Patents
Literature
470 results about "Heatable glass" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
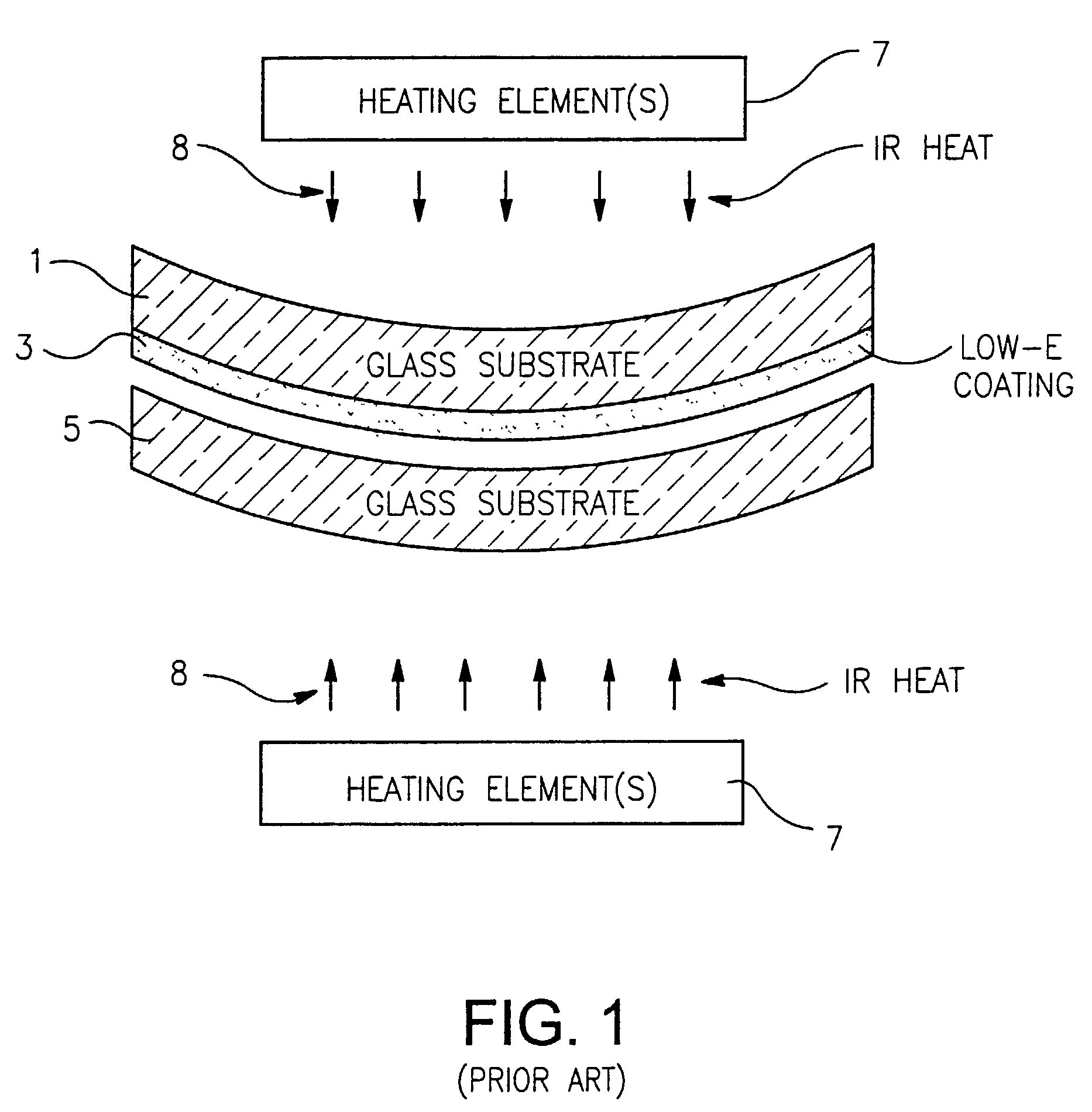
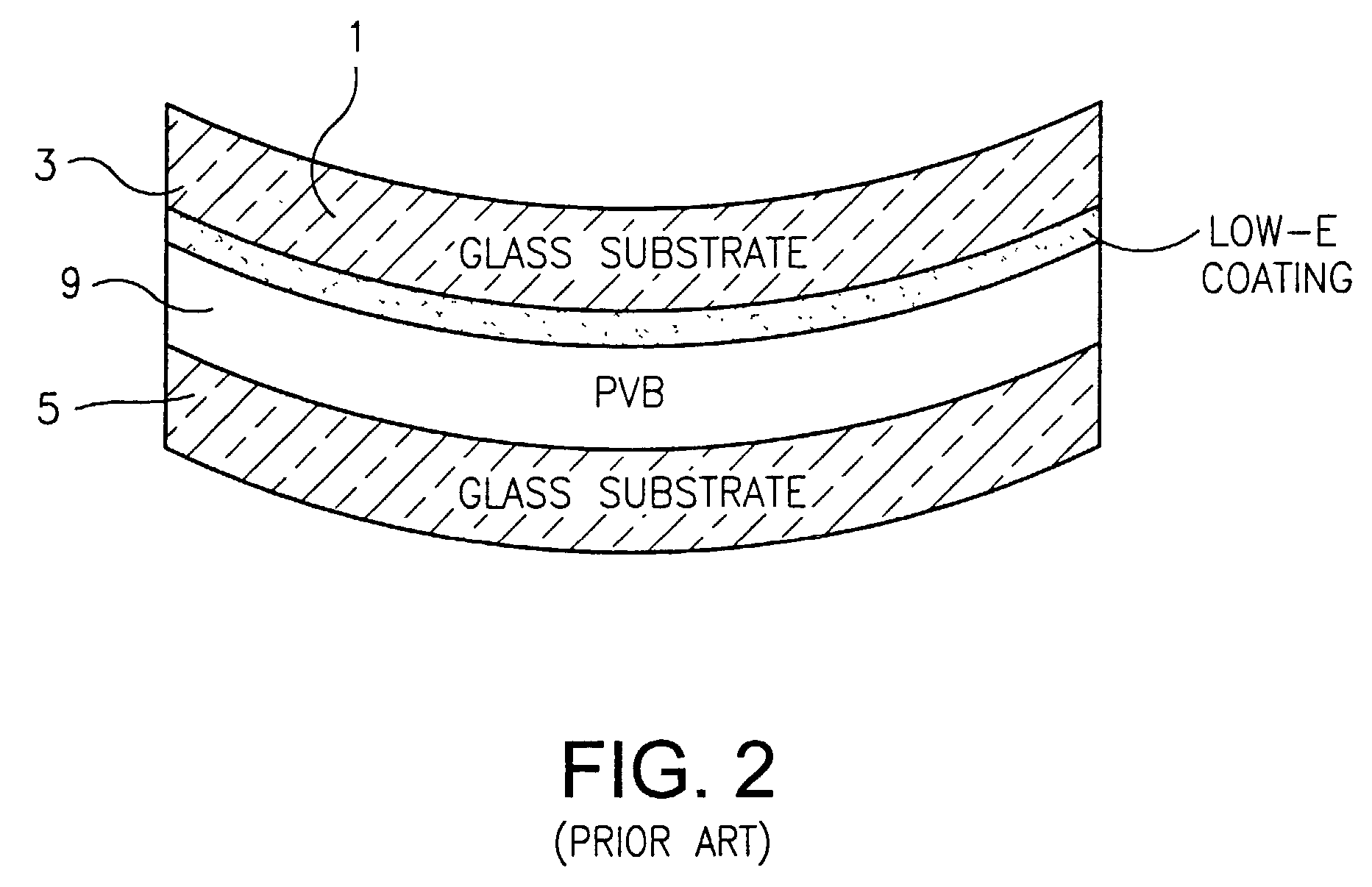
Electrically heatable glass and windows are relatively new products, which help solve problems in the design of buildings and vehicles. The idea of heating glass is based on the use of energy-efficient low-emissive glass, which is generally simple silicate glass with a special metallic oxides coating. Low-emissive coating decreases heat loss by approximately 30%. Heatable glass can be used in all kinds of standard glazing systems, whether wood, plastic, aluminum or steel.
Method of forming a glass melt
ActiveUS7454925B2Promote vigorous boilingReduce partial pressureCharging furnaceGlass furnace apparatusMolten glassExcessive Cooling
A method of forming a glass melt including heating a glass feed material in a first melting furnace to form a glass melt, flowing the glass melt into a second melting furnace through a refractory metal connecting tube, and further heating the glass melt in the second melting furnace. The refractory metal connecting tube is heated to prevent the molten glass from excessive cooling, and to ensure that the glass melt entering the second melting furnace is equal to or greater than the temperature of the glass melt in the second melting furnace. An apparatus for performing the method is also disclosed.
Owner:CORNING INC
Boro-silicate glass frits for hermetic sealing of light emitting device displays
InactiveUS20080124558A1Problem be addressLamination ancillary operationsSolid-state devicesFritSilicate glass
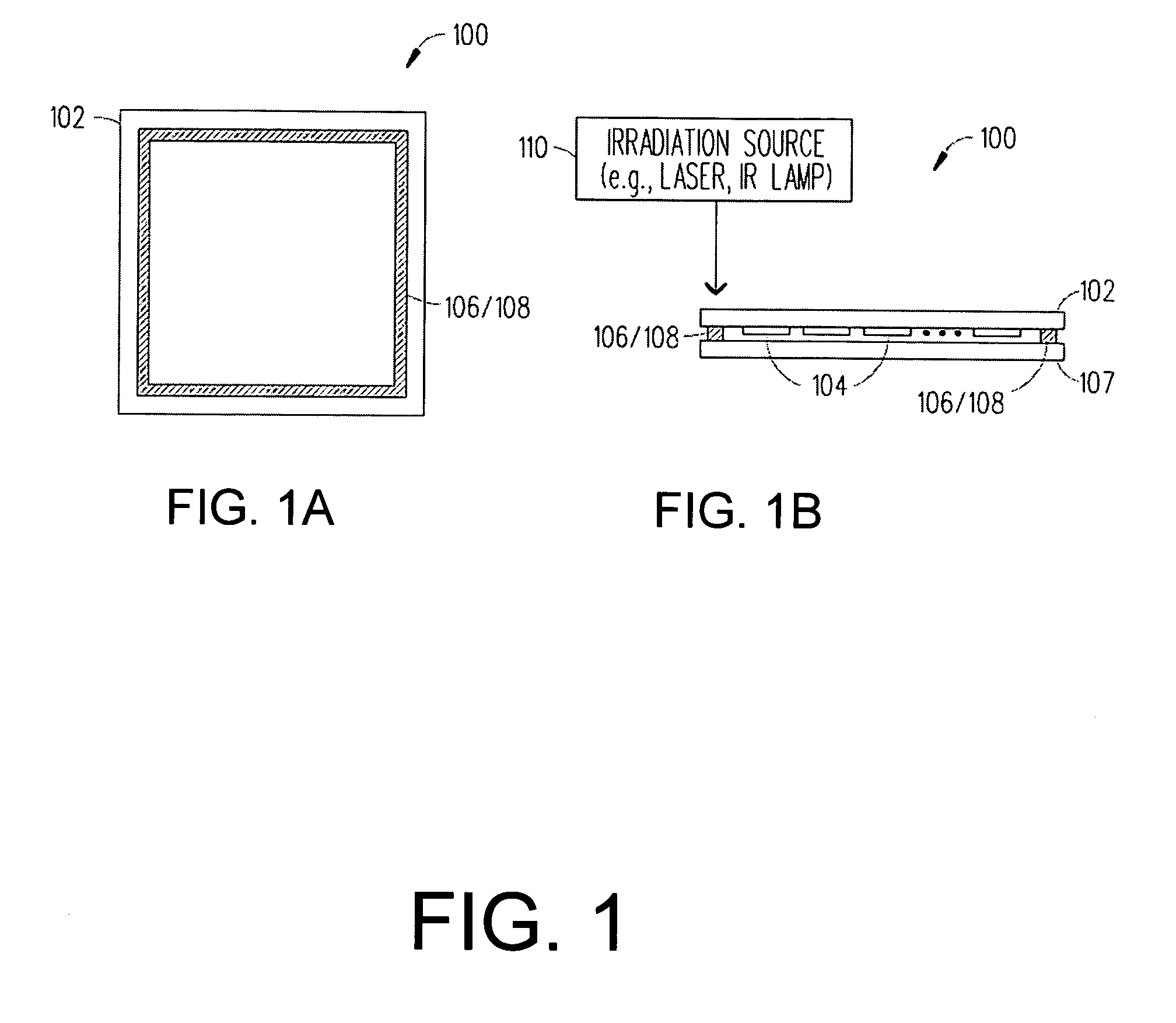
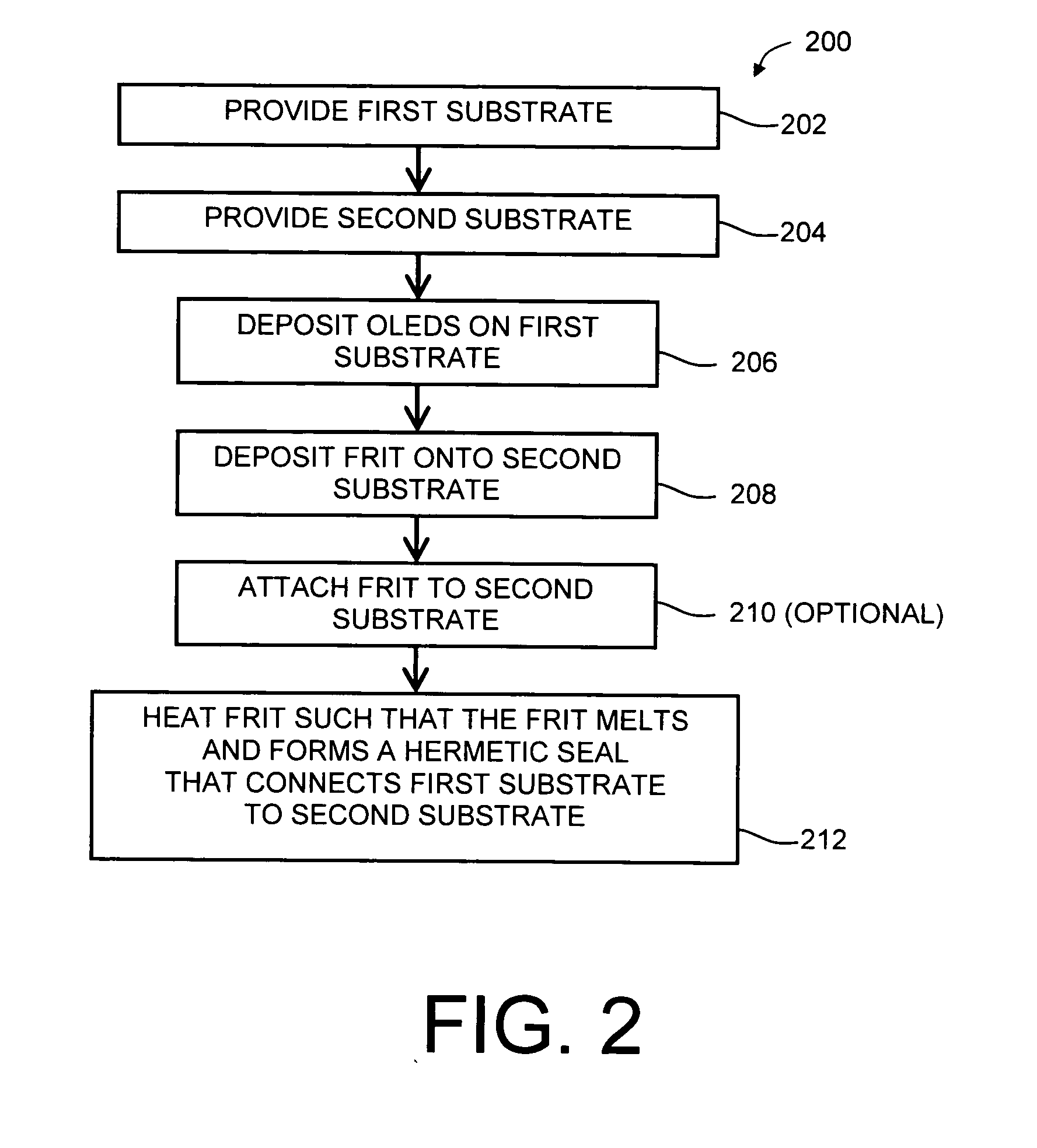
A frit composition useful for sealing a light emitting device is disclosed. The frit composition comprises a glass portion comprising a base component and at least one absorbing component. The glass portion of the frit comprises silica, boron oxide, optionally alumina, and (a) cupric oxide and / or a (b) combination of ferric oxide, vanadium pentoxide, and optionally titanium dioxide. Also disclosed is an article comprising a substrate and a frit, and a glass package comprising two substrates and a frit positioned between the substrates. A method for manufacturing a hermetically sealed glass package comprising the deposition of a glass frit and heating of the glass frit to form a hermetic seal is also disclosed.
Owner:CORNING INC
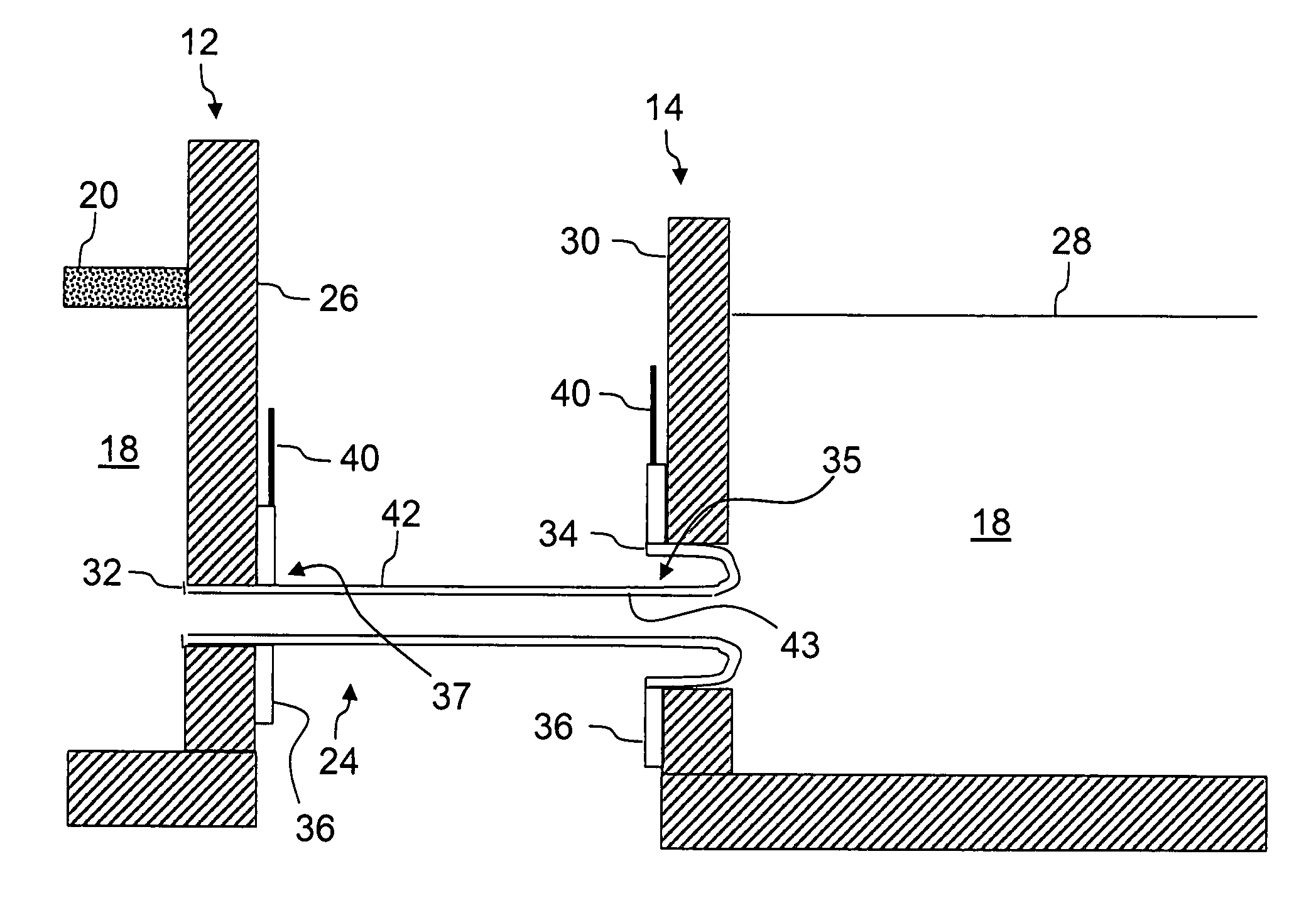
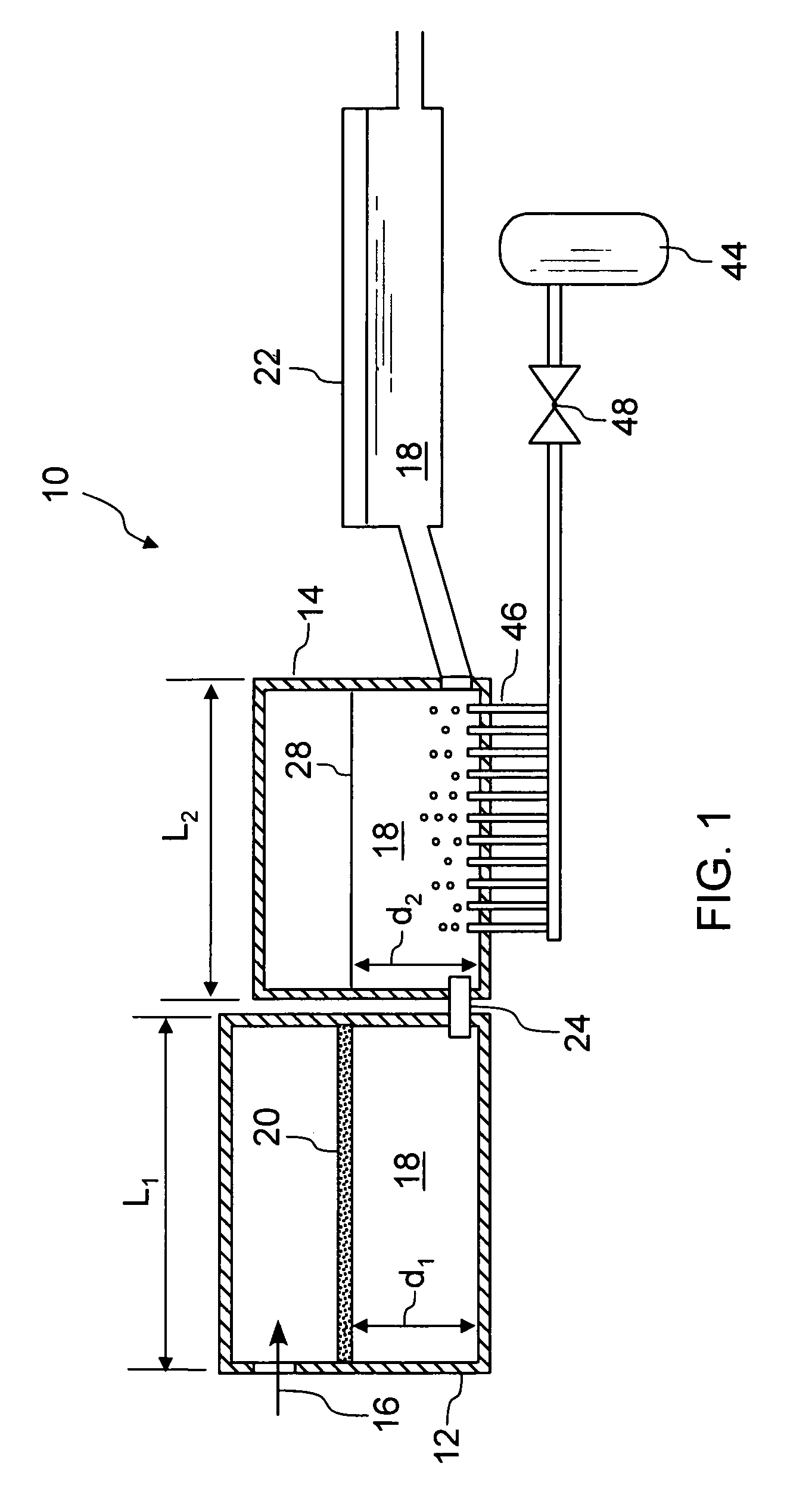
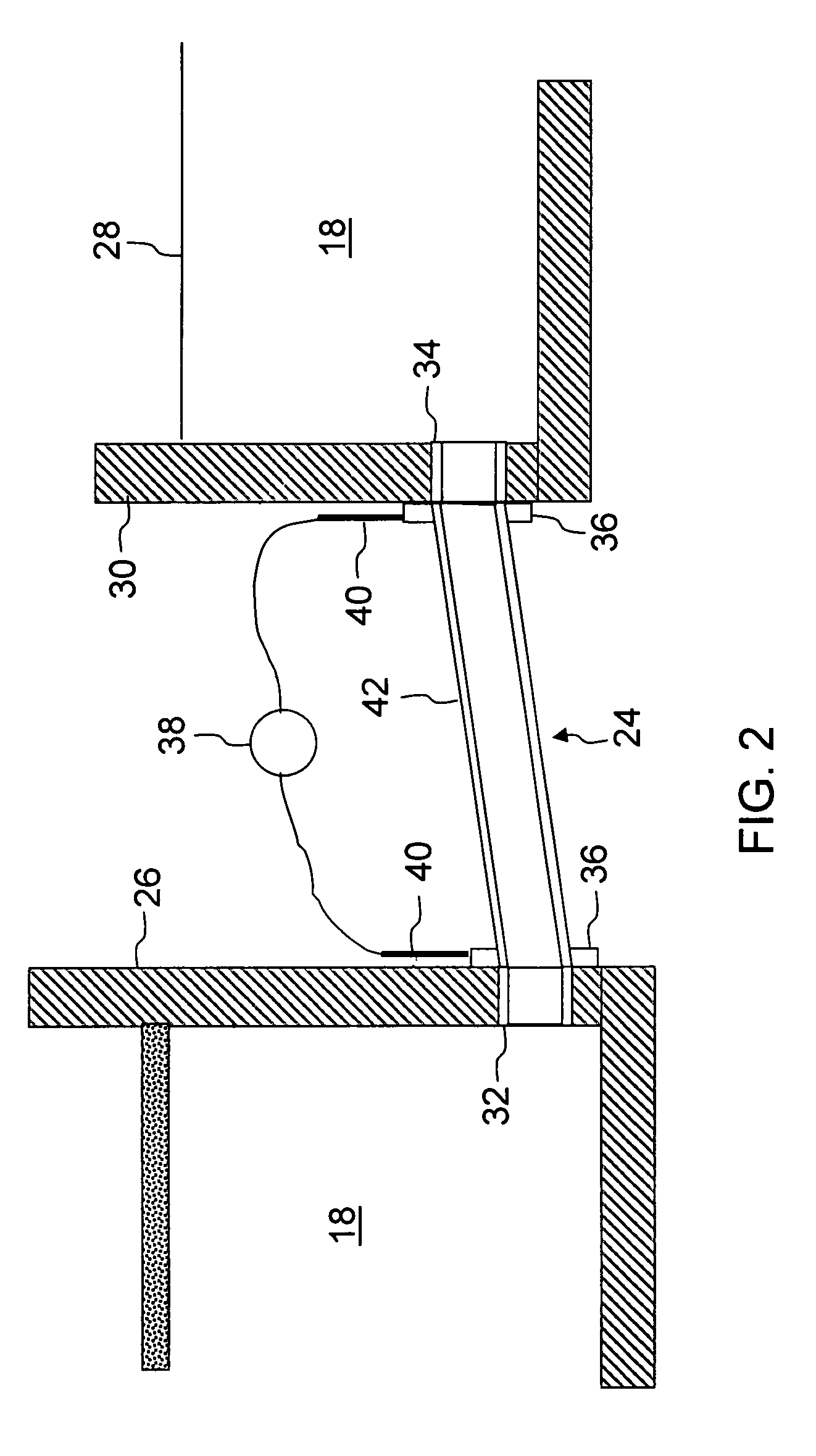
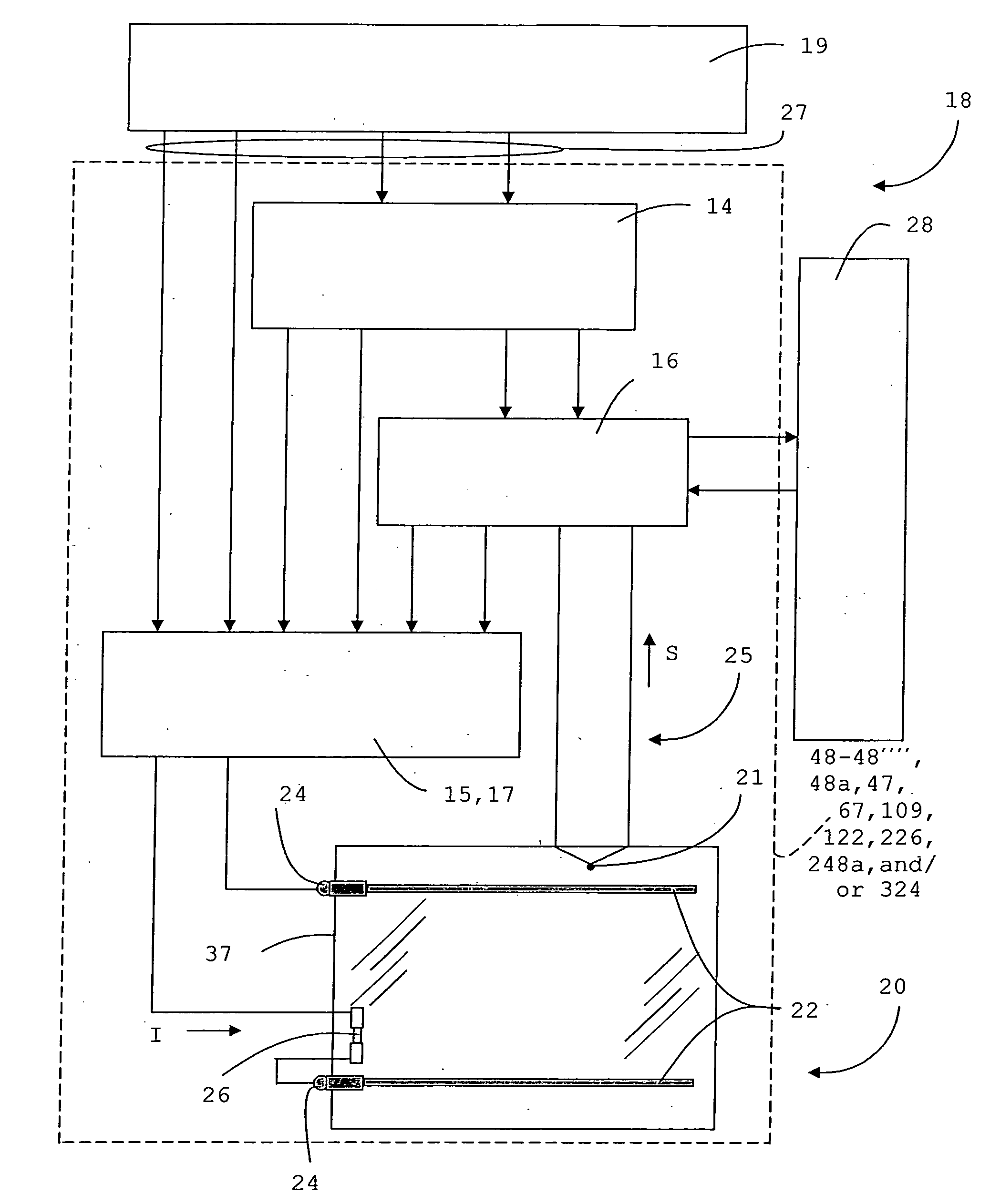
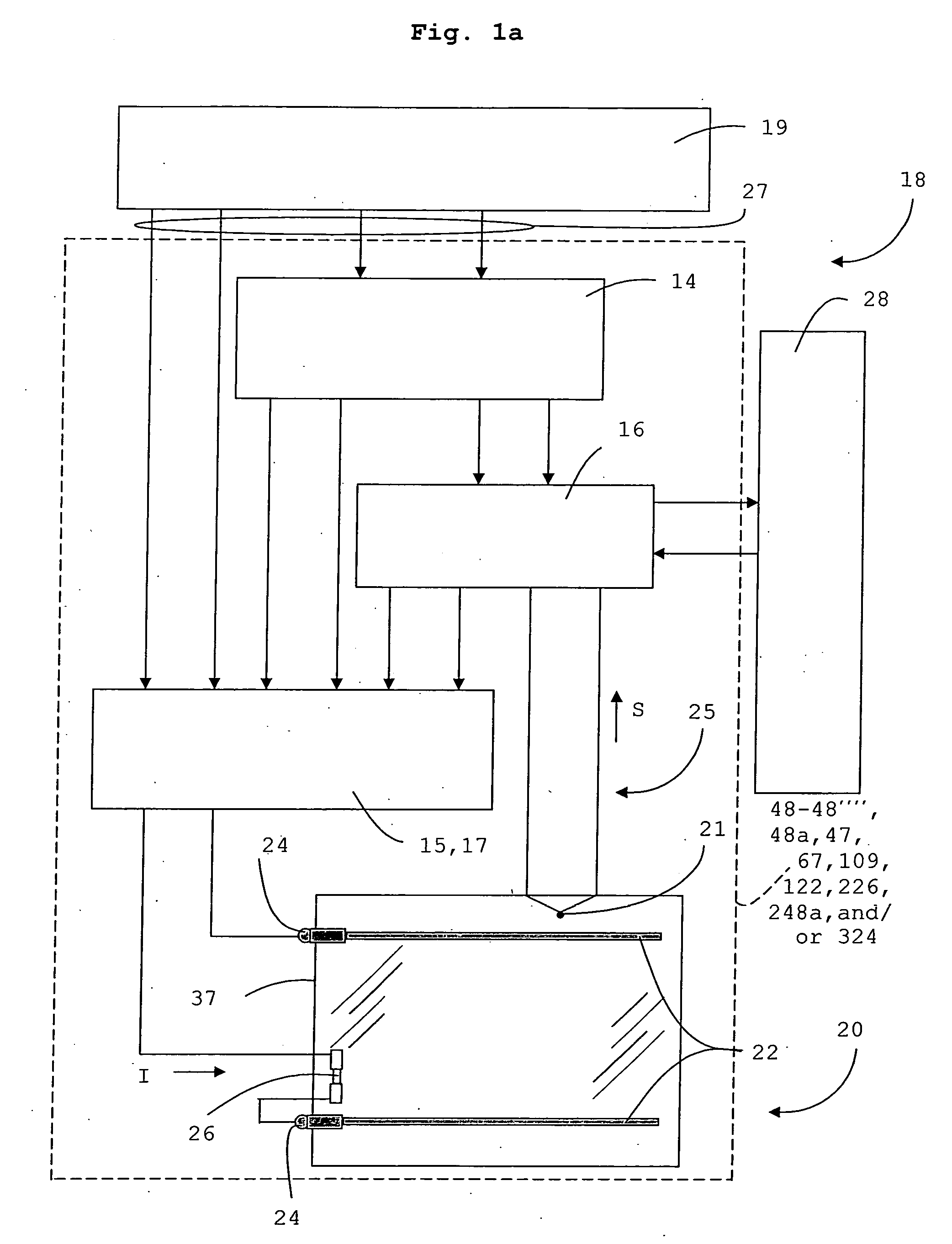
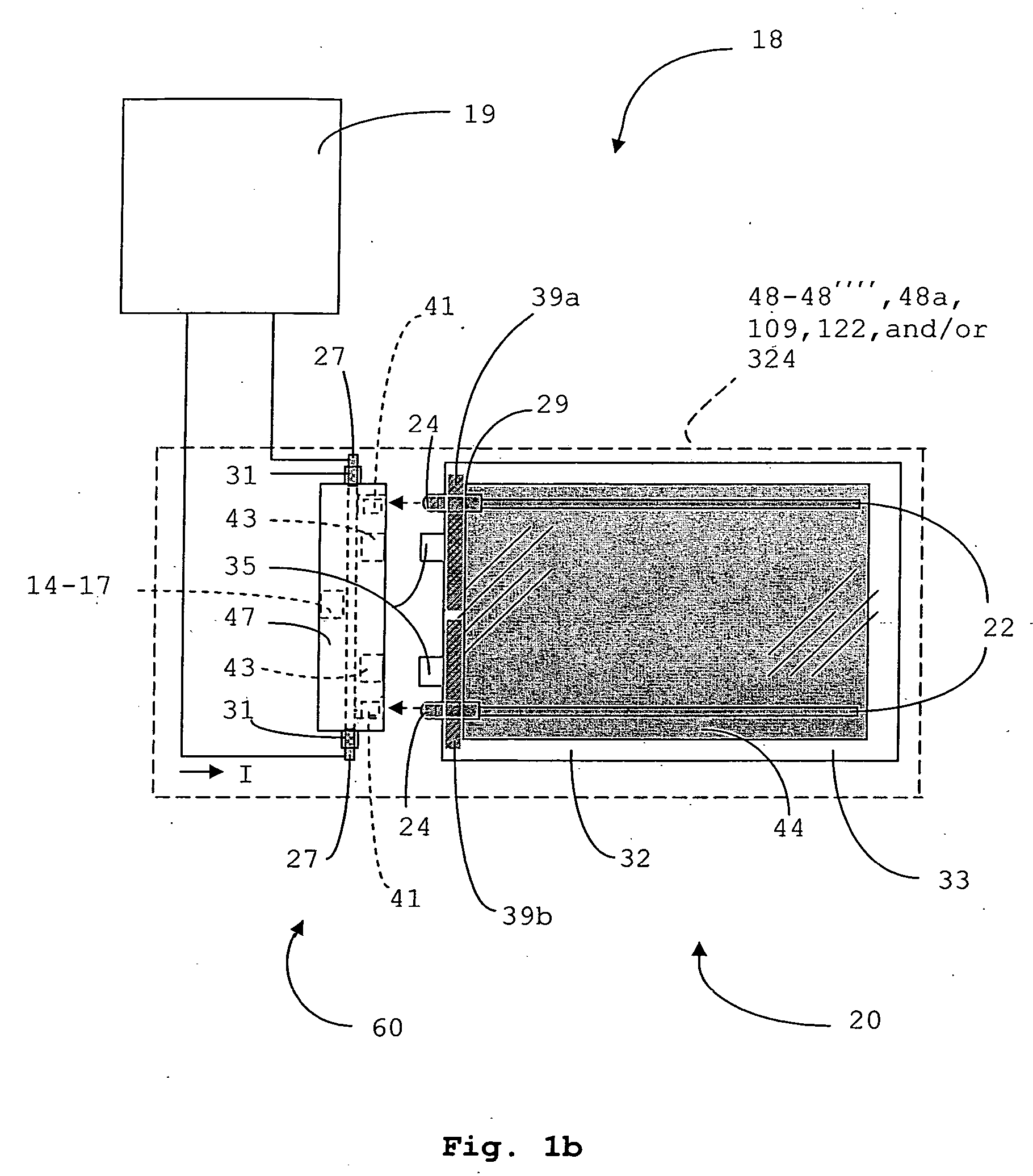
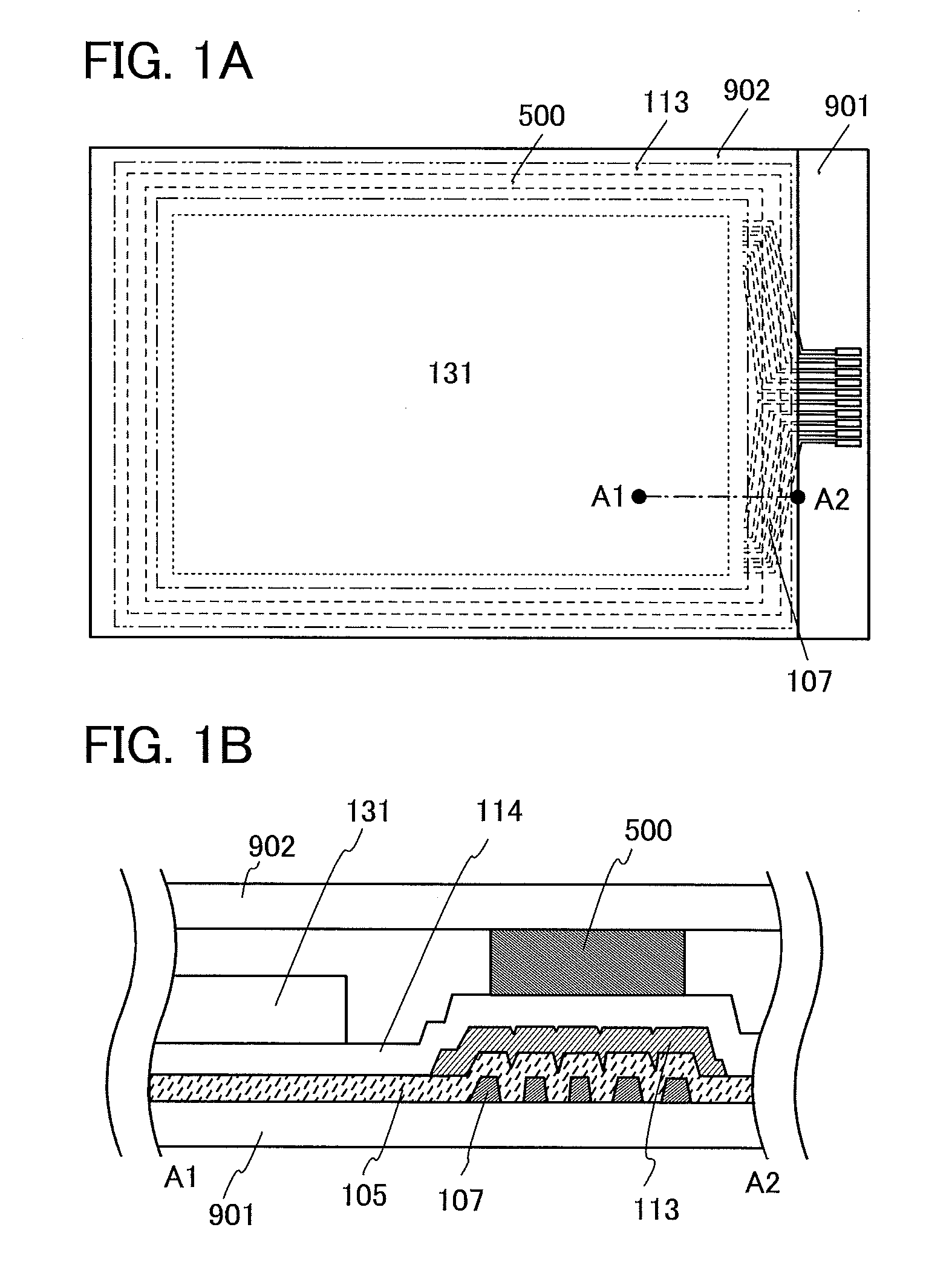
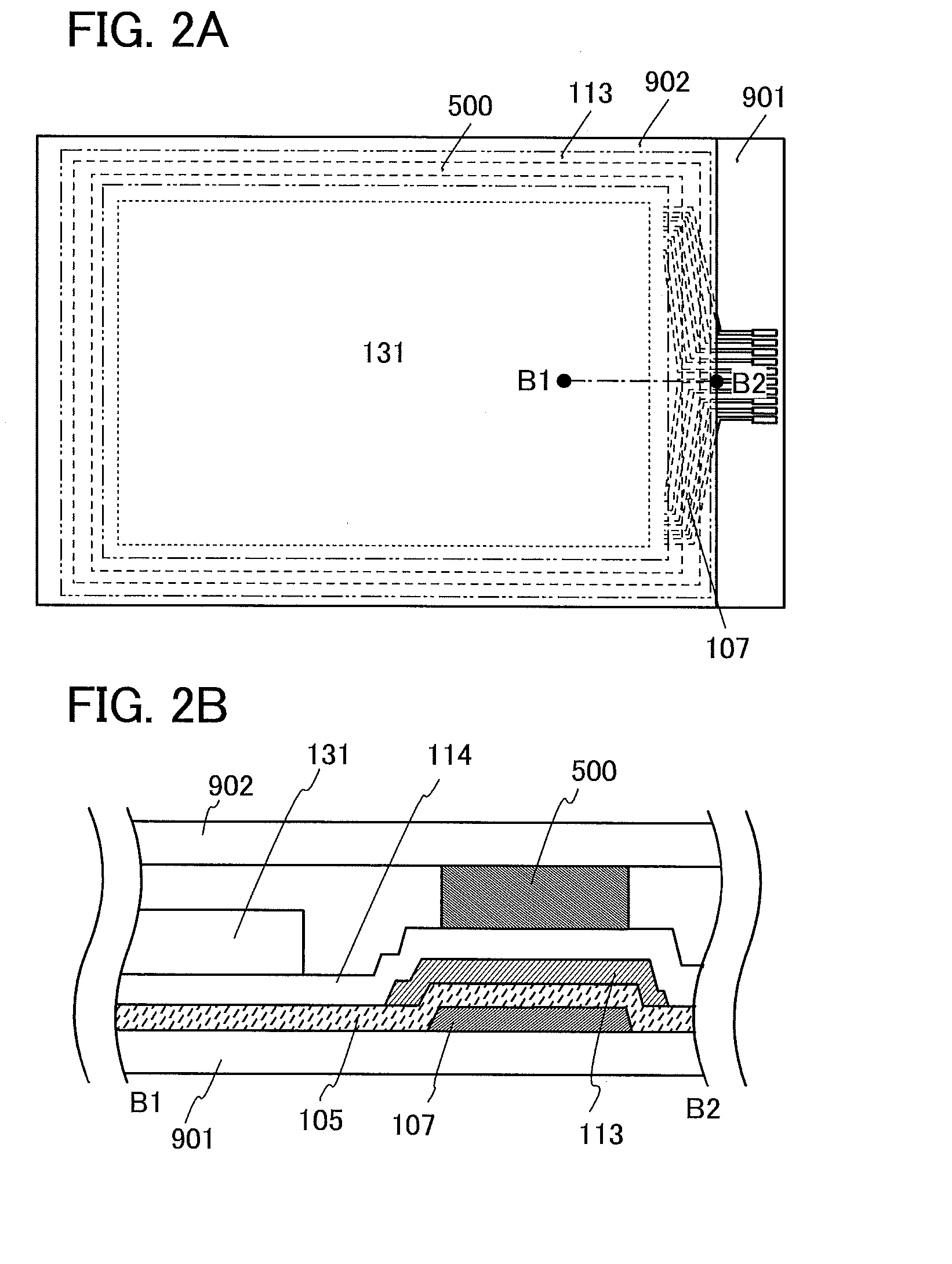
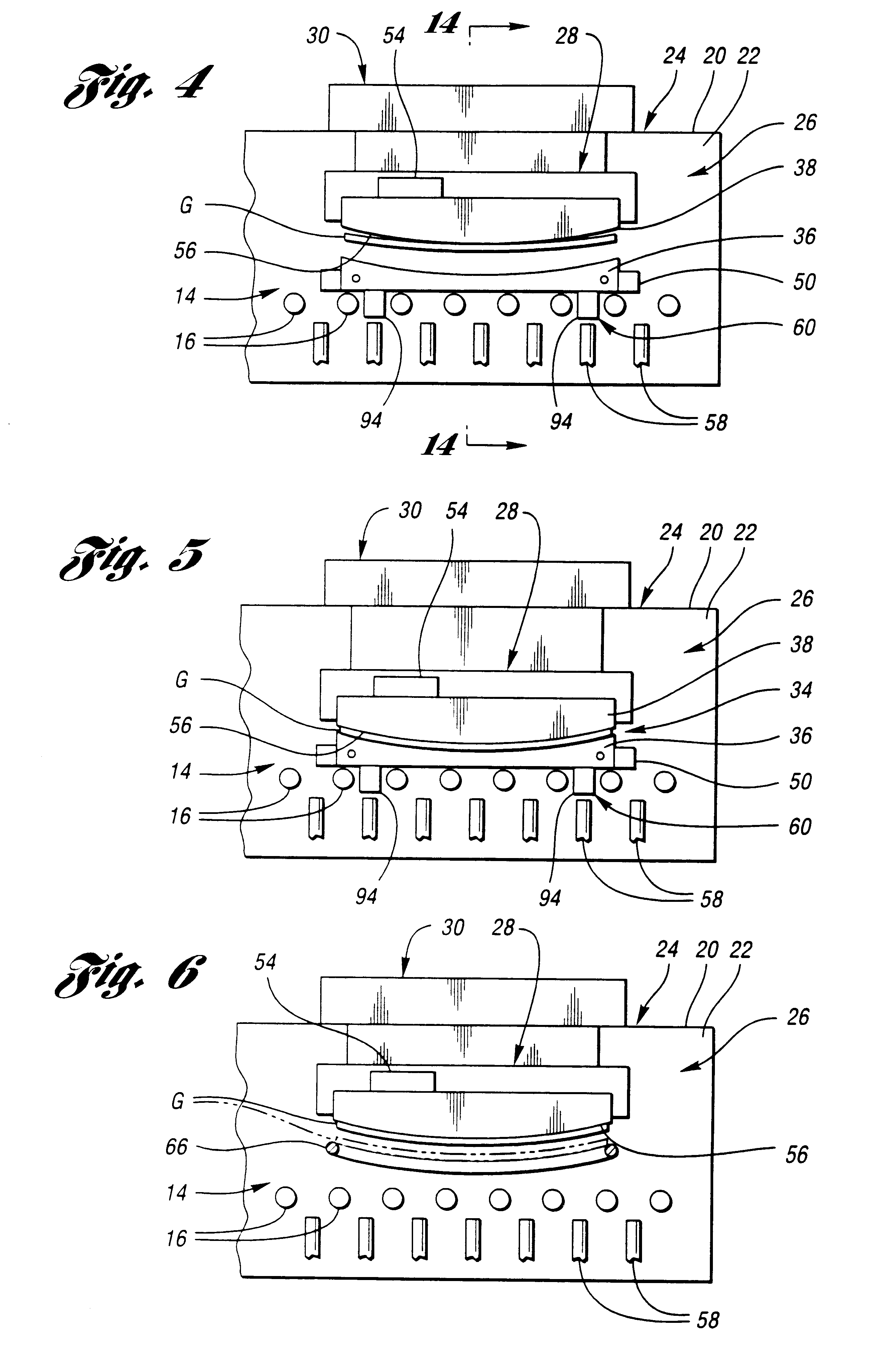
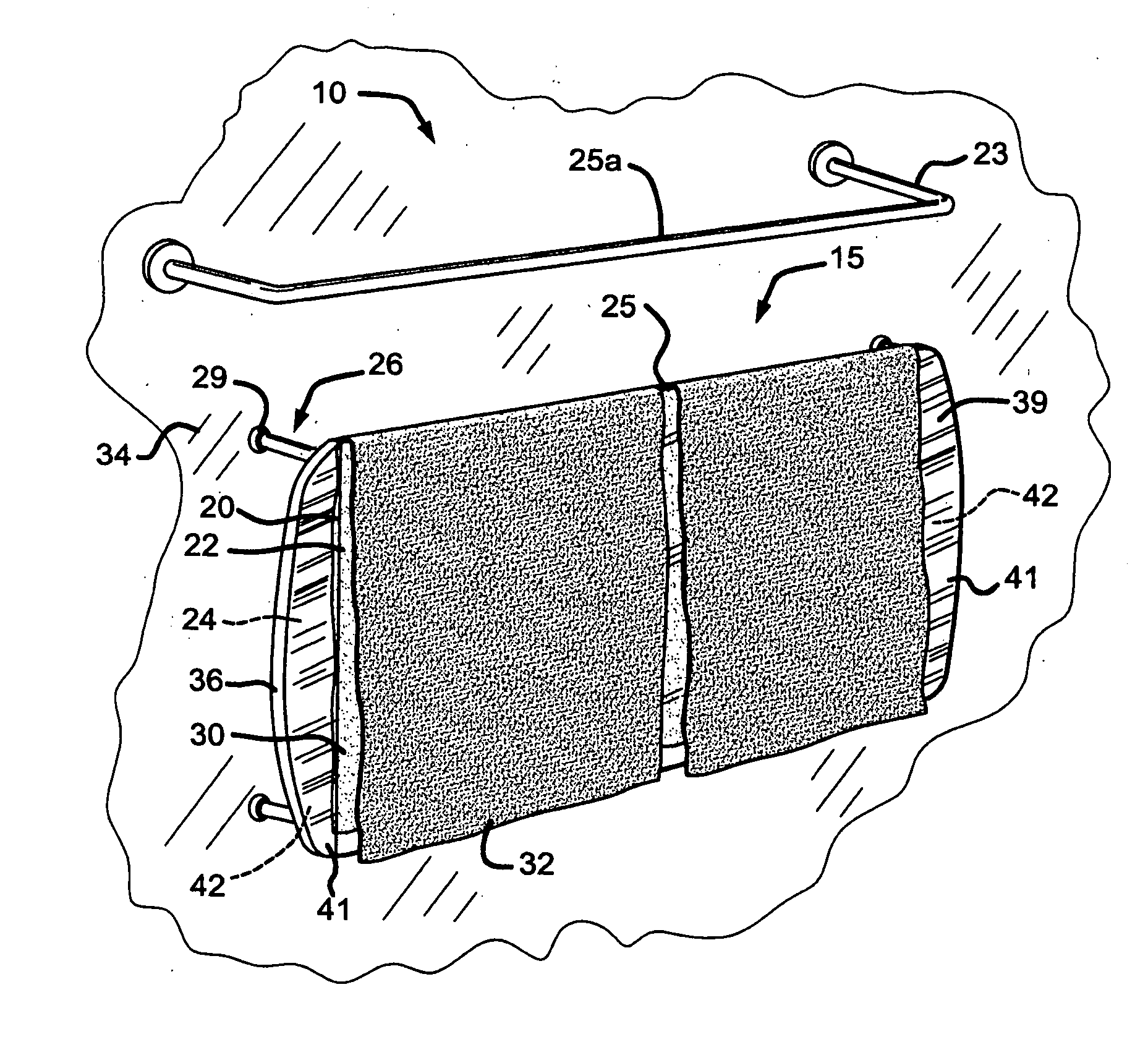
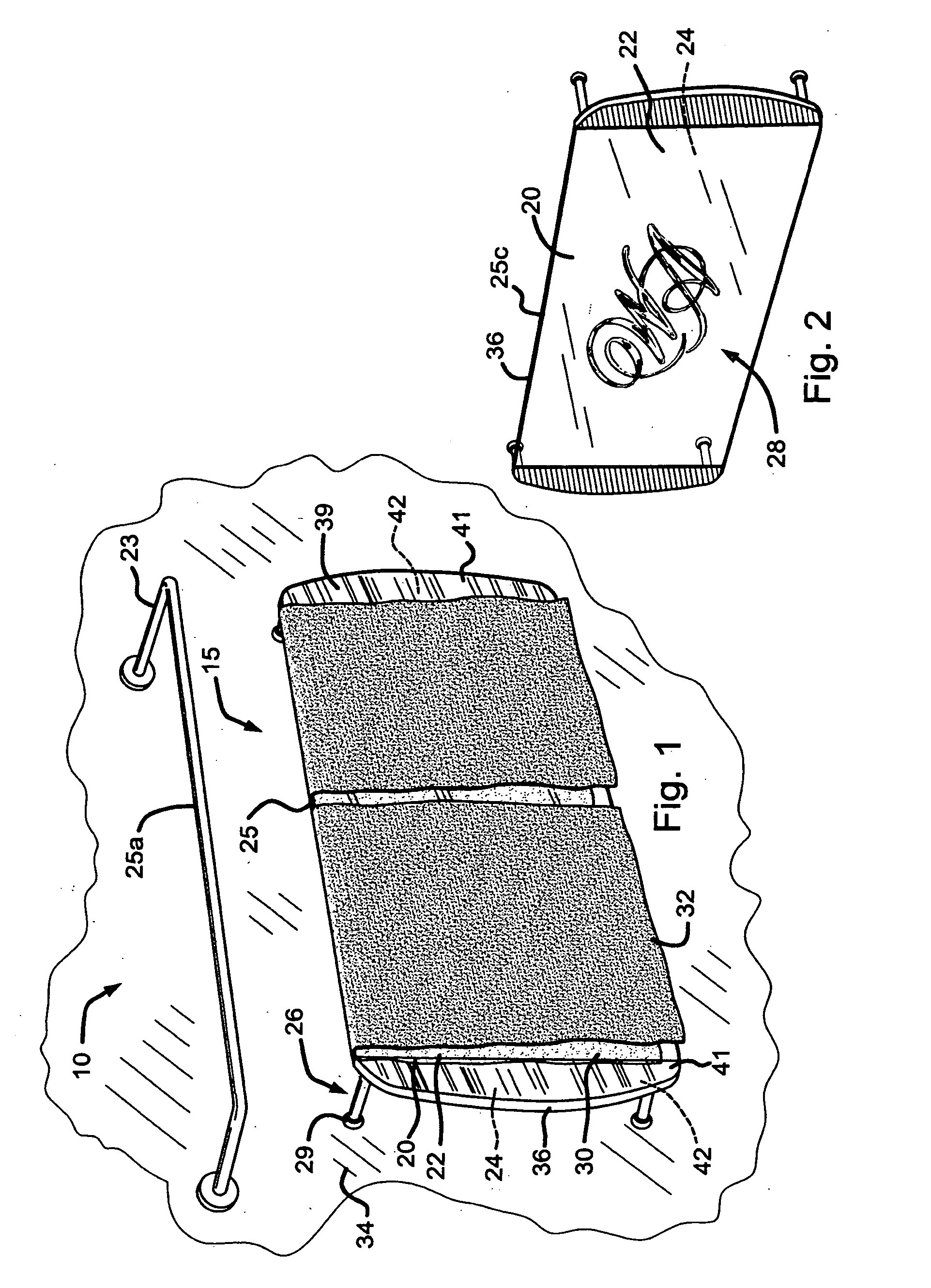
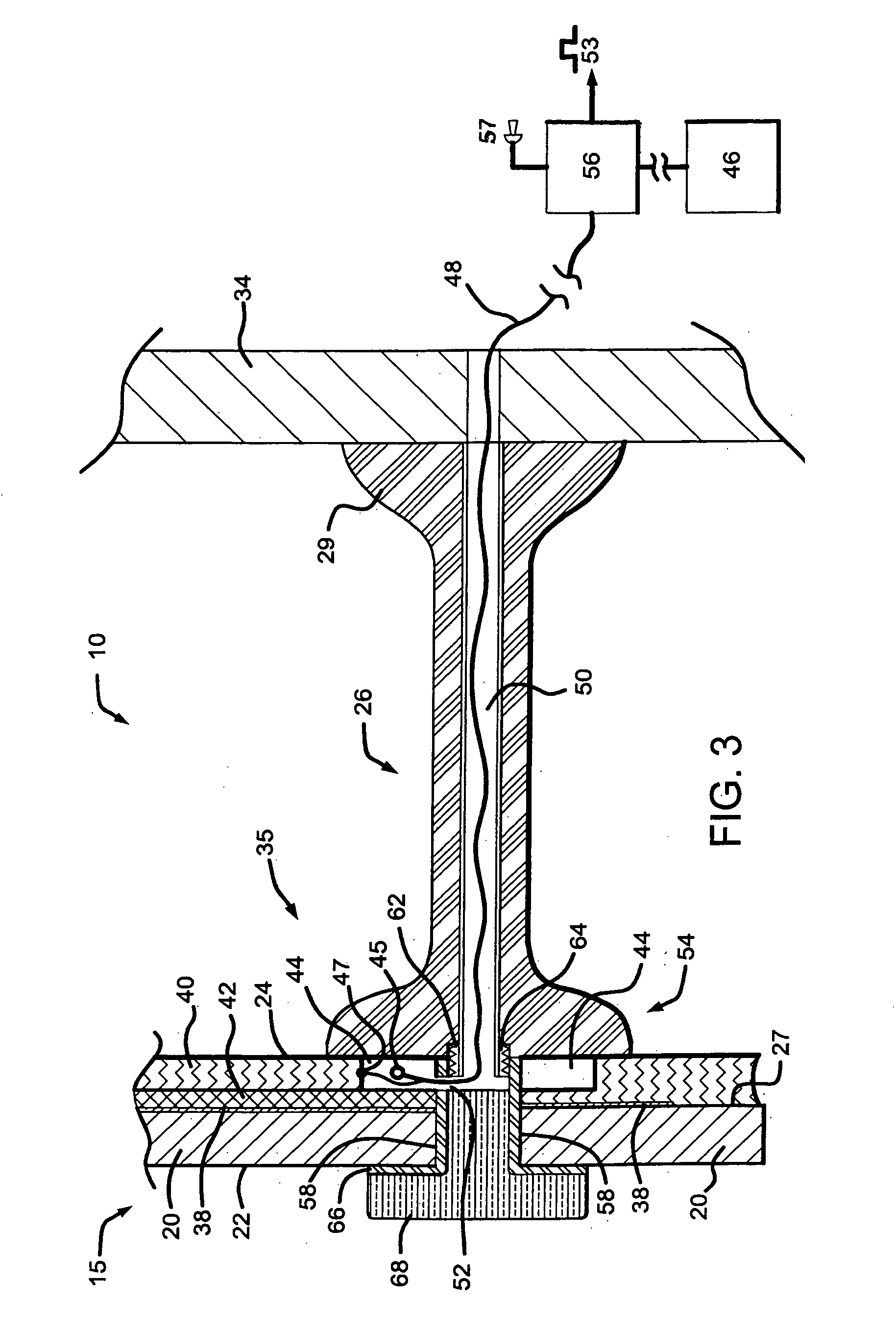
Heated glass panels and methods for making electrical contact with electro-conductive films
InactiveUS7362491B2Lighting and heating apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectrical conductorEngineering
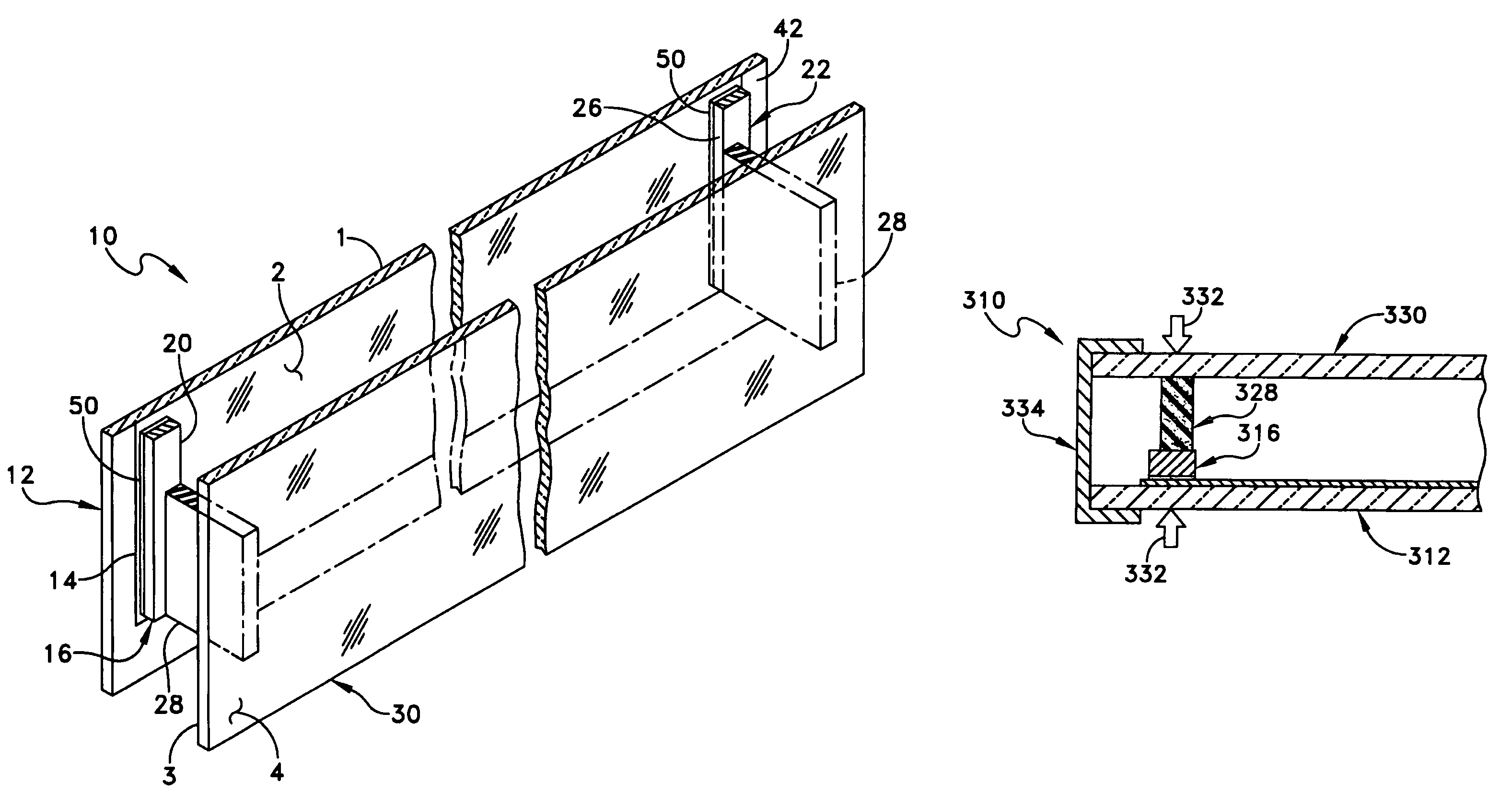
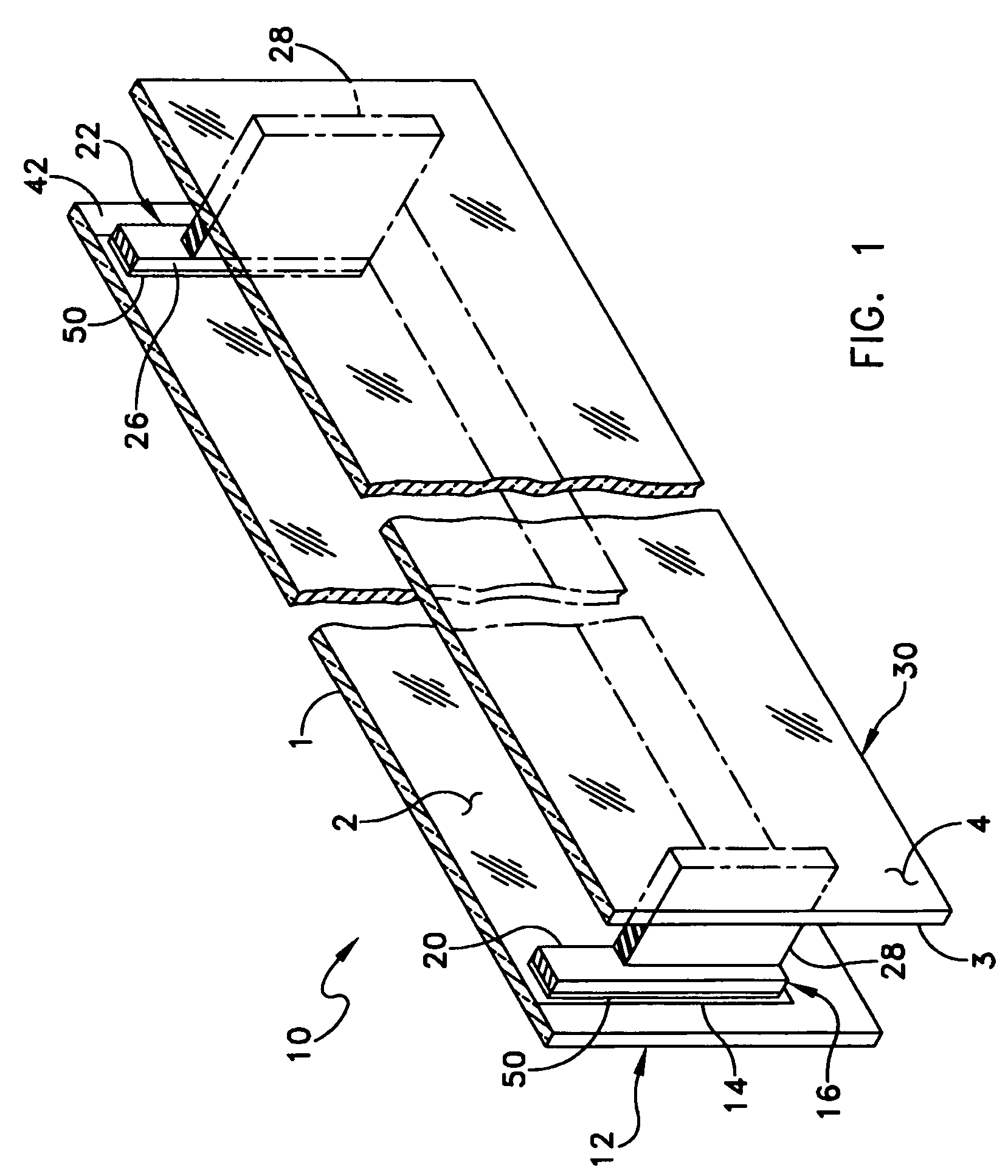
