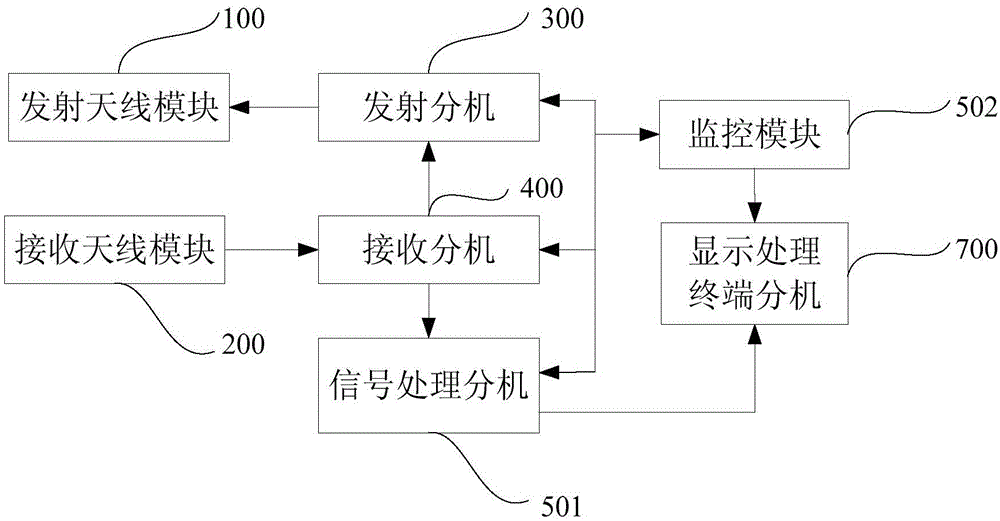
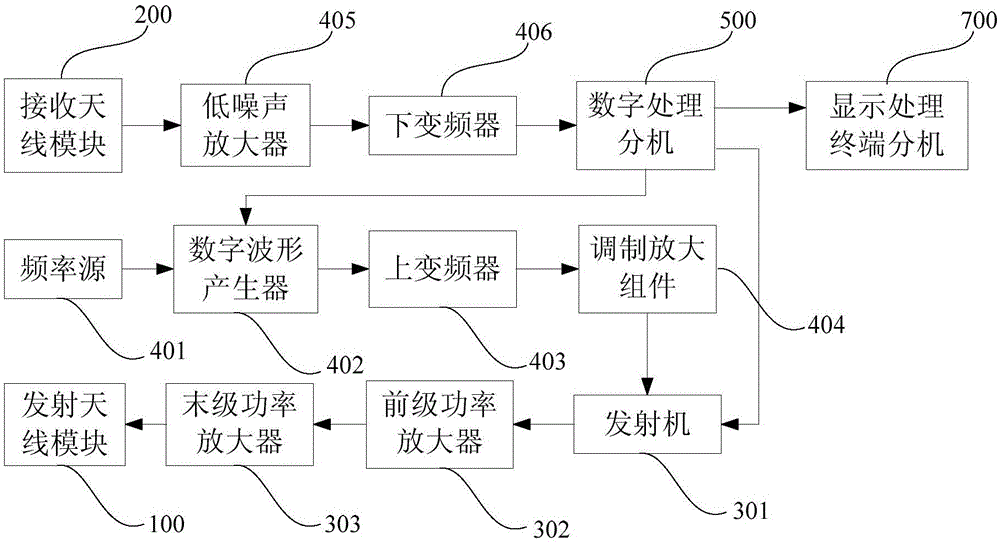
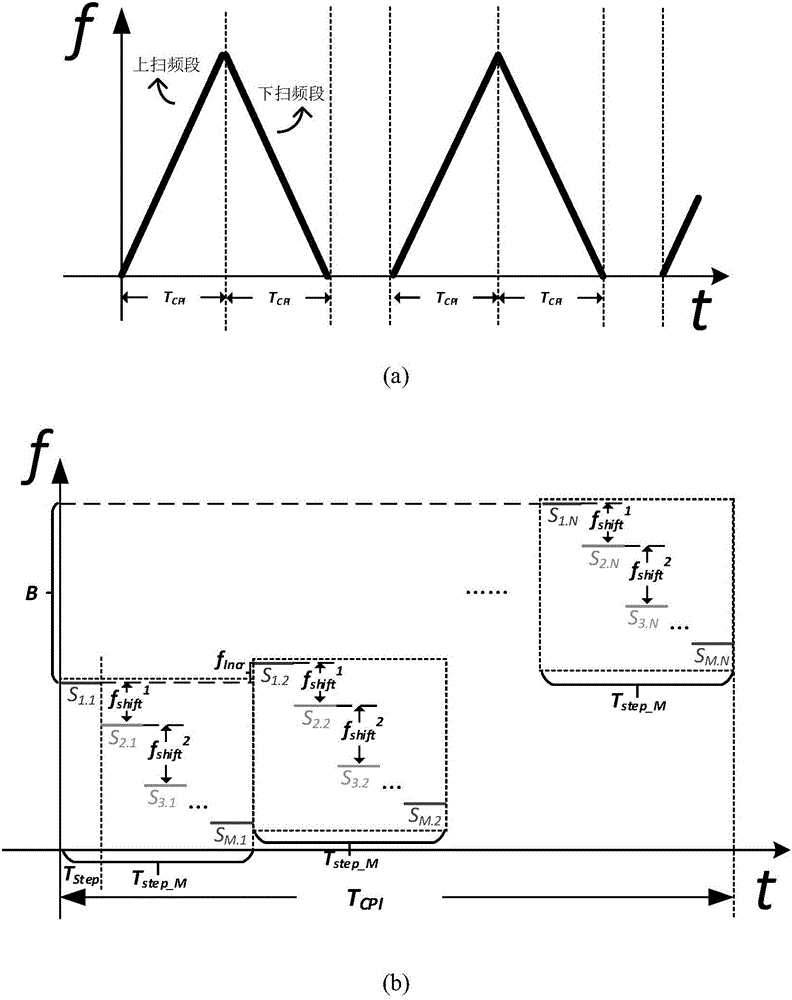
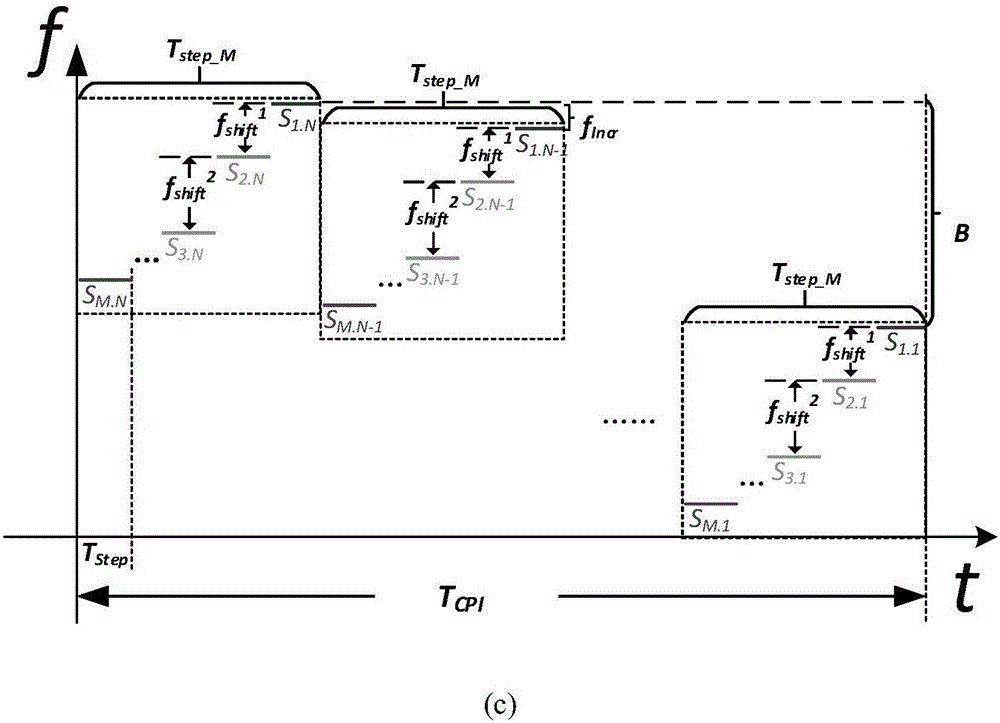
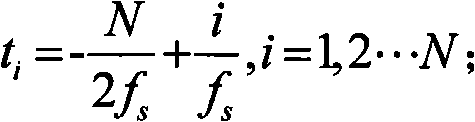Patents
Literature
341 results about "Continuous wave signal" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Inter-vehicle communication and warning apparatus
InactiveUS20070096885A1Enhance traffic transportation safetyEasy to transportDigital data processing detailsDetection of traffic movementRadarEngineering
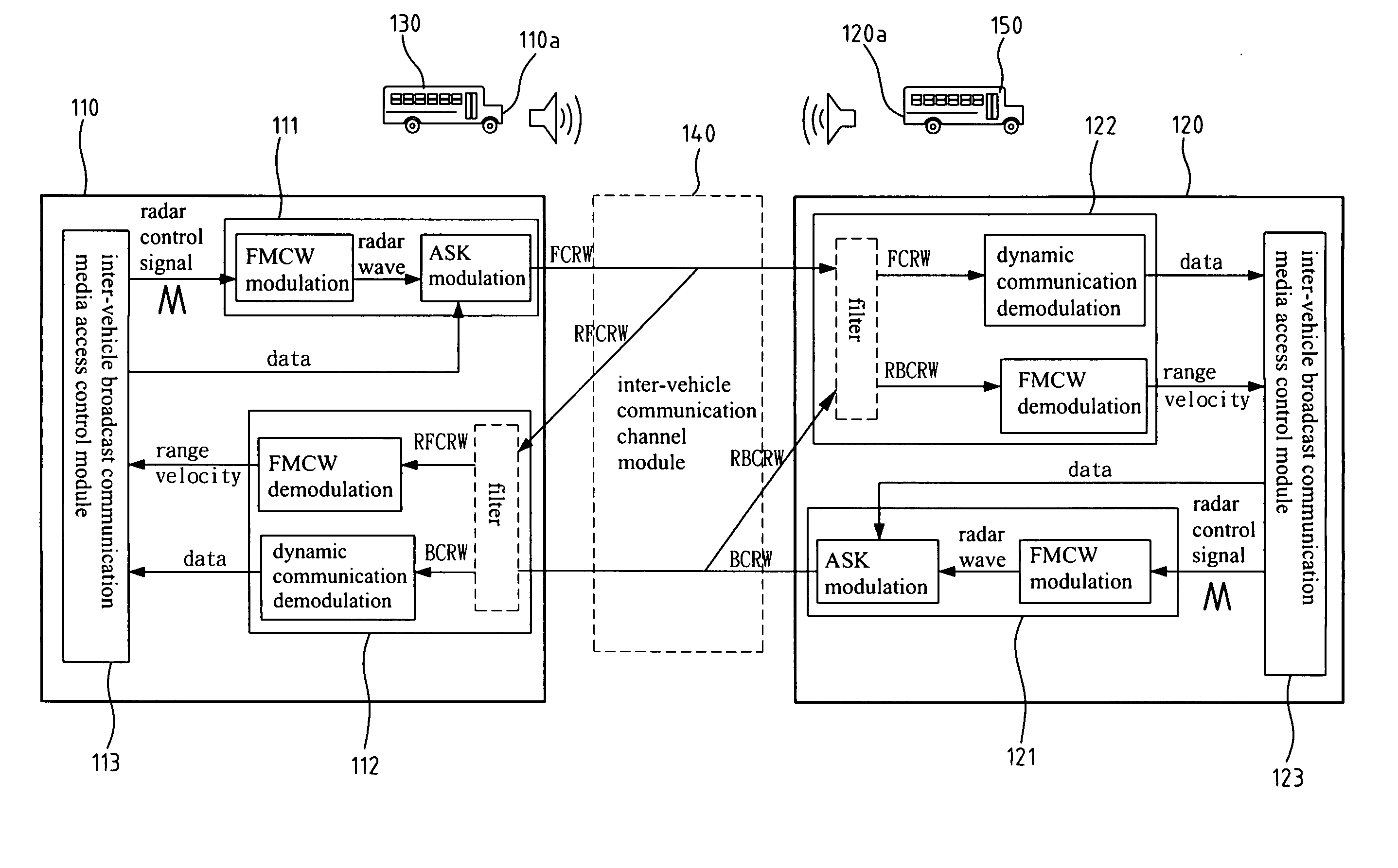
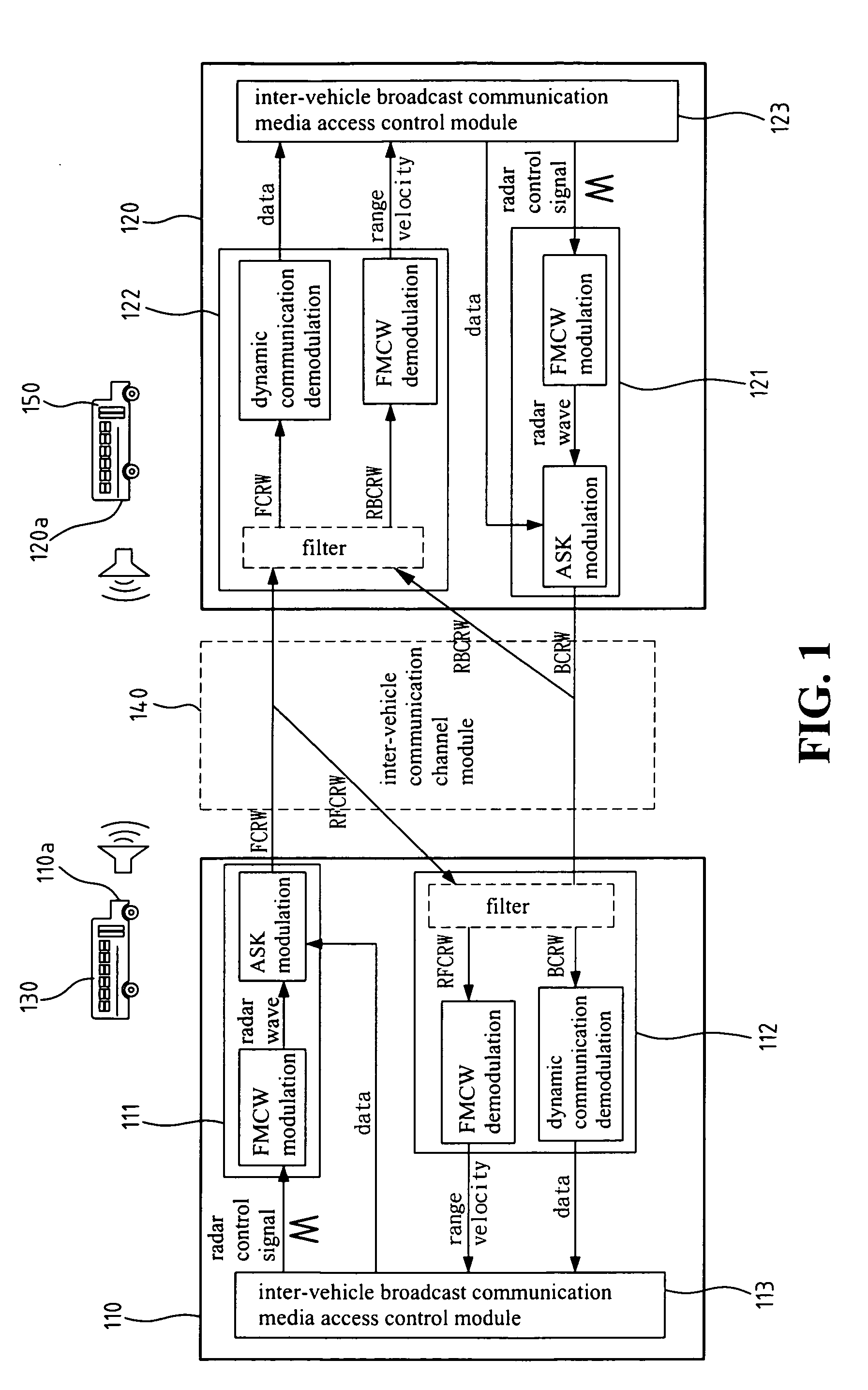
A short-range inter-vehicle communication and warning apparatus comprises a forward radar and a backward radar. The apparatus uses the radars to generate Frequency Modulation / Continuous Wave (FMCW) signals, uses amplitude shift keying for data modulation and arranges a special packet format, to realize such a low cost and fast response device of collision avoidance for vehicles. The invention has the dual capabilities of detecting and communicating simultaneously. It can also measure the relative speed of a preceding / rear vehicles and the relative inter-vehicle distance. The invention also exchanges the real-time traffic information with the preceding / rear vehicles at the same time. It is applicable to a one-to-one or one-to-many inter-vehicle channel model.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
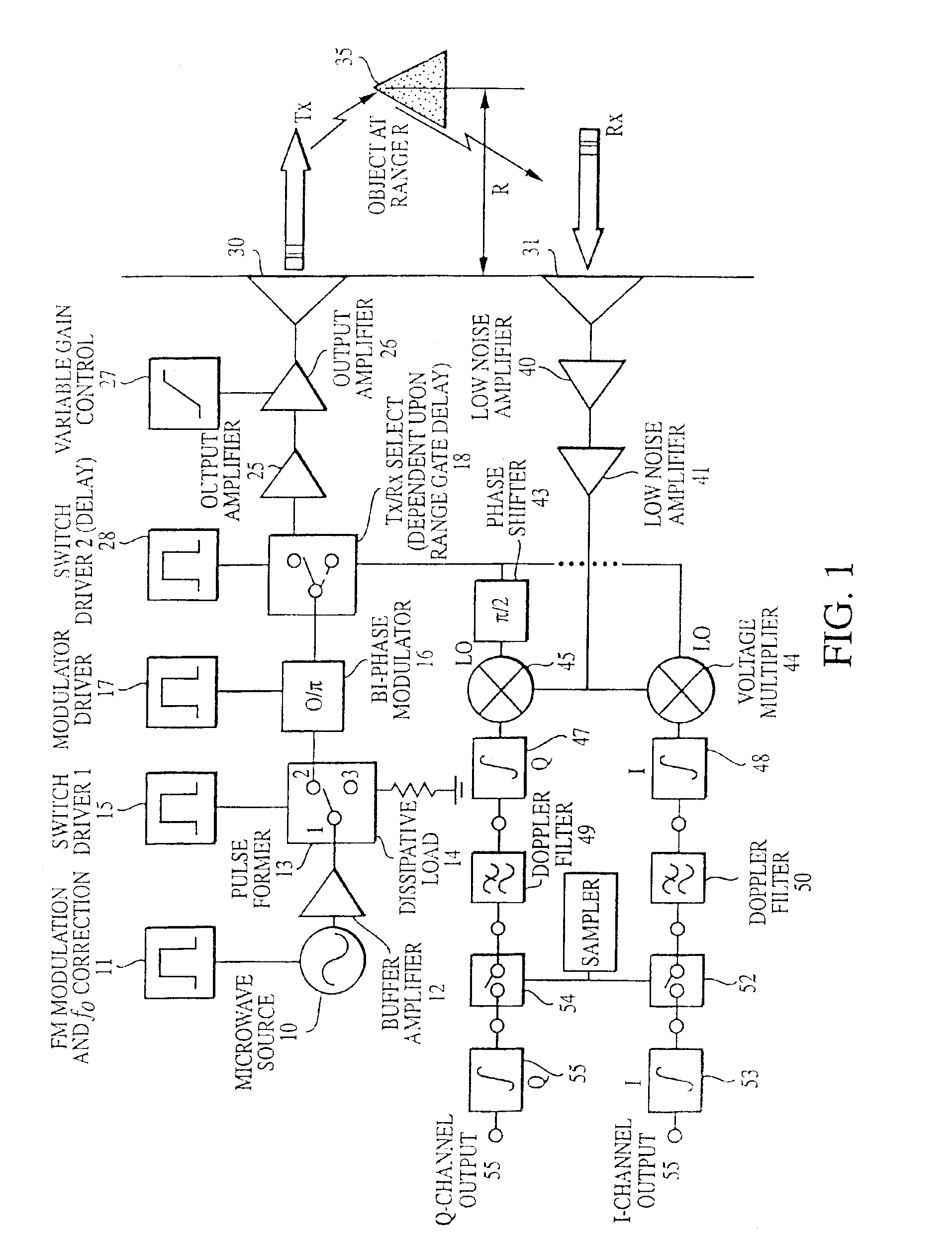
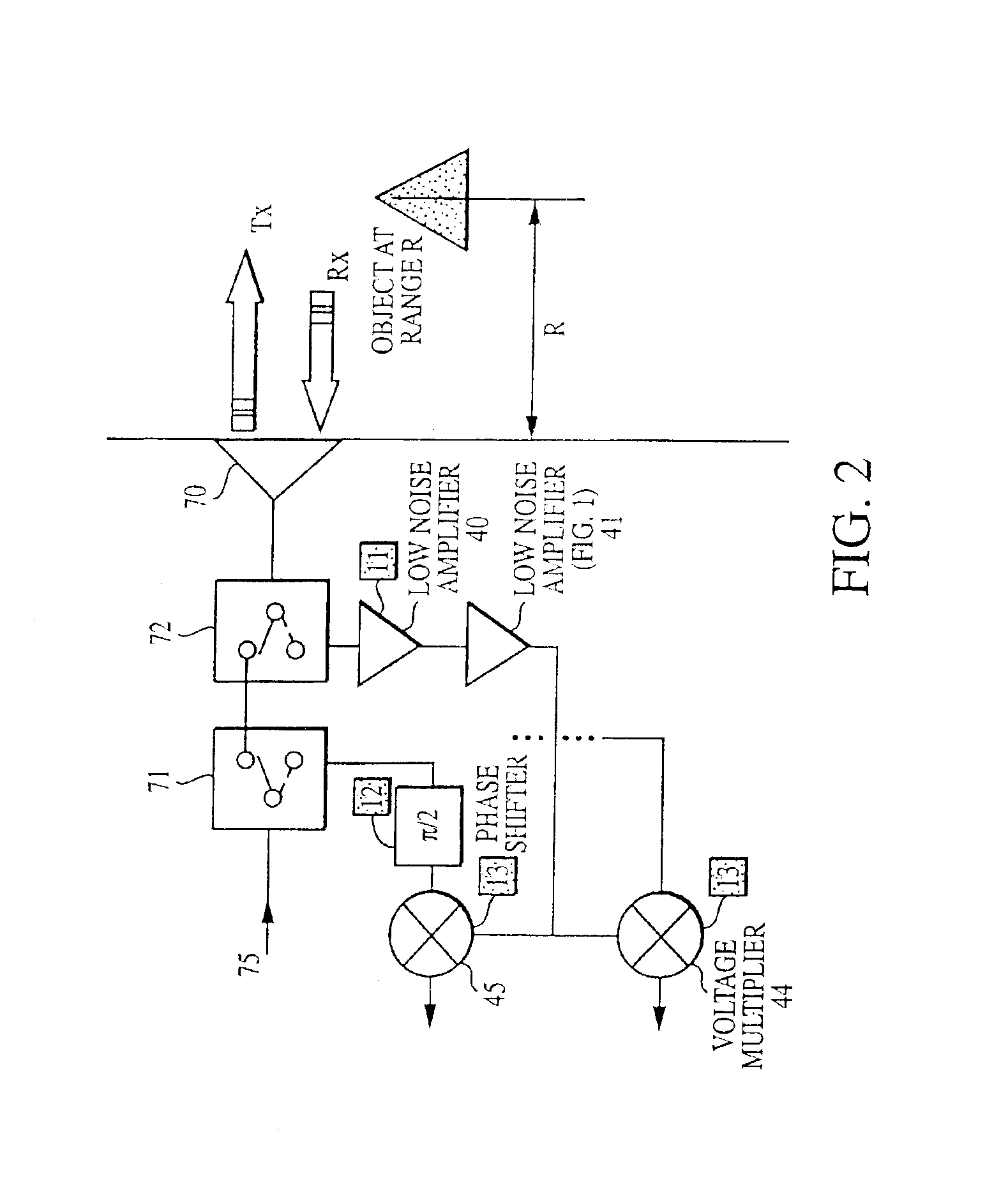
Pulse radar detection system
InactiveUS6879281B2Improve immunityShort-range discriminationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsRadar detection
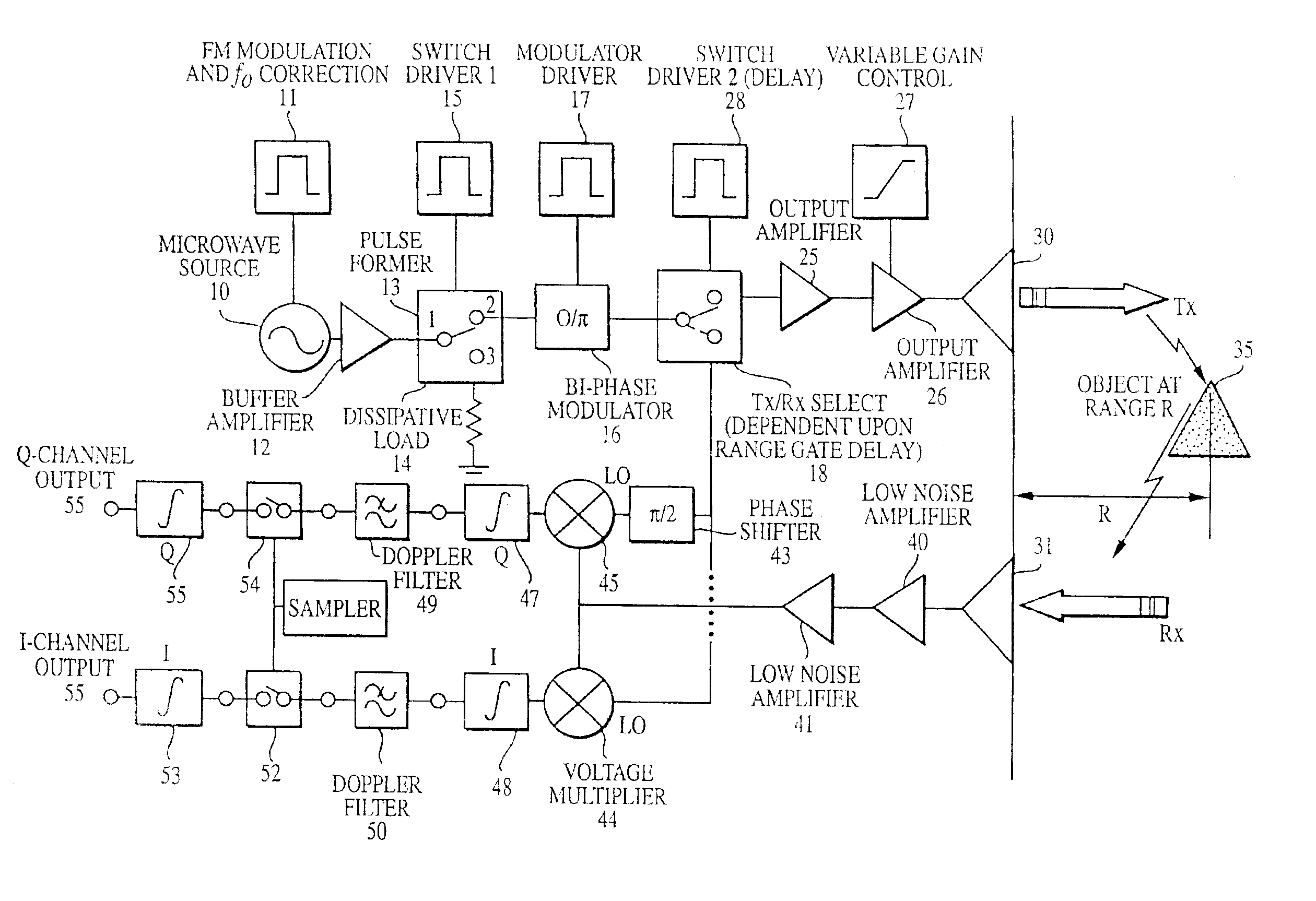
A radar based sensor detection system comprises a microwave source operative to provide a continuous wave signal at an output. A pulse-former is coupled to the output of the source and is operative to provide at an output a variable length pulse that increases the transmitted energy of the radar system according to the range of object detection. A modulator is coupled to the output of the pulse-former for providing a modulated pulse signal when required. A transmit / receive switch coupled to the output of the modulator is selectively operative between a first transmit position and a second receive position. A transmit channel coupled to the transmit / receive switch transmits the pulse signal when the switch is operated in the transmit position. A receiving channel coupled to the transmit / receive switch receives the modulator signal when the switch is operated in the receive position. First and second voltage multipliers each have a local oscillator input for receiving the modulator signal in the receive position, and each have an input signal port, and an output port. A receiver channel receives a reflected transmitted signal from an object and applies the received signal to the receive signal input ports of the voltage multipliers. An autocorrelator coupled to the output ports of the voltage multipliers correlates the received signal to produce an output signal indicating the detection and position of the object.
