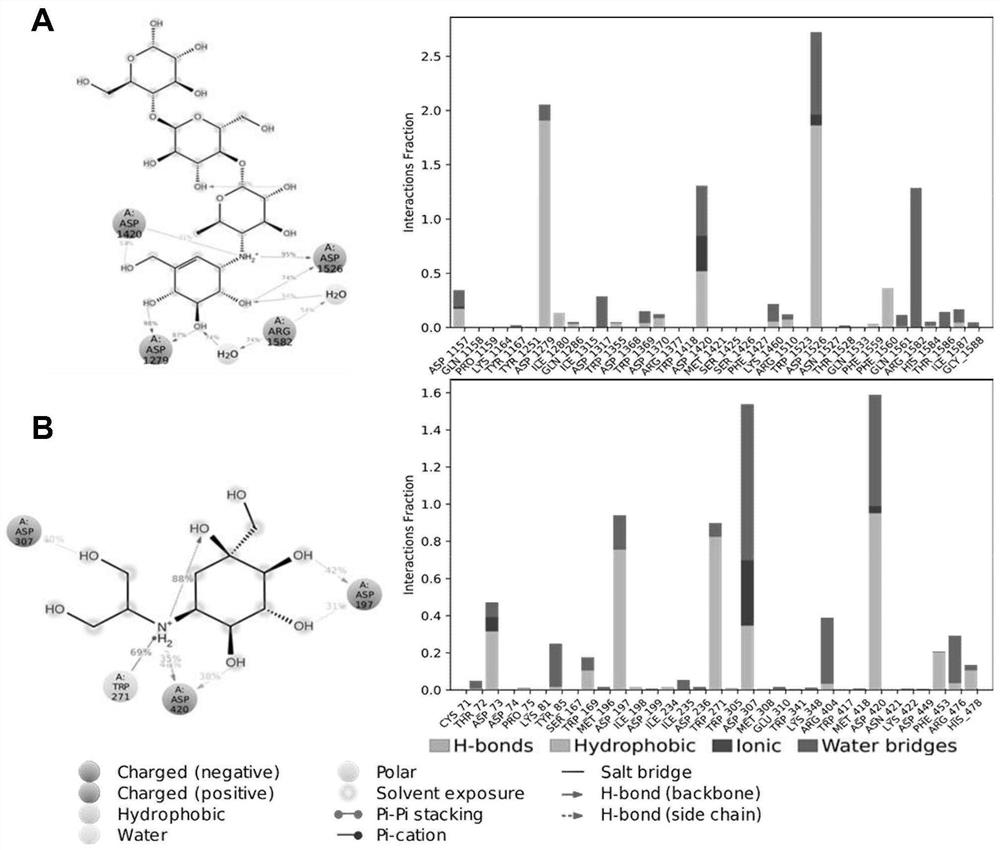
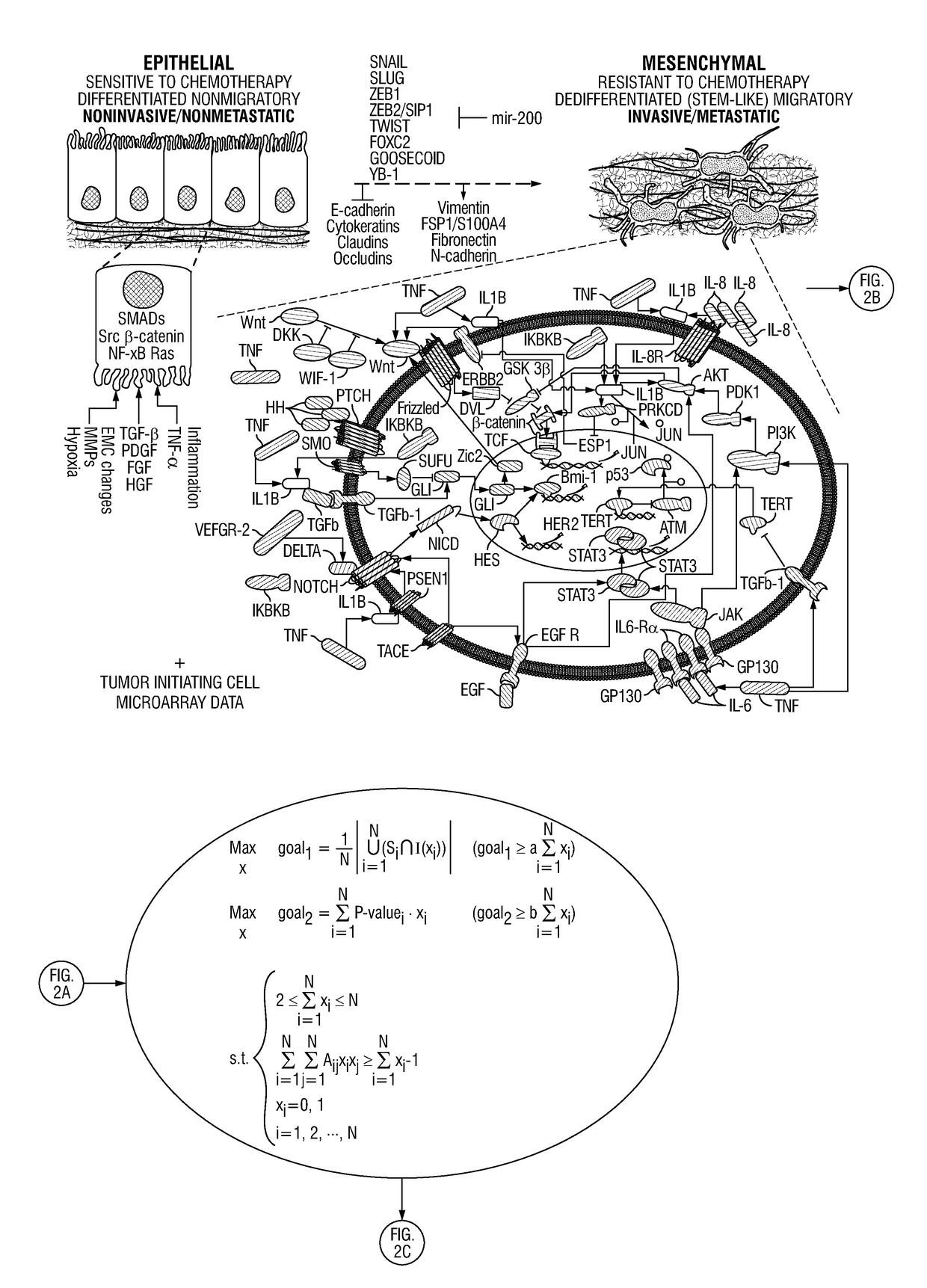
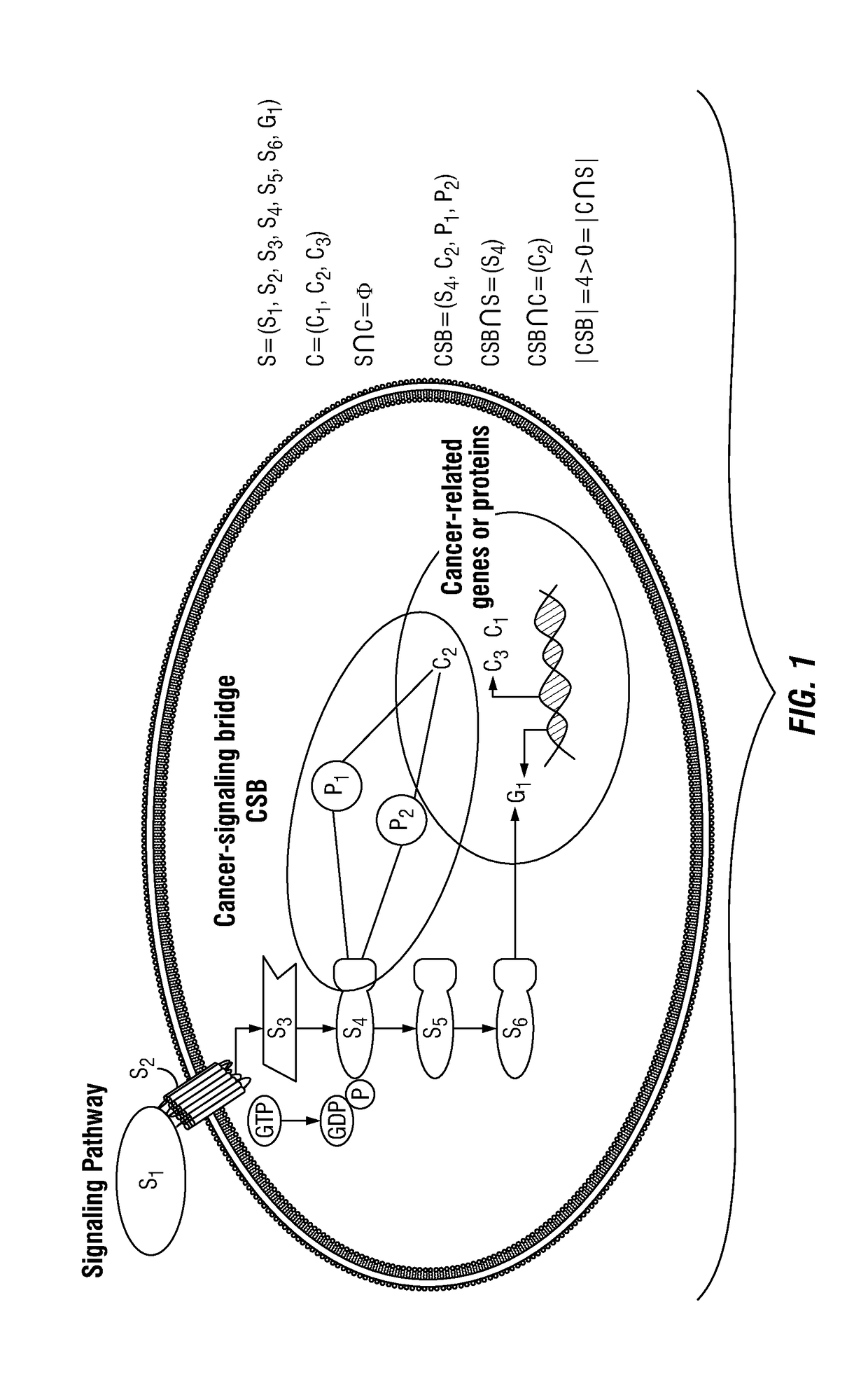
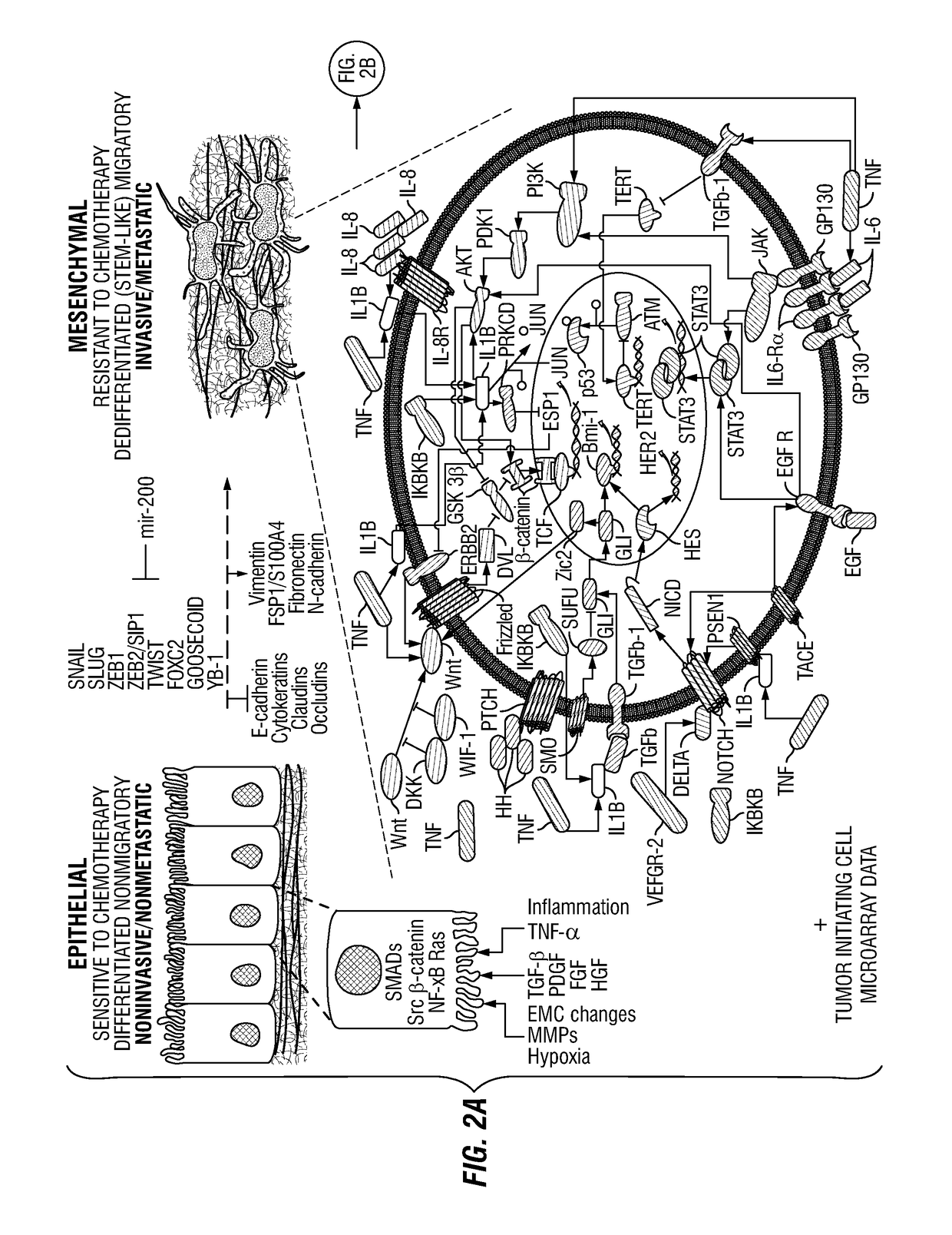
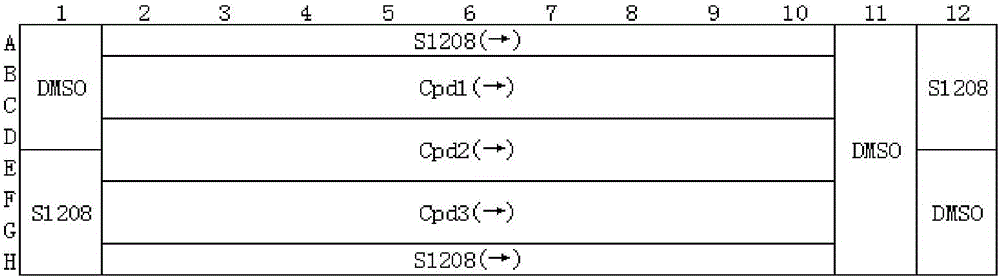
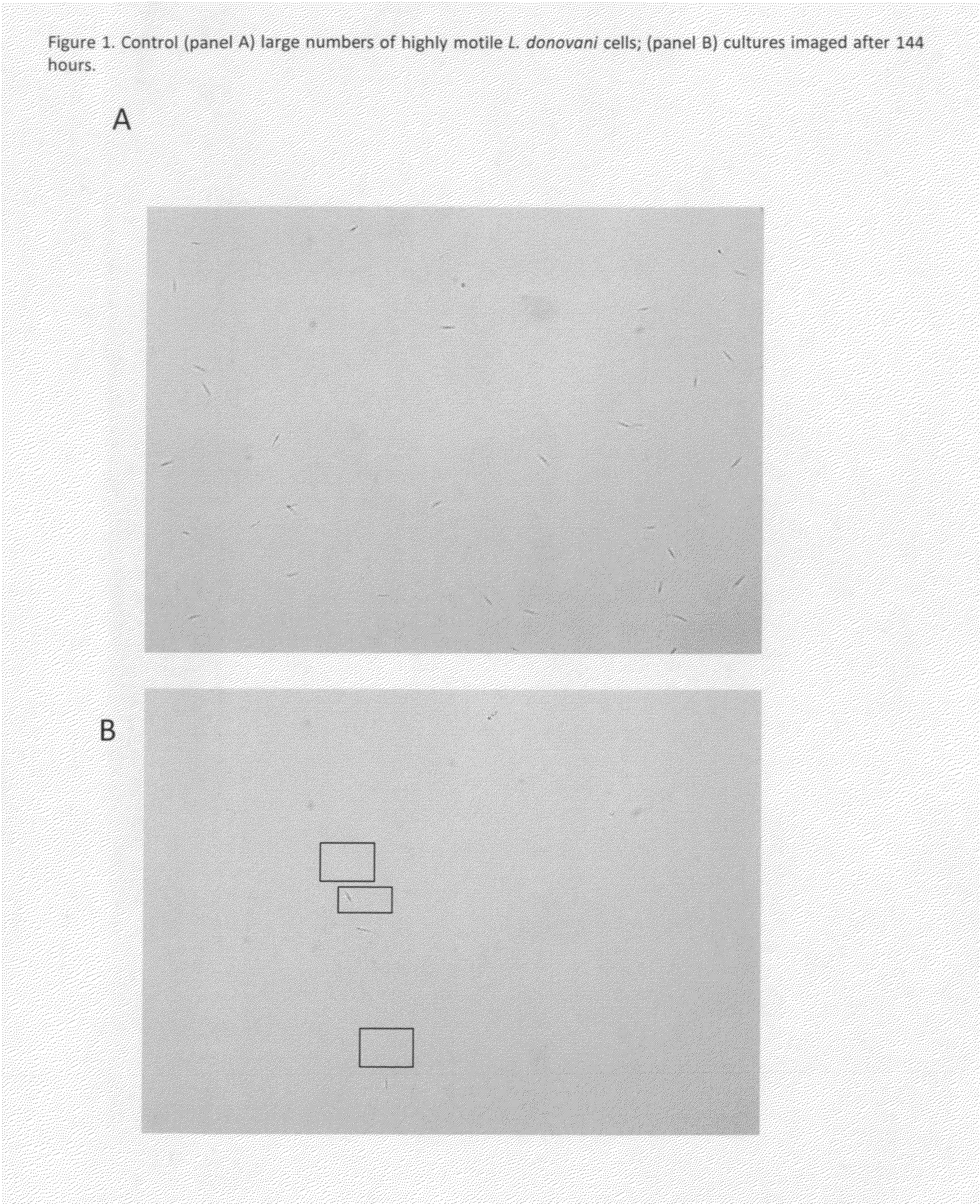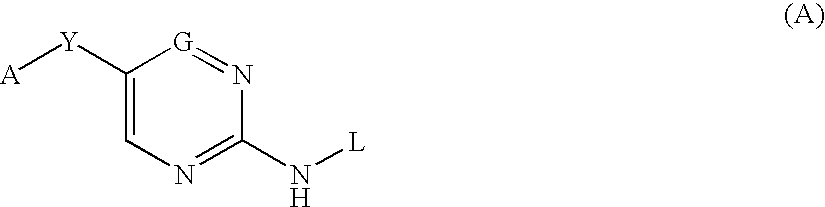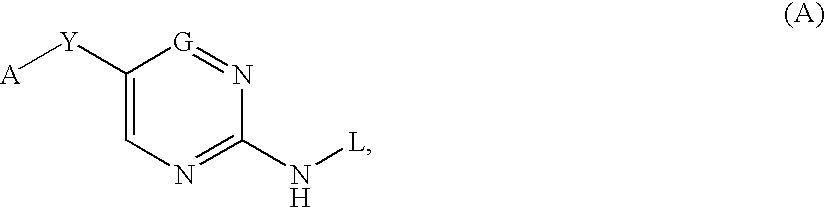Patents
Literature
69 results about "Approved drug" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An approved drug is a preparation that has been validated for a therapeutic use by a ruling authority of a government. This process is specific by country.
Compositions & formulations for preventing and treating chronic diseases that cluster in patients such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, obesity, polycystic ovary syndrome, hyperlipidemia and hypertension, as well as for preventing and treating other diseases and conditions
InactiveUS20140271923A1Good for healthImproving well-beingHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideSide effectPolycystic ovary
Patients inflicted with various clustering chronic diseases require treatment with multiple drugs having distinct mechanisms of action. Accordingly, patients with multiple conditions suffer from cumulative side effects of multiple drugs as well as drug-drug interactions. Embodiments, agents, compounds or drugs of the present invention, such as sesquiterpenes, e.g., Zerumbone, replace an equal or larger number of approved drugs during patient treatment. Examples of disorders prevented or ameliorated by administration of the formulations of this invention include but are not limited to inflammatory diseases that may be, oncological, genetic, ischemic, infectious, neurological, hematological, ophthalmological, rheumatoid, orthopedic, neurological, hematological, kidney, vascular, dermatological, gynecological, or obstetric. The present invention further relates to a method of identifying agents, compounds or drugs useful in preventing or treating CDCP related diseases and conditions as well as other disorders, diseases and conditions treatable or preventable by the same agents, compounds or drugs.
