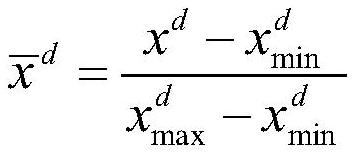Patents
Literature
97 results about "Molecular descriptor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
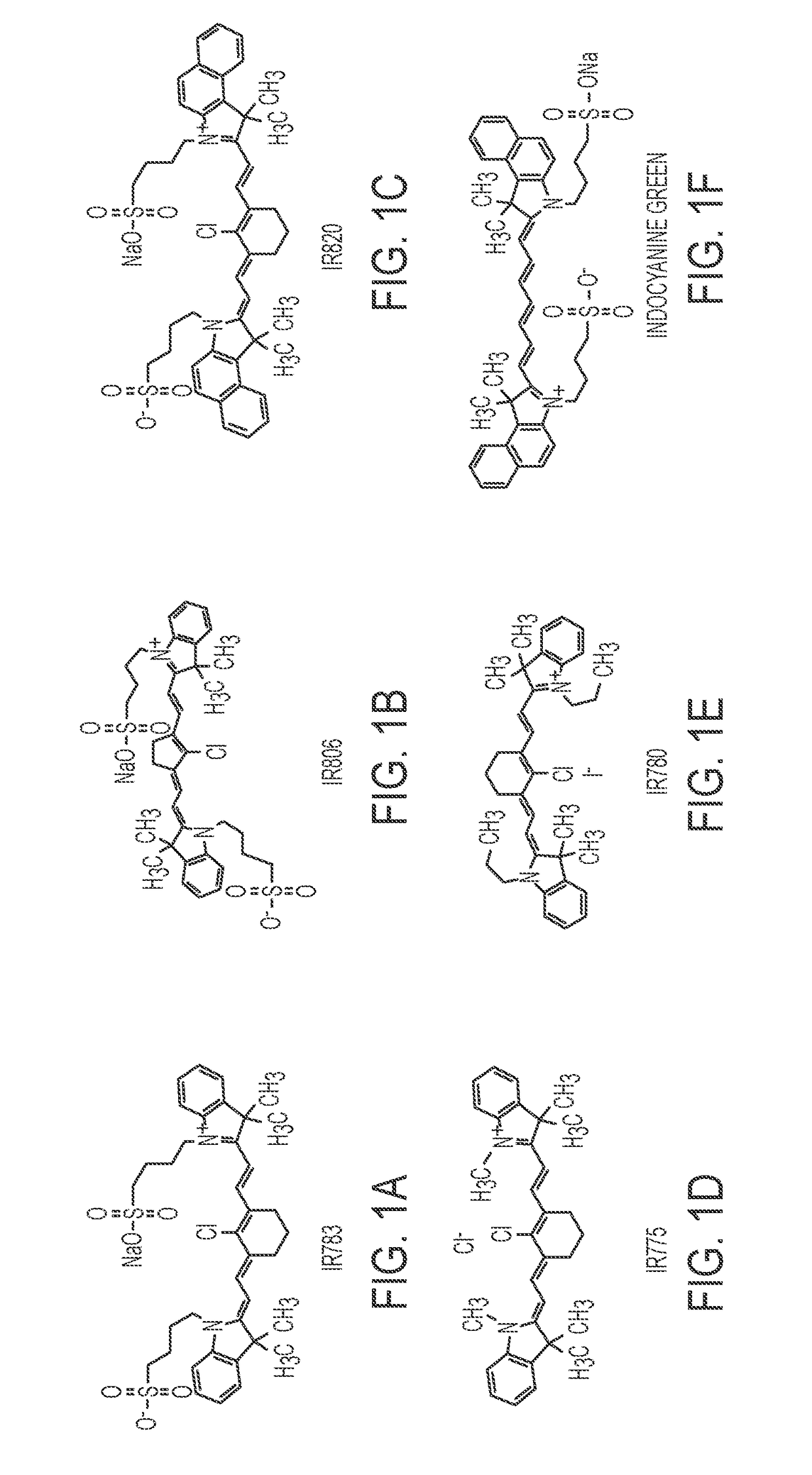
Molecular descriptors play a fundamental role in chemistry, pharmaceutical sciences, environmental protection policy, and health researches, as well as in quality control, being the way molecules, thought of as real bodies, are transformed into numbers, allowing some mathematical treatment of the chemical information contained in the molecule.
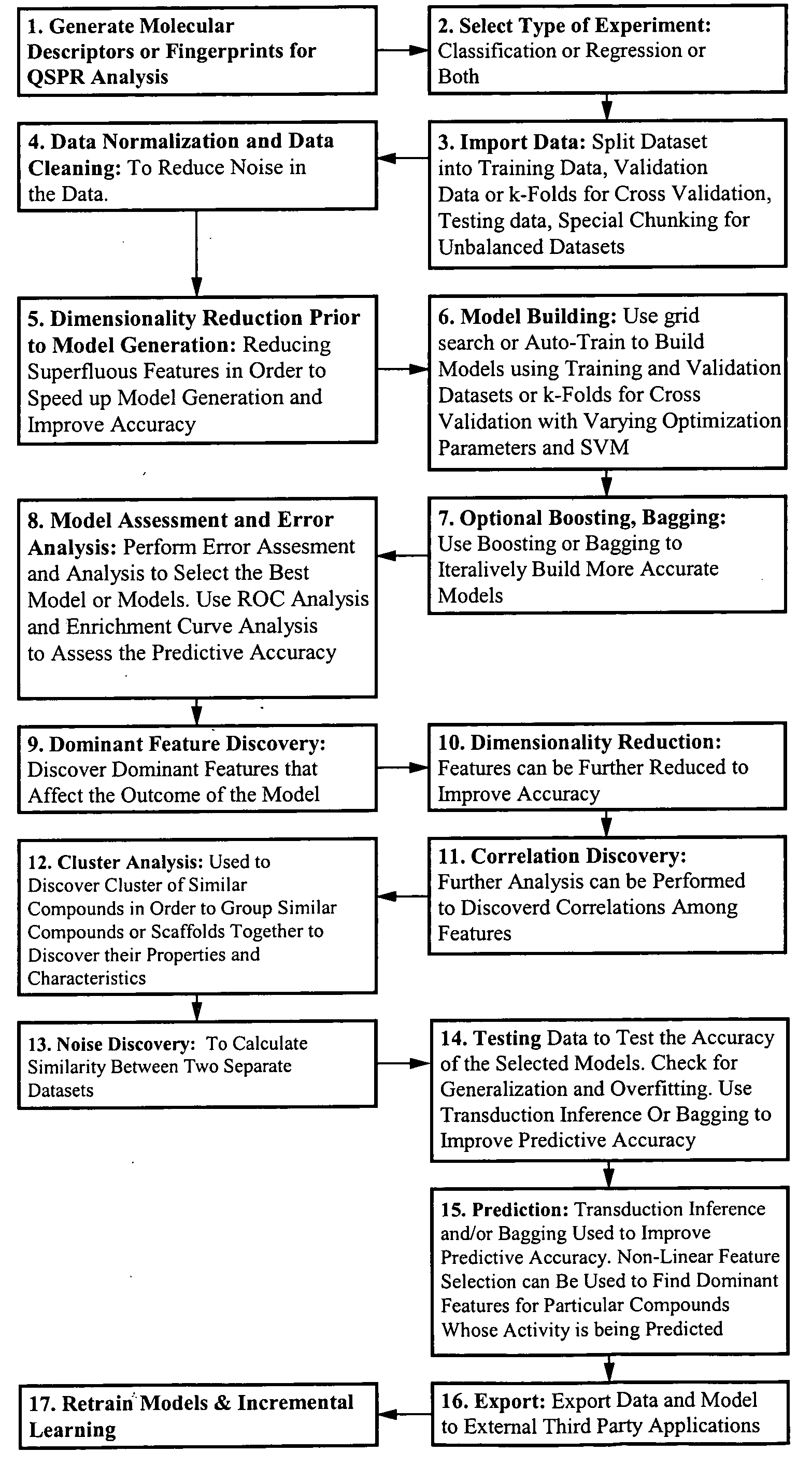
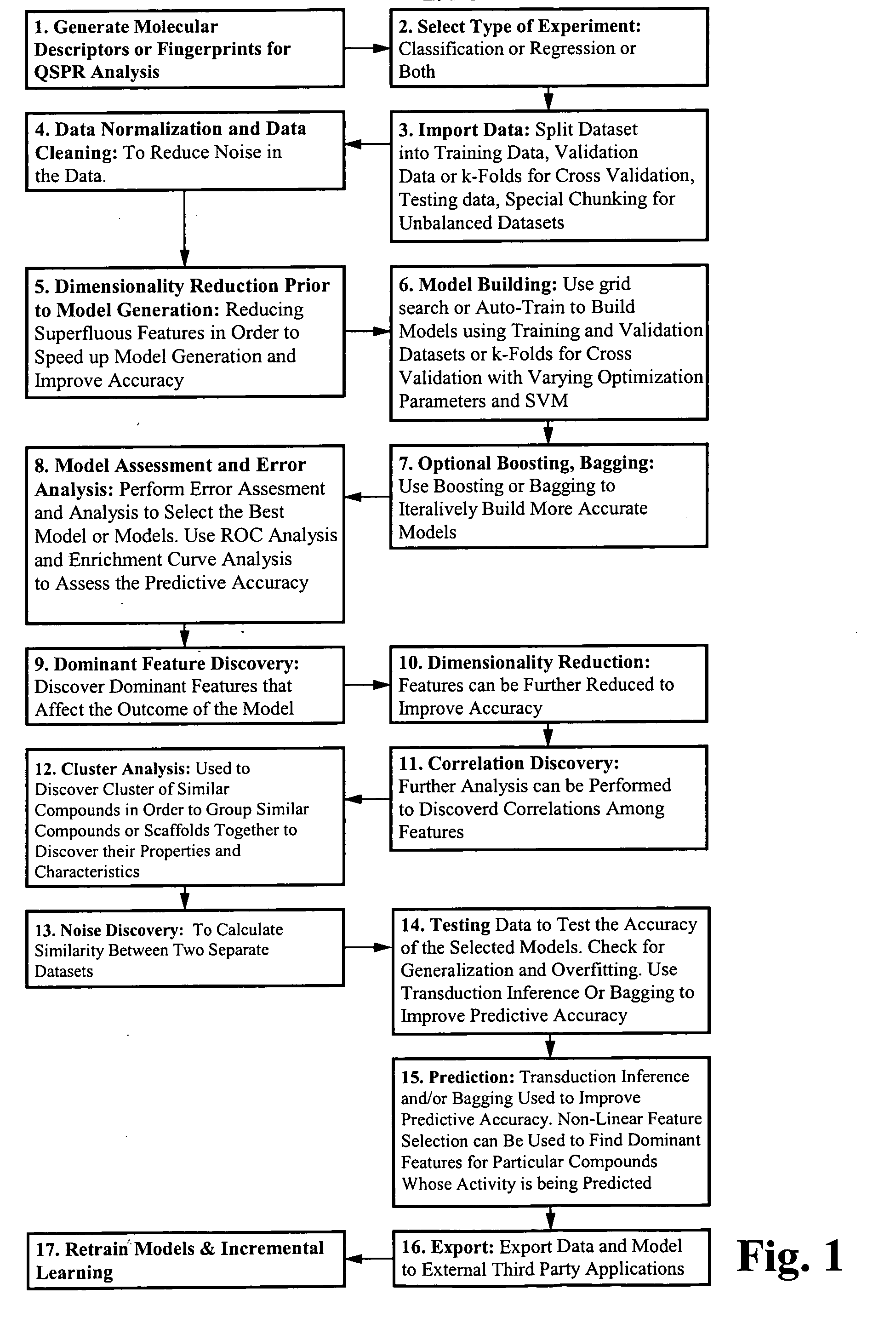
Method and apparatus for predictive modeling & analysis for knowledge discovery
A device and method designed to carry out the computation of a wide range of topological indices of molecular structure to produce molecular descriptors, representing important elements of the molecular structure information including but not limited to molecular structure variables such as; the molecular connectivity chi indices, mXt, and mXtv; kappa shape indices, mκ and mκα; electrotopological state indices, Si; hydrogen electrotopological state indices, HESi; atom type and bond type electrotopological state indices; new group type and bond type electrotopological state indices; topological equivalence indices and total topological index; several information indices, including the Shannon and the Bonchen Trinajstic information indices; counts of graph paths, atoms, atoms types, bond types; and others.
Owner:ASAR ADNAN +3
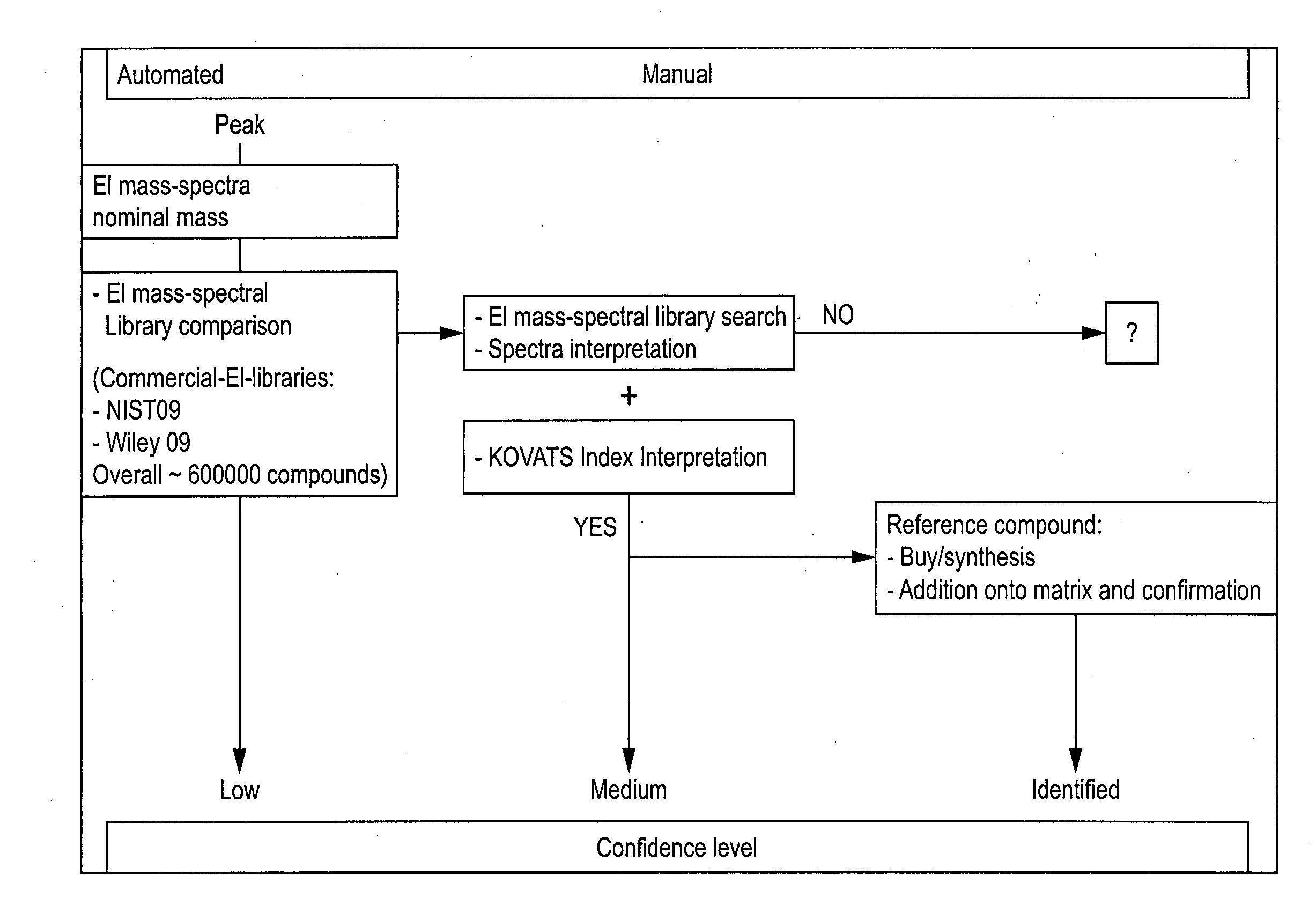
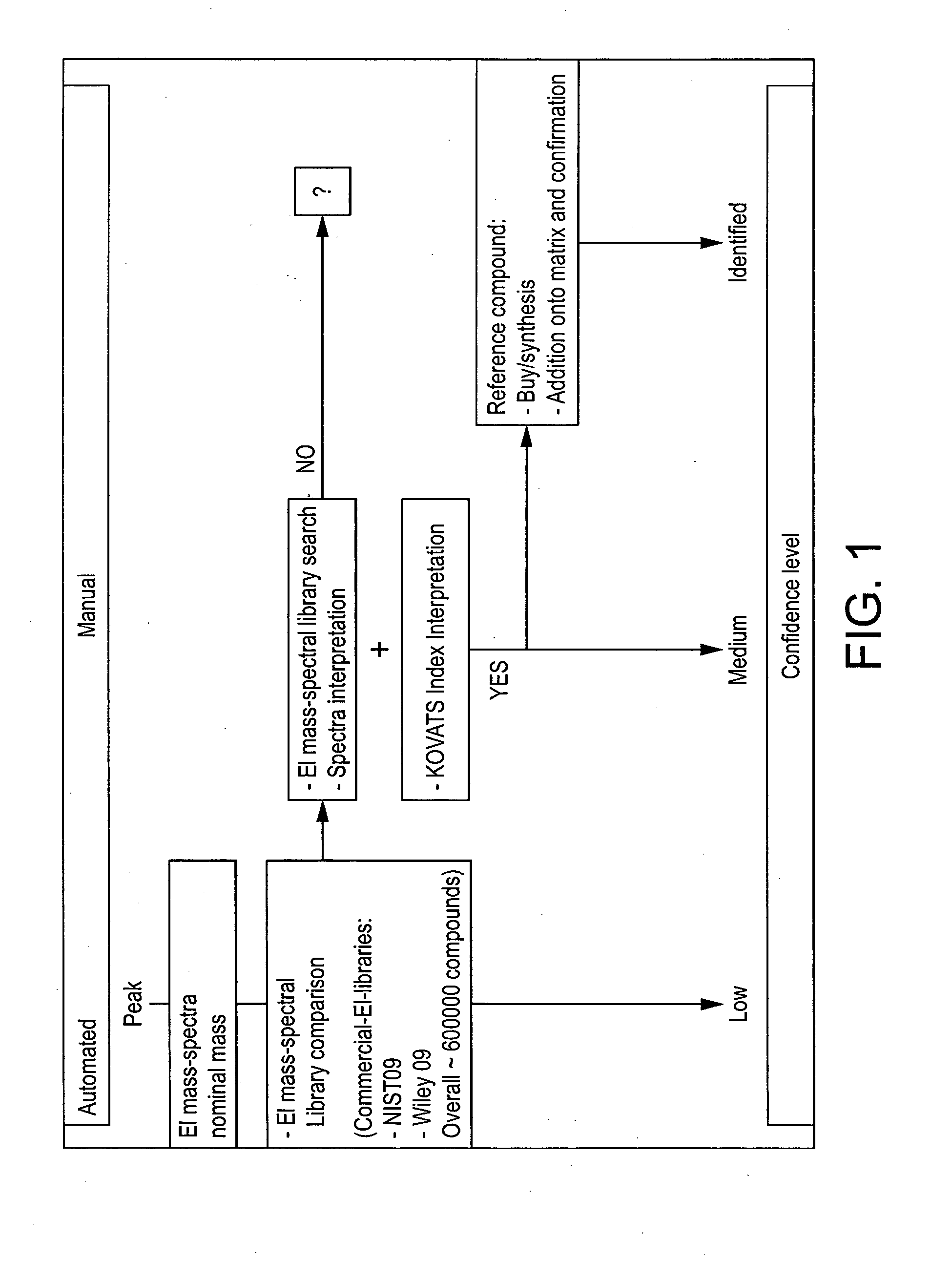
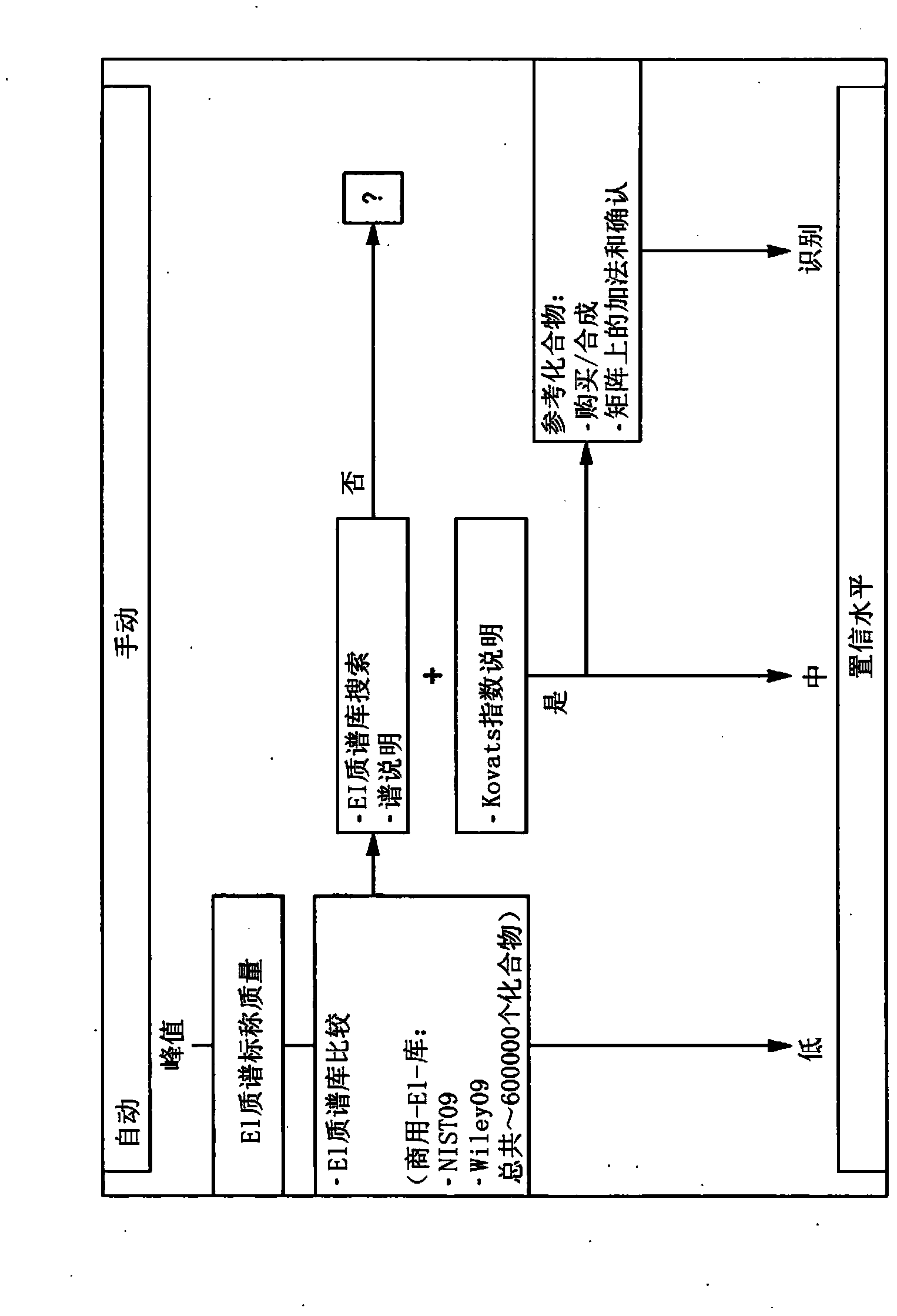
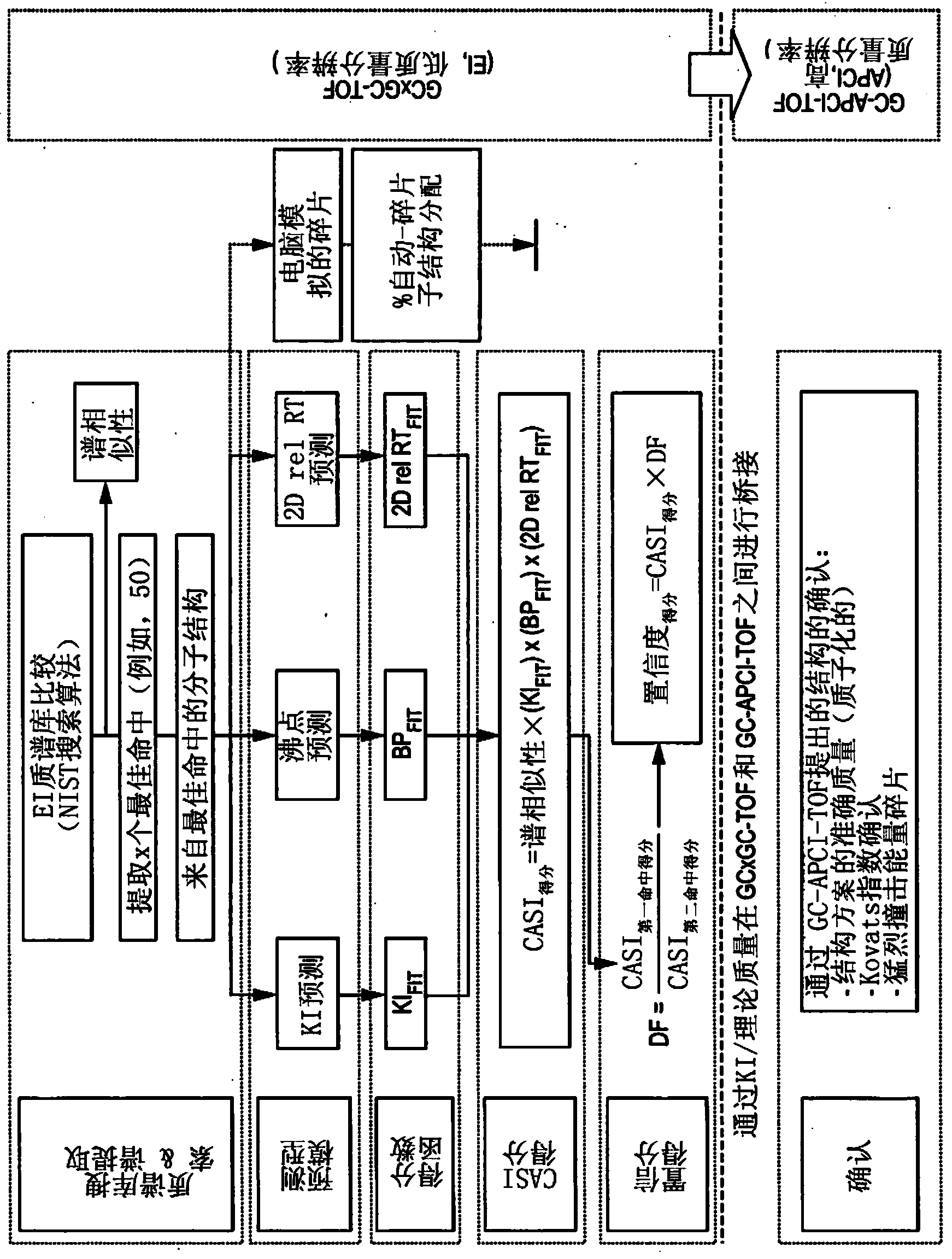
Computer-assisted structure identification
InactiveUS20140297201A1Promote resultsHigh resolutionParticle separator tubesComponent separationAnalyteMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
The invention relates to a method for analysing mass spectral data obtained from a sample in GC×GC (2-dimensional) mass spectrometry, comprising: (a) comparing mass spectral data of an analyte with mass spectral data of candidate compounds of known structure in a data library; (b) identifying a plurality of candidate compounds from the library based on similarities of mass spectral data; (c) predicting, for each candidate compound, a value of at least one analytical property using a quantitative model based on a plurality of molecular descriptors; and (d) calculating a match score for each candidate compound based on the value predicted in step (c) and a measured value of the analytical property for the analyte.
