Patents
Literature
68results about How to "Temperature variation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Exposure system and pattern formation method using the same
InactiveUS20050136361A1Good body shapeAbnormal exposureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusResistEngineering
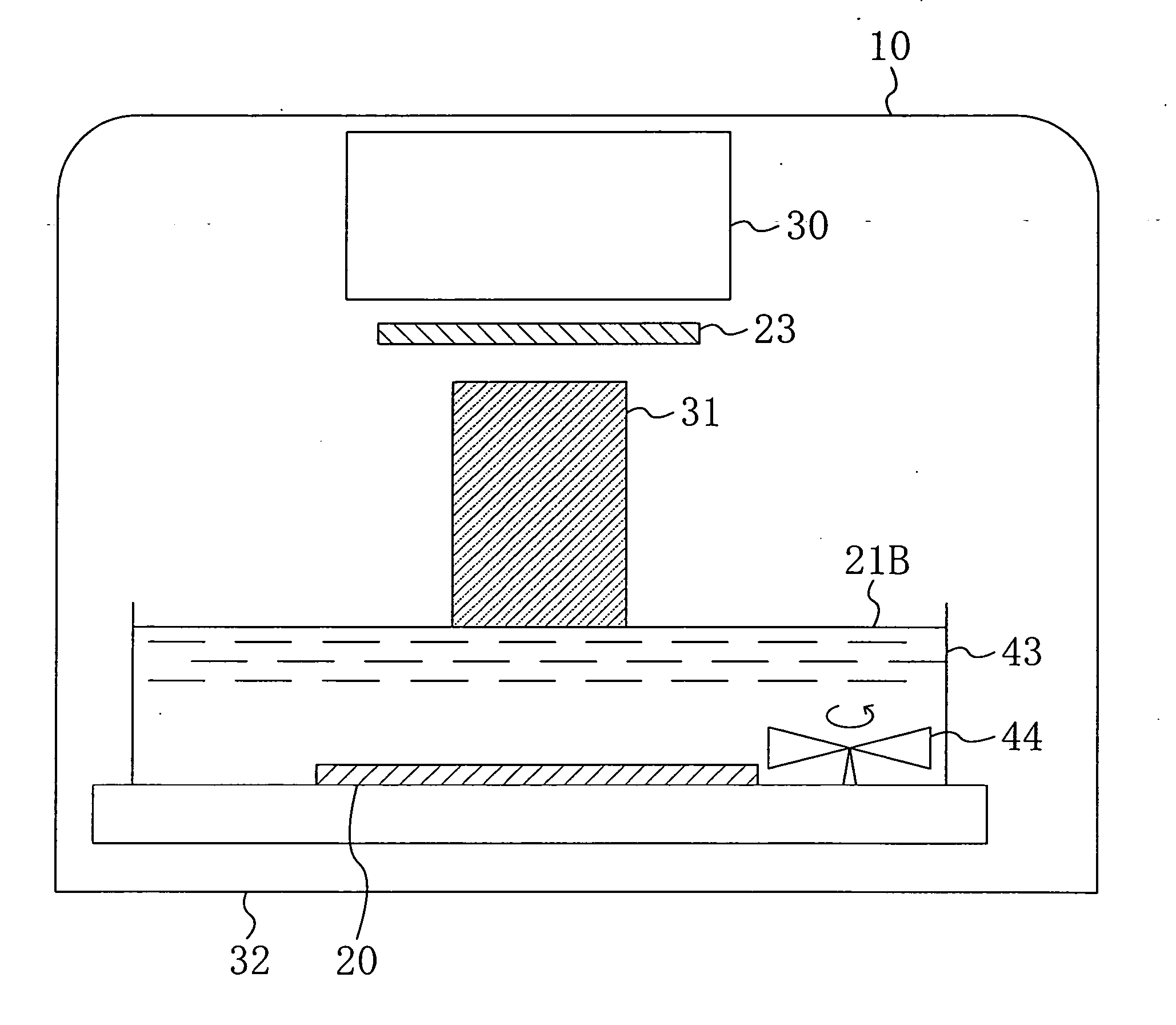
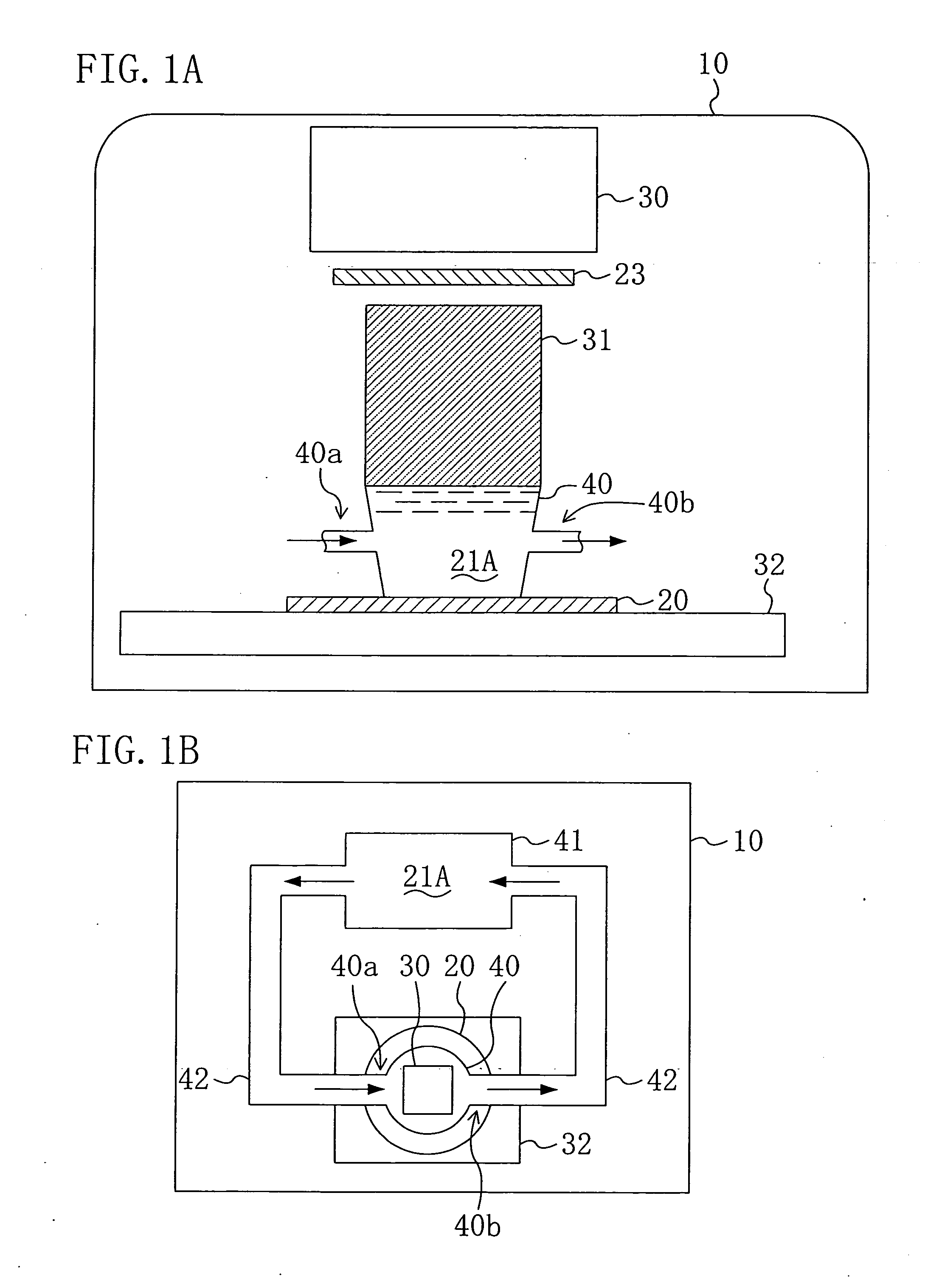
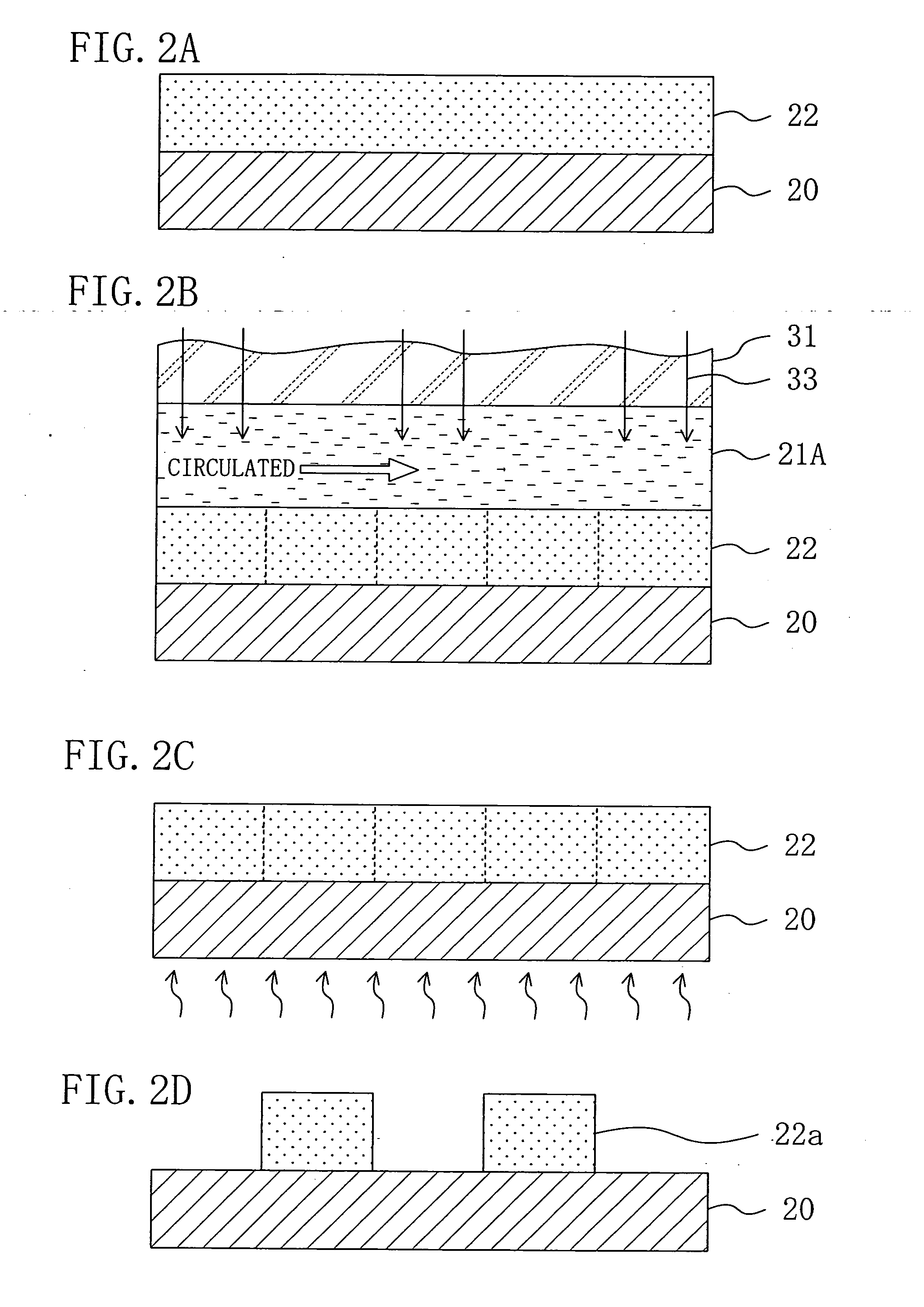
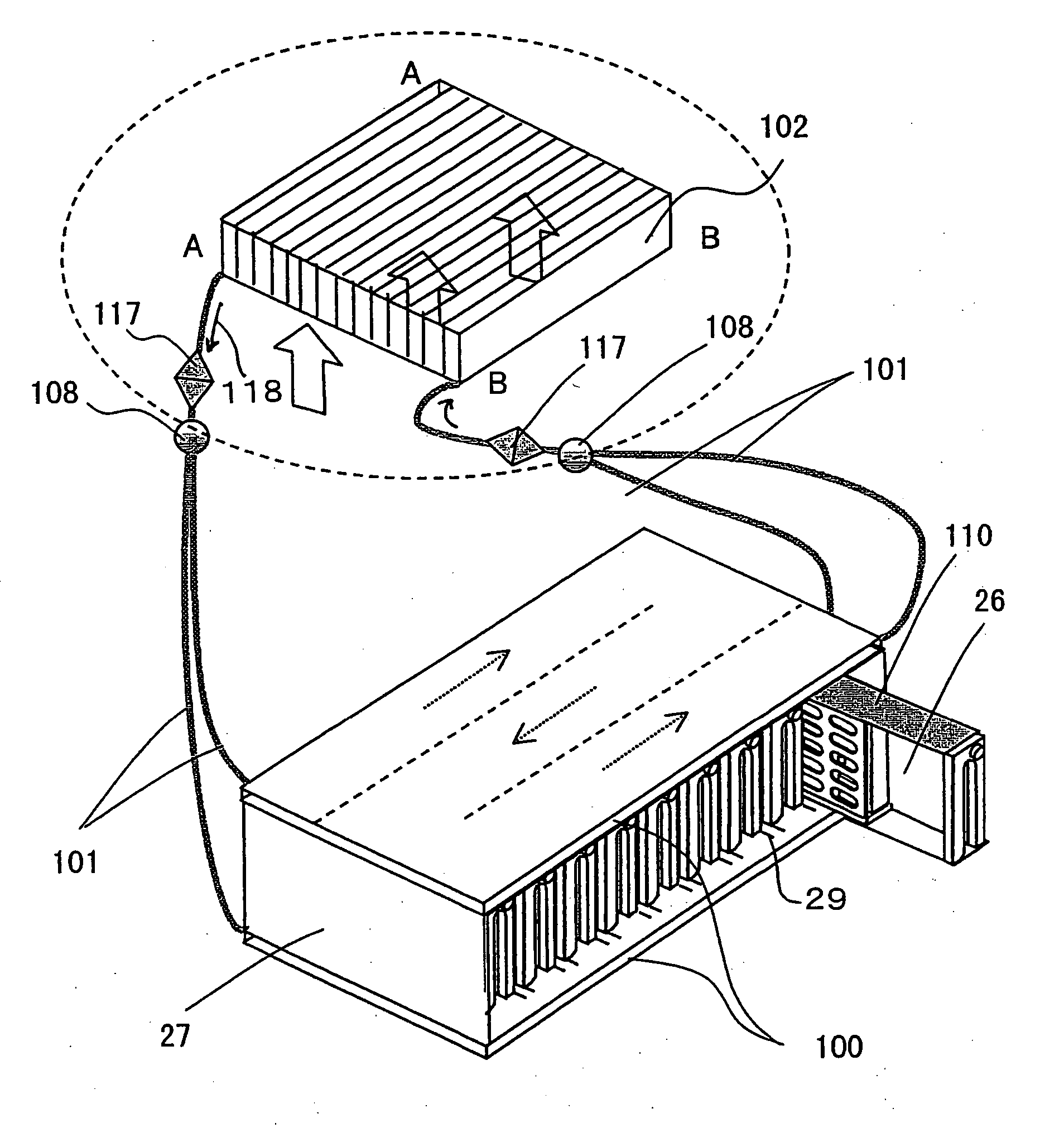
An exposure system includes a liquid supply section for supplying an immersion liquid onto a resist film formed on a substrate; and an exposure section for irradiating the resist film with exposing light through a mask with the immersion liquid provided on the resist film. The liquid supply section includes an immersion liquid tank for circulating the immersion liquid during exposure.
Owner:RPX CORP
Disk array system
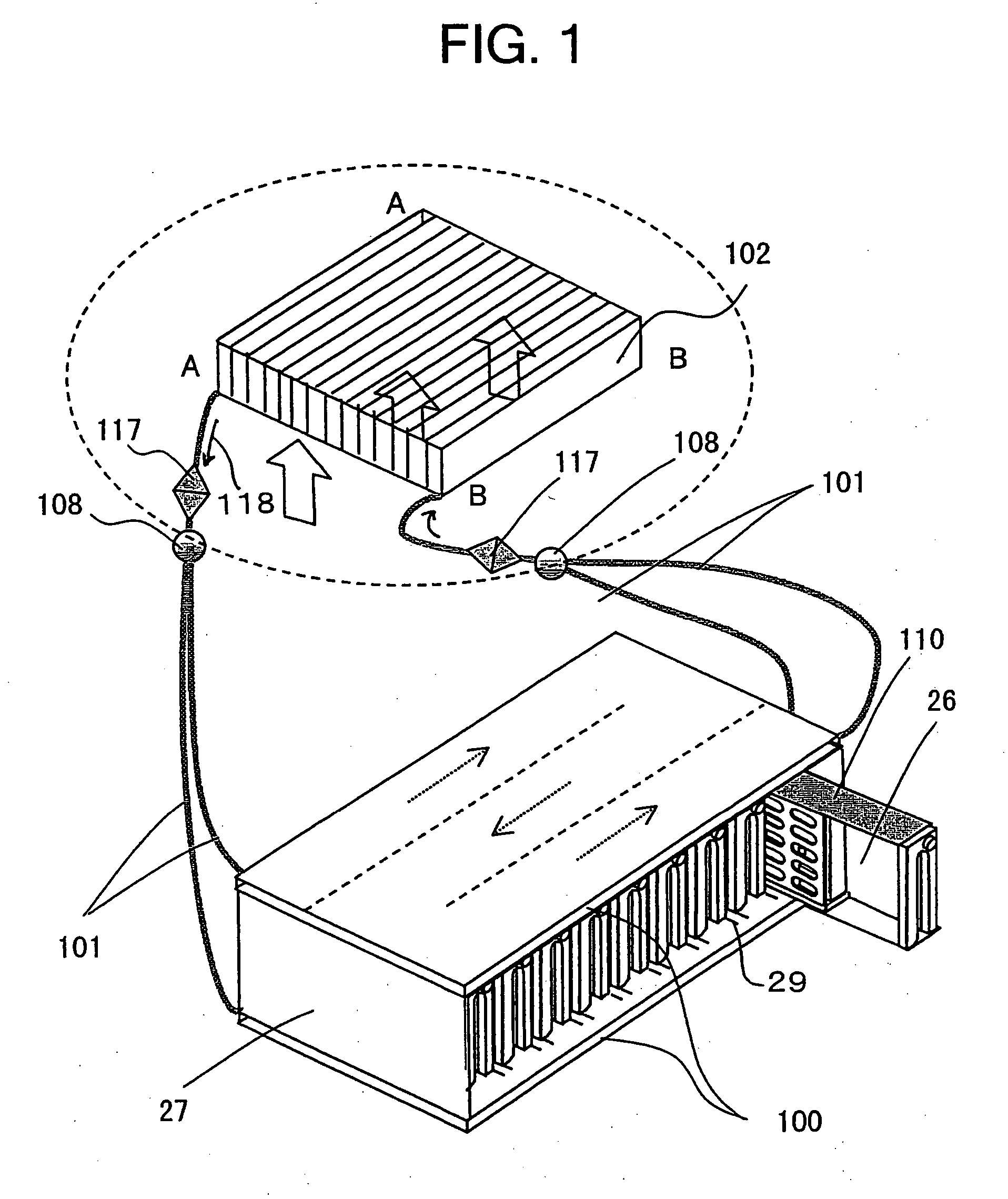
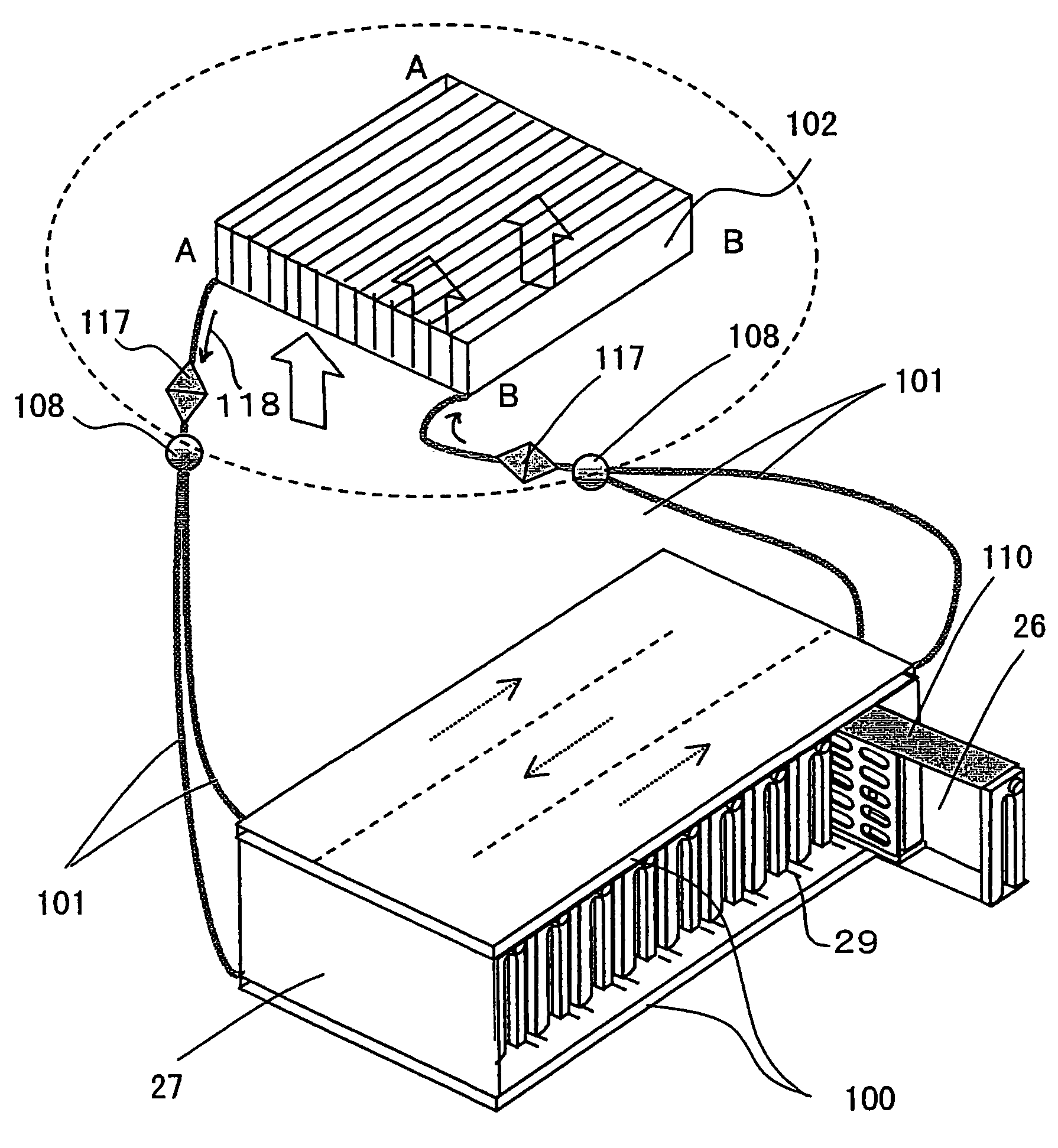
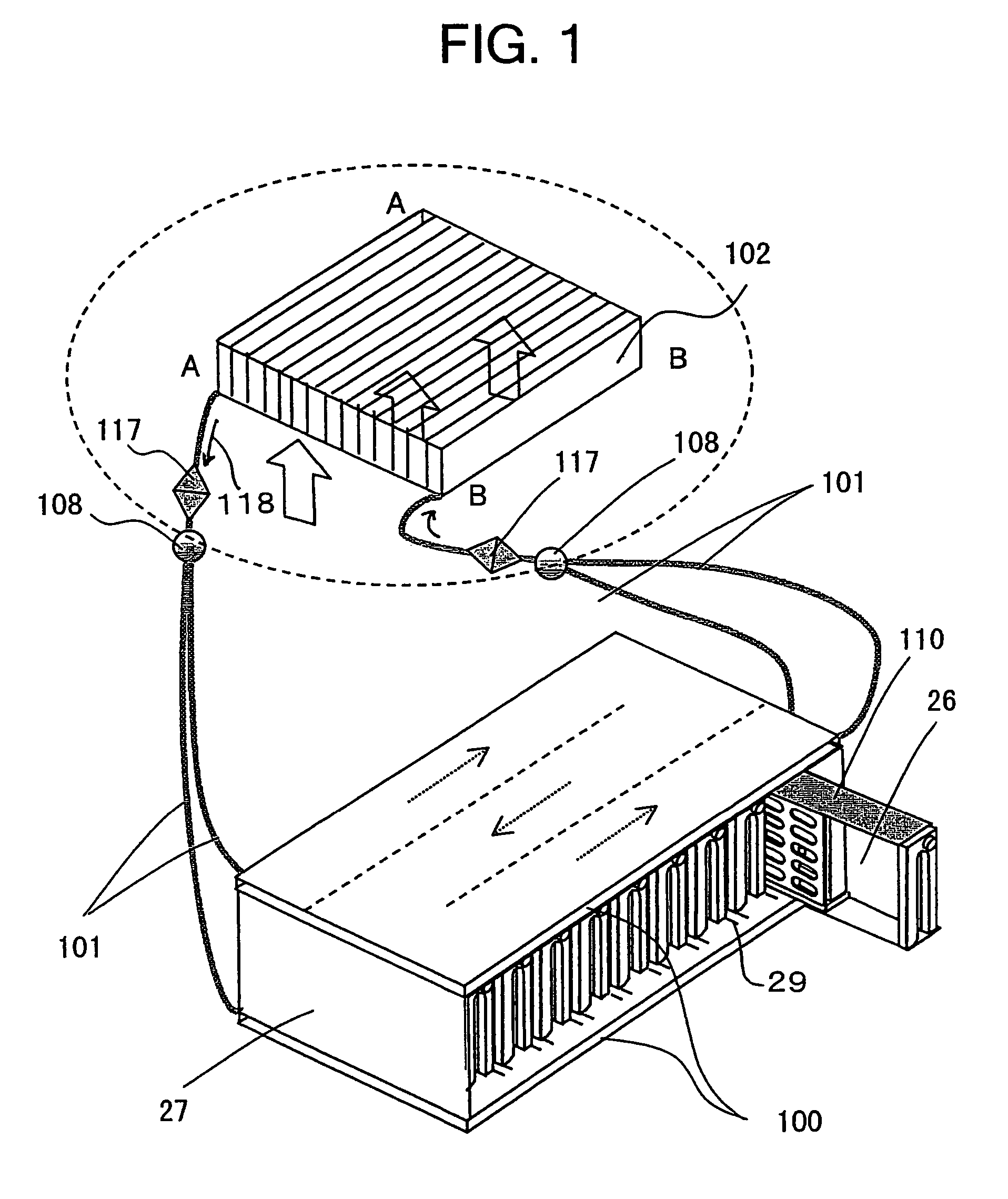
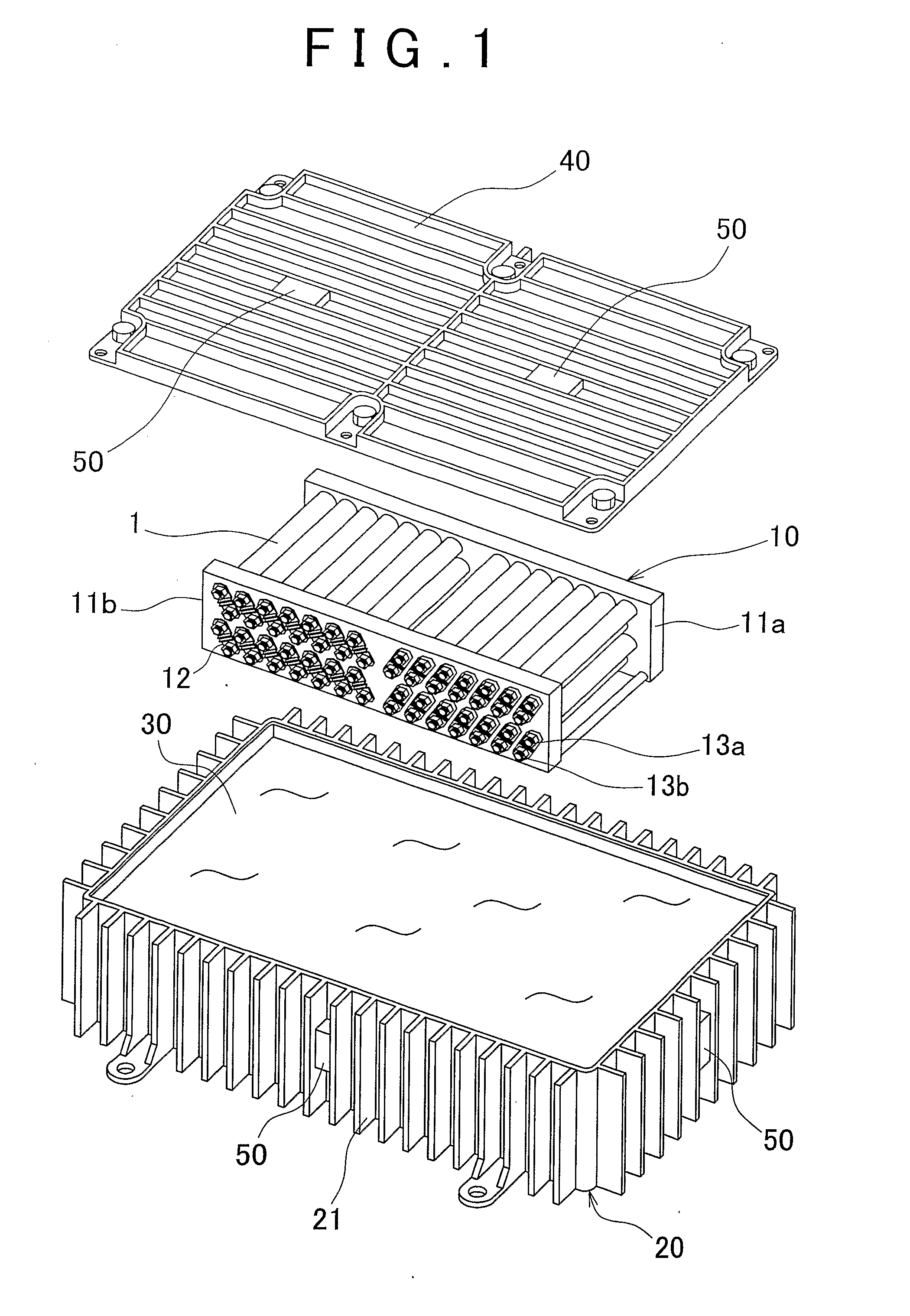
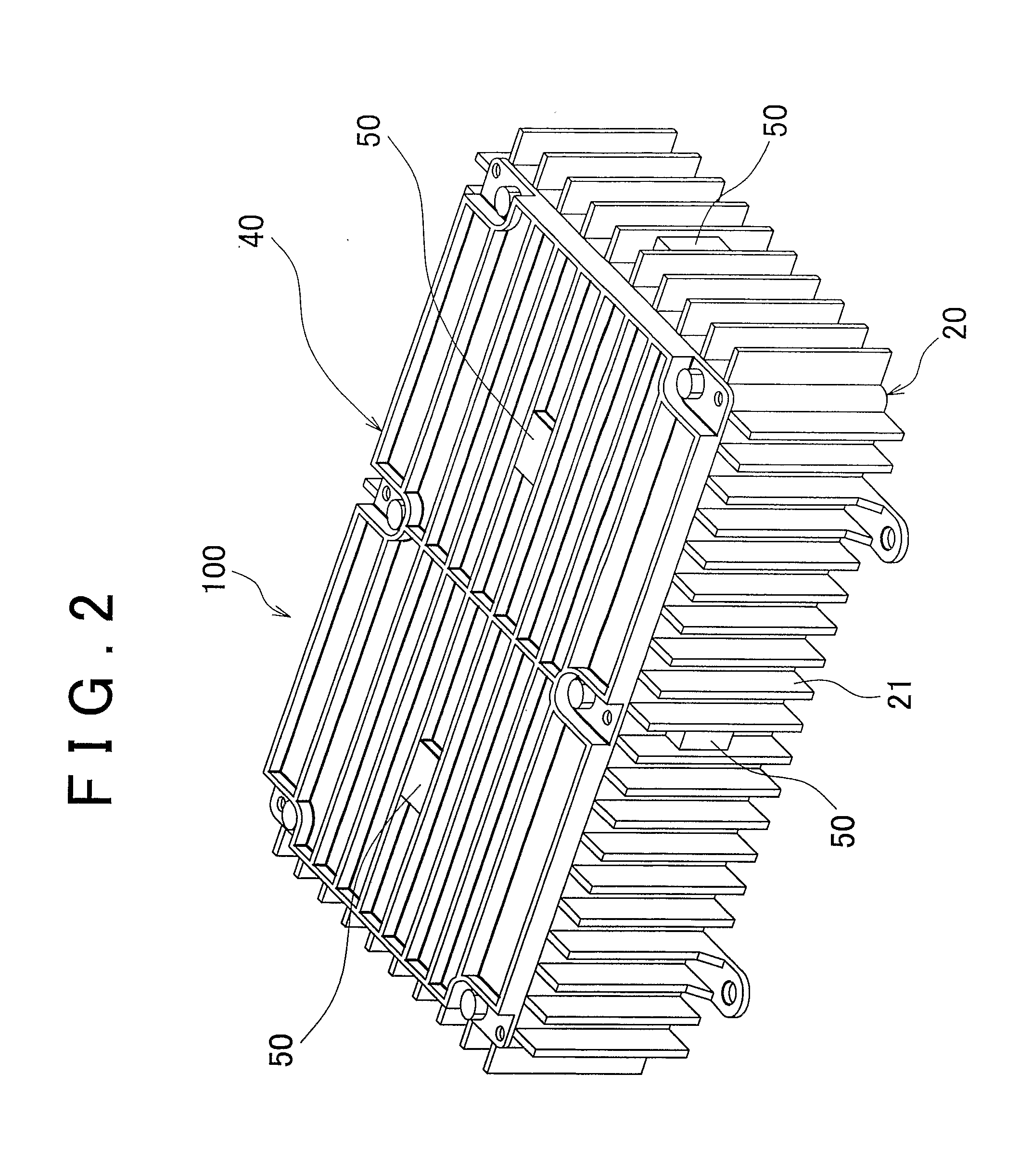
InactiveUS20060077776A1Improve cooling effectImprove reliabilityReducing temperature influence on carrierDigital data processing detailsEngineeringConductive materials
A disk array system includes a plurality of disk drives and at least one unit box including the plurality of disk drives aligned in the thickness direction of the disk drive, each disk drive including a thin case accommodating a recording disk, a read / write head, and a driving mechanism for driving the recording disk and the read / write head, and a control board for controlling the driving mechanism, the control board being mounted on the thin case. In the disk array system, the thin case and the unit box are composed of a thermally-conductive material, the unit box includes surfaces parallel to the thickness direction of the plurality of disk drives, and at least one of the surfaces has a cold plate filled with a refrigerant. Heat generated at the disk drives is transferred to the cold plate, thereby improving cooling performance.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Disk array system
InactiveUS7675748B2Improve cooling effectImprove reliabilityReducing temperature influence on carrierDigital data processing detailsEngineeringConductive materials
A disk array system includes a plurality of disk drives and at least one unit box including the plurality of disk drives aligned in the thickness direction of the disk drive, each disk drive including a thin case accommodating a recording disk, a read / write head, and a driving mechanism for driving the recording disk and the read / write head, and a control board for controlling the driving mechanism, the control board being mounted on the thin case. In the disk array system, the thin case and the unit box are composed of a thermally-conductive material, the unit box includes surfaces parallel to the thickness direction of the plurality of disk drives, and at least one of the surfaces has a cold plate filled with a refrigerant. Heat generated at the disk drives is transferred to the cold plate, thereby improving cooling performance.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
