Patents
Literature
45 results about "Microvascular Network" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
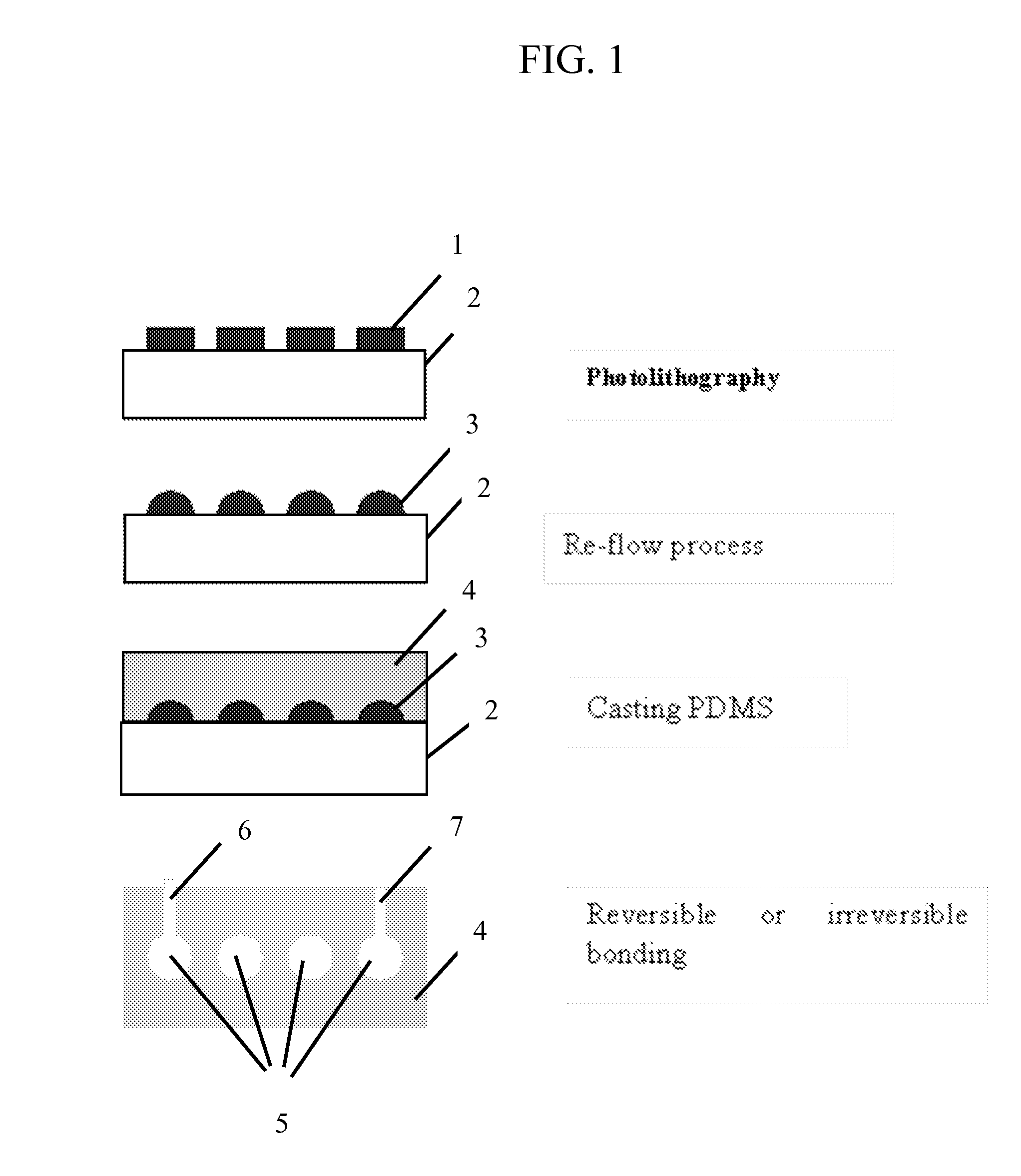
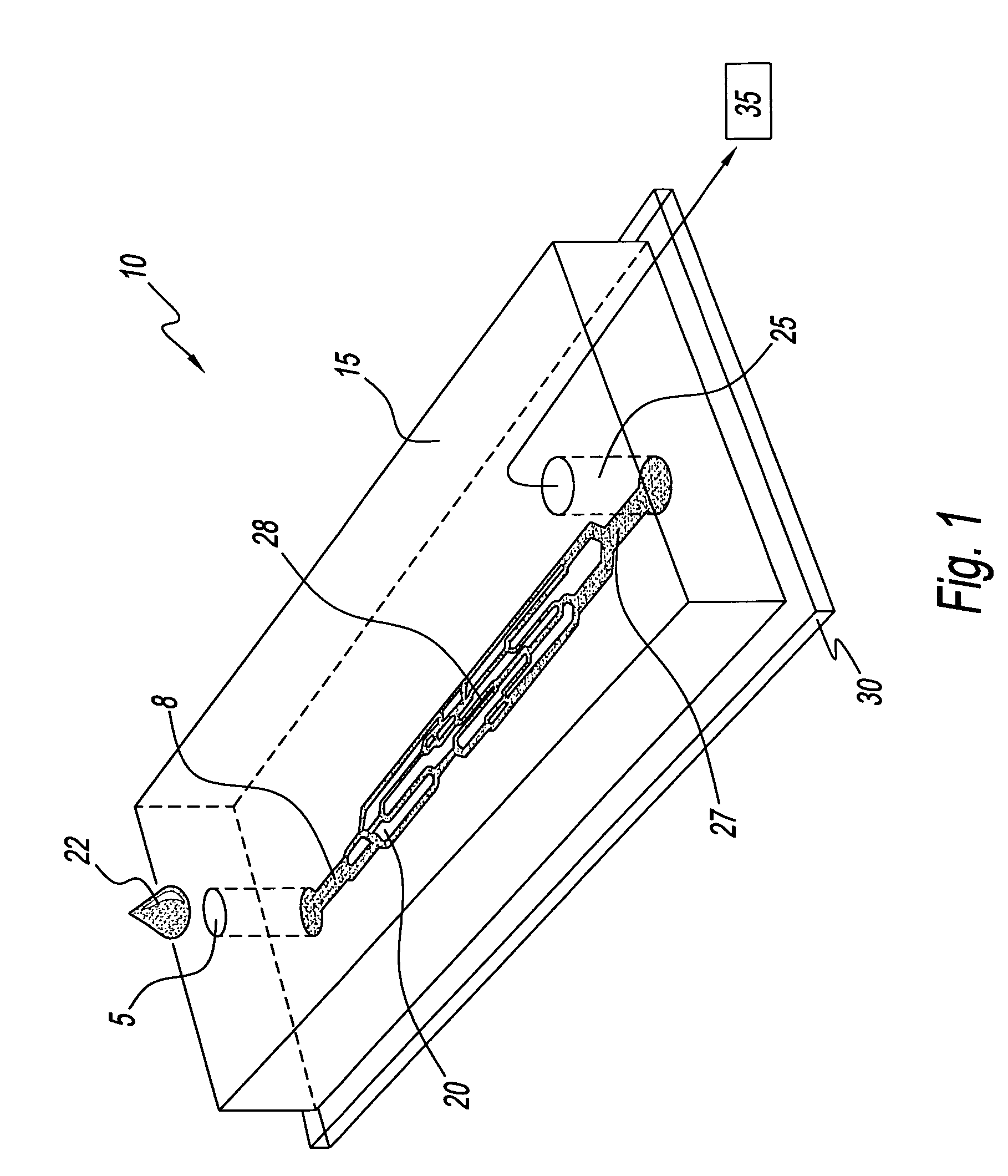
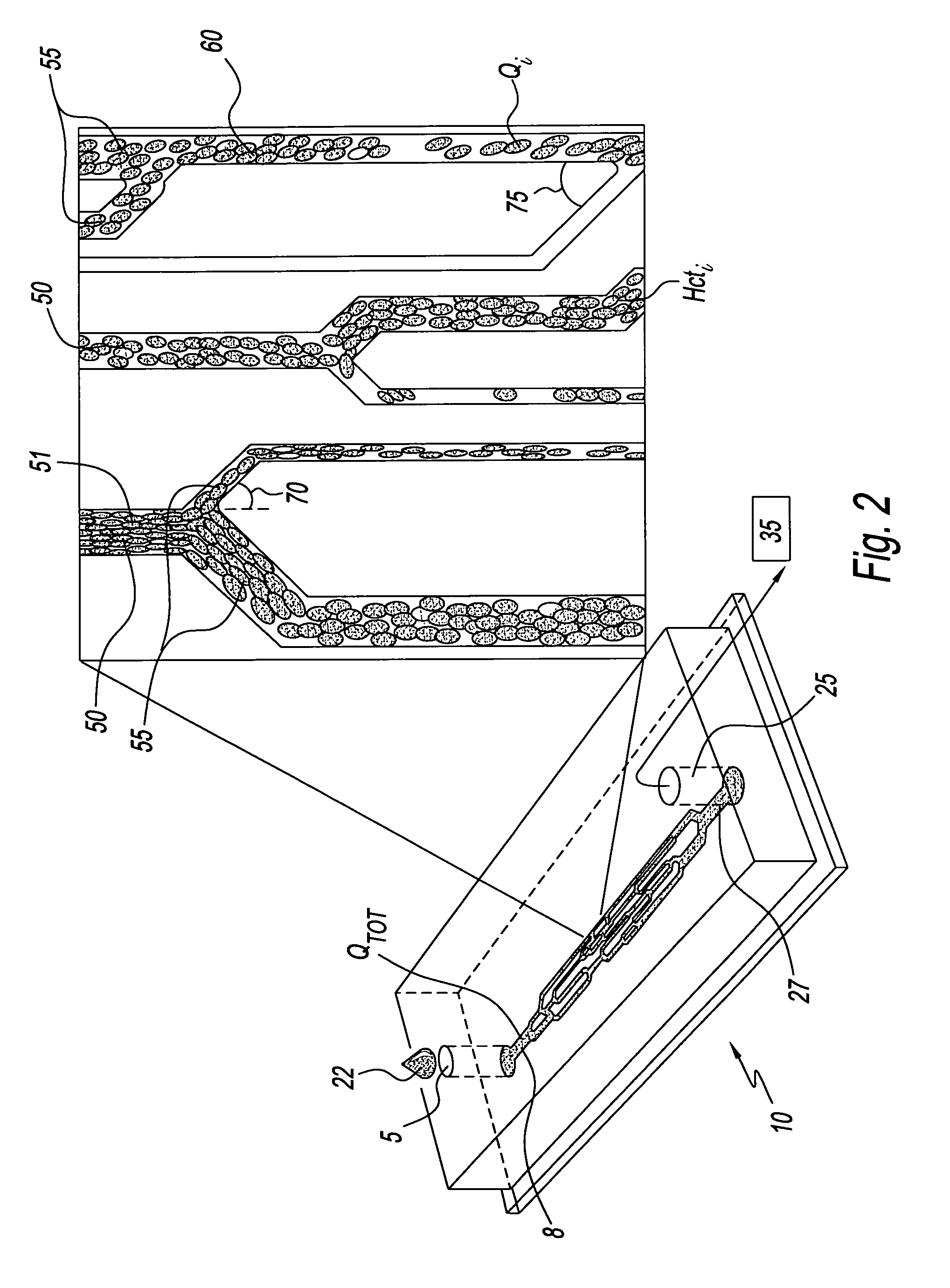
System for assessing the efficacy of stored red blood cells using microvascular networks
InactiveUS20090269837A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicrovascular NetworkEngineering
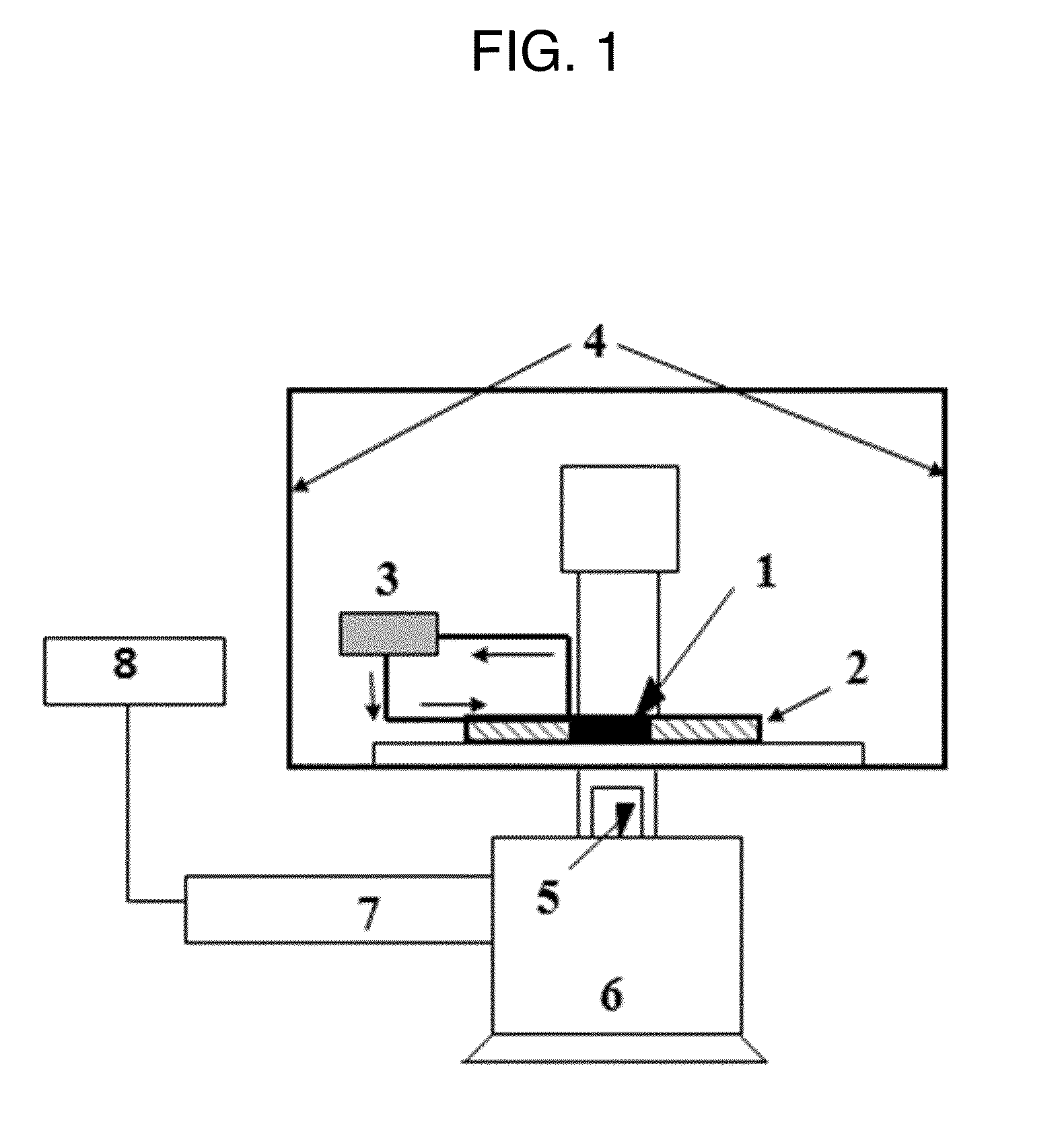
A system for assessing the microvascular fitness of a sample of stored red blood cells. The system has a network device having at least one network unit. The network unit has a single inlet and a single outlet for the sample and a plurality of microchannels. The plurality of microchannels receive the sample from the single inlet and drain the sample into the single outlet. The network unit includes an aspiration pressure means for providing movement of liquid sample through the at least one network unit. The system further includes an analysis unit that receives the network device therein. The analysis unit includes a sensor for capturing measurements related to the sample and a processor capable of comparing the captured measurements to measurements stored in a database of healthy red blood cells to determine the microvascular fitness of the stored red blood cells.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Three-Dimensional Microfabricated Bioreactors with Embedded Capillary Network
InactiveUS20110033887A1Promote growthFacilitating growth and expansionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCapillary networkEngineering
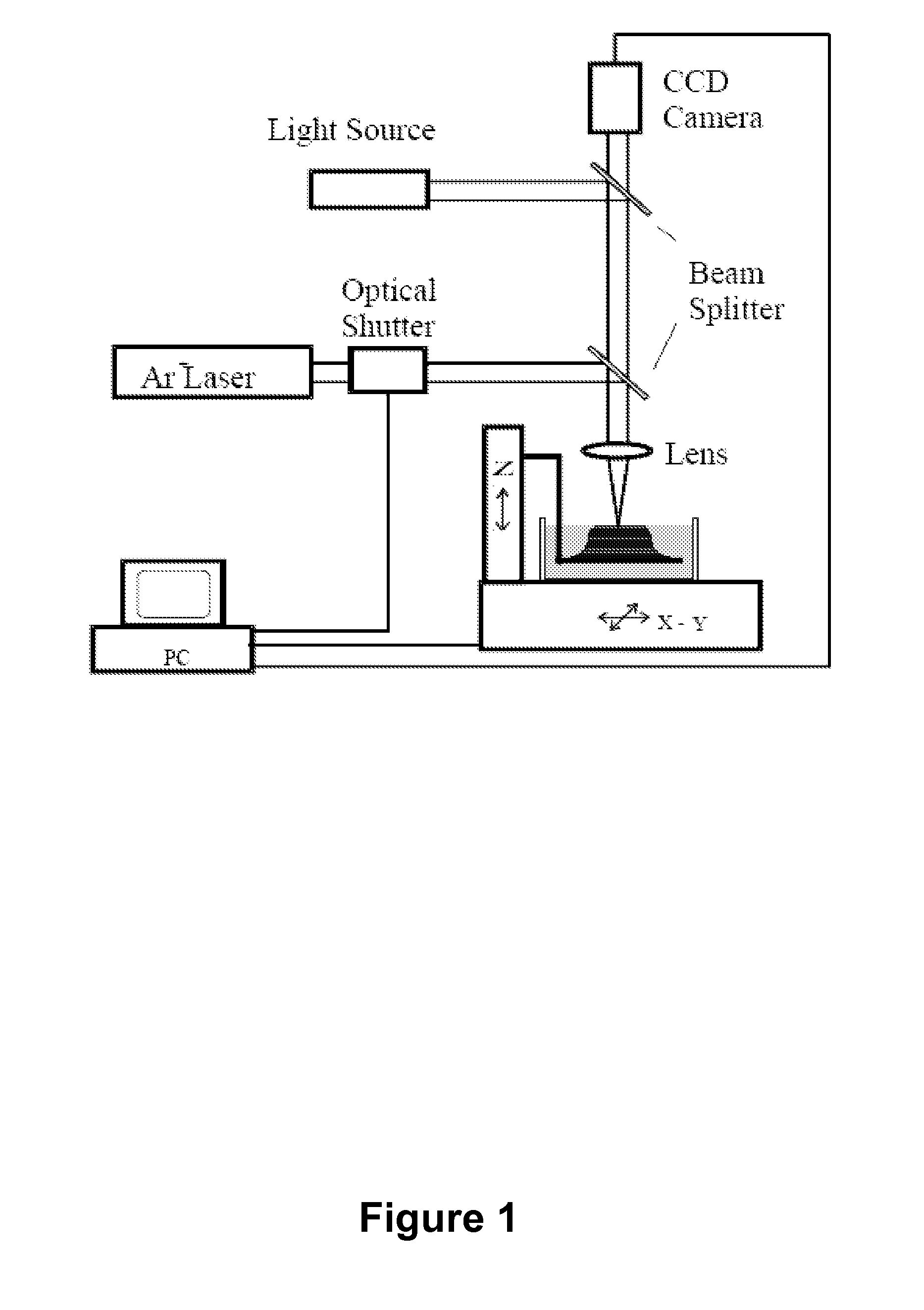
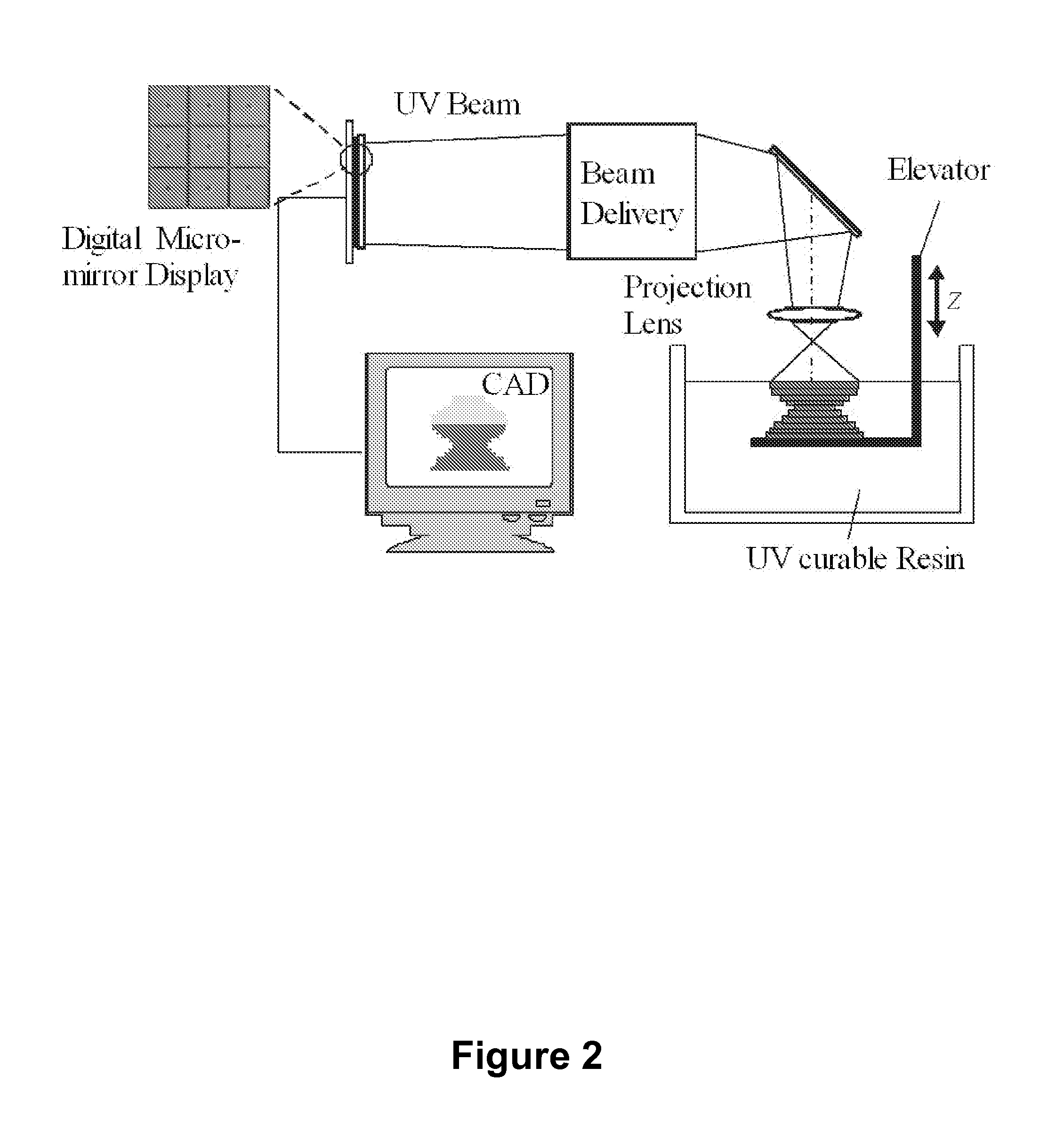
