Patents
Literature
34results about How to "Dynamic range" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
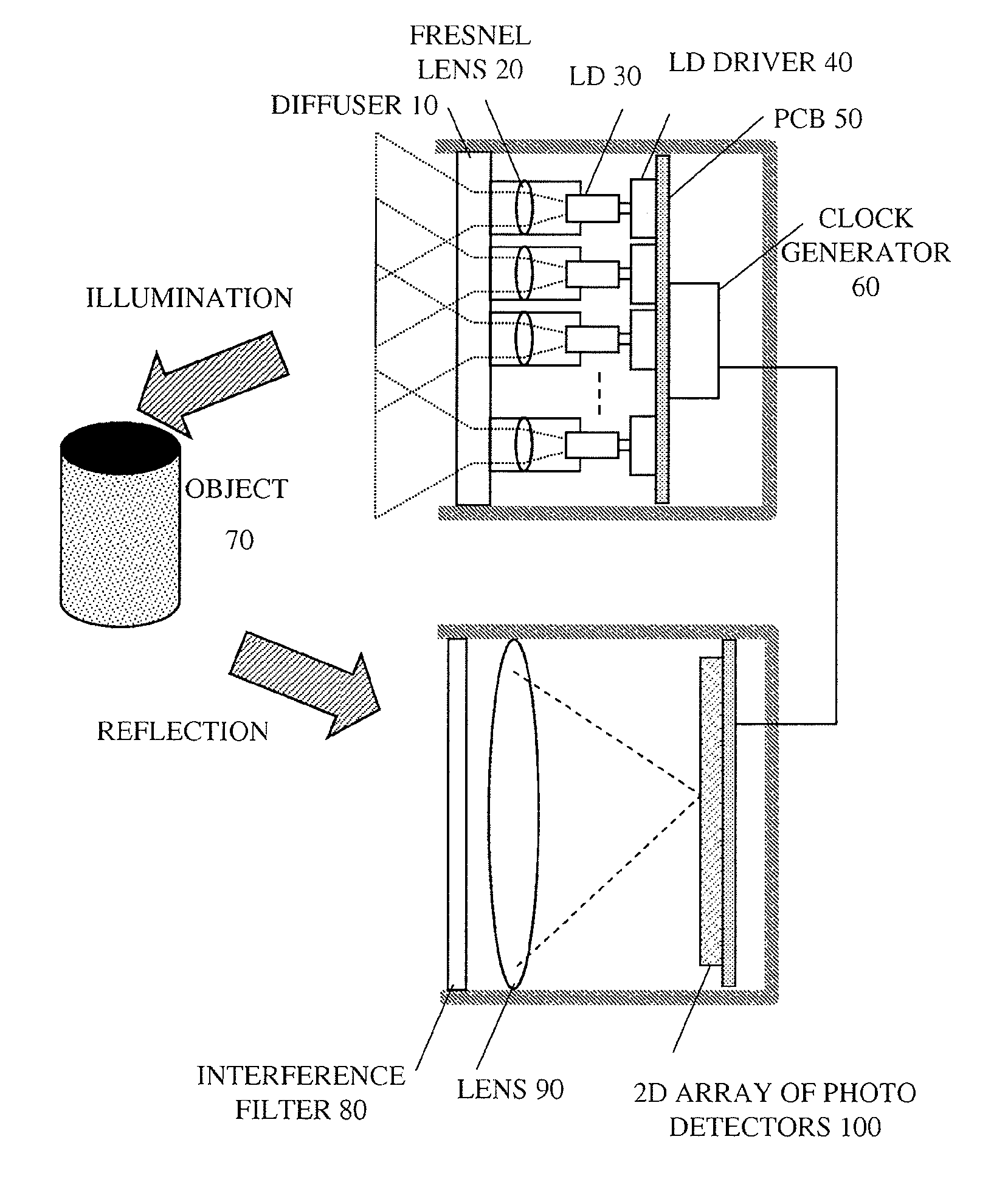
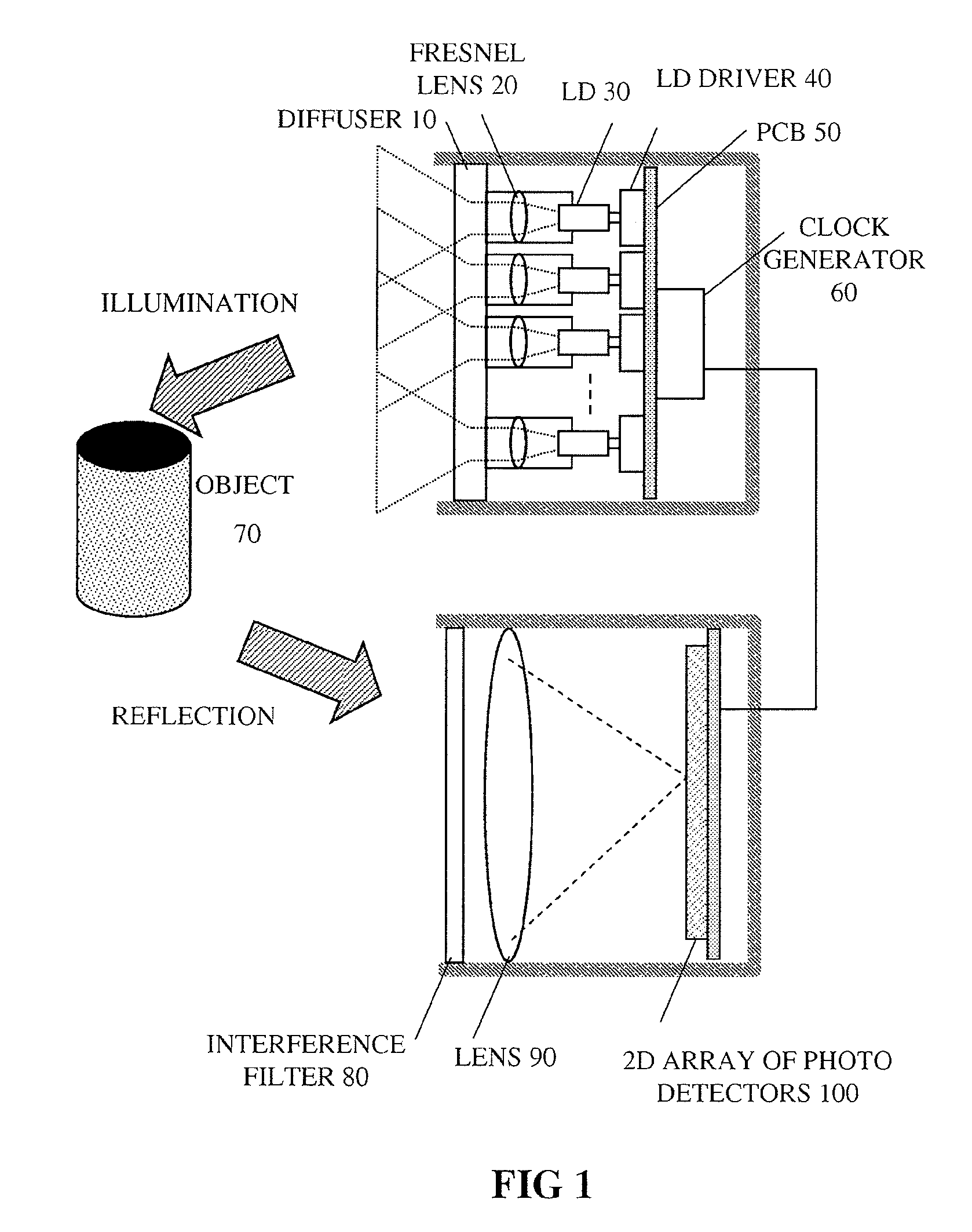
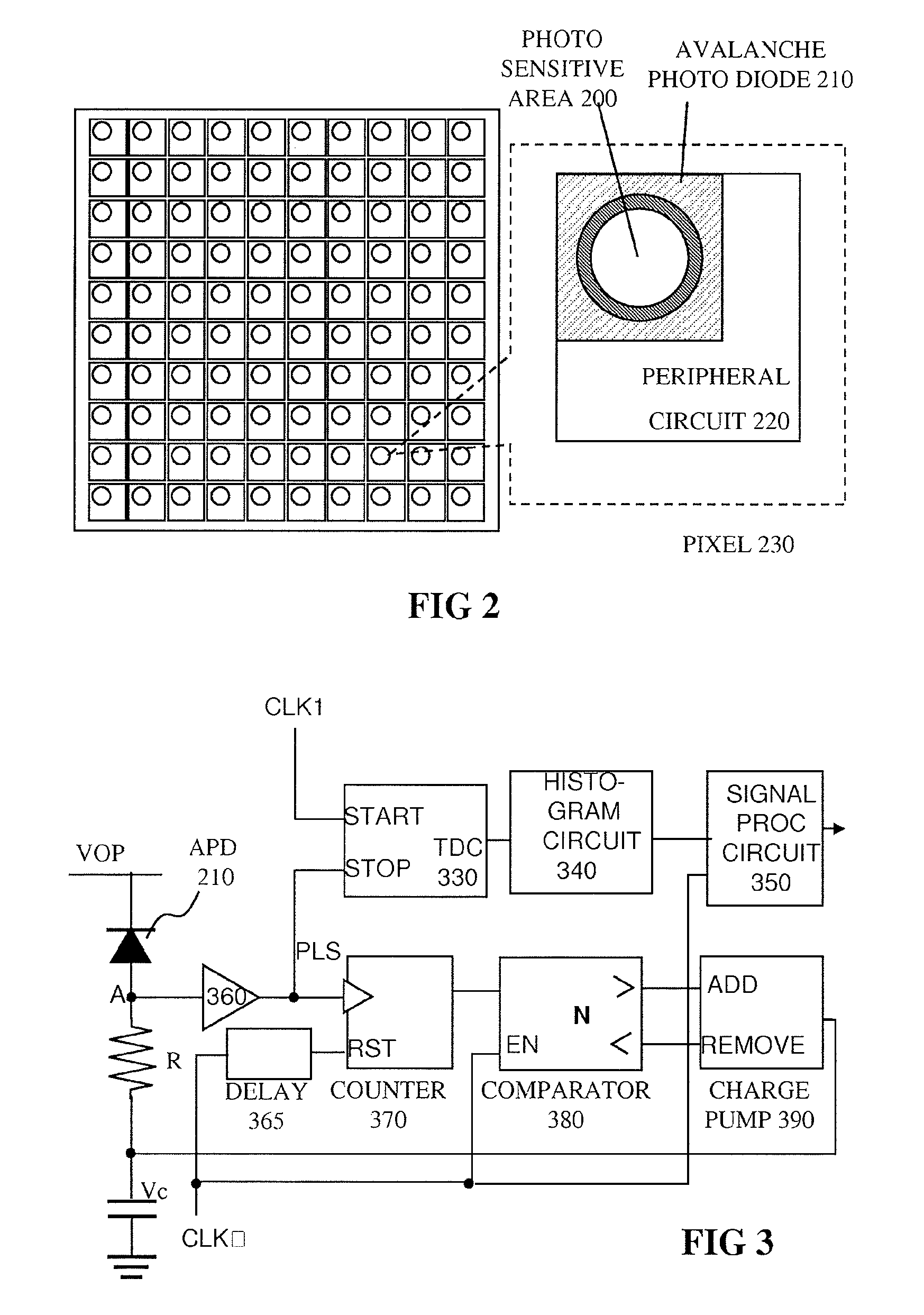
Pulsed light optical rangefinder
ActiveUS20120075615A1Improve dynamic rangeAvoid saturationOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationPhoton detectionTime of flight
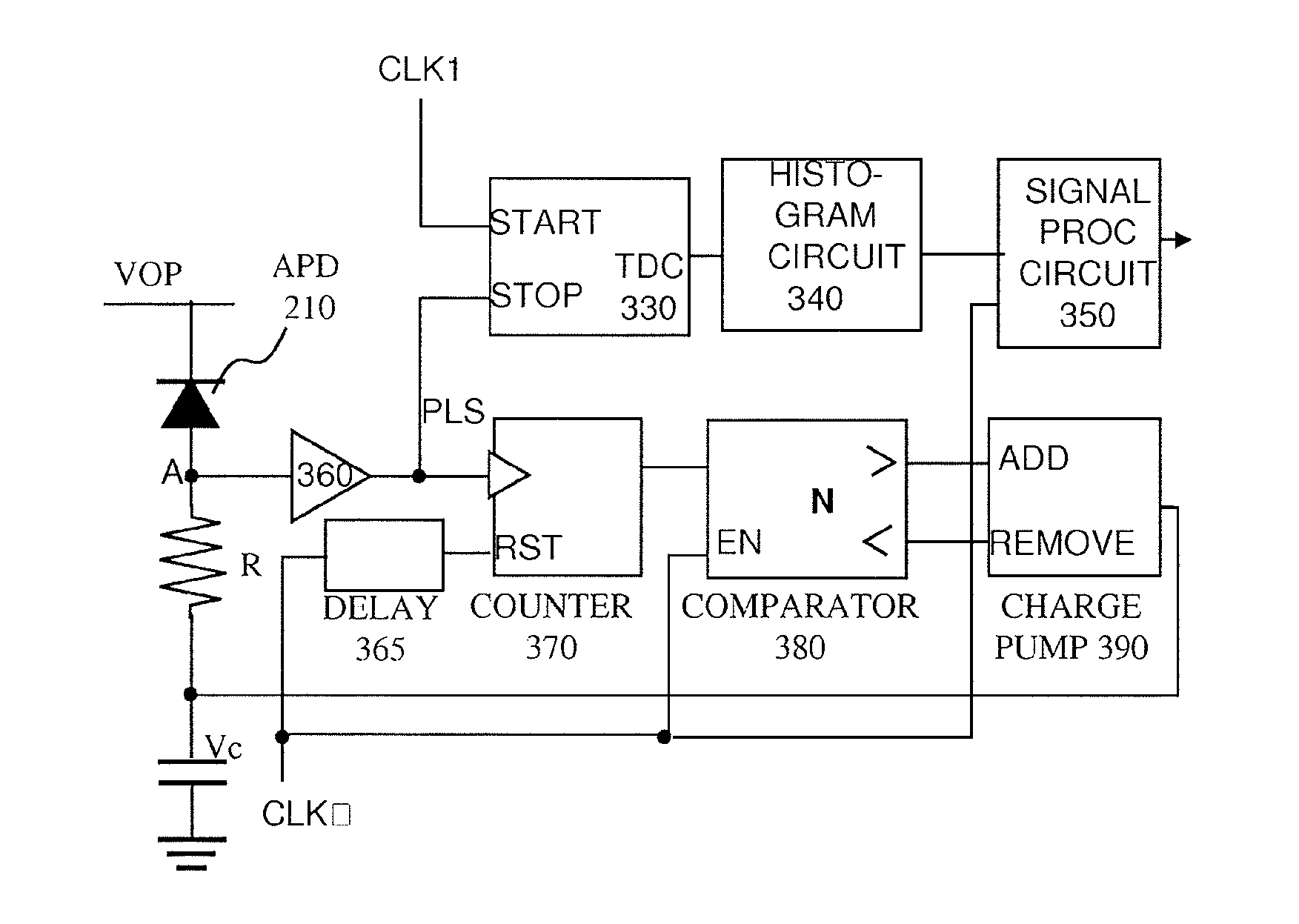
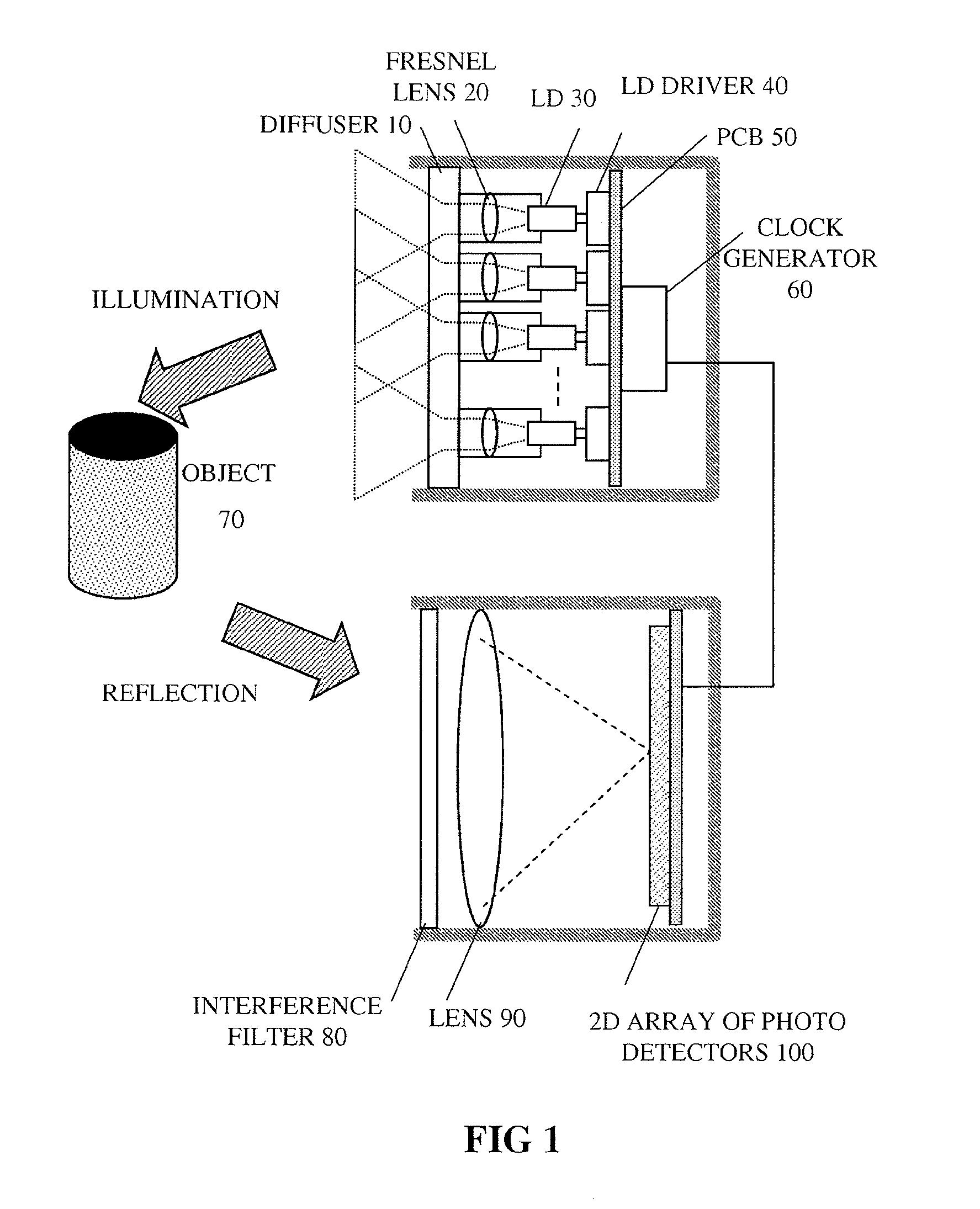
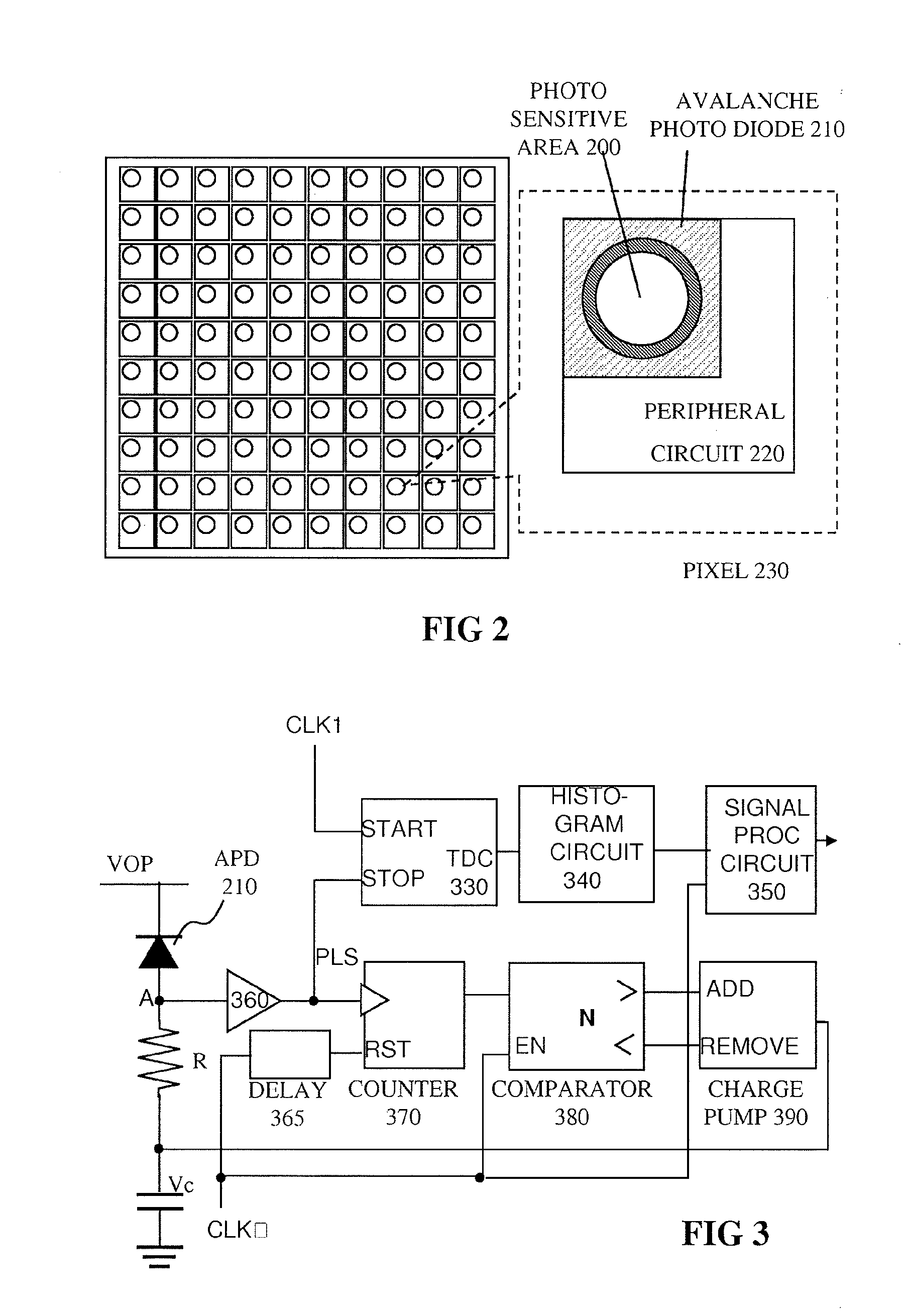
An optical rangefinder based on time-of-flight measurement, radiates pulsed light toward an object (70), and receives reflected light from the object, the receiver operating in a photon counting mode, so as to generate a pulse for a detected photon. There is a variable probability of a photon detection on the receiver, and a controller (370, 380, 390; 365, 470, 475, 380, 390; 570, 580, 590, 390) controls the photon detection probability of the receiver, based on a light level. By controlling the detection probability according to a light level, the receiver can have an increased dynamic range, and without the expense of using optical components. This can apply even while detecting very weak signals since the receiver can still be in a photon counting mode while the detection probability is controlled. The light level can be indicated by an output of the receiver itself, or by another detector external to the receiver.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
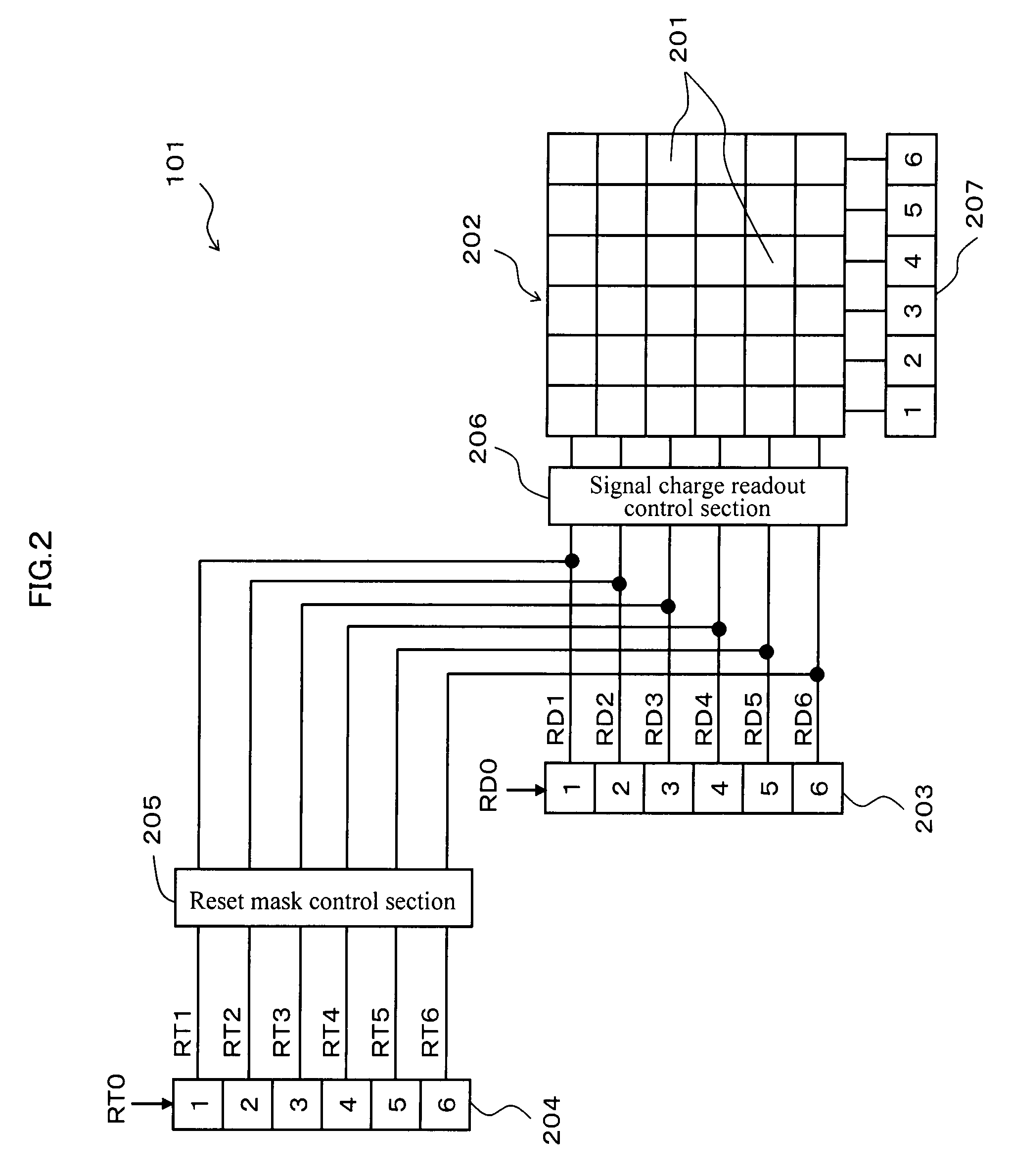
Image Sensor
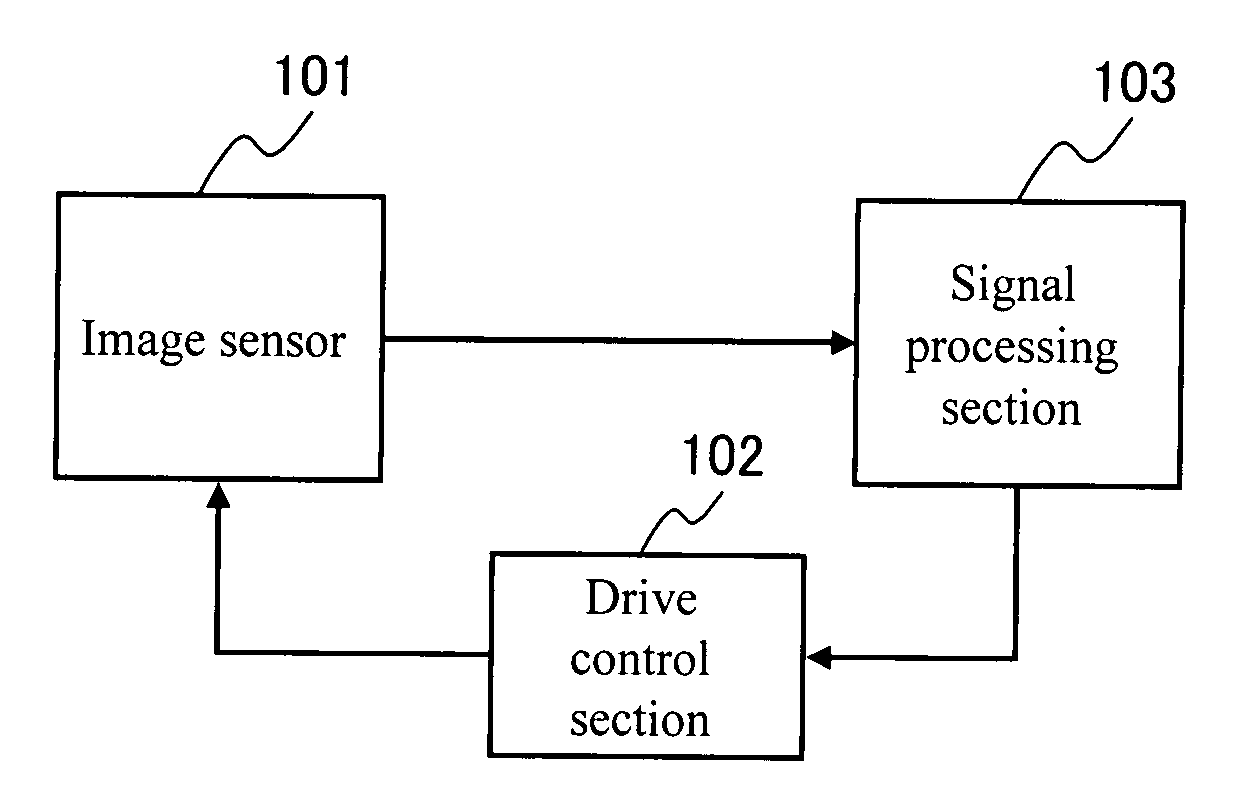
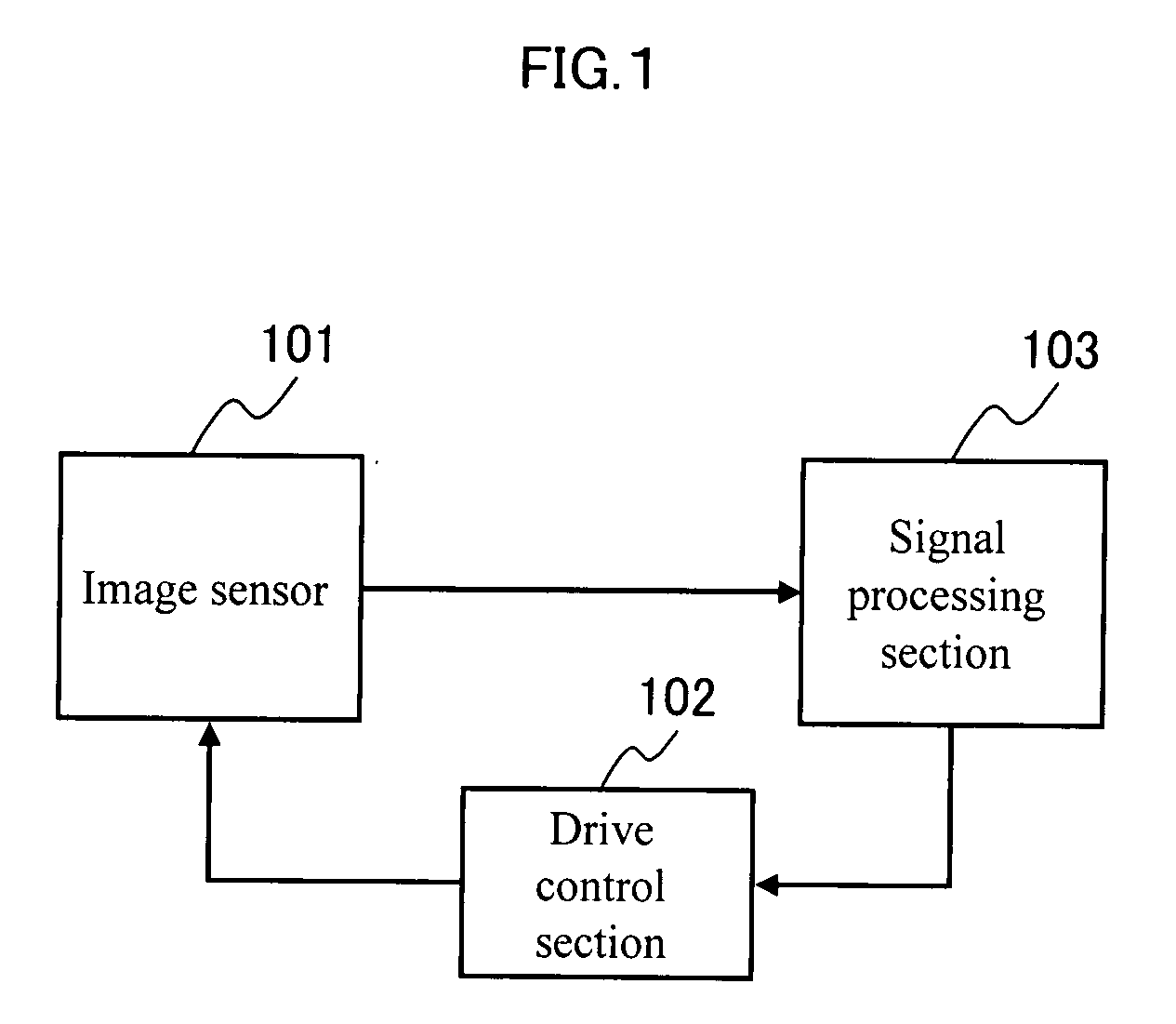
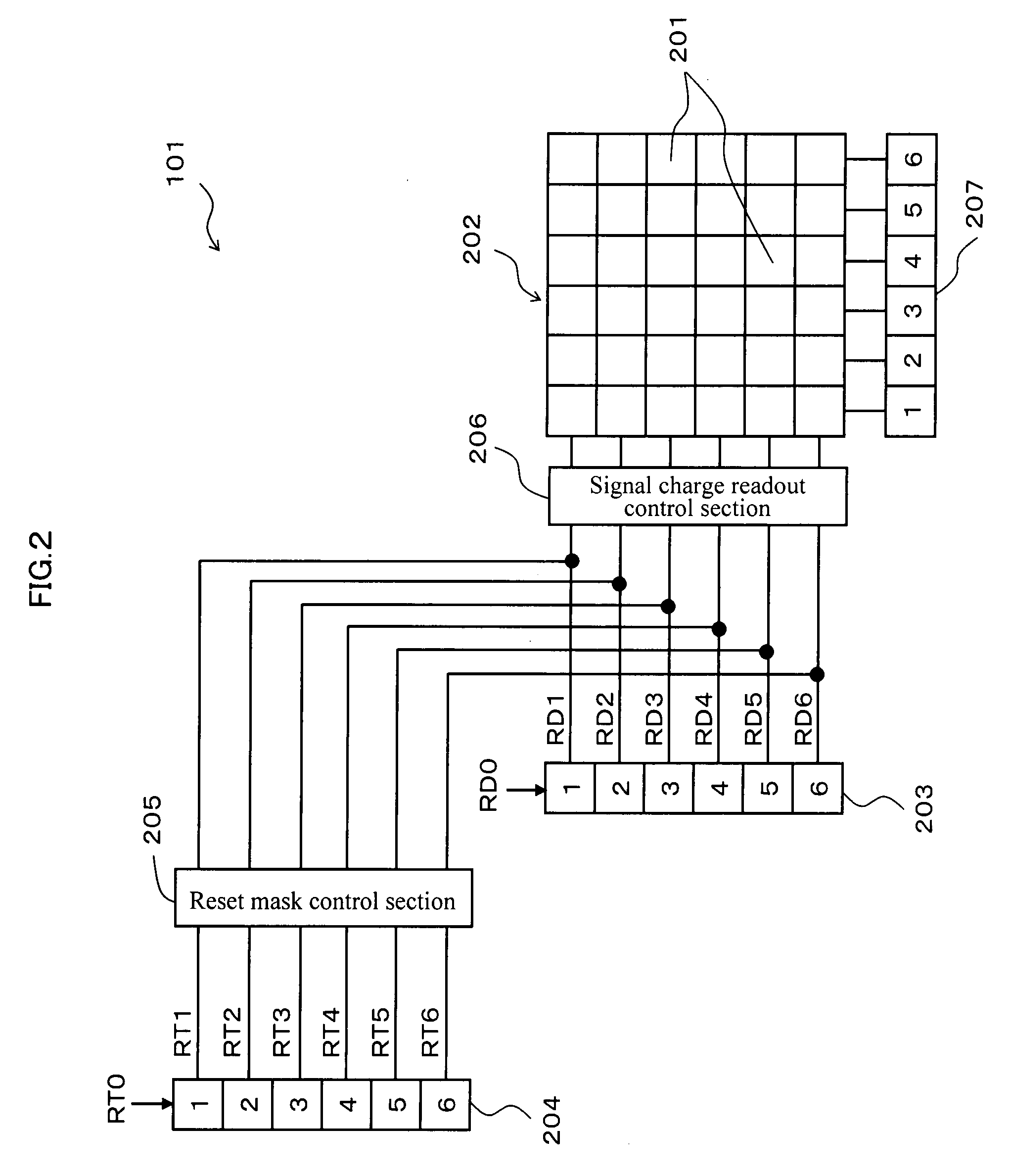
InactiveUS20070273785A1Expansion of dynamic rangeSuppresses deterioration of image qualityTelevision system detailsExposure controlComputer scienceDynamic range
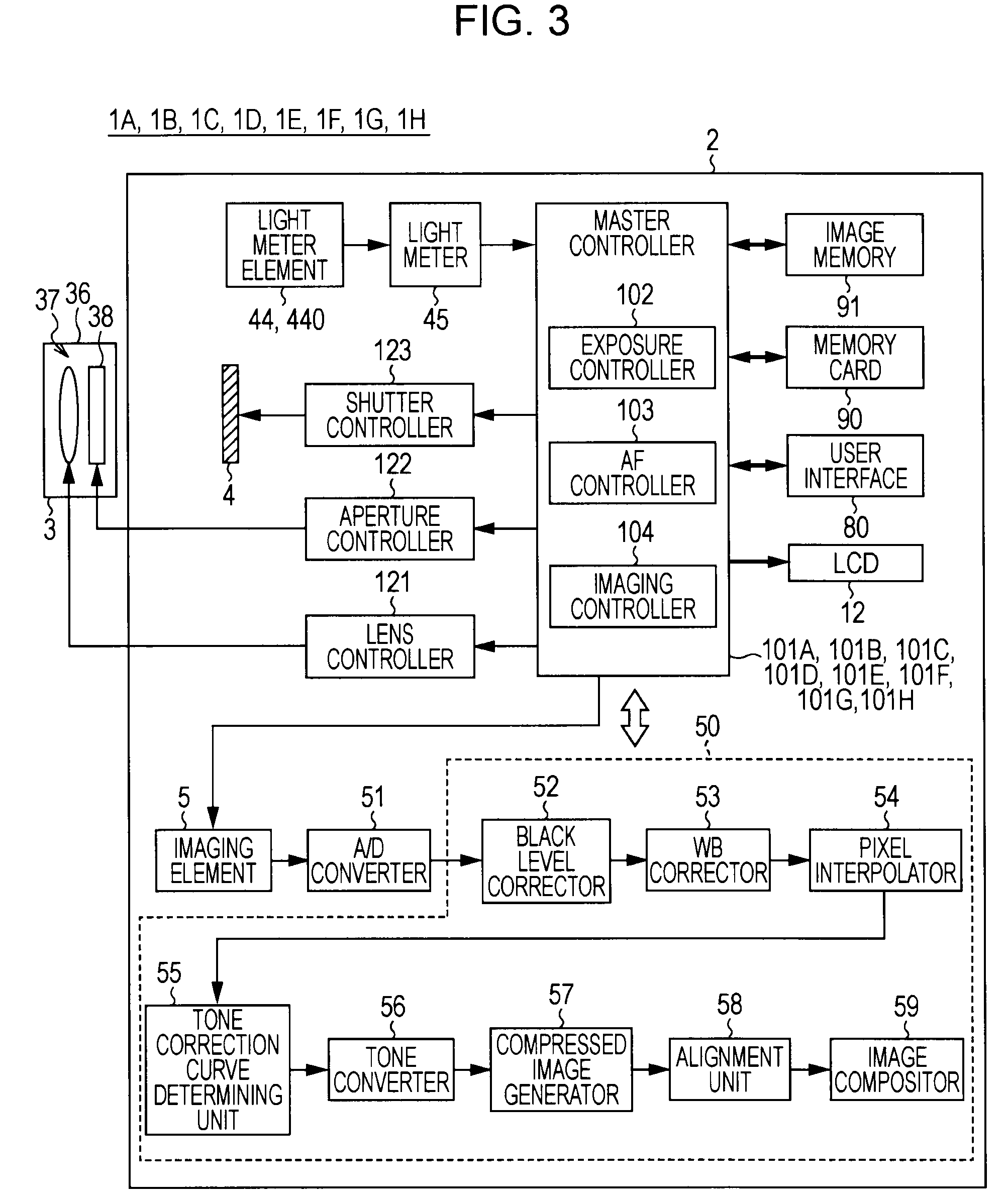
[PROBLEMS] suppress deterioration in picture qualities while achieving expansion in a dynamic range. [MEANS FOR SOLVING PROBLEMS] An image sensor readout method that reads out, from an area sensor where a plurality of image pickup elements are arranged in matrix, signal charges that are accumulated in the image pickup elements is constituted as follows. First, plural kinds of exposure time different in length from each other are set, and the exposure time is then individually allocated to each line of the area sensor. Next, the signal charges accumulated in the image pickup elements in the allocated exposure time are read out through a line unit of the area sensor. Then, the read out signal charges are synthesized through a screen unit of the area sensor.
