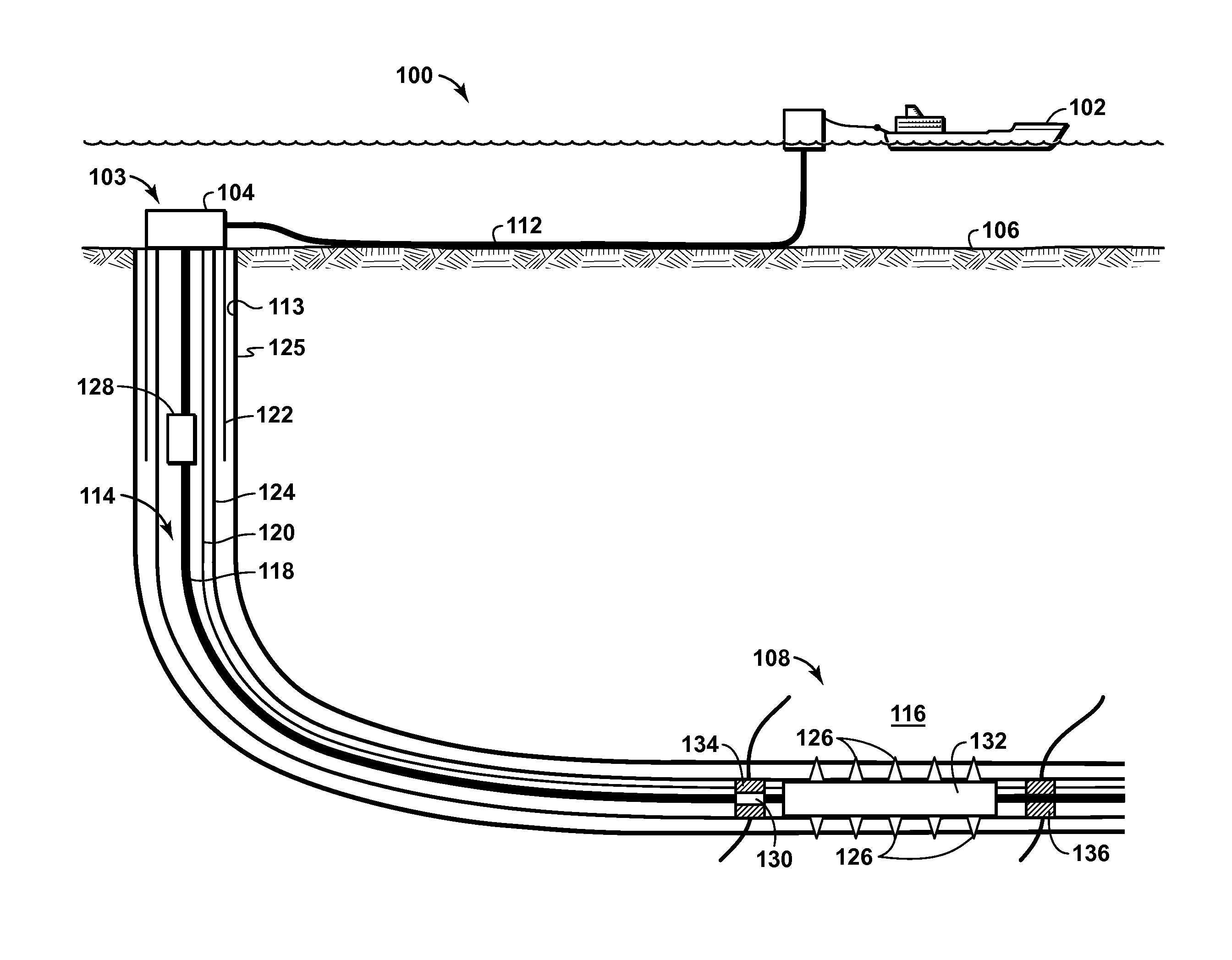
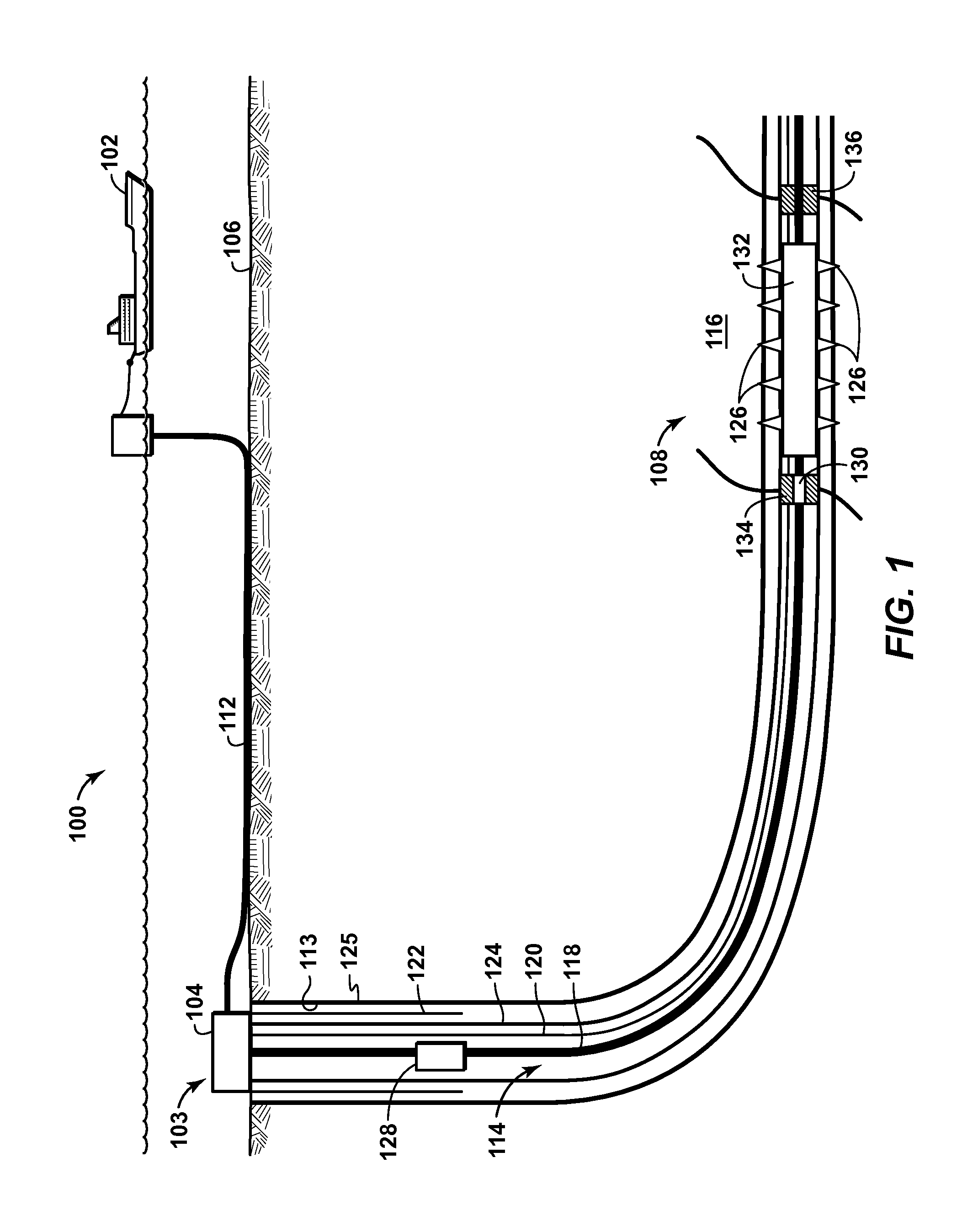
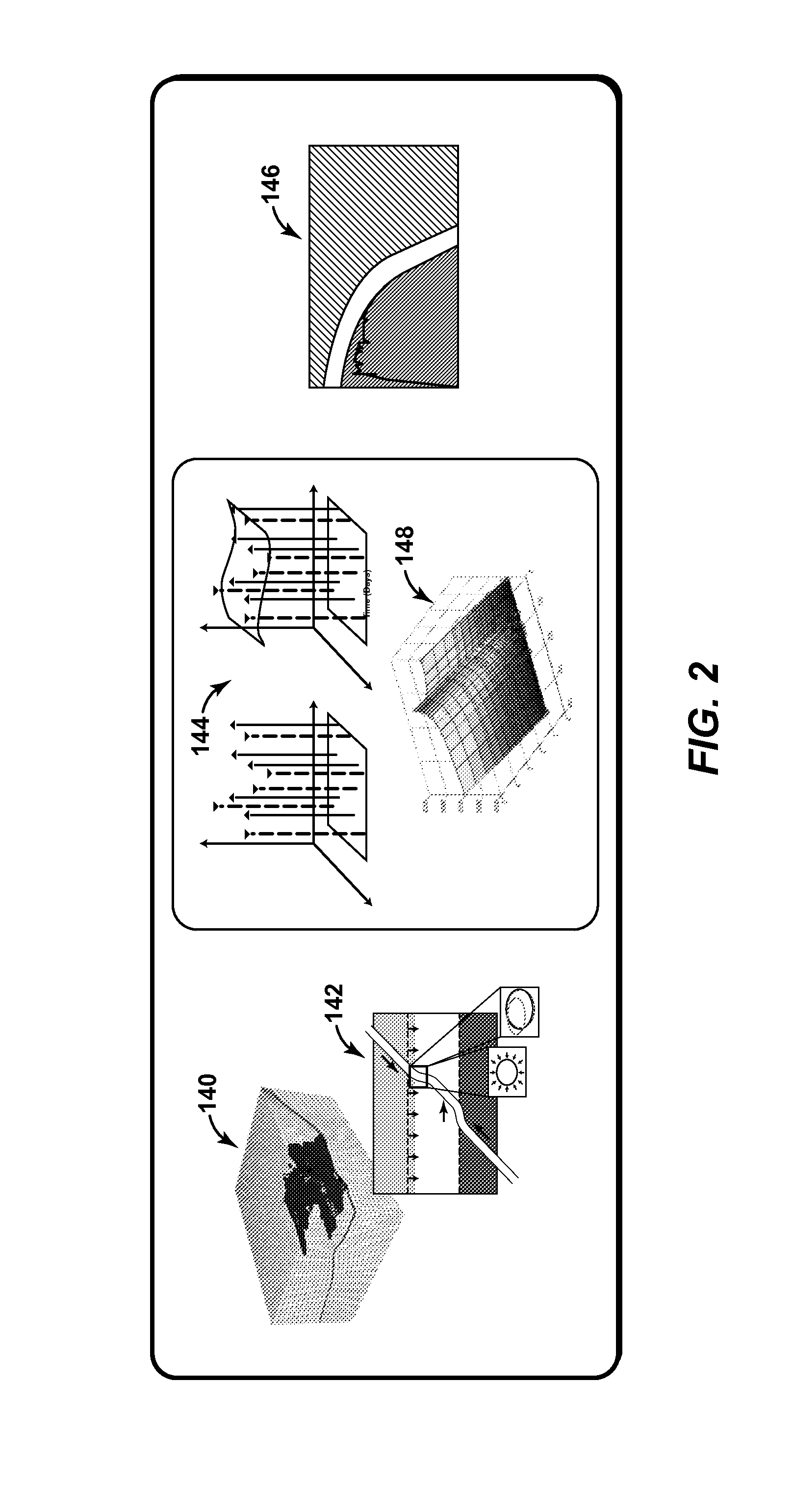
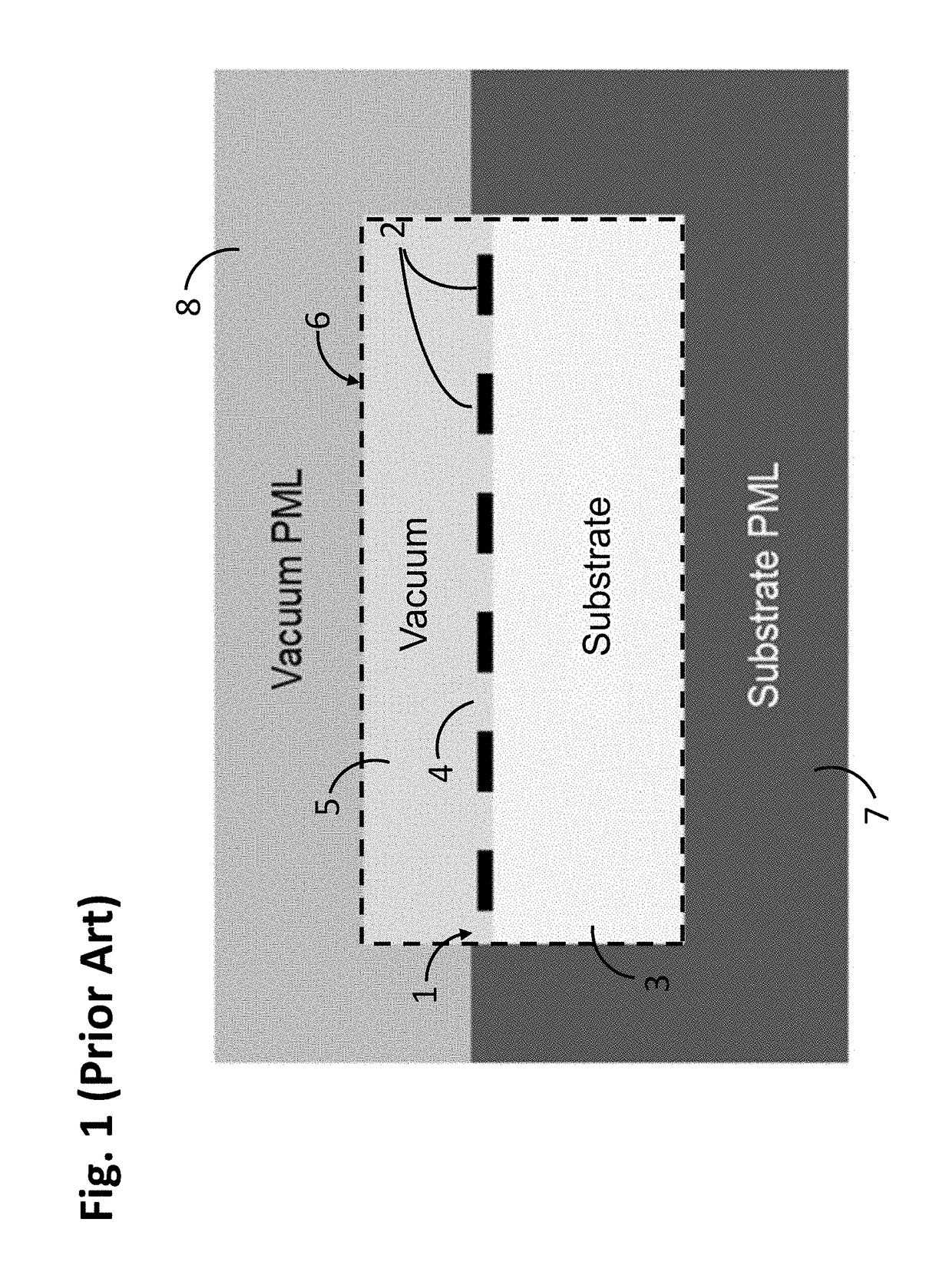
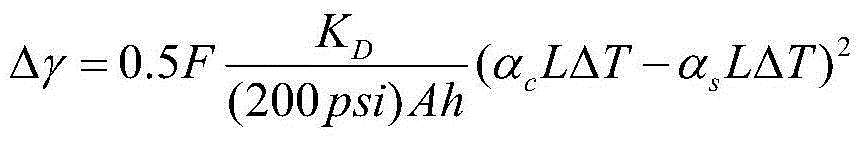Patents
Literature
262 results about "Physical modelling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Physical Modeling. Physical modeling is a way of modeling and simulating systems that consist of real physical components. It employs a physical network approach, where Simscape™ blocks correspond to physical elements, such as pumps, motors, and op-amps. You join these blocks by lines corresponding to the physical connections that transmit power.
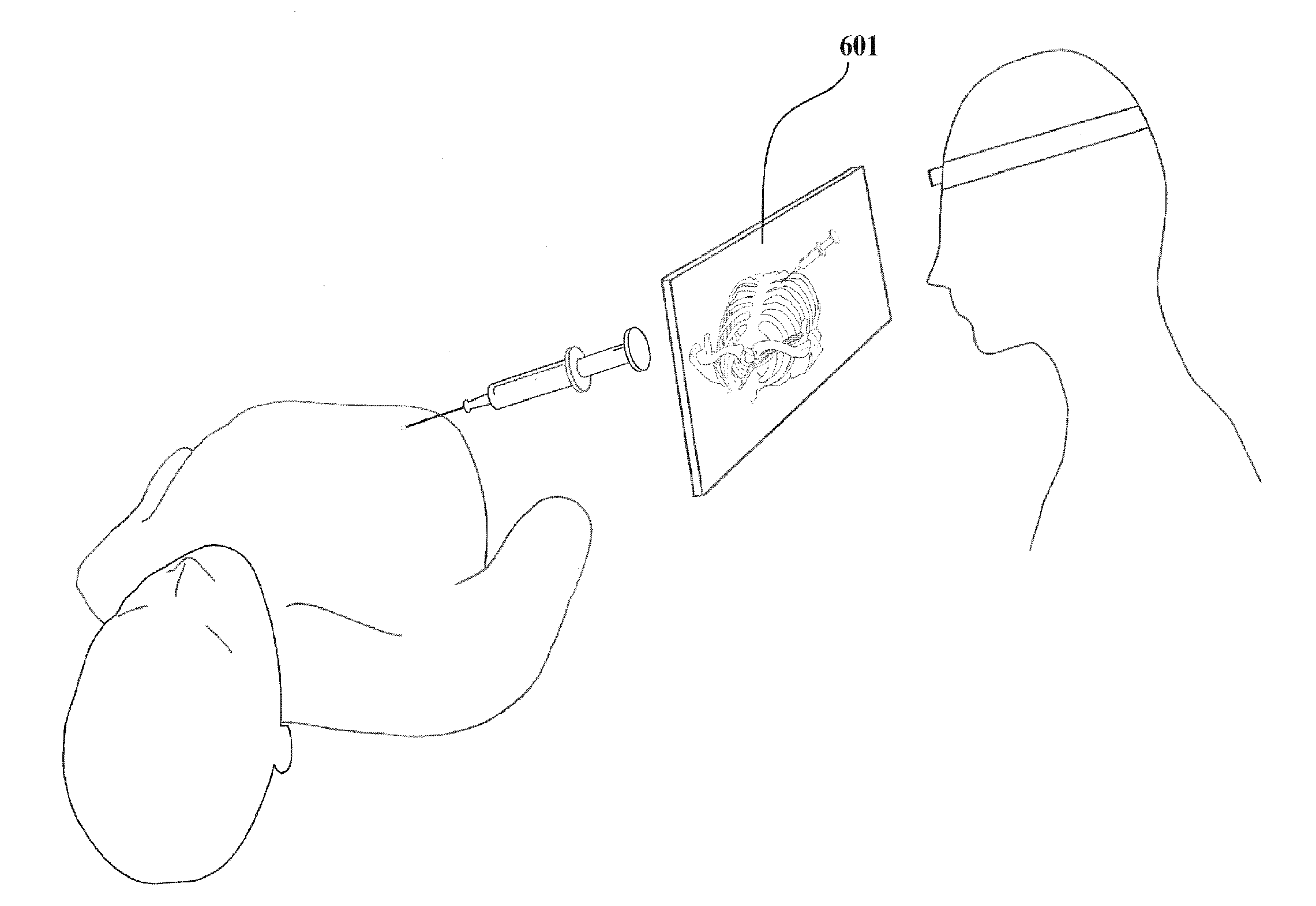
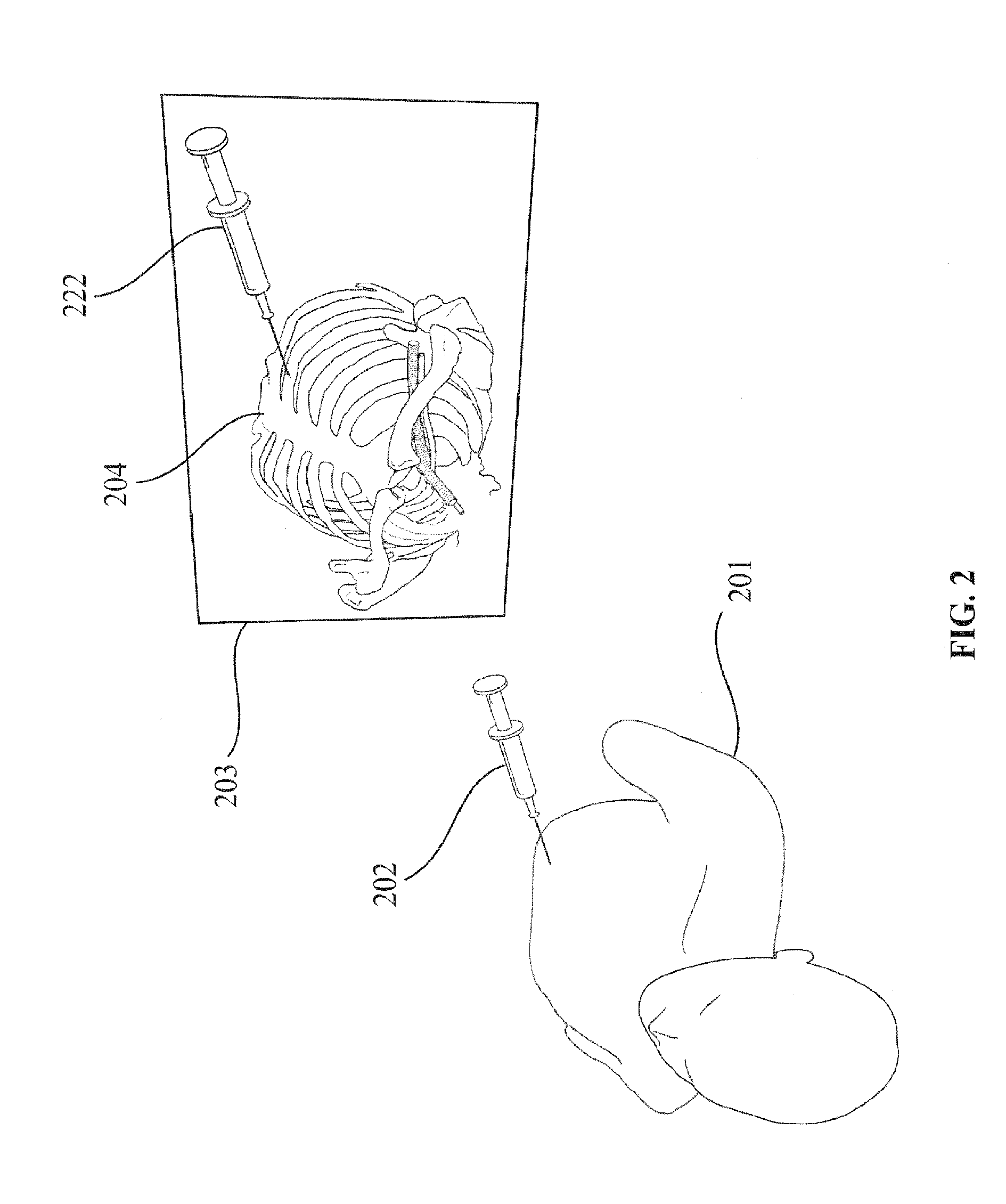
Interactive mixed reality system and uses thereof
ActiveUS20120280988A1Eliminate timeAdditive manufacturing apparatusColor television detailsMixed realityPhysical body
An interactive mixed reality simulator is provided that includes a virtual 3D model of internal or hidden features of an object; a physical model or object being interacted with; and a tracked instrument used to interact with the physical object. The tracked instrument can be used to simulate or visualize interactions with internal features of the physical object represented by the physical model. In certain embodiments, one or more of the internal features can be present in the physical model. In another embodiment, some internal features do not have a physical presence within the physical model.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
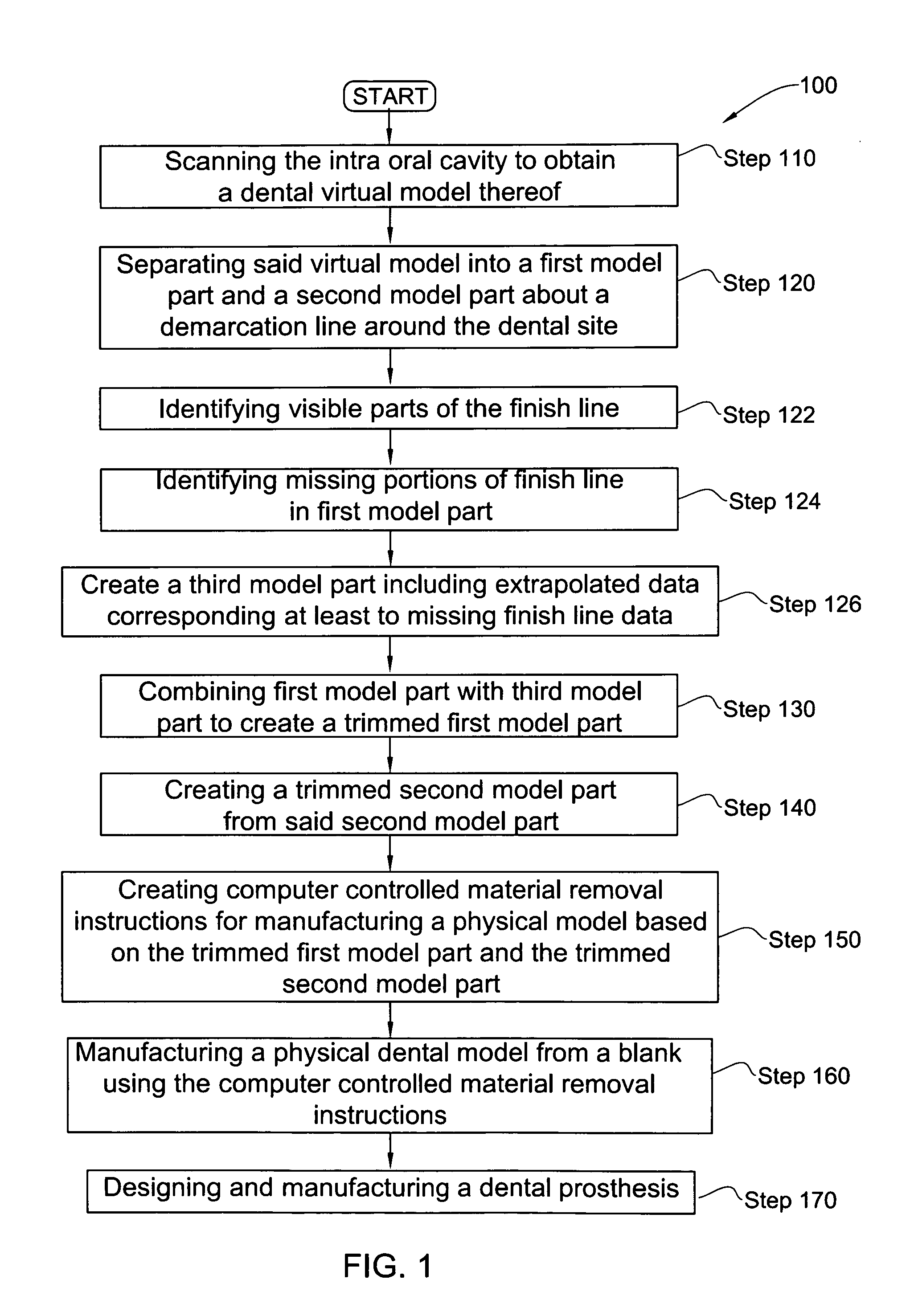
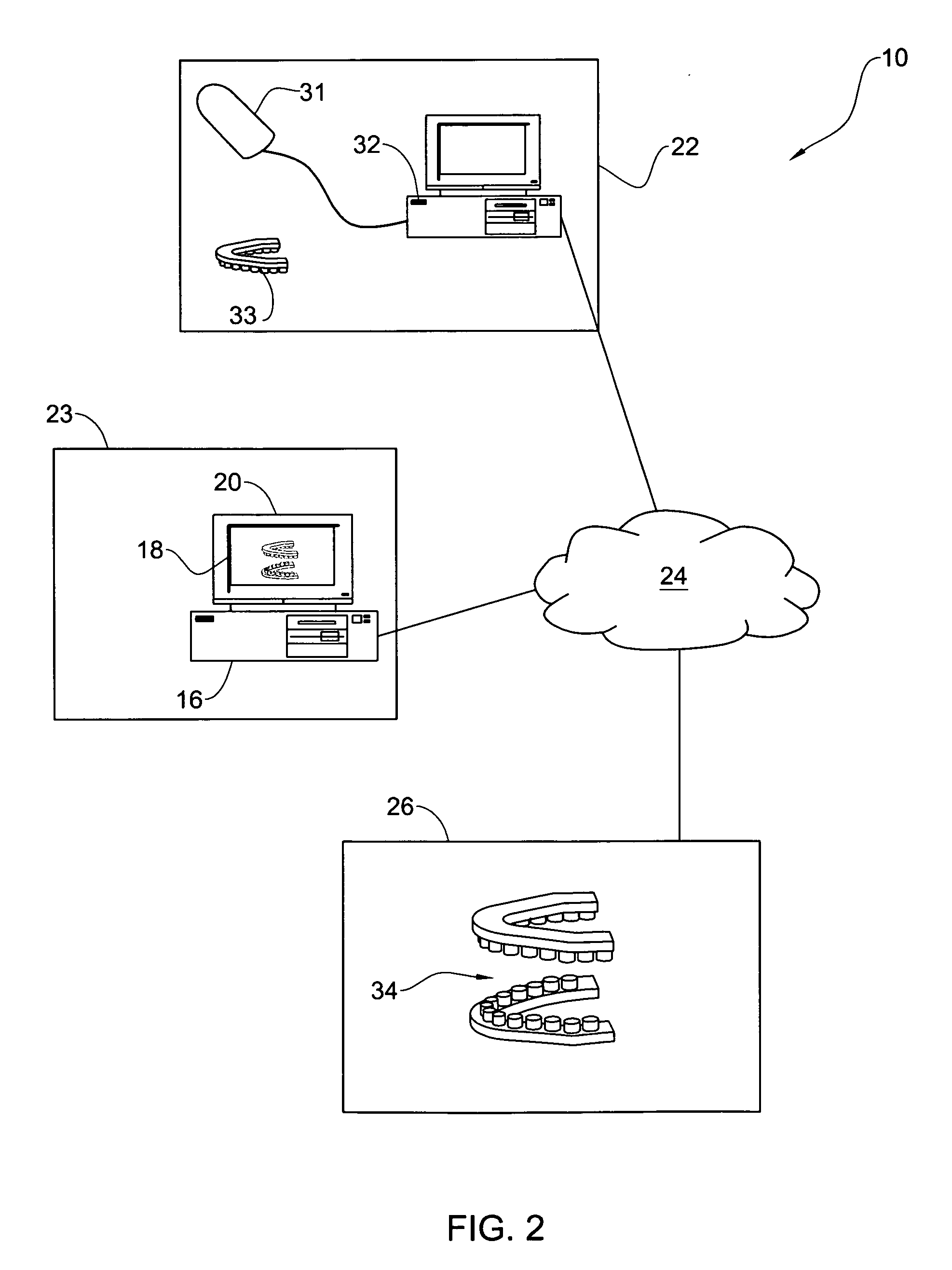
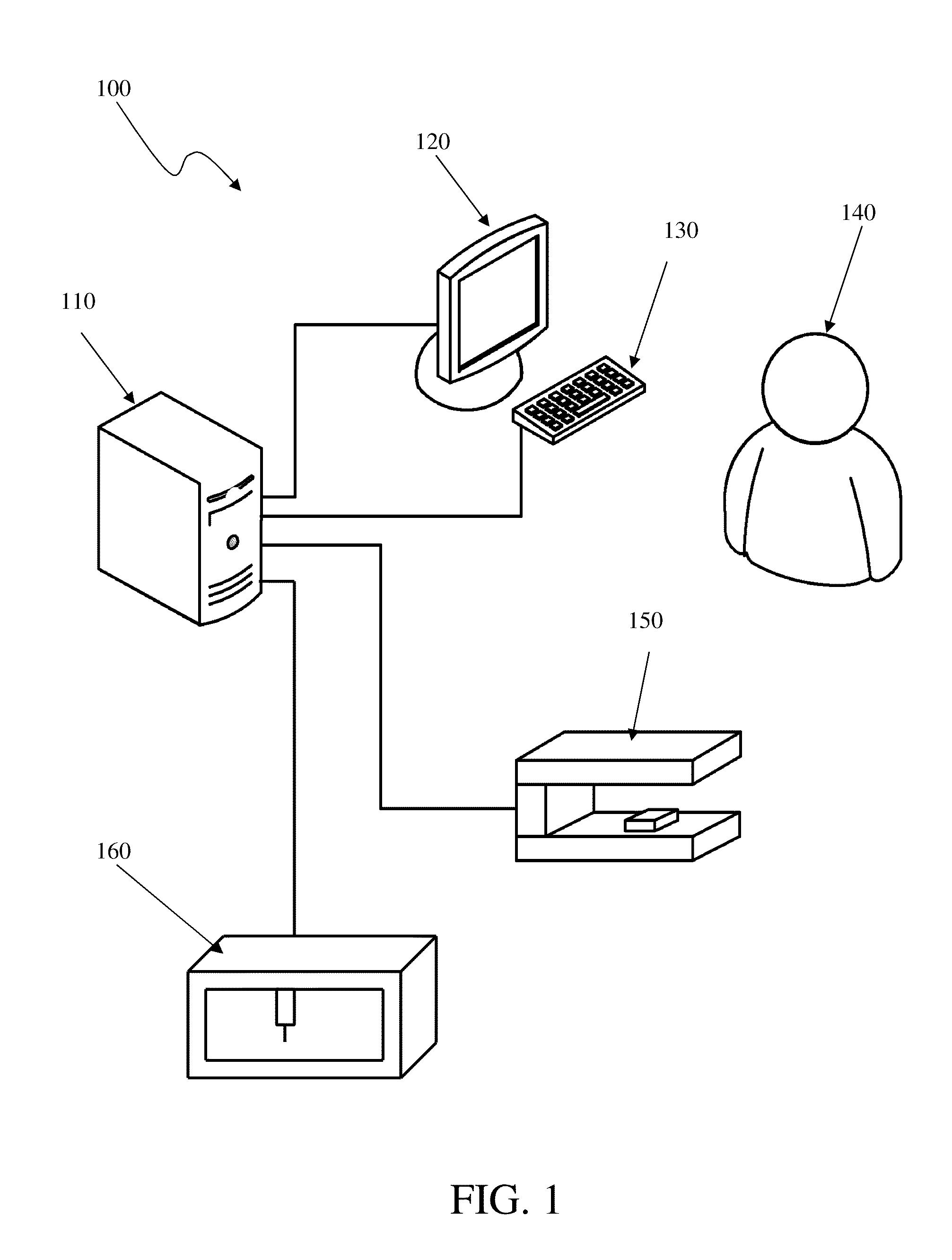
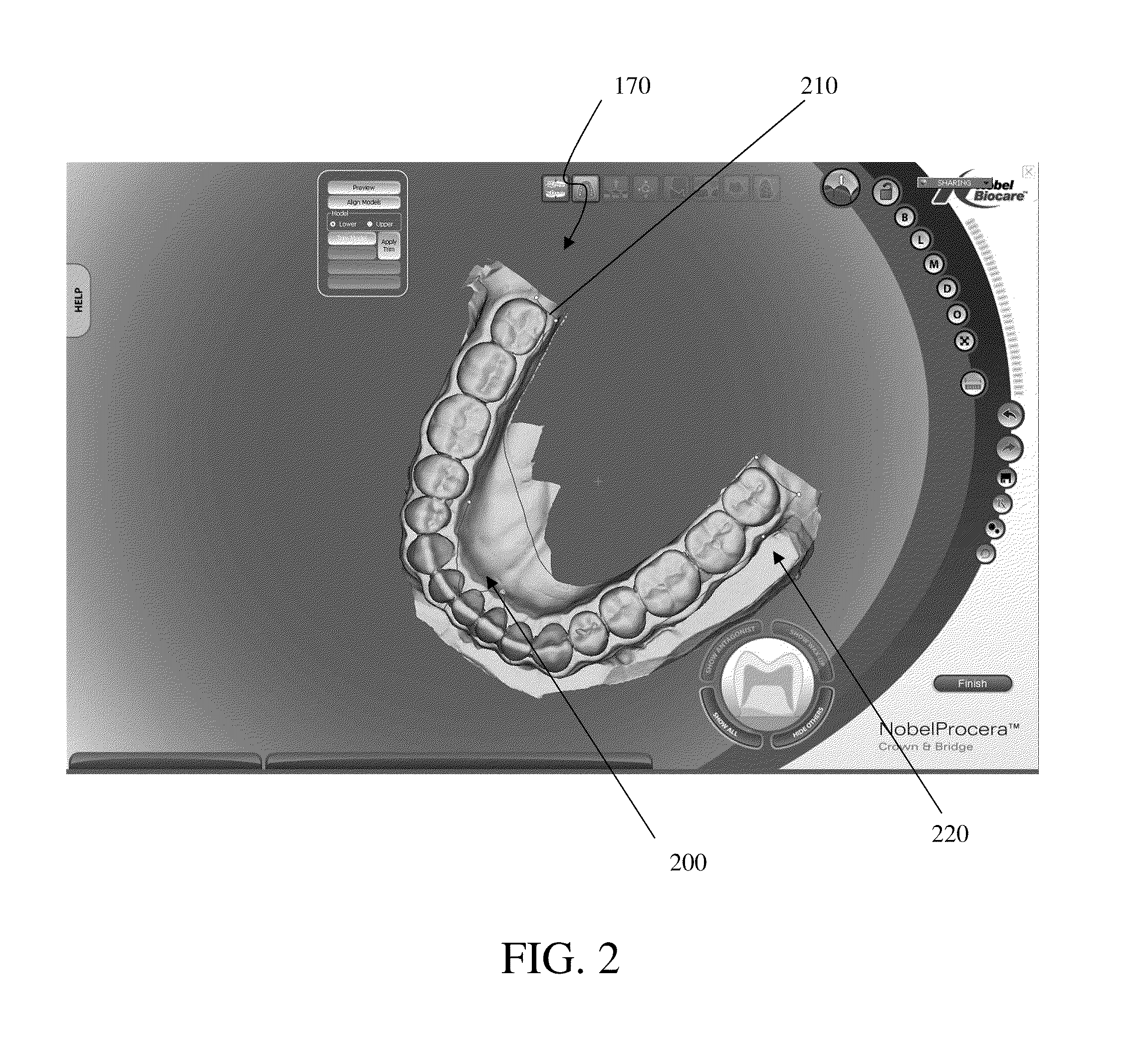
Method for manipulating a dental virtual model, method for creating physical entities based on a dental virtual model thus manipulated, and dental models thus created
ActiveUS20080300716A1Impression capsAnalogue computers for chemical processesVirtual spaceProsthesis
A 3D virtual model of an intra oral cavity in which at least a part of a finish line of a preparation is obscured is manipulated in virtual space by means of a computer or the like to create, recreate or reconstruct finish line data and other geometrical corresponding to the obscured part. Trimmed virtual models, and trimmed physical models, can then be created utilizing data thus created. The virtual models and / or the physical models may be used in the design and manufacture of copings or of prostheses.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
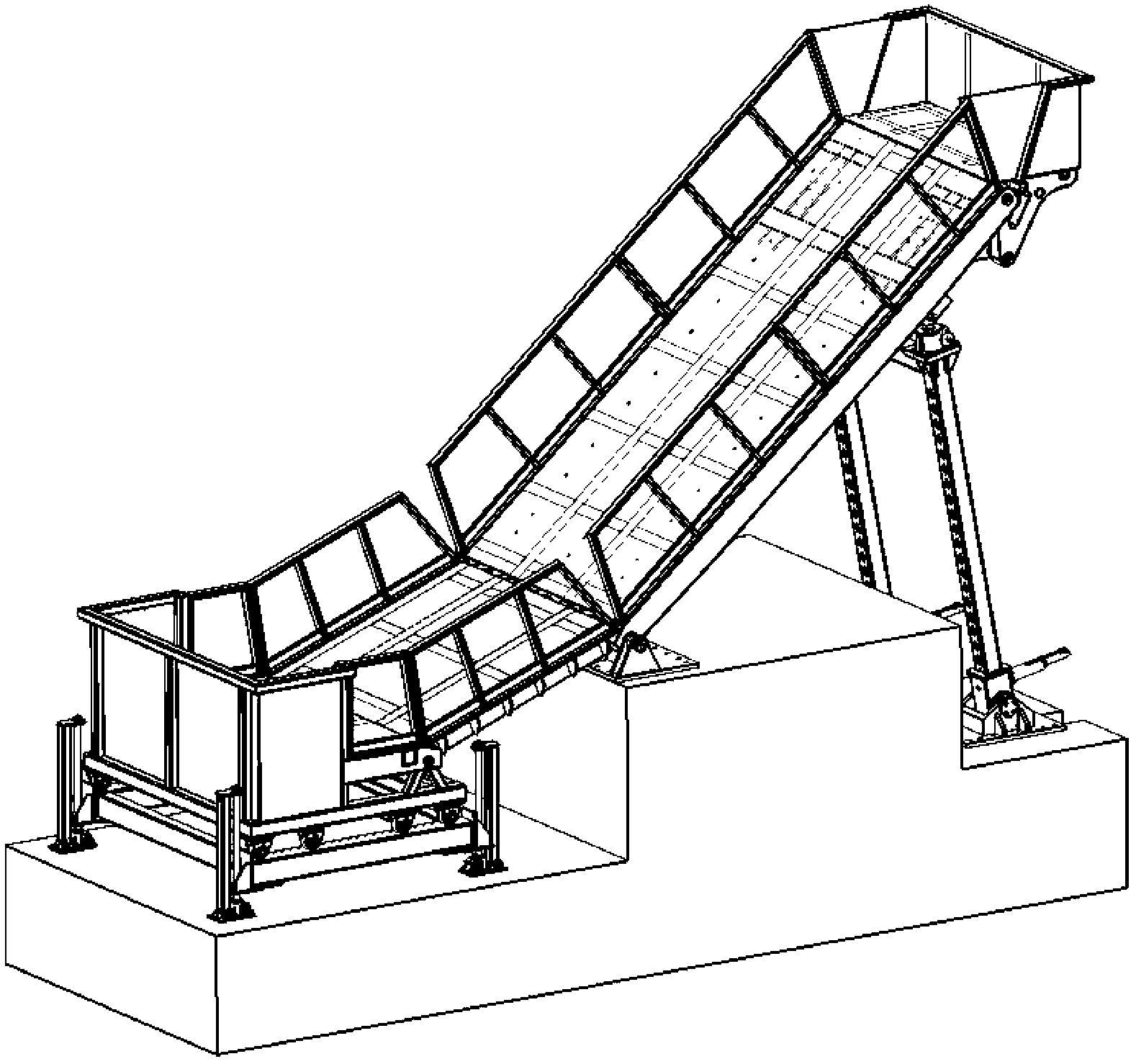
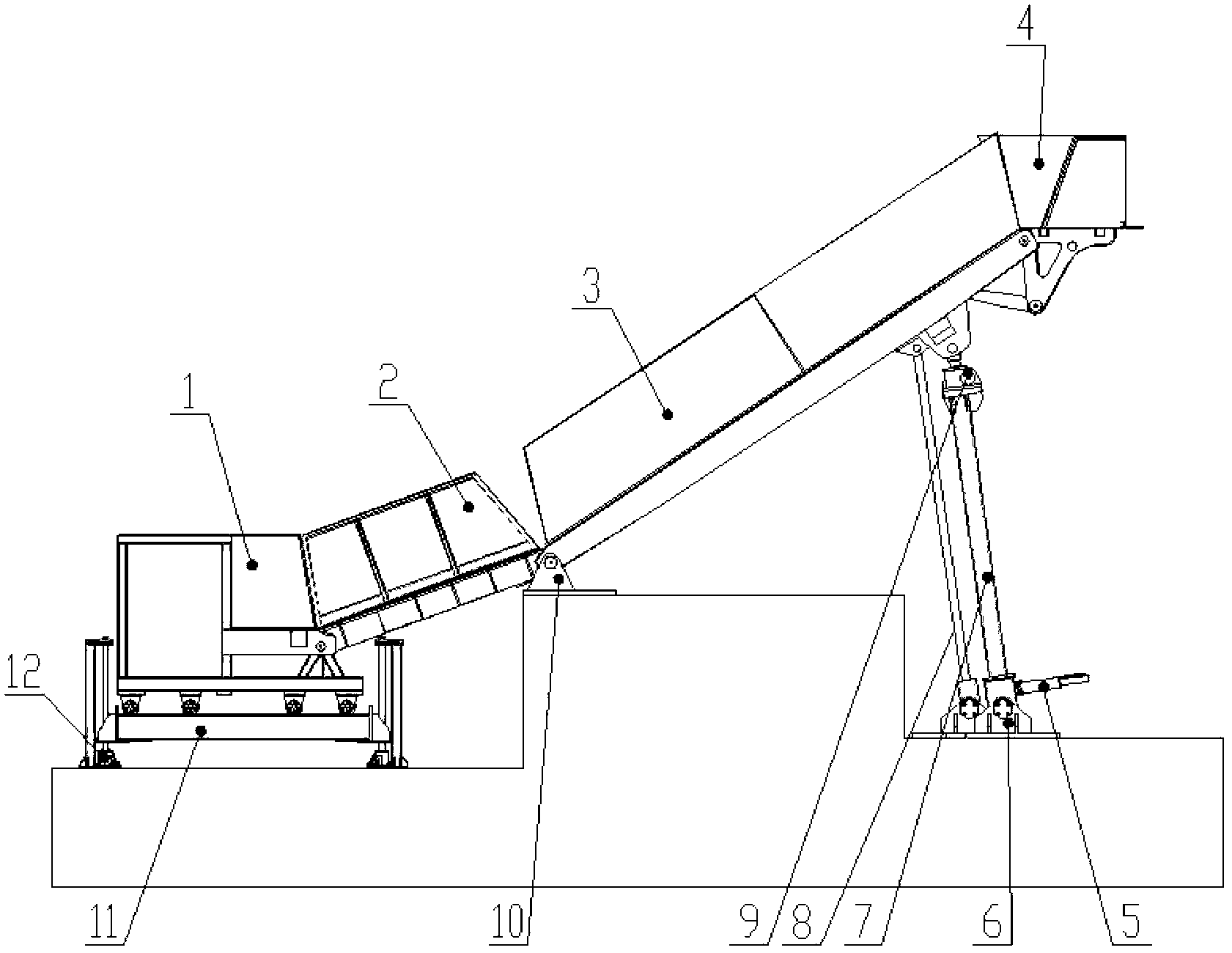
Experimental device with physical landslide model