In an aspect, the present invention uses projection micro stereolithography to generate three-dimensional microvessel networks that are capable of supporting and fostering growth of a cell population. For example, provided is a method of making a microvascularized bioreactor via layer-by-layer polymerization of a photocurable liquid composition with repeated patterns of illumination, wherein each layer corresponds to a layer of the desired microvessel network. The plurality of layers are assembled to make a microvascular network. Support structures having different etch rates than the structures that make up the network provides access to manufacturing arbitrary geometries that cannot be made by conventional methods. A cell population is introduced to the external wall of the network to obtain a microvascularized bioreactor. Provided are various methods and related bioreactors, wherein the network wall has a permeability to a biological material that varies within and along the network.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
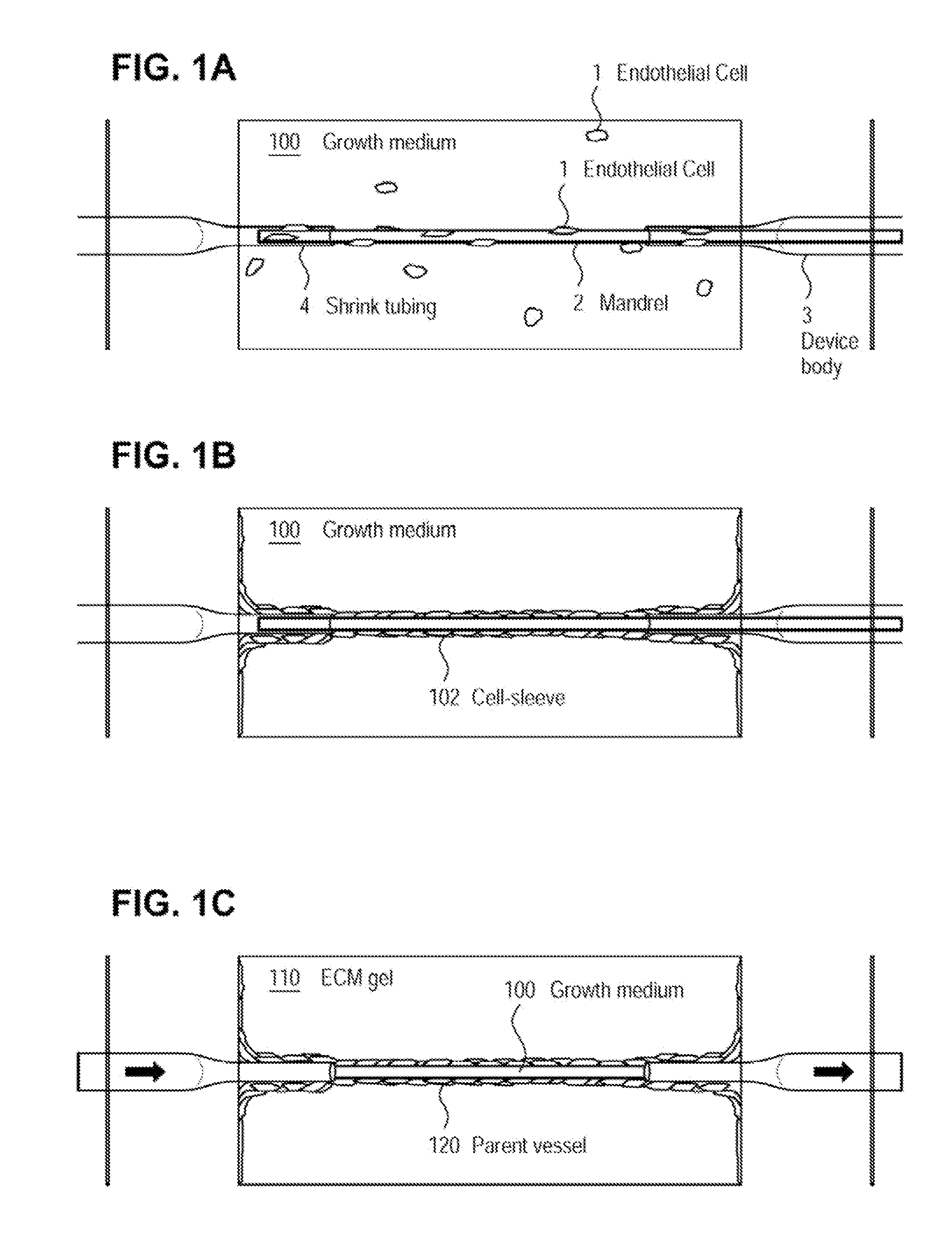
Method for creating perfusable microvessel systems
ActiveUS20070224677A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell-Extracellular MatrixECM Protein
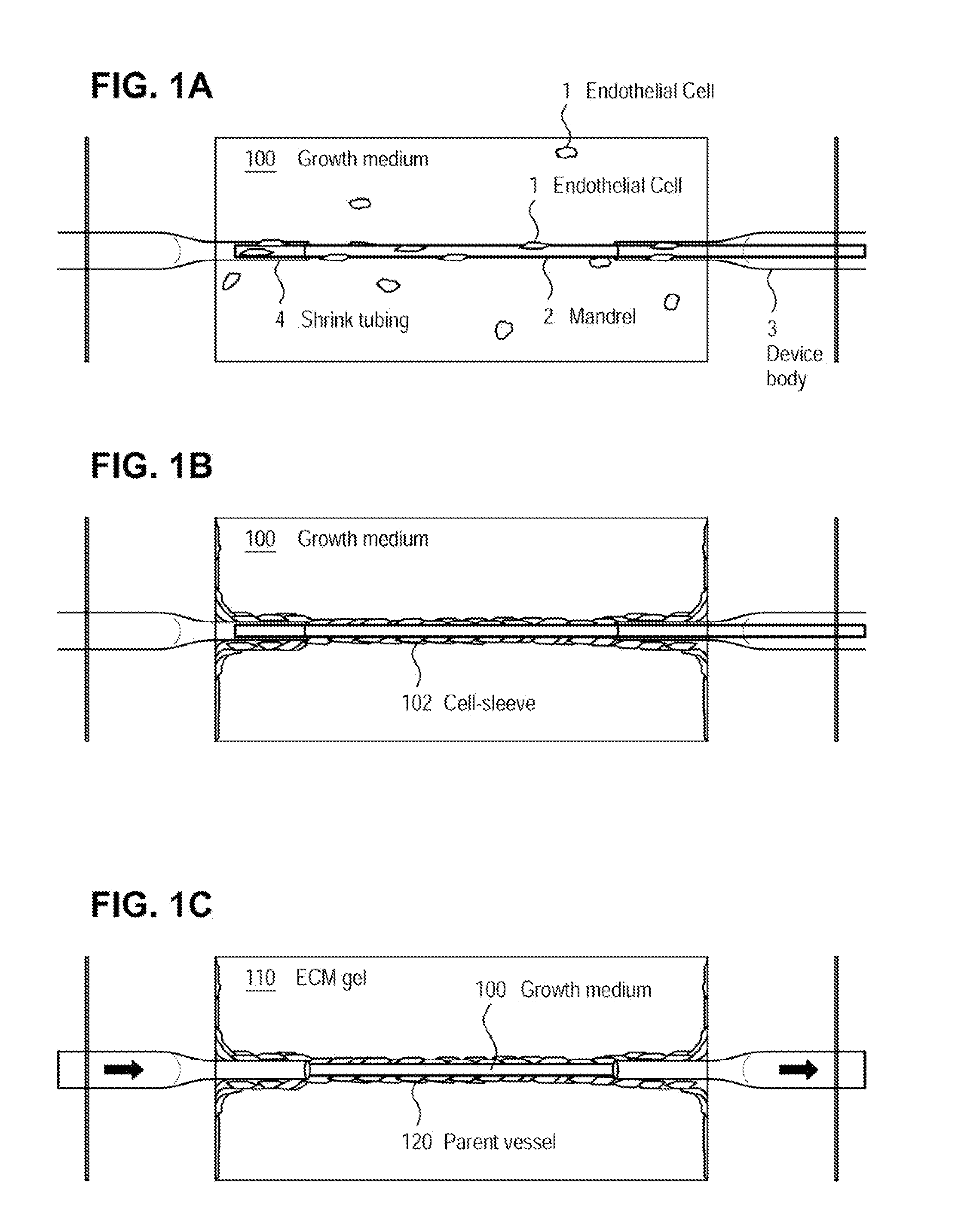
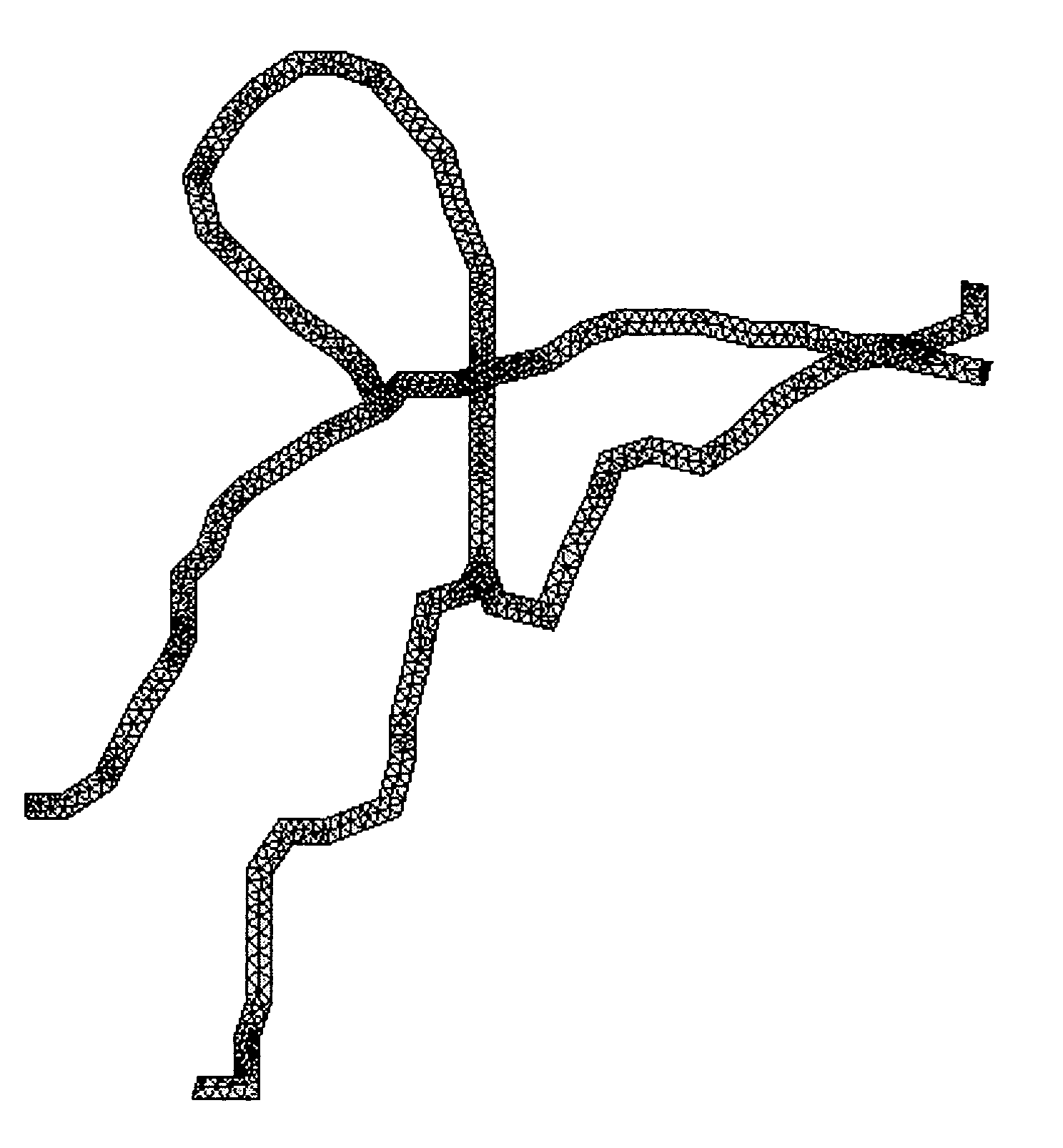
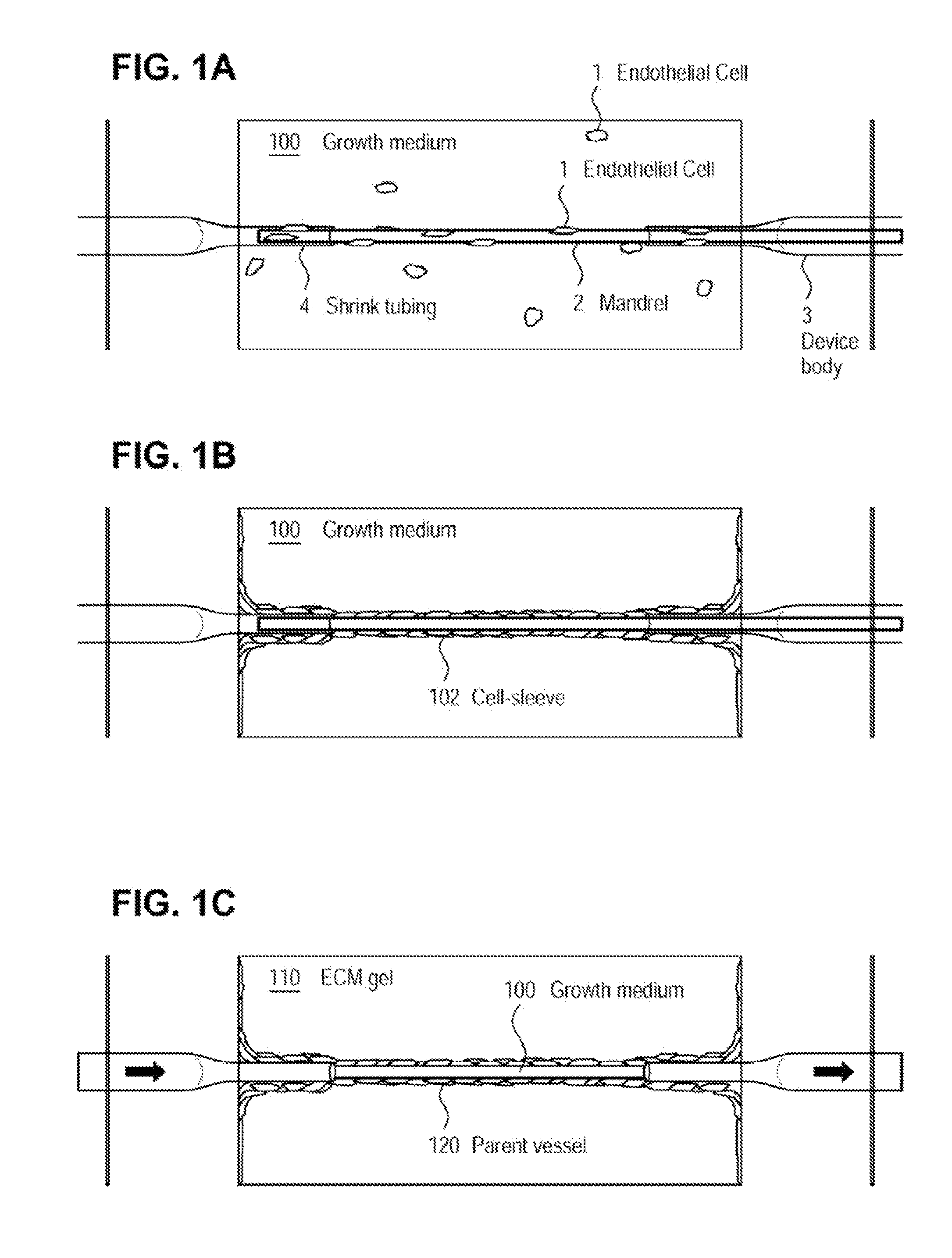
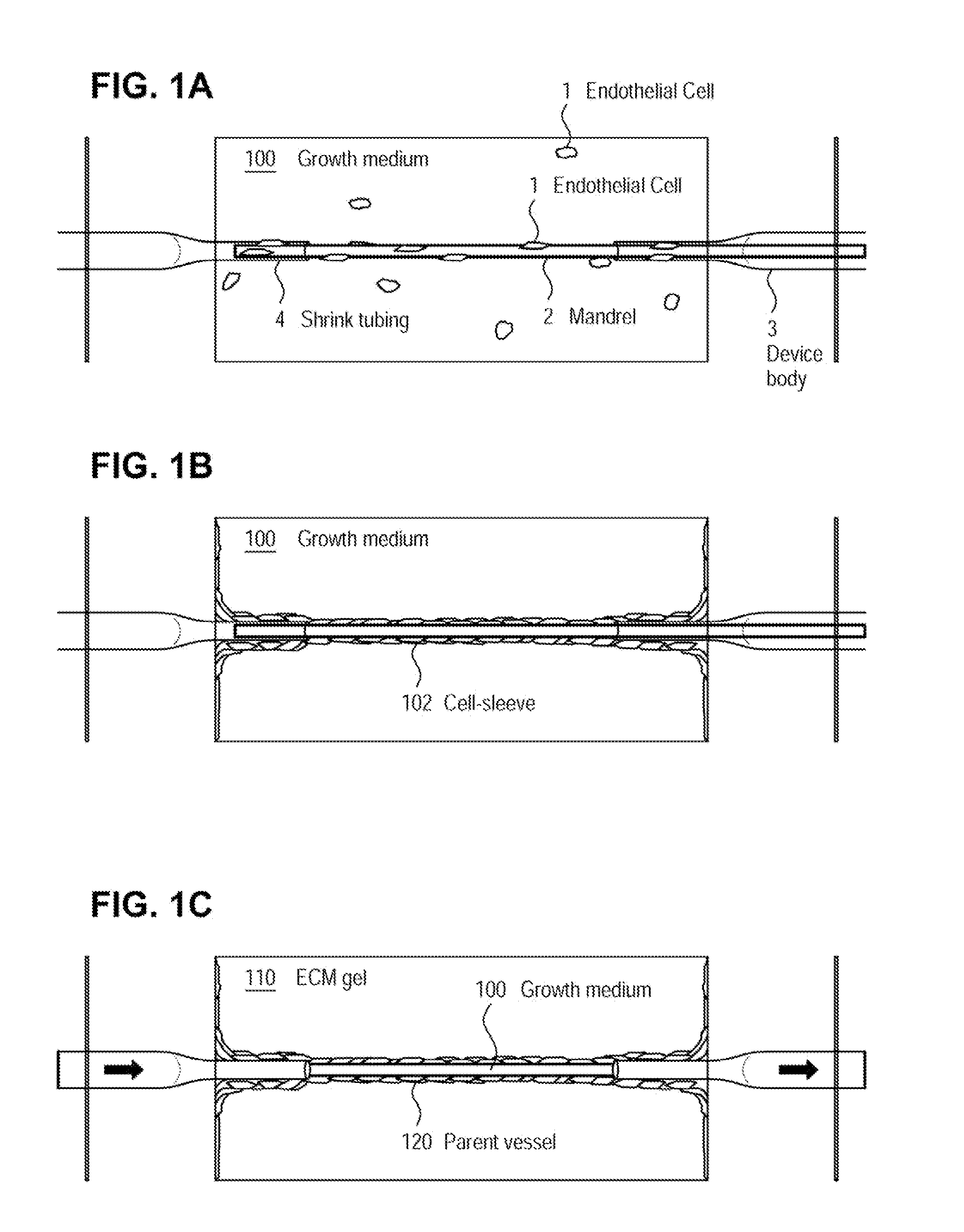
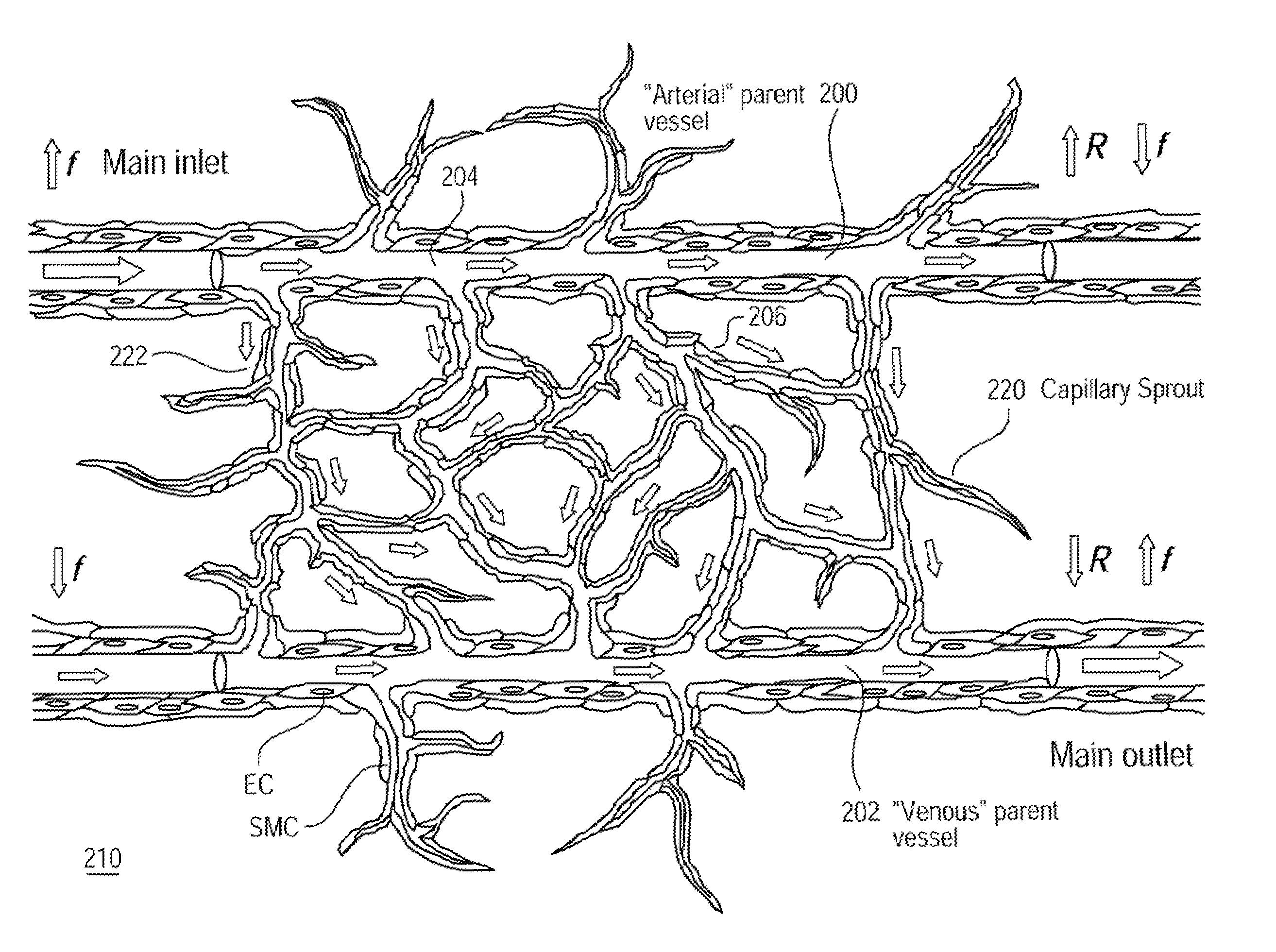
Microvessel networks are produced in vitro from tissue-engineered parent vessels sprouting into a supporting matrix, as for example gels, of extracellular matrix proteins. The microvessel systems are integrated into devices that allow for controlled perfusion with fluids. The vessels may include cells from one cell type, for example, endothelial cells, or from combinations of two or more cell types.