Owner:REID CHRISTOPHER BRIAN
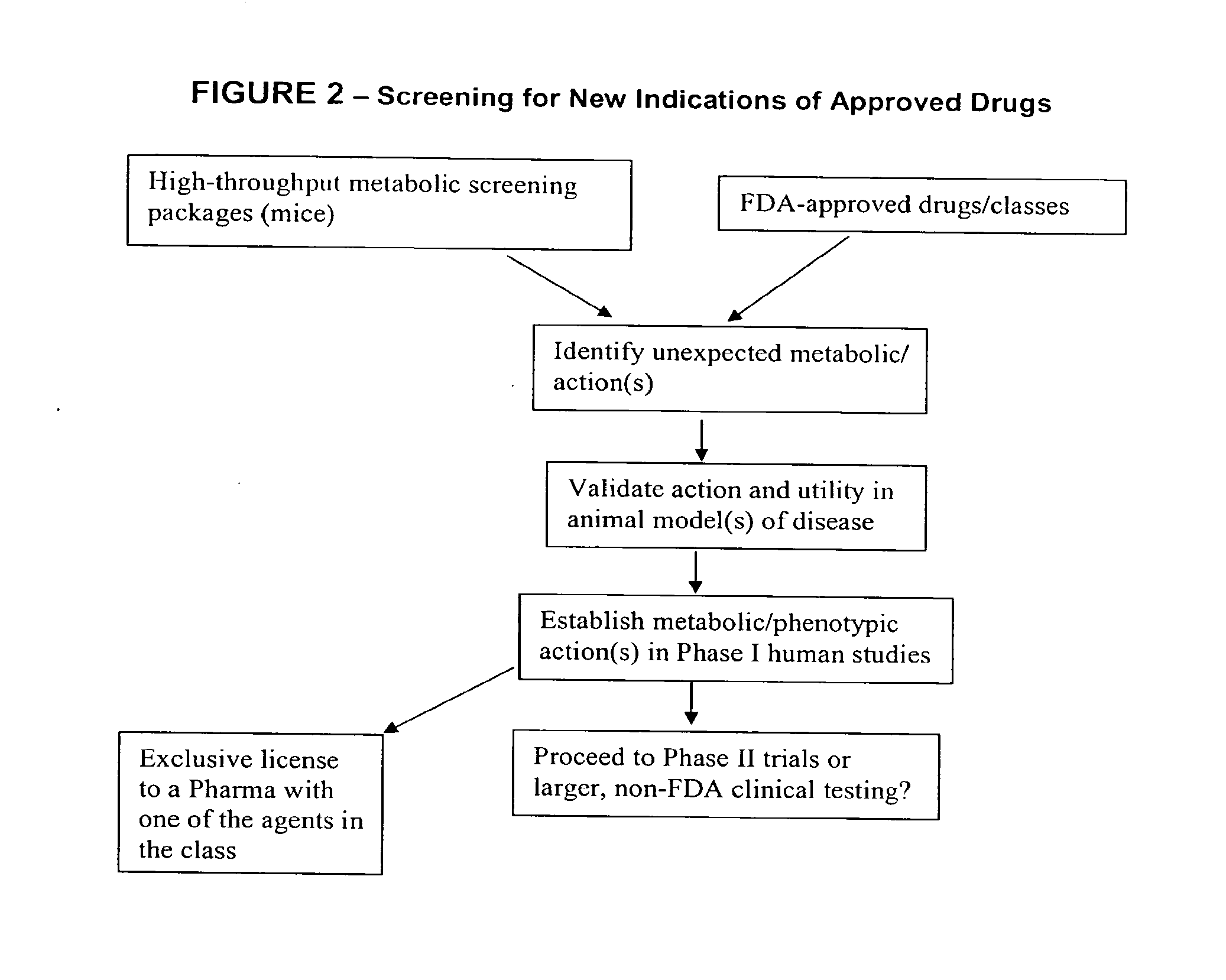
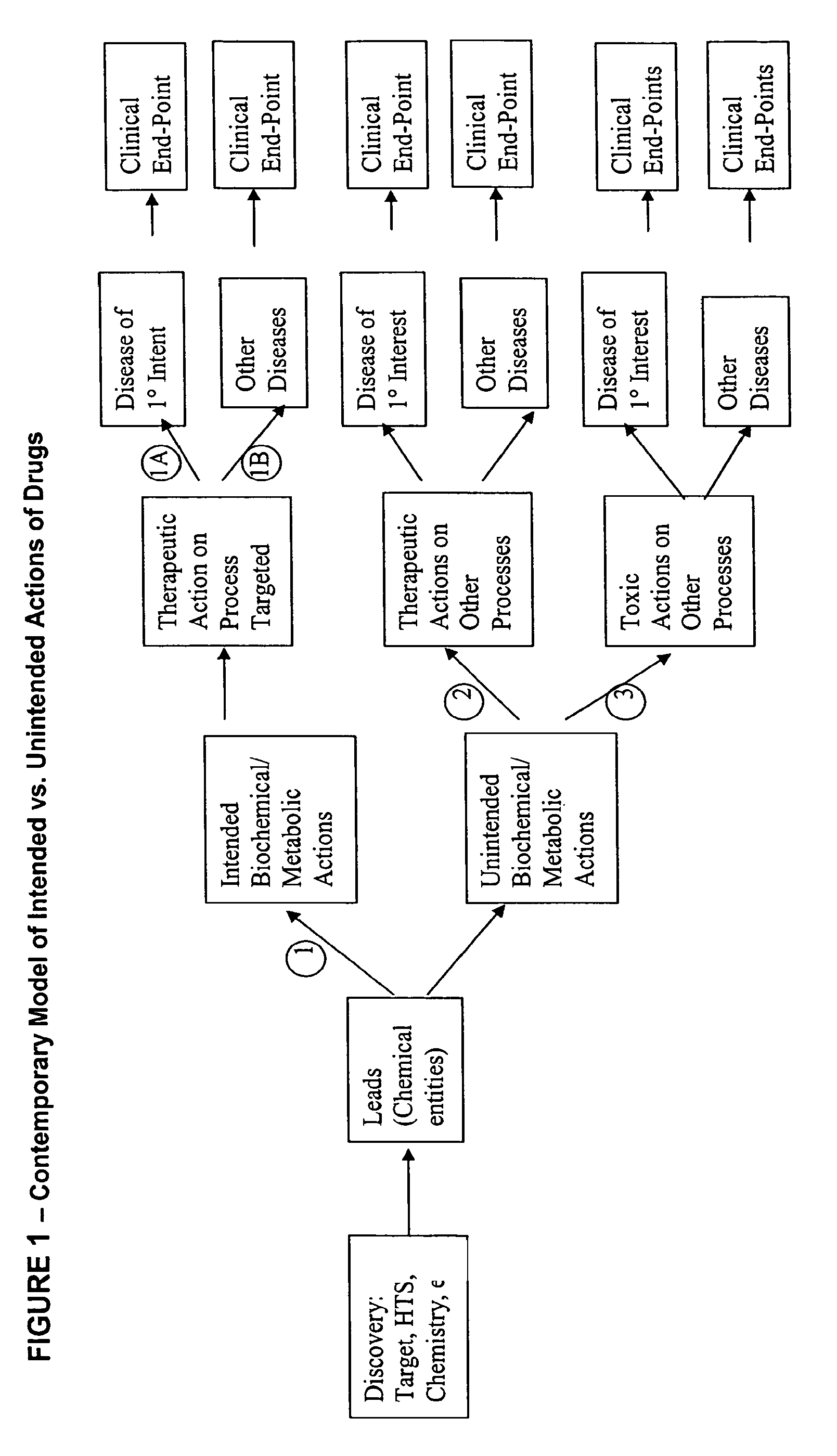
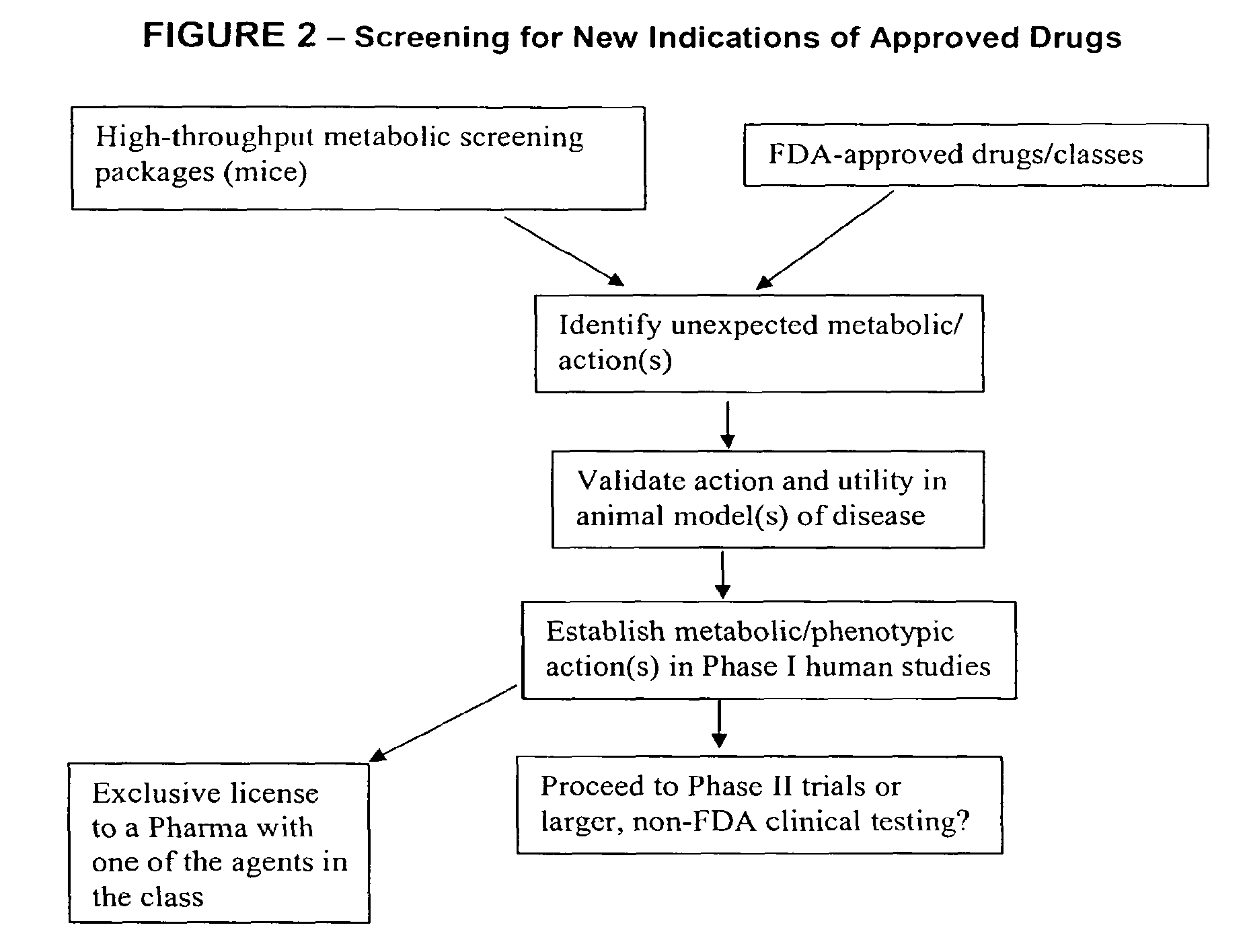
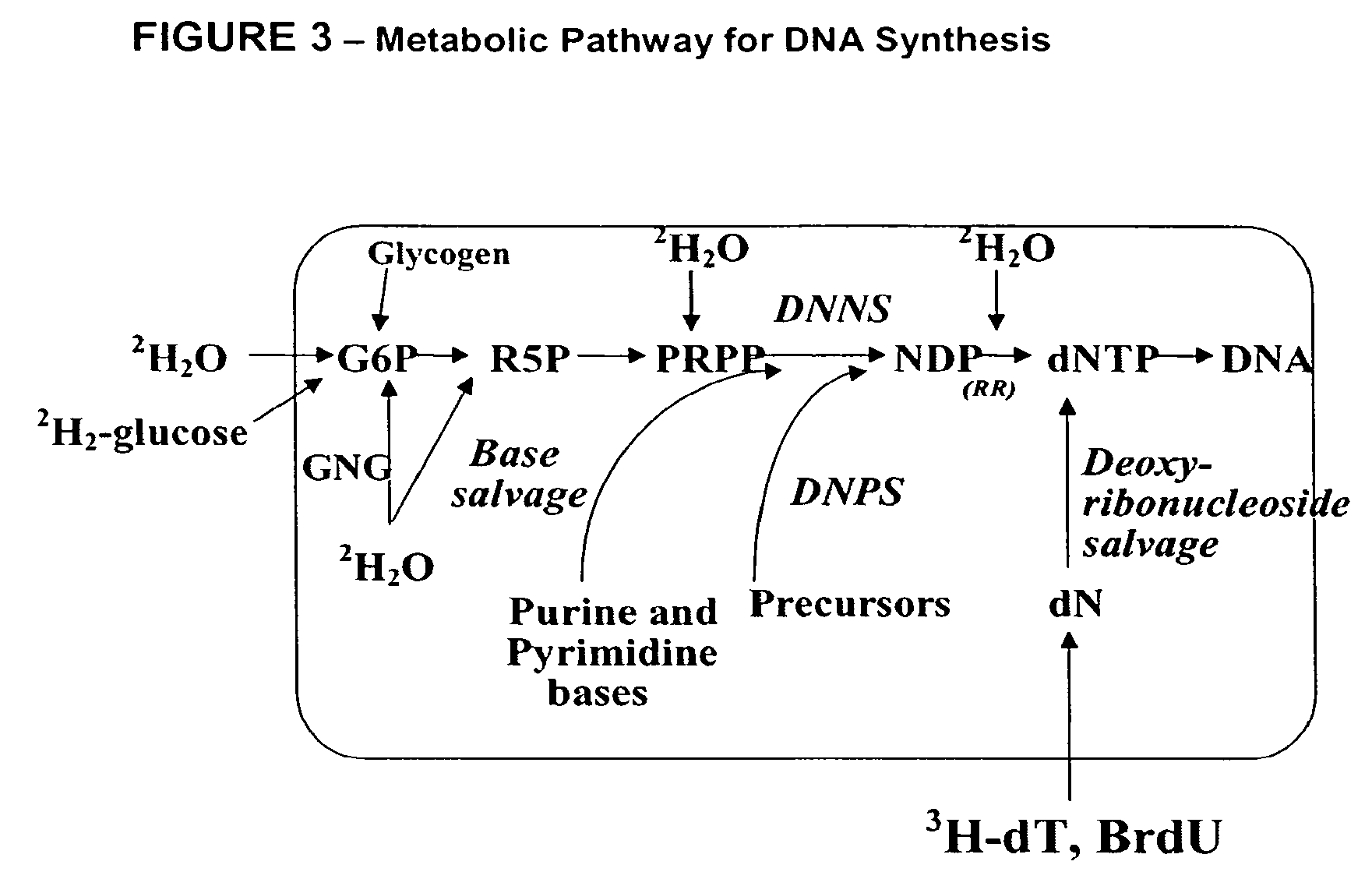
Method for high-throughput screening of compounds and combinations of compounds for discovery and quantification of actions, particularly unanticipated therapeutic or toxic actions, in biological systems
InactiveUS20050202406A1Compounds screening/testingMicrobiological testing/measurementLiving systemsIsotopic labeling
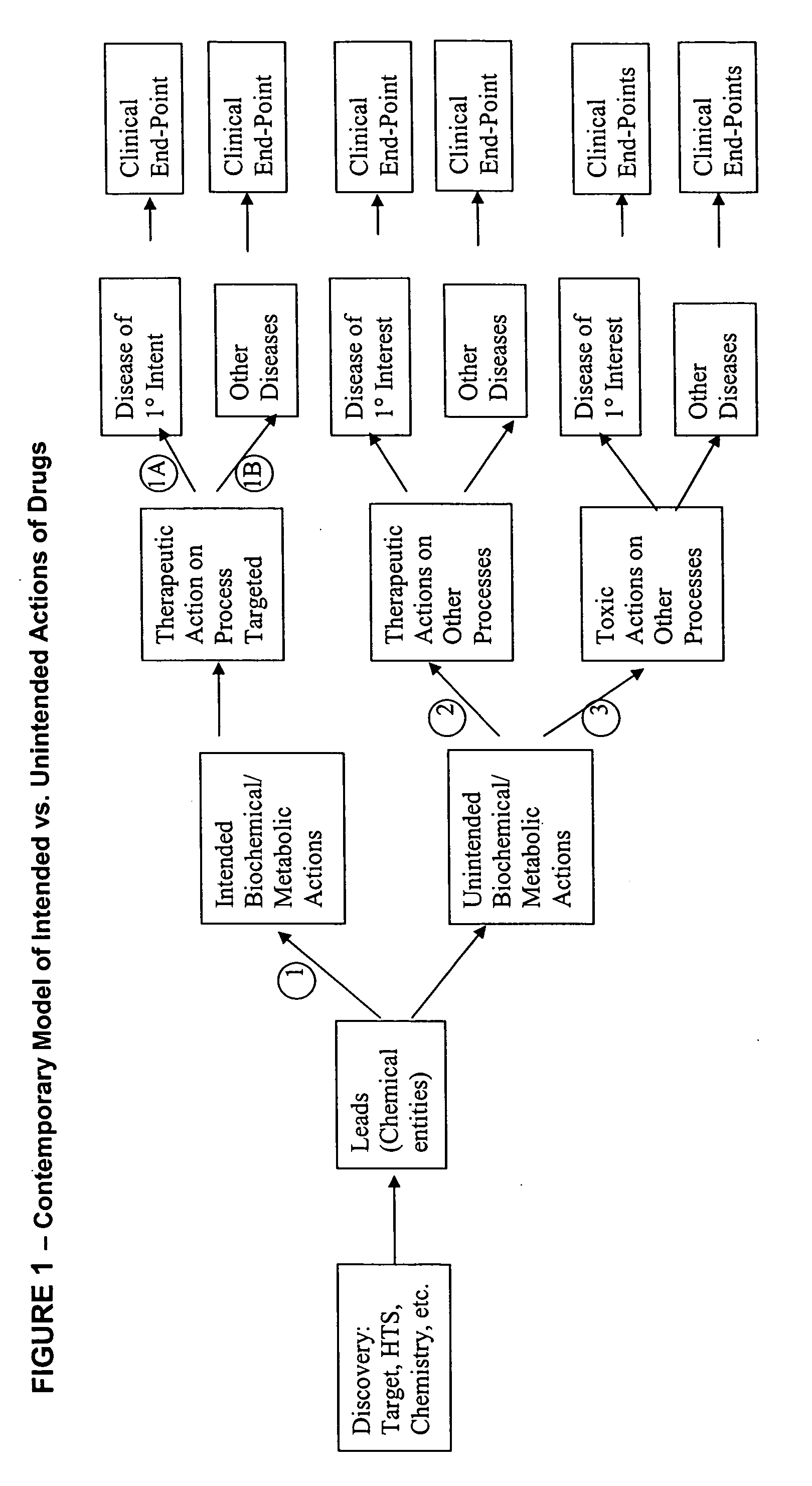
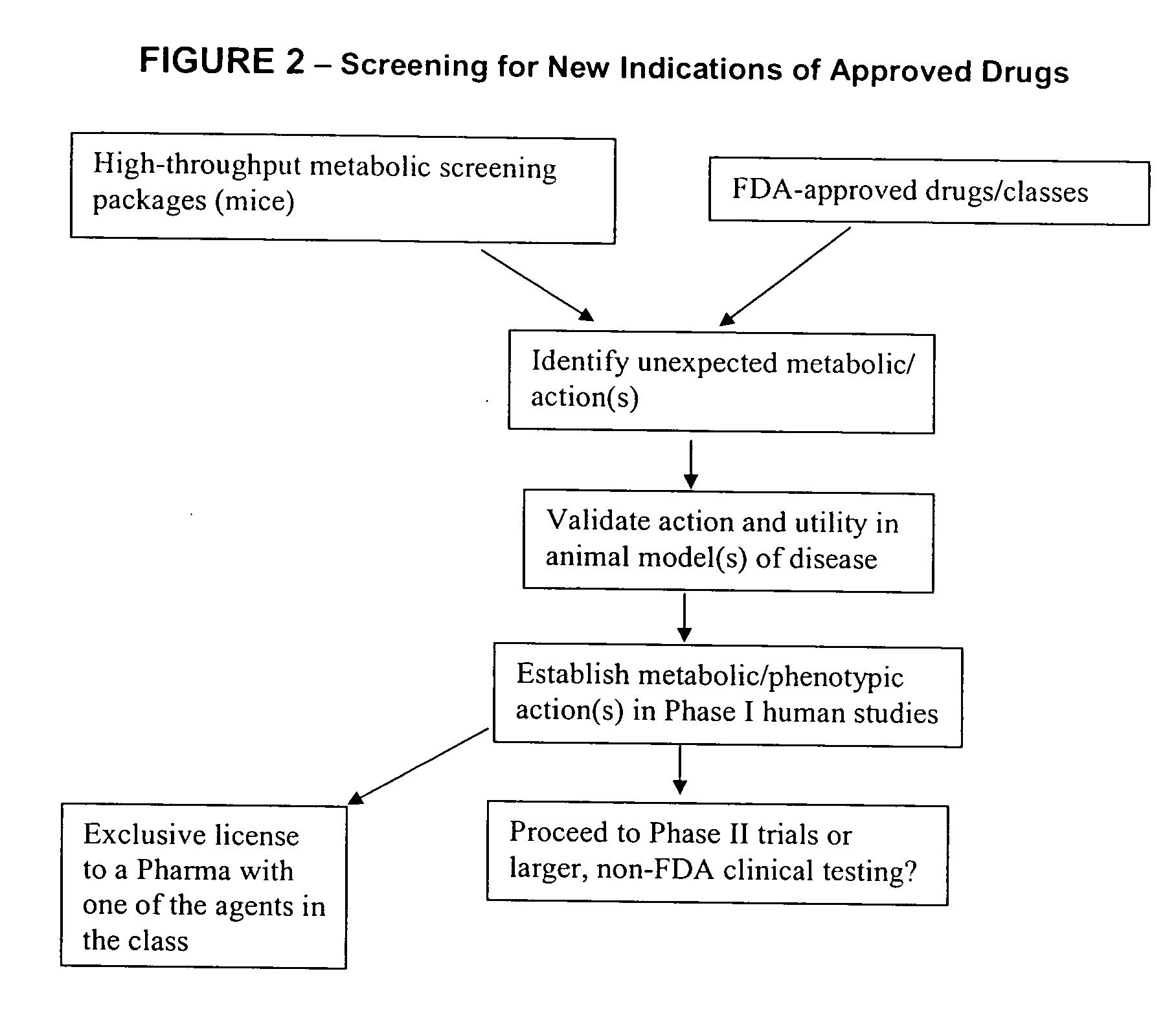
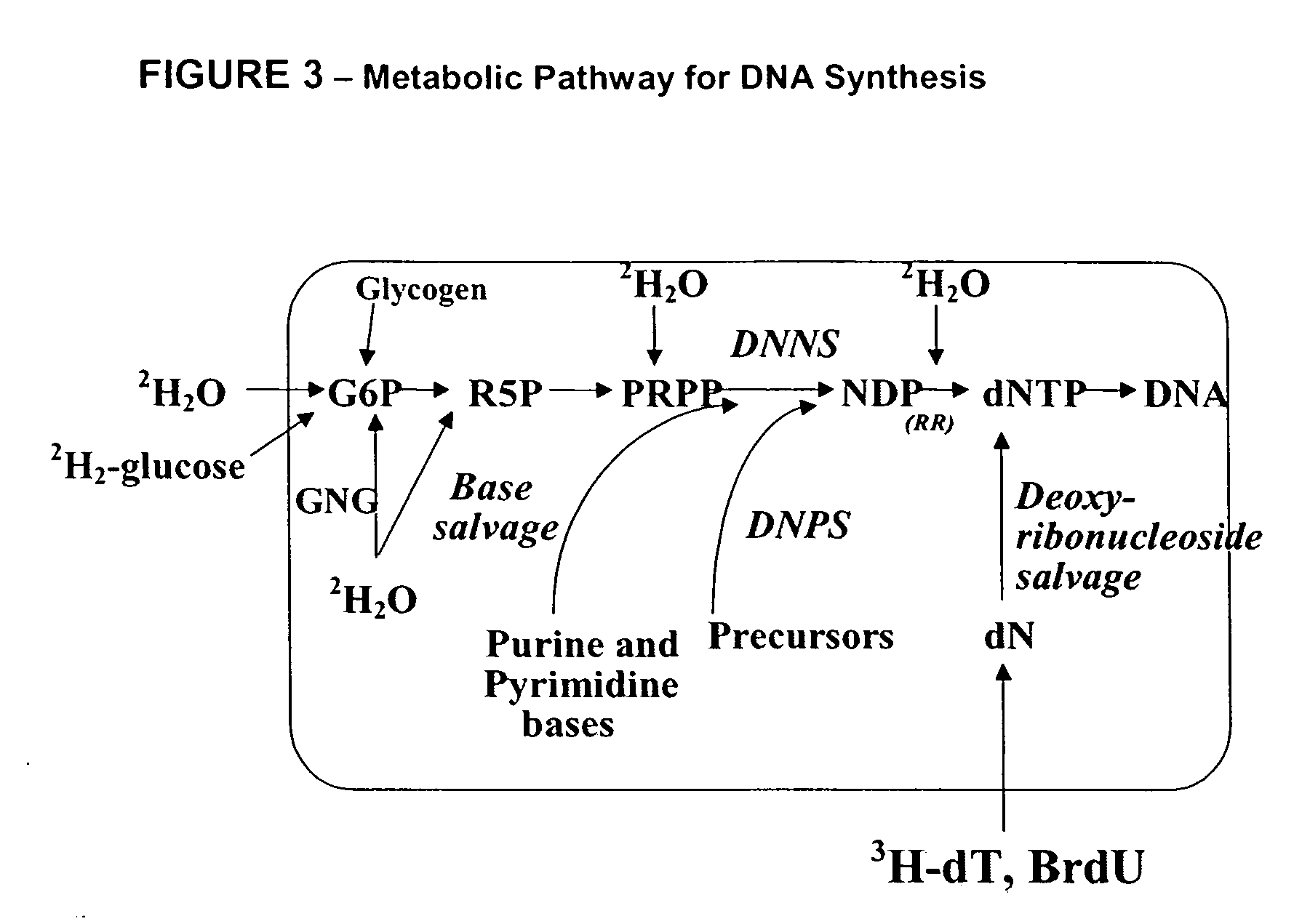
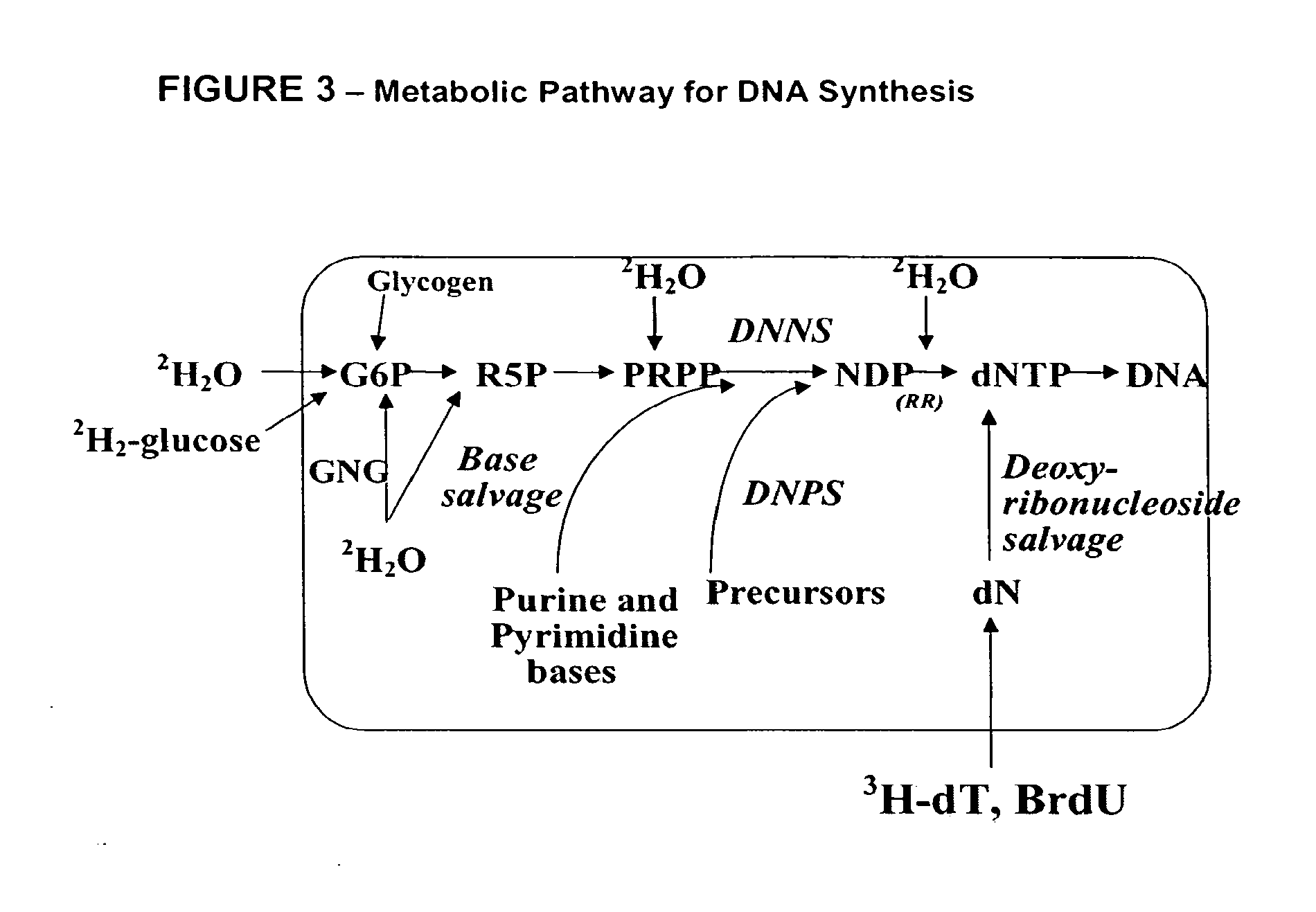
The invention enables high-throughput screening of compounds in living systems to detect unanticipated or unintended biological actions. The invention also allows for screening, detection, and confirmation of new indications for approved drugs. Screening and detection of toxic effects of compounds also can be achieved by using the methods of the invention. The methods comprise administering isotope-labeled substrates to a living system so that the label is incorporated into molecules in a manner that reveals flux rates through metabolic pathways thought to be involved in a disease. Comparisons between living systems exposed to compounds and living systems not so exposed reveals the effects of the compounds on the flux rates through the metabolic pathways. Combinations or mixtures of compounds can be systematically screened to detect unanticipated or unintended biological actions, including synergistic actions, in the same manner.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
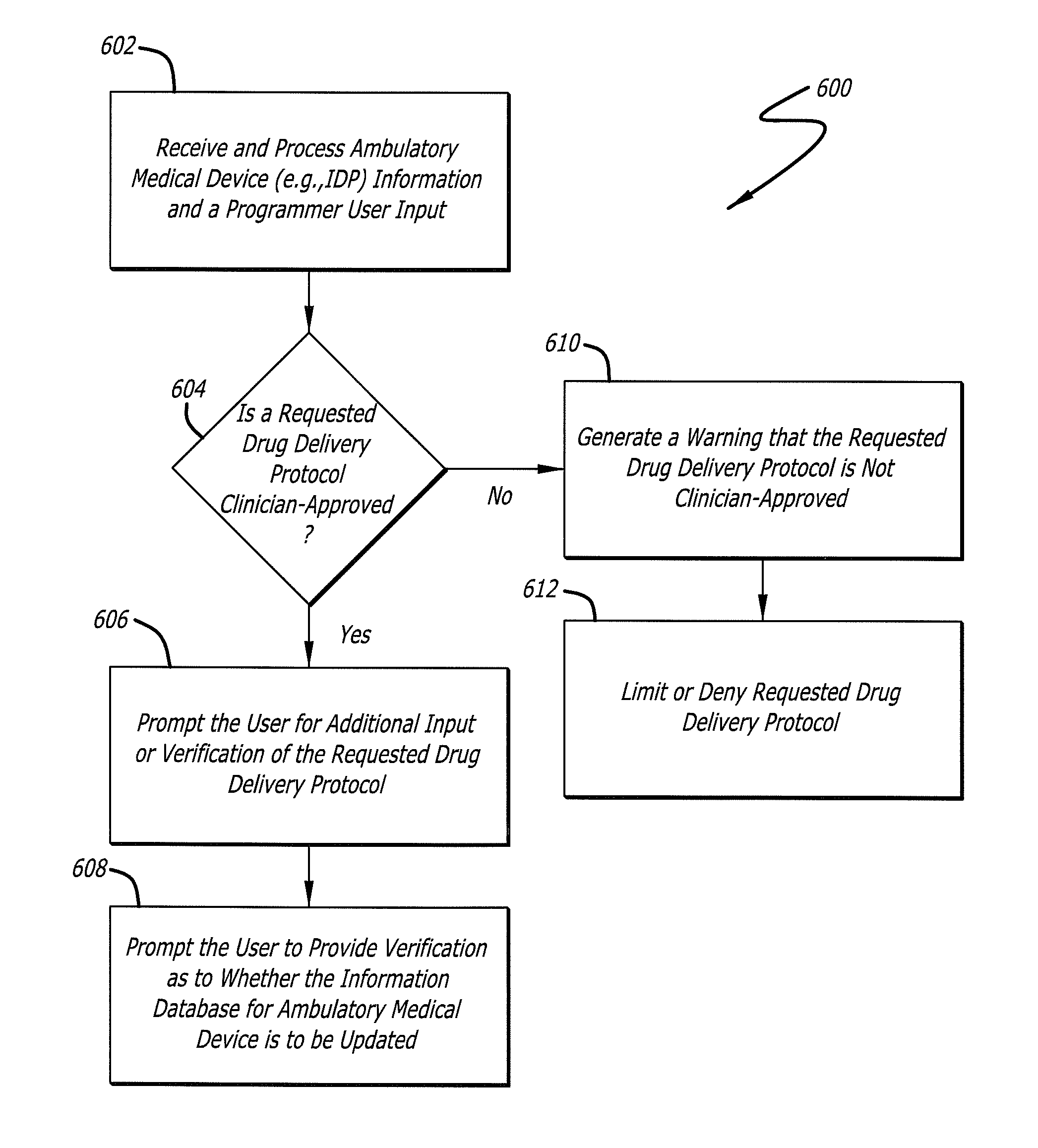
Drug Delivery Safety System
ActiveUS20090043290A1Drug and medicationsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismGraphicsGraphical user interface
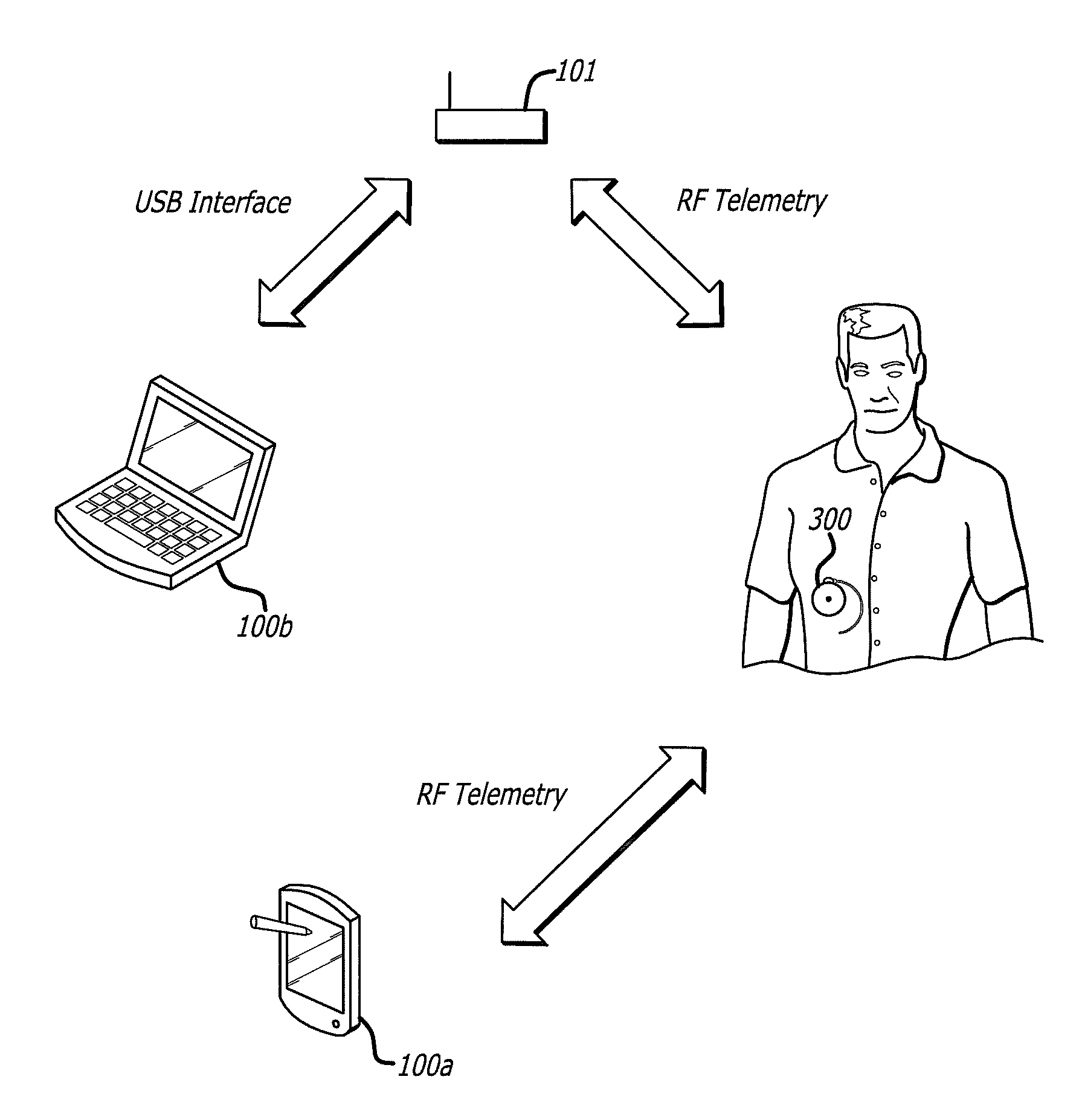
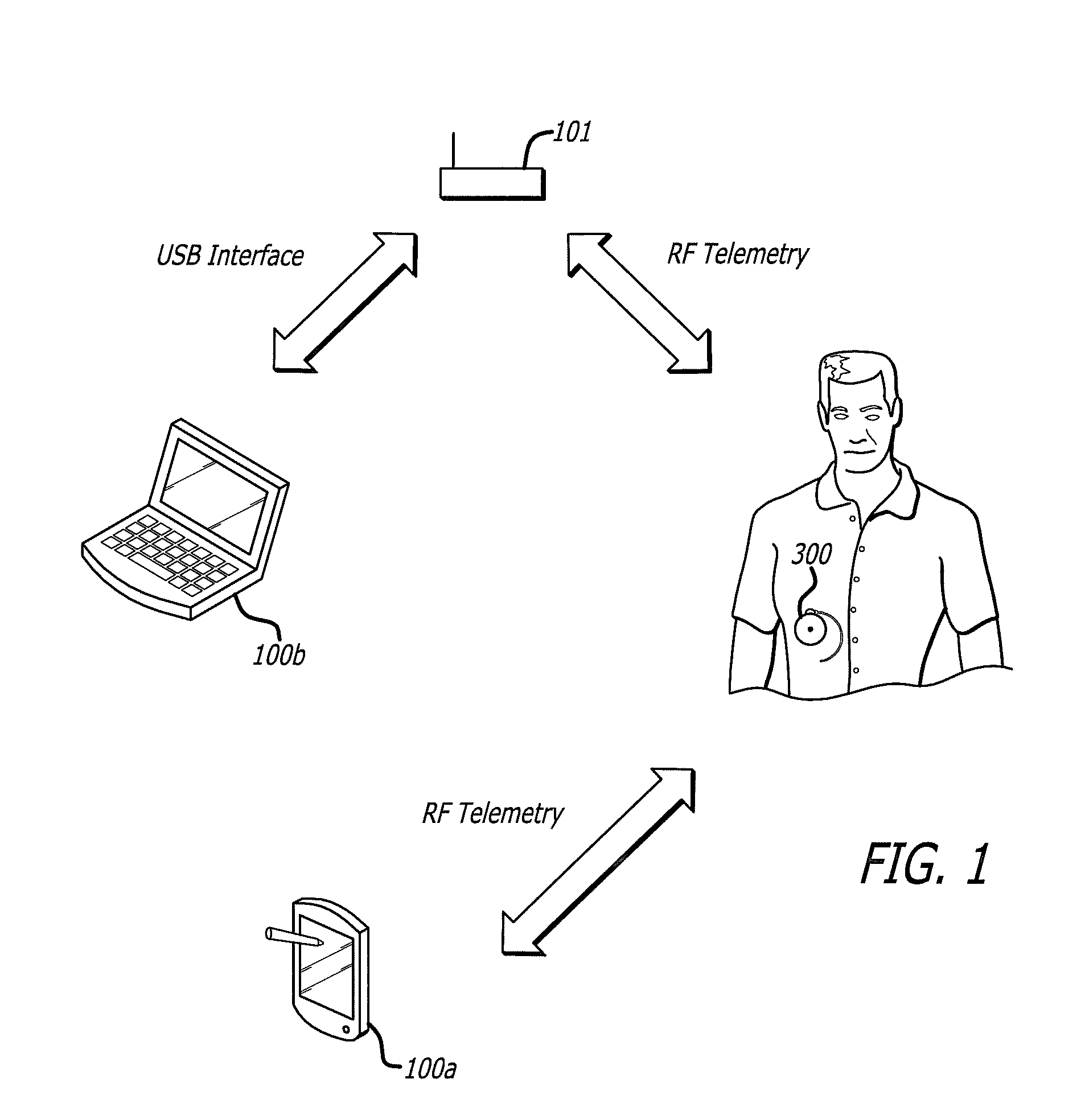
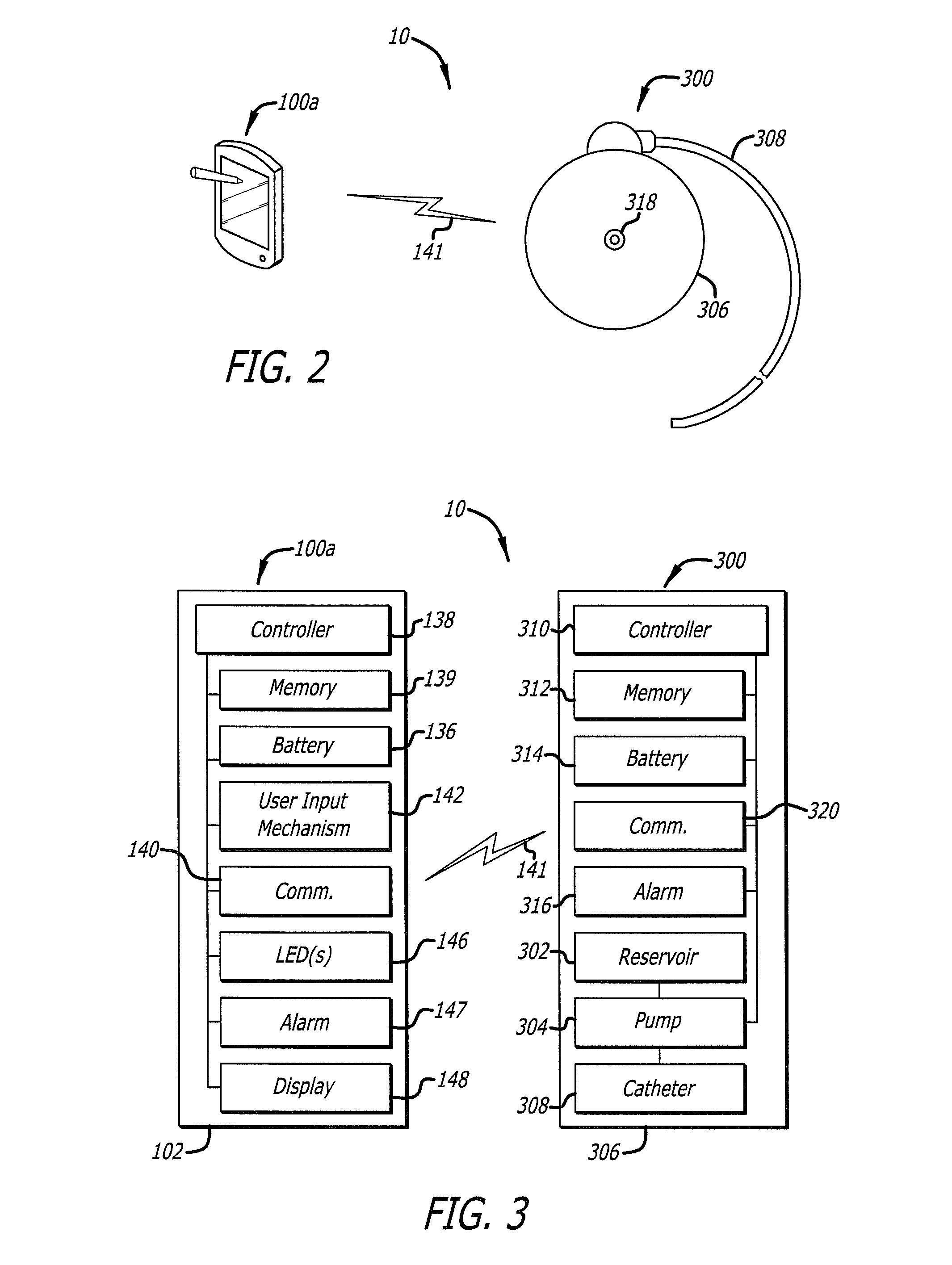
A drug delivery safety system includes a programmer with a display and a communications device adapted to communicate with an ambulatory medical device. The programmer has access to a database of information, and is adapted to receive and process the information and a user input and to control the display to provide a graphical user interface that prompts a user of the programmer to provide an additional user input when the user input requests a drug delivery protocol for the ambulatory medical device that is not already stored in the database as a clinician-approved drug delivery protocol.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
