Patents
Literature
51results about How to "Improved" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Fuzzy logic based system and method for information processing with uncertain input data
InactiveUS6282526B1ImprovedReduce the possibilityWave based measurement systemsDigital computer detailsGuidance systemData input
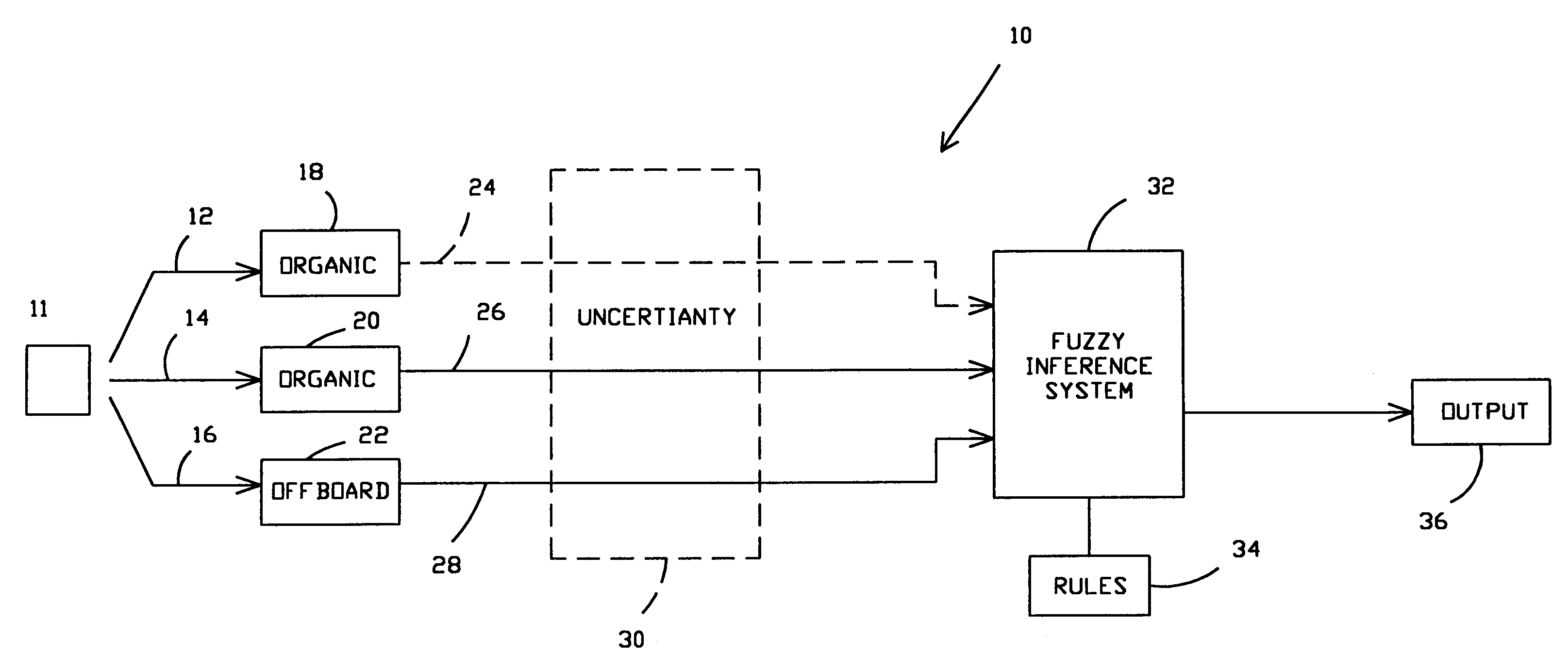
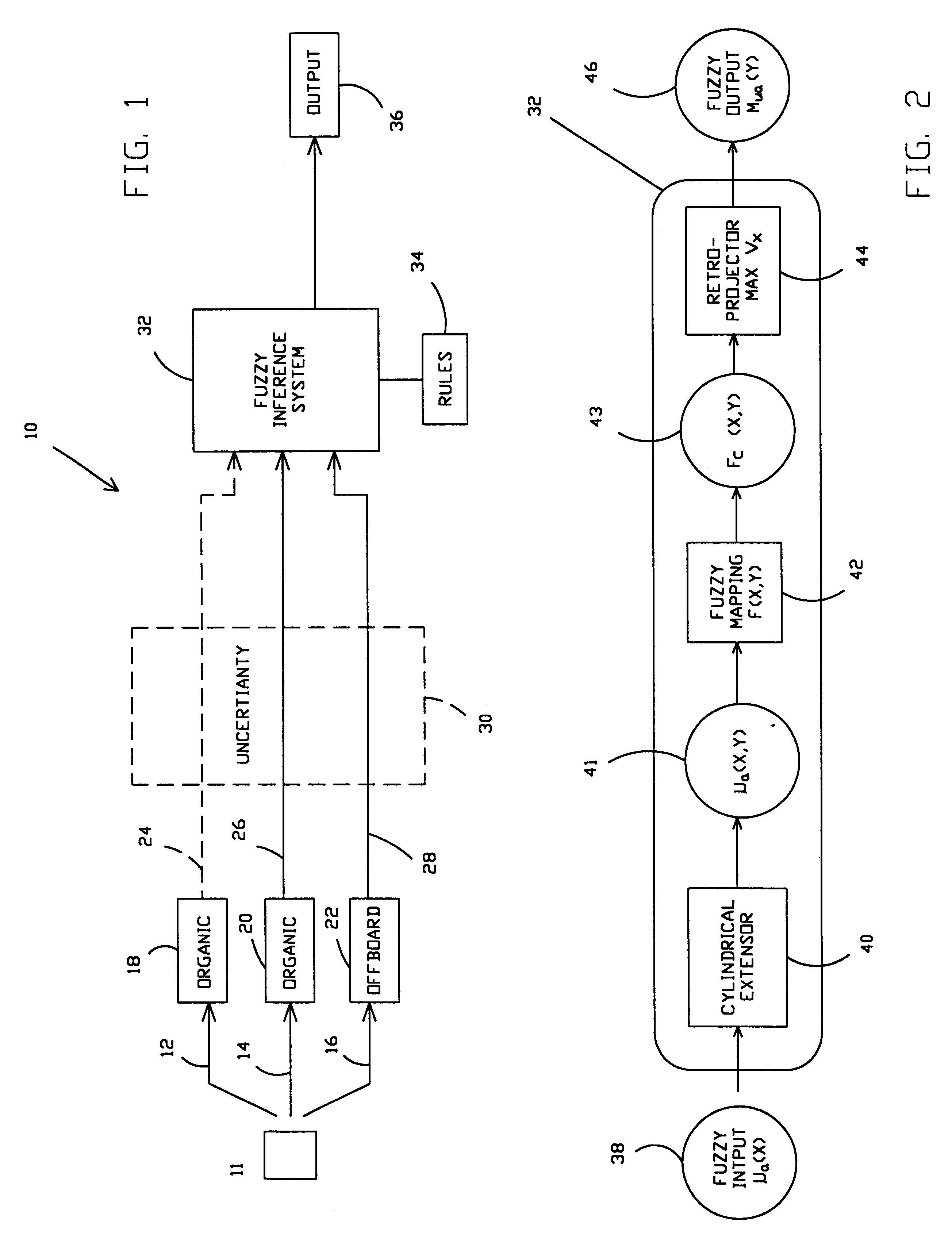
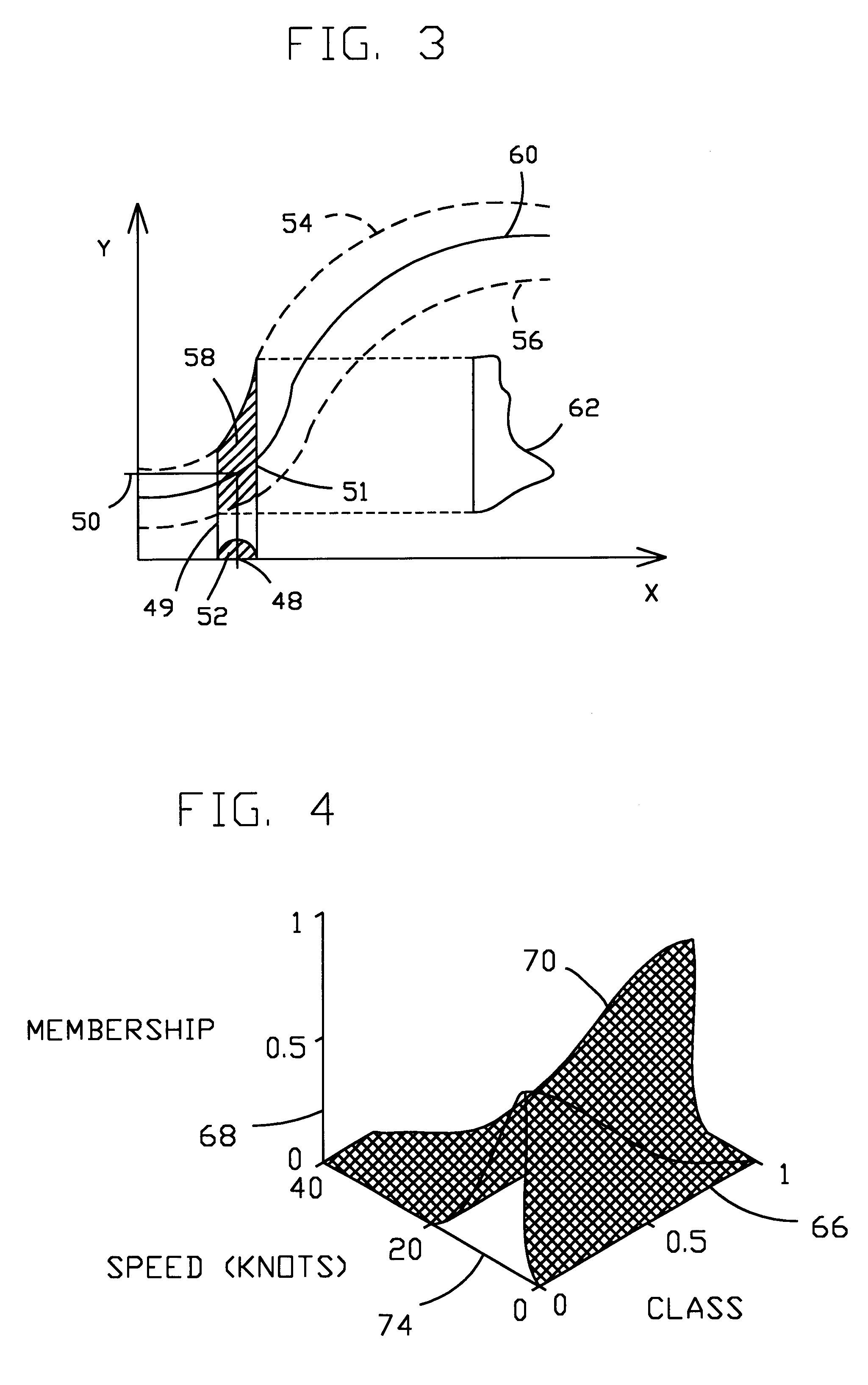
A fuzzy logic information processing system and method are disclosed that may be used not only with known or definite data input but also with uncertain data input. The uncertain data input may be represented by a set of values wherein the possibility of any particular or specific value within the set being the true or accurate value is uncertain. The preferred embodiment of the system provides for an extensor to extend or map a representation of the uncertain data into at least one additional dimension related to dimensions of a set of rules used for making fuzzy logic inferences. The set of rules may be provided effectively in a mapped or graphed form. The set of rules and uncertain data are combined, for instance by locating intersection regions, to produce an output set that may be also be described as a map or plot. In a presently preferred embodiment the uncertain inputs and rules are represented mathematically or symbolically and then operated on to produce an output set. A projector then projects the output set to the desired output dimension as an output for the system. The system output may then be used for control purposes such as, for example only, a combat control system to provide a tactical picture, decision aid, presets for a guidance system, or the like.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
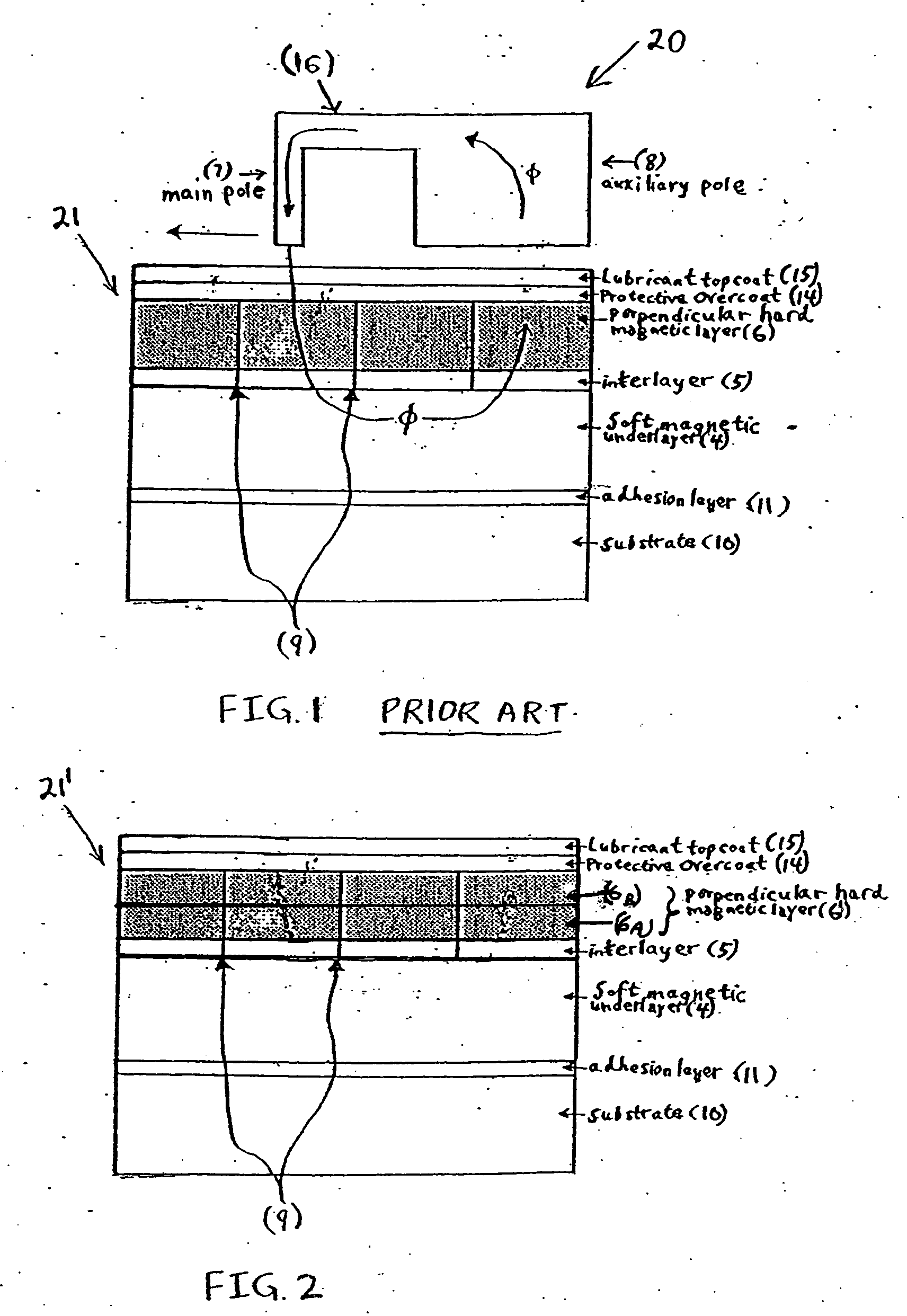
Granular perpendicular magnetic recording media with dual recording layer and method of fabricating same
InactiveUS20060139799A1ImprovedImprove methodConstruction of head windingsRecord information storageNuclear magnetic resonanceMagnetic layer
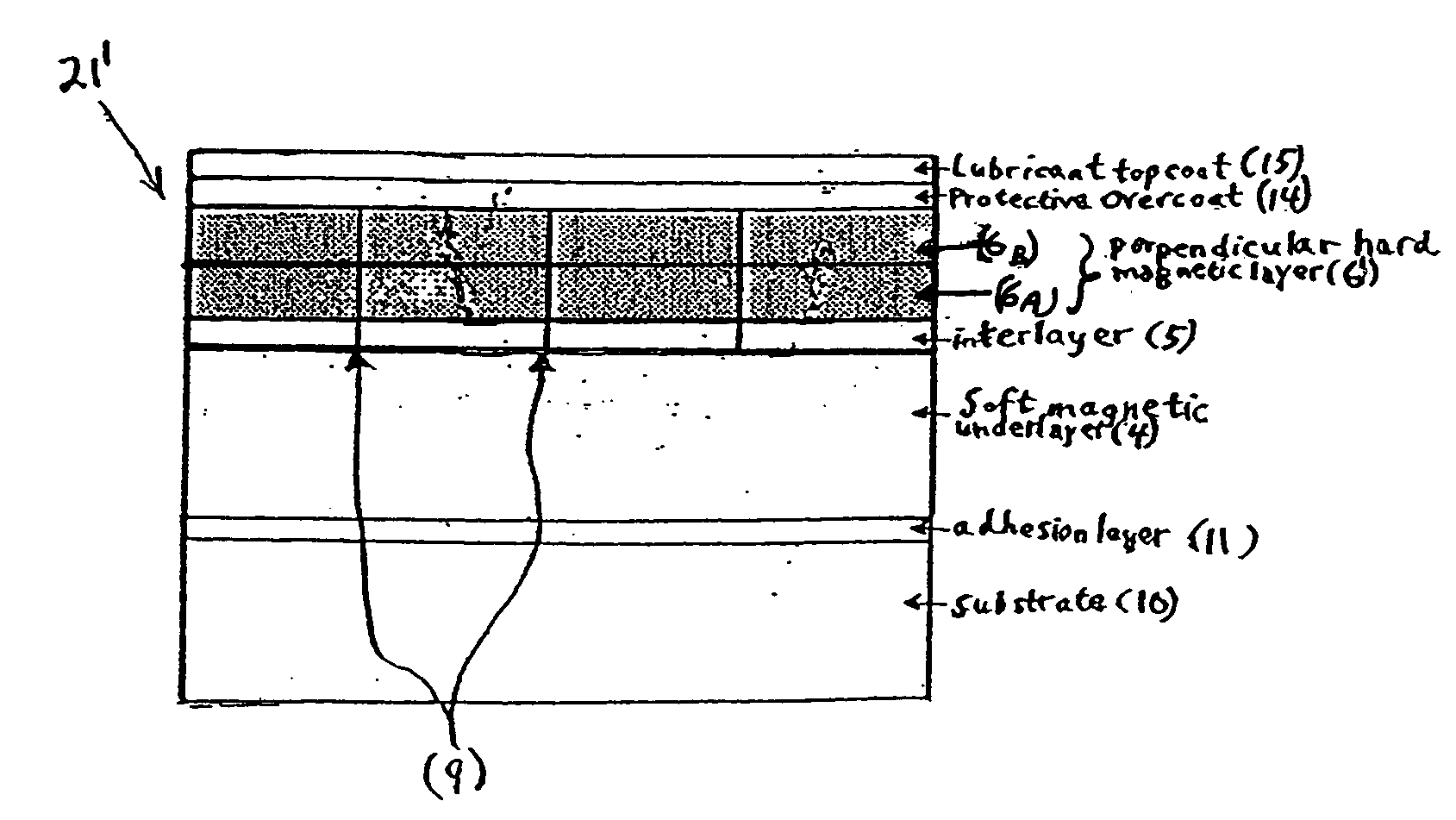
A granular perpendicular magnetic recording medium comprises a non-magnetic substrate and a granular perpendicular magnetic recording layer overlying the substrate, comprising a first granular perpendicular magnetic layer proximal the substrate and having a first saturation magnetization (Ms)1, and a second granular perpendicular magnetic layer distal the substrate and having a second, different saturation magnetization (Ms)2. Also disclosed is a method of fabricating the granular perpendicular magnetic recording medium.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Individually paced table game tournaments
ActiveUS8684830B1ImprovedEasy accessApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingVideo gamesCommunication interfaceMatch play
Table game tournament systems can include player terminal(s), electronic gaming table(s), and / or a remote server. A player terminal can have an outer housing, a controller located therewithin or thereabout, input and output component(s), and a communications interface to an outside gaming network having other functionally similar gaming device(s), gaming table(s), and a remote server. The controller and / or server can facilitate providing tournament information to a player, which information can include whether the player would qualify for the next tournament round, who is the most serious opponent to the player, and / or the chip difference therebetween. A terminal can also facilitate asynchronous and individually paced tournament play, switching between different tournament tables on demand, and play of other non-tournament table games thereat simultaneously with the play of the table game tournament. Portable computing devices can be used as player terminals and can permit players to play in actual or practice play-along modes.