Owner:NORTIS
Apparatus and Method for Capturing a Vital Vascular Fingerprint
ActiveUS20140241596A1Effective imagingAccurate identificationPrint image acquisitionMatching and classificationPattern recognitionDermal papillae
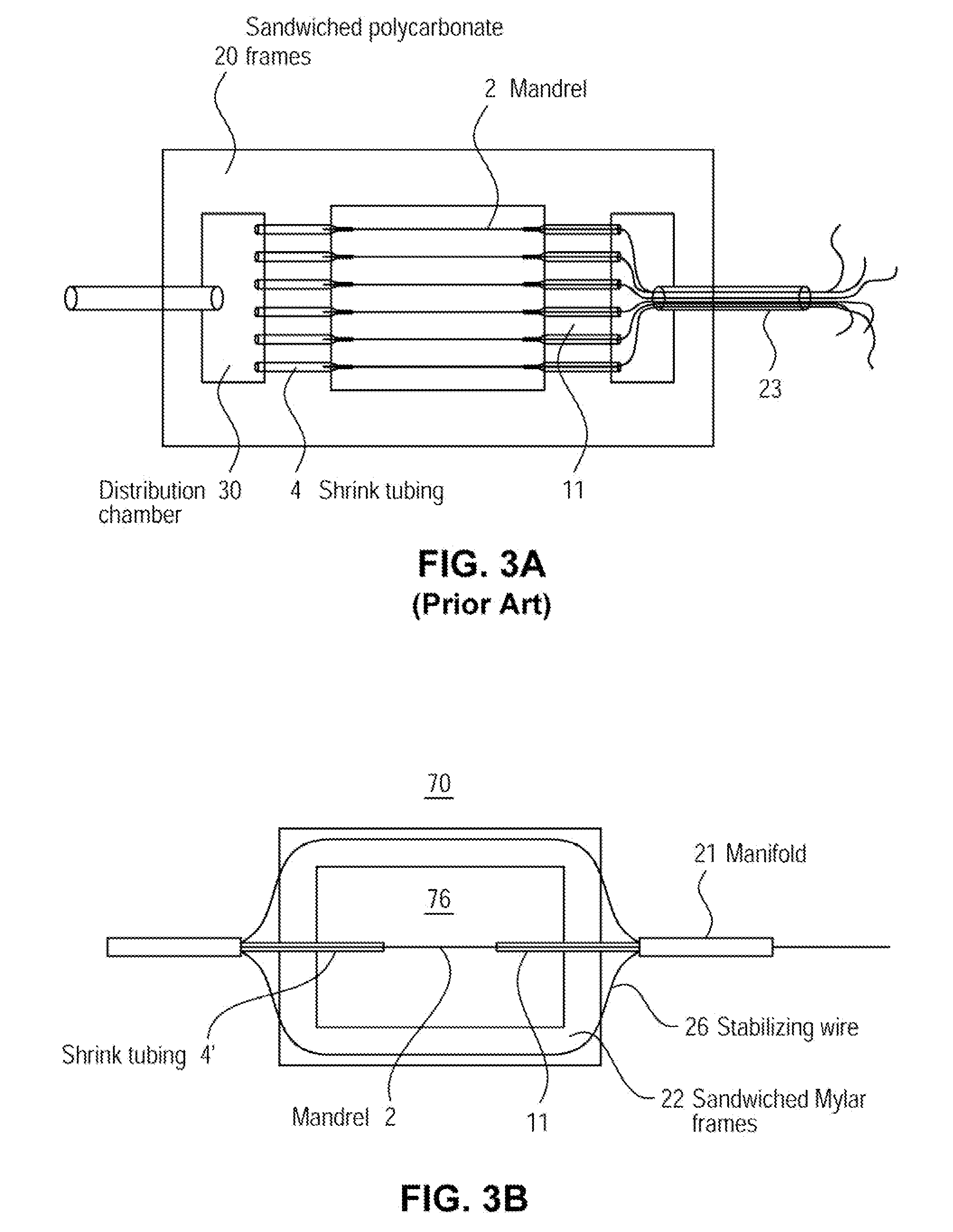
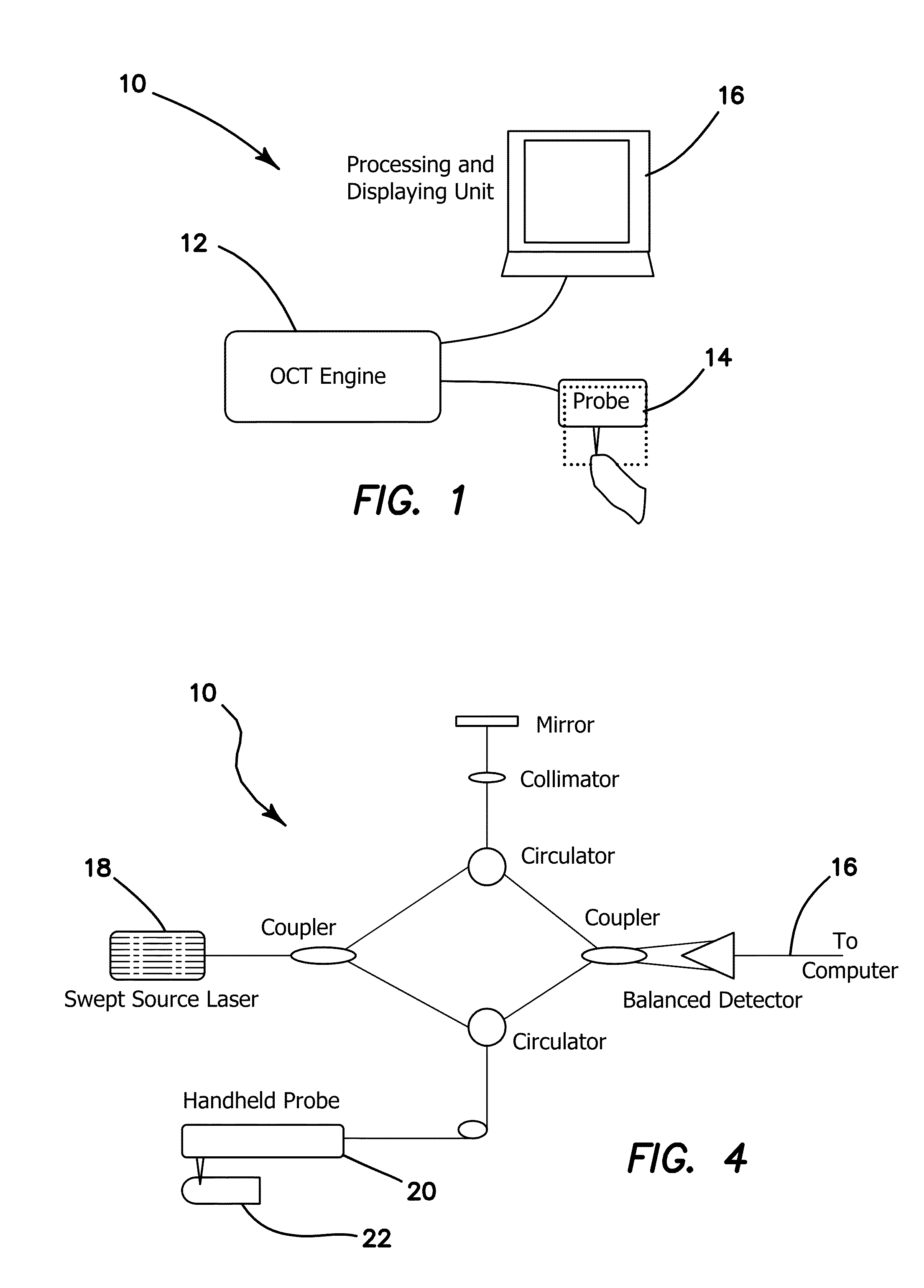
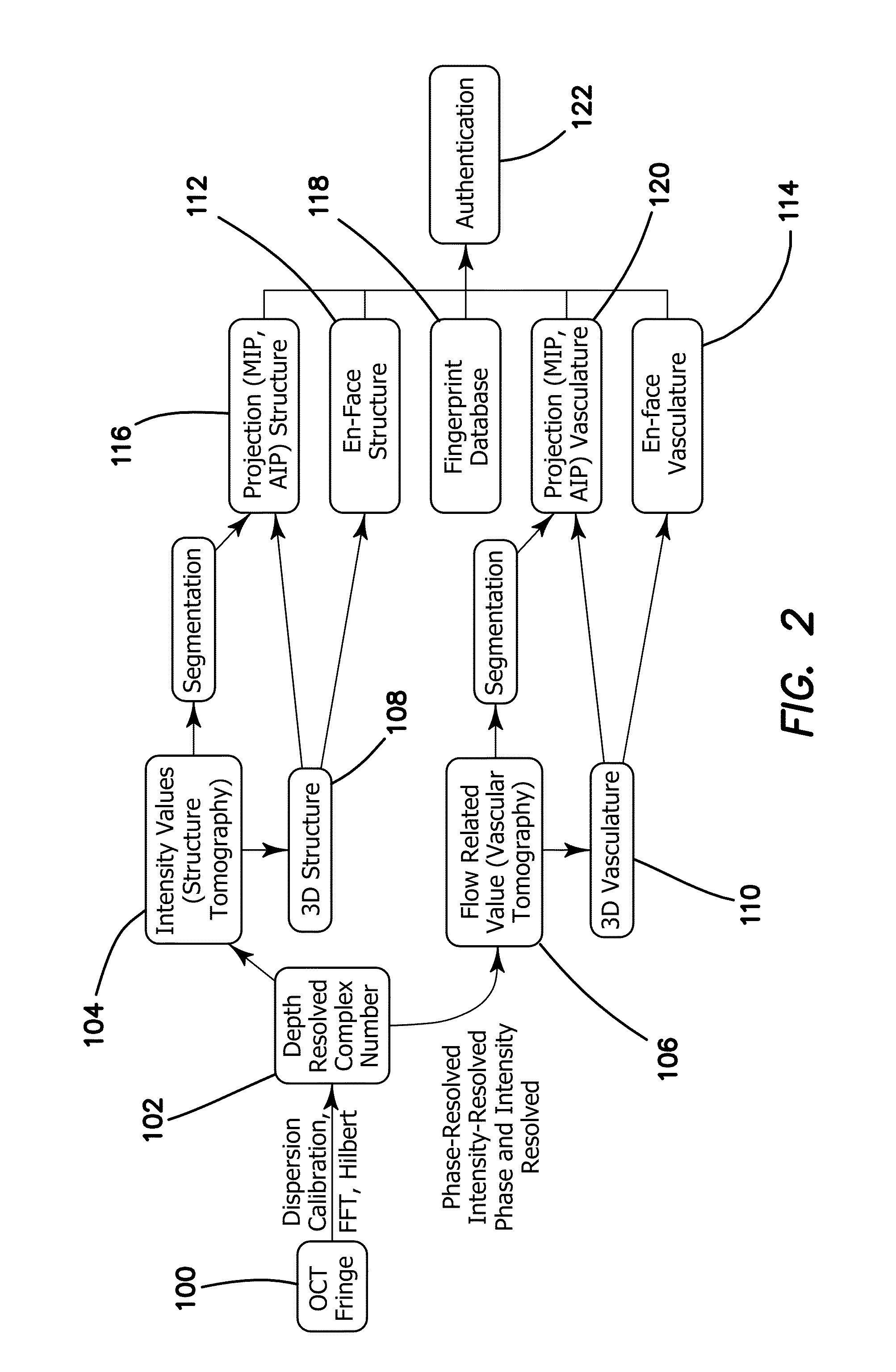
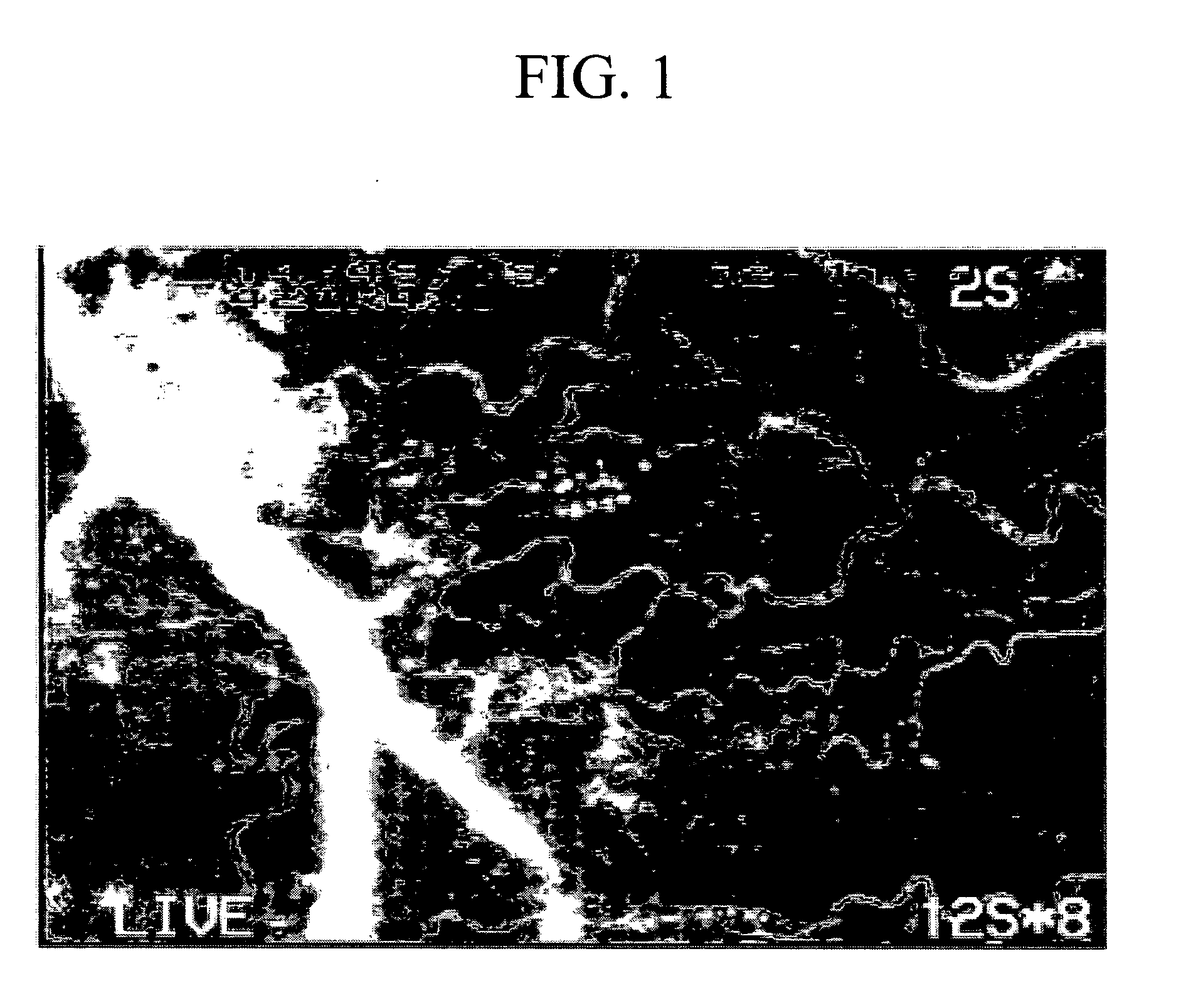
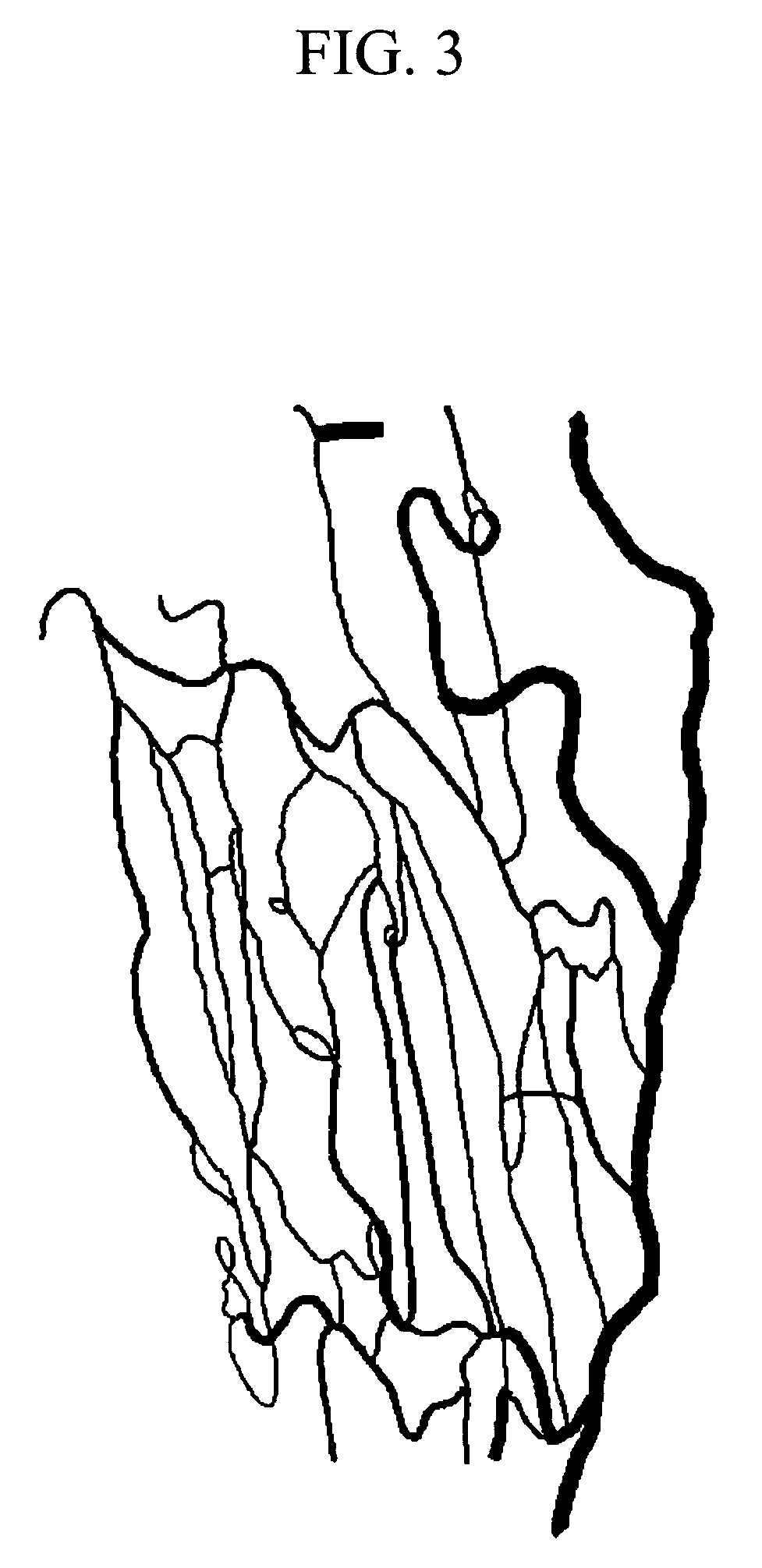
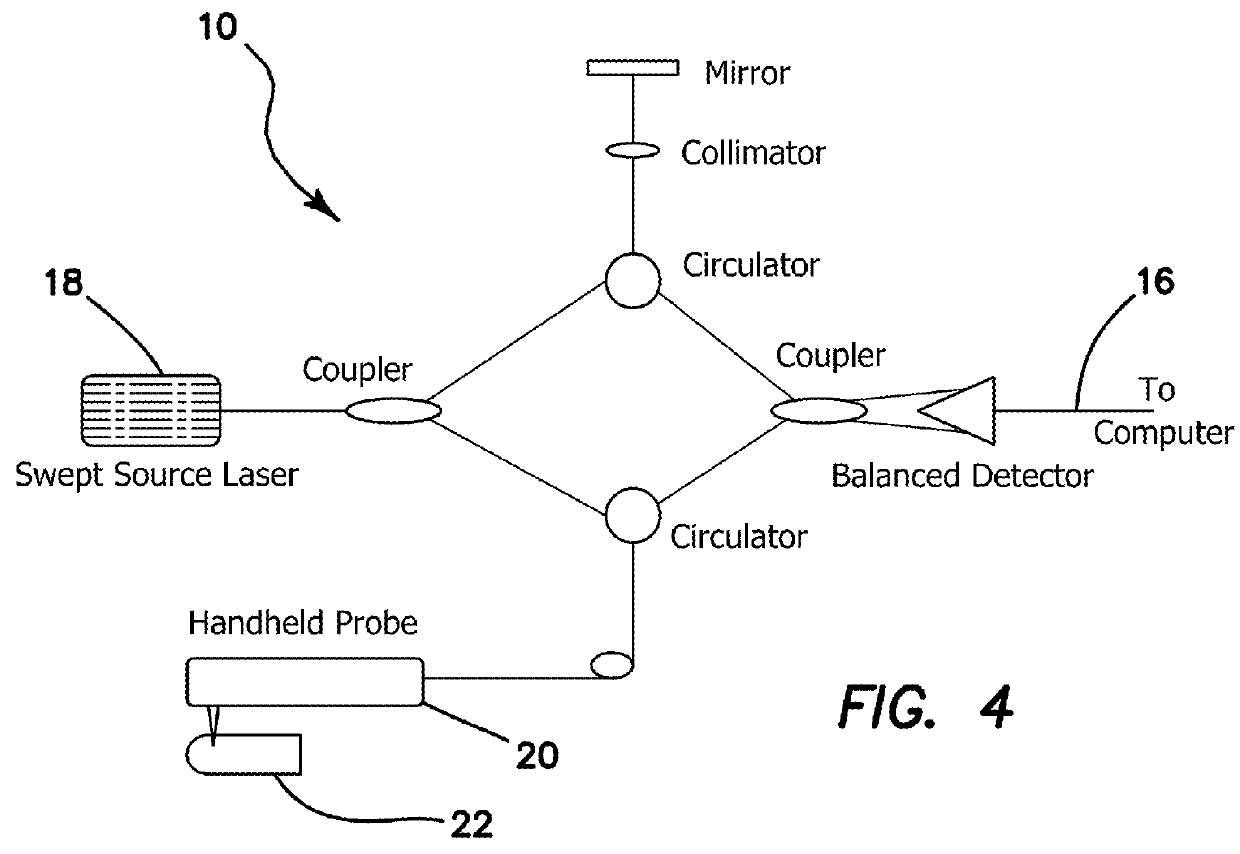
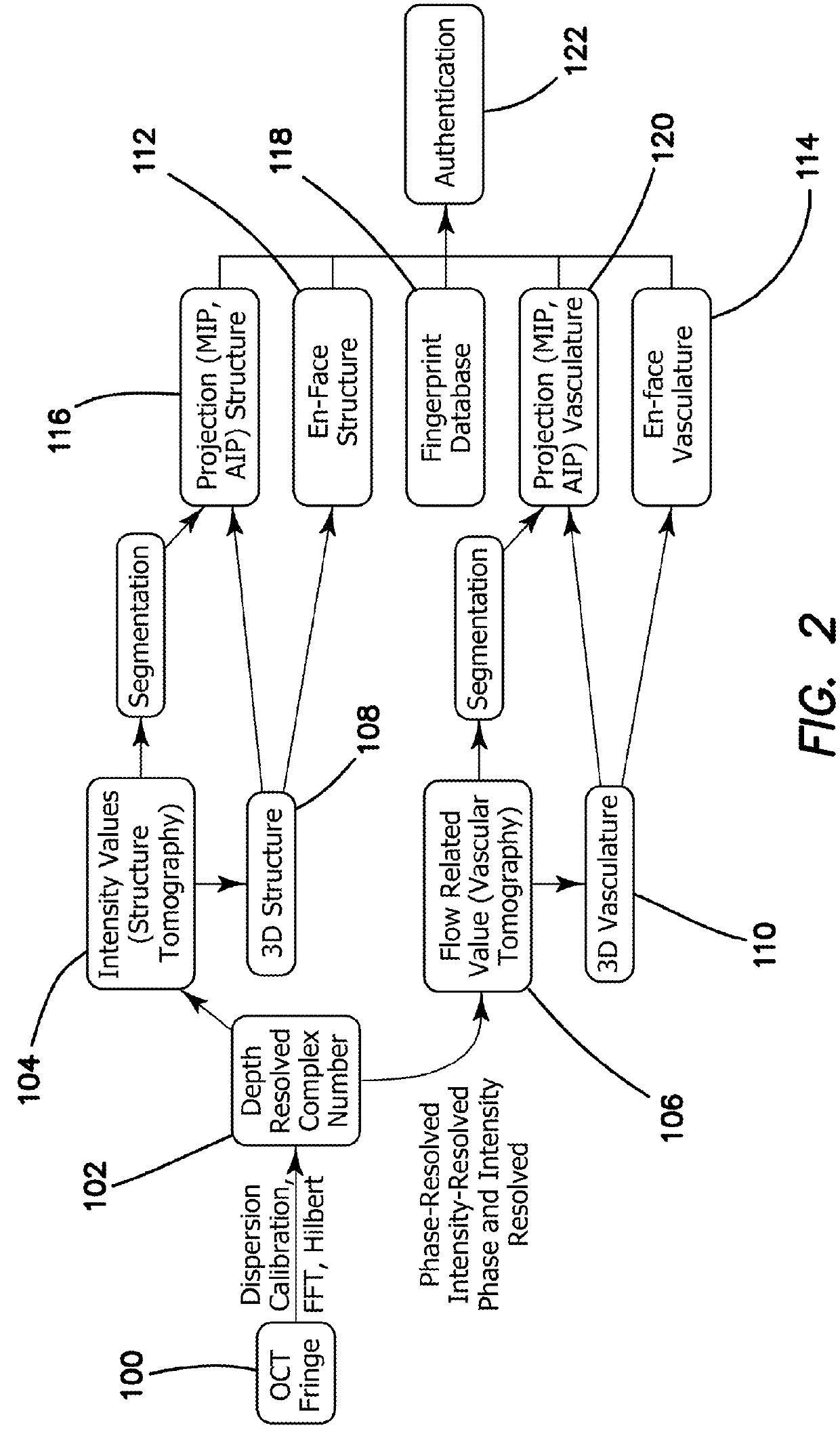
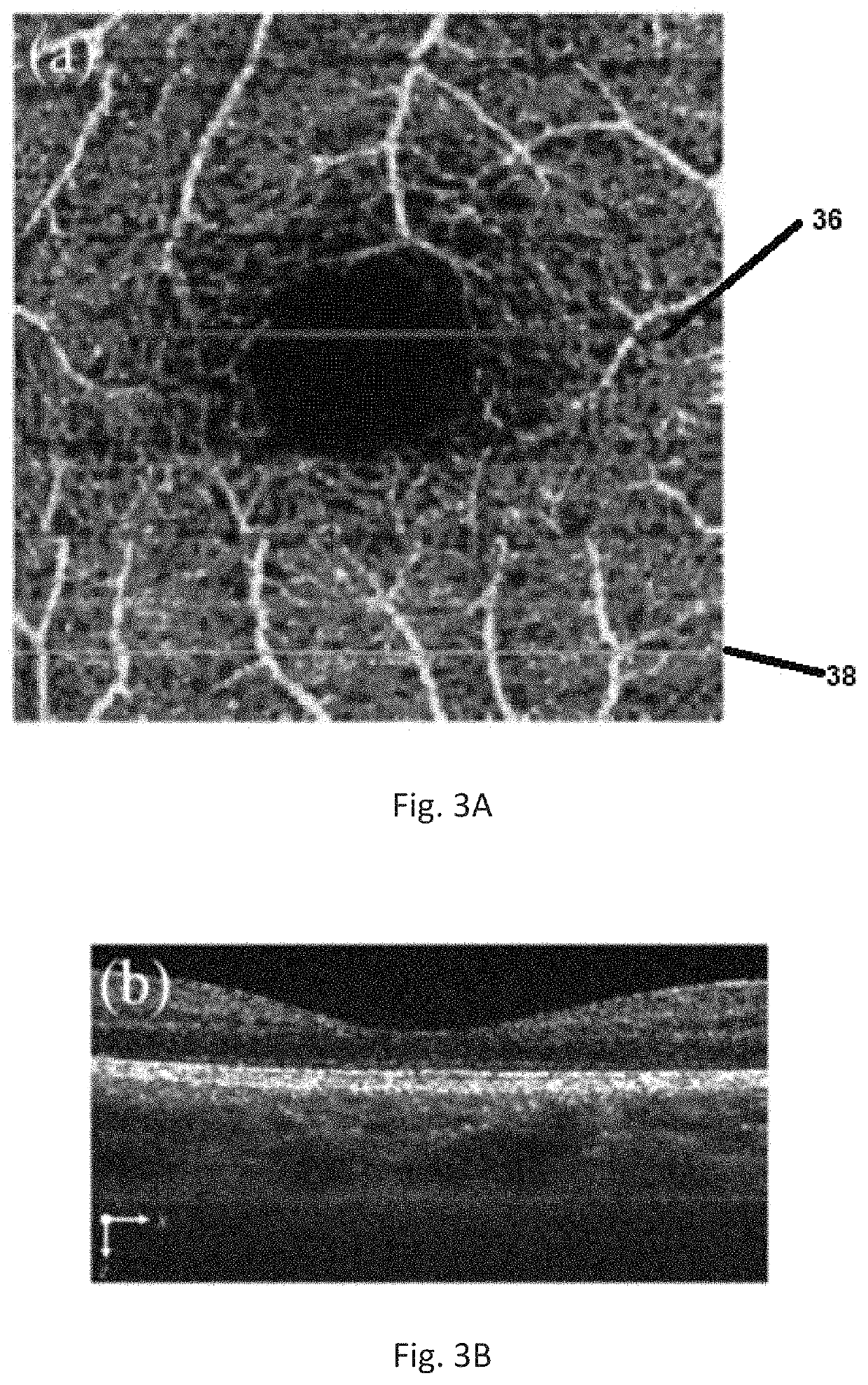
A method using optical coherence tomography to capture the microvascular network of the superficial layer of the finger skin for the purpose of fingerprint authentication and liveness detection. At the dermal papilla region, the vascular pattern follows the same pattern of the fingerprint and this vascular pattern forms a live vascular fingerprint. This live vascular fingerprint provides for ultrahigh security and a unique way for fingerprint-based personal verification. Because the system is based on blood flow, which only exists in a living person, the technique is robust against spoof attaching. After performing non-contact in-vivo imaging of a human fingertip, a three dimensional vasculature image is reconstructed from a plurality of vasculature tomography images and at least one vasculature fingerprint image which corresponds to the fingertip is extracted from the three dimensional vasculature image. This extracted image may then be compared to known fingerprint database for authentication or for liveness detection.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
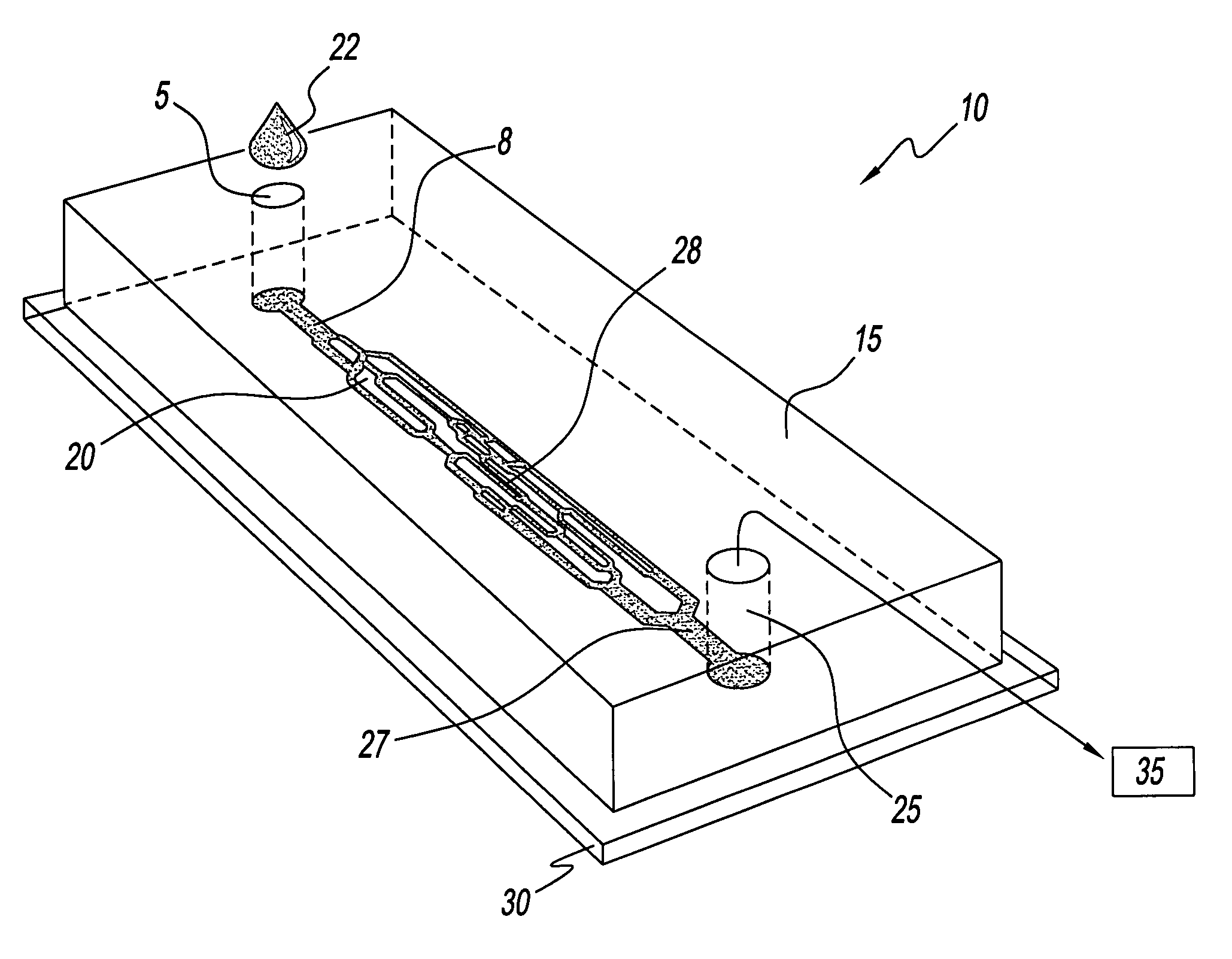
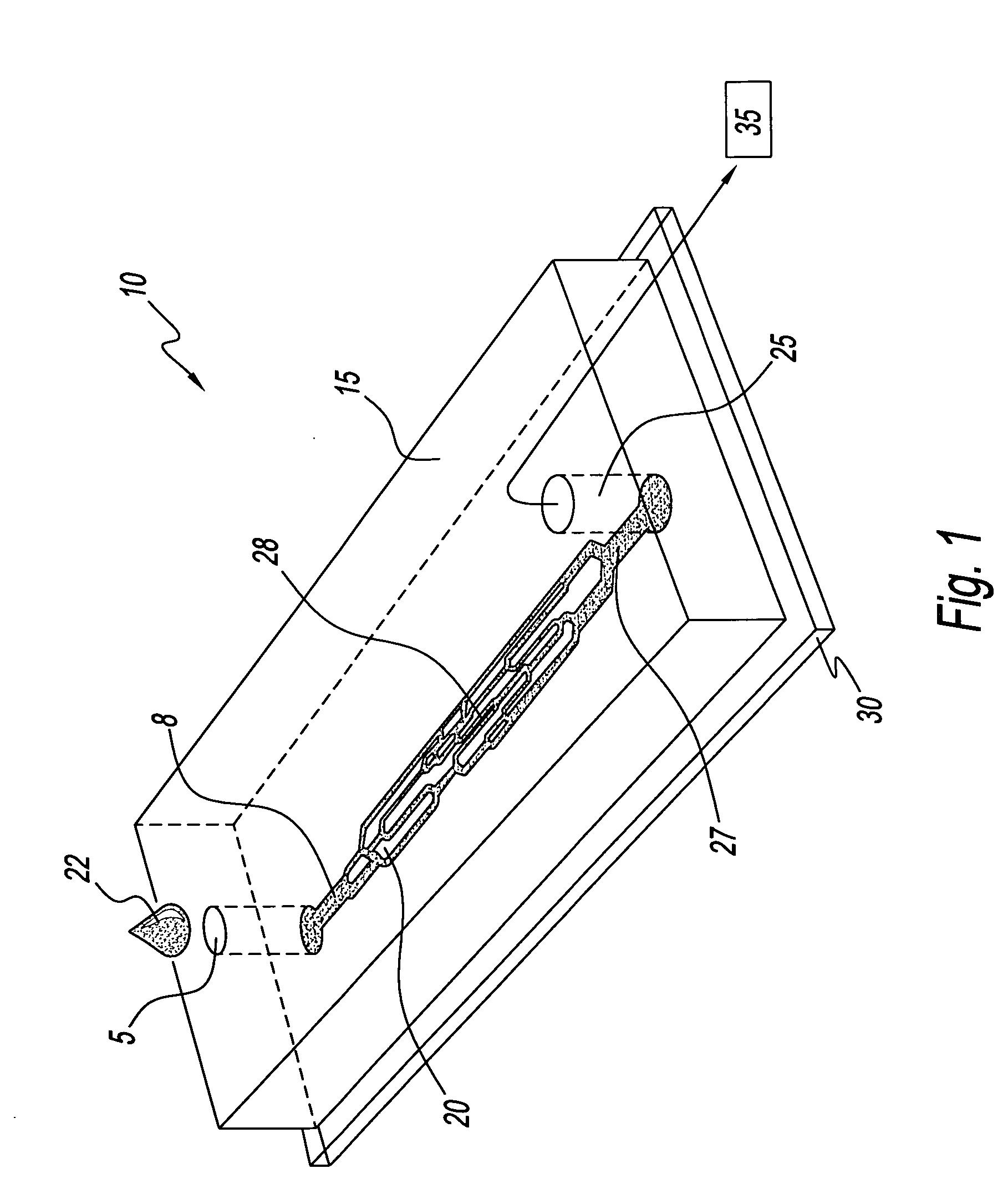
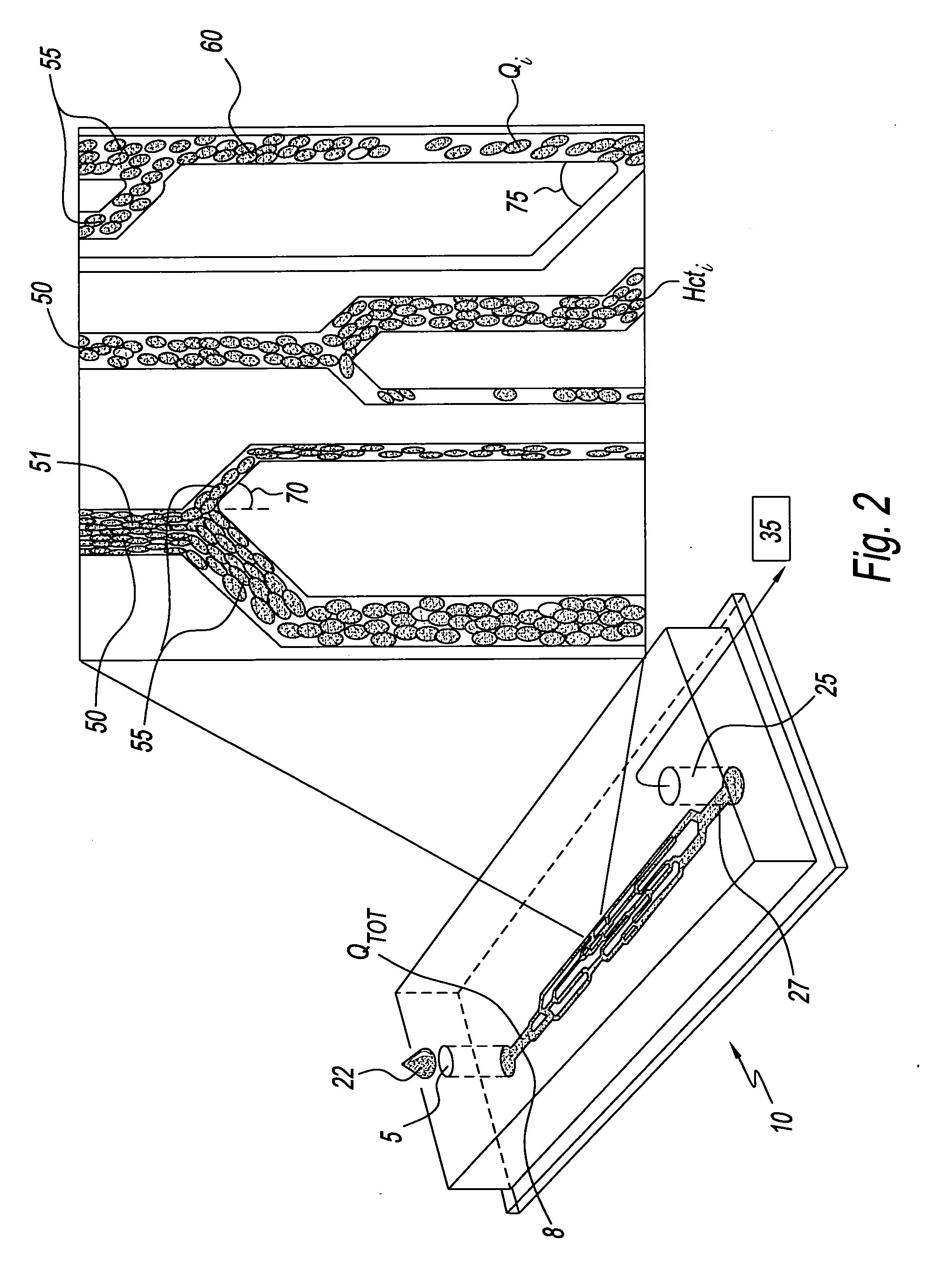
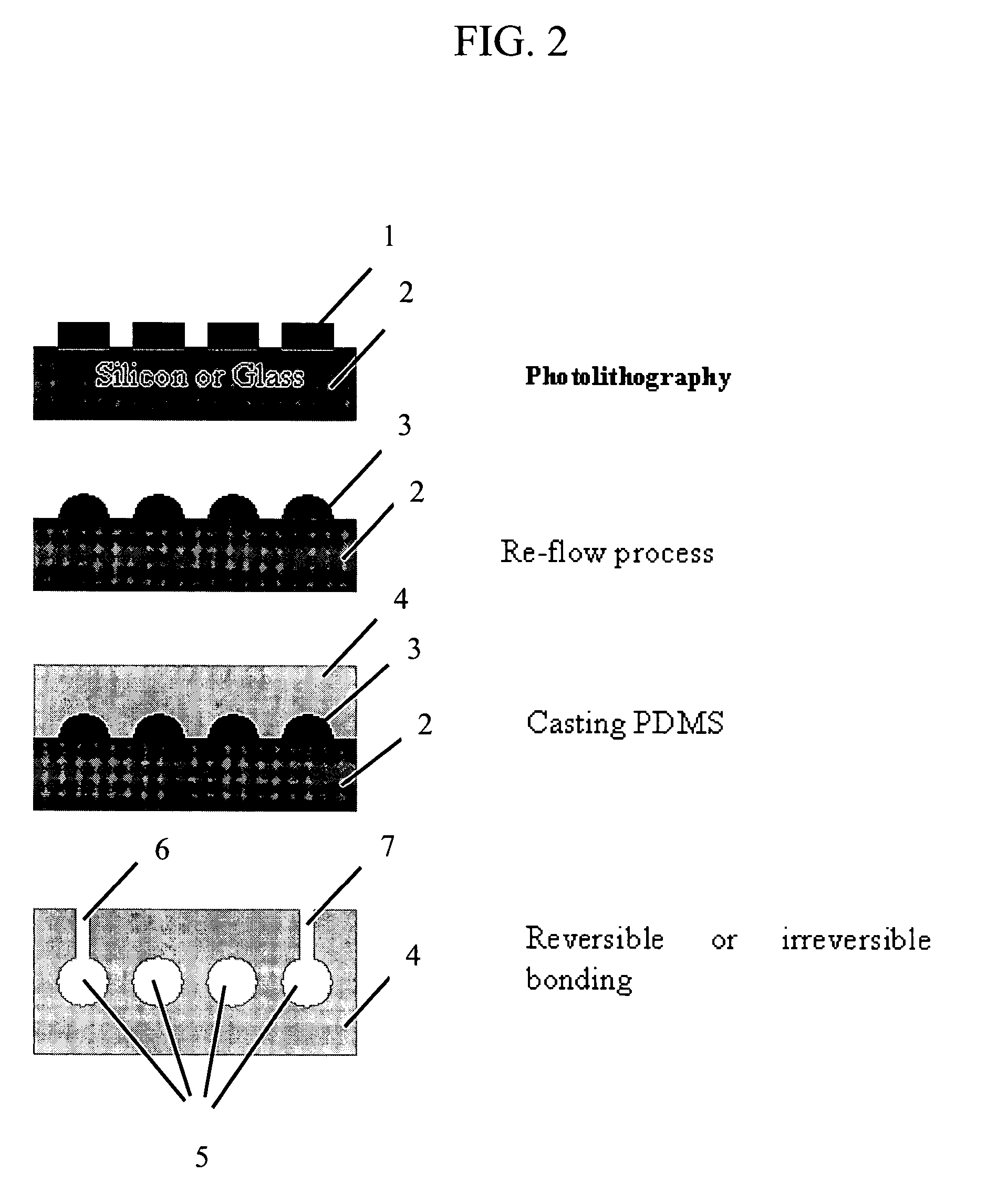
