Patents
Literature
72results about "Offset printing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
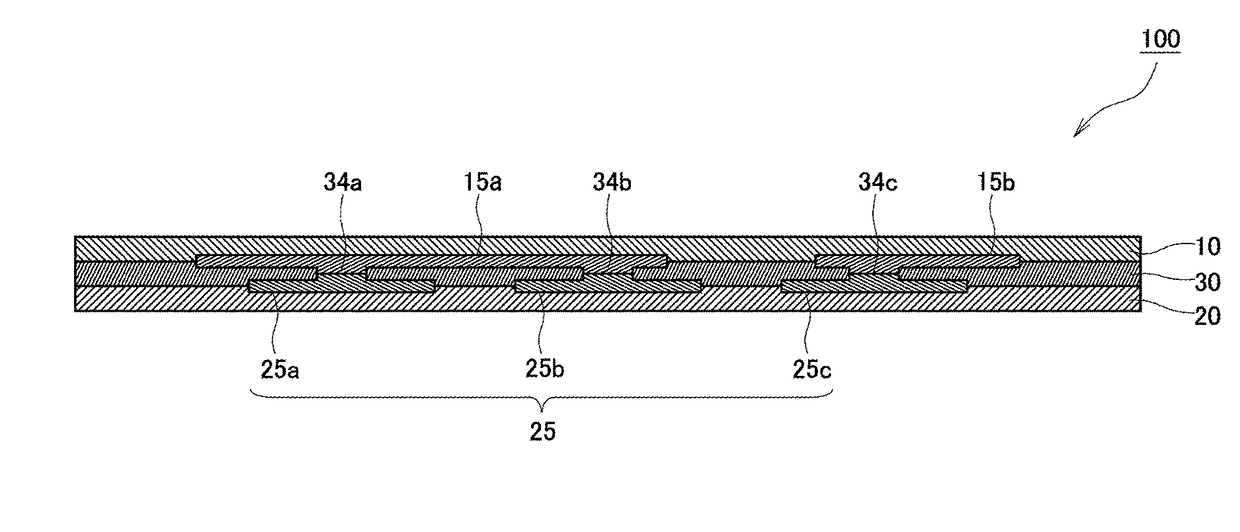
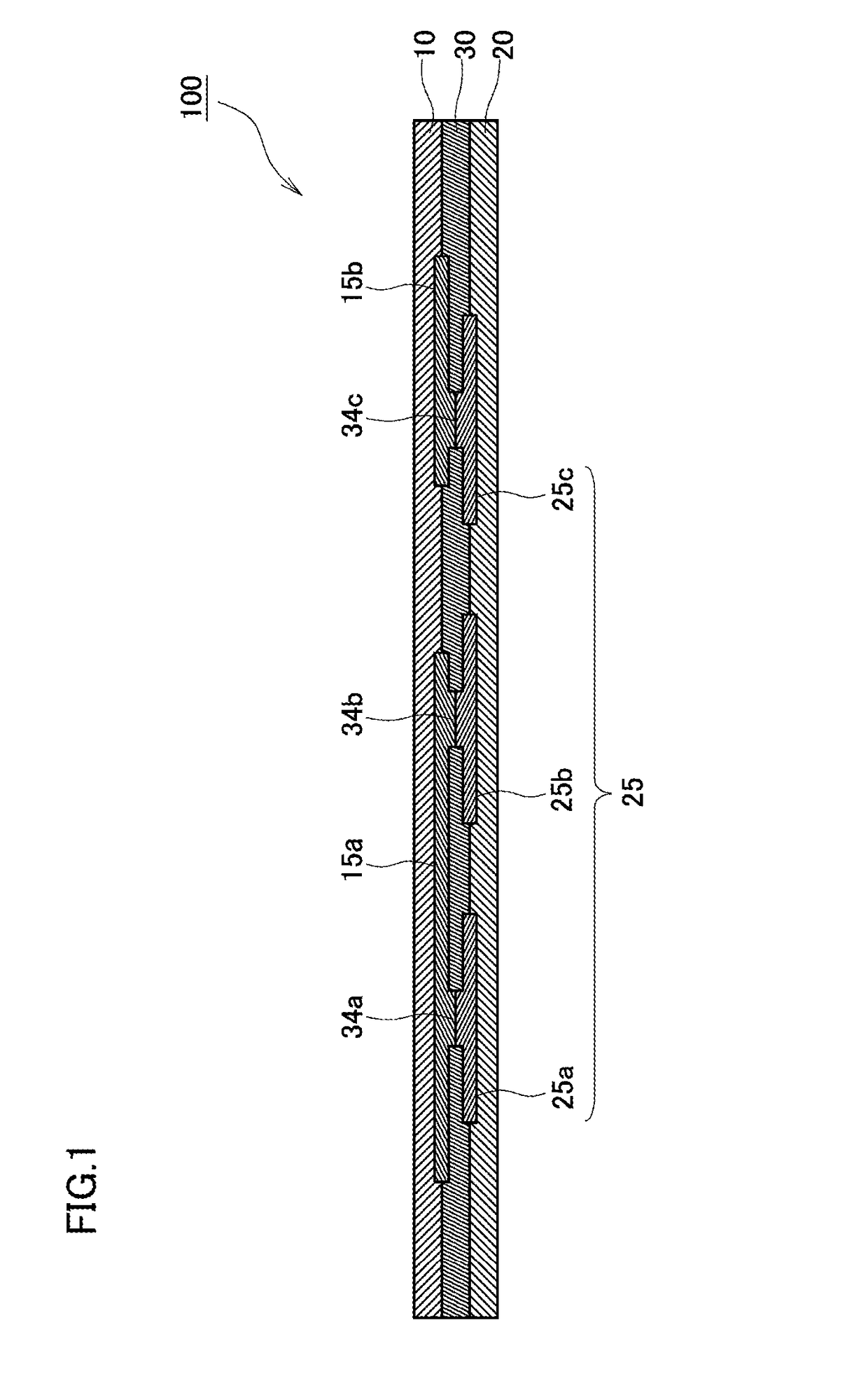
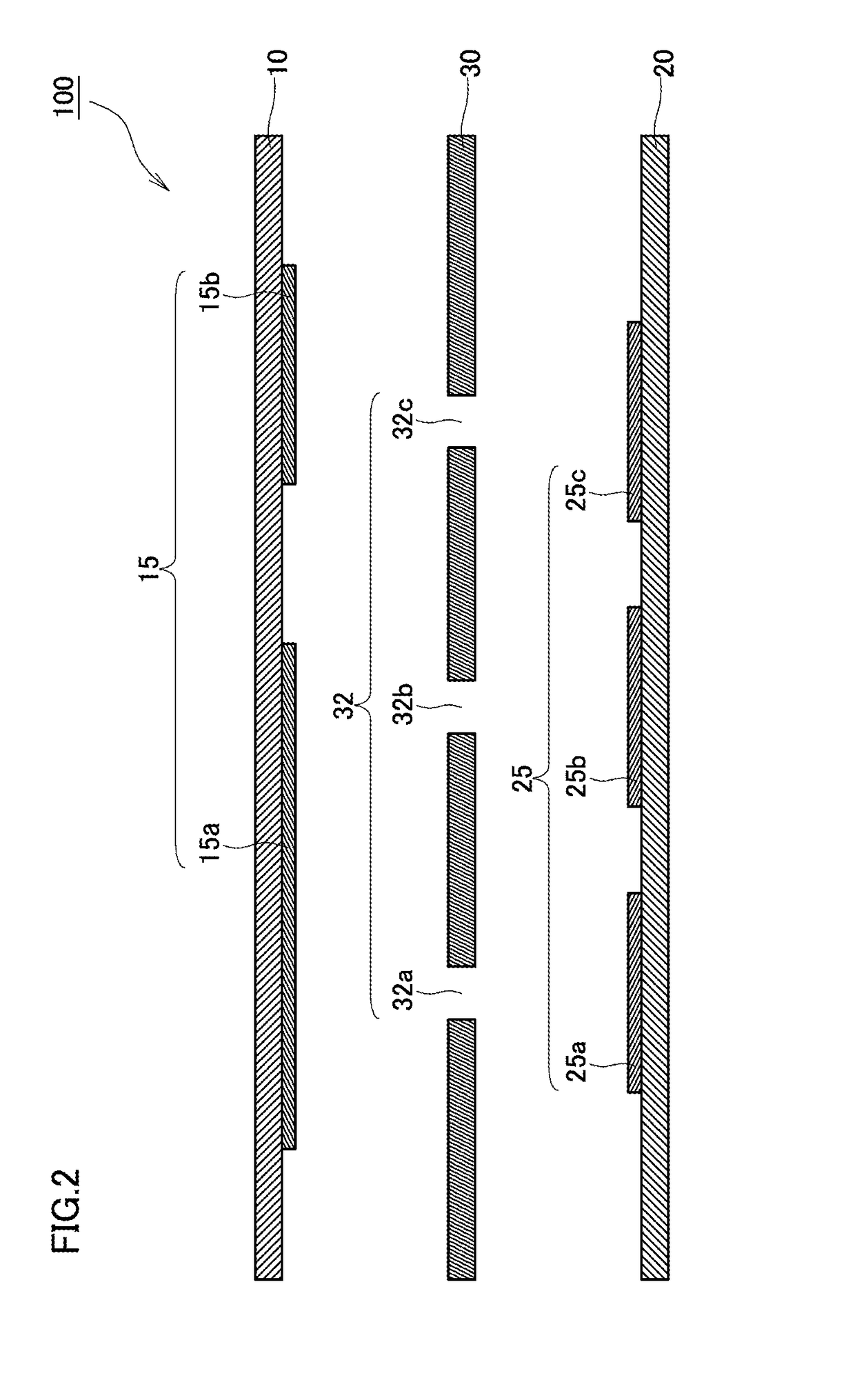
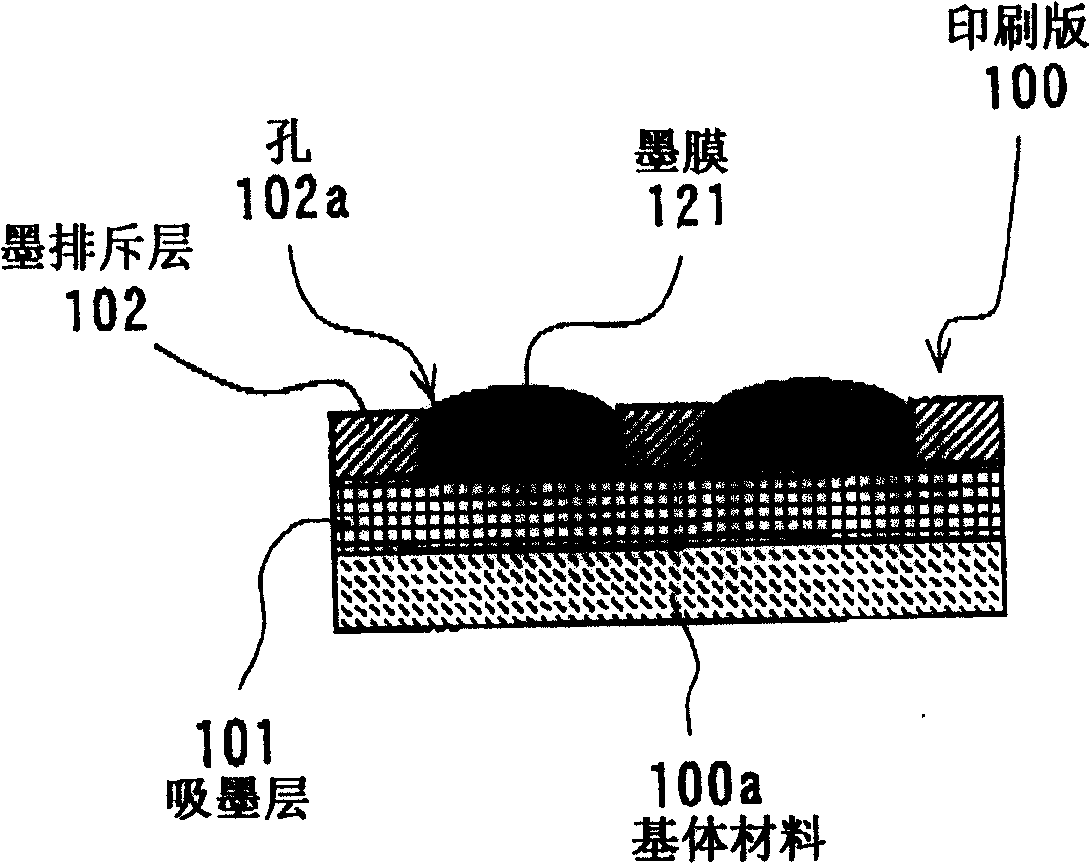
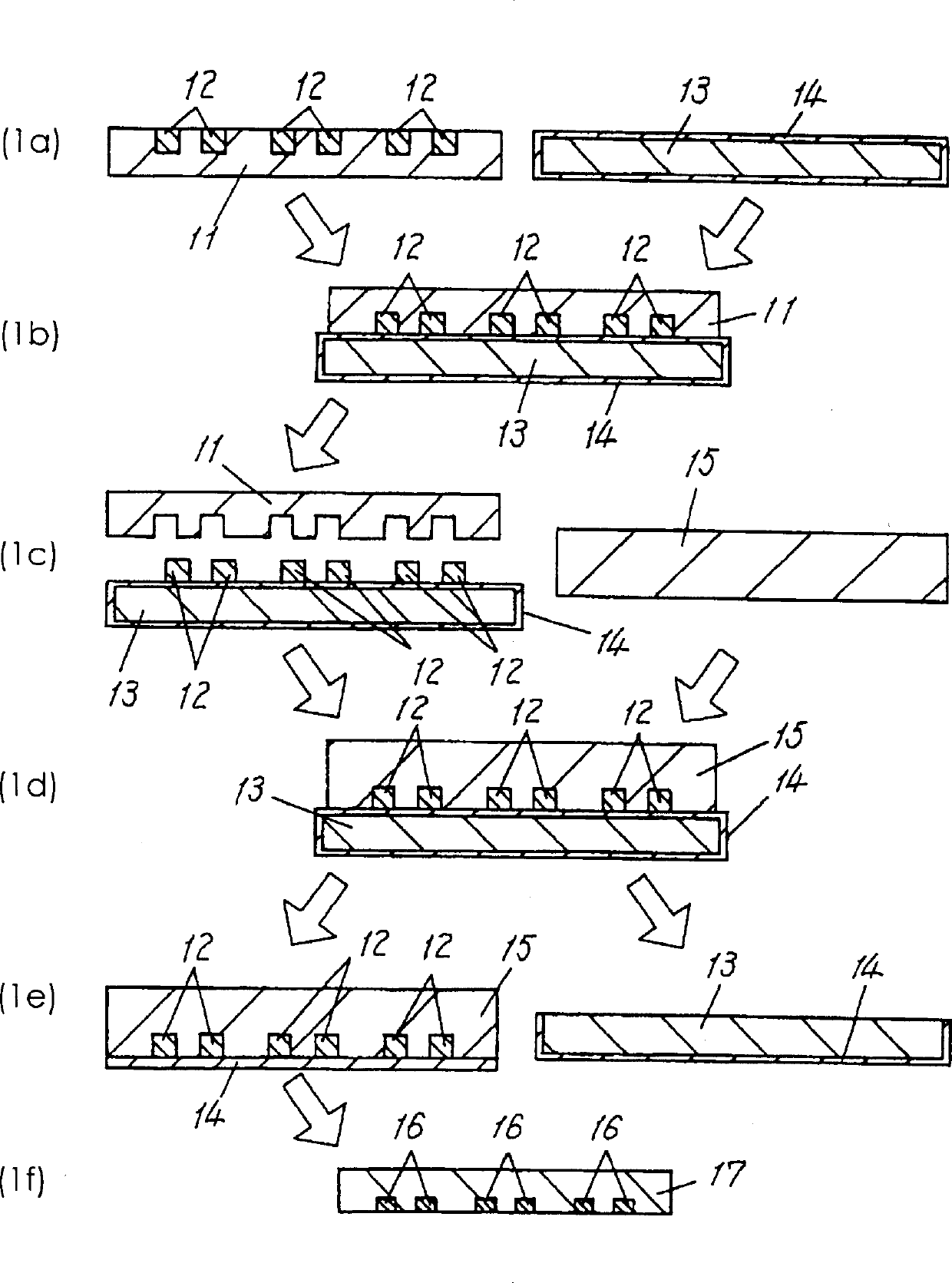
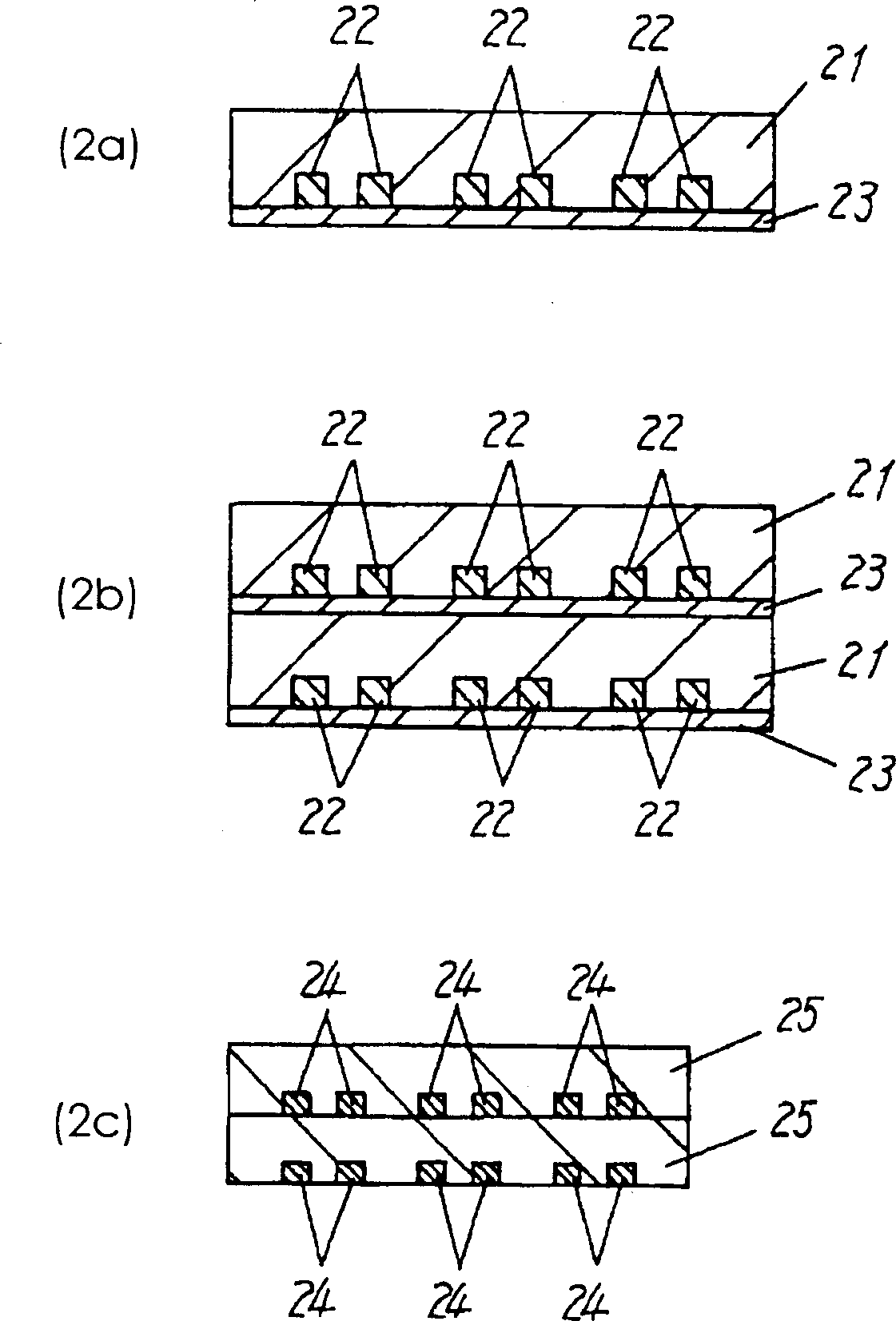
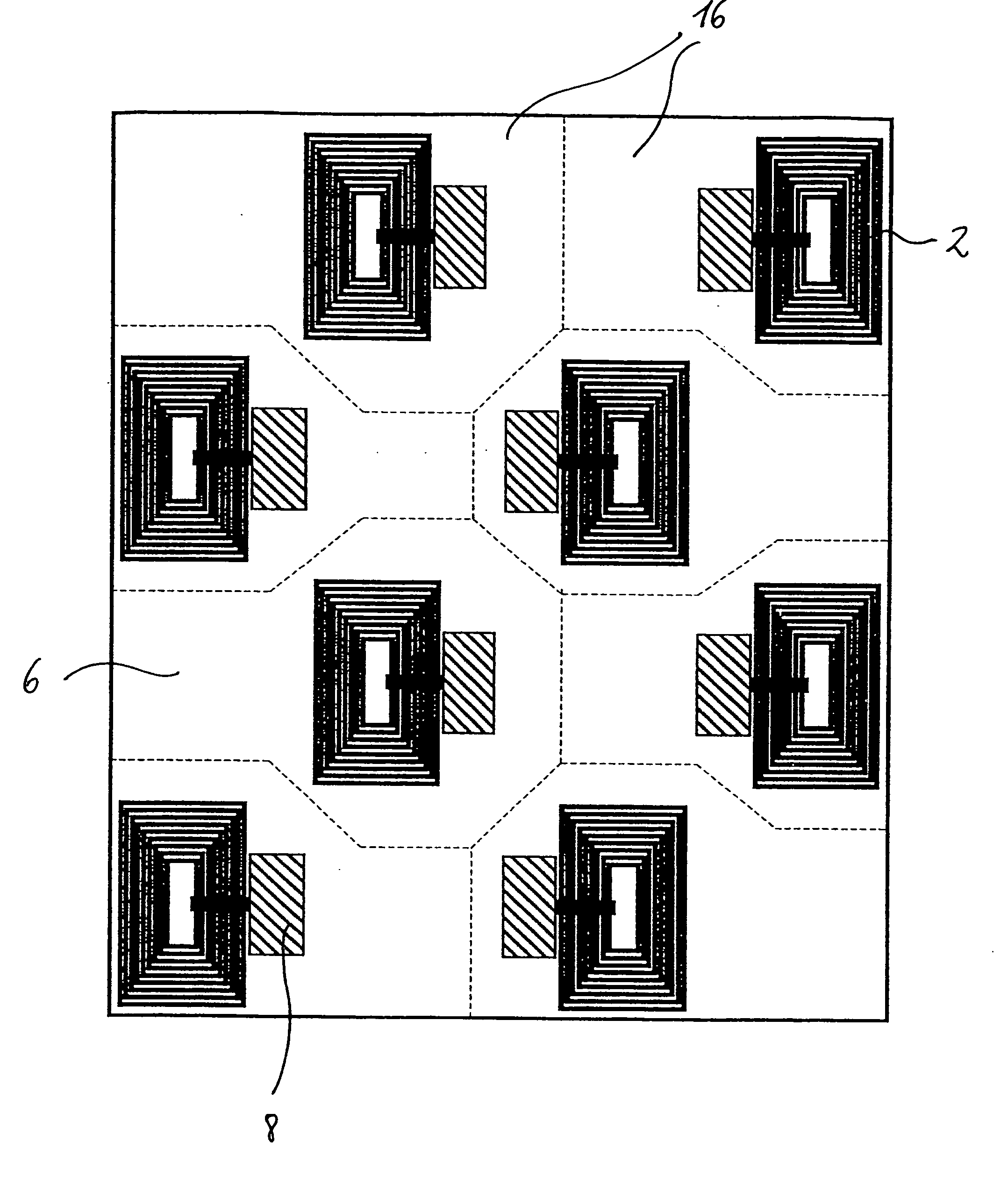
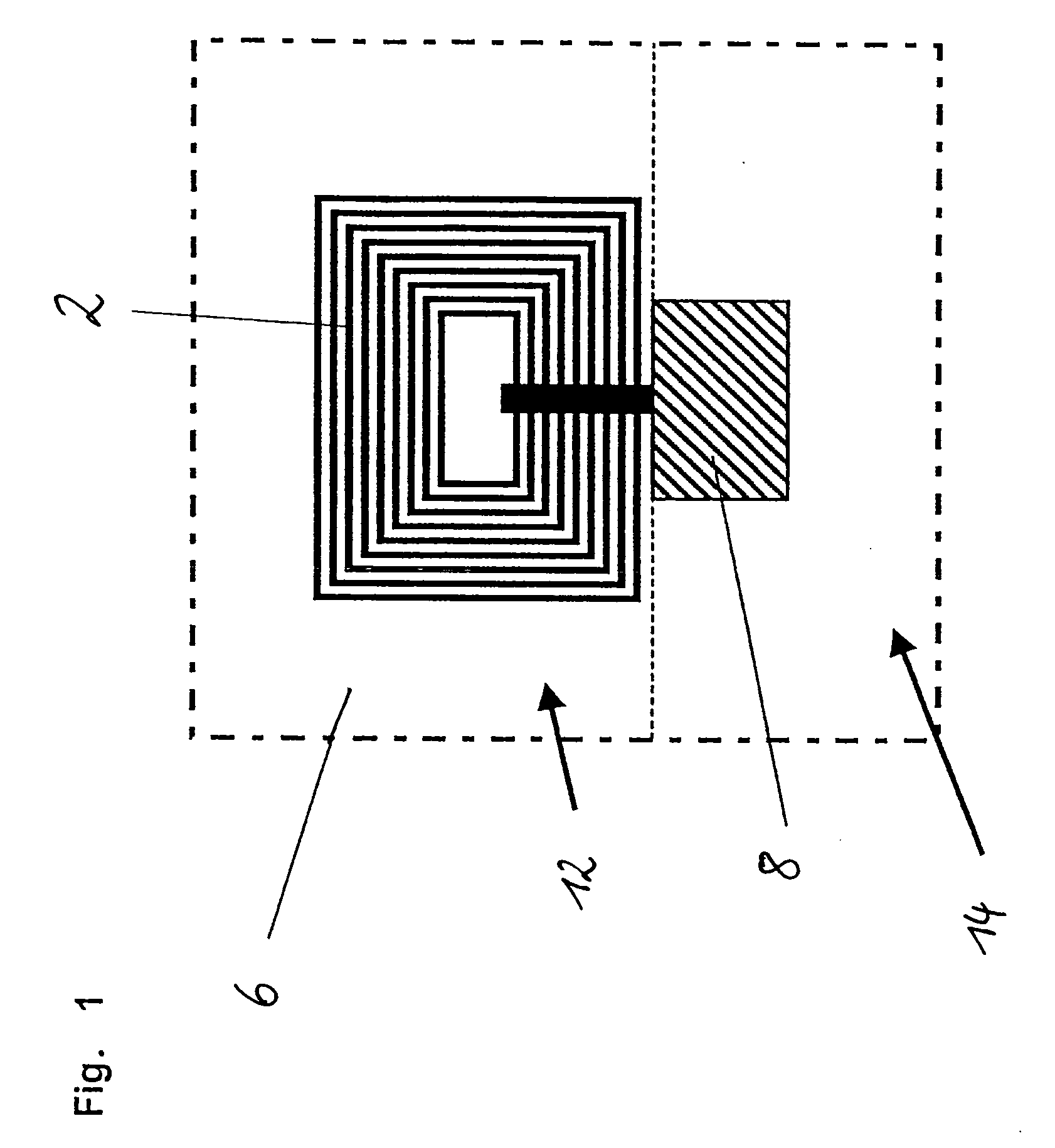
Method for transferring a picture to a surface
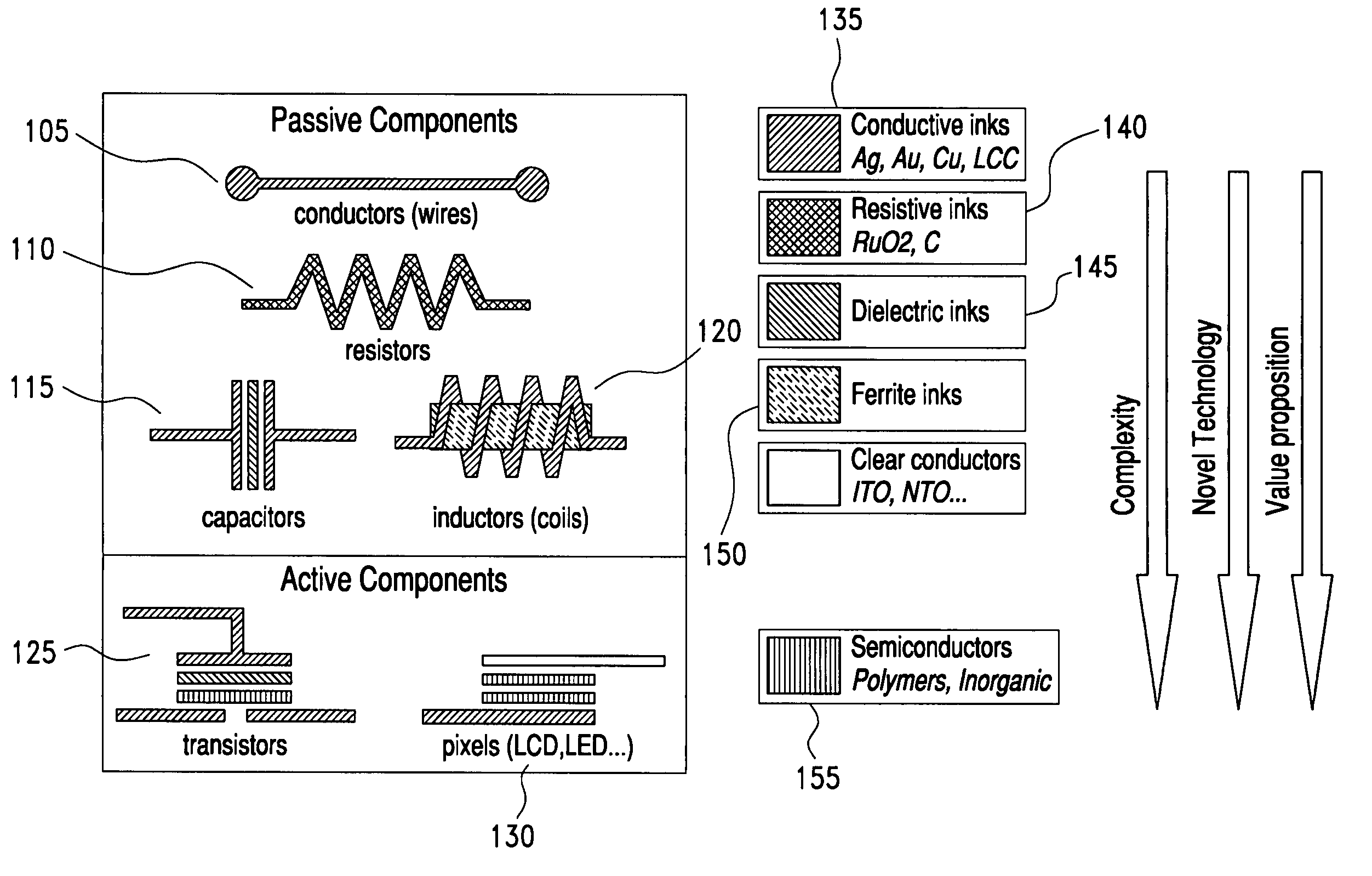
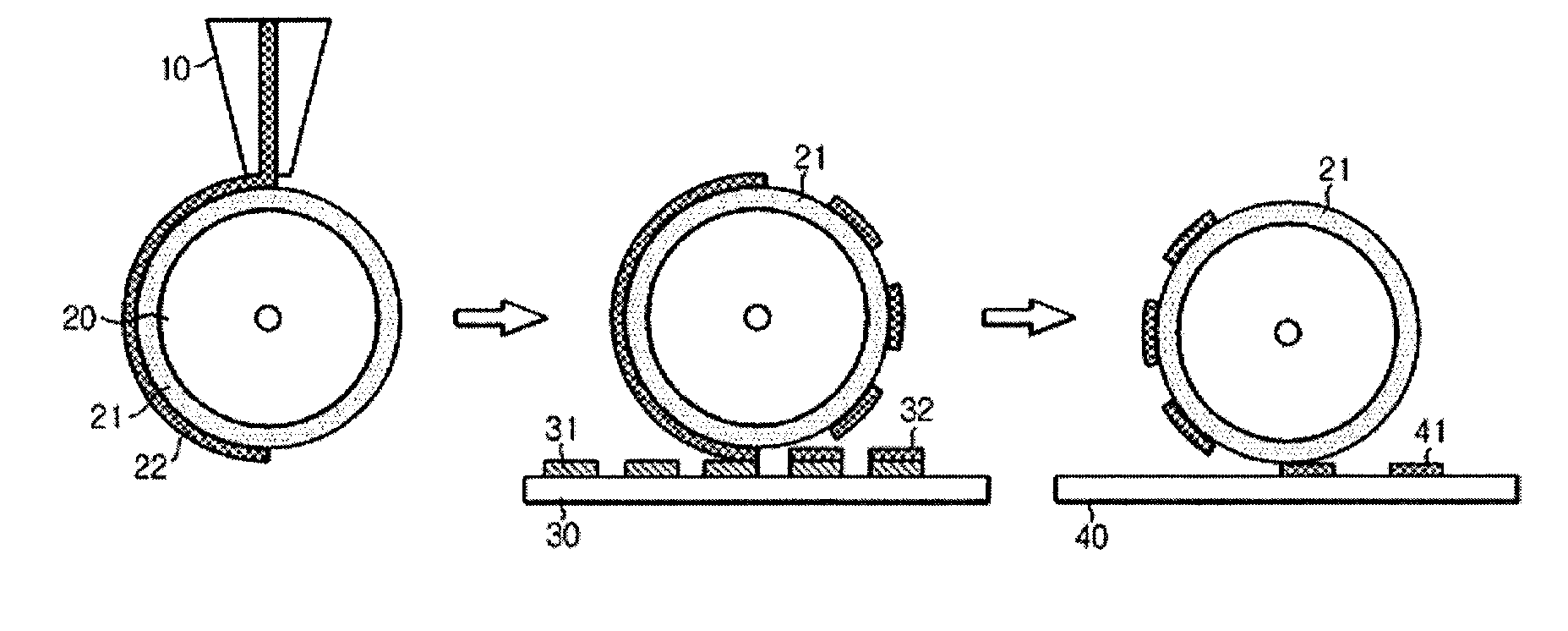
InactiveUS6158341AEasy to coverDesign specification3D rigid printed circuitsPrinted circuit aspectsElectromagnetic radiationTampon
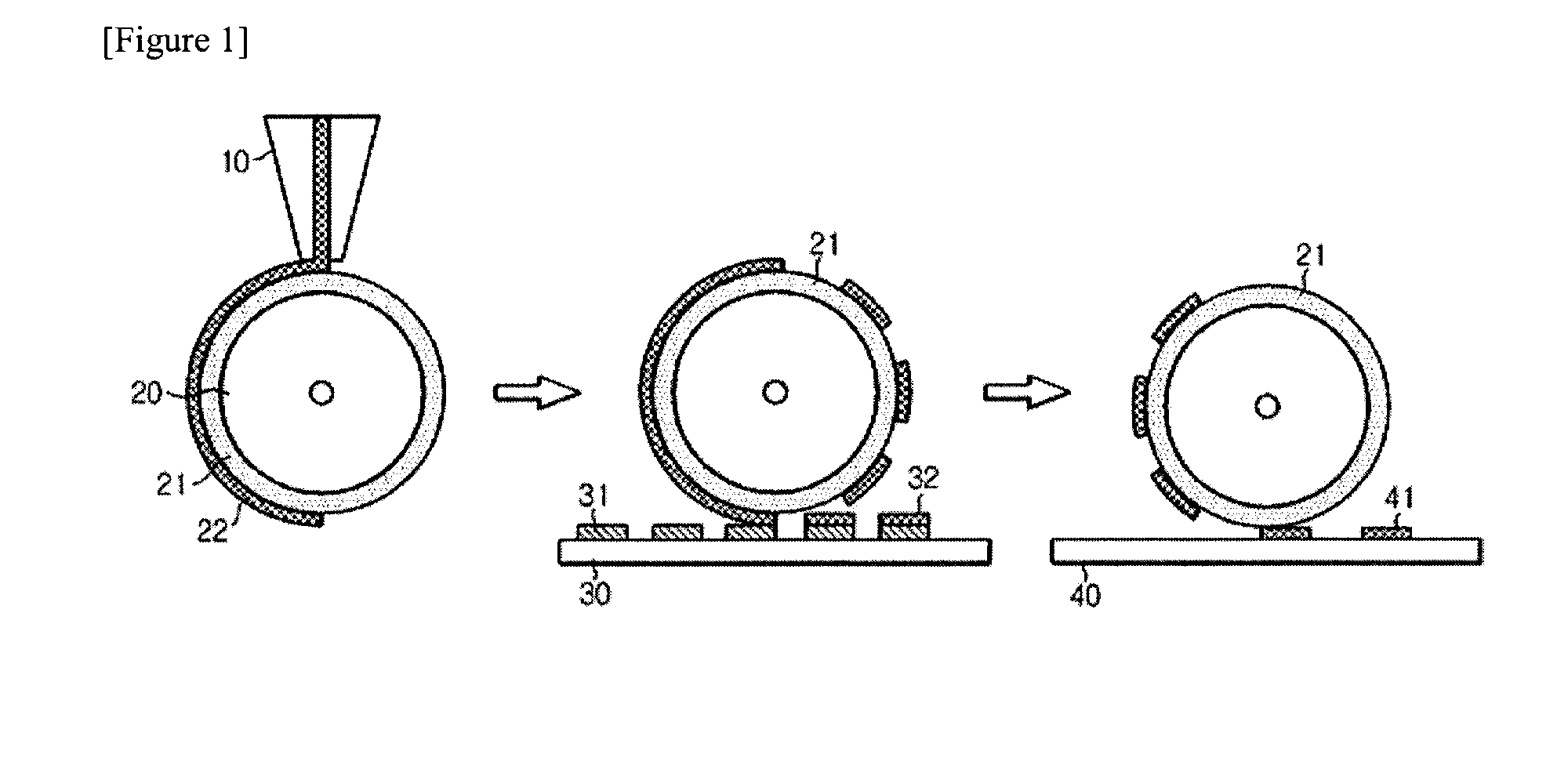
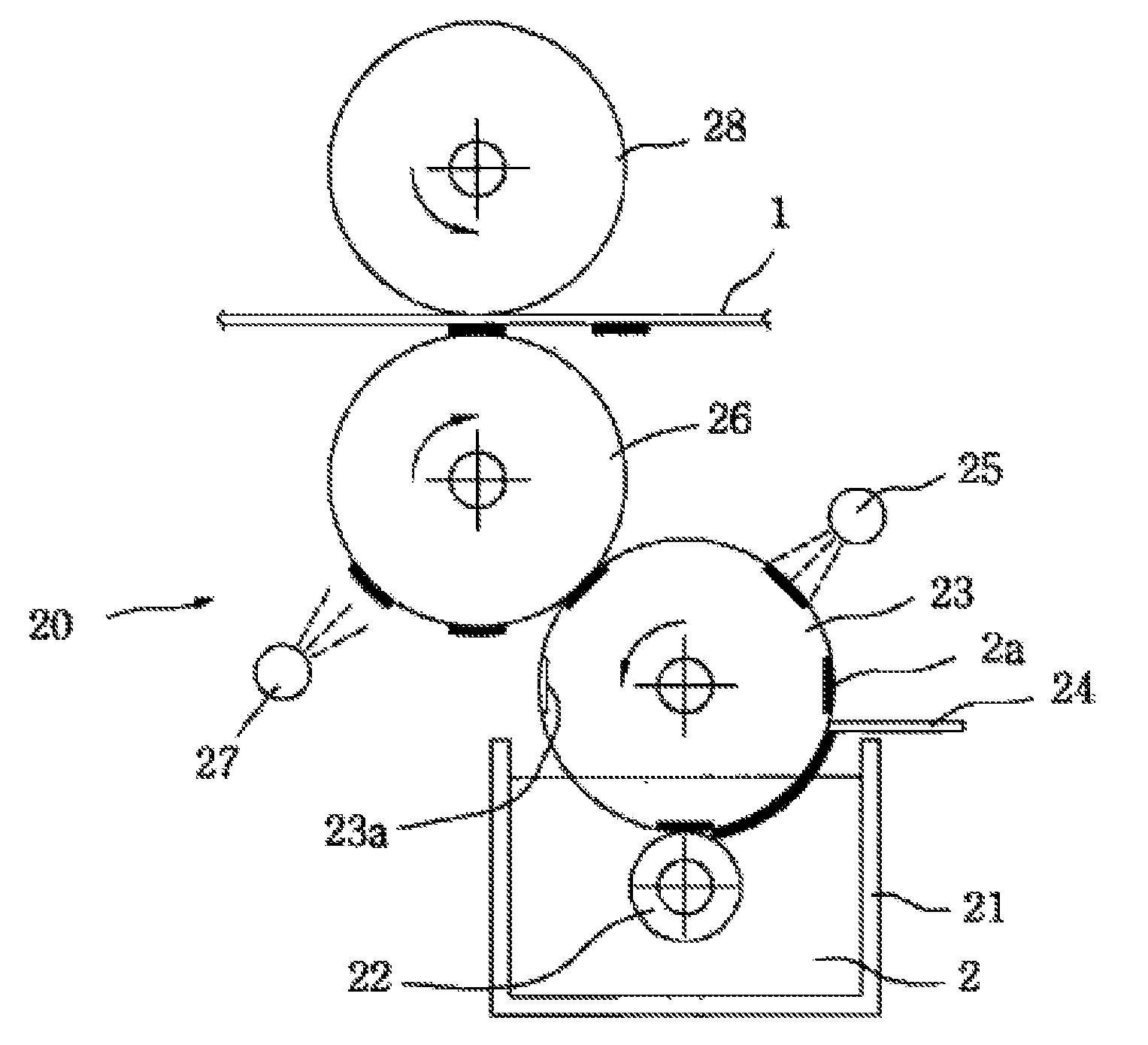
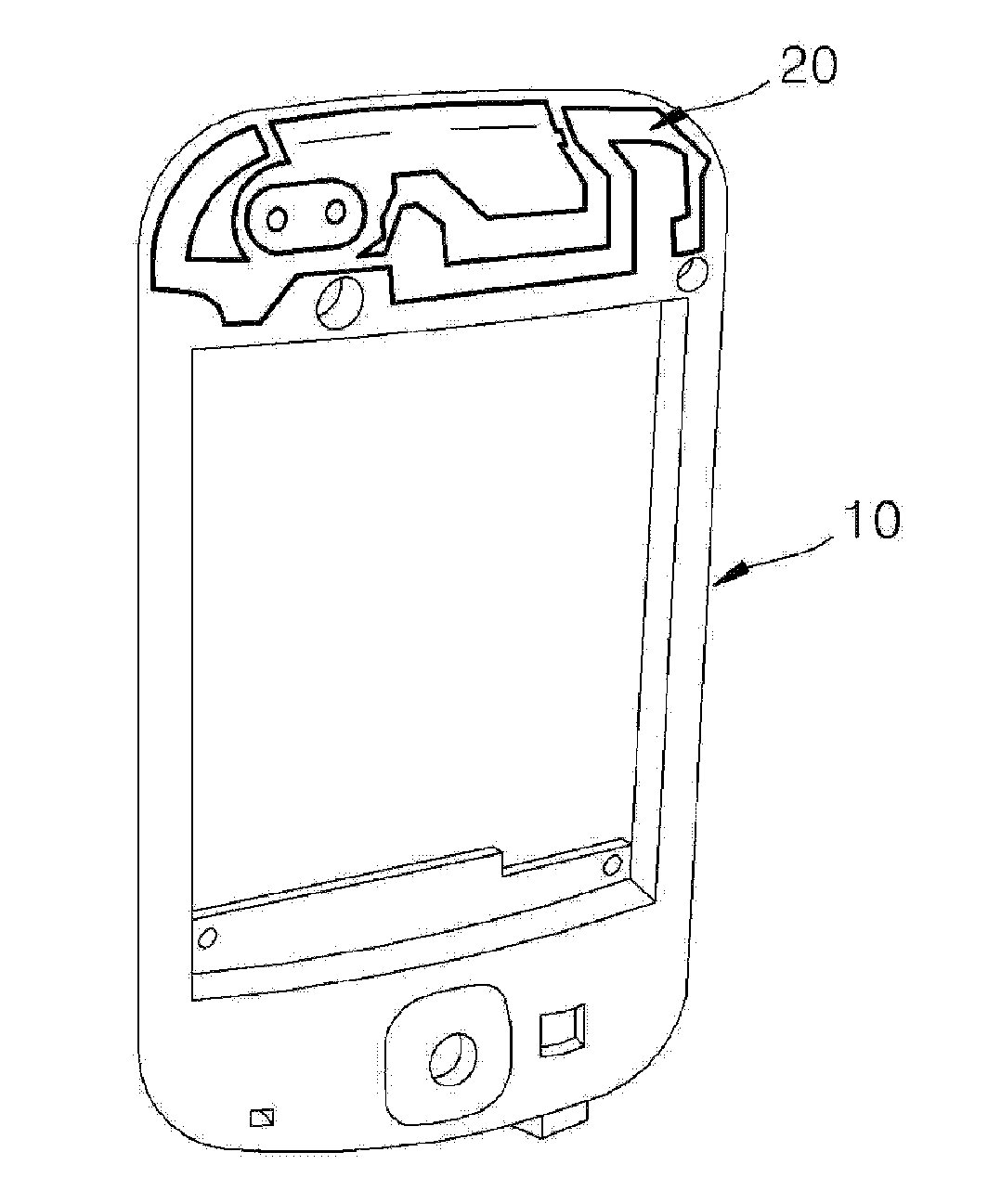
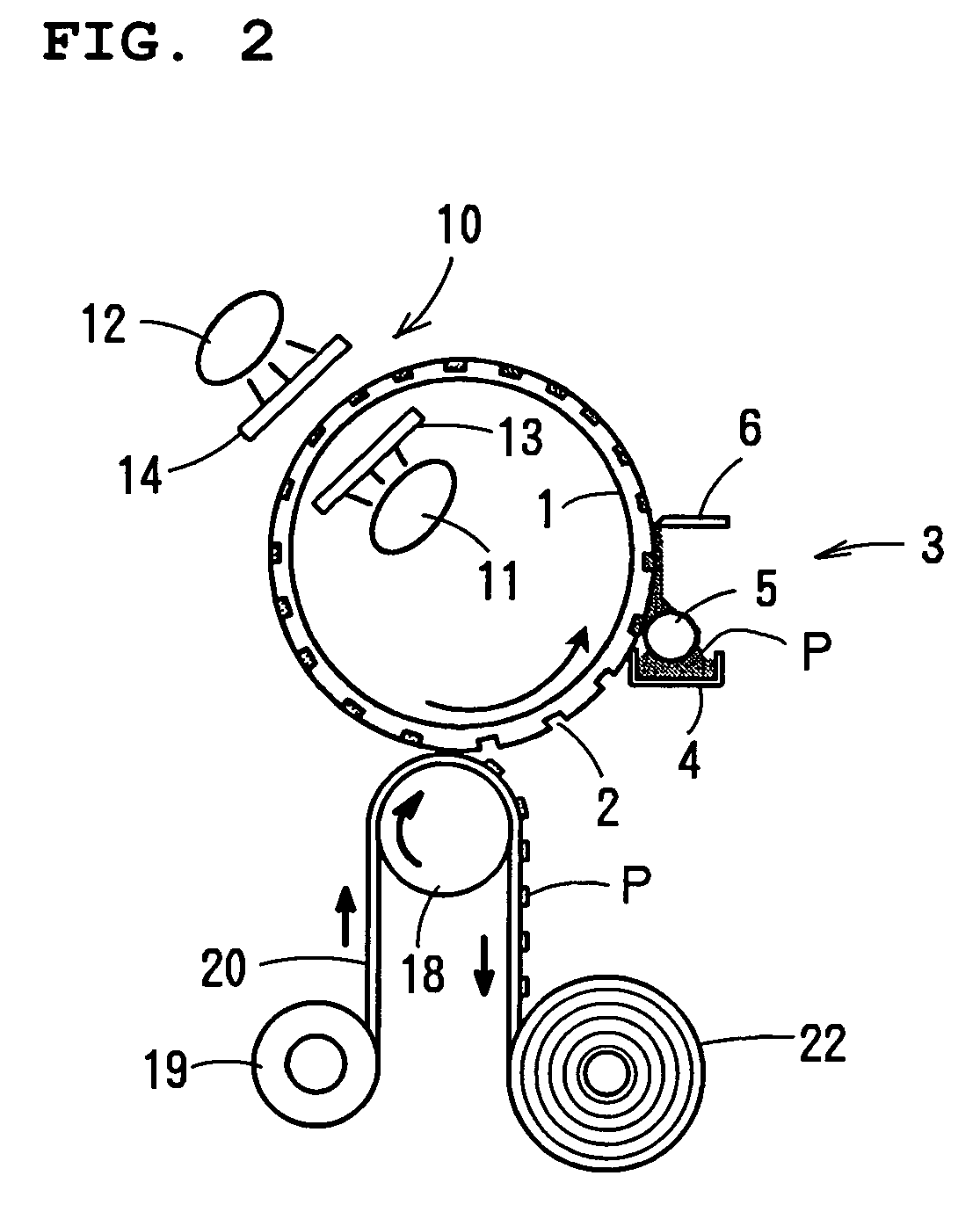
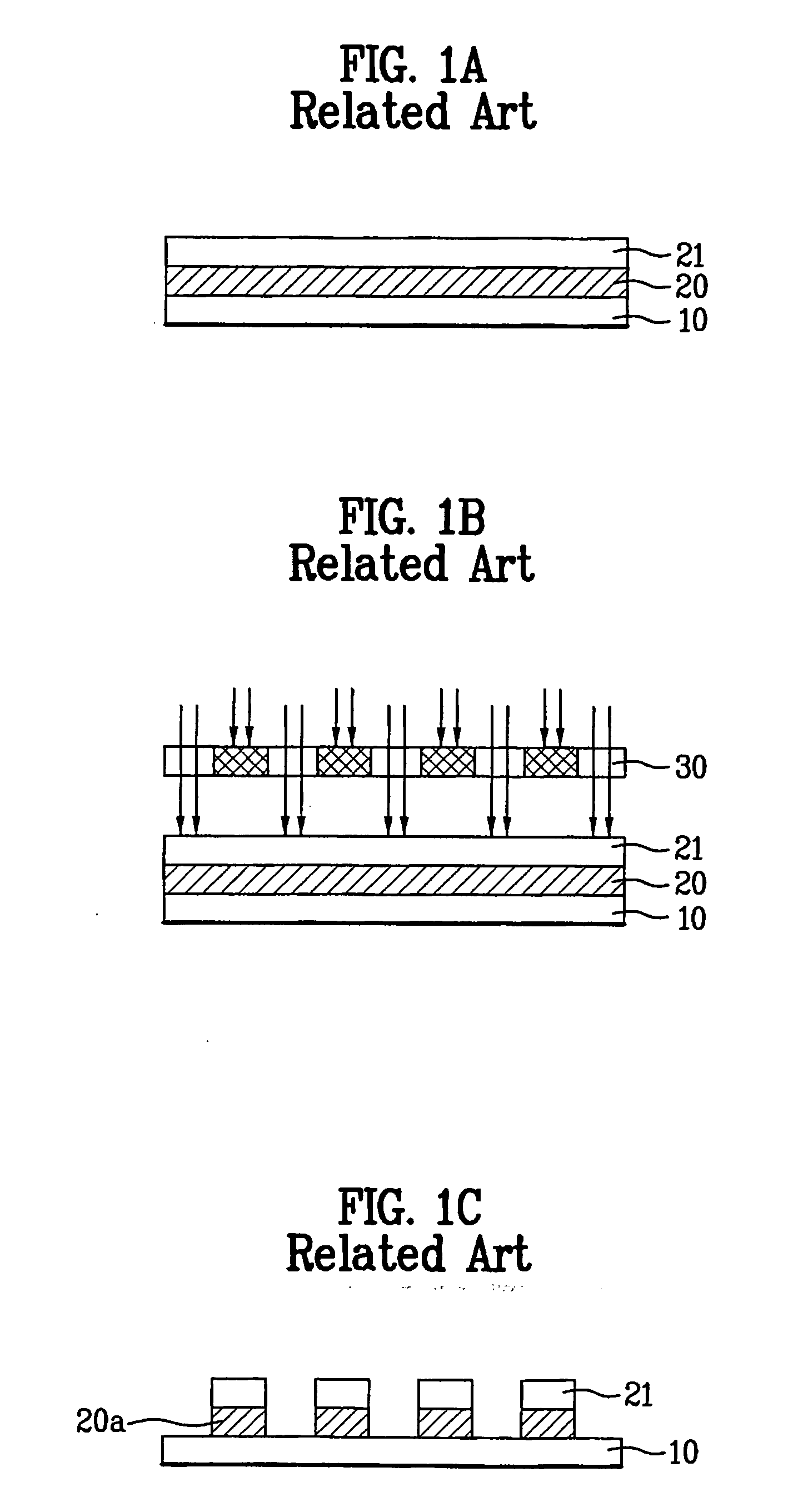
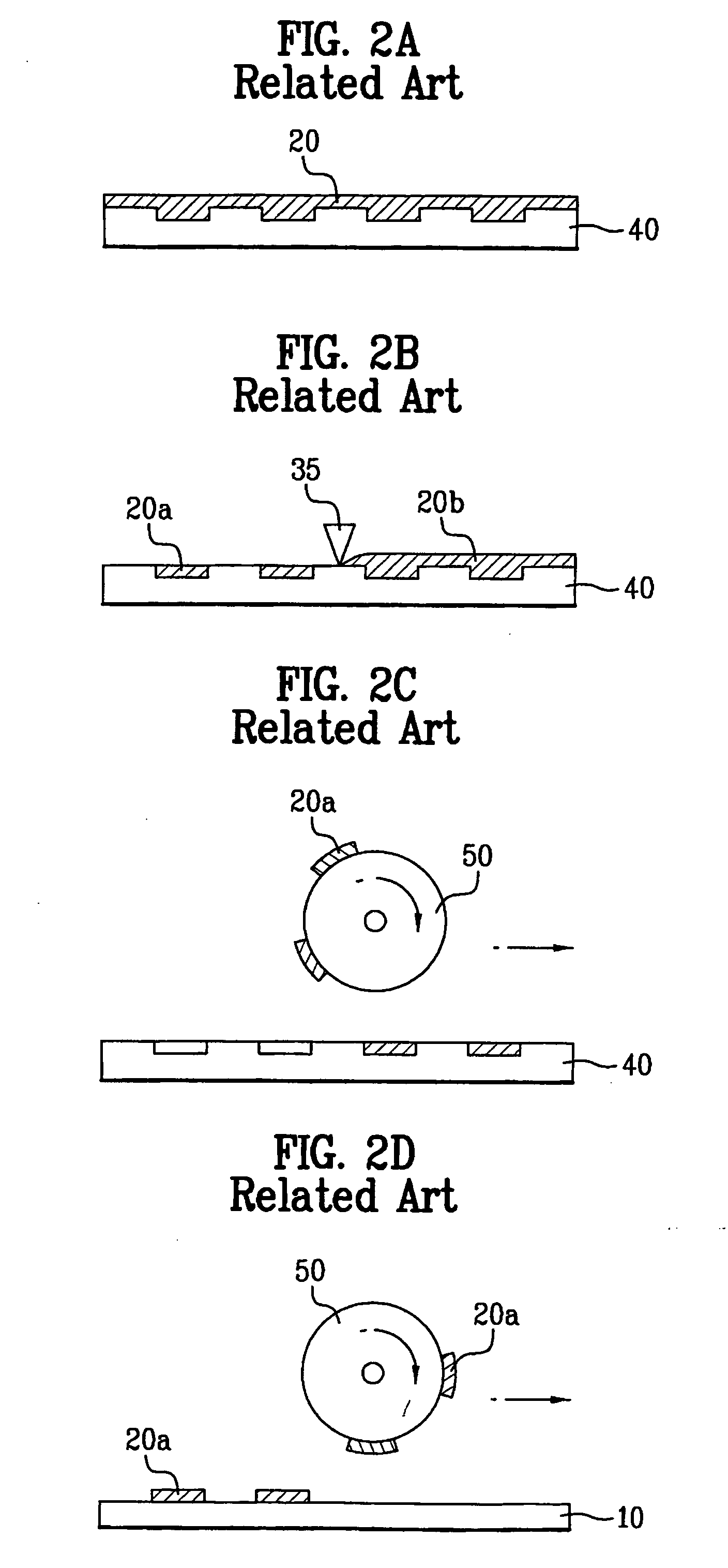
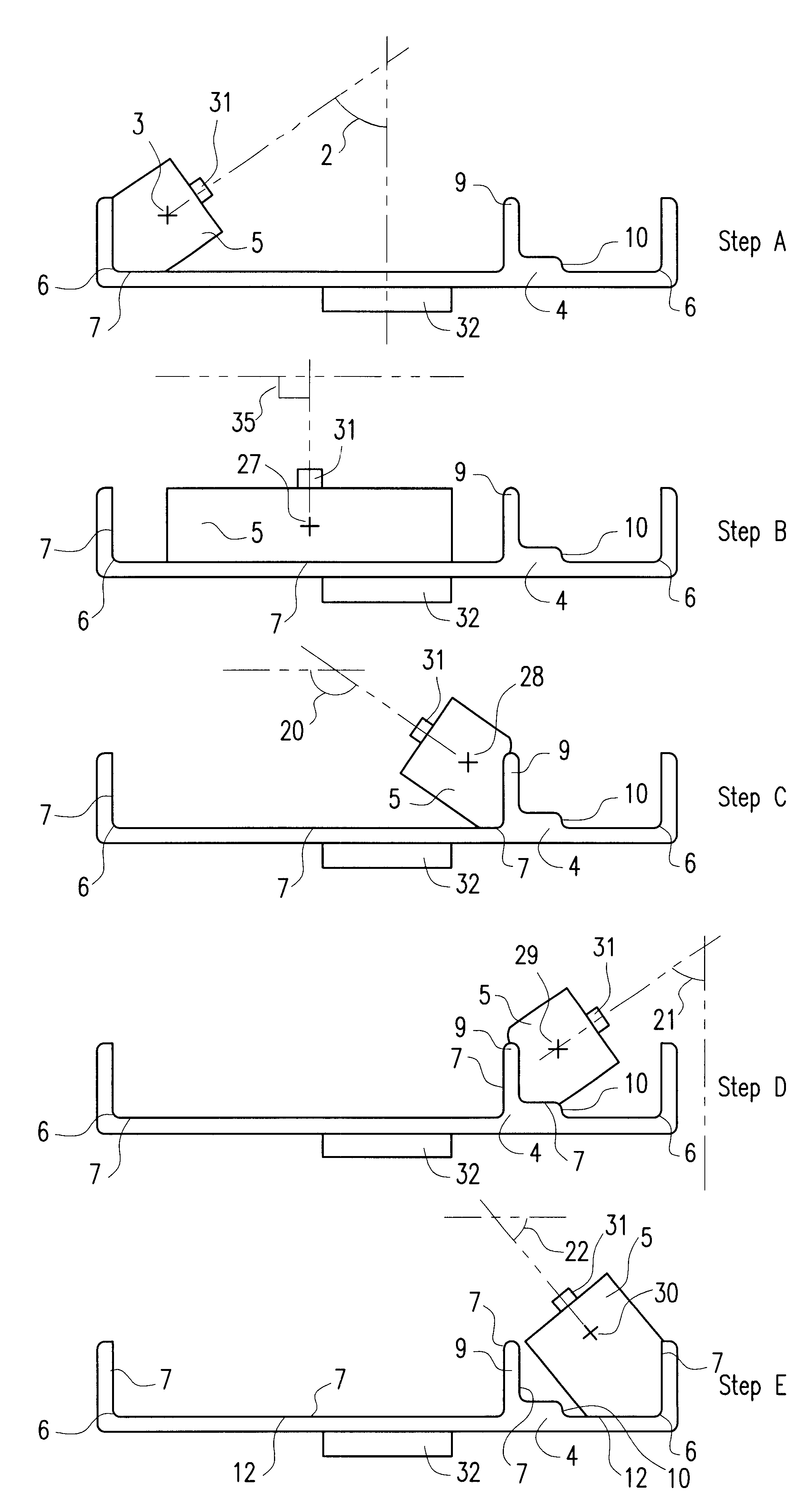
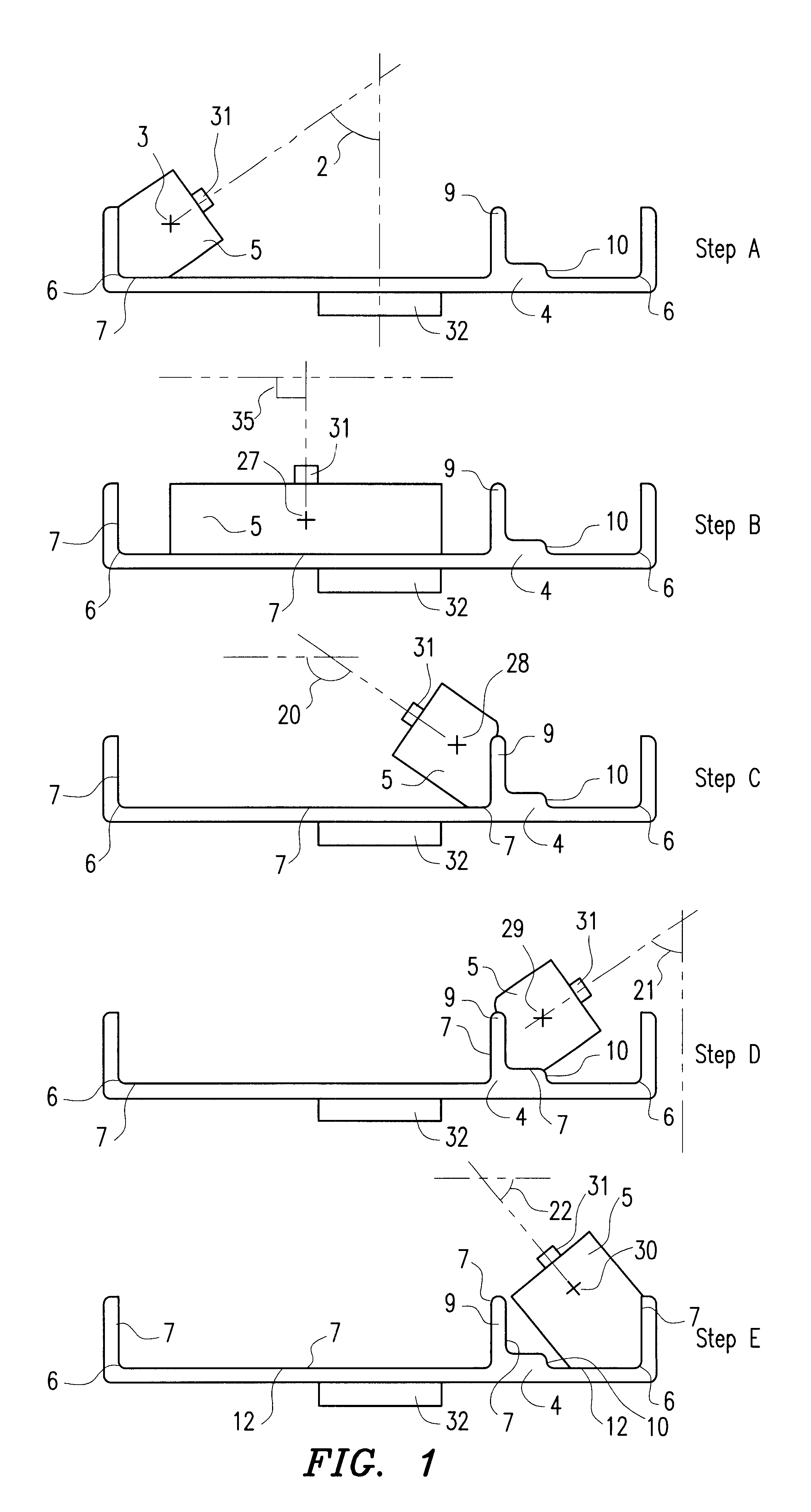
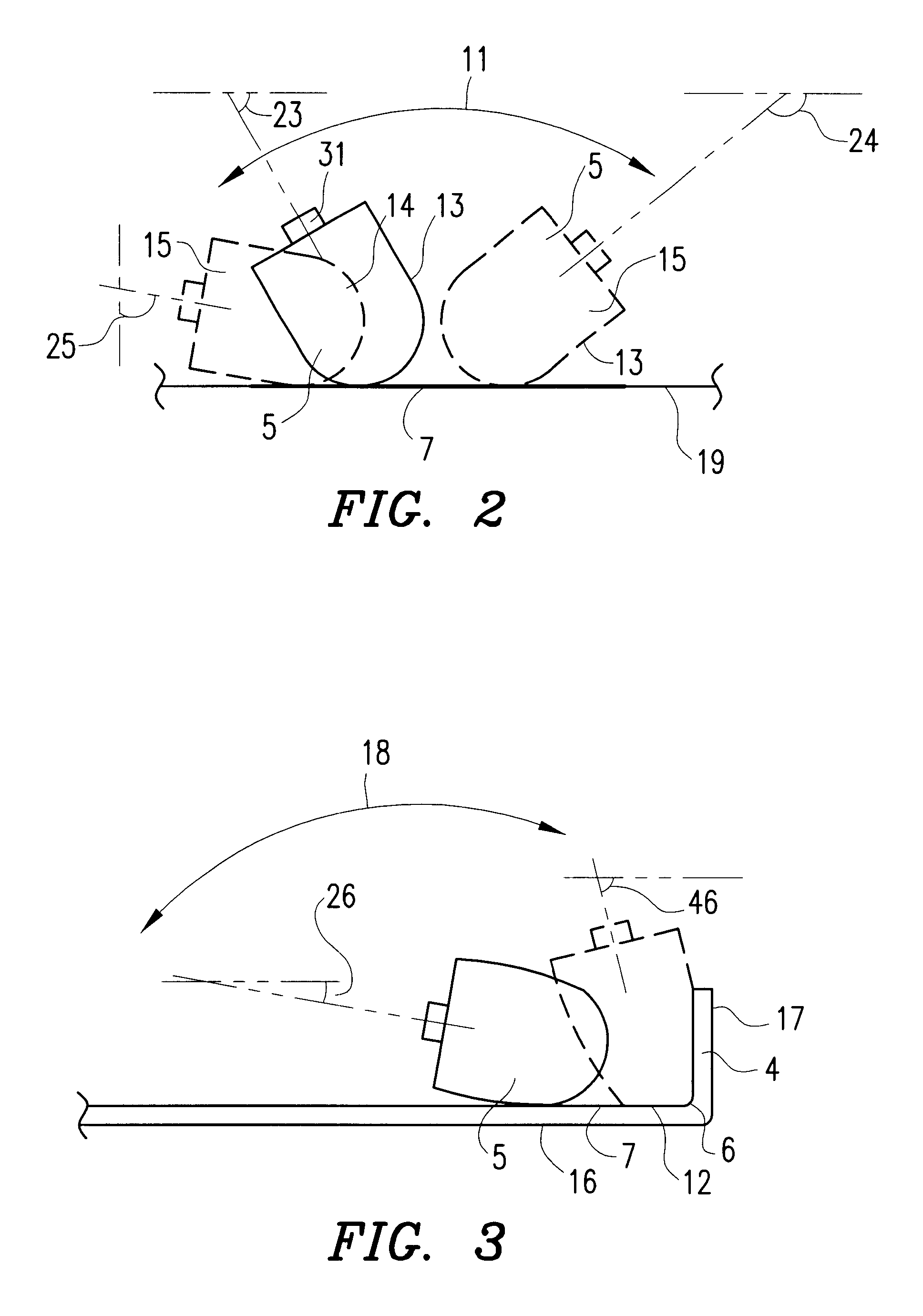
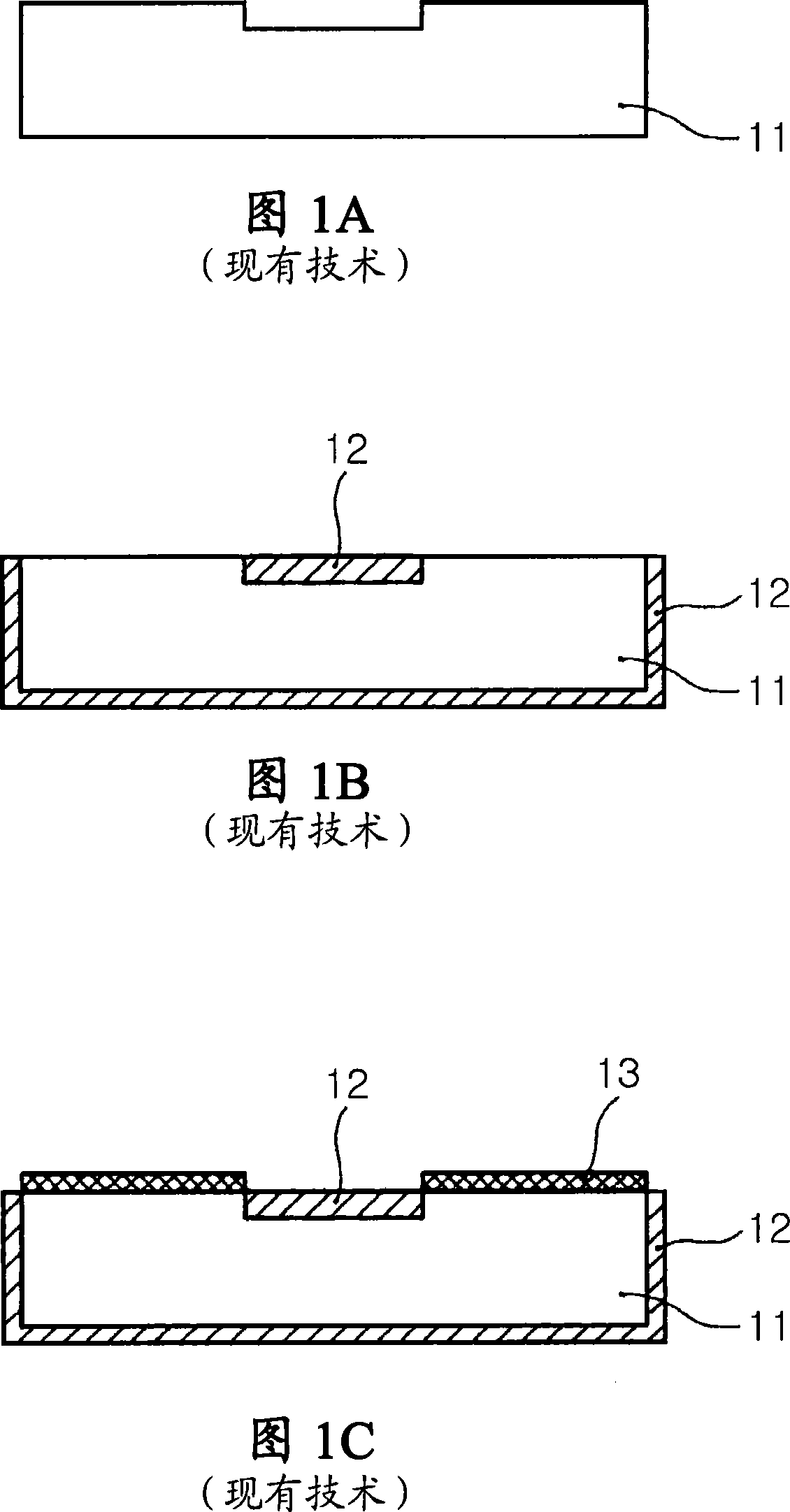
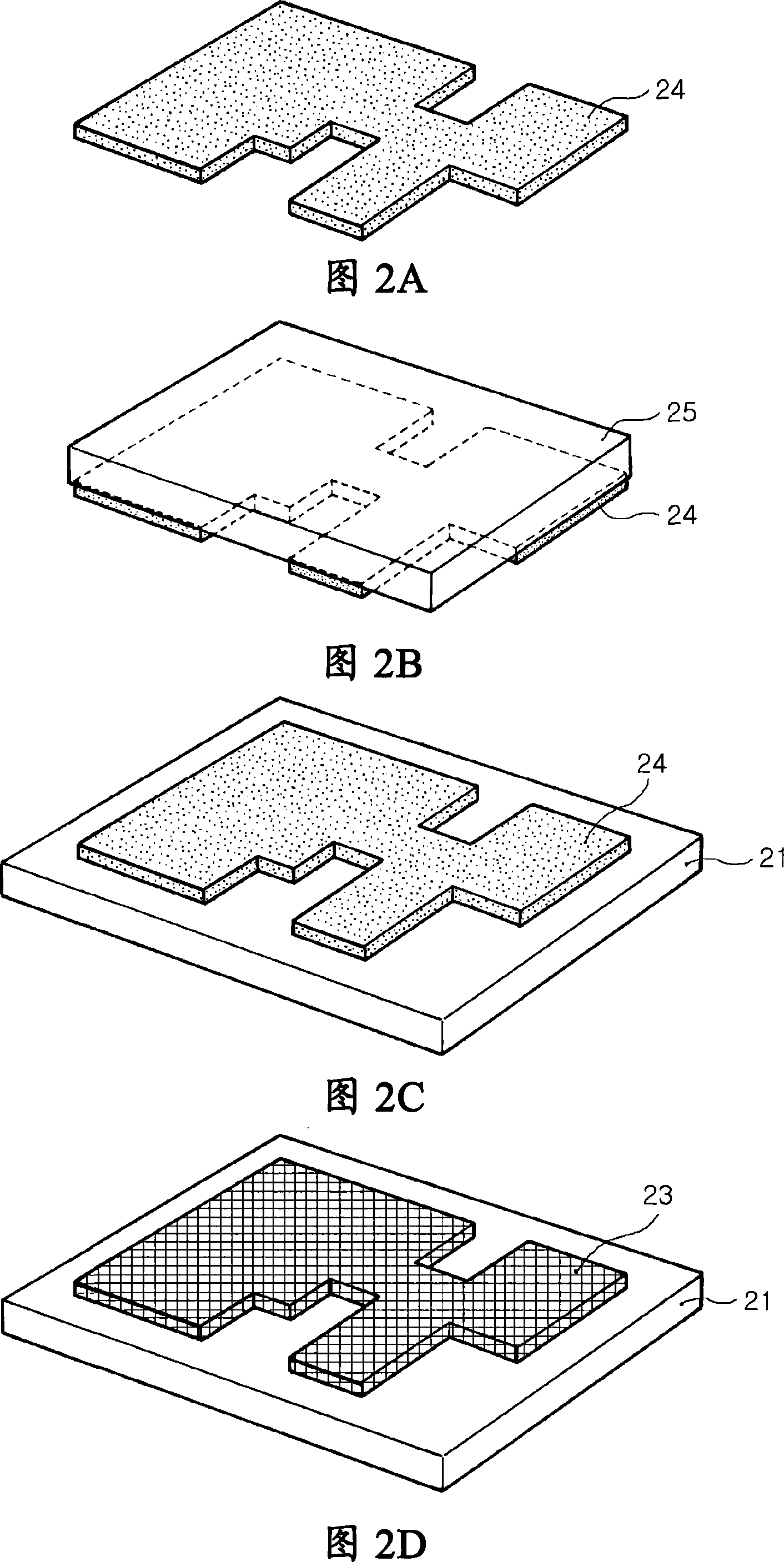
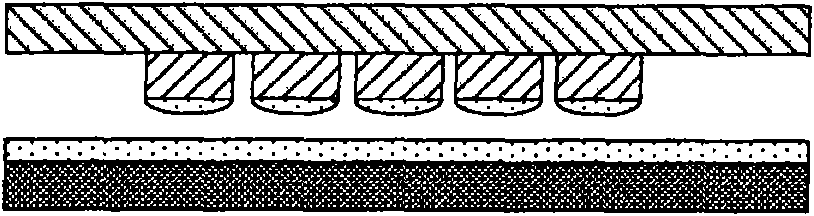
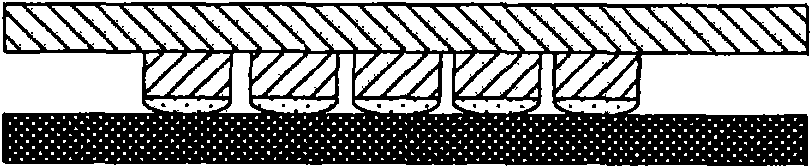
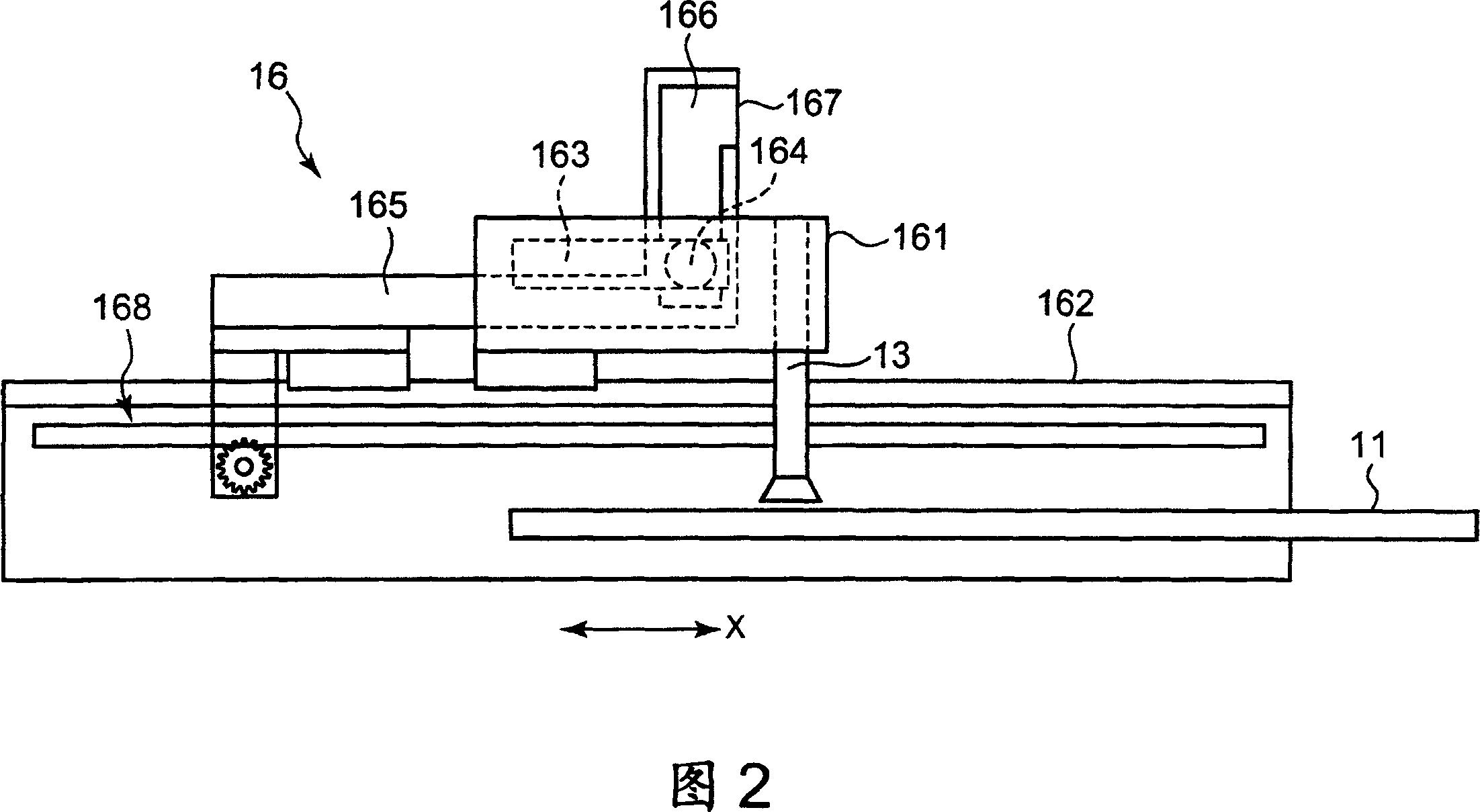
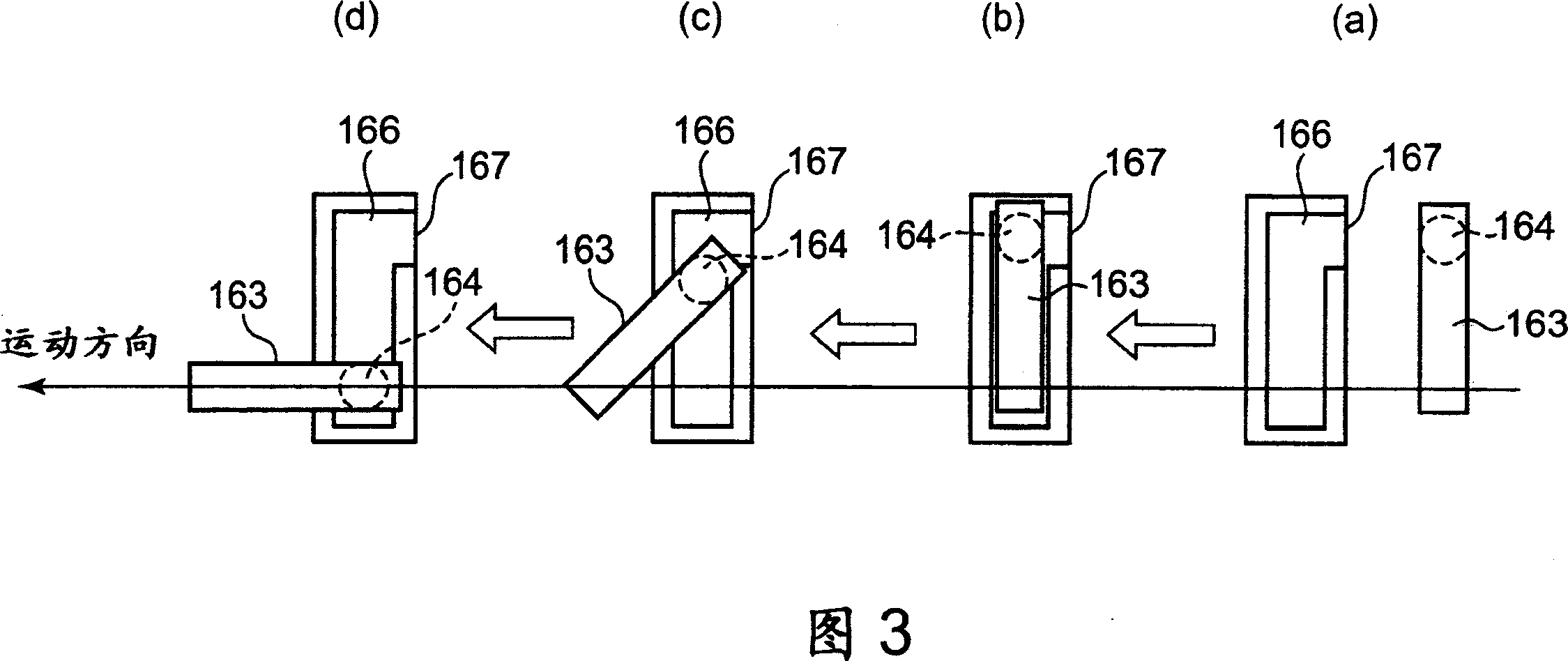
The present invention relates to a method and an arrangement for transferring a conductive picture (12) to an irregular surface of a mobile phone casing (4) for shielding the mobile phone casing from electromagnetic radiation. It also relates to the printing colour used for the conductive picture and tampon pads (5) used for the transferring of the conductive printing colour to the phone casing (4). Conductive partial pictures (7) are printed on the irregular surface of the casing (4) step by step by means of tampon pads until the complete conductive picture (12) is achieved. The tampon pad has a shape corresponding to the surface of the phone casing. The printing colour has a composition, which facilitates the adhering on the tampon pad. The invention also describes a method for printing an electrical circuit pattern on a phone casing (4) by using the above mentioned tampon pads and printing colour.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
