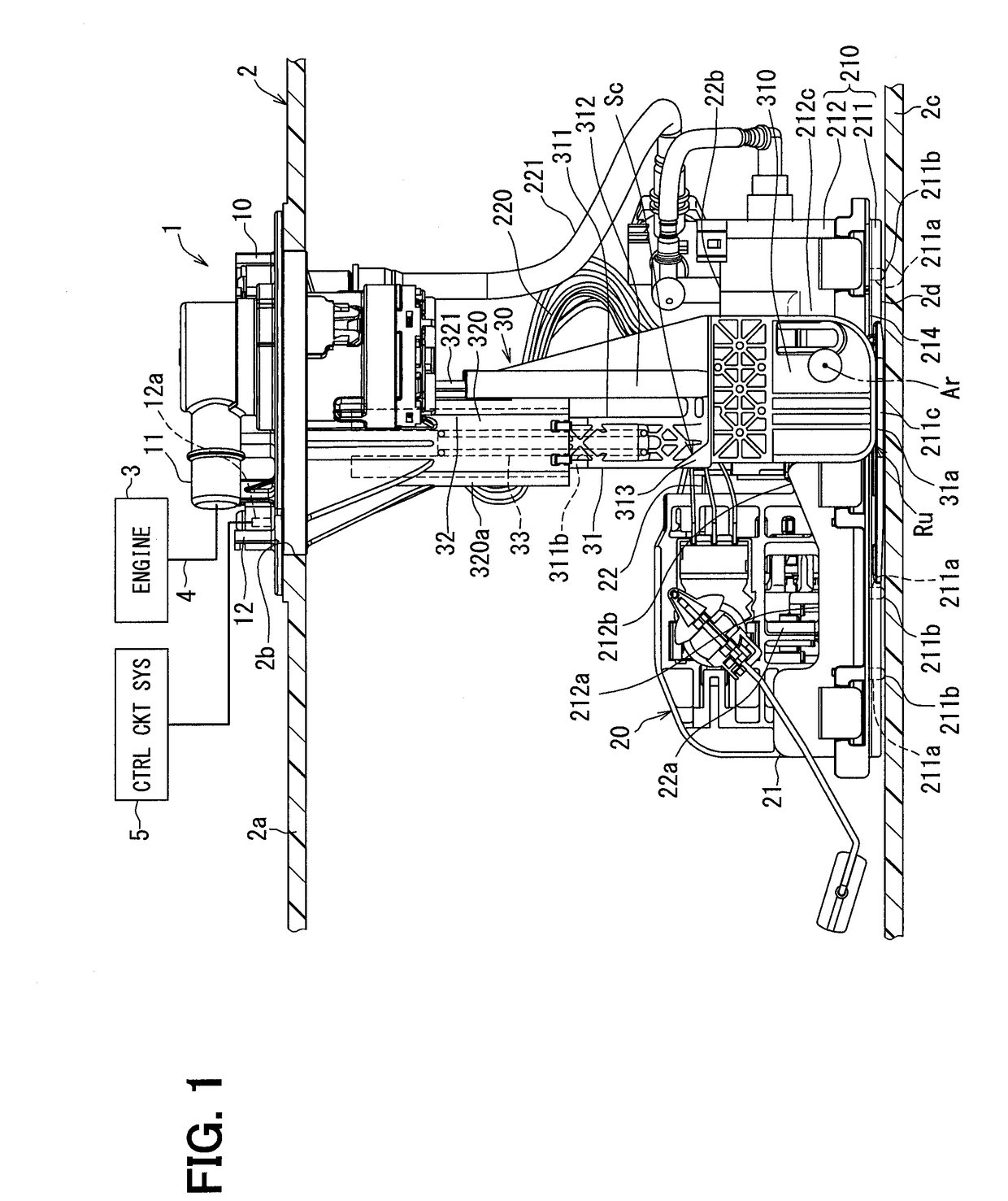
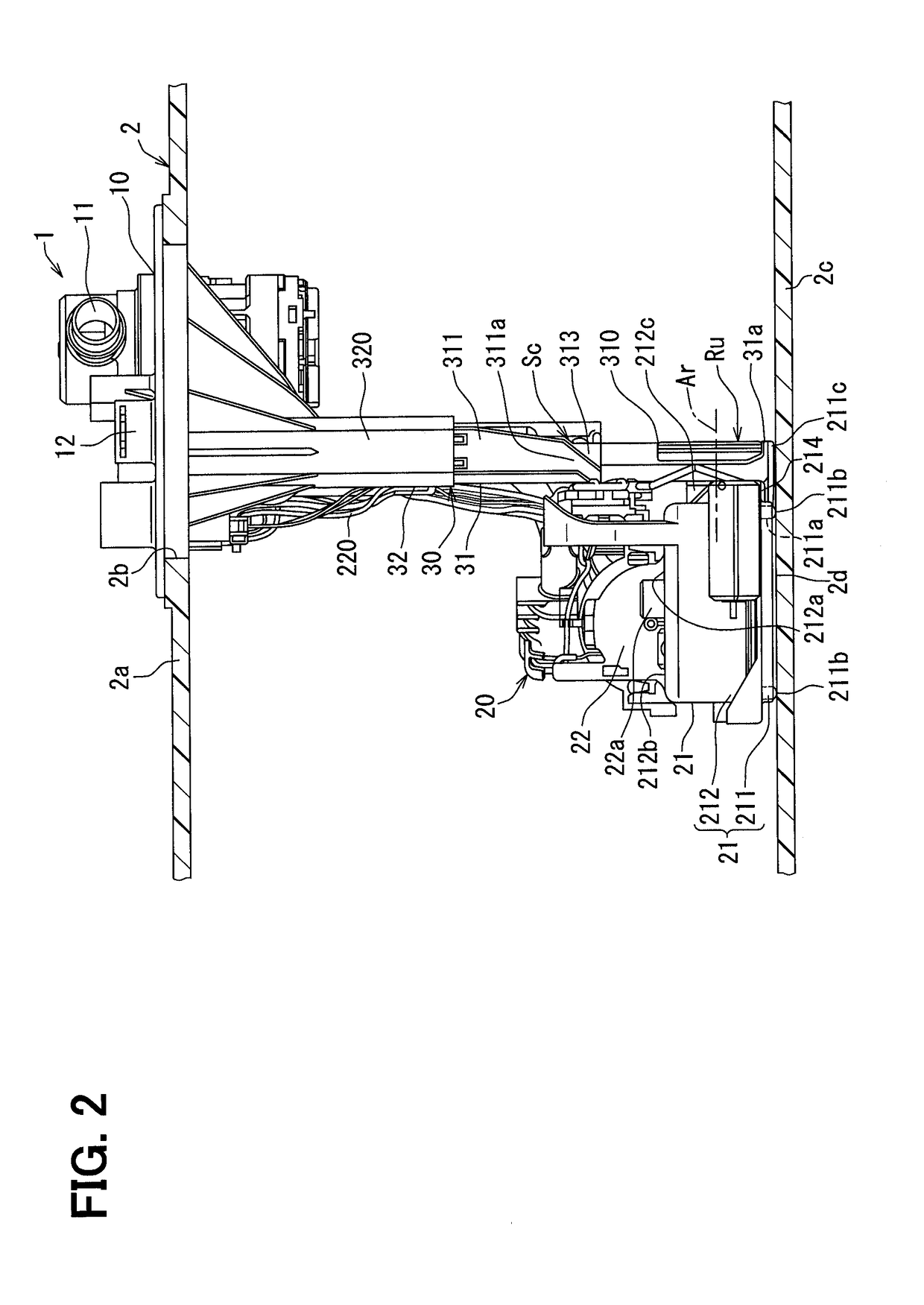
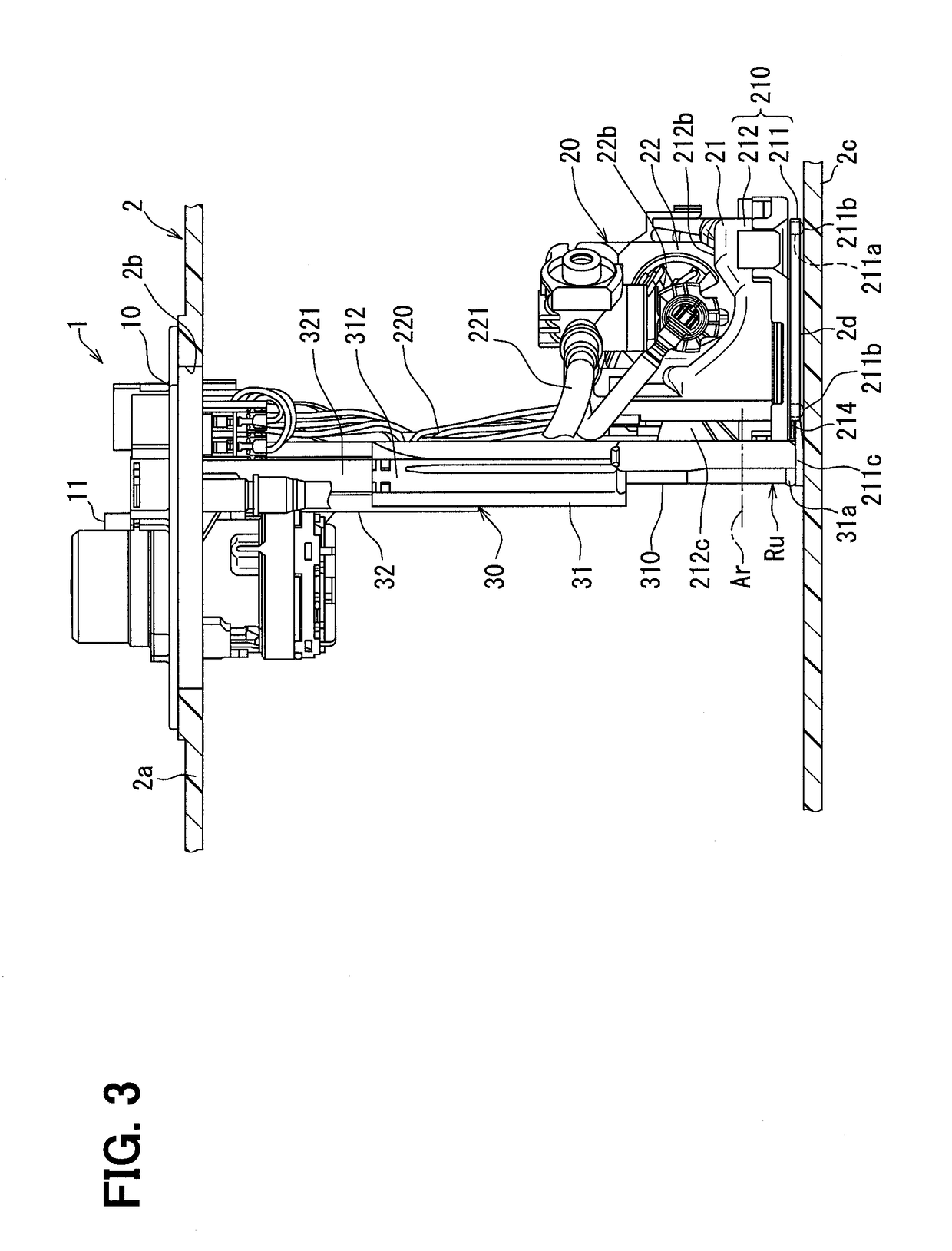
Patents
Literature
113 results about "Section modulus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Section modulus is a geometric property for a given cross-section used in the design of beams or flexural members. Other geometric properties used in design include area for tension and shear, radius of gyration for compression, and moment of inertia and polar moment of inertia for stiffness. Any relationship between these properties is highly dependent on the shape in question. Equations for the section moduli of common shapes are given below. There are two types of section moduli, the elastic section modulus and the plastic section modulus. The section moduli of different profiles can also be found as numerical values for common profiles in tables listing properties of such.
Length-to-waist silhouette(s) of absorbent article(s) comprising beamed elastics
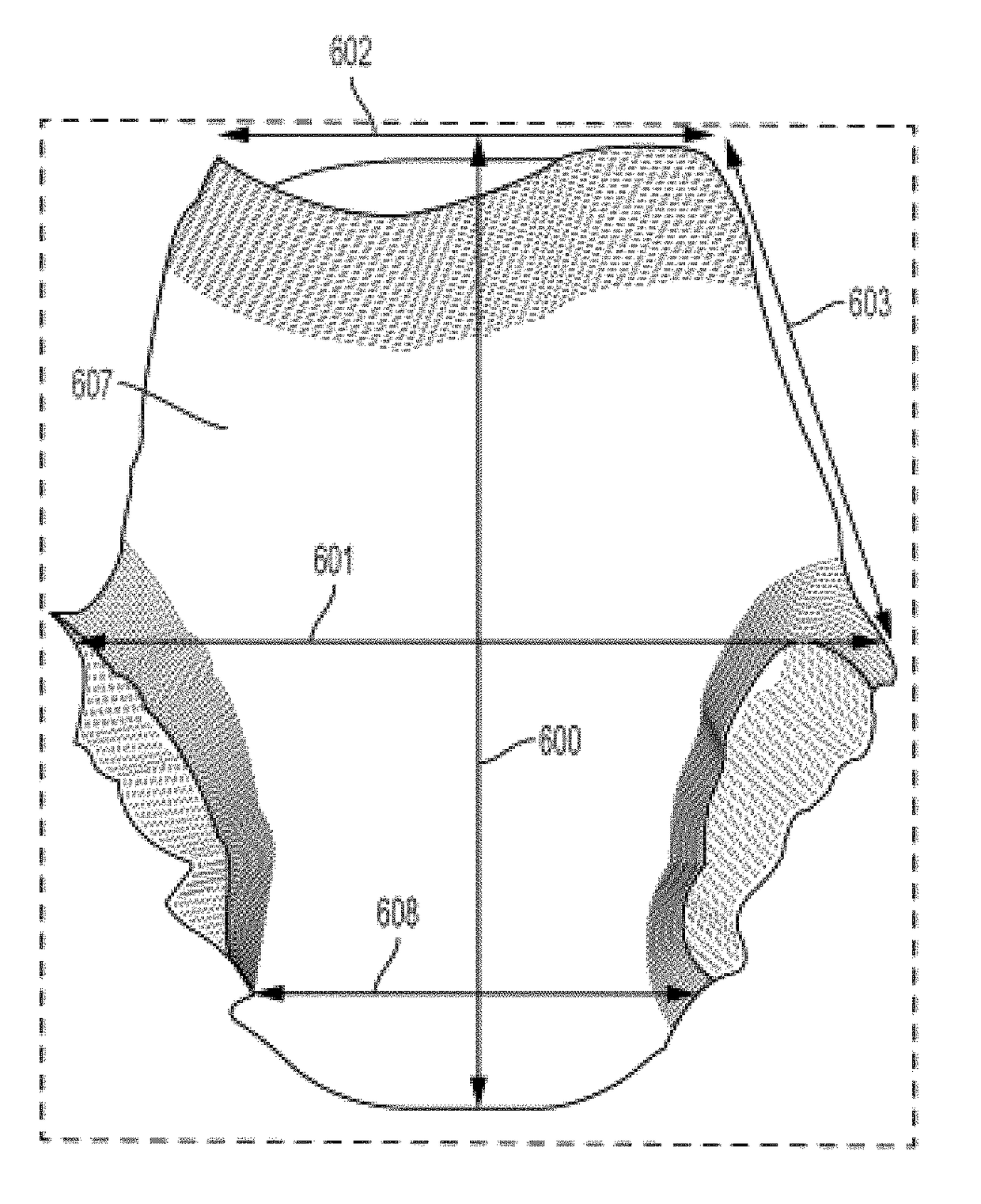
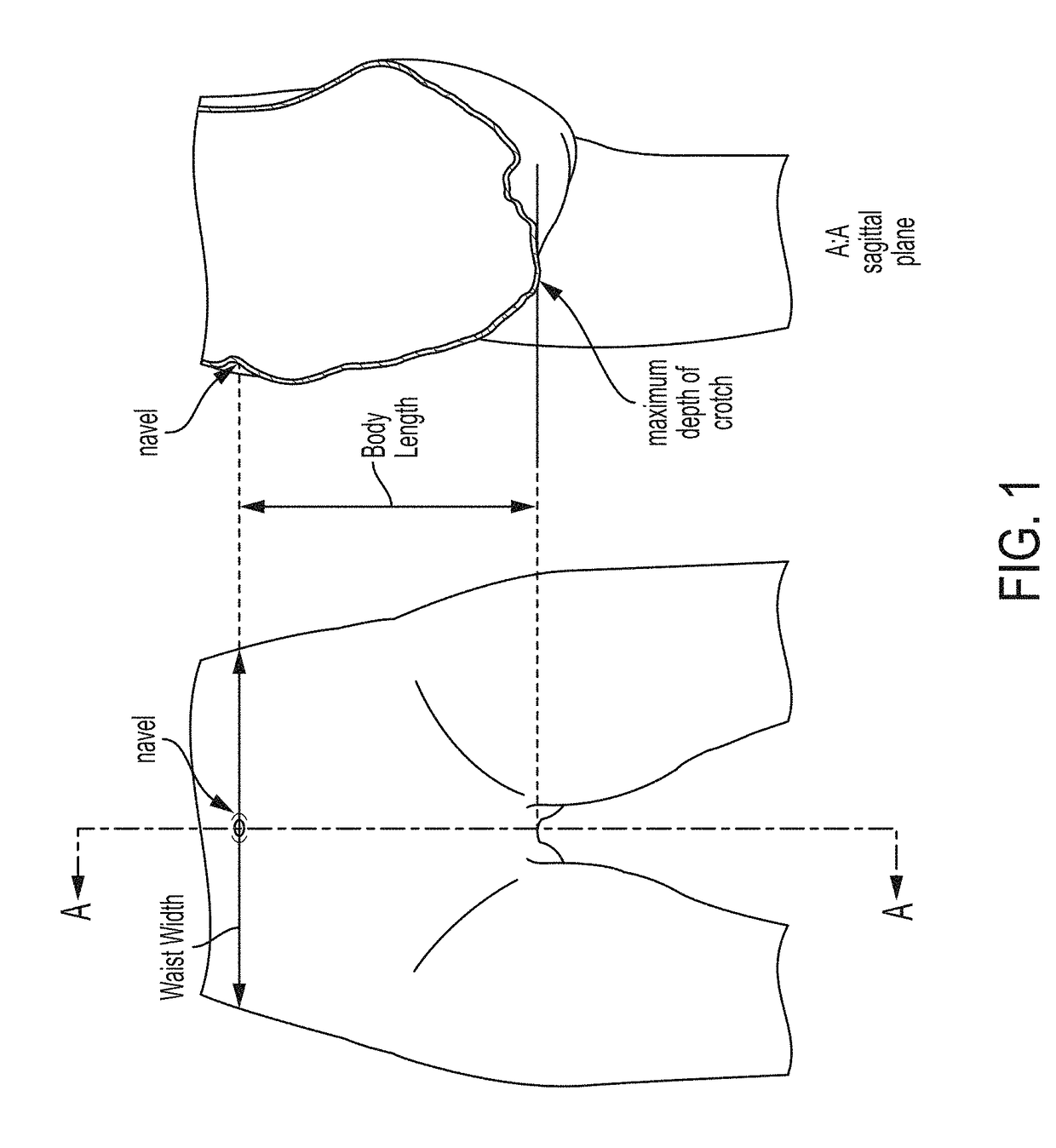
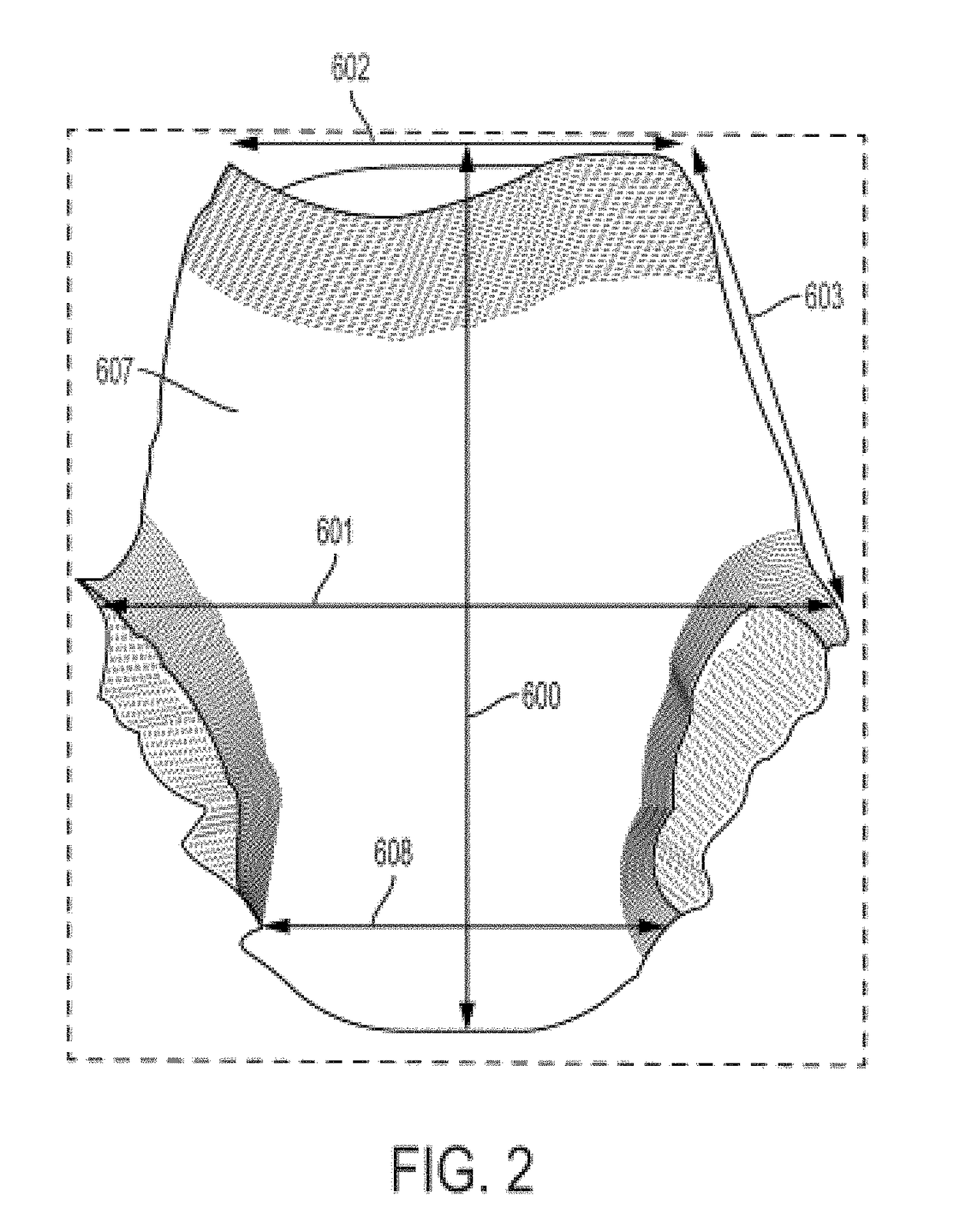
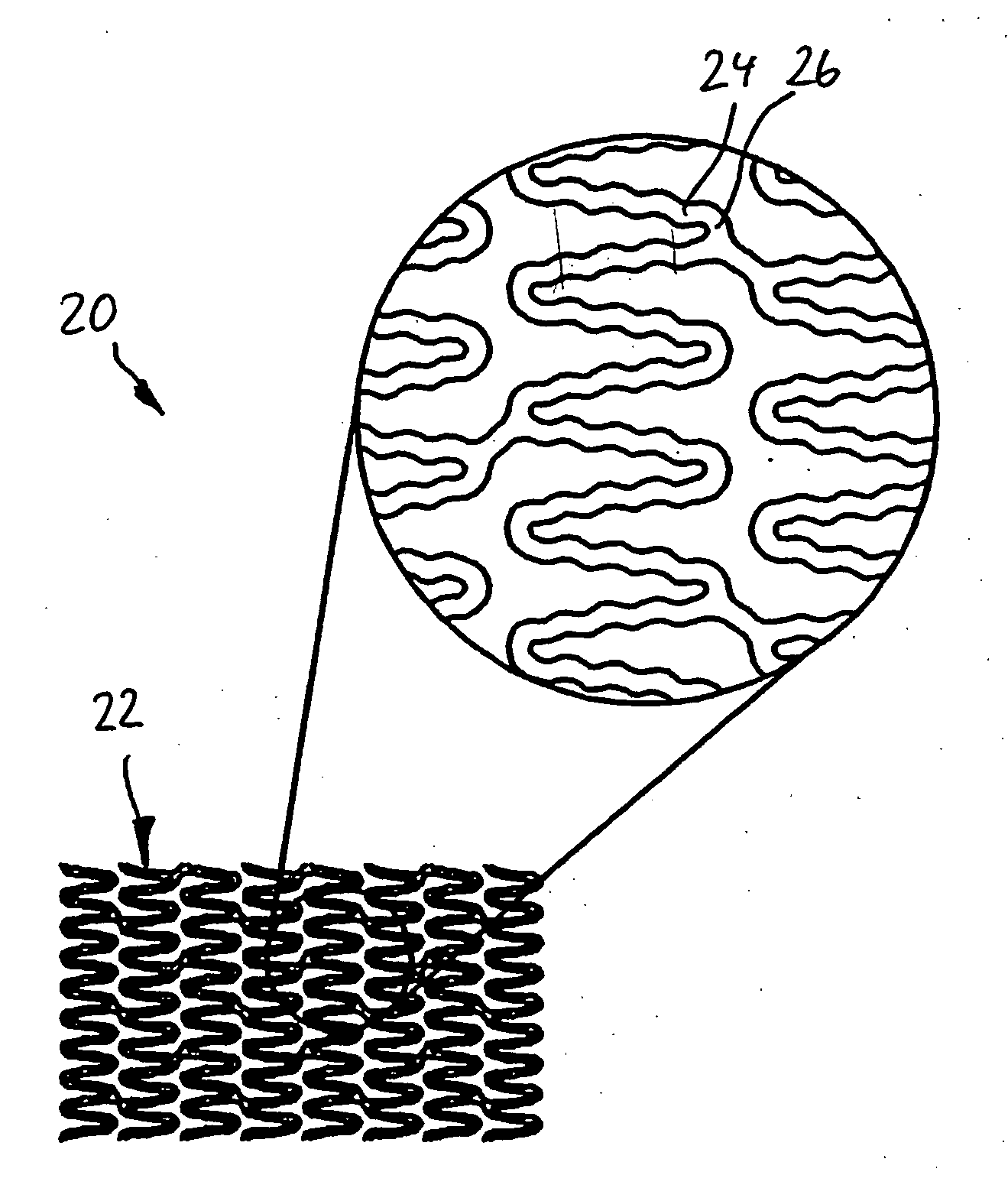
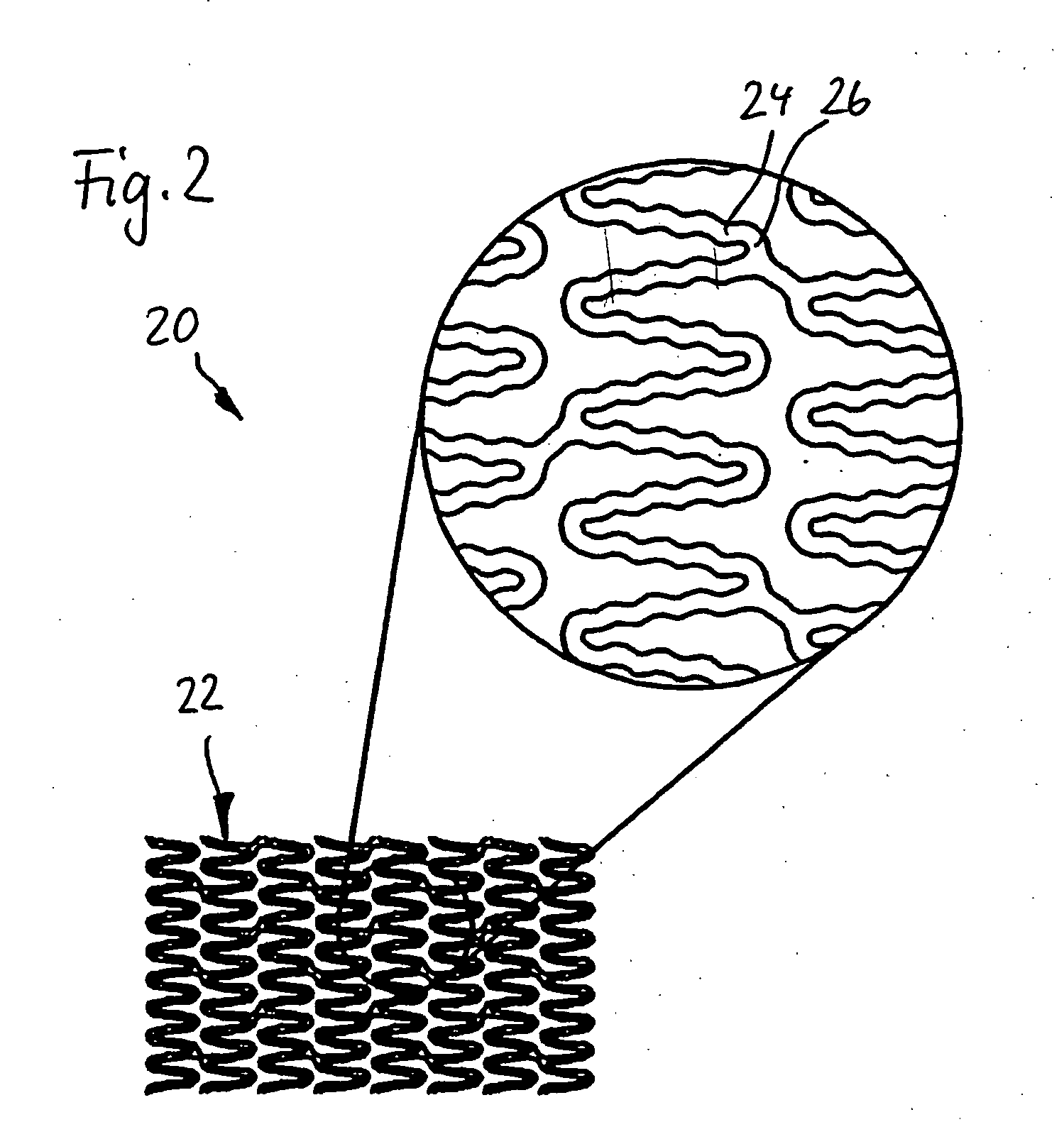
The present disclosure relates to absorbent articles comprising belts comprising one or more pluralities of tightly spaced (less than 4 mm, less than 3 mm, less than 2 mm, and less than 1 mm) and / or low decitex (less than 300, less than 200, less than 100 dtex) and / or low strain (less than 300%, less than 200%, less than 100%) elastics to deliver low pressure less than 1 psi (according to the conditions defined by the Pressure-Under-Strand Test in the Method below) under the elastics, while providing adequate Section-Modulus of (between about 2 gf / mm and 15 gf / mm), resulting in a Product Length-to-Waist Silhouette that is within from about −0.3 to about 0.3 of the Target Body Length-to-Waist Silhouette to make the article conform better to the body of the wearer at a lower Pressure-Under-Strand, even with a loaded core (holding at least 50 mls of liquid), to provide for the advantages described above.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
