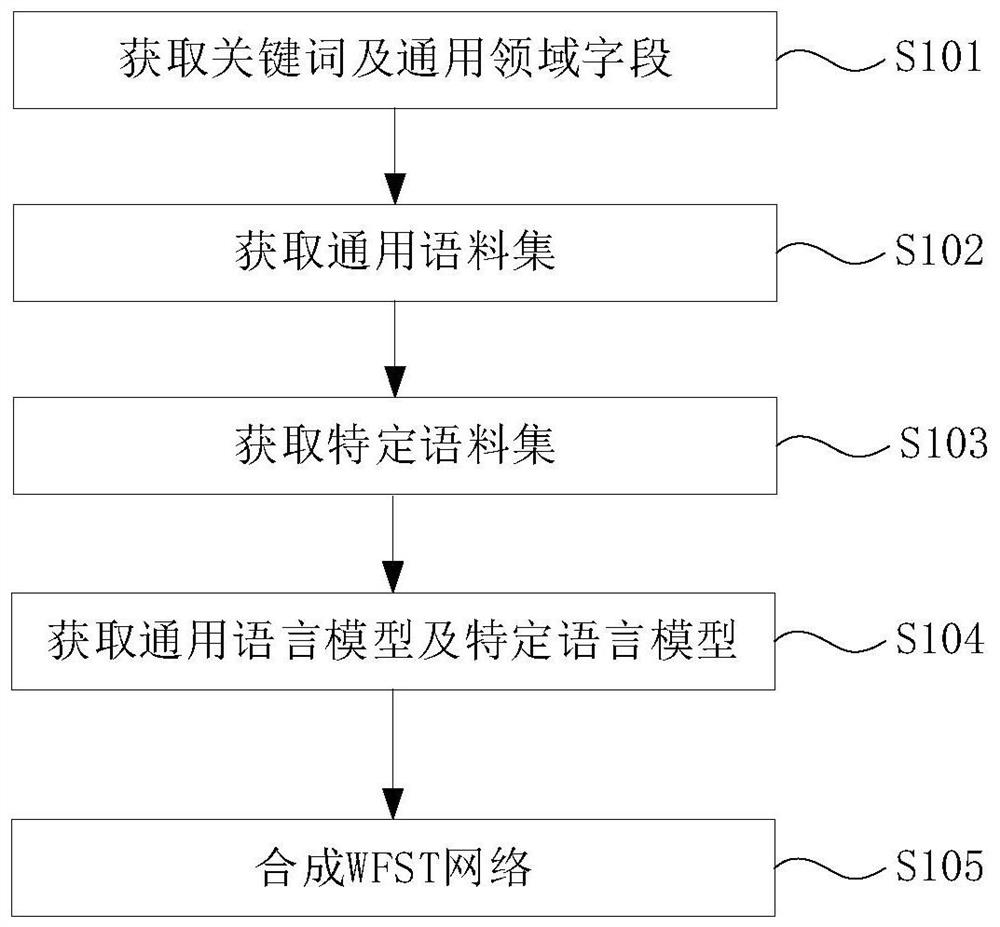
Patents
Literature
49results about How to "Shorten product cycle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Electric melting forming method of metal component
ActiveCN104526171AHigh strengthImprove toughnessLiquid surface applicatorsManufacturing heating elementsElectricityElectrical resistance and conductance
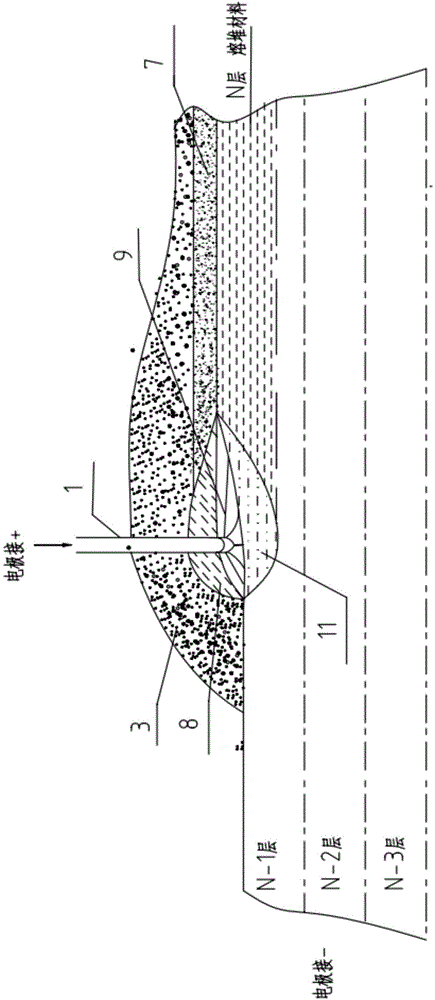
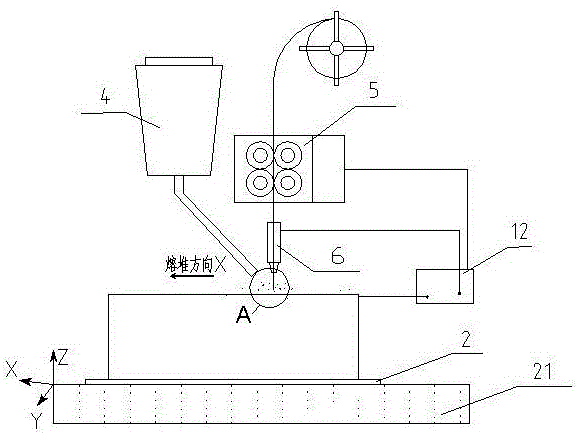
The invention provides an electric melting forming method of a metal component, which has the advantages of high efficiency, low cost and excellent mechanical performance. In the method, an electric melting head and a substrate are connected to two poles of a power supply; a raw metal wire is conveyed to the surface of the substrate by a conveying mechanism and the electric melting head in forming; under the stacking protection of granular accessories, an electric arc is generated between the raw metal wire and the substrate; a molten part is overlaid on the accessories to form a molten slag pool; current flows through the raw metal wire and the molten slag pool to form resistance heat and electroslag heat; the raw metal wire is molten under the effect of three thermal compound high-energy heat sources of electric arc heat, the resistance heat and the electroslag heatto form a local molten pool on the surface of the base material; the raw metal wire and the accessories are continuously conveyed; the relative movement of the electric melting head and the substrate is controlled by a computer according to hierarchical slicing data of the formed component to realize quick cooling and layer-by-layer condensation and accumulation of the molten pool on the substrate; and finally, the metal component with the needed shape and size is formed through layer-by-layer accumulation.
Owner:NANFANG ADDITIVE MFG TECH
Electric smelting forming method of hydrogenation reactor barrel
The invention mainly aims at providing a forming method of a hydrogenation reactor barrel. The method is efficient, low in cost and good in mechanical property. The method comprises the steps that an electric smelting head and a base material are connected to two electrodes of a power source, and in the forming process, metal raw material wires are conveyed to the surface of the base material through a conveying mechanism and the electric smelting head; under accumulation protection of granular auxiliary materials, an electric arc is generated between the raw material wires and the base material, and a molten slag pool is formed by stacking and laying the auxiliary materials on the smelting portion; current flows through the raw material wires and the molten auxiliary material slag pool to form resistance heat and electric slag heat; under the effect of three component high-energy heat sources of electric arc heat, the resistance heat and the electric slag heat, the raw material wires are molten; a local molten pool is formed on the surface of the base material, and the raw material wires and the auxiliary materials are continuously conveyed; according to layered section data of a forming component, a computer is adopted to control relative movement of the electric smelting head and the base material; and the aim that the molten pools are rapidly cooled, solidified and stacked layer by layer on the base material is achieved, and finally the hydrogenation reactor barrel is formed.
Owner:NANFANG ADDITIVE MFG TECH
Electric smelting forming method for nuclear power station pressure vessel shell
ActiveCN104526115AHigh strengthImprove toughnessAdditive manufacturing apparatusNuclear energy generationMelting tankNuclear power
The invention provides an electric smelting forming method for a nuclear power station pressure vessel shell. The method is efficient and low in cost and has the good mechanical property. The method comprises the steps that an electric smelting head and a base material are connected to two electrodes of a power source, and in the forming process, a metal raw material wire is conveyed to the surface of the base material through a conveying mechanism and the electric smelting head; under accumulation protection of a granular auxiliary material, an electric arc is generated between the raw material wire and the base material, and a molten slag pool is formed by smelting part of the accumulated laid auxiliary material; a current flows through the raw material wire and the molten auxiliary material slag pool to form resistant heat and electric slag heat; under the effect of three composite high-energy heat sources of the electric arc heat, the resistance heat and the electric slag heat, the raw material wire is smelted, and a local smelting pool is formed on the surface of the base material; the raw material wire and the auxiliary material are continuously conveyed; according to hierarchy slicing data of a forming component, a computer is adopted to control relative moving of the electric smelting head and the base material; and the aim that the smelting pool is rapidly cooled on the base material and solidified and stacked layer by layer, and finally the nuclear power station pressure vessel shell is formed is achieved.
Owner:NANFANG ADDITIVE MFG TECH
Electric smelting forming method of ultra-supercritical low-pressure rotor
ActiveCN104526113AHigh strengthImprove toughnessArc welding apparatusMetal working apparatusMelting tankElectricity
The invention provides an electric smelting forming method of an ultra-supercritical low-pressure rotor. The method is efficient and low in cost and has the good mechanical property. An electric smelting head and a base material are connected to two electrodes of a power source; in the forming process, a metal raw material wire is conveyed to the surface of the base material through a conveying mechanism and the electric smelting head; under the accumulation protection of granular auxiliary materials, an electric arc is generated between the raw material wire and the base material, and the auxiliary materials are molten to form a melting slag pool; under the composite high-energy heat source effect of the electric arc heat, resistance heat and electric slag heat, the raw material wire is molten, and the raw material wire and the auxiliary materials are continuously conveyed; according to layered slicing data of a forming component, relative moving of the electric smelting head and the base material is controlled, and rapid cooling and layer-by-layer solidification and accumulation of the smelting pool on the base material are achieved; layer-by-layer accumulation is carried out to form a rotor component, and the ultra-supercritical low-pressure rotor is made of 3.5 percent NiCrMoV materials; and the content of C of the metal raw material wire used by an electric smelting device ranges from 0.20 percent to 0.30 percent, the content of C of the materials manufactured through electric smelting ranges from 0.10 percent to 0.18 percent, and the grain size ranges from 7 levels to 10 levels.
Owner:NANFANG ADDITIVE MFG TECH
Electric smelting forming method for ultra-supercritical high intermediate pressure rotor
ActiveCN104526170AGuaranteed performanceAchieve Layered FormingWelding apparatusMelting tankElectricity
The invention provides an electric smelting forming method for an ultra-supercritical high intermediate pressure rotor. The method is efficient and low in cost and has the good mechanical property. The method comprises the steps that an electric smelting head and a base material are connected to two electrodes of a power source; in the forming process, metal raw material wires are conveyed to the surface of the base material through a conveying mechanism and the electric smelting head; under accumulation protection of granular auxiliary materials, an electric arc is generated between the raw material wires and the base material, and the auxiliary materials are accumulated and laid on a smelting portion to form a melting slag pool; currents flow through the raw material wires and the melting auxiliary material slag pool to form resistance heat and electric slag heat; under the effect of three heat composite high-energy heat sources of electric arc heat, resistance heat and electric slag heat, the raw material wires are smelted, and a local smelting pool is formed on the surface of the base material; the raw material wires and the auxiliary materials are continuously conveyed, and according to layered section data of a forming component, a computer is adopted to control relative moving between the electric smelting head and the base material; and rapid cooling layer-by-layer solidification accumulation of the smelting pools on the base material is achieved, and finally layer-by-layer accumulation is carried out to form a rotor component.
Owner:NANFANG ADDITIVE MFG TECH
Electric smelting forming method of CAP1400 main steam pipe penetration piece
The invention provides an electric smelting forming method of a CAP1400 main steam pipe penetration piece which is efficient, low in cost and excellent in mechanical properties. According to the method, an electric smelting head and a substrate are connected to the two poles of a power source; while forming, a metal raw material wire is conveyed to the surface of the substrate by a conveying mechanism and the electric smelting head; under the protection of the accumulation of granular accessories, the electric arc is generated between the raw material wire and the substrate to melt partial surfacing accessories to form a molten slag pool; the current flows through the raw material wire and the molten slag pool to form resistance heat and electro-slag heat; under the actions of the three composite high-energy heat sources, namely the electric arc heat, the resistance heat and the electro-slag heat, the raw material wire is melted to form a local molten pool on the surface of the substrate; the raw material wire and the accessories are fed continuously; the relative movement of the electric smelting head and the substrate is controlled by a computer according to the stratified slicing data of a formed part so as to realize quick cooling and layer-by-layer solidification accumulation of the molten pool on the substrate, and finally, the main steam pipe penetration piece is formed by virtue of layer-by-layer accumulation.
Owner:NANFANG ADDITIVE MFG TECH
Electric melting forming method of nuclear power conventional island low-voltage rotor
ActiveCN104526172AGuaranteed performanceAchieve Layered FormingWelding apparatusMelting tankElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention provides an electric melting forming method of a nuclear power conventional island low-voltage rotor, which has high efficiency, low cost and excellent mechanical performance. The method comprises the following steps: an electric melting head and a substrate are connected to two poles of a power supply; a raw metal wire is sent to the surface of the substrate by a conveying mechanism and the electric melting head; under the stacking protection of particle accessories, an electric arc is generated between the raw metal wire and the substrate for melting the accessories to form a molten slag pool; the raw metal wire is molten under the effect of three thermal compounding high-energy heat sources of electric arc heat, resistance heat and electroslag heat to form a molten pool; the raw metal wire and the accessories are continuously conveyed; the relative movement of the electric melting head and the substrate is controlled; quick cooling and layer-by-layer solidification and accumulation of the molten pool on the substrate are realized; finally, the nuclear power conventional island low-voltage rotor is formed through layer-by-layer accumulation; the rotor adopts a 30 Cr2Ni4MoV material; the raw metal wire prepared through electric melting contains 0.20-0.28% of C; the material prepared through electric melting contains 0.10-0.18% of C; and the grain size is 7-10 grade.
Owner:NANFANG ADDITIVE MFG TECH
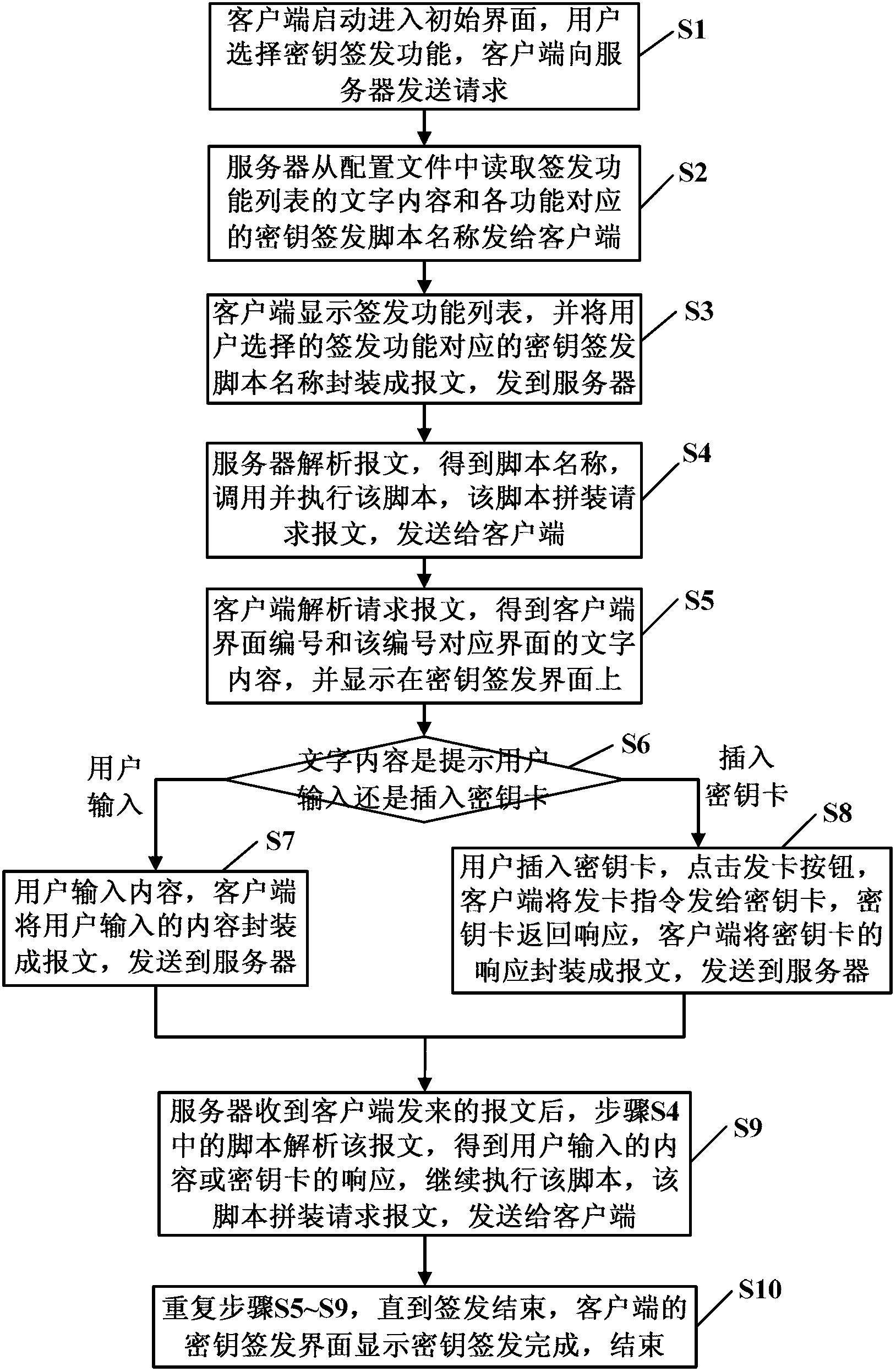
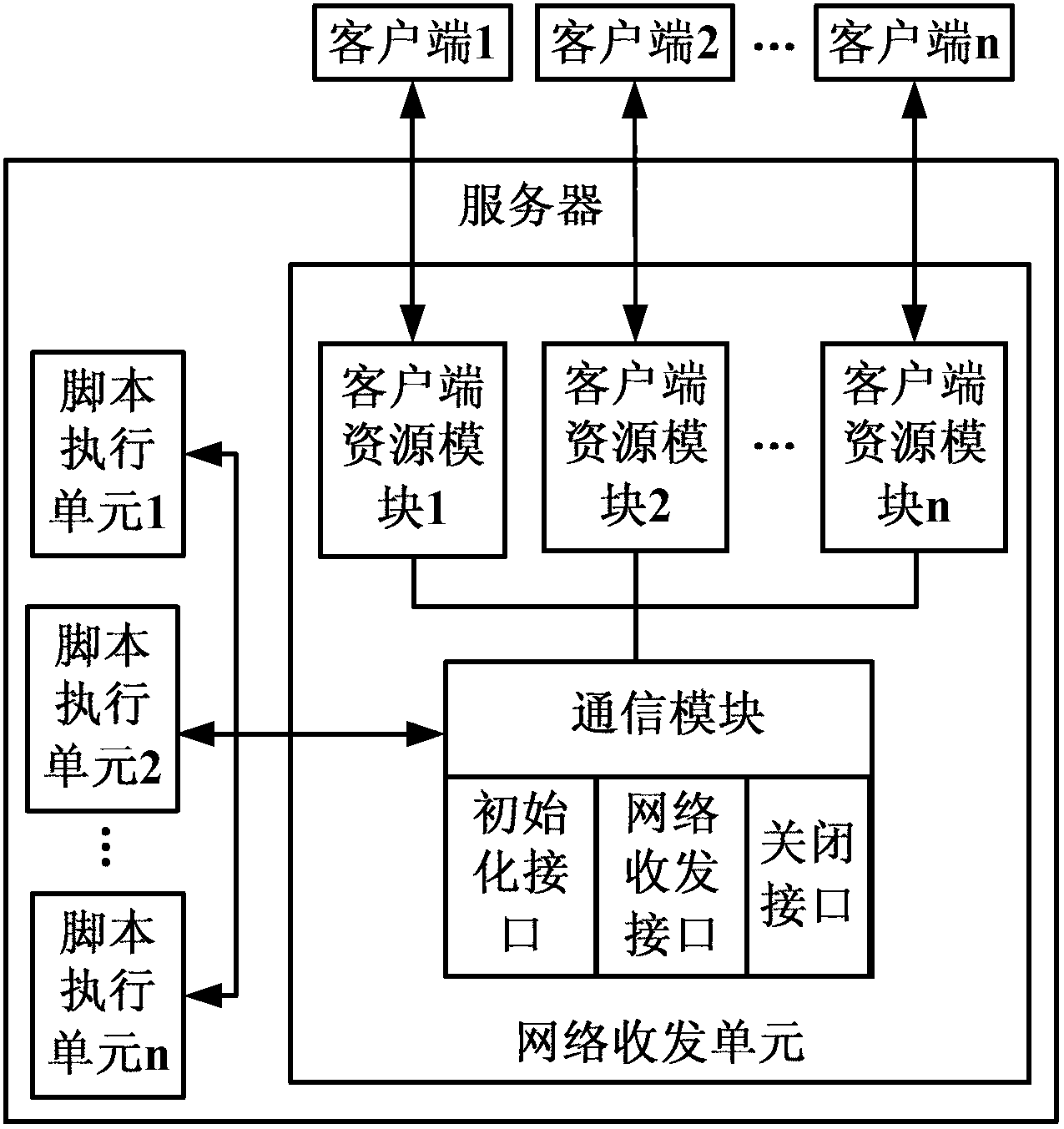
Method and system used for dynamic key network issue and interface control and based on script
ActiveCN103067173AShorten product cycleSave labor costUser identity/authority verificationKey issuesSoftware engineering
The invention discloses a method and a system used for dynamic key network issue and interface control and based on a script, and relates to the field of financing institution network transaction safety. According to the method and the system used for the dynamic key network issue and the interface control and based on the script, multi-client-end concurrent access is supported, a multi-client-end interface layout is pre-configured, file names and layout files of the multi-client-end interface layout are stored in a server, according to a Python script, a dynamic control secret key issue process is configured, an interface display layout is called, verbal content of the interface display is configured, a user interface is dynamically generated according to the process, the universal functions in the issue process are divided into small functional modules which can be recombined and replaced, the method and the system can be applied to various business application scenarios. Once a business application scenario and an industry application scenario are changed, the control script of a server end is just required to be modified, the issue process and the interface display of a client end can be changed, and a client-end interface is not required to be redeveloped. A product cycle is shortened, cost of manpower and time is saved, and maintenance is convenient to achieve.
