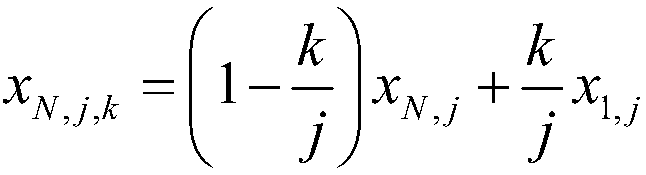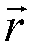Patents
Literature
40 results about "Antenna geometry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
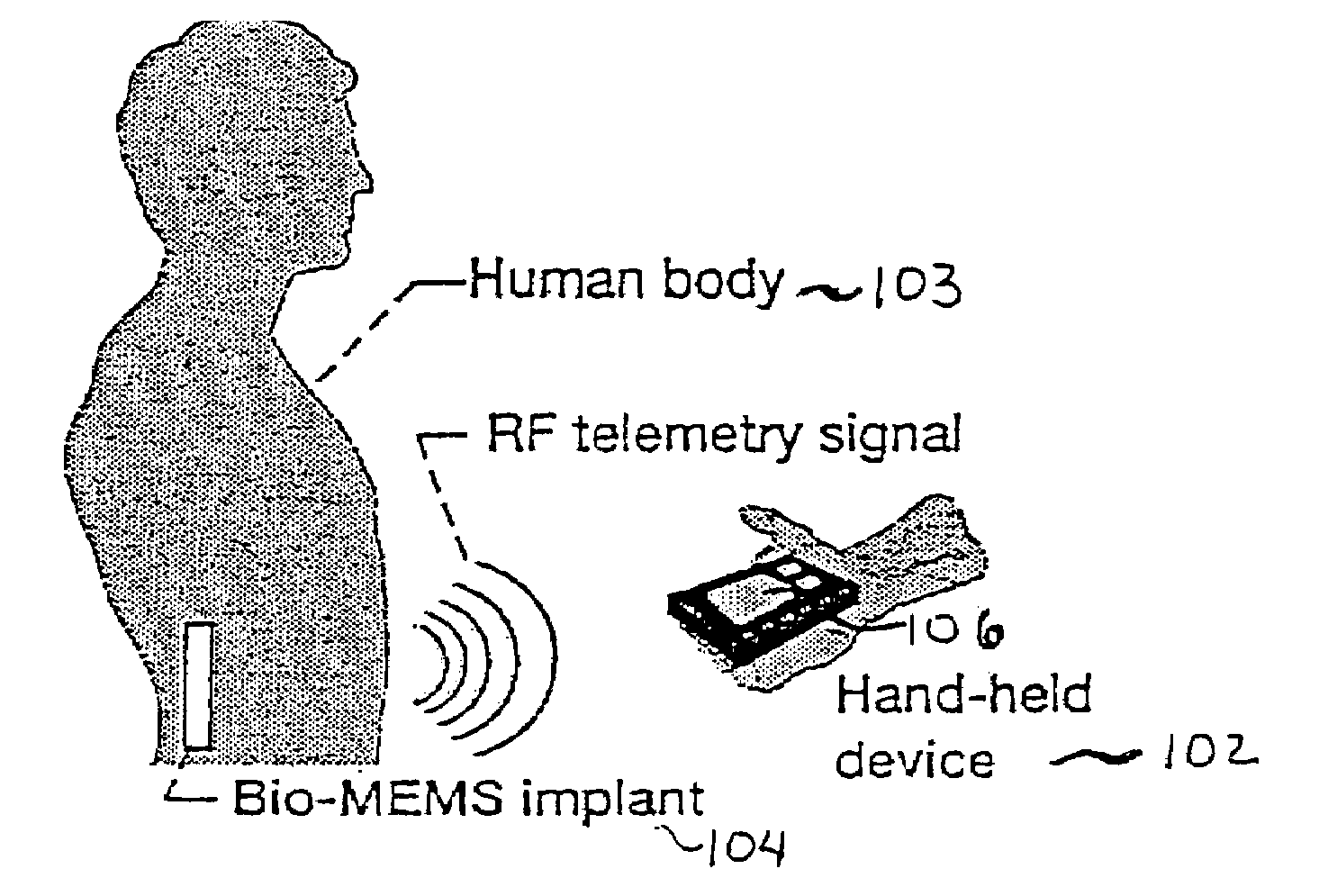
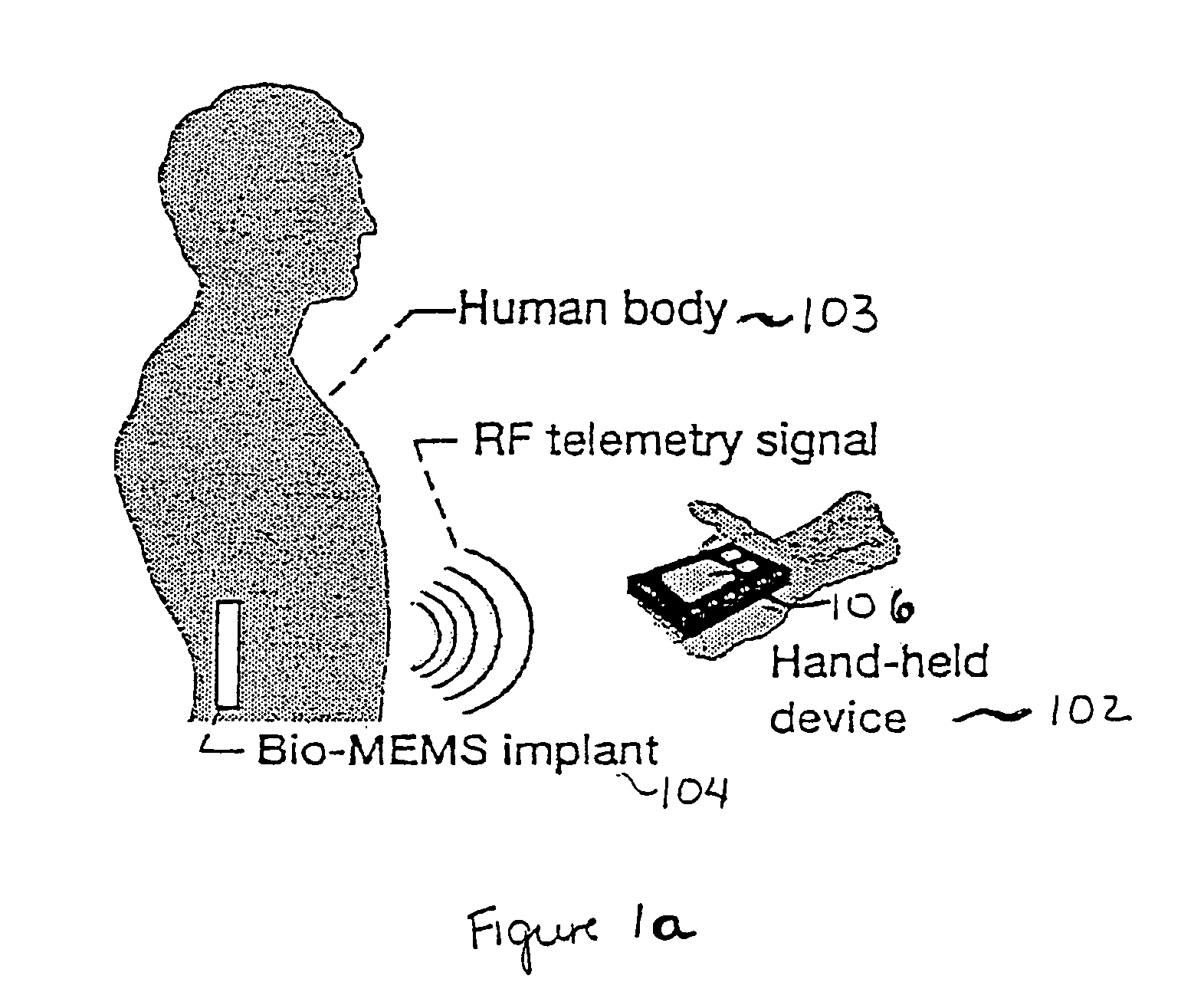
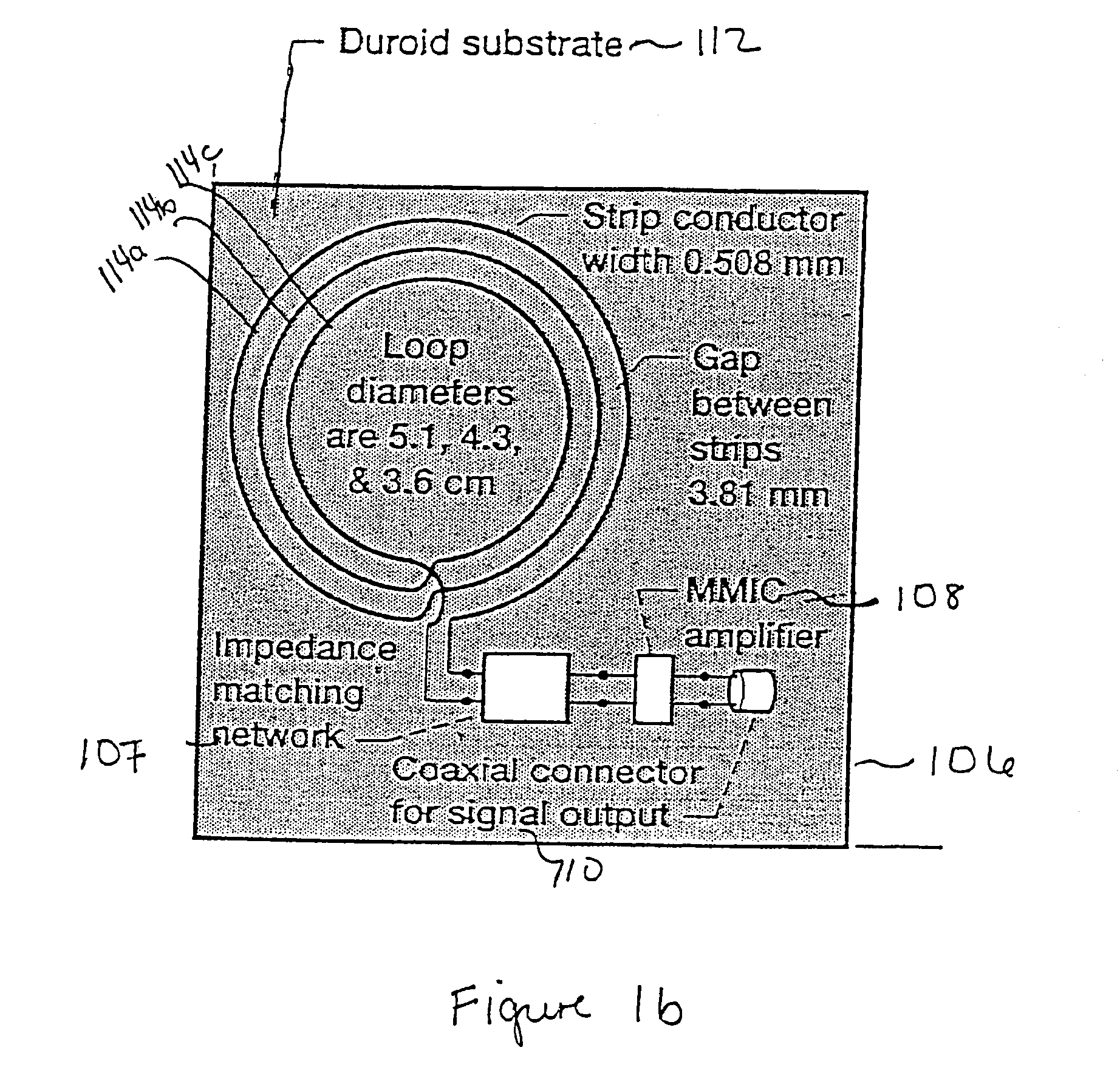
Hand held device for wireless powering and interrogation of biomems sensors and actuators
ActiveUS7191013B1Facilitate communicationElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringElectromagnetic couplingData retrieval
A compact, hand-held device for wireless powering, interrogation and data retrieval from at least one implanted sensor. The hand-held device includes an antenna for powering an implanted sensor and for receiving data from the implanted sensor to the hand-held device for at least one of storage, display or analysis. The hand-held device establishes electromagnetic coupling with a low radiating radio frequency power inductor in the implanted sensor at a predefined separation and the antenna geometry allows for the antenna to power, interrogate and retrieve data from the implanted sensor without strapping the hand-held device to a human body housing the implanted sensor The hand-held device optionally allows for activation of the implanted sensor only during interrogation and data retrieval.
Owner:NASA UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRSENTED BY THE ADMINISTATOR
Microcomputer electric stacking type millimeter wave antenna
ActiveCN101141023AReduce distractionsHigh bandwidthDecorative surface effectsRadiating elements structural formsMicrocomputerAnisotropic substrate
The invention provides a micro electromechanical cascade millimeter wave antenna, comprising an upper anisotropic substrate, a middle anisotropic substrate and a lower anisotropic substrate. The upper surface deposit of the upper anisotropic substrate is provided with metal and forms a first metal radiation patch by mechanical erosion. The upper surface deposit of the middle anisotropic substrate is provided with metal and forms a second metal radiation patch by mechanical erosion. The upper surface deposit of the lower anisotropic substrate is provided with metal and forms a FGCPW-MS feeder or a MS feeder by mechanical erosion. The upper anisotropic substrate, the middle anisotropic substrate and the lower anisotropic substrate form a unit by MEMS bonding technology. The antenna has small size and light weight, which is also easy for the further integration.
Owner:NO 55 INST CHINA ELECTRONIC SCI & TECHNOLOGYGROUP CO LTD
Branching RF antennas and plasma processing apparatus
InactiveUS6868800B2Improve uniformityReduce standing wave effectElectric discharge tubesElectric arc lampsAntenna designProcess region
The inductively coupled plasma source and antenna geometry are significant factors in determining plasma and process uniformity inside the chamber. Growing demands for processing larger and larger wafers or LCD substrates and providing higher and higher degrees of plasma uniformity challenge the current ICP type antenna designs and push development of sources. Branching RF antenna, featuring a plurality of major and minor branches, provides improved coverage of processing area, reduced standing wave effect, improved uniformity of inductively coupled electromagnetic field, more uniform plasma production, and more homogeneous processing conditions throughout the whole processing area.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Method for designing a small antenna matched to an input impedance, and small antennas designed according to the method
InactiveUS7057574B2Reduce areaImprove performanceRadiating elements structural formsElectrically short antennasCapacitanceEngineering
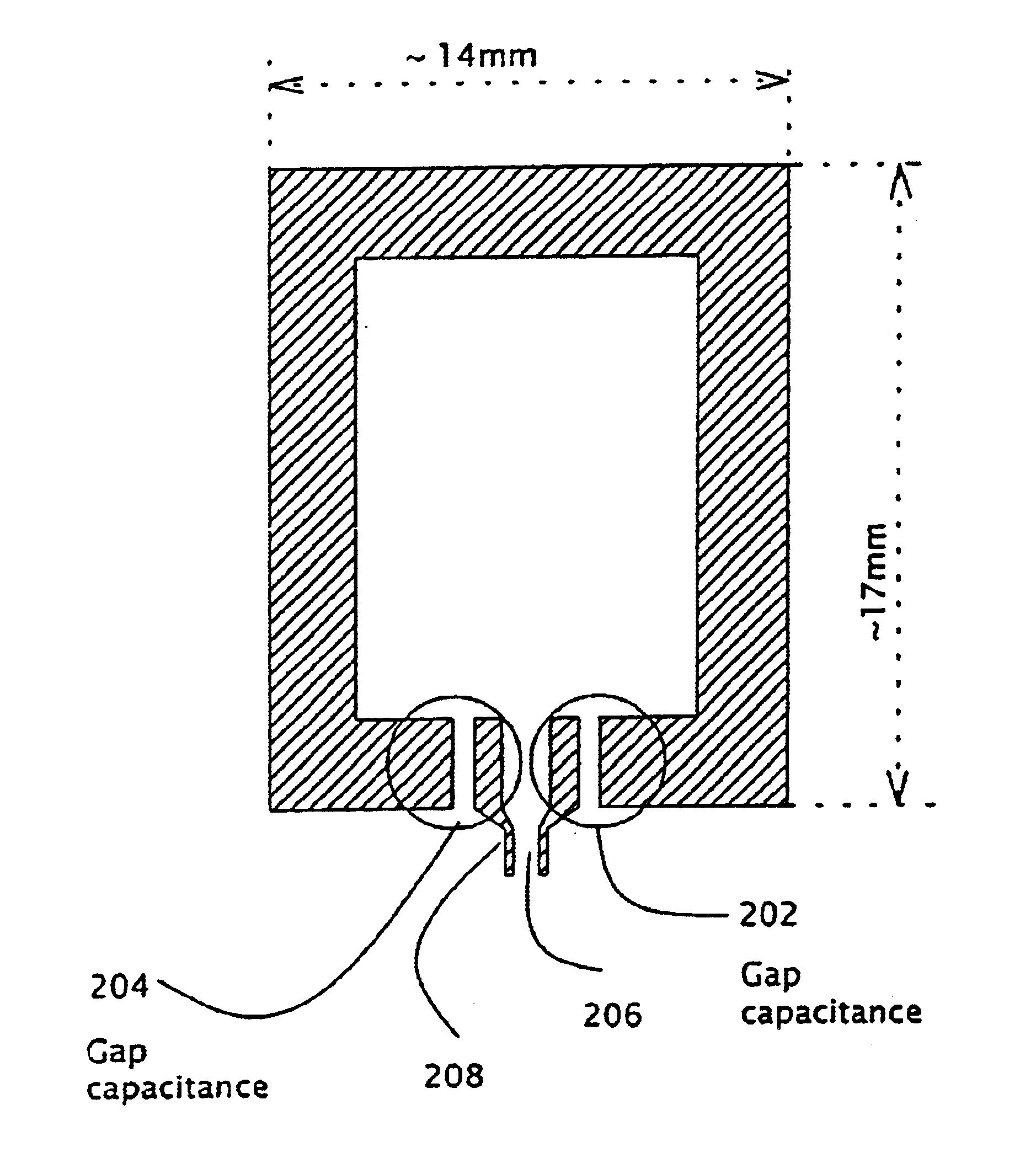
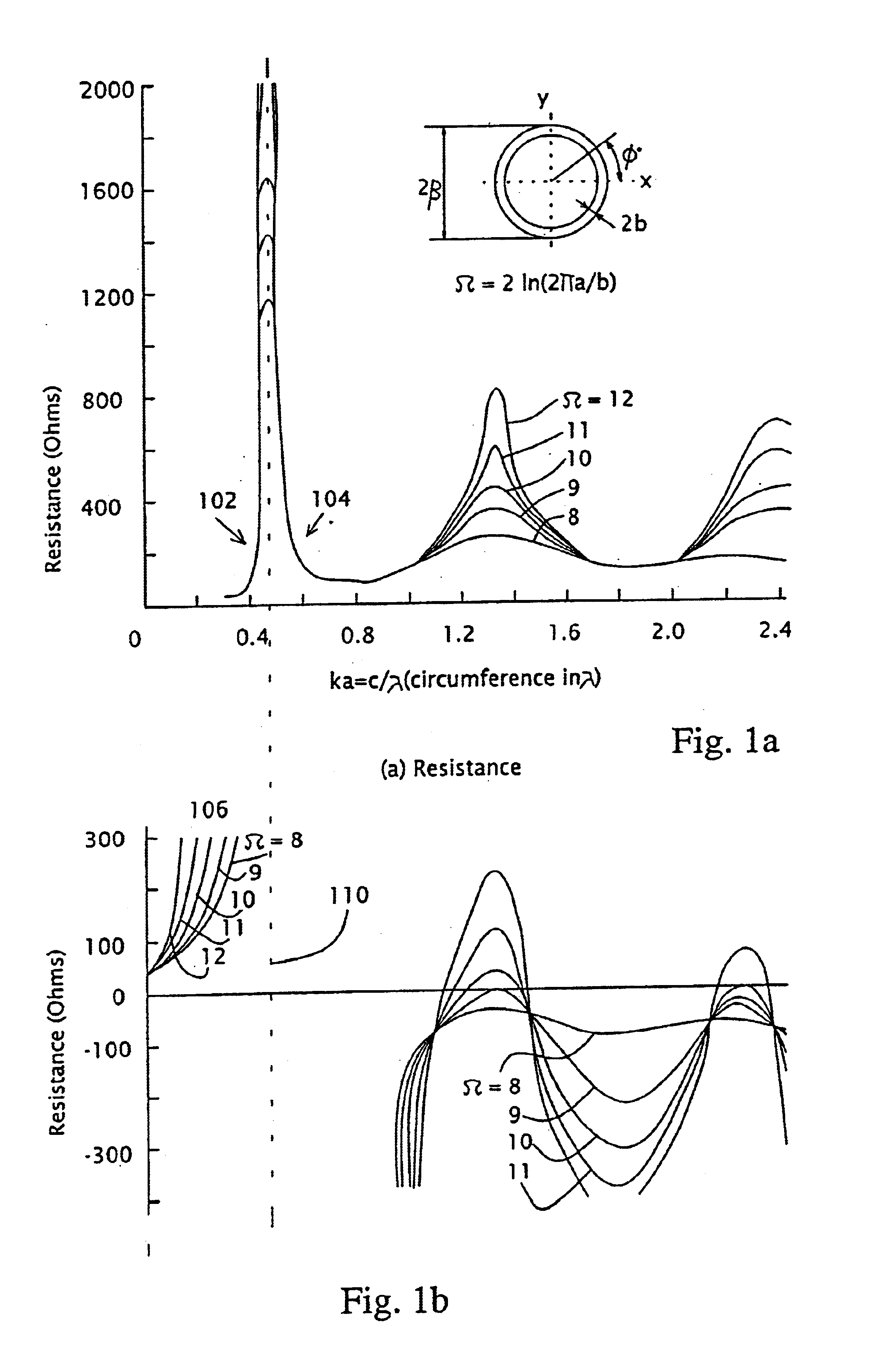
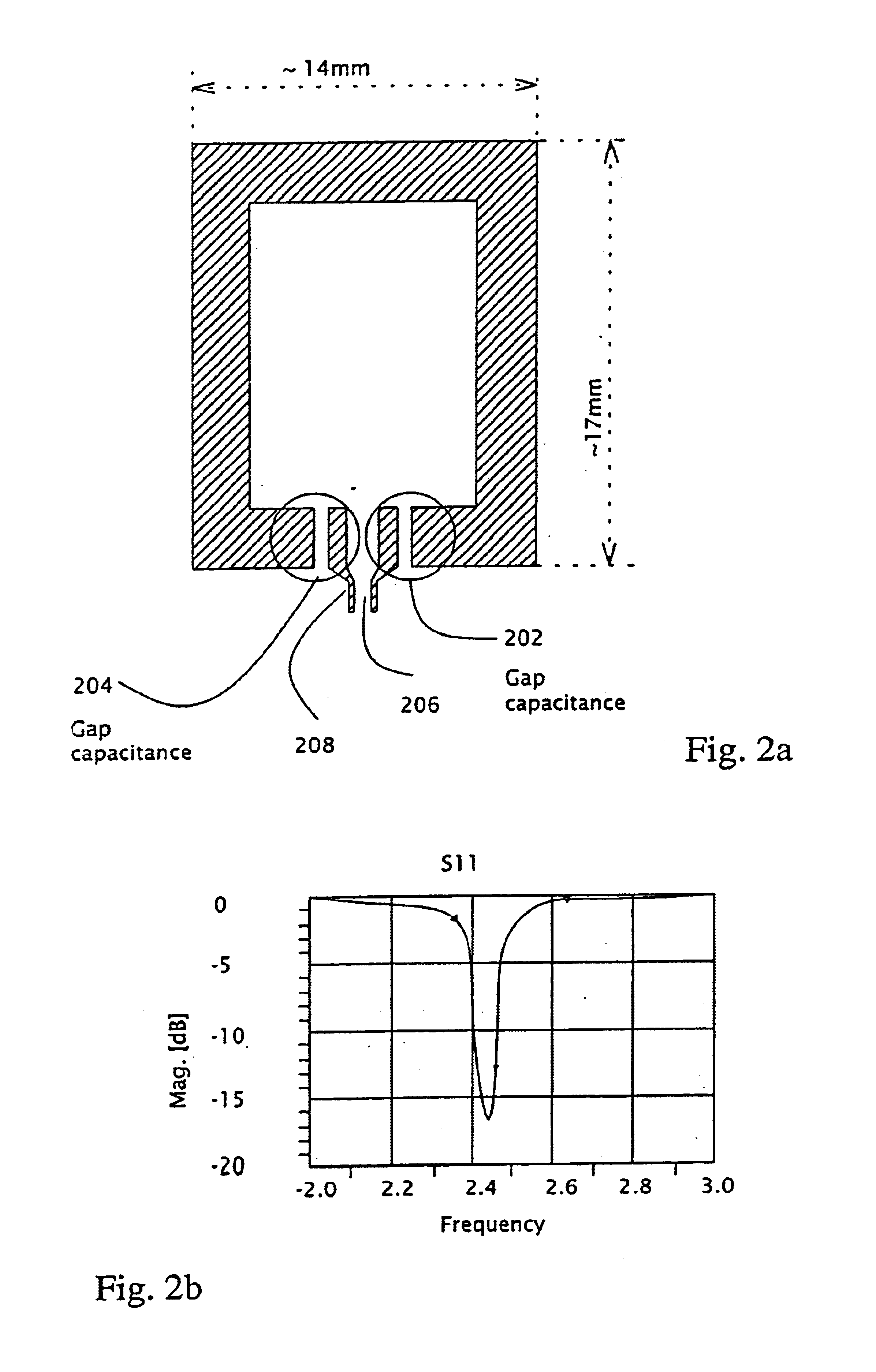
A method for designing a high performance, small antenna that is matched to a required output impedance, does not require filtering, is simple and inexpensive to manufacture, and is easily integrable with an RF power amplifier- with minimum cost, minimum external components and minimum energy losses. The method includes finding a singular point (102) in the impedance vs. antenna geometrical dimension / wavelength ratio graph, the singular point (102) exhibiting a high very high positive reactance, setting the antenna geometry to match this point, and canceling the very high positive reactance (high inductance) resulting from this match by adding to the antenna a very small capacitance, preferably provided by at least one gap capacitor (202) The antenna is preferably a loop antenna (200), and both the antenna and the gap capacitor (202) (204) are preferably implemented by printing methods on printed circuit board or ceramic substrates. The antenna (200) may also be implemented in non-differential designs.