Owner:COLLABO INNOVATIONS INC
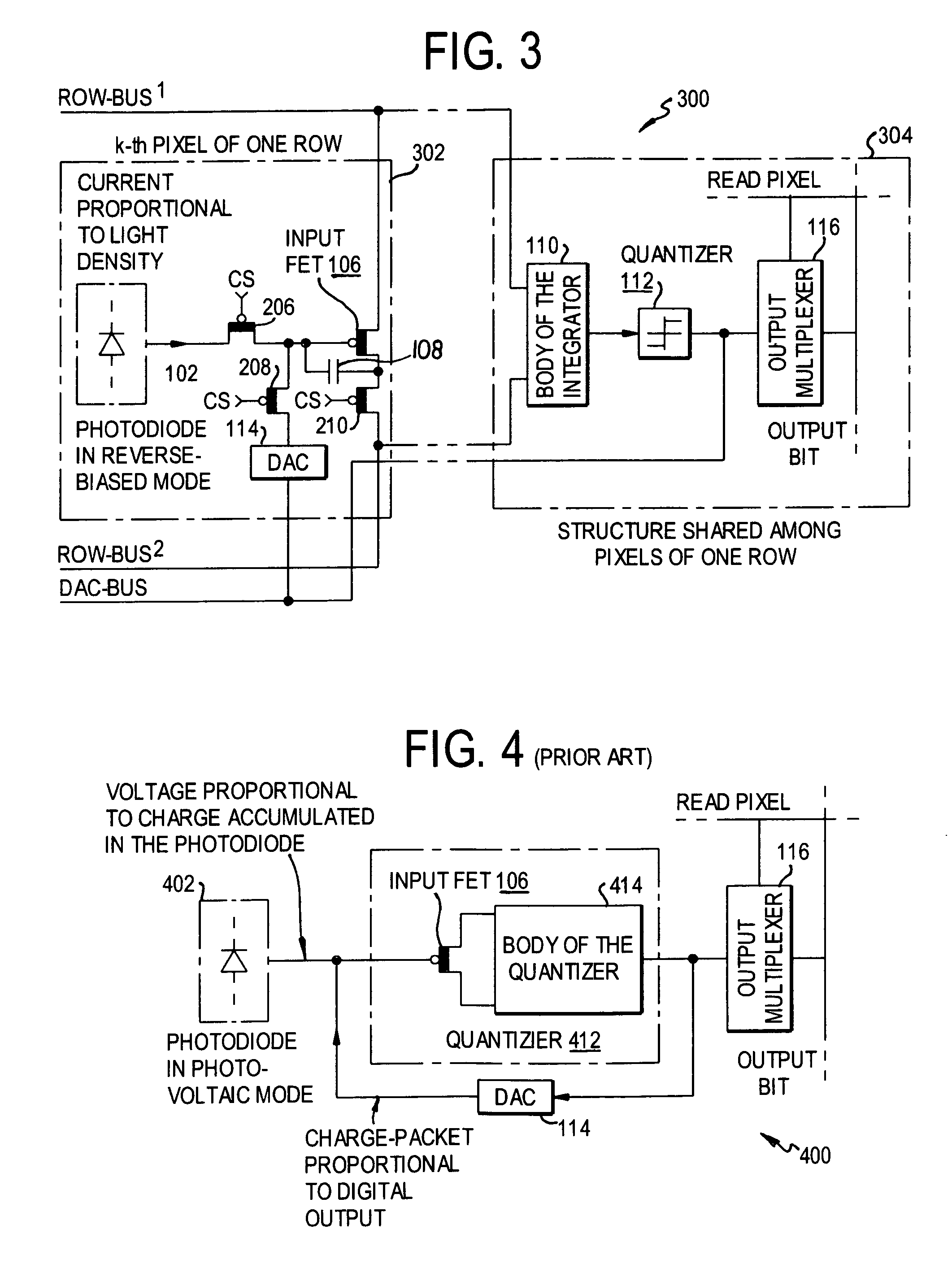
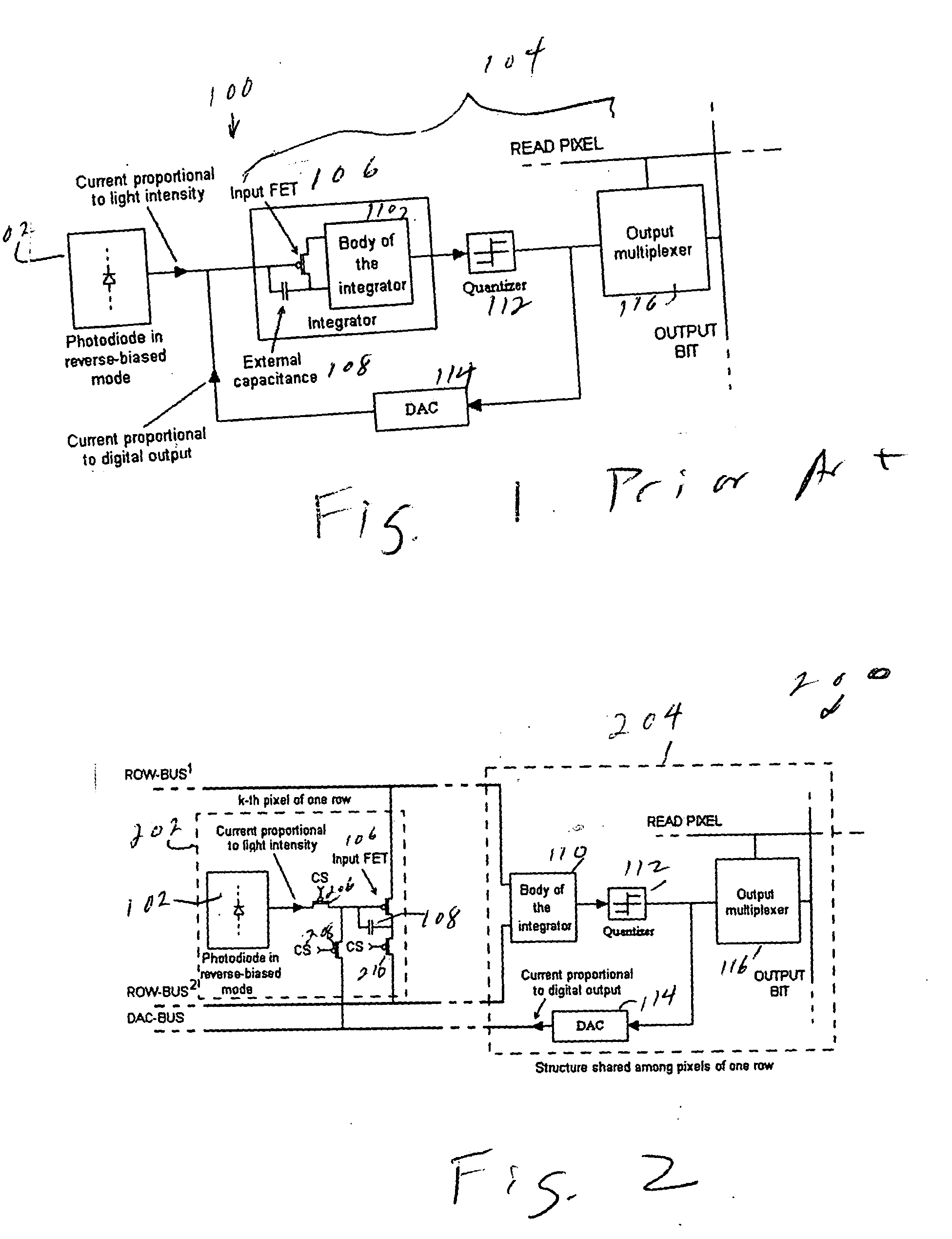
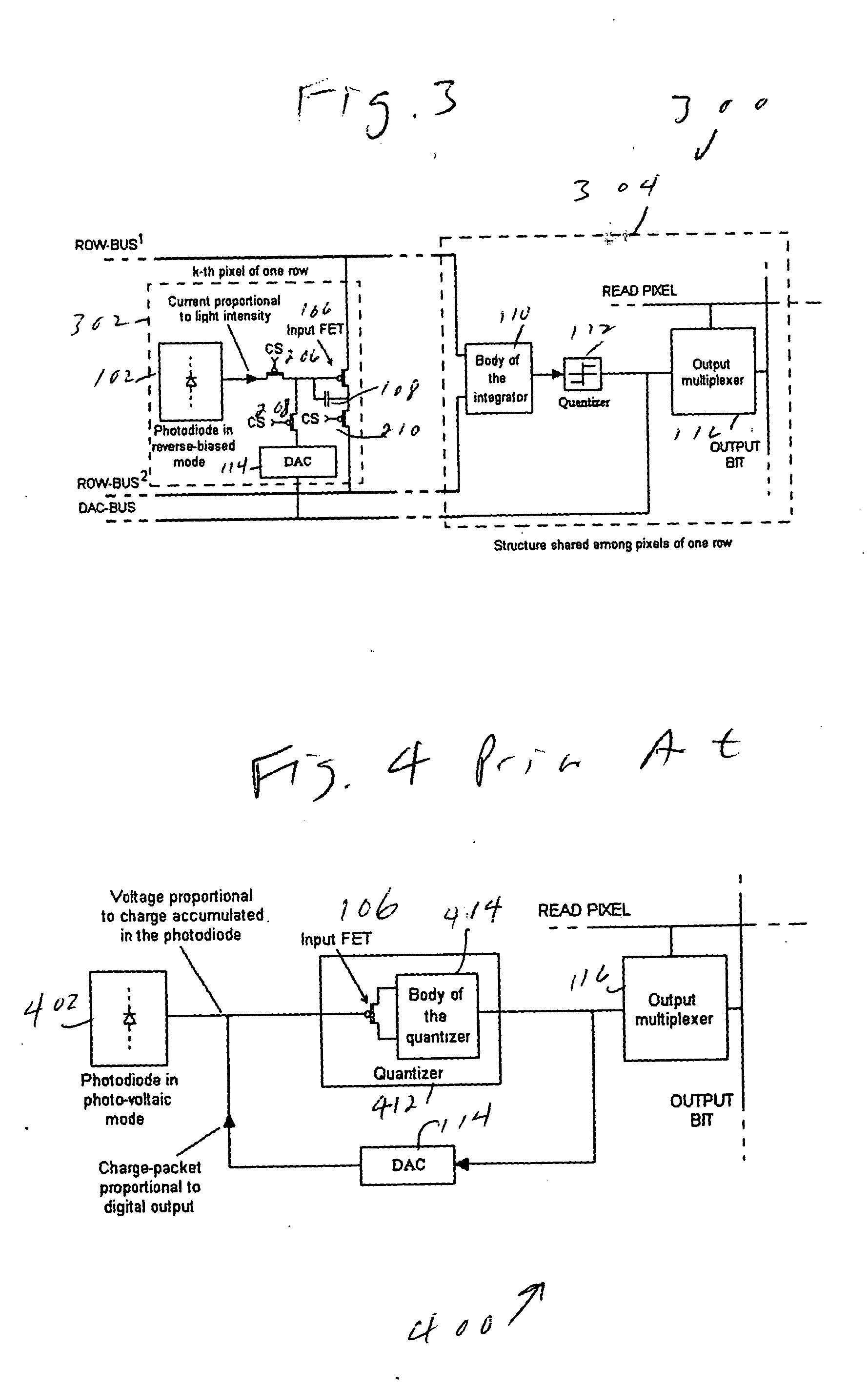
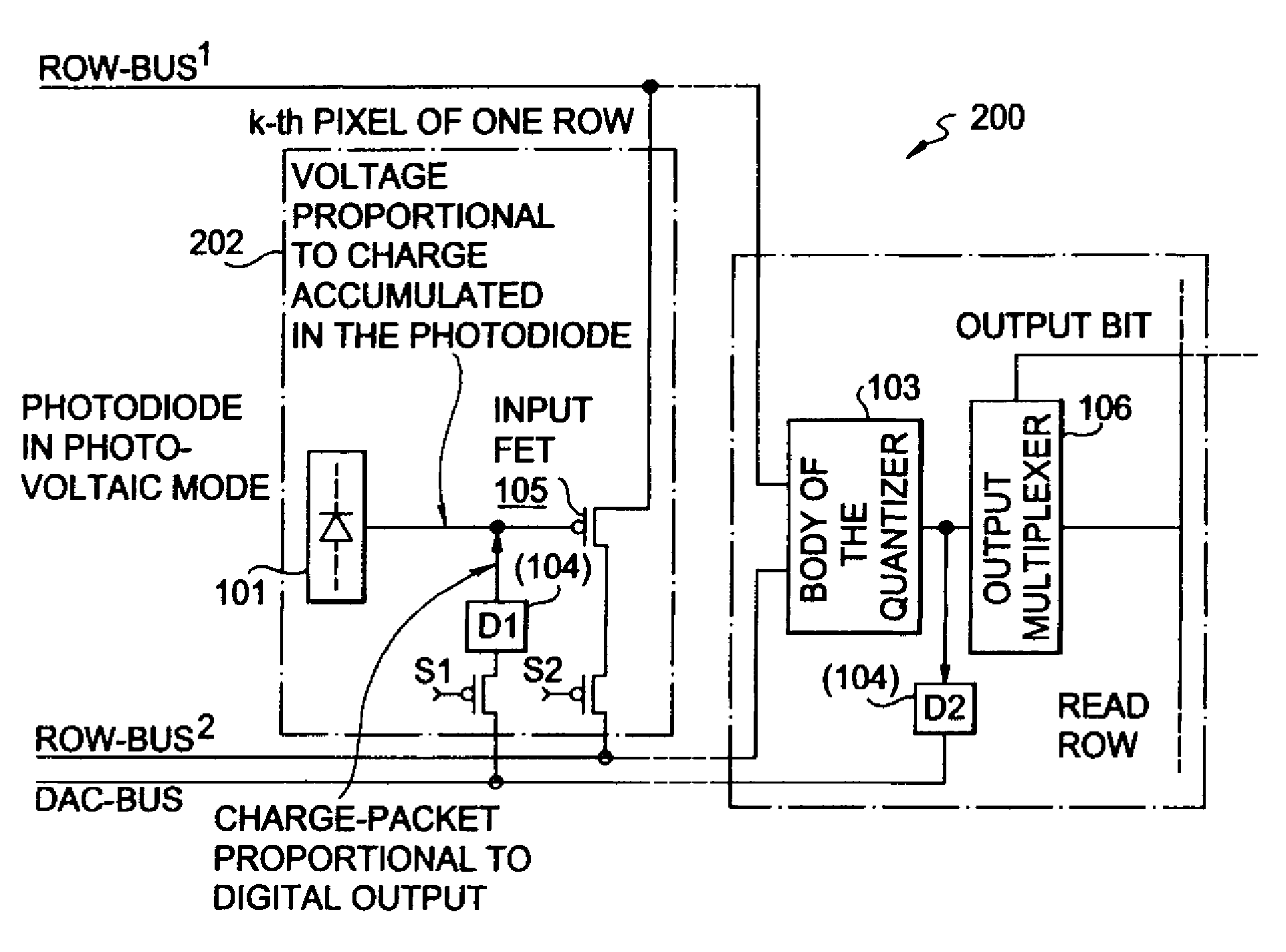
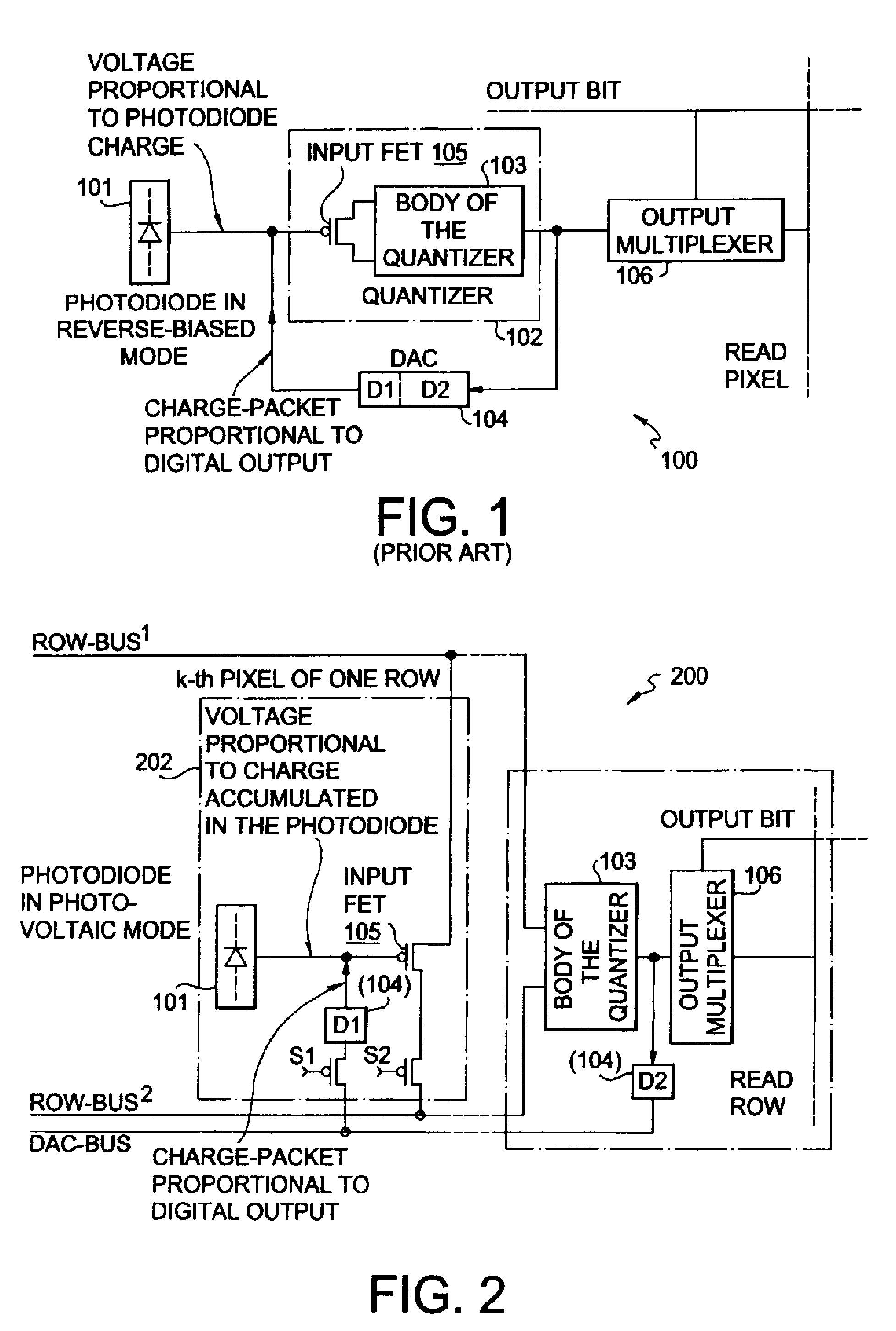
Multiplexed-input-separated sigma-delta analog-to-digital converter design for pixel-level analog-to-digital conversion
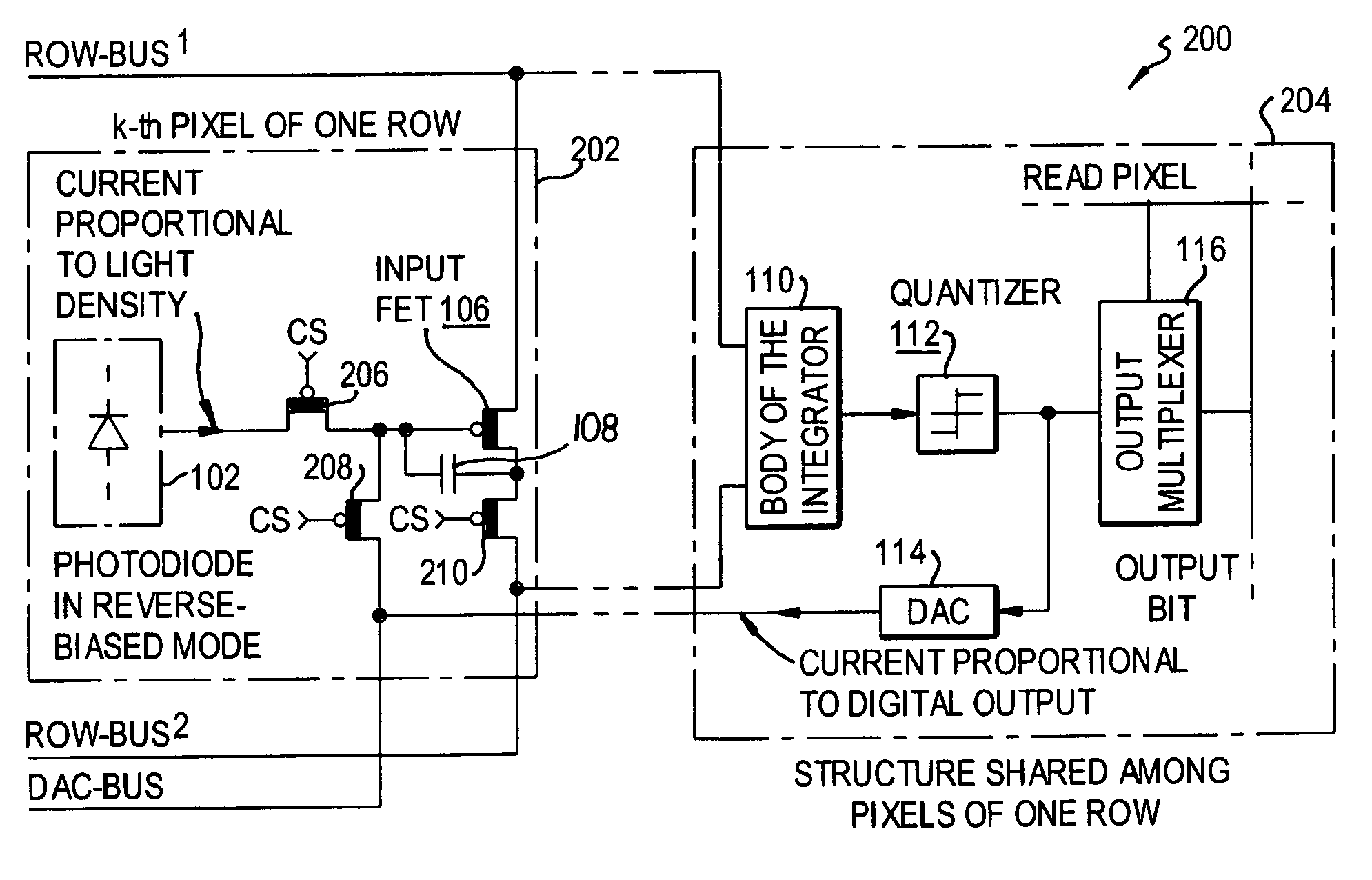
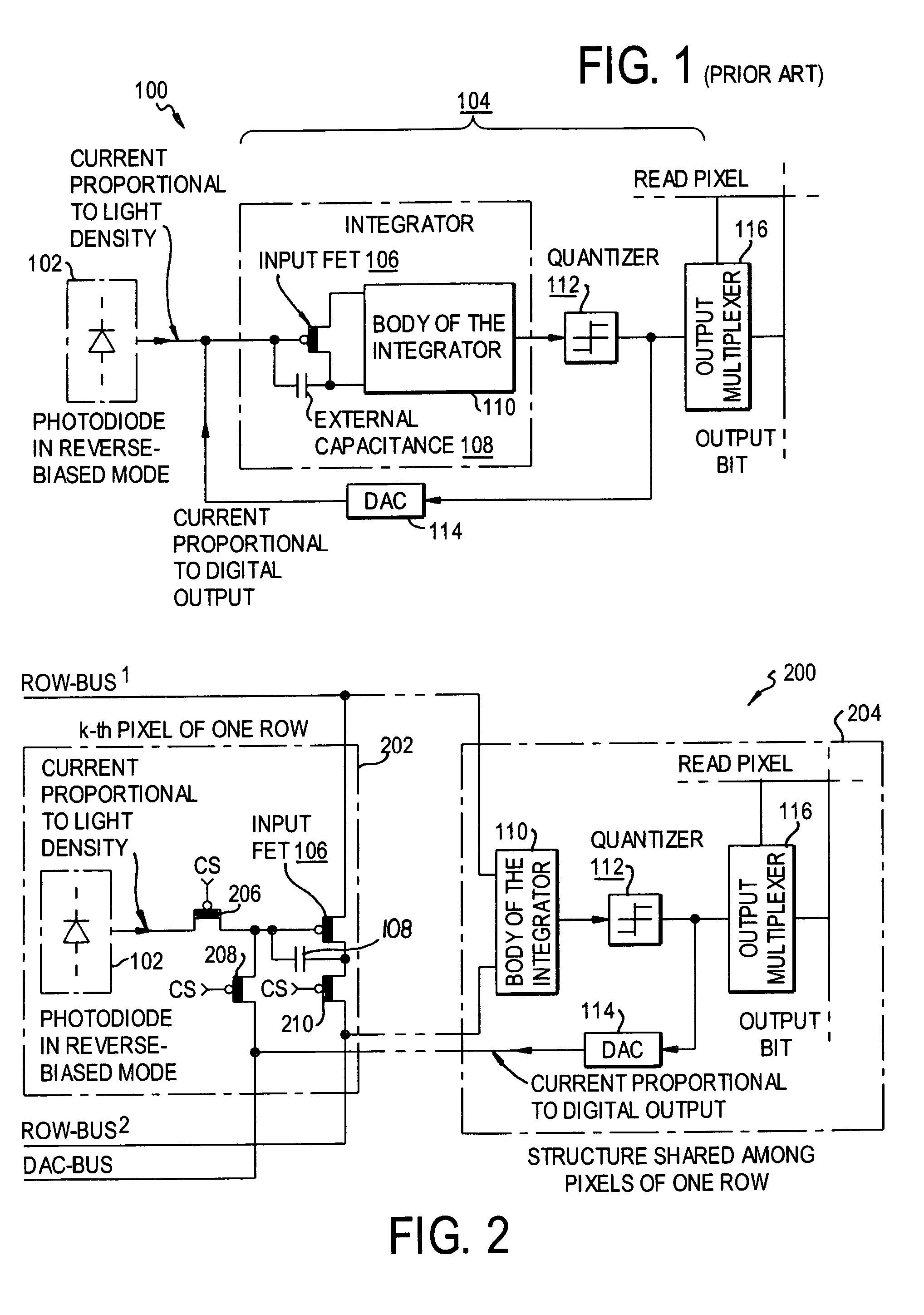
InactiveUS7023369B2Improve linearityReduce power consumptionTelevision system detailsElectric signal transmission systemsMultiplexingIntegrator
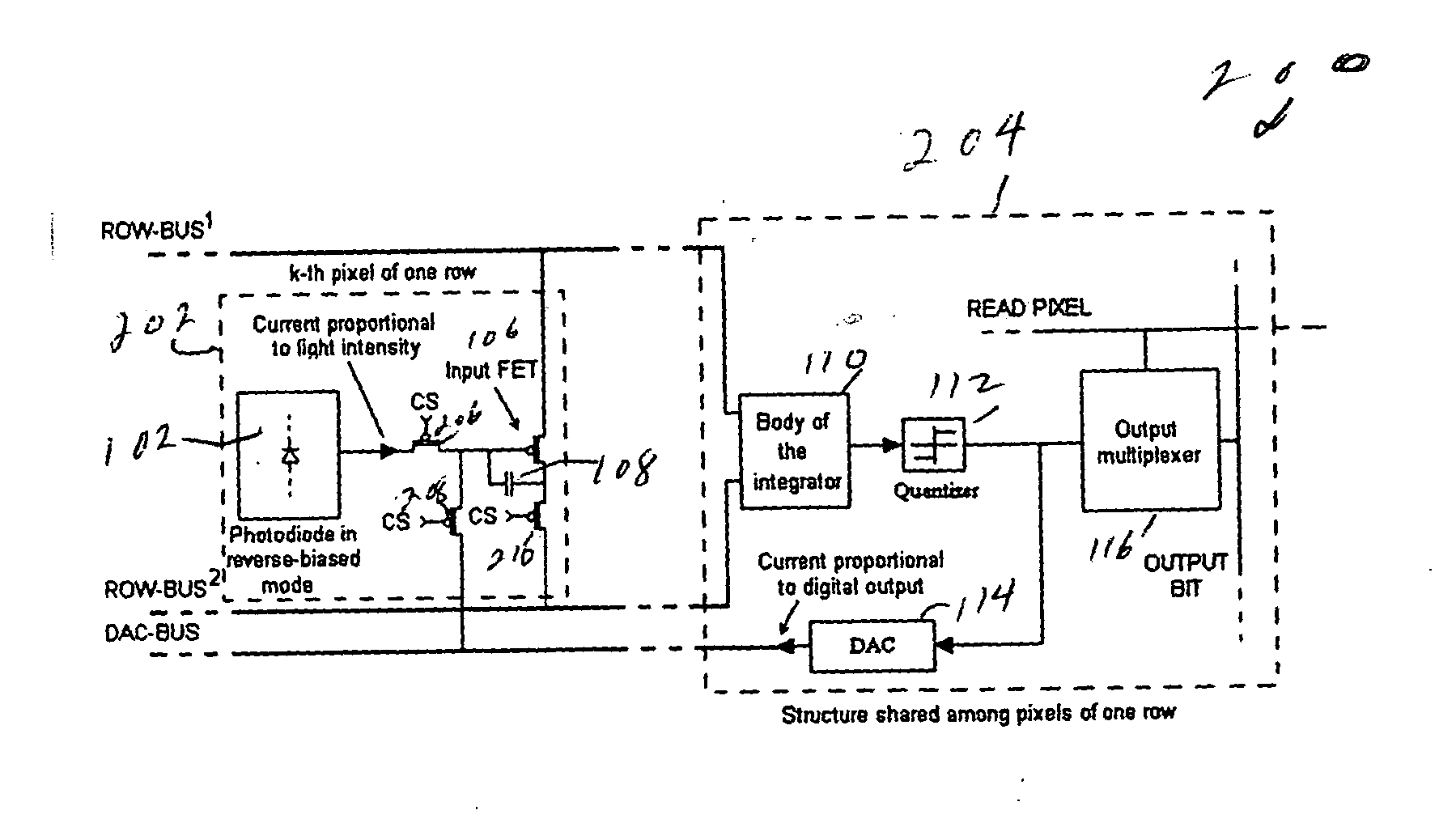
An image-sensing element has an array of photodiodes or other photodetecting elements and performs sigma-delta analog-to-digital conversion on the outputs of the photodetecting elements. The sigma-delta analog-to-digital converters have components divided between pixel-level and row-level structures, with each row-level structure connected to its pixel-level structures to define a multiplexed-input-separated sigma-delta analog-to-digital converter. The converter can include an integrator or can rely on an integration effect of the photodetecting element. The feedback required for sigma-delta analog-to-digital conversion can involve digital-to-analog converters located at each row-level structure or at each pixel-level structure.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
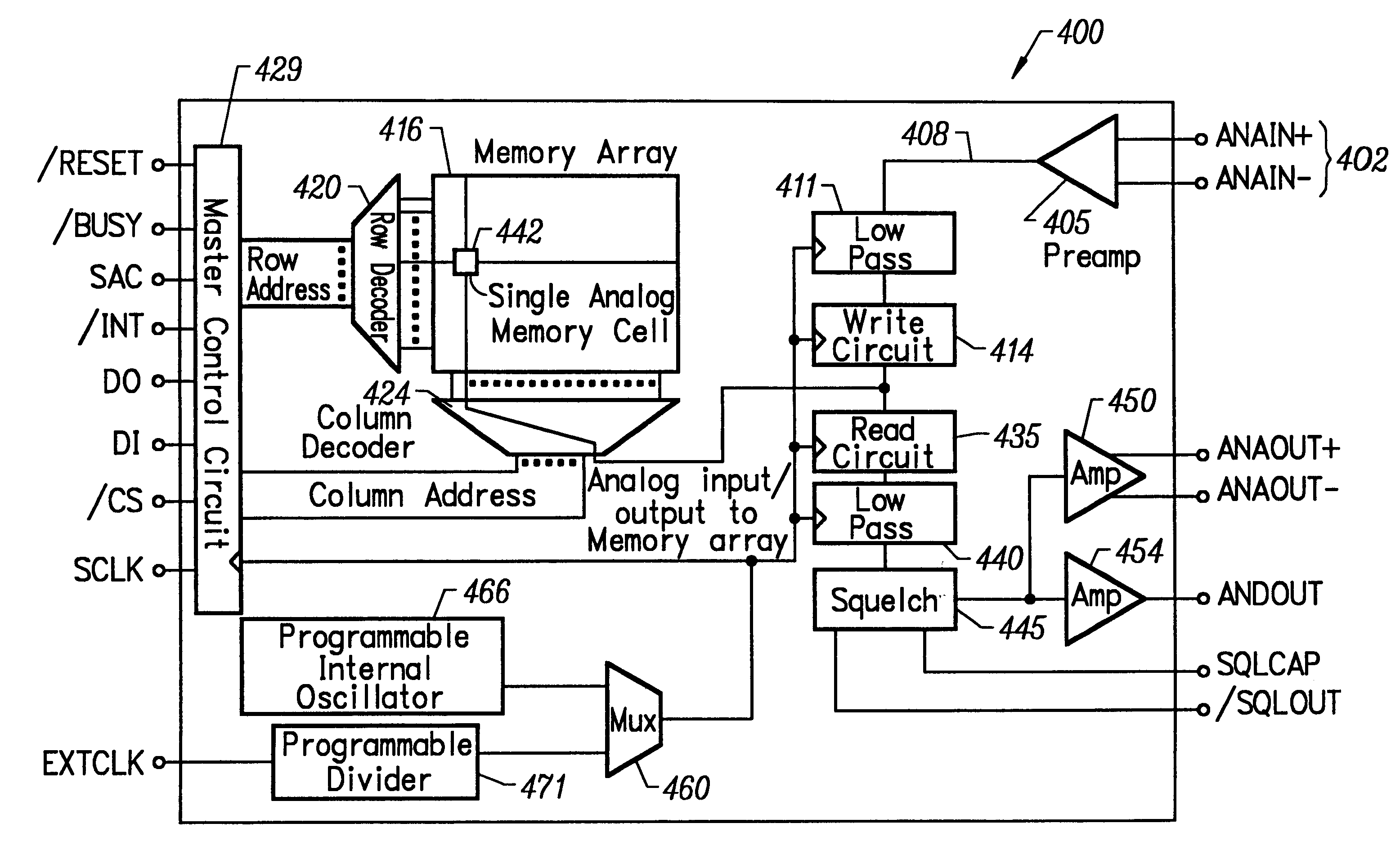
Analog memory IC with fully differential signal path
InactiveUS6185119B1High precisionImproved noise suppressionElectric analogue storesRead-only memoriesDifferential signalingAnalog signal
An integrated circuit memory is capable of storing analog information without the need for A / D conversion. Samples of a analog signal input are stored in nonvolatile memory cells. The integrated circuit is also capable of storing digital information in digital form. The sampling rate at which the analog signal input is sampled is user selectable. An internal signal path of the integrated circuit memory is differential, which enhances the precision with which the analog signal is stored in the memory cells.
