Patents
Literature
50 results about "Cryometer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A cryometer is a thermometer used to measure very low temperatures of objects.
Apparatus and methods for monitoring and testing coolant recirculation systems
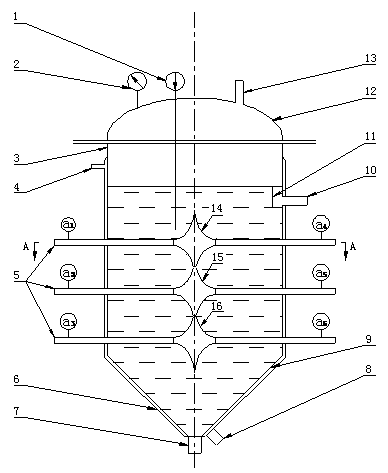
Apparatus for monitoring, characterizing, and testing coolant recirculation systems has, in combination, a heat load, a flow meter measuring flow rate of the coolant, inlet and outlet thermometers, and a data recorder connected to the flow meter, inlet thermometer, and outlet thermometer for recording their data outputs. The data recorder has an output representing flow rate, coolant inlet temperature, and coolant outlet temperature, whereby the coolant-recirculating heat exchanger system is characterized. A computer connected to the data recorder output is operable for computing heat removal capacity. The apparatus is specially adapted for methods of monitoring, characterizing, and testing coolant recirculation systems, including determining their maximum heat removal capacities.
Owner:RYAN WILLIAM J +2
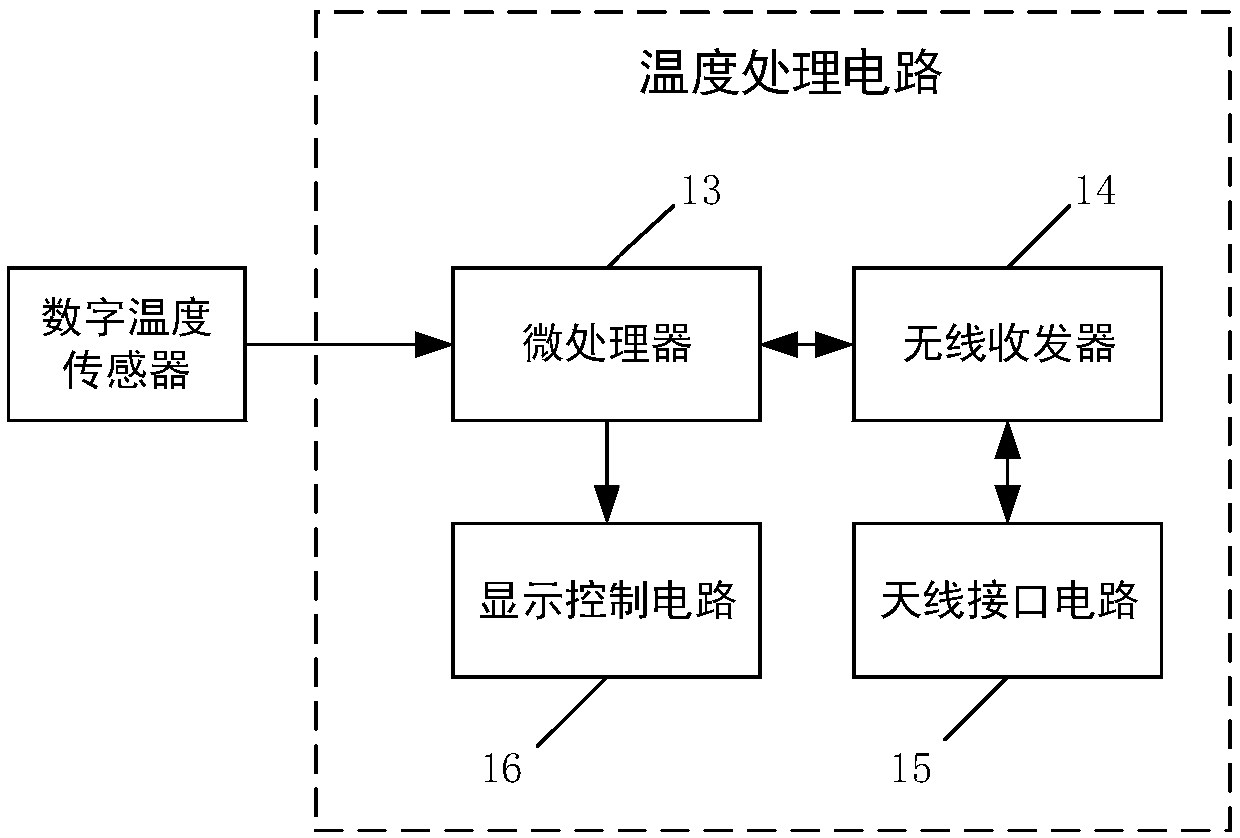
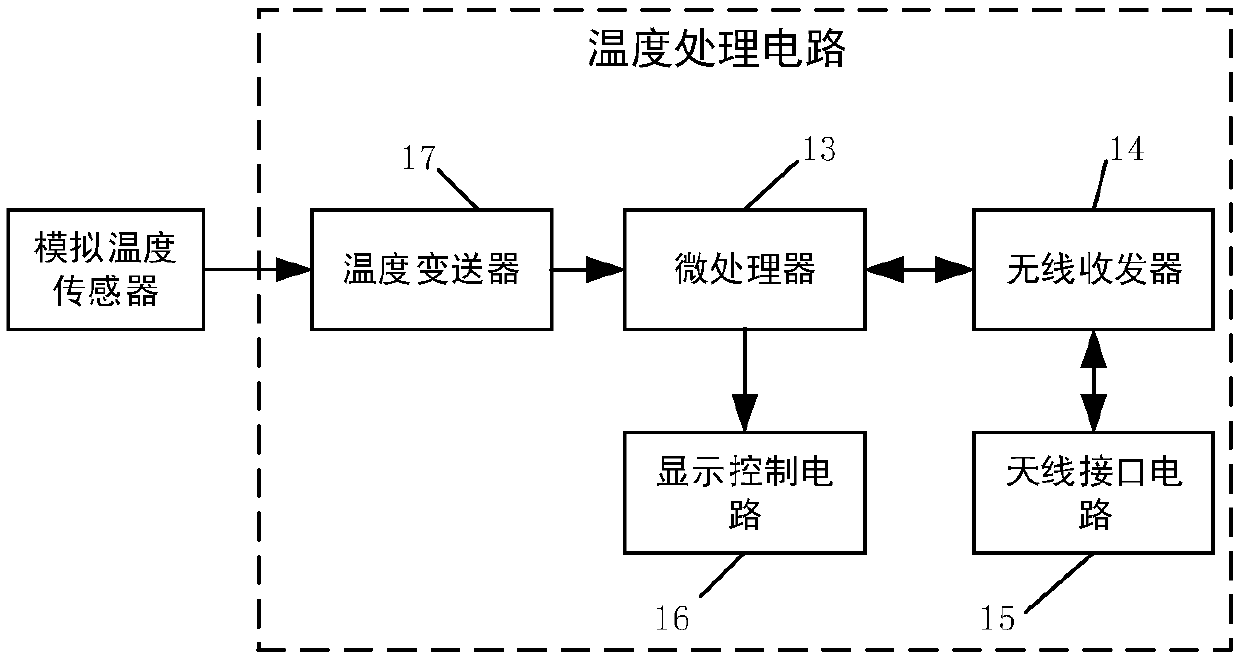
Compensation process for detecting temperature for temperature sensor
InactiveCN101424572AConvenient verificationSimple methodThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsUsing electrical meansMathematical modelEngineering
The invention provides a method for compensating the temperature detected by a temperature sensor, belonging to the sensing measurement and control field. Firstly, a Chinese Standard No.1 mercury thermometer is taken as the temperature detecting standard, a mathematic model of the temperature sensor Pt100 is established, and a transfer function is determined; secondly, parameters of the transfer function of the temperature sensor Pt100 is determined through experiments, a third-order model is introduced to describe the temperature property of the temperature sensor, an MATLAB software is used to fit the experimental data, a penalty function is introduced, and a penalty algorithm is determined; and finally, a difference equation realized by computer language is transferred to fulfill the purpose of automatically detecting the temperature. The compensating method ensures that the dynamic property of the temperature sensor Pt100 approaches the dynamic property of the Chinese Standard No.1 mercury thermometer well, which is verified in the practical application well. The method is convenient and easy to implement and has accurate measurement result.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
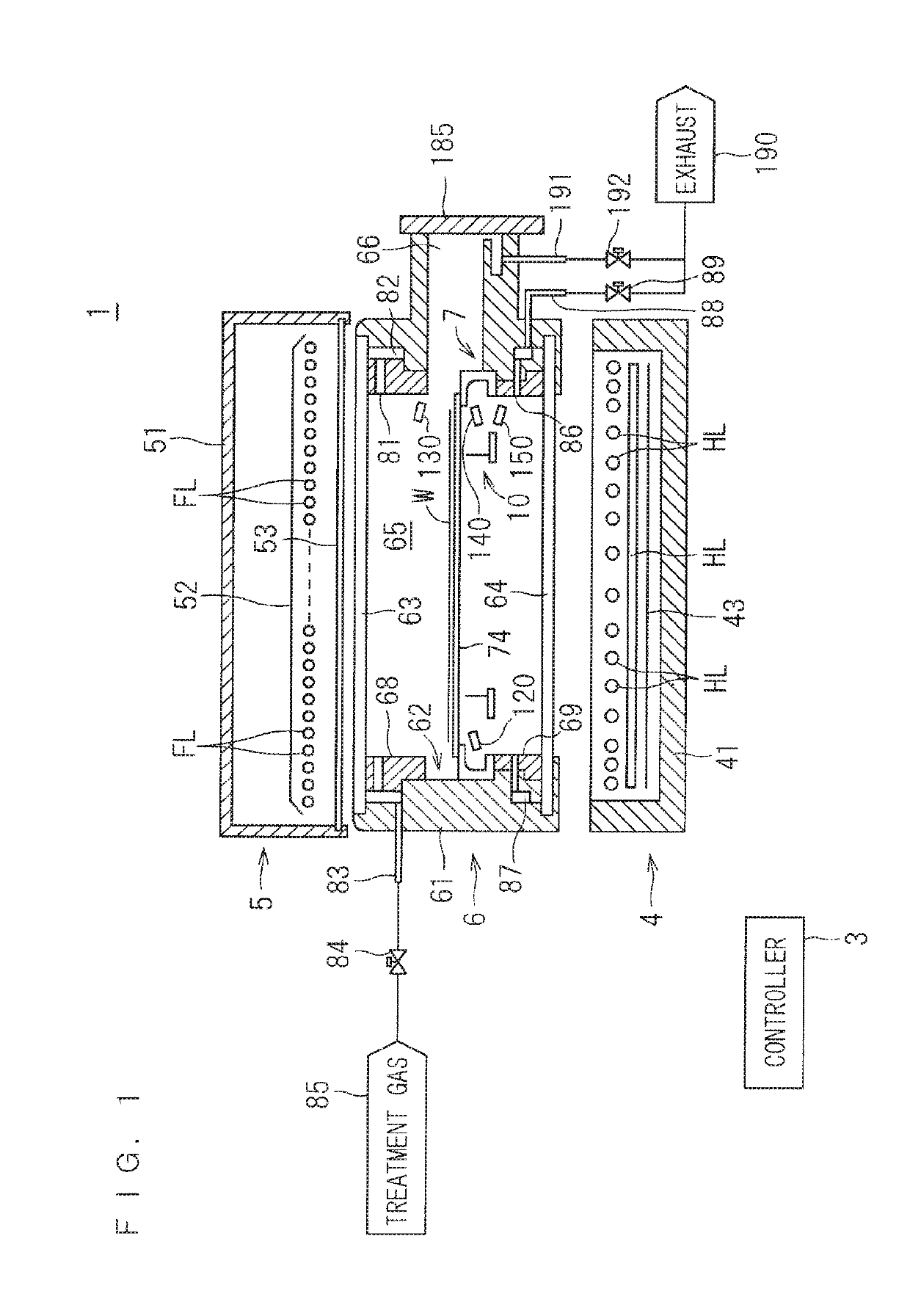
Light-irradiation type thermal processing method and thermal processing apparatus
ActiveUS20170053818A1Simple structureSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesLight irradiationRadiation thermometer
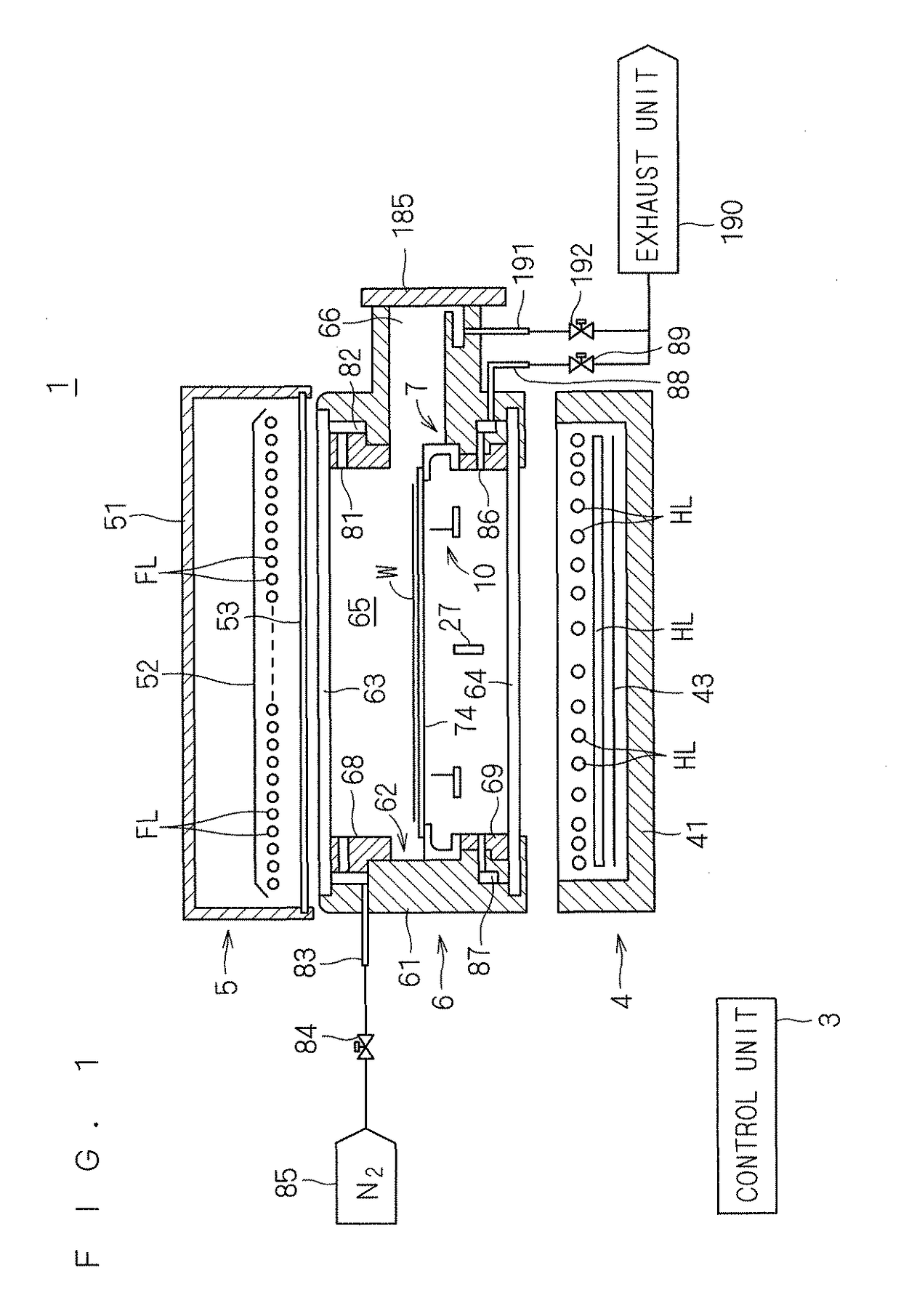
From a stage of preheating by a halogen lamp to irradiation with a flash by a flash lamp, a radiation thermometer is used for measuring the temperature of a back surface of a semiconductor wafer. A increased temperature ΔT is determined by which the back surface of the semiconductor wafer is increased in temperature from the preheating temperature by irradiation with a flash. The specific heat of the semiconductor wafer has a known value. Further, the increased temperature ΔT is proportionate to the magnitude of energy applied to a front surface of the semiconductor wafer by irradiation with a flash. Thus, a front surface attained temperature of the semiconductor wafer can be determined using the increased temperature ΔT of the back surface of the semiconductor wafer during irradiation with a flash.