Owner:VEONEER US LLC
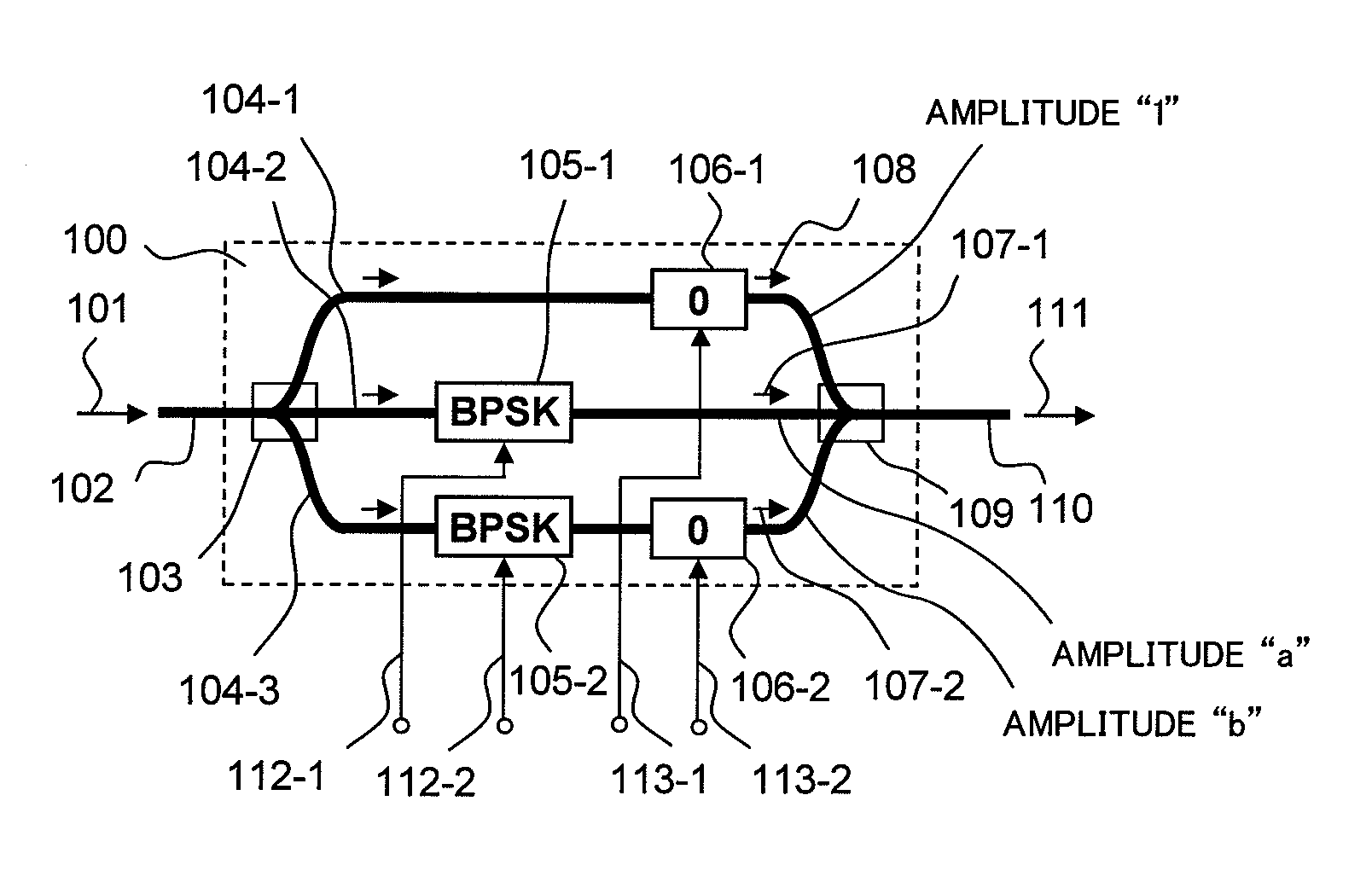
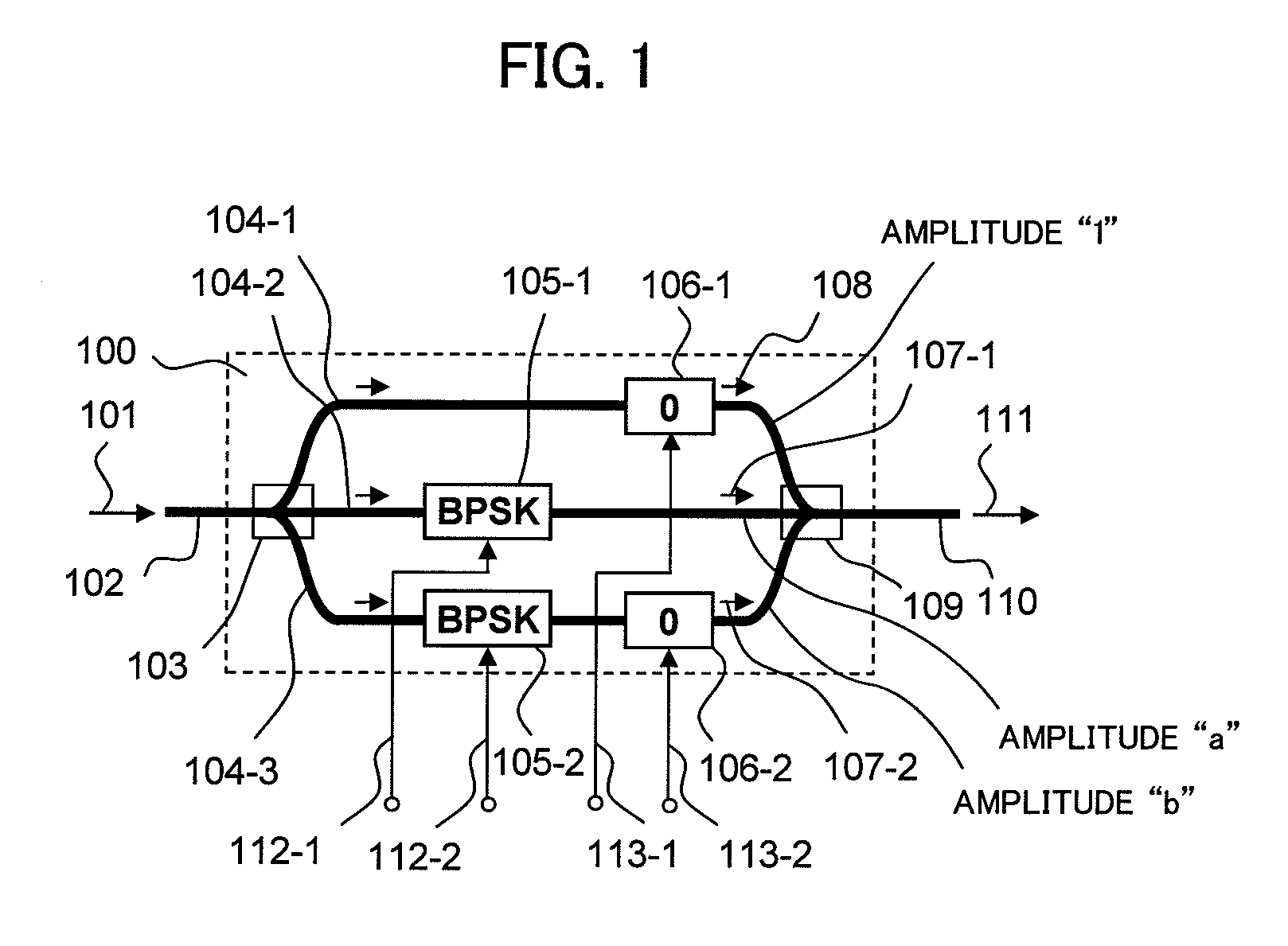
Optical modulator
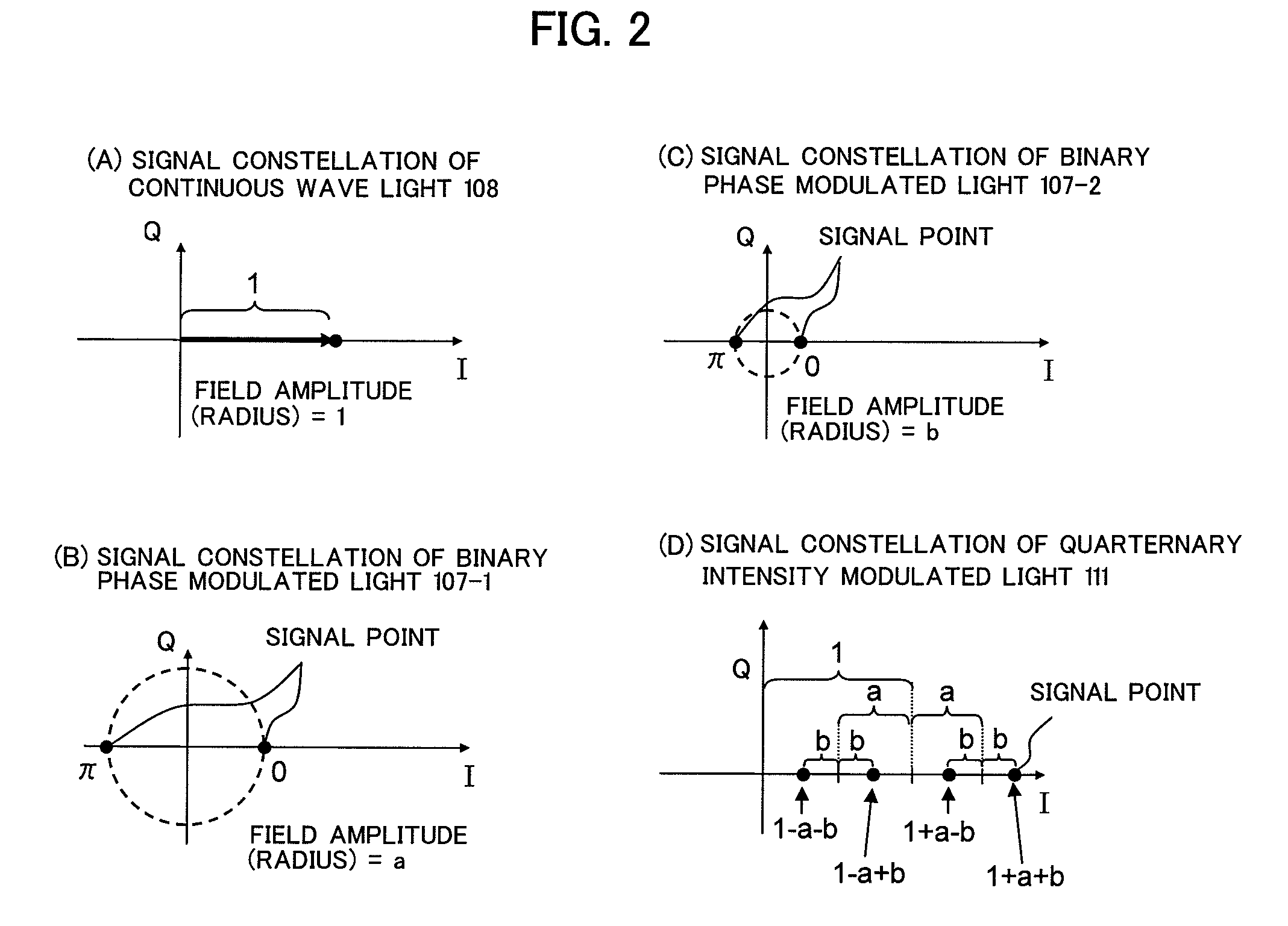
InactiveUS7978390B2Improve optical signal receiving sensitivityEfficiently transmitting informationElectromagnetic transmittersNon-linear opticsContinuous wave signalOptical modulator
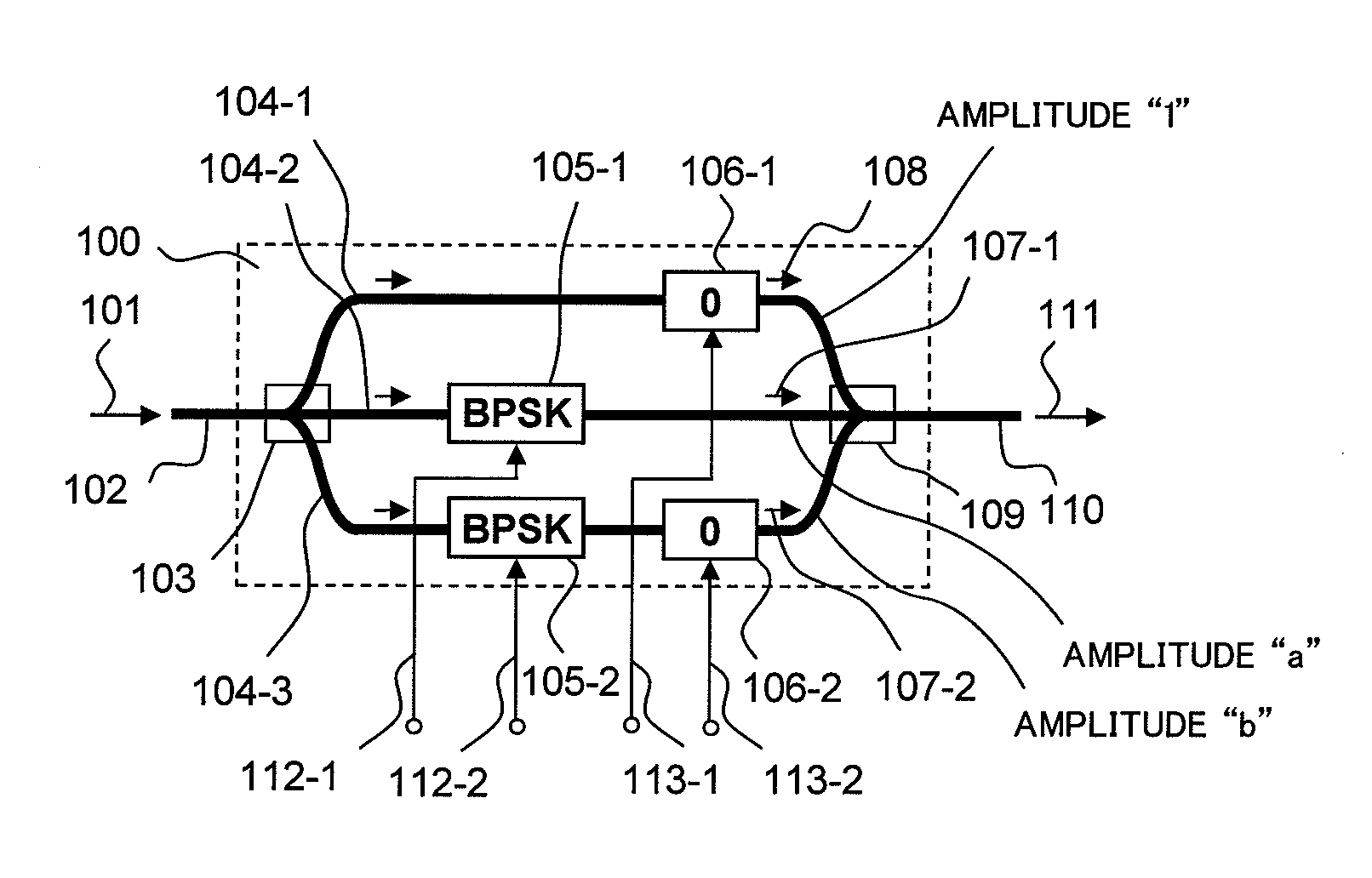
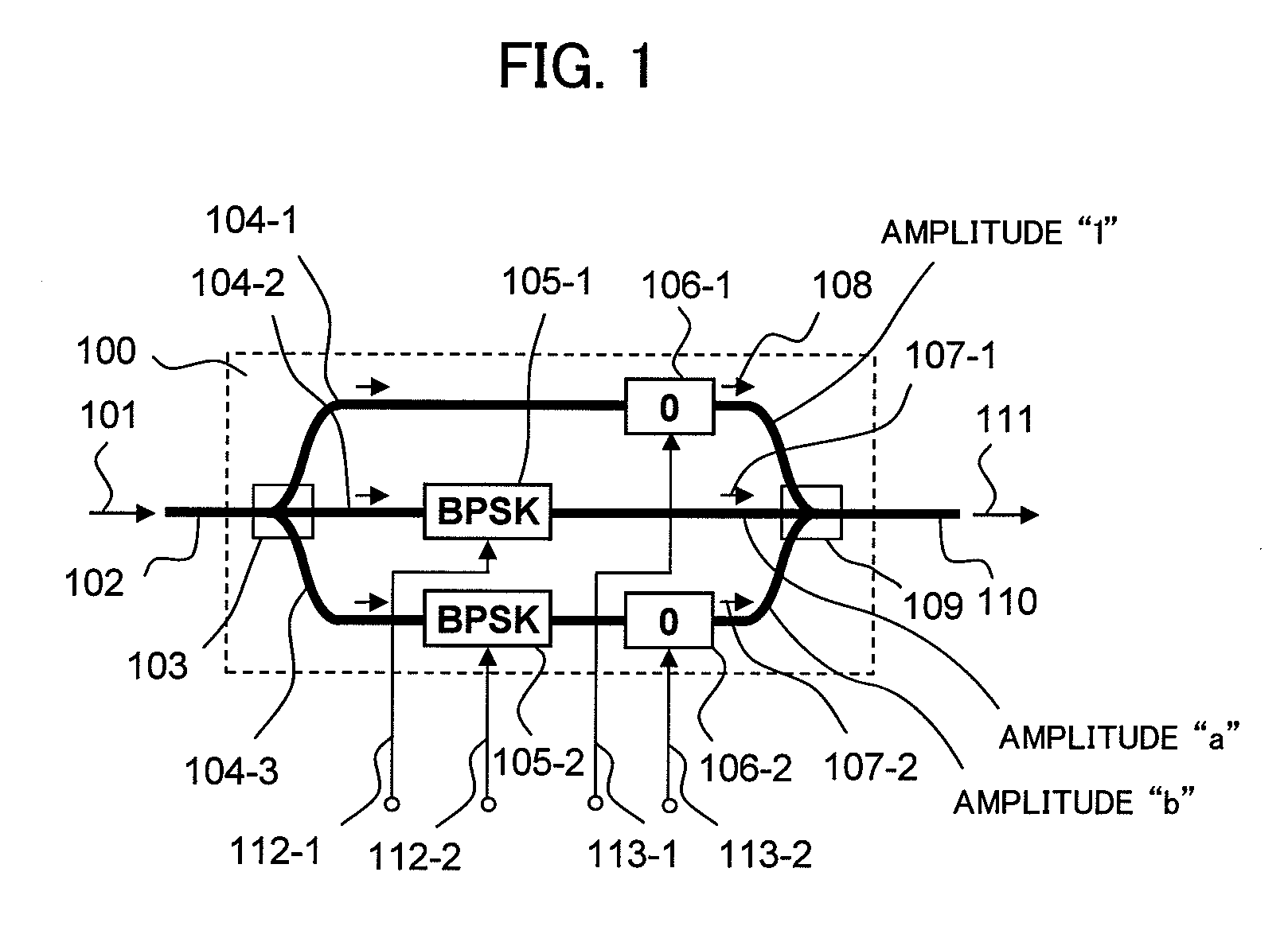
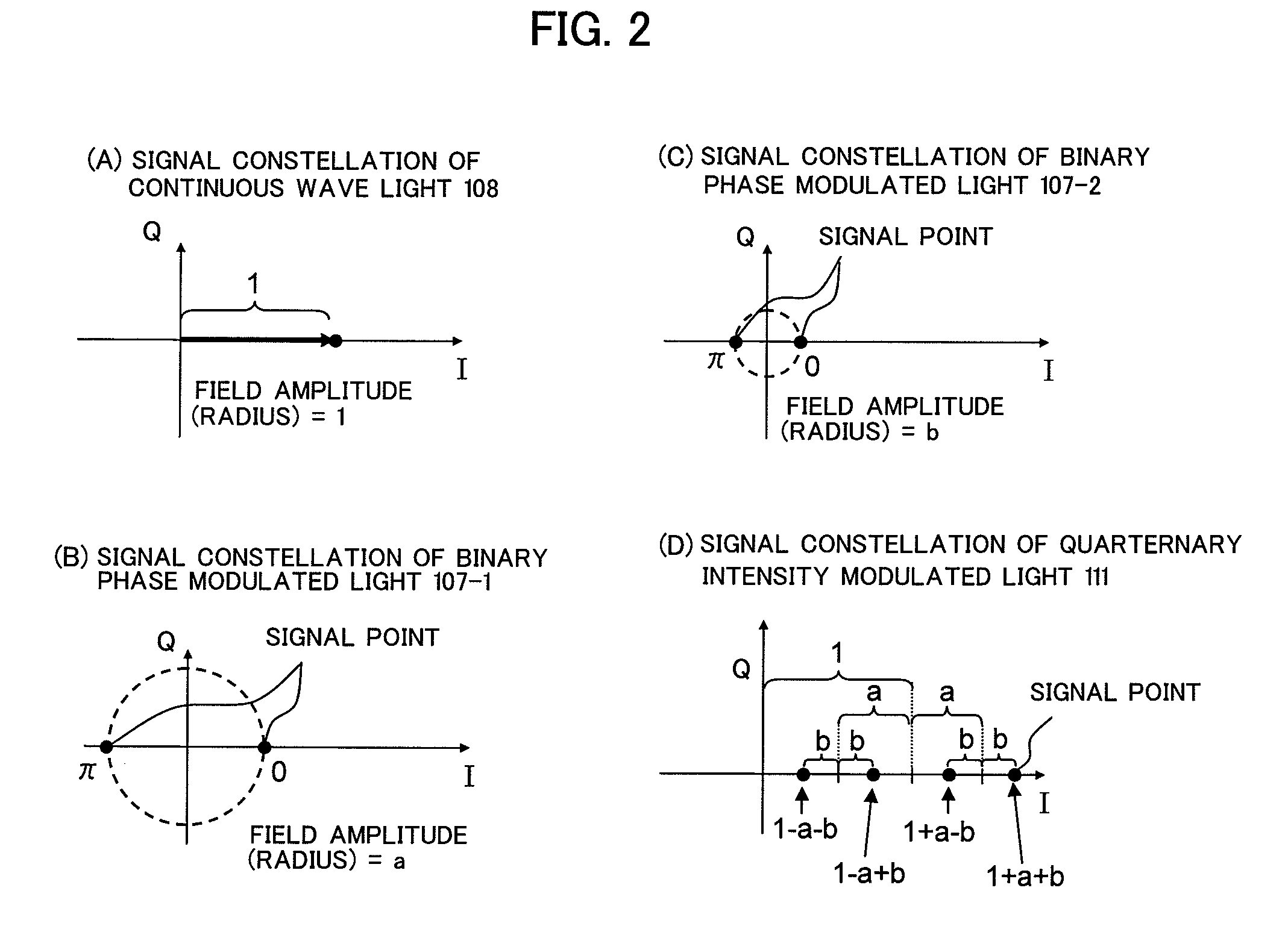
The present invention relates to an optical modulator that generates quaternary amplitude modulated light without inter-symbol-interference by splitting input light into three optical paths, generating a continuous wave signal in a first optical path, generating binary phase modulated lights using a single drive MZ type optical phase modulator in second and third optical paths, and interfering them at in-phase and at field amplitude 1:a:b.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Radar sensing of vehicle occupancy
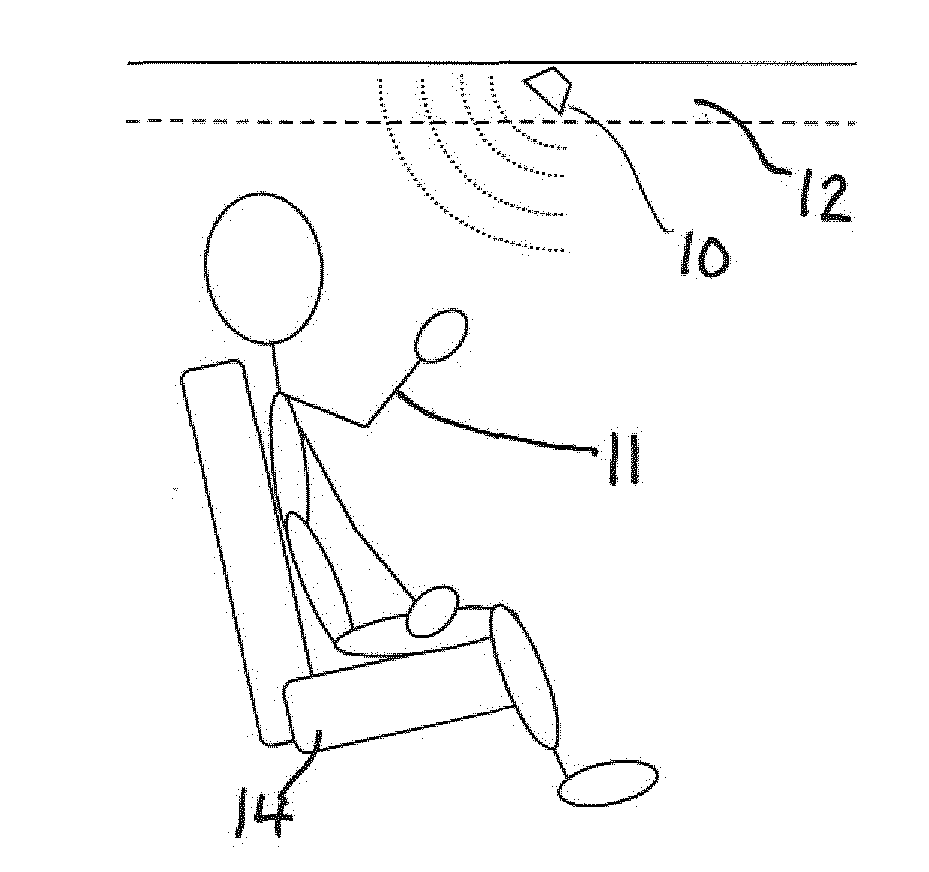
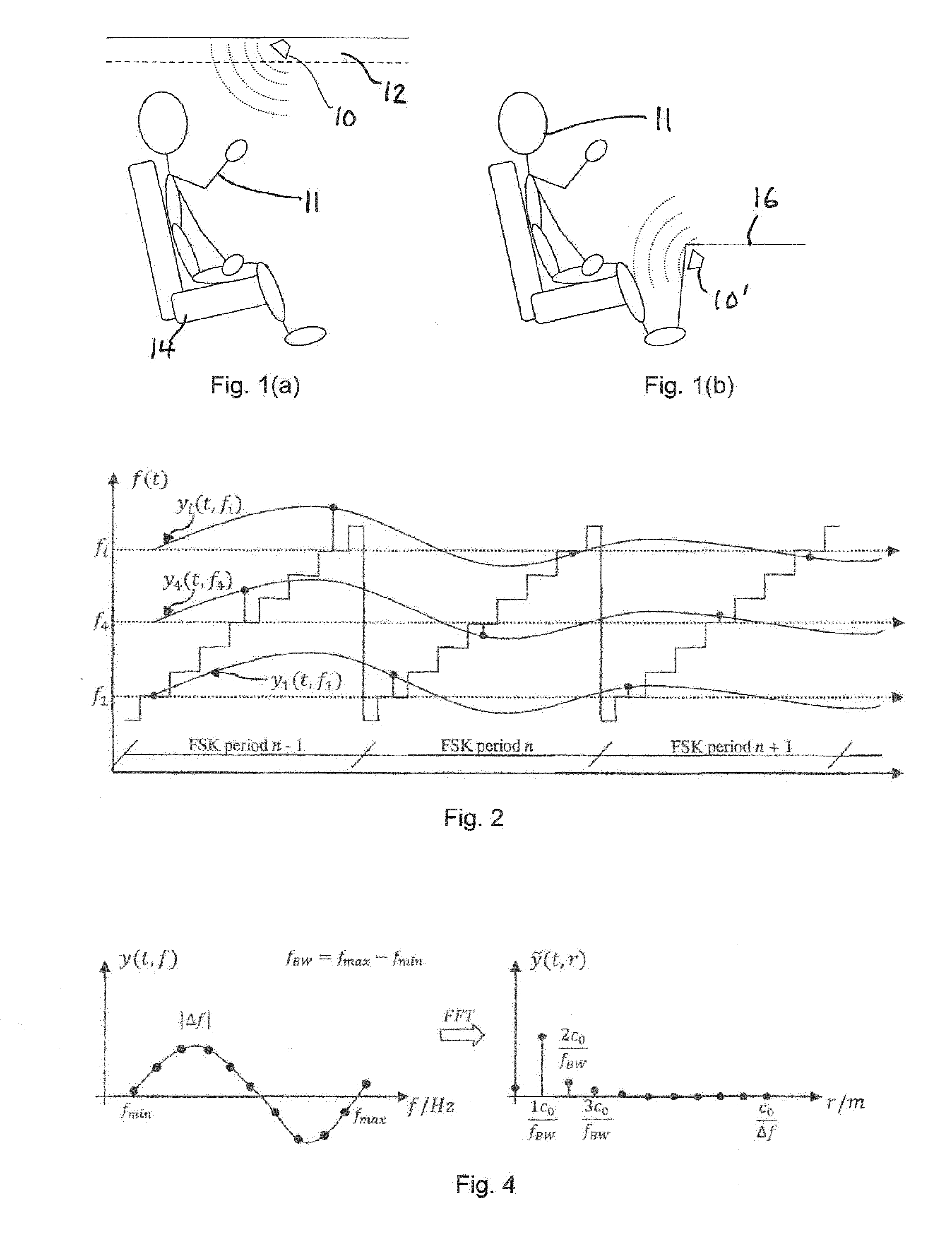
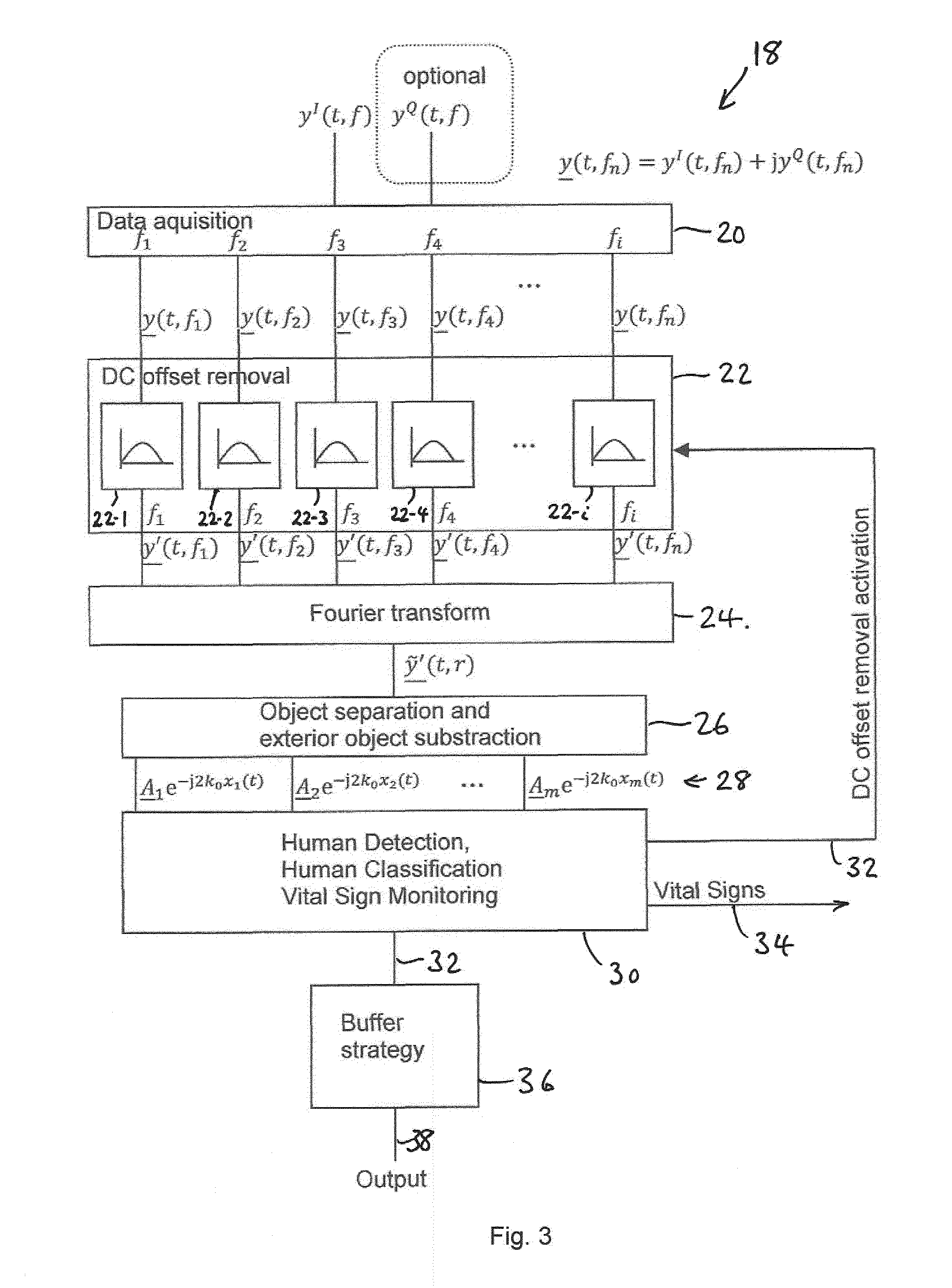
ActiveUS20160200276A1Pedestrian/occupant safety arrangementDiagnostic recording/measuringRadar systemsAirbag
A method for sensing occupancy status within an automotive vehicle uses a radar sensor system, the radar sensor system comprising an antenna system, at least one sensor (10) and processing circuitry (18). The method comprises illuminating, using the antenna system, at least one occupiable position within the vehicle with continuous wave (CW signals), the CW signals being frequency modulated in time. At least one sensor signal (a) reflected as a result of the CW signals, is received using at least one sensor (10) the at least one sensor (10) defining a plurality of receive channels (1 . . . i), each channel having a different frequency (f1 . . . fi). Processing circuitry (18) is operable for applying, for each receive channel (1 . . . i), DC offset removal to the corresponding sensor signal (a) to generate a modified signal (b); and generating, based on the modified signals (b) one or more occupancy status signals (34, 38), the occupancy status signal indicating a property related to said at least one occupiable position. A system for carrying out the