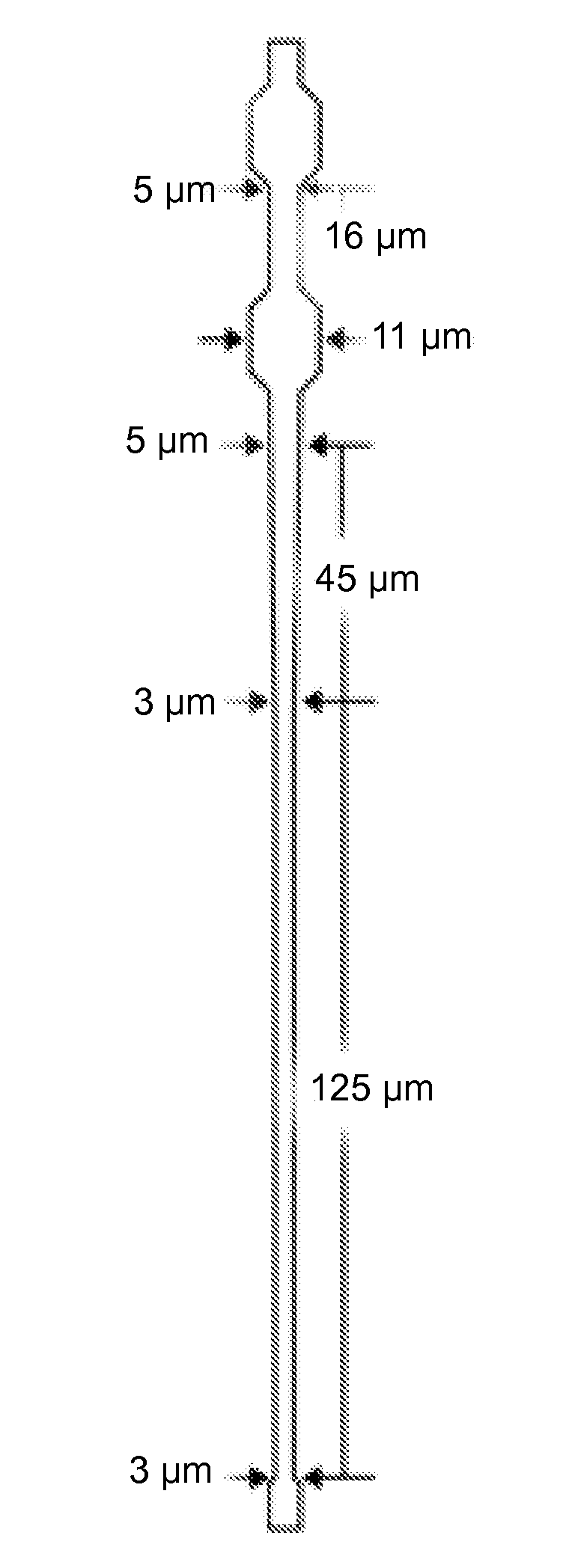
Microvascular network device
A microvascular network device comprising: a substrate; at least one microchannel; at least one opening to the microchannel for sample entry; at least one opening to the microchannel for sample exit; and an aspirator which causes the sample to traverse the microchannel.
Owner:HEMANEXT +1
Automatic three-dimensional segmentation method for oct and doppler oct angiography
ActiveUS20170164825A1Early diagnosisAccurate monitoringScattering properties measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringData treatmentTomographic image
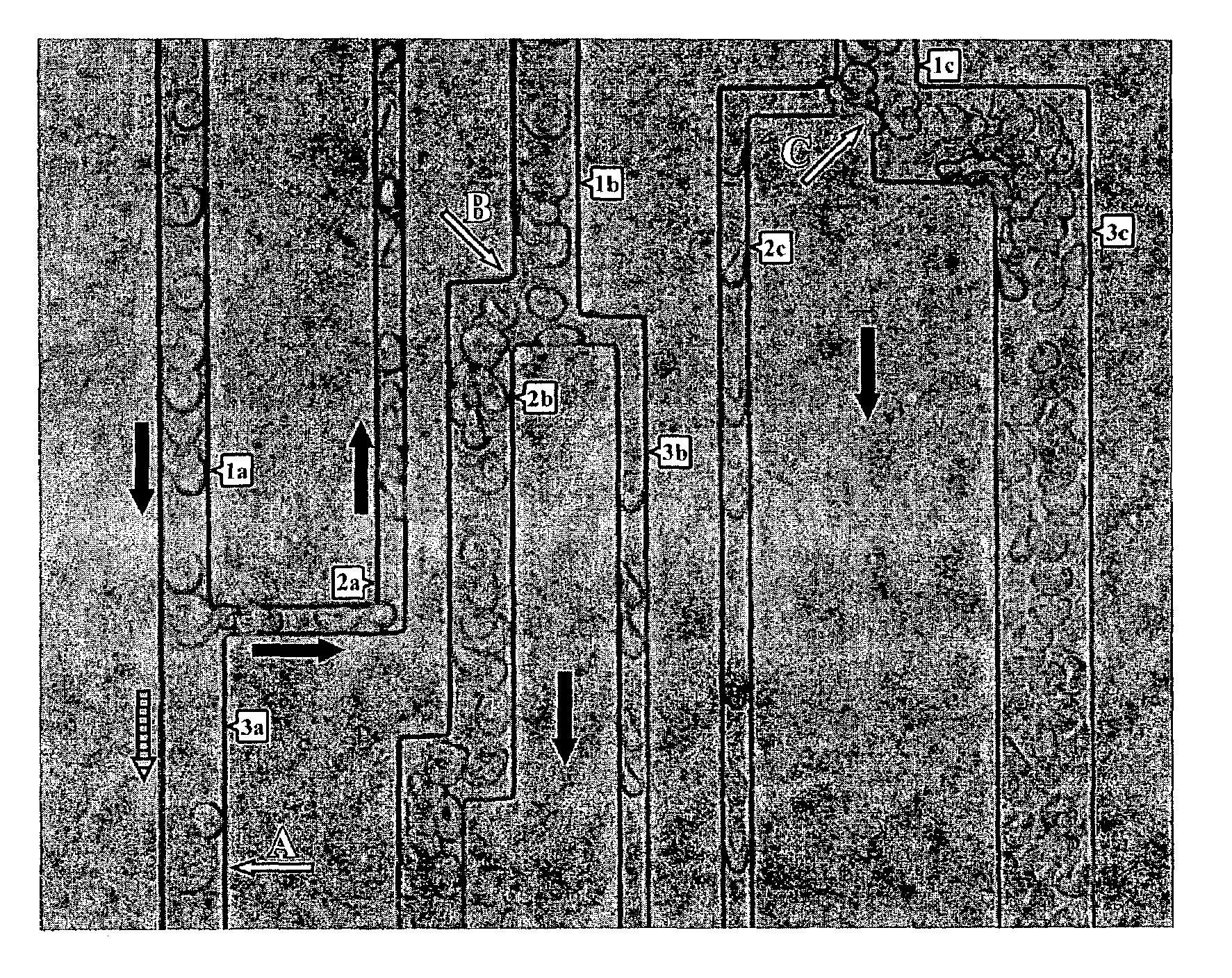
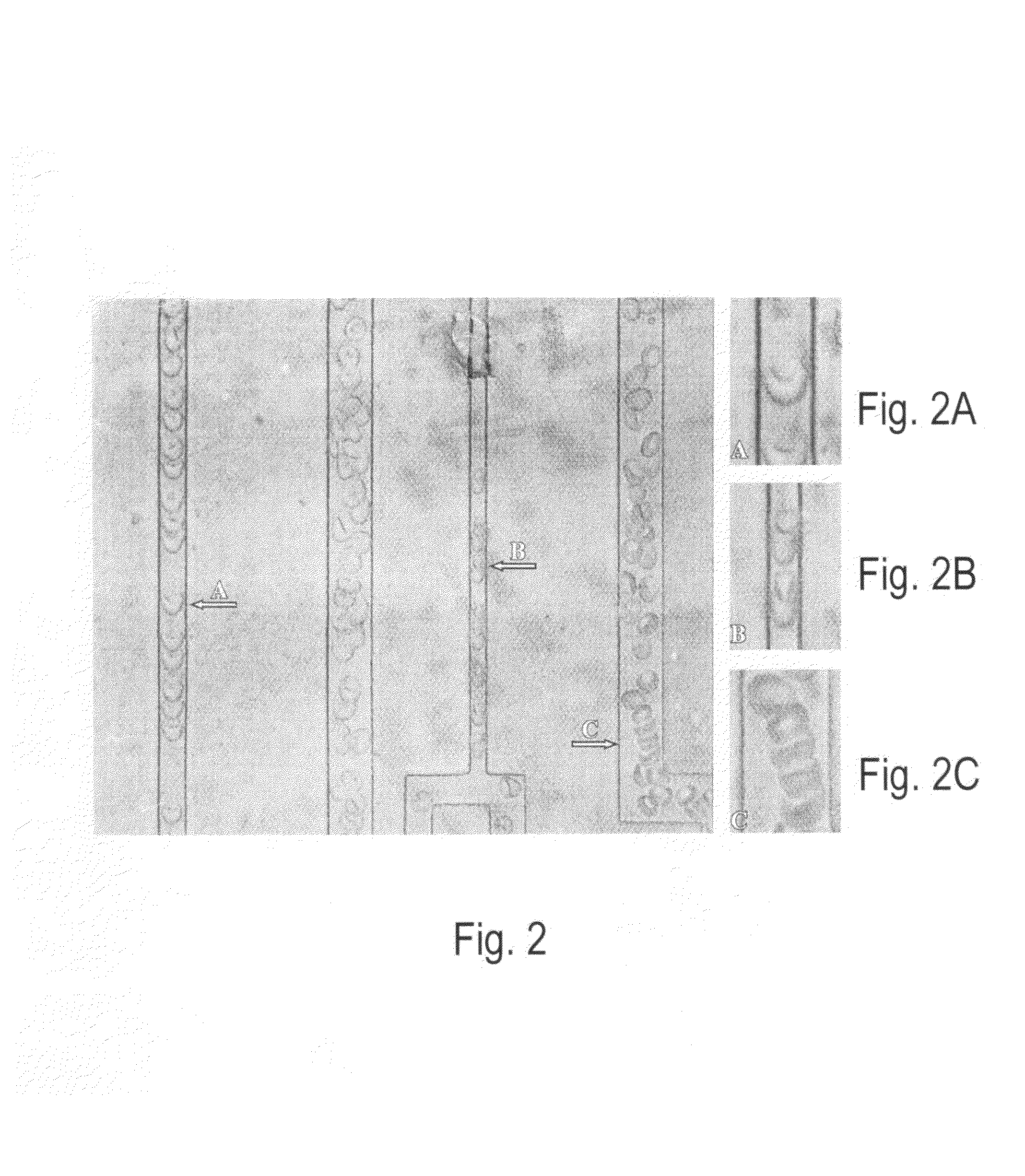
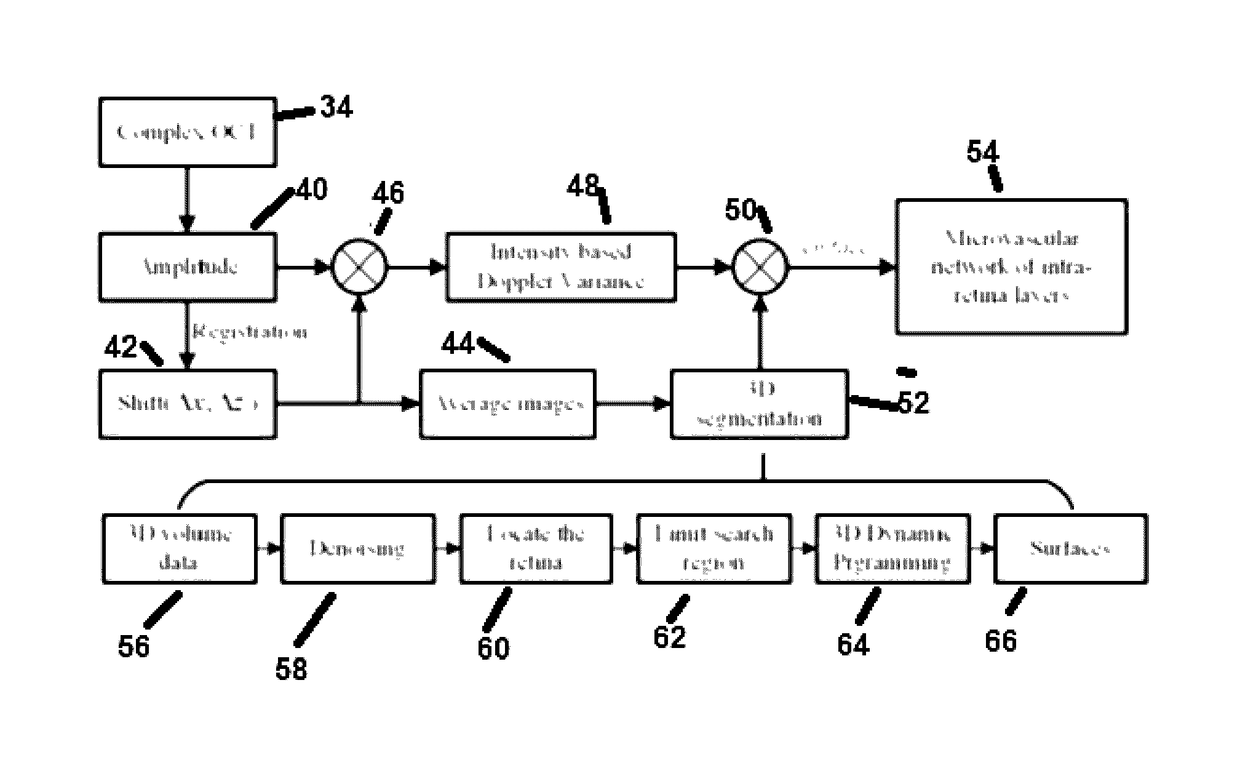
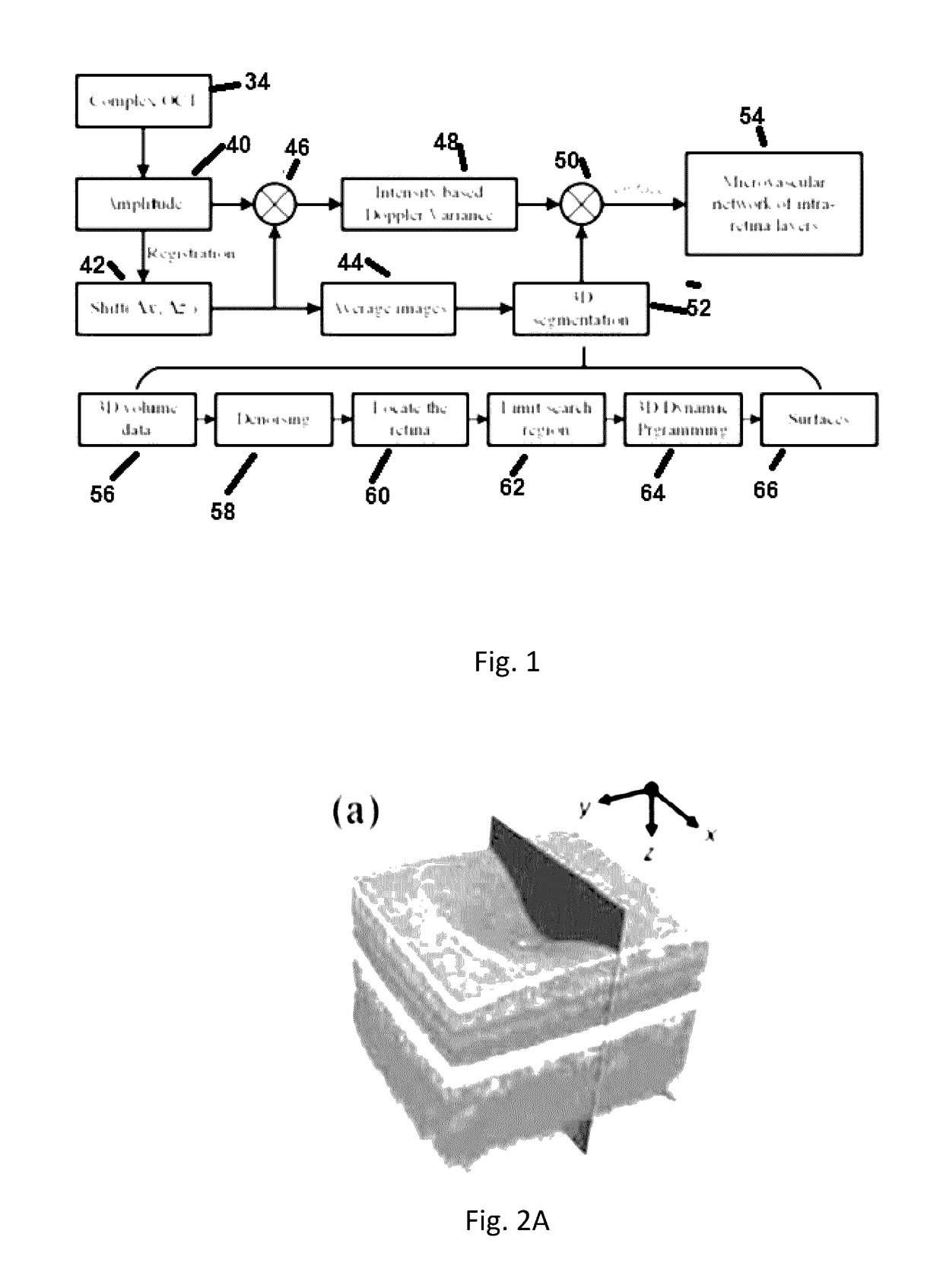
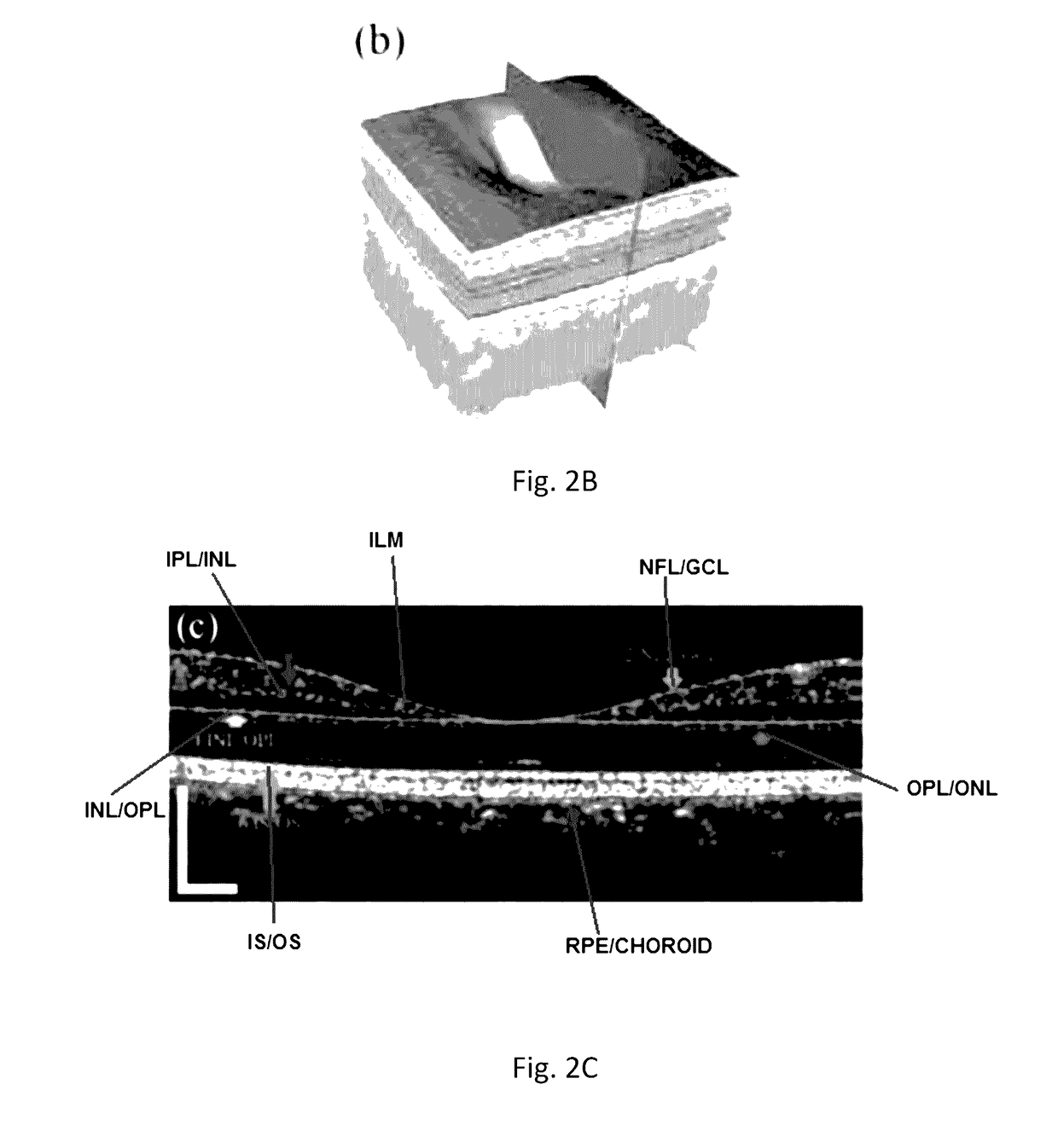
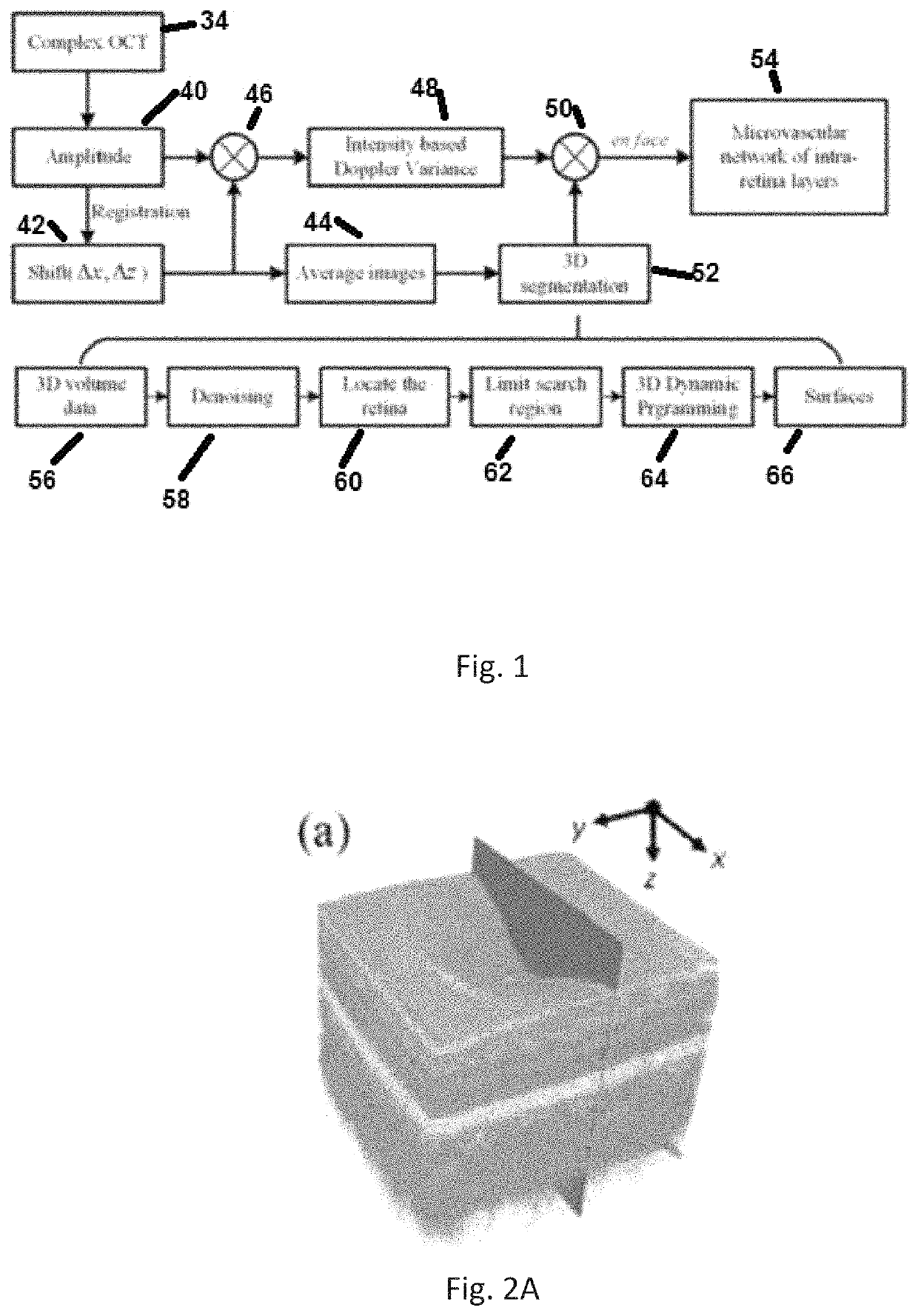
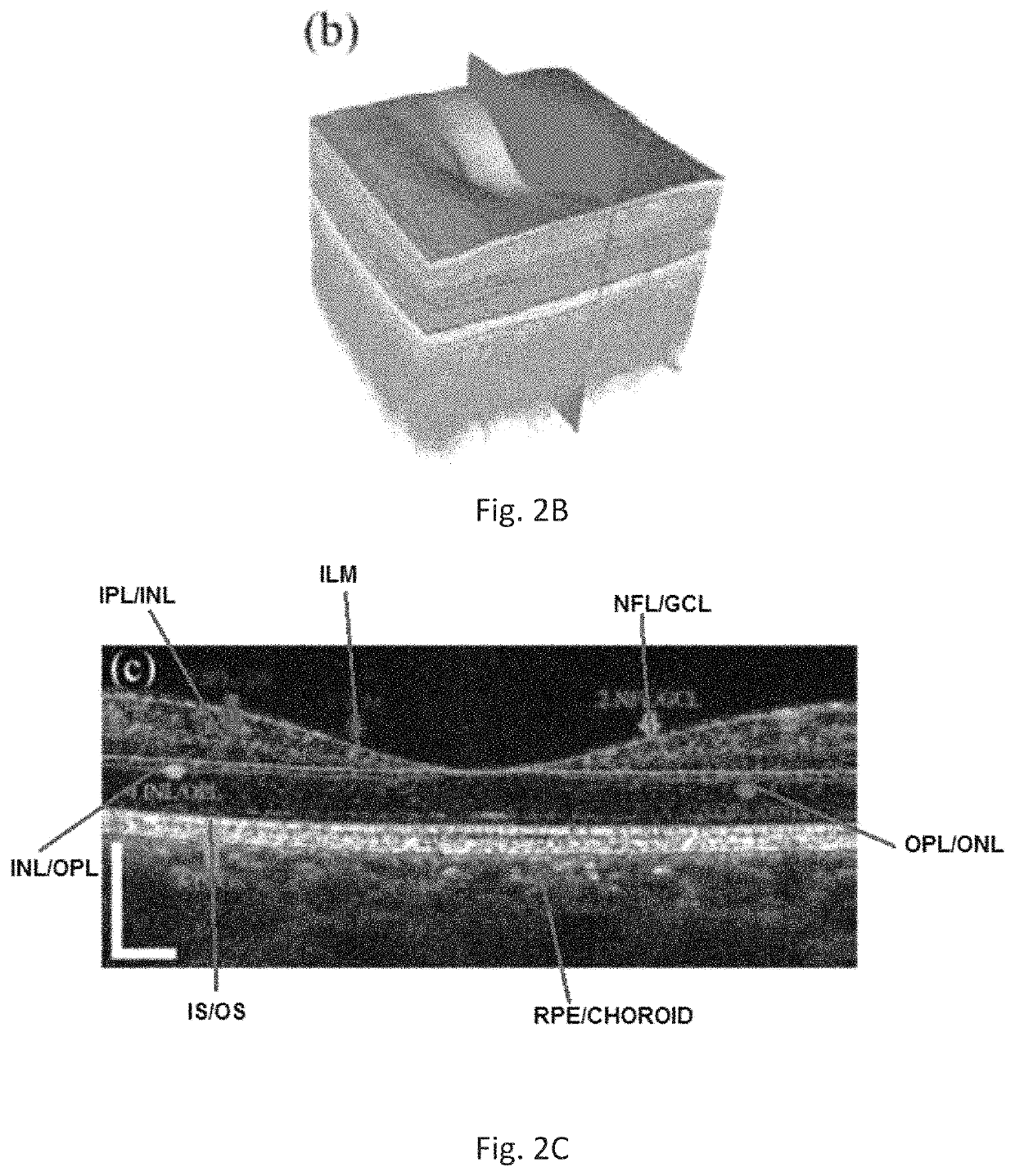
A three-dimensional (three dimensional) segmentation method with intensity-based Doppler variance (IBDV) based on swept-source OCT. The automatic three dimensional segmentation method is used to obtain seven surfaces of intra-retinal layers. The microvascular network of the retina, which is acquired by the IBDV method, can be divided into six layers. The microvascular network of the six individual layers are visualized, and the morphology and contrast images can be improved by using the segmentation method. This method has potential for earlier diagnosis and precise monitoring in retinal vascular diseases. Each tomographic image is composed of eight repeat scans at the same position, which achieves a high time difference to improve the sensitivity of the angiographic method. A subpixel registration algorithm is used to reduce the eye movement. The GPU was used to accelerate the data processing to achieve real-time preview of the acquired data.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Repairing or replacing tissues or organs