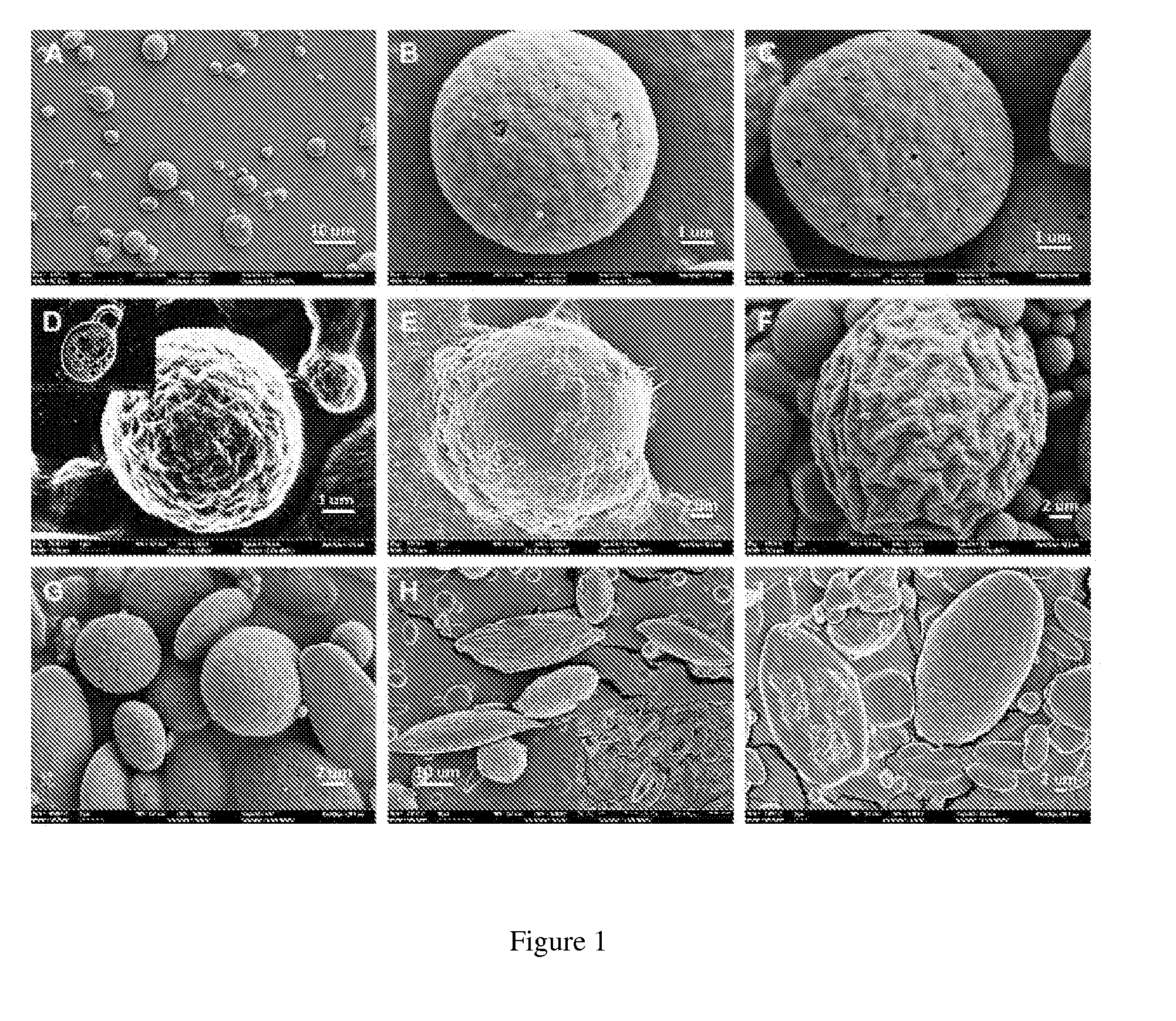
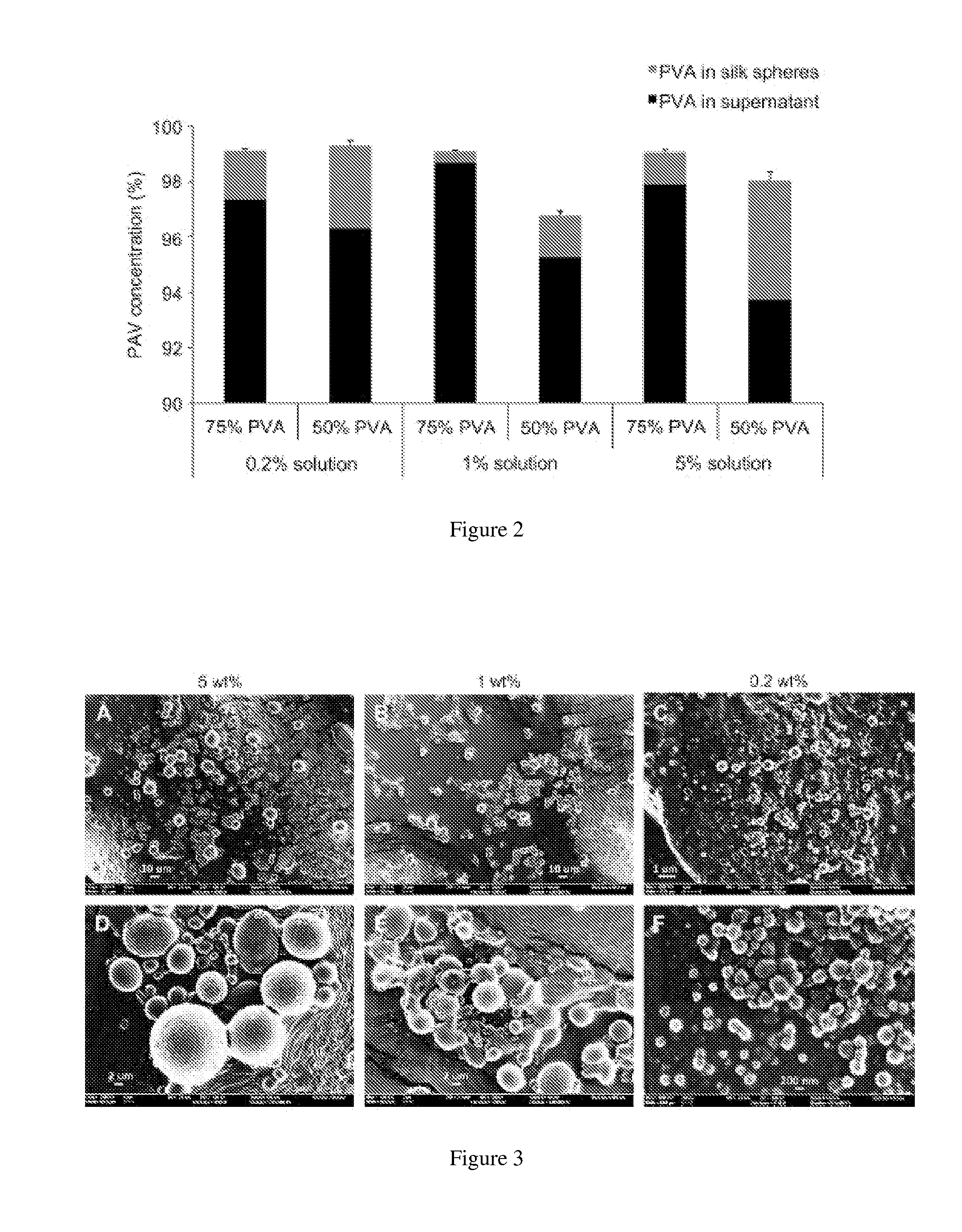
Silk nanospheres and microspheres and methods of making same
ActiveUS20120187591A1Organic active ingredientsMaterial nanotechnologyPolymer sciencePolyvinyl alcohol
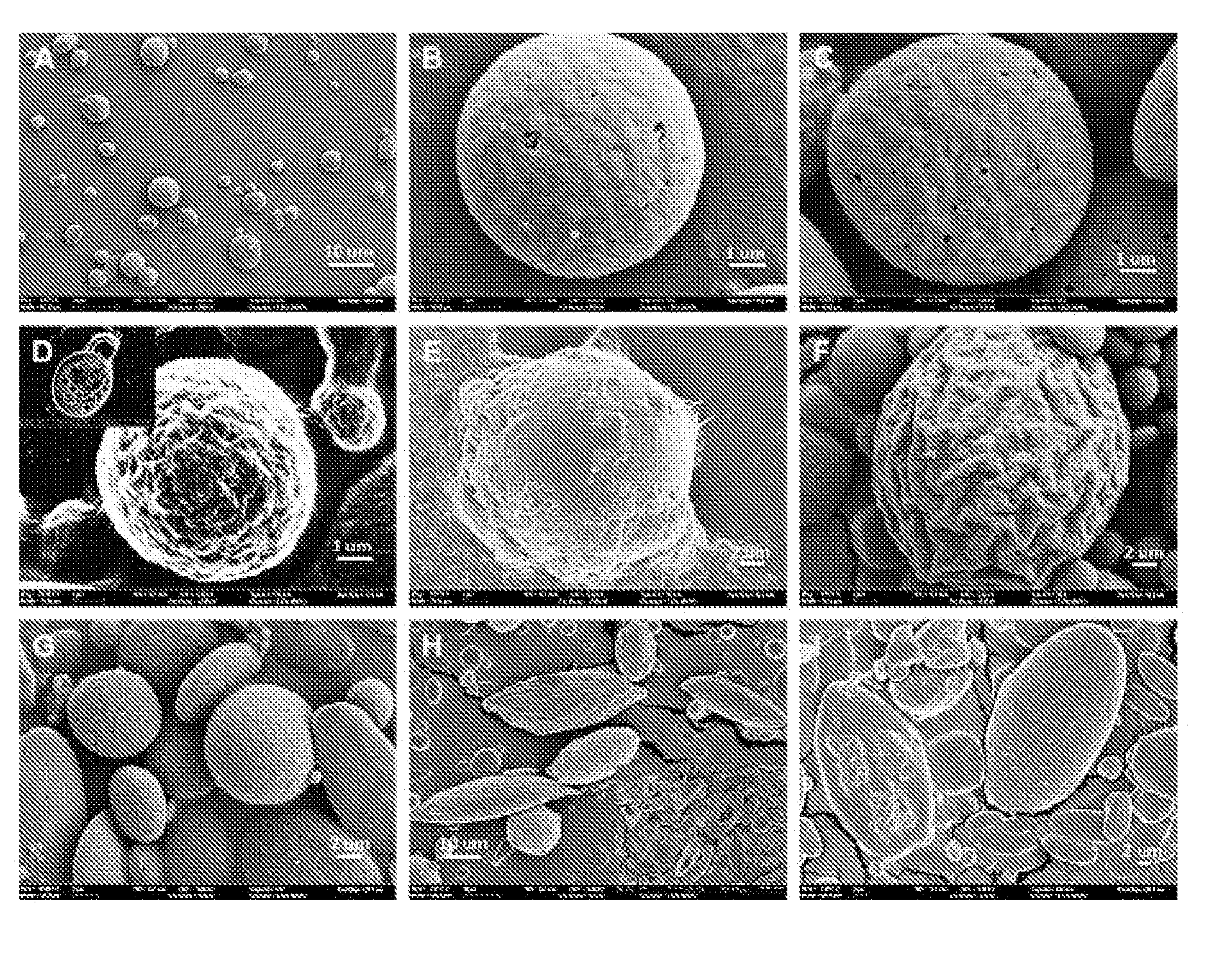
The present invention provides for methods of preparing silk nanoparticles and microparticles, methods of encapsulating an active agent into the silk nano- and microparticles and compositions comprising these silk particles. In particular, the silk spheres are prepared from phase separation of silk and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), without exposure to an organic solvent. The method employs a chemical, PVA, which is an FDA-approved ingredient in drug formulations. Different parameters can be adjusted to control the size and shape of the silk spheres during the fabrication process. The silk particle compositions of the present invention may also encapsulate active agents or chemicals. Such compositions allow the active agents to be controllably and sustainably released to the target organs or tissues. The silk composition entrapping active agents also provides for a long-term storage medium for the active agents so entrapped. The silk nano- and microparticles of the present invention are thus suitable for a variety of biomedical and pharmaceutical applications, such as drug delivery or tissue engineering.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGE TUFTS UNIV
Six membered heteroaromatic inhibitors targeting resistant kinase mutations
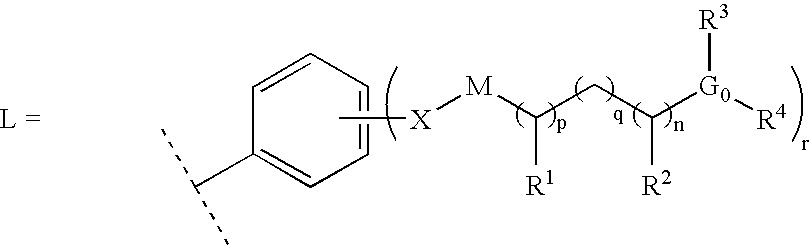
A compound is provided, having the general structure (A): wherein A is an (un)substituted aryl or (un)substituted heteroaryl moiety, G is N, CH, or CR, R is an unsubstituted or substituted lower alkyl, Y is a hydrophobic linking moiety, and L is a substitutent as defined. The compound (A) can be used for treatment of various angiogenic and hematological-associated disorders, such as myeloproliferative disorder in patients who do not respond to kinase-inhibition therapy that comprises administering approved medications.