method is also disclosed. The techniques provide for in-vehicle occupant detection and classification (airbag suppression), for passenger presence detection and passenger's vital sign monitoring and for seat-belt reminder functionality (SBR). The radar system may consist of one or two (or four) outputs (I / Q) per channel. The received signal may be mixed down with a single channel demodulator or an I / Q demodulator into the baseband. An advanced signal processing including an auto calibration routine and clutter removal may be used to detect occupants and their vital sign (breathing and heart beat) and to determine their distance to the radar system.
Owner:IEE INT ELECTRONICS & ENG SA
Space-borne multichannel microwave switch testing device
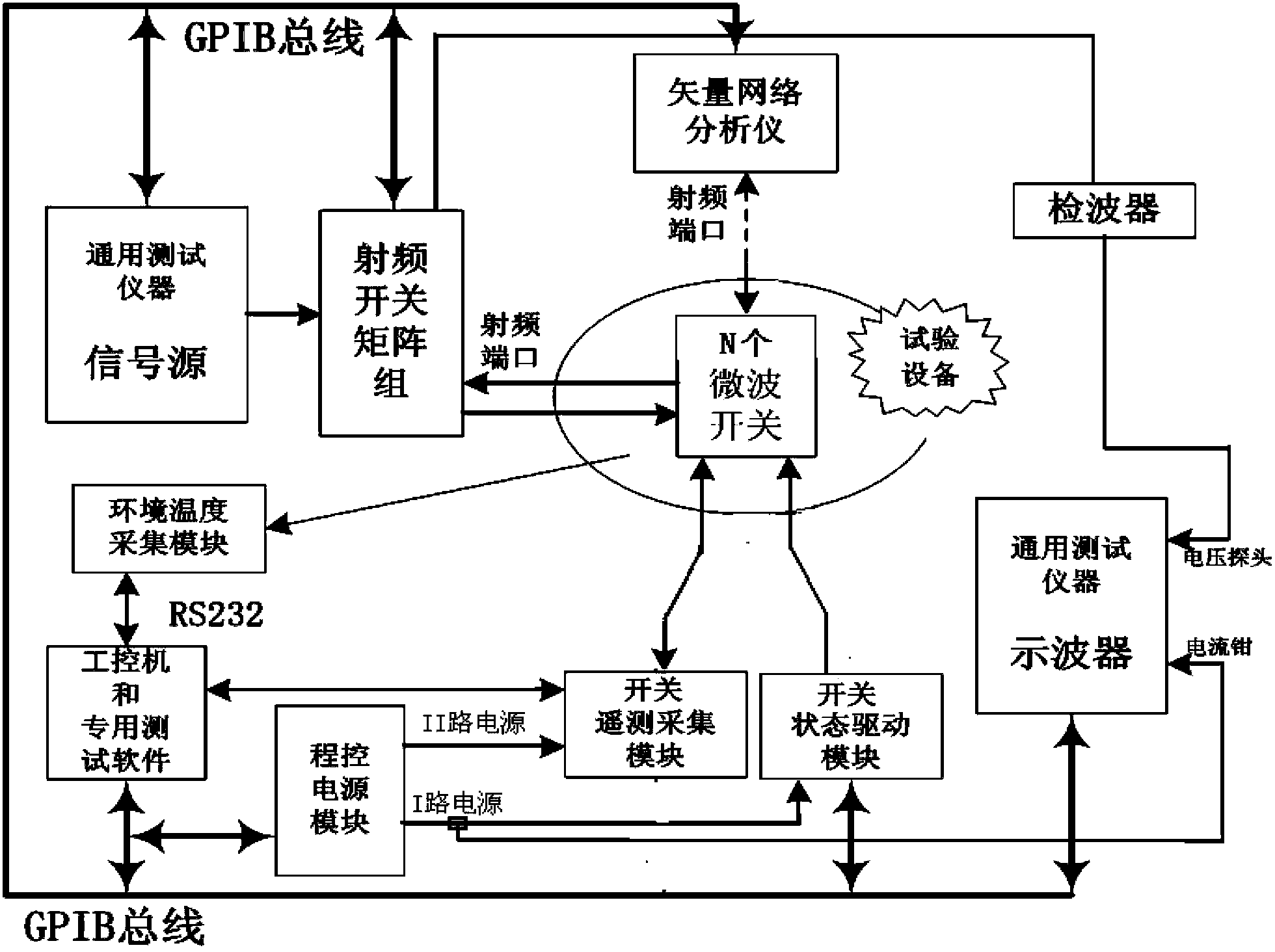
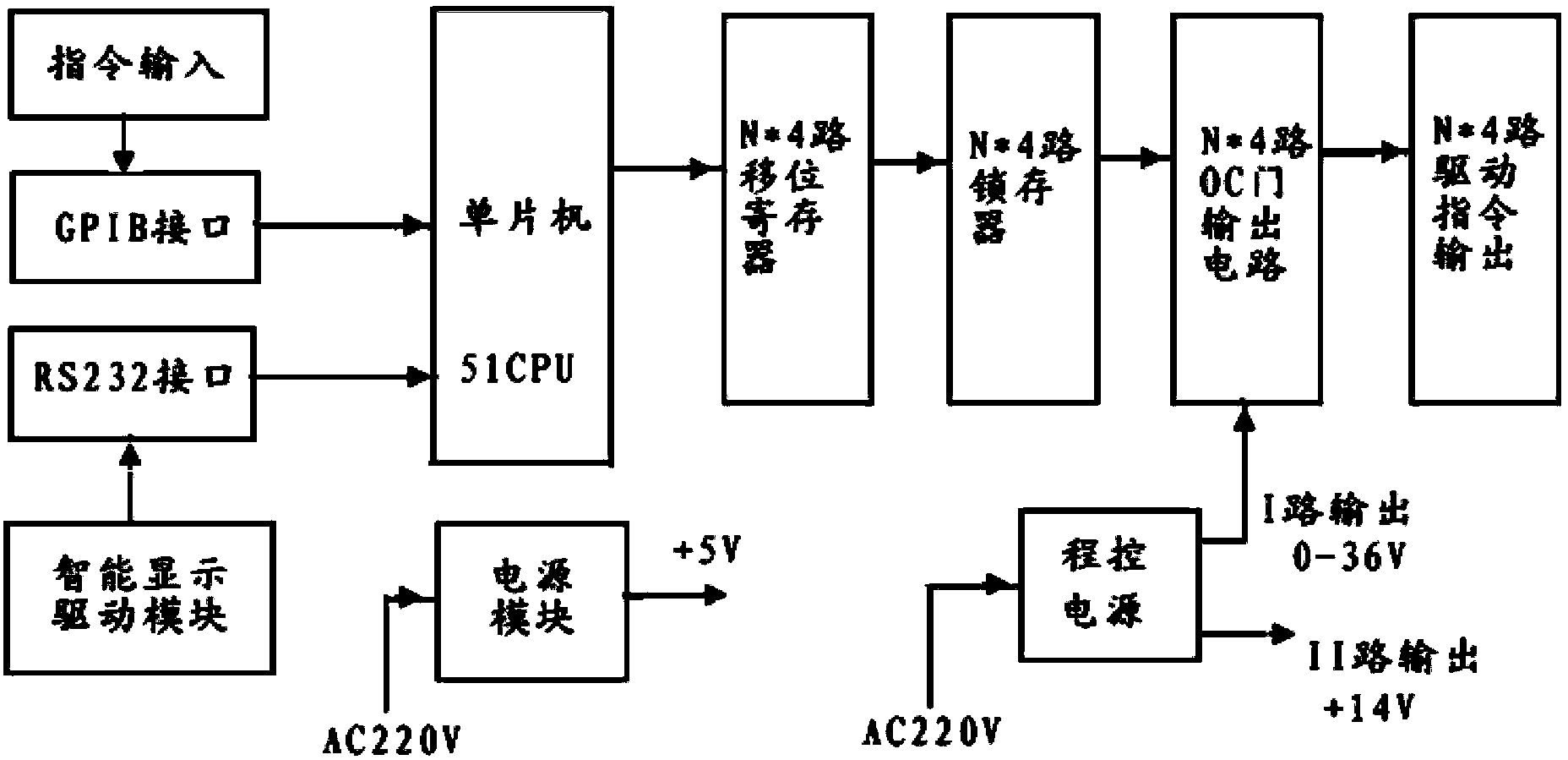
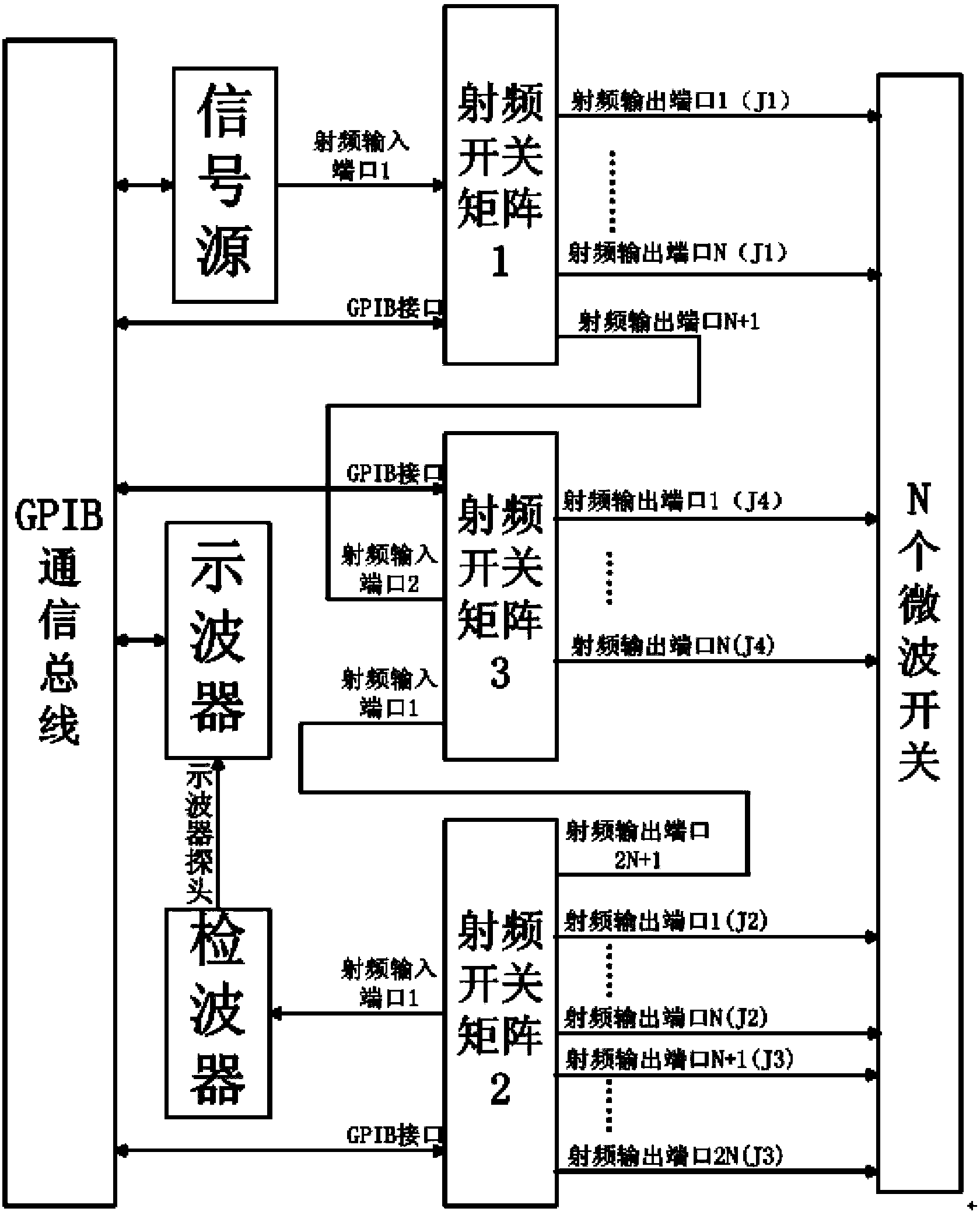
ActiveCN103412255AShort possession timeRealize free conversion connectionCircuit interrupters testingControl signalEngineering
A space-borne multichannel microwave switch testing device comprises a programmable power supply, a switch state driving module, a switch telemetering acquisition module, a radio frequency switch matrix set, a detector, a signal source, an oscilloscope, a vector network analyzer and an industrial personal computer. The industrial personal computer controls the value of voltage outputted by the programmable power supply through a network, controls switching of the radio frequency switch matrix set, controls the switch state driving module to produce commands of independent driving switches in N*4 channels, controls the switch telemetering acquisition module to collect state telemetering signals of independent detected switches in N*4 channels, controls the signal source to produce continuous wave signals, controls the oscilloscope to obtain driving current values of the detected switches and switching time of the detected switches, and controls the vector network analyzer to obtain radio frequency S parameters of the detected switches; state conversion threshold voltage of the detected switches is obtained by changing driving ranges of driving commands; the service life of the detected switches is obtained by recording accurate state conversion frequency of the detected switches.
