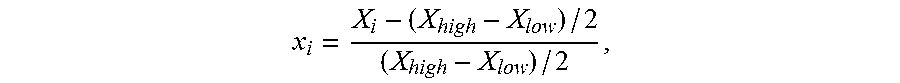Patents
Literature
39 results about "Programmable Array Logic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
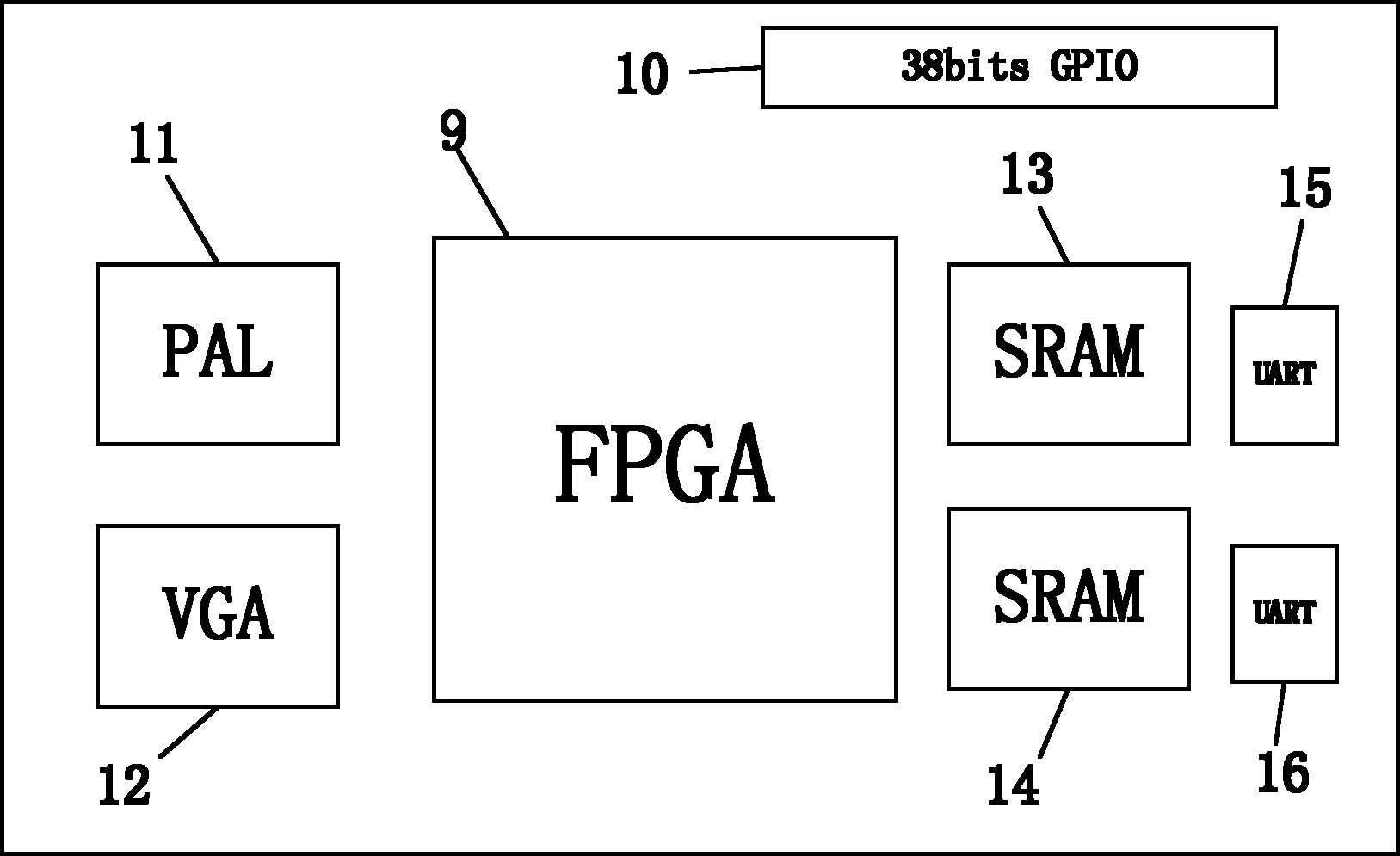
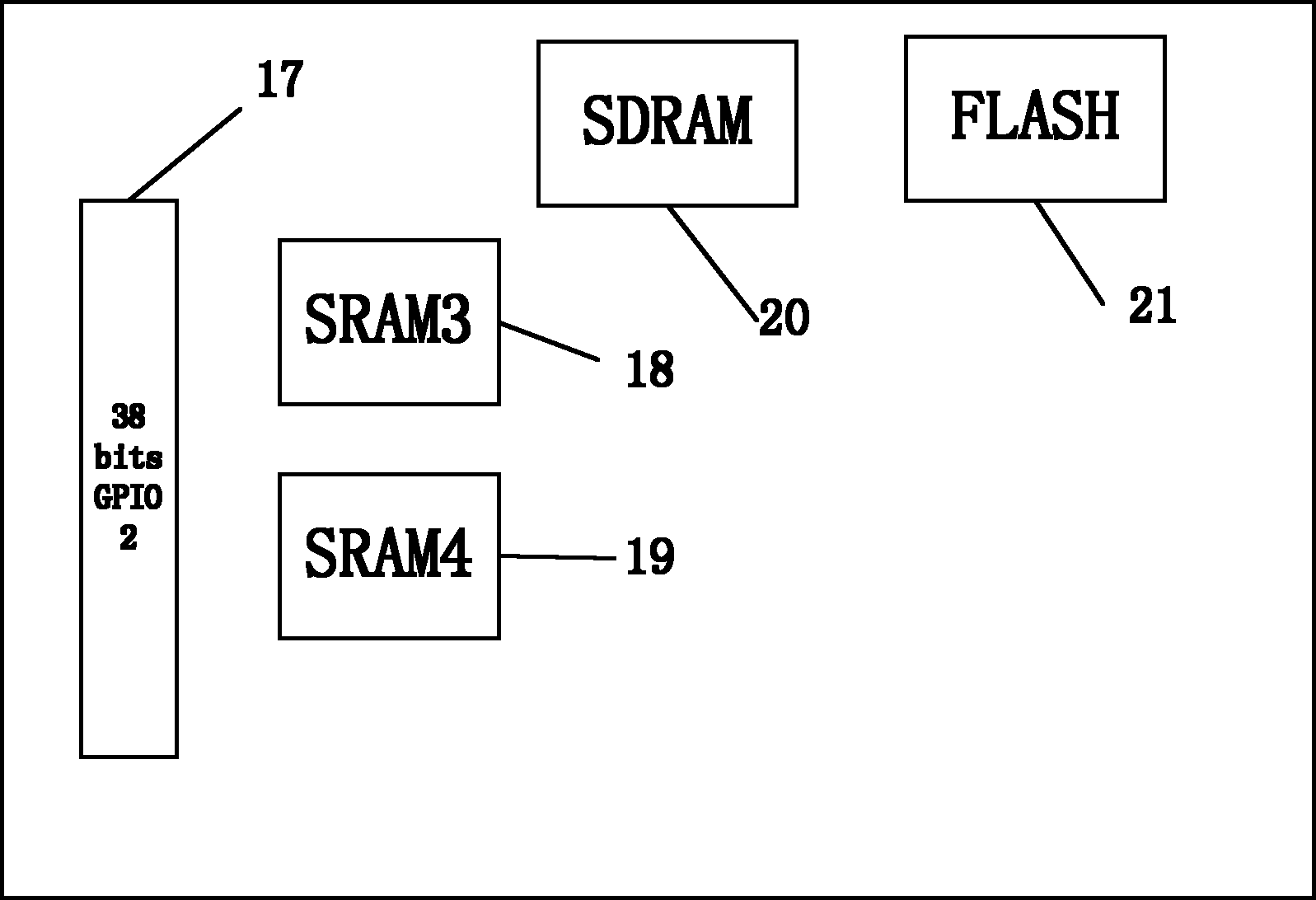
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
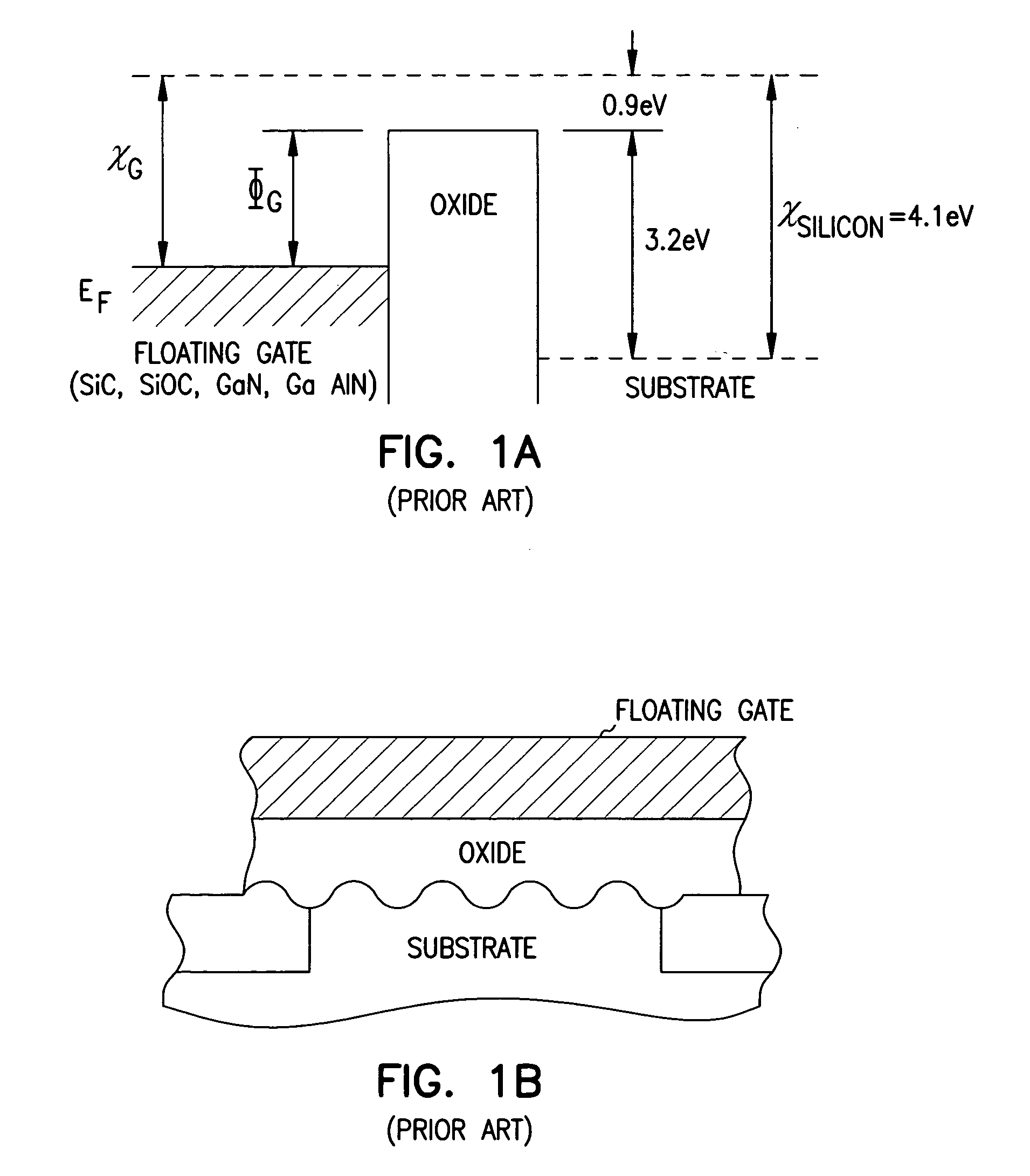
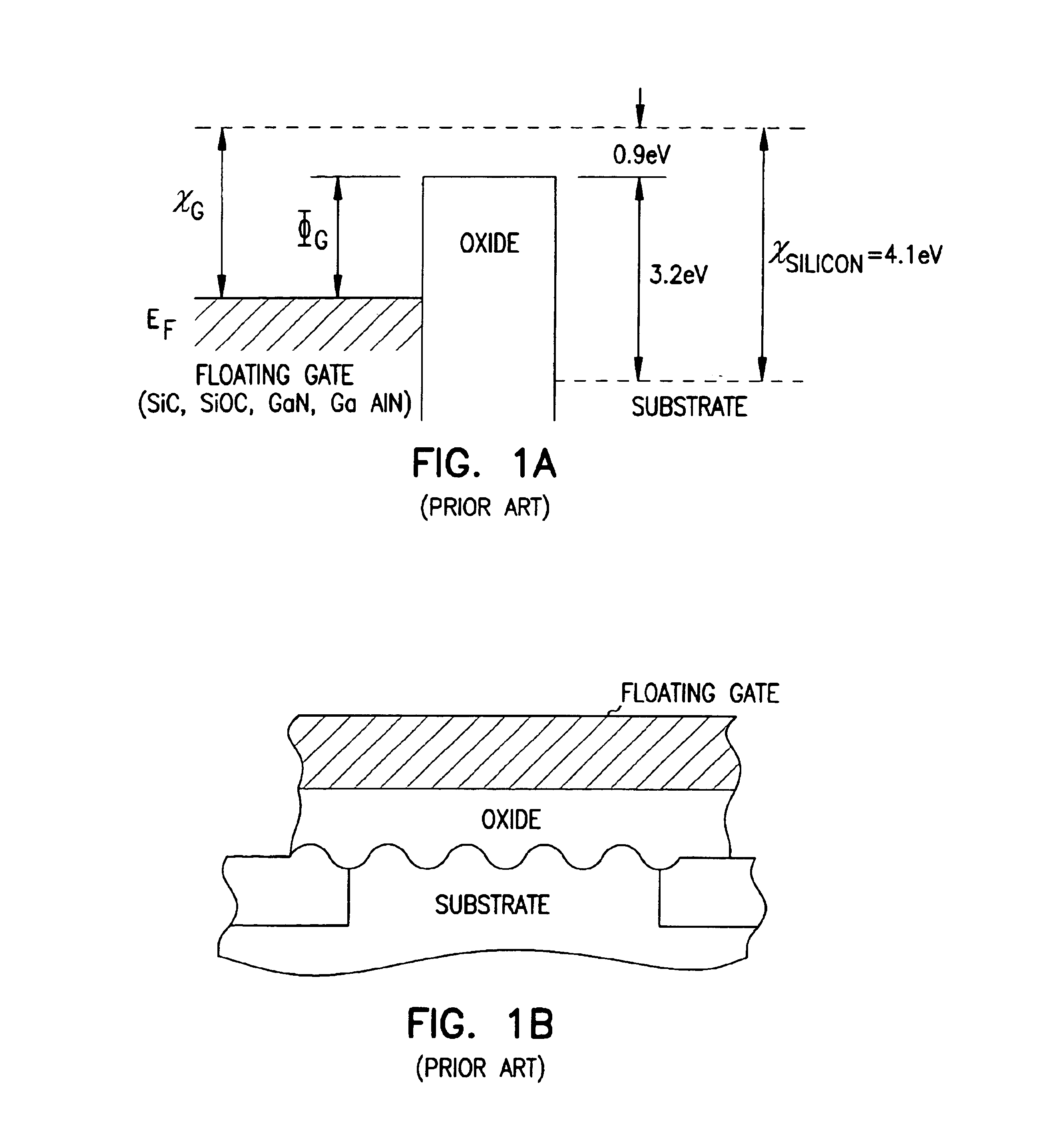
Programmable Array Logic (PAL) is a family of programmable logic device semiconductors used to implement logic functions in digital circuits introduced by Monolithic Memories, Inc. (MMI) in March 1978. MMI obtained a registered trademark on the term PAL for use in "Programmable Semiconductor Logic Circuits". The trademark is currently held by Lattice Semiconductor.
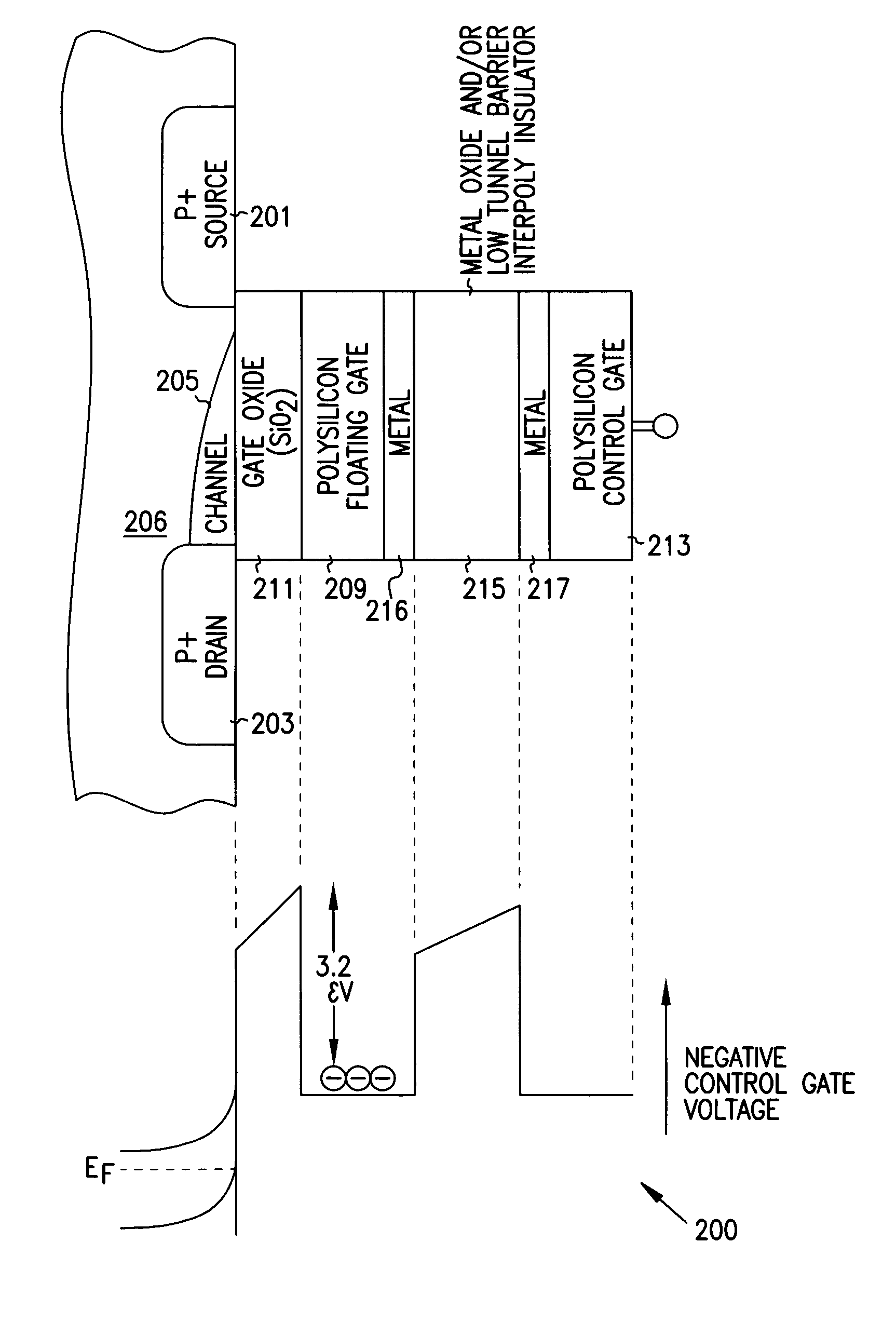
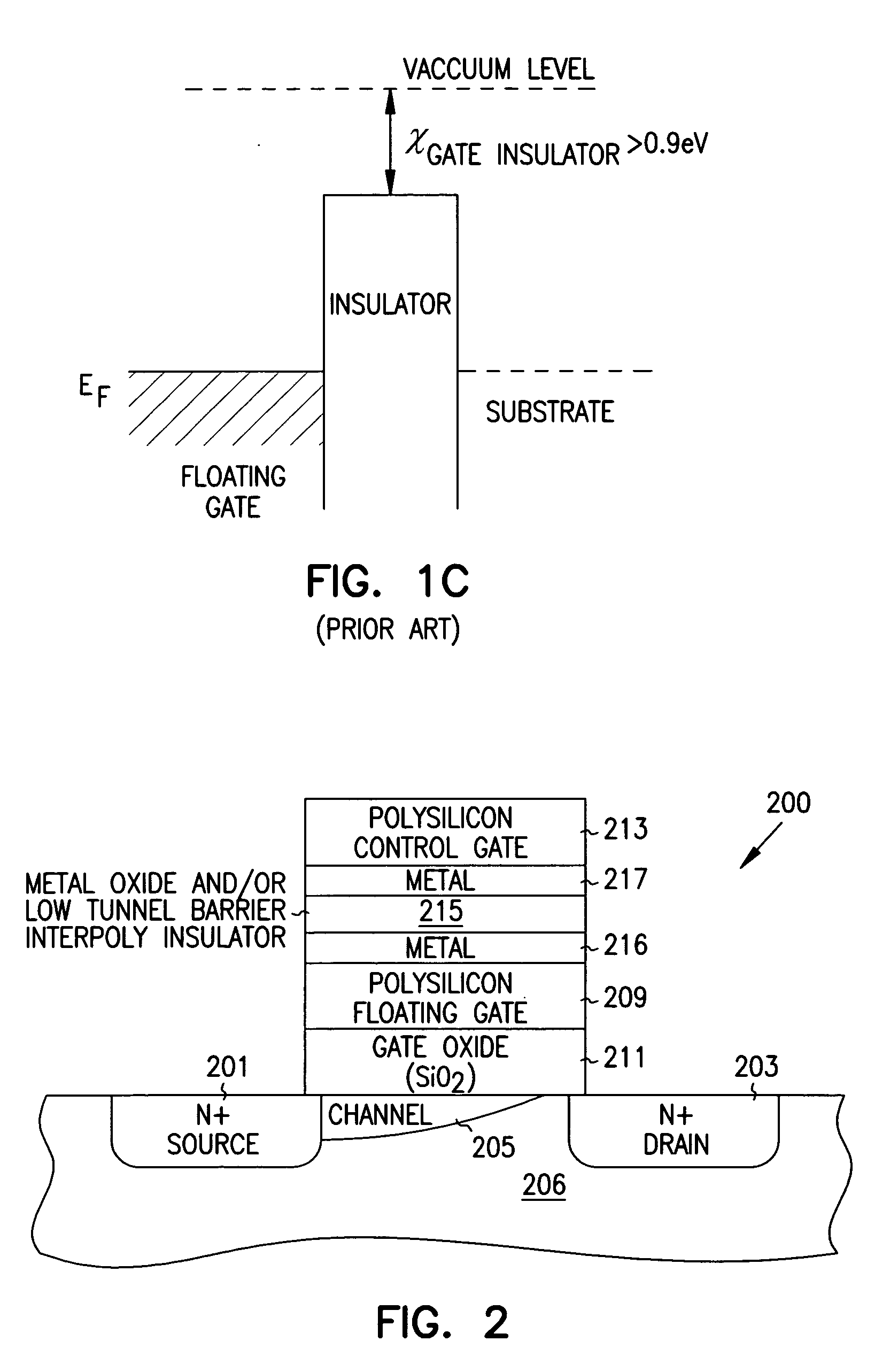
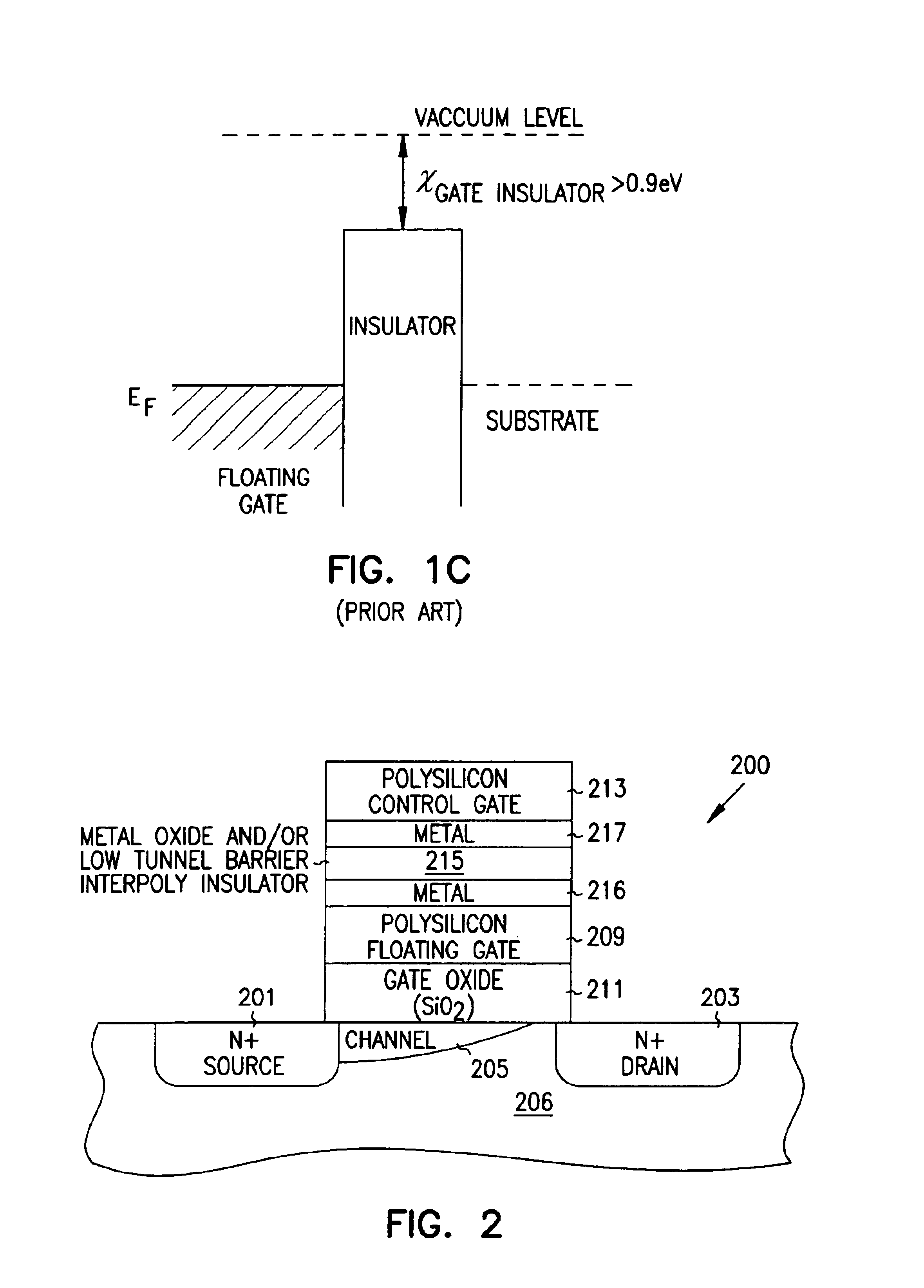
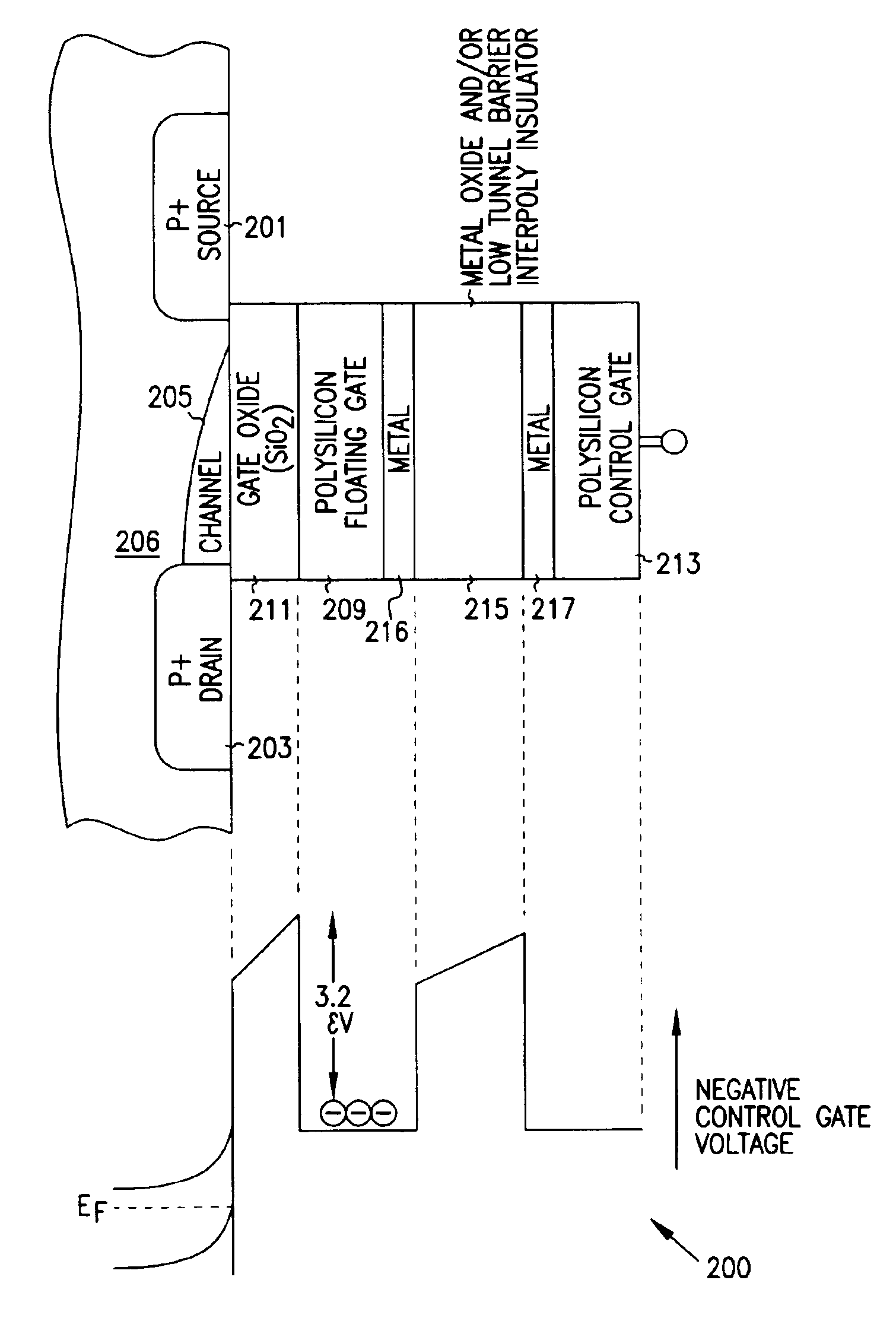
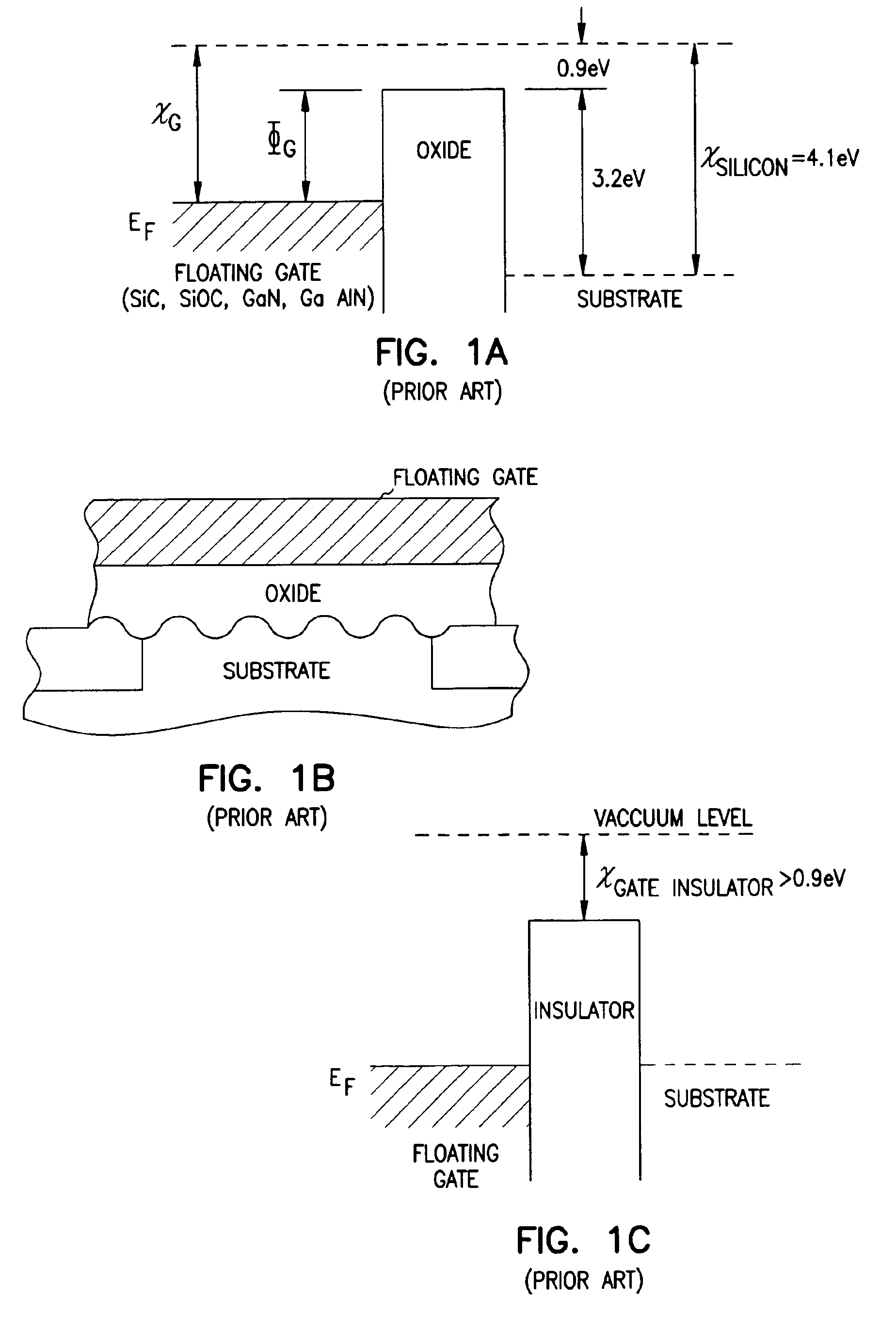
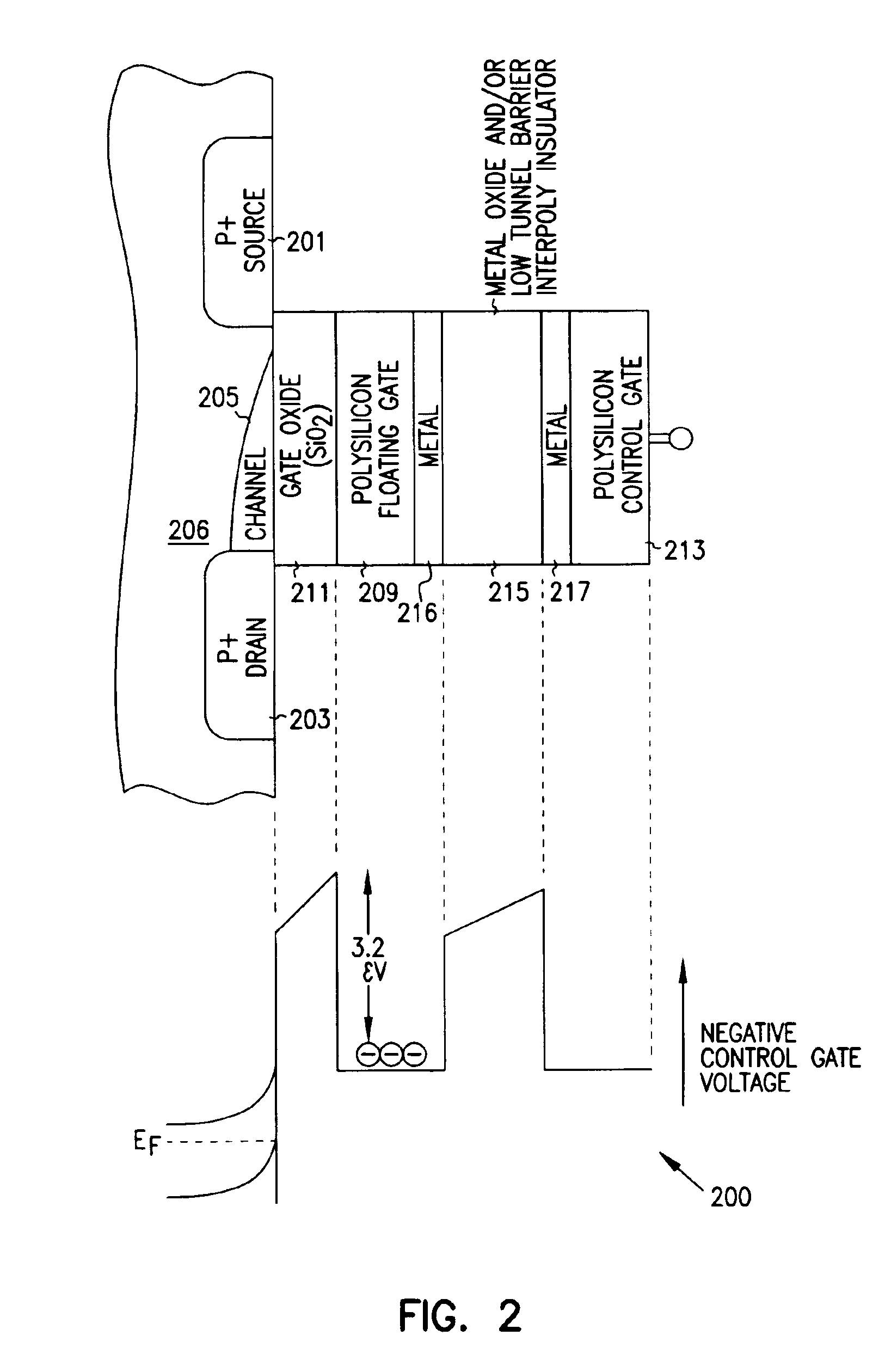
Programmable array logic or memory with p-channel devices and asymmetrical tunnel barriers
Structures and methods for programmable array type logic and / or memory with p-channel devices and asymmetrical low tunnel barrier intergate insulators are provided. The programmable array type logic and / or memory devices include p-channel non-volatile memory which has a first source / drain region and a second source / drain region separated by a p-type channel region in an n-type substrate. A floating gate opposing the p-type channel region and is separated therefrom by a gate oxide. A control gate opposes the floating gate. The control gate is separated from the floating gate by an asymmetrical low tunnel barrier intergate insulator. The asymmetrical low tunnel barrier intergate insulator includes a metal oxide insulator selected from the group consisting of Al2O3, Ta2O5, TiO2, ZrO2, Nb2O5, SrBi2Ta2O3, SrTiO3, PbTiO3, and PbZrO3. The floating gate includes a polysilicon floating gate having a metal layer formed thereon in contact with the low tunnel barrier intergate insulator. And, the control gate includes a polysilicon control gate having a metal layer, having a different work function from the metal layer formed on the floating gate, formed thereon in contact with the low tunnel barrier intergate insulator.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
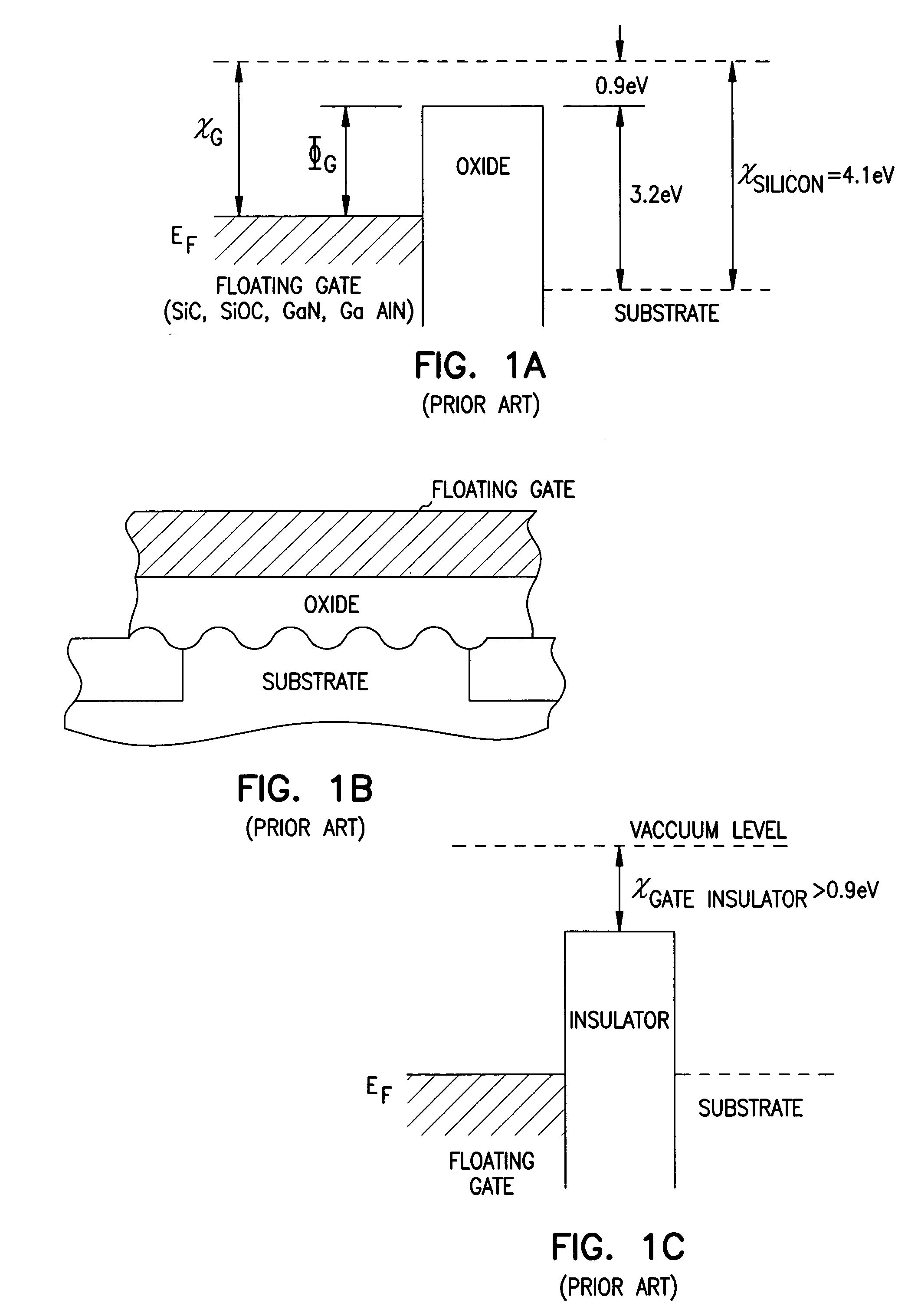
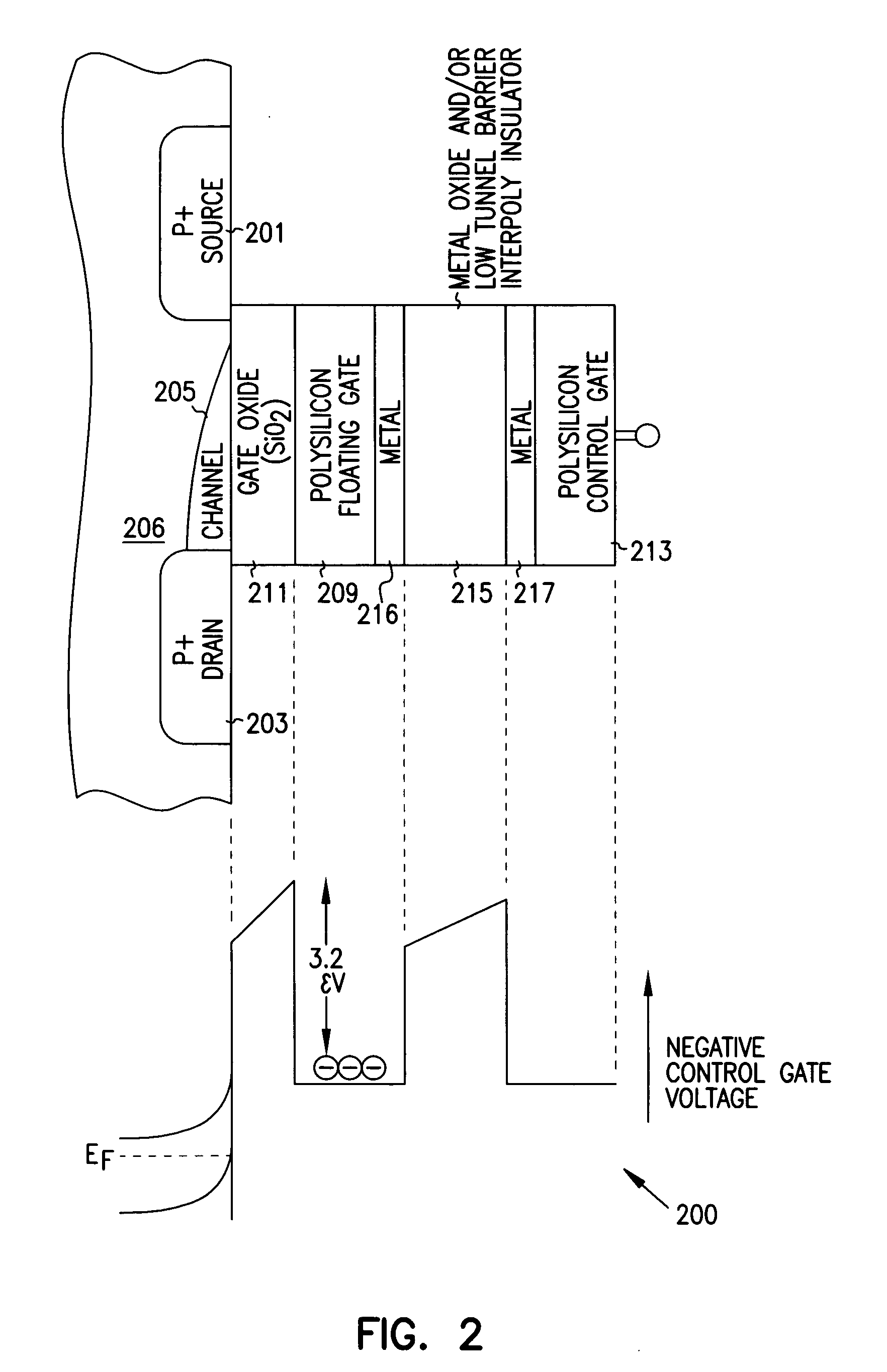
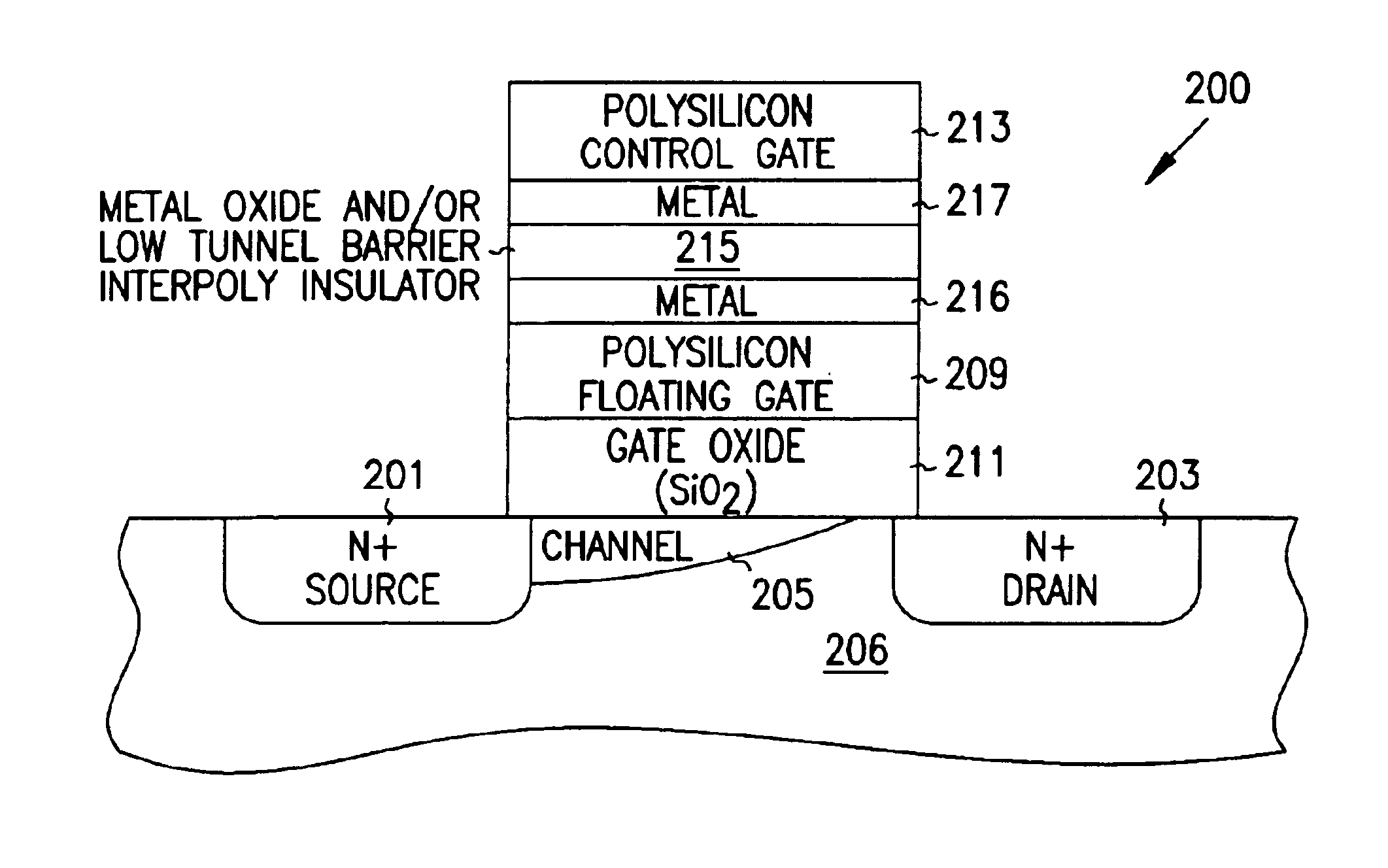
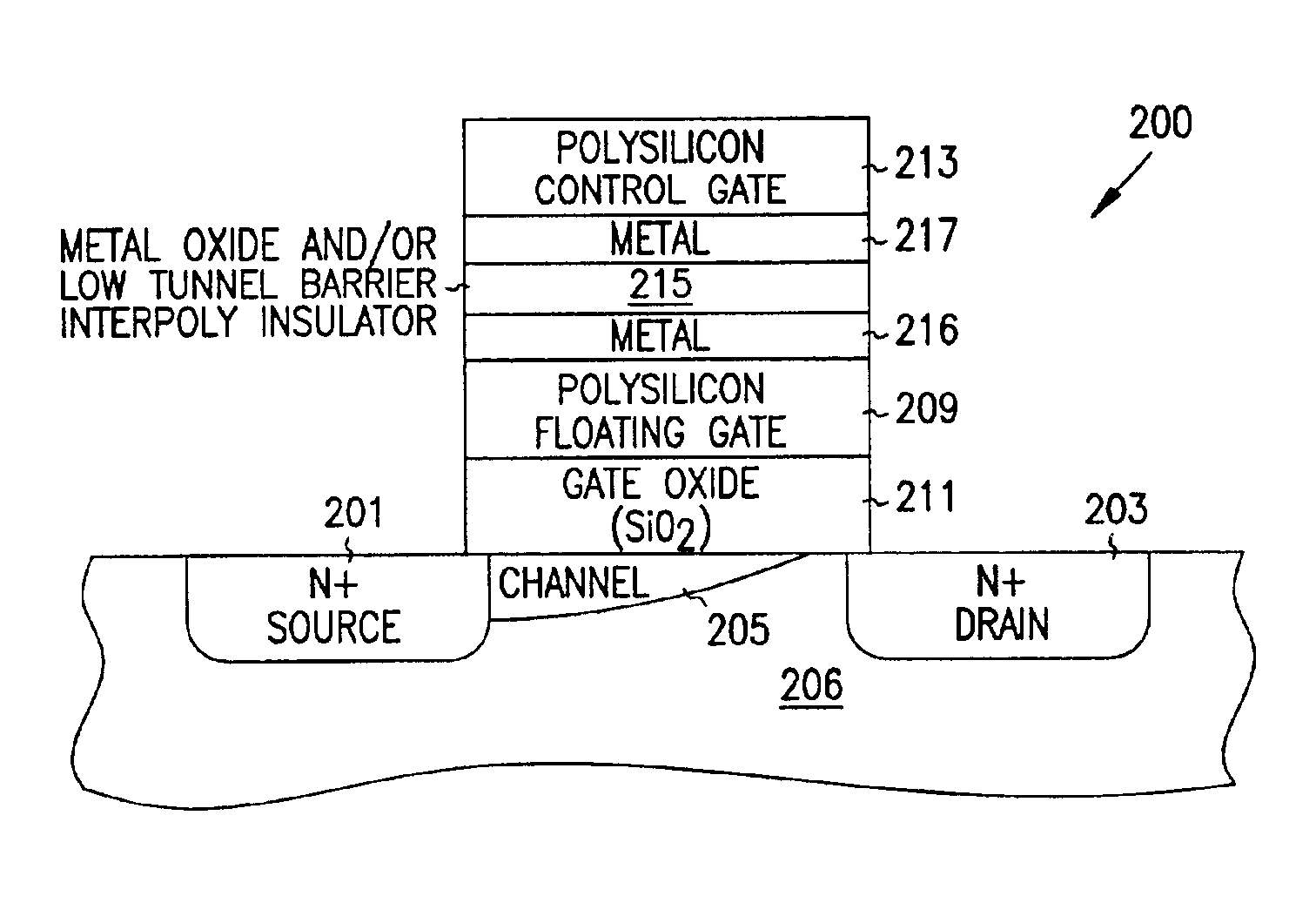
Programmable array logic or memory devices with asymmetrical tunnel barriers
Structures and methods for programmable array type logic and / or memory devices with asymmetrical low tunnel barrier intergate insulators are provided. The programmable array type logic and / or memory devices include non-volatile memory which has a first source / drain region and a second source / drain region separated by a channel region in a substrate. A floating gate opposing the channel region and is separated therefrom by a gate oxide. A control gate opposes the floating gate. The control gate is separated from the floating gate by an asymmetrical low tunnel barrier intergate insulator. The asymmetrical low tunnel barrier intergate insulator includes a metal