Owner:PHILIP MORRIS PROD SA
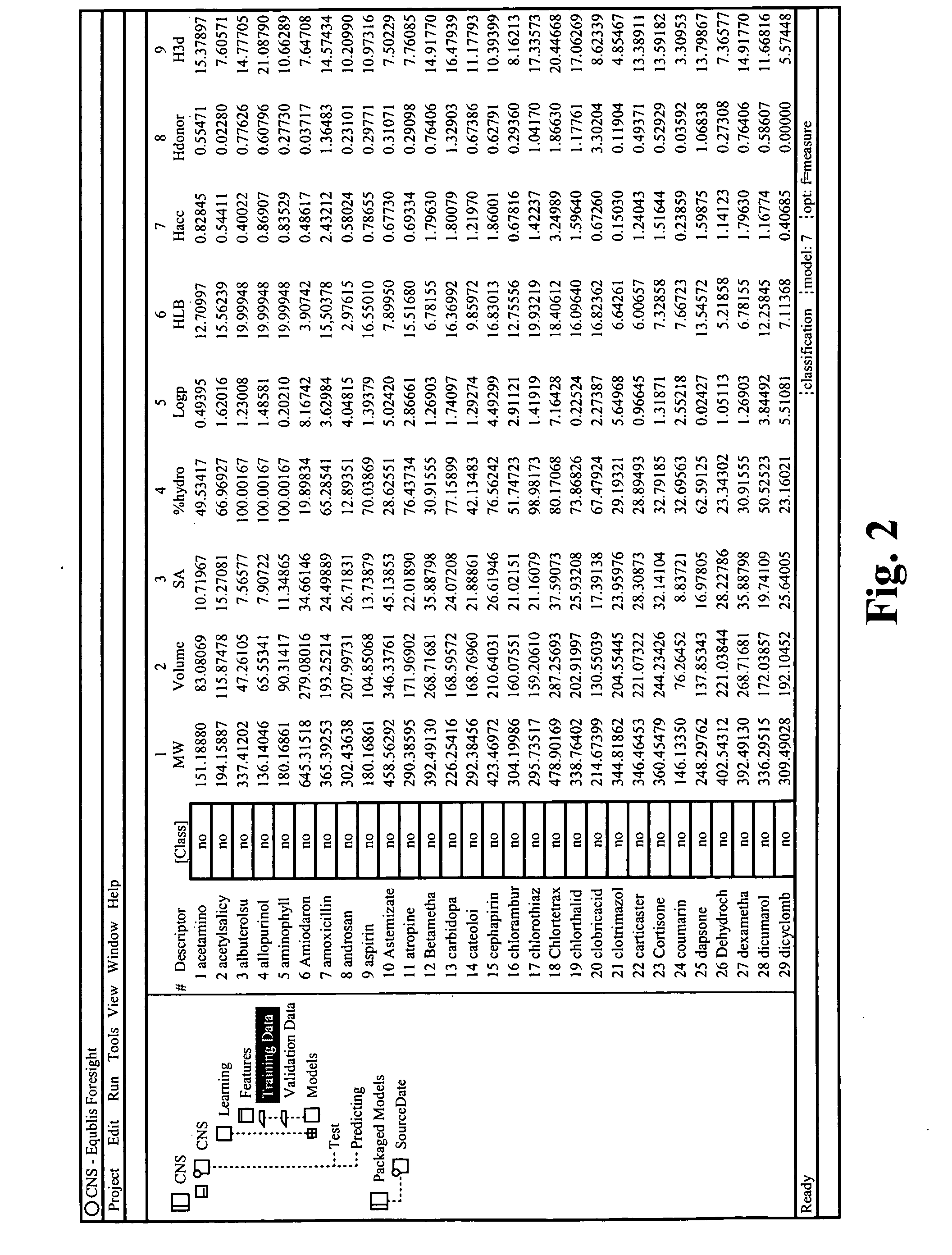
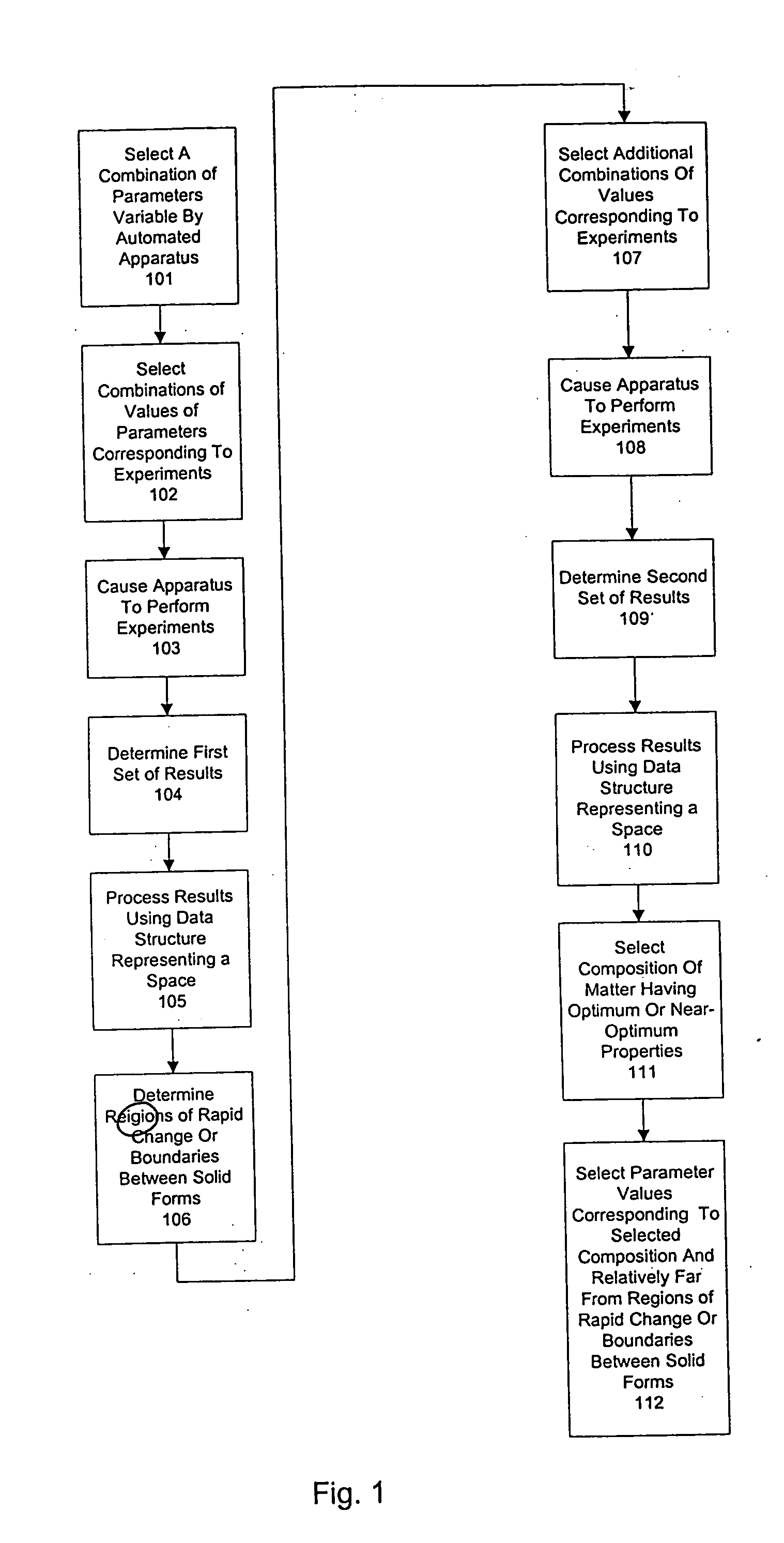
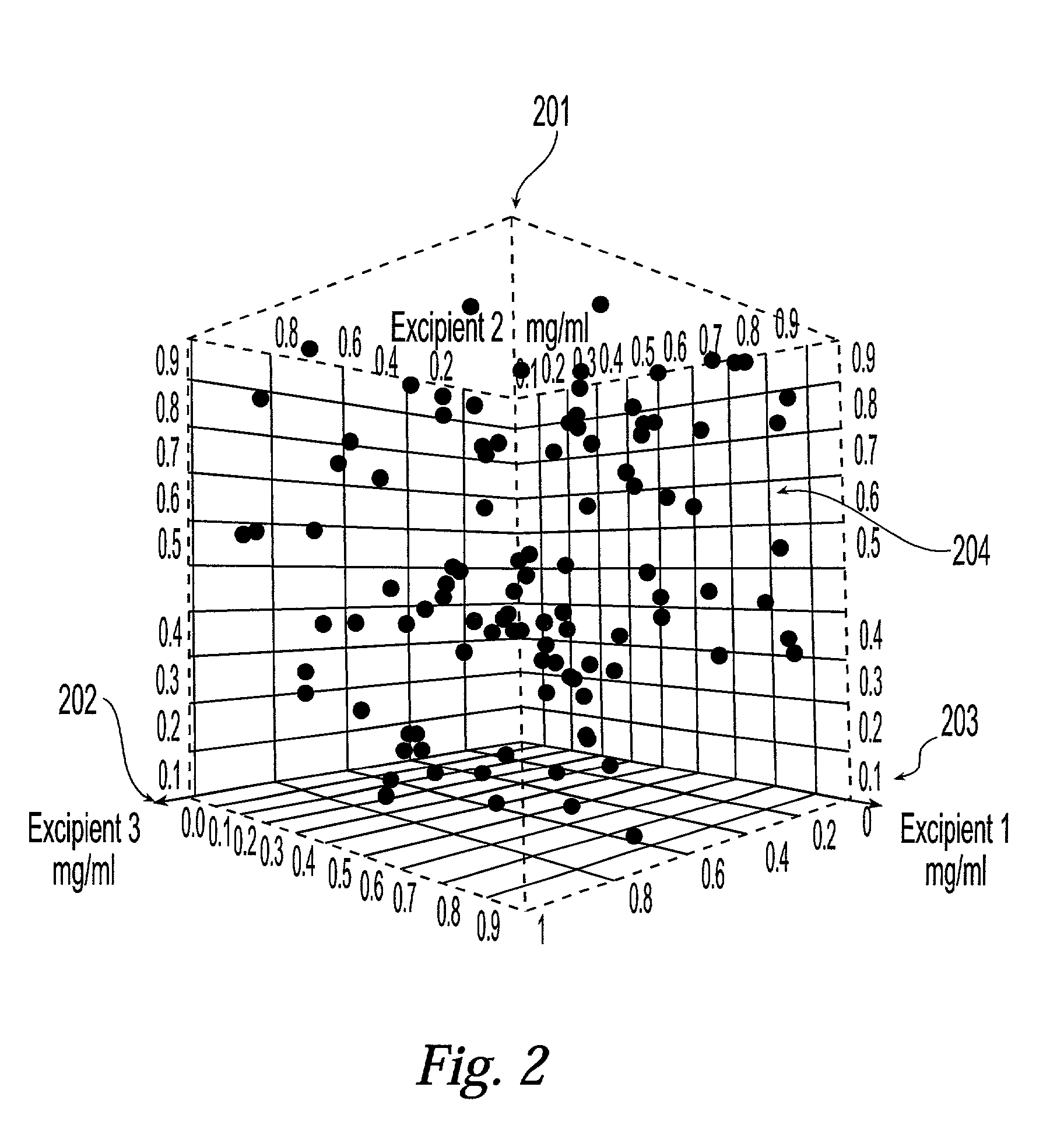
Method and system for planning, performing, and assessing high-throughput screening of multicomponent chemical compositions and solid forms of compounds
InactiveUS20050118637A9Library screeningCheminformatics programming languagesHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsChemical composition
The present application is directed to the use of computerized data processing to plan, perform, and assess the results of high-throughput screening of multicomponent chemical compositions and solid forms of compounds. Systems utilized include databases of molecular descriptors and related compounds and their properties as determined empirically and through simulation, along with multidimensional visualization tools. Methods include methods for determining chemical compositions by performing steps including selecting a plurality of combinations of values of experimental parameters that can be varied by an automated experiment apparatus, determining a set of experimental results, and determining a second plurality of combinations of values based on the set of experimental results. Additional methods include selecting values of parameters that produce a composition, the values being relatively far from areas of rapid change or boundaries between solid forms.
Owner:TRANSFORM PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Protein-ligand affinity predicting method based on molecule descriptors
InactiveCN102930181AReduce dependenceImprove predictive abilitySpecial data processing applicationsCrystal structureConjugate gradient method
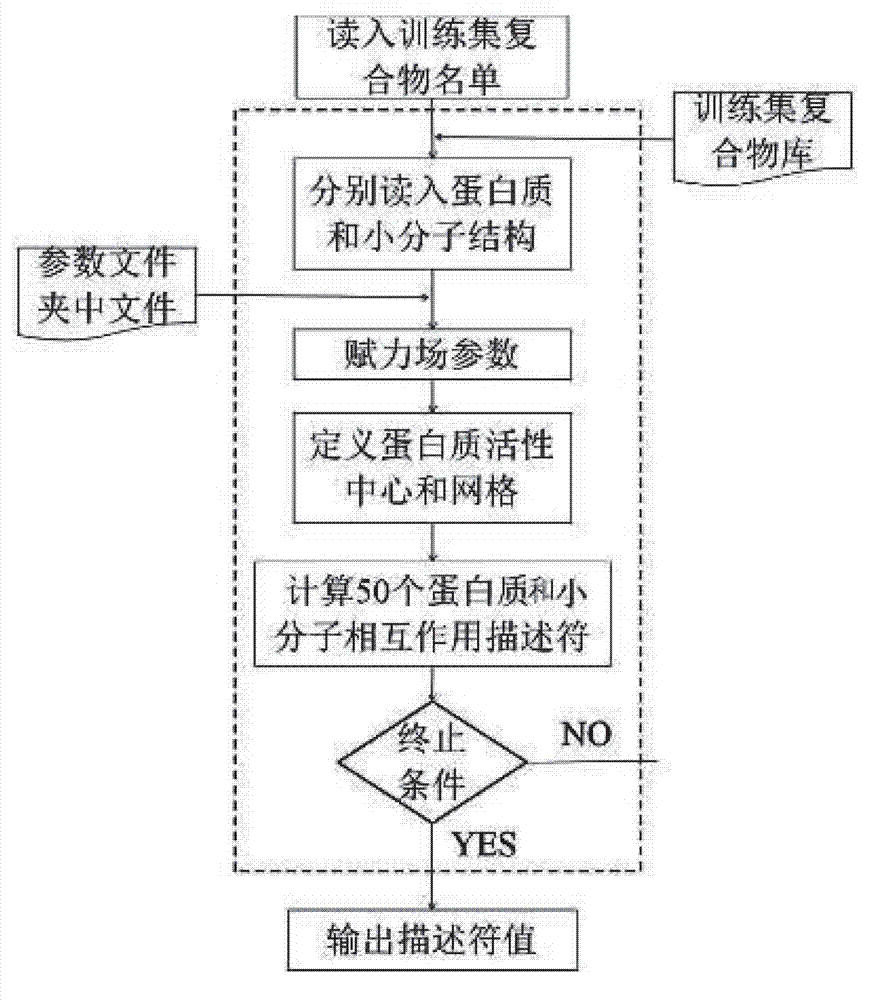
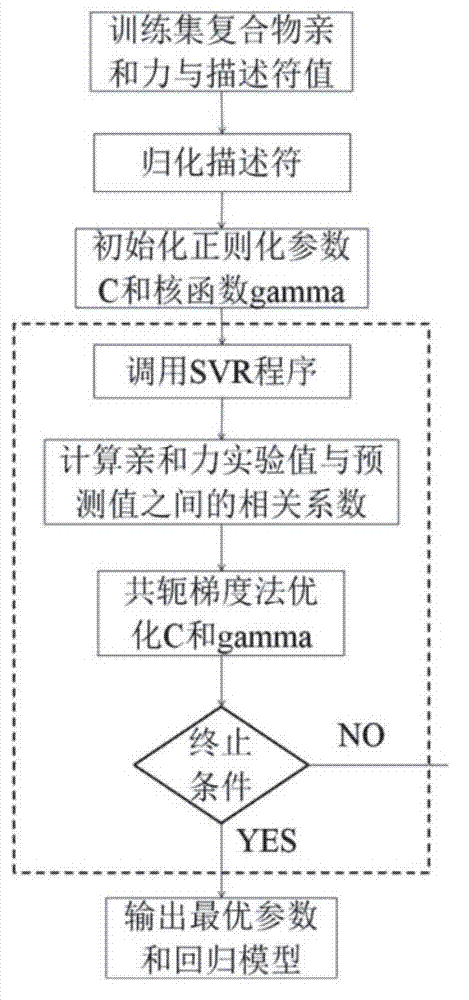
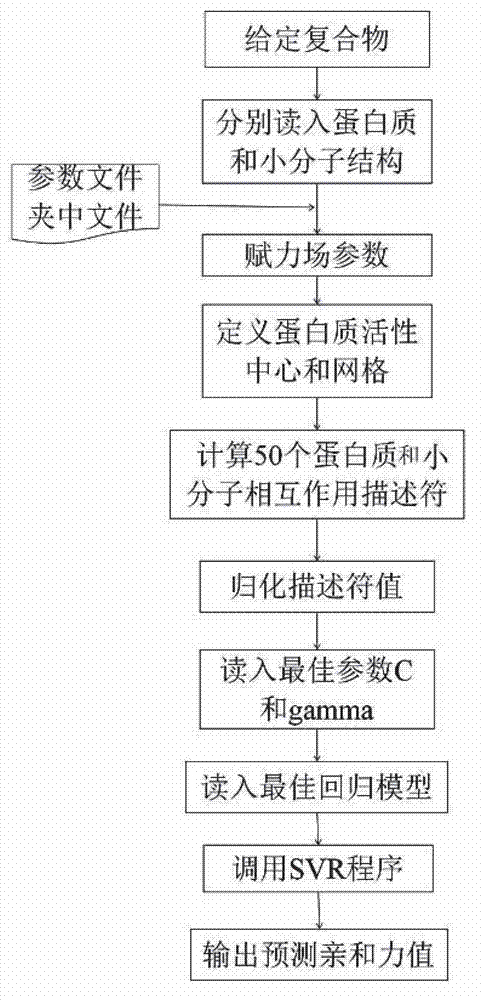
Disclosed is a protein-ligand affinity predicting method based on molecule descriptors. The protein-ligand affinity is reflected through construction of perfect and systematic molecule descriptors, and the relation between the descriptors and the affinity is constructed through a supporting vector regression (SVR) mode. The method includes the steps of training set preparation: preparing a large amount of data containing the crystal structure and the affinity of a protein-ligand complex; construction and calculation of the molecule descriptors: constructing 50 kinds of molecule descriptors which belong to nine categories, and calculating concrete values of all the complex descriptors in the training set; regression model construction: fitting the relation between the descriptors and the affinity through the SVR mode, and introducing a conjugate gradient method to optimize a penalty factor C and a kernel function parameter; and novel scoring function building which is used for predicting the affinity of the complex. The method has the advantages of being high in prediction capacity, small in target dependence, high in homolog sensitivity and the like.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Method for predicting n-octyl alcohol air distribution coefficient (KOA) at different temperatures through quantitative structure-activity relationship and solvent model
InactiveCN102999705AWide range of applicationsReliable predictive dataSpecial data processing applicationsSolventPhysics
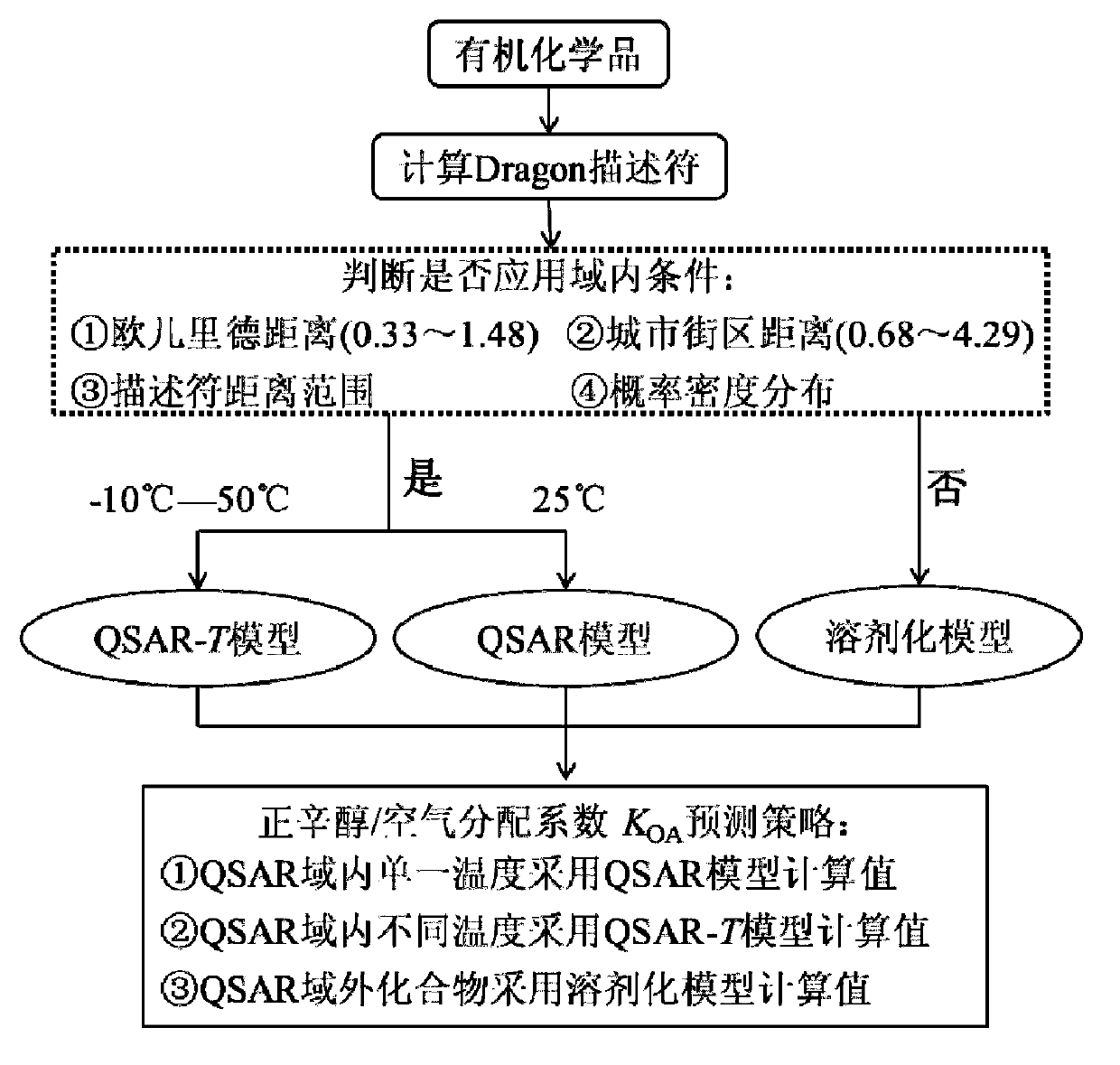
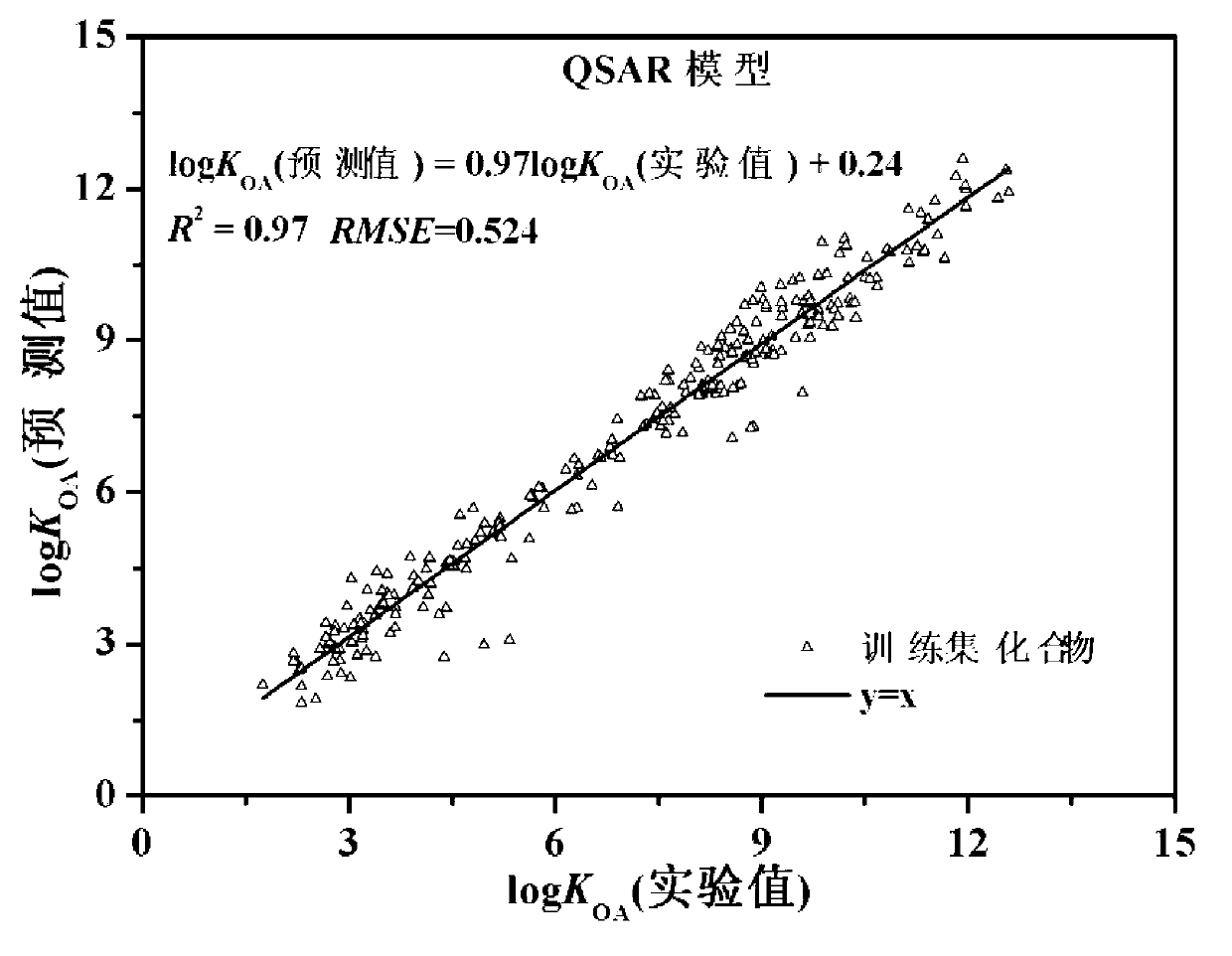
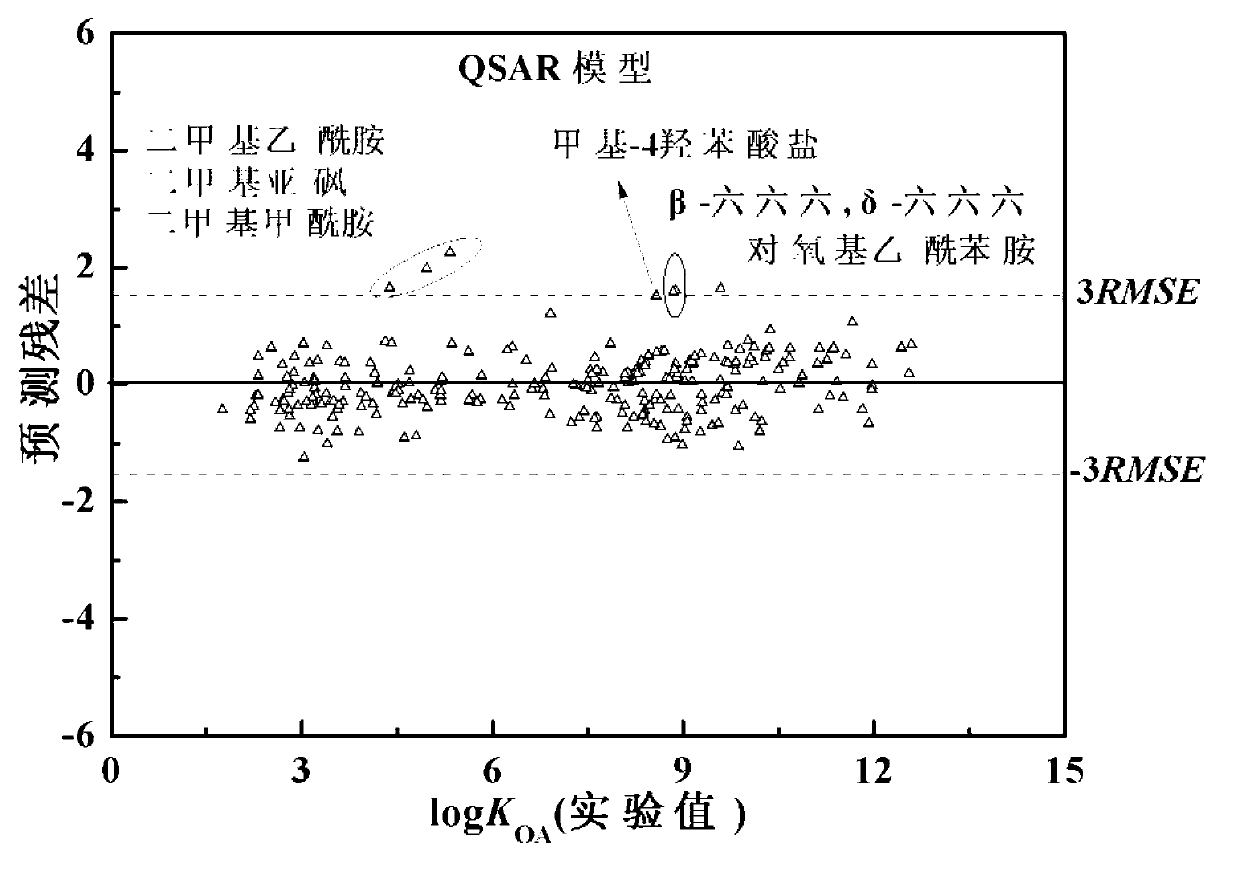
The invention discloses a theoretical prediction method for organic chemical n-octyl alcohol / air distribution coefficient (KOA) and belongs to the field of ecological risk assessment testing strategy. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) based on a molecular Dragon descriptor of a compound and calculating free melting energy based on a thermodynamic principle by adopting an open source solvent model, and transforming to obtain the KOA according to a thermodynamic principle formula of logKOA=-deltaGOA / 2.303RT. A general strategy of predicting the KOA of the compound is provided based on the method, namely whether the molecule is in the application range is judged according to the Dragon descriptor, if so, a QSAR model is preferentially adopted (QSAR-T is adopted at different temperatures), otherwise, the compound is predicted by adopting an SM8AD solvent model. The method and strategy are adopted and accorded, the KOA of different compounds at different temperatures can be rapidly and effectively predicted, lots of manpower, material resources and financial resources are saved, and important essential data is provided for large-scale ecological risk assessment and environment supervision of chemicals.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for predicting fish bio-concentration factors of organic chemicals by quantitative structure-activity relationship
