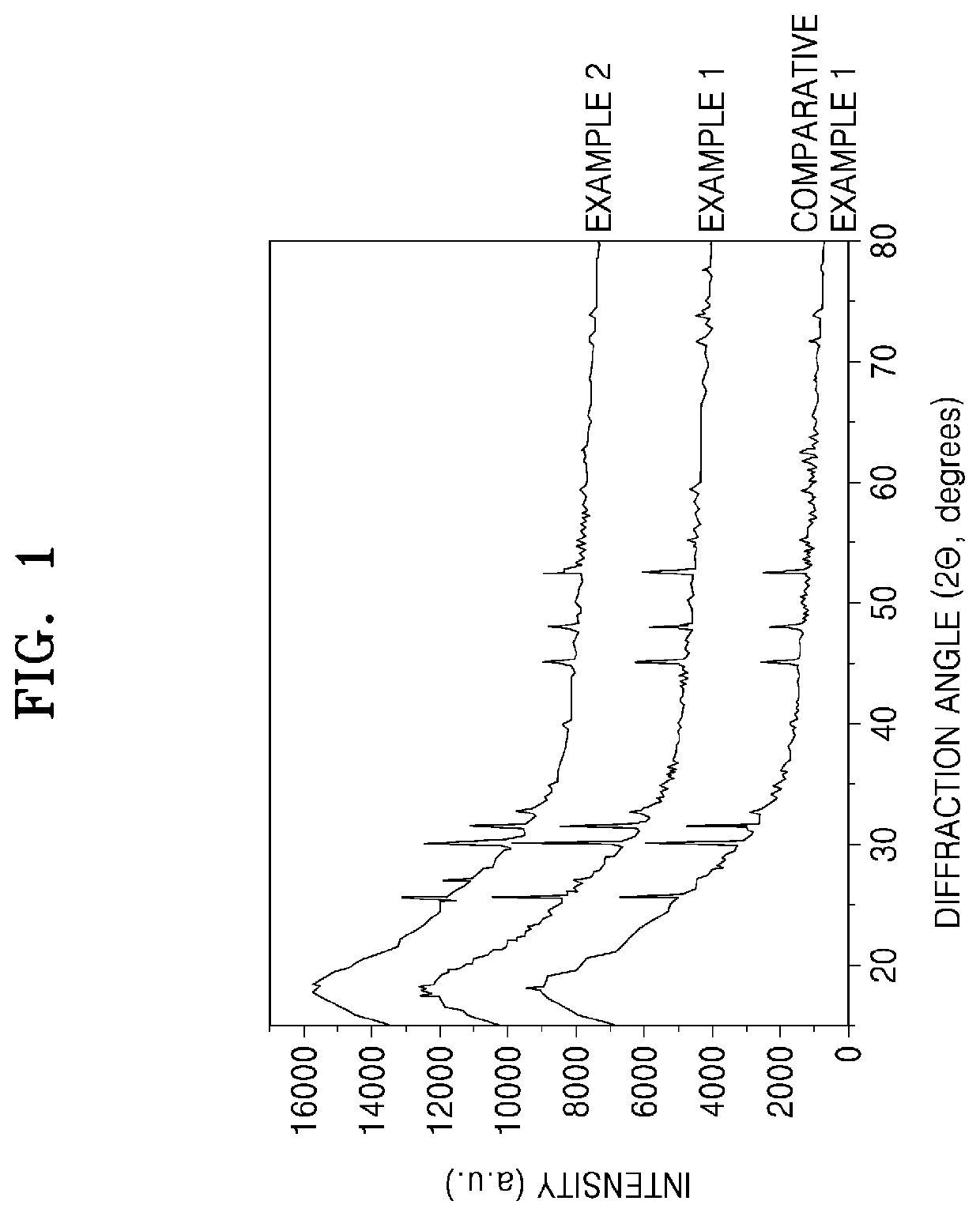
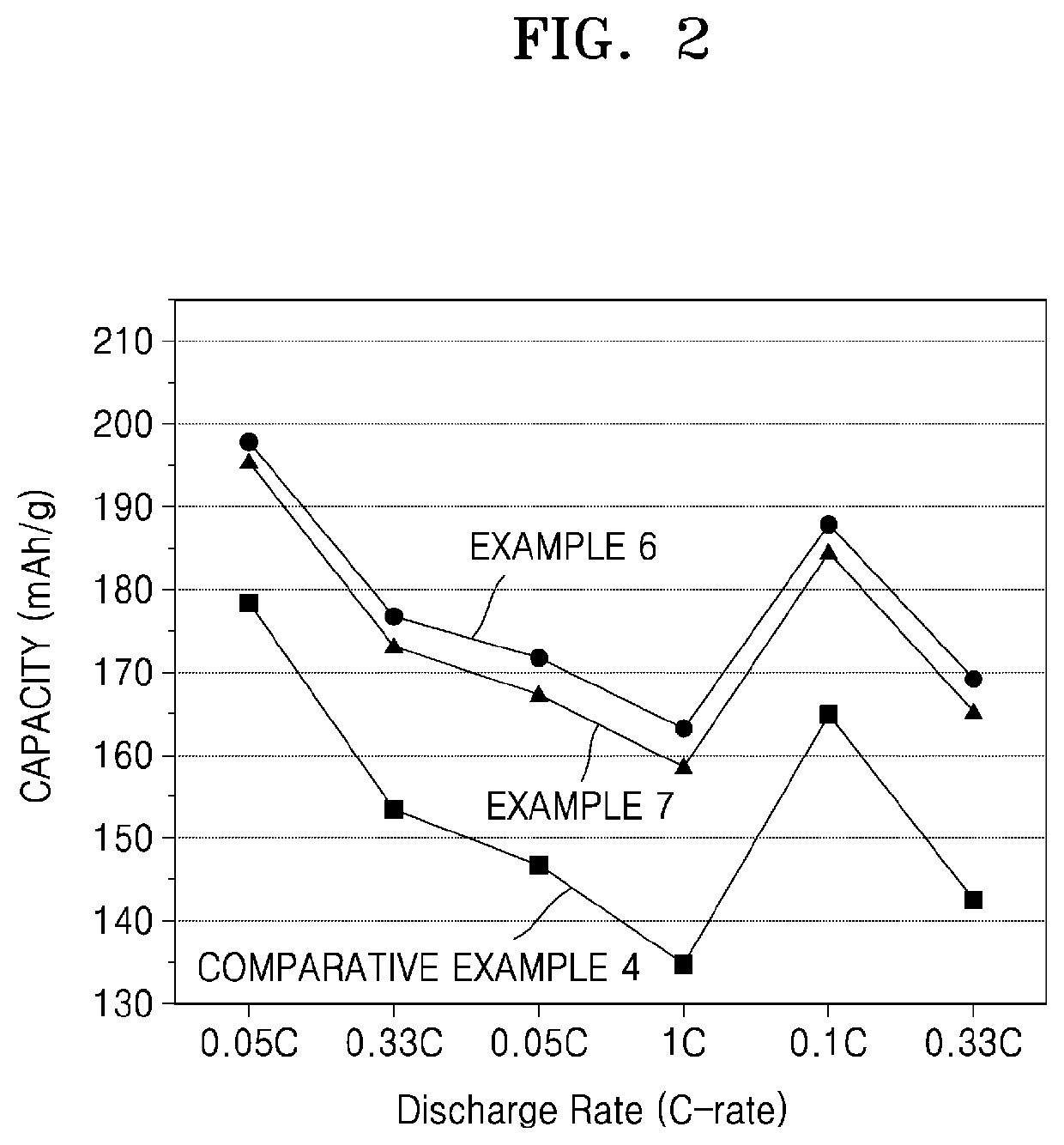
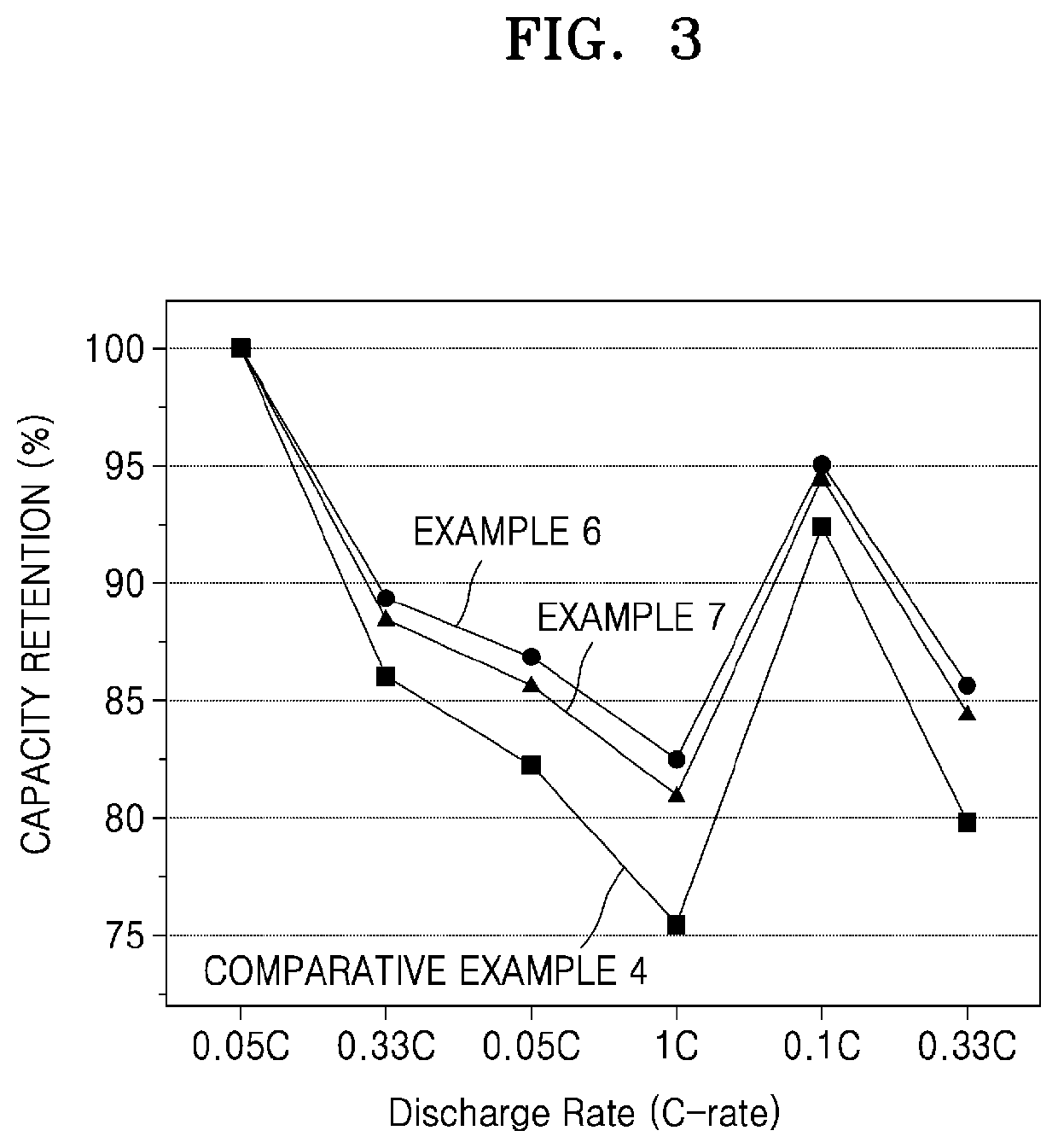
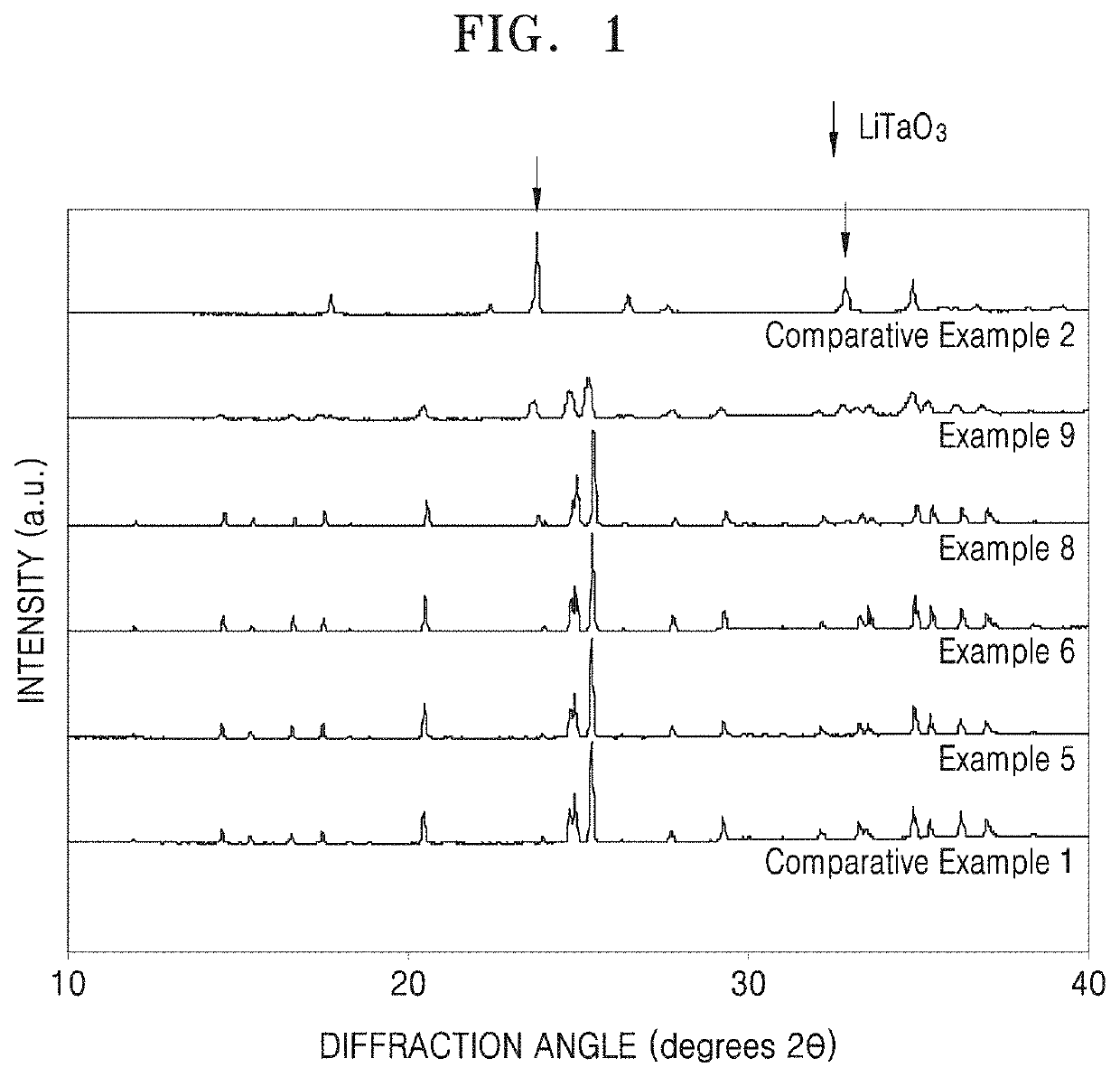
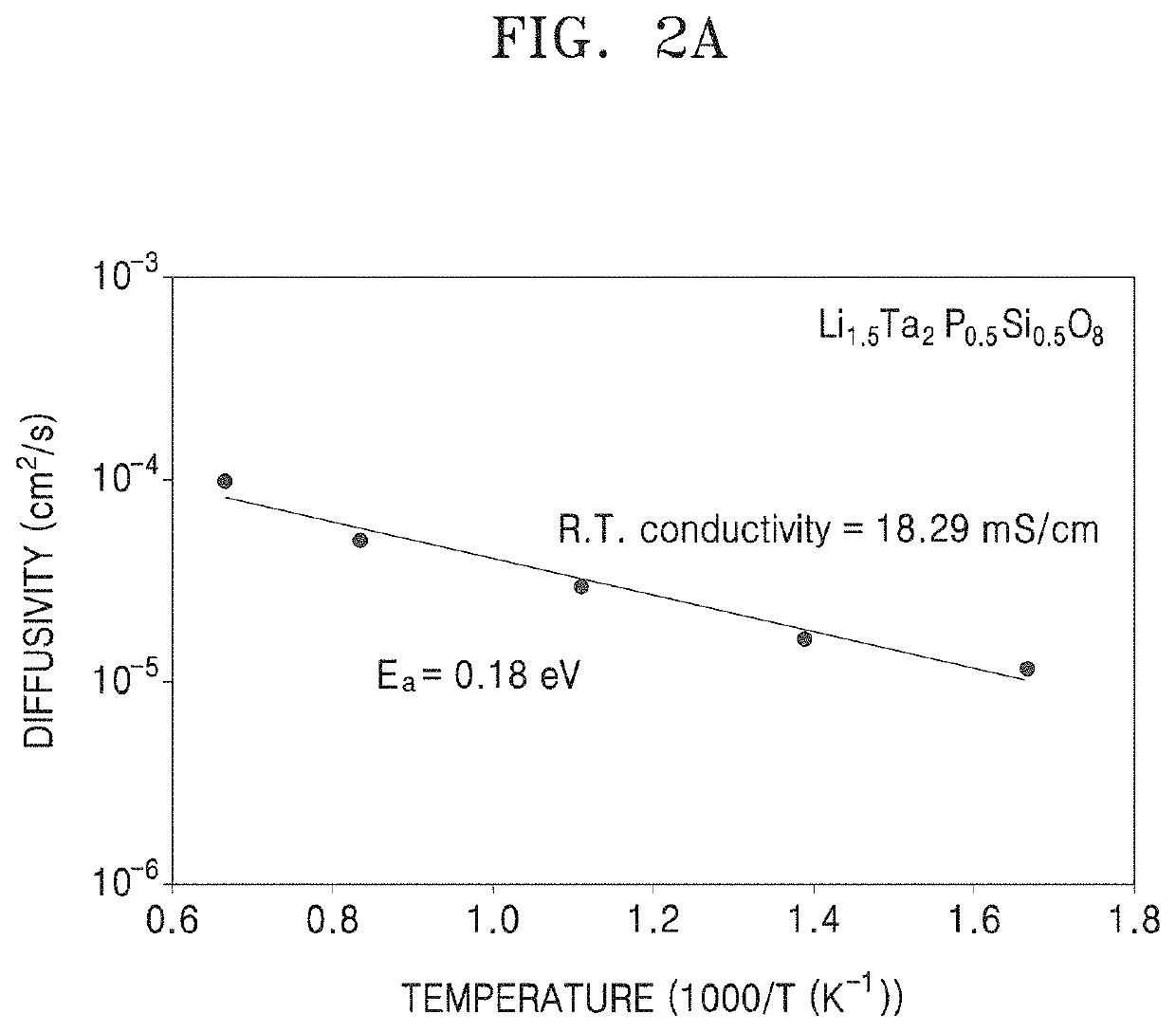
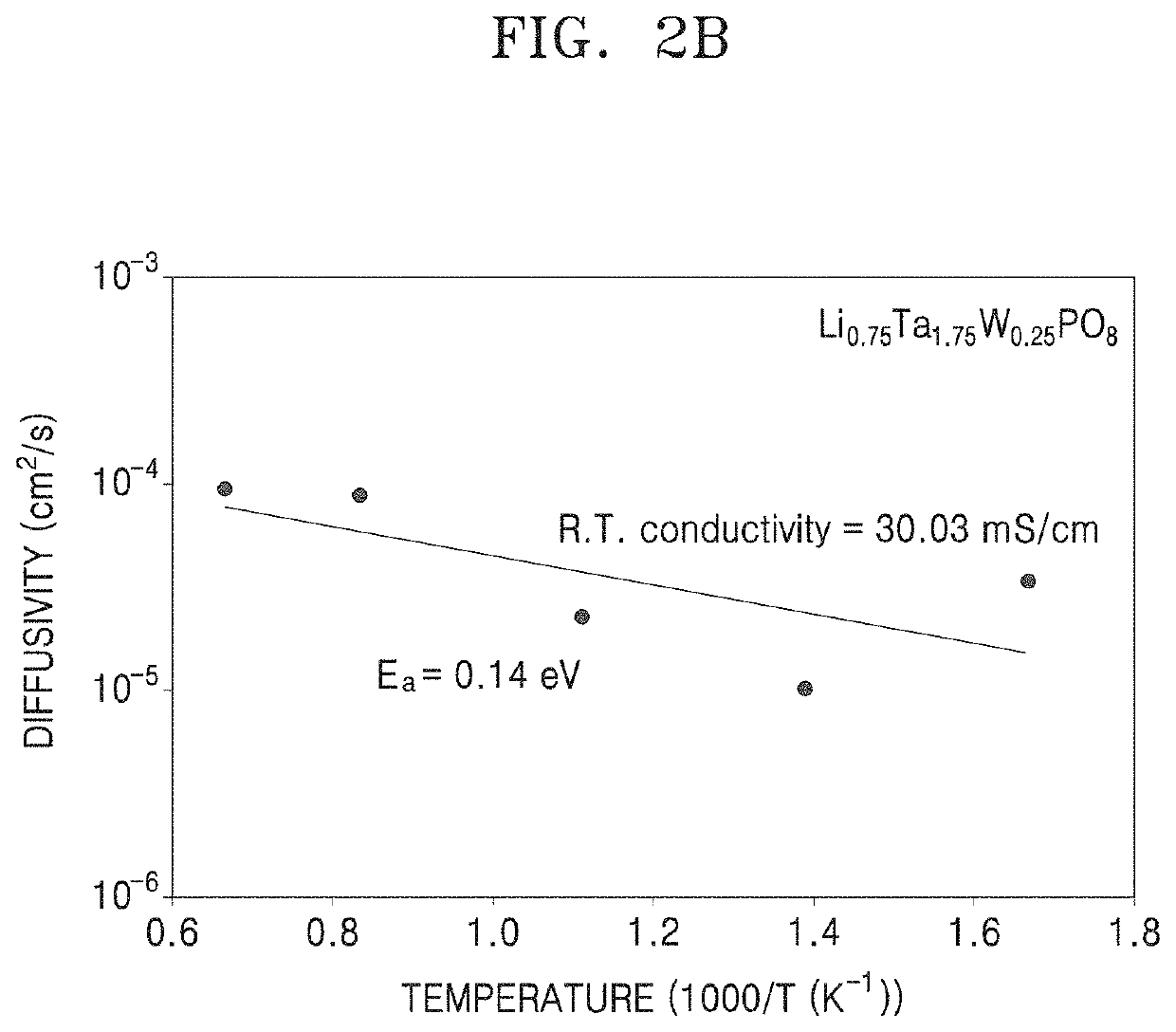
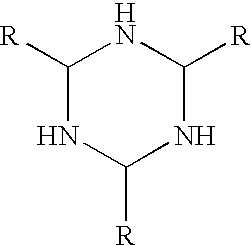
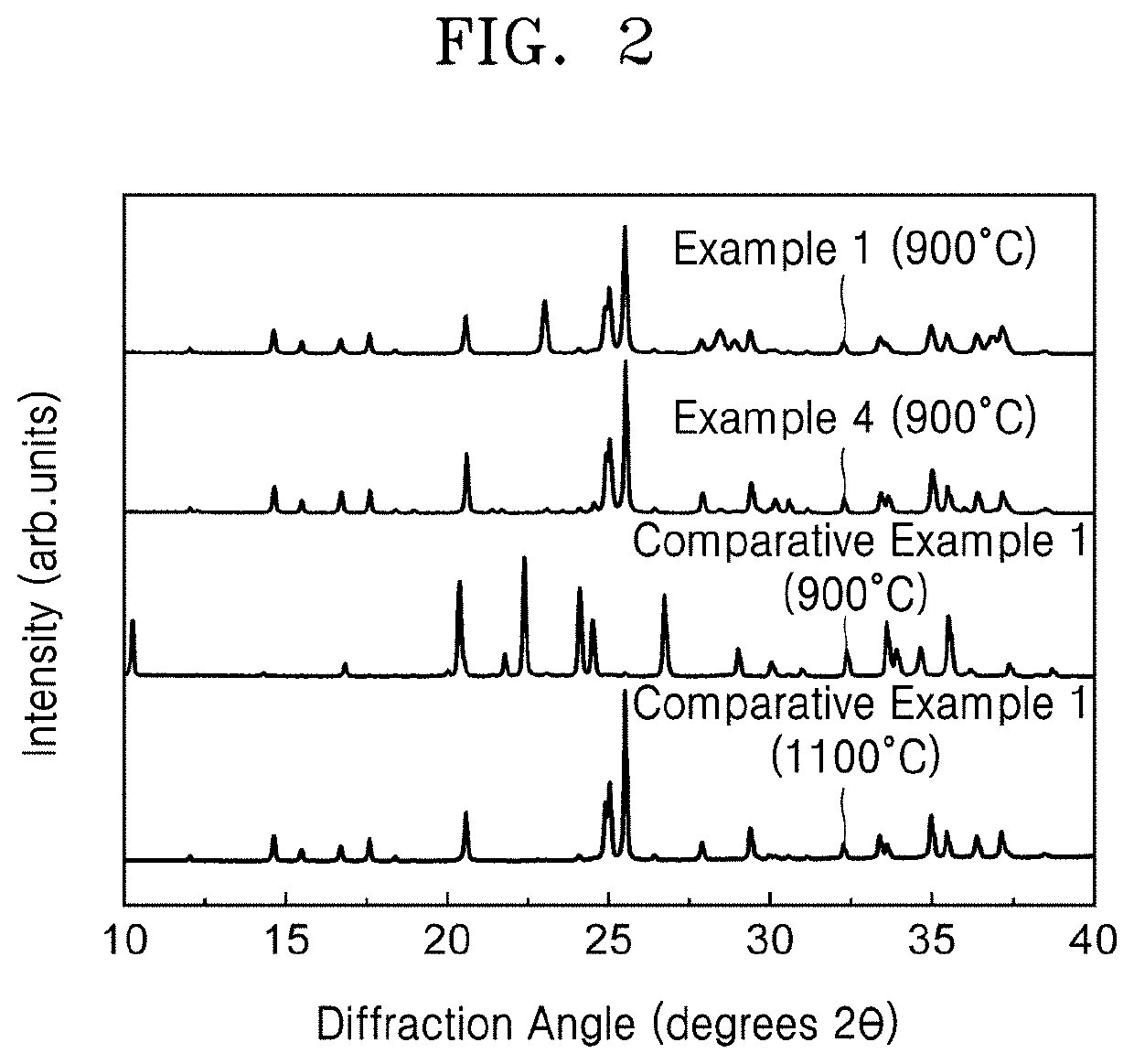
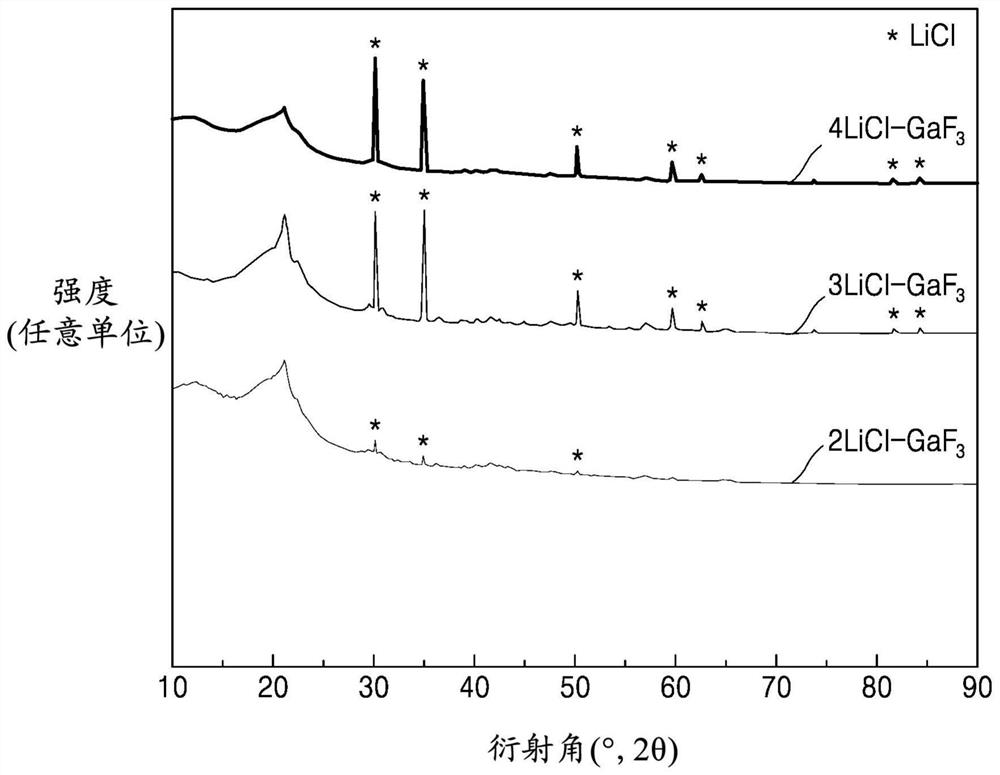
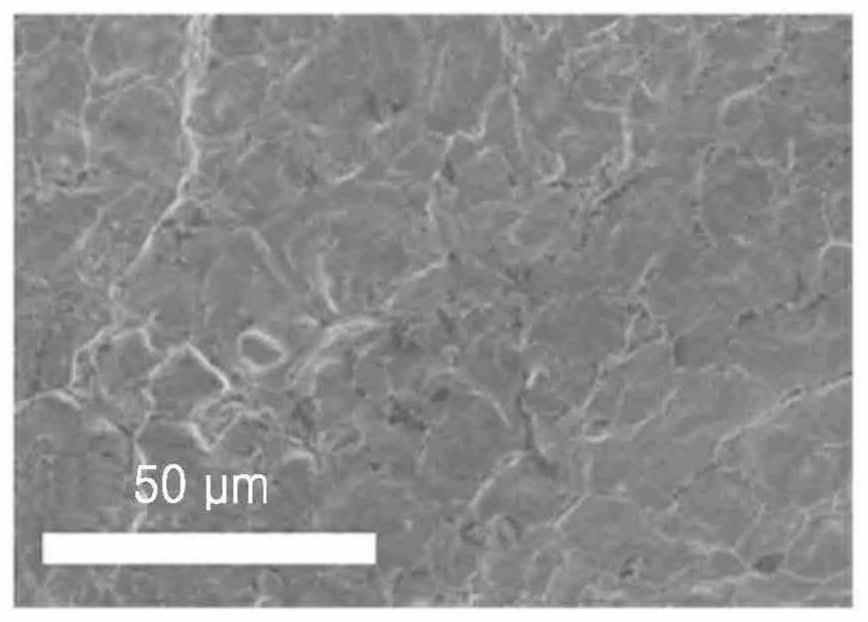
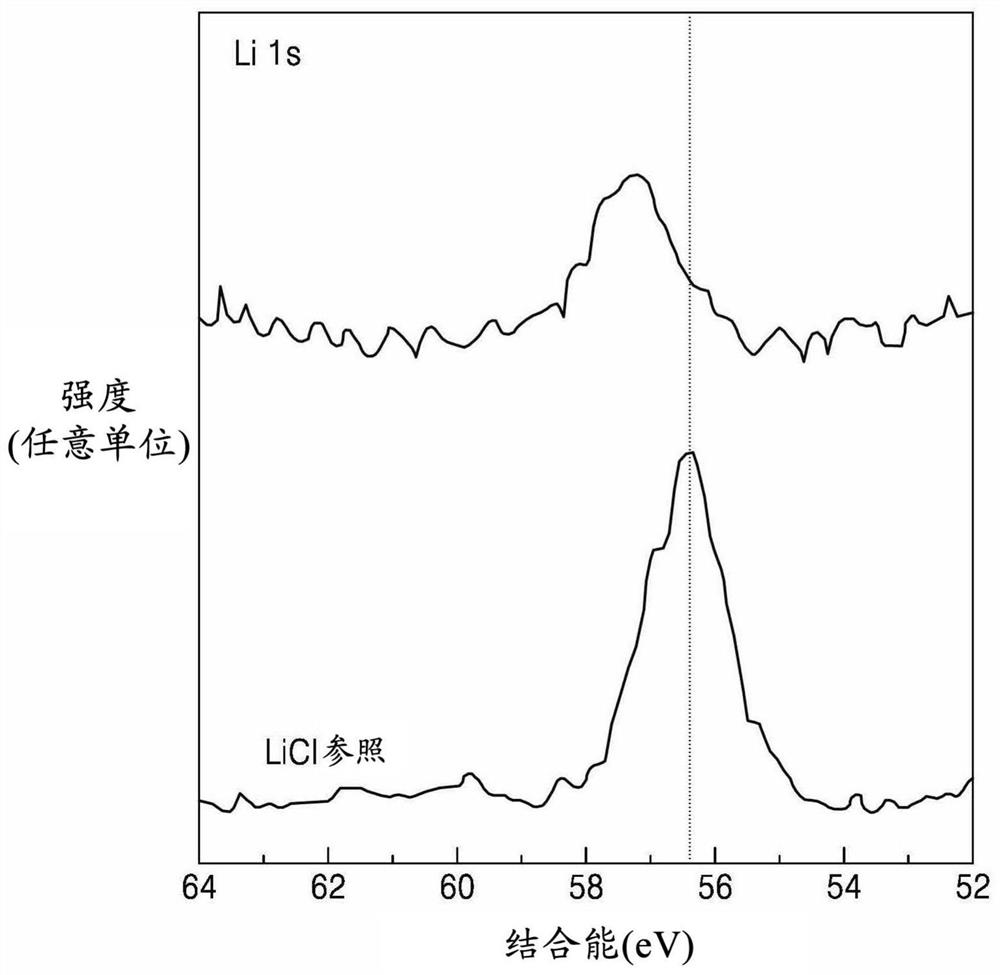
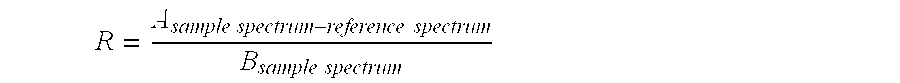Patents
Literature
34 results about "Pseudohalogen" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The pseudohalogens are polyatomic analogues of halogens, whose chemistry, resembling that of the true halogens, allows them to substitute for halogens in several classes of chemical compounds. Pseudohalogens occur in pseudohalogen molecules, inorganic molecules of the general forms Ps–Ps or Ps–X (where Ps is a pseudohalogen group), such as cyanogen; pseudohalide anions, such as cyanide ion; inorganic acids, such as hydrogen cyanide; as ligands in coordination complexes, such as ferricyanide; and as functional groups in organic molecules, such as the nitrile group. Well-known pseudohalogen functional groups include cyanide, cyanate, thiocyanate, and azide.