Owner:SANDISK CORP
Radiation detector with extended dynamic range
InactiveUS7705309B1Improve dynamic rangeLarge dynamic temperature sensing rangeRadiation pyrometrySolid-state devicesSensor arrayOptical property
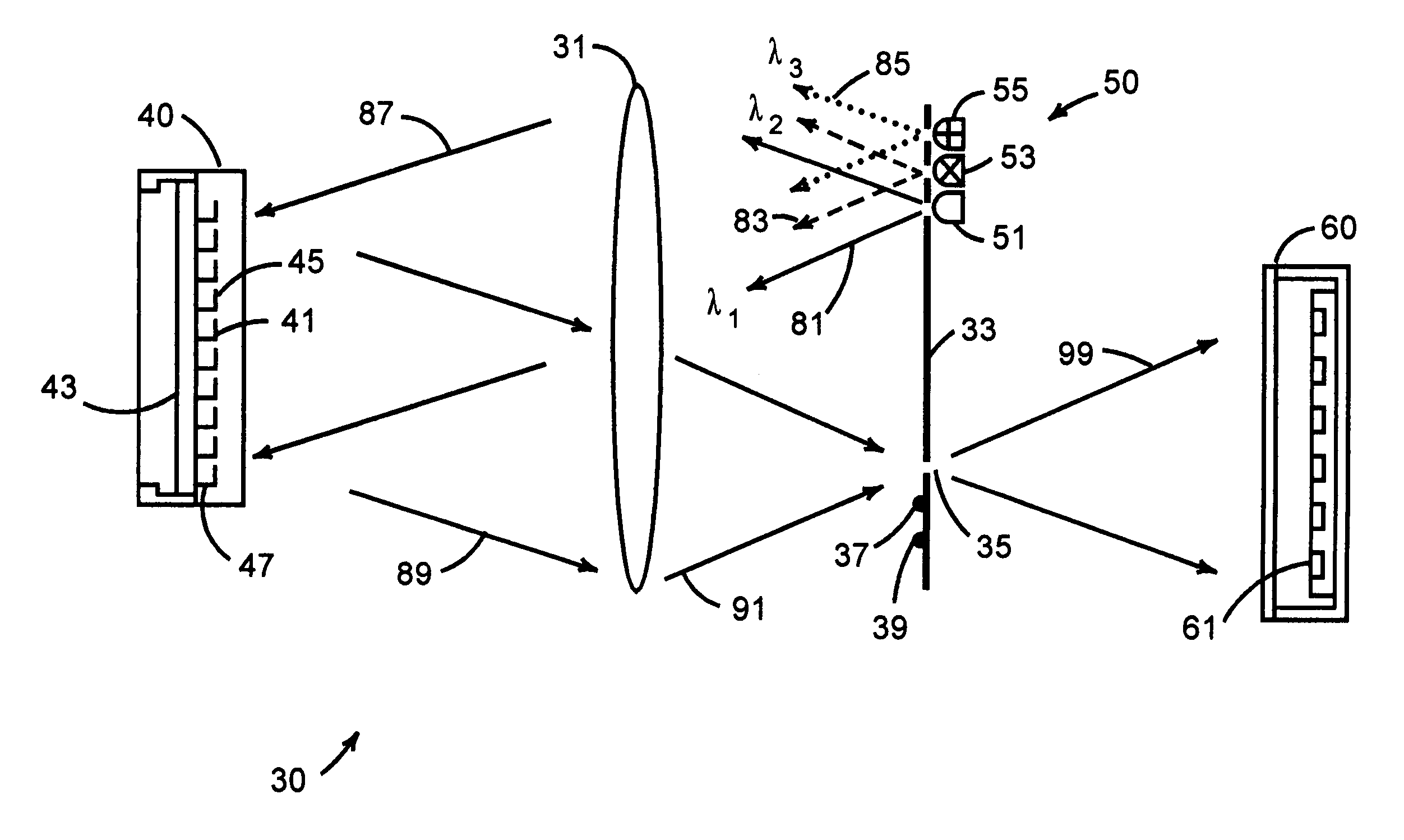
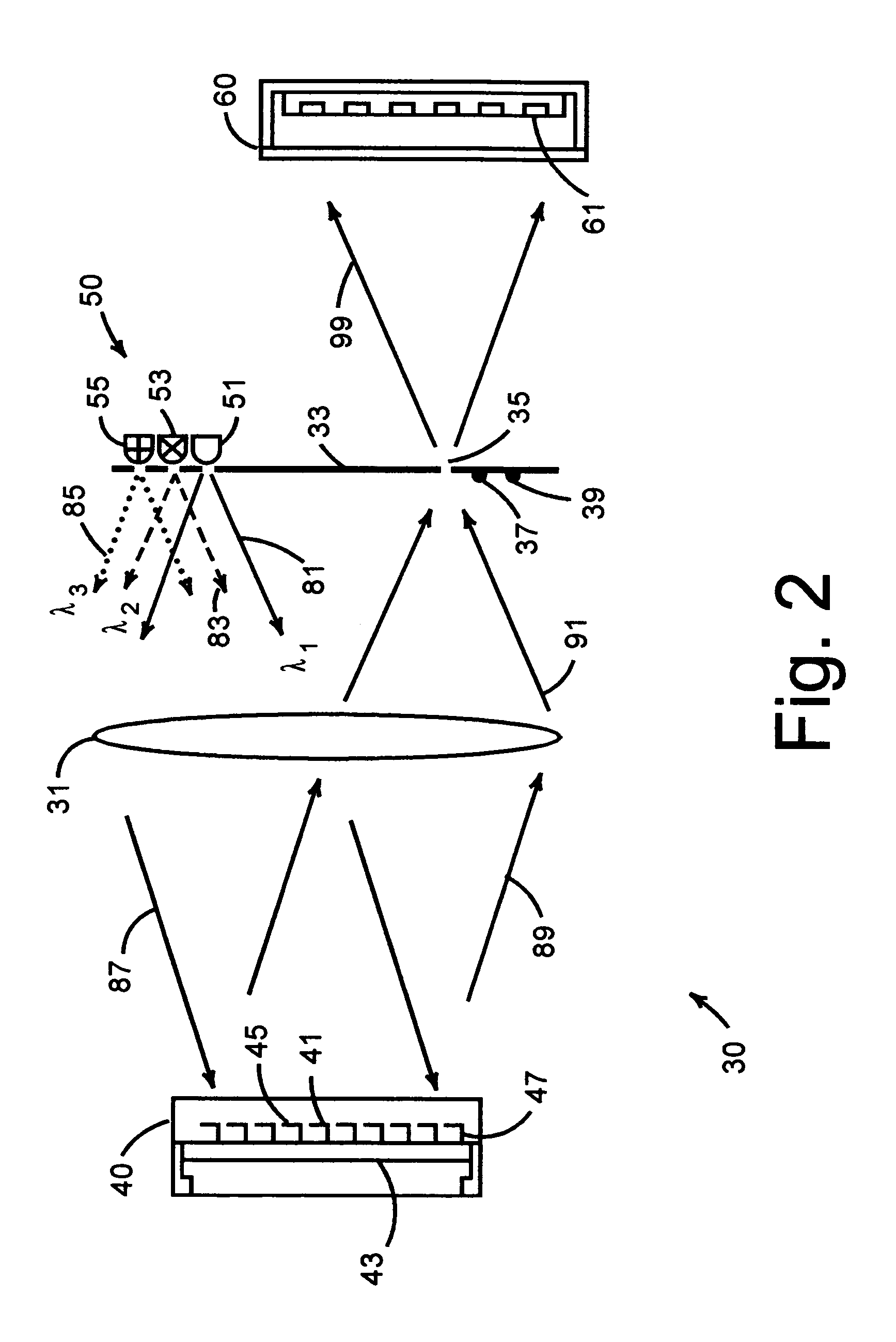
A mechanical-optical transducer comprises a readout illumination source providing light having different wavelengths or different polarization states; an image sensor array for sensing the light from the readout illumination source; and a mechanical-optical device including sensing pixels whose optical property change in response to incident thermal infrared radiation, the mechanical-optical device having a reflective surface disposed to selectively reflect light from the readout illumination source to the image sensor array.
Owner:FLIR COMML SYST
Multiplexed-input-separated sigma-delta analog-to-digital converter design for pixel-level analog-to-digital conversion
InactiveUS20050073451A1Improve linearityReduce power consumptionTelevision system detailsElectric signal transmission systemsMultiplexingIntegrator
An image-sensing element has an array of photodiodes or other photodetecting elements and performs sigma-delta analog-to-digital conversion on the outputs of the photodetecting elements. The sigma-delta analog-to-digital converters have components divided between pixel-level and row-level structures, with each row-level structure connected to its pixel-level structures to define a multiplexed-input-separated sigma-delta analog-to-digital converter. The converter can include an integrator or can rely on an integration effect of the photodetecting element. The feedback required for sigma-delta analog-to-digital conversion can involve digital-to-analog converters located at each row-level structure or at each pixel-level structure.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Pulsed light optical rangefinder
ActiveUS9417326B2Improve dynamic rangeLower detection rateElectromagnetic wave reradiationPhoton detectionTime of flight
An optical rangefinder based on time-of-flight measurement, radiates pulsed light toward an object (70), and receives reflected light from the object, the receiver operating in a photon counting mode, so as to generate a pulse for a detected photon. There is a variable probability of a photon detection on the receiver, and a controller (370, 380, 390; 365, 470, 475, 380, 390; 570, 580, 590, 390) controls the photon detection probability of the receiver, based on a light level. By controlling the detection probability according to a light level, the receiver can have an increased dynamic range, and without the expense of using optical components. This can apply even while detecting very weak signals since the receiver can still be in a photon counting mode while the detection probability is controlled. The light level can be indicated by an output of the receiver itself, or by another detector external to the receiver.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Solid-state imaging device and electronic device
ActiveUS20190096933A1Improve dynamic rangeDynamic rangeTransistorSolid-state devicesOptical axisEngineering
The present technology relates to a solid-state imaging device and an electronic device that can expand a dynamic range in a pixel having a high-sensitivity pixel and a low-sensitivity pixel. The solid-state imaging device includes a pixel array unit in which a plurality of pixels is arranged in a two-dimensional manner, in which the pixel includes a first photoelectric conversion unit and a second photoelectric conversion unit having lower sensitivity than the first photoelectric conversion unit, and a size of the second photoelectric conversion unit in an optical axis direction in which light enters is smaller than a size of the first photoelectric conversion unit in the optical axis direction. The present technology can be applied to a backside-illumination CMOS image sensor, for example.
Owner:SONY CORP
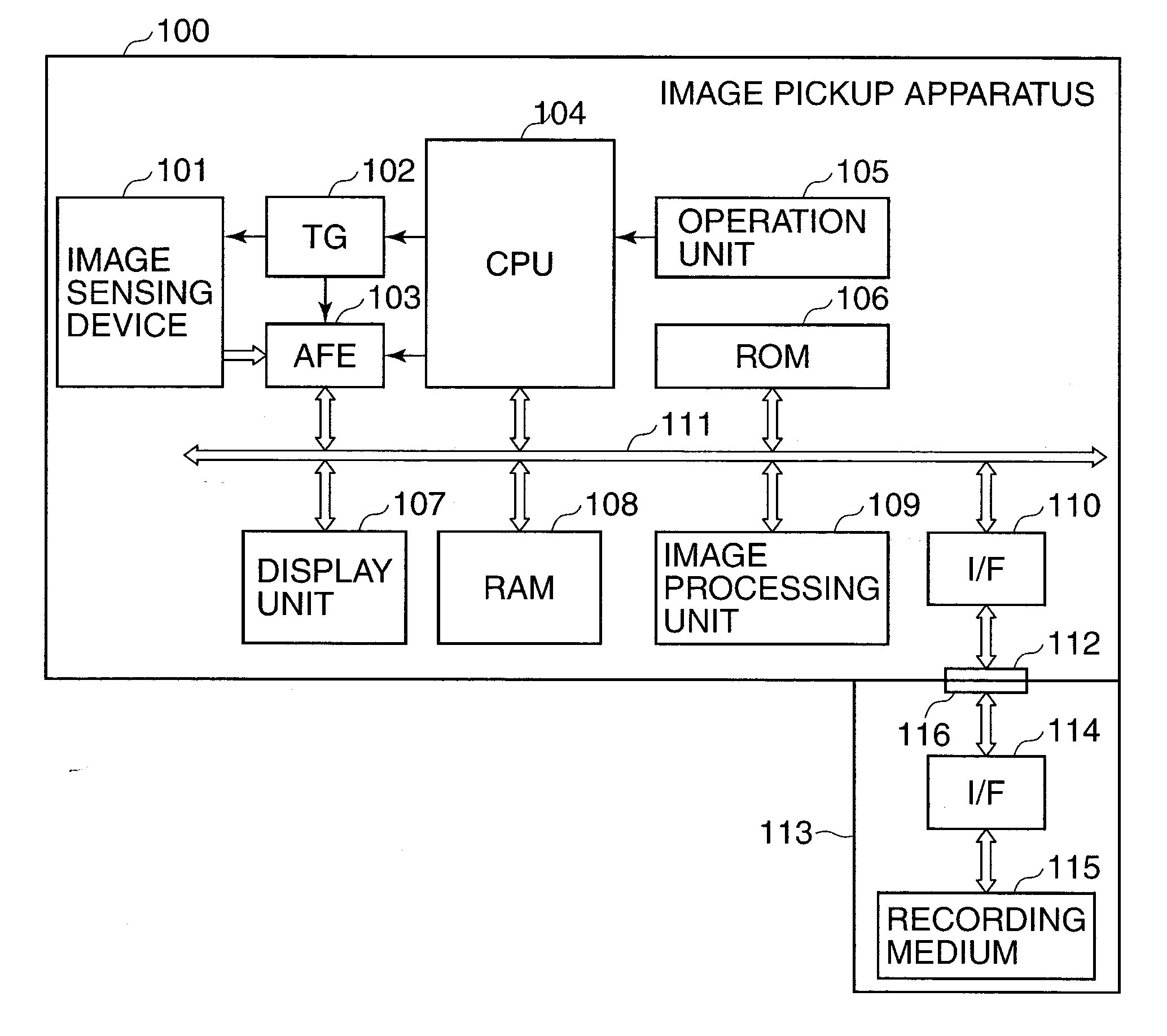
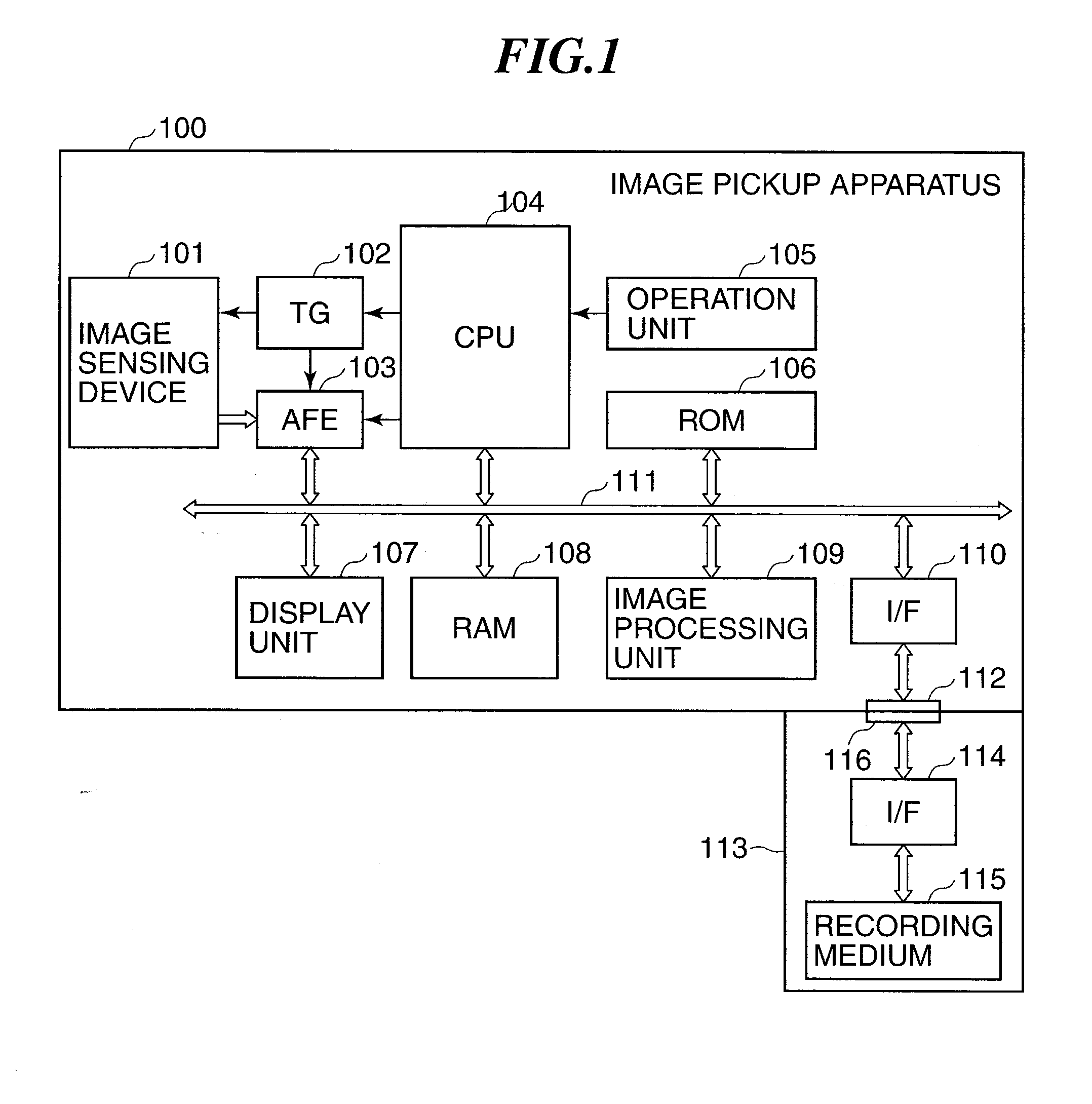
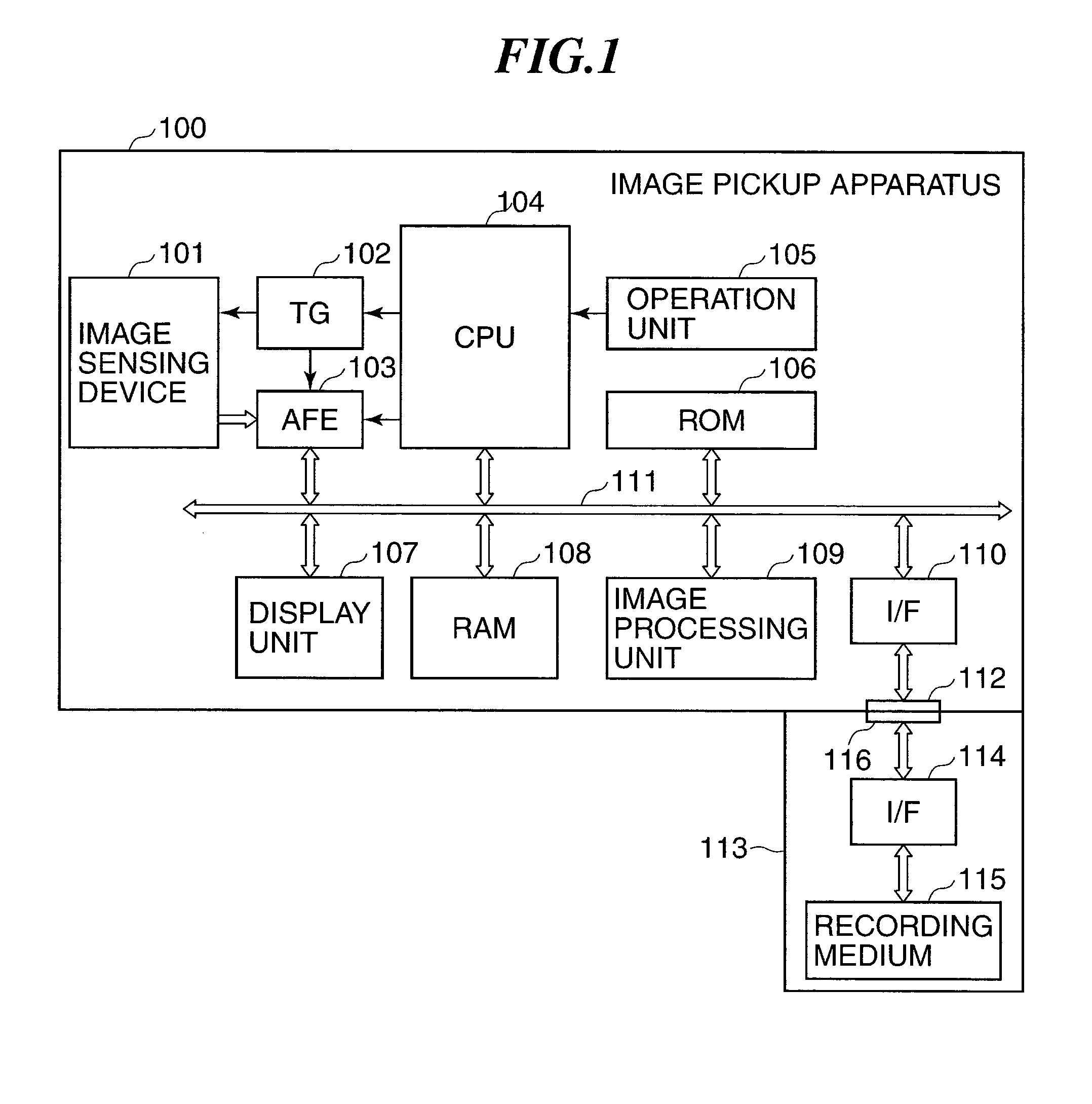
Image pickup apparatus capable of changing operation condition of image sensing device and control method therefor
ActiveUS20130021510A1Reduce noiseDynamic rangeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsVoltageImage sensing
An image pickup apparatus capable of ensuring a dynamic range suitable for an image shooting condition and capable of reducing noise. The image pickup apparatus includes an image sensing device having floating diffusion units that are provided corresponding to pixels and that convert electrical charges accumulated in the pixels into voltage signals, which are output as pixel signals from pixel amplifiers. At that time, according to an image shooting condition, at least parts of connection switches corresponding to the floating diffusion units are sequentially turned on or all the connection switches are turned off, whereby the connection switches are connected to or disconnected from connection lines to thereby change capacity components connected to pixel amplifiers. This contributes to dynamic range expansion or noise reduction.