A heated glass panel assembly according to one embodiment of the invention may include a substrate having an electro-conductive film provided thereon. A conductor is positioned in contact with the electro-conductive film. A resilient material is positioned in contact with the conductor so that at least a portion of the conductor is located between the resilient material and the electro-conductive film. A retainer is positioned in contact with the resilient material so that at least a portion of the resilient material and at least a portion of the conductor are located between the retainer and the electro-conductive film. The retainer applies a compressive pressure to the resilient material which transfers at least a portion of the compressive pressure to the conductor to hold the conductor in contact with the electro-conductive film.
Owner:RADIANT GLASS INDS
Process and device for manufacturing glass sheet
InactiveUS7231786B2Minimizes warpGlass furnace apparatusGlass drawing apparatusFlat glassGlass sheet
The present invention relates to a process for manufacturing flat sheets of a glass-based material and to an apparatus therefor. The process comprises providing a glass preform, heating the glass preform in a furnace, forming a gob and a pre-sheet, removing the gob and drawing the glass pre-sheet into a flat glass sheet. Also provided is an apparatus for drawing a glass preform into a glass sheet, the apparatus comprising a draw furnace, stretching arms for stretching and drawing the pre-sheet into a glass sheet, and opposing edge rollers for applying a downward force on the glass sheet. The draw furnace may include a plurality of individual heating elements, the temperature of each heating element capable of being separately controlled. The apparatus may further include an annealing furnace for annealing the glass sheet.
Owner:CORNING INC
Process and device for manufacturing glass sheet
InactiveUS20060021385A1Minimizes warpGlass furnace apparatusGlass drawing apparatusFlat glassGlass sheet
The present invention relates to a process for manufacturing flat sheets of a glass-based material and to an apparatus therefor. The process comprises providing a glass preform, heating the glass preform in a furnace, forming a gob and a pre-sheet, removing the gob and drawing the glass pre-sheet into a flat glass sheet. Also provided is an apparatus for drawing a glass preform into a glass sheet, the apparatus comprising a draw furnace, stretching arms for stretching and drawing the pre-sheet into a glass sheet, and opposing edge rollers for applying a downward force on the glass sheet. The draw furnace may include a plurality of individual heating elements, the temperature of each heating element capable of being separately controlled. The apparatus may further include an annealing furnace for annealing the glass sheet.
Owner:CORNING INC
Method of molding glass parts and molding apparatus
InactiveUS8099982B2Reduced size and costSmall sizeElectric discharge heatingGlass drawing apparatusShell moldingAlkali metal
A molding apparatus of a glass material according to the present invention is characterized by containing means for holding a glass material and a molding die in contact with each other, means for heating the glass material and the molding die, and means for applying a voltage across the glass material and the molding die, in which press-molding is performed by electrostatic attraction acting between a surface of the glass material and a surface of the molding die. Further, a molded product of a glass material according to the present invention is characterized by including an alkali metal as a component, in which a concentration of the alkali metal is lowered in vicinity of a surface to be molded as compared with that of a glass base material.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
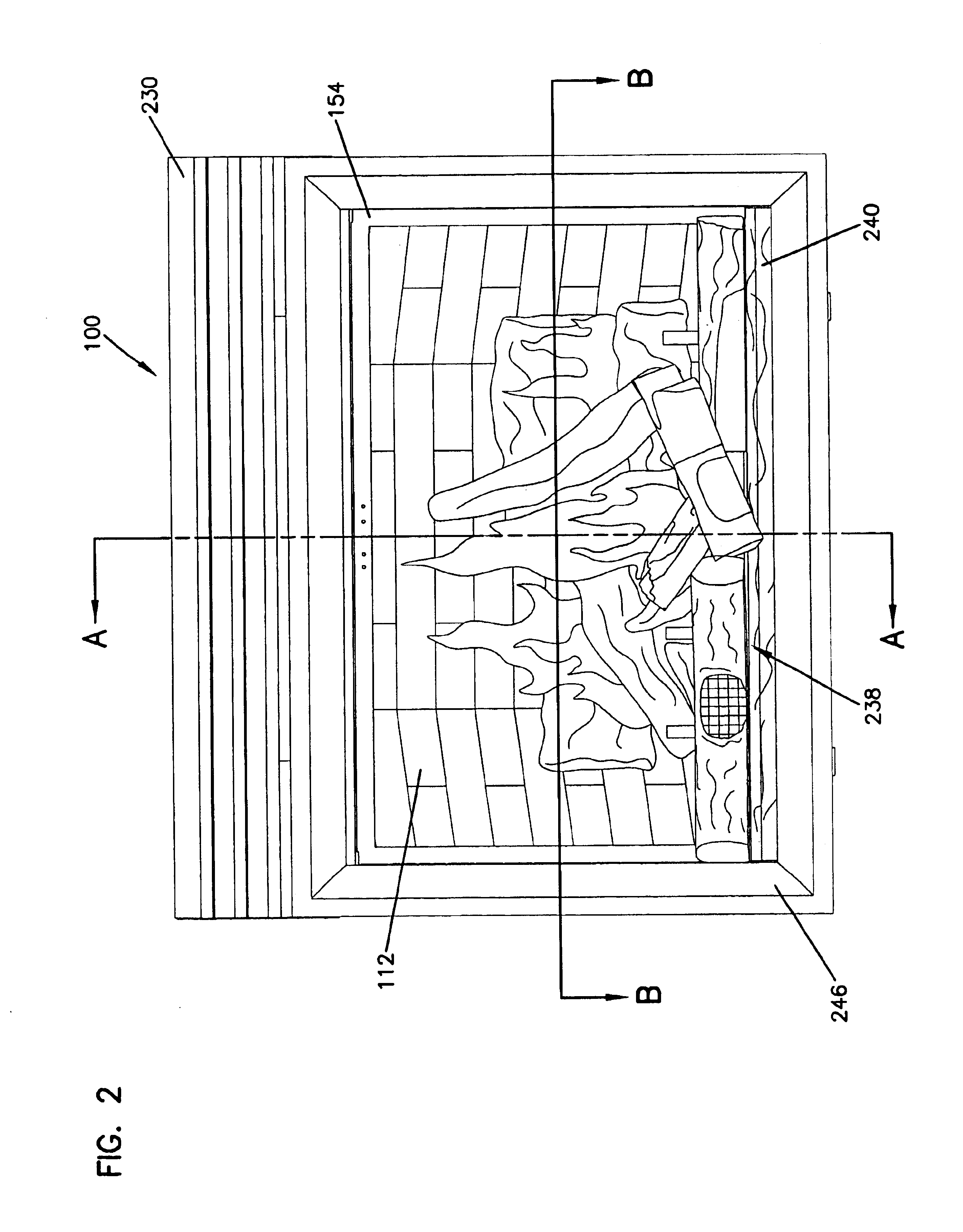
Lenticular fireplace
InactiveUS6880275B2Domestic stoves or rangesElectrical heating fuelLenticular lensPhase-change material
