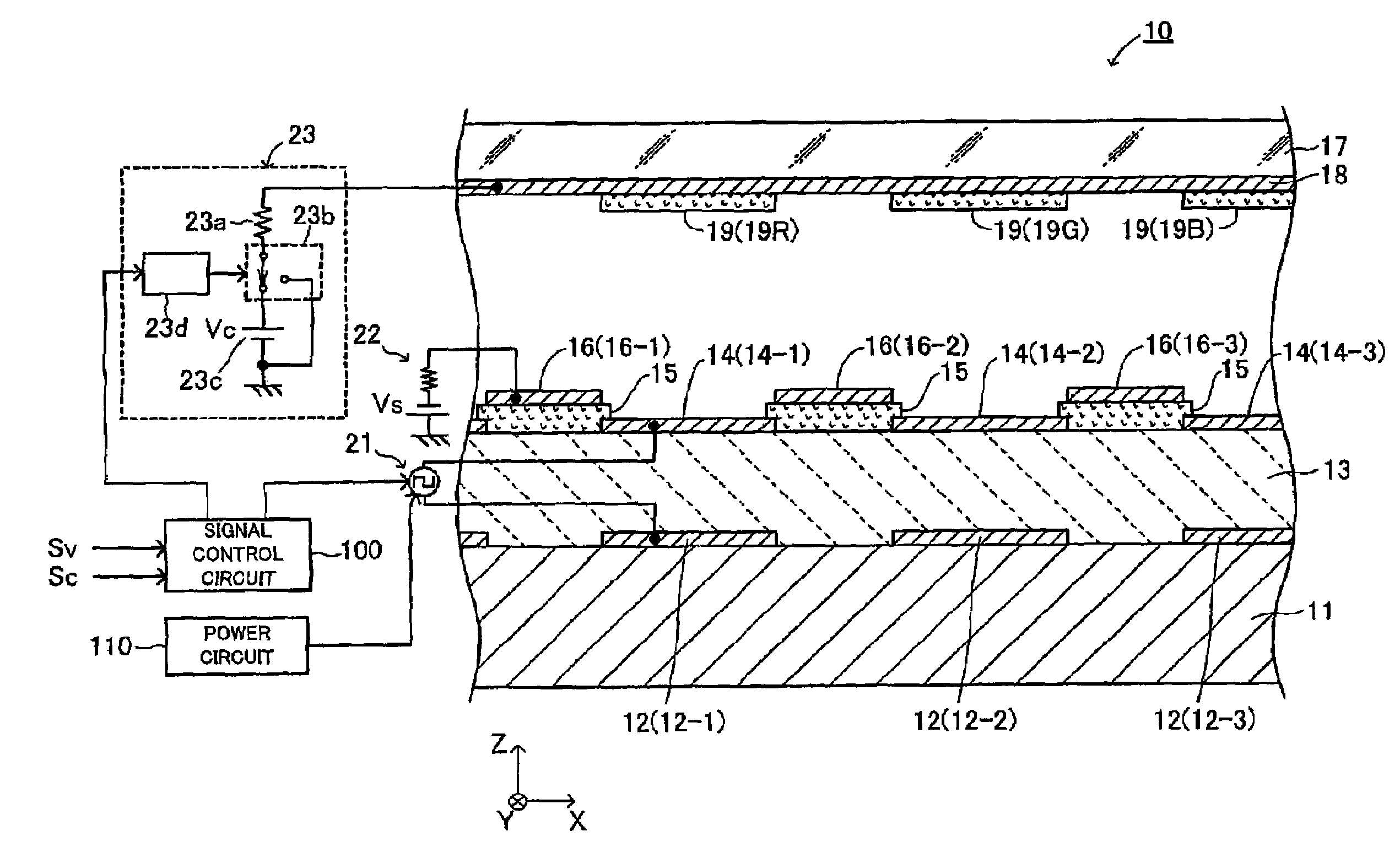
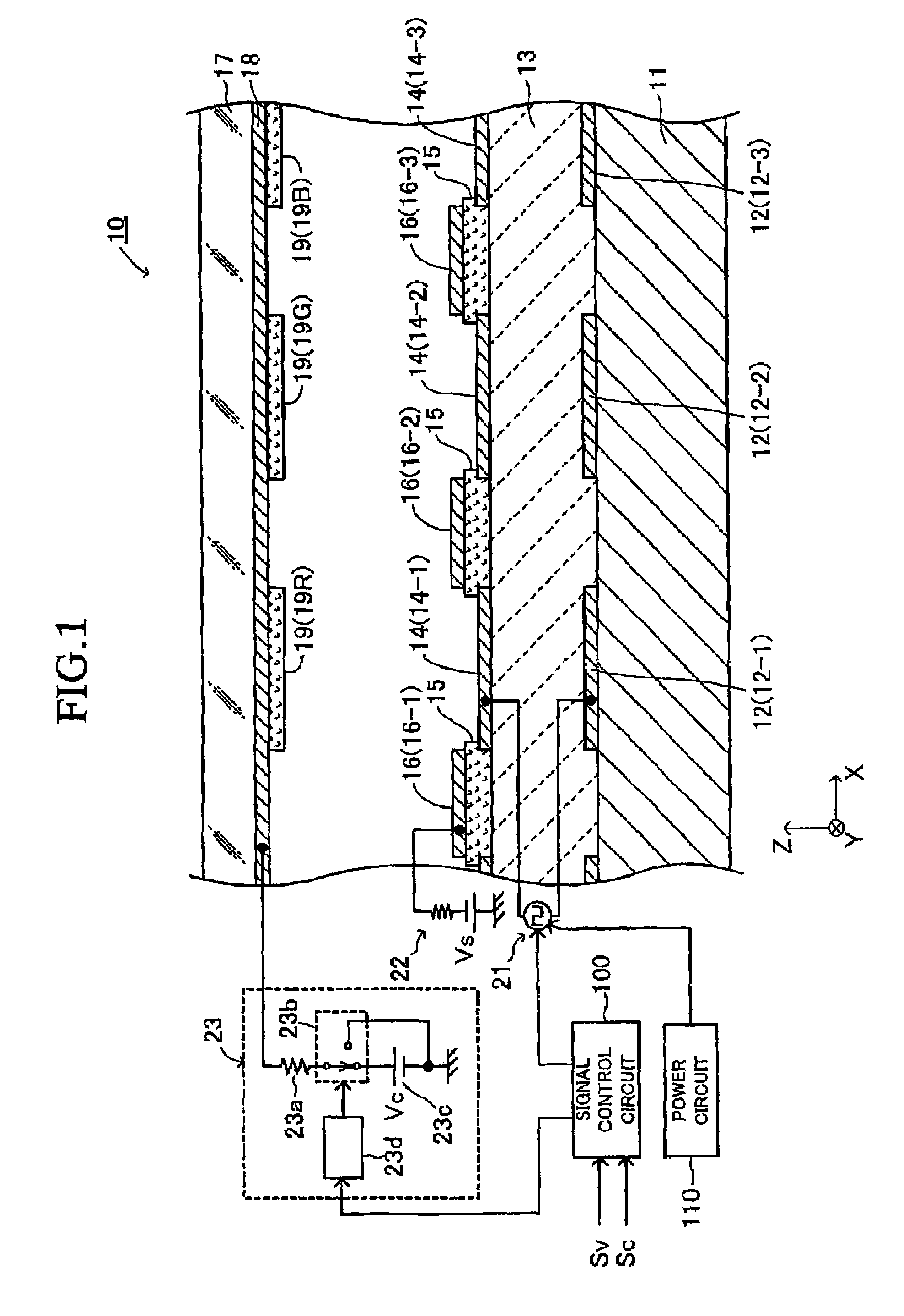
An electron emitting apparatus includes a lower electrode, an emitter section made of a dielectric material, a plurality of upper electrodes having micro through holes, and a collector electrode opposing the upper electrodes. In this electron-emitting apparatus, electrons are accumulated in the emitter section by controlling the potential difference (drive voltage) between the lower and upper electrodes with respect to the potential of the lower electrode to a negative predetermined voltage. At this time, the collector electrode of the electron-emitting apparatus is grounded. Thus, unnecessary electron-emitting is suppressed. Subsequently, the drive voltage is changed to a positive predetermined voltage. As a result, polarization reversal occurs in the emitter section, and accumulated electros are emitted through the micro through holes in the upper electrodes by Coulomb repulsion. At this time, a positive voltage Vc is applied to the collector electrode to give large energy to accelerate the electrons.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Electron beam directed energy device and methods of using same
InactiveUS20070029497A1Avoid excessive distanceLess detectableThermometer detailsStability-of-path spectrometersX-rayLight beam
A method and apparatus is disclosed for an electron beam directed energy device. The device consists of an electron gun with one or more electron beams. The device includes one or more accelerating plates with holes aligned for beam passage. The plates may be flat or preferably shaped to direct each electron beam to exit the electron gun at a predetermined orientation. In one preferred application, the device is located in outer space with individual beams that are directed to focus at a distant target to be used to impact and destroy missiles. The aimings of the separate beams are designed to overcome Coulomb repulsion. A method is also presented for directing the beams to a target considering the variable terrestrial magnetic field. In another preferred application, the electron beam is directed into the ground to produce a subsurface x-ray source to locate and / or destroy buried or otherwise hidden objects including explosive devices.