Organic room-temperature phosphorescent material and electroluminescent device
PendingCN110724088AImprove structural stabilityLong room temperature phosphorescenceOrganic chemistry methodsSolid-state devicesBenzeneChemical physics
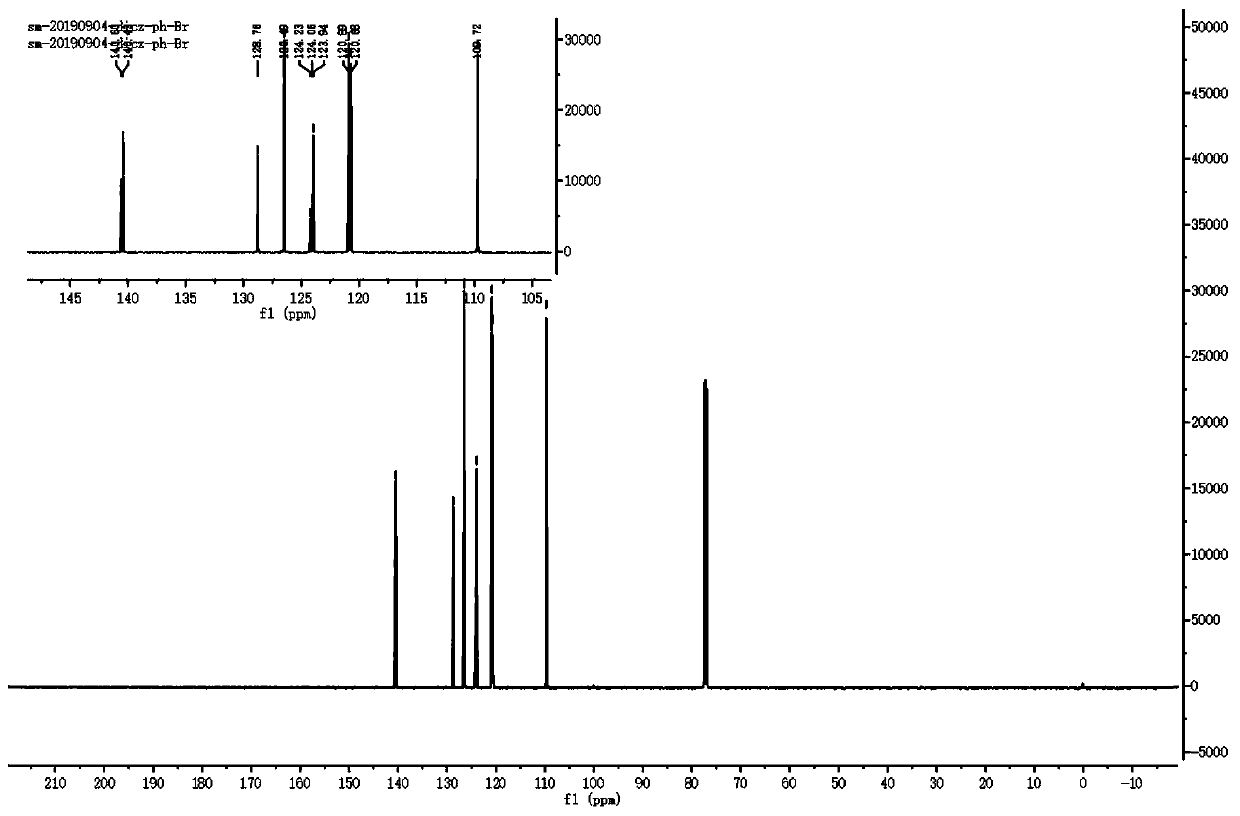
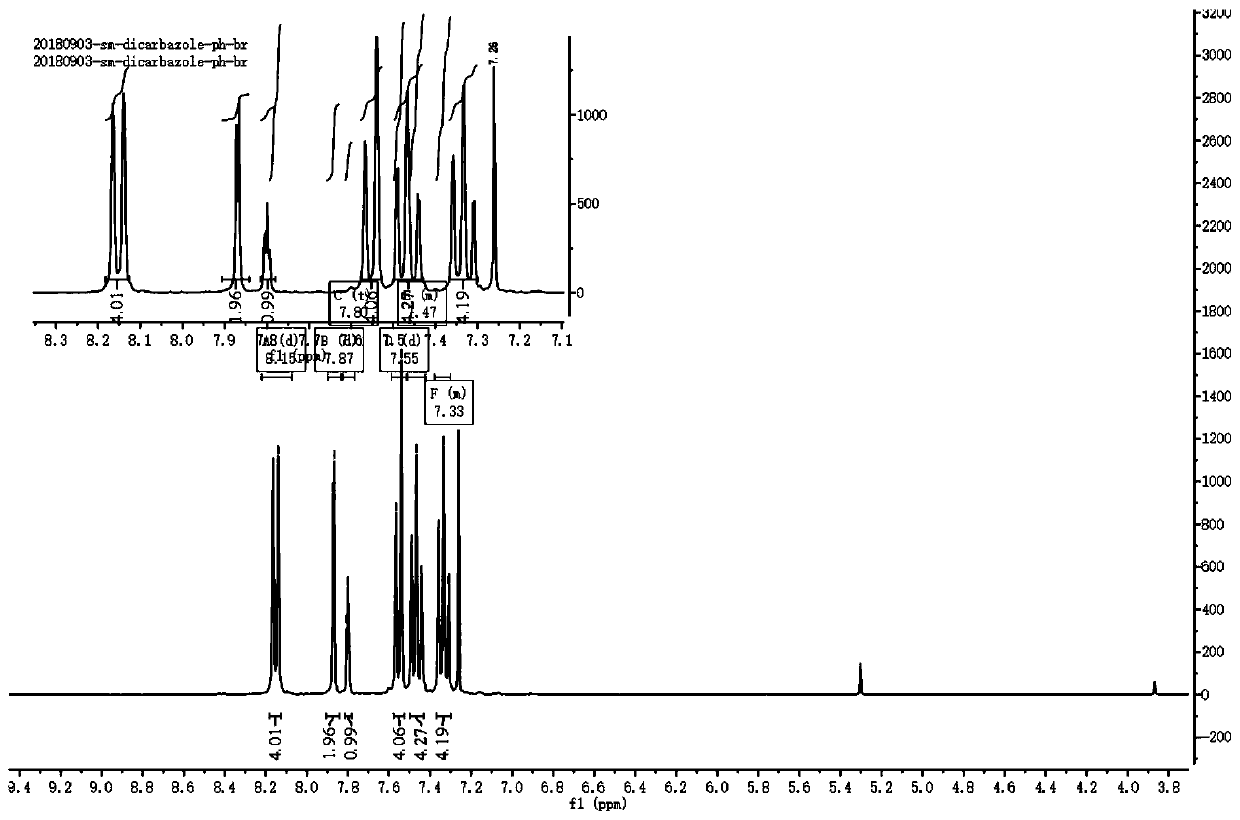
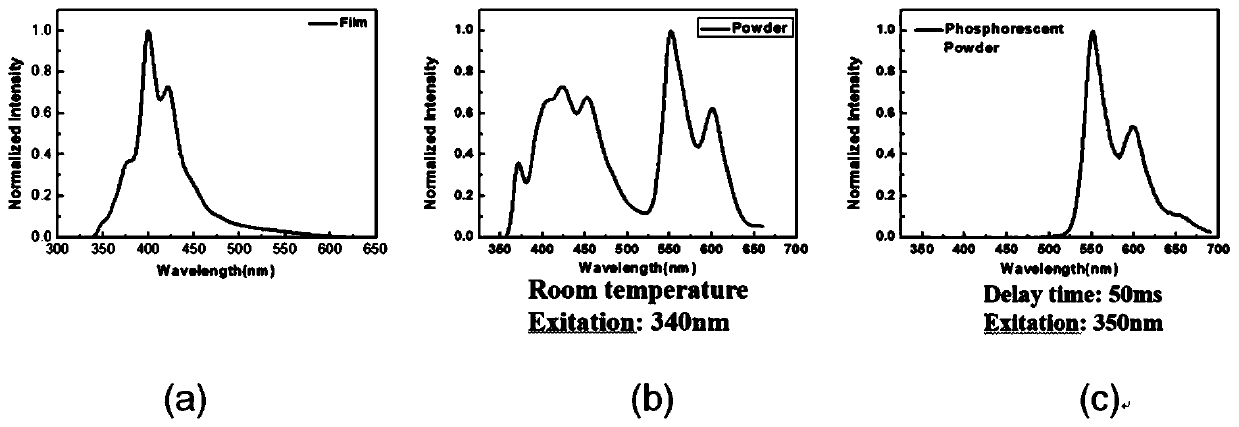
The invention discloses an organic room-temperature phosphorescent material and an electroluminescent device. The material is based on a structure with 1,3-dicarbazolyl benzene as a mother nucleus andmodified by halogen atoms or pseudo-halogen groups, may have very long room-temperature phosphorescence (with lifetime as long as several seconds), and also has very high phosphorescent quantum yield(up to 40% or above). Furthermore, on the basis of the structure, the structural stability of molecules can be improved by introducing a modification group or deuteration to a carbazolyl group, and phosphorescence lifetime can be further prolonged by deuteration because of the self heavy-atom effect, so triplet-state molecular orbital coupling effect is improved. Furthermore, a series of new mother nucleuses are designed through the replacement of carbazole similar structures and the replacement of phenyl groups, but the main body structure is not changed, and super-long room-temperature phosphorescence and strong phosphorescence quantum yield are also realized after the same modification.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Percolation efficiency of the conductivity of electrically conductive adhesives
InactiveCN101602929ANon-macromolecular adhesive additivesNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialPolymer resinPseudohalogen
The present invention relates to percolation Efficiency of the conductivity of electrically conductive adhesives. The present invention further relates to an electroconductive bonding material consists of a resin matrix and a modified conductive filler. The resin matrix if formed by providing a thermosetting or thermoplastic resin-based polymer resin. The conductive filler is a metal filler material suitable for use as conductive filler for the resin matrix. The metal filler is modified by applying a material selected from one of halogens, pseudohalogens or their precursors.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Pseudohalogen induction-based two-dimensional perovskite electric storage device and preparation method therefor
ActiveCN107316939ASolving Manufacturing ComplexitySolve yieldSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectricityPseudohalogen
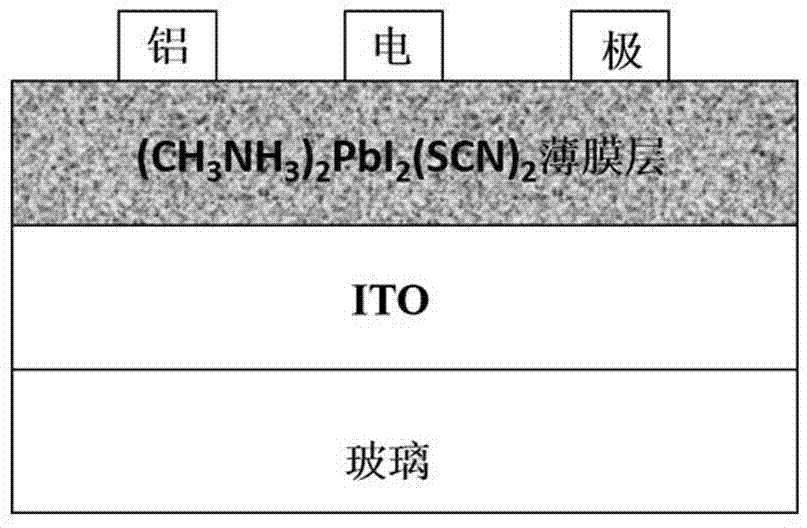
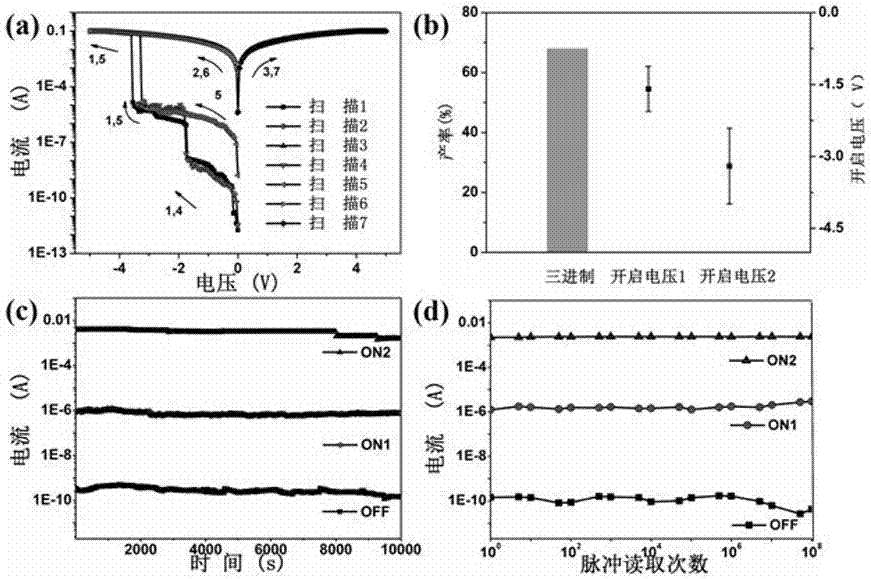
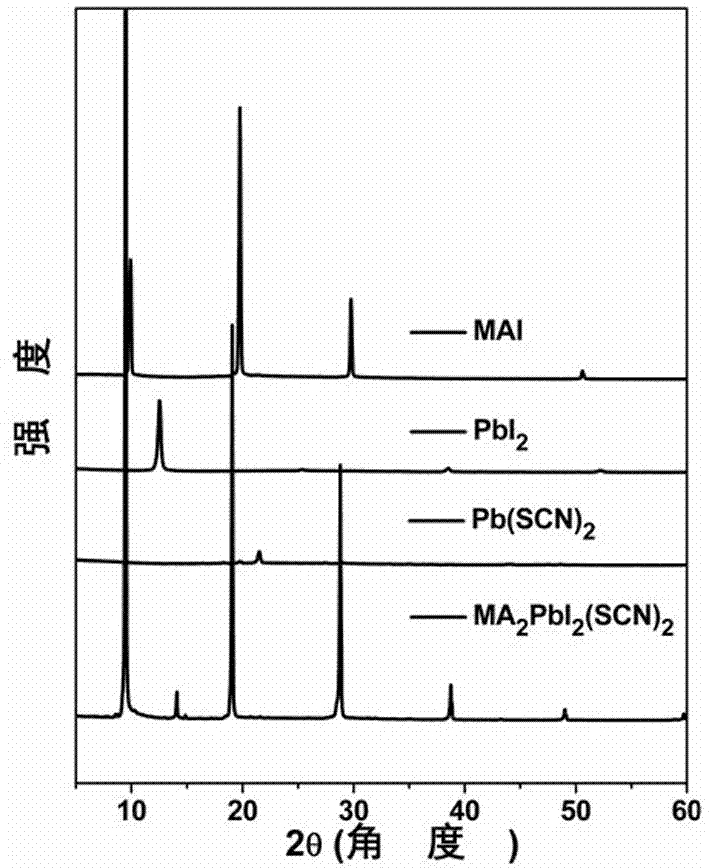
The invention discloses a pseudohalogen induction-based two-dimensional perovskite (CH<3>NH<3>)<2>PbI<2>(SCN)<2> electric storage device and a preparation method therefor. The preparation method comprises the following steps of dissolving methyl amine iodide into a DMF solvent, and then adding lead thiocyanate into the solution, fully oscillating and preparing into a yellow perovskite solution; coating a substrate with the perovskite solution to prepare an active layer; and next, preparing an electrode on the active layer to obtain the pseudohalogen induction-based two-dimensional perovskite (CH<3>NH<3>)<2>PbI<2>(SCN)<2> electric storage device. The pseudohalogen induction-based two-dimensional perovskite material is formed by organic amine salt and the inorganic metallic compound through a coordination effect so as to prepare the organic electric storage device with the sandwich structure, so that an organic electric storage behavior is realized successfully; meanwhile, the preparation method is simple and the ternary electric storage behavior is high in yield; and therefore, the invention also discloses an application of the two-dimensional perovskite material in the preparation of the electric storage device.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Process for making a fluoropolymer having nitrile end groups
The present invention discloses a process for making a fluoropolymer having nitrile endgroups. The process comprises a free radical polymerization of one or more fluorinated monomers in the presence of a nitrile group containing salt or a nitrile group containing pseudohalogen compound.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Fluorescent compound and preparation method and application thereof, and writing medium
ActiveCN111253265AOrganic compound preparationGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsPhosphoniumFluorescence
The invention provides a fluorescent compound and a preparation method and application thereof, and a writing medium. The fluorescent compound comprises a crystalline compound formed by quaternary ammonium salt (phosphonium) cations and metal halide anions, and has a structural formula of [R<1>R<2>R<3>R<4>X][MY<c>][Z]<d>, wherein X is nitrogen or phosphorus; M is a main group metal element or a transition metal element; Y is halogen or pseudo-halogen; Z is a volatile compound; a is a natural number in a range of 1 to 6; b is a natural number in a range of 1 to 6; c is a natural number ina range of 3 to 20; d is a natural number in a range of 0 to 6; substituent groups R<1>, R<2>, R<3> and R<4> of X are respectively, independently and optionally selected from a group consisting of hydrogen, C1-C18 alkyl groups, C2-C18 alkenyl groups, C2-C18 alkynyl groups, aromatic compound groups and heterocyclic compound groups. The fluorescent compound provided by the invention can be combinedwith volatile liquid molecules to cause the change of fluorescence or color, and is separated from the volatile liquid molecules under heat treatment to recover the fluorescence or color, so the effect of repeatable writing is realized; the preparation method is simple; and the mode of changing fluorescence duration is simple.