Owner:IGT
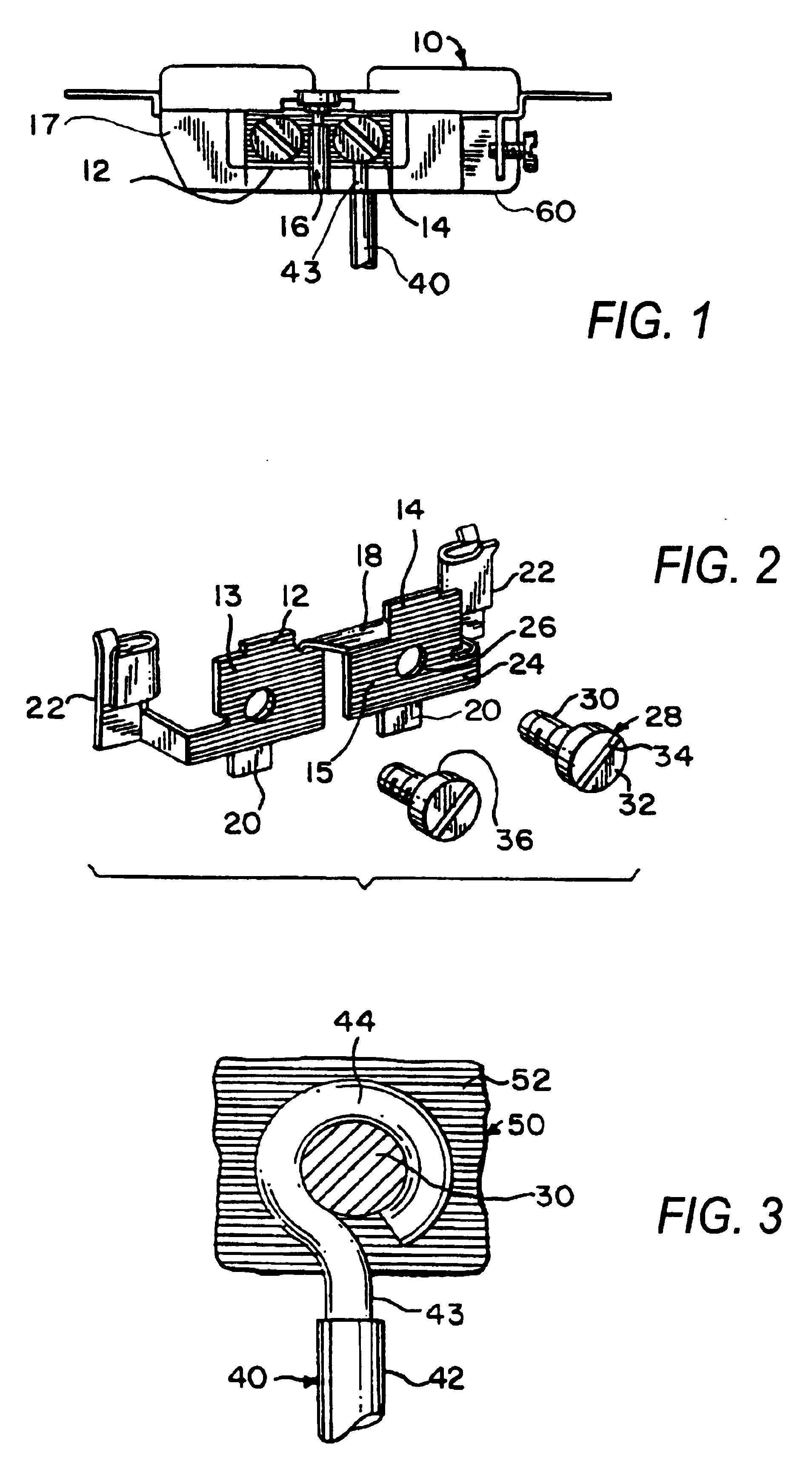
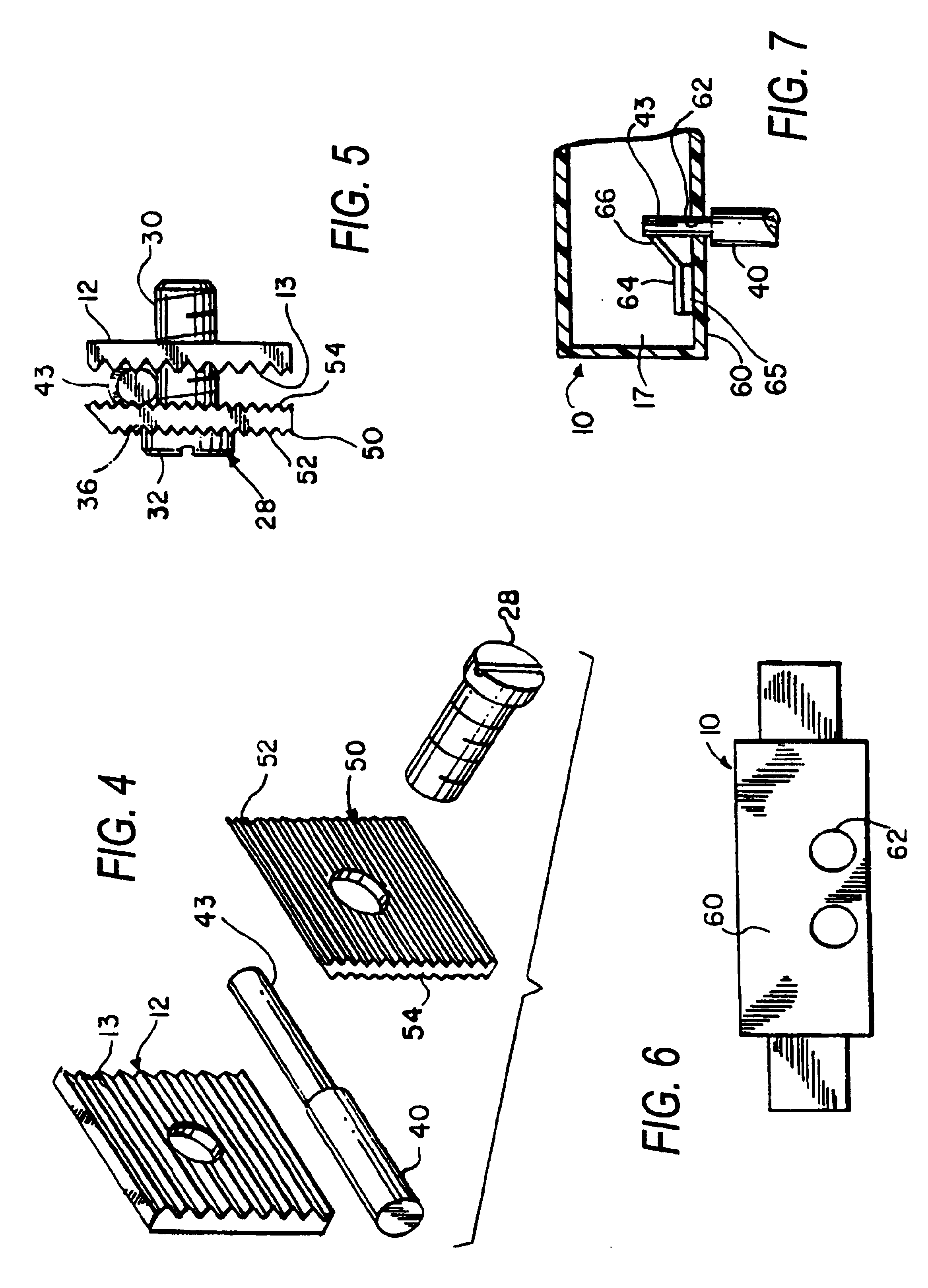
Relay having two switches that can be actuated in opposite directions
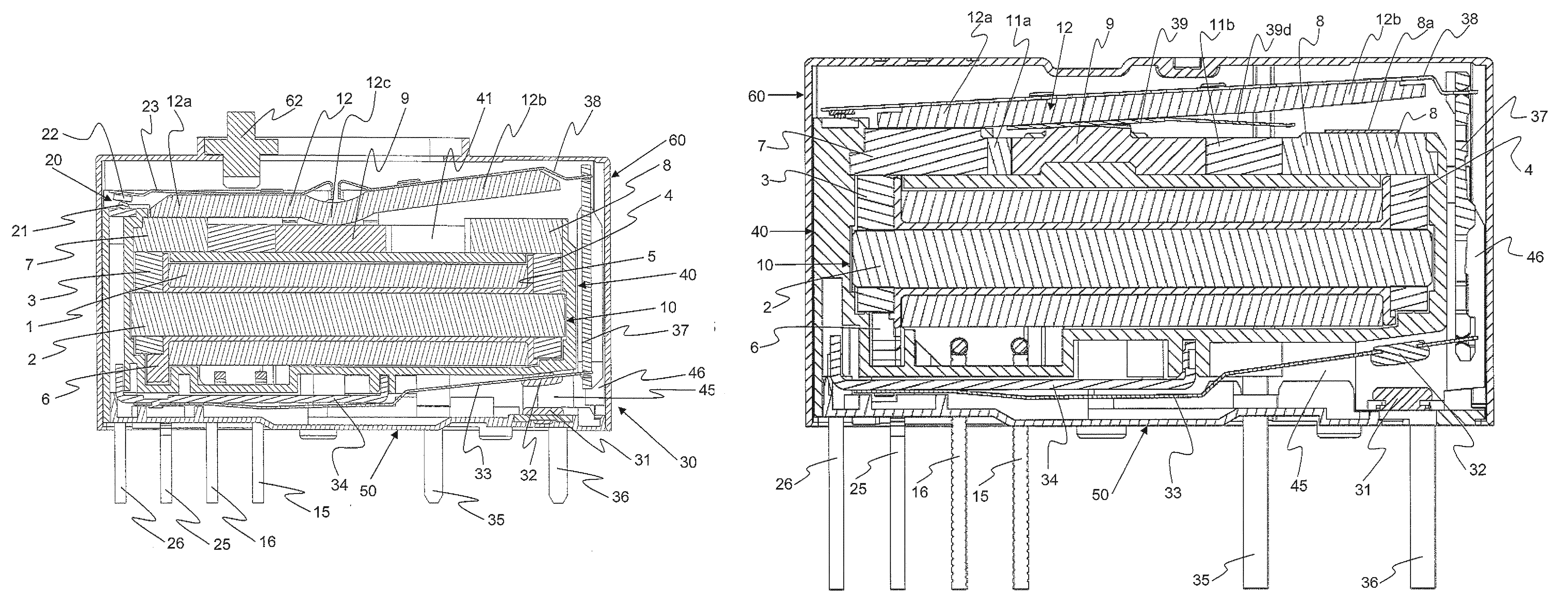
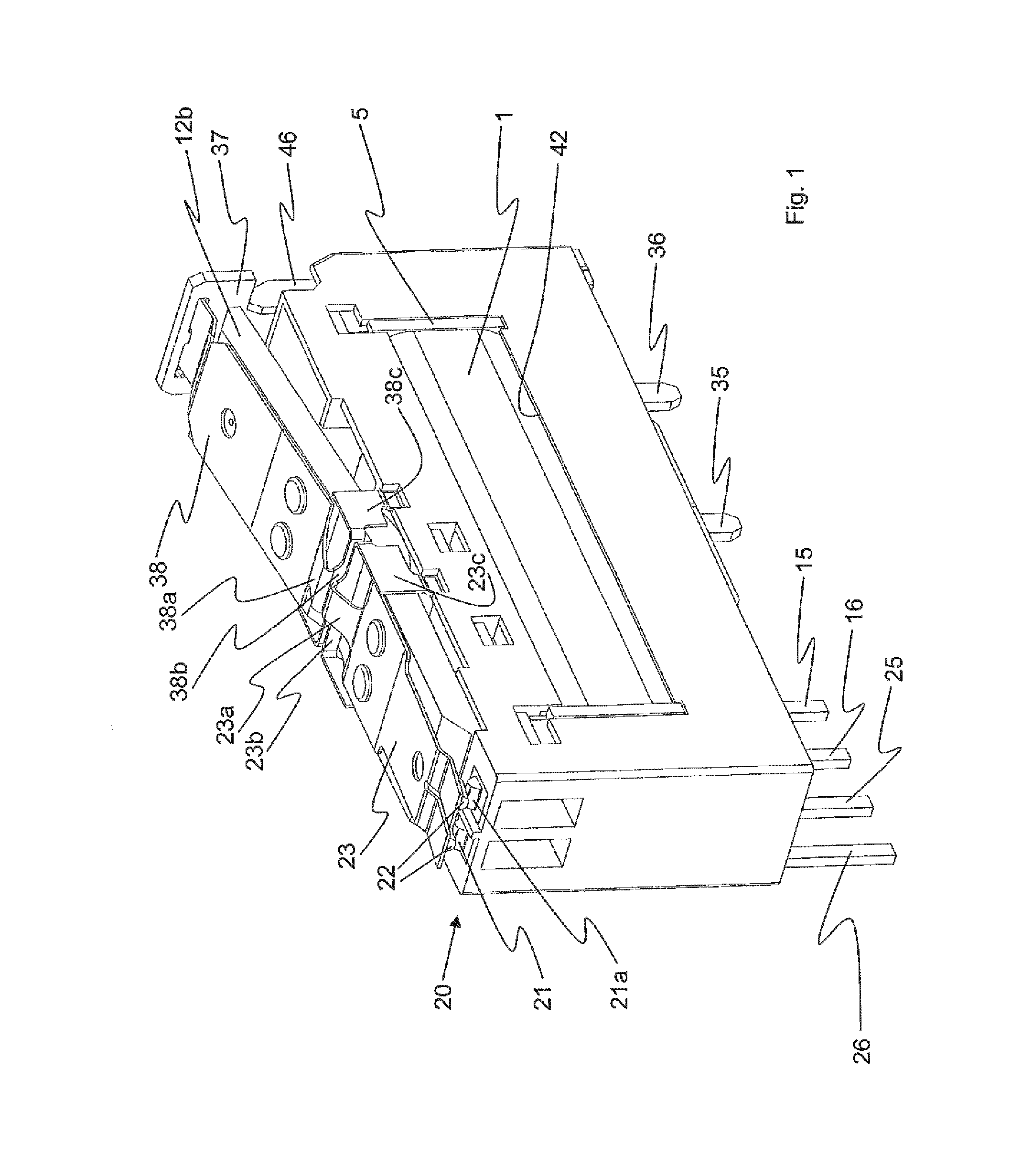
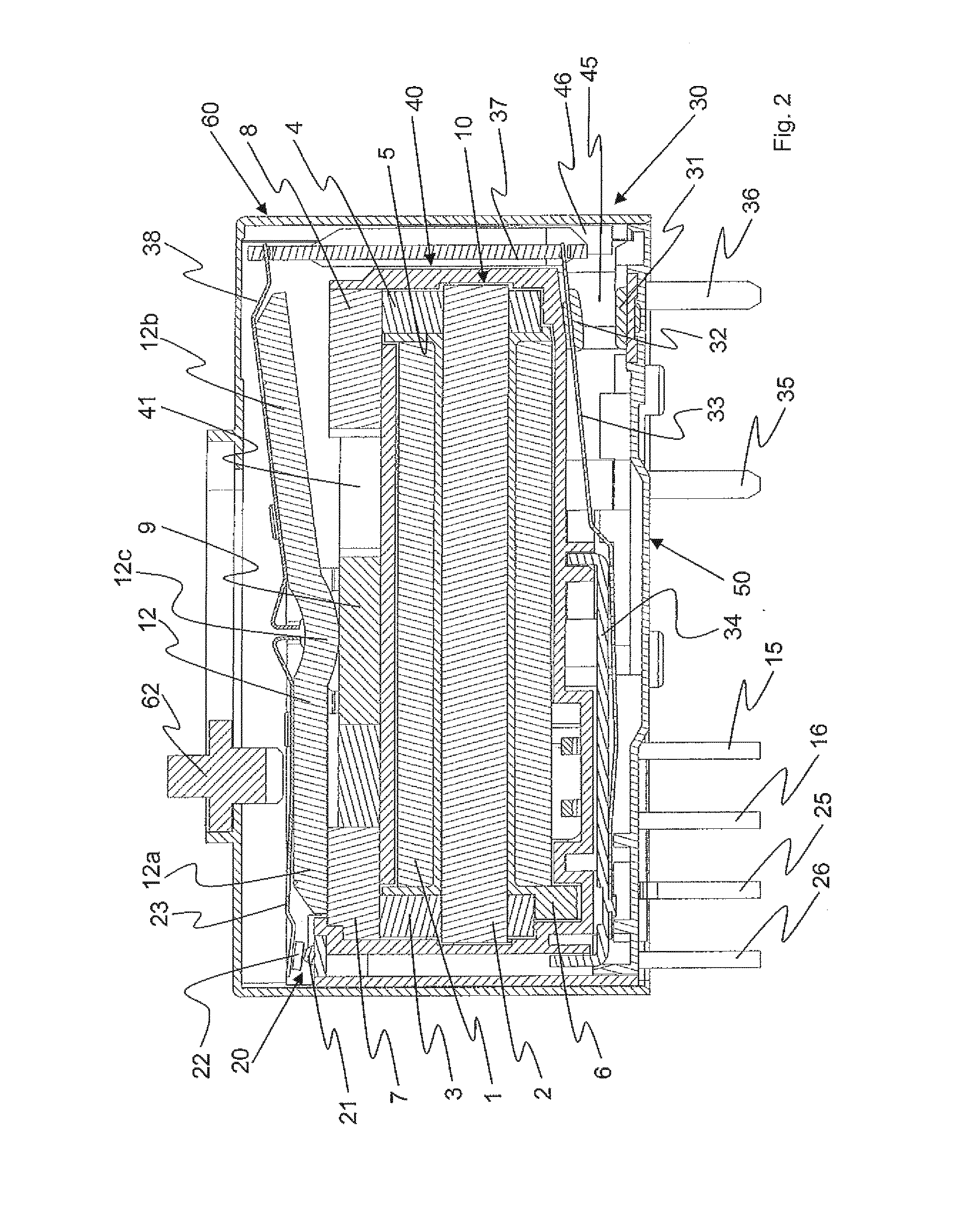
ActiveUS9275815B2Function increaseImprovedElectromagnetic relay detailsPolarised relaysRelayEngineering
An electromechanical relay is provided, comprising a magnetic system and a pivotable armature. A diagnostic switch is arranged on one side of the relay, and the set of contacts of the diagnostic switch is driven by the adjacent leg of the armature. A load switch is arranged on the bottom side of the relay and is driven by the second leg of the armature via an insulating coupling member.
Owner:PHOENIX CONTACT GMBH & CO KG
Low profile magnetic element
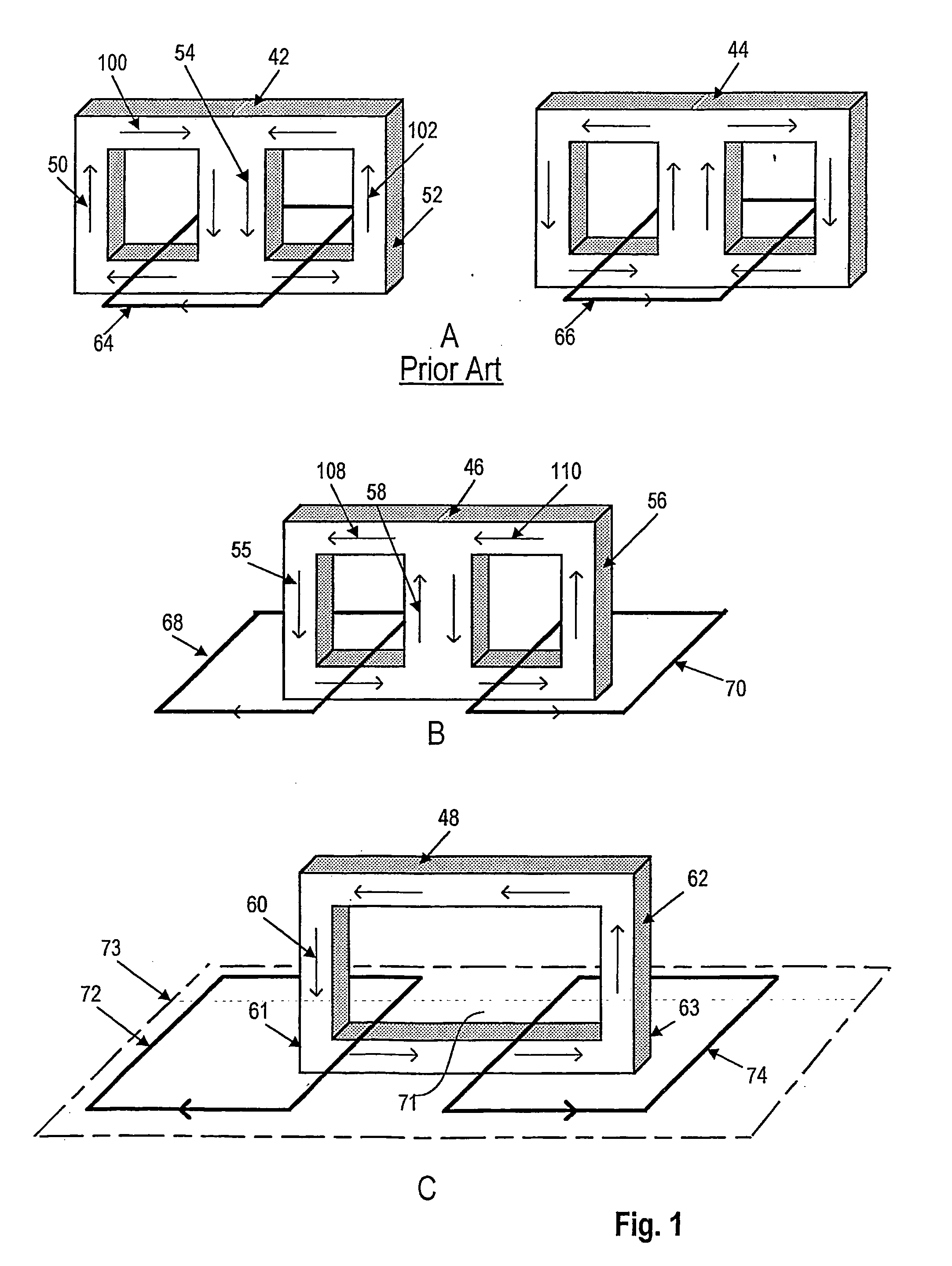
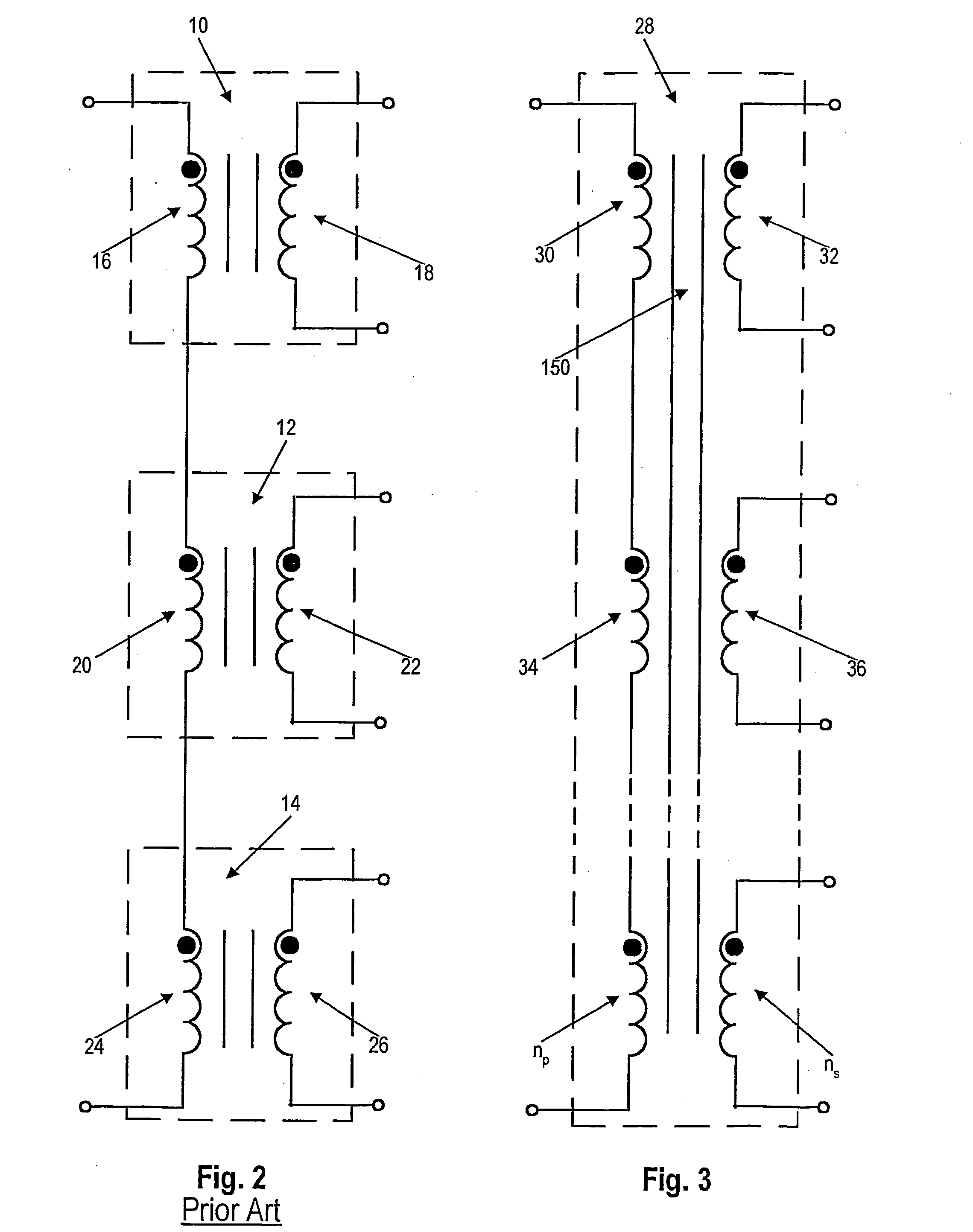
ActiveUS20060006975A1ImprovedConduction loss can be minimizedTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsTransformers/inductances magnetic coresMagnetic corePrinted circuit board
A low profile magnetic element used in cooperation with a multilayer printed circuit board has two or more core arms penetrating the board from one outer surface to the other and a series of magnetic core elements, at least one on each side of the board, bridging pairs of the core arms to form a closed, unbranched flux path. Series-connected windings form a transformer primary and are wound on the core arms that penetrate the board. Parallel-connected windings form a transformer secondary and are also wound on the core arms. The series-connected windings and the parallel-connected windings may be buried windings printed on internal surfaces of the multilayer board. The connected in series primary windings all have the same number of turns and the parallel-connected secondary windings all have the same number of turns. The parallel secondary windings are connected in current additive fashion to afford a high current transformer output. Output treating circuitry can treat each output separately in parallel and identically, being connected between the winding outputs and their point of connection. The transformer core can be assembled entirely of C and I magnetic elements. In one embodiment, a pair of magnetic plates overlying the outer surfaces of the multilayer circuit board are in flux-conducting relation with all of the core arms penetrating the board.