Owner:RETSKY MICHAEL W
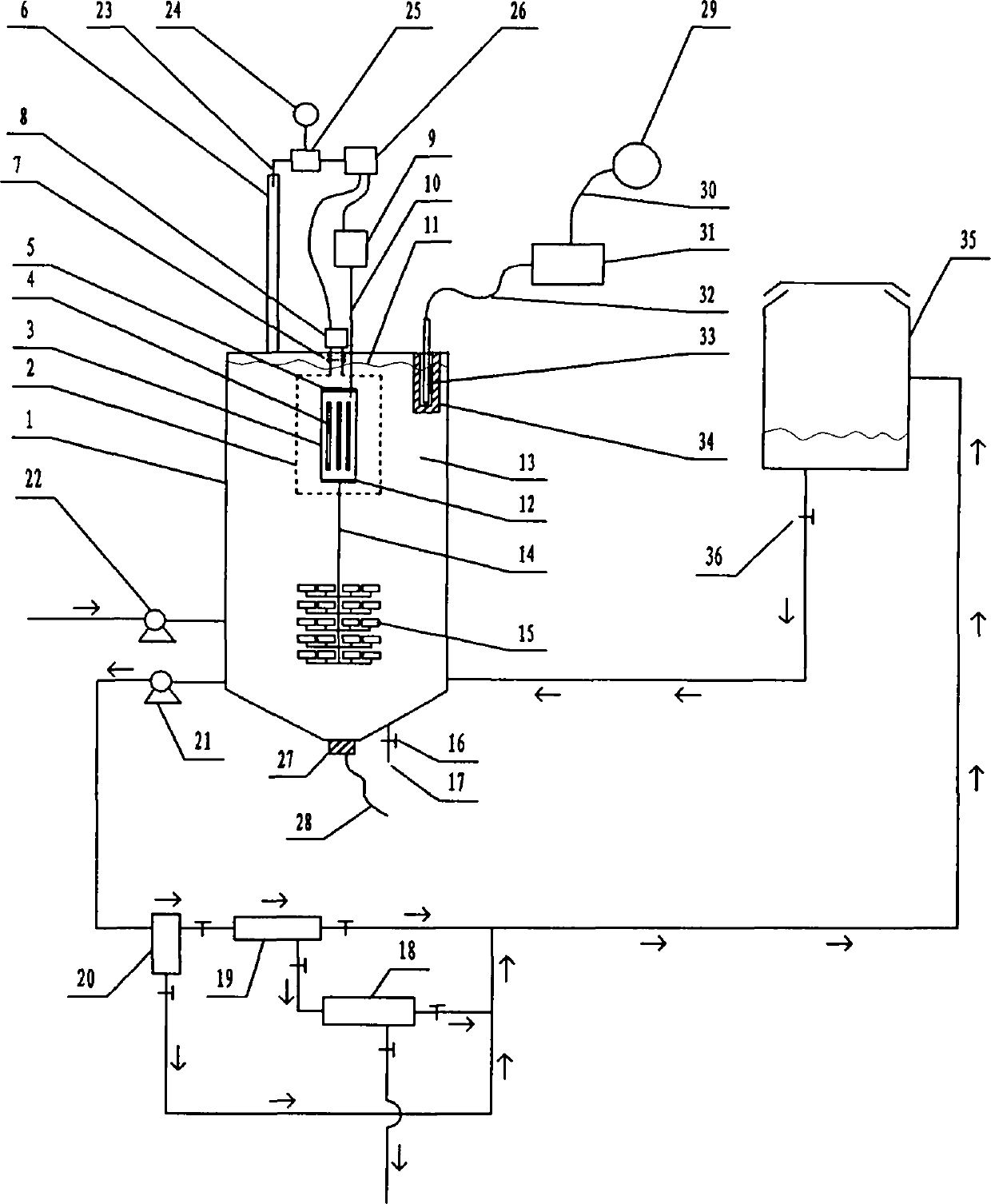
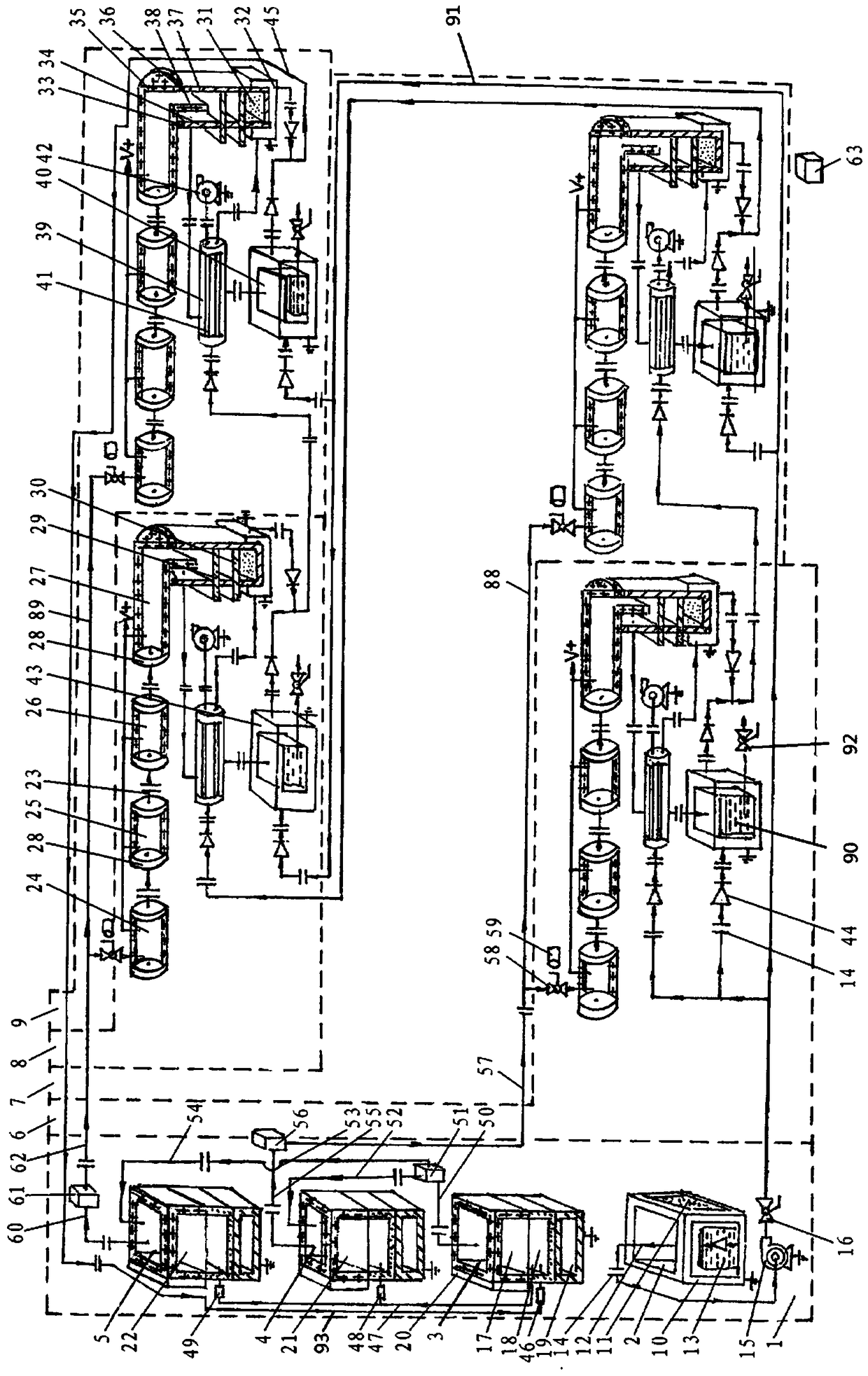
Large-capacity wastewater degradation reactor capable of infusing charge characteristics of photocatalyst particles
InactiveCN103253808AWeaken stubborn attachmentResists stubborn attachmentWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisElectricityMicrowave
The invention relates to a large-capacity wastewater degradation reactor capable of infusing charge characteristics of photocatalyst particles and belongs to the field of a wastewater treatment technology. The existing related background technique has the problems that a nano photocatalyst runs off, microwave energy is wasted, the single-pot wastewater treatment amount of a reactor is relatively small, a finishing moment of a degradation reaction is difficult to distinguish, a contact agent reunited object can not be forcedly dissipated in situ, the contact agent reunion can not be observed in time, the charge characteristics of contact agent particles can not be greatly utilized and the like, and the scheme aims to solve the problems. In the scheme, a metal cage can be used for restricting microwaves so as to greatly enlarge the reactor; the structure in the scheme strengthens inner liquid to be greatly circulated; the structure strengthens the interception of a contact agent by using a charge negative electricity hollow fiber membrane by Coulomb repulsion; the structure can forcedly dissipate the contact agent reunited object in situ and incidentally cleans a quartz tube in an ultrasound manner; the structure can automatically switch off a related power supply in time at a finishing point of degradation; and the structure can automatically detect main incentive parameters of the reunion of the contact agent.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Electron-emitting apparatus
InactiveUS20060132024A1Reduce power consumptionDischarge tube luminescnet screensCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesElectric fieldAtomic physics
An electron-emitting apparatus includes an emitter section made of a dielectric material, lower electrodes, upper electrodes having micro through holes, insulating layers disposed on the upper surface of the emitter section and between the adjacent upper electrodes, and focusing electrodes to which a predetermine potential is applied and which are disposed on the insulating layers. The electron-emitting apparatus applies a negative potential to the upper electrode to accumulate electrons in the emitter section and then applies a positive potential to the upper electrode. As a result, the polarization of the emitter section is reversed, and the accumulated electrons are emitted through the micro through holes in the upper electrodes by Coulomb repulsion. Owing to electric fields generated by the focusing electrodes, the emitted electrons travel in the upward direction of the upper electrode without spreading into a shape of a cone.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
High-capacity microwave photocatalysis wastewater degrading device capable of self-detecting states of electrodeless ultraviolet lamp
InactiveCN103466864AWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment with mechanical oscillationsUltravioletEngineering
The invention relates to a high-capacity microwave photocatalysis wastewater degrading device capable of self-detecting the states of an electrodeless ultraviolet lamp, and belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment. In the prior related technology, the problems that the functional state of an electrodeless lamp is difficult to obtain timely, water burst in a tube cavity occurs as a quartz tube is used for the screen protection of the electrodeless lamp, secondary ozone channeling in the reverse direction corrodes a magnetron, and the electrical charge characteristics of a contact agent is not well utilized exist, and the high-capacity microwave photocatalysis wastewater degrading aims to solve the series of problems. An optical fiber extending into a reactor inner chamber and attached components of the optical fiber in the structure of the high-capacity microwave photocatalysis wastewater degrading device can achieve the purpose of monitoring the functional state of the electrodeless lamp in a real-time manner; an additionally arranged small-type diaphragm pump in the structure is used for continuously injecting air into a quartz tube cavity in small flux, so as to avoid the water burst of the quartz tube cavity; a contact agent interception mechanism in the structure comprises a charge negative electricity filtering film, so that an interception link of contact agent particles is strengthened by virtue of the coulomb repulsion; a waveguide tube of the device is separated by wave-transmitting materials in an air sealing manner, so that the structure facilitates preventing the ozone channeling in the reverse direction, and the like.