A lenticular fireplace and methods for simulating a fire within a fireplace are disclosed. In one respect, a fire is simulated with a lenticular screen. The lenticular screen includes a lenticular lens layer and an image layer, wherein the image layer comprises one or more images of a fire. A device is coupled to the lenticular screen that moves the lenticular screen to alter a viewed image of the fire. In another respect, the lenticular screen is disposed within a fireplace enclosure. In another respect, a fireplace includes a convertible heated glass apparatus. The apparatus is used in a front wall of an enclosure. The front wall includes an electrically conductive panel coupled to a phase change material. Electrical terminals are operatively connected to the electrically conductive panel for applying a voltage across the electrically conductive panel to heat the front wall and convert the phase change material from an opaque solid to a less opaque liquid to allow viewing through the front wall. In another respect, a flame simulation apparatus simulates a flickering flame effect on a translucent screen. The flame simulation apparatus includes the translucent screen having a front surface and a back surface, a bobble-flame, a device to move the bobble-flame, and a light source to reflect light off of the bobble-flame and onto the translucent screen. In another respect, a fireplace includes the lenticular screen, the convertible heated glass apparatus, and the flame simulation apparatus.
Owner:HNI TECH INC
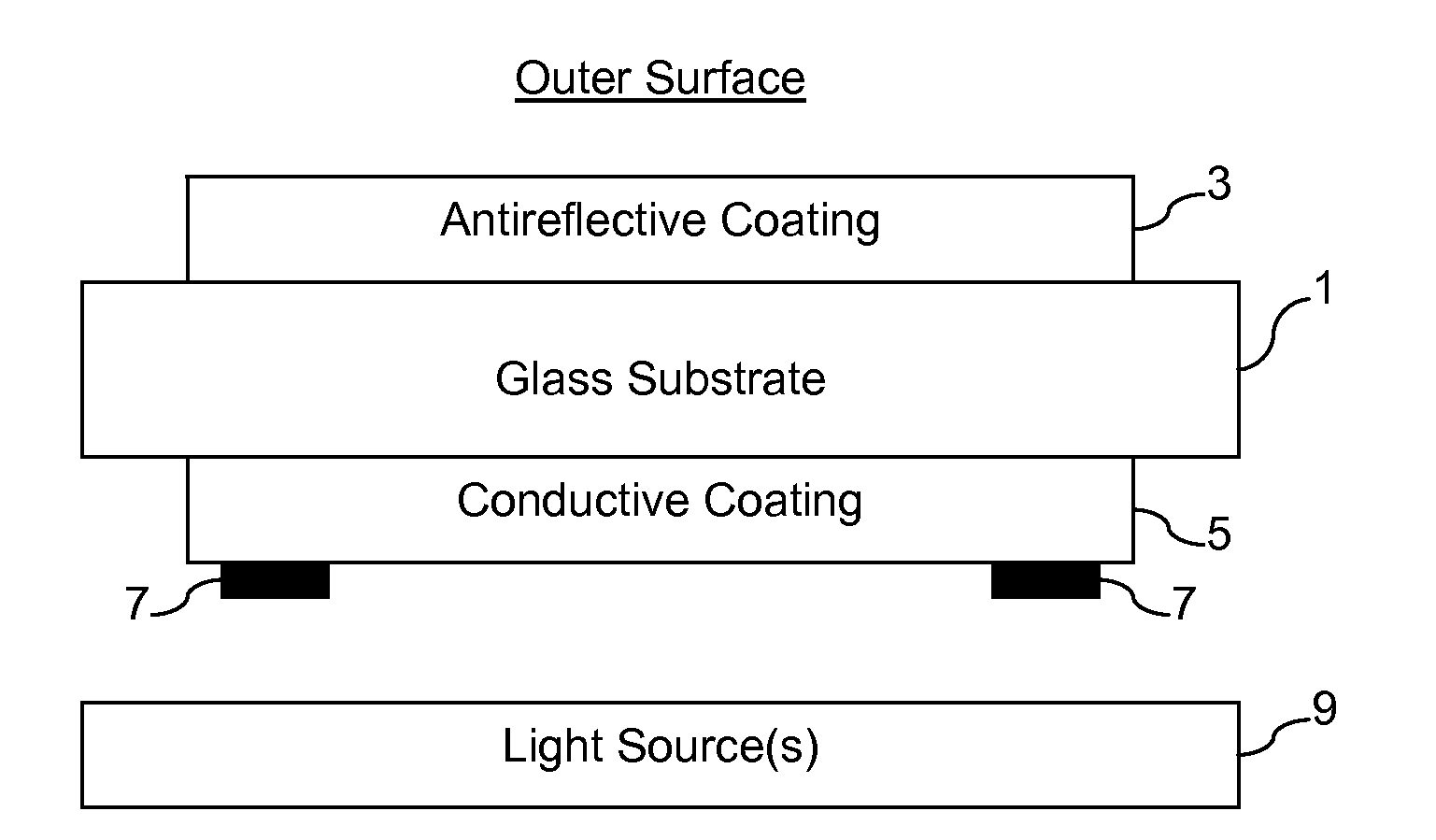
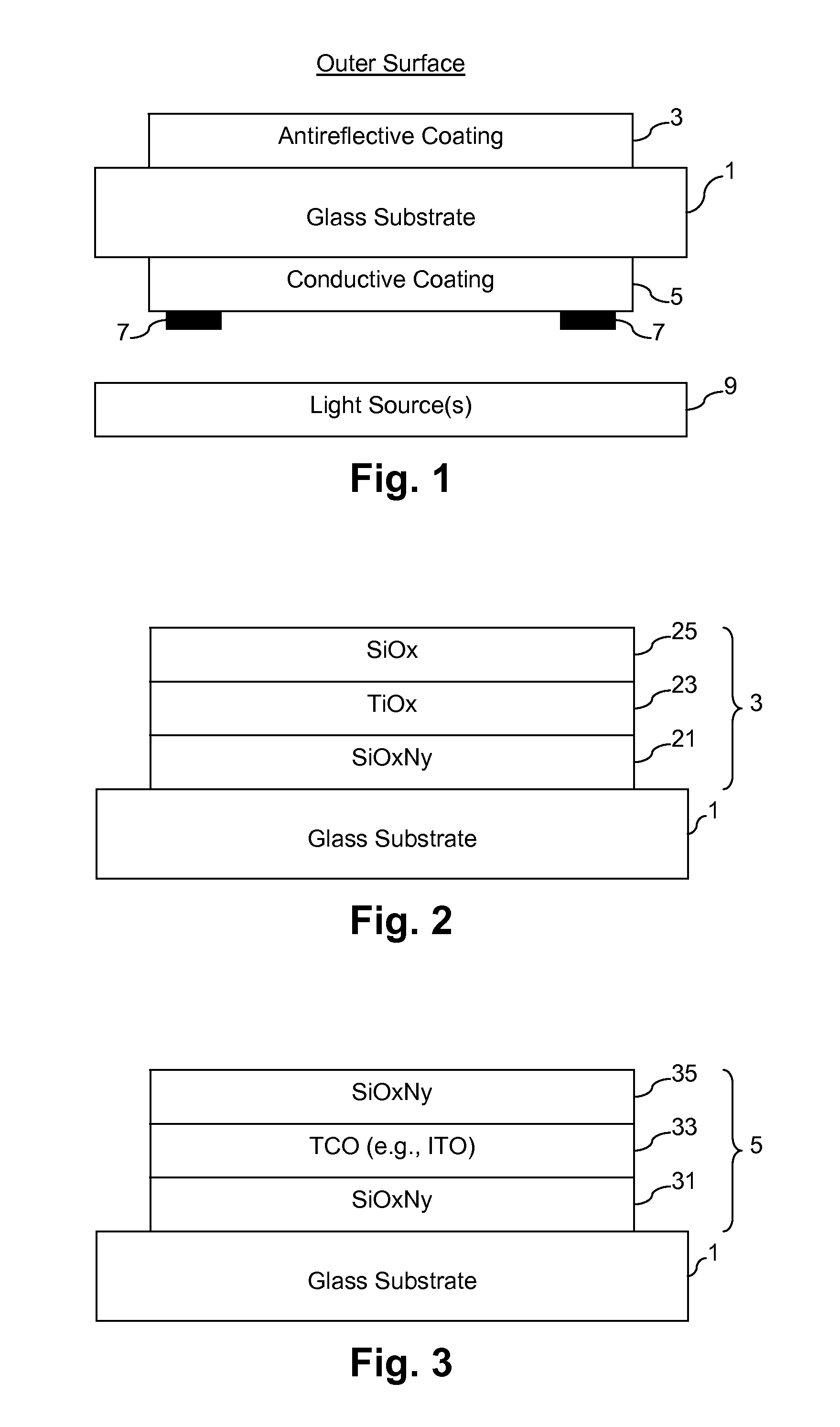
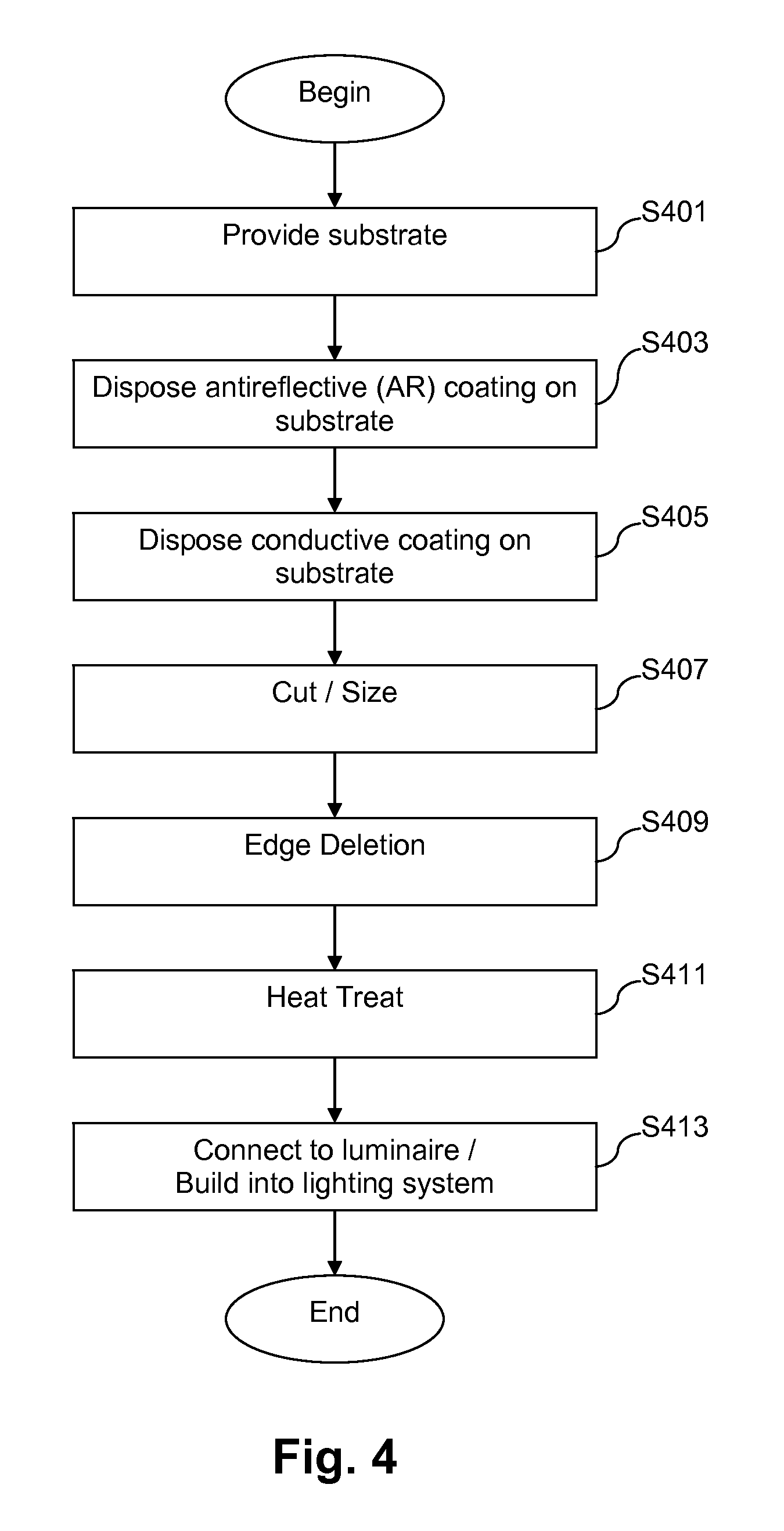
Heatable lens for luminaires, and/or methods of making the same
InactiveUS20120250314A1Fast heatingImprove efficiencyNon-electric lightingPoint-like light sourceConductive coatingEffect light
Certain example embodiments of this invention relate to heatable glass substrates that may be used in connection with lighting applications, and / or methods of making the same. In certain example embodiments, a glass substrate supports an antireflective (AR) coating on a first major surface thereof, and a conductive coating on a second, opposite major surface thereof. Bus bars connect the conductive coating to a power source in certain example embodiments. The substrate may be heat treated (e.g., heat strengthened and / or thermally tempered), with one or both coatings thereon. The heatable glass substrate thus may help provide a chemical and / or environmental barrier for the luminaire or lighting system disposed behind it. In addition, or in the alternative, the heatable glass substrate may help reduce the amount of moisture (e.g., snow, rain, ice, fog, etc.) that otherwise could accumulate on the luminaire or lighting system.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
Heated glass panel frame with electronic controller and triac
The present invention places an electronic controller and / or a triac in a frame, a cover, a chase, or a mounting member of a heated glass panel assembly, where the panel has a conductive coating dispose on it. By placing the controller in the panel frame, the cover, the chase, or the mounting member, field wiring of the panel assembly is greatly reduced, wire lengths are standardized, production glazing, wiring, and pre-testing are facilitated, and installation time and complexity are minimized. By placing the triac in thermal contact with the panel frame, the cover, the chase, or the mounting member, the heat from the triac may be used to complement the heat supplied by the assembly.