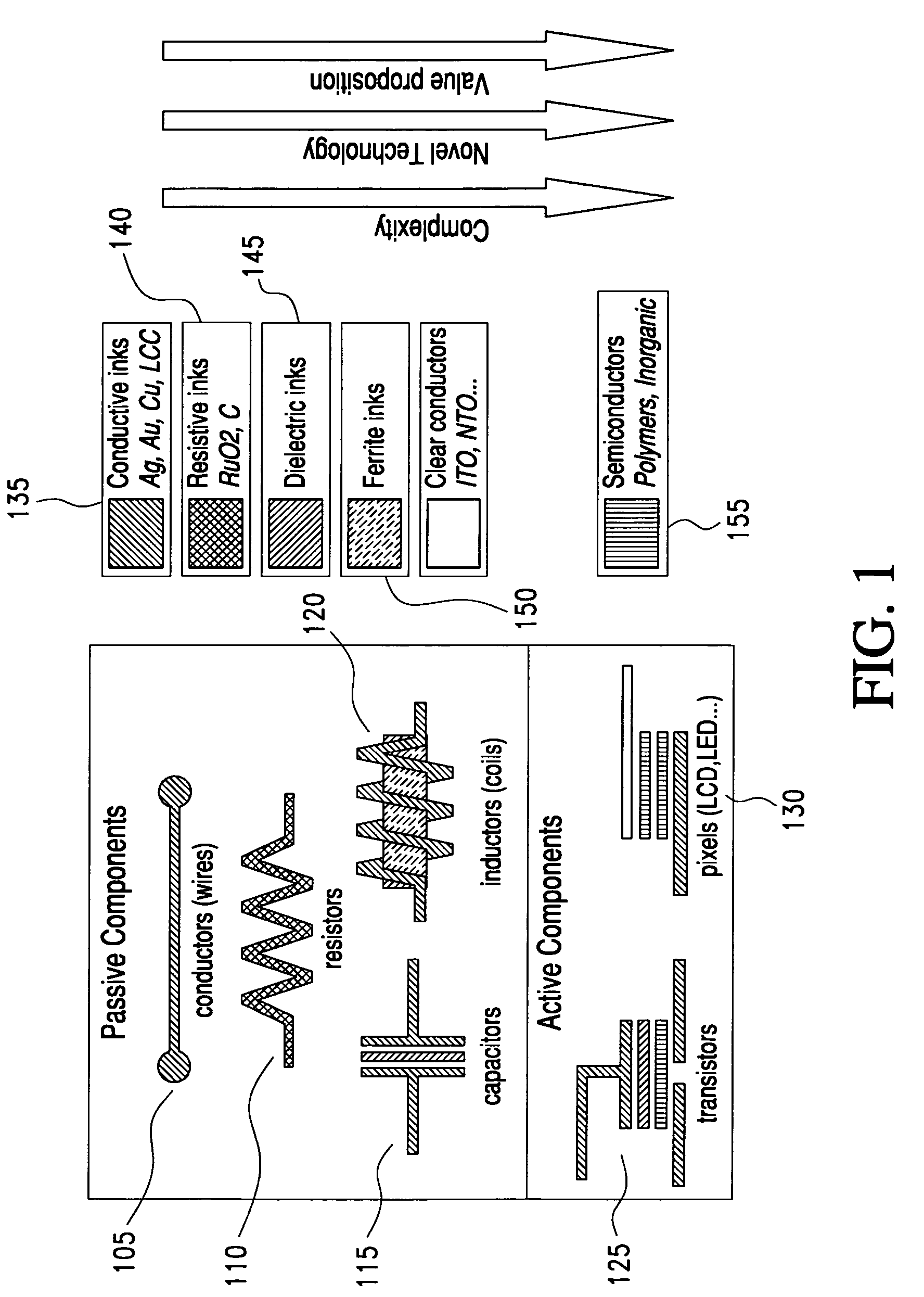
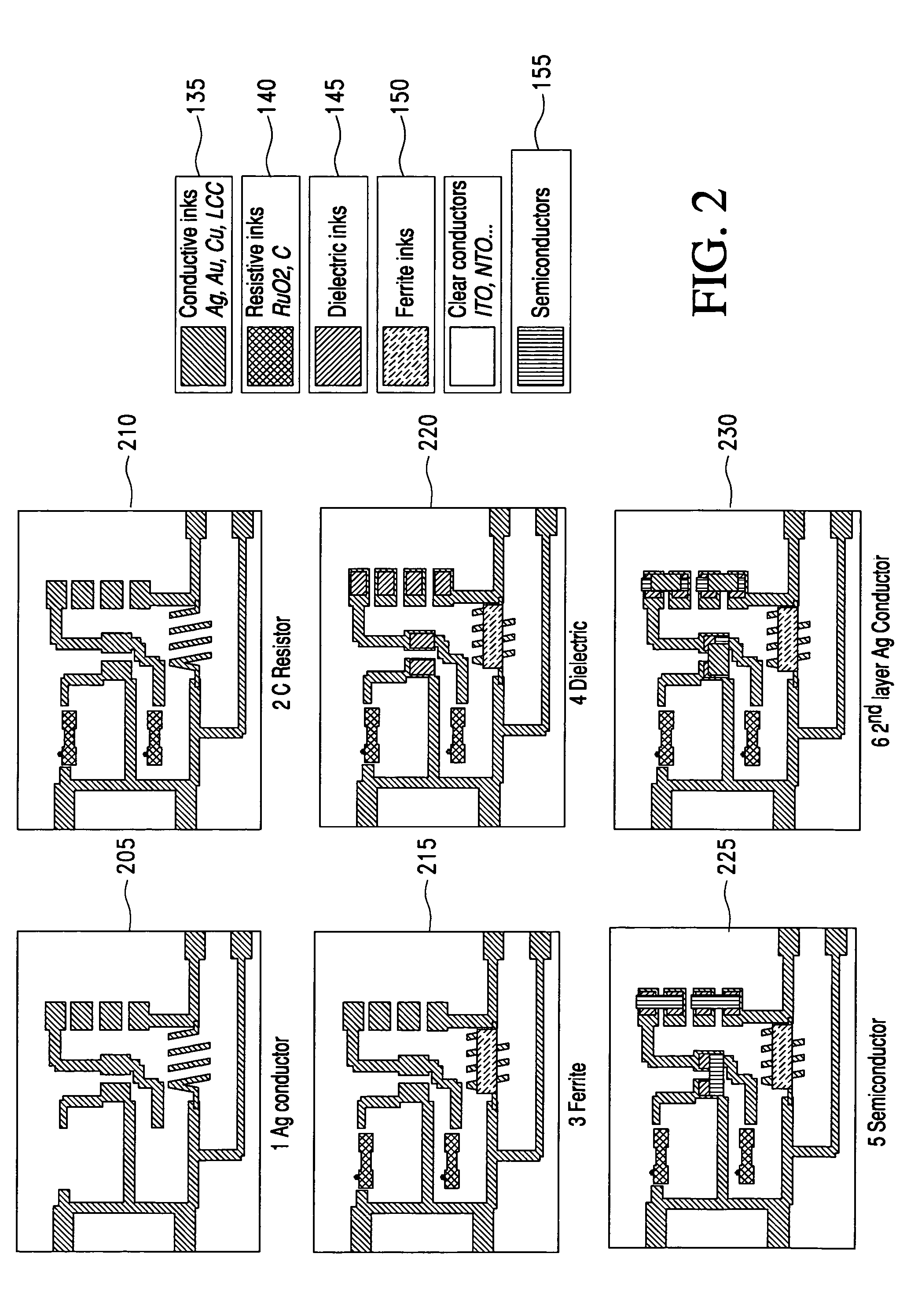
Optimized multi-layer printing of electronics and displays
InactiveUS8334464B2Printed electric component incorporationPrinted circuit aspectsDisplay devicePrinted circuit board
An apparatus and method for making a printed circuit board comprising a substrate and an electrical circuit is provided. The circuit is formed by deposition of a plurality of electronic inks onto the substrate and curing of each of the electronic inks. The deposition may be performed using an ink-jet printing process. The inkjet printing process may include the step of printing a plurality of layers, wherein a first layer includes at least one electronic ink deposited directly onto the substrate, and wherein each subsequent layer includes at least one electronic ink deposited on top of at least a portion of a previous layer when the previous layer has been cured. One or more of the layers may include at least two of the electronic inks.
Owner:CABOT CORP
Conductive metal ink composition, and method for preparing a conductive pattern
ActiveUS20130277096A1Improve conductivityGood adhesionConductive materialInksPolymer coatingsSolvent
The present invention relates to a conductive metal ink composition, comprising: a first metal powder having conductivity; a non-aqueous solvent; an attachment improving agent; and a polymer coating property improving agent, and a method for forming a conductive pattern by using the conductive metal ink composition, and the conductive metal ink composition can be appropriately applied to a roll printing process and a conductive pattern exhibiting more improved conductivity and excellent attachment ability with respect to a board can be formed.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Method of manufacturing a device
InactiveUS7131194B2Wave amplification devicesPrinted circuit secondary treatmentEngineeringAdhesive materials