Owner:李榕生
Electron-emitting apparatus
InactiveUS20060118827A1Suppress electron emissionAvoiding excessive electron emissionStatic indicating devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPotential differenceEngineering
An electron emitting apparatus includes a lower electrode, an emitter section made of a dielectric material, a plurality of upper electrodes having micro through holes, and a collector electrode opposing the upper electrodes. In this electron-emitting apparatus, electrons are accumulated in the emitter section by controlling the potential difference (drive voltage) between the lower and upper electrodes with respect to the potential of the lower electrode to a negative predetermined voltage. At this time, the collector electrode of the electron-emitting apparatus is grounded. Thus, unnecessary electron-emitting is suppressed. Subsequently, the drive voltage is changed to a positive predetermined voltage. As a result, polarization reversal occurs in the emitter section, and accumulated electros are emitted through the micro through holes in the upper electrodes by Coulomb repulsion. At this time, a positive voltage Vc is applied to the collector electrode to give large energy to accelerate the electrons.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Plasma seawater purifying equipment
InactiveCN108706670AStable temperatureWater/sewage treatment by irradiationSeawater treatmentAtmospheric airX-ray
The invention discloses plasma seawater purifying equipment. The plasma seawater purifying equipment mainly comprises a seawater plasma supplying network, a first seawater purifying unit, a second seawater purifying unit, a third seawater purifying unit, a fourth seawater purifying unit and a decay nuclear energy online detection instrument, wherein the seawater plasma supplying network, comprisesa sweater supplying network, a seawater evaporation and ionization network, a first seawater boiling and ionization network, a second seawater boiling and ionization network; and the decay nuclear energy online detection instrument is connected to each part and is used for controlling each part to work. The seawater plasma supplying network is used for supplying 106-DEG C seawater plasma gas to the four seawater purifying units through an X-ray photoelectric effect, 106-DEG C plasma is enhanced, multiplied and superimposed by the four seawater purifying units through the X-ray photoelectric effect, ionized oxygen atoms (O<e+>) generate Coulomb repulsion with pollution particles such as heavy metal positive charges so as to purify the seawater, regenerated gas state purified water is collected by virtue of a stainless steel water tank, and regenerated air is discharged into atmosphere.
Owner:标胜环球(天津)实业有限公司
High-capacity reactor capable of monitoring the degradation of photocatalysis waste water under lamp source state in real time
The invention relates to a high-capacity reactor capable of monitoring the degradation of photocatalysis waste water under a lamp source state in real time, and belongs to the technical field of waste water treatment. The high-capacity reactor aims to fully solve the problems of the prior art that a functional state of an electrodeless lamp is hard to instantly know, a pipe cavity of a quartz pipe for protecting an electrodeless lamp screen outputs water, an accelerant charge electrical property is not fully utilized, and secondary ozone conversely and crossly flows to erode a magnetron. The high-capacity reactor provided by the invention has the advantages that one end of an optical fiber is led to the periphery of the quartz pipe and the tip end of the optical fiber points to an inner cavity of the quartz pipe, the other end of the optical fiber closes to and points to a detecting window of an ultraviolet light intensity detection instrument, and the functional state of the electrodeless lamp can be instantly monitored with the structure; a tail end filter membrane of a multi-level accelerant interception mechanism of the reactor adopts a charge negative electricity filter membrane, and coulomb repulsion is utilized to strengthen and intercept accelerant particles. According to the structure, a minitype diaphragm pump connected in a bypass way assists to supplement air, the positive pressure state of air in a pipe cavity of the quartz pipe is maintained, and the high-capacity reactor also solves multiple other problems.
Owner:李榕生
Heating equipment for producing hydrogen, oxygen and purified water by ionizing water vapor through photoelectric effect
PendingCN114703489ALow costGet rid of pollutionElectrolysis componentsHydrogen separationWater vaporParticle physics
The invention discloses a heating device for preparing hydrogen, oxygen and purified water by ionizing water vapor through a photoelectric effect. The invention relates to an atomic photoelectric effect probability formula tau which is provided by Philips Lenard in 1902 according to the principle of photoelectric effect and the formula tau of atomic photoelectric effect, wherein the ionization of gas can be generated only when electrons pass through gas and have certain minimum energy when the electrons pass through the gas, and the formula tau of atomic photoelectric effect is taught by Bushu Holy of Beijing University. According to the invention, a mercury-lead particle and radioactive particle photoelectric effect detection collection chamber, a water vapor H2O (g) photoelectric effect ionization chamber, a mercury-lead particle and radioactive particle detection oxygen plasma reducer, a positive electricity coulomb repulsion monel alloy sieve plate and other key components are used for preparing low-cost purified water without alpha, beta and beta particles, and hydrogen and oxygen with the purity of 99.9999%. And heat can be supplied, and a large amount of rare and precious gases such as tritium deuterium 3He (g) and 4He (g) in clear water can be collected.
Owner:湖南红砖新能源有限公司
Systems and methods for nuclear fusion
PendingCN114270451ANuclear energy generationLow temperature fusion reactorNuclear engineeringNuclear fusion
The present disclosure provides methods and systems for generating heat from nuclear fusion. The methods and systems utilize a host material (e.g., metal nanoparticles) to carry a fusible material (e.g., deuterium). The host material and / or the fusible material is irradiated with electromagnetic radiation that causes phonon vibrations in the host material and / or the fusible material. The phonon vibration shields coulomb repulsive forces between the nuclei of the fusible material, thereby improving the rate of nuclear fusion even at relatively low temperatures and pressures. The methods and systems cause nuclear fusion reactions that produce energy or heat. The heat can be converted to useful energy using systems and methods for efficient heat dissipation and thermal management.