oxide insulator selected from the group consisting of Al2O3, Ta2O5, TiO2, ZrO2, Nb2O5, SrBi2Ta2O3, SrTiO3, PbTiO3, and PbZrO3. The floating gate includes a polysilicon floating gate having a metal layer formed thereon in contact with the low tunnel barrier intergate insulator. And, the control gate includes a polysilicon control gate having a metal layer, having a different work function from the metal layer formed on the floating gate, formed thereon in contact with the low tunnel barrier intergate insulator.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
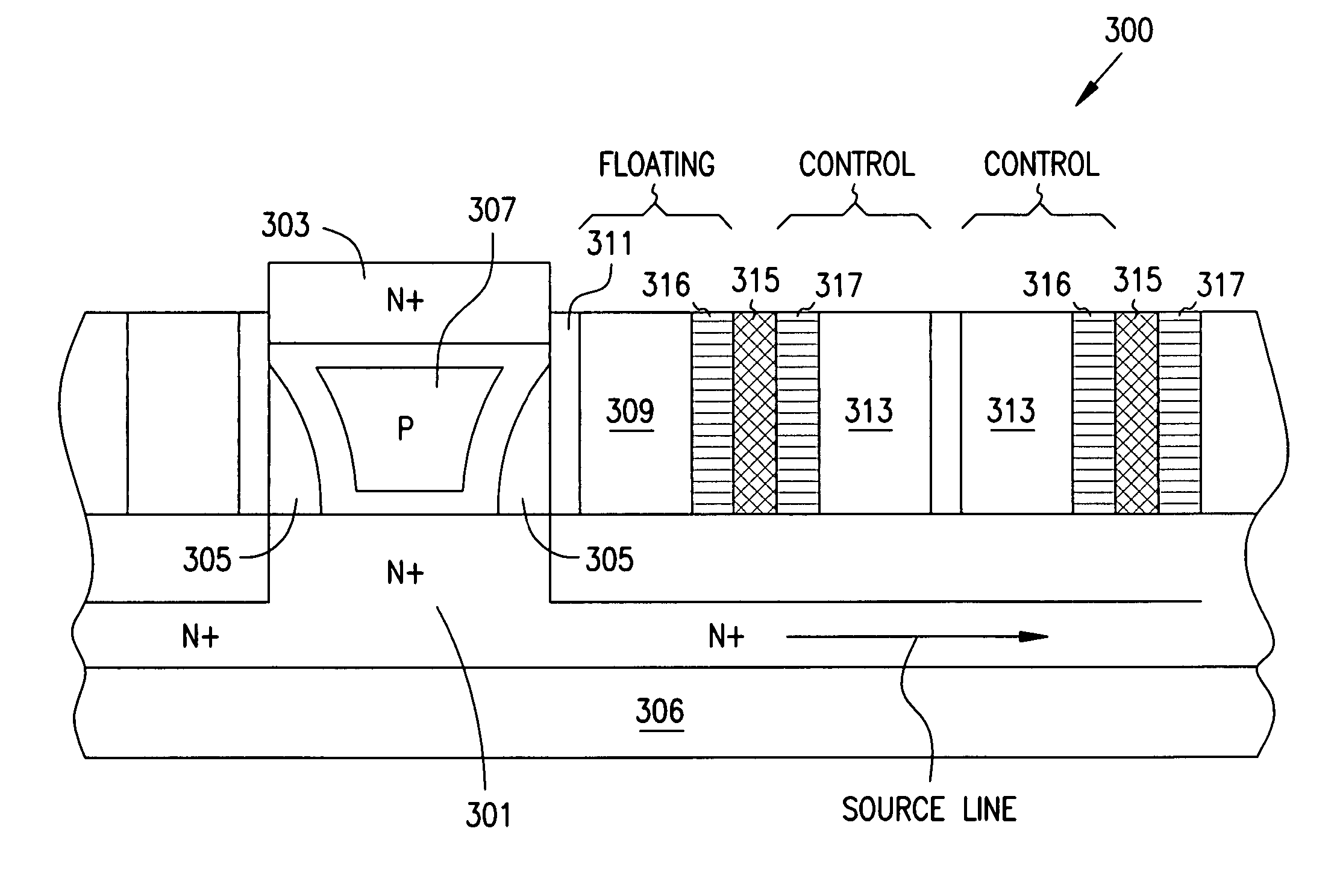
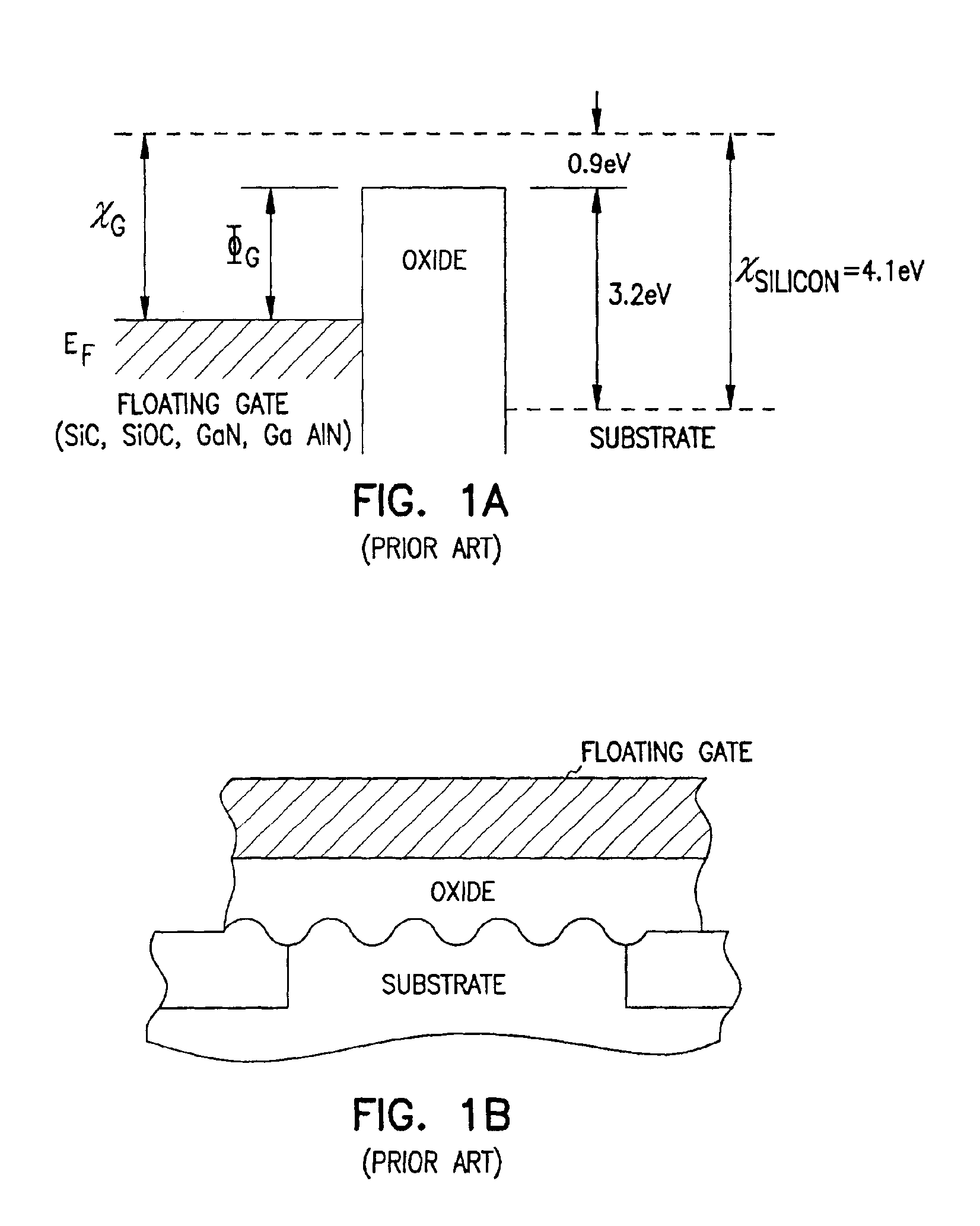
Programmable array logic or memory devices with asymmetrical tunnel barriers
Structures and methods for programmable array type logic and / or memory devices with asymmetrical low tunnel barrier intergate insulators are provided. The programmable array type logic and / or memory devices include non-volatile memory which has a first source / drain region and a second source / drain region separated by a channel region in a substrate. A floating gate opposing the channel region and is separated therefrom by a gate oxide. A control gate opposes the floating gate. The control gate is separated from the floating gate by an asymmetrical low tunnel barrier intergate insulator. The asymmetrical low tunnel barrier intergate insulator includes a metal oxide insulator selected from the group consisting of Al2O3, Ta2O5, TiO2, Zro2, Nb2O5, SrBi2Ta2O3, SrTiO3, PbTiO3, and PbZrO3. The floating gate includes a polysilicon floating gate having a metal layer formed thereon in contact with the low tunnel barrier intergate insulator. And, the control gate includes a polysilicon control gate having a metal layer, having a different work function from the metal layer formed on the floating gate, formed thereon in contact with the low tunnel barrier intergate insulator.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
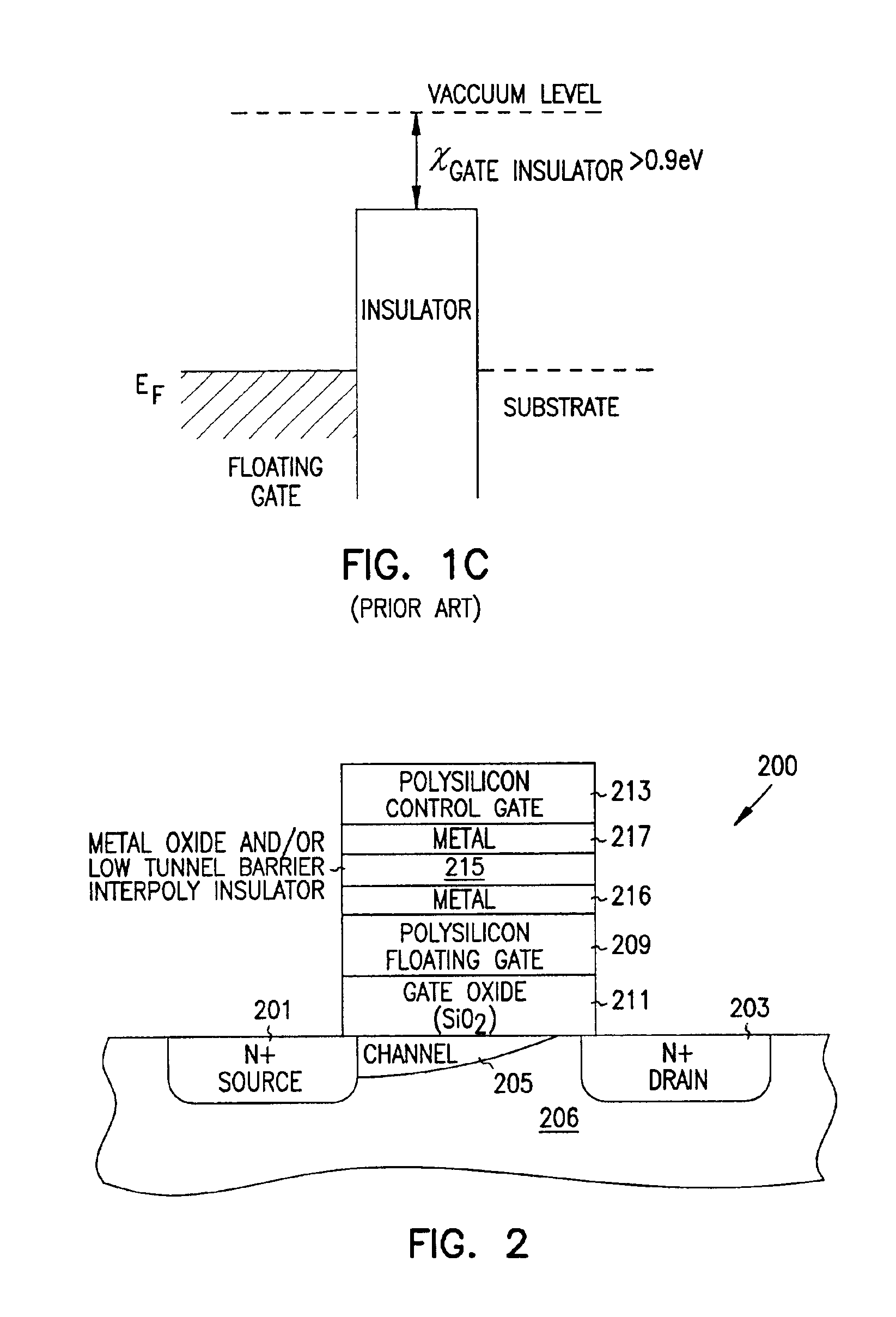
Programmable array logic or memory devices with asymmetrical tunnel barriers
Structures and methods for programmable array type logic and / or memory devices with asymmetrical low tunnel barrier intergate insulators are provided. The programmable array type logic and / or memory devices include non-volatile memory which has a first source / drain region and a second source / drain region separated by a channel region in a substrate. A floating gate opposing the channel region and is separated therefrom by a gate oxide. A control gate opposes the floating gate. The control gate is separated from the floating gate by an asymmetrical low tunnel barrier intergate insulator. The asymmetrical low tunnel barrier intergate insulator includes a metal oxide insulator selected from the group consisting of Al2O3, Ta2O5, TiO2, ZrO2, Nb2O5, SrBi2Ta2O3, SrTiO3, PbTiO3, and PbZrO3. The floating gate includes a polysilicon floating gate having a metal layer formed thereon in contact with the low tunnel barrier intergate insulator. And, the control gate includes a polysilicon control gate having a metal layer, having a different work function from the metal layer formed on the floating gate, formed thereon in contact with the low tunnel barrier intergate insulator.