The invention discloses an experimental device with a physical landslide model. The experimental device comprises a landslide experiment tank which comprises a base and four segments of platforms, wherein the first segment of platform is located above the base, the first segment of platform, the second segment of platform, the third segment of platform and the fourth segment of platform are connected in sequence, the first segment of platform is horizontal, and the inclination angles of the second segment of platform, the third segment of platform and the fourth segment of platform are adjustable. The experimental device with the physical landslide model disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of large scale, sectional type, multi-factor and overall process, and can truly simulate the overall damage evolution process of a landslide disaster chain under hydrodynamic force induction factors.
Owner:INST OF MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
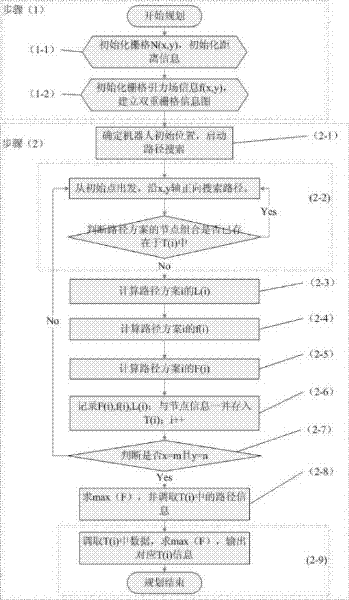
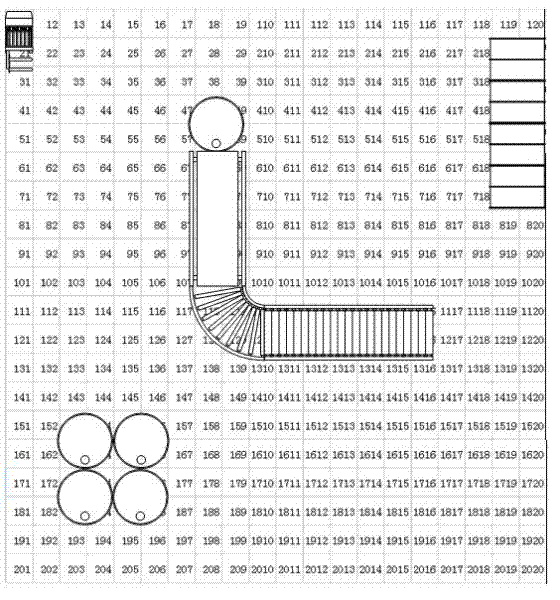
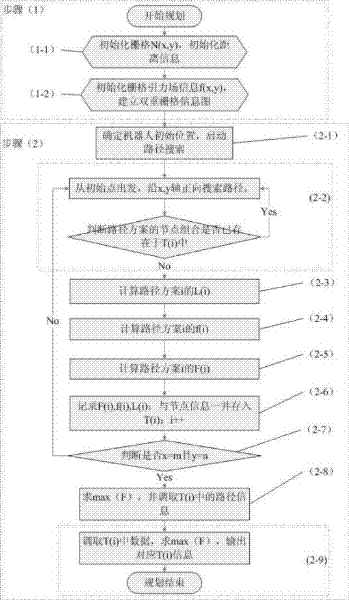
Physical modeling-based robot obstacle avoidance path planning method
InactiveCN102520718AImprove efficiencyOvercome the disadvantage of not considering geometric attributesPosition/course control in two dimensionsObstacle avoidanceControl theory
The invention discloses a physical modeling-based robot obstacle avoidance path planning method, which comprises the following steps of: setting a gravitational field grid and a distance information grid of a robot working region to establish a robot double-grid information graph; based on the double-grid information graph, searching all feasible paths by using a directional ergodic method; calculating a comprehensive evaluation value of a gravity value and a distance value; and taking a path scheme corresponding to the maximum value as a robot optimal obstacle avoidance path planning scheme.By using the method, the defect that geometric attributes of moving objects and obstacles in robot path planning are not considered is overcome; during path searching after double grids are established by the method, robot obstacle avoidance path planning is performed according to the value of the double grids; and thus, the problems of the shortest path and moving safety are both taken into consideration, the efficiency of path planning is increased, and damage accidents which probably occur in path optimization are reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
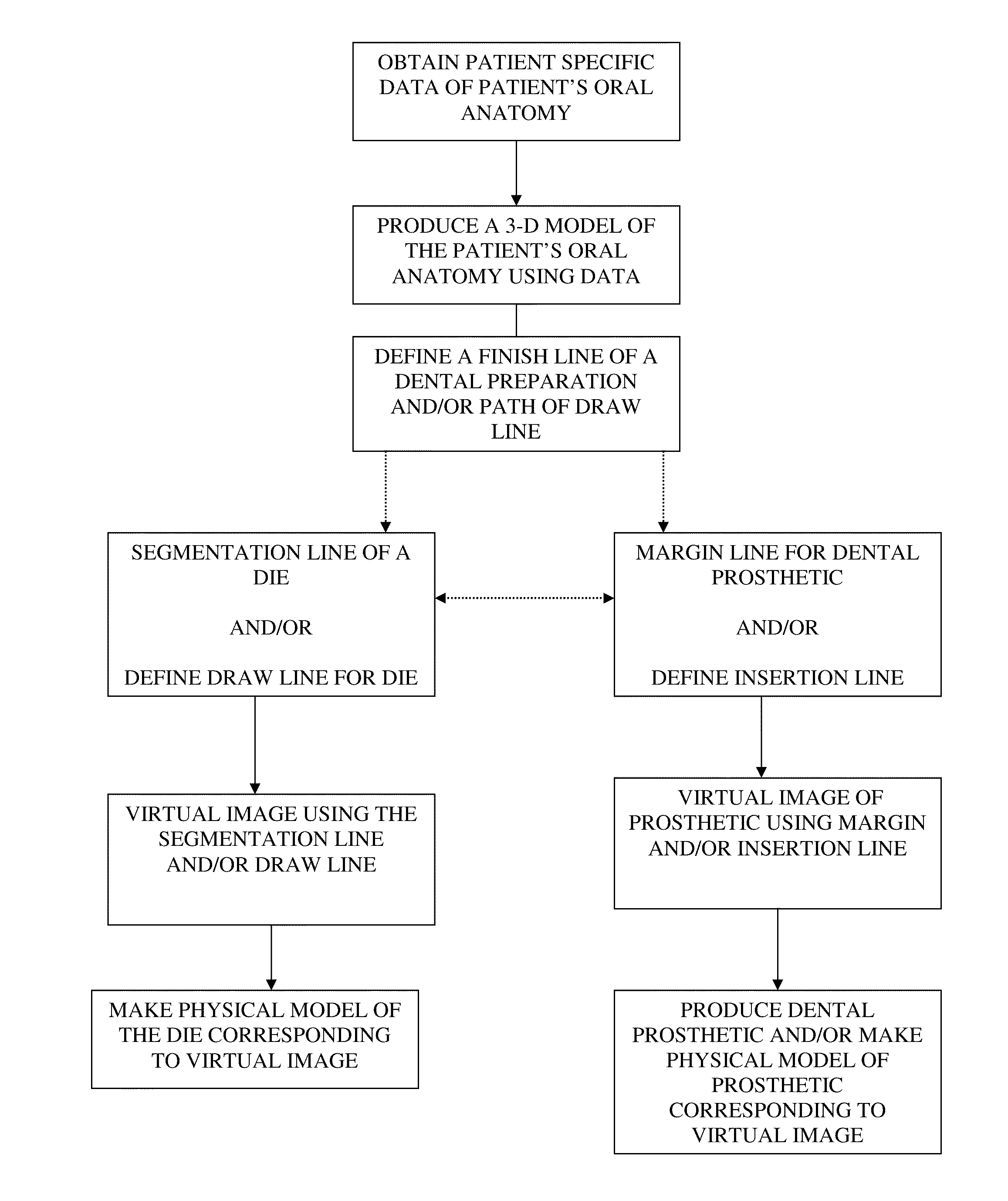
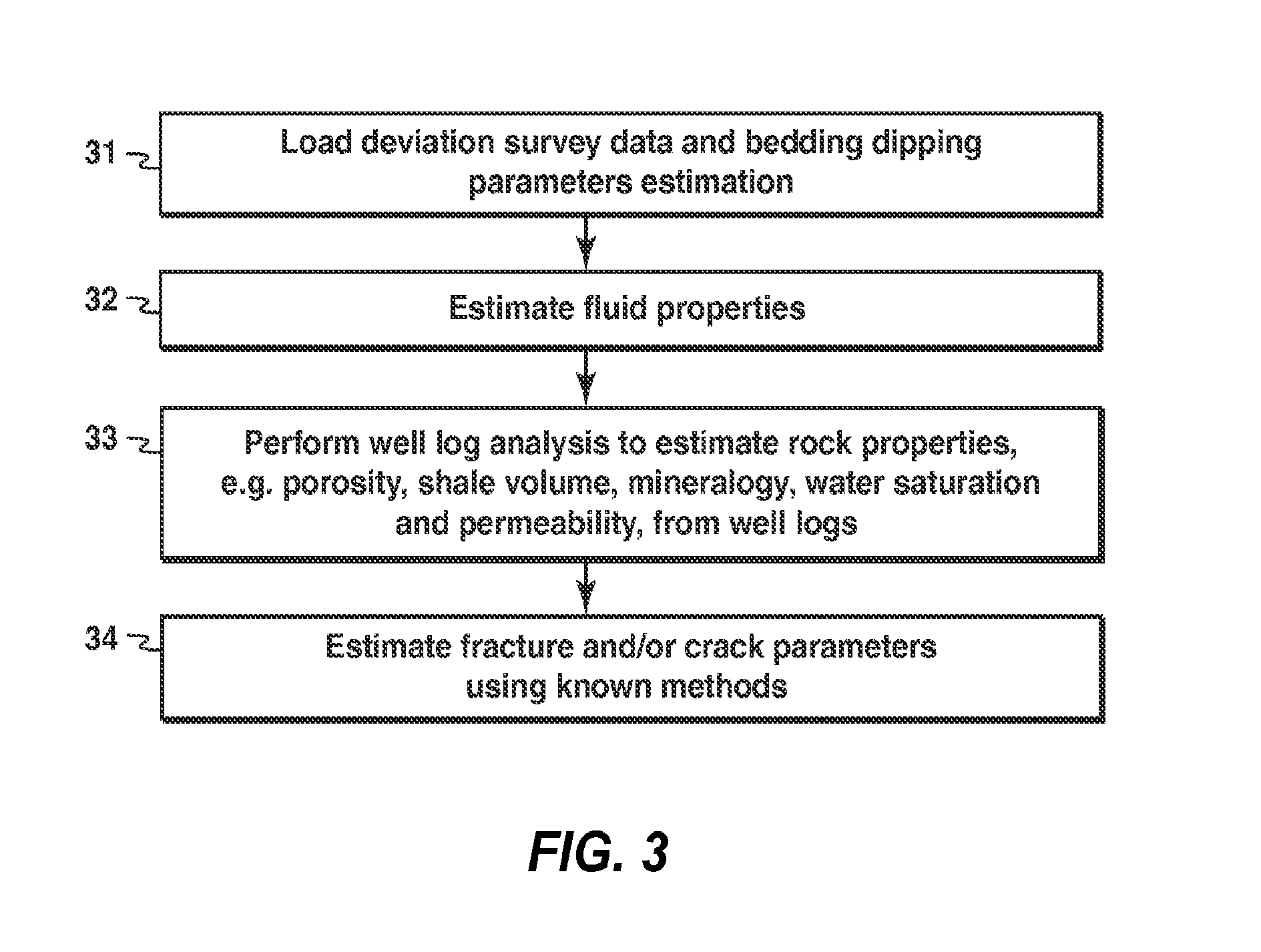
Method for planning a dental component
Presented herein are methods and devices for designing dental components, such as physical models of a patient's anatomy, crowns and bridges. An operator of a prosthetic designing system can receive information, such as from a scanner, which provides information on the topology of the patient's dentition. The operator can use this information to design a custom prosthetic to fit the patient. Part of the designing process involves using a finish line defined for a preparation as a segmentation line for a physical die corresponding to the preparation, and using a path of draw line as an insertion axis line for a dental prosthetic.