InactiveUS20060140914A1Increase the number ofImprove biological activityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsMicrovascular NetworkBiology
In general, this invention provides methods and compositions for stabilizing, repairing, or replacing damaged or diseased tissues or organs by engineering blood vessels in such tissues or organs. In addition, the invention further provides methods and compositions for producing functional microvascular networks useful in tissue engineering.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Method for Creating Perfusable Microvessel Systems
ActiveUS20080261306A1Prolong survival timeOvercome limitationsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicrovascular NetworkPerfusion
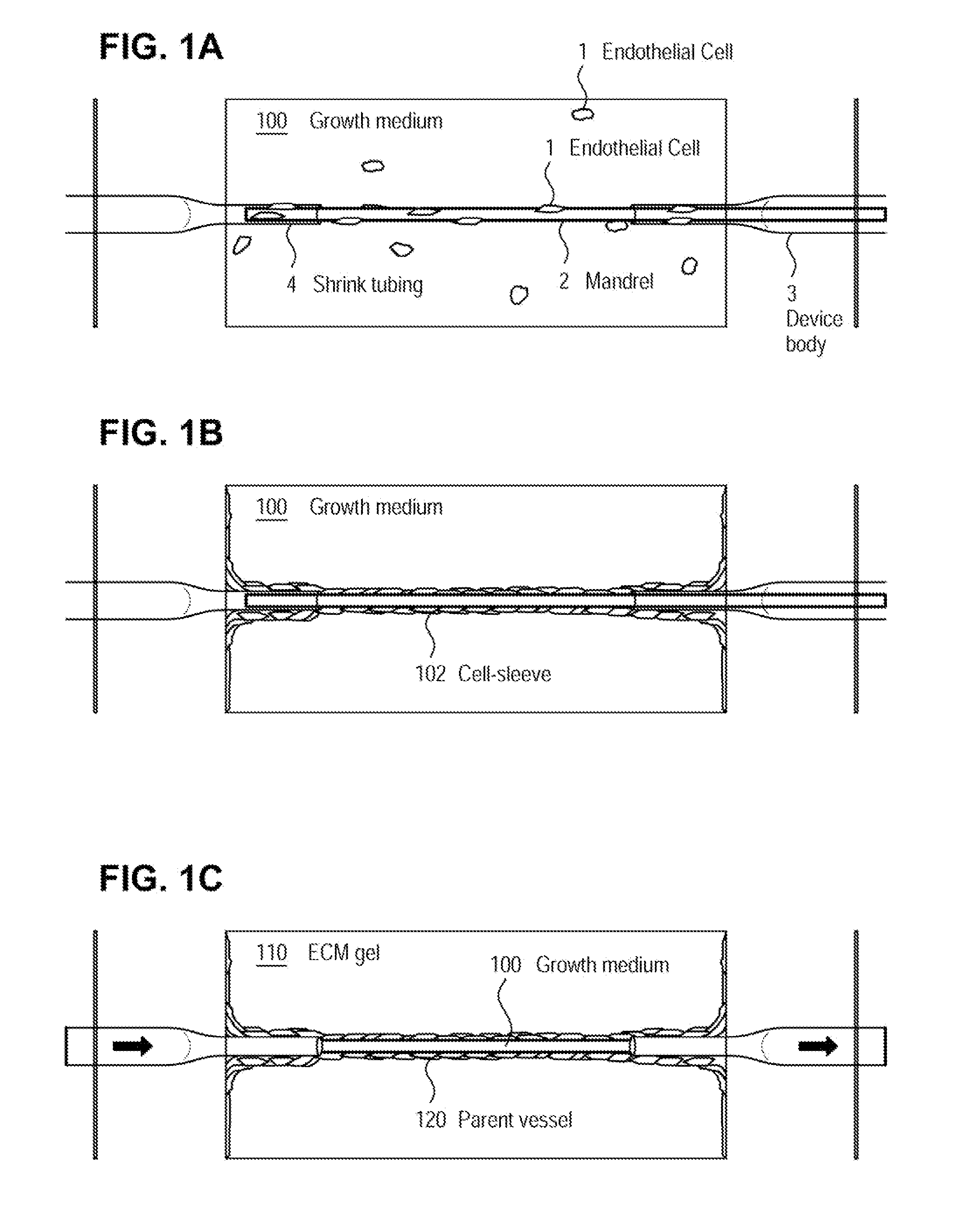
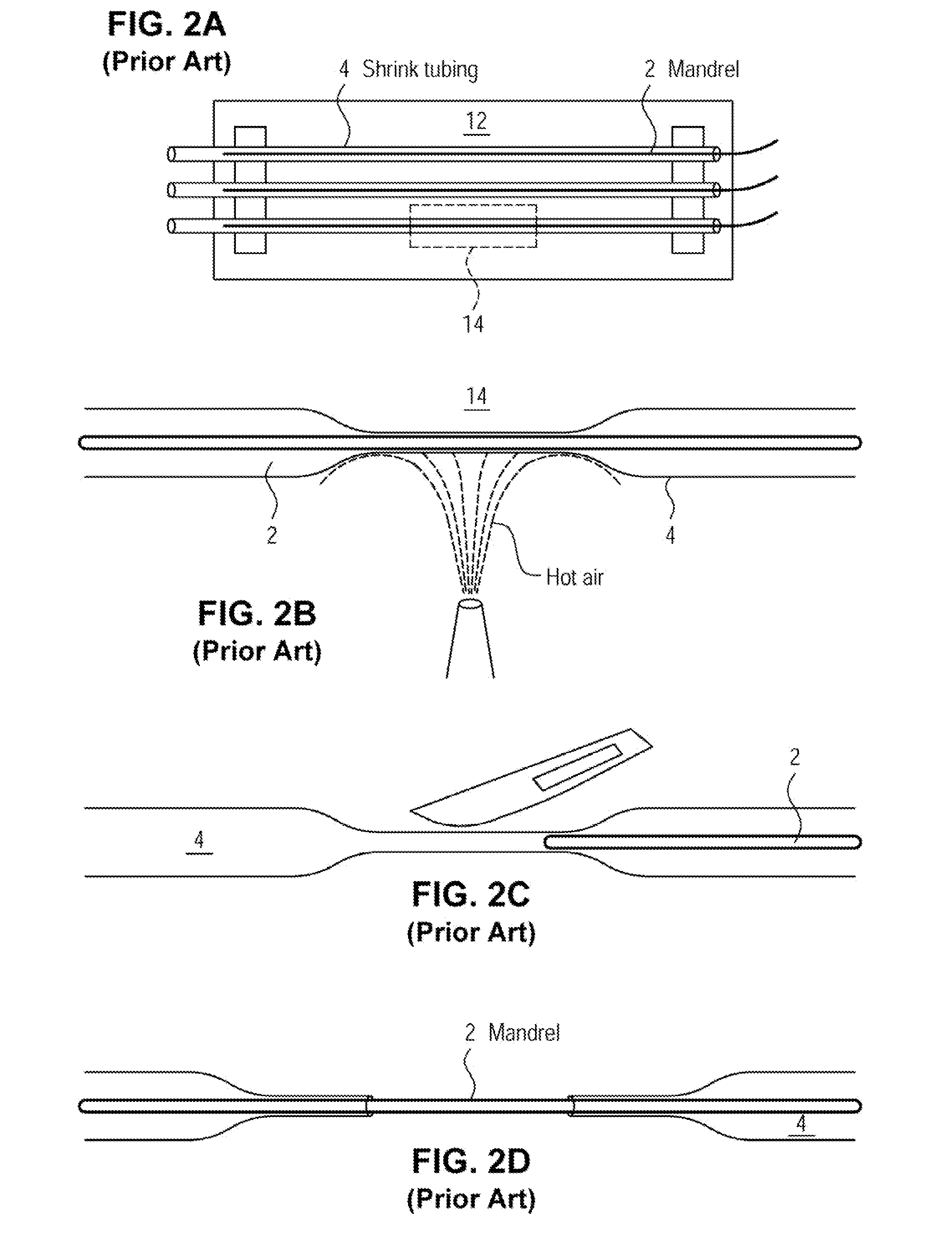
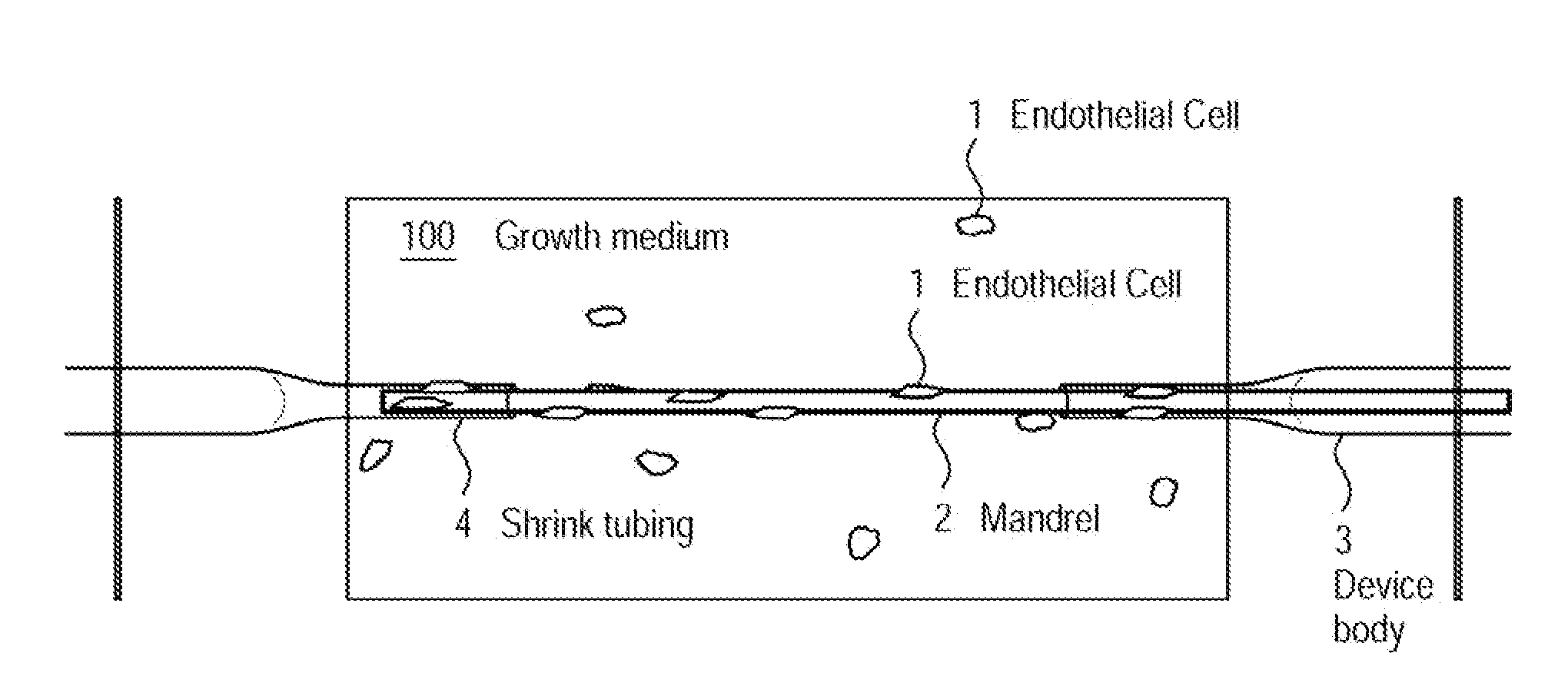
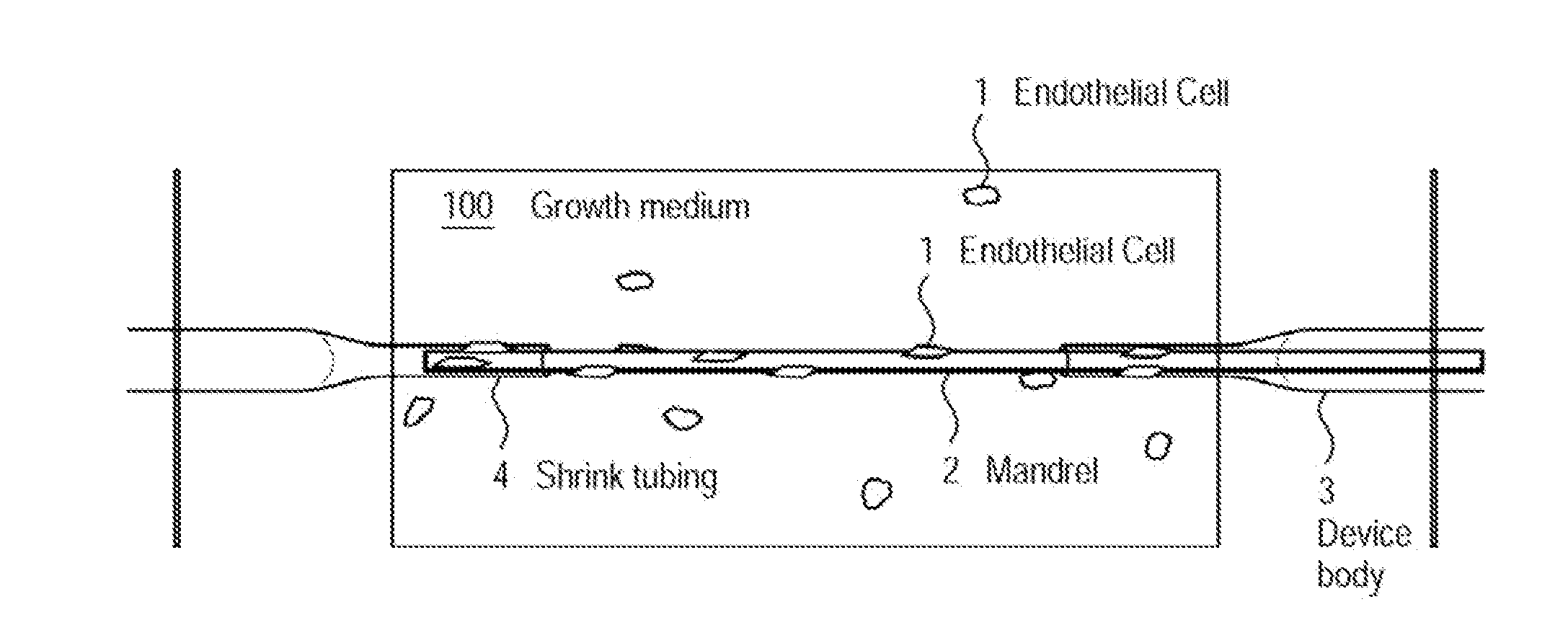
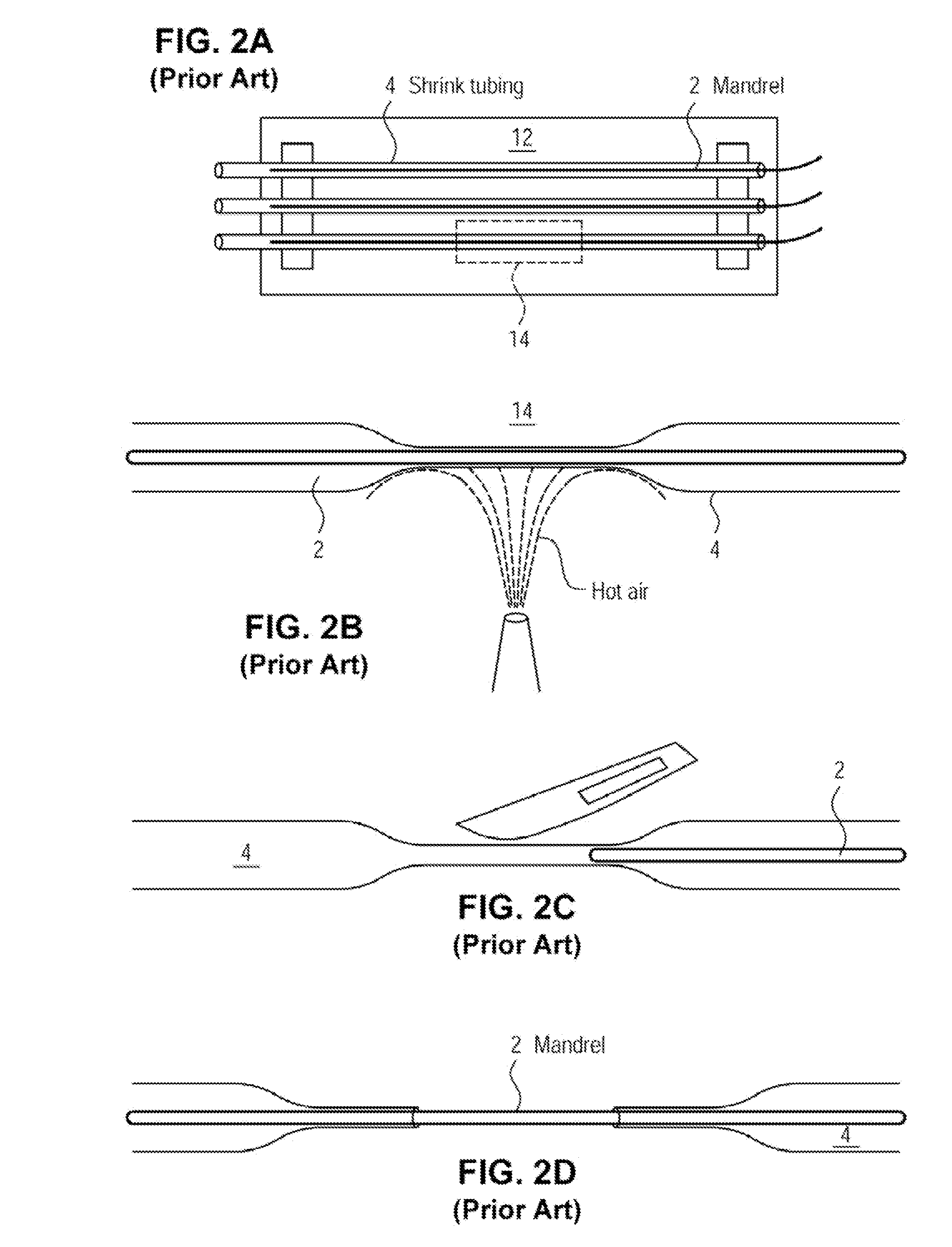
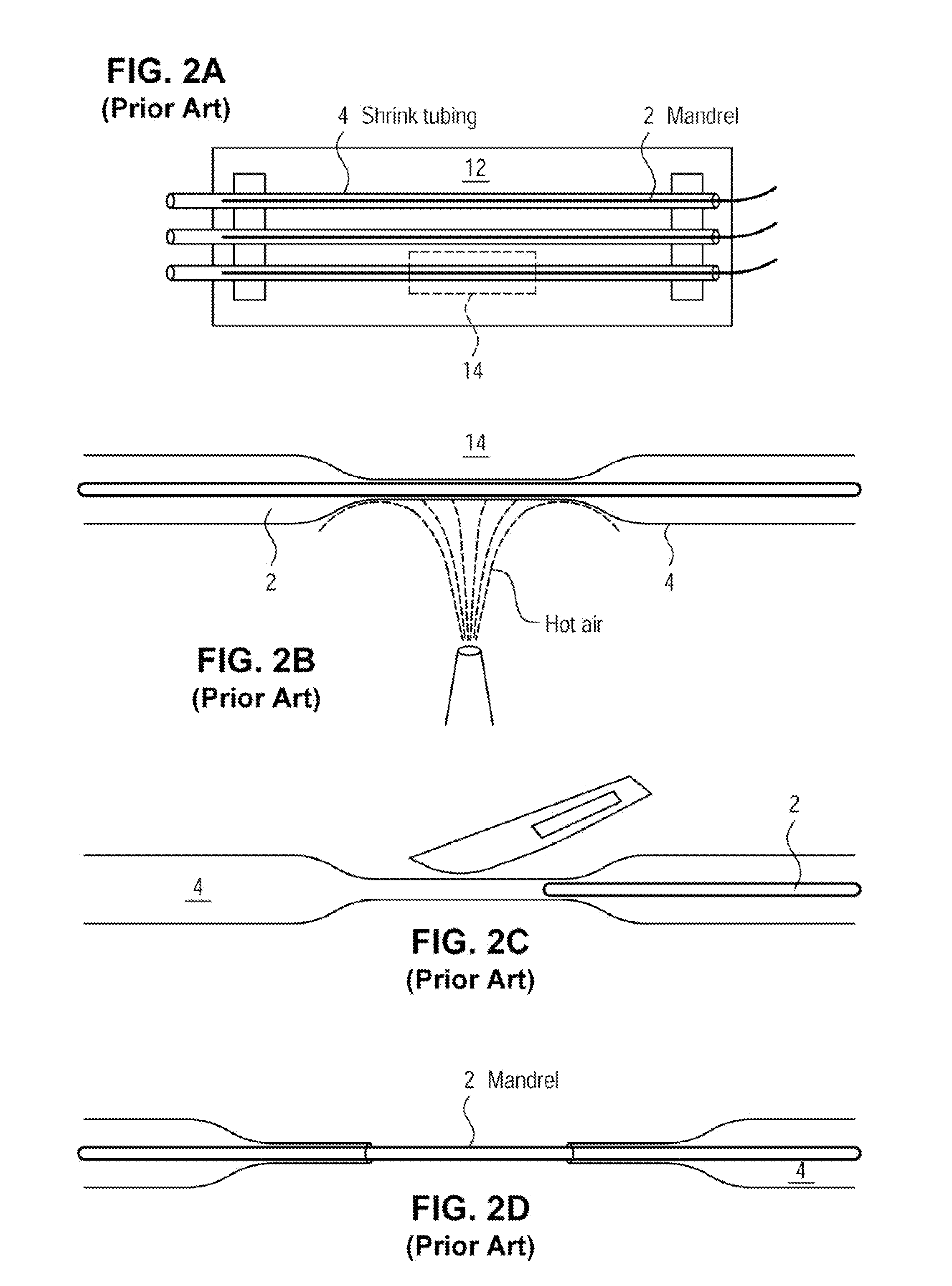
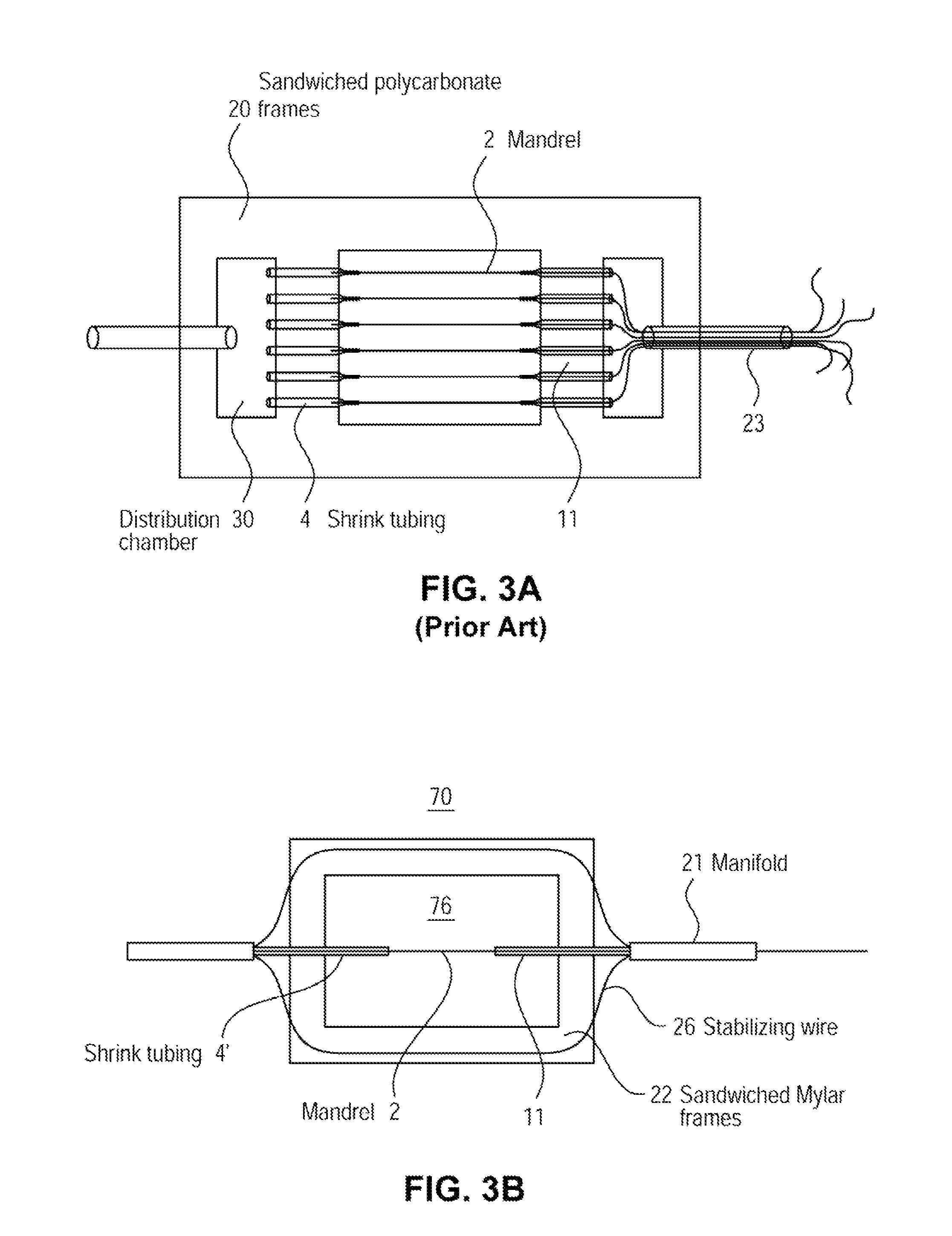
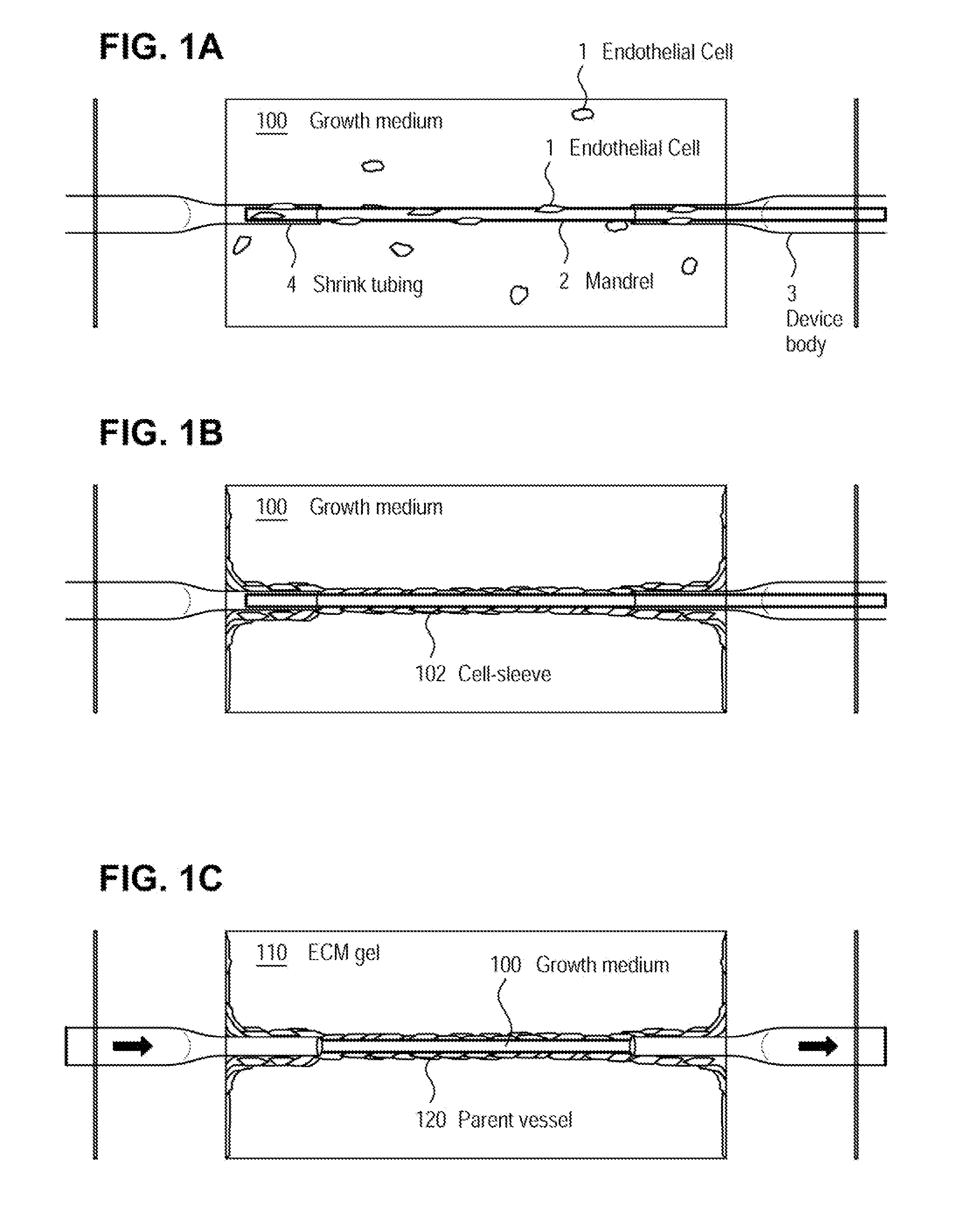
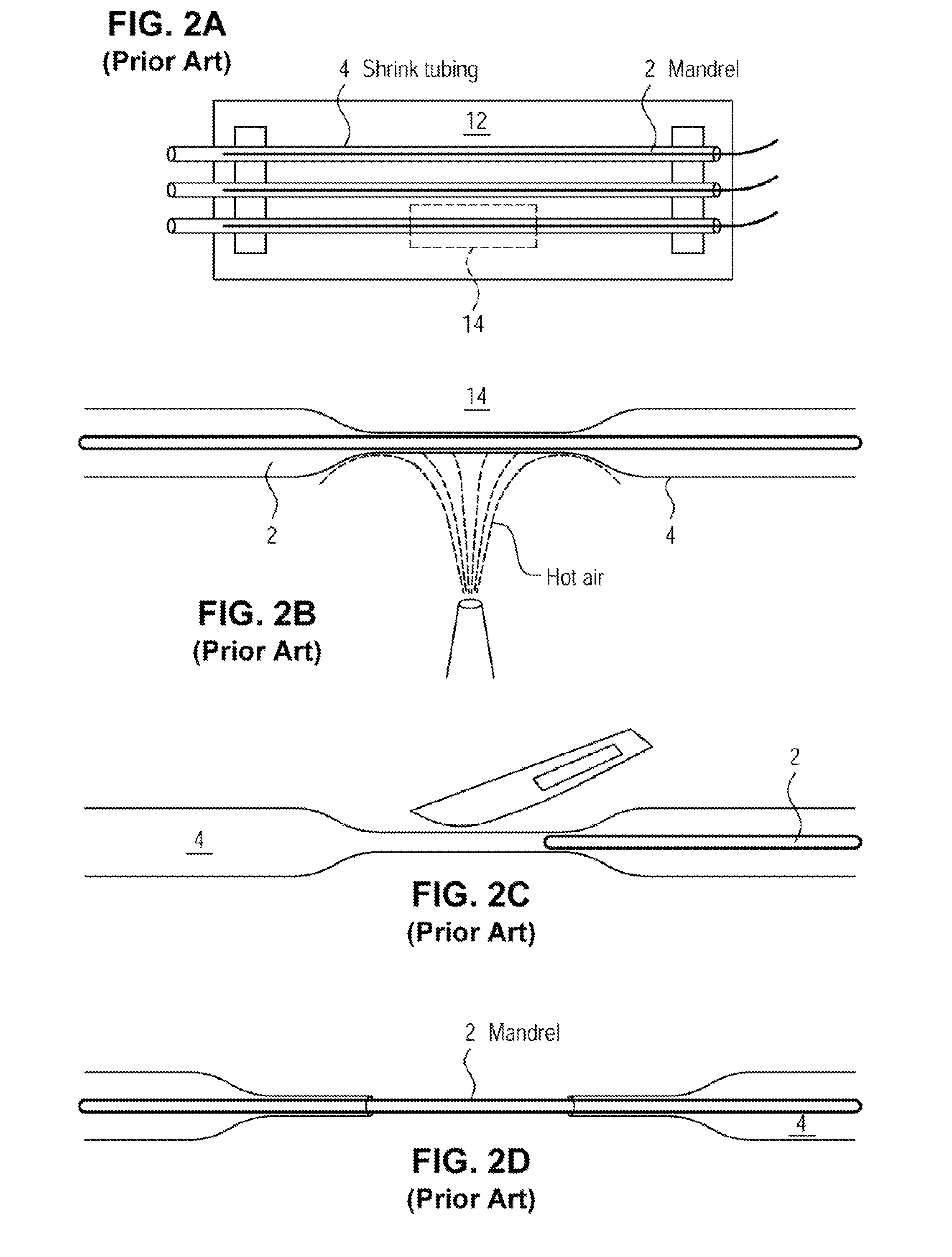
A method for creating networks of perfusable microvessels in vitro. A mandrel is drawn through a matrix to form a channel through the matrix. Cells are injected into the channel. The matrix is incubated to allow the cells to attach inside the channel. The channel is perfused to remove unattached cells to create a parent vessel, where the parent vessel includes a perfusable hollow channel lined with cells in the matrix. The parent vessel is induced to create sprouts into the surrounding matrix gel so as to form a microvessel network. The microvessel network is subjected to luminal perfusion through the parent vessel.