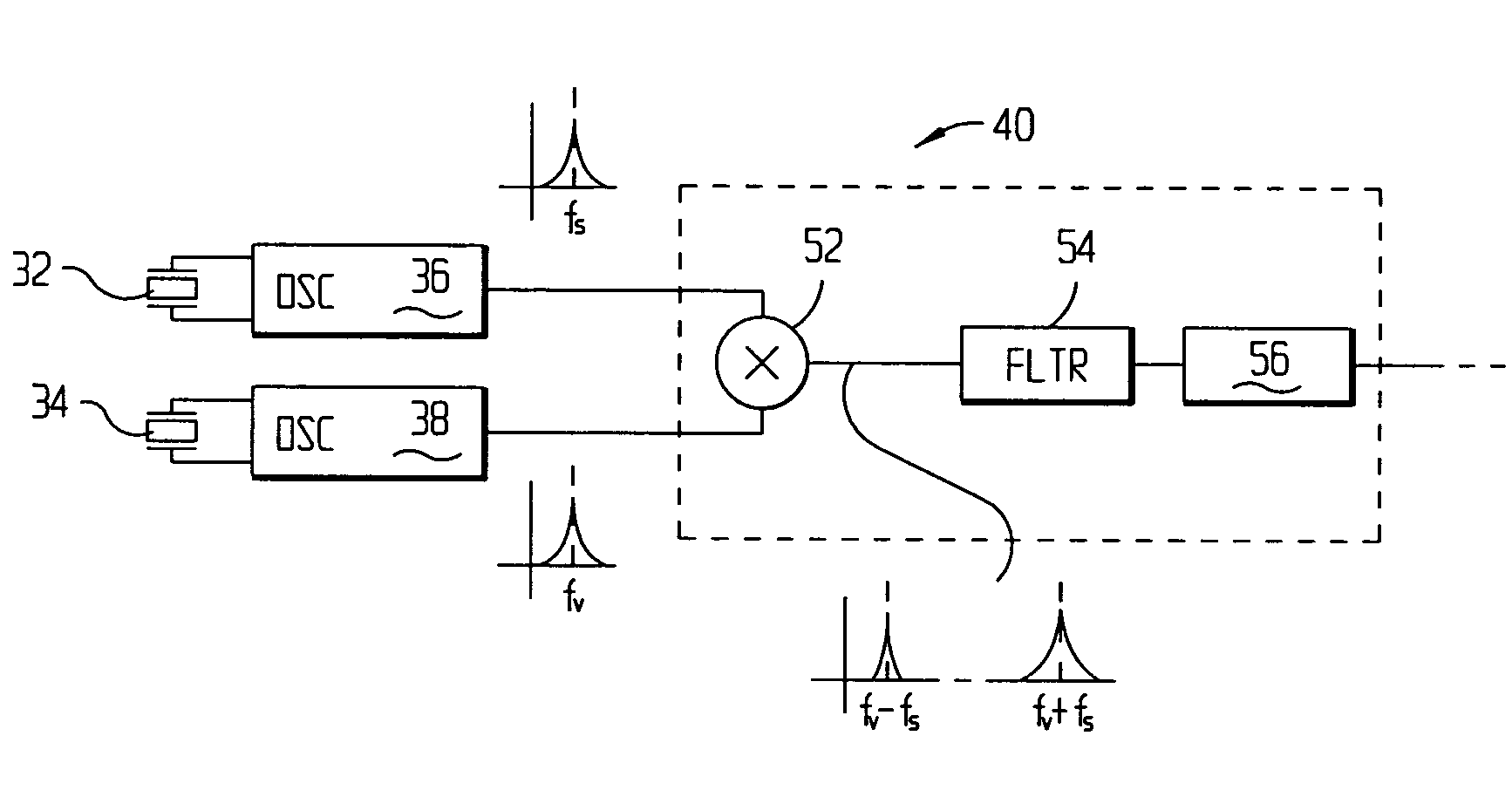
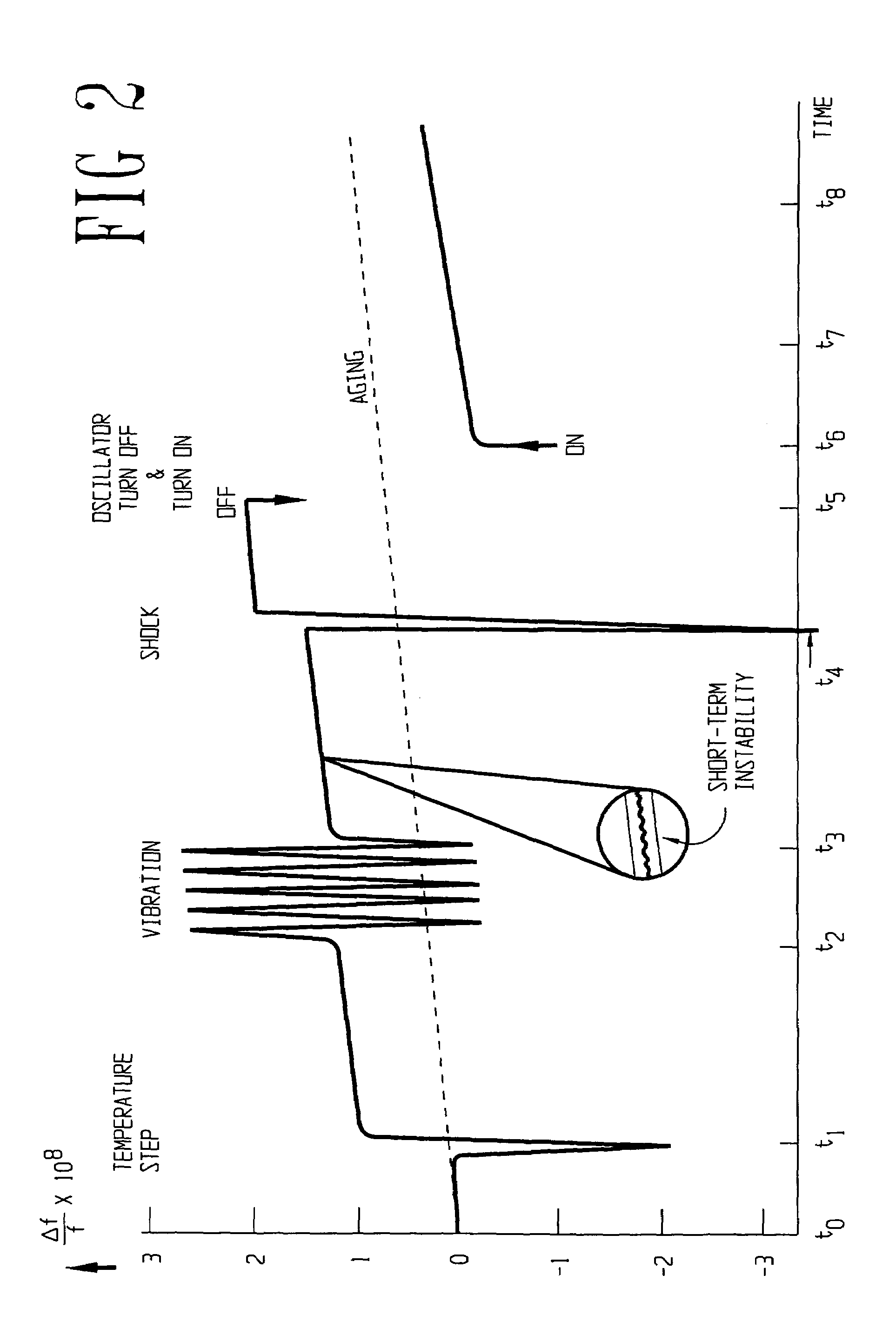
Downhole clock having temperature compensation
ActiveUS7212075B2Improve frequency stabilityTemperature variationPulse automatic controlGenerator stabilizationEngineeringCrystal base
A downhole crystal-based clock that is substantially insensitive to the factors that may cause frequency deviation as a result of downhole temperature. The clock may include a plurality of crystals, where a first crystal may be more stable, with respect to temperature, than a second crystal. The crystals may be thermally coupled together so that they may have substantially the same temperature. An error detector may monitor the differences between the frequencies associated with each crystal and provide this information to a storage device. This information may be determined prior to deploying the clock downhole. When deployed downhole, the signal from the error detector may be interpreted in light of the information in the storage device to provide a temperature measurement of the two crystals. The downhole temperature measurement then may be used to reduce frequency deviations in the downhole clock that may result from downhole temperatures.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Surface acoustic wave device and surface acoustic wave oscillator
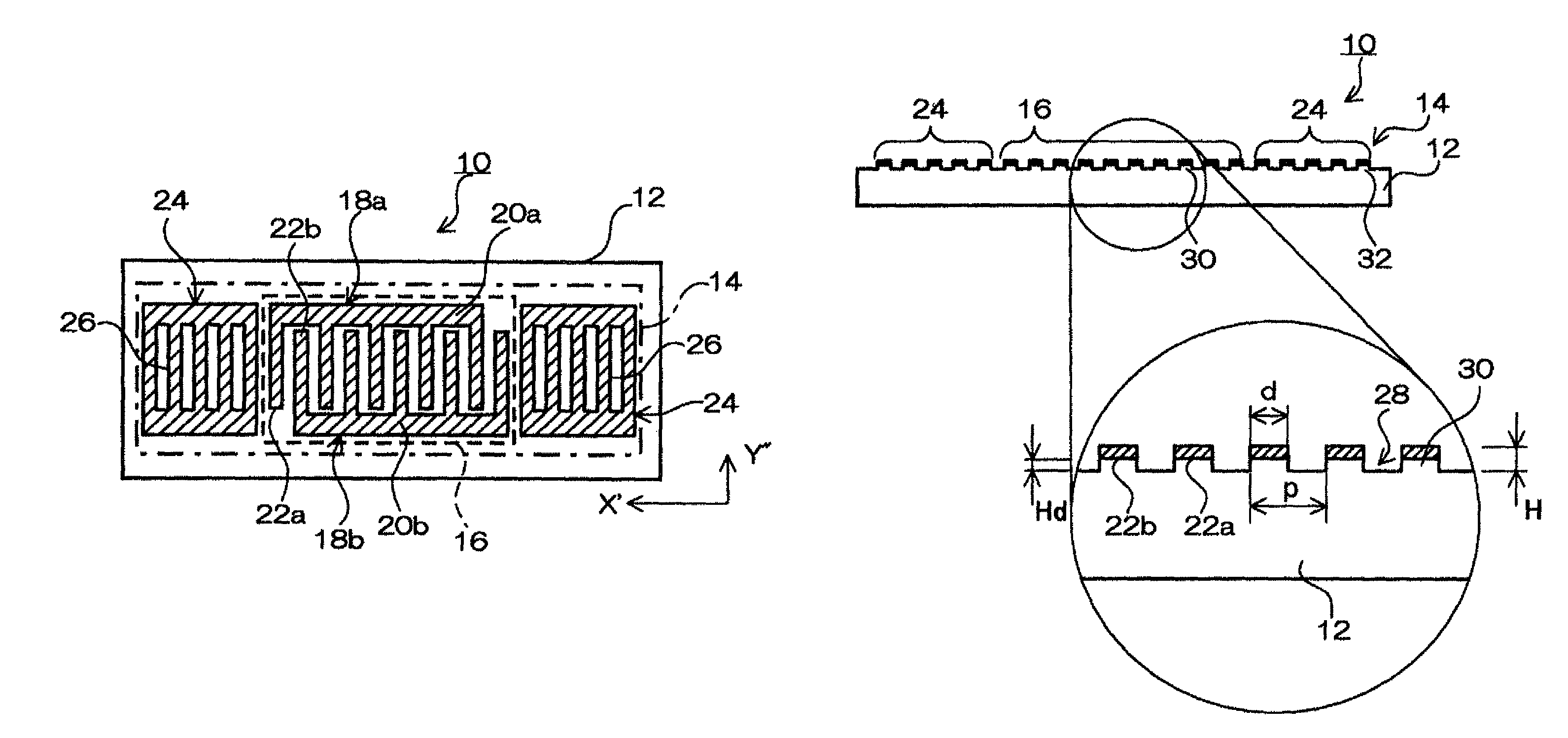
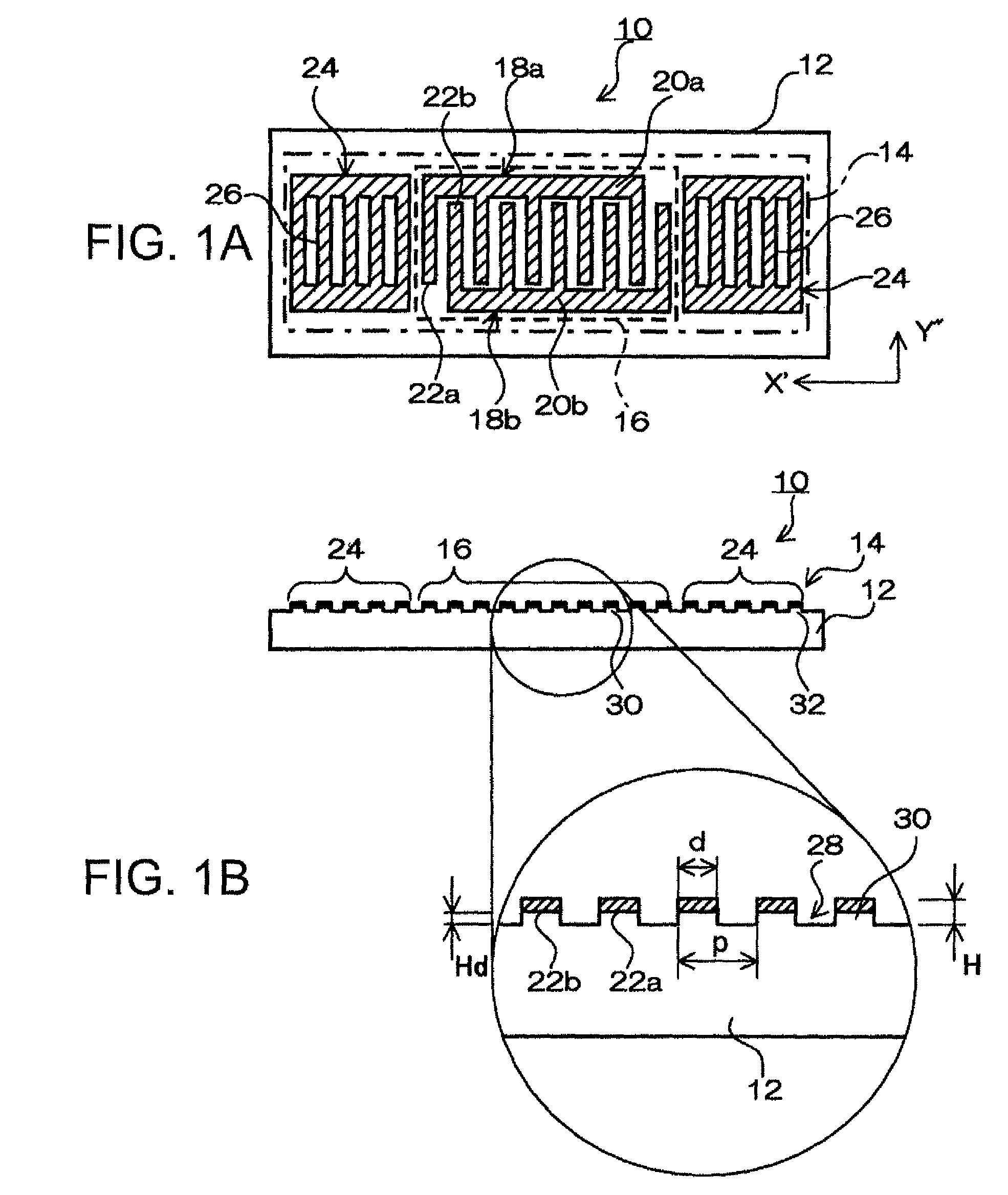
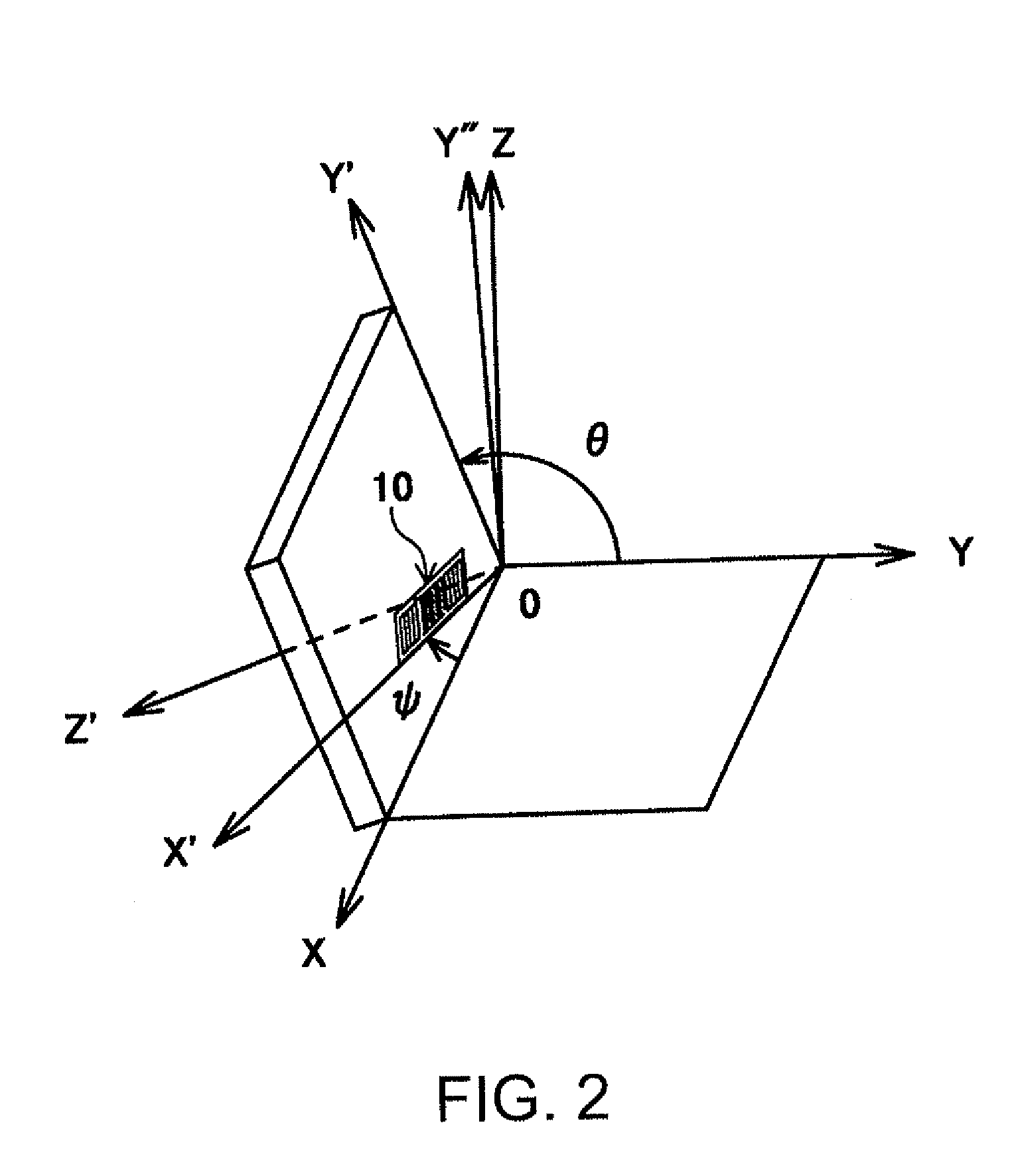
ActiveUS20090206955A1Suitable for mass-productionReduce disagreementImpedence networksInterdigital transducerStopband
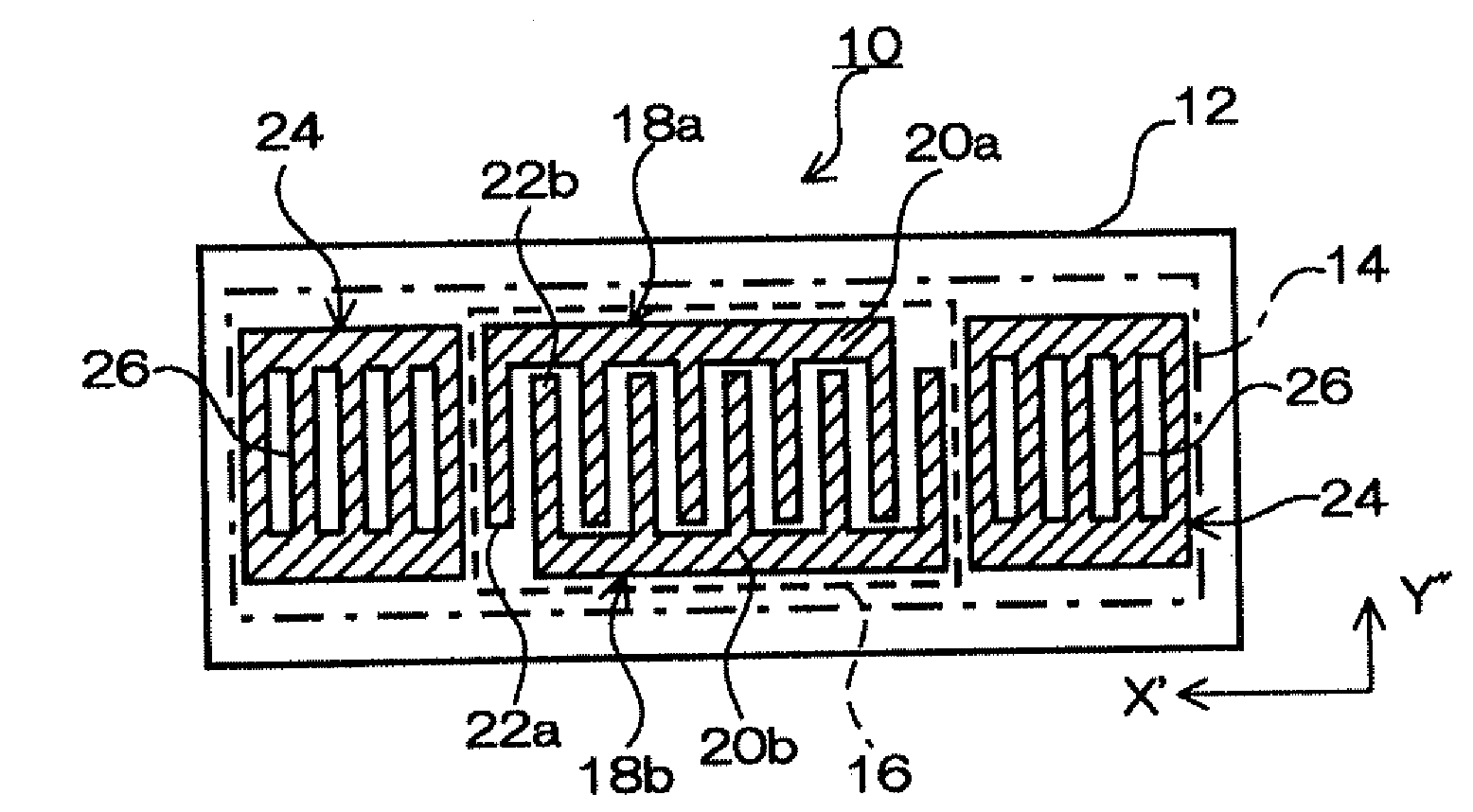
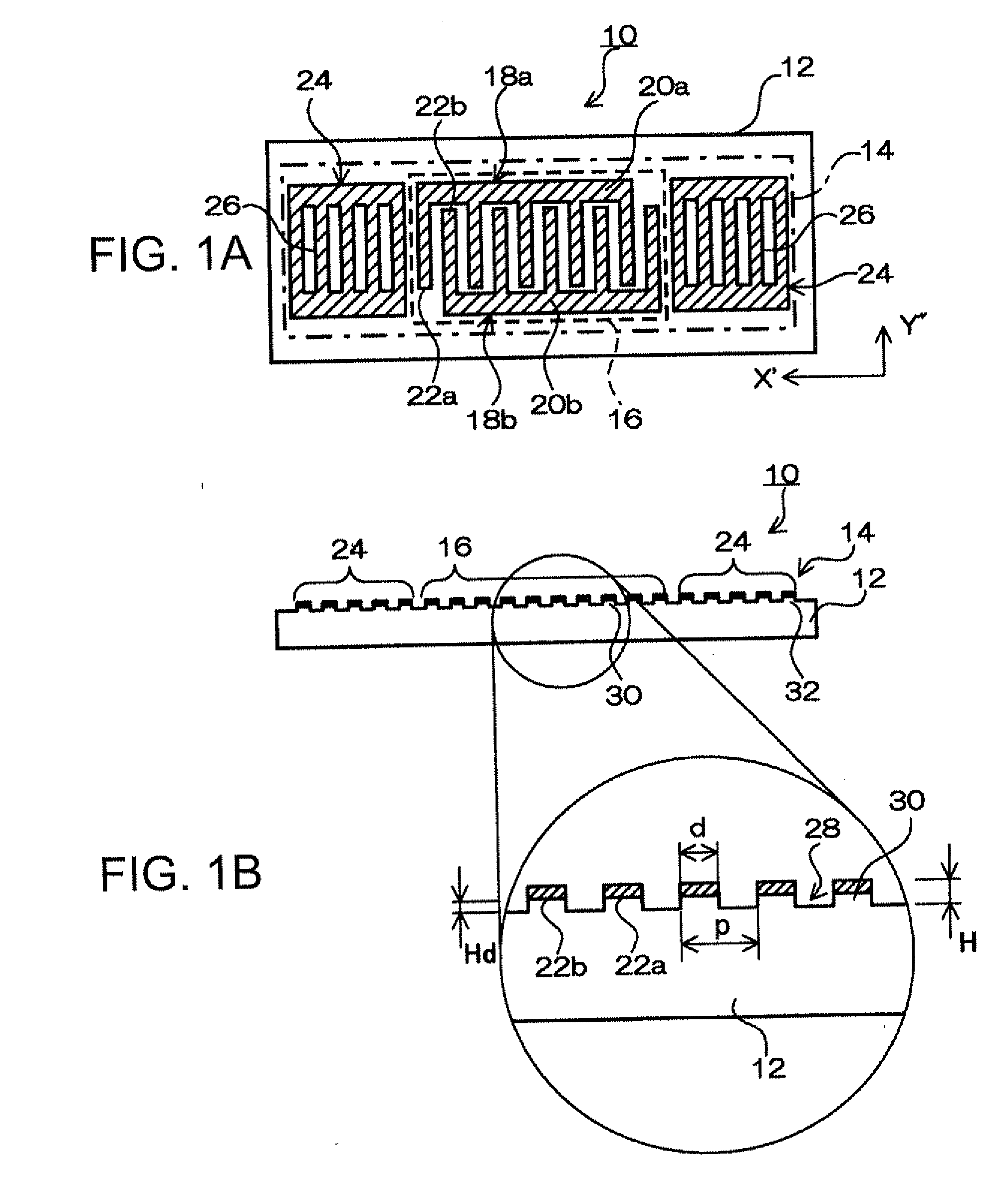
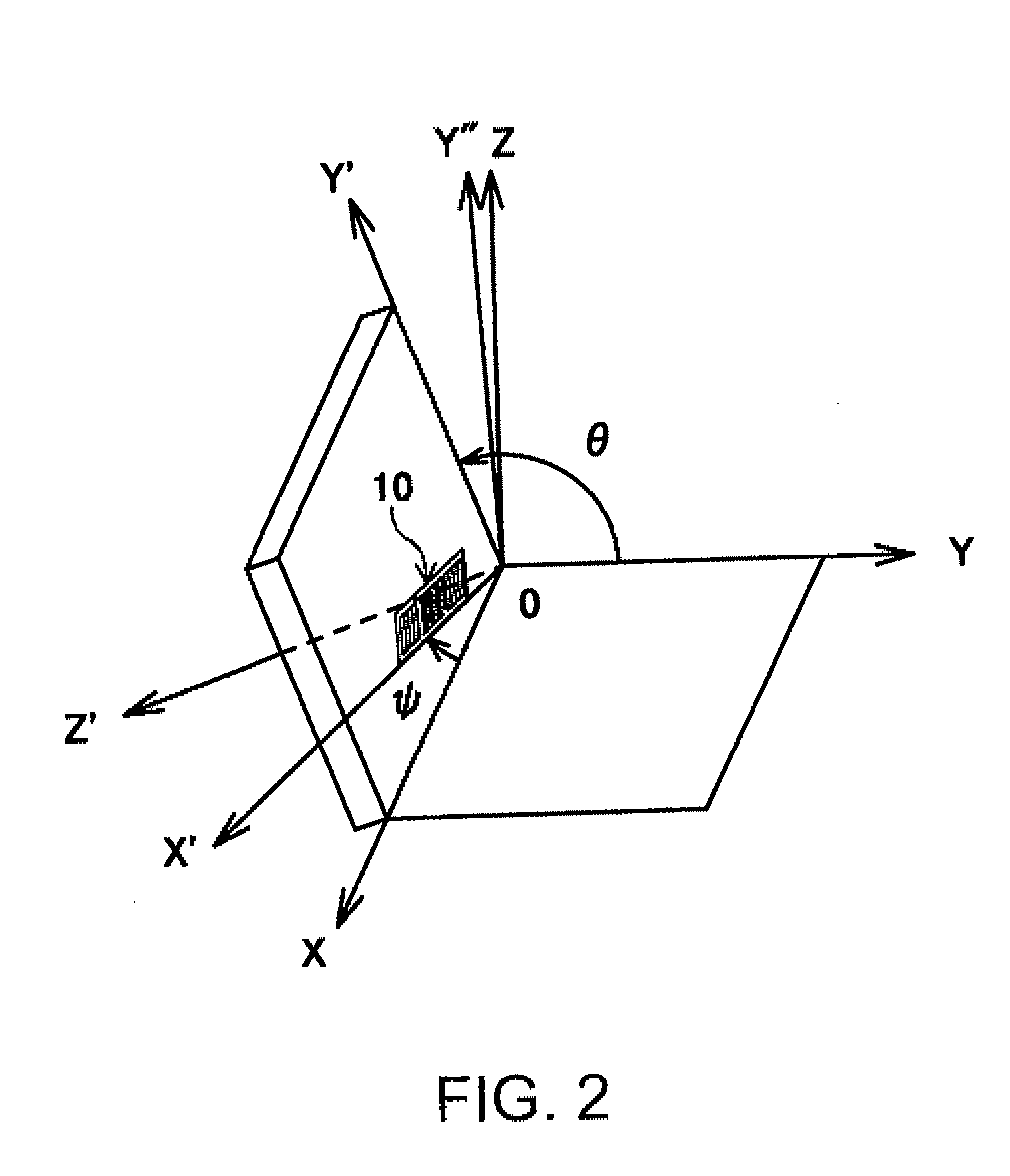
A surface acoustic wave device, includes: an interdigital transducer serving as an electrode pattern to excite a Rayleigh surface acoustic wave, the interdigital transducer including a comb-tooth-shaped electrode having a plurality of electrode fingers; a piezoelectric substrate on which the interdigital transducer is formed, the piezoelectric substrate being made of a quartz substrate that is cut out at a cut angle represented by an Euler angle representation (φ, θ, Ψ) of (0°, 95°≦θ≦155°, 33°≦|Ψ|≦46°); electrode finger grooves formed between the electrode fingers of the comb-tooth-shaped electrode; and electrode finger bases being quartz portions sandwiched between the electrode finger grooves and having upper surfaces on which the electrode fingers are positioned The surface acoustic wave device provides an excitation in an upper limit mode of a stop band of the surface acoustic wave.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
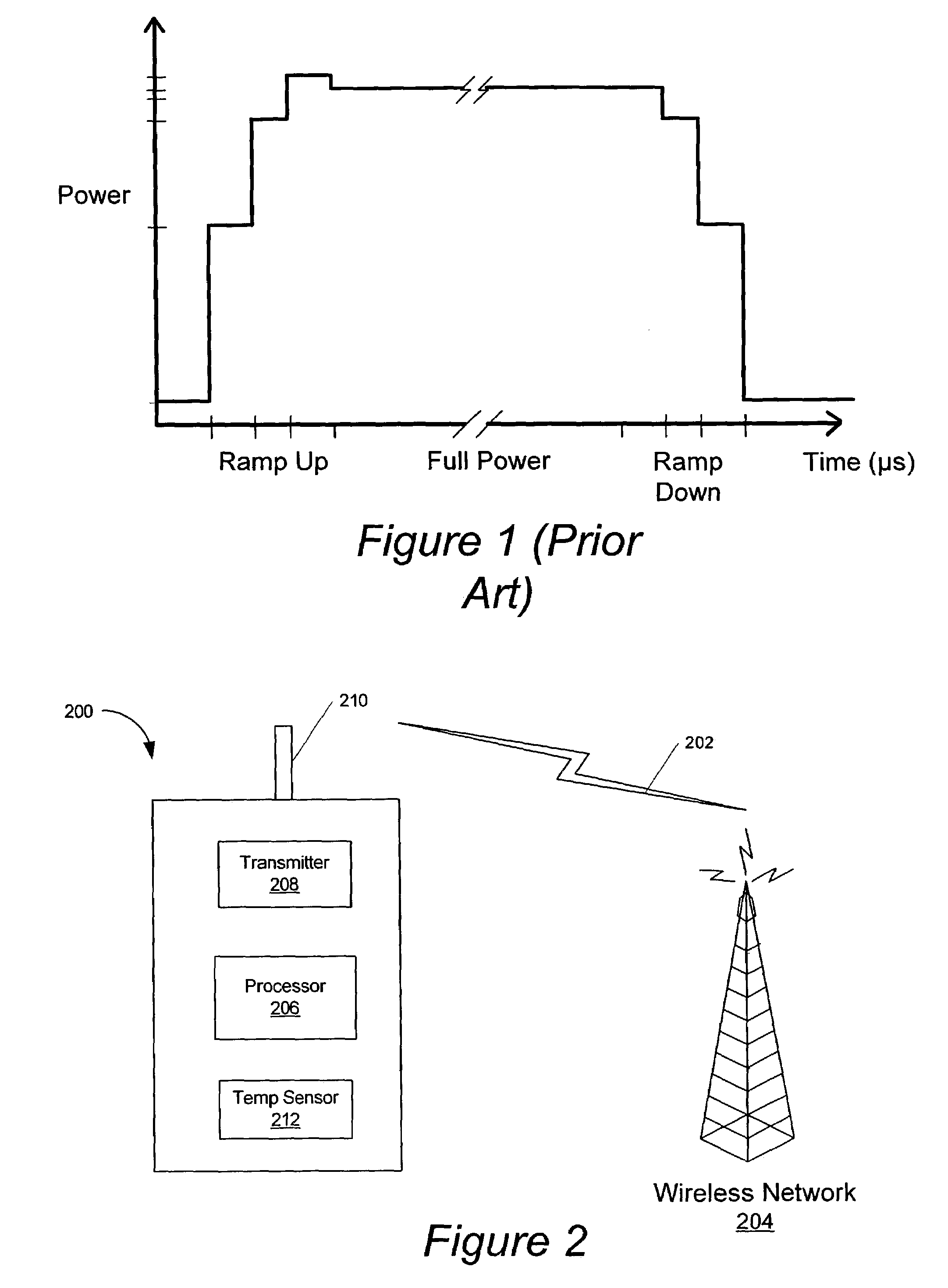
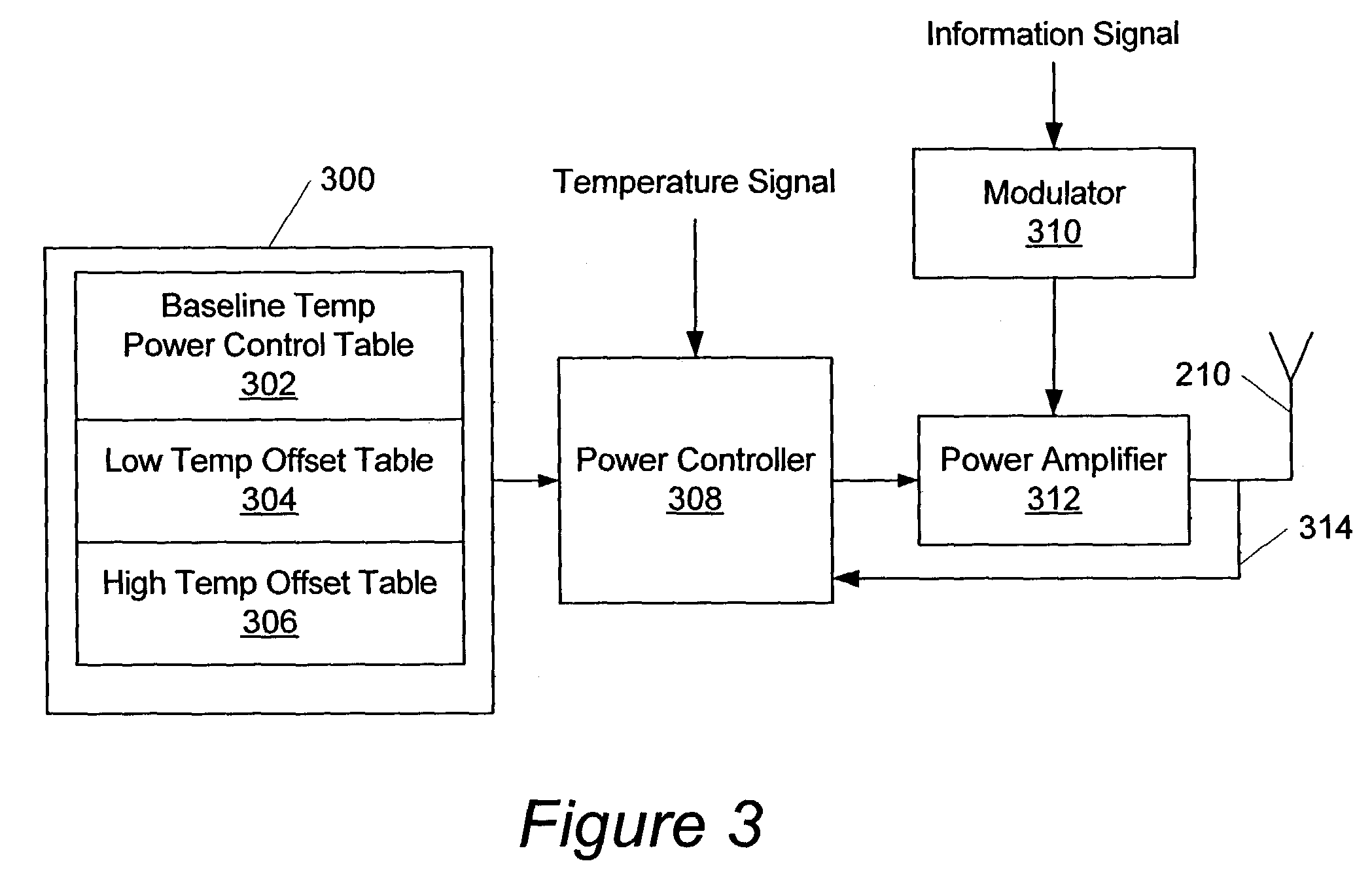
Radio transmitters with temperature compensated power control profiles and methods of operating same
ActiveUS7068985B2Compensation effectTemperature variationPower managementResonant long antennasPower controllerAudio power amplifier
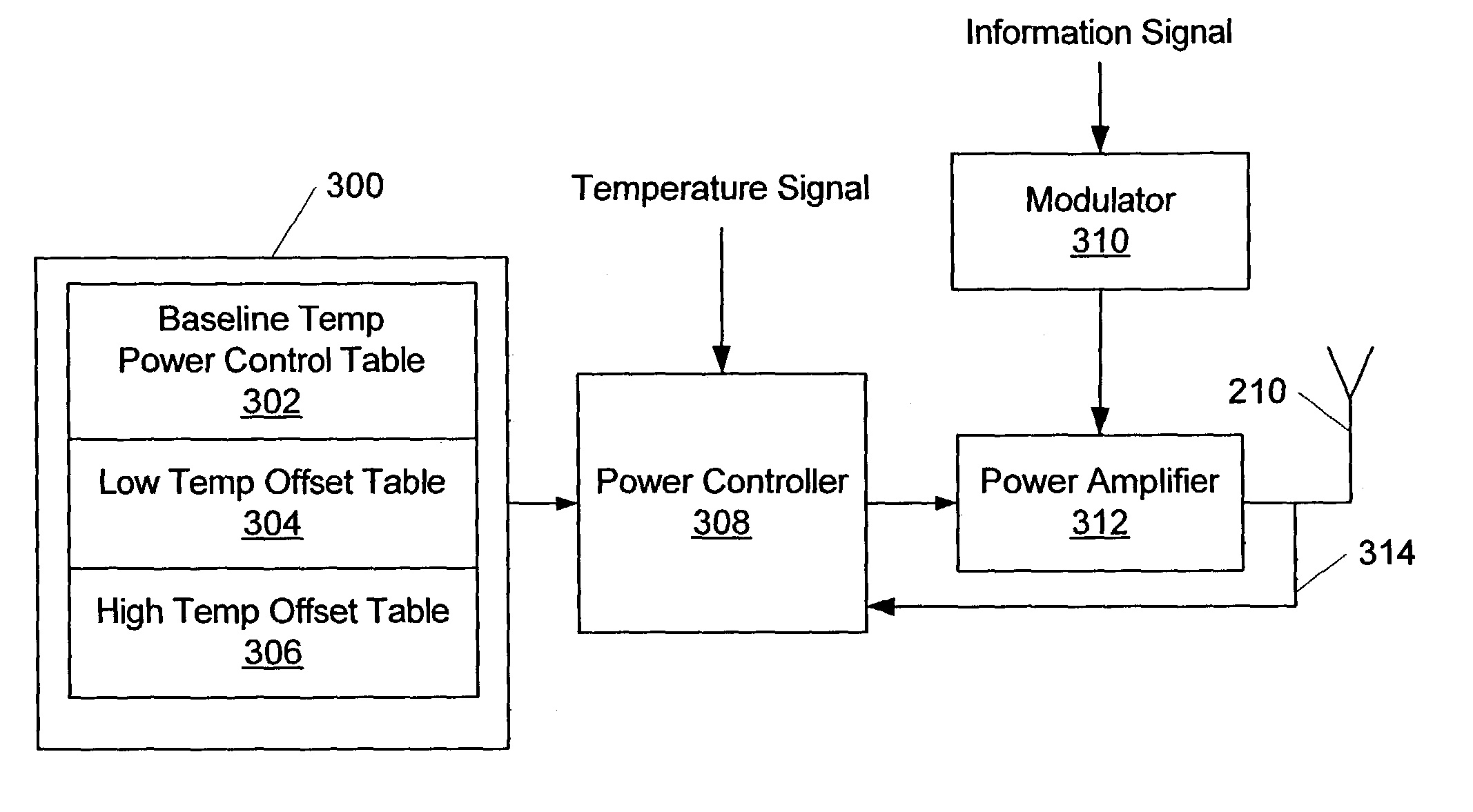