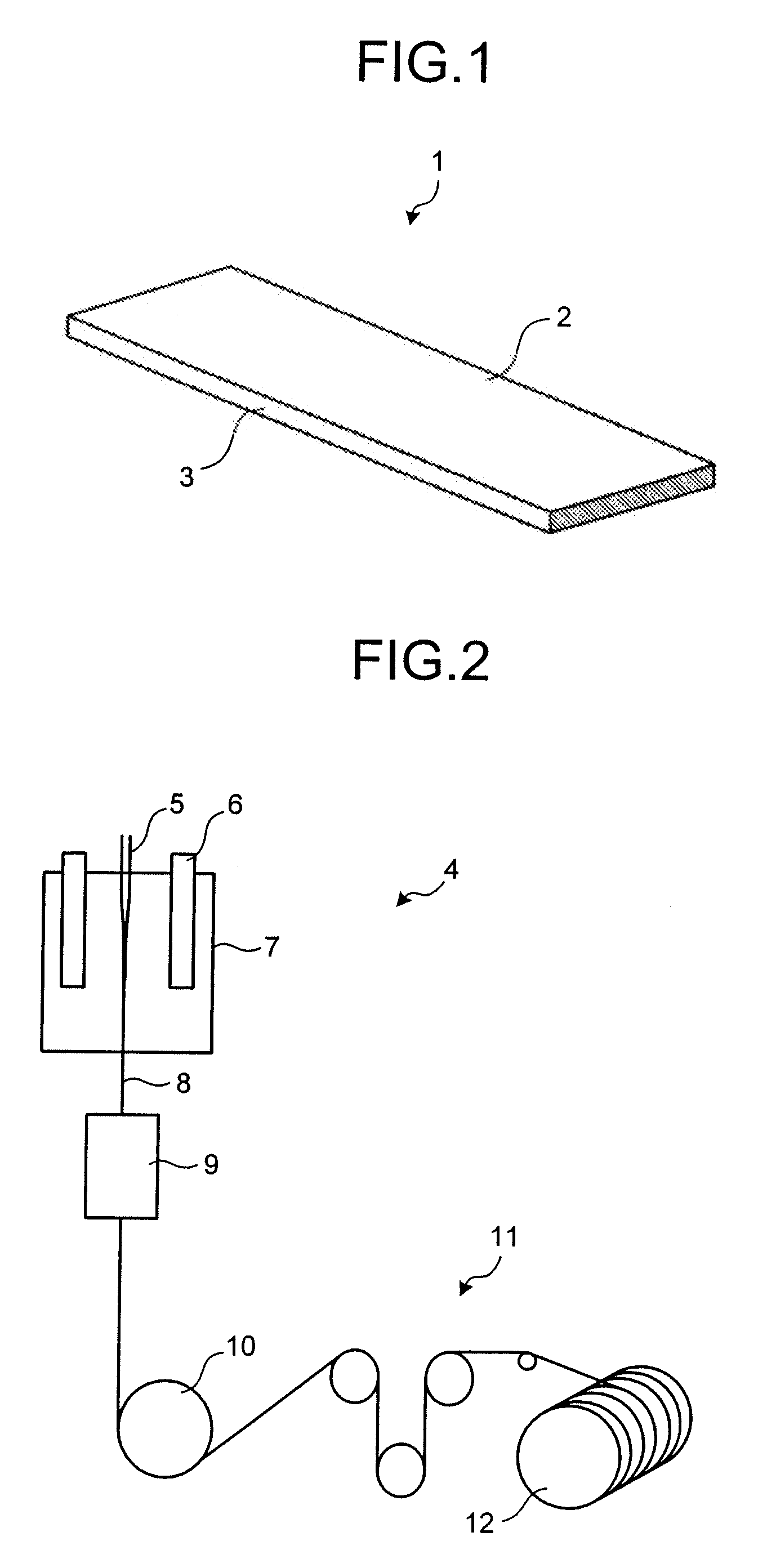
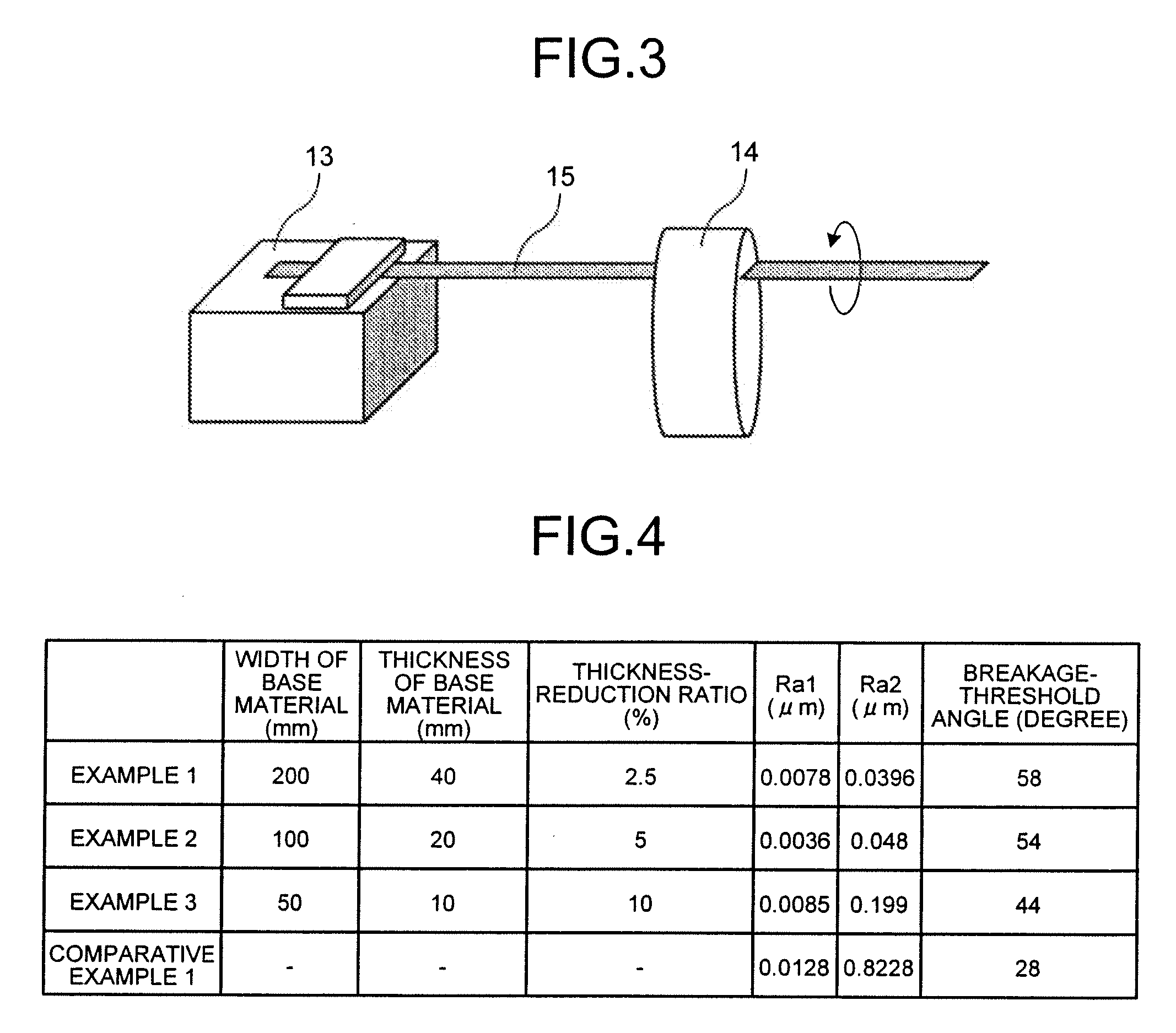
Sheet glass and method for manufacturing sheet glass
InactiveUS20070178281A1Solve problemsSynthetic resin layered productsRecord information storageFlat glassSurface roughness
A sheet glass that has a side surface with an average surface roughness equal to or less than 0.2 μm is provided. Furthermore, a method of manufacturing a sheet glass is provided that includes processing a base-material glass sheet to obtain a sheet glass that has a side surface with an average surface roughness equal to or less than 0.2 μm. Moreover, a method of manufacturing a sheet glass is provided that includes processing a base-material glass sheet so that an average surface roughness of a side surface becomes equal to or less than a predetermined value according to a section modulus of the sheet glass that is to be manufactured.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
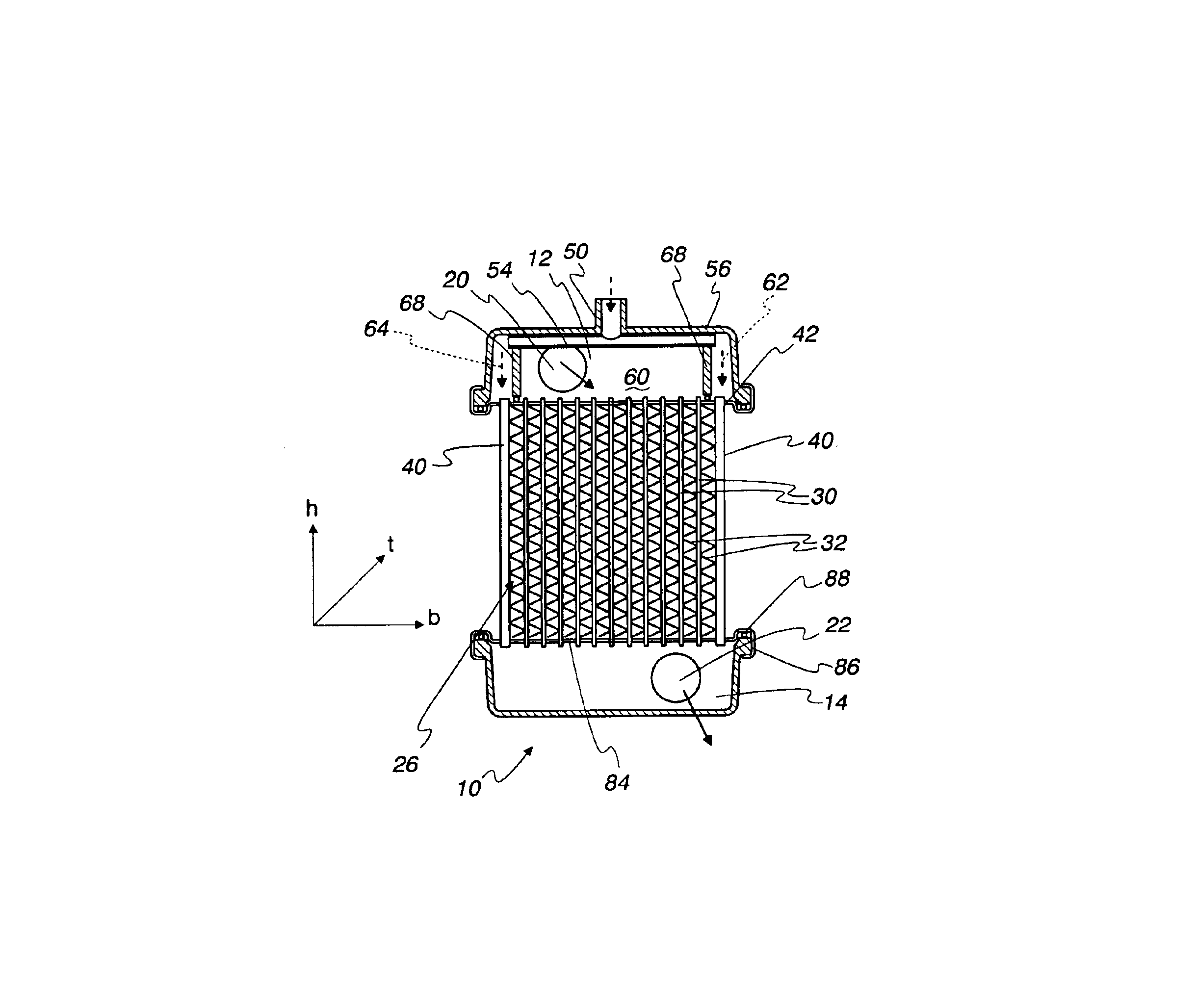
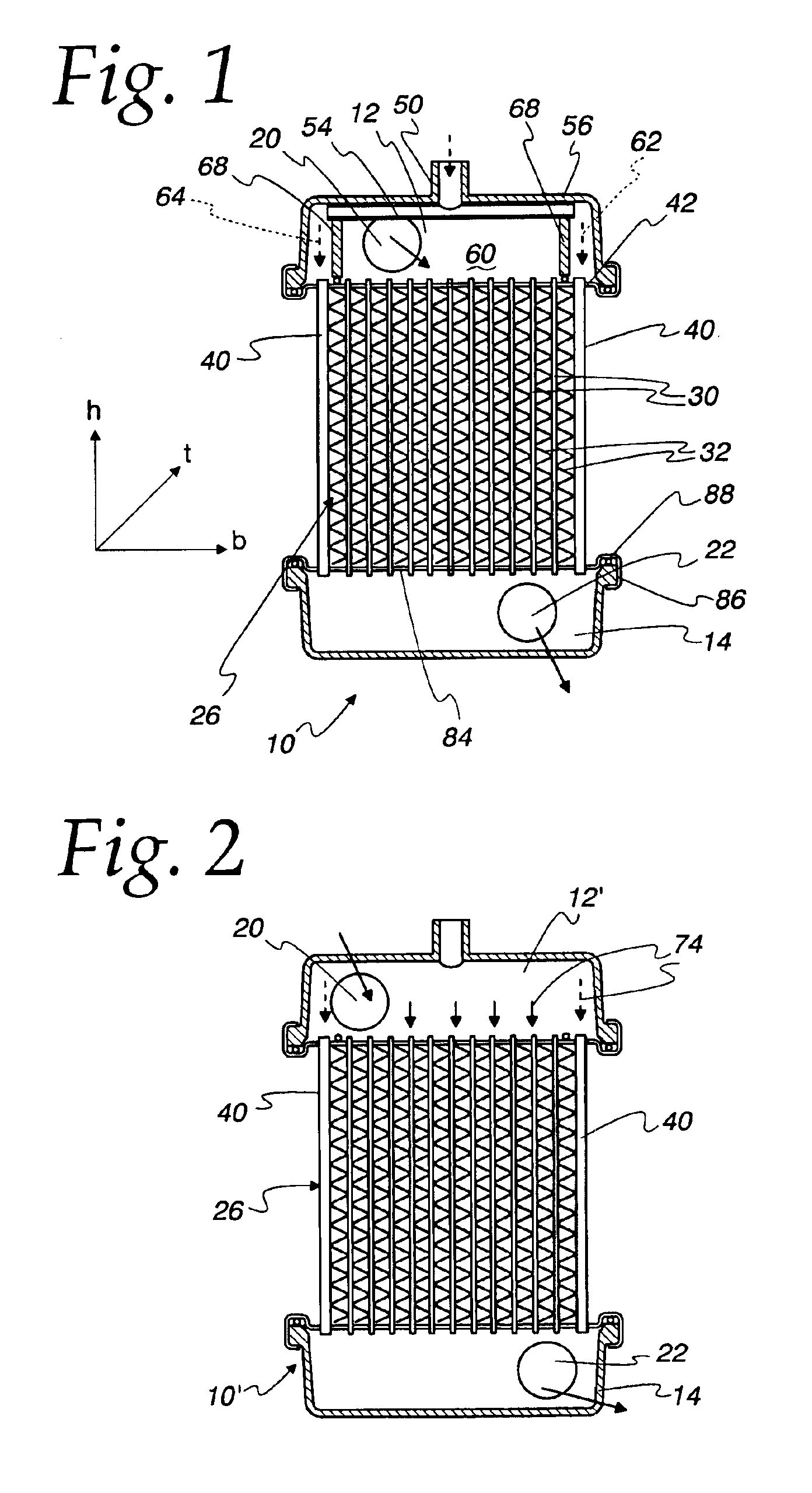
Radiator with side flat tubes
A vehicle radiator including inlet and outlet headers, a soldered core having a plurality of coolant flat tubes joining the inlet header and the outlet header with cooling fins on opposite sides of the coolant flat tubes, and a multifunction flat tube on at least one side of the core. The multifunction flat tube has a greater section modulus than the coolant flat tubes, and is soldered to adjacent cooling fins and the inlet and outlet headers whereby the multifunction flat tube carries coolant from the inlet header to the outlet header. The multifunction flat tubes each also have an inner flow resistance which is substantially smaller than the inner flow resistance of individual coolant flat tubes whereby more coolant flows through each multifunction flat tube than flows through an individual coolant flat tube per unit time.