Owner:重庆平创半导体研究院有限责任公司
Catalyst of load type bimetallic cyaniding complex, preparation method and application
This invention discloses a method for preparing double-metal cyanide complex supported catalyst and its application. The composition is : S-M11a[M(CN)BL1c].xM11X2.y1L2.y2L3.zH2O, wherein, S is the carrier, and is SiO2, TiO2 or their mixture; M11 is divalent metal ion; M is divalent, trivalent or valency-changeable metal ion; X is halogen anion or analog of halogen anion; L1 is high molecular or low molecular mono-tooth or double-tooth ligand of M; L2 is water-soluble alcohol or cyclic ether; L3 is water-soluble or alcohol-soluble compound, and can be high molecular or low molecular mono-toothor double-tooth ligand; a and b are positive integers; c is 0 or positive integer; x, y1, y2 and z are 0 or positive numbers. The catalyst is stable in air, and is insensitive to water vapor. The catalyst can be adequately utilized due to supporting, and can be easily removed from reaction products.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Solid electrolyte, electrochemical cell including solid electrolyte, and method of preparing solid electrolyte
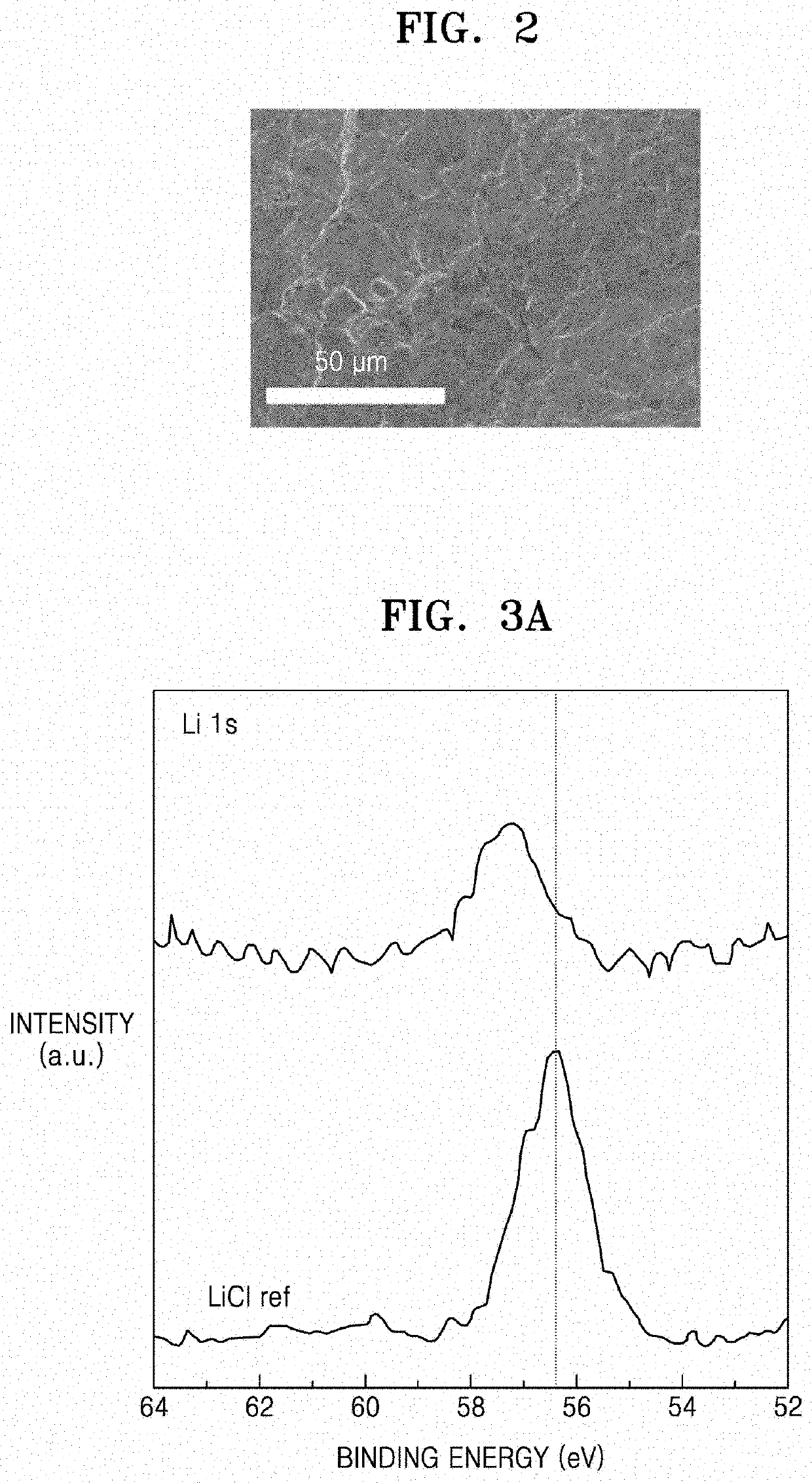
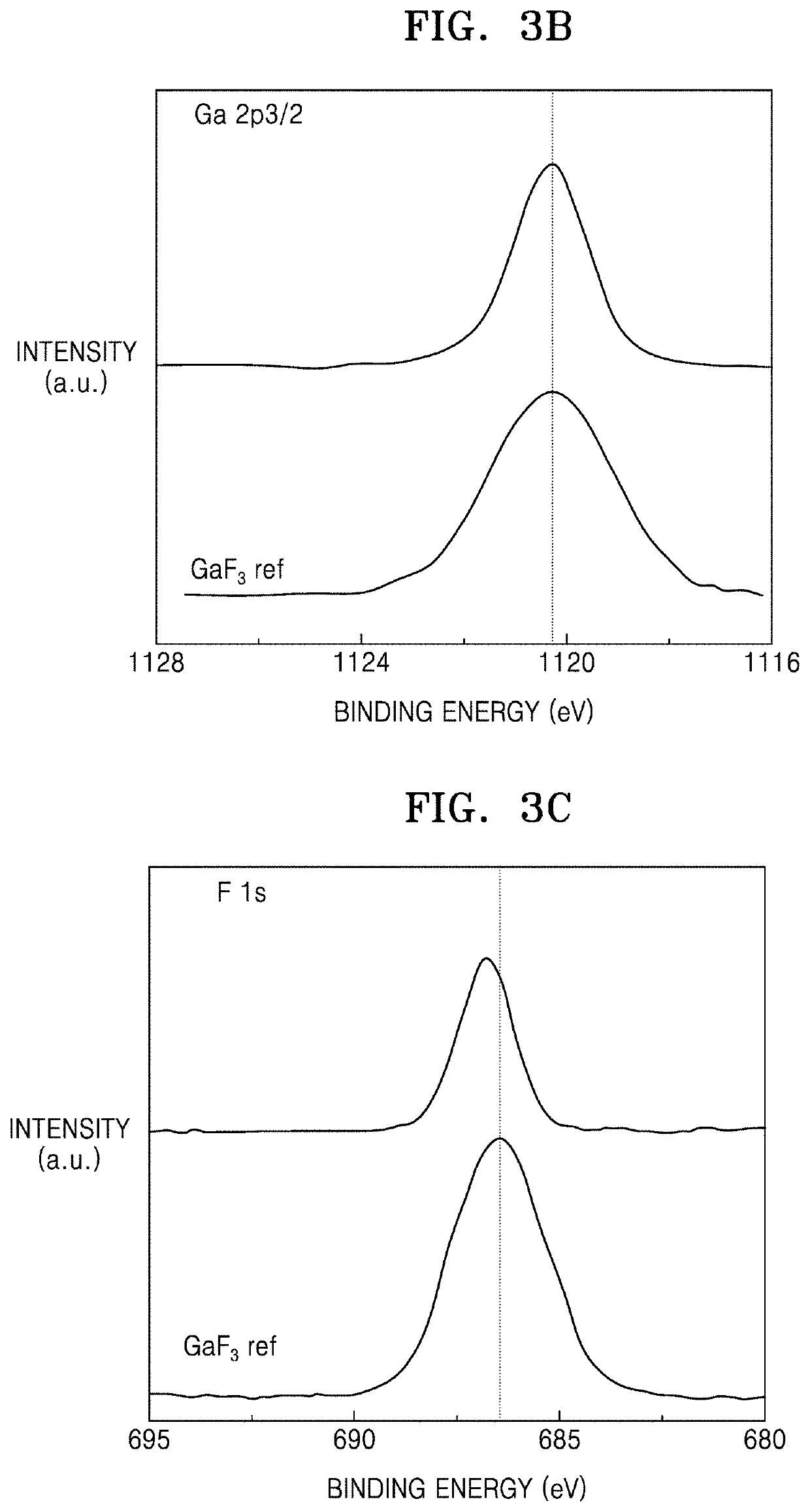
PendingUS20210143468A1Improved rate capability and lifetime characteristicSolid electrolytesPhosphorus sulfur/selenium/tellurium compoundsPseudohalogenPhysical chemistry
A solid electrolyte including a compound represented by Formula 1:(Li1-aMa)7-d+xPS6-d-x+kNxXd Formula 1wherein, in Formula 1,M is Na, K, Ca, Fe, Mg, Ag, Cu, Zr, Zn, or a combination thereof;X is Cl, Br, F, I, a pseudohalogen, or a combination thereof; and0<x<1, 0≤a<1, 0<d≤1.8, and 0≤k<1, andwherein the compound has an argyrodite crystal structure.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
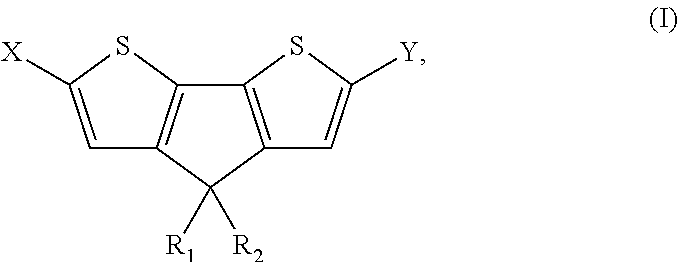
4, 4' disubstituted 4h-cyclopentadithiophene and new methods for synthesising the same
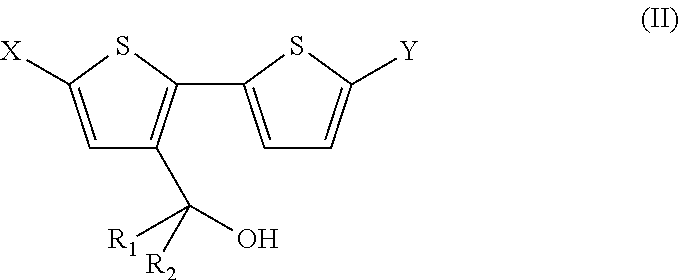
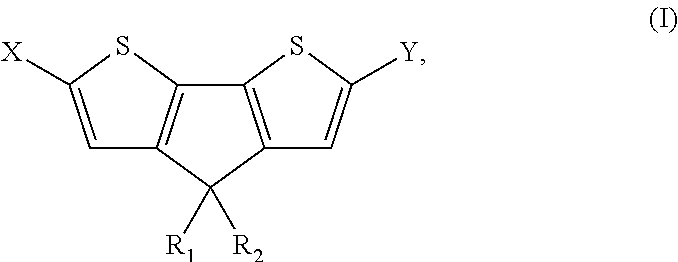
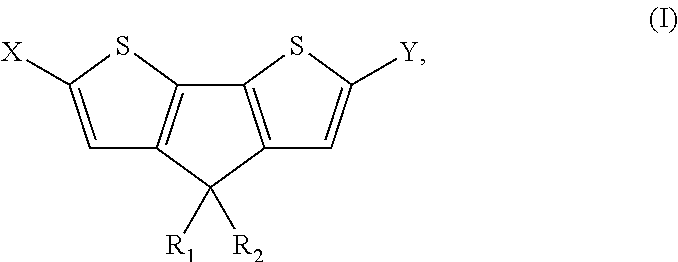
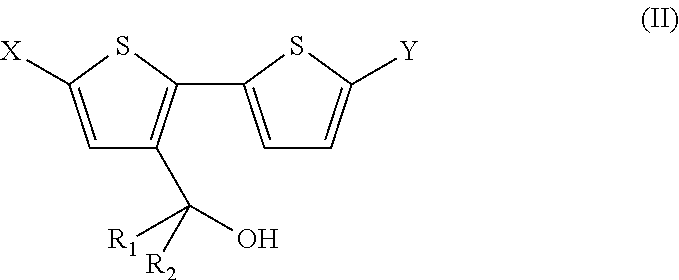
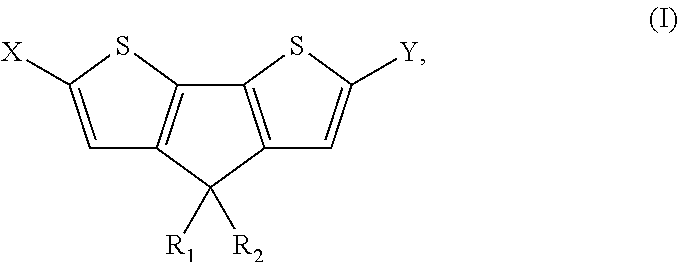
The present preferred embodiments relate to a method for the synthesis of a compound having the following general formula:the method comprising the step of reacting, in presence of a diprotic acid having a negative pKa, a compound having the general formula:wherein R1 and R2 are organic groups and wherein X and Y are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, chloro, bromo, iodo, boronic acid, boronate esters, borane, pseudohalogen and organotin. It further relates to compounds so obtained and to compounds resulting from the ring closure of compound (II).