A radio transmitter includes a power control table, a power amplifier, and a power controller. The power control table includes a plurality of control values. The power amplifier amplifies an RF signal for transmission with an adjustable gain. The power controller adjusts the gain of the power amplifier based on the power control table and a temperature signal that is indicative of a temperature of at least a portion of the radio transmitter.
Owner:SONY ERICSSON MOBILE COMM AB
Underwater cutting pelletizer
InactiveUS7470118B2Uniform retention timeVariations in temperature of the pellets can be kept to a minimumMouldsConfectioneryRetention timeUnderwater
An underwater cutting pelletizer is disclosed wherein a water chamber is circular in plan, an inlet portion is formed on one side in a diametrical direction of the water chamber to introduce cooling water into the water chamber, and an outlet portion is formed on the other side in the diametrical direction of the water chamber to discharge the cooling water from the interior of the water chamber to the exterior, the inlet portion being in a divergent shape in an inflow direction of cooling water. The retention time of pellets in the interior of the water chamber can be made as short as possible.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
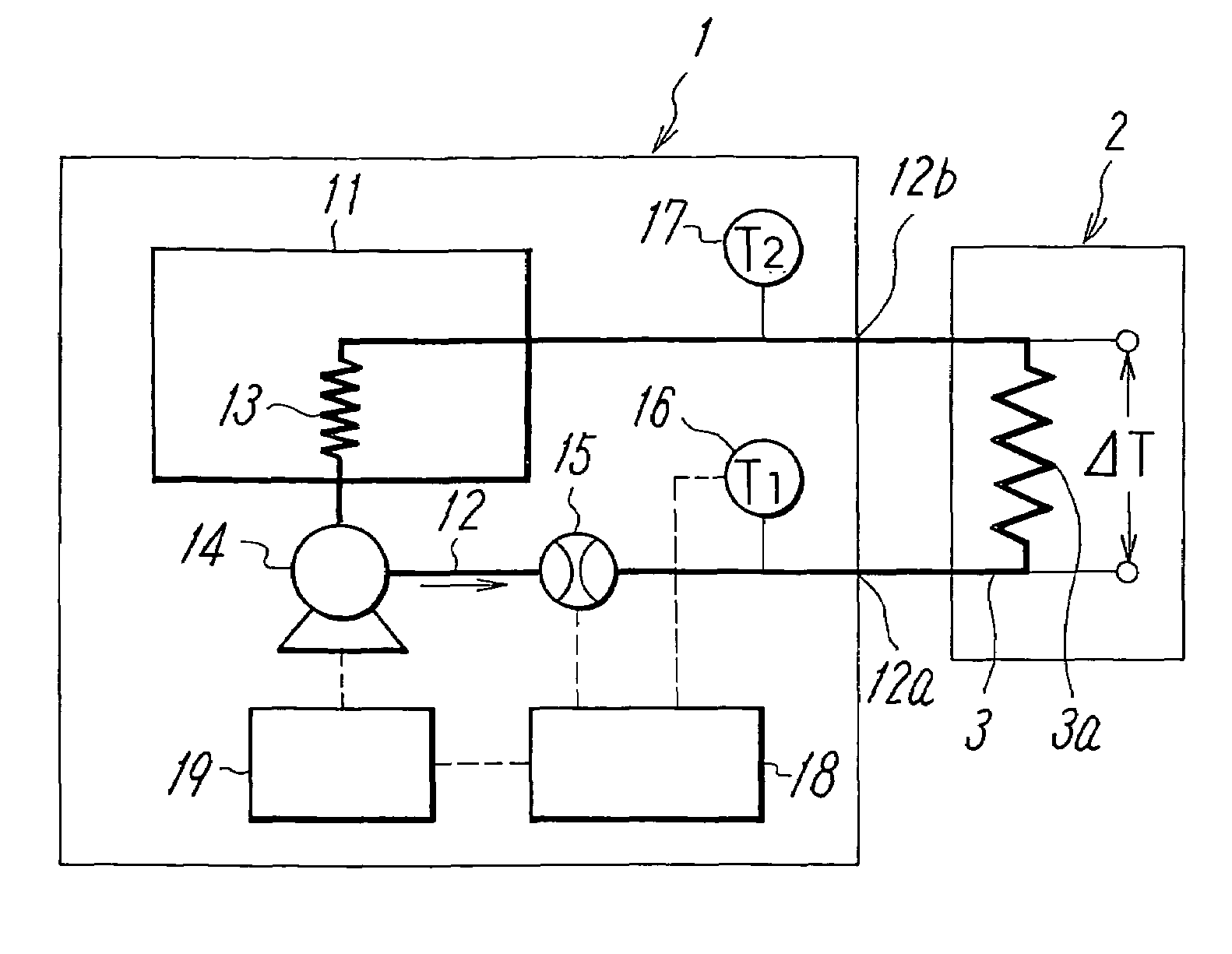
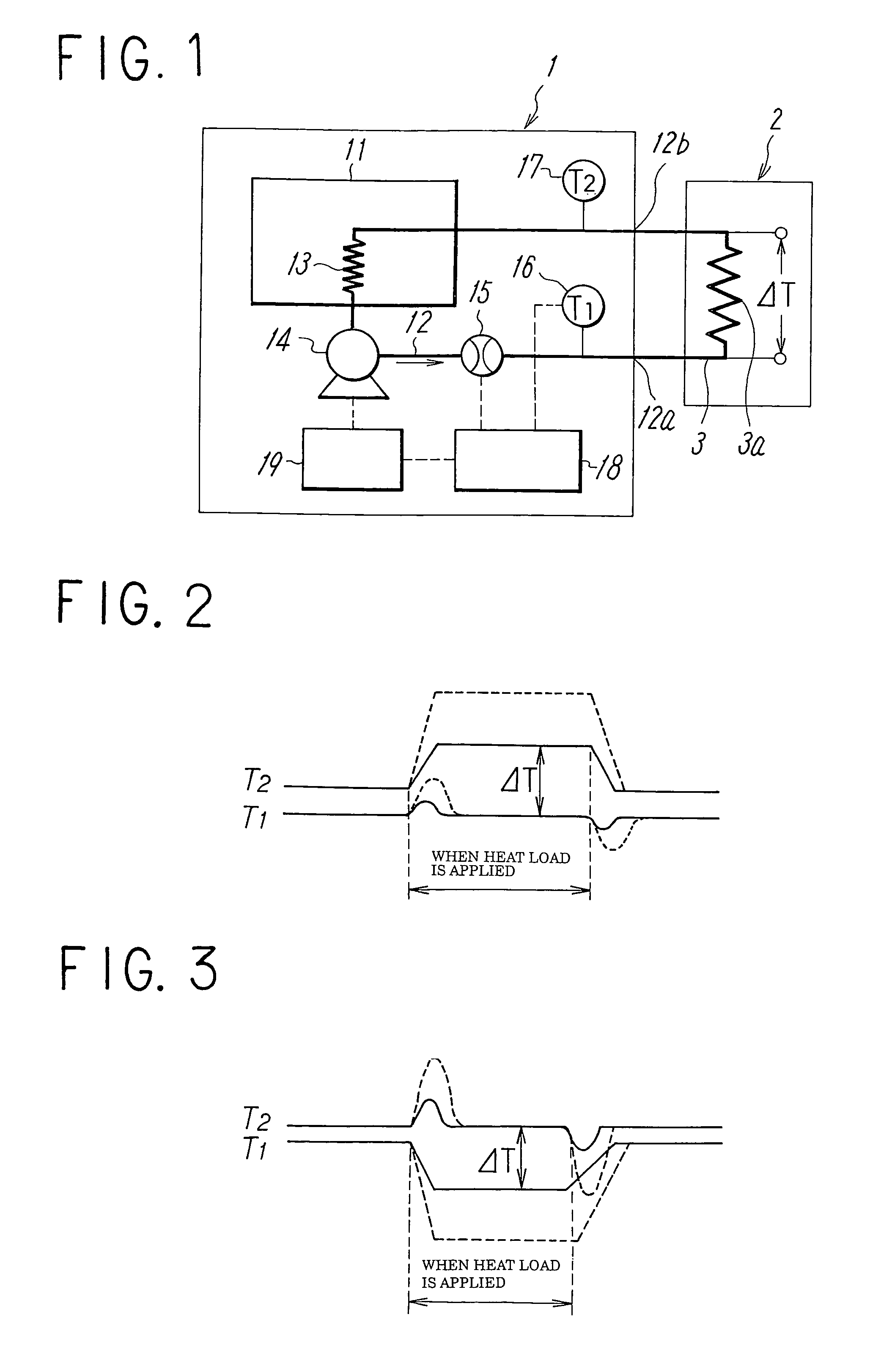
Constant temperature liquid circulating device and method of controlling temperature in the device
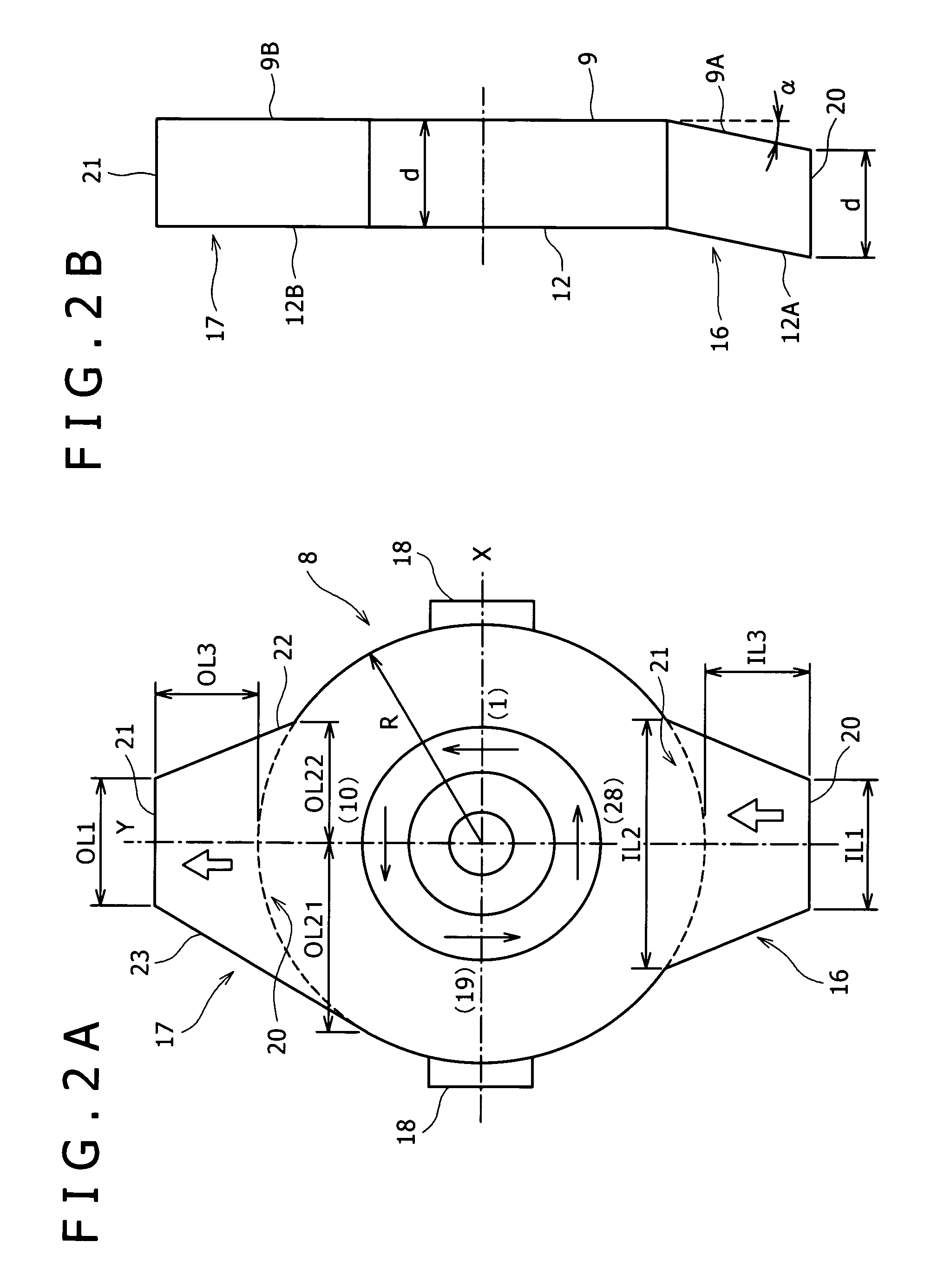
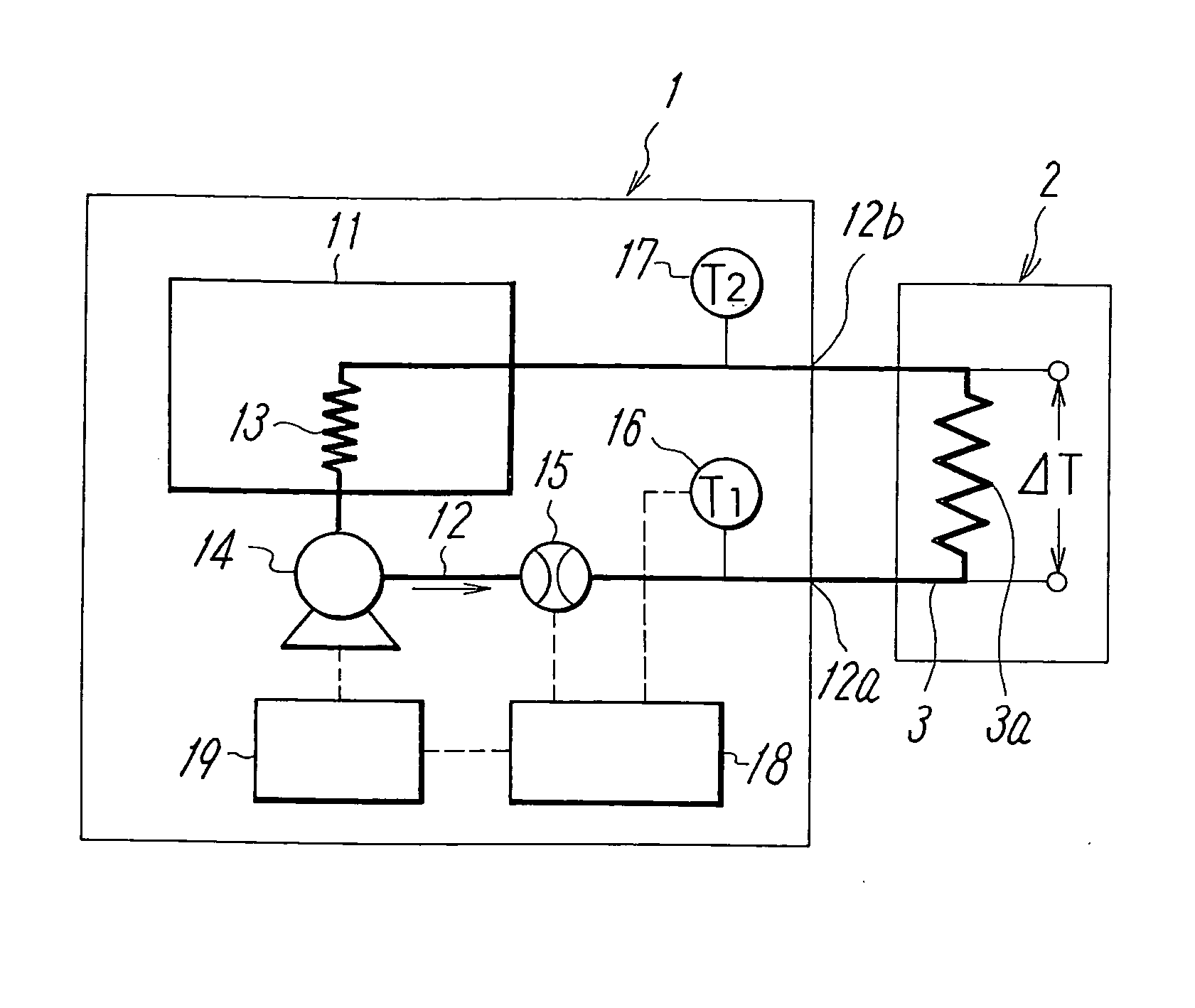
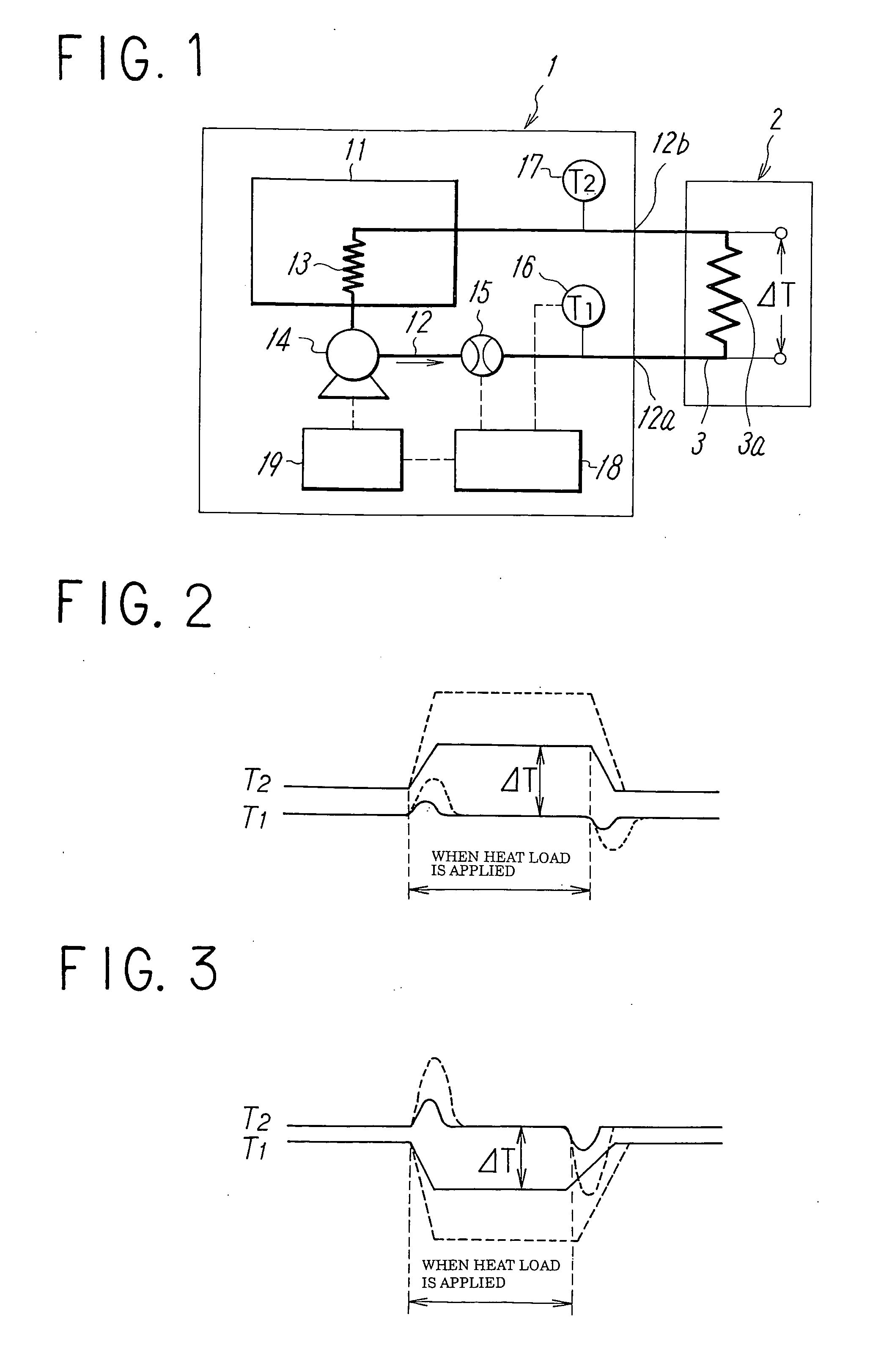
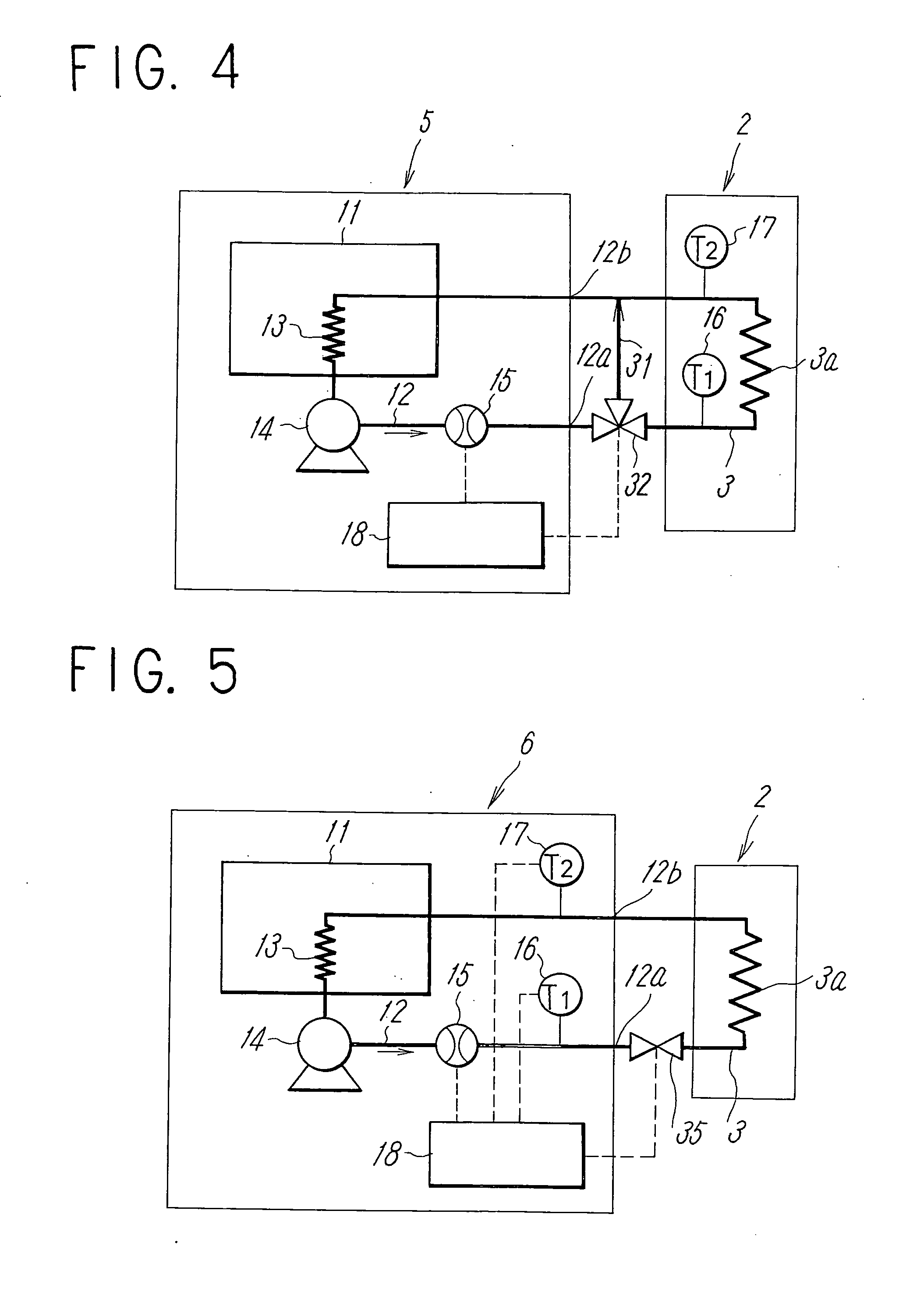
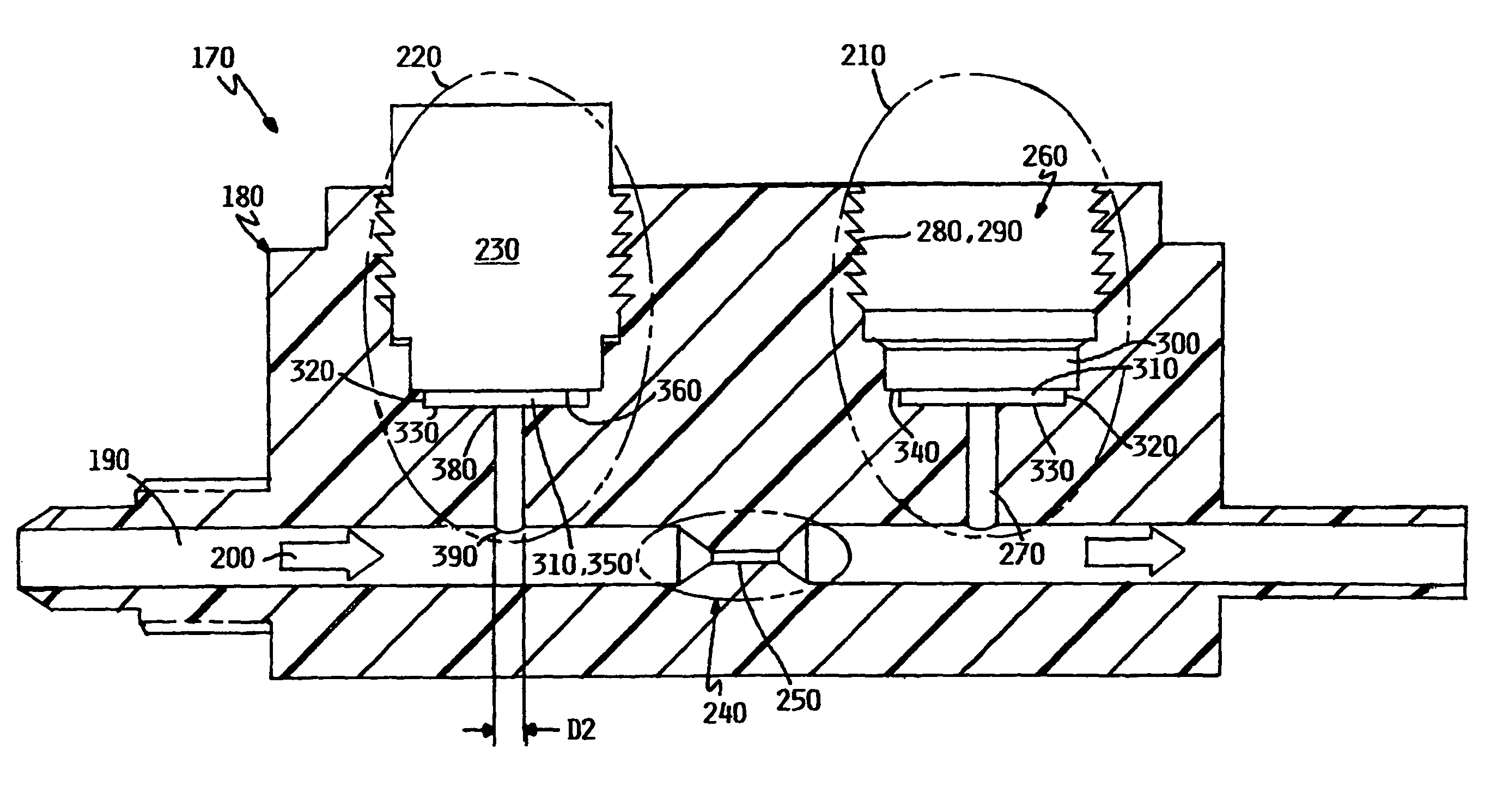
ActiveUS20070074863A1Reduce variationTemperature variationTemperature control without auxillary powerSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsTemperature controlFlow transducer
To reduce the width of variations in temperature of circulating liquid due to a variation in a heat load of an external device to a low level to stabilize the performance of the external device in a constant temperature liquid circulating device. In a constant temperature liquid circulating device that connects a piping of circulating liquid in an external device between a discharge port and a return port of a conduit for delivering the circulating liquid at a constant temperature by a pump, a flow amount sensor and temperature sensors for detecting discharge temperature (T1) of the circulating liquid from the conduit and the return temperature (T2) of the circulating liquid are provided in the conduit, so that the flow amount and the temperature of the circulating liquid is controlled by a controller according to the heat load of the external device obtained on the basis of the outputs from the temperature sensors. The control is such that when the difference between the discharge temperature and the return temperature is smaller than the preset value, the temperature of the circulating liquid is controlled corresponding to the heat load, and when the temperature difference is larger than the preset value, the temperature of the circulating liquid is controlled corresponding to the heat load by increasing the flow amount of the circulating liquid to the piping of the external device in addition to the temperature control described above.