Owner:ENGINEERED GLASS PRODS
Machining Of Fusion-Drawn Glass Laminate Structures Containing A Photomachinable Layer
ActiveUS20140238078A1Glass forming apparatusPhotosensitive material processingGlass structureCrystallization
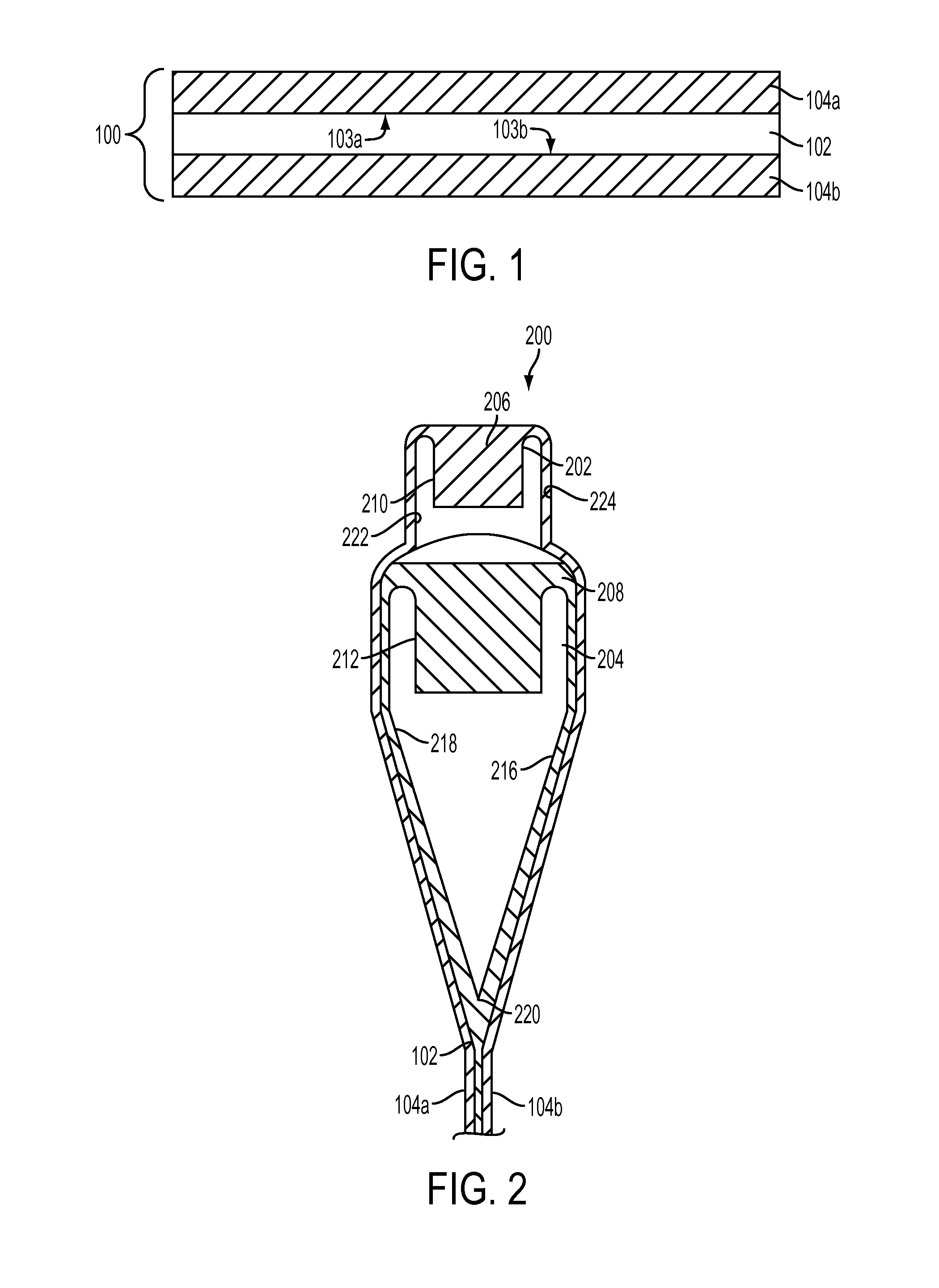
Methods for machining glass structures may be performed on fusion-drawn glass laminates having a core layer interposed between a first cladding layer and a second cladding layer. The core layer may be formed from a core glass composition having a core photosensitivity, the first cladding layer may be formed from a glass composition having a photosensitivity different from the core photosensitivity, and the second cladding layer may be formed from a glass composition having a photosensitivity different from the core photosensitivity. At least one of the core layer, the first cladding layer, and the second cladding layer is a photomachinable layer. The methods may include exposing a selected region of a photomachinable layer in the fusion-drawn laminate to ultraviolet radiation; heating the glass structure until the selected region crystallizes; and removing the crystallized material selectively from the photomachinable layer.
Owner:CORNING INC
Process and apparatus for scoring a brittle material
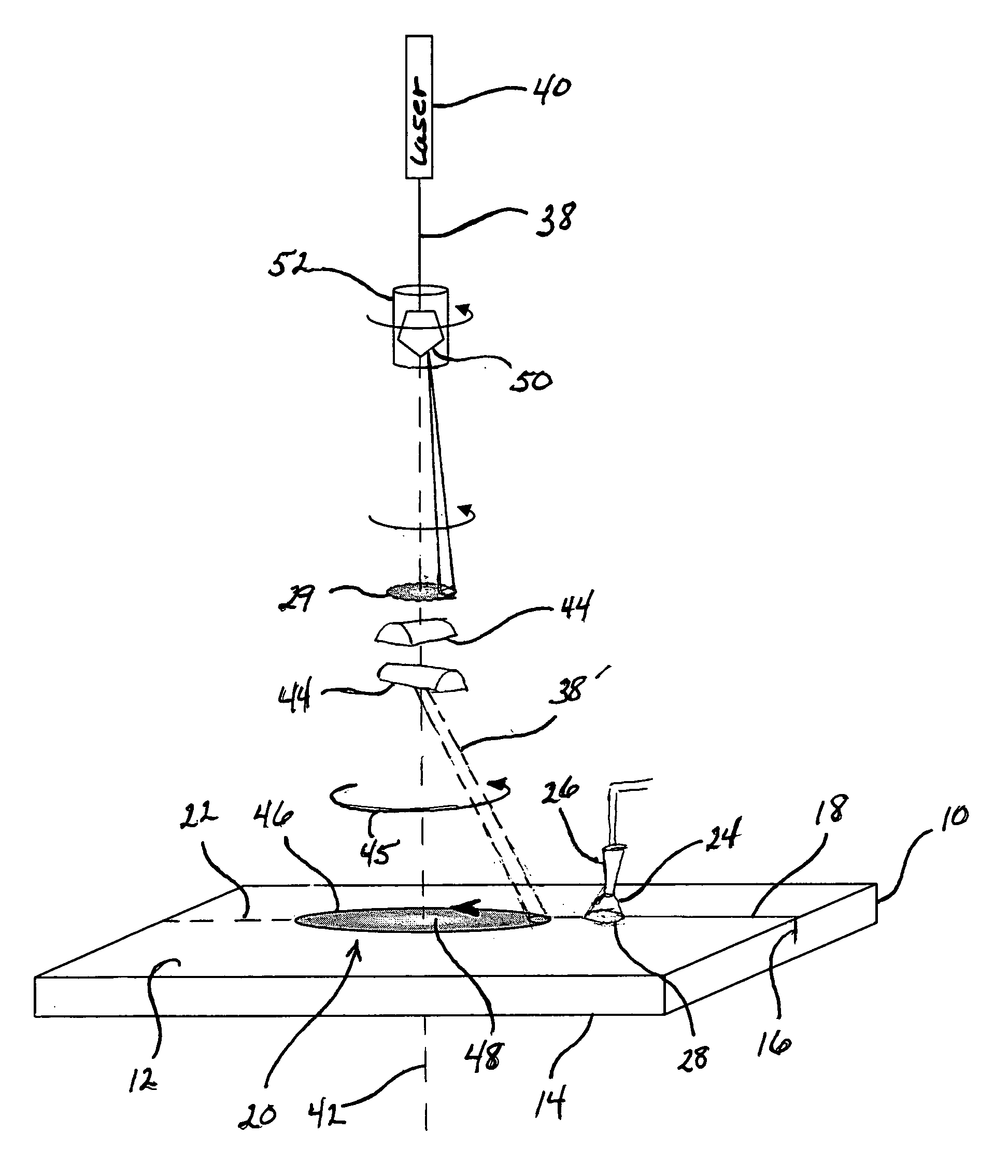
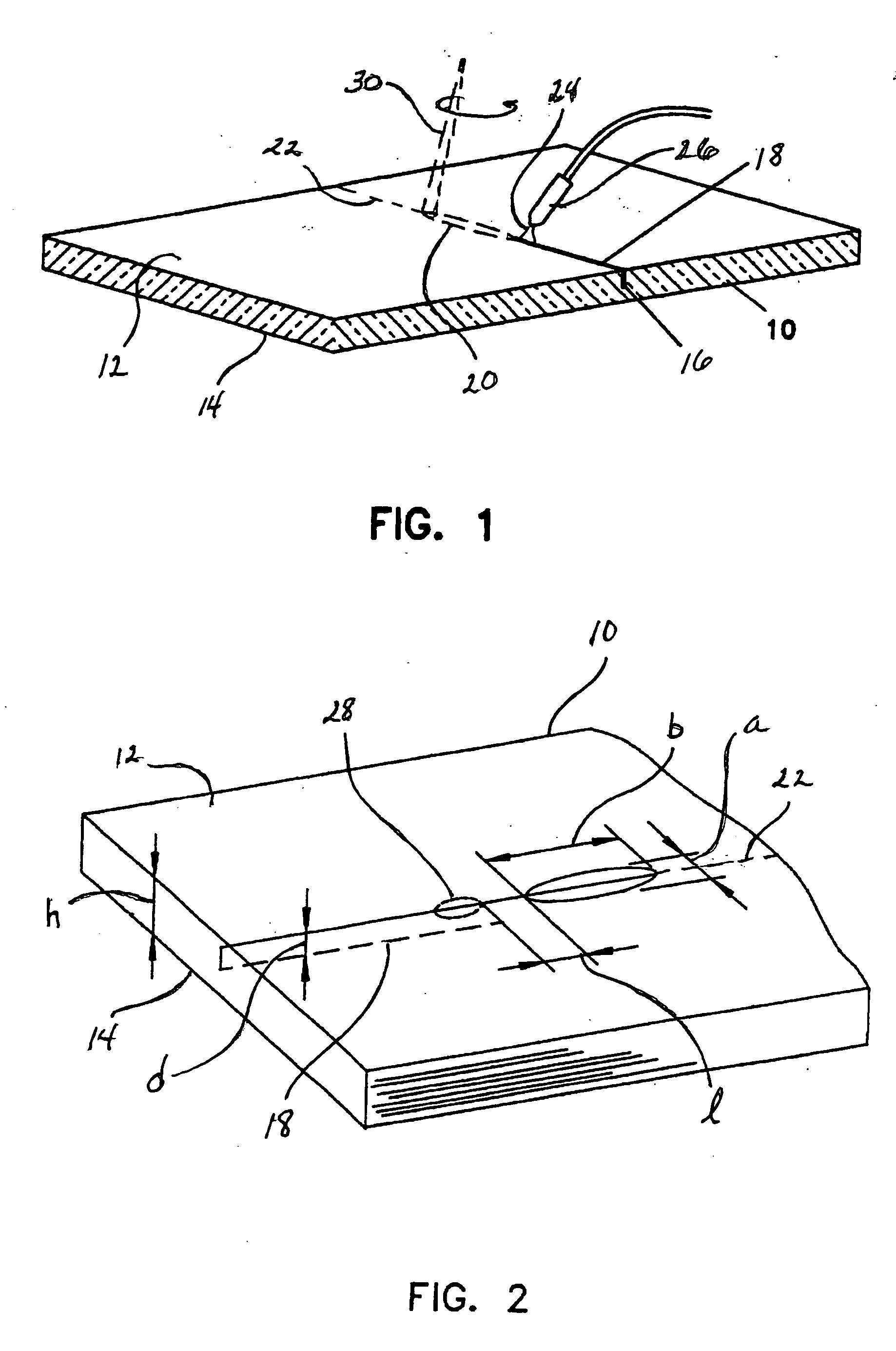
InactiveUS20060022008A1Easy to understandGlass severing apparatusWelding/soldering/cutting articlesFlat glassLaser beams
The present invention relates to a process for laser scoring of flat glass sheets. The process comprises manipulating a laser beam having a substantially Gaussian intensity profile to produce an elongated heating zone on the glass sheet to be scored, the elongated heating zone having a central portion with a lower temperature than a temperature of an outer portion of the heating zone. An initial crack is made in the glass sheet, the elongated heating zone is traversed across the glass sheet coincident with the initial crack, and the heated glass is thermally shocked by directing a cooled liquid against the heated glass, thus propagating the crack. The scored glass sheet may thereafter be broken by applying bending techniques as are known in the art.