Owner:宝瓶能源公司
Microwave photocatalysis wastewater degradation reactor dilation method for integrating Coulomb repulsion action
InactiveCN103253814AWeaken stubborn attachmentResists stubborn attachmentWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisUltrasoundChemistry
The invention relates to a microwave photocatalysis wastewater degradation reactor dilation method for integrating Coulomb repulsion action, and belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The problems of extremely weak catalyst interception link, extremely small single-tank treatment amount of a reactor and difficult discrimination of degradation reaction terminal time and the problems that catalyst aggregations can not be intensively dissipated in situ, the catalyst aggregations can not be perceived in time, the charged characteristics of catalyst particles is not properly utilized, and the like exist in the related prior art. Aiming at the problems, the microwave photocatalysis wastewater degradation reactor dilation method comprises the following main steps of: limiting a microwave radiation region; bunching bubble flows, and guiding the bubble flows into an important degradation reaction region; intensifying catalyst interception by using hollow fiber membrane with negative electric charges; intensively dissipating the catalyst aggregations in situ by using ultrasonic waves emitted from the bottom of the reactor, and incidentally cleaning a quartz tube; monitoring reaction progress by using an ozone sensor, and automatically switching off a relative power supply when reaching a degradation terminal; and actively warning a catalyst aggregation tendency.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Method for expanding volume of photocatalysis wastewater degradation reactor taking coulomb repulsion function into account
InactiveCN103253805AIncrease design capacityKnow the energy input in timeWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisParticulatesEngineering
The invention relates to a method for expanding the volume of a photocatalysis wastewater degradation reactor taking a coulomb repulsion function into account, belonging to the technical field of wastewater treatment. An existing related technology has the problems that the microwave energy is wasted, the single-tank wastewater treating capacity is small, the oxygen supply concentration of a key area is insufficient, a catalyst flows away, the end time of a degradation reaction is difficult to distinguish, a catalyst agglomerate cannot be subjected to in situ strong dissipation, the agglomeration of the catalyst cannot be detected in time, the particulate charged characteristics of the catalyst are not put into good use, and the like. The method is provided for solving the series of problems, and mainly comprises the following steps of: restricting a microwave radiation airspace by using a metal cage to facilitate large-scale volume expansion of the reactor; releasing bubble flows to an important degradation reaction area in a concentrated mode; enhancing catalyst interception by using a negatively charged hollow fiber membrane; carrying out in situ strong dissipation on the catalyst agglomerate by using ultrasonic waves emitted from the bottom of the reactor, and cleaning a quartz tube at the same time; sensing the degradation end point by using an ozone sensor, and automatically turning off a power supply at the degradation end point; and automatically detecting the tendency of the agglomeration of the catalyst.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Method for expanding volume of photocatalysis wastewater degradation reactor integrating coulomb repulsion function
InactiveCN103253806AWeaken stubborn attachmentResists stubborn attachmentMultistage water/sewage treatmentParticulatesEngineering