Owner:SMC CORP
Surface acoustic wave device and surface acoustic wave oscillator
InactiveUS8063534B2Reduce disagreementReduce frequency differenceImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSurface acoustic wave oscillatorsQuartz substrate
A surface acoustic wave device, includes: an interdigital transducer serving as an electrode pattern to excite a Rayleigh surface acoustic wave, the interdigital transducer including a comb-tooth-shaped electrode having a plurality of electrode fingers; a piezoelectric substrate on which the interdigital transducer is formed, the piezoelectric substrate being made of a quartz substrate that is cut out at a cut angle represented by an Euler angle representation (φ, θ, Ψ) of (0°, 95°≦θ≦155°, 33°≦|Ψ|≦46°); electrode finger grooves formed between the electrode fingers of the comb-tooth-shaped electrode; and electrode finger bases being quartz portions sandwiched between the electrode finger grooves and having upper surfaces on which the electrode fingers are positioned. The surface acoustic wave device provides an excitation in an upper limit mode of a stop band of the surface acoustic wave.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
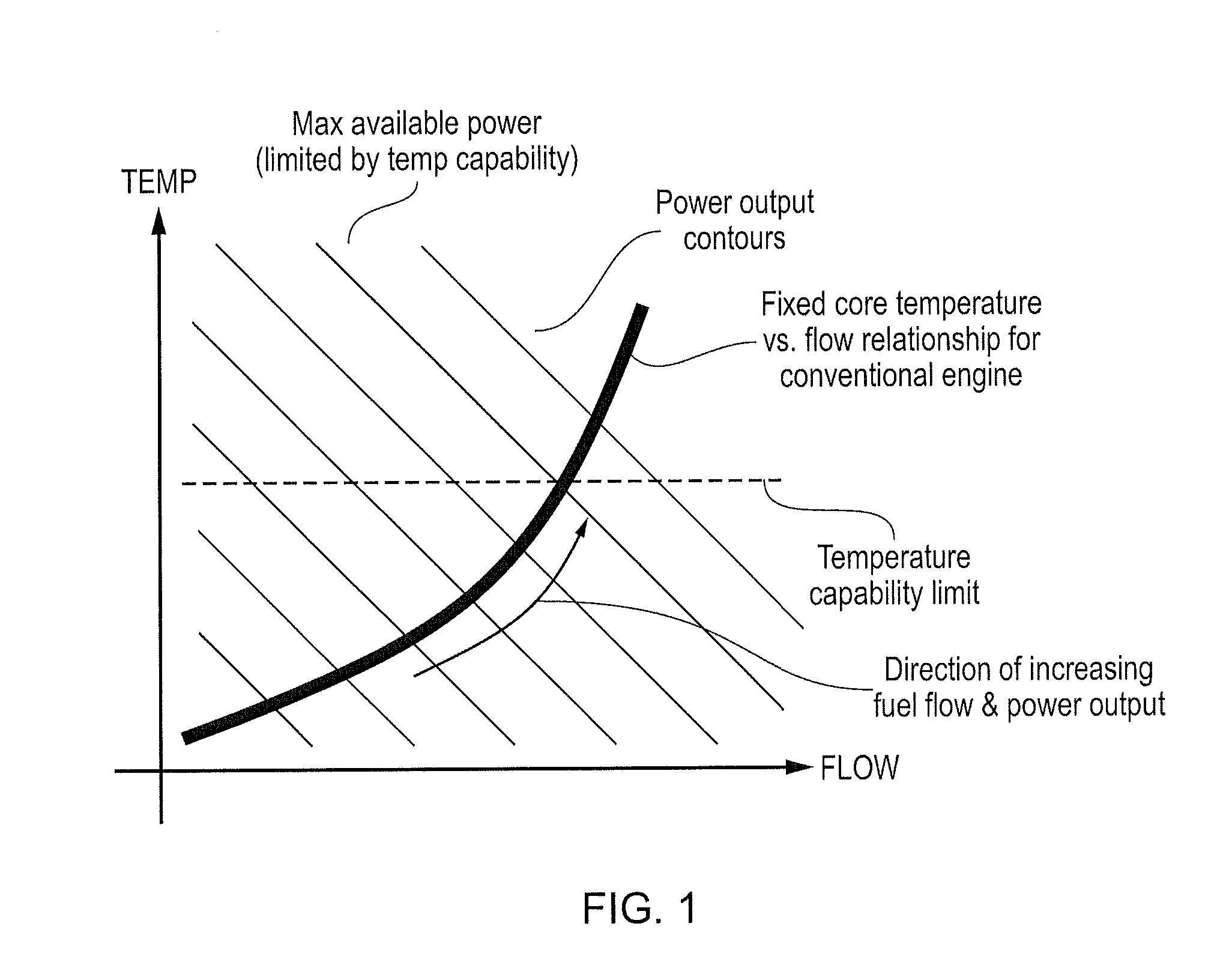
Control of a gas turbine engine
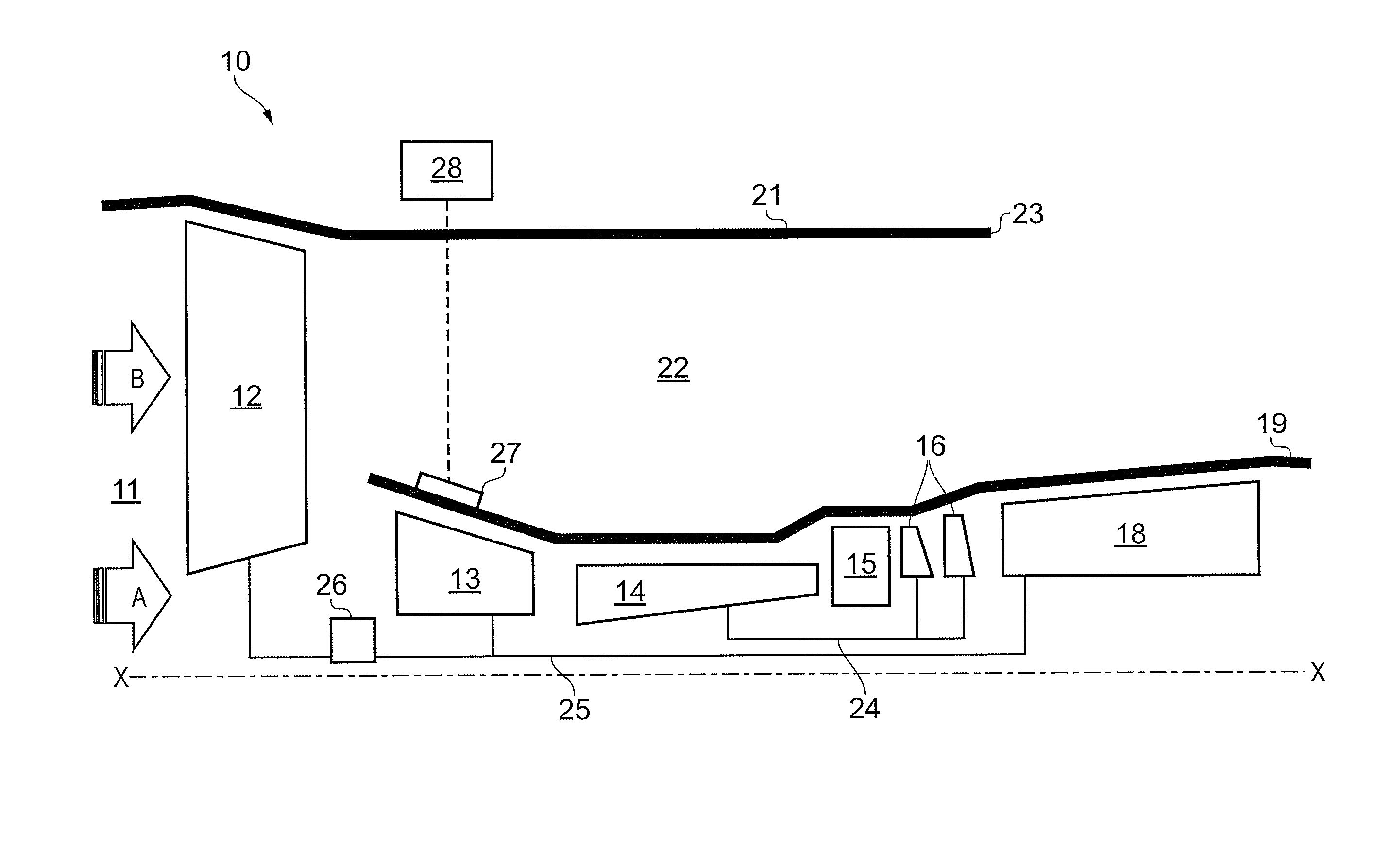
ActiveUS20150308353A1Temperature variationHigh power outputGas turbine plantsEfficient propulsion technologiesCombustionHigh pressure
An engine that has, in axial flow series, booster compressor, core compressor, combustion equipment, core turbine, and low-pressure turbine. Core turbine drives core compressor via an interconnecting high-pressure shaft. Low-pressure turbine drives booster compressor via an interconnecting low-pressure shaft. Low-pressure turbine also drives external load having a defined speed characteristic that dictates speed of the low-pressure turbine and booster compressor. Booster compressor has one or more rows of variable stator vanes. The method includes: scheduling variation in the angle of variable stator vanes as a function of speed of the booster compressor wherein the vanes open as booster compressor speed increases; measuring or setting one or more operational parameters which are determinative of temperature at entry to core turbine; and biasing scheduling of angle variation of variable stator vanes as a function of operational parameter(s) to reduce variation in temperature at entry to core turbine.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
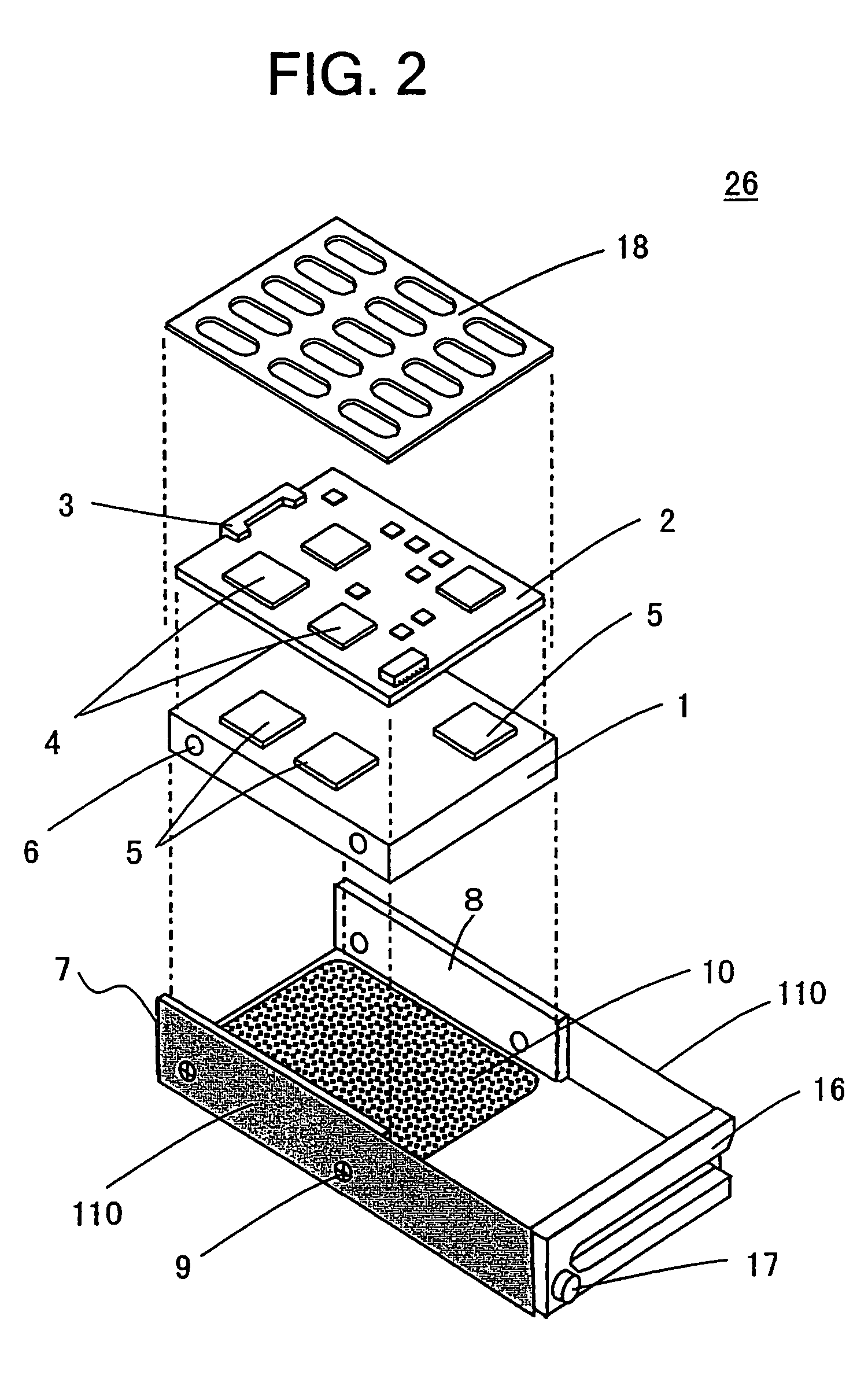
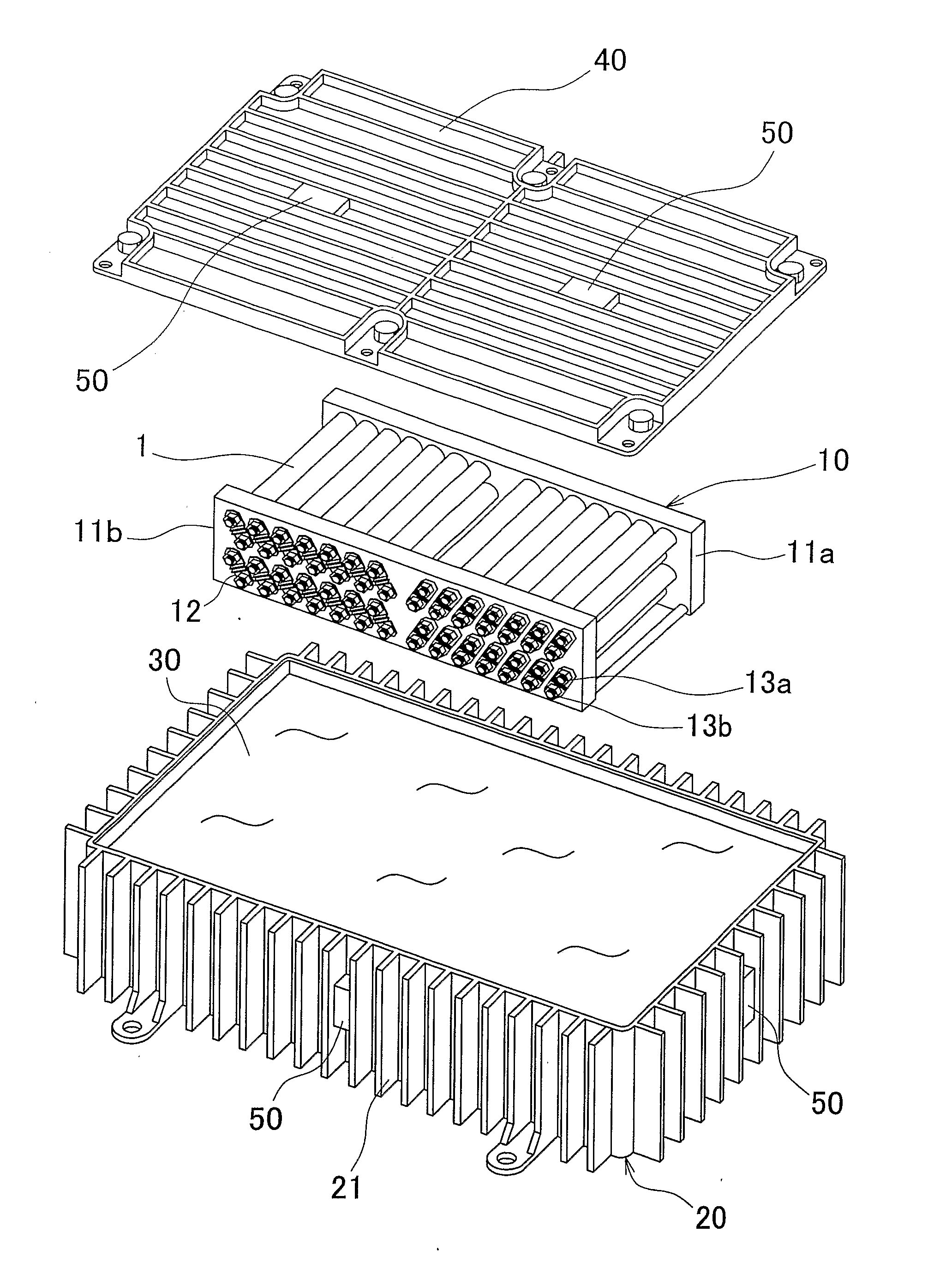
Multilayer wiring board
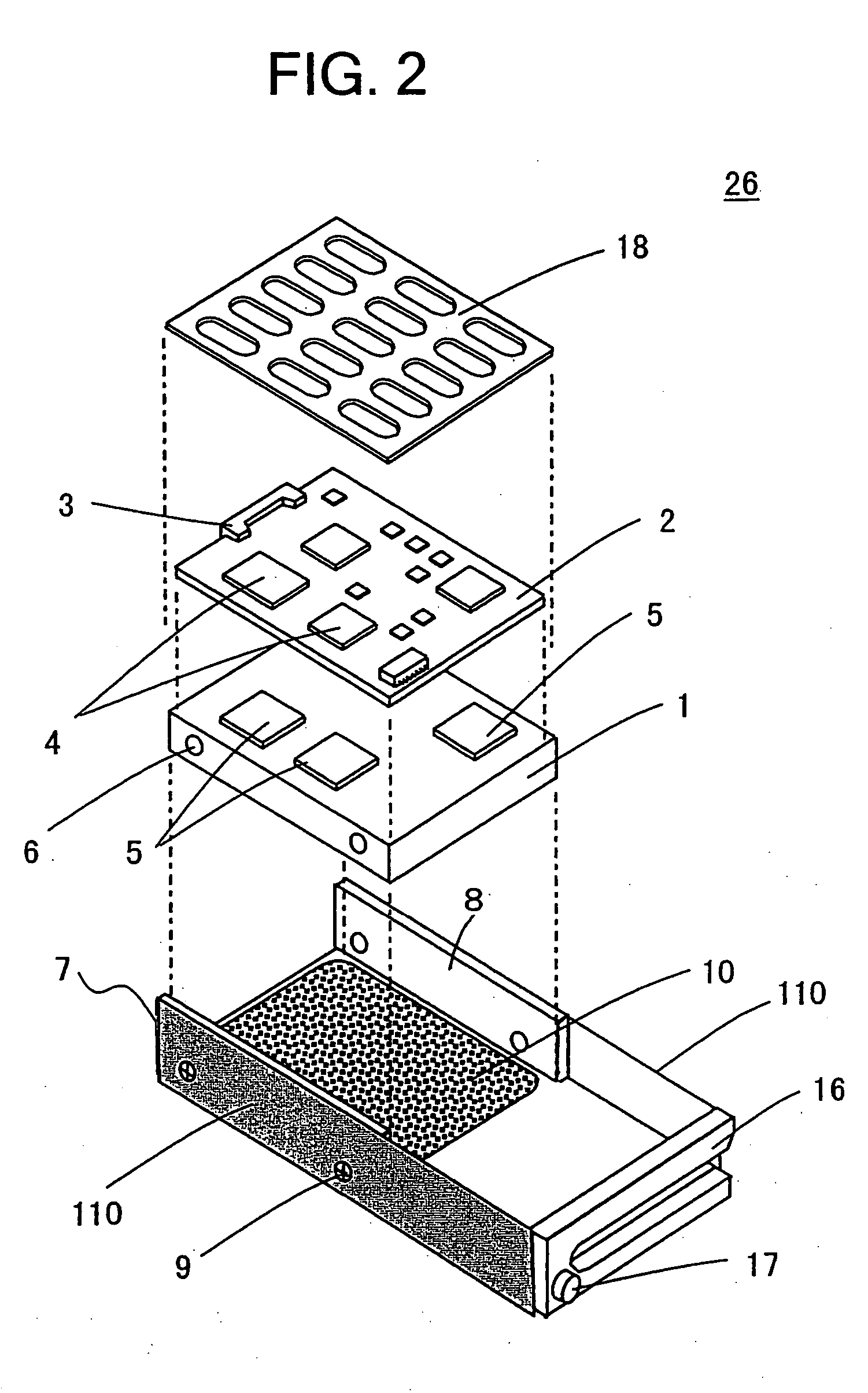
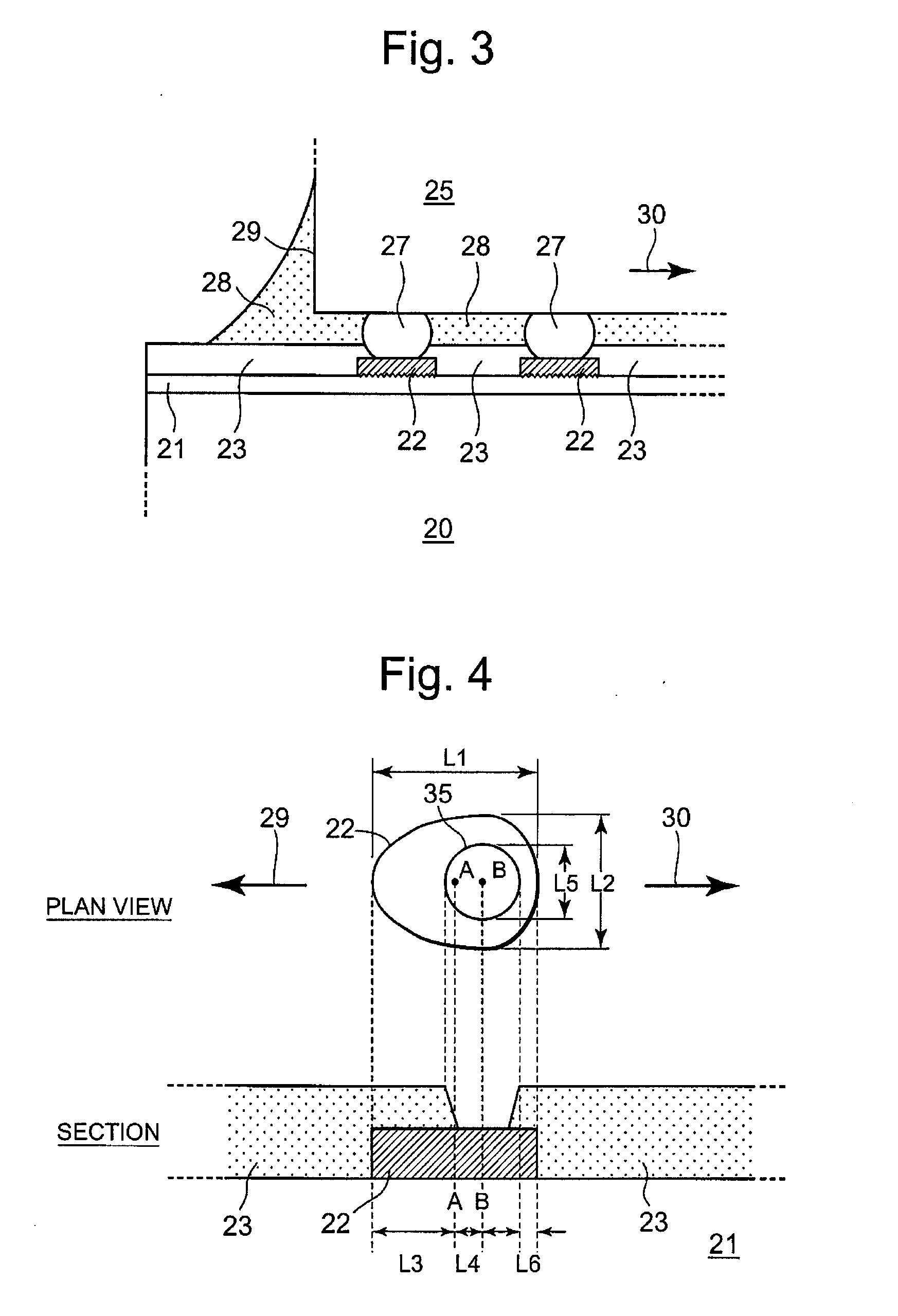
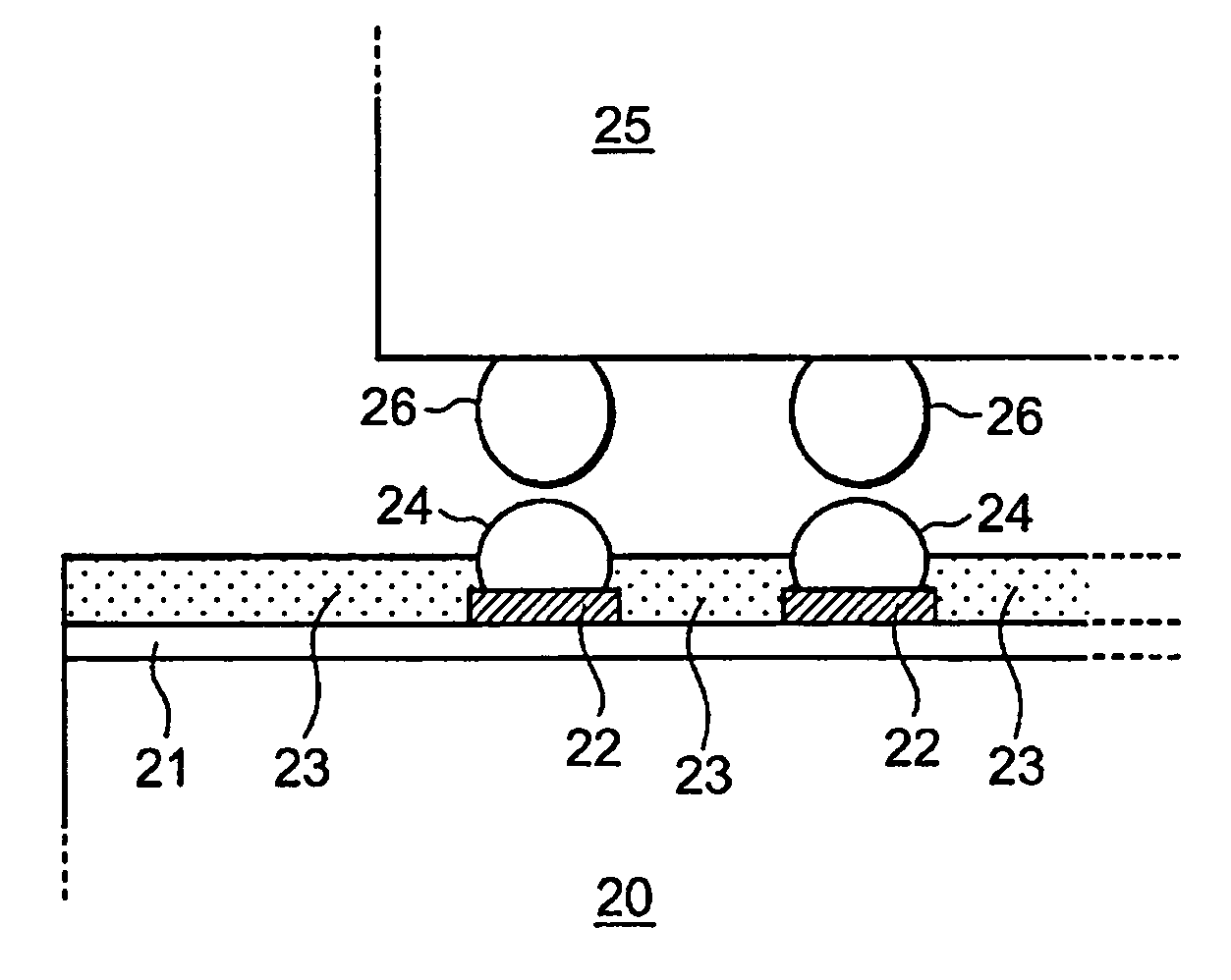
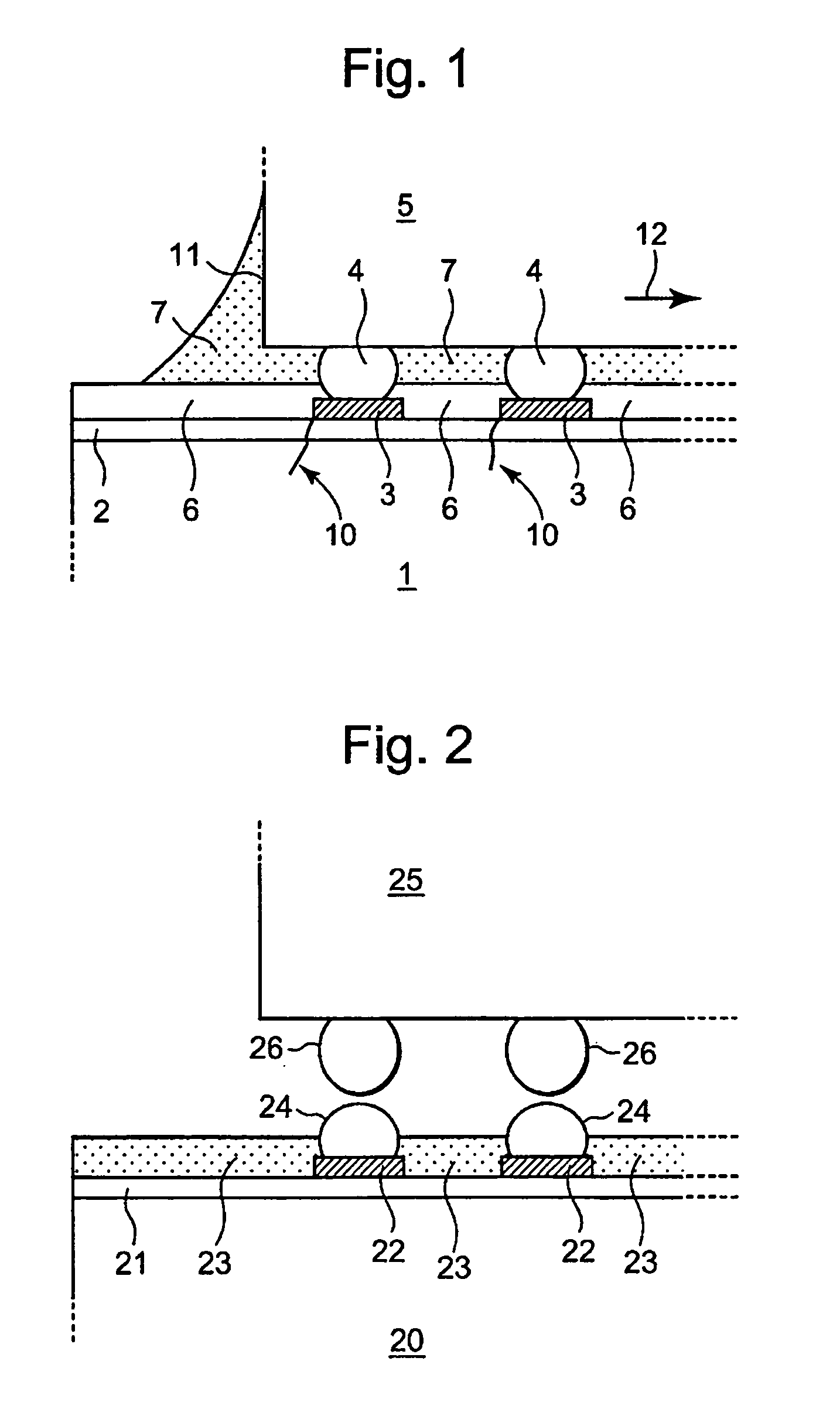
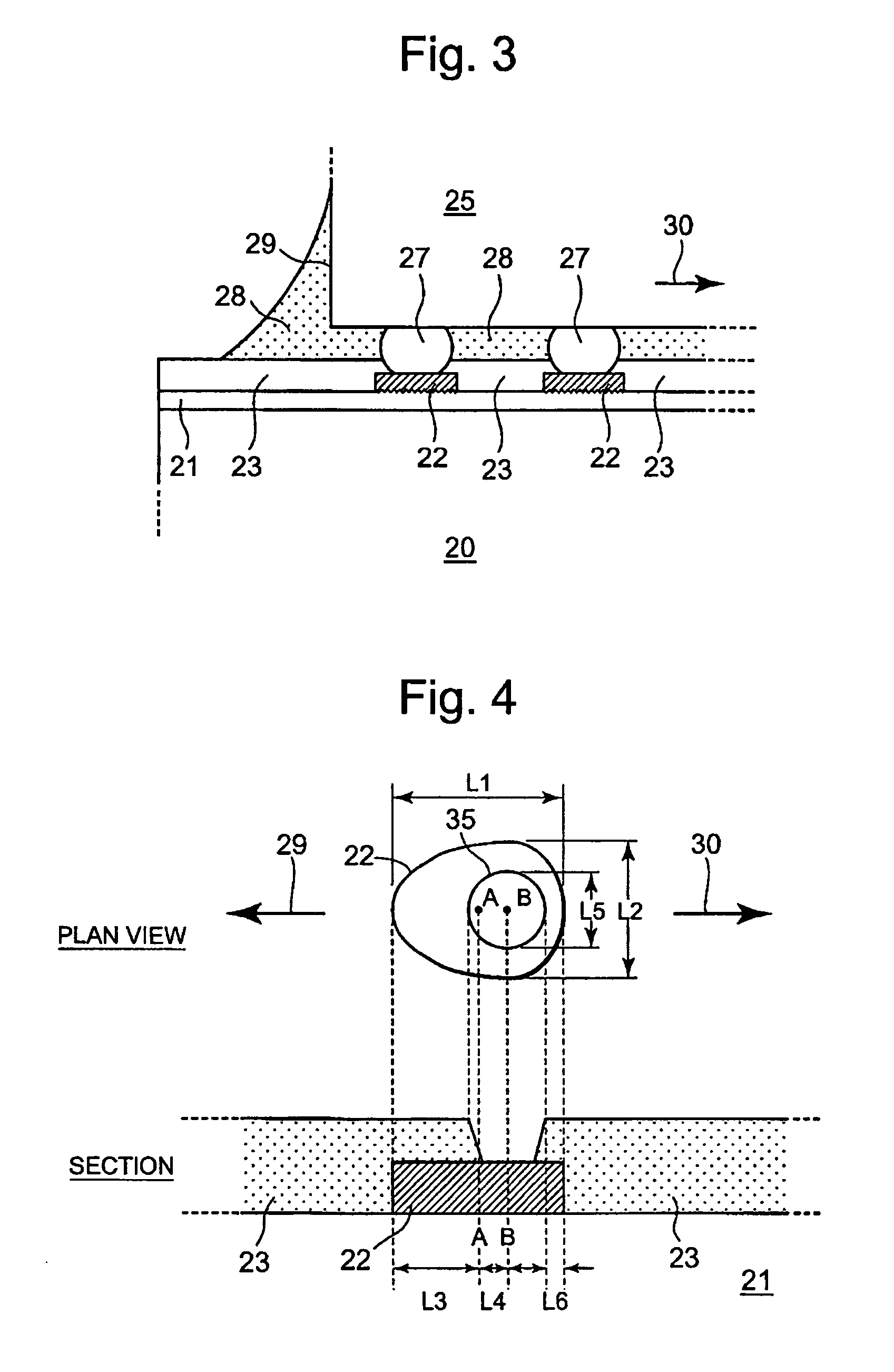
InactiveUS20050087364A1Reduce the possibility of disconnectionImprove reliabilityPrinted circuit assemblingFinal product manufactureResistSemiconductor chip
To prevent, in a multilayer wiring board to which a semiconductor chip is flip-chip bonded, occurrence of cracks in the board at portions adjacent to electrode pads due to a difference in thermal expansion coefficient between the semiconductor chip and the board. A multilayer wiring board (20) of the present invention has features that electrode pads (22) corresponding to electrodes of a semiconductor chip (25) located near an outer periphery (29) of the semiconductor chip each have an oblong shape, openings (35) of a solder resist (23) are each smaller than the oblong shape, and the center (B) of the opening is located to be offset from the center (A) of the oblong shape by a distance (L4) in a direction (30) toward the center of the semiconductor chip. Therefore, in the multilayer wiring board of the present invention, thermal stresses applied to portions (L3) of the electrode pads (22) on the board near the outer periphery of the semiconductor chip are relaxed. Consequently, the multilayer wiring board of the present invention can prevent occurrence of cracks in the board at portions adjacent to the electrode pads near the outer periphery of the semiconductor chip due to a difference in thermal expansion coefficient between the semiconductor chip and the board.