Owner:NORTIS
Synthetic microfluidic microvasculature network
ActiveUS20070231783A1Optimize drug deliveryEliminate concernsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsParticle adhesionDiabetes mellitus
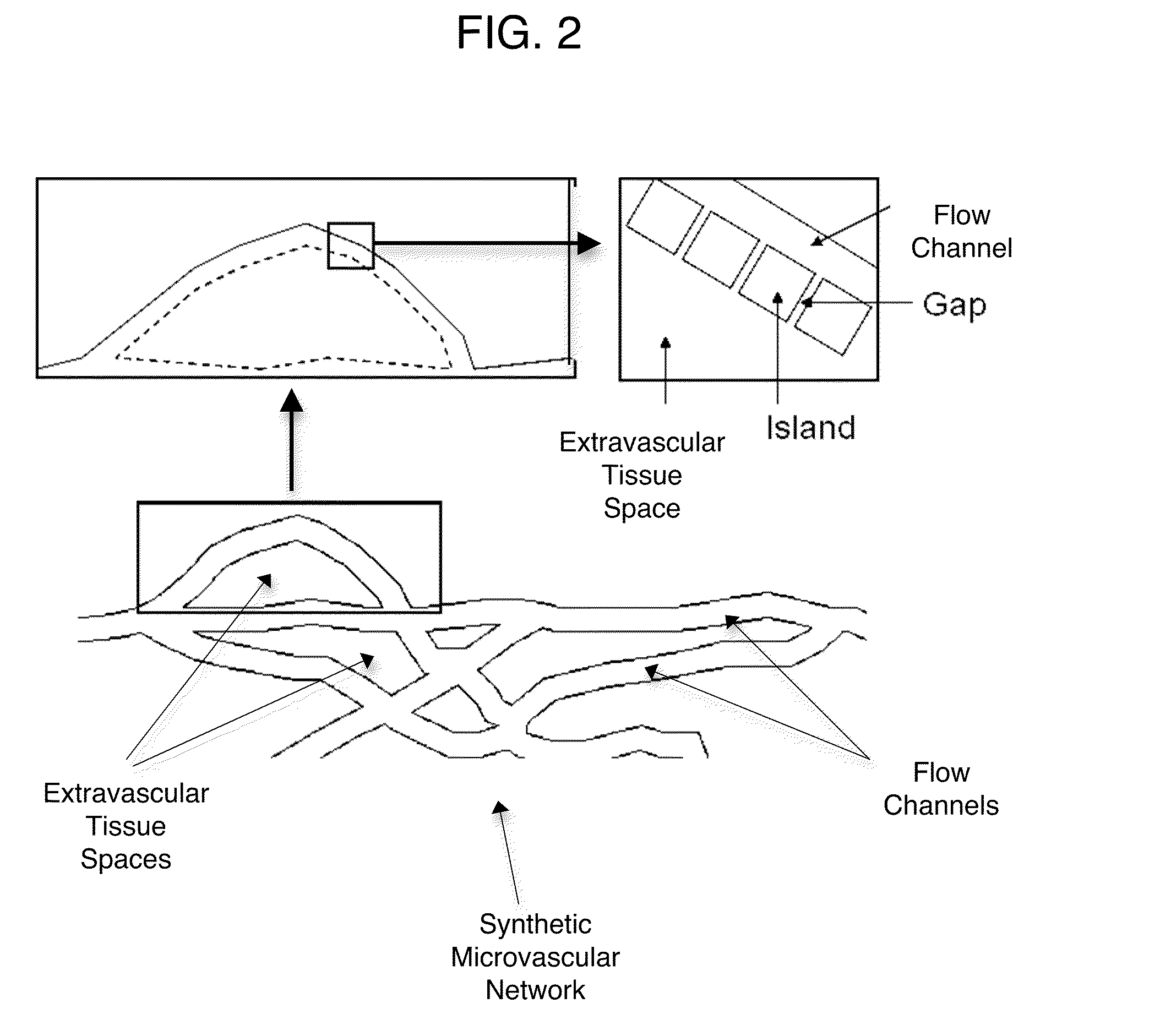
The present invention is a synthetic microfluidic microvasculature network and associated methods. The synthetic microfluidic microvasculature network mimics the structure, fluid flow characteristics, and physiological behavior of physiological microvasculature networks. Computational methods for simulating flow and particle adherence in synthetic and physiological microvascular systems and methods for determining parameters influencing particle adhesion and drug delivery are also described. The invention has many uses including the optimization of drug delivery and microvascular treatments and in describing disease mechanisms that affect the microvasculature such as inflammation, diabetes and hypertension.
Owner:SYNVIVO INC
Microfluidic Assay for Selection and Optimization of Drug Delivery Vehicles to Tumors
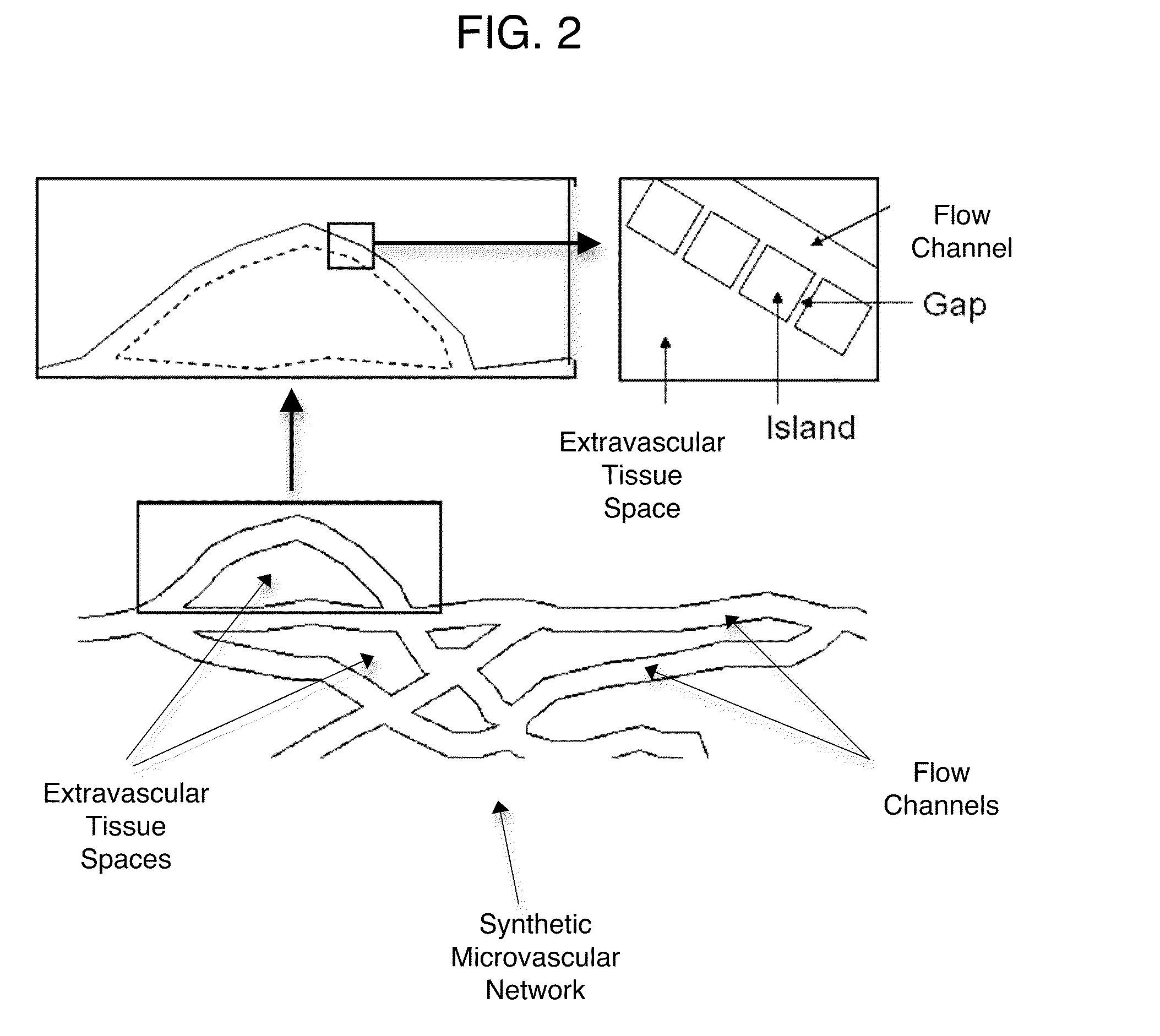
ActiveUS20100099136A1Improve breathabilityHigh interstitial pressureBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAssayMicrovascular Network
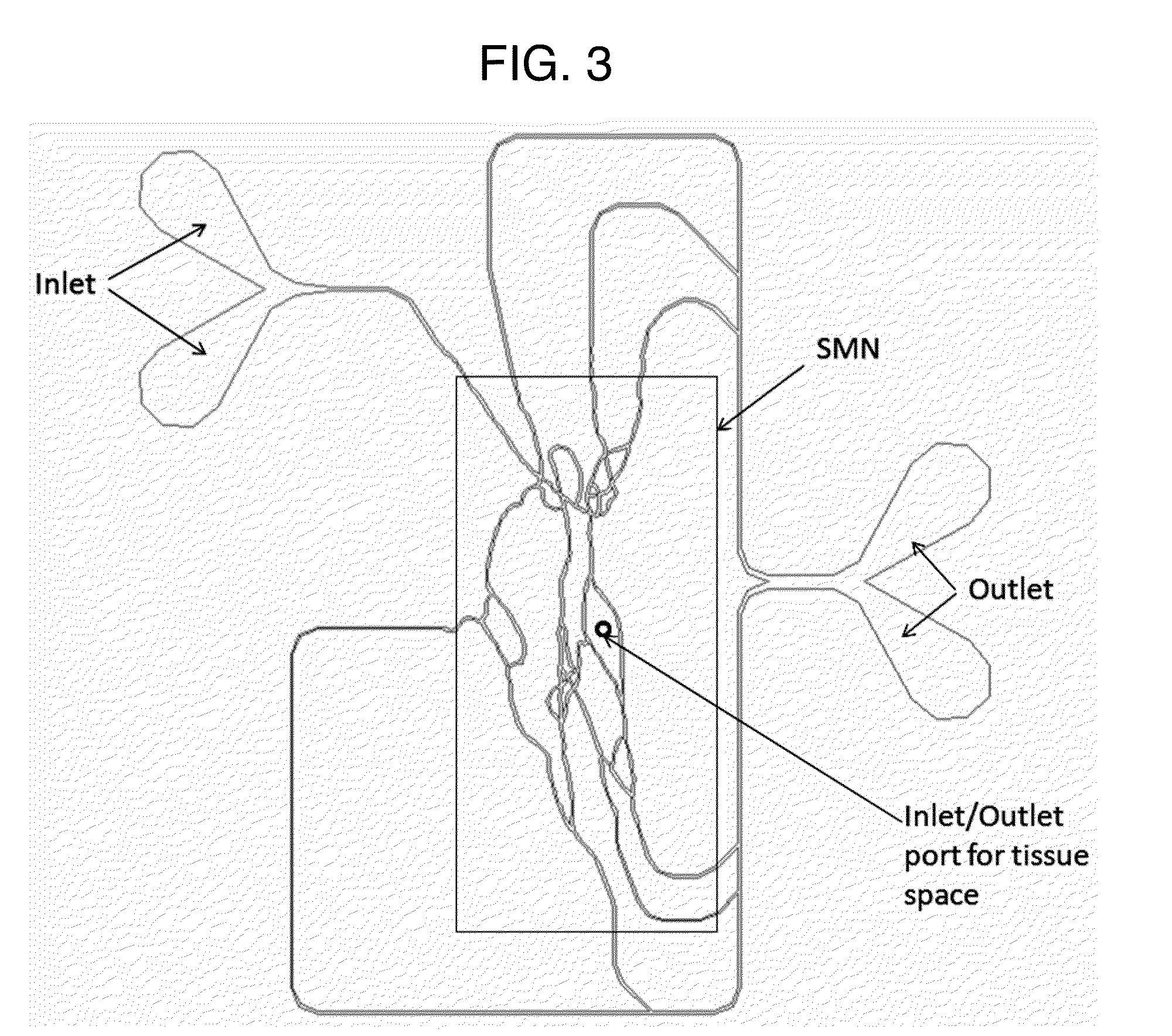
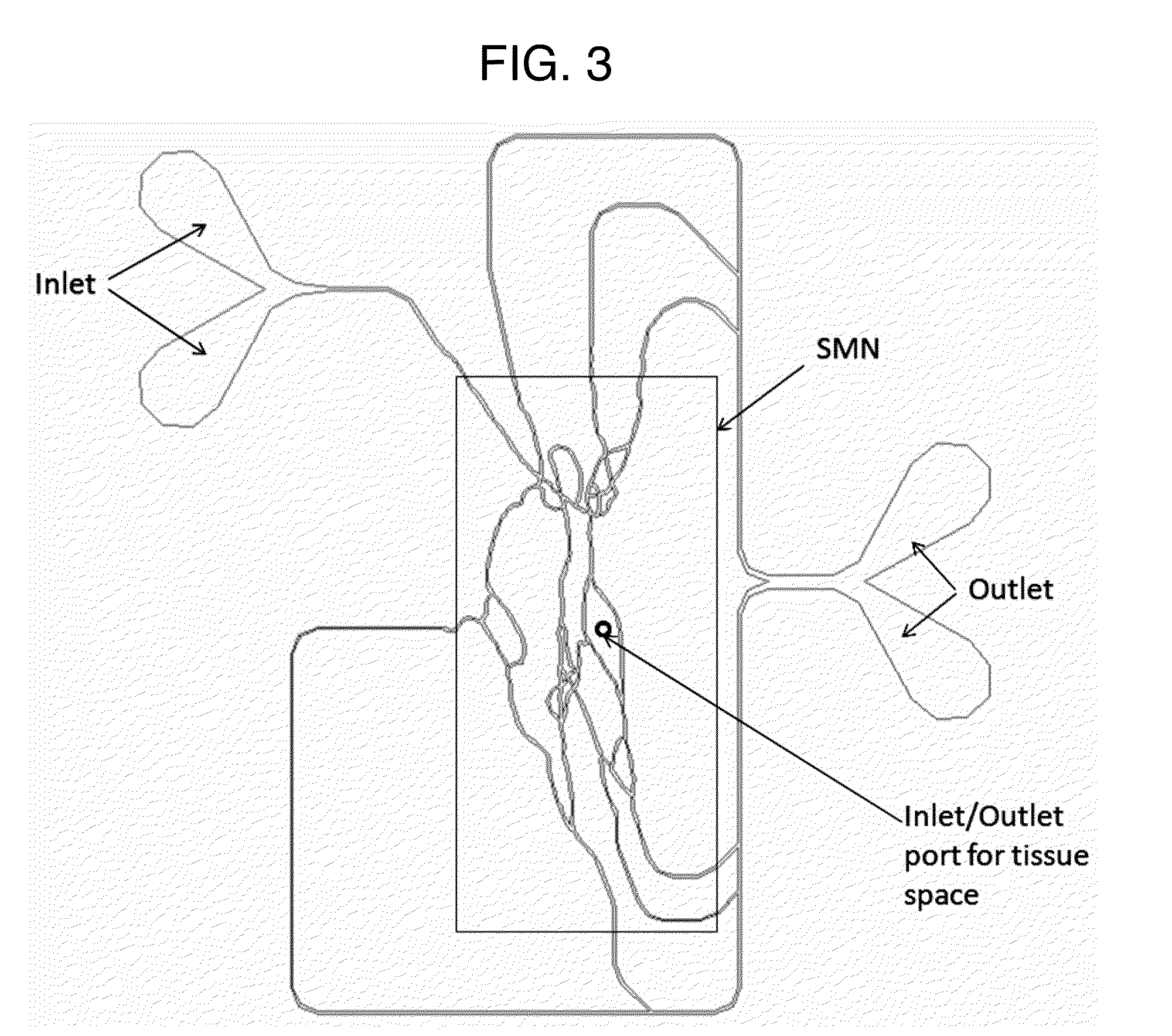
An apparatus and method for assaying a tumor drug delivery vehicle comprises a synthetic microvascular network of interconnected flow channels in fluid communication through a porous wall with a tissue space containing animal cells and means for quantifying drug delivery from the microvascular network to the animal cells.