The invention relates to a method for expanding the volume of a photocatalysis wastewater degradation reactor integrating a coulomb repulsion function, belonging to the technical field of wastewater treatment. An existing related technology has the problems that the microwave energy is wasted, the single-tank wastewater treating capacity is small, the oxygen supply concentration of a key area is insufficient, a catalyst flows away, the end time of degradation is difficult to distinguish, a catalyst agglomerate cannot be subjected to in situ strong dissipation, the agglomeration of the catalyst cannot be detected in time, the particulate charged characteristics of the catalyst are not put into good use, and the like. The method is provided for solving the series of problems, and mainly comprises the following steps of: obstructing a microwave radiation airspace; expanding the size of the reactor; guiding bubble flows to intensively release the bubble flows to an important area; enhancing catalyst interception by using a negatively charged hollow fiber membrane; carrying out in situ strong dissipation on the catalyst agglomerate by using ultrasonic waves emitted from the bottom of the reactor, and cleaning a quartz tube at the same time; sensing the reaction process by using an ozone sensor, and turning off a power supply immediately at the degradation end point; and automatically detecting main incentive parameters of the agglomeration of the catalyst.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Microwave synergistic photocatalytic wastewater degradation reactor taking electrostatic repulsion effect into consideration
InactiveCN103253812AWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment with mechanical oscillationsFiberMicroparticle
The invention relates to a microwave synergistic photocatalytic wastewater degradation reactor taking the electrostatic repulsion effect into consideration, and belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The scheme aims to solve the series of problems that the accelerant intercepting link is weaker, the single tank handling capacity of the reactor is smaller, the repetitive operation is highly frequent, the finish point of the degradation reaction is hard to identify, the accelerant agglomerates cannot be powerfully eliminated in situ, the accelerant agglomeration cannot be immediately detected, the charge characteristics of the accelerant particles are not better used and the like in one package. According to the scheme, the structure is blocked and the microwave irradiation area is limited. In the structure, ozone containing bubbles are guided to key degradation reaction areas. Accelerant interception is strengthened by an electronegative hollow fibrous membrane by means of Coulomb repulsion. The accelerant agglomerates can be eliminated in situ in the structure, and an ultrasonic cleaning quartz tube is carried at the same time. Associated power supplies can be automatically powered off when the degradation reaction reaches the finish point in the structure. Accelerant agglomeration trend can be automatically sensed by the structure, and the trend is automatically warned.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Microwave Photocatalytic Wastewater Degradation Reactor Capacity Expansion Method Combining Coulomb Repulsion
InactiveCN103253814BWeaken stubborn attachmentResists stubborn attachmentWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisUltrasoundChemistry
The invention relates to a microwave photocatalysis wastewater degradation reactor dilation method for integrating Coulomb repulsion action, and belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The problems of extremely weak catalyst interception link, extremely small single-tank treatment amount of a reactor and difficult discrimination of degradation reaction terminal time and the problems that catalyst aggregations can not be intensively dissipated in situ, the catalyst aggregations can not be perceived in time, the charged characteristics of catalyst particles is not properly utilized, and the like exist in the related prior art. Aiming at the problems, the microwave photocatalysis wastewater degradation reactor dilation method comprises the following main steps of: limiting a microwave radiation region; bunching bubble flows, and guiding the bubble flows into an important degradation reaction region; intensifying catalyst interception by using hollow fiber membrane with negative electric charges; intensively dissipating the catalyst aggregations in situ by using ultrasonic waves emitted from the bottom of the reactor, and incidentally cleaning a quartz tube; monitoring reaction progress by using an ozone sensor, and automatically switching off a relative power supply when reaching a degradation terminal; and actively warning a catalyst aggregation tendency.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
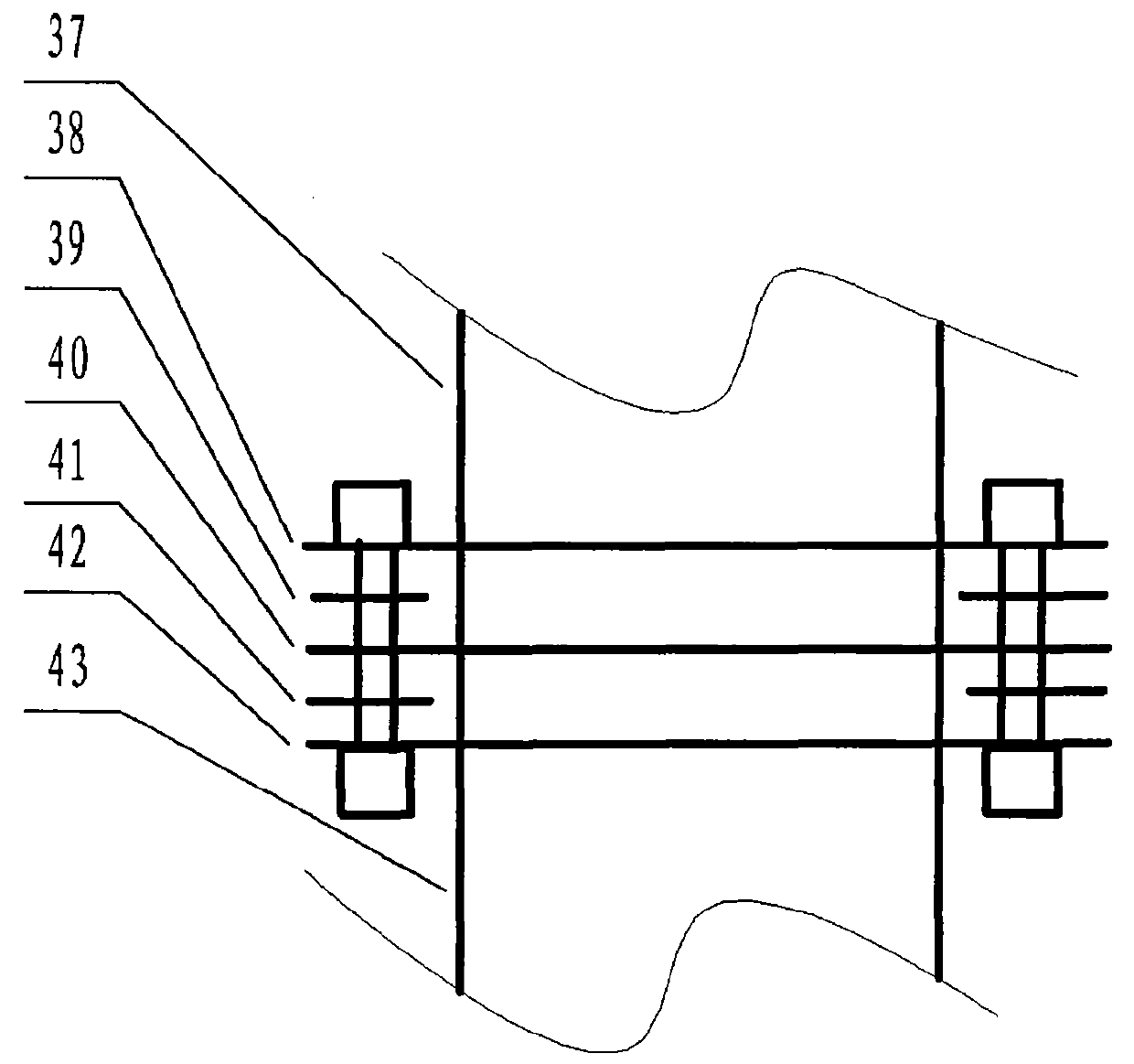
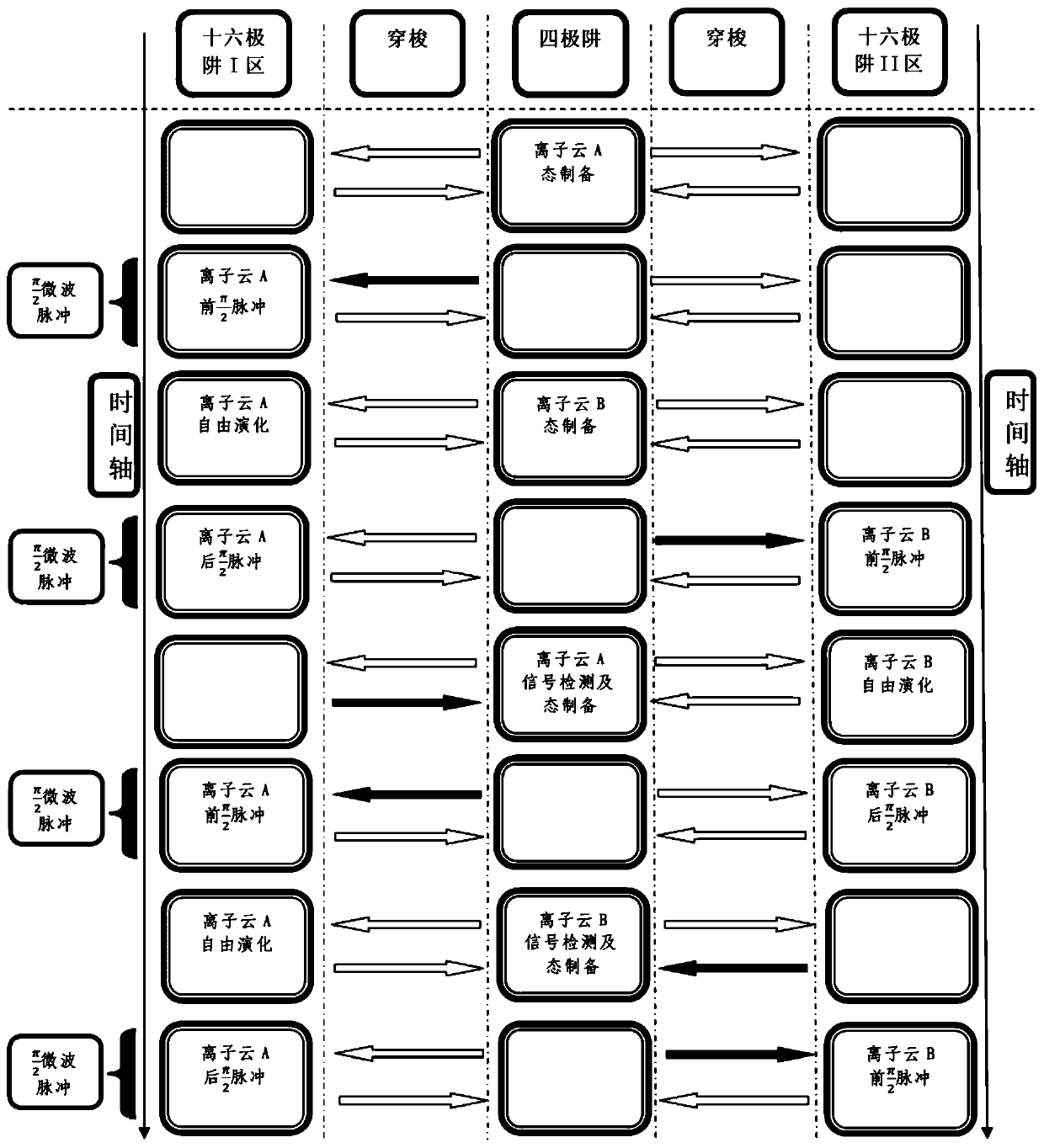
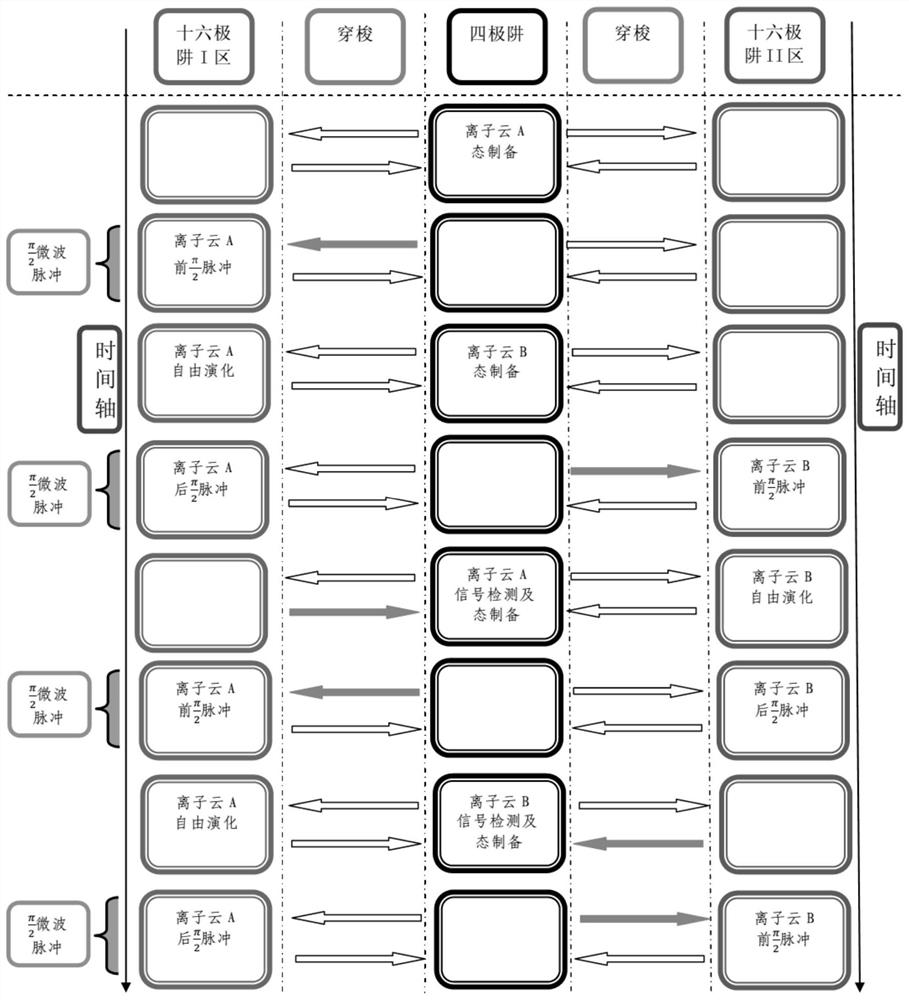