Owner:BIOCAD MEDICAL
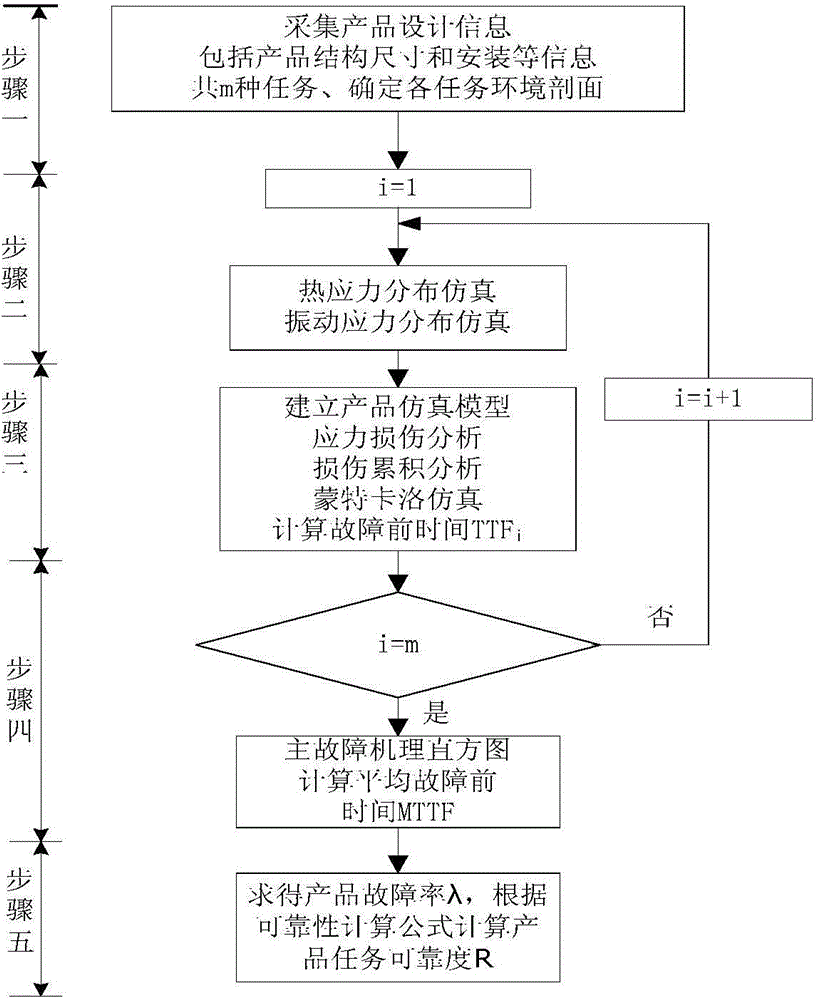
PoF (physics of failure) based method for calculating mission reliability of electronic product
ActiveCN103559418AIn line with the real situationReflect the stress situationSustainable transportationSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationComputing MethodologiesDesign improvement
A PoF based method for calculating mission reliability of an electronic product comprises steps as follows: step one, information of all mission profiles of the product is collected, and an environment profile of each mission is determined; step two, thermal simulation and vibration simulation of environmental stress of each mission are performed, and a local response of the product to an environmental load is obtained; step three, a product simulation model is established; step four, simulation calculation of the product in all the mission profiles is completed, and the mean time to failure and a main failure mechanism of the product are obtained; and step five, the mission reliability of the product is calculated according to the mean time to failure. According to the PoF based method for calculating the mission reliability of the electronic product, all missions of the product during lifetime use are considered, the environmental stress of each mission is simulated, and the mean time to failure and the mission reliability of the product are comprehensively calculated. By means of a PoF model, the direction relation between parameters of a product material, structure, process and the like and the reliability can be obtained, and a design improvement direction is clearly and directly provided for the product.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
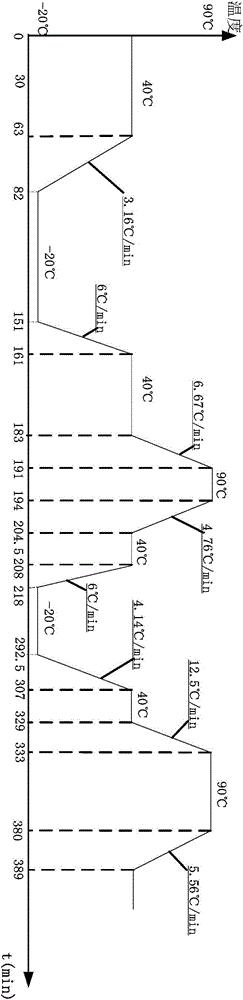
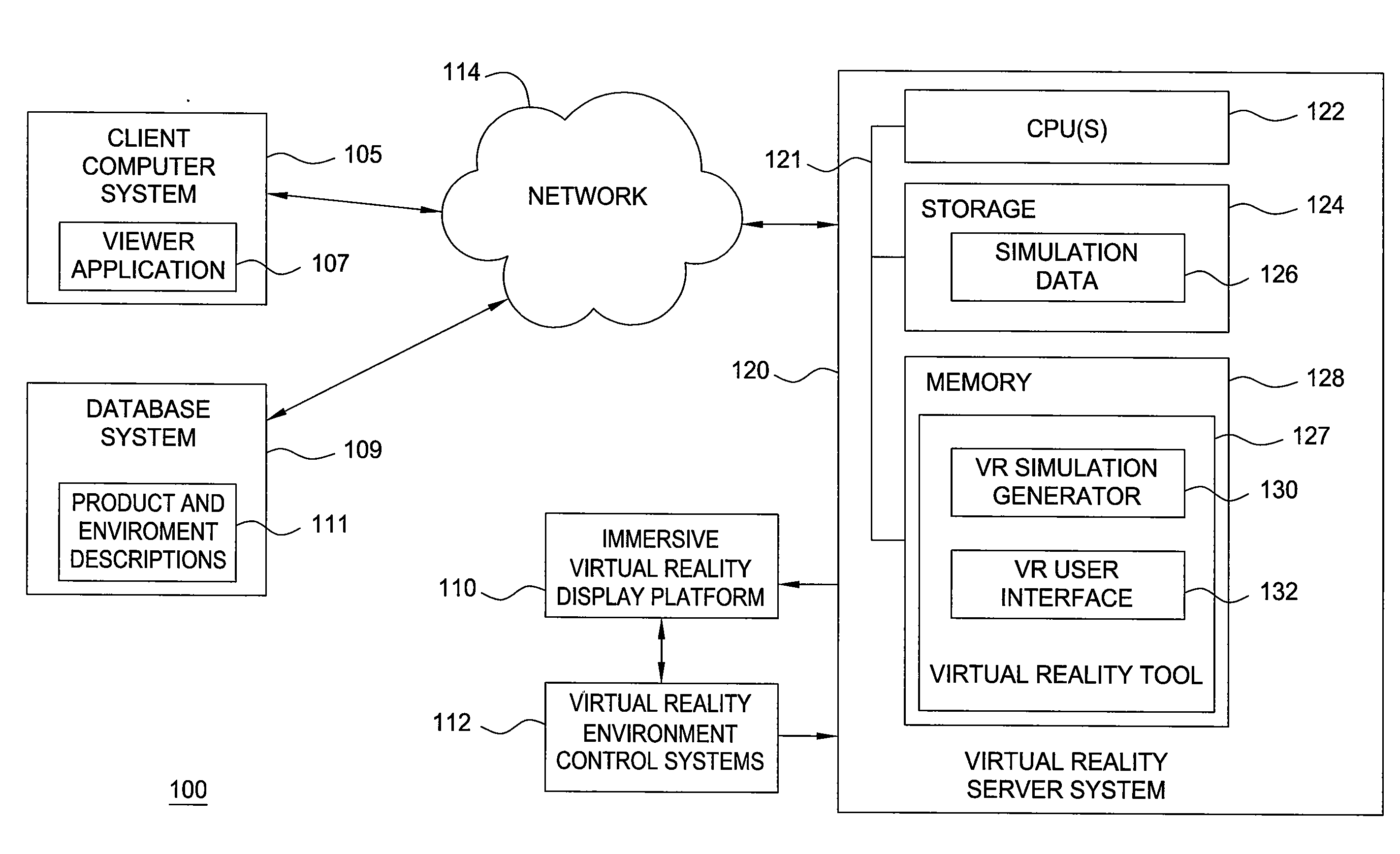
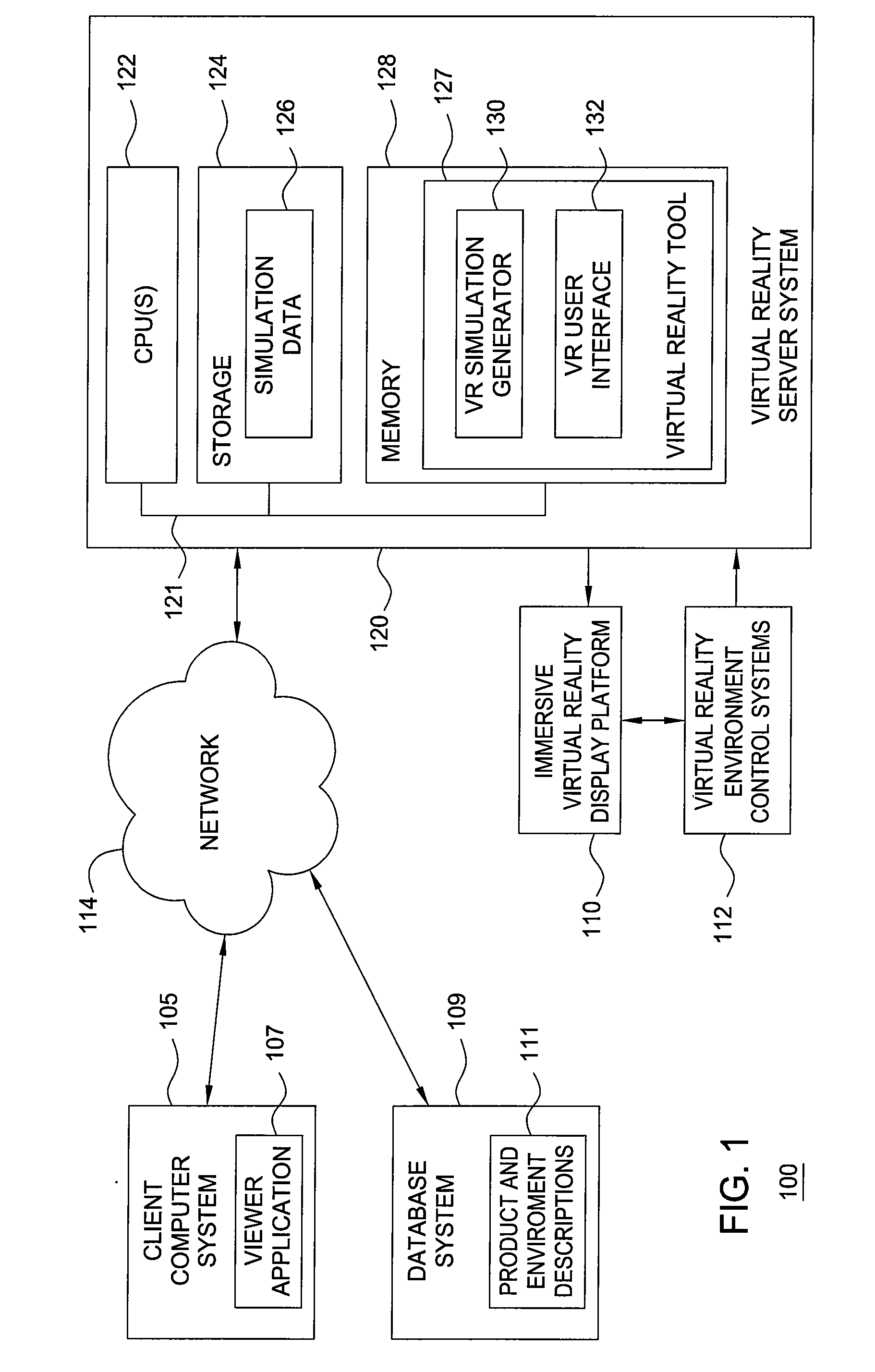
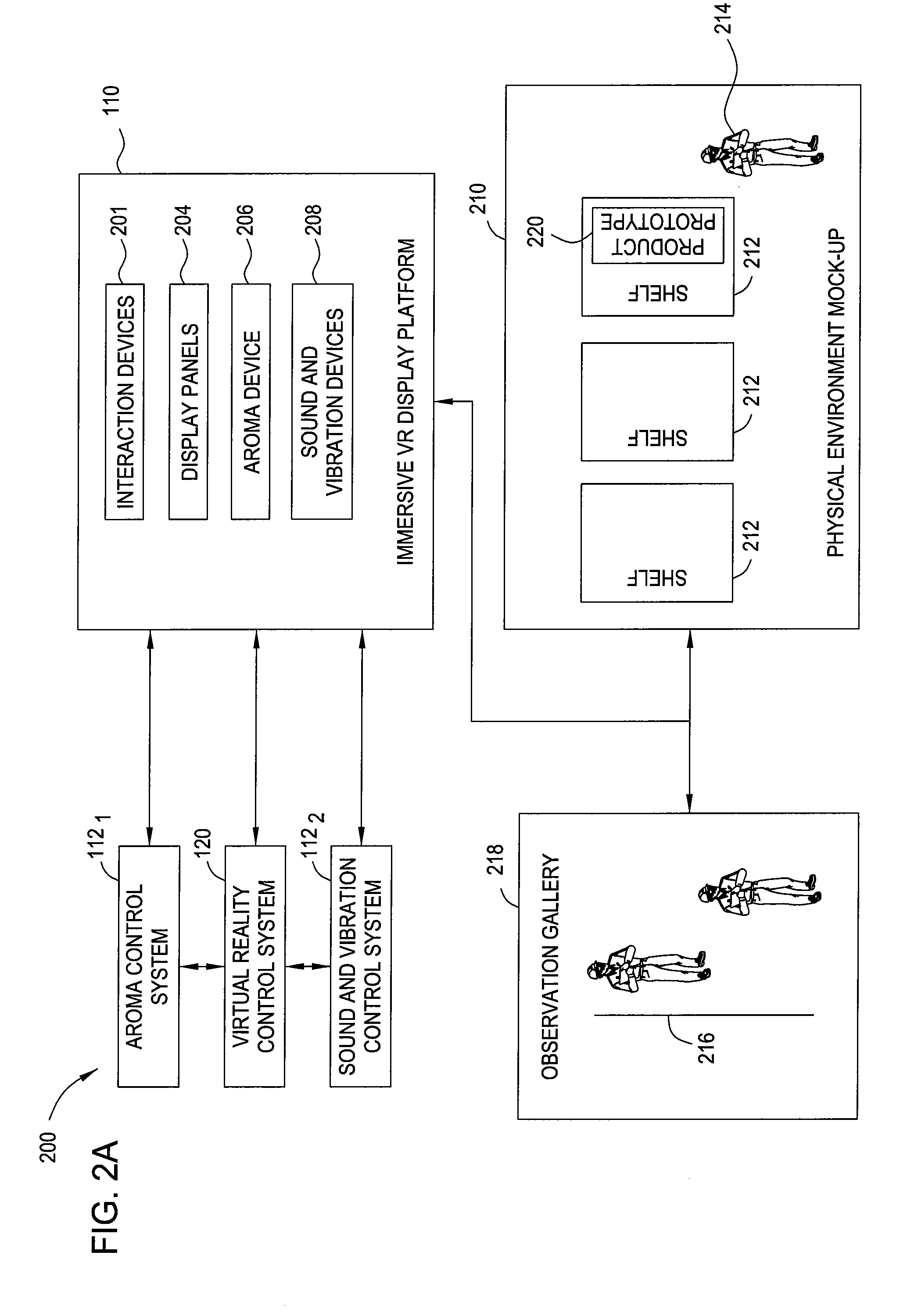
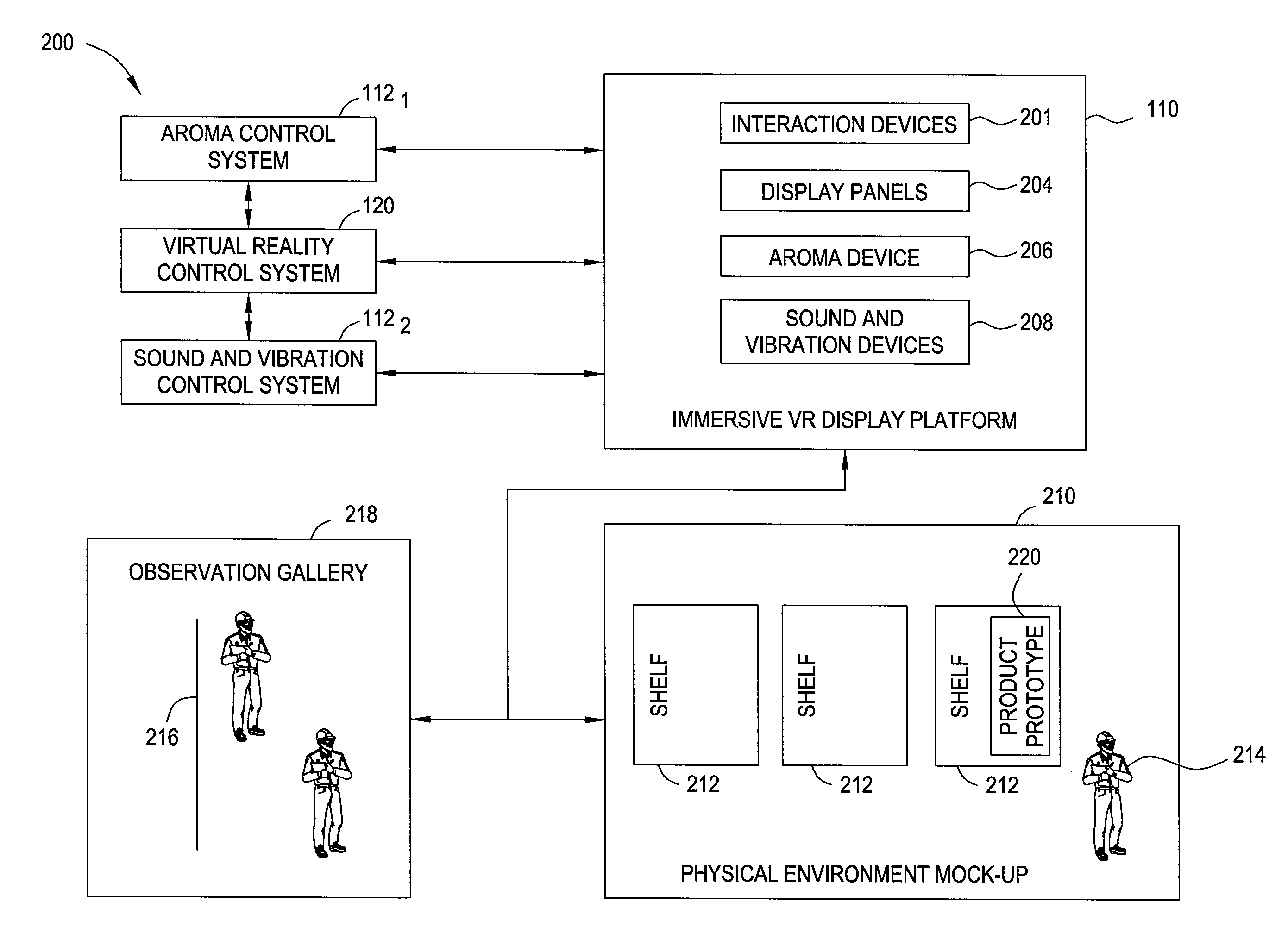
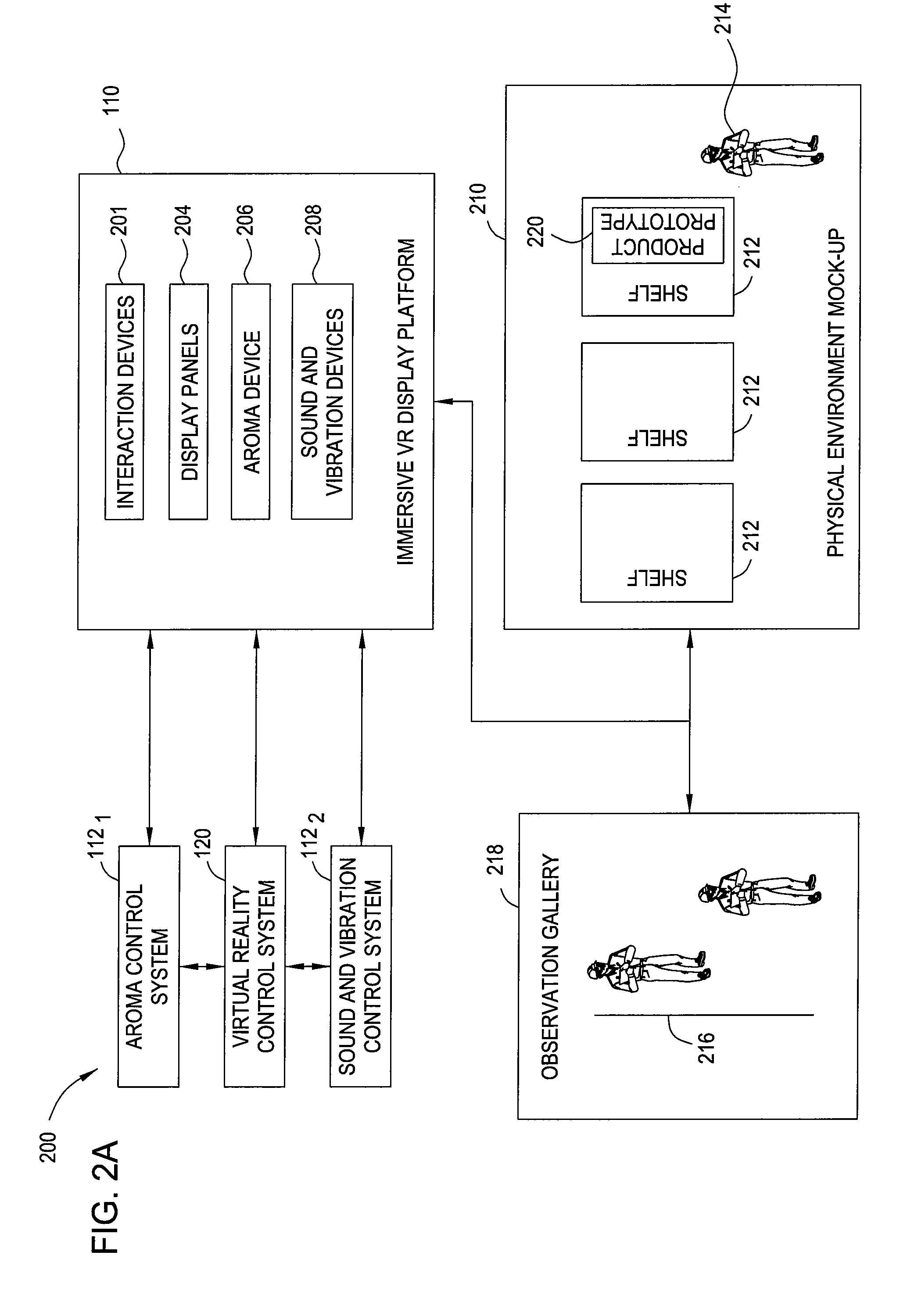
Immersive visualization center for creating and designing a "total design simulation" and for improved relationship management and market research
InactiveUS20080162262A1Special data processing applicationsMarketingCustomer relationship managementMock ups
Embodiments of the invention include methods, apparatuses, and articles of manufacture for generating and using virtual reality simulations to conduct market research and related activities. An immersive visualization center may be used to manage relationships with customers, choosers, shoppers, and users. The visualization center may allow customers (or other relevant parties) to interact with virtual representations of products or solutions in a virtual reality environment appropriate for the product. The immersive visualization center may also include a physical mock-up of the environment and or products simulated by the virtual reality simulation.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Space-Time Surrogate Models of Subterranean Regions
Methods for creating and using space-time surrogate models of subsurface regions, such as subsurface regions containing at least one hydrocarbon formation. The created surrogate models are explicit models that may be created from implicit models, such as computationally intensive full-physics models. The space-time surrogate models are parametric with respect to preselected variables, such as space, state, and / or design variables, while also indicating responsiveness of the preselected variables with respect to time. In some embodiments, the space-time surrogate model may be parametric with respect to preselected variables as well as to time. Methods for updating and evolving models of subsurface regions are also disclosed.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
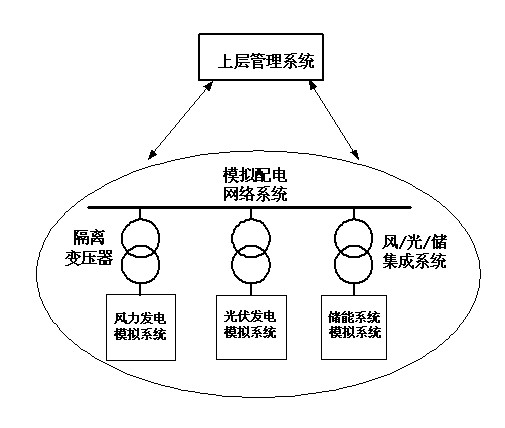
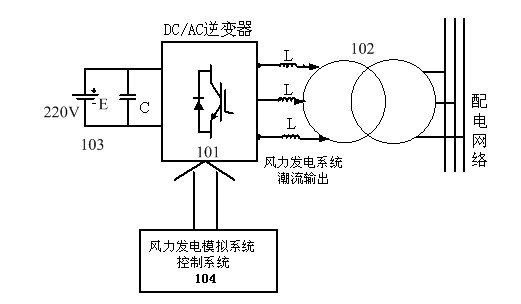
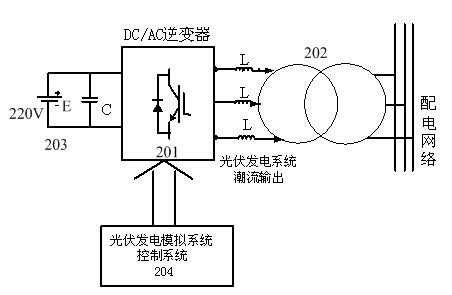
Physical modeling system with wind power generation, photovoltaic power generation and energy storage integration system
ActiveCN102437571AAchieving two-way flowSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsEnergy storagePhysical modelPhysical system
The invention discloses a physical modeling system with a wind power generation, photovoltaic power generation and energy storage integration system. The physical modeling system is based on power output characteristics of a wind power generation system, a photovoltaic power generation system and an energy storage system, and a converter system is utilized to simulate the wind power generation system, the photovoltaic power generation system and the energy storage system. The physical modeling system comprises an upper layer management module, a wind power generation simulation module, a photovoltaic power generation simulation module, an energy storage simulation module and a simulation power distribution network module. The wind power generation simulation module and the photovoltaic power generation simulation module can simulate power trends of a wind power field and a photovoltaic power station according to a set environment parameter. The energy storage simulation module employs a set of reversely connected current transformers to carry out simulation. Charge and discharge characteristics of a storage battery can be simulated, and an instruction of the upper layer management module can be received. According to a practical requirement, active and reactive power is sent or absorbed to stabilize voltage or frequency fluctuation of the power distribution network module. According to the invention, an inverter is utilized to establish a physical model, and a bottleneck problem that wind power, photovoltaic power and energy storage integration generation research can not be realized in a laboratory physical system is solved well.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE, CHINA SOUTHERN POWER GRID CO LTD +1
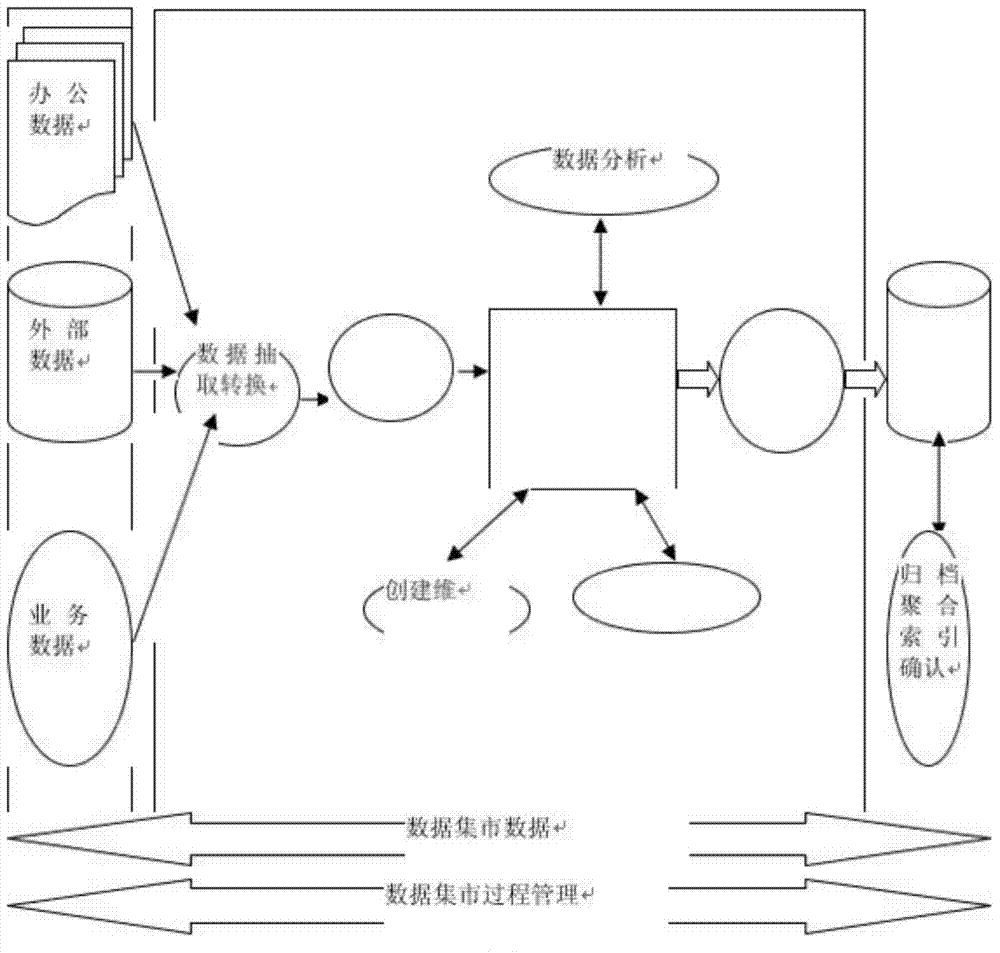
Marketing analysis data market system
The invention provides a marketing analysis data market system. The marketing analysis data market system comprises a data access layer, a data extraction module, a data conversion module, a data cleaning module, a log and alarm sending module and a data downloading module, a data packet of the data access layer contains office data, external data and service data, and models of the system includes a data logic model and a data physics module. Firstly, necessity in designing the marketing data market is analyzed and ETL data processing including noise data processing, data uniformity and data quality and the like is analyzed by discussing a data integration method, and various data sources can be reorganized and processed by a data transition tool. In addition, the physics model in the data market is realized according to the physic list structure of the logic model. Finally, application prospect of the data market in the marketing analysis is expected.