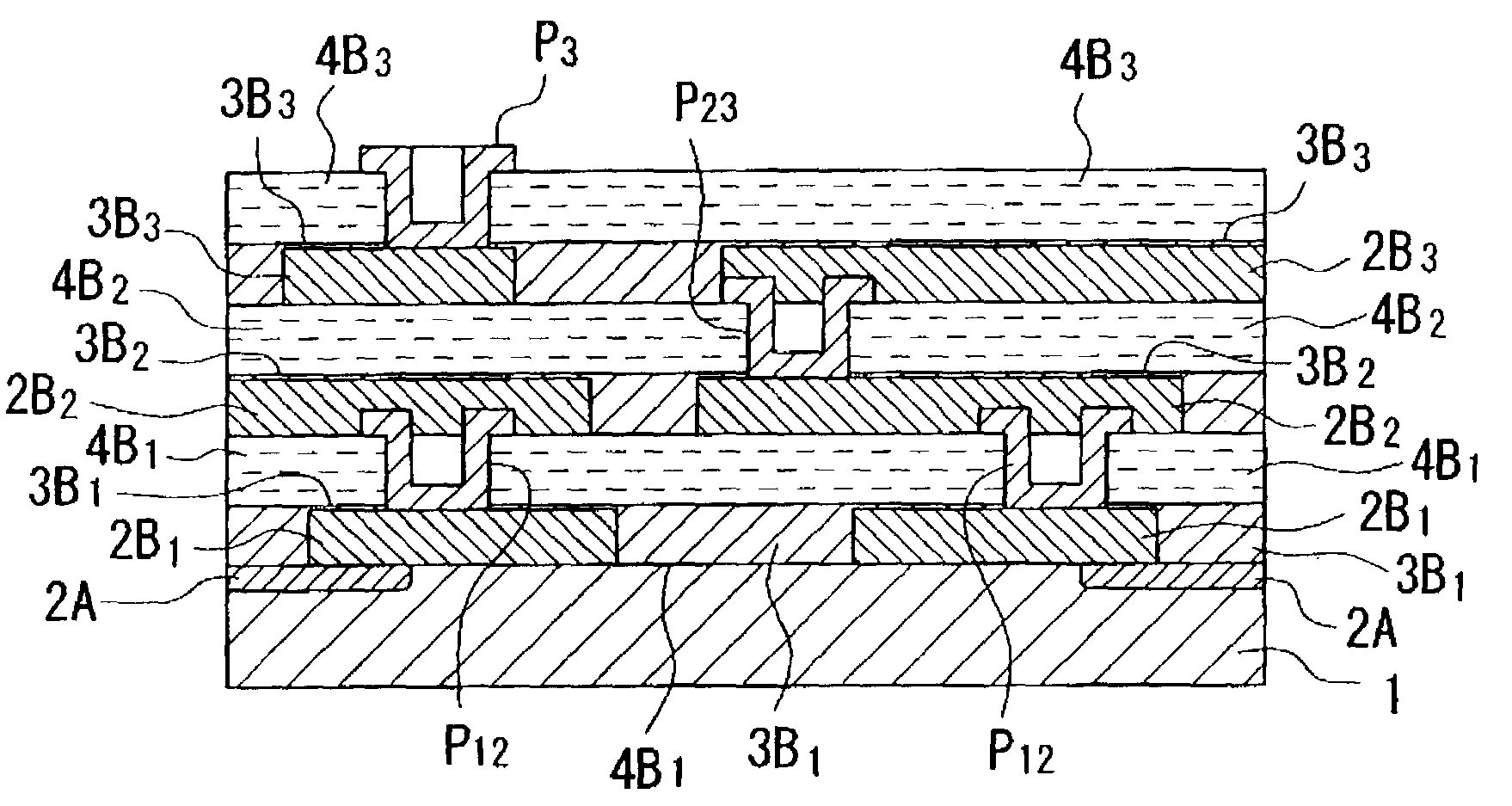
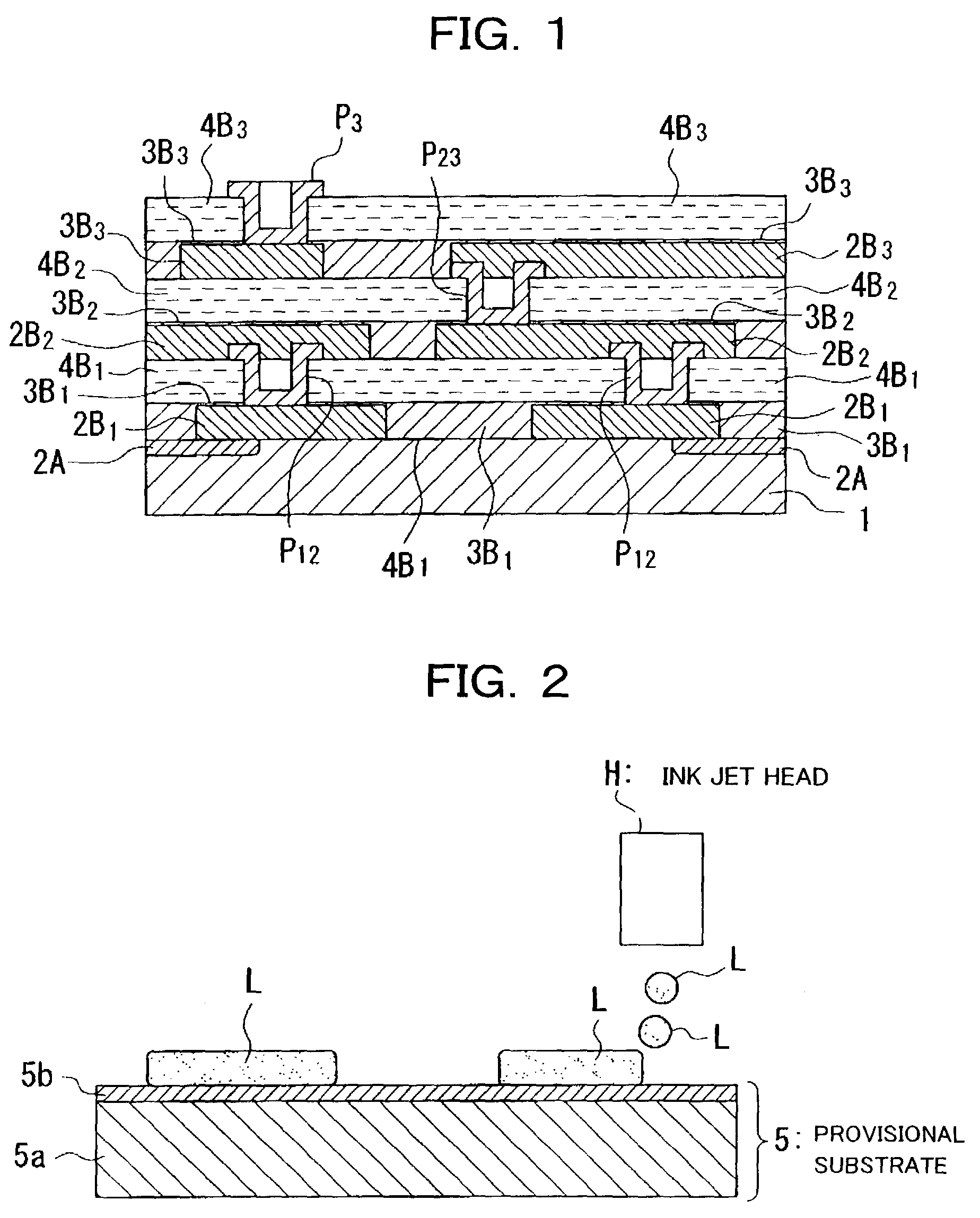
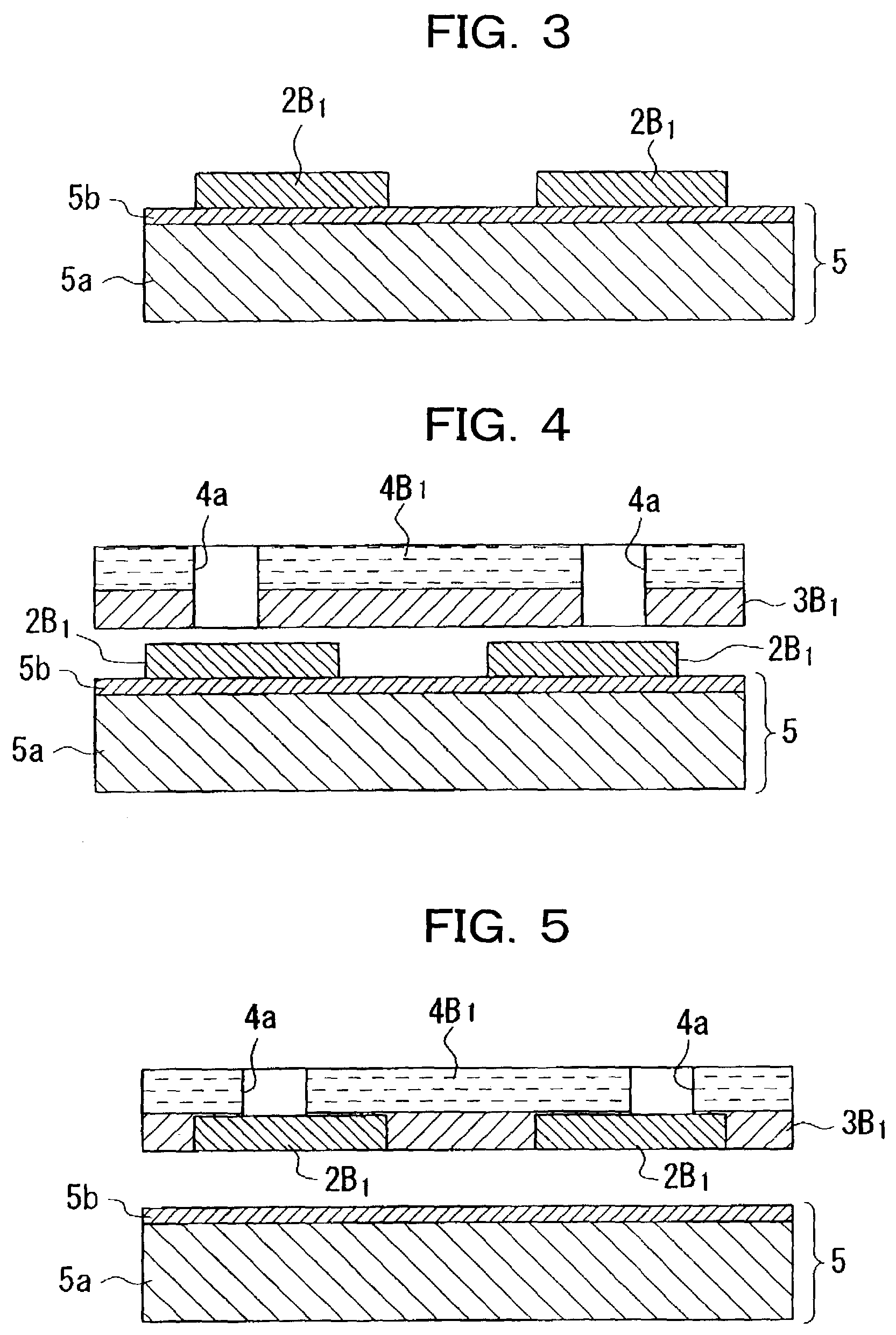
Wirings 2B1 are formed by application of heat treatment after an ink jet system is used to discharge a conductive liquid L onto a provisional substrate 5 having a predetermined repellent property, bonding an insulating layer 4B1 to the wirings 2B1 with an adhesive material 3B1 therebetween, peeling and removing the provisional substrate 5, and bonding and fixing the wirings 2B1 together with the insulating film 4B1 to a main substrate 1 by an adhesive material 3B1.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Method of manufacturing thin film device
InactiveUS20100051178A1Simple processImprove equipment reliabilityLamination ancillary operationsLayered product treatmentOptoelectronics
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
High spread highly randomized generatable interleavers
InactiveUS20070234180A1Minimize negative impactIncrease the number ofOther decoding techniquesCode conversionCommunications systemTheoretical computer science
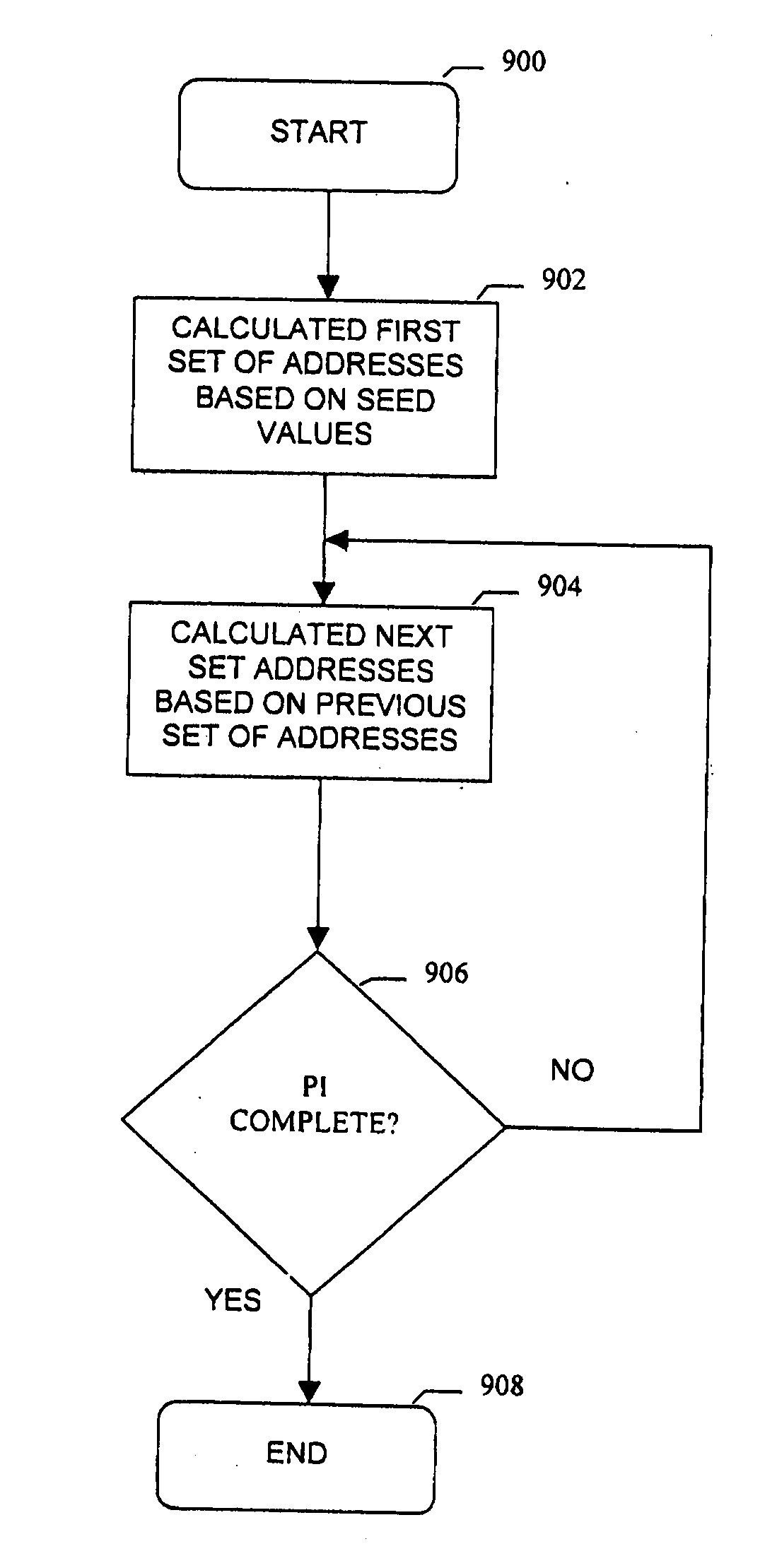
Methods and apparatus for generating and performing digital communications using a randomized generatable interleaver. In accordance with one exemplary embodiment of the invention, a pseudo random interleaver of size n*m with excellent randomness and spread properties may be generated from a set of seed values. The interleaver of size N=n*m is defined by dividing the N possible address in the interleaver (0-N−1) into n subsets. The subsets are preferably generatable from a single value within the subset either using an algorithm or a memory based lookup table. The set of n seeds comprises one value selected from each subset. An improved communication system incorporating the aforementioned interleaver and using turbo codes or other concatenated coding systems is also disclosed.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and apparatus for manufacturing electronic device using roll-to-roll rotary pressing process
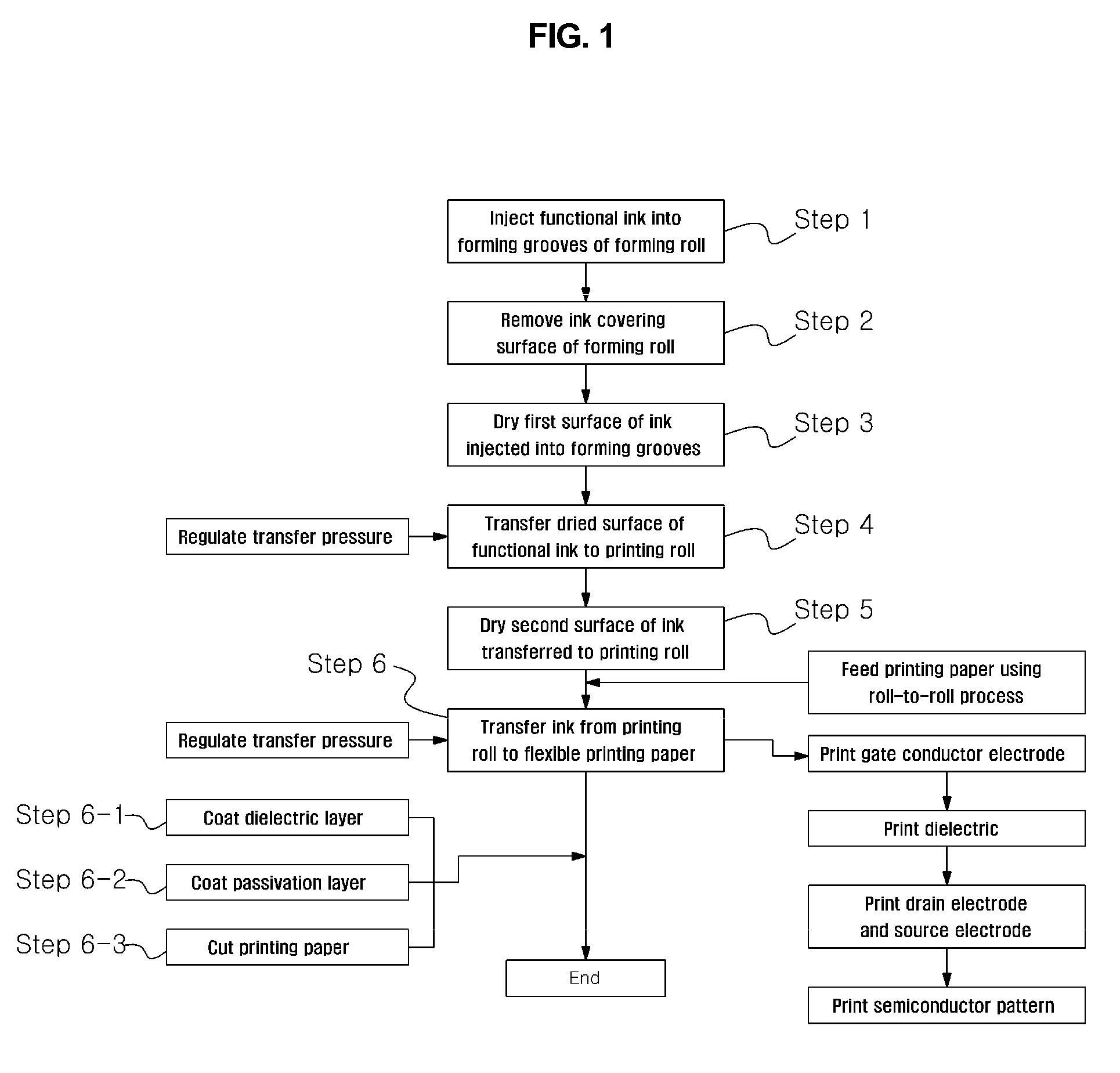