Owner:西安航天恒星精密机电有限责任公司
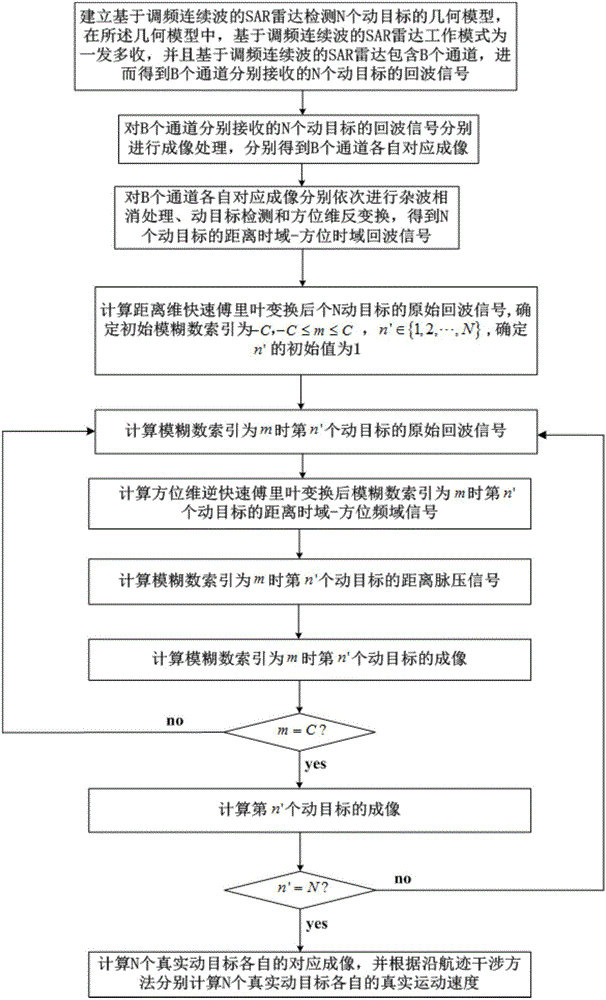
SAR radar moving target detecting and imaging method based on FM continuous wave
InactiveCN106443671AIncrease duty cycleLow powerRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFast Fourier transformTime domain
The invention discloses an SAR radar moving target detecting and imaging method based on an FM continuous wave. The method comprises the steps of establishing a geometric model of an SAR radar based on the FM continuous wave for detecting N moving targets, wherein the SAR radar based on the FM continuous wave comprises B channels, a first channel is a reference channel and N moving targets transmit the FM continuous wave signal, respectively receiving echo signals of the N moving targets by the B channels; after obtaining the echo signals of the N moving targets which are respectively received by the B channels, respectively performing imaging processing, and respectively obtaining images which correspond with the B channels; further successively performing clutter cancellation processing, moving target detecting and orientation dimension reversal conversion, and obtaining distance time domain-orientation time domain echo signals of the N moving targets; performing distance dimension FFT, obtaining original echo signals of the N moving targets after distance dimension fast Fourier transform; further calculating corresponding images of N real moving targets, and respectively calculating respective real moving speeds of the N real moving targets according to an along-track interferometry method.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Simulation method of linear frequency modulation continuous wave synthetic aperture radar video signal
InactiveCN101295019AEasy to getImprove general performanceRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsSynthetic aperture radar
The invention provides a simulation method for a linear frequency modulation continuous wave synthetic aperture radar video signal, which comprises the following steps: simulated synthetic aperture radar system parameter information is set and read; the information parameter of a target is set; a simulated time is treated with discretization; the instantaneous positions of a radar platform and the target are respectively calculated, and a distance vector between a phase center and the target is obtained according to geometric position relation; a one-dimension echo signal is obtained by combining the echo signal mathematic model of the synthetic aperture radar and radar system parameters; the one-dimension signal is divided according to pulse repetition period and formatted into a two-dimension signal, the two-dimension signal with Na multiplied by Nr is obtained after the total data is stored, thus finishing the fine simulation of the linear frequency modulation continuous wave synthetic aperture radar video signal. The more accurate echo simulation signal can be obtained by utilizing the simulation method, and the simulation method is especially suitable for a frequency modulation continuous wave signal with high-speed movement, long distance and severe oblique observation condition of the radar and has more excellent realization efficiency, and stronger adaptability and compatibility.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Optical modulator
InactiveUS20090324247A1Improve optical signal receiving sensitivityEfficiently transmitting informationElectromagnetic transmittersNon-linear opticsContinuous wave signalOptical modulator
The present invention relates to an optical modulator that generates quaternary amplitude modulated light without inter-symbol-interference by splitting input light into three optical paths, generating a continuous wave signal in a first optical path, generating binary phase modulated lights using a single drive MZ type optical phase modulator in second and third optical paths, and interfering them at in-phase and at field amplitude 1:a:b.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
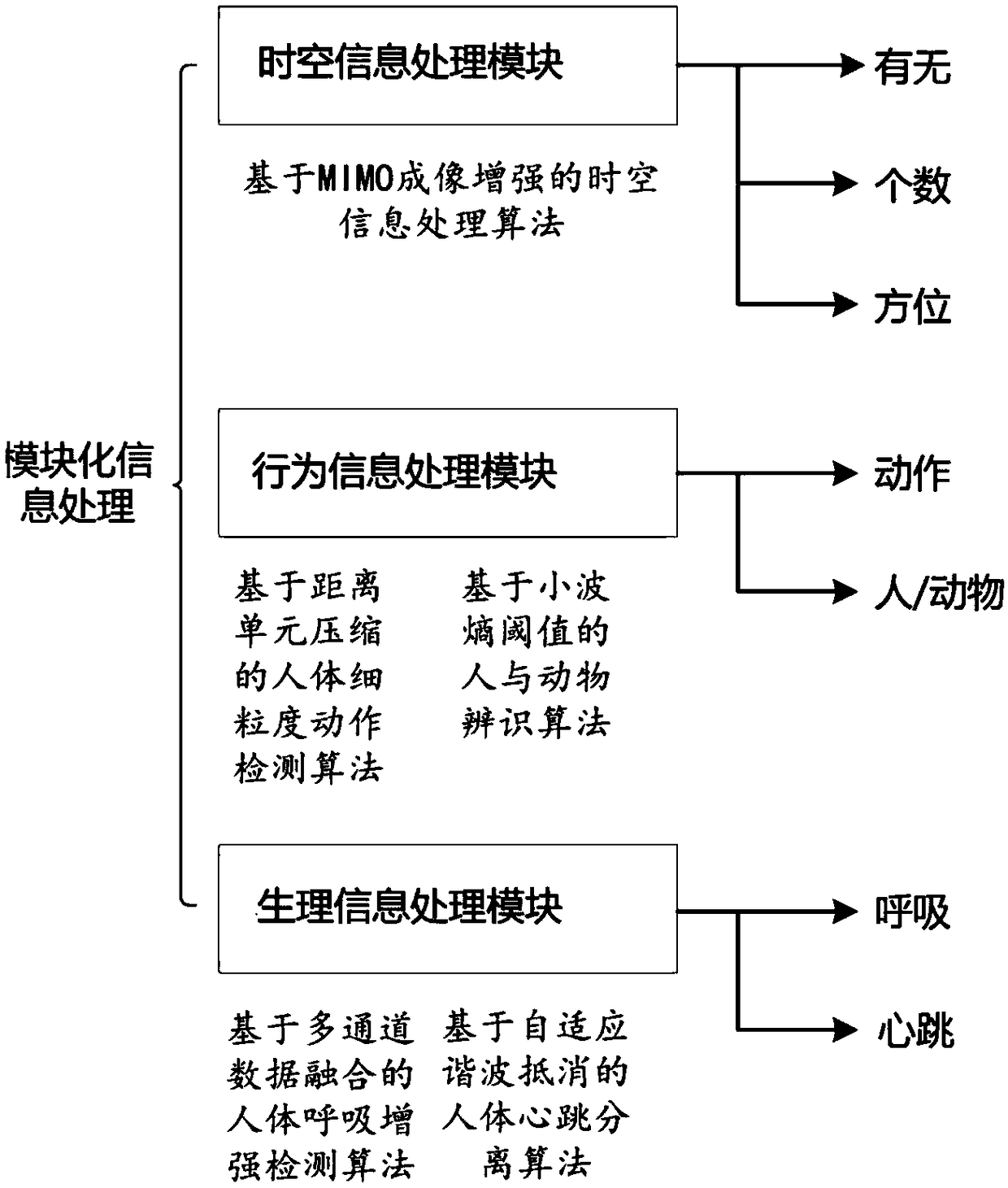
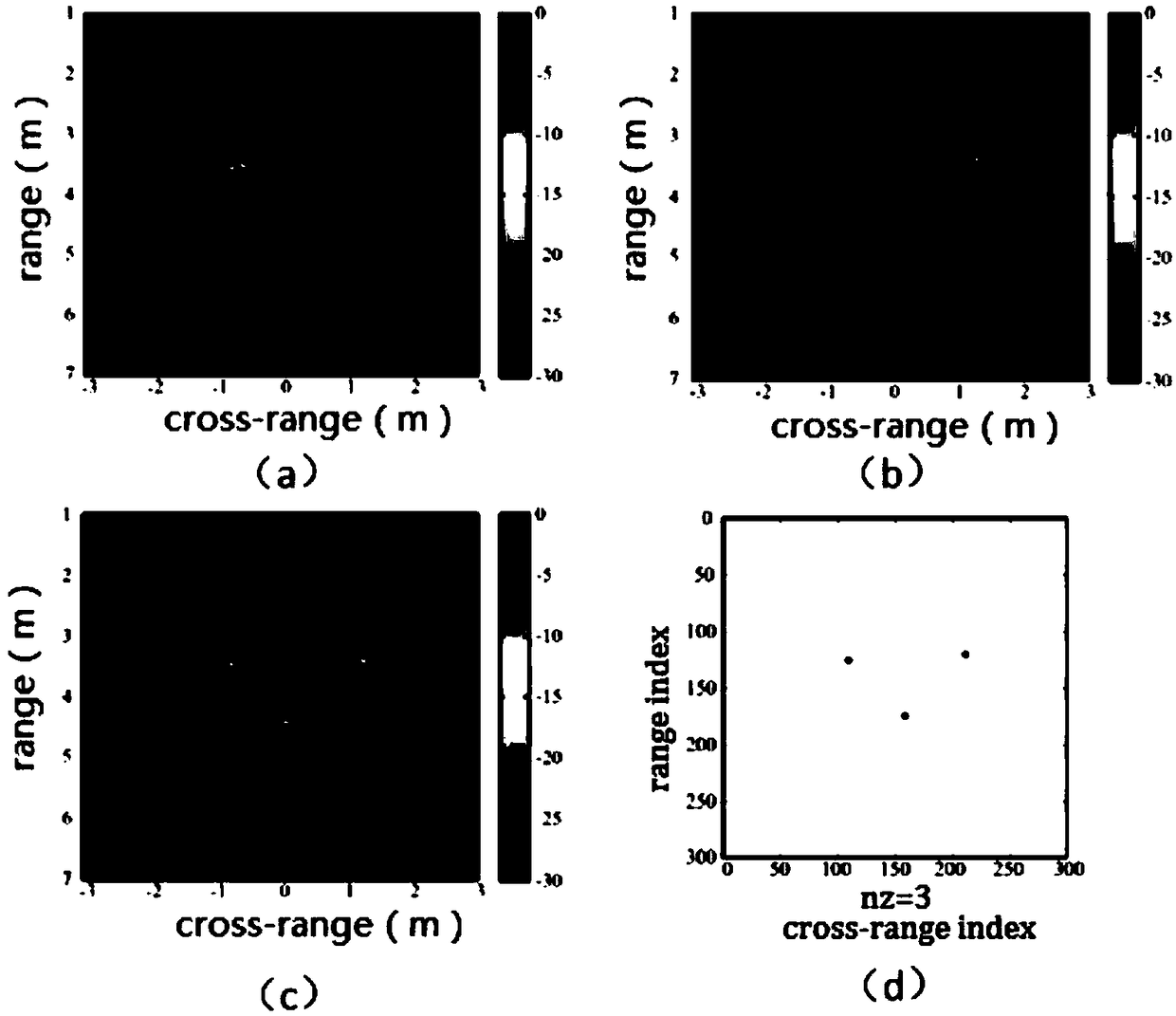
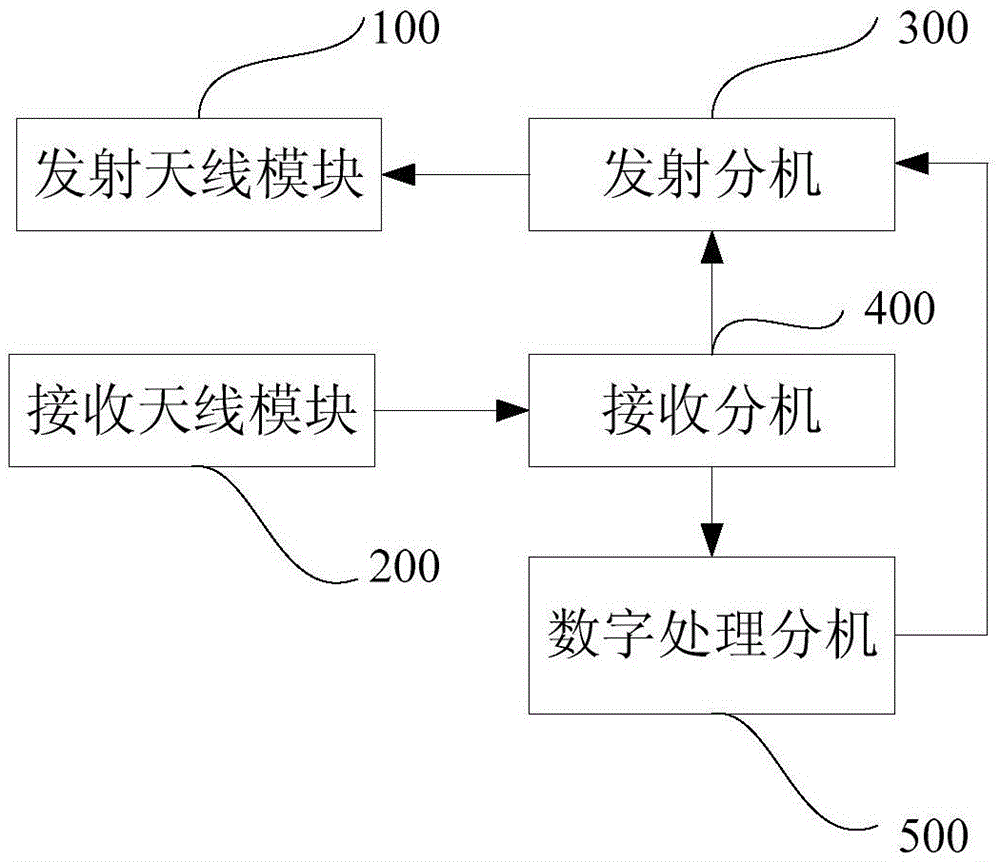
UWB (Ultra-Wide Band) based multi-information perception bioradar system and method thereof for obtaining target information
PendingCN109507653AImprove information perceptionImprove practicalityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionInformation processingSignal on
The invention particularly discloses a UWB (Ultra-Wide Band) based multi-information perception bioradar system and a method thereof for obtaining target information. The multi-information perceptionbioradar system comprises a transmitter system, a receiver system, an antenna system and a control and processing system, wherein the antenna system adopts the configuration of an array antenna with two transmitting antennas and four receiving antennas; the transmitter system is used for receiving a working instruction of the control and processing system, generating equally spaced step frequencycontinuous wave UWB signals on the basis of a constant-temperature crystal oscillator and sending the signals to the transmitting antennas; the receiver system is of a superheterodyne structure; a receiver sends a bioradar echo signal into the control and processing system; and the control and processing system comprises a spatio-temporal information processing module, a behavior information processing module and a physiological information processing module. Through adopting a step frequency continuous wave signal system, a multi-channel antenna array and a module information processing technique, the comprehensive perception, about the spatio-temporal, behavior and physiological information of a human body, of a bioradar is realized; and the information perception ability and the utilityvalue of the bioradar are improved.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Meteorological radar system based on continuous wave system and control method
InactiveCN105158763AHigh range resolutionSuitable for refined weather detectionICT adaptationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionWeather radarRadar systems
The invention relates to a meteorological radar system based on continuous wave system and a control method, wherein the system comprises an emission extension which is used to receive a linear frequency modulation continuous wave signal from an extension and obtain a continuous wave emission signal after amplification processing, and output the signal to an emission antenna module; a reception extension which is used to output the linear frequency modulation continuous wave signal to the emission, receive a meteorological echo signal from an antenna module, and output the signal to a digital processing extension after frequency conversion amplification processing; an emission antenna module, which is used to emit the continuous wave emission signal; a reception antenna module, which is used to receive the meteorological echo signal; and a digital processing extension, which is used to receive the signal from the extension and process it to obtain the meteorological data information and perform instruction control to the radar system state at the same time. According to the continuous wave system, the emission signal employs continuous wave signal, which has a higher distance resolution compared to a pulse system radar, therefore the meteorological radar system is especially suitable for refined meteorological detection.
Owner:ANHUI SUN CREATE ELECTRONICS
Target detection method of auxiliary vehicle driving radar
ActiveCN106338727AReduce distanceReduce precisionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionBlind zoneEngineering
The invention discloses a target detection method of an auxiliary vehicle driving radar. The method comprises steps that an emission waveform mode of the radar is determined to be a multi-order frequency stepping continuous wave MS-FSCW, one integral MS-FSCW waveform comprises two parts of an upper frequency sweeping segment and a lower frequency sweeping segment, and signals of each frequency sweeping segment are composed of multiple frequency stepping dot frequency continuous wave signals arranged in an alternative mode; MS-FSCW emission waveform parameters of the radar are determined, waveform parameters are determined according to a largest distance measurement scope, a largest speed measurement scope, distance measurement precision and a system detectable smallest signal to noise ratio, and the waveform parameters comprises frequency sweeping band width, a frequency sweeping period, a sampling rate, the quantity of frequency stepping continuous wave signals and initial frequency difference among the frequency stepping continuous wave signals; an MS-FSCW emission signal echo of the radar is processed to acquire a target distance and the speed information. Through the method, distance and speed detection blind zones caused by transceiving leakage can be reduced, and target distance measurement and speed measurement precision is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Unmanned airborne system for SAR imaging and moving-target detection by utilizing Ka-frequency-band frequency modulated continuous waves
InactiveCN104698458AObvious angular features of the targetGood for target recognitionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionLow frequency bandBand width
The invention discloses an unmanned airborne system for SAR imaging and moving-target detection by utilizing millimeter-wave Ka-frequency-band frequency modulated continuous waves. Ka-frequency-band wavelength is shorter, and an antenna is smaller than a lower-frequency-band antenna in size under the condition of the same beam width. A millimeter-wave device is smaller than a lower-frequency-band device in size, weight and power consumption. The system can be miniaturized, images finer than other lower-frequency-band images can be obtained by utilizing millimeter-wave Ka-frequency-band signals to perform SAR imaging, target edge and corner characteristics are obvious, and target recognition is facilitated. Ka-frequency-band signals of higher relative band width can be obtained, so that higher image resolution can be obtained compared with lower-frequency-band signals. The system for SAR imaging by utilizing the frequency modulated continuous waves is simple in device, low in complexity, small in data volume by adopting a de-chirp mode and capable of performing real-time imaging processing.
Owner:山东华宇航天空间技术有限公司北京分部
Radar system
ActiveUS20100103023A1Prevent radio wave interferenceAvoid interferenceRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsEngineering
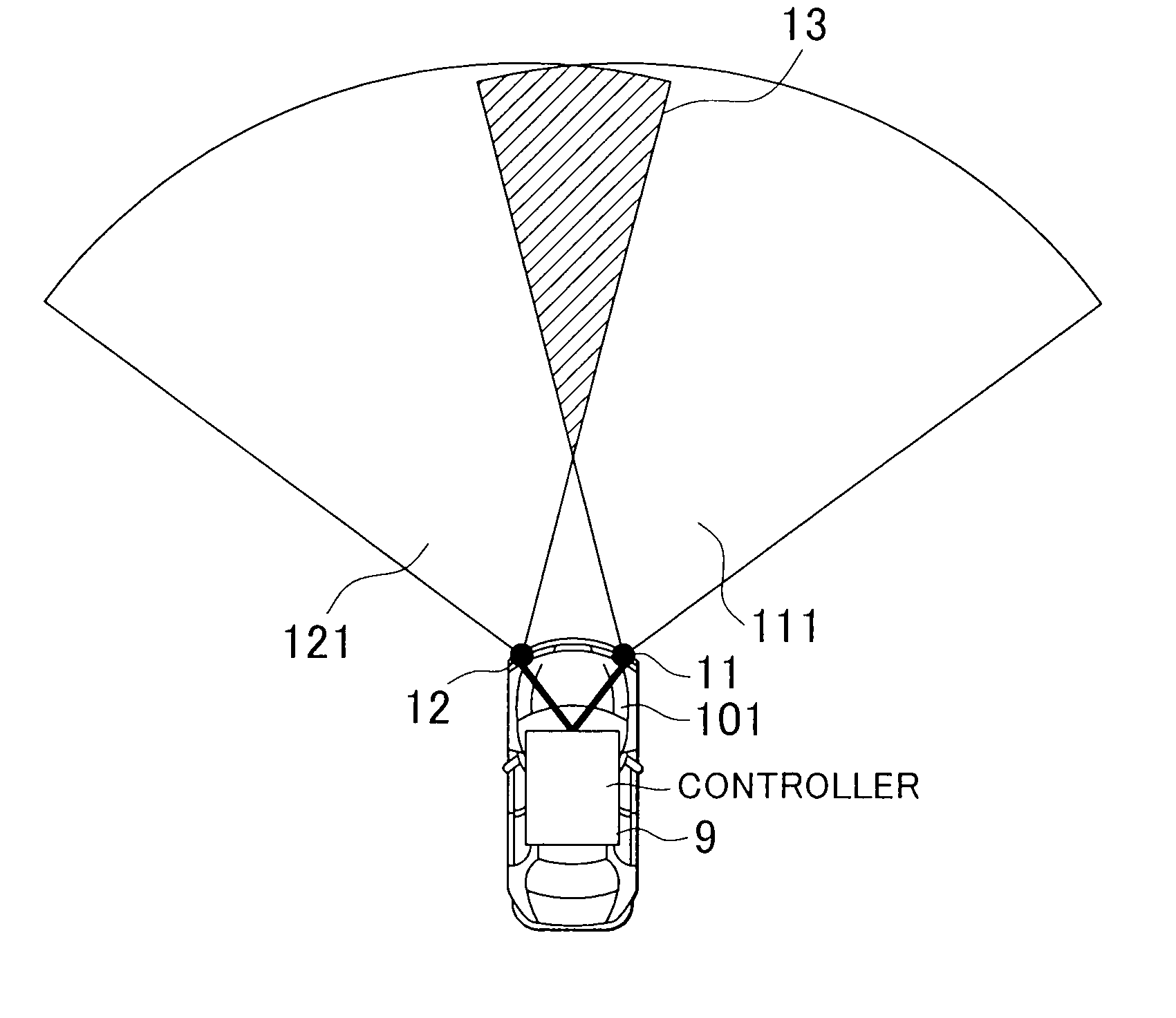
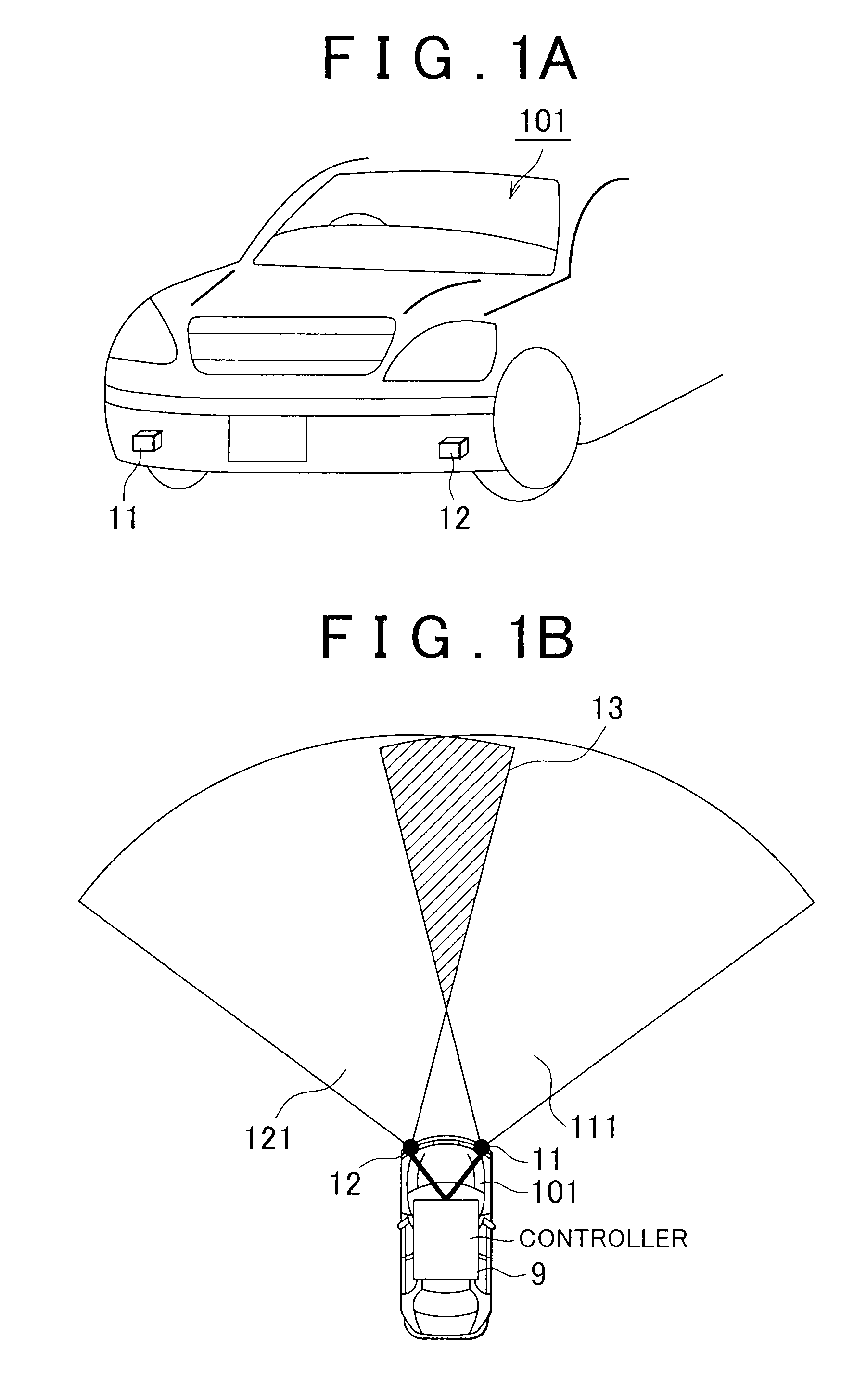
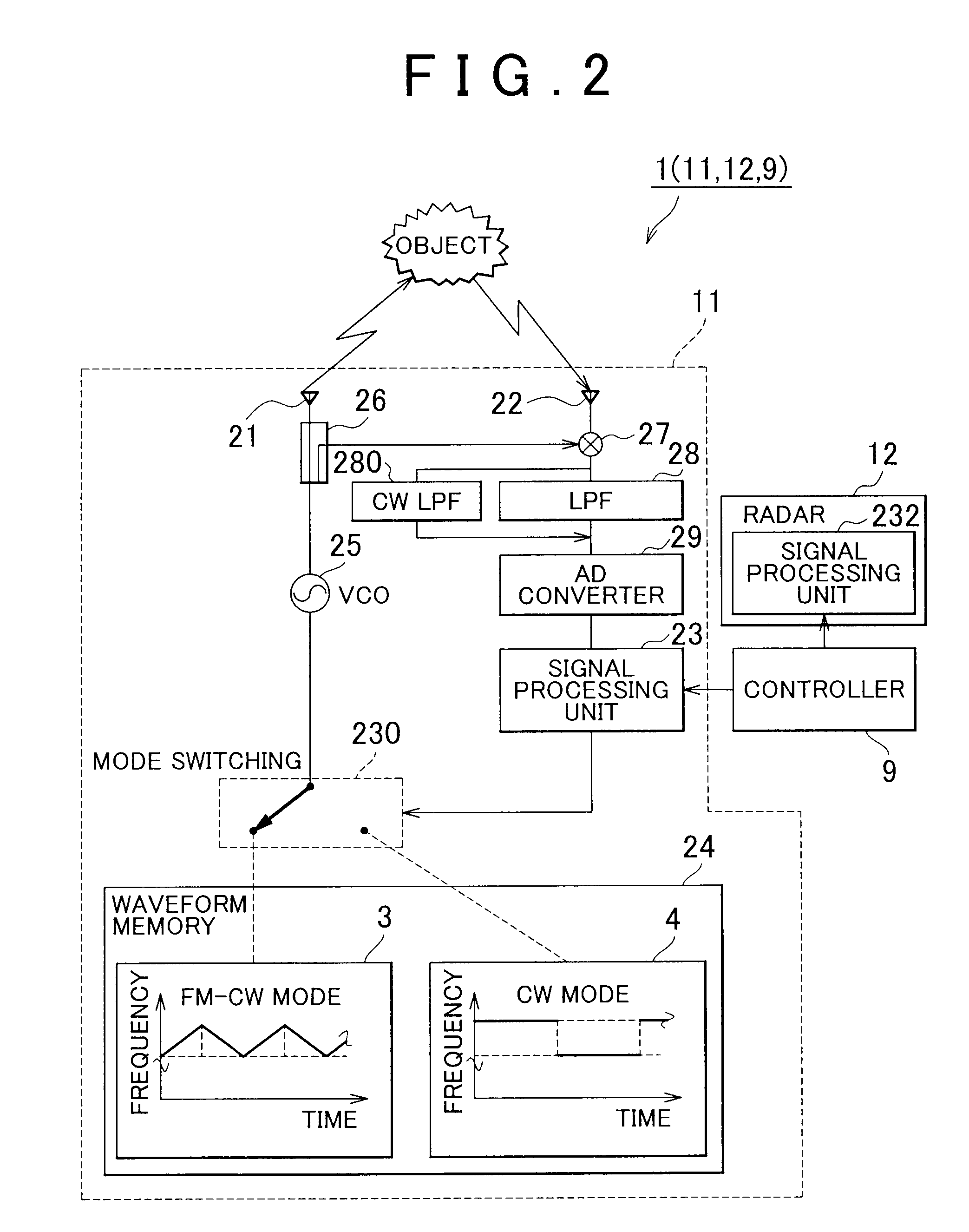
A radar system includes radars and a controller. The controller controls waveform patterns of the radars. As a signal processing unit of each of the radars receives an instruction from the controller, the signal processing unit selects a frequency modulation pattern of a VCO between an FM-CW mode and a CW mode stored in a waveform memory to perform mode switching, and then outputs a radio wave from a transmission antenna. Then, the controller instructs each signal processing unit for a frequency modulation pattern of each radar or an output timing of each pattern so that a time, at which continuous wave signals output from the radars have the same frequency, is not continuous.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Forward and reverse passive inter-modulation (PIM) testing device and method for isolator
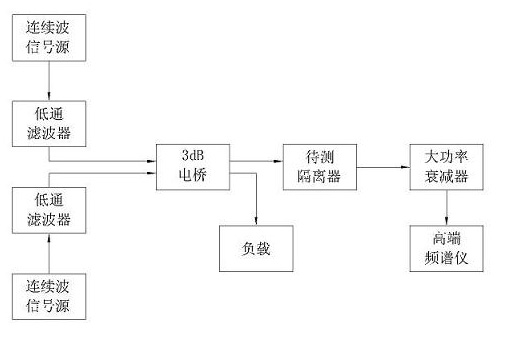
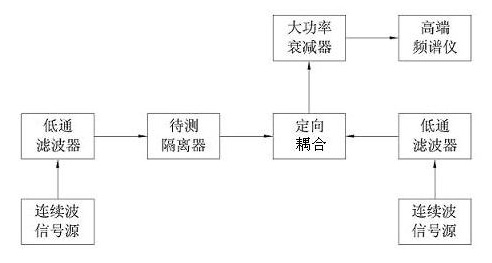
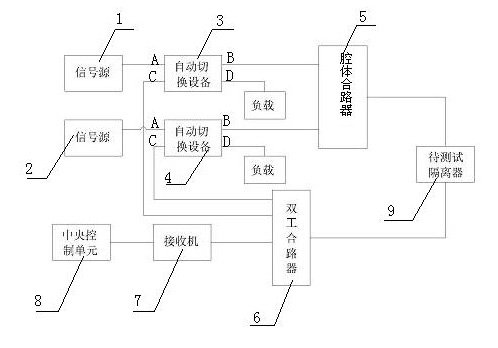
InactiveCN102025432ALower requirementReduce the burden onTransmitters monitoringTest efficiencyRadio frequency signal
The invention discloses a forward and reverse passive inter-modulation (PIM) testing device and method for an isolator. The testing device comprises a first continuous wave signal source, a second continuous wave signal source, first automatic switching equipment, second automatic switching equipment, a cavity combiner, a duplex combiner, a receiver and a central control unit. The testing method comprises the following steps: setting the testing mode to be forward or reverse testing; setting carrier frequency and carrier power required in a test; testing the forward or reverse PIM level of the isolator; and calculating the difference value between a PIM level value and a carrier power value, wherein, the difference value is the relative inter-modulation level. In the invention, different test platforms are not required in the case of the forward and reverse PIM testing, thus improving the maneuverability and the testing efficiency, lowering the residual inter-modulation of a system, improving the testing accuracy, eliminating power consumption of a 3dB electrical bridge, and enhancing the transmission efficiency and performance of a radio frequency signal; and a central processingunit is adopted instead of a frequency spectrograph, so the testing result can be directly obtained.