Owner:DONGYANG AIWEIDE ADVERTISING MEDIA
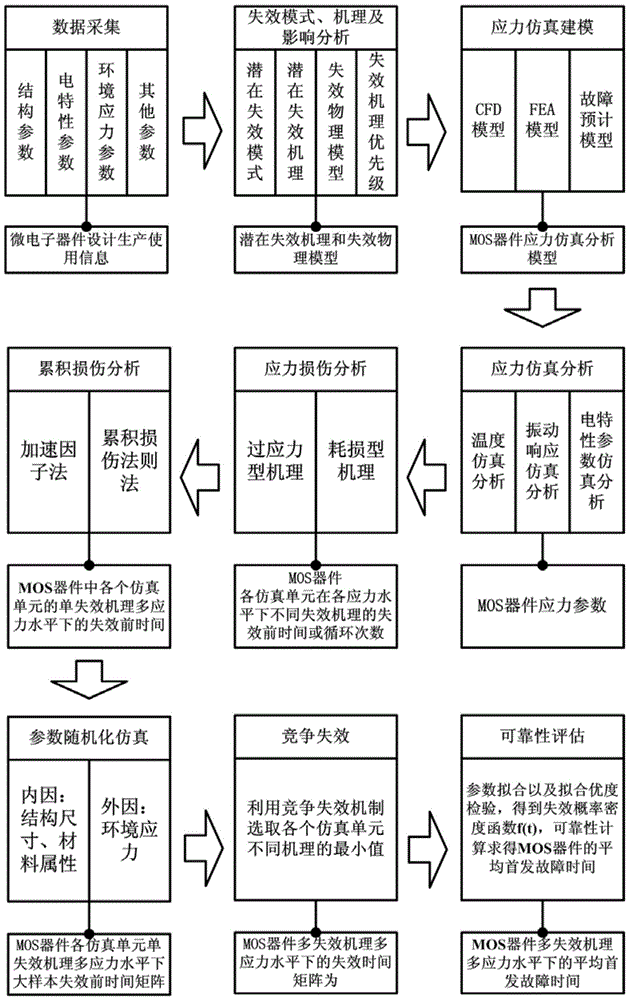
Physics-of-failure-based MOS (metal oxide semiconductor) device reliability simulation evaluation method
InactiveCN103955568ASoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationSpecial data processing applicationsElement analysisFailure mechanism
The invention relates to a physics-of-failure-based MOS (metal oxide semiconductor) device reliability simulation evaluation method. The method comprises the following steps: first, acquiring related parameters of an MOS device; second, analyzing a failure mode, a mechanism and an influence; third, establishing CFD (computational fluid dynamics), FEA (finite element analysis) and failure prediction models; fourth, carrying out the simulation analysis on temperature, vibration and electrical characteristics; fifth, performing stress damage analysis; sixth, performing cumulative damage analysis; seventh, considering deviation and performing parameter randomization simulation; eighth, obtaining a time vector before a failure by utilizing a competition failure mechanism; ninth, estimating the average starting failure time of the device. According to the method, a potential failure mechanism and a corresponding failure physical model of the device are obtained by analyzing, the using stress of the device is determined by simulating and analyzing, and finally, the average starting failure time of the MOS device under using conditions is obtained by calculating from the possible failure reasons of the MOS device on the basis of a failure physical theory. The method belongs to the technical field of MOS device reliability simulation and evaluation.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
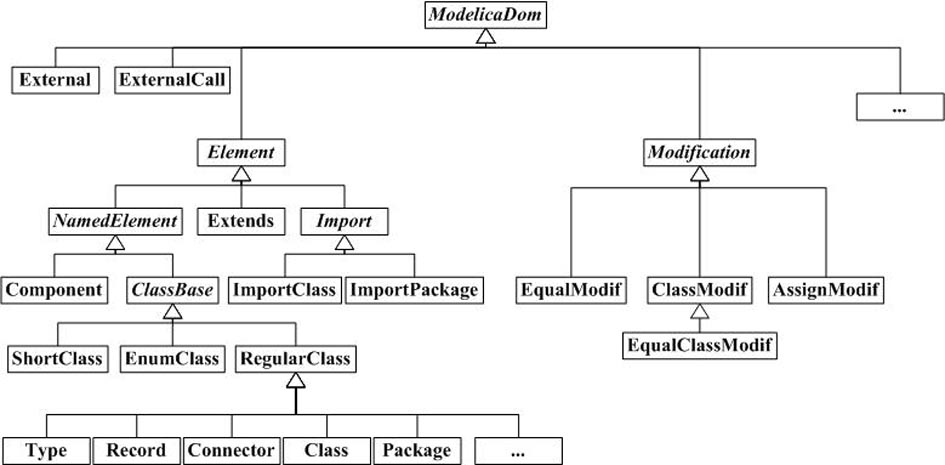
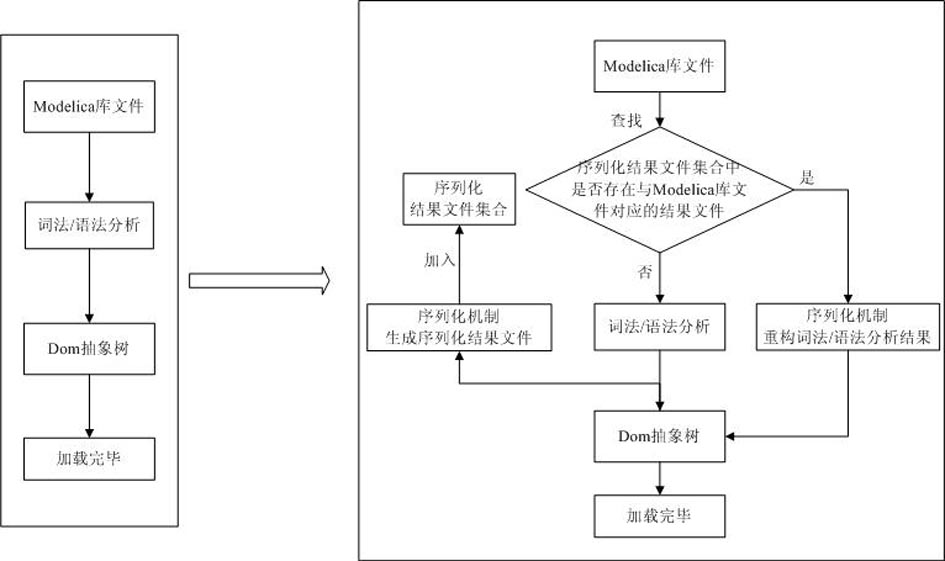
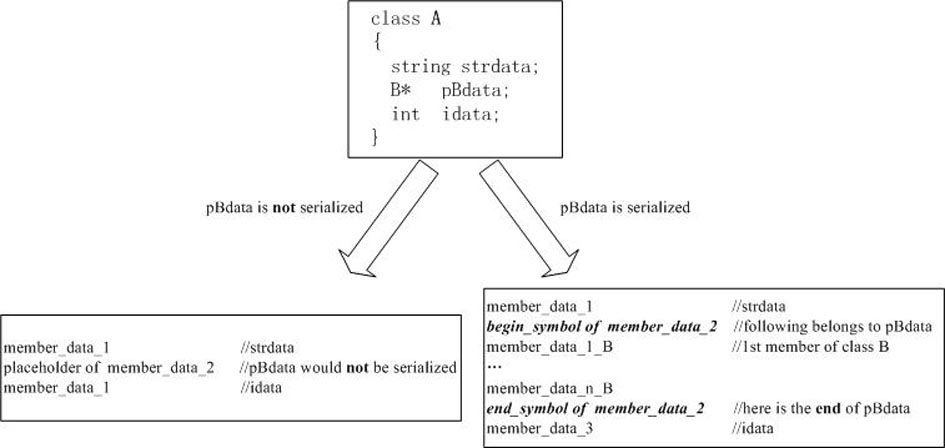
File serialization method of model library of physical modeling language Modelica
InactiveCN102043657AImprove loading speedAvoid parsingProgram loading/initiatingModelicaTheoretical computer science
The invention discloses a file serialization method of a model library of physical modeling language Modelica. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: while loading the model library for the first time, lexical / syntactic analysis is carried out on source files of the Modelica model library; a document object model (DOM) abstract syntax tree is established; and the data of the DOM abstract syntax tree is saved in serialization destination files by a serialization technology. Meanwhile the invention further discloses a corresponding deserialization method. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that by means of the preprocessing course, while loading the model library for the first time, the serialization destination files are generated so as to facilitate loading the model library next time only by directly reading the destination files, thus avoiding lexical / syntactic analysis of the model library every time and greatly accelerating the loading speed of the model library. A Modelica2.1 standard library is taken as an example: while not using the method, the loading time is 300 seconds; and while using the method, the loading time is only 600 milliseconds.
Owner:苏州同元软控信息技术有限公司
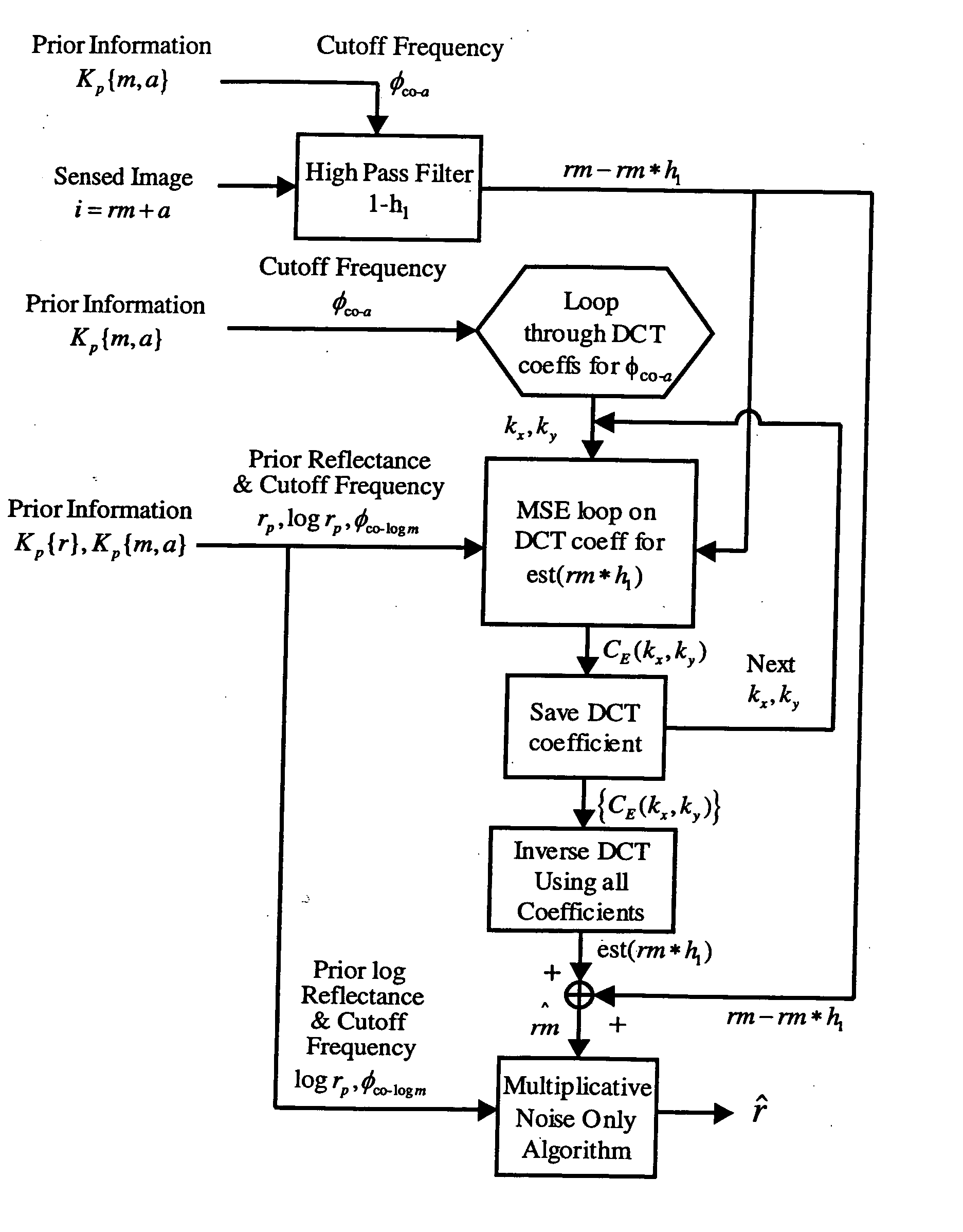
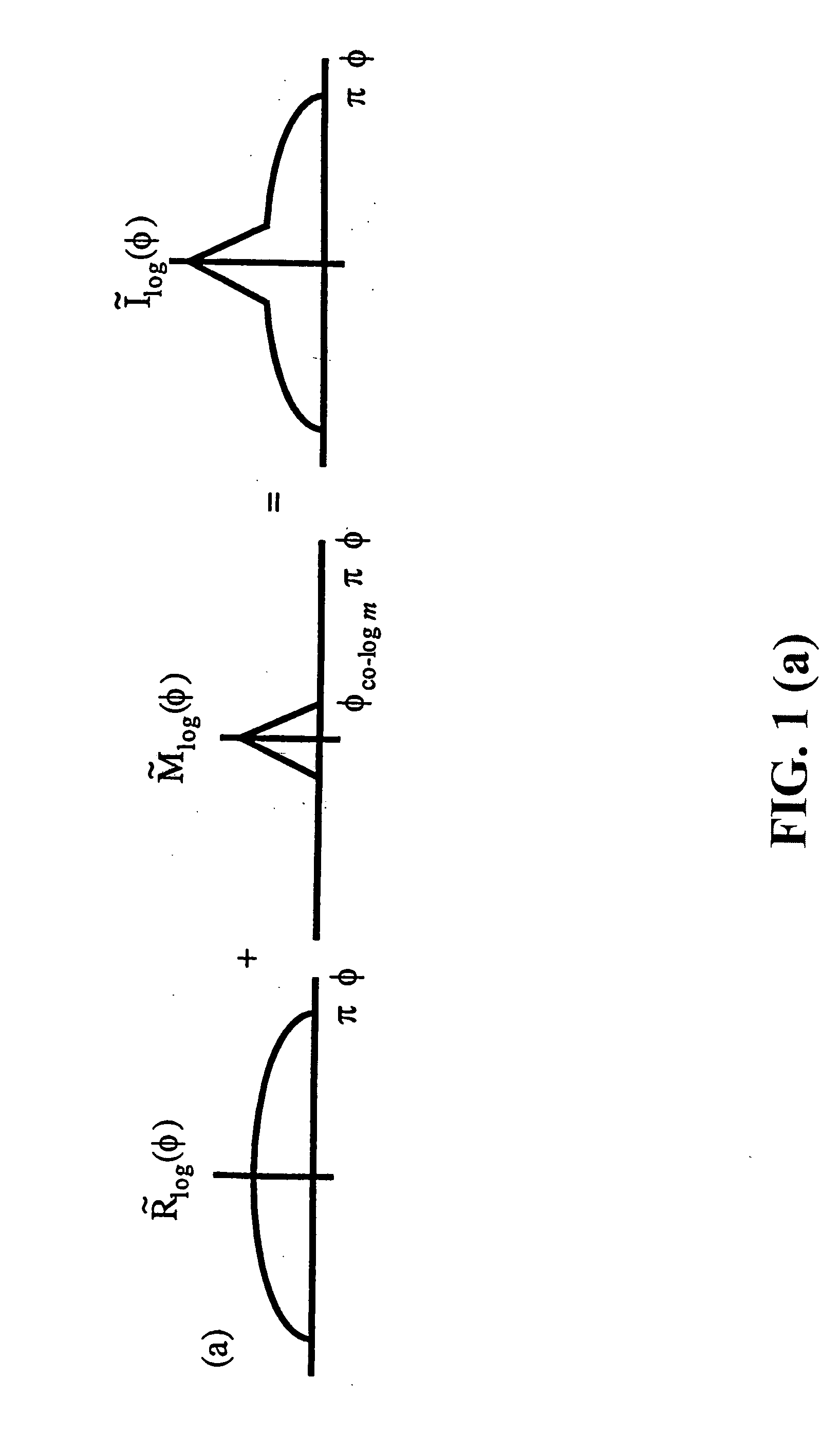
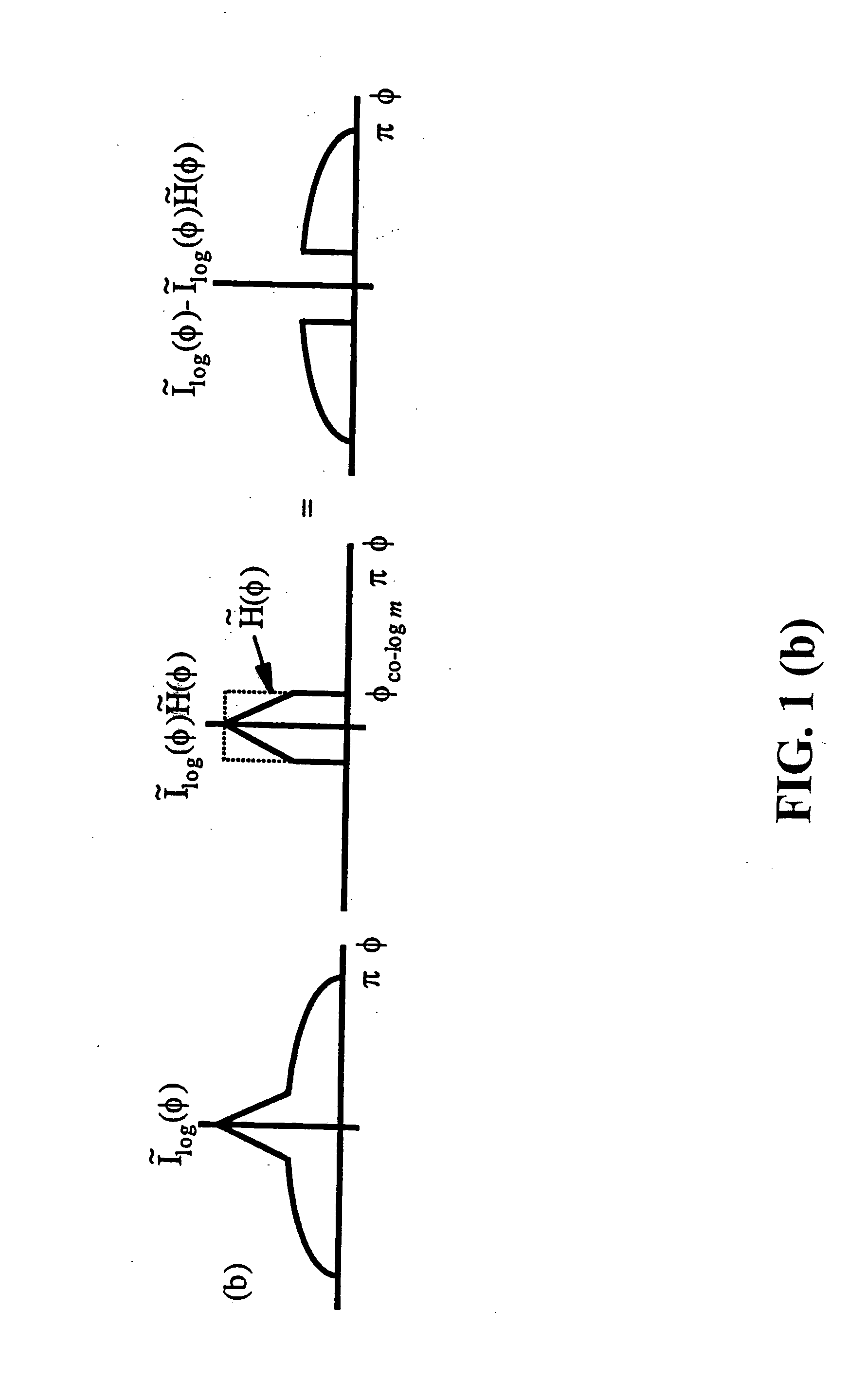
Spatial surface prior information reflectance estimation (SPIRE) algorithms
InactiveUS20050036661A1Remove additive noiseScattering properties measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionGround truthAtmospherics
A new class of algorithms has been developed to estimate spectral reflectance in remote sensing imagery. These algorithms are called Surface Prior Information Reflectance Estimation (SPIRE) algorithms and estimate surface spectral reflectance using prior spatial and spectral information about the surface reflectance. This paper describes SPIRE algorithms that employ spatial processing of single channel data to estimate local changes in spectral reflectance under spatially and spectrally varying multiplicative and additive noise caused by variations in illumination and atmospheric effects. Rather than modeling the physics of the atmosphere and illumination (using a physics-based code such as ATREM), or using ground truth spectra at known locations to compensate for these effects (using the Empirical Line Method), prior information about the low spatial frequency content of the scene in each spectral channel is used instead. HYDICE VNIR-SWIR hyperspectral data were used to compare the performance of SPIRE, ATREM, and ELM atmospheric compensation algorithms. The Spatial SPIRE algorithm performance was found to be nearly identical to the ELM ground-truth based results, while Spatial SPIRE performed better than ATREM overall, and significantly better under high clouds and haze.