Owner:CORNING INC
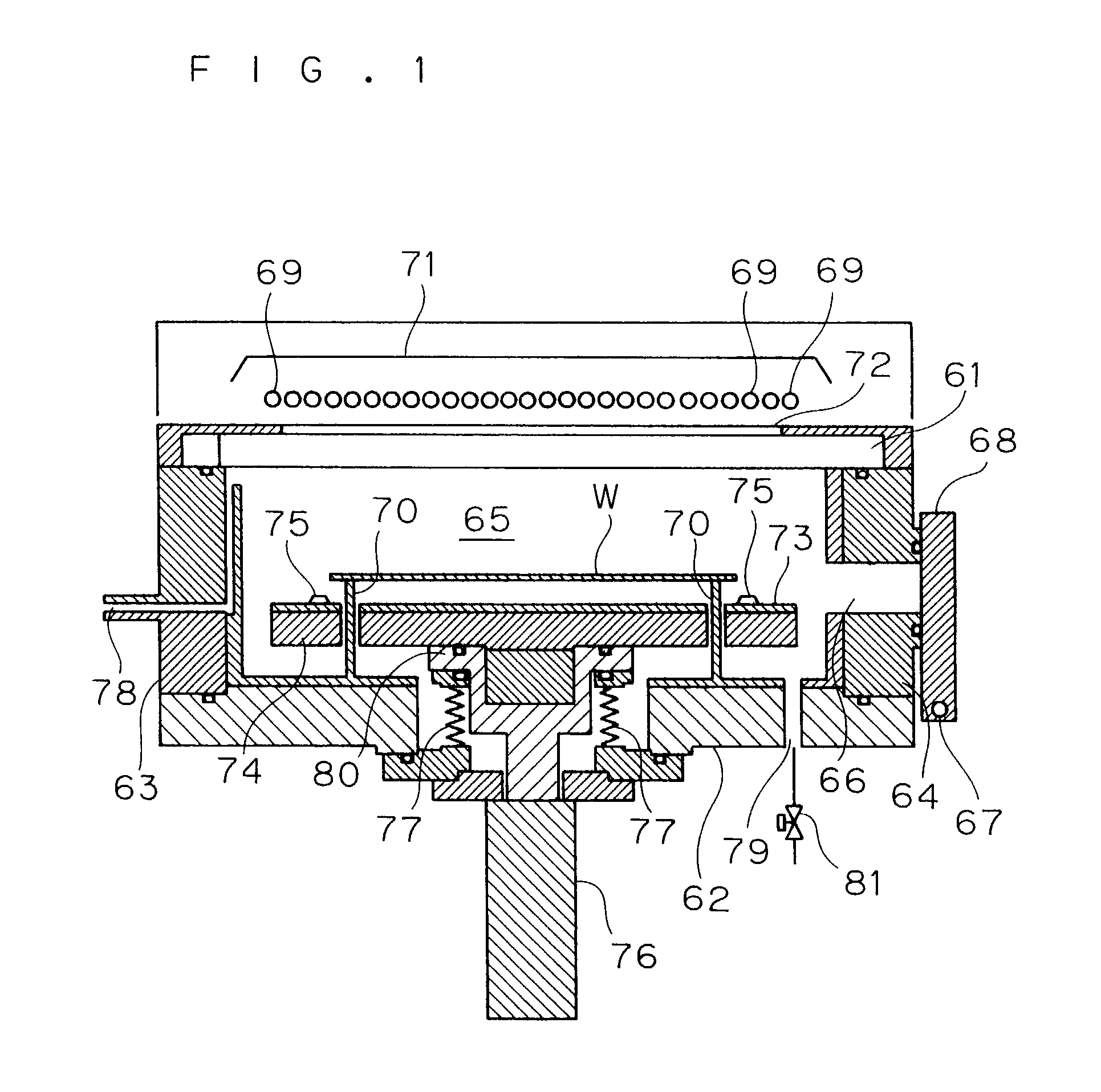
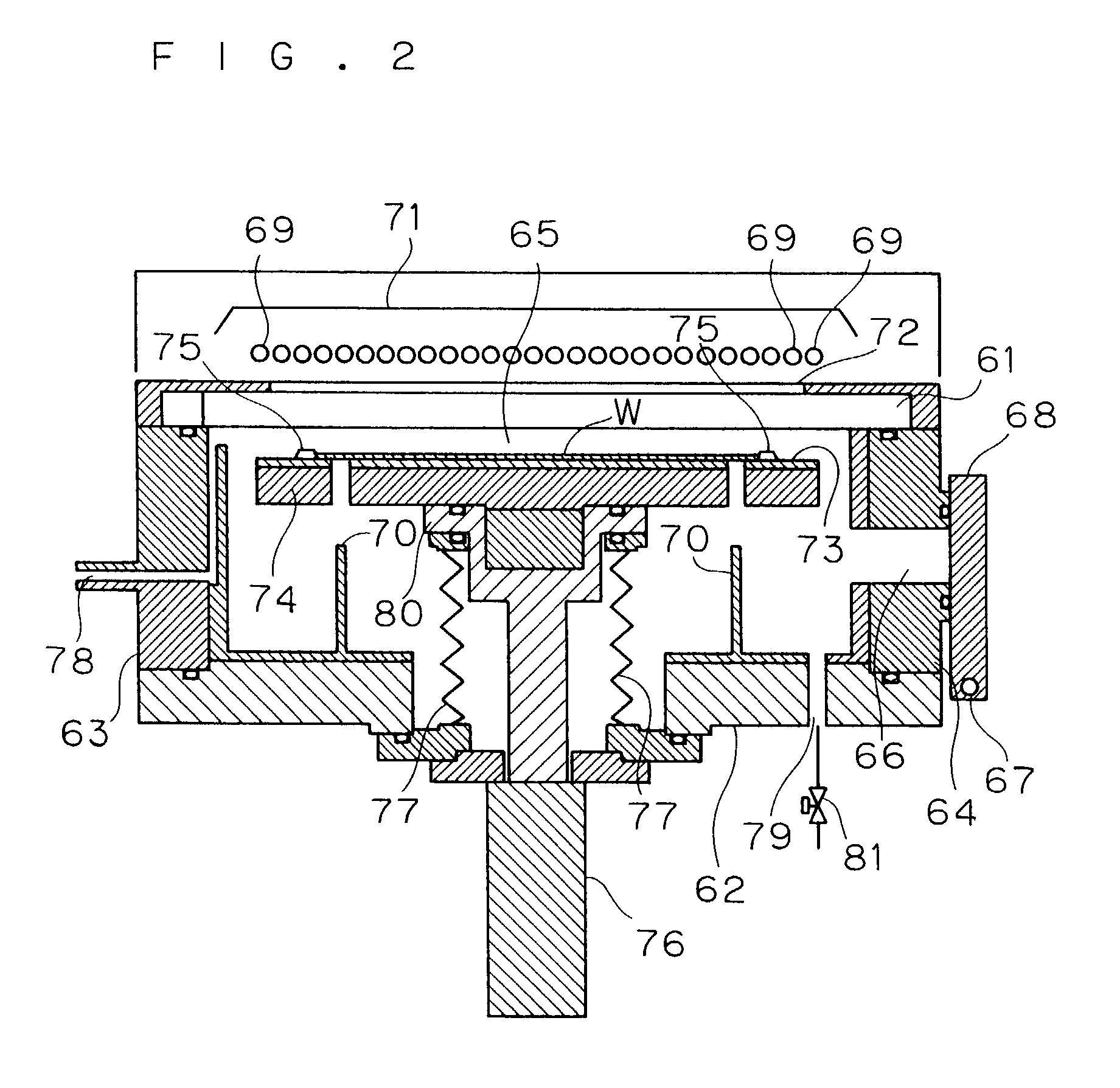
Apparatus for vacuum impulse forming of heated glass sheets
InactiveUS6227008B1Reduced optical distortionIncrease vacuumGripping headsGlass reforming apparatusGlass sheetMaterials science
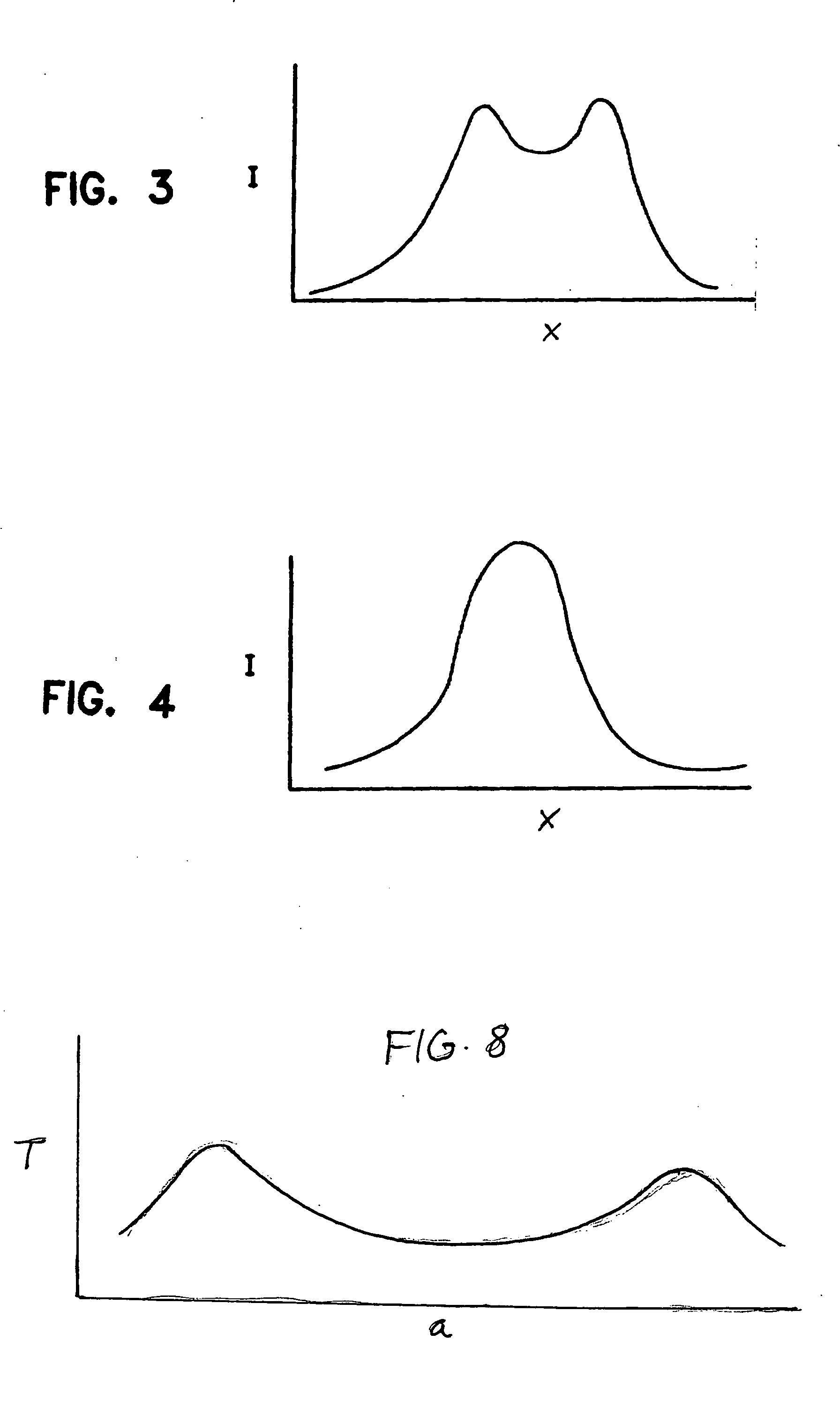
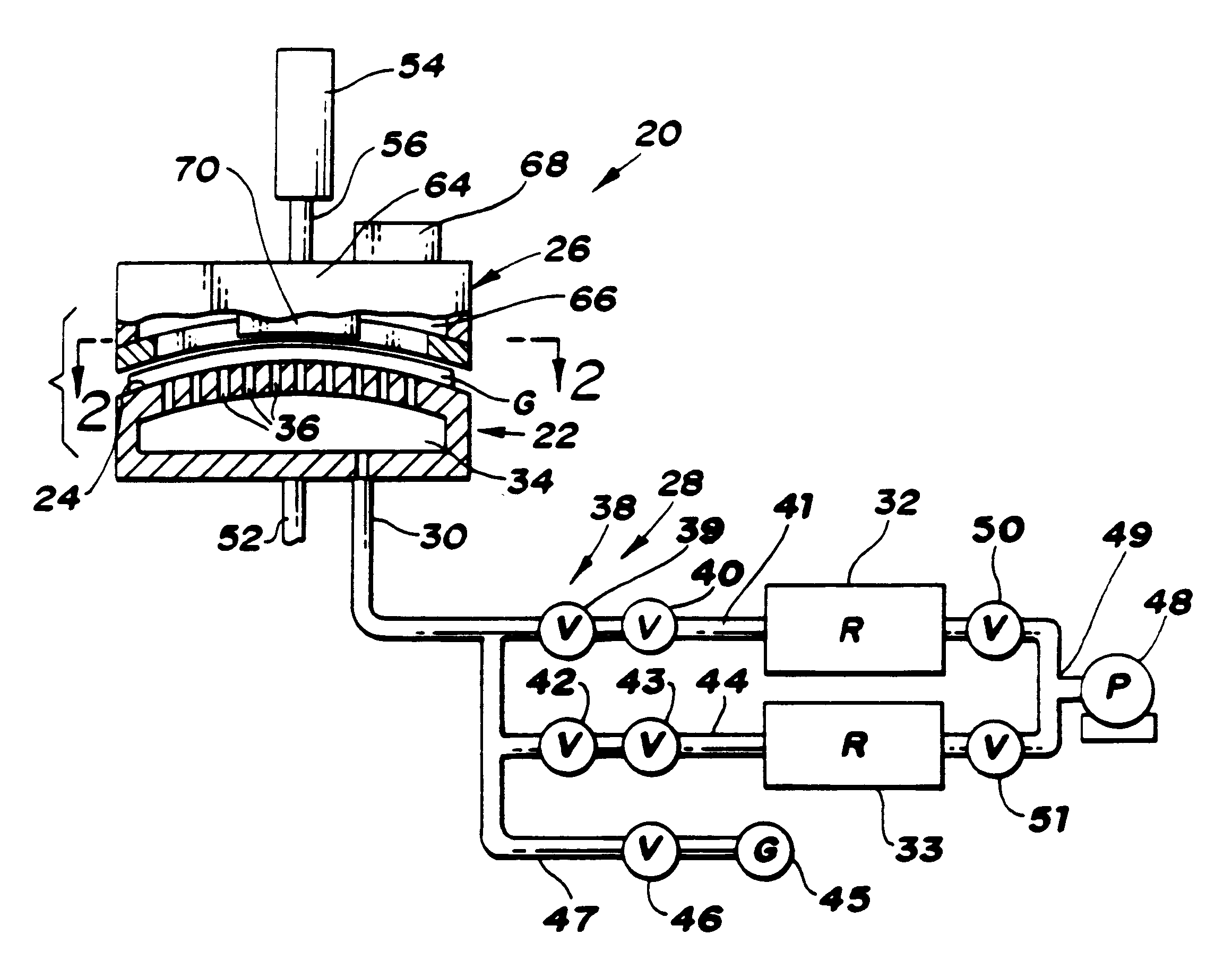
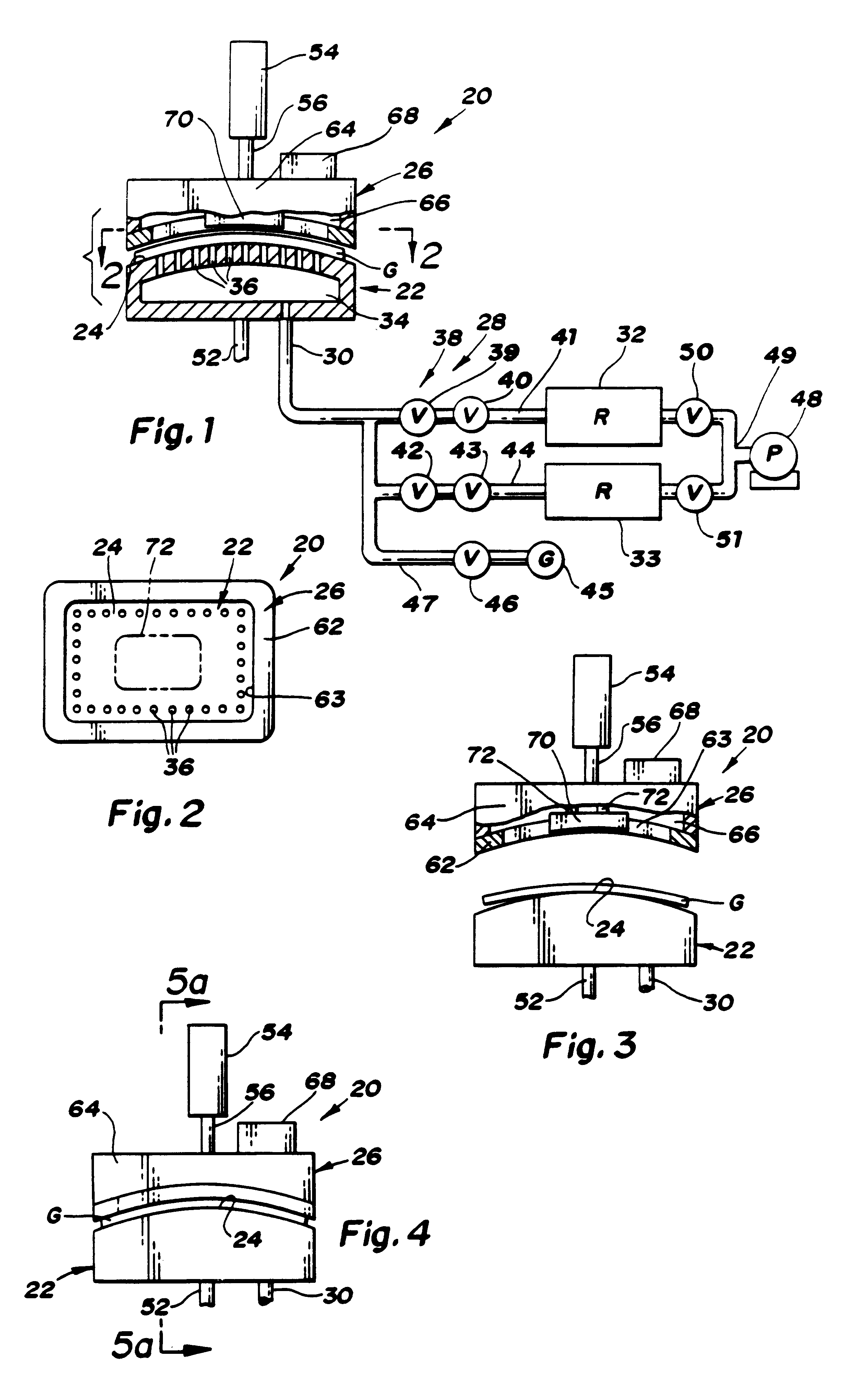
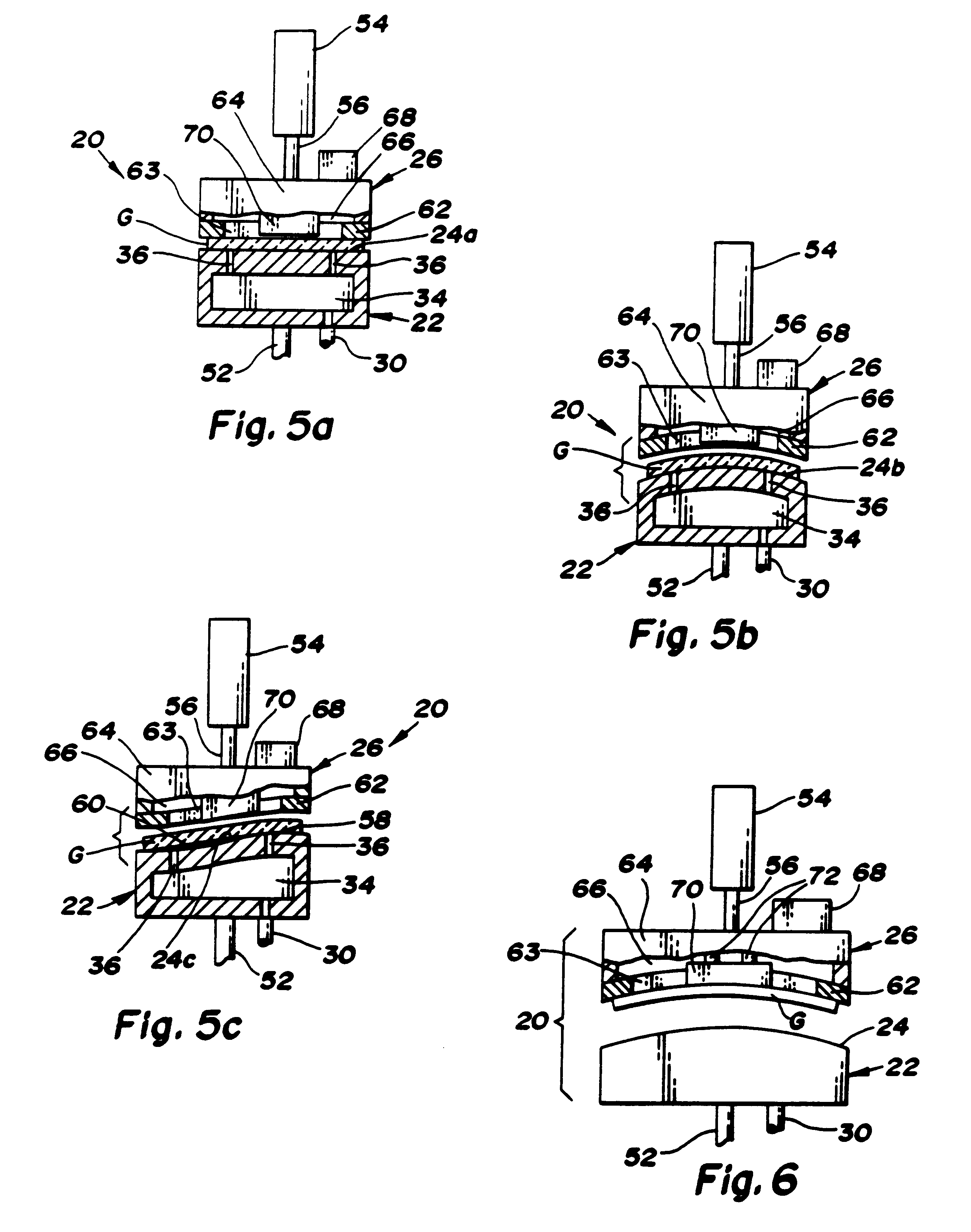
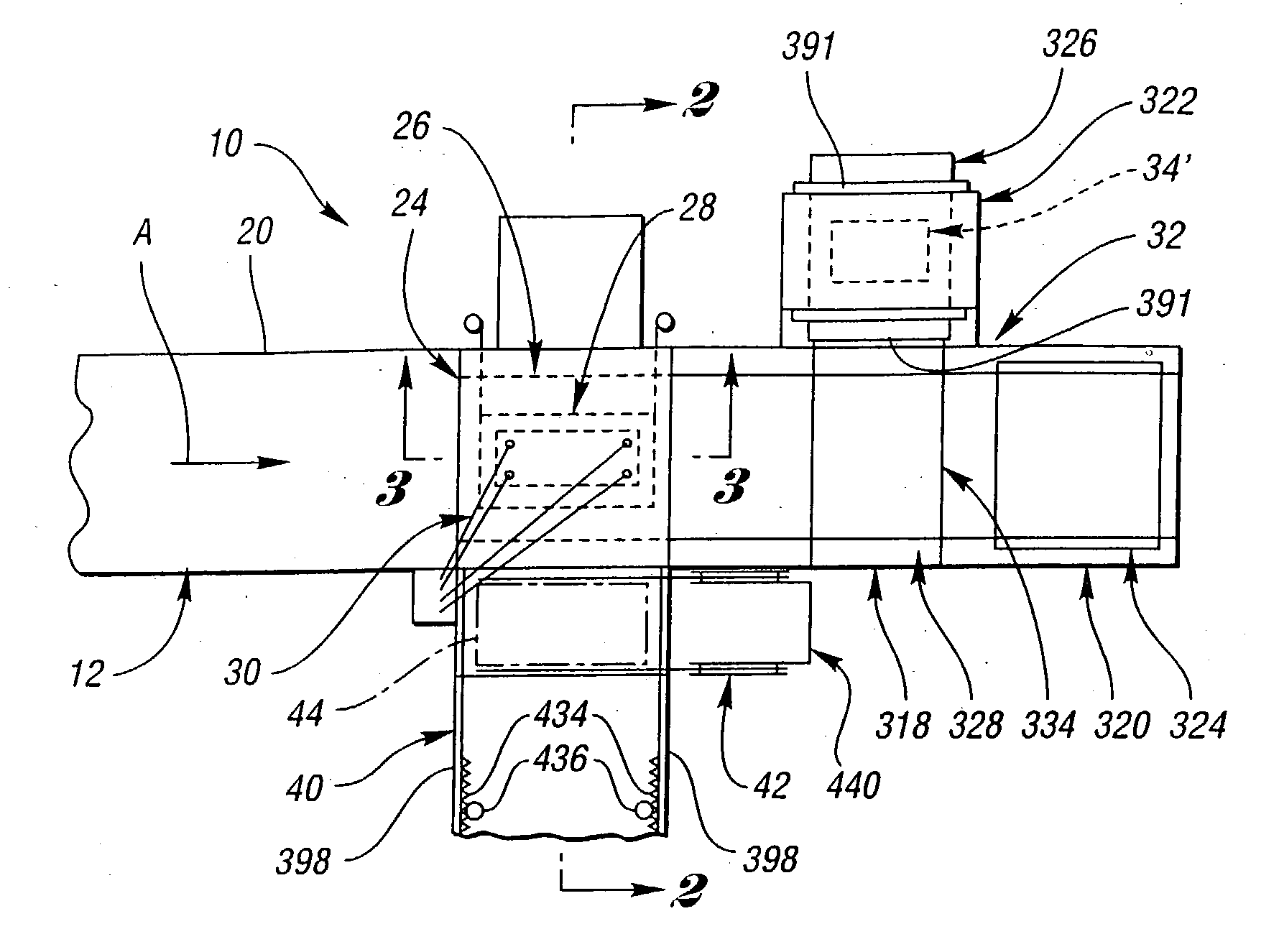
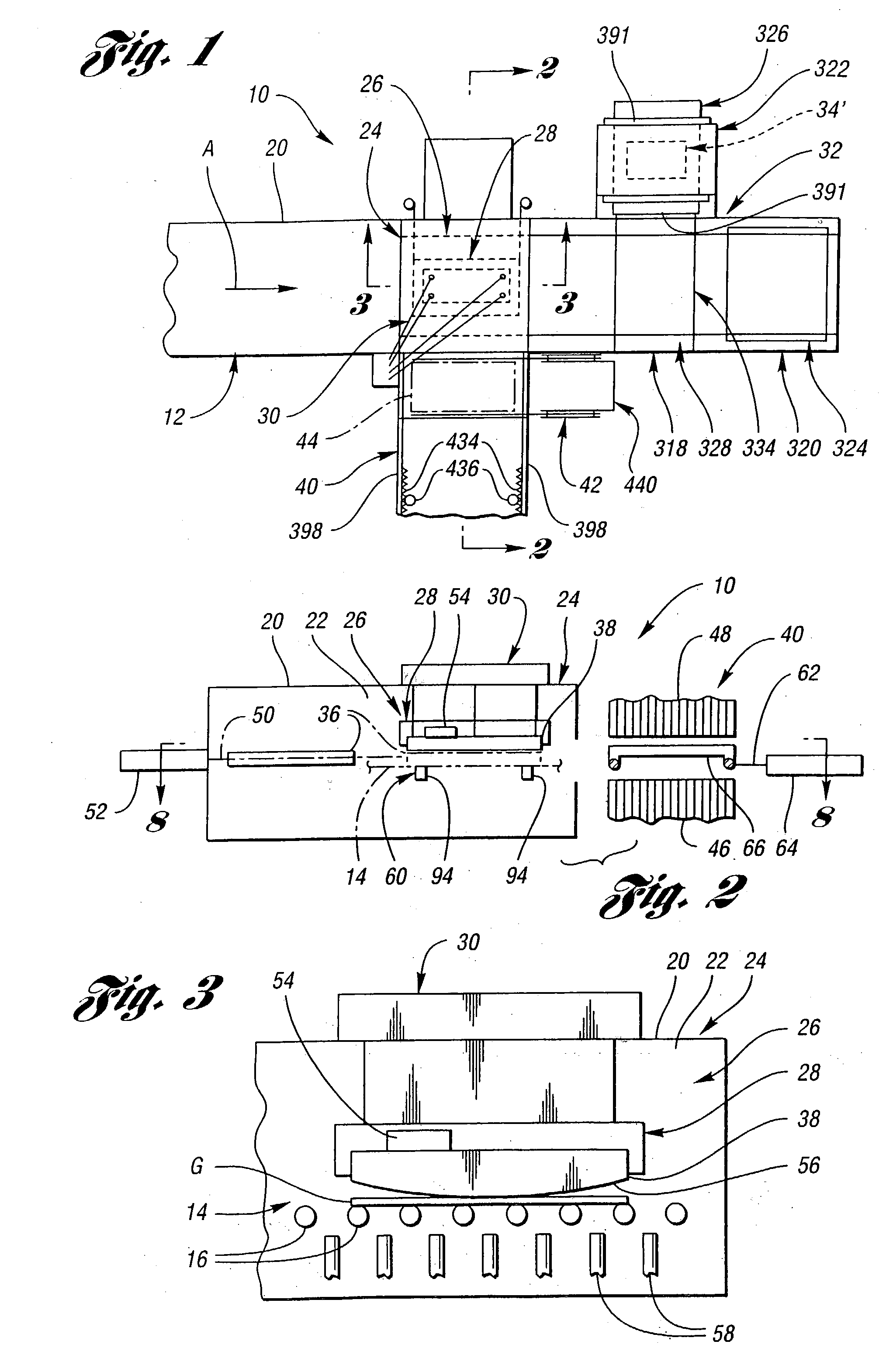
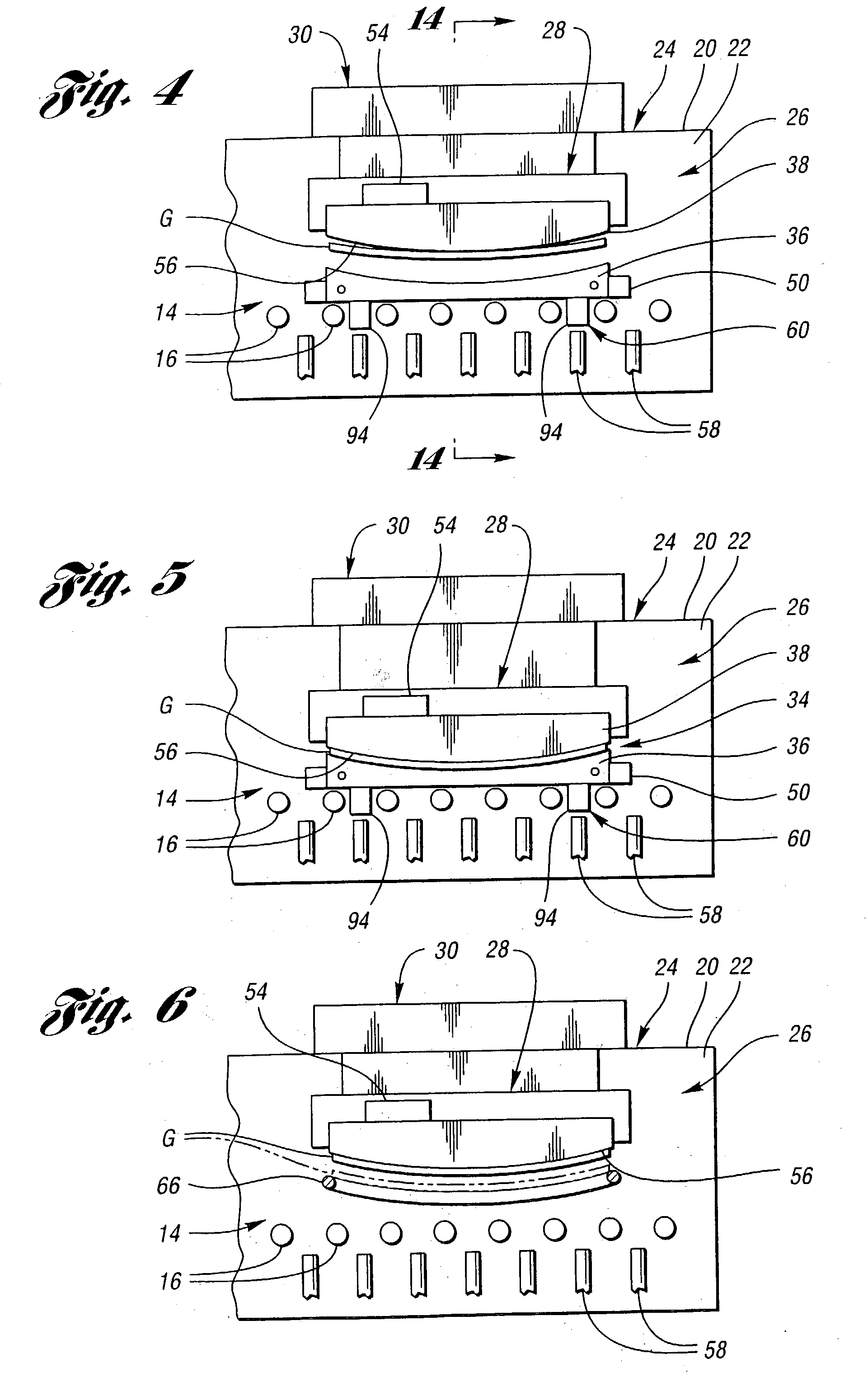
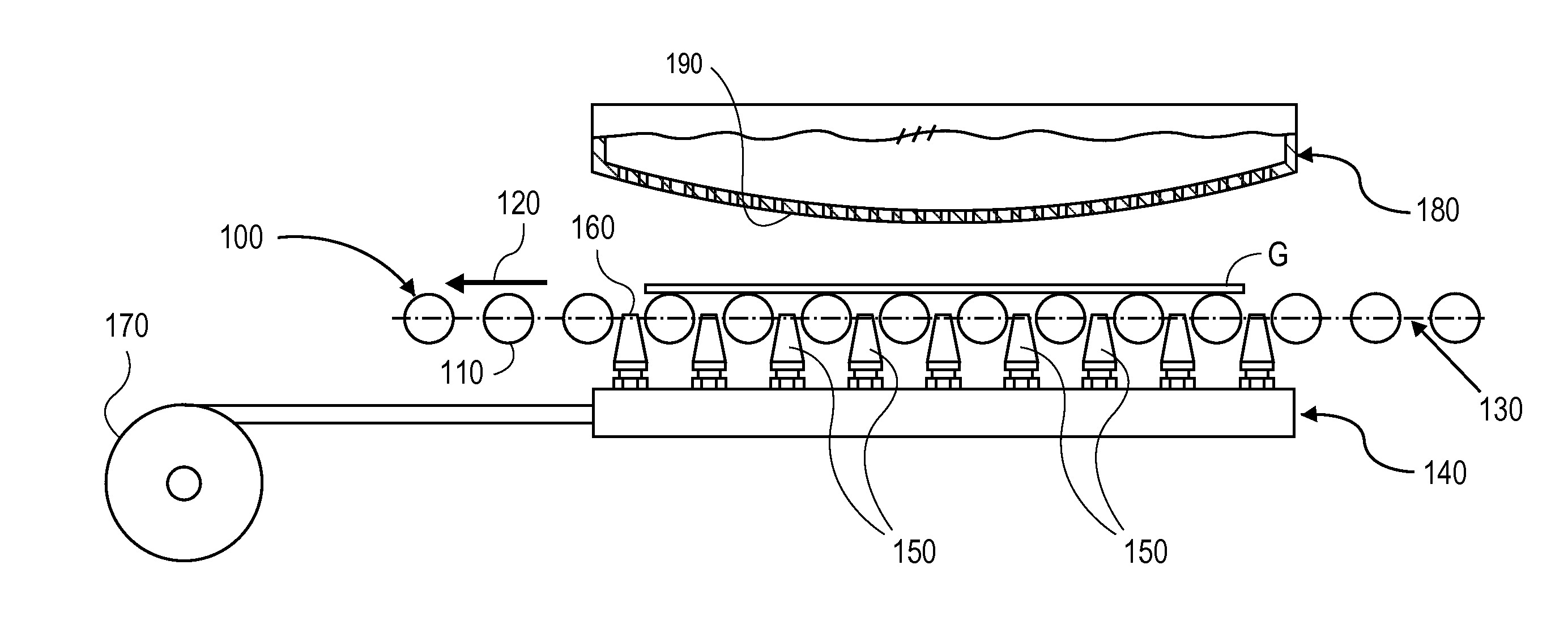
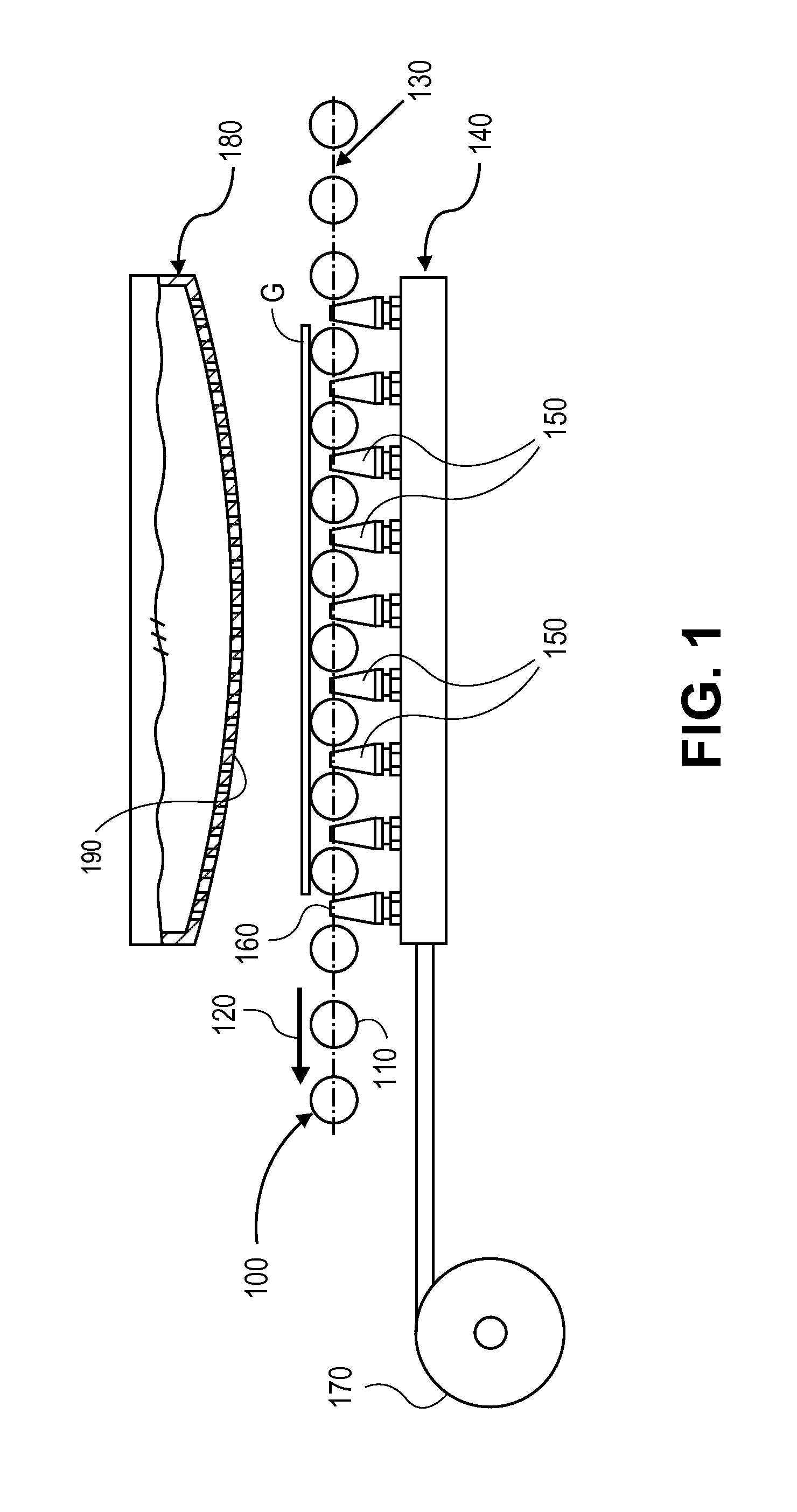
Apparatus (20,120) for forming a heated glass sheet G is disclosed as including a vacuum mold (22,22a,122,122a) having a full surface (24,24a,124,124a) against which a peripheral mold (26,26a,126,126a) presses the glass sheet periphery and with which at least one vacuum reservoir (32,33) is communicated within the interior of the sealed glass sheet periphery to form the glass sheet to the shape of the vacuum mold surface. Valving (38) of a vacuum system (28) is preferably operable to provide the vacuum impulse in two stages with an initial limited extent of vacuum and a subsequent greater extent of vacuum by communication first with one vacuum reservoir (32) and subsequently with another vacuum reservoir (33). Different embodiments of the vacuum mold have the vacuum mold surface facing upwardly and downwardly with convex and concave shapes. Glass sheet shapes including straight line elements such as cylindrical and conical bends as well as shapes including curvatures in transverse directions and inverse curvatures can be effectively provided by this vacuum impulse forming.