Owner:MODINE MFG CO
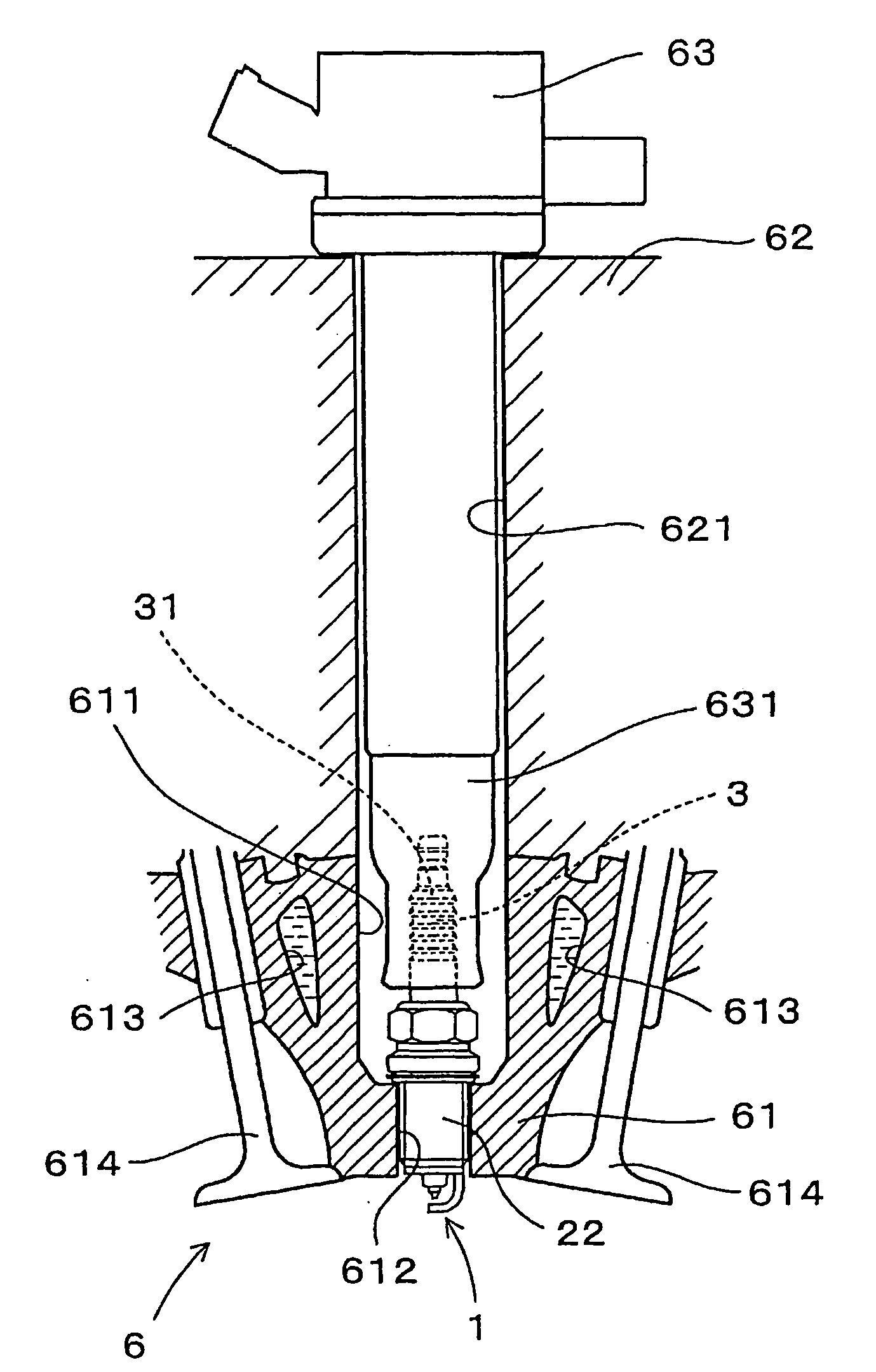
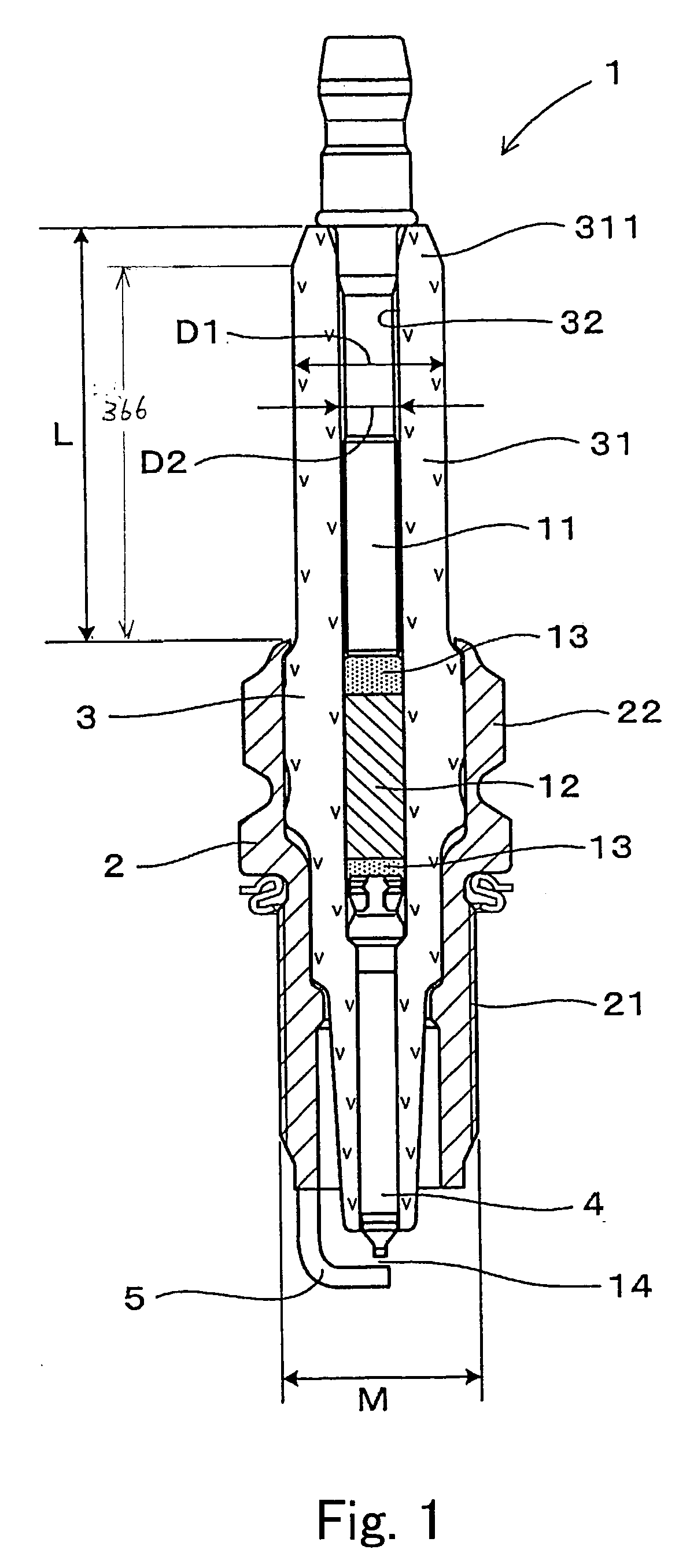
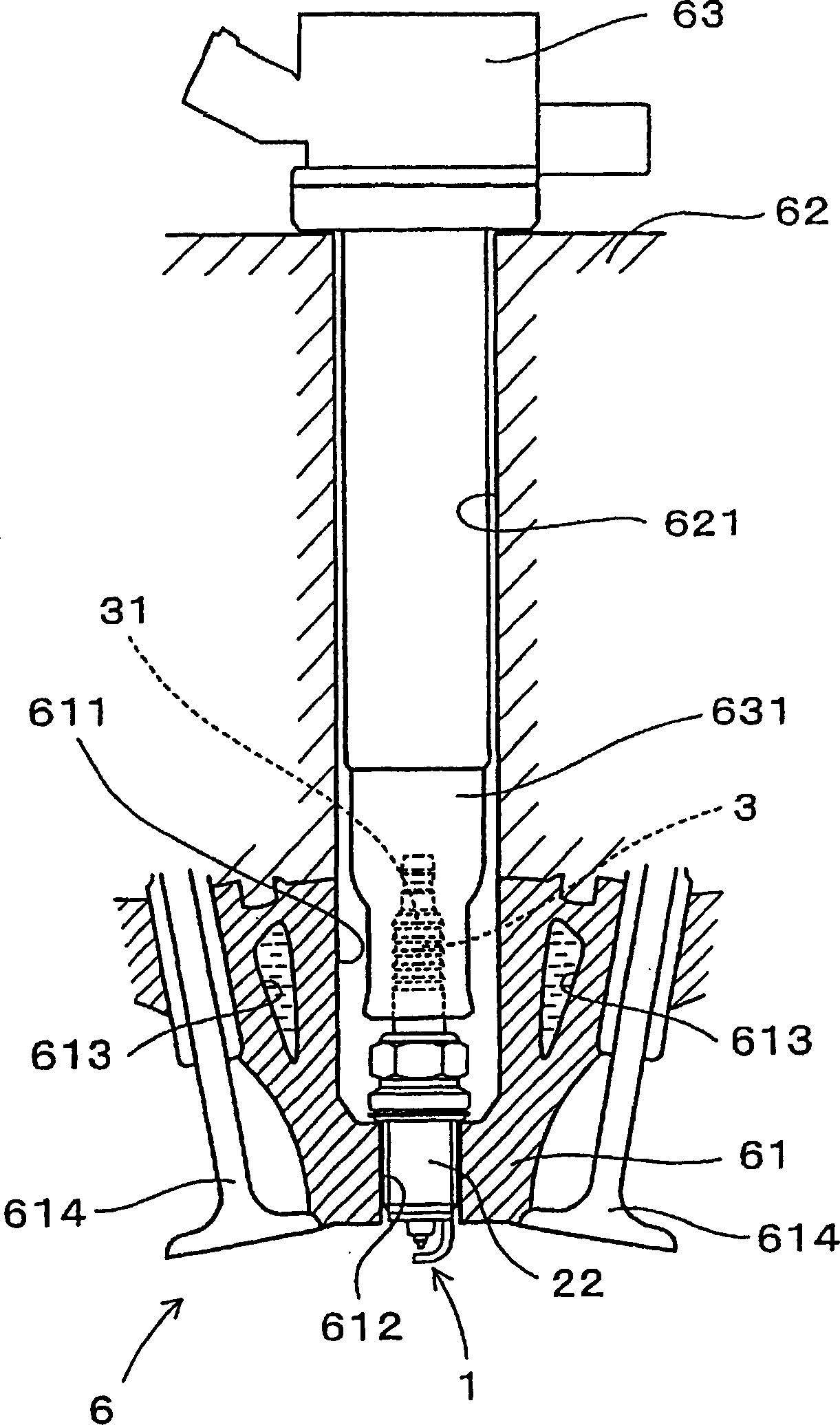
Spark plug with increased durability
InactiveUS20060042610A1Desired strengthSmall sizeSparking plugsMachines/enginesEndurabilityEngineering
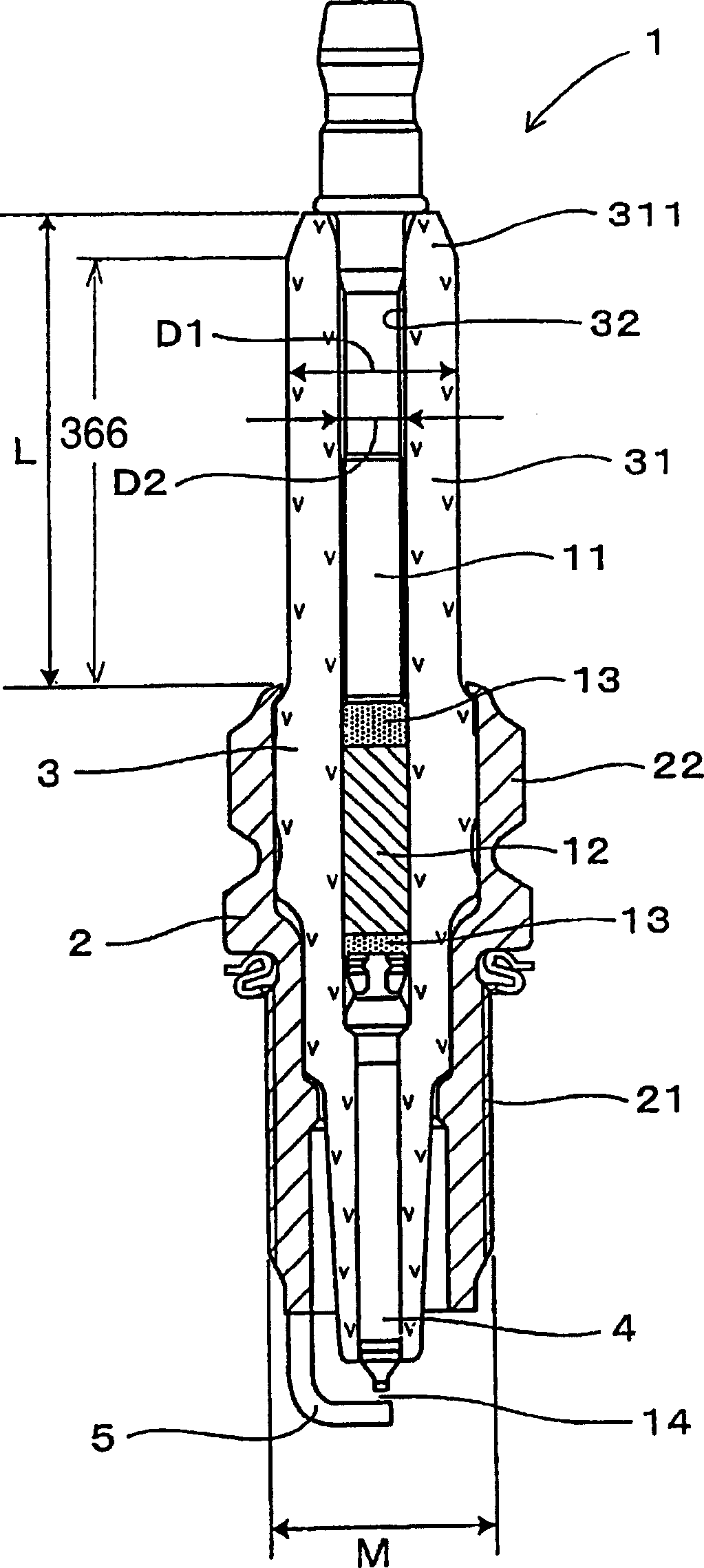
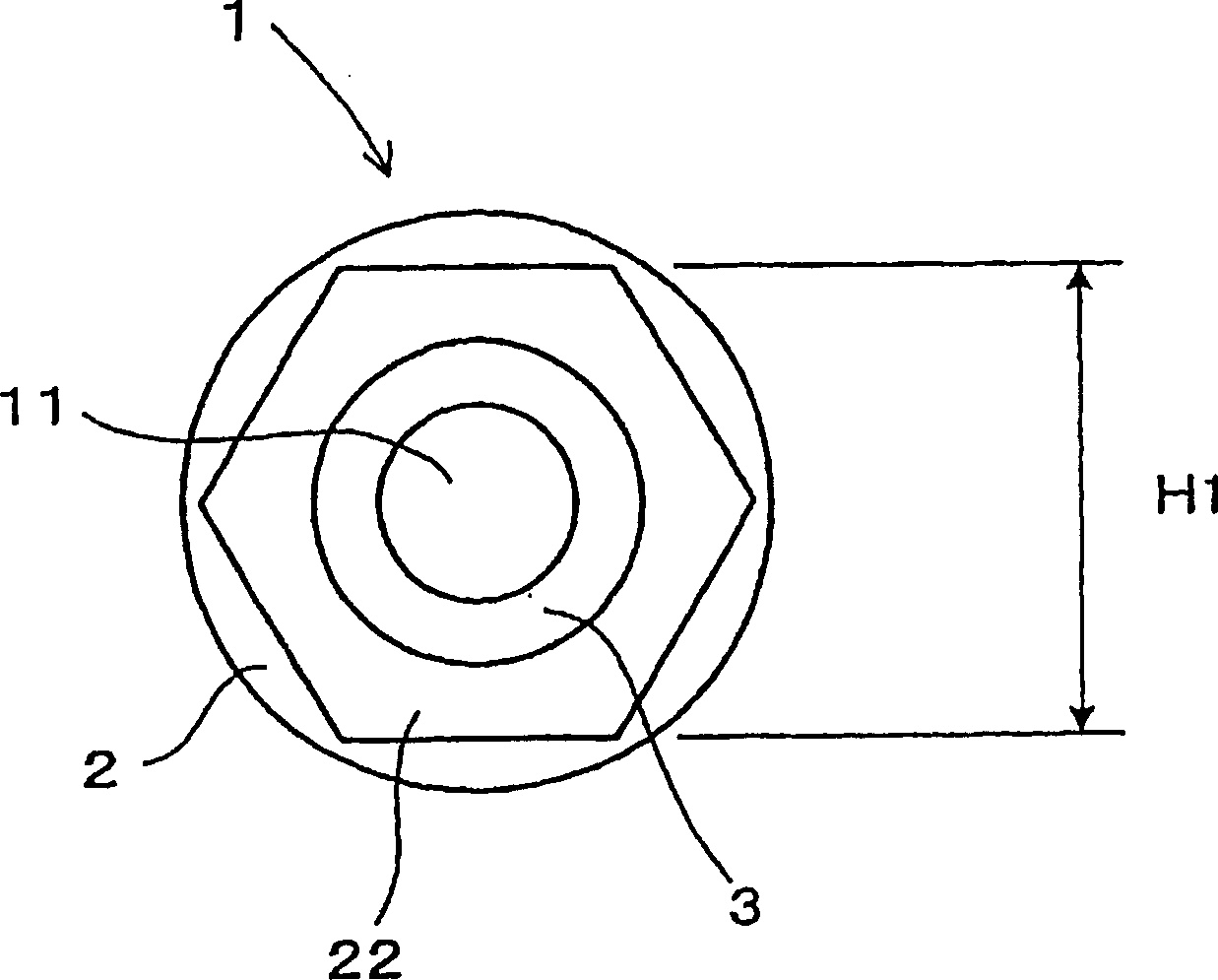
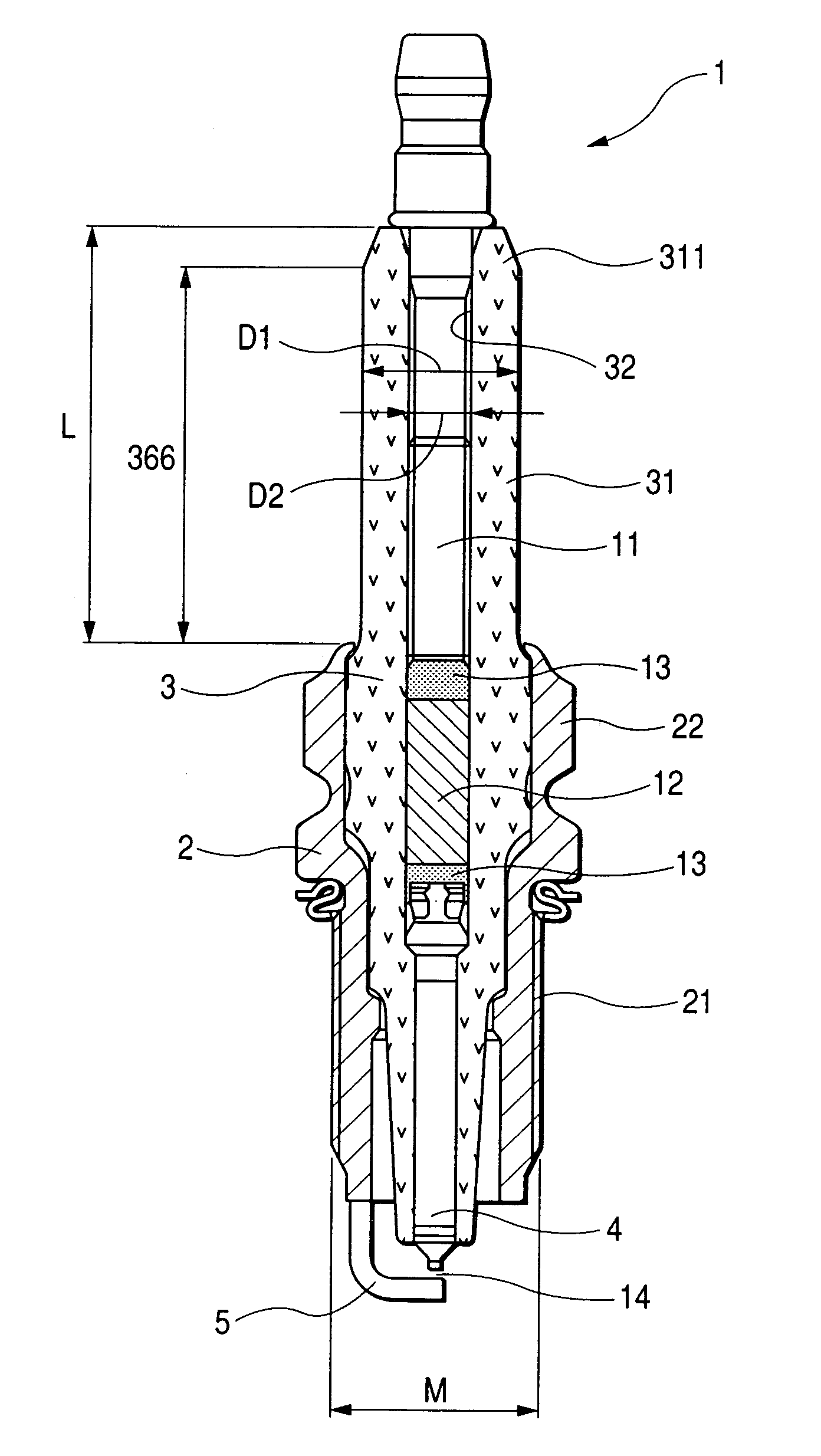
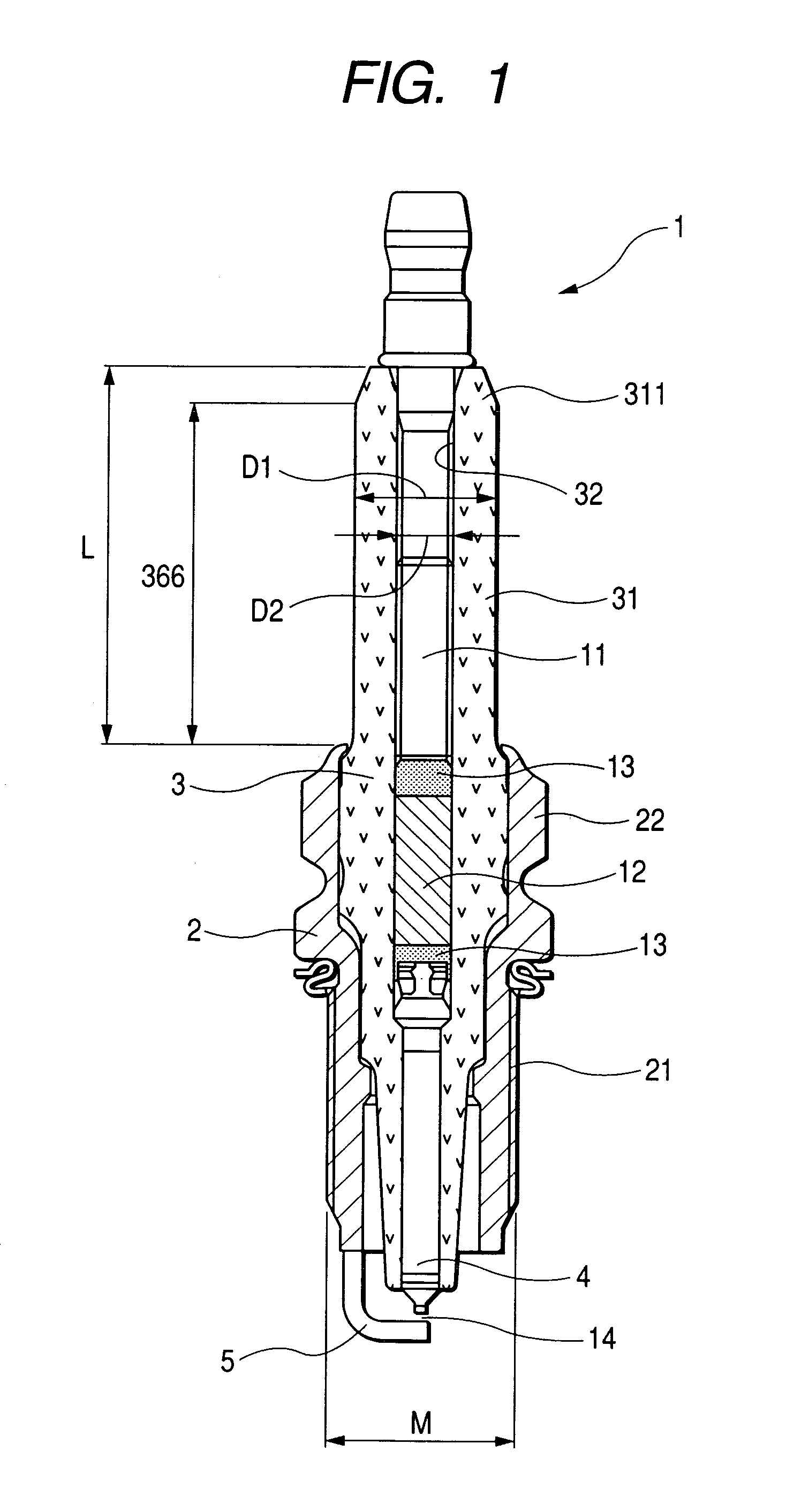
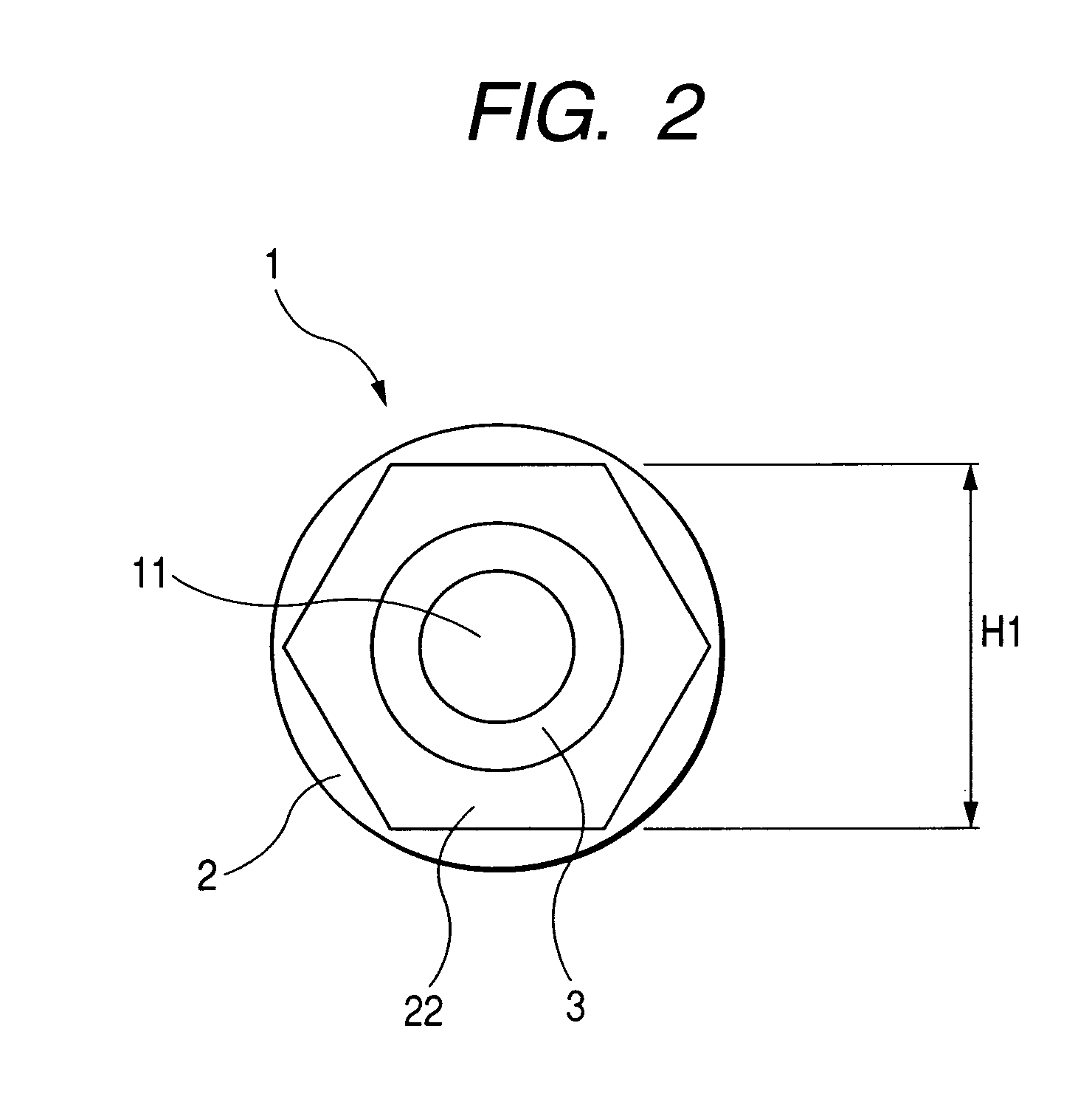
A spark plug is provided which is designed to be compact without sacrificing a mechanical strength of a porcelain insulator. The spark plug includes a metal shell having a base end and a top end. The porcelain insulator is made of a hollow cylinder which includes a body and an insulator head. The body is retained within the metal shell. The insulator head extends from the base end of the metal shell in a lengthwise direction of the porcelain insulator and has