Owner:镇江市澳华测控技术有限公司
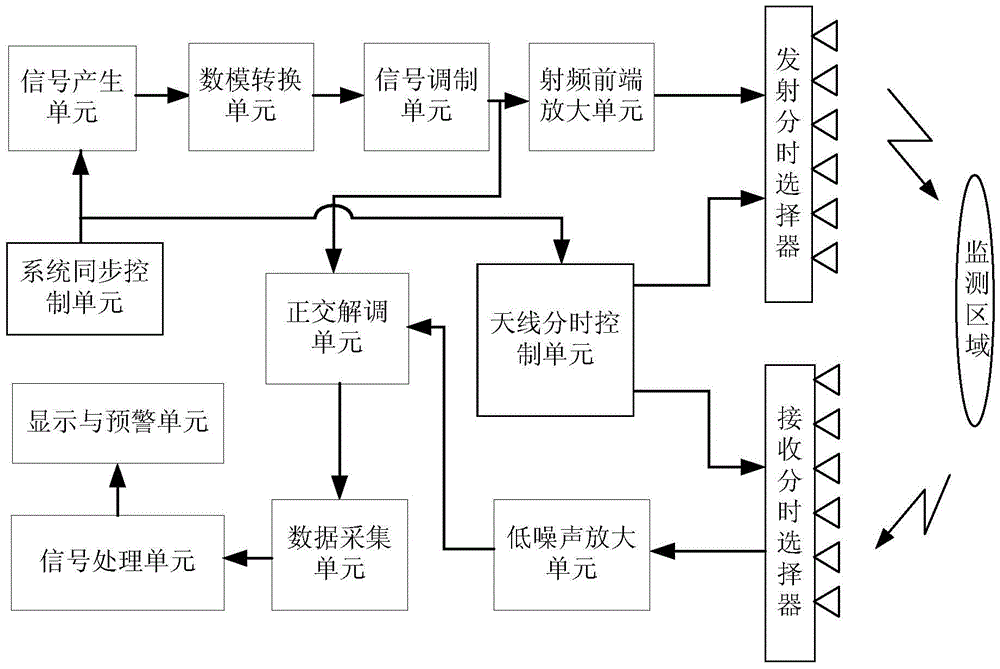
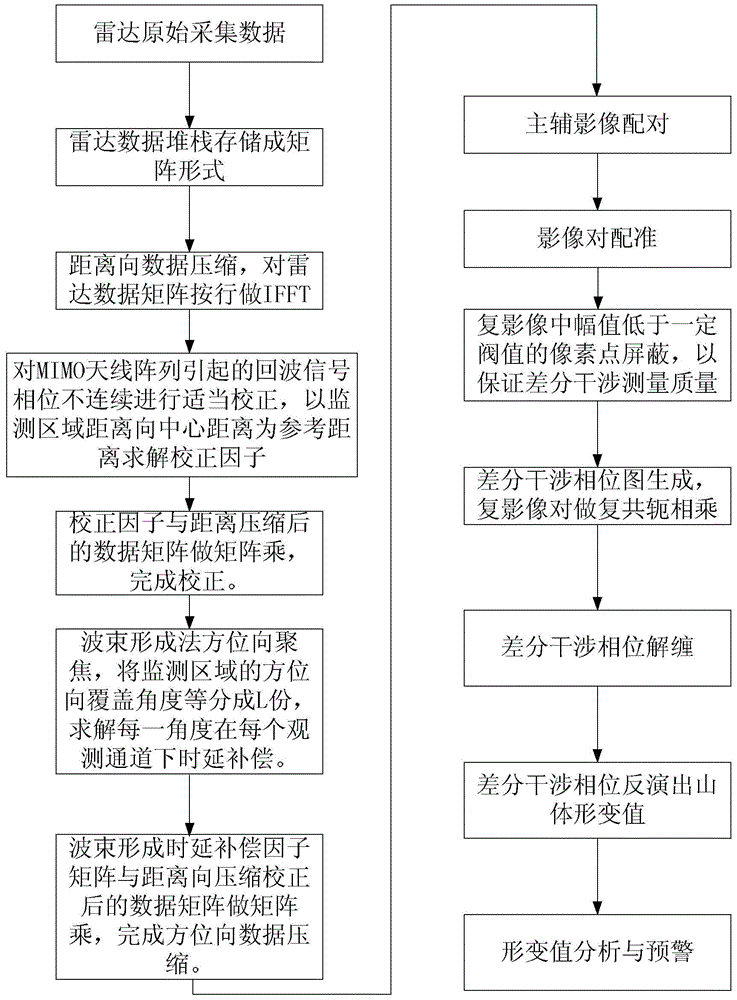
Landslide MIMO radar monitoring system and monitoring method
ActiveCN104991249AFast data collectionAdjustable arrayRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTime delaysData acquisition
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
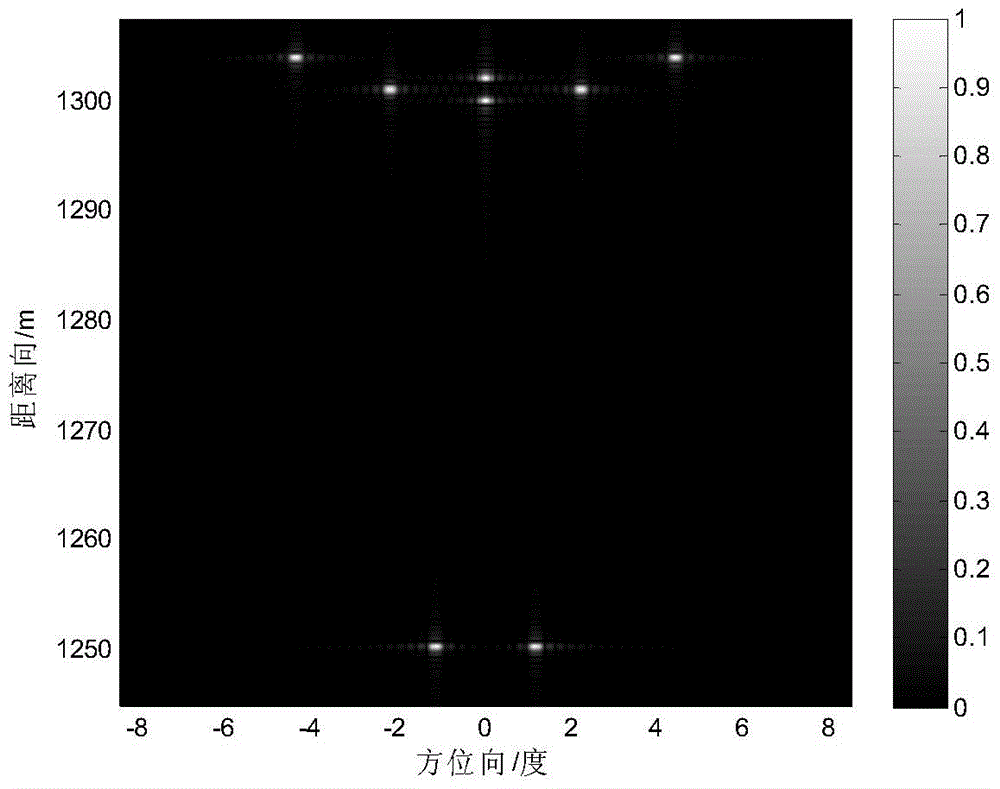
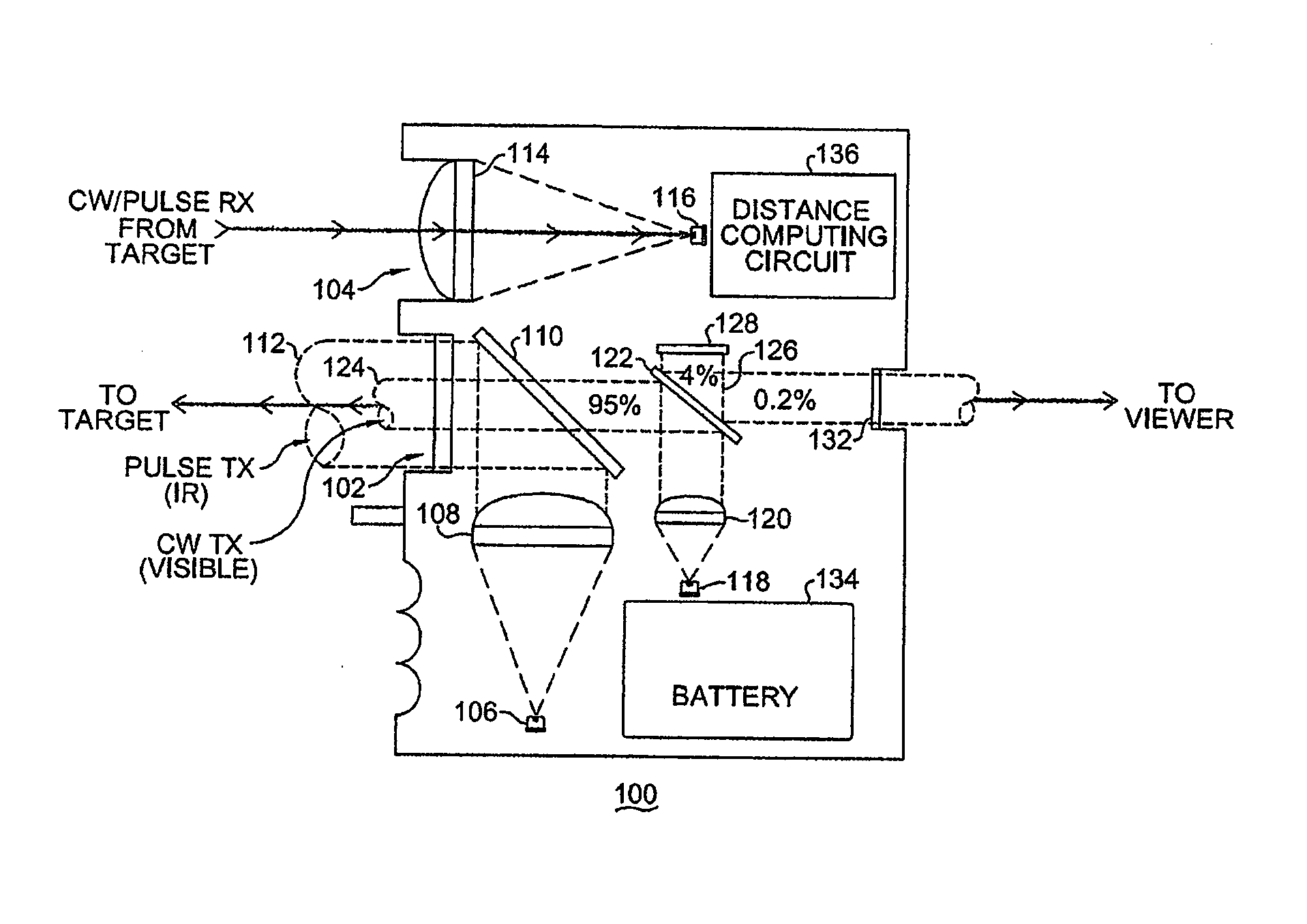
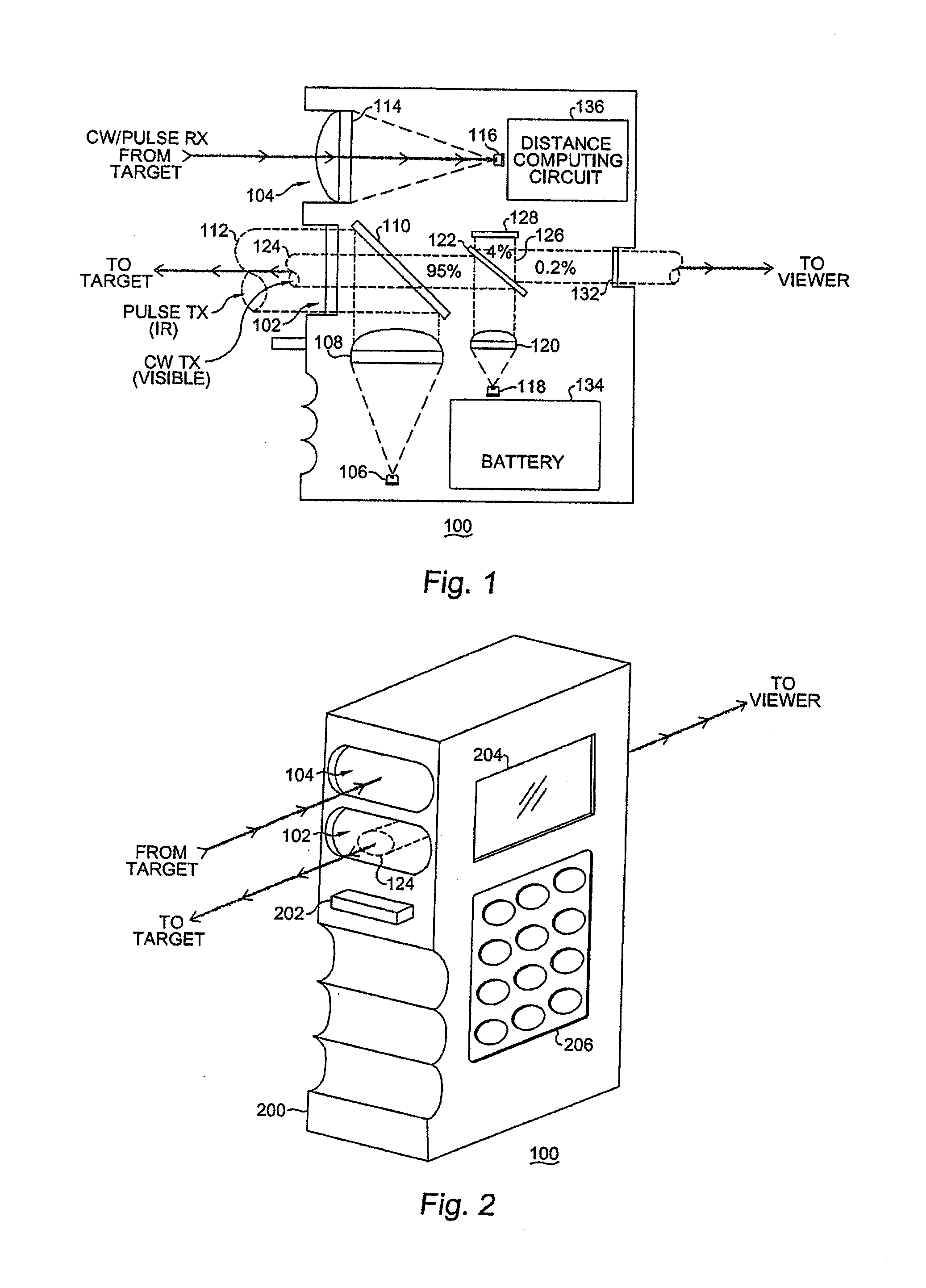
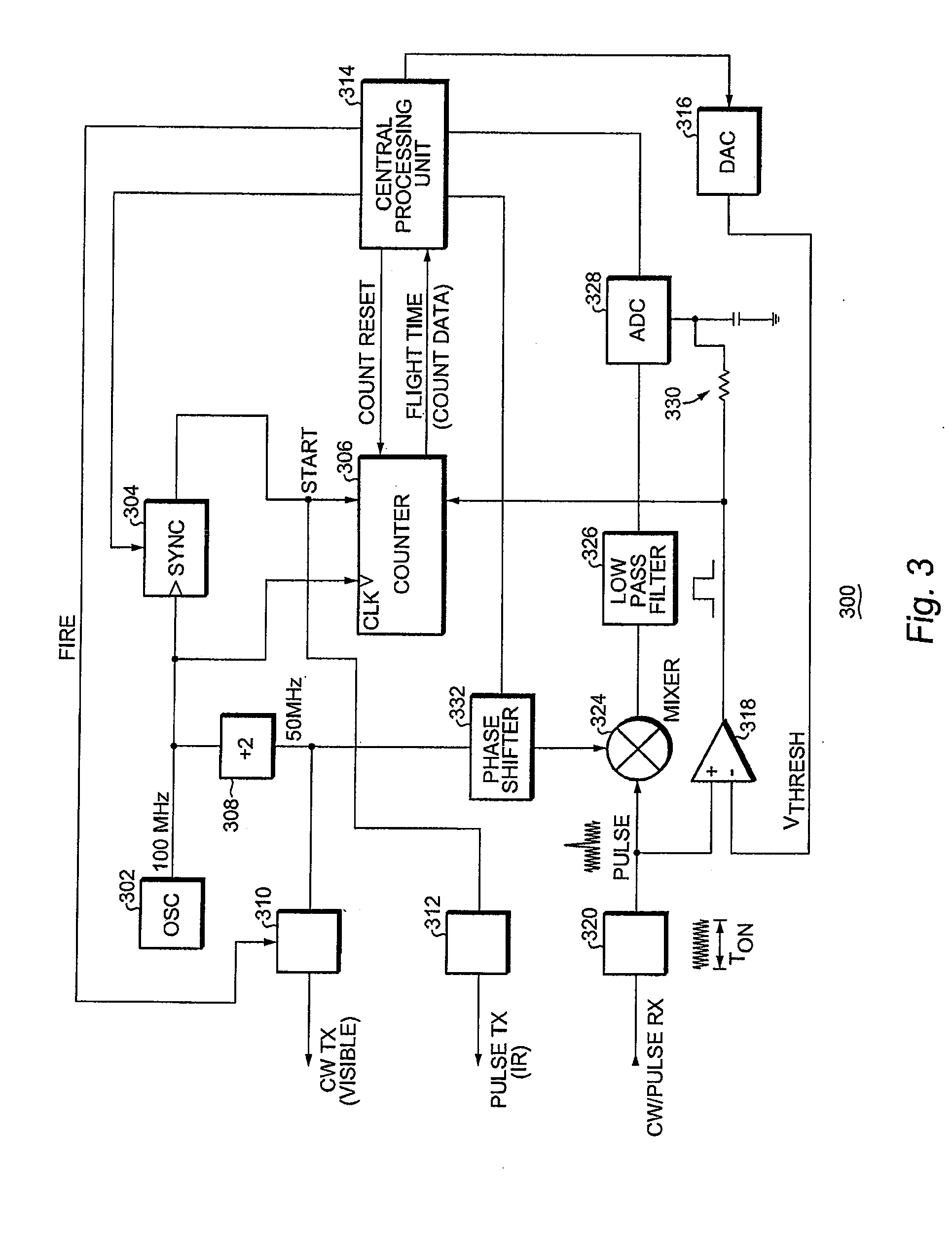
System and method for a rangefinding instrument incorporating pulse and continuous wave signal generating and processing techniques for increased distance measurement accuracy
ActiveUS20140071432A1Improve ranging accuracyEfficient solutionOptical rangefindersActive open surveying meansAmbiguityContinuous wave signal
A system and method for a rangefinding instrument incorporating pulse and continuous wave signal generating and processing techniques for increased distance measurement accuracy. The use of the former technique effectively solves the ambiguity issues inherent in the latter while allowing for relatively simple circuit implementations. Thus, a potentially more accurate phase-based distance measurement technique can be utilized which is also completely independent of the maximum range to the target.
Owner:LASER TECH INC +1
Full-duplex ultrasonic through-wall communication and power delivery system with frequency tracking
ActiveUS20150049587A1Accurate signalSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionHigh level techniquesElectric power transmissionEngineering
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
TD-SCDMA signal generator and its regulating method
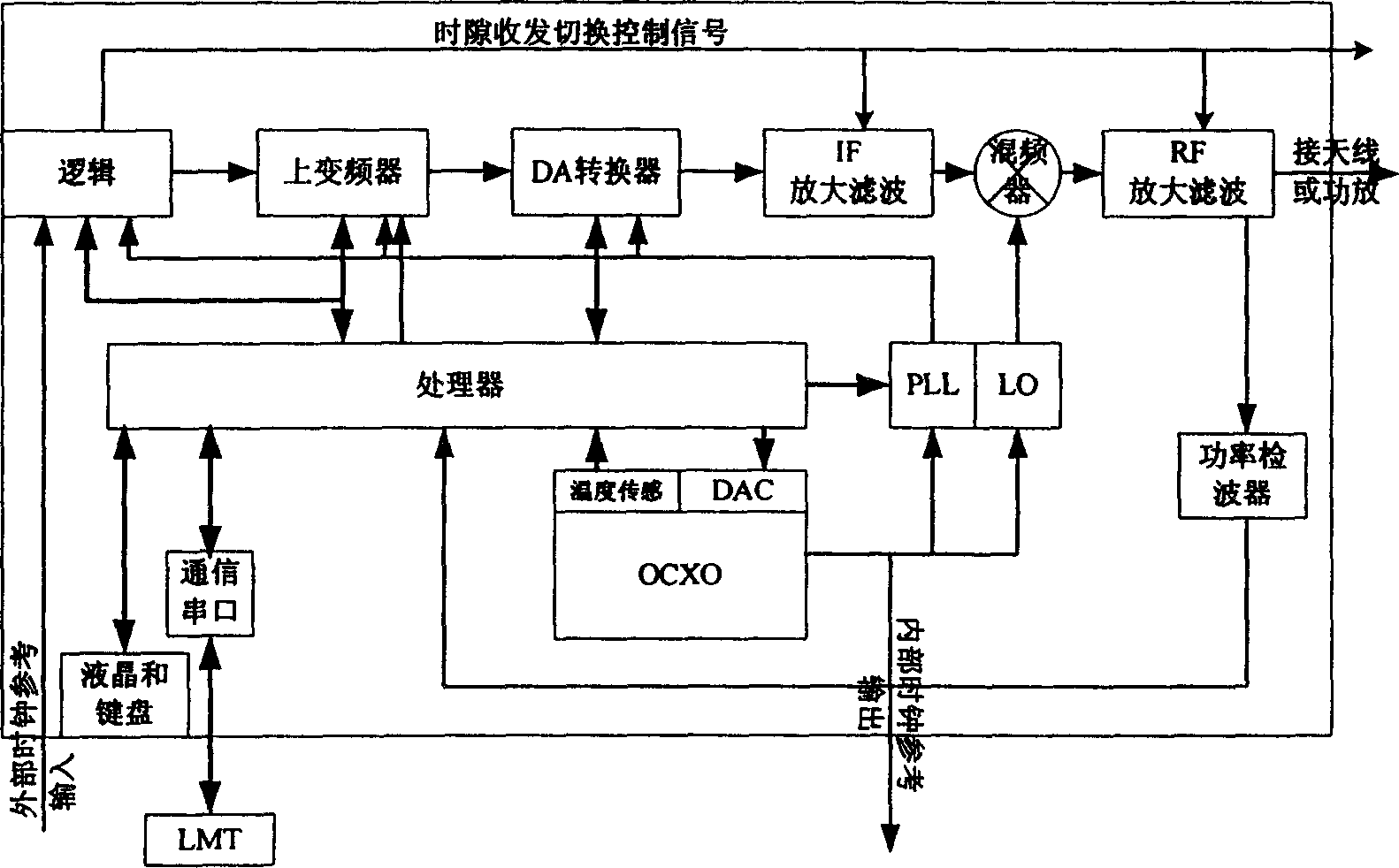
ActiveCN1866799AEasy to testMultiplex code generationTransmission monitoringFrequency changerPower detector
The invention discloses a signal generating device and calibration method of TD-SCDMA system net rule, net optimization and facility test, which comprises the following parts: logical module, up converter, DA converter, IF magnification filtering modular, frequency mixer, RF magnification filtering modular, power detector, handler, thermostatic crystal oscillator, temperature sensing modular, voltage controller, phase-locked loop, local oscillator, communication serial port, wherein the device can launch continuous wave signal of base station work frequency band, TD-SCDMA signal of launching base station or terminal, which can realize TD-SCDMA network planning, network optimization and device test work.