Owner:DAINIPPON SCREEN MTG CO LTD
Special auxiliary device for continuous measurement of molten iron temperature and molten iron temperature continuous measurement system
ActiveCN101556188AAvoid errorsExtended service lifeRadiation pyrometryContinuous measurementRadiation thermometer
The invention relates to a special auxiliary device for continuous measurement of molten iron temperature. The device comprises an air-cooling jacket, wherein an auxiliary tube of the air-cooling jacket is communicated with a first end part and a second end part of a main tube; the first end part is provided with an air inlet; a mounting position for an infrared radiation thermometer positioned between the first end part and the second end part is arranged in the main tube; and preferably, an air path which is communicated with the auxiliary tube and oriented to the mounting position of the infrared radiation thermometer is arranged in the second end part. The device also comprises a light shading tube which is inserted and fixed in the second end part, an adjusting device and an air supply component, wherein the adjusting device comprises a fixed link and an adjusting part; the first end part is fixed on the fixed link; the adjusting part is fixed with the fixed link and the second end part respectively; and an air outlet pipeline of the air supply component is connected with the air inlet. The invention also relates to a molten iron temperature continuous measurement system with the special auxiliary device. The special auxiliary device has smart design, and can accurately and continuously measure the molten iron temperature, thereby realizing real application of the infrared radiation thermometer in molten iron temperature measurement.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANTECH AUTOMATION ENG
Contacting/non-contacting molten metal high temperature measuring apparatus and measuring method
InactiveCN101034010ARadiation pyrometryThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsMeasurement deviceRadiation thermometer
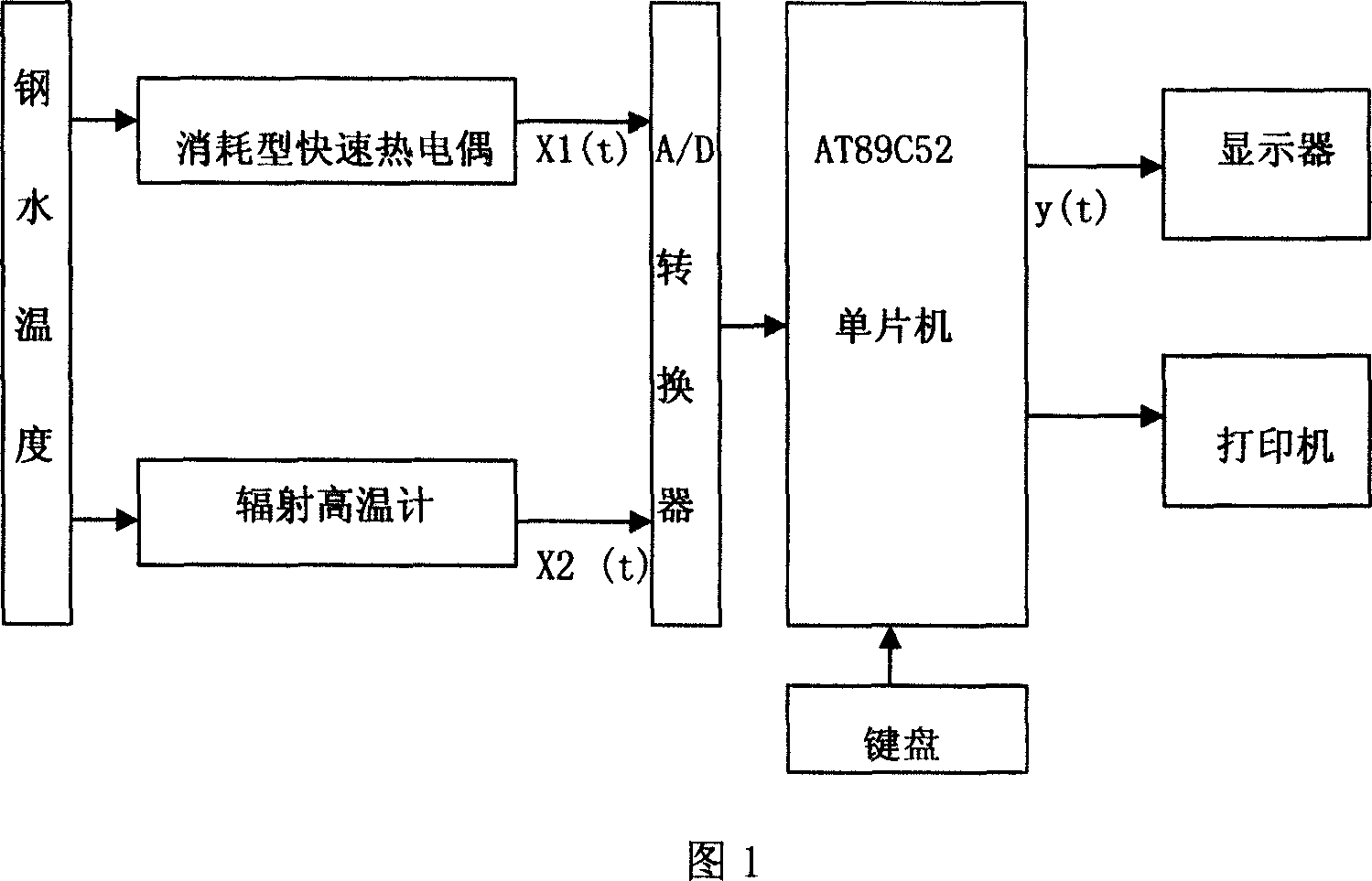
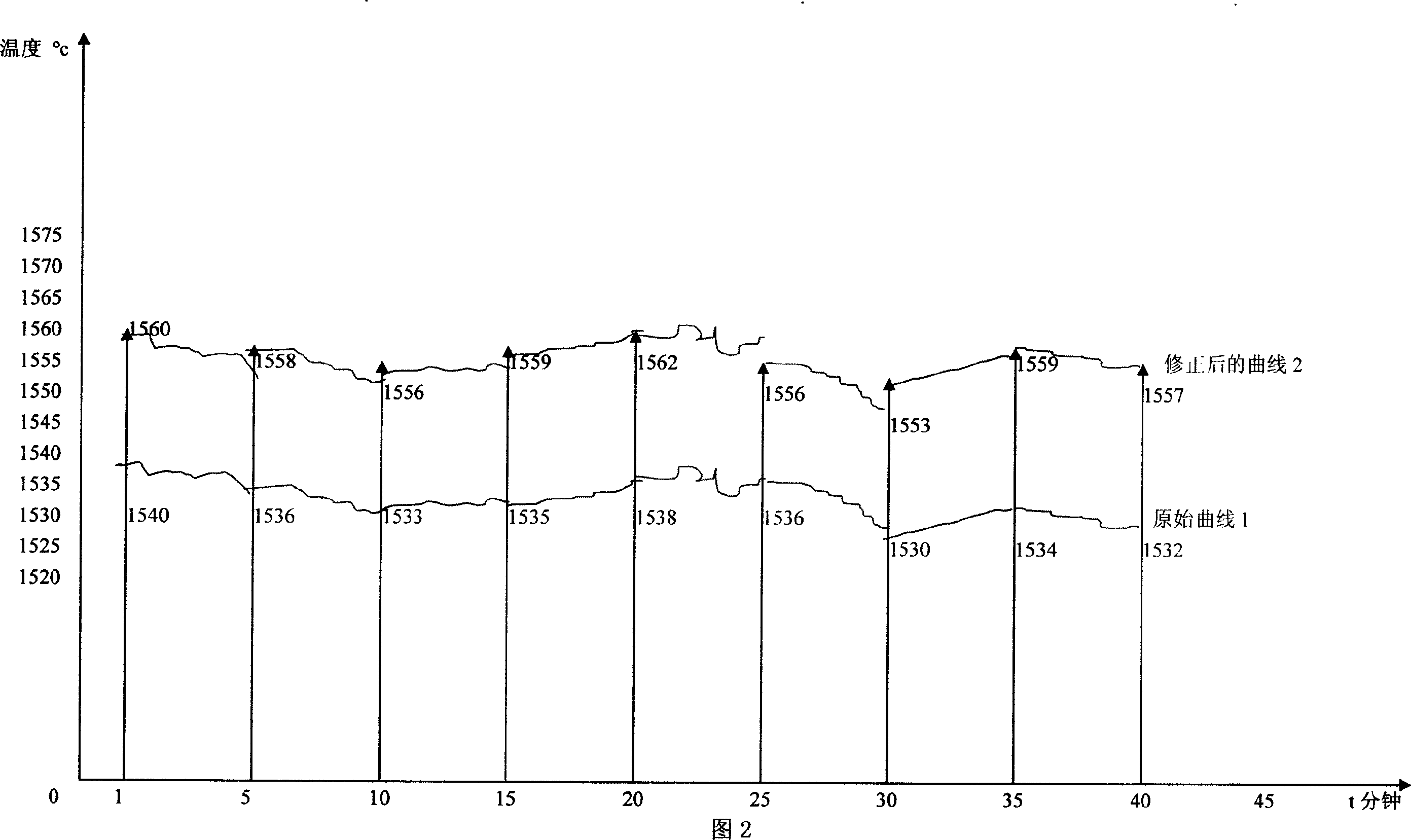
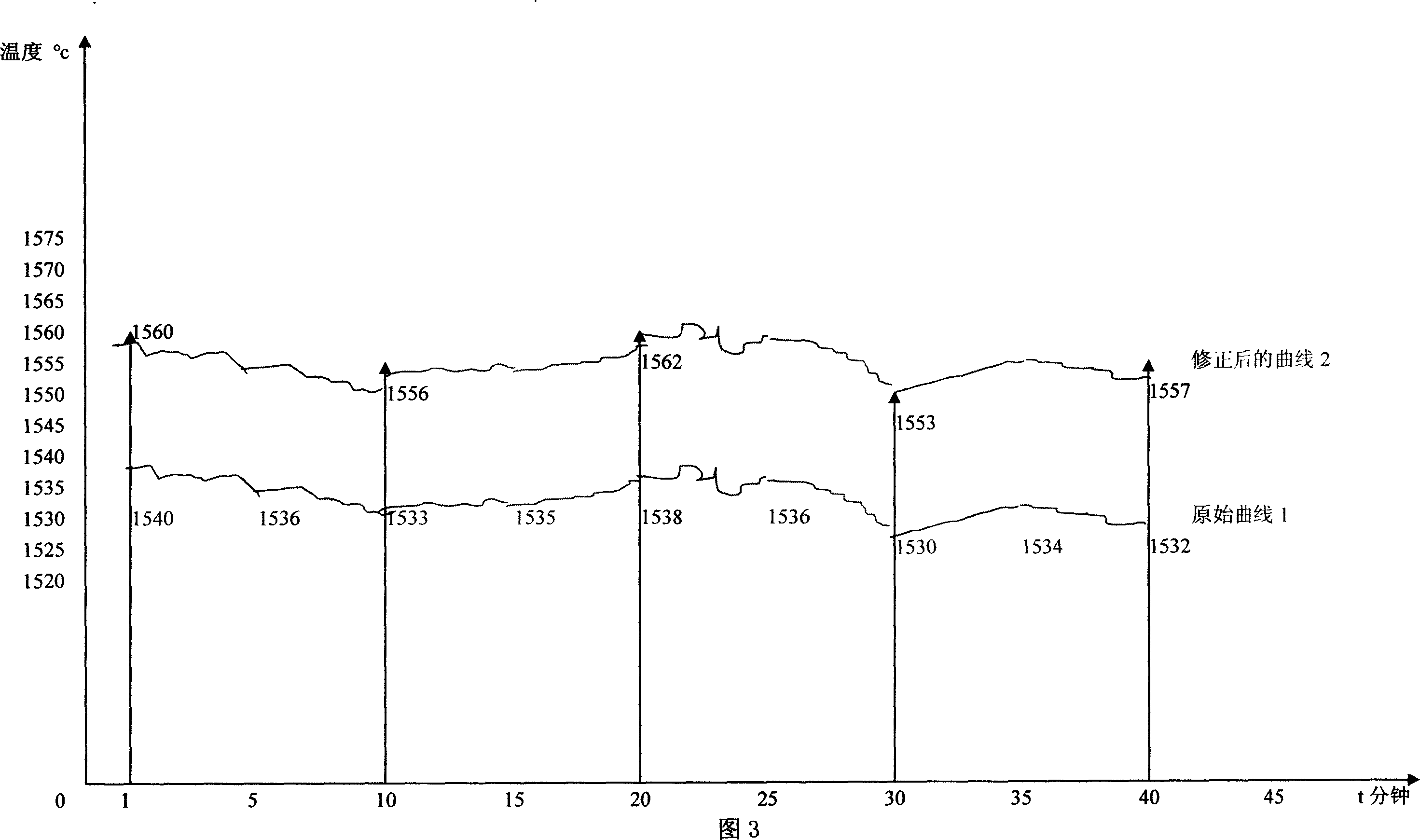
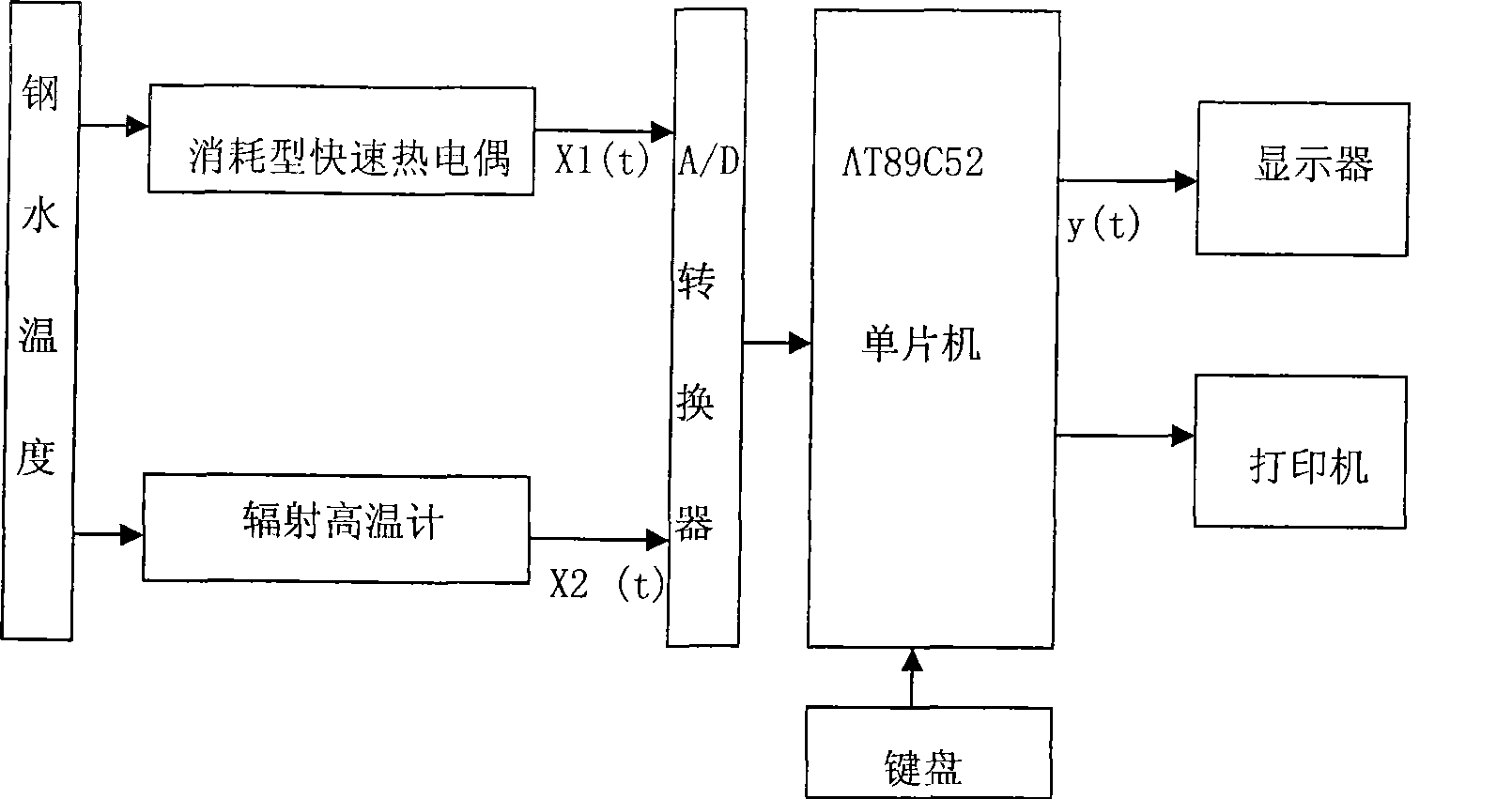
This invention relates to a high temperature measuring method of contact / non- contact molten metal. Specifically the invention is a measuring device and measuring means, which aim at temperature of iron and molten steel, to use discrete temperature signal X1 (T) of asynchronism expending electro heat to continual modify continually varying temperature signal x2 ( T) of high temperature radiation thermometer. The invention includes expend type fast thermocouple, high temperature radiation thermometer, A / D data converter, single chip and output equipment. The described expend type fast thermocouple and high temperature radiation thermometer respectively connect with A / D data converter's input end; A / D data converter's output port connect with single chip; single chip respectively connect with keyboards, display unit and printer.
Owner:武钢集团有限公司
Test device and use method of long-rod platinum resistance thermometer
InactiveCN101319940ASimple structureEasy to useThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsUsing electrical meansWater bathsElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention belongs to the technical field of product testing and relates to a testing device for a long rod platinum resistance thermometer with a length over 700mm in particular. The testing device include a constant temperature water bath device and at least two standard thermometers; the constant temperature water bath device includes a water bath chamber which can be inserted into the long rod platinum resistance thermometer to be tested; the two standard thermometers are respectively inserted into the two ends of the water bath chamber as well. The testing device not only has a simple structure and is conveniently used, but also greatly reduces the testing cost. The invention also relates to a method for testing the long rod platinum resistance thermometer with the testing device; the method includes the steps as follows: firstly inserting the long rod platinum resistance thermometer into any end of the water bath chamber; then setting the temperature value of the constant temperature water bath device and waiting for a temperature field to be stable; then reading the values of each thermometer in turn and working out a standard temperature value by utilizing the values of the standard thermometers; then comparing the temperature value of the long rod platinum resistance thermometer to be tested with the standard temperature value and judging the measuring characteristic of the standard temperature value; resetting at least two temperature values to the constant temperature water bath device and repeating the steps.
Owner:DAYA BAY NUCLEAR POWER OPERATIONS & MANAGEMENT
Multi-group layered submerged impinging steam reactor
ActiveCN104338492AIncrease the level of mixingIncrease reaction rateChemical/physical/physico-chemical nozzle-type rreactorsLiquid-liquid reaction processesChemical reactorNuclear engineering
The invention discloses a multi-group layered submerged impinging steam reactor and relates to a chemical reactor. The reactor is of a multi-group layered structure; top, middle and lower three layers of feed pipes are arranged on a reactor body; the feed pipes on the same layer are coaxially and oppositely arranged; the outlet end of each feed pipe is provided with a nozzle adjustable in structure, diameter and spacing; the reactor body is in the shape of a vertical cylinder; the upper end of the reactor body is provided with an elliptical head cover; a gas outlet, a pressure gage insertion hole and a temperature gauge insertion hole are formed in the elliptical head cover; the lower end of the reactor body is a conical reactor bottom, and a discharge hole is formed in the reactor bottom; an overflow outlet is formed in the side wall of the upper part of the reactor body, and can be used for leading out light components after reaction; the outer side of a column wall is provided with a jacket, and the jacket is used for heating or cooling. When the reactor works, fluid is sprayed through the nozzles of the feed pipes, and violently impinges in an impinging area in the reactor body so as to achieve the goals of full mixing and full reaction; the radial liquid flow of the impinging fluid can impinge for the second time, so that the reaction (mixing) efficiency is improved. According to the reactor, the feed pipes can be increased or reduced by groups according to the actual requirement, and therefore multiple working conditions can be adapted; the reactor is convenient to install and low in maintenance cost.
Owner:SHENYANG INSTITUTE OF CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
Non-conducting zirconium dioxide
ActiveUS20110305259A1Good reproducibilityIncrease productionTemperature measurement in motorsThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsZirconium hydrideNiobium
A resistance thermometer is provided having a measuring resistor in a form of a 0.1 to 10 μm thick structured platinum layer applied to an electrically insulated surface of a substrate and an electrically insulating coating layer covering the platinum layer. The substrate or its surface contains zirconium dioxide, which is stabilized with oxides of a trivalent and a pentavalent metal. Preferably, the trivalent metal is yttrium and the pentavalent metal is tantalum or niobium. The characteristic curve of the measuring resistor preferably conforms to DIN-IEC 751. For mass production of resistance thermometers having high and reproducible measurement accuracy, a structured platinum layer having a thickness of 0.1 to 10 μm is applied to an electrically insulating substrate having a thermal expansion coefficient in the range of 8.5 to 10.5×10−6 / ° K and a roughness less than 1 μm, and the structured platinum layer is covered by an electrical insulator. The resistance thermometers allow precise temperature measurement between −200° C. and +850° C., preferably as a sensor in an exhaust gas treatment system. In a substance-sensitive sensor having a circuit path structure on a substrate, the circuit path structure has an epitaxially applied base layer, and a substance-sensitive metal layer attached to the epitaxially applied base layer.
Owner:HERAEUS NEXENSOS GMBH
Non-conducting zirconium dioxide
ActiveUS8730002B2Good reproducibilityIncrease productionTemperature measurement in motorsThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsZirconium hydrideNiobium
A resistance thermometer is provided having a measuring resistor in a form of a 0.1 to 10 μm thick structured platinum layer applied to an electrically insulated surface of a substrate and an electrically insulating coating layer covering the platinum layer. The substrate or its surface contains zirconium dioxide, which is stabilized with oxides of a trivalent and a pentavalent metal. Preferably, the trivalent metal is yttrium and the pentavalent metal is tantalum or niobium. The characteristic curve of the measuring resistor preferably conforms to DIN-IEC 751. For mass production of resistance thermometers having high and reproducible measurement accuracy, a structured platinum layer having a thickness of 0.1 to 10 μm is applied to an electrically insulating substrate having a thermal expansion coefficient in the range of 8.5 to 10.5×10−6 / ° K and a roughness less than 1 μm, and the structured platinum layer is covered by an electrical insulator. The resistance thermometers allow precise temperature measurement between −200° C. and +850° C., preferably as a sensor in an exhaust gas treatment system. In a substance-sensitive sensor having a circuit path structure on a substrate, the circuit path structure has an epitaxially applied base layer, and a substance-sensitive metal layer attached to the epitaxially applied base layer.