a length made up of a major body leading to the body of the porcelain insulator and an end portion lying far away from the body. The major body has an outer diameter D1, an inner diameter D2, and a section modulus Z at a smallest-outer diameter portion thereof which meet relations of 7.1 mm≦D1≦8.8 mm, D2≧2.8 mm, and Z≧33 mm3.
Owner:DENSO CORP
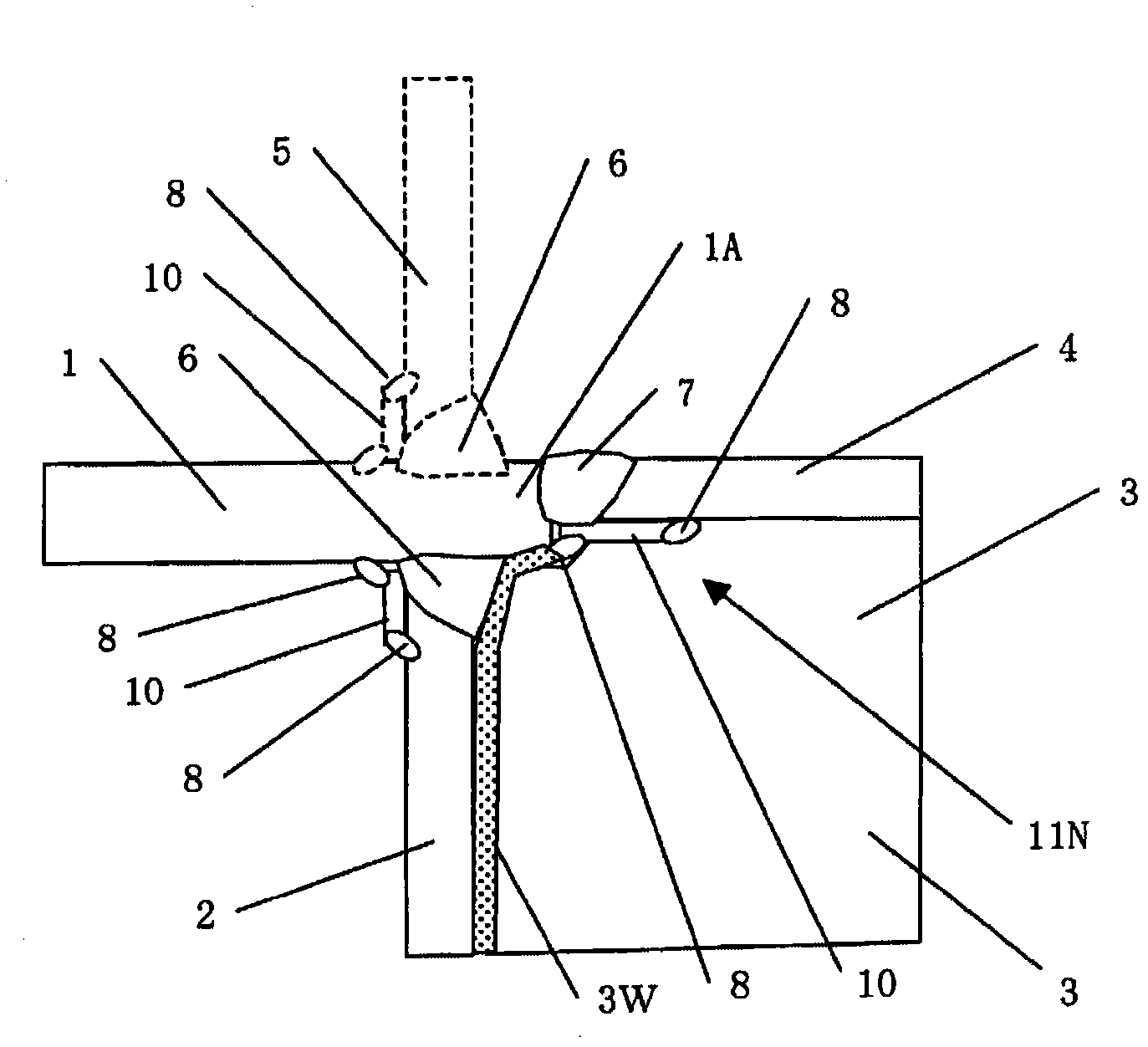
Stent having a bridge structure
InactiveUS20060085059A1Great possible diameter ratioEnsure supportStentsBlood vesselsMedicineInsertion stent
In a stent intended for implantation in a living body and having a bridge structure in which at least two bridges are coupled to one another at at least one node region on at least one of the bridges near the node region, the section modulus of the bridge varies along the length thereof, and the stresses arising at the node region upon deformation of the stent are distributed in the longitudinal direction of the bridge.