Owner:AIR FORCE GOVERNMENT OF THE US SEC THE
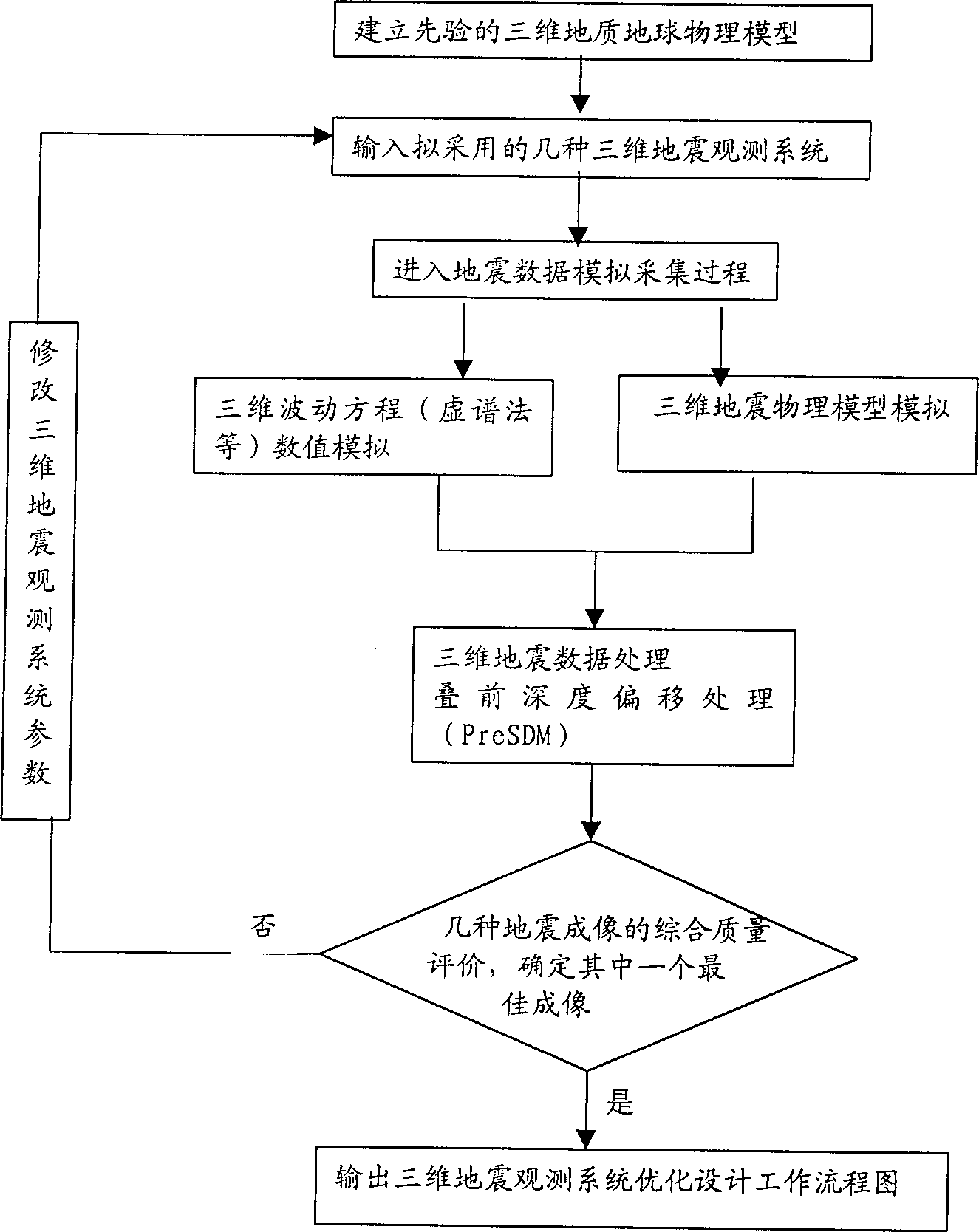
Optimizing design method of 3D seismic observation system based on geologic geophysical model
The optimized design method of geological geophysical model based three-dimensional seismological observation system includes the following steps: A). creating geological geophysical model; B). designing two kinds of several kinds of observation systems with three-dimentional geological data acquisition; C). adopting imaginary spectrum method and combinatino of three-dimensional wave equation numerical analog and three-dimensional geophysical model analog two methods of implement data acquisitino work; D). using common-reflection point as basis, making depth deviation treatment of acquired data before superposition to obtain several kinds of imaging results of seismic treatment; and E). making comprehensive comparison and evaluation of imaging quality of said imaging results and defining one optimum seismic imaging result. The invention is extensive in application range, can obtain good effect for making seismic exploration of petroleum and natural gas.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
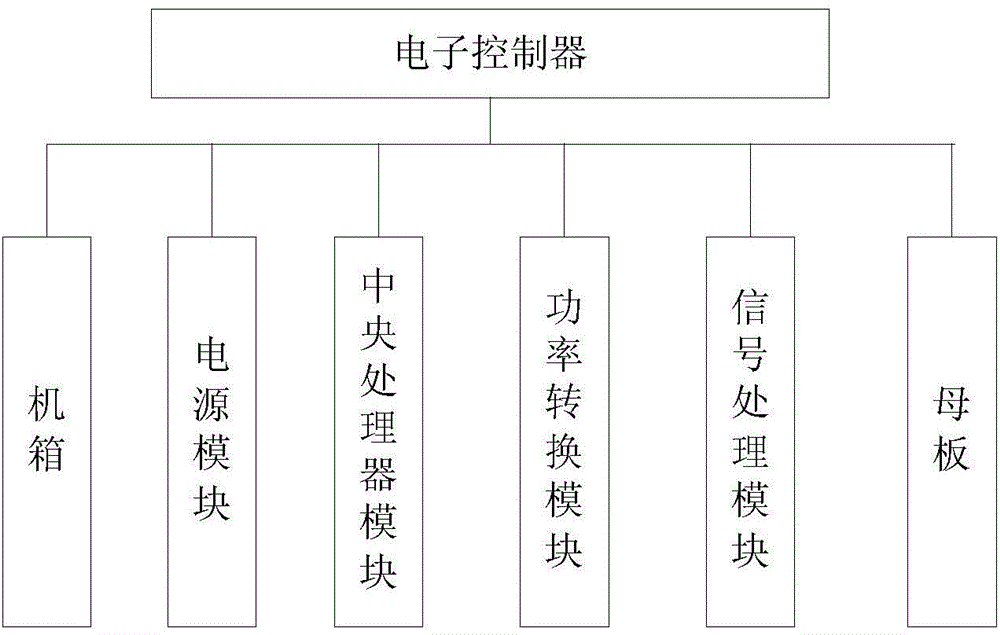
Electronic product reliability accelerated test method based on failure physics
ActiveCN104392073AImprove accuracyHigh precisionSpecial data processing applicationsTested timeDependability
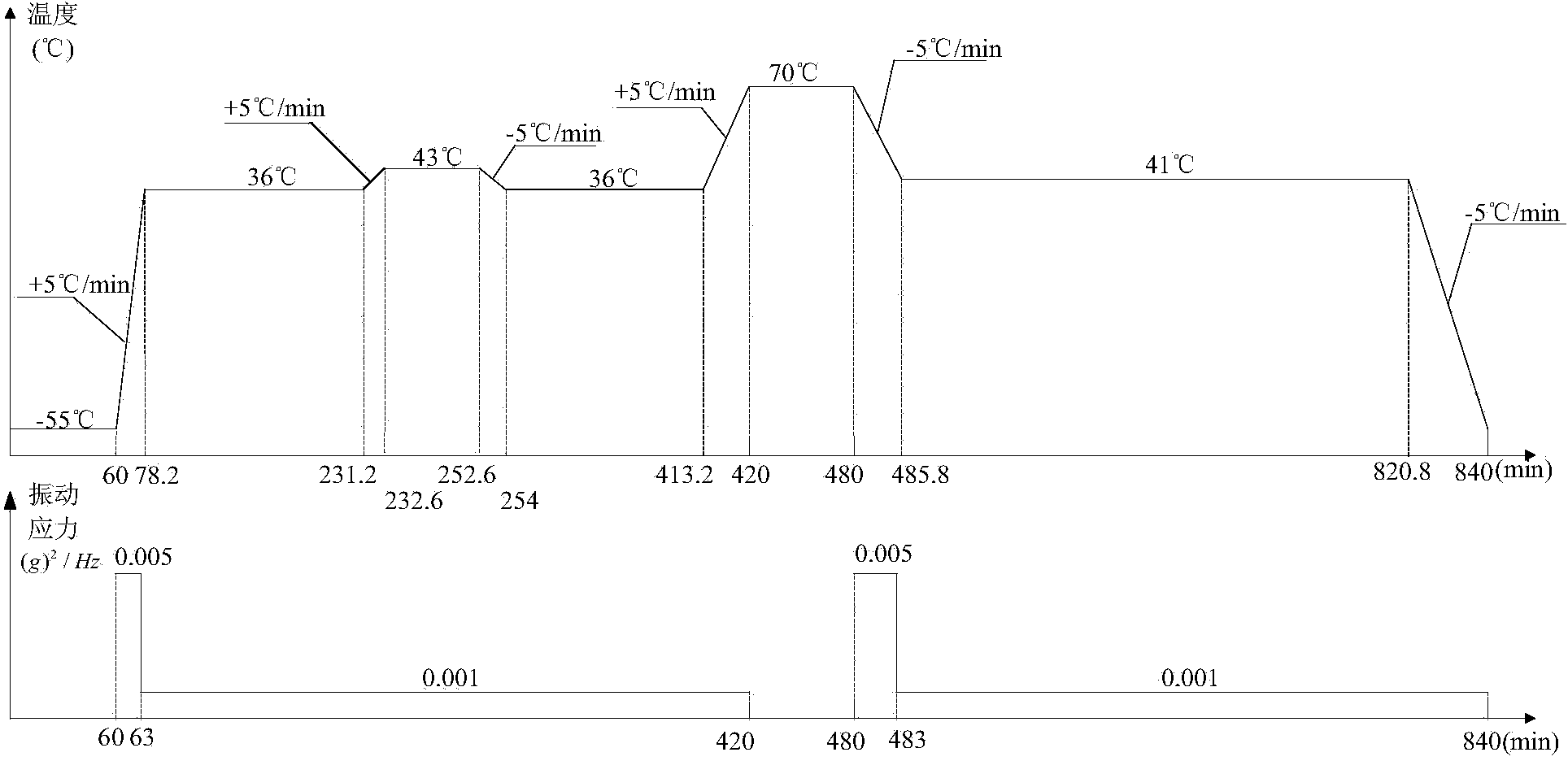
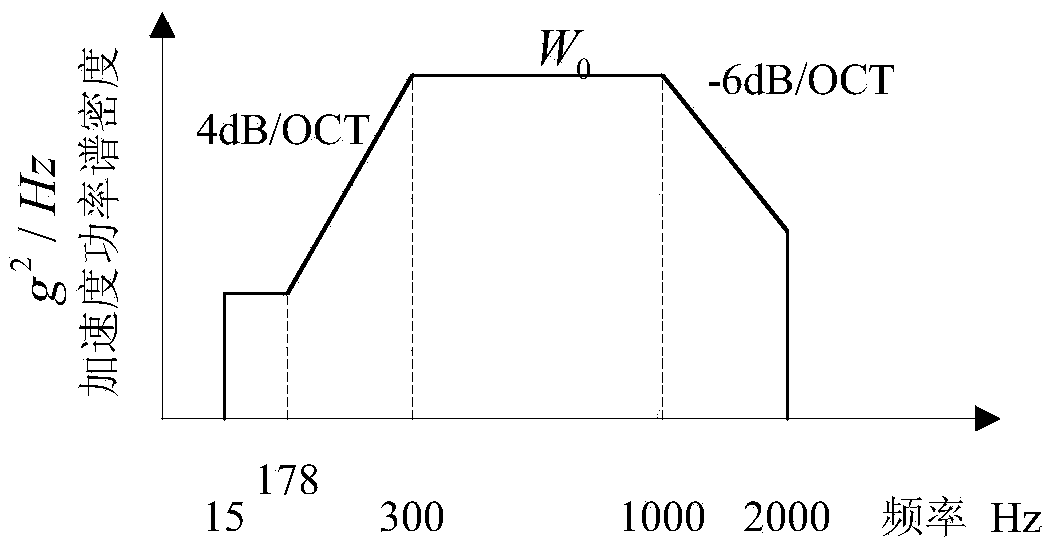
The invention belongs to an electronic product reliability technology and relates to an electronic product reliability accelerated test method based on failure physics. The electronic product reliability accelerated test method is characterized by comprising the following steps: building a digital prototype model of an electronic product; analyzing a thermal stress state and a vibration stress state; determining a failure mechanism of the electronic product; determining a failure physics model of the electronic product; providing temperature conditions for reliability accelerated test; calculating accelerated test time; calculating the vibration conditions of the reliability accelerated test; evaluating test implementation and test results. The electronic product reliability accelerated test method provided by the invention has the benefits that the transfer effect of stress in a product structure can be considered, the accuracy of the model is improved, and further, the test result accuracy is improved.
Owner:CHINA AERO POLYTECH ESTAB
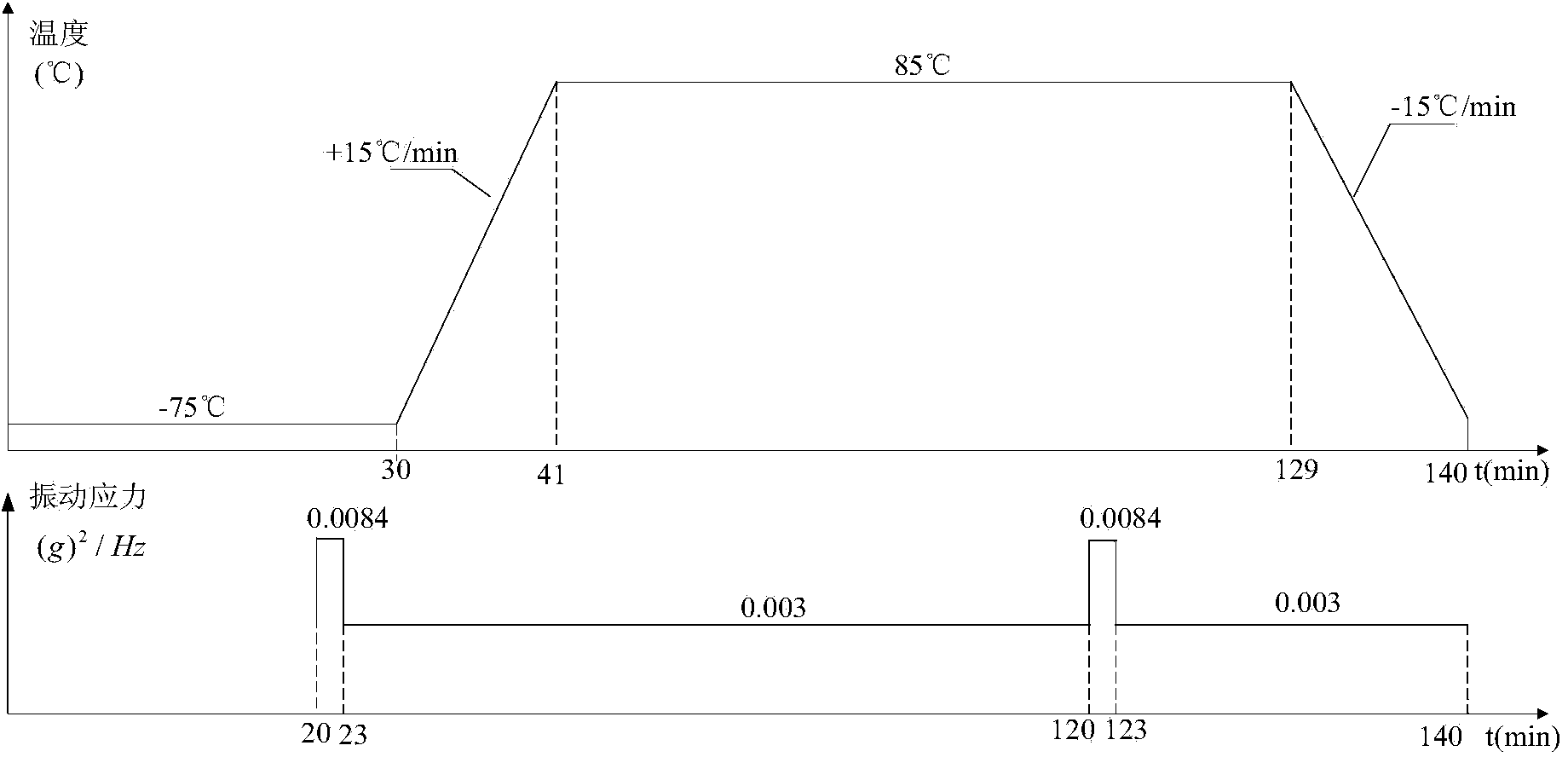
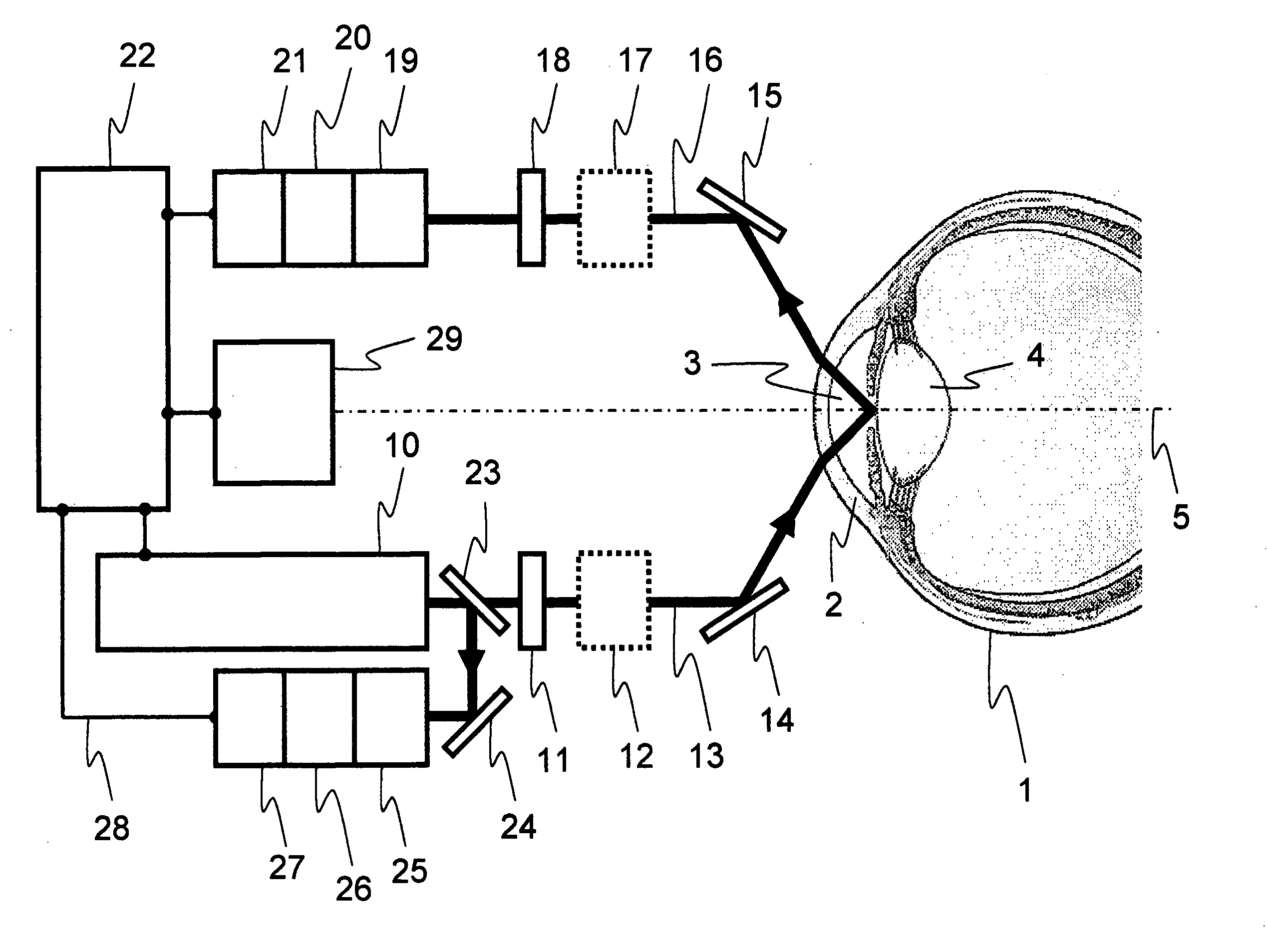
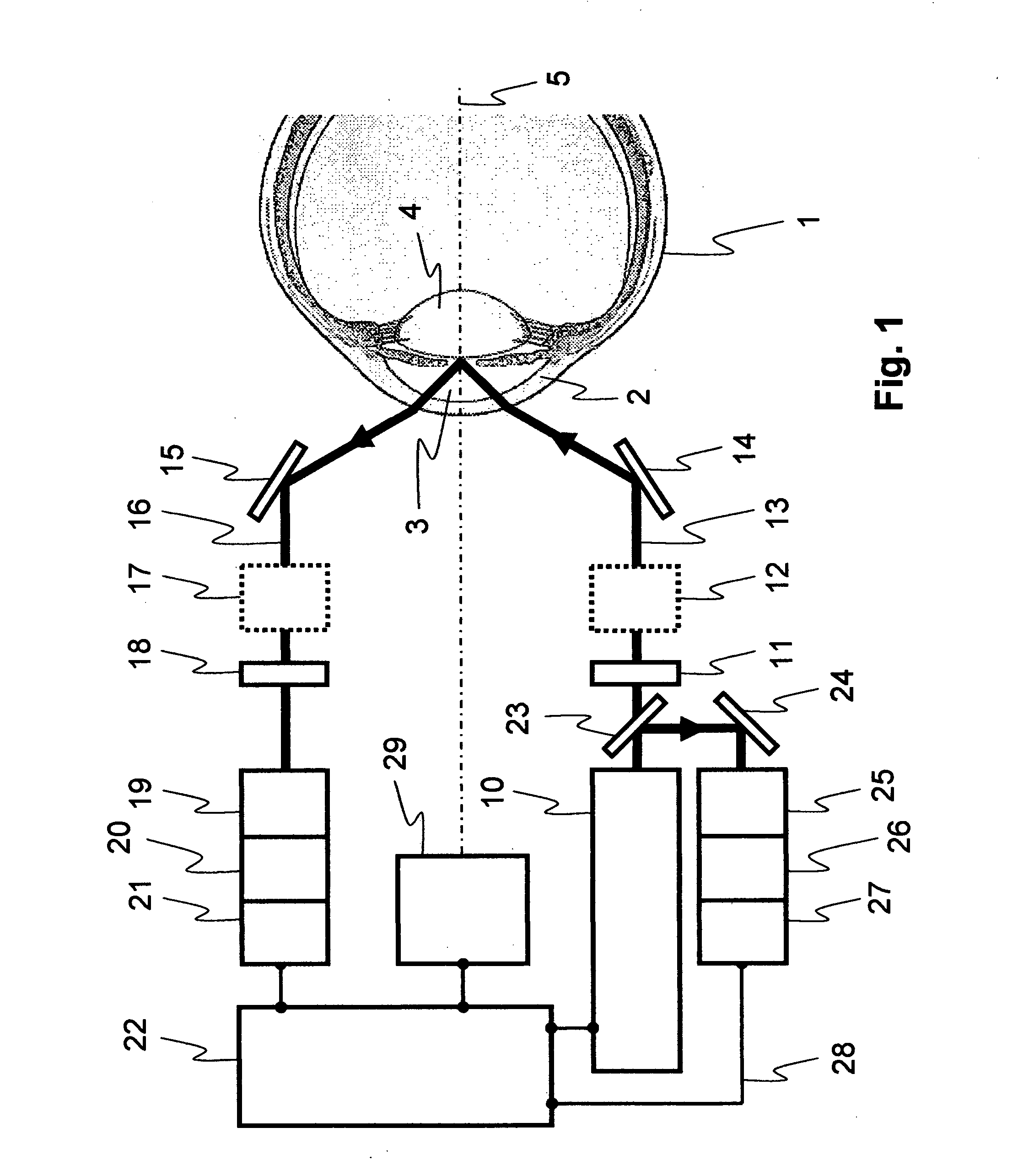
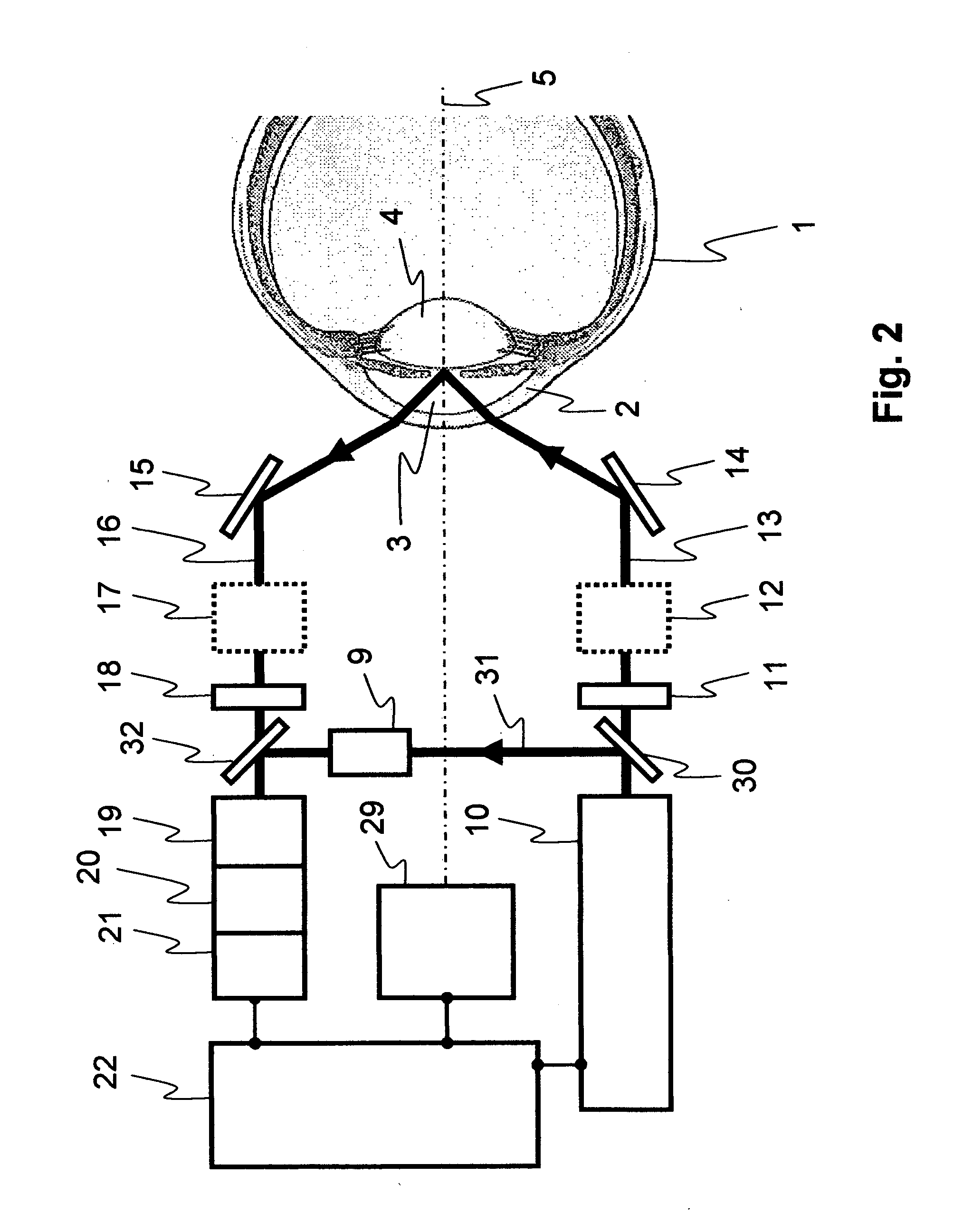
Method and device for measuring dissolved substances in human or animal intraocular fluid
The present invention relates to the non-invasive optical measurement of glucose and other dissolved substances in human or animal intraocular fluid. For this purpose, a method and devices for carrying out the method are proposed. The method according to the invention takes advantage of the fact that the wave dependence of optical activity is fundamentally different from corneal birefringence. The optical activity of substances dissolved in the intraocular fluid, such as glucose, lactate, ascorbic acid or amino acids, is scaled as a first approximation with the reciprocal value of the wavelength square. Upon closer review, higher orders must be taken into consideration and effectively an exponent varying from a value of 2 may occur. For glucose, the exponent shall be denoted as 2+xG, with the value xG being approximately 0.2. Accordingly, the exponents for lactate are denoted as 2+xLak, for ascorbic acid as 2+xAsc and for amino acids as 2+xAm. In contrast, corneal birefringence is scaled with the reciprocal value of the wavelength and therefore behaves considerably different from the optical activity. For the method according to the invention, a physical model is used, which describes the influence on the polarization of measurement radiation by the components of the eye, particularly by the intraocular fluid and the cornea.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Immersive visualization center for creating and designing a total design simulation and for improved relationship management and market research
InactiveUS8321797B2MarketingInput/output processes for data processingCustomer relationship managementMock ups
Embodiments of the invention include methods, apparatuses, and articles of manufacture for generating and using virtual reality simulations to conduct market research and related activities. An immersive visualization center may be used to manage relationships with customers, choosers, shoppers, and users. The visualization center may allow customers (or other relevant parties) to interact with virtual representations of products or solutions in a virtual reality environment appropriate for the product. The immersive visualization center may also include a physical mock-up of the environment and or products simulated by the virtual reality simulation.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