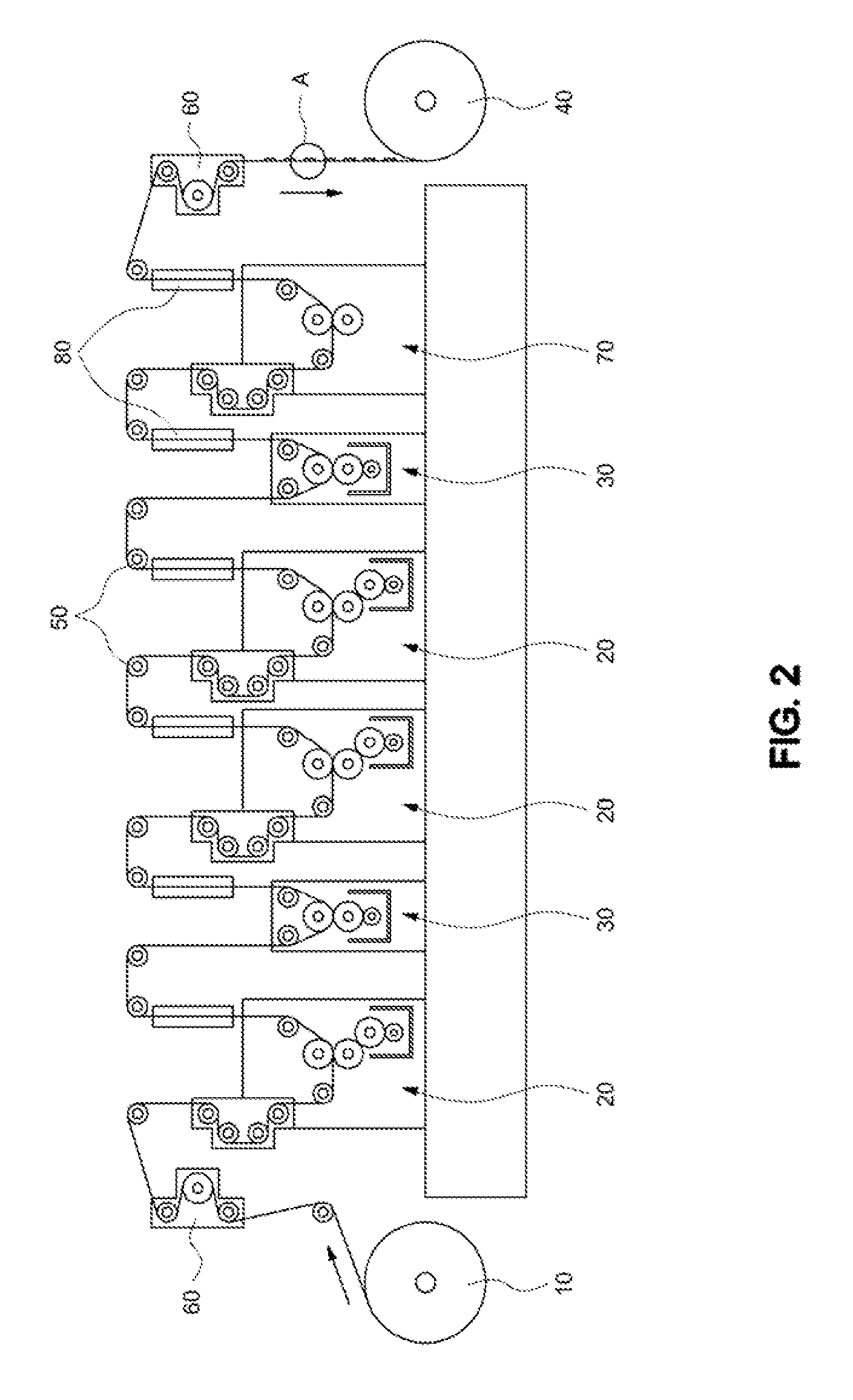
InactiveUS20090288567A1Rotary intaglio printing pressPattern printingEngineeringMechanical engineering
The present invention discloses an apparatus for manufacturing electronic devices using a roll-to-roll rotary pressing process, comprising a winding roll around which flexible printing paper is wound; a plurality of printing units arranged in a straight line; at least one coating unit; a rewinding roll to rewind the printing paper when printing has been completed; a plurality of guide rolls arranged between the winding roll and the rewinding roll, thus guiding the printing paper; a plurality of drying units, each drying unit being provided on a printing paper-path between the printing unit and the adjacent guide roll to dry ink transferred to the printing paper or on a printing paper-path between the coating unit and the adjacent guide roll to dry the printing paper on which coating agent is supplied; and tension regulating units installed around the winding roll and the rewinding roll, respectively, for regulating tension of the printing paper.
Owner:KOREA INST OF MACHINERY & MATERIALS
Printing conductive inks
InactiveUS20060260493A1Reduce conductivityImprove conductivityPlaten pressesMounting boardsDielectricEngineering
A conductive ink containing conductive, metallic particulates is printed onto a substrate by waterless printing on a lithographic press using a relief image plate in a flexographic coating unit or in a lithographic printing unit without fountain solution to provide a layer of conductive print on the substrate. The other units of a sheetfed press may be used to print decorative ink, including full-color printing, further conductive layers, and / or dielectric materials.
Owner:FLINT INK
Ink for printing a mobile phone antenna pattern, method for manufacturing a synthetic resin part for a mobile phone on which an antenna pattern is printed using the ink, and synthetic resin part for a mobile phone on which an antenna pattern is printed
InactiveUS20130076572A1Improve manufacturing productivityReduce the environmentSimultaneous aerial operationsConductive materialProduction ratePolystyrene