Owner:HERAEUS NEXENSOS GMBH
Non-contact type infrared temperature detecting system based on micromachine thermopile
InactiveCN103344343AHigh sensitivityImprove temperature measurement accuracyPyrometry using electric radation detectorsThermopileContact type
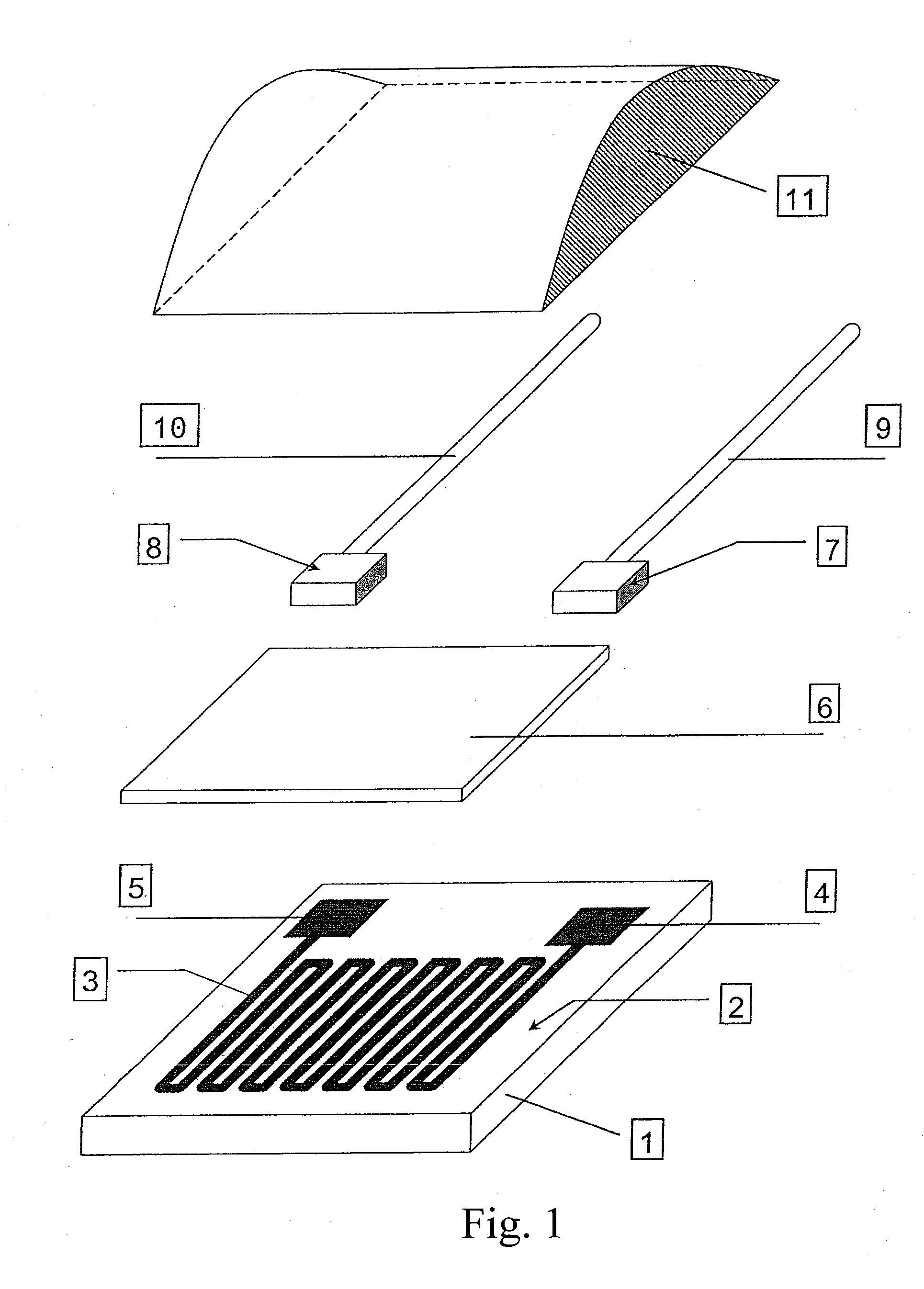
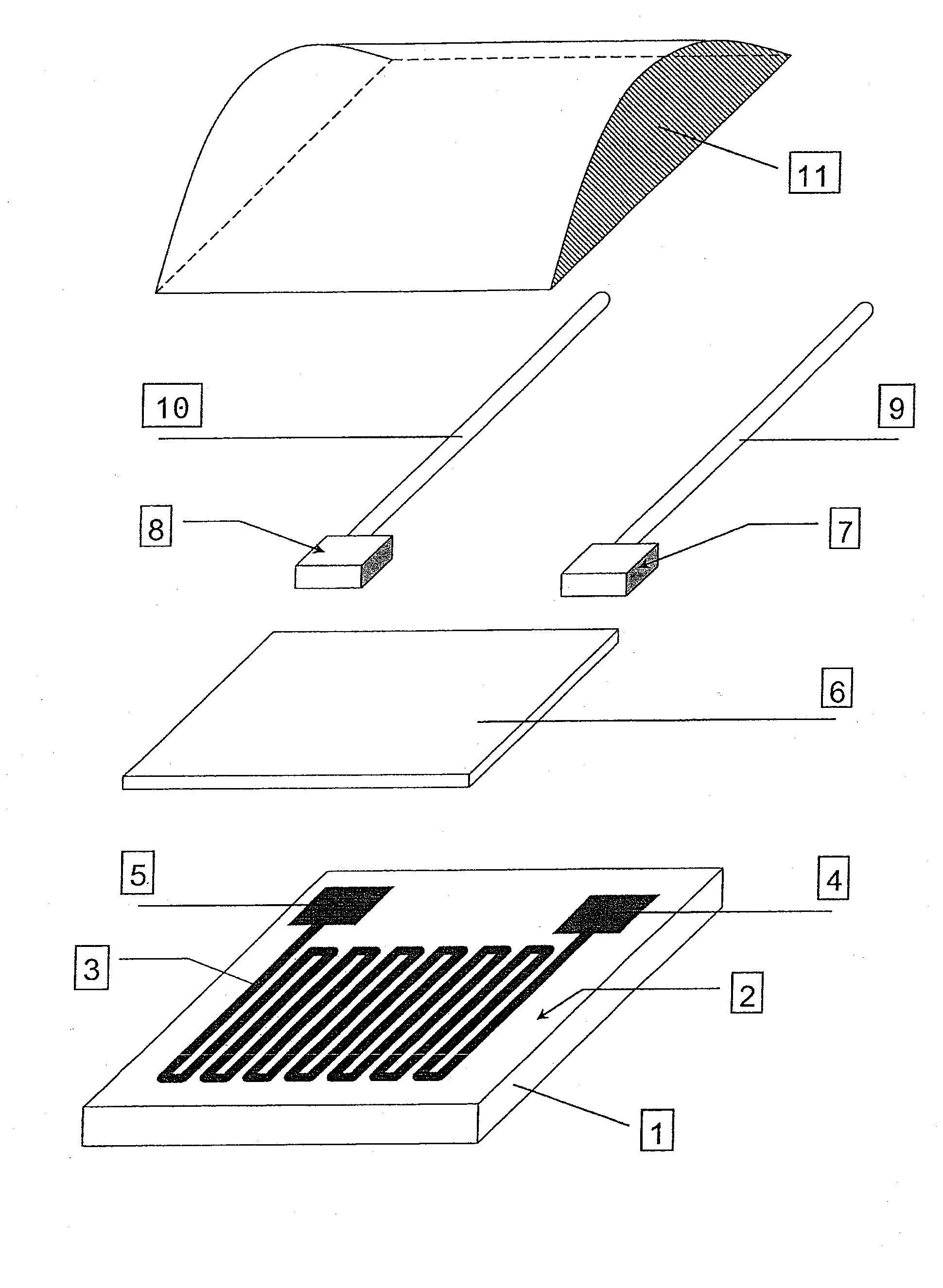
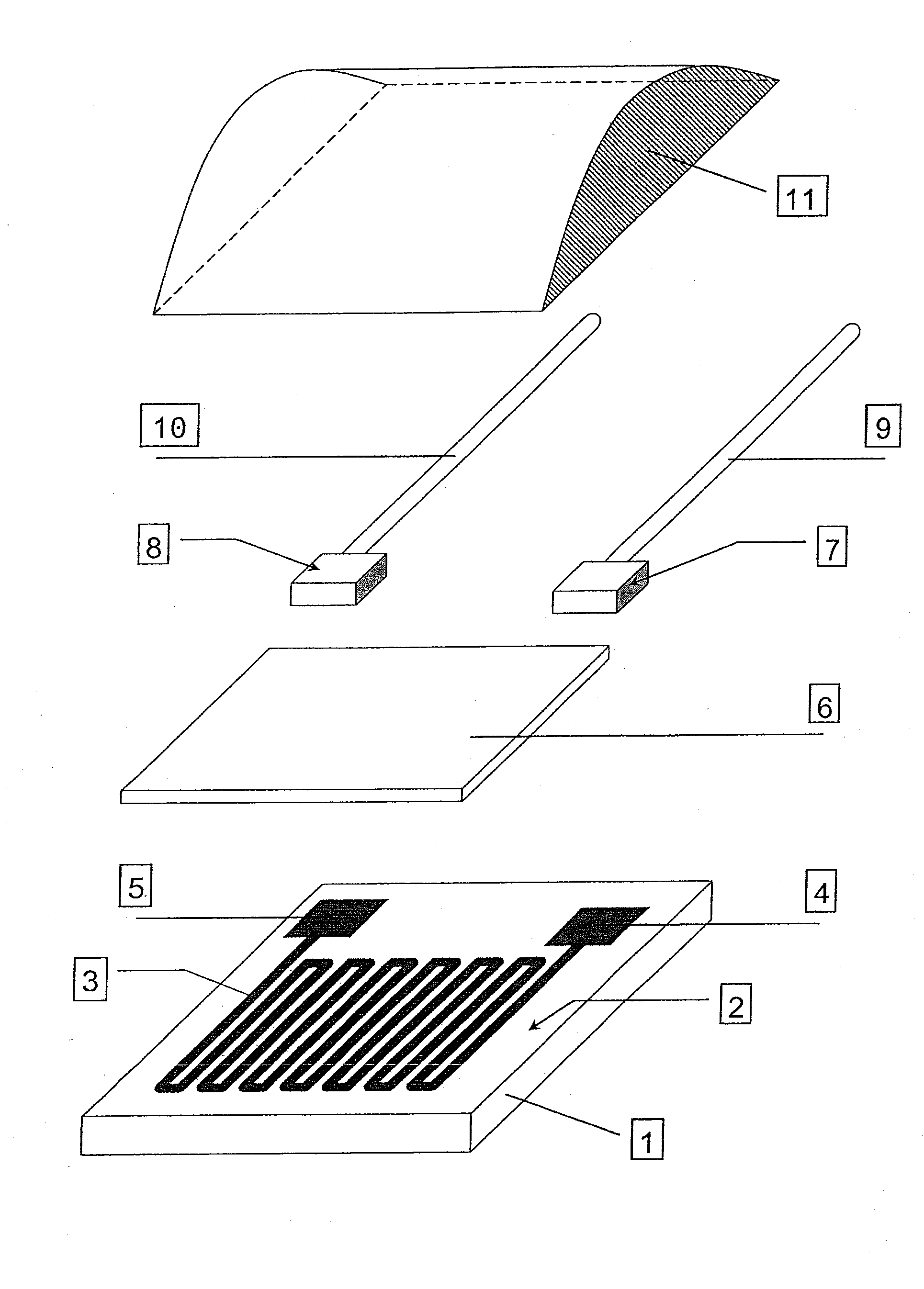
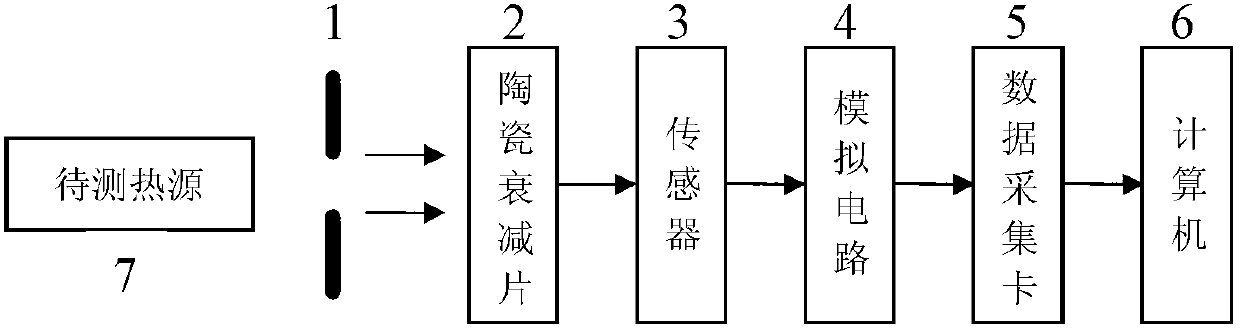
A non-contact type infrared temperature measuring system based on a micromachine thermopile comprises a diaphragm, a ceramic damping piece, a sensor, a simulation circuit, a data collecting card and a computer. The non-contact type infrared temperature measuring system based on the micromachine thermopile is suitable for temperature measuring of a long-distance target, a high-speed moving target, an electrification target and other untouchable targets especially in some dangerous environments. Compared with a traditional thermocouple, a thermometer and other thermodetectors, the system does not need to be in contact with a measured object by infrared temperature measuring, long-distance temperature measuring can be achieved, and meanwhile tiny temperature fluctuation of the object can cause large changing of radiation energy, so that an infrared thermodetector is high in sensitivity, and the minimum measurable temperature difference of the micromachine thermopile infrared thermodetector can reach 0.01 DEG C. In addition, the system has the advantages of being reasonable and simple in structural design, low in cost, high in temperature measuring accuracy and the like.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
Thermal-energy meter checking device
A calibrating device of heat energy meter consists of temperature detecting system including the same two of temperature setting units prepared as connecting water box to warm field , placing silicone oil in warm field cavity ,setting temperature sensor and thermometer of heat energy meter in silicone oil and having water rising along spiral sheet in jacket of internal cavity ; flow rate detecting system prepared as connecting water box to flow stabilization tank and connecting said tank separately to two flow test piping with heat energy meter ; and computer processing system .
Owner:睿能太宇(沈阳)能源技术有限公司
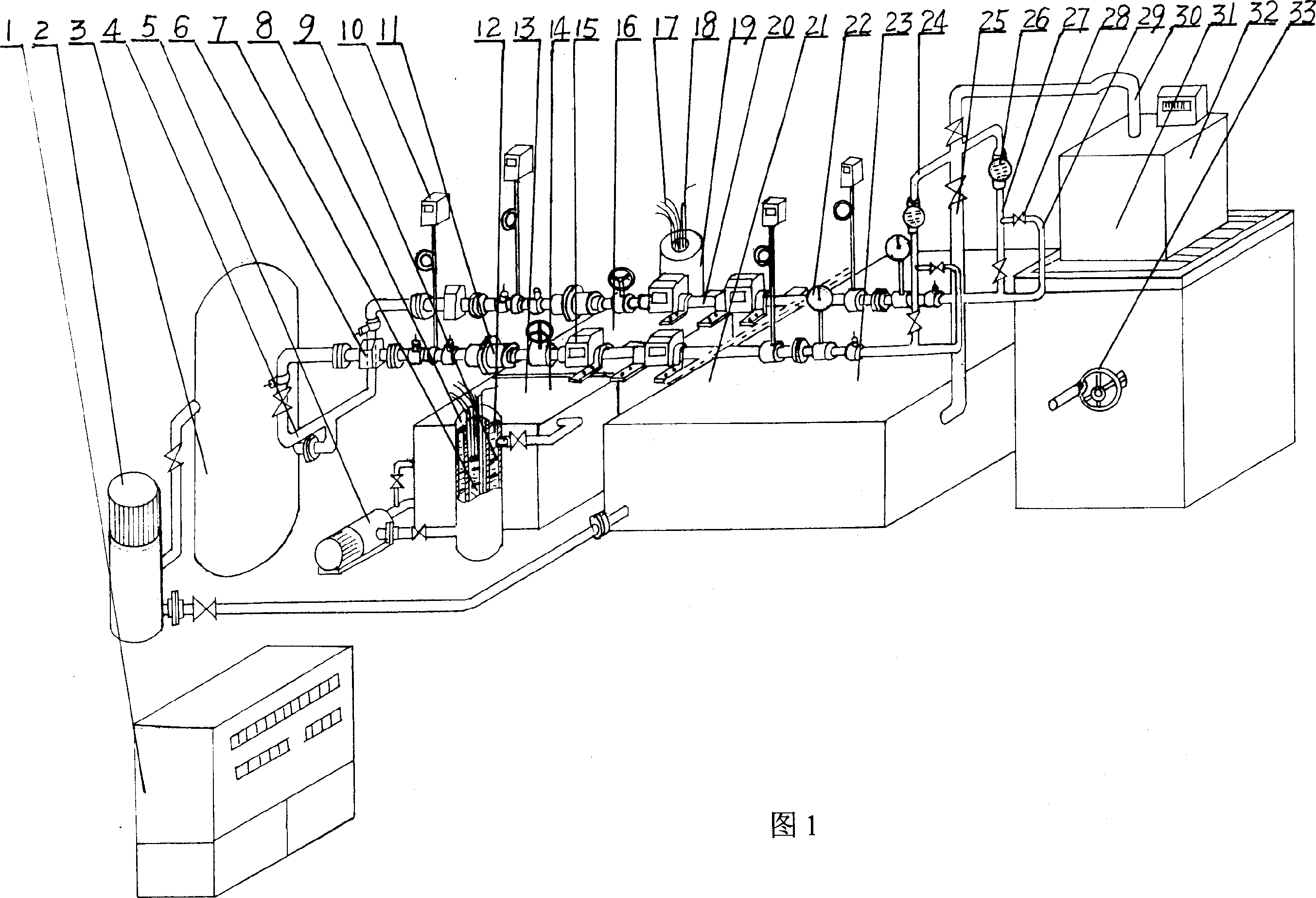
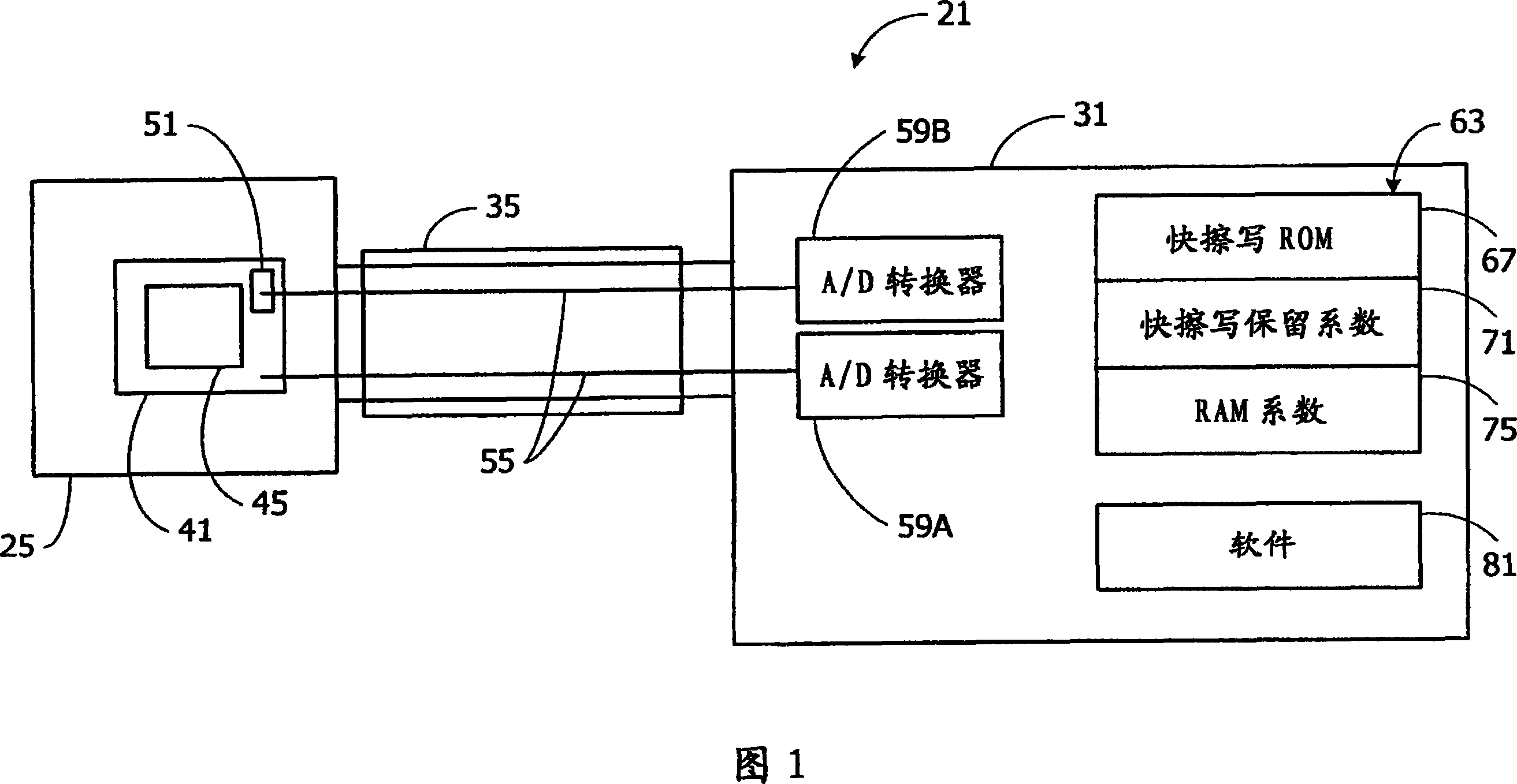
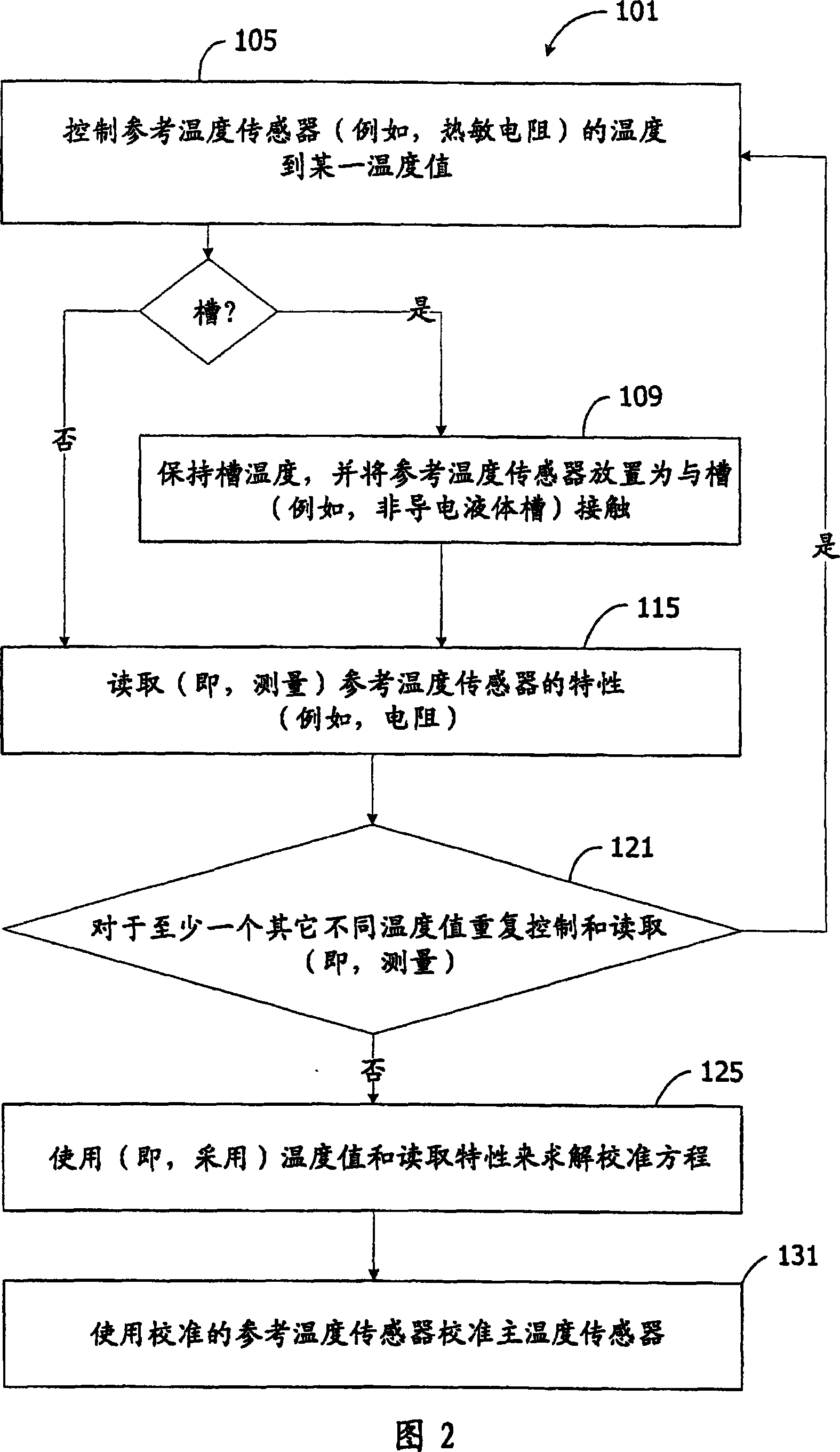
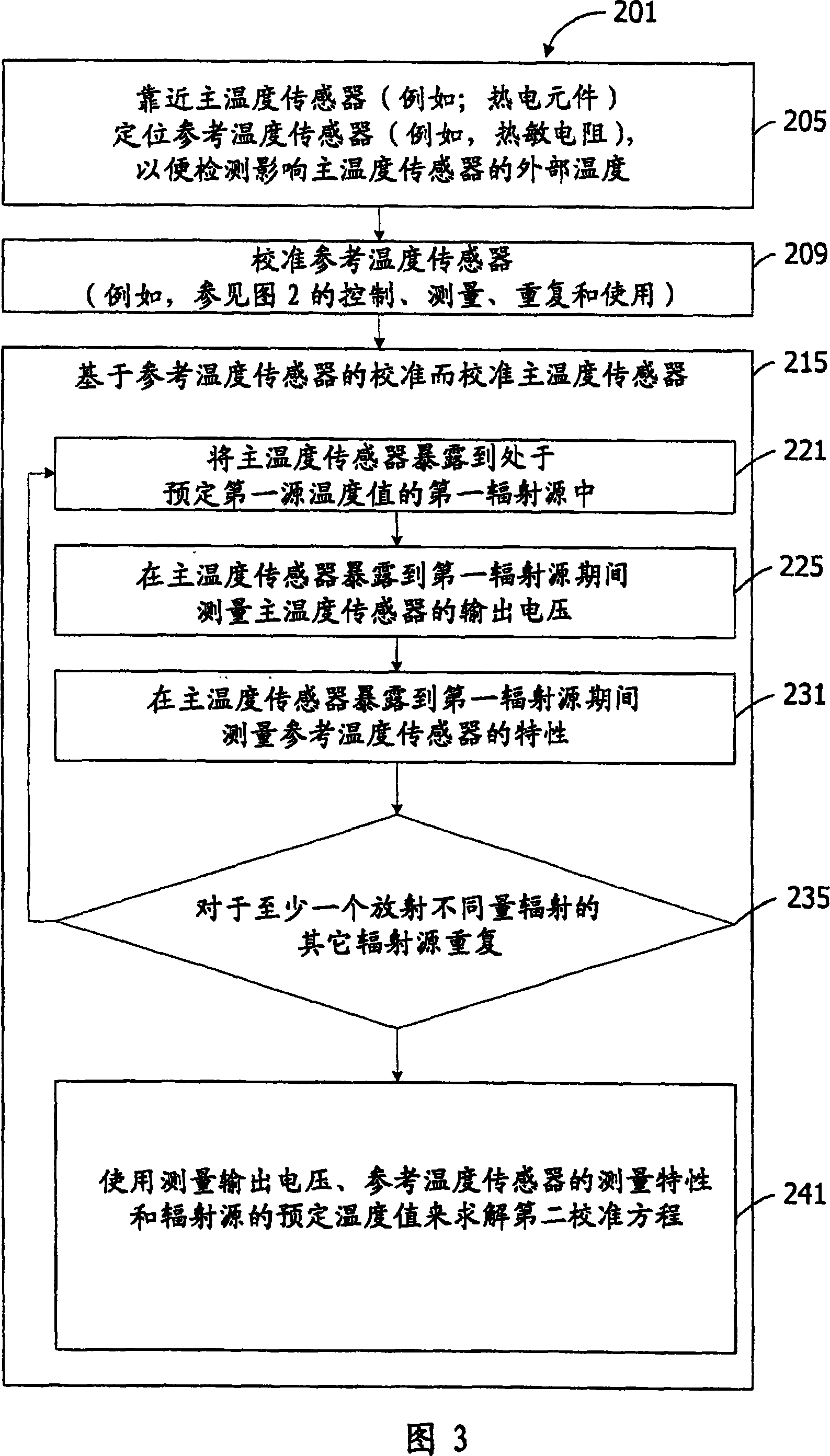
Thermometer calibration by immersion in non-electrically conductive liquid
InactiveCN101078655AEasy CalibrationThermometer testing/calibrationPyrometry using electric radation detectorsTemperature controlEngineering
A method for calibrating a thermometer is disclosed. The thermometer comprises a primary temperature sensor for determining the temperature of a target. The thermometer also comprises a reference temperature sensor positioned proximate to the primary temperature sensor and being responsive to an extraneous temperature affecting the primary temperature sensor. One calibration method calibrates the reference temperature sensor. This calibration can utilize a non-electrically conductive liquid bath for temperature control. Another calibration method calibrates the reference temperature sensor and the primary temperature sensor.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Light irradiation type heat treatment apparatus and heat treatment method
InactiveUS20190141790A1Accurate measurementAccurate temperature measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPyrometry using electric radation detectorsLight irradiationRadiation thermometer
A semiconductor wafer held in a chamber by a susceptor is heated by irradiating the semiconductor wafer with light directed through an upper chamber window and a lower chamber window. A radiation thermometer measures the temperature of the semiconductor wafer held by the susceptor. A temperature correction part corrects temperature measurement of the semiconductor wafer with the radiation thermometer, based on the value of temperature measurement of the upper chamber window, the value of temperature measurement of the lower chamber window, and the value of temperature measurement of the susceptor. Thus, the temperature of the semiconductor wafer is accurately measured irrespective of the temperatures of in-chamber structures including the susceptor and the like.