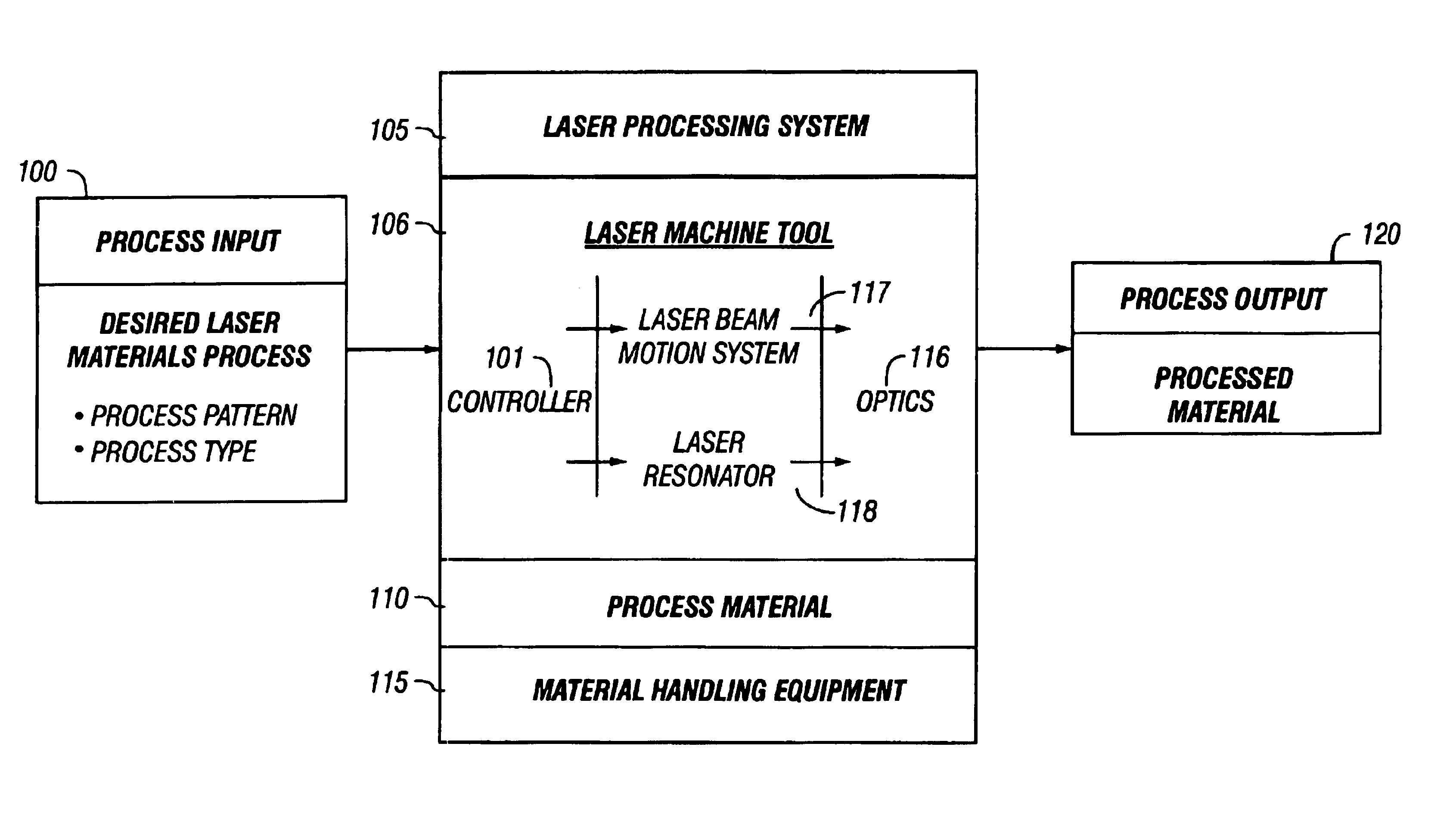
Controller for a laser using predictive models of materials processing
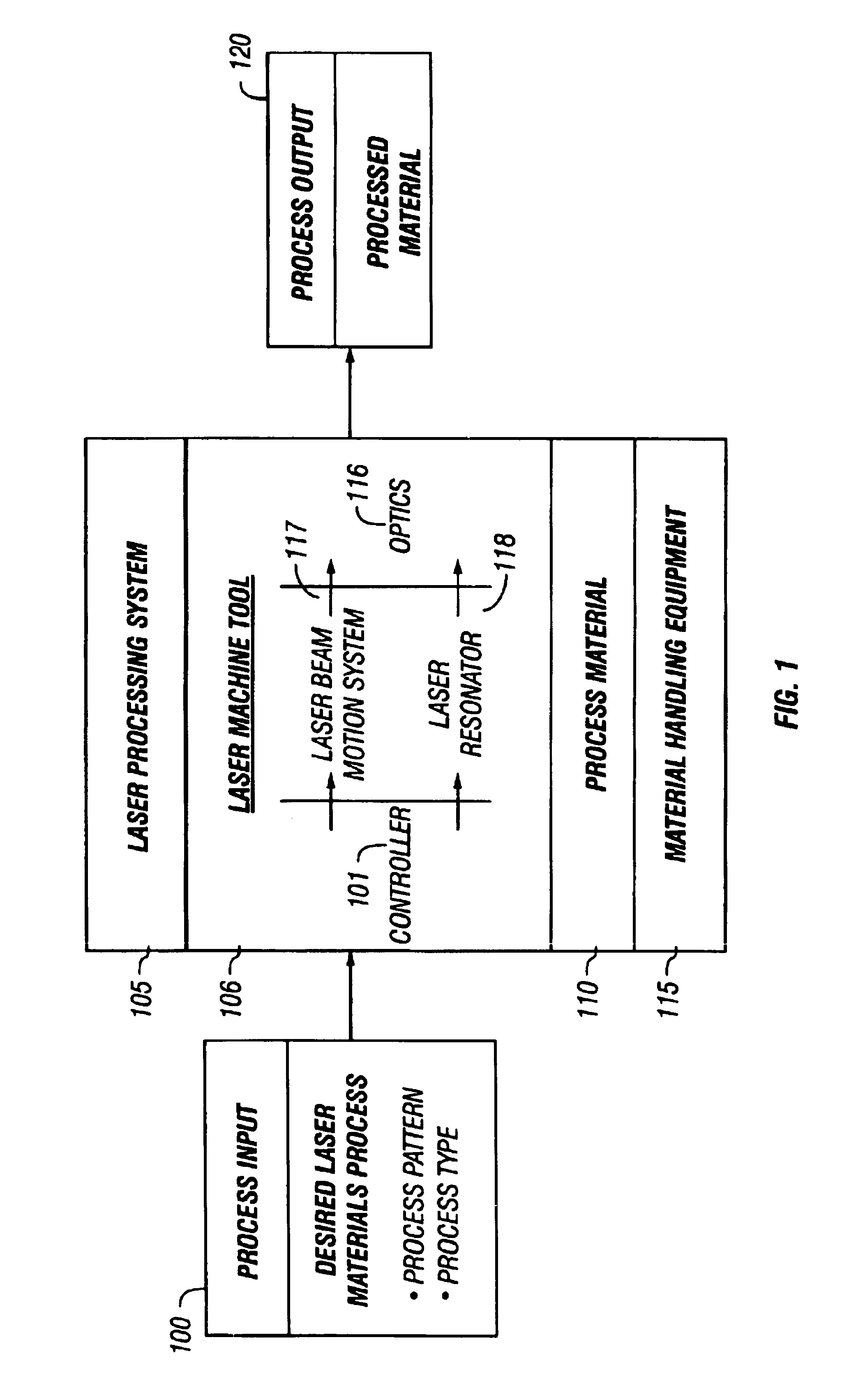
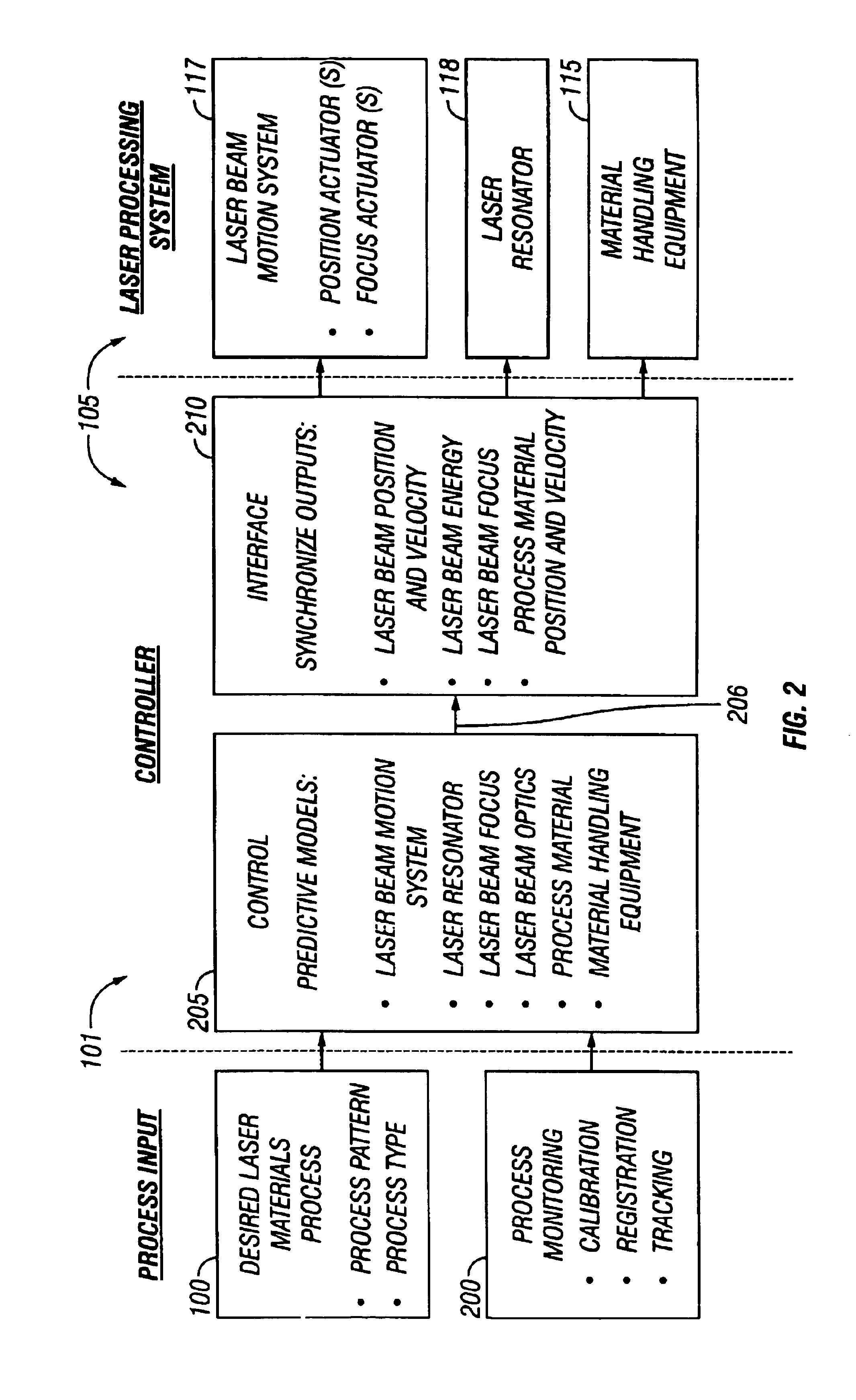
InactiveUS6850812B2Simulator controlSpecial data processing applicationsLaser processingControl signal
Predictive models of physical parts of the laser processing system part determined. These predictive models are used to determine how the physical system will actually react. The predicted reaction from the models is used as feedback in order to produce the control signals. These physical models therefore adjust to the operation of the system, much in the way that actual feedback would adjust the operation of the system. However, the system may be used at faster speeds, where the actual feedback could not be produced fast enough. Different kinds of modeling are described, including in-position feedback which models sharp movements of the laser system, trajectory models which superimpose the commanded curve over the predicted actual curve to determine errors in trajectory, and constant / variable energy density controls.
Owner:LASX INDS
Tooth preparation-based data flexible fusion method
ActiveCN103871097AMeet design needsImprove the internal organizational structureComputerised tomographsTomographyData acquisitionComputer-aided
The invention discloses a tooth preparation-based data flexible fusion method, and belongs to the field of CAD (computer aided design). The method comprises four steps: data collection and pretreatment; characteristic curve self-adaptive extractive technique; data pre-registration; data dynamic registration. According to the method, only simple man-machine interactive operation is included; the degree of automation is high; a fused model not only has high-precision surface information, but also has a perfect internal structure; due to complete information which truly reflects a physical model, efficiency and accuracy of subsequent design and manufacturing can be improved; the method has important application value in the field of CAD for the oral cavity.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
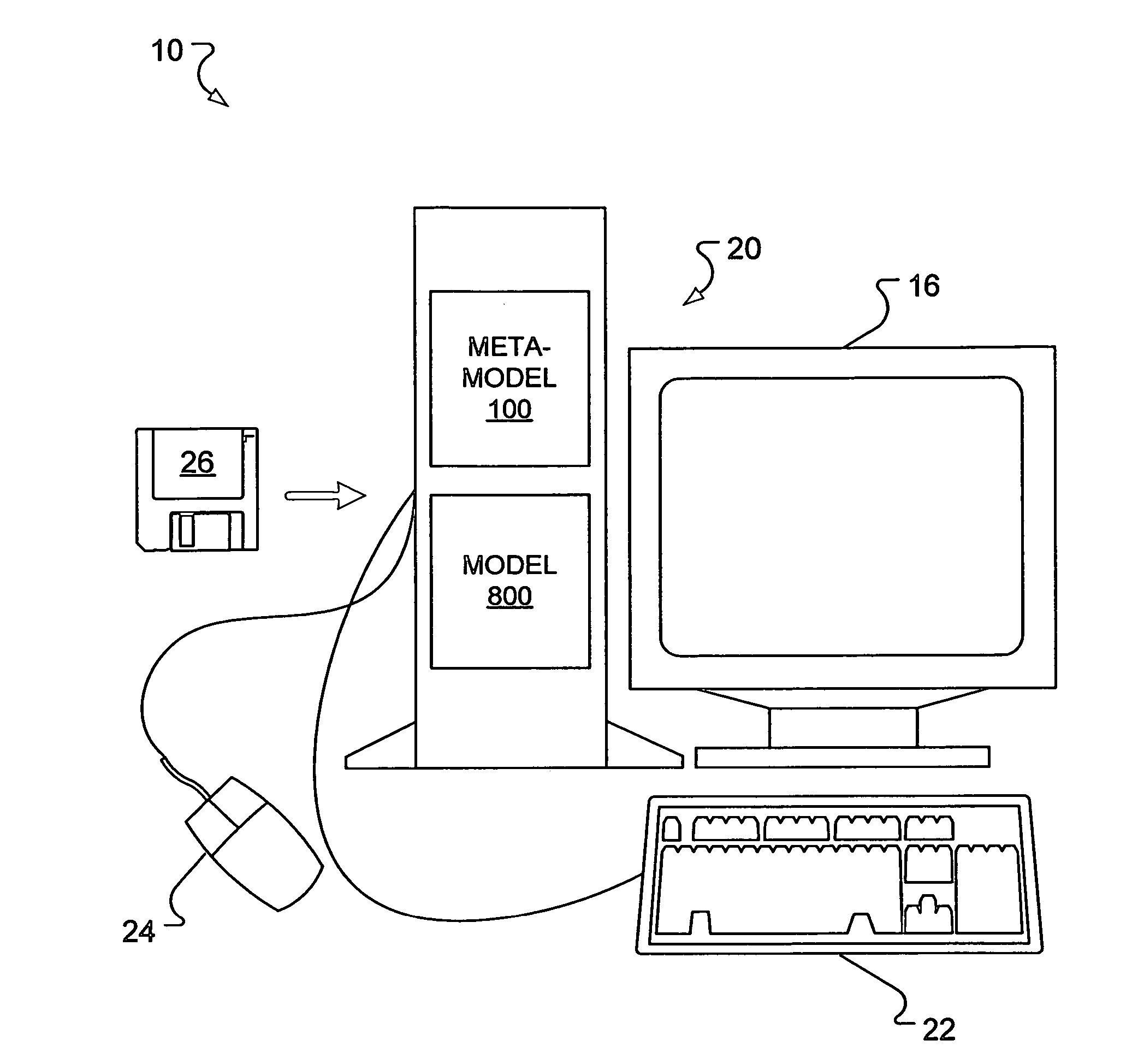
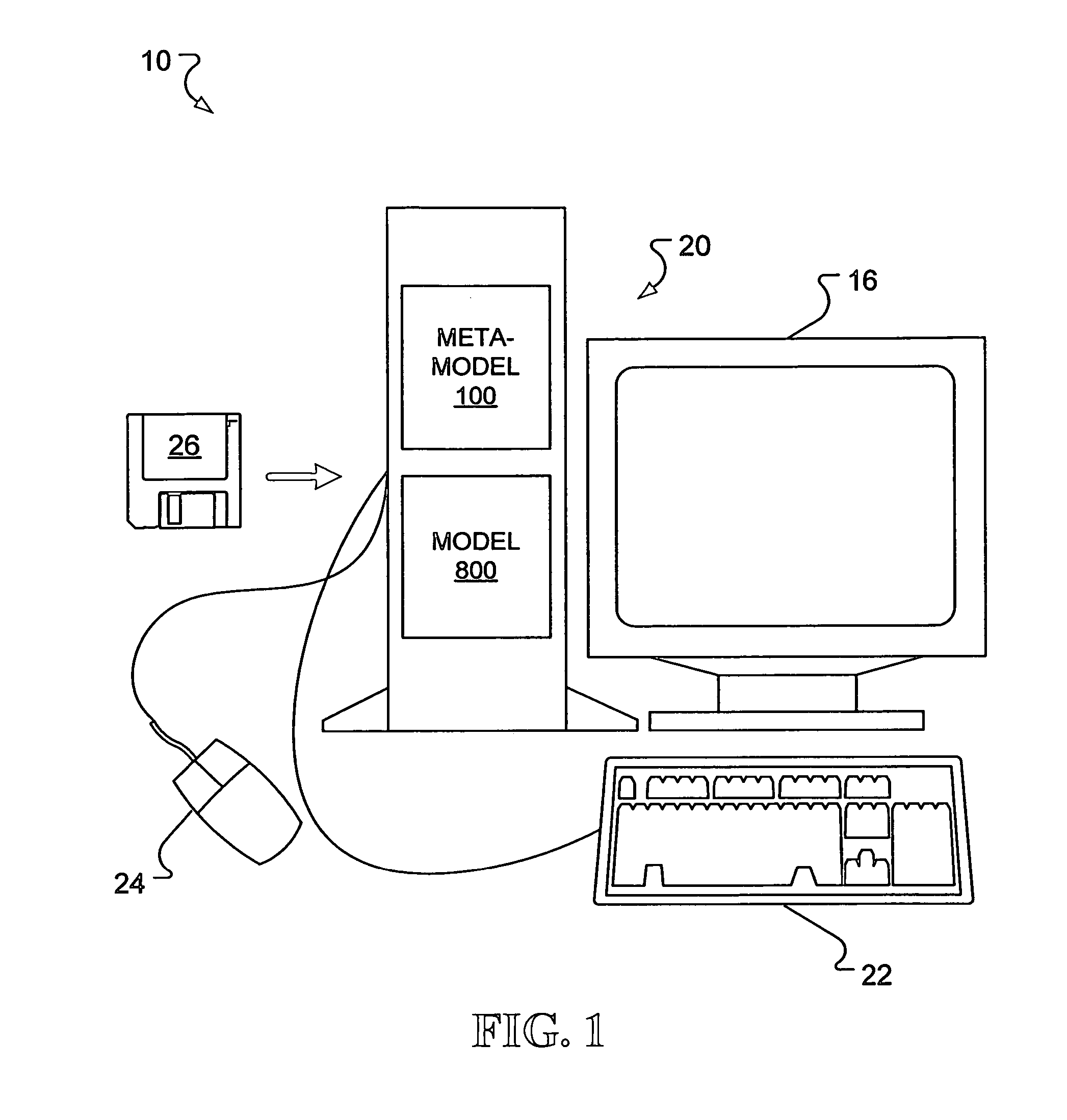
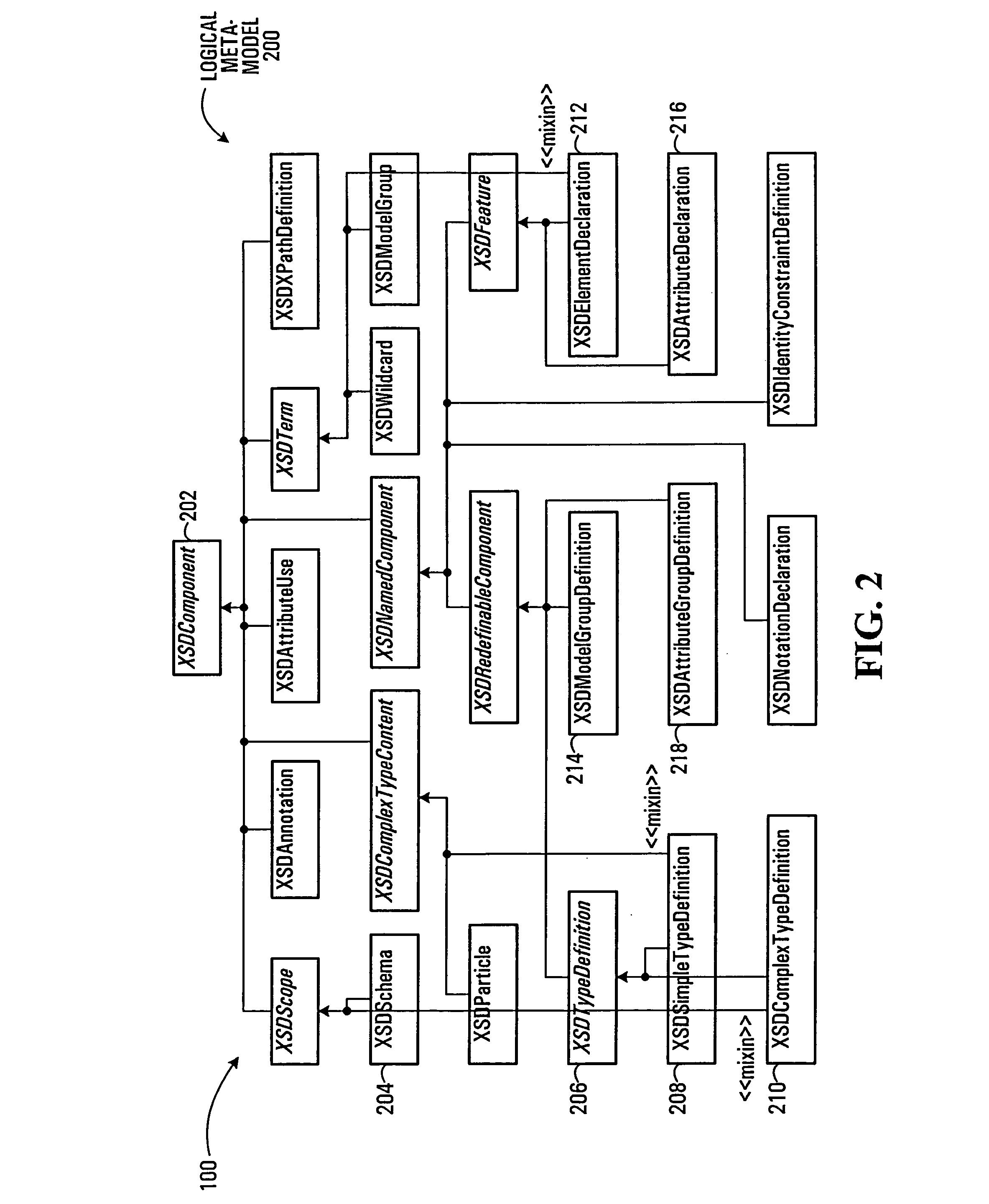
Meta-model for associating multiple physical representations of logically equivalent entities in messaging and other applications
ActiveUS7559052B2Reduce redundancyEfficient “sparse” modelsDigital data information retrievalSoftware engineeringXML schemaBase class
Owner:MAPLEBEAR INC
Experimental facility for simulating shield tunnel dynamically boring causing ground loss and surface subsidence
An experimental facility for simulating shield tunnel dynamically boring causing ground loss and surface subsidence includes a model case which is provided with a tunnel simulation mechanism and lifting regulating mechanisms. The model case is formed by splicing four lateral plates and a base plate, wherein through grooves are correspondingly formed on two lateral plates which are opposite to each other. The tunnel simulation mechanism is provided with a shield pipe and a tunnel pipe, the shield pipe is sleeved outside the tunnel pipe, and at least two sets of elastic support pieces are arranged between the shield pipe and the tunnel pipe in an axial direction of the pipes. Each of the through grooves is provided with a set of lifting regulating mechanism which includes lifting plates, wherein the lifting plates are attached firmly to the lateral plates of the model case on the positions of the through grooves and connected with a climbing mechanism or a lifting mechanism, through holes are formed on the position of the lifting plates, which is corresponding to the position of the shield pipe, and the tunnel simulation mechanism is arranged in the through holes and through grooves in a penetrating mode. The experimental facility for simulating shield tunnel dynamically boring causing ground loss and surface subsidence solves the problem in existing indoor physical modeling experiment method that the influence effect and influence rule of influence factors such as cutting depth and cutting diameter on ground displacement can not be considered.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
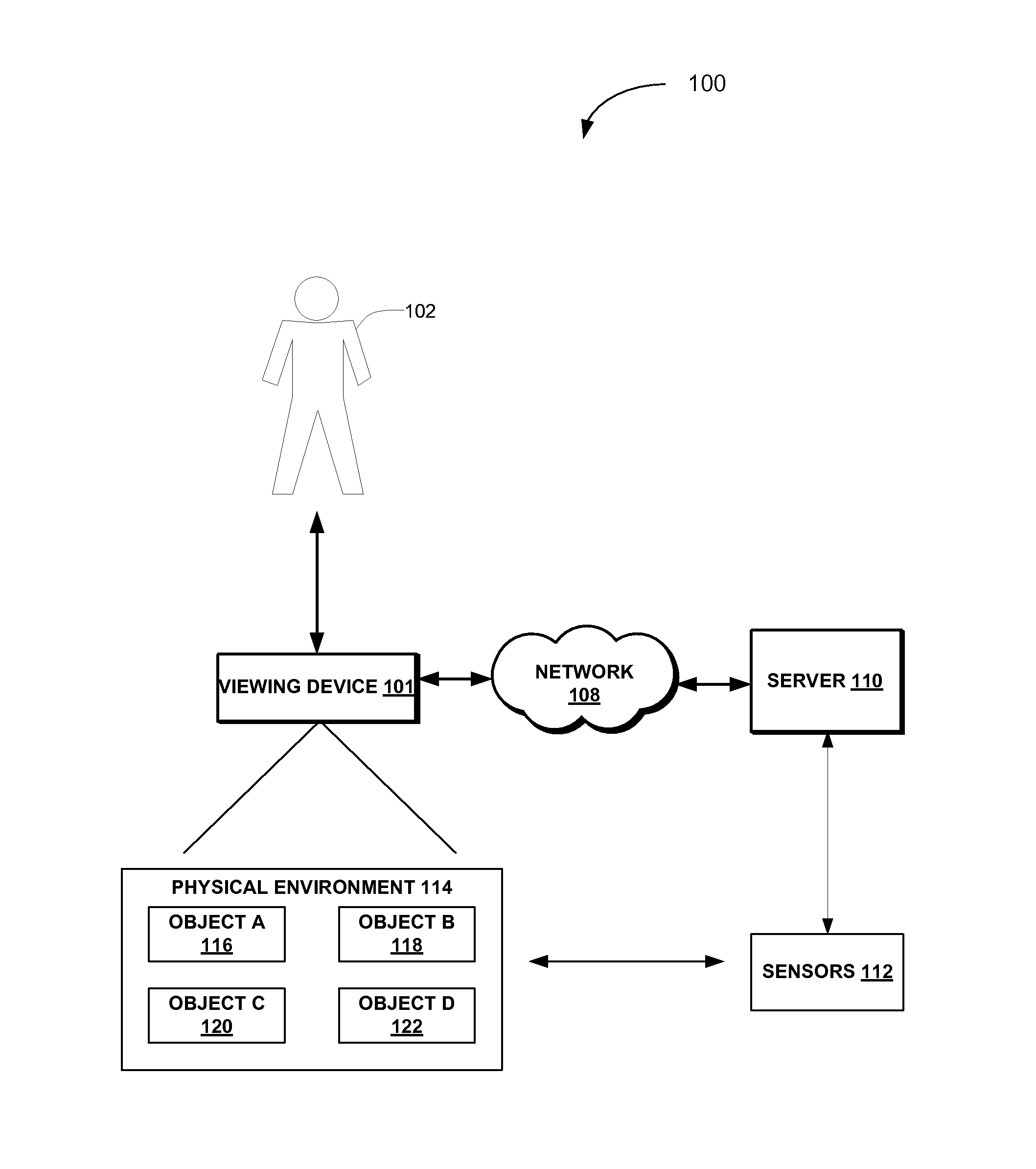
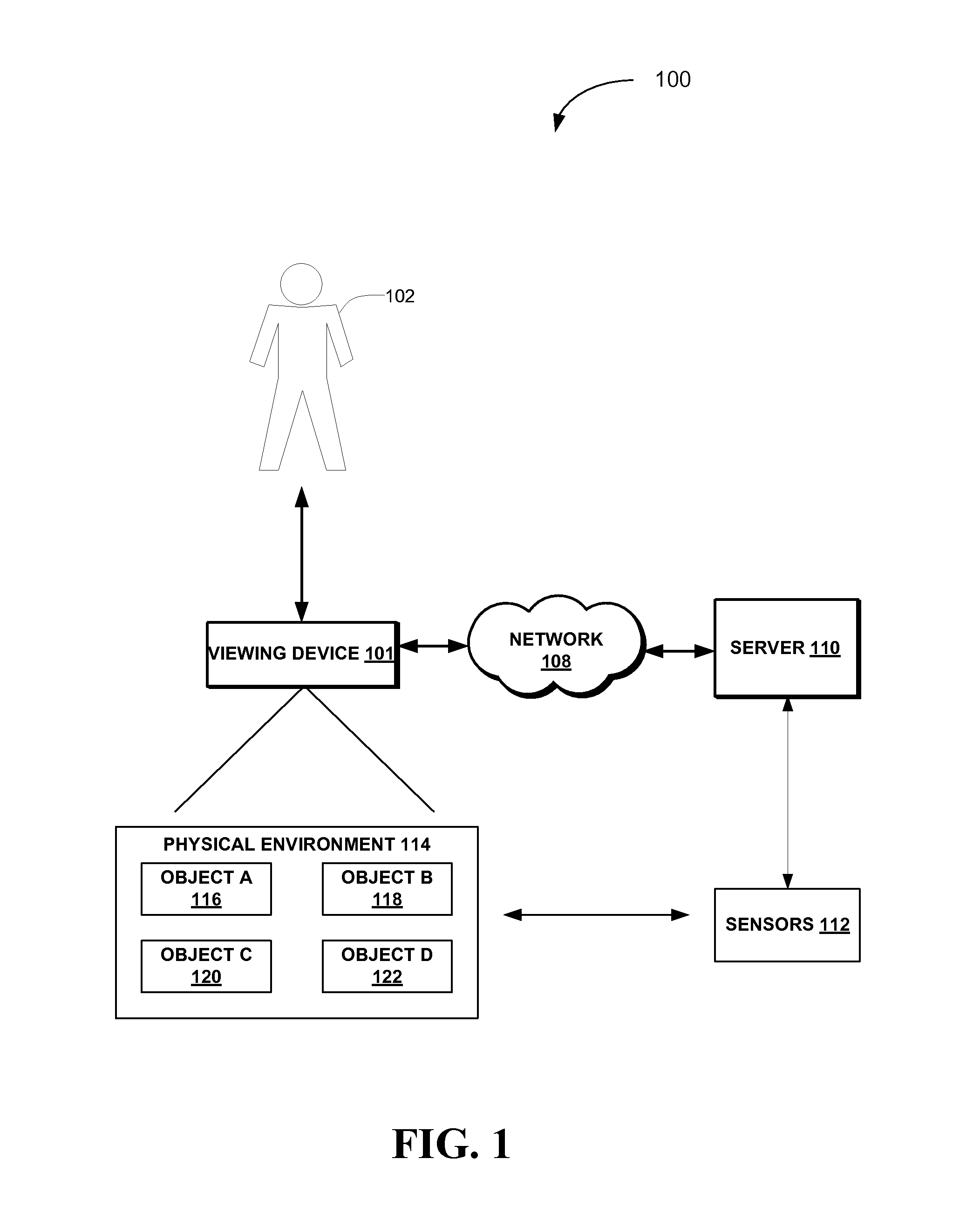
Visualization of physical interactions in augmented reality
A system and method for visualization of physical interactions are described. Objects in a scene are captured with a viewing device. Physical characteristics of the objects are computed using data from at least one sensor corresponding to the objects. A physics model of predicted interactions between the one or more objects is generated using the physical characteristics of the objects. An interaction visualization is generated based on the physics model of the predicted interactions between the one or more objects. An image of the one or more objects is augmented with the interaction visualization in a display of the viewing device.