Owner:VISHAY ADVANCED TECH LTD +1
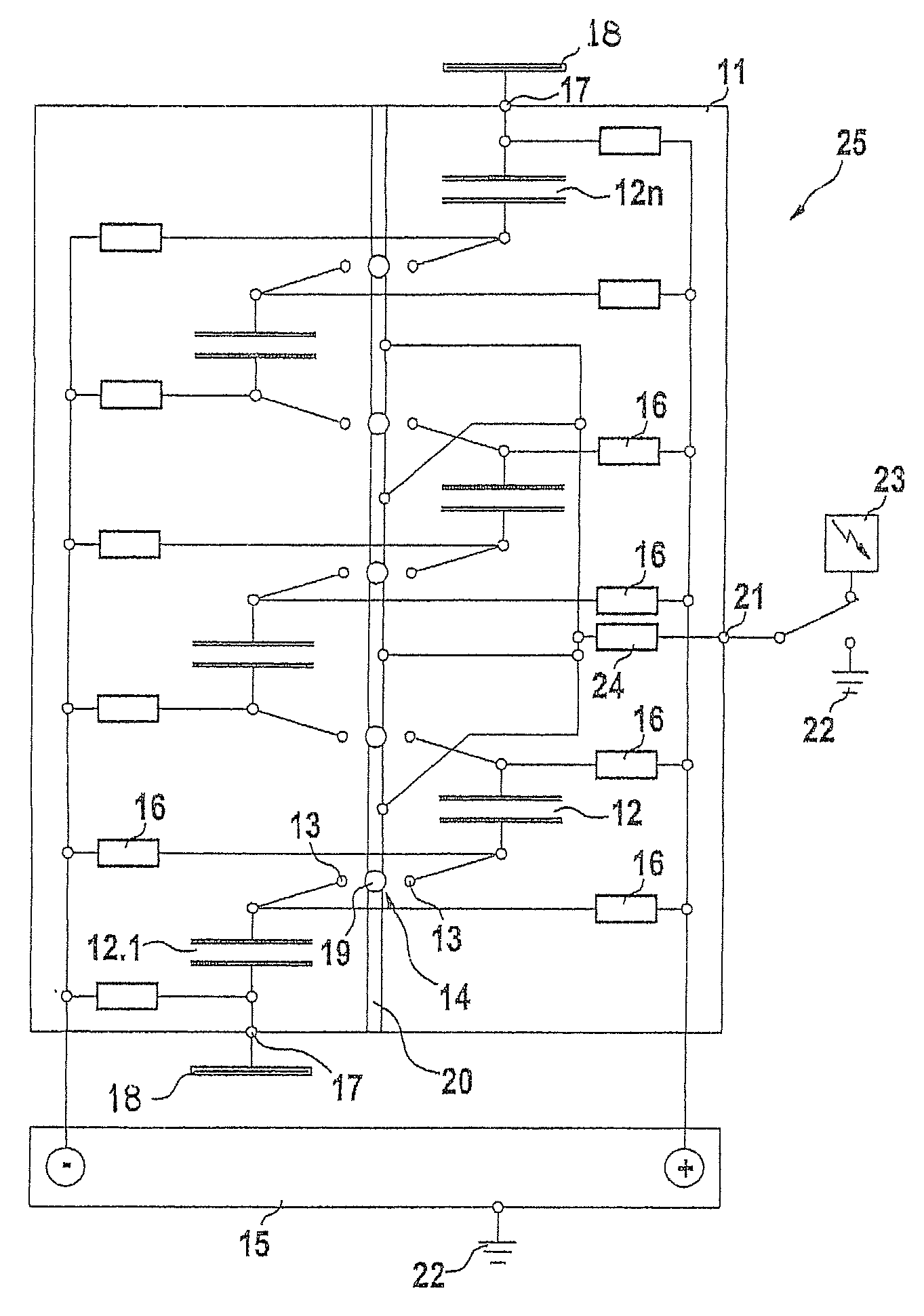
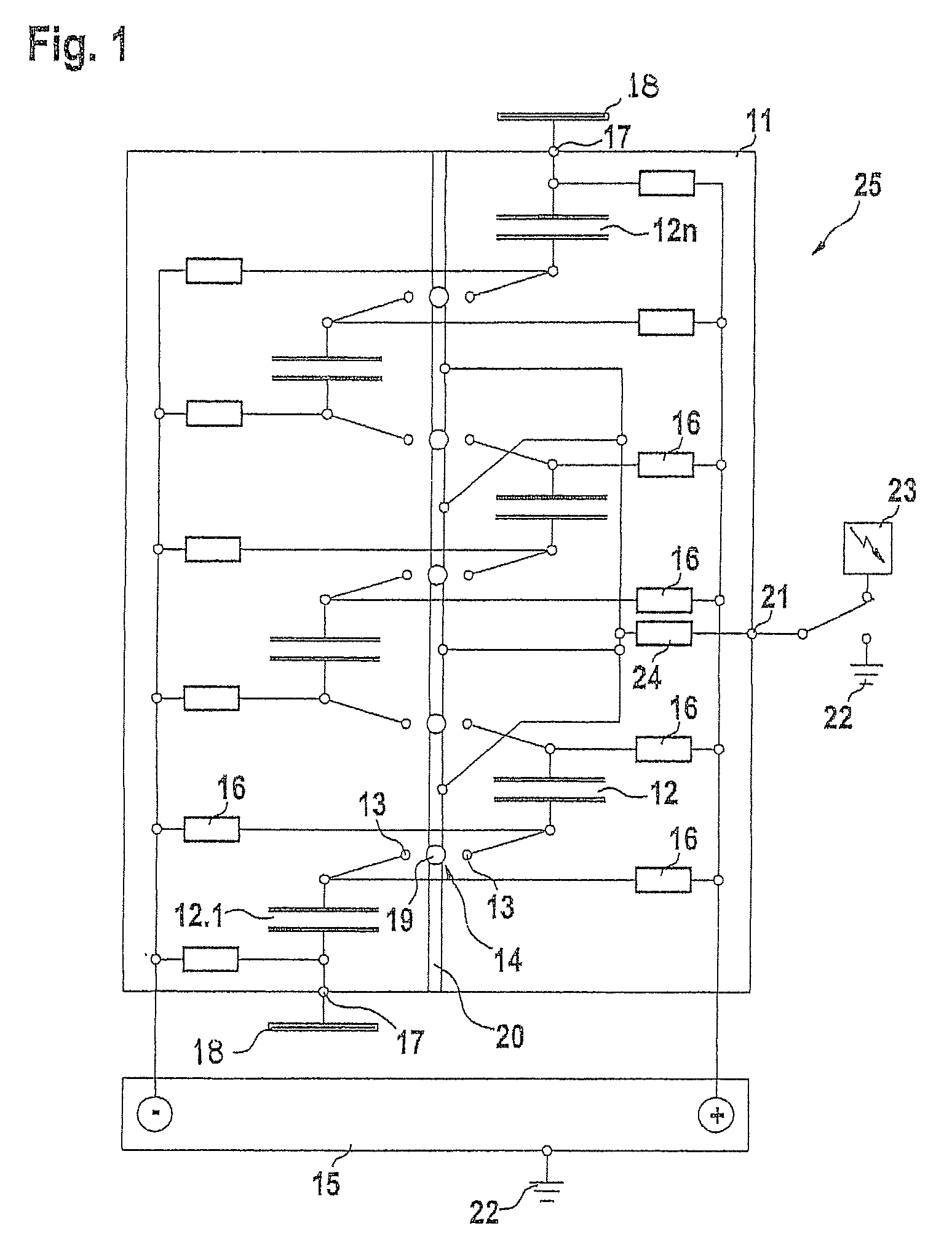
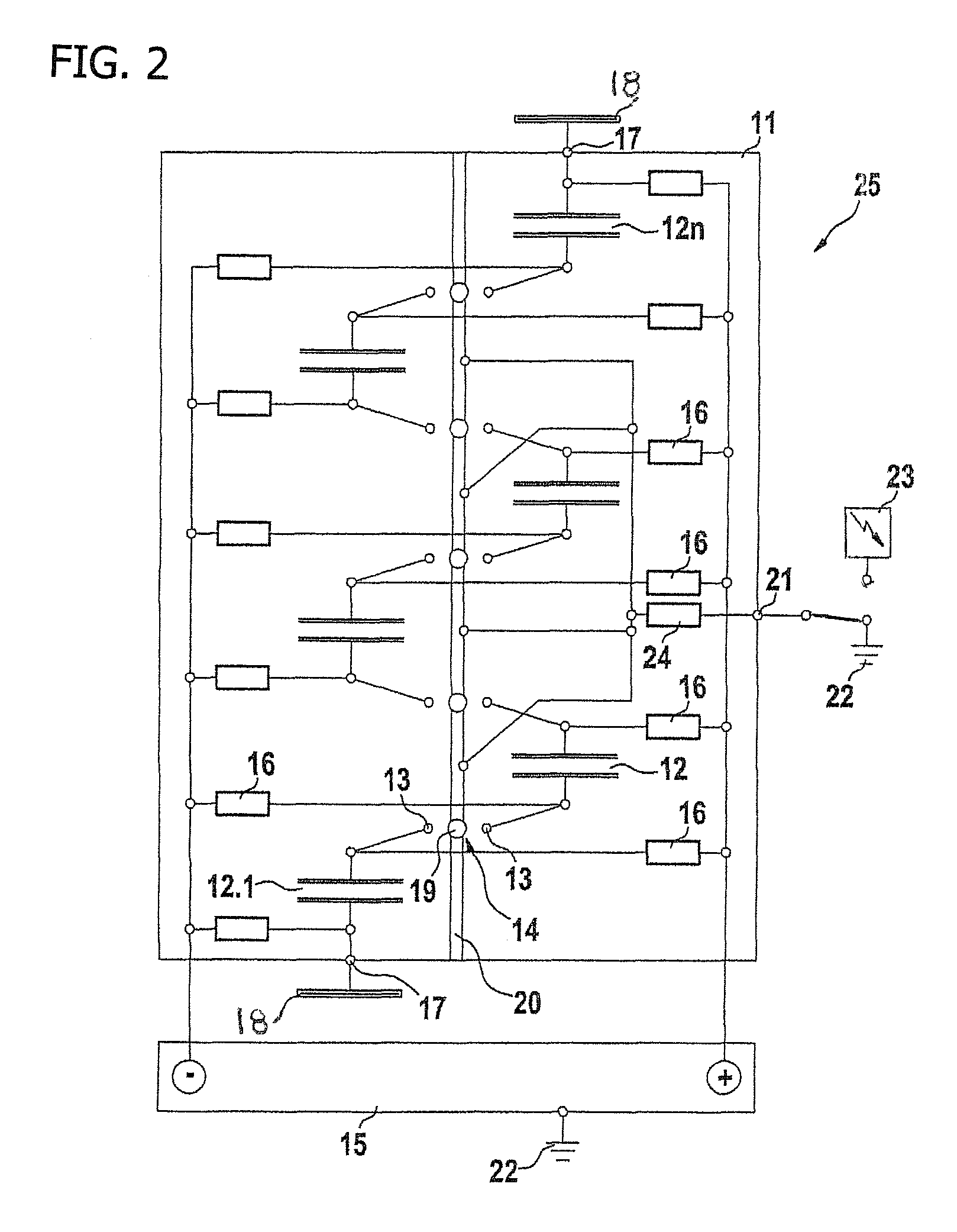
Method and device for production and emission of a high-power microwave pulse
InactiveUS20080191559A1Improvement in radio-frequency oscillation responseReduction in charging resistanceApparatus without intermediate ac conversionOscillations generatorsCapacitanceMicrowave
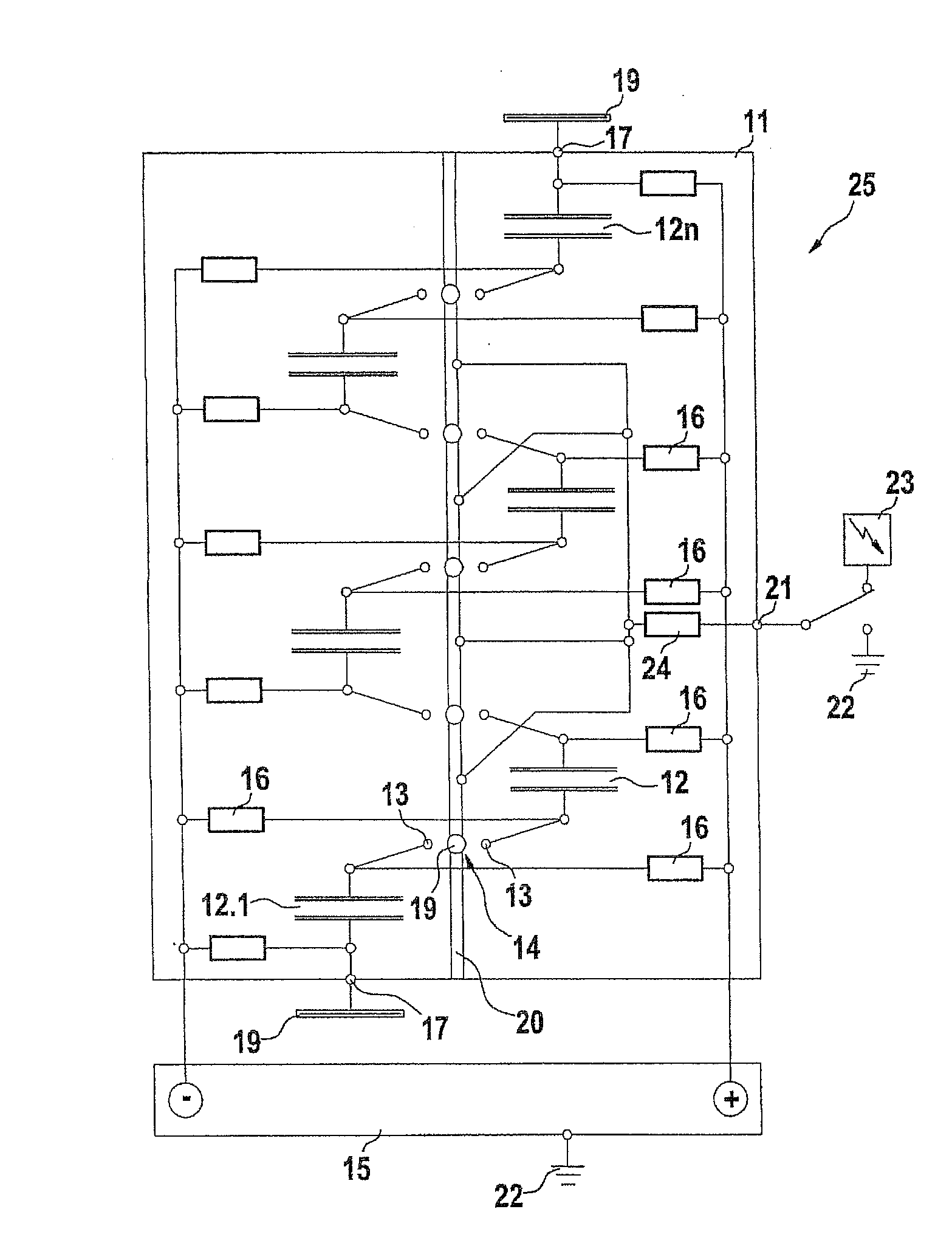
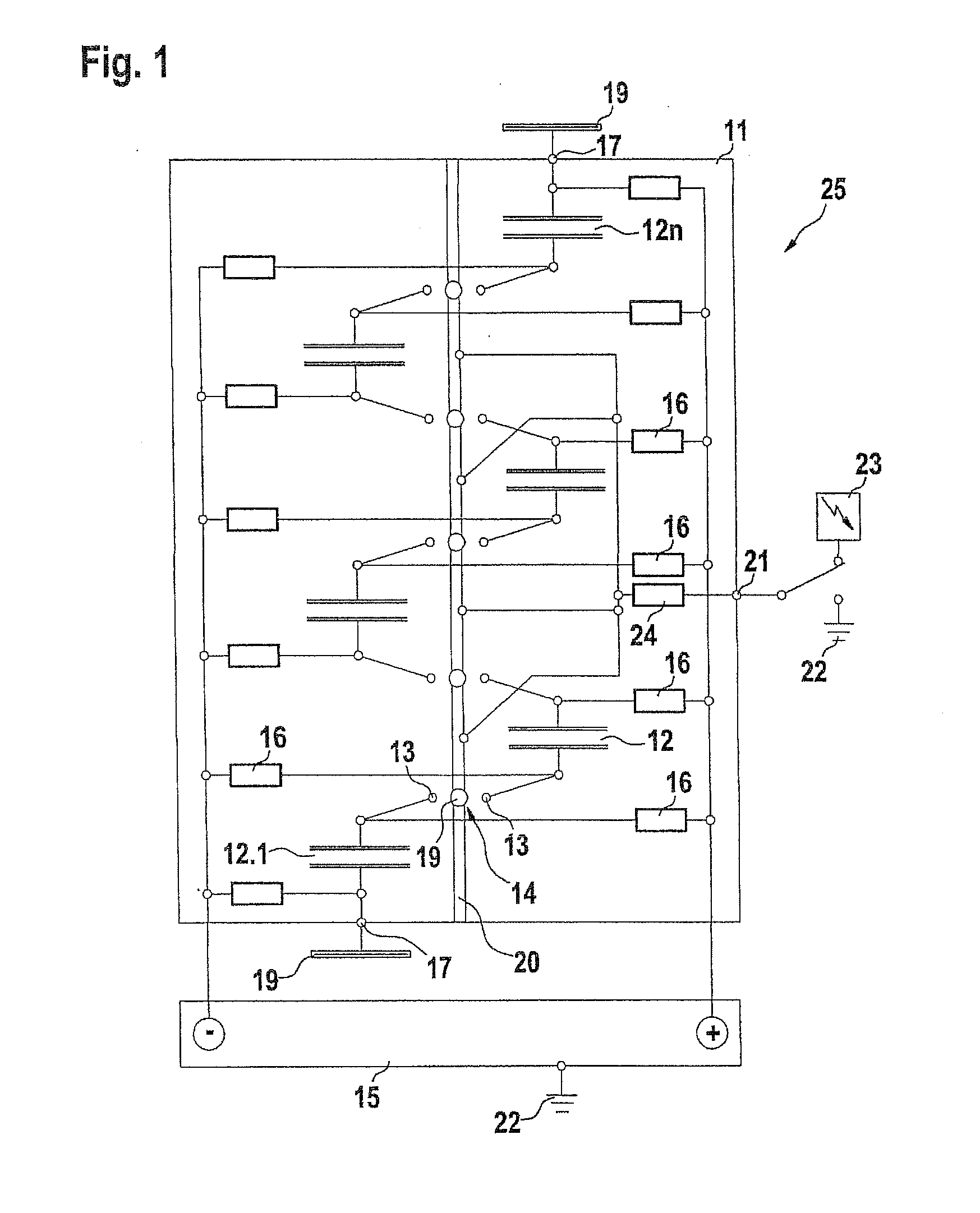
The production and emission of high-energy microwave pulses are made possible by means of a device with a particularly compact design if the capacitor column (12-12) of the Marx generator (11) whose series circuit conventionally itself feeds a microwave generator with a matched antenna geometry, is now itself used—dispensing with the microwave generator and its antenna—directly as a resonator and Hertzian antenna dipole (24). Its oscillation response can be optimized by triggered spark gaps (14) for the switching of capacitors (12), and by means of plates (19) connected at the ends, in order to increase the stray capacitances.