Owner:DET INT HLDG LTD
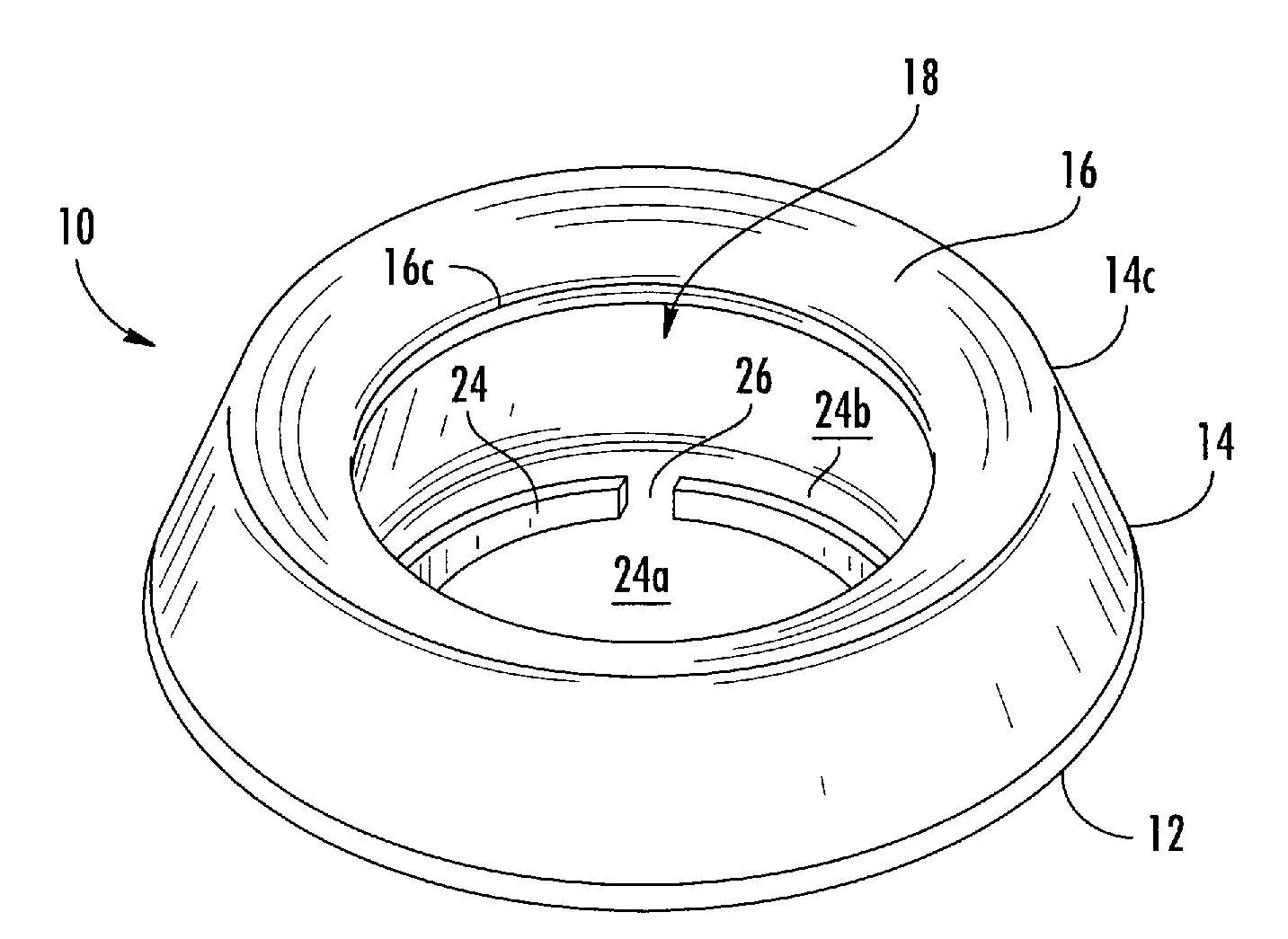
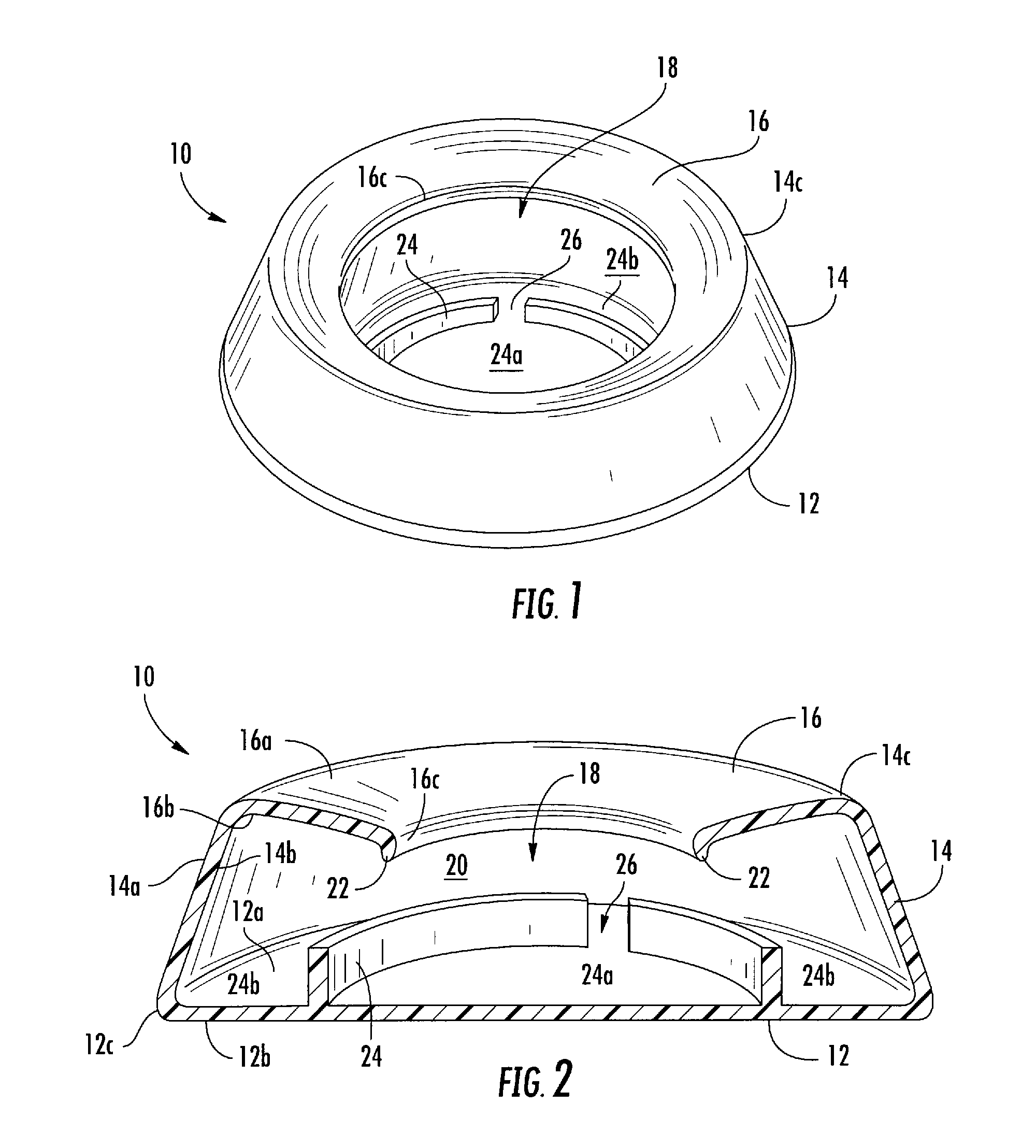
Pet Water Dish
The present invention provides an improved spill-resistant container for providing water to pets. The container generally includes a base member, annular sidewall integral with a periphery of the base member, and an annular lip extending partially inward from the sidewall forming an aperture through which the pet access the fluid (e.g., water). The base member, annular sidewall, and lip together form an inner cavity adapted to hold fluid for a pet. A circular anti-splash ring is centrally disposed within the inner cavity and extends slightly upward from the base to resist horizontal sloshing (wave action) of the fluid within the inner cavity. The anti-splash ring further includes a flow aperture, allowing fluid communication throughout the inner cavity.
Owner:PET SPILL PROOF
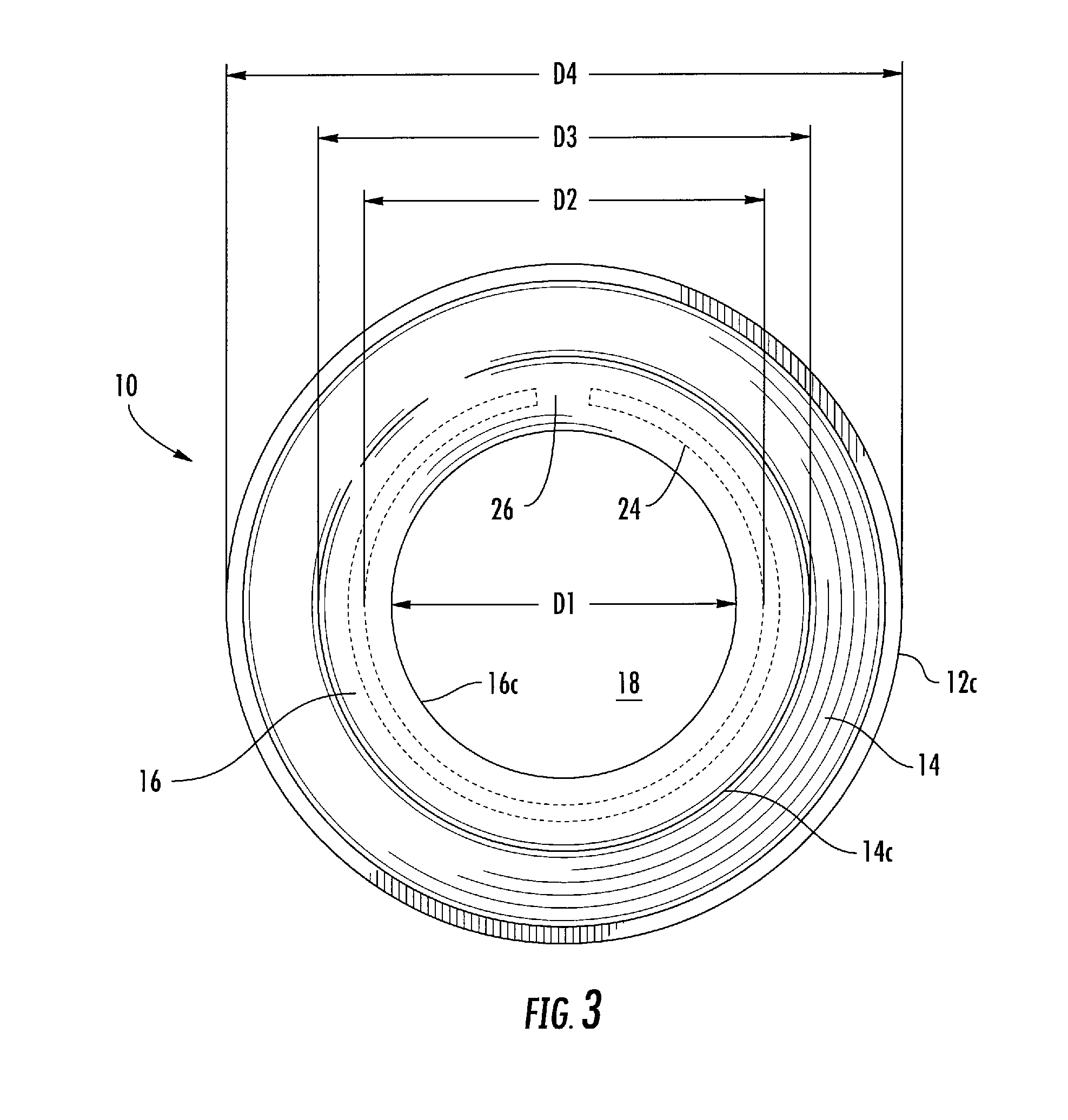
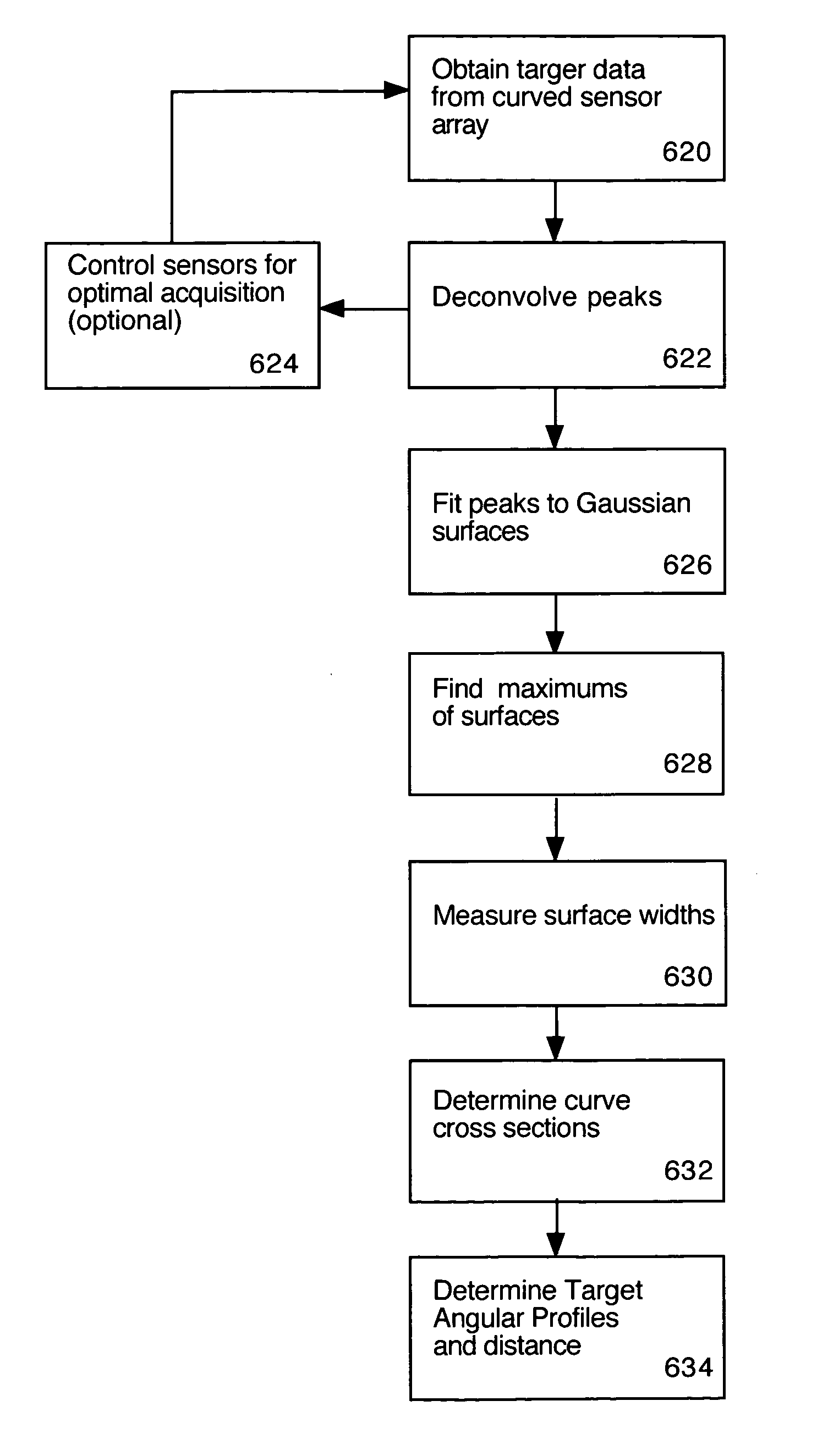
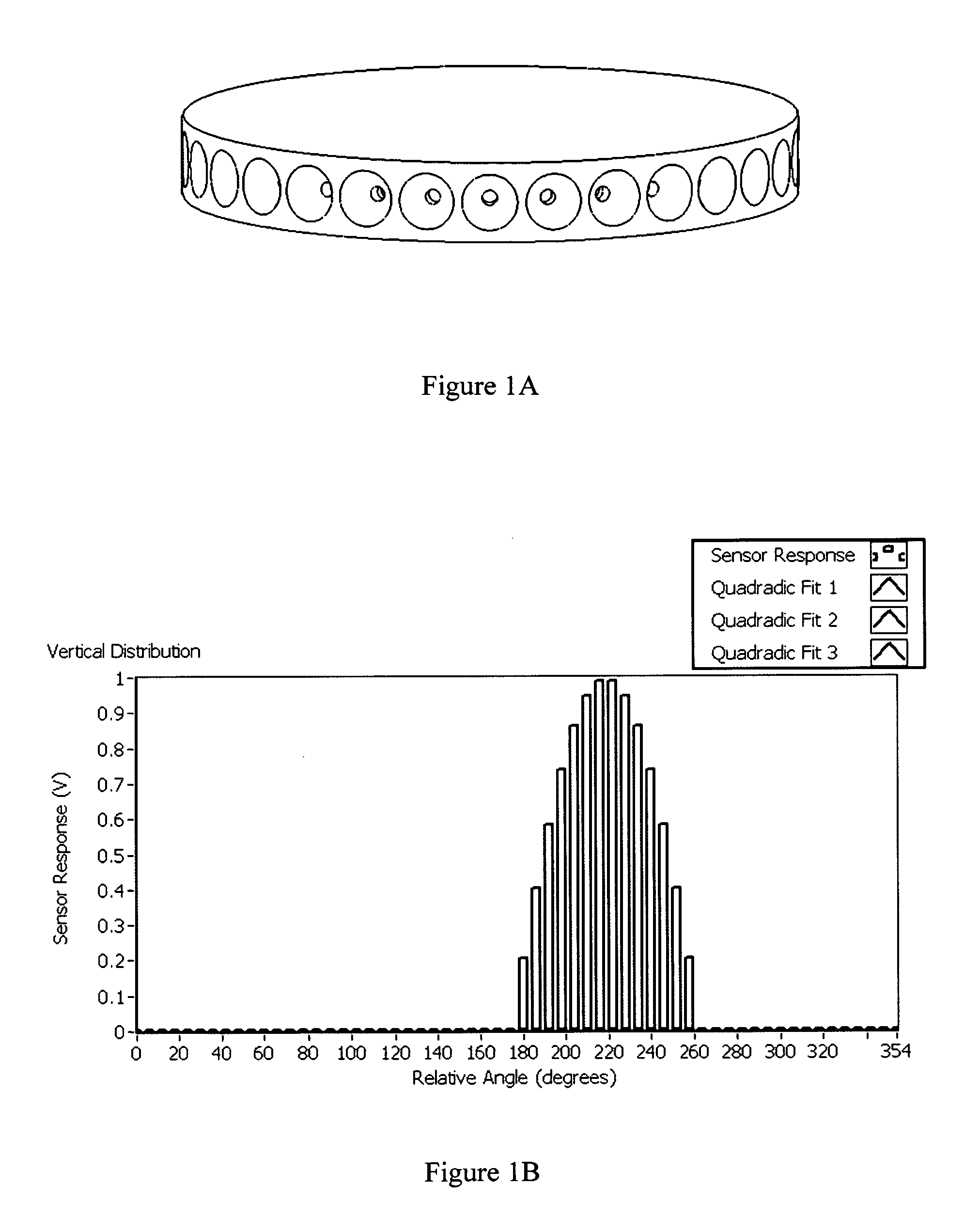
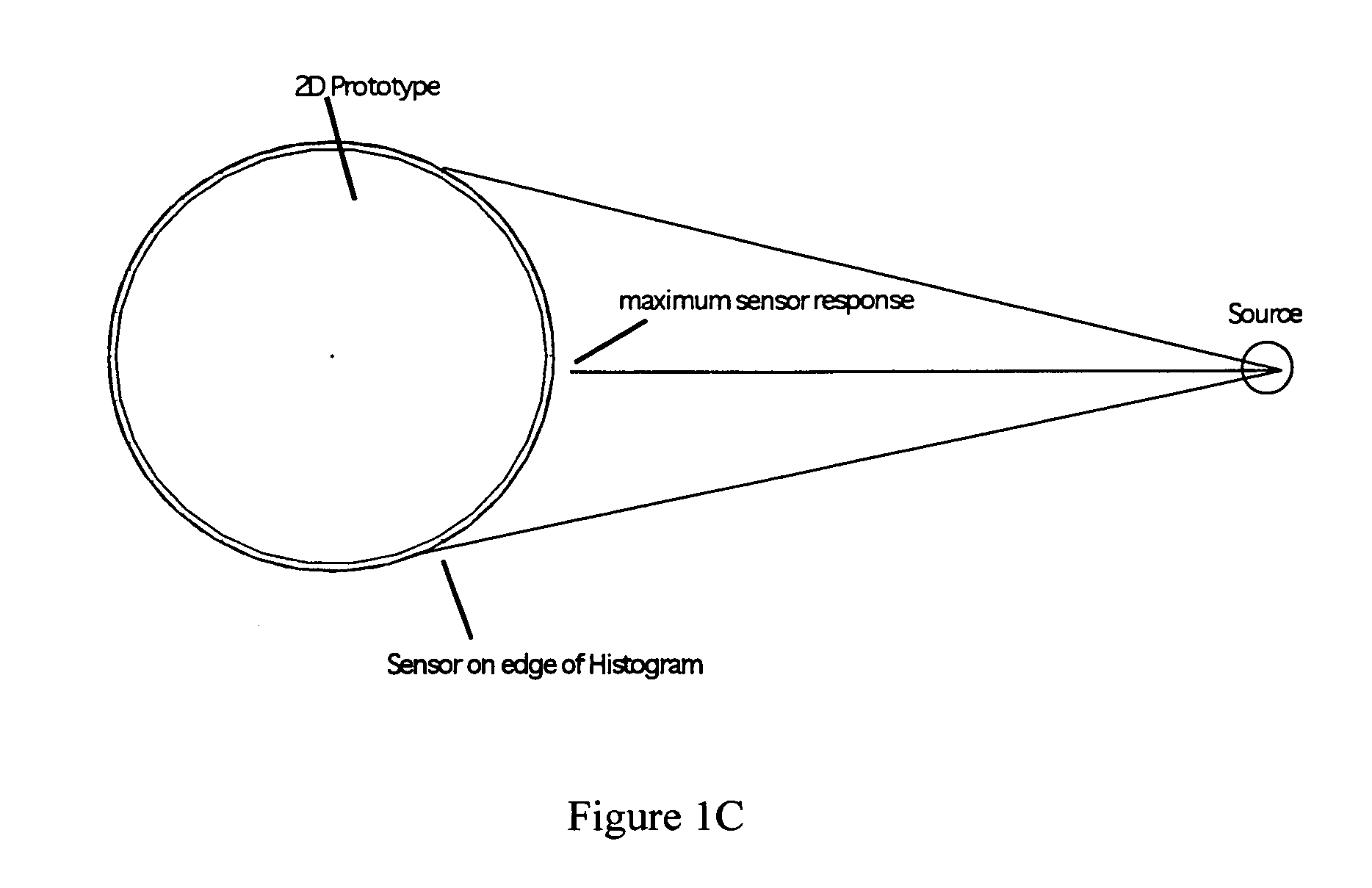
Curved sensor array apparatus and methods
InactiveUS7619754B2ImprovedAccurate calculationRadiation pyrometryOptical rangefindersSpatial OrientationsResponse Amplitude
Curved sensor array configurations and methods of processing the data gathered by the sensors. A 2 dimensional embodiment comprises singular ring of sensors that can monitor sources in a 2 dimensional plane. A sensor directly facing a target produces a maximum response. As the angle of a sensor relative to the target increases, the response decreases. Fitting the sensor response amplitudes to a 2D Gaussian curve and calculating the peak of the curve allows a very accurate calculation of the angular direction of the target. A 3D embodiment comprises sensors distributed over the surface of a sphere in order to monitor multiple targets in any spatial orientation. Again, the sensor amplitude data is fitted to a 3D curve or surface such as a Gaussian surface. The present invention can resolve more than one target using deconvoluting techniques.