Owner:CANON KK
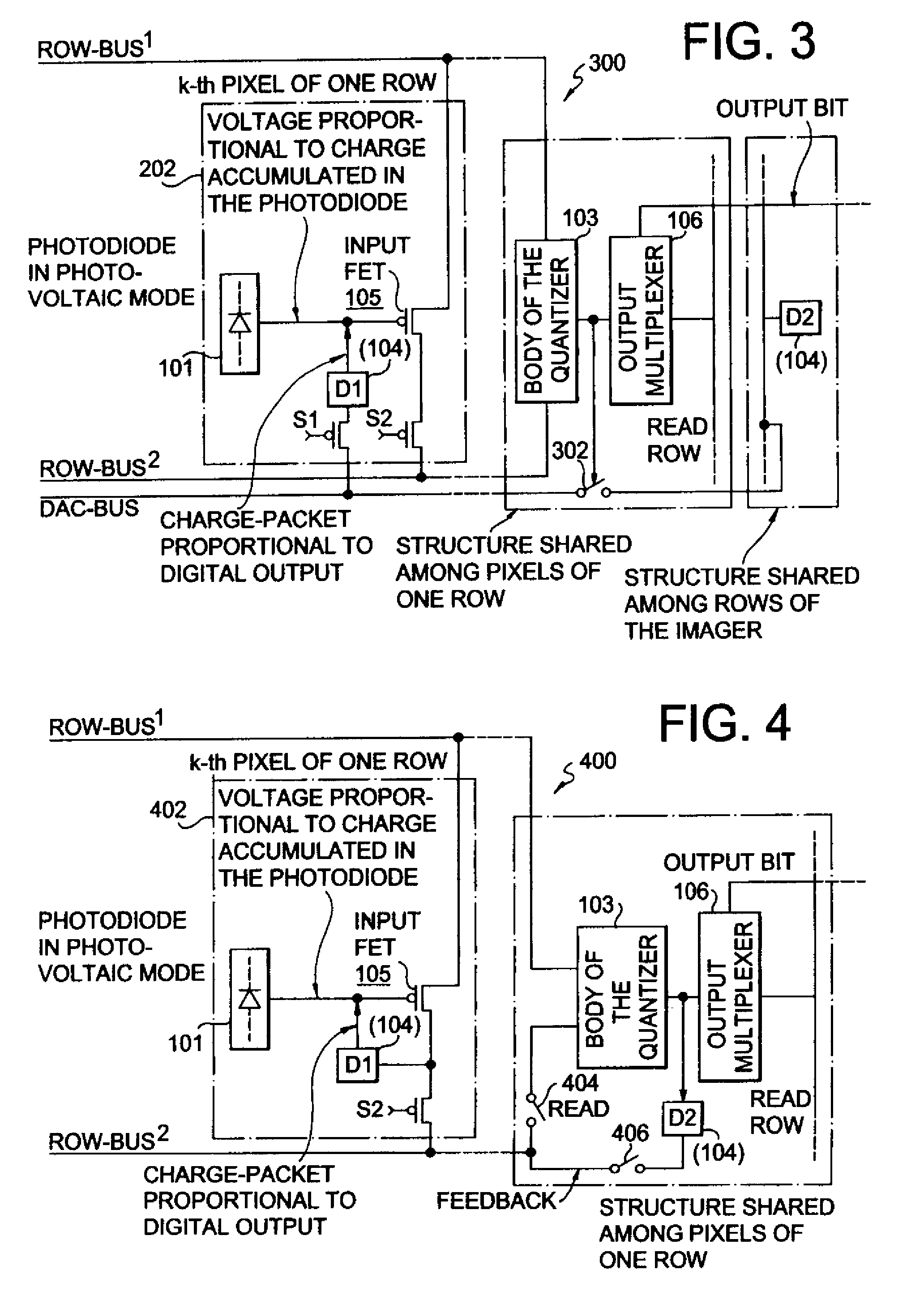
Multiplexed-input-separated Sigma-Delta analog-to-digital converter for pixel-level analog-to-digital conversion utilizing a feedback DAC separation
InactiveUS7466255B1Improve linearityReduce power consumptionTelevision system detailsElectric signal transmission systemsMultiplexingEngineering
In an array of imaging elements, a pixel level analog-to-digital-converter design splits the quantizer into an input transistor at the pixel location and a quantizer body for each row. The feedback digital-to-analog converter is also split into two components, one at the pixel location and one provided either for each row or for the entire array.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Amplifier
ActiveUS20100117650A1Noise figure is lowDynamic rangeMagnetic property measurementsVariable-capacitor element amplifiersLocal oscillator signalSideband
A two port parametric amplifier has a first port that receives an input signal to be amplified and upconverted and a second port that receives a local oscillator signal. The amplified upconverted input signal is emitted as an output at upper and lower sideband frequencies. The amplifier further has a pair of varactor diodes connected between the first port and the second port. The diodes are connected in parallel from the first port and in series from the second port.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Electro-acoustic transducer device
InactiveUS7860258B2Drift suppressionInhibit deteriorationPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSemiconductor electrostatic transducersUltrasonic sensorTransducer
A transducer for transmitting and receiving ultrasonic waves to a diaphragm-based ultrasonic transducer device using silicon as a base material. An electro-acoustic transducer device which can have a first electrode formed on top of, or inside, a substrate and having a thin film provided on top of the substrate. The device can also have a second electrode formed on top of, or inside, the thin film. A void layer can be provided between the first electrode and the second electrode. A charge-storage layer can be provided between the first electrode and the second electrode. A source electrode and a drain electrode can also be provided for measuring a quantity of electricity stored in the charge-storage layer.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
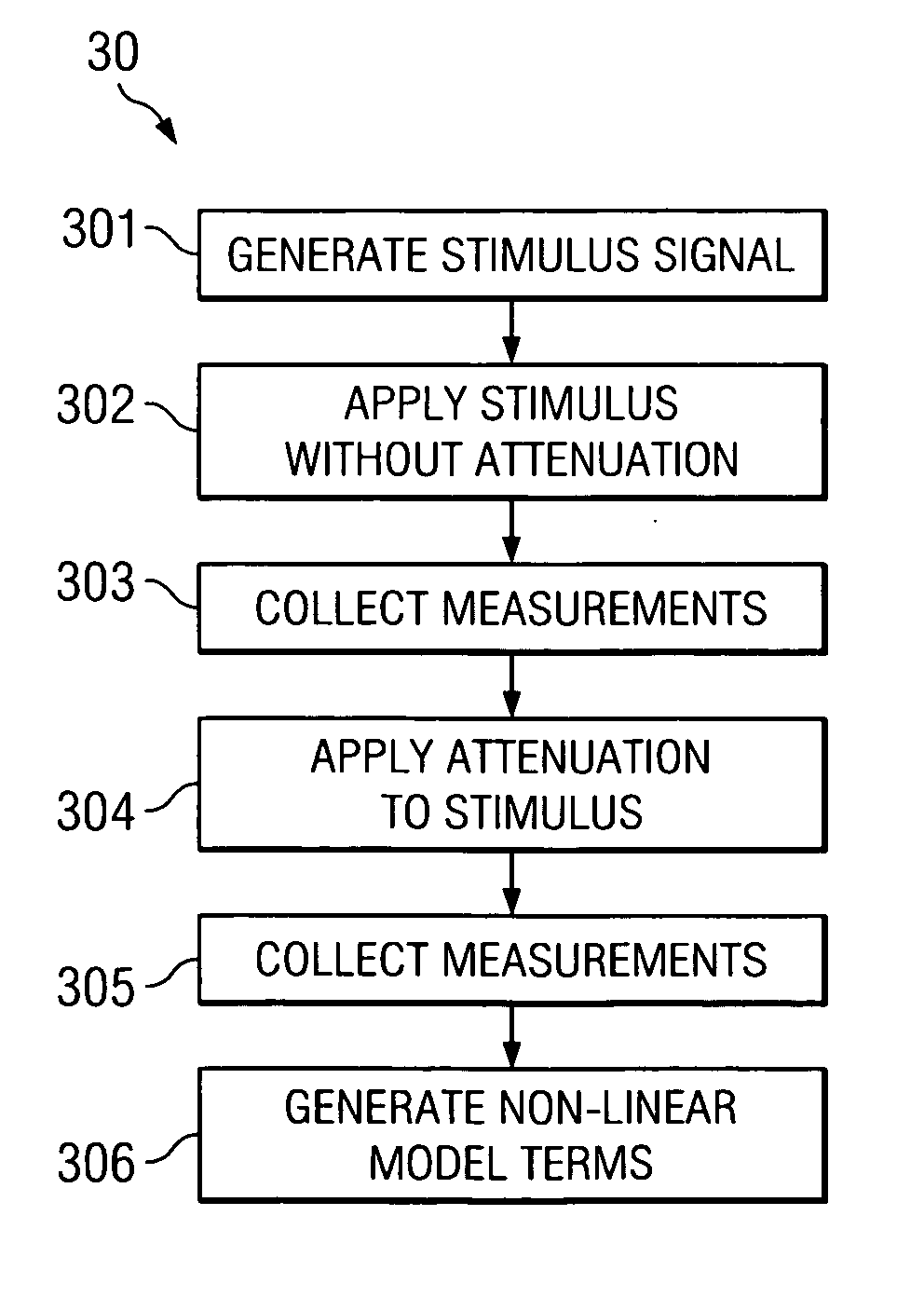
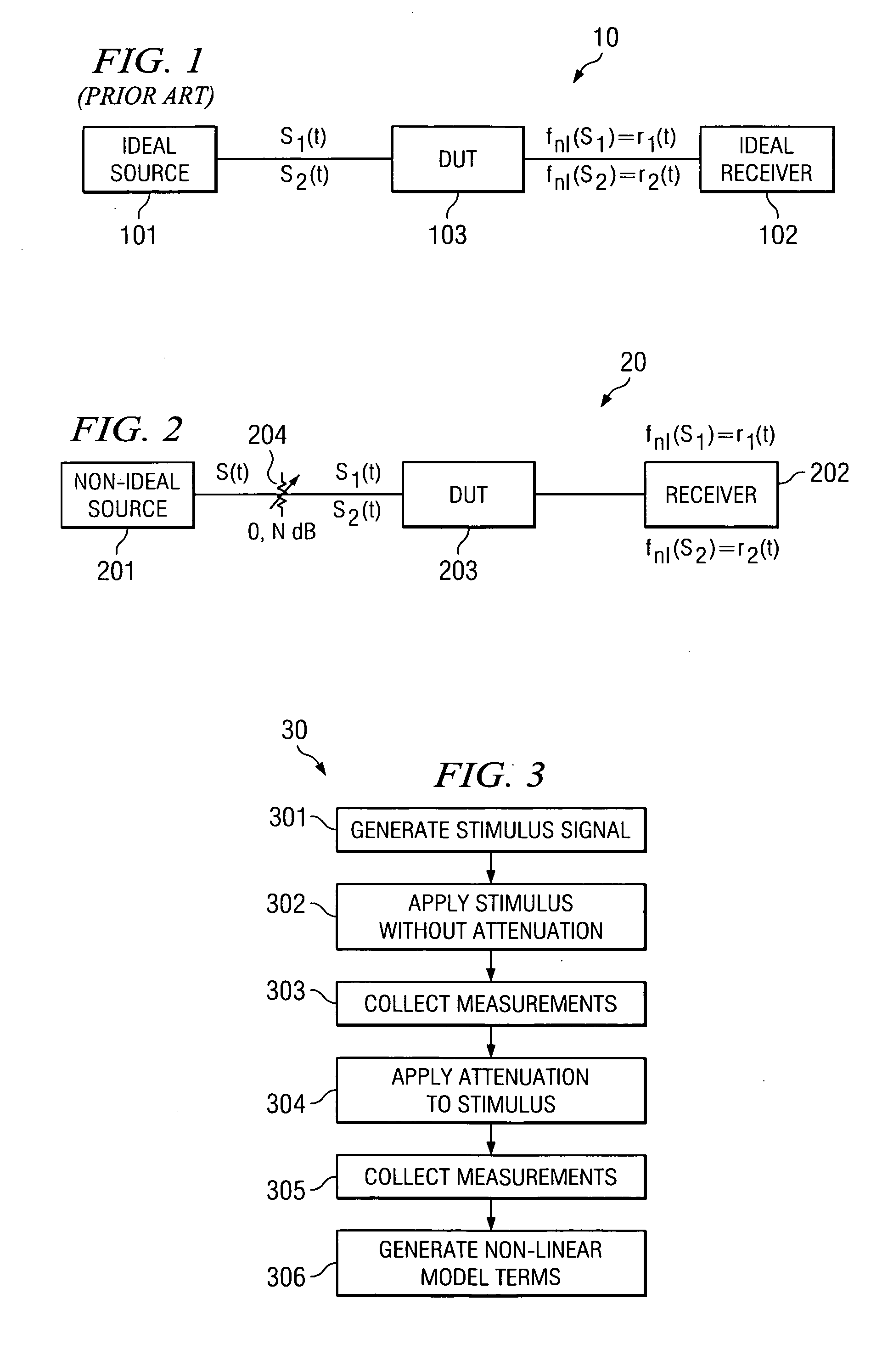
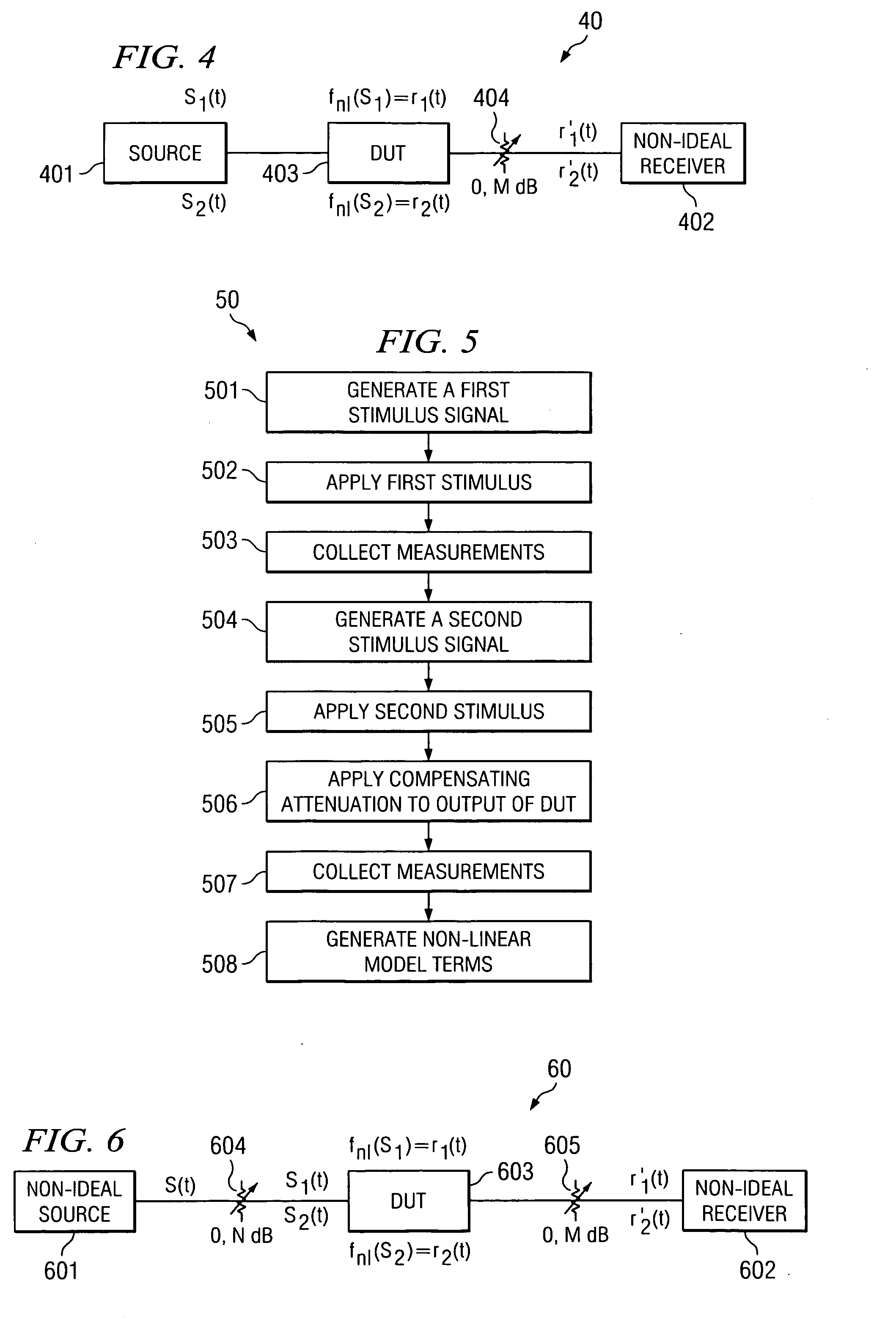
Nonlinear model calibration using attenuated stimuli
InactiveUS20070136018A1Minimize effect of nonlinearitiesRecovers dynamic rangeElectrical testingTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesUltrasound attenuationNonlinear model
A system and method are disclosed for calibrating non-linear behavior using attenuated stimuli and responses which allows for calibration with unknown stimulus and less expensive sources and receivers. The device under test is stimulated with a signal and then an attenuated version of the same signal, so that non-linear differences between responses can be attributed to the device rather than the signal source. Alternatively, or in conjunction with attenuation of the stimulus, the output of the device at different response amplitudes can be selectively attenuated such that the receiver measures approximately the same amplitude. This allows non-linear differences between measurements to be attributed to the device rather than the receiver. Two or more different signal sources can also be used, where responses are measured for each signal individually and then for at least one linear combination of signals.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
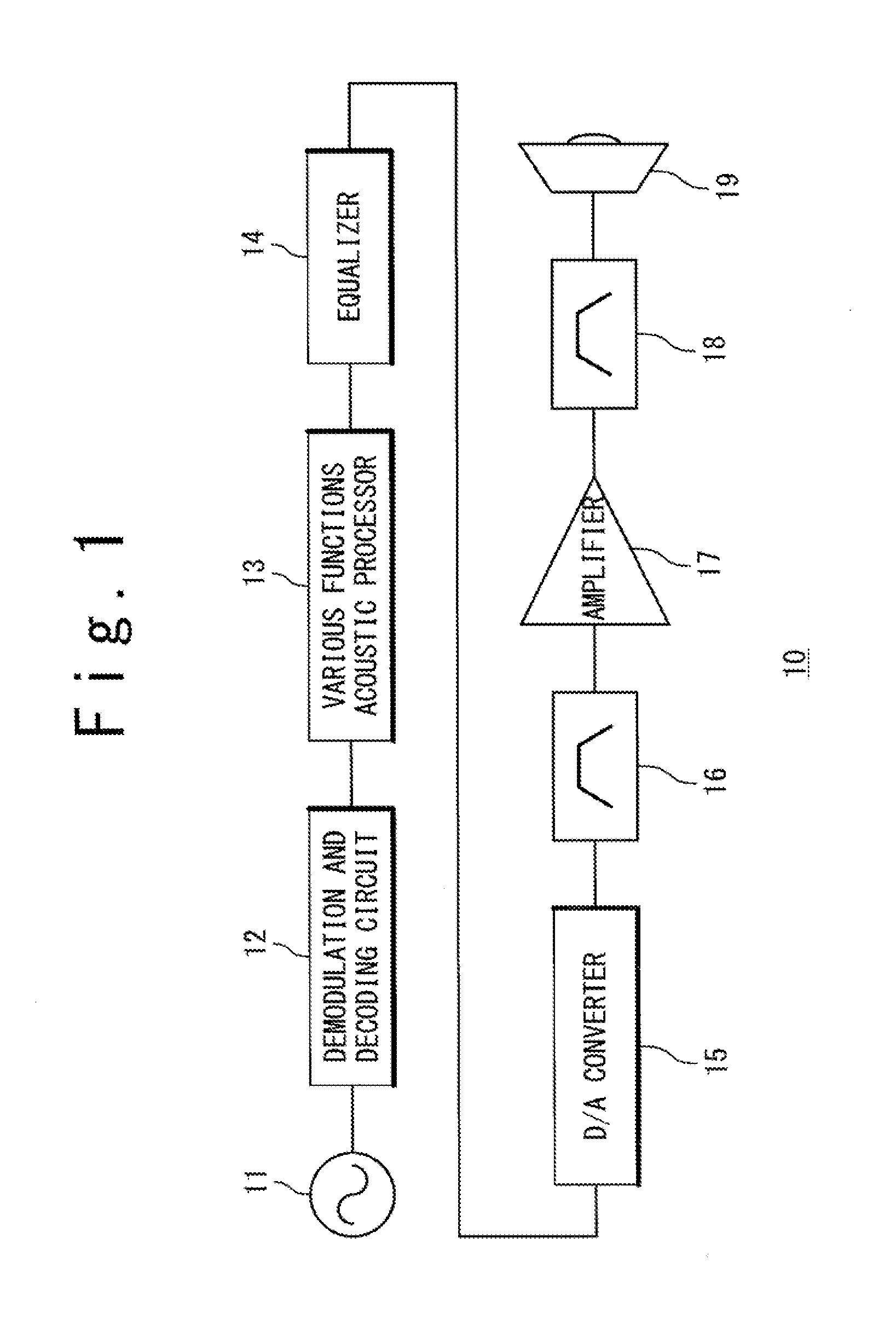
Acoustic processing system and method for electronic apparatus and mobile telephone terminal
InactiveUS20100086149A1Compression of dynamic rangeIncrease valueVolume compression/expansion in untuned/low-frequency amplifiersVolume compression/expansion in digital/coded amplifiersEngineeringLoudspeaker
An acoustic processing system for an electronic device includes: an equalizer processor which boosts or cuts a digital signal which has been subjected to an acoustic process for each of frequency components; a low-pass filter which extracts a low-range signal from the signal from the equalizer processor and outputs the signal; a high-pass filter which extracts a high-range signal from the signal from the equalizer processor and outputs the signal; a high-frequency compressor which compresses the high-range signal; an adder which generates an addition of the low-range signal and the compressed high-range signal; and a speaker which outputs a sound in accordance with the addition of the signal.
Owner:NEC CORP
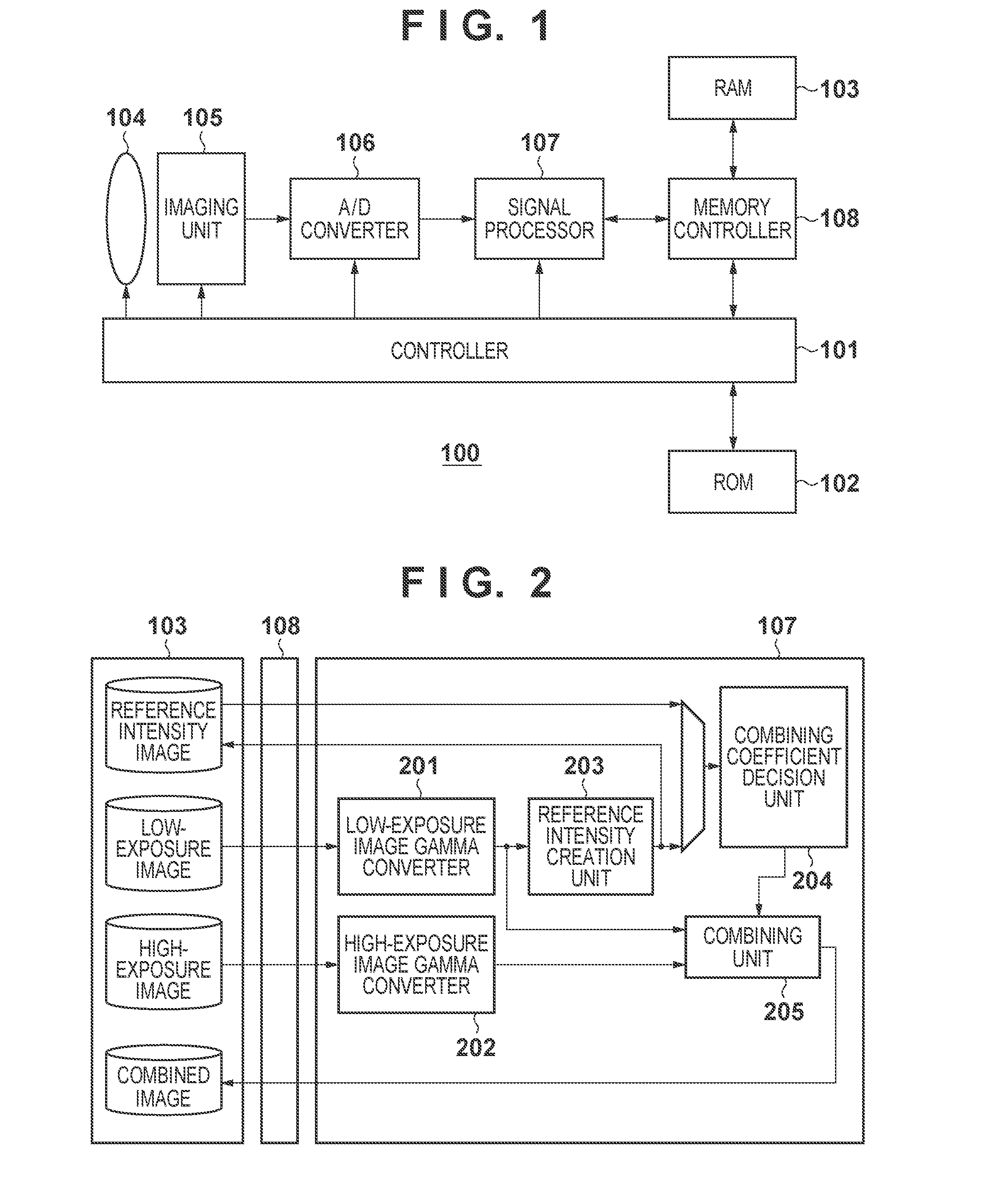
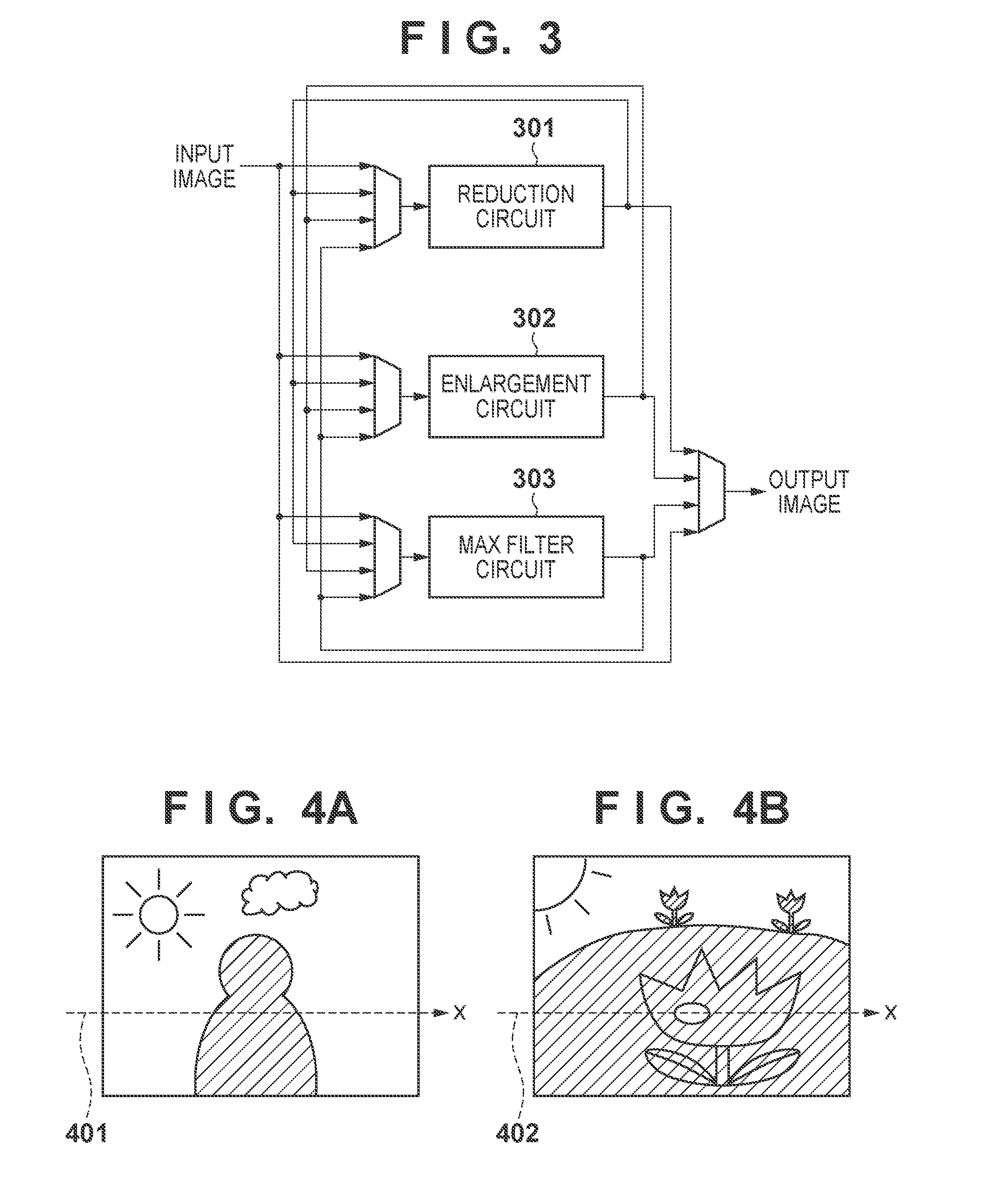
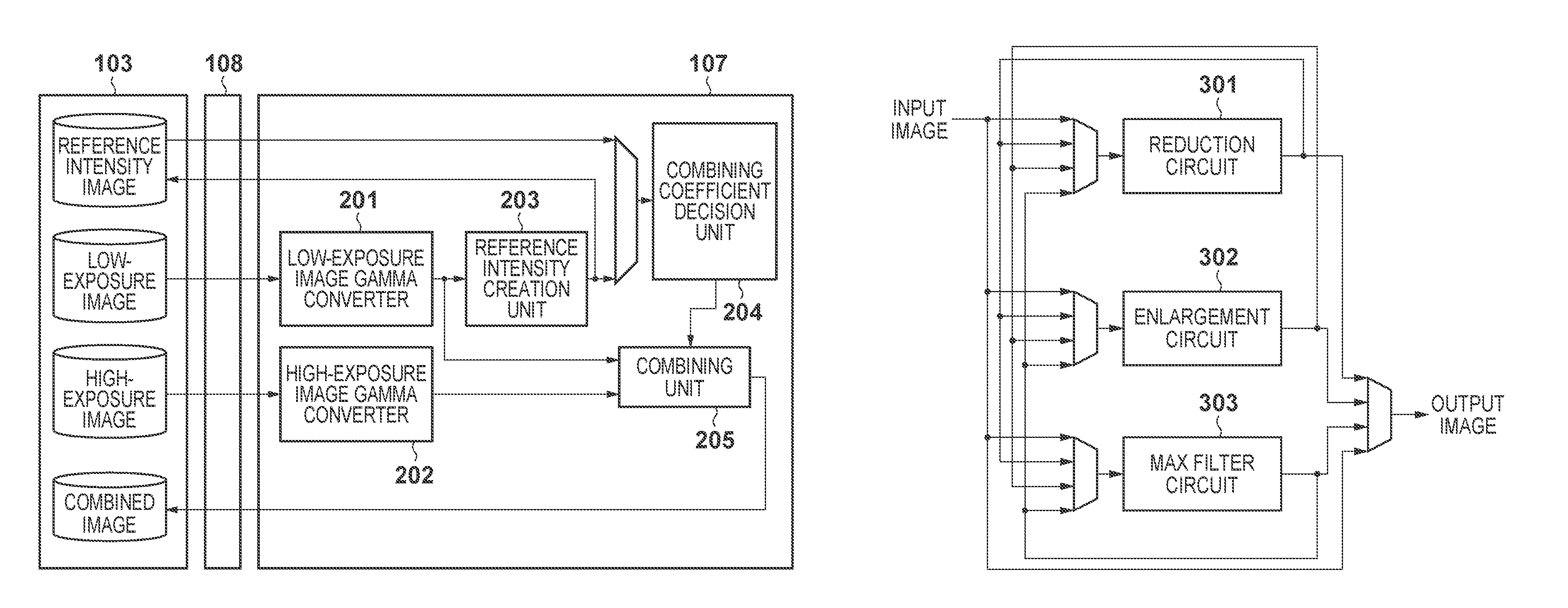
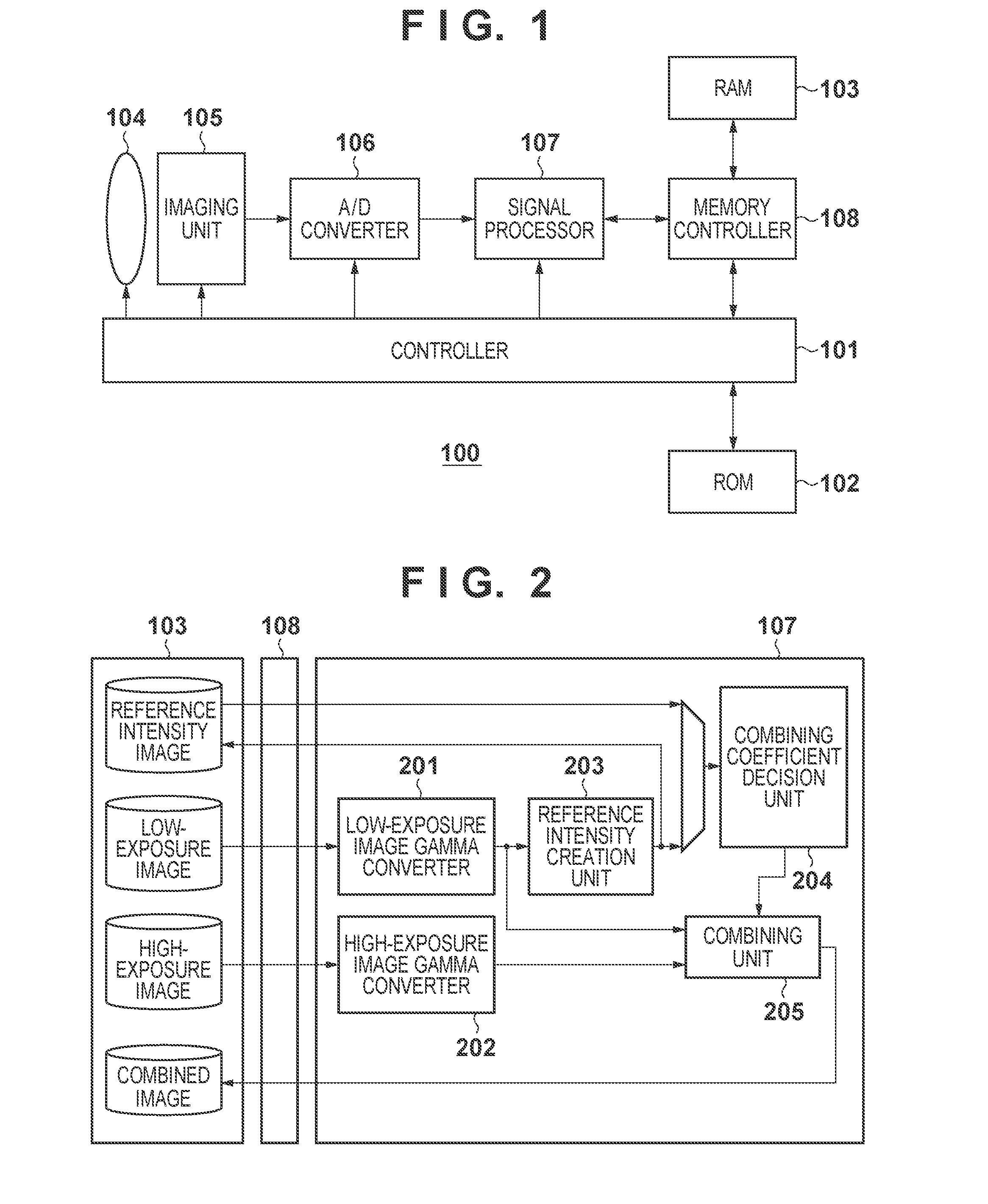
Image processing apparatus, control method thereof, and recording medium
ActiveUS20120200744A1Dynamic rangeTelevision system detailsImage enhancementImaging processingComputer science
A first image captured using a first exposure and a second image captured using a second exposure higher than the first exposure are obtained. A third image used as a reference for combining processing is created from the first image. An image, a dynamic range of which is extended, is created by weighted-combining the first and second images using adding coefficients, which are associated with pixel values of the third image in advance.