Owner:DIEHL BGT DEFENCE GMBH & CO KG
GNSS attitude real-time measurement device and method based on three antennas
InactiveCN110850461AThere is no problem of error accumulationAchieving real-time attitude measurementSatellite radio beaconingCarrier signalRemote sensing
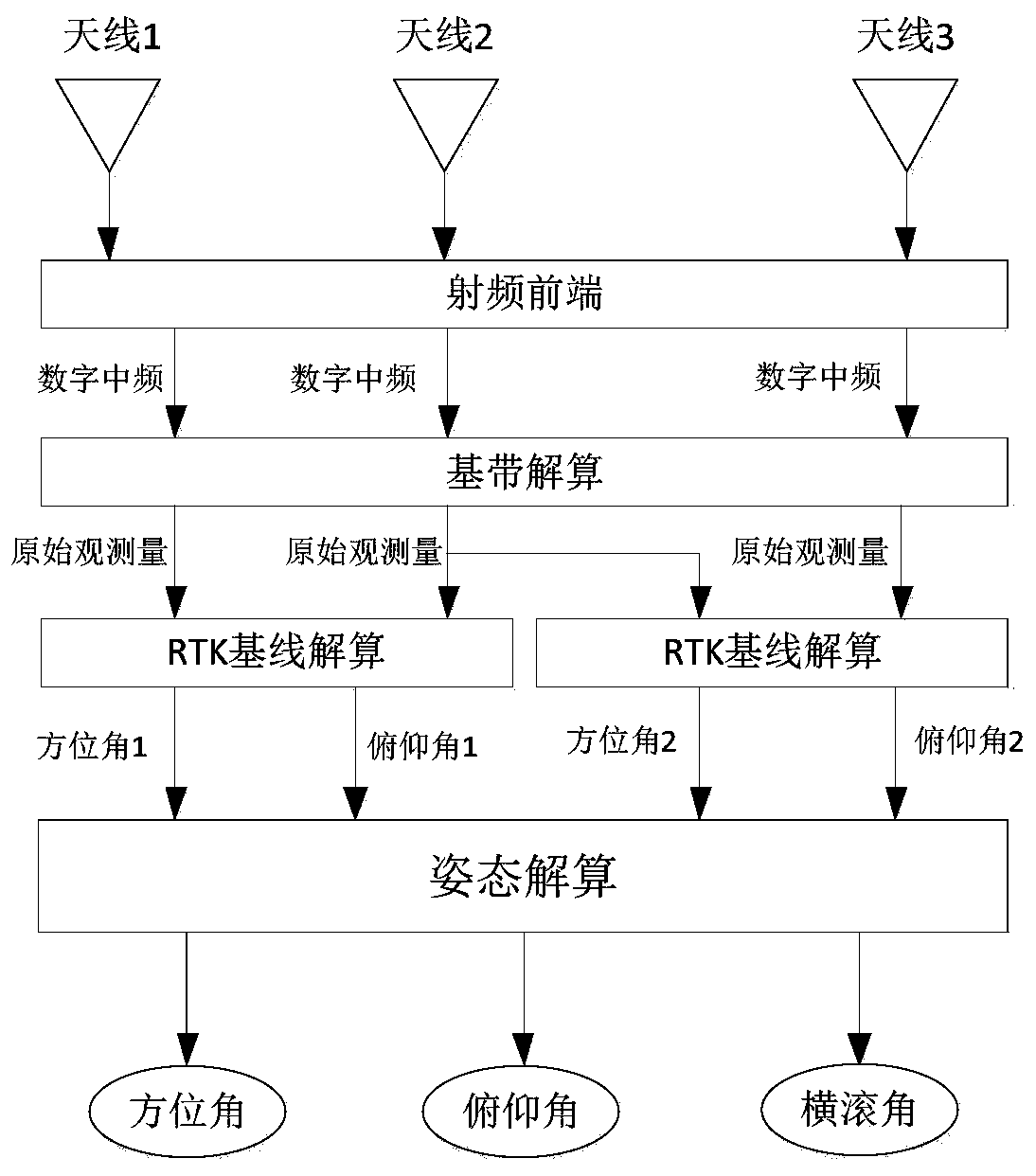
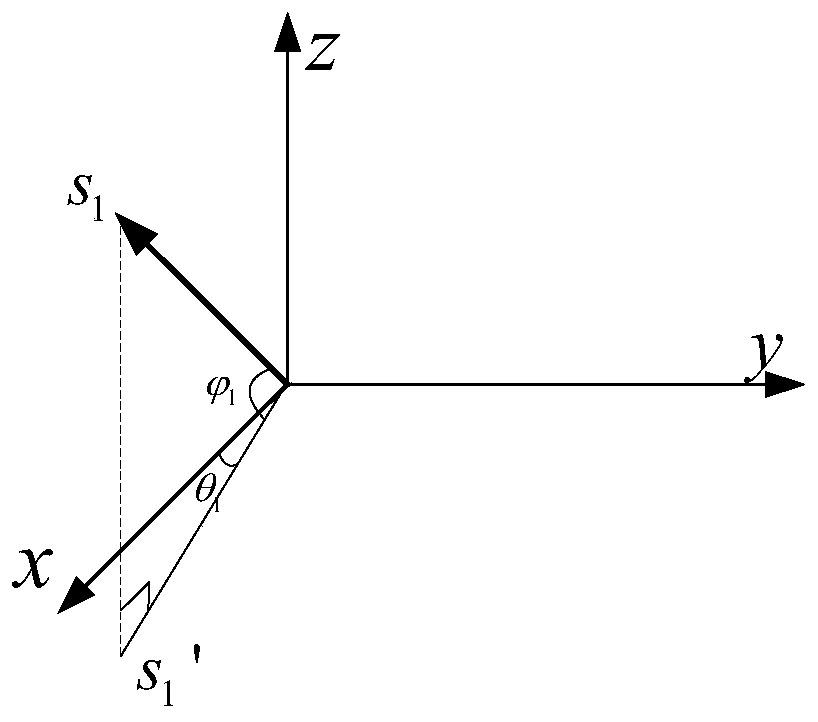
The invention discloses a GNSS attitude real-time measurement device and measurement method based on three antennas, and belongs to the technical field of measurement and surveying and mapping. A three-antenna GNSS receiver structure is adopted, and an azimuth angle, a pitch angle and a roll angle of a plane where the antennas are located are obtained by measuring carrier phase difference values of GNSS satellite signals received by the three antennas; due to the fact that satellite signals are updated and resolved in real time, the problem of error accumulation does not exist, high-precisionreal-time attitude measurement can be achieved, and positioning and attitude measurement are integrated. The three antennas can be placed at will without being limited by geometrical shapes of the antennas, and compared with a single-point positioning attitude measurement system and other attitude measurement systems, the precision is high, and the real-time performance is good; compared with a double-antenna RTK receiver, a three-dimensional attitude angle can be obtained; and according to the invention, GNSS signals are used for position, baseline and attitude calculation, and the system canautomatically calculate the azimuth angle, the pitch angle and the roll angle.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIS TECH INSTR CO LTD
Self-structuring hybrid antenna system
InactiveUS20050219142A1Reduce search timeAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesIndividually energised antenna arraysGeneral purposeCommunications system
A self-structuring antenna (SSA) system selects a predetermined antenna geometry as a preliminary configuration based on a particular communication band in which the SSA system is operating. The preliminary configuration provides an initial or default antenna configuration for the particular communication band. The SSA system may use a preliminary configuration when the communication system is first activated. In addition, the SSA system may use a predetermined antenna geometry as a general purpose default configuration until a configuration producing better antenna characteristics can be identified.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
System and method for downlink channel estimation in massive multiple-input-multiple-output (MIMO)
It is possible to reduce the overhead associated with downlink channel estimation in massive Multiple-Input-Multiple-Output (MIMO) networks by processing training sequences according to a transformation matrix. The transformation matrix maps a generic dictionary to a non-generic dictionary associated with an antenna geometry of a MIMO antenna array. The transformation matrix can be computed basedon the two dictionaries. In one embodiment, the training reference signal is precoded to obtain a precoded training reference signal, which is then transmitted over a MIMO antenna array. The trainingprecoder used to precode the training reference signal is designed according to the transformation matrix to mitigate a dependence that the training reference signal transmission has on the antenna geometry.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Geometric modeling method for panel slot antenna