ActiveCN103761431ATransparent prediction rulesEasy to understand and analyzeSpecial data processing applicationsDensity functional theoryOrganic compound
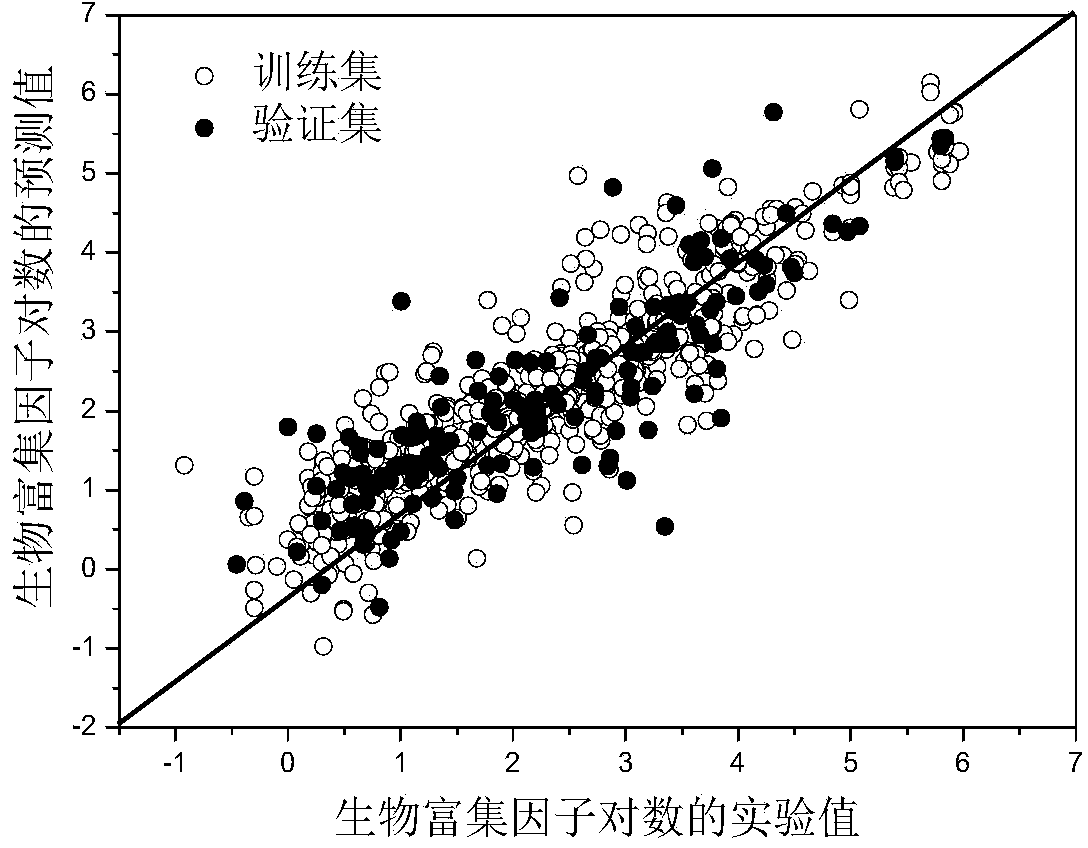
The invention discloses a method for predicting fish bio-concentration factors of organic chemicals by the quantitative structure-activity relationship, and belongs to the field of ecological risk assessment and test strategies. According to the method, bio-concentration factor data of 780 types of organic compounds are collected from public databases or published papers; molecular structures of the organic compounds are optimized according to the density functional theory, and 4885 types of molecule descriptors of the organic compounds are preliminarily screened on the basis of the optimized molecular structures to acquire 3480 molecule descriptors; the organic compounds are divided into a training set and a verification set according to a ratio of 4:1, the training set is used for creating a predication model, and the verification set is used for external verification after model creation. The method has the advantages that the model is clear in application field and covers new pollutants, has good imitative effect, robustness and predication capability, and can effectively predict bio-concentration factors of different types of organic compounds; predication results of the method can provide important data support for risk assessment and management of the organic chemicals and are of great significance in ecological risk assessment.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
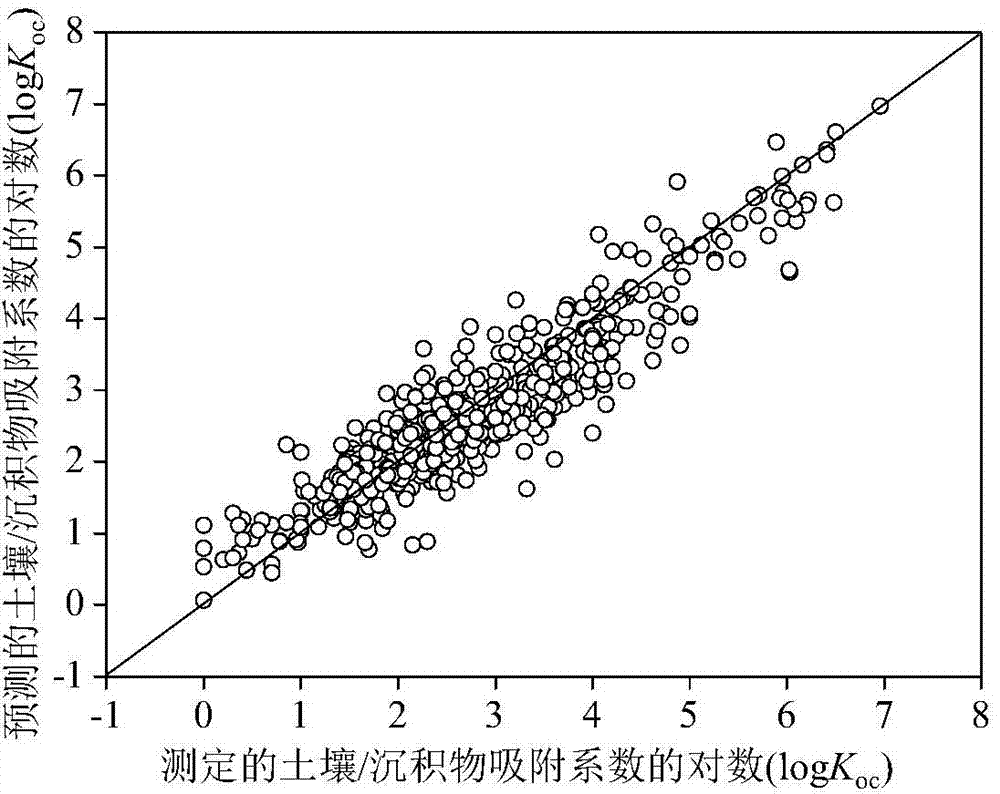
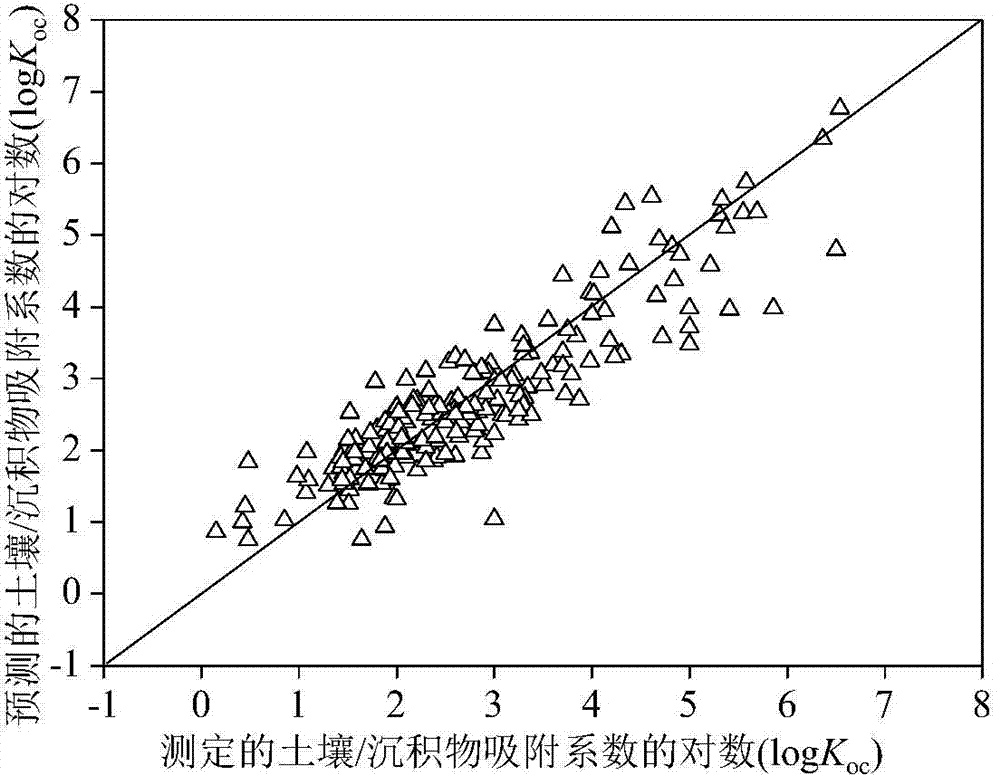
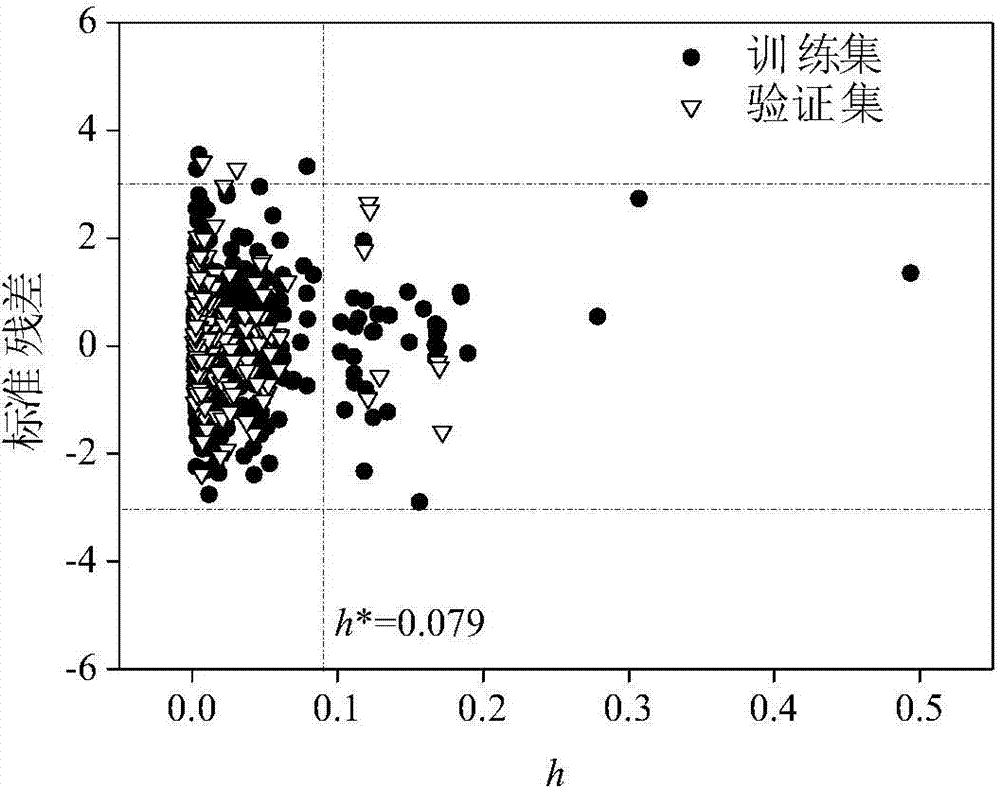
Method for adopting quantitative structure-activity relationship model to predicting soil or sediment adsorption coefficients of organic compound
ActiveCN103488901AThe method is simple and fastLow costSpecial data processing applicationsRelational modelMultiple linear regression analysis
The invention discloses a method for adopting a quantitative structure-activity relationship model to predicting soil or sediment adsorption coefficients of an organic compound. On the basis that a molecular structure of the organic compound is known, the soil or sediment adsorption coefficients of the organic compound can be quickly and efficiently predicted only by calculating a molecular descriptor with the molecular structure and applying a built QSAR (quantitative structure-activity relationship) model. The method is simple, quick, low in cost and capable of saving manpower, material resources and financial resources needed for experiment testing. Modeling is performed according to guidelines on building and using the QSAR model of the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, and a simple and transparent multiple linear regression analysis method is applied, so that easiness in understanding and applying is realized; the method has clear application domain, good fitting capacity, robustness and predicting capability; by the method, the soil or sediment adsorption coefficients of the organic compound in the application domain can be effectively predicted, and necessary basic data are provided for ecological risk evaluation and management of the compound; the method has important significance.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Modeling method and device of compound toxicity prediction model and application of compound toxicity prediction model
InactiveCN110890137AReliable Toxicity Prediction ResultsReduce false positive rateMolecular designSystems biologyProtein targetDrug biological activity
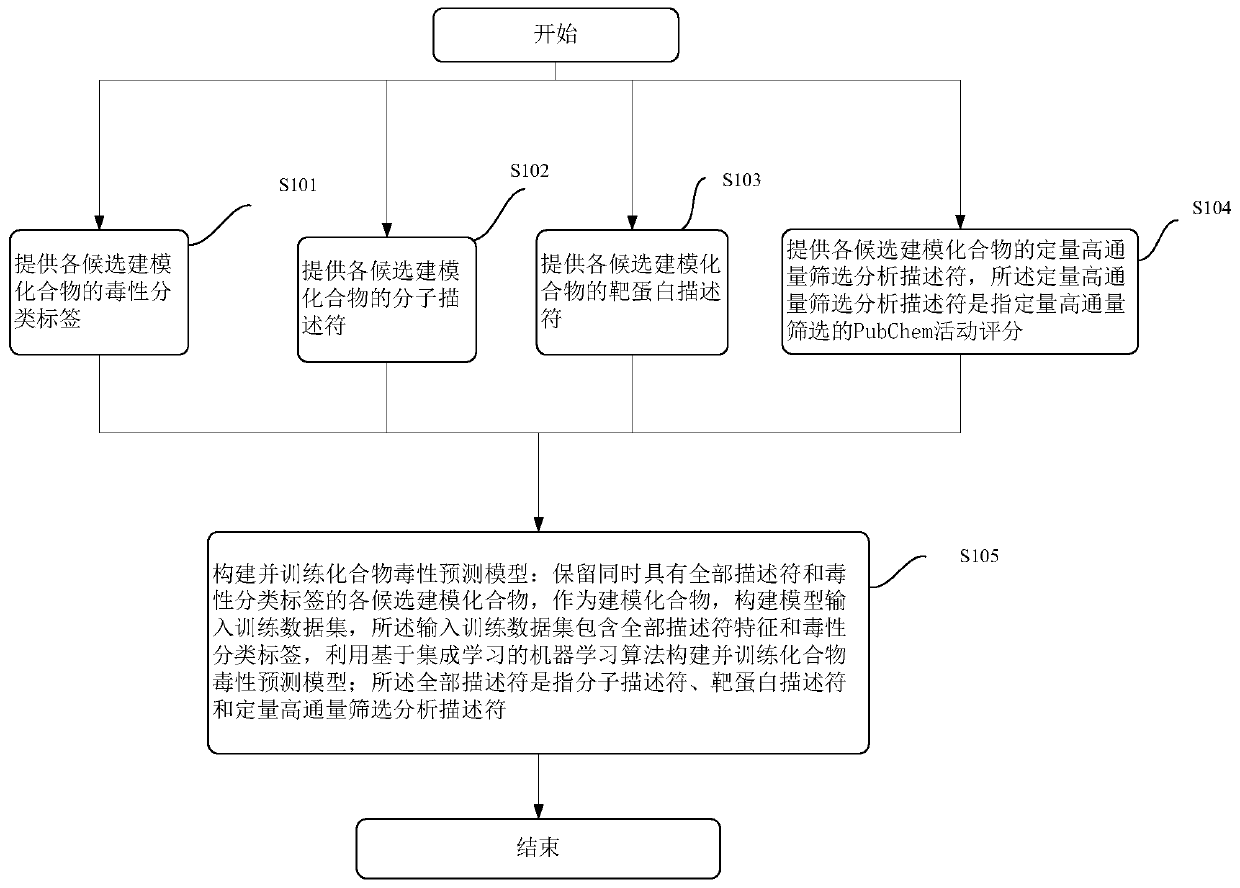
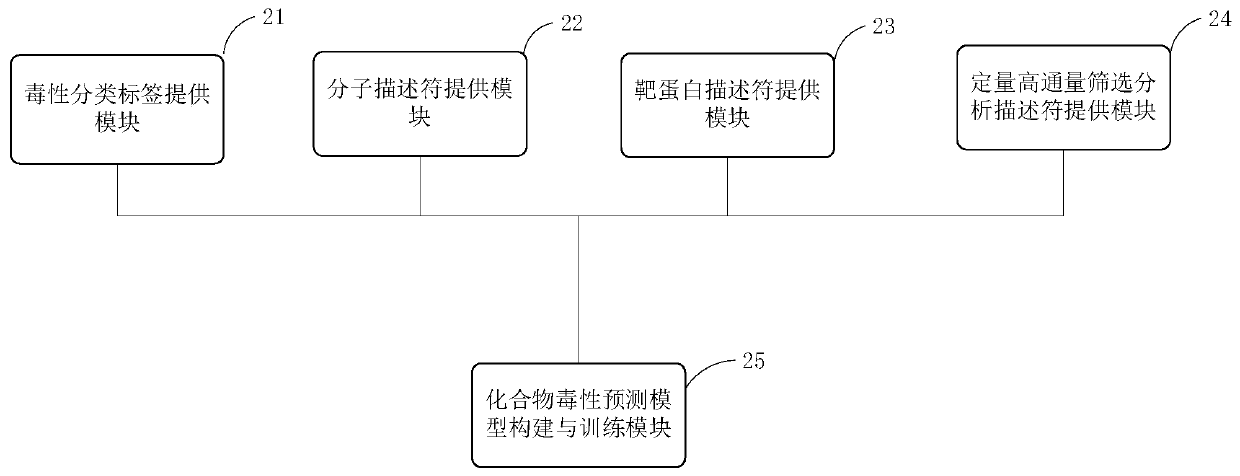
The invention provides a modeling method of a compound toxicity prediction model. The modeling method at least comprises the following steps of: S101, providing toxicity classification labels of candidate modeling compounds; S102, providing a molecular descriptor of each candidate modeling compound; S103, providing a target protein descriptor of each candidate modeling compound; S104, providing aquantitative high-throughput screening analysis descriptor of each candidate modeling compound, wherein the quantitative high-throughput screening analysis descriptor is a PubChem activity score of aspecified amount of high-throughput screening; and S105, constructing and training a compound toxicity prediction model. According to the method, physicochemical properties, biological activity and target protein action properties of drug candidate compounds can be fully utilized, and a drug toxicity prediction system is constructed by utilizing statistical modeling advantages of a machine learning algorithm based on ensemble learning, so that the model has interpretability and prediction performance, and has the better physicochemical and biological significance and research value.