Owner:CANON KK
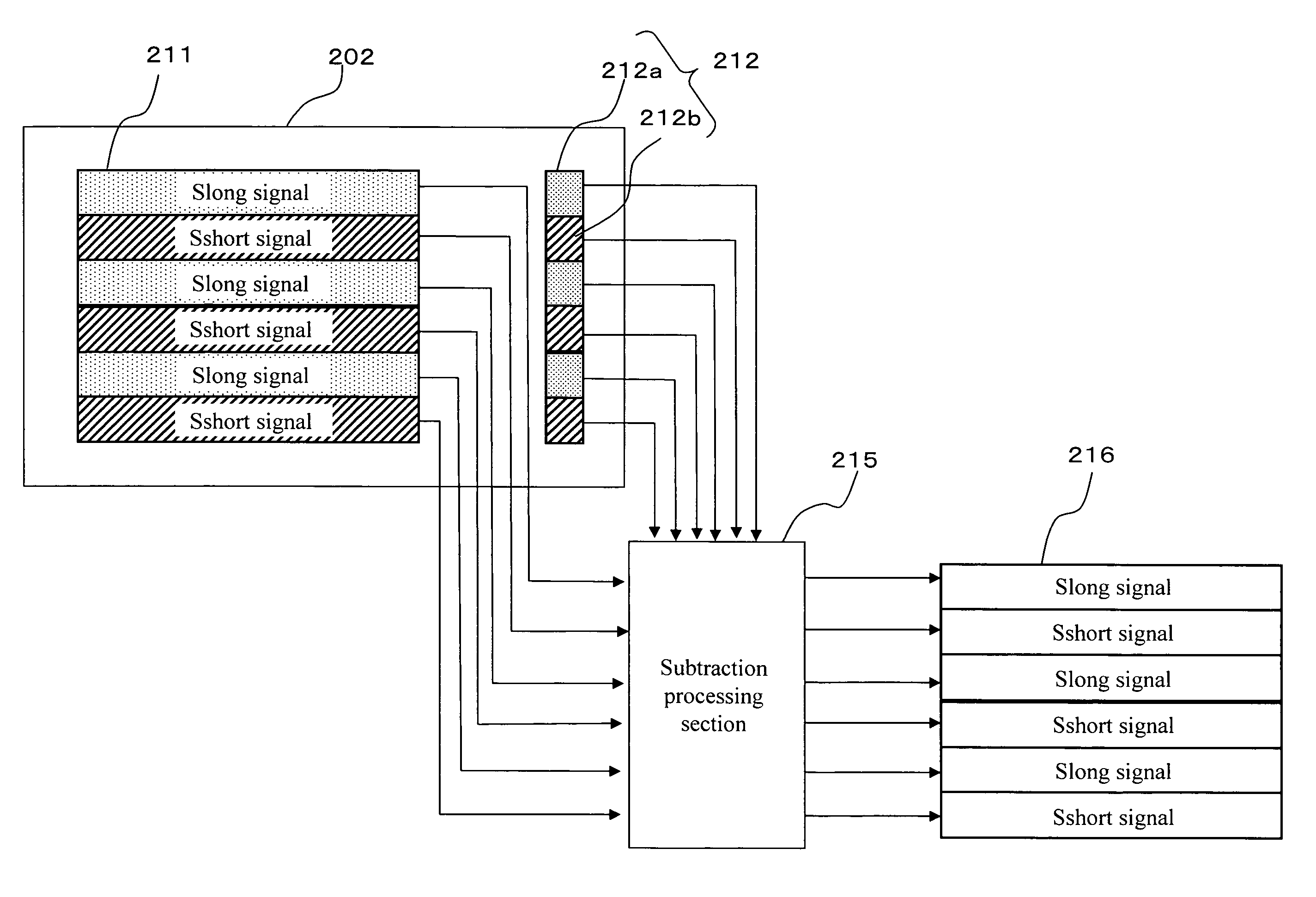
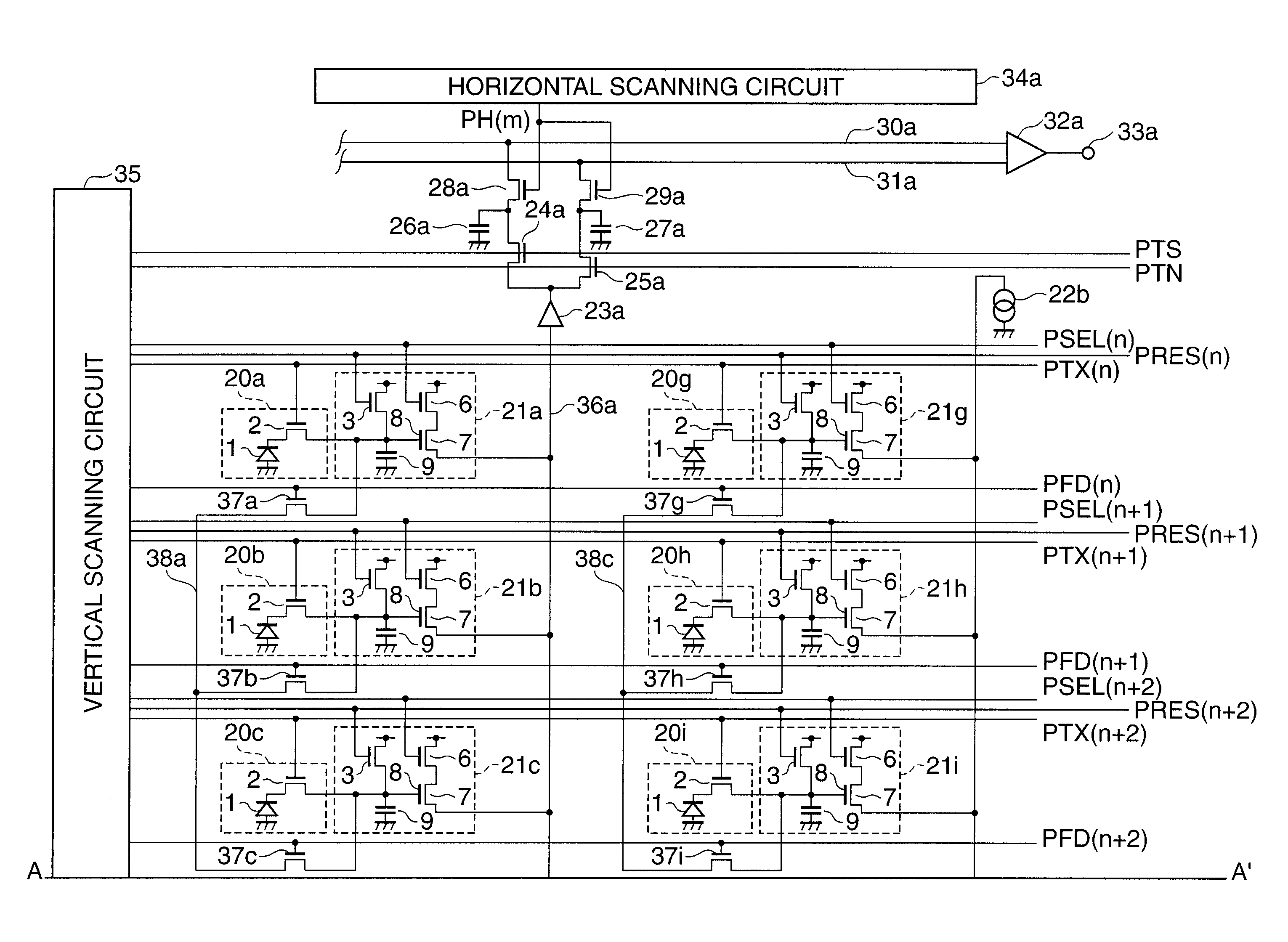
Method for reading out signal charges from an image sensor having different exposure times
InactiveUS7956925B2Suppresses deterioration of image qualityDynamic rangeTelevision system detailsExposure controlEngineeringDynamic range
Suppress deterioration in picture qualities while achieving expansion in a dynamic range.An image sensor readout method that reads out, from an area sensor where a plurality of image pickup elements are arranged in matrix, signal charges that are accumulated in the image pickup elements is constituted as follows. First, plural kinds of exposure time different in length from each other are set, and the exposure time is then individually allocated to each line of the area sensor. Next, the signal charges accumulated in the image pickup elements in the allocated exposure time are read out through a line unit of the area sensor. Then, the read out signal charges are synthesized through a screen unit of the area sensor.
Owner:COLLABO INNOVATIONS INC
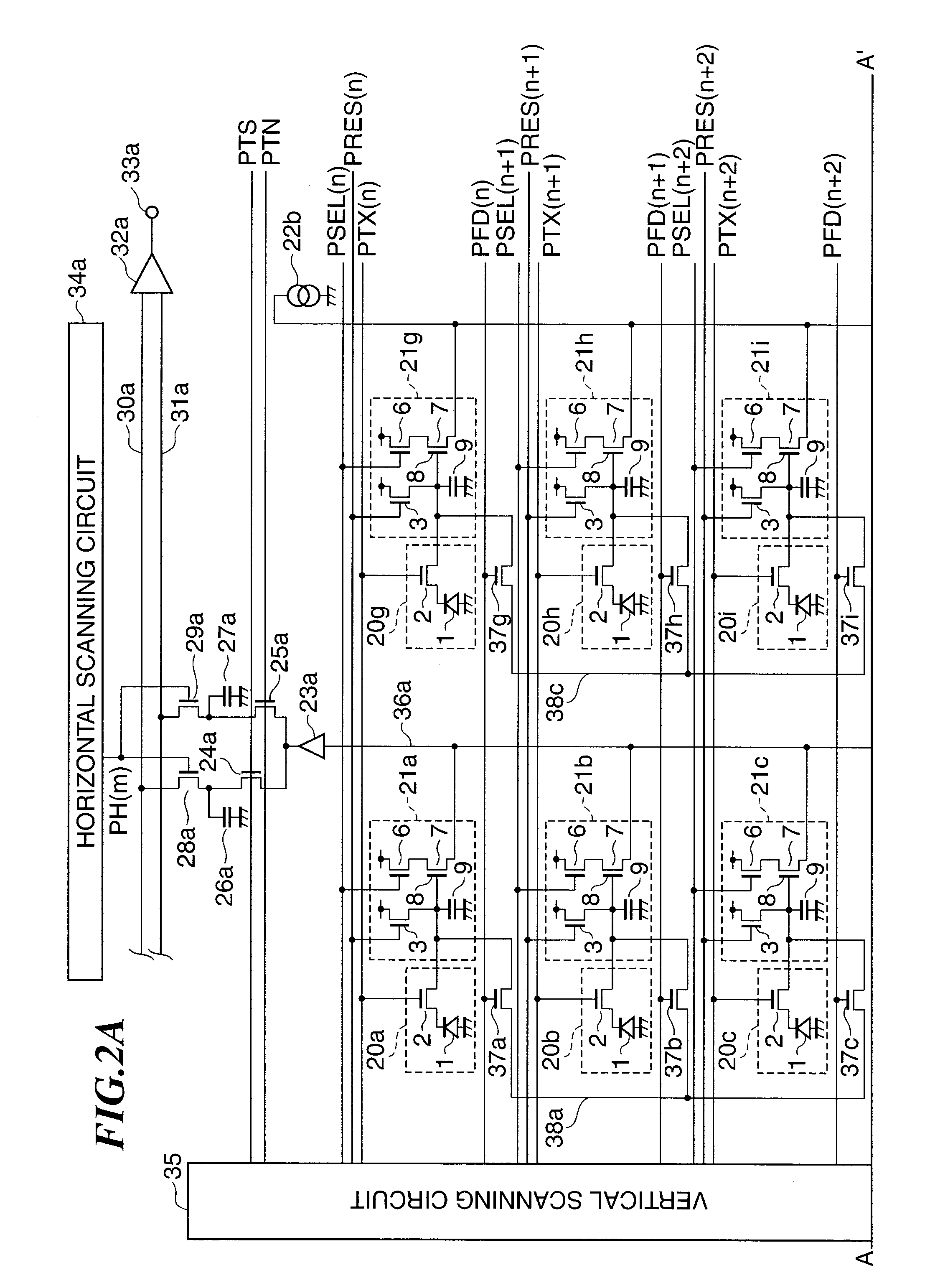
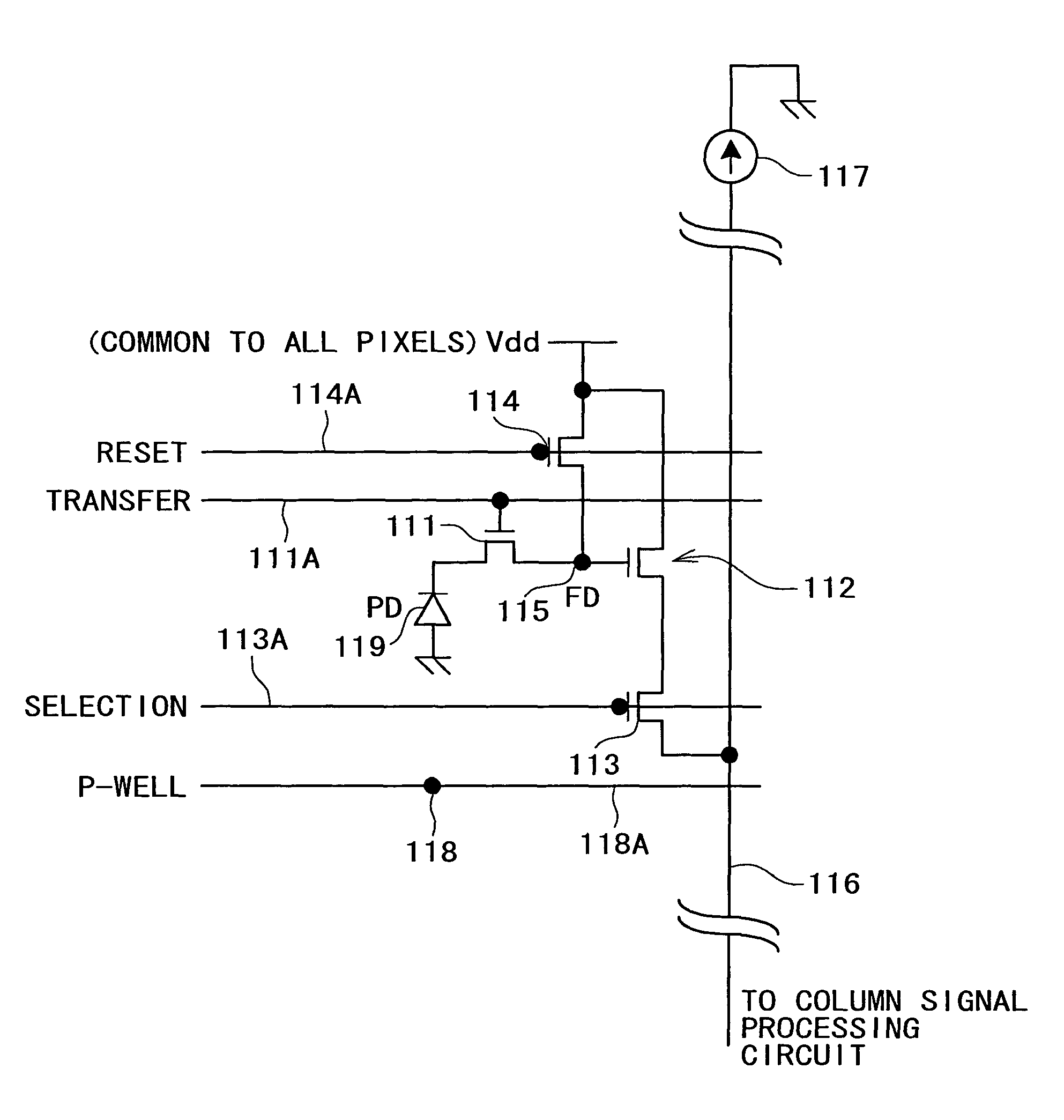
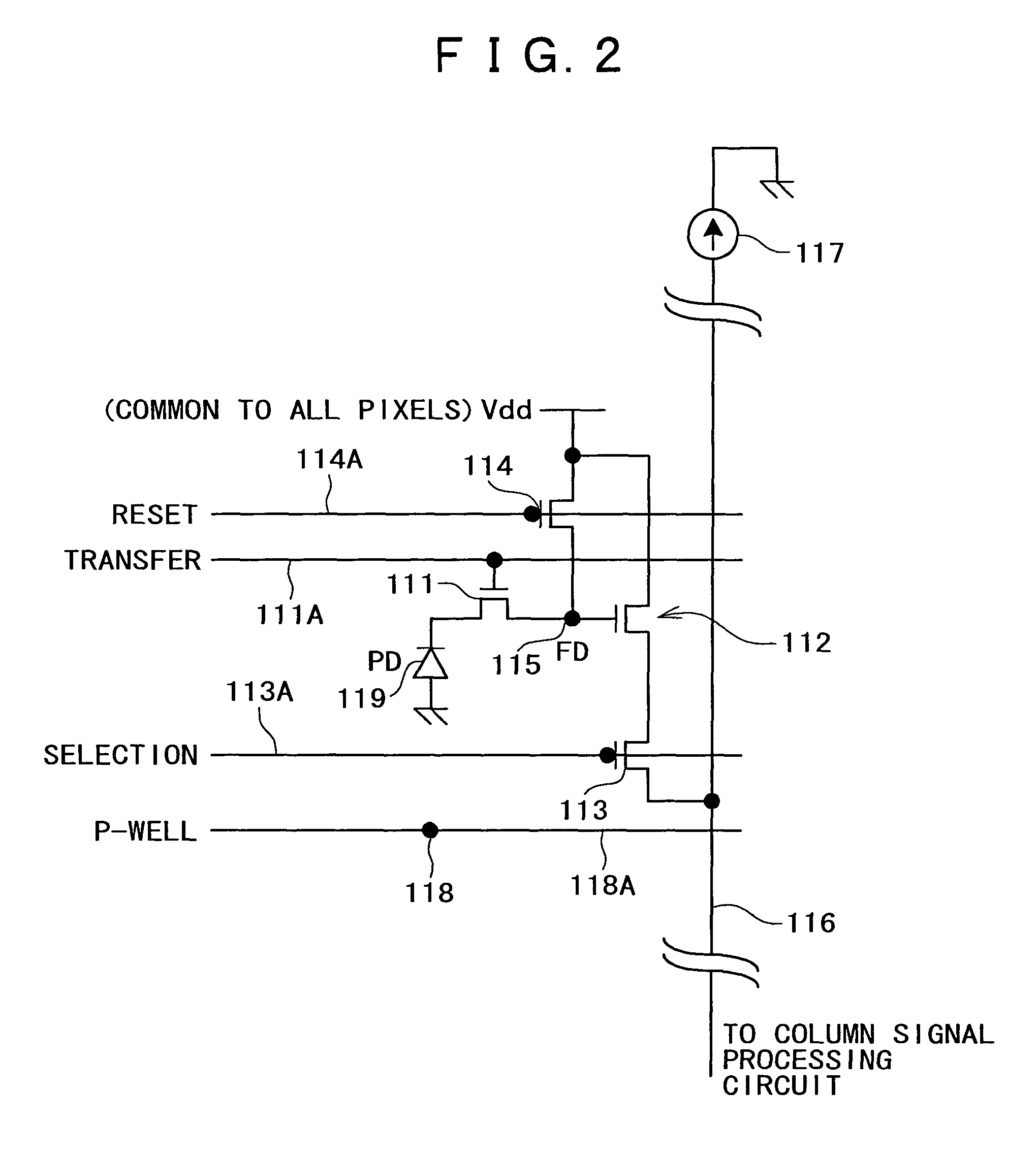
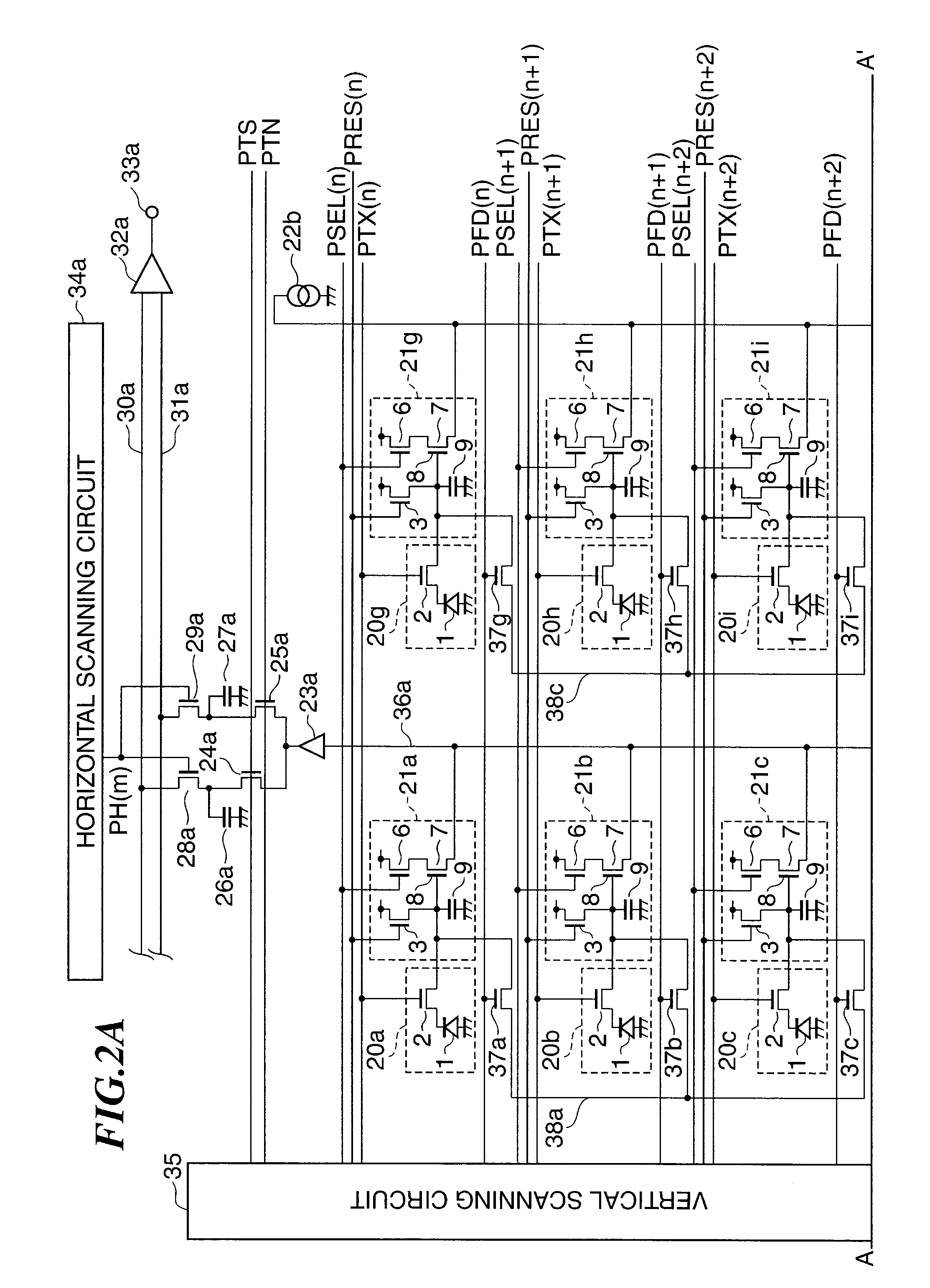
Solid-state image pickup device and driving method therefor
ActiveUS7787038B2Expansion of dynamic rangeReduce voltageTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCMOSFloating diffusion
A CMOS image sensor is disclosed which can achieve reduction of the voltage used to read out signal charge and can achieve expansion of the dynamic range. A P-well region is formed on a semiconductor substrate, and an embedded photodiode, a transfer transistor, an amplification transistor, a selection transistor, a reset transistor, a floating diffusion and so forth are provided in the P-well region. Signal charge of the photodiode is transferred to the floating diffusion by operation of the transfer transistor. A substrate bias voltage in the form of a negative voltage is applied to the P-well region in synchronism with the charge transfer operation of the transfer transistor to control the potential balance between the photodiode and the transfer gate portion to reduce the voltage for charge transfer. Further, during charge storage of the photodiode, the substrate bias voltage is varied to modify the angle of the sensitivity curve to achieve expansion of the dynamic range.
Owner:SONY CORP
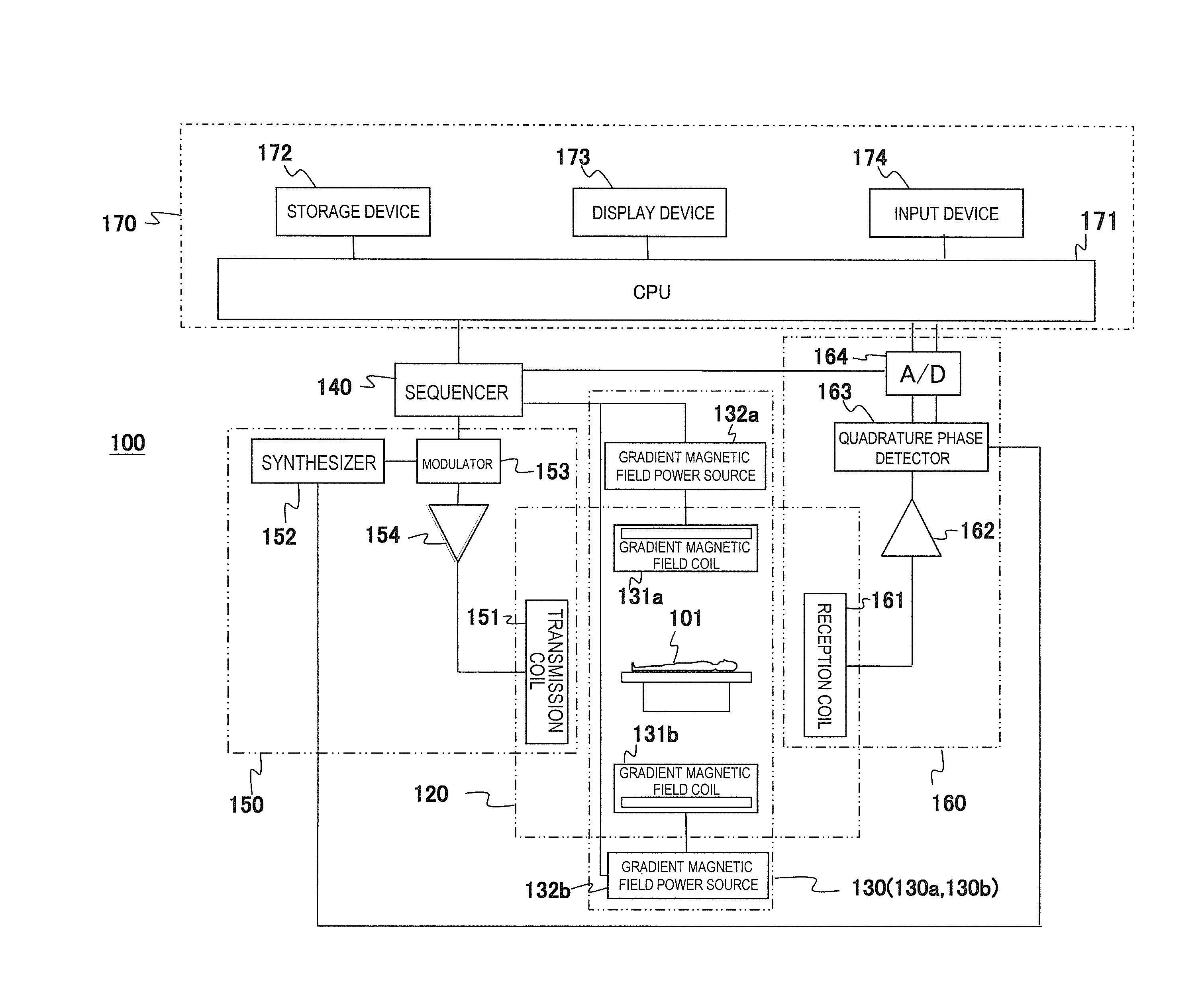
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus
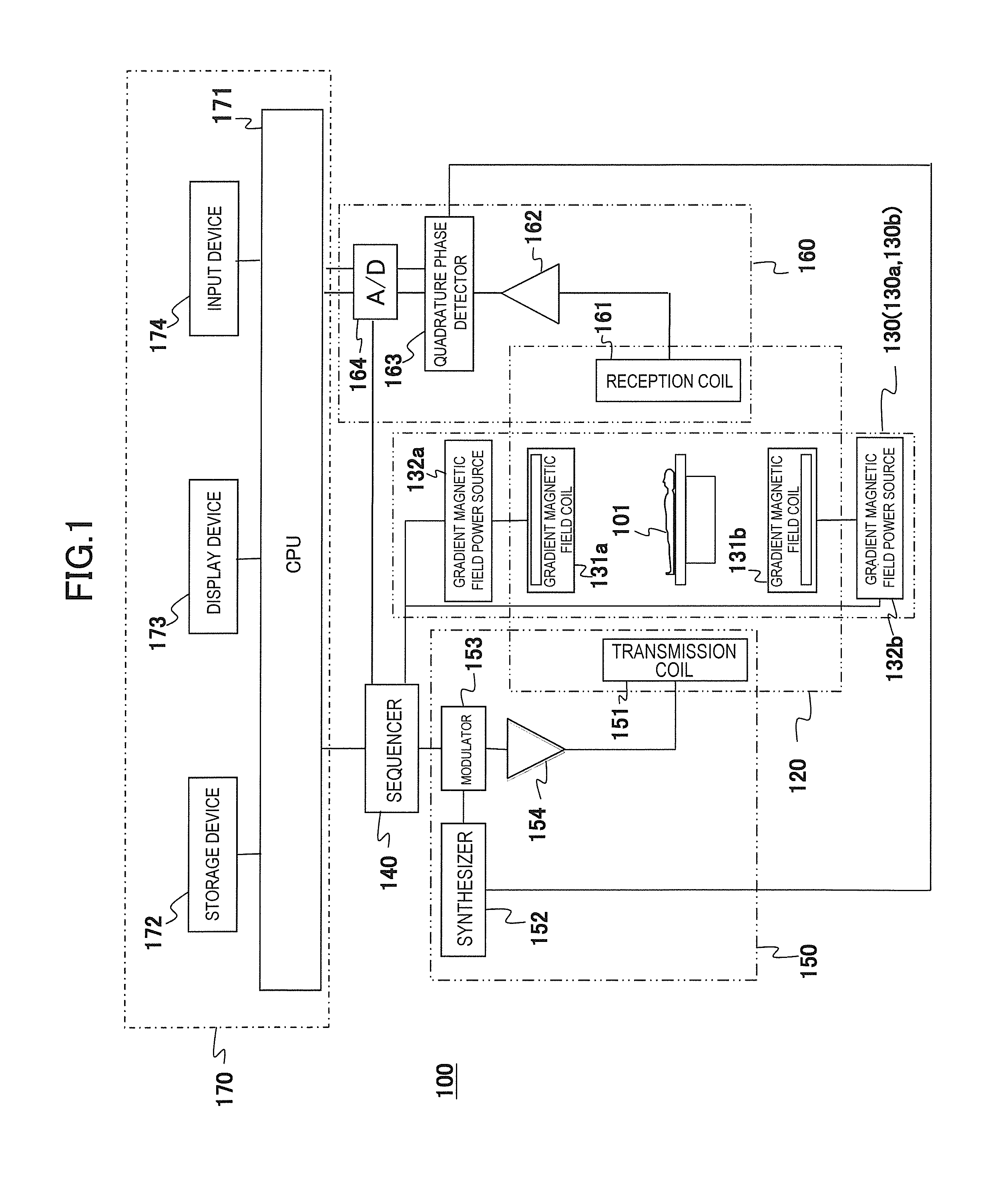
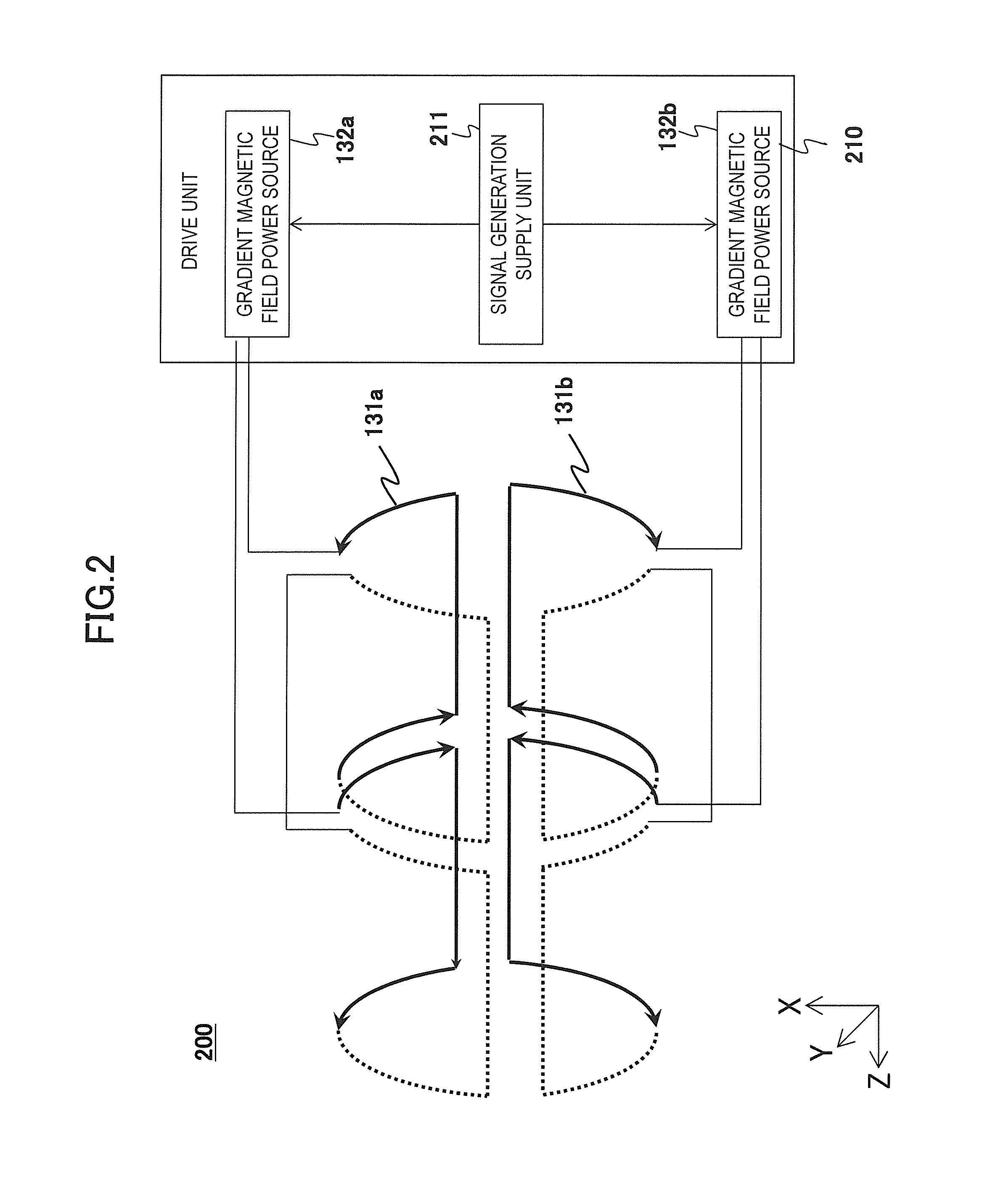
ActiveUS20160266221A1Reduce errorsImprove accuracyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Frequency encoding
In order to obtain highly accurate images with a high SNR without extending measurement time or increasing hardware costs and software processing costs, the present invention narrows a dynamic range (amplitude) of an NMR signal to be received by a reception coil (reception NMR signal) in an MRI apparatus. In order to narrow the amplitude of the reception NMR signal, according to the position of an imaging region, a peak position of the reception NMR signal is shifted from the said position in the present embodiment. The shift is achieved by applying frequency encoding gradient magnetic field pulses whose application amount in the time direction is different according to the position. This is realized by a plurality of gradient magnetic field generating systems that can be driven independently.