InactiveCN101958459ASpeed up the geometric modeling processShorten the development cycleAntenna arraysRadiating elements structural formsSimulationGeometric modeling
The invention discloses a geometric modeling method for a panel slot antenna, mainly overcoming the defects of poor generality and long modeling period in the traditional geometric modeling method. The geometric modeling method comprises the following modeling steps of: firstly, splitting the antenna into a plurality of subassemblies according to the characteristic of local similarity of a panel slot antenna structure; secondly, establishing a geometric model of each subassembly and translating the geometric models to the corresponding spatial positions through circulating the structural parameter information of each subassembly; and finally, combining according to the affiliation relationship of each subassembly and a submatrix to obtain the geometric model of the whole panel slot antenna. The invention has the advantages of strong generality and high modeling efficiency and can be used for parametrically modeling a large-caliber panel slot antenna.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
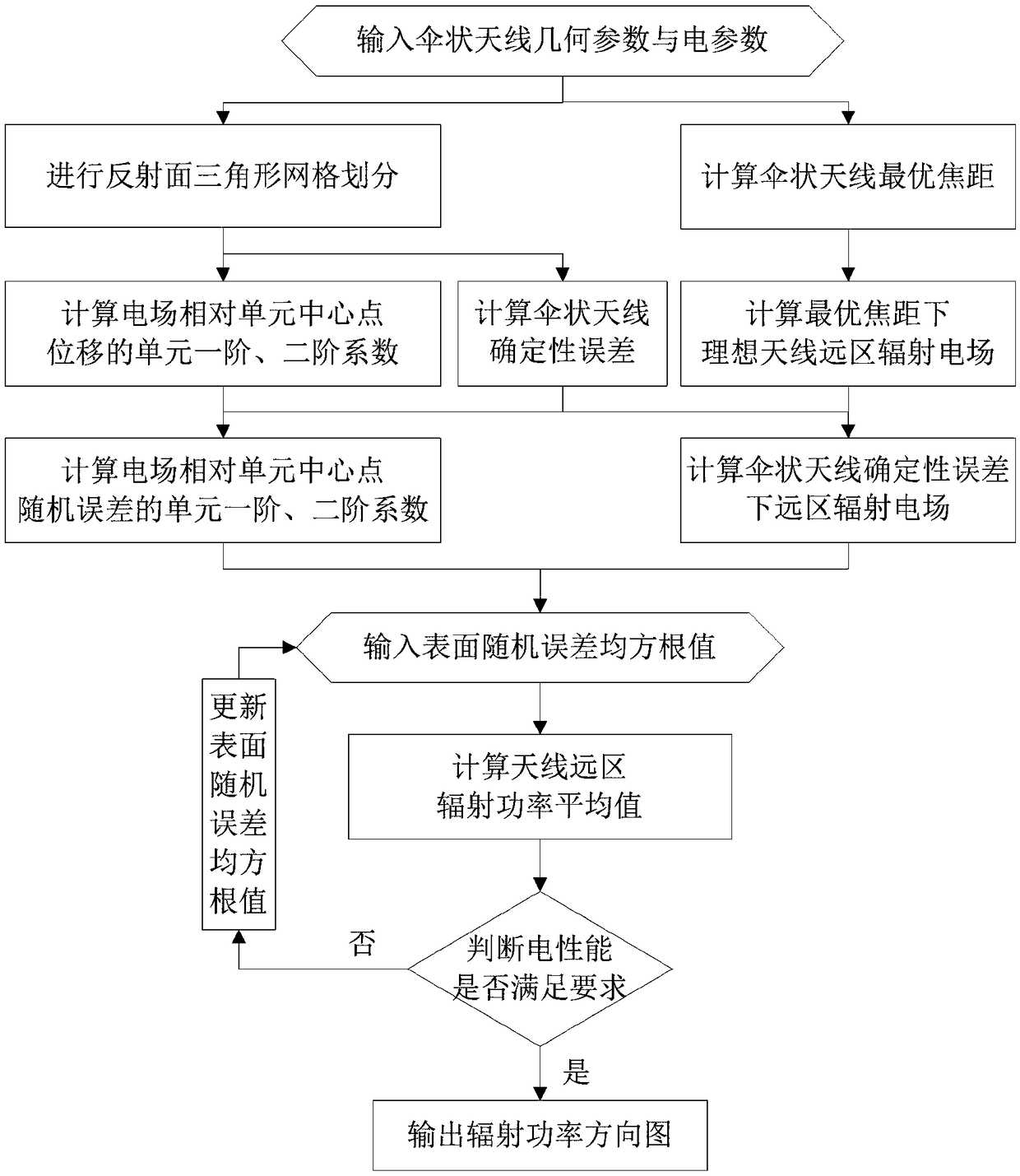
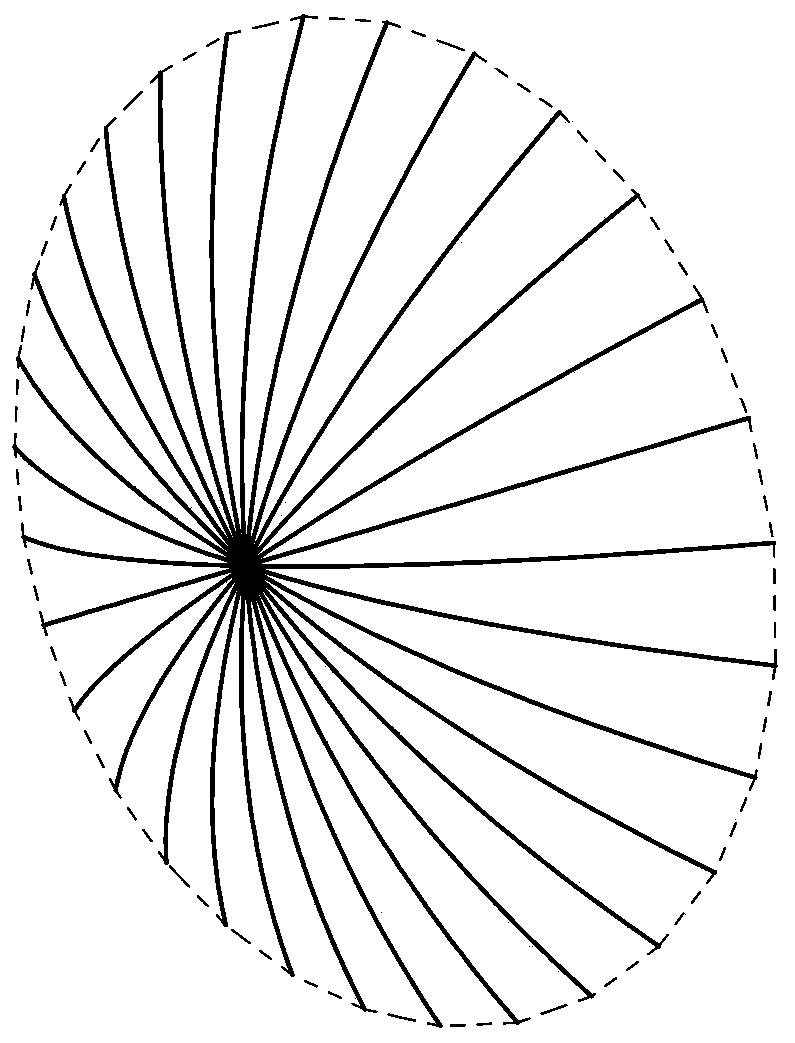
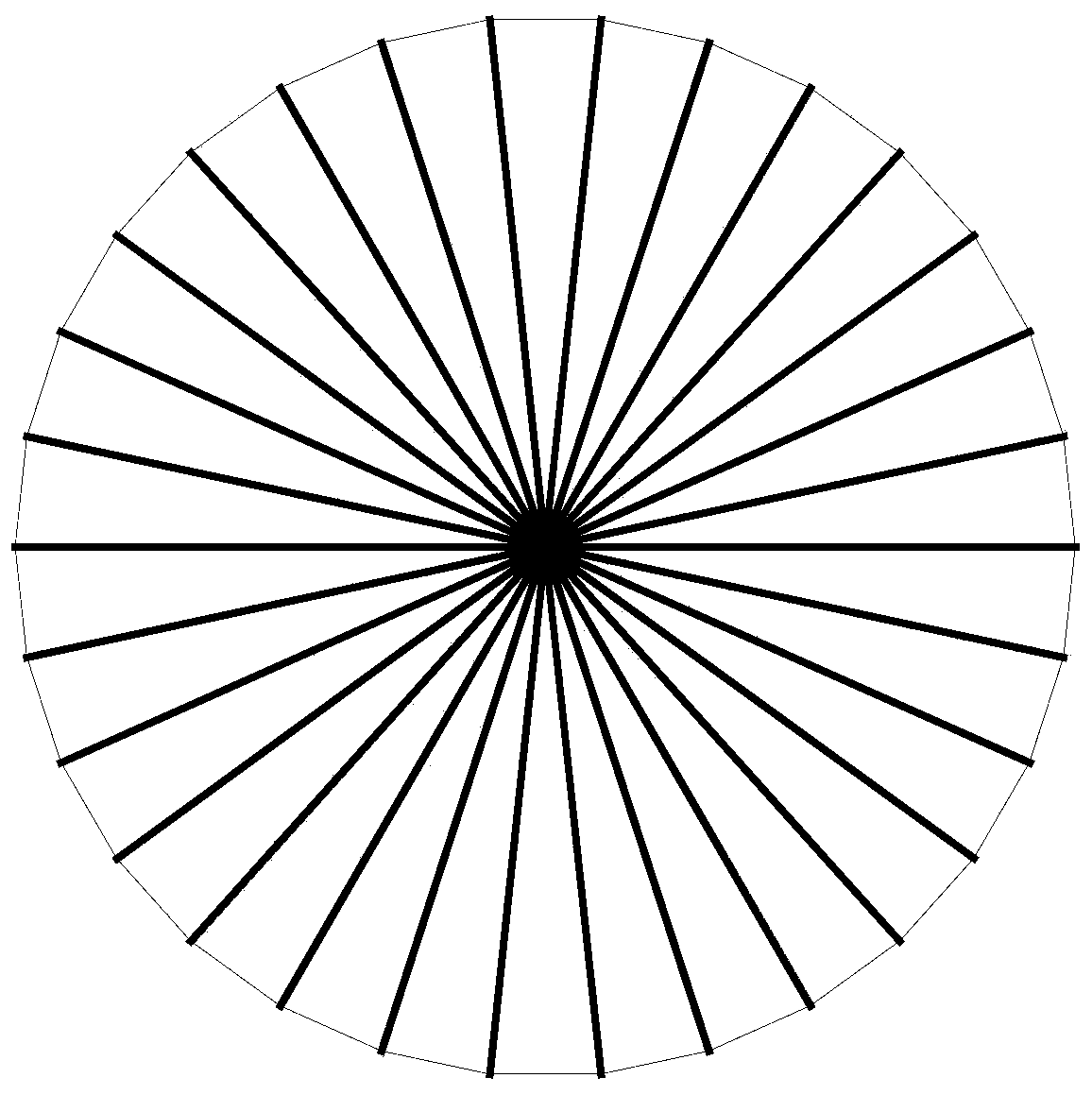
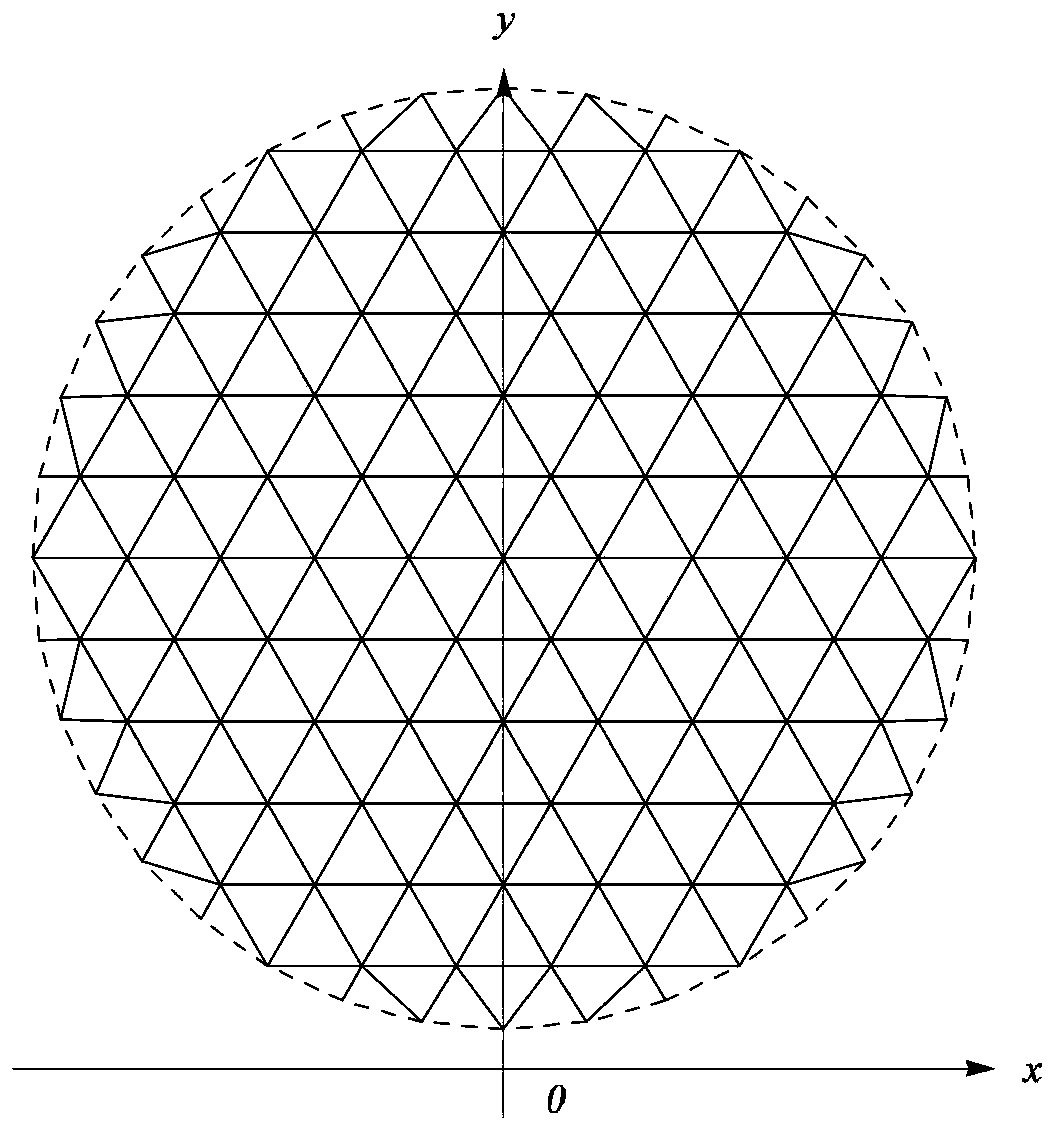
Modeling method of average power pattern of umbrella antenna considering patch splicing error
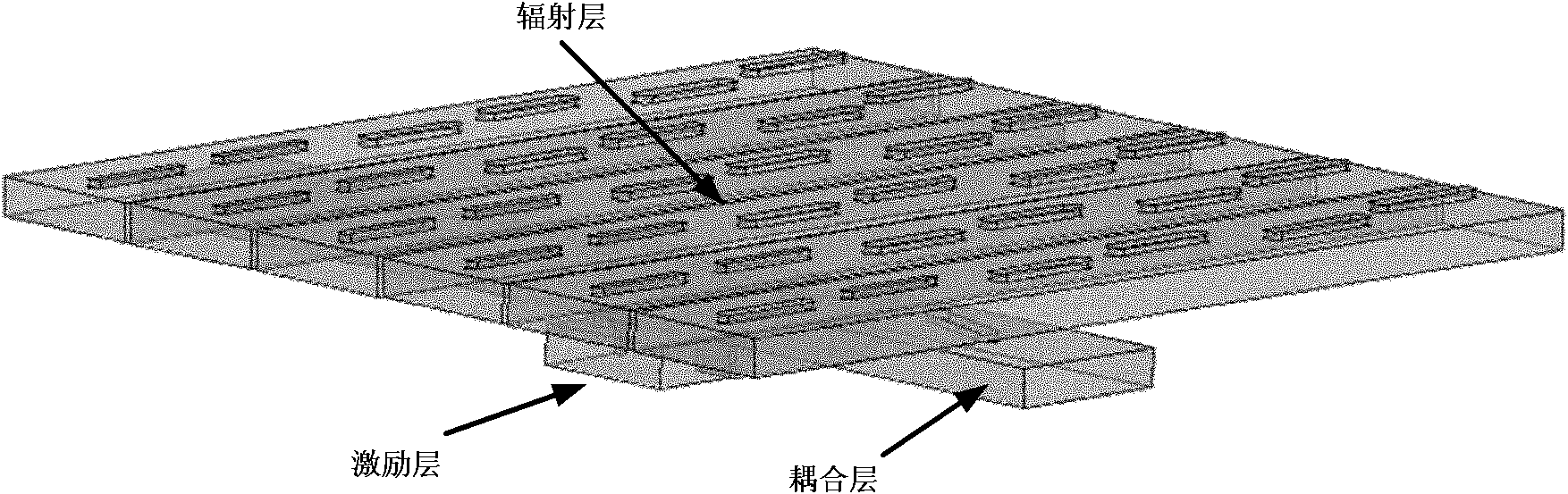
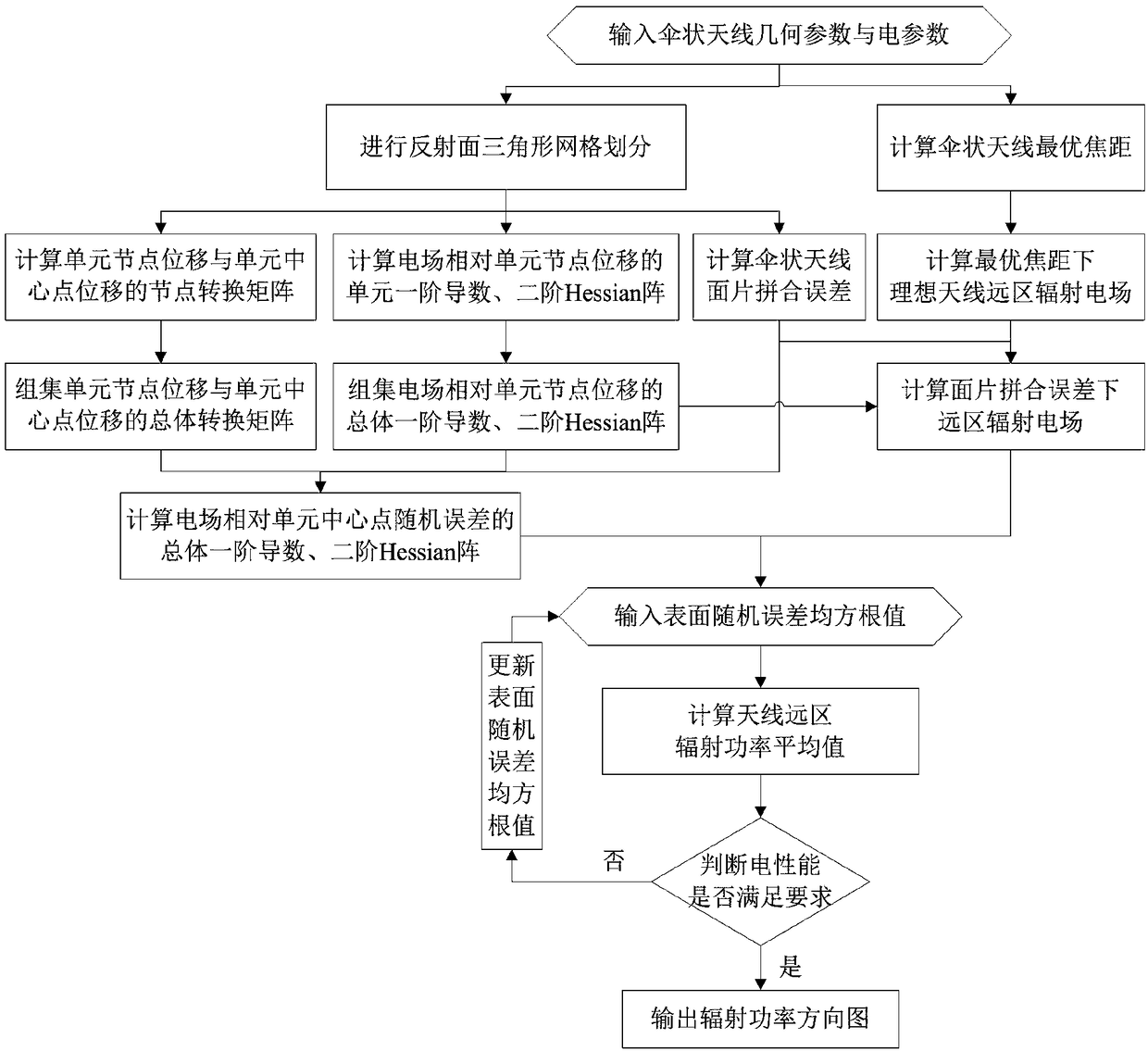
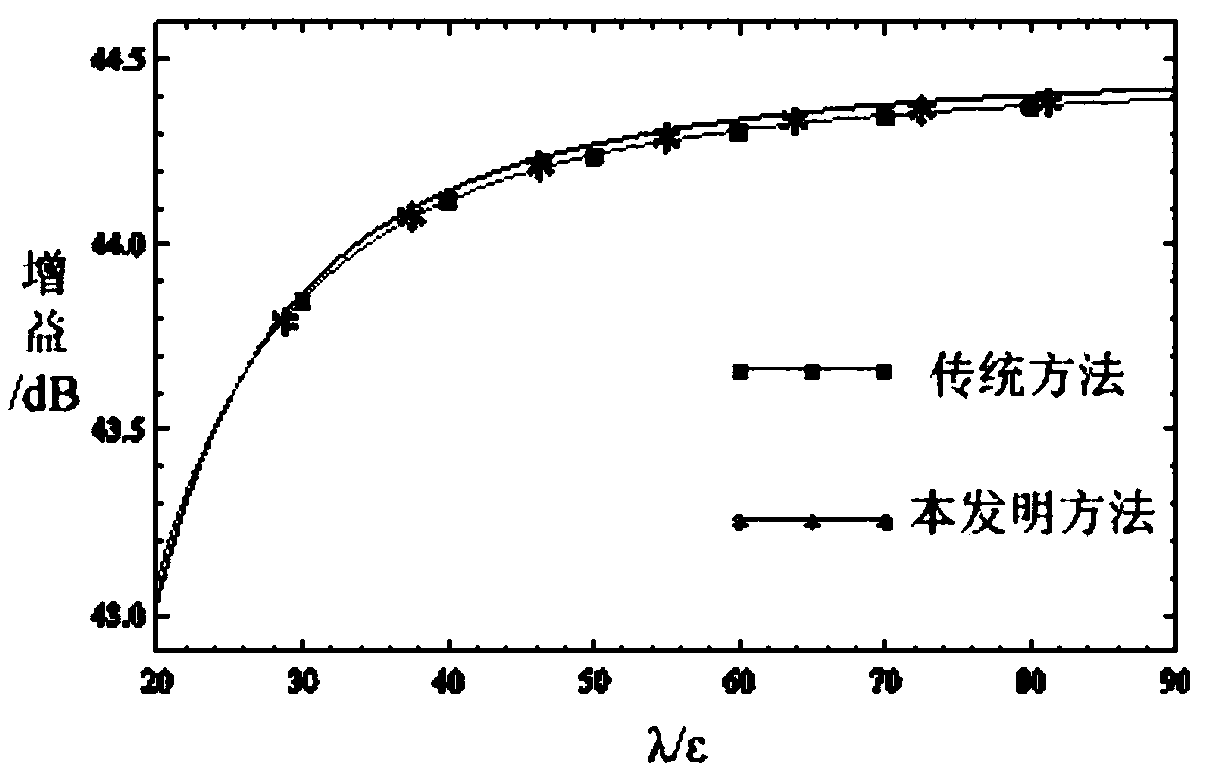
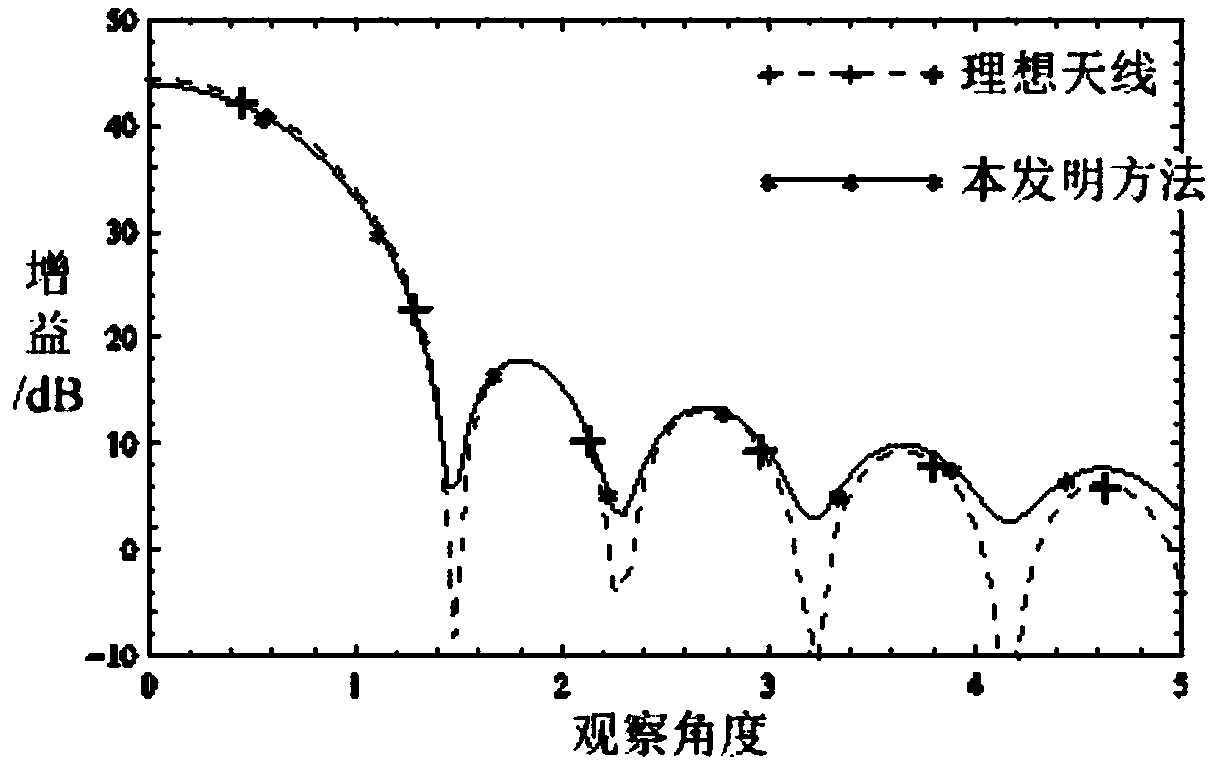
ActiveCN109408958AGuaranteed calculation accuracyAvoid formula derivationSpecial data processing applicationsTransformation matrixModelling methods
The invention relates to an umbrella antenna average power pattern modeling method considering surface patch splicing error, which comprises the following steps of: inputting umbrella antenna geometryand electric parameters; the far field of the ideal antenna is calculated under the optimal focal length and the optimal focal length of the umbrella antenna. Reflector triangular mesh generation; the nodal transformation matrix of the patch splicing error and the element node displacement and the element center displacement of the umbrella antenna is calculated. The Overall Transformation Matrixbetween the Node Displacement and the Center Displacement of the Group Element; the first derivative of the element and the second Hessian matrix of the electric field relative to the node displacement of the element are calculated. The global first derivative of the group electric field relative to the node displacement of the element, the second order Hessian matrix; the total first derivativeand second order Hessian matrix of the far field and the random error of the electric field relative to the center point of the element are calculated under the patch splicing error. RMS value of input surface random error; calculating an average value of the far-field radiation power of the antenna; judging whether the electrical performance is satisfied; outputting radiated power pattern; updatingthe surface random error rms value.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