Owner:DAINIPPON SCREEN MTG CO LTD
Infrared thermometer
InactiveUS20080267254A1Accurate temperature measurementImprove stabilityThermometer detailsWave amplification devicesAir cycleEngineering
This invention discloses an infrared thermometer for ear or skin temperature. The infrared thermometer comprises a body, an infrared sensing element, and a heat dissipating means. The heat dissipation means is provided behind or below the infrared sensing element for urging the air flowing in and out of the body, so as to contribute better heat dissipation and air circulation around the infrared sensing element. Hence the accuracy and stability of the infrared thermometer are improved.
Owner:ACTHERM INC
Method for manufacturing toner
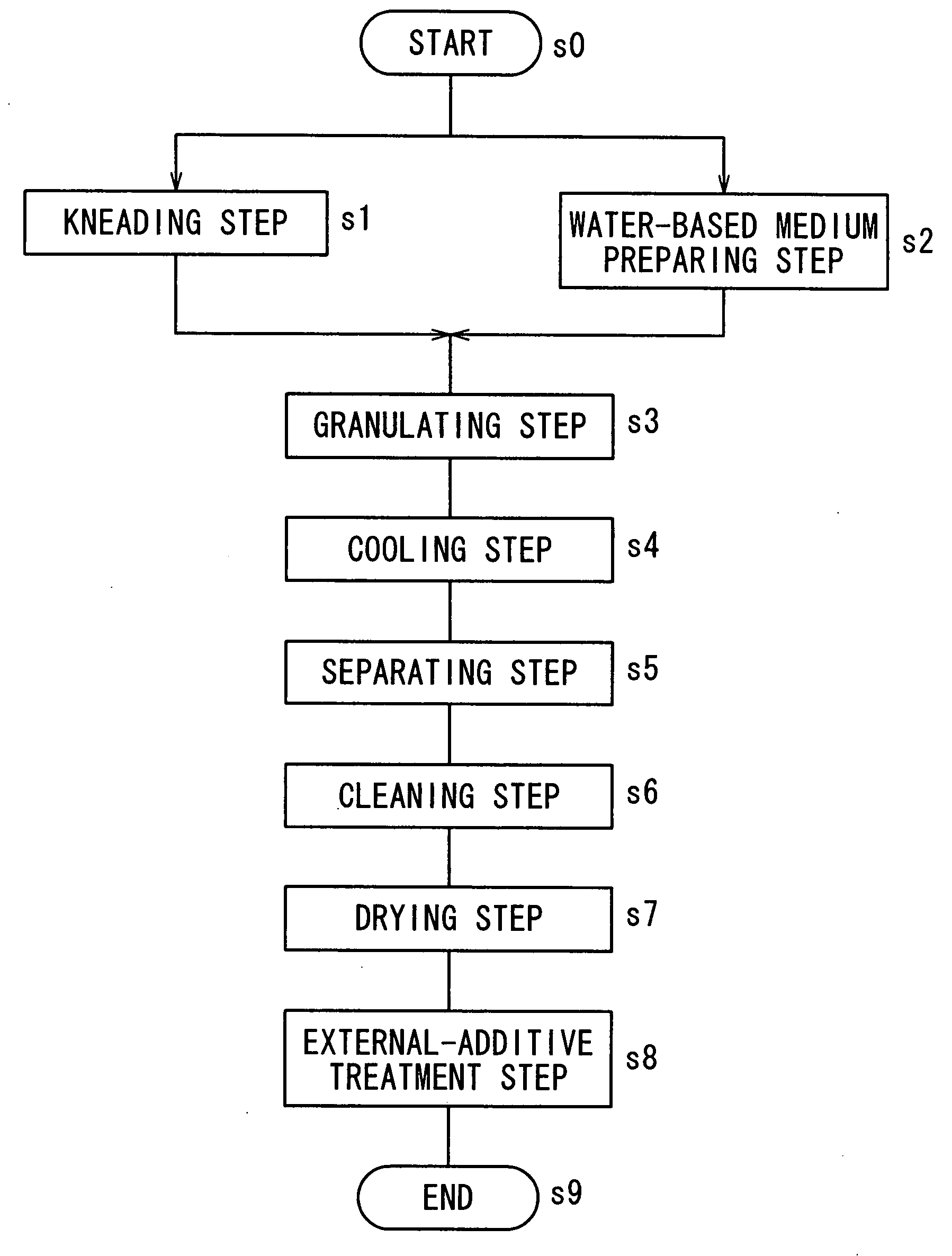
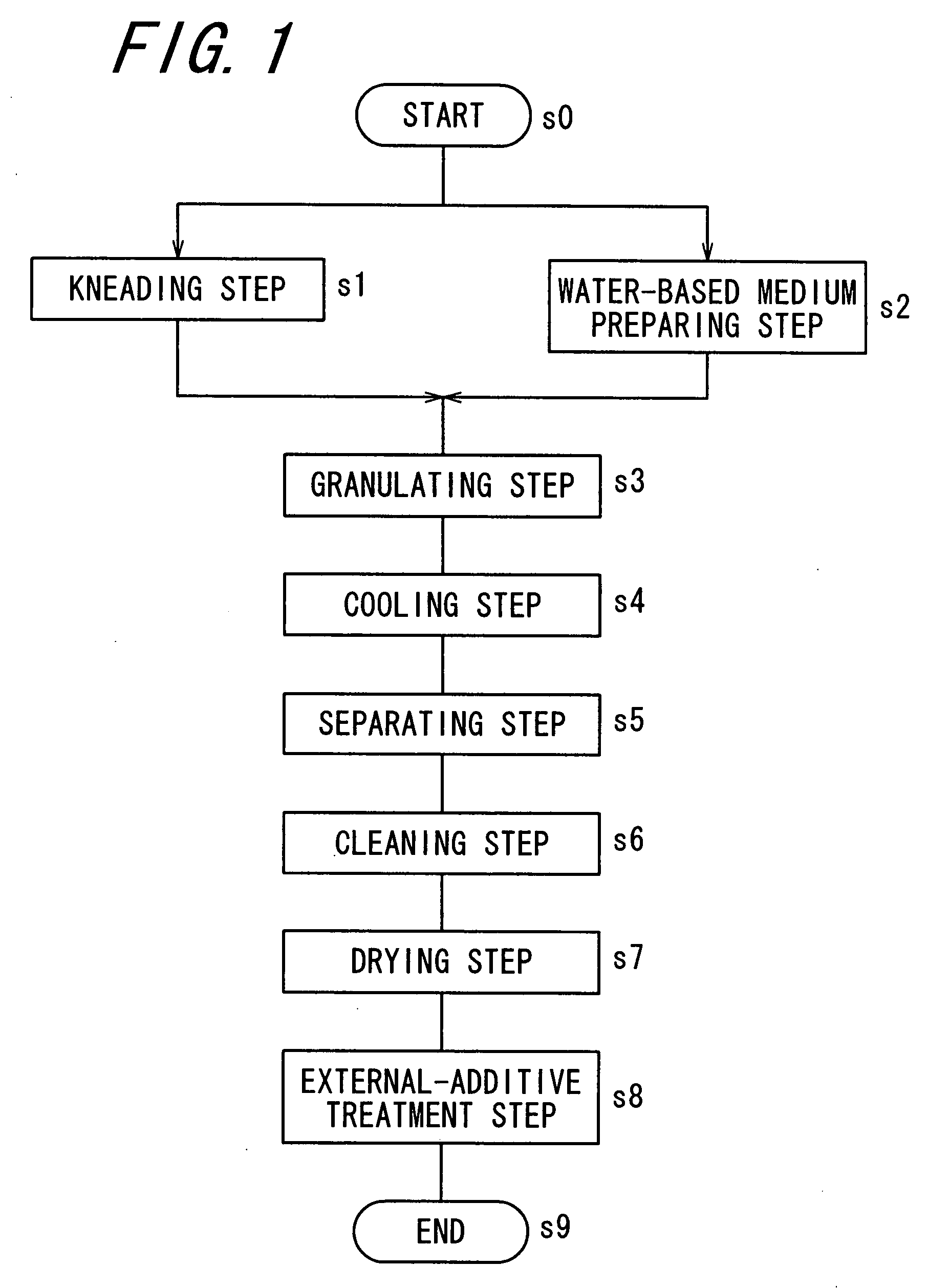
InactiveUS20070224533A1Avoid it happening againReduce the amount requiredDevelopersWater basedEngineering
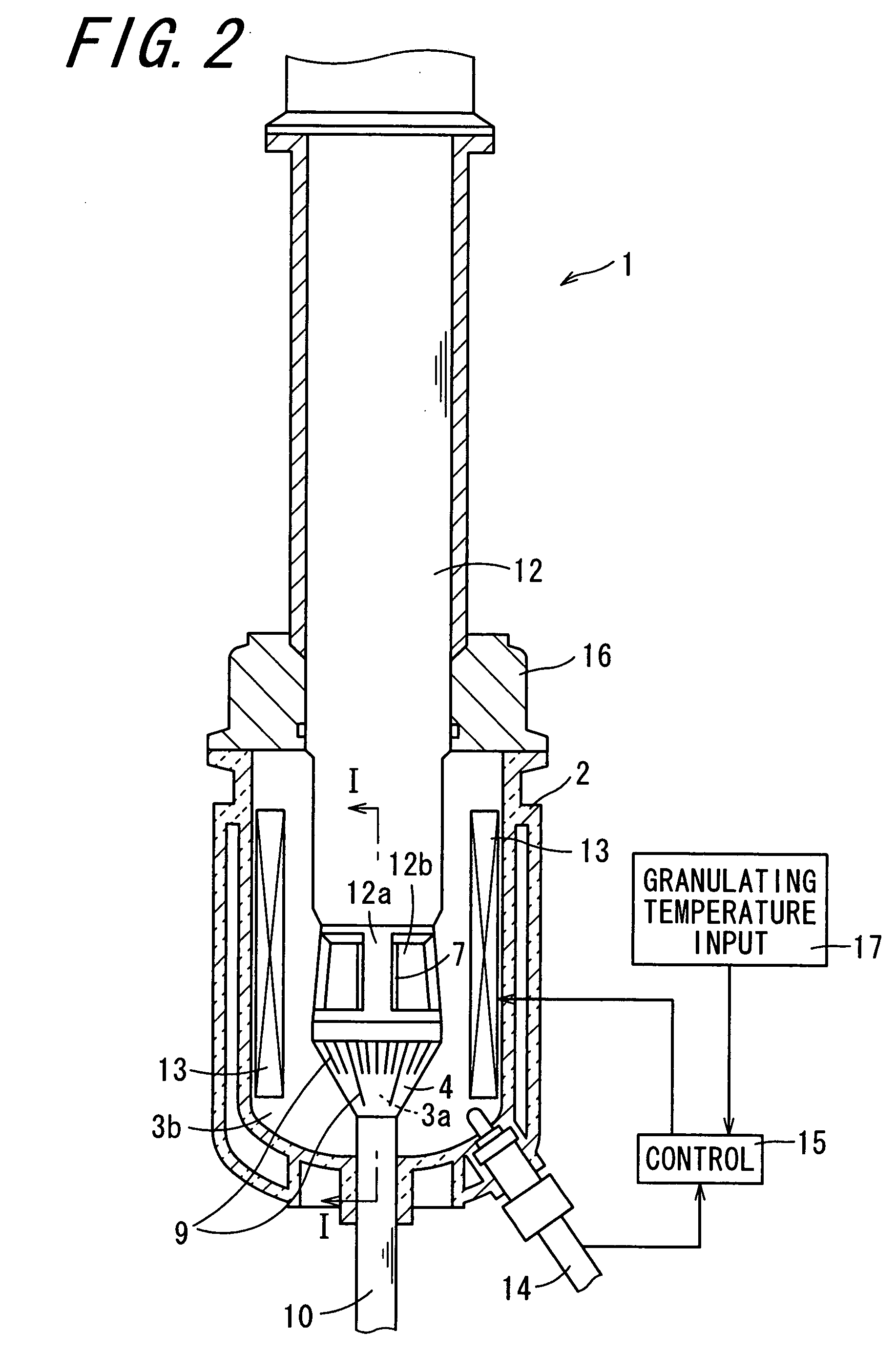
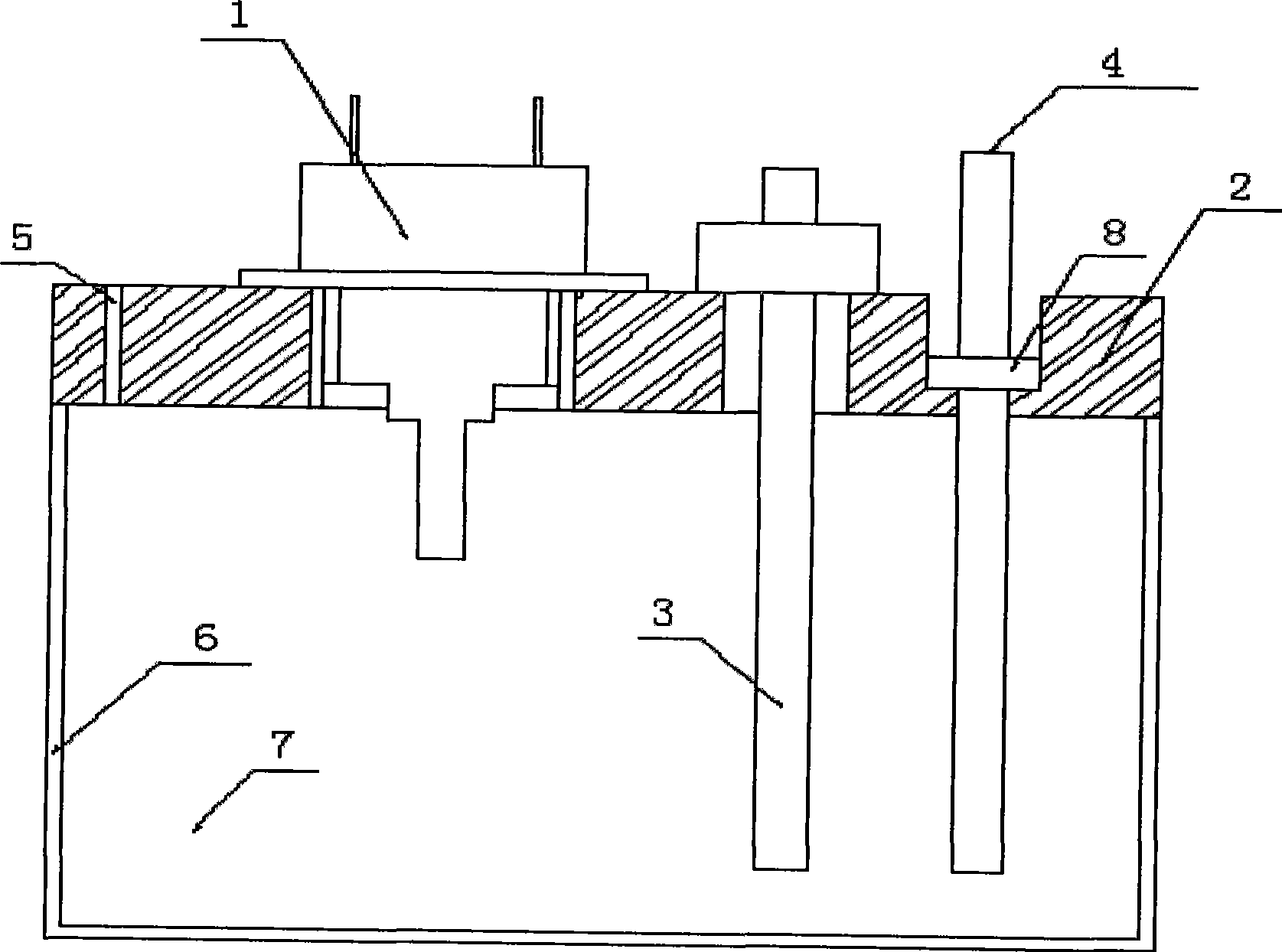
A kneaded material obtained by heating and melt-kneading a toner composition and a water-based medium containing water are put into a container of a granulating apparatus, and heated by a heater while agitating, to disperse the kneaded material into the water-based medium in its softened state. A temperature at which a loss tangent value of the kneaded material reaches a predetermined loss tangent value A, specifically, 0.5 or more and less than 5.0, is inputted to a granulating temperature input section as a setting granulating temperature T1. The heater is then controlled by a control section so that a granulating temperature as a temperature of the water-based medium measured by a thermometer reaches the setting granulating temperature T1 inputted to the input section. Accordingly, the granulating temperature as a temperature of the water-based medium, and thus a temperature of the kneaded material in the water-based medium is adjusted to T1.
Owner:SHARP KK
Water temperature sensor detection device and detecting method thereof
InactiveCN101458130ADetermine whether to failEngine testingThermometer testing/calibrationEngineeringWater temperature
The invention relates to a detecting device of a water temperature sensor and a detecting method thereof, comprising a transparent container, an approach slab, a heating device and a thermograph; wherein, a main body consisting of the transparent container and the approach slab is filled with water, the heating system and the thermograph are arranged on the approach slab and contacted with the water, an air outlet hole is arranged on the approach slab, and another hole is arranged on the approach slab and is used for installing the water temperature sensor. The invention can rapidly and accurately identify whether the water temperature sensor is invalid or not.