The ink for printing an antenna pattern for a mobile phone according to an embodiment of the present invention includes a mixture of one of silver (Ag) powder, nickel (Ni) powder, copper (Cu) powder, and gold (Au) powder, liquid acrylonitrile, liquid polystyrene, liquid butadiene, and methyl ethyl ketone (MEK) as a diluent. The present invention does not include a plating process, and thus allows a significant improvement in productivity.
Owner:YEN AN TECH +1
Electrode substrate of plasma display panel and method for making the same
InactiveUS20020125486A1Reduce manufacturing costNot to wasteSolid-state devicesPattern printingEngineeringSolvent
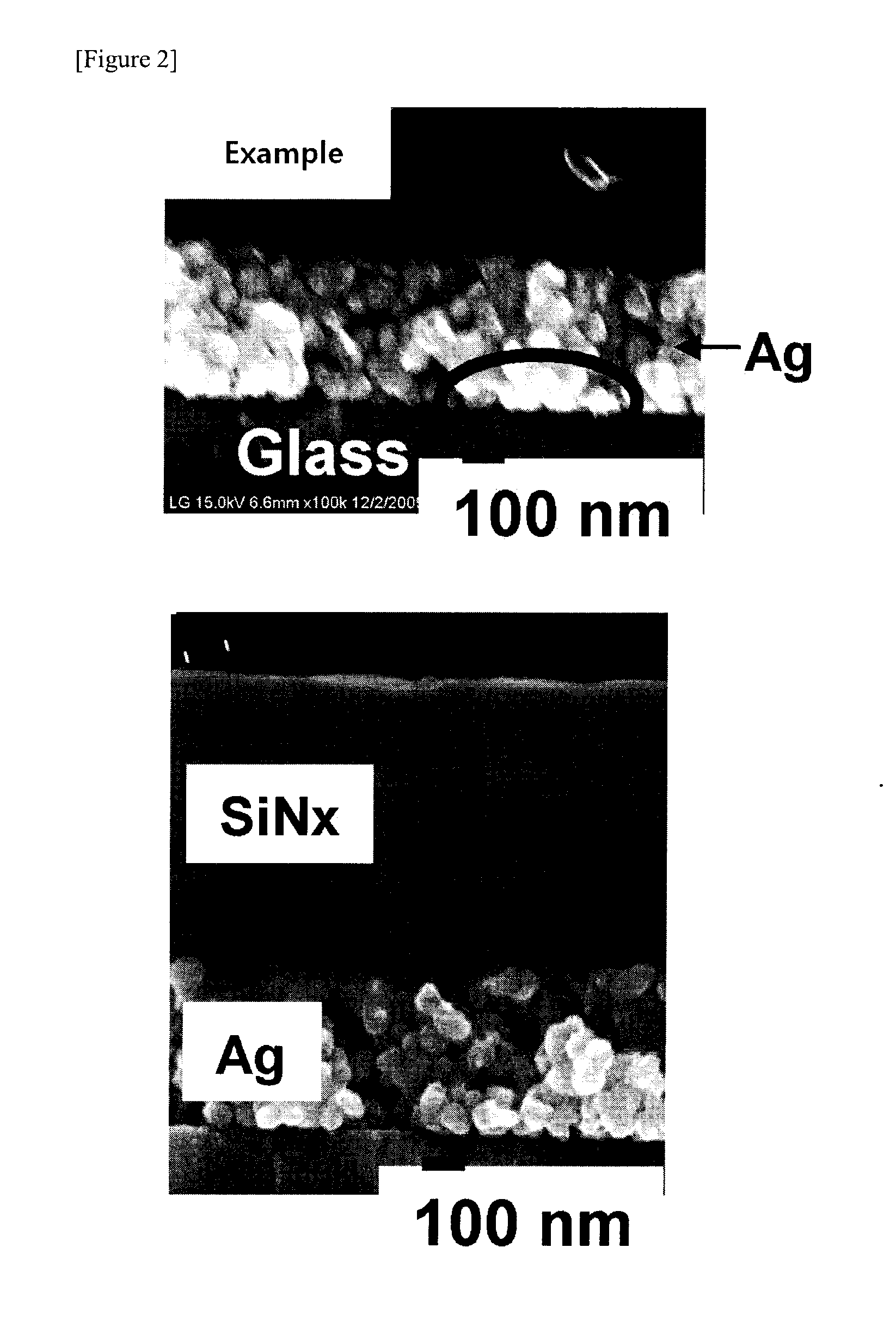
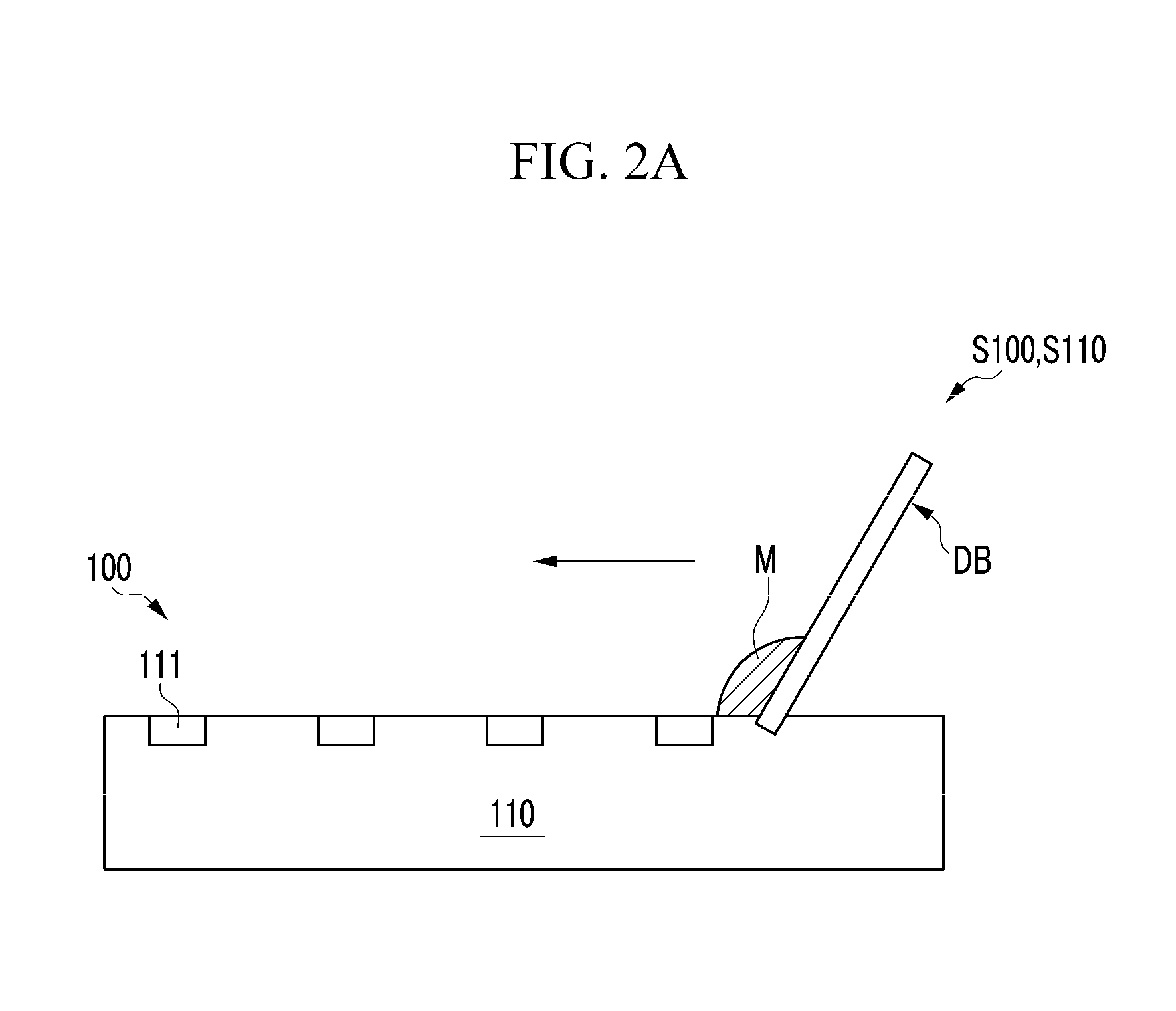
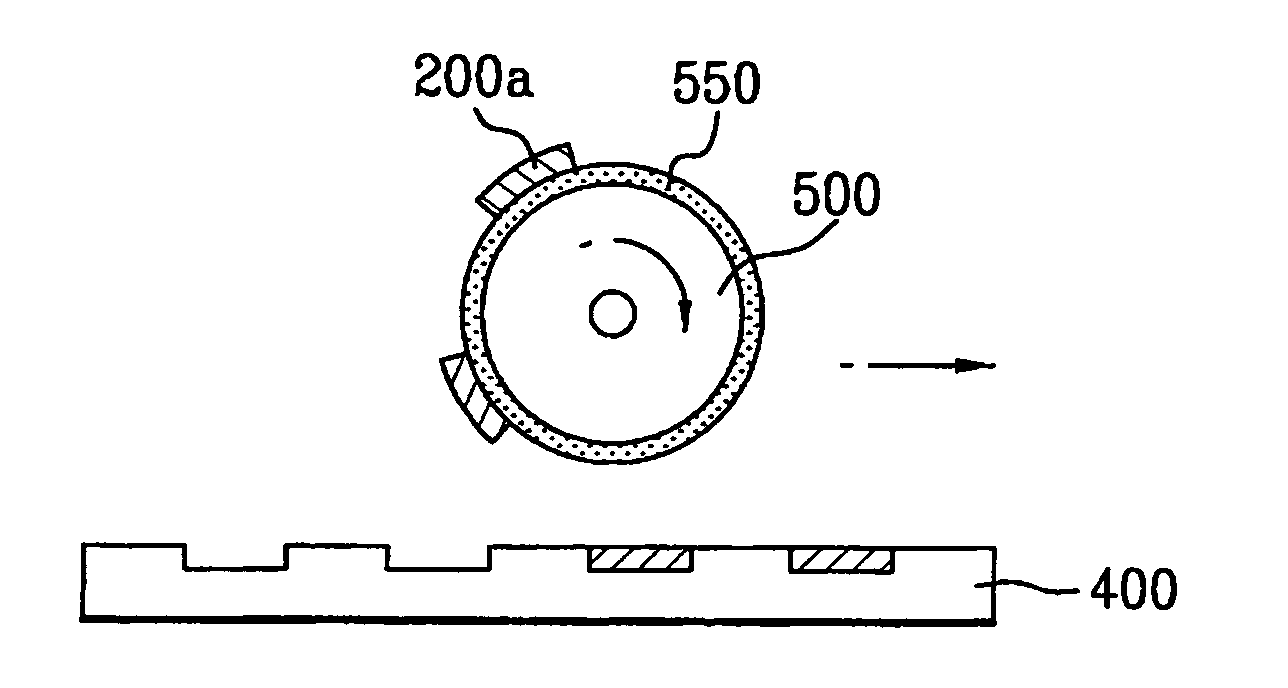
An electrode substrate of a PDP has an electrode pattern on a glass substrate and is made by baking and removing a resin binder in a conductive pattern composed of a conductive ink. The conductive pattern is formed by printing the conductive ink on the glass substrate by an intaglio offset printing method. The conductive ink is formed by dispersing or dissolving a metal powder and a resin binder into a solvent. A printing blanket used for printing the conductive pattern has a rubber layer on the surface of the printing blanket, and the rubber layer poses a volume increasing rate under 20% when the rubber is immersed in the solvent for 24 hours at 23° C. The printing blanket is heated such that a surface temperature TB of the printing blanket is about 40~200° C., and then the printing blanket is cooled in a condition that the surface temperature TB (° C.) of the printing blanket with respect to a surface temperature TP (° C.) of the intaglio satisfies the equation |TP-TB|<=5° C. As a result, the electrode substrate has a tiny and highly precise electrode pattern.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
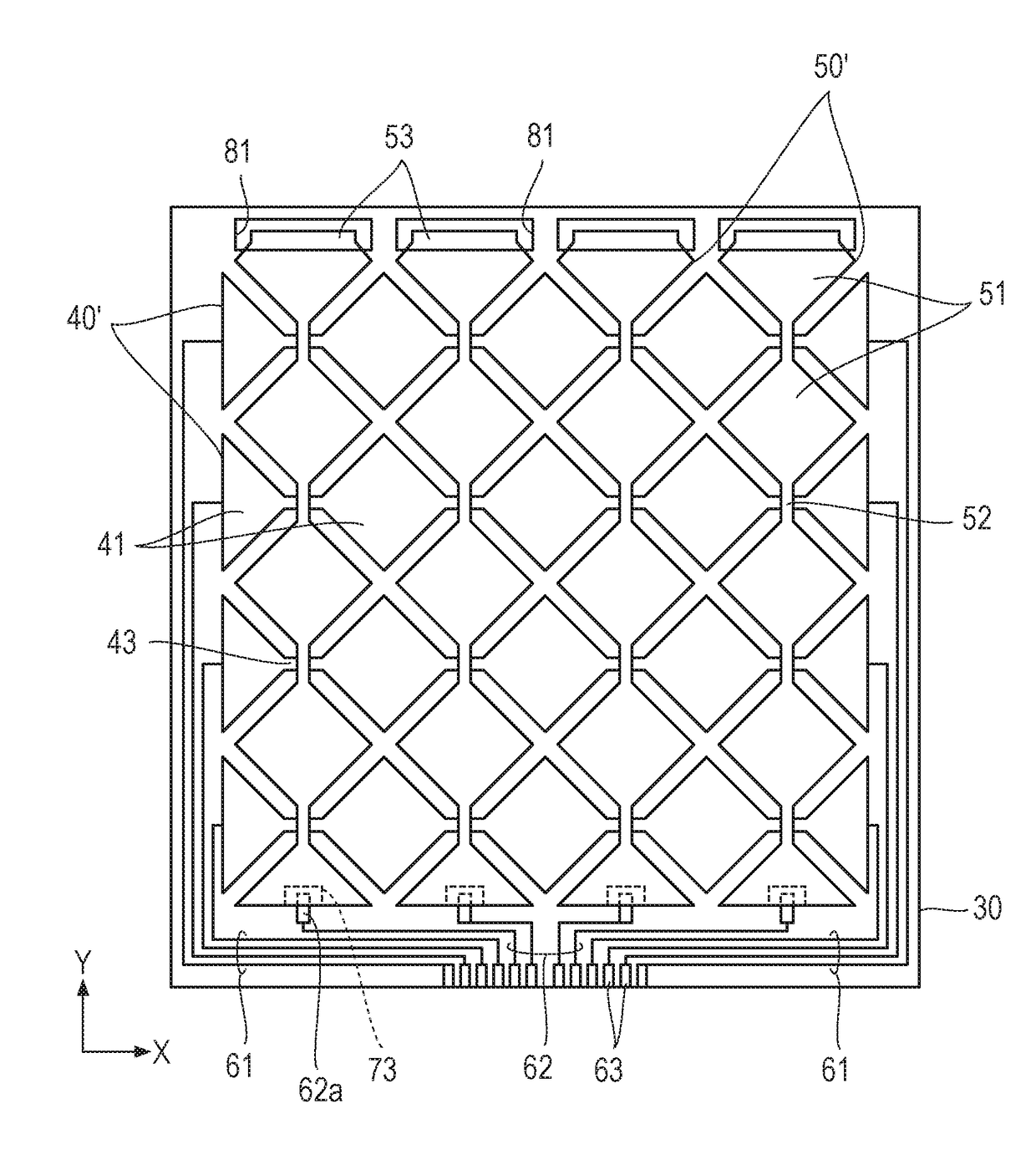
Cliche for off-set printing and product manufactured using the same
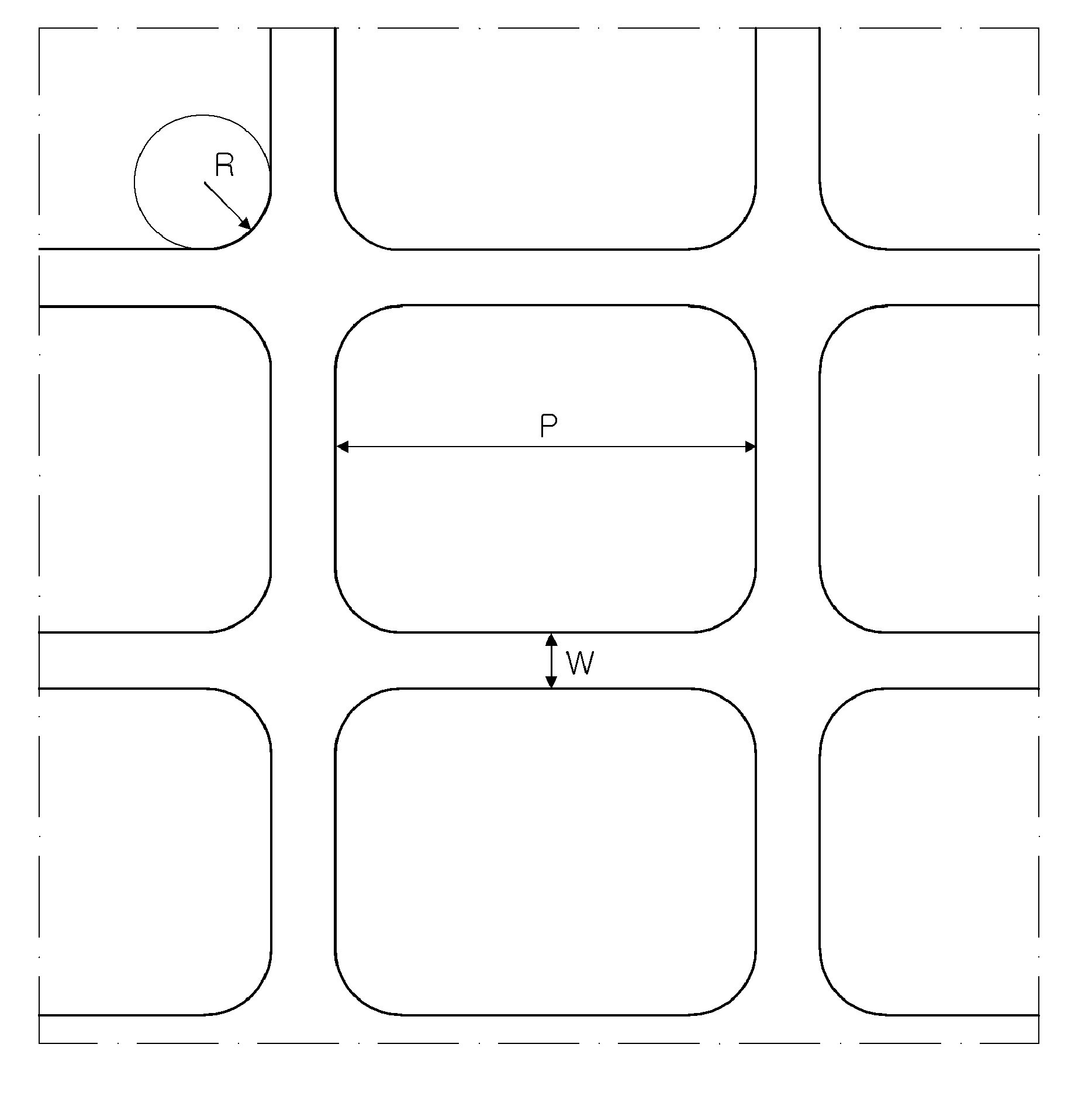