Owner:上海尔云信息科技有限公司
Medicament module pharmacokinetic property and toxicity predicting method based on capsule network
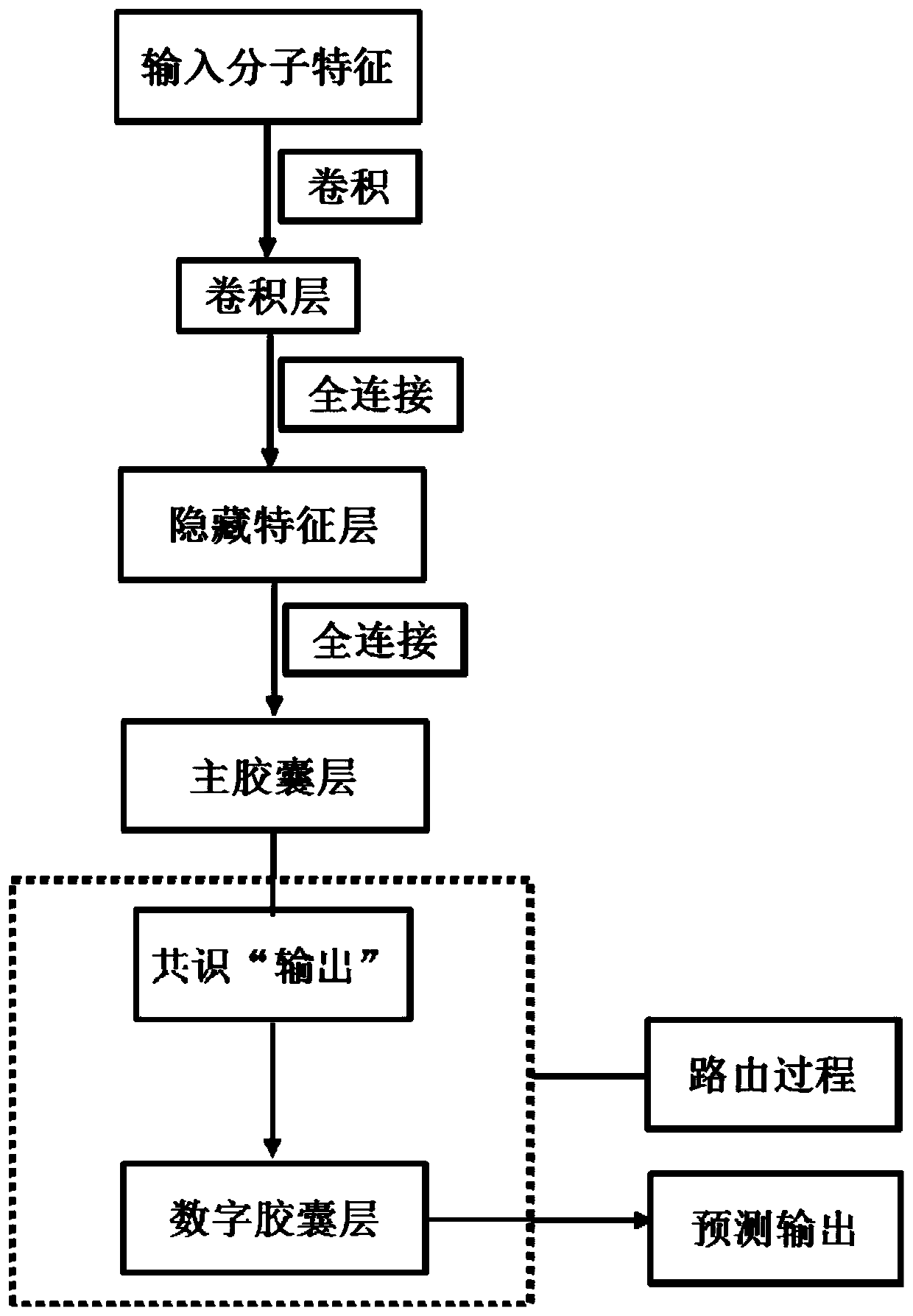
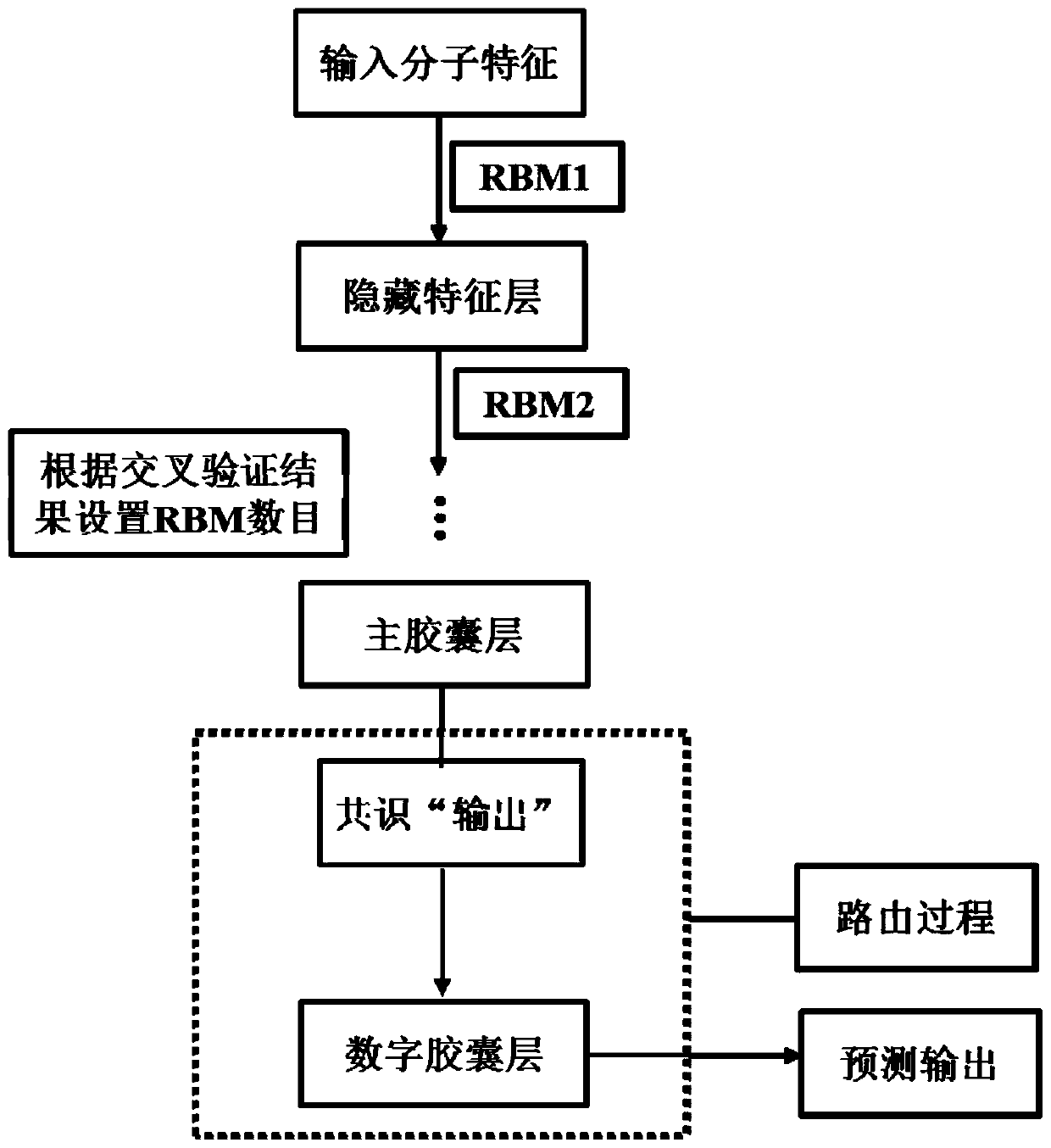
InactiveCN109979541AGood forecastPreserve Hierarchical Positional RelationshipsChemical property predictionComputational theoretical chemistryData setRestricted Boltzmann machine
The invention provides a medicament module pharmacokinetic property and toxicity predicting method based on a capsule network. After a comprehensive module fingerprint and a module descriptor are constructed and early-period preparing operation for establishing model is performed, a low-grade characteristic content of a molecule is extracted from an upper-layer low-grade characterized through convolutional or restricted Boltzmann machine operation; then a capsule network method is used for abstracting the high-grade characteristic of the molecule in a lower-layer high-grade characteristic; a relation between the high-grade characteristic and an active label is fit through a dynamic routing algorithm, thereby predicting the pharmacokinetic property and the toxicity class of an unknown smallmolecule. The method does not require collection of large scale datasets for training, optimization is performed on input through end-to-end and furthermore automatic dimension reduction is realized.A coupling coefficient is updated through iterating a dynamic routing process. The dynamic routing conveys all characteristics of an upper-layer capsule to a random lower-layer capsule, thereby greatly reserving a hierarchical position relation. The method realizes a better predicting effect than that of a traditional machine learning method.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Method for predicting inhibiting concentration of pyridazine HCV NS5B polymerase inhibitor based on particle swarm optimization support vector machine
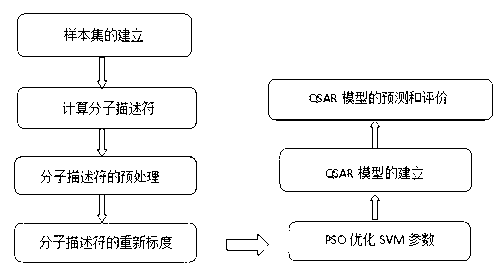
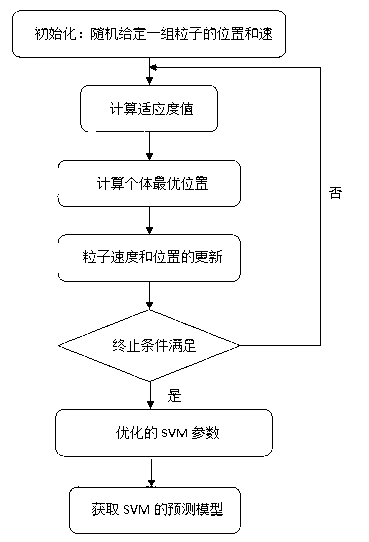
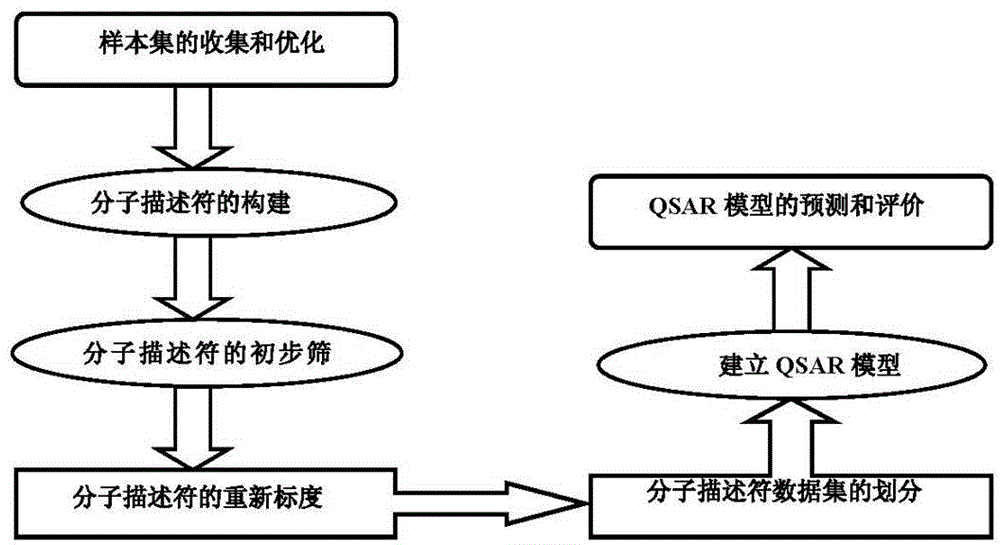
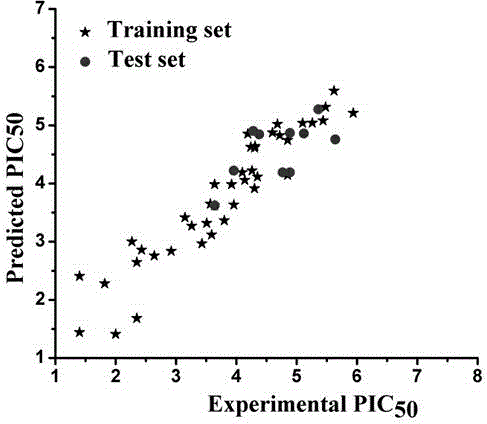
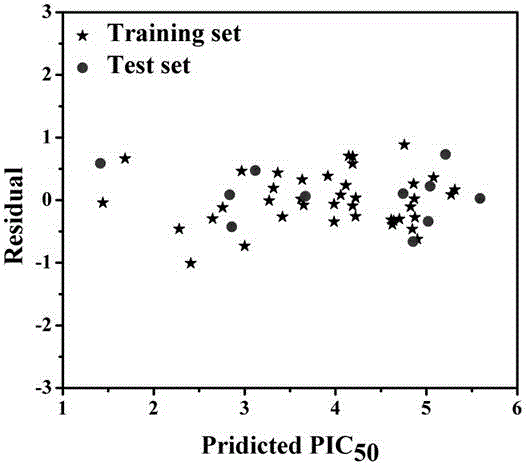
The invention discloses a method for predicting inhibiting concentration of a pyridazine HCV NS5B polymerase inhibitor based on a particle swarm optimization (PSO) support vector machine (SVM). The method comprising the following steps: establishing and optimizing a sample set, calculating inhibitor molecule descriptor, preprocessing a molecule descriptor data set, rescaling the inhibitor molecule descriptor data set, dividing the data set, optimizing support vector machine parameters, establishing a model and predicting. The method for predicting the inhibiting concentration of the pyridazine HCV NS5B polymerase inhibitor based on the particle swarm optimization support vector machine is an SVM parameter selecting method based on a PSO algorithm, the optimization of the model is achieved by using the high global searching ability of the PSO, a relational model is established through the structure and the inhibiting concentration of the pyridazine HCV NS5B polymerase inhibitor, accurate predicting is conducted on the inhibiting concentration of the pyridazine HCV NS5B polymerase inhibitor, effectiveness of the method is verified, an excellent method for predicting the inhibiting concentration of other inhibitors is provided, and predicting conducted on unknown output can be accurate as far as possible.
Owner:NORTHWEST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Computer aided design system for predicting energetic molecule based on machine learning performance
ActiveCN110728047AEfficient designRapid designMolecular computersDesign optimisation/simulationComputer Aided DesignData set
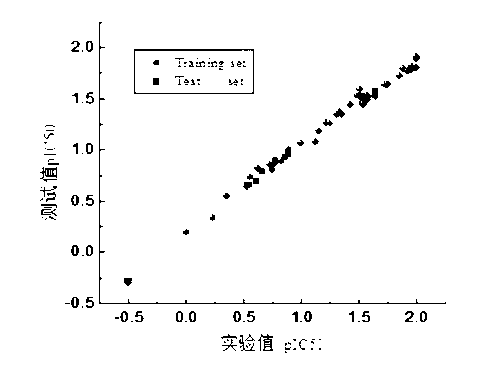
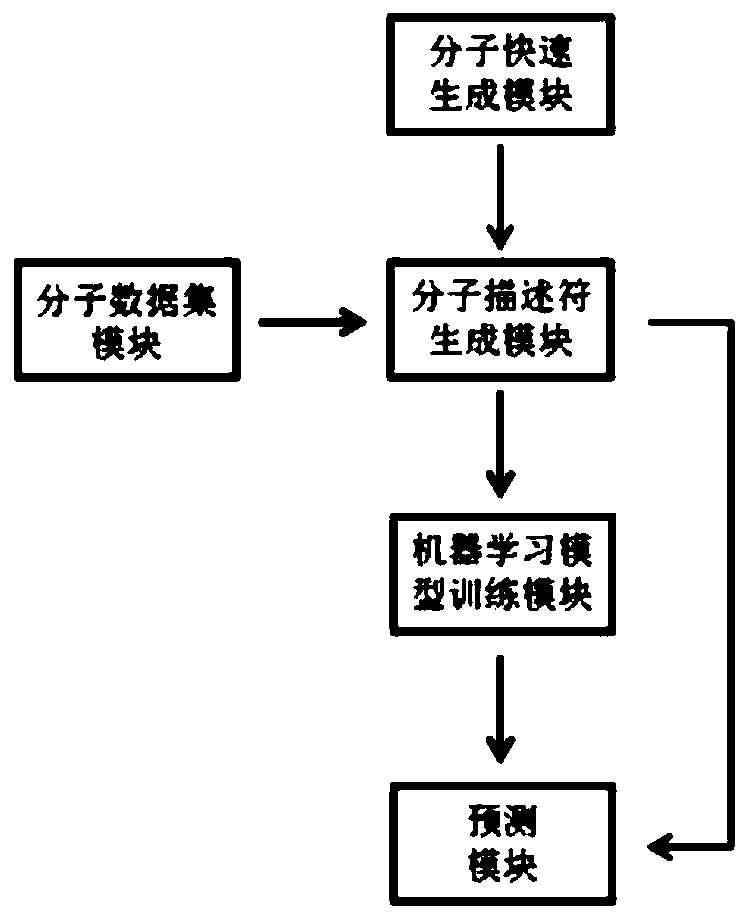
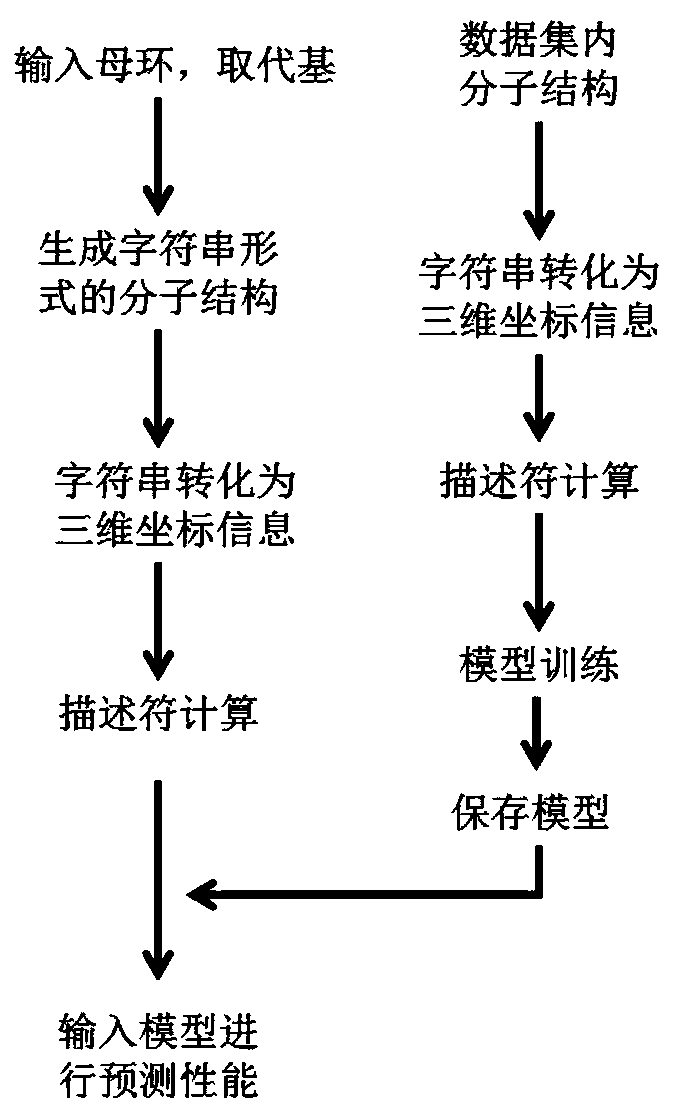
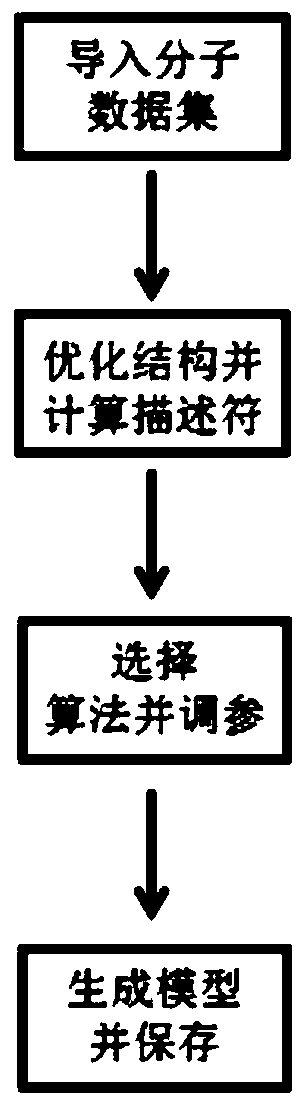
The invention discloses a computer aided design system for predicting energetic molecules based on machine learning performance, and belongs to the technical field of computer aided design systems. The system comprises: a molecule rapid generation module, which is used for generating all possible molecular structural formulas according to permutation and combination of a molecular mother ring anda substituent group input by a user, and removing a repeated structure; a molecular data set module used for recording reported energetic molecular performance data, and the energetic molecular performance data being mainly used as a training set of the machine learning model training module; a molecular descriptor generation module used for calculating molecular descriptors of molecules generatedby the molecular rapid generation module or molecules in the molecular data set module or molecules input by a user; a machine learning model training module used for training and storing a model byadopting a machine learning algorithm according to the data of the molecular descriptor set; and a performance prediction module used for reading the model and carrying out performance prediction on the molecules generated by the molecule rapid generation module or the molecules input by the user.