Owner:武汉烽合智达信息技术有限责任公司
Radar system
ActiveUS7567202B2Easy to controlGenerate accuratelyAntennasRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
Embodiments of the invention are concerned with a radar system, and relates specifically to scanning radar systems that are suitable for detecting and monitoring ground-based targets.In one aspect, the radar system is embodied as a scanning radar system comprising a frequency generator, a frequency scanning antenna, and a receiver arranged to process signals received from a target so as to identify a Doppler frequency associated with the target, wherein the frequency generator is arranged to generate a plurality of sets of signals, each set having a different characteristic frequency, the frequency generator comprising a digital synthesiser arranged to modulate a continuous wave signal of a given characteristic frequency by a sequence of modulation of patterns whereby to generate a said set of signals, and wherein the frequency scanning antenna is arranged to cooperate with the frequency generator so as to transceive radiation over a region having an angular extent dependent on the said generated frequencies.Embodiments of the invention thus combine digital synthesiser techniques, which are capable of precise frequency generation and control, with passive frequency scanning and Doppler processing techniques. This enables accurate control of range and of scan rates, and enables optimisation of range cell size for factors such as slow and fast target detection and Signal to Noise ratio, and thus enables detection of targets located at distances considerably farther away than is possible with known systems having similar power requirements.
Owner:BLIGHTER SURVEILLANCE SYST LTD
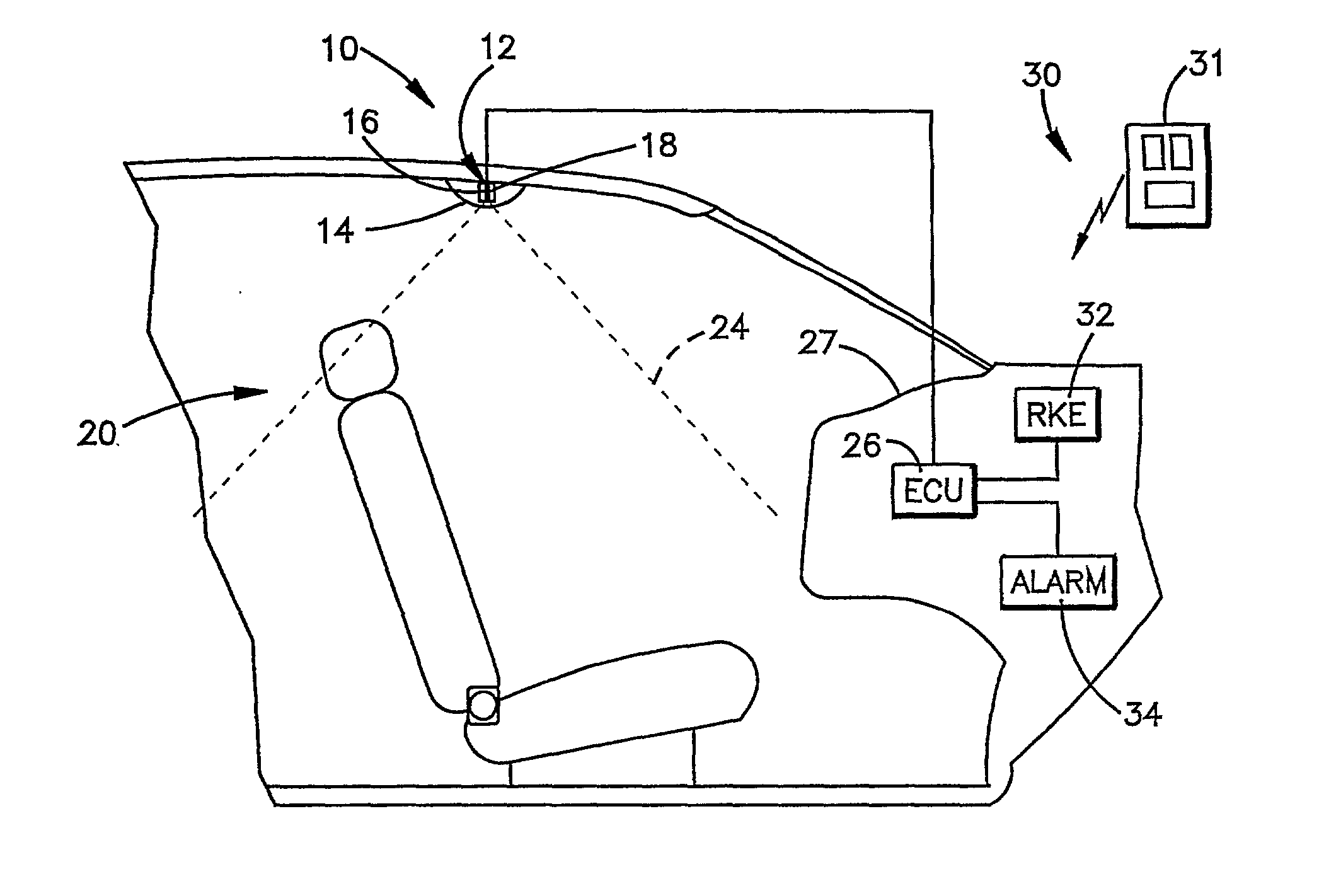
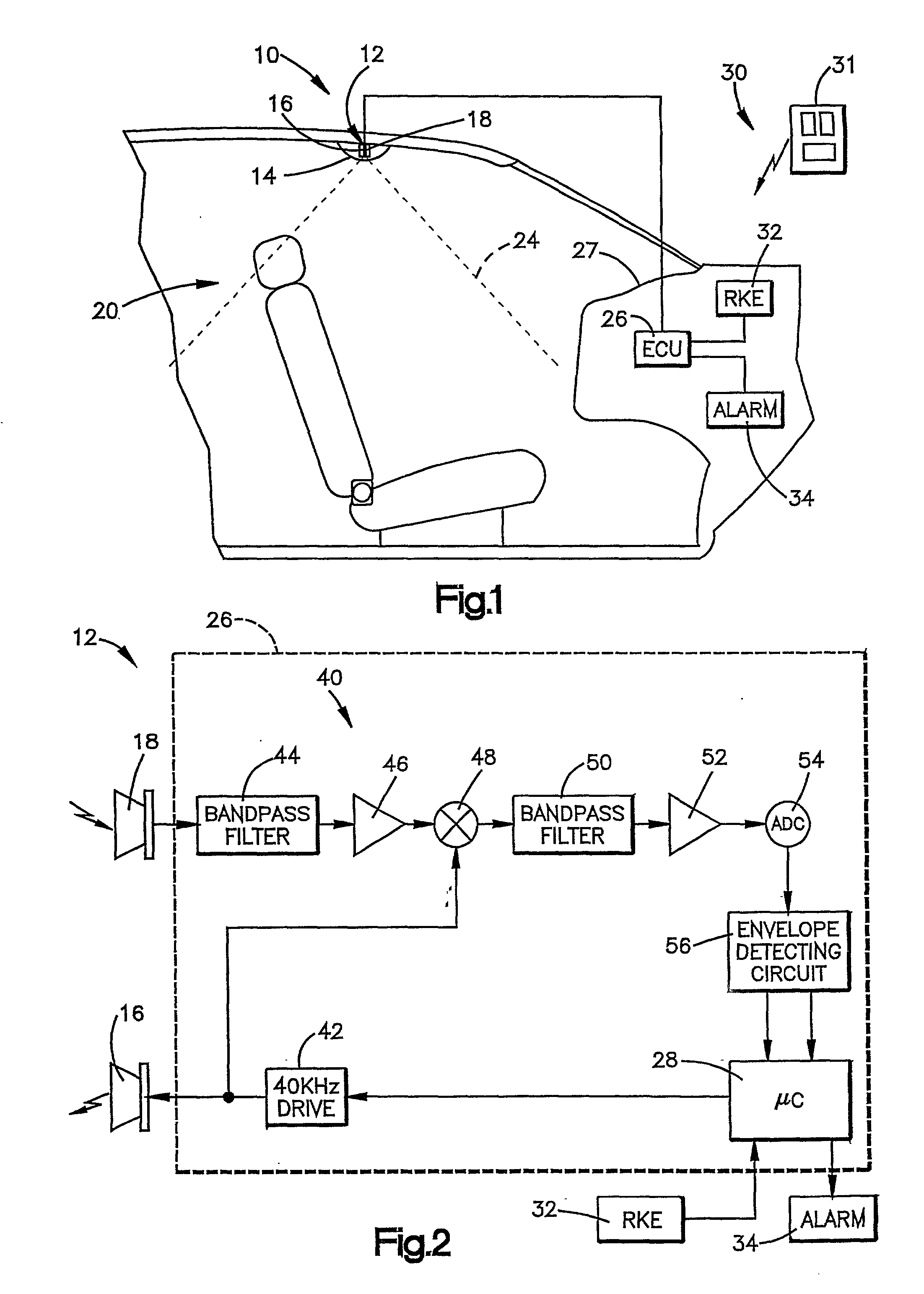
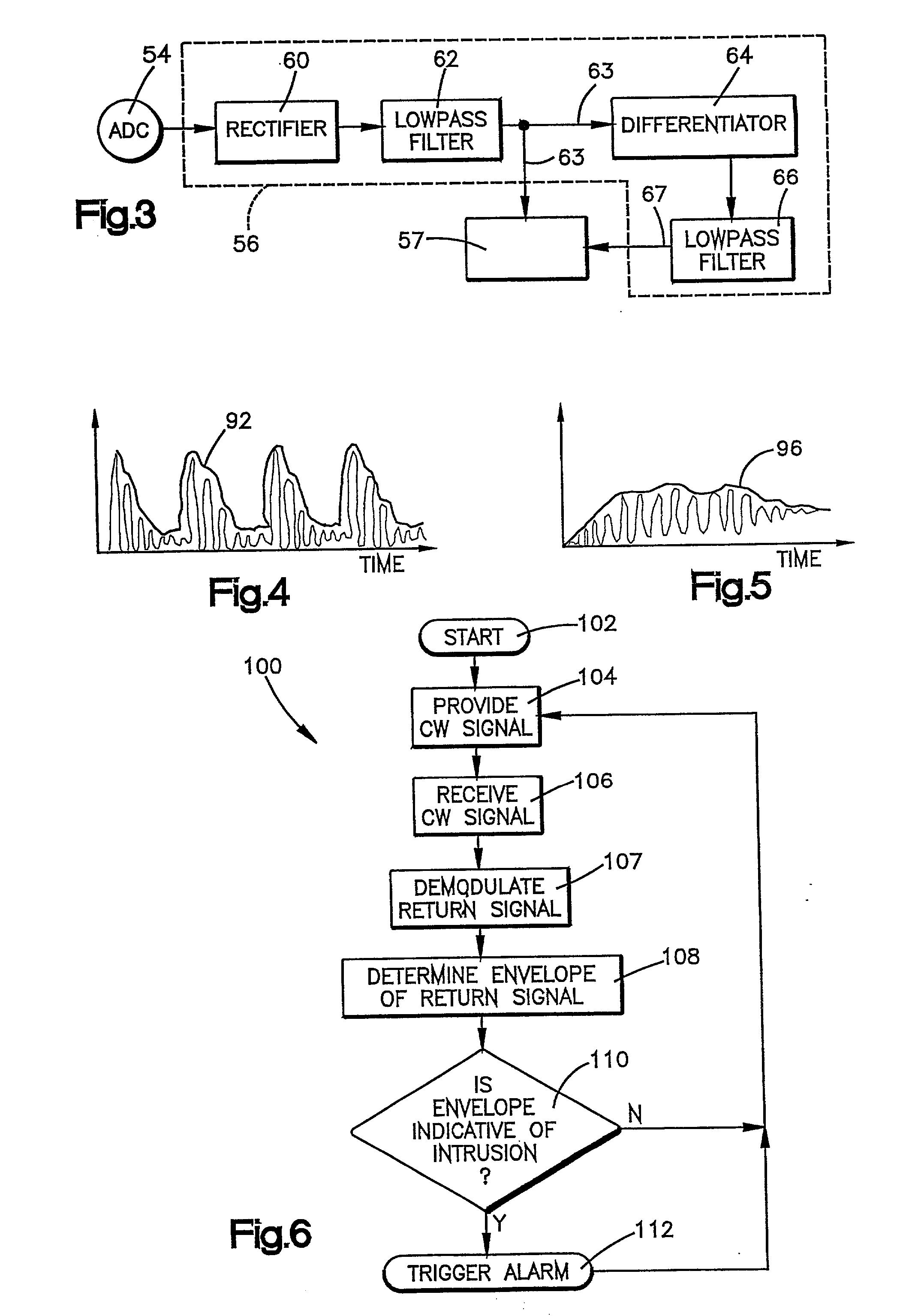
Method and apparatus for detecting intrusion and non-intrusion events
InactiveUS20020105417A1Anti-theft devicesBurglar alarm short radiation actuationControl signalEmbedded system
An intrusion detection system that differentiates between a vehicle intrusion event and a non-intrusion event includes transmitter (16) for transmitting a continuous wave signal that is reflected of surfaces within the vehicle's interior and / or a moving object (i.e., an intruder). The associated reflected signals subsequently return to a receiver (18). An ECU (26) demodulates the return signal into frequency and amplitude components. The ECU (26) further determines a waveform envelope of the demodulated return signals and monitors the envelope waveform during time windows to determine whether their corresponding envelope waveform is indicative of an intrusion event or an non-intrusion event. When an intrusion event is detected, the ECU (26) outputs a control signal to actuate an alarm (34).
Owner:TRW INC
Method for distance measurement and data transmission in a continuous wave radar system
ActiveUS20090309780A1Improve performanceRadio wave reradiation/reflectionEngineeringData transmission
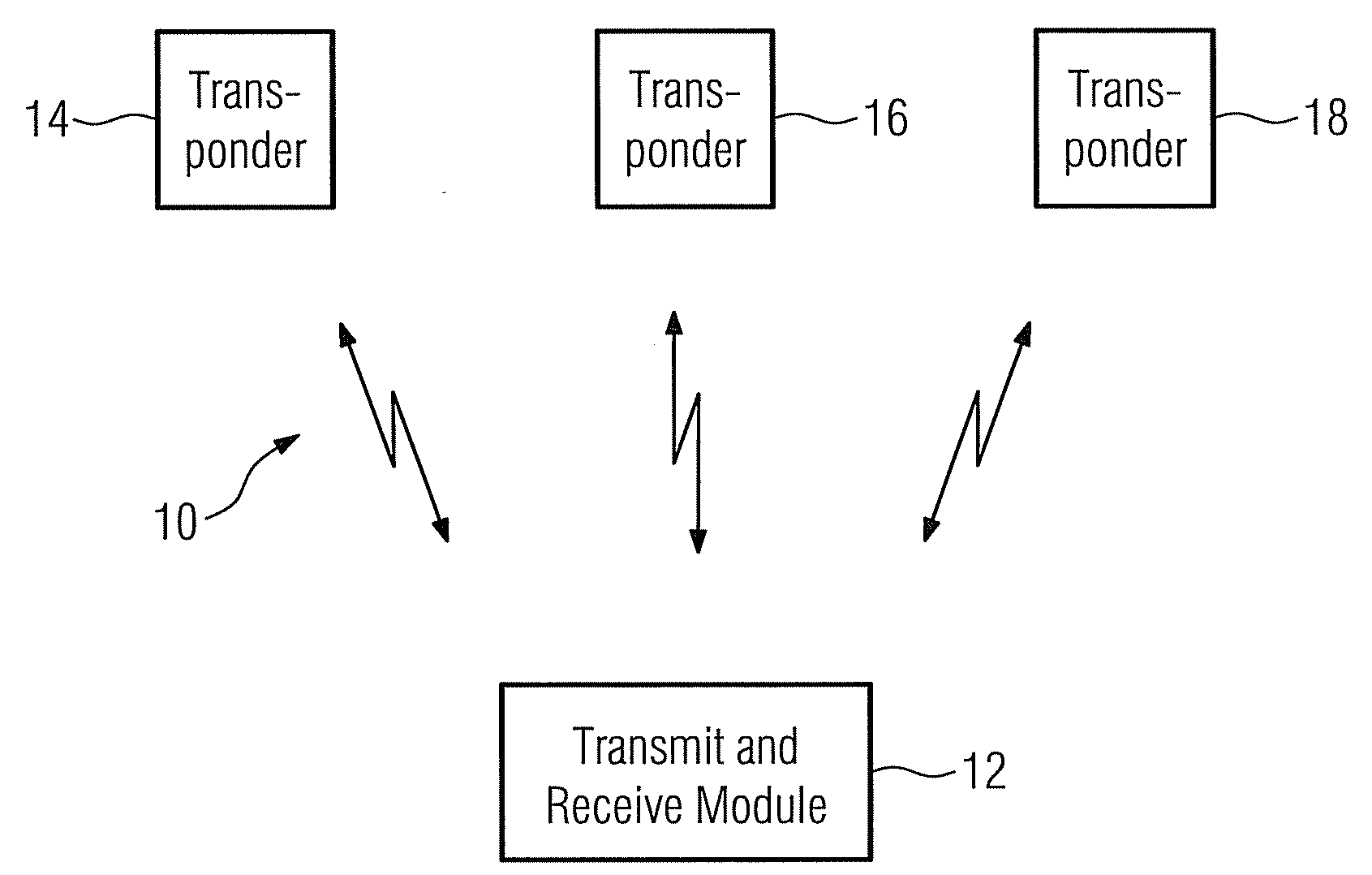
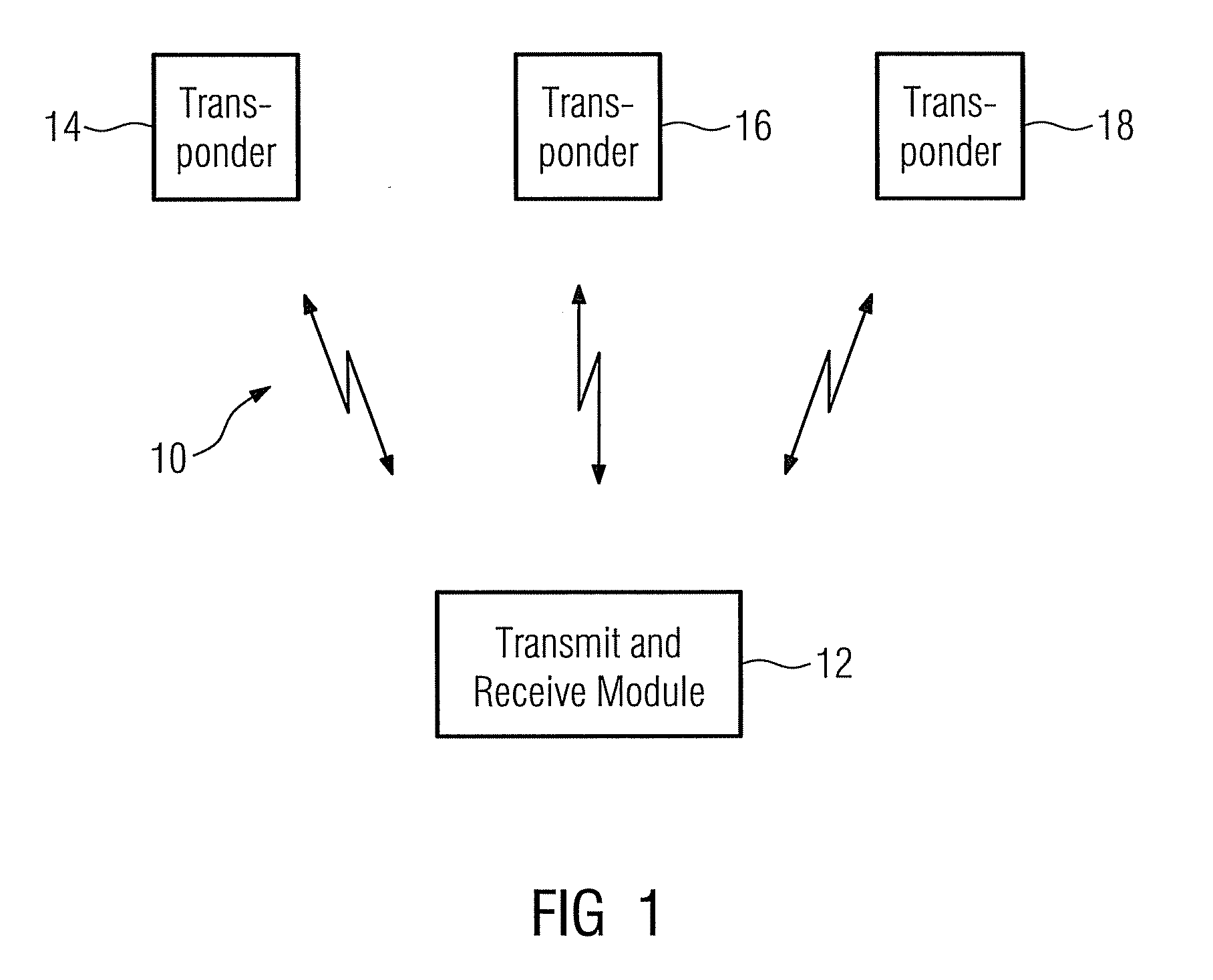
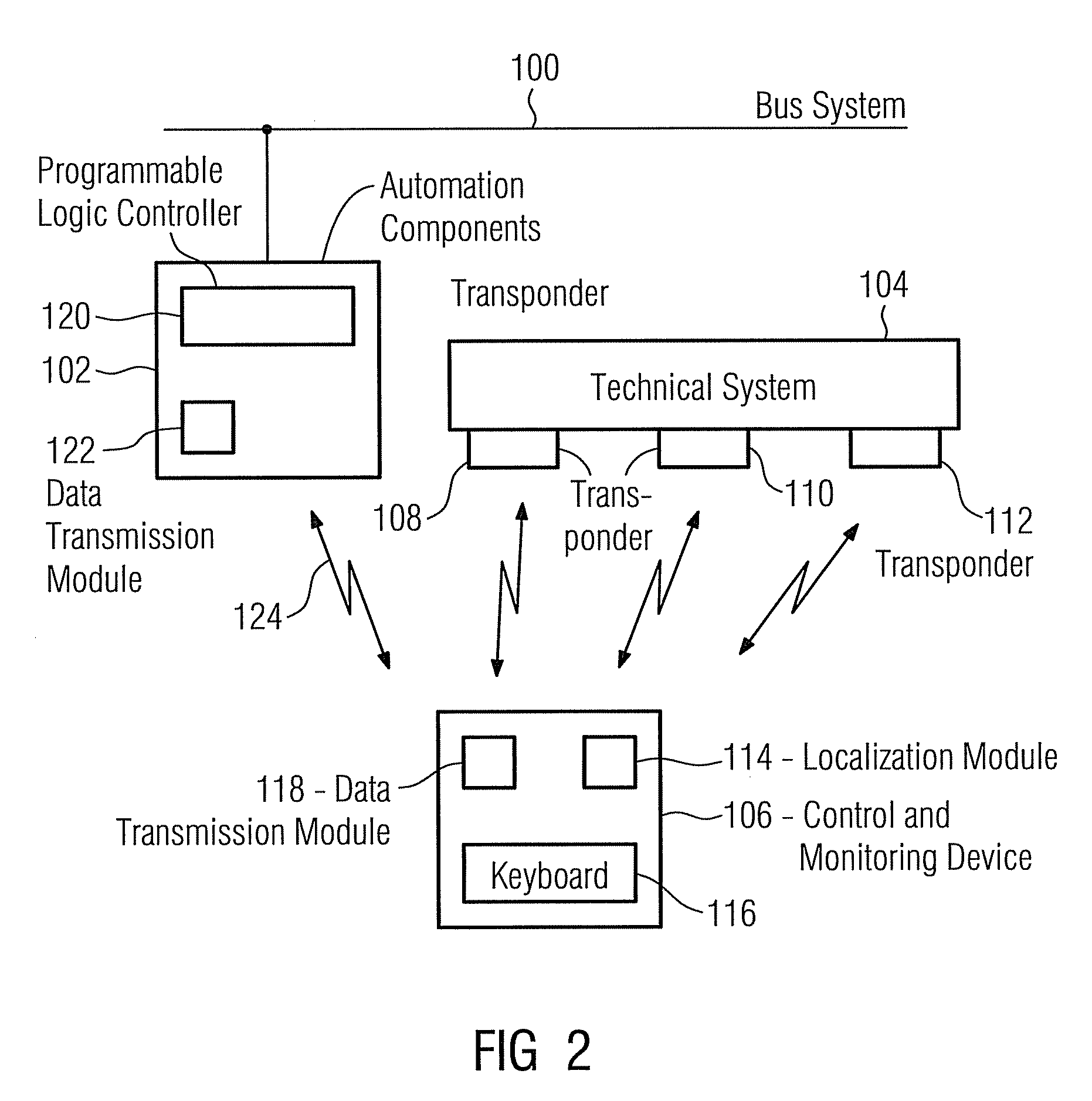
A method for distance measurement and data transmission in a continuous wave radar system is described. A continuous wave radar system has a transmit and receive module and at least one transponder device, a mobile control and monitoring device and an HMI system. Transponder devices are searched for with the aid of an unmodulated continuous wave signal as an interrogation signal, such that the transponder device can send a radio response signal to the transmit and receive module in response to the interrogation signal, as a result of which a data transmission takes place from the transponder device to the transmit and receive module. Upon completion of the data transmission a frequency-modulated continuous wave signal is generated in order to measure, on the basis thereof, a distance between the transponder device and the transmit and receive module.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
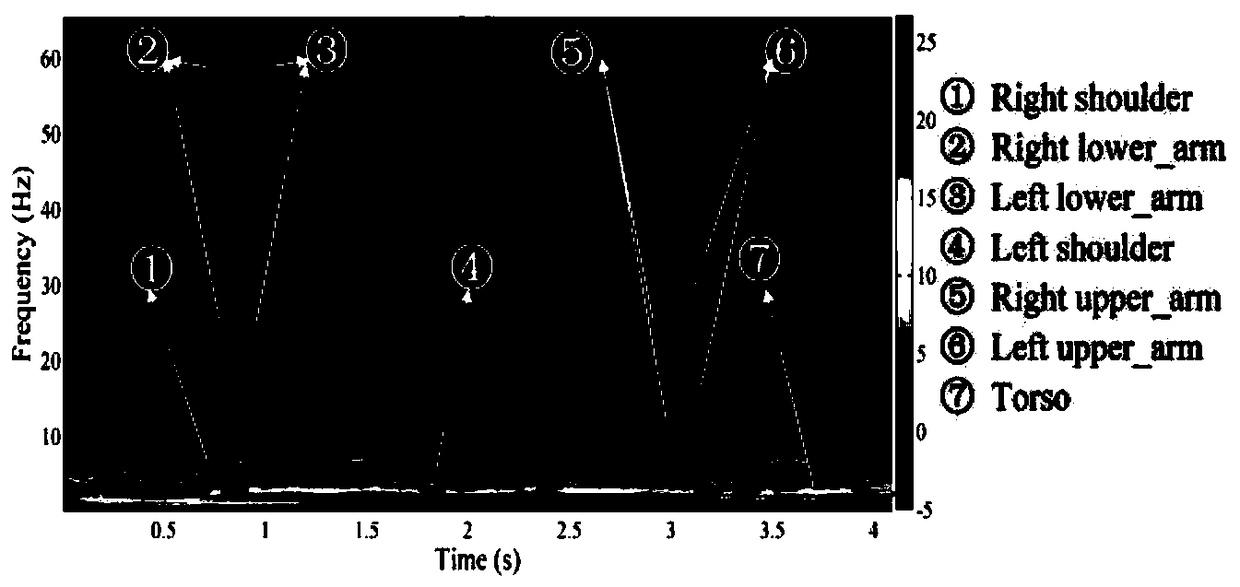
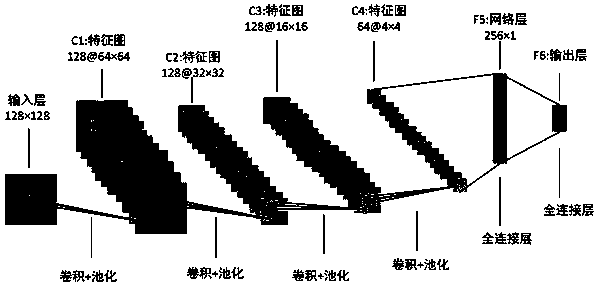
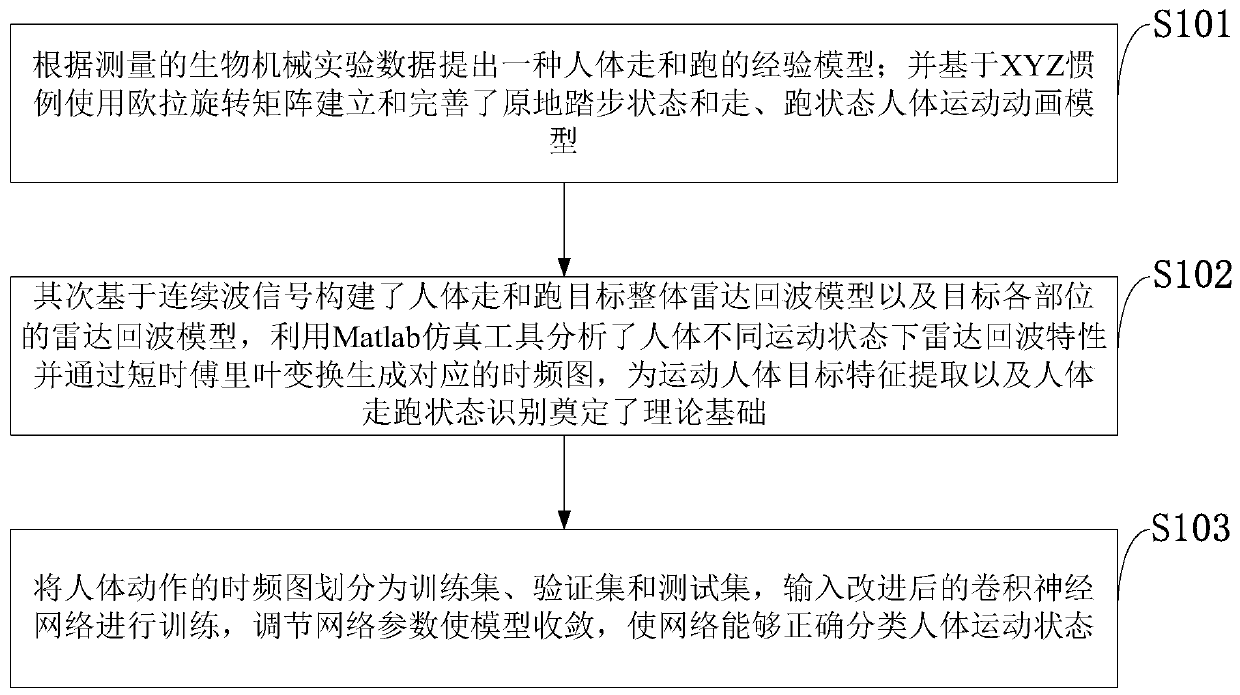
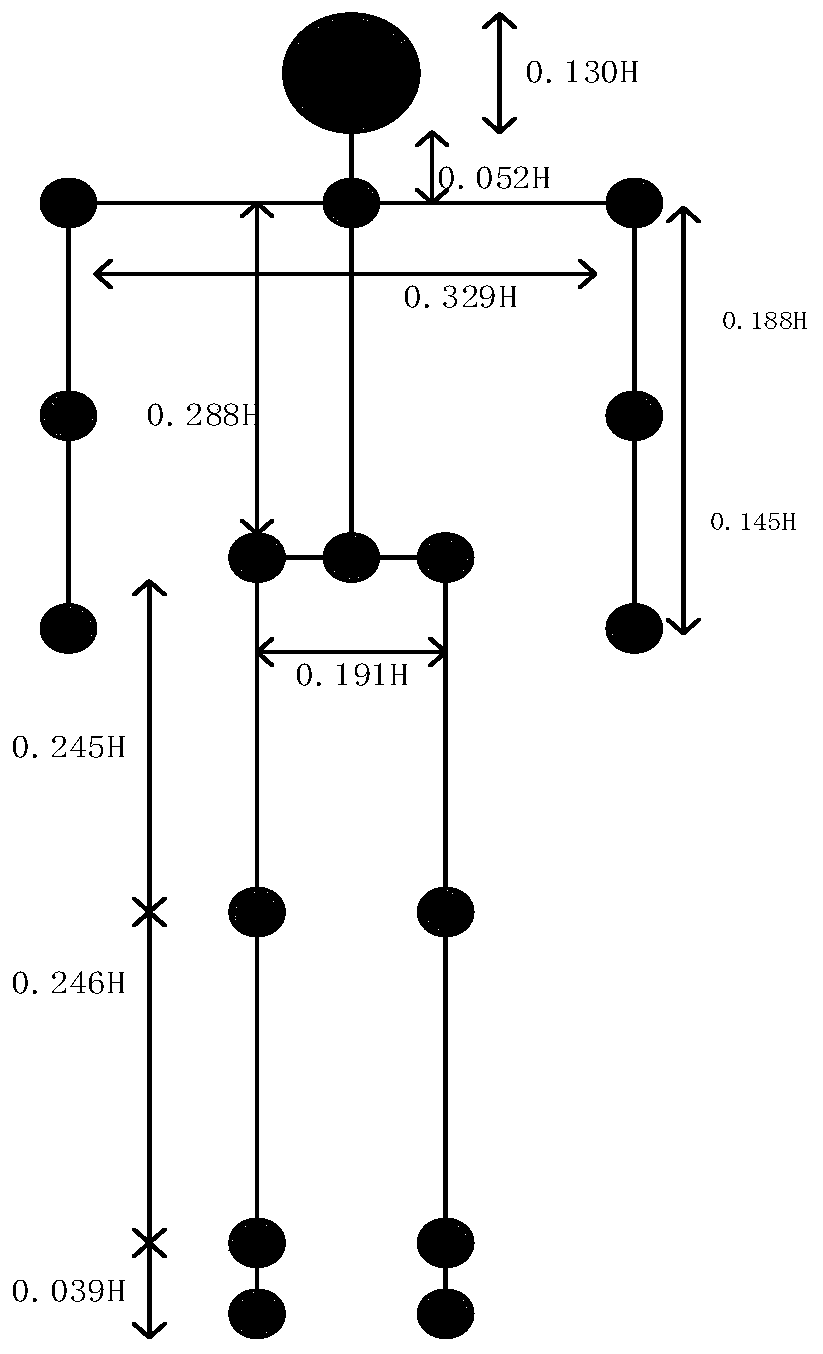
Human body motion state classification method based on improved convolutional neural network
PendingCN110045348AReduce the amount of parametersAccurate classificationWave based measurement systemsCharacter and pattern recognitionHuman bodyClassification methods
The invention firstly simplifies a human body target motion into a compound motion of a typical motion form, and puts forward a human body walking and running empirical model according to measured biomechanical experiment data. On the basis of an XYZ convention, an Euler rotation matrix is used for establishing and perfecting human body motion animation models under a state of marching on the spotand a walking and running state; then, on the basis of a continuous wave signal, an integral radar echo model of a human body walking and running target and a radar echo model of each position of thetarget are constructed; and a Matlab simulation tool is used for analyzing radar echo characteristics under different human body motion states and generating a corresponding time domain graph throughthe short-time Fourier transform so as to lay a theoretical foundation for the moving human body target characteristic extraction and the walking and running state of the human body. The time domaingraph of the human body motion is divided into a training set, a verification set and a testing set, the improved convolutional neural network is input for training, the network parameter is regulatedto realize model convergence, and the network can correctly classify the human body motion state.
Owner:SHANGHAI FIRE RES INST OF MEM
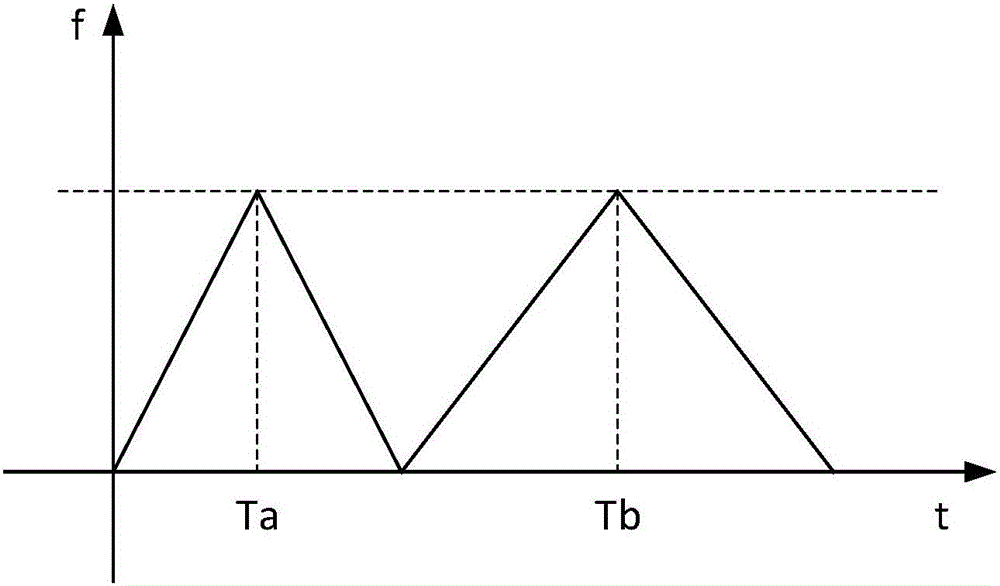
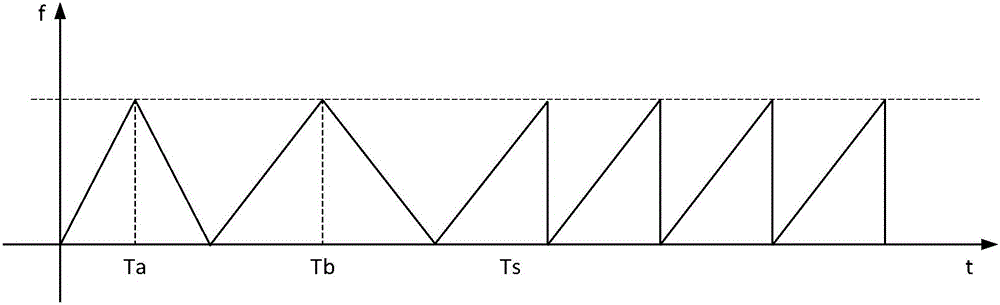
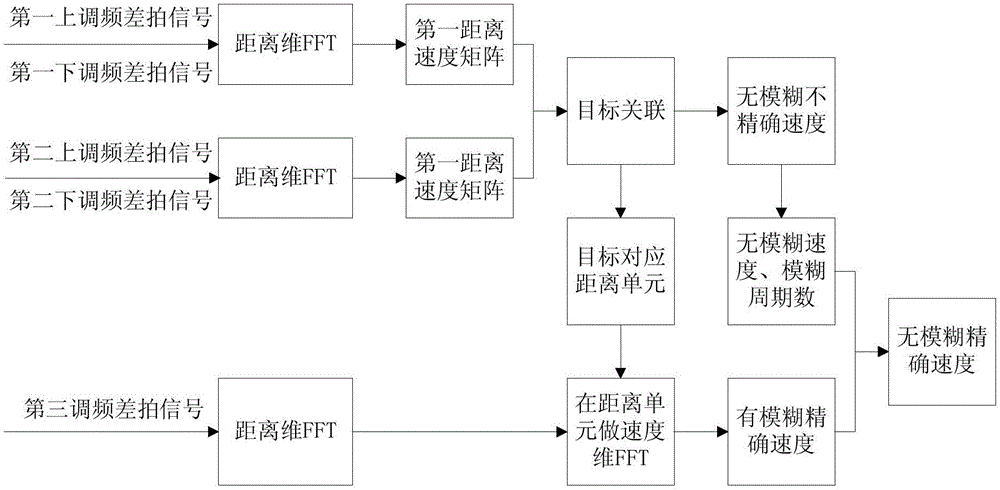
Frequency modulated continuous wave speed measurement and distance measurement method
ActiveCN105738889AImproving the Accuracy of FM Continuous Wave Distance Measurement and Velocity MeasurementRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTime domainContinuous wave signal