Owner:RIEL RYAN D +2
Capacitive angular position sensor
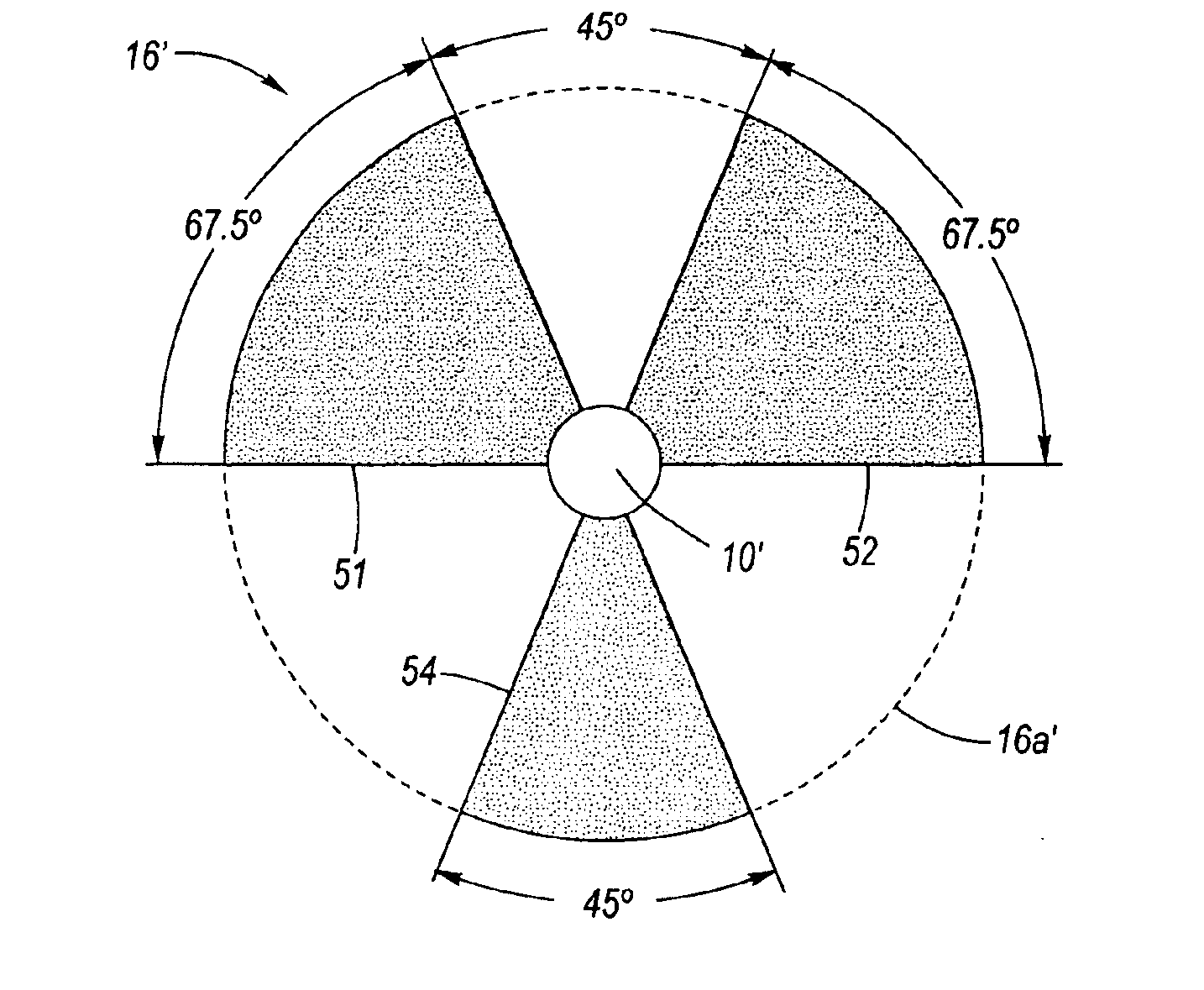
InactiveUS6876209B2ImprovedResistance/reactance/impedenceSolid-state devicesElectricityElectrode pair
A sensor assembly for sensing angular position of one object relative to another object. A capacitor is formed between a transmitter capacitor plate having a pair of transmitter electrodes and a receiver capacitor plate having preferably eight receiver electrodes forming four receiver electrode pairs. A dielectric rotor rotates between the plates, the rotor having first and second segments each subtending 67.5 which are mutually separated by a vacancy subtending 45 degrees, and further having a third segment subtending 45 degrees disposed between the first and second segments diametrically opposite the vacancy. An electrical circuit measures net charge induced on each of the receiver electrode pairs, wherein the charges indicate the angular position of said rotor relative to said transmitter and receiver capacitor plates.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
Ignition disconnect
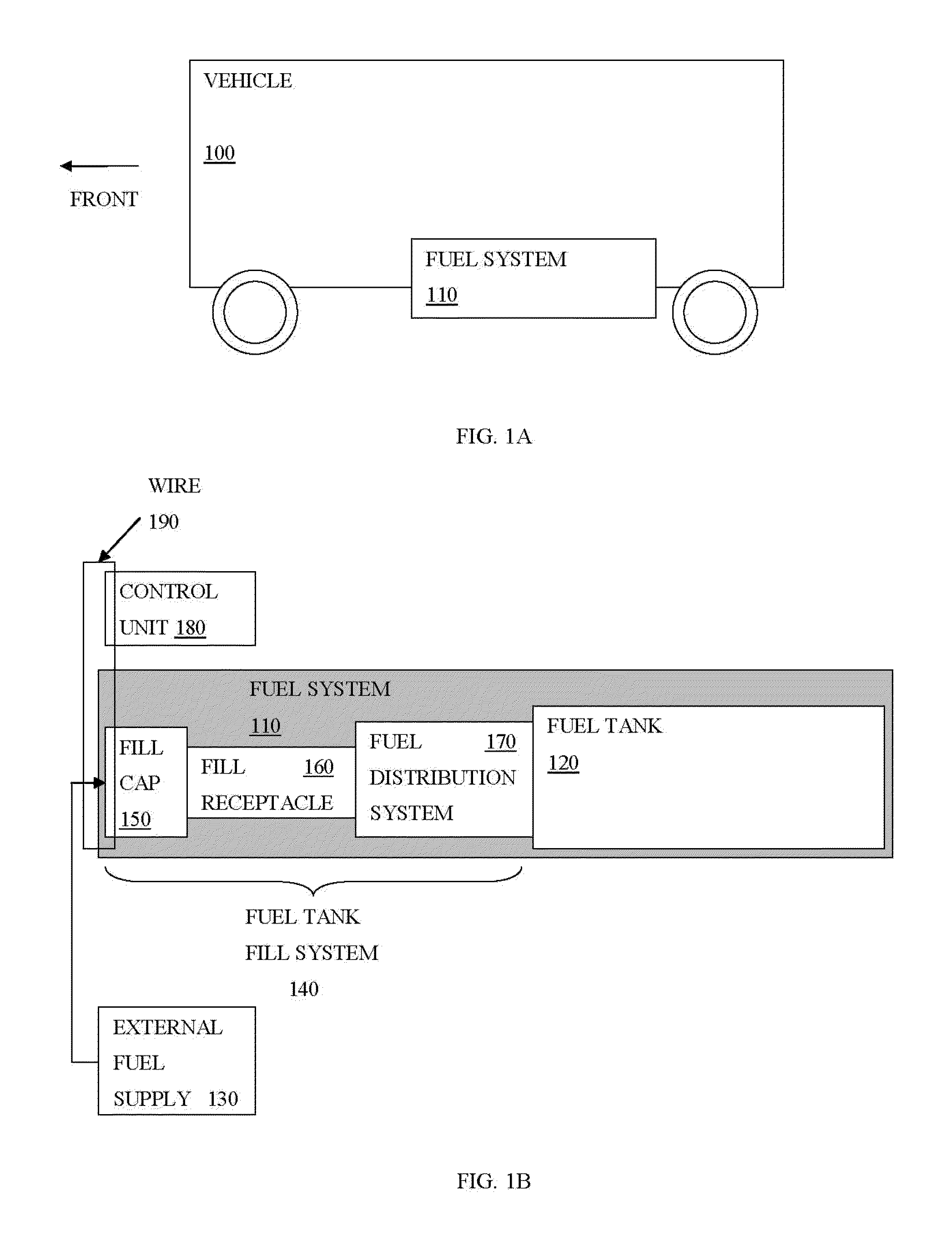
ActiveUS20130291825A1ImprovedInternal combustion piston enginesEngine controllersNatural gas fuelFuel tank
The invention provides devices, systems and methods for filling, capping and electronically monitoring the closure of a fuel tank. In some embodiments, the invention provides devices, systems and methods for filling, capping and providing an ignition disconnect mechanism upon uncapping of a natural gas fuel tank.
Owner:AGILITY FUEL SYST LLC
Passenger dorsal support
InactiveUS7523993B1ImprovedSimple structureSeating arrangementsPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementEngineeringBack support
Owner:NOVA BUS DIV DE GRP VOLVO CANADA INC
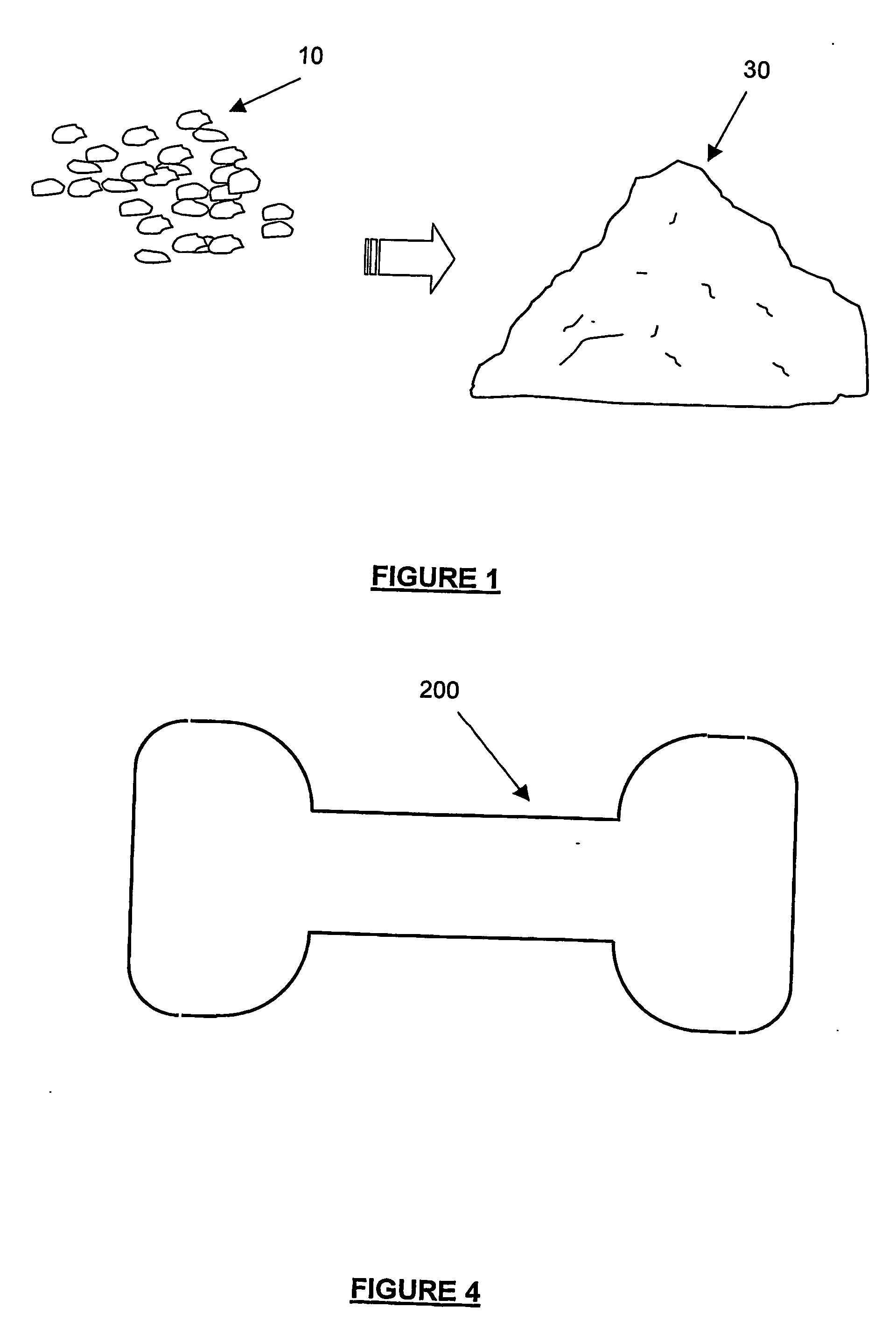
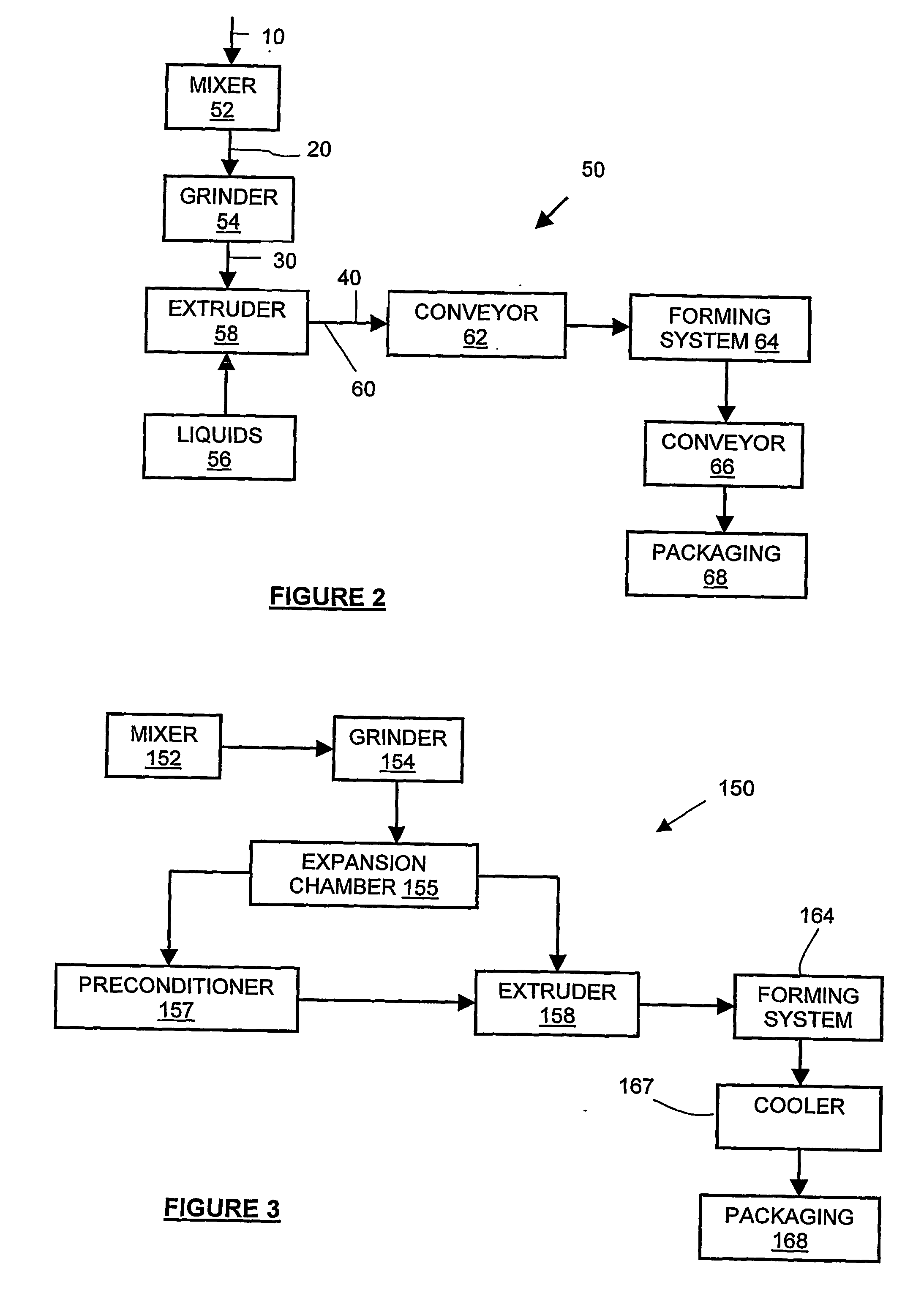
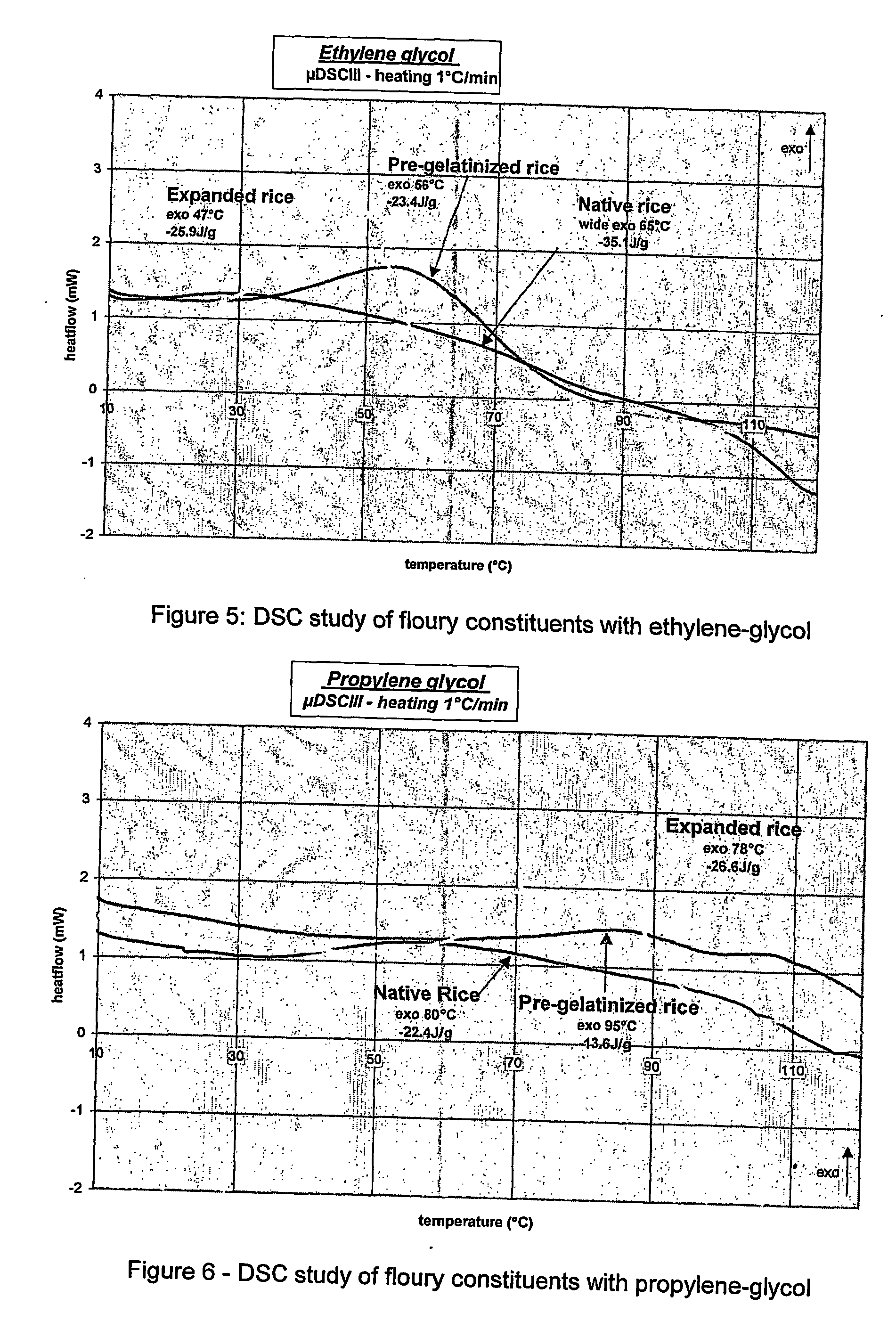
Use of expanded constituents and manufacture of products therefrom
InactiveUS20060292288A1Reduce requirement and emissionImprovedConfectioneryAnimal feeding stuffChemistryHeat processing
The present invention provides methods and products made thereby, wherein a pre-expanded constituent, including an edible constituent, is thermally treated to melt it, preferably in a dynamic process environment, to produce products ranging from high to quite low densities and from very strong to soft to apparently dry textures. The wide range of textures enables the provision of food products such as low calorie, digestible and safe, long duration pet food chews. Non-food products suitable for use in manufacture may also be produced. Cooking is preferably carried in an extruder, preferably at low moisture or in the total absence of added water. The methods of dynamic cooking reduce cost in a number of ways including but not limited to decreased process steps, increased throughput, decreased capital expenses and decreased raw product cost.
Owner:NESTEC SA
Cross-linking compositions for polymer-modified asphalt compositions
ActiveUS20060223915A1Easy to useImprovedIn situ pavingsWorking-up pitch/asphalt/bitumen by chemical meansPolymer chemistrySulfur containing
The present invention relates to a bituminous composition comprising a bituminous component, an elastomeric polymer component, and a specific cross-linking composition component comprising elemental sulfur, a sulfur-containing derivative, a sulfur activator, a fatty acid or fatty acid derivative and a polymeric carrier. Compositions according to the invention are particularly useful in preparing polymer-modified asphalt (“PMA”) for road applications.
Owner:KRATON POLYMERS US LLC
Electrical wiring device with multiple types of wire terminations
InactiveUS6926543B2ImprovedGood gripContact members penetrating/cutting insulation/cable strandsClamped/spring connectionsClutchElectrical conductor
A wiring device is provided with three different ways in which the bared end of an electrical conductor can be coupled to the contacts inside the body of a wiring device. A clamping plate is placed upon the threaded body of a terminal screw. In a first arrangement the bared end is formed about the terminal screw and trapped between the head of the terminal screw and a first surface of the clamping plate which forces the conductor into firm contact with the first surface of the clamping plate. In another arrangement the straight bared end of the conductor is trapped between a second surface of the clamping plate and a contact plate. The movement of the conductor and clamping plate is controlled by the terminal screw. Apertures are placed in the bottom of the device housing adjacement the contacts in the housing. A contact arm, formed as a one-way clutch grips the straight bared end of a conductor to make contact with the contacts of the device but prevents withdrawal of the conductor.