Owner:WUHAN TIANYU INFORMATION IND
Electric melting molding method of nuclear power conventional island low-pressure rotor
InactiveCN106271141AGuaranteed performanceAchieve Layered FormingWelding apparatusMelting tankHigh energy
The invention provides an electric melting molding method of a nuclear power conventional island low-pressure rotor, which includes the following procedures: using high energy heat sources which is composited by electric arc heat, resistance heat and electro slag heat to fuse raw metal wire materials transported continuously, solidifying and accumulating the base materials layer by layer to mold and to make rotor components; using computers to control relative move of the electric melting heads and the base materials, thus achieving that a molten pool cools quickly on the base materials and solidifies and accumulates layer by layer, and finally accumulating the molded rotor components layer by layer. The material of the rotor is 30Cr2Ni4MoV, the content of C in the raw metal wire materials used for preparing electric melting is 0.20-0.28 %, the content of C in the materials made by electric melting is 0.10-0.18 % and the grain size is 7-10 levels. The electric melting molding method of a nuclear power conventional island low-pressure rotor has the advantages of high efficiency, low costs and good mechanical properties.
Owner:NANFANG ADDITIVE MFG TECH
Novel preparing method of multi-metal compounded bar with irregular cross section shape
A novel preparing method of a multi-metal compounded bar with an irregular cross section shape is provided. The method comprises following processes: remodeling a base metal substrate according to product specifications; removing dirt on the inner and outer surfaces of a solid substrate and a hollow auxiliary material; assembling the solid substrate and the hollow auxiliary material; reducing caliber of ends of the solid substrate and the hollow auxiliary material; cleaning surface of the substrate tube material, and coating; performing cold drawing and forming of double metals or multi metals; and preforming fine alignment. Composite materials with different cross-section shapes can be prepared by the method. A cladding process between metals is emitted. Cold drawing and forming are directly preformed after the surface of an outer auxiliary material of a substrate-auxiliary material composite is coated with the coating having lubrication and protection functions, thus effectively increasing the production efficiency and reducing the production cost.
Owner:BAOJI SHENGKE NEW METAL
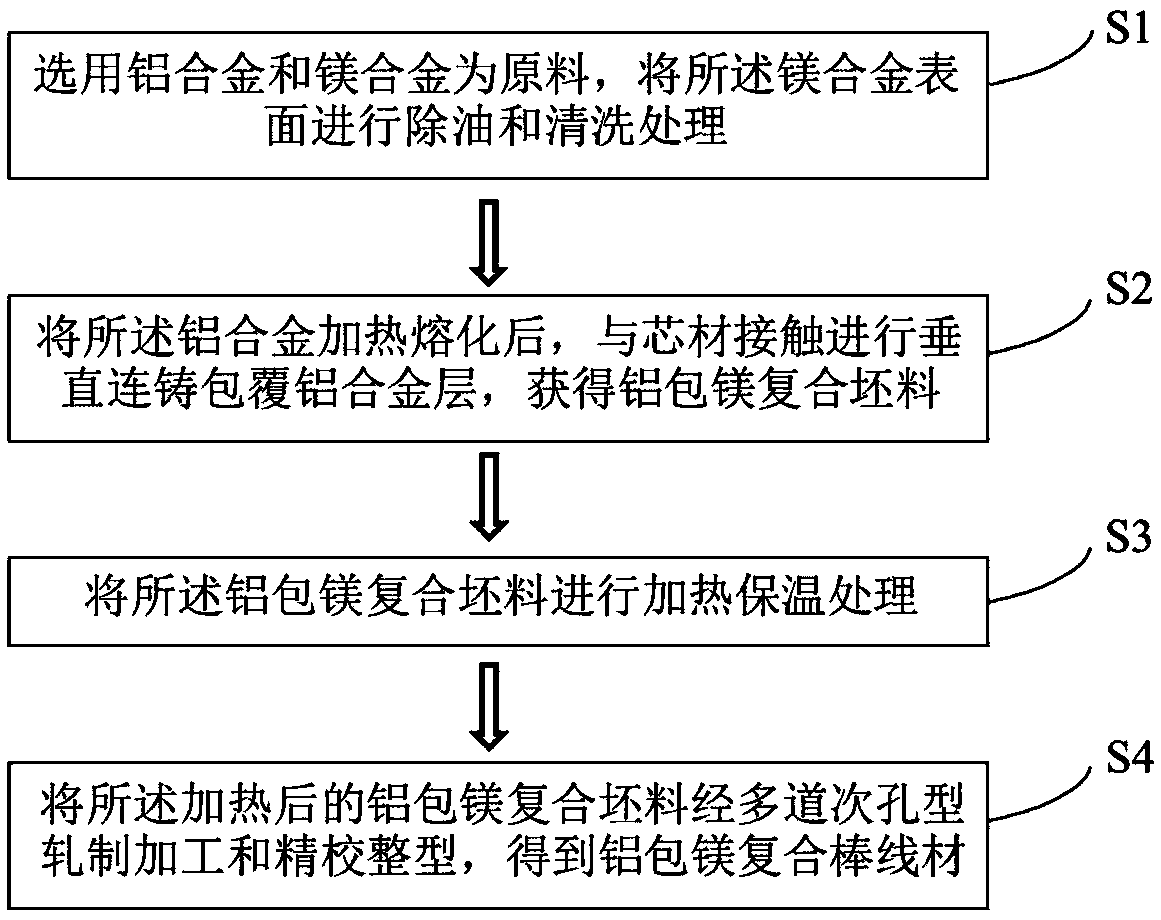
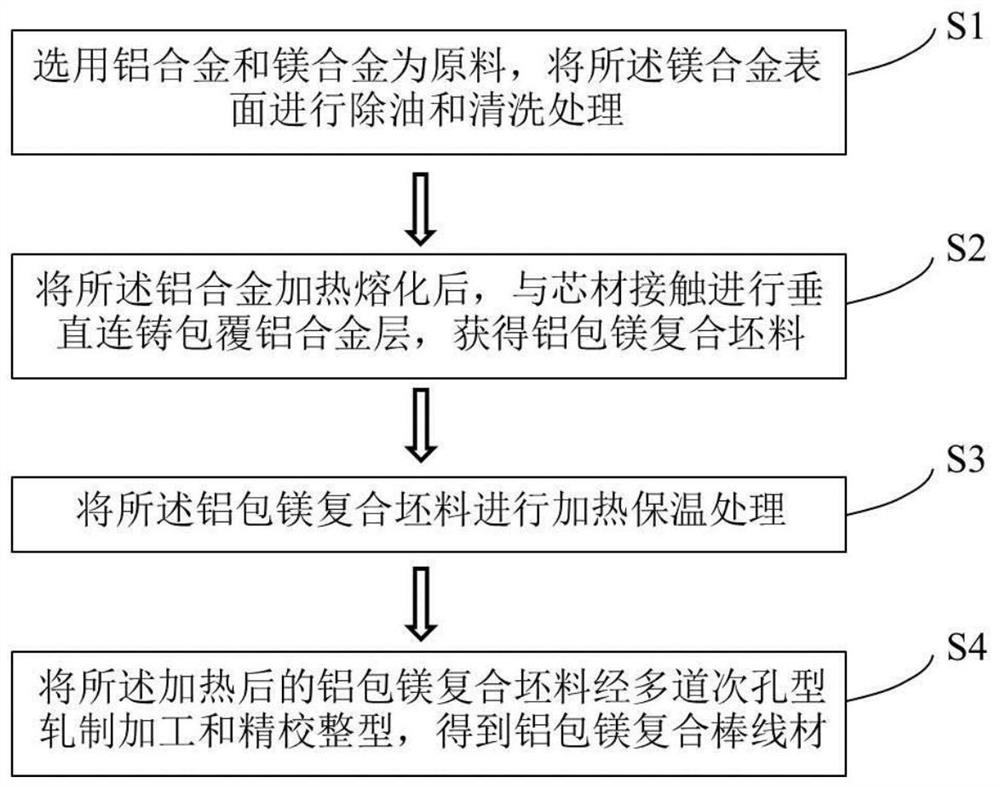
Preparation method of aluminum-coated magnesium composite rod wire rod
The invention provides a preparation method of an aluminum-coated magnesium composite rod wire rod. The preparation method comprises the following steps that the surface of a magnesium alloy core material is cleaned, and then is placed in the central position of a crystallizer and is fixedly connected with a traction device; after an aluminum alloy is heated and melted, the aluminum alloy is poured into a casting inner cavity of the crystallizer, aluminum alloy liquid is in contact with the magnesium alloy core material, the aluminum alloy layer is formed by cooling and solidifying the surfaceof the core material, and meanwhile, the traction device is started, and the composite blank is pulled out from the lower part of the crystallizer, so that continuous coating can be realized; the size ratio of the inner diameter of the casting inner cavity of the crystallizer to the inner diameter of the magnesium alloy core material is 1.5-2.3:1; and after the aluminum-coated magnesium compositeblank is heated, continuous multi-pass rolling is carried out, and the aluminum-clad magnesium composite bar materials with different section sizes and section shapes are prepared by adjusting the rolling pass and the shape of rolling holes. The material has good tissue performance, and is low in cost, high in efficiency and wide in applicability.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Quick-change die for forming wire
InactiveCN103331374AReduce resource development wasteShorten product cycleShaping toolsProduction rateEngineering
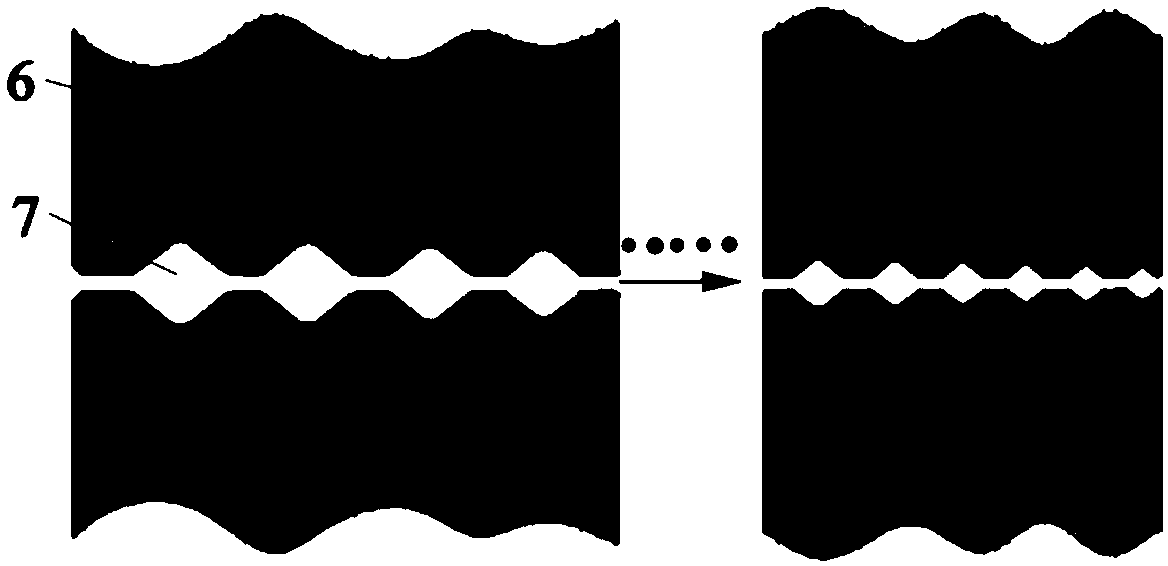
The invention provides a quick-change die for forming a wire, which includes an upper die base (1), an upper die plate (2), a pressing plate (3), a backing support (4), a lower die plate (5), a stripping plate (6), a lower die base (7), a downward flanging cutter block (8) and an upward flanging cutter block (9), wherein the upper die plate (2) is embedded in the upper die base (1) and is fixed in the upper die base (1); the backing support (4) and the lower die plate (5) are embedded in the lower die base (7); the stripping plate (6) moves up and down along the lower die plate (5); the upward flanging cutter block (9) and the downward flanging cutter block (8) are both of quick change type. The quick-change die for forming the wire is high in production rate and low in cost, can realize universality easily, and is particularly suitable for mass production in batches.
Owner:NANJING HUIDE MACHINERY
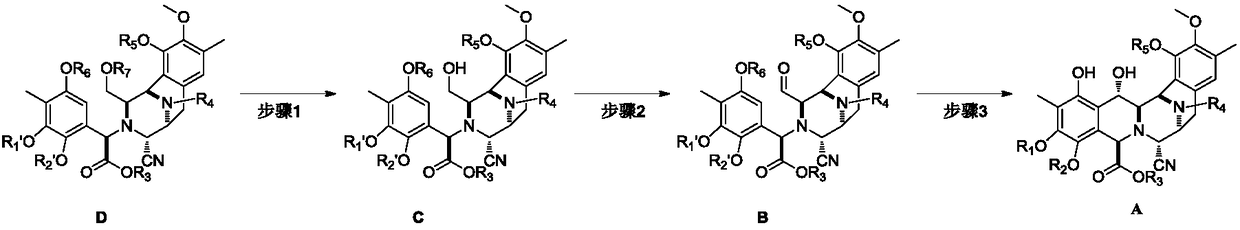
Intermediate product of trabectedin as well as preparation method and application thereof
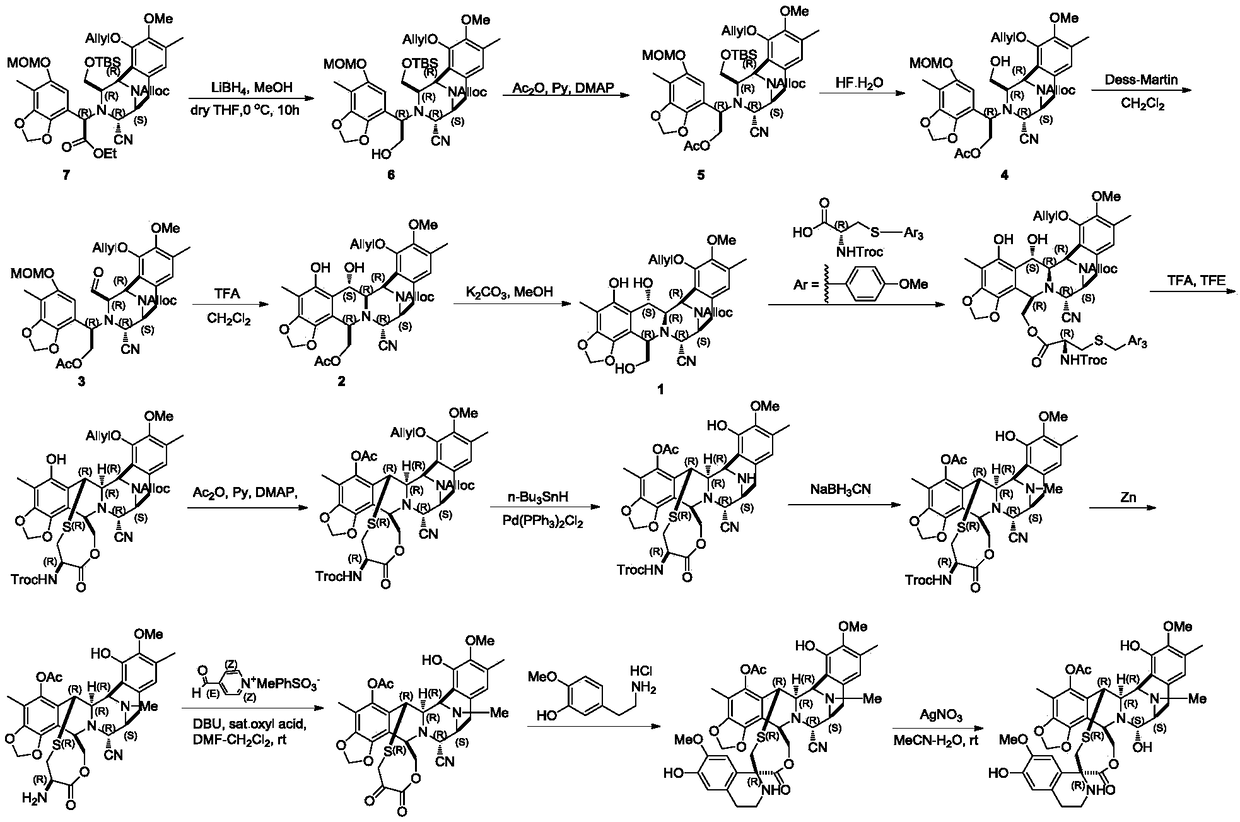
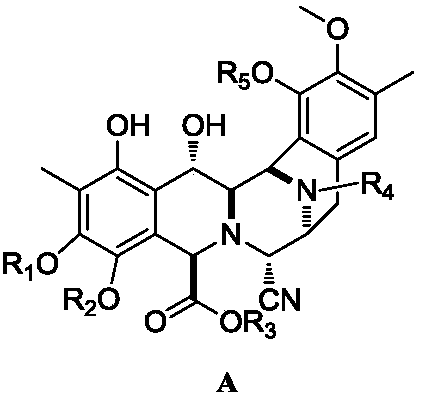
ActiveCN108276408ASimple and fast operationEasy to zoom inOrganic chemistryCompound aCombinatorial chemistry
The invention relates to a key intermediate product compound A for preparing trabectedin and a method for preparing the compound A by using a compound D. According to the method disclosed by the invention, three-step reaction can be continuously operated, and individual separation and purification are not needed, and therefore, an operation is simple and convenient. The invention also relates to amethod for preparing a compound E through reduction of the compound A and application of the intermediate product. The method has the advantages of controllability, simpleness and convenience in operation and stable yield. The formula (1) is shown in the description.
Owner:SHANGHAI HAOYUAN CHEMEXPRESS
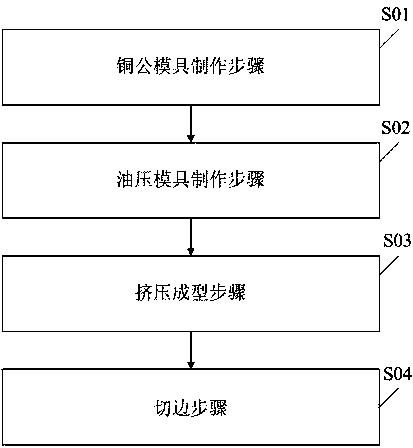
Manufacturing technology of glasses legs
ActiveCN104741481AShorten product cycleIncrease production capacityShaping toolsManufacturing technologyEyewear
The invention relates to the field of glasses manufacturing and provides a manufacturing technology of glasses legs. The manufacturing technology comprises the first step of copper male die manufacturing, the second step of oil-pressure die manufacturing, the third step of extrusion forming and the fourth step of edge cutting. A merging principle is adopted in the manufacturing technology of the glasses legs, a fine machining edge is arranged on a lower fine plate of a lower edge cutting die, and a rough machining edge is arranged on a lower rough plate of the lower edge cutting die. Thus, rough machining and fine machining for the glasses legs can be completed at the same time in the edge cutting process of the glasses legs, an original technological process is effectively simplified, and the product cycle is shortened. Meanwhile, one set of equipment and one operator can be omitted. Besides, productivity is improved by a half, and standard performance is more stable.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRAND OPTICAL
Hydrogenation reactor barrel electric-smelting forming method
The invention provides a hydrogenation reactor barrel electric-smelting forming method, which comprises the steps of adopting a high-energy heat source compounded by electric arc heat, resistance heat and electroslag heat for melting a continuously conveyed metal raw material wire, and solidifying, stacking and forming layer by layer on a base material to manufacture a metal component; and adopting a computer for controlling the relative motion of an electric smelting head and the base material, quickly cooling a molten bath and solidifying and stacking layer by layer on the base material, and finally forming a hydrogenation reactor barrel. The hydrogenation reactor barrel electric-smelting forming method provided by the invention has the advantages of high efficiency, low cost, favorable mechanical property and the like.
Owner:NANFANG ADDITIVE MFG TECH
Electric smelting forming method for nuclear power plant evaporator barrel body
The invention provides an electric smelting forming method for a nuclear power plant evaporator barrel body. According to the electric smelting forming method, a high energy heat source formed by combining electric arc heat, electric resistance heat and electric slag heat is used for smelting continuously conveyed metal raw material wires, and metal components are formed and manufactured through layer-by-layer solidification and accumulation on a substrate; and a computer is used for controlling the relative movement of an electric smelting head and the substrate, rapid cooling and layer-by-layer solidification and accumulation of a molten pool on the substrate are realized, and finally the nuclear power plant evaporator barrel body is formed. The electric smelting forming method for the nuclear power plant evaporator barrel body has the advantages of high efficiency, low cost, good mechanical performance and the like.
Owner:NANFANG ADDITIVE MFG TECH
CAP 1400 main steam pipe penetration assembly electric smelting forming method
The invention discloses a CAP 1400 main steam pipe penetration assembly electric smelting forming method. Through a heating source of high energy which comprises arc heat, resistance heat and electro slag heat, metal wires transported continuously are smelted, the smelted product is solidified and accumulated layer by layer on a base material to be made into shaped metal components; according to layered section data of the shaped components and through relative movement between an electric smelting head controlled by a computer and the base material, a molten pool is fast cooled, and solidified and accumulated layer by layer on the base material, and the CAP 1400 main steam pipe penetration assembly are formed finally. The CAP 1400 main steam pipe penetration assembly has the advantages of high efficiency, low cost, good mechanical property and the like.