Owner:GLASSTECH
Reducing corrosion and particulate emission in glassmelting furnaces
ActiveUS20060150677A1Reduces alkali corrosionCharging furnaceGlass furnace apparatusParticulatesCombustion
A glassmelting furnace is heated by combustion of fuel having an atomic ratio of hydrogen to carbon of 0.9 or less.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
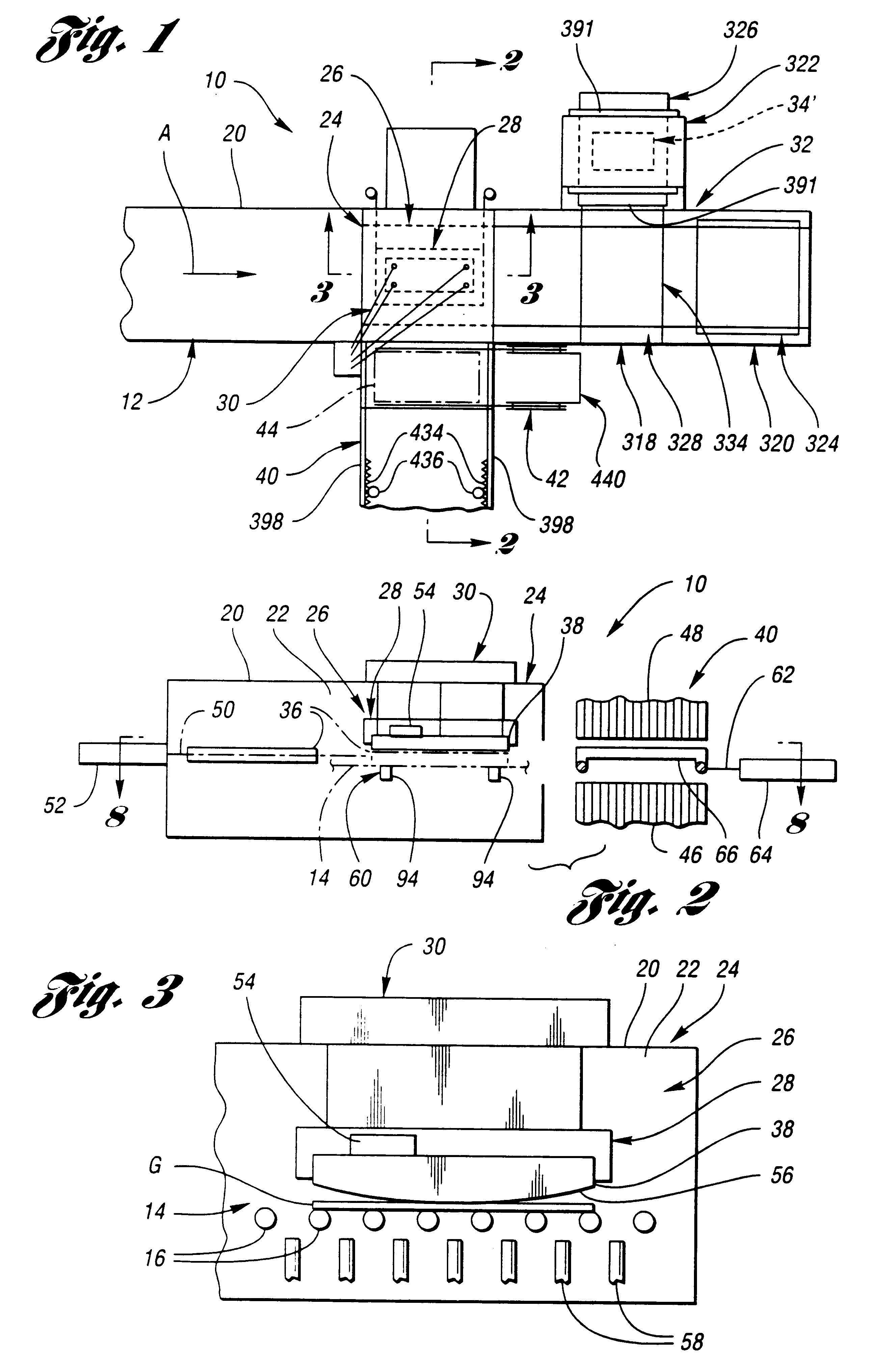
Method for forming heated glass sheets
InactiveUS20030106340A1Blowing machine gearingsGlass drawing apparatusMechanical engineeringGlass sheet
Apparatus (26) and a method for forming heated glass sheets in a heated chamber (22) of a housing (20) includes an upper mold support assembly (28) for supporting an upper mold (38) within the heated chamber for cyclical vertical movement between upper and lower positions. A lower mold shuttle (50) supports a lower mold (36) for movement between an idle position horizontally spaced from the upper mold and a use position below the lower mold. The apparatus also includes a lower mold support assembly (60) to which the lower mold is transferred from the lower mold shuttle (50) to provide support thereof while permitting horizontal alignment with the upper mold upon each cycle of downward movement to form a heated glass sheet between the molds. The lower mold shuttle (50) is supported by vertically movable rollers (70) to provide the transfer between the lower mold shuttle and the lower mold support assembly (60). A quench station (40) includes a quench shuttle (62) that moves a quench ring (66) to receive the formed glass sheet from the upper mold (38) and to then move the formed glass sheet between lower and upper quench modules (46,48) of the quench station for quenching.
Owner:GLASSTECH
Sealing Structure and Organic Electroluminescence Device
ActiveUS20140027743A1Improve air tightnessIncrease flexibilityLamination ancillary operationsElectroluminescent light sourcesFritOptoelectronics
A sealing structure with high air-tightness and an organic electroluminescence device with high air-tightness are provided regardless of a pattern of a first metal layer overlapping with glass frit. A second metal layer is provided in a region where a common power supply line overlaps with the glass frit. Since laser light is absorbed or reflected by the second metal layer, the glass frit can be uniformly heated. Therefore, an object to be sealed can be sealed with a low-melting-point glass in which a crack is not easily generated.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
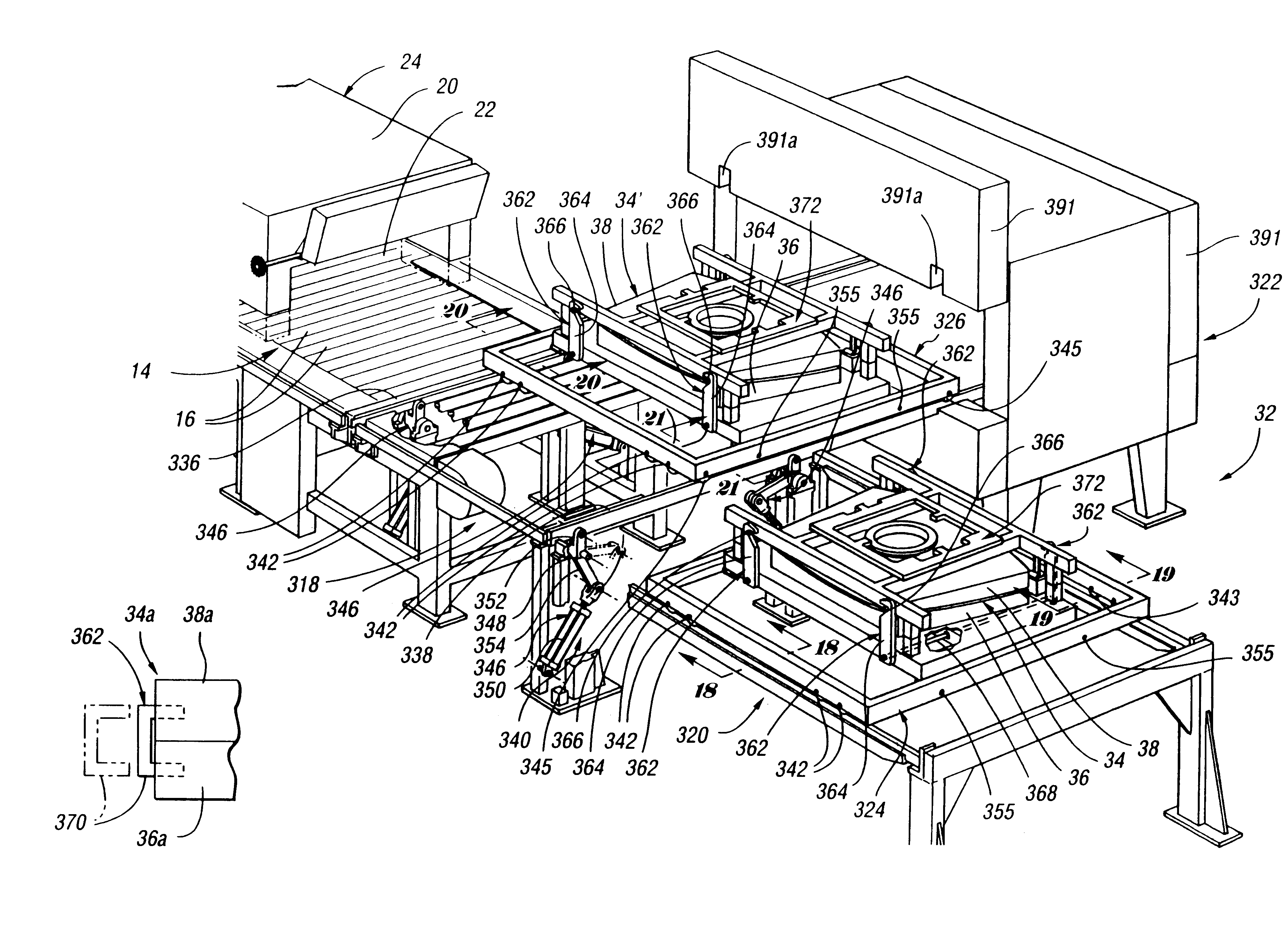
Method for installing mold assembly
InactiveUS6173587B1Simple methodBlowing machine gearingsGlass transportation apparatusGlass sheetMaterials science
A mold assembly (34) for cyclically forming heated glass sheets includes a lower mold (36) having an upwardly oriented mold face (356) and an upper mold face having a downwardly oriented mold face (56) that opposes the upwardly oriented mold face of the lower mold to form a heated glass sheet during movement of the molds toward each other. Alignment guides (122,124) align the molds (36,38) with each other as necessary during movement of the molds toward each other. Detachable connectors (362) detachably connect the molds to each other for installation and are disconnectable to permit the molds to be used for glass sheet forming. In one embodiment, the detachable connectors (362) are latches that include a latch member (364) and a keeper (366), and in another embodiment the detachable connectors are retainers (370) engageable and disengageable from the molds to provide their detachable securement. The upper mold (38) includes a support plate (372) having mounting portions (374,376) and mounting guide portions (378,380,382) for providing alignment during mounting.
Owner:GLASSTECH
Method and apparatus for a cloth heater
A cloth heater and method for using the heater are provided. The heater utilizes a horizontally disposed surface, a heated glass panel, and support members. The horizontally disposed surface may comprise the top edge or surface of the heated glass panel, or a surface on a separate rack that is above and vertically inline with the top edge of the heated glass panel. The heated glass panel also has two opposing major surfaces. The support members physically support the heated glass panel and have electrical leads that communicate electrical power to the heated glass panel, thus heating the heated glass panel. When a cloth is placed across the horizontally disposed surface, the horizontally disposed surface supports the cloth, and the cloth makes contact with the two opposing major surfaces of the heated glass panel, thus heating the cloth at both opposing major surfaces.
Owner:ENGINEERED GLASS PRODS
Method and lift jet floatation system for shaping thin glass
InactiveUS20150274571A1Glass transportation apparatusGlass reforming apparatusEngineeringGlass sheet
Disclosed herein are systems for shaping a glass sheet comprising a roll conveyor comprising a plurality of rollers for conveying the glass sheet along a plane; a lift jet array comprising a plurality of nozzles, one or more of the plurality of nozzles comprising a tip having a plurality of orifices; and a shaping mold located above the roll conveyor, wherein the lift jet array is positioned below the roll conveyor such that each nozzle tip is located above the centerline of the plurality of rollers. Also disclosed herein are methods for shaping a glass sheet comprising heating the glass sheet and conveying the glass sheet on a roll conveyor to a position between the lift jet array and the shaping mold, wherein gas flows from the lift jet array with a force sufficient to lift the glass sheet from the roll conveyor.
Owner:CORNING INC
Method of molding glass parts, molding apparatus, and molded product of glass material
InactiveUS20100112341A1Good effectElectric discharge heatingGlass drawing apparatusShell moldingMetal
In order to solve problems involved in micromolding of a glass, according to the present invention, there can be provided a technology for enabling molding of a glass without applying a large load.A molding apparatus of a glass material according to the present invention is characterized by containing means for holding a glass material and a molding die in contact with each other, means for heating the glass material and the molding die, and means for applying a voltage across the glass material and the molding die, in which press-molding is performed by electrostatic attraction acting between a surface of the glass material and a surface of the molding die. Further, a molded product of a glass material according to the present invention is characterized by including an alkali metal as a component, in which a concentration of the alkali metal is lowered in vicinity of a surface to be molded as compared with that of a glass base material.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
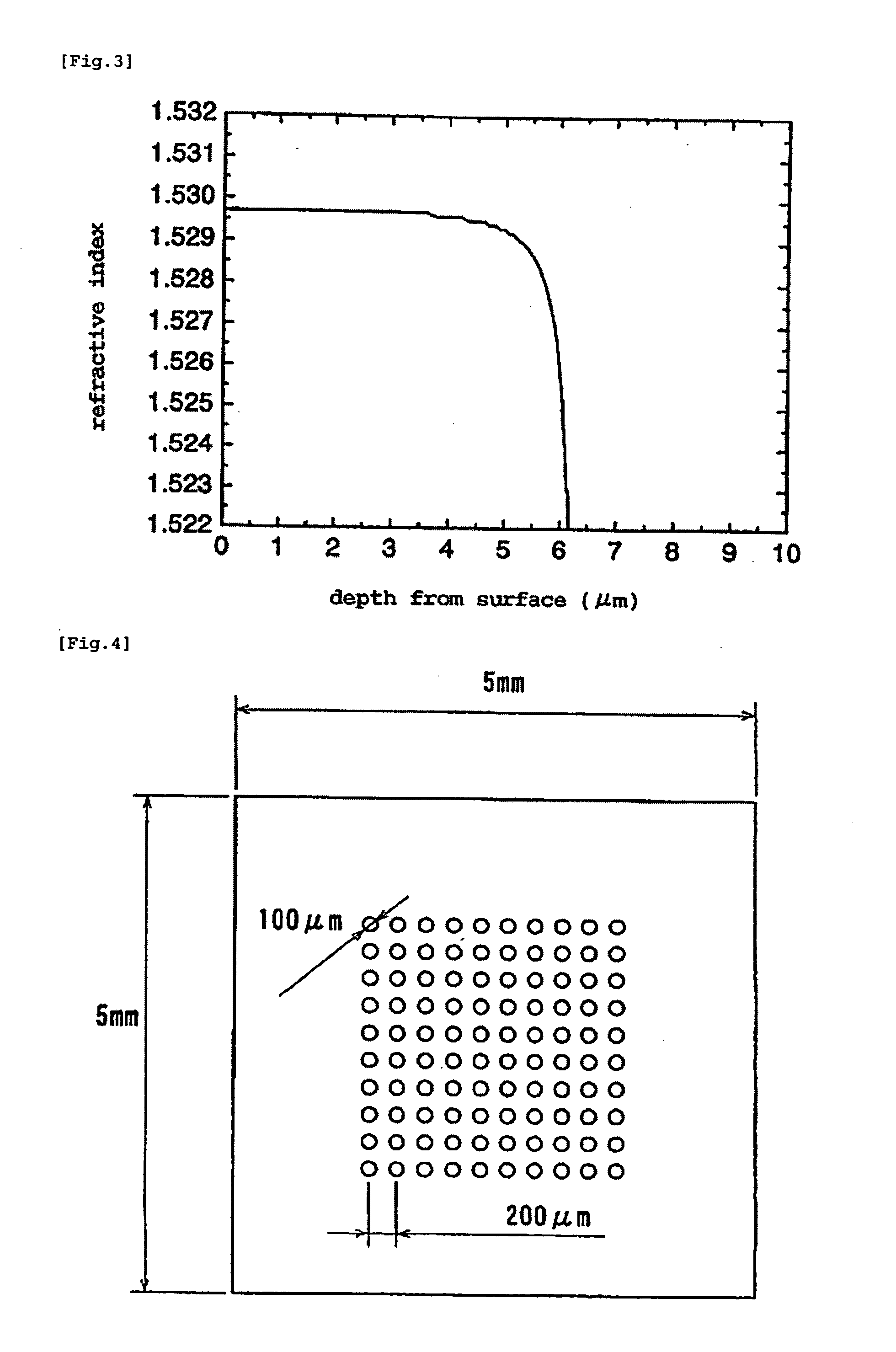
Method for Manufacturing Gradient-Index Optical Element Having Infrared Absorbing Ability
InactiveUS20100165454A1Low costProductionElectrostatic spraying apparatusCoatingsRubidium compoundGradient-index optics
A method of readily producing a gradient optical element having infrared absorbing ability by easily forming a refractive index distribution in a desired portion of a glass substrate having infrared absorbing ability without requiring a specific treatment atmosphere nor using a molten salt.More specifically, the present invention provides a method for producing a gradient-index optical element having infrared absorbing ability, the method comprising applying a paste containing an organic resin, an organic solvent, and at least one compound selected from the group consisting of lithium compounds, potassium compounds, rubidium compounds, cesium compounds, silver compounds, copper compounds, and thallium compounds onto a glass substrate containing an alkali metal component, at least one member selected from the group consisting of iron, copper, cobalt and vanadium, and over 3 wt. % of iron, when contained singly among iron, copper, cobalt and vanadium, on an Fe2O3 basis, taking the total weight of the glass as 100 wt. %, and heating the glass substrate at a temperature below the softening temperature of the glass substrate.
Owner:ISUZU GLASS +1
Apparatus and method for bending and/or tempering glass
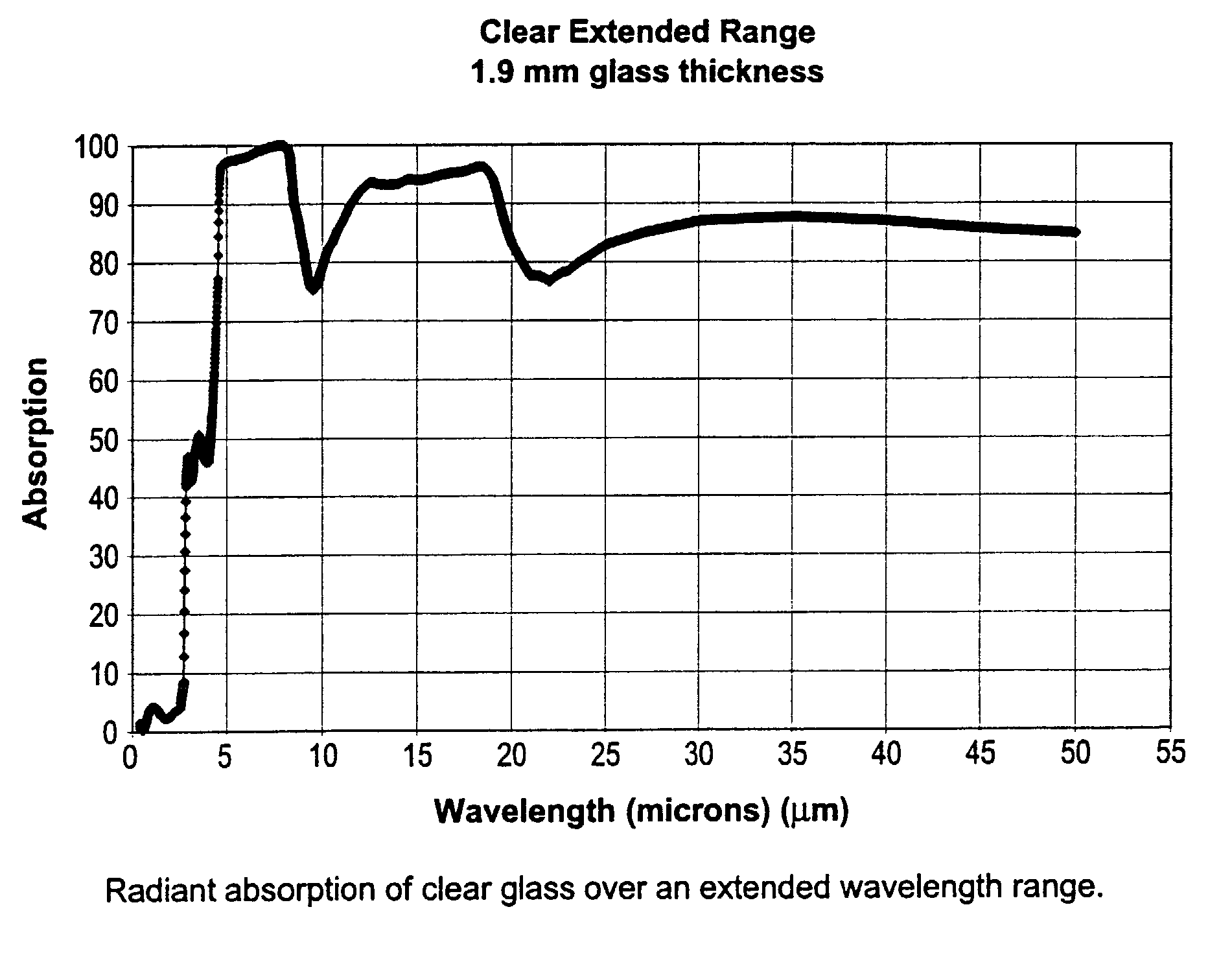
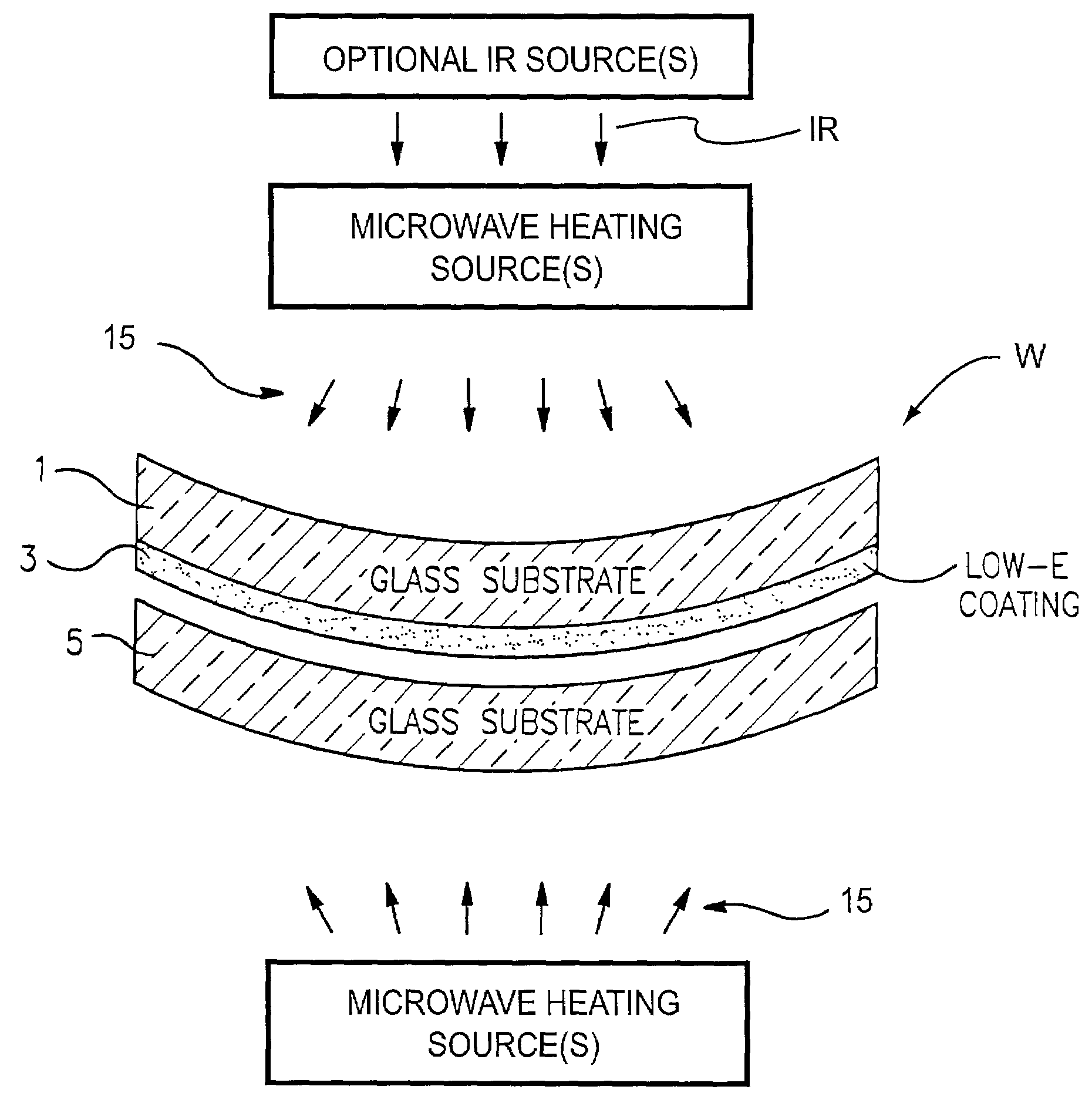
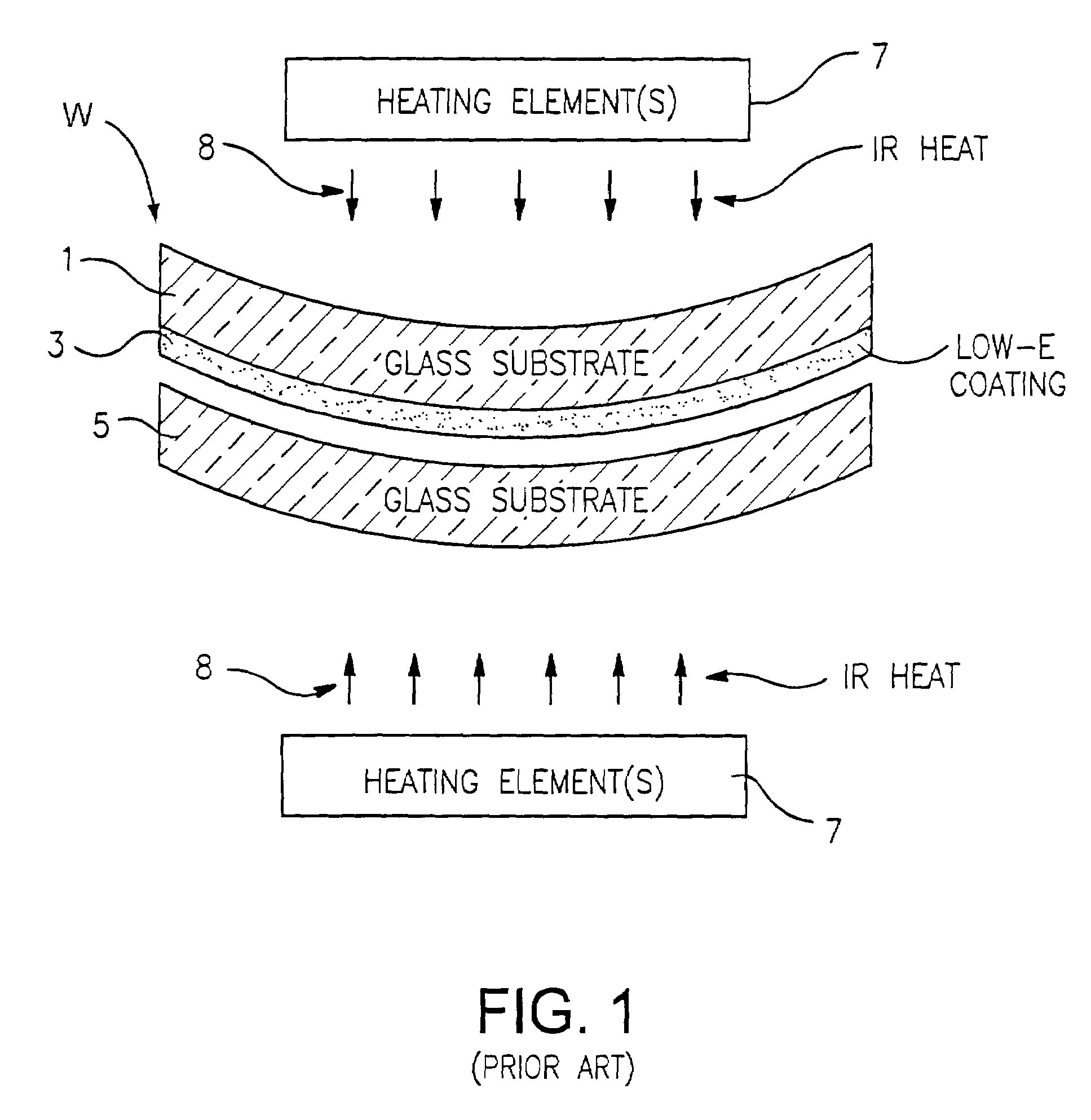
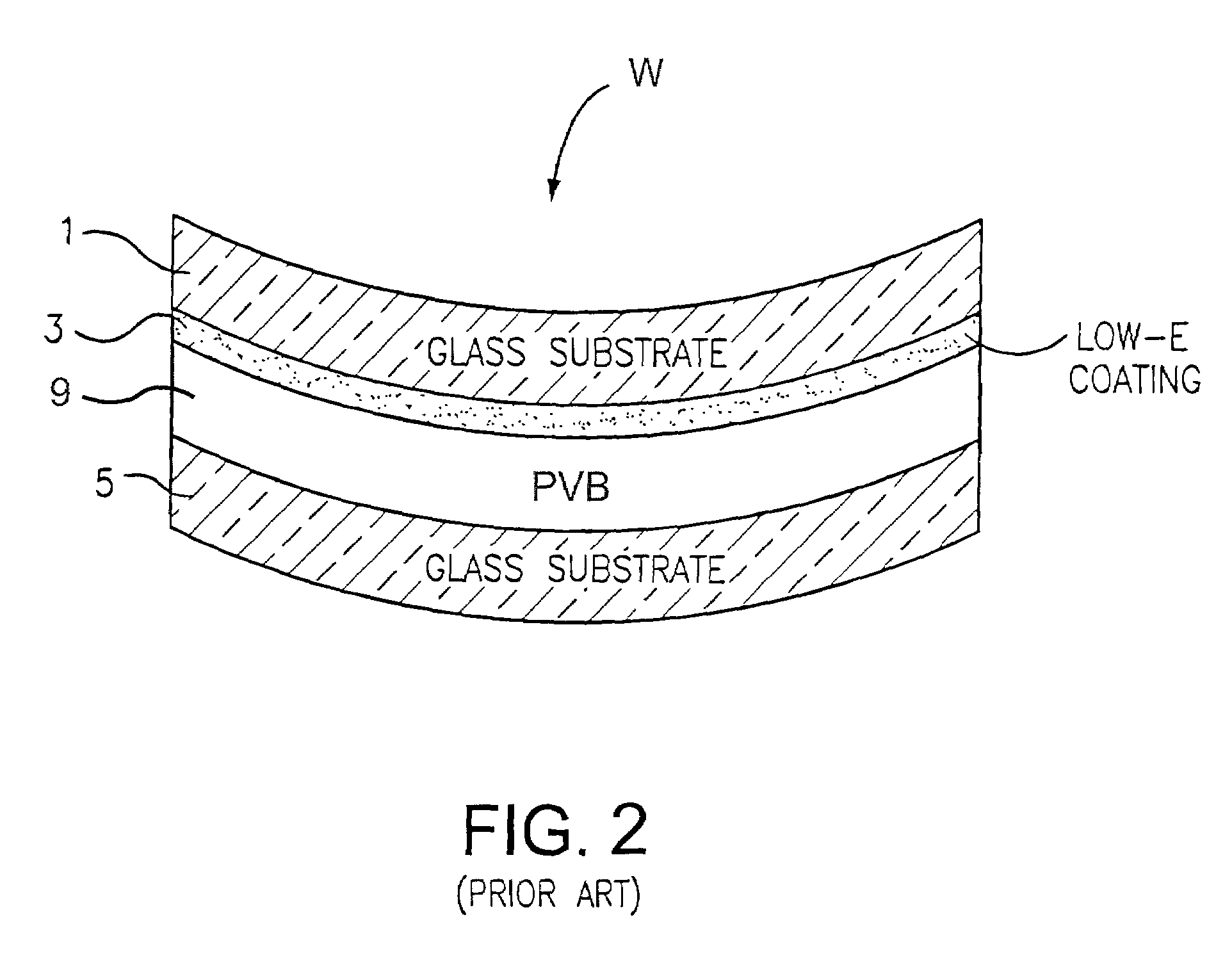
An apparatus and method for bending and / or tempering glass substrate(s) are provided. The amount of near-IR radiation which reaches the glass to be bent and / or tempered is limited (e.g., via filtering or any other suitable technique). Thus, the IR radiation (used for heating the glass) which reaches the glass to be bent and / or tempered includes mostly mid-IR and / or far-IR radiation, and not much near-IR. In such a manner, coating(s) provided on the glass can be protected and kept at lower temperatures so as to be less likely to be damaged during the bending and / or tempering process. Heating efficiency can be improved. A ceramic (e.g., aluminosilicate) filter or baffle may be used in certain embodiments in order to reduce the amount of mid-IR and / or far-IR radiation reaching the glass to be tempered and / or bent.