Owner:LEVITON MFG
Relay Having Two Switches That Can Be Actuated In Opposite Directions
ActiveUS20150042423A1Easy to manufactureAvoid damageElectromagnetic relay detailsSelector switchesRelay
An electromechanical relay is provided, comprising a magnetic system and a pivotable armature. A diagnostic switch is arranged on one side of the relay, and the set of contacts of the diagnostic switch is driven by the adjacent leg of the armature. A load switch is arranged on the bottom side of the relay and is driven by the second leg of the armature via an insulating coupling member.
Owner:PHOENIX CONTACT GMBH & CO KG
Magnetic fishing reel clicker
A clicker mechanism for a fishing reel is described. A typical fishing reel has a spool defining an orifice and a shaft passing through the orifice. A component having an irregular surface, such as a gear-like component with teeth or a ring defining a serrated inner surface engages the shaft. A clicker assembly may be affixed to the spool. The clicker assembly includes a clicker for engaging the clicker gear. The clicker alternately moves from a first position to a second position. The clicker assembly utilizes a magnet that provides a magnetic force to return the clicker to the first position from the second position. Two magnets may be used to exert magnetic force against one another, either with an attracting or a repelling force.
Owner:W C BRADLEY ZEBCO HLDG LLC
Optical discriminator for transmitting and receiving in both optical fiber and free space applications
InactiveUS6925256B1ImprovedConstructed moreWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic receiversLight sourceOptical fiber cable
A bi-directional communication assembly is provided with commonly available optoelectronic components in a compact package. Diplex functionality is achieved by orienting the receiving detector at an angle with respect to the transmitting beam. An interference coating inside the detector, on the detector surface, or on a surface in intimate contact with the detector, reflects the transmitted beam while simultaneously allowing the receiving beam to pass through the coating to the light absorbing region. The combined function of the receiving detector, providing advantages of a common beam path and close proximity of the components, enable a compact package that can be placed within the space usually occupied by the transmitter light source alone.
Owner:MOOG INC
Switching elements and devices, memory devices and methods of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20130320286A1Easy to optimizeHeat stableBulk negative resistance effect devicesSemiconductor devicesNitrogenEngineering
A switching element includes: a first electrode; a second electrode; and a silicon-containing chalconitride layer between the first electrode and the second electrode. A switching device includes: a threshold switch material layer between a first electrode and a second electrode. The threshold switch material layer includes a cationic metal element, a chalcogen element, a silicon element and a nitrogen element. A memory device include: a plurality of first wirings arranged in parallel with each other; a plurality of second wirings crossing the first wirings, and arranged in parallel with each other; and a memory cell formed at each intersection of the plurality of first wirings and the plurality of second wirings. The memory cell includes a laminate having a silicon-containing chalconitride layer, an intermediate electrode, and a memory layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
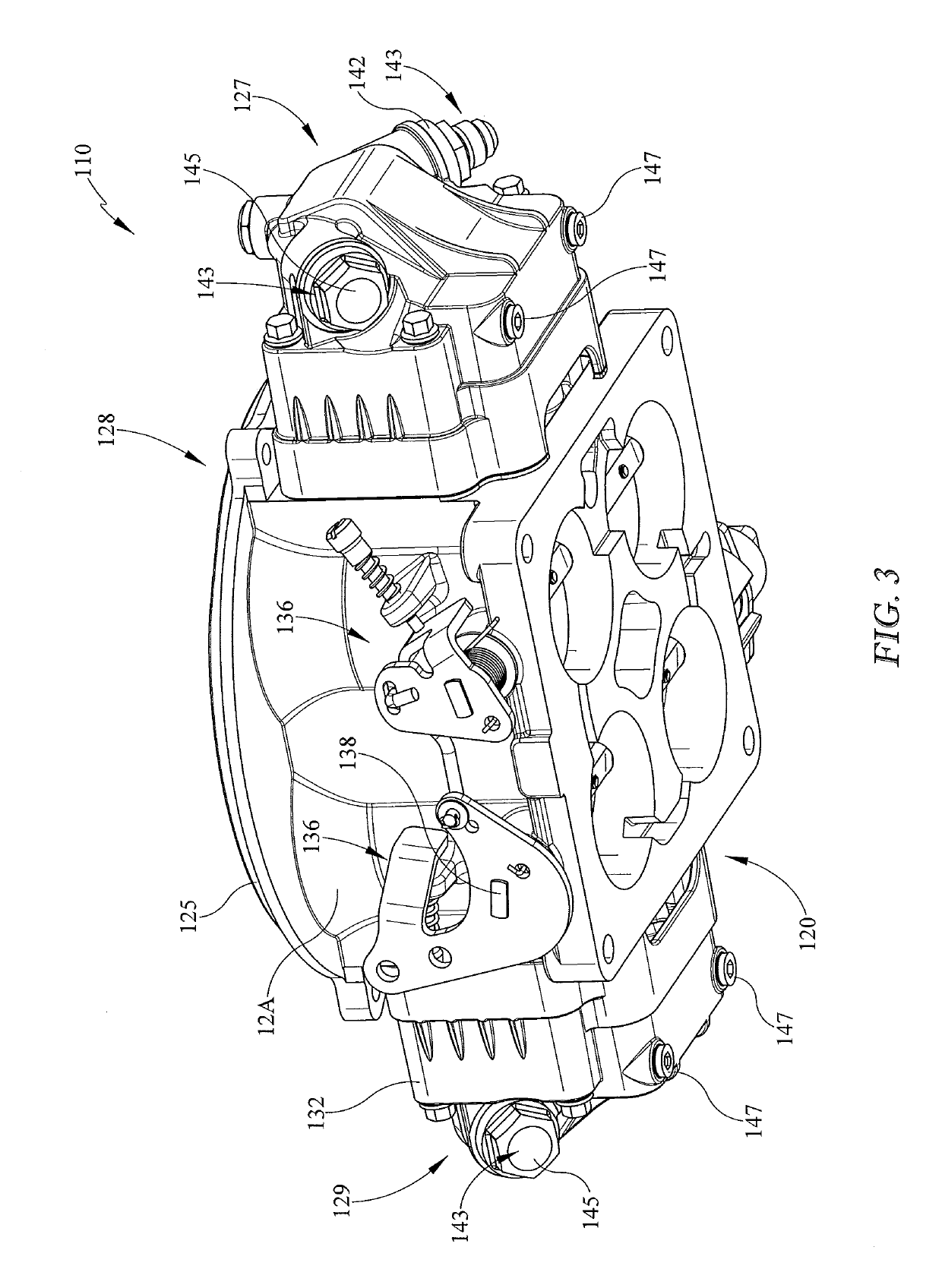
Electronic Fuel Injection Throttle Body Assembly
ActiveUS20190170069A1ImprovedImproved configurationLow pressure fuel injectionEngine controllersInjectorThrottle
Present embodiments provide a throttle body which may be used with a variety of engines of different manufacturers. The throttle body may be used to replace mechanical or hydraulically controlled carburetors with electronic fuel injection. The throttle body may provide improved fuel pathways and fuel injector placement.
Owner:HOLLEY PERFORMANCE PRODUCTS
Design structure for chip identification system
InactiveUS20090094566A1ImprovedReduce power consumptionProgram controlRecord carriers used with machinesElectrical conductorIdentification system
Disclosed is a design structure for an on-chip identification circuitry. In one embodiment, pairs of conductors (e.g., metal pads, vias, lines) are formed within one or more metallization layers. The distance between the conductors in each pair is predetermined so that, given known across chip line variations, there is a random chance (i.e., an approximately 50 / 50 chance) of a short. In another embodiment different masks form first conductors (e.g., metal lines separated by varying distances and having different widths) and second conductors (e.g., metal vias separated by varying distances and having equal widths). The first and second conductors alternate across the chip. Due to the different separation distances and widths of the first conductors, the different separation distances of the second conductors and, random mask alignment variations, each first conductor can short to up to two second conductors. In each embodiment the resulting pattern of shorts and opens, can be used as an on-chip identifier or private key.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
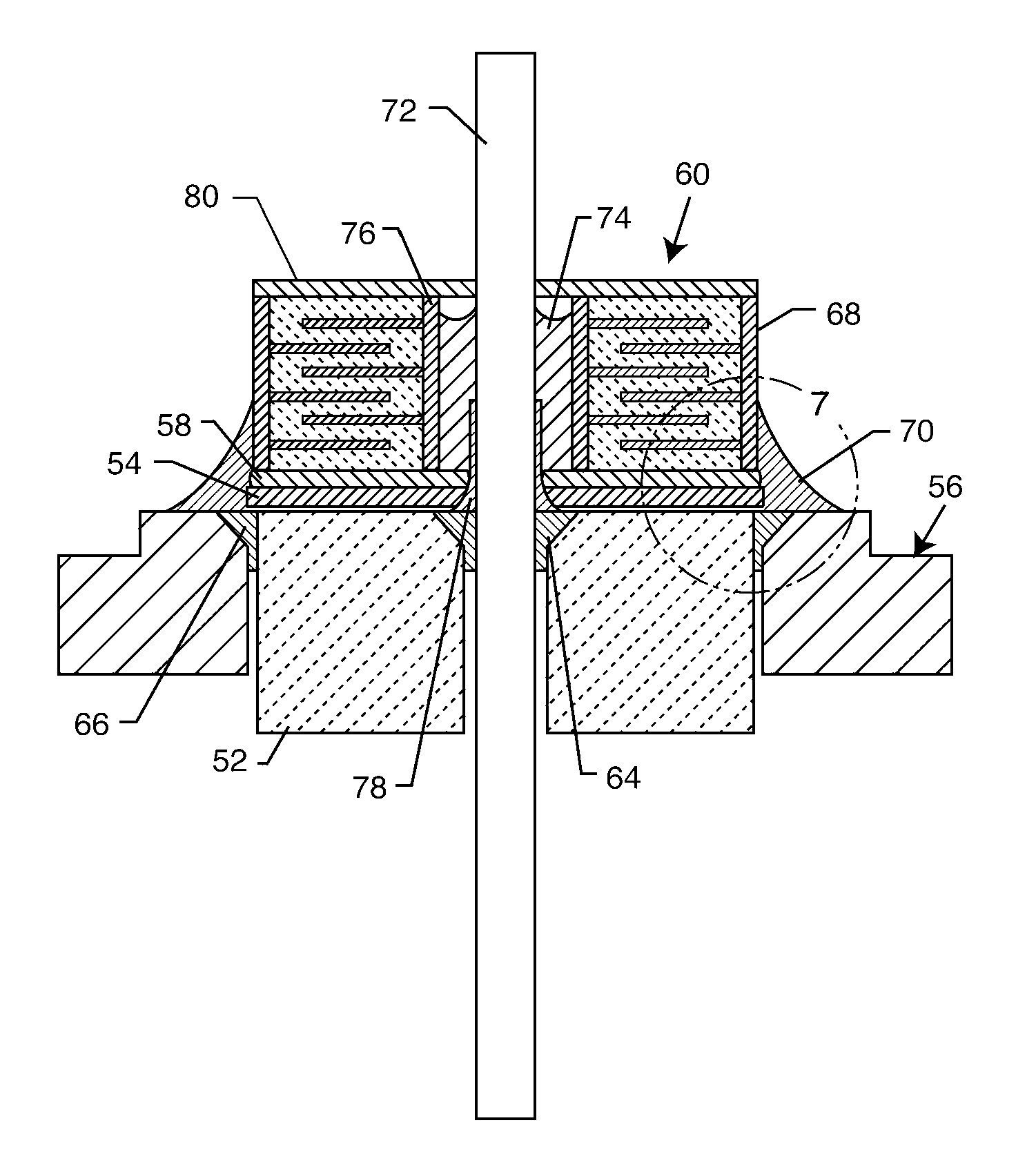
Feedthrough capacitor filter assemblies with laminar flow delaminations for helium leak detection
A feedthrough filter capacitor assembly includes a capacitor having first and second sets of conductive electrode plates embedded within a dielectric body and mounted to the hermetic terminal of an implantable medical device. A laminar delamination gap is provided between the capacitor sealing materials and the hermetic terminal assembly to facilitate helium leak detection. At least one feedthrough terminal pin extends through the capacitor in conductive relation with the first set of electrode plates, and an outer ferrule is mounted about the capacitor in conductive relation with the second set of electrode plates. The mounting washer is spaced against the hermetic seal and is adhesively connected to the feedthrough capacitor. The mounting washer forms a laminar flow delamination through which helium molecules can flow during a helium leak detection test. Provision is made for a pre-connection to the gold braze so that the capacitor inside diameter termination is not electrically isolated from the lead wire.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
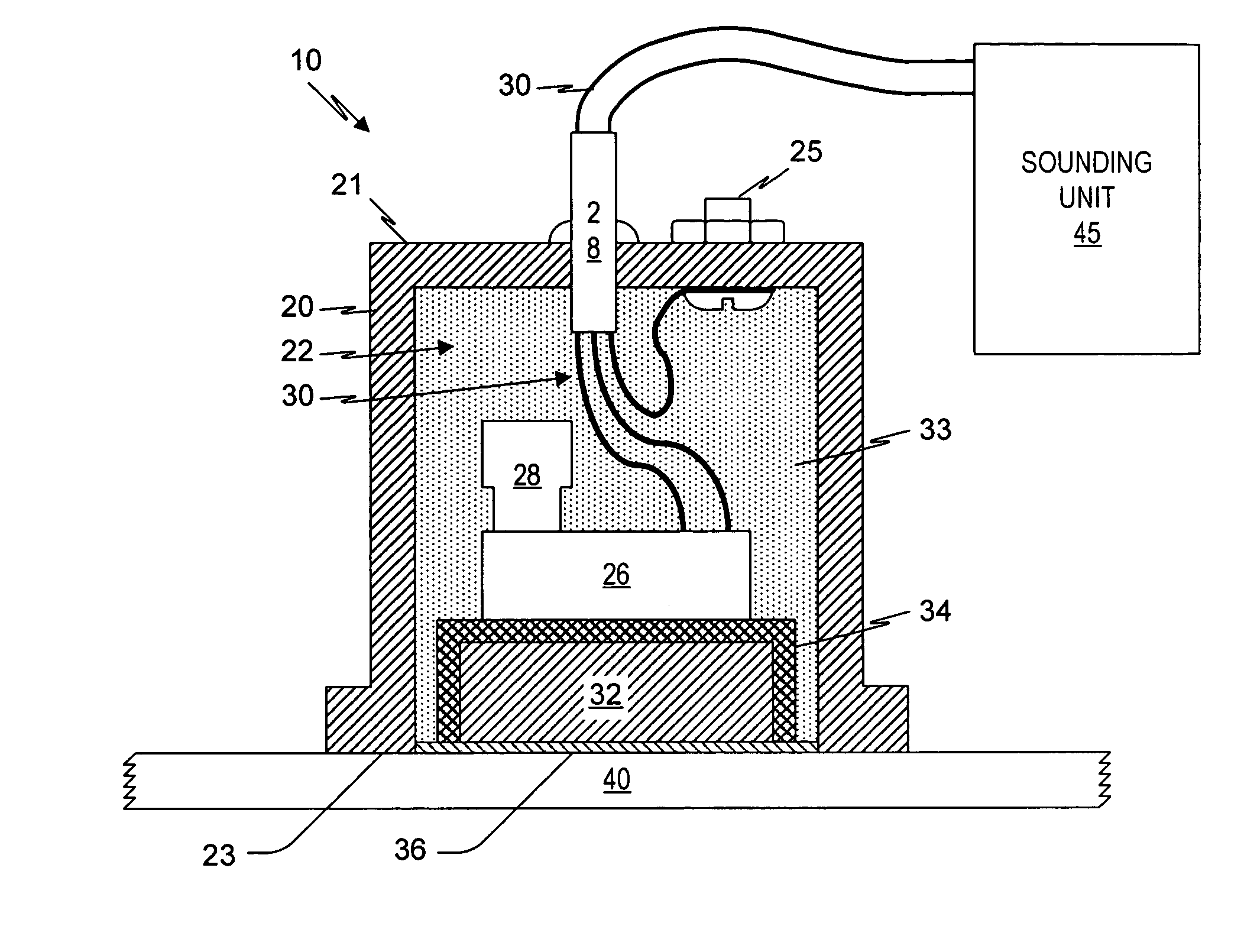
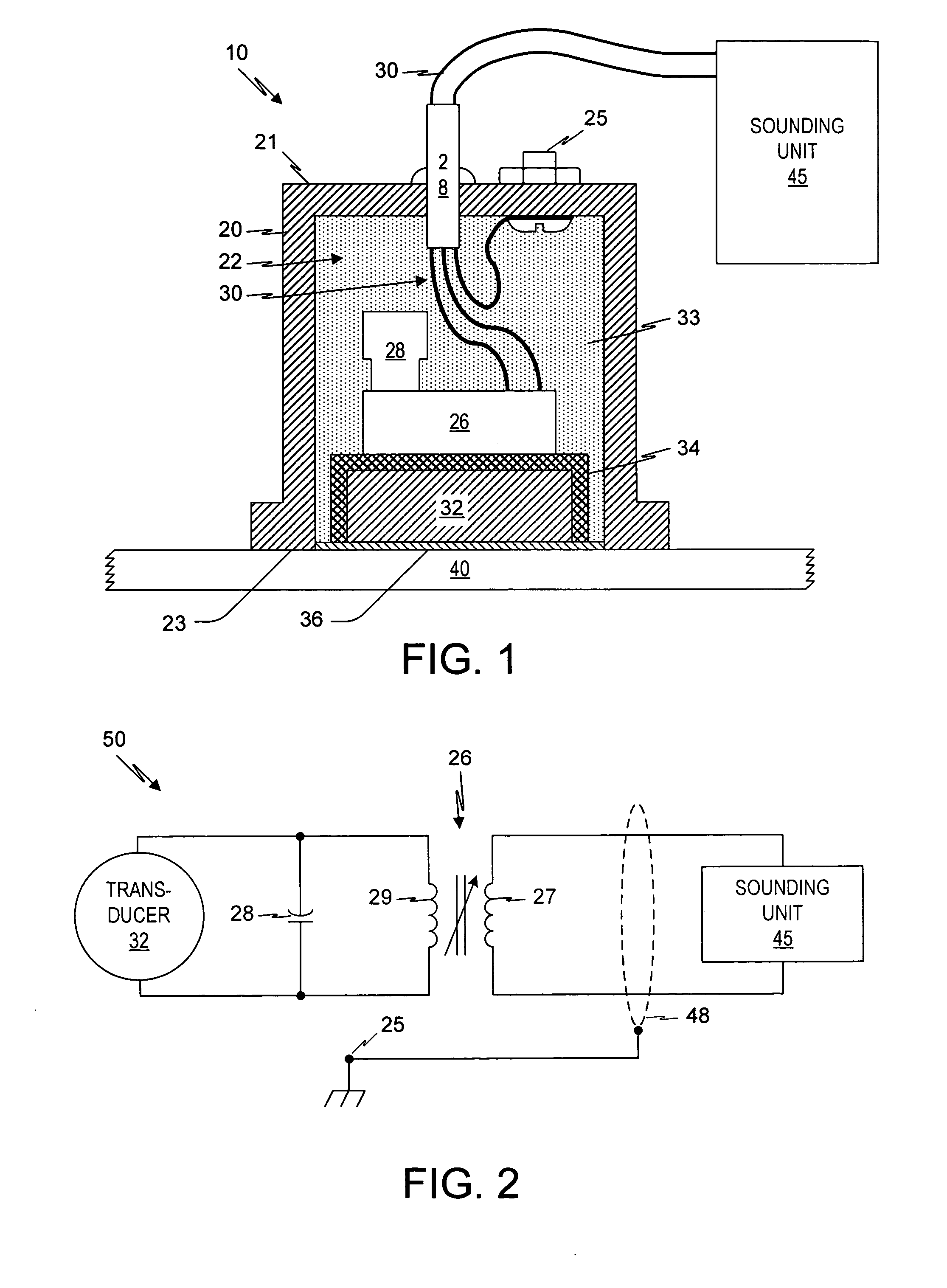
Acoustic transducer assembly for aluminum hulled vessels
InactiveUS20050201205A1ImprovedIncrease acoustic noiseMechanical vibrations separationSound producing devicesUltrasound pulseAdhesive
A transducer assembly is provided with an ultrasonic transducer, a capacitor, and a transformer enclosed within a protective housing, and an acoustic block. The transducer is adhered to the acoustic block, and the materials of the transducer, acoustic block, and adhesive are selected so that when the transducer assembly is adhered to an aluminum boat hull, acoustic energy loss due to attenuation is mitigated. The secondary winding of the transformer and the capacitor form a resonant circuit that is wired to the ultrasonic transducer and helps to reject some of the acoustic-generated hull noise that may reach the transducer. The transformer steps up the voltage pulses to the transducer. In use, the transducer assembly is wired to a sounding unit, which provides the voltage pulses for generating ultrasonic pulses, and processes electrical signals from the transducer that correspond to ultrasonic echoes.