Owner:MICRON TECHNOLOGY INC
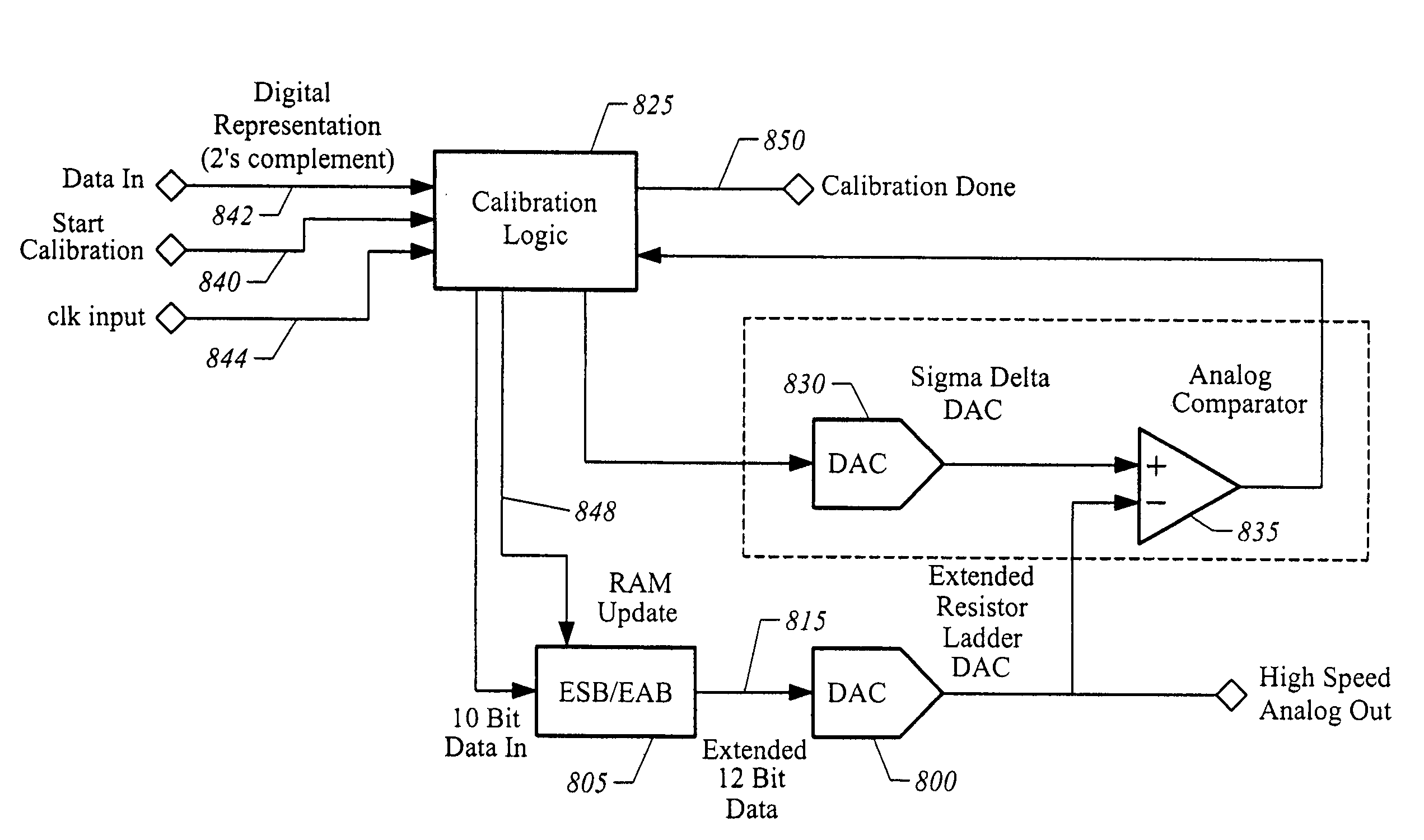
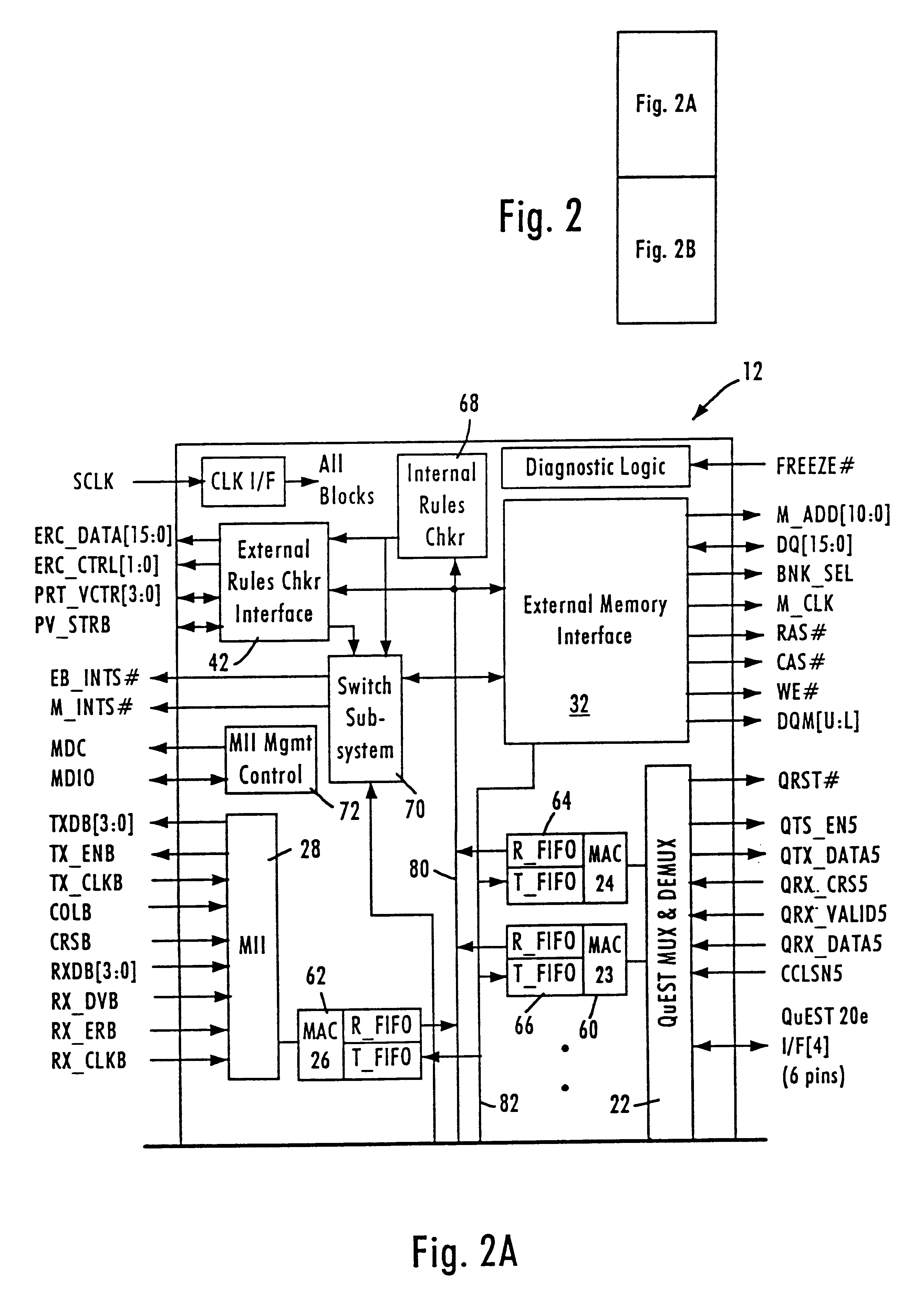
Analog-to-digital converter for programmable logic
InactiveUS6956512B1Electric signal transmission systemsResistance/reactance/impedenceProgrammable logic deviceLogic cell
Digital-to-analog and analog-to-digital conversion are implemented in or using programmable logic. The DAC and ADC circuits may be hardwired in a programmable logic integrated circuit or may be implemented using an intellectual property (IP) core. The IP core would be a series of bits to configure the logic cells and other programmable logic of an integrated circuit to include one or more DACs or ADC, or both on the same integrated circuit. The DAC may be a sigma-delta-modulator-based implementation or a resistor-ladder-based implementation.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Programmable array logic or memory with p-channel devices and asymmetrical tunnel barriers
Structures and methods for programmable array type logic and / or memory with p-channel devices and asymmetrical low tunnel barrier intergate insulators are provided. The programmable array type logic and / or memory devices include p-channel non-volatile memory which has a first source / drain region and a second source / drain region separated by a p-type channel region in an n-type substrate. A floating gate opposing the p-type channel region and is separated therefrom by a gate oxide. A control gate opposes the floating gate. The control gate is separated from the floating gate by an asymmetrical low tunnel barrier intergate insulator. The asymmetrical low tunnel barrier intergate insulator includes a metal oxide insulator selected from the group consisting of Al2O3, Ta2O5, TiO2, ZrO2, Nb2O5, SrBi2Ta2O3, SrTiO3, PbTiO3, and PbZrO3. The floating gate includes a polysilicon floating gate having a metal layer formed thereon in contact with the low tunnel barrier intergate insulator. And, the control gate includes a polysilicon control gate having a metal layer, having a different work function from the metal layer formed on the floating gate, formed thereon in contact with the low tunnel barrier intergate insulator.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
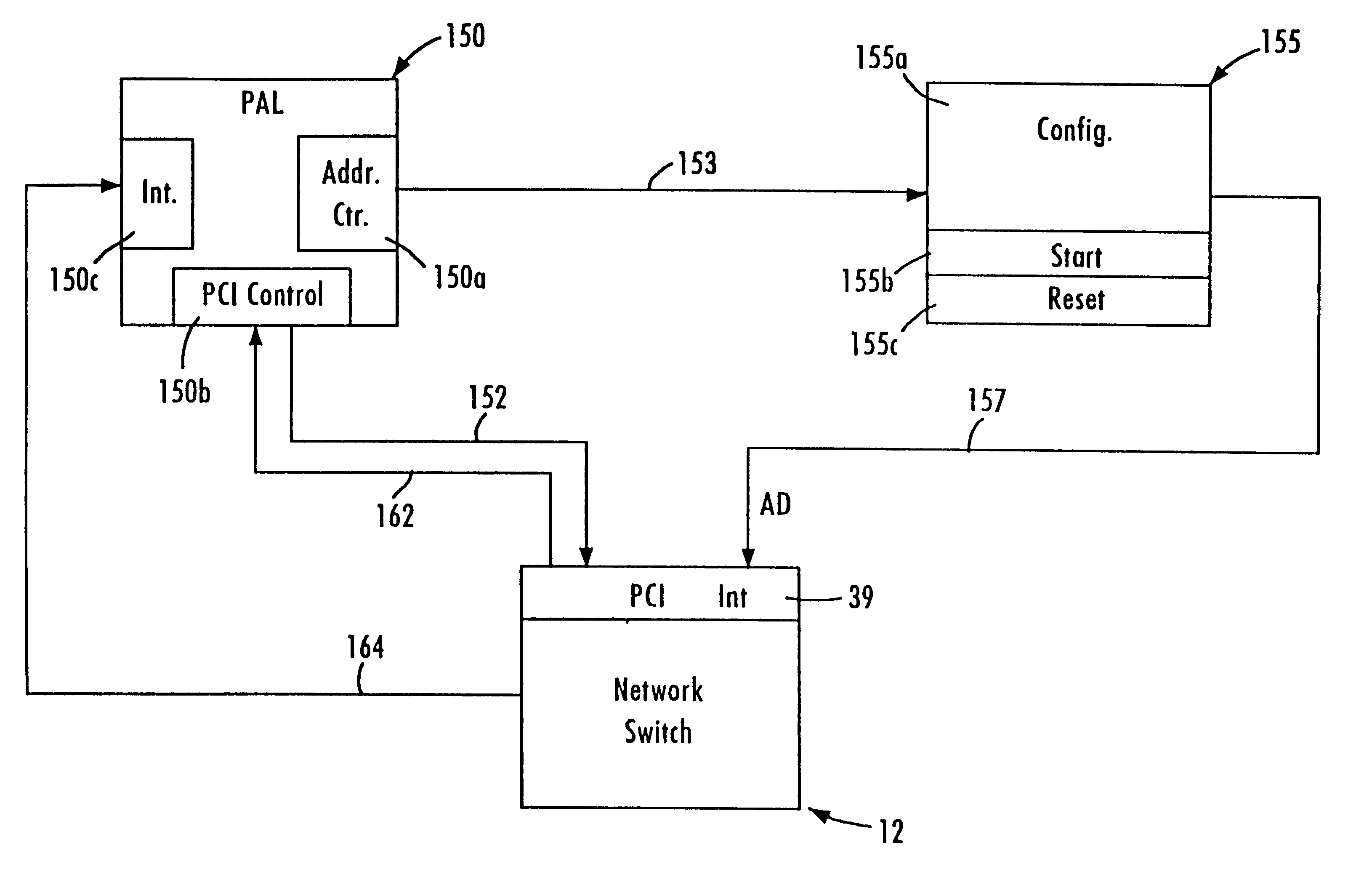
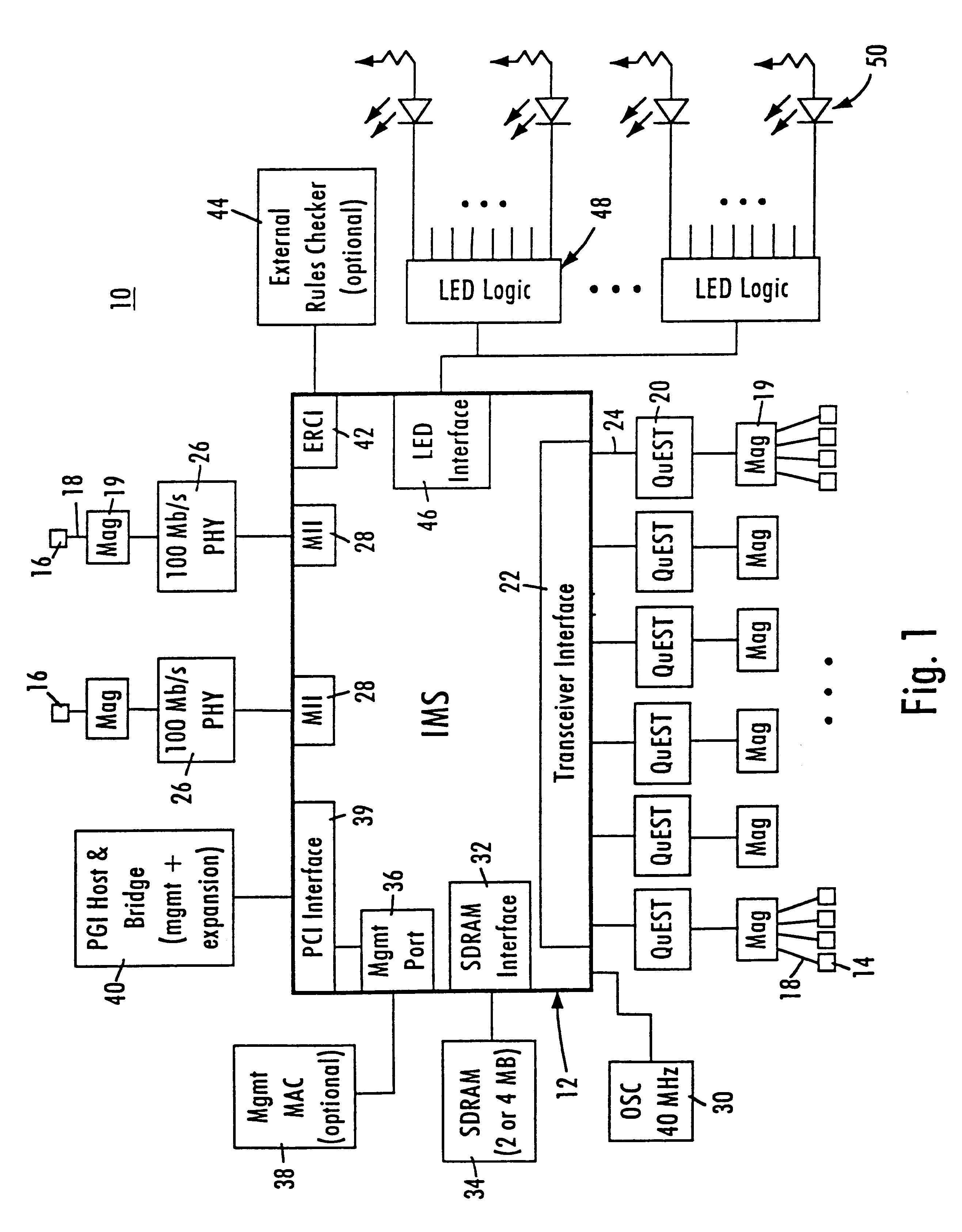
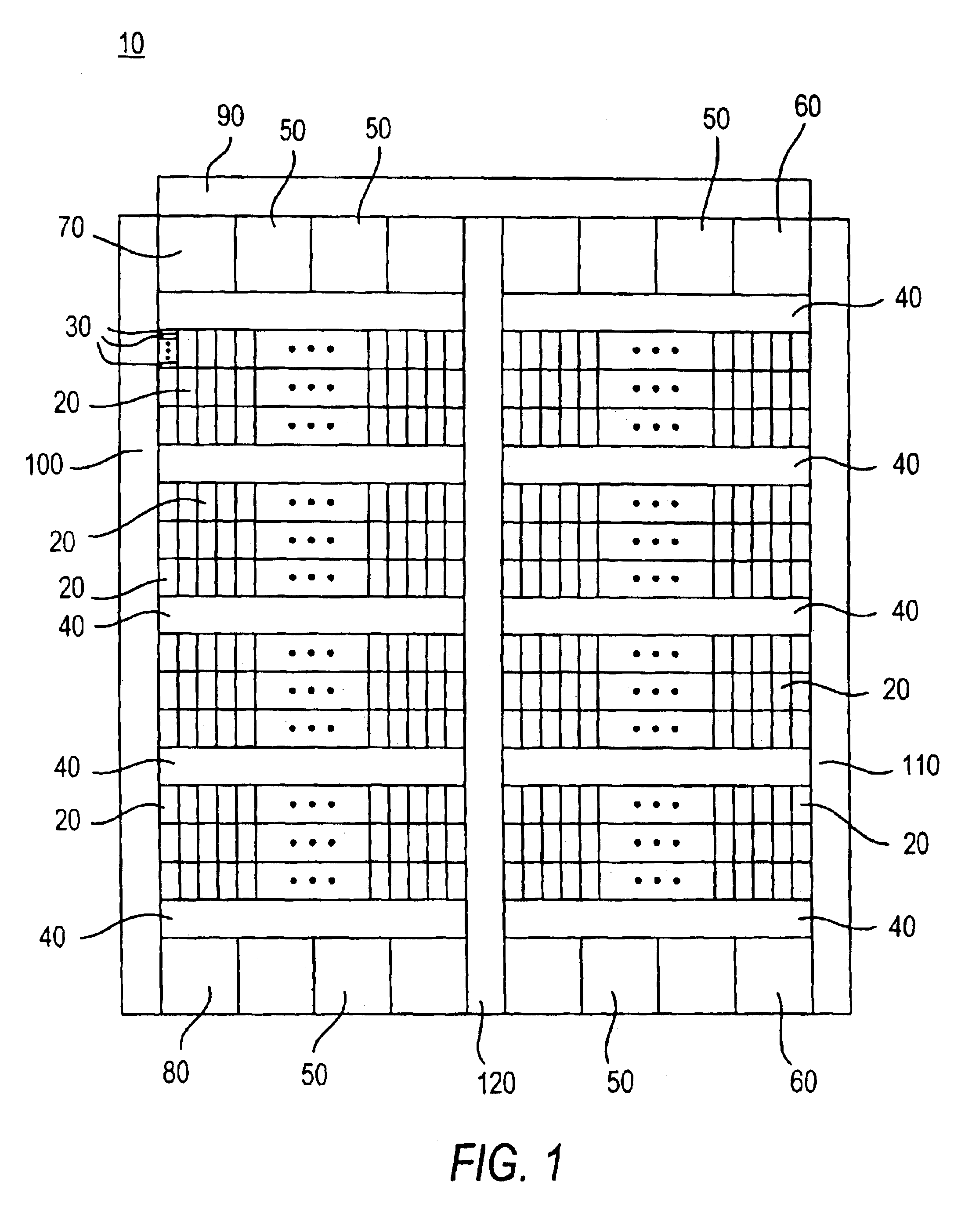
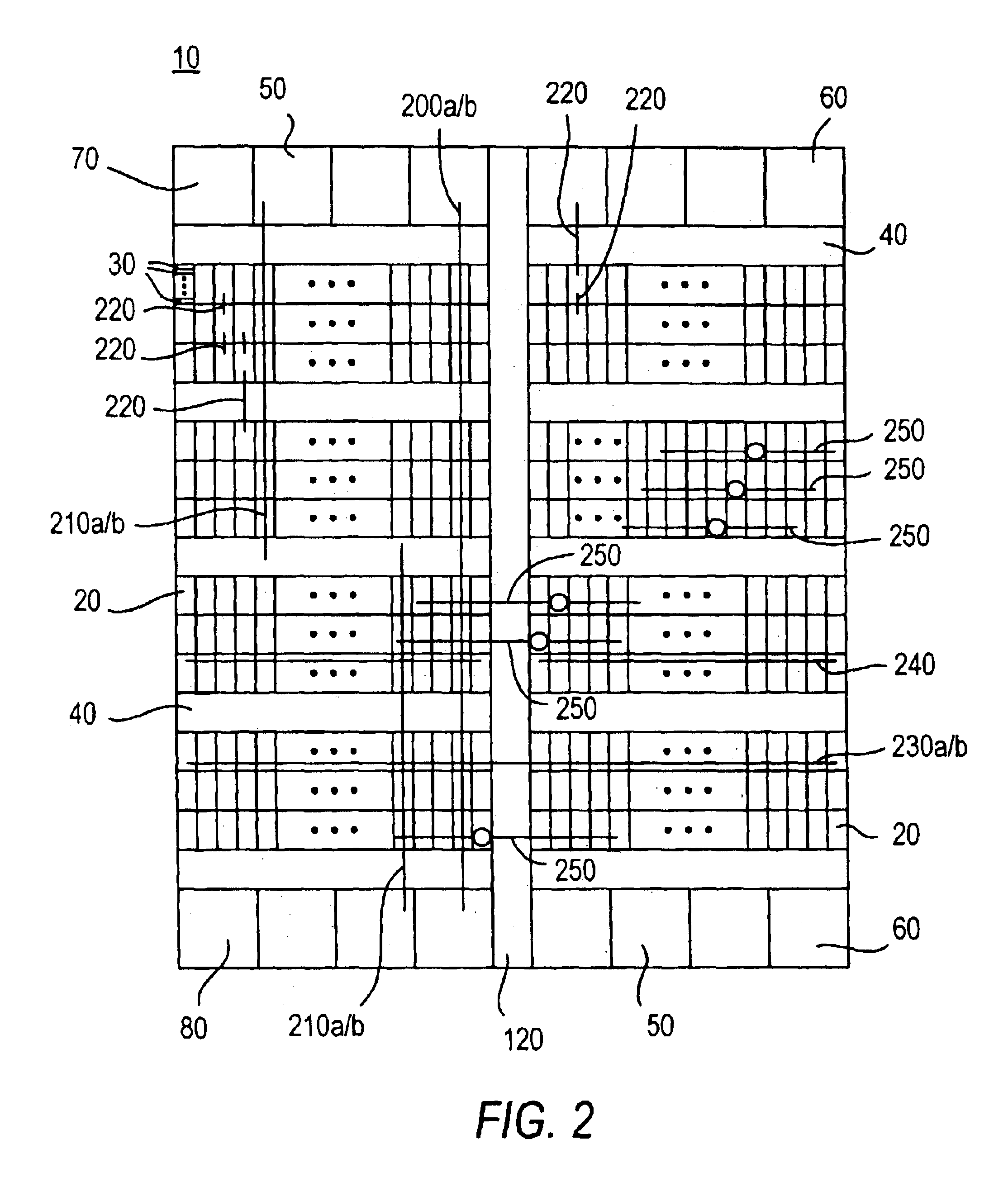
Device initializing system with programmable array logic configured to cause non-volatile memory to output address and data information to the device in a prescribed sequence
InactiveUS6185630B1Low-cost arrangementLow costSpecial service provision for substationDigital storageData informationControl signal
A low-cost implementation of a switching system using a multiport network switch avoids the necessity of a microprocessor by using programmable array logic (PAL) configured to drive a non-volatile memory. The PAL includes an address generator state machine, a PCI control signal state machine, and an interrupt state machine. The non-volatile memory sequentially outputs address and data information, under the control of the address generator state machine, onto a bus connected to the network switch in order to initialize the network switch with initialization and configuration data. The PCI control signal state machine provides control signals causing the output address and data information to mimic a PCI burst transfer. Once the network switch has been configured, the non-volatile memory outputs a start command causing the network switch to begin running in a free-running mode. A memory overflow interrupt in the network switch is also enabled, causing the PAL to reset the network switch if overloaded.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
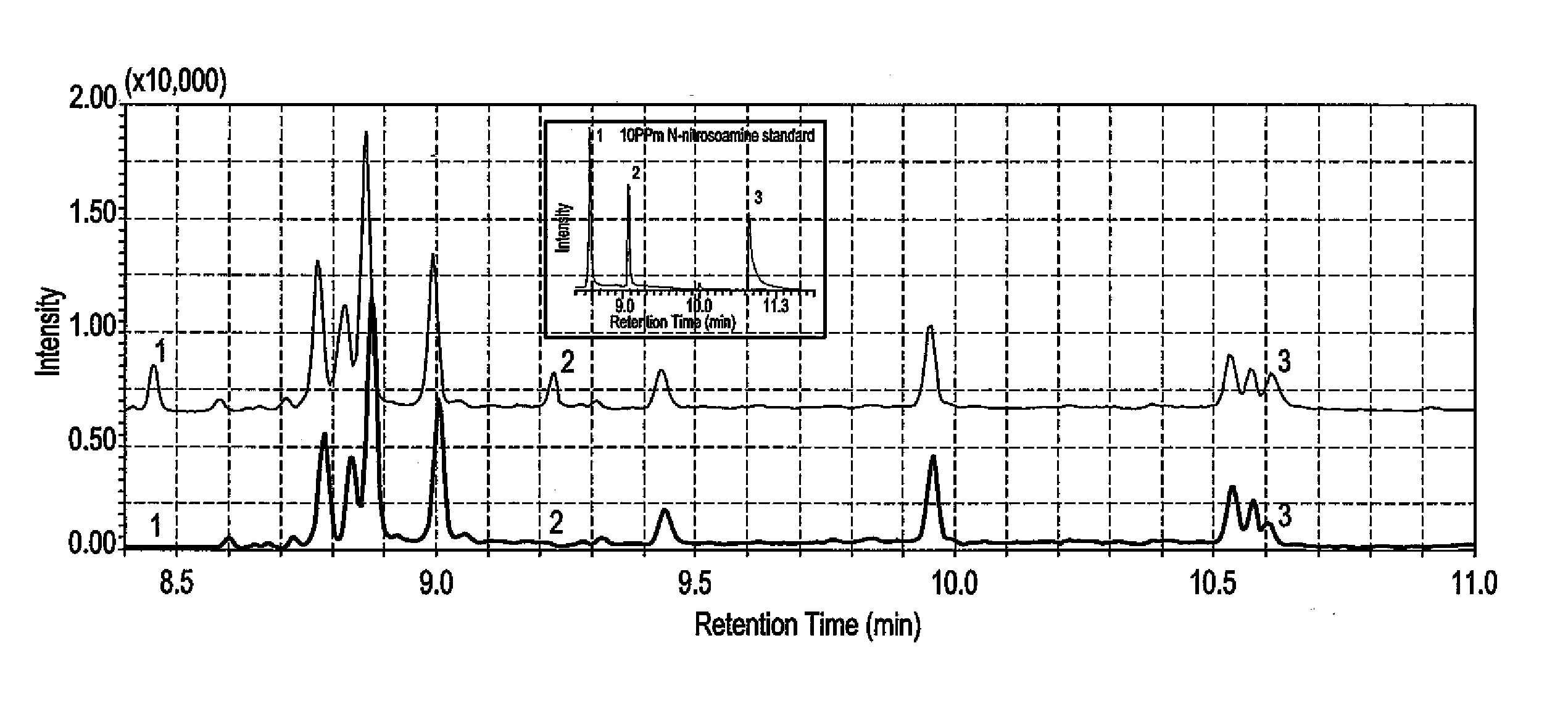
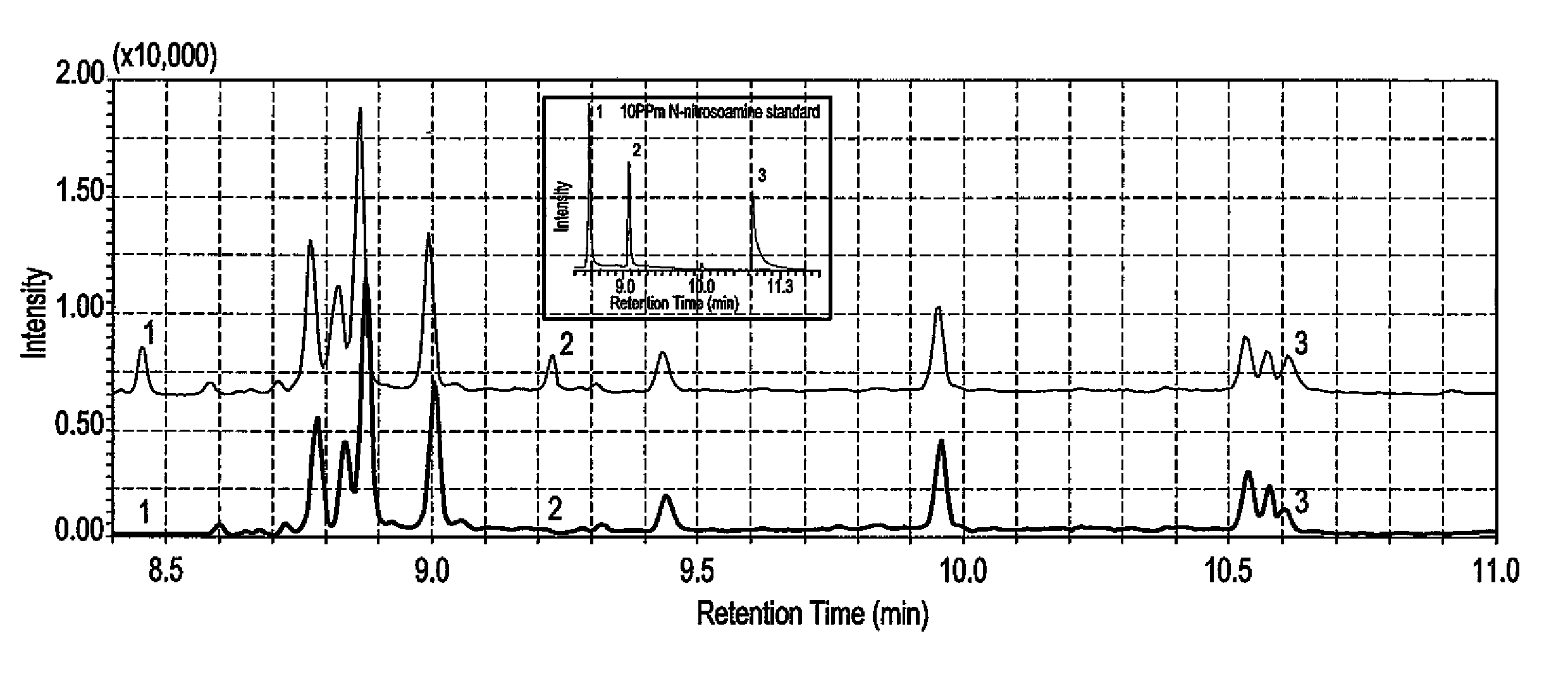
Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction method of detecting n-nitrosoamines
ActiveUS20150121993A1Readily apparentSamplingComponent separationVapor phase chromatographyProgrammable Array Logic
The dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction (DLLME) method of detecting N-nitrosoamines (NAs) is a DLLME performed with a xylene extraction solvent and a methanol disperser solvent. The microextraction is preferably performed by a programmable array logic (PAL) auto-sampler. Determination and measurement of concentration of the NAs in the water sample being found by a gas chromatograph coupled with a mass spectrometer (GC-MS).