Direct-connected three-zone linear ion well and ion alternating frequency-discrimination locking method thereof
ActiveCN109786206AImprove production efficiencyImprove microwave clock signal-to-noise ratioStability-of-path spectrometersMicrowaveSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention discloses a direct-connected three-zone linear ion well and an ion alternating frequency-discrimination locking method thereof. In the realization process of a microwave clock, the ion state preparation and signal detection are completed in a quadrupole well, and the exploration of ions and microwaves are completed in a hexadecapole well; the ions trapped by the ion alternating frequency-discrimination locking method are divided into A and B ion clouds, which are respectively trapped and shuttled between I and II regions of the quadrupole well and the hexadecapole well to finallyrealize ion alternating frequency-discrimination locking. The method provided by the invention can further reduce the second-order Doppler shift caused by the collision and Coulomb repulsion betweenthe ions when the ions and the microwave interact while improving the ionic state preparation efficiency and enhancing the signal detection intensity to improve the signal-to-noise ratio of the microwave clock, and can separately perform good closed electromagnetic shielding and ionic state preparation on the microwave exploration region and perform good optical path design on the signal detectionregion.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SPACE TECH
Large-capacity microwave-photocatalytic wastewater degradation device combined with function of coulomb repulsion force
InactiveCN103253813AWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisElectricityEngineering
The invention relates to a large-capacity microwave-photocatalytic wastewater degradation device combined with the function of coulomb repulsion force, and belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment. In order to completely solve the problems in the relevant prior art that the contact agent is weak in the intercept link; a small amount of wastewater can be treated by using a reactor with a single tank; the moment at the end of a degradation reaction is difficult to distinguish; a contact agent agglomeration matter cannot be forcedly dissipated in situ; the agglomeration of the contact agent is not perceived in time; the charged characteristic of contact agent particles is not utilized well and the like, the large-capacity microwave-photocatalytic wastewater degradation device is provided. According to the structure of the device, a microwave irradiation airspace is limited; the capacity of the reactor can be expanded substantially; bubble flows are led to be released to a key reaction area; a hollow fiber membrane changed with negative electricity is utilized to strengthen the interception of the contact agent; the contact agent agglomeration matter can be forcedly dissipated in situ as well as a quartz tube is ultrasonically cleaned at the same time; relevant power supplies are automatically closed at the end of the degradation reaction; and the main inducement parameter of the contact agent agglomeration is automatically detected as well as an automatic alarm is given.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
A Directly Connected Three-Zone Linear Ion Trap and Its Ion Alternating Frequency Discrimination and Locking Method
ActiveCN109786206BAlternate Frequency Discrimination and Locking RealizationImprove production efficiencyStability-of-path spectrometersIon trap mass spectrometryMicrowave - action
The invention discloses a direct-connected three-zone linear ion well and an ion alternating frequency-discrimination locking method thereof. In the realization process of a microwave clock, the ion state preparation and signal detection are completed in a quadrupole well, and the exploration of ions and microwaves are completed in a hexadecapole well; the ions trapped by the ion alternating frequency-discrimination locking method are divided into A and B ion clouds, which are respectively trapped and shuttled between I and II regions of the quadrupole well and the hexadecapole well to finallyrealize ion alternating frequency-discrimination locking. The method provided by the invention can further reduce the second-order Doppler shift caused by the collision and Coulomb repulsion betweenthe ions when the ions and the microwave interact while improving the ionic state preparation efficiency and enhancing the signal detection intensity to improve the signal-to-noise ratio of the microwave clock, and can separately perform good closed electromagnetic shielding and ionic state preparation on the microwave exploration region and perform good optical path design on the signal detectionregion.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SPACE TECH