Owner:IBM CORP
Fluid handling device with isolating chamber
ActiveUS7942069B2Avoiding undesirable signal bias and noiseAvoiding regionOperating means/releasing devices for valvesFluid pressure measurement using ohmic-resistance variationEngineeringFluid handling
A fluid handling device includes a body portion defining a flow passage and an impulse chamber extending from the flow passage. The impulse chamber is fluidly coupled with the flow passage and has a pair of opposing ends defining a length dimension therebetween. The impulse chamber further presents a diameter dimension transverse to the length dimension, wherein the length dimension is at least 3 times and not greater than 10 times the diameter dimension. The device further includes at least one sensor operably coupled with the body portion. The sensor is disposed proximate the end of the impulse chamber opposite the flow passage and presents a sensing face facing into the impulse chamber.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
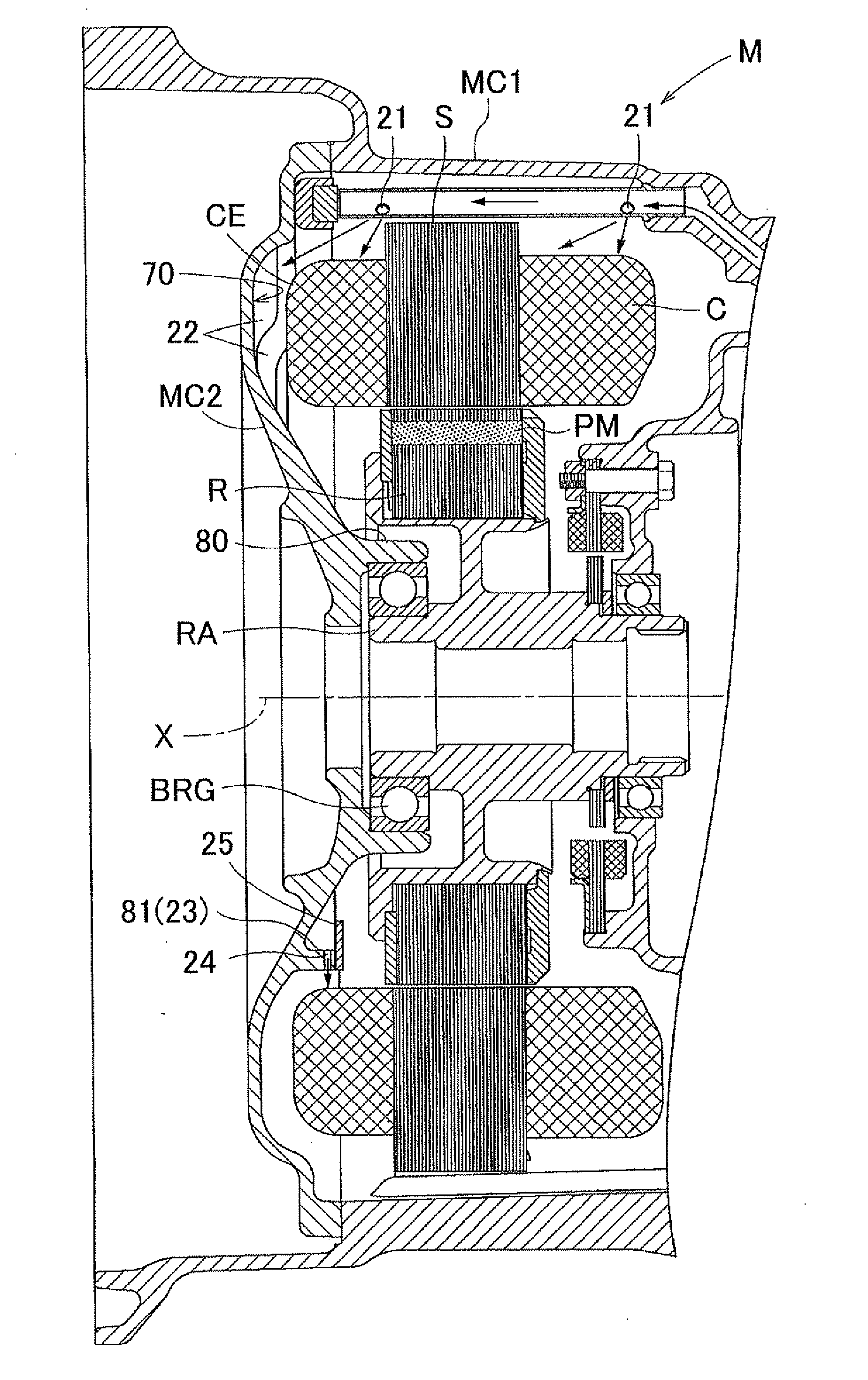
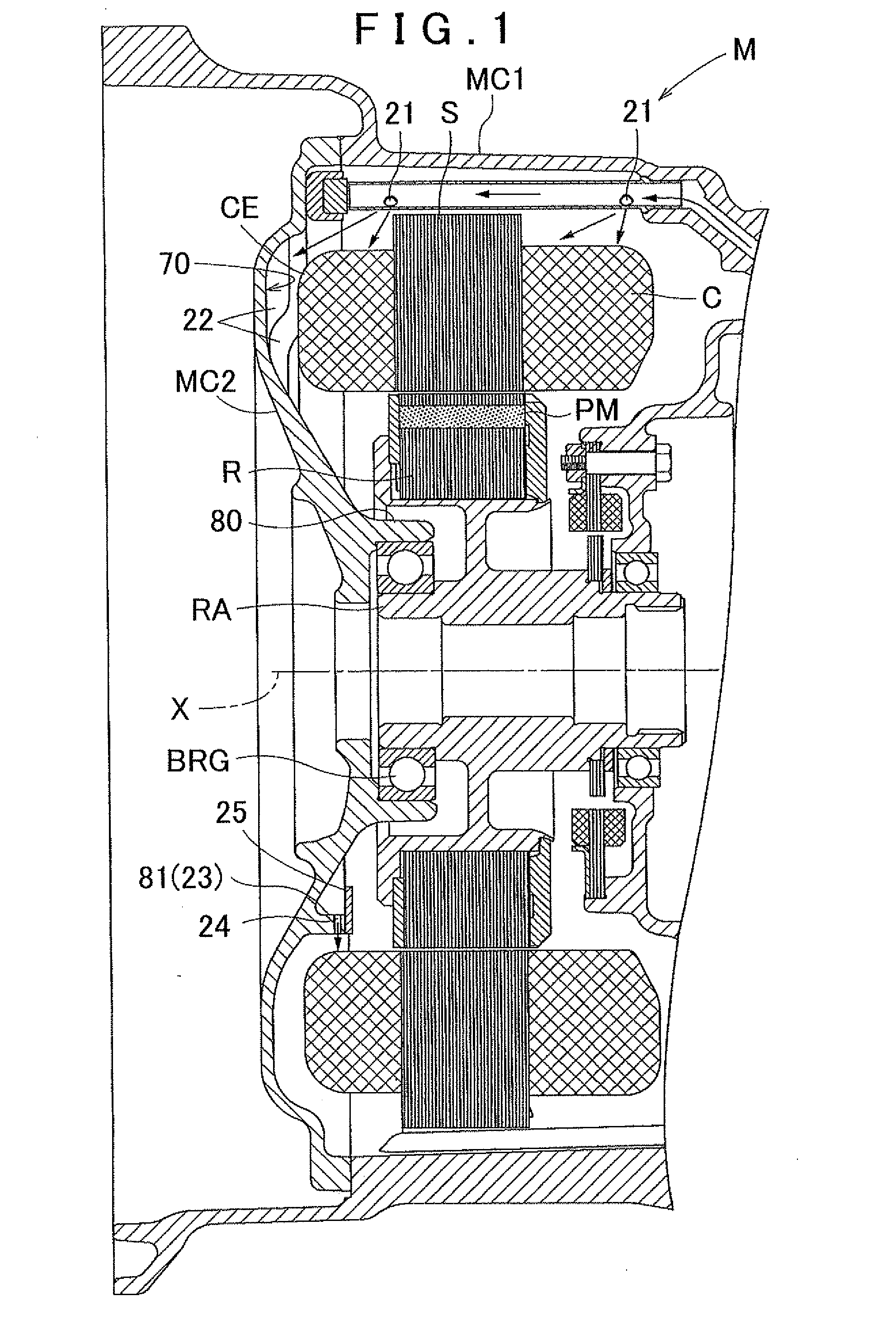
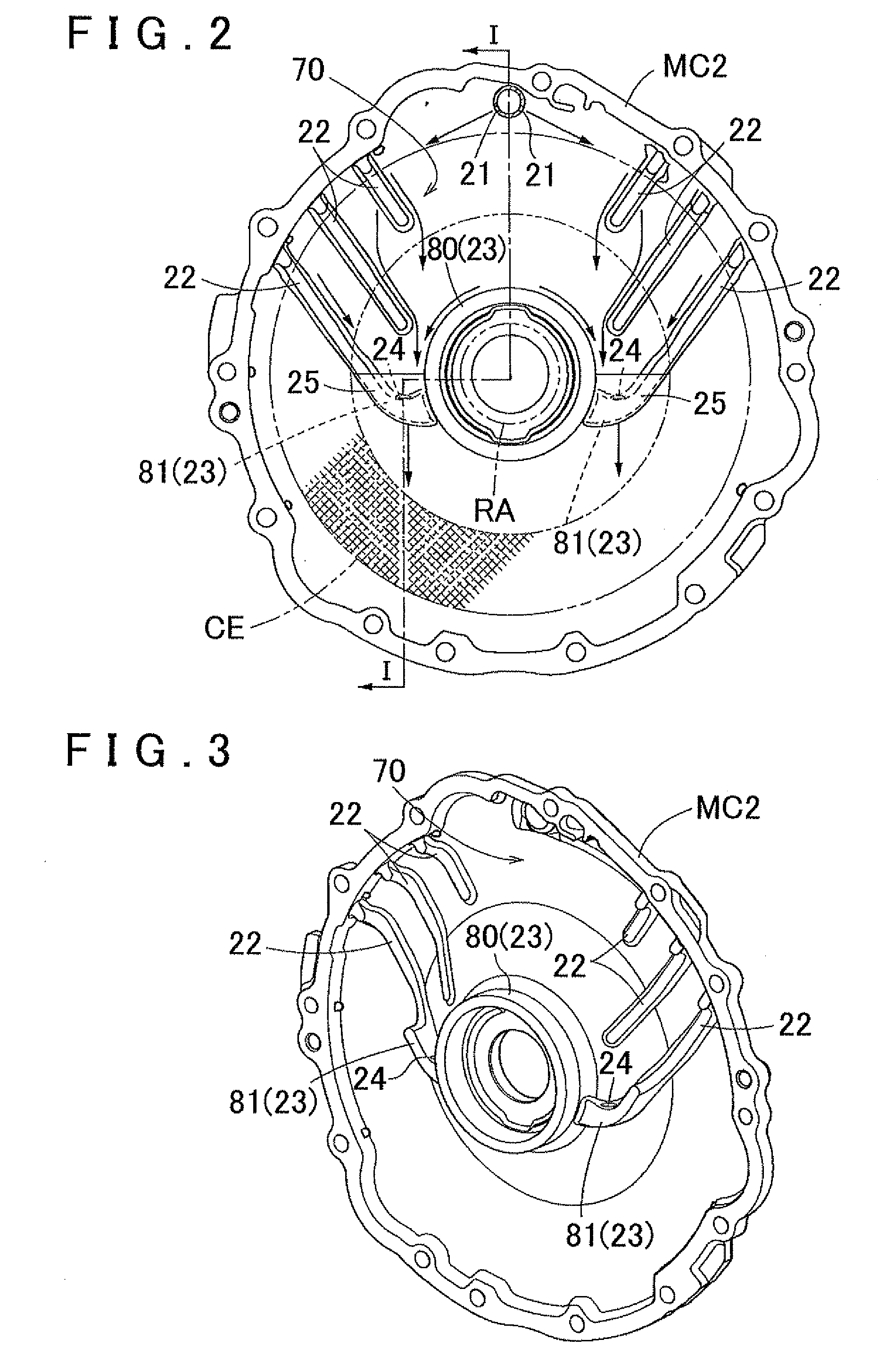
Cooling structure for rotating electric machine
InactiveUS20120062055A1Improve cooling efficiencyEfficient collectionCooling/ventillation arrangementSupports/enclosures/casingsStatorEngineering
A cooling structure for a rotating electric machine, having a coolant supply portion, and configured to supply a coolant to a coil end portion of a stator. A protrusion portion is provided on a portion of a coil end facing area, and projects toward the coil end portion side and extends downward and toward a radially inner side of the coil end portion, wherein the coil end facing area is a section that faces the coil end portion on an inner wall surface of a case that accommodates the stator. A collection portion collects the coolant distributed along the protrusion portion. A drip portion is disposed on the radially inner side of the coil end portion at a position that axially overlaps with the coil end portion as viewed from the radial direction, wherein the coolant collected in the collection portion drips from the drip portion.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
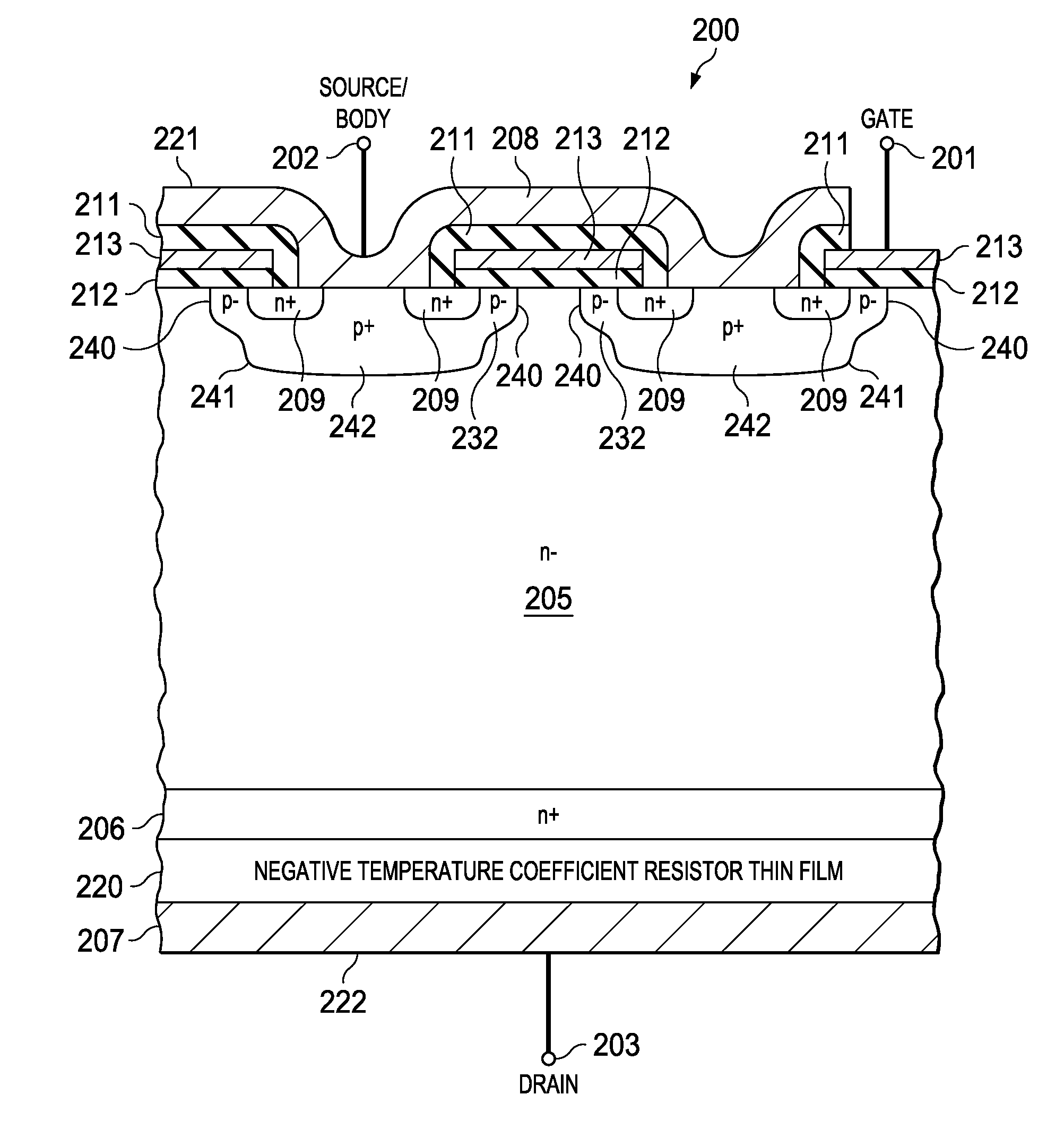
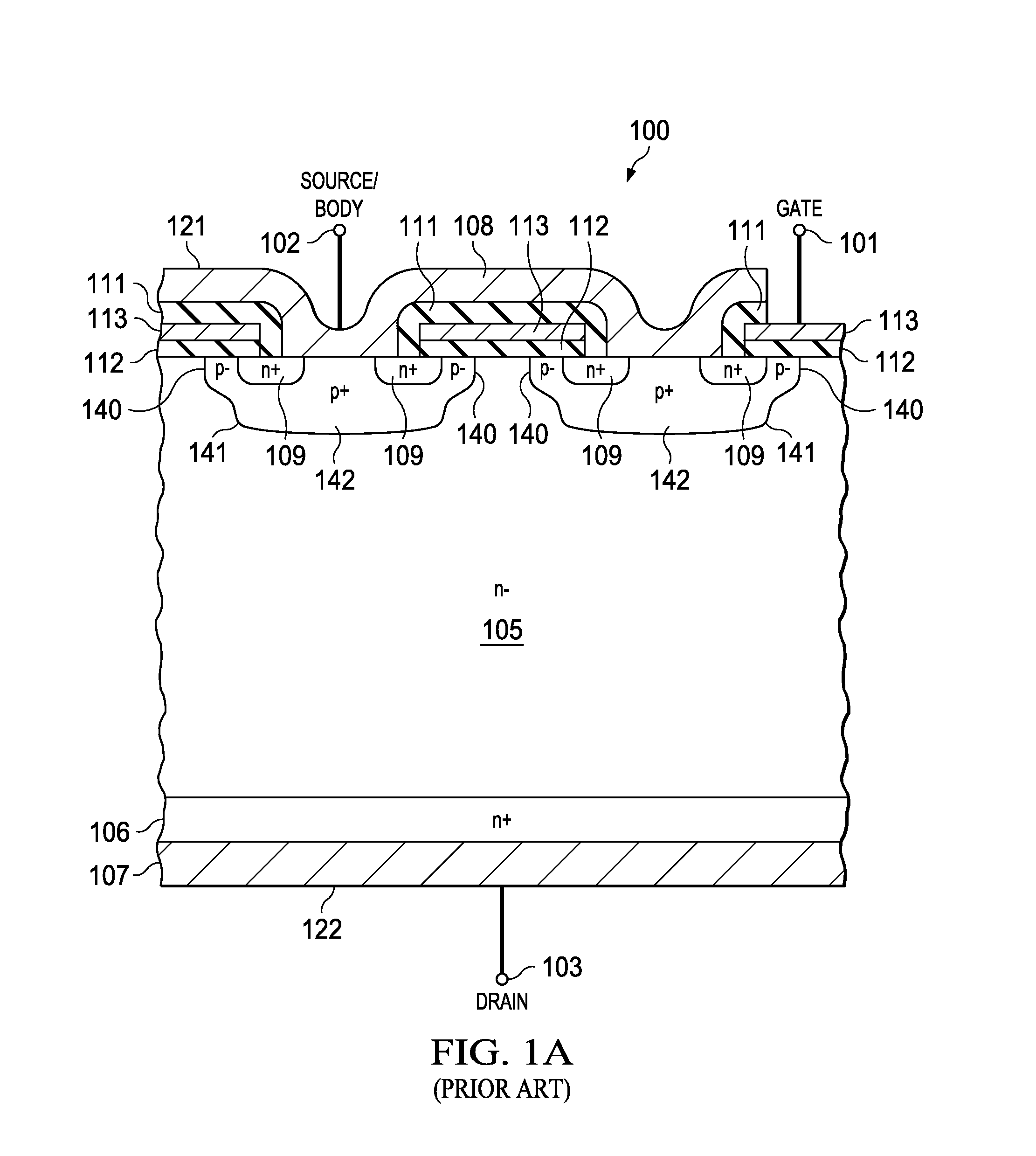
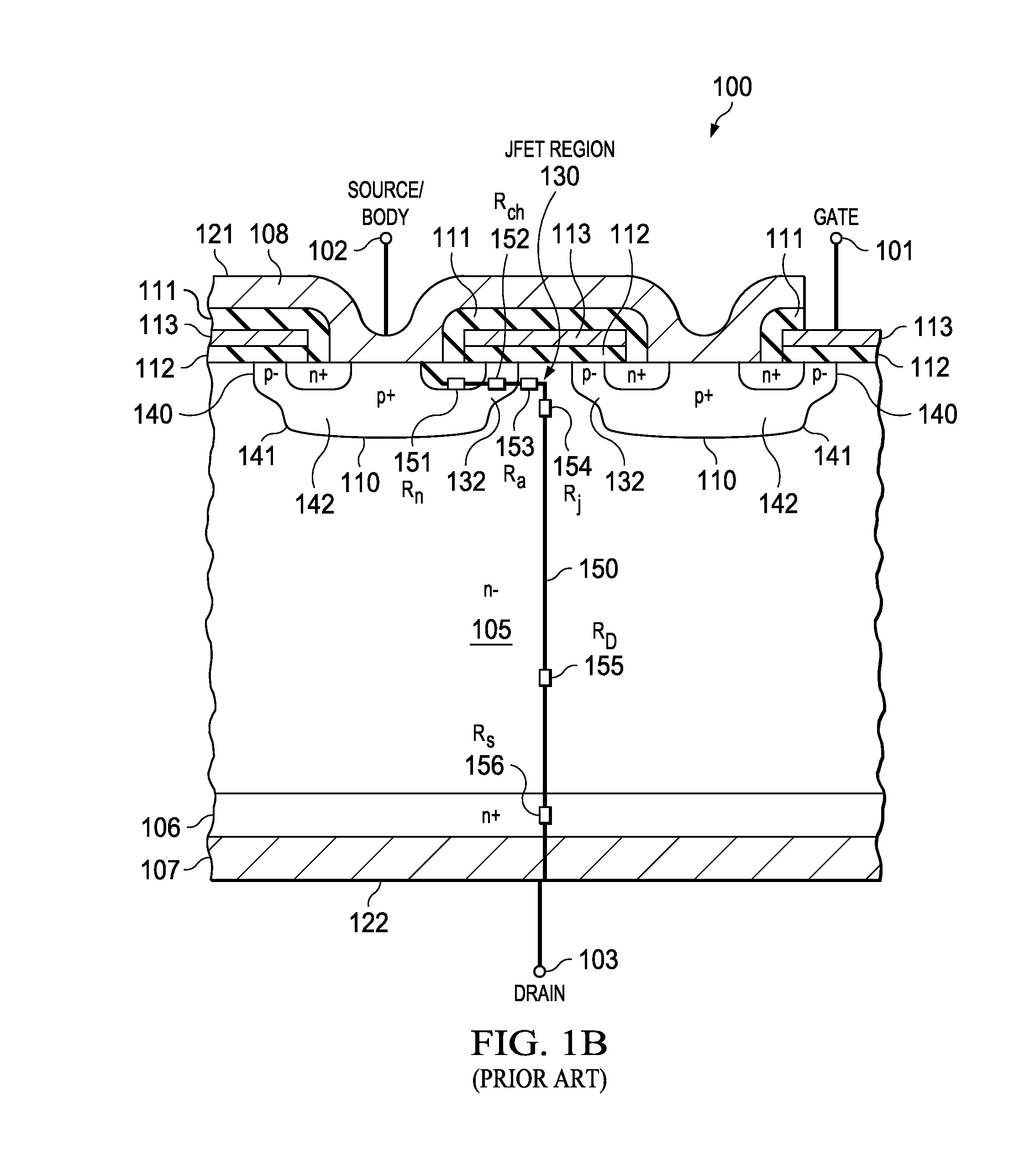
Device architecture and method for temperature compensation of vertical field effect devices
InactiveUS20140264343A1Reduce temperature changesReduce variationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceNegative temperature
A field effect device is disclosed that provides a reduced variation in on-resistance as a function of junction temperature. The field effect device, having a source junction, gate junction and drain junction, includes a resistive thin film adjacent the drain junction wherein the resistive thin film comprises a material having a negative temperature coefficient of resistance. The material is selected from one or more materials from the group consisting of doped polysilicon, amorphous silicon, silicon-chromium and silicon-nickel, where the material properties, such as thickness and doping level, are chosen to create a desired resistance and temperature profile for the field effect device. Temperature variation of on-resistance for the disclosed field effect device is reduced from the temperature variation for a similar field effect device without the resistive thin film.