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW) +1
Process and method for recovery of halogens
InactiveUS20070207083A1Suitable for useFlow fastCellsPhotography auxillary processesPseudohalogenElectrochemical cell
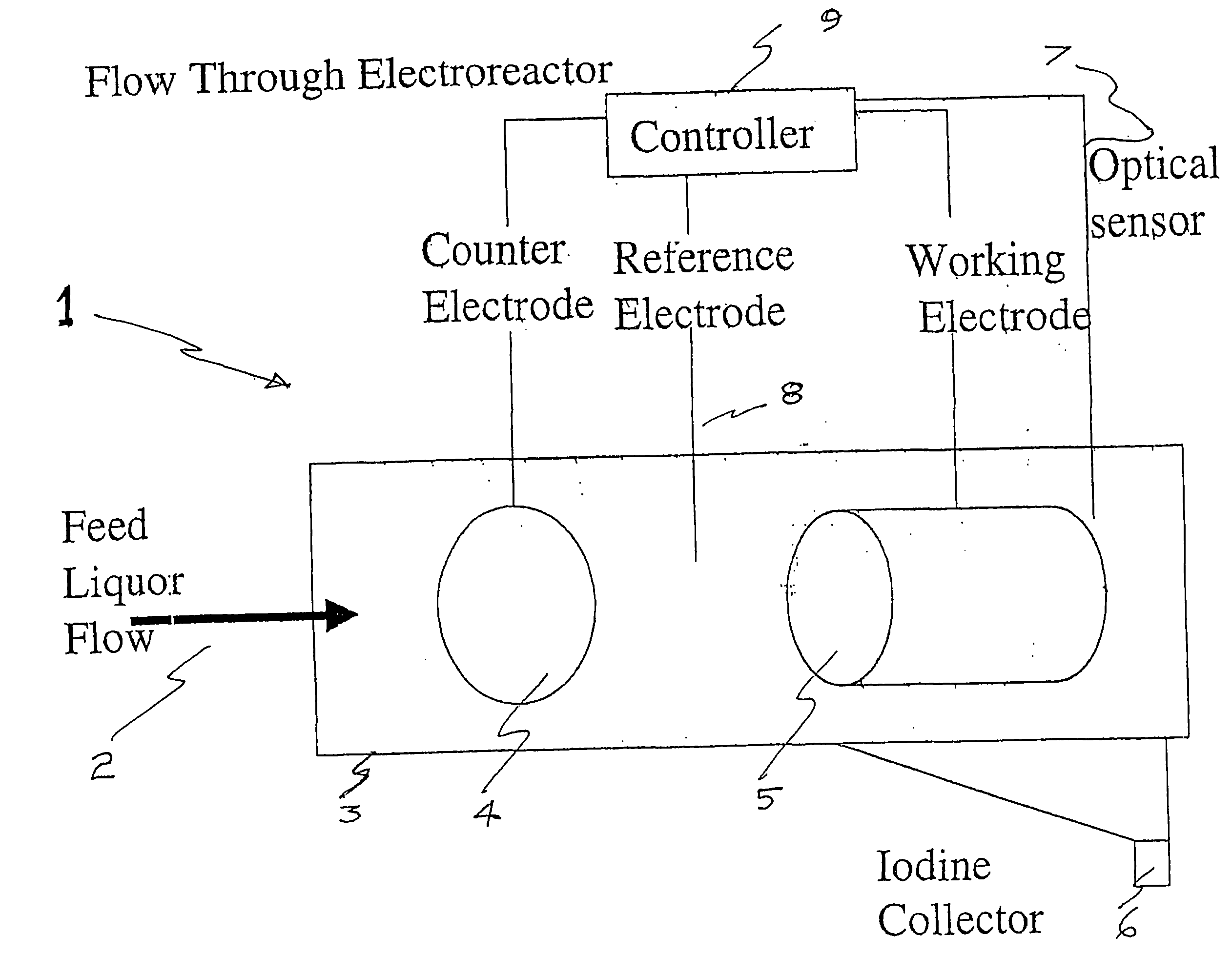
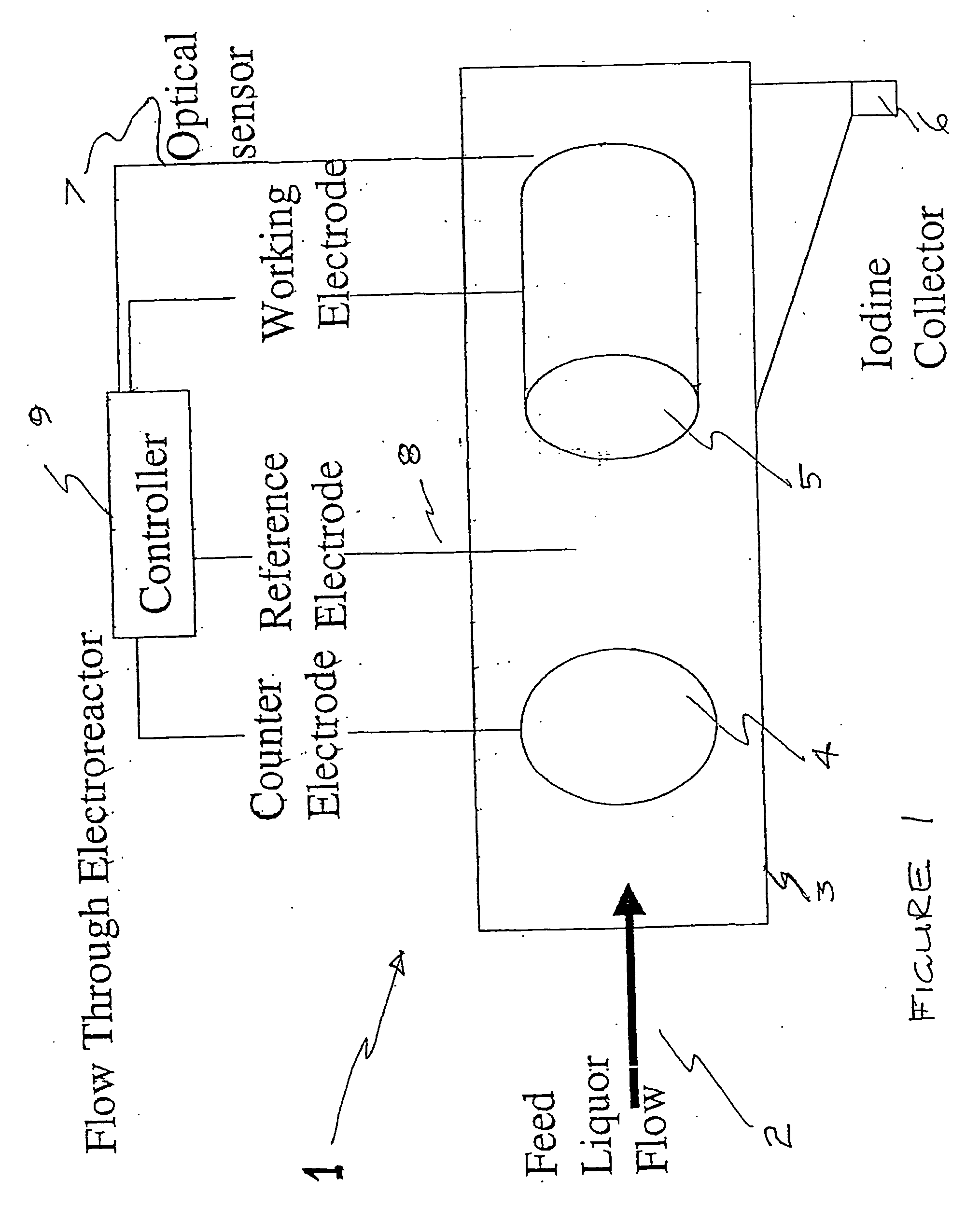
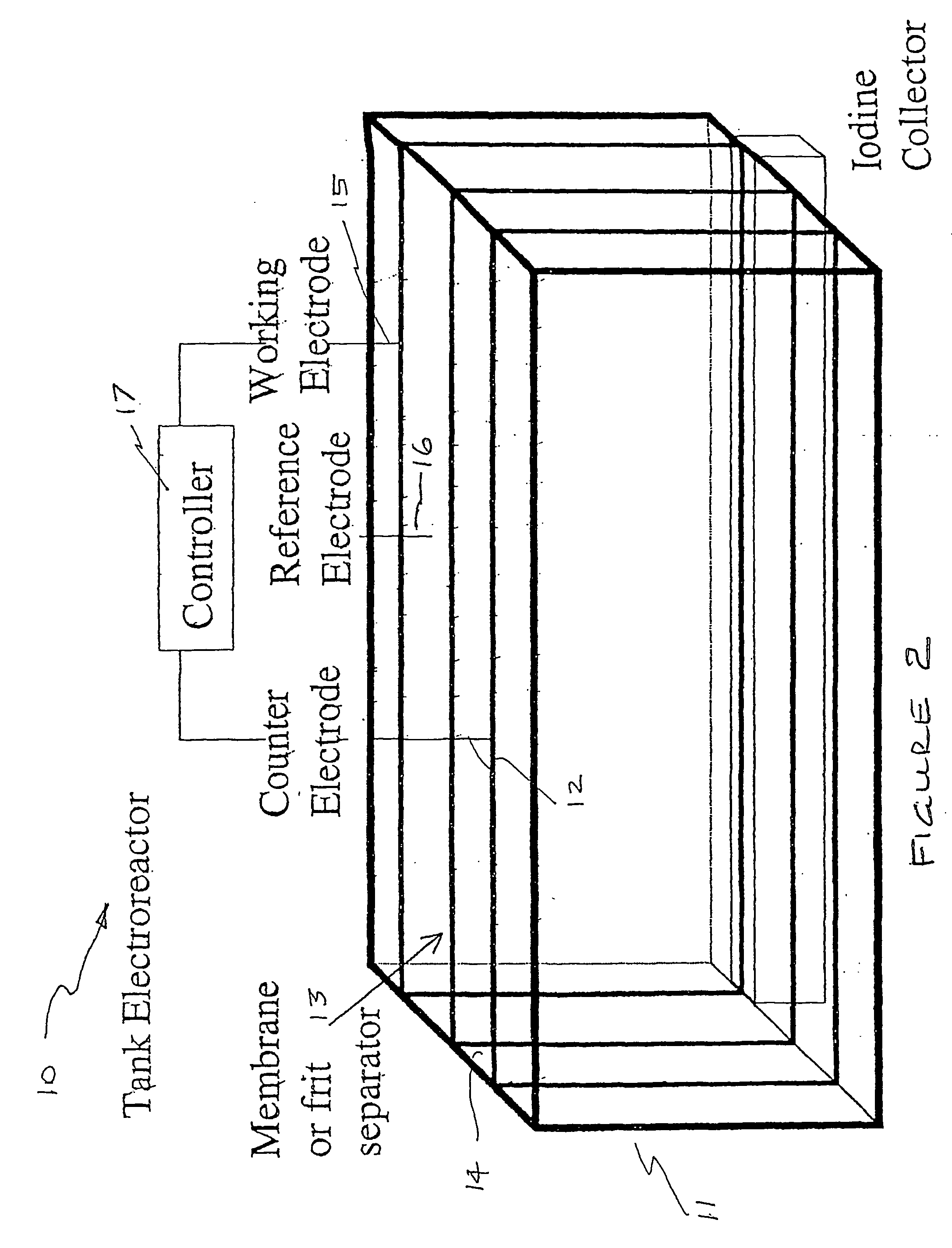
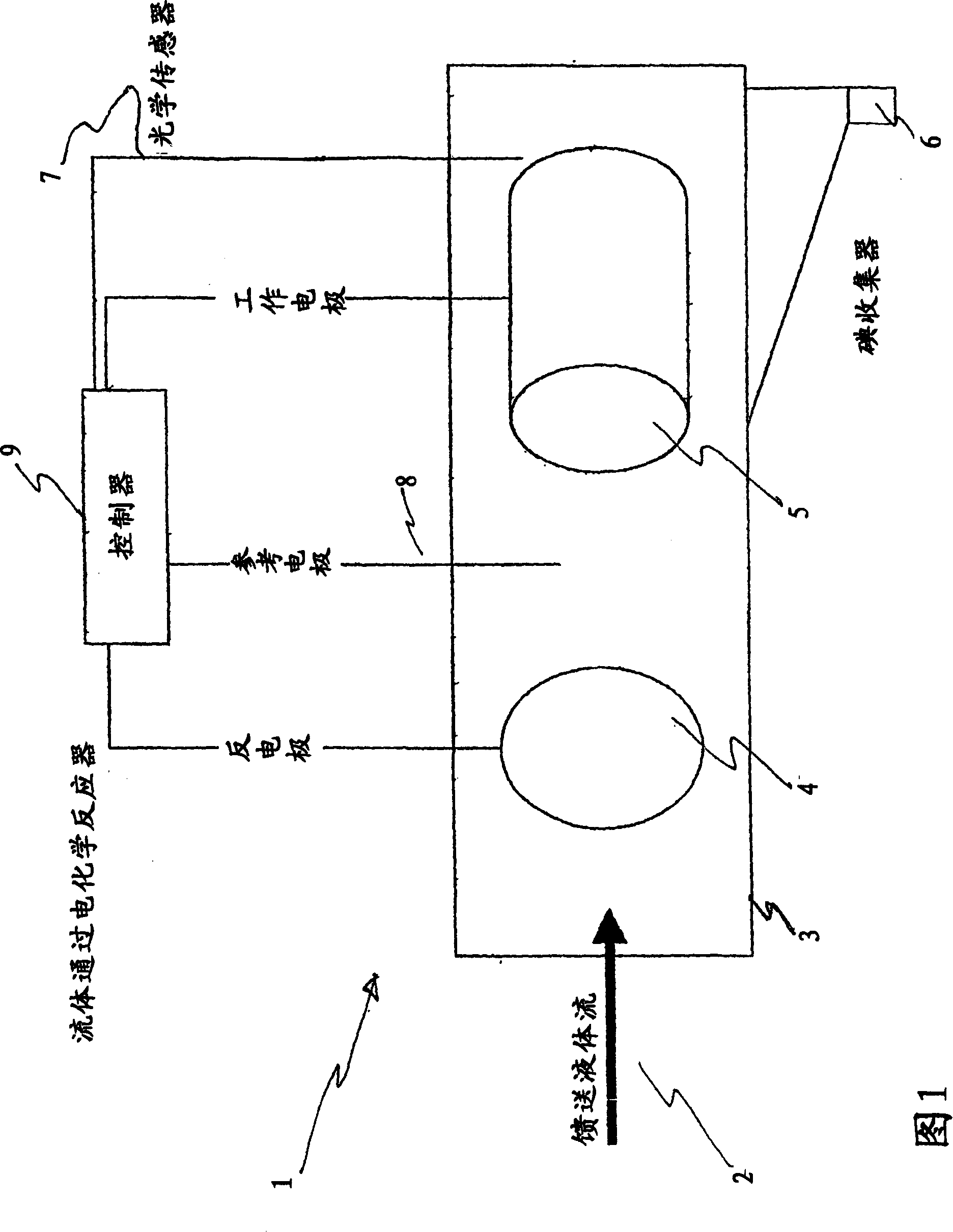
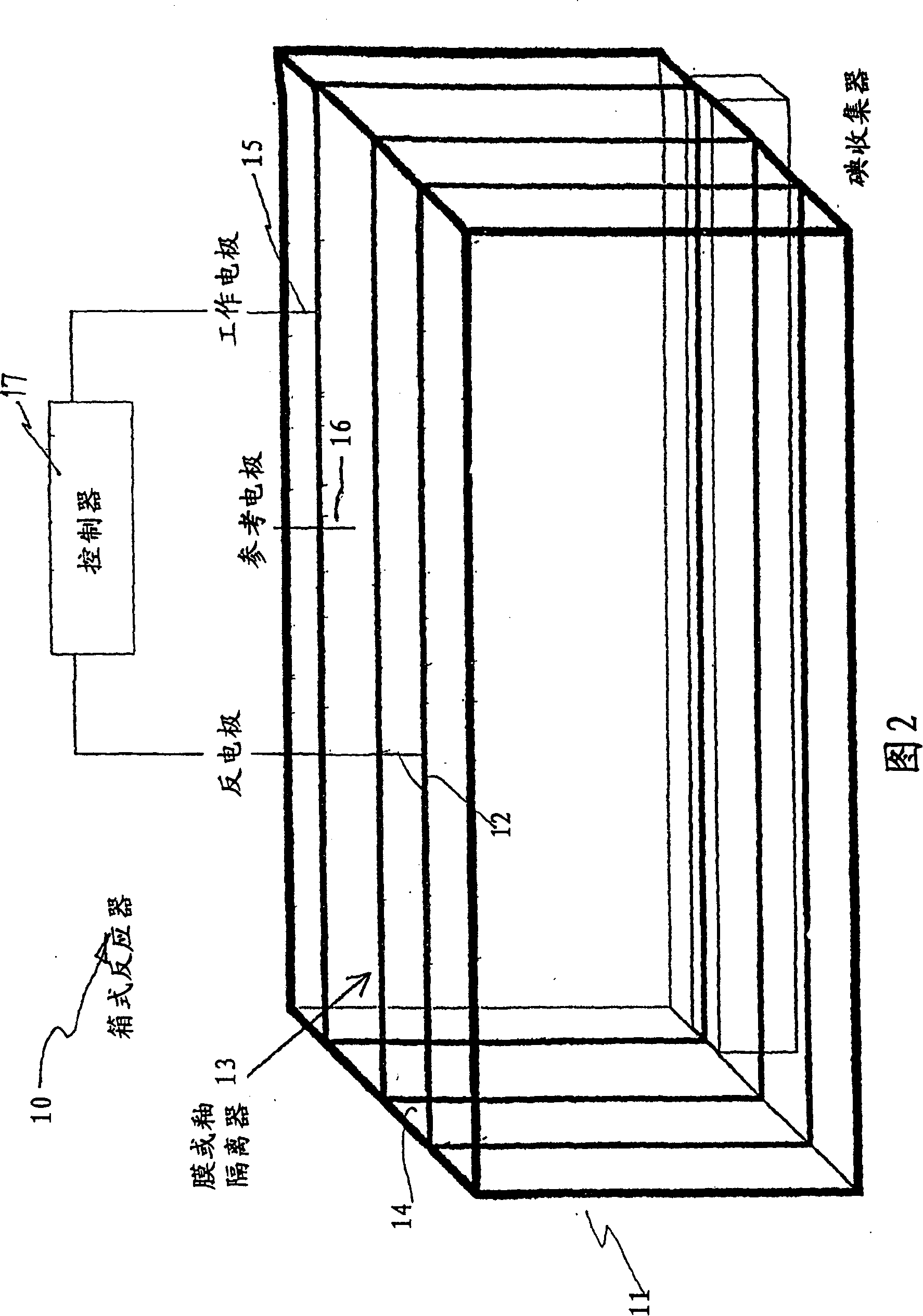
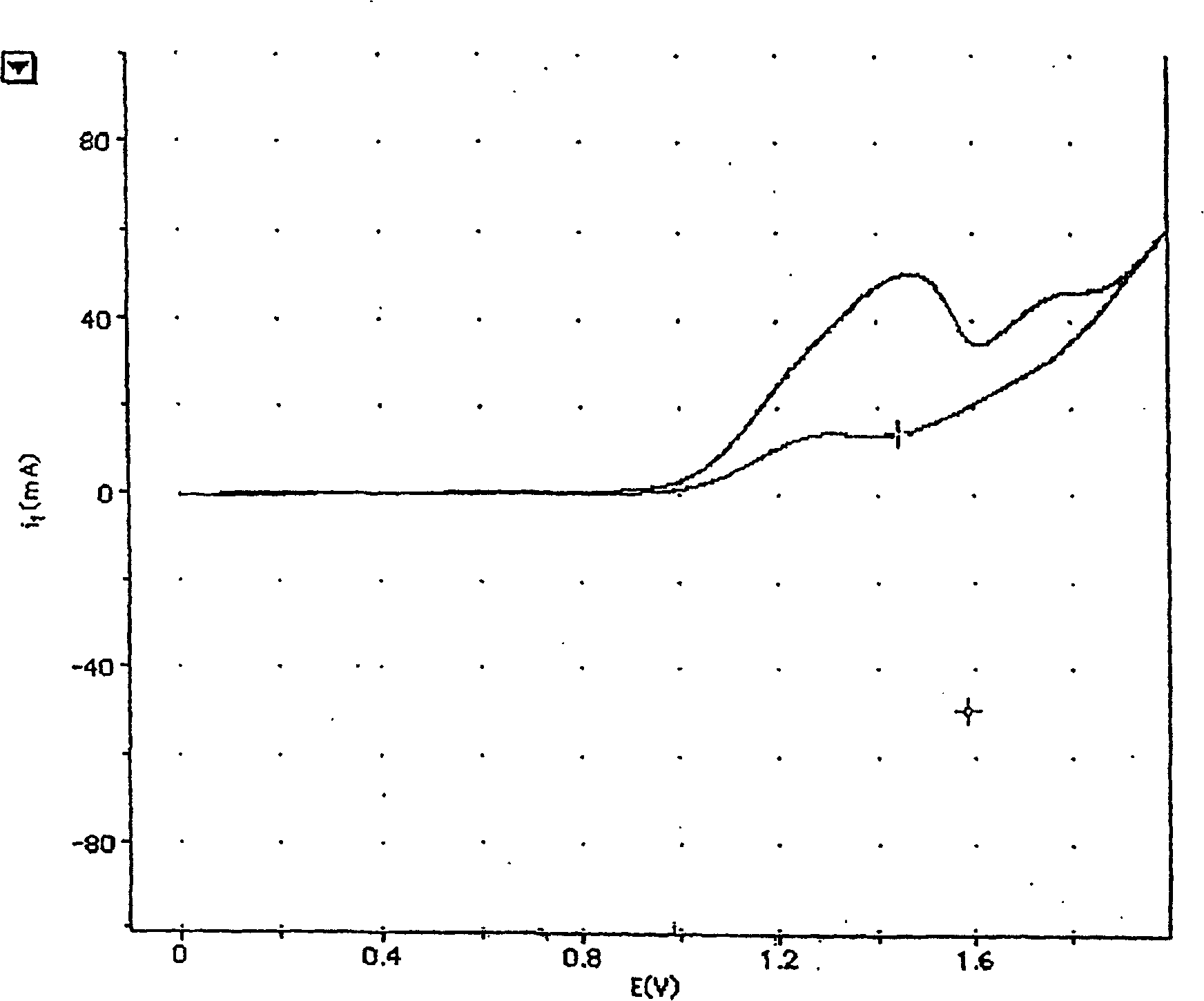
An apparatus for the recovery of a halogen or pseudohalogens from a halide compound in solution; wherein the apparatus includes an electrochemical cell including, an electrode assembly including at least a first and second electrodes in communication with a controller for providing a current to at least two of the electrodes; wherein, upon delivery of a predetermined voltage, the halide compound is oxidised at one or more of the electrodes to form a halogen corresponding to the halide in solution whereupon the halogen is deposited on said one or more electrode upon completion of oxidation.