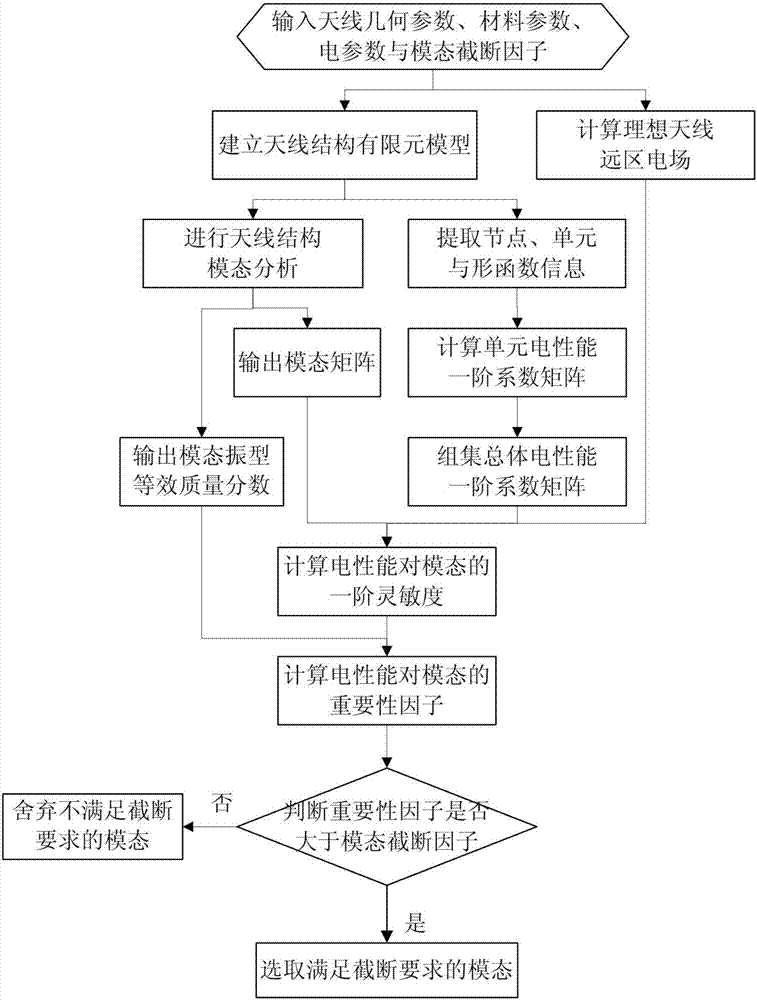
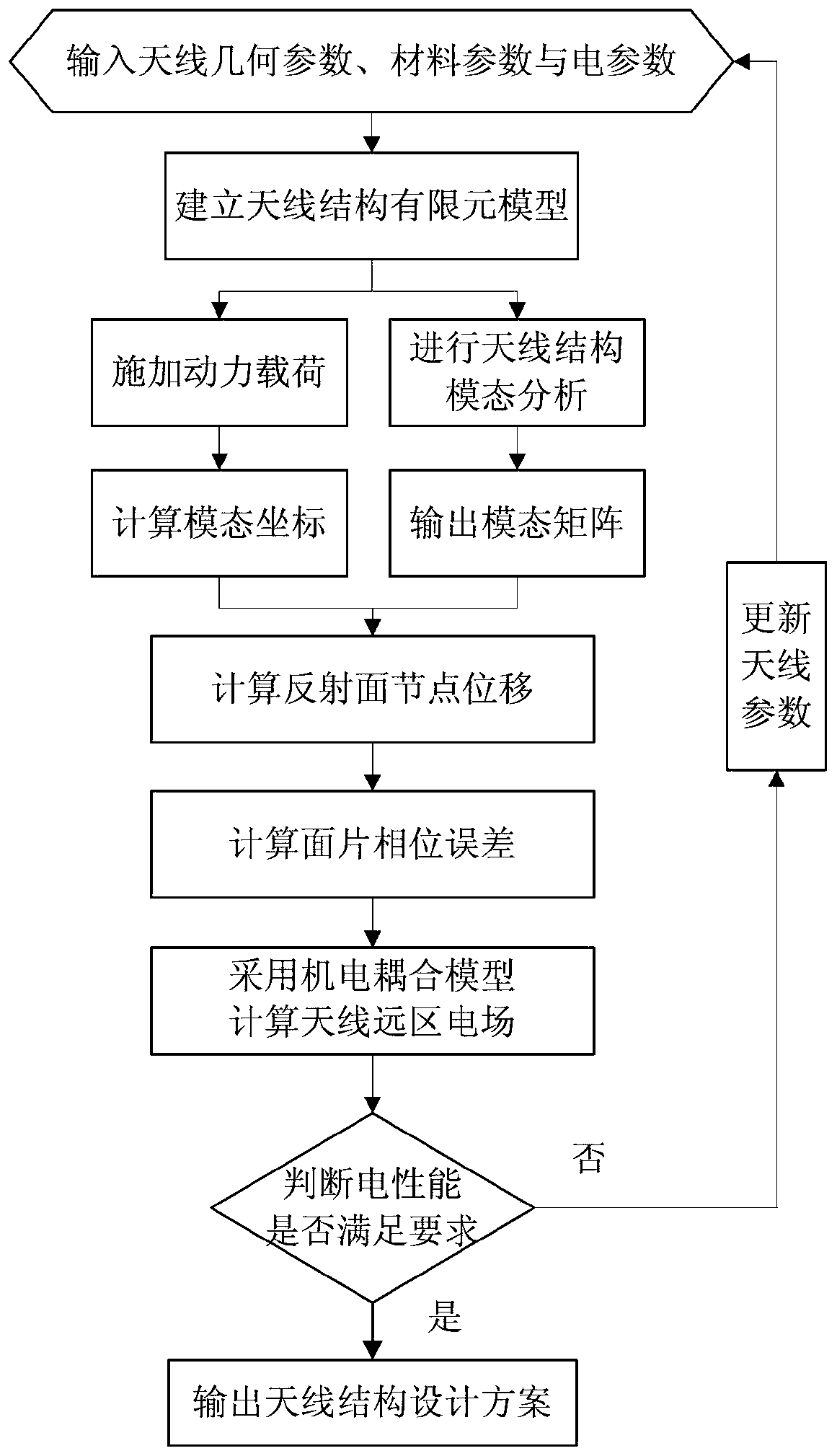
Electric performance-oriented space mesh antenna key dynamical modal selection method
ActiveCN106934097AGet first order sensitivityOvercome the inability to consider the lack of electrical performanceDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsNODALElement model
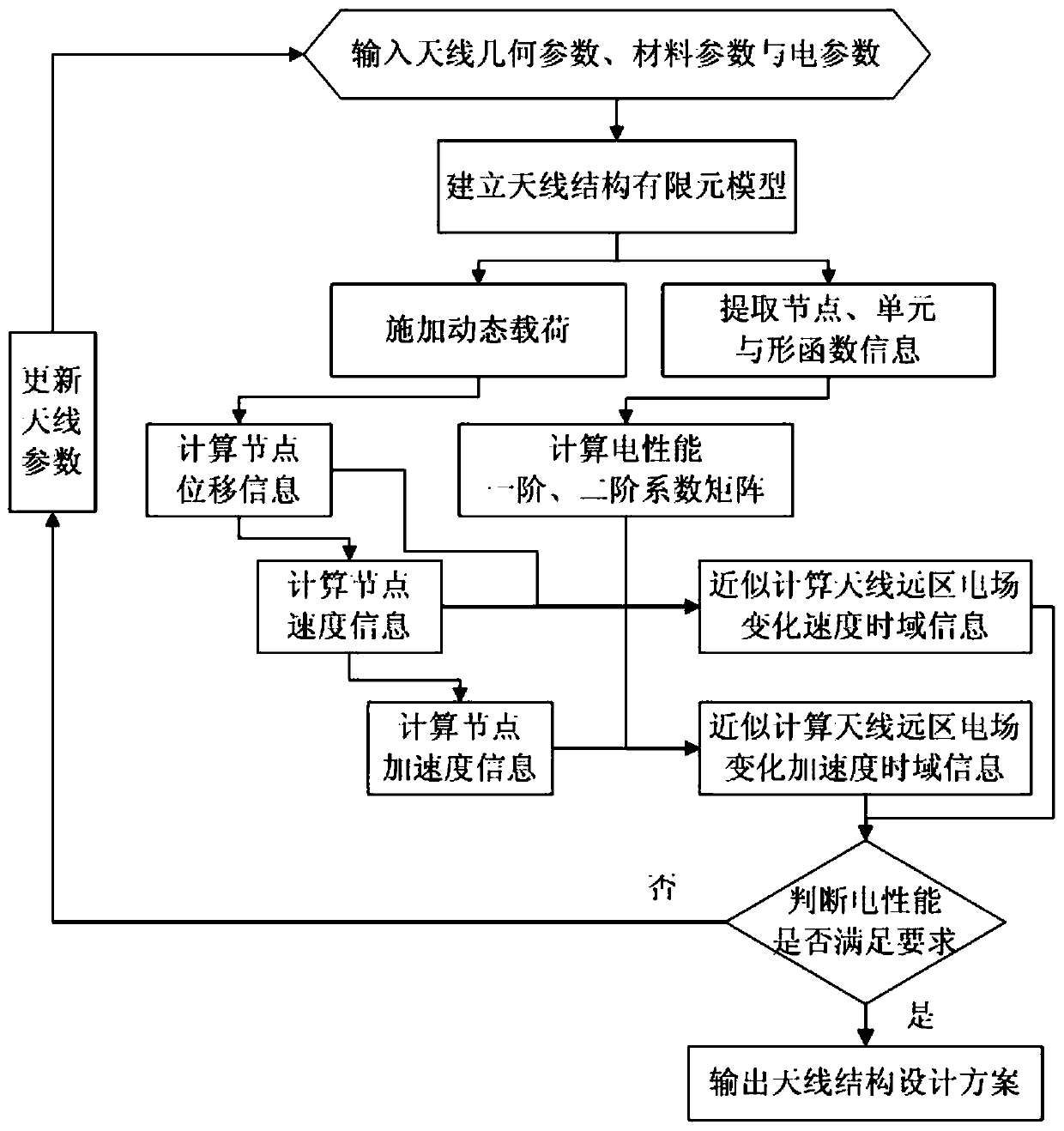
The invention discloses an electric performance-oriented space mesh antenna key dynamical modal selection method. The method comprises the following steps of: inputting geometric parameters, material parameters, electric parameters of modal guillotine factors; calculating an ideal antenna far electric field; establishing an antenna structure finite element model; extracting node, unit and shape function information; calculating a unit electric performance first-order coefficient matrix; grouping an overall electric performance first-order coefficient matrix; carrying out antenna structure modal analysis; outputting a modal matrix; calculating a first-order sensitivity, for the modal, of the electric performance; outputting a modal shape equivalent mass fraction; calculating significance factors, for the modal, of the electric performance; judging whether the significance factors are greater than the modal guillotine factors or not; if the judging result is positive, selecting the significance factors; and otherwise, abandoning the significance factors. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the deficiencies of the traditional dynamical modal selection method are overcome, the influences, on the electric performance of antennas, of modals in different orders are integrally considered in the modal selection process, and the problem of electric performance-oriented space mesh antenna key dynamical modal selection is solved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
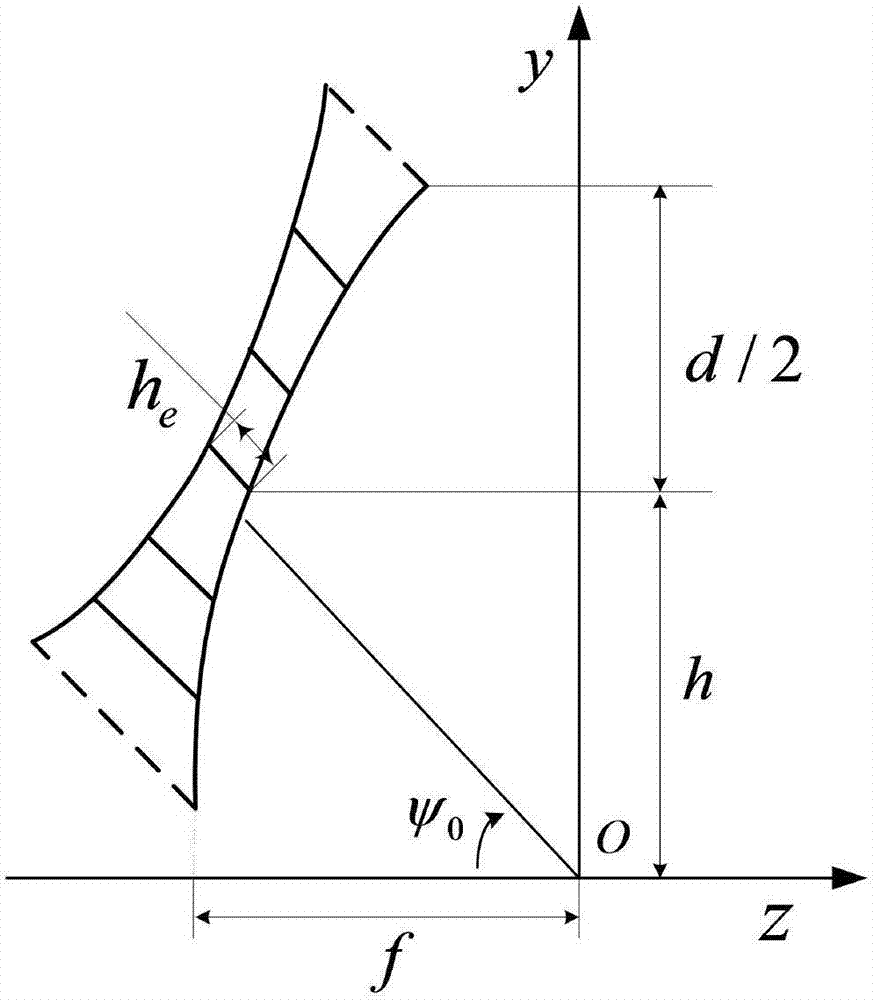
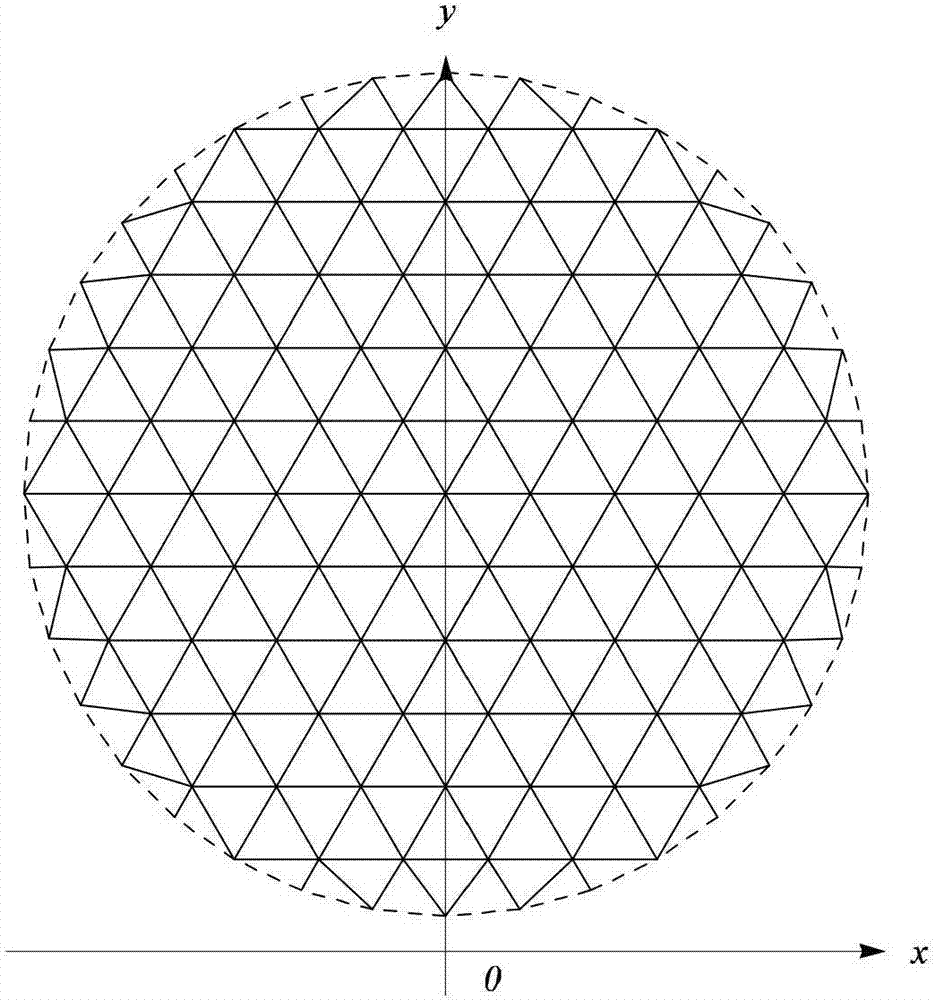
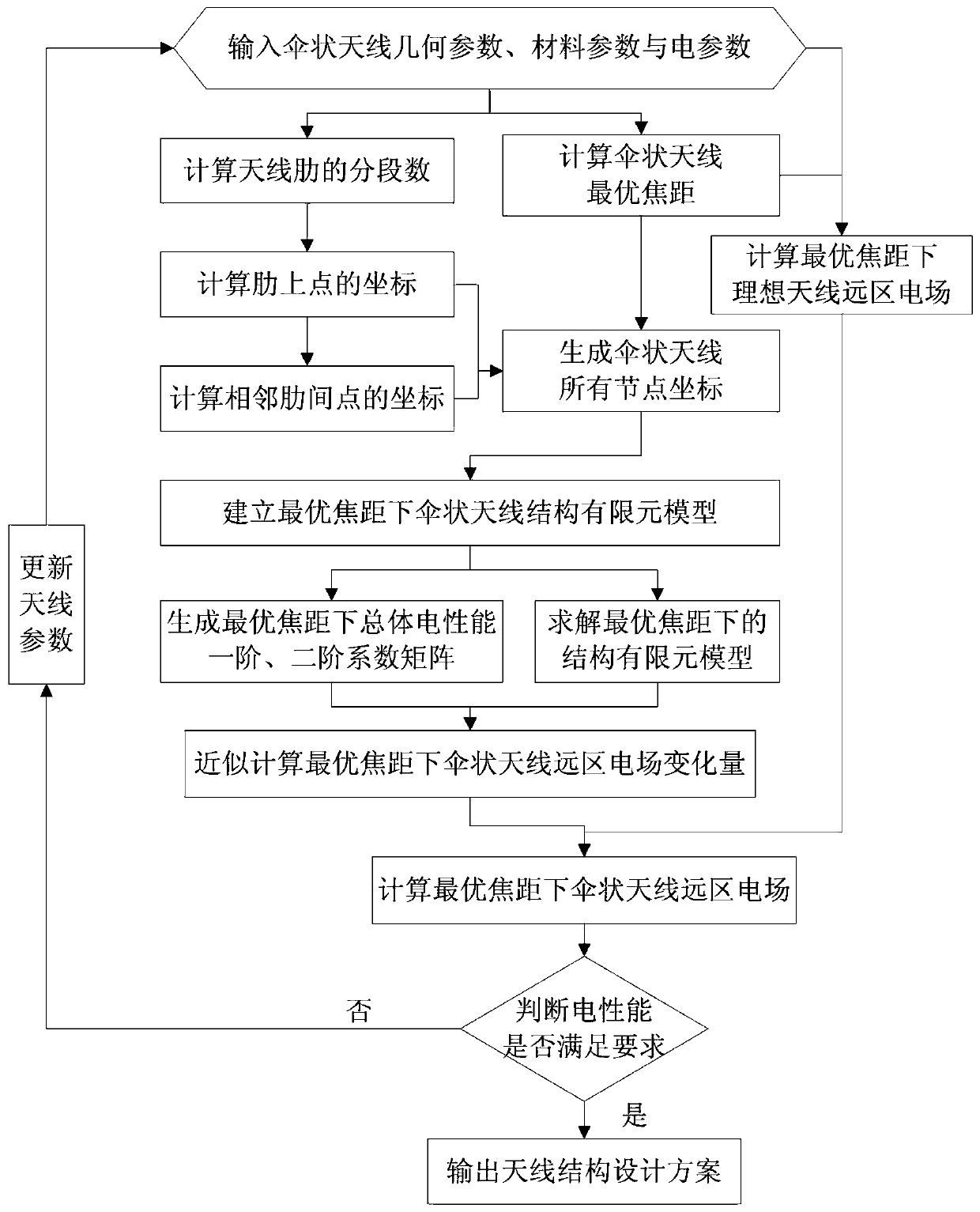
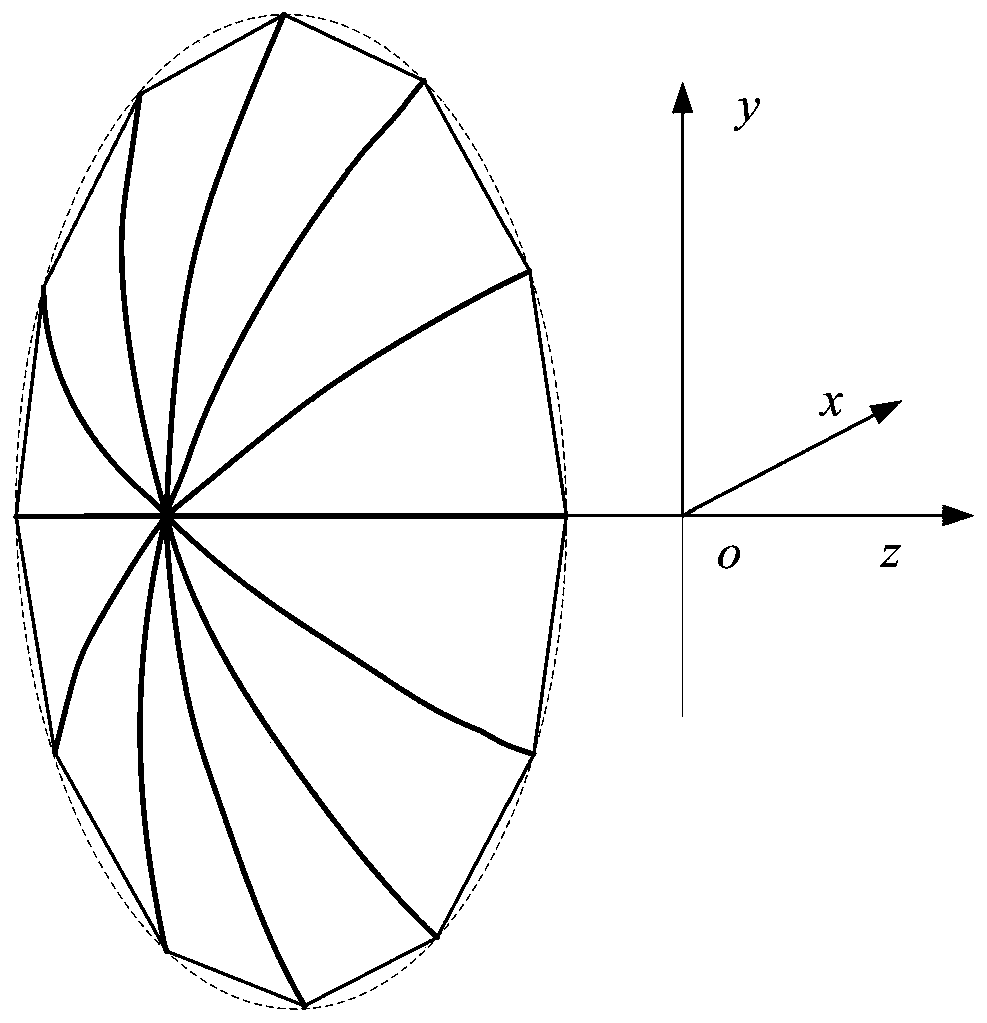
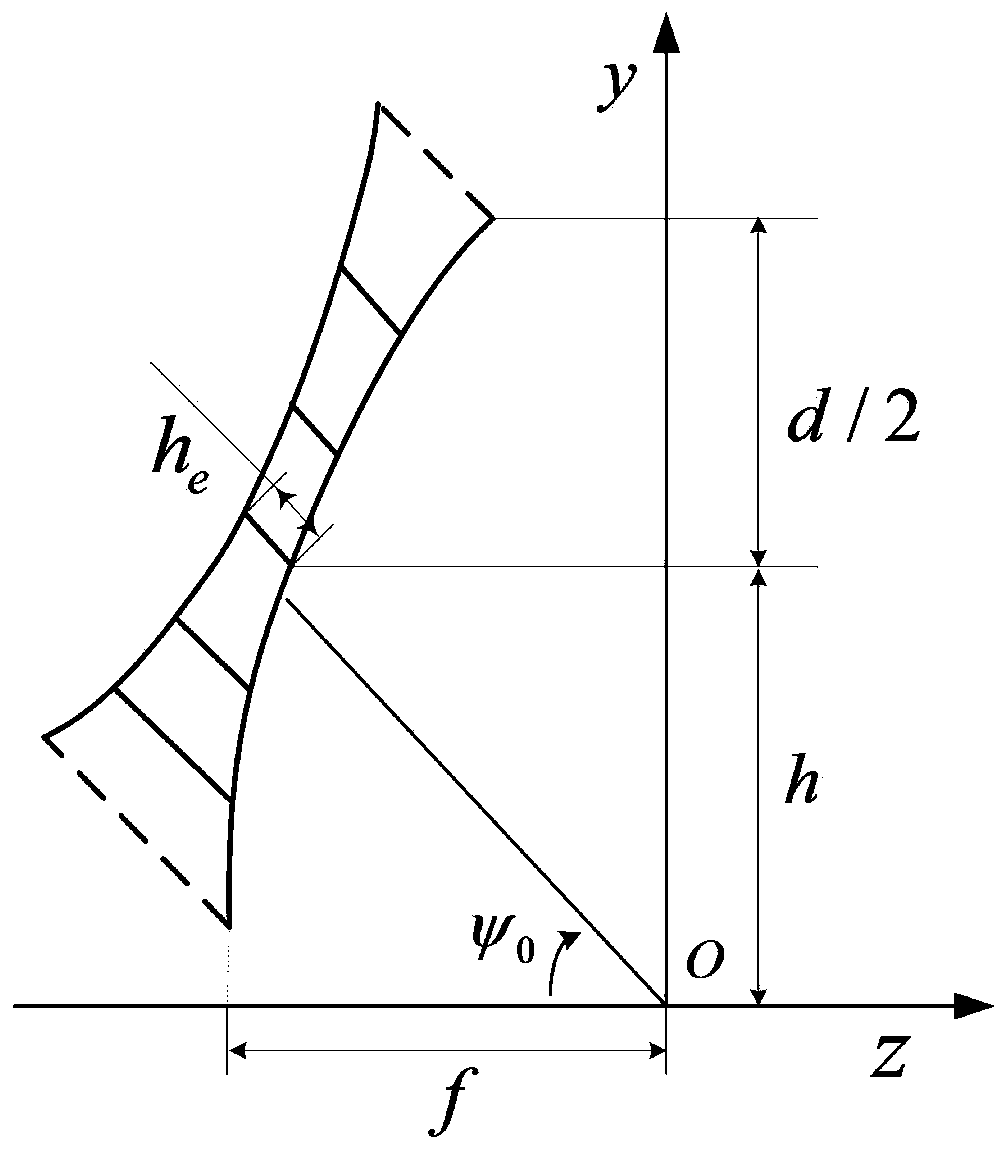
Electromechanical integration optimization design method for umbrella-shaped antenna under optimal focal distance
ActiveCN107169174AAvoid loss of electrical performanceGuaranteed calculation accuracyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationElectricityElement model
The invention discloses an electromechanical integration optimization design method for an umbrella-shaped antenna under an optimal focal distance. The method comprises the steps of inputting a geometrical parameter, a material parameter and an electrical parameter of the umbrella-shaped antenna; calculating the optimal focal distance of the umbrella-shaped antenna; calculating an ideal antenna far electric field under the optimal focal distance; calculating the number of segments of antenna ribs; calculating coordinates of points on the ribs; calculating the coordinates of the points between the adjacent ribs; generating all node coordinates of the umbrella-shaped antenna; establishing a structure finite element model of the umbrella-shaped antenna under the optimal focal distance; generating first-order and second-order coefficient matrixes of