Owner:CHERY AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
Method for testing temperature of explosive ignition point
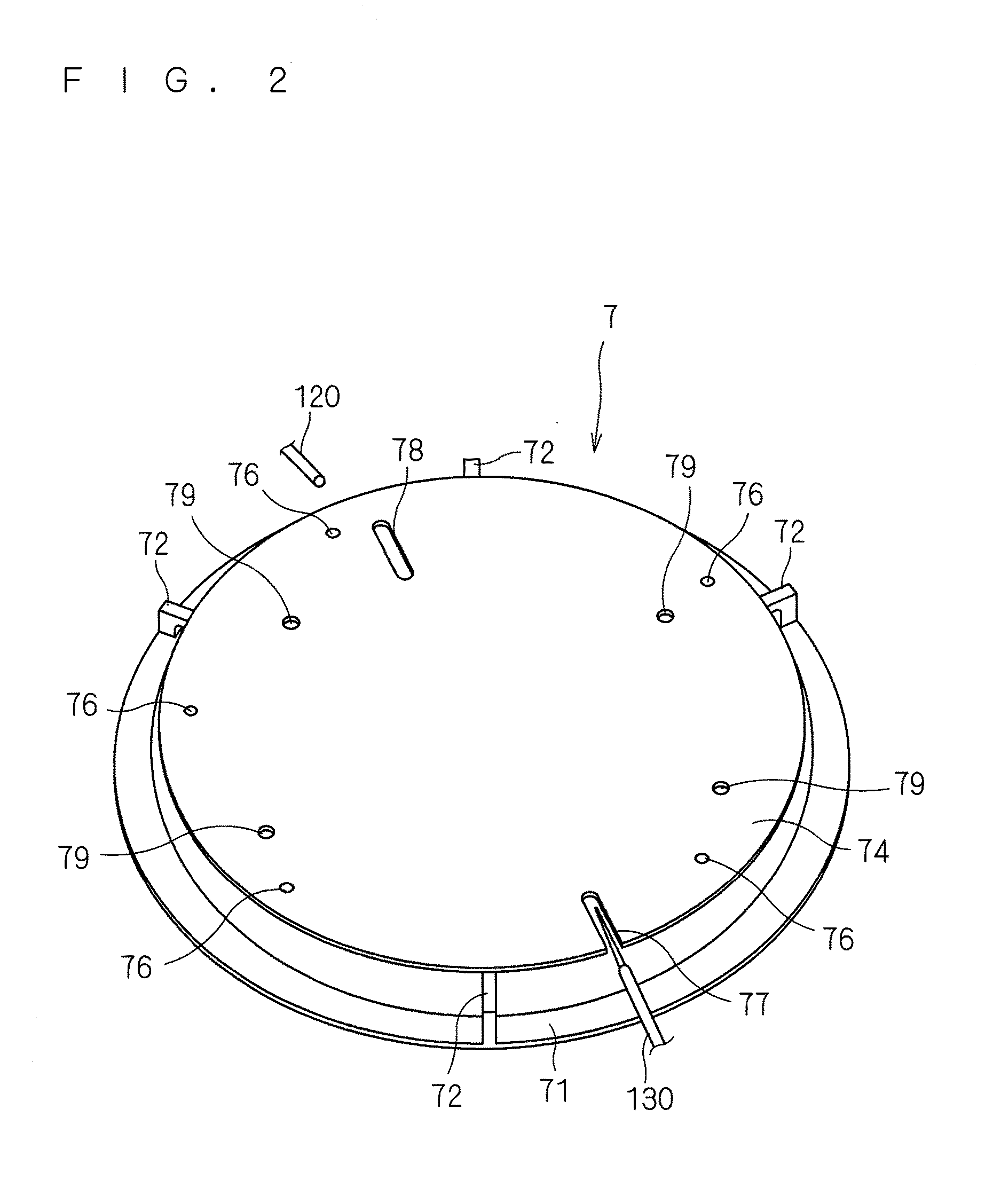
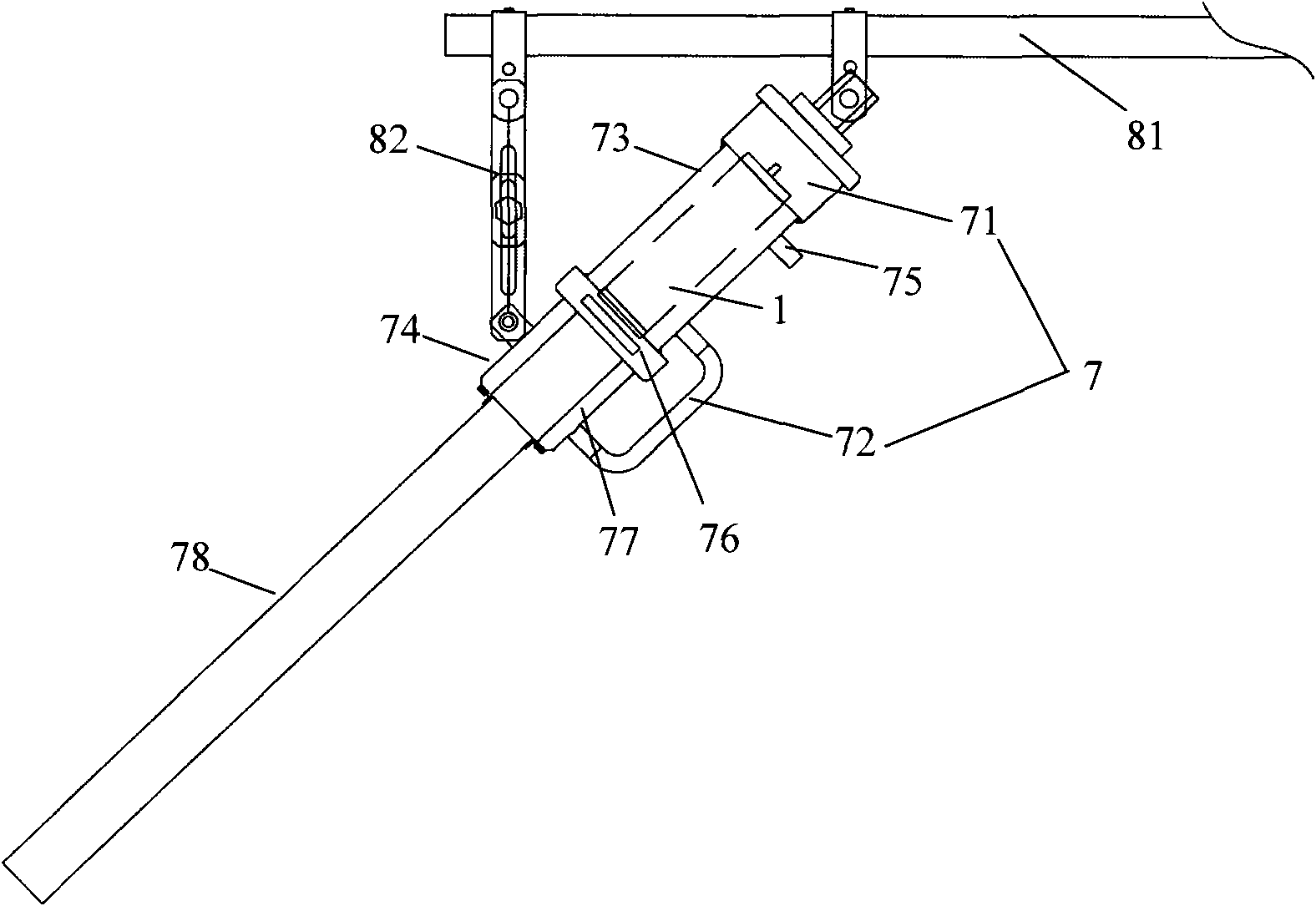
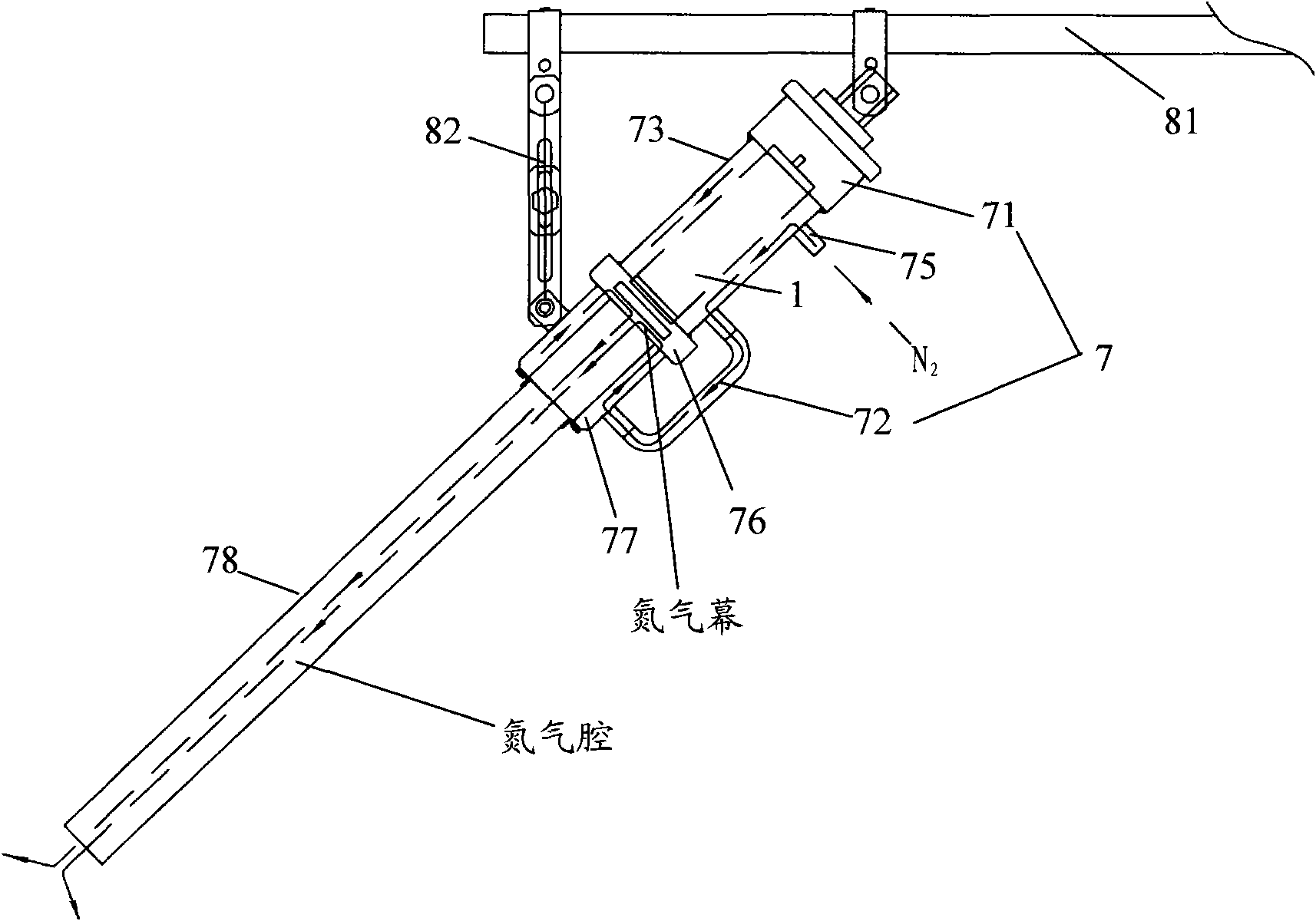
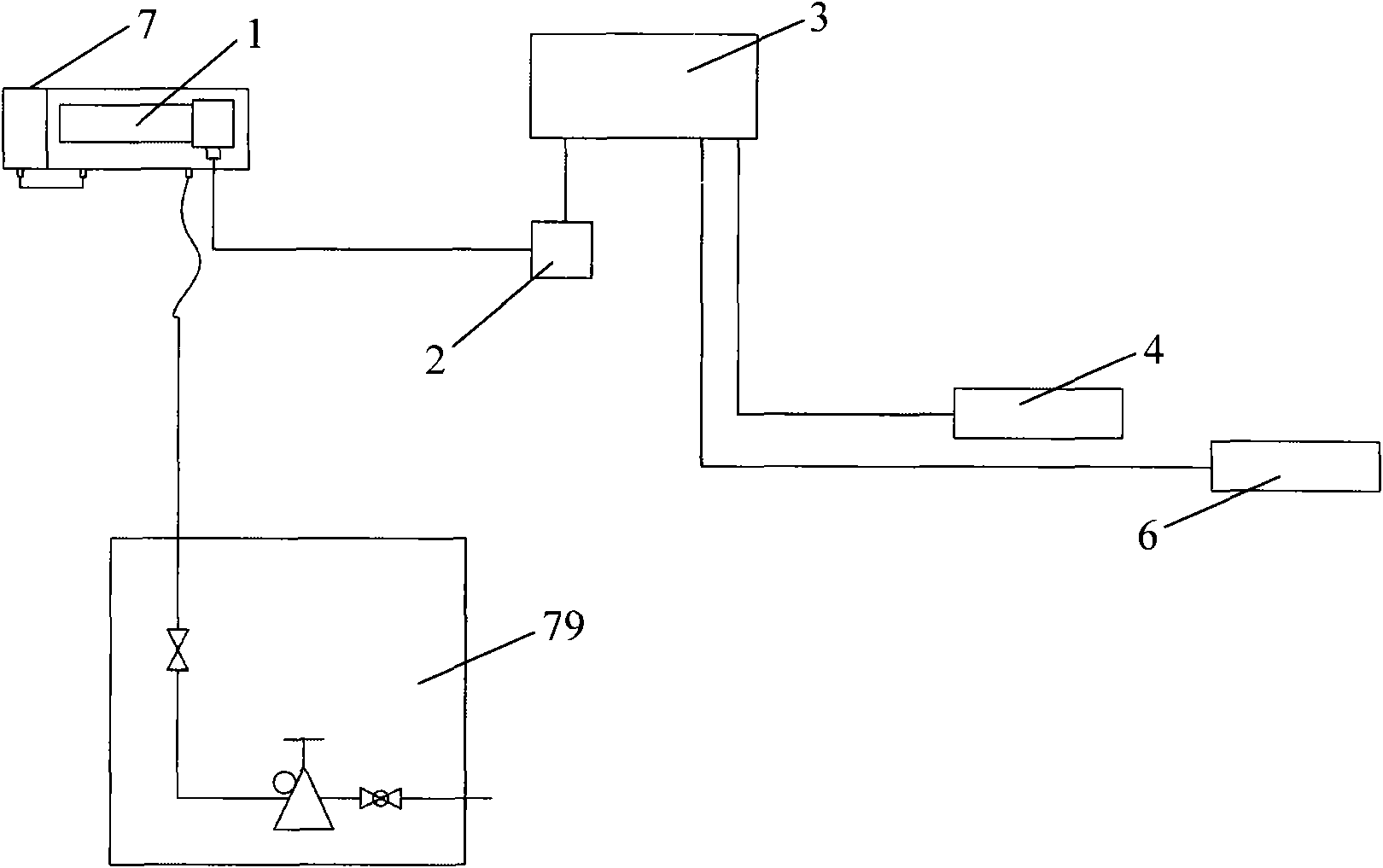
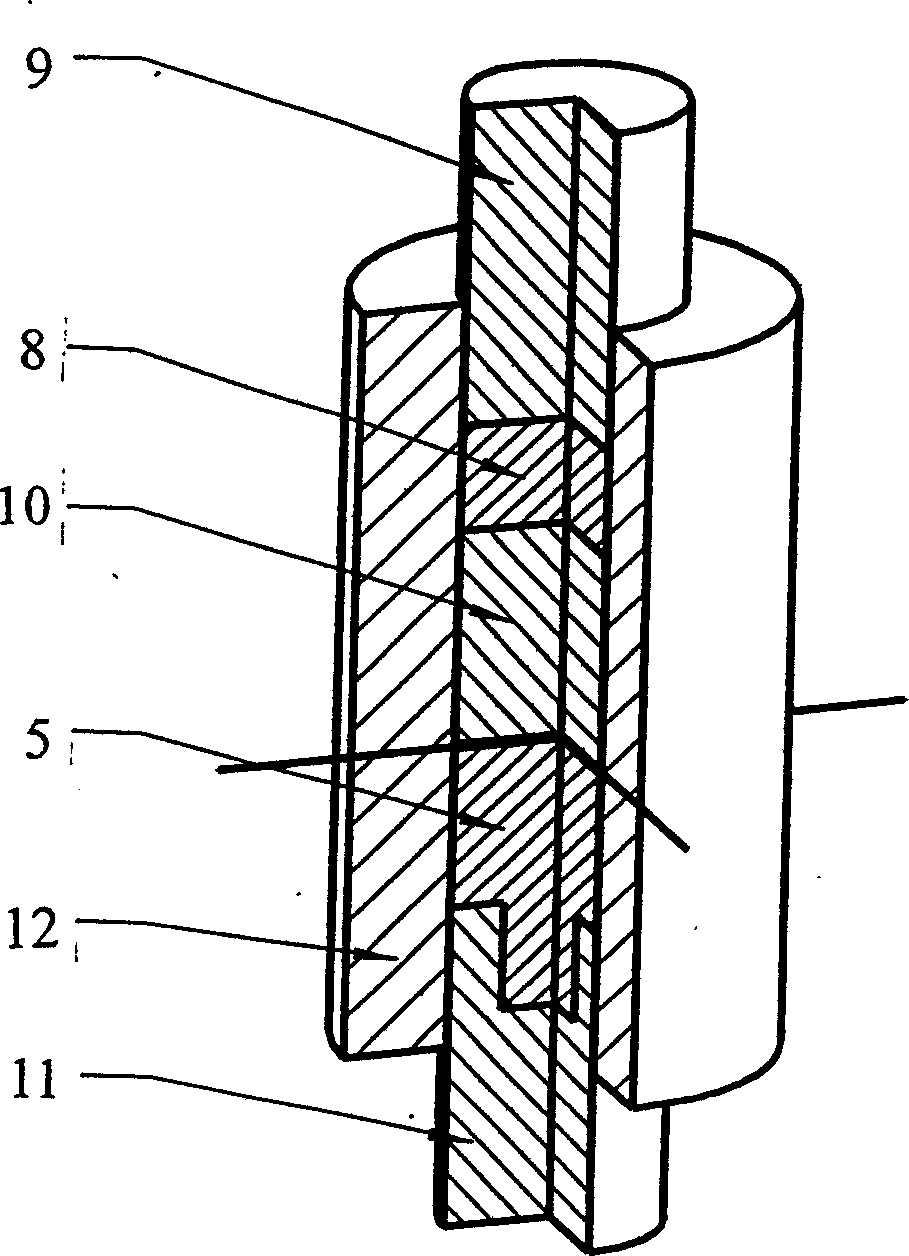
InactiveCN1504734AEasy to operateThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsUsing electrical meansEngineeringCryometer
The invention relates to a method for measuring explosive firing temperature, which comprises the steps of, (1) contacting the tested explosive with a selected temperature gauge, (2) heating-up temperature gauge through a heating arrangement, (3) recording the heating-up process of the explosive and interpreting the explosive ignition temperature. The method can facilitate the extensive use in the real world engineering.