Owner:D3 SEMICON
Constant temperature liquid circulating device and method of controlling temperature in the device
ActiveUS7637315B2Temperature variationImprove responseTemperature control without auxillary powerTemperature control using plurality of sensorsLiquid circulationHeat load
In a constant temperature liquid circulating device that connects a piping of circulating liquid in an external device between a discharge port and a return port of a conduit for delivering the circulating liquid at a constant temperature by a pump, a flow amount sensor and temperature sensors for detecting discharge temperature (T1) of the circulating liquid from the conduit and the return temperature (T2) of the circulating liquid are provided in the conduit, so that the flow amount and the temperature of the circulating liquid is controlled by a controller according to the heat load of the external device obtained on the basis of the outputs from the temperature sensors.
Owner:SMC CORP
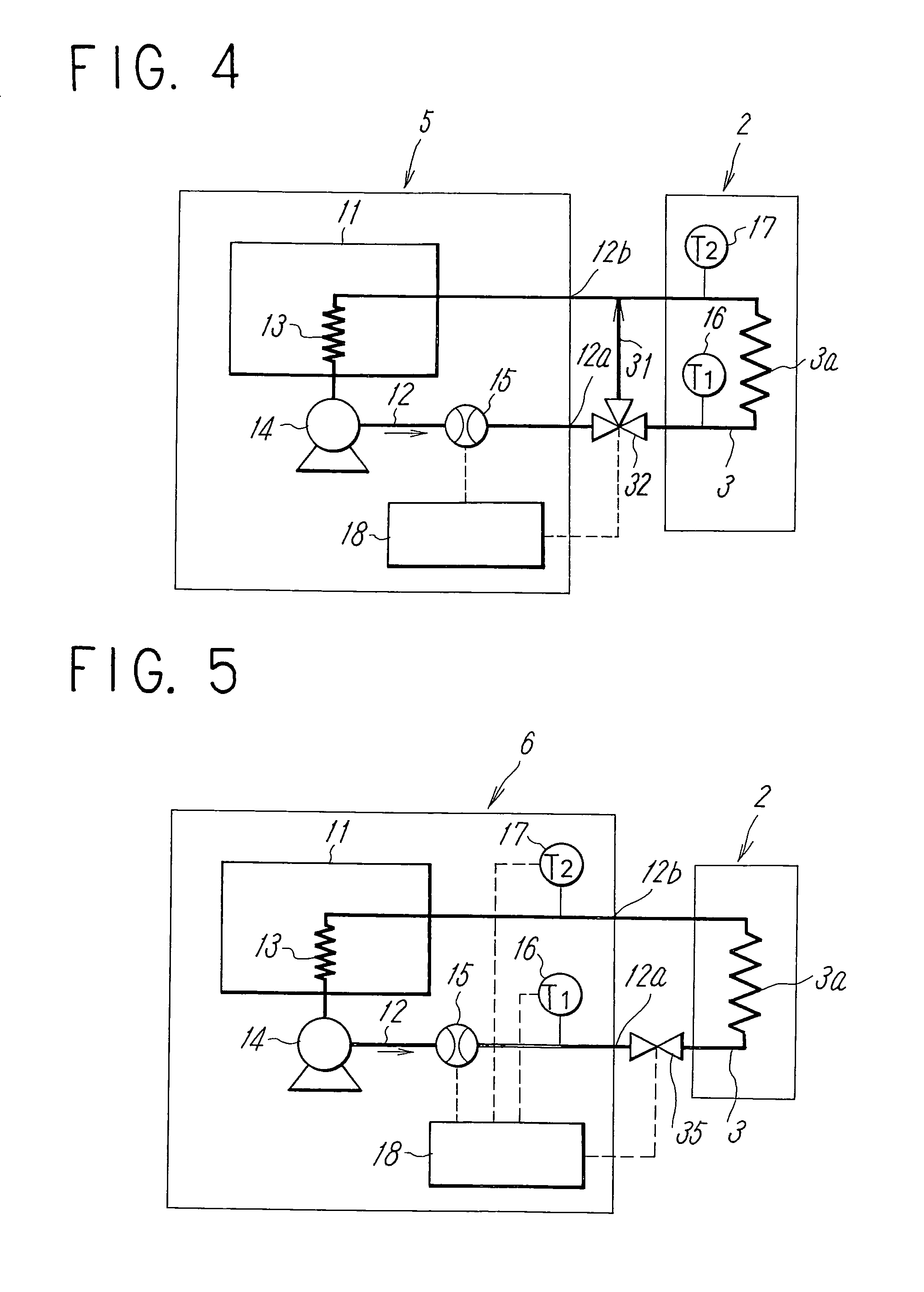
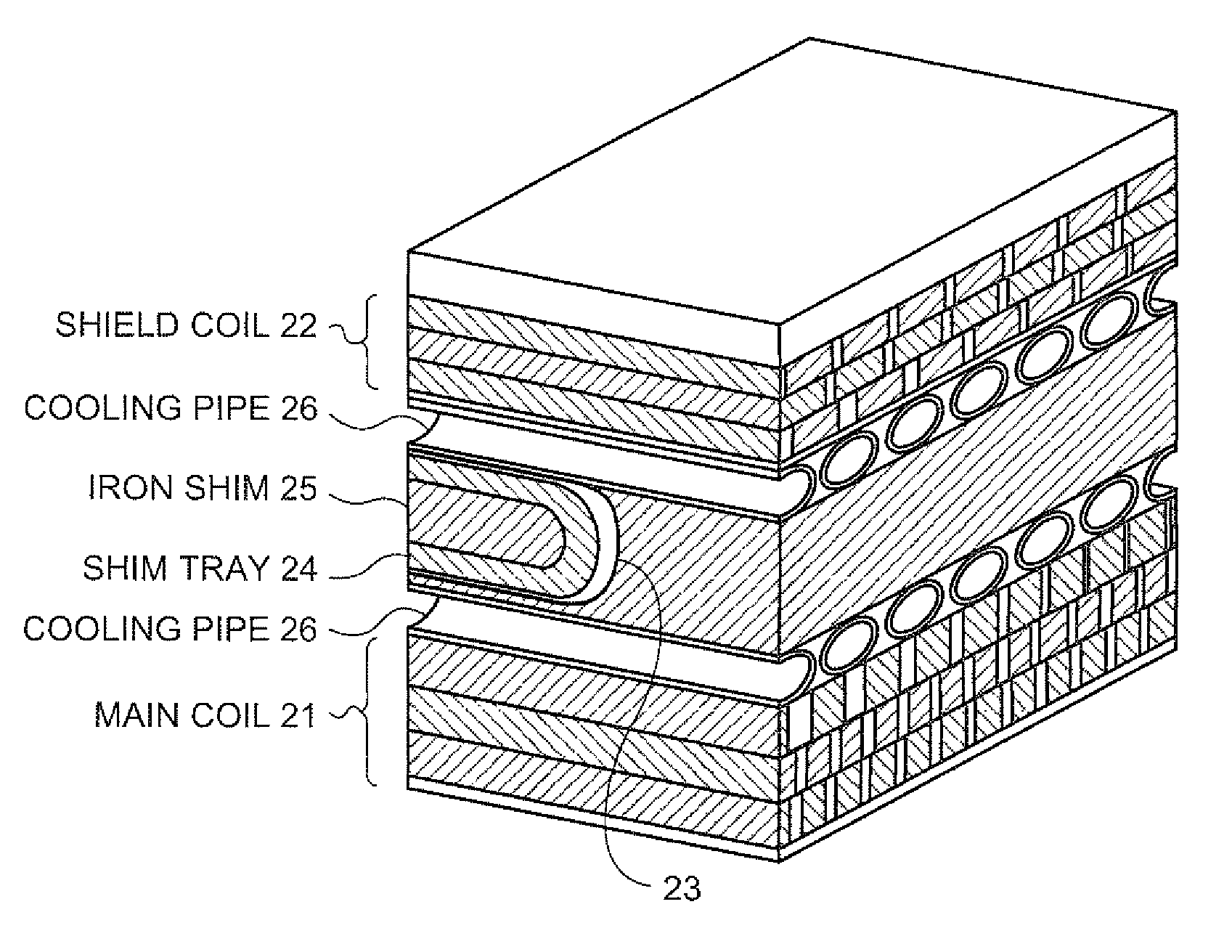
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and chiller
ActiveUS8188741B2Suppress mutationTemperature variationMagnetic measurementsSuperconducting magnets/coilsWater flowEngineering
By using a temperature monitor, a coil-dedicated chiller measures an amount of change in temperature of cooling water flowing out from a cooling pipe of a gradient magnetic field, determines an amount of change in temperature of cooling water to be flowed into the cooling pipe in accordance with the measured amount of change in temperature of the cooling water; and changes the temperature of cooling water to be flowed into the cooling pipe of the gradient magnetic field based on the determined amount of change in temperature.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
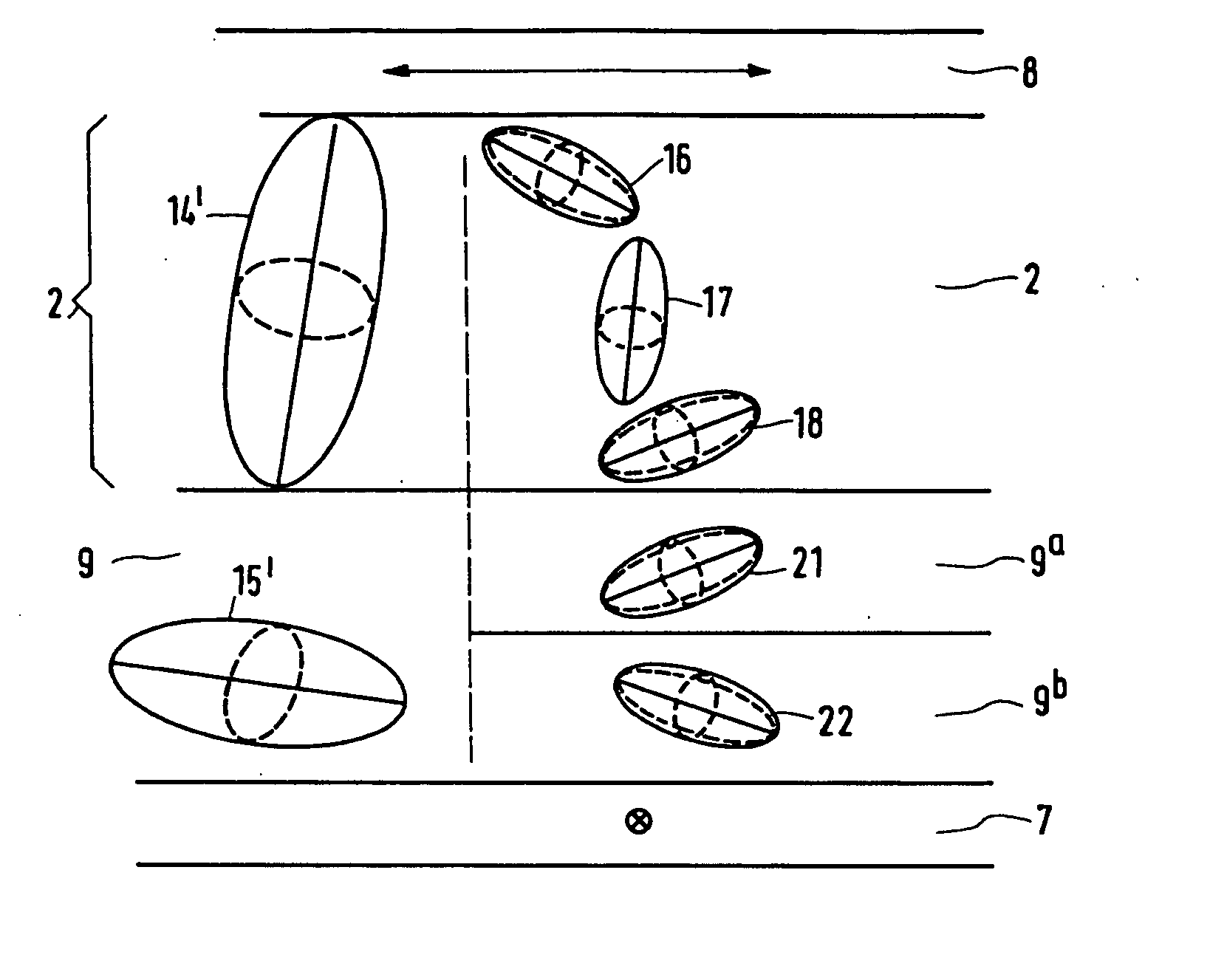
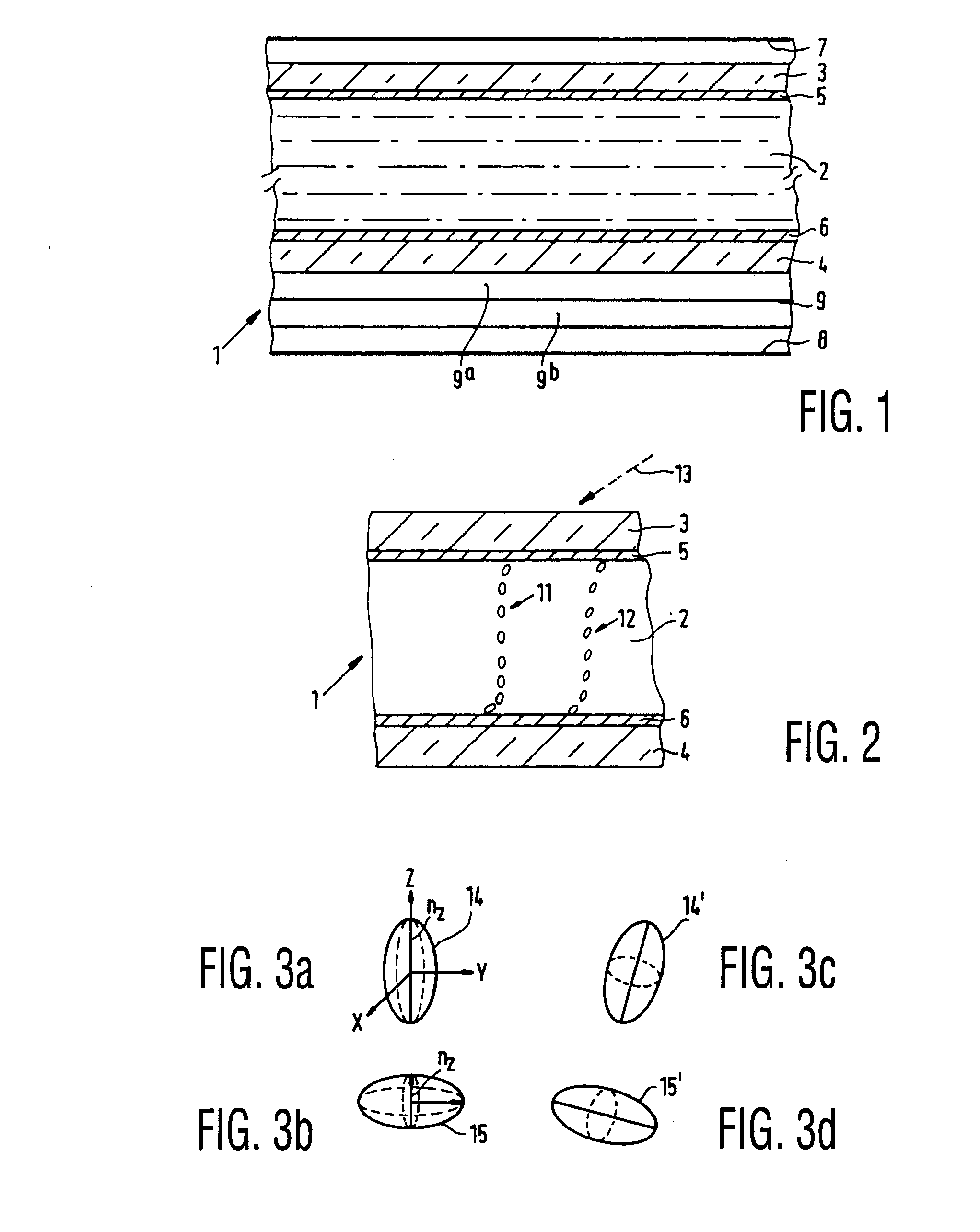
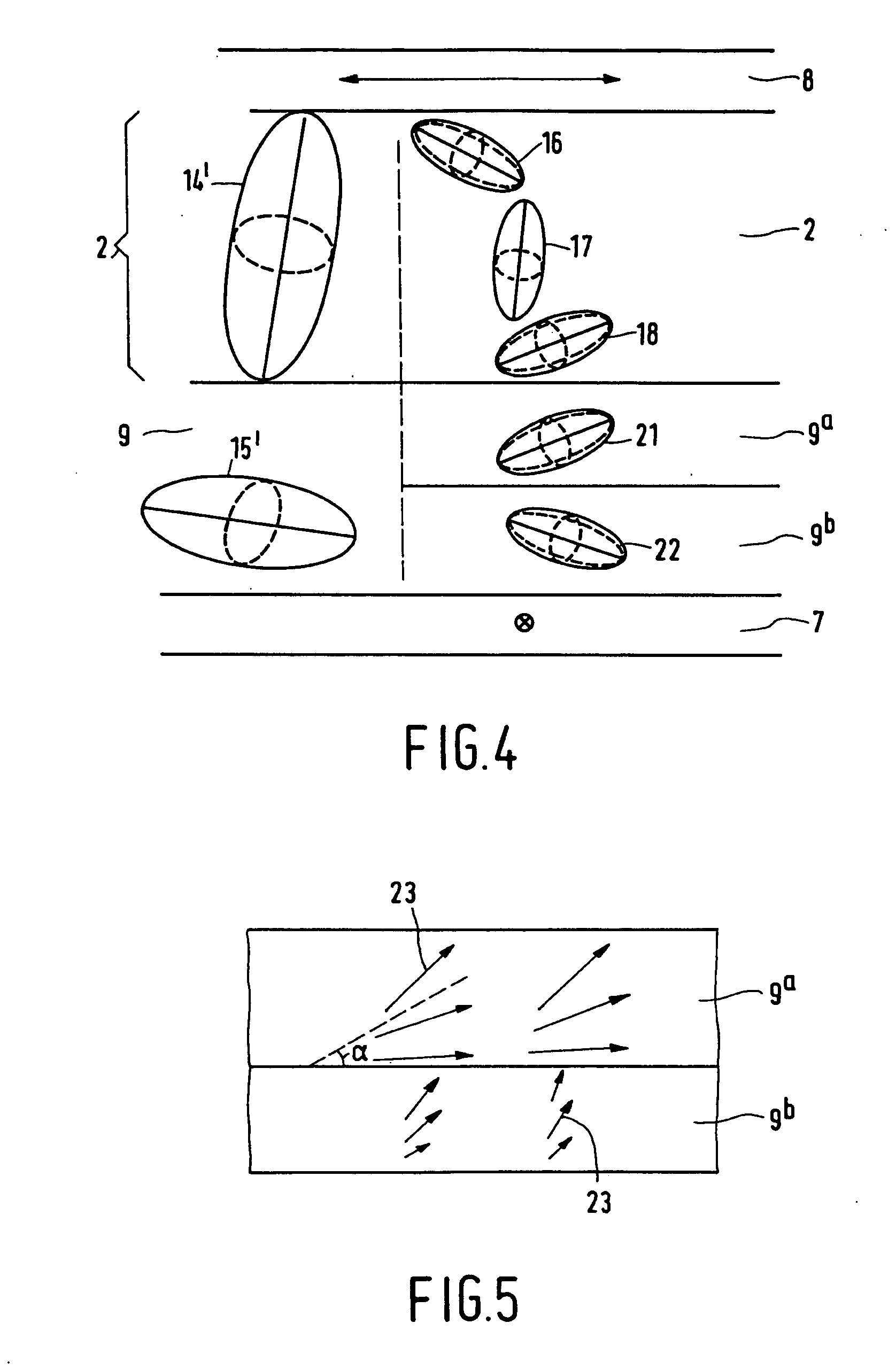
Liquid-crystal display device, compensator layer and method of manufacturing retardation foil
InactiveUS20040257508A1Angle-dependence can be substantially eliminatedImprove machinabilityLiquid crystal compositionsPolarising elementsVitrificationEngineering
A method of forming a liquid-crystal display device having a display cell comprises forming retardation foils on substrates using polymerized or vitrified liquid-crystal material wherein the liquid-crystal molecules of the polymerized or vitrified liquid-crystal material have a tilt angle with respect to a plane parallel to the substrates and so that the retardation foils have substantially complementary indicatrices and so that each one of the retardation foils brings about the compensation of approximately half the display cell in the driven state.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Power supply device
InactiveUS20090317698A1Reduce temperatureReduce variationPrimary cell maintainance/servicingElectrolytic capacitorsPower storageEngineering
In a power supply device, a power storage body is disposed in a casing that houses a cooling liquid. The power supply device includes oscillation means that oscillates the cooling liquid.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Light-bulb type LED lamp and illumination apparatus
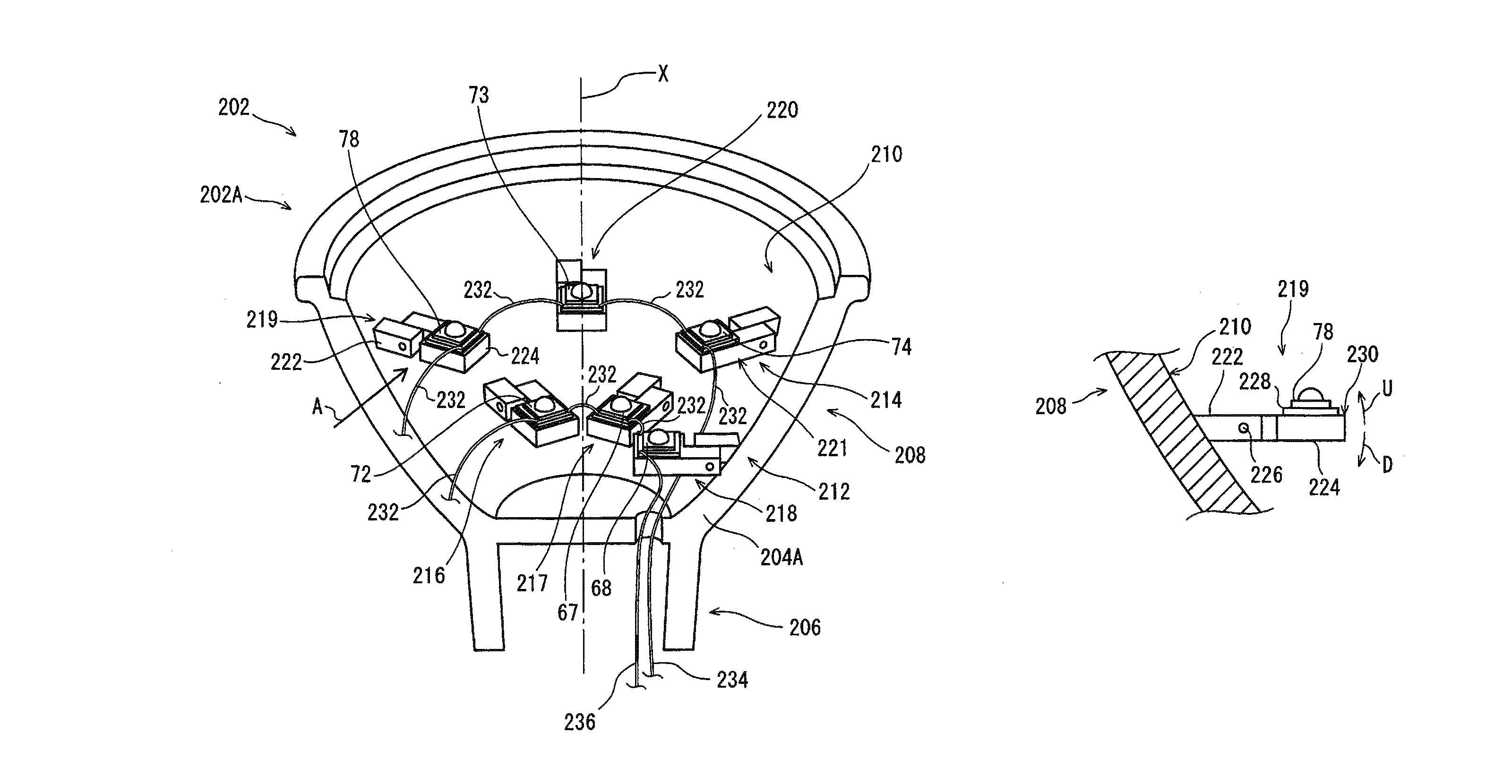
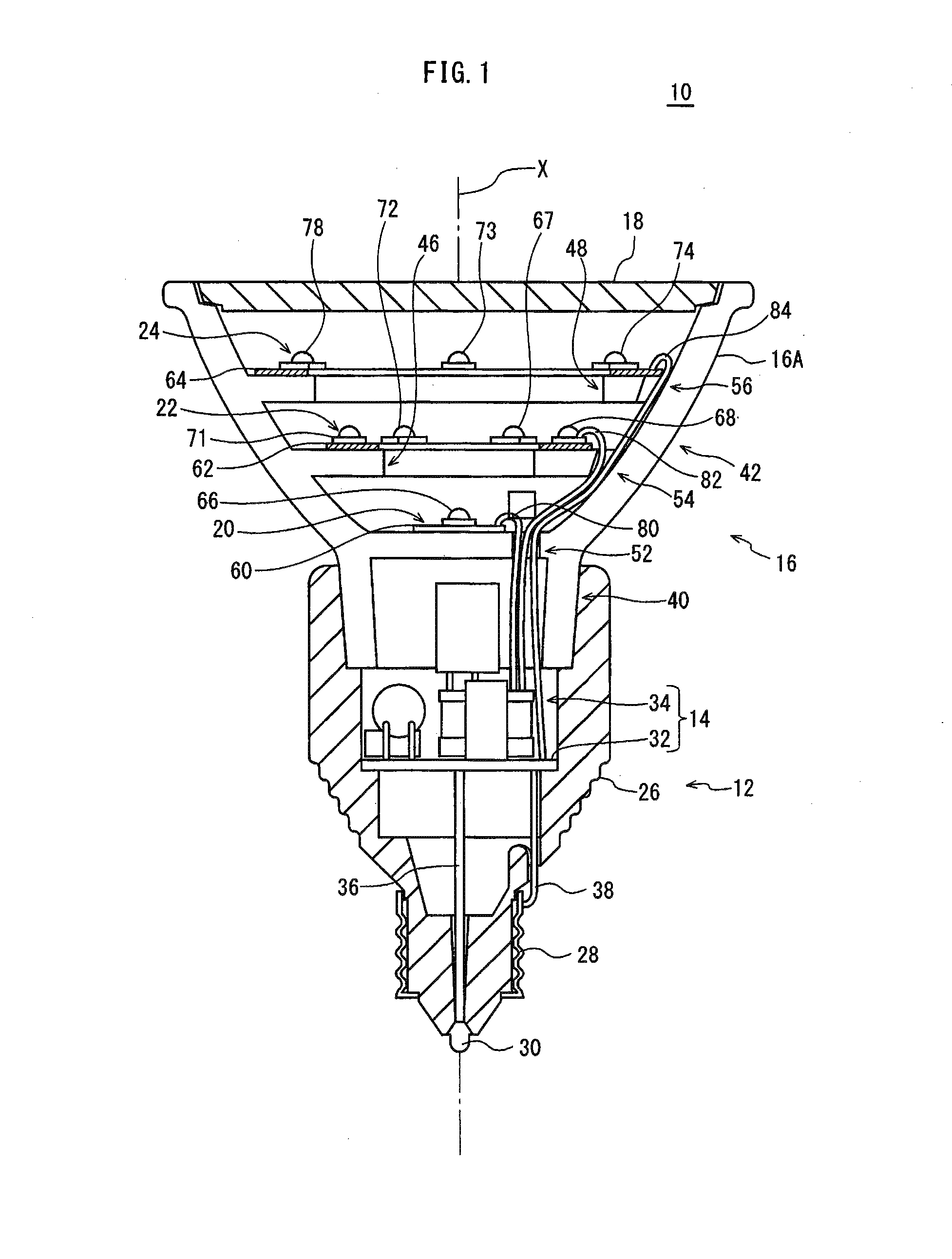
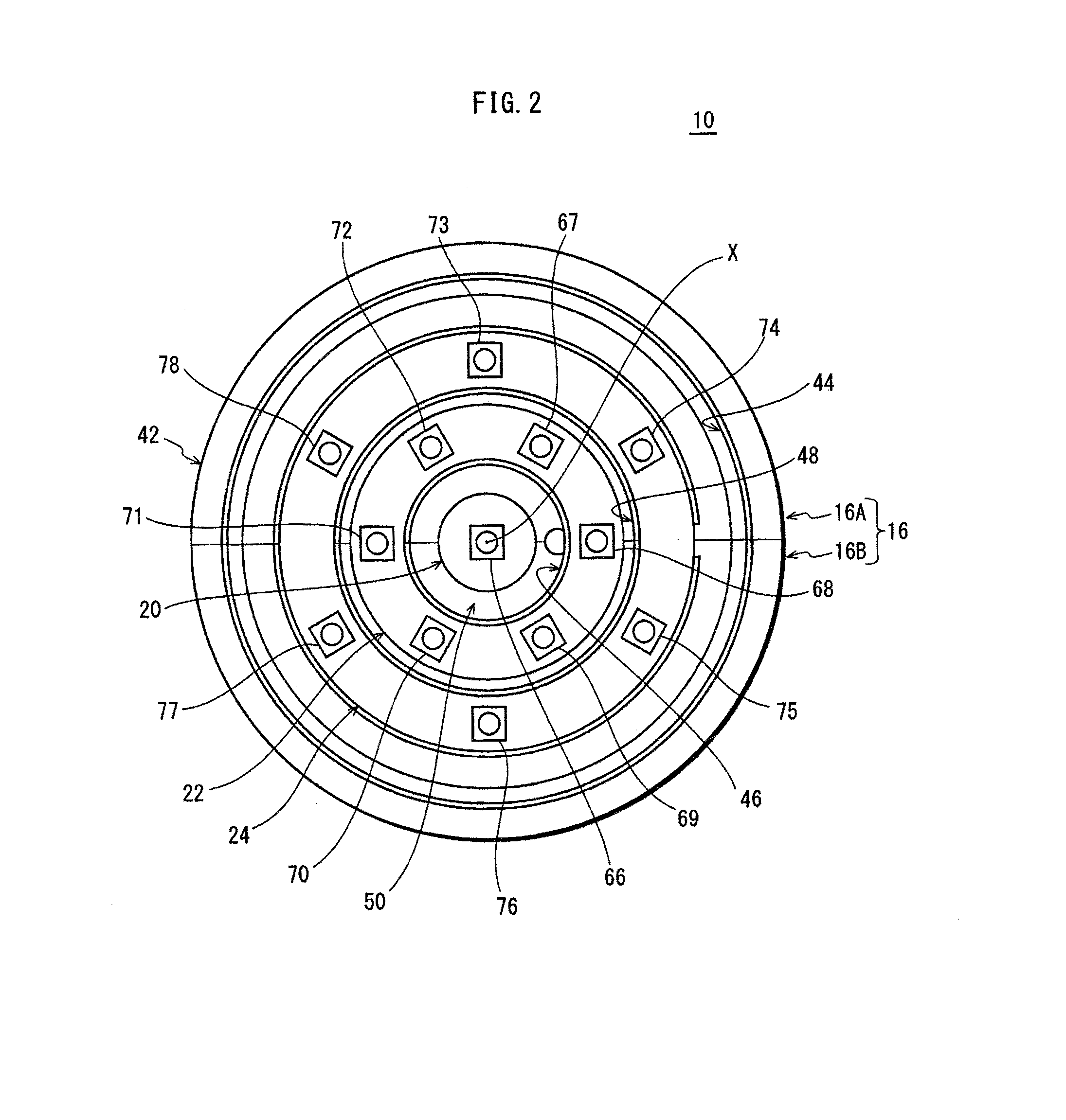
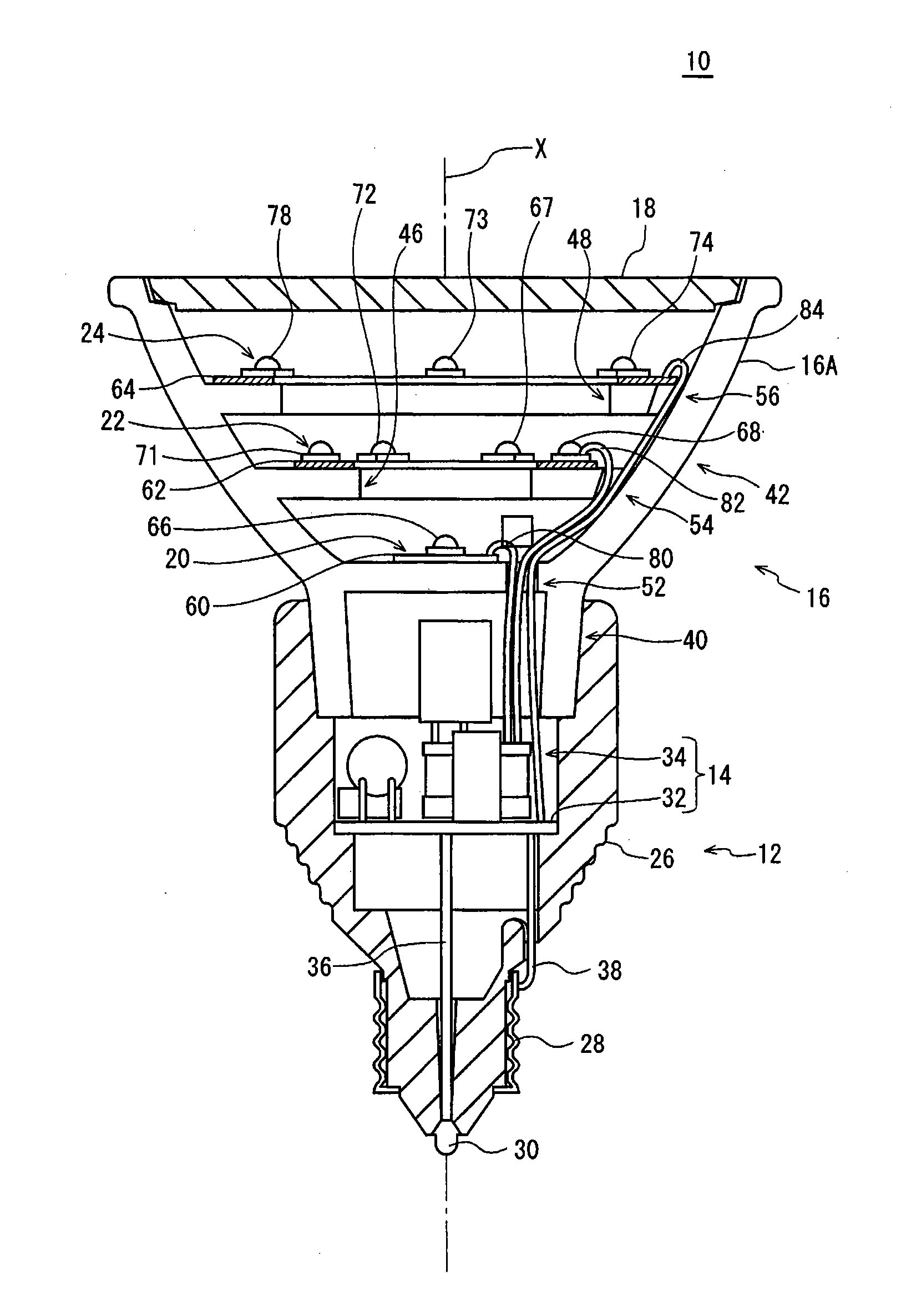
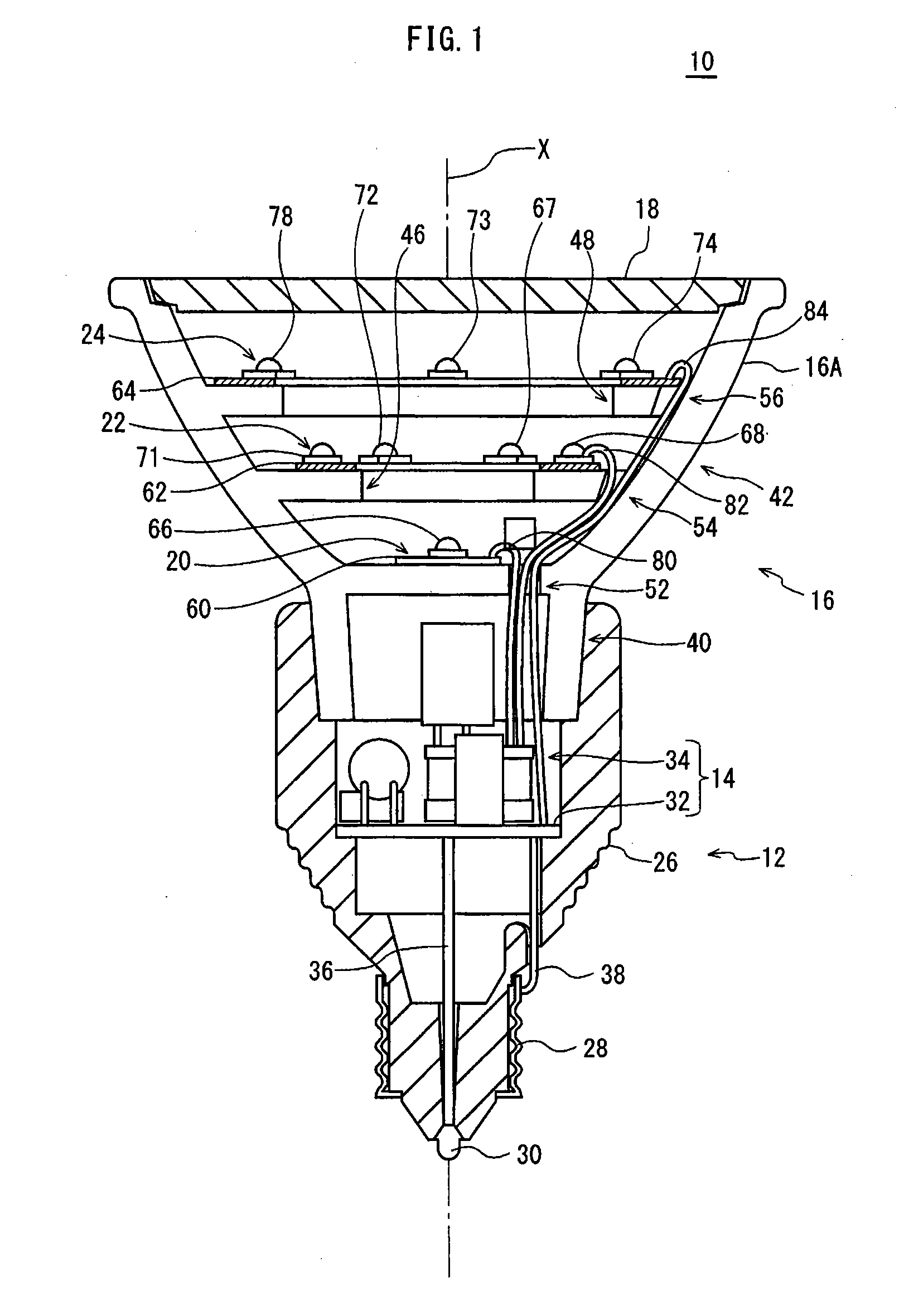
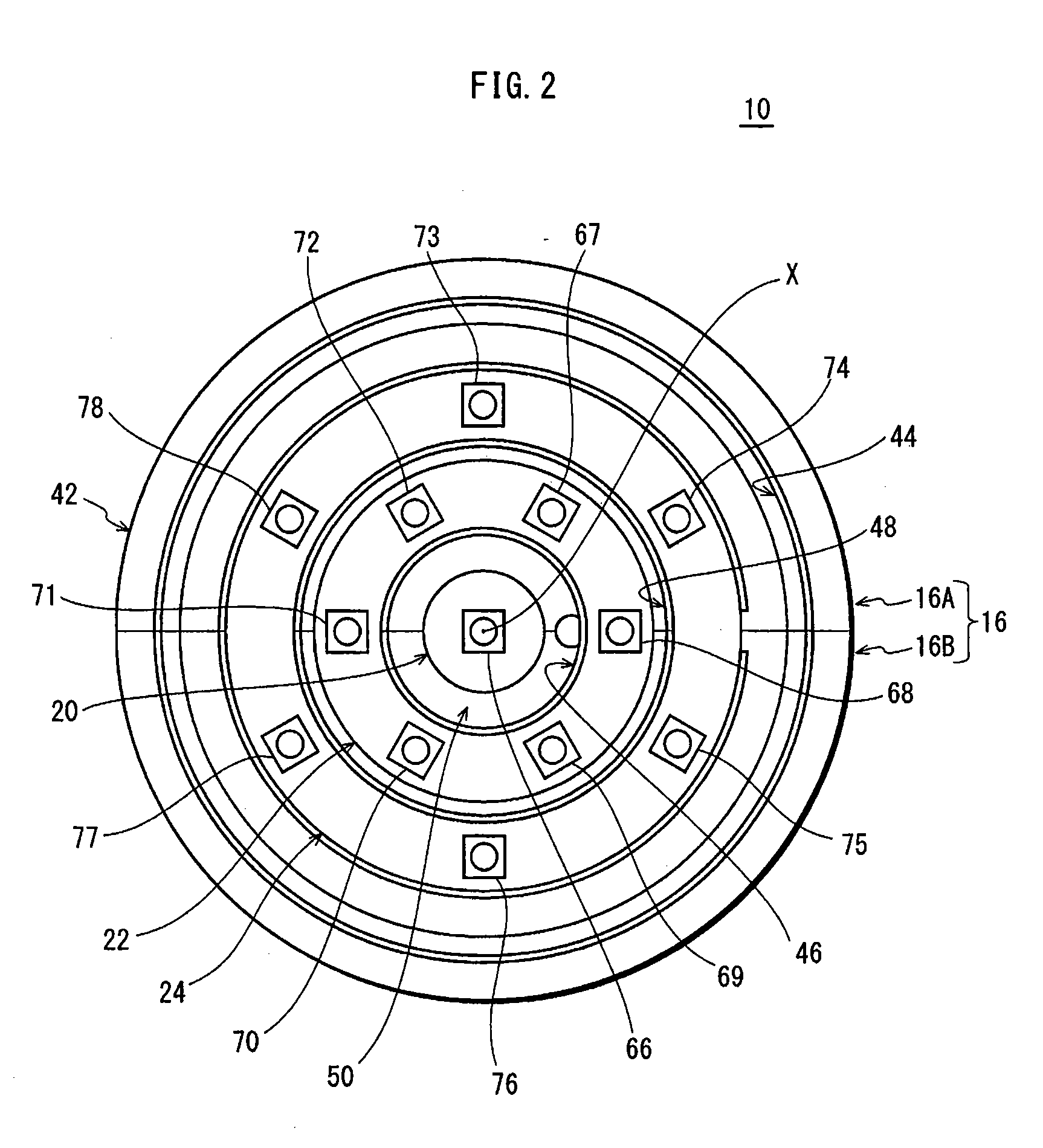
ActiveUS8393757B2Reduce thermal effectsTemperature variationLighting support devicesPoint-like light sourceEffect lightThermal radiation
Provided is a light-bulb type LED lamp 10 including a plurality of LEDs 67-78, a base 12, a lighting circuit unit that converts commercial power provided through the base 12 into power for lighting the LEDs 67-78, and a heat radiation member 16 that includes a bowl-shaped portion 42. Two stages 46 and 48, extending inwards from an inner circumferential surface 44 of the bowl-shaped portion 42, are provided in a direction of a central axis X of the bowl-shaped portion 42. The LEDs 67-78 are mounted on the stages 46 and 48 in a circumferential direction around the central axis X.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Light-bulb type LED lamp and illumination apparatus
ActiveUS20120120661A1Reduce thermal effectsTemperature variationPoint-like light sourceLighting support devicesEffect lightEngineering
Provided is a light-bulb type LED lamp 10 including a plurality of LEDs 67-78, a base 12, a lighting circuit unit that converts commercial power provided through the base 12 into power for lighting the LEDs 67-78, and a heat radiation member 16 that includes a bowl-shaped portion 42. Two stages 46 and 48, extending inwards from an inner circumferential surface 44 of the bowl-shaped portion 42, are provided in a direction of a central axis X of the bowl-shaped portion 42. The LEDs 67-78 are mounted on the stages 46 and 48 in a circumferential direction around the central axis X.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Hydrogen storage device