Owner:IODINE TECH AUSTRALIA PTY LTD
Process and method for recovery of halogens
An apparatus for the recovery of a halogen or pseudohalogens from a halide compound in solution; wherein the apparatus includes; an electrochemical cell including, an electrode assembly including at least a first and second electrodes in communication with a controller for providing a current to at least two of said electrodes; wherein, upon delivery of a predetermined voltage, said halide compound is oxidised at one or more said electrodes to form a halogen corresponding to said halide in solution whereupon said halogen is deposited on said one or more electrode upon completion of oxidation.
Owner:IODINE TECH AUSTRALIA PTY LTD
Oxide, preparation method thereof, solid electrolyte including the oxide, and electrochemical device including the oxide
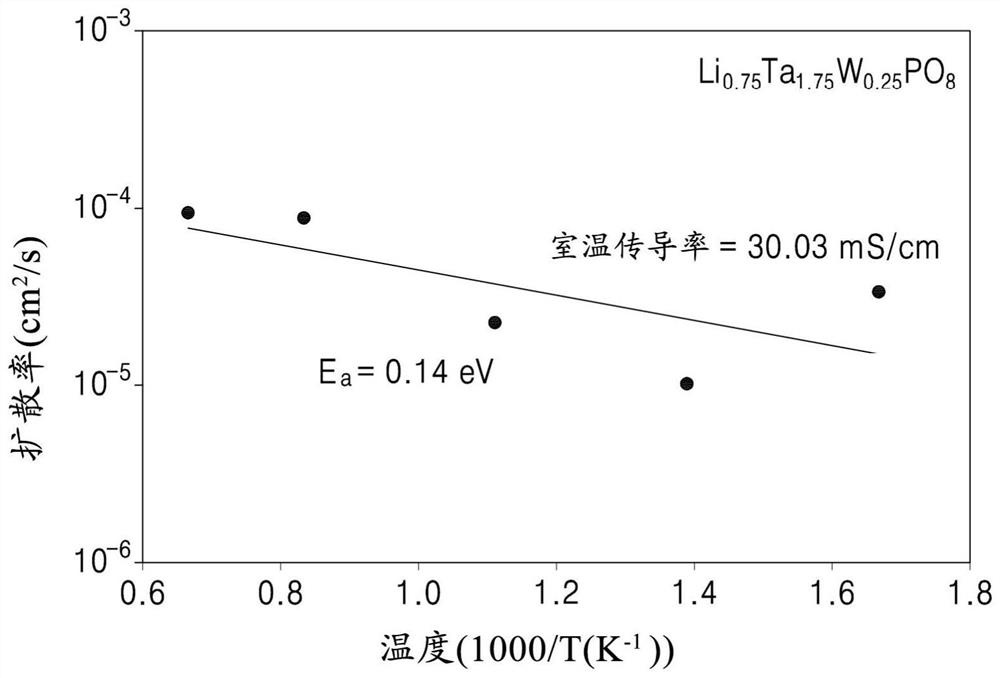
ActiveUS20210408576A1Improve ionic conductivityImproved lithium stabilityCell electrodesTantalum compoundsPseudohalogenPhysical chemistry
An oxide includes a compound represented by Formula 1, a compound represented by Formula 2, or a combination thereof:Li1−x+y−zTa2−xMxP1−yQyO8−zXz Formula 1wherein, in Formula 1,M is an element having an oxidation number of 5+ or 6+,Q is an element having an oxidation number of 4+,X is a halogen atom, a pseudohalogen, or a combination thereof,0≤x<0.6, 0≤y<1, and 0≤z<1, wherein x and y are not 0 at the same time,Li1−x+yTa2−xMxP1−yQyO8.zLiX Formula 2wherein, in Formula 2,M is an element having an oxidation number of 5+ or 6+,Q is an element having an oxidation number of 4+,X is a halogen atom, a pseudohalogen or a combination thereof,0≤x<0.6, 0≤y<1, and 0≤z<1, wherein x and y are not 0 at the same time, andwherein in Formulas 1 and 2, M, Q, x, y, and z are independently selected.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Process for making a fluoropolymer having nitrile and groups
The present invention discloses a process for making a fluoropolymer having nitrile endgroups. The process comprises a free radical polymerization of one or more fluorinated monomers in the presence of a nitrile group containing salt or a nitrile group containing pseudohalogen compound.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Solid electrolyte, method of preparing the same, and electrochemical device including the same
ActiveUS20210376378A1Gallium/indium/thallium compoundsNegative electrodesVitrificationChemical physics
A solid electrolyte including a compound represented by Formula 1 or 3, the compound having a glass transition temperature of −30° C. or less, and a glass or glass-ceramic structure,AQX-Ga1-zMz1(F1-kClk)3-3zZ3z1 Formula 1wherein, in Formula 1,Q is Li or a combination of Li and Na, K, or a combination thereof,M is a trivalent cation, or a combination thereof,X is a halogen other than F, pseudohalogen, OH, or a combination thereof,Z is a monovalent anion, or a combination thereof,1<A<5, 0≤z≤1, 0≤z1≤1, and 0≤k<1,AQX-aMz1Z3z1-bGa1-z(F1-kClk)3-3z Formula 3wherein, in Formula 3, Q is Li or a combination of Li and Na, K, or a combination thereof;M is a trivalent cation, or a combination thereof,X is a halogen other than F, pseudohalogen, OH, or a combination thereof,Z is a monovalent anion, or a combination thereof,0<a≤1, 0<b≤1, 0<a+b, a+b=4−A, 1<A<5, 0≤z<1, 0≤z1≤1, and 0≤k<1.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
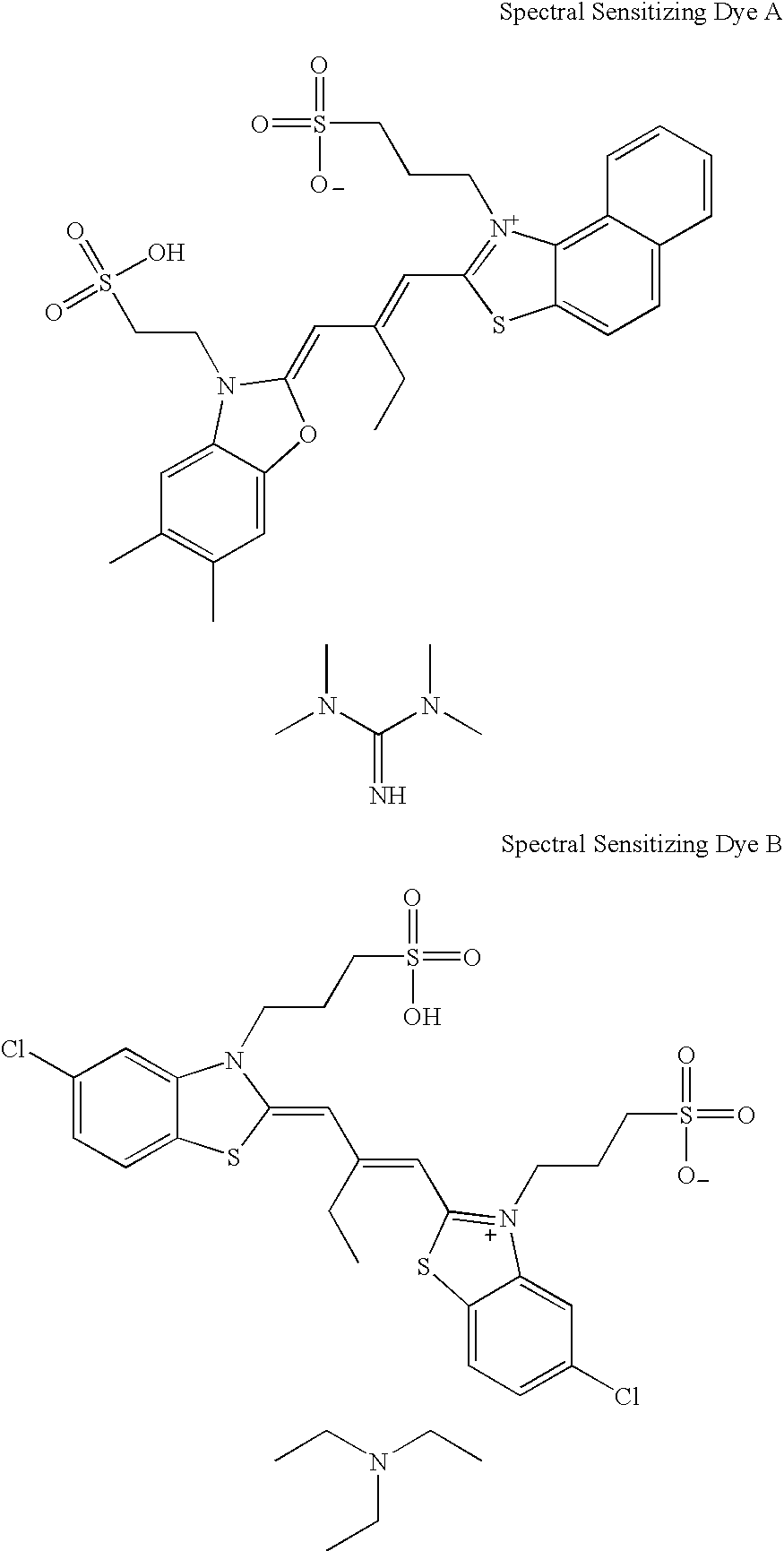
Silver halide emulsion containing iridium dopant
InactiveUS6969582B2Improving reciprocity performanceMinimal or no impact on other aspects of photographic performanceMulticolor photographic processingPhotothermographic systemsIridiumCoordination complex
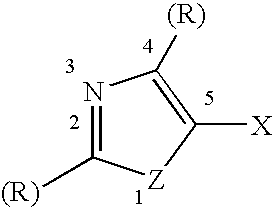
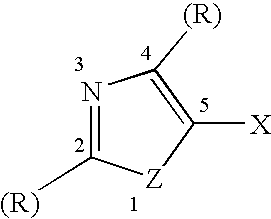
A silver halide emulsion comprising radiation sensitive silver halide grains exhibiting a face centered cubic crystal lattice structure containing a hexacoordination complex of an iridium ion in which at least half of the coordination sites in the hexacoordination complex are provided by halogen or pseudohalogen ligands, and at least one coordination site is provided by a ligand comprising a azole ring containing a chalcogen atom and a nitrogen atom, wherein the azole ring is substituted at the 5-position with a halide ion. The invention provides emulsions containing with a preferred class of iridium dopants which are especially useful for improving reciprocity performance in silver halide emulsions with minimal or no impact on other aspects of photographic performance. These dopants give a superior balance of reciprocity and other photographic properties compared to other iridium dopants exemplified in the prior art.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Silver halide emulsion containing iridium dopant
InactiveUS20050233266A1Improving reciprocity performanceMinimal or no impact on other aspects of photographic performanceMulticolor photographic processingPhotothermographic systemsIridiumPhotochemistry
A silver halide emulsion comprising radiation sensitive silver halide grains exhibiting a face centered cubic crystal lattice structure containing a hexacoordination complex of an iridium ion in which at least half of the coordination sites in the hexacoordination complex are provided by halogen or pseudohalogen ligands, and at least one coordination site is provided by a ligand comprising a azole ring containing a chalcogen atom and a nitrogen atom, wherein the azole ring is substituted at the 5-position with a halide ion. The invention provides emulsions containing with a preferred class of iridium dopants which are especially useful for improving reciprocity performance in silver halide emulsions with minimal or no impact on other aspects of photographic performance. These dopants give a superior balance of reciprocity and other photographic properties compared to other iridium dopants exemplified in the prior art.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Oxide, method of preparing the same, solid electrolyte including the oxide, and electrochemical device including the oxide
PendingUS20220158229A1Improve ionic conductivityImprove methodFinal product manufactureCell electrodesChemical physicsPseudohalogen
Provided are an oxide including a compound represented by Formula 1, a method of preparing the same, a solid electrolyte including the oxide, and an electrochemical device including the oxide:LiaTa2-yAyP1-xMxO8-zXz Formula 1wherein, in Formula 1, M is an element having an oxidation number of +3,A is an element having an oxidation number of +4, +5, or +6, or a combination thereof,when A is an element having an oxidation number of +4, a is 1+y+2x−z,when A is an element having an oxidation number of +5, a is 1+2x−z,when A is an element having an oxidation number of +6, a is 1−y+2x−z,X is a halogen atom or a pseudohalogen, and0≤y<0.6, 0≤x<1, and 0≤z<1, except that x, y and z are 0 at the same time.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Solid electrolyte, preparation method thereof, protected positive electrode comprising same, electrochemical cell and electrochemical device
The invention relates to a solid electrolyte, a preparation method thereof, a protected positive electrode comprising same, an electrochemical cell and an electrochemical device. A solid electrolyte includes a compound represented by Formula 1 or 3, the compound having a glass transition temperature of -30 DEG C or less, and a glass or glass-ceramic structure, AQX-Ga1-zMz1(F1-kClk)3-3zZ3z1 Formula 1, wherein, in Formula 1,Q is Li or a combination of Li and Na, K, or a combination thereof,M is a trivalent cation, or a combination thereof, X is a halogen other than F, pseudohalogen, OH, or a combination thereof, Z is a monovalent anion, or a combination thereof, 1<A<5, 0<=z<=1, 0<=z1<=1, and 0<=k<1, AQX-aMz1Z3z1-bGa1-z(F1-kClk)3-3z Formula 3, wherein, in Formula 3, Q is Li or a combination of Li and Na, K, or a combination thereof; M is a trivalent cation, or a combination thereof, X is a halogen other than F, pseudohalogen, OH, or a combination thereof, Z is a monovalent anion, or a combination thereof, 0<a<=1, 0<b<=1, 0<a+b, a+b=4-A, 1<A<5, 0<=z<1, 0<=z1,=1, and 0<=k<1.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Process for the preparation of aryl alcohols and heteroaryl alcohols
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
A kind of phosphorus anion reagent and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN108910847BPhosphorus anion activity is highLow reaction energySilicon halogen compoundsSodium/potassium compoundsO-Phosphoric AcidStructural formula
The invention discloses a phosphorus anionic reagent as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The phosphorus anionic reagent has the structural formula as shown in the figure I in thespecification, wherein X is any one of elements of aluminum, boron, silicon and titanium, the valence state of X is m, Z is halogen or pseudohalogen, and n is equal to m-1, R<+> is any one of an ammonium positive ion, a sulfur onium ion and a phosphorus onium ion. The preparation method comprises the following step that under the protection of inert gas, a phosphoric acid derivative reacts with areducing agent in an organic solvent so as to prepare the phosphorus anionic reagent, wherein the reducing agent has the structural formula as shown in the figure II in the specification, and in the structural formula of the reducing agent, R1 is any one of hydrogen, C1-6 alkyl, C1-3 alkoxy, phenyl and substituted phenyl. According to the phosphorus anionic reagent as well as the preparation method and application thereof, the preparation process of the phosphorus anionic reagent is simple, the obtained phosphorus anionic reagent is high in activity and can be applied to prepare a compound containing any one or more of chemical bonds such as a P-C bond, a P-S bond, a P-F bond and a P-H bond, the range of synthesized phosphorus compounds is wide, the use of phosphorus trichloride can be avoided, and the the phosphorus anionic reagent as well as the preparation method and application thereof are green, environmentally friendly, safe and efficient.