Owner:NANFANG ADDITIVE MFG TECH
Sweet-scented osmanthus screen weaving branch healing method
InactiveCN105961164AShorten product cycleExpand application formGrowth substratesCulture mediaOsmanthusHormone
The invention relates to a sweet-scented osmanthus screen weaving branch healing method. The method includes the following steps that firstly, a sweet-scented osmanthus variety is selected; secondly, sweet-scented osmanthus seedlings are cultivated; thirdly, sweet-scented osmanthus is planted; fourthly, the period from April to November every year is selected for weaving; fifthly, weaving is conducted, wherein rhombic gaps formed by weaving branches are uniform in size; sixthly, the branches are healed, wherein the contact portion of every two branches is peeled by the depth 1 / 5 of the diameter of a tree stem, hormone is sprayed on the wound portion, after hormone is completely absorbed, the wound portion is bound and fixed with cloth strips, and hormone is sprayed once every other month; seventhly, maintenance is conducted after weaving. According to the sweet-scented osmanthus screen weaving branch healing method, the screen weaving branches are healed, so that the sweet-scented osmanthus styling product cycle is shortened, the application forms of the sweet-scented osmanthus seedlings are widened, and the method plays a practical role in development of sweet-scented osmanthus.
Owner:HANGZHOU LANDSCAPING
Cylindrical cavity charging pressing, vacuum pumping and screwing sealing integrated device
InactiveCN105691708AImprove working conditionsImprove labor productivityPackaging by pressurising/gasifyingPackaging automatic controlVacuum pumpingControl system
The invention discloses a cylindrical cavity charging pressing, vacuum pumping and screwing sealing integrated device. The cylindrical cavity charging pressing, vacuum pumping and screwing sealing integrated device consists of a control system, a vacuum pump, a vacuum pumping part and a pressing and screwing part; by the vacuum pumping part, the inside of a cylindrical cavity has vacuum degree in a charging process and in the end; and the pressing and screwing part is used for pressing materials placed in the cylindrical cavity, after charging is finished, a blanking cover at the tail end is screwed and sealed, and therefore, a charging process is finished. A PMAC+ industrial personal computer is used in the control system, the vacuum pumping part and the pressing and screwing part are controlled, and independent operations of different mechanisms are realized as needed. The vacuum pump is positioned outside the device, and two air channels are led out from the vacuum pump, and are respectively connected to an end effector through a first electromagnetic valve and connected to a vacuum sealing cover through a second electromagnetic valve. After the first electromagnetic valve is switched on, the tail end of the end effector generates negative pressure to adsorb materials to be charged. A screwing pin stretches and retracts through a telescopic cylinder, and is matched with a lead screw to fulfill a screwing function.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
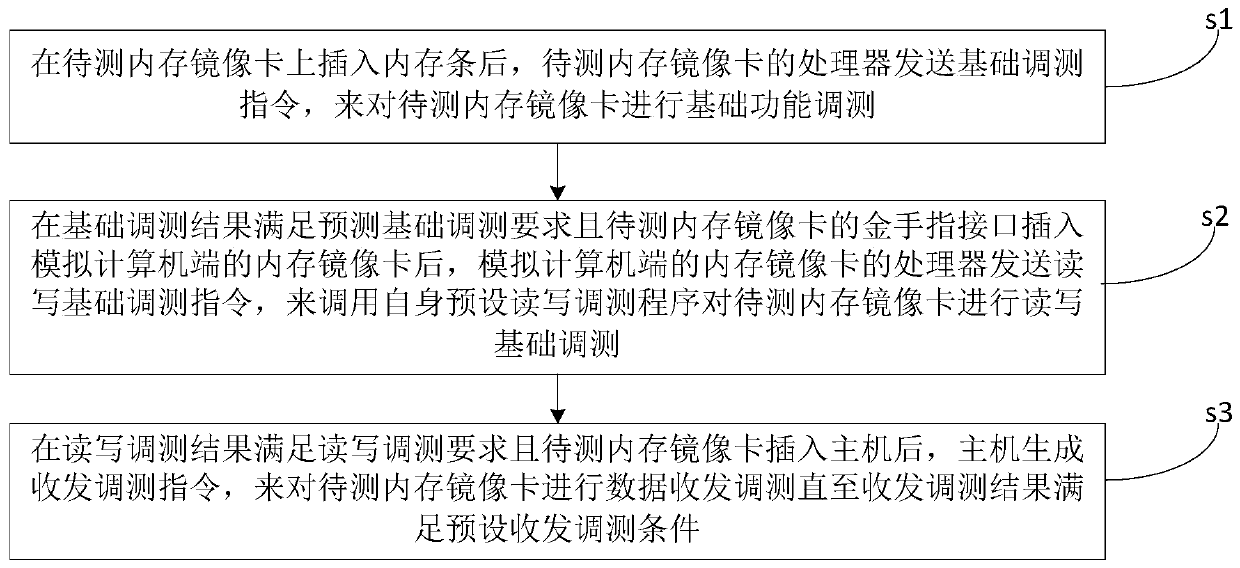
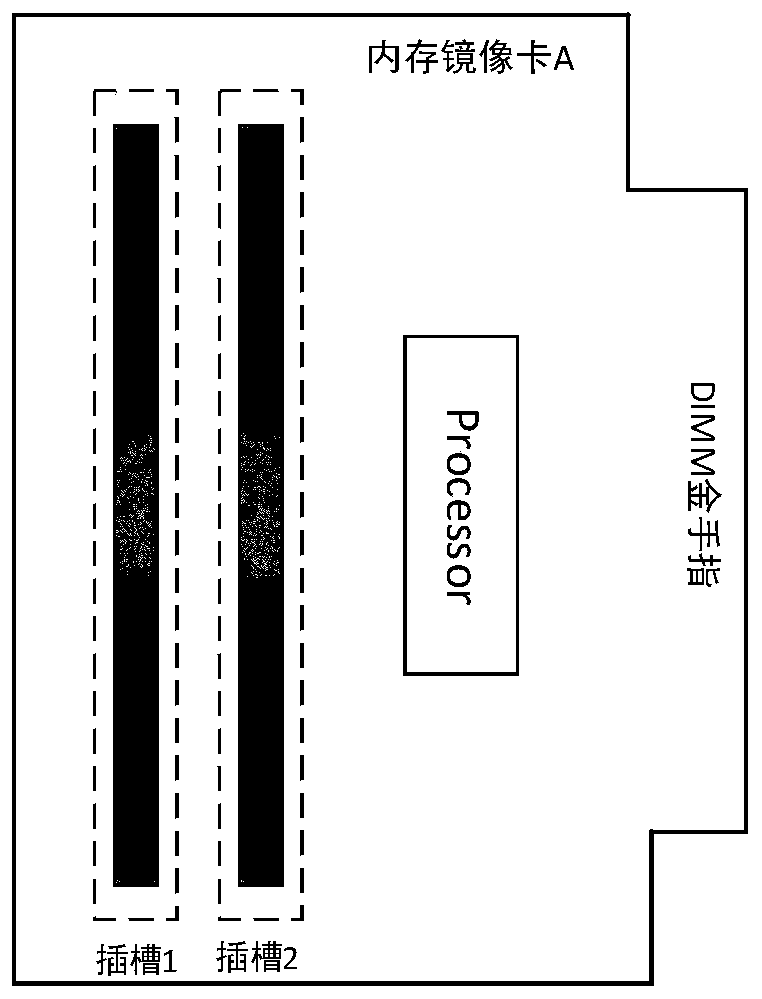
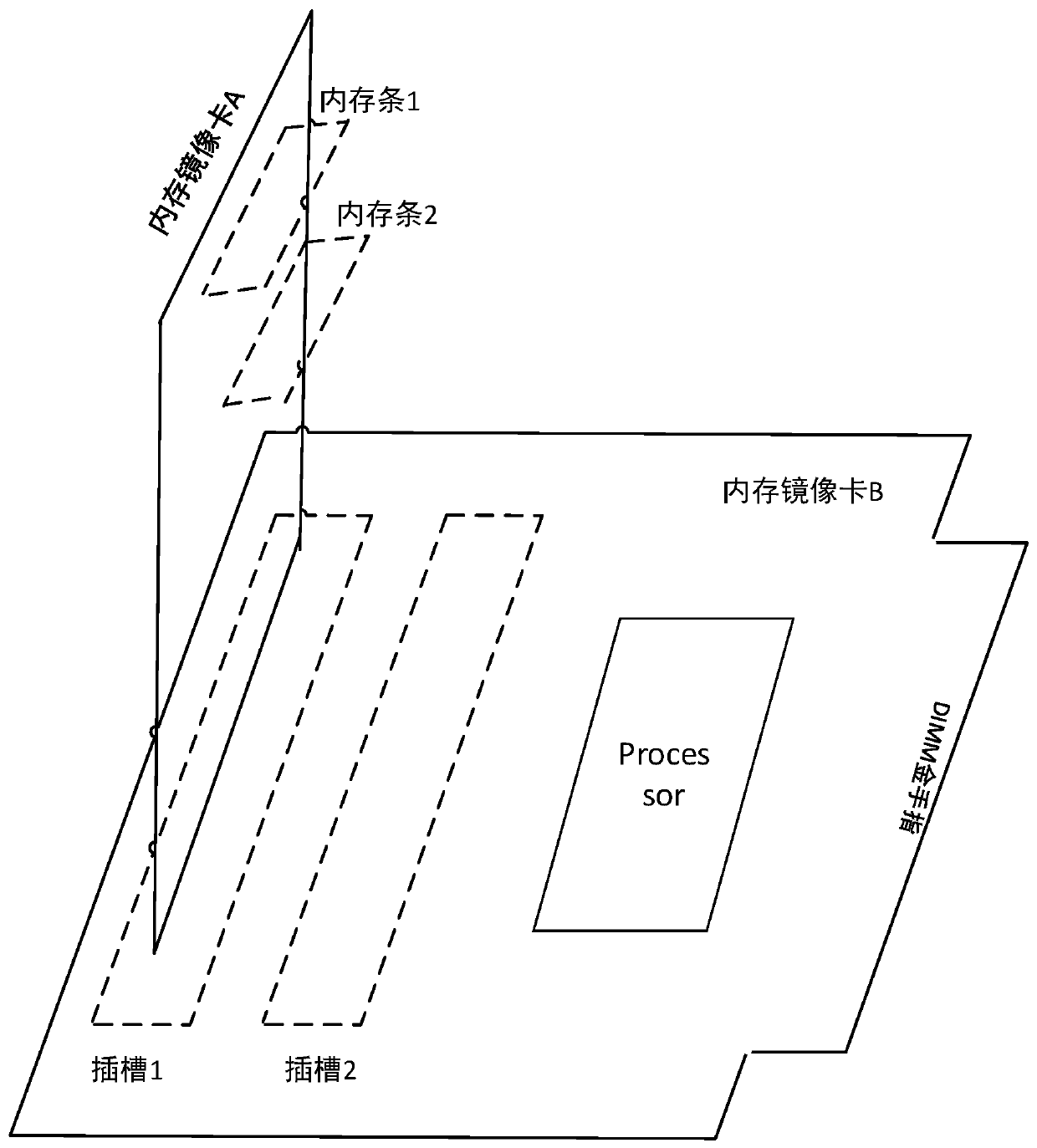
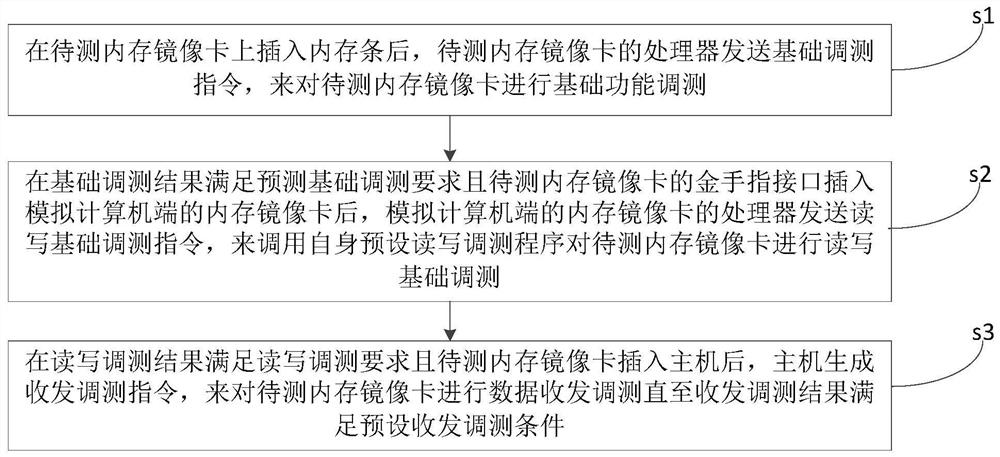
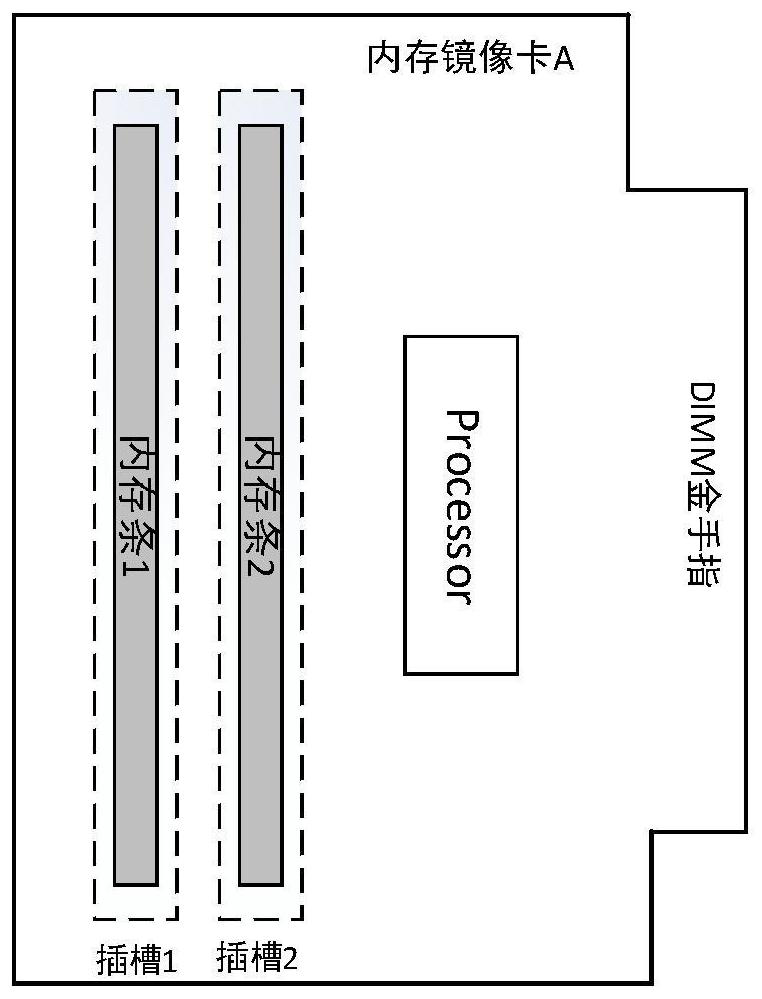
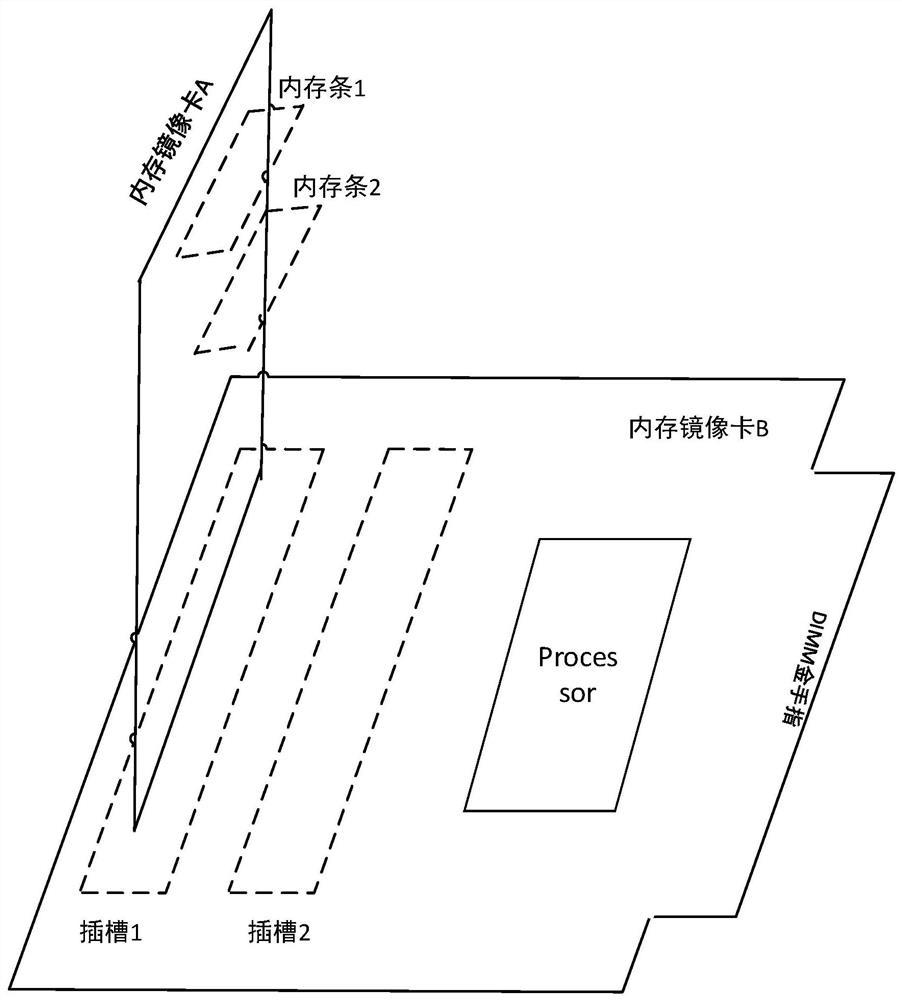
A memory mirror image card debugging method and system
ActiveCN109710480AQuick debuggingQuickly locate faultsDetecting faulty computer hardwareComputer hardwareAnalog computer
The invention discloses a memory mirror image card debugging method and system, and the method comprises the steps: enabling a processor of a to-be-tested memory mirror image card to send a basic debugging instruction to carry out the basic function debugging of the to-be-tested memory mirror image card after a memory bank is inserted into the to-be-tested memory mirror image card; after the basicdebugging result meets the prediction basic debugging requirement and the golden finger interface of the memory mirror image card to be tested is inserted into the memory mirror image card of the analog computer end; a processor of the memory mirror image card of the simulation computer end sends a read-write basic debugging instruction to call a self-preset read-write debugging program to carryout read-write basic debugging on the memory mirror image card to be tested; and after the read-write debugging result meets the read-write debugging requirement and the to-be-tested memory mirror image card is inserted into the host, the host generates a transceiving debugging instruction to perform data transceiving debugging on the to-be-tested memory mirror image card until the transceiving debugging result meets a preset transceiving debugging condition. The test process can be set according to requirements, the limitation is small, and the test reliability is higher after the host is inserted subsequently.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU YUNHAI INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Aluminum heat radiating module of LED (Light Emitting Diode)
InactiveCN103438409AImprove cooling effectReduce thermal resistancePoint-like light sourceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectricityHeat conducting
The invention provides an aluminum heat radiating module of an LED (Light Emitting Diode). The aluminum heat radiating module of the LED comprises an aluminum heat radiator, an LED chip and a common PCB (Printed circuit board), wherein circuit bonding pads which correspond to two electrodes of the LED chip are arranged on an electricity conducting layer of the common PCB; a heat conducting face is arranged on the aluminum heat radiator; a concave camber for the arrangement of the common PCB is arranged in a position near the heat conducting face; the common PCB board is arranged inside the concave camber of the heat radiator; the insulating face of the LED chip is adhered onto a corresponding part of the heat conducting face of the aluminum heat radiator by adopting bonding glue; the two electrodes of the LED chip and the two circuit bonding pads on the common PCB are correspondingly connected by electricity conducting wires. The aluminum heat radiating module of the LED provided by the invention is convenient to manufacture and has a good heat radiation effect.