Owner:TARGEGEN
Drug recommendation algorithm based on depth learning
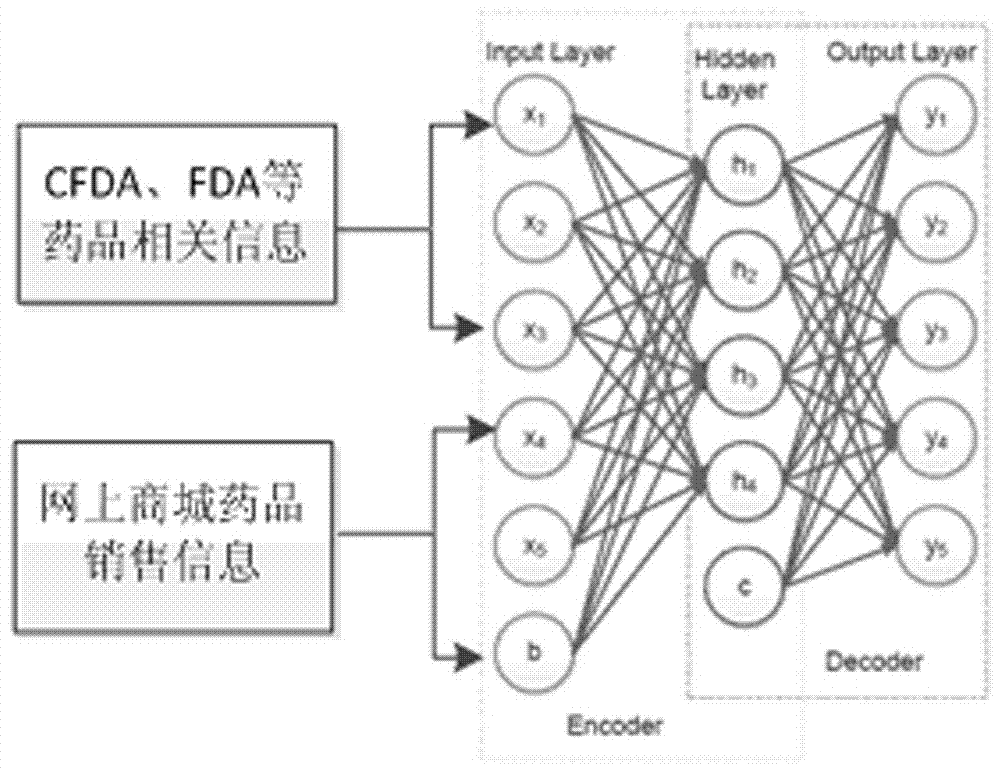
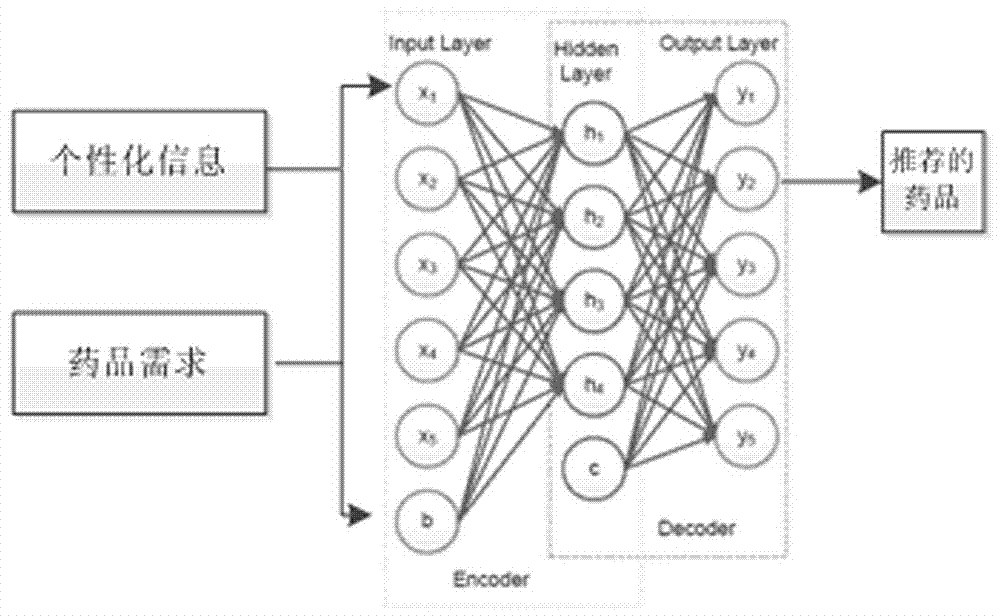
InactiveCN107092797AEfficient Online Drug PurchaseSolve the problem of lack of expert guidance on drug purchaseMedical automated diagnosisBuying/selling/leasing transactionsDiseasePersonalization
The present invention provides a drug recommendation algorithm based on depth learning. The present invention belongs to the field of computer software. a model of correspondence between drug effects and diseases is constructed in a framework of depth learning, and based on the mode, a personalized drug recommendation algorithm is proposed. The recommendation algorithm provided by the present invention comprises three parts: first, a drug-related information acquisition process, which comprises acquiring a name of an approved drug as well as a disease treated thereby, a side effect of the drug, precautions for use and other information from CFDA, and acquiring information such as sales data, user comments and price of the drug from an online drug mall; next, a depth learning feature training process, which comprises construction of a training network based on depth learning, a feature parameter training process, and output of drug classification information; and finally, individual recommendation, which comprises drug recommendation based on long-term personal health features and an implementation process thereof. The algorithm provided by the present invention better solves the problem that users lack instructions on drug purchasing from experts.
Owner:广东亿荣电子商务有限公司 +1
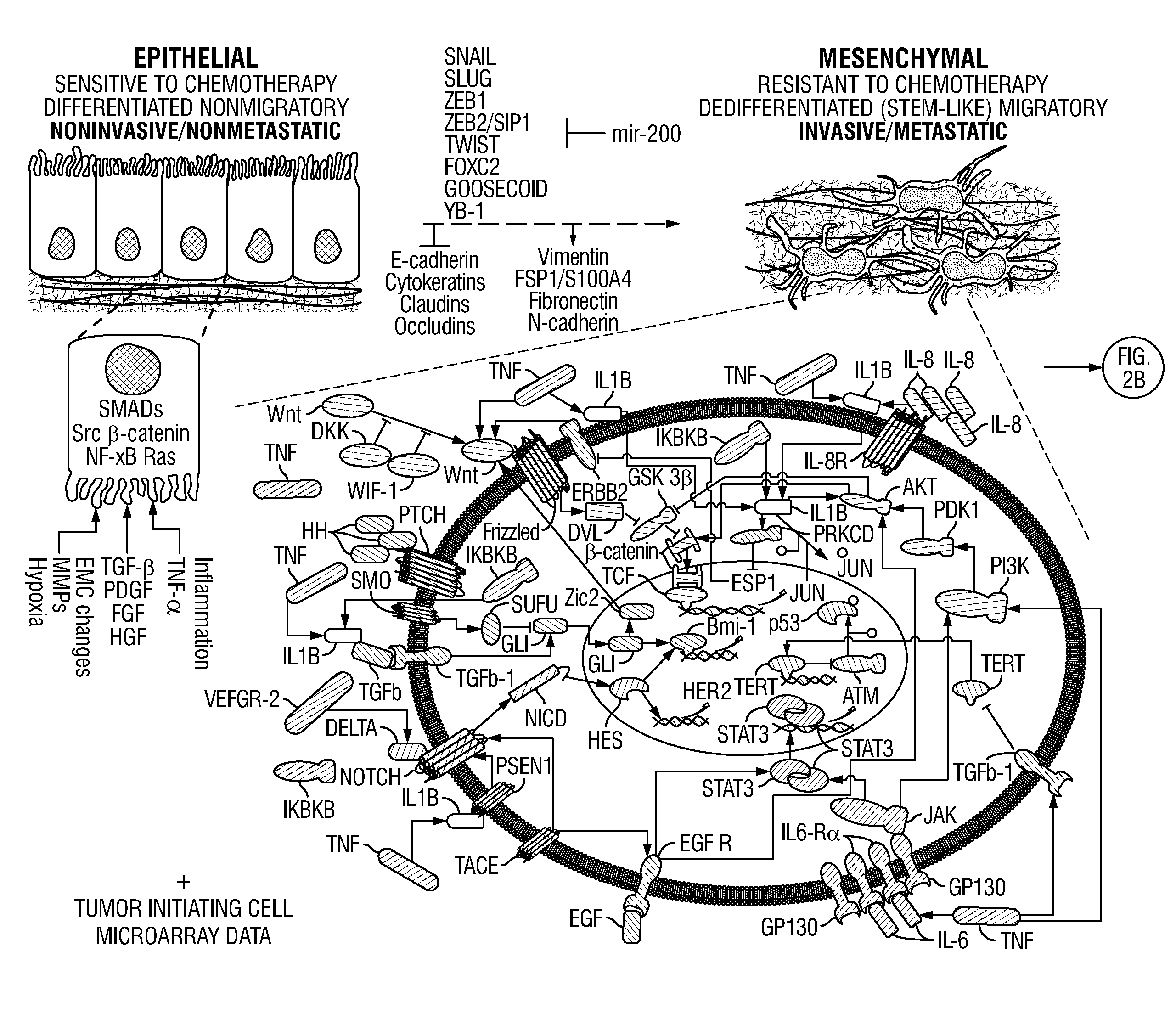
Drug Repositioning Methods For Targeting Breast Tumor Initiating Cells
InactiveUS20120296090A1Quick translationInhibit breast TICsMedical simulationOrganic chemistryOncologyPharmacology
Disclosed are systems biology-based methods for repositioning known pharmaceutical compounds to new indications, through the identification of network-based signatures. In particular, the invention provides new and useful methods for selecting drugs or combinations of drugs (and preferably previously-approved drugs) for use in new therapeutic indications. Also disclosed are methods for identifying anti-breast tumor initiating cell (TIC)-based therapeutics from within populations of target compounds. In illustrative embodiments, the invention provides methods and computer programs for the repositioning of FDA-approved pharmaceutical compounds to new indications using network-based signature analysis coupled with conventional in vitro and in vivo testing of identified drug candidates. The invention also allows identification of drugs or drug combinations for treating unmet medical needs including, for example, “orphan” diseases.
Owner:THE METHODIST HOSPITAL RES INST
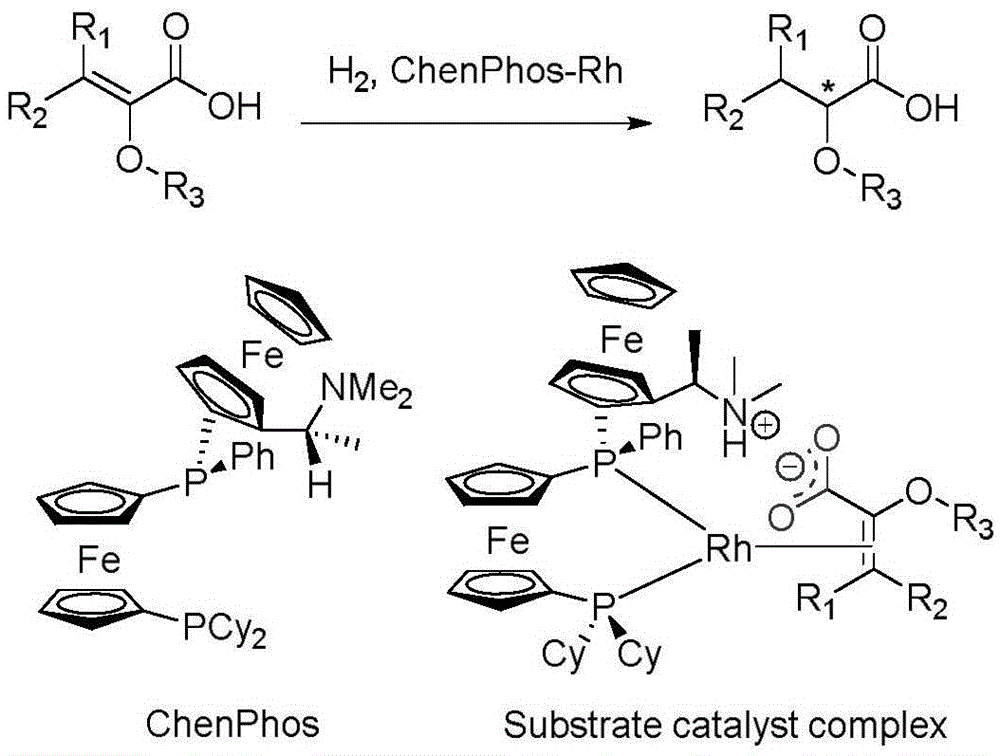
Asymmetric hydrogenation method of alpha-oxo-alpha, beta-unsaturated carboxylic acid
InactiveCN105481622AHigh catalytic activityHigh enantioselectivityOrganic reductionOrganic compound preparationEnkephalinase inhibitorAsymmetric hydrogenation
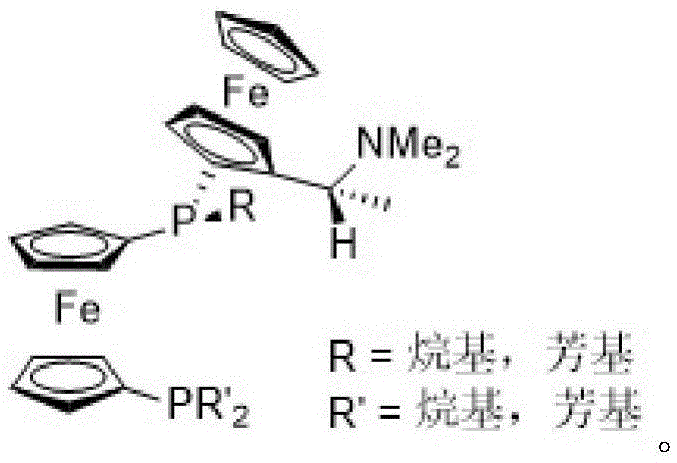
The invention relates to an asymmetric hydrogenation method of alpha-oxo-alpha, beta-unsaturated carboxylic acid. A metal complex containing ChenPhos chiral ligand is a catalyst high in conversion efficiency, and particularly, the catalyst can be used for synthesizing a core framework in enkephalinase inhibitor Sacubitril through asymmetric hydrogenation. The inhibitor is one of components of medicine LCZ 696 approved by American Food and Drug Administration. The asymmetric hydrogenation method of the alpha-oxo-alpha, beta-unsaturated carboxylic acid is efficient, and the application range of substrate is wide.
Owner:WUHAN CATALYS TECH CO LTD
Rare cell isolation device and method of use thereof
ActiveUS20180106805A1Faster cell captureQuick snapComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementPopulation sampleLymphatic Spread
This invention concerns patentable devices configured to capture cancer stem cells and cell clusters. After capturing such cells and / or clusters, the cancerous cells are subjected to whole genome sequencing. The resulting genomic sequence information is then compared to that for “normal” or non-diseased tissue (obtained, for example, from either the same patient, or a population sample, etc.) in order to identify the specific genetic mutation(s) present in the CSCs. Further analysis then correlates the genetic mutations with cell growth signaling pathways typically found with tumor metastases. Armed with this information, an oncologist can then develop a specifically targeted therapy that utilizes approved drugs or drug candidates undergoing clinical testing to address the identified driver mutations and thus effect a “targeted” therapy tailored to the particular patient's disease.
Owner:TUMORGEN INC
Techniques for Purposing a New Compound and for Re-Purposing a Drug
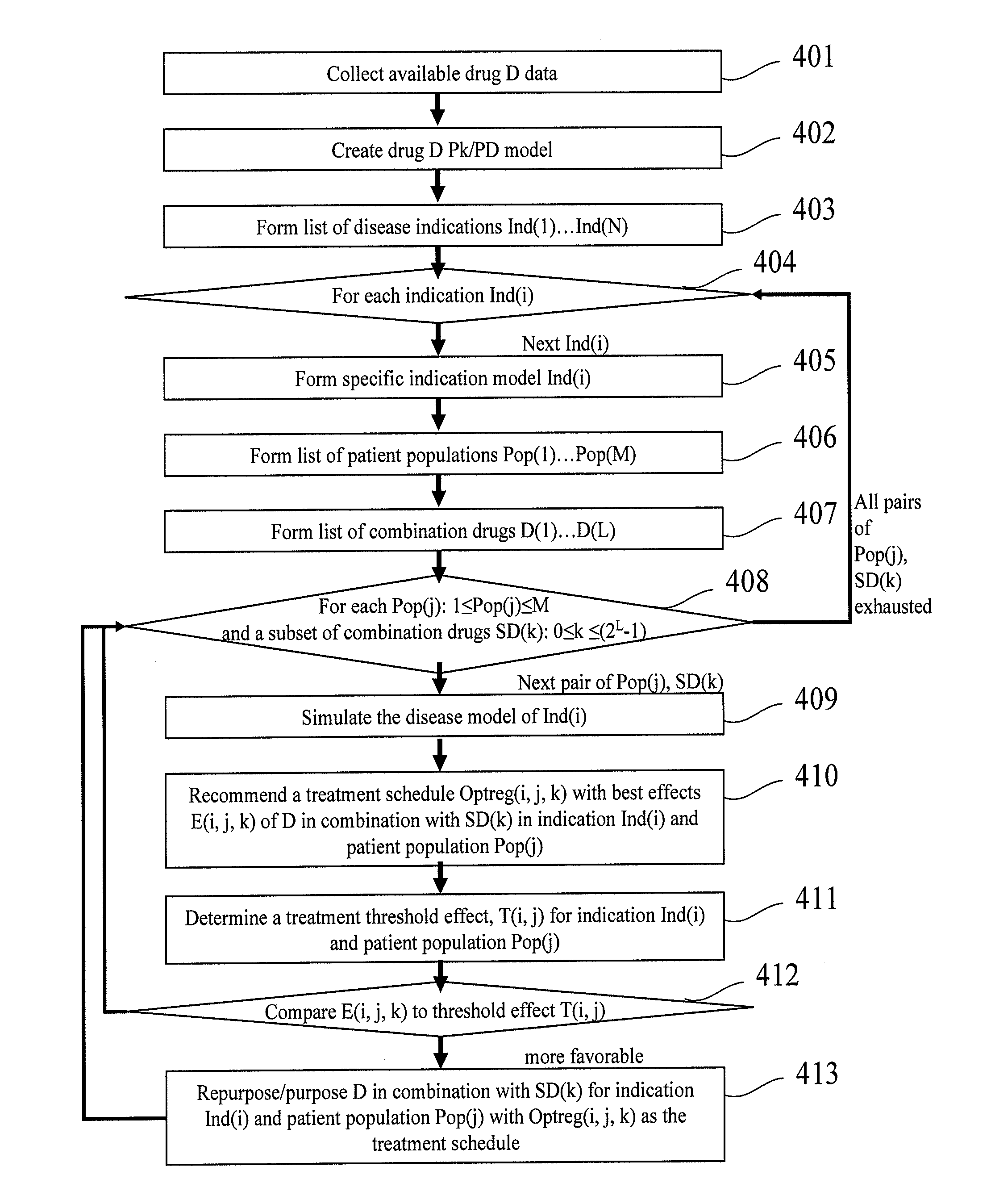
InactiveUS20100161301A1Reduce drug toxicityImprove efficacyChemical property predictionAnalogue computers for chemical processesTrial drugMathematical model
A method for repurposing a pharmaceutical compound. The method includes identifying a pharmaceutical compound, the pharmaceutical compound corresponding to a drug that has failed in clinical development or an approved drug. A mathematical model describing the physiological processes related to at least one disease and the effects of the pharmaceutical compound on the disease is created. The model is adjusted based upon information from preclinical or clinical trials. A new treatment protocol is suggested to salvage the failed drug or a new way to use an approved drug. The suggested treatment protocol is displayed. Systems and computer program products encompassing the above techniques are also disclosed.