Owner:INST OF CHEM MATERIAL CHINA ACADEMY OF ENG PHYSICS
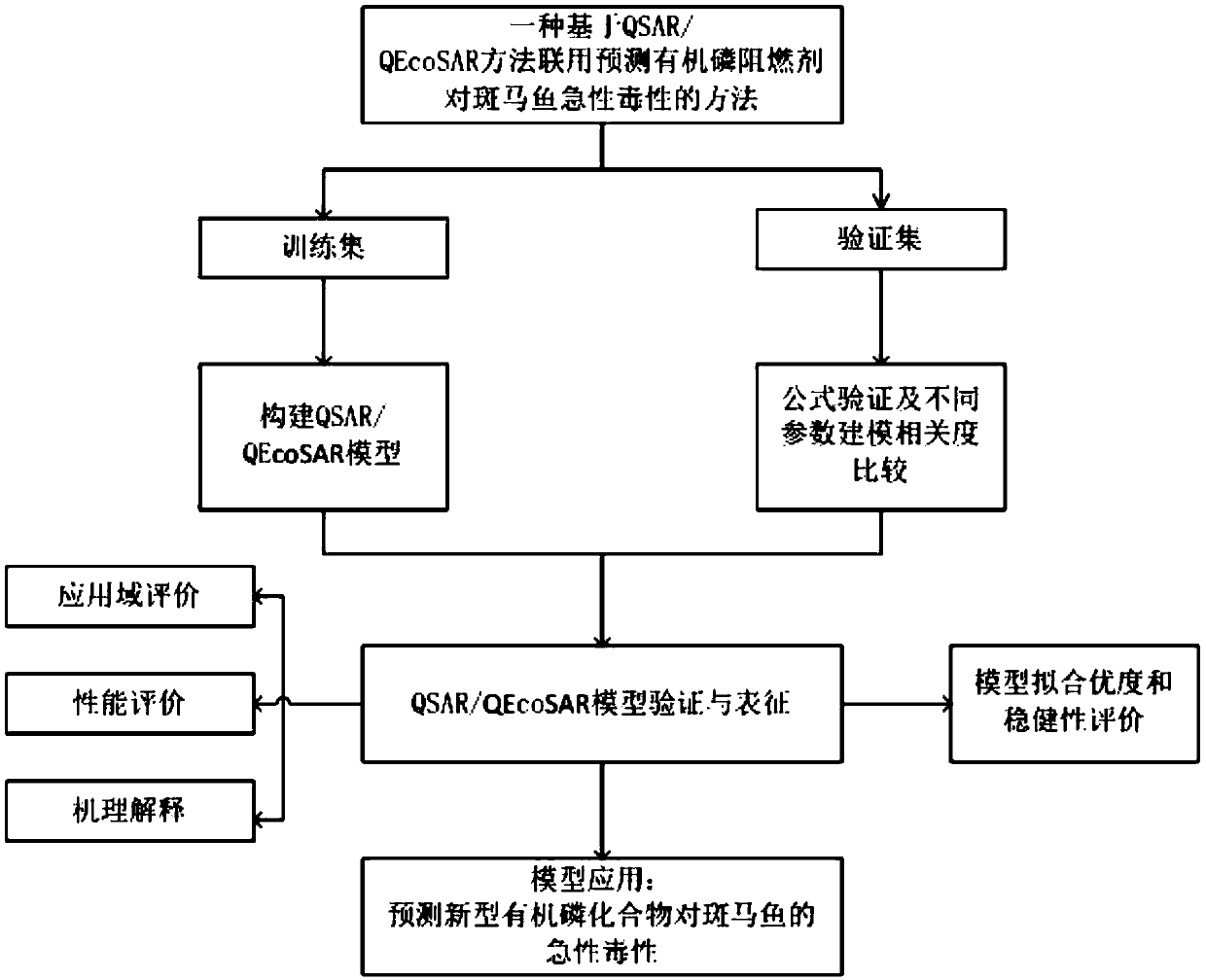
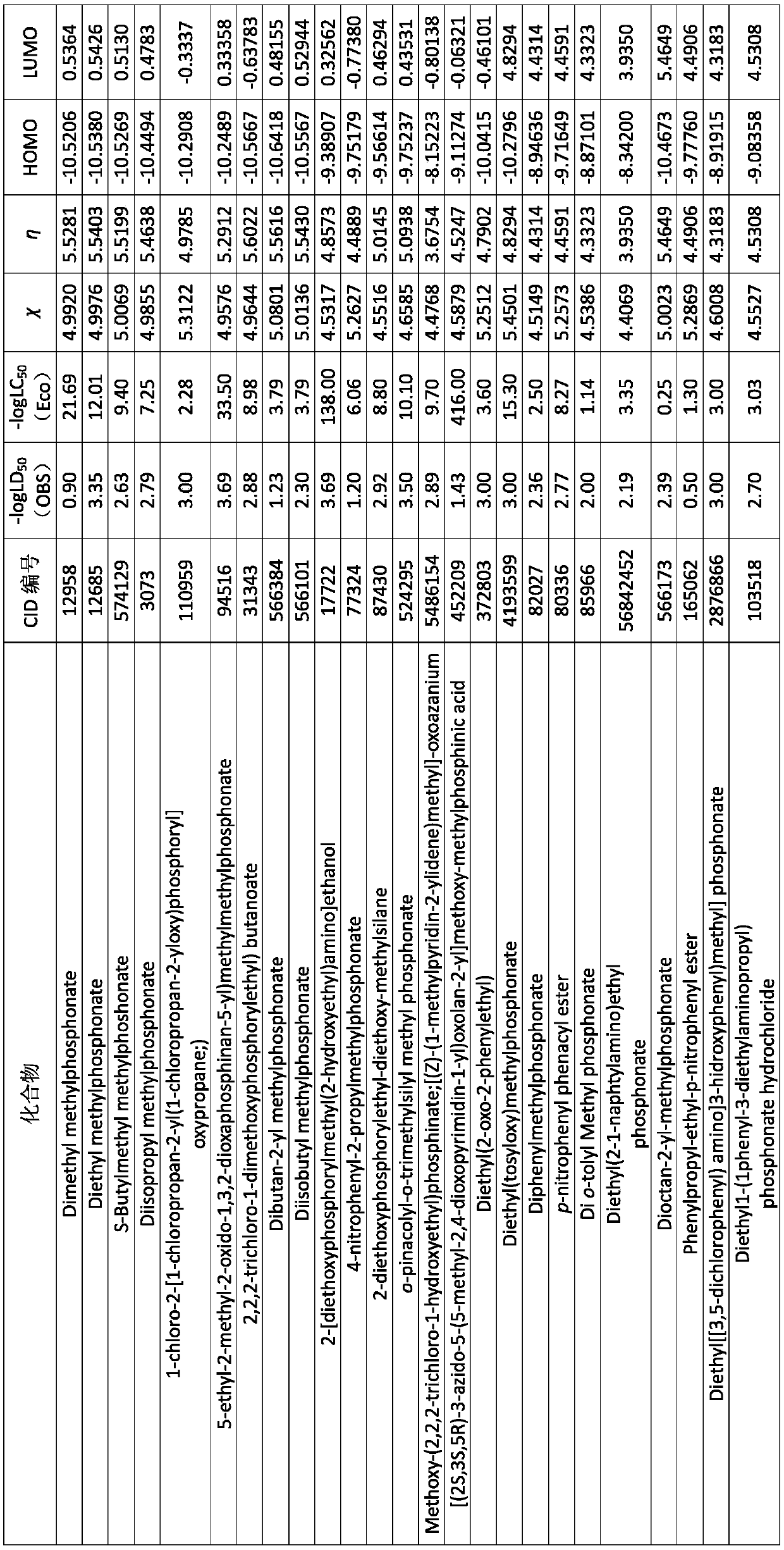
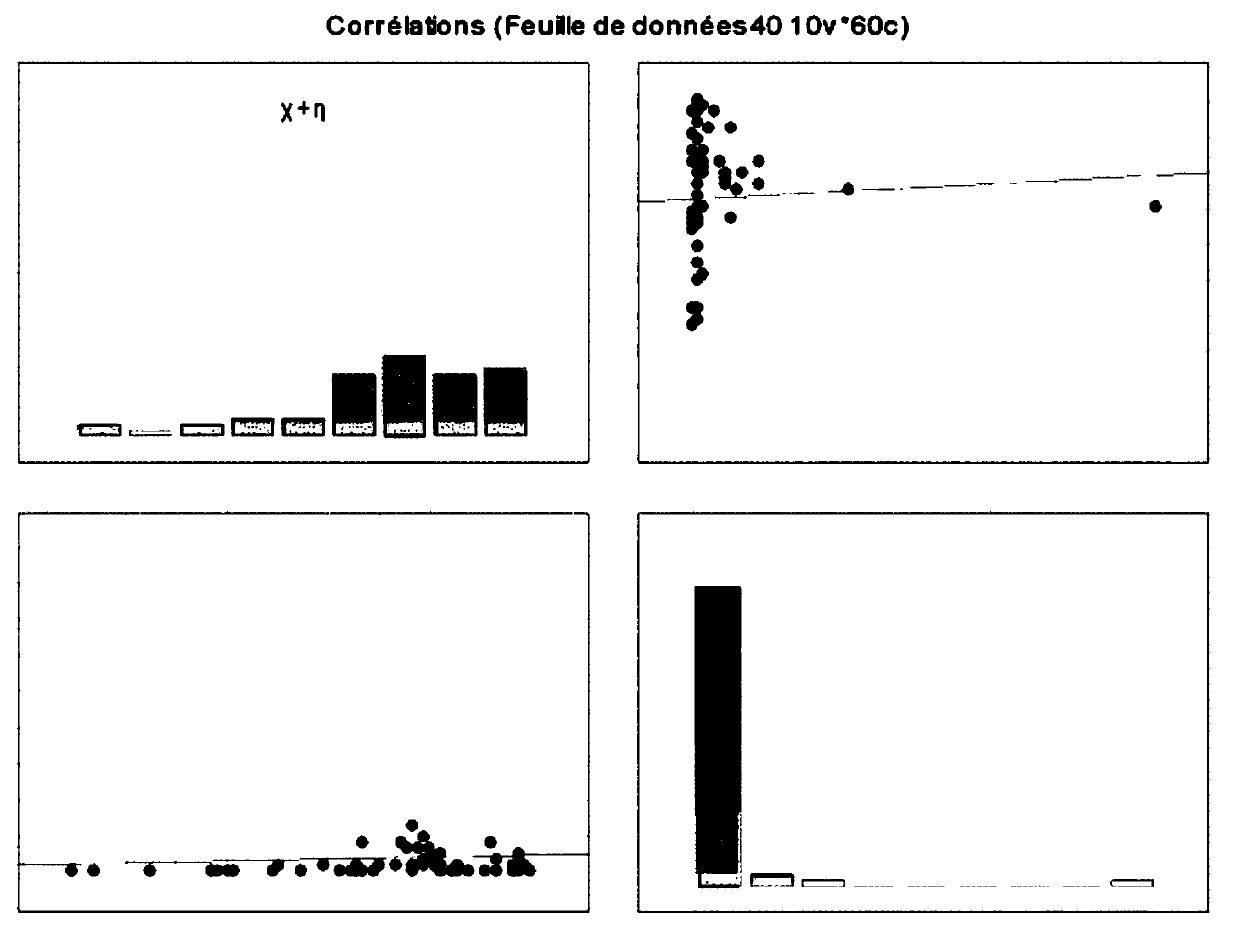
Method for predicting acute toxicity of organophosphorous flame retardant on zebra fish based on QSAR/QEcoSAR method combination
InactiveCN108733970APredict acute toxicityShortcut structureSpecial data processing applicationsAcute toxicity testingChemical reaction
The invention discloses a method for predicting acute toxicity of an organophosphorous flame retardant on a zebra fish based on QSAR / QEcoSAR method combination and belongs to the technical field of quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) for chemical environment supervision. The method comprises the steps that based on the chemical reaction principle and the minimum energy principle, QSAR and QEcoSAR are combined, and a multivariate linear regression method is adopted to construct a QSAR model of LC50 and training set compound molecule descriptors (electronegativity, chemical hardness, chemical force, eletrophilicity and other characteristics). The method is low in cost and convenient and fast to use, and a large amount of manpower, cost and time needed in experimental testingcan be saved; and by use of the prediction result, important data support can be provided for ecological risk evaluation and management of organophosphorous chemicals, and therefore the method has important realistic significance and theoretical value.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
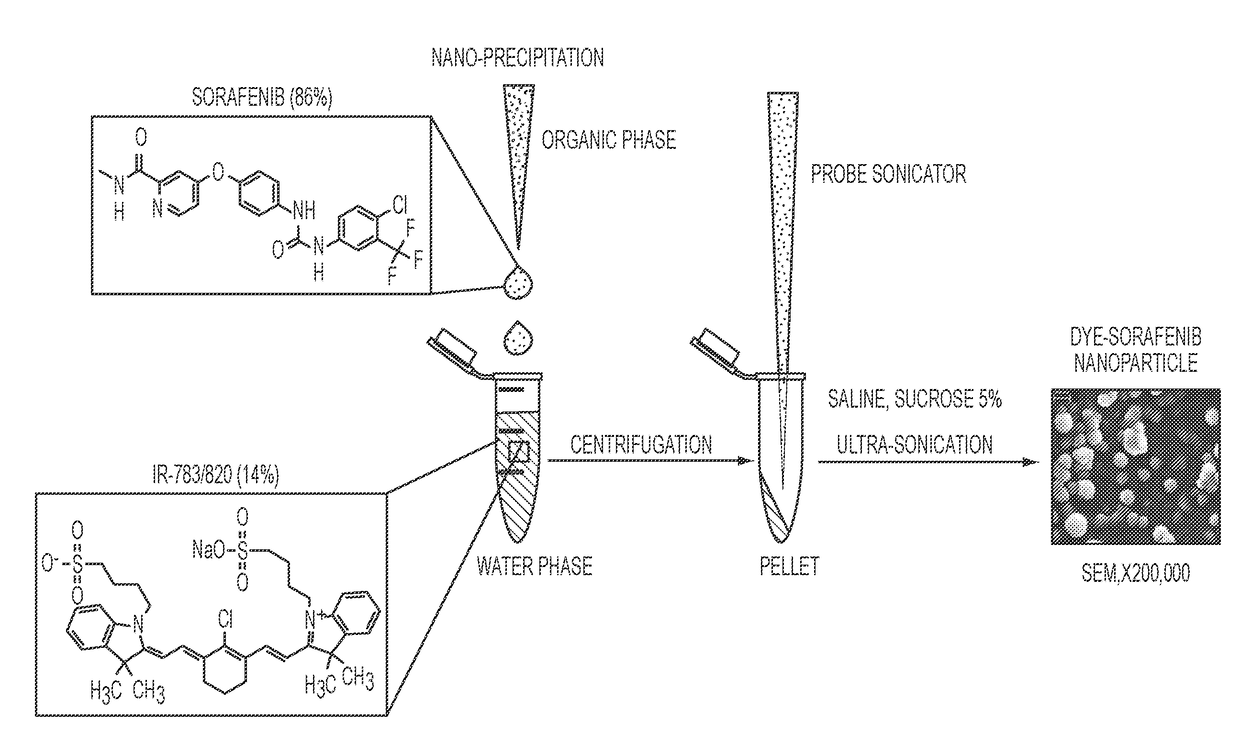
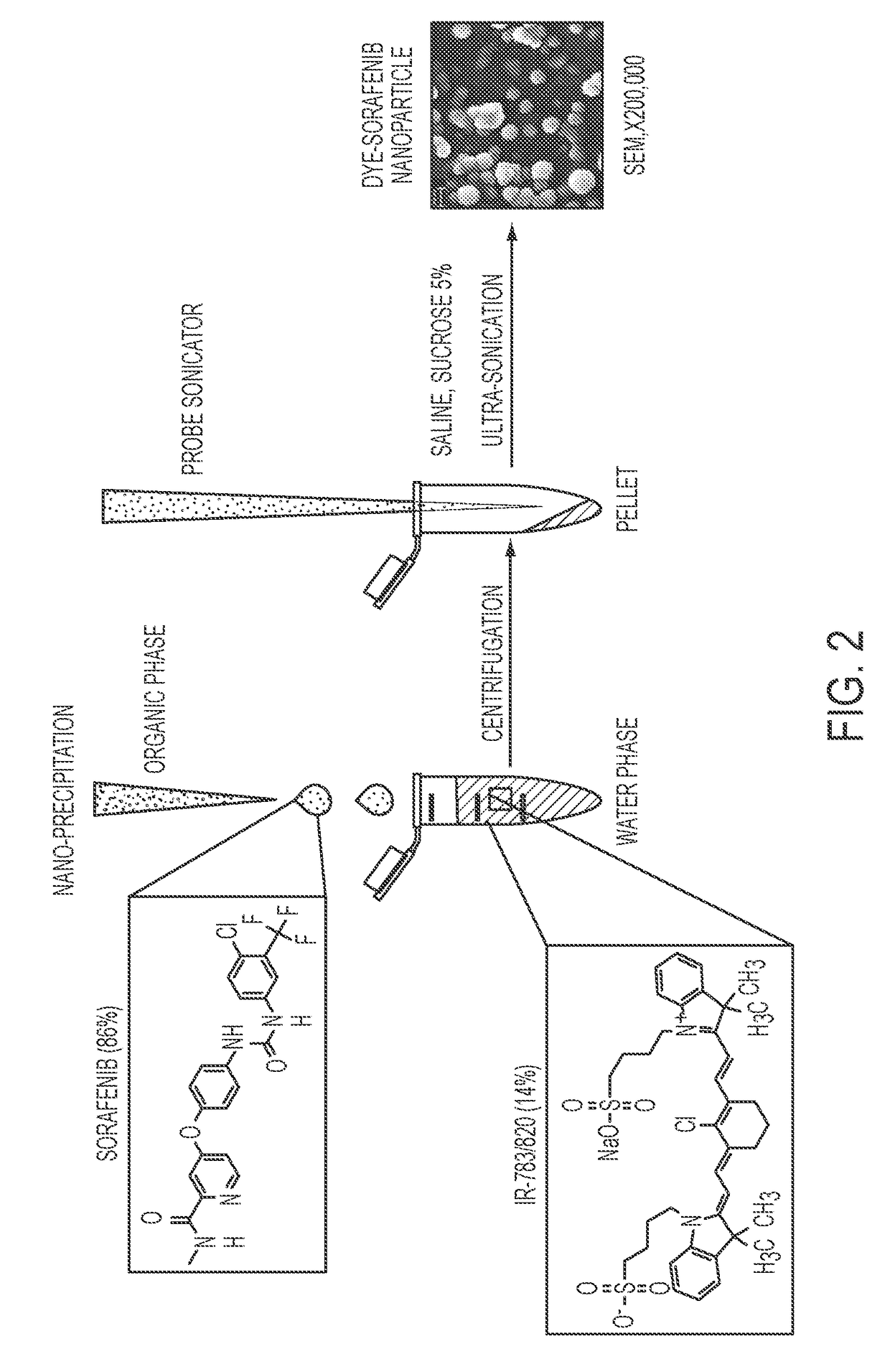
Dye-stabilized nanoparticles and methods of their manufacture and therapeutic use
InactiveUS20180021259A1Increase surface chargeEasily lyophilzedPowder deliveryMolecular designTherapeutic effectIn vivo
Described herein are nanoparticles which are largely made of (e.g., 90 wt. %) hydrophobic drugs and are stabilized by water soluble dyes. The nanoparticles can range in size from 30 nm to 150 nm and have highly negative surface charge (e.g., −55 mV). These nanoparticles are highly soluble in water, stable for days in PBS buffer and can be easily lyophilzed and reconstituted in water. Using quantitative self-assembly prediction calculations, topochemical molecular descriptors were identified and validated as highly predictive indicators of nano-assembly, nanoparticle size, and drug loading. The resulting nanoparticles selectively targeted kinase inhibitors to caveolin-1-expressing human colon cancer and autochthonous liver cancer models to yield striking therapeutic effects while avoiding pERK inhibition in healthy skin. The nanoparticles exhibited remarkable anti-tumor efficacy in vitro and in vivo in models of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
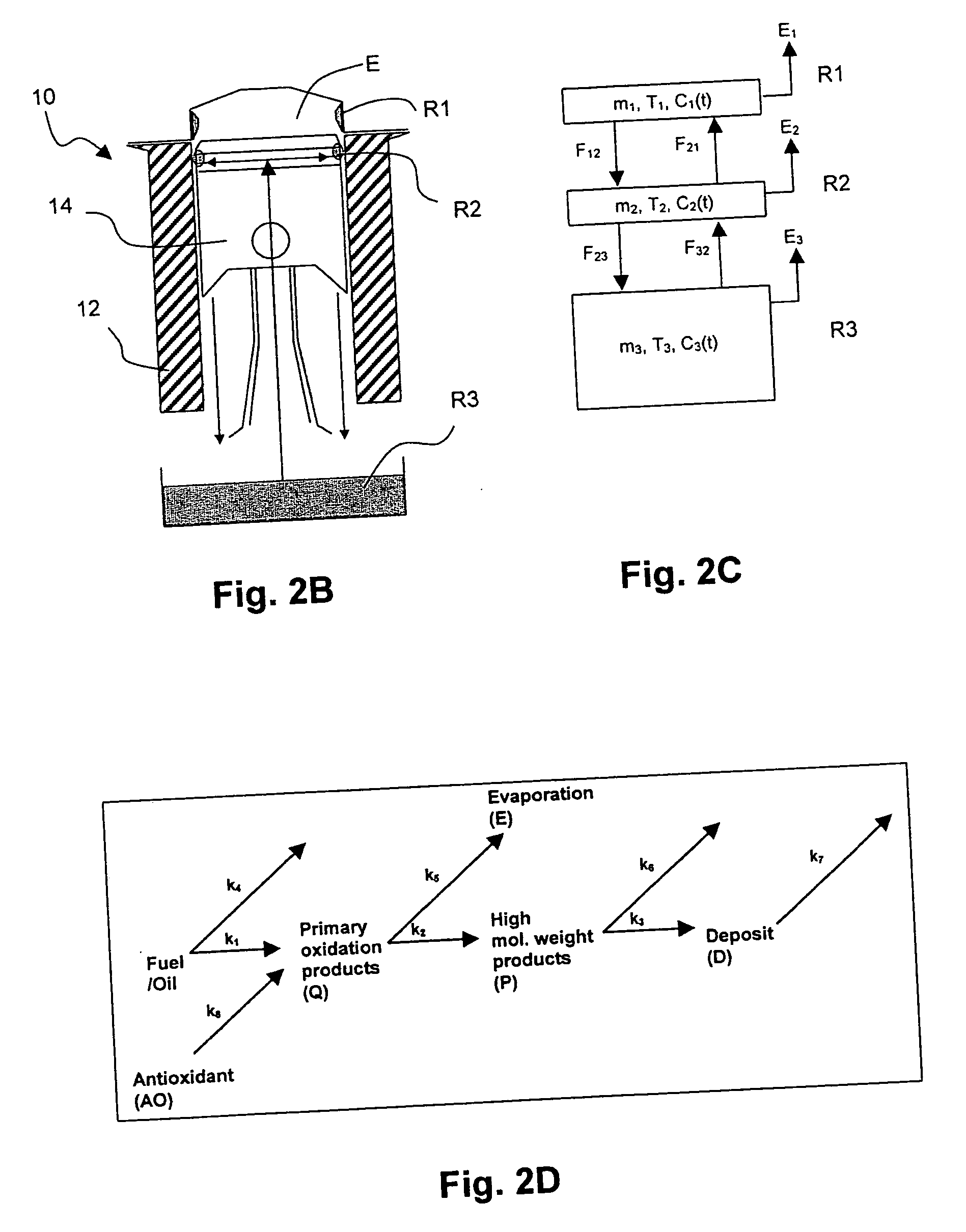
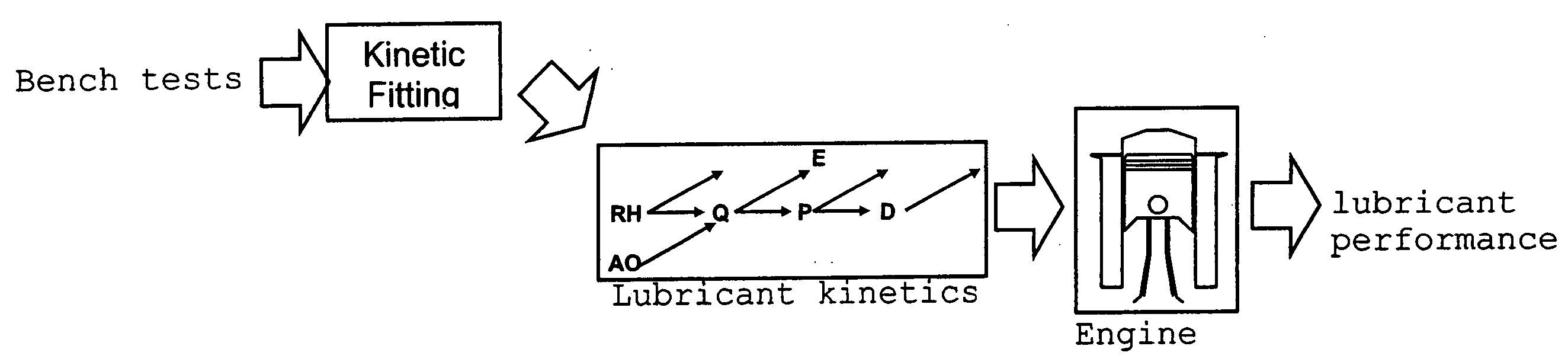
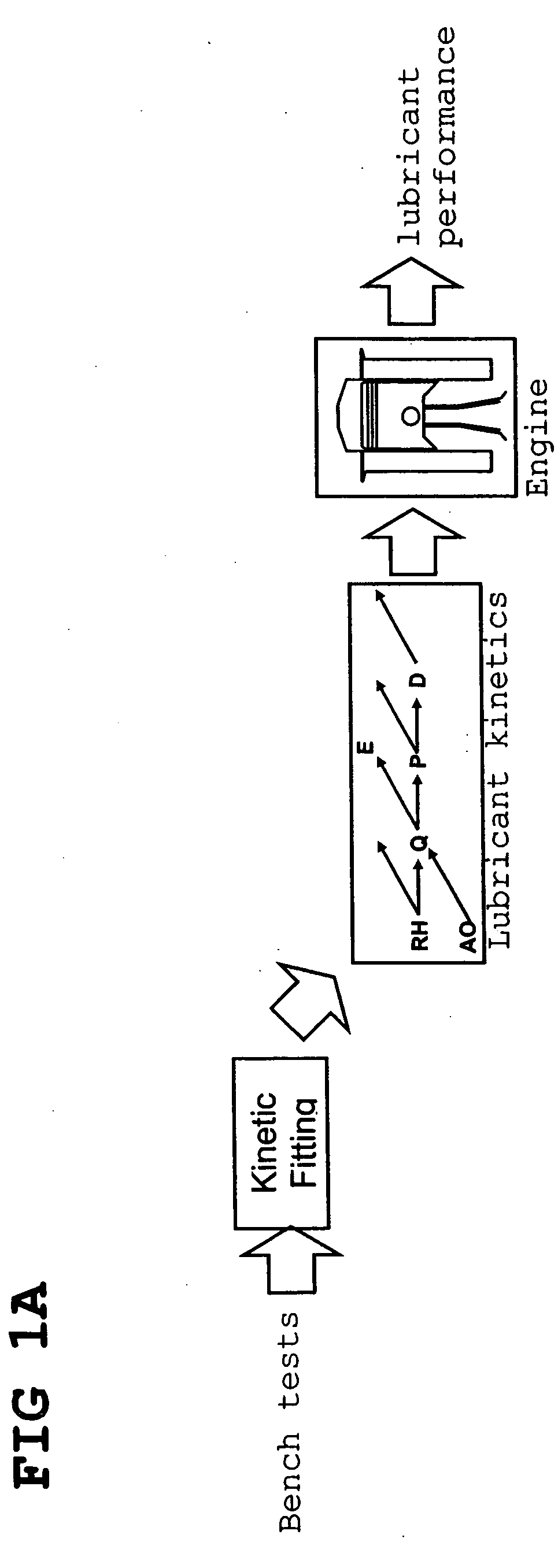
Predictive technologies for lubricant development
InactiveUS20070112527A1Alter its performanceImprove stabilityChemical property predictionMaterial testing goodsChemical structureEngineering
In a method for predicting and / or correlating additive chemical structure to engine performance, at least one molecular descriptor for one or more additives are used to characterize the chemical structure. Based on the selected molecular descriptors, a value or functional relation of model parameters of a mechanistic engine model for the engine performance e.g. using reaction kinetics parameters is determined. For example, a functional relation between the molecular descriptors and the kinetic parameters by testing compositions comprising one or more additives is determined. Based on the mechanistic engine model a QSPR library describing the relation between the molecular descriptors of the additives and the kinetic parameters an engine performance of other additives may be estimated.