Owner:FUJIFILM HEALTHCARE CORP
Imaging apparatus and imaging control method
ActiveUS8421882B2Efficient use ofEnhance the imageTelevision system detailsColor television detailsValue setSingle exposure
In an imaging apparatus, an imaging unit generates an acquired image of a subject. A luminance information acquirer acquires the subject's luminance information. A detector detects the subject's luminance range on the basis of the acquired luminance information. An imaging controller sets a range of exposure control values having a step that corresponds to a value obtained by multiplying the detected luminance range by a predetermined coefficient k (where 0<k<1), and then uses the imaging unit to take multiple shots (i.e., multiple imagings) set with respectively different exposure control values within the range of exposure control values. An image compositor generates a composite image by compositing image portions extracted from the plurality of images obtained via the multiple shots. When just one shot is taken, the single exposure control value set for the one shot is contained within the range of the exposure control values.
Owner:SONY CORP
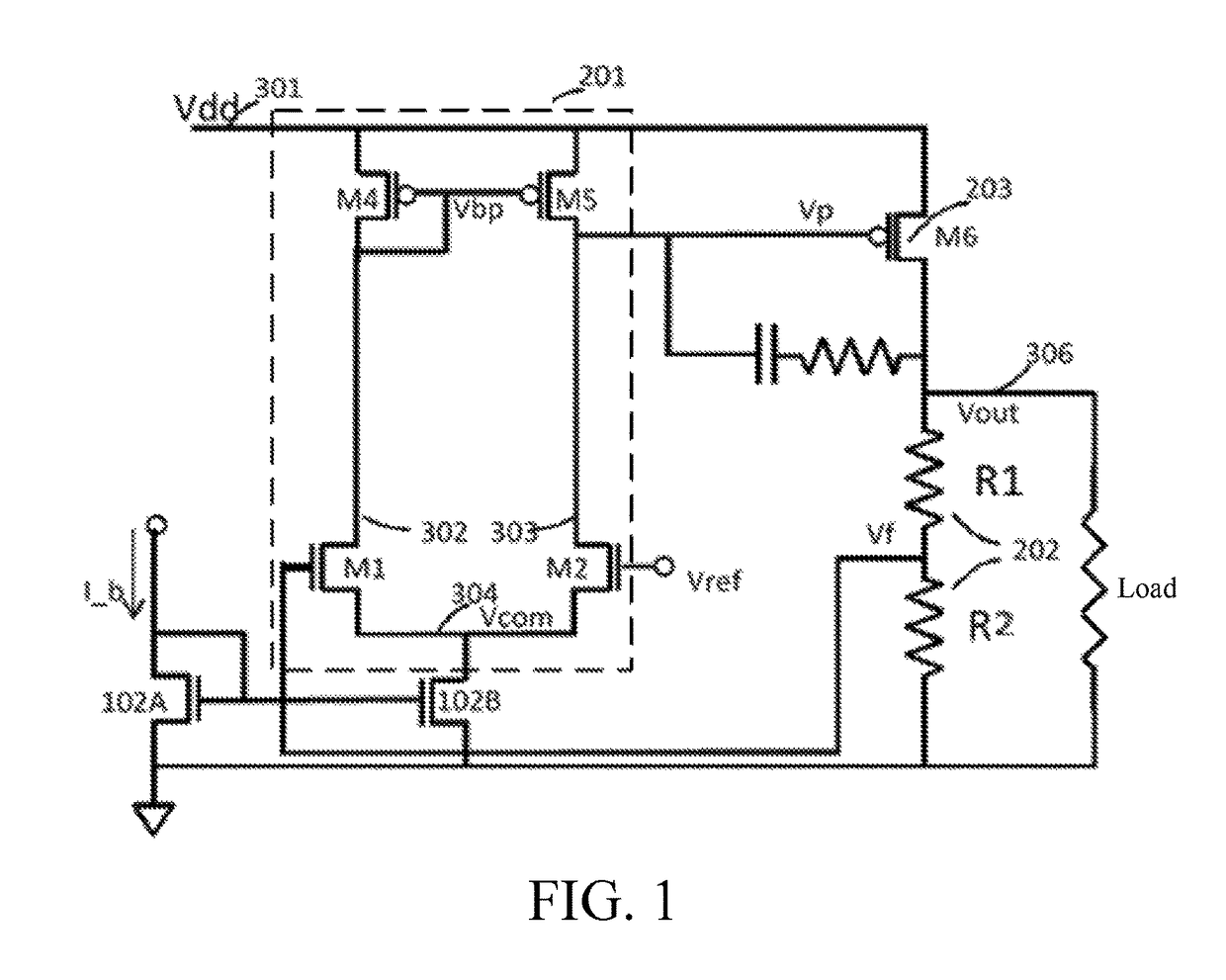
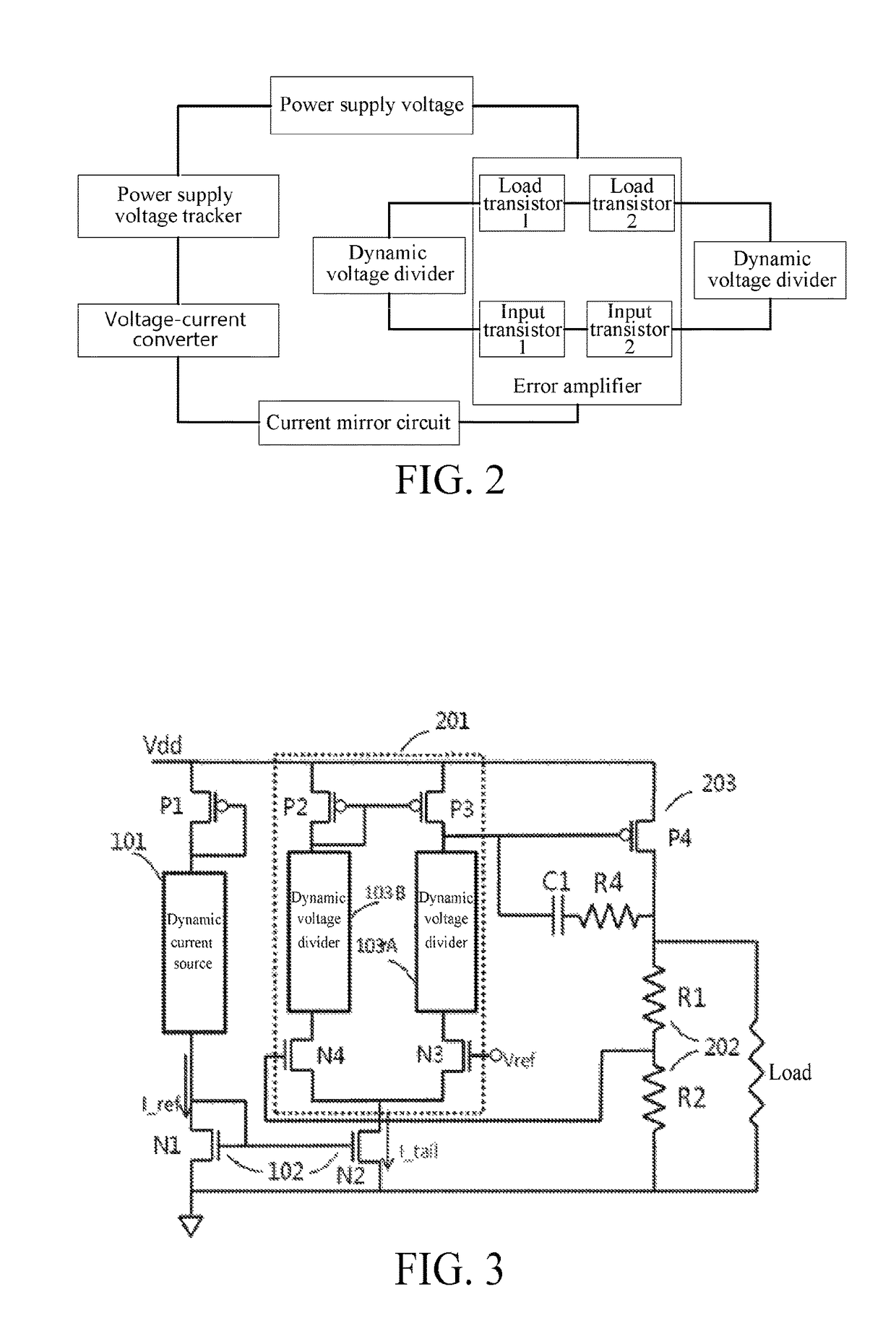
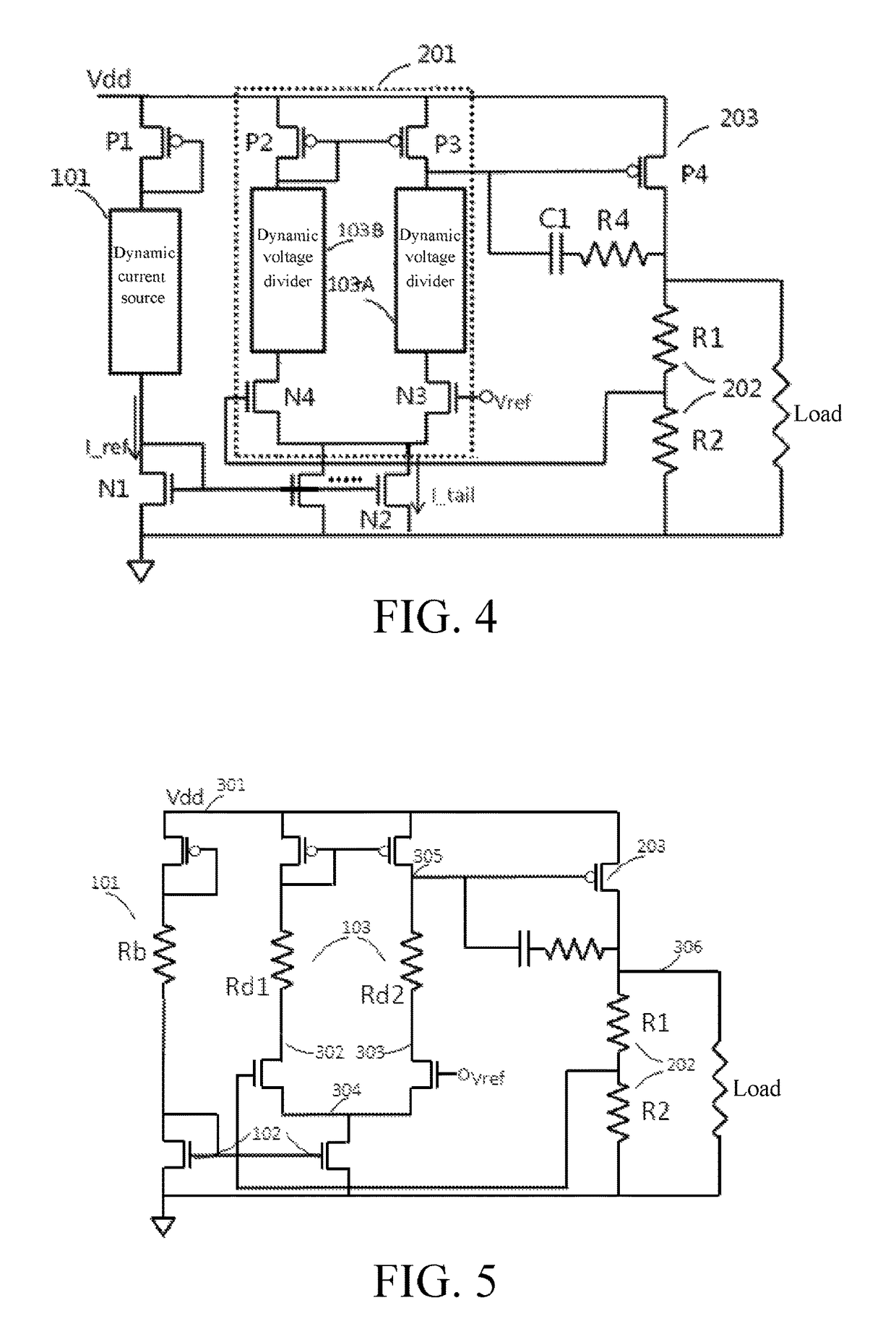
Adaptive low-dropout regulator having wide voltage endurance range, chip and terminal
ActiveUS20180067512A1Adjustable rangeHigh voltageAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesAmplifier modifications to reduce detrimental impedenceEngineeringField-effect transistor
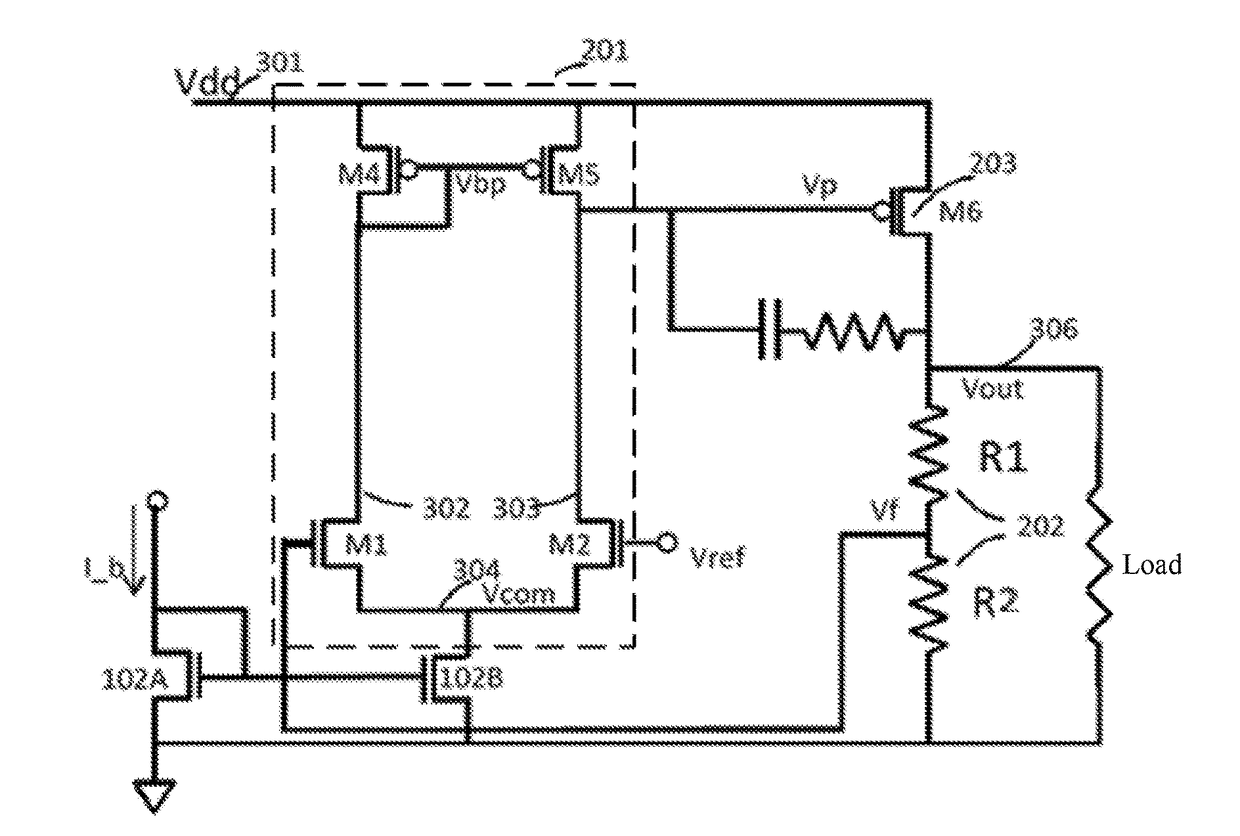
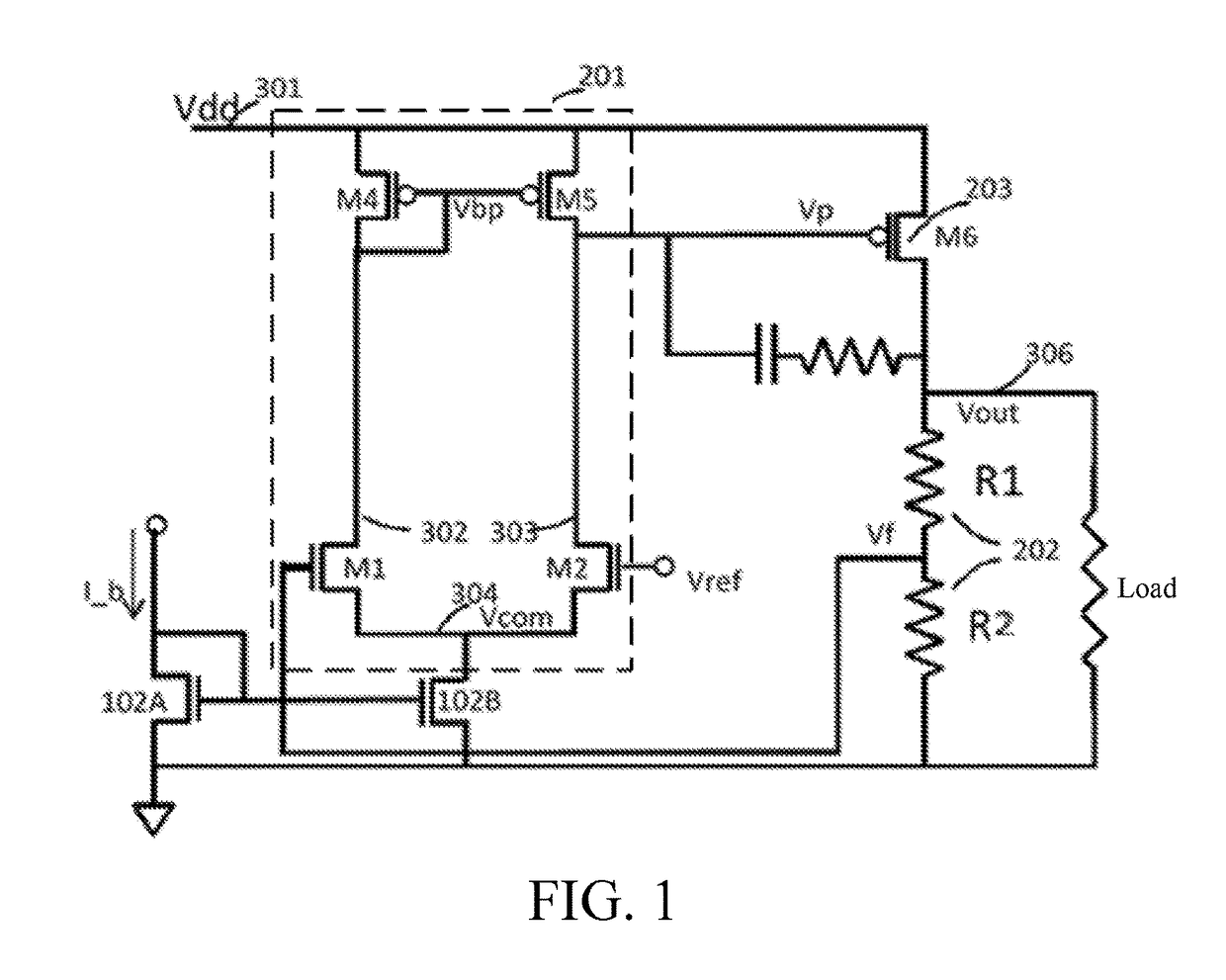
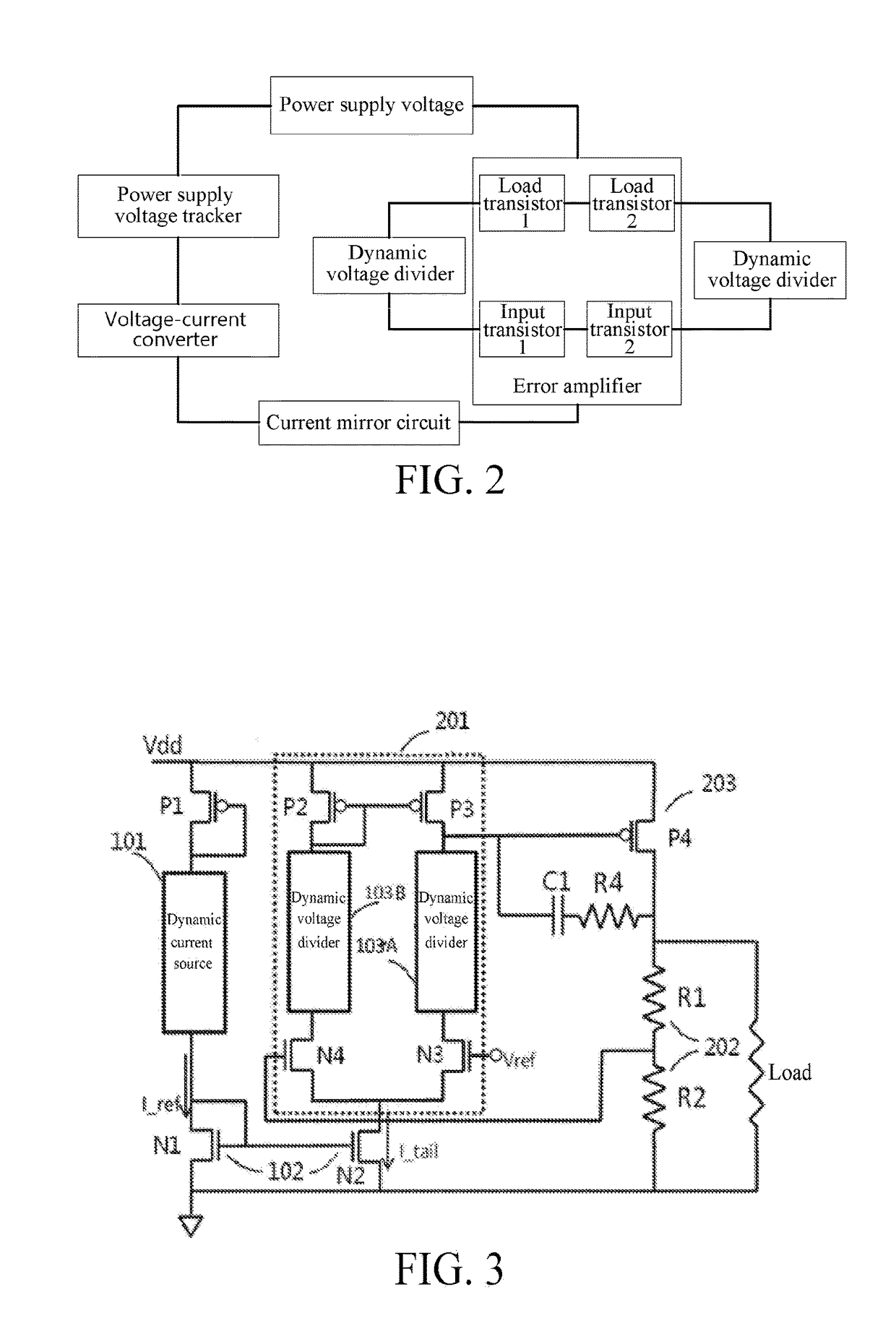
An adaptive low-dropout regulator (LDO) having a wide voltage endurance range includes a power supply voltage tracker (P1), a voltage-current converter (101), an error amplifier (201), a current mirror circuit (102), and a dynamic voltage divider (103). One end of the power supply voltage tracker (P1) is connected to a Vdd, the other end thereof is connected to the voltage-current converter (101) connected to an input end of the current mirror circuit (102), and an output end of the current mirror circuit (102) is connected to sources of two input field effect transistors (N3, N4) in the error amplifier (201). Sources of two load field effect transistors (P2, P3) in the error amplifier (201) are connected to the Vdd. Dynamic voltage dividers (103A, 103B) are connected respectively between each of the input field effect transistors (N3, N4) and the corresponding load field effect transistors (P2, P3).
Owner:VANCHIP TIANJIN TECH
Image processing apparatus and method in which first and second images are combined in a weighted manner based on a third image
ActiveUS9426382B2Dynamic rangeImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImaging processingImage capture
A first image captured using a first exposure and a second image captured using a second exposure higher than the first exposure are obtained. A third image used as a reference for combining processing is created from the first image. An image, a dynamic range of which is extended, is created by weighted-combining the first and second images using adding coefficients, which are associated with pixel values of the third image in advance.