Owner:OPTIMATA
Method for high-throughput screening of compounds and combinations of compounds for discovery and quantification of actions, particularly unanticipated therapeutic or toxic actions, in biological systems
InactiveUS20110195865A1Compounds screening/testingMicrobiological testing/measurementLiving systemsIsotopic labeling
The invention enables high-throughput screening of compounds in living systems to detect unanticipated or unintended biological actions. The invention also allows for screening, detection, and confirmation of new indications for approved drugs. Screening and detection of toxic effects of compounds also can be achieved by using the methods of the invention. The methods comprise administering isotope-labeled substrates to a living system so that the label is incorporated into molecules in a manner that reveals flux rates through metabolic pathways thought to be involved in a disease. Comparisons between living systems exposed to compounds and living systems not so exposed reveals the effects of the compounds on the flux rates through the metabolic pathways. Combinations or mixtures of compounds can be systematically screened to detect unanticipated or unintended biological actions, including synergistic actions, in the same manner.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
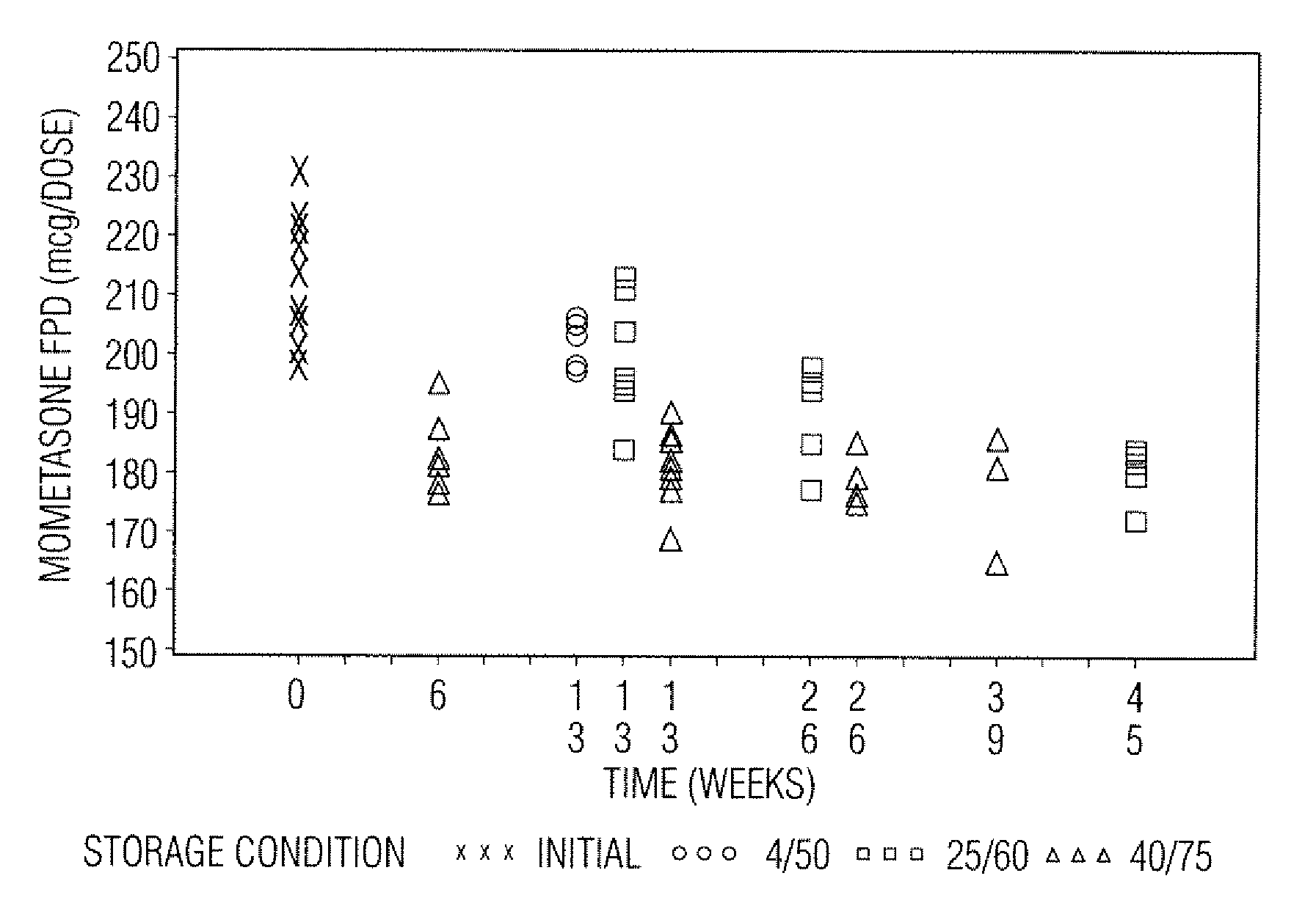
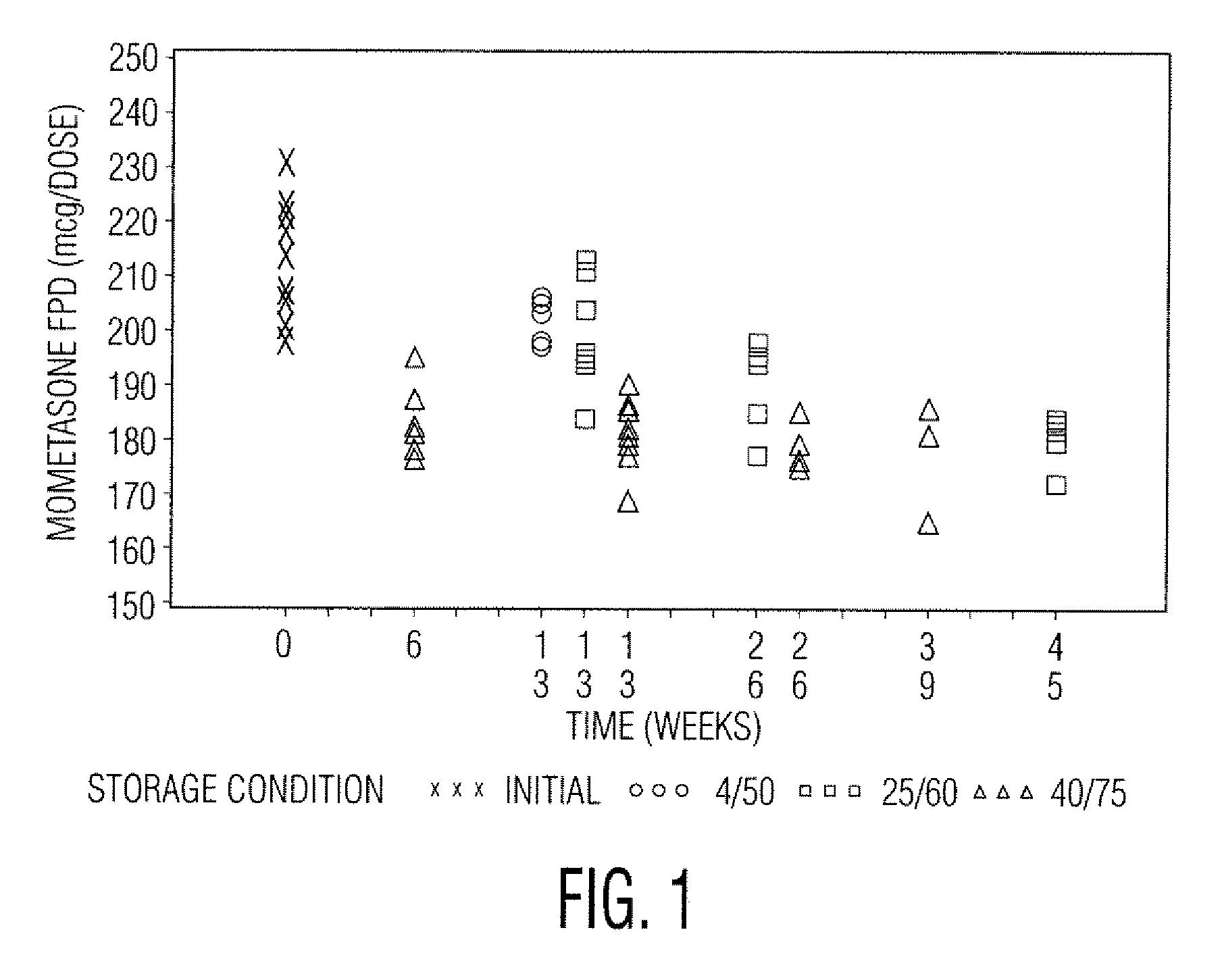
Stable pharmaceutical drug aerosols
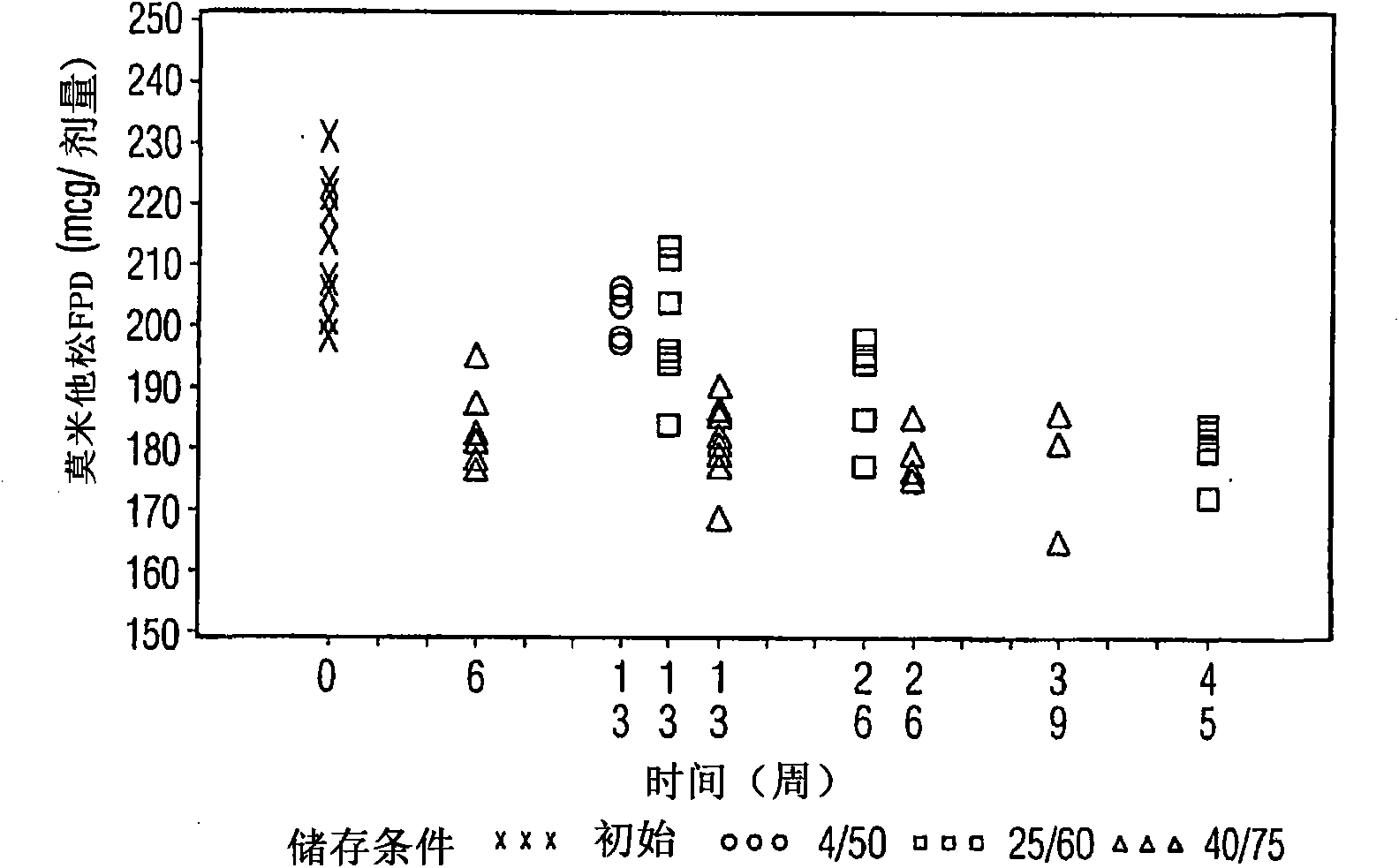
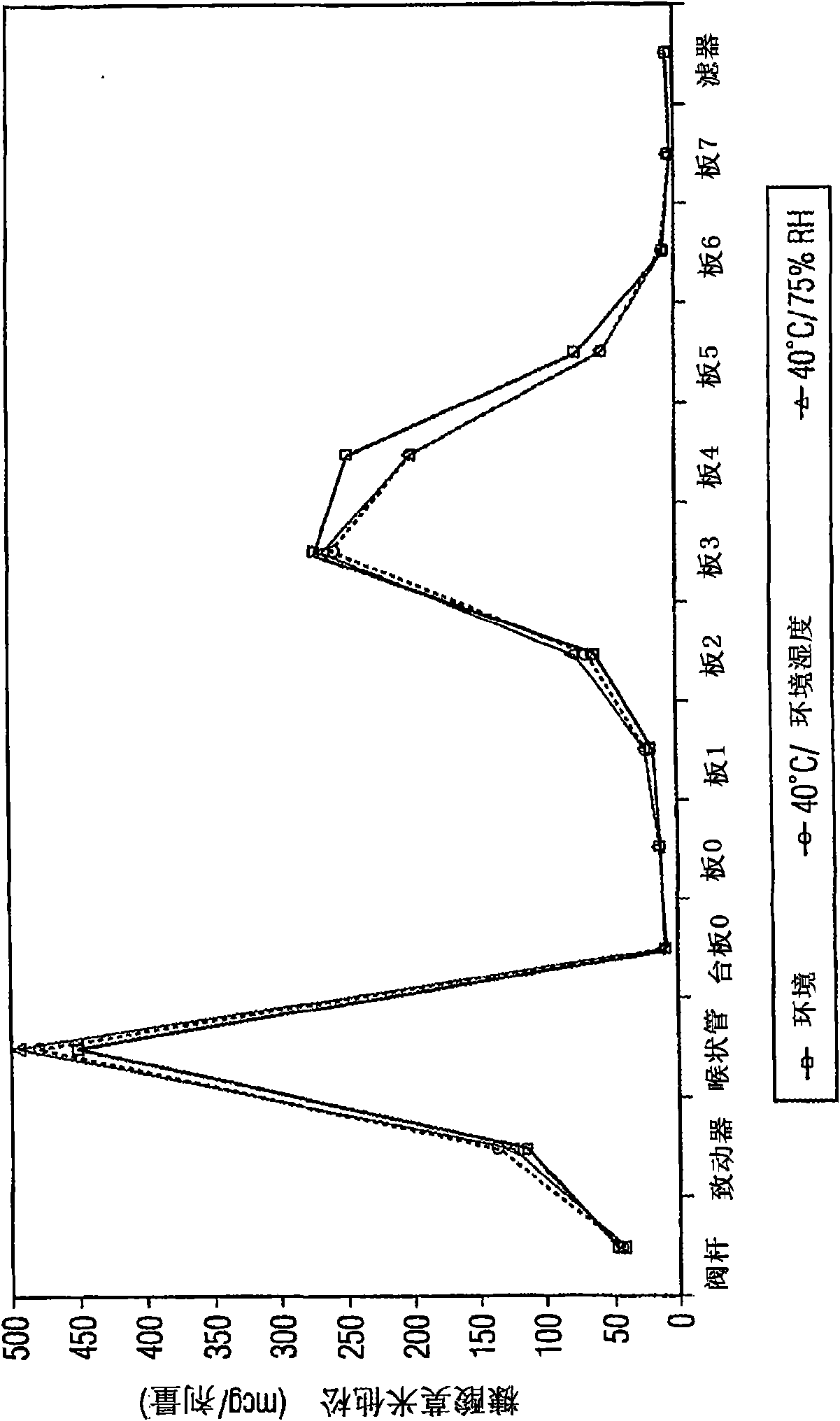
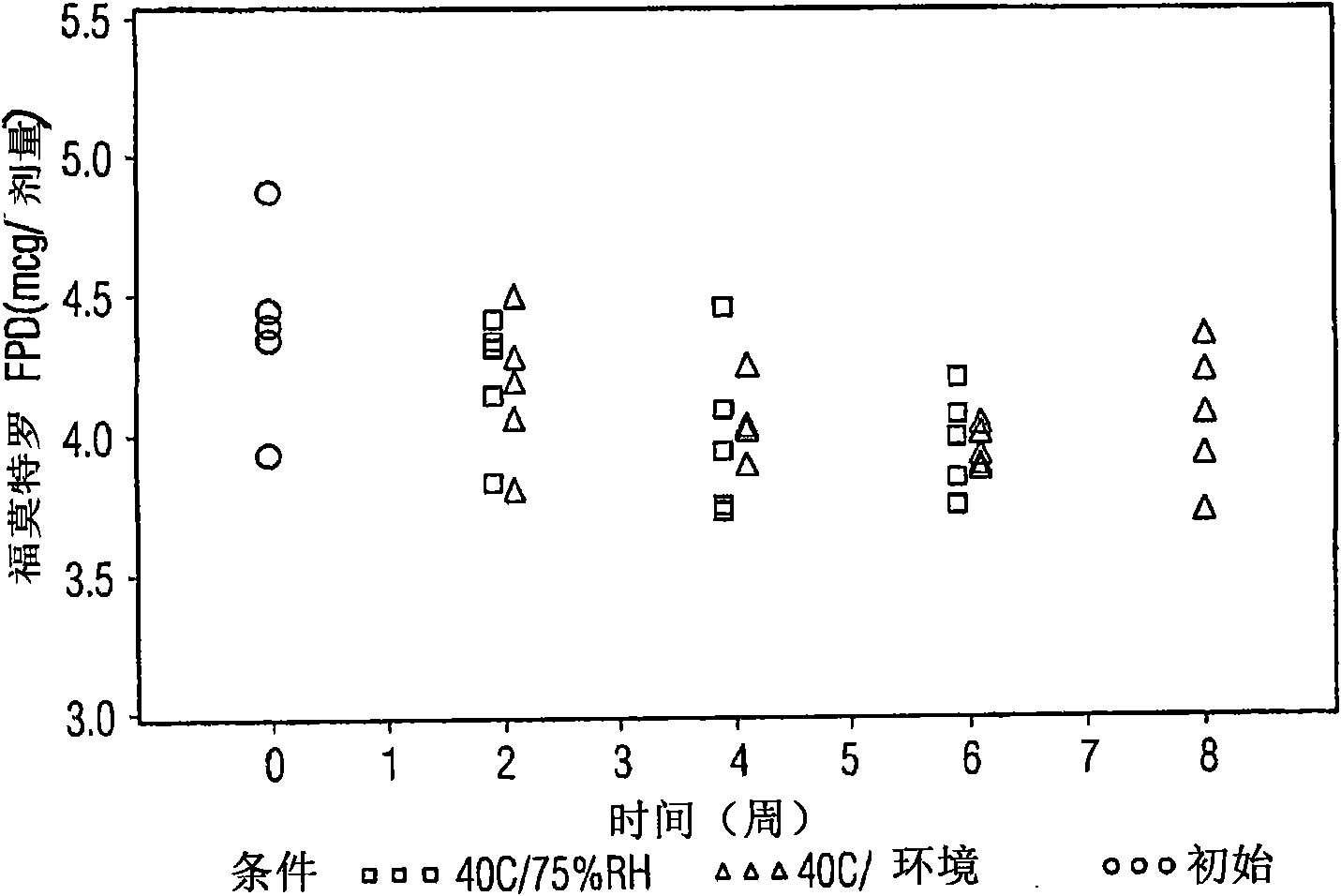
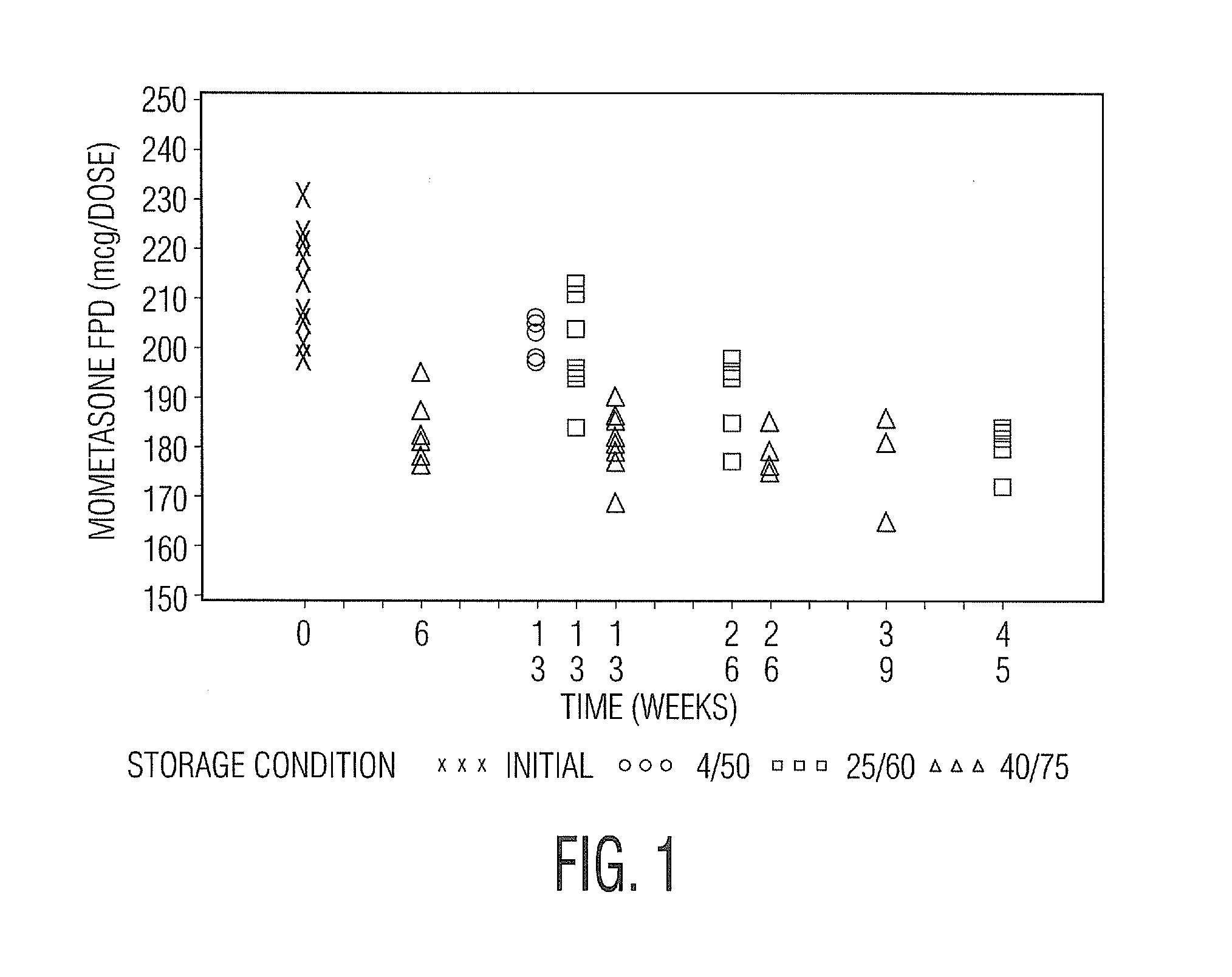
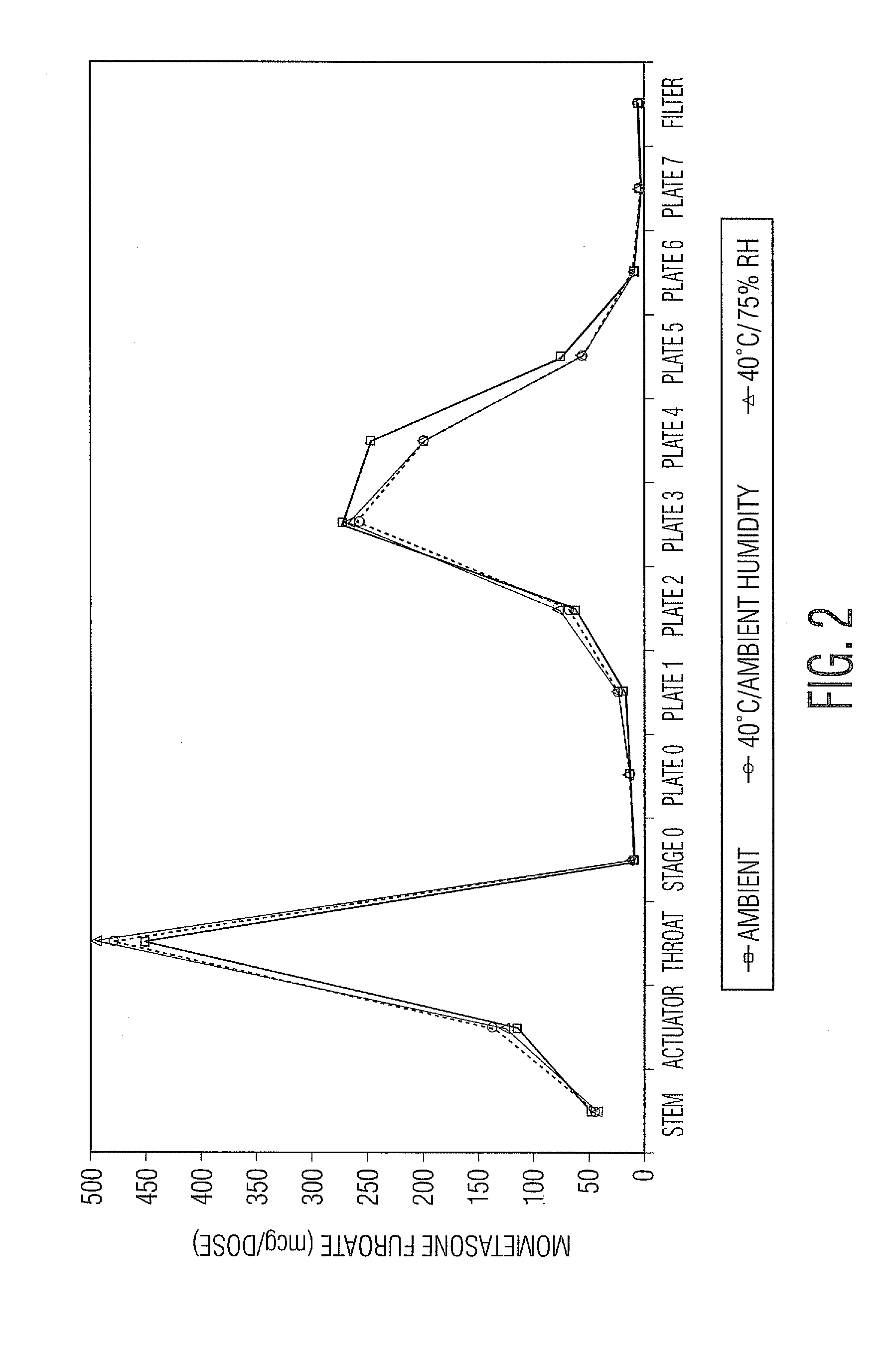
Various aspects of the present invention provide for methods of manufacturing a pharmaceutical drug product, which include storing a container at a temperature greater than ambient conditions for at least about seven days and conducting release testing on the container after storing. Products manufactured by this method have a more consistent fine particle size distribution (FSD) and fine particlefraction (FPF) at ambient conditions and at accelerated stability conditions over the life of the drug product. Advantageously, such products may more reliably and regularly pass testing requirementsas required for an approved drug product by regulatory authorities such as the United States Food and Drug Administration (USFDA).
Owner:SCHERING AG
Method for high-throughput screening of compounds and combinations of compounds for discovery and quantification of actions, particularly unanticipated therapeutic or toxic actions, in biological systems
The invention enables high-throughput screening of compounds in living systems to detect unanticipated or unintended biological actions. The invention also allows for screening, detection, and confirmation of new indications for approved drugs. Screening and detection of toxic effects of compounds also can be achieved by using the methods of the invention. The methods comprise administering isotope-labeled substrates to a living system so that the label is incorporated into molecules in a manner that reveals flux rates through metabolic pathways thought to be involved in a disease. Comparisons between living systems exposed to compounds and living systems not so exposed reveals the effects of the compounds on the flux rates through the metabolic pathways. Combinations or mixtures of compounds can be systematically screened to detect unanticipated or unintended biological actions, including synergistic actions, in the same manner.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
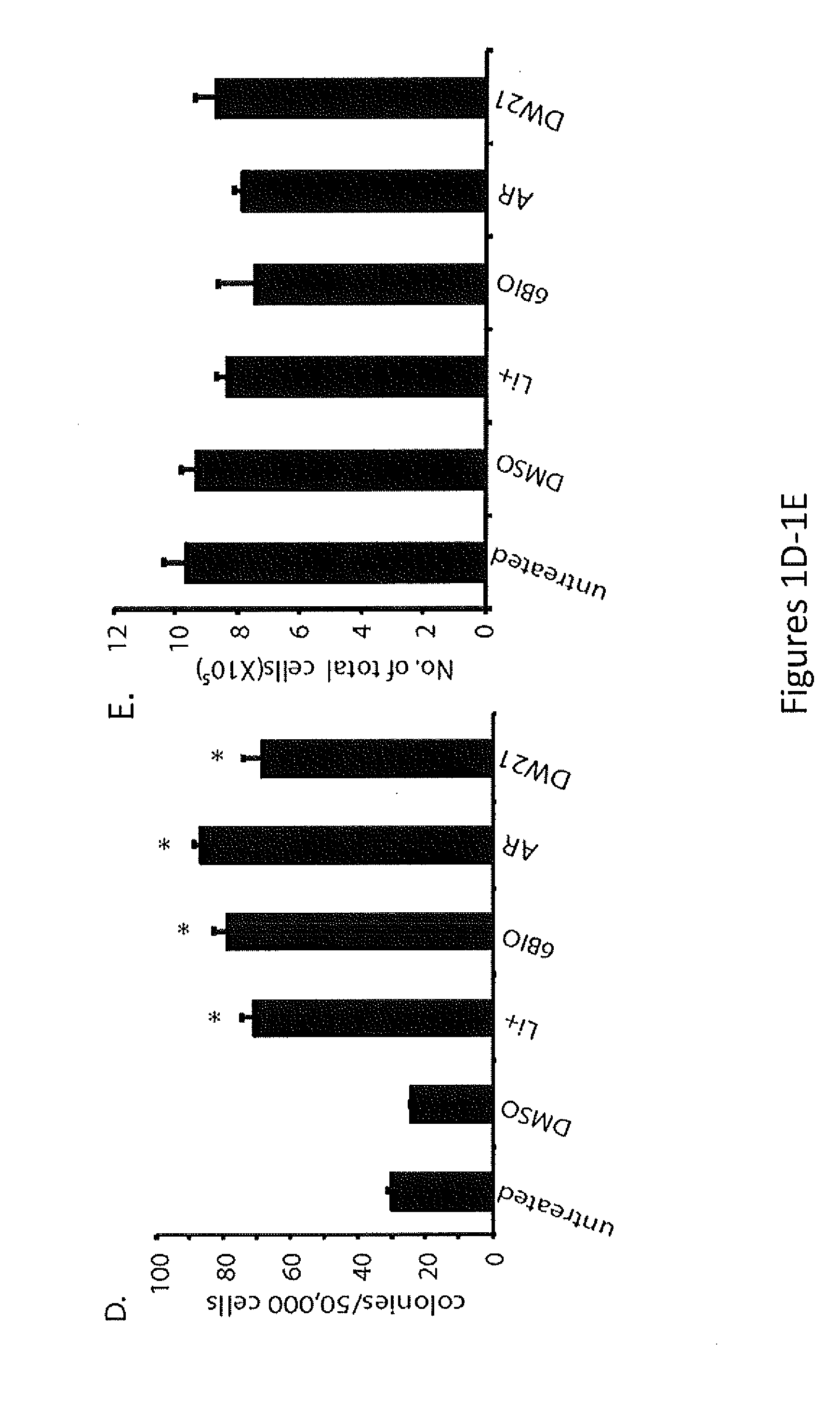
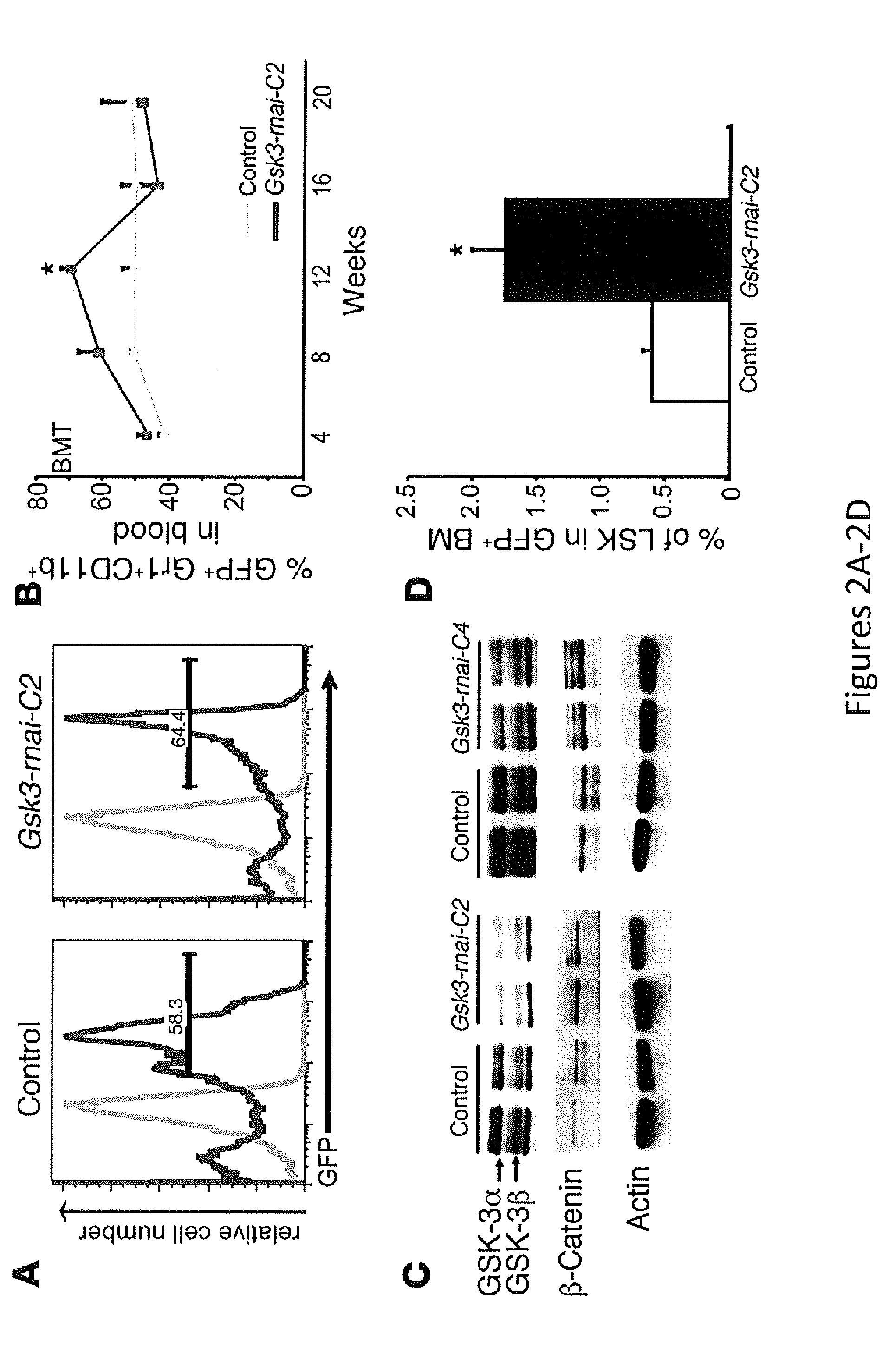
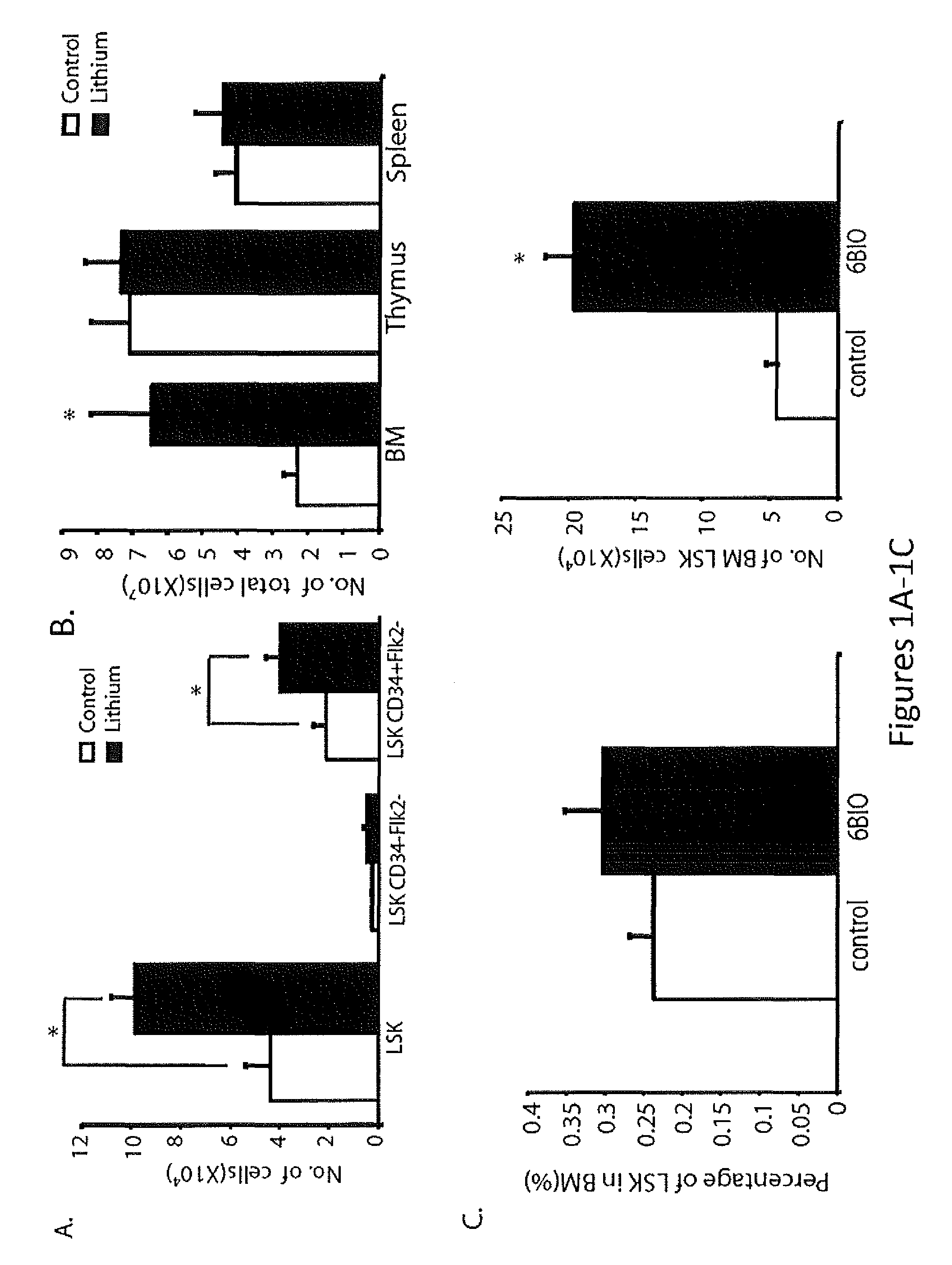
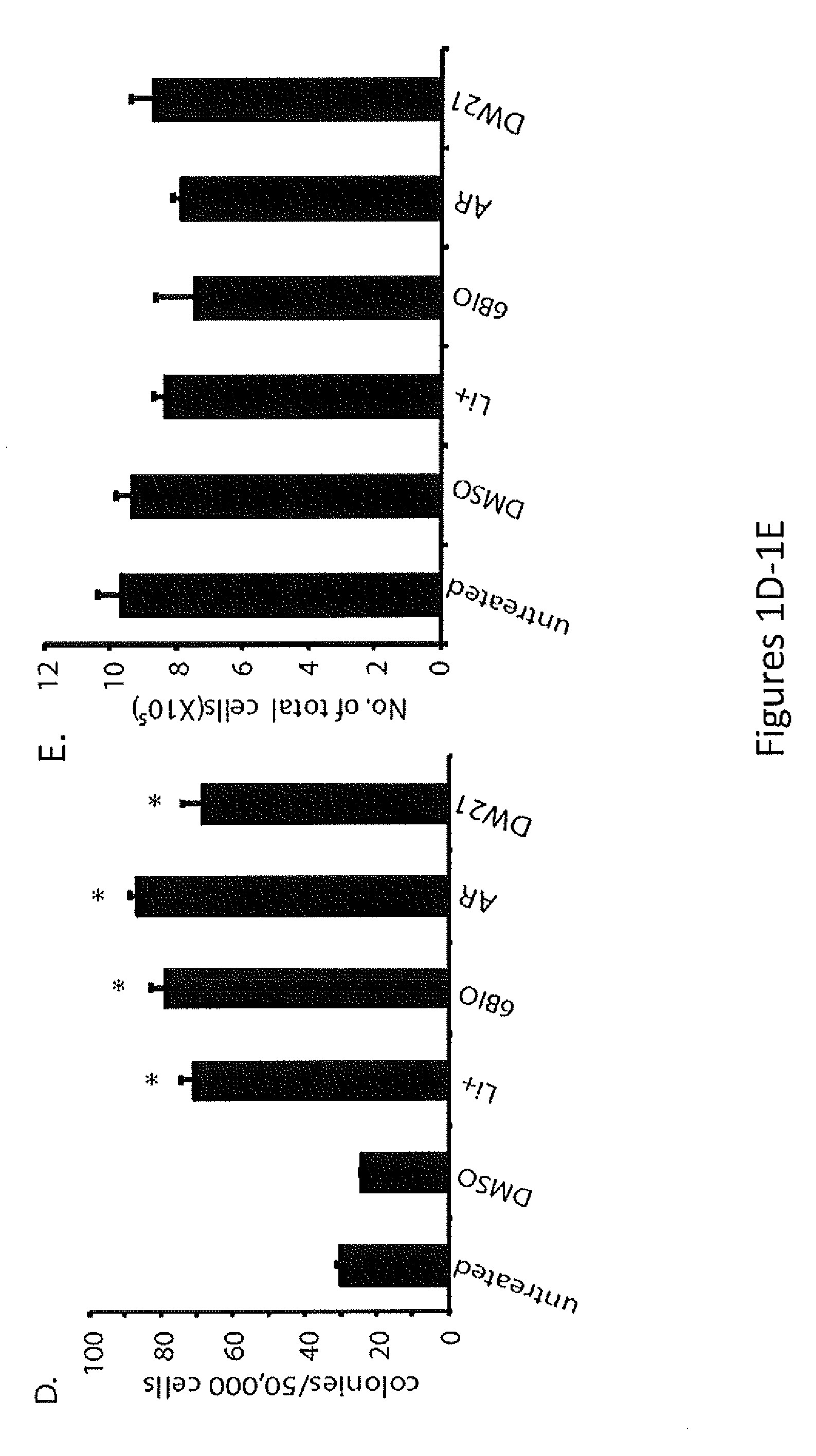
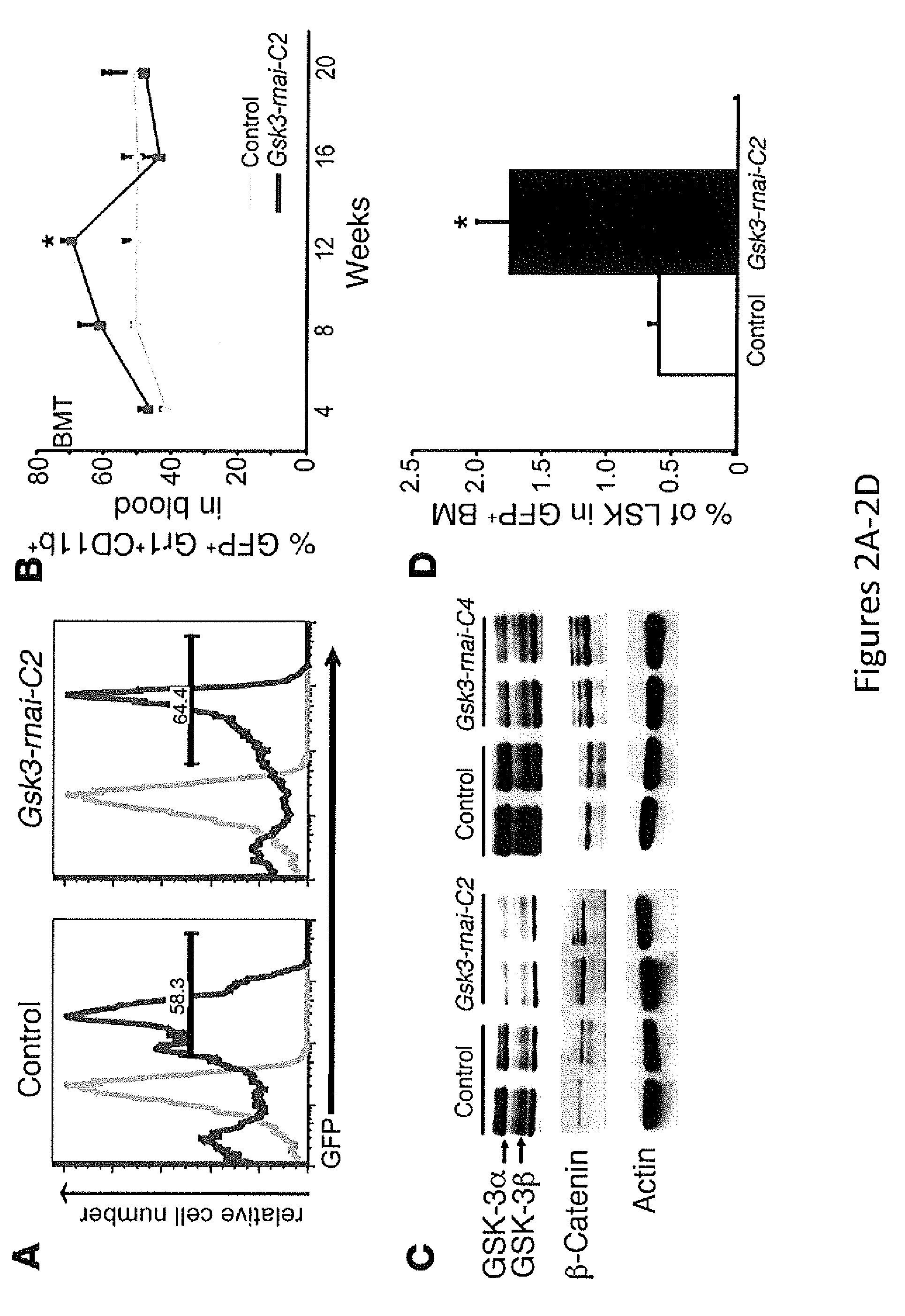
In Vivo and Ex Vivo Expansion of Hematopoietic Stem Cells With a Targeted Combination of Clinically Tested, FDA Approved Drugs
The present invention provides a therapeutic approach to maintain and expand HSCs in vivo using currently available medications that target GSK-3 and mTOR. The present invention also provides a system and method for the ex vivo culturing of HSCs, where an mTOR inhibitor is combined with a GSK-3 inhibitor within the culturing conditions.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Stable Pharmaceutical Drug Products
InactiveUS20080253970A1Avoid security issuesAvoid efficacy concernDispersion deliveryAerosol deliveryRegulatory authorityApproved drug
Various aspects of the present invention provide for methods of manufacturing a pharmaceutical drug product, which include storing a container at a temperature greater than ambient conditions for at least about seven days and conducting release testing on the container after storing. Products manufactured by this method have a more consistent fine particle size distribution (FSD) and fine particle fraction (FPF) at ambient conditions and at accelerated stability conditions over the life of the drug product. Advantageously, such products may more reliably and regularly pass testing requirements as required for an approved drug product by regulatory authorities such as the United States Food and Drug Administration (USFDA).