Owner:GUARDIAN EURO S A R L +1
Machining of fusion-drawn glass laminate structures containing a photomachinable layer
ActiveUS9340451B2Glass forming apparatusPhotosensitive material processingGlass structureCrystallization
Methods for machining glass structures may be performed on fusion-drawn glass laminates having a core layer interposed between a first cladding layer and a second cladding layer. The core layer may be formed from a core glass composition having a core photosensitivity, the first cladding layer may be formed from a glass composition having a photosensitivity different from the core photosensitivity, and the second cladding layer may be formed from a glass composition having a photosensitivity different from the core photosensitivity. At least one of the core layer, the first cladding layer, and the second cladding layer is a photomachinable layer. The methods may include exposing a selected region of a photomachinable layer in the fusion-drawn laminate to ultraviolet radiation; heating the glass structure until the selected region crystallizes; and removing the crystallized material selectively from the photomachinable layer.
Owner:CORNING INC
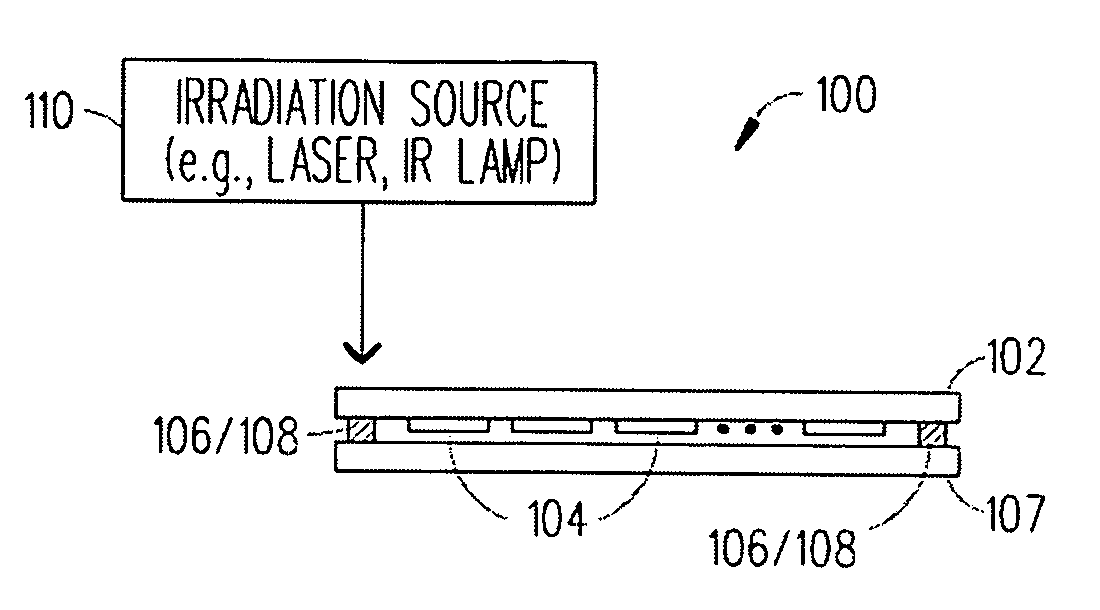
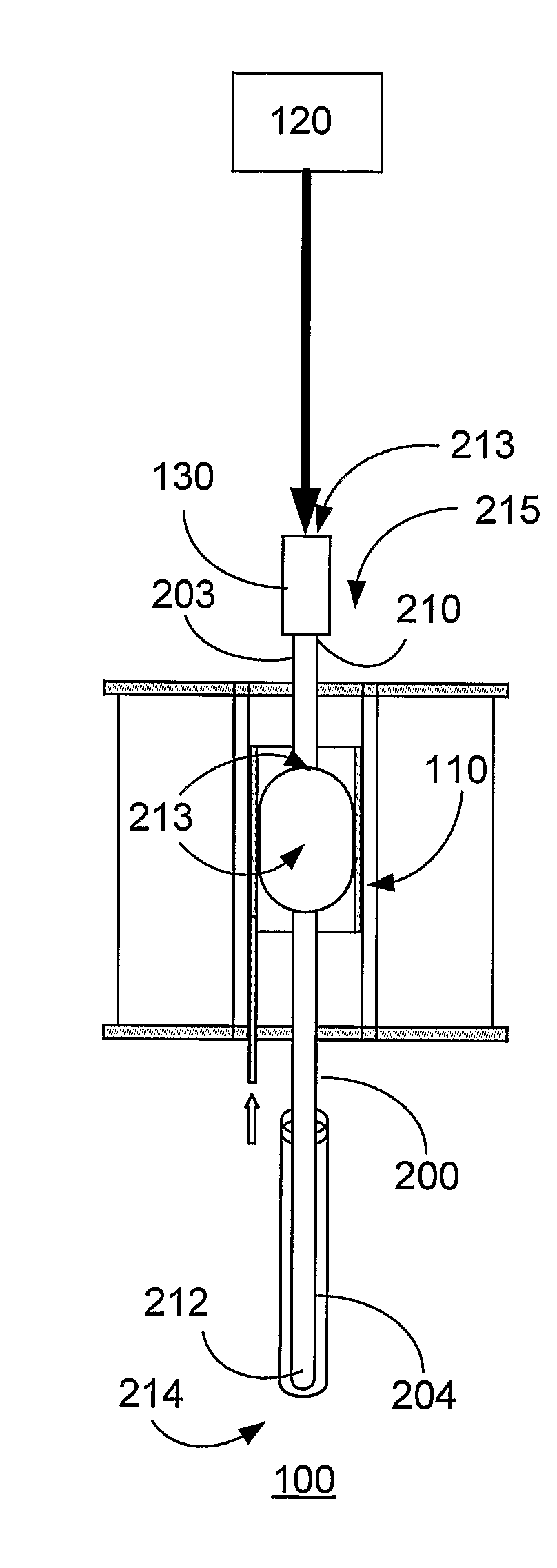
Method and device for the homogenous heating of glass and/or glass-ceramic articles using infrared radiation
InactiveUS7017370B1Quality improvementImprove overall utilizationElectric discharge heatingTank furnacesGlass-ceramicHeat treating
A method for the homogeneous heating of semitransparent and / or transparent glass and / or glass-ceramic articles using infrared radiation so that the glass and / or glass-ceramic articles undergo heat treatment at between 20 and 3000° C., notably at between 20 and 1705° C. Heating is achieved by a component of infrared radiation which acts directly on the glass and / or glass-ceramic articles and by a component of infrared radiation which acts indirectly on said glass and / or glass-ceramic articles. The radiation component indirectly acting on the glass and / or glass-ceramic articles accounts for more than 50% of total radiation output.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Heat treatment apparatus and heat treatment method of substrate
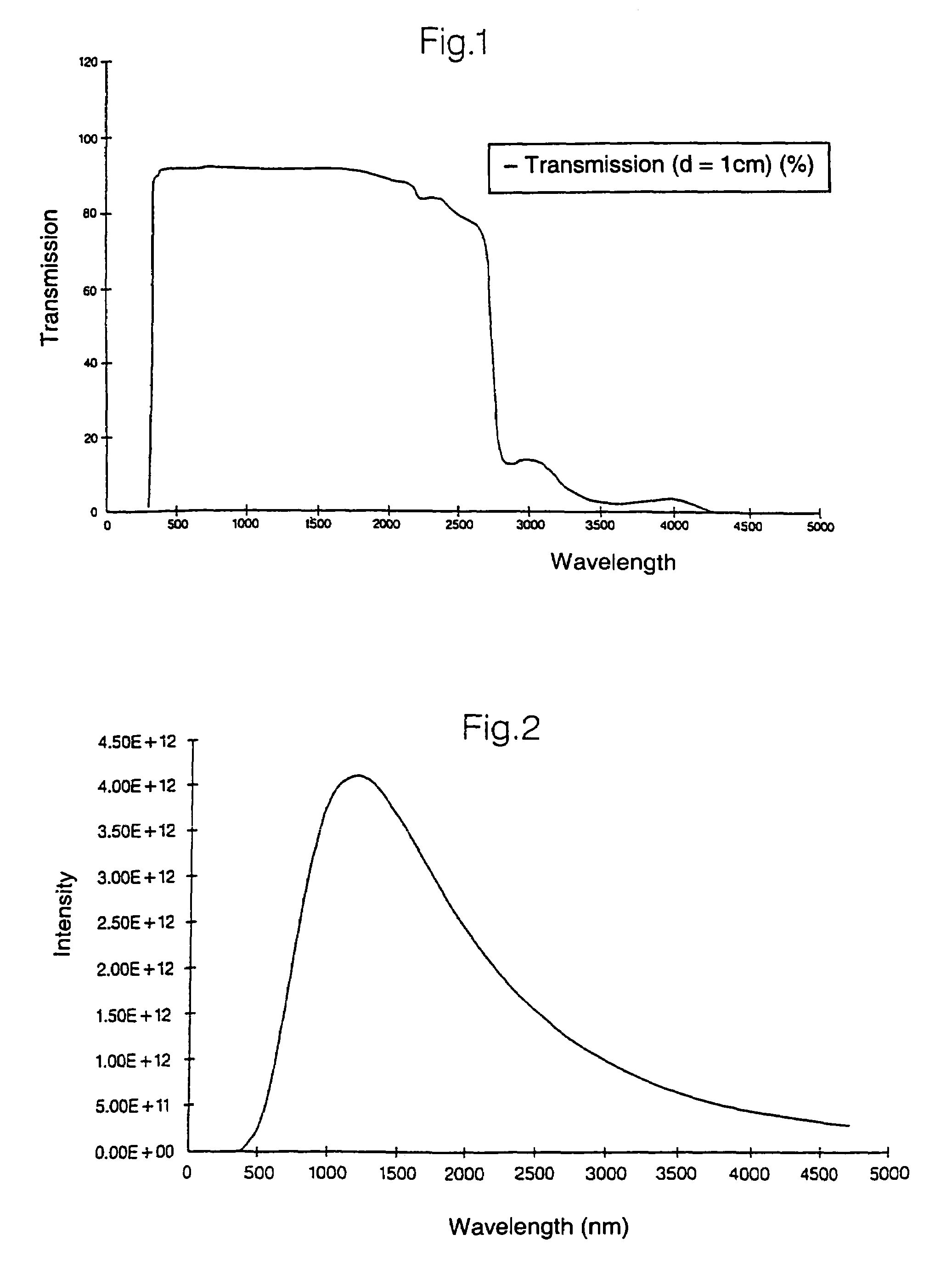
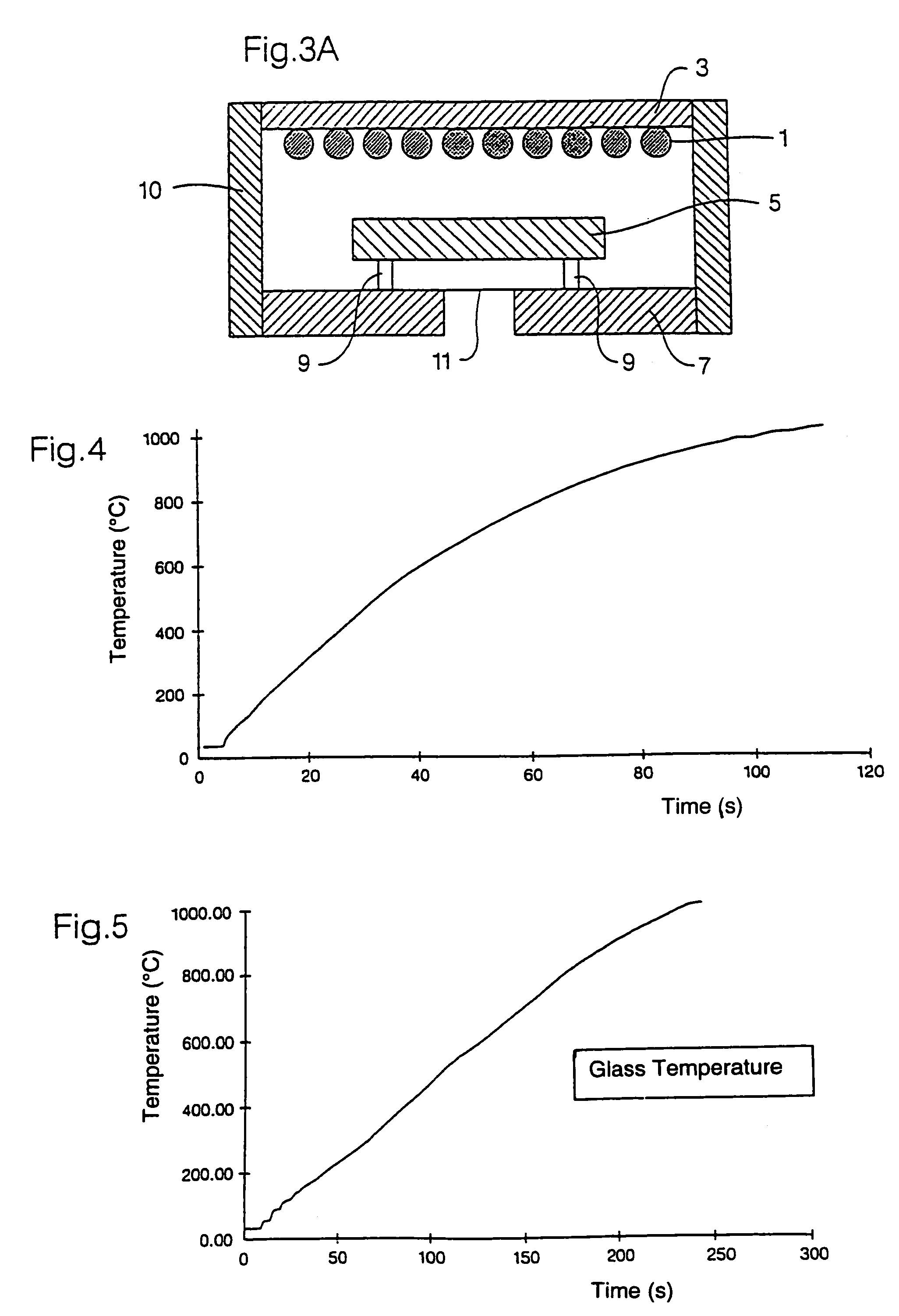
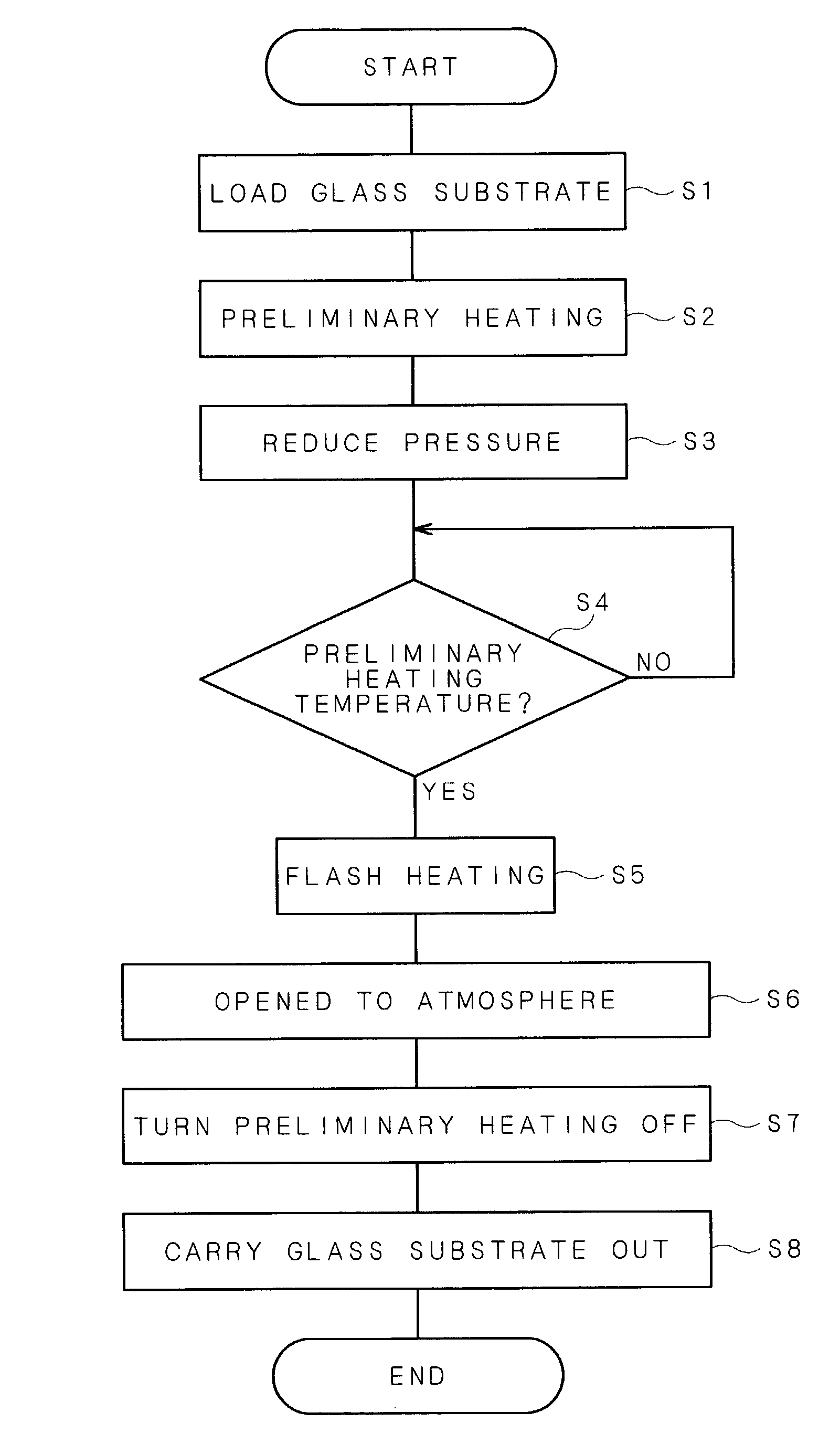
ActiveUS7255899B2Well formedExcellent characteristicsBlowing machine gearingsGlass furnace apparatusAmorphous siliconIrradiation
A heat diffusion plate and a heating plate are placed in a heat treatment chamber in this order. The heating plate is used for preliminarily heating a glass substrate to a temperature in a range from 200° C. to 400° C. The glass substrate thus preliminarily heated is subjected to a heat treatment by flash light irradiation by a xenon flash lamp. The flash light irradiation makes it possible to uniformly heat an amorphous silicon film on the glass substrate, and consequently to be poly-crystallized. Thus, it becomes possible to provide a heat treatment technique capable of carrying out a uniform heat treatment on the silicon film on the glass substrate sufficiently.
Owner:DAINIPPON SCREEN MTG CO LTD
Method of producing glass products from glass product material and an assembly for performing said method
ActiveUS20140174127A1Eliminate the effects ofBlowing machine gearingsGlass furnace apparatusMaterials scienceRadiation
The invention is related to a method of producing glass products from glass product material. Said method comprises the steps of heating the glass product material, shaping the heated glass product material into a glass product, cooling the shaped glass product, and inspecting the shaped glass products by means of at least one sensor sensitive to infrared radiation In said inspecting step a first image of the glass product is taken under a first viewing angle. In addition a second image of said glass product is taken under a second viewing angle which is different from the first viewing angle. The first image is compared with the second image for eliminating parasite reflections. The first and second images are analyzed for detecting whether said glass product is defective or not. An assembly is described for performing said method of producing glass products from glass product material.
Owner:CENT VOOR TECHN INFORMATICA
Apparatus and method for bending glass using microwaves
ActiveUS7140204B2Reduce the amount requiredGlass/slag layered productsGlass reforming apparatusEngineeringMicrowave irradiation
An apparatus and method for bending glass substrate(s) are provided. Microwave radiation is used to heat glass substrate(s) for bending. As a result, a coating supported by the substrate(s) is not heated as much during the bending process compared to if only conventional IR radiation was used. Thus, more extreme degrees of glass bending may be achieved, and / or the likelihood of coating damage reduced.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
Ultra Thin Glass Drawing and Blowing
InactiveUS20100107694A1Large thin sheet widthReduce widthRibbon machinesGlass drawing apparatusAir bearingDisplay device
Systems, methods, apparatus and products relate to drawing and blowing of ultra thin glass substrates, such as flexible display glass sheets, for example, organic light emitting diode (OLED) displays, liquid crystal displays (LCDs), and / or other flexible substrate applications, such as lighting, and / or other technologies, such as electro-wetting (EW), electro-phoretic display applications, etc. A localized heat source centripetally heats a vertical glass pre-form, while a pressurized air source blows the heated glass to expansion. An air bearing may centripetally blow air against the expanding pre-form to limit expansion and prevent contact of the pre-form with the localized heat source. Meanwhile, the pre-form is pulled vertically to draw the heated glass. The pre-form may float in a floatation mechanism to compensate for gravity when the pre-form is pulled upward. The blown and drawn pre-form may be cooled, coated with a polymer layer, and cut into a ribbon by in-line devices as it exits the air bearing. For example, a laser may helicoidally cut a polymer-coated blown and drawn pre-form into a ribbon, which may be rolled for collection.