Owner:FUJIAN YDJ LIGHT
Method, system and platform for visual generation of speech recognition network
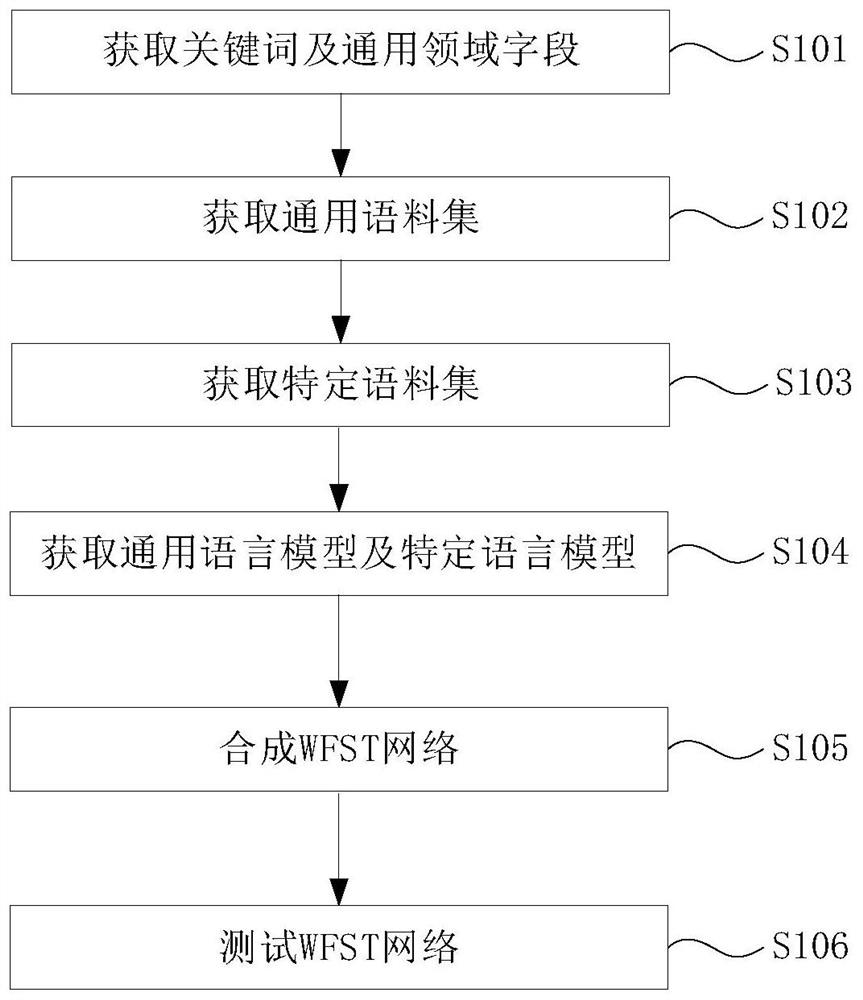
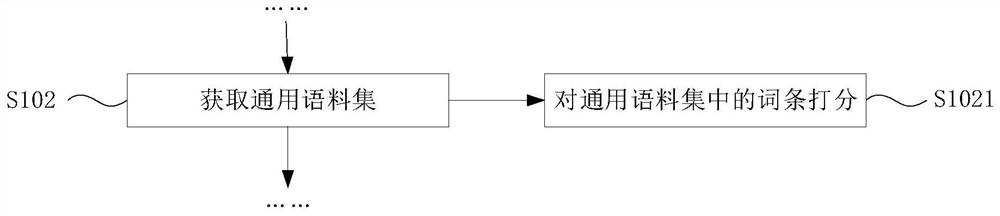
ActiveCN110427459BIncrease training speedImprove accuracySemantic analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionInteraction interfaceEngineering
The invention discloses a method for generating visualization of a speech recognition network, and the method includes: receiving keywords through a human-computer interaction interface. The current domain field is selected from a plurality of preset general domain fields, and each general domain field corresponds to a plurality of preset crawlers and corresponds to a plurality of preset web crawling pages. Get a general corpus. Get a specific corpus. Train the general corpus to obtain the general language model and the specific language model. After the WFST speech recognition network of the general language model and the WFST speech recognition network of the specific language model are connected in parallel, combined with the acoustic model and pronunciation dictionary, the WFST speech recognition network is synthesized through combination, determinization, and minimization operations. By configuring the system on the same platform, the training speed of the language model is accelerated, the product cycle is shortened, the labor consumption is shortened, and the labor cost is saved. At the same time, through the combination of general language model network and specific language model, the accuracy and efficiency of language recognition can be improved.
Owner:AISPEECH CO LTD
A memory mirroring card debugging method and system thereof
ActiveCN109710480BQuick debuggingQuickly locate faultsDetecting faulty computer hardwareComputer hardwareComputer architecture
The invention discloses a memory mirroring card debugging method and system thereof, comprising: after inserting a memory bar into the memory mirroring card to be tested, the processor of the memory mirroring card to be tested sends basic commissioning instructions to perform basic functions of the memory mirroring card to be tested Commissioning: After the basic commissioning results meet the predicted