Owner:SCHERING CORP
Method for treating a protozoal infection
InactiveUS20160354370A1Good for healthPatient benefitPeptide/protein ingredientsKetone active ingredientsSide effectKidney
Patients inflicted with various clustering chronic diseases require treatment with multiple drugs having distinct mechanisms of action. Accordingly, patients with multiple conditions suffer from cumulative side effects of multiple drugs as well as drug-drug interactions. Embodiments, agents, compounds or drugs of the present invention, such as sesquiterpenes, e.g., Zerumbone, replace an equal or larger number of approved drugs during patient treatment. Examples of disorders prevented or ameliorated by administration of the formulations of this invention include but are not limited to inflammatory diseases that may be, oncological, genetic, ischemic, infectious, neurological, hematological, ophthalmological, rheumatoid, orthopedic, neurological, hematological, kidney, vascular, dermatological, gynecological, or obstetric. The present invention further relates to a method of identifying agents, compounds or drugs useful in preventing or treating CDCP related diseases and conditions as well as other disorders, diseases and conditions treatable or preventable by the same agents, compounds or drugs.
Owner:REID CHRISTOPHER BRIAN
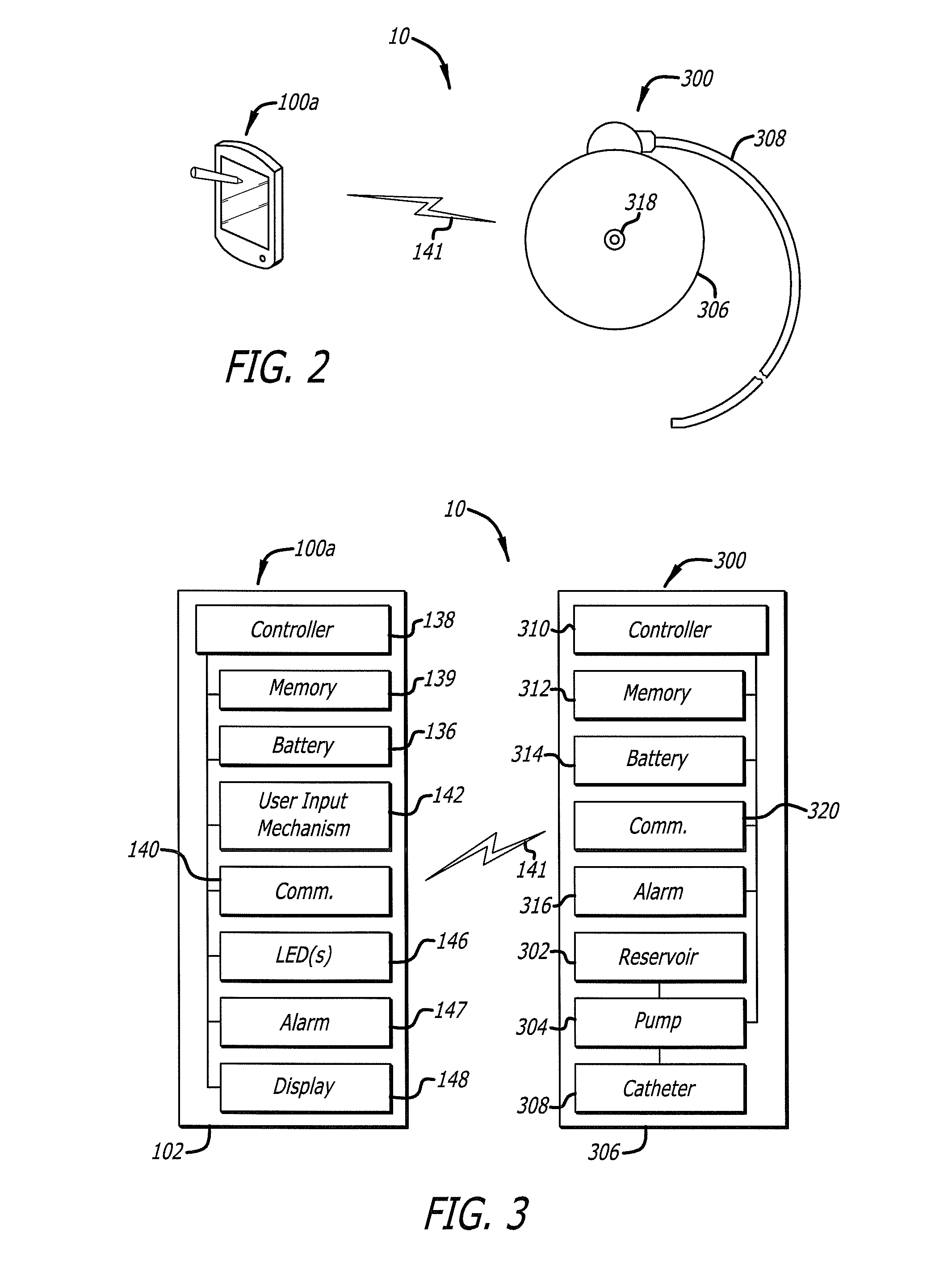
Drug delivery safety system
ActiveUS8683381B2Drug and medicationsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismGraphicsGraphical user interface
A drug delivery safety system includes a programmer with a display and a communications device adapted to communicate with an ambulatory medical device. The programmer has access to a database of information, and is adapted to receive and process the information and a user input and to control the display to provide a graphical user interface that prompts a user of the programmer to provide an additional user input when the user input requests a drug delivery protocol for the ambulatory medical device that is not already stored in the database as a clinician-approved drug delivery protocol.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
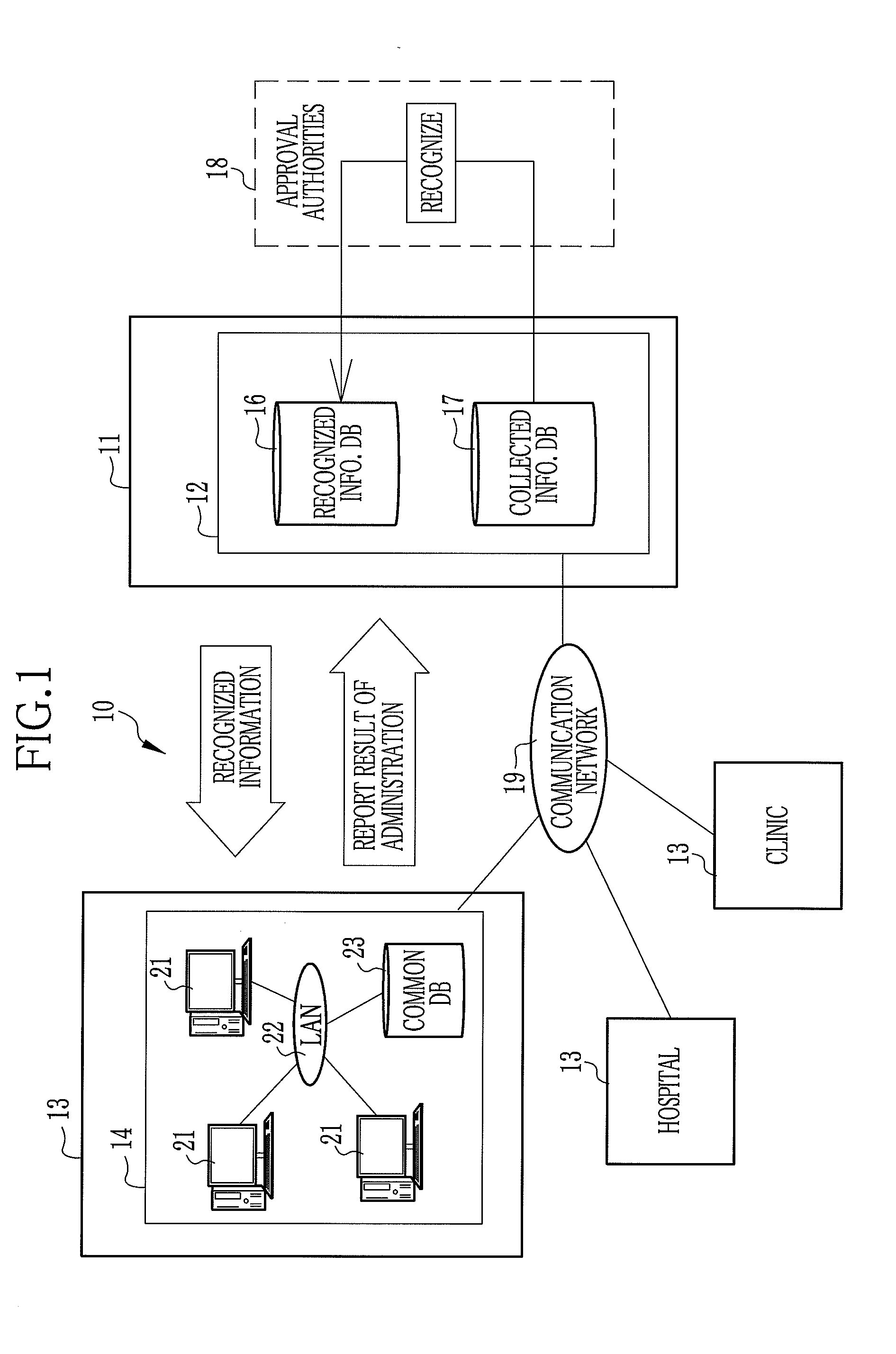
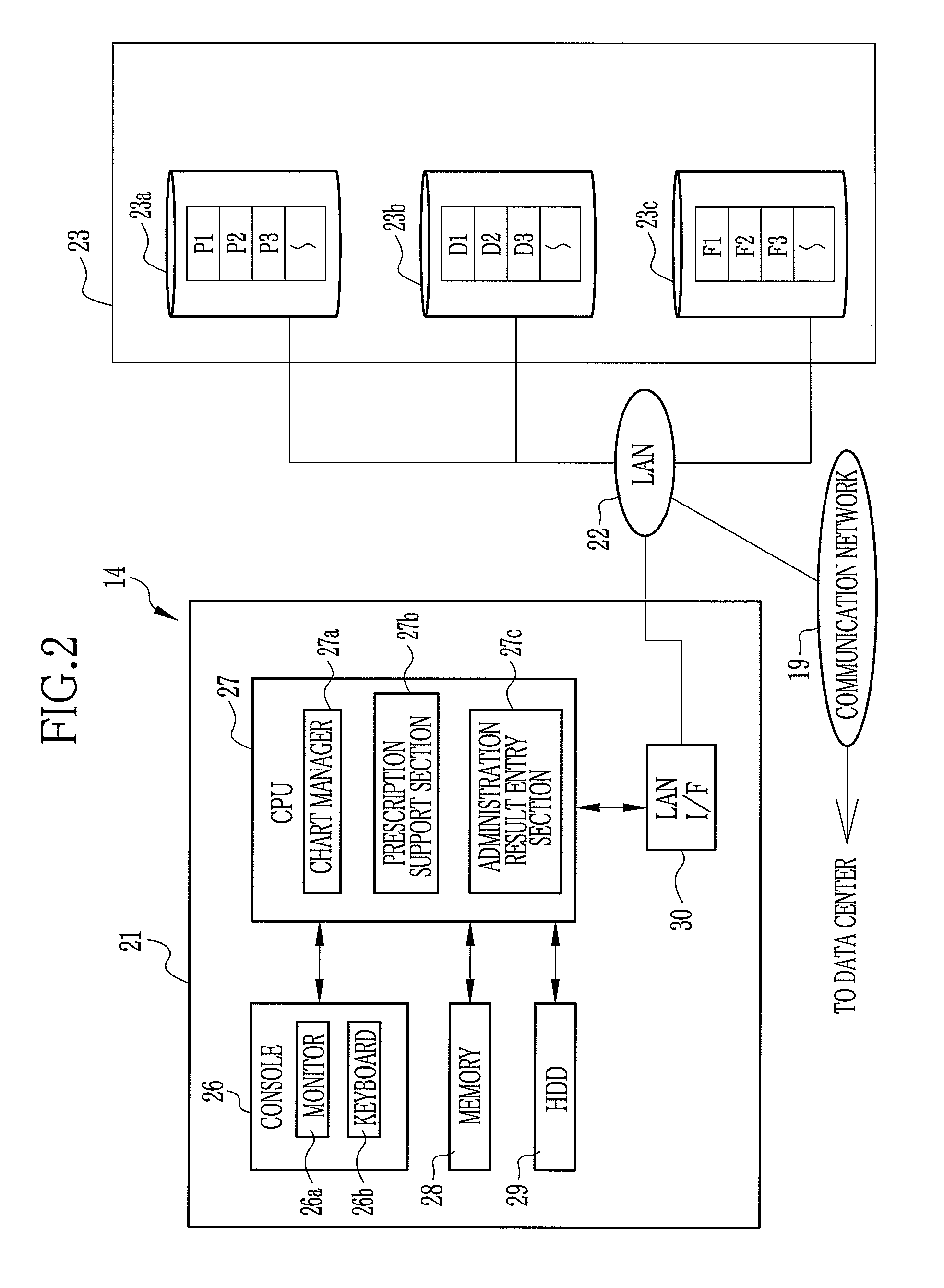
Drug information collecting network system and electronic chart apparatus
InactiveUS20080243552A1Efficient collectionEasily and swiftly collectData processing applicationsDrug and medicationsMedication informationData center
An electronic chart system consists of terminal apparatuses and a common database. The common database is provided with a chart data storage storing chart data of individual patients, a drug information storage storing recognized information on approved drugs and an administration result storage storing information on such results from administration of some drugs that were unexpected when the drugs were approved. The terminal apparatus is provided with an administration result entry section for entering the unexpected results of administration. As the unexpected administration result is entered, the administration result entry section records it in the administration result storage in association with chart data of the patients who get the unexpected results, and also sends the unexpected result together with the chart data to a data center.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
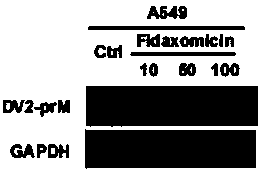
Application of fidaxomicin in preparing medicines for treating related diseases and/or symptoms caused by dengue virus infection
ActiveCN107929300AImprove securityHigh activityOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsDiseaseClostridium difficile infections
The invention discloses an application of fidaxomicin in preparing medicines for treating related diseases and / or symptoms caused by dengue virus infection. The fidaxomicin, as a clinically approved drug for resisting clostridium difficile infection, is high in safety; and in addition, the fidaxomicin, which is high in activity of inhibiting the dengue virus infection and relatively strong in binding capacity with dengue virus non-structural protein NS5, is expected to function as a novel drug for resisting the dengue virus infection.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
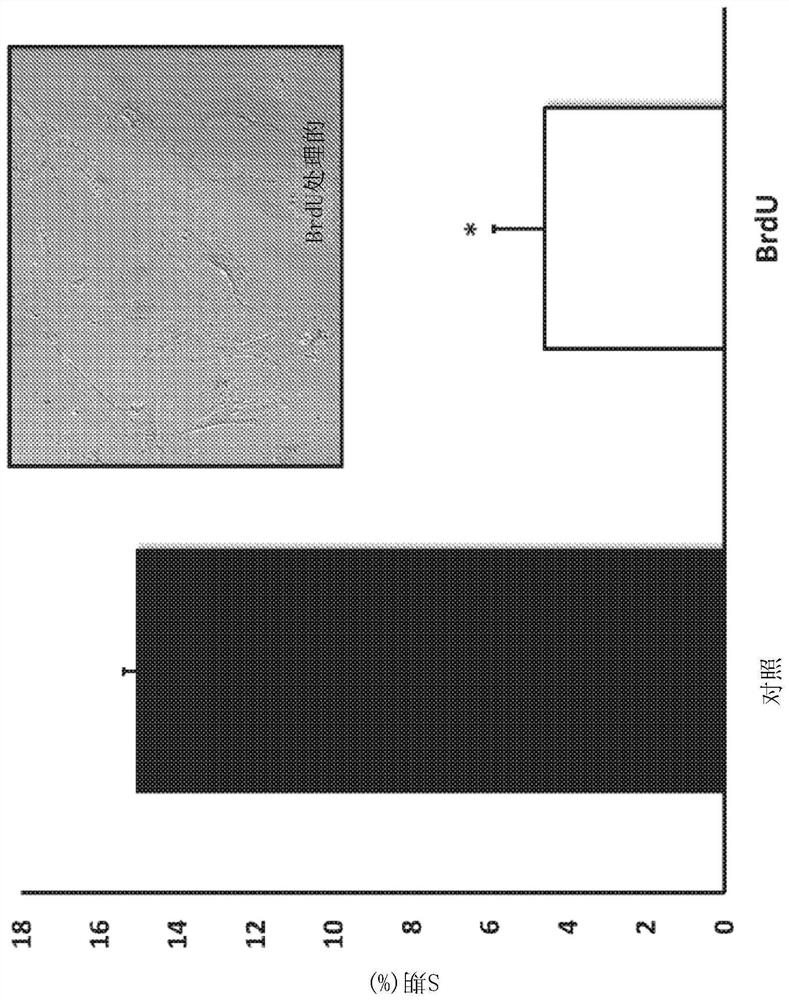
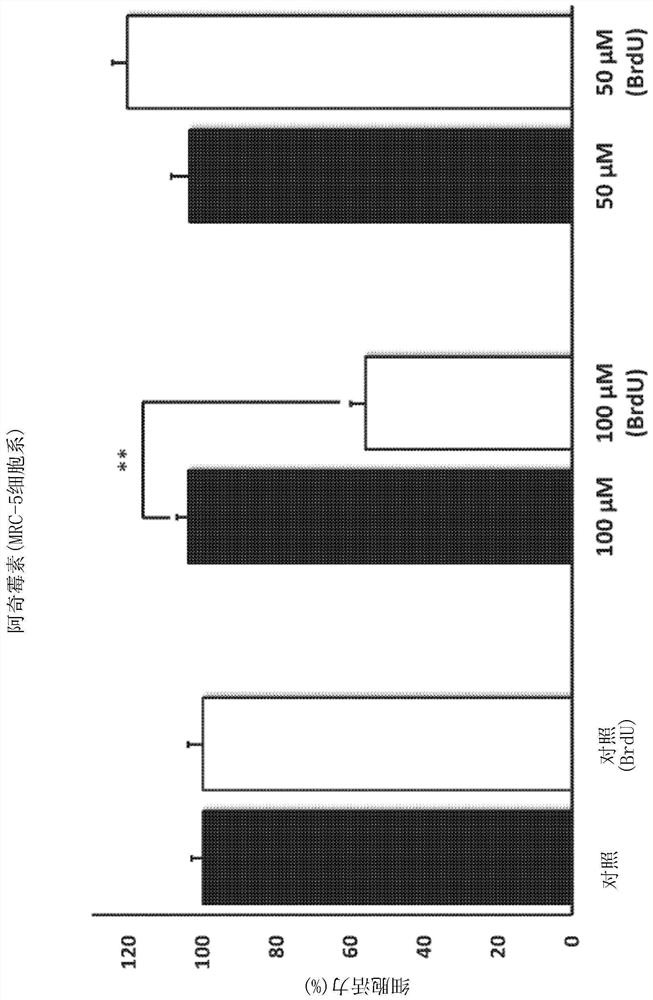
Azithromycin and roxithromycin derivatives as senolytic drugs
PendingCN113164504AAntibacterial agentsTetracycline active ingredientsFibroblast cell lineTelithromycin
This disclosure describes the use of azithromycin, roxithromycin, and telithromycin, including derivatives thereof, as senolytic drugs. BrdU was used to induce senescence in model human fibroblast cell lines. Also disclosed are methods for screening compounds for senolytic activity. The SRB assay was used to measure cell viability through protein content. Azithromycin roxithromycin, and telithromycin, clinically-approved pharmaceuticals, were found to be senolytic drugs. However, the closely-related parent compound, erythromycin, showed no senolytic activity. Azithromycin strongly induced both aerobic glycolysis and autophagy in human fibroblasts, but showed bi-phasic effects including on mitochondrial oxygen consumption rates with inhibitory activity at 50 muM and stimulatory activity at 100 muM. The xCELLigence real-time assay system showed that azithromycin preferentially targets senescent cells, removing approximately 97% (nearly a 25-fold reduction in senescent cells).