Owner:SYNVIVO INC
Method for creating perfusable microvessel systems
ActiveUS20100279268A1Fast formingPromote growthBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell typeMicrovascular Network
A method for creating networks of perfusable microvessels in vitro. Cells including cell types capable of sprouting are seeded 1300 into a channel in a matrix at to activate competency 1304 of the cells for sprouting as microvessels based on the seeding density. The matrix channel is perfused with medium to allow parent vessels to form and for viability 1324. The parent vessels and matrix are incubated and perfused to provide for sprouting of microvessels from parent vessels into the surrounding matrix 1328. The sprouting parent vessels are grown until network forms 1332.
Owner:NORTIS
Synthetic Microfluidic Microvasculature Networks
ActiveUS20120330629A1Computation using non-denominational number representationBiological testingParticle adhesionMedicine
A synthetic microfluidic microvasculature network and associated methods mimic the structure, fluid flow characteristics, and physiological behavior of physiological microvasculature networks. Computational methods for simulating flow and particle adherence in synthetic and physiological microvascular systems and methods for determining parameters influencing particle adhesion and drug delivery are described with applications in the optimization of drug delivery and microvascular treatments and in describing disease mechanisms that affect the microvasculature.
Owner:SYNVIVO INC
In-vitro construction method for simulating blood brain barrier through human brain microangiogenesis
ActiveCN108823145AReduce dosageAvoid inaccurate test resultsNervous system cellsArtificial cell constructs3D cell cultureCell culture media
The invention discloses an in-vitro construction method for simulating a blood brain barrier through human brain microangiogenesis. The method comprises the following steps: preparing human brain microvascular endothelial cell suspension and human astrocyte suspension, and preparing fibrinogen mother liquor and thrombin mother liquor; mixing the endothelial cell suspension, the astrocyte suspension, a DMEM (Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium) medium, the fibrinogen mother liquor and the thrombin mother liquor, and preparing a mixed cell gel solution; injecting the mixed cell gel solution into amicro-fluidic chip, performing thermostatic incubation to gelation, adding an endothelial growth medium into the micro-fluidic chip, and constructing a 3D cell culture chip; performing continuous culture on the 3D cell culture chip, and enabling the endothelial cells and astrocyte to grow into a brain microvascular network structure, namely correspondingly producing the simulated blood brain barrier. According to the technical scheme provided by the invention, the in-vitro model of the blood brain barrier is successfully constructed, and the characteristics of the blood brain barrier are clearly and accurately reflected.
Owner:WUHAN CHOPPER BIOLOGY
Controllable formation of microvascular networks using sacrificial microfiber templates
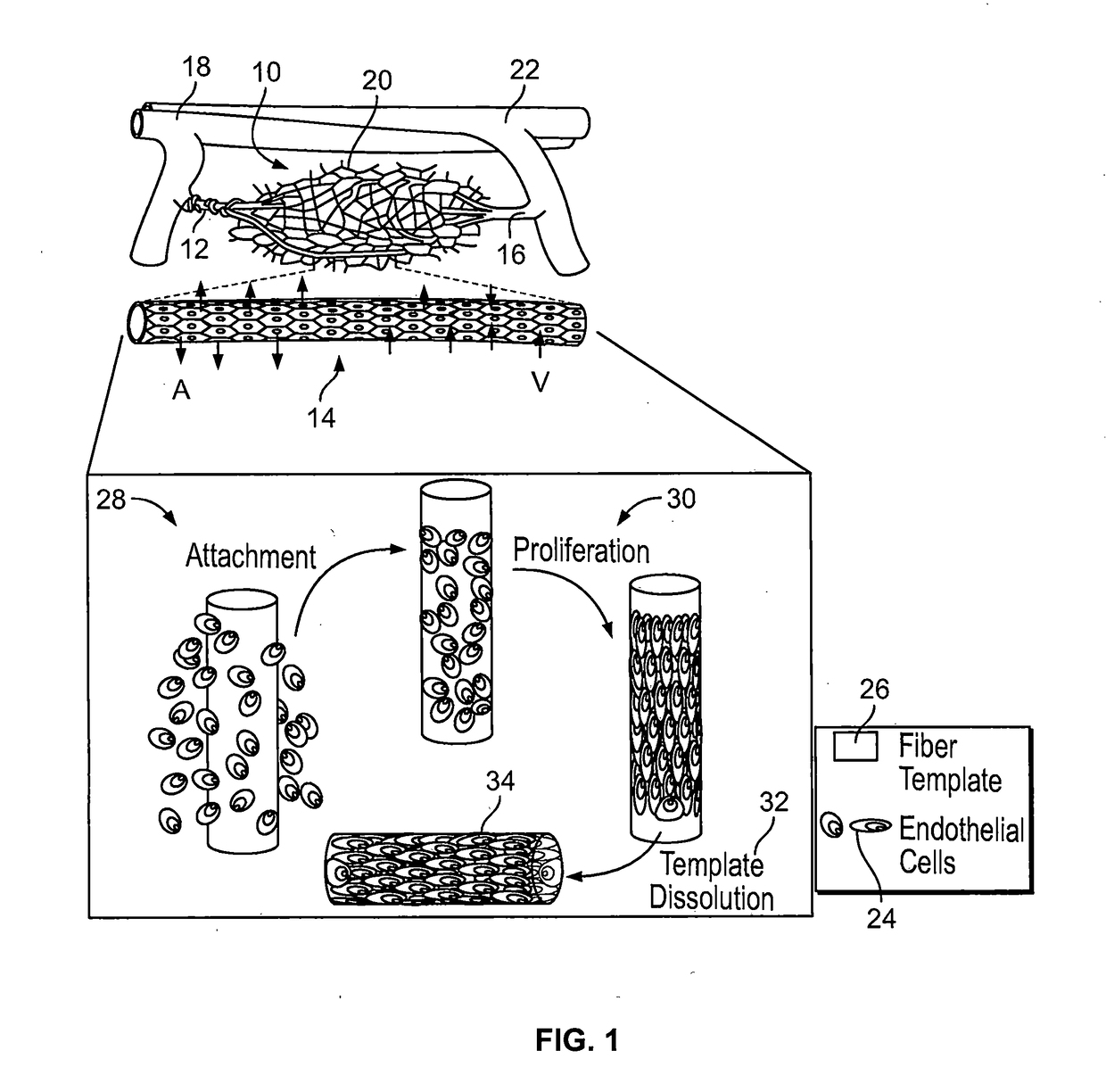
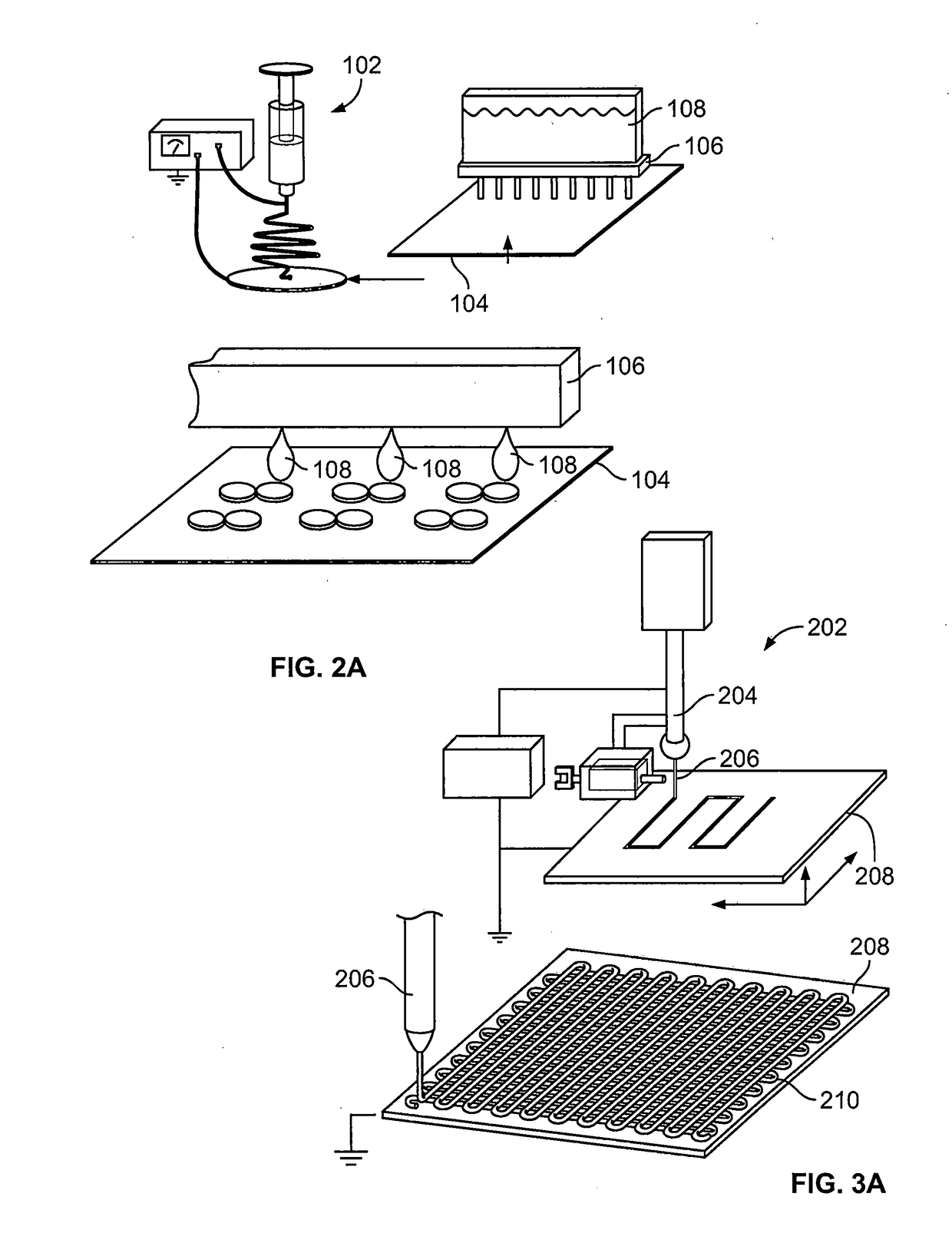
InactiveUS20170088815A1Easily integrated into tissue-engineered tissue constructRaise the potentialCell culture supports/coatingCell culture active agentsProgenitorMicrovascular Network
The present disclosure relates to fabricating sacrificial microfiber templates from any biocompatible and resorbable materials depending on the time needed for dissolving the microfiber template to free the endothelial tube with open lumen. Microfiber networks with distinct patterns and defined diameters initially serve as a template to support the growth of vascular cells (endothelial cells or their progenitor cells, or combined with mural cells such as pericytes) and then dissolve to form an empty endothelium lumen. The incorporation of sacrificial microfiber networks encapsulated with vascular cells into 3D cell-rich constructs allows for the creation of various vascularized tissues.
Owner:STEVENS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Microfluidic assay for selection and optimization of drug delivery vehicles to tumors
ActiveUS8355876B2Improve breathabilityImprove pressure resistanceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMedicineMicrovascular Network
An apparatus and method for assaying a tumor drug delivery vehicle comprises a synthetic microvascular network of interconnected flow channels in fluid communication through a porous wall with a tissue space containing animal cells and means for quantifying drug delivery from the microvascular network to the animal cells.
Owner:SYNVIVO INC
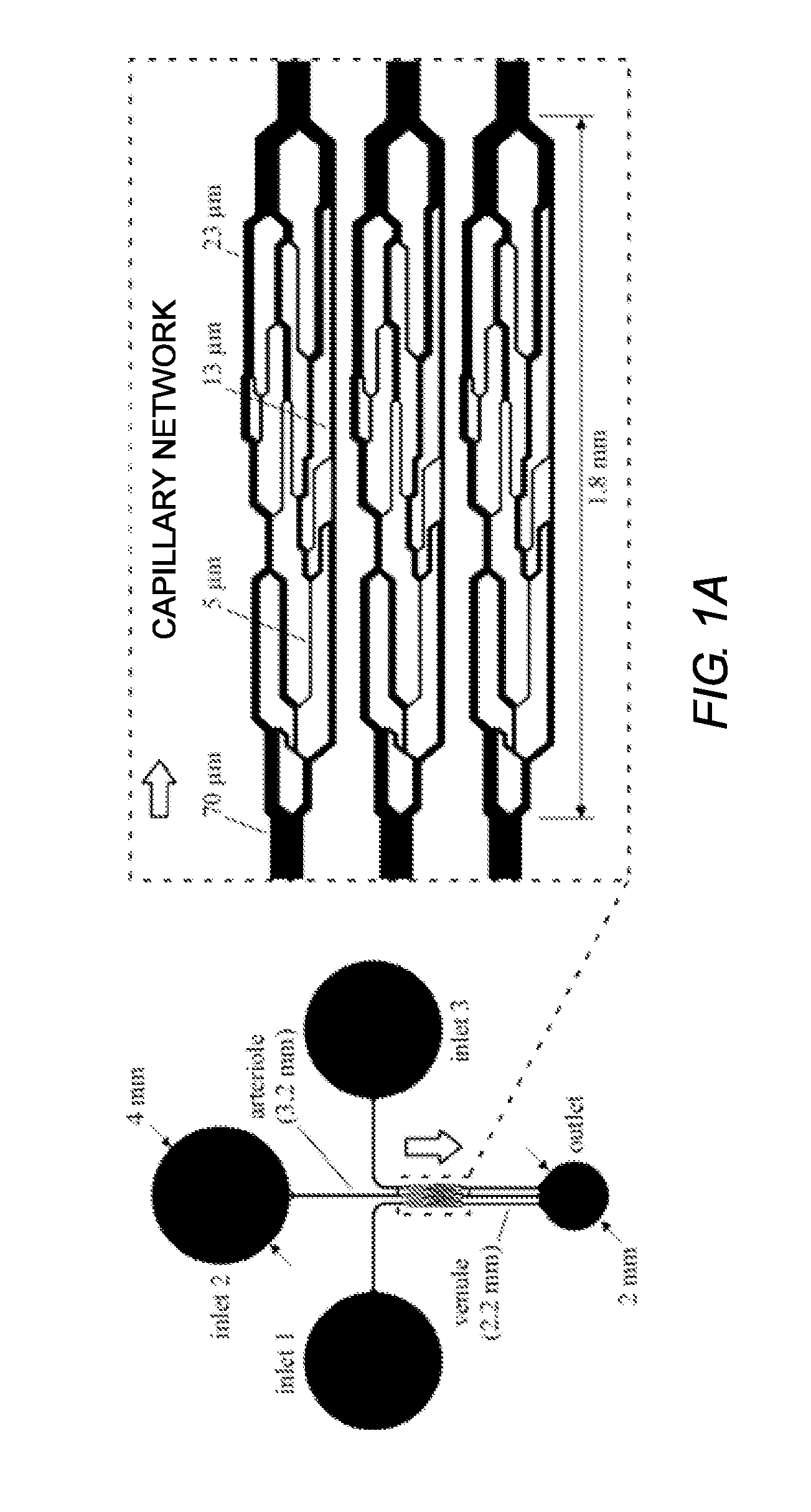
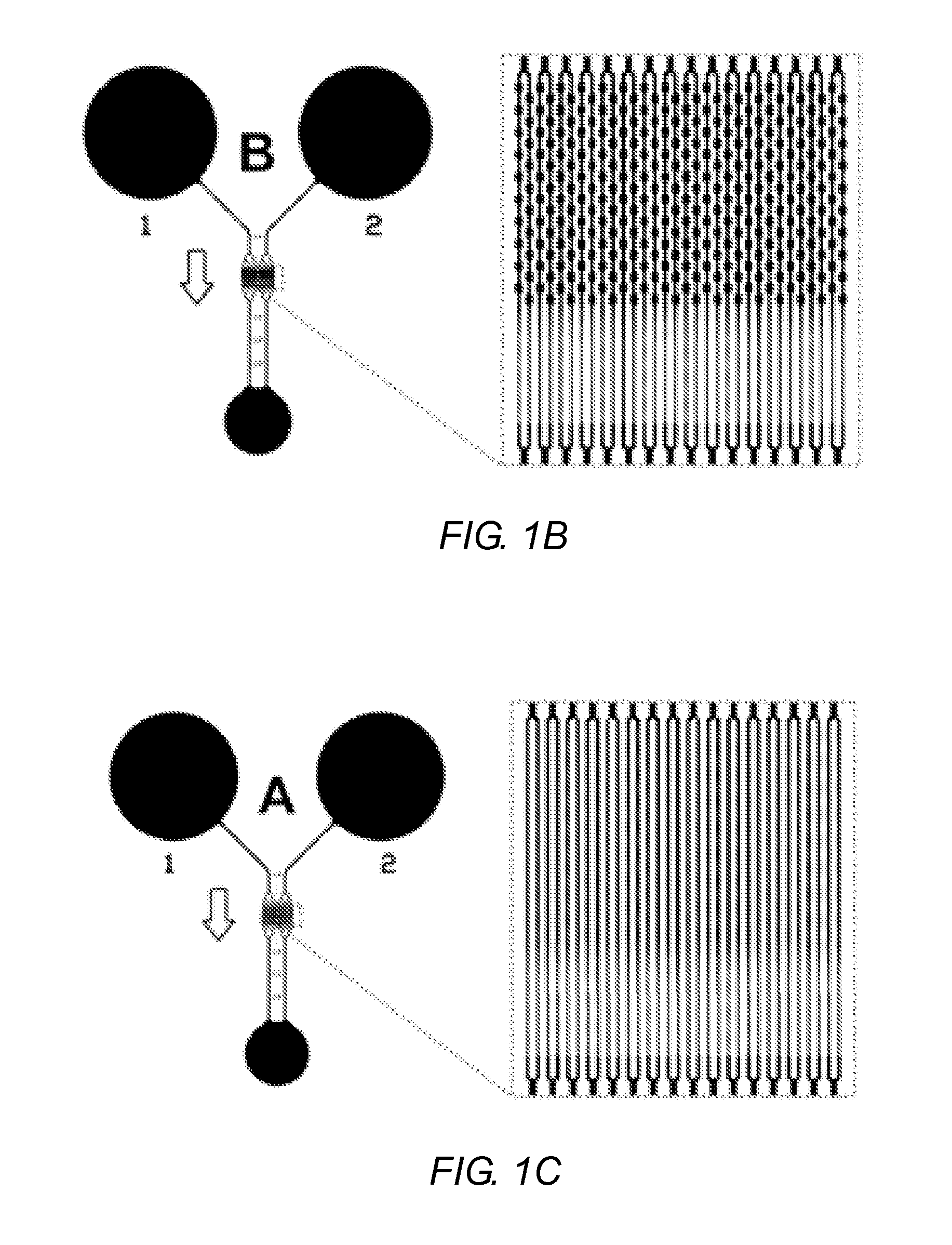
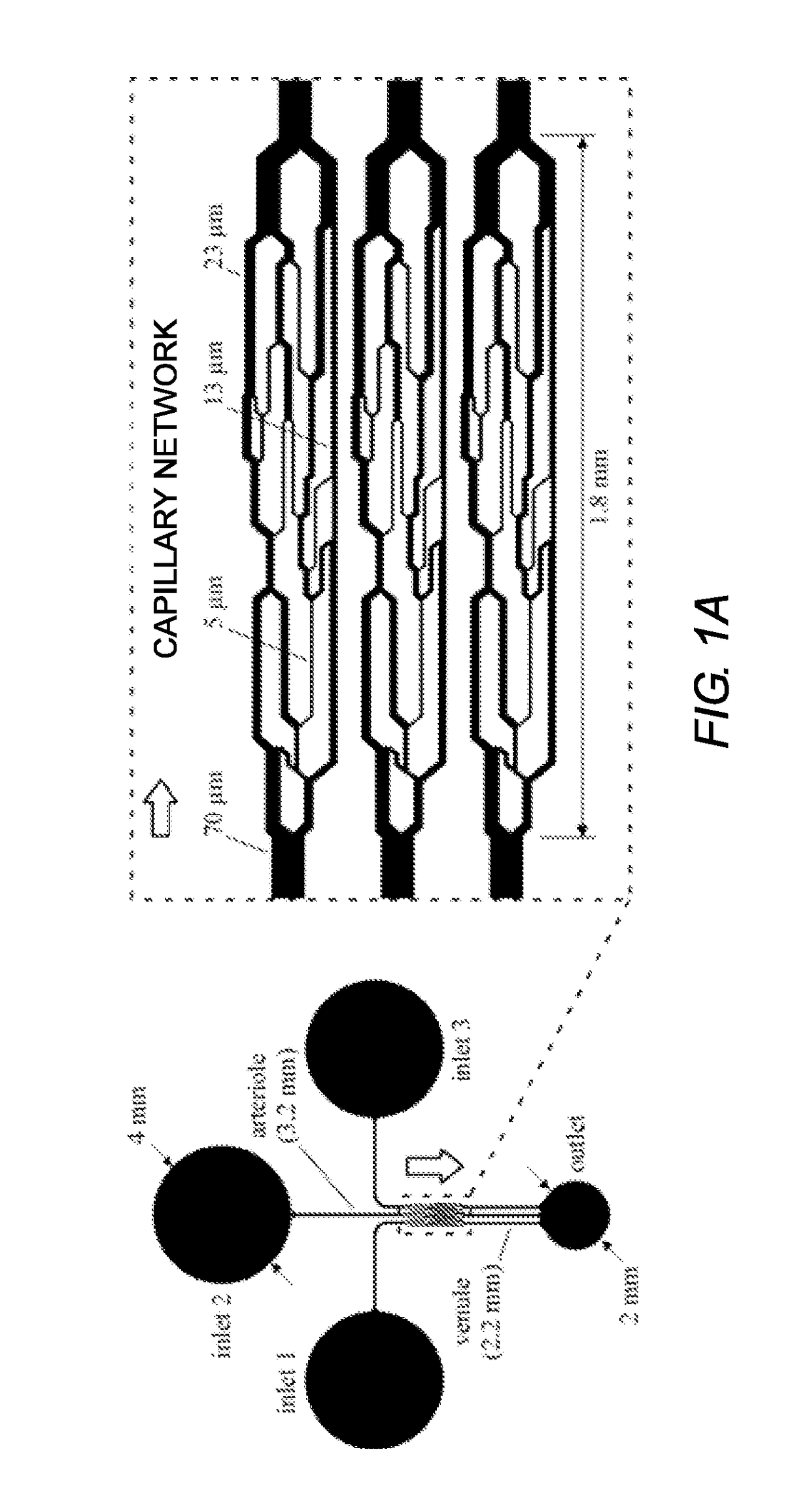
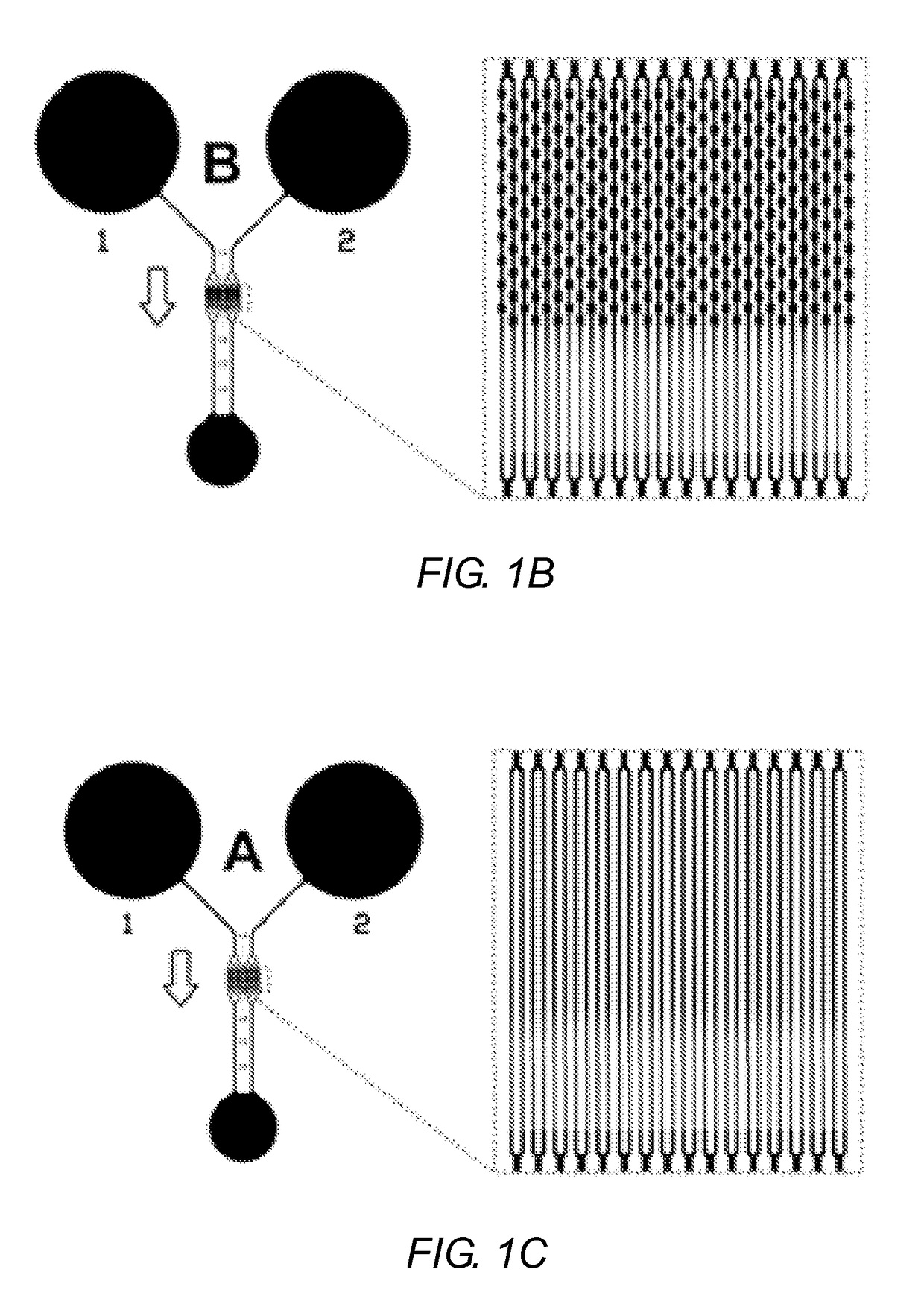
Capillary network devices and methods of use
ActiveUS20150153367A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCapillary networkEngineering
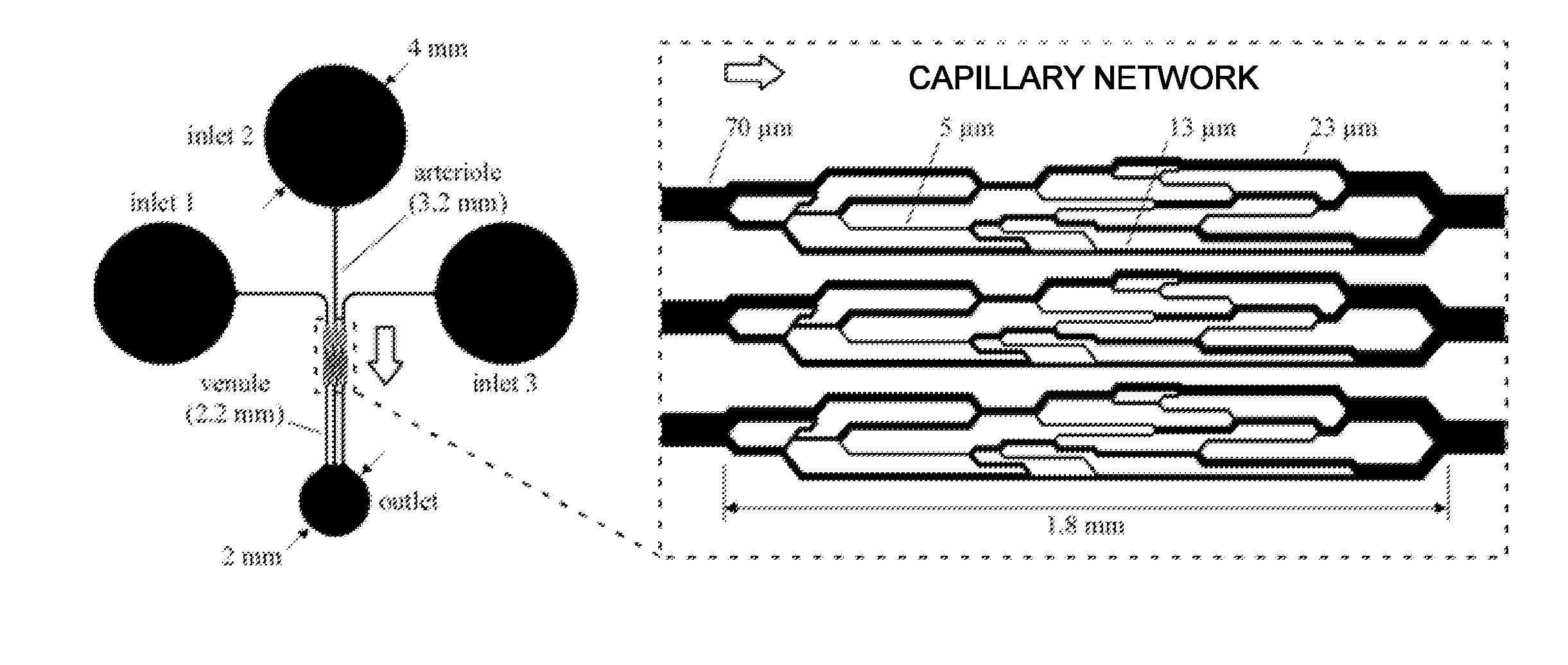
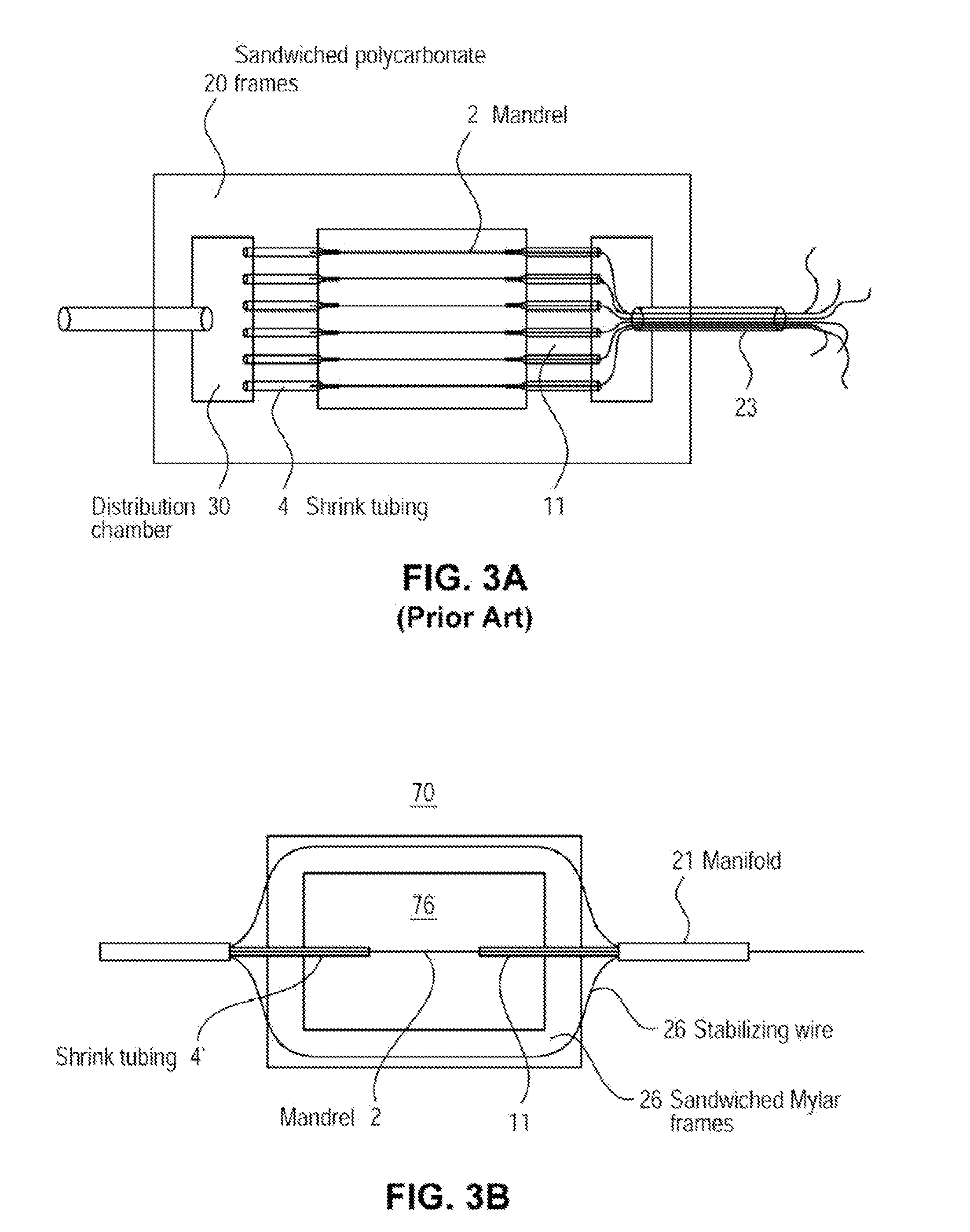
Artificial microvascular network (AMVN) devices are provided and related methods of making and methods of using such devices are provided. The present disclosure generally relates to an AMVN device comprising a substrate including a capillary network configured so as to simulate those actually encountered in the circulation of various humans and animal model systems. In certain aspects, the AMVN devices may be used, e.g., to investigate the effect of storing RBCs under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. However, the use of such AMVN devices is not so limited.