basic commissioning requirements and the gold finger interface of the memory mirroring card to be tested is inserted into the memory mirroring card on the simulated computer side, the processor of the memory mirroring card on the simulated computer side sends a basic commissioning command for reading and writing, To call its own preset read-write commissioning program to perform basic read-write commissioning of the memory mirror card to be tested; after the read-write commissioning results meet the read-write commissioning requirements and the memory mirror card to be tested is inserted into the host, the host generates sending and receiving commissioning commands , to perform data sending and receiving commissioning on the memory mirroring card to be tested until the sending and receiving commissioning results meet the preset sending and receiving commissioning conditions. The test process of the present invention can be set according to requirements, has less limitations, and the test reliability after being inserted into the host is higher.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU YUNHAI INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
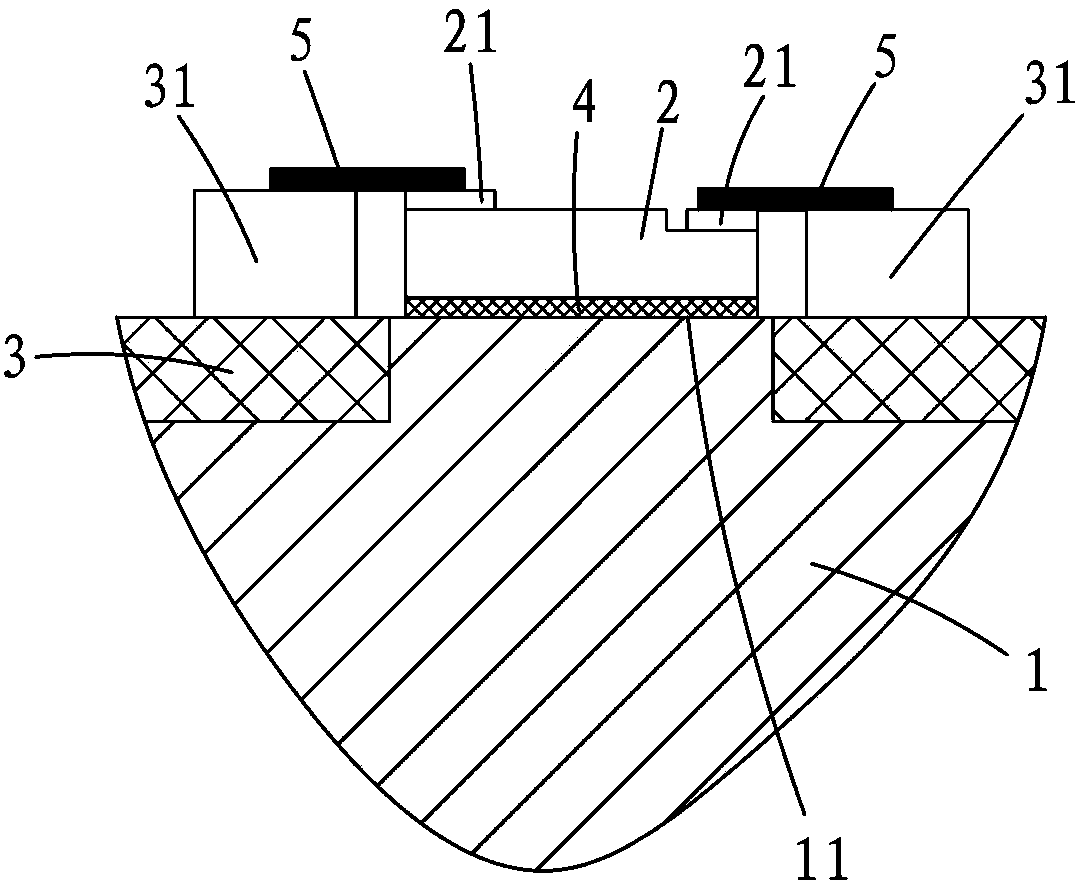
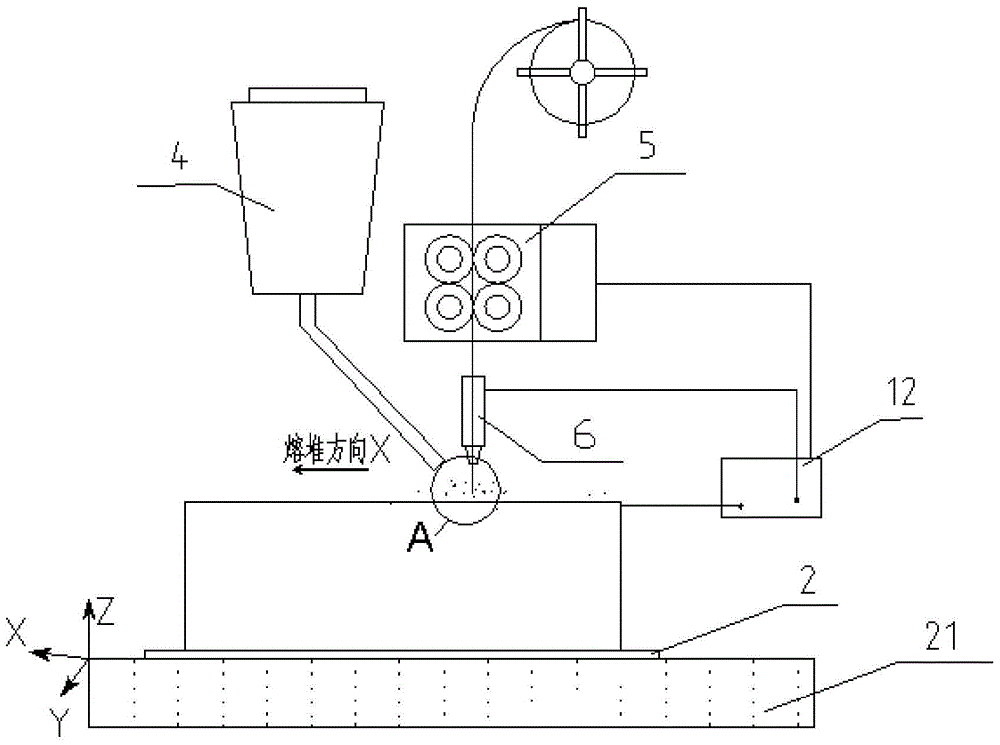
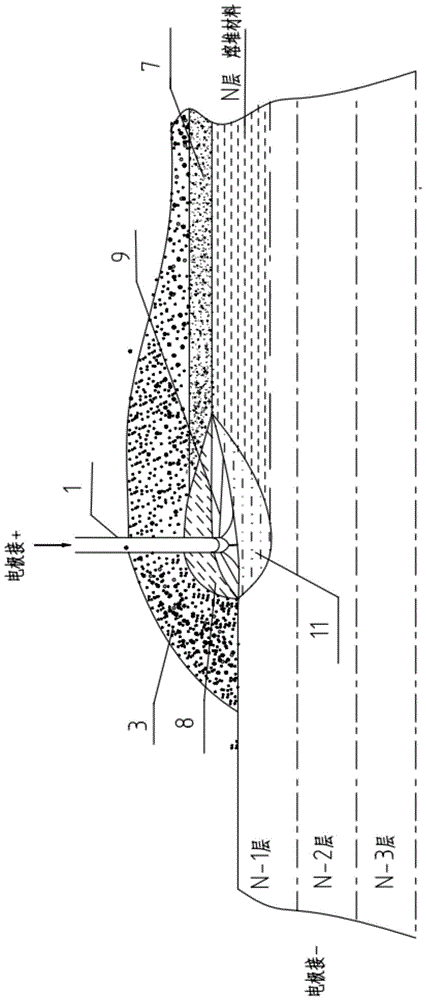
Electrofusion Forming Method for Nuclear Power Station Voltage Stabilizer Cylinder
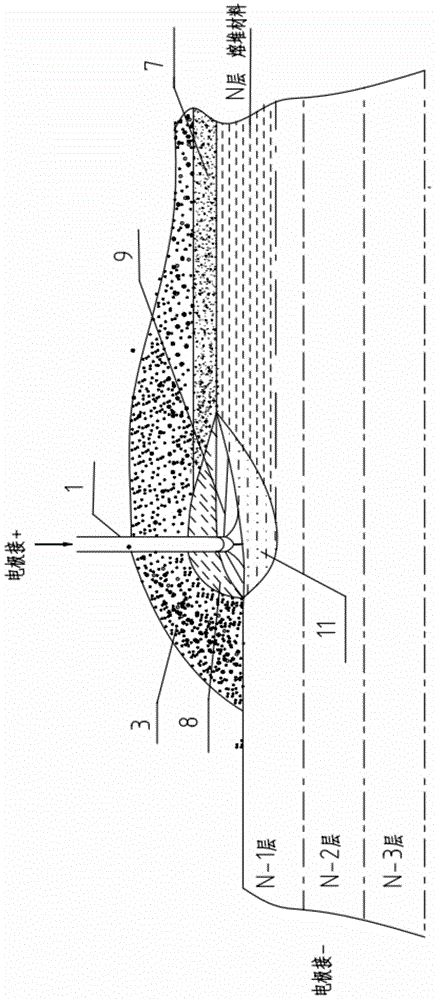
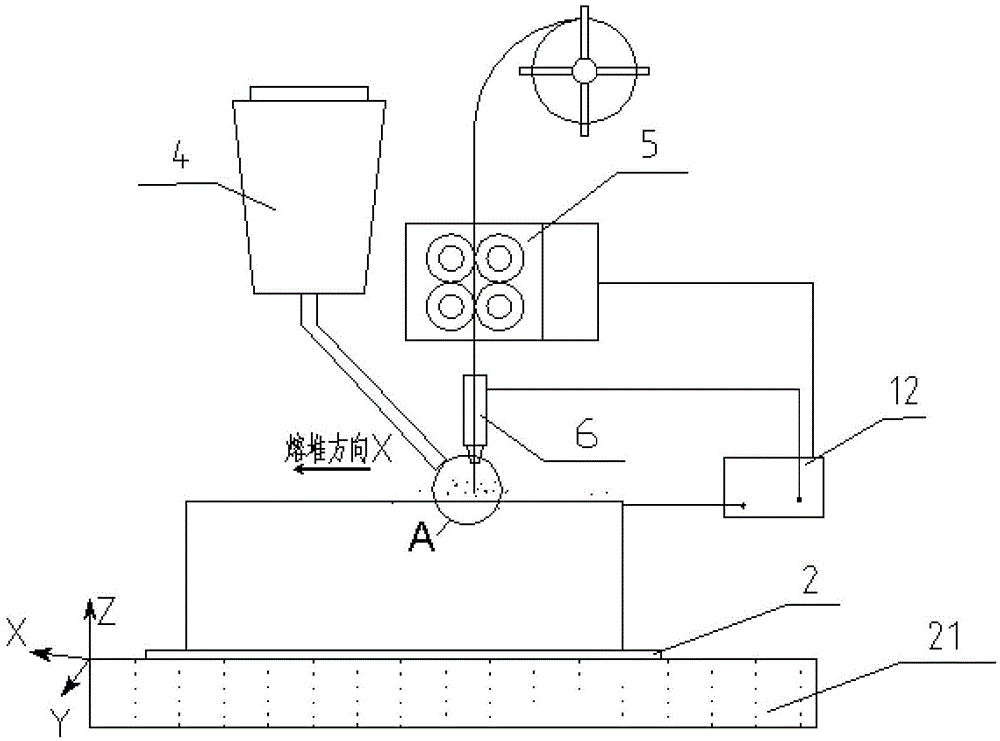
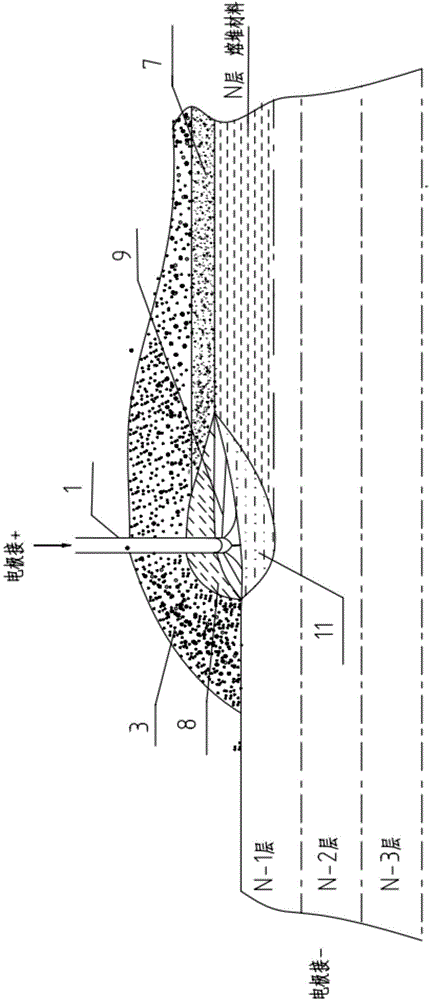
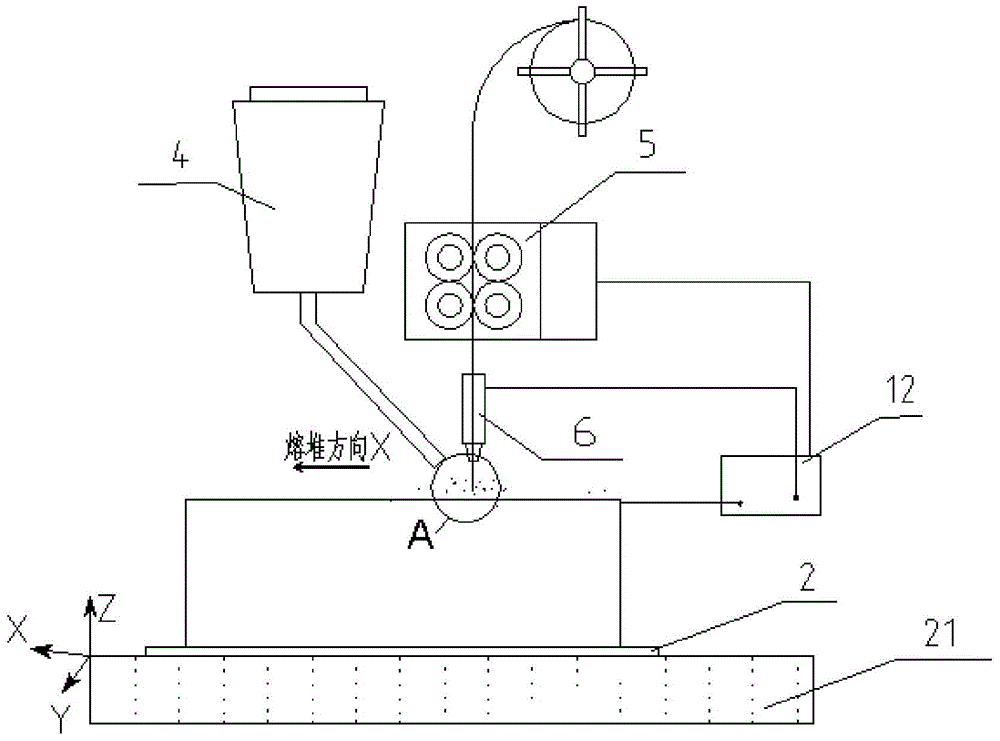
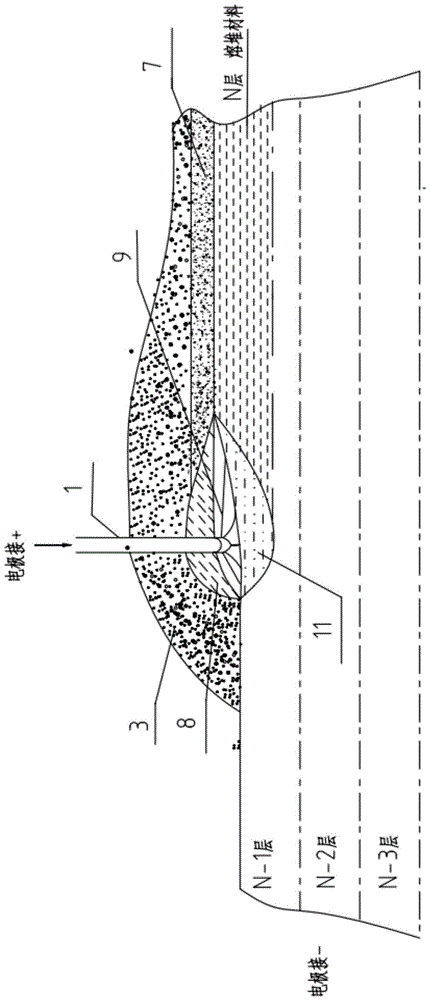
ActiveCN104532236BHigh strengthImprove toughnessMetallic material coating processesMelting tankHigh energy
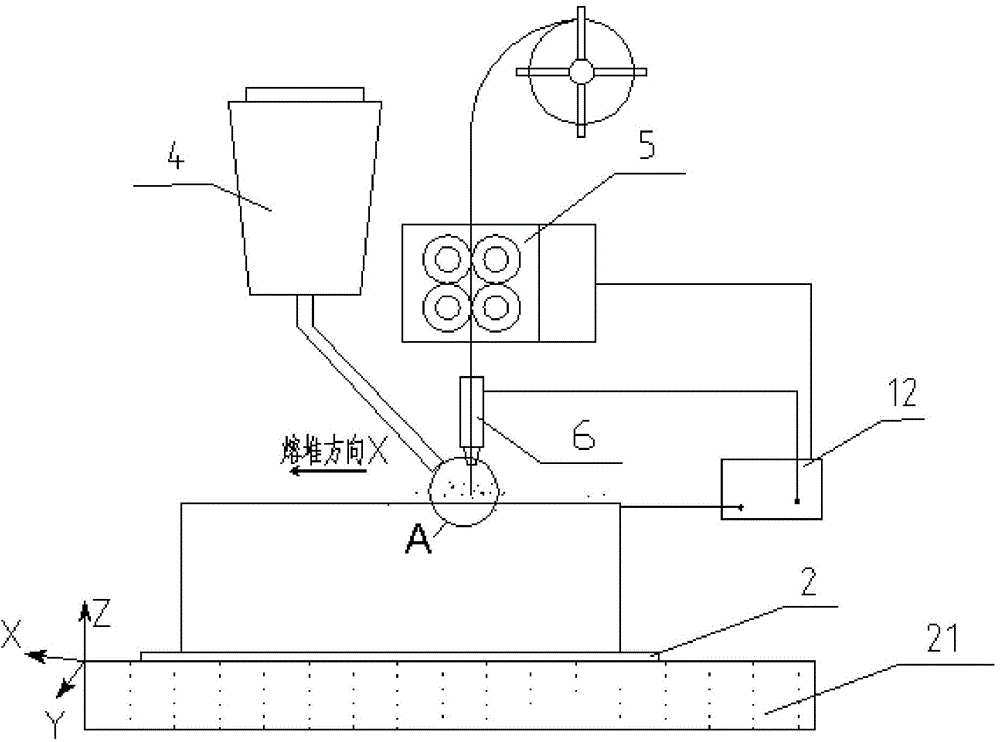
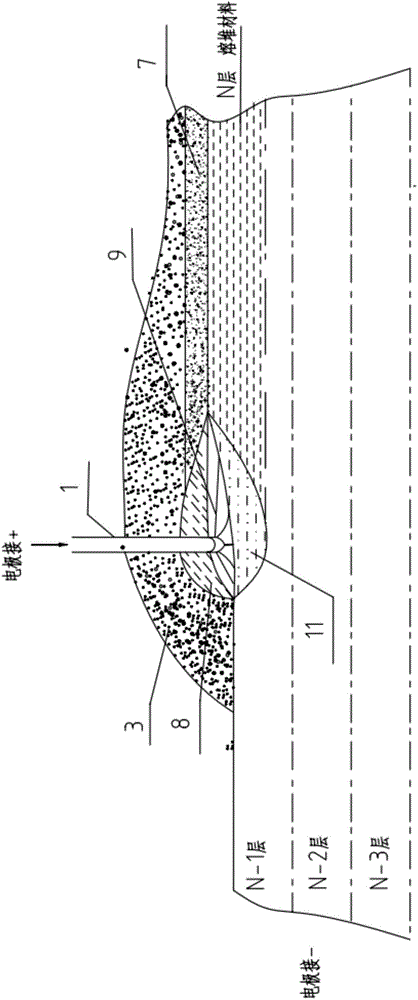
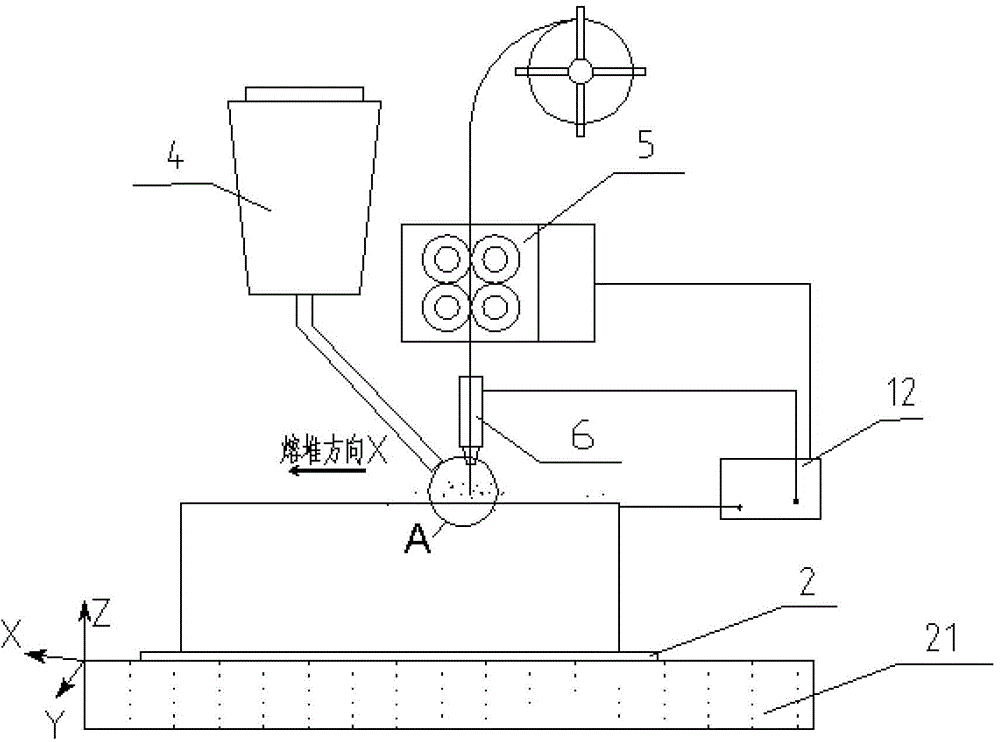
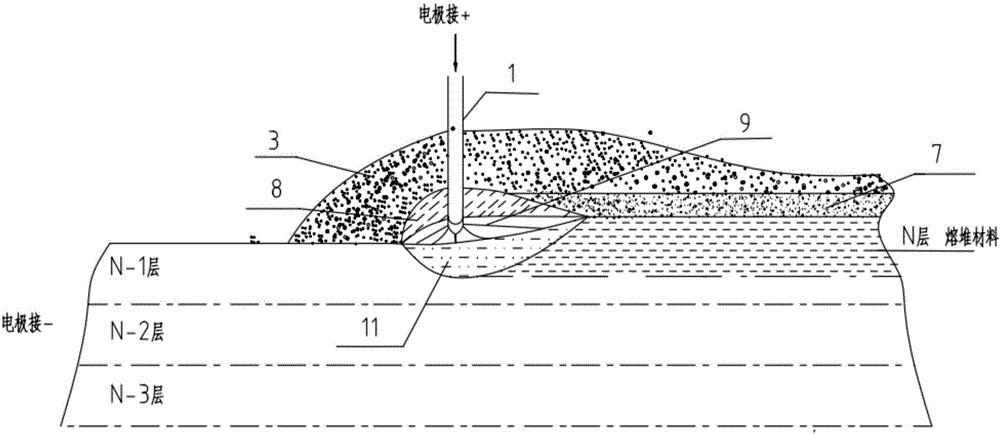
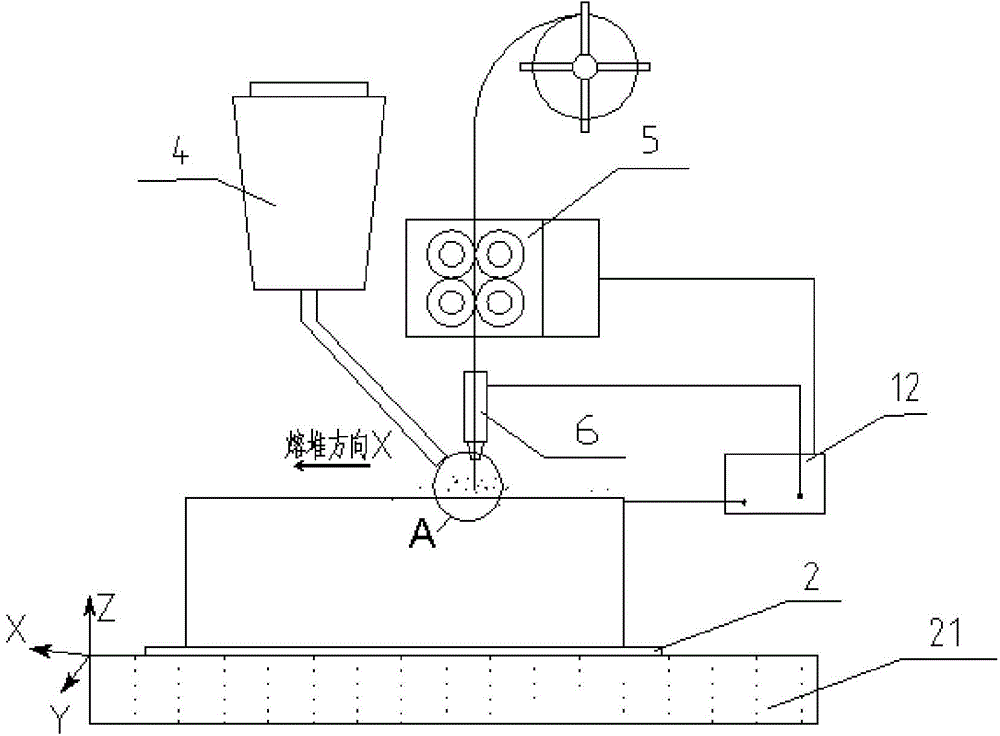
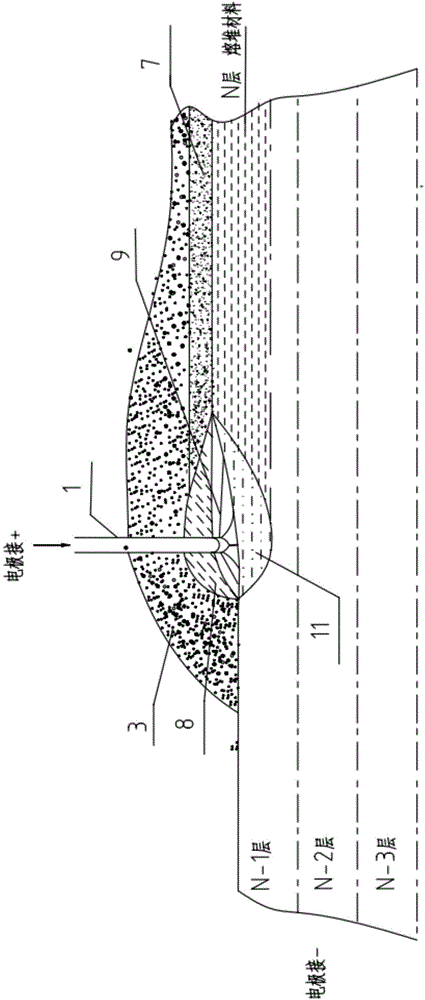
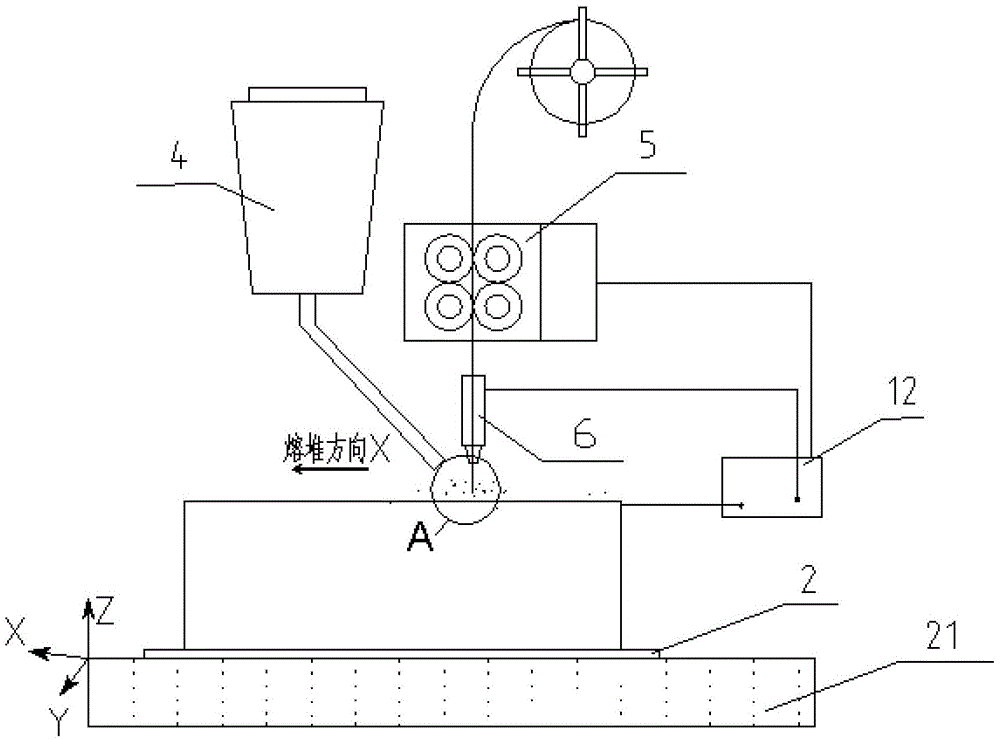
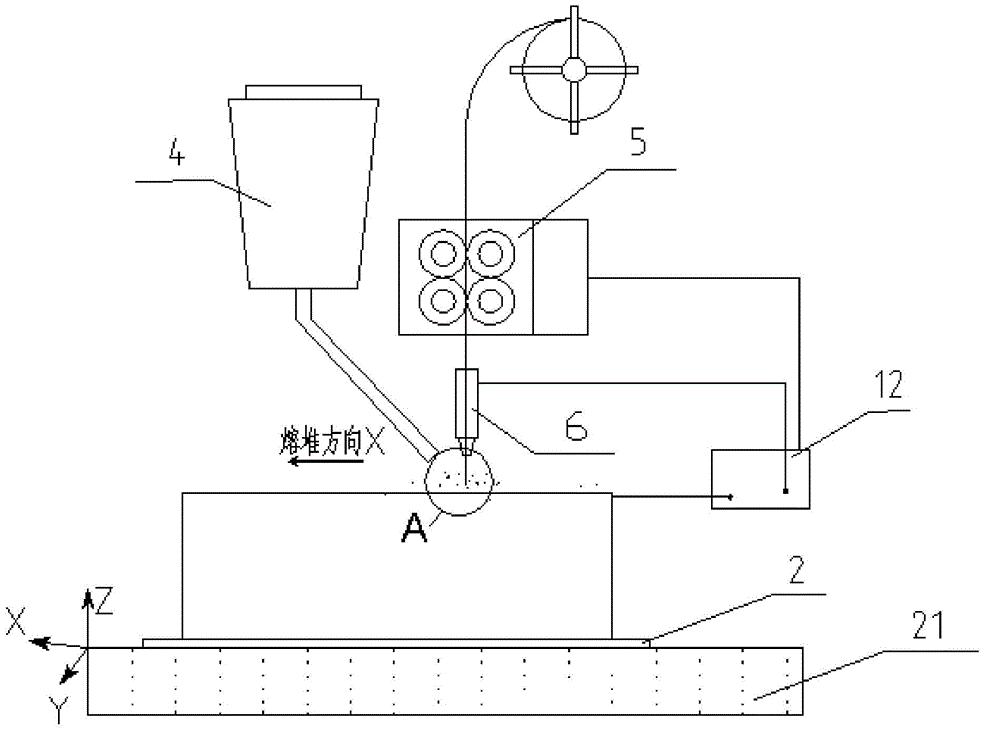
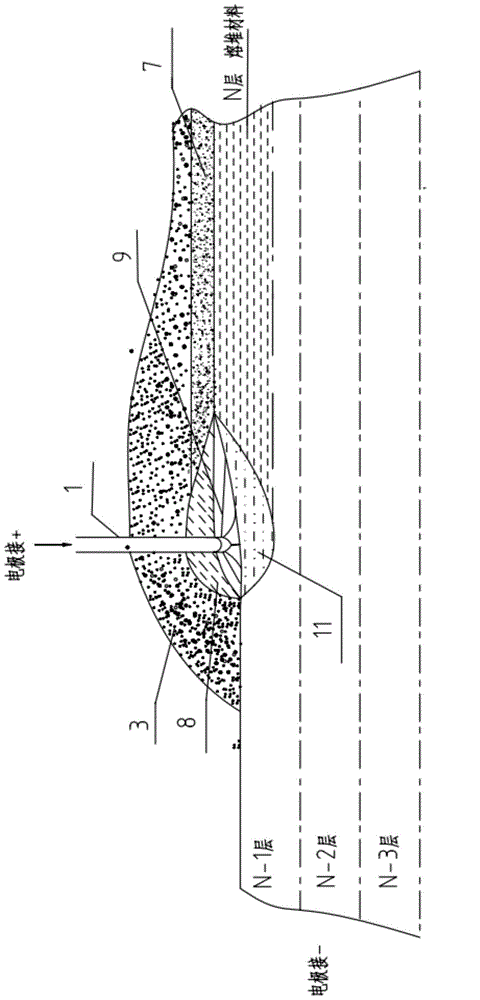
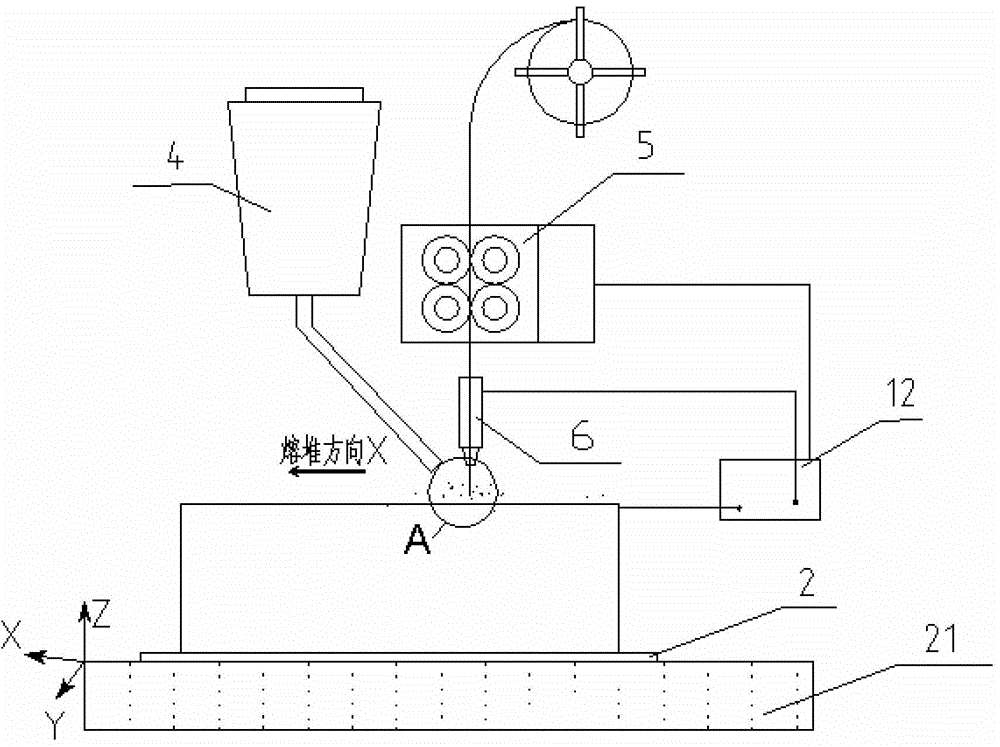
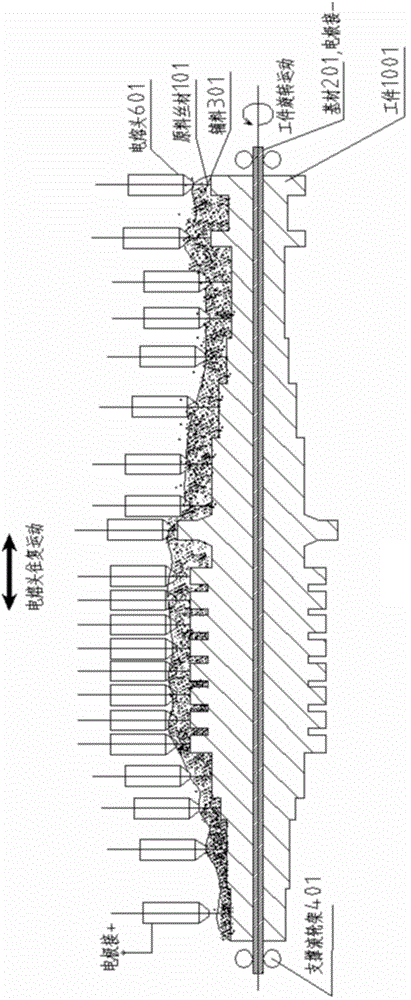
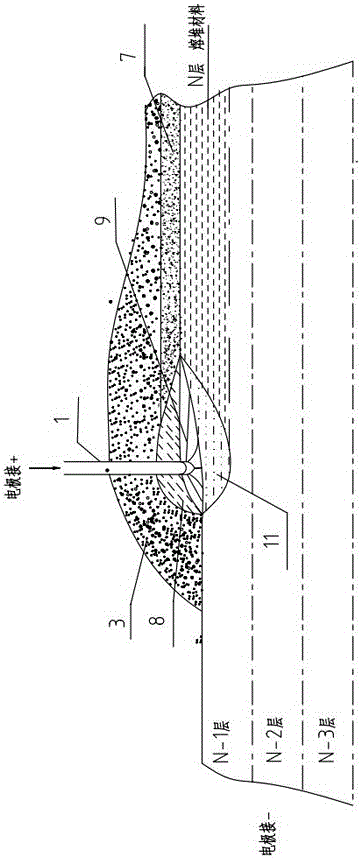
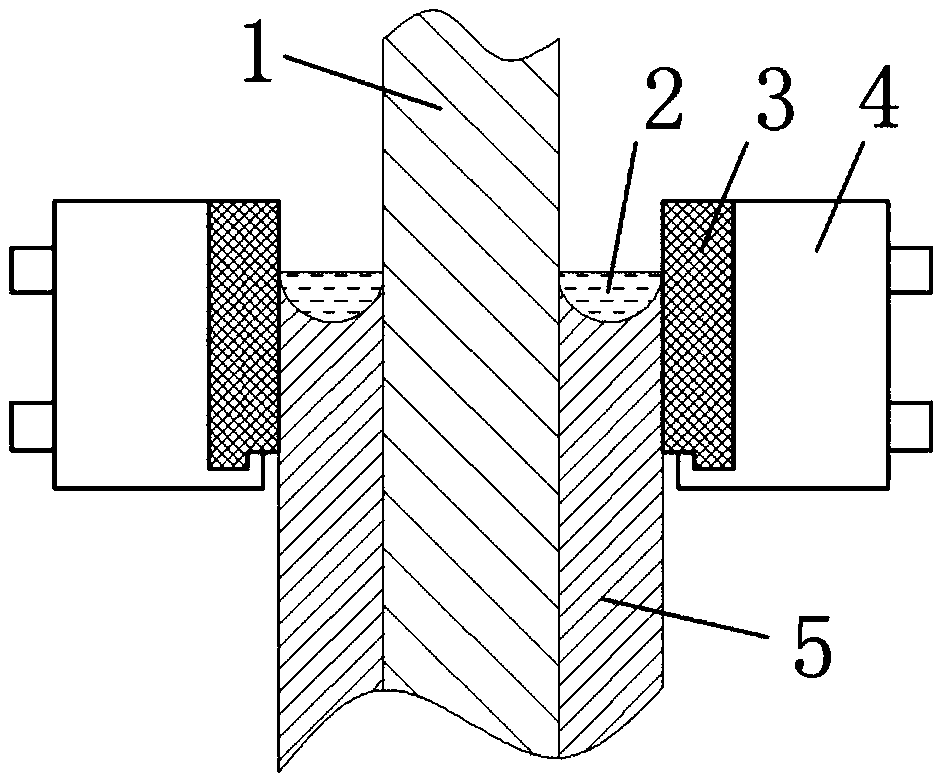