Owner:AVANTIUM INT
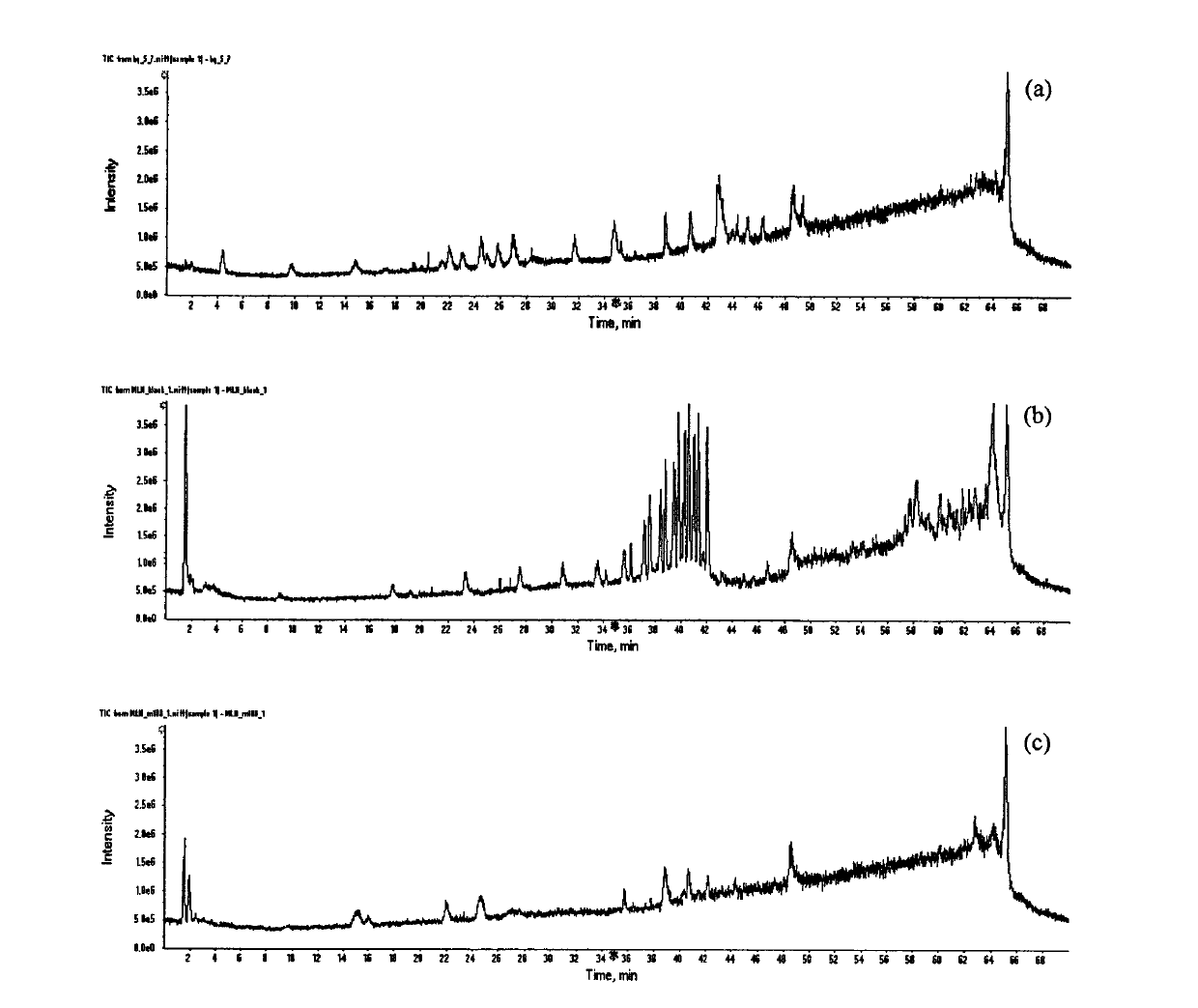
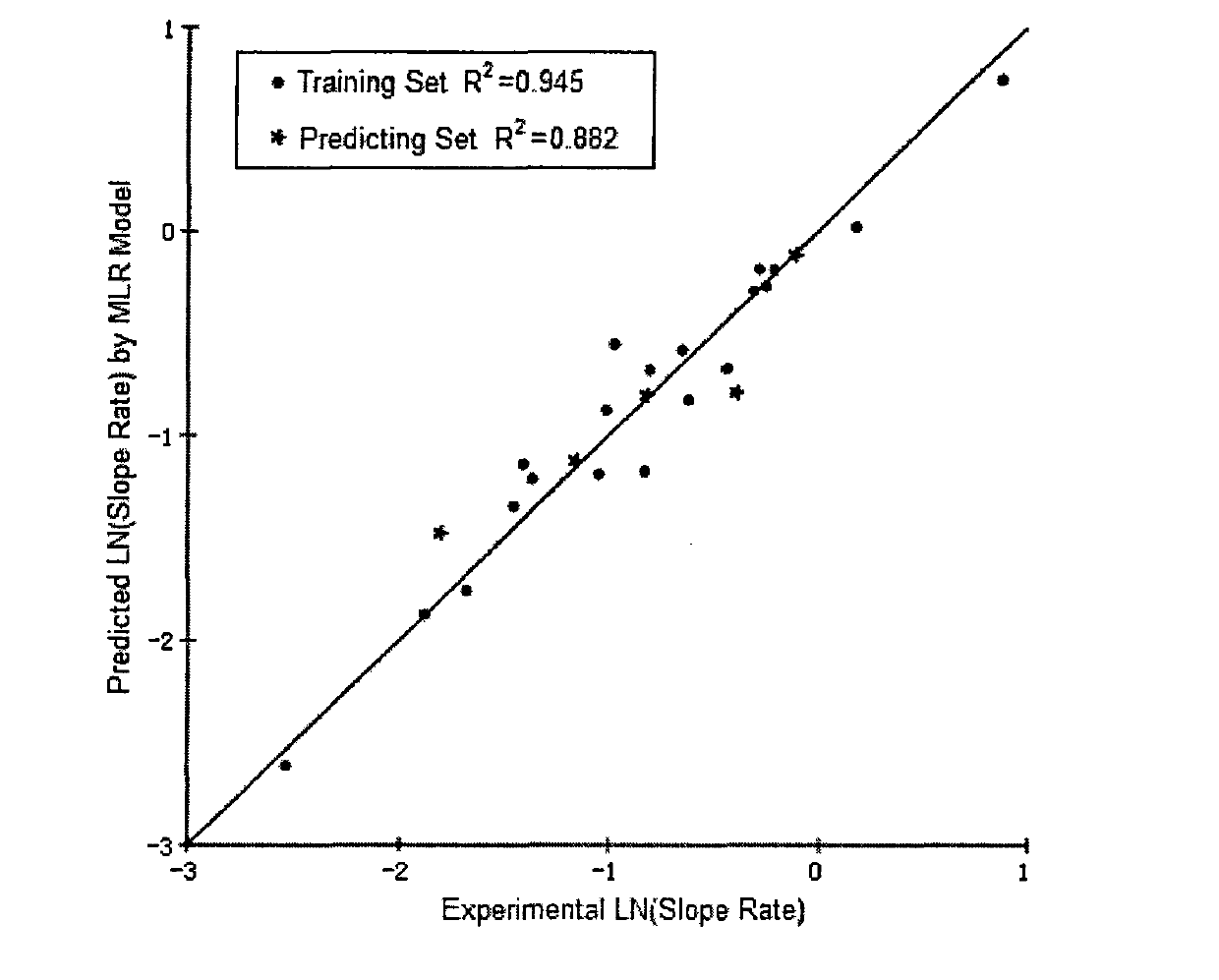
Novel non-standard-dependence quantitative analysis method based on study on homologous/similar compound structure-mass-spectrum response relationship
InactiveCN103018317AMass Spec Response High and LowQuantitatively accurateMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMethodological researchCompound structure
The invention belongs to the field of analysis, relates to a quantitative analysis method for homologous / similar compounds, and particularly relates to a quantitative compound analysis method for a complicated matrix sample which does not contain a standard substance. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) selecting a series of homologous / similar compounds, and carrying out mass-spectrum quantitative methodological study and textual research on the homologous / similar compounds; (2) carrying out zero-intercept linear fitting according to established standard curves of all the compounds; (3) carrying out structural optimization on the compounds by using molecular simulation software, and calculating related molecular descriptors; (4) carrying out establishment and verification on the relationship between the structures and mass-spectrum responses of the compounds by using the molecular simulation software; (5) carrying out qualitative analysis on the complicated matrix sample by employing related mass spectrometry technologies; (6) calculating the slope coefficients of linear fit standard curves of the verified series compounds according to a structure-mass-spectrum response relationship equation established previously; and (7) obtaining the concentrations of the compounds in the complicated matrix sample by using the fit standard curves of the series compounds. Thus, the non-standard-dependence quantitative analysis is realized.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
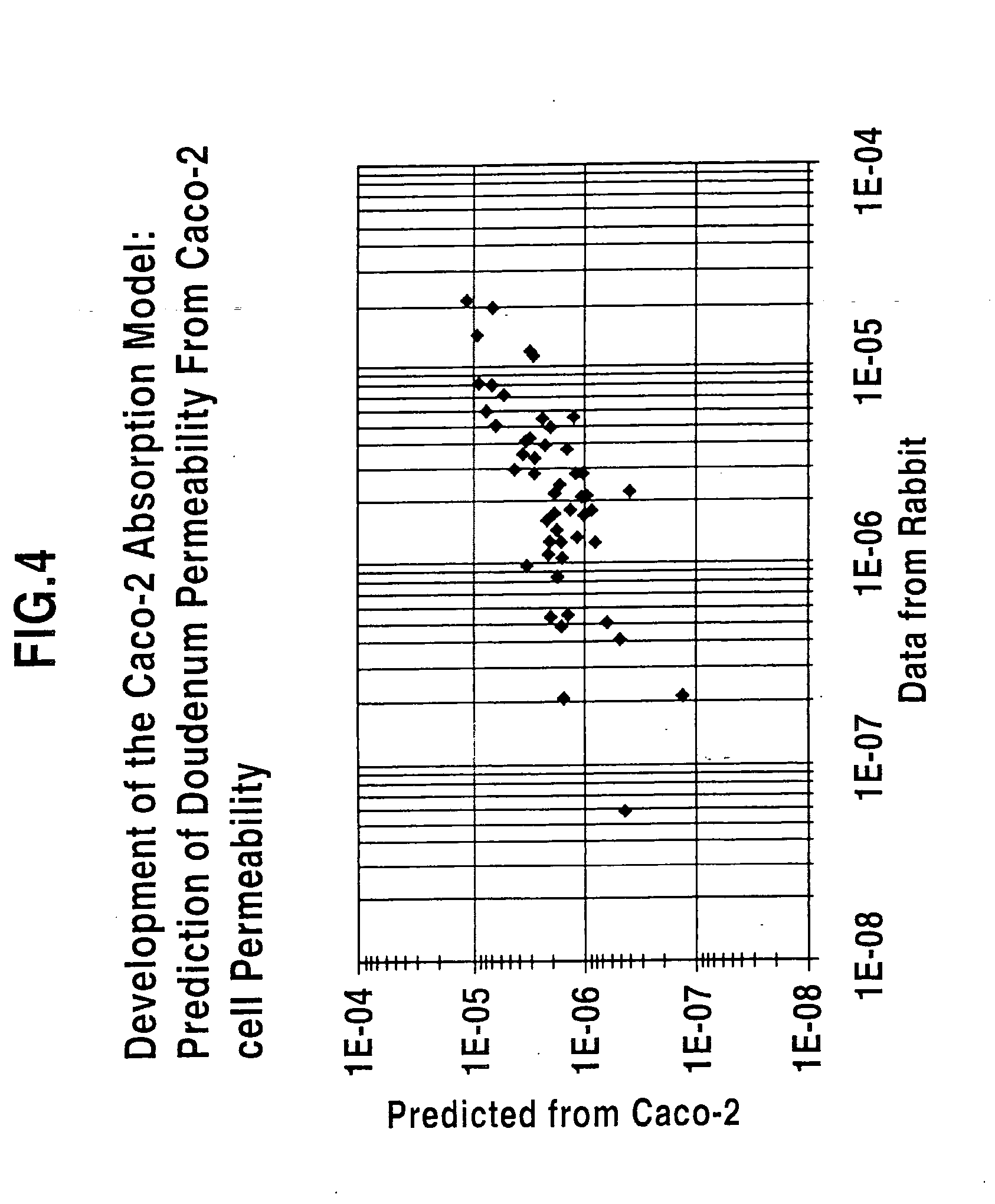
Regional intestinal permeability model
Permeability models and methods for creating the models are disclosed. The models include receiving as an input in vitro permeability and structure data for a particular compound. Then the data is mapped to at least one permeability. In some models the data is mapped to a plurality of permeabilities, each associated with a specific region in a mammalian GI tract. Some models may take into consideration solubility, permeability and at least one molecular descriptor associated with the compound of interest.
Owner:LION BIOSCIENCE AG
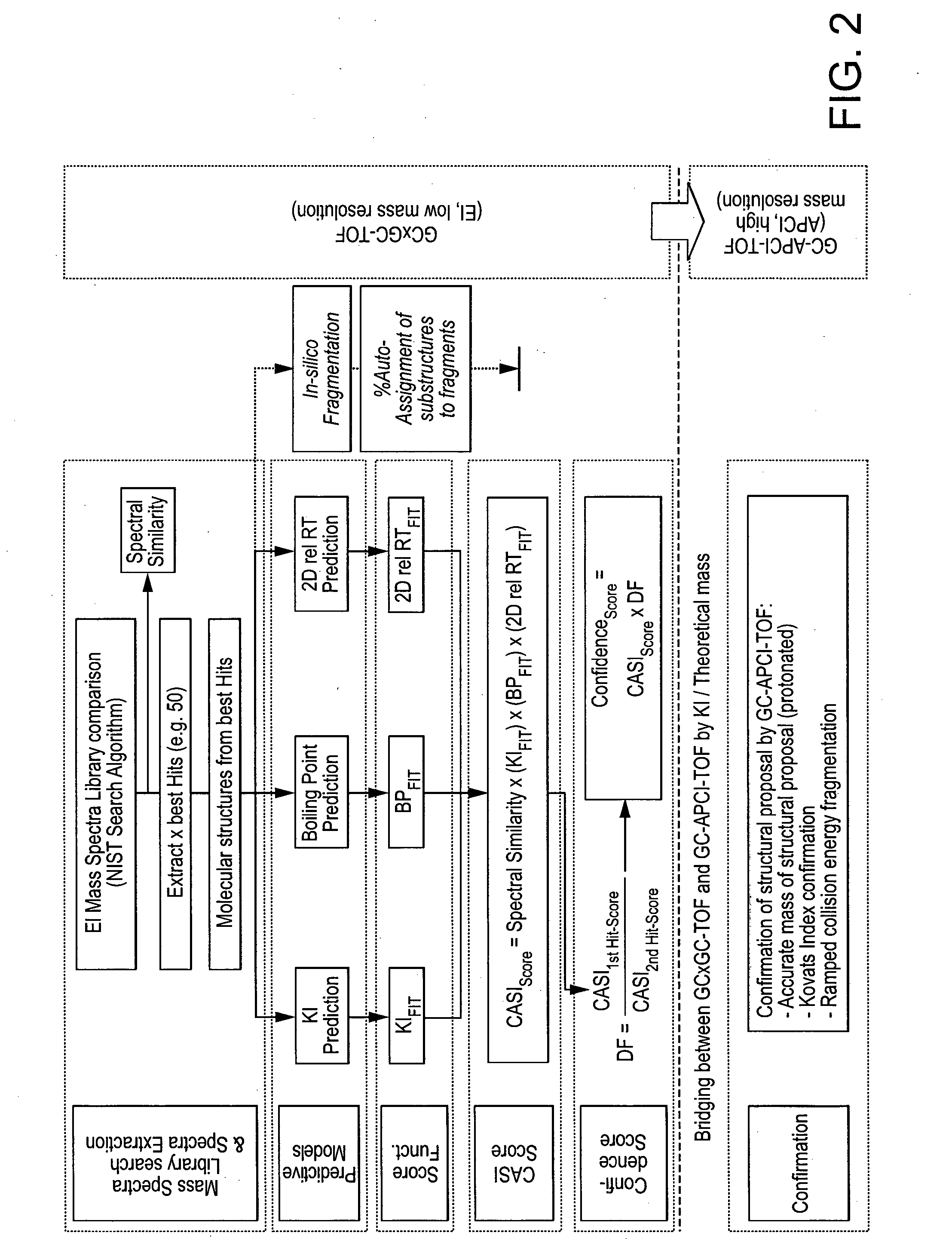
Computer-assisted structure identification
InactiveCN103650100AParticle separator tubesComponent separationAnalyteMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
The invention relates to a method for analysing mass spectral data obtained from a sample in GC*GC (2-dimensional) mass spectrometry, comprising: (a) comparing mass spectral data of an analyte with mass spectral data of candidate compounds of known structure in a data library; (b) identifying a plurality of candidate compounds from the library based on similarities of mass spectral data; (c) predicting, for each candidate compound, a value of at least one analytical property using a quantitative model based on a plurality of molecular descriptors; and (d) calculating a match score for each candidate compound based on the value predicted in step (c) and a measured value of the analytical property for the analyte.
Owner:PHILIP MORRIS PROD SA
Method for predicting inhibition concentration of cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP1A2 inhibitor by utilizing simplified partial least squares
ActiveCN104866710AReduce development riskImprove forecast qualitySpecial data processing applicationsCytochrome P450 InhibitorsCYP1A2
The invention discloses a method for predicting inhibition concentration of a cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP1A2 inhibitor by utilizing simplified partial least squares. The method comprises the steps of: 1) collecting, processing and optimizing sample sets; 2) constructing molecular descriptors of the inhibitor; 3) preliminarily screening molecular descriptors of the inhibitor; 4) scaling data sets of molecular descriptors of the inhibitor again; 5), dividing data sets of molecular descriptors of the inhibitor; 6), setting up a QSAR model; and 7) predicting inhibition concentration of the cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP1A2 inhibitor.The method utilizes the method of partial least squares (PLS) to further estimate and simplify constituents of partial least squares (PLS) in the presence of serious multiple correlations of independent variables on the basis of regression modeling and uses the simplified method of partial least squares (SIMPLS) to precisely predict inhibition concentration of the cytochrome P450 inhibitor.
Owner:居李生物科技(北京)有限公司
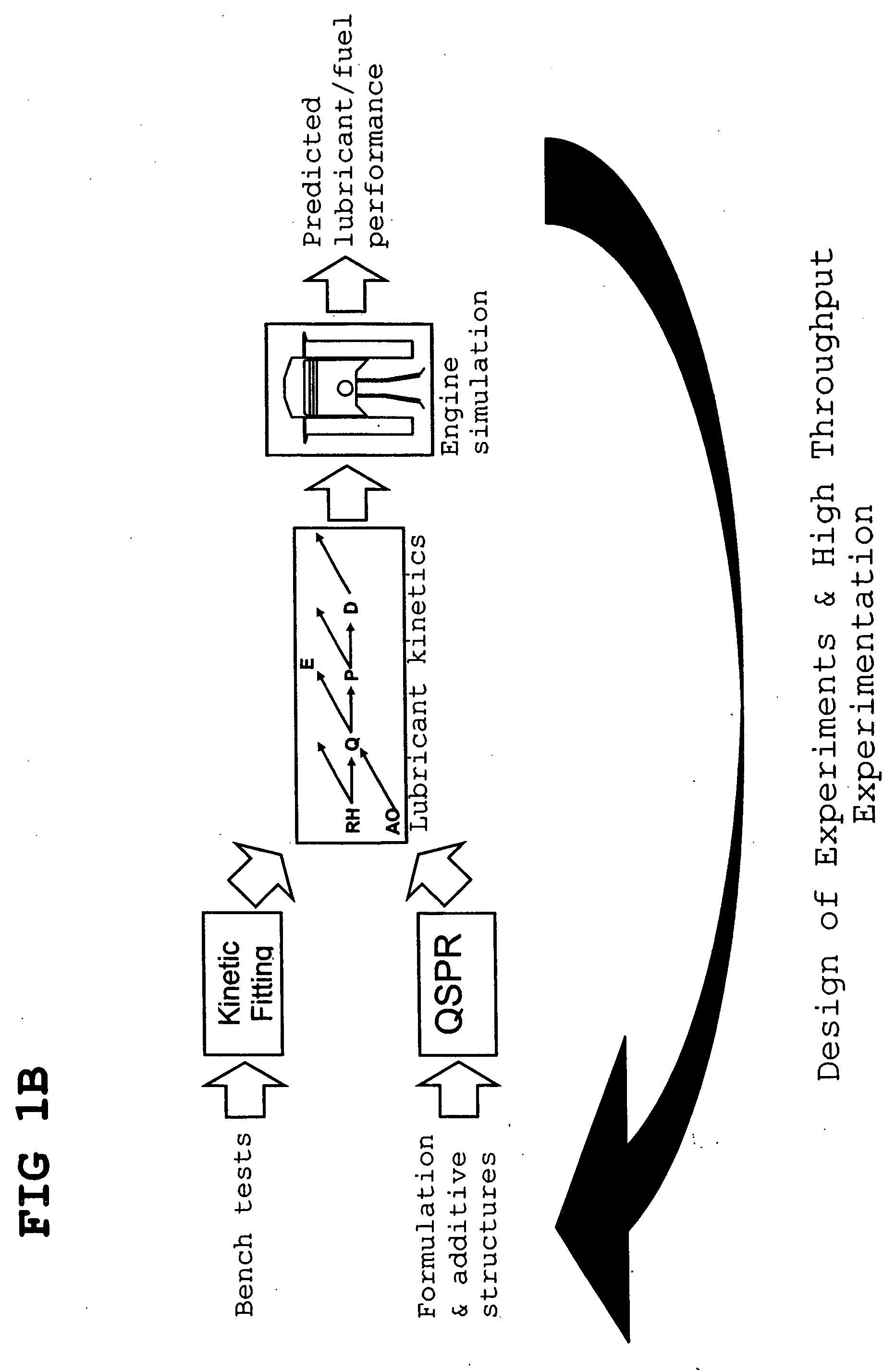
Predictive technologies for lubricant development
InactiveUS20070106477A1Alter its performanceShorten the timeChemical property predictionBiological testingEngineeringLubricant
Method for predicting and / or correlating additive structure to engine performance includes developing molecular descriptors for one or more additives, developing a kinetic model for the engine performance using kinetic parameters, determining the relation between the molecular descriptors and the kinetic parameters by testing compositions comprising one or more additives, developing a QSPR library describing the relation between the molecular descriptors of the additives and the kinetic parameters and by predicting the engine performance of other additives using the QSPR library.
Owner:AVANTIUM INT
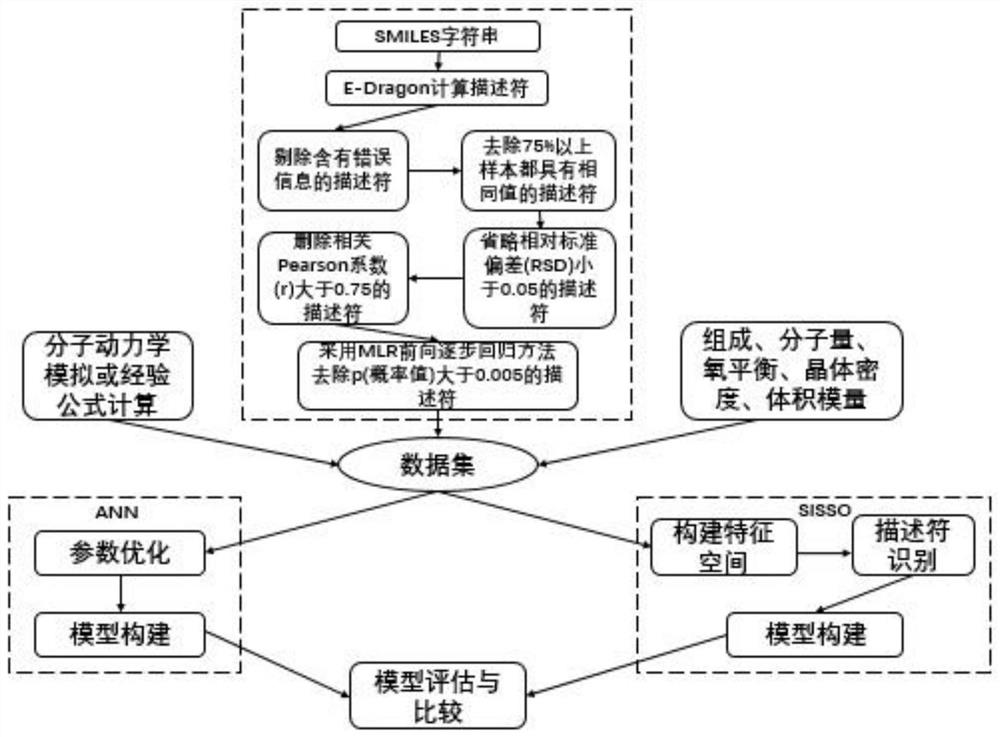
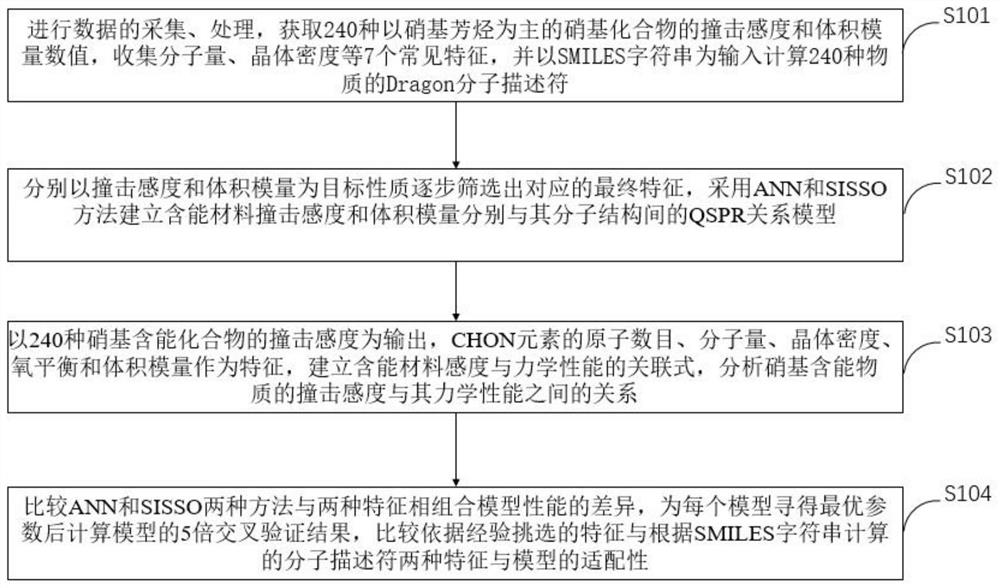
Machine learning estimation method for sensitivity and mechanical properties of energetic substances and relationship between the sensitivity and the mechanical properties of the energetic substances
ActiveCN112382350AImprove accuracyReduce processChemical property predictionChemical machine learningExperimental researchChemical physics
The invention belongs to the technical field of compound performance evaluation, and discloses a machine learning estimation method for sensitivity and mechanical properties of energetic substances and a relationship between the sensitivity and the mechanical properties of the energetic substances. The estimation method comprises the following steps: constructing a quantitative structure-activityrelationship model of impact sensitivity and bulk modulus of seven nitro energetic substances based on an artificial neural network and a method for determining independent screening and sparse operators by taking a molecular descriptor and molecular structure information calculated by E-Dragon as characteristics; and determining the relationship between the impact sensitivity and the mechanical property of the nitro energetic substance and the quantitative relationship between the impact sensitivity and the mechanical property of the nitro energetic substances respectively with the molecularstructure by utilizing the constructed quantitative structure-activity relationship model of the impact sensitivity and the bulk modulus of the nitro energetic substances. According to the method, seven QSPR models of the impact sensitivity and the bulk modulus of the nitro nitro energetic substances are established on the basis of molecular descriptors calculated by EDragon and several common molecular structure information, so that the process of experimental research on energetic materials is shortened, and design and comprehensive evaluation of novel energetic compounds are facilitated.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
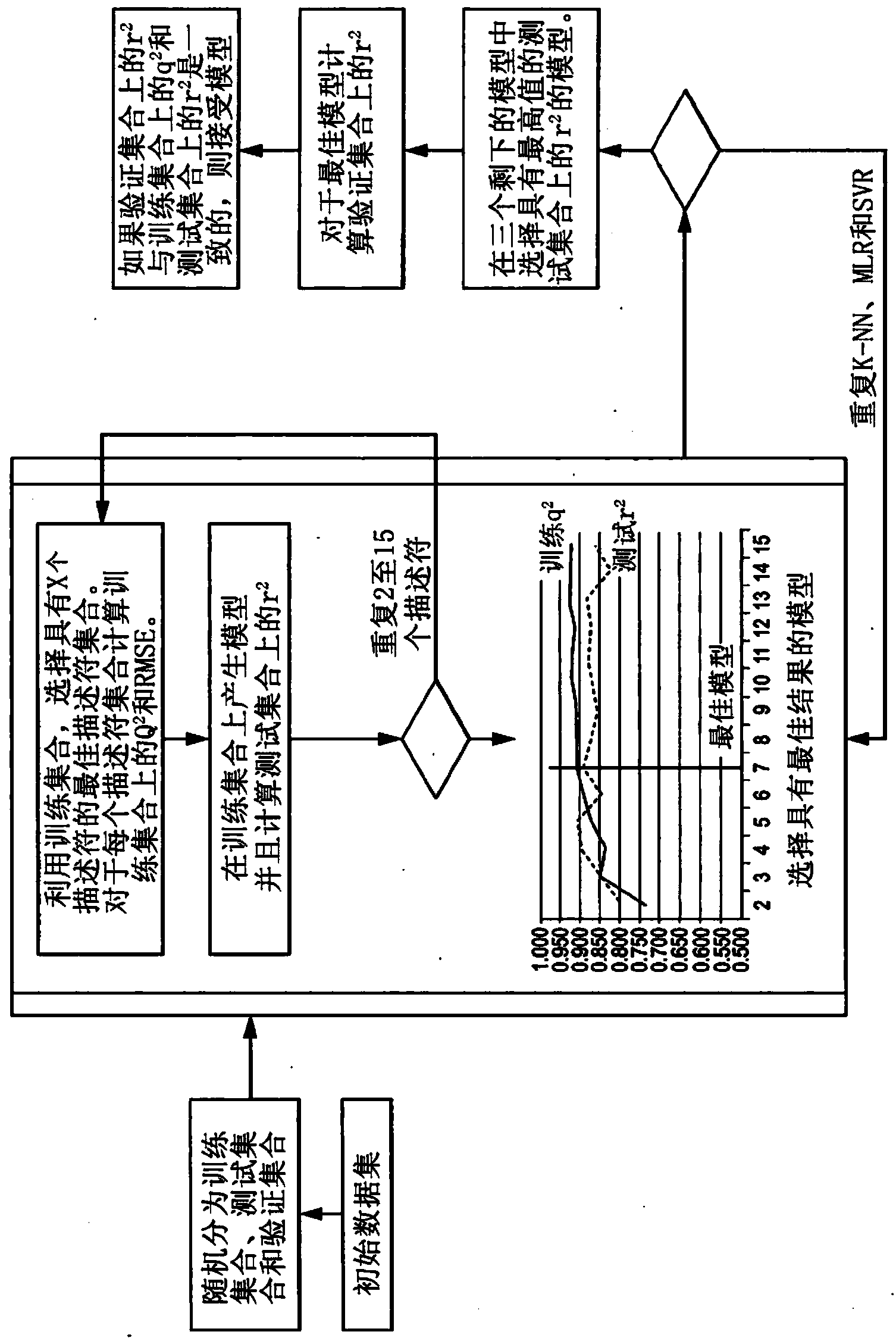
Method for selecting an optimally diverse library of small molecules based on validated molecular structural descriptors
InactiveUS7184893B2Good varietyAvoiding oversamplingChemical property predictionData processing applicationsData setValidation methods
The use for biological screening purposes of a subset (library) of a large combinatorially accessible chemical universe increases the efficiency of the screening process only if the subset contains members representative of the total diversity of the universe. In order to insure inclusion in the subset of molecules representing the total diversity of the universe under consideration, valid molecular descriptors which quantitatively reflect the diversity of the molecules in the universe are required. A unique validation method is used to examine both a new three dimensional steric metric and some prior art metrics. With this method, the relative usefulness / validity of individual metrics can be ascertained from their application to randomly selected literature data sets. By the appropriate application of validated metrics, the method of this invention selects a subset of a combinatorial accessible chemical universe such that the molecules of the subset are representative of all the diversity present in the universe and yet do not contain multiple members which represent the same diversity (oversample). The use of the neighborhood definition of a validated metric may also be used to combine (without oversampling the same diversity) any number of combinatorial screening libraries.