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS +1
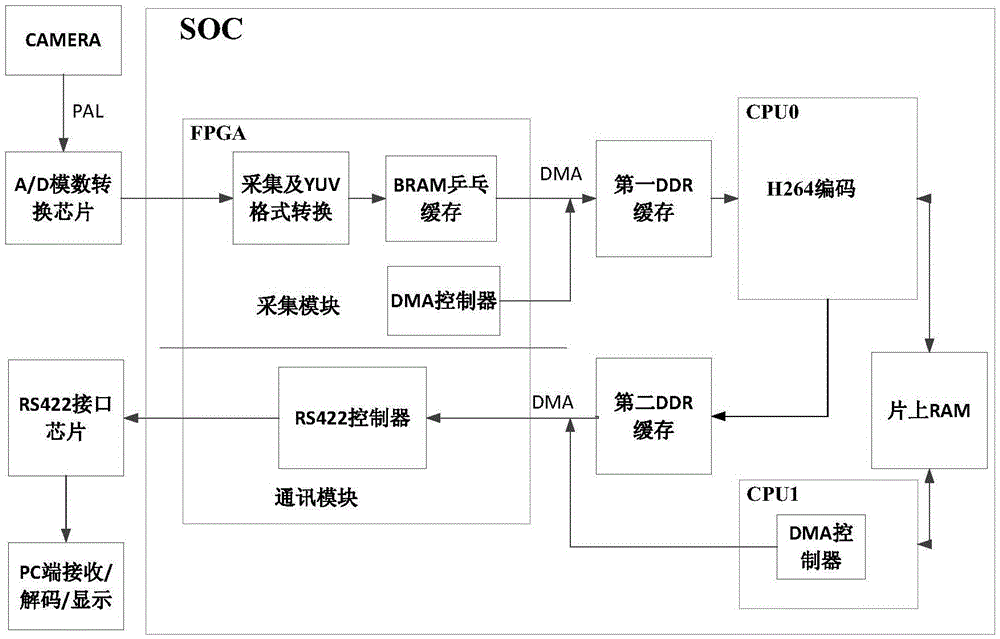
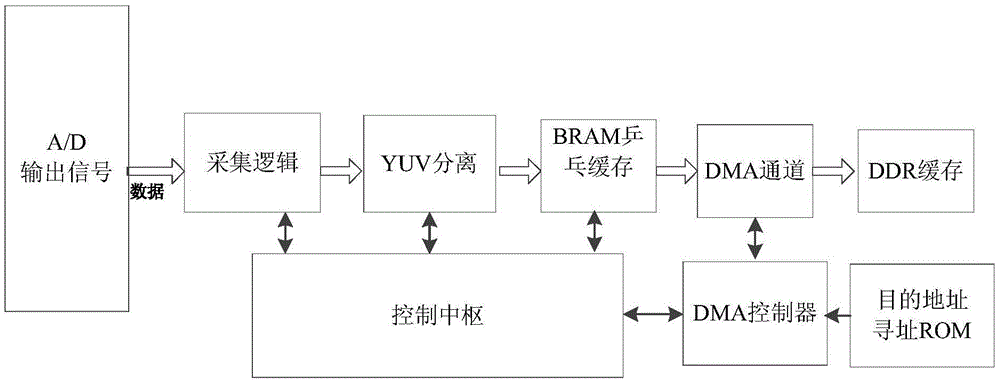
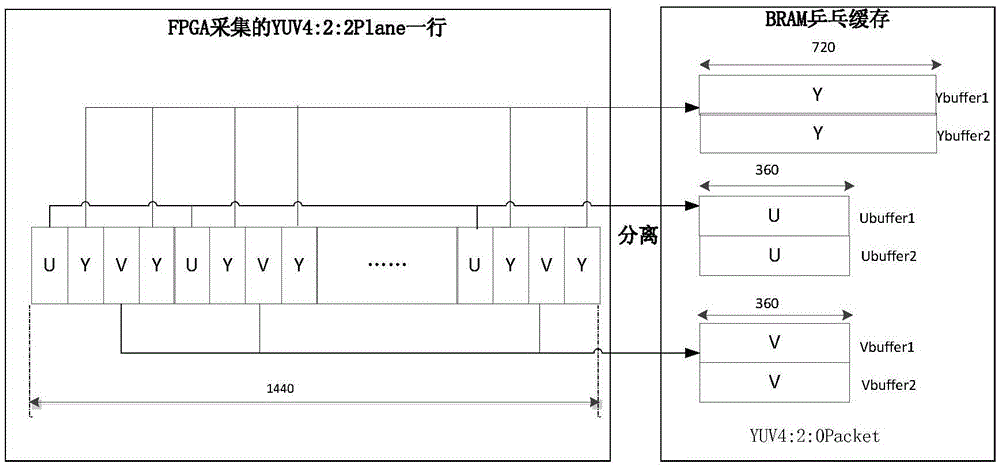
System and method for implementing video capture, compression and transmission on SOC (System On Chip)
ActiveCN105611295ADoes not occupy clock resourcesConvert in real timeDigital video signal modificationDigital videoAnalog-to-digital converter
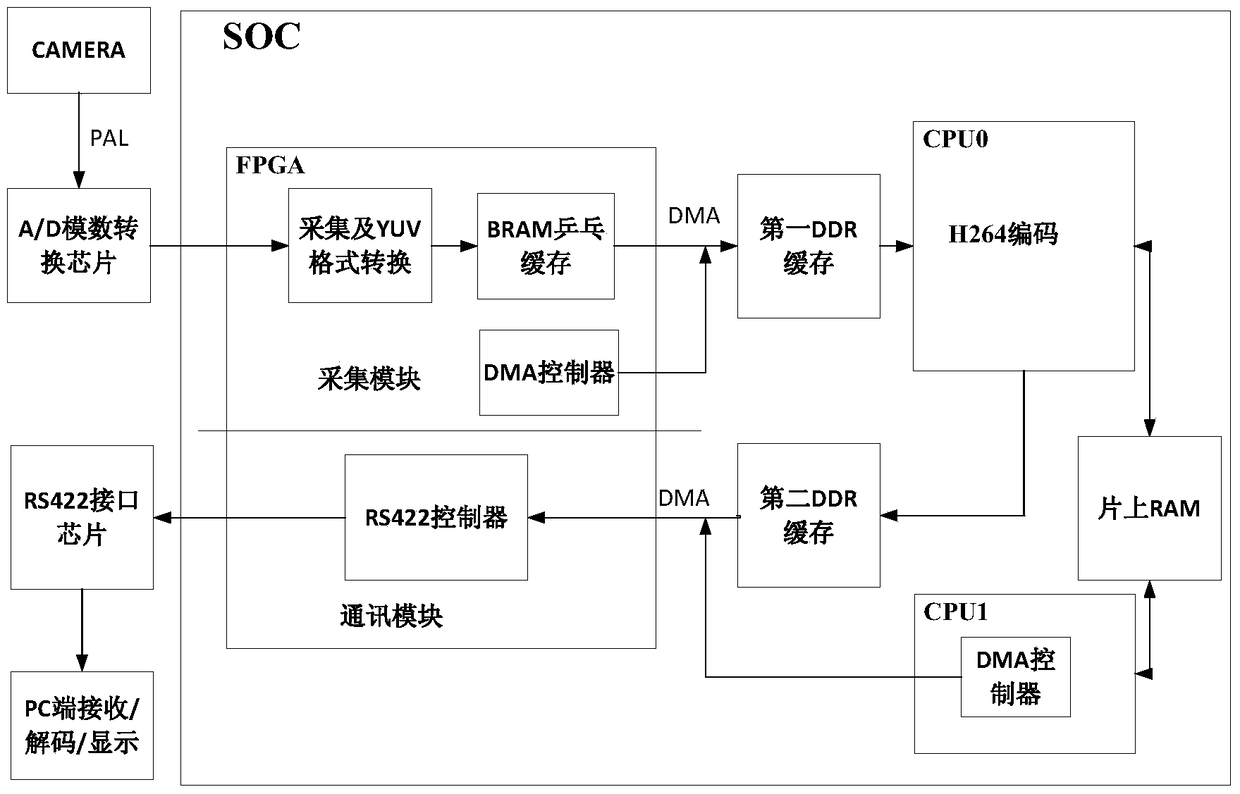
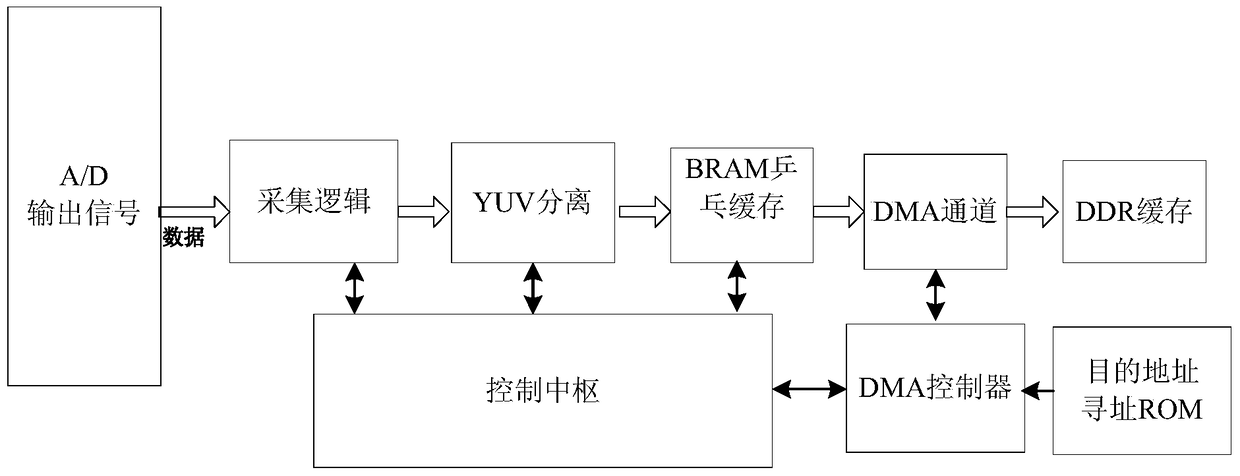
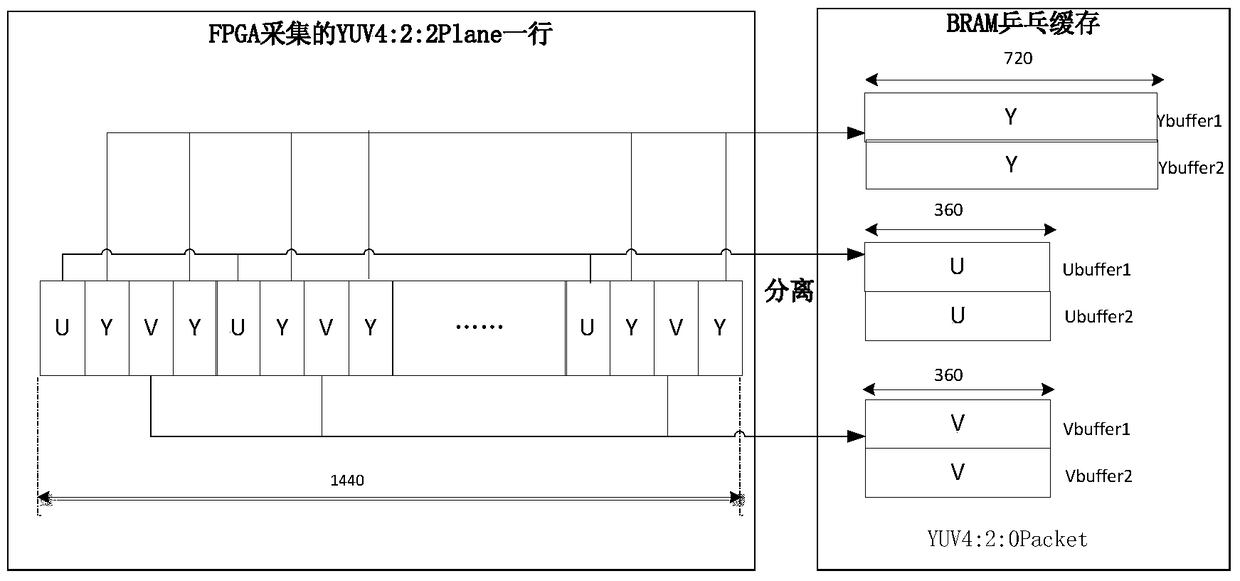
The invention relates to a system and method for implementing video capture, compression and transmission on a system on chip. The system captures a PAL (Programmable Array Logic) standard video, and then transmits the PAL standard video to a computer terminal through a serial port after the PAL standard video is compressed through an H.264 protocol, decodes and displays the PAL standard video synchronously; the system comprises video capture, video coding, code stream transmission and computer terminal decoding and display; in video capture, an analog to digital converter is used foracquiring the PAL standard video to obtain a digital video signal, and separating a YUV 4 to 2 to 0 video signal from the digital signal; in video coding,compressed encoding based on the H.264 protocol is performedon an obtained YUV 4 to 2 to 0 video frame; in code stream transmission,a compressed code stream generated by a coding module is transmitted to a computer terminal program through the serial port; and the computer terminal program decodes the received code stream and displays images in real time. The system has the characteristics of being miniaturized, and flexible in application; two CPU (Central Processing Unit) cores using an SOC (System On Chip) processor perform coding and transmission control, and the processing capacity is strong; and an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) is used for performing video capture and separation and controlling direct memory access and transmission.
Owner:CHINA AEROSPACE TIMES ELECTRONICS CORP
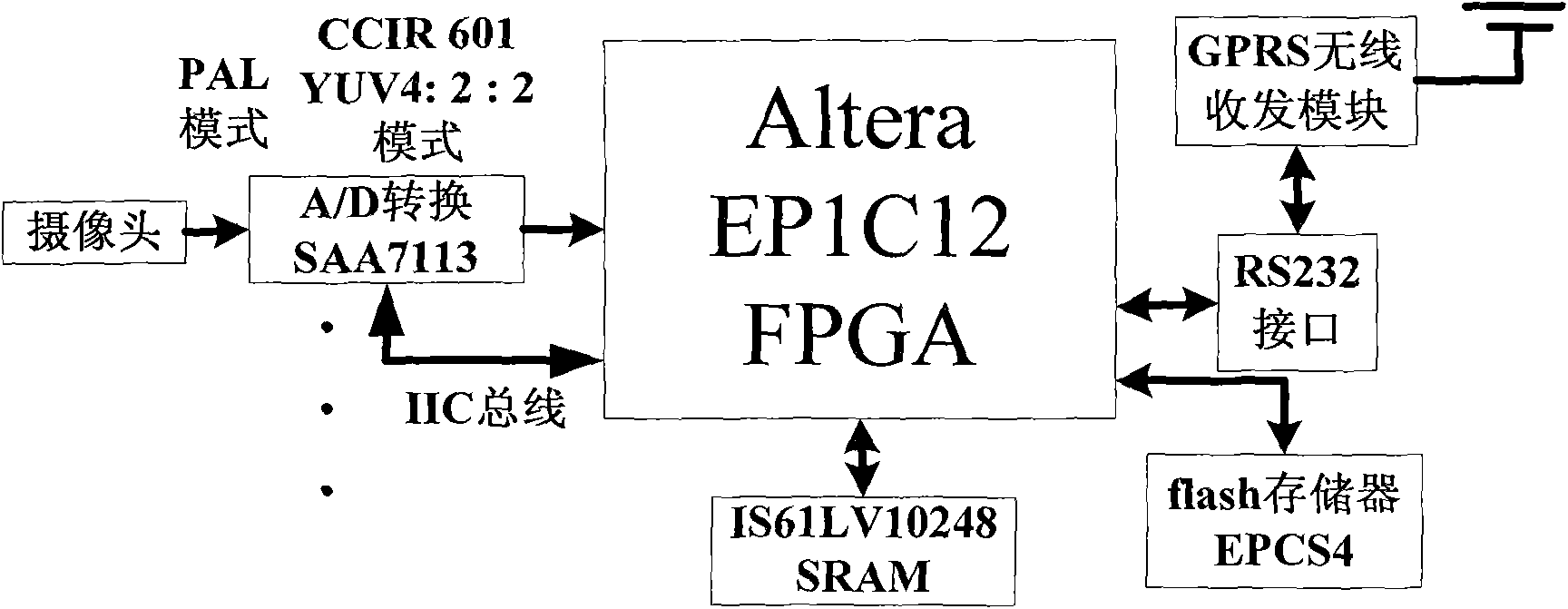
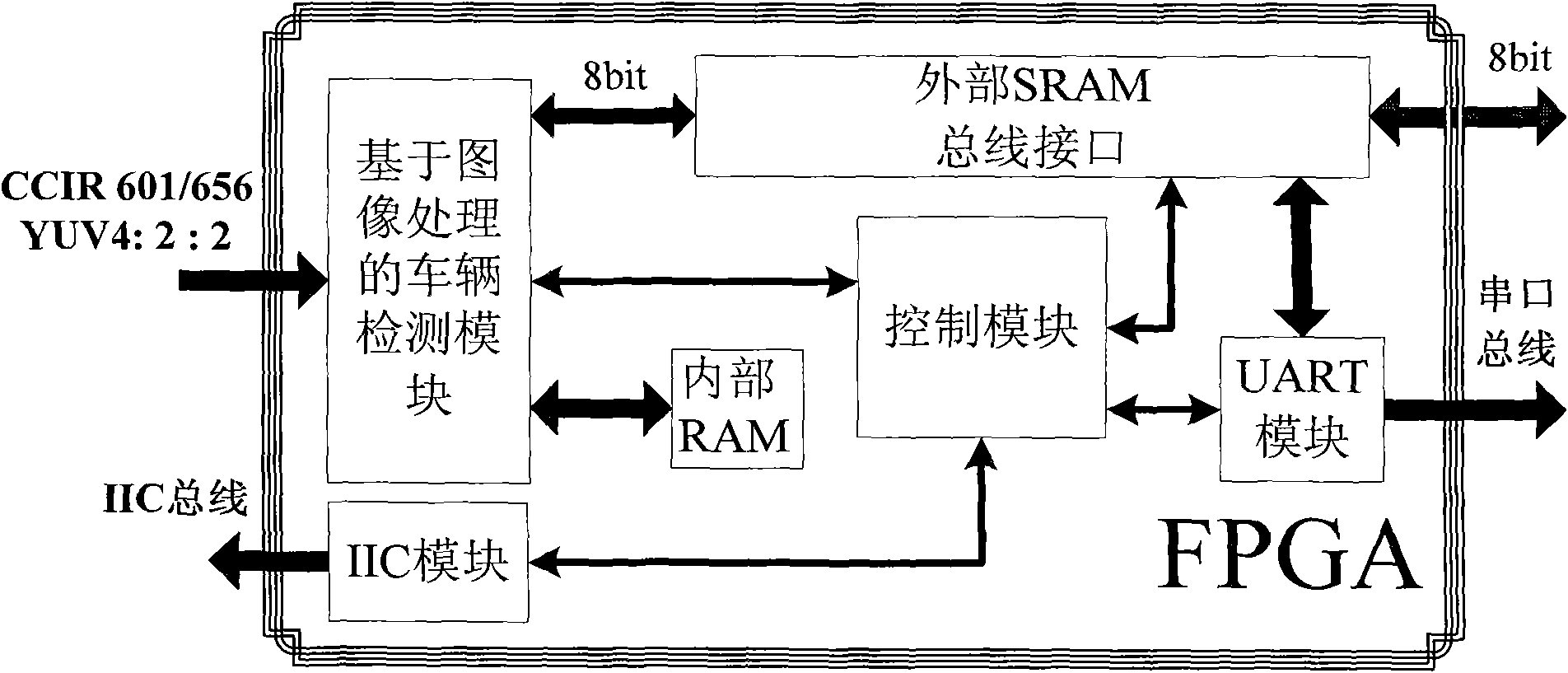
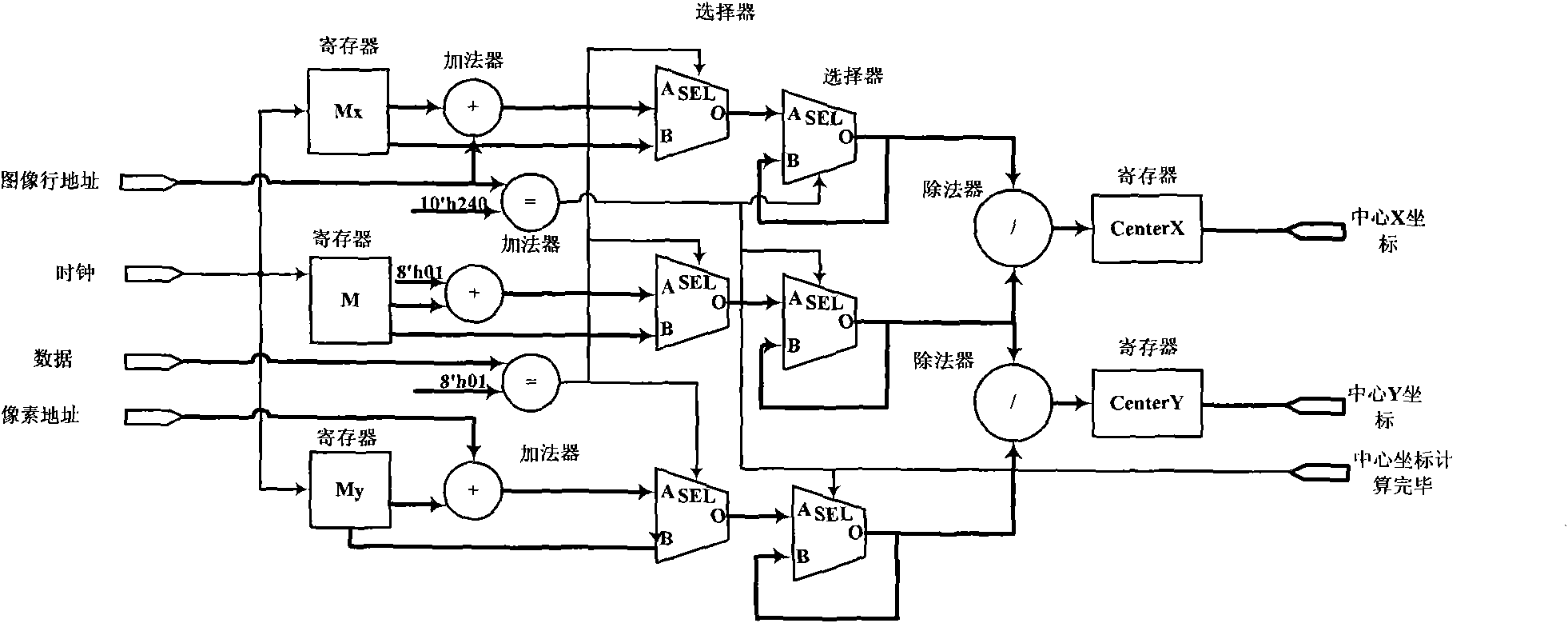
Embedded super-speed video detection method based on FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array)
InactiveCN101853576AEasy to handleQuick checkEnergy efficient ICTRoad vehicles traffic controlVideo monitoringGeneral Packet Radio Service
The invention discloses an embedded super-speed video detection method based on an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array), aiming to solve the technical problem of high power consumption of the traditional intelligent traffic integrated video monitoring system. The method comprises the following steps of: monitoring an appointed detection region of a highway by using a high-speed clock of 200Mhz through a plurality of CCD (Charge Coupled Device) cameras of a PAL (Programmable Array Logic) system and processing images; carrying out image threshold segmentation by directly using the FPGA, judging whether a vehicle is overspeed or not and determining the position of the vehicle in the images; capturing images containing the type and a license plate number of the overspeed vehicle and exactly measuring the speed of the overspeed vehicle; and sending the information of the obtained speed of the overspeed vehicle, the captured images, the incident time and place, and the like to a radio transmission module and transmitting the information to a monitoring station through a GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) network. In the invention, the FPGA is directly adopted to process all image acquisition and image segmentation calculation, and the quick processing and super-speed detection of multiple paths of images are realized by utilizing the parallel processing capacity of the FPGA to the images; and other core processing units are not needed, thus the system power consumption is reduced.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
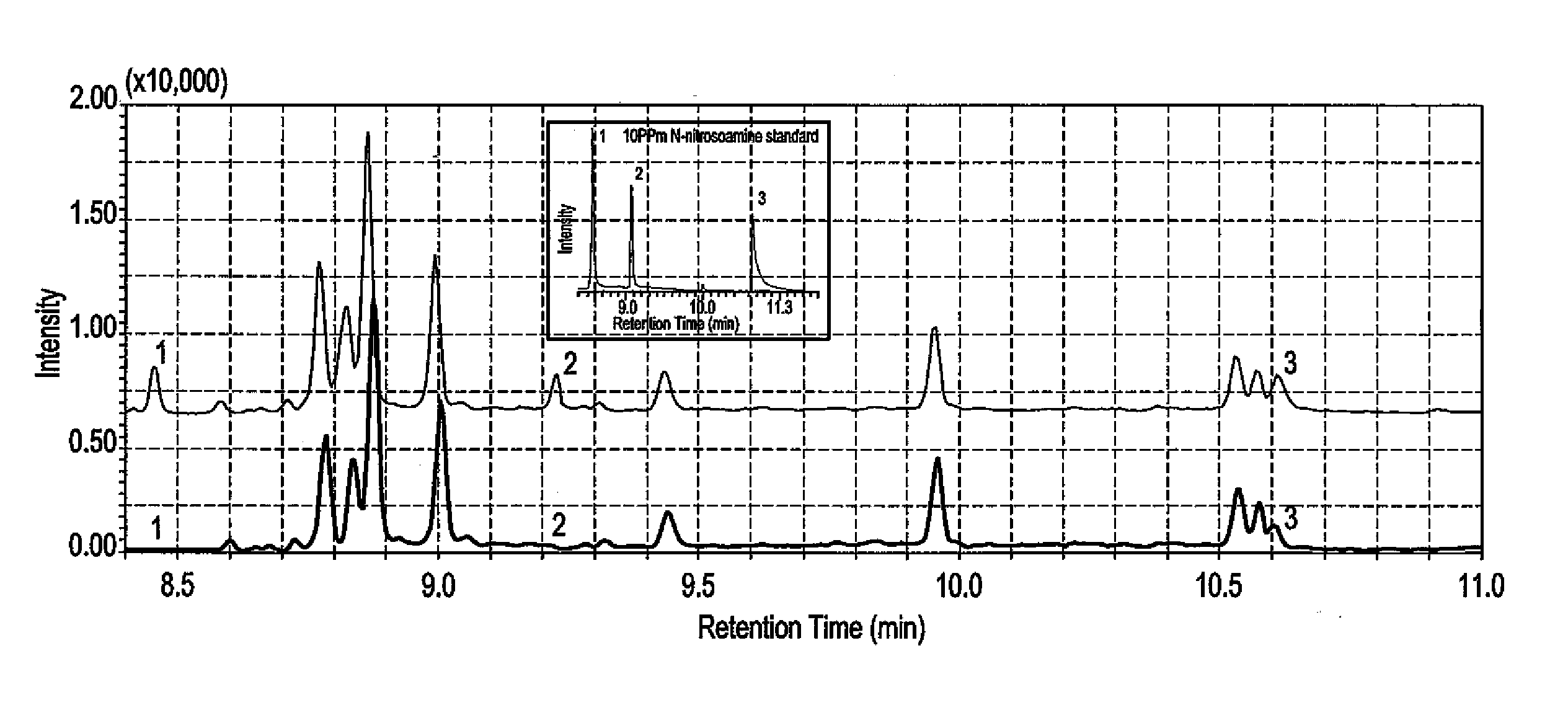
Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction method of detecting N-nitrosoamines
The dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction (DLLME) method of detecting N-nitrosoamines (NAs) is a DLLME performed with a xylene extraction solvent and a methanol disperser solvent. The microextraction is preferably performed by a programmable array logic (PAL) auto-sampler. Determination and measurement of concentration of the NAs in the water sample being found by a gas chromatograph coupled with a mass spectrometer (GC-MS).
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS +1
Video system conversion method and conversion device in ultrasonic imaging equipment
ActiveCN102523417ADisplay image effect is goodReduce data volumeStandards conversionDigital videoExternal storage
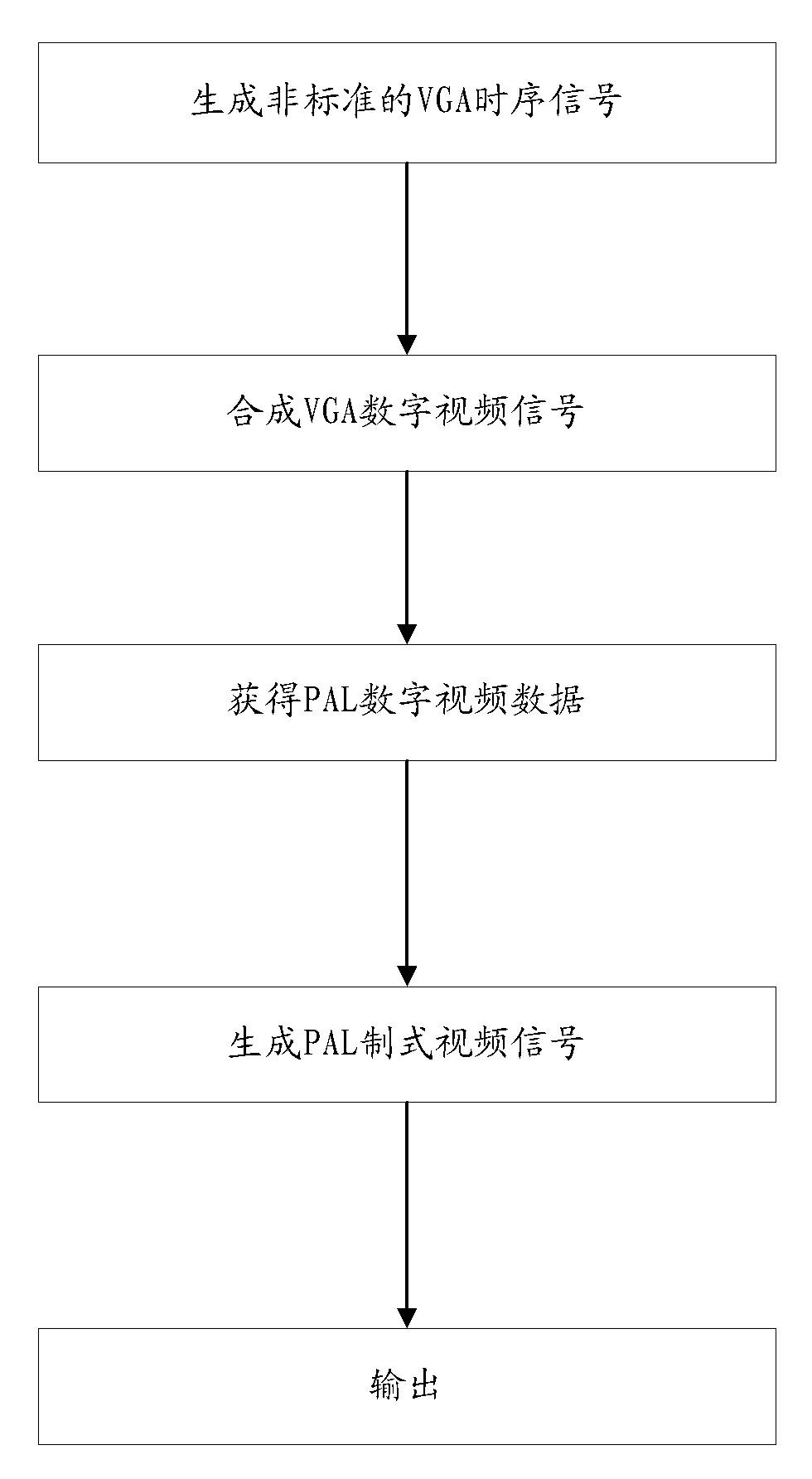
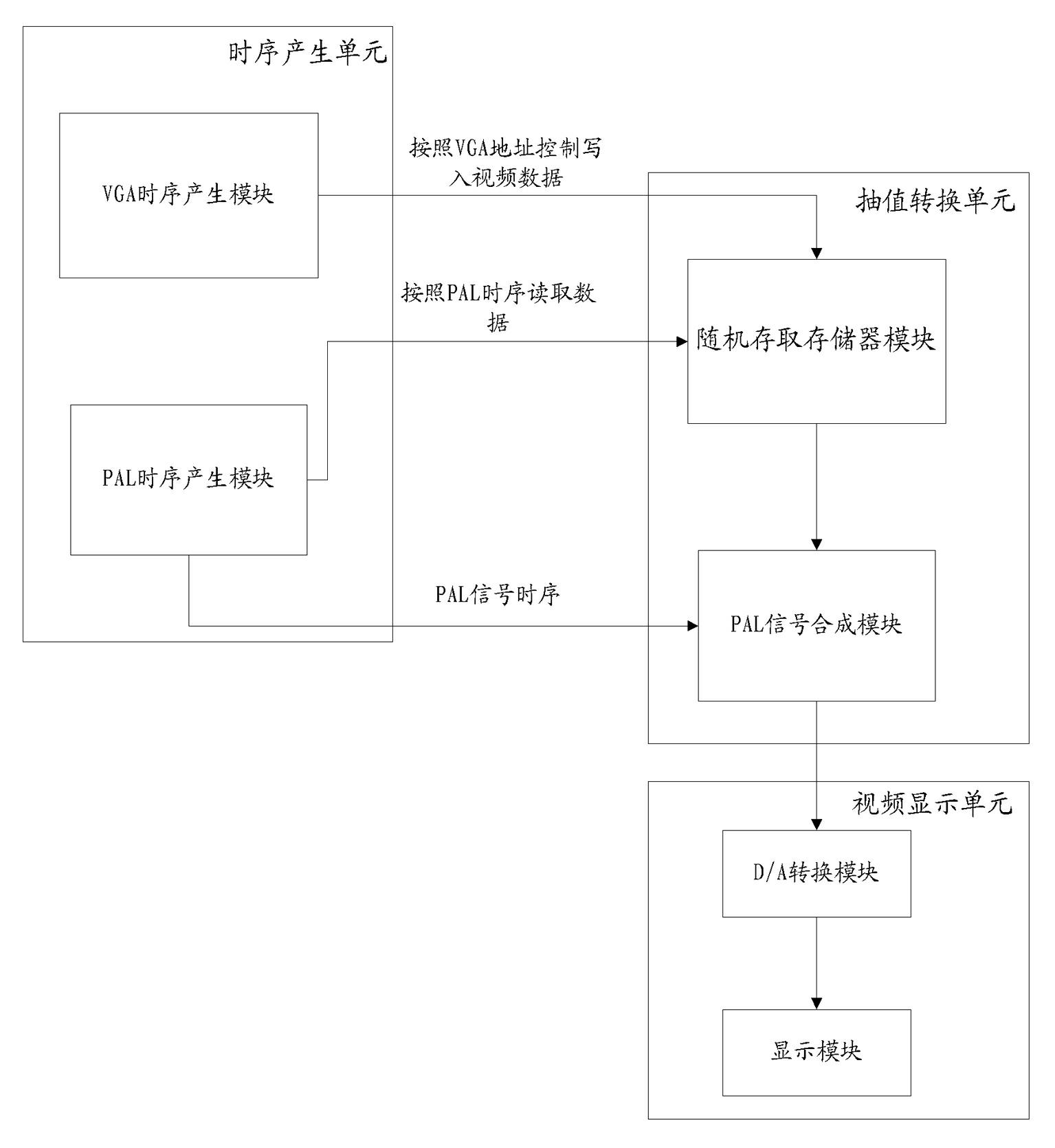
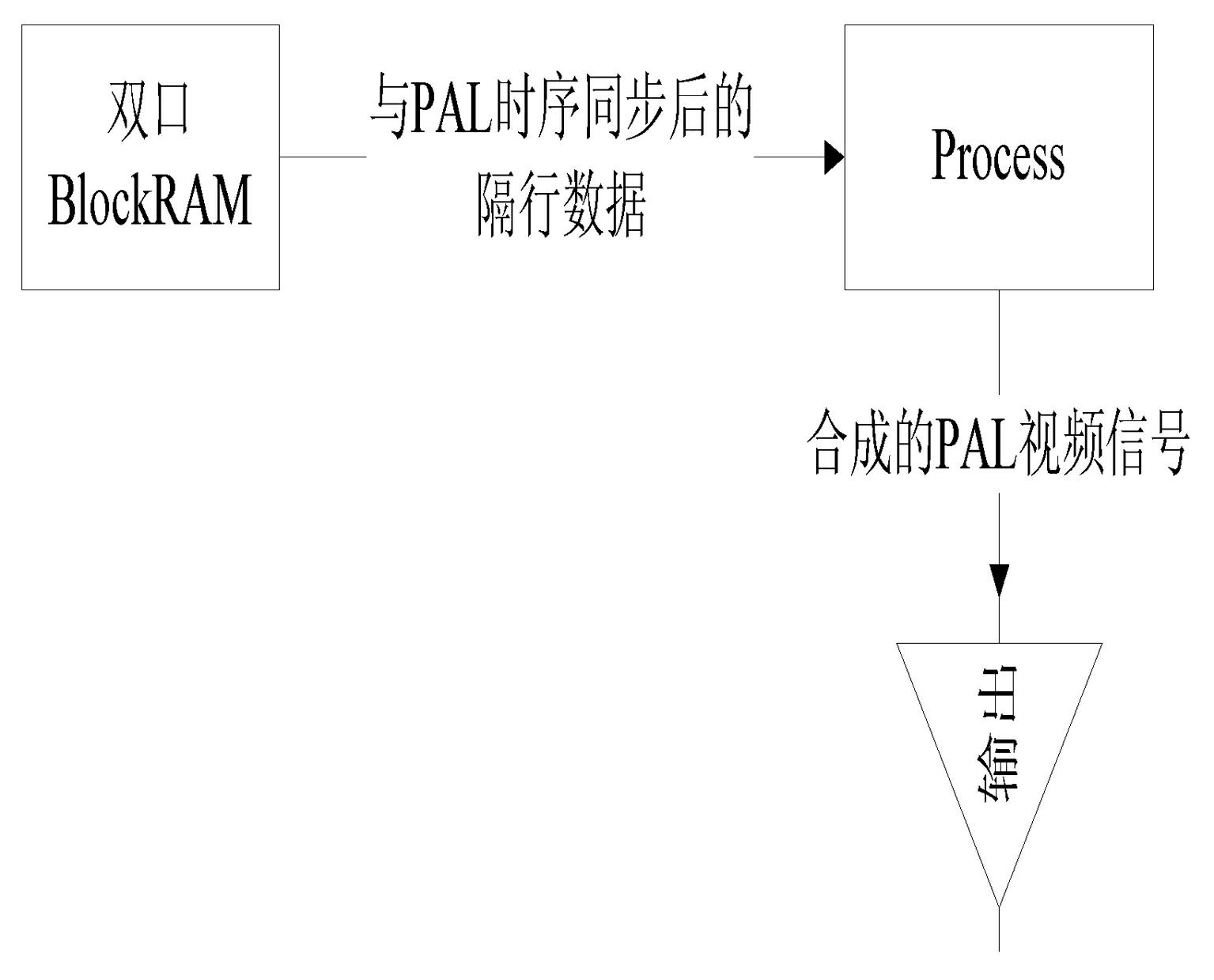
The invention provides a video system conversion method in ultrasonic imaging equipment, which includes: producing VGA (video graphic array) time sequence and address information, converting VGA time sequence signals to non-standard VGA time sequence signals, converting VGA digital video signals into simulation signals to be output, writing the address information into an external storage unit, loading standard PAL (programmable array logic) address information into the external storage unit, acquiring PAL digital video data generated by the external storage unit by reading the external storage unit, combining with the PAL time sequence, overlapping the PAL digital video data on the standard PAL time sequence waveform to generate PAL system video signals and outputting the PAL system video signals to the outside. The video system conversion method is capable of extracting original VGA data directly without interpolation zoom, PAL image display effect is excellent, particularly the bottom and the top of an image are displayed well, cached data quantity is reduced greatly, external storage units are omitted, and cost is saved. Meanwhile, a conversion device utilizing the video system conversion method also has the above advantages.