Owner:CORNING INC
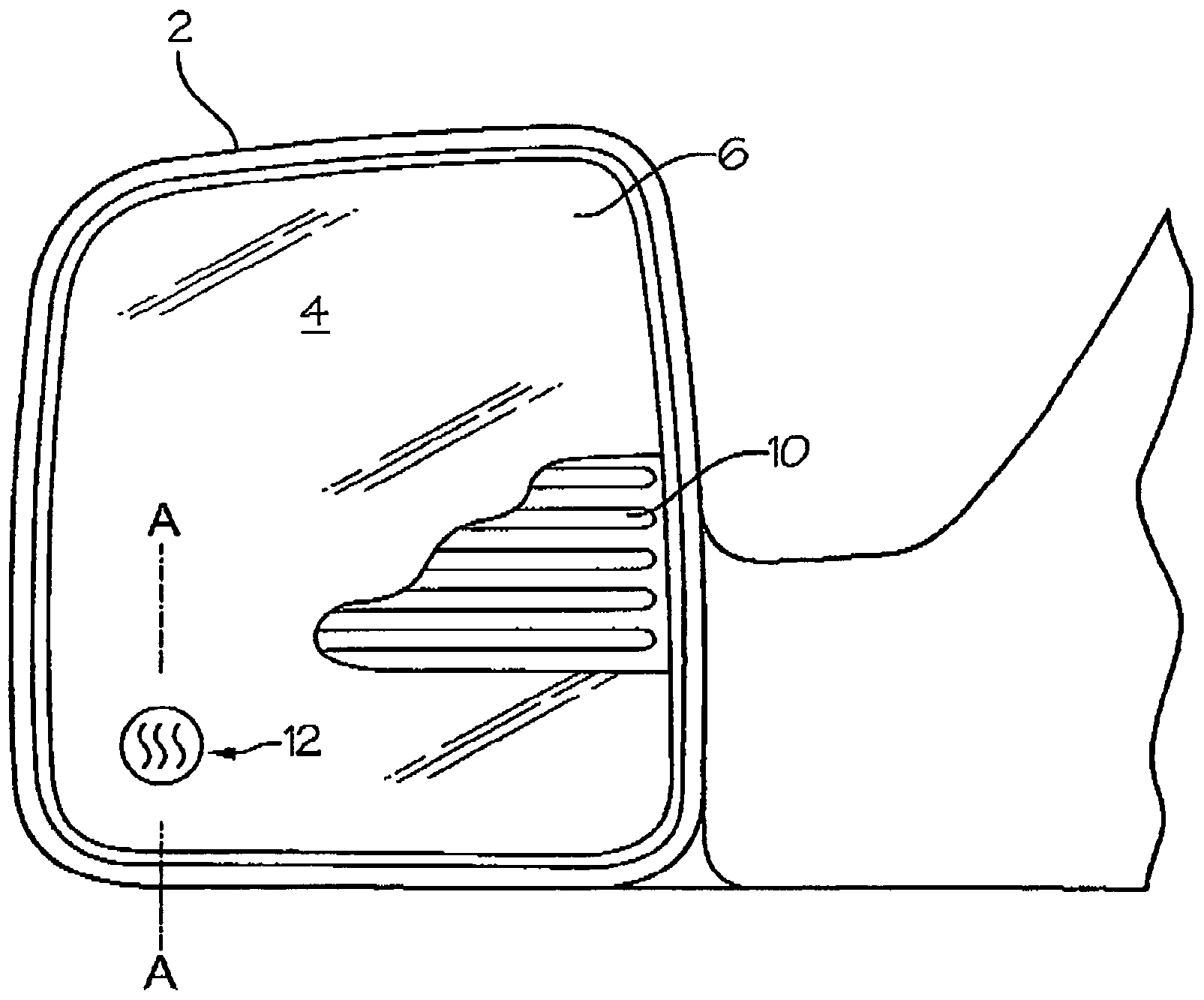
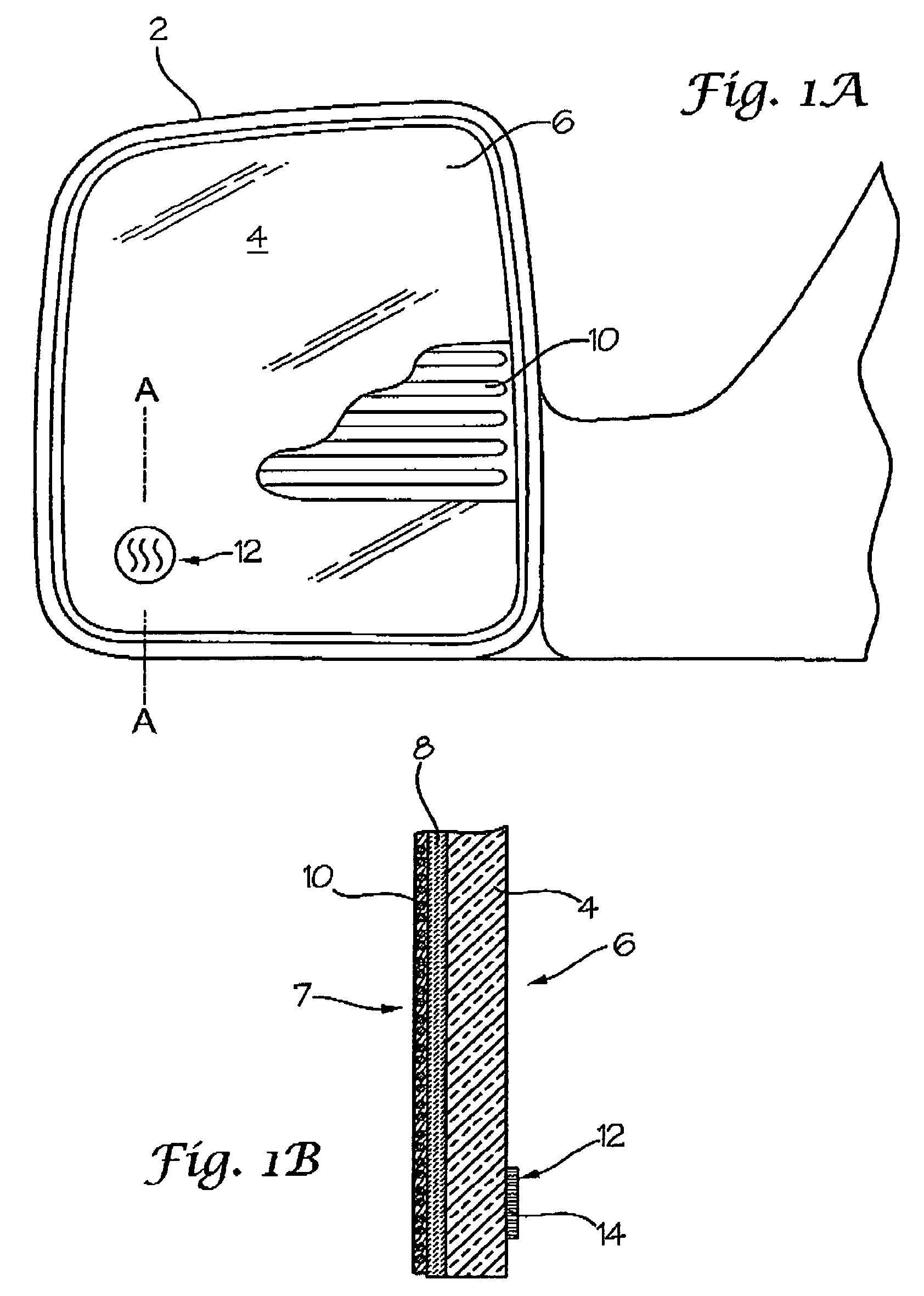
Heatable external mirror for motor vehicles
InactiveUS7230207B2Expanded indicationsOhmic-resistance heatingPower to electric heating circuitsMobile vehicleHeat conducting
A heatable external rearview mirror including a mirror housing for attachment to the vehicle and a mirror pane with a reflecting surface carried in the housing. A heating element is located adjacent the mirror pane for heating the pane to remove precipitation. A thermochromic heating indicator is provided in heat conducting contact with at least one of the heating element and the mirror pane that reacts to temperature changes for detecting heating of the mirror pane by the heating element and providing a visual indication of the operation of the heating element.
Owner:LANG MEKRA NORTH AMERICA LLC
Electrically heatable glass pane, method for production of same and window
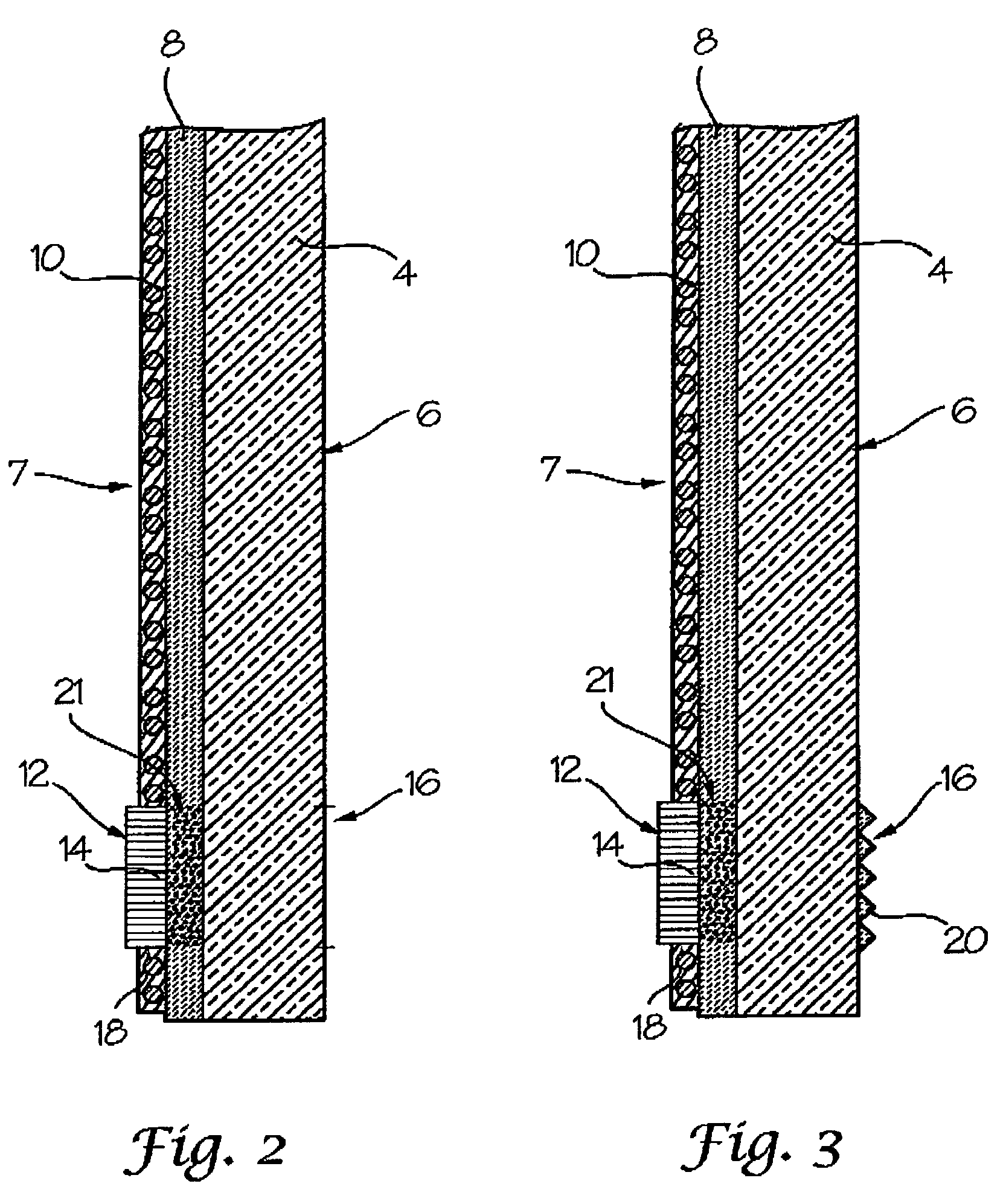
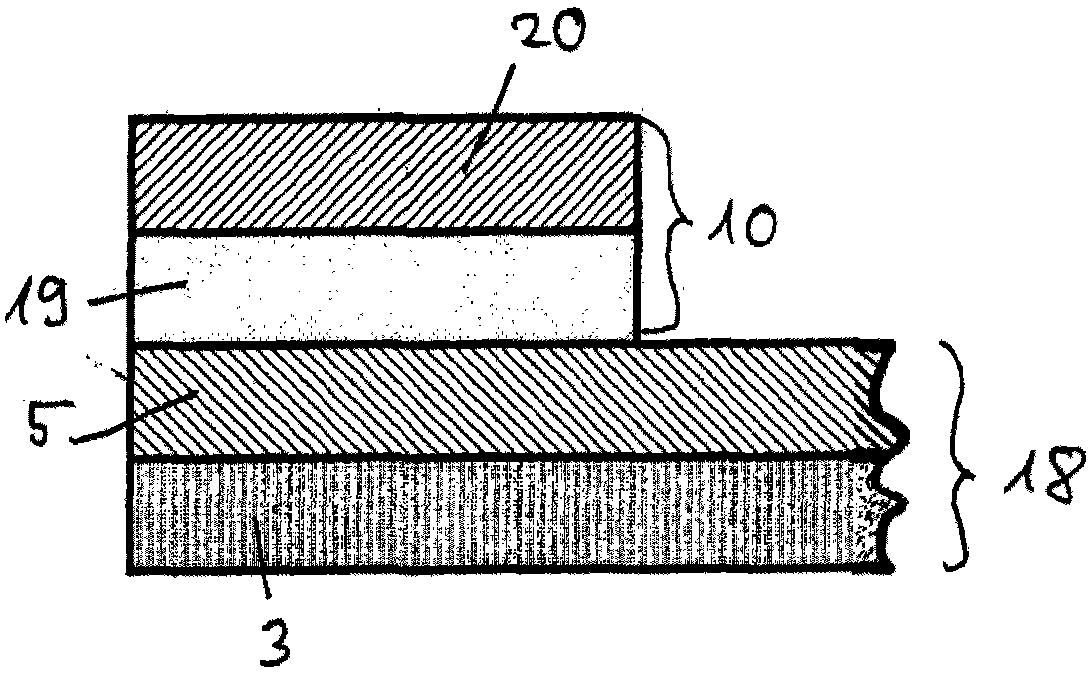
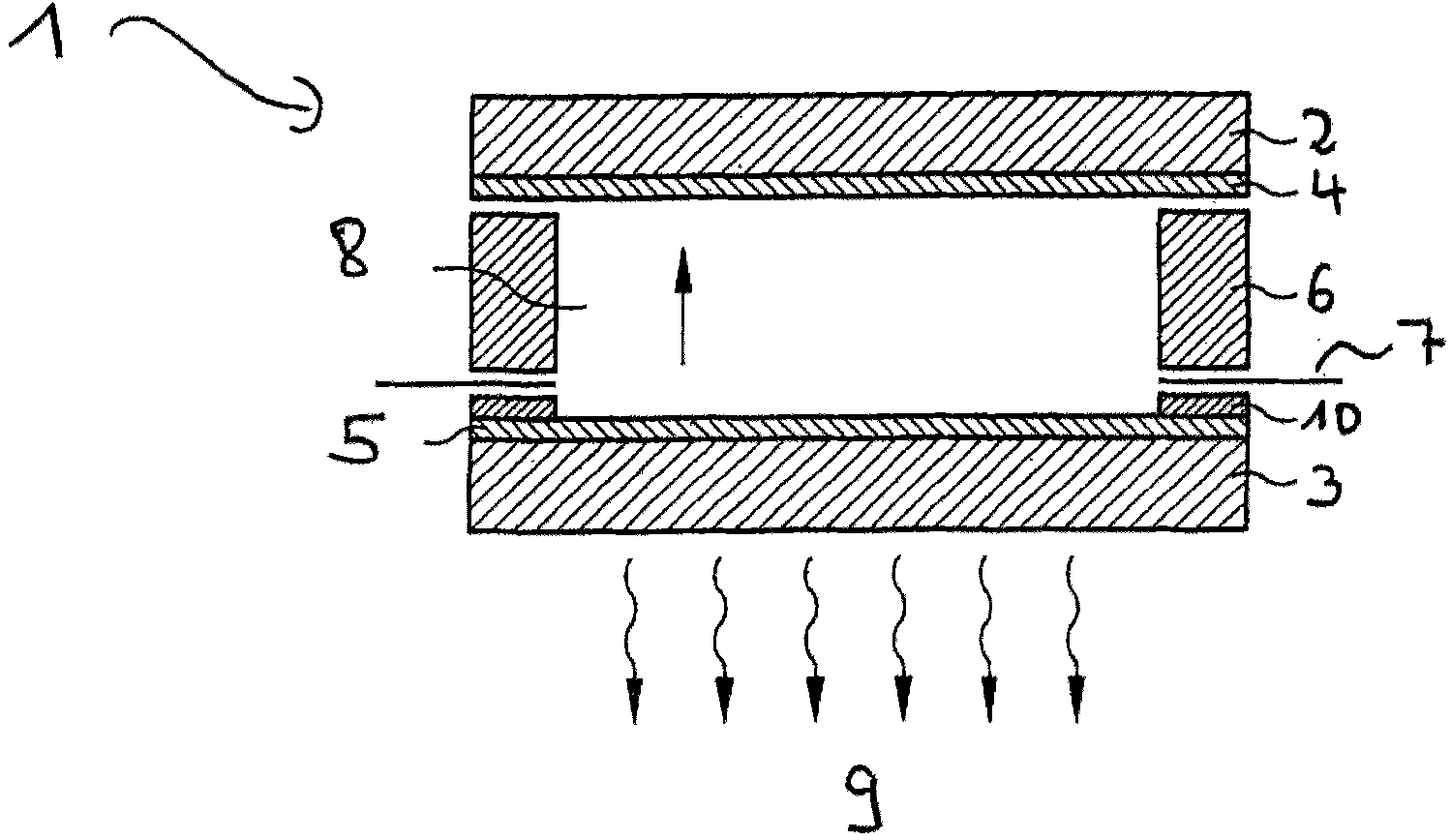
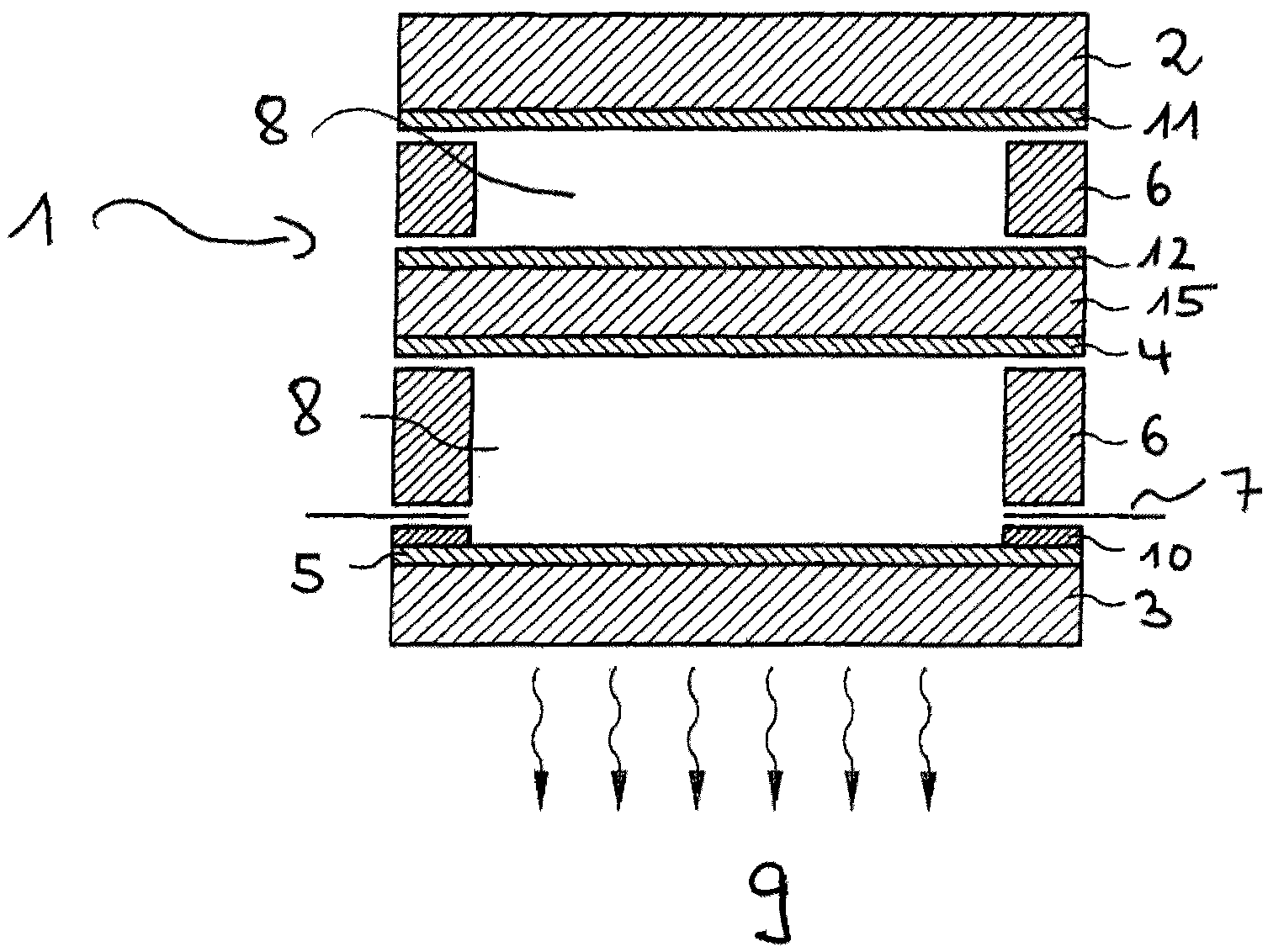
The invention relates to an electrically heatable sheet of glass (10), including at least one electrically conductive coating applied on at least one side of the sheet of glass and also to at least one contacting applied at least in regions on the coating, the contacting being configured as a spray coating.
Owner:THERM IC PRODS NFG
Method for preparing single layer glass by glass tube
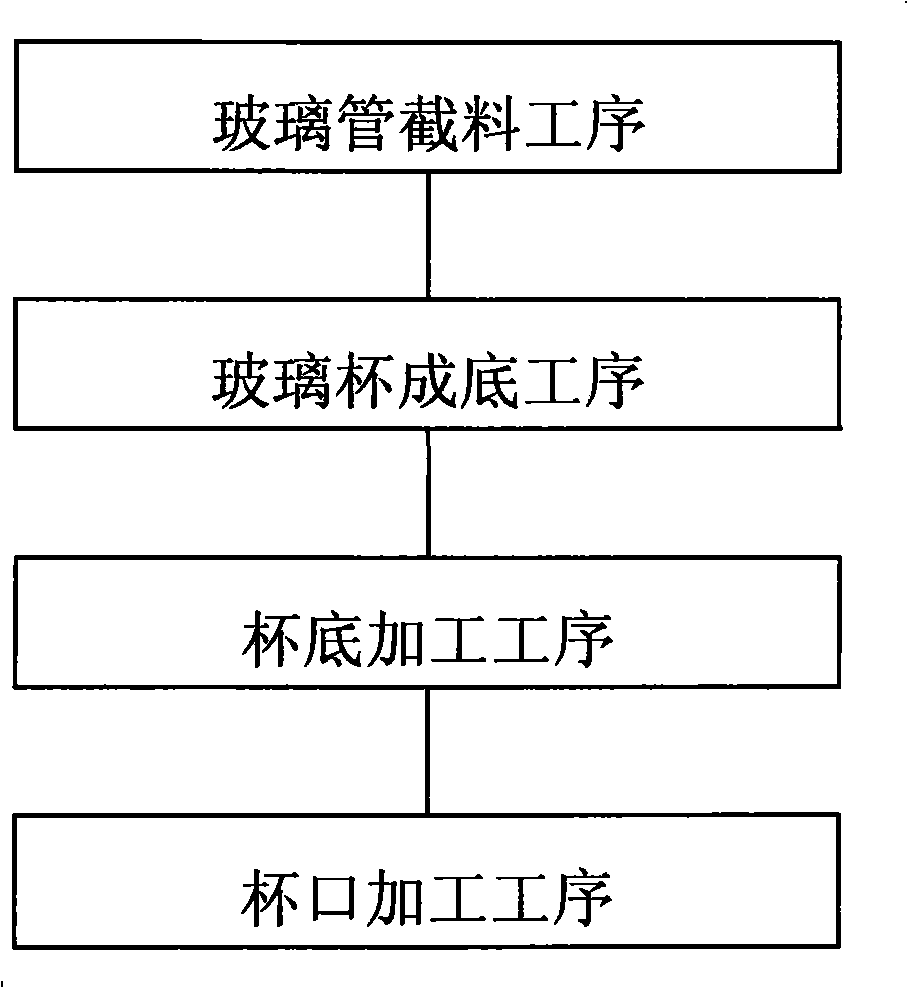
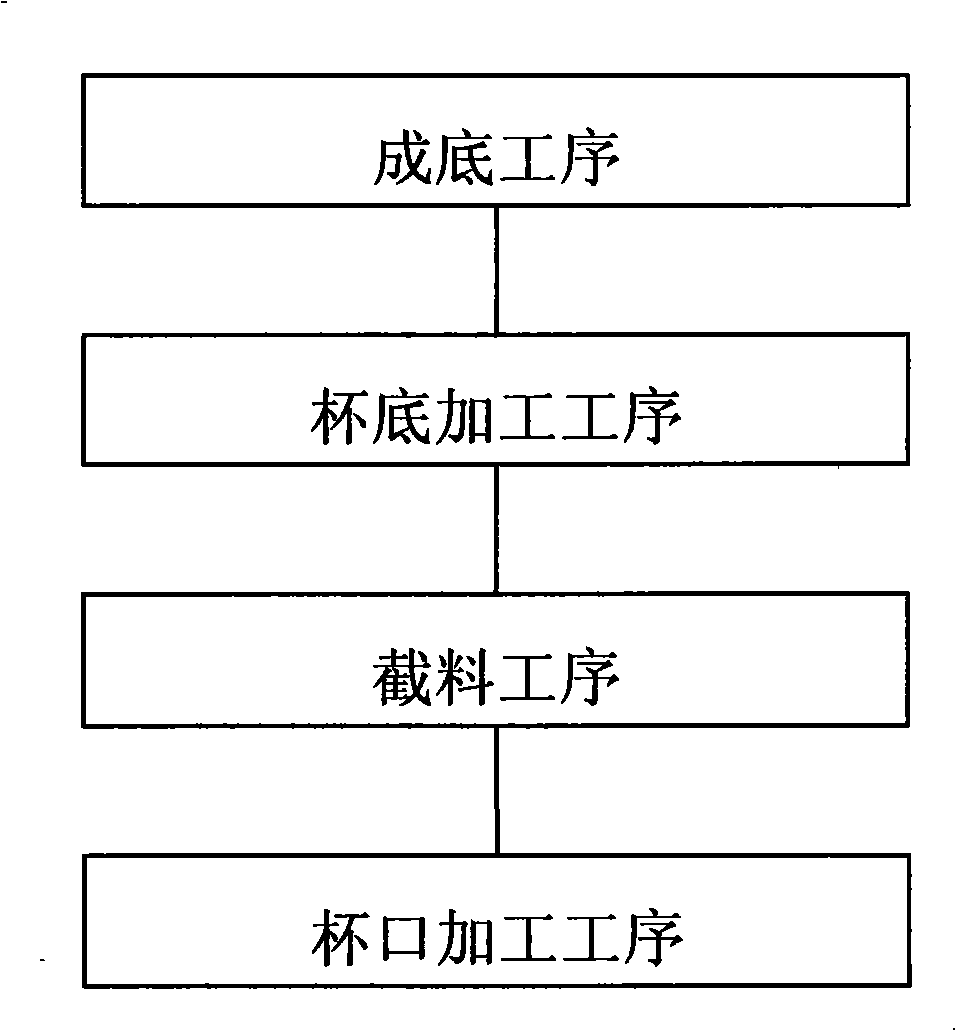
InactiveCN101357820AGood light transparencyImprove yieldGlass reforming apparatusGlass productionCutting glassSoftening
The invention relates to a method for producing a single-layer glass cup by using a glass tube. The method comprises the following steps: A. material cutting process: the glass tube is cut into the glass tube material section with the height which is twice that of the finished glass cup; B. bottom forming process: the both ends of the cut glass tube material are clamped on a rotary device to locally heat the middle part of the tube material till the softening of the glass, a heat-resistant material blade with the thickness which is less than the width of a heating zone and does not have the affinity with the glass is used for cutting the middle part of the heating zone to form blanks of two cup bottoms; C. cup bottom processing process: the cup-shaped glass tube material is clamped on the rotary device, flames are used for heating the bottom part of the glass cup-shaped tube material along the transverse direction at the same time of rotation till the melting of the glass, and the cup bottoms are thickened to meet the design requirements. The method has simple production technology, greatly improved yield, good overall transparency of the cup and no need of polishing. The production efficiency is greatly improved, and the method can be used for large-scale production and family workshop operation. The equipment cost is greatly reduced, and the method can be used for the production by only using a special burning device, thereby eliminating the constraints of a kiln on the production scale and the place.
Owner:郝身峙
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com