Owner:CANON KK
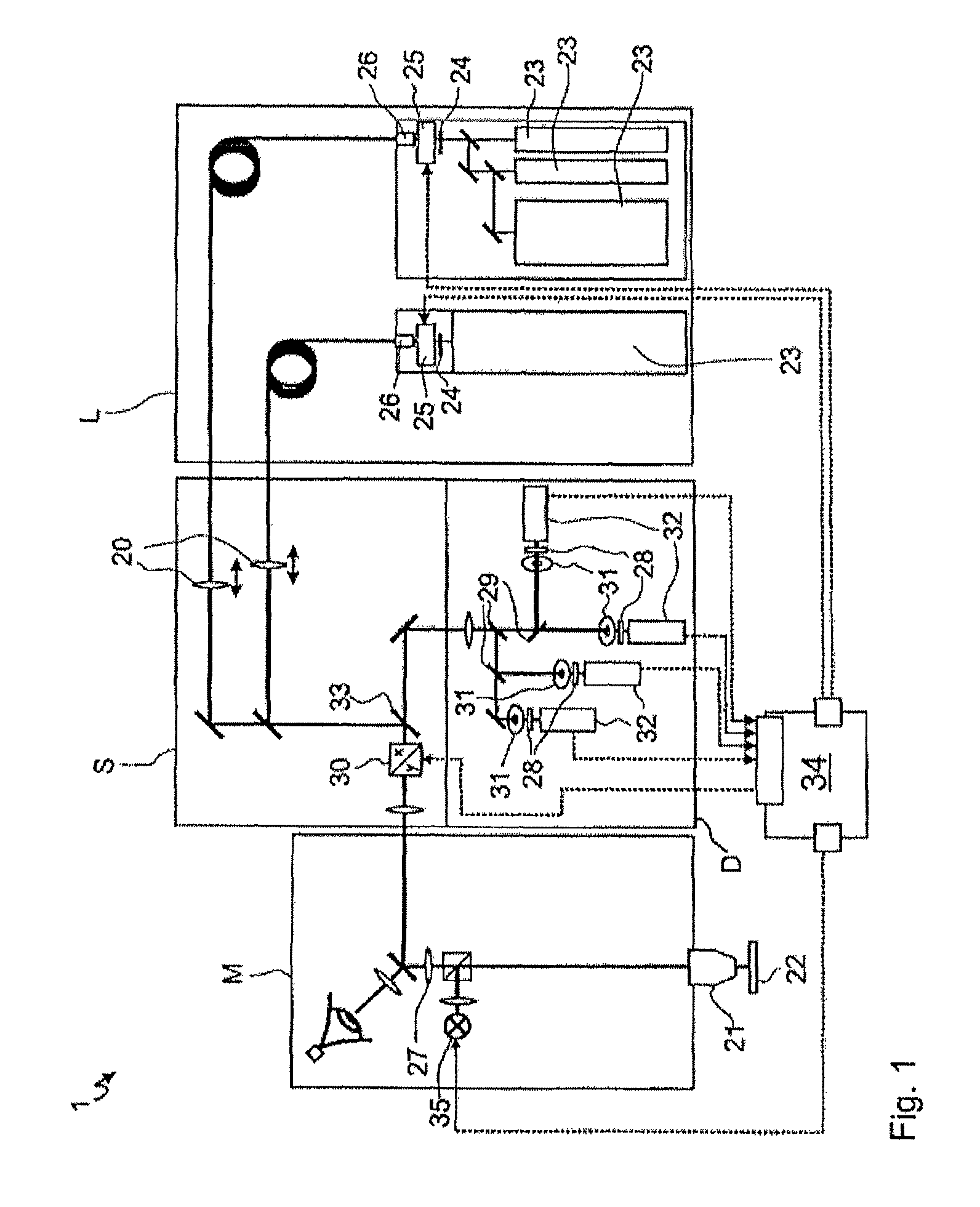
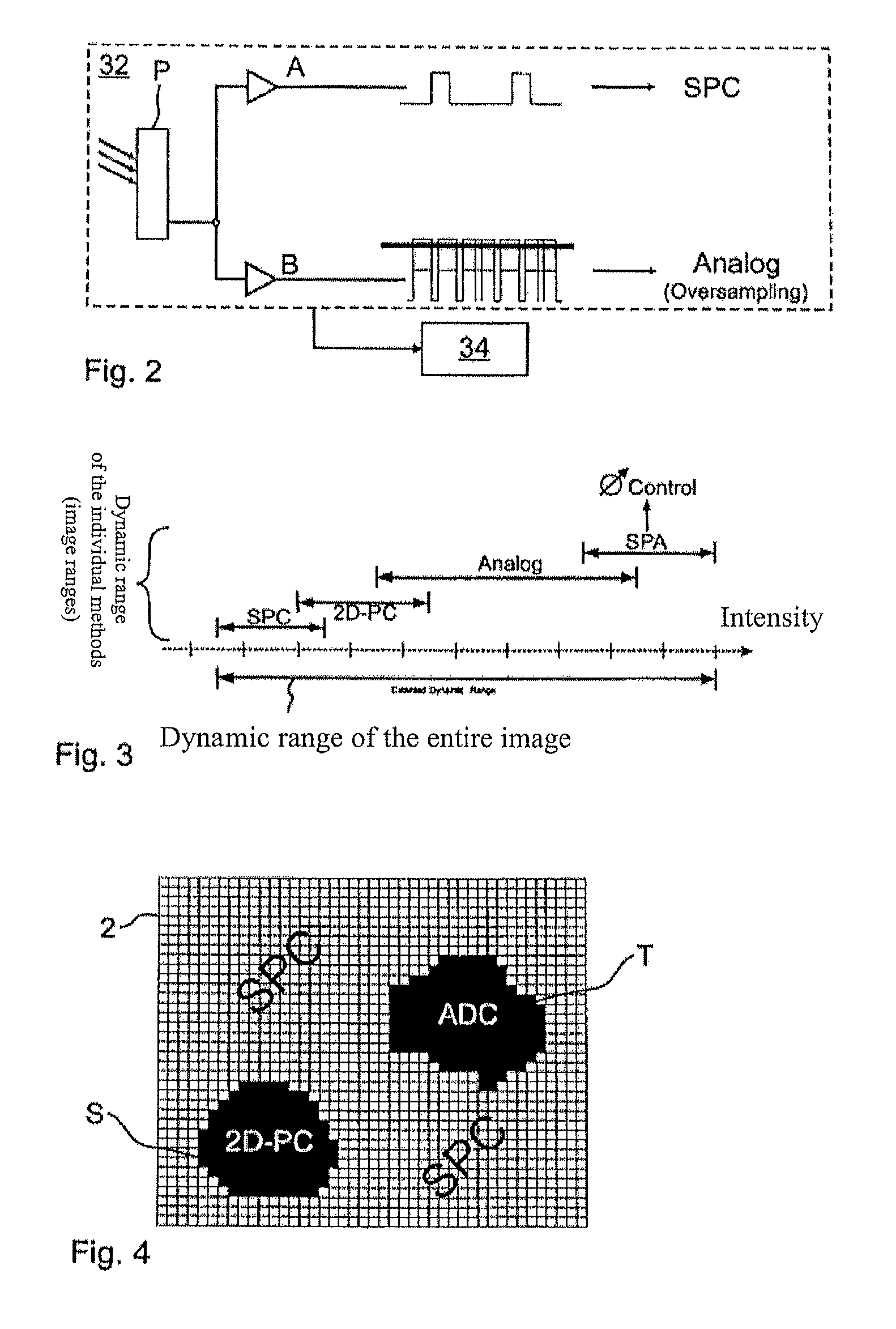
Method for generating images with an expanded dynamic range and optical device for carrying out such a method, in particular a laser scanner microscope
ActiveUS8633430B2Reduce noiseTime-consuming sequential acquisition of several individual images can be eliminatedPhotometry using reference valueSolid-state devicesLaser scanningLight signal
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
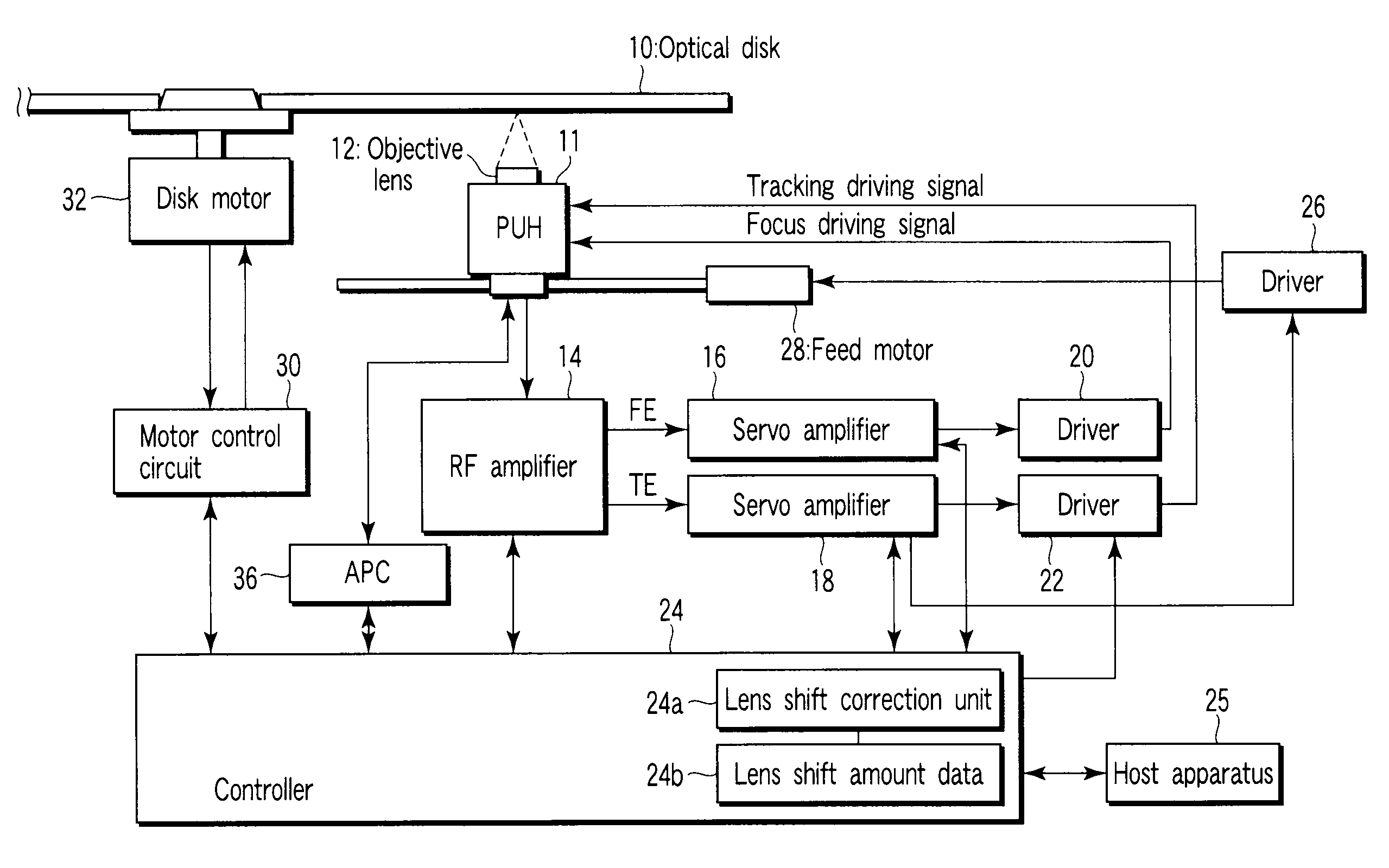
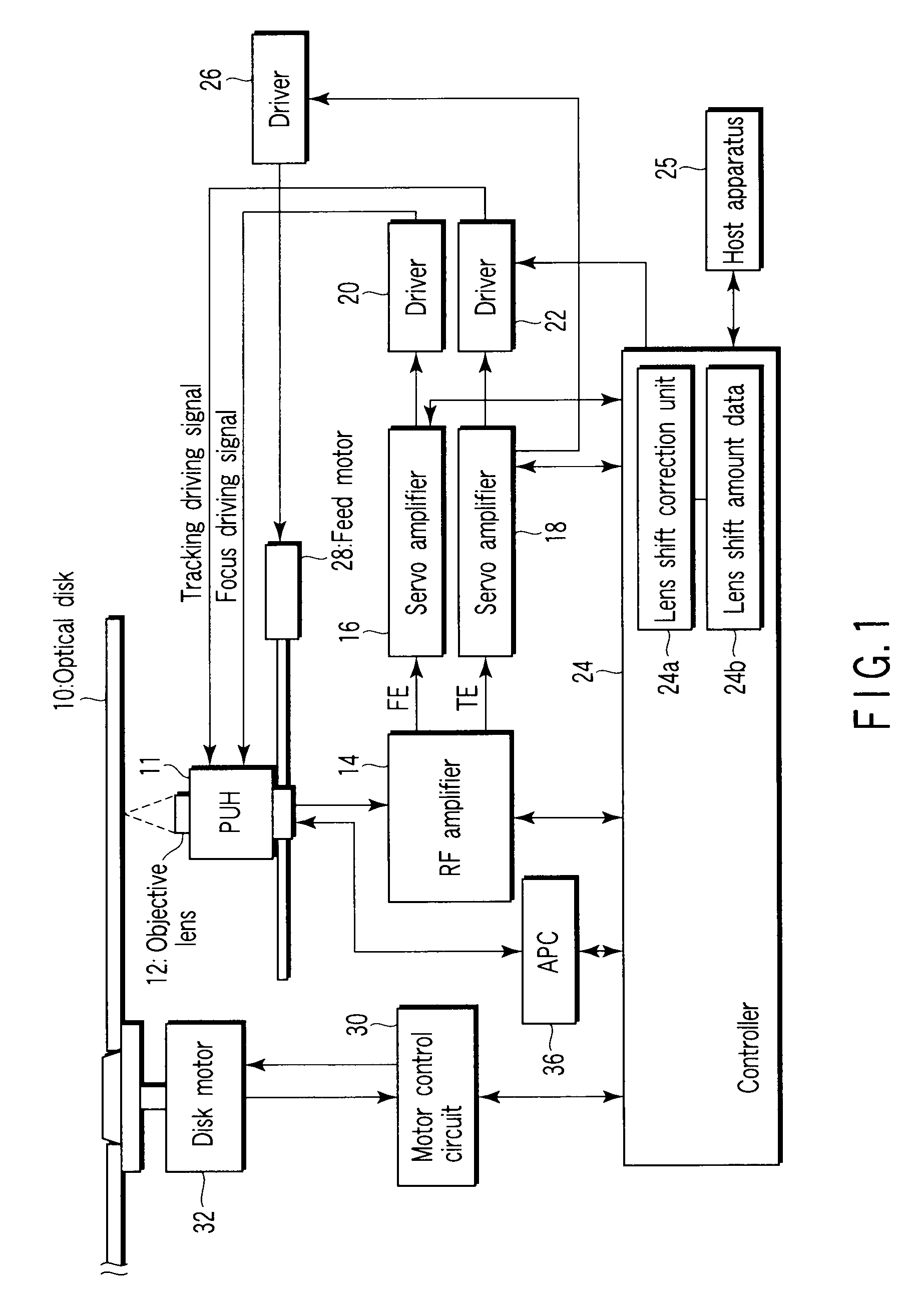
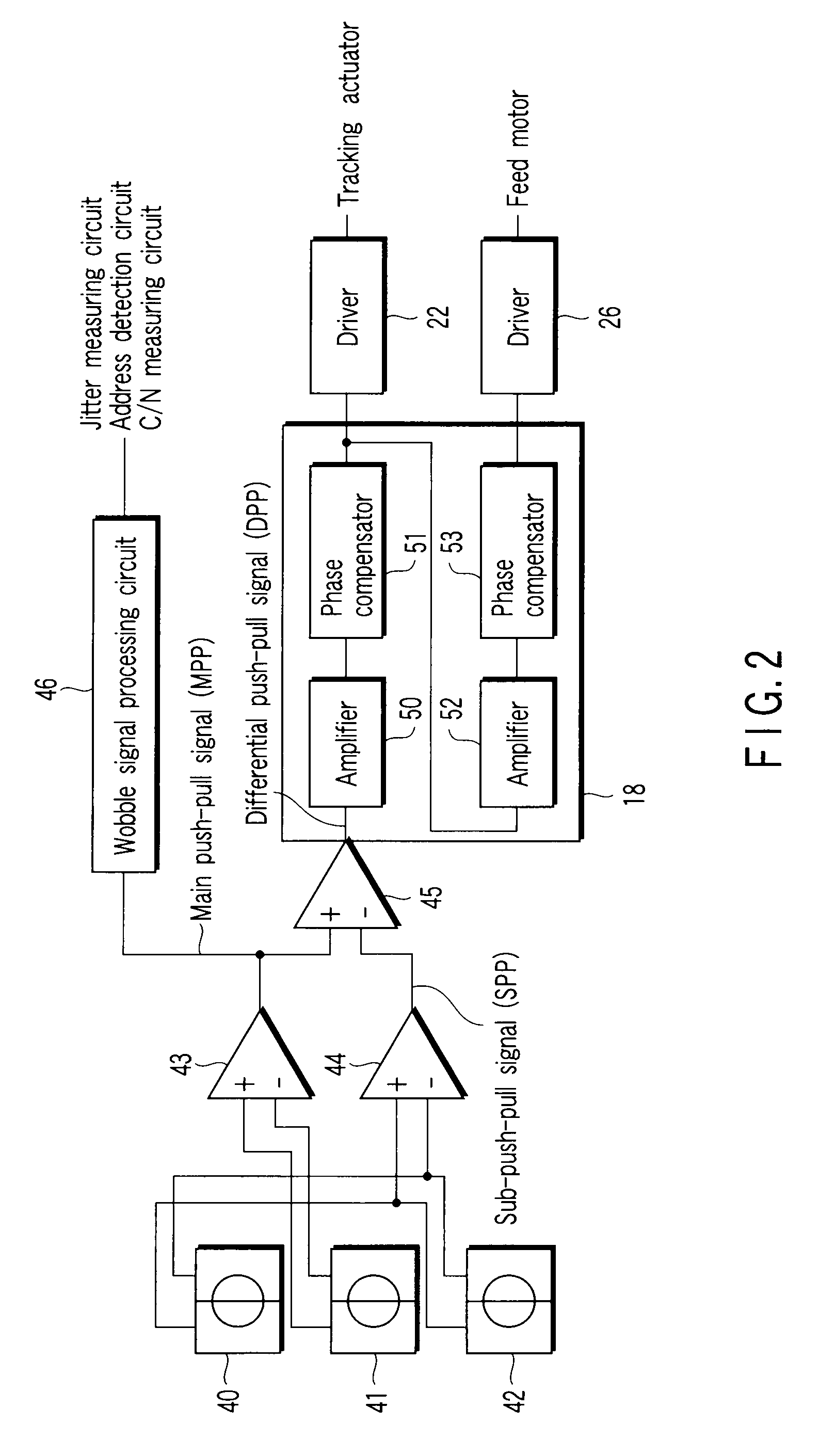
Optical disc apparatus and lens shift correction method
InactiveUS20090103403A1Improve balanceImprove dynamic rangeRecord information storageDisposition/mounting of headsPhysicsCamera lens
An optical disc apparatus, which executes tracking control for an objective lens by generating a push-pull signal, includes a determination unit which detects symmetry of the push-pull signal and determines whether balance of signal characteristics of the push-pull signal is good, a lens shift amount detection unit which detects, in a case where the determination unit determines that the balance of the signal characteristics of the push-pull signal is not good, a lens shift amount of the objective lens in such a manner as to improve the balance of the signal characteristics, a memory unit which stores the lens shift amount that is detected by the lens shift amount detection unit, and an addition unit which constantly applies the lens shift amount, which is stored in the memory unit, to a tracking actuator which shifts the objective lens.
Owner:TOSHIBA SAMSUNG STORAGE TECHNOLOGY
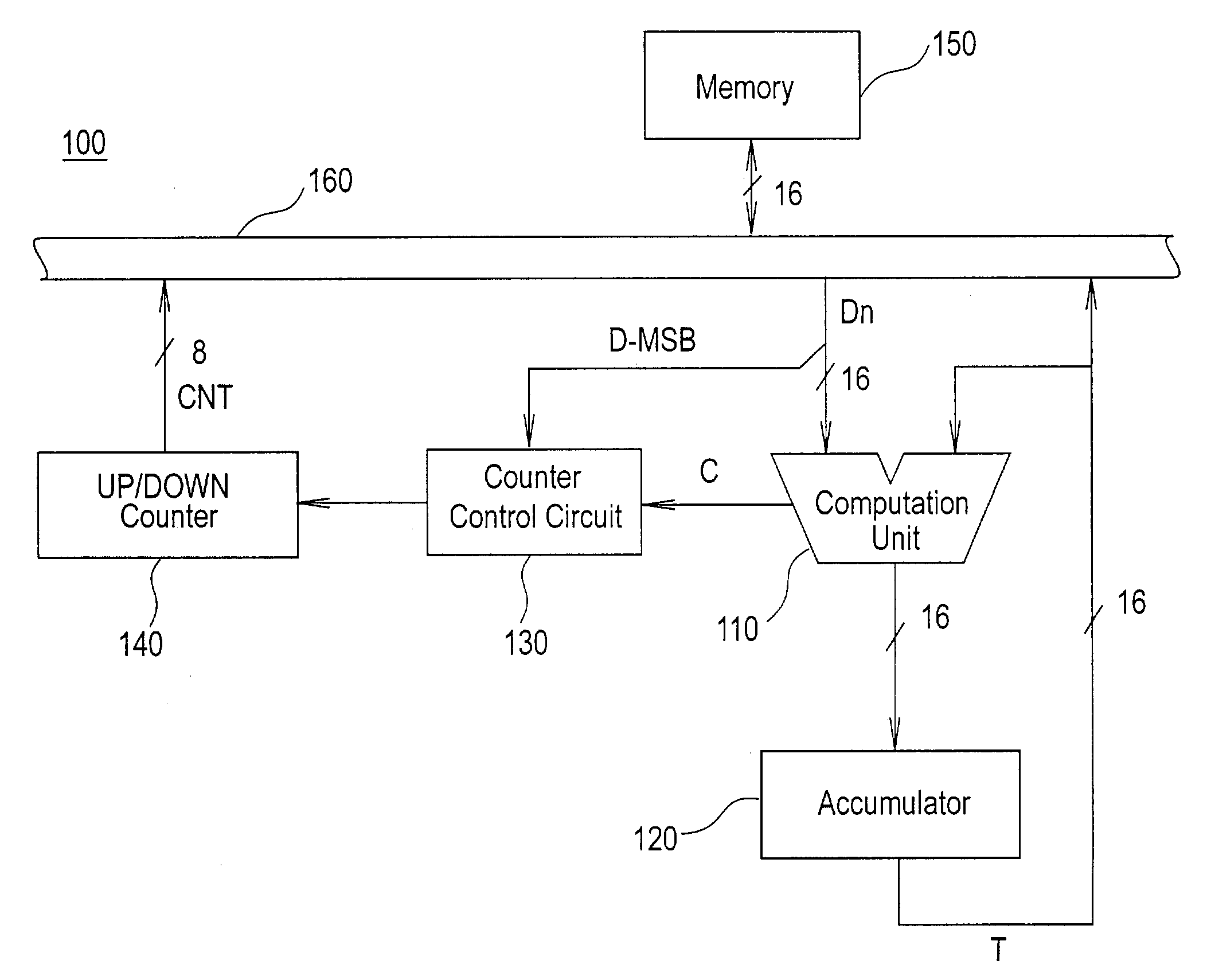
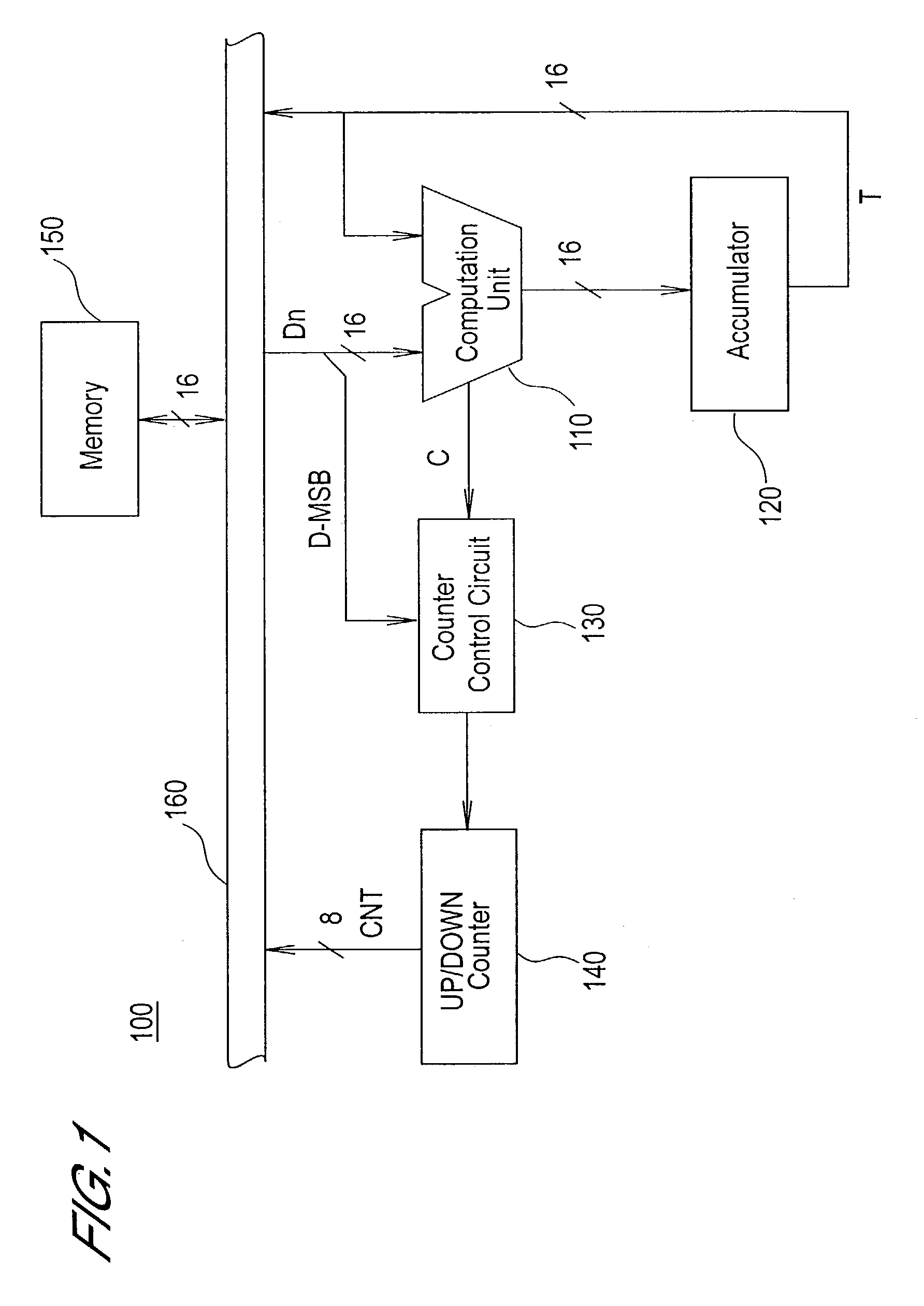
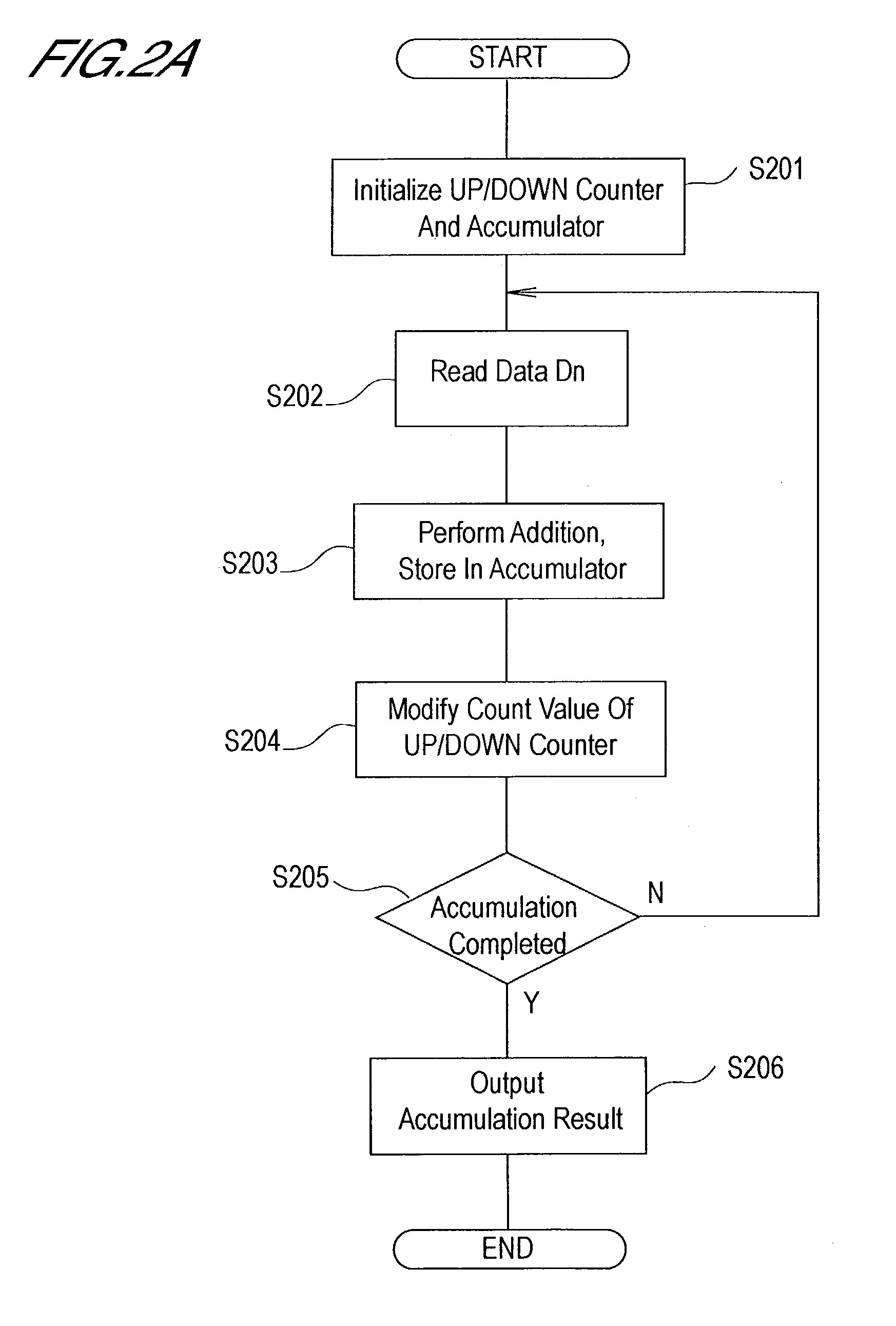
Computation circuit having dynamic range extension function
InactiveUS7089277B2Low costReduce circuit sizeComputation using non-contact making devicesNumber-of-one countersParallel computingControl circuit
A computation circuit which can obtain n+m-digit accumulation results by using an n-digit computation unit. This computation circuit comprises a computation unit which performs additions of n-digit data; an m-digit up / down counter; and a control circuit which uses the up / down counter to generate the upper m digits of the computation result. In a preferred embodiment, the control circuit increments by one the up / down counter when carry-over occurs in the computation unit, and when the input data of the computation unit is negative, decrements by one the up / down counter. In another preferred embodiment, the control circuit increments or decrements by one the up / down counter when positive or negative overflow occurs in the computation unit, and decrements by one the up / down counter when the final computation result of the computation unit is negative or is a positive number greater than 2n−1−1.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
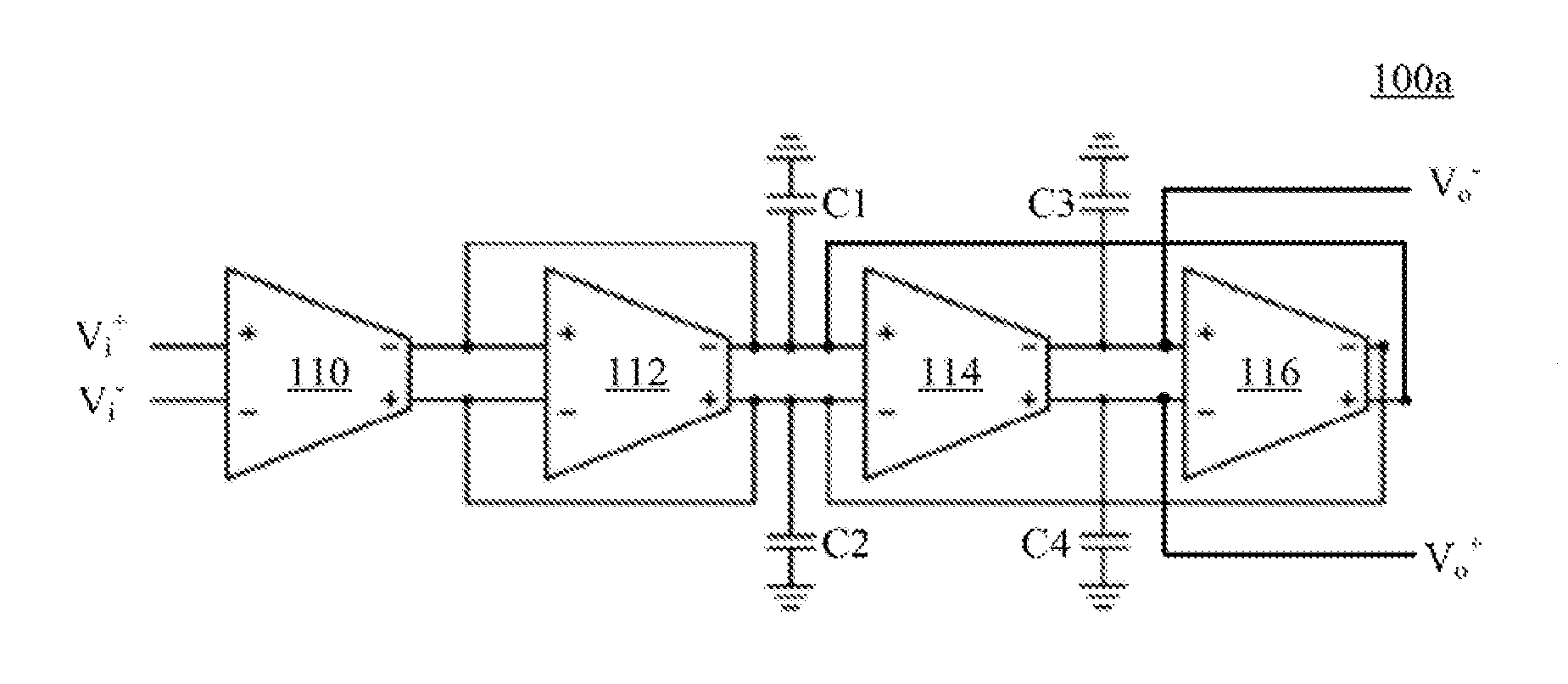
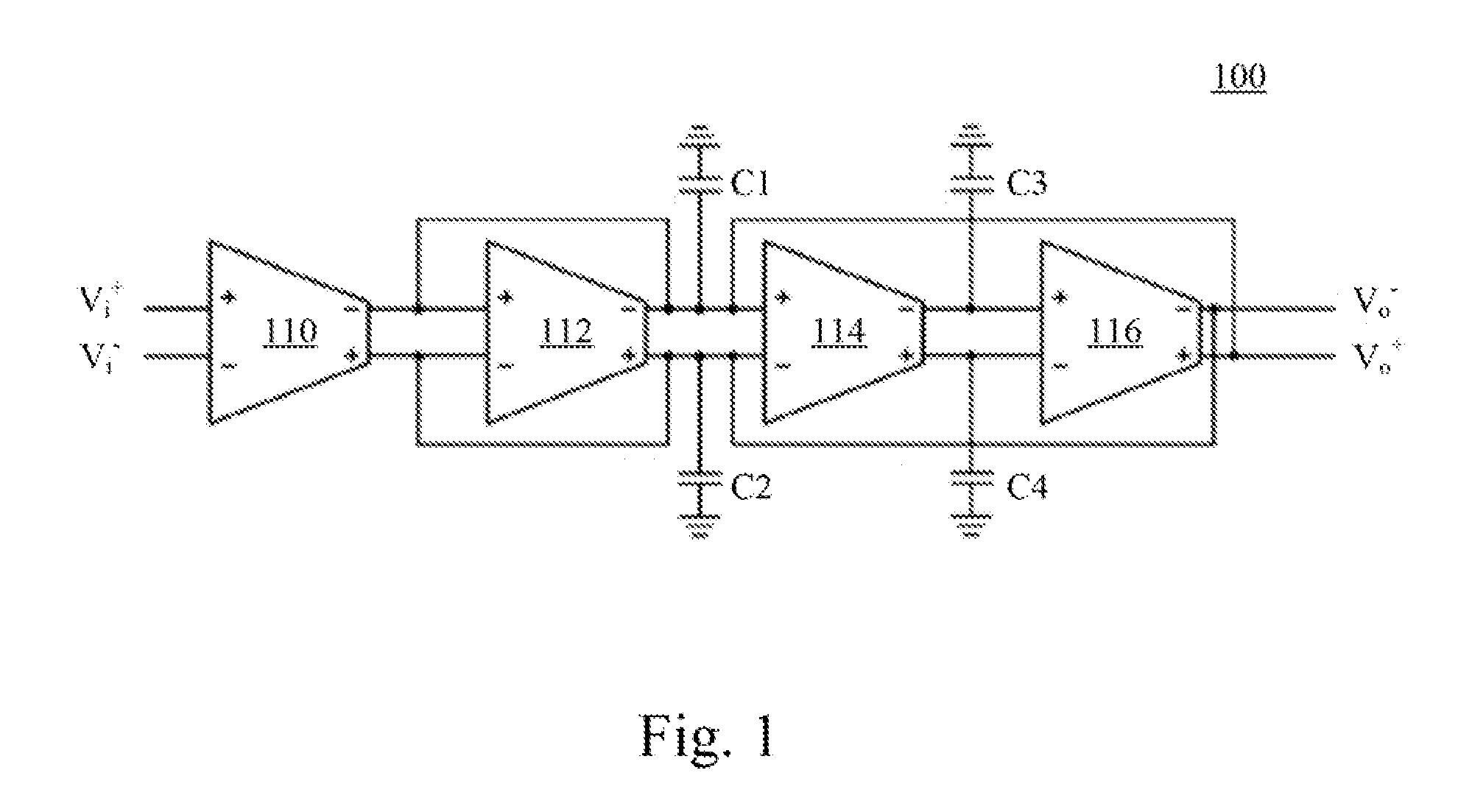
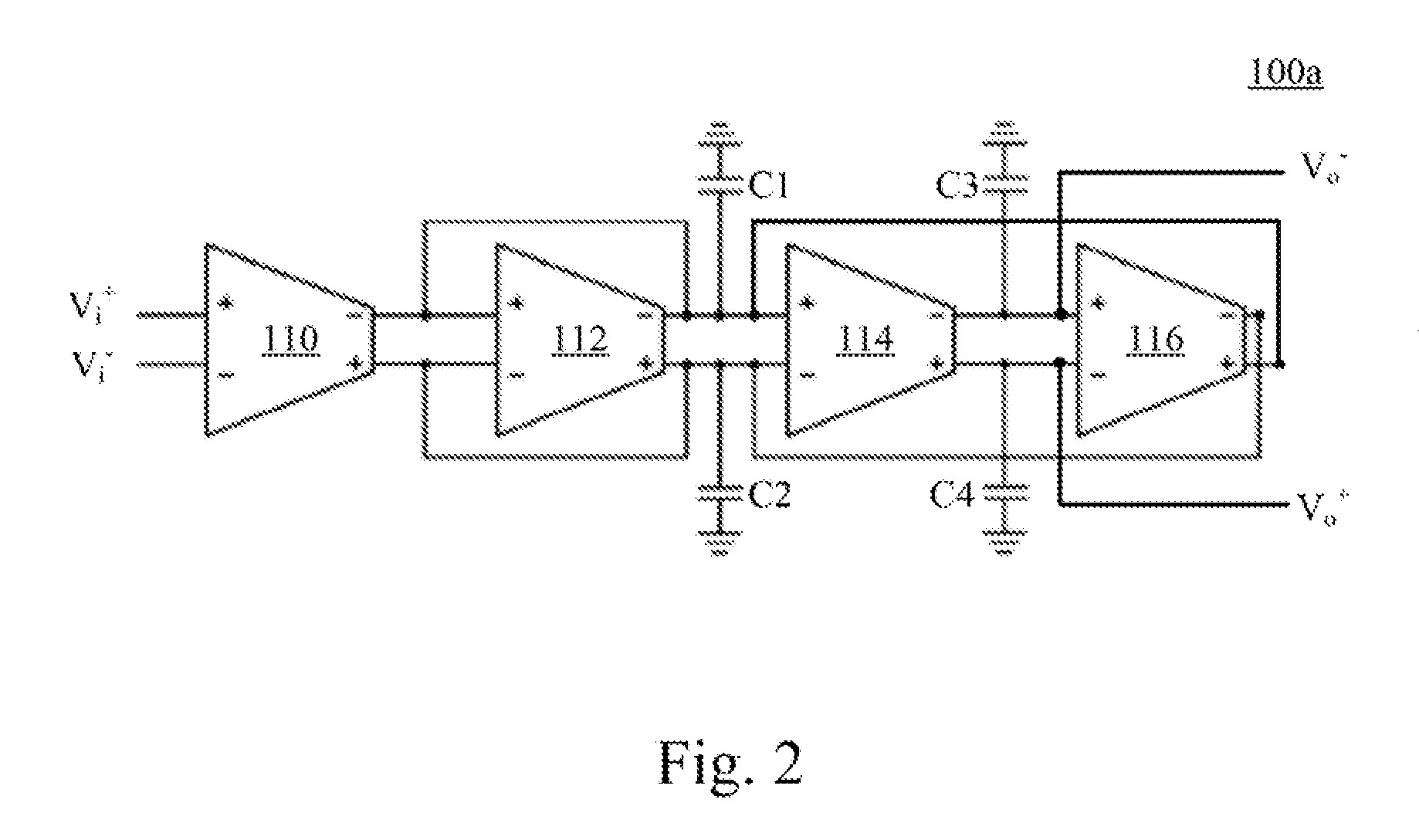
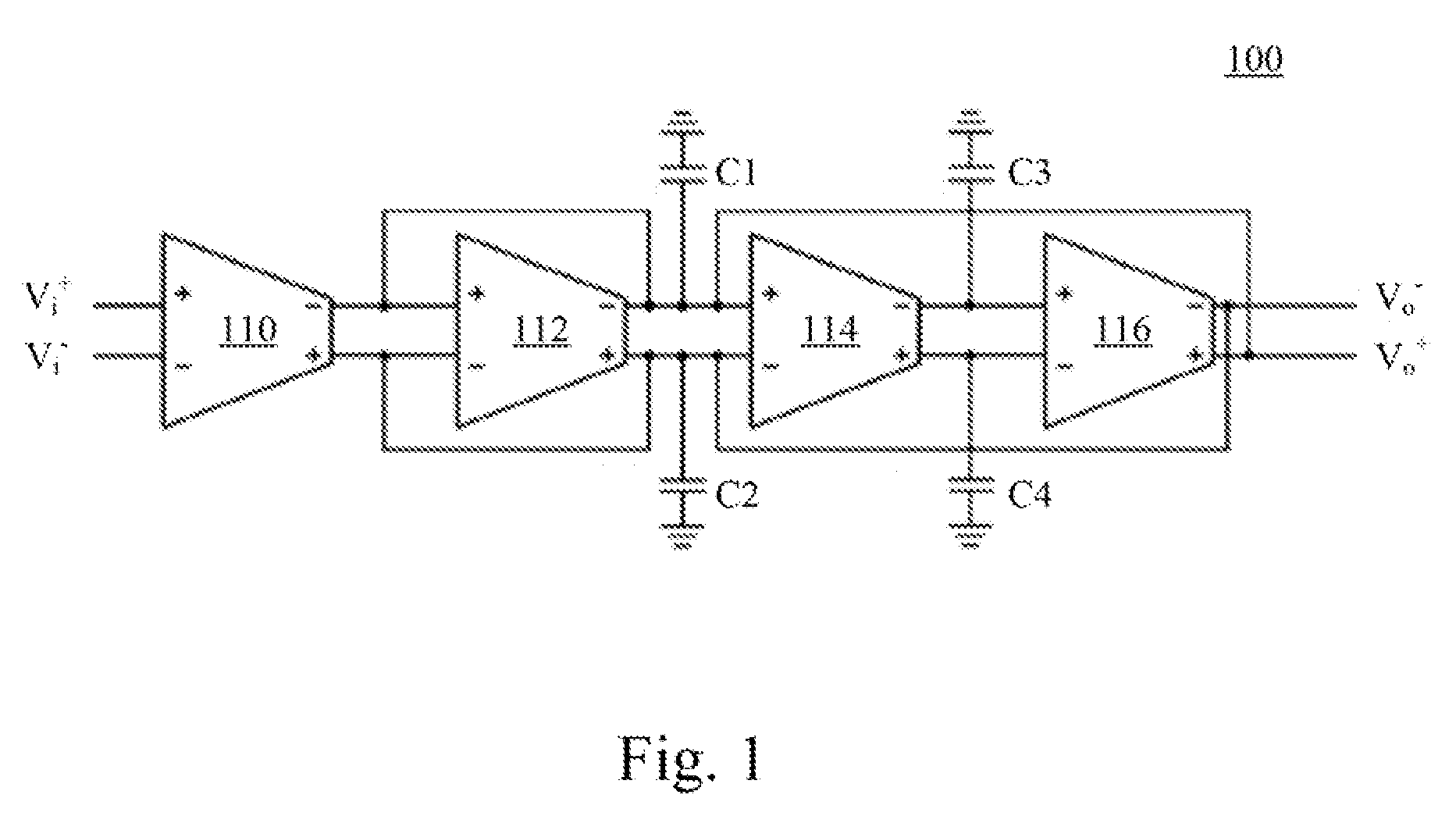
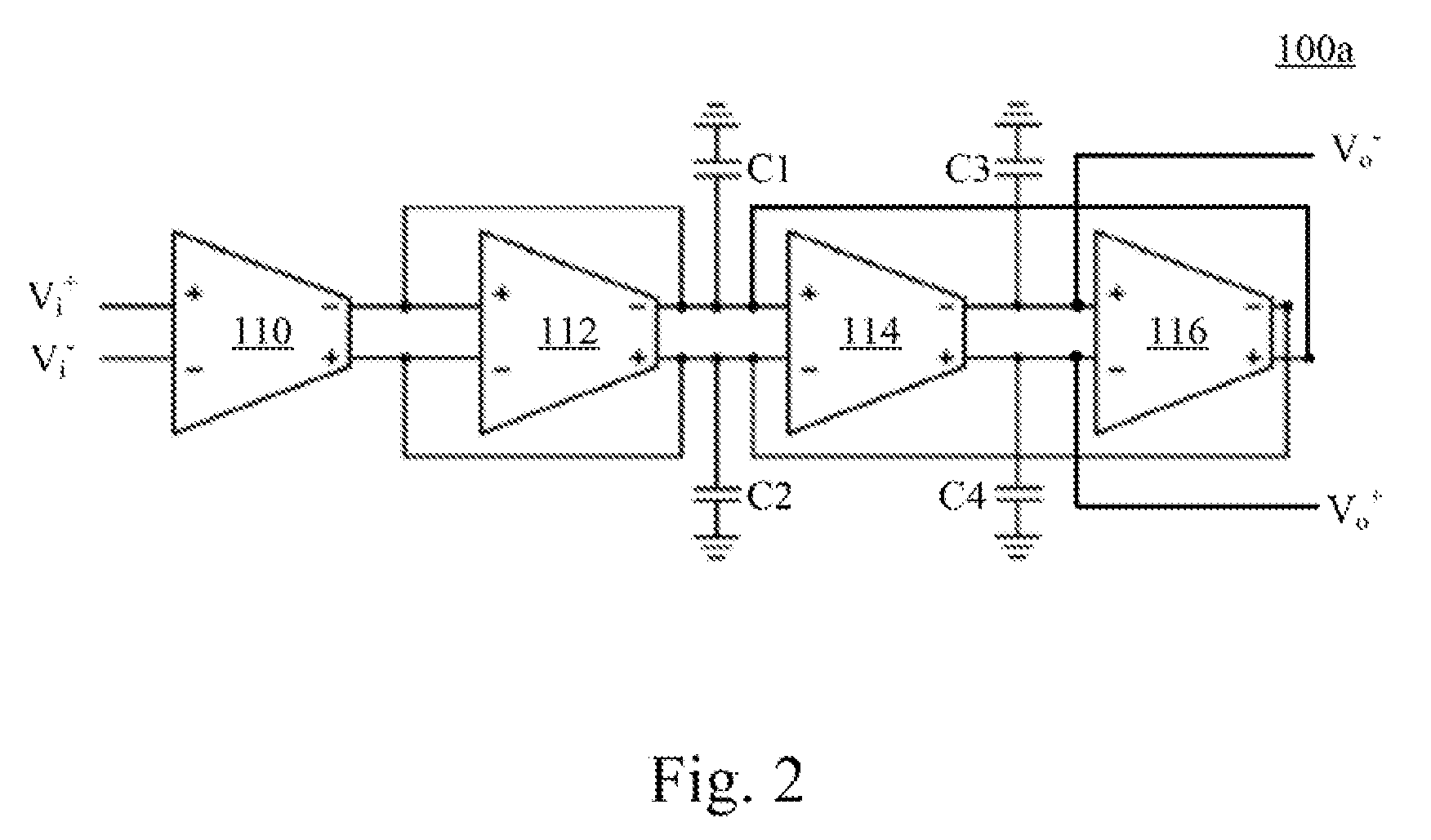
Operational transconductance amplifier, operational transconductance amplifier-capacitor filter and high order reconfigurable analog filter
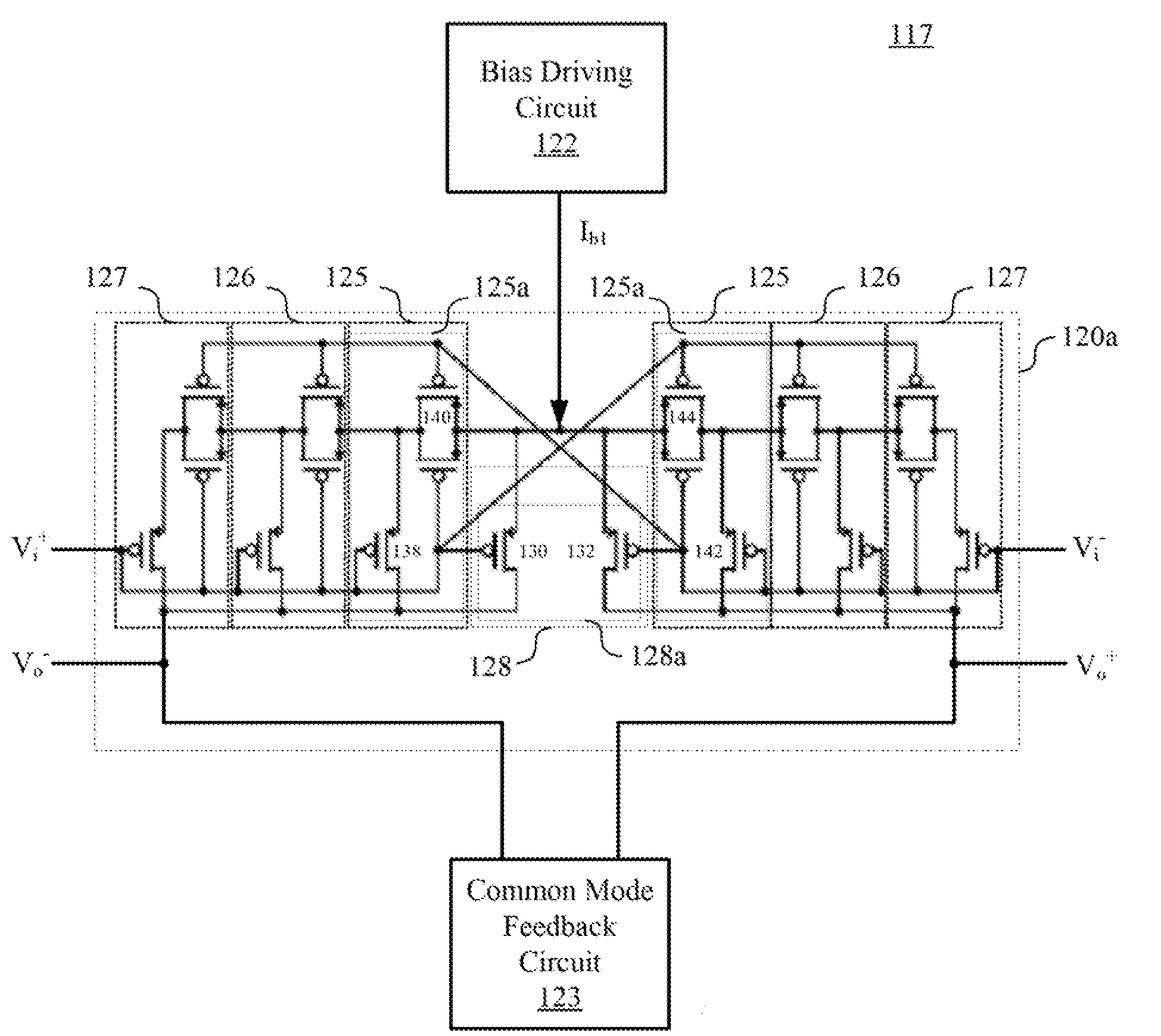
ActiveUS20150200648A1Improve linear rangeReduce outputAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyDifferential amplifiersPower flowAudio power amplifier
An operational transconductance amplifier includes a fully-differential amplifying circuit, a bias driving circuit, and a common mode feedback circuit. The fully-differential amplifying circuit is configured for receiving a differential input voltage and providing a differential output voltage. The fully-differential amplifying circuit includes a plurality of diffusor-differential-pair circuits. The bias driving circuit is configured for providing at least one first bias current to drive the fully-differential amplifying circuit and adjust the transconductance of the transconductance amplifier. The common mode feedback circuit is configured for stabilizing the differential output voltage. An operational transconductance amplifier-capacitor (OTA-C) filter and a high order filter are disclosed herein as well.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Image pickup apparatus capable of changing operation condition of image sensing device and control method therefor
ActiveUS8792033B2Reduce noiseDynamic rangeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsAudio power amplifierFloating diffusion