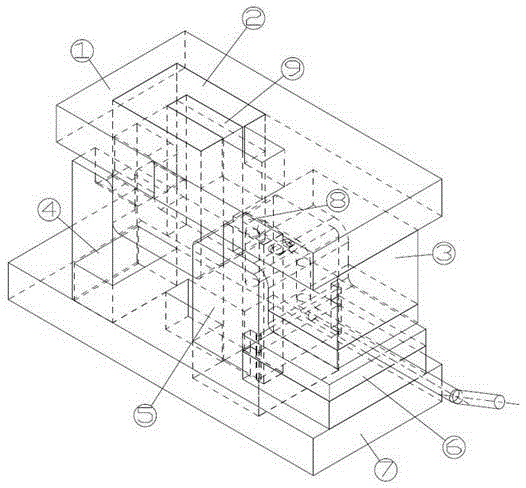
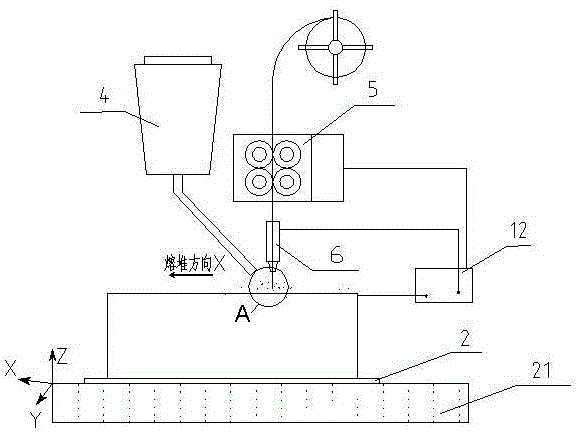
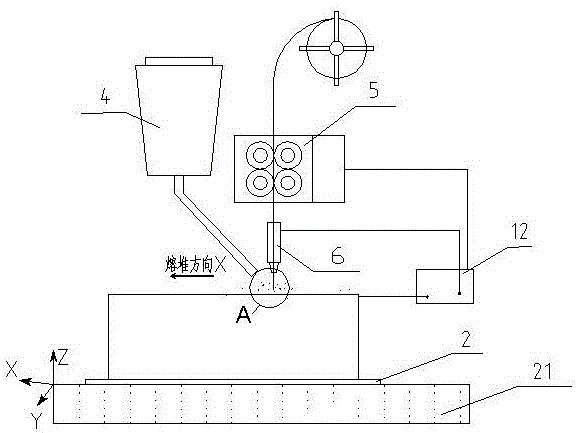
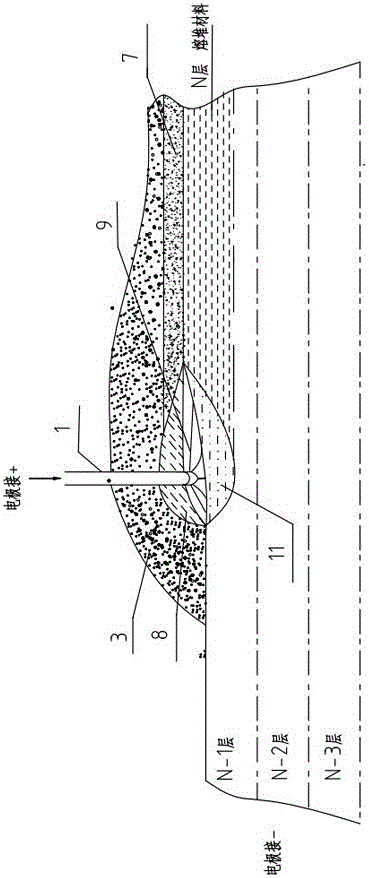
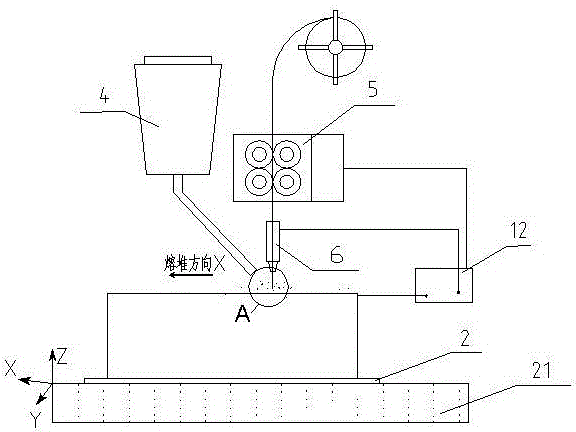
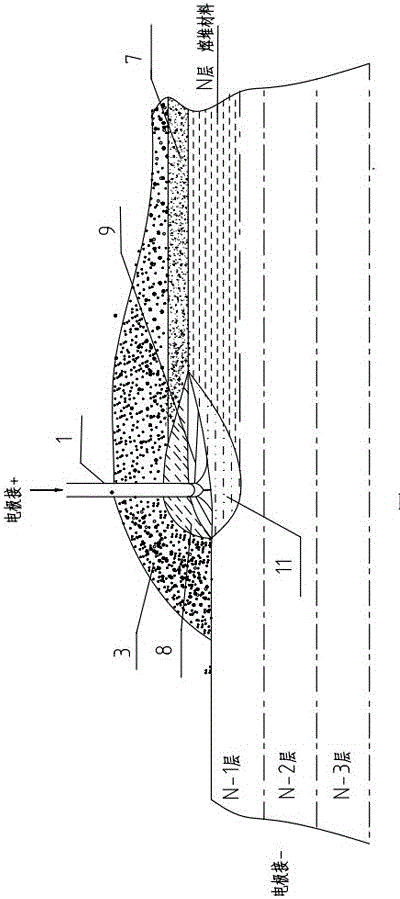
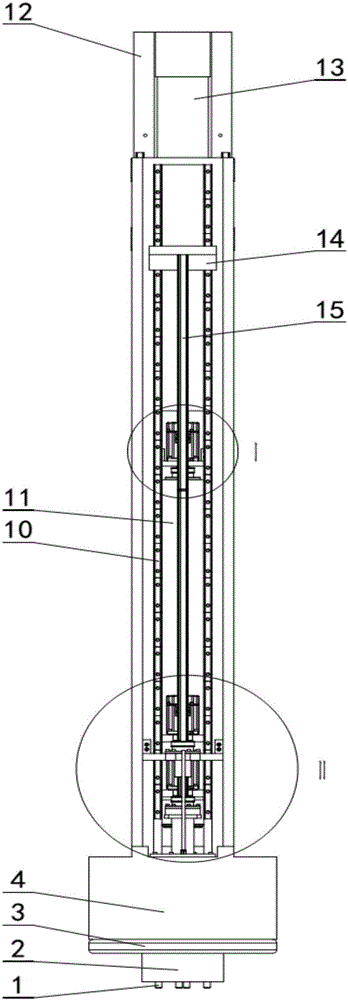
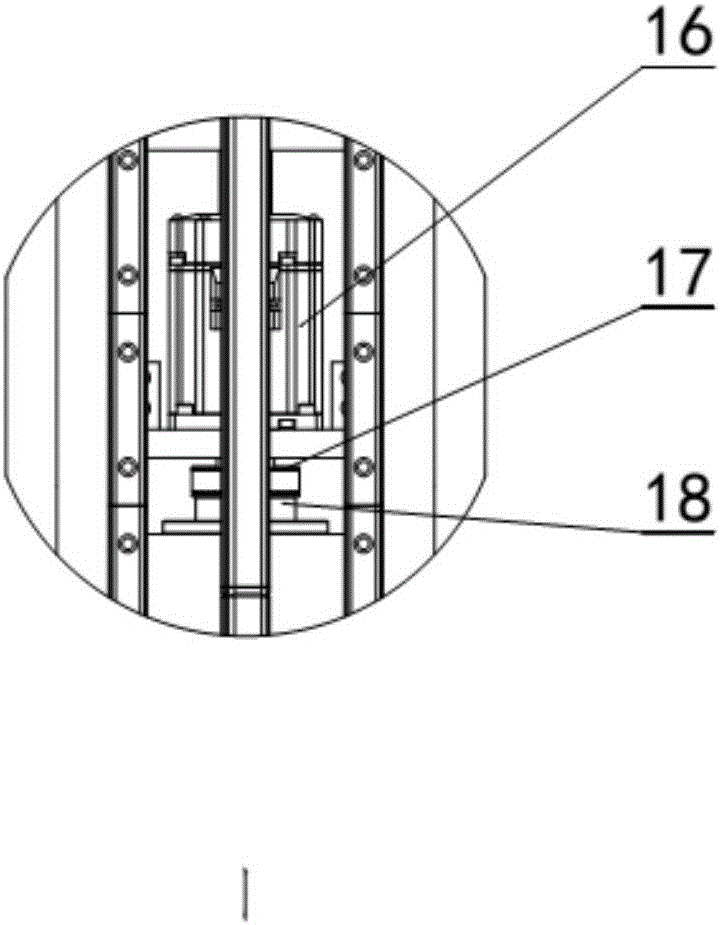
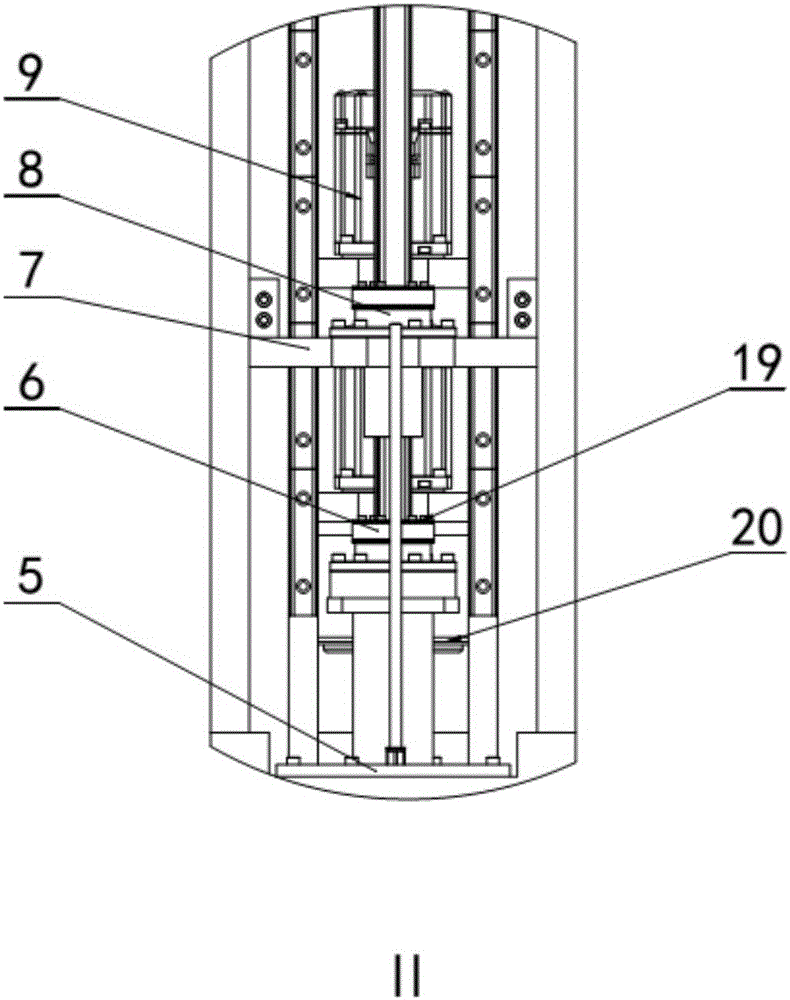
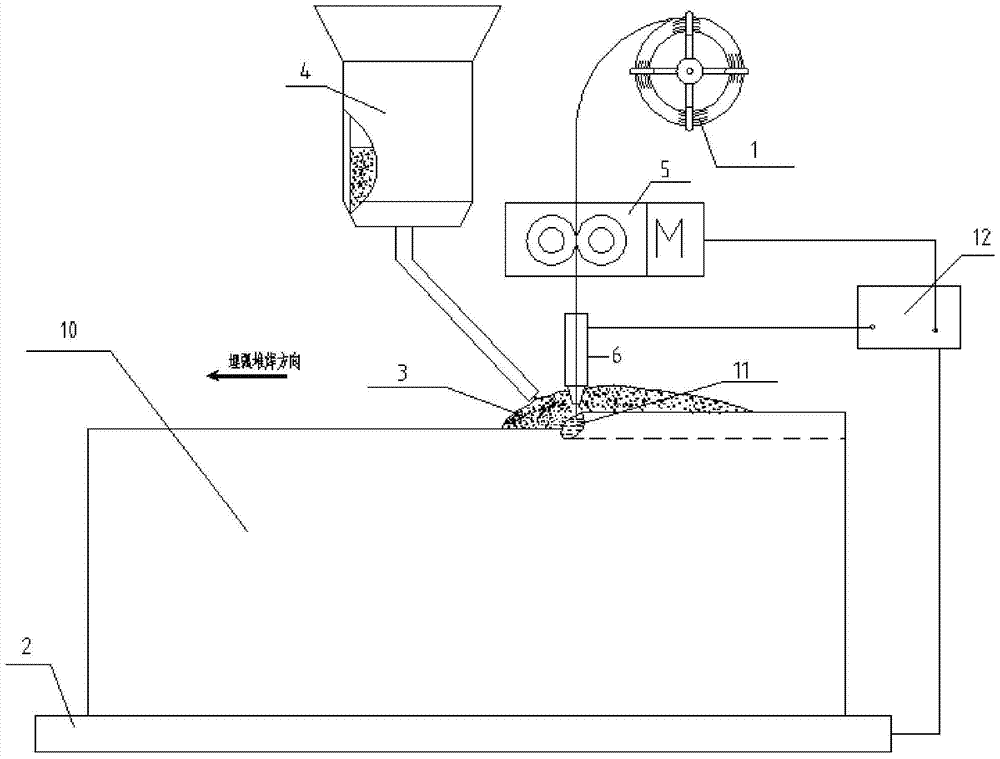
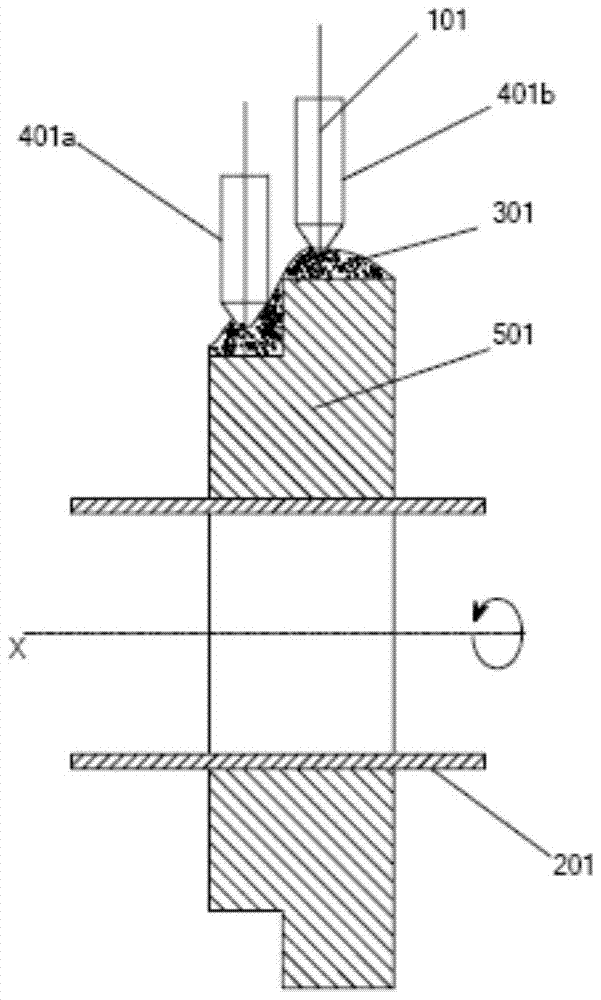
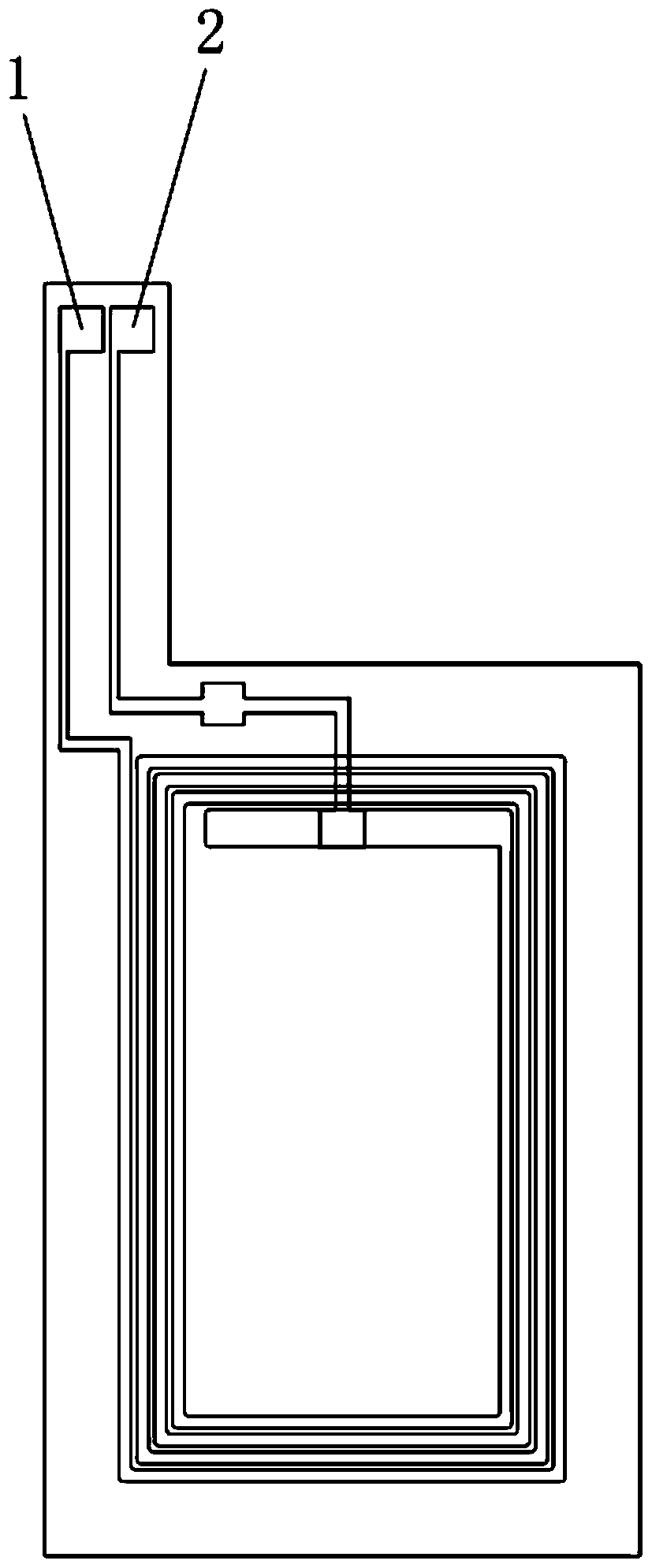
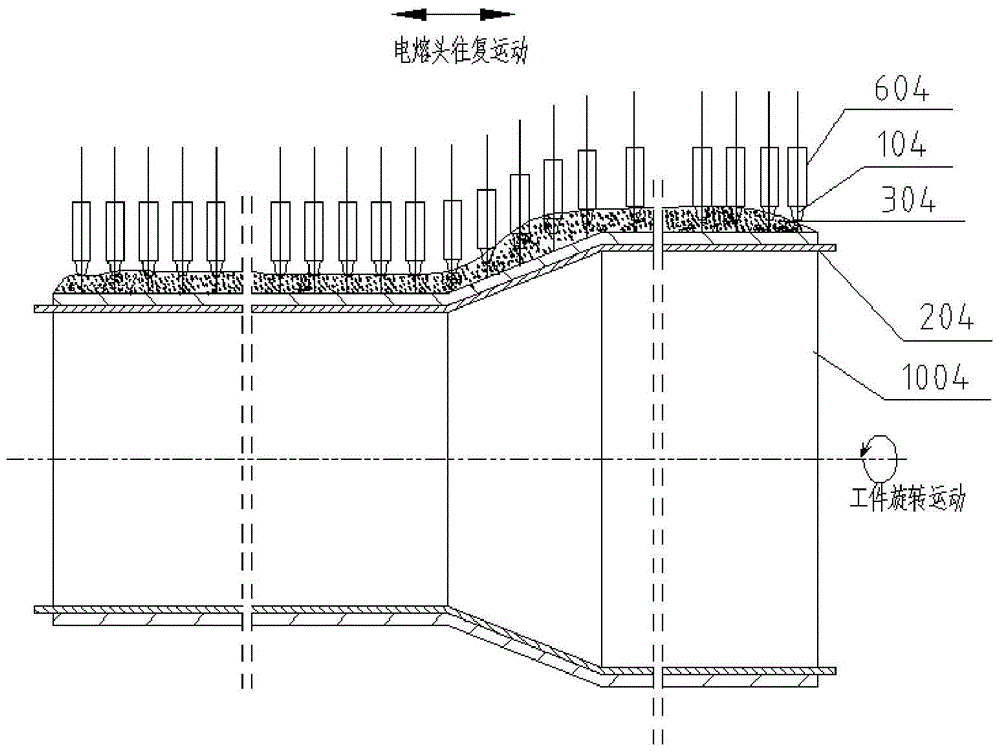
An electric melting method for forming a nuclear power plant voltage regulator cylinder: a high-energy heat source formed by combining electric arc heat, resistance heat, and electroslag heat is employed to melt a continuously conveyed raw material metal wire (1), which is solidified and deposited layer-by-layer on a substrate (2) to form a manufactured metal structure; an electric melting head (6) and a substrate (2) are connected to either electrode of a power source, when forming, the raw material metal wire (1) is fed to a surface of the substrate (2) via a conveyor mechanism (5) and the electric melting head (6), under the protection of a stack of a granular auxiliary material (3), an electric arc (9) is produced between the raw material wire (1) and the substrate (2) to partly melt the surfacing auxiliary material (3) to form a molten slag pool (8), an electric current flows through the raw material wire (1) and the molten auxiliary material slag pool (8) to form resistance heat and electroslag heat, the raw material wire (1) is molten under the effect of the high-energy heat source combining the electric arc heat, the resistance heat, the electroslag heat, a partly molten pool (11) is formed on the surface of the substrate (2), conveyance of the raw material wire (1) and the auxiliary material (3) is continued, a computer is employed to control relative movements of the electric melting head (6) and of the substrate (2) on the basis of layer slicing data of a forming component, rapid cooling and layer-by-layer solidification and deposition of the molten pool on the substrate (2) is implemented, and finally, the voltage regulator cylinder is formed by layer-by-layer deposition.