The present invention relates to a frequency modulated continuous wave speed measurement and distance measurement method. The method comprises the steps of S1 transmitting a frequency modulated continuous wave signal of which the frequency changes along a combined waveform modulating signal to N targets, and obtaining a corresponding beat signal; S2 carrying out the one-dimensional FFT processing of a fast time domain on the beat signals within a cycle TTa and a cycle TTb to extract the spectral peak frequencies corresponding to the N targets in the cycle TTa and the cycle TTb; S3 calculating to obtain the corresponding distance speed matrixes in the cycle TTa and the cycle TTb; S4 finishing the correlation matching of multiple targets to obtain the distance r and the unambiguous inaccurate speed v corresponding to each target; S5 calculating to obtain the ambiguous accurate speed vapre corresponding to each target; S6 calculating to obtain the unambiguous accurate speed vpre corresponding to each target. According to the present invention, by utilizing an improved modulating signal and combining a two dimension FFT method, the purpose of high-precision speed measurement and distance measurement can be achieved under a smaller FFT point number.
Owner:HUAYU AUTOMOTIVE SYST
Accurate positioning method based on linear frequency modulation continuous wave technology and accurate positioning devices based on linear frequency modulation continuous wave technology
ActiveCN103558598AEfficient use ofOffsetting timing differencesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionLocal oscillatorPositioning technology
The invention relates to an accurate positioning method based on the linear frequency modulation continuous wave technology, and accurate positioning devices based on the linear frequency modulation continuous wave technology. The accurate positioning method based on the linear frequency modulation continuous wave technology includes the following steps that in the one-time distance measurement process, the device B transmits linear frequency modulation continuous wave signals, the device A receives the signals, both the device A and the device B generate linear frequency modulation continuous wave signals periodically, and supposing that local oscillators at the two ends of the device A and the two ends of the device B have fixed difference t0, the oscillators of the device A are in front of the oscillators of the device B, the flying time of the linear frequency modulation continuous wave signals in air is tau, and the signals received by the device A are the signals transmitted by the device B and having been delayed in the air for the time of tau. The invention further provides the accurate positioning devices based on the linear frequency modulation continuous wave technology. The method and the devices have the advantage that on the basis of the accurate positioning technology of the FMCW technology, accurate measurement between two points is achieved by measuring the flying time of radio waves in the air.
Owner:SHENZHEN YIRI TECH
Continuous wave mud pulse generator
ActiveCN103410503AReduce consumptionMeet job requirementsSurveyHydraulic motorElectrical energy consumption
The invention relates to a continuous wave mud pulse generator. A hydraulic motor is utilized for replacing a high-power motor to provide a driving force, the driving force is greater, the electrical energy consumption is lower, continuous wave signals are generated by swinging a shutoff valve rotor, and the generator works more stably.
Owner:上海神开石油测控技术有限公司 +2
Velocity ambiguity resolution angle measurement method for vehicle-mounted LFMCW radar
ActiveCN110488270AReduce processing timeIncrease data rateRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDigital signal processingRadar systems
The invention discloses a velocity ambiguity resolution angle measurement method for vehicle-mounted LFMCW radar, belongs to the signal processing technology, and particularly relates to the velocityambiguity resolution and radar virtual aperture direction of arrival measurement technology. According to the invention, velocity ambiguity resolution and MIMO radar virtual aperture angle measurementprocessing are carried out in one frame of signal, a two-transmitting four-receiving radar system is taken as an example, a radar transmitting end transmits linear frequency modulation continuous wave signals with different slope durations and the same bandwidth by using a time division multiplexing technology, and a radar receiving end simultaneously receives signals reflected by two transmitting antennas through an object by using four receiving antennas. Echo signals are subjected to frequency mixing, low-pass filtering and analog-to-digital conversion and finally enter a digital signal processor DSP. 2D-FFT and two-dimensional constant false alarm detection are performed in the DSP, then resolution of velocity ambiguity and phase compensation are conducted, and finally MIMO radar virtual aperture angle measurement processing is carried out, thus realizing the purpose of the invention. The method has the effects of reducing the signal processing time and improving the radar data rate.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
LFMCW signal rapid detection and estimation method
ActiveCN106443588AResolve interceptionSolve the characteristicsWave based measurement systemsParametric searchPeak value
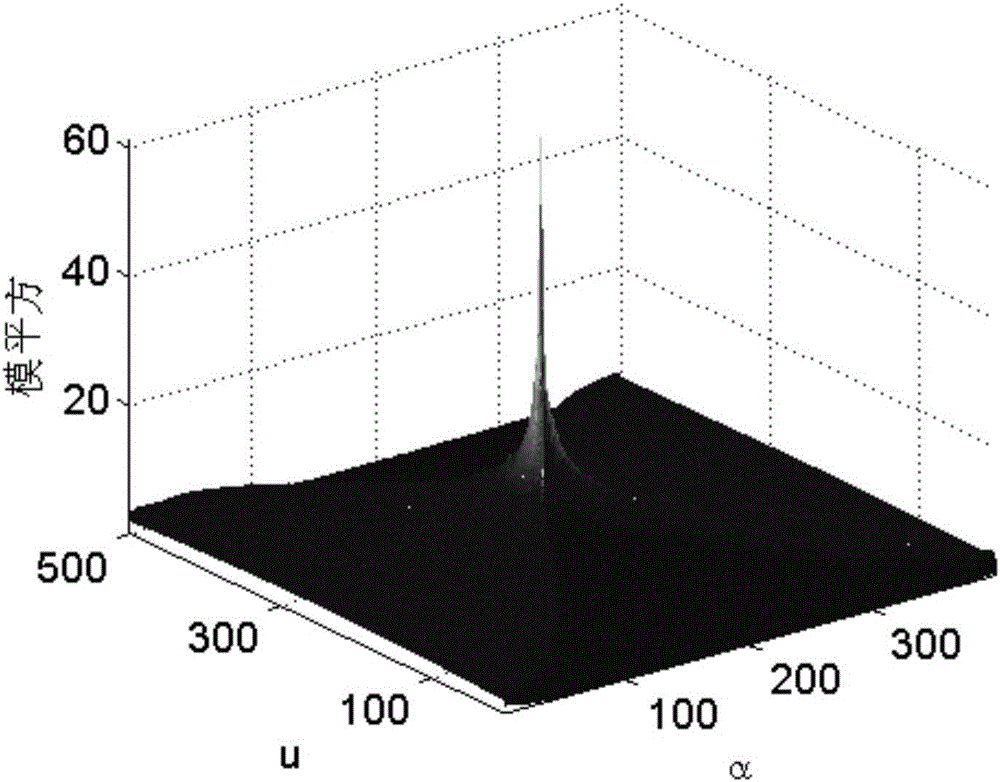
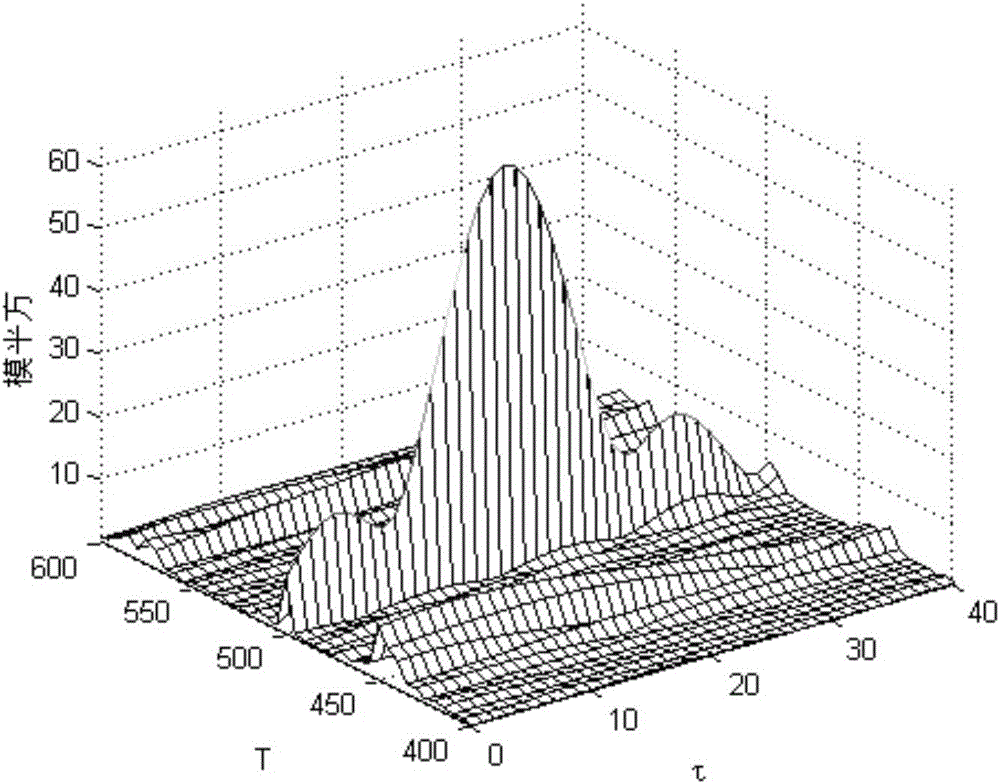
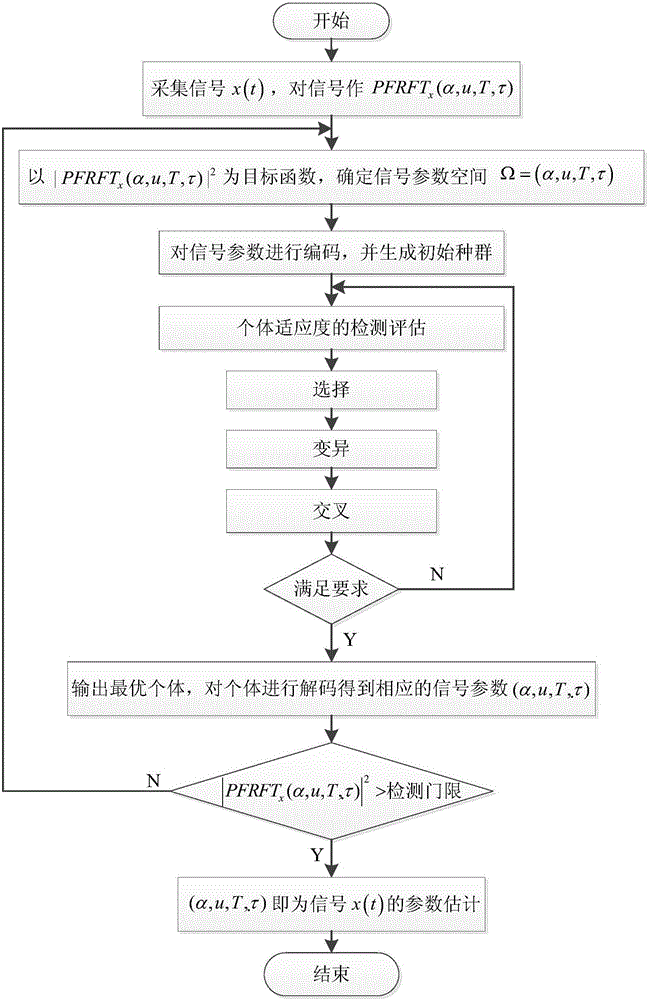
The invention belongs to the technical field of radar signal analysis, and discloses an LFMCW signal rapid detection and estimation method. Quasi-coherent accumulation is performed on the LFM part of each period of the same modulation frequency in LFMCW signals according to PFRFT energy so that the signals are enabled to have great energy concentration characteristic in the PFRFT domain, i.e. the PFRFT of the signals has an obvious peak value in two sections. Firstly rapid period fractional order Fourier transform is performed on the linear frequency modulation continuous wave signals, the maximum modulus square of period fractional order Fourier transform act as a target function to establish an optimization model, and the optimization model is solved by using a genetic algorithm so that the optimal parameter estimation of the signals can be obtained. Four-dimensional parameter searching is performed on the PFRFT energy of the linear frequency modulation continuous wave signals by using the genetic algorithm so that detection and estimation of radar weak signals can be realized, the method is especially applied to the design of a signal analysis system of low interception probability radar and thus the theoretical and project application of the PFRFT algorithm can be realized.