Owner:INST OF MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
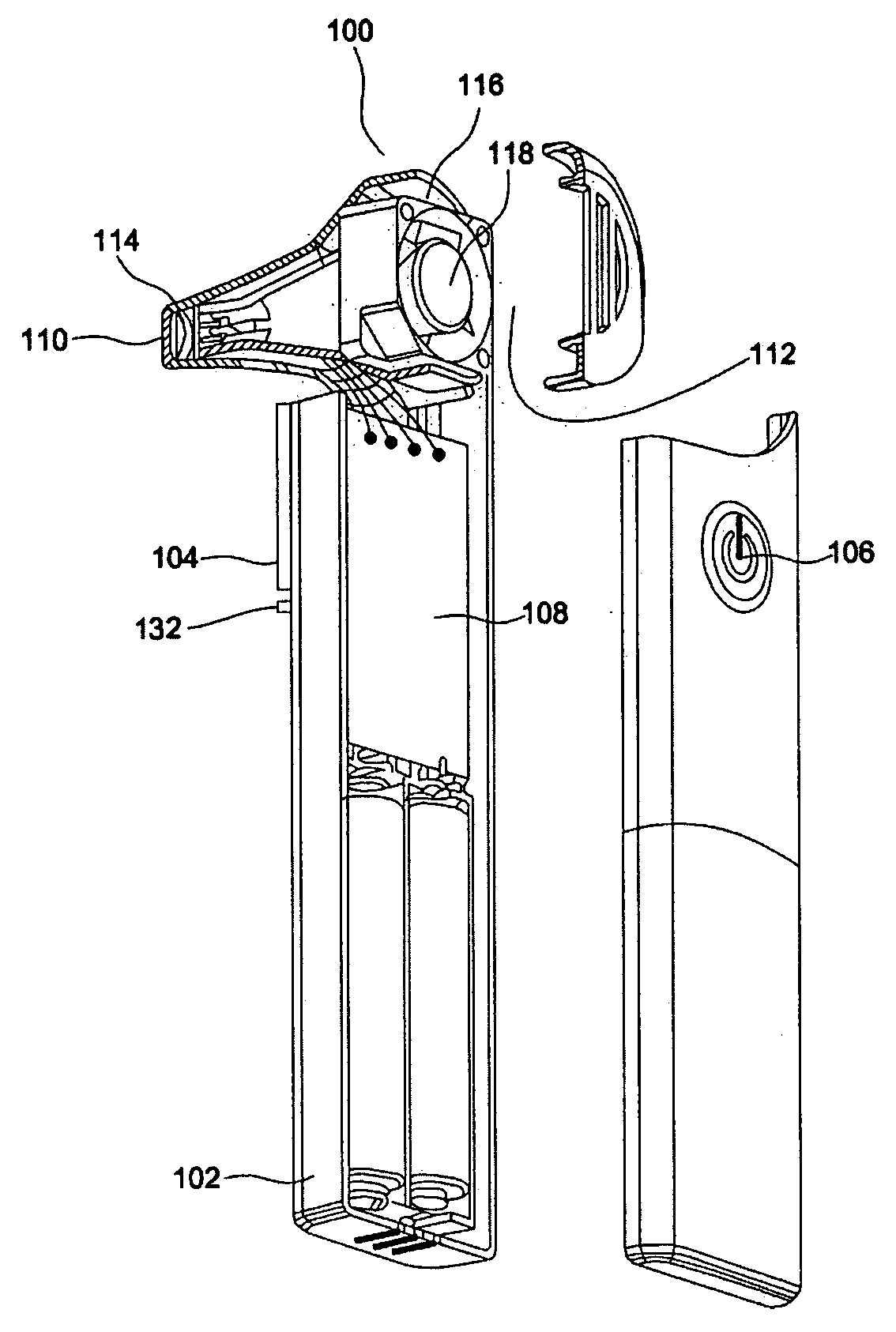
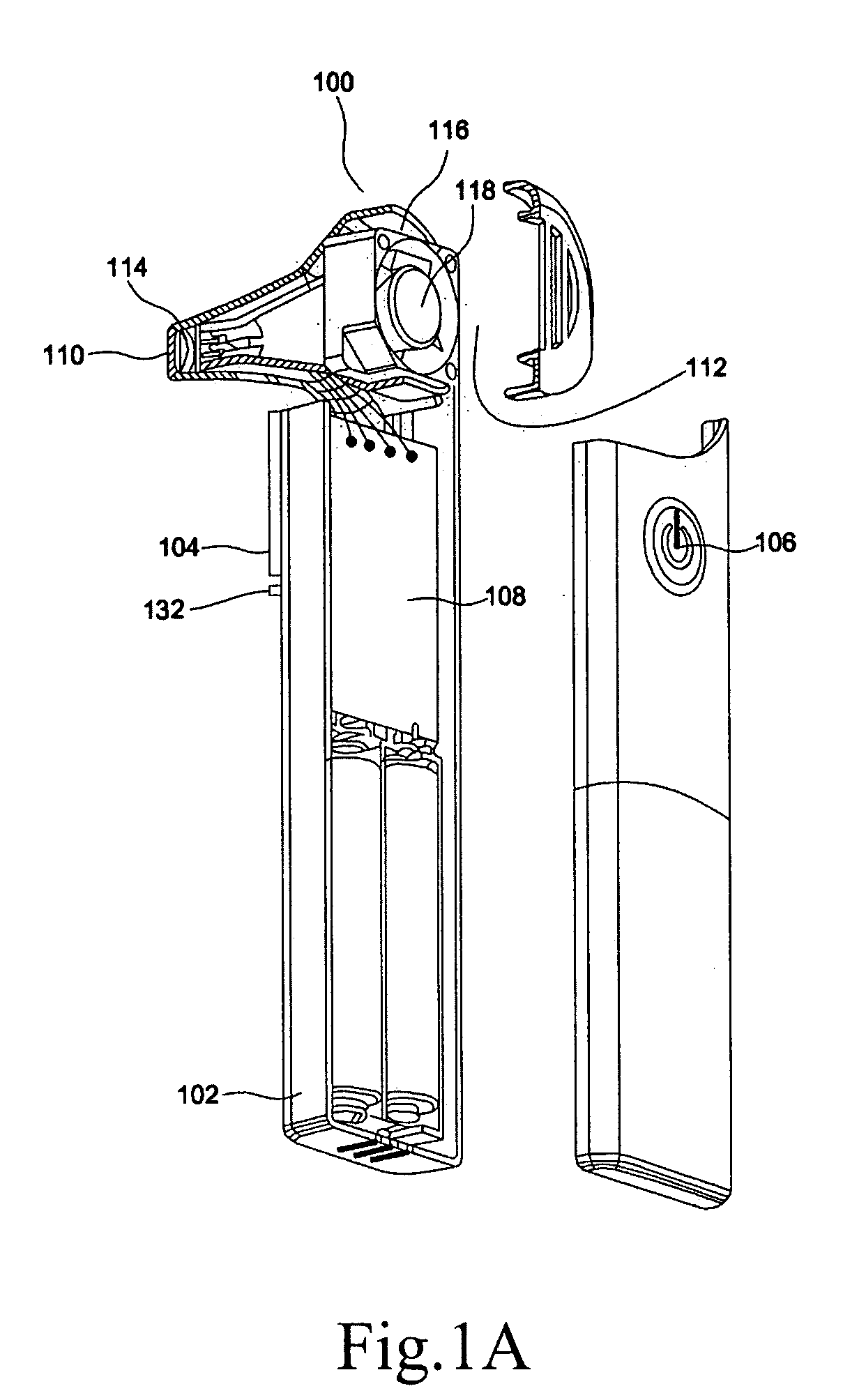
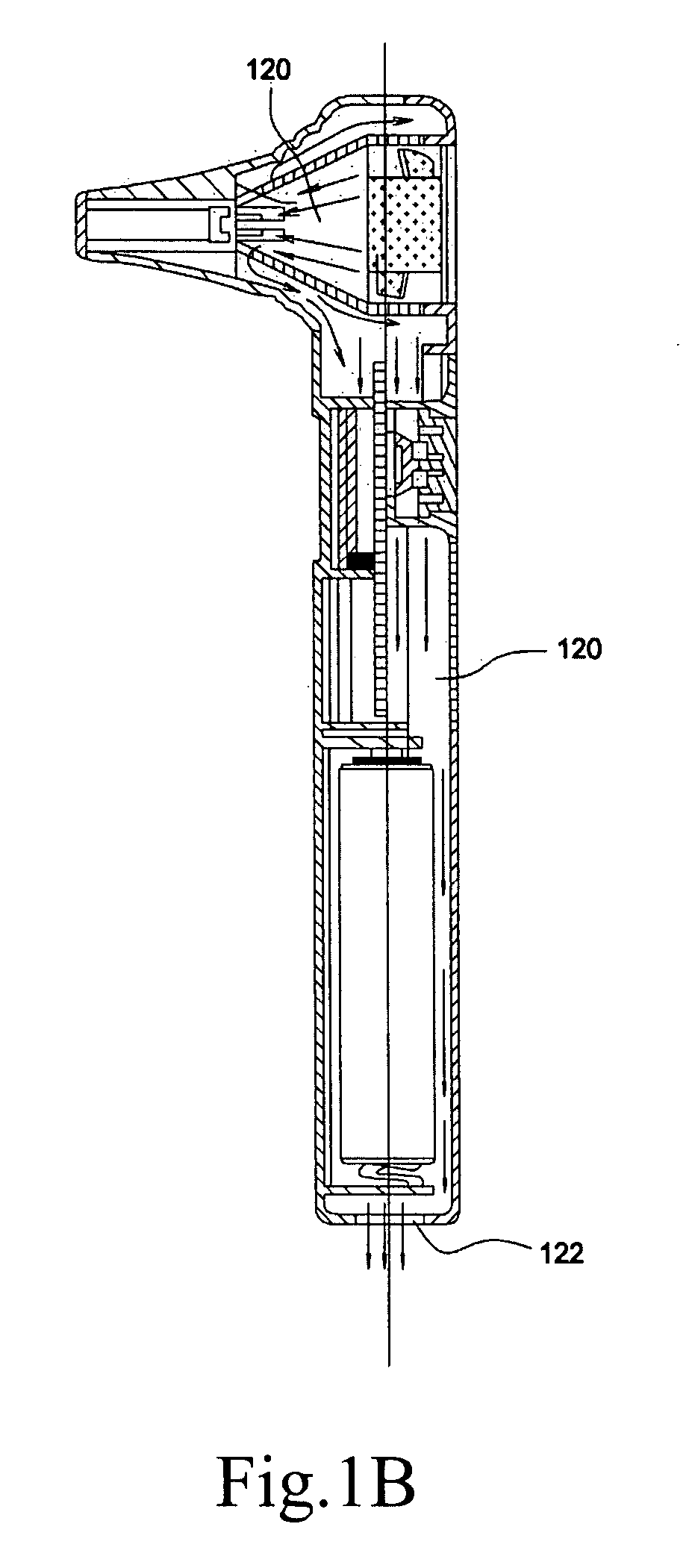
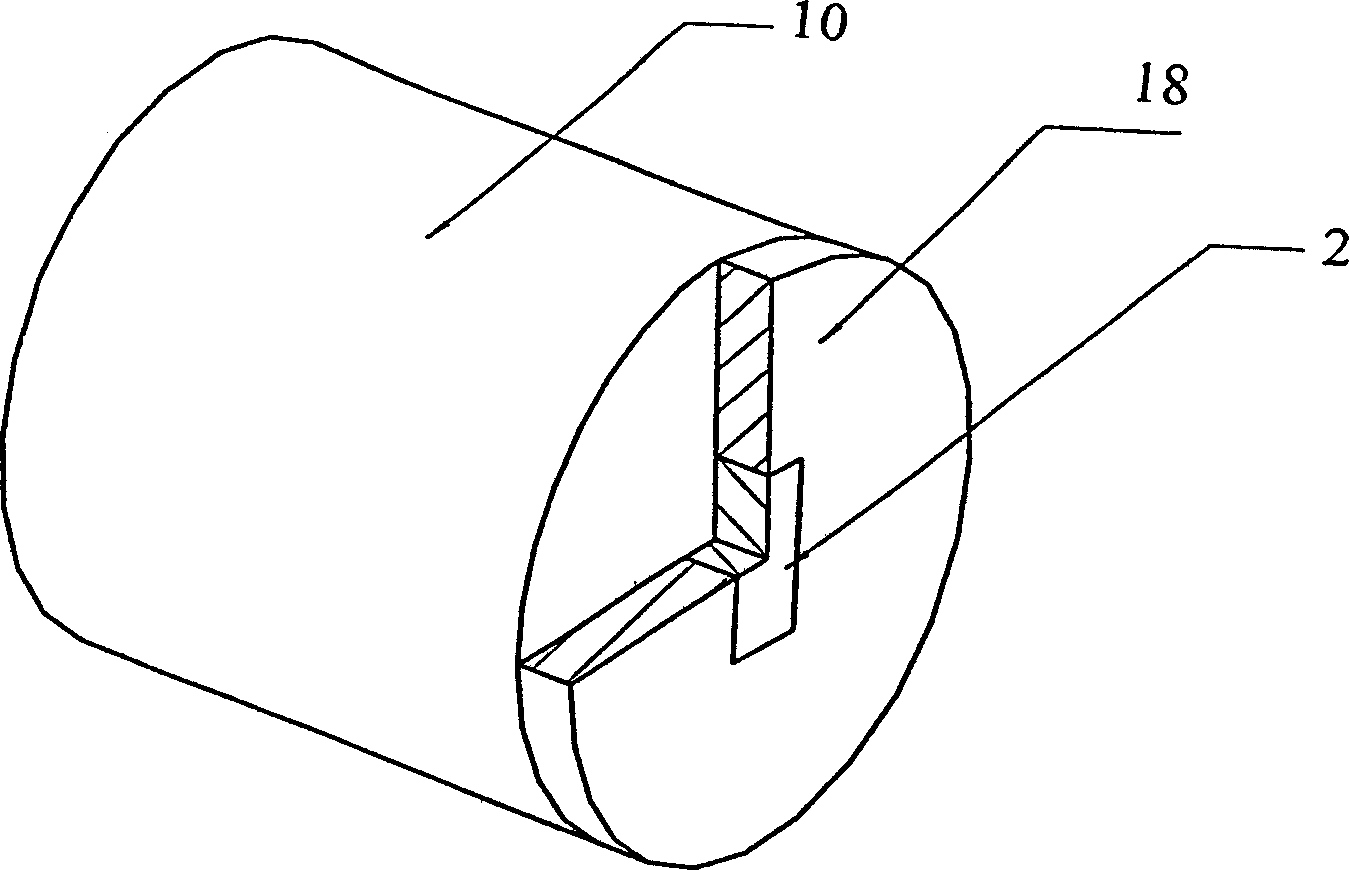
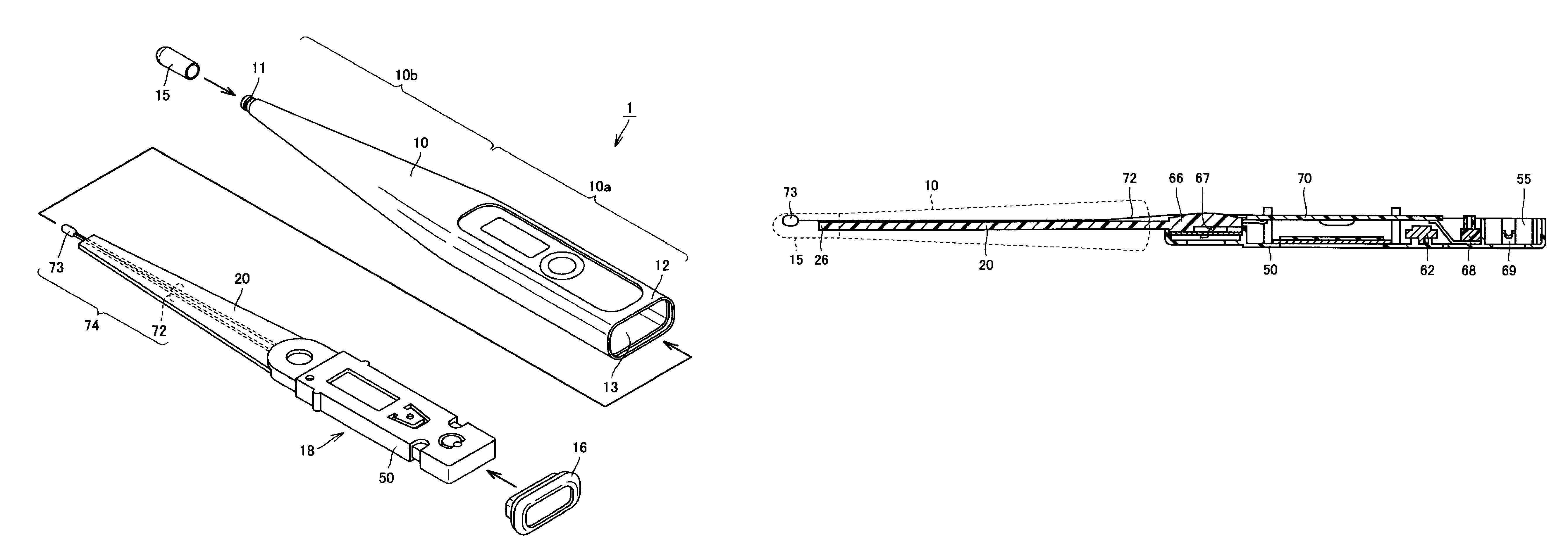
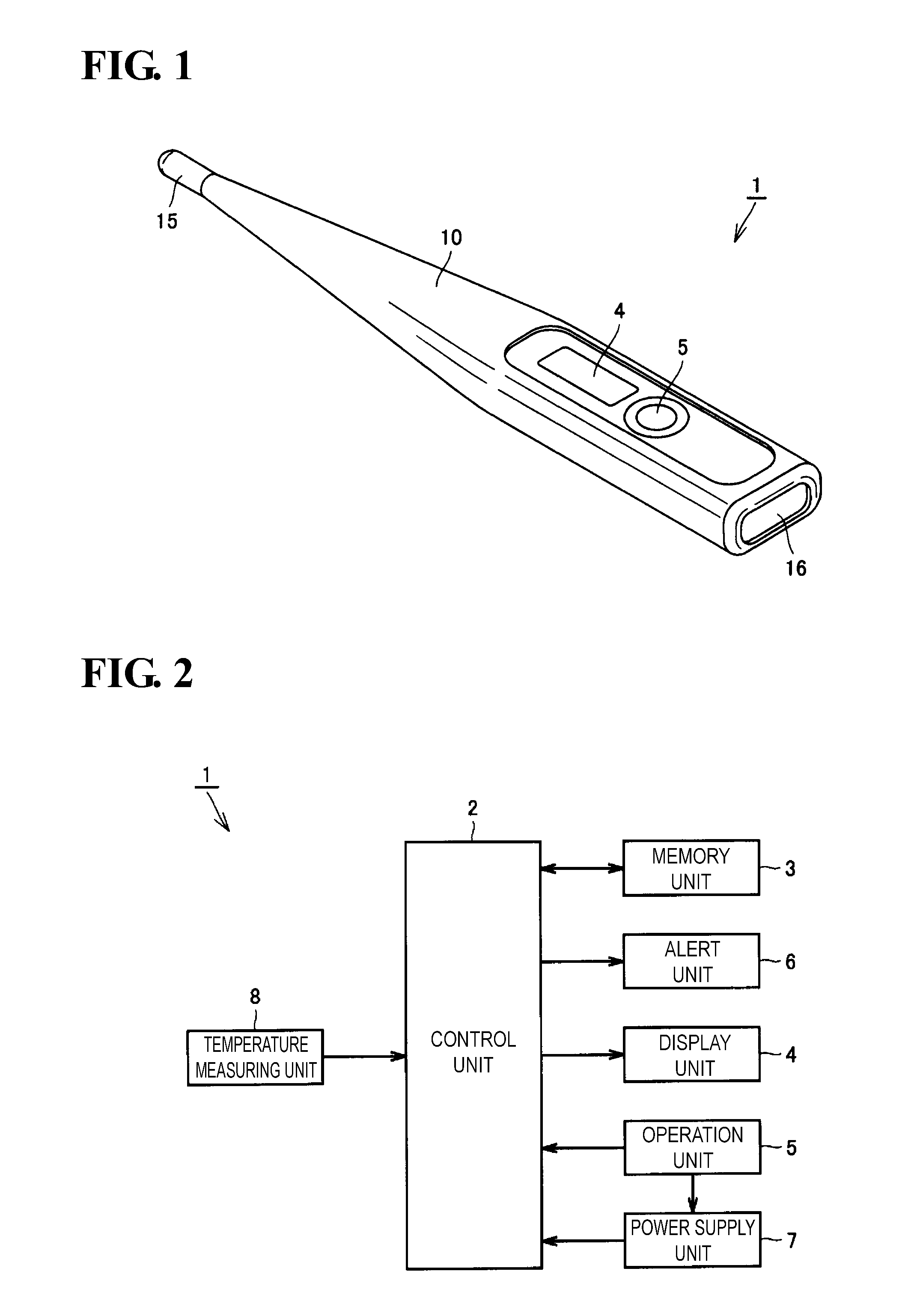
Electronic thermometer and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS9316544B2Fast thermal responseSuppresses bending and directional misalignmentThermometer detailsLine/current collector detailsPrinted circuit boardCryometer
Provided is an electronic thermometer that is inexpensive, has fast thermal response, and suppresses bending and directional misalignment of the lead of the temperature sensor during assembly of the electronic thermometer. The electronic thermometer includes: a temperature sensor that includes a temperature sensing unit that measures the body temperature of a measurement subject and a lead having one end that is fixed to the temperature sensing unit; a hollow housing that houses the lead, and in which the temperature sensing unit is arranged on the tip side; a printed circuit board to which the other end of the lead is fixed; and an assembly that includes the printed circuit board and is housed in the housing. The assembly includes an extension portion extending toward the tip side of the housing. The extension portion has a guide portion that orients the extending direction of the lead.
Owner:OMRON HEALTHCARE CO LTD
Probe cover cassette with improved probe cover support
A cassette of tympanic thermometer probe covers includes a frame and probe covers releasably attached to the frame. The probe covers can be individually attached over a probe of a tympanic thermometer to protect the probe from contamination. The probe covers are constructed to releasably secure themselves to the probe. The force required to secure the probe covers to the frame is less that the force which is required to detach the probe covers from the frame so that the probe cover is held by the frame while being attached to the thermometer probe. The probe cover is connected to the frame by frangible connections that are arranged to inhibit pivoting of the probe cover when being attached to the thermometer probe. A method of securing a probe cover to a probe of a tympanic thermometer is also disclosed.