Owner:META PLATFORMS TECH LLC
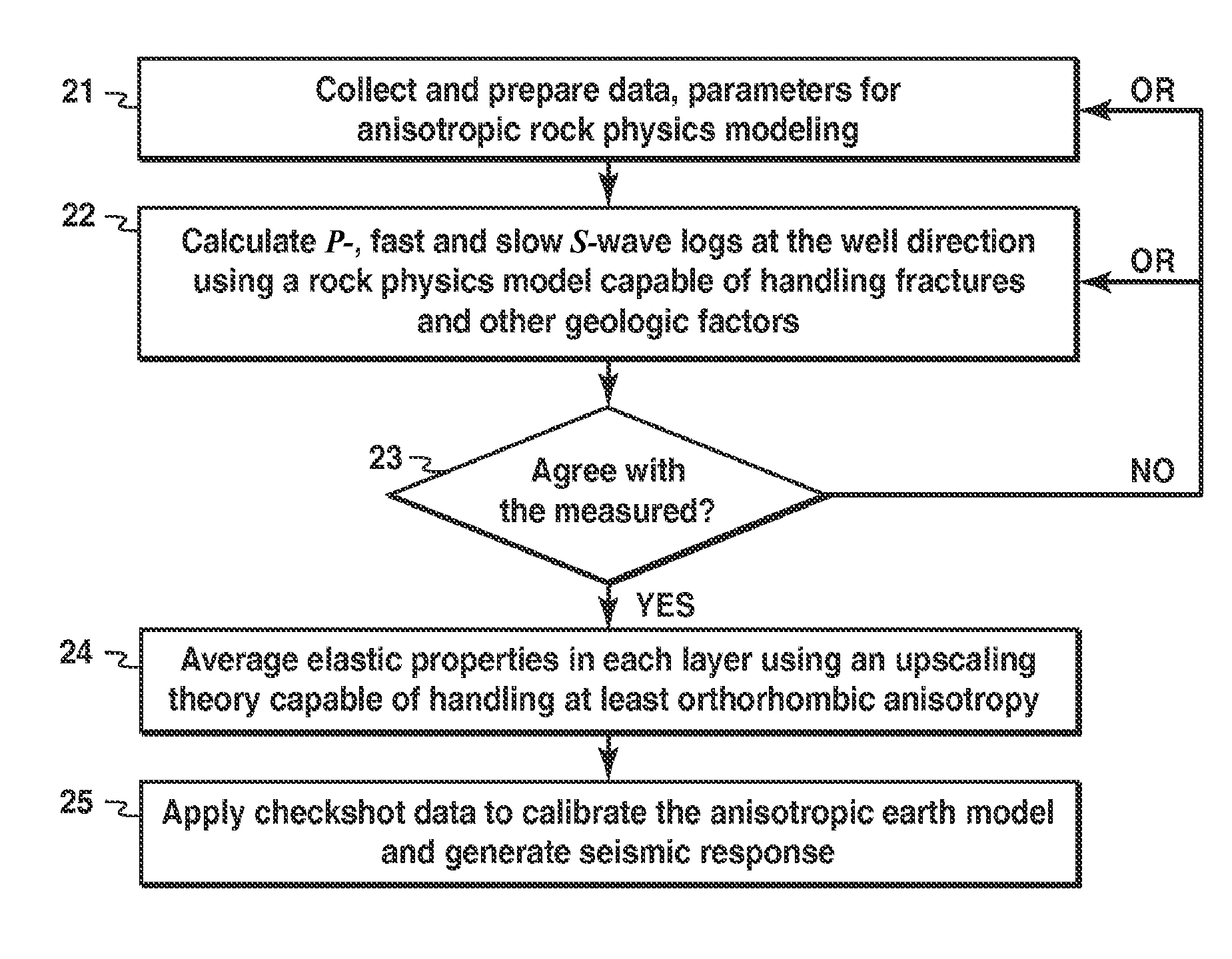
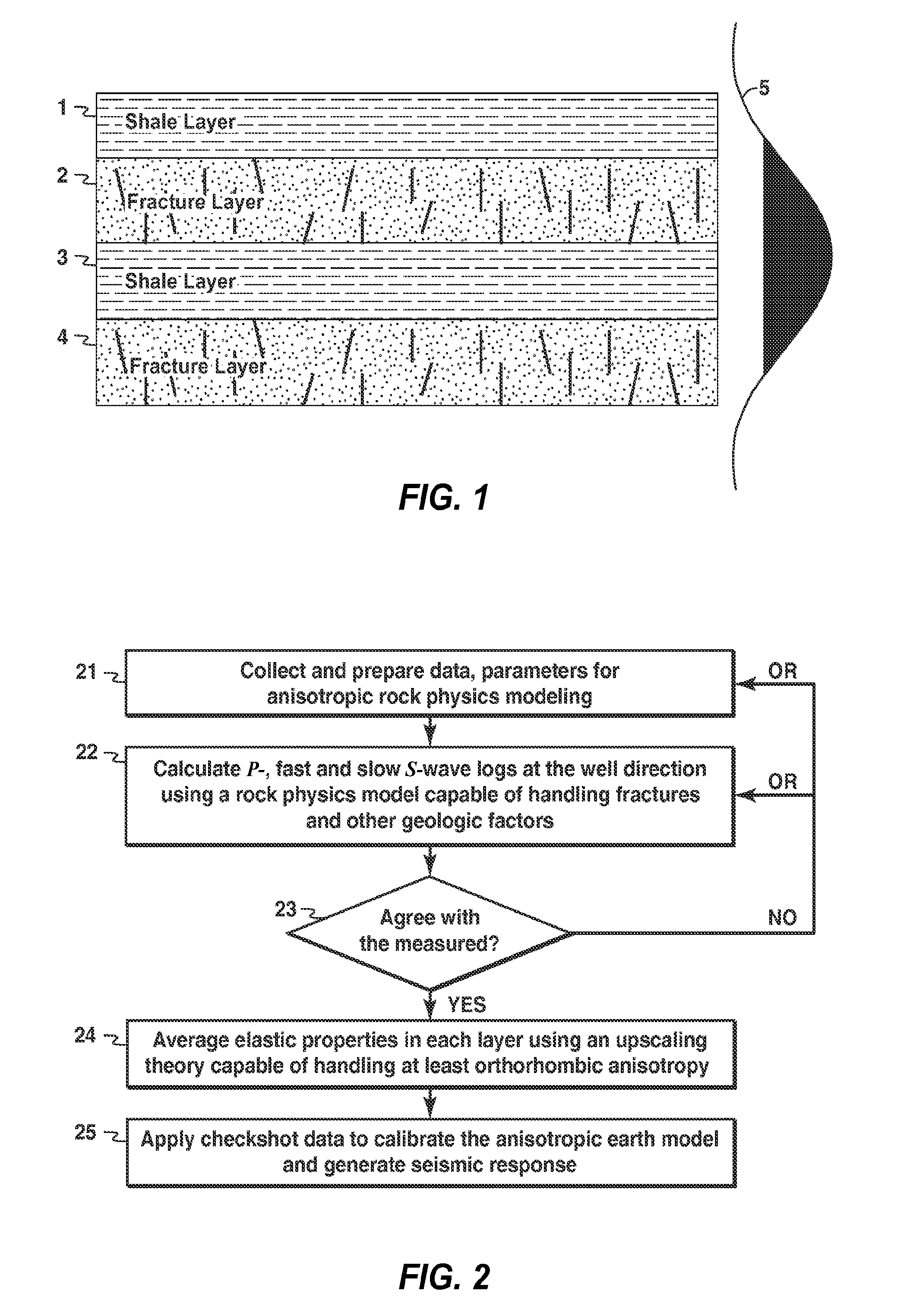
Rock physics model for simulating seismic response in layered fractured rocks
ActiveUS8184502B2Computation using non-denominational number representationAnalogue computers for heat flowS-waveIterative method
Method for modeling anisotropic elastic properties of a subsurface region comprising mixed fractured rocks and other geological bodies. P-wave and fast and slow S-wave logs are obtained, and an anisotropic rock physics model of the subsurface region is developed (21). P- and fast and slow S-wave logs at the well direction are calculated using a rock physics model capable of handling fractures and other geological factors (22). Calculated values are compared to measured values in an iterative model updating process (23). An upscaled ID model is developed by averaging elastic properties in each layer using an upscaling theory capable of handling at least orthorhombic anisotropy (24). The ID model may be used to generate synthetic seismic response for well ties or AVO modeling (25). Further, a method is disclosed for estimating anisotropy parameters from P- and fast / slow S-wave logs from one or more deviated wells.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
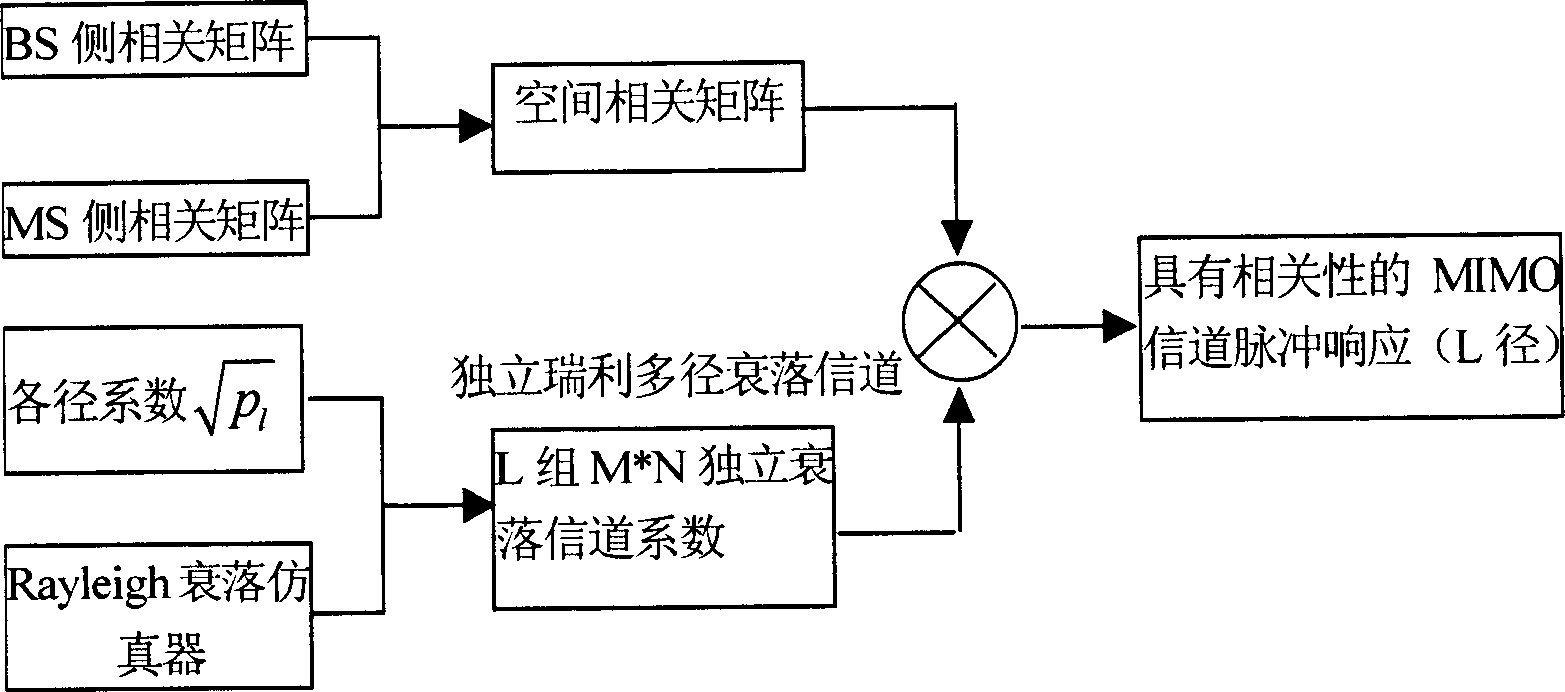
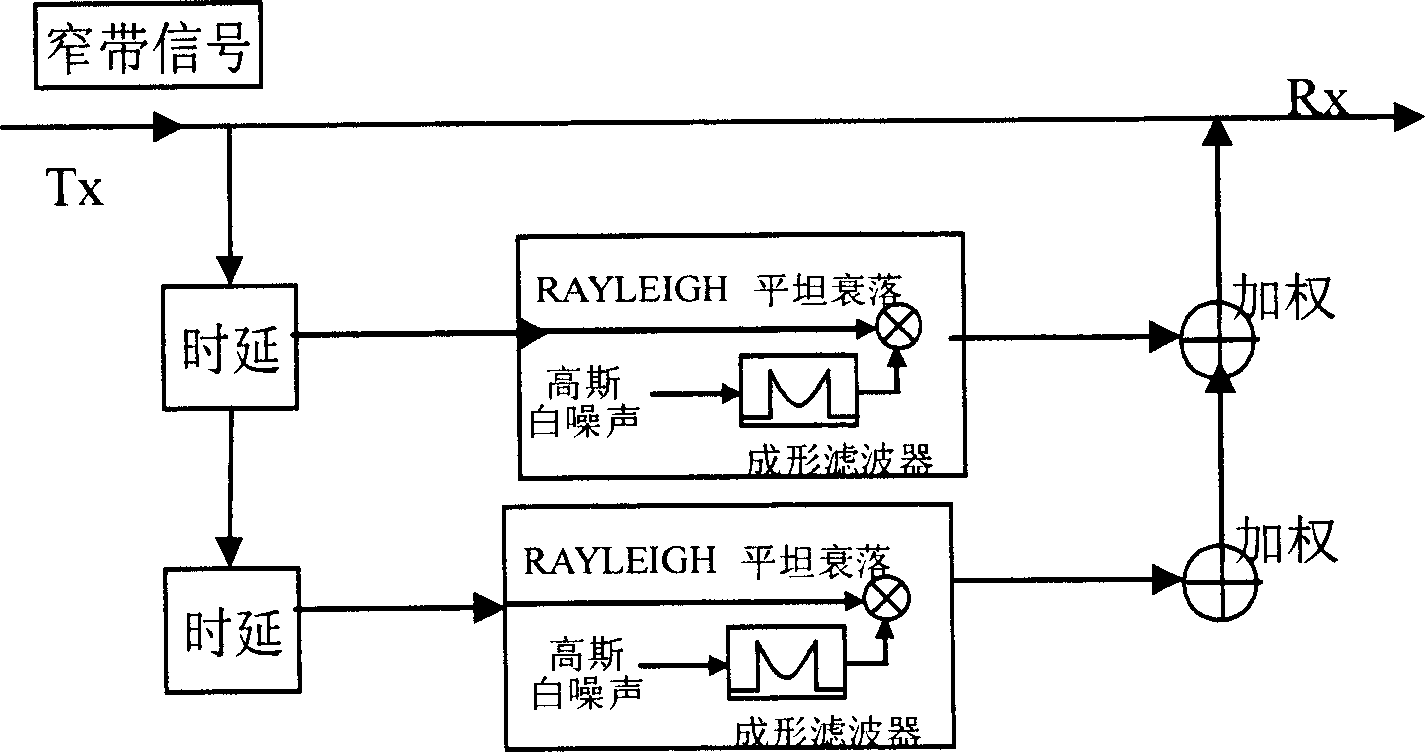
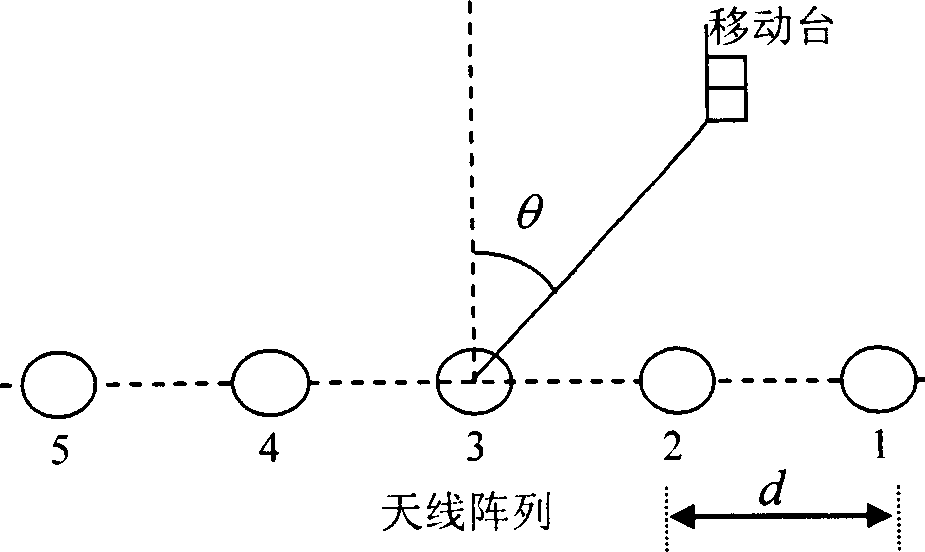
Non-physical modeling and emulation method for channels in multi-input and multi-output communication system
InactiveCN1808949AFully embodies the characteristics of spaceReflect the characteristics of spaceSpatial transmit diversityTransmission monitoringMulti inputSpatial correlation
This invention relates to multiple input and output communication system signal one non-physical module establishing and artificial method, which comprises the following steps: Firstly establishing multiple input and output communication system non-physical relative matrix; then generating independent multiple path declining channel; then valuating the generated independent declining parameters; finally computing space relative matrix and using third partner plan to give angle power spectrum intensity form to get space relative parameters and to use MIMO system channel non-physical module formula to get the channel space relative matrix.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for correcting brain tissue deformation in navigation system of neurosurgery
InactiveCN1582863AEffective correctionEasy to implementDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsBiomechanicsData field
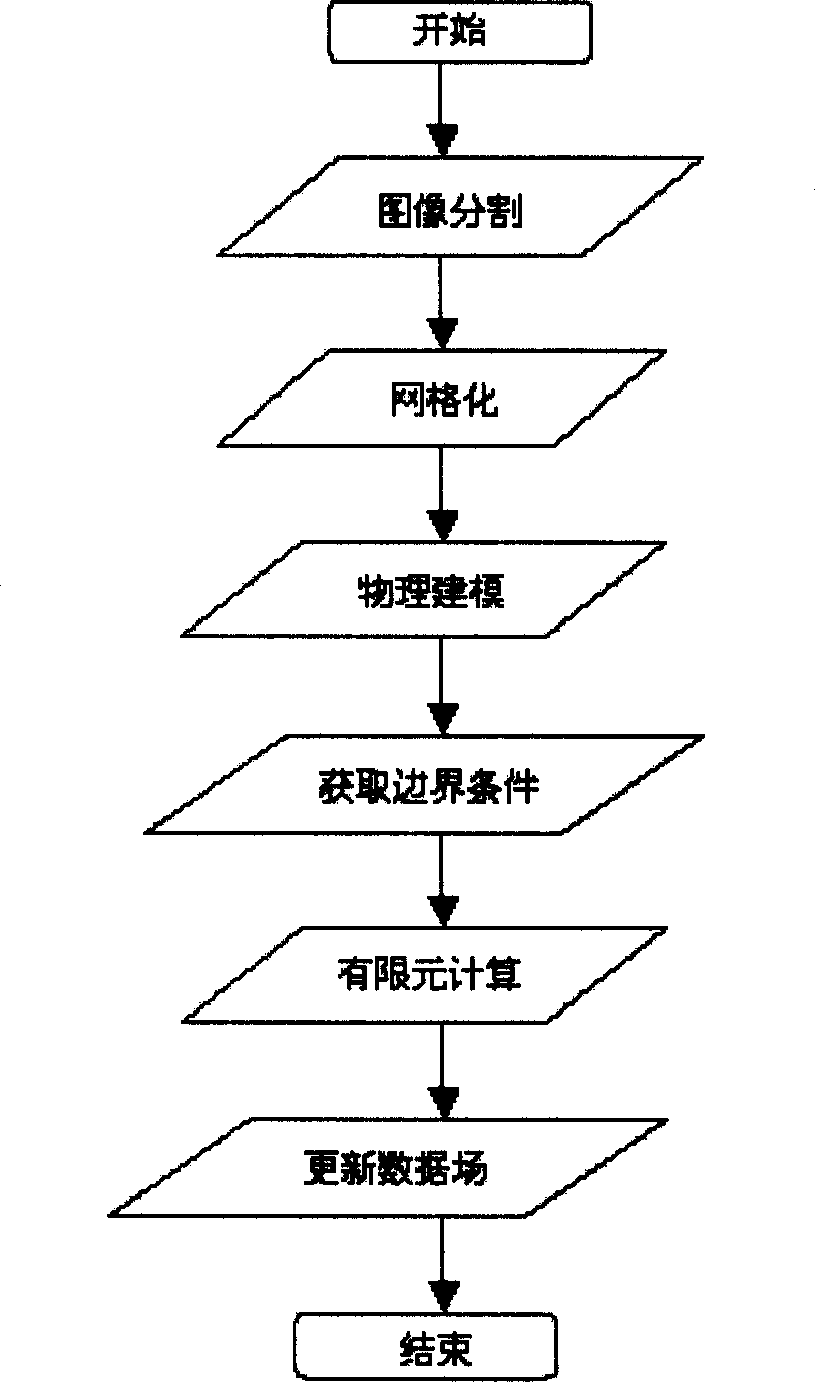
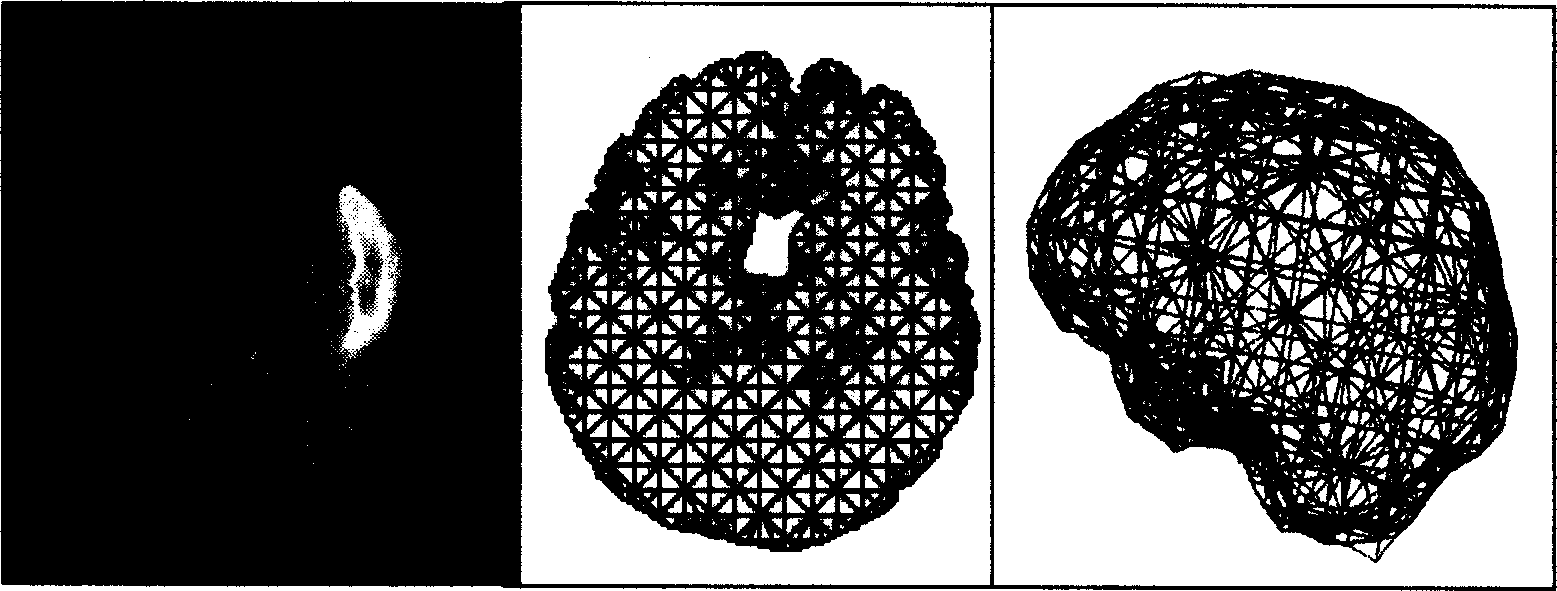
A method for correcting the deformation of cerebral tissue in the navigation system of neurosurgical operation includes such steps as obtaining target tissue (cerebral tissue) by 3D automatic division algorithm based on MRI, generating the lattice of cerebral tissue, assigning the relative biomechanical attribute to each lattice unit, creating physical mode, tracking the movement of exposed cerebral cortex layer, finit element calculating to obtain the deformation for cerebral tissue, and updating the 3D data field before operation by an algorithm to direct the operation.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Electronic product reliability simulation test method based on physics of failure
InactiveCN104462700AExposing design flawsShorten the timeSpecial data processing applicationsStressed statePhysical modelling
The invention belongs to electronic product reliability test technology, and relates to an electronic product reliability simulation test method based on physics of failure. The method is characterized by including the following steps: constructing a digital prototype model; analyzing thermal stress state and vibration stress state under the loading condition; analyzing potential failure; determining a physics-of-failure model; performing thermal stress damage analysis and vibration stress damage analysis; performing electronic product reliability assessment. By the method, design defects of electronic products can be revealed as soon as possible, time for electronic product reliability test is reduced, efficiency of reliability test is increased, and accordingly development cycle of the electronic products is shortened, and development cost of the electronic products is lowered.