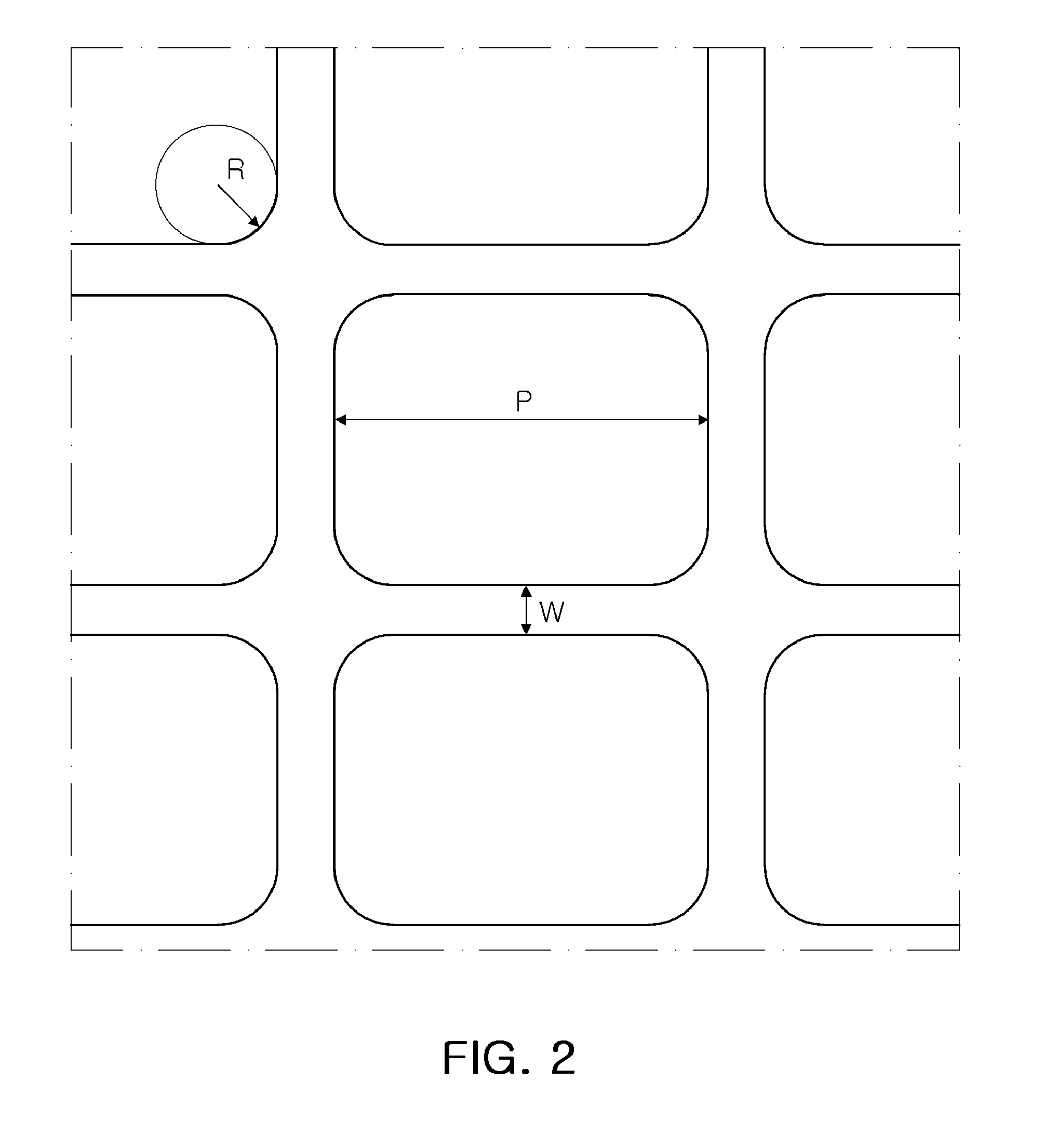
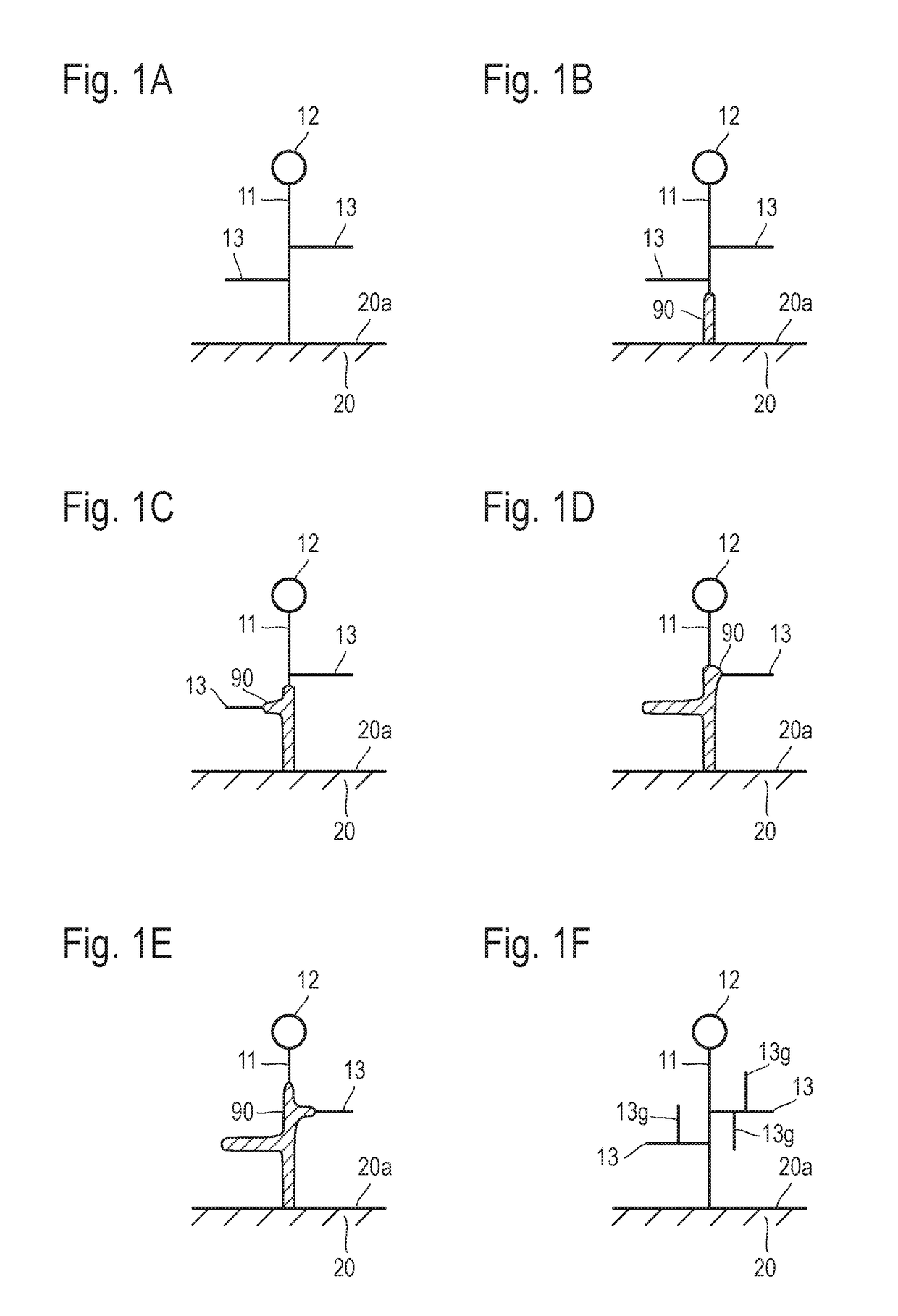
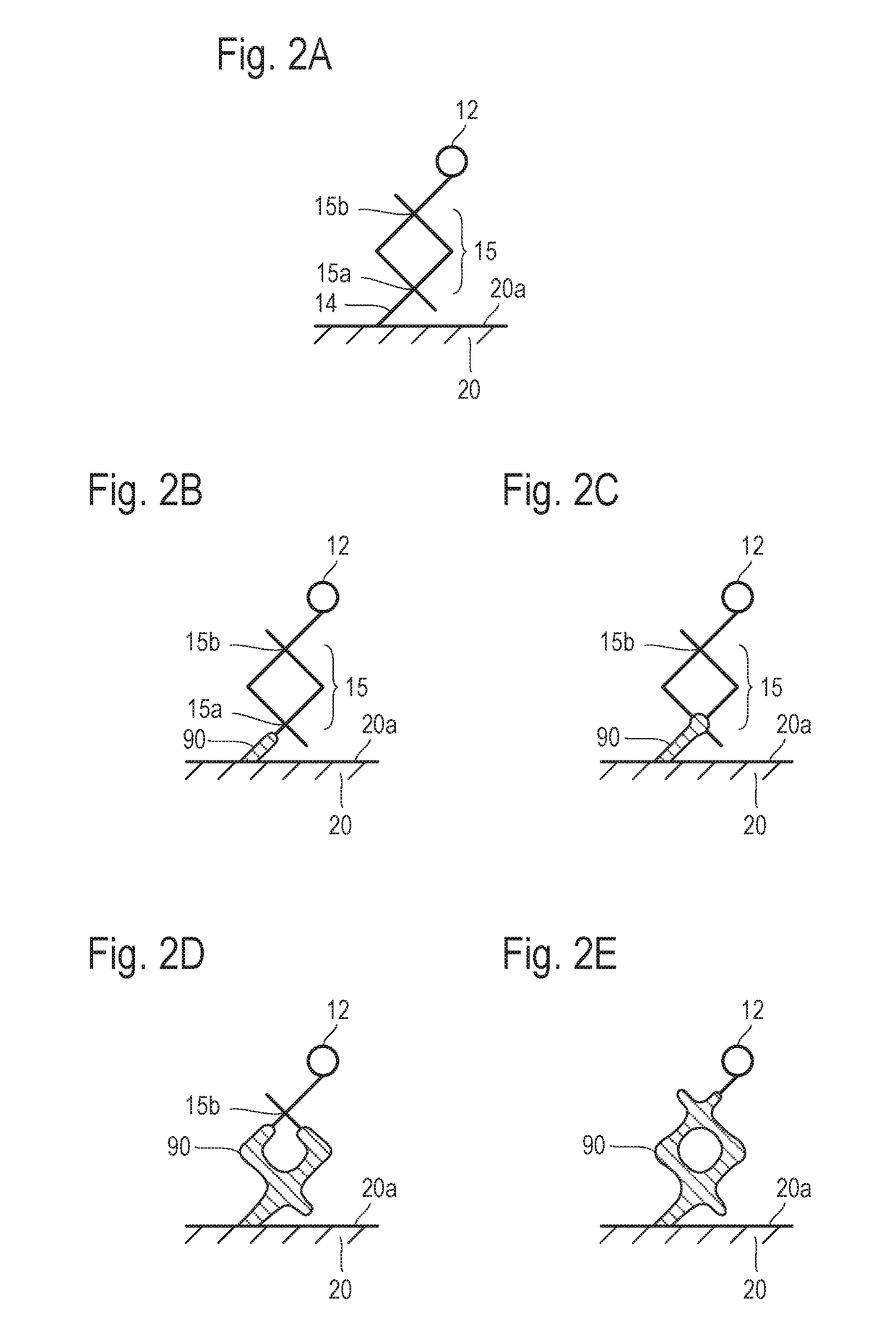
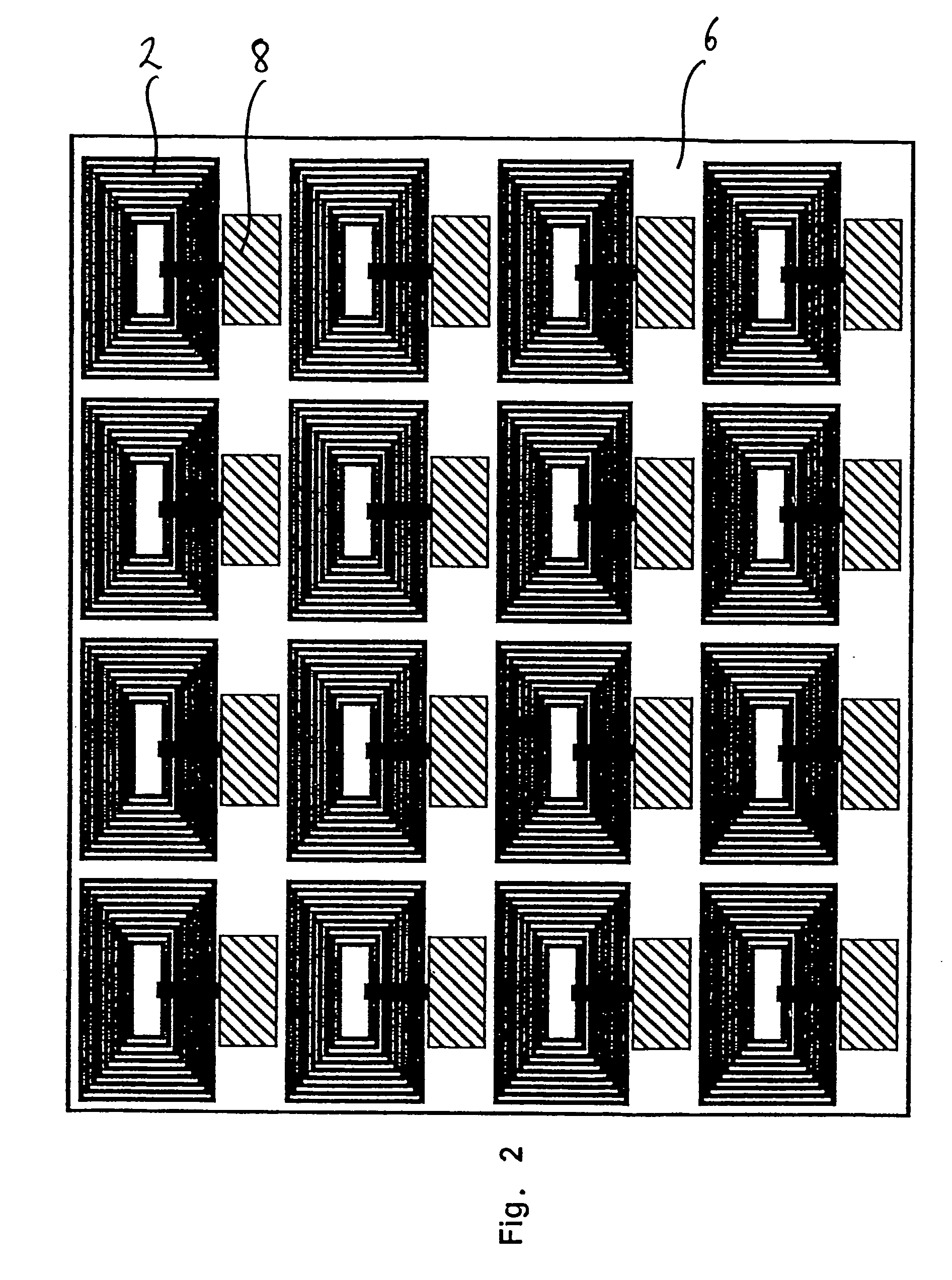
ActiveUS20110174176A1Increase line widthLine width is preventedPrinted circuit detailsMagnetic/electric field screeningEngineeringMesh grid
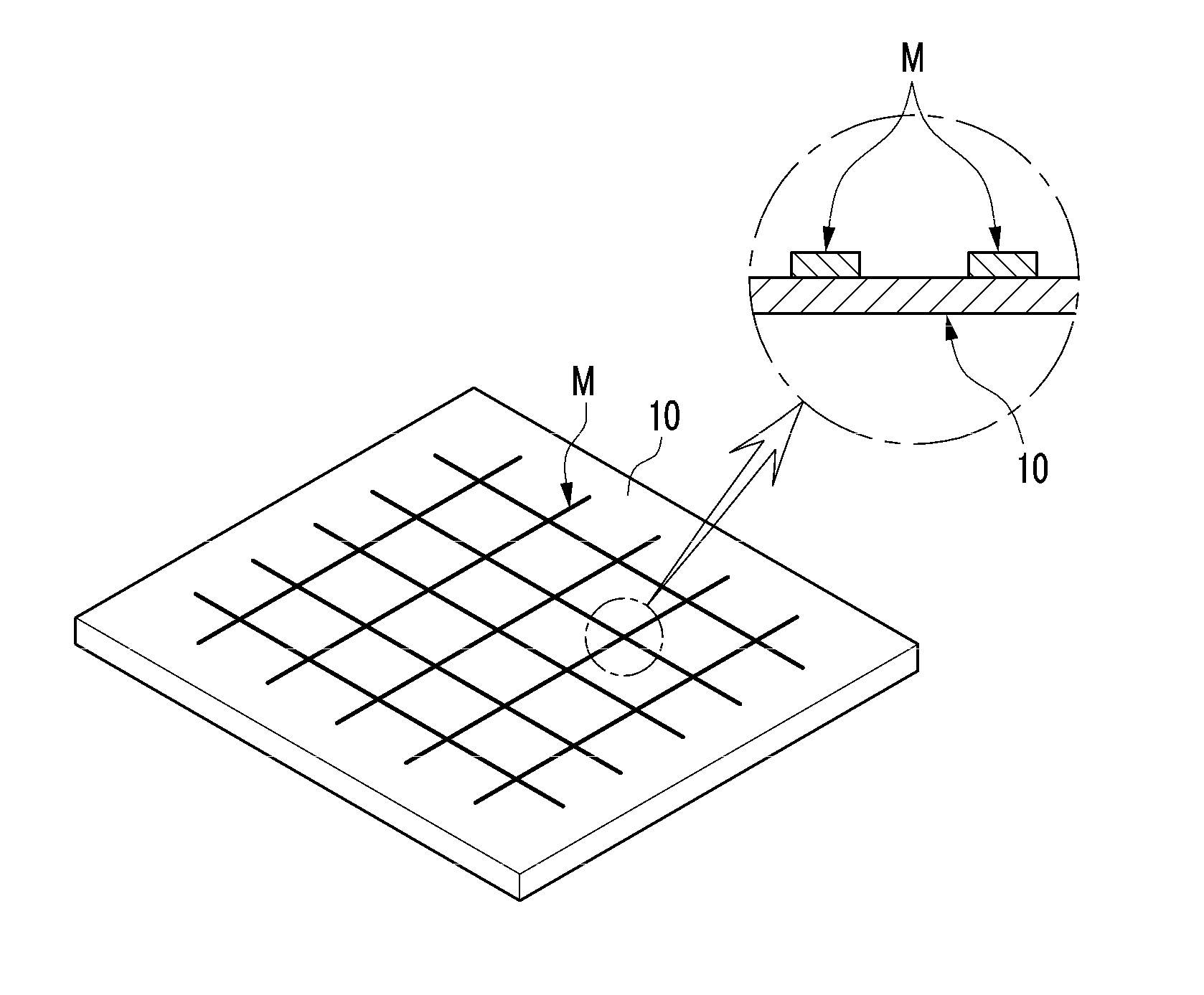
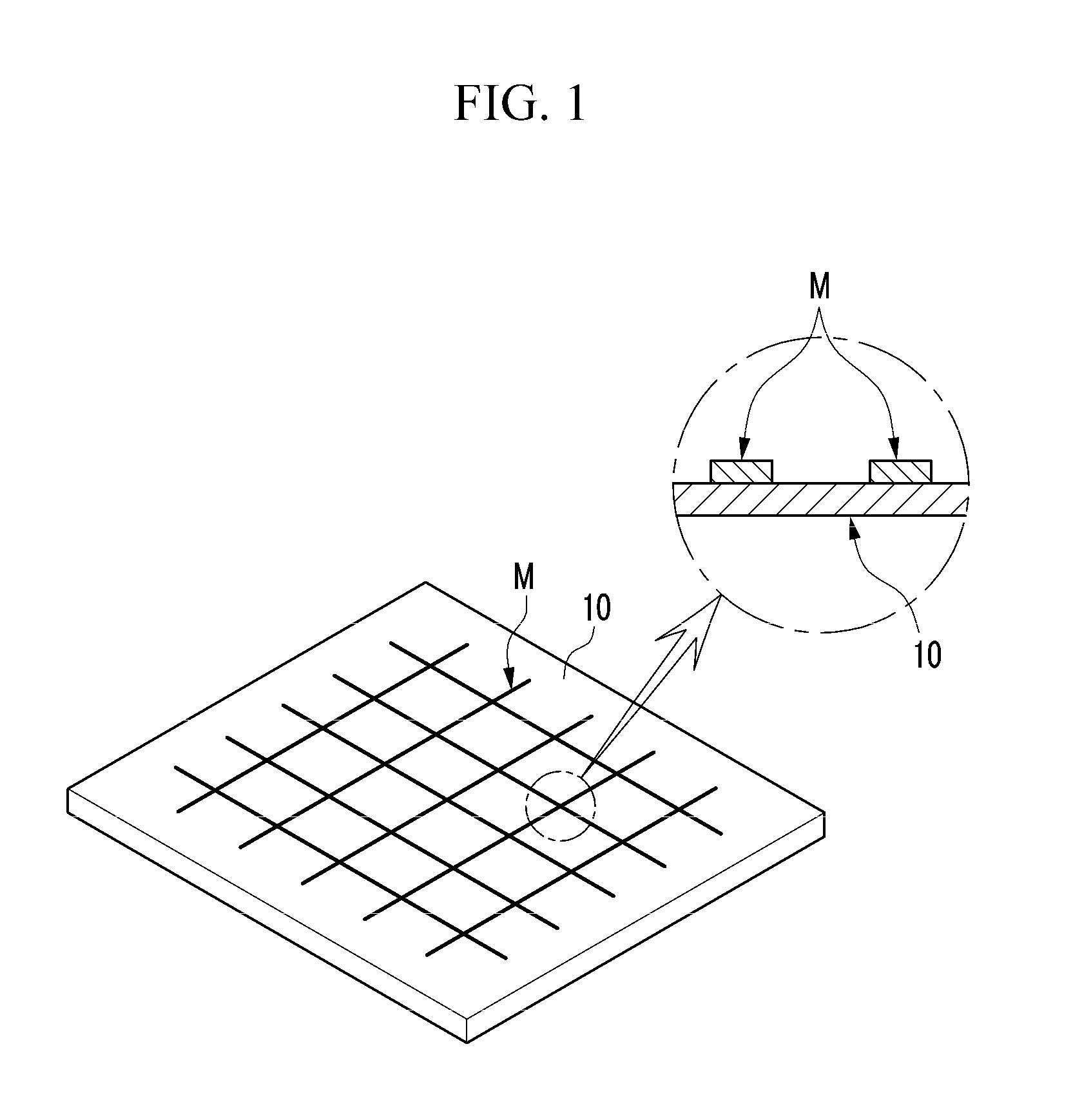
The present invention relates to a cliche for offset printing for forming a mesh pattern, and more specifically, to a cliche for offset printing comprising a mash pattern with a plurality of intersection units, wherein the plurality of intersection units are formed in a curved shape with a radius of curvature 0.6 to 4 times that of a mesh line width.When the cliche for offset printing of the present invention is used, line width reductions generated around the intersection units during mesh pattern printing may be reduced. As a result, when a final product is manufactured by using the cliche for printing of the present invention, the surface resistance properties of the product may be improved.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Paste coater and PoP automatic mounting apparatus employing the same
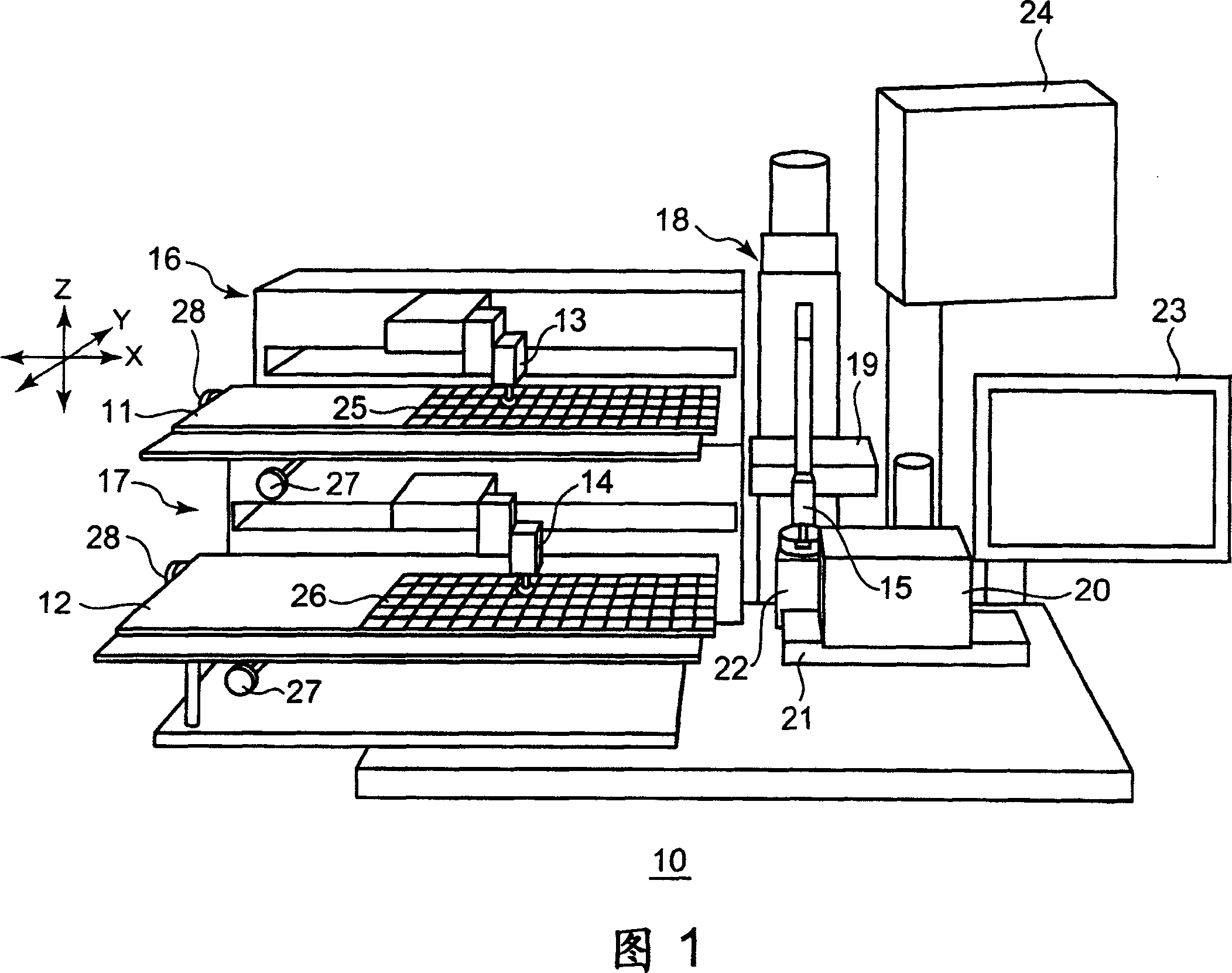
InactiveUS7497365B2Easy to adjustLiquid surface applicatorsPrinted circuit aspectsRotational axisEngineering
A paste coater that can apply an amount of a solder paste to small-diameter bump electrodes at a narrow pitch is described. A paste coater includes: a transfer roller, supported by a sub frame; a roller drive mechanism for rotating the transfer roller; a paste storage unit for storing paste to be supplied to the surface of the transfer roller; a squeegee having a distal edge, parallel to the rotary shaft of the transfer roller, separated by a gap from the distal edge to the surface of the transfer roller; a squeegee holder for holding and including biasing means for pushing the squeegee in a first direction thereby widening the gap; and a gap adjustment mechanism with biasing means for pushing the squeegee in a second direction thereby narrowing the gap.