Owner:EHRLINSPIEL MICHAEL +2
Flexible tube made from polypropylene and method for production of said tube
InactiveUS20060188676A1Synthetic resin layered productsThin material handlingEngineeringPolypropylene
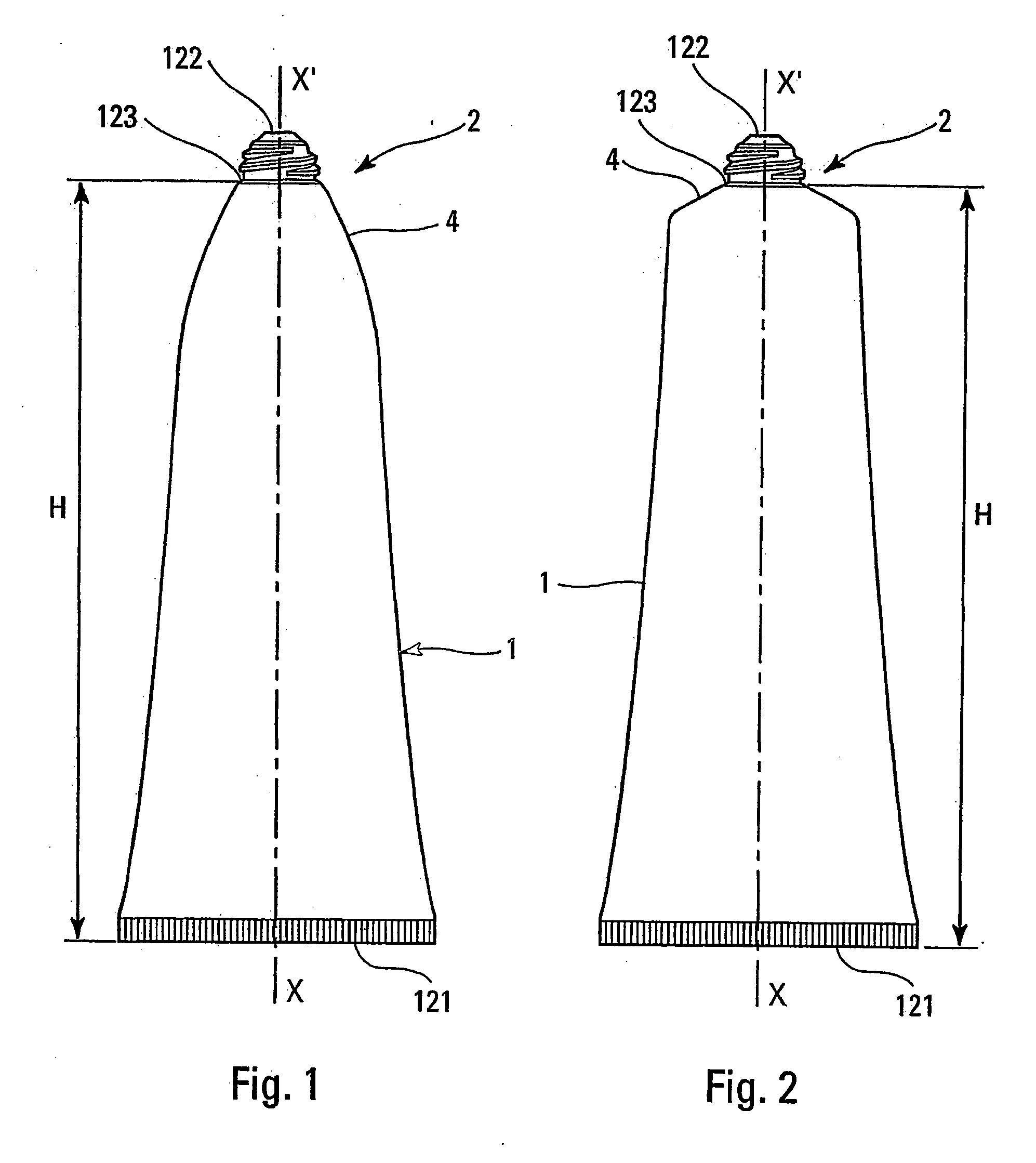
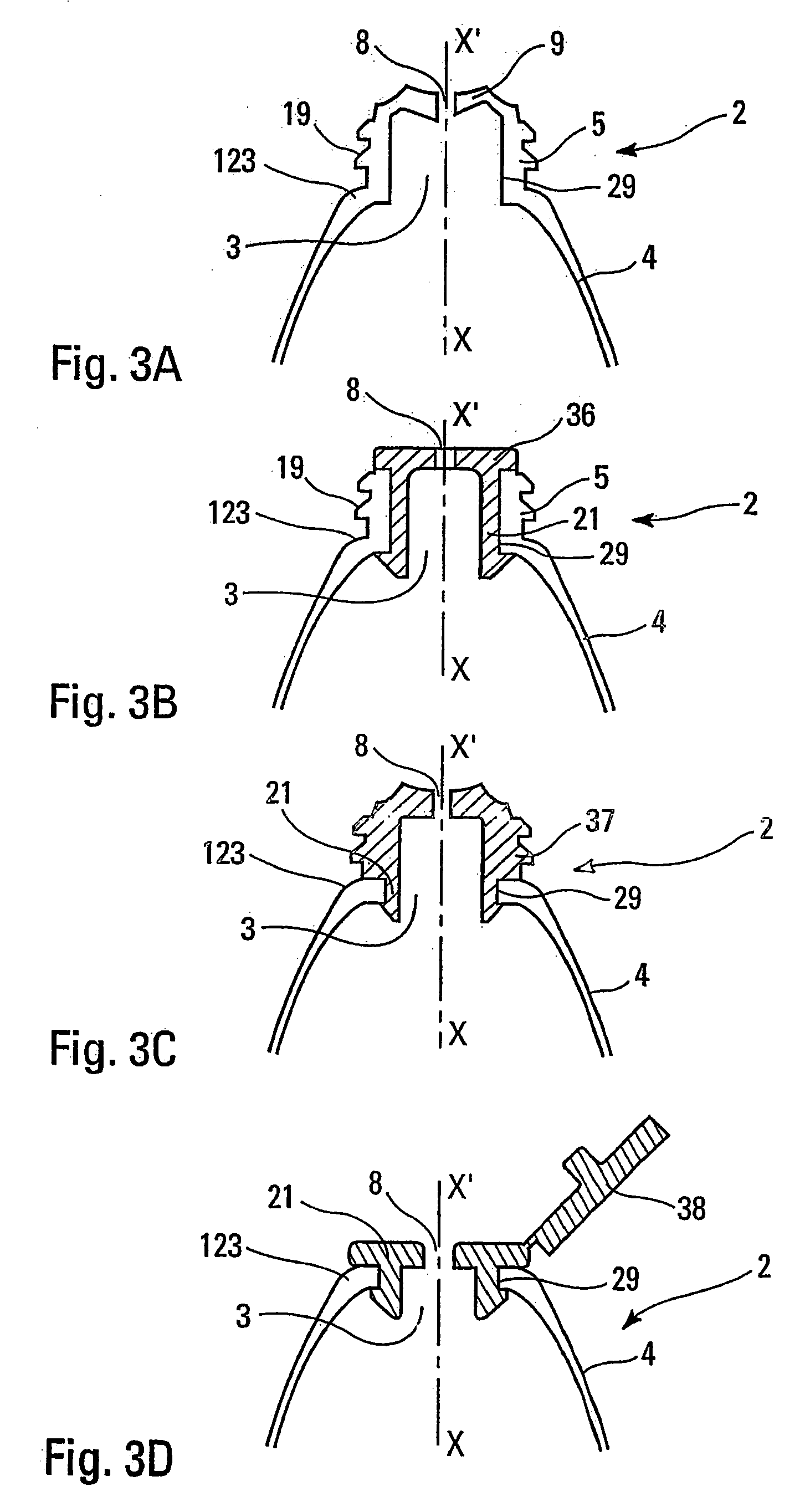
A flexible tube comprising a skirt and a distribution head, resistant to cracking under stress and forming a barrier to water. The wall of the tube is made from at least one first polymer from the group of polypropylenes, with, at the mid-point from the end of the skirt furthest from the head to the end of the neck forming the distribution hole of the tube, a thickness of between 0.30 mm and 1.00 mm, with a section modulus of between 700 MPa and 80 MPa, the section moduli of the components of the wall being chosen to follow a law of maximum dispersion. The tube finds application in the storage of all products, in particular pasty bodies in cosmetics and pharmaceuticals.
Owner:CEP IND
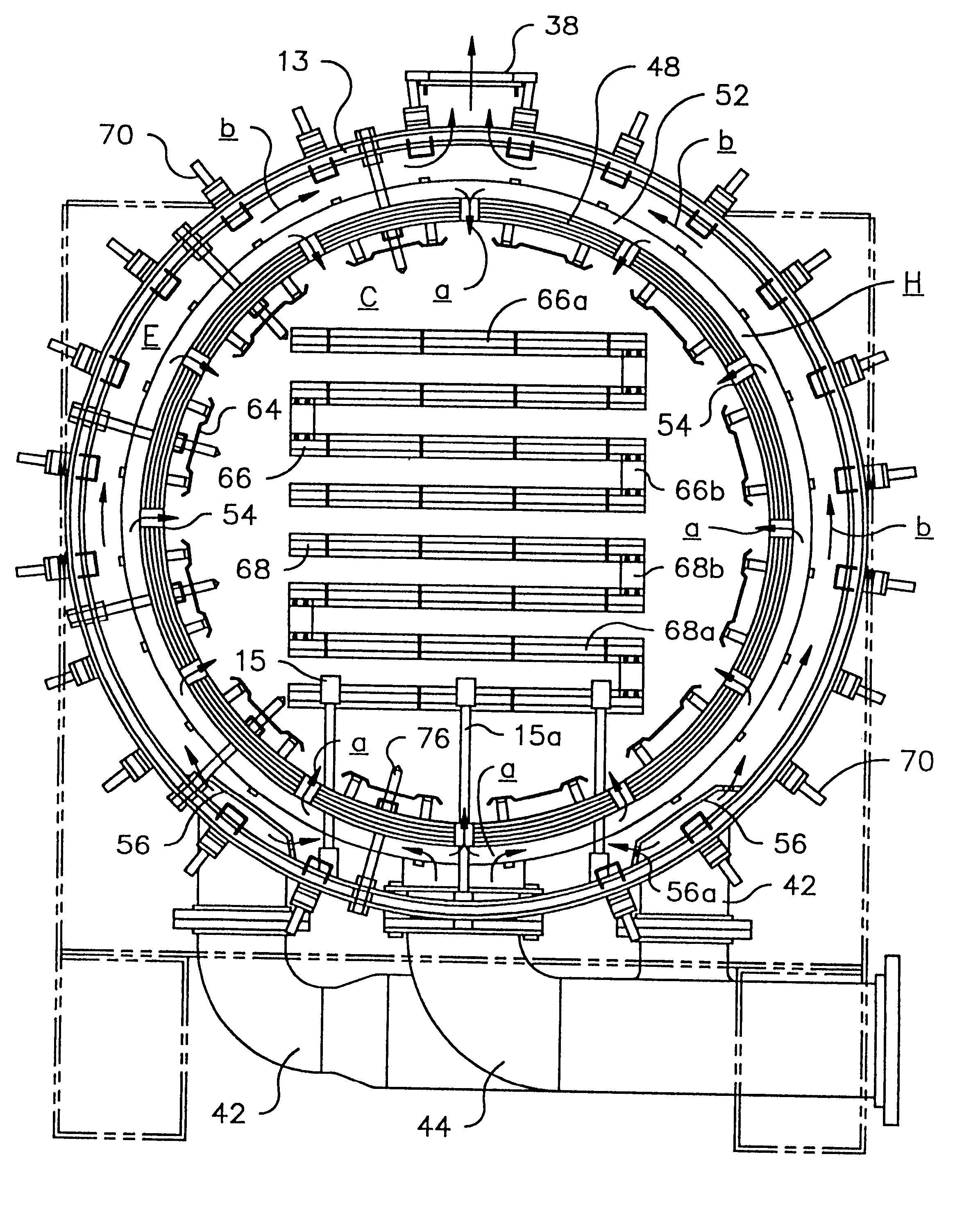
High temperature vacuum furnace
InactiveUS6349108B1Improve uniformityEffective dispersionMuffle furnacesMaintainance of heating chambersEngineeringDirect radiation
An electric resistance high temperature vacuum furnace having radiant heating units evenly spaced around the sides and ends of the furnace hot zone. Pairs of units are automatically regulated both radially and longitudinally according to the temperature required by the workload in the hot zone. The units each comprise parallel aligned elements electrically connected in series at their one ends. Each element has lengthwise surfaces angularly disposed from each other to form a beam structure of high section modulus for stiffness and resistance to sagging. Also, the angles of the element surfaces facing a heat-reflective assembly substantially enable all of the energy radiated toward the assembly to be reflected into the hot zone in addition to the direct radiation from the surfaces facing the hot zone. The furnace includes a re-circulating cooling system for rapid cooling of the furnace and workload. An inert cooling fluid bypasses the hot zone, passing instead around the outside of the heat assembly and through a heat exchanger until the circulated fluid temperature drops below the maximum tolerated by all component parts in the cooling system, after which the fluid passes directly through the hot zone.
Owner:PVT
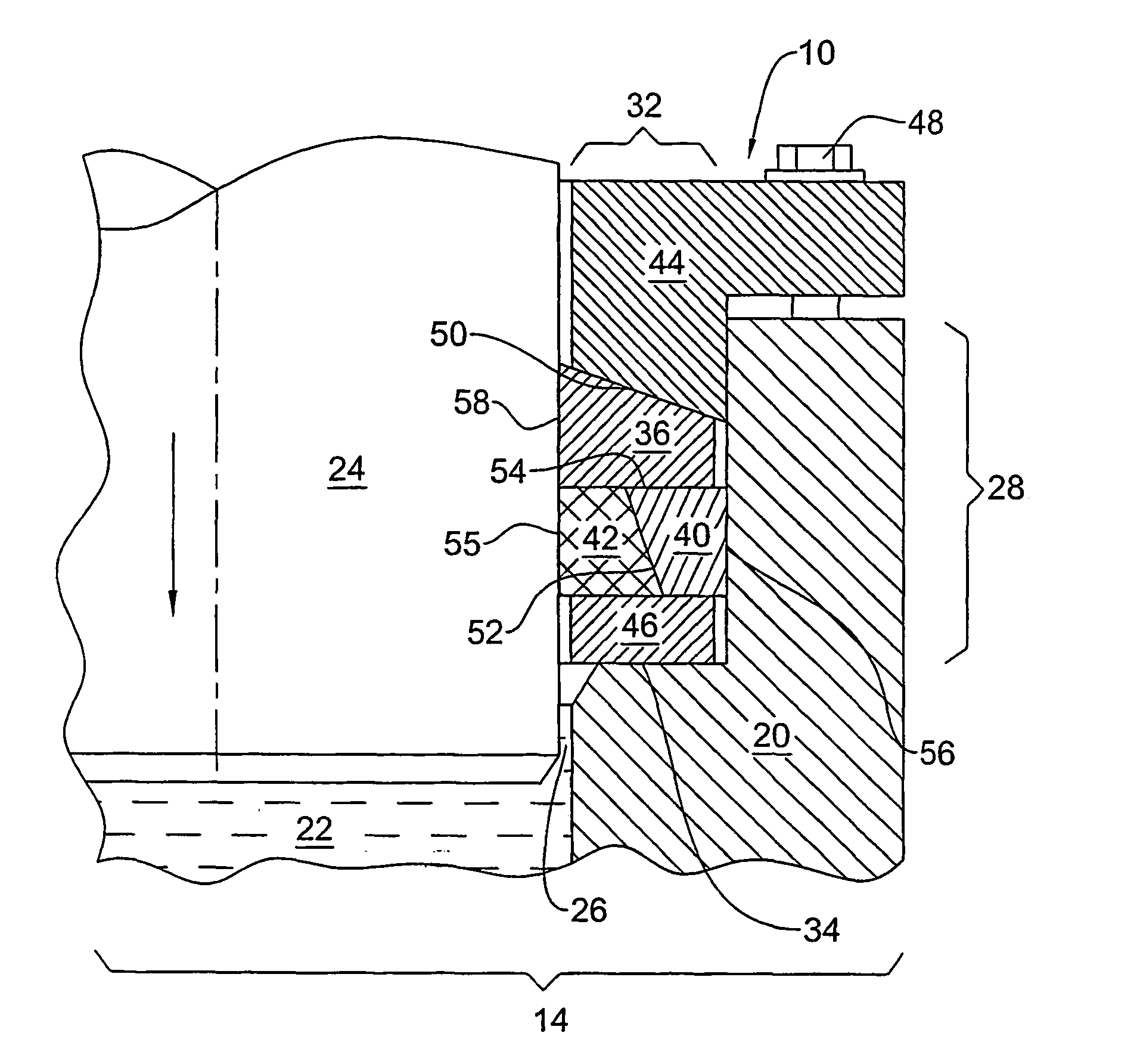
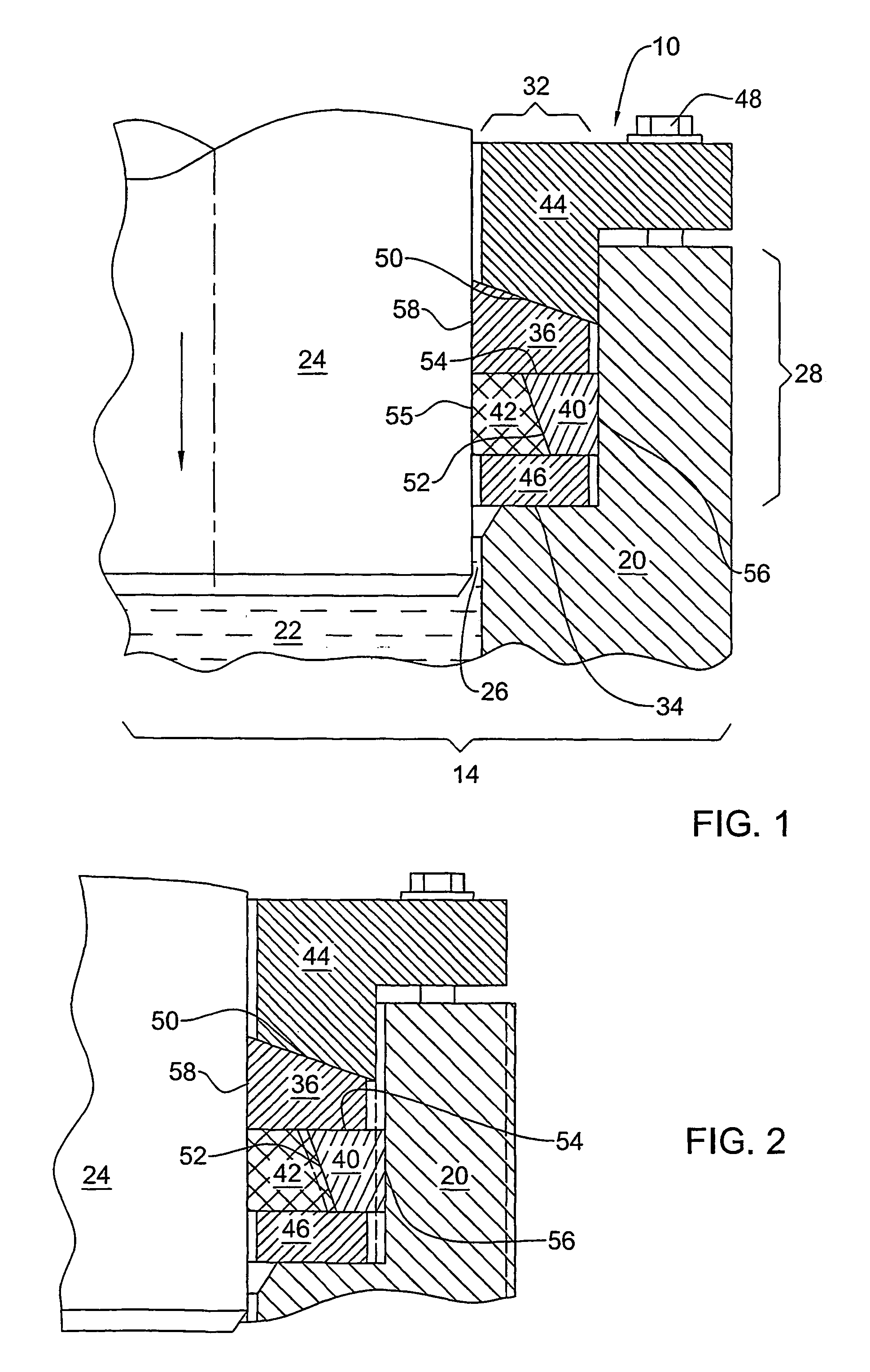
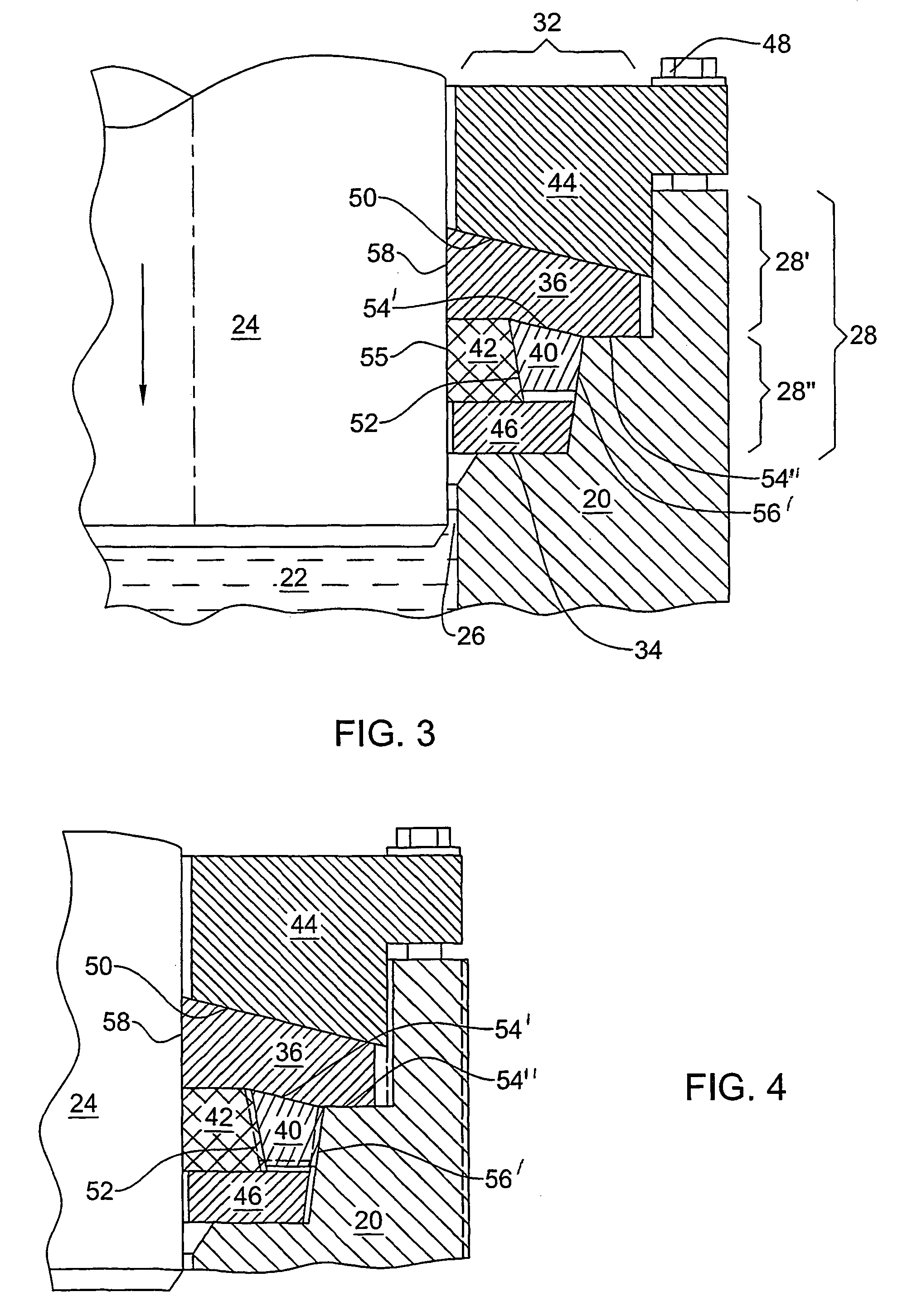
Fixing device and image forming apparatus
A fixing device includes: a rotatable endless fixing belt; a nip forming member arranged inside the fixing belt; a facing rotating body that abuts the nip forming member via the fixing belt to form a nip portion with the fixing belt; a heat source that directly heats up the fixing belt at a portion other than the nip portion; and a supporting member that supports the nip forming member. The fixing device conveys a recording medium carrying an unfixed image to the nip portion to fix the unfixed image to the recording medium, and the supporting member includes a rising portion extending in an abutting direction of the facing rotating body against the fixing belt and having a tip close to an inner circumferential surface of the fixing belt, and is set to have a section modulus of 200 mm3 or higher.