total electrical property under the optimal focal distance; solving the structure finite element model under the optimal focal distance; approximately calculating a variation of the far electric field of the umbrella-shaped antenna under the optimal focal distance; calculating the far electric field of the umbrella-shaped antenna under the optimal focal distance; judging whether the electrical property meets the requirement; outputting an antenna structure design scheme; and updating the antenna parameters. According to the method, surface patch splicing characteristics of the umbrella-shaped antenna are considered, the electrical property under the optimal focal distance is acquired based on a second-order approximate calculation formula, and the electromechanical integration optimization design efficiency can be improved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
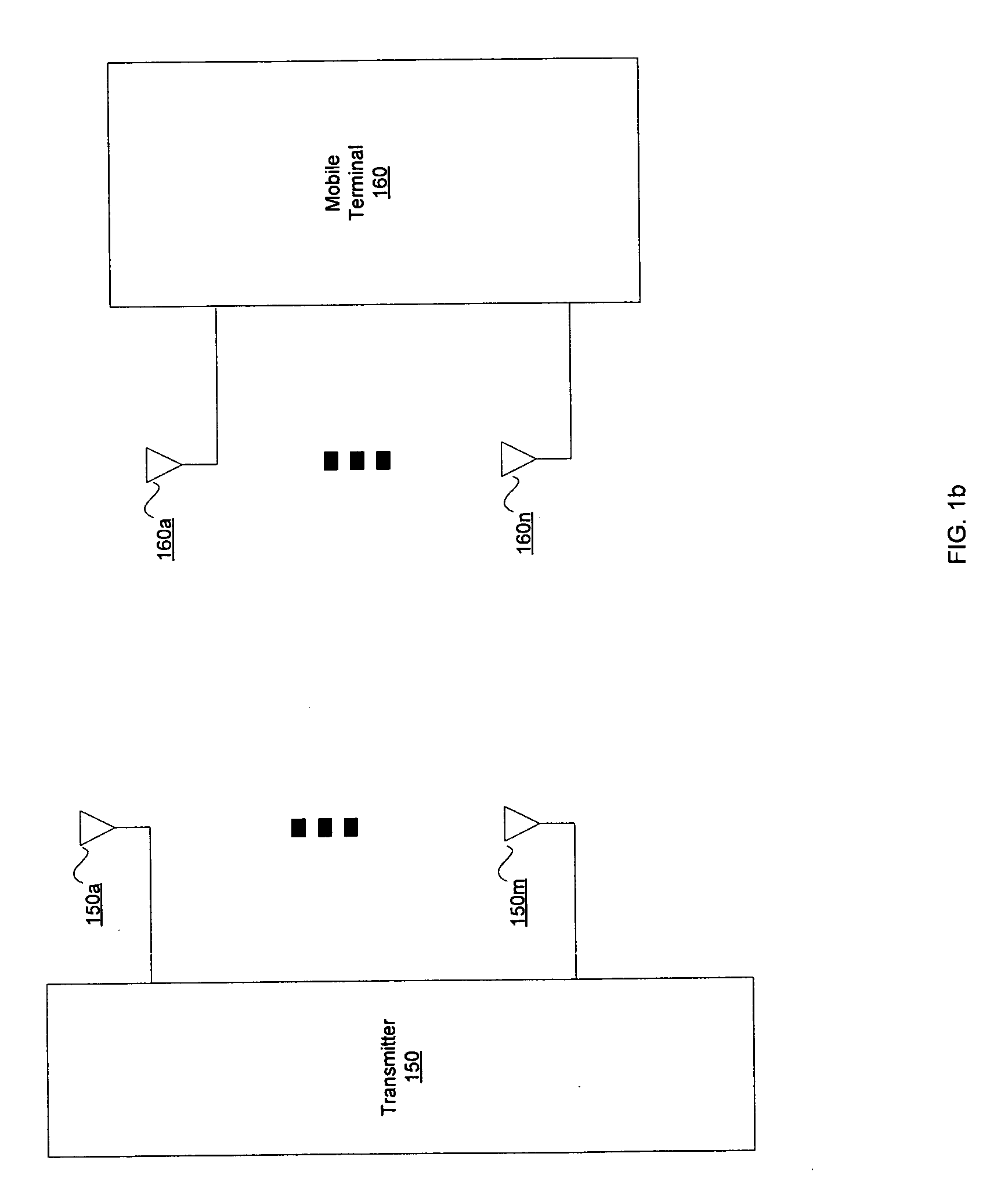
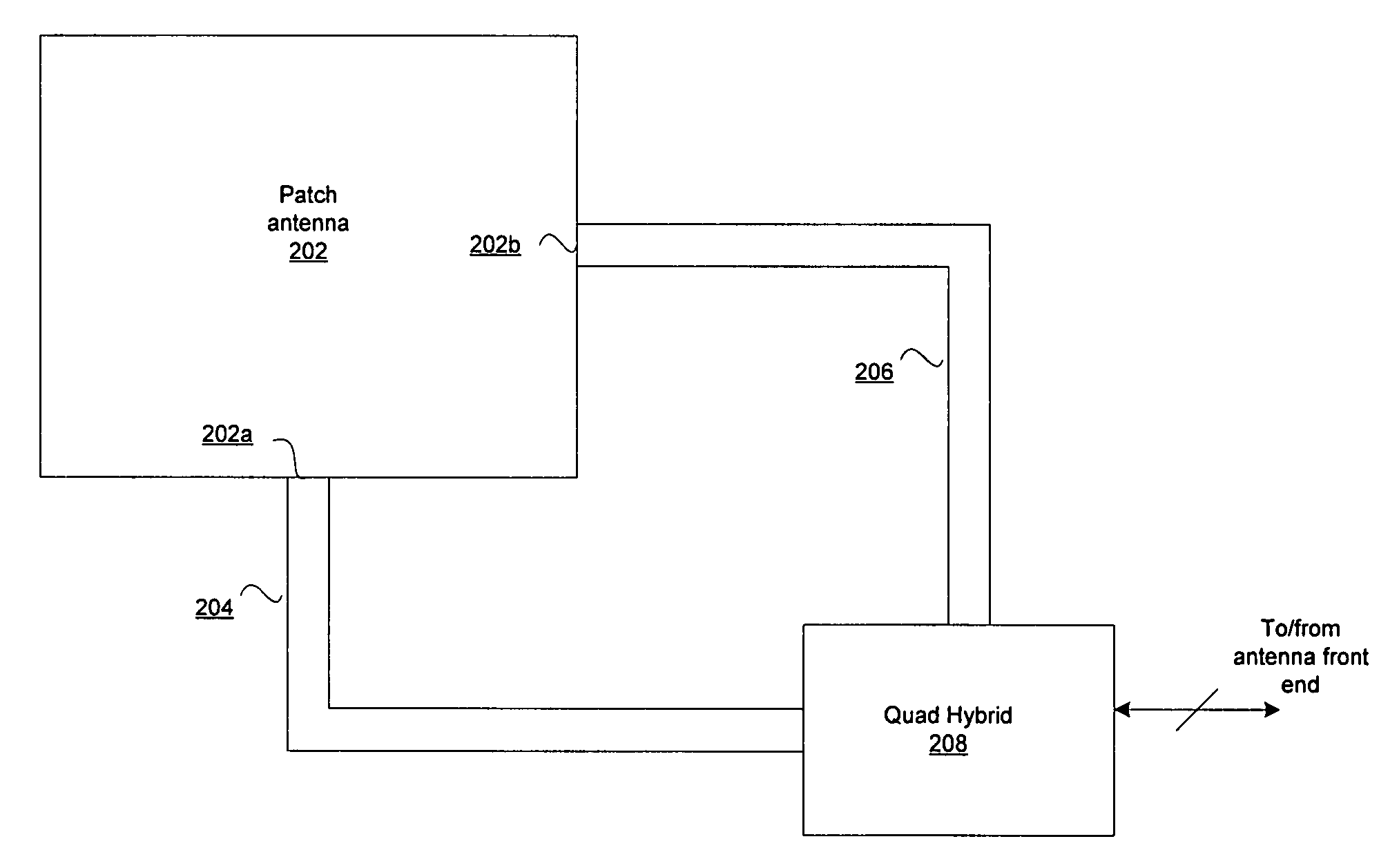
Method and system for antenna geometry for multiple antenna handsets
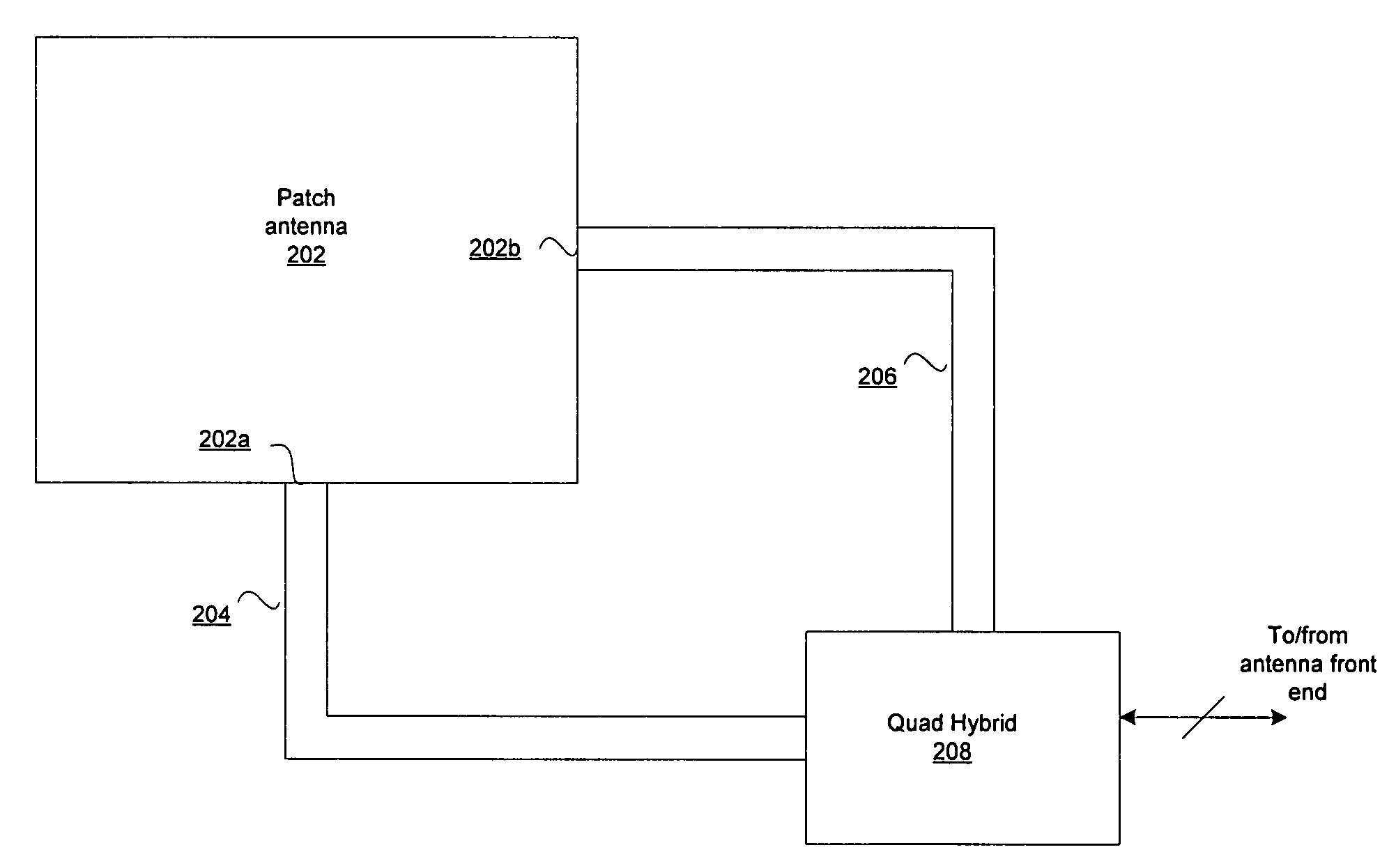
InactiveUS20070159397A1Simultaneous aerial operationsPolarisation/directional diversitySignal processing circuitsAntenna geometry
Certain embodiments for antenna geometry for multiple antenna handsets may include receiving RF signals via a patch antenna coupled to a signal processing circuitry within a mobile terminal. The signal processing circuitry may process the RF signals, comprising at least one of a plurality of polarizations that are received by the patch antenna. The patch antenna may be a dual-polarized antenna, and may comprise a plurality of ports. RF signals at a first of the plurality of ports may be orthogonally polarized with respect to RF signals at a second of the plurality of ports. The patch antenna may be optimized to receive multiple RF bands. Each of the multiple RF bands may be communicated via different ports to be processed.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and device for production and emission of a high-power microwave pulse
InactiveUS7795758B2Saves complexityReduced space requirementsApparatus without intermediate ac conversionOscillations generatorsCapacitanceMicrowave
Owner:DIEHL BGT DEFENCE GMBH & CO KG
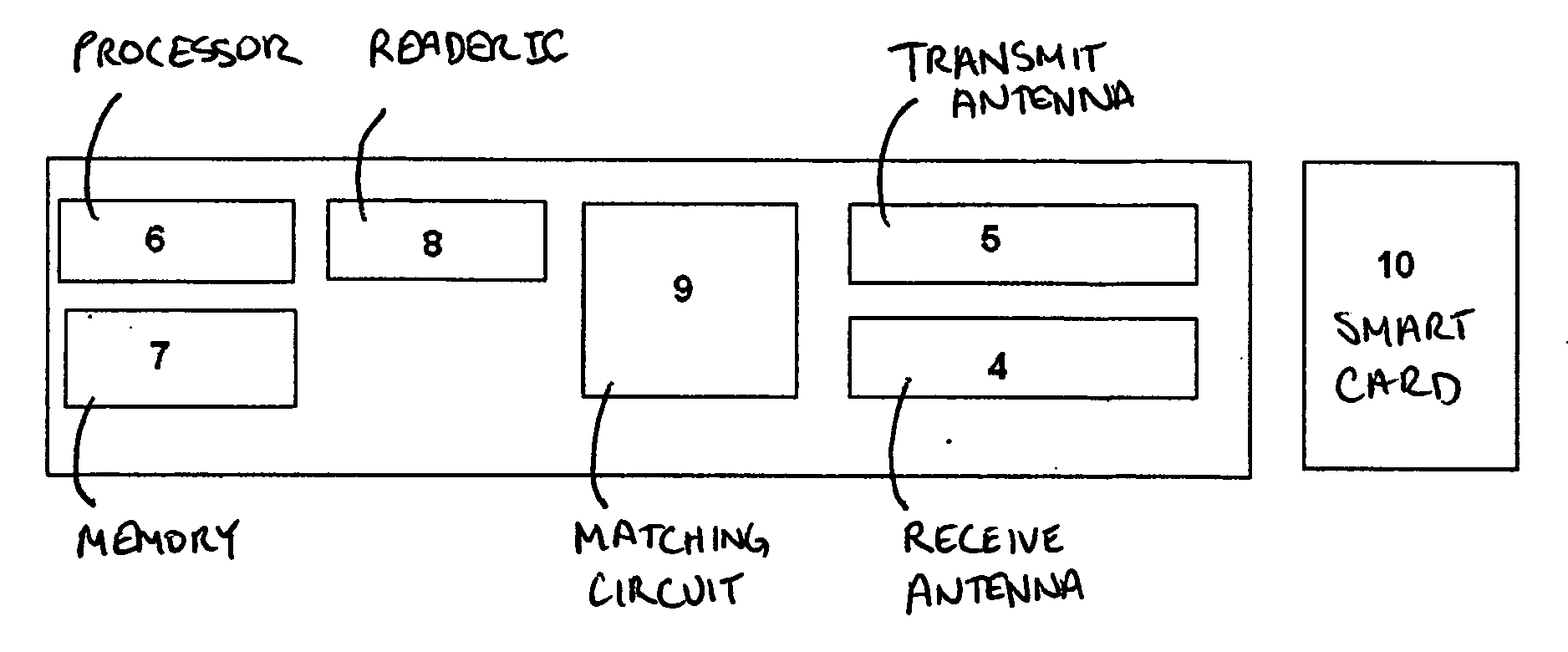
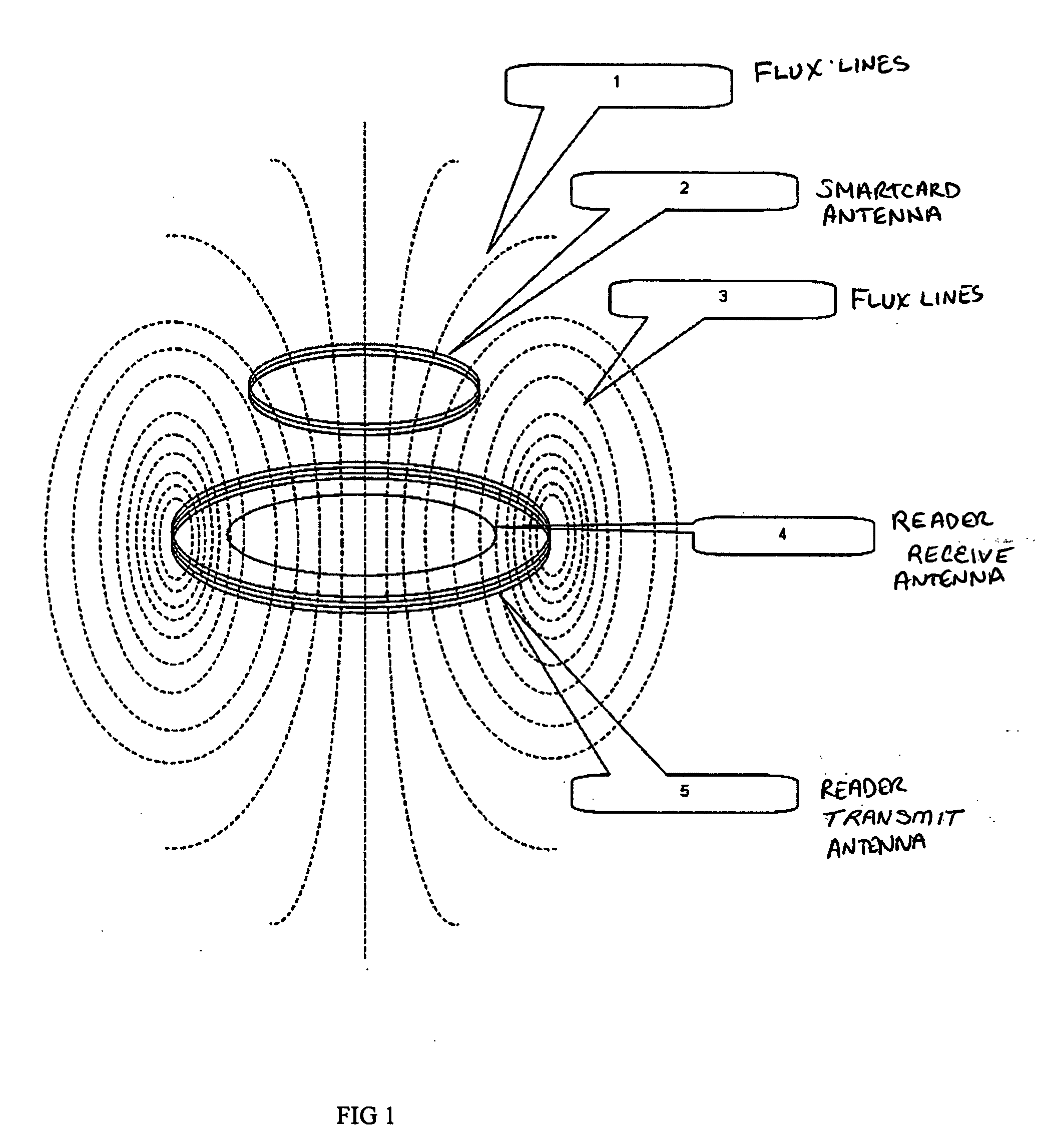
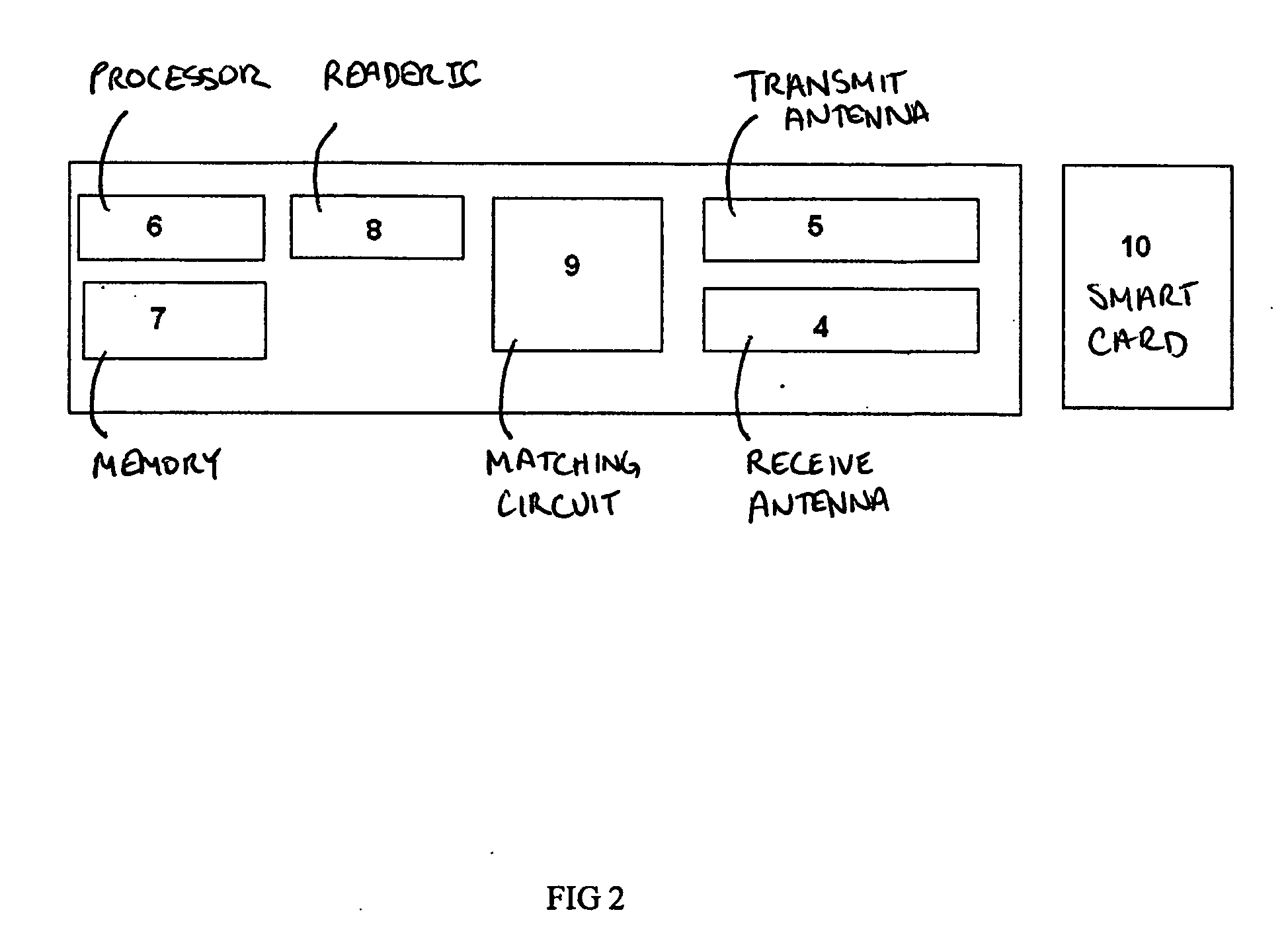
Contact-less smart card reader
InactiveUS20090078763A1Enhanced signalIncrease signal strengthSensing by electromagnetic radiationSignal qualitySignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
An improved contact-less smart card reader is disclosed that includes at least one separate transmit antenna and at least one separate receive antenna for transmitting and receiving respectively, wherein the antenna geometry of said reader is adapted to capture a maximum number of flux lines that pass through the corresponding smartcard and a minimum number of flux lines that do not pass though the corresponding smartcard, thereby increasing the signal to noise ratio in the reader and consequently, increasing the strength of the signal qualities received from the smart card, particularly in the event of operation of the smart card from a substantial operating distance. A method is also provided for assembling an improved contact-less smartcard reader as described above.