Owner:CHAVEZ ALFRED MAX +1
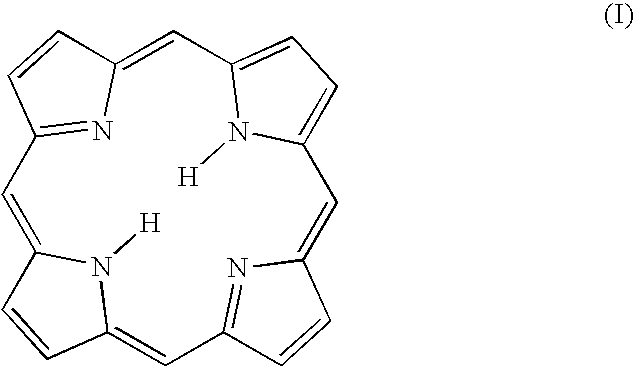
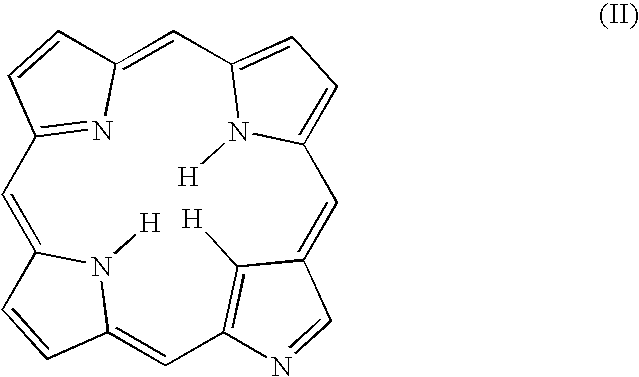
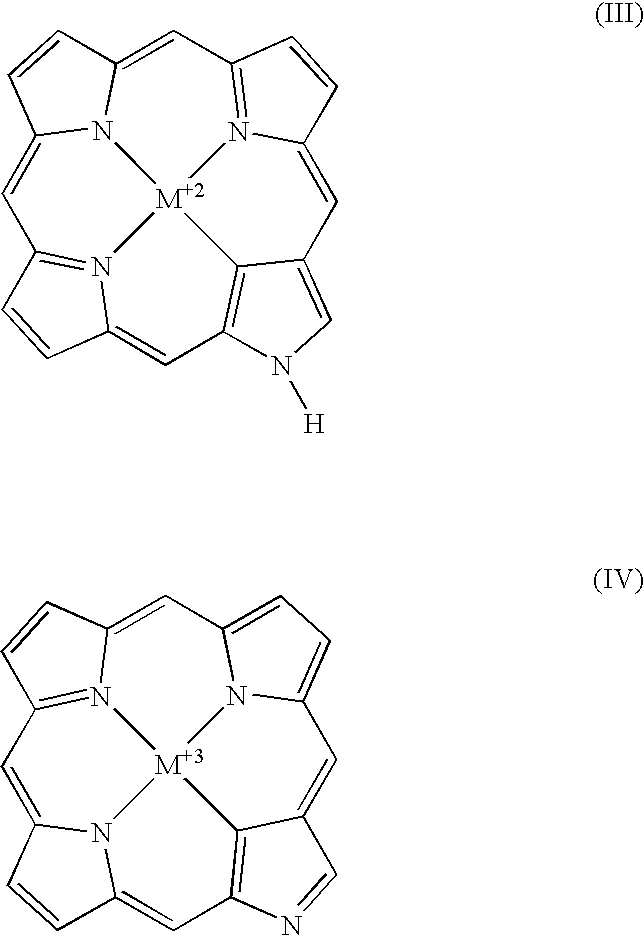
Carbene porphyrins and carbene porphyrinoids, methods of preparation and uses thereof
The present invention includes novel N-heterocyclic carbene substituted porphyrins and porphyrinoids. The invention also includes complexes of metals and N-heterocyclic carbene substituted porphyrins and porphyrinoids. The invention further includes N-heterocyclic carbene substituted porphyrins and porphyrinoids, and metal complexes of N-heterocyclic carbene substituted porphyrins and porphyrinoids that also includes a targeting moiety or group. The compositions of the present invention are useful in the fields of diagnosis and treatment of many medical ailments.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON
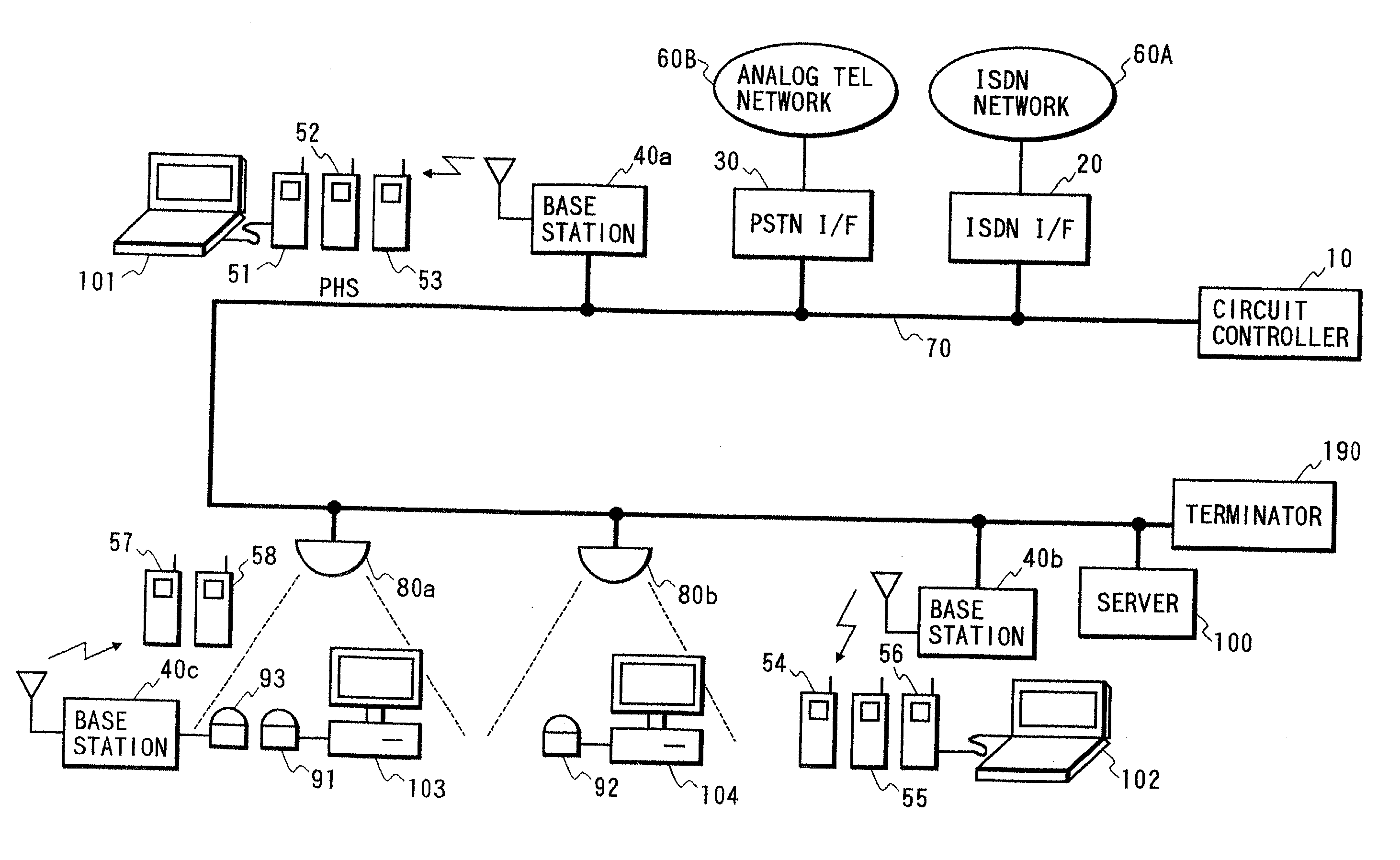
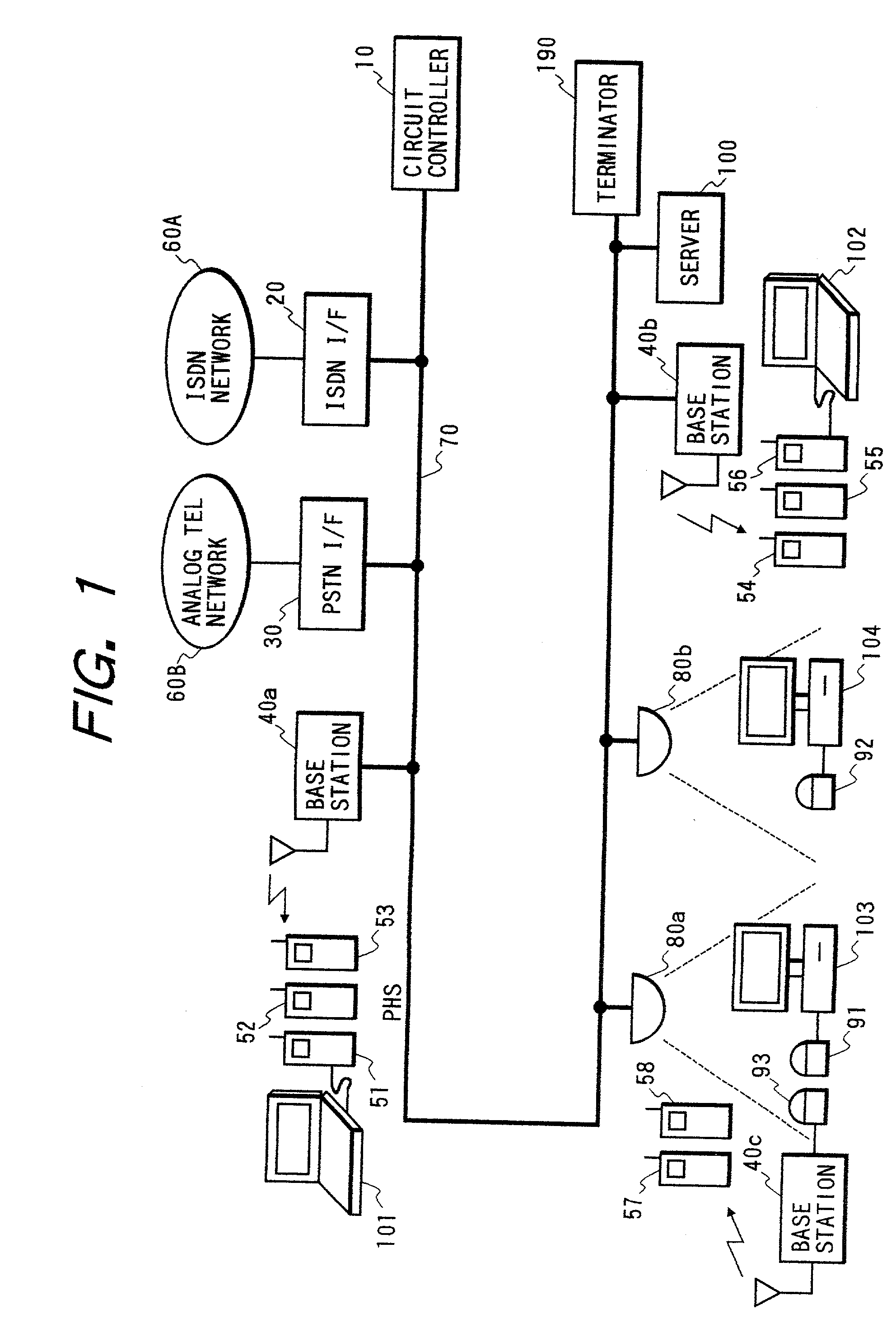
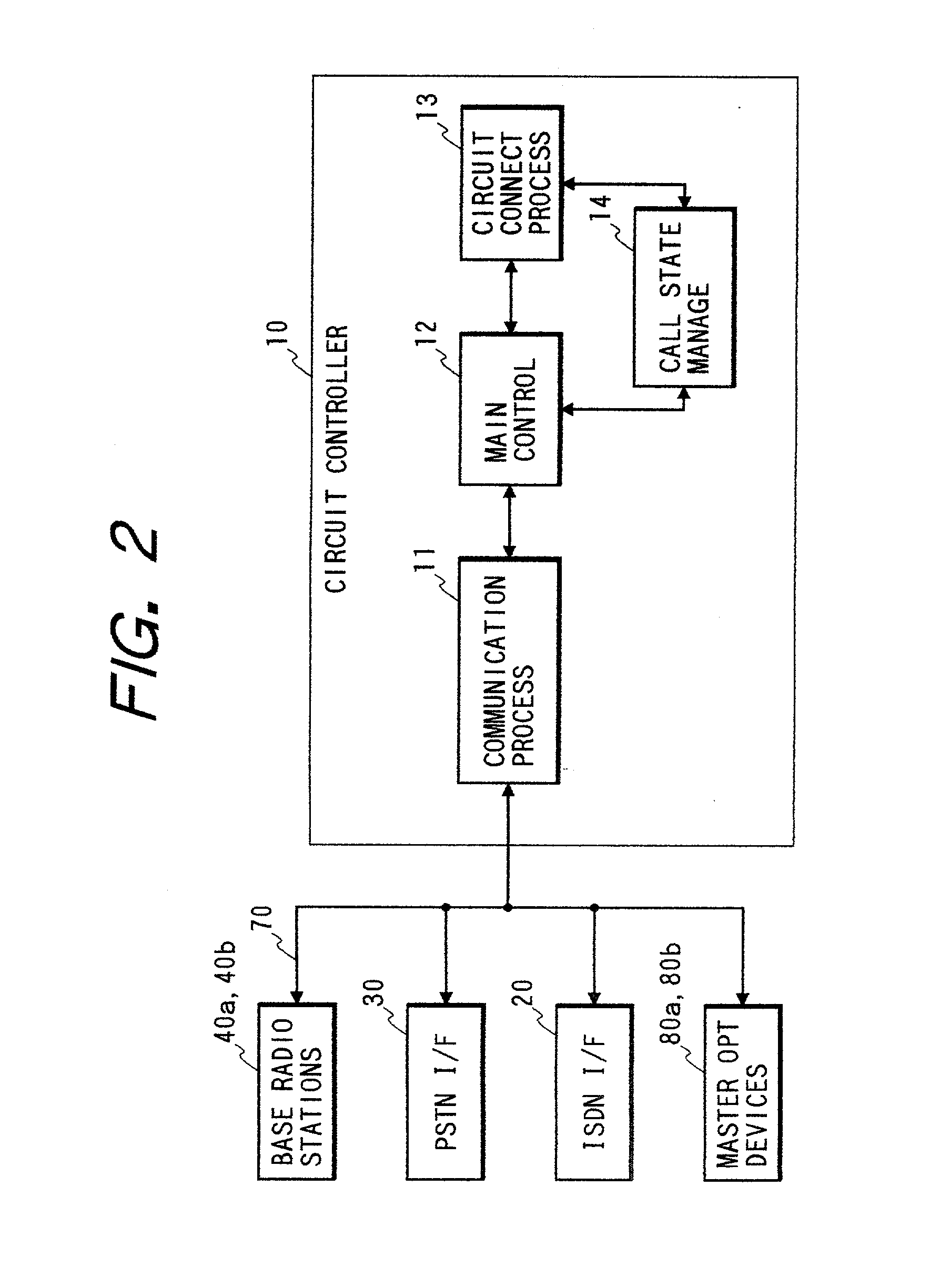
Communication system and circuit controller
InactiveUS20020126696A1ImprovedNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesCable networkData rate
A communication system includes a wire network, a first terminal device, and a second terminal device. A first master device connected to the wire network transmits and receives data to and from the first terminal device by wireless at a first data rate. For example, light is used by the wireless data transmission between the first master device and the first terminal device. A second master device connected to the wire network transmits and receives data to and from the second terminal device by wireless at a second data rate lower than the first data rate. For example, radio is used by the wireless data transmission between the second master device and the second terminal device. A server connected to the wire network manages addresses of the first and second master devices.
Owner:VICTOR CO OF JAPAN LTD
Channel frequency response estimator for a wireless RF channel
ActiveUS20140079109A1ImprovedImprove receptionModulated-carrier systemsTransmission monitoringChannel frequency responseEngineering
A channel frequency response estimator for estimating the channel frequency response of a wireless RF channel having a time or frequency varying channel frequency response is disclosed. The channel frequency response estimator includes a wireless receiver. An ambiguous channel frequency response estimator is also included and configured to establish multiple channel frequency response estimate candidates for the channel frequency response of the channel. An ambiguity resolver is configured to select a channel frequency response estimate from the multiple channel frequency response estimate candidates that maximizes a goodness of fit of the selected first channel frequency response estimate, and at least two further channel frequency response estimates to a channel model. The channel model models the time or frequency dependent variance of the channel frequency response.
Owner:NXP BV
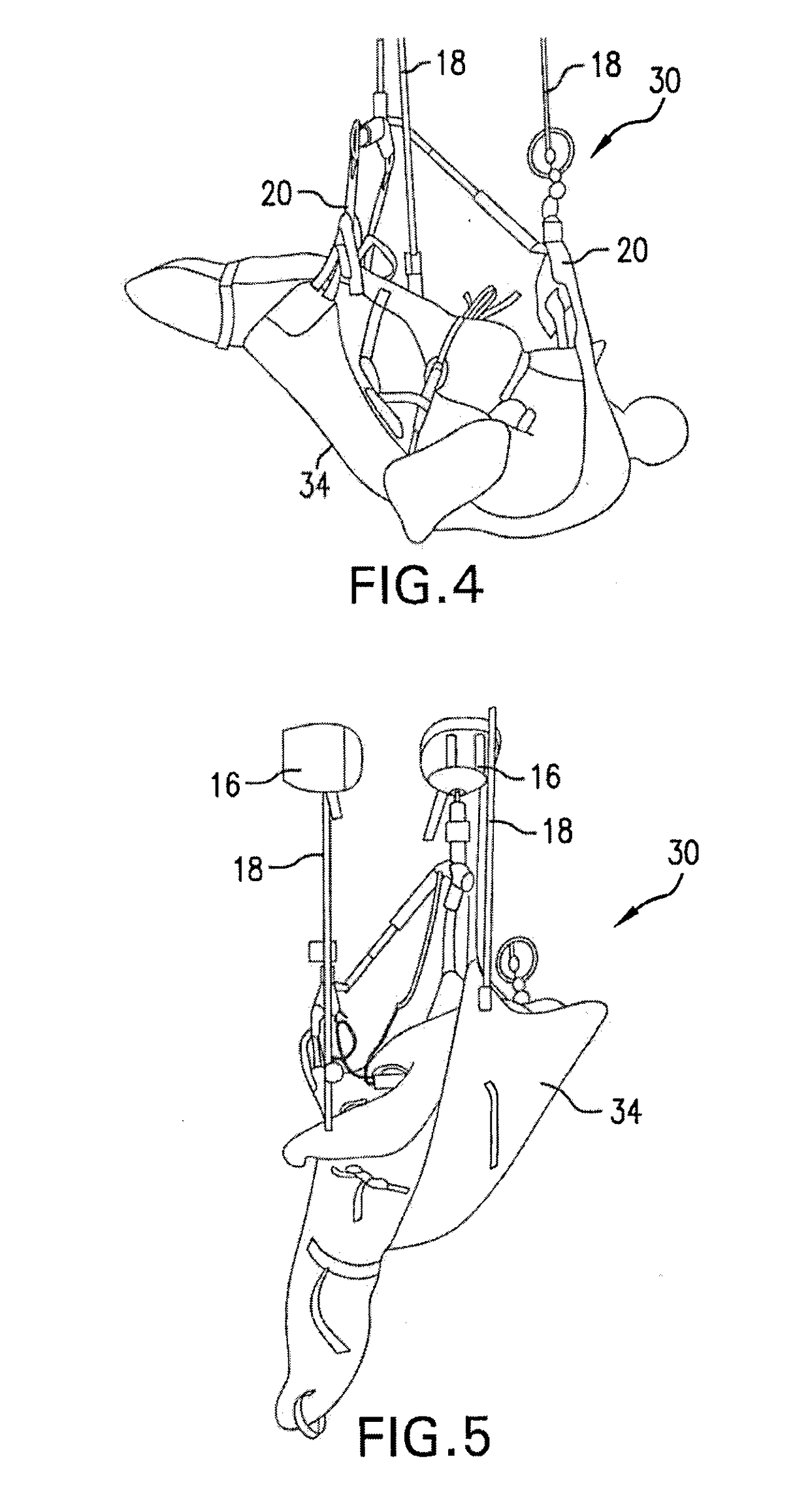
Ceiling Lift Tilt Management System
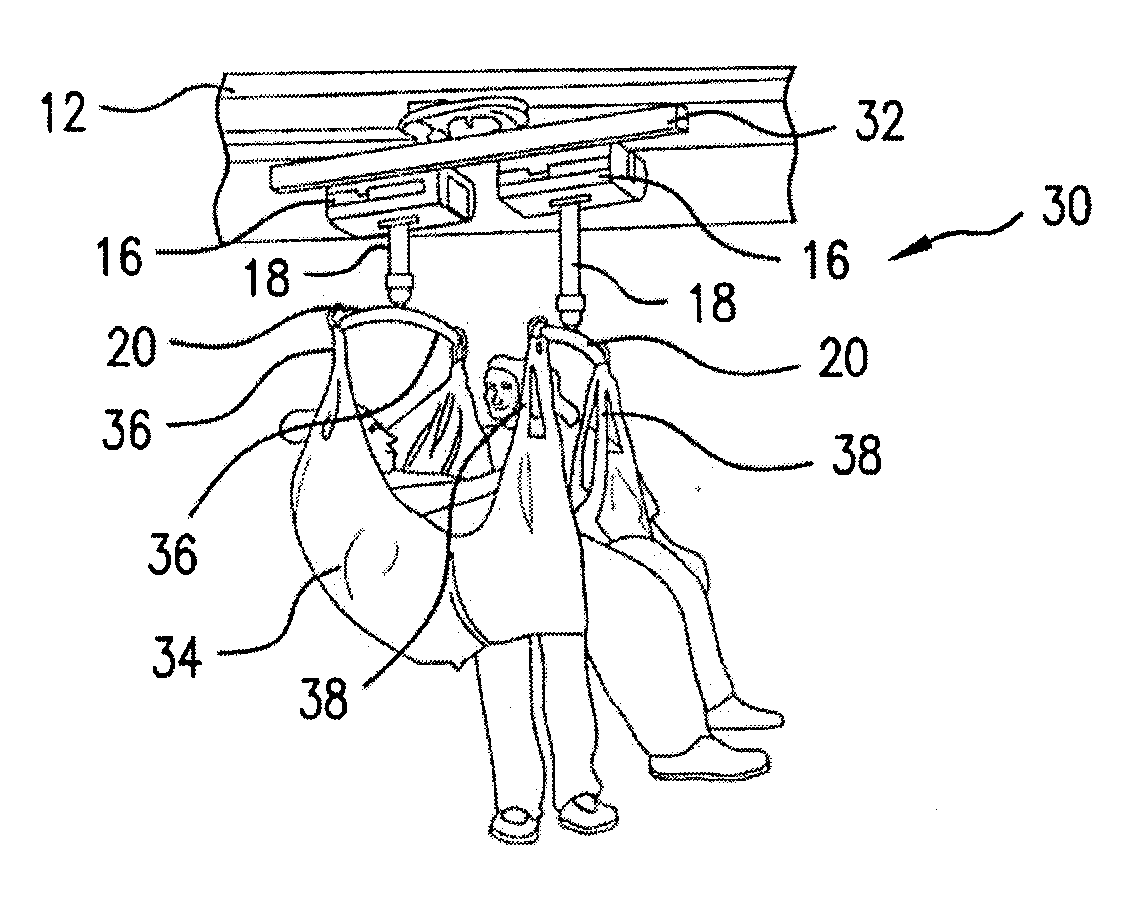
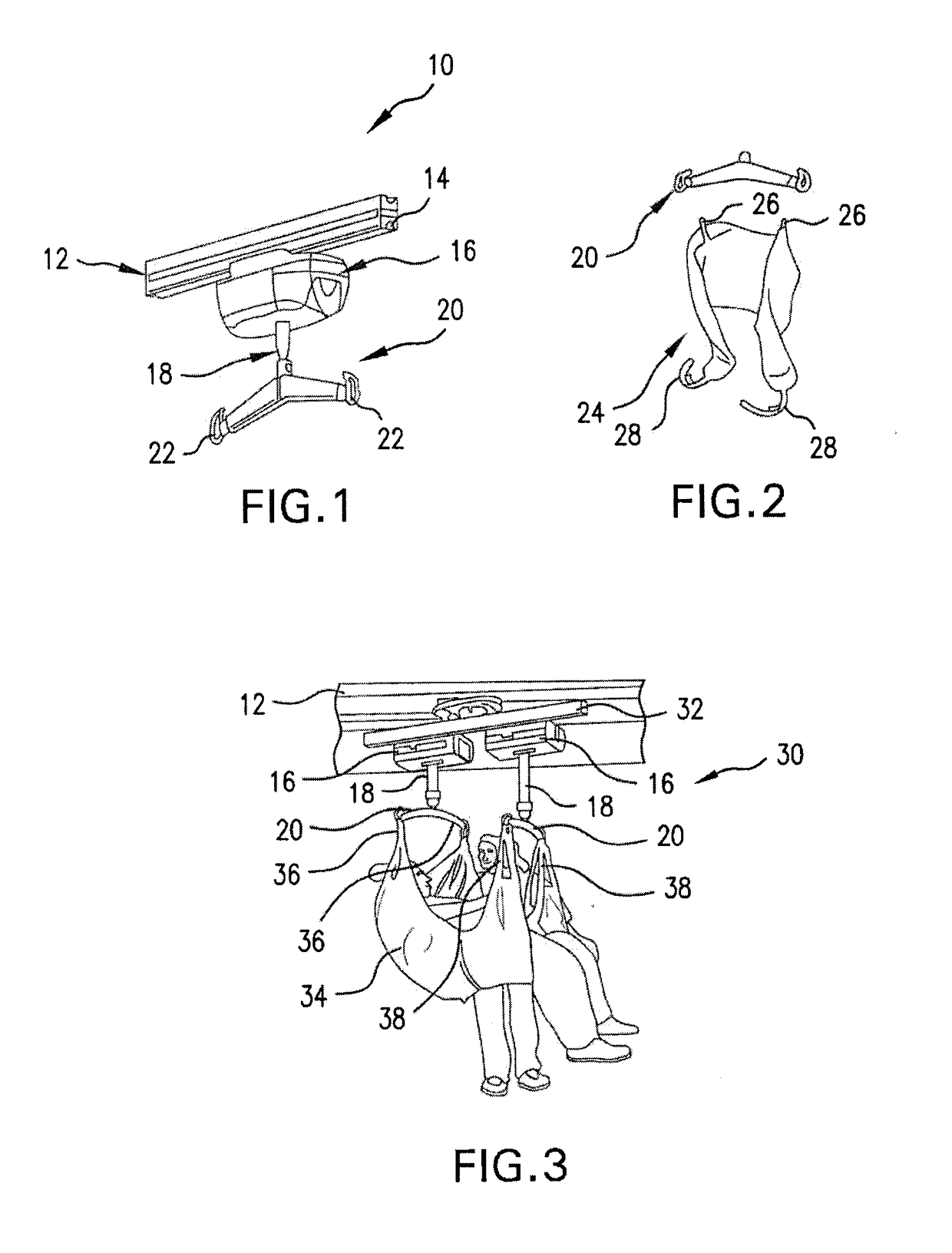
ActiveUS20170354559A1ImprovedIncrease the differenceTravelling sacksNursing bedsManagement systemPatient comfort
A ceiling lift tilt management system includes first and second motor units, which are attachable to a rail system of a medical care facility. Each motor unit includes a flexible strap, which can be coiled or uncoiled within the motor unit to raise or lower a spreader bar attached thereto. Coiling or uncoiling of the straps can cause raising or lowering of a sling attached to the spreader bars. The system also allows for tilting of the spreader bars by coiling or uncoiling a leading motor unit strap. The system includes a control system that measures the relative lengths of the two straps in order to ensure that relative tilt between the spreader bars does not exceed a threshold. Once a threshold tilt for height difference is reached, further user requests for additional tilting are prohibited. Patient comfort and safety are therefore ensured.