Owner:LUNELLA BIOTECH INC
Protection of tcr signaling chains in cancer patients and enhancement of car-t cell therapy
InactiveUS20160231323A1Organic active ingredientsBiological material analysisAbnormal tissue growthCAR T-cell therapy
Disclosed are means of protecting signaling integrity of T cells in cancer patients through reduction of neutrophil and other cellular induced oxidative stress. In one embodiment the FDA approved drug Mucomyst is administered at a concentration of 50-150 mg / kg to increase expression of T cell receptor (TCR)-zeta chain in patients with cancer. In other embodiments enhancement of CAR-T cell therapy is performed through modulation of inflammatory and oxidative stress in a tumor bearing patient.
Owner:BATU BIOLOGICS
In vivo and ex vivo expansion of hematopoietic stem cells with a targeted combination of clinically tested, FDA approved drugs
The present invention provides a therapeutic approach to maintain and expand HSCs in vivo using currently available medications that target GSK-3 and mTOR. The present invention also provides a system and method for the ex vivo culturing of HSCs, where an mTOR inhibitor is combined with a GSK-3 inhibitor within the culturing conditions.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Application of mesenchymal stem cells combined with TPO and analogues thereof in treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia
PendingCN113750220APrevent proliferationPromote apoptosisOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsMyeloid leukemiaReceptor
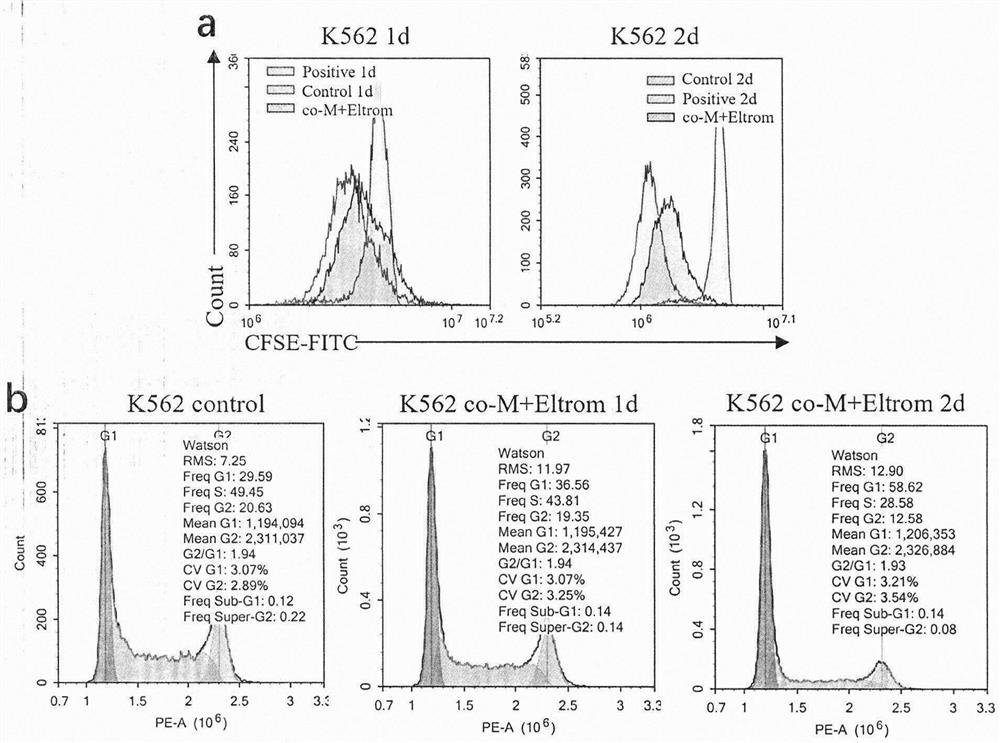
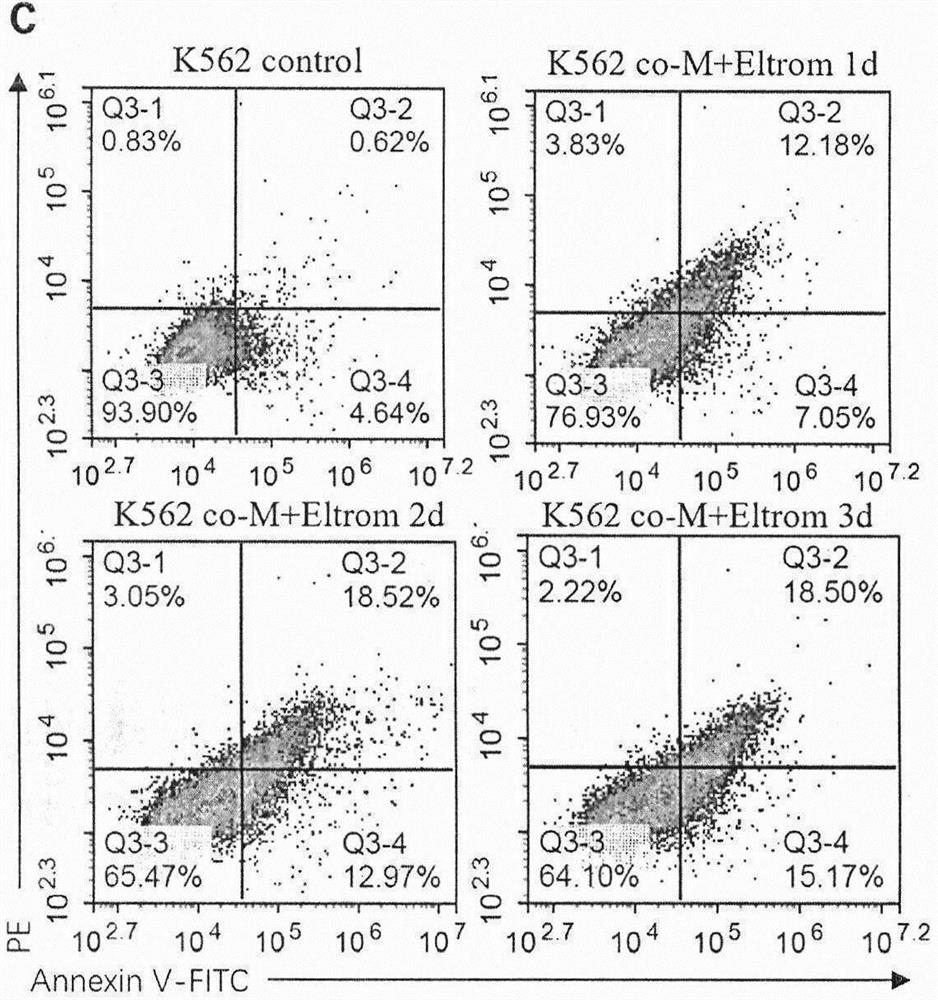
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical biology, and particularly relates to application of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells combined with TPO and analogues thereof in preparation of drugs for treating chronic myelogenous leukemia. The mesenchymal stem cells are human-derived umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (UC-MSCs), can efficiently induce differentiation of chronic myeloid leukemia cells after being combined with a TPO analogue Eltrombopag, and the capability is realized by secreting TPO by MSCs and inducing leukemia cells to express a TPO receptor (MPL); and compared with chemotherapy, mesenchymal stem cell transplantation is lower in toxic and side effects, has low immunogenicity and meets clinical requirements, and the Eltrombopag is a clinically approved drug. The method provides a new thought for stem cell transplantation treatment of myeloid leukemia, and can be applied to differentiation treatment of myeloid leukemia.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Application of benserazide as alpha-glucosidase inhibitor
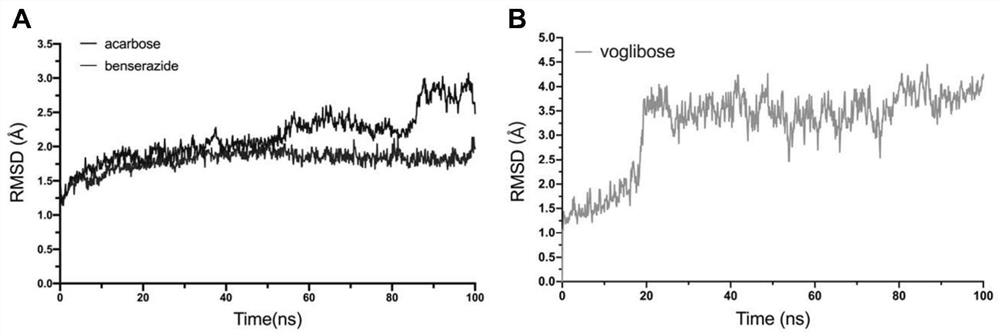
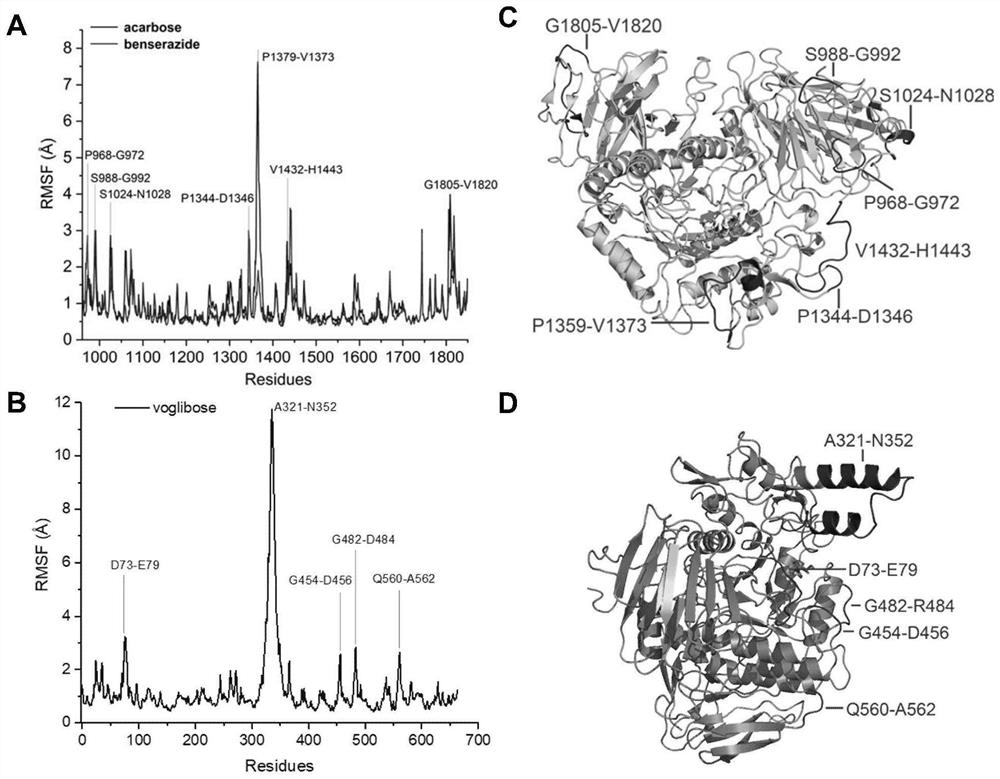
PendingCN111627504AImprove bindingPromote rapid developmentChemical property predictionComputational theoretical chemistryBenserazidePharmacophore
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicine. The invention in particular relates to the applicatoin of benserazide (The International Nonproprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Substances (INN) is Benserazide) as an alpha-glucosidase inhibitor, and a structure-based computational simulation screening method. Benserazide can be stably combined with an active site of alpha-glucosidase to inhibit the activity of alpha-glucosidase, so that the effect of reducing blood sugar is achieved. According to the invention, based on a thought of new use of old drugs, FDA-approved drugs are subjected to pharmacophore-based virtual screening, molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation processes, and it is found that benserazide can be stably combined at an active site of alpha-glucosidase, and in-vitro experiments show that benserazide is an alpha-glucosidase inhibitor, so that the new application of the benserazide in reducing blood sugar is excavated. The invention not only provides a new angle for benserazide as a hypoglycemic drug, but also provides an example for rapid development of a novel alpha-glucosidase inhibitor.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
Drug repositioning methods for targeting breast tumor initiating cells
InactiveUS20170286630A1Quick translationInhibit breast TICsMedical simulationSpecial data processing applicationsDiseaseIn vivo
Disclosed are systems biology-based methods for repositioning known pharmaceutical compounds to new indications, through the identification of network-based signatures. In particular, the invention provides new and useful methods for selecting drugs or combinations of drugs (and preferably previously-approved drugs) for use in new therapeutic indications. Also disclosed are methods for identifying anti-breast tumor initiating cell (TIC)-based therapeutics from within populations of target compounds. In illustrative embodiments, the invention provides methods and computer programs for the repositioning of FDA-approved pharmaceutical compounds to new indications using network-based signature analysis coupled with conventional in vitro and in vivo testing of identified drug candidates. The invention also allows identification of drugs or drug combinations for treating unmet medical needs including, for example, “orphan” diseases.
Owner:THE METHODIST HOSPITAL
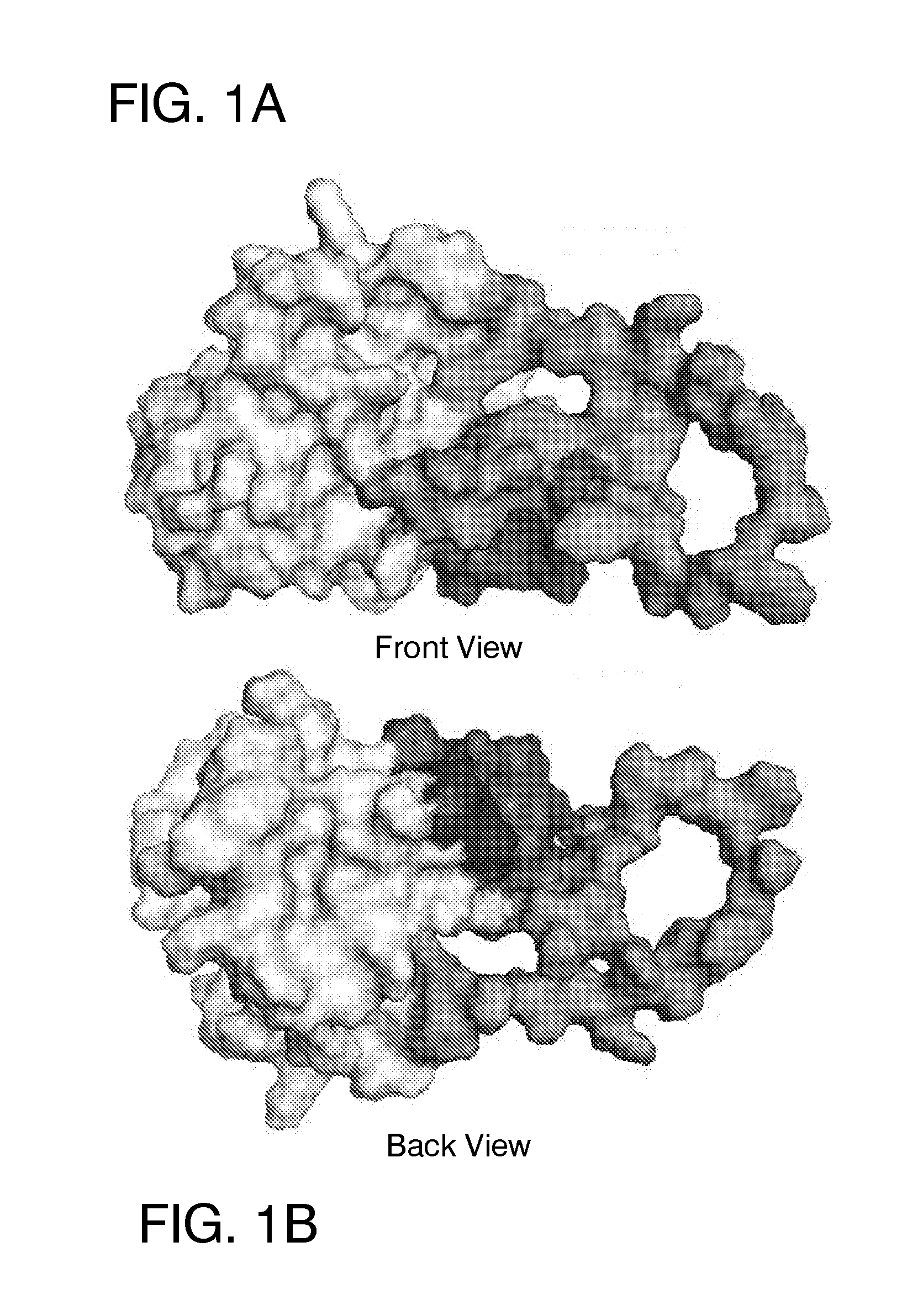
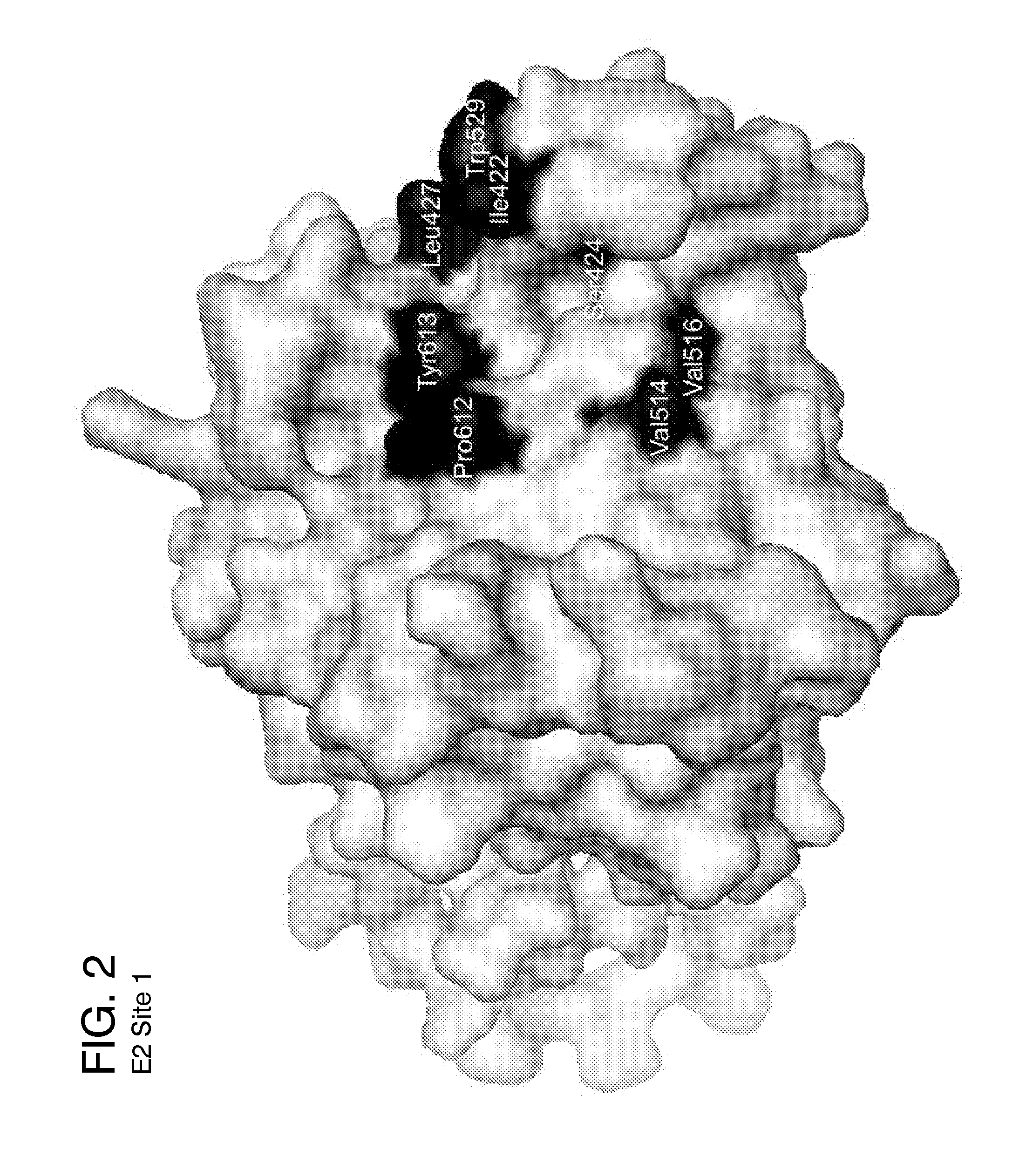
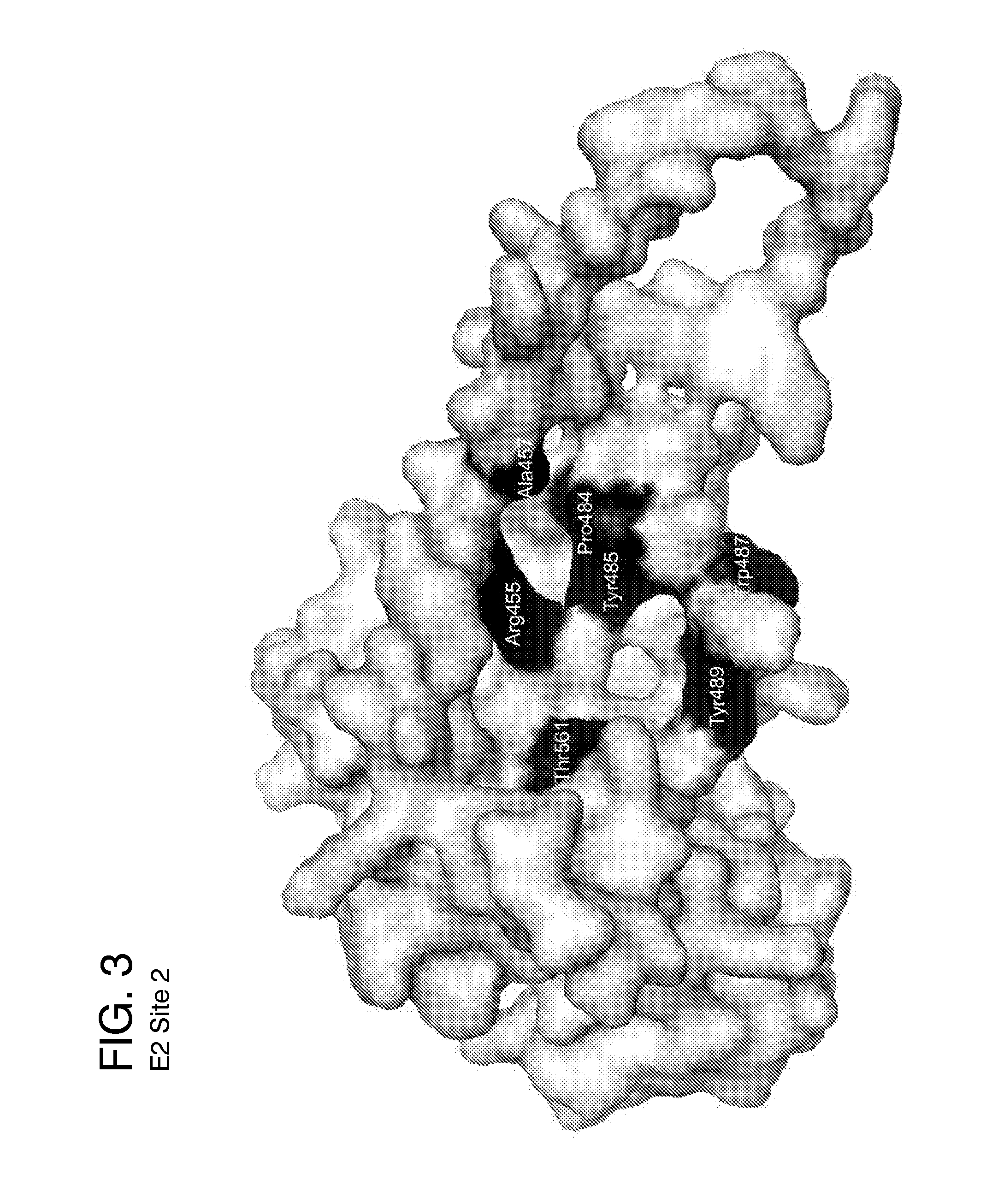
Ligands that target hepatitis c virus e2 protein
InactiveUS20160361311A1Reduce severityPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsPolymerase LInterferon alpha
Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) infects 200 million individuals worldwide. Although several FDA approved drugs targeting the HCV serine protease and polymerase have shown promising results, there is a need for better drugs that are effective in treating a broader range of HCV genotypes and subtypes without being used in combination with interferon and / or ribavirin. Recently, the crystal structure of the core of the HCV E2 protein (E2c) has been determined, providing structural information that can now be used to target the E2 protein and develop drugs that disrupt the early stages of HCV infection by blocking E2's interaction with different host factors. By targeting sites containing conserved E2 amino acids in the CD81 binding site on HCV E2, one might also be able to develop drugs that block HCV infection in a genotype-independent manner. Using the E2c structure as a template, a structural model of the E2 protein core (residues 421-645) was developed that includes the three amino acid segments that are not present in the E2c crystal structure. Blind docking of a diverse library of 1715 small molecules to this model led to the identification of a set of 34 ligands predicted to bind near conserved amino acid residues involved in the HCV E2:CD81 interaction. Surface plasmon resonance was used to screen the ligand set for binding to recombinant E2 protein, and the best binders were subsequently tested to identify compounds that inhibit the infection of hepatocytes by HCV. One compound, 281816, blocked E2 binding to CD81 and inhibited hepatocyte infection by HCV genotypes 1a, 1b, 2a, 2b, 4a and 6a with IC50's ranging from 2.2 μM to 4.6 μM. Methods are described for preventing or treating HCV infection using small molecule inhibitors such as 281816 that target E2 and disrupt its interactions.