Owner:RICOH KK
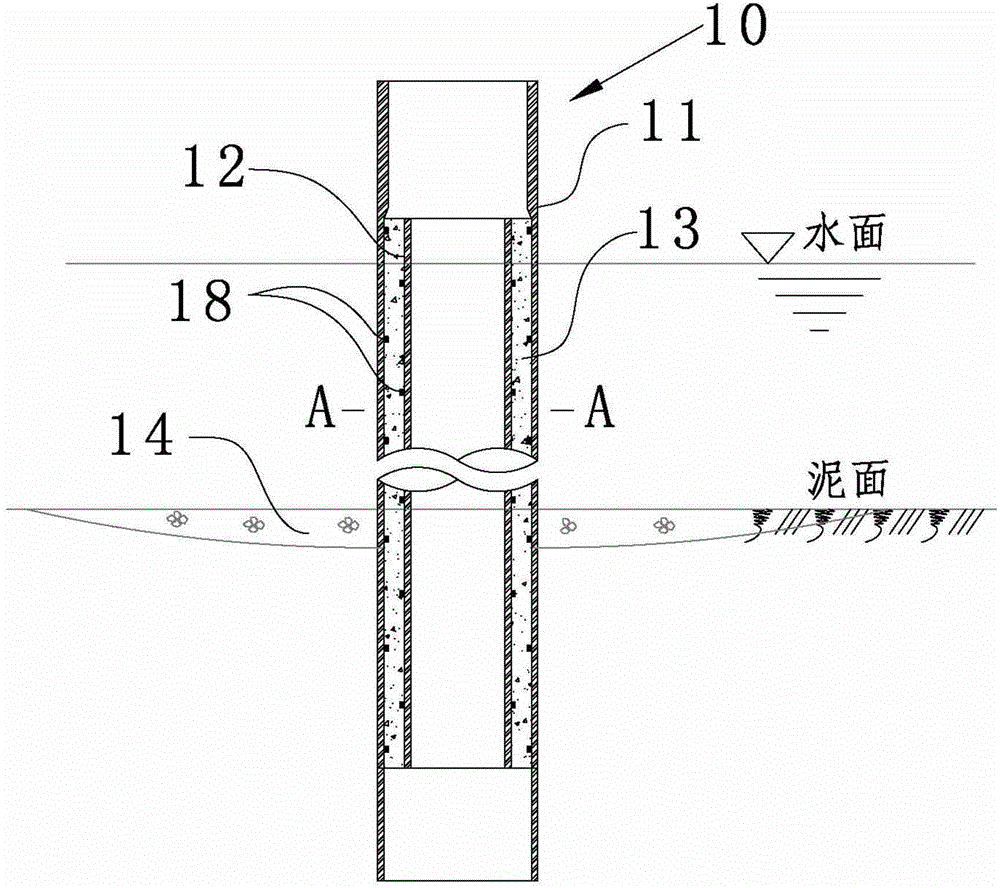
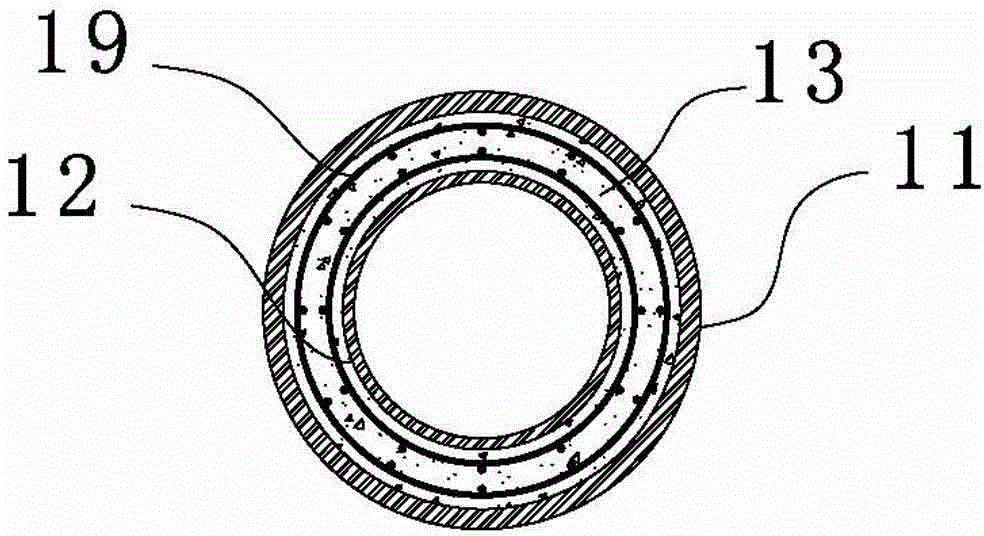
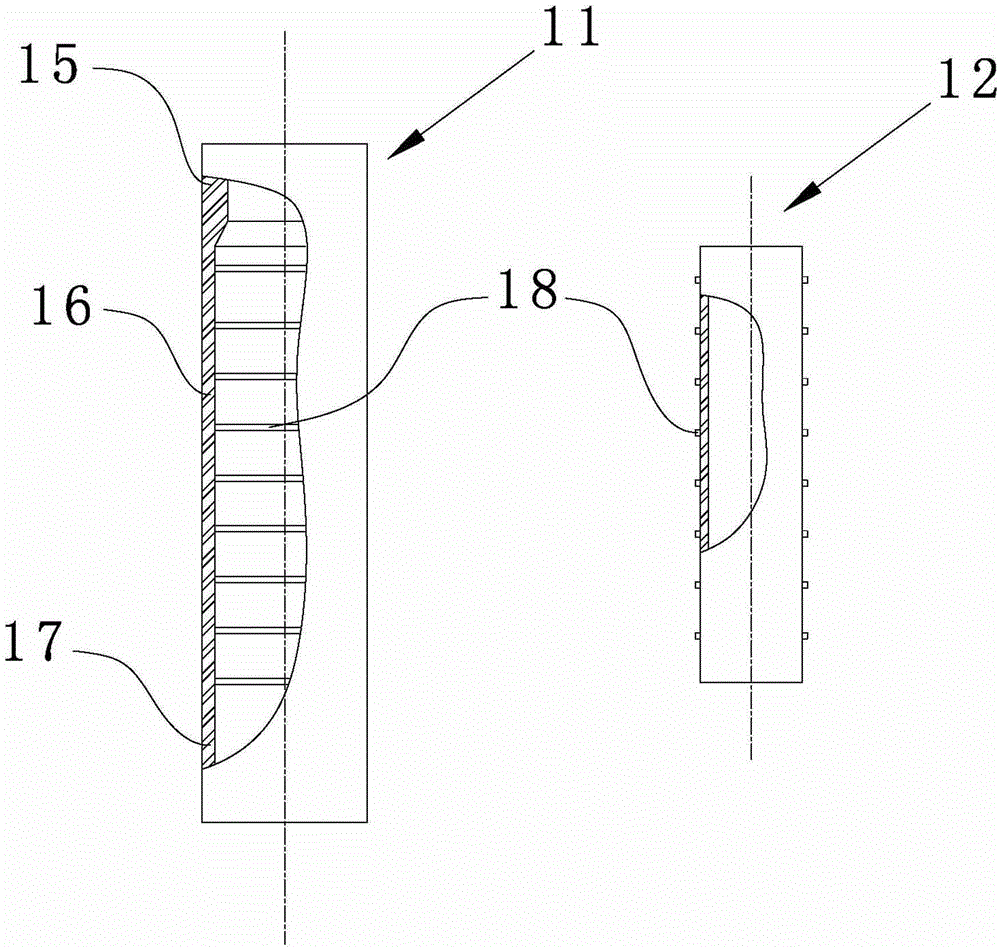
On-sea sandwich steel pipe pile foundation and construction method
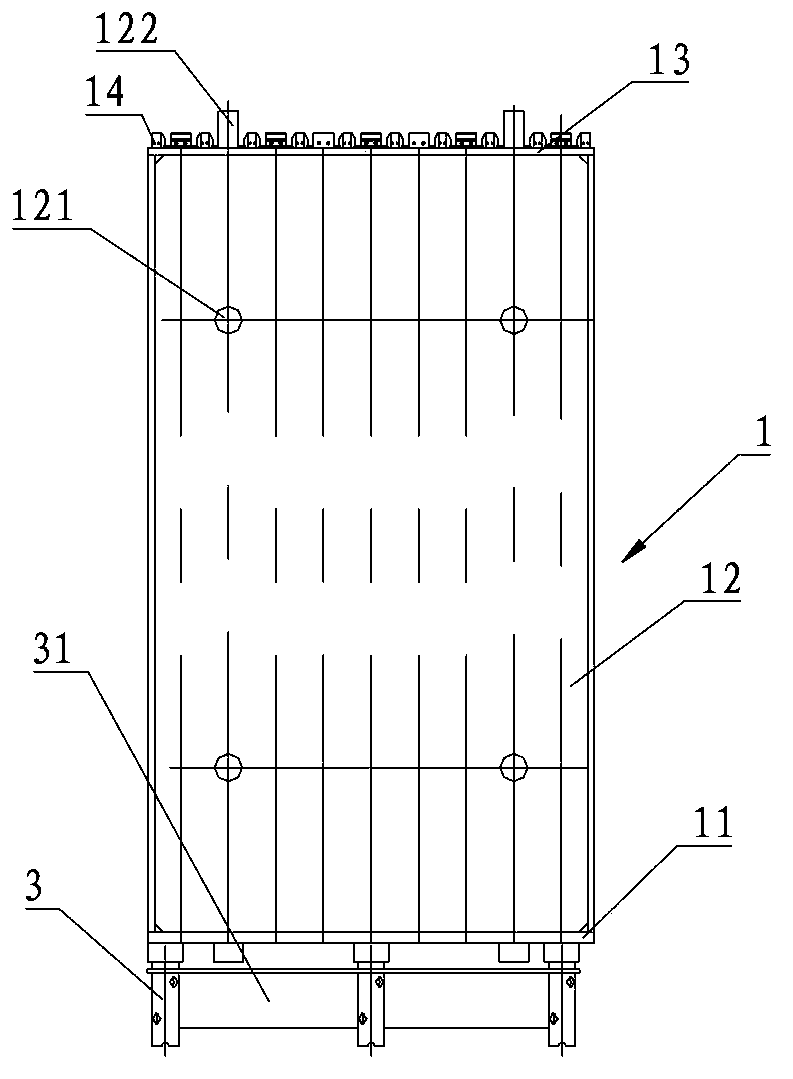
The invention discloses an on-sea sandwich steel pipe pile foundation and a construction method. The on-sea sandwich steel pipe pile foundation comprises an outer steel pipe (11) and an inner steel pipe (12), the inner steel pipe (12) is arranged in the outer steel pipe (11), an annular space is formed between the inner steel pipe (12) and the outer steel pipe (11), and reinforced concrete (13) is cast and formed in the annular space. Through organic combination of a steel structure and a reinforced concrete structure, the section modulus and the structural rigidity of a single-pile structure are obviously increased, and the defects that in the use period, the single-pile structure is too large in deformation and not suitable for the large water depth are overcome. The sandwich steel pipe pile foundation can effectively reduce the wall thickness and the weight of an outer steel pile which is piled firstly, when the hoisting capacity is fixed, pile-sinking construction of the pipe pile of the larger diameter can be achieved, and the on-sea sandwich steel pipe pile foundation can be suitable for the engineering area with the larger water depth. The construction method of the on-sea sandwich steel pipe pile foundation is further disclosed.
Owner:熊翱
Beam shoe
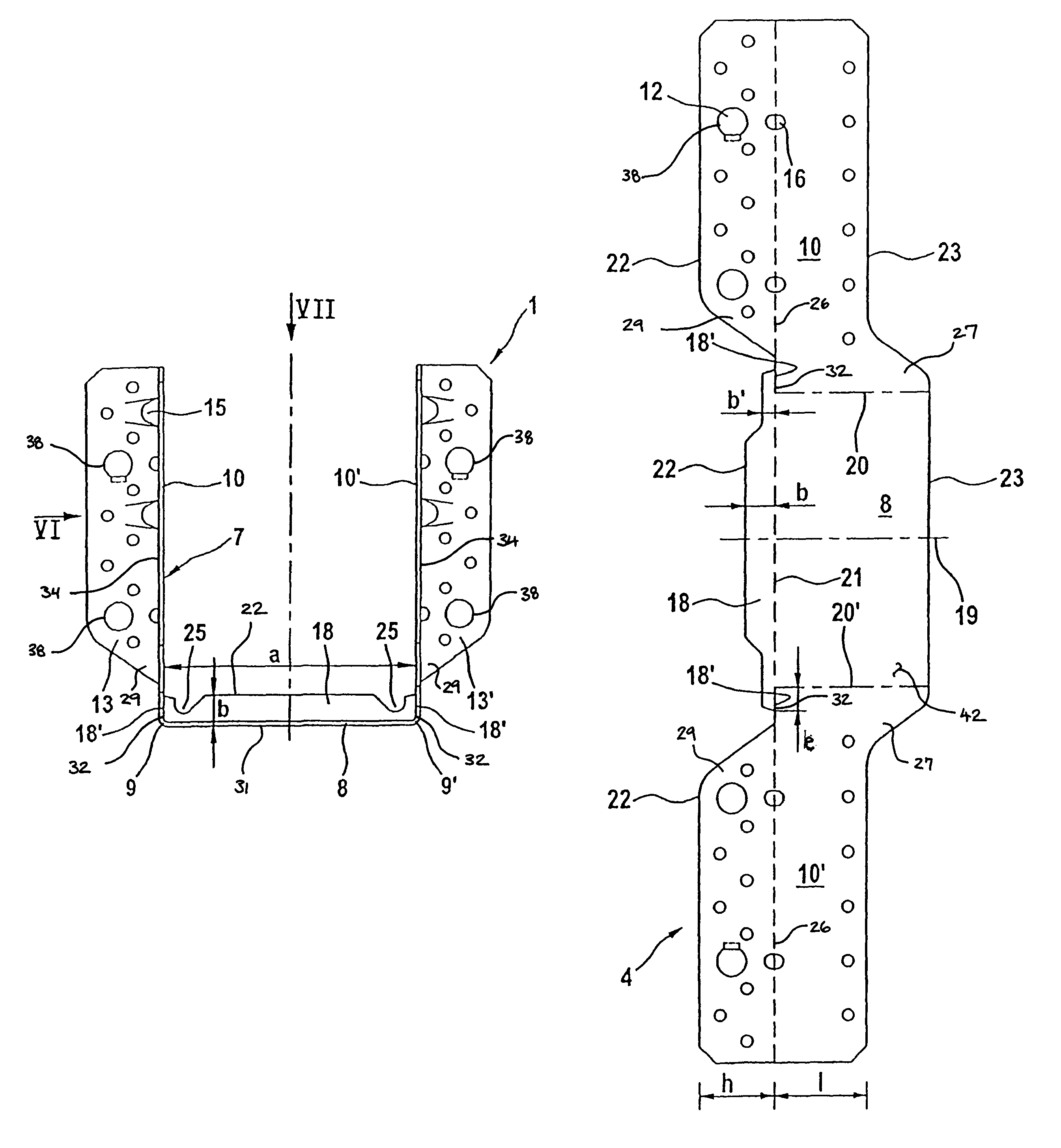
A beam shoe for attaching a (first) beam end-on to a load-bearing construction, especially to a second beam disposed in the same plane as the beam to be attached and running at right angles thereto, the beam shoe comprising an originally flat, one-piece, strip-like sheet-metal portion or blank, which is shaped to an upwardly open channel-shaped retaining member having a web-like rectangular bottom for bracing the beam to be attached on the beam shoe as well as two web-like, parallel retaining legs, the retaining member embracing, in assembled condition, an end portion of the beam to be attached at the underside and side faces thereof, the legs, which are bent over upwardly from the bottom at right angles and disposed along two opposite borders of the bottom, being provided with through holes for rod-like fasteners such as nails in particular in order to join the beam shoe to the beam to be attached, the inside spacing of the legs therefore being (at least) as large as (and if necessary somewhat larger than) the width of the beam to be attached, wherein a fastening flange provided with through holes for rod-like fasteners such as nails and / or screws is bent over at right angles along that longitudinal border of each retaining leg which faces the load-bearing construction (or if necessary the second beam), the fastening flange being designed to be placed with its outside face remote from the channel-shaped retaining member of the beam shoe on the load-bearing construction / the second beam and to be fastened thereto with rod-like fasteners such as nails and / or screws, and wherein the web-like bottom is reinforced by a (bottom) reinforcing flange or the like in order to increase its section modulus against sagging under relatively large load.
Owner:SIMPSON STRONG TIE
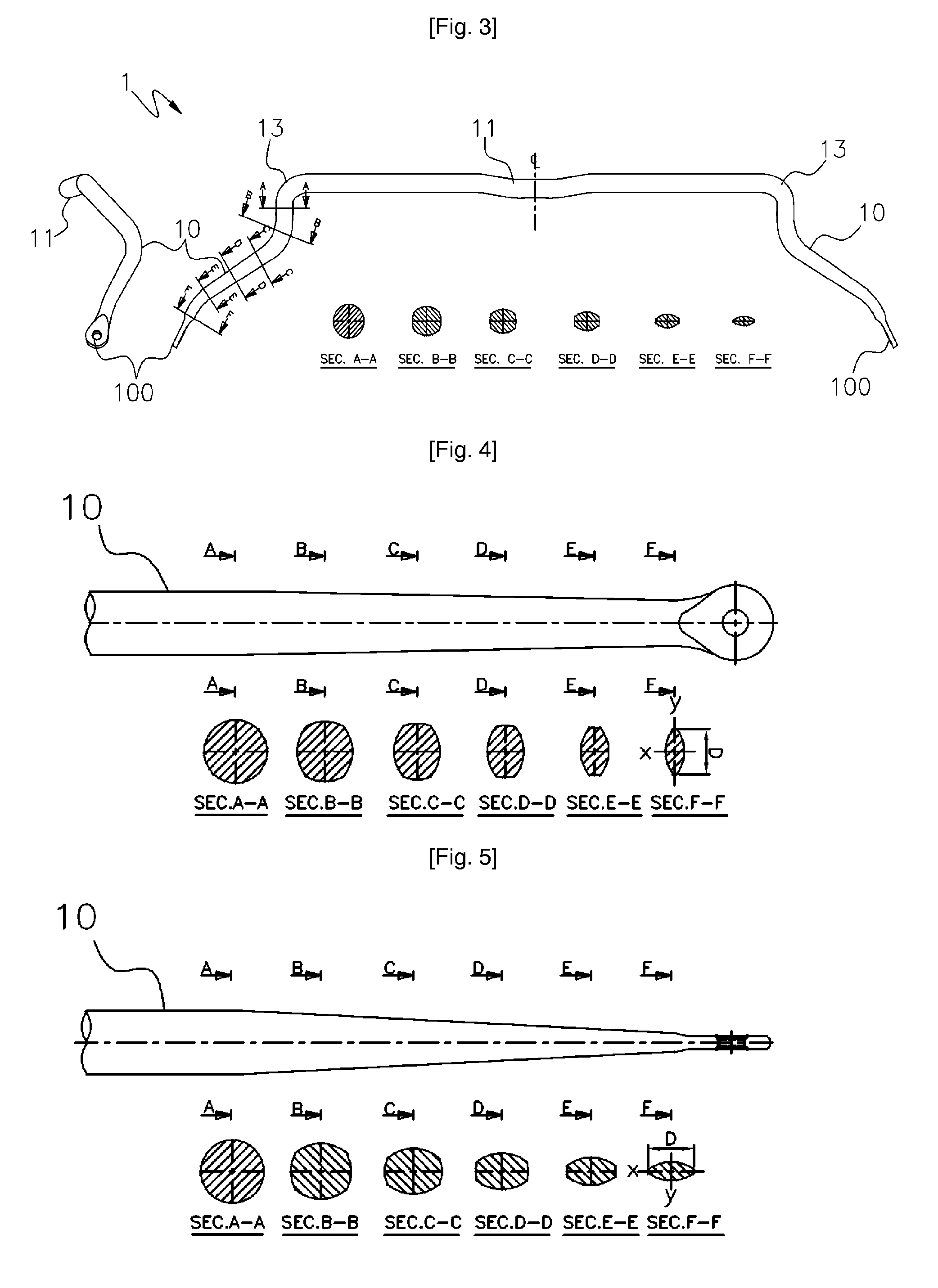
Tapered stabilizer bar having continuously changing cross-section and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20100225083A1Reduce manufacturing costLow weight costMetal-working apparatusInterconnection systemsSection modulusFastener
A stabilizer bar includes a parallel bar which is secured with respect to a frame via fasteners in each of which a bush is fitted, and leg bars which extend from both ends of the parallel bar with distal ends of the leg bars connected to suspension arms. Each leg bar is tapered from an upper end toward a lower end thereof to continuously decrease a section modulus of the leg bar from the upper end toward the lower end thereof so that the stress generated by a load applied to the lower end of the leg bar is not concentrated on a bent part of the stabilizer bar and is distributed over the entire leg bar so as to prevent the stabilizer bar from being broken at the bent part.