Owner:ARJOHUNTLEIGH MAGOG
Straight-through rotary valve structure
InactiveUS20100275759A1ImprovedReduce rotational frictionPlug valvesWind musical instrumentsRotary valveEngineering
A straight-through rotary valve structure includes: a case having an internal conic receiving space with an opening, a first extension section being disposed at a tip of the receiving space, a second extension section being disposed beside the first extension section; a conic rotary valve block having a pivot shaft and formed with a first hole and a second hole, the first hole communicating with a third hole formed at a tip of the rotary valve block in communication with the first extension section, the second hole communicating with a fourth hole formed on a conic face of the rotary valve block; and an outer cover blocking the opening of the case. The outer cover is formed with a central shaft hole through which the pivot shaft passes. The outer cover is further formed with a first perforation and a second perforation corresponding to the first and second holes respectively.
Owner:HSIAO KUO MING
Power line device with directional coupler
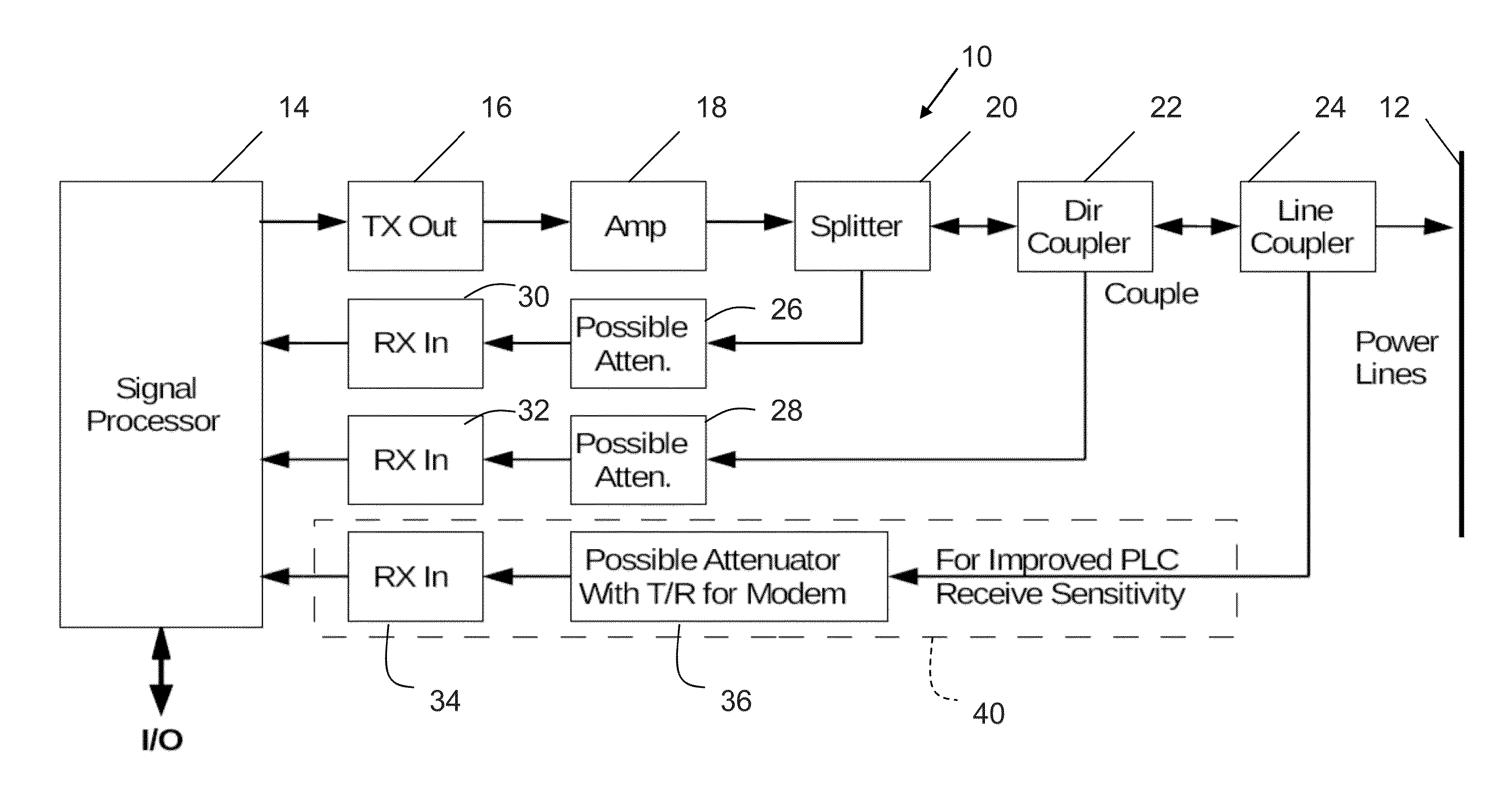
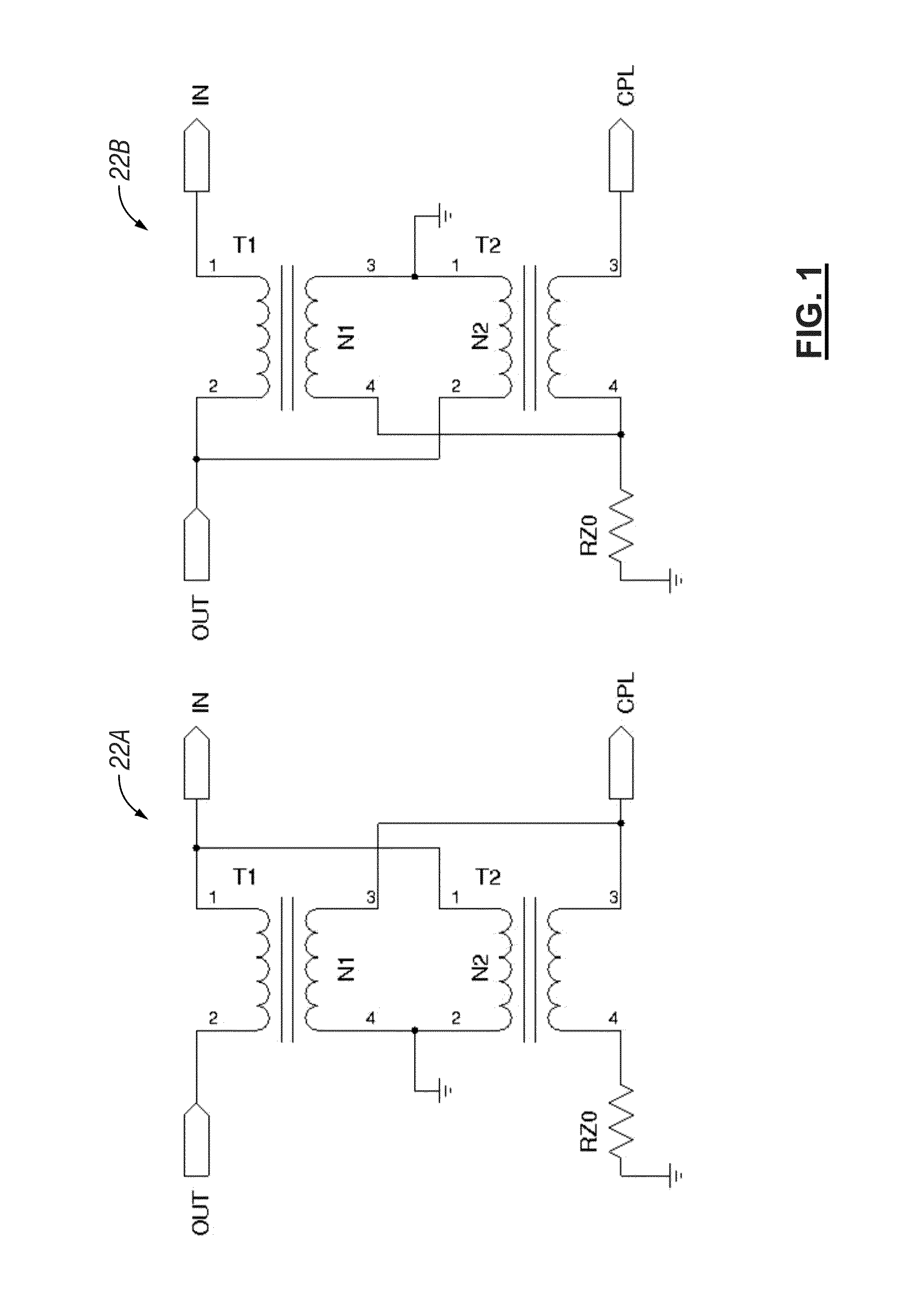
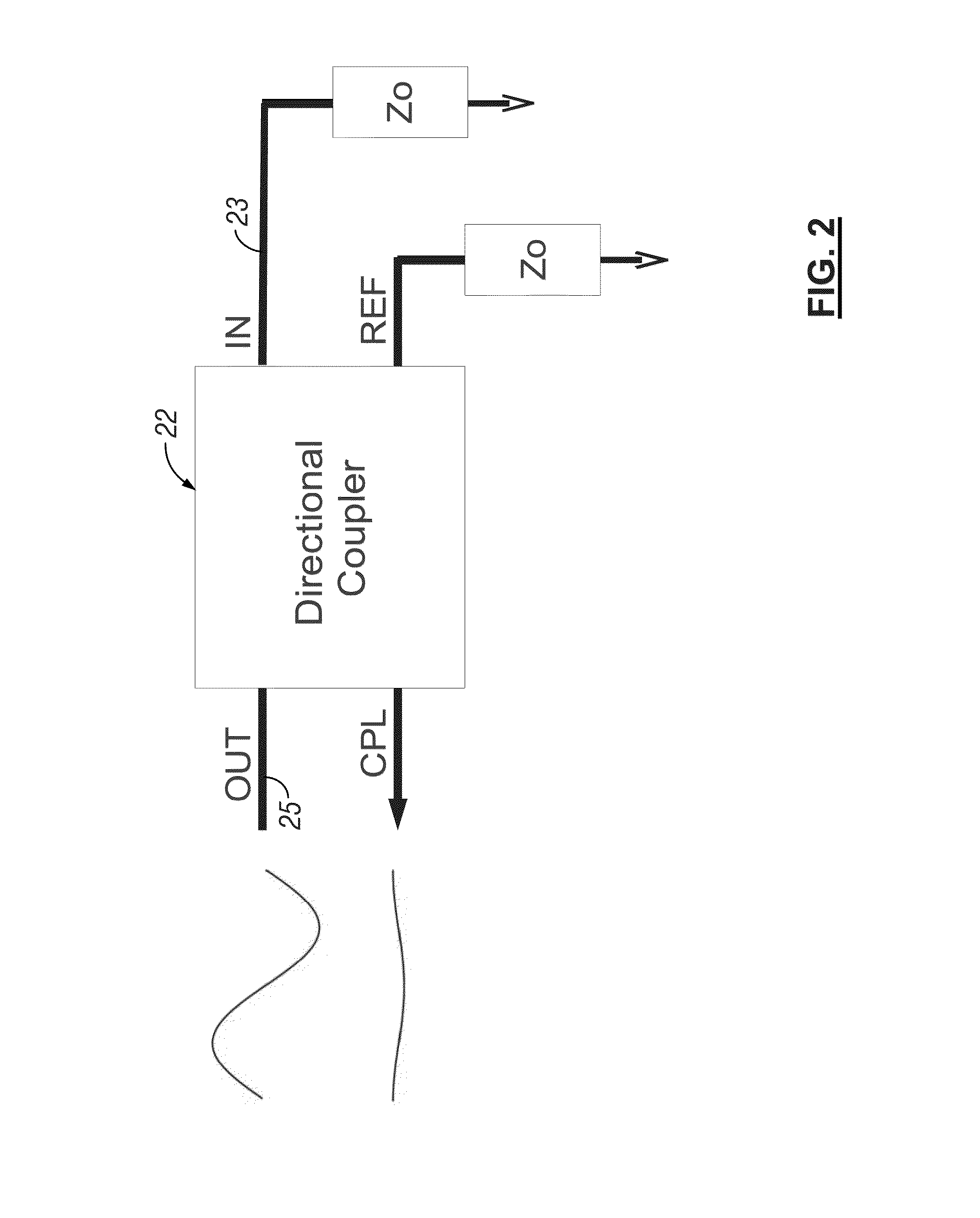
ActiveUS8989243B1ImprovedAvoids problem associated with impedance mismatchPower distribution line transmissionImproving S/N for transmission/receivingCarrier signalReceiver function
A power line carrier modem is configured for coupling to AC power lines. The power line carrier modem includes a processor, an output from the processor, a plurality of inputs to the processor, and a directional coupler operatively connected to the output, the plurality of inputs, and the AC power lines. The power line carrier modem may further include a digital-to-analog-converter operatively connected to the output from the processor. The output from the processor may be an output bus. The power line carrier modem further includes an analog-to-digital-converter operatively connected to the plurality of inputs to the processor. The power line carrier modem may be configured to perform Vector Network Analysis functions. The power line carrier modem may be configured to indicate PLC modem transmit frequencies being reflected from the AC power lines or the line coupler. The transmitter functions may be implemented in software by the processor to provide a transmit output on the output line. Receiver functions may also be implemented in software by the processor.
Owner:SOLAIRENC LLC
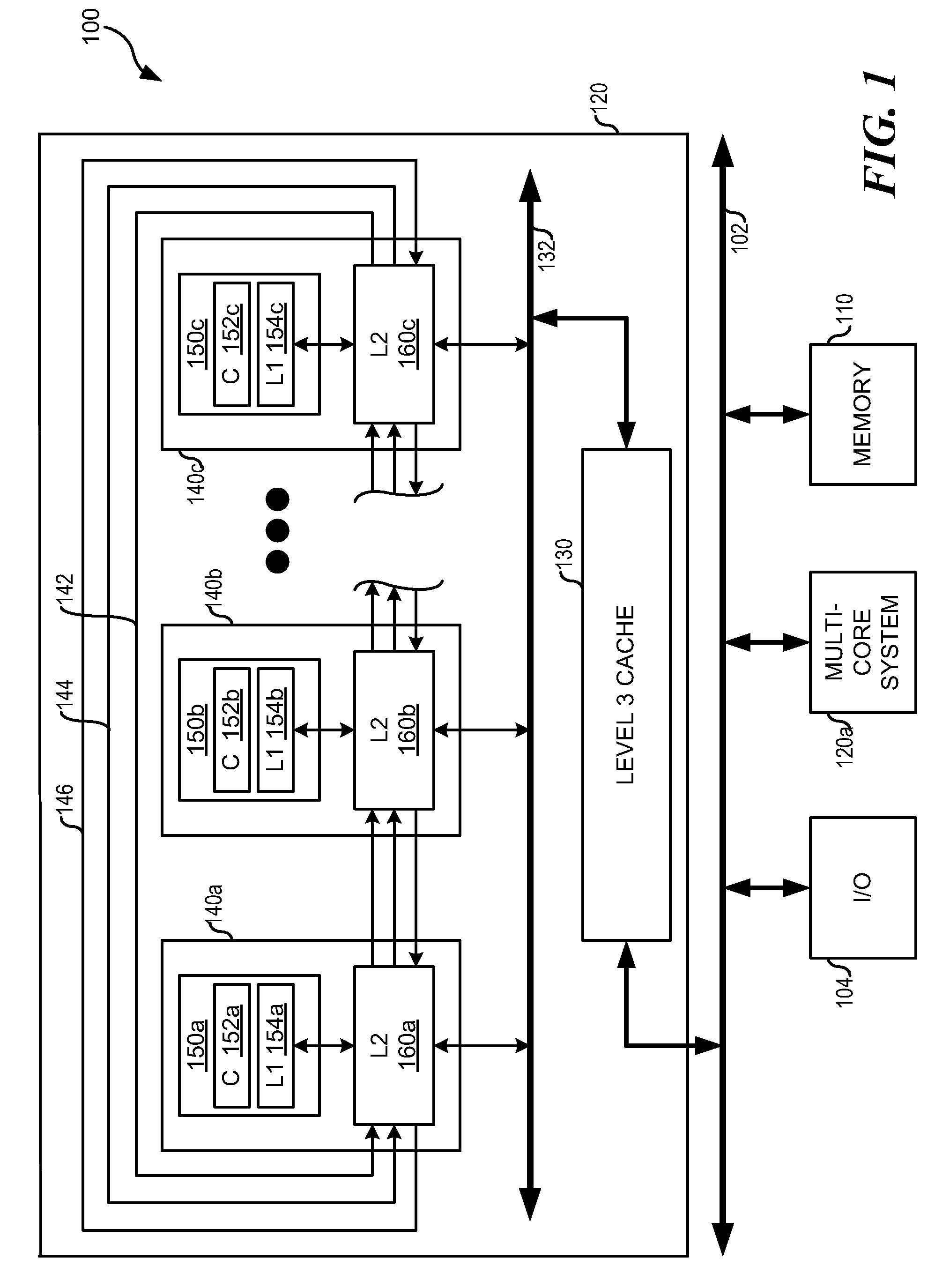
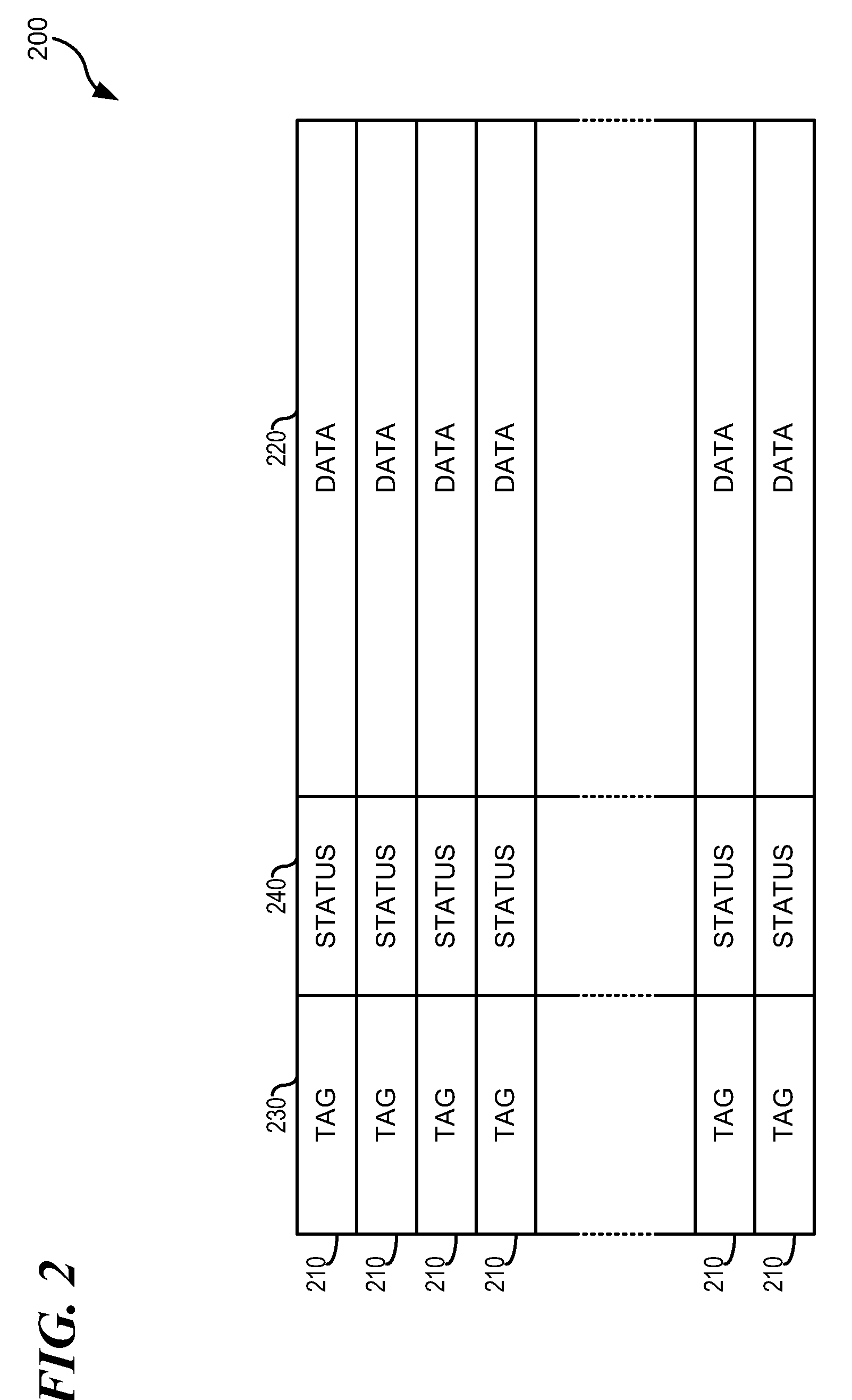
System and Method for Cache Coherency In A Multiprocessor System
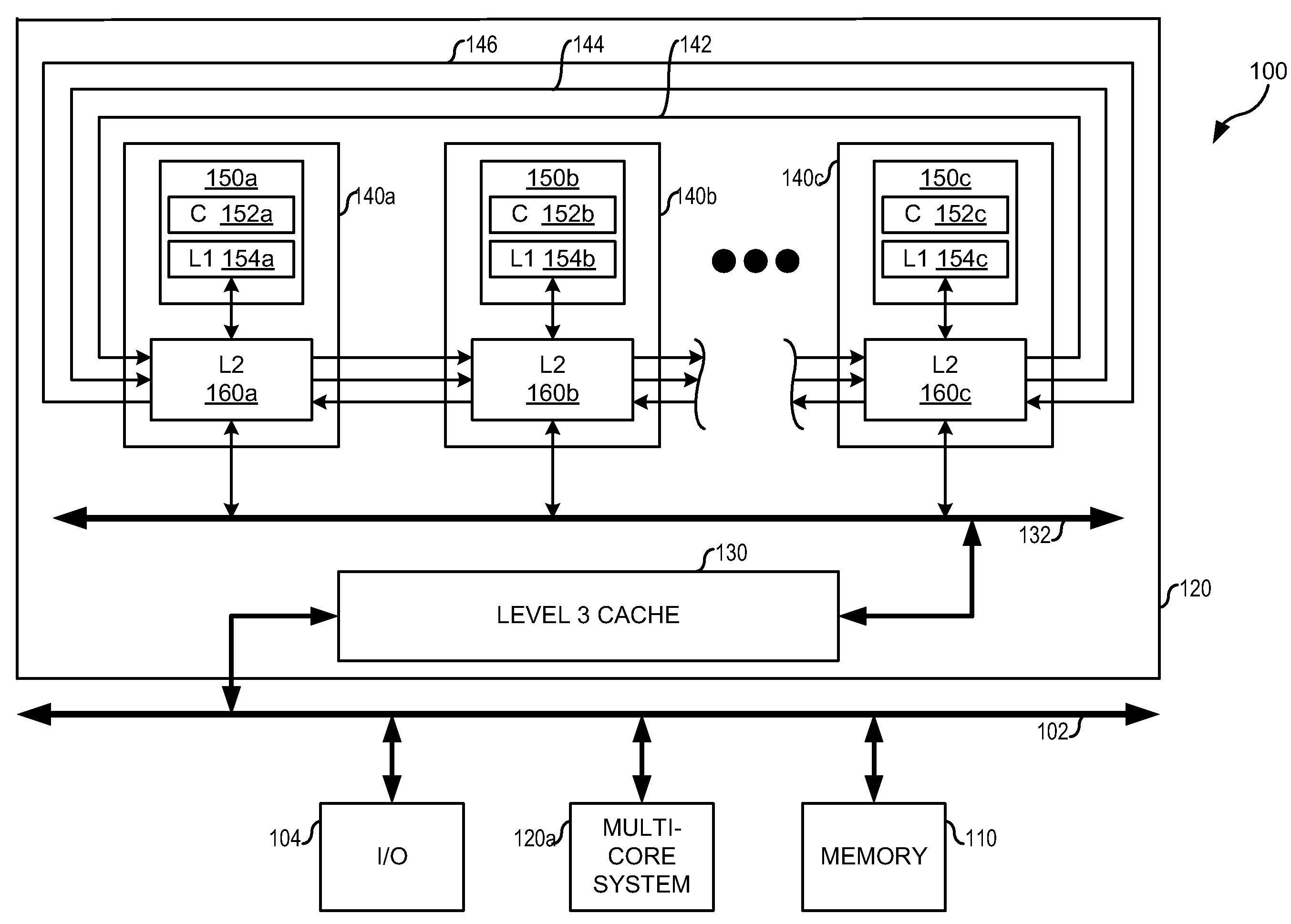
ActiveUS20090164735A1Improved cache coherency methodImprovedMemory systemsCache coherenceMulti processor
A method for maintaining cache coherency operates in a data processing system with a system memory and a plurality of processing units (PUs), each PU having a cache, and each PU coupled to at least another one of the plurality of PUs. A first PU receives a first data block for storage in a first cache of the first PU. The first PU stores the first data block in the first cache. The first PU assigns a first coherency state and a first tag to the first data block, wherein the first coherency state is one of a plurality of coherency states that indicate whether the first PU has accessed the first data block. The plurality of coherency states further indicate whether, in the event the first PU has not accessed the first data block, the first PU received the first data block from a neighboring PU.