Owner:武汉中科先进材料科技有限公司
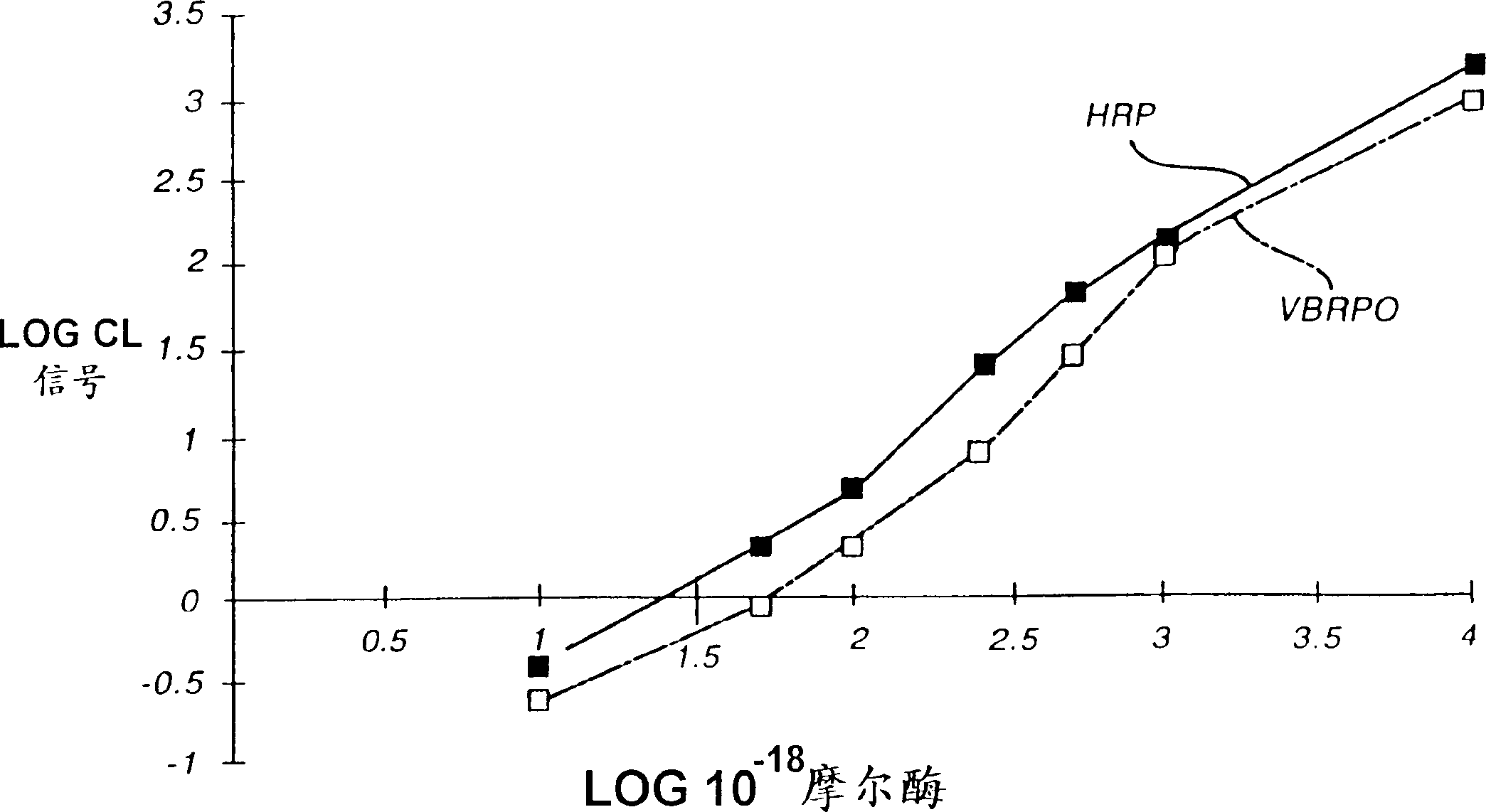
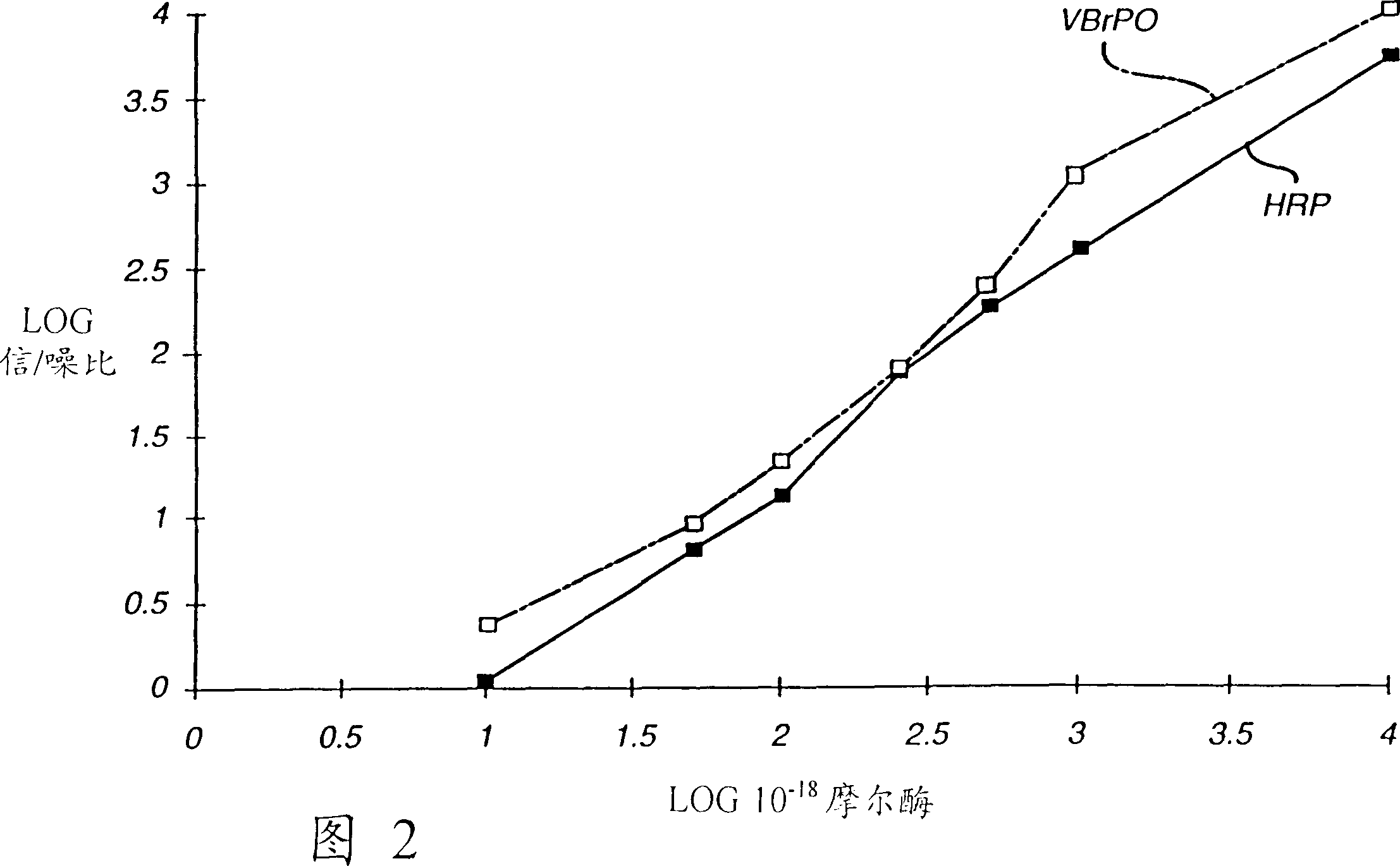
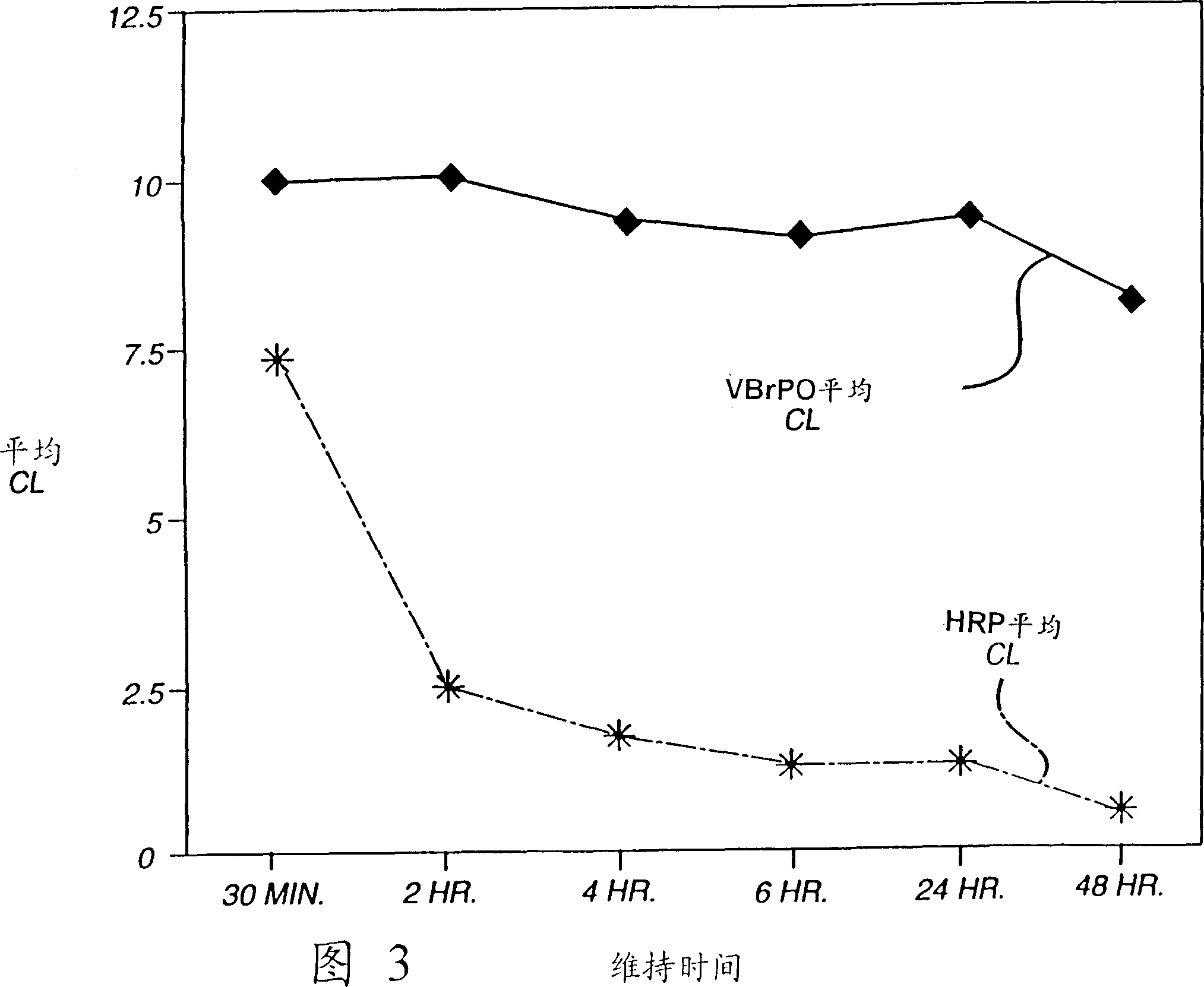
Analytical element and method for determination of specific binding ligand using vanadium bromoperoxidase as signal-generating enzyme
InactiveCN1113105CHigh sensitivityRapid detectionMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementVanadium bromoperoxidasePseudohalogen
An analytical element can be used to sensitively and rapidly detect a wide variety of specific binding ligands in either a competitive or sandwich assay format. The assays are carried out using a vanadium bromoperoxidase-labeled immunoreactant and a chemiluminescent signal-providing wash composition which comprises a 2,3-dihydro-1,4-phthalazinedione derivative; a halogen, pseudohalogen, halogen-providing source or pseudohalogen-providing source; and a peroxide or a peroxide-generating reagent composition.
Owner:ORTHO-CLINICAL DIAGNOSTICS
Phosphorus anionic reagent as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108910847APhosphorus anion activity is highLow reaction energySilicon halogen compoundsSodium/potassium compoundsPhosphoric acidStructural formula
The invention discloses a phosphorus anionic reagent as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The phosphorus anionic reagent has the structural formula as shown in the figure I in thespecification, wherein X is any one of elements of aluminum, boron, silicon and titanium, the valence state of X is m, Z is halogen or pseudohalogen, and n is equal to m-1, R<+> is any one of an ammonium positive ion, a sulfur onium ion and a phosphorus onium ion. The preparation method comprises the following step that under the protection of inert gas, a phosphoric acid derivative reacts with areducing agent in an organic solvent so as to prepare the phosphorus anionic reagent, wherein the reducing agent has the structural formula as shown in the figure II in the specification, and in the structural formula of the reducing agent, R1 is any one of hydrogen, C1-6 alkyl, C1-3 alkoxy, phenyl and substituted phenyl. According to the phosphorus anionic reagent as well as the preparation method and application thereof, the preparation process of the phosphorus anionic reagent is simple, the obtained phosphorus anionic reagent is high in activity and can be applied to prepare a compound containing any one or more of chemical bonds such as a P-C bond, a P-S bond, a P-F bond and a P-H bond, the range of synthesized phosphorus compounds is wide, the use of phosphorus trichloride can be avoided, and the the phosphorus anionic reagent as well as the preparation method and application thereof are green, environmentally friendly, safe and efficient.