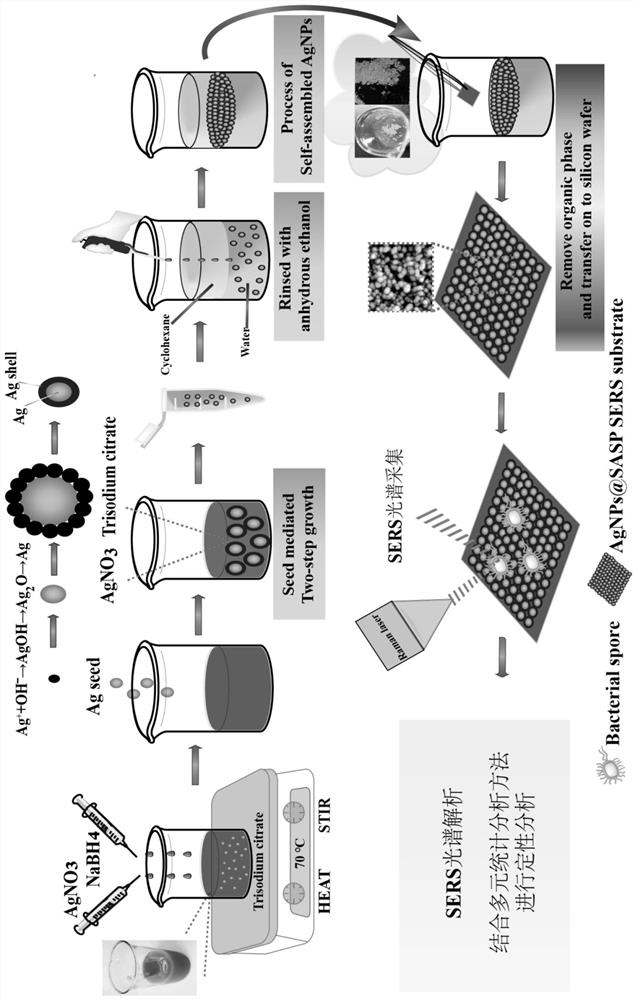
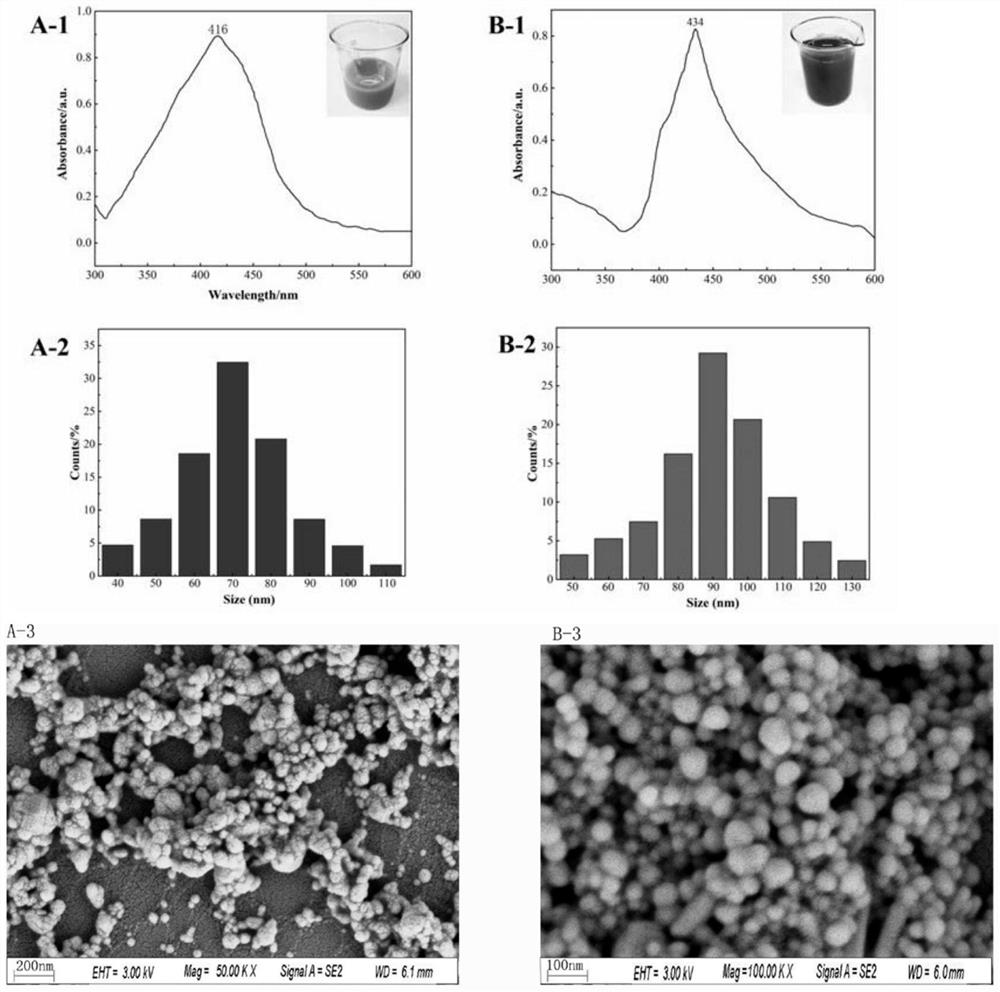
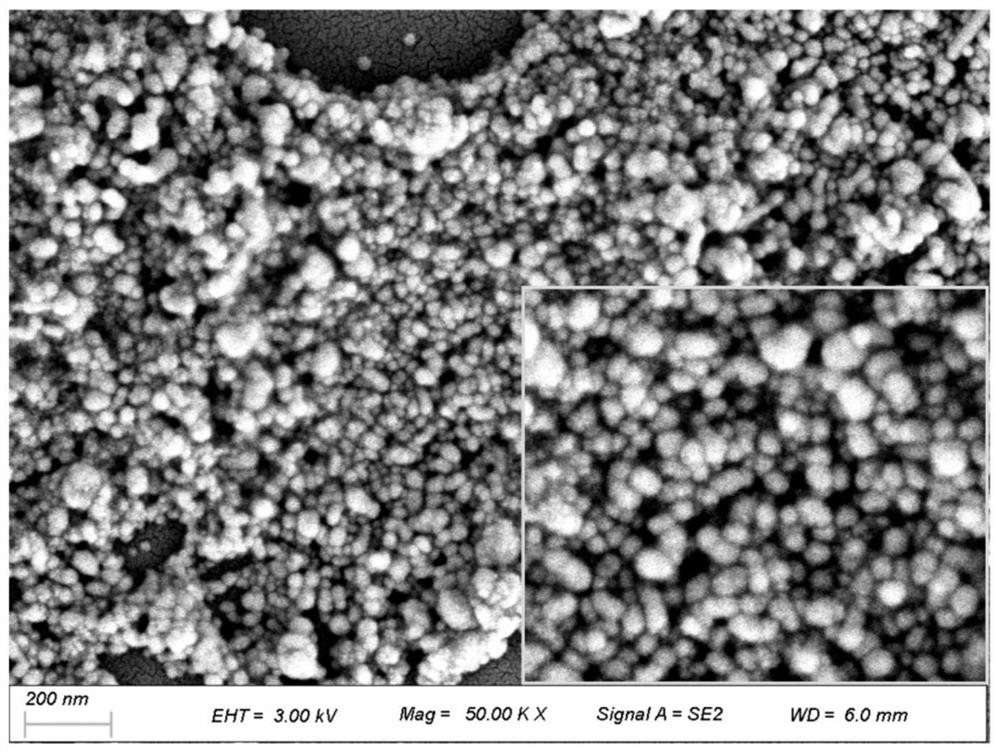
Preparation method and application of AgNPs (at) SASP substrate material
ActiveCN114535593AQuick identificationReduced charge density results inMaterial nanotechnologyLiquid-phase epitaxial-layer growthSporeChemical physics
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of an AgNPs (at) SASP substrate material, cyclohexane is taken as an organic phase, ethanol is taken as an inducer, and self-assembly is carried out by utilizing interfacial tension of an organic / water interface, so that nanoparticles are arranged in a single layer. A low-dielectric solvent is added to serve as an inducer to reduce the charge density result on the nanoparticles, Van der Waals force and coulomb repulsive force are reduced, so that the nanoparticles have the tendency of reassembling on an organic / water interface, a new balance is formed, and an SERS platform of a two-dimensional AgNPs array is formed. Different food-borne pathogenic bacteria spores are subjected to SERS (Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering) detection and peak position attribution analysis, and qualitative analysis is performed through a multivariate statistics method, so that rapid identification of spore bacteria is realized.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Photocatalytic Wastewater Degradation Reactor Capacity Expansion Method Incorporating Coulomb Repulsion
InactiveCN103253806BWeaken stubborn attachmentResists stubborn attachmentMultistage water/sewage treatmentParticulatesEngineering
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
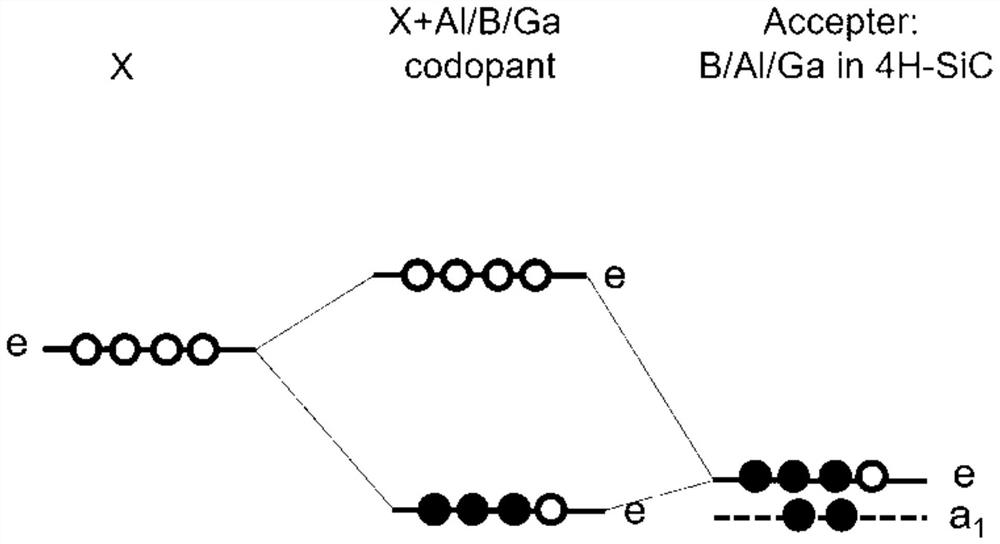
Method for preparing p-type 4H-SiC by co-doping IVB group atoms and aluminum
ActiveCN113279065ASolve the problem of high ionization energyIncrease the effective concentrationPolycrystalline material growthDiffusion/dopingPhysical chemistryElectric resistivity
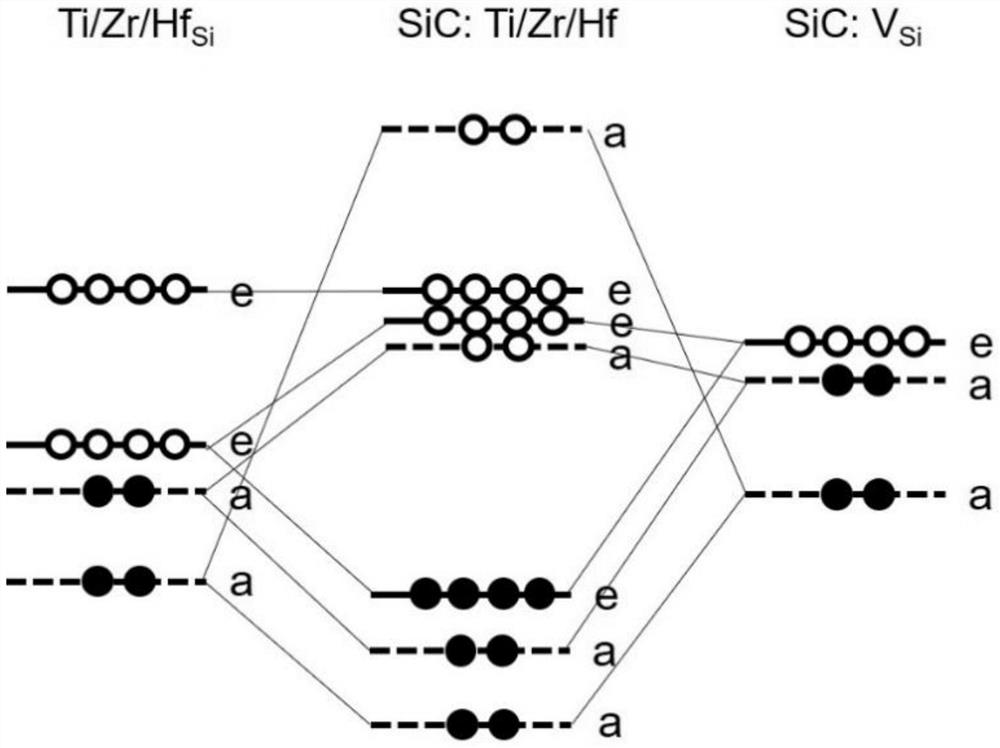
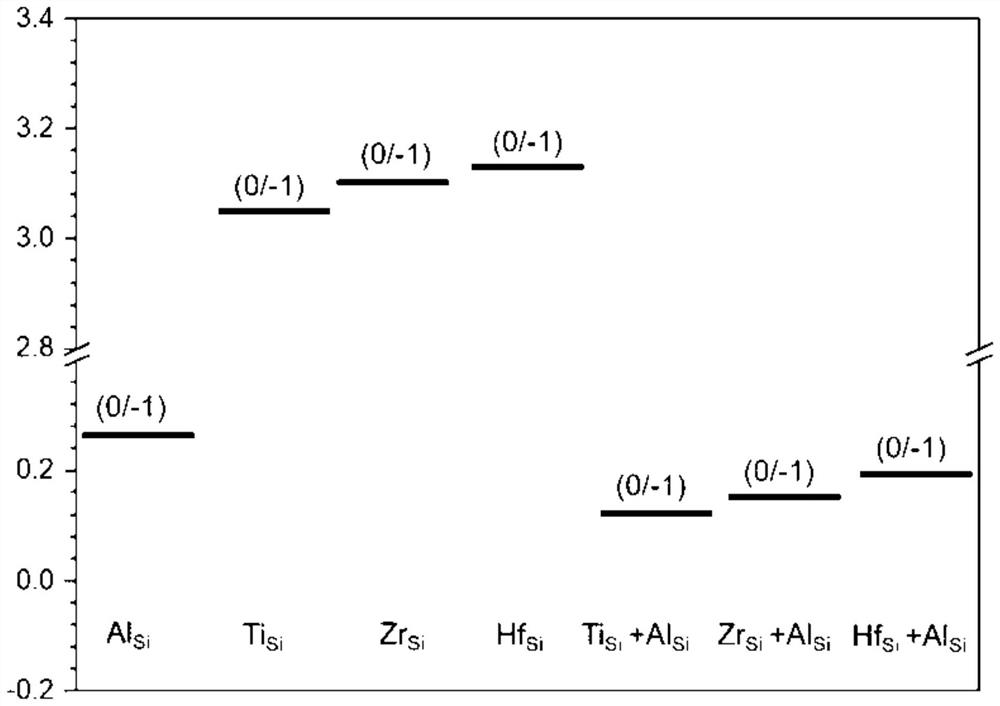
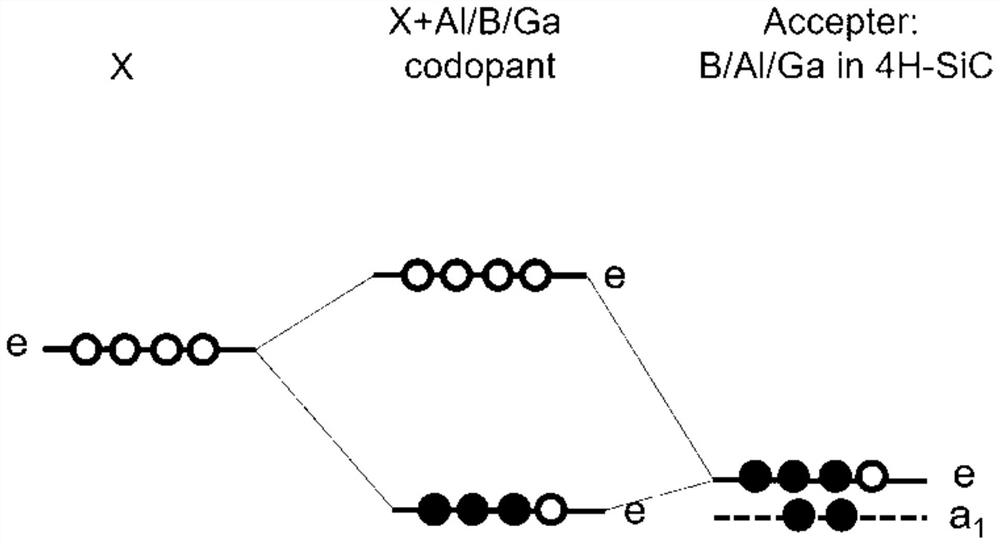
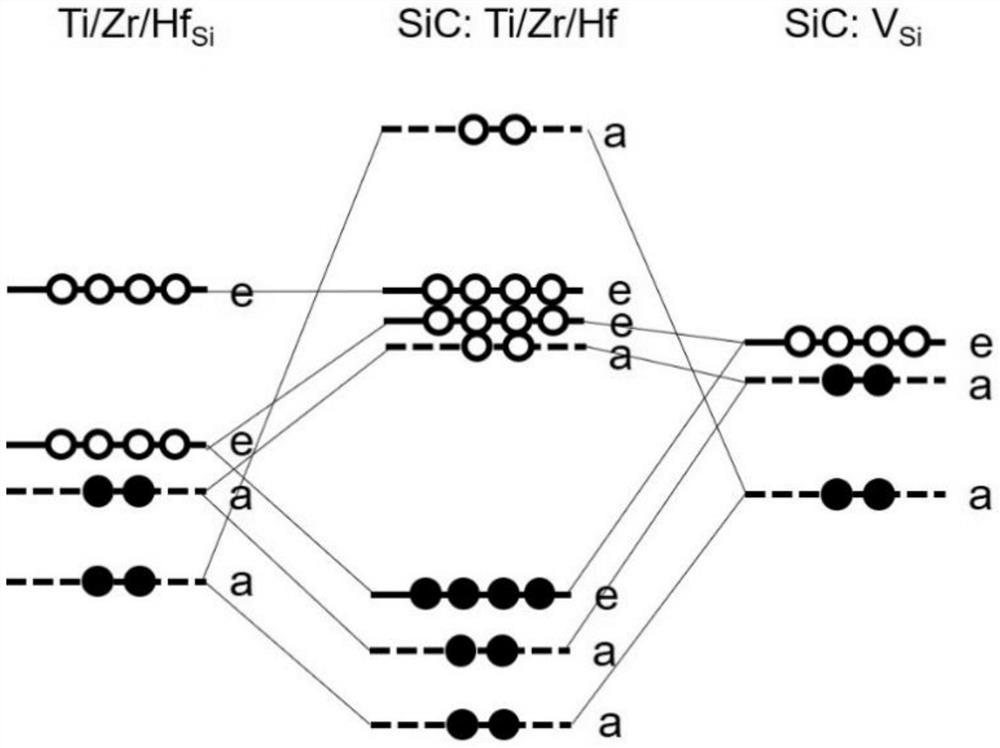
The invention relates to a method for preparing p-type 4H-SiC by co-doping IVB group atoms and aluminum. According to the preparation method, the aluminum atoms and IVB group atoms are doped into 4H-SiC, so that the ionization energy of aluminum in a silicon carbide crystal is effectively reduced, and the preparation of low-resistance p-type 4H-SiC is realized. After the IVB group atoms are doped, an empty impurity orbital e energy level is introduced to form effective coulomb repulsion with an e orbital occupied by 3 / 4 of Al, so that the ionization energy of Al impurities is reduced. The doping concentration of the IVB group atoms is ensured to be more than 1017 cm <-3 >, and the doping concentration of the aluminum atoms is ensured to be about 1020 cm <-3 >. The problem that the ionization energy of the aluminum atoms in 4H-SiC is high is solved, the effective concentration of carriers in silicon carbide is increased, the resistivity of the 4H-SiC silicon carbide crystal is reduced; and the method has important significance on manufacturing of various electronic devices in the field of power electronics.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV HANGZHOU GLOBAL SCI & TECH INNOVATION CENT
A method for preparing p-type 4h-sic by co-doping of group IVb atoms and aluminum
ActiveCN113279065BSolve the problem of high ionization energyIncrease the effective concentrationPolycrystalline material growthDiffusion/dopingCarbide siliconMetallurgy
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV HANGZHOU GLOBAL SCI & TECH INNOVATION CENT
Large-capacity wastewater degradation reactor with photocatalyst particle charging characteristics integrated into it
InactiveCN103253808BWeaken stubborn attachmentResists stubborn attachmentWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisEngineeringWastewater disposal