Owner:SCOLIS TECHNOLOGIES (INDIA) PVT LTD
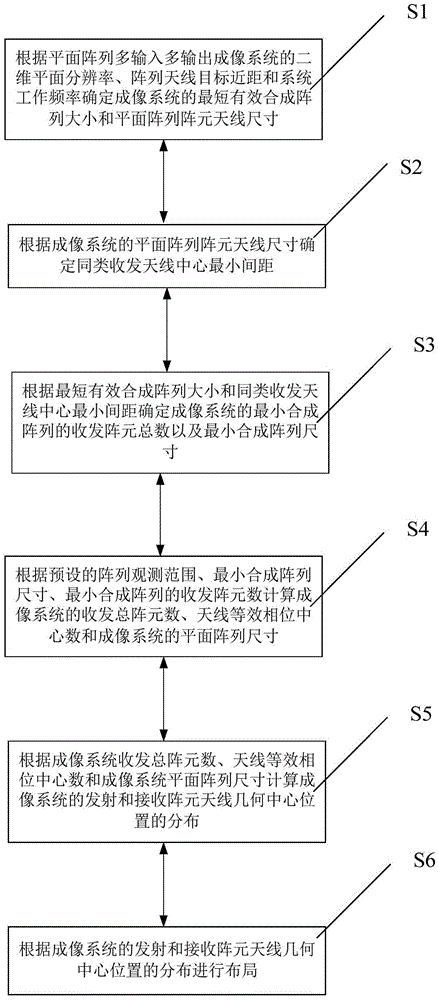
Layout method of multiple-input multiple-output imaging antenna in close range planar array
ActiveCN104269612BGuaranteed efficiencyReduce in quantityAntenna arraysRadiating elements structural formsTransceiverMicrowave
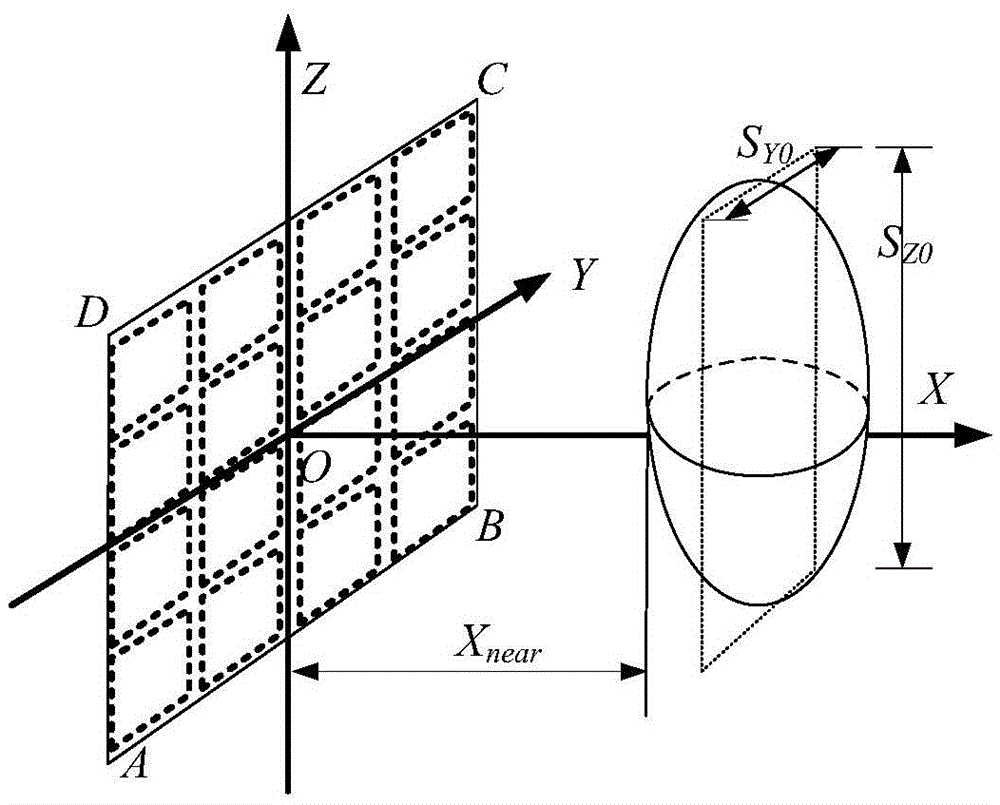
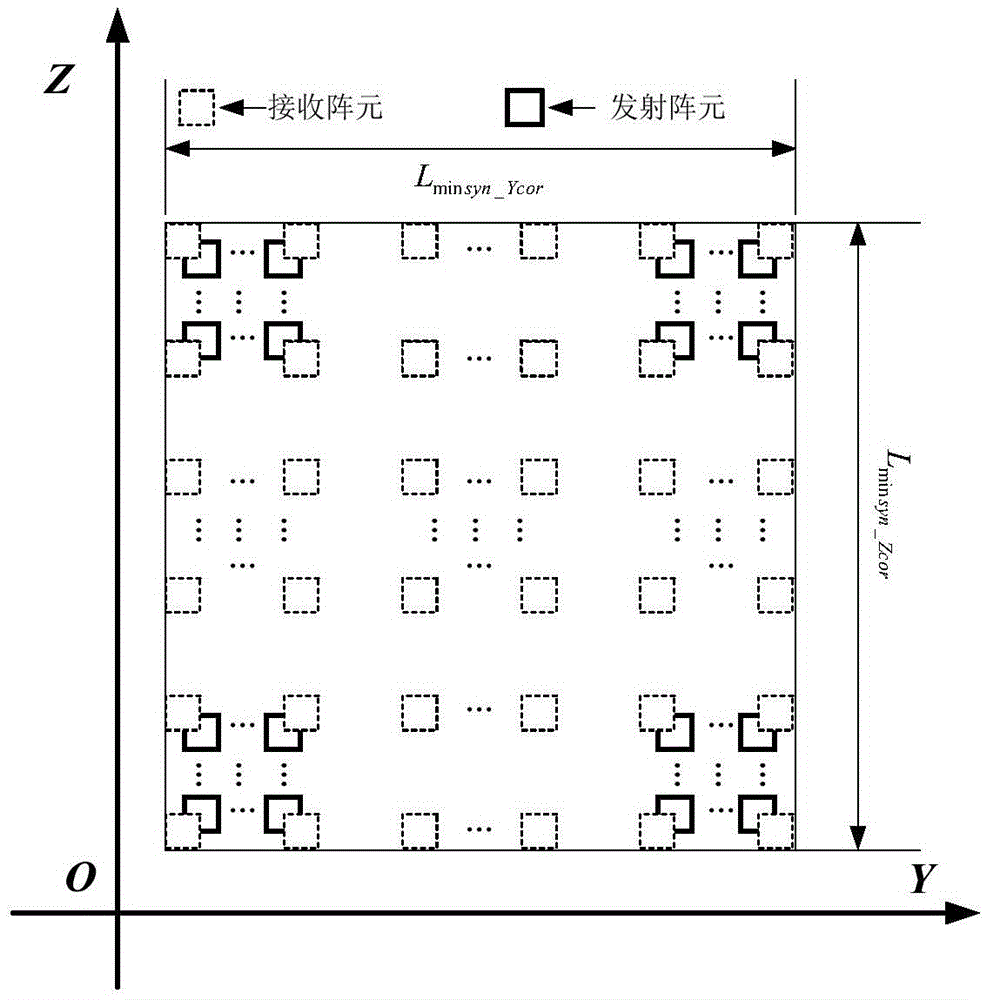
The invention discloses a layout method of a short-distance planar array MIMO imaging antenna, comprising: step S1: determining the shortest effective synthetic array size and the size of the planar array element antenna of the imaging system; step S2: determining the minimum distance between the centers of the receiving and transmitting antennas of the same type; step S3: Determine the total number of transceiver elements and the size of the minimum composite array of the imaging system; Step S4: Calculate the total number of transceiver elements of the imaging system, the number of antenna equivalent phase centers, and the planar array size of the imaging system; Step S5: Calculating the distribution of the geometric center positions of the transmitting and receiving array element antennas of the imaging system; Step S6: performing layout according to the distribution of the geometric center positions of the transmitting and receiving array element antennas of the imaging system. The layout method of the present invention solves the problem that the effective synthesis array length is affected by the observation distance in planar array MIMO imaging, and further improves the data acquisition efficiency on the premise of ensuring the quality of short-distance microwave images.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV OF TECH
Antenna switching system and method
InactiveUS8035523B2Sensing record carriersBurglar alarm by hand-portable articles removalCouplingEngineering
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
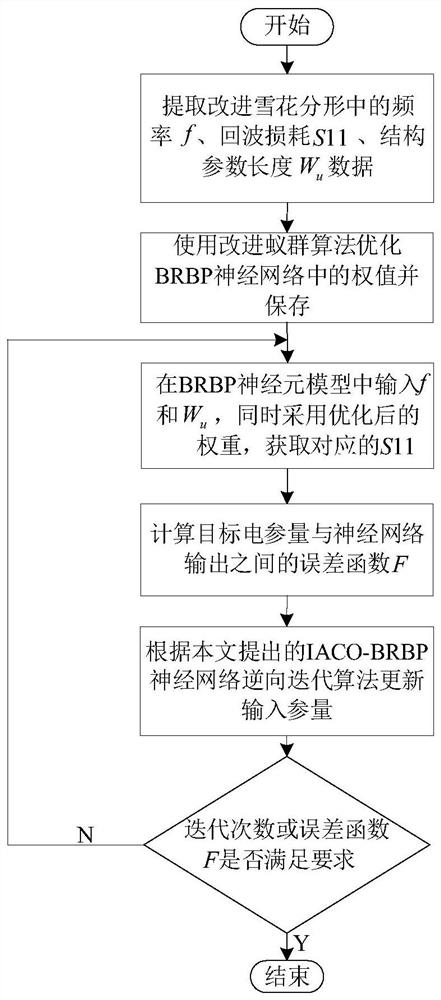
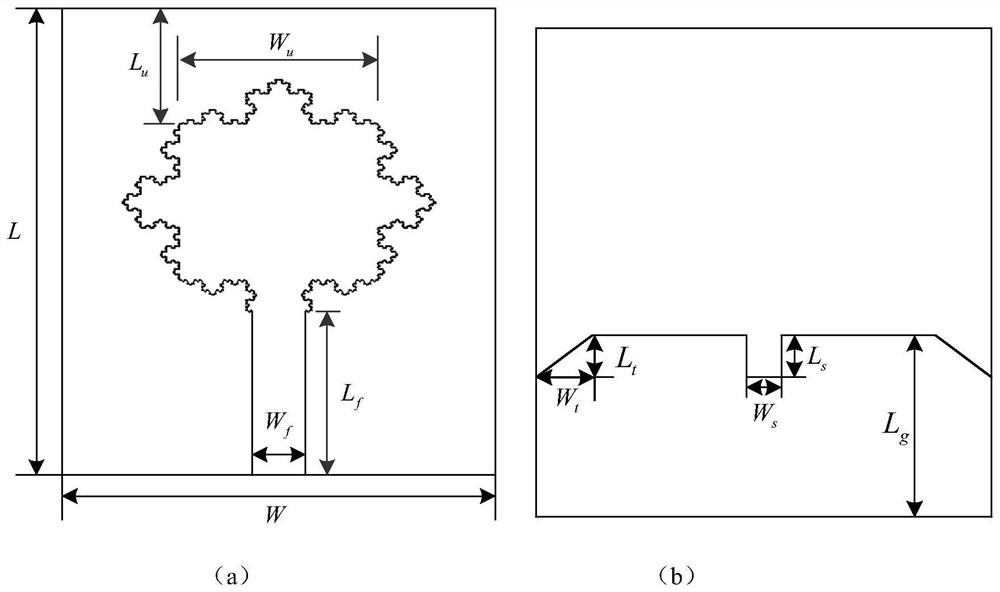
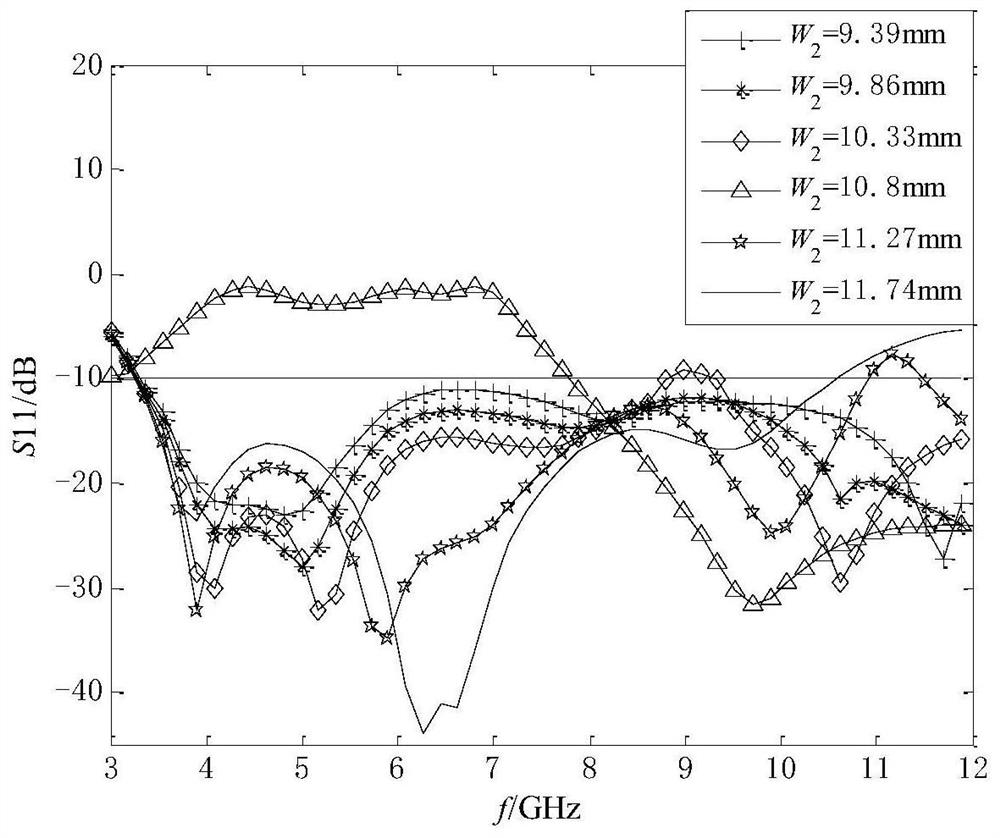
Koch snowflake ultra-wideband antenna reverse modeling method based on IACO-BRBP neural network
PendingCN112861386AReduce running timeSolve multiple problemsArtificial lifeDesign optimisation/simulationUltra wideband antennasSimulation
The invention discloses a Koch snowflake ultra-wideband reverse modeling method based on an IACO-BRBP neural network, and the method mainly comprises the steps: 1, obtaining experimental data, and dividing the experimental data into a training set and a test set; 2, improving a traditional ant colony algorithm; 3, training the BRBP forward model by using the improved ant colony algorithm, and storing the optimized weight; 4, keeping the weight unchanged, and inputting an electric parameter in the established IACO-BRBP model to realize a reverse solving process; 5, calculating an evaluation function between the output parameter and the target parameter; 6, updating the input parameters by using a reverse iteration algorithm. According to the method, the IACO-BRBP neural network reverse modeling method is applied to the improved Koch snowflake-type ultra-wideband antenna, so that corresponding structural parameters can be solved according to given antenna electrical parameters; once the training of the reverse model is completed, the geometric parameters of the antenna can be quickly simulated only by inputting target electrical parameters; therefore, the design period is greatly shortened while the design requirement is basically met.
Owner:LIAONING TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY
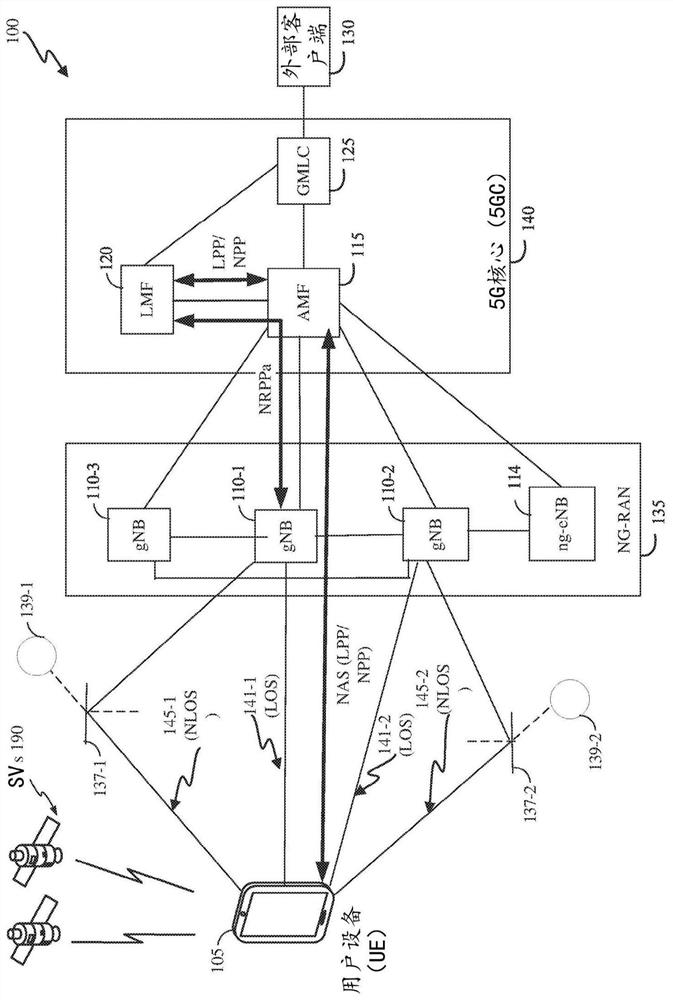
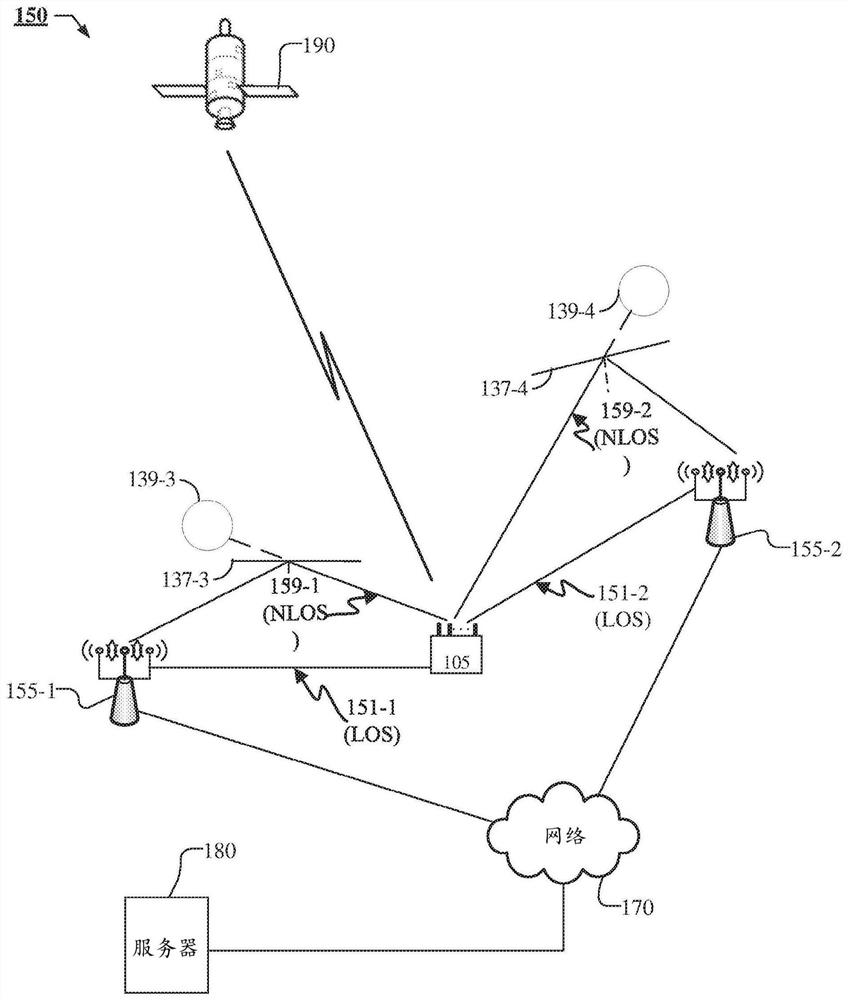
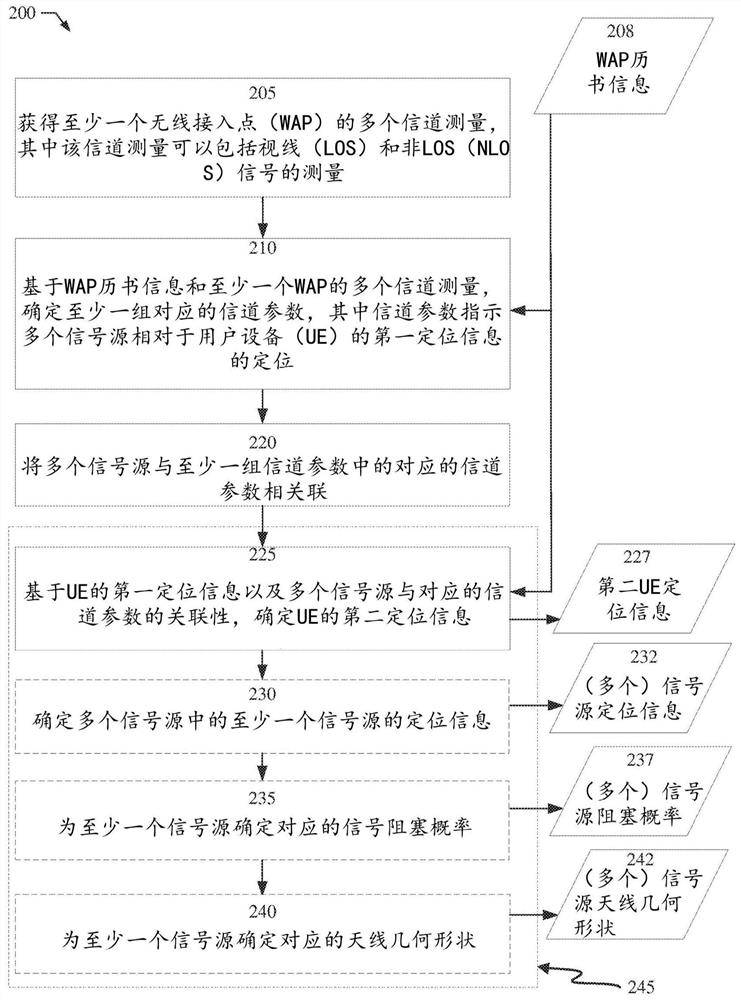
Systems and methods for positioning with channel measurements
Position determination of user equipment (UE) is supported using channel measurements obtained for Wireless Access Points (WAPs), wherein the channel measurements are for Line of Sight (LOS) and Non-LOS (NLOS) signals. Based on WAP almanac information and the channel measurements, channel parameters indicative of positions of signal sources relative to a first position of UE may be determined. Using the first position of the UE and an association of the signal sources with corresponding channel parameters, a second position of the UE may be determined. The position of the UE may be a probability density function. Additionally, position information for signal sources may be determined, such as a probability density function, as well as signal blockage probability and an antenna geometry and the WAP almanac information may be updated accordingly.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
An umbrella antenna random error analysis methodconsidering deterministic error
ActiveCN109408957AGuaranteed calculation accuracyAvoid formula derivationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElectricityUmbrella antenna
The invention discloses an umbrella antenna random error analysis method considering deterministic error, which comprises the following steps: inputting umbrella antenna geometrical parameter and electric parameter; calculating the optimal focal length of the umbrella antenna; Calculation of Far Area Radiation Electric Field of Ideal Antenna at Optimal Focal Length; Reflector triangular mesh generation; calculating the deterministic error of the umbrella antenna; the first-order and second-order coefficients of the electric field displacement relative to the center point of the element are calculated. The first-order and second-order coefficients of the random error of the electric field relative to the center point of the element are calculated. Calculation of Far Area Radiated Electric Field under Deterministic Error of Umbrella Antenna; RMS value of input surface random error; calculating an average value of the far-field radiation power of the antenna; Judge whether the electricalperformance meets the requirements; Output radiated power pattern; Update the surface random error rms value. By obtaining the influence of the surface random error of the umbrella antenna on the electric performance, the invention can guide the processing and manufacturing of the umbrella antenna components.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
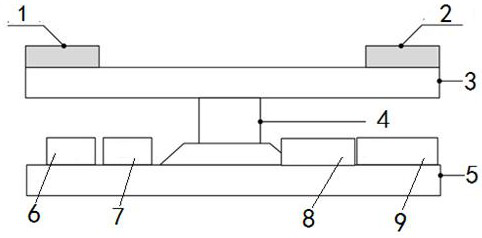
MEMS Stacked Millimeter-Wave Antenna
ActiveCN101141023BReduce distractionsHigh bandwidthDecorative surface effectsRadiating elements structural formsCouplingDielectric substrate
The micro-electromechanical stacked millimeter-wave antenna provided by the present invention includes an upper dielectric substrate, a middle dielectric substrate and a lower dielectric substrate, the upper surface of the upper dielectric substrate is deposited with metal and etched to form a first metal radiation patch , the upper surface of the middle dielectric substrate is deposited with metal and etched to form a second metal radiation patch, the upper surface of the lower dielectric substrate is deposited with metal and etched to form a ground plane with an aperture coupling gap, the lower layer Metal is deposited on the lower surface of the dielectric substrate and etched to form a FGCPW-MS feeder or MS feeder, and the upper dielectric substrate, middle dielectric substrate and lower dielectric substrate are integrated through a MEMS bonding process. The antenna has a small geometry, light weight and is easy to further integrate.