Owner:IBM CORP
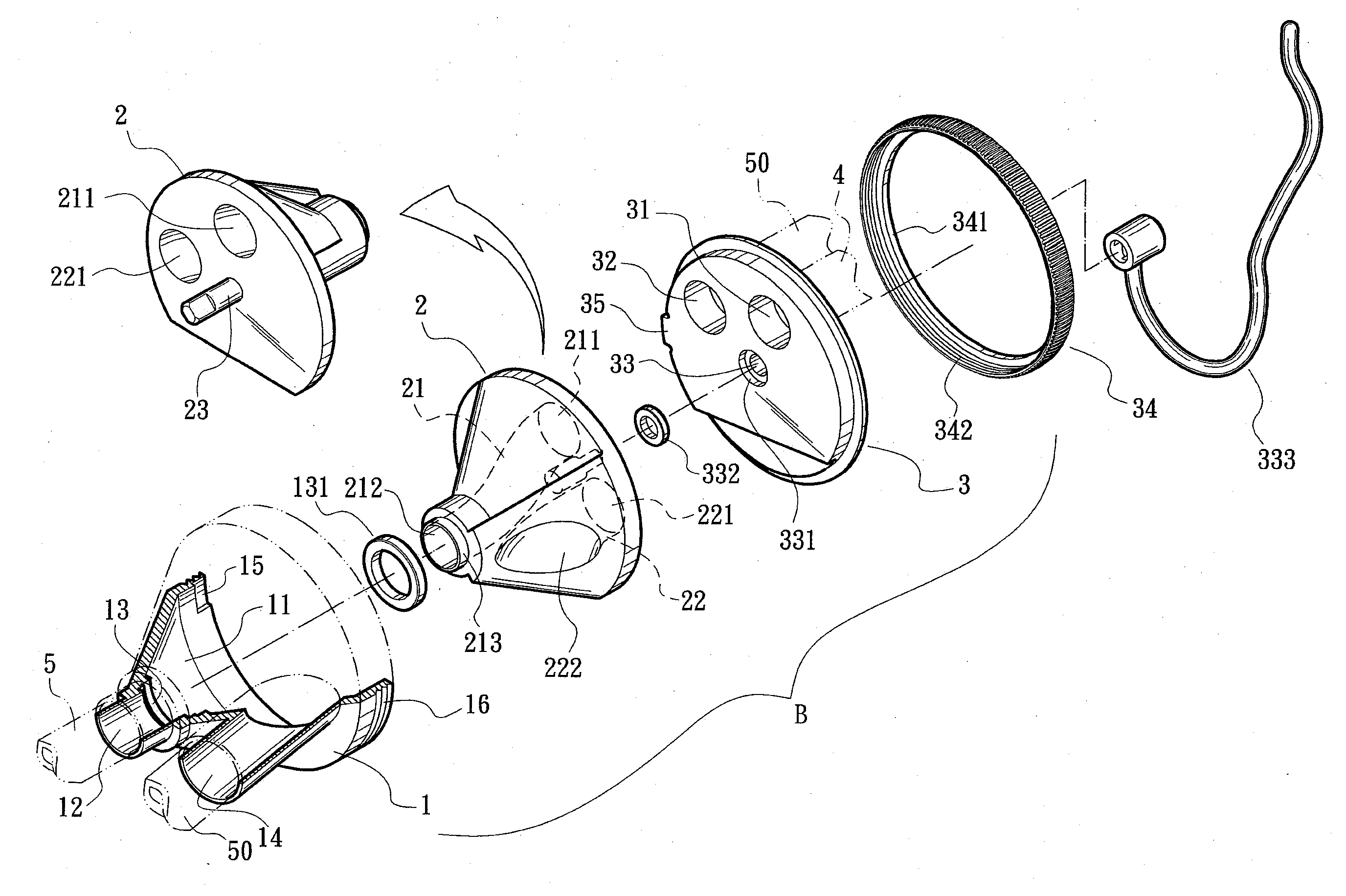
Breather filter
InactiveUS20060113236A1ImprovedAvoid contaminationDispersed particle filtrationLighting and heating apparatusMajor and minorPrimary channel
The present invention is directed to a filter for placement over a breather opening of an enclosure, such as a headlamp. The filter includes an elastomeric body having a primary channel extending from a first end to a second end of the elastomeric body, and a plurality of secondary channels extending from the first end to the second end of the elastomeric body. A cap is configured to at least partially cover the elastomeric body, the cap having an interior surface and an exterior surface. Filter material is arranged in fluid communication with the primary and secondary channels, the filter material configured to filter air flowing through the primary and secondary channels.
Owner:DONALDSON CO INC
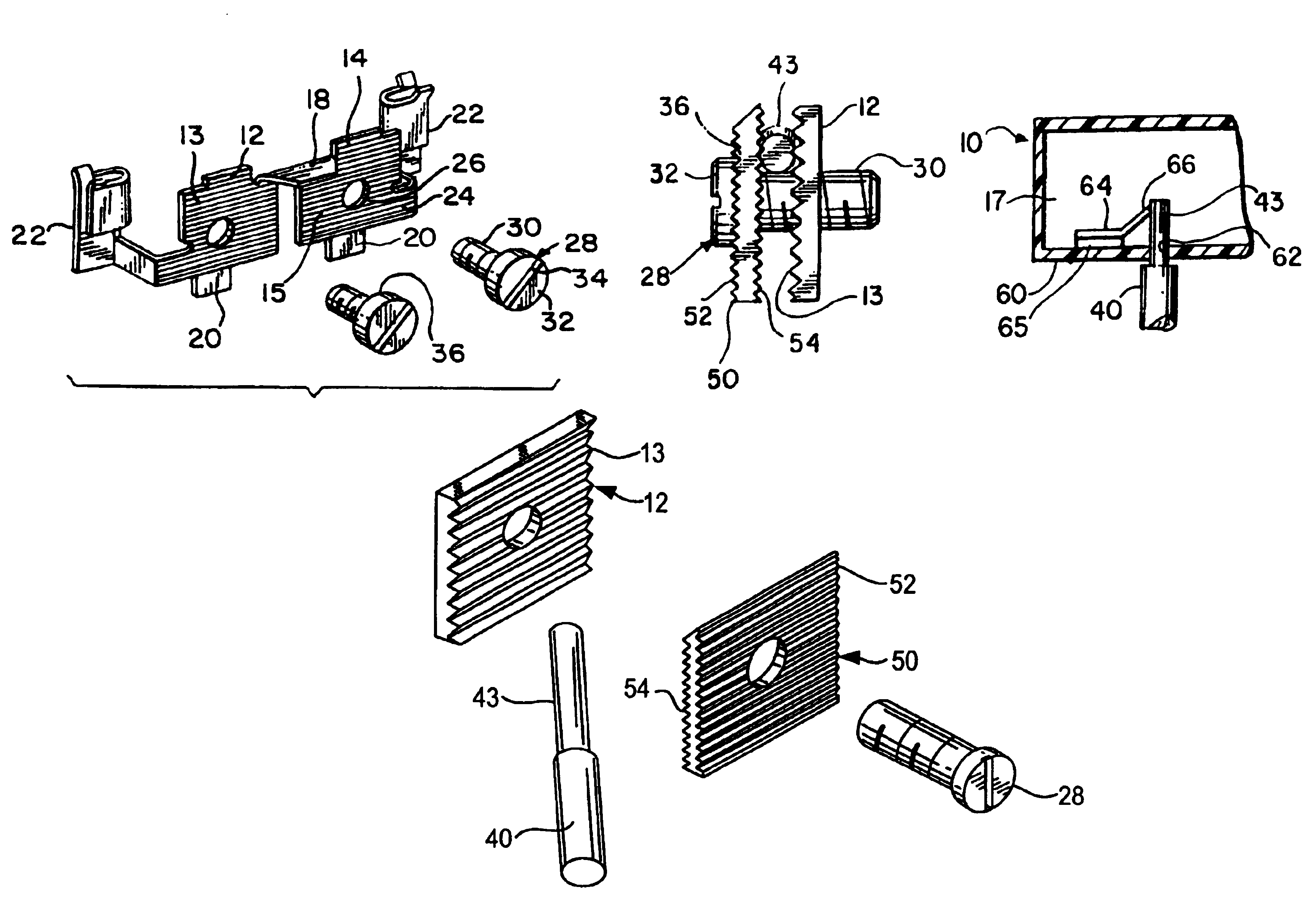
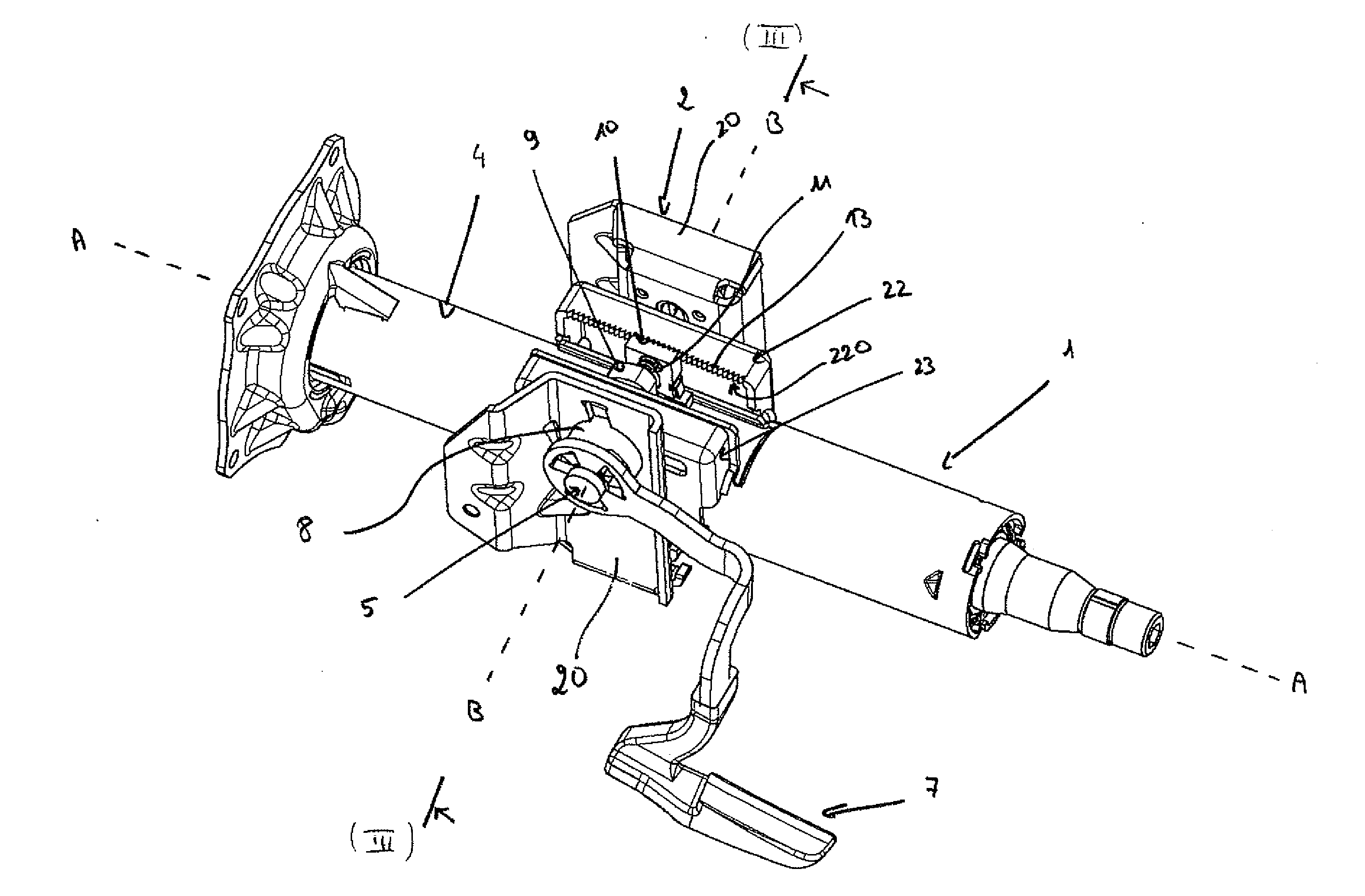
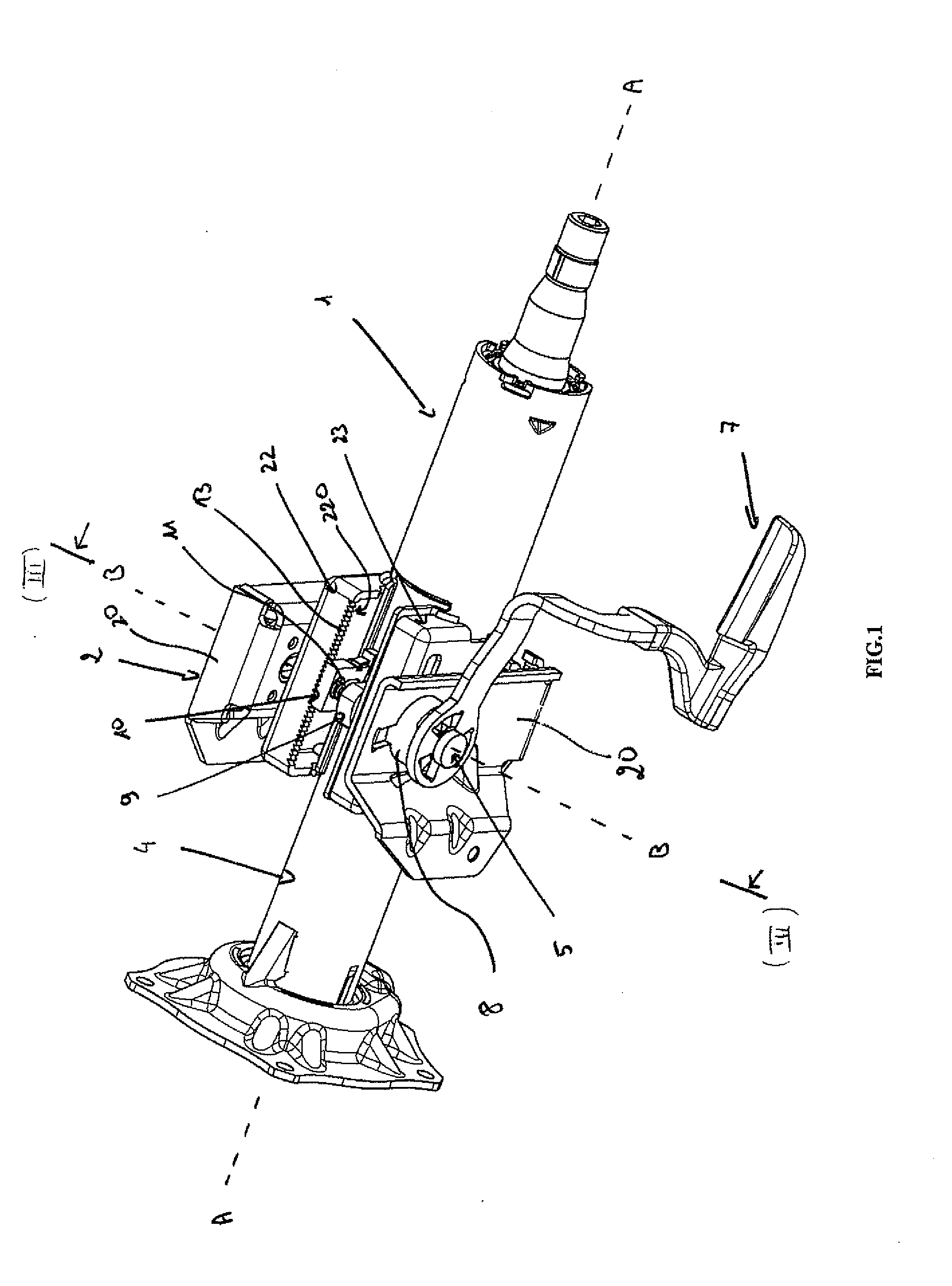
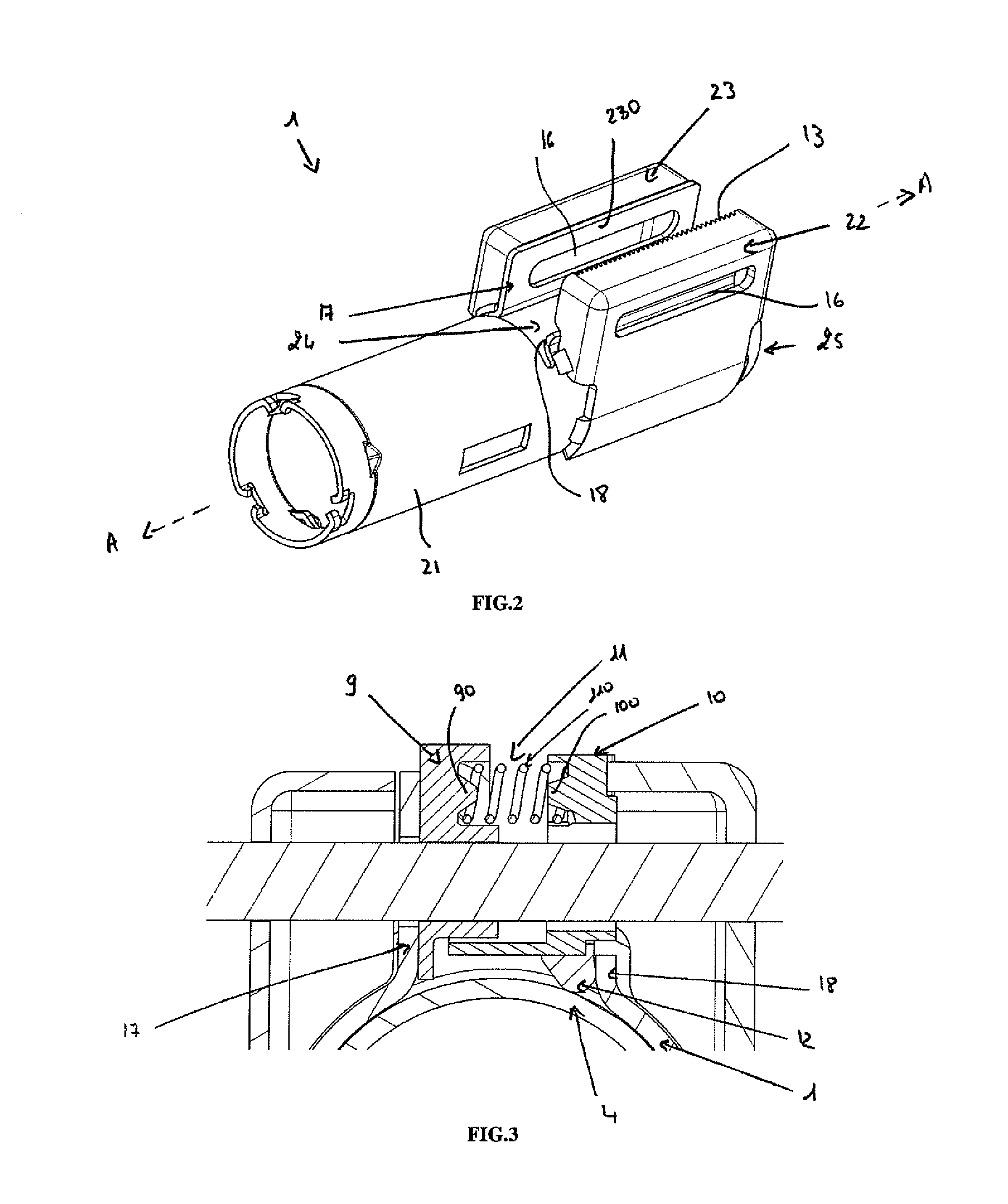
Steering column comprising an improved depth-blocking mechanism
A steering column including an upper body, two connection flanges for connecting the upper body to a support element, and a tightening and blocking device the upper body in position on an internal tube, where the tightening and blocking device includes a clamp screw extending through the flanges, a set of cams comprising a fixed cam and a movable cam mounted such that it can move freely in translation along the clamp screw and arranged so that it can bear on one of the flanges, a rack capable of cooperating with a notched arrangement provided on the other flange, and a resilient means arranged between the movable cam and the rack in order to exert a return force on the rack in the direction of the notched flange.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH AUTOMOTIVE STEERING VENDOME
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com