Owner:CARDINAL HEALTH IRELAND UNLTD
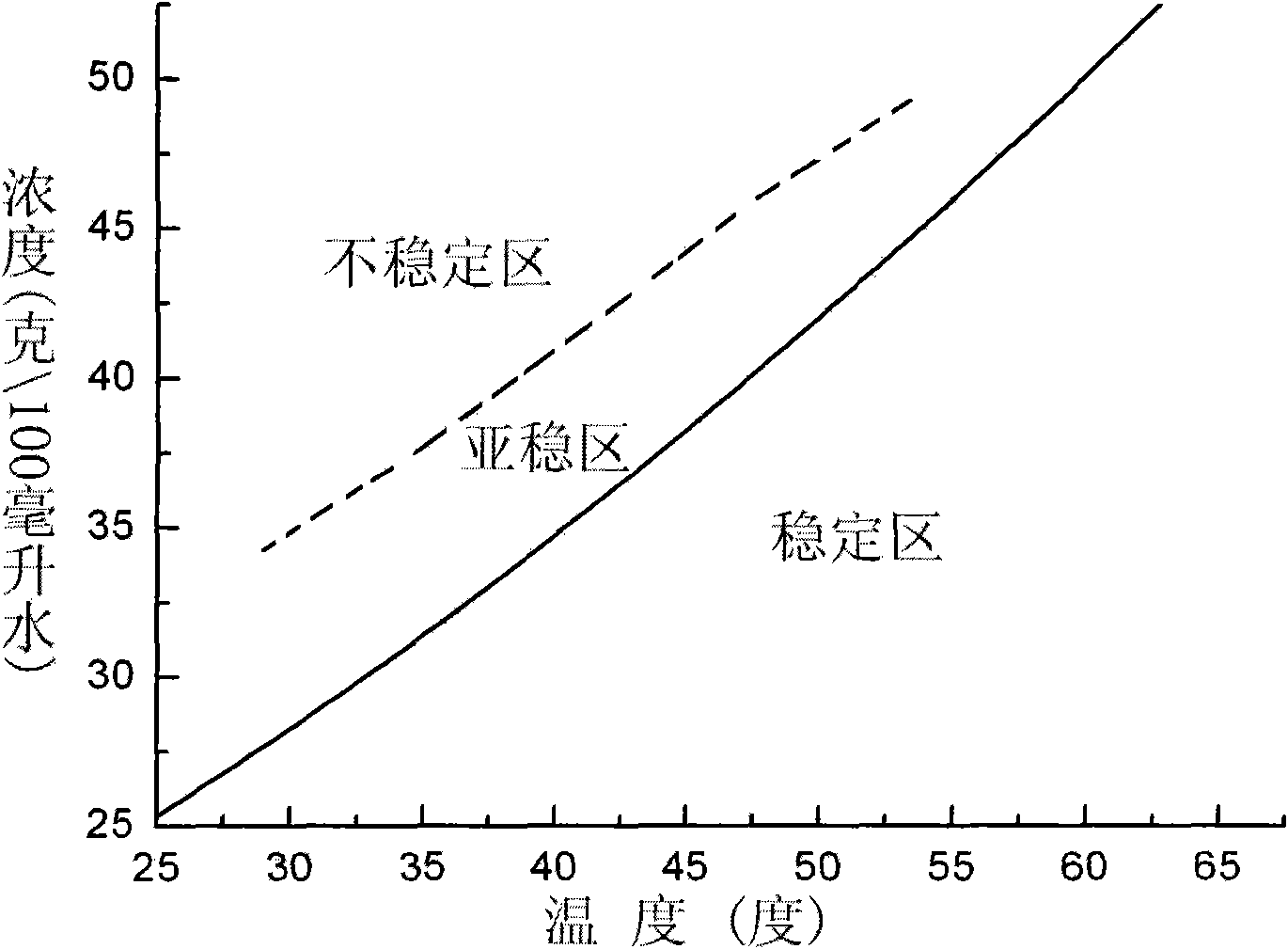
Metastable zone width measuring method of KDP saturated solution in tonner crystal growth tank
The invention relates to a metastable zone width measuring method of KDP saturated solution in a tonner crystal growth tank. In a dosing tank, after saturated KDP growth solution is prepared, the saturation temperature of the saturated solution is measured in a crystal hanging method accurately. After the consistent superheat temperature of the saturated solution is kept for 24 hours, the saturated solution is filtered and introduced into a crystal growth tank which is provided with a rapid growth crystal loading frame, seed crystals are not placed on the crystal loading frame, and the water bath temperature out of the growth tank is the same as the superheat temperature of the saturated solution. The rotation mode of the crystal loading frame is the same as that of rapid growth, and the cooling mode of the saturated solution is the same as that of rapid growth. When the temperature of the growth solution drops to the saturation temperature, the growth tank is observed. When observing that a first spontaneous crystal appears in the growth tank, the reading on a thermometer is recorded, and the difference of the temperature and the saturation temperature is the metastable zone width. By using the method, the metastable zone width of the KDP saturated solution in a large-scale crystal growth tank can be accurately measured.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Thermal processing method and thermal processing apparatus through light irradiation
ActiveUS9922889B2Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementVacuum evaporation coatingSusceptorLight irradiation
Owner:DAINIPPON SCREEN MTG CO LTD
Method and apparatus for manufacturing vitreous silica crucible
InactiveUS20120167623A1Improve temperature measurement accuracyImprove accuracyPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltRadiation thermometerCrucible
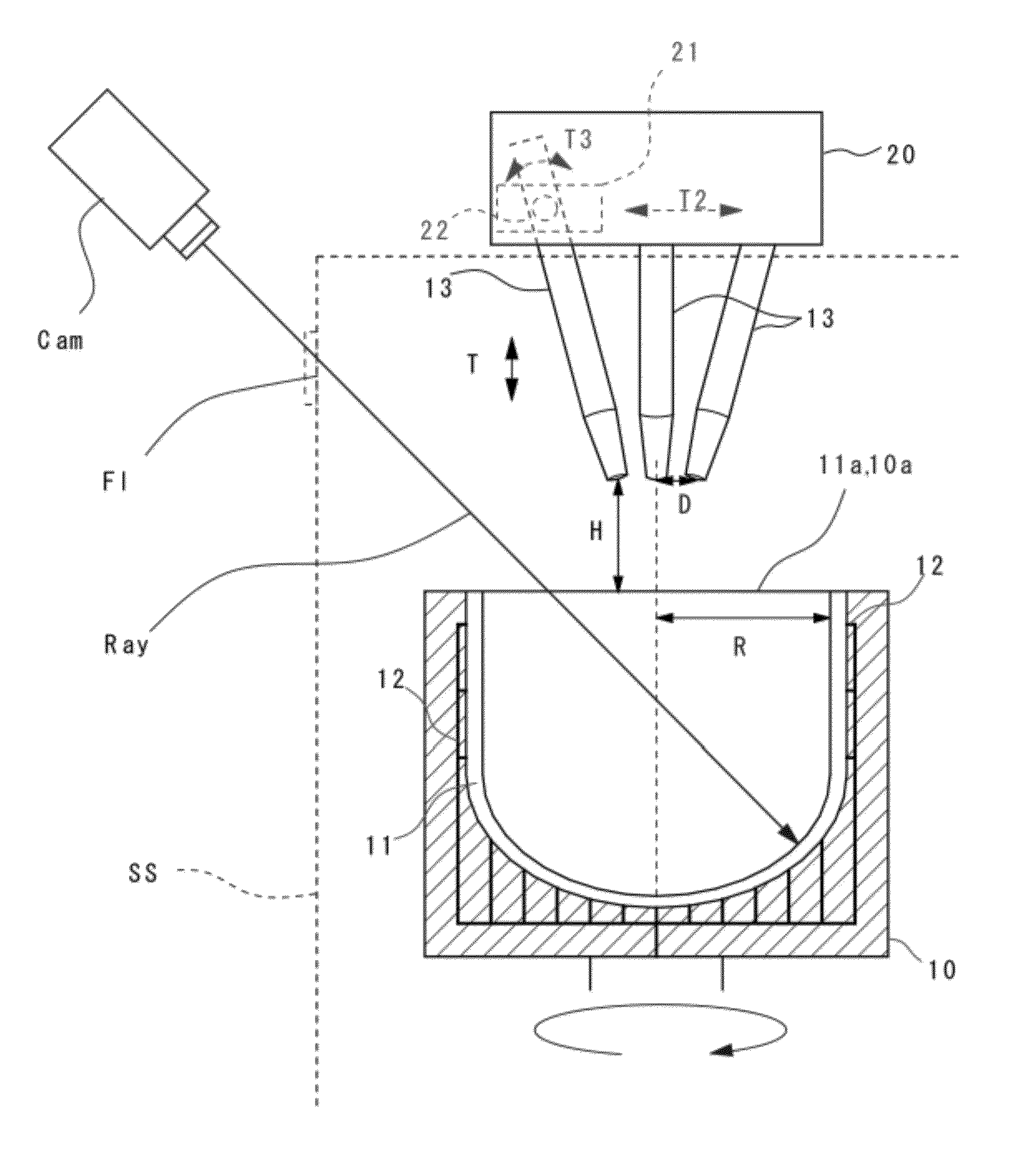
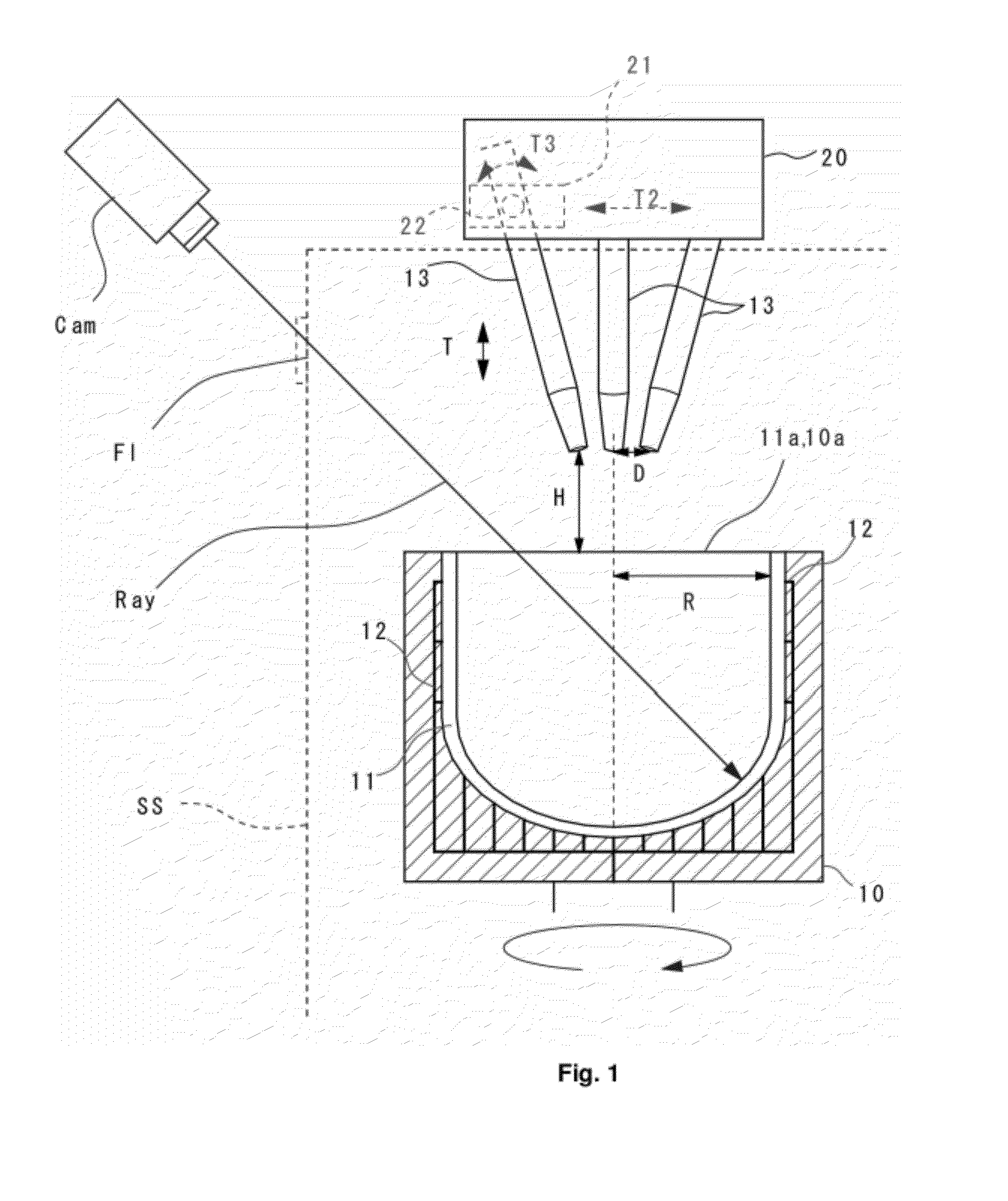
Accurate temperature measurement during manufacturing a vitreous silica crucible is enabled. The present invention provides an apparatus for manufacturing a vitreous silica crucible including: a mold for forming a silica powder layer by supplying silica powder therein; an arc discharge unit having carbon electrodes and a power supply unit and for heating and fusing the silica powder layer by arc discharge; and a temperature measurement unit for measuring temperature of a fused portion in the mold, wherein the temperature measurement unit is an radiation thermometer for measuring temperature by detecting radiation energy of a wavelength of 4.8 to 5.2 μm.
Owner:SUMCO CORP
Sealed constant temperature bath
InactiveCN104180928ASolve the smokeSolve the problem of direct emission of hydrogen hydrocarbons and other components into the atmosphereThermometer testing/calibrationEngineeringOpen structure
The invention discloses a sealed constant temperature bath which comprises a bath body, a flange cover and a sealing ring. The bath body is made of materials which are resistant to corrosion and pressure and cannot react with oil products. The flange cover and the bath body are sealed. The sealing ring is arranged between the bath body and the flange cover. At least one installation hole is formed in the flange cover. A temperature gauge insertion tube is connected with the flange cover through the installation hole. According to the sealed constant temperature bath, the normal-pressure sealing structure is achieved, the open-type structure of a traditional constant temperature oil bath is improved fundamentally, and oil and oil steam are automatically recycled in the heating process, so that a sealed self-circulation system is formed, no pollution is caused to the environment, and green verification and calibration are achieved.
Owner:BEIJING THREE YUAN ZHAOXING TECH
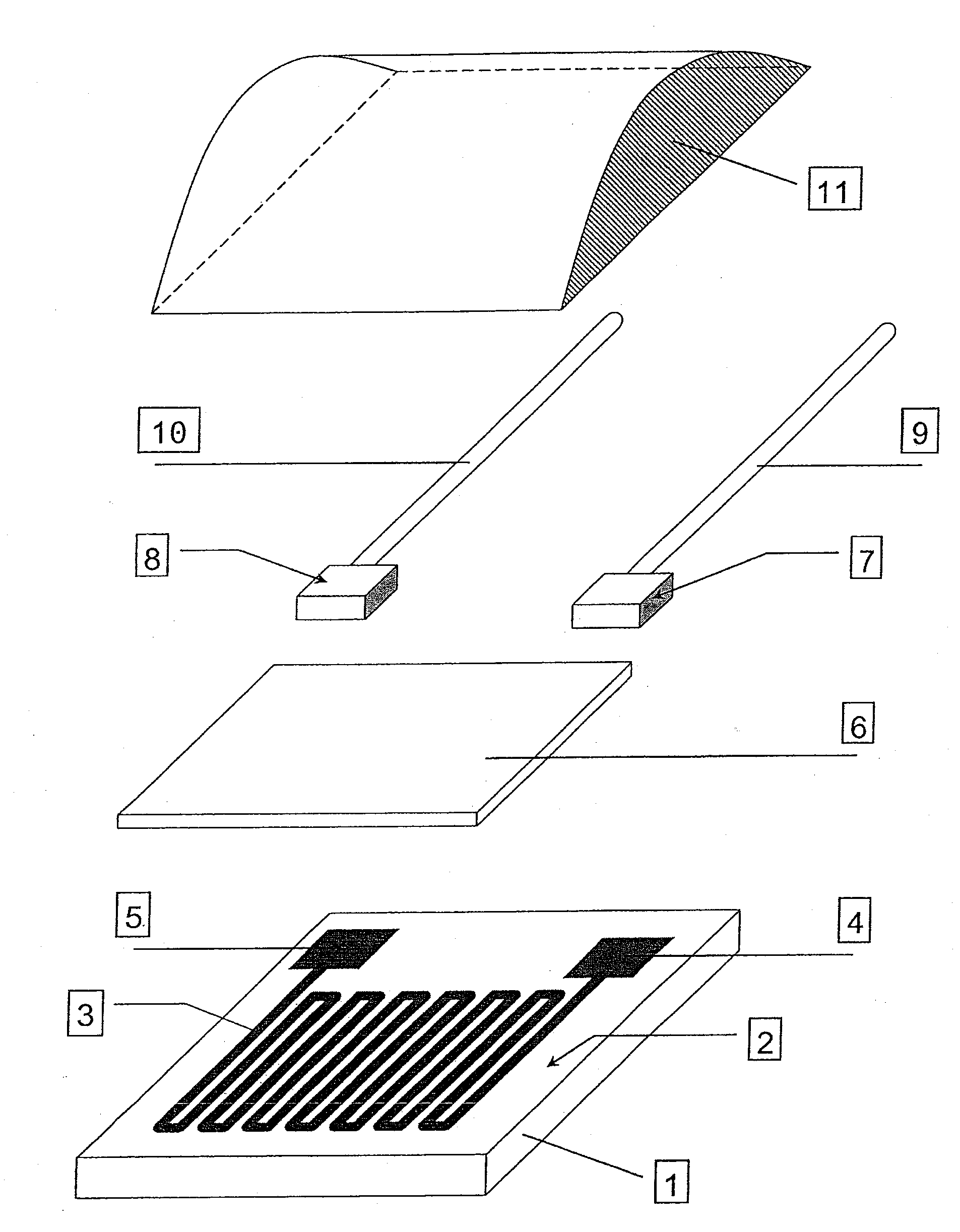
Platinium heat resistor of 8-shape laying wire
InactiveCN1821733AGuaranteed uptimeThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsUsing electrical meansDisturbance voltageElectrical resistance and conductance
This invention relates to an embedded Pt thermal resistor wired in 8-shape used in a resistance thermometer for testing the temperature of the coil or the core of a motor including Pt wires and a carrier, in which, said carrier is a plate-type bracket, two circular slots are opened on it to surround two same inside tracks, the Pt wire is laid around the slot in a 8-shape and an insulating layer is set at the cross exchange place of the Pt wires between the two slots. When a Pt thermo-resistor is embedded in the core slot, the alternating leakage-flux in the slot will turn the interference voltage induced at the lead end of the resistor to drop to zero so as to ensure the normal operation of the resistor.
Owner:上海电机成套联合有限公司
Internet of things digital thermometer suitable for industrial field
InactiveCN109632116AImprove accuracyEasy to installThermometer detailsThermometer applicationsDigital thermometersThe Internet
Owner:波思环球(北京)科技有限公司
Radiation thermometer, radiation temperature measurement system, storage medium having program for radiation thermometer stored therein, and radiation temperature measurement method
InactiveUS20170138794A1Accurate measurementPyrometry using electric radation detectorsInfraredRadiation thermometer
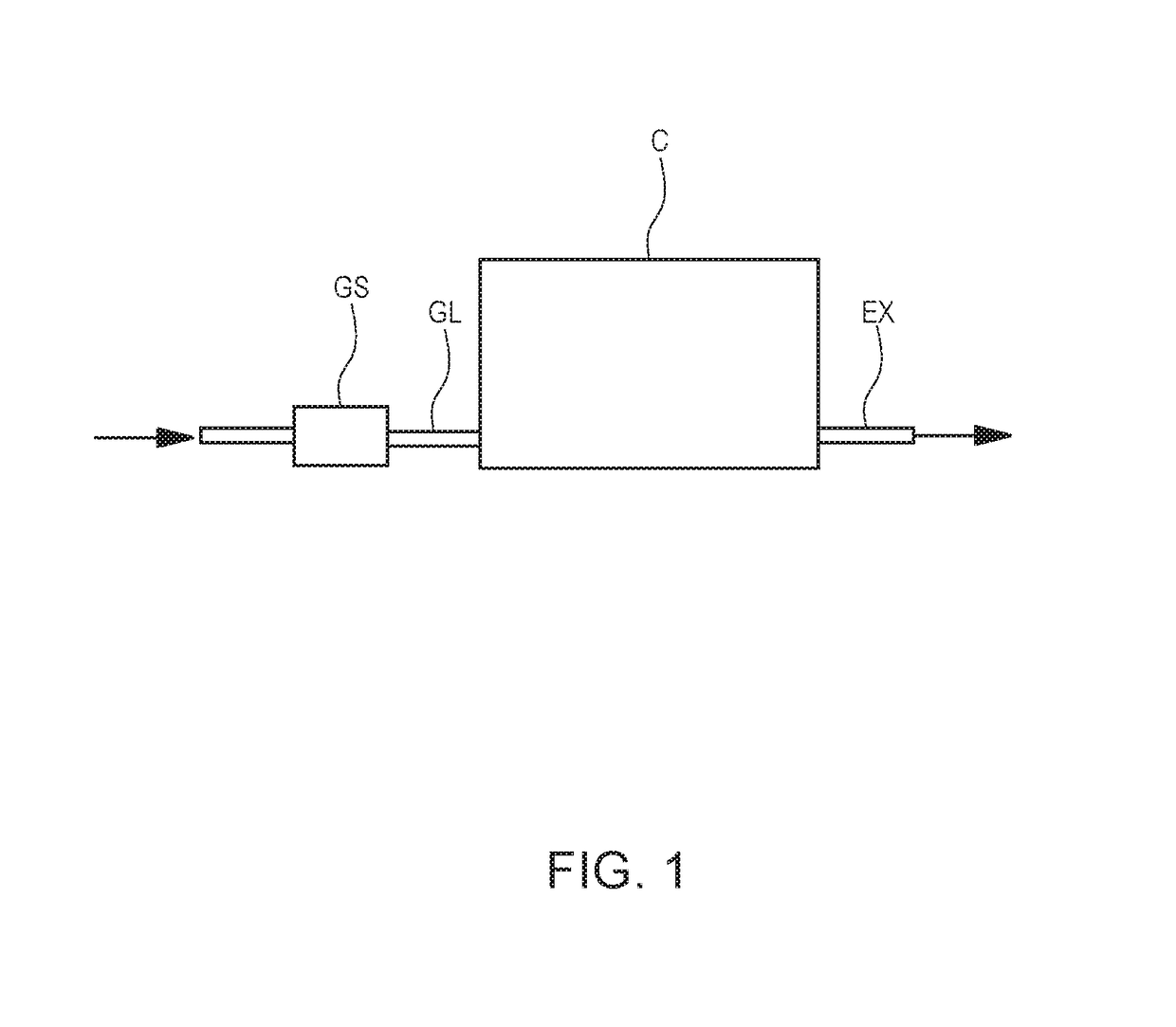
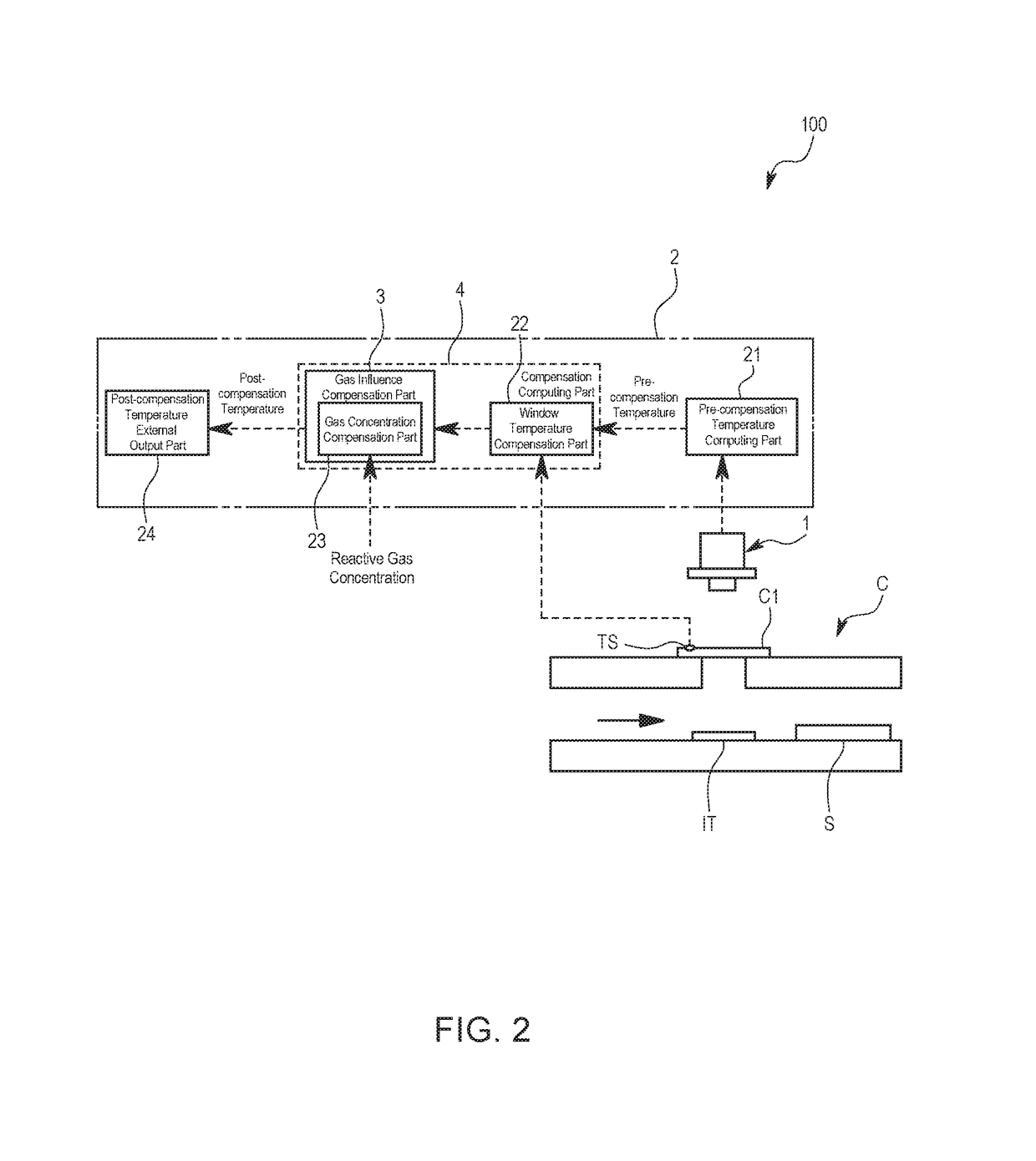
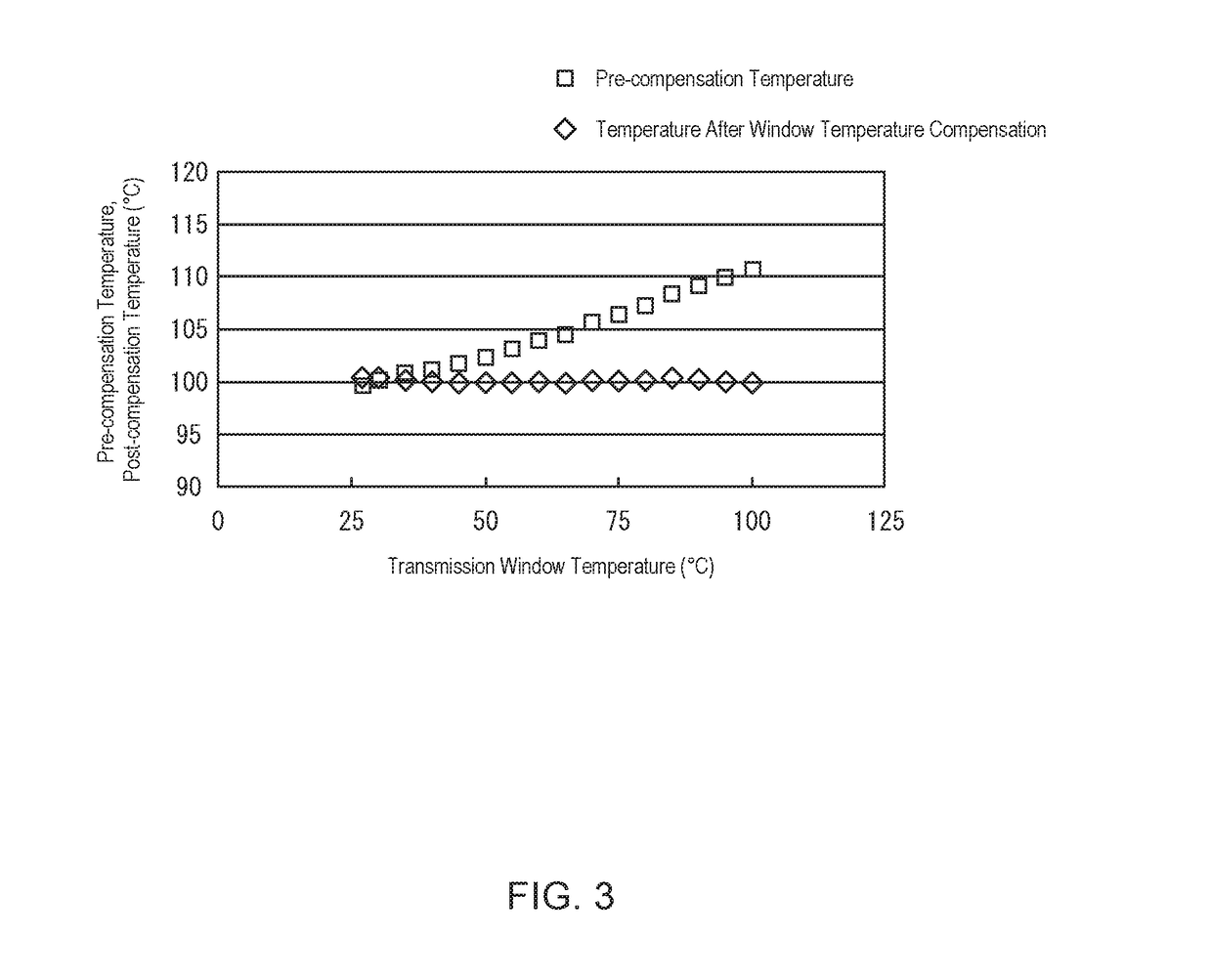
In order to provide a radiation thermometer with which a temperature of a measurement object disposed in a chamber configured to form plasma therein can be accurately measured in a noncontact manner from outside of the chamber, the radiation thermometer includes an infrared sensor and a window temperature compensation part. The infrared sensor is disposed outside the chamber configured to form plasma therein, and is configured to detect infrared ray emitted from the measurement object in the chamber through a transmission window provided in the chamber. The infrared sensor is configured to output an output signal according to energy of detected infrared ray. The window temperature compensation part is configured to compensate for a pre-compensation temperature of the measurement object being indicated by the output signal of the infrared sensor, on the basis of a temperature of the transmission window.