The invention relates to a large-capacity wastewater degradation reactor capable of infusing charge characteristics of photocatalyst particles and belongs to the field of a wastewater treatment technology. The existing related background technique has the problems that a nano photocatalyst runs off, microwave energy is wasted, the single-pot wastewater treatment amount of a reactor is relatively small, a finishing moment of a degradation reaction is difficult to distinguish, a contact agent reunited object can not be forcedly dissipated in situ, the contact agent reunion can not be observed in time, the charge characteristics of contact agent particles can not be greatly utilized and the like, and the scheme aims to solve the problems. In the scheme, a metal cage can be used for restricting microwaves so as to greatly enlarge the reactor; the structure in the scheme strengthens inner liquid to be greatly circulated; the structure strengthens the interception of a contact agent by using a charge negative electricity hollow fiber membrane by Coulomb repulsion; the structure can forcedly dissipate the contact agent reunited object in situ and incidentally cleans a quartz tube in an ultrasound manner; the structure can automatically switch off a related power supply in time at a finishing point of degradation; and the structure can automatically detect main incentive parameters of the reunion of the contact agent.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Ion accelerator
PendingCN109688690ASimple configurationNo repulsionLinear acceleratorsPlasma techniqueIon beamIon acceleration
The invention provides an ion accelerator, which comprises a plasma generating source, a vacuum container, an ionic linear accelerator and a high-voltage power supply used for increasing the voltage of the vacuum container to required voltage. The vacuum container is mounted at an ion inlet of the ionic linear accelerator, and an ion beam generated by the plasma generating source is directly emitted into the ionic linear accelerator from the vacuum container. According to the ion accelerator, the complexity of a combination of an ion source, a bunch and the ionic linear accelerator can be greatly reduced, and the effect of coulomb repulsion is further reduced.
Owner:广东太微加速器有限公司
A method for expanding the capacity of photocatalytic wastewater degradation reactor taking into account the Coulomb repulsion
InactiveCN103253805BIncrease design capacityKnow the energy input in timeWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisFiberParticulates
The invention relates to a method for expanding the volume of a photocatalysis wastewater degradation reactor taking a coulomb repulsion function into account, belonging to the technical field of wastewater treatment. An existing related technology has the problems that the microwave energy is wasted, the single-tank wastewater treating capacity is small, the oxygen supply concentration of a key area is insufficient, a catalyst flows away, the end time of a degradation reaction is difficult to distinguish, a catalyst agglomerate cannot be subjected to in situ strong dissipation, the agglomeration of the catalyst cannot be detected in time, the particulate charged characteristics of the catalyst are not put into good use, and the like. The method is provided for solving the series of problems, and mainly comprises the following steps of: restricting a microwave radiation airspace by using a metal cage to facilitate large-scale volume expansion of the reactor; releasing bubble flows to an important degradation reaction area in a concentrated mode; enhancing catalyst interception by using a negatively charged hollow fiber membrane; carrying out in situ strong dissipation on the catalyst agglomerate by using ultrasonic waves emitted from the bottom of the reactor, and cleaning a quartz tube at the same time; sensing the degradation end point by using an ozone sensor, and automatically turning off a power supply at the degradation end point; and automatically detecting the tendency of the agglomeration of the catalyst.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Solid electrolyte materials for lithium-ion batteries
ActiveCN103401018BImprove structural stabilityIncrease attractivenessSecondary cellsSolid state electrolyteSpace group
Owner:CONTEMPORARY AMPEREX TECH CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com