Owner:EDAN INSTR
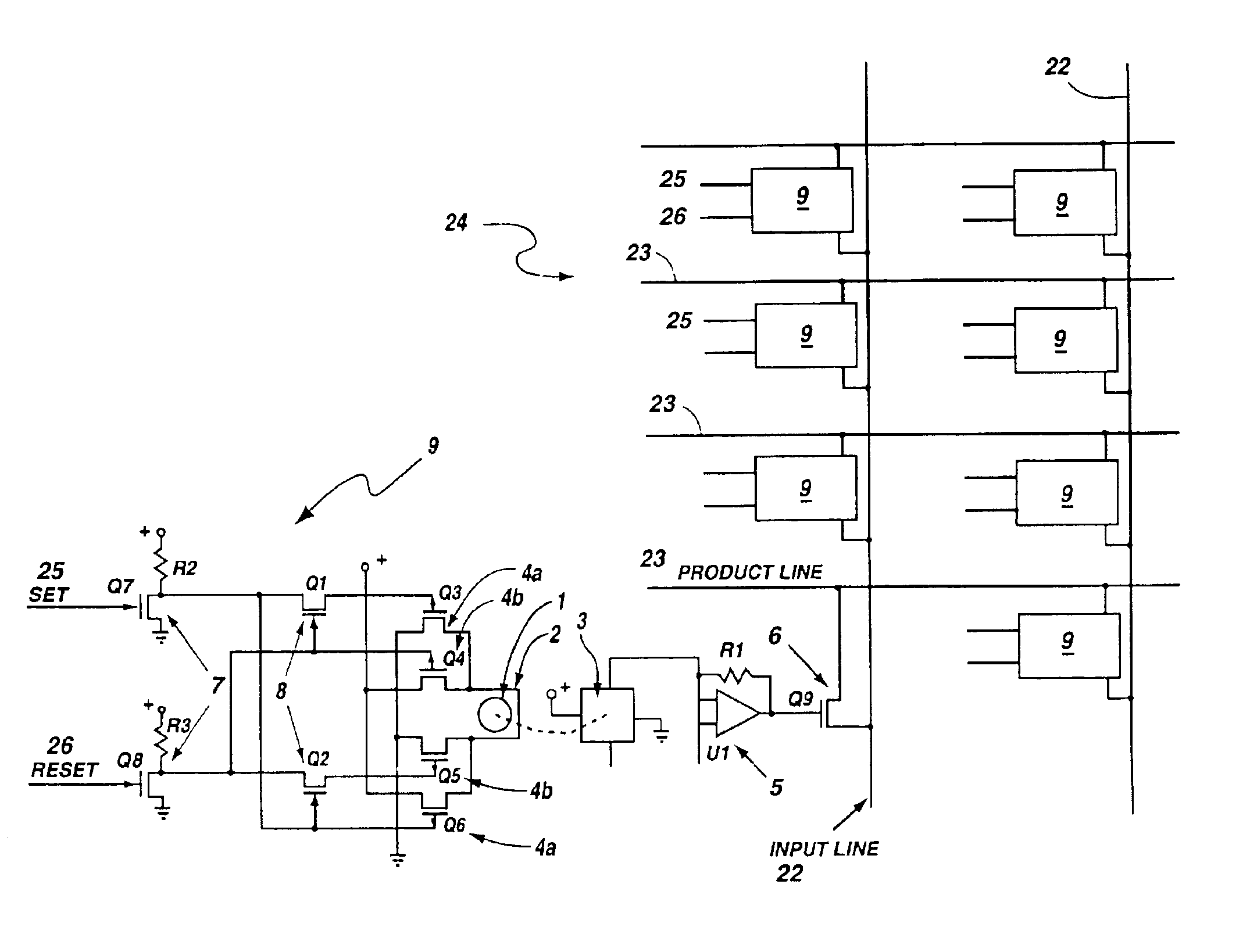
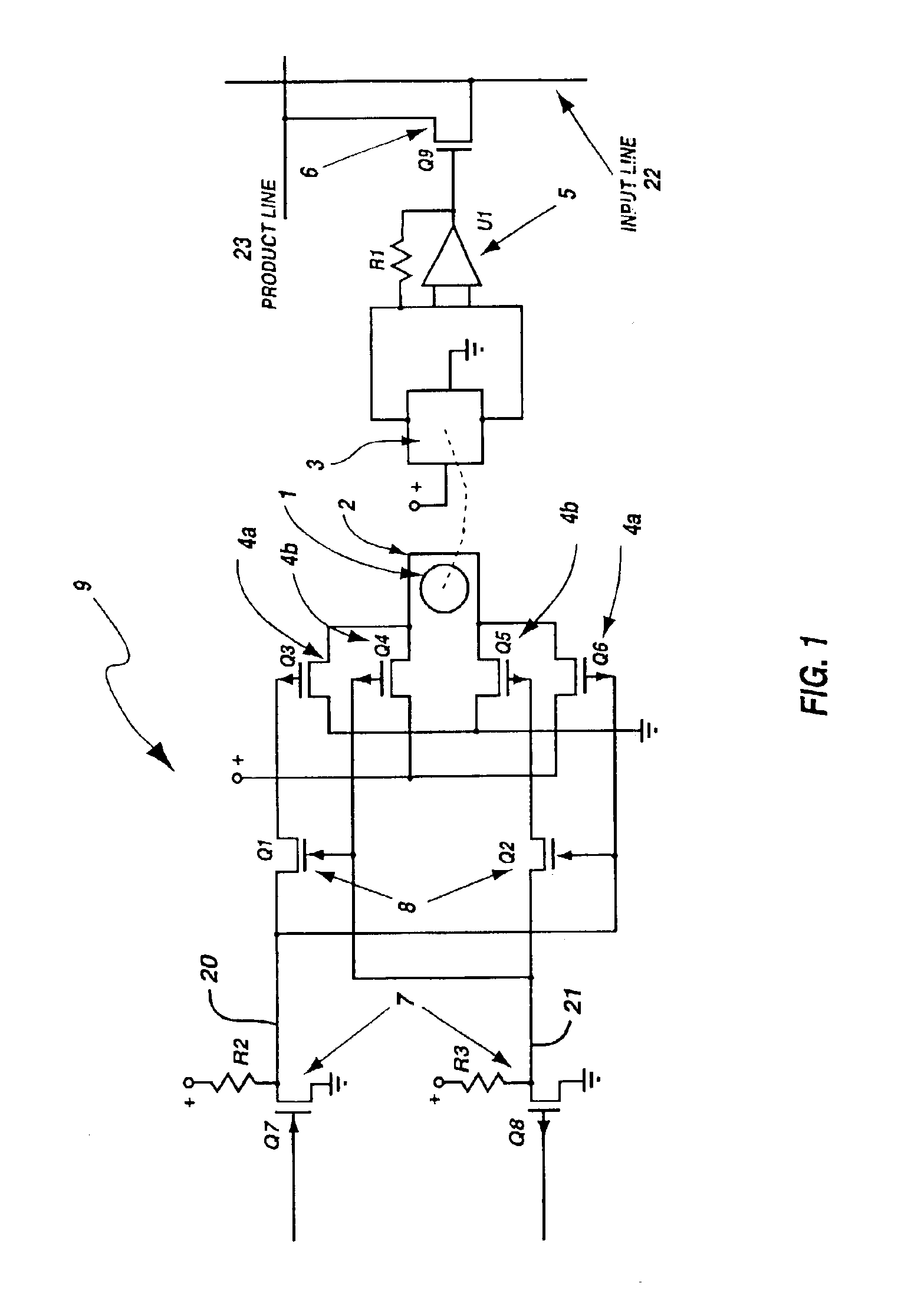
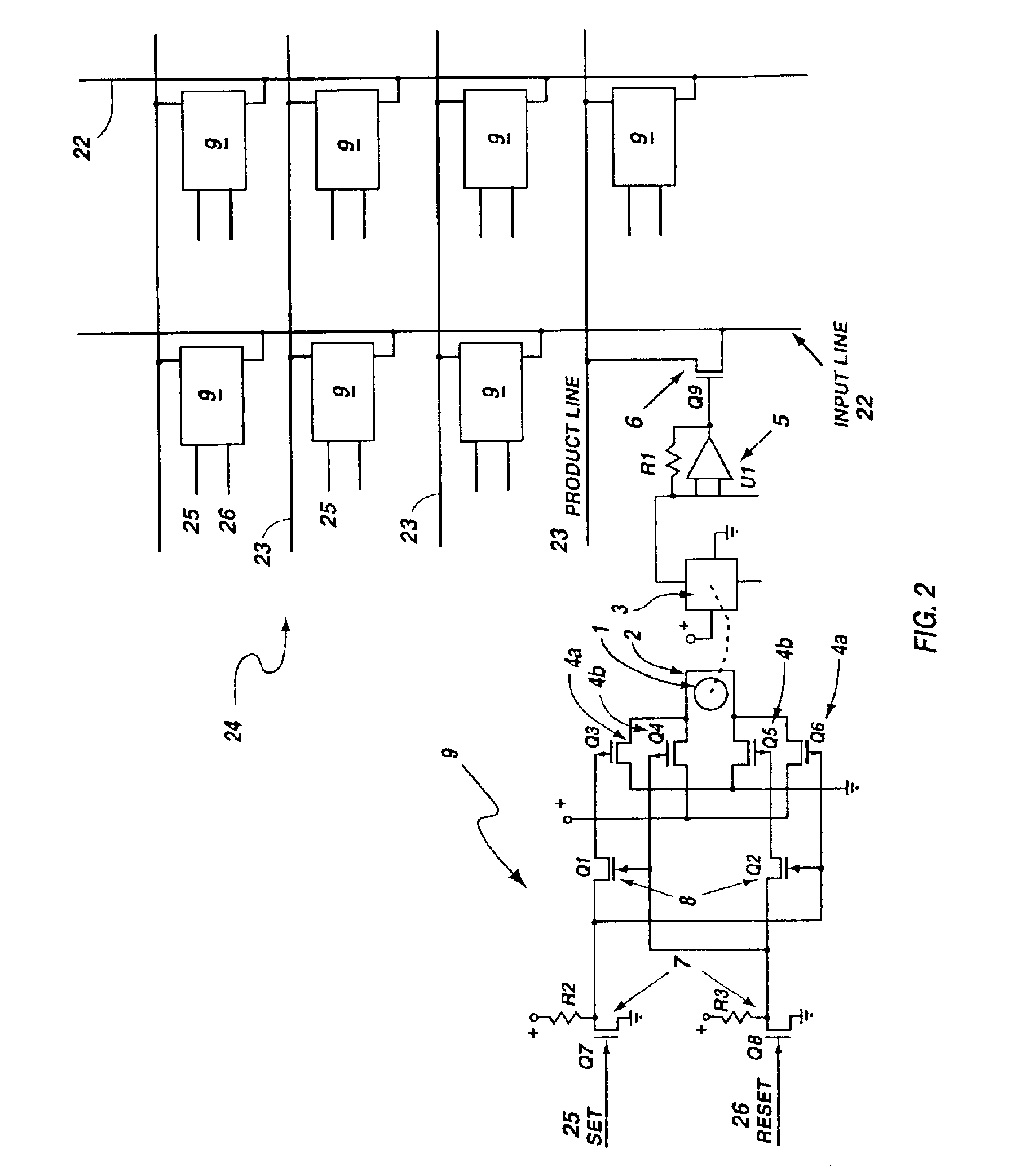
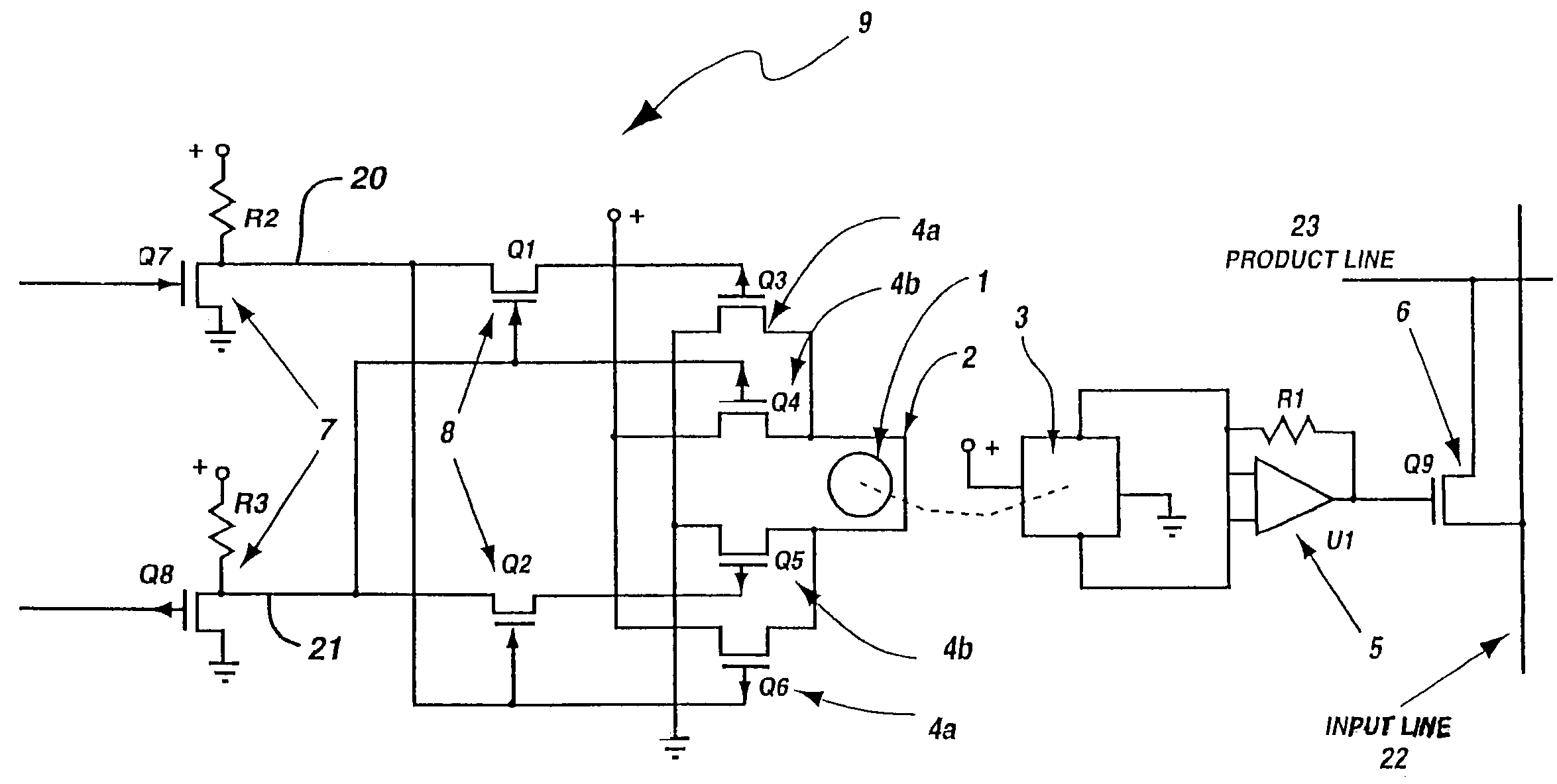
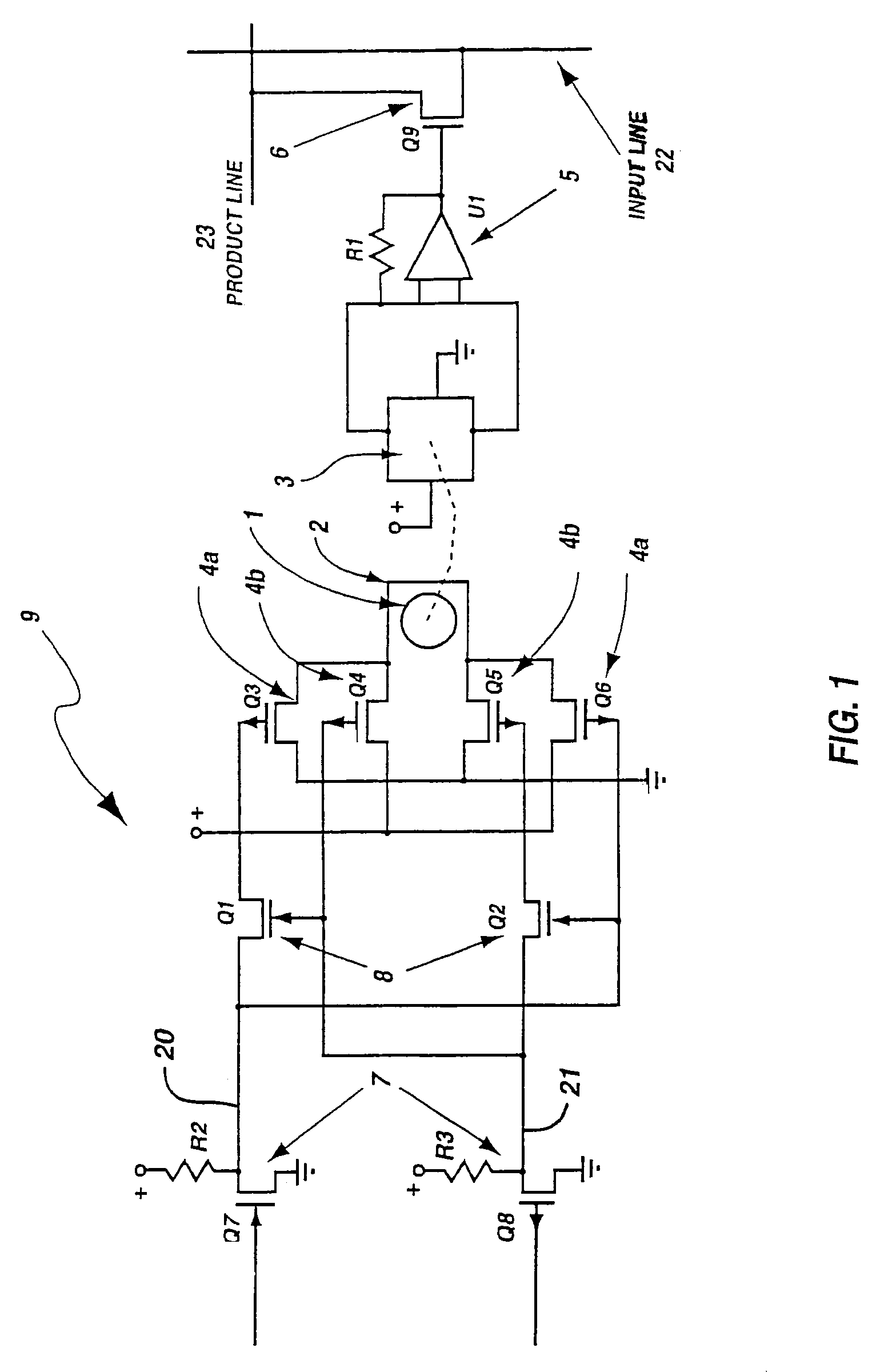
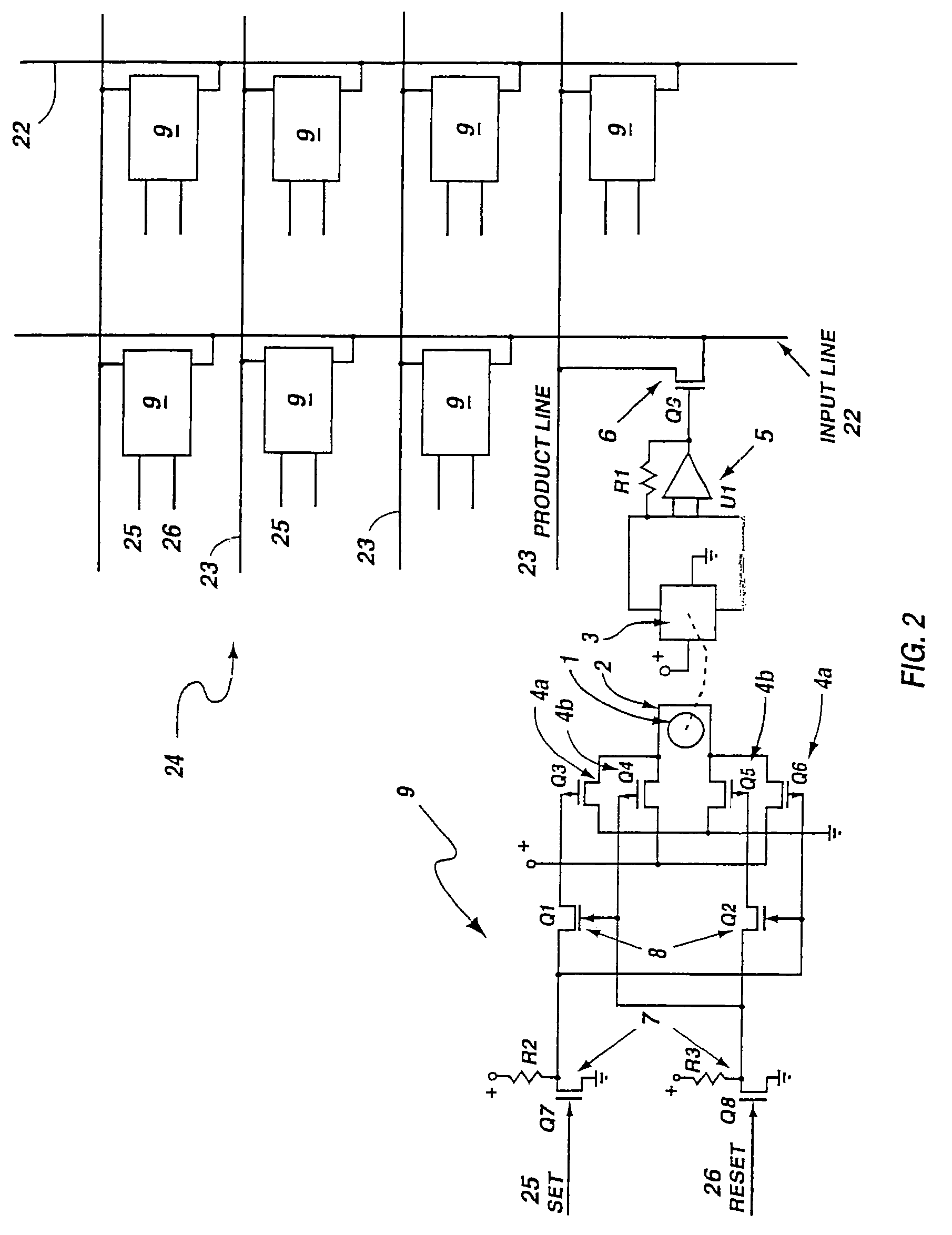
Programmable array logic circuit whose product and input line junctions employ single bit non-volatile ferromagnetic cells
InactiveUS6864711B2Save powerNo lossSolid-state devicesPulse modulationProduction lineControl signal
A programmable array logic circuit whose temporary memory circuitry employs single bit non-volatile ferromagnetic memory cells. The ferromagnetic memory cells or bits store data even when there is no power provided to the circuitry, thus saving power during operation of the programmable logic circuitry, and ensuring that there is no loss of the data should there be a temporary power shut down. Additionally, the ferromagnetic cells provide for indefinite number of switching actions on the data without degradation to the capacity to store data therein. The invention provides an integrated circuit, comprising a programmable logic circuit array having product lines and input lines therein, and a storage register circuit. The storage register circuit has a ferromagnetic bit and sensor coupled to store a remnant control signal and an output transistor, coupled to be responsive to the remnant control signal on its gate, and coupled between an input and product line. Additionally, the integrated circuit may further include a logical AND array and a logical OR array.
Owner:MXRAM LLC A NEW MEXICO LIMITED LIABILITY +1
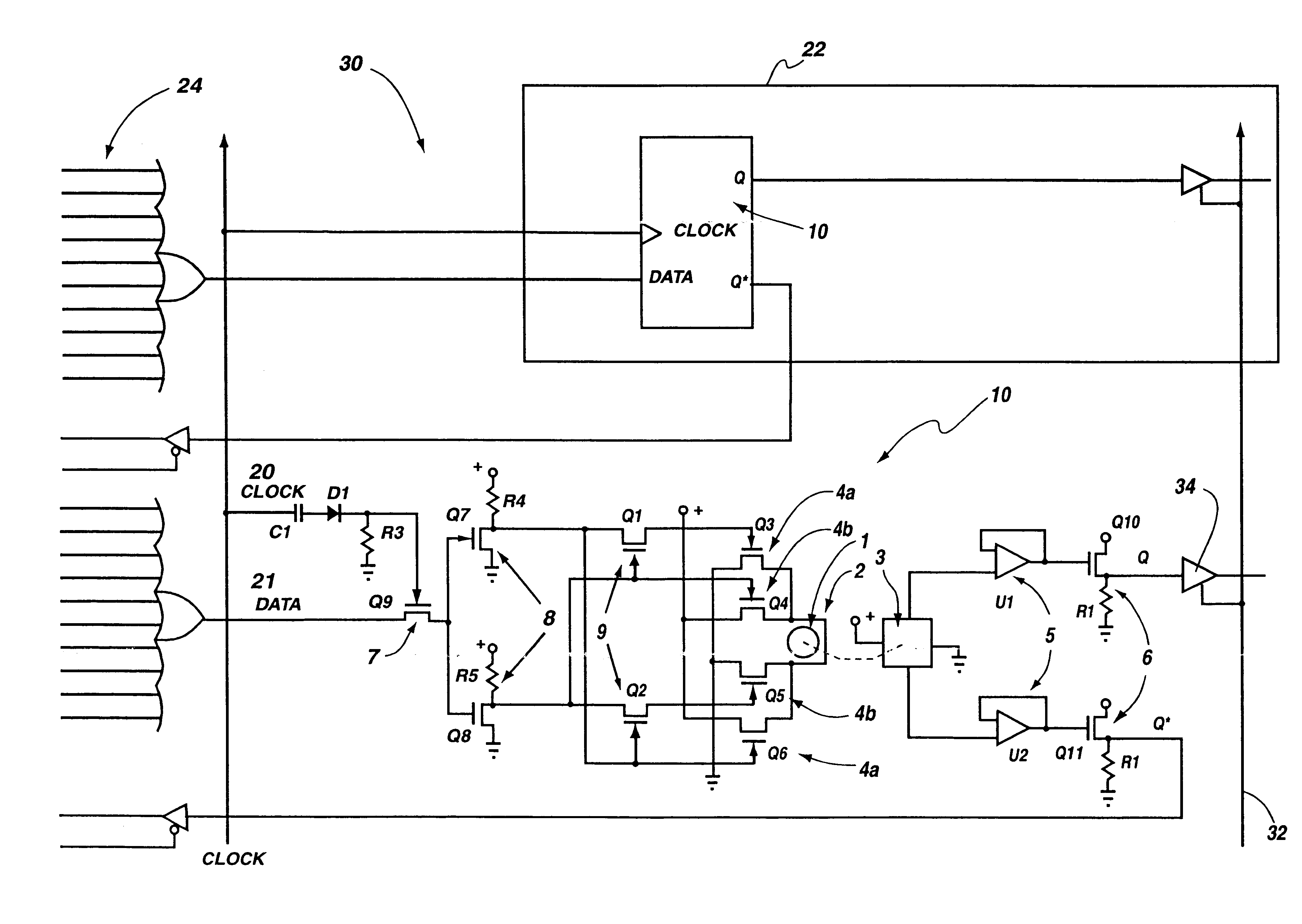
Programmable array logic circuit macrocell using ferromagnetic memory cells
InactiveUS6710624B2No lossOperational savingPulse modulationLogic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsComputer architectureHemt circuits
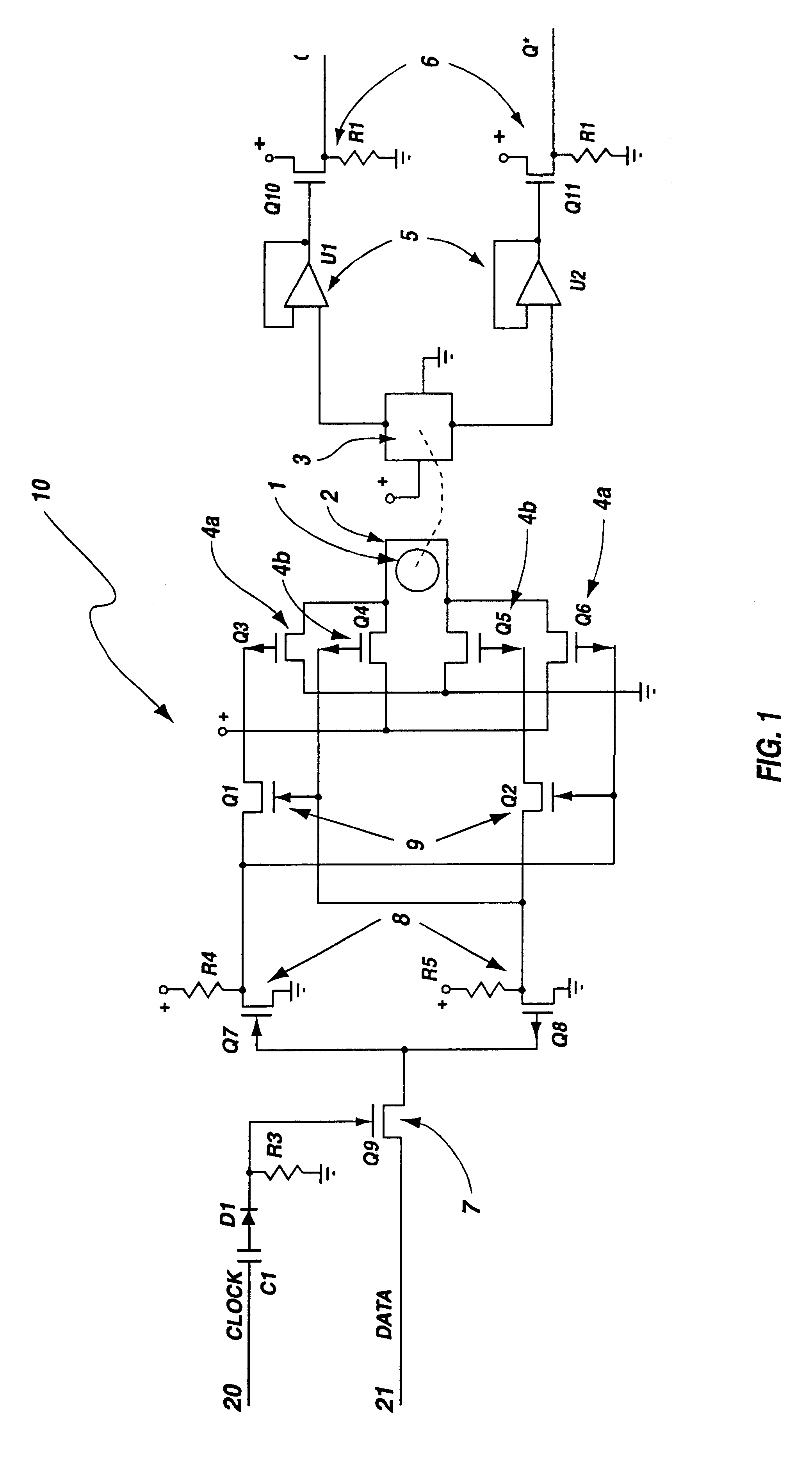
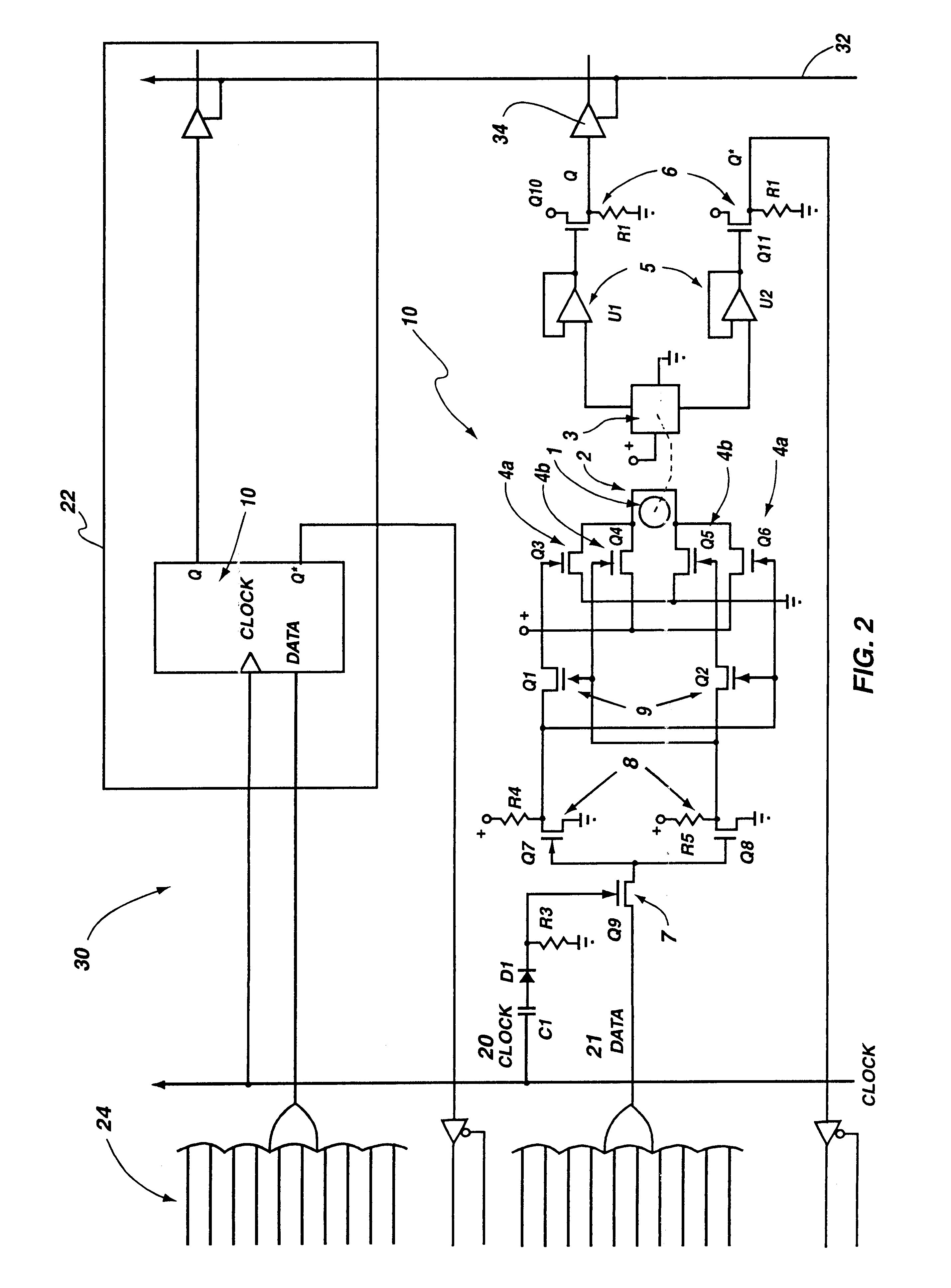
A programmable array logic circuit macrocell using ferromagnetic memory cells. More particularly, the present invention uses a non-volatile ferromagnetic memory cell to temporarily store binary data. It is an advantage of the invention to have the ferromagnetic memory cells or bits to store data even when there is no power provided to the circuitry, thus saving power during operation of the programmable logic circuitry, and ensuring that there is no loss of the data should there be a temporary power shutdown. Additionally, the ferromagnetic cells provide for indefinite number of switching actions on the data without degradation to the capacity to store data therein, thus eliminating "write fatigue". The invention provides an integrated circuit, comprising a programmable OR array (24), a programmable AND array (28), coupled to the programmable OR array, and a macrocell output circuit (22). The macrocell uniquely has a ferromagnetic bit (11) and sensor (12) coupled to store remnant output signal, and an output buffer (34), coupled to output the remnant output signal upon receiving an output enable signal. The macrocell may further include a DQ register that contains the ferromagnetic bit. The DQ register may also include a drive coil, which at least partially surrounds the ferromagnetic bit. Drive coils may have a bi-directional current that sets the polarity of the ferromagnetic bit. The bi-directional current may be switched by two sets of transistor pairs (Q10 and Q11). The two sets of transistor pairs may, in turn, be gated by first and second transistor respectively. The first and second transistors may be responsive to a DATA signal that is received when a CLOCK signal is received.