Owner:HORIBA LTD +1
Contacting/non-contacting molten metal high temperature measuring apparatus and measuring method
InactiveCN100494925CRadiation pyrometryThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsMeasurement deviceRadiation thermometer
This invention relates to a high temperature measuring method of contact / non- contact molten metal. Specifically the invention is a measuring device and measuring means, which aim at temperature of iron and molten steel, to use discrete temperature signal X1 (T) of asynchronism expending electro heat to continual modify continually varying temperature signal x2 ( T) of high temperature radiation thermometer. The invention includes expend type fast thermocouple, high temperature radiation thermometer, A / D data converter, single chip and output equipment. The described expend type fast thermocouple and high temperature radiation thermometer respectively connect with A / D data converter's input end; A / D data converter's output port connect with single chip; single chip respectively connect with keyboards, display unit and printer.
Owner:武钢集团有限公司
Integral temperature indicator
InactiveCN101858792ADisplayableFunctionalThermometers using material expansion/contactionThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsElectrical resistance and conductanceWhole body
The invention relates to an integral temperature indicator. The temperature indicator comprises a field temperature indicator, a remote transmitting temperature indicator and a protection pipe which are formed into a whole body, wherein temperature sensing elements of the field temperature indicator and the remote transmitting temperature indicator are all arranged at the bottom of the protection type, the field temperature indicator adopts a bimetal temperature indicator, a bimetal strip is arranged at the bottom of the protection pipe, the remote transmitting temperature indicator adopts a thermal resistor temperature indicator or a thermocouple temperature indicator, and a thermal resistor or a thermocouple is arranged at the bottom of the protection pipe. The invention integrates the field temperature indicator and the remote transmitting temperature indicator into an integral temperature measuring instrument with the field display and signal remote transmitting functions. The invention has the advantages of compact structure, convenient installation and lower cost, and is widely applied to industries such as petroleum, chemical engineering, iron and steel, dye printing, pharmacy and the like.
Owner:常州双环热工仪表有限公司
Temperature indication pipe joint
ActiveUS8167484B2Simple structureLow costThermometer detailsPlug valvesHeat transmissionDigital thermometers
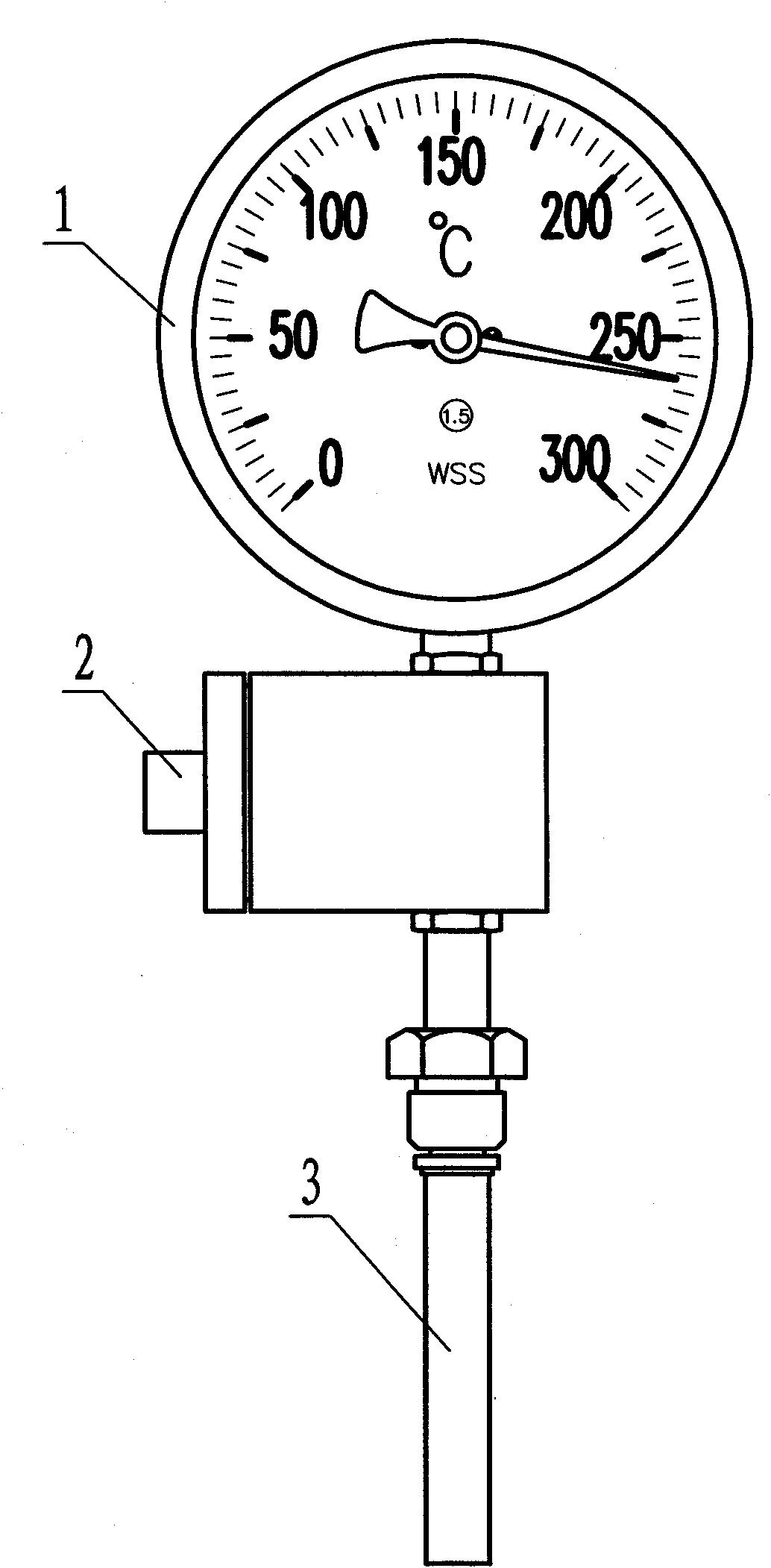
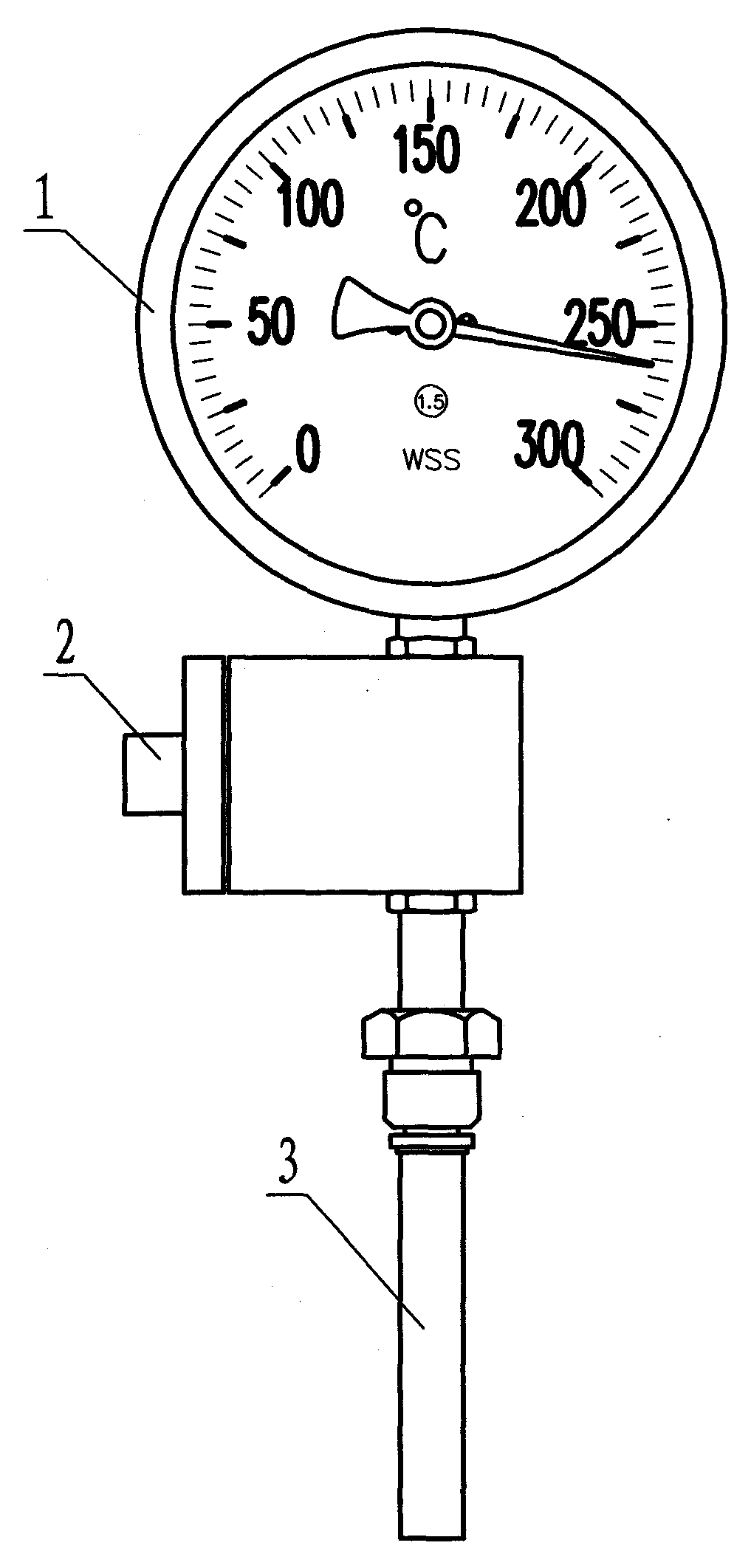
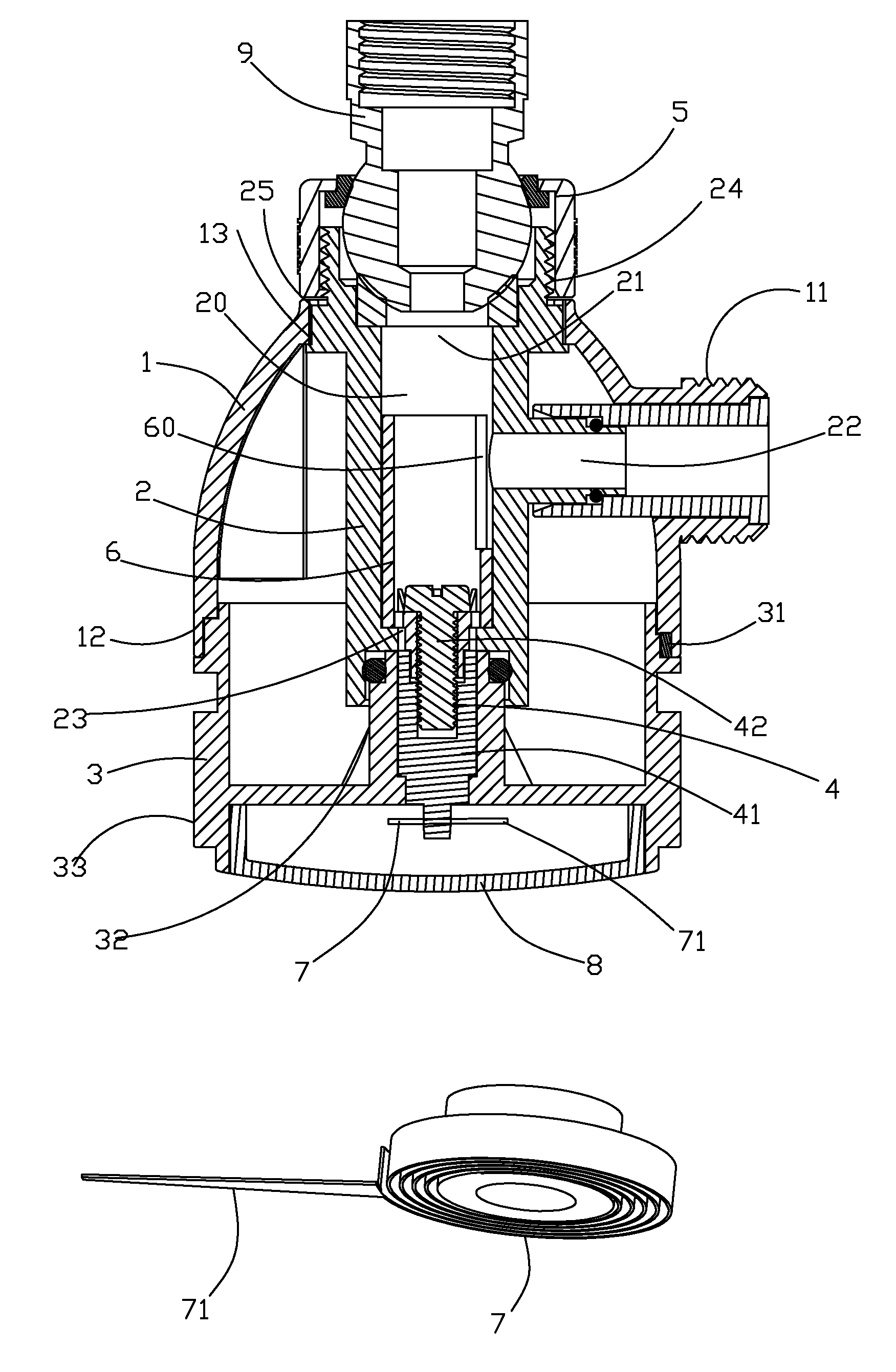
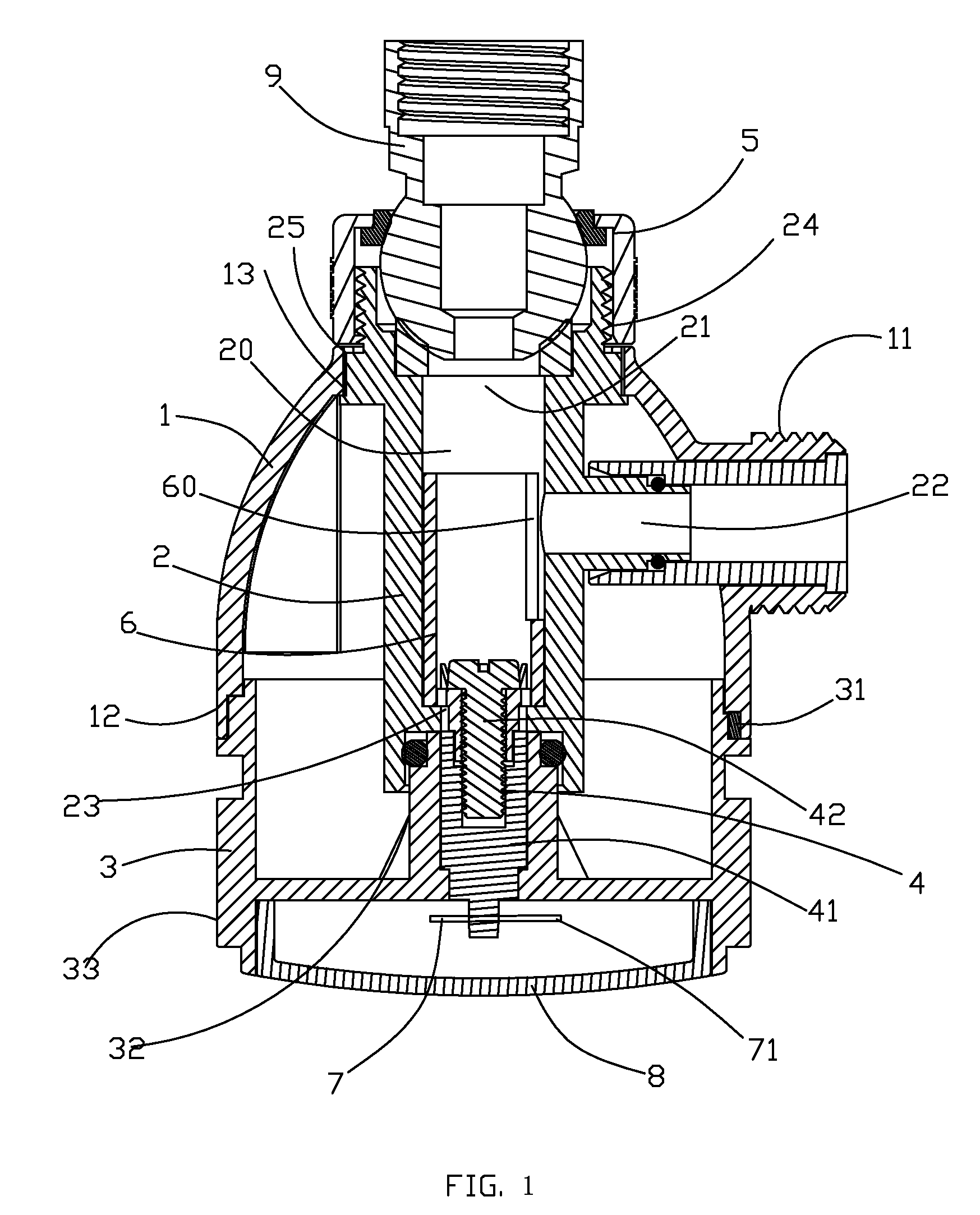
A temperature indication pipe joint, including a shell, wherein a water conduit is arranged in said shell, and including a heat transmission unit which has a first end in said water conduit and a second end connected to the center of a spiral double sheet metal, said spiral double sheet metal further has an indicating needle extended from its other end. By utilizing the double sheet metal to sense the change of temperature and deform accordingly, the water temperature can be indicated, which can reduce the cost and achieve a simpler structure compared to the digital thermometer used before; when rotating the cover of the present invention, the quantity of water stream will be adjusted.
Owner:XIAMEN SOLEX HIGH TECH IND CO LTD
Temperature measurement and calibration platform in space vacuum environment
ActiveCN102539019BSolve the problem of large differences in measurement resultsSolve the traceability problemThermometer testing/calibrationVacuum pumpingSpace environment
The invention relates to a temperature measurement and calibration platform in space vacuum environment. The temperature measurement and calibration platform is favorable for realizing the simultaneous calibration of contact type temperature measurement and non-contact type temperature measurement, so the temperature measurement and calibration platform is served for heat vacuum and heat balance experiments of spacecrafts such as satellites, spaceship and the like. The temperature measurement and calibration platform comprises a constant temperature bath, wherein a double-sub-cavity vacuum cavity, the double-sub-cavity vacuum cavity comprises a first vacuum cavity body and a second vacuum cavity body, the first vacuum cavity body and the second vacuum cavity body are connected with a vacuum pumping device through a three-way valve, standard temperature indicator sensors are respectively arranged on the outer wall of the first vacuum cavity body and on the outer wall of the second vacuum cavity body, the standard temperature indicator sensors are connected with a temperature secondary meter, a laser light path reflecting device is arranged in the vacuum cavity of the first vacuum cavity body for calibrating a non-contact type temperature measuring system based on the tunable diode laser absorption spectrum technology, and the vacuum cavity of the second vacuum cavity body is used for accommodating a temperature sensor for calibrating a contact type temperature measuring system adopting the temperature sensor.
Owner:BEIJING DONGFANG MEASUREMENT & TEST INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com