InactiveUS20110192732A1Avoid deformationAvoid distortionOther accessoriesContainer/bottle contructionProcess engineeringDistortion
The present invention discloses a hydrogen storage device. The hydrogen storage device includes a first casing, at least one hydrogen container, at least one stress buffering unit, and a second casing. The hydrogen container is set inside the first casing. The stress buffering unit is set between the hydrogen container and the first casing. The second casing surrounds the first casing forming a second space to contain heat transfer media, thereby controlling the temperature of the hydrogen container. While the hydrogen storage materials loaded in the hydrogen container absorb hydrogen gas, the stress buffering unit can eliminate the stress caused by the volume expansion of the hydrogen storage materials so as to prevent the first casing from distortion and deformation. Thus, the hydrogen gas can be stored efficiently and safely.
Owner:CHUNG HSIN ELECTRIC & MACHINERY MFG
Power storage apparatus
ActiveUS20160126604A1Reduce temperature changesCooling performance is deterioratedCurrent conducting connectionsSecondary cellsPower storageElectrical and Electronics engineering
A power storage apparatus includes a plurality of spacers. The plurality of spacers is alternately stacked with the power storage devices. Each of the spacers defines a space through which cooling air flows. The spacers include first spacer and second spacer. The first spacer is a spacer disposed between the end plate and one of the plural power storage devices that is located adjacent to the end plate. The first spacer includes guide member. The guide member is arranged in a circumference of the opening of at least one of the inflow port and the outflow port so as to narrow the opening.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Method of Mixing Rubber Composition and System for Mixing Rubber Composition
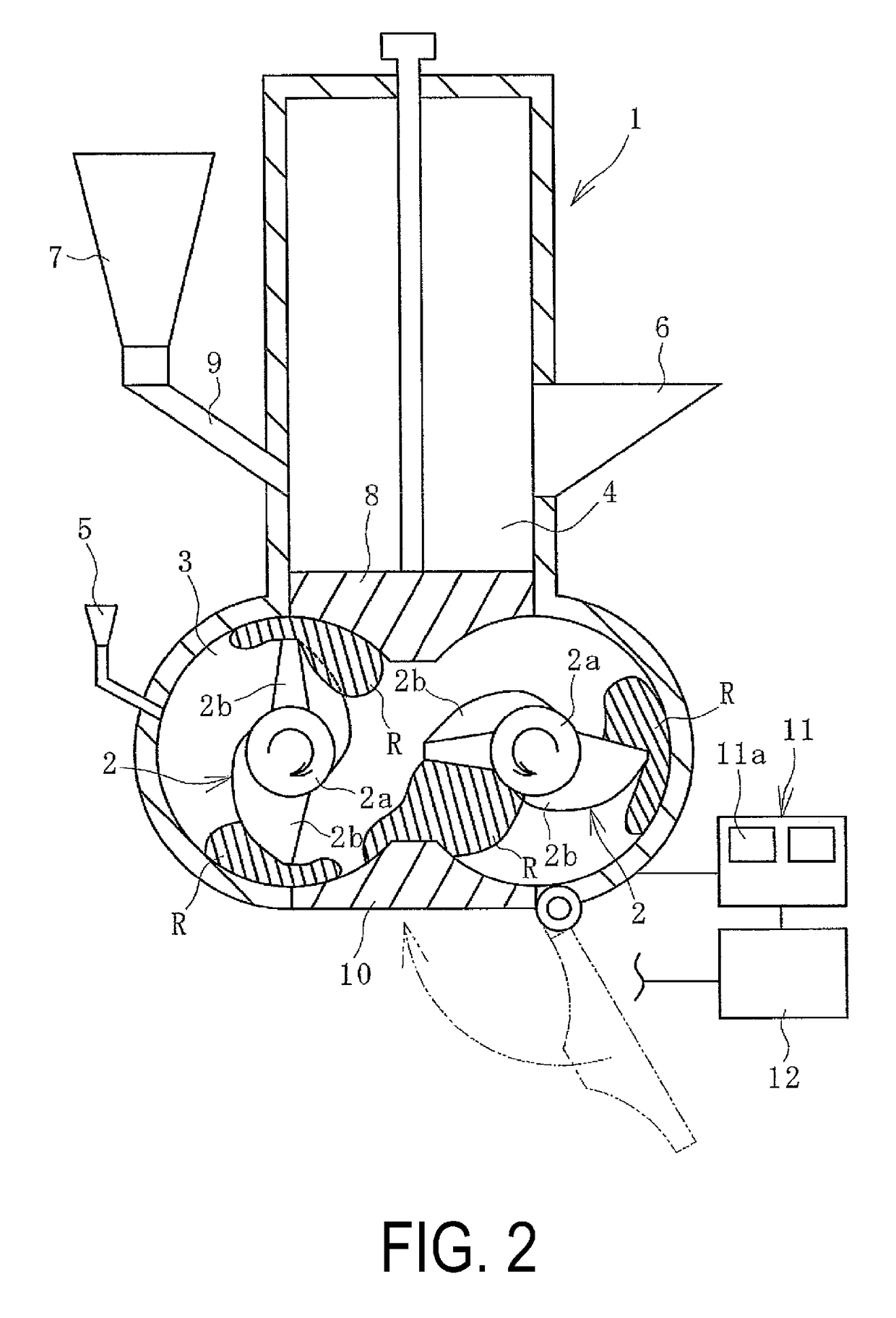
ActiveUS20170225132A1Rate of temperature increaseReduce variationTransportation and packagingMixer accessoriesPolymer scienceRam pressure
A method of mixing a rubber composition includes a carbon introduction step and a uniform dispersion step. In the carbon introduction step, on the basis of a deviation between a rate of temperature increase of the rubber mixture (R) and a target value, at least one of a ram pressure (Pr) and a rotational speed (N) of the mixing rotor (2) is PID controlled so that the ultimate temperature of the rubber mixture (R) at the conclusion of the step is within a tolerance range. In the uniform dispersion step, the ram pressure (Pr) or the rotational speed (N) of the mixing rotor (2) is adjusted to reduce a deviation between a value based on successively detected data associated with a predetermined control target and a target value.
Owner:THE YOKOHAMA RUBBER CO LTD
Multilayer wiring board
InactiveUS7078629B2Blocking may occurImprove reliabilityPrinted circuit assemblingFinal product manufactureResistSemiconductor chip
To prevent, in a multilayer wiring board to which a semiconductor chip is flip-chip bonded, occurrence of cracks in the board at portions adjacent to electrode pads due to a difference in thermal expansion coefficient between the semiconductor chip and the board. A multilayer wiring board (20) of the present invention has features that electrode pads (22) corresponding to electrodes of a semiconductor chip (25) located near an outer periphery (29) of the semiconductor chip each have an oblong shape, openings (35) of a solder resist (23) are each smaller than the oblong shape, and the center (B) of the opening is located to be offset from the center (A) of the oblong shape by a distance (L4) in a direction (30) toward the center of the semiconductor chip. Therefore, in the multilayer wiring board of the present invention, thermal stresses applied to portions (L3) of the electrode pads (22) on the board near the outer periphery of the semiconductor chip are relaxed. Consequently, the multilayer wiring board of the present invention can prevent occurrence of cracks in the board at portions adjacent to the electrode pads near the outer periphery of the semiconductor chip due to a difference in thermal expansion coefficient between the semiconductor chip and the board.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Concentrated cooling apparatus of refrigerator
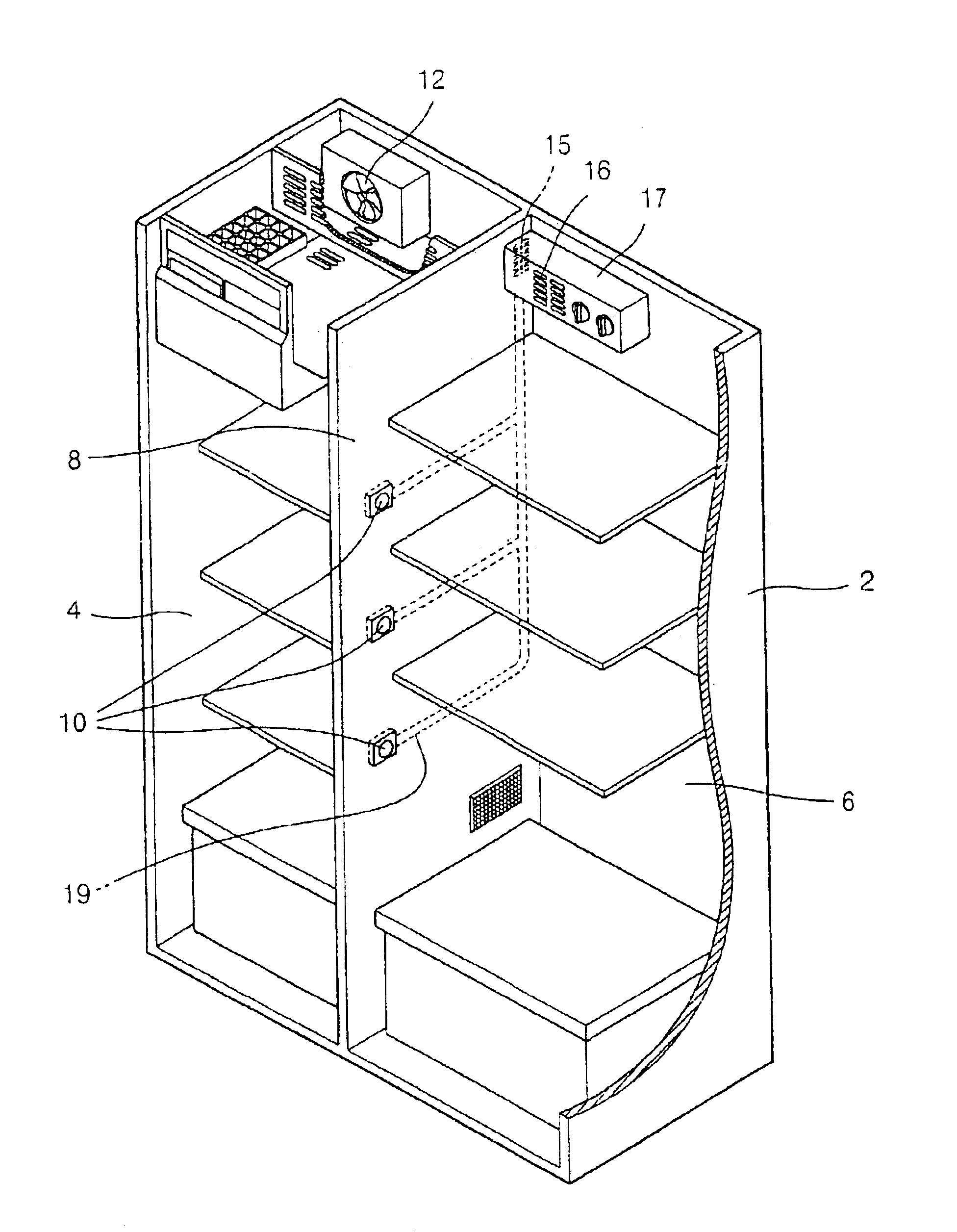
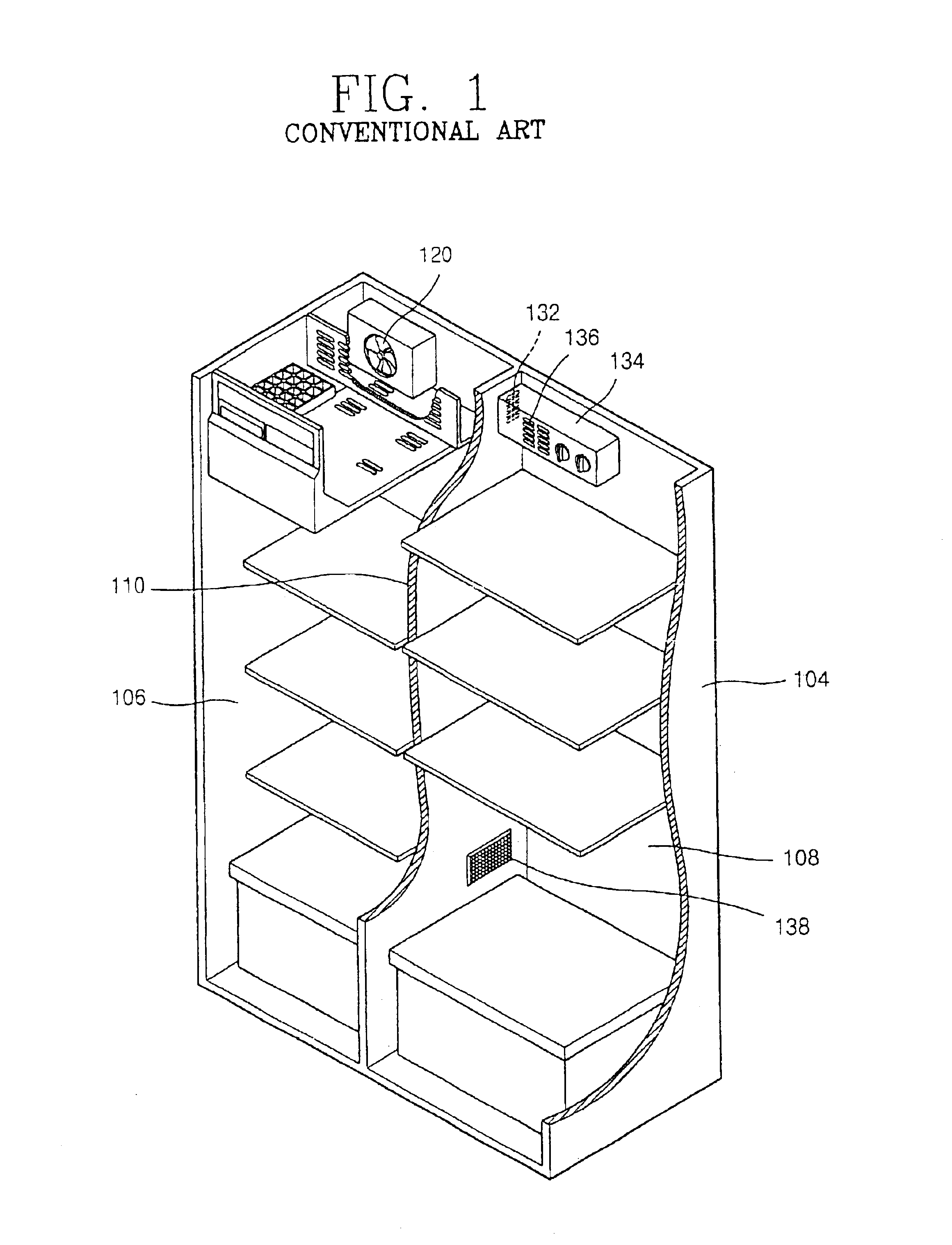
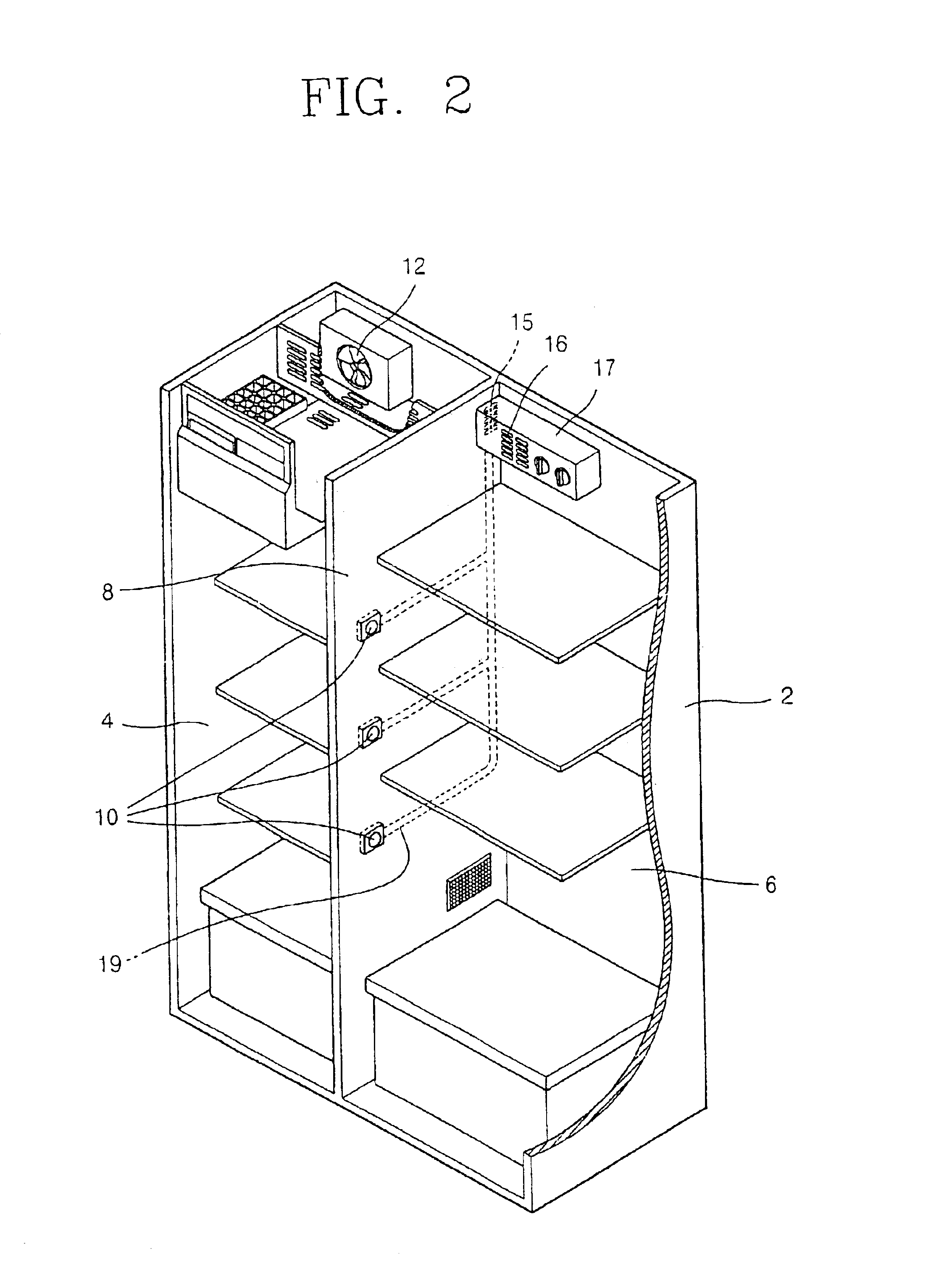