Owner:MXRAM LLC A NEW MEXICO LIMITED LIABILITY +1
Digital television set top box based on LED visible light communication
InactiveCN102595222AFast transmissionReduce power consumptionSelective content distributionDigital tuningVisible light communication
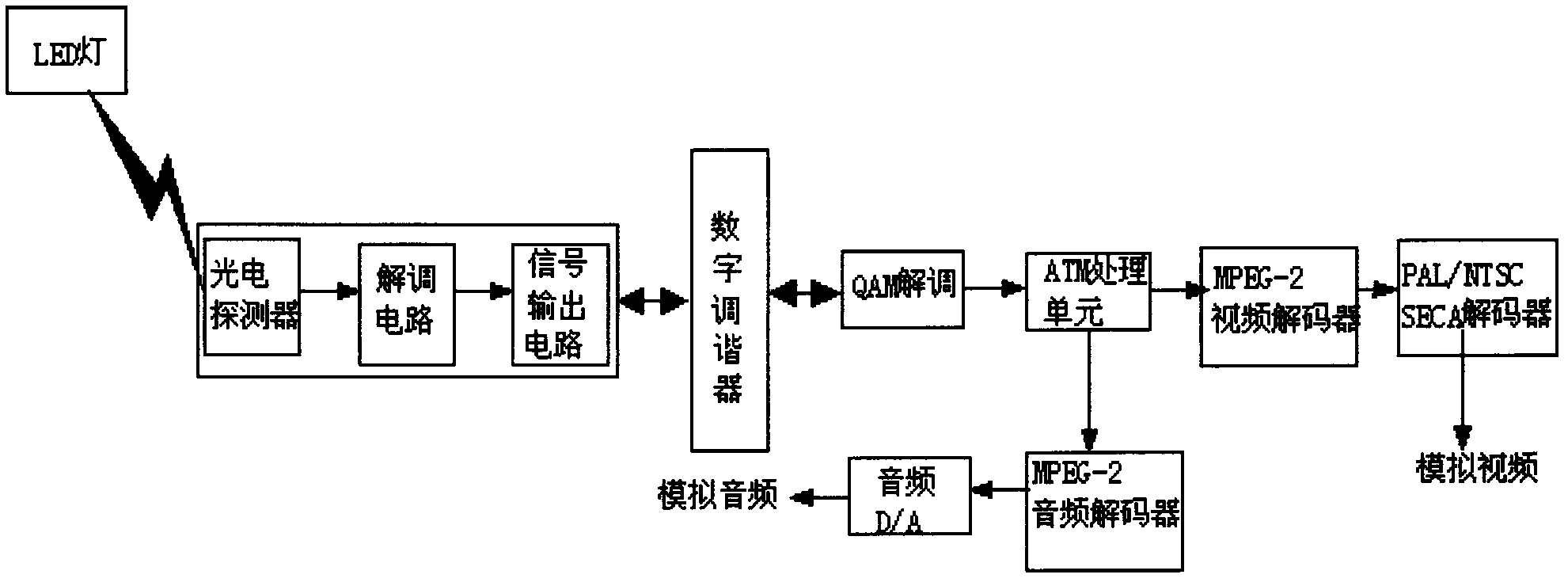
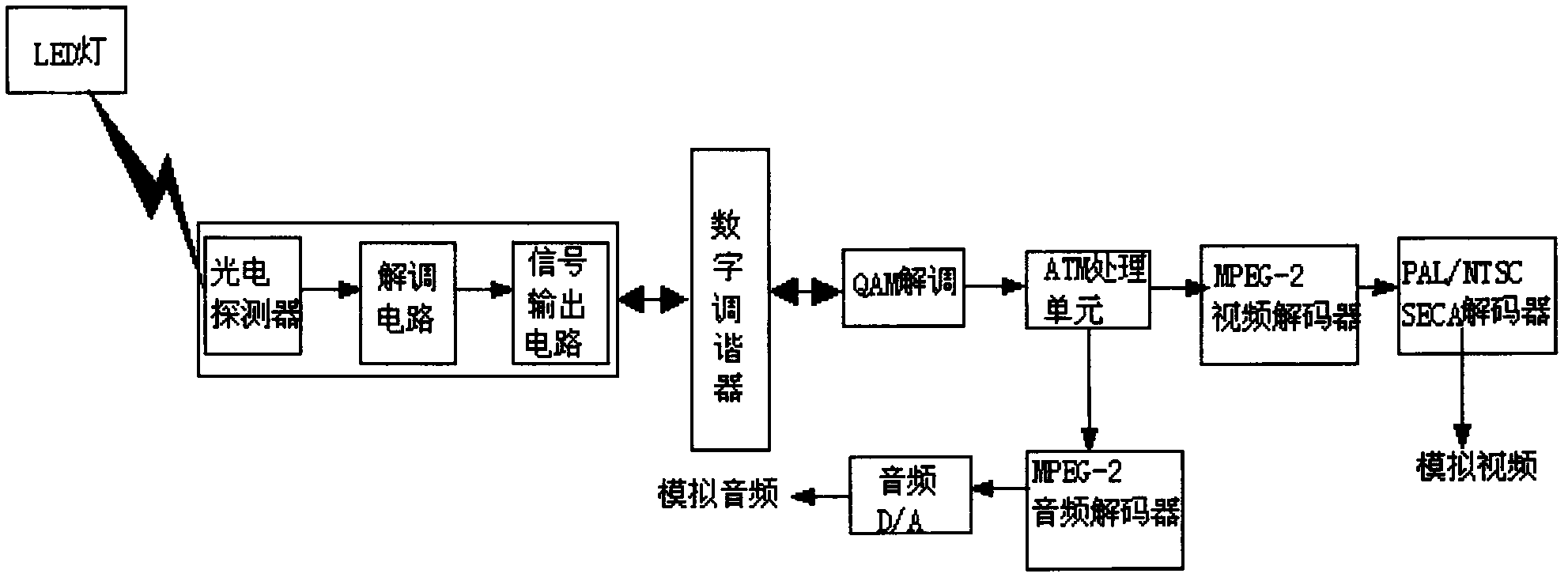
The invention discloses a digital television set top box based on LED visible light communication, belonging to the field of digital television set top boxes and comprising a digital tuner, a quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) and demodulation module, an ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) processing unit, an MPEG (Moving Picture Experts Group)-2 video and audio decoder, an audio digital analogy (D / A) conversion unit, a PAL / NTSC / SECAM (Programmable Array Logic / National Television System Committee / Sequential Colour and Memory) decoder and an optical receiver; and an LED visible light communication technology is applied to the digital television set top box so that the wireless communication between a television program signal and the set top box is realized. In such a way, a television signal can be input to the digital television set top box in a wireless way so as to be decoded and output; and the digital television set top box based on LED visible light communication has the advantages of simple structure, higher image definition and better practicability.
Owner:郭丰亮
Programmable array logic circuit employing non-volatile ferromagnetic memory cells
A programmable array logic circuit whose temporary memory circuitry employs single bit non-volatile ferromagnetic memory cells. The ferromagnetic memory cells or bits store data even when there is no power provided to the circuitry, thus saving power during operation of the programmable logic circuitry, and ensuring that there is no loss of the data should there be a temporary power shut down. Additionally, the ferromagnetic cells provide for indefinite number of switching actions on the data without degradation to the capacity to store data therein. The invention provides an integrated circuit, comprising a programmable logic circuit array having product lines and input lines therein, and a storage register circuit. The storage register circuit has a ferromagnetic bit and sensor coupled to store a remnant control signal and an output transistor, coupled to be responsive to the remnant control signal on its gate, and coupled between an input and product line. Additionally, the integrated circuit may further include a logical AND array and a logical OR array.
Owner:LIENAU RICHARD M
Interconnection and input/output resources for programmable logic integrated circuit devices
InactiveUS6894533B2Double speedHalve propagation time of signalComputation using non-contact making devicesSolid-state devicesProgrammable logic deviceComputer module
A programmable logic integrated circuit device has a plurality of regions of programmable logic disposed on the device in a plurality of intersecting rows and columns of such regions. Interconnection resources (e.g., interconnection conductors, signal buffers / drivers, programmable connectors, etc.) are provided on the device for making programmable interconnections to, from, and / or between the regions. At least some of these interconnection resources are provided in two forms that are architecturally similar (e.g., with similar and substantially parallel routing) but that have significantly different signal propagation speed characteristics. For example, a major or larger portion of such dual-form interconnection resources may have what may be termed normal signal speed, while a smaller minor portion may have significantly faster signal speed. Secondary (e.g., clock and clear) signal distribution may also be enhanced, and so may be input / output circuitry and cascade connections between adjacent or nearby logic modules on the device.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
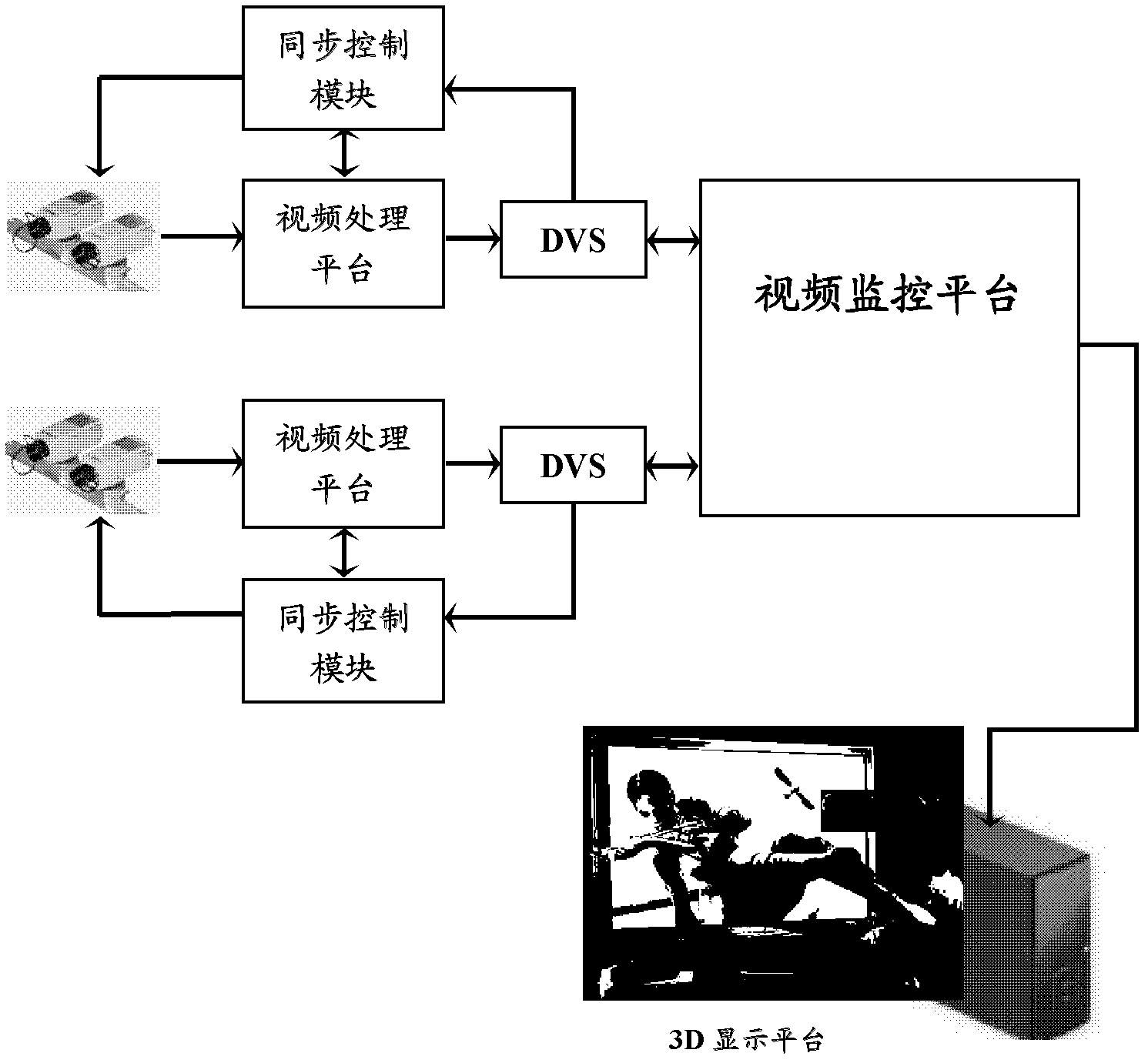
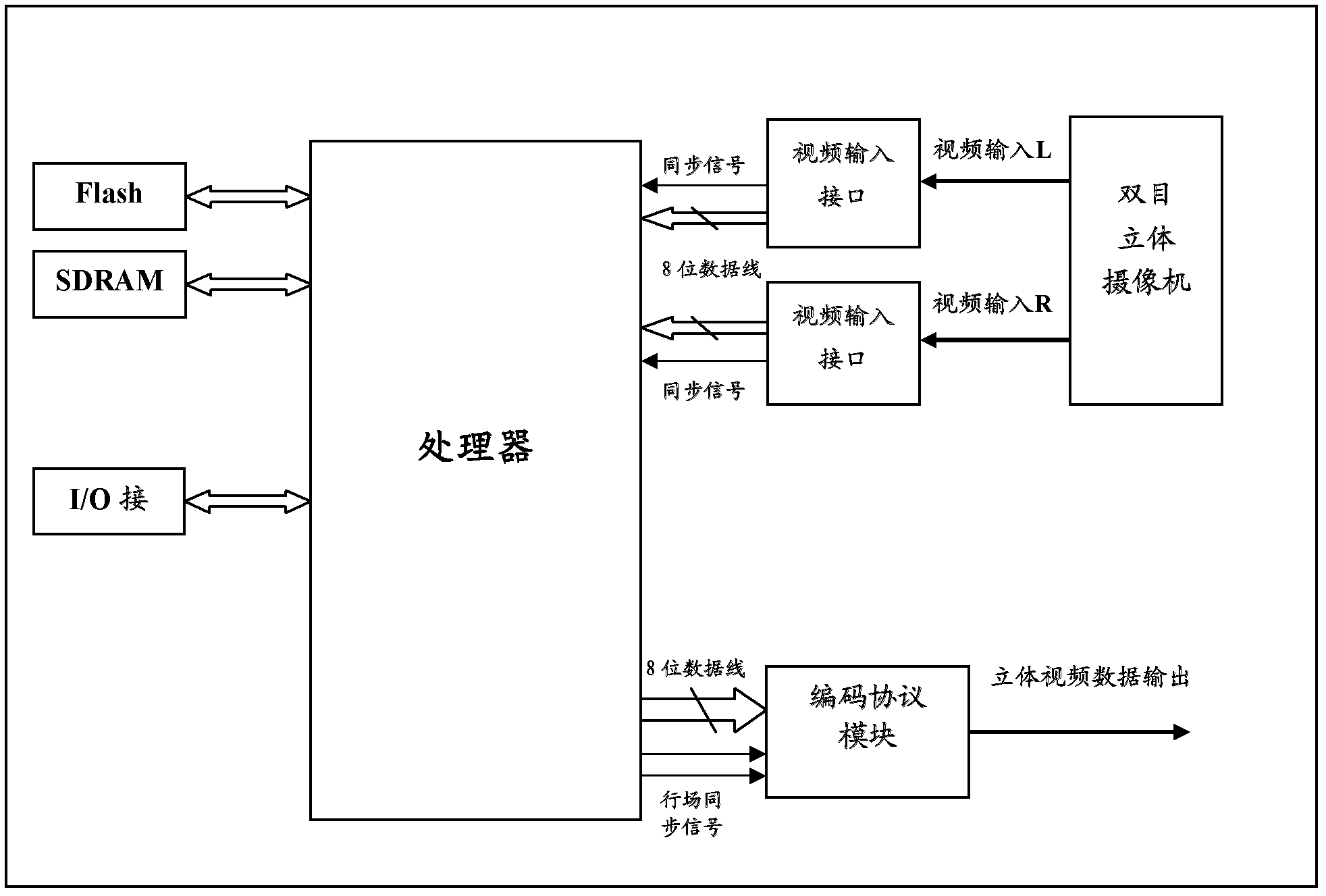
Network 3D (three dimensional) video monitoring system and method and video processing platform
ActiveCN103051866ARealize monitoringTelevision system detailsColor television detailsVideo monitoringVideo processing
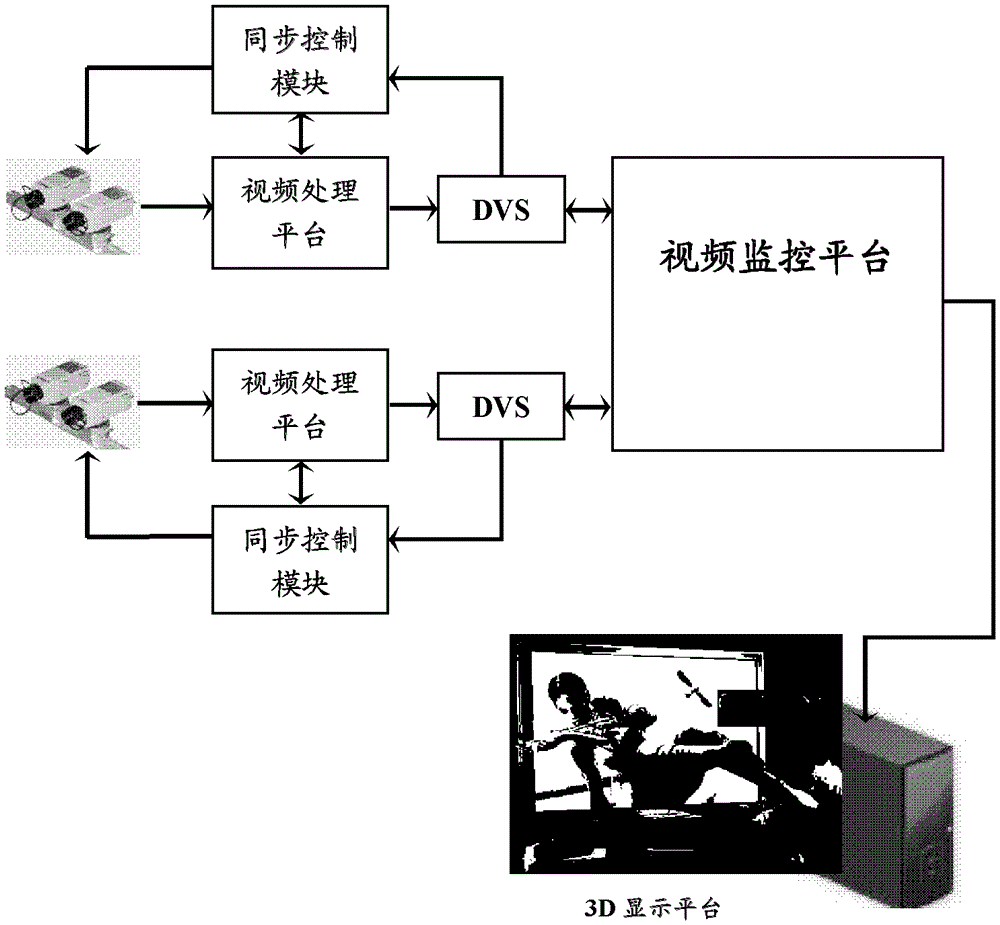
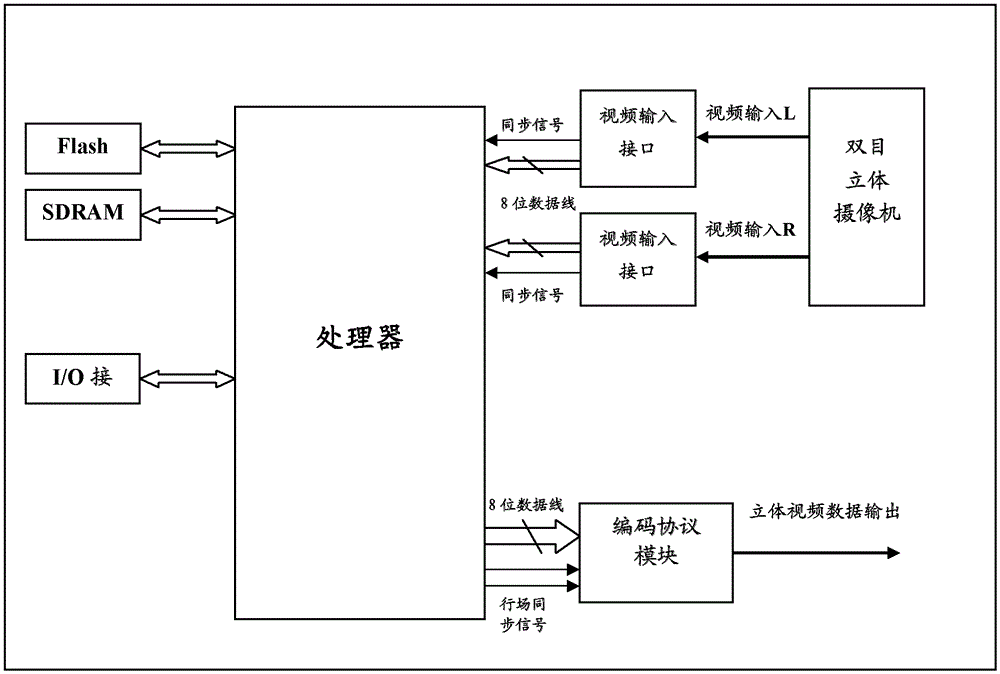
The invention provides a network 3D (three dimensional) video monitoring system and method and a video processing platform. A binocular stereo-camera acquires two paths of video signals of a 3D scene under the control of synchronous signals and transmits the two paths of video signals to the video processing platform; the video processing platform is used for merging the two paths of 3D video signals into a PAL (Programmable Array Logic) video signal which is compatible with a 3D video JPS (JPEG Stereo) format and transmitting the PAL video signal to the video monitoring platform; and the video monitoring platform is used for transmitting the PAL video signals to a 3D display platform and displaying videos in the 3D display platform. According to the invention, network 3D video monitoring is achieved.