Owner:CHINA AERO POLYTECH ESTAB
Automatic checking method for change influence degree of model
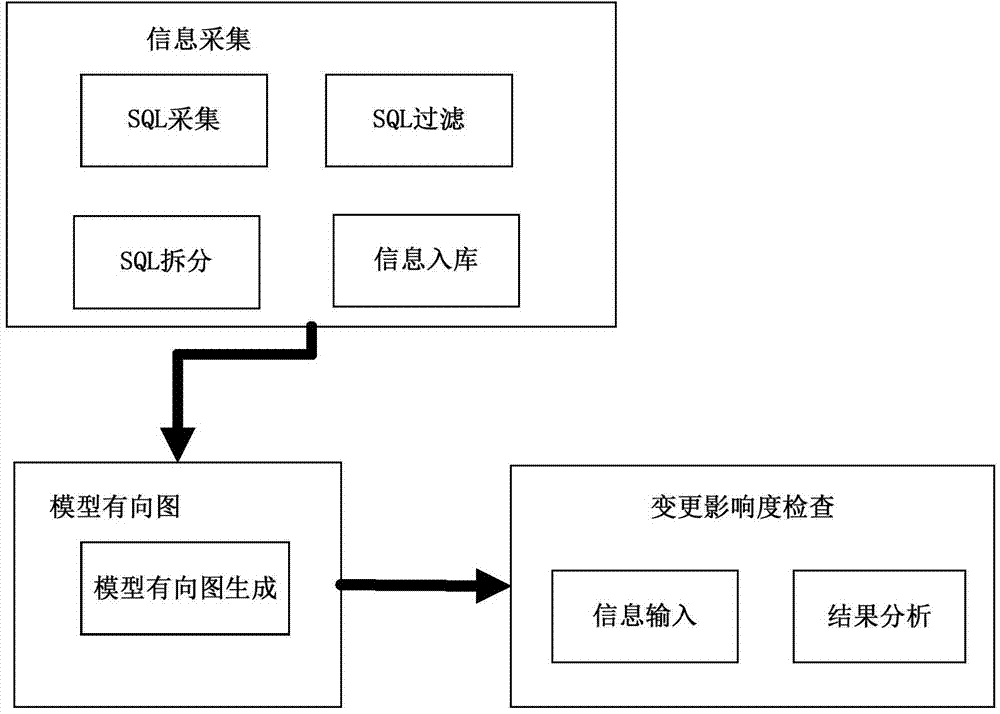
ActiveCN104750496AComprehensive riskImprove intuitivenessSpecific program execution arrangementsSoftware systemPhysical modelling
The invention discloses an automatic checking method for change influence degree of a model. The automatic checking method comprises the following steps: a), collecting and analyzing SQL (structured query language) sentences performed by a database, and recording correlation between tables in the database; b) generating a correlation base line of a system data model to obtain a constrained graph of a system physical model, generating a physical model digraph according to the system service flow, and constructing a data model-service functional diagraph; c) when the software system has model changes, inputting the corresponding change information, and distinguishing the change influence range and the service functions according to the digraph and the functional digraph. According to the automatic checking method for change influence degree of the model disclosed by the invention, the SQL information of the database is collected, the model digraph is generated, the software change influence degree is analyzed from the software system physical model, the change influence range and the service function pots of the model are intelligently judged, and the risk and design defects are distinguished in advance, so that the intuition, the sufficiency and the efficiency of the change influence degree analysis are improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI SNC NET INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
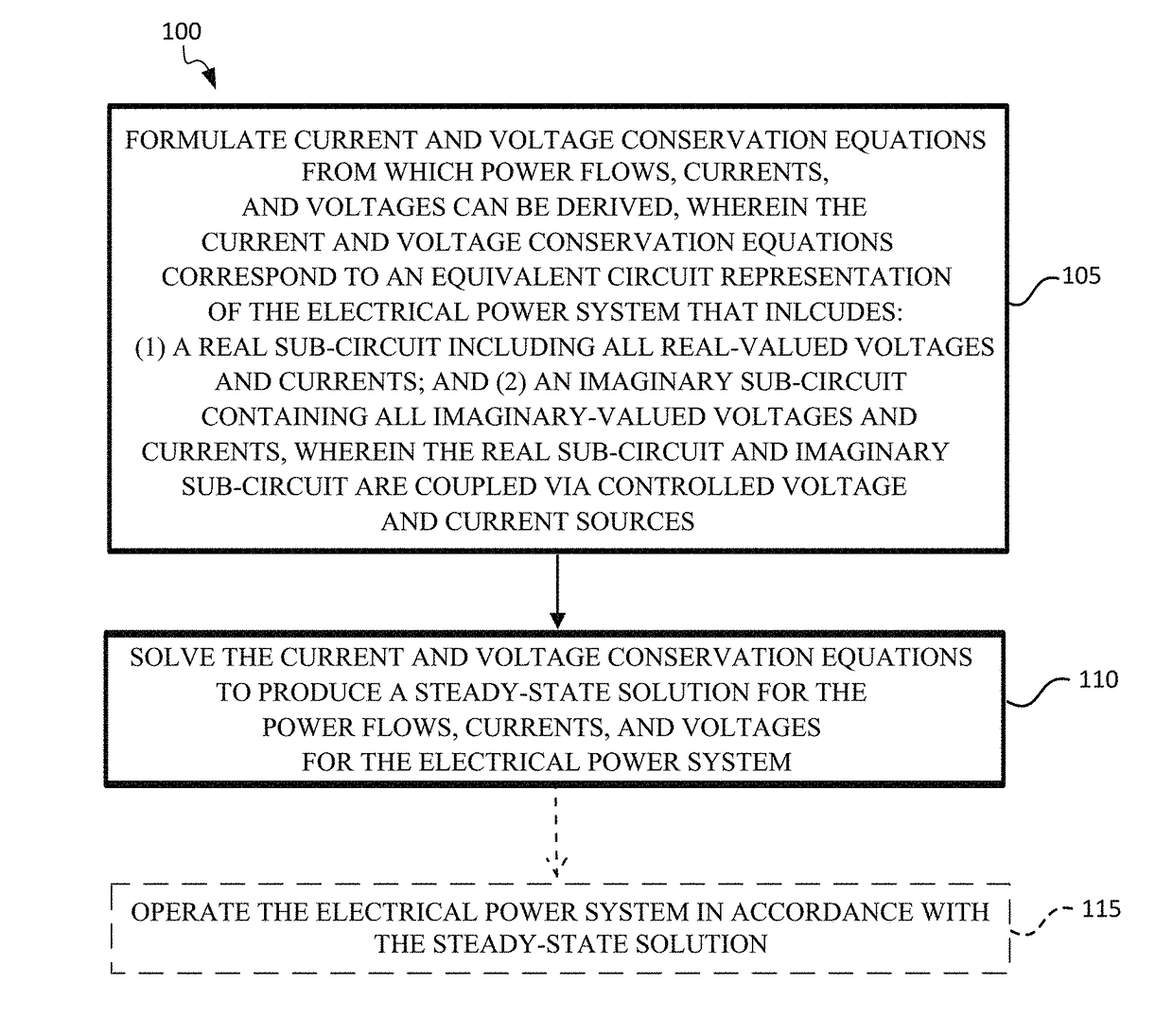
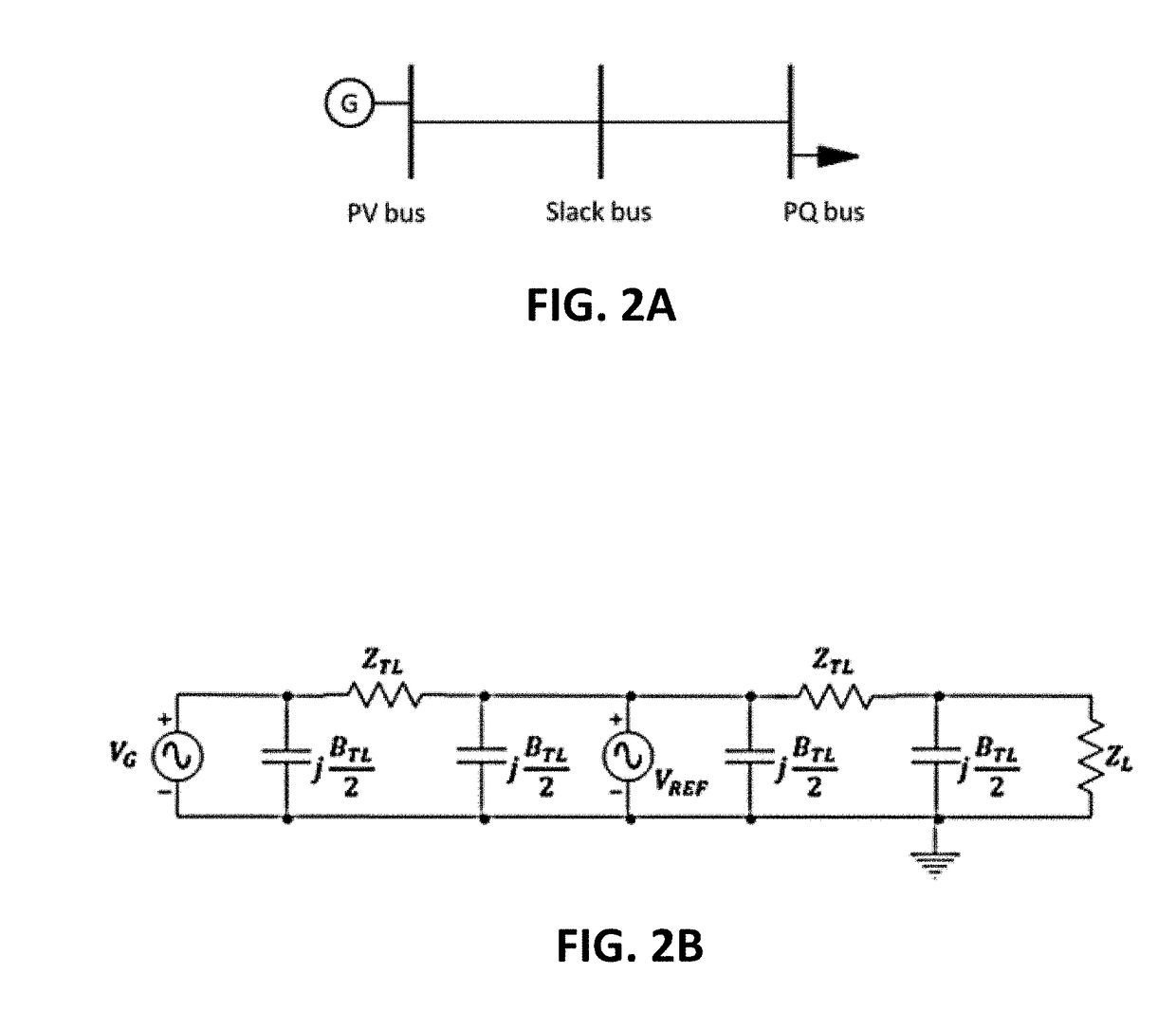
Systems, Methods, and Software for Planning, Simulating, and Operating Electrical Power Systems
InactiveUS20170184640A1Single network parallel feeding arrangementsWind energy generationOperant conditioningPhysical modelling
An approach to modeling the nonlinear steady-state behavior of an electrical power grid in terms of equivalent circuits with currents and voltages as state variables is provided. Current and voltage conservation equations are formulated with circuit-theoretic algorithms that offer demonstrably superior robustness relative to traditional approaches. Generalized bus and line models are accommodated by the equivalent circuit-based approach, allowing for simulation of physical models not compatible with traditional methods. Unbalanced three-phase systems are handled without loss of generality. The provided methods allow for robust, efficient power flow simulation for contingency analysis, power system planning, power system design, power system control, component configurations and operating conditions, real-time scheduling, and optimization, among other applications.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
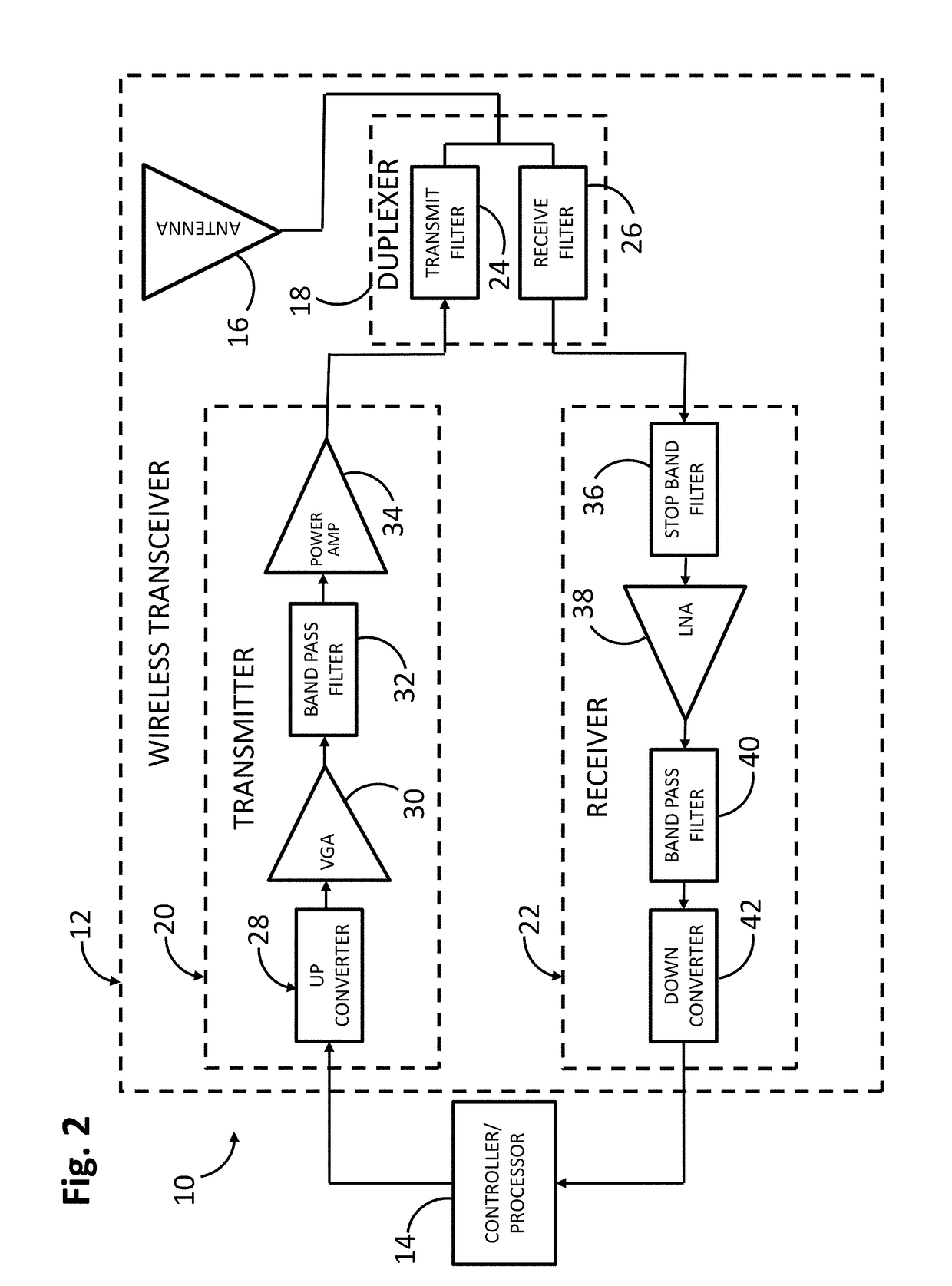
Hierarchical cascading in two-dimensional finite element method simulation of acoustic wave filter devices
A method of analyzing a microwave acoustic wave (AW) structure comprises defining a physical model of the AW structure, partitioning the physical model into a plurality of unit blocks, identifying at least one core block within the plurality of original unit blocks, computing characteristics of each of the at least one core block, deriving characteristics for each of the original unit blocks from the computed characteristics of the core block(s), combining the original unit blocks into a single block having computed characteristics derived from the characteristics of the unit blocks, such that the single block subsumes the plurality of original unit blocks, and deriving at least one electrical response of the physical model at least partially from the computed characteristics of the single block.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
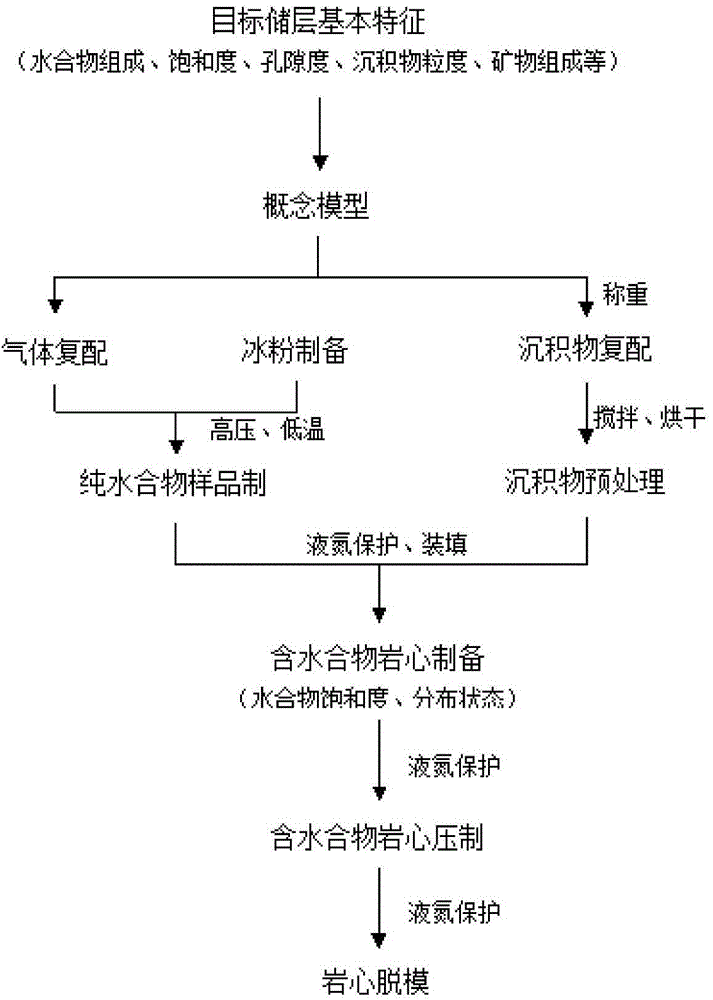
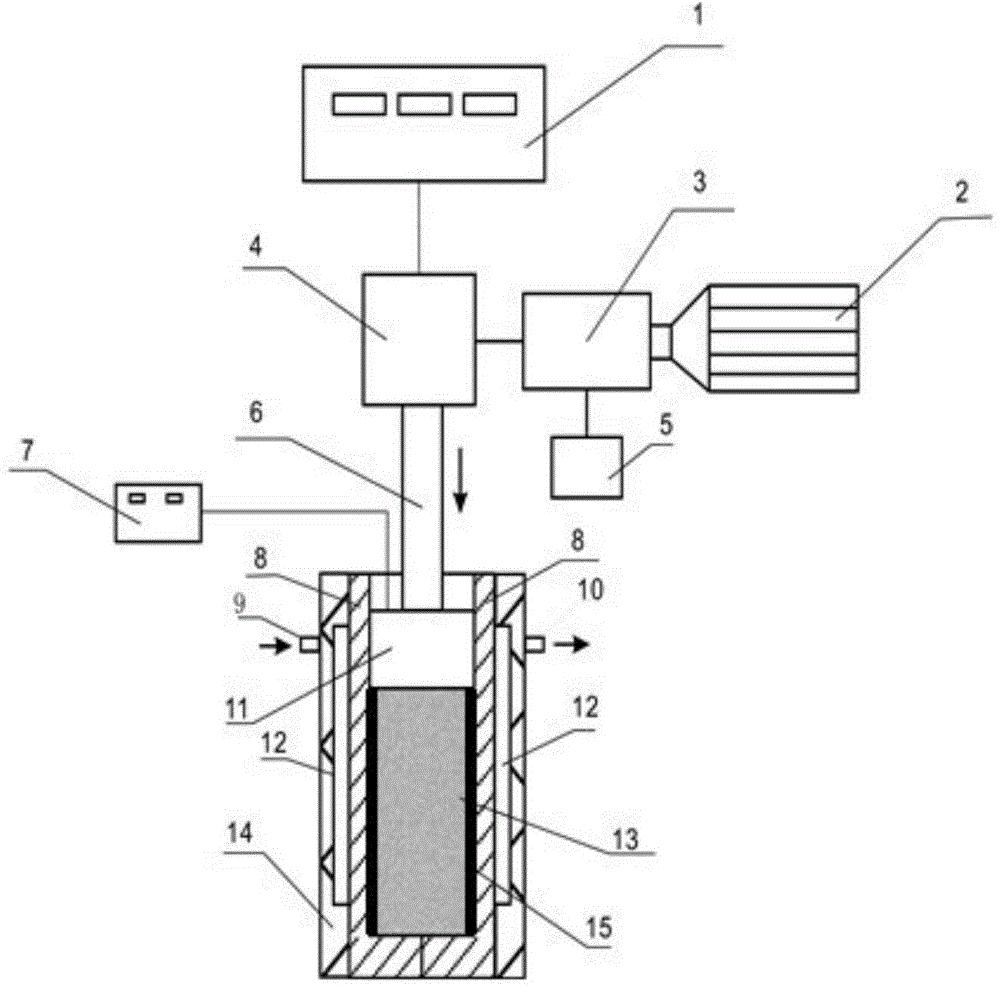
Pressing method for methane hydrate containing rock core sample
ActiveCN104949870AThe basic characteristics are the samePreparing sample for investigationRock corePre treatment
The invention discloses a pressing method for a methane hydrate containing rock core sample. The pressing method comprises the following steps: firstly, confirming the basic characteristics of an actual physical model; secondly, carrying out sediment compounding; thirdly, carrying out sediment pretreatment; fourthly, stirring and mixing a hydrate and the compound and pretreated sediment at low temperature; fifthly, manually pressing a rock core; finally, demoulding the pressed iron core. The pressing method has the benefit of better ensuring that the basic characteristics of the pressed methane hydrate containing rock core sample are basically consistent with those of a target reservoir.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF MARINE GEOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com