Owner:IBM CORP
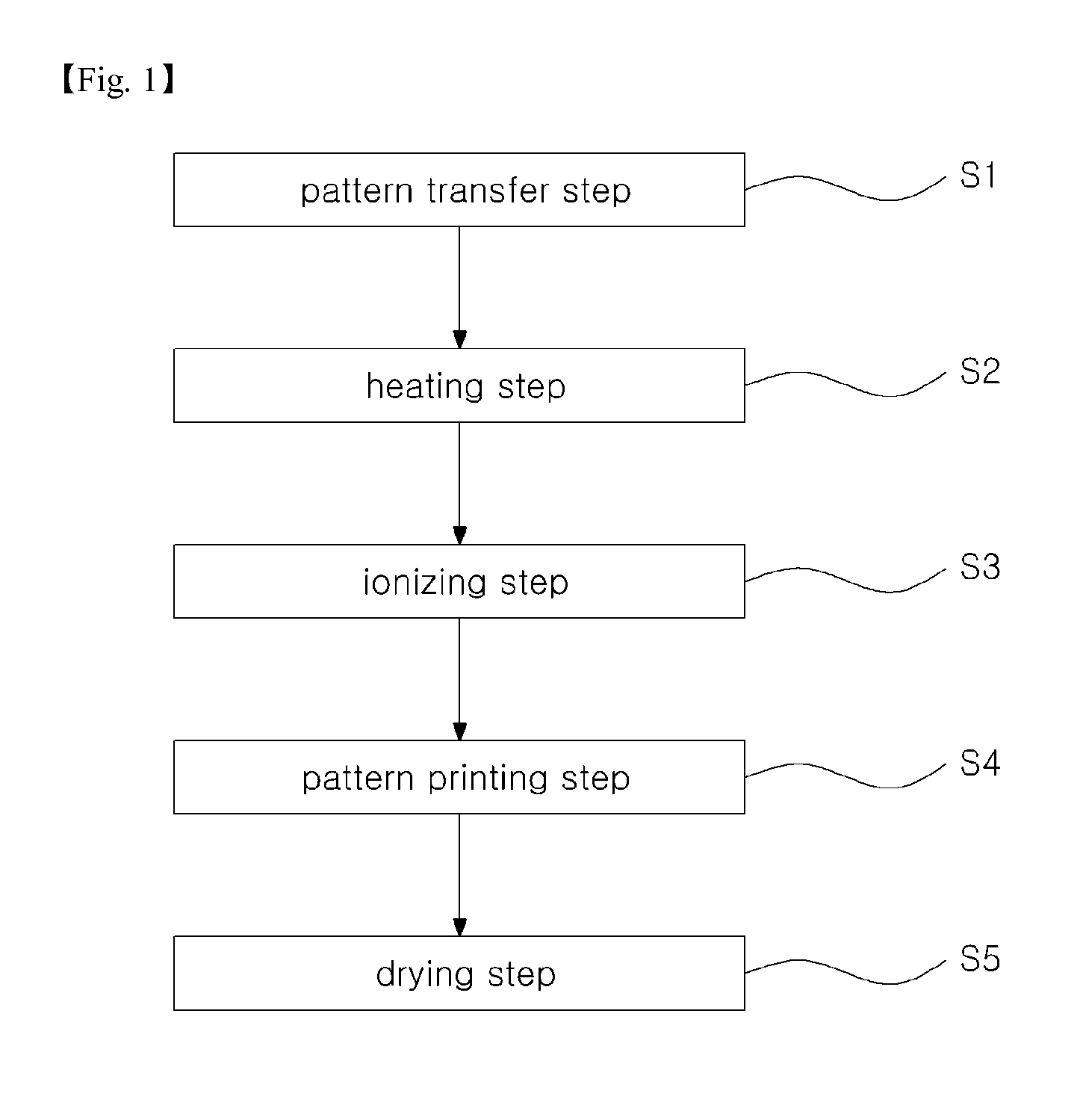
Method for forming pattern using printing process
A method for forming a pattern using a printing process is disclosed in the present invention. The method includes forming a resist layer on a substrate having an etching layer thereon, locating a master having a convex pattern over the substrate, pressing the master against the substrate until the convex pattern of the master directly contacts the etching layer, and removing a portion of the resist layer to expose a surface over the substrate, the removed portion of the resist layer having a width substantially the same as the convex portion of the master.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Stretchable circuit board and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20170245362A1Preventing a wire from breakingCircuit bendability/stretchabilityInsulating substrate metal adhesion improvementEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:NIPPON MEKTRON LTD
Printing plate for intaglio offset and manufacturing method thereof, methods for manufacturing substrate and display apparatus
InactiveCN101301827AEnhance ink affinityHigh transfer accuracyPlate printingOther printing apparatusDisplay deviceMechanical engineering
Owner:NEC LCD TECH CORP
Method of forming thick-film wiring and method of producing laminated electronic component
InactiveUS7049176B2Rotary intaglio printing pressSoldered/welded conductive connectionsHardnessOptoelectronics
In a method of forming a thick-film wiring on a substrate, photosensitive-electroconductive paste is filled into a pattern groove formed on the surface of a light-transmitting intaglio plate. The pattern groove corresponds to a desired thick-film wiring pattern. The photosensitive-electroconductive paste filled in the pattern groove are irradiated with light-rays from the front and back sides of the intaglio plate to cause the paste to harden until the overall peripheral surface of the electroconductive paste has a predetermined hardness. The electroconductive paste hardened in the pattern grooves of the intaglio plate is transferred to an intermediate piece. Then, the electroconductive paste is transferred from the intermediate piece to a substrate. Thereafter, the electroconductive paste is fired, whereby a thick-film wiring is formed on the substrate.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Printing plate, method of fabricating the same, and method of fabricating flat panel display using the same
ActiveUS20070048667A1Improve accuracyHigh precision formingNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesResistDisplay device
A method of fabricating a printing plate includes: preparing a substrate; forming a metal layer on an entire surface of the substrate; forming a resist pattern on the metal layer, the resist pattern having a fine pattern exposing a portion of the metal layer; wet etching the exposed metal layer, and removing the resist pattern to form a metal layer pattern exposing a portion of the substrate; wet etching the exposed substrate, and removing the metal layer pattern to form a recessed pattern; and forming a compensation layer on an entire surface of the substrate where the recessed pattern is formed.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Method for burying conductive mesh in transparent electrode
ActiveUS20130031781A1Improve contact effectPrevent protrudingPrinted circuit aspectsApparatus for manufacturing conducting/semi-conducting layersOptoelectronicsElectrode
Owner:KOREA INST OF MASCH & MATERIALS
Patterning method and method for manufacturing liquid crystal display device using the same
ActiveUS20070157841A1Improve accuracyLow costCylinder pressesPlaten pressesLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
A patterning method and a method for manufacturing an LCD device using the same are disclosed. The patterning method includes preparing a printing plate having concave and convex portions; coating a pattern material in the concave portion of the printing plate; rolling a printing roller on the printing plate to print the pattern material of the concave portion on the printing roller; and rolling the printing roller on a substrate to print the pattern material of the printing roller on the substrate.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
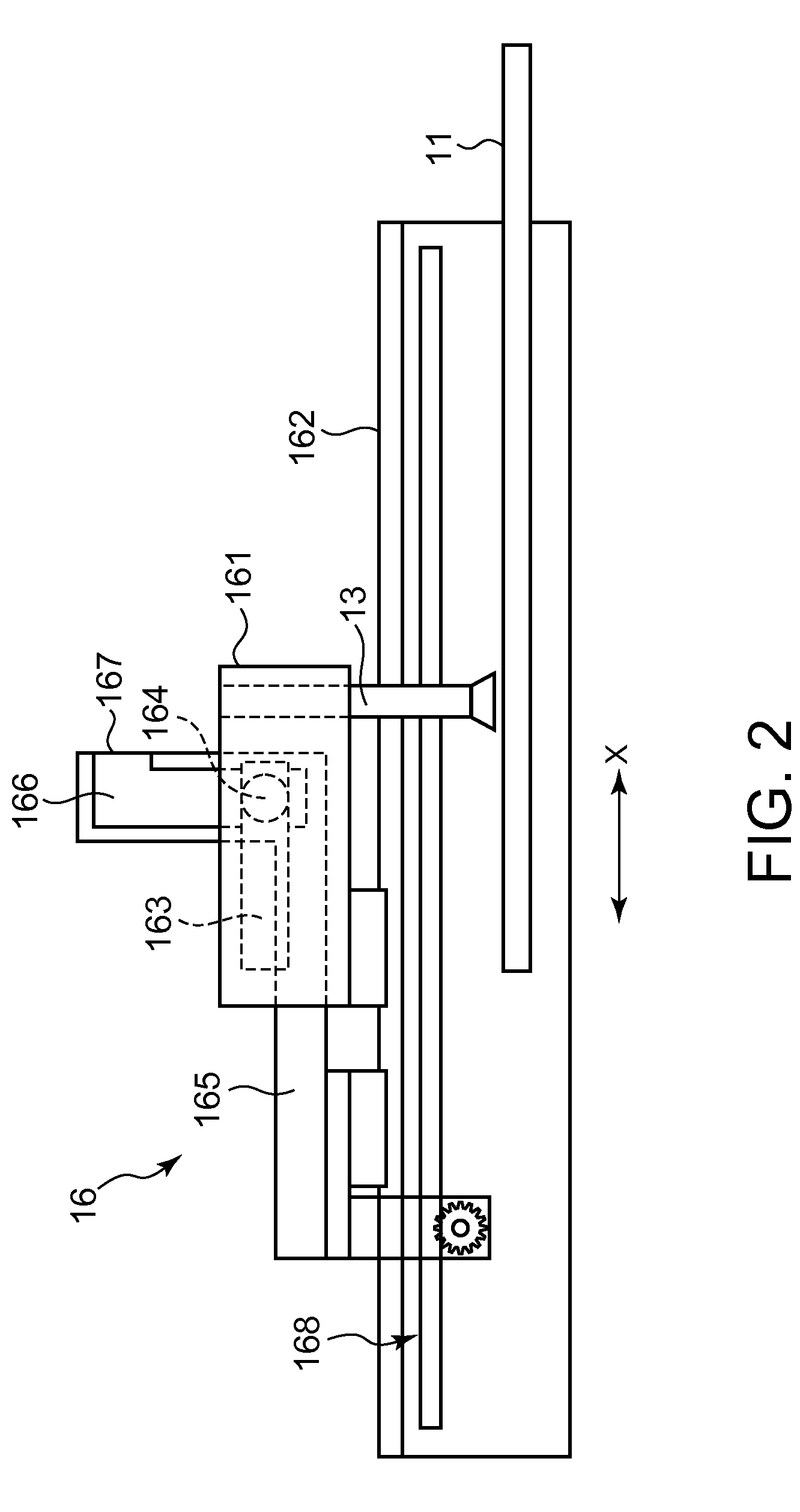
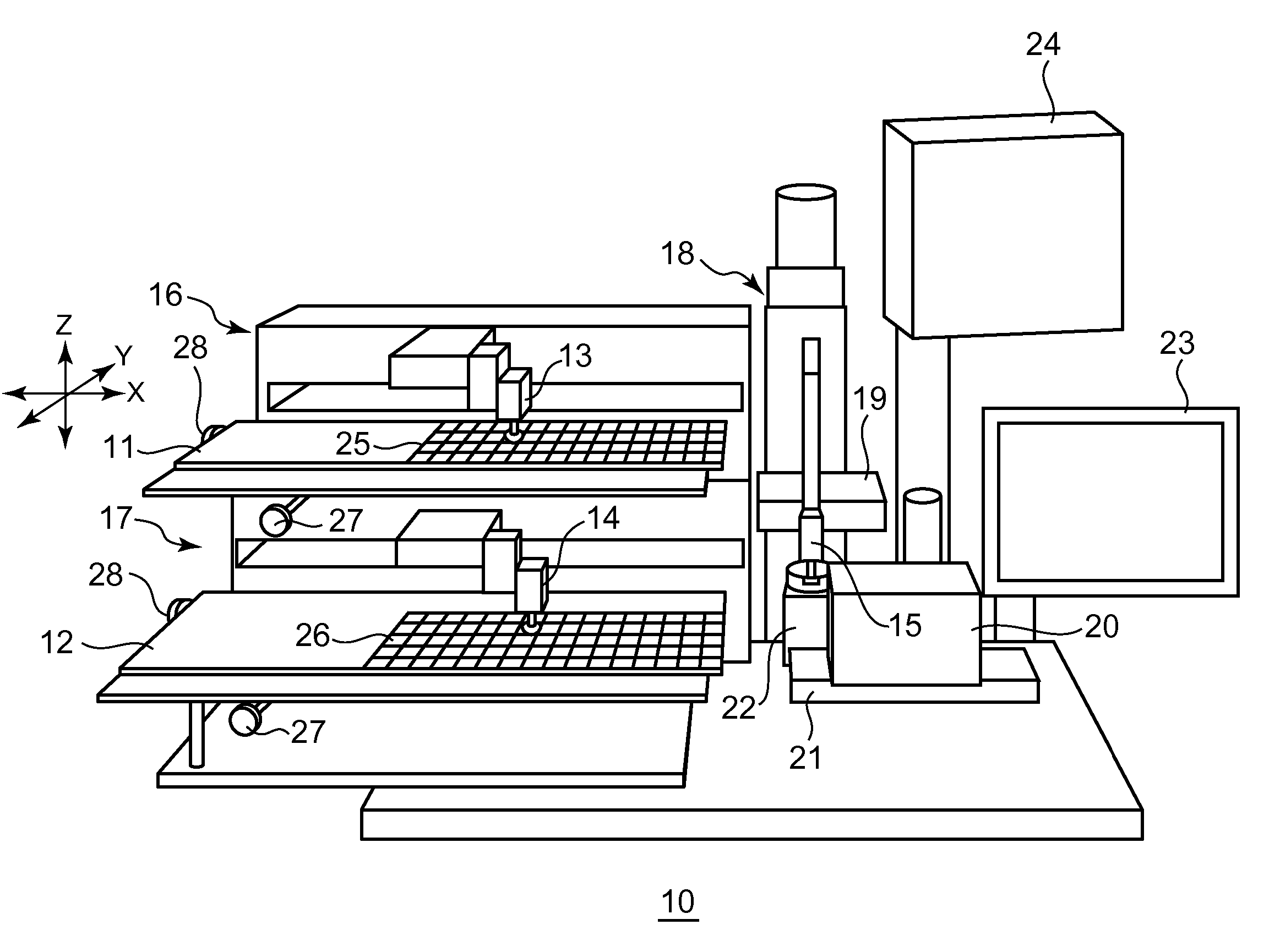
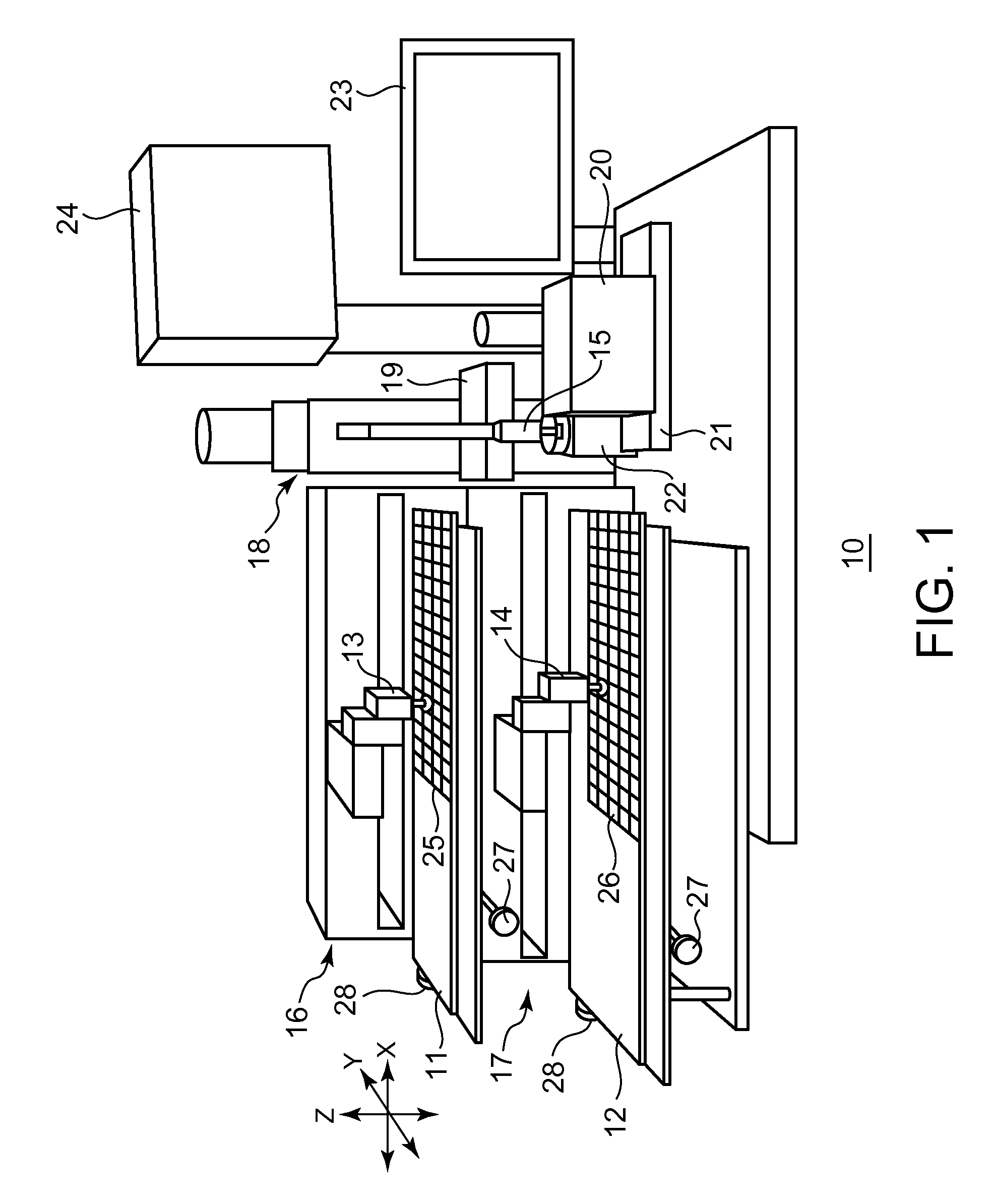
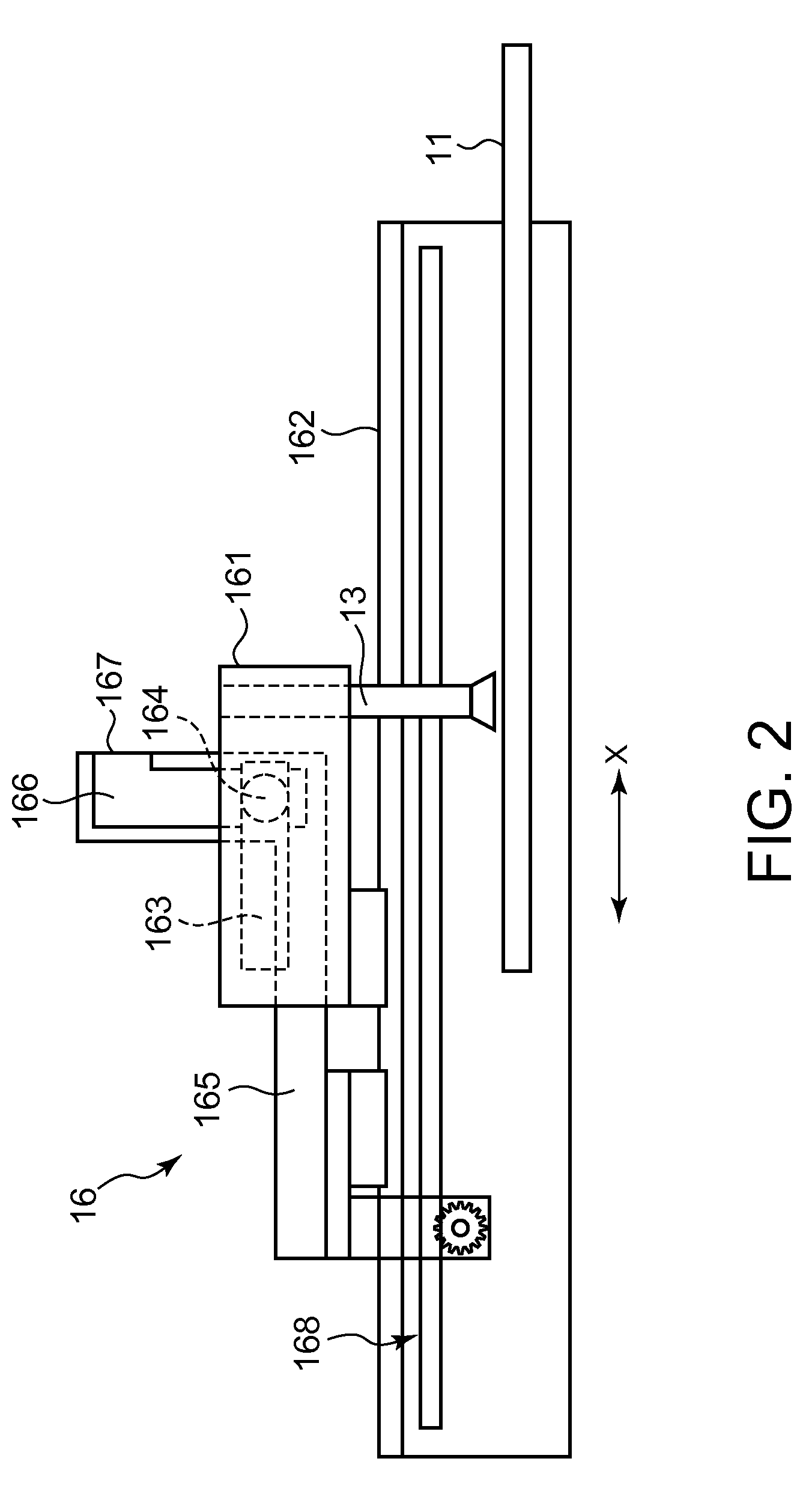
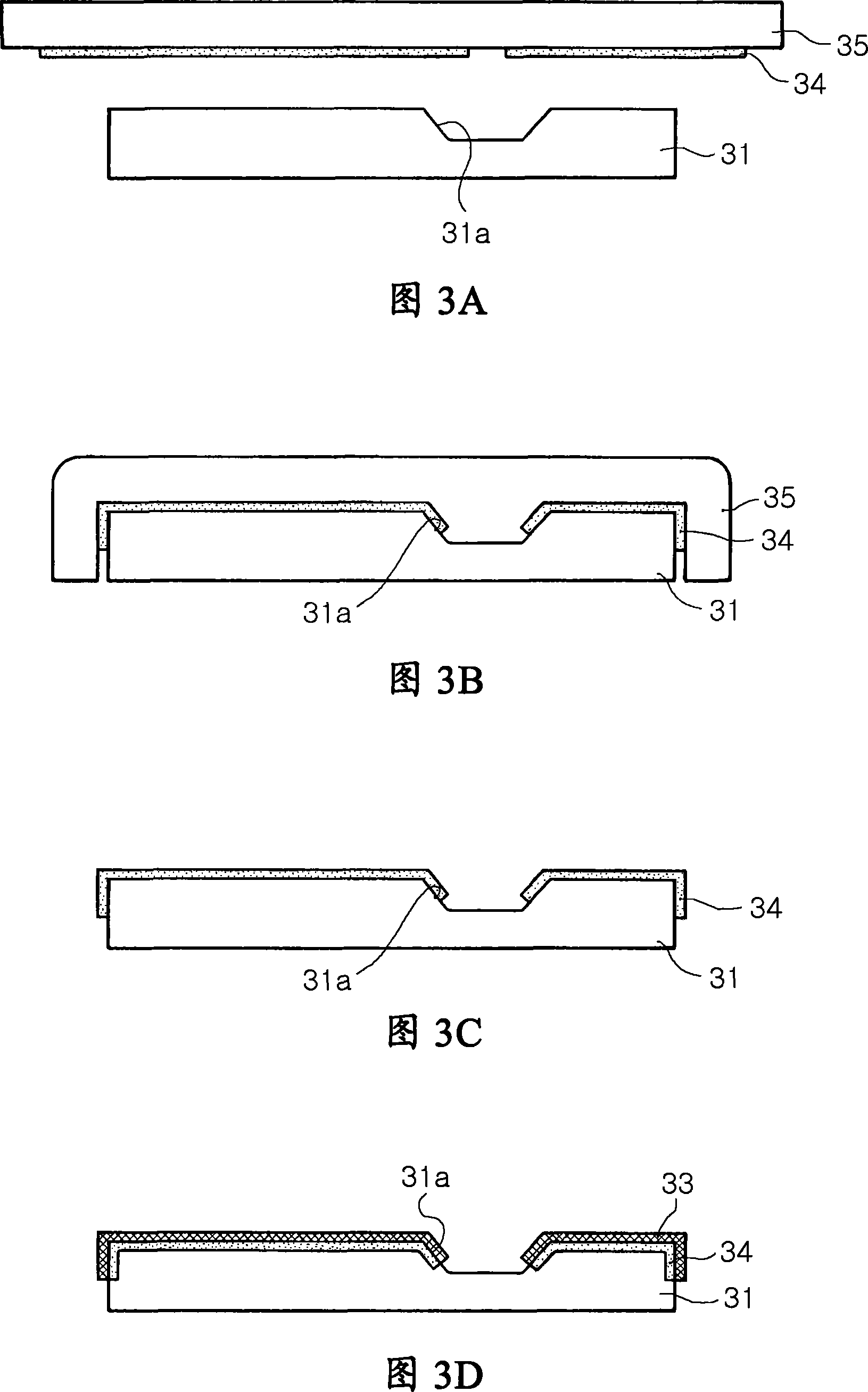
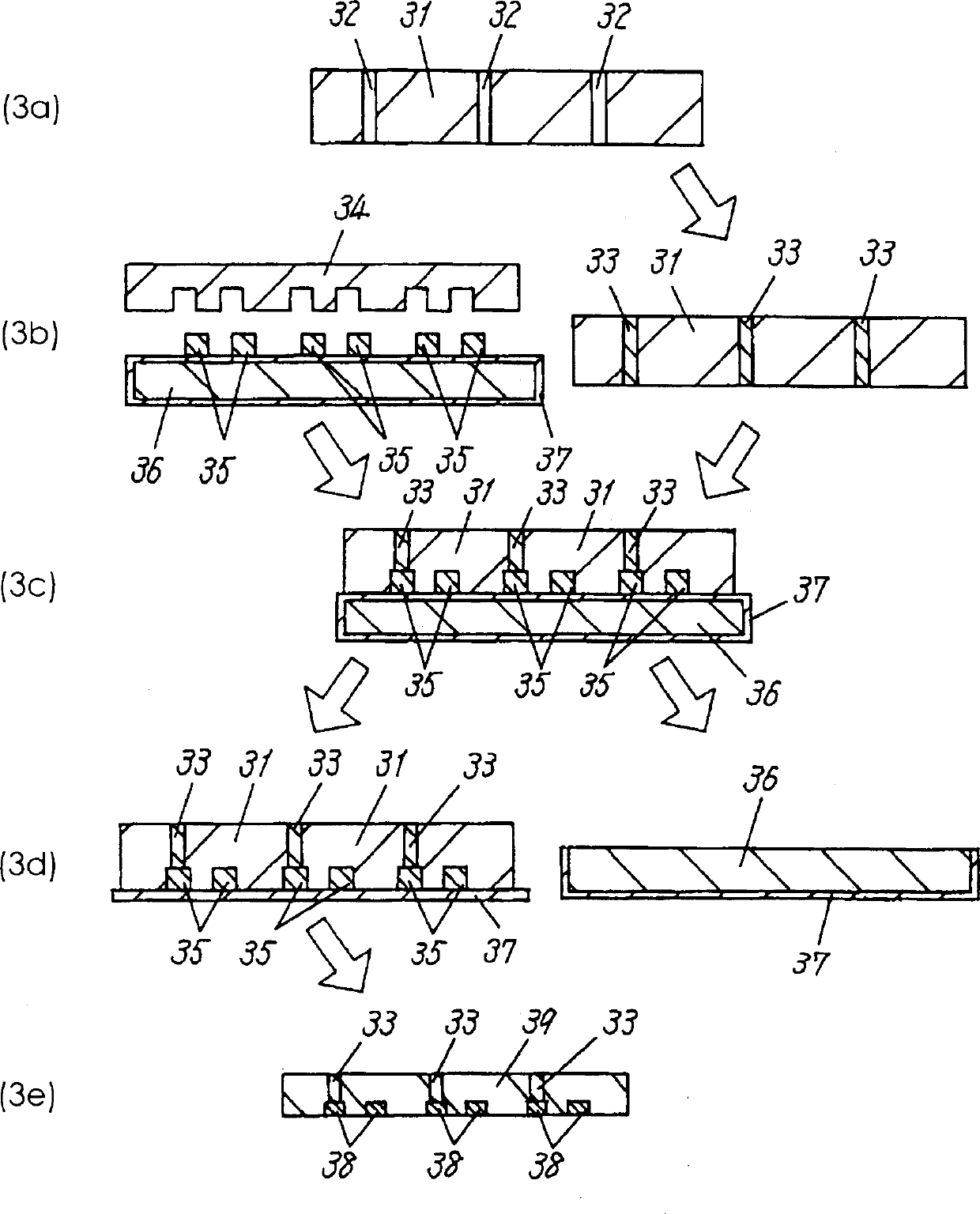
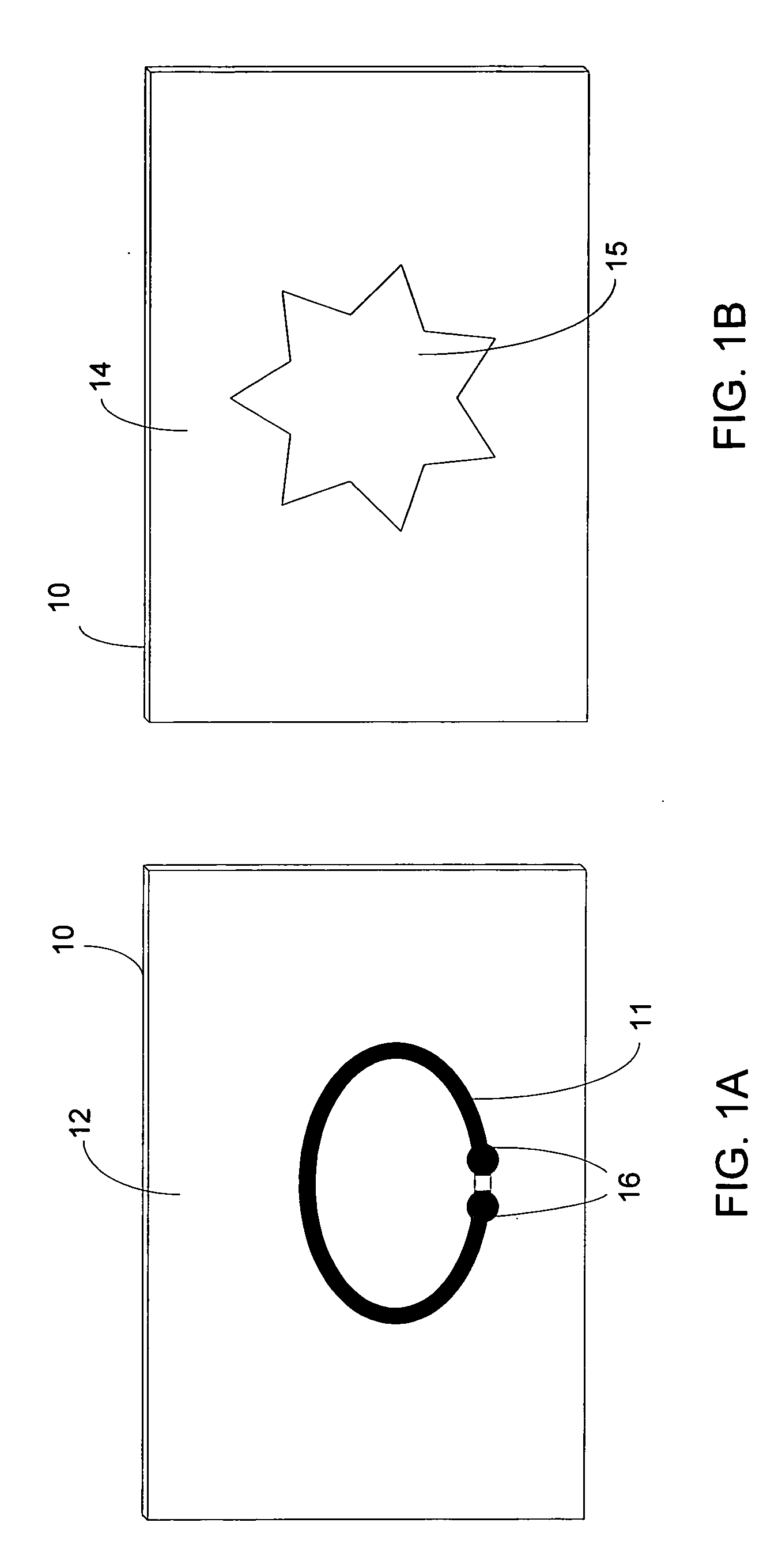
Apparatus for pad printing a conductive picture on an irregular surface
InactiveUS6470797B1Easy to coverImprove accessibility3D rigid printed circuitsPlaten pressesPad printingEngineering
The present invention relates to a method and an arrangement for transferring a conductive picture (12) to an irregular surface of a mobile phone casing (4) for shielding the mobile phone casing from electromagnetic radiation. It also relates to the printing color used for the conductive picture and tampon pads (5) used for the transferring of the conductive printing color to the phone casing (4). Conductive partial pictures (7) are printed on the irregular surface of the casing (4) step by step by means of tampon pads until the complete conductive picture (12) is achieved. The tampon pad has a shape corresponding to the surface of the phone casing. The printing color has a composition, which facilitates the adhering on the tampon pad. The invention also describes a method for printing an electric circuit pattern on a phone casing (4) by using the above mentioned tampon pads and printing color.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
Method for the manufactur of a printed circuit and planar antenna manufactured with this printed circuit
InactiveCN1528109APrinted circuit aspectsRadiating elements structural formsEngineeringCircuit models
In a method for the manufacture of a printed circuit on a dielectric carrier (2), in a first step a circuit pattern (1) is applied with an electrically conductive ink and, in a second step, the circuit model is plated, the electrically conductive ink being applied by means of a method of gravure printing and the plating being done by electrolytic or chemical means.
Owner:MICROCONNECTIONS
Paste Coater and PoP Automatic Mounting Apparatus Employing the Same
InactiveUS20070137559A1Easy to adjustLiquid surface applicatorsPrinted circuit aspectsSolder pasteMechanical engineering
A paste coater that can apply an amount of a solder paste to small-diameter bump electrodes at a narrow pitch is described. A paste coater includes: a transfer roller, supported by a sub frame; a roller drive mechanism for rotating the transfer roller; a paste storage unit for storing paste to be supplied to the surface of the transfer roller; a squeegee having a distal edge, parallel to the rotary shaft of the transfer roller, separated by a gap from the distal edge to the surface of the transfer roller; a squeegee holder for holding and including biasing means for pushing the squeegee in a first direction thereby widening the gap; and a gap adjustment mechanism with biasing means for pushing the squeegee in a second direction thereby narrowing the gap.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for forming insulating layer, method for producing electronic device, and electronic device