An image pickup apparatus capable of ensuring a dynamic range suitable for an image shooting condition and capable of reducing noise. The image pickup apparatus includes an image sensing device having floating diffusion units that are provided corresponding to pixels and that convert electrical charges accumulated in the pixels into voltage signals, which are output as pixel signals from pixel amplifiers. At that time, according to an image shooting condition, at least parts of connection switches corresponding to the floating diffusion units are sequentially turned on or all the connection switches are turned off, whereby the connection switches are connected to or disconnected from connection lines to thereby change capacity components connected to pixel amplifiers. This contributes to dynamic range expansion or noise reduction.
Owner:CANON KK
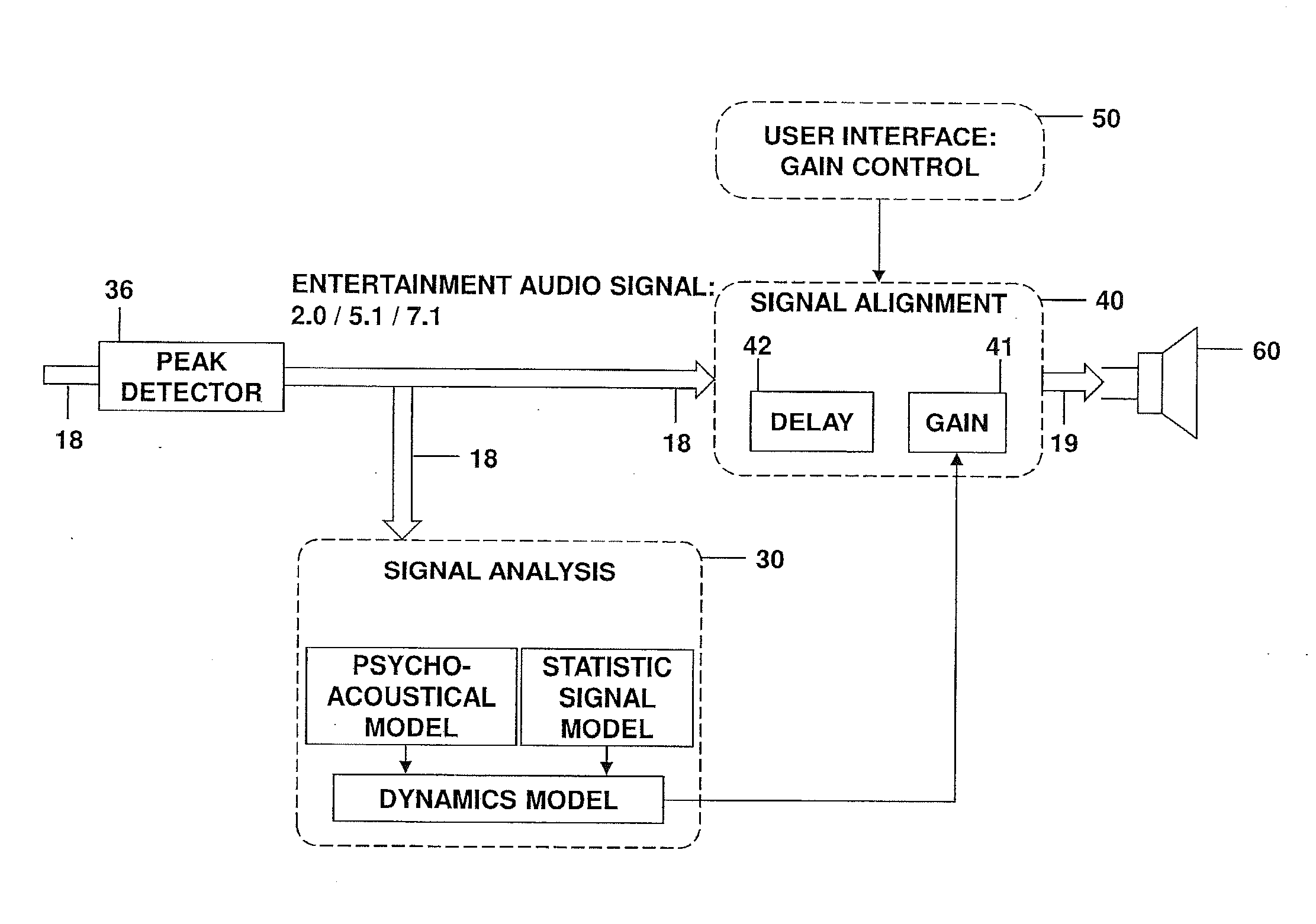
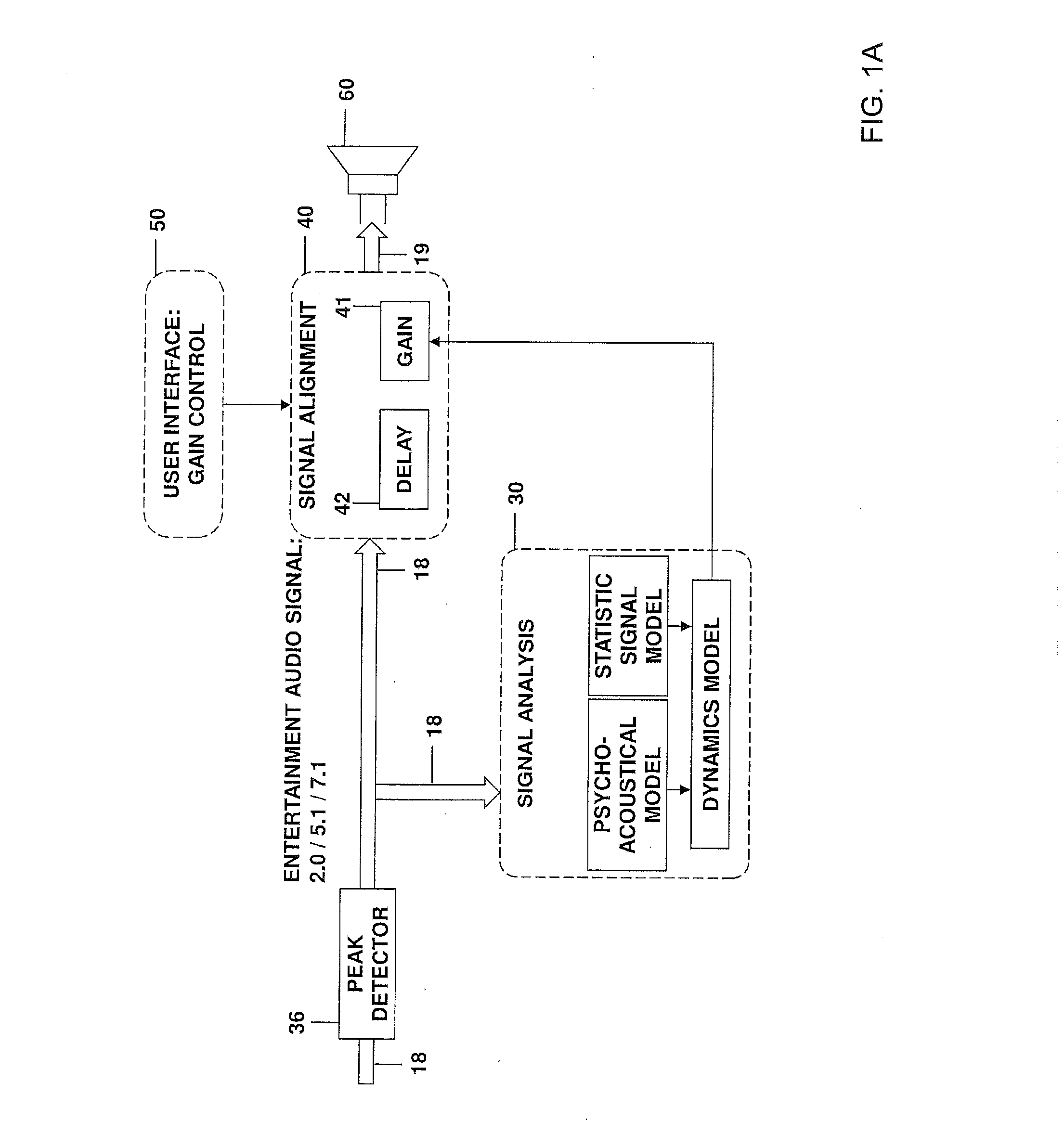
Peak detection when adapting a signal gain based on signal loudness
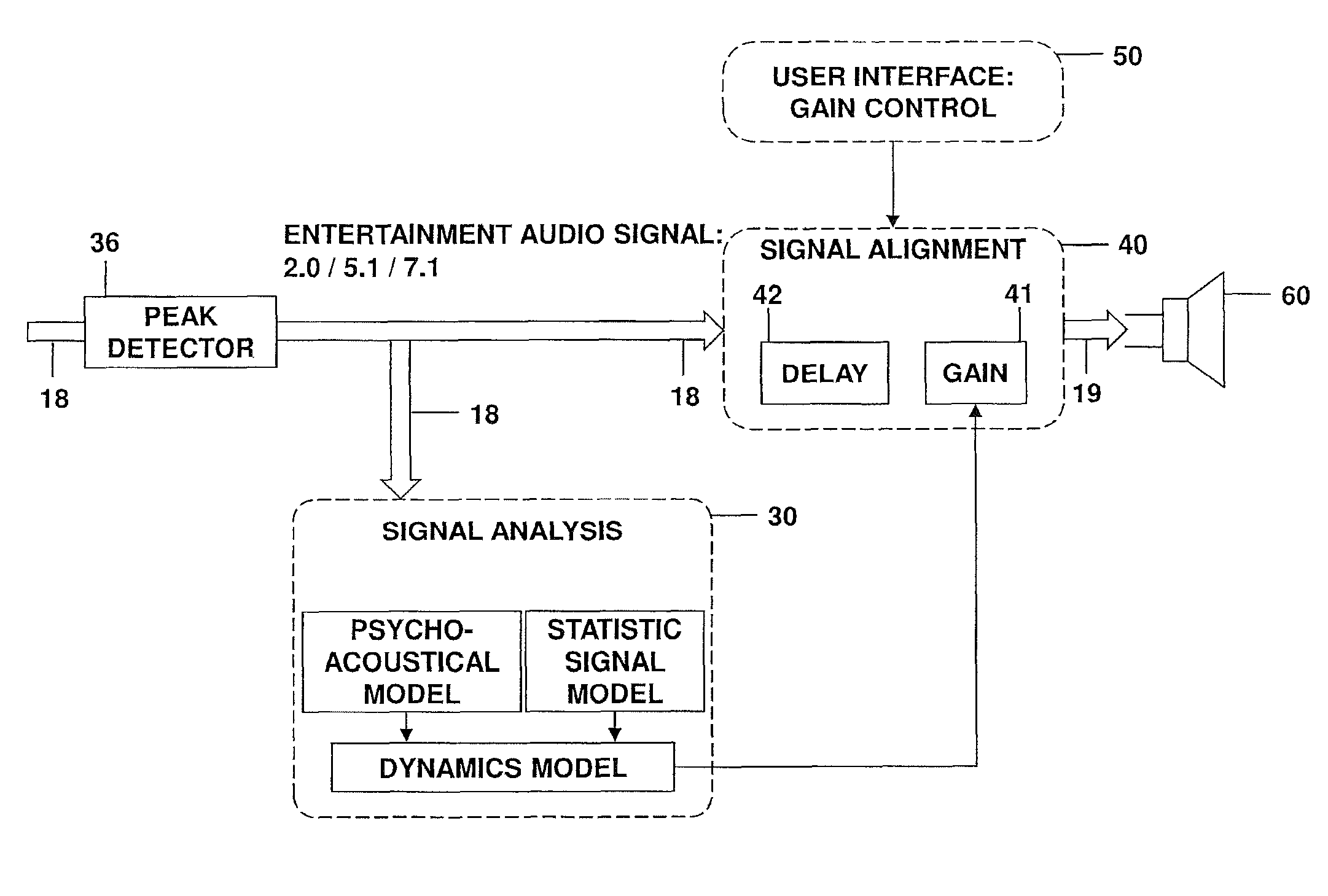
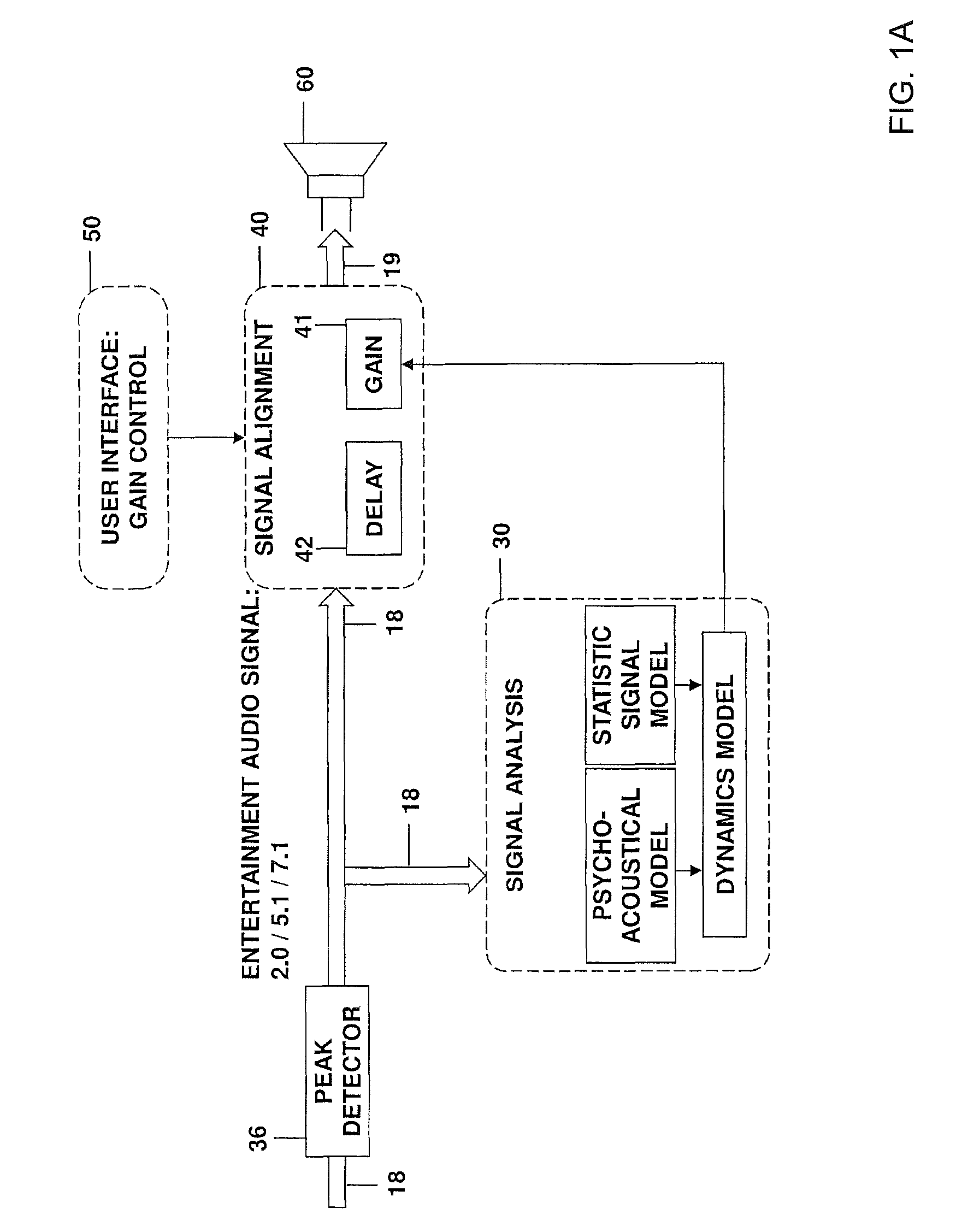
ActiveUS20130195279A1Increase control flexibilityIncrease flexibilityGain controlDigital signal tone/bandwidth controlContinuous signalTime constant
Various embodiments relate to a system for adapting a signal gain, which comprises a peak detector configured to receive an audio input signal containing consecutive signal blocks and to dynamically establish a current input signal level of the audio input signal, and a loudness determination unit configured to dynamically determine a perceived loudness of a current signal block of the audio input signal based on a psycho-acoustic model of a human hearing. Furthermore the system comprises a time constant generation unit configured to determine a time constant based on the perceived loudness of the current signal block and the perceived loudness of a preceding signal block, wherein the time constant describing a change of the signal gain. A gain determination unit is configured to determine the signal gain for the current signal block based on the time constant and the current input signal level.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
Adaptive low-dropout regulator having wide voltage endurance range, chip and terminal
ActiveUS10168727B2Dynamic rangeHigh voltageAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesAmplifier modifications to reduce detrimental impedencePower flowAudio power amplifier
An adaptive low-dropout regulator (LDO) having a wide voltage endurance range includes a power supply voltage tracker (P1), a voltage-current converter (101), an error amplifier (201), a current mirror circuit (102), and a dynamic voltage divider (103). One end of the power supply voltage tracker (P1) is connected to a Vdd, the other end thereof is connected to the voltage-current converter (101) connected to an input end of the current mirror circuit (102), and an output end of the current mirror circuit (102) is connected to sources of two input field effect transistors (N3, N4) in the error amplifier (201). Sources of two load field effect transistors (P2, P3) in the error amplifier (201) are connected to the Vdd. Dynamic voltage dividers (103A, 103B) are connected respectively between each of the input field effect transistors (N3, N4) and the corresponding load field effect transistors (P2, P3).
Owner:VANCHIP TIANJIN TECH
Peak detection when adapting a signal gain based on signal loudness
ActiveUS9219455B2Increase signal gainReduce signalingGain controlCombination control in untuned amplifierPeak detectionSignal gain
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
Operational transconductance amplifier, operational transconductance amplifier-capacitor filter and high order reconfigurable analog filter
ActiveUS9401694B2Improve linear rangeReduce outputAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAudio power amplifierEngineering
An operational transconductance amplifier includes a fully-differential amplifying circuit, a bias driving circuit, and a common mode feedback circuit. The fully-differential amplifying circuit is configured for receiving a differential input voltage and providing a differential output voltage. The fully-differential amplifying circuit includes a plurality of diffusor-differential-pair circuits. The bias driving circuit is configured for providing at least one first bias current to drive the fully-differential amplifying circuit and adjust the transconductance of the transconductance amplifier. The common mode feedback circuit is configured for stabilizing the differential output voltage. An operational transconductance amplifier-capacitor (OTA-C) filter and a high order filter are disclosed herein as well.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com