Owner:THE ADMINISTRATORS OF THE TULANE EDUCATIONAL FUND +1
Experimental method for promoting tissue engineering pre-vascularization by umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells
InactiveCN107748260APromote angiogenesisPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansIn vivoMicrovascular Network
The invention discloses an experimental method for promoting tissue engineering pre-vascularization by umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells; according to the method, vascular endothelial cells and umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells with different proportions are co-cultured in a two-dimensional manner, and a rule of promoting vascular endothelial cell proliferation and hematopoietic differentiation by the umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells is studied. In addition, a micron-sized network microvascular scaffold is prepared by high temperature molten monosaccharide and is dissolved in hydrogel to construct a continuous microchannel culture system of a three-dimensional hydrogel female die, the two cells are subjected to perfusion and suspension culture, an in-vitro constructed microvascular network structure and an engineered bone tissue in-vivo transplantation effect based on the structure are evaluated, and a mechanism of the two cells participating and promoting microvascular network construction is illuminated. A new solution and an experimental basis are provided for in-vitro pre-vascularization of engineered tissues and organs.
Owner:XIAN TISSUE ENG & REGENERATIVE MEDICINE RES INST
Method for creating perfusable microvessel systems
ActiveUS8445280B2Improve stabilityExtension of timeDead animal preservationCell culture supports/coatingCell typeMicrovascular Network
A method for creating networks of perfusable microvessels in vitro. Cells including cell types capable of sprouting are seeded 1300 into a channel in a matrix at to activate competency 1304 of the cells for sprouting as microvessels based on the seeding density. The matrix channel is perfused with medium to allow parent vessels to form and for viability 1324. The parent vessels and matrix are incubated and perfused to provide for sprouting of microvessels from parent vessels into the surrounding matrix 1328. The sprouting parent vessels are grown until network forms 1332.
Owner:NORTIS
Synthetic microfluidic microvasculature network
ActiveUS7725267B2Reduce deliveryEliminate concernsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsParticle adhesionDiabetes mellitus
Owner:SYNVIVO INC
Apparatus and method for capturing a vital vascular fingerprint
ActiveUS9384404B2Effective imagingAccurate identificationPrint image acquisitionSubcutaneous biometric featuresPattern recognitionDermal papillae
A method using optical coherence tomography to capture the microvascular network of the superficial layer of the finger skin for the purpose of fingerprint authentication and liveness detection. At the dermal papilla region, the vascular pattern follows the same pattern of the fingerprint and this vascular pattern forms a live vascular fingerprint. This live vascular fingerprint provides for ultrahigh security and a unique way for fingerprint-based personal verification. Because the system is based on blood flow, which only exists in a living person, the technique is robust against spoof attaching. After performing non-contact in-vivo imaging of a human fingertip, a three dimensional vasculature image is reconstructed from a plurality of vasculature tomography images and at least one vasculature fingerprint image which corresponds to the fingertip is extracted from the three dimensional vasculature image. This extracted image may then be compared to known fingerprint database for authentication or for liveness detection.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for creating perfusable microvessel systems
ActiveUS8003388B2Prolong survival timeOvercome limitationsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicrovascular NetworkPerfusion
Owner:NORTIS
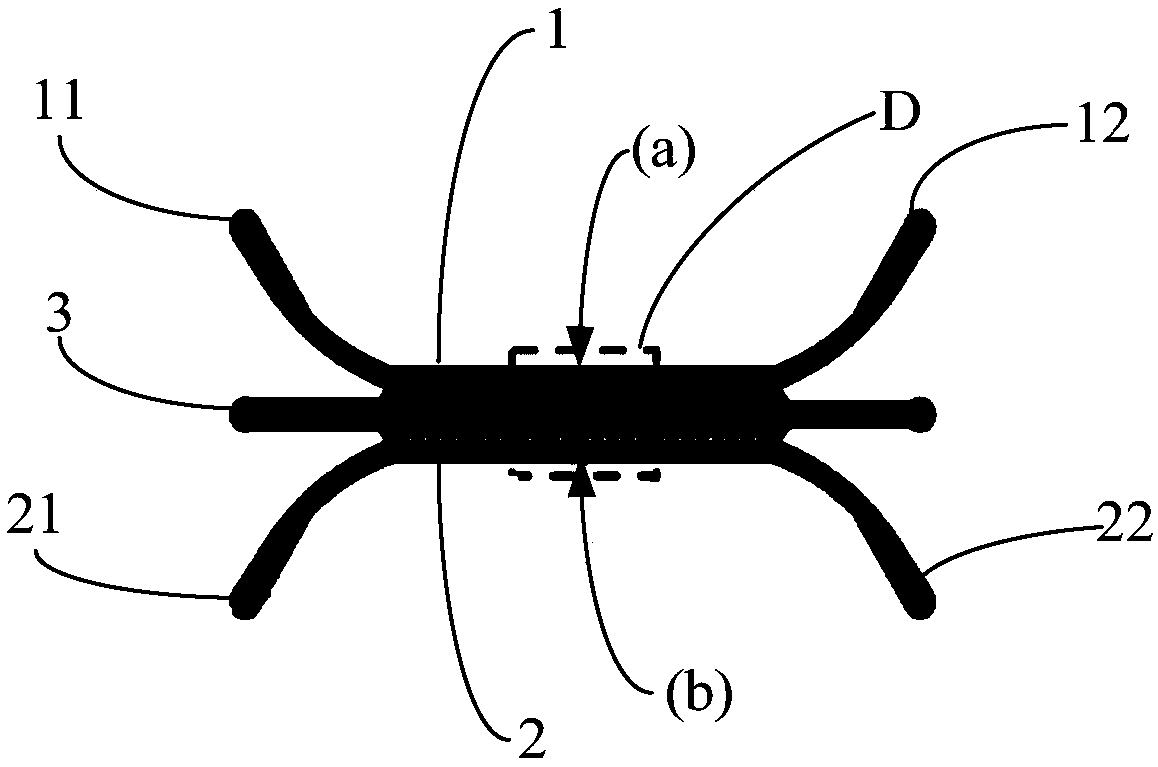
Cycle pathway micro-vessel network structure and application thereof
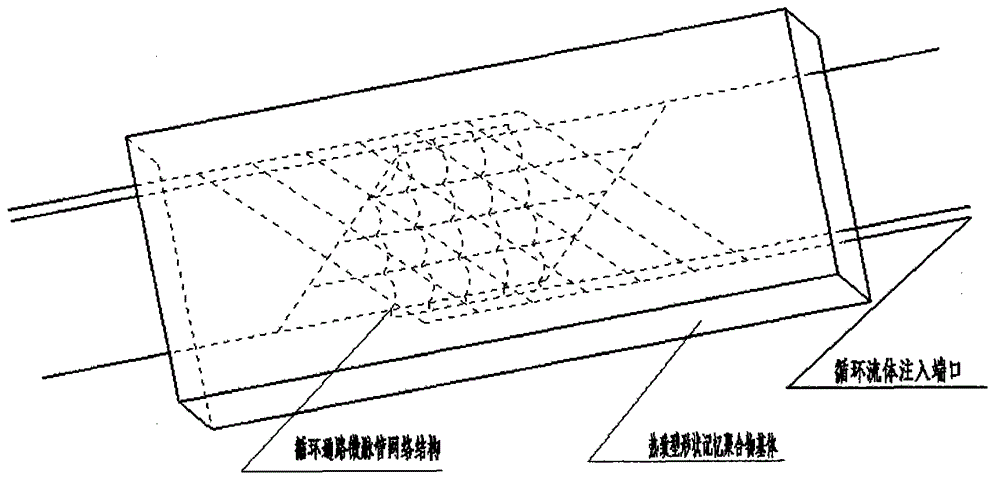
ActiveCN102745323ASolve the problem of sharp decrease in stiffnessStrong load bearing capacityFuselage bulkheadsWorking fluidEngineering
The invention relates to a cycle pathway microvascular network structure and an application thereof. The network structure comprises cycle pathway micro-vessels, the cycle pathway micro-vessels have a multi-array penetrating type structure or a three-dimensional penetrating type structure, the structure is in a thermotropic shape memory polymer matrix, the communication ports at the ends of the micro-vessel networks are preset outside the shape memory polymer matrix, and a work fluid flows through the whole cycle networks through the communication ports at the ends of the micro-vessel networks. The cycle pathway micro-vessel network structure is applied to the thermotropic shape memory polymer. The network structure has the advantages of high heating efficiency, uniform heating and simple technology, and solves a problem that the rigidity of the shape memory polymer rapidly reduces at a glass transition temperature. The network structure enables the shape memory polymer to be effectively heated and simultaneously guarantee that the shape memory polymer has a certain rigidity and a certain strength to oppose a certain load, so the load bearing capability of the shape memory polymer is substantially improved, and application fields of the shape memory polymer are extended.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for creating perfusable microvessel systems
ActiveUS7622298B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell-Extracellular MatrixECM Protein
Microvessel networks are produced in vitro from tissue-engineered parent vessels sprouting into a supporting matrix, as for example gels, of extracellular matrix proteins. The microvessel systems are integrated into devices that allow for controlled perfusion with fluids. The vessels may include cells from one cell type, for example, endothelial cells, or from combinations of two or more cell types.
Owner:NORTIS
Automatic three-dimensional segmentation method for OCT and doppler OCT angiography
ActiveUS10463247B2Early diagnosisAccurate monitoringScattering properties measurementsEye diagnosticsData treatmentMicrovascular Network
A three-dimensional (three dimensional) segmentation method with intensity-based Doppler variance (IBDV) based on swept-source OCT. The automatic three dimensional segmentation method is used to obtain seven surfaces of intra-retinal layers. The microvascular network of the retina, which is acquired by the IBDV method, can be divided into six layers. The microvascular network of the six individual layers are visualized, and the morphology and contrast images can be improved by using the segmentation method. This method has potential for earlier diagnosis and precise monitoring in retinal vascular diseases. Each tomographic image is composed of eight repeat scans at the same position, which achieves a high time difference to improve the sensitivity of the angiographic method. A subpixel registration algorithm is used to reduce the eye movement. The GPU was used to accelerate the data processing to achieve real-time preview of the acquired data.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Capillary network devices and methods of use
Artificial microvascular network (AMVN) devices are provided and related methods of making and methods of using such devices are provided. The present disclosure generally relates to an AMVN device comprising a substrate including a capillary network configured so as to simulate those actually encountered in the circulation of various humans and animal model systems. In certain aspects, the AMVN devices may be used, e.g., to investigate the effect of storing RBCs under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. However, the use of such AMVN devices is not so limited.
Owner:THE ADMINISTRATORS OF THE TULANE EDUCATIONAL FUND +1
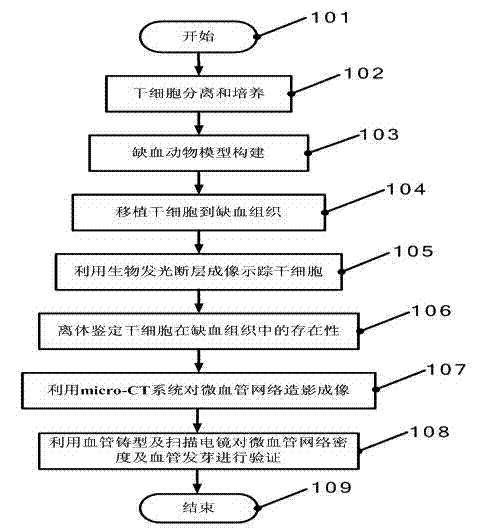
Multi-mode molecular imaging monitoring method of ischemia model
ActiveCN102389297ADisadvantages of avoiding dead small animal modelsComputerised tomographsDiagnostic recording/measuringDiagnostic Radiology ModalityIn vivo
The invention relates to the technical field of multi-mode molecular imaging, in particular to a multi-mode molecular imaging monitoring method of an ischemia model. By the observation method and the verification means of stem cell tracking and angiogenesis, a biological light-emitting tomography imaging method and a micro-CT (computed tomography) vascular imaging method adopted by the invention in vivo are confirmed, and the angiogenesis situation is analyzed by the survival of stem cells, three-dimensional positioning and quantitative observation and the density change of a microvascular network. The method overcomes the defect that small animal models are killed at different time points, and the continuous long-range observation of animals can be carried out.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY +1
Bionic pre-vascularization material as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111450319AImprove survival rateEasy to getTissue regenerationProsthesisVascularizesHuman body
The invention relates to the technical field of biological medicines, and discloses a bionic pre-vascularization material as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method of the pre-vascularization material comprises the steps of preparing a biological material with a vein structure, performing in-vitro cell culture and performing in-vivo transplantation. The pre-vascularization material can be applied to preparation of a wound repair material, a scaffold material, an organ reconstruction material, a tissue replacement material, a tissue filling material or a wrapping material and the like. A vein network structure of a pre-lymphatic vascularization material is similar to a lymphatic network structure of the human body; and a mesh branch structure of the leafvein of the pre-vascularization material is similar to a microvascular network structure of the human body. The bionic pre-vascularization material has the mechanical properties suitable for expectable application and can keep sufficient integrity until tissues grow inwards and heal; and the bionic pre-vascularization material has the characteristic of being easily processed and shaped into a product and the acceptable storage life, but does not cause significant inflammatory or toxic response in vivo.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SUN YAT SEN UNIV
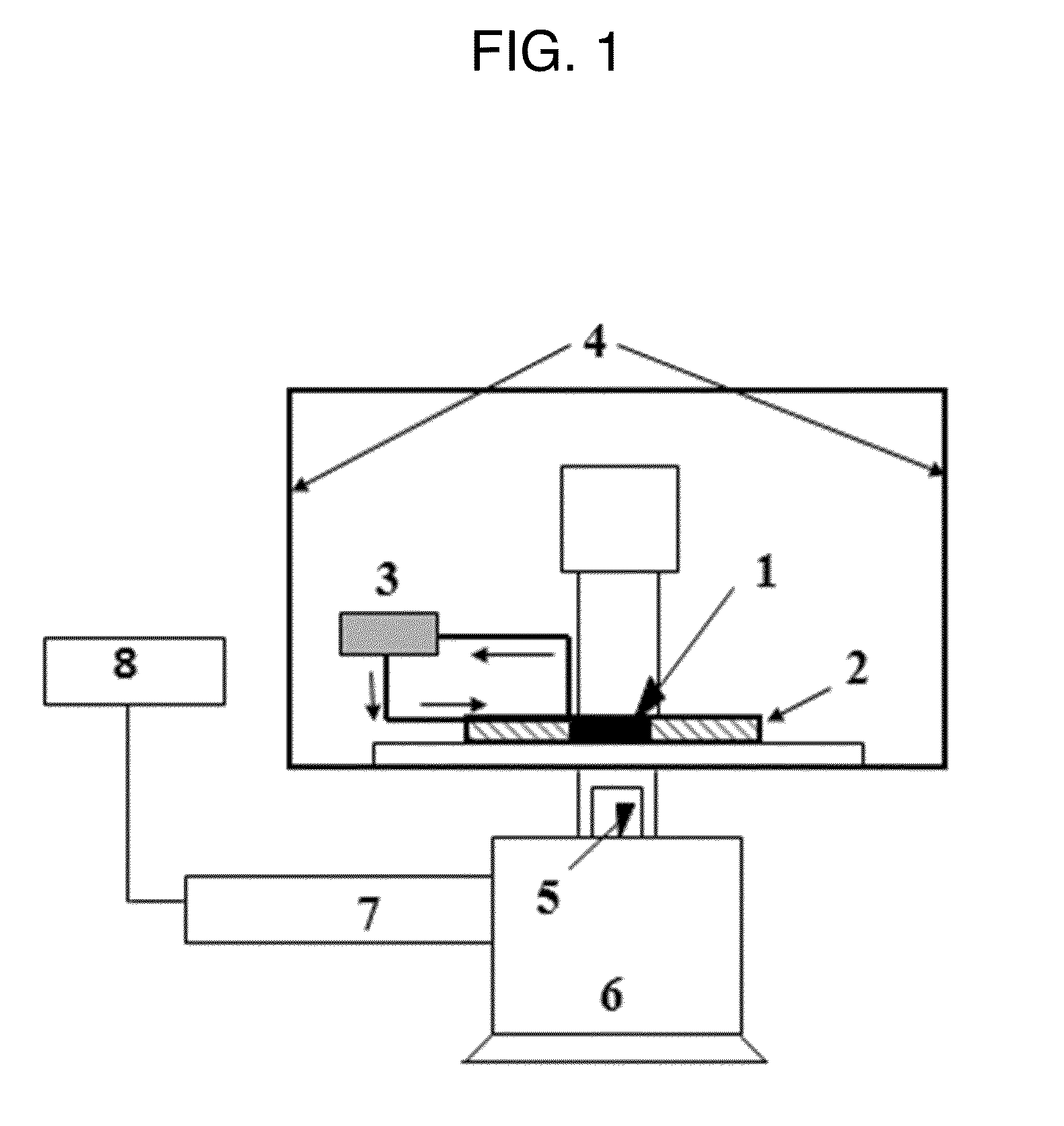
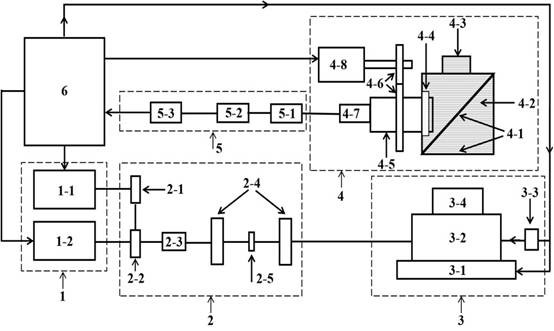
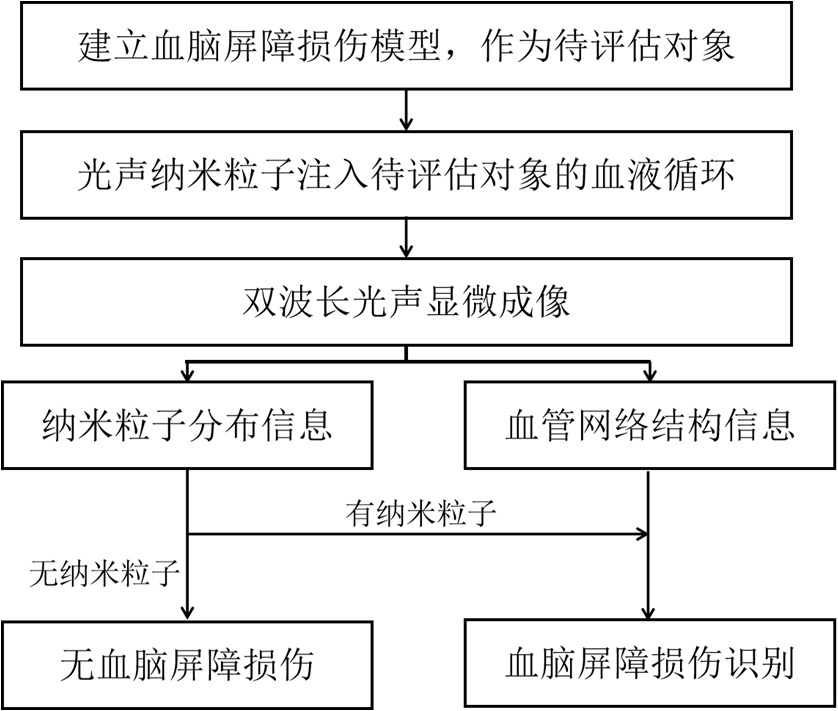
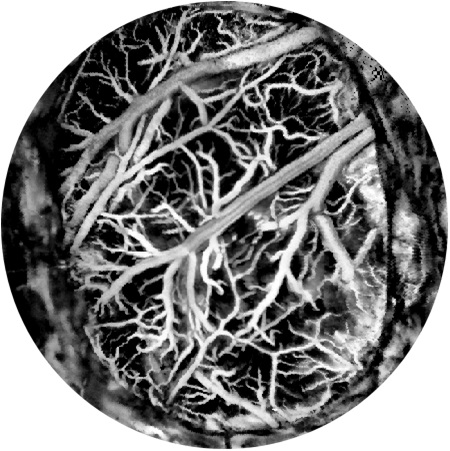
Blood brain barrier injury assessment device and method based on dual-wavelength photoacoustic microscopic imaging
ActiveCN114010152APositive technical effectImprove resolutionOrgan movement/changes detectionCatheterCapillary networkBeam scanning
The invention discloses a blood-brain barrier injury assessment device and method based on dual-wavelength photoacoustic microscopic imaging, and the device and mehtod are used for realizing high-resolution three-dimensional real-time assessment of blood-brain barrier injury. The device comprises a laser source assembly, a light beam transmission assembly, a light beam scanning assembly, a reflective imaging port assembly, a signal acquisition assembly and a computer. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a blood-brain barrier injury model; injecting a photoacoustic nanoparticle suspension into the blood of the established model through femoral vein; adopting a dual-wavelength photoacoustic microscopic imaging mode to conduct high-resolution brain imaging on the established model to obtain photoacoustic data, wherein pulse laser of a first wavelength and pulse laser of a second wavelength are used for exciting hemoglobin and nanoparticles respectively; reconstructing the photoacoustic data to obtain a capillary network structure of the brain and a distribution condition of nano particles; and identifying the damage area of the blood brain barrier according to the distribution condition of the nano particles on the outer side of the blood vessel, calculating the concentration of the nano particles outside the blood vessel, and analyzing the damage degree quantitatively.
Owner:SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY OF CHINA
System for assessing the efficacy of stored red blood cells using microvascular networks
InactiveUS8828226B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEfficacyEngineering
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Preparation method of microvascular self-repairing coating layer
ActiveCN108299666AImprove repair efficiencyImprove applicabilityEpoxy resin coatingsSurface layerMicrovascular Network
The invention discloses a preparation method of a microvascular self-repairing coating layer. The coating prepared by the method consists of a bottom layer coating layer and a surface layer coating layer. A microvascular network is constructed in the bottom layer coating layer and a repair agent is injected to the microvascular network, and a curing agent is added to a surface layer coating. Whenthe surface layer coating is damaged, the repair agent spills out at a damaged position through the microvascular network and reacts with the curing agent in the surface layer coating to heal damage.The constructed microvascular network system consists of 'aorta' and 'capillary', the aorta has large diameter, large reserve amount of the repair agent, and deep implantation and is not easily damaged, while the capillary has small diameter, relatively dense arrangement and shallow implantation and is easily damaged with the surface layer coating synchronously; the coating layer is guaranteed tohave high repair efficiency, and can achieve multiple times of repair at a same position.
Owner:SHAANXI SCI TECH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com