Owner:AMERICAN UNIV OF CAIRO
Stable pharmaceutical drug products
InactiveUS20120055469A1Avoid safety and efficacy concernReduce surface tensionRespiratorsLiquid surface applicatorsBiochemical engineeringApproved drug
Various aspects of the present invention provide for methods of manufacturing a pharmaceutical drug product, which include storing a container at a temperature greater than ambient conditions for at least about seven days and conducting release testing on the container after storing. Products manufactured by this method have a more consistent fine particle size distribution (FSD) and fine particle fraction (FPF) at ambient conditions and at accelerated stability conditions over the life of the drug product. Advantageously, such products may more reliably and regularly pass testing requirements as required for an approved drug product by regulatory authorities such as the United States Food and Drug Administration (USFDA).
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
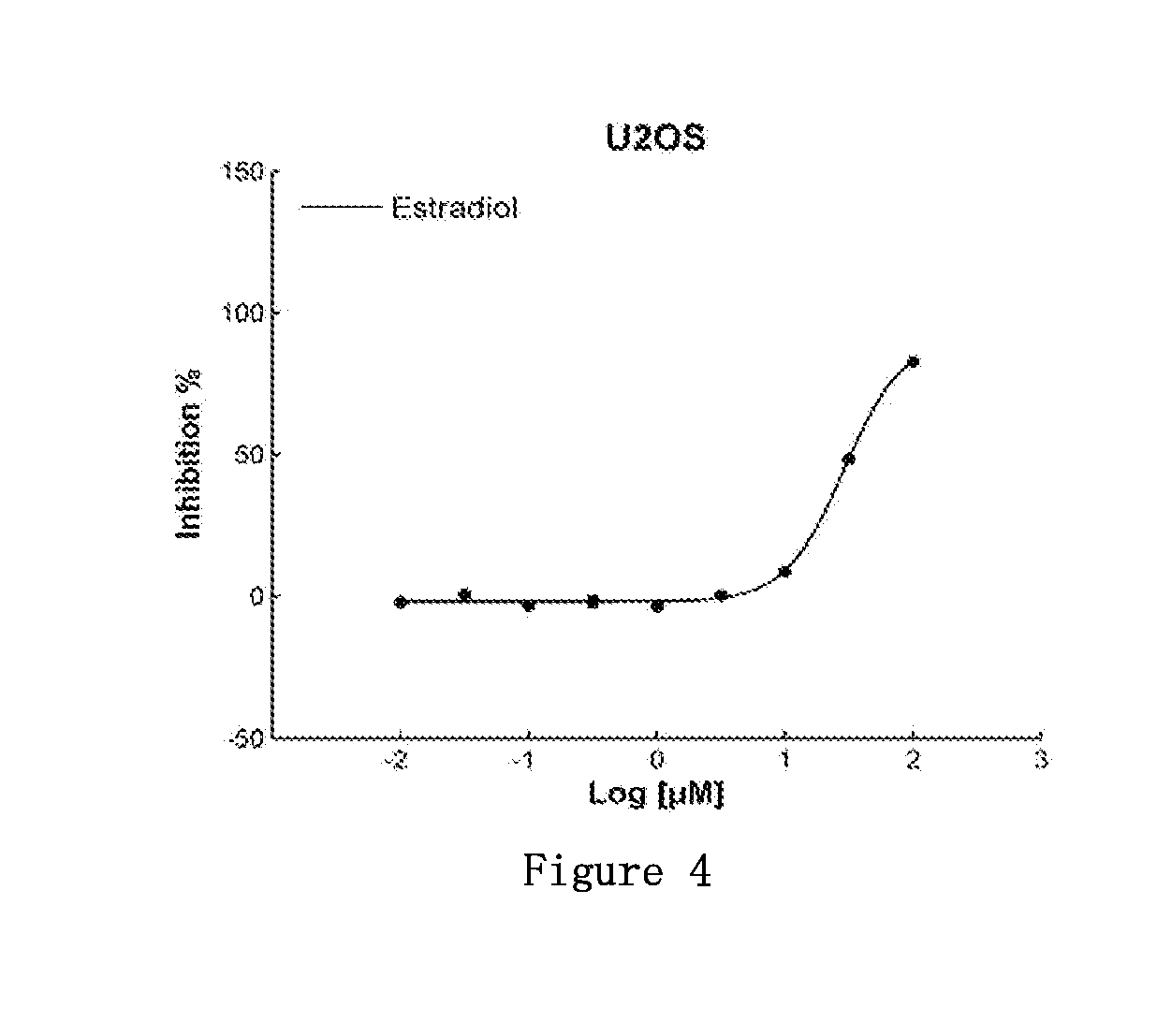
Applications for estradiol in preparing Anti-small cell lung cancer and/or ovarian cancer and/or osteosarcoma products
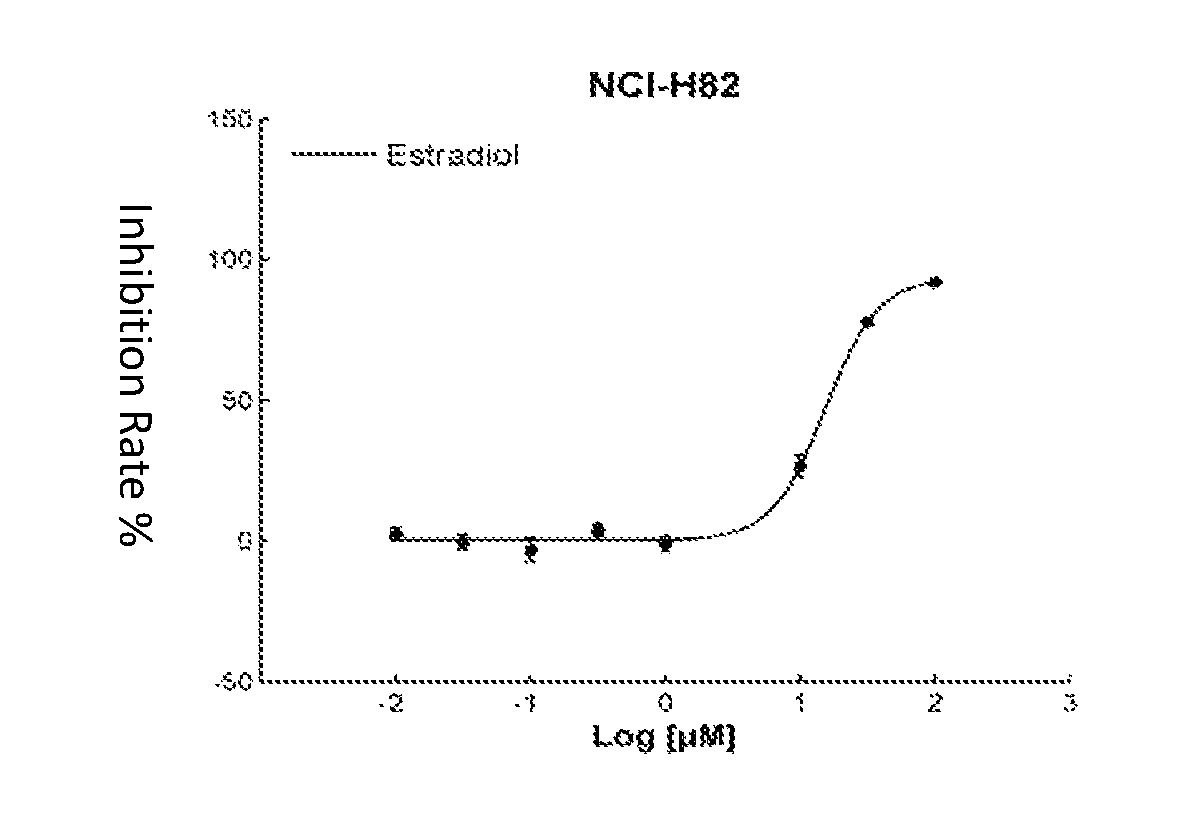
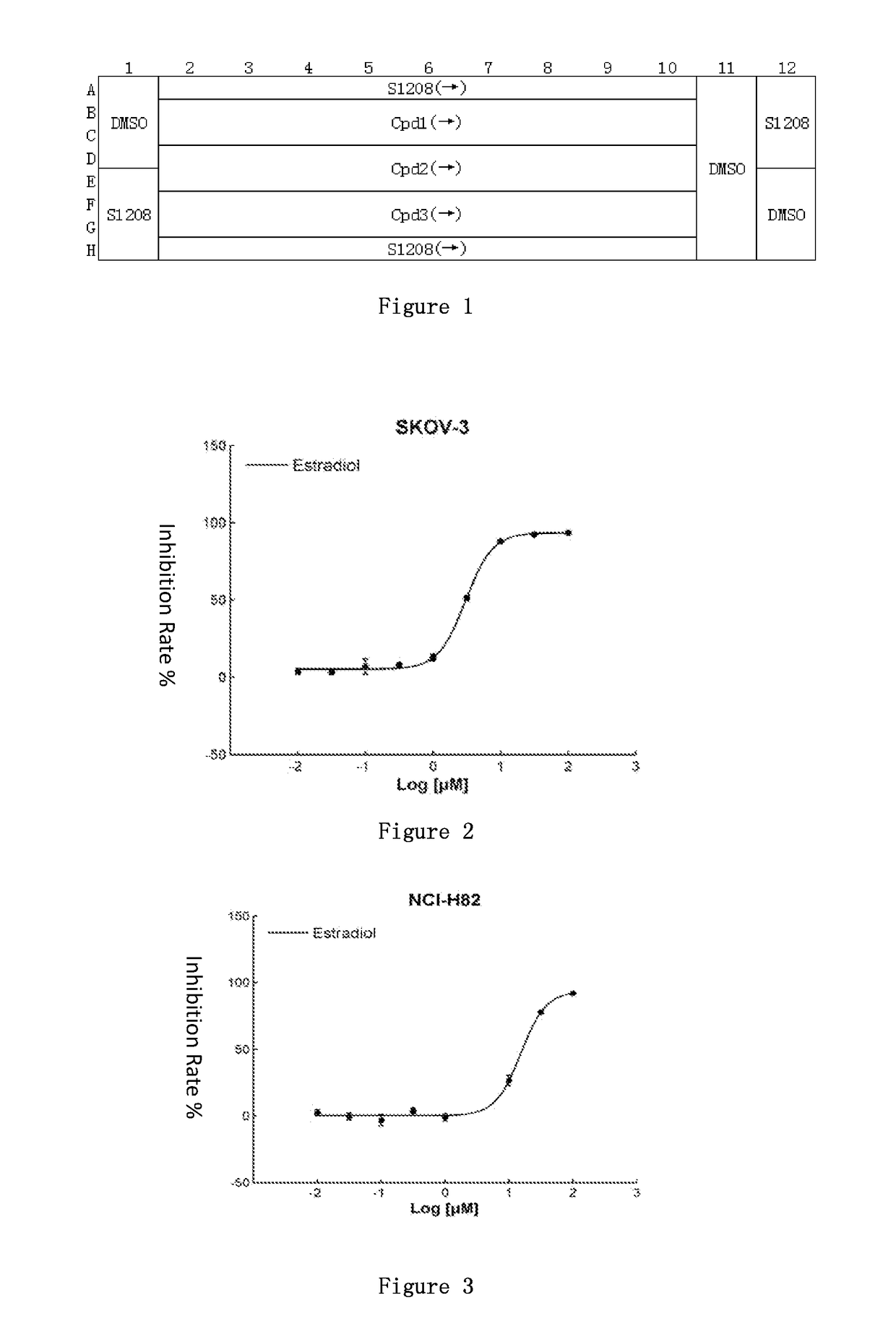
This invention discloses uses for estradiol in preparing anti-small cell lung cancer and / or ovarian cancer and / or osteosarcoma products. This invention provides uses for estradiol in preparing anti-small cell lung cancer and / or ovarian cancer and / or osteosarcoma products. From carrying out cancer drug repositioning for the FDA- and CFDA-approved drug estradiol, experiments for this invention show, based on screening of non-anti-cancer drugs for various cancer cell lines (tissue types) and mutation sites, that estradiol has a new use as an anti-small cell lung cancer and / or ovarian cancer and / or osteosarcoma medication, thus achieving a new purpose for an old drug.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
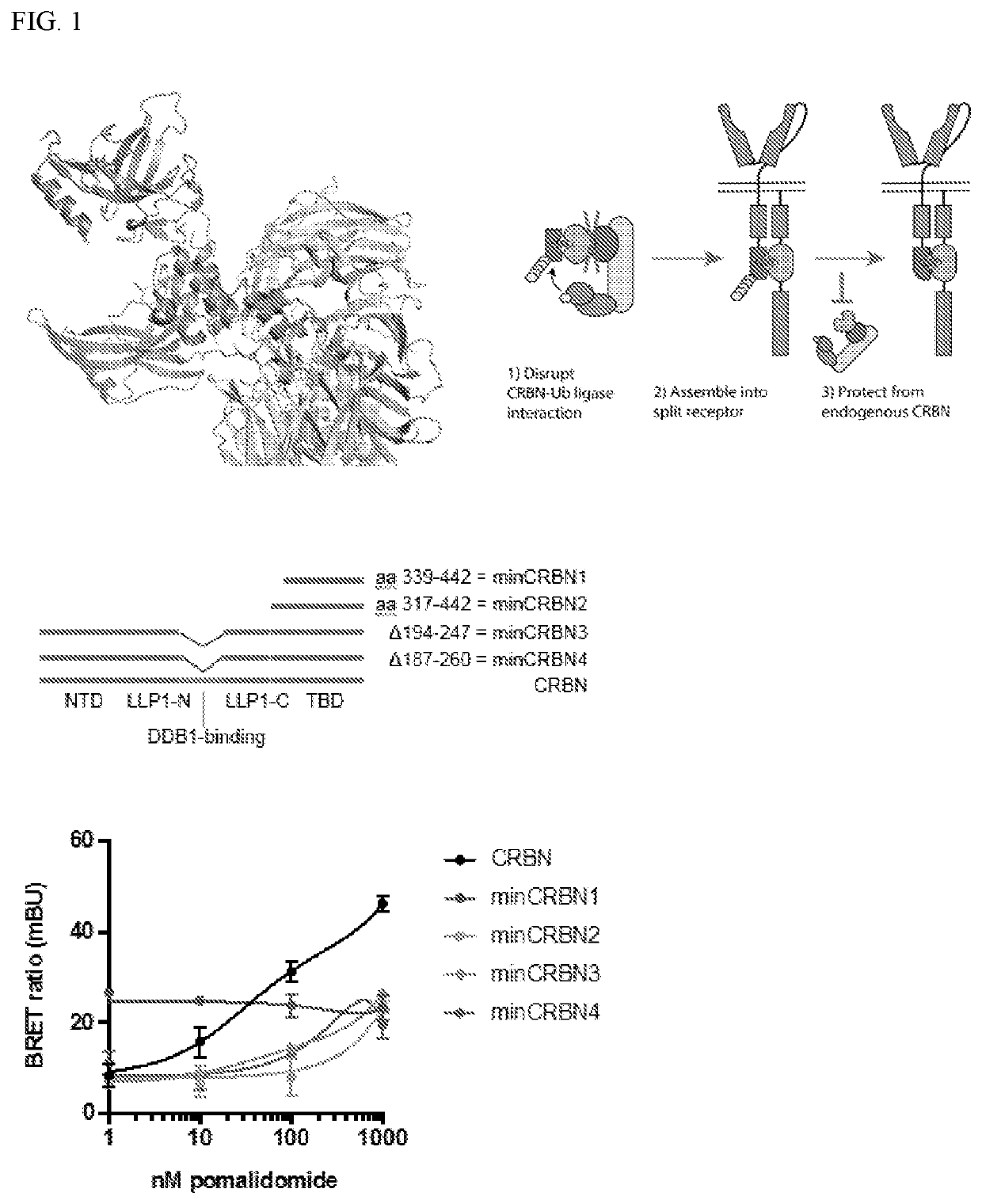
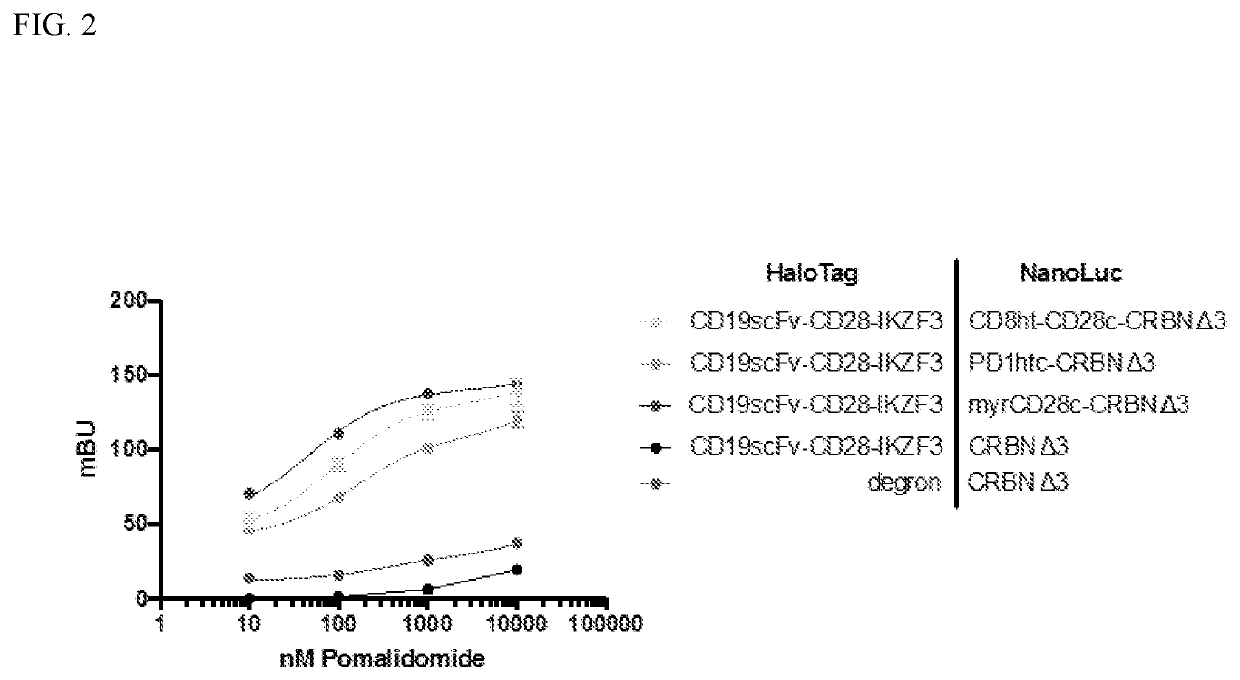
Molecular switch-mediated control of engineered cells
PendingUS20210040166A1Convenient treatmentReduces and avoids symptomPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyThalidomide AnalogAntigen receptors
The present disclosure relates to therapeutic methods and clinically useful molecular switches, for which activity or degradation of a switch-presenting polypeptide can be precisely induced via administration or withdrawal of an FDA-approved drug. Certain aspects of the disclosure relate to an engineered drug-inducible heterodimeric system including a first polypeptide presenting a CRBN polypeptide disrupted for or lacking a DDB1-interacting domain and a second polypeptide presenting a CRBN polypeptide substrate, where binding between the CRBN polypeptide and the CRBN polypeptide substrate are inducible via administration of an FDA-approved thalidomide analog immunomodulatory drug (IMiD). Another aspect of the disclosure relates to a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) that presents a minimal fragment of the CRBN polypeptide substrate IKZF3 capable of triggering proteasomal degradation of CAR upon administration of an FDA-approved IMiD.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +2
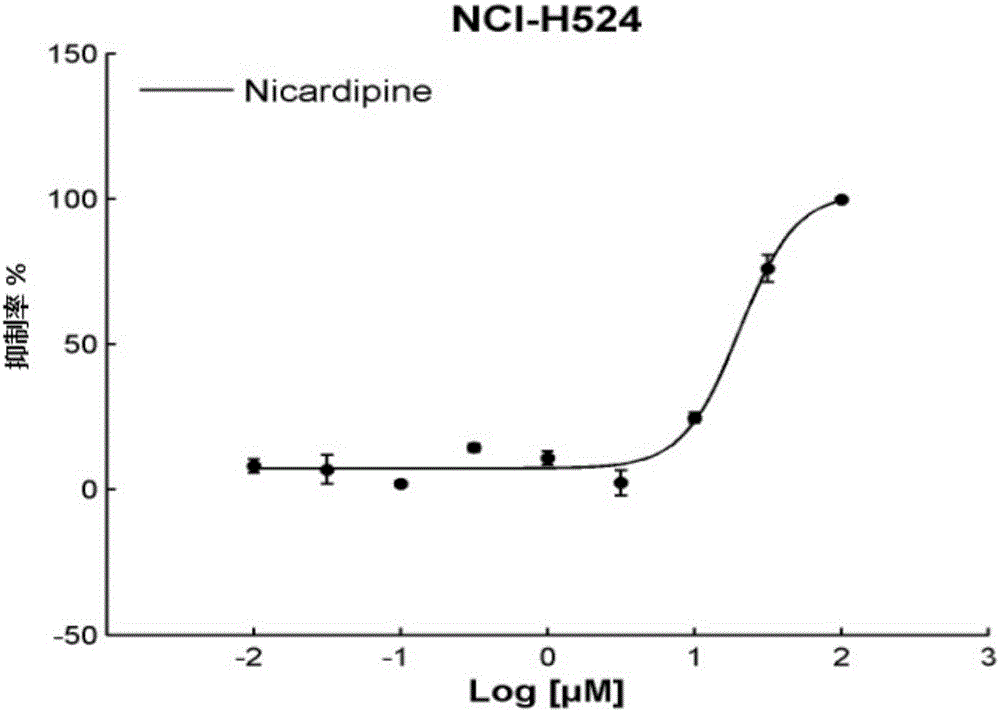
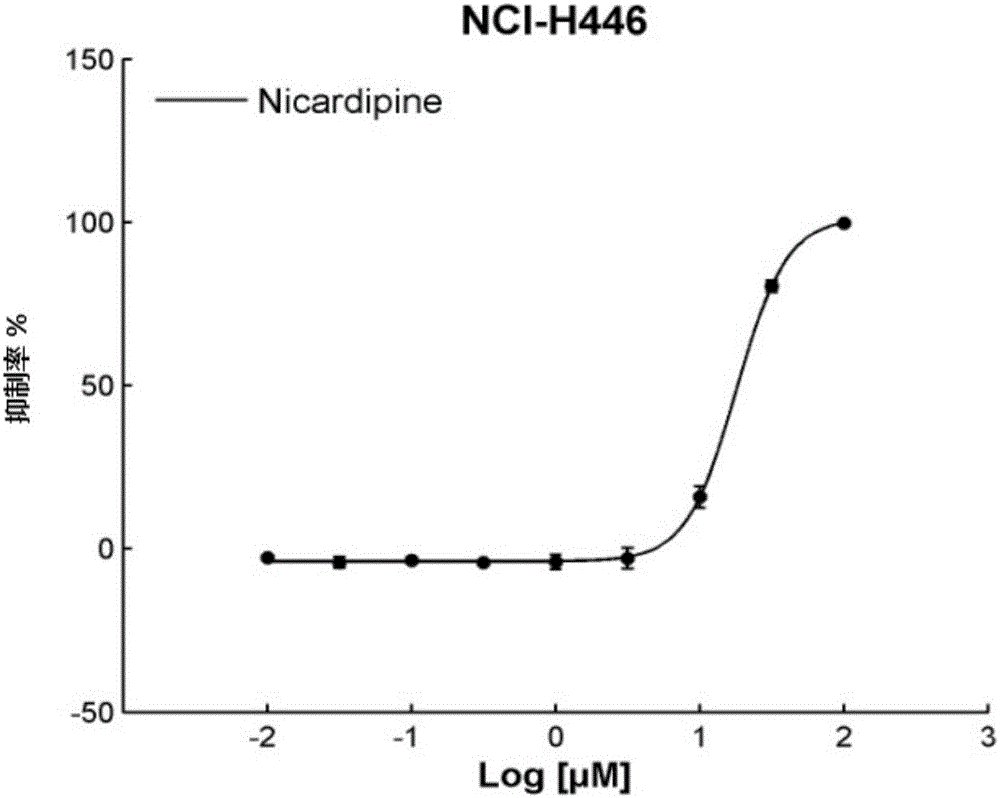
Application of Nicardipine in preparation of lung cancer resistant product
ActiveCN104983733ARealize the new use of old medicineOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsApproved drugTissues types
The invention discloses an application of Nicardipine in preparation of a lung cancer resistant product, and provides an application of the Nicardipine in preparation of a lung cancer curing product. An experiment of the application proves that relocation of an anti-tumor drug is carried out on the Nicardipine which is approved by the FDA and the CFDA, according to different cell lines (histopathological types) and mutation sites of a tumor, screening is carried out to screen out drugs showing indications which are not resistant to tumors, novel uses / a novel use of being resistant to small cell lung cancer and / or resistant to non-small cell lung cancer of the Nicardipine are / is found, and the novel uses / the novel use for the approved drug are / is achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com