Owner:NANFANG ADDITIVE MFG TECH
A metal component submerged arc surfacing welding forming method
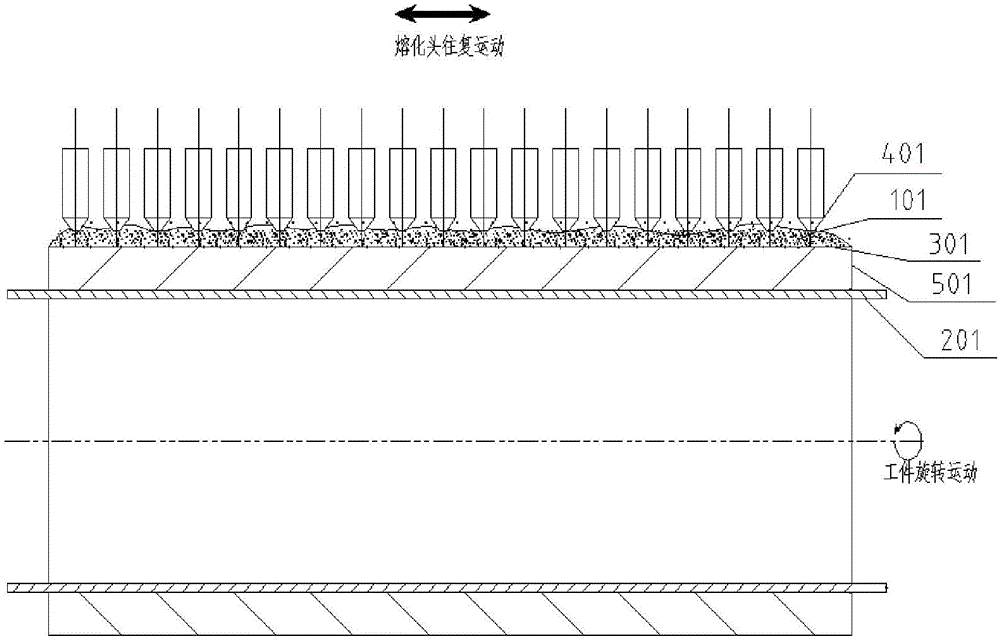
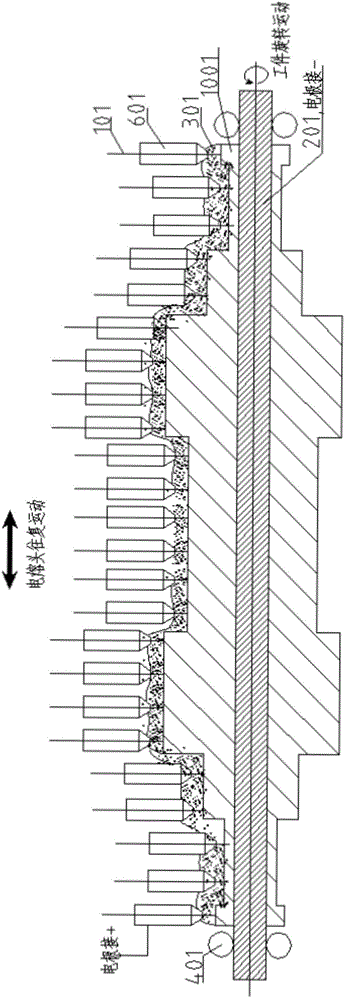
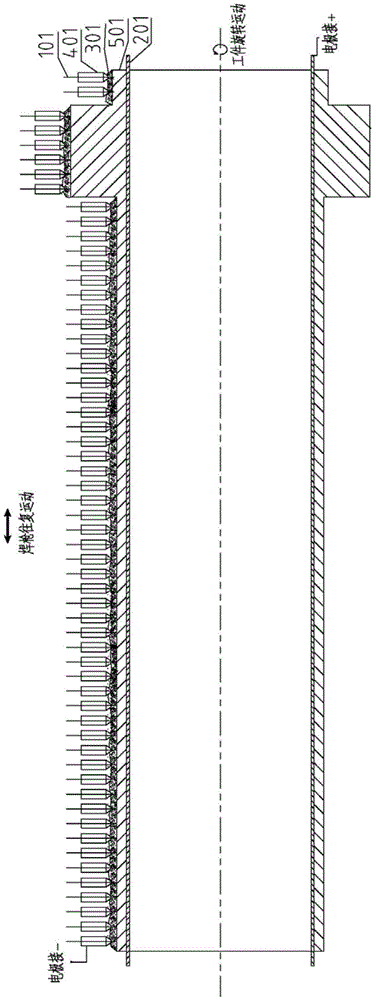
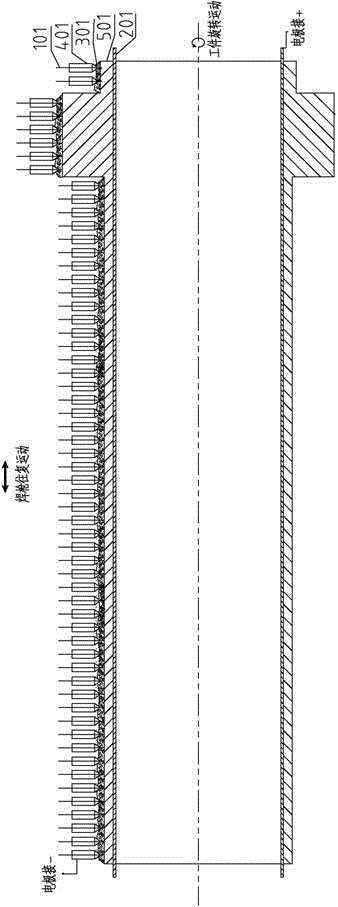
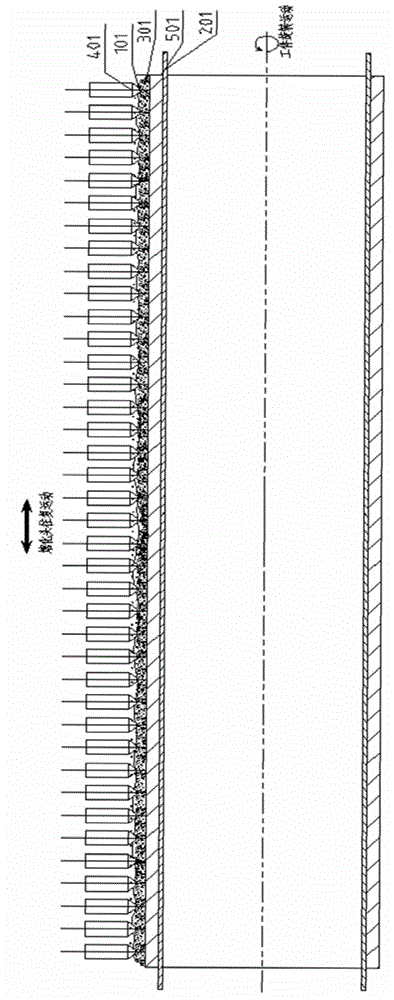
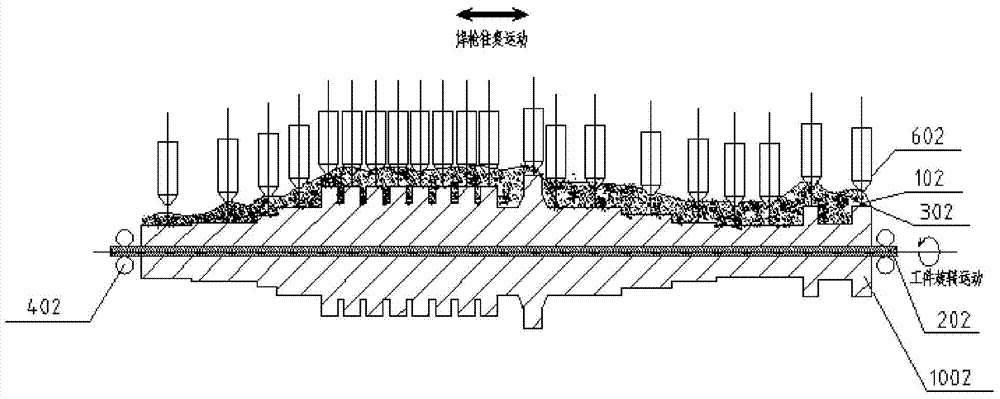
ActiveCN104526114BHigh strengthImprove toughnessArc welding apparatusWelding power supplyEngineering
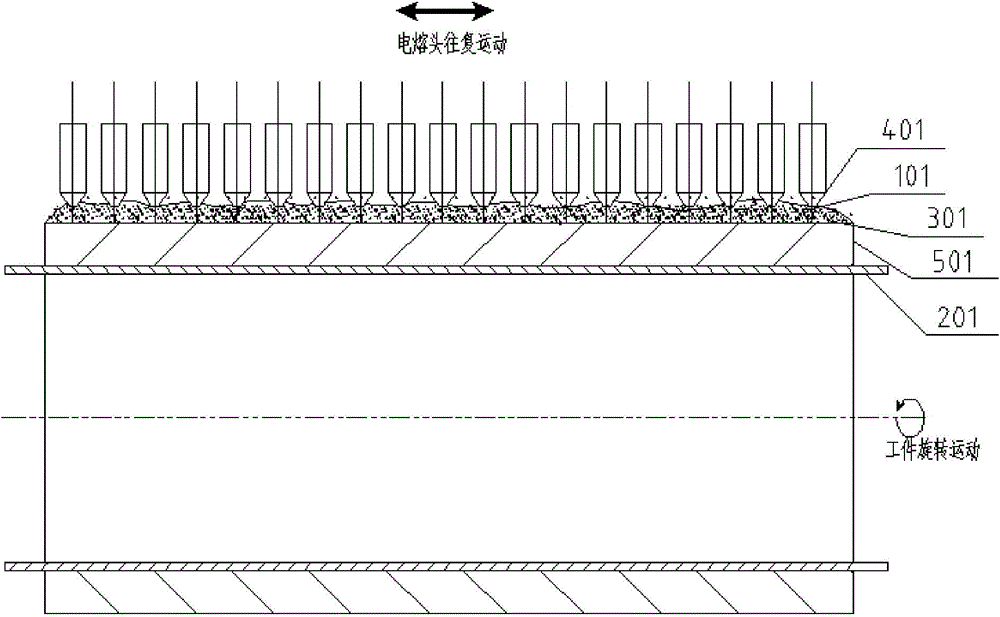
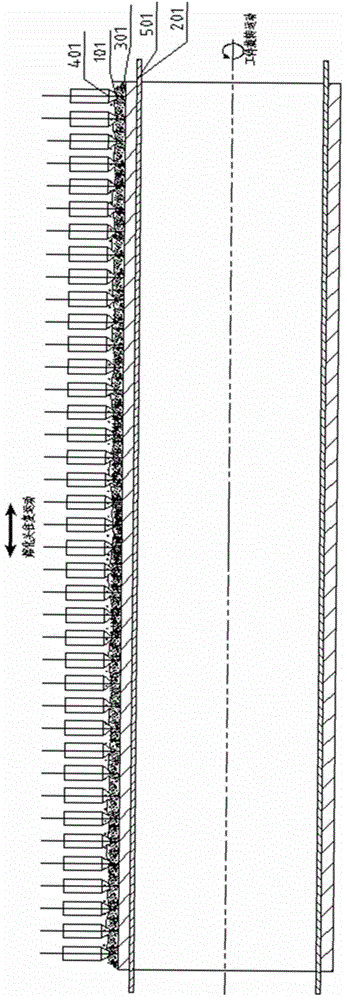
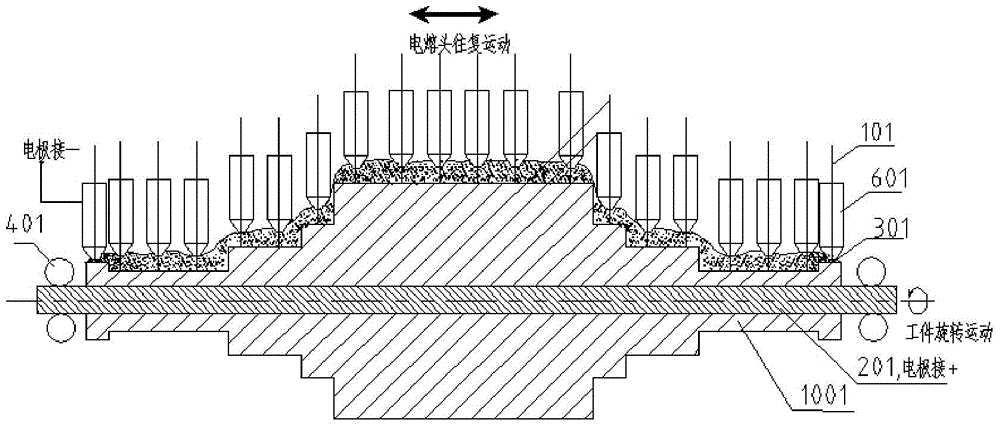
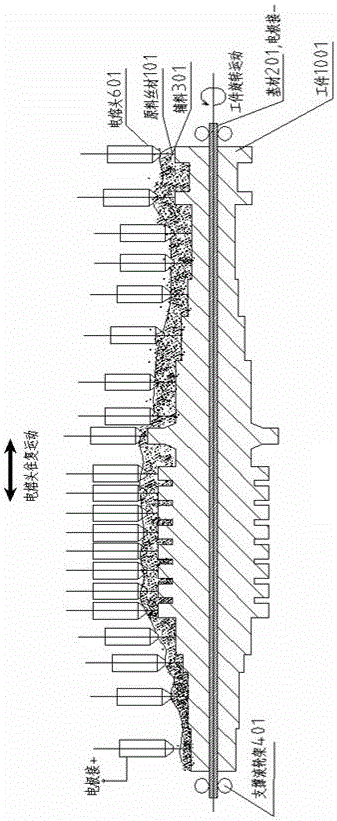
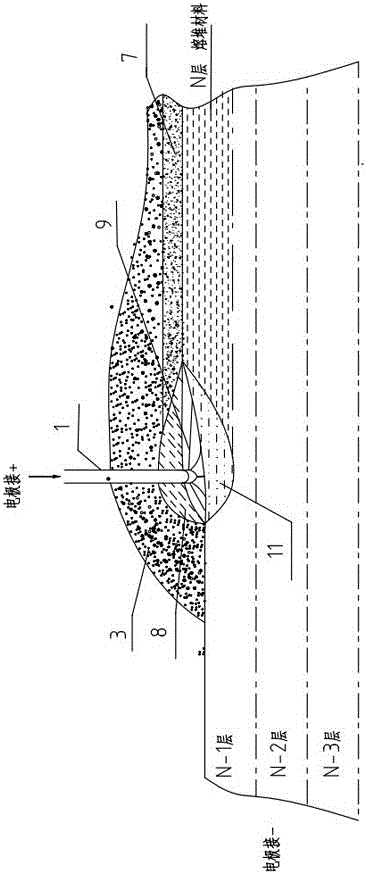
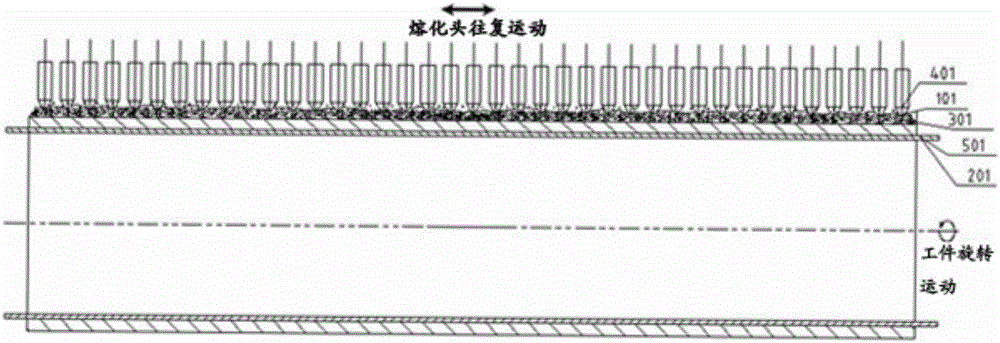
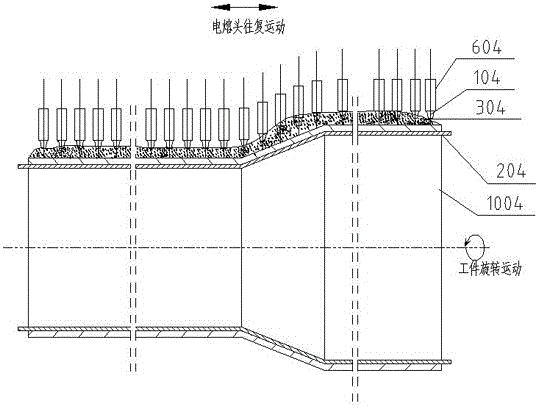
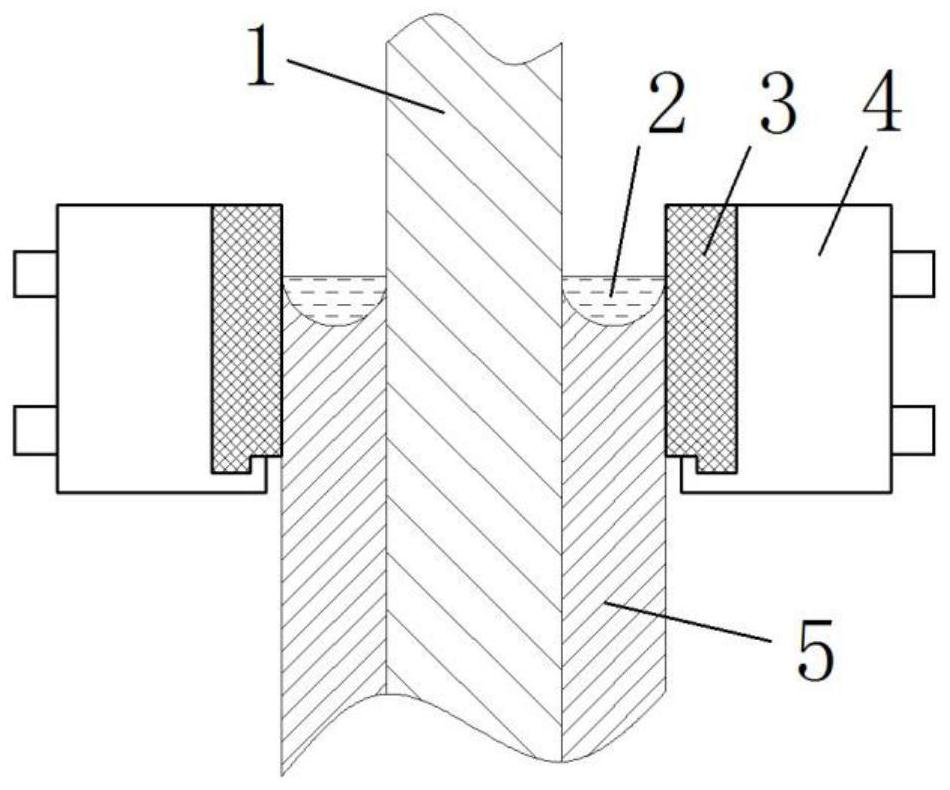
A submerged arc additive manufacturing method for a metal structure having great mechanical properties. The submerged arc welding method for forming the metal structure is such that: two electrodes of a welding power source (12) respectively are connected to a welding torch (6, 401, 602, and 603) and to a substrate (2, 201, 202, and 203), a granular flux (3, 301, 302, and 303) and a metal welding wire (1, 101, 102, and 103) are simultaneously conveyed onto a surface of the substrate, power is turned on, an electric arc is produced between the substrate and the welding wire covered by the flux, thus allowing the welding wire and the surface of the substrate to be partly molten to form a weld pool on the surface of the substrate, conveyance of the welding wire and the flux is continued, and relative movement paths of the welding torch and of the substrate are controlled on the basis of modulus data of parts, thus implementing layer-by-layer hardfacing deposition on the substrate to form the metal structure.