Owner:CHINA TELECOM CORP LTD
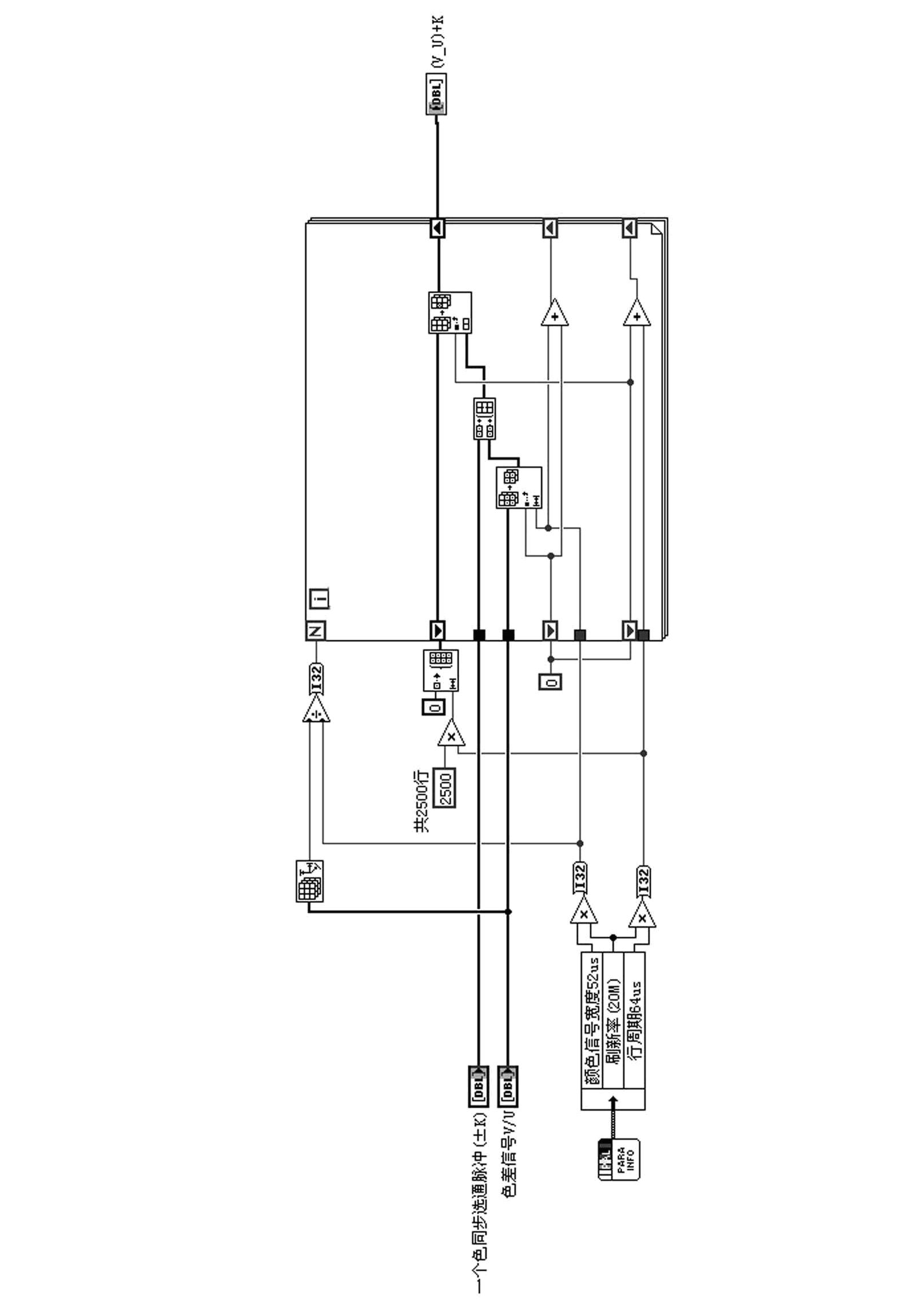
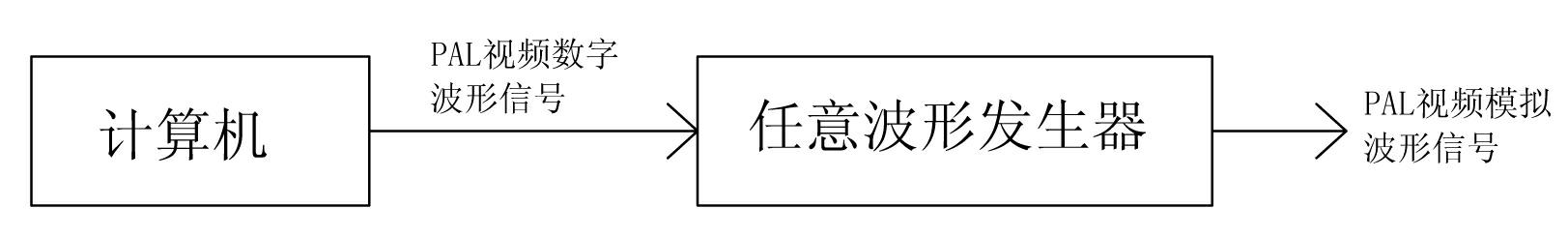
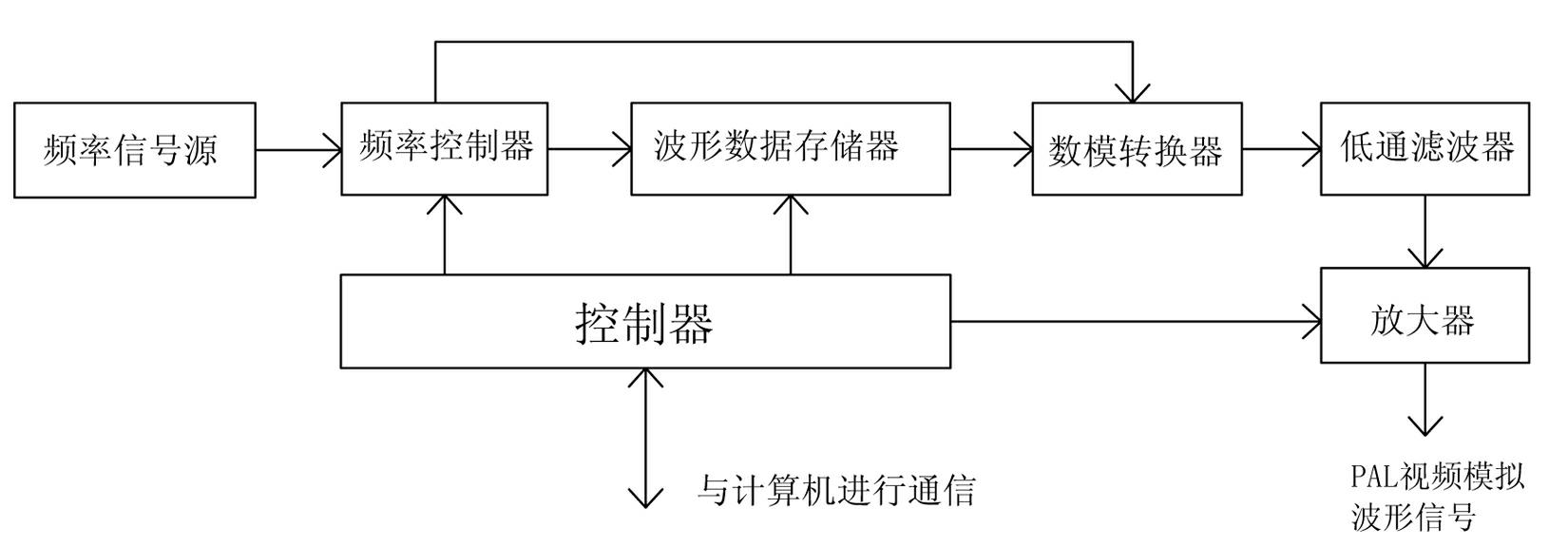
Programmable array logic (PAL) video signal generation device based on arbitrary waveform generator
The invention discloses a programmable array logic (PAL) video signal generation device based on an arbitrary waveform generator. The PAL video signal generation device comprises a computer and the arbitrary waveform generator, wherein the computer generates PAL video digital waveform signals which are stored in the arbitrary waveform generator, and the arbitrary waveform generator converts the stored PAL video digital waveform signals to PAL video simulation waveform signals and then outputs the PAL video simulation waveform signals. According to the PAL video signal generation device, red / blue / green (RBG) value of image pixels is obtained by aid of the computer image processing technology, luma and chroma (YUV) value of the pixels is obtained through conversion, PAL video signal waveform is formed by using the YUV value as input of the software algorithm, and PAL video signals are output through the arbitrary waveform generator. Compared with the existing PAL television signal encoder, the PAL video signal generation device is greatly reduced in volume, is easy to install and debug and low in cost, has generality, usability and extendibility, is strong in stability, flexibility and function, and can be applied to the fields of tests related to PAL signals.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HANGXIN AVIATION TECH CO LTD
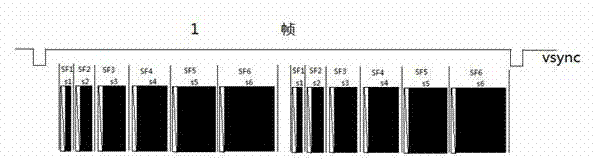
Method for self-adaptively adjusting overflow of sustaining pulses under programmable array logic (PAL) mode
InactiveCN102968951ANo flickeringPrevent overflowStatic indicating devicesTime rangeProgrammable Array Logic
Owner:SICHUAN COC DISPLAY DEVICES
Method and system for system detection under weak signal
ActiveCN102595183AImprove accuracyHigh strengthTelevision systemsTelevision systemProgrammable Array Logic
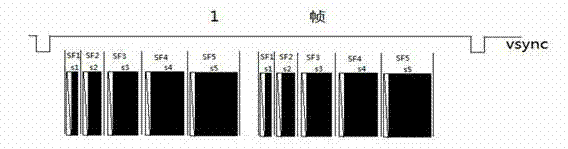
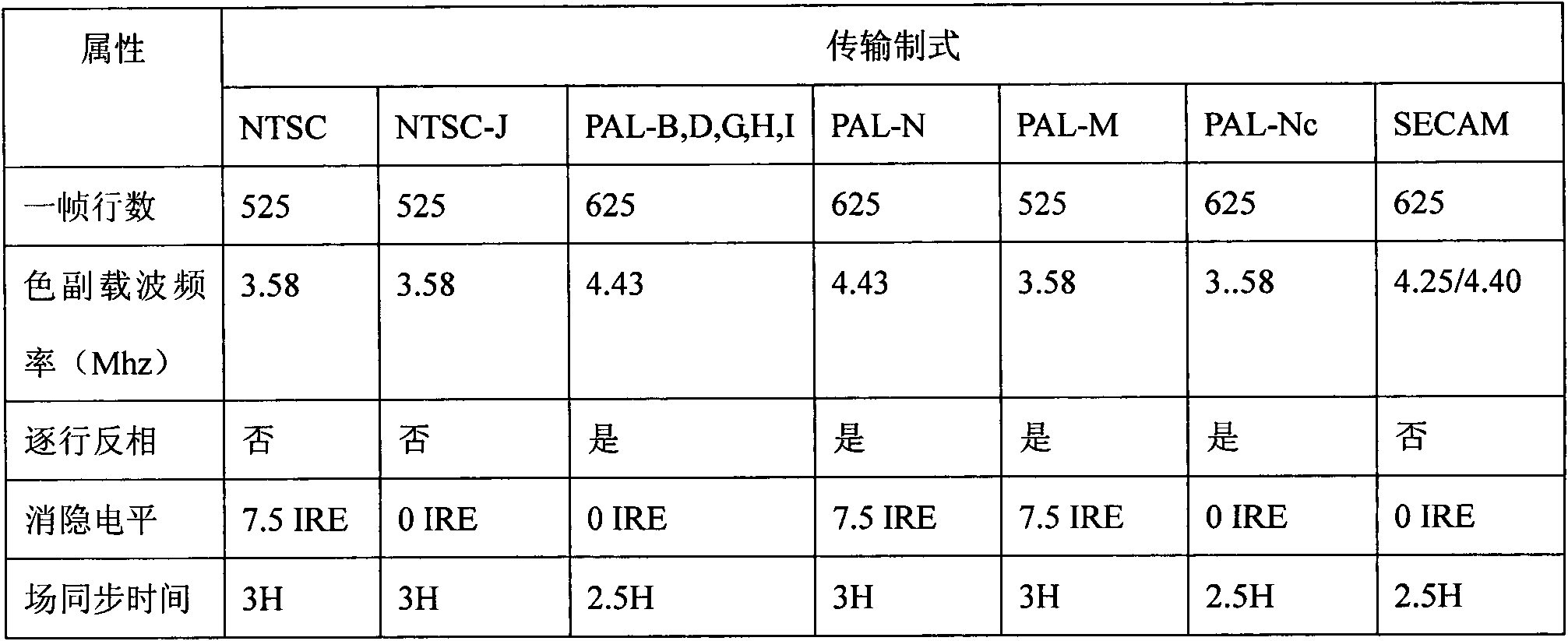
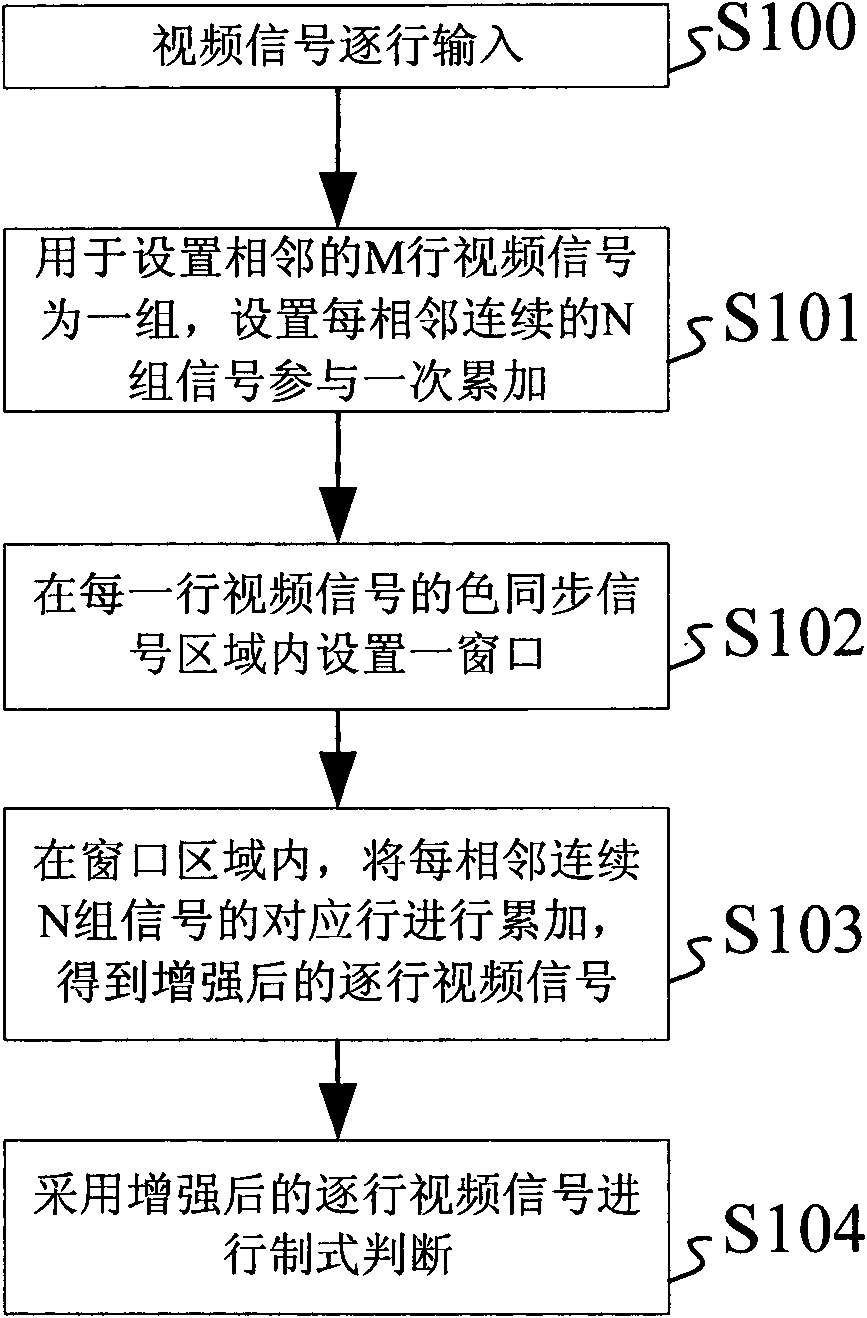
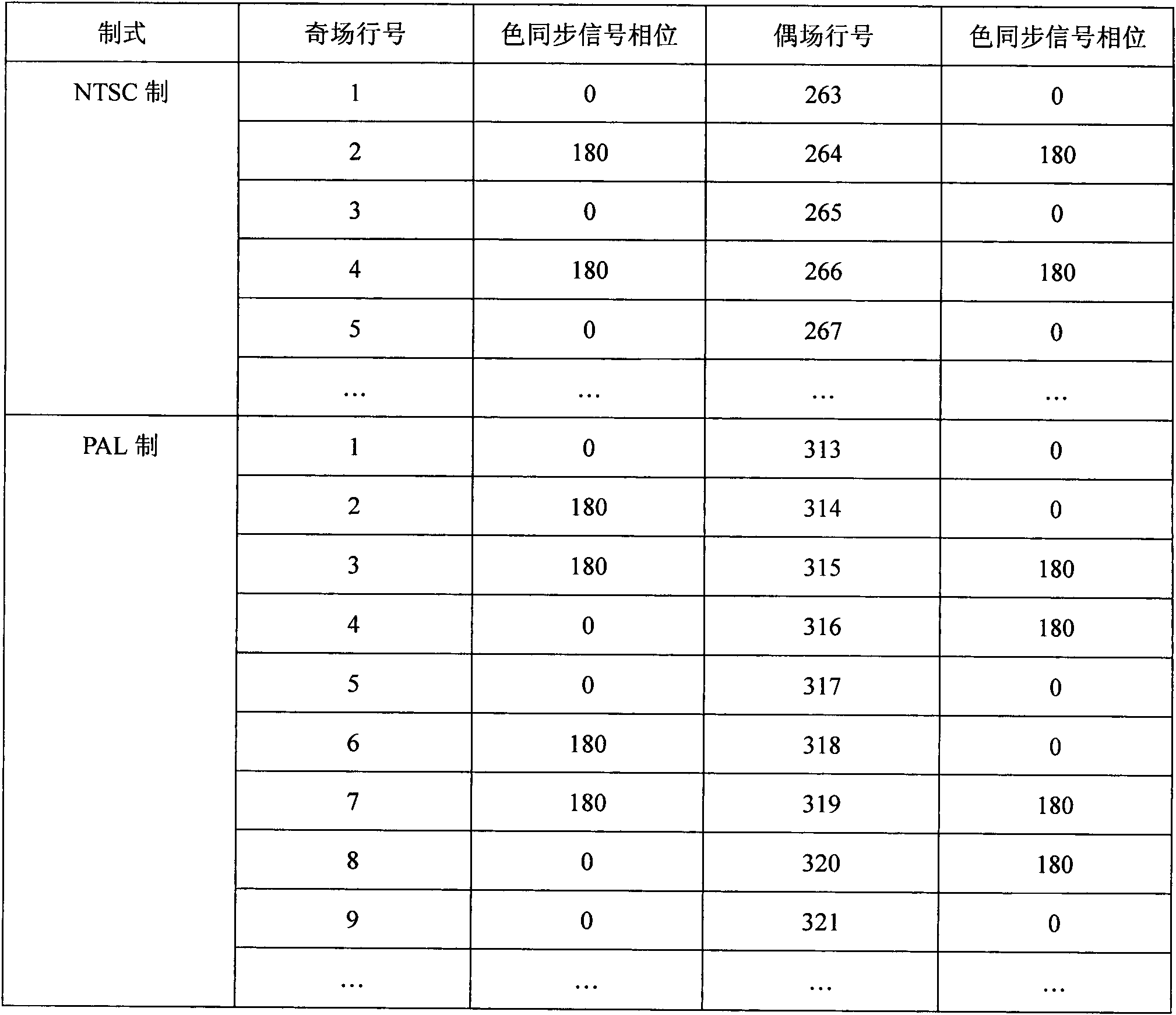
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method for system detection under a weak signal, which comprises the following steps of: inputting video signals line by line; setting adjacent M lines of video signals as one group, and setting each adjacent continuous N group of signals to be participated in one-time accumulation; setting a window in a color sync signal zone of each line of video signals; in each window zone, accumulating corresponding lines of each adjacent continuous N group of signals to obtain enhanced line-by-line video signals; and carrying out system judgment through adopting the enhanced line-by-line video signals. The embodiment of the invention also discloses a system for system detection under the weak signal, which comprises a signal input unit, a parameter confirming unit, a window setting unit, an accumulation unit, and a system judging unit. According to the technical scheme of the invention, through analysis of phase positions and frequency characteristics of color sync signals of a PAL (Programmable Array Logic) system and an NTSC (National Television System Committee) system, and the adoption of an accumulation method, the accuracy of detection of the PAL system and NTSC system is effectively improved.
Owner:ARKMICRO TECH
System and method for dealing with component obsolescence in microprocessor-based control units
InactiveUS20060282254A1Error detection/correctionSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationField programmable logic devicesComplex programmable logic device
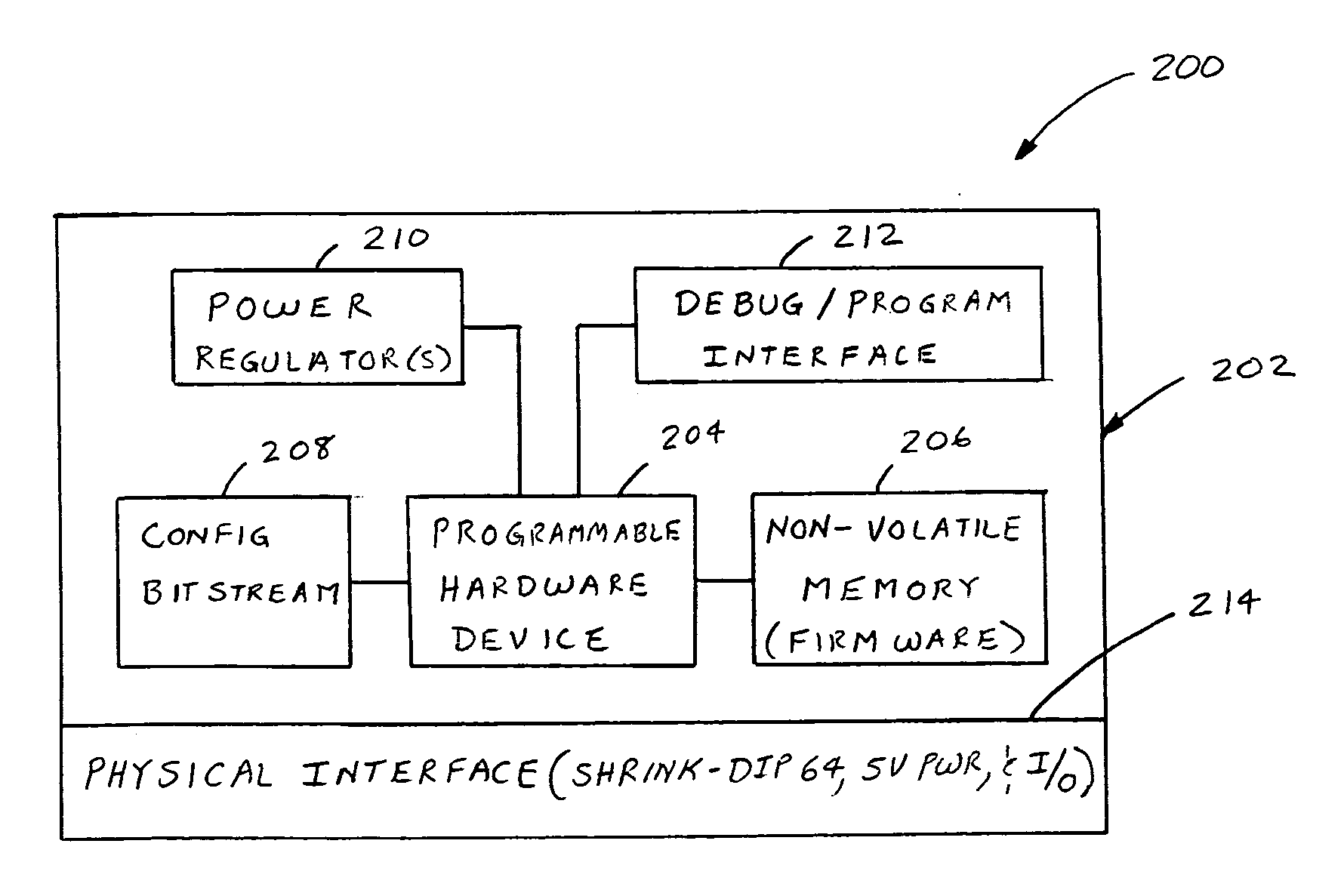
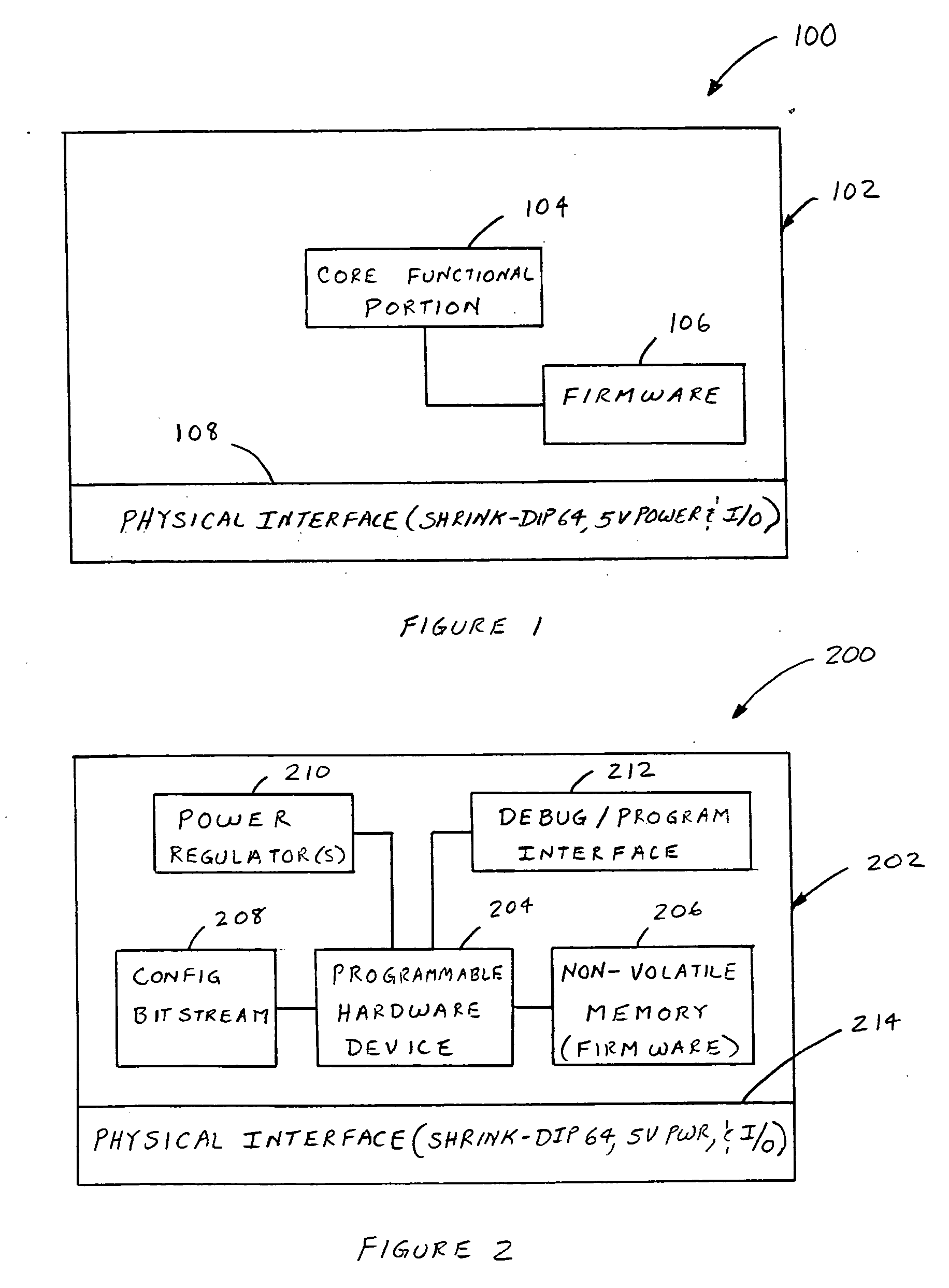
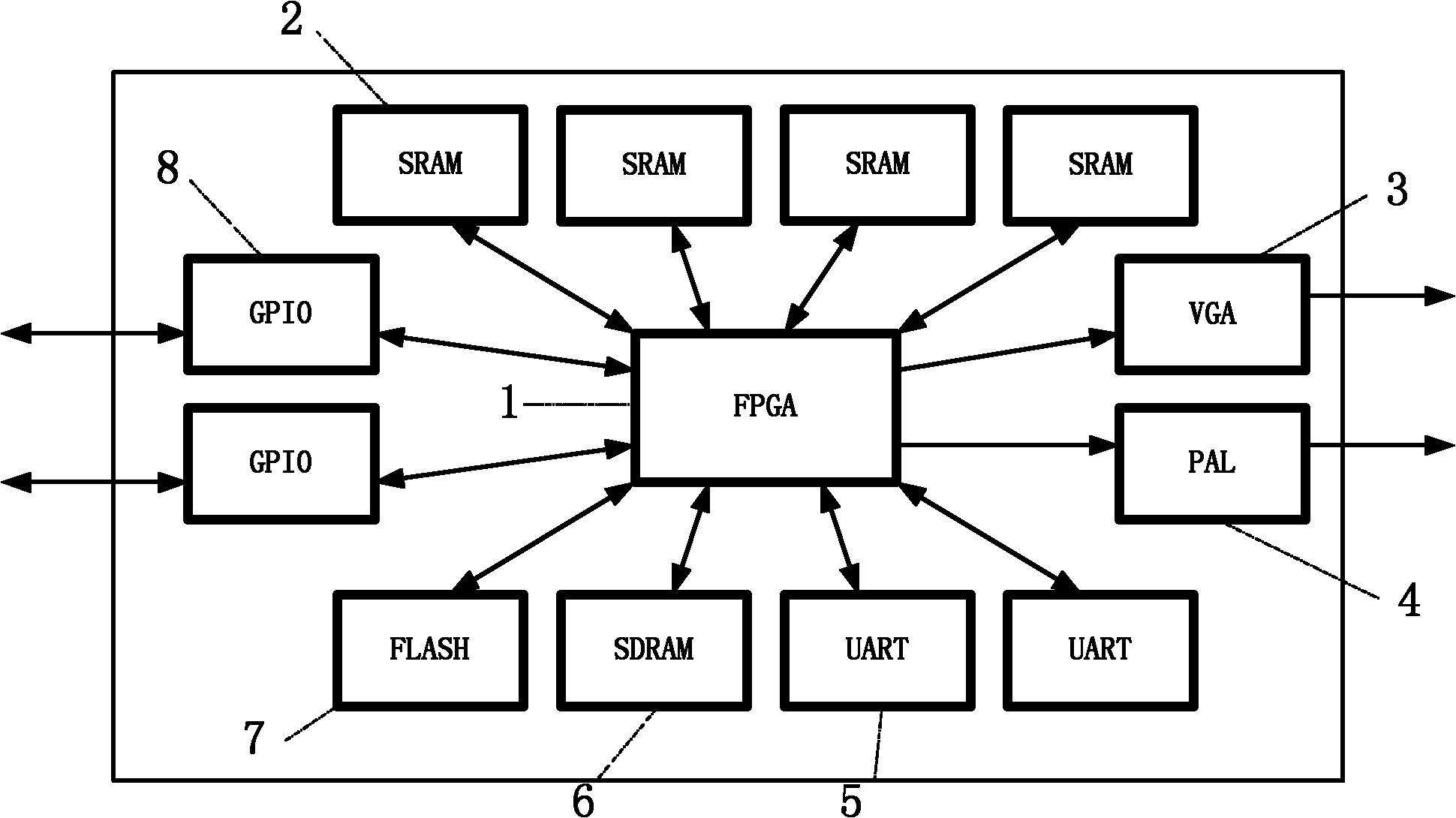
A method of dealing with a microprocessor used in a first vehicle system control unit becoming obsolete. The method comprises providing a second vehicle system control unit for performing substantially the same operation as that of the first vehicle system control unit, wherein the second vehicle system control unit includes a microprocessor emulation unit having a programmable hardware device adapted to emulate the operation of the core functional portion of the microprocessor. The programmable hardware device may comprise a field programmable gate array (FPGA) device, a field programmable logic device (FPLD), a programmable logic array (PLA), a mask programmable logic device (MPLD), a programmable array logic (PAL) device, or a complex programmable logic device (CPLD). The microprocessor emulation unit may include substantially the same firmware and physical interface of the obsolete microprocessor.
Owner:BAYERISCHE MOTOREN WERKE AG
General digital image processing system
InactiveCN102158679ASmall footprintFlexible receptionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsGraphicsTransceiver
The invention relates to a general digital image processing system comprising a digital processing module, a storage module, a VGA (Video Graphics Array) module, a PAL (Programmable Array Logic) module, a general input-output interface module and a general asynchronous serial transceiver, wherein the digital processing module is used for compiling and processing programs according to specific application and realizing core calculation and processing; the storage module is used for storing images and parameter data; the VGA module is used for converting a digital signal output by the digital processing module into a VGA signal and outputting the VGA signal; the PAL module is used for converting the digital signal output by the digital processing module into a PAL signal and outputting the PAL signal; the general input-output interface module provides an user-defined I / O (Input / Output) interface connected with the digital processing module for users; and the general asynchronous serial transceiver realizes conversion between an RS422 difference electrical level and a single-end electrical level so as to realize full duplex communication with an upper computer. The invention providesa small general digital image processing system which has small circuit occupying space and complete function, and can be applied under various situations.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Multifunctional set top box
InactiveCN102665121AEasy to useRecord information storageSelective content distributionKey pressingDigital video
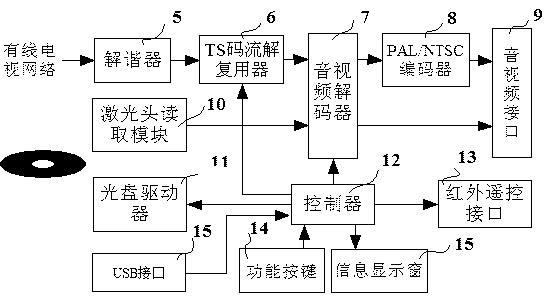
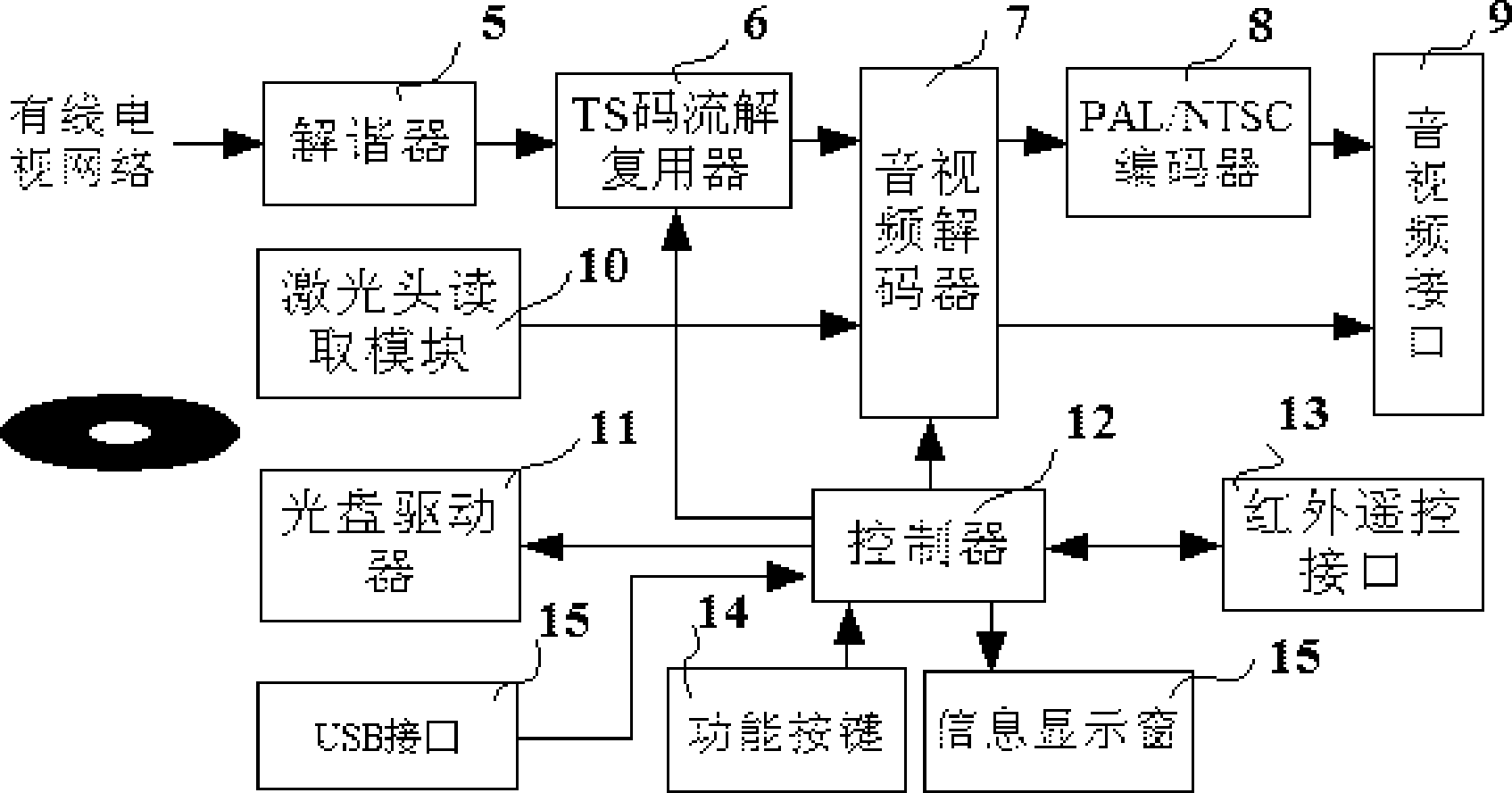
The invention discloses a multifunctional set top box, comprising a machine case, functional buttons, an information display window and a DVD (digital video disk) optical driver, and further comprising an electronic controller, wherein the functional buttons, the information display window and the DVD optical driver are arranged on the machine case, the electronic controller comprises a detuning device and a TS (transport stream) code stream demultiplexing device, the TS code stream demultiplexing device is connected with a first audio and video port of an audio and video decoder, the audio and video decoder is provided with a video output port connected with a PAL / NTSC (programmable array logic / national television system committee) encoder, the PAL / NTSC encoder is connected with an audio and video interface, the audio and video decoder is provided with the audio output port which is connected with the audio and video interface, the multifunctional set top box further comprises a controller which is connected with an infrared remote-control interface, the functional buttons, the information display window and the TS code stream demultiplexing device, the controller is connected with a control port of the audio and video decoder, and the multifunctional set top box further comprises an optical driver, a USB (universal serial bus) interface and a laser head reading module, wherein the optical driver is connected with the controller, and the laser head reading module is connected with a second audio and video port of the audio and video decoder.