InactiveUS6837066B2Temperature variationMaintain freshnessLighting and heating apparatusCooling fluid circulationCold airRefrigerated temperature
A concentrated cooling apparatus of a refrigerator is capable of improving the reliability of an infrared sensor by preventing moisture from being condensed onto the surface of the infrared sensor. The concentrated cooling apparatus includes a nozzle rotationally supported by a cold air guide path, the nozzle intensively jetting cold air to a high-temperature load region when a high-temperature load is placed inside a chilling chamber of the refrigerator. An infrared sensor is installed at the front of the nozzle, and the infrared sensor senses the high-temperature load region while being rotated together with the nozzle. A moisture removing device is formed at a side of the nozzle, the moisture removing device jetting cold air on the surface of the infrared sensor to remove moisture condensed on the surface of the infrared sensor.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
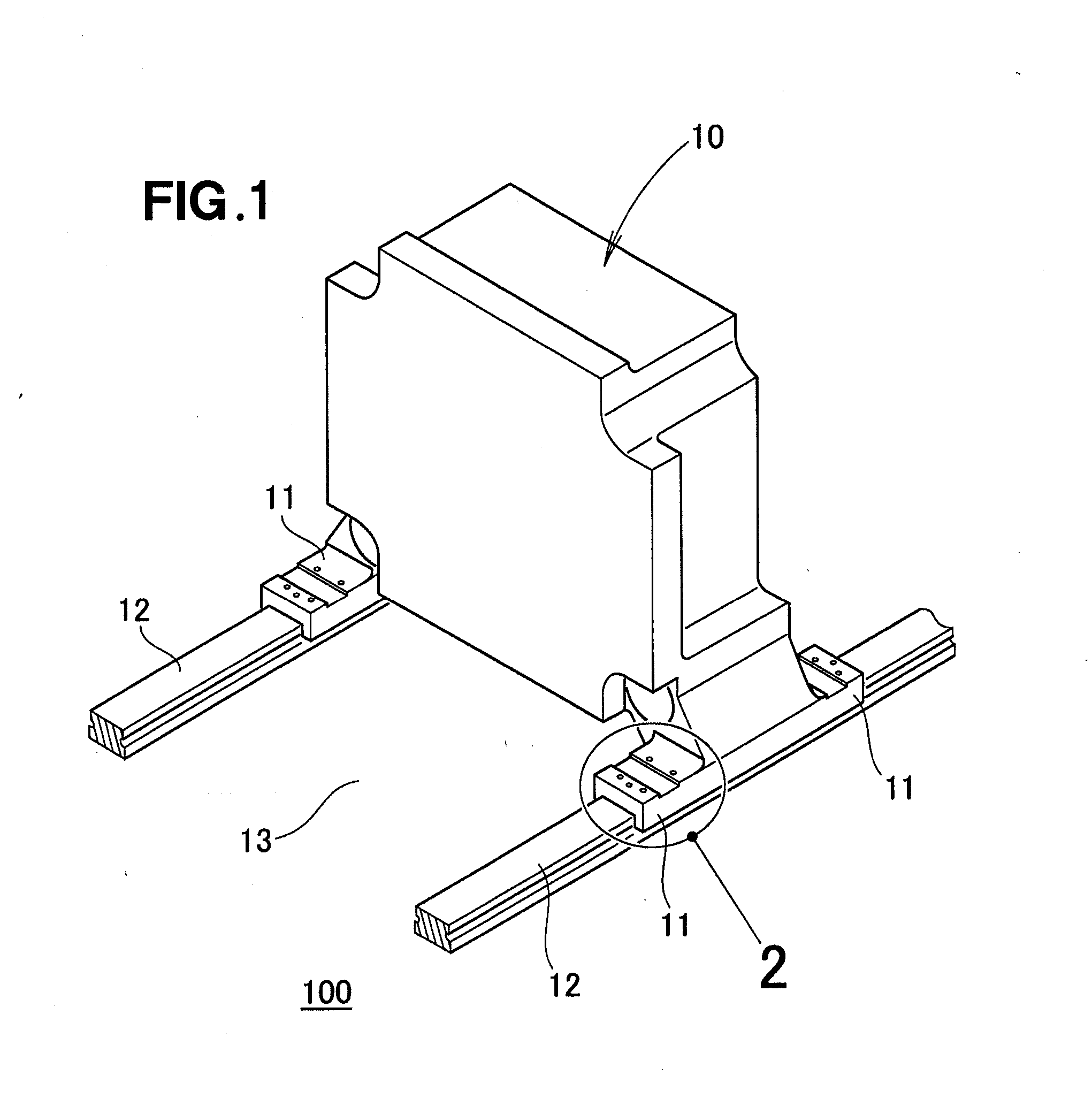
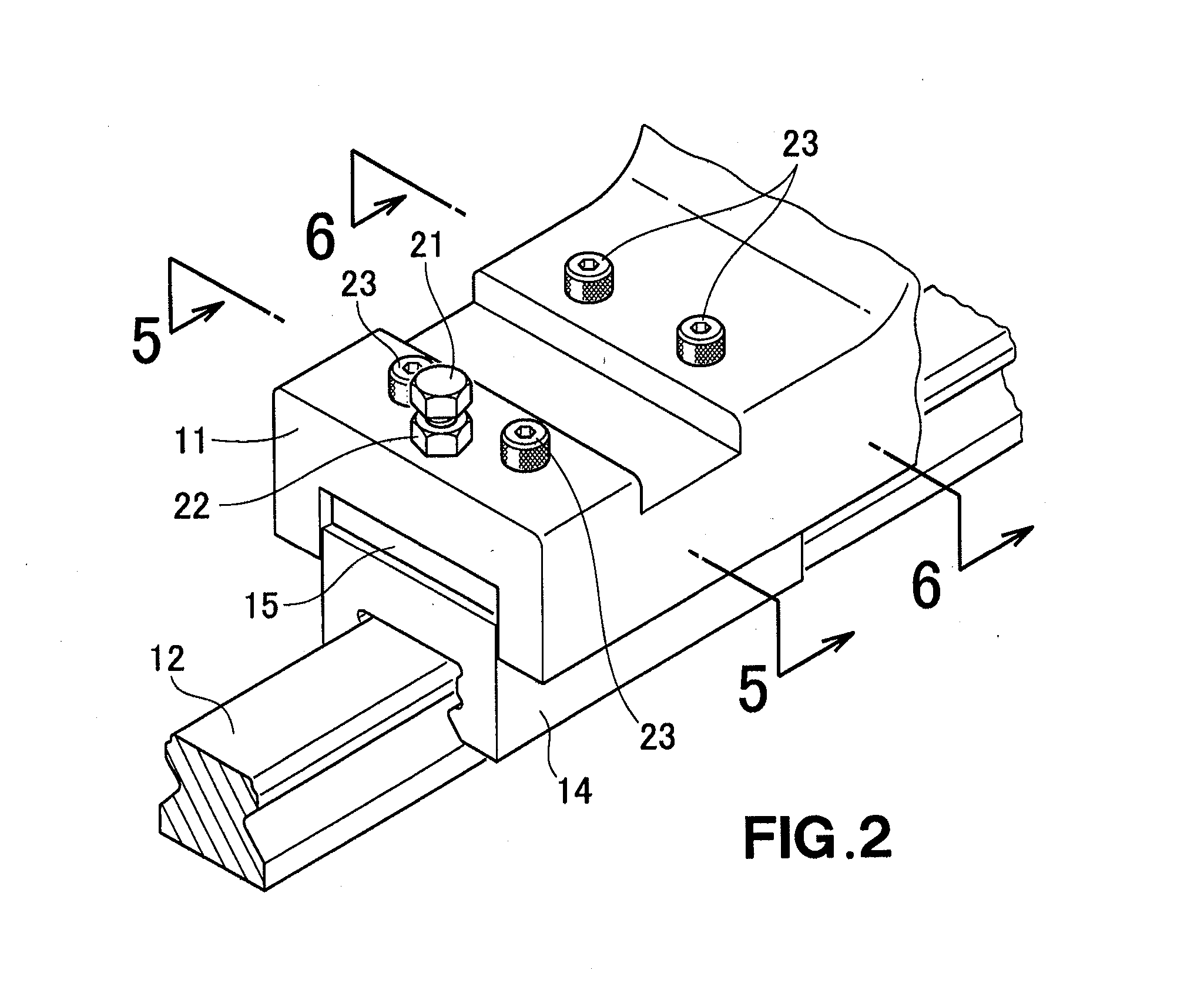
Movable platen support structure for injection molding apparatus
Owner:NISSEI PLASTIC IND CO LTD
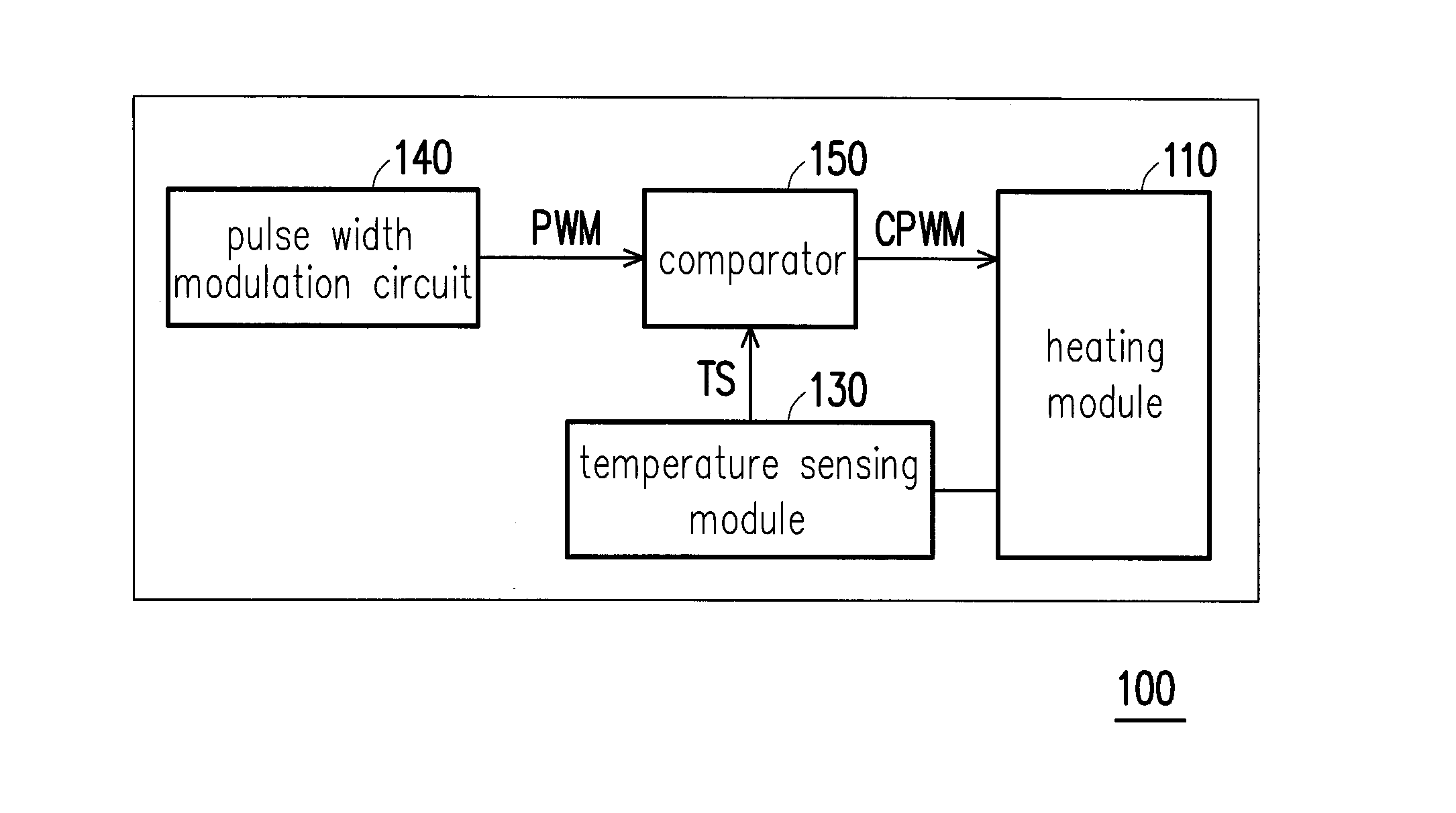
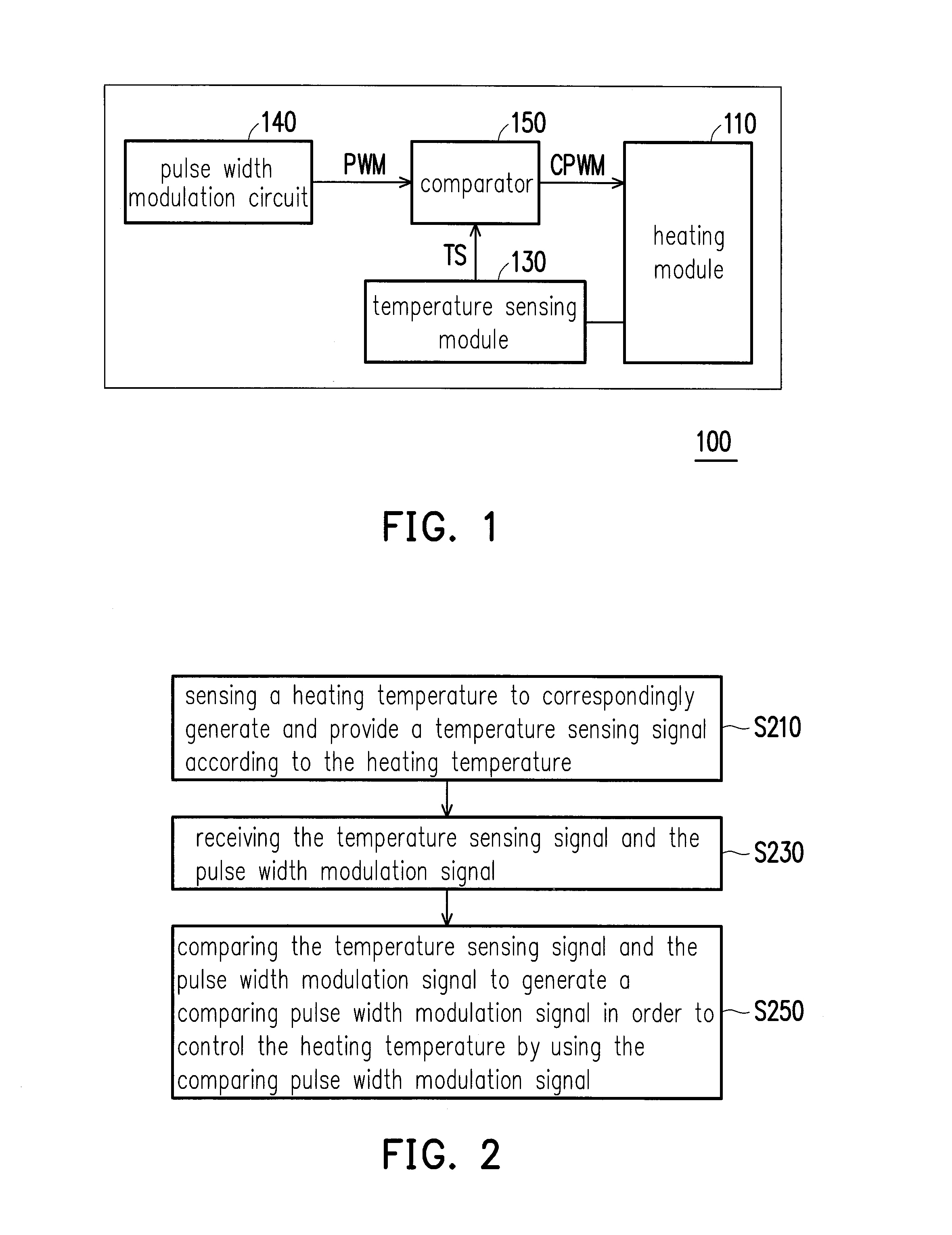
Heating control apparatus and control method thereof
ActiveUS9482586B2Instantly controllingReduce temperature changesAdditive manufacturing apparatusThermometer applicationsEngineeringHeat control
A heating control apparatus and a control method thereof are provided. The heating control apparatus includes a heating module, a temperature sensing module, a pulse width modulation circuit, and a comparator. Input terminals of the comparator are respectively coupled to the temperature sensing module and the pulse width modulation circuit, and an output terminal of the comparator is coupled to the heating module. In the control method, a heating temperature of the heating module is sensed by the temperature sensing module, so as to provide a temperature sensing signal. The comparator receives the temperature sensing signal and a pulse width modulation signal generated by the pulse width modulation circuit and compares the temperature sensing signal and the pulse width modulation signal to generate a comparing pulse width modulation signal, so as to control the heating temperature of the heating module by using the comparing pulse width modulation signal.
Owner:XYZPRINTING +2
Spacecraft
ActiveUS9828116B1Low costMore reliableCosmonautic environmental control arrangementCosmonautic vehiclesEngineeringDrive motor
The invention relates to a spacecraft comprising a body having two opposite faces; a first radiator carried by at least one face; the first radiator having an outer face; a first supporting arm extending substantially perpendicularly to the outer face of the first radiator; a drive motor suitable for rotating the first supporting arm about its longitudinal axis a first assembly carried by the first supporting arm, said first assembly comprising a plurality of slats stationary with respect to the first supporting arm; said slats being attached one above the other and separated from each other by a free space.
Owner:AIRBUS DEFENCE & SPACE
High-power microwave tube with beam spreading in the collector
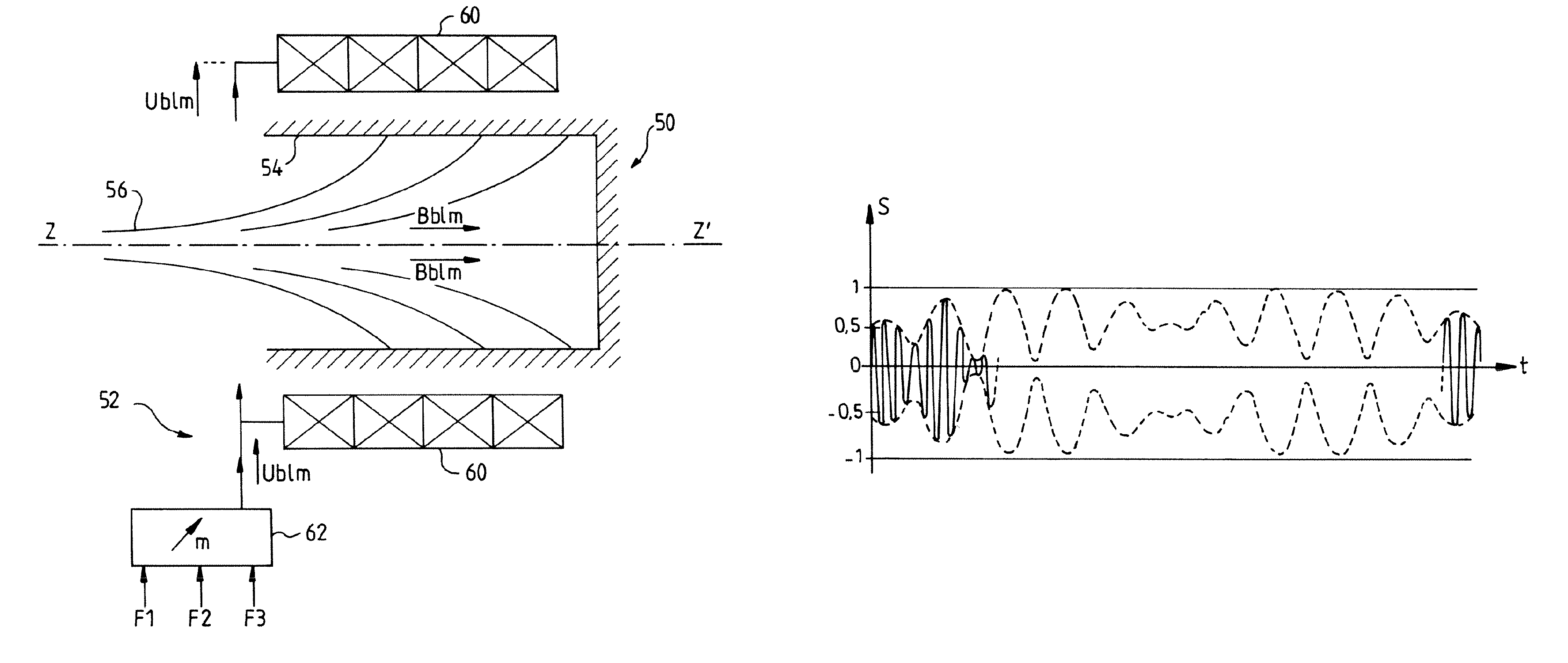
InactiveUS7750572B2Temperature variationVariation in timeTransit-tube collectorsKlystronsMicrowave tubeLight beam
The invention relates to a microwave power tube consisting of an electron gun comprising a cathode that generates an electron beam in a microwave structure of the tube, and a collector for collecting electrons from the beam. In addition, the tube comprises a magnetic device for spreading the beam in the collector, which generates a periodic amplitude-modulated magnetic spread field Bblm. The invention is suitable for microwave power tubes.
Owner:THALES SA
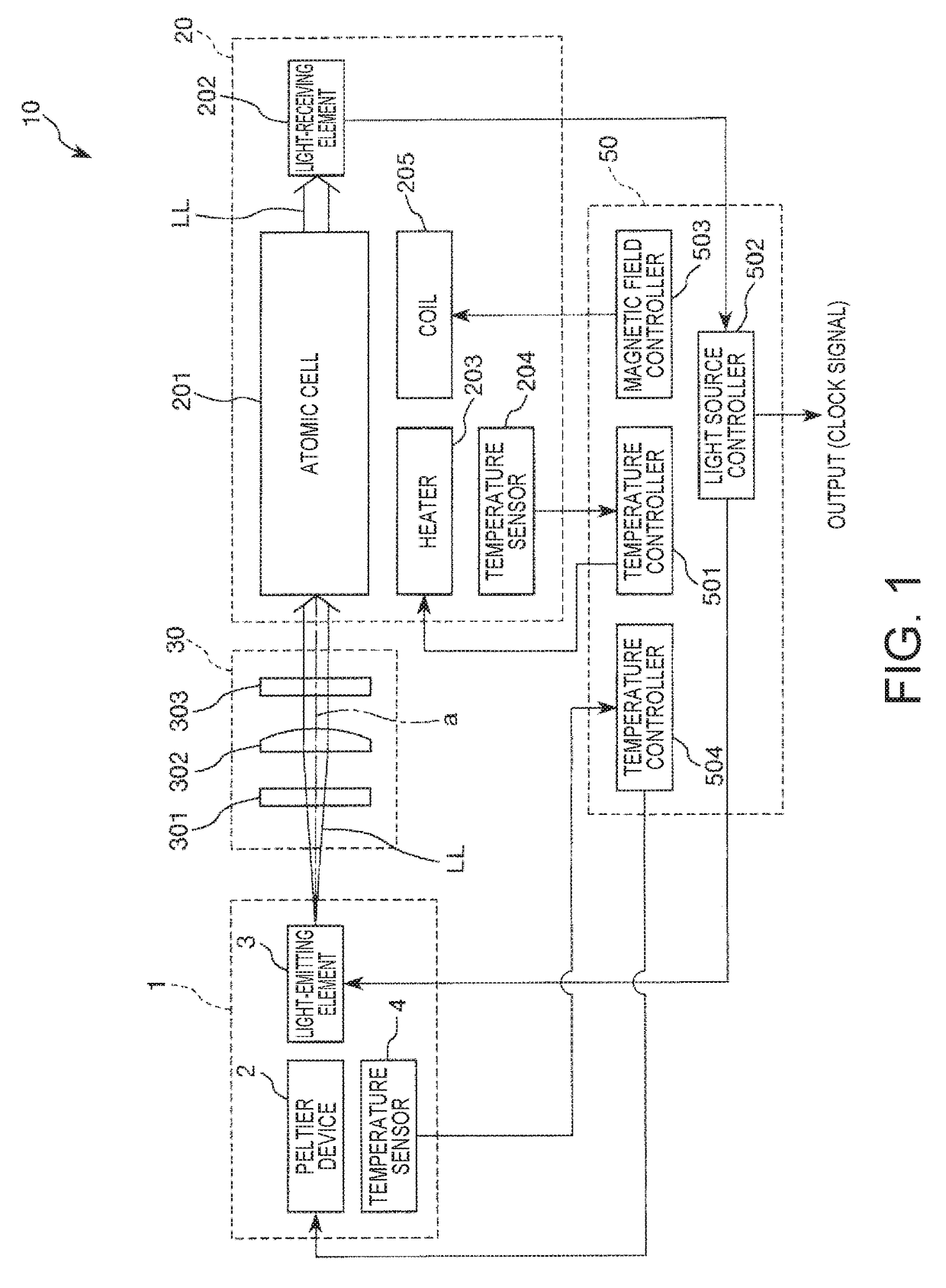
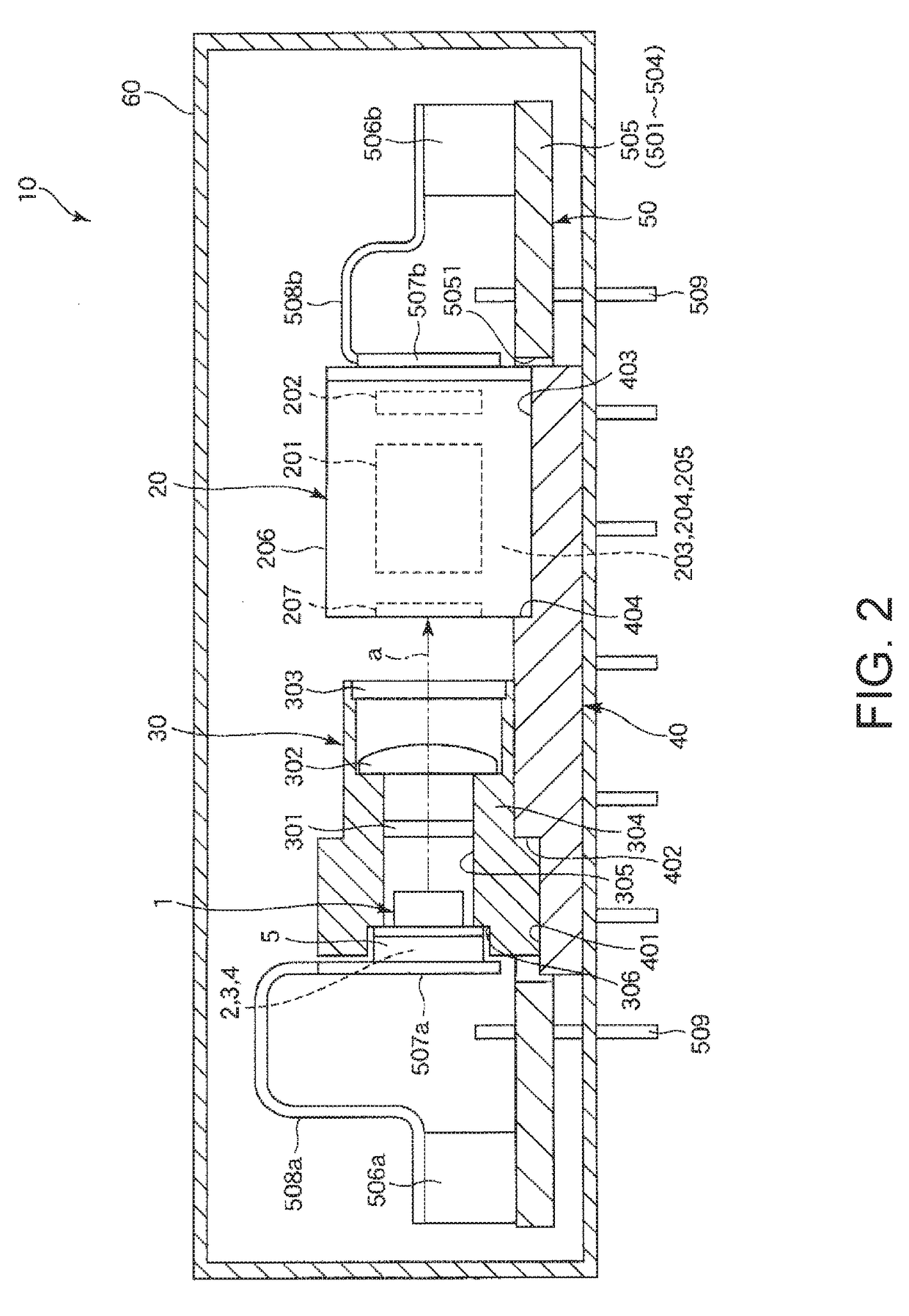
Light-emitting element module, atomic oscillator, and electronic apparatus
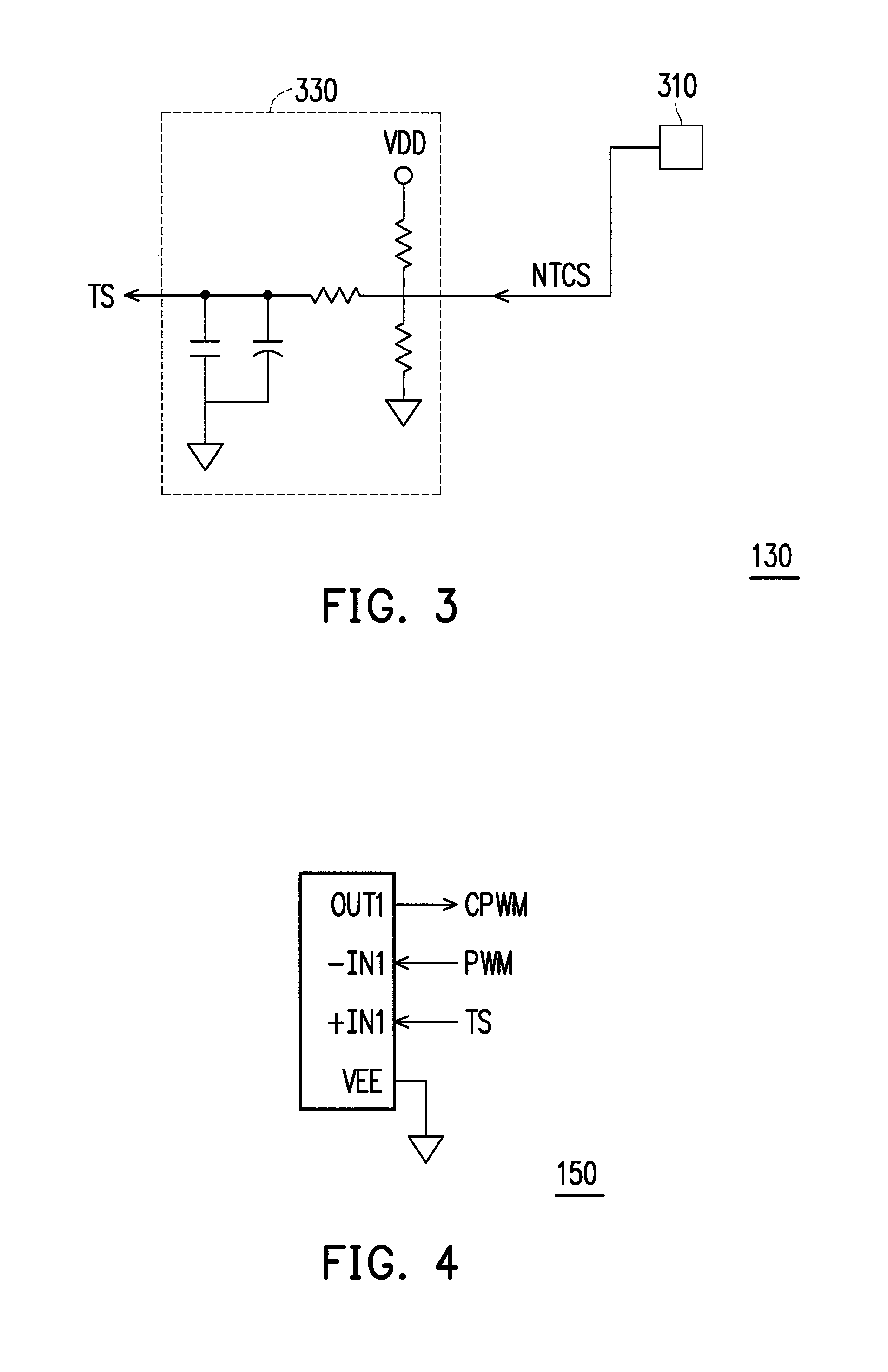
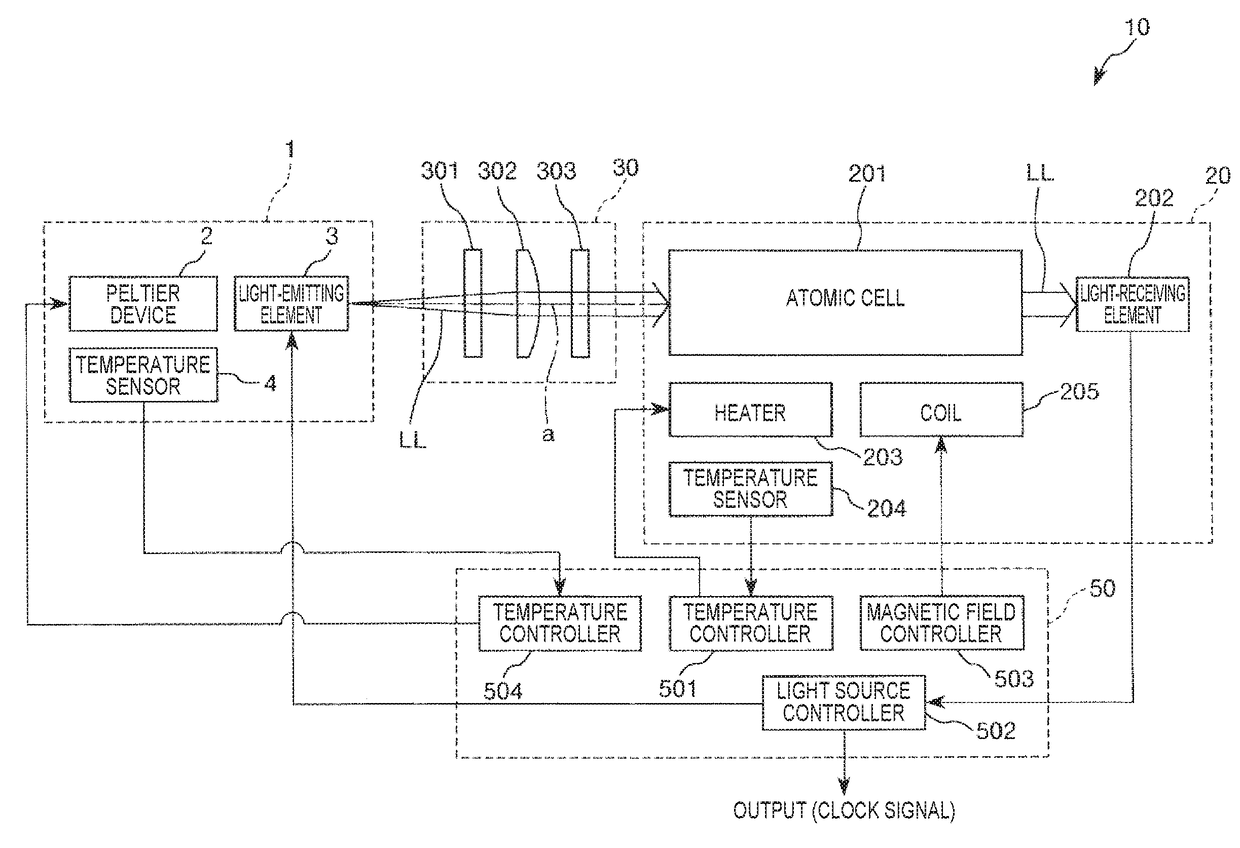
ActiveUS20180069372A1Temperature variationImprove reliabilityLaser detailsPulse automatic controlElectronElectrical and Electronics engineering
A light-emitting element module includes: a Peltier device; a light-emitting element that is disposed on the Peltier device; and a package that accommodates the Peltier device and the light-emitting element, the package including a base on which the Peltier device is disposed and a lid joined to the base and. When Ts is external temperature of the package, Tv is temperature of the light-emitting element, Tc1 is temperature of the base, and Tc2 is temperature of the lid, Ts<Tc2<Tc1 is satisfied in a case of Tv<Ts.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com