Owner:DAEWON KANG UP CO LTD
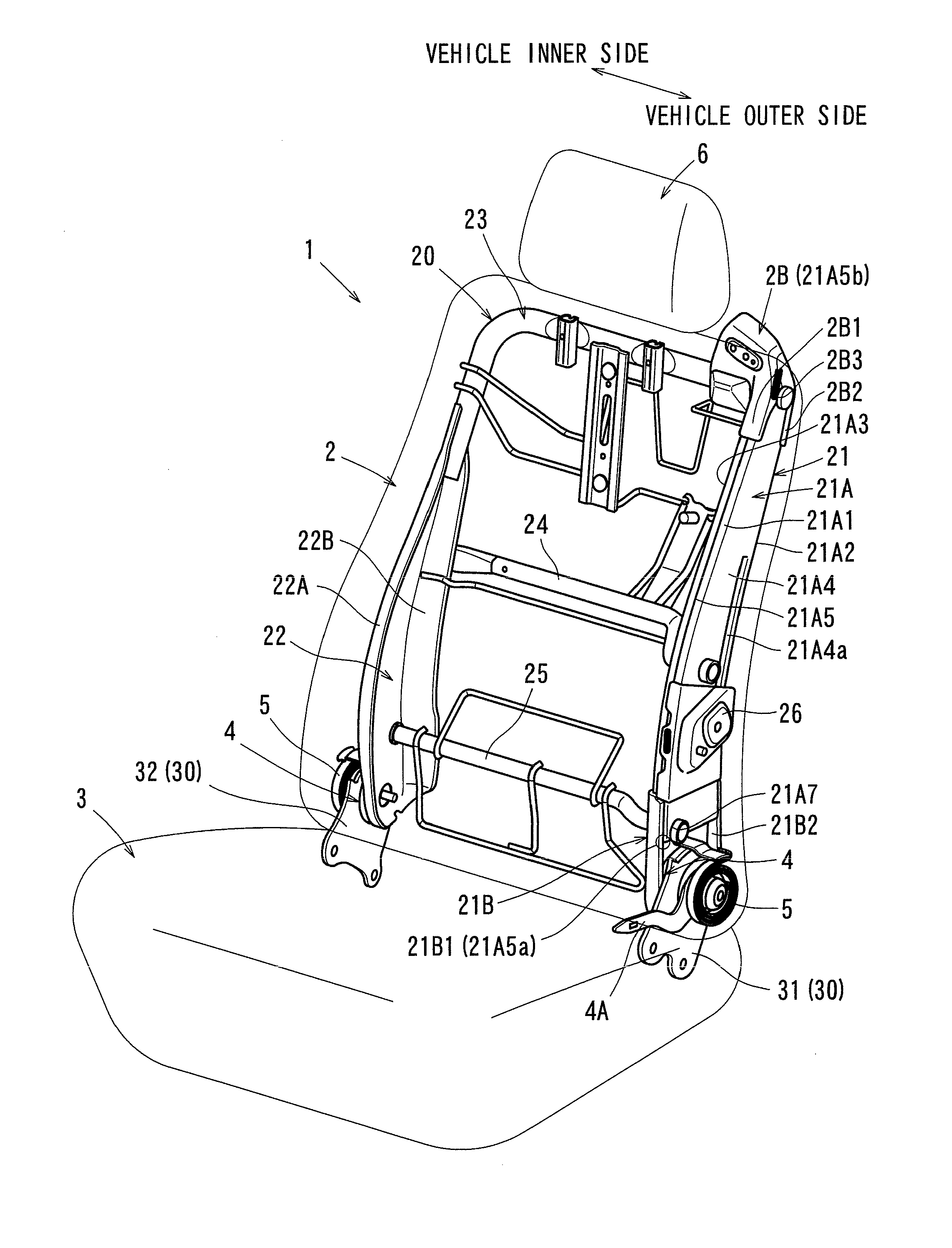
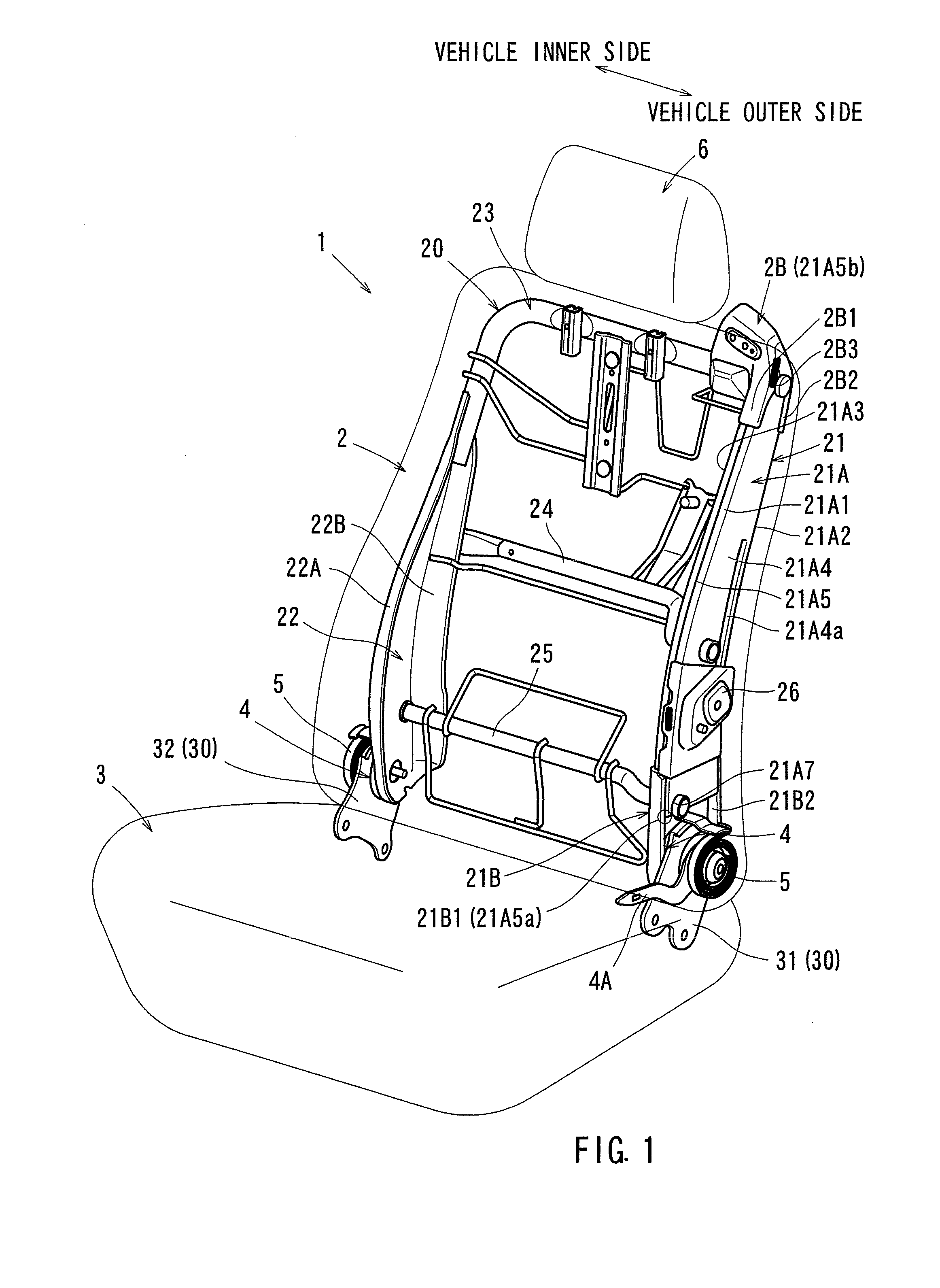
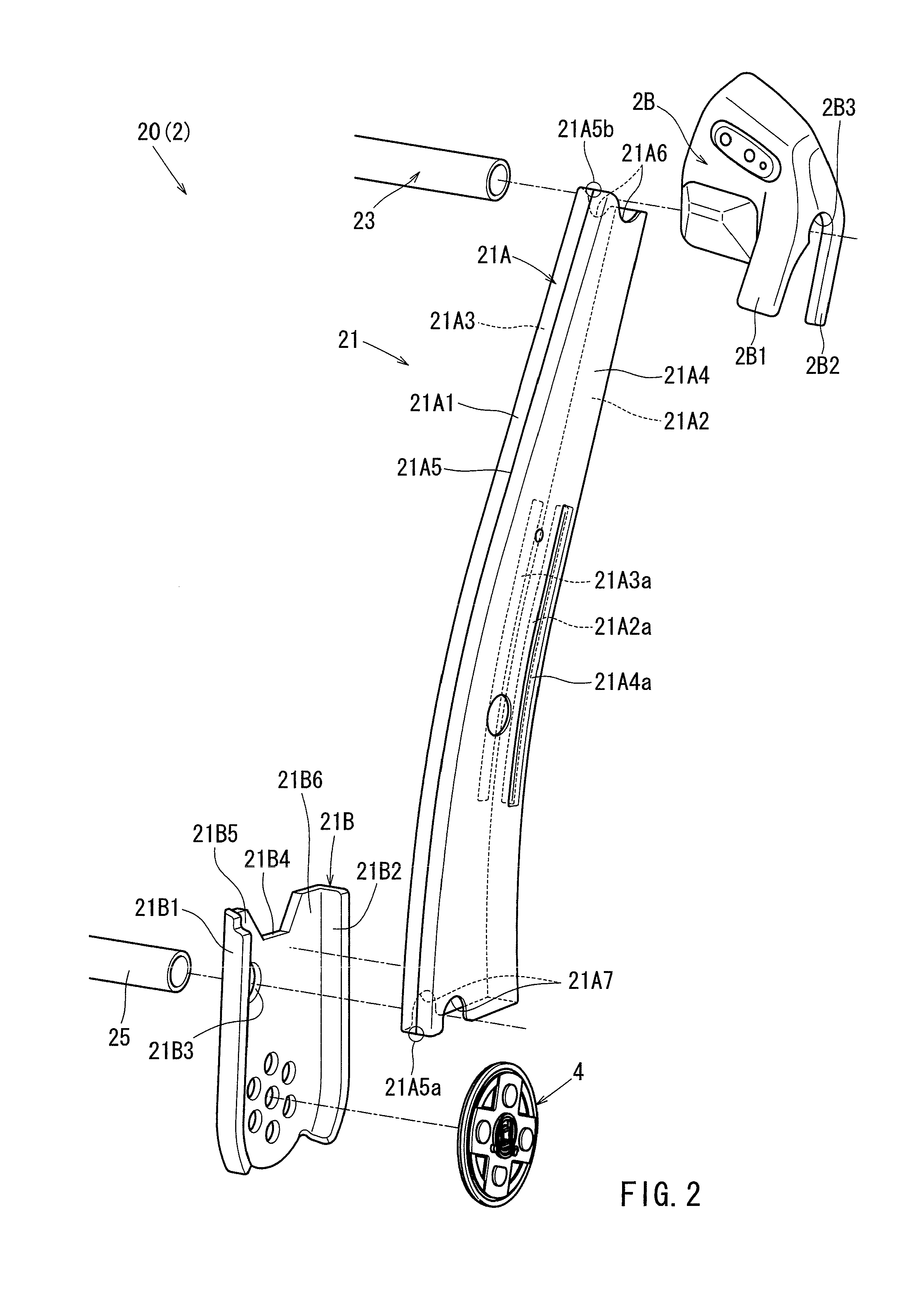
Frame structures for vehicle seats
ActiveUS20140232161A1Reduce structural strengthEasy to produceSeat framesStoolsMechanical engineeringSection modulus
Embodiments of the present invention may include a frame structure for a vehicle seat having two frames, a pile portion, and a section modulus reducing configuration. The two frames extend in a specific direction. At the pile portion, the two frames abut each other in a direction perpendicular to the specific direction and connected to each other.The section modulus reducing configuration is formed at an edge portion in the specific direction of the pile portion, and is configured to achieve a reduction in section modulus.
Owner:TOYOTA BOSHOKU KK
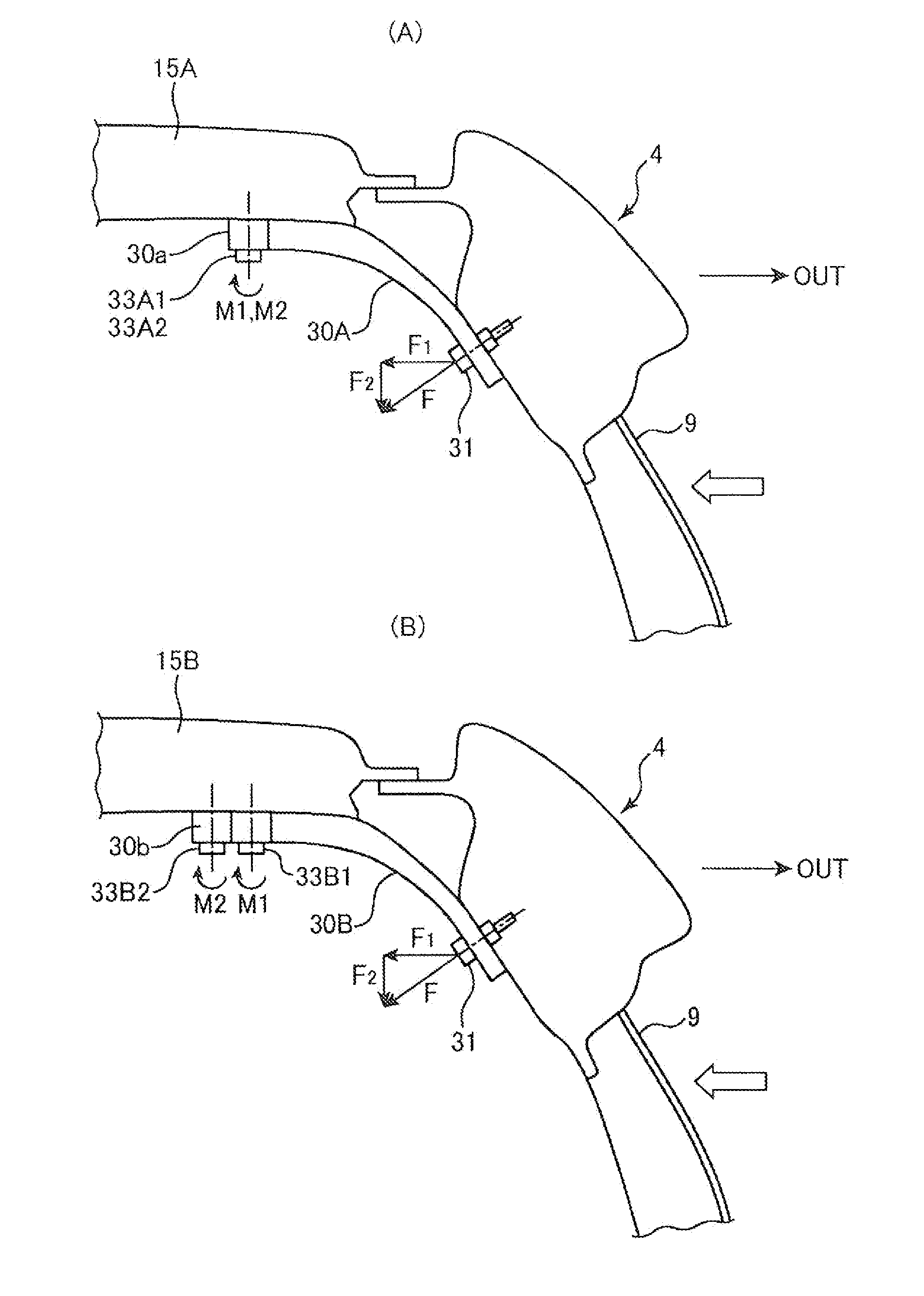
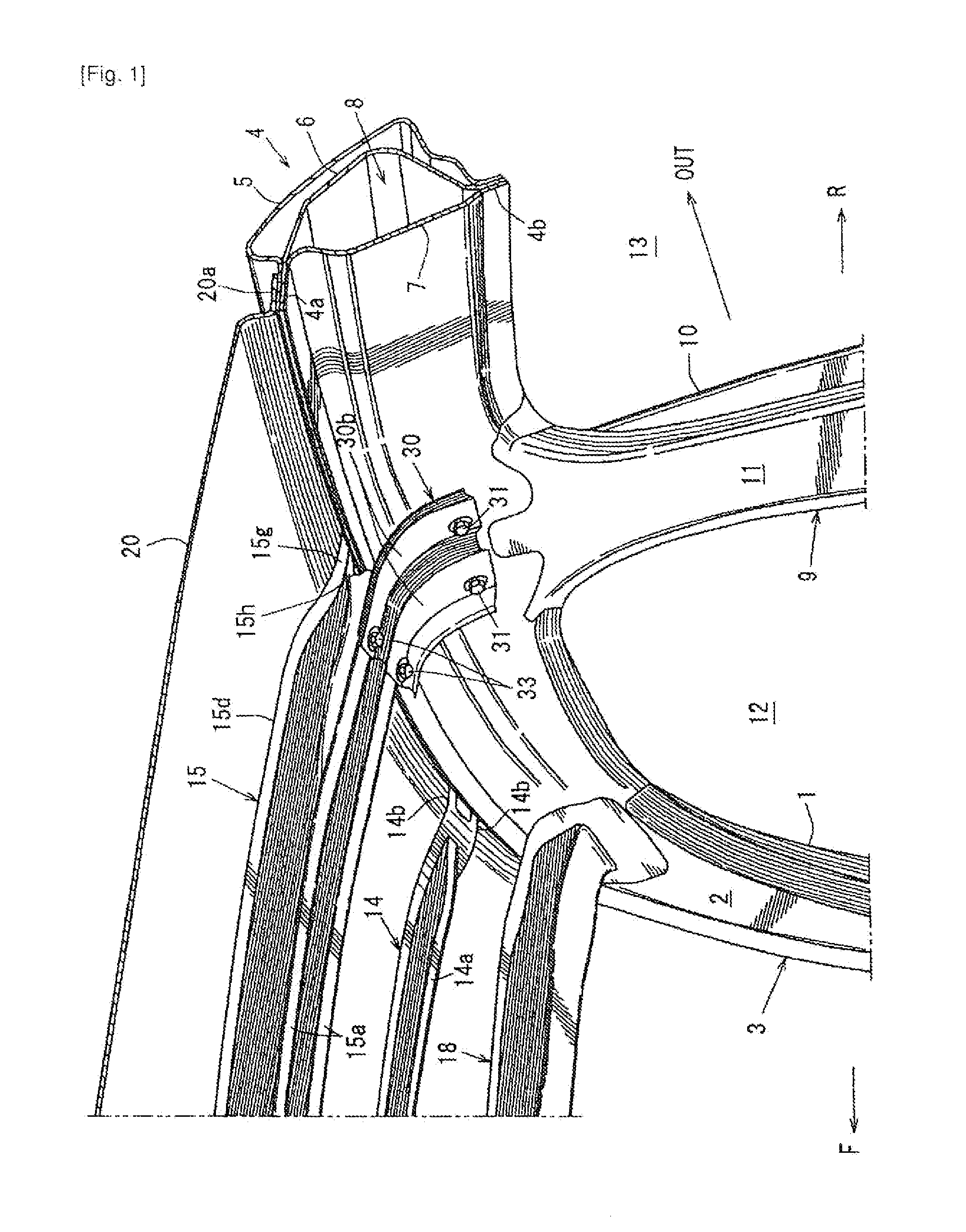
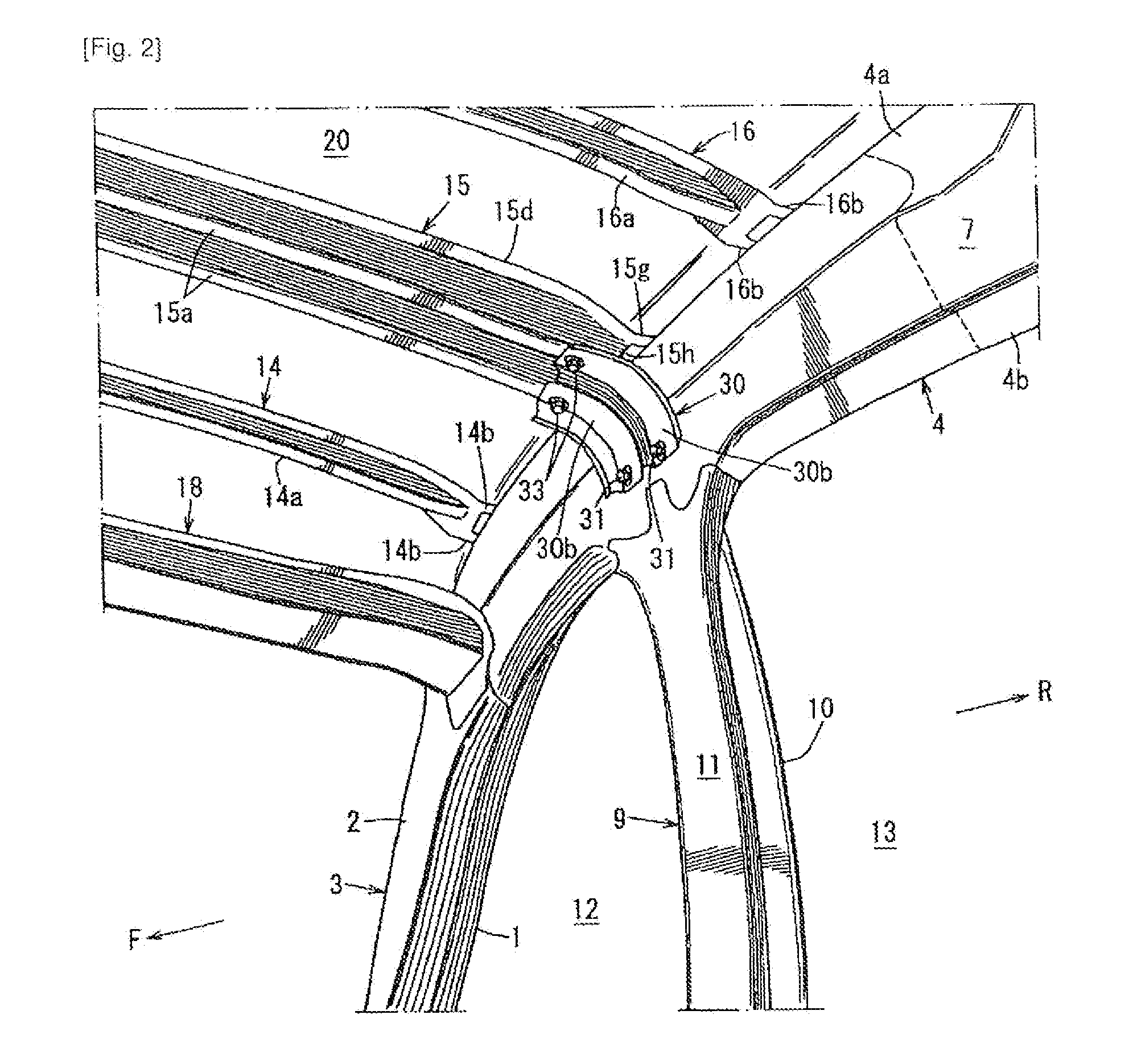
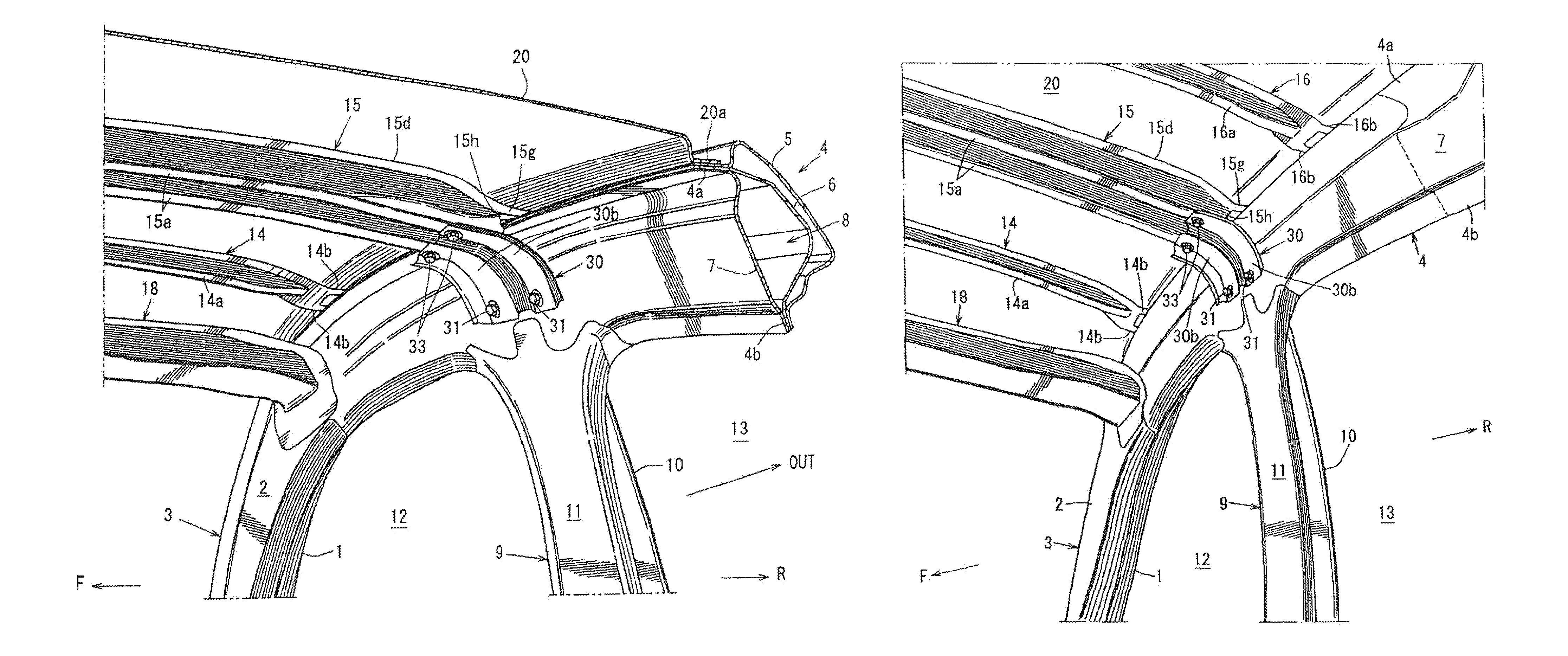
Vehicle upper structure
ActiveUS20130320716A1Counteracting forceEffective dispersionSuperstructure subunitsRoofsGusset plateSide impact
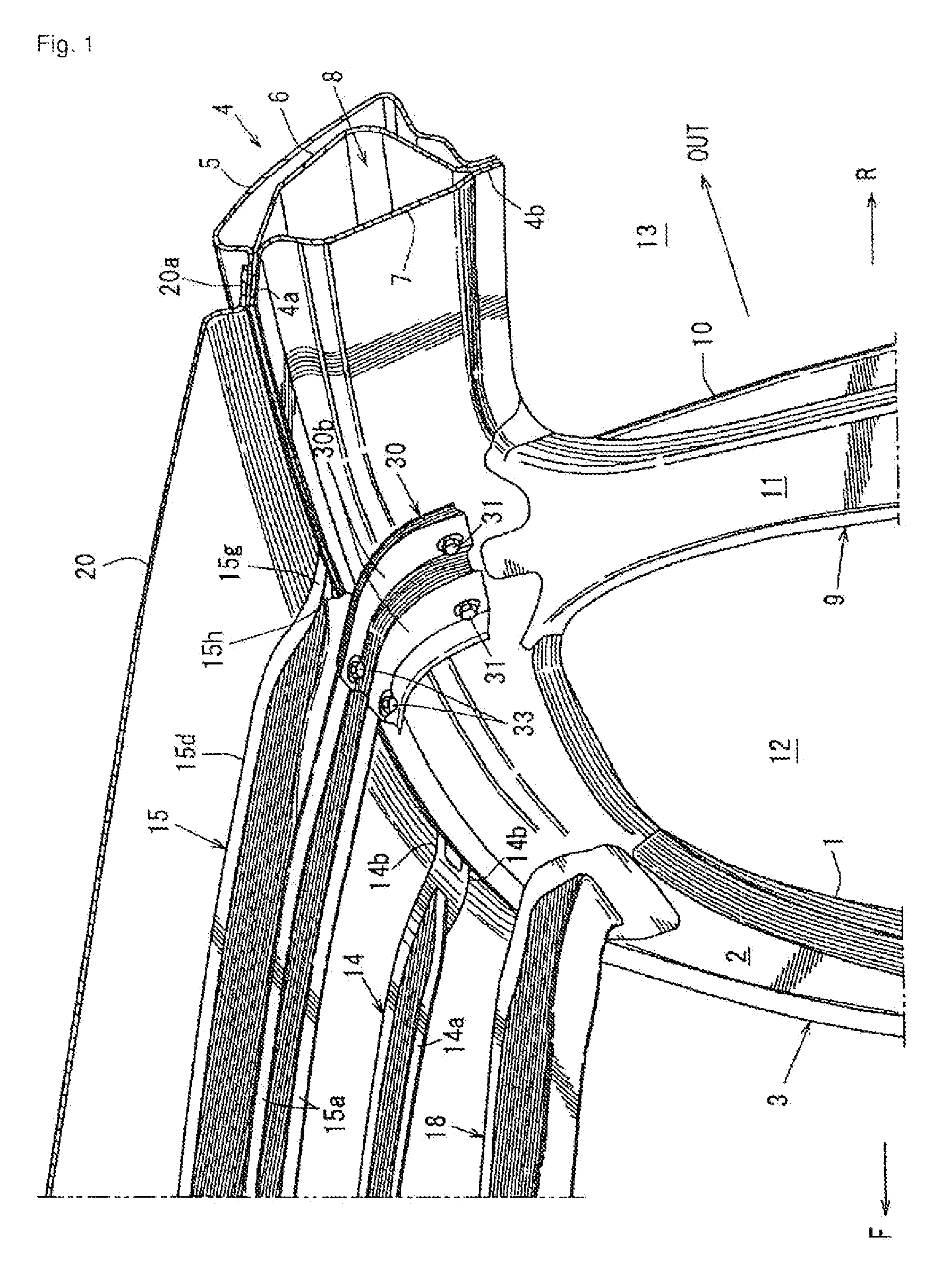
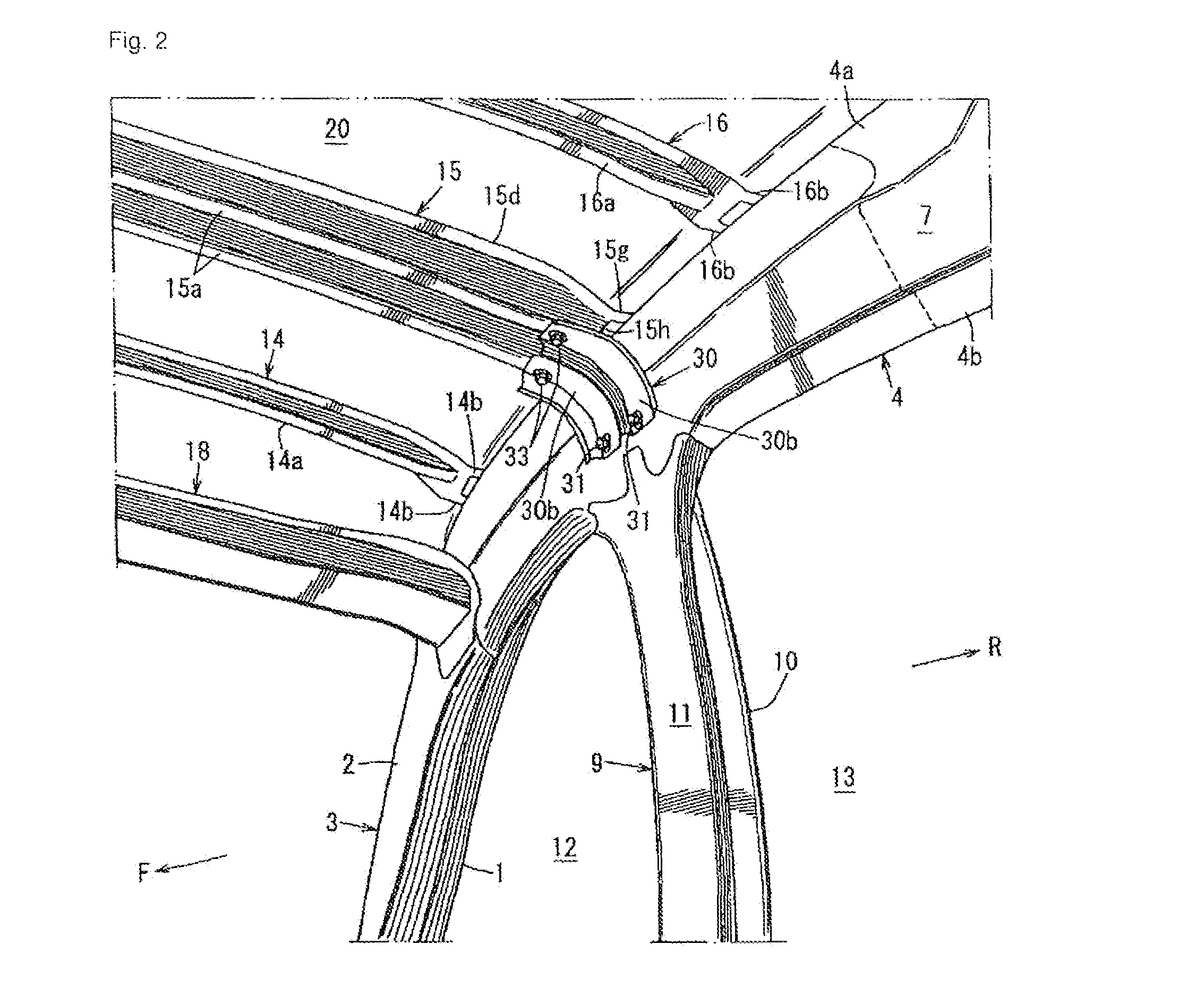
Provided is a vehicle upper structure which is capable of increasing, in a simple manner, a section modulus (resistive force) against a bending moment to be imposed on a roof reinforcement by a swinging phenomenon of a gusset occurring when a side impact load input into a center pillar and a roof side rail member is applied to the roof reinforcement from the gusset during a vehicle side impact event, to allow the load to be effectively dispersed to the roof reinforcement. The vehicle upper structure comprises a roof side rail member 4, a roof reinforcement 15 and a gusset 30, wherein an end of the gusset 30 on a side fastened to the roof reinforcement 15 has a shape which inclines with respect to a line L1 oriented in a vehicle front-rear direction, in top plan view.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
Vehicle upper structure
ActiveUS8915540B2Counteracting forceEffective dispersionSuperstructure subunitsRoofsGusset plateEngineering
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
Spent fuel rod storage grillwork for nuclear power plant
InactiveCN103400617AIncrease storage capacityIncrease the moment of inertiaNuclear energy generationReactor fuel elementsNuclear engineeringNuclear power
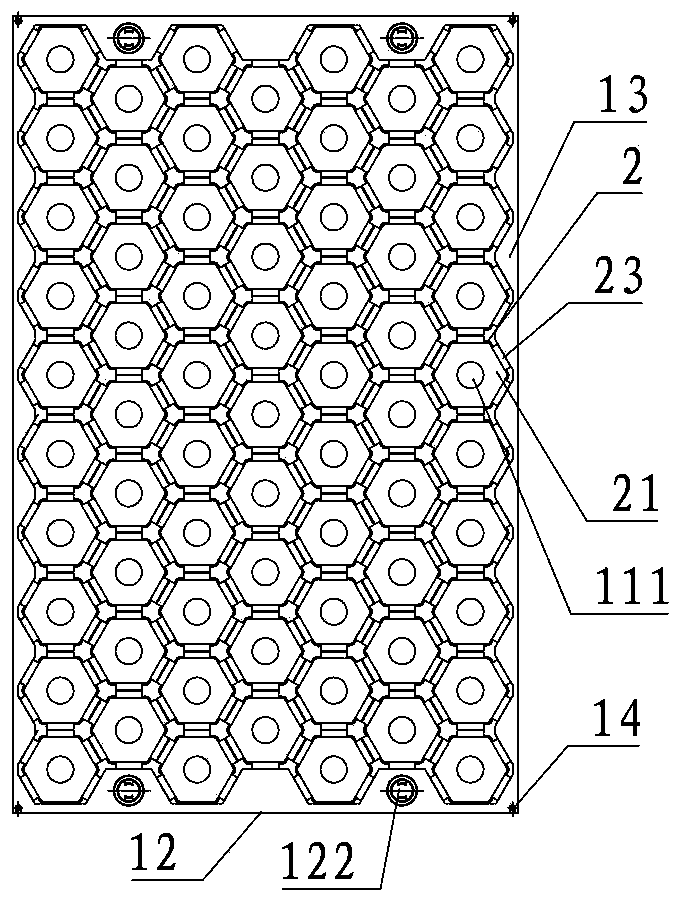
The invention discloses a spent fuel rod storage grillwork for a nuclear power plant in the field of nuclear power equipment. The spent fuel rod storage grillwork comprises a lower supporting plate and a grillwork body defined by a plurality of peripheral plates, wherein a plurality of small spent fuel rod storage chambers which are positioned on the top of the lower supporting plate and are regularly hexagonally prismatic steel pipes are arranged in the grillwork body; the small spent fuel rod storage chambers are arranged on the top of the lower supporting plate in a honeycomb manner; a spent fuel rod storage cavity with openings in two ends is formed in the center of each small spent fuel rod storage chamber; a bottom overflowing through hole formed in the lower supporting plate is positioned right under the spent fuel rod storage cavity of each small spent fuel rod storage chamber. The spent fuel rod storage grillwork has the technical effects that the inertia moment, the section modulus and the anti-bending capacity of the single small spent fuel rod storage chamber in the spent fuel rod storage grillwork for the nuclear power plant are improved, and the spent fuel rod storage amount in a unit volume in the spent fuel rod storage grillwork for the nuclear power plant can be increased.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR POWER ENG CO LTD
Combined steel sheet pile and integrated vertical wall used for bay dock or dock basin
The invention discloses a combined steel sheet pile for a bay dock or a dock, which is characterized in that the combined steel sheet pile is combined by a steel sheet pile and profile steel, two sides of the steel sheet pile are provided with wide U-shaped steel sheet piles with locking notches, and the profile steel is H-shaped; and the H-shaped profile steel is arranged on the convex back of the U-shaped steel sheet pile, and a flange of the H-shaped profile steel is fixedly connected with the U-shaped steel sheet pile by welding or through a bolt. The invention also discloses an integrative upright wall for the bay dock or the dock. Compared with the prior art, the combined steel sheet pile has various section moduli; and under the same section modulus, the utilization rate of the steel is higher, the home-made rate can reach about 60 percent, the using amount of the import steel sheet pile is greatly reduced, the construction cost is lowered, the manufacturing process is simple, the assembly speed is high, and the integral structural property is good.
Owner:ZHONGCHUAN NO 9 DESIGN & RES INST +1
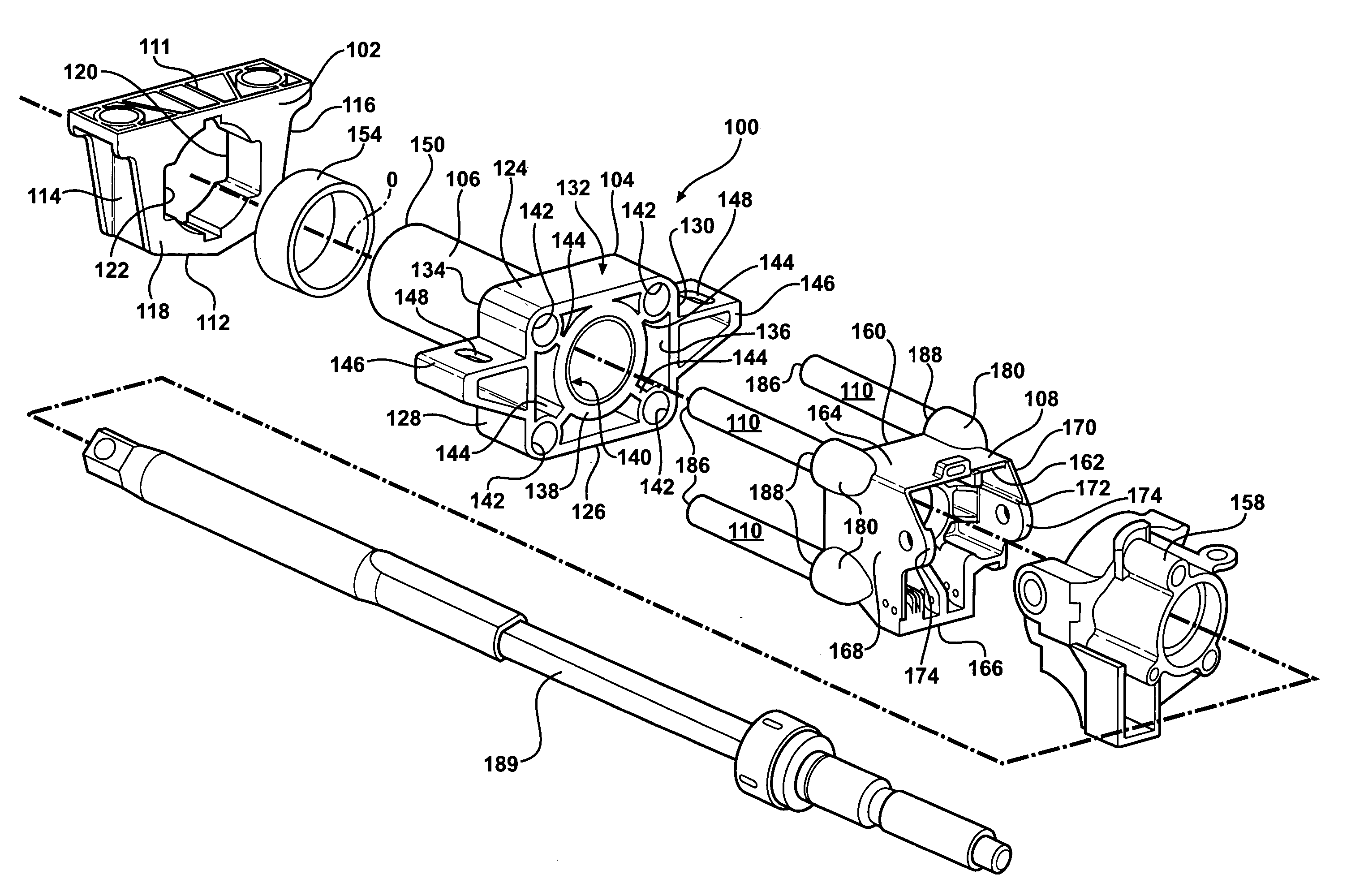