Owner:CERTARA
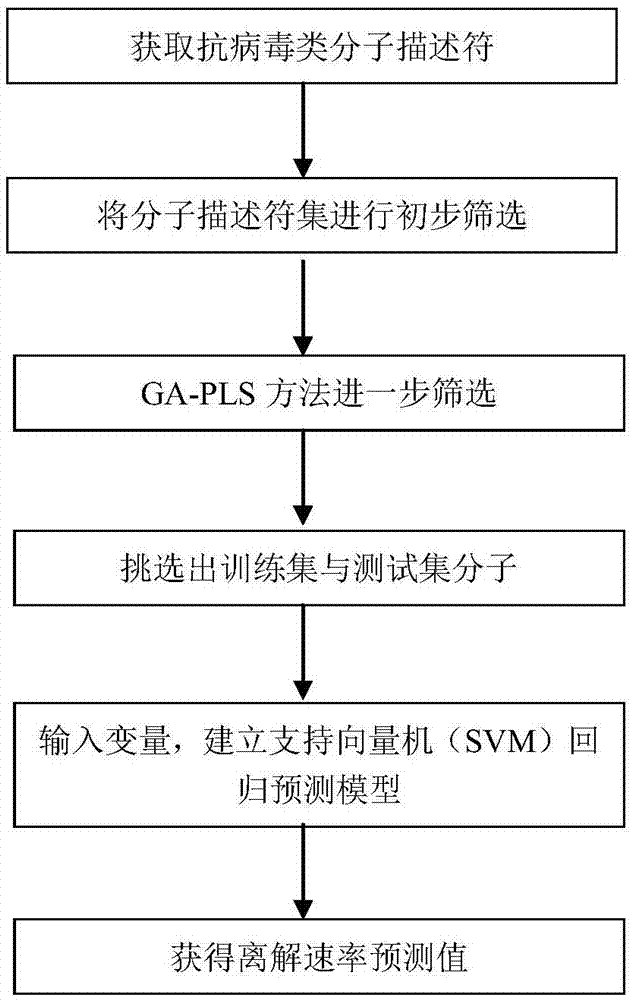
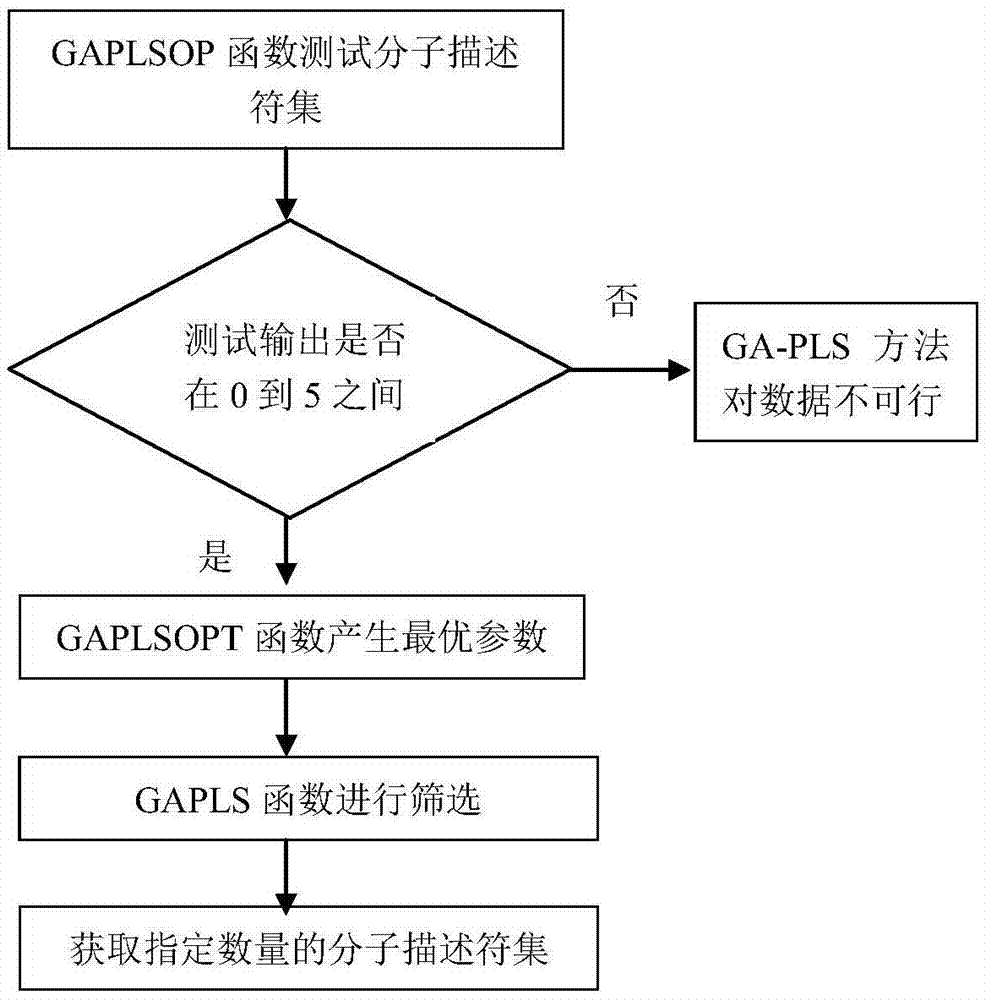
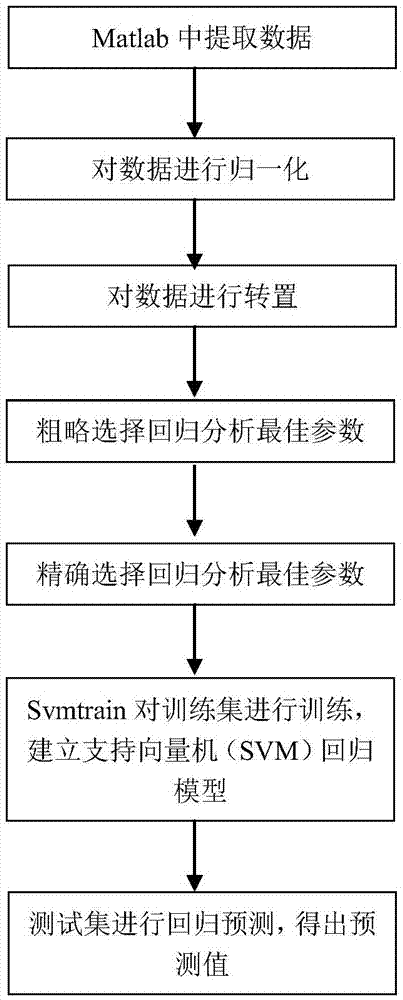
Support vector machine based antiviral inhibitor dissociation rate constant prediction method
The present invention discloses a support vector machine based antiviral inhibitor dissociation rate constant prediction method, and belongs to the field of bioinformatics. The method comprises: obtaining a molecular descriptor dataset of anti-viral drugs, screening the dataset by using medical and statistical software SPSS and partial least squares Genetic Algorithms (GA-PLS), inputting the screened dataset into a Matlab, and establishing a regression model by using a support vector machine method. According to the method disclosed by the present invention, the regression prediction model is established by using the molecular descriptor of the drug and a corresponding Koff value, and the Koff value prediction is realized by using the simple and practical method, so that a research process of a relation between the chemical structure and the binding dynamics can be promoted, development efficiency of drug development is improved, and the development cost is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
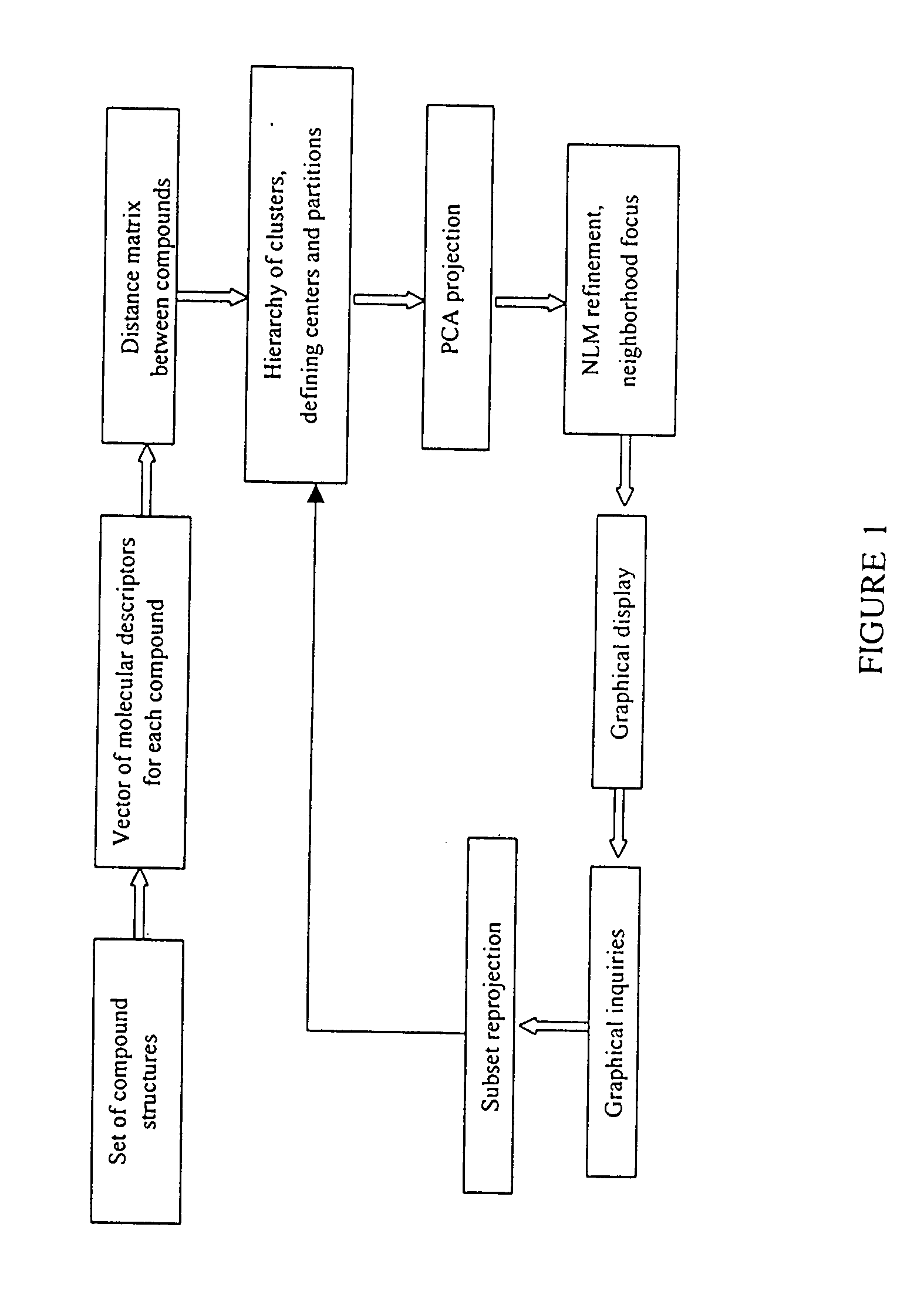
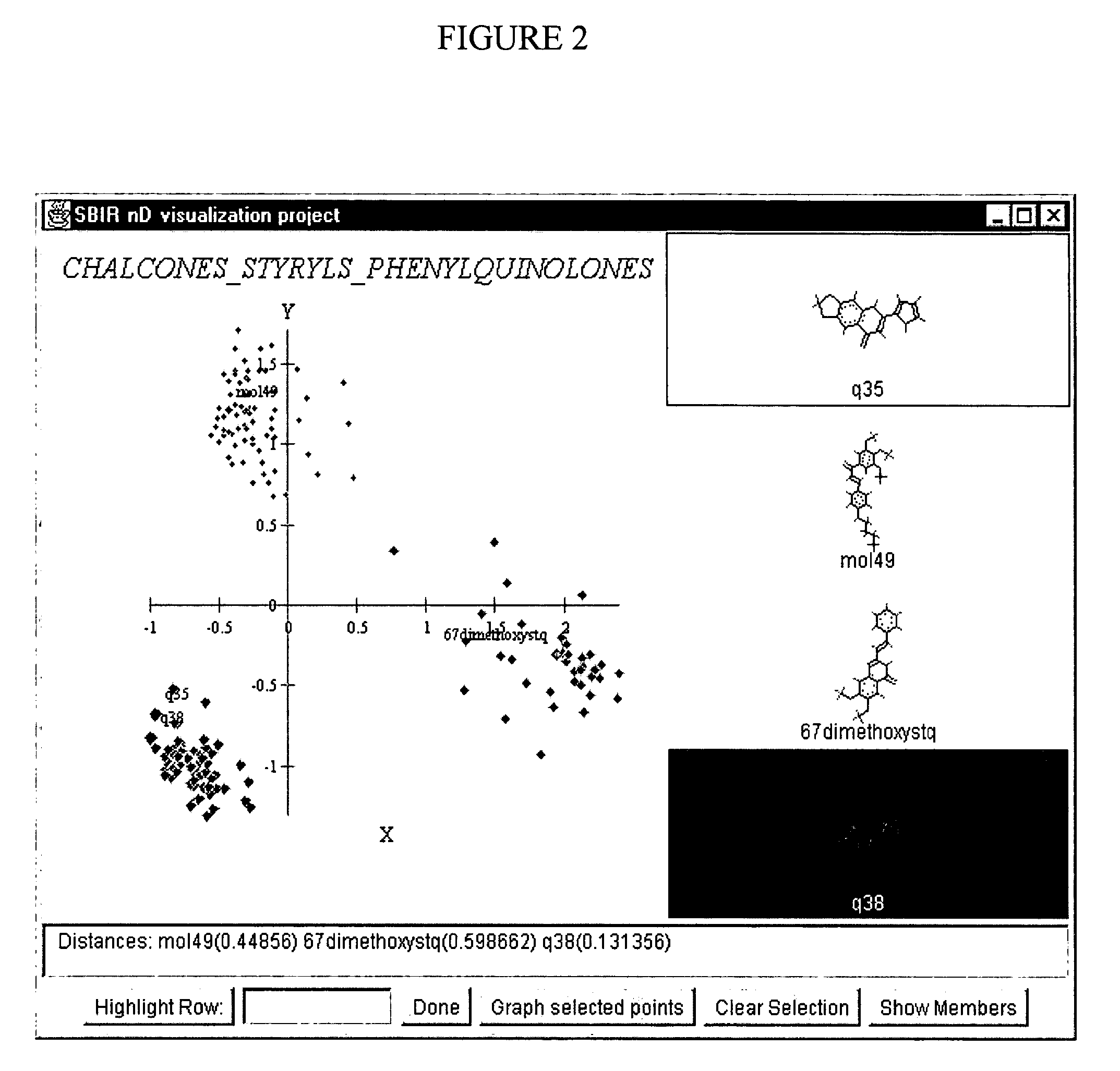
Visualizing high dimensional descriptors of molecular structures
InactiveUS20040241709A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHorizonData set
The distribution of chemical compounds in high-dimensional molecular descriptor space can be viewed in two dimensions by applying the projection method of this invention. This method has particular usefulness for viewing the relationships of a large number of compounds such as found in a large scale HTS or virtual combinatorial library. After selecting a representative subset of the larger data set of compounds, initially components from the high-dimensional descriptor space are determined by PCA. In order to relax an NLM projection using the PCA components as a start, the stress function is modified to reflect a local horizon beyound which the separation of the compounds is not meaningfully measureable. The resulting two dimensional projections provide a clear insight into the distribution of the chemical compounds in the higher dimensional space. The method is clearly generalizable to viewing descriptor space in three dimensions and to using high dimensional descriptors other than those used to describe molecular structure.
Owner:PATTERSON DAVID E
Method for predicting elimination rate coefficient of gas state sulfur compound on low-temperature hydrolysis condition
InactiveCN105678069APredicted elimination rate constantLow costInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsMaterial resourcesLinear regression
The invention discloses a method for predicting the elimination rate coefficient of a gas state sulfur compound on the low-temperature hydrolysis condition by building a Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationship (QSAR) model, and belongs to the technical field of quantitative structure-activity relationships of ecological risk assessment. The elimination rate coefficient of the gas state sulfur compound on the low-temperature hydrolysis condition can be rapidly and efficiently predicted only calculating a molecule descriptor with the structural feature and applying the built QSAR model on the basis of the known gas state sulfur compound molecule structure. The method is simple, rapid and low in cost, and labor, material resources and financial resources needed by experimental tests can be saved. The simple and transparent multiple linear regression method is applied and is easy to understand and apply. The method has the specific application field, and good fitting ability, robustness and predictive ability, and can effectively predict the elimination rate coefficient of the gas state sulfur compound on the low-temperature hydrolysis condition in the application field.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
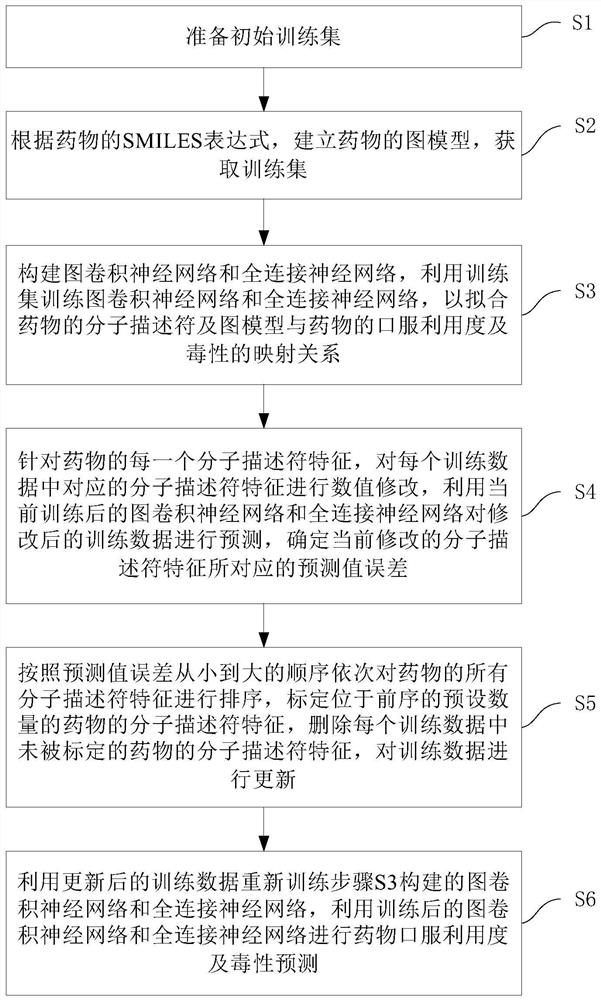
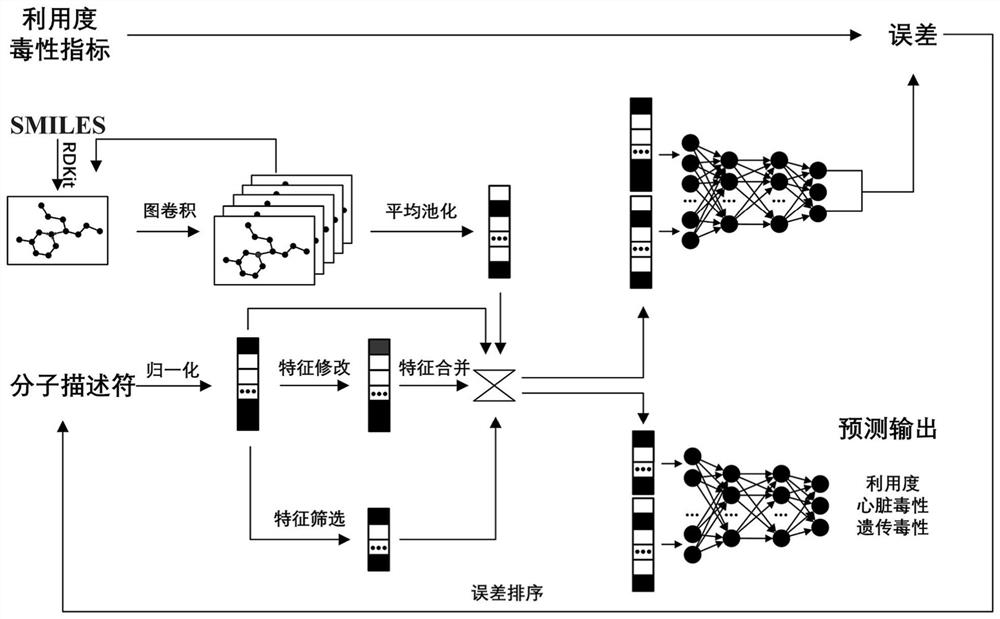
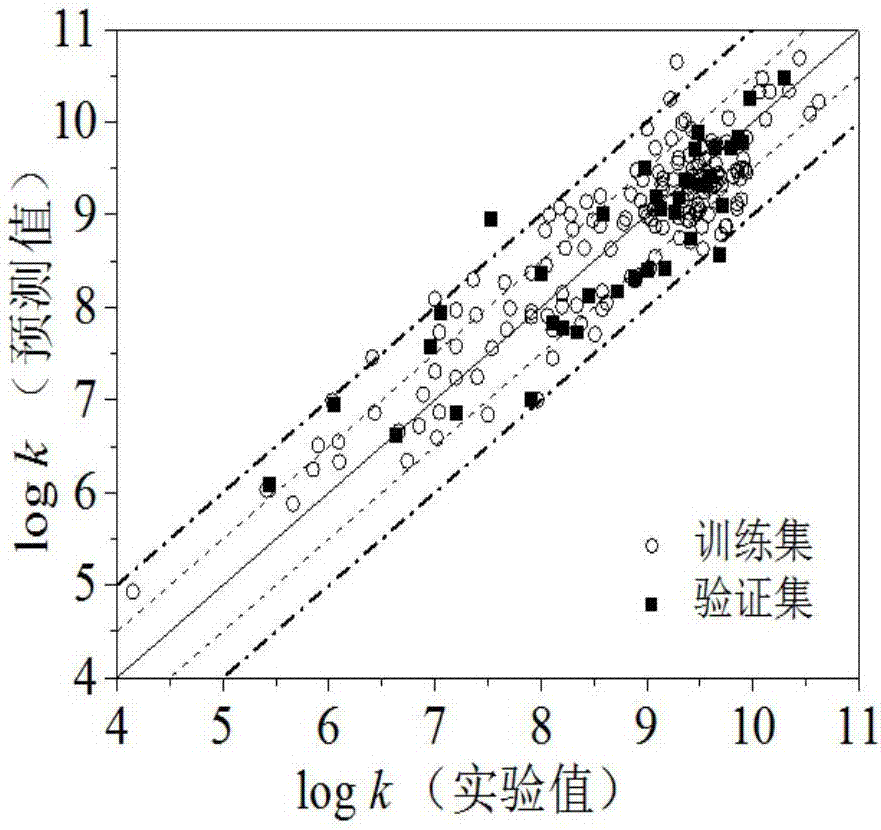
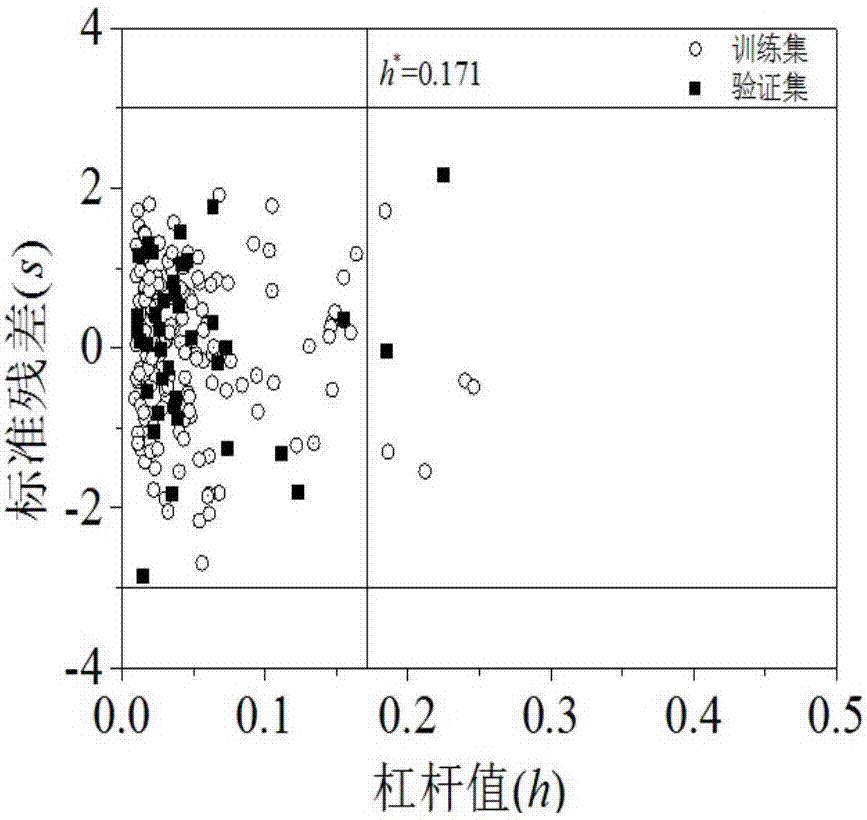
Drug oral availability and toxicity prediction method based on graph convolutional neural network
PendingCN114550847AImprove forecast accuracyMolecular designDrug referencesPharmaceutical drugEngineering
The invention discloses a graph convolutional neural network-based drug oral availability and toxicity prediction method. The method comprises the steps of S1, preparing an initial training set; s2, establishing a graph model of drugs, and obtaining a training set; s3, training a graph convolutional neural network and a full-connection neural network by using the training set, and fitting a molecular descriptor of the drug and a mapping relationship between a graph model and oral availability and toxicity of the drug; s4, performing numerical modification on each molecular descriptor feature in the training data, predicting the modified training data by using a neural network, and determining a corresponding predicted value error; s5, sorting all the molecular descriptor features of the medicine, calibrating the molecular descriptor features located in the preorder, deleting the molecular descriptor features of the medicine which are not calibrated, and updating the training data; and S6, retraining the graph convolutional neural network and the full-connection neural network constructed in the step S3. According to the method, the drug oral availability and toxicity prediction model with high prediction precision can be obtained.