ActiveUS20170156218A1Facilitate conductionTransparent dielectricsConductive pattern formationElectrical conductorElectrical connection
By flexographic printing or inkjet printing, insulating ink is applied on a wiring pattern in accordance with a predetermined printing pattern. The insulating ink is hardened, whereby an insulating layer is formed. A contact region of the wiring pattern that is used for electrical connection with a conductor other than the wiring pattern is not covered with the insulating layer. The printing pattern is delimited by the outline of a non-printing region including the contact region. The wiring pattern includes, in the non-printing region, a trunk wiring line leading, to the contact region, from a position on the wiring pattern at which the wiring pattern overlaps with the outline and a branch wiring line extending from a point on at least one side of the trunk wiring line and terminating without making contact with the outline.
Owner:JAPAN AVIATION ELECTRONICS IND LTD
Method of manufacturing metal film pattern forming body
InactiveCN101145630ALiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingConductive pattern formationEngineeringMetal
A method of manufacturing a metal film pattern forming body, the method including: forming a desired metal film pattern on one surface of a stamp by using a catalyst for activating a surface of a plastic base; activating the surface of the plastic base by transferring the catalyst formed on the surface of the stamp onto the surface of the plastic base; and plating the surface of the activated plastic base.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Method for producing ceramic substrate
InactiveCN1381160AEasy to manufactureInsulating substrate metal adhesion improvementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectrical conductorHigh density
Provided is a method for manufacturing a ceramic circuit substrate in which a high-density pattern obtained by a thick-film gravure (11) replication method is used as an inner layer conductor. The adhesive (14) is coated on the heat-resistant substrate (13), and the conductor pattern (12) is temporarily copied on the heat-resistant substrate. A green sheet (15) is laminated on the conductor pattern side of the heat-resistant substrate and heated and compressed, whereby the conductor pattern is reproduced on the green ceramic green sheet and cut into the green sheet. A conductor pattern is thus formed on the green sheet. After the green sheet and the pattern are debonded and sintered, a ceramic circuit board with a high-density pattern obtained by the thick film gravure replication method as the inner layer conductor can be manufactured.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method for printing an electronic circuit component on a substrate using a printing machine
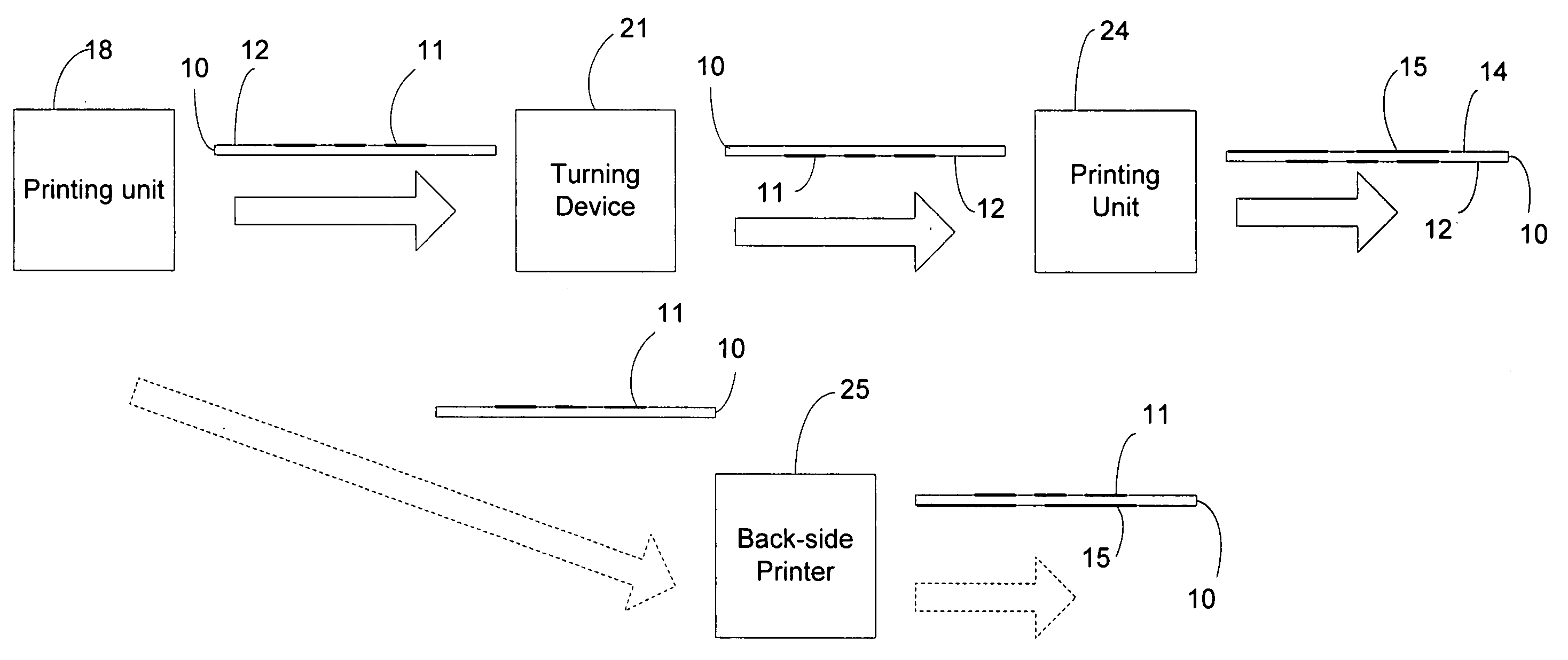
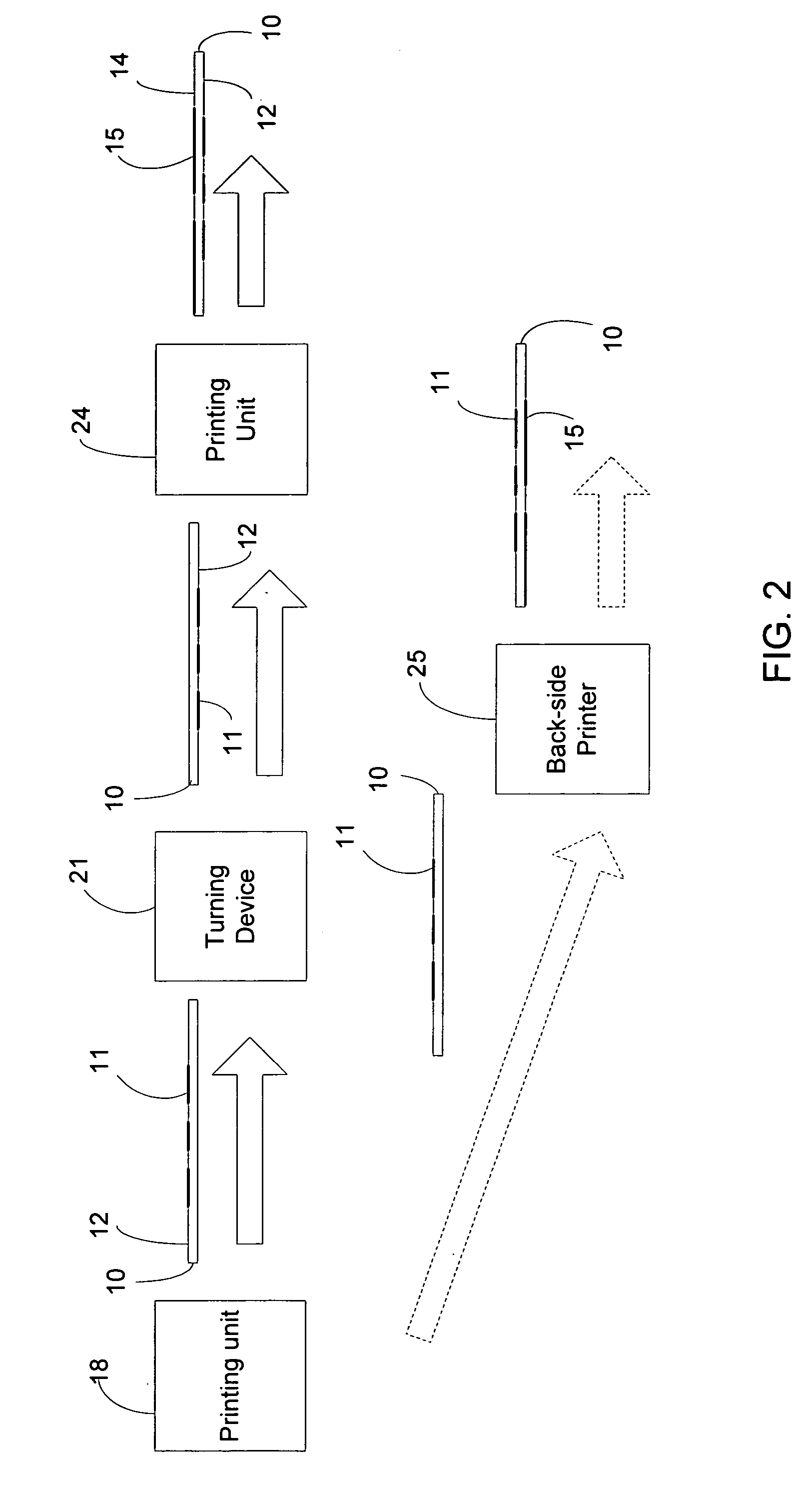
A method of printing an electronic circuit or components thereof uses a printing machine to print a conductive structure on the front printing side (back side of the sheet) of a printing substrate. The sheet is then reversed and a decorative printing motif is printed on the back side in one work step. Alternatively, the circuit or components of a circuit may be printed by having a printing machine for color printing preceded by a printing machine for printing on the back side of the printing substrate. A chip is applied to the printing substrate where the back side of the printing sheet with the printing motif is cooled to prevent any negative effect on the printing motif and / or the printing substrate.
Owner:MANROLANAD AG
Printing using a structure coated with ultraviolet radiation responsive material
The present invention relates to a printing method using a structure coated with ultraviolet radiation responsive material. Wetting and print transfer from a printing patterned transfer surface is enhanced by applying an ultraviolet radiation responsive material to the patterned transfer surface. Ultraviolet activation of the ultraviolet responsive coating is performed during a transfer of printing material to a substrate. The technique increases precision of the printing process and is useful for transfer of printing material to a substrate in order to establish printed circuit components such as circuit traces and printed circuit elements on the substrate. In a particular configuration the ultraviolet radiation responsive material can be made of azobenzene material or free radical initiators.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Application of RFID labels
InactiveUS20090017578A1Minimal technical effortEfficient use ofSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringRelief printing
Disclosed is a method for producing an RFID label with the aid of a printing process. The aim of the invention is make it easy to apply the parts required onto the label while completing the label in a simple manner. Said aim is achieved by applying at least one portion of the antenna and the resonant circuit required for the function to the printing material by means of sheet-fed offset printing or directly or indirectly with the aid of a relief printing plate. The resonant circuits or chips are applied individually or to a packaging that is to be created or filled in the same alignment once several copies of the labels have been produced on one sheet and have been separated therefrom.
Owner:MANROLANAD AG
Process for contact printing of patterns of electroless deposition catalyst
InactiveUS20060236884A1High resolutionLow costLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingConductive pattern formationElectroless depositionContact print
A process comprising the step of: contact printing a pattern of an electroless deposition catalyst via a hydrophilic phase to a receiving medium, wherein said electroless deposition catalyst requires no activation prior to electroless deposition.
Owner:AGFA GEVAERT AG
Paste coater and PoP automatic mounting apparatus employing the same
InactiveCN1981941ALiquid surface applicatorsPrinted circuit aspectsSolder pasteMechanical engineering
A paste coater that can apply an amount of a solder paste to small-diameter bump electrodes at a narrow pitch is described. A paste coater includes: a transfer roller, supported by a sub frame; a roller drive mechanism for rotating the transfer roller; a paste storage unit for storing paste to be supplied to the surface of the transfer roller; a squeegee having a distal edge, parallel to the rotary shaft of the transfer roller, separated by a gap from the distal edge to the surface of the transfer roller; a squeegee holder for holding and including biasing means for pushing the squeegee in a first direction thereby widening the gap; and a gap adjustment mechanism with biasing means for pushing the squeegee in a second direction thereby narrowing the gap.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com