Owner:NANFANG ADDITIVE MFG TECH
An nfc antenna
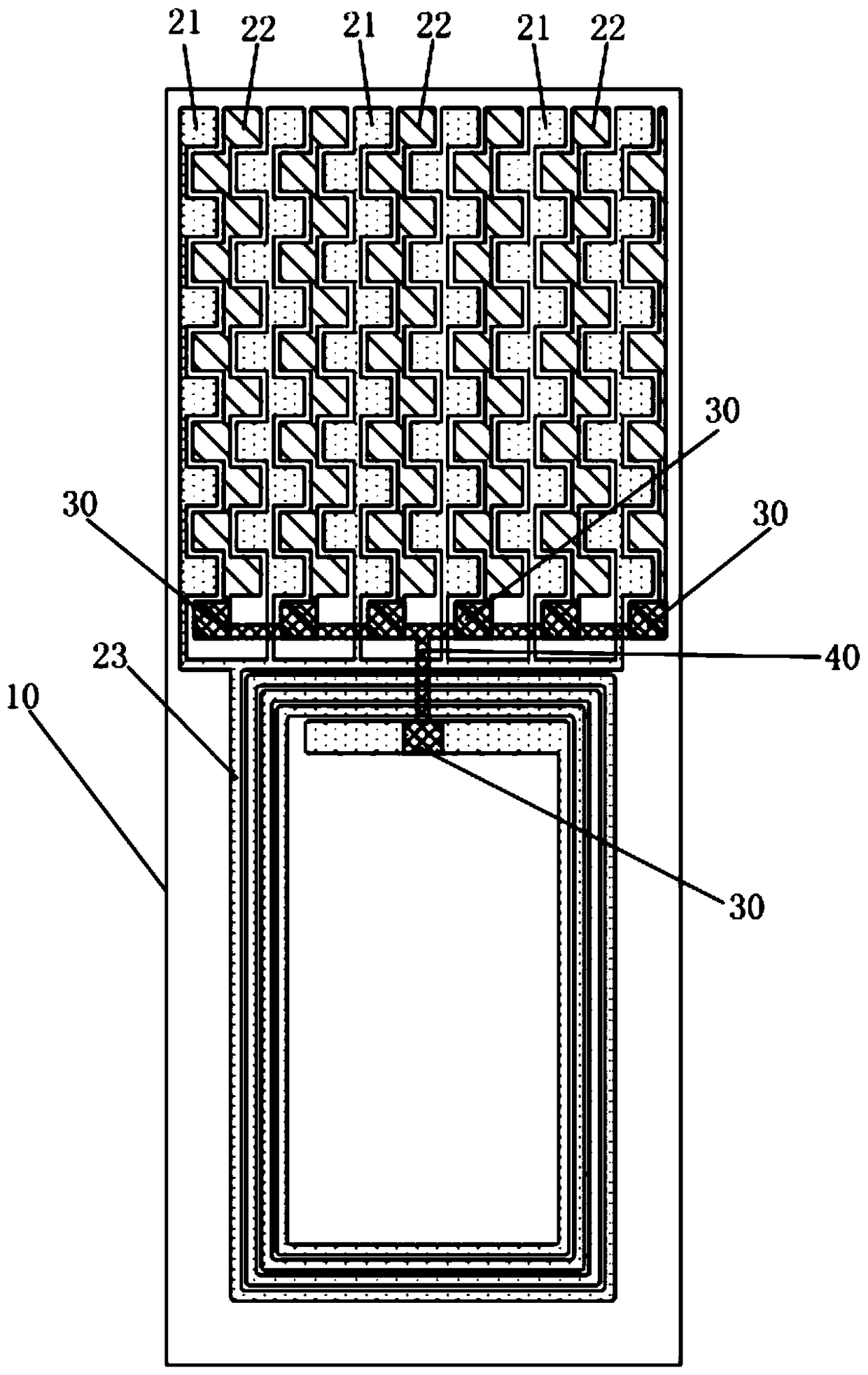
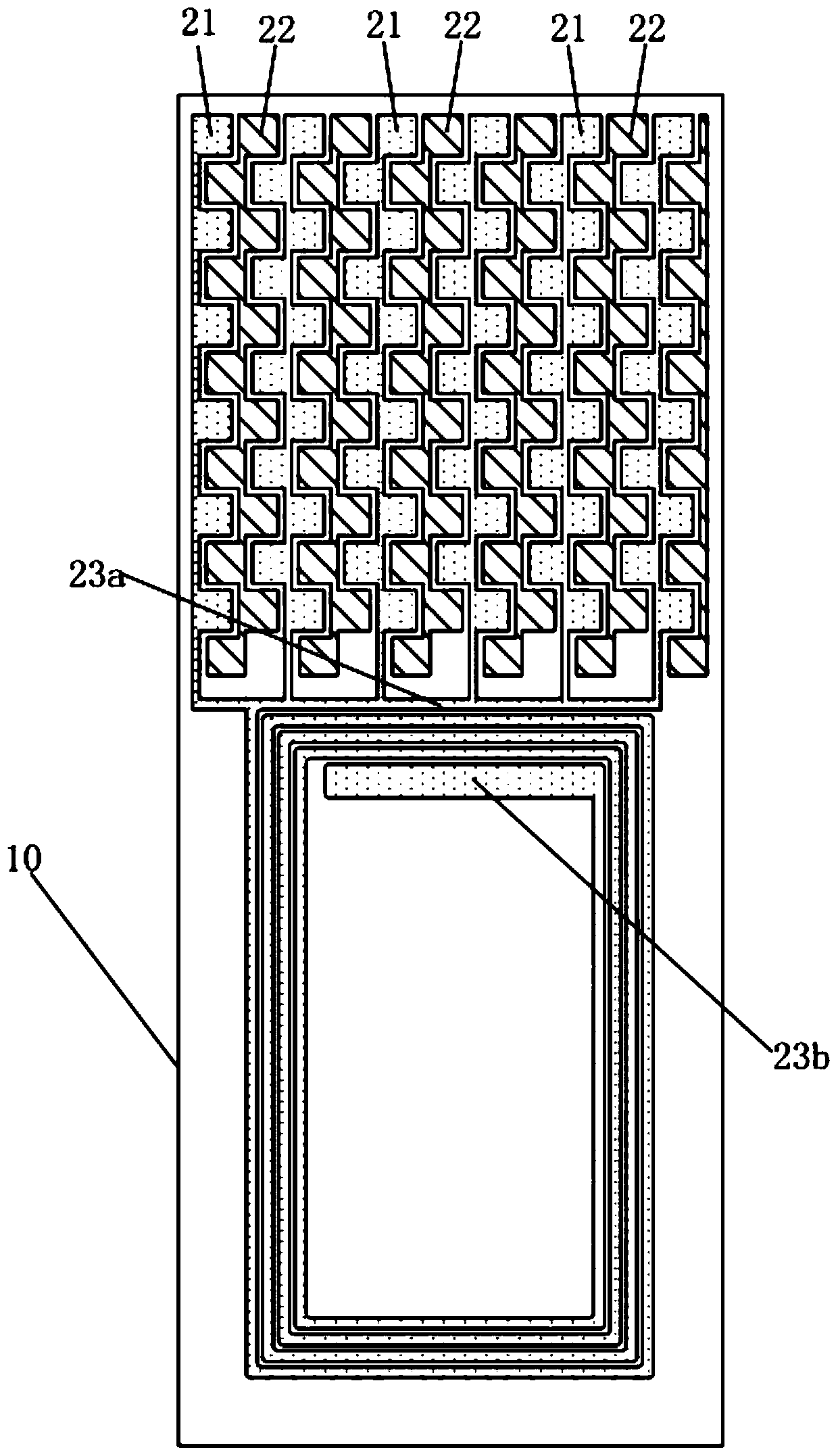
ActiveCN105071039BMeet needsWide applicabilityAntennas earthing switches associationLoop antennasDot matrixEngineering
The invention discloses an NFC antenna, which is connected to a circuit board through a thimble, comprising: a substrate; a first contact unit, a second contact unit and a conductive coil located on the upper surface of the substrate; wherein the first contact unit includes multiple a first contact for connecting to the positive pole of the thimble, the second contact unit includes a plurality of second contacts for connecting to the negative pole of the thimble; a plurality of conductive via holes penetrating the substrate, Connected to each other through the conductive pattern located on the lower surface of the substrate; the first contact is connected to the outer ring of the conductive coil, and the second contact is connected to the inner ring of the conductive coil through the conductive via hole and the conductive pattern The connection; the first contacts and the second contacts are arranged in a dot matrix, and each row includes the first contacts and the second contacts arranged at intervals, and each column includes the first contacts arranged at intervals. contact and the second contact. The array contact design can meet a variety of thimble contacts, without the need for custom-designed antennas.
Owner:SHENZHEN SUNLORD ELECTRONICS
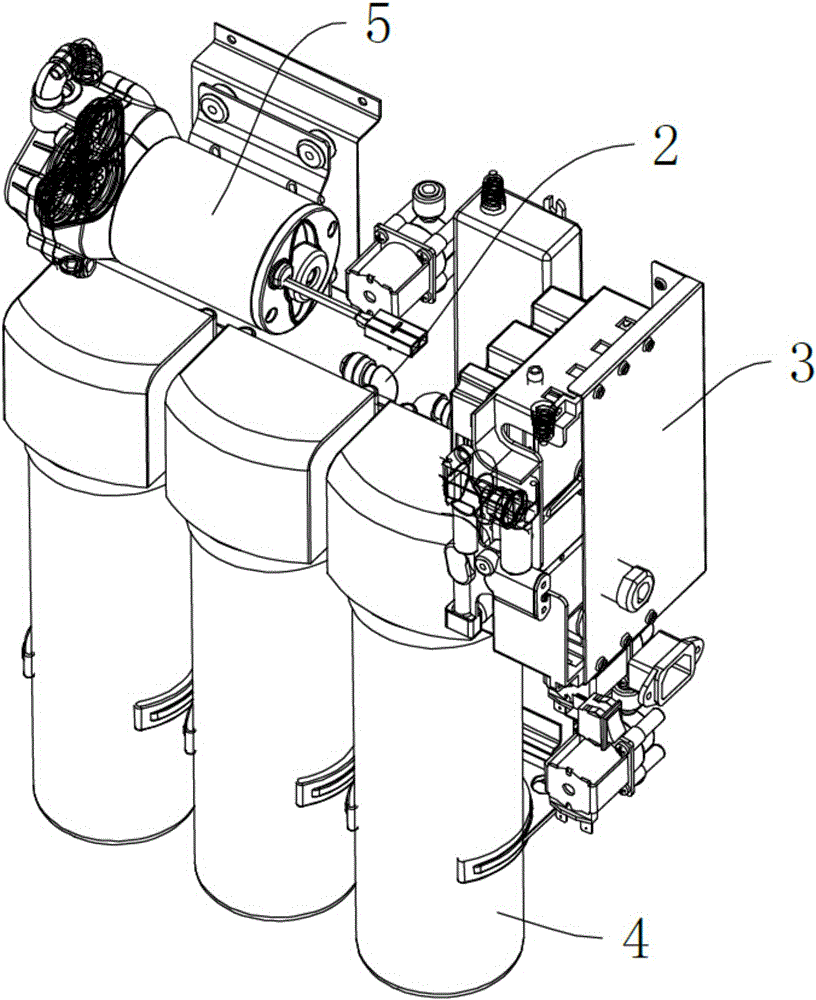
Water purifier capable of being produced flexibly
InactiveCN106277095ASmooth connectionUnlimited hardware upgradesTreatment involving filtrationWater treatment locationComputer moduleEngineering
The invention discloses a water purifier capable of being produced flexibly. The water purifier comprises a case, a water path, a circuit, a valve, a valve element, a water pump and a control display module. The water purifier is characterized in that the case is of a metal plate spliced structure, and the control display module is arranged on the outer side of the case.
Owner:贺天山
Electrofusion forming method for evaporator cylinder in nuclear power plant
Owner:NANFANG ADDITIVE MFG TECH
A kind of preparation method of aluminum-clad magnesium composite rod and wire
The invention provides a preparation method of an aluminum-coated magnesium composite rod wire rod. The preparation method comprises the following steps that the surface of a magnesium alloy core material is cleaned, and then is placed in the central position of a crystallizer and is fixedly connected with a traction device; after an aluminum alloy is heated and melted, the aluminum alloy is poured into a casting inner cavity of the crystallizer, aluminum alloy liquid is in contact with the magnesium alloy core material, the aluminum alloy layer is formed by cooling and solidifying the surfaceof the core material, and meanwhile, the traction device is started, and the composite blank is pulled out from the lower part of the crystallizer, so that continuous coating can be realized; the size ratio of the inner diameter of the casting inner cavity of the crystallizer to the inner diameter of the magnesium alloy core material is 1.5-2.3:1; and after the aluminum-coated magnesium compositeblank is heated, continuous multi-pass rolling is carried out, and the aluminum-clad magnesium composite bar materials with different section sizes and section shapes are prepared by adjusting the rolling pass and the shape of rolling holes. The material has good tissue performance, and is low in cost, high in efficiency and wide in applicability.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
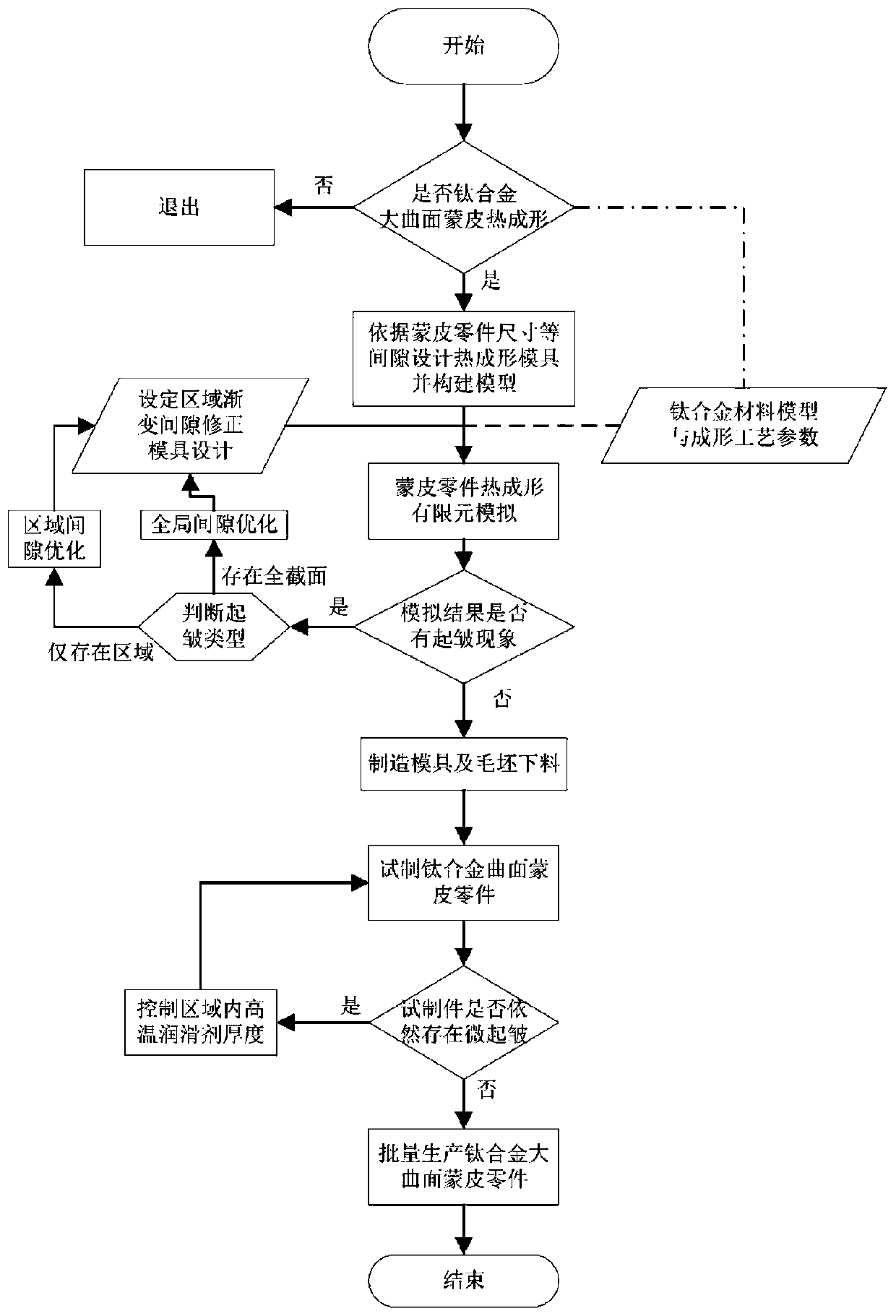
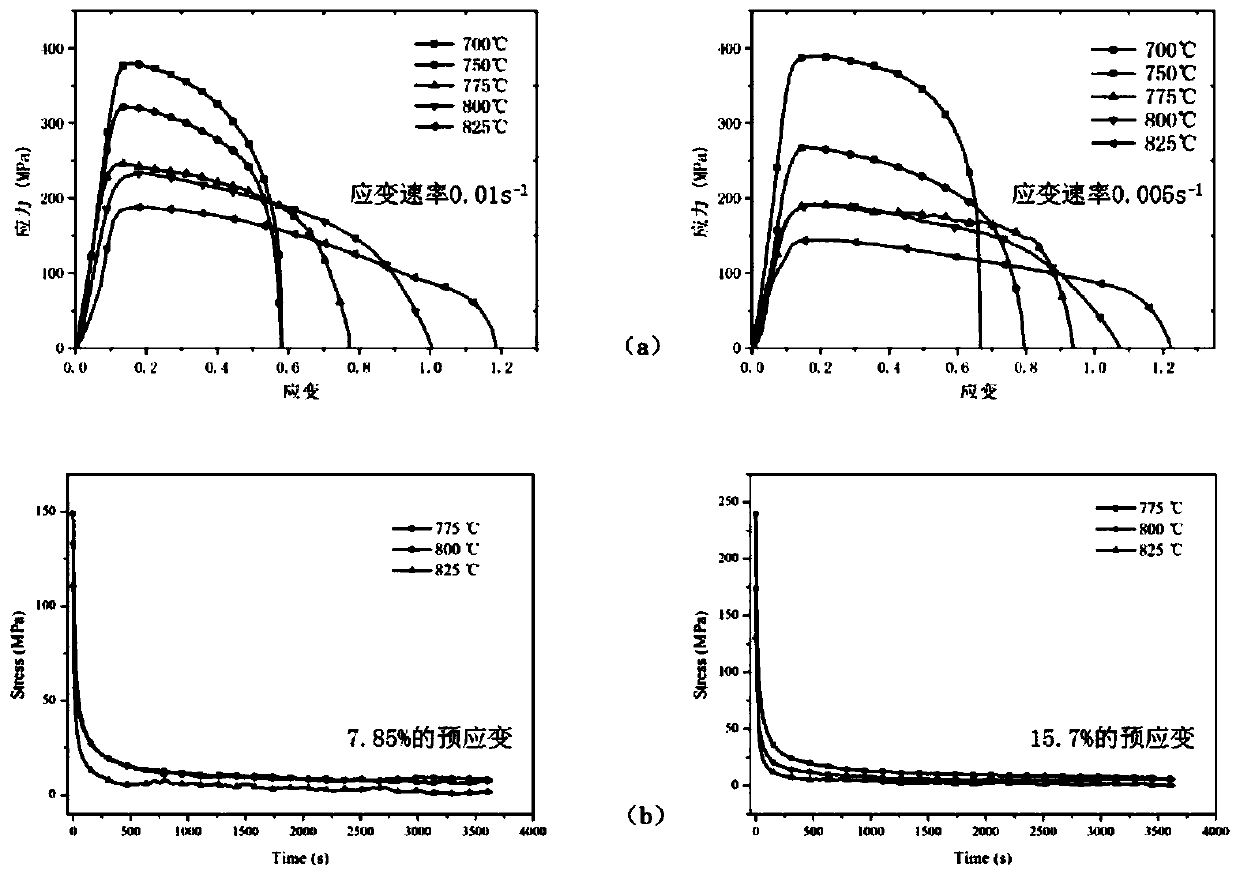
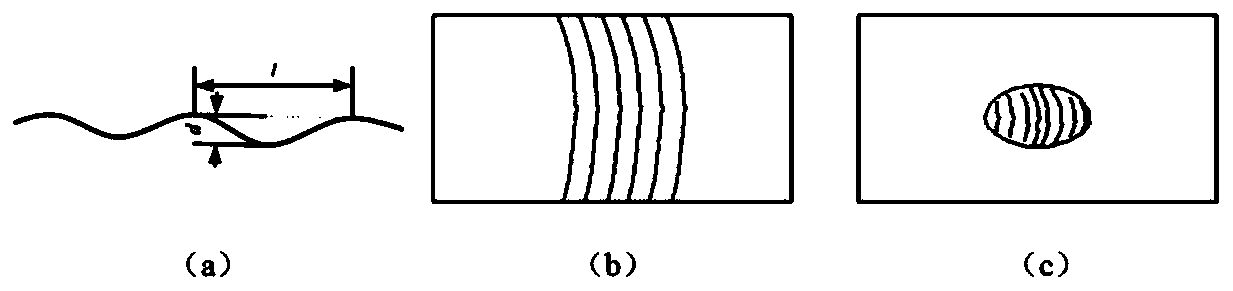
A Method of Eliminating Wrinkling of Large Curved Surface Based on Gradient Gap Die
The invention discloses a method of eliminating skin wrinkles of a large surface based on a gradient gap die and belongs to the field of techniques of removing skin formation wrinkles. Batch production of high-quality skin can be implemented herein by optimally designing die gaps and manufacturing; the method herein is applicable to the formation of skin parts of various high-intensity materials,particularly manufacturing of titanium alloy skin parts; pressure-pressure stress state is a main cause to wrinkling; gaps are reasonably designed, gradient frictional resistance is utilized to form acontrollable resistance field, and therefore, mobility during plate forming process is limited, the pressure-pressure stress state in plates is reduced, wrinkle removal is achieved, and high-qualityparts with corrugation meeting technical requirements are met. The method herein may be used as a new method to eliminate wrinkles in thermal formation of titanium alloy large-surface skin so as to obtain high-quality parts.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com