Owner:NAT INNOVATION INST OF DEFENSE TECH PLA ACAD OF MILITARY SCI
Quantitative structure activity relationship model for predicting water-phase reaction rate constant of organic matter and sulfuric acid free radical in water phase
ActiveCN107330254AAccurate predictionLow costChemoinformaticsComputational theoretical chemistryAdvanced oxidation processLinear regression
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for constructing quantitative structure-activity relationship model to predict silicone oil-air partition coefficient of hydrophobic compound
ActiveCN107516016ASimple methodFast wayChemical machine learningSpecial data processing applicationsPolarizabilityOrbit
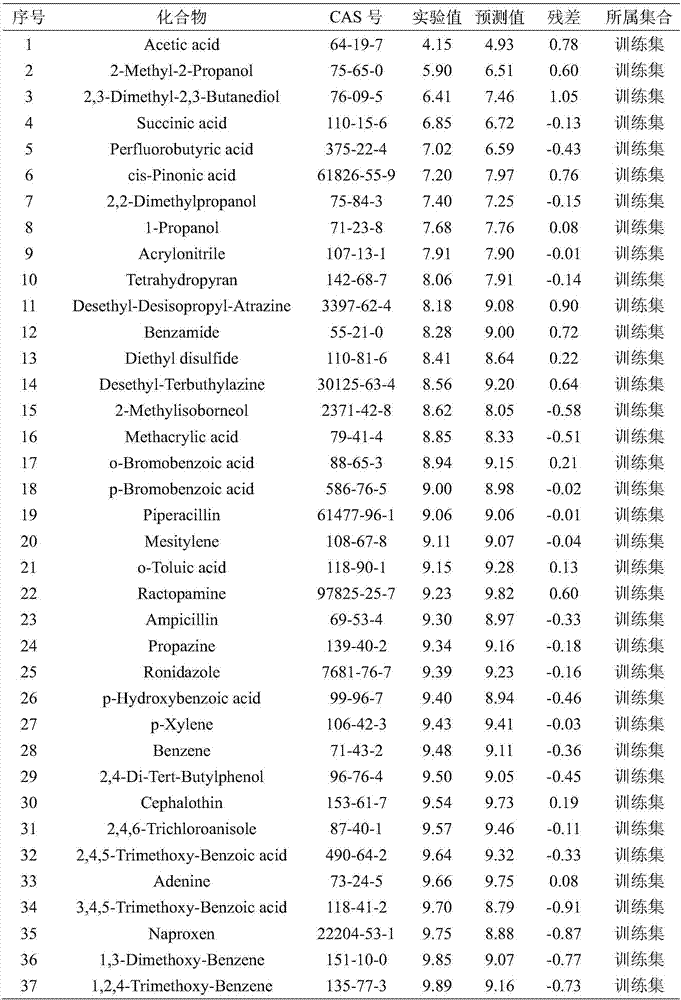
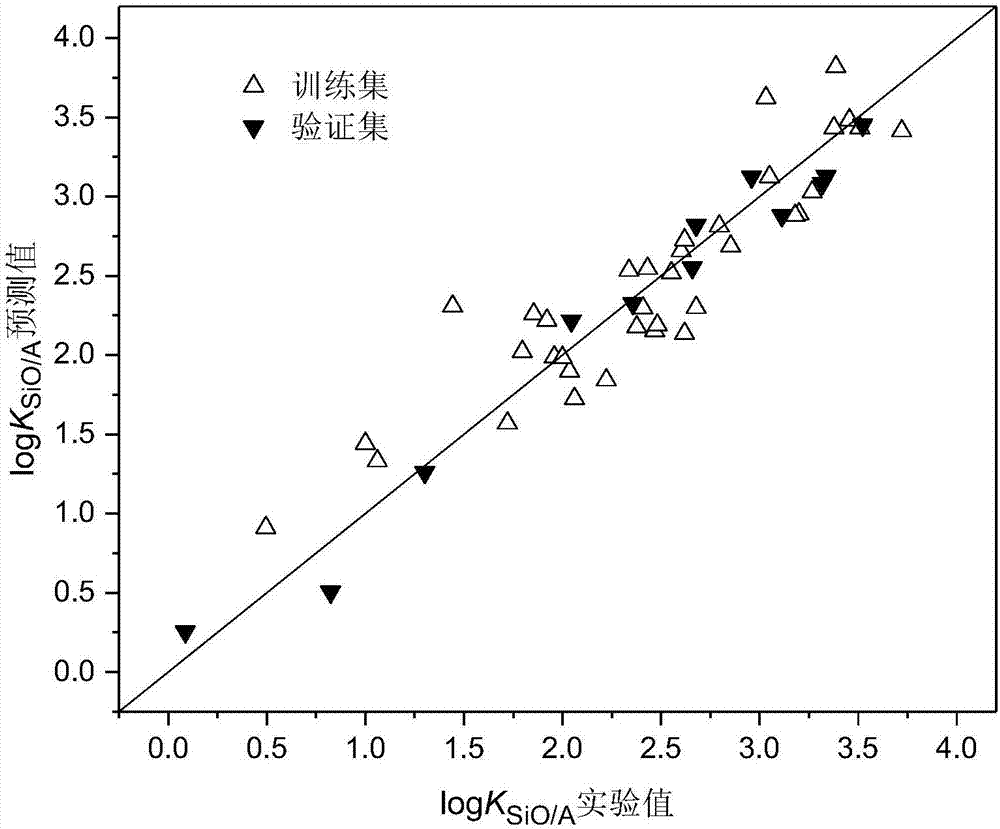
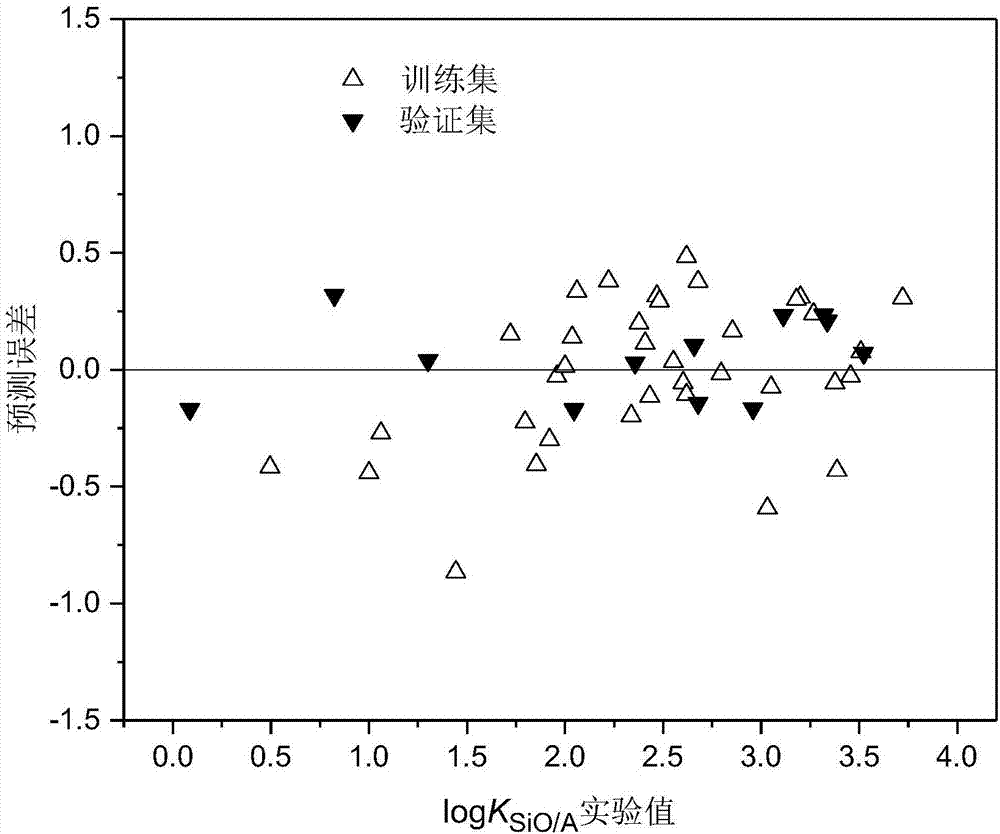
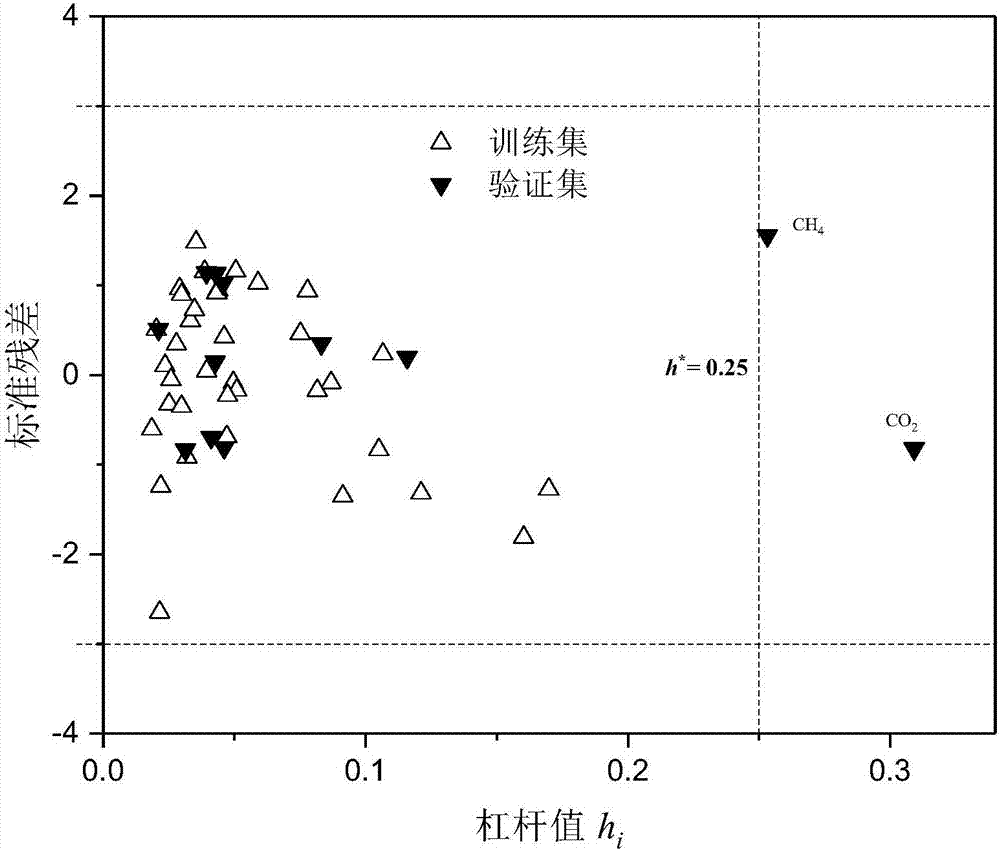
The invention discloses a method for constructing a quantitative structure-activity relationship model to predict a silicone oil-air partition coefficient of a hydrophobic compound. According to the method, the model is adopted for predicting the silicone oil-air partition coefficient, wherein logKSiO / A = 2.888 + 0.025 * alpha - 0.244 * (ELUMO-EHOMO), logKSiO / A represents the silicone oil-air partition coefficient, alpha represents an average molecular polarizability, and (ELUMO-EHOMO) represents an energy difference between a lowest unoccupied molecular orbit and a highest occupied molecular orbit. According to the method, the silicone oil-air partition coefficient of the hydrophobic compound can be quickly and efficiently predicted simply by calculating molecular descriptors with structural characteristics and applying the constructed QSAR model; the method is simple, quick and low in cost, and the labor, materials and financial resources needed for experimental tests can be saved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for predicting toxicity of chemicals taking zebra fish embryos as receptors by establishing QSAR model
ActiveCN110910970AValidate predictive powerVerify robustnessChemical property predictionChemical machine learningExperimental testingMultiple linear regression analysis
The invention discloses a method for predicting toxicity of chemicals taking zebra fish embryos as receptors by establishing a QSAR model. On the basis of a known compound molecular structure, the half lethal concentration of the compound taking zebra fish embryos as receptors can be quickly and efficiently predicted only by calculating molecular descriptors with structural characteristics and applying the constructed QSAR model, and the method is simple, quick, low in cost and capable of saving manpower, material resources and financial resources required by experimental testing. According tothe method, modeling is carried out according to the construction of the QSAR model and the use guide rule of the economic cooperation and development organization, and a simple and transparent multiple linear regression analysis method is applied, so the method is easy to understand and apply; the method has a clear application domain and good fitting ability, robustness and prediction ability,can effectively predict the median lethal concentration of the compound in the application domain by taking zebra fish embryos as receptors, provides necessary basic data for ecological risk evaluation and management of the compound, and has important significance.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Building method of modified bioadsorbent structure-activity relationship model and application thereof
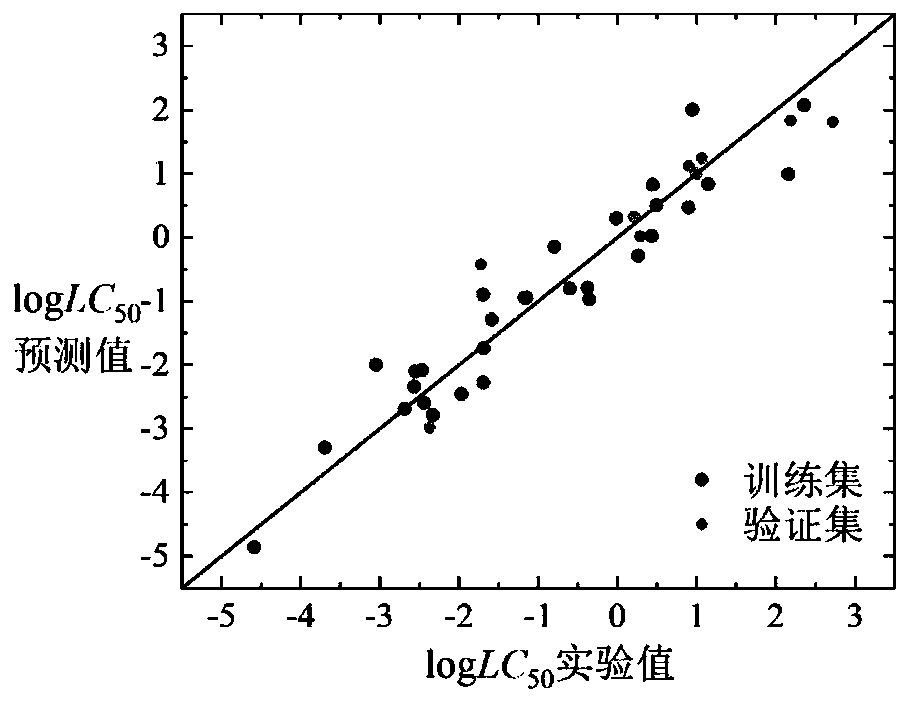
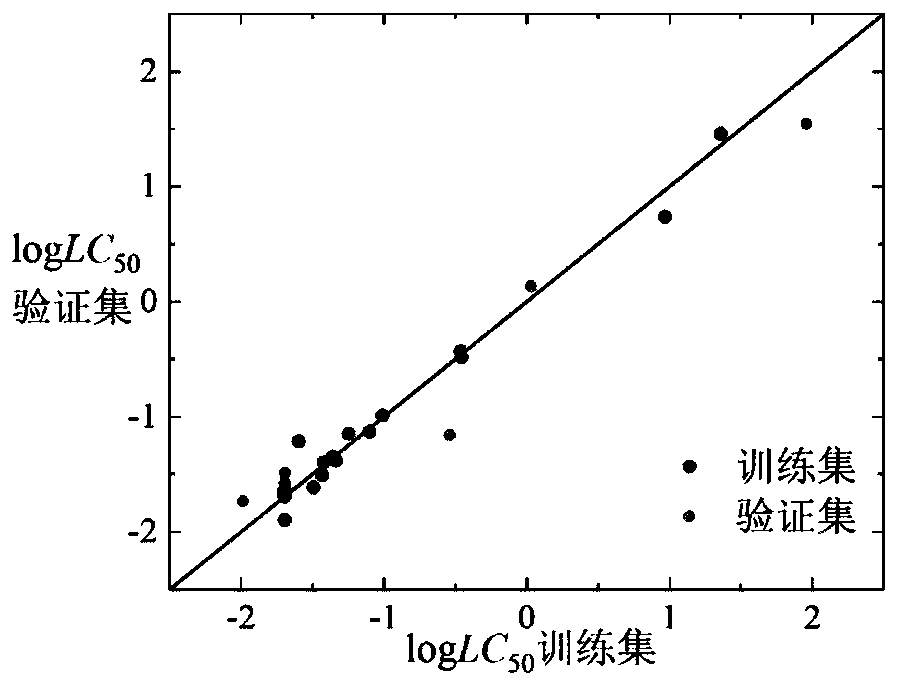
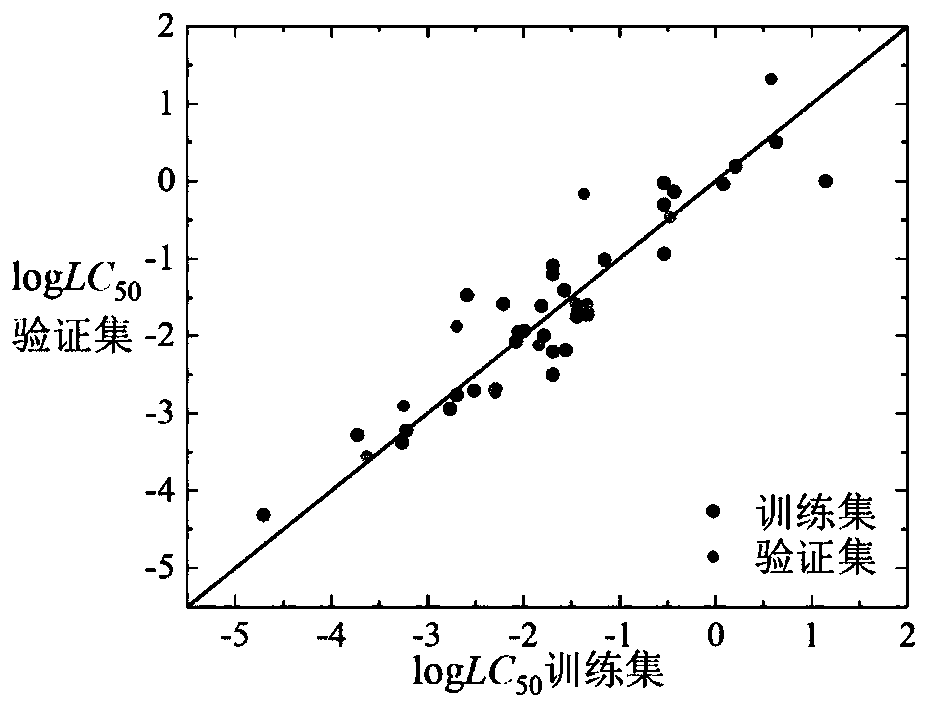
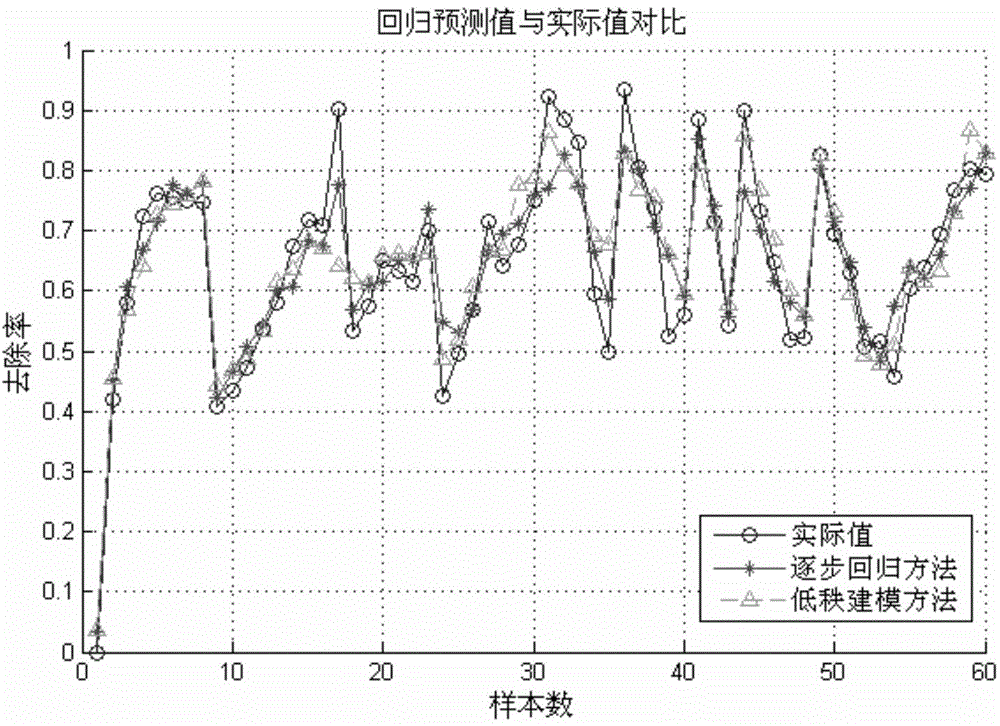
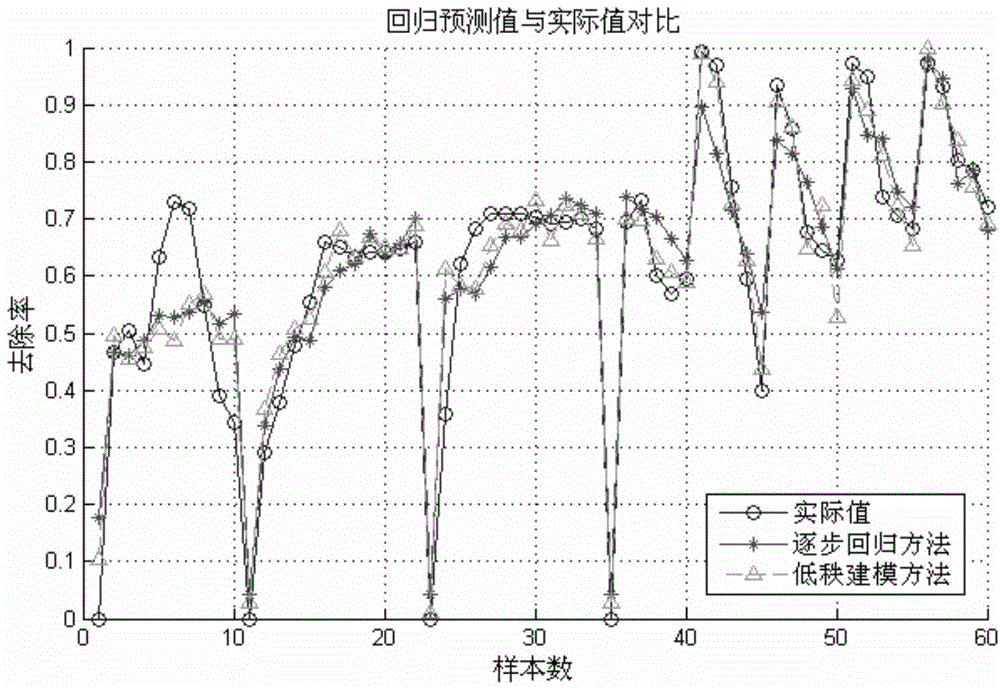
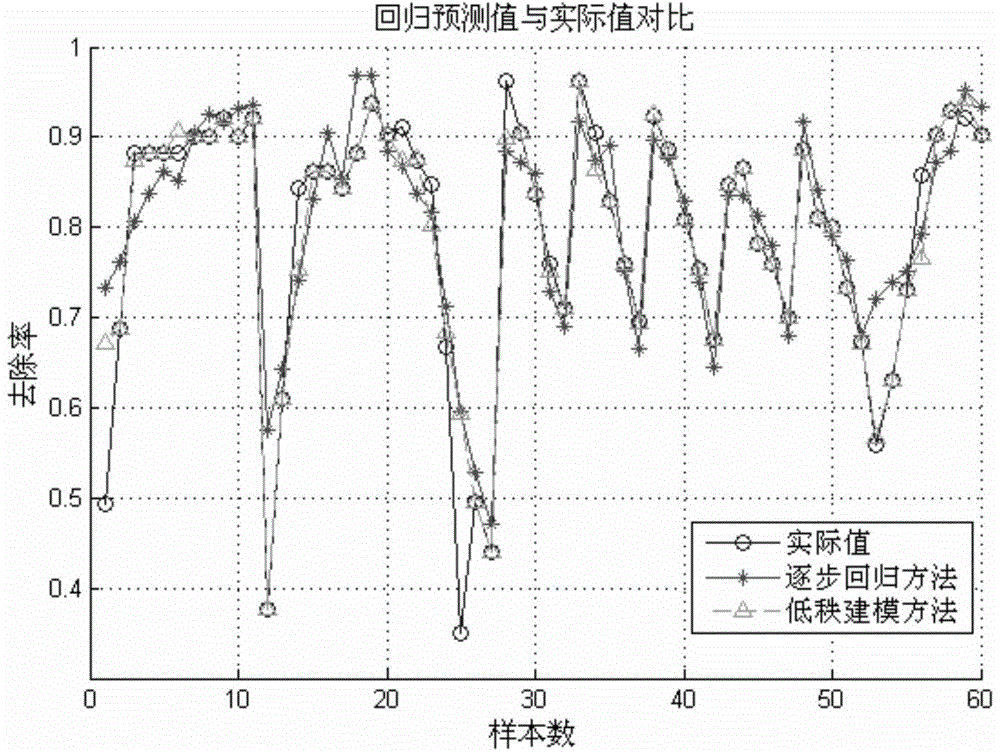
InactiveCN104573273AShorten the development cycleStrong descriptive abilitySpecial data processing applicationsEntity–relationship modelRelational model
The invention relates to a novel method of building a structure-activity relationship model of modified biomaterial adsorbing heavy metal ions and application thereof. The method includes the steps of 1, selecting biomaterial which is low in price, easy to obtain and rich in lignocellulose; 2, measuring an index of removal rate of heavy metal ions in water by means of a series of physiochemical modifications; 3, preprocessing acquired test data; 4, selecting the type of a molecular structure descriptor of the biomaterial, performing calculation, and building a molecular structure descriptor set; 5, screening molecular descriptors on the basis of low-rank modeling; 6, building the structure-activity relationship model of modification conditions, post-screening molecular descriptors and the index of removal rate of heavy metal ions in the water (waste water) on the basis of a support vector machine, and optimizing parameters. The method has the advantages that the design and synthesis of high-performance adsorbent can be effectively guided, the development cycle of efficient adsorbent of heavy metal ions is greatly shortened, and waste of financial and material resources is avoided.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Computer-implemented method of merging libraries of molecules using validated molecular structural descriptors and neighborhood distances to maximize diversity and minimize redundancy
InactiveUS7096162B2Good varietyAvoiding oversamplingChemical property predictionData processing applicationsData setValidation methods
The use for biological screening purposes of a subset (library) of a large combinatorially accessible chemical universe increases the efficiency of the screening process only if the subset contains members representative of the total diversity of the universe. In order to insure inclusion in the subset of molecules representing the total diversity of the universe under consideration, valid molecular descriptors which quantitatively reflect the diversity of the molecules in the universe are required. A unique validation method is used to examine both a new three dimensional steric metric and some prior art metrics. With this method, the relative usefulness / validity of individual metrics can be ascertained from their application to randomly selected literature data sets. By the appropriate application of validated metrics, the method of this invention selects a subset of a combinatorial accessible chemical universe such that the molecules of the subset are representative of all the diversity present in the universe and yet do not contain multiple members which represent the same diversity (oversample). The use of the neighborhood definition of a validated metric may also be used to combine (without oversampling the same diversity) any number of combinatorial screening libraries.
Owner:CERTARA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com