Owner:NO 55 INST CHINA ELECTRONIC SCI & TECHNOLOGYGROUP CO LTD
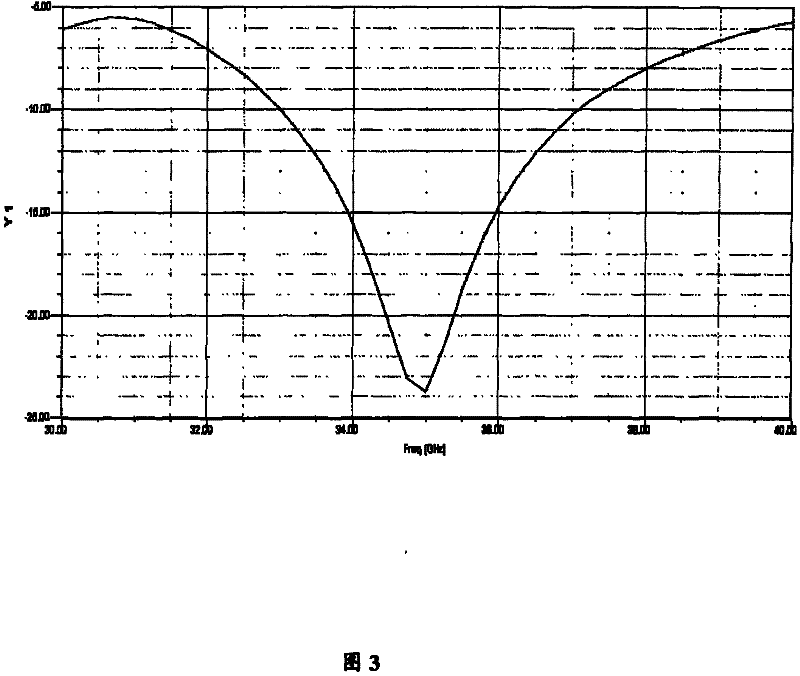
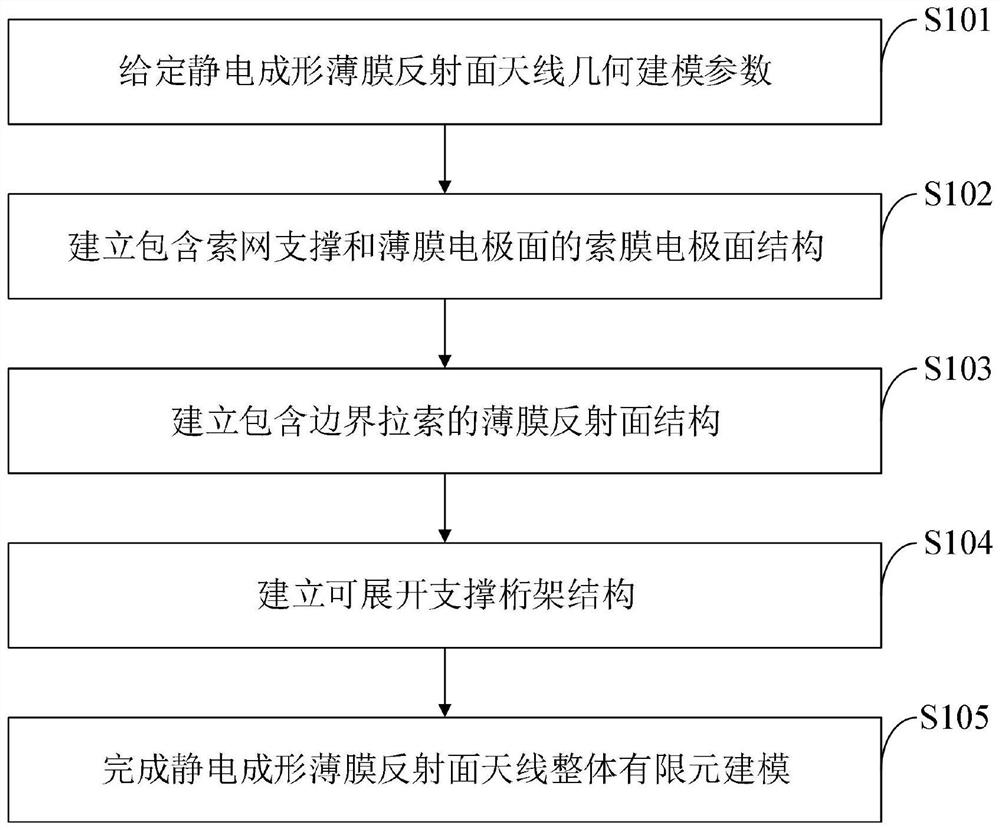
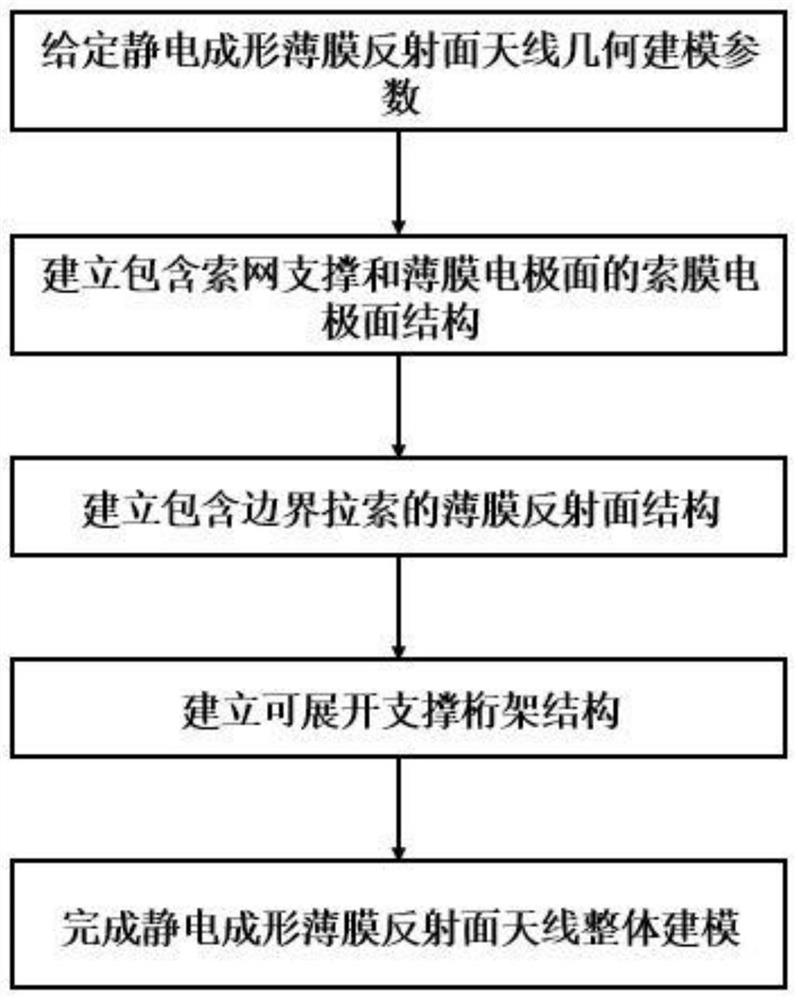
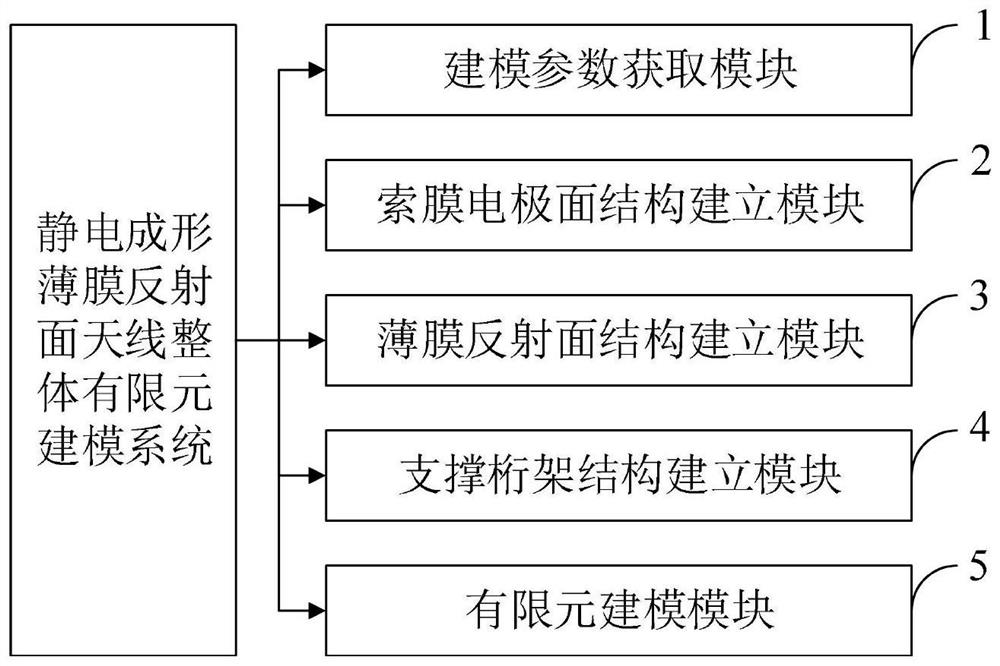
Electrostatic forming film reflector antenna integral finite element modeling method and system
PendingCN114117837AEasy to set upFast and reasonable finite element modelingGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationThin film electrodeGeometric modeling
The invention belongs to the technical field of spaceborne antenna simulation, and discloses an overall finite element modeling method and system for an electrostatic forming film reflector antenna, and the method comprises the steps: giving geometric modeling parameters of the electrostatic forming film reflector antenna; establishing a cable membrane electrode surface structure comprising a cable net support and a membrane electrode surface; establishing a thin film reflecting surface structure comprising a boundary inhaul cable; establishing an expandable support truss structure; and integral finite element modeling of the electrostatic forming thin film reflector antenna is completed. According to the method, parametric modeling is carried out on the deployable supporting truss, the cable membrane electrode surface and the thin film reflecting surface of the electrostatic forming thin film reflecting surface antenna, so that high-precision finite element modeling analysis and structure optimization of the electrostatic forming thin film reflecting surface antenna can be carried out; the static forming film reflector antenna integral model with different size parameters can be conveniently established, and a basis is provided for high-precision analysis and structure optimization of the static forming film reflector antenna.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Electromechanical integration optimization design method of umbrella antenna under optimal focal length
ActiveCN107169174BAvoid loss of electrical performanceGuaranteed calculation accuracyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationElement modelAlgorithm
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
A positioning and orientation device for mimu/rotating Beidou short baseline dual antennas
ActiveCN109282812BHigh precisionImprove reliabilityAngle measurementNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsOriginal dataCarrier signal
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Analysis Method of Mesh Antenna Electrical Performance in Time Domain Based on Approximate Calculation Formula
ActiveCN107590309BGuaranteed calculation accuracyReduce computing timeDesign optimisation/simulationTime informationTime domain
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
System and method for downlink channel estimation in massive multiple-input multiple-output (mimo)
By processing the training sequence according to the transformation matrix, the overhead associated with downlink channel estimation in massive multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) networks can be reduced. The transformation matrix maps a generic dictionary to a non-generic dictionary associated with the antenna geometry of the MIMO antenna array. The transformation matrix can be calculated based on these two dictionaries. In an embodiment, the training reference signal is precoded to obtain a precoded training reference signal, and then the precoded training reference signal is sent through a MIMO antenna array. A training precoder for precoding the training reference signal is designed according to the transformation matrix to alleviate the dependence of the training reference signal transmission on the antenna geometry.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Dynamic load analysis method of space mesh antenna based on electromechanical coupling model
ActiveCN106599504BReduce vibration frequencyLow modal densityDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelControl engineering
The invention discloses an electromechanical coupling model-based space net-shaped antenna power load analysis method. The method specifically comprises the steps of (1) inputting antenna geometrical parameter, material parameters and electrical parameters; (2) establishing an antenna structure finite element model; (3) performing antenna structure modal analysis; (4) outputting a modal matrix; (5) applying power load; (6) calculating modal coordinates; (7) calculating reflective surface node displacement; (8) calculating surface patch phase error; (9) calculating an antenna far-zone electric field by adopting an electromechanical coupling model; (10) determining whether electrical performance satisfies requirement or not; and (11) outputting an antenna structure design scheme, or (12) updating the antenna parameters and continuing to perform the step (1). By virtue of the electromechanical coupling model-based space net-shaped antenna power load analysis, the space net-shaped antenna electrical performance analysis and electromechanical integration optimization design can be guided under the effect of vibration load.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method and system for antenna geometry for multiple antenna handsets
InactiveUS7525485B2Simultaneous aerial operationsPolarisation/directional diversitySignal processing circuitsAntenna geometry
Certain embodiments for antenna geometry for multiple antenna handsets may include receiving RF signals via a patch antenna coupled to a signal processing circuitry within a mobile terminal. The signal processing circuitry may process the RF signals, comprising at least one of a plurality of polarizations that are received by the patch antenna. The patch antenna may be a dual-polarized antenna, and may comprise a plurality of ports. RF signals at a first of the plurality of ports may be orthogonally polarized with respect to RF signals at a second of the plurality of ports. The patch antenna may be optimized to receive multiple RF bands. Each of the multiple RF bands may be communicated via different ports to be processed.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
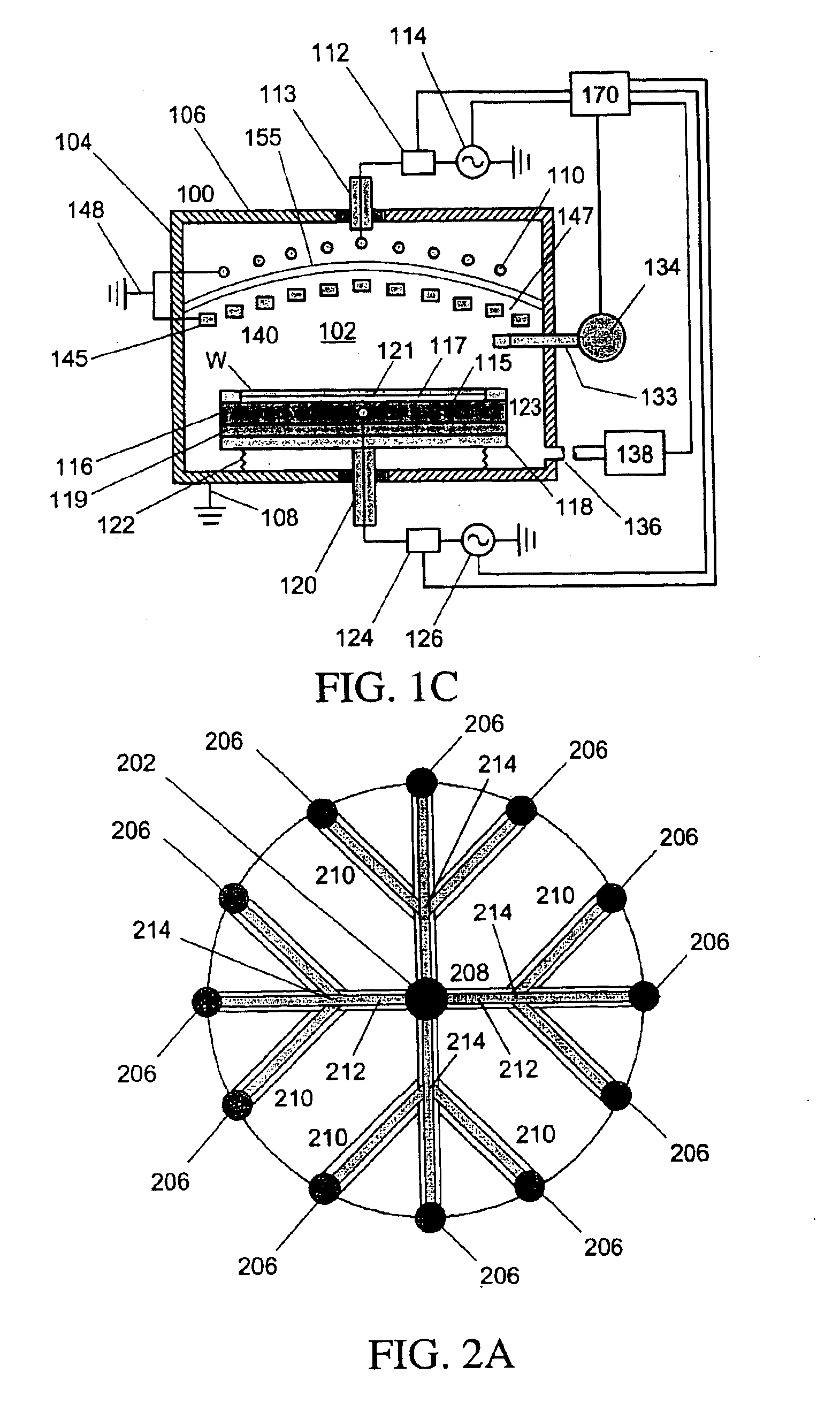
Ribbon antenna for versatile operation and efficient RF power coupling
ActiveCN104081492AImprove coupling efficiencyHigh densityElectric discharge tubesPower couplingPlasma density
Owner:VARIAN SEMICON EQUIP ASSOC INC
Stacked microstrip antenna based on nested recursive rotationally symmetric csrr distribution array
ActiveCN104466382BHigh gainReduce gainSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsElectrical conductorMicrostrip antenna array
The invention relates to a microstirp antenna, in particular to a stacked microstirp antenna based on a nested recursion rotational symmetry CSRR distribution array. The stacked microstirp antenna is of a five-layer structure formed by stacking good conductors and dielectric substrates without gaps and sequentially comprises the upper good conductor layer, the upper substrate, the middle good conductor layer, the lower substrate and the lower good conductor layer from top to bottom. The upper good conductor layer is a one-order Minkowski fractal upper radiation patch with a nested recursion rotational symmetry CSRR distribution array structure and a chamfer structure, the nested recursion rotational symmetry CSRR distribution array structure is provided with eight array elements geometrically centrosymmetric with the antenna, the array elements are of a complementary opening resonance ring structure, the distribution array structure is formed by a two-order array in a nested recursion mode and composed of a first-order four-element array near the center of the patch and a second-order four-element array scattered at four corners of the patch, the included angle between four array elements of the first-order four-element array or four array elements of the second-order four-element array and the edge of the antenna is 45 degrees, and the four array elements of the first-order four-element array and the four elements of the second-order four-element array are both arranged in a 90-degree rotational symmetry mode; the center of each complementary opening resonance ring is located in the diagonal of the patch; the middle good conductor layer is a one-order Minkowski fractal lower radiation patch with small holes and chamfers.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com