Owner:武汉中科先进材料科技有限公司
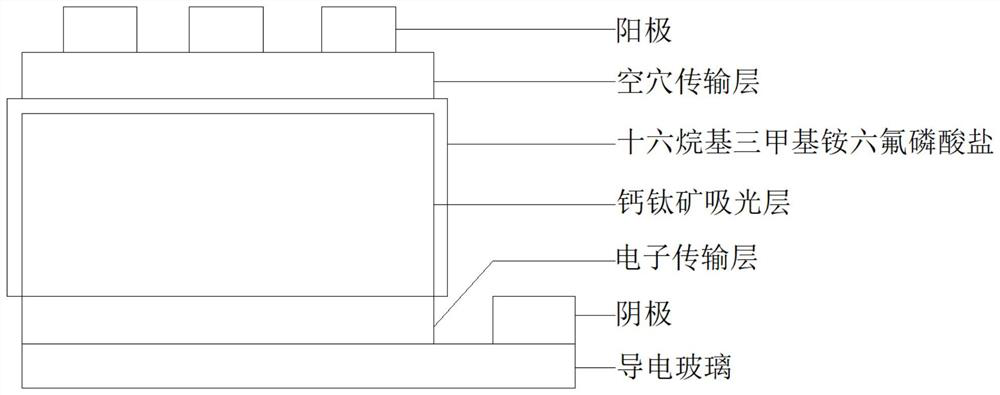
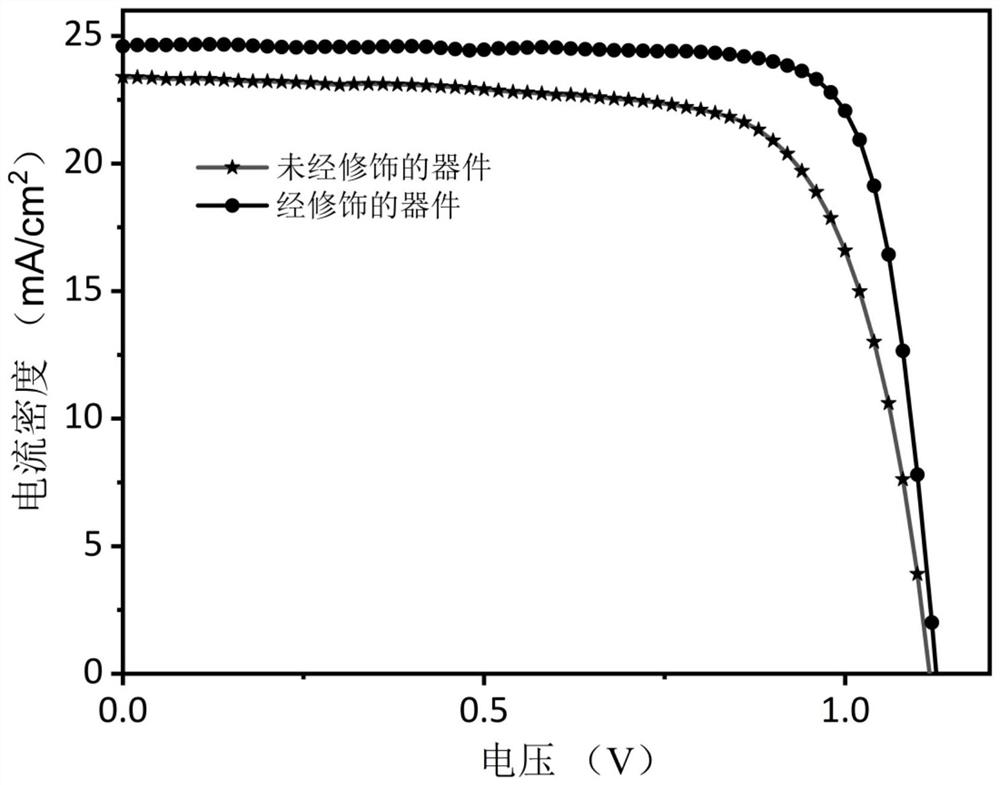
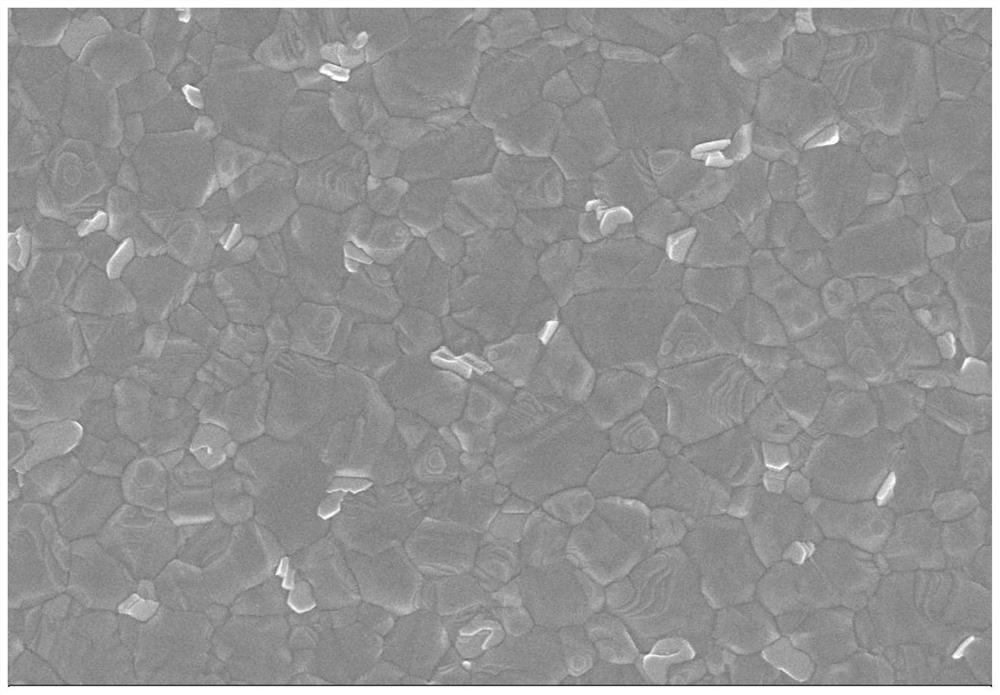
Interface modification method for improving environmental stability of perovskite solar cell
PendingCN114566597AGood environmental stabilityImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHole transport layerAbsorption layer
The invention provides an interface modification method for improving the environmental stability of a perovskite solar cell. The interface modification method comprises the following steps: cleaning an ITO conductive glass substrate; preparing a SnO2 electron transport layer on the ITO conductive glass substrate; preparing a perovskite precursor solution; preparing the perovskite precursor solution on the electron transport layer through a spin-coating method, and then annealing to prepare a perovskite light absorption layer; the preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium hexafluorophosphate in an isopropanol solution to prepare an interface modifier precursor solution; spin-coating the surface of the perovskite thin film with the interface modifier precursor solution, and then annealing; preparing a hole transport layer on the perovskite thin film; and evaporating an electrode on the hole transport layer. According to the invention, the pseudo-halogen molecules and the long-chain organic cations with super-strong hydrophobicity are introduced for interface modification, so that the surface defects of the perovskite thin film can be effectively reduced, the surface hydrophobicity of the thin film is improved, and the stability and efficiency of the perovskite solar cell are enhanced.
Owner:安徽速牛智能科技有限公司
Process for making a fluoropolymer having nitrile end groups
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Oxide, method for preparing same, protected positive electrode, electrochemical device, and electrochemical cell
Provided are an oxide including a compound represented by Formula 1, a method for preparing the same, a protected positive electrode, an electrochemical device, and an electrochemical cell. Wherein, in Formula 1, M is an element having an oxidation value of + 3, A is an element having an oxidation value of + 4, + 5, or + 6, or a combination thereof, when A is an element having an oxidation value of + 4, a is 1 + y + 2x-z, when A is an element having an oxidation value of + 5, a is 1 + 2x-z, when A is an element having an oxidation value of + 6, a is 1-y + 2x-z, X is a halogen atom or pseudo-halogen, and 0 < = ytt; 0.6, 0 < = xlt; 1, and 0 < = zlt; and x, y and z are 0 at the same time. The formula 1 is LiaTa (2-y) AyP (1-x) MxO (8-z) Xz.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
4, 4′ disubstituted 4H-cyclopentadithiophene and new methods for synthesizing the same
The present preferred embodiments relate to a method for the synthesis of a compound having the following general formula:the method comprising the step of reacting, in presence of a diprotic acid having a negative pKa, a compound having the general formula:wherein R1 and R2 are organic groups and wherein X and Y are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, chloro, bromo, iodo, boronic acid, boronate esters, borane, pseudohalogen and organotin. It further relates to compounds so obtained and to compounds resulting from the ring closure of compound (II).
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW) +1
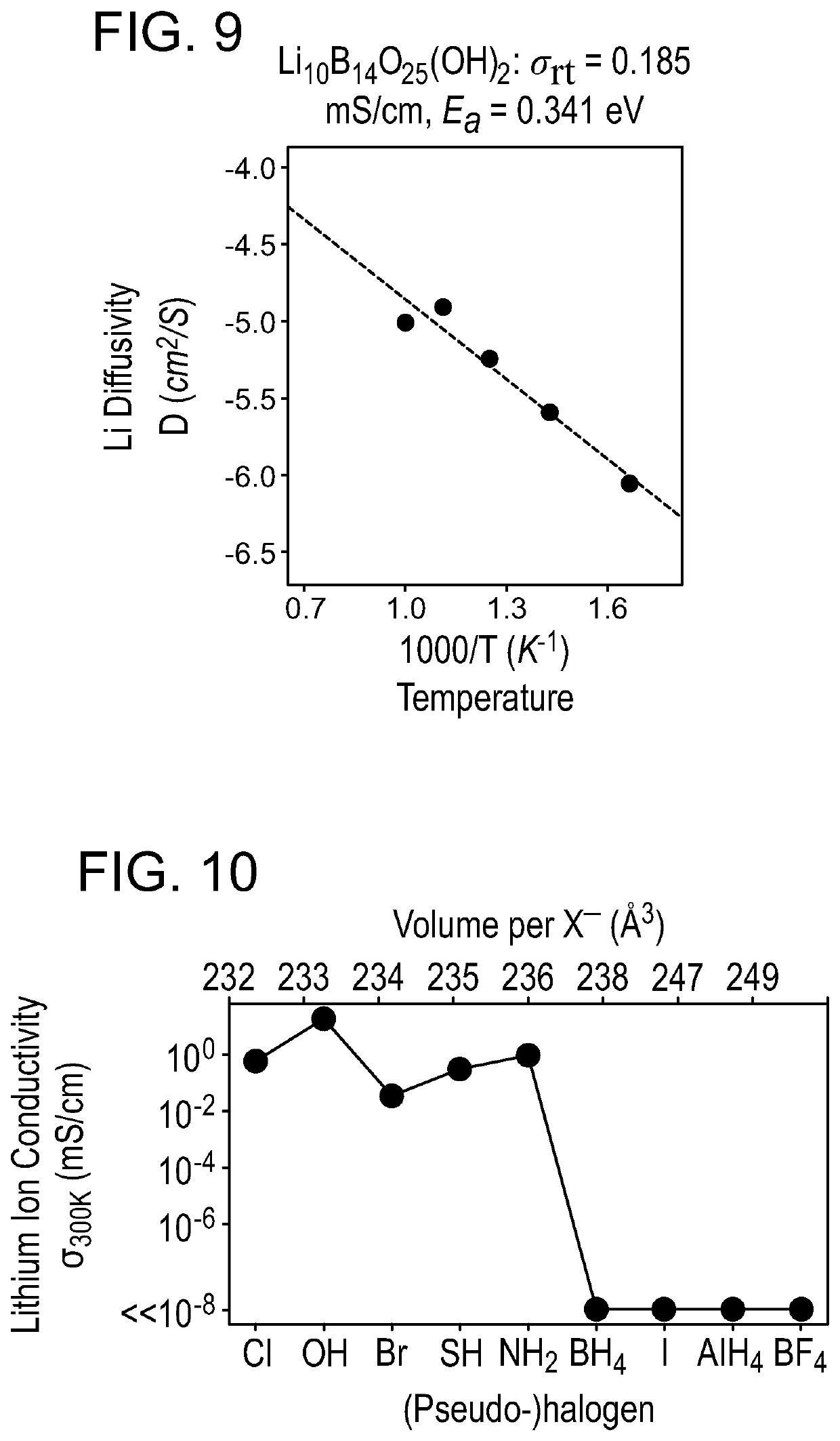
Solid-state lithium-ion conductor and methods of manufacture thereof
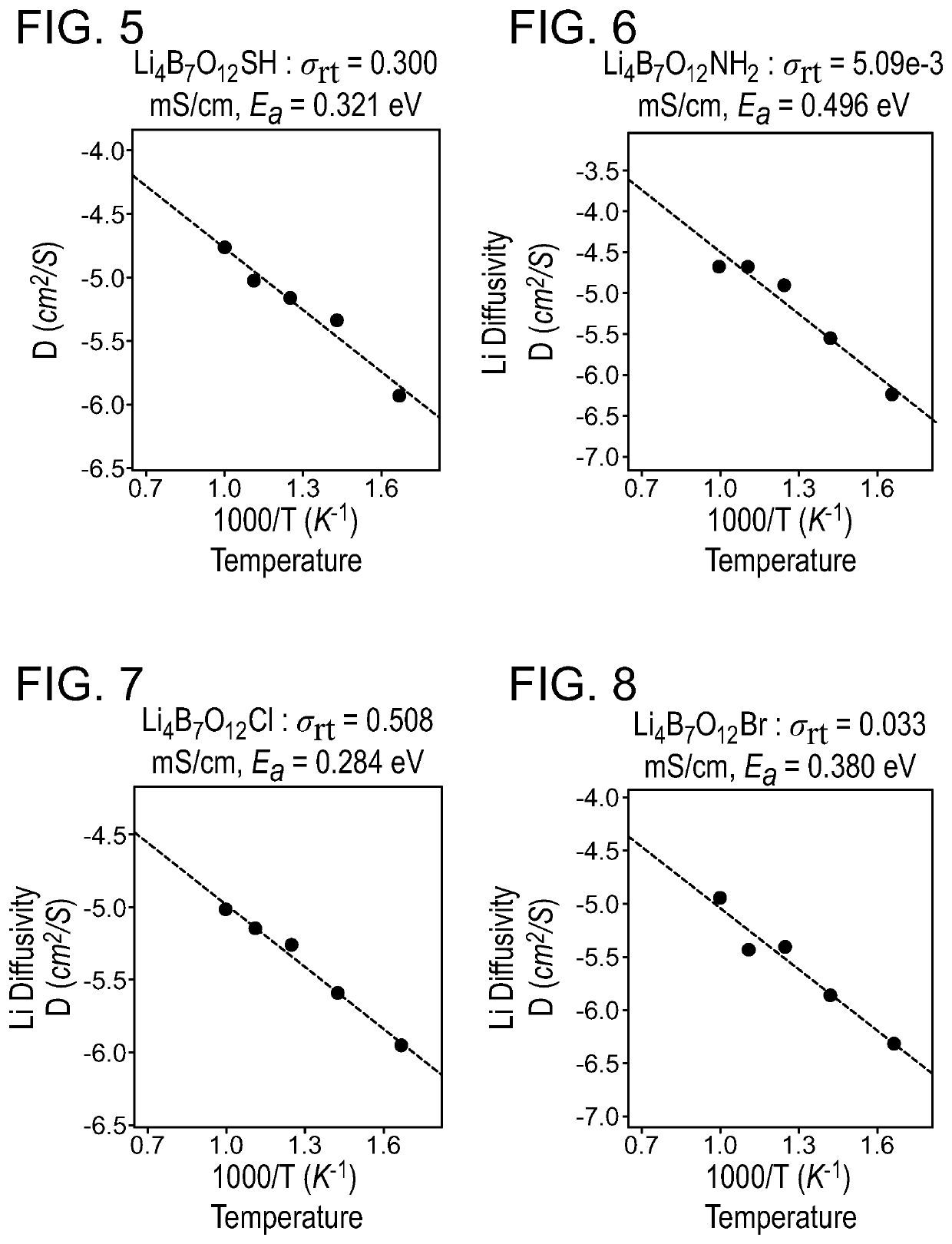
A solid-state ion conductor includes a compound of Formula (I):Li4+xB7O12+0.5xX1aX21−a Formula (I)wherein, in Formula (I), 0≤x≤1; X1 is a pseudohalogen; X2 is a halogen; and 0<a≤1.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Solid electrolyte, electrochemical cell including solid electrolyte, and method of preparing solid electrolyte
PendingCN112786952ASolid electrolytesPhosphorus sulfur/selenium/tellurium compoundsPseudohalogenArgyrodite
The present invention relates to a solid electrolyte, an electrochemical cell including solid electrolyte, and a method of preparing the solid electrolyte. The solid electrolyte includes a compound represented by Formula 1: Formula 1 (Li1-aMa)7-d+xPS6-d-x+kNxXdwherein, in Formula 1, M is Na, K, Ca, Fe, Mg, Ag, Cu, Zr, Zn, or a combination thereof; X is Cl, Br, F, I, a pseudohalogen, or a combination thereof; furthermore 0<x<1, 0<=a<1, 0<d<=1.8 and 0<=k<1, and wherein the compound has an argyrodite crystal structure. Formula1 (Li1-aMa)7-d+xPS6-d-x+kNxXd.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Percolation efficiency of the conductivity of electrically conductive adhesives
InactiveCN101602929BNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialPseudohalogenPolymer resin
An electroconductive bonding material is formed as a Modified Electrically Conductive Adhesive (MECA), and consists of a resin matrix and a modified conductive filler. The resin matrix if formed by providing a thermosetting or thermoplastic resin-based polymer resin. The conductive filler is a metal filler material suitable for use as conductive filler for the resin matrix. The metal filler is modified by applying a material selected from one of halogens, pseudohalogens or their precursors.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Oxide, preparation method thereof, solid electrolyte including the oxide, and electrochemical device including the oxide
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
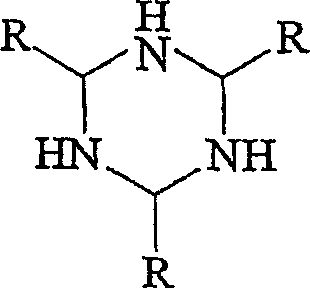
A kind of living/controllable radical polymerization method of water-soluble monomer
The invention discloses a living / controllable free radical polymerization method of a water-soluble monomer, which comprises the following steps: adding a water-soluble monomer, a pseudohalogen initiator, a catalyst and a solvent into a polymerization reaction vessel, and removing the water-soluble monomer with an inert gas Seal the polymerization reaction container after oxygen, and then carry out the polymerization reaction at 20~90°C for 0.5~53 hours, wherein the molar ratio between the water-soluble monomer, the pseudohalogen initiator and the catalyst is 50~1000:1:0.005~0.5 . The present invention makes full use of the special effect between the catalyst copper acetate and the initiator dithiocarbamate, constructs a simple and efficient active / controllable free radical polymerization system in water, and successfully obtains the molecular weight can be designed and the molecular weight distribution is relatively Narrow water-soluble polymers and amphiphilic block copolymers. In addition, the polymerization method of the present invention avoids the use of expensive ligands, which reduces production costs; at the same time, it does not need any additives, which simplifies the polymerization operation.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com