Owner:UNIT 63892 OF PLA
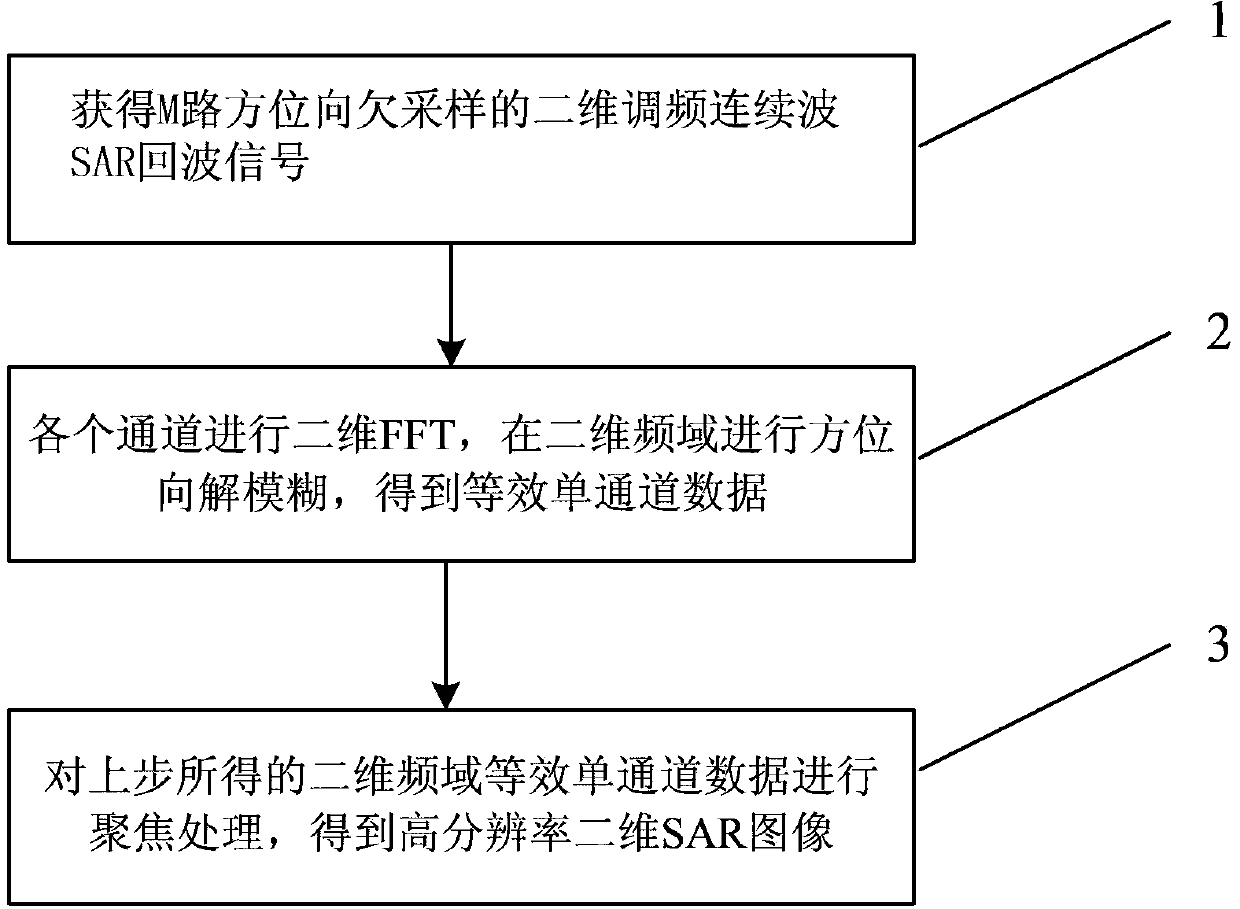
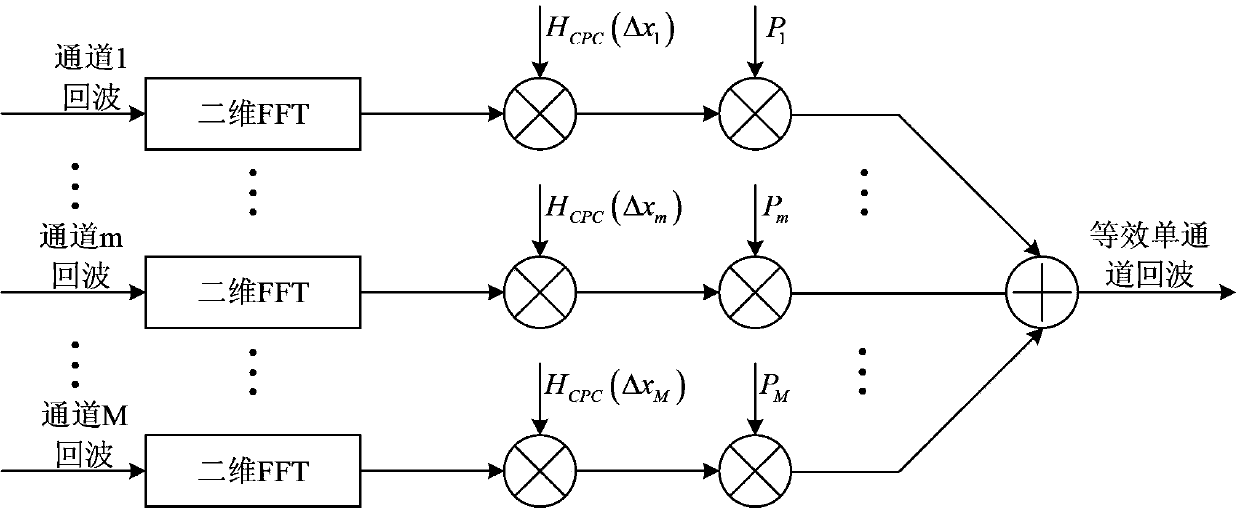
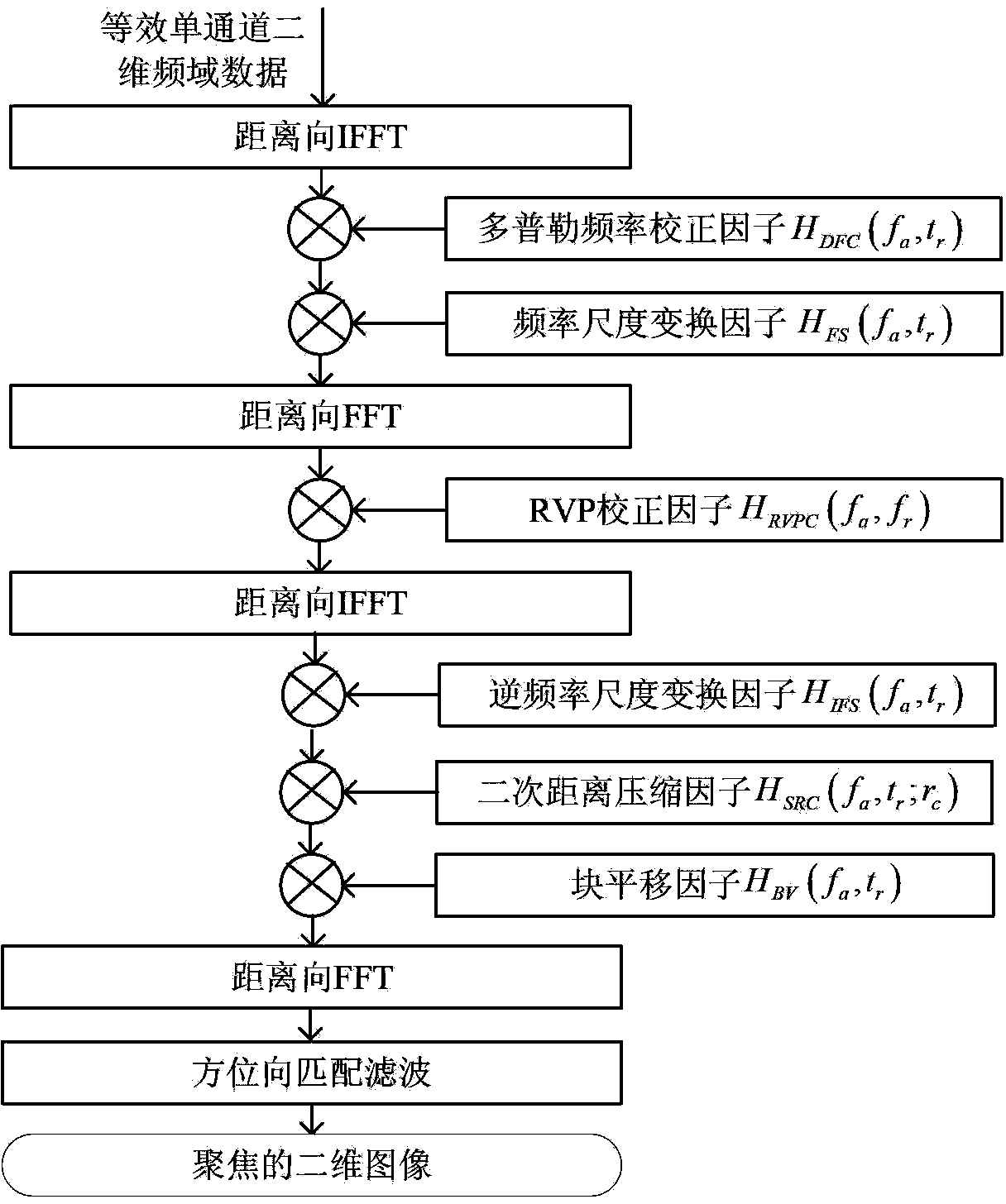
Multichannel frequency modulated continuous wave SAR (synthetic aperture radar) imaging method
InactiveCN103969644ARemove constraintsHigh resolutionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture sonarInverse synthetic aperture radar
The invention provides a multichannel frequency modulated continuous wave SAR (synthetic aperture radar) imaging method. The technical scheme includes that the multichannel frequency modulated continuous wave SAR imaging method includes transmitting frequency modulated continuous wave signals by a channel and receiving the same by M channels simultaneously, and acquiring M channels of azimuths of undersampled two-dimensional frequency modulated continuous wave SAR echo signals; subjecting the acquired M channels of signals to two-dimensional Fourier transform, performing Doppler defuzzification in a two-dimensional frequency domain and acquiring equivalent single-channel signals eliminating azimuth aliasing; focusing the equivalent single-channel signals in the two-dimension frequency domain to obtain two-dimensional high-resolution frequency modulated continuous wave SAR images. Compared with existing single-channel frequency modulated continuous wave SAR imaging method, the multichannel frequency modulated continuous wave SAR imaging method can be operated in the mode with longer operation distance, wider measuring band width and higher imaging resolution under the condition of same transmission power, and application of the frequency modulated continuous wave SAR is broadened.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
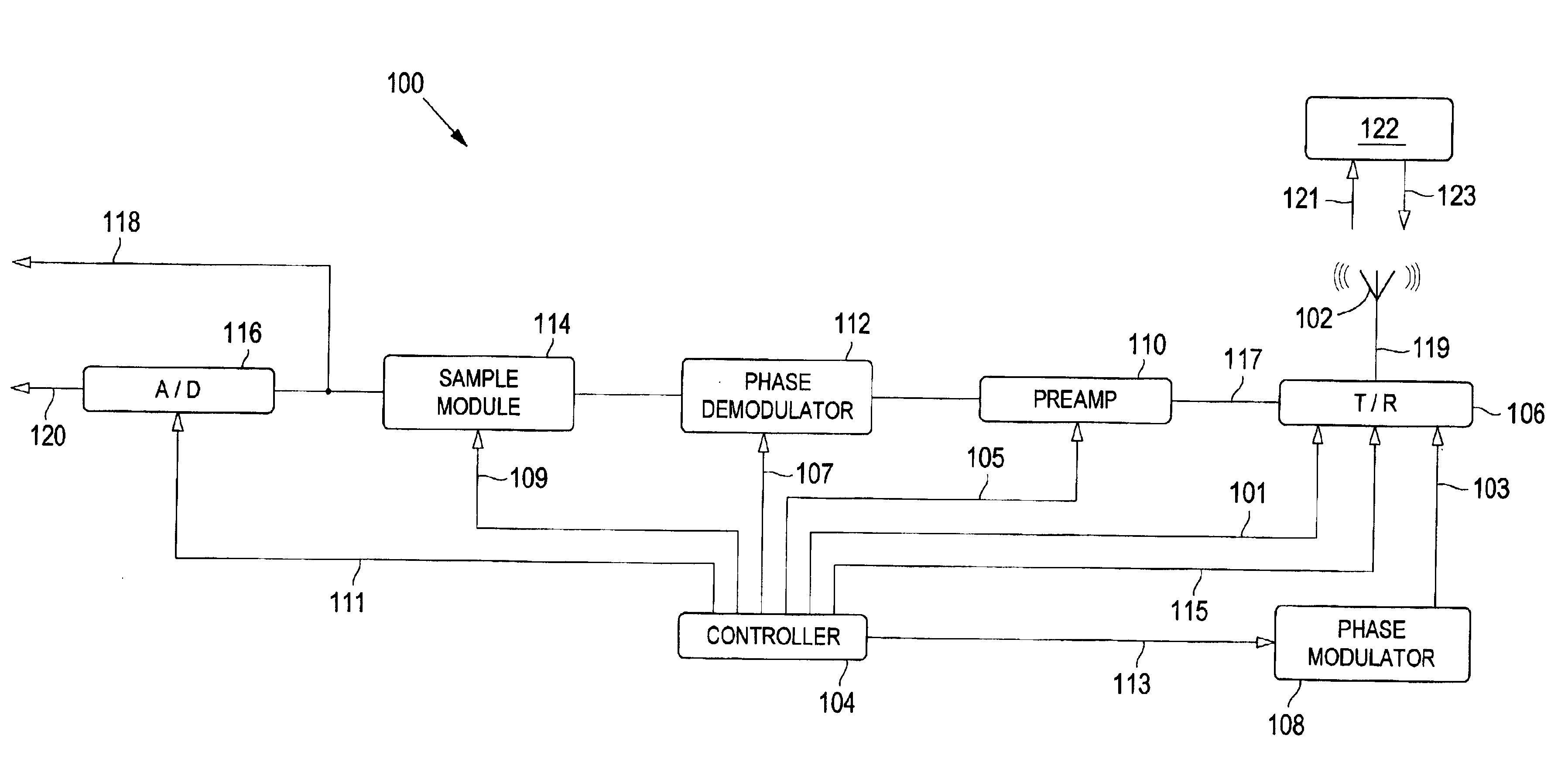
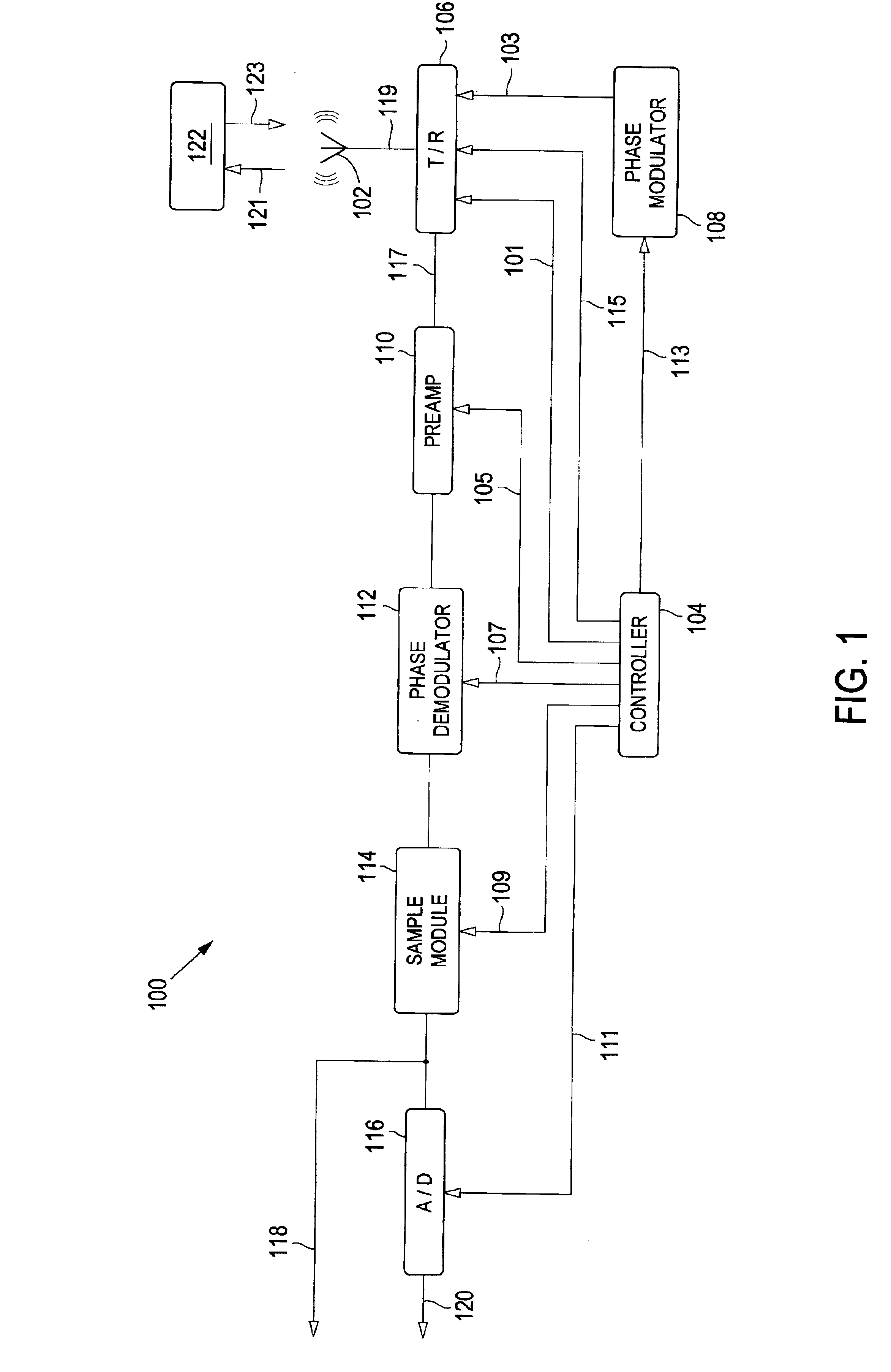
Sensor front-end with phase coding capability
A sensor front end for an electronic radar sensor is disclosed that provides for a lower parts count while providing technical functionality by using multifunction parts, i.e., parts that are used both in transmitting and receiving. The sensor front end includes a continuous wave signal source that functions as a signal source when the front end is transmitting a signal and as a local oscillator when the front end is receiving a signal. The sensor front end also includes a tri-mode mixer that functions as a phase-modulator and transmit switch when the front end is transmitting a signal and as a mixer / down-converter when the front end is receiving a signal. The sensor front end further includes a common aperture antenna that acts as both a transmitting antenna for transmitting a sensor signal and for receiving a reflected signal from a object. A phase shifter can be added to provide a predetermined phase shift in the transmitted sensor signal, the received reflected signal, or both, such that in-phase and quadrature signal components are provided. In addition, phase coding may be added to the signal to reduce the degenerative impact of interfering signals. A receiver module is coupled to the tri-mode mixer such that, when receiving a reflected signal, the receiver provides a baseband sensor output signal that can be used to determined the position and velocity of the object. A sampling module can be added such that the sensor output signal is sampled and provided as an analog signal, or the sampled sensor output signal can be provided to an analog-to-digital converter to convert the sensor output signal into a digital format, or both.
Owner:VEONEER US LLC
3R optical signal regeneration
InactiveUS6775481B2Logic circuits using opto-electronic devicesElectromagnetic transmittersSignal regenerationOptical power
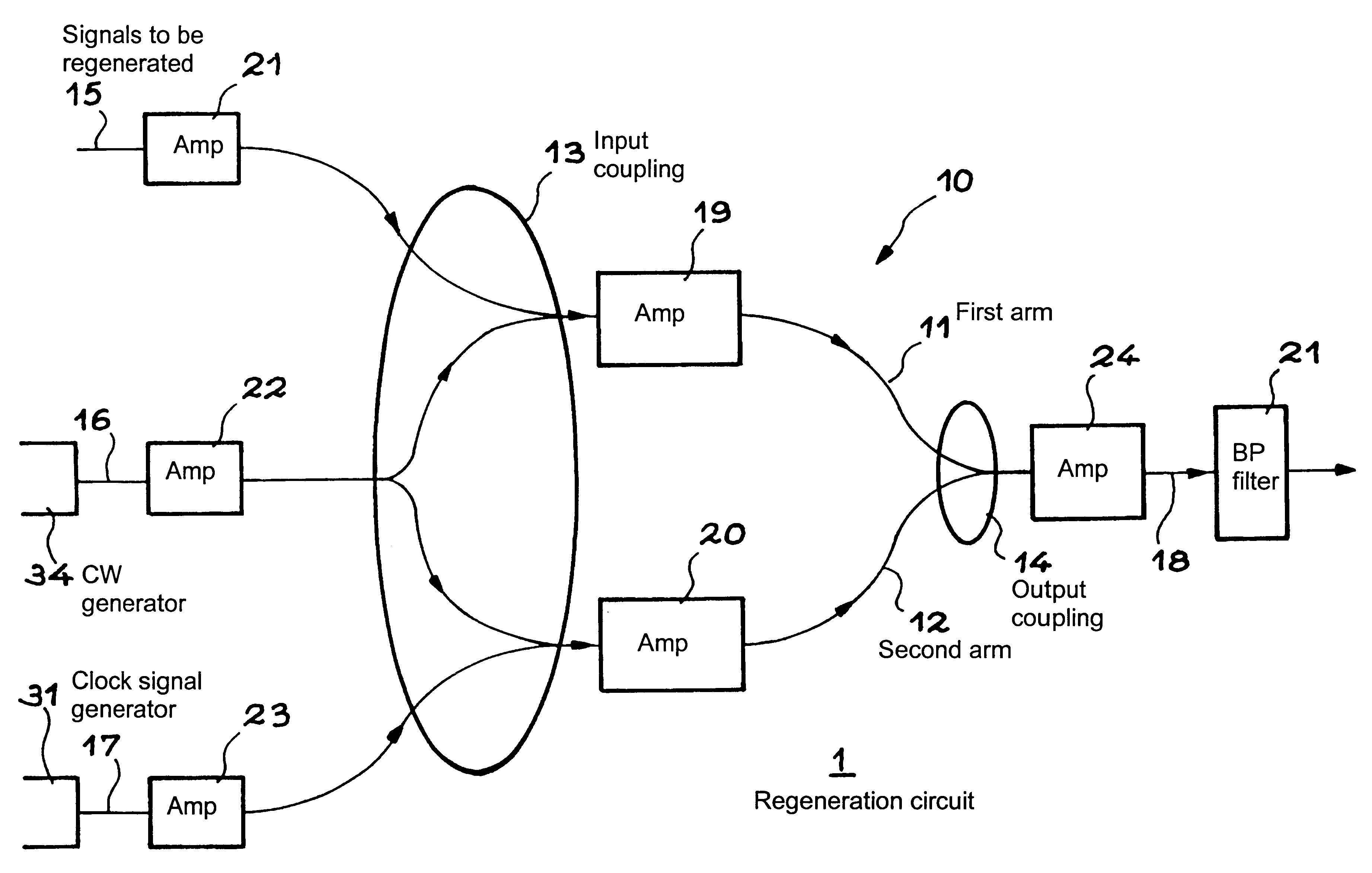
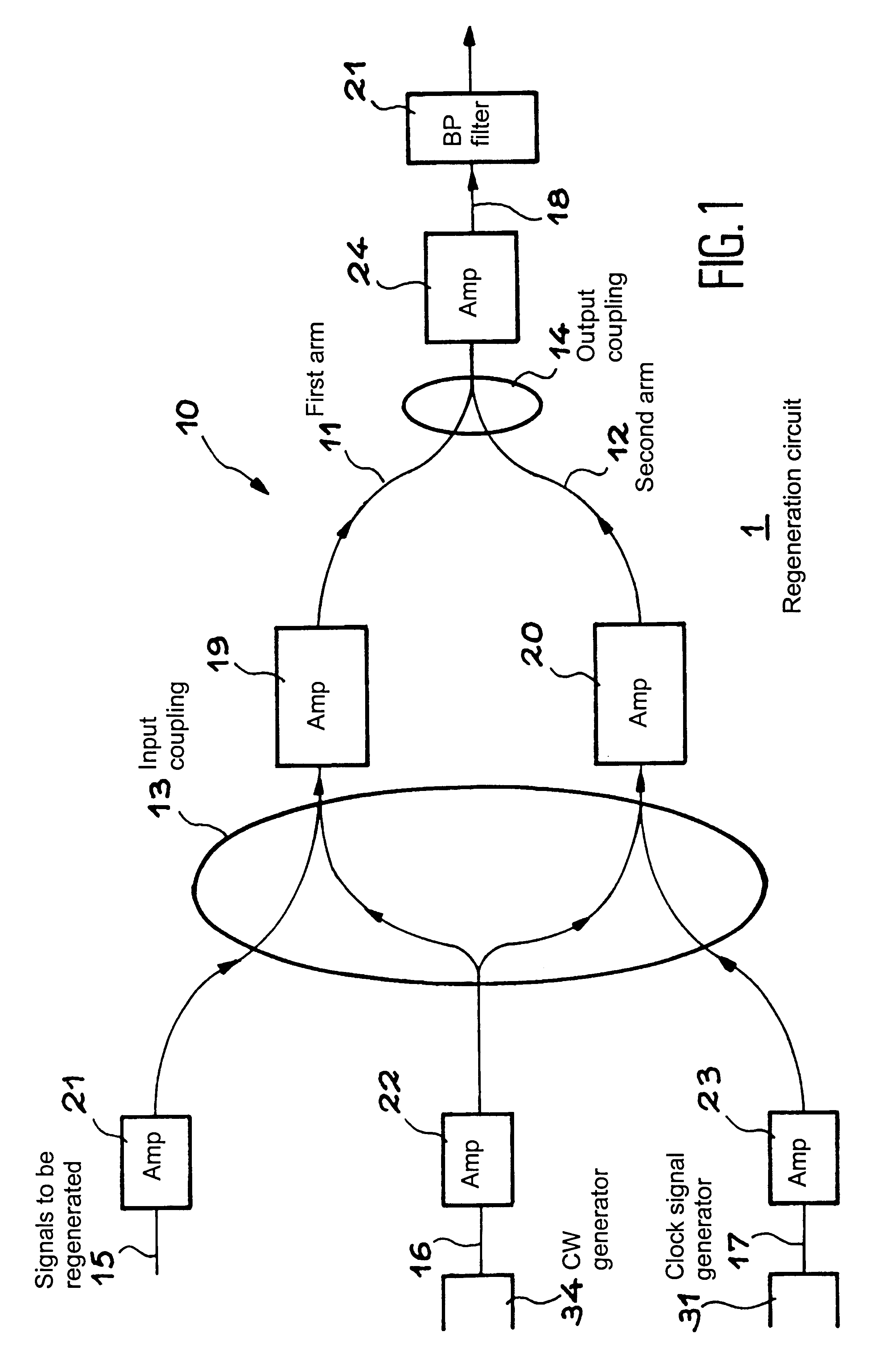
An optical signal regeneration device having an interferometric structure with two arms. Each of the arms has a medium, the optical power output of which is variable with the optical power input. The first arm receives, through an input coupler, a continuous wave and the signal to be regenerated. The second arm receives through the input coupler, a continuous wave signal and a clock signal. A filter, centered on the continuous wave wavelength, receives the output signal of the interferometric structure through the coupler. The filter output signal constitutes the regenerated 3R signal.
Owner:RPX CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com