Owner:CIXI MAISTE ELECTRONICS TECH
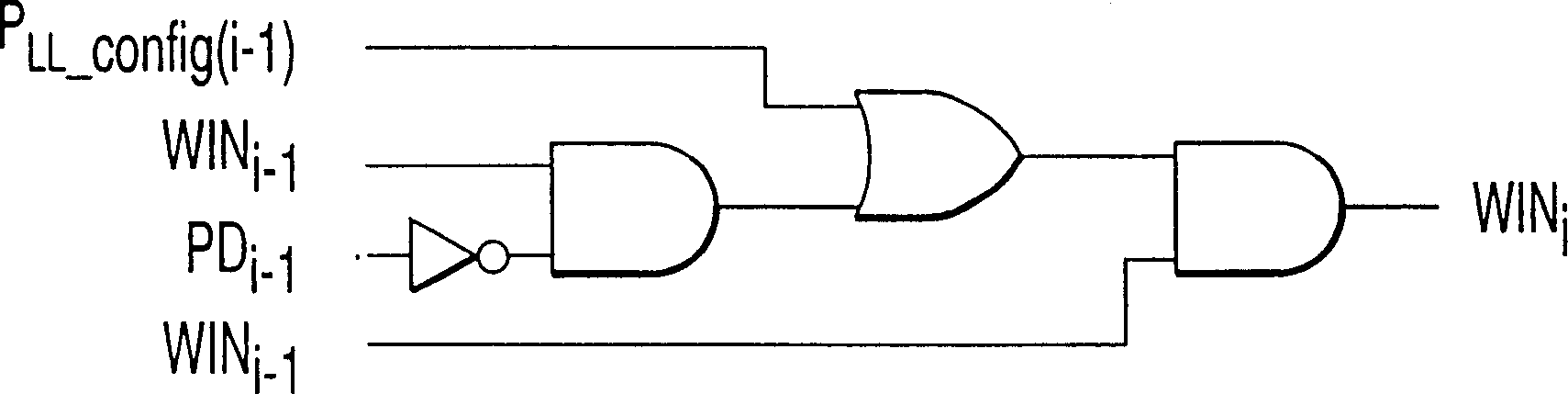
Field Programmable Logic Array
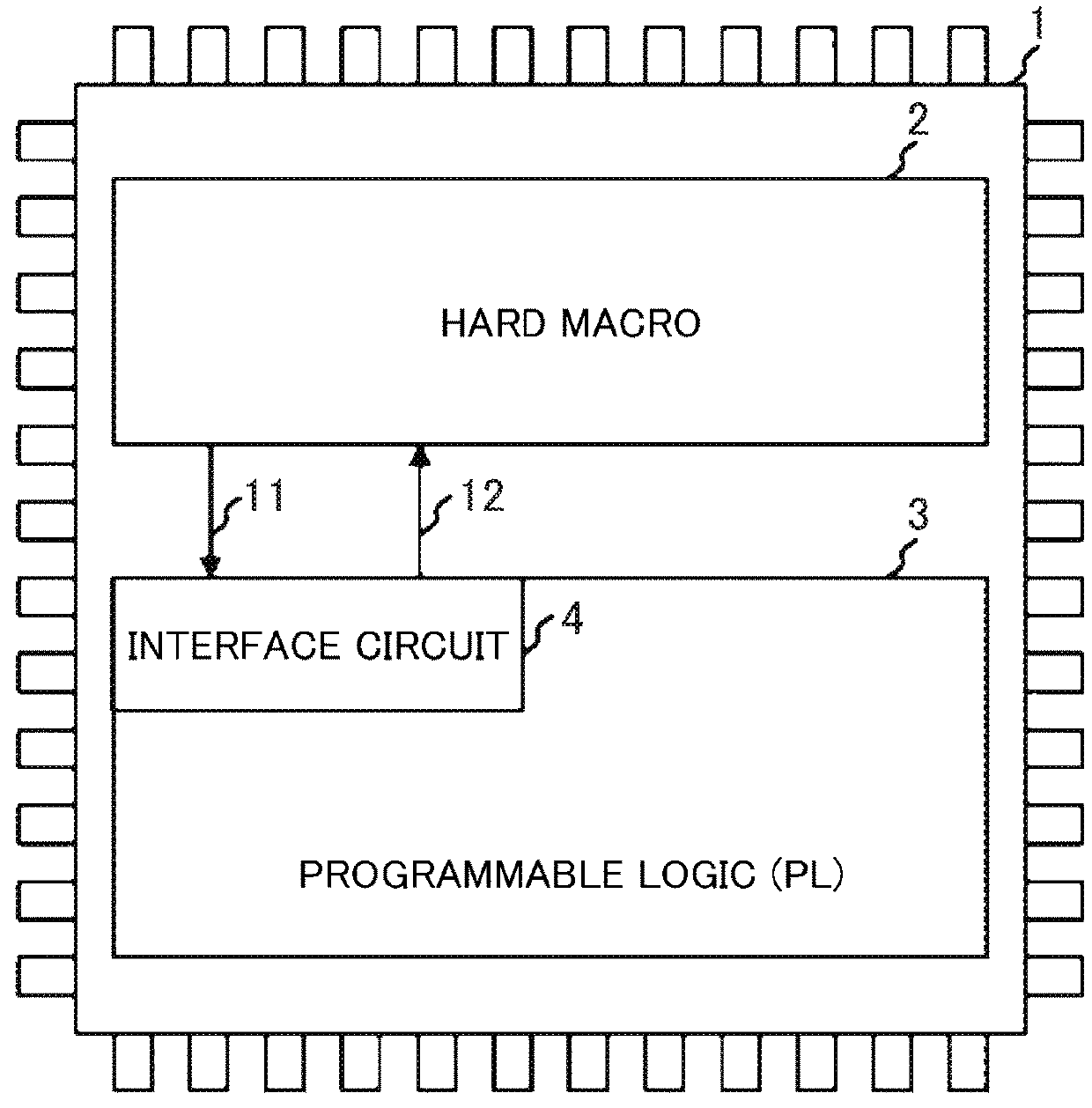
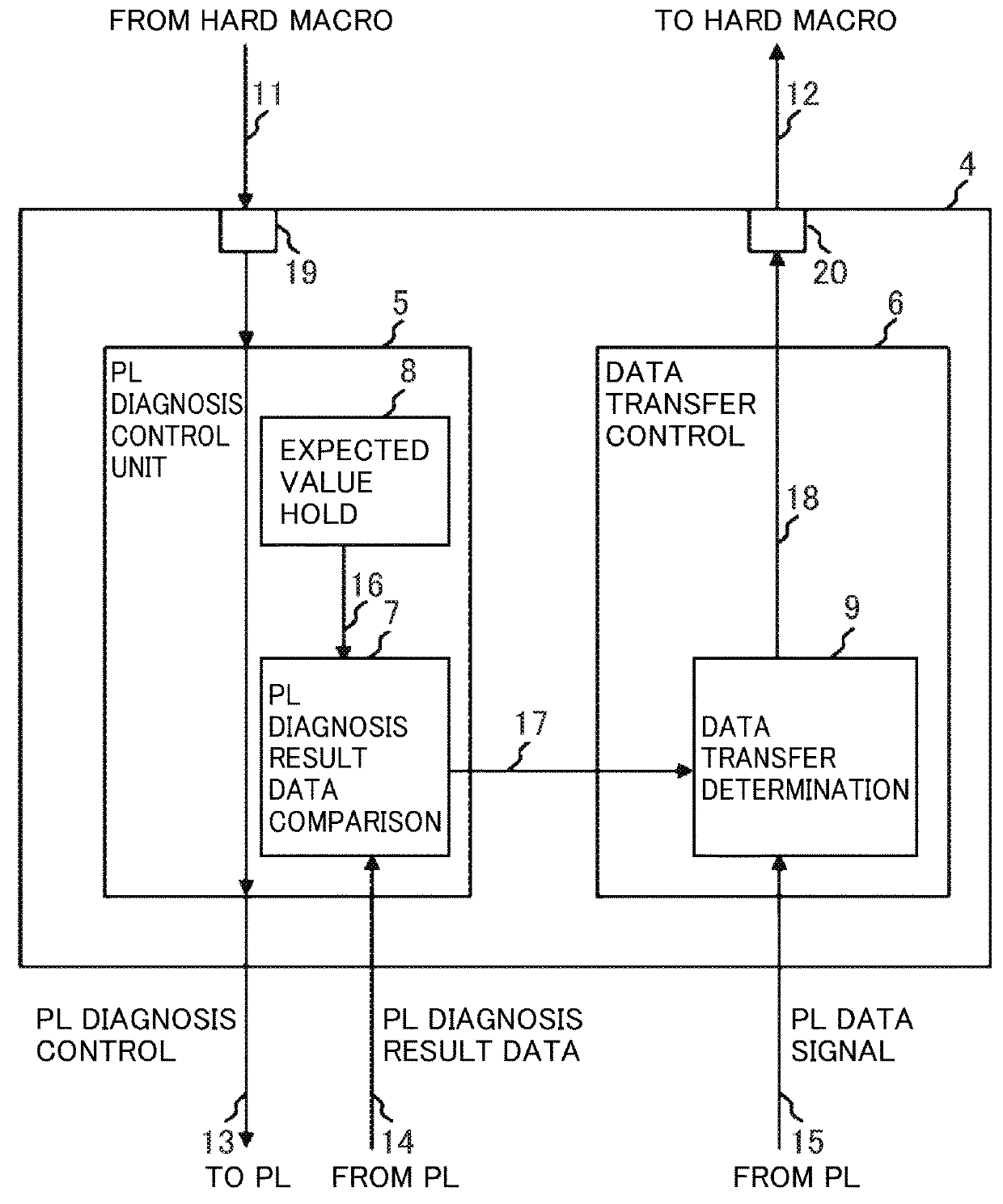
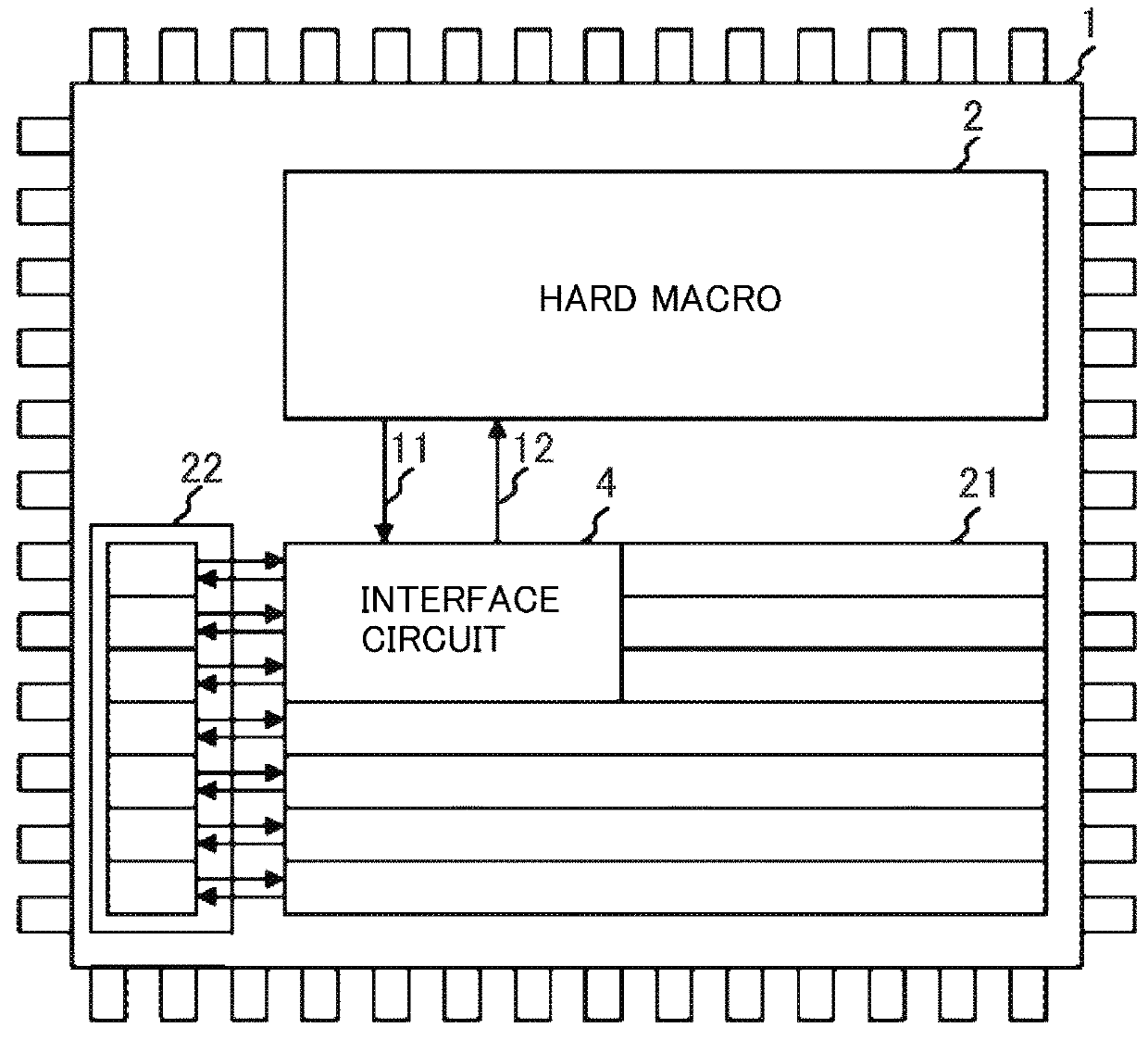
To realize control of a system for which a high level of safety is demanded by one SRAM-type FPGA, it is to eliminate a possibility that an undesirable control signal is output to the outside of the FPGA because of influence of failure by a soft error and the like and a problem. To solve this problem, there is provided a hard macro having fixed circuitry structure, programmable logic arranged via an interval close to the hard macro and having a changeable circuitry structure, and an I / F circuit which is provided inside the programmable logic and outputs a processing result in the programmable logic to the hard macro. It is a characteristic that the I / F circuit monitors soundness of the programmable logic and stops output of the processing result to be transmitted to the hard macro on the basis of a monitoring result.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Control circuitry for high speed video camera operation
InactiveUS6856342B1Accurate and inexpensive to controlEasy to manufactureTelevision system detailsColor television detailsComputer graphics (images)High speed video
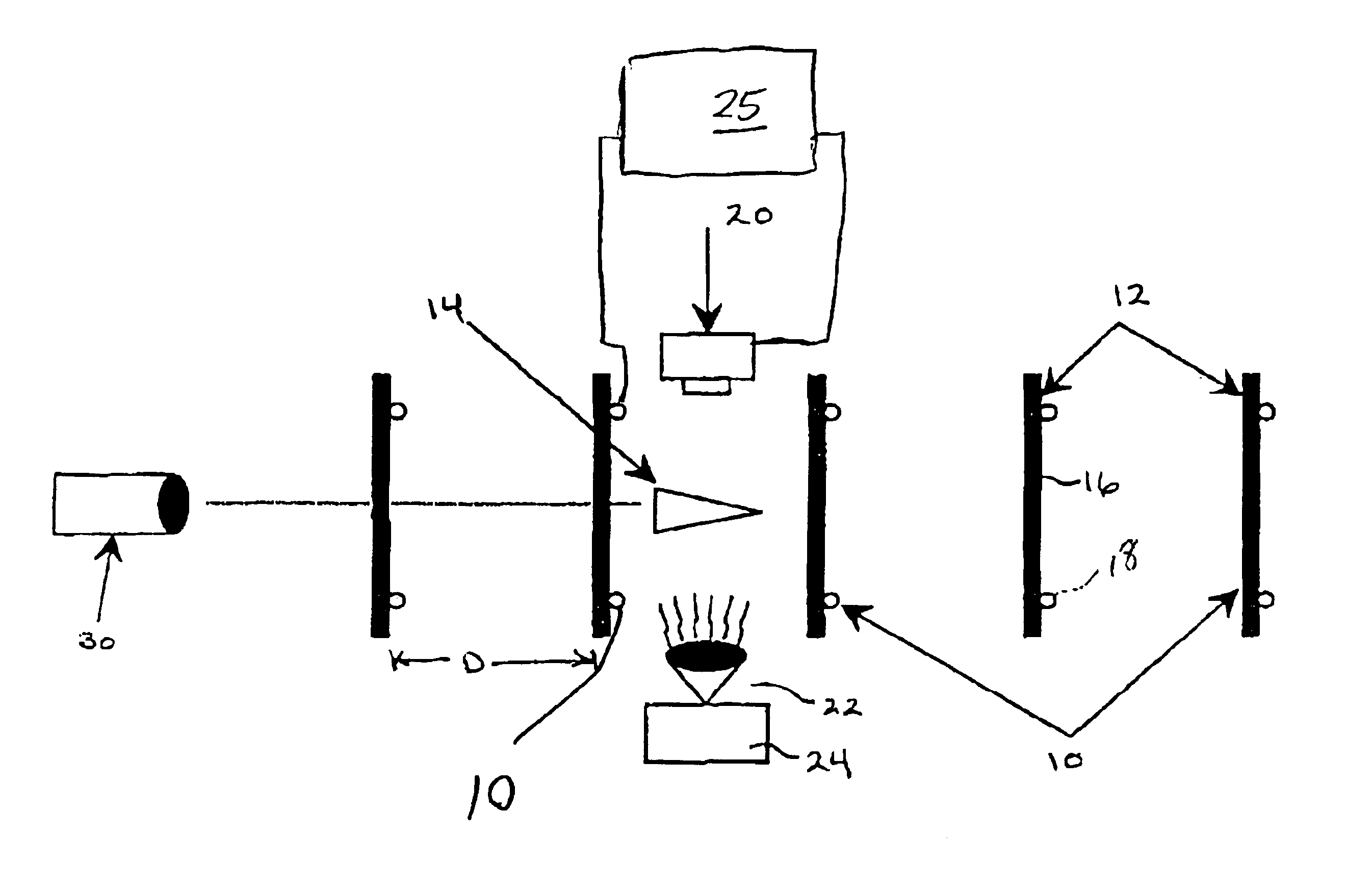
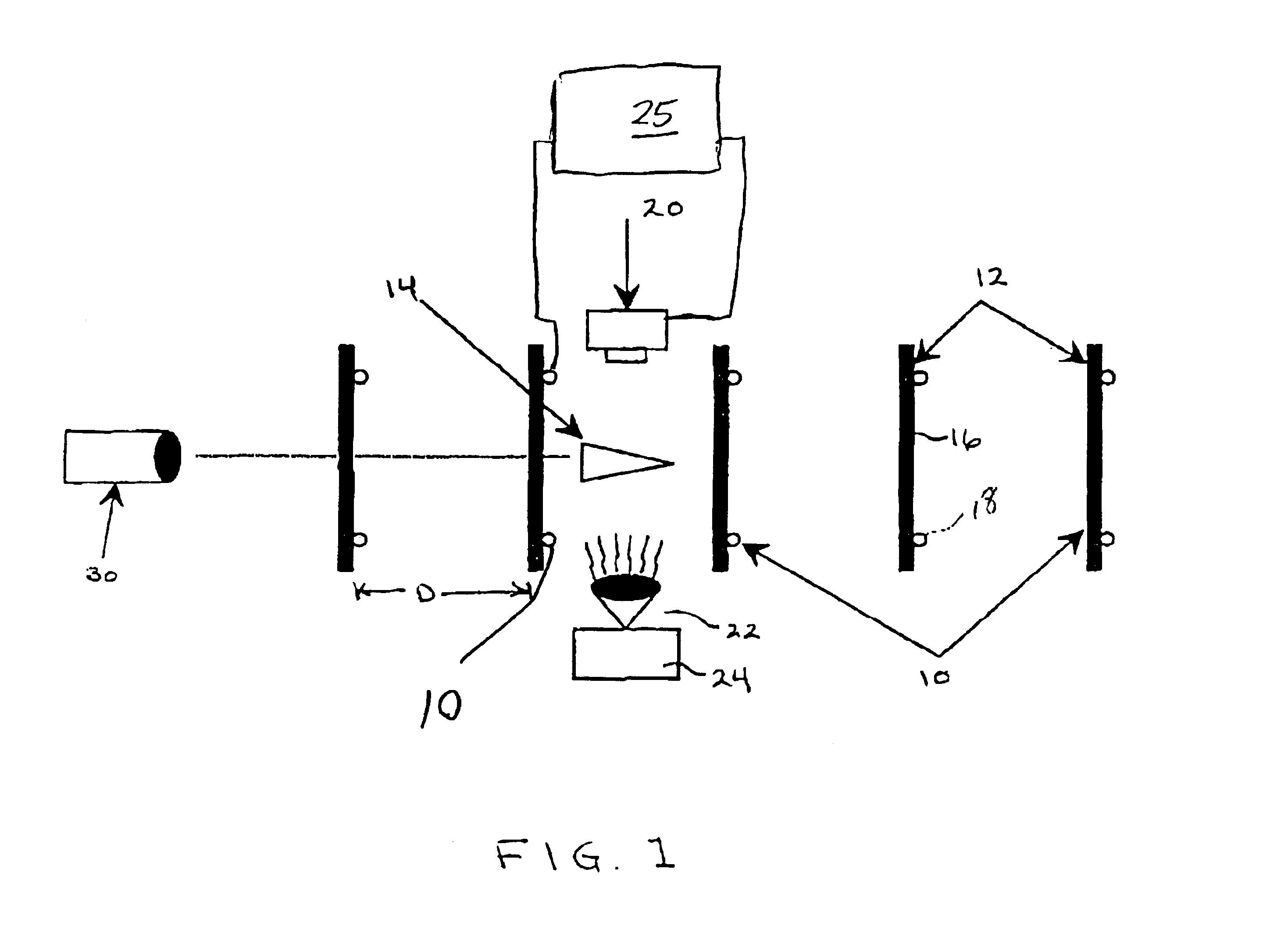
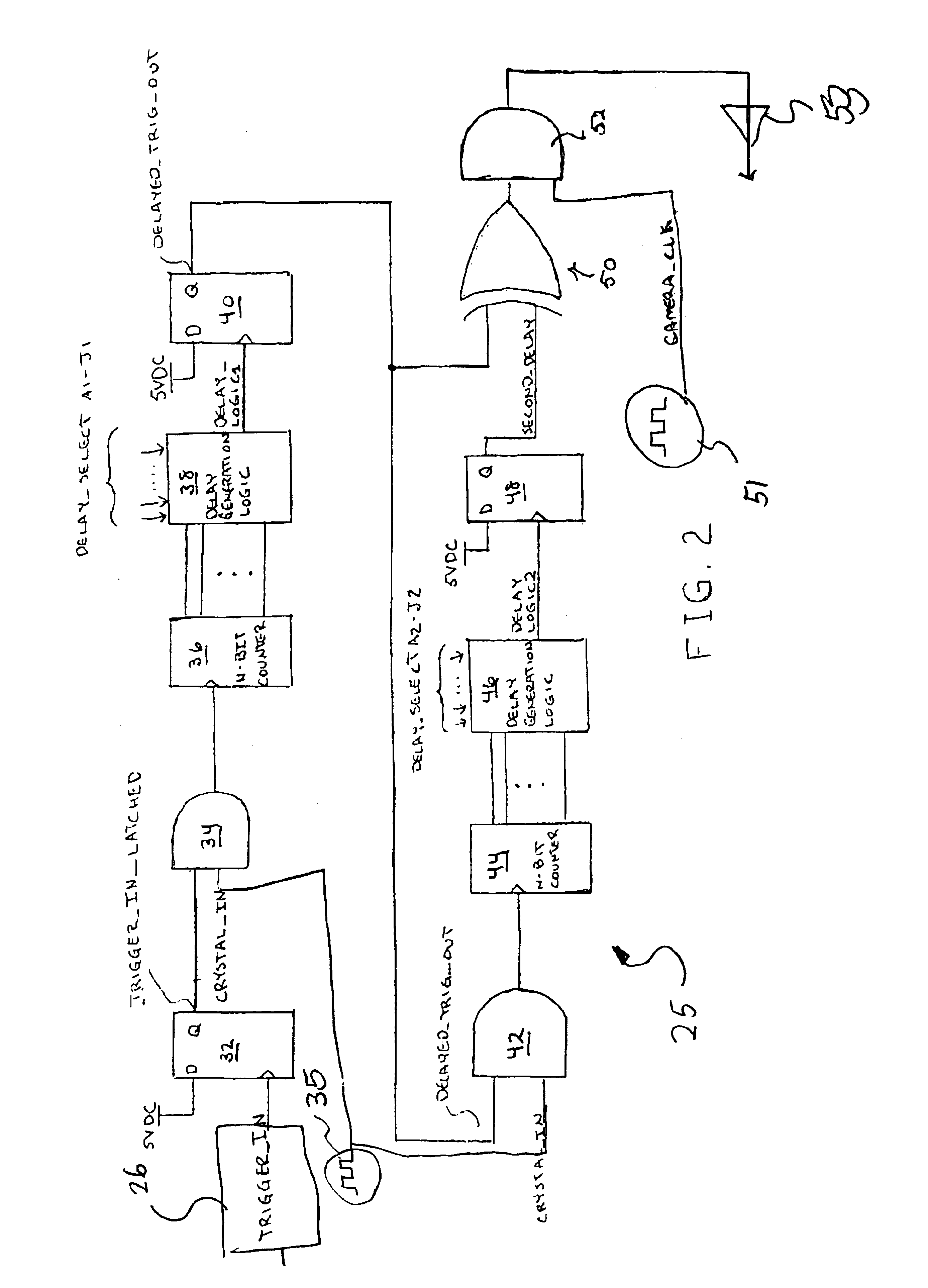
A device for controlling a video camera in underwater high speed photography in a first aspect includes a plurality of spaced break screen or sense coil members, a projectile for launch through the series of break screen or sense coil members, a video camera operated to video at a predetermined timing upon release of the projectile, and a source of illumination to aid in the video photography. A trigger device such as a break screen or sense coil is positioned immediately up-range of the video camera. With a time delay programmed into a Programmable Array Logic (PAL), a control circuitry receives the trigger information and creates a timed signal to control the operation of the video camera. In accordance with another aspect of this invention, the control circuitry includes discrete logic devices programmed such that gating of the video camera is controlled by the control circuitry at the time the projectile passes the lens of the camera.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE NAVY NAVAL RES LAB WASHINGTON
Adaptive double iris and facial image recognition machine
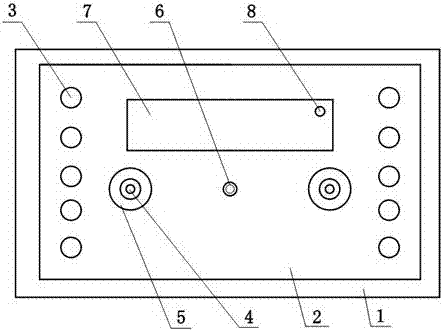
ActiveCN104091165BWork humanizationImprove comfortCharacter and pattern recognitionDisplay deviceIris image
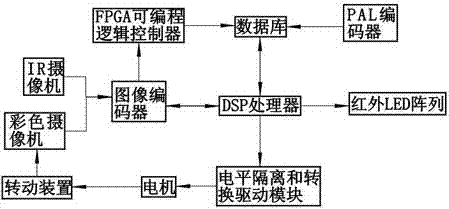
The invention discloses an adaptive double-iris and facial image register recognizing machine which comprises a DSP (Digital Signal Processor) embedded microprocessor, an image encoder, a stepping motor and a database, wherein the DSP embedded microprocessor is connected with the image encoder, the stepping motor and the database; the image encoder is connected with IR (iris) cameras, a color camera and an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) programmable logic controller; the database is connected with the FPGA programmable logic controller and a PAL (Programmable Array Logic) encoder; a level isolation and conversion driving module is arranged between the stepping motor and the DSP embedded microprocessor; the stepping motor is connected with the color camera by virtue of a rotating device; the DSP embedded microprocessor is connected with an infrared LED array and a display interface. The adaptive double-iris and facial image register recognizing machine can be used for automatically detecting and tracking faces and eyes, improvement is performed on the basis of existing equipment, a mode that the equipment is searched passively by human bodies is changed into human-computer interaction to adapt to each other, and single display of an iris image is changed into simultaneous display of a double-iris image and a facial image.
Owner:河南华辰智控技术有限公司
A system and method for realizing video capture, compression and transmission on a SOC
ActiveCN105611295BDoes not occupy clock resourcesConvert in real timeDigital video signal modificationDigital videoAnalog-to-digital converter
The invention relates to a system and method for implementing video capture, compression and transmission on a system on chip. The system captures a PAL (Programmable Array Logic) standard video, and then transmits the PAL standard video to a computer terminal through a serial port after the PAL standard video is compressed through an H.264 protocol, decodes and displays the PAL standard video synchronously; the system comprises video capture, video coding, code stream transmission and computer terminal decoding and display; in video capture, an analog to digital converter is used foracquiring the PAL standard video to obtain a digital video signal, and separating a YUV 4 to 2 to 0 video signal from the digital signal; in video coding,compressed encoding based on the H.264 protocol is performedon an obtained YUV 4 to 2 to 0 video frame; in code stream transmission,a compressed code stream generated by a coding module is transmitted to a computer terminal program through the serial port; and the computer terminal program decodes the received code stream and displays images in real time. The system has the characteristics of being miniaturized, and flexible in application; two CPU (Central Processing Unit) cores using an SOC (System On Chip) processor perform coding and transmission control, and the processing capacity is strong; and an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) is used for performing video capture and separation and controlling direct memory access and transmission.
Owner:CHINA AEROSPACE TIMES ELECTRONICS CORP
Network 3D video surveillance system, method and video processing platform
ActiveCN103051866BRealize monitoringTelevision system detailsColor television detailsVideo monitoringVideo processing
The invention provides a network 3D (three dimensional) video monitoring system and method and a video processing platform. A binocular stereo-camera acquires two paths of video signals of a 3D scene under the control of synchronous signals and transmits the two paths of video signals to the video processing platform; the video processing platform is used for merging the two paths of 3D video signals into a PAL (Programmable Array Logic) video signal which is compatible with a 3D video JPS (JPEG Stereo) format and transmitting the PAL video signal to the video monitoring platform; and the video monitoring platform is used for transmitting the PAL video signals to a 3D display platform and displaying videos in the 3D display platform. According to the invention, network 3D video monitoring is achieved.
Owner:CHINA TELECOM CORP LTD
Multi-purpose system and method and device using processors of different speeds
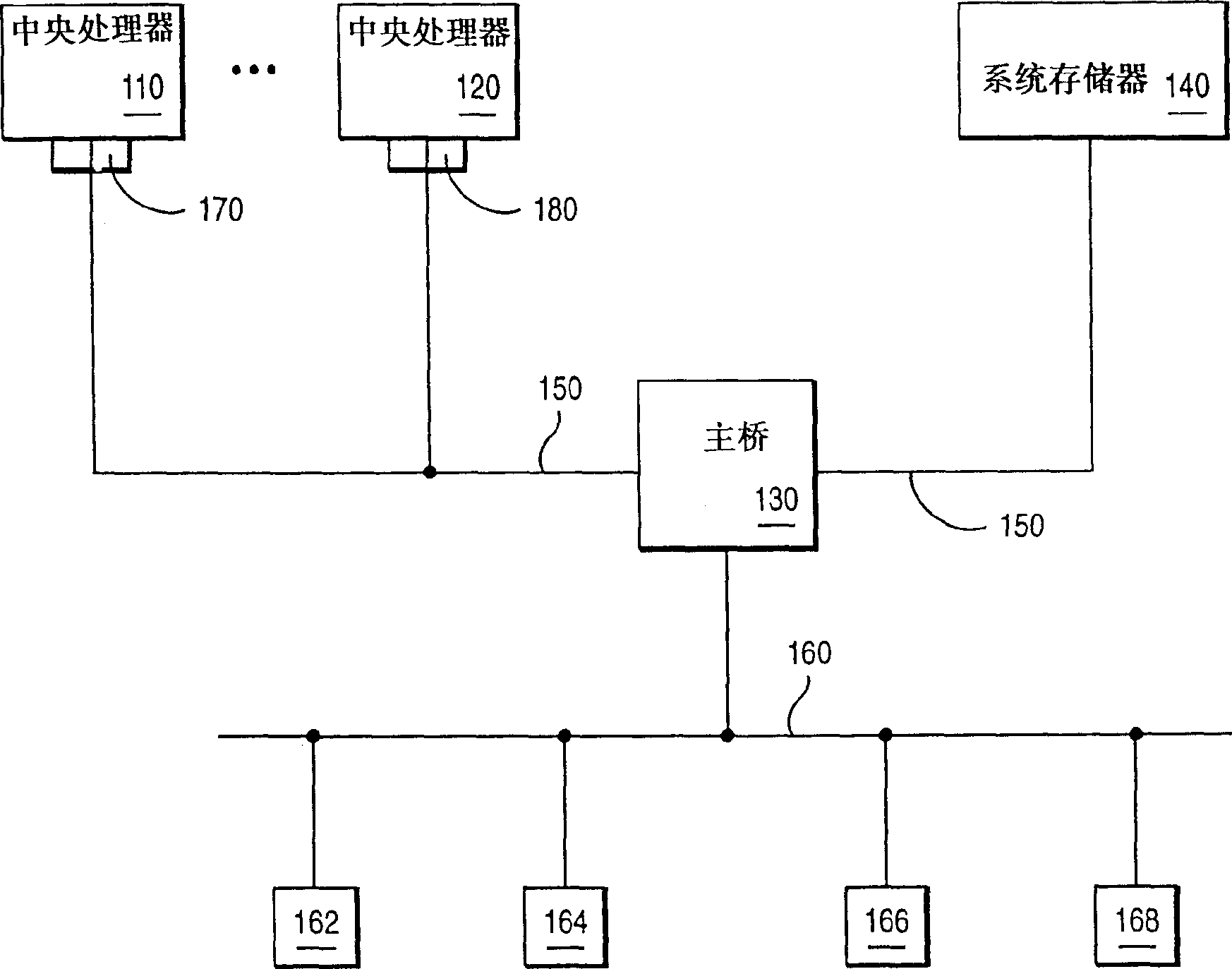
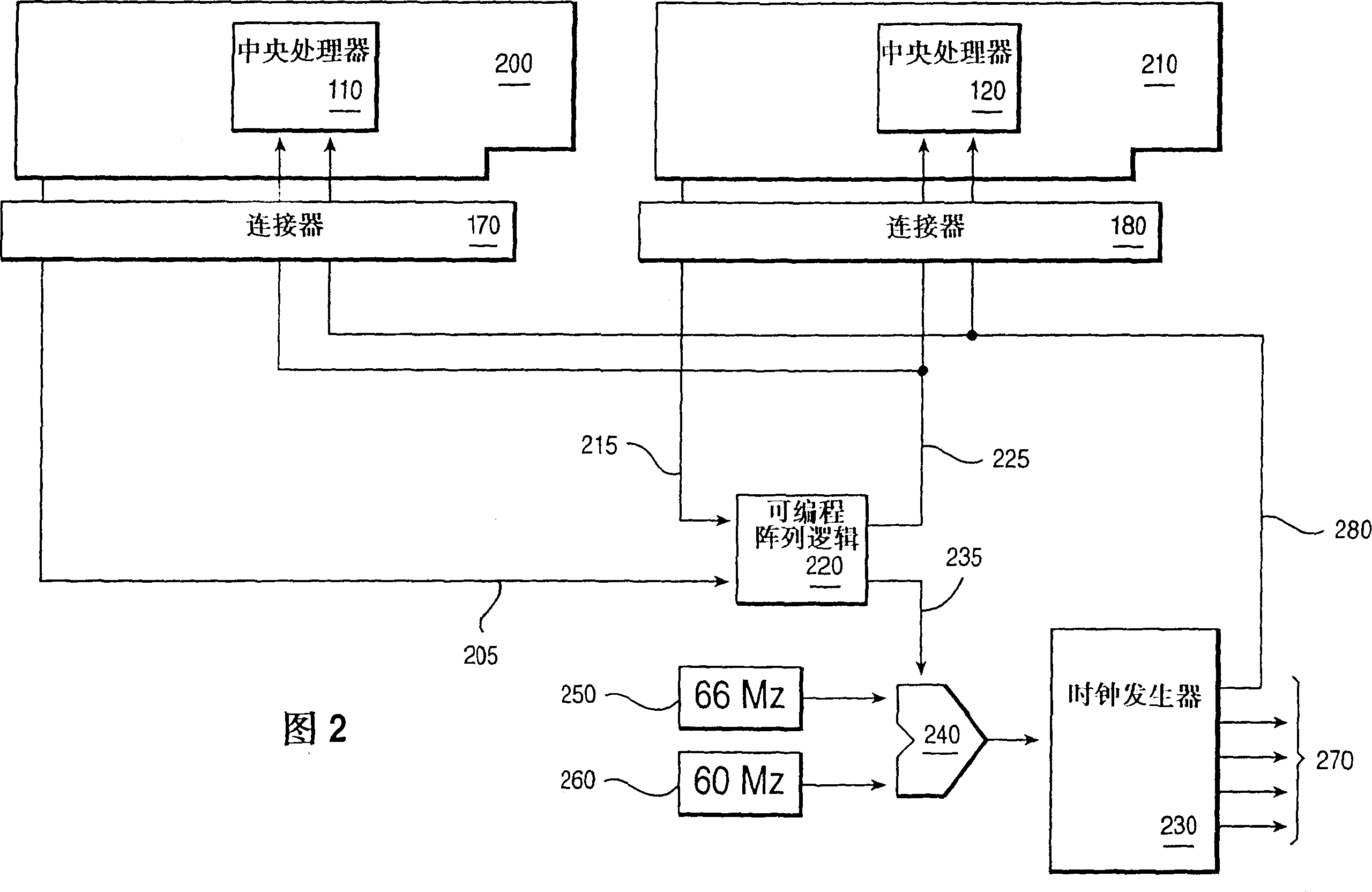
InactiveCN1117327CMultiple digital computer combinationsGenerating/distributing signalsMulti processorProgrammable Array Logic
A method and apparatus of allowing processors of different speeds to be used in a multi-processor system are disclosed. The method and apparatus comprise a programmable array logic (PAL) or field programmable gate array (FPGA) that detects each of the processors maximum speed and selects a speed common to all of the processors as the operating speed of the processors. The method and apparatus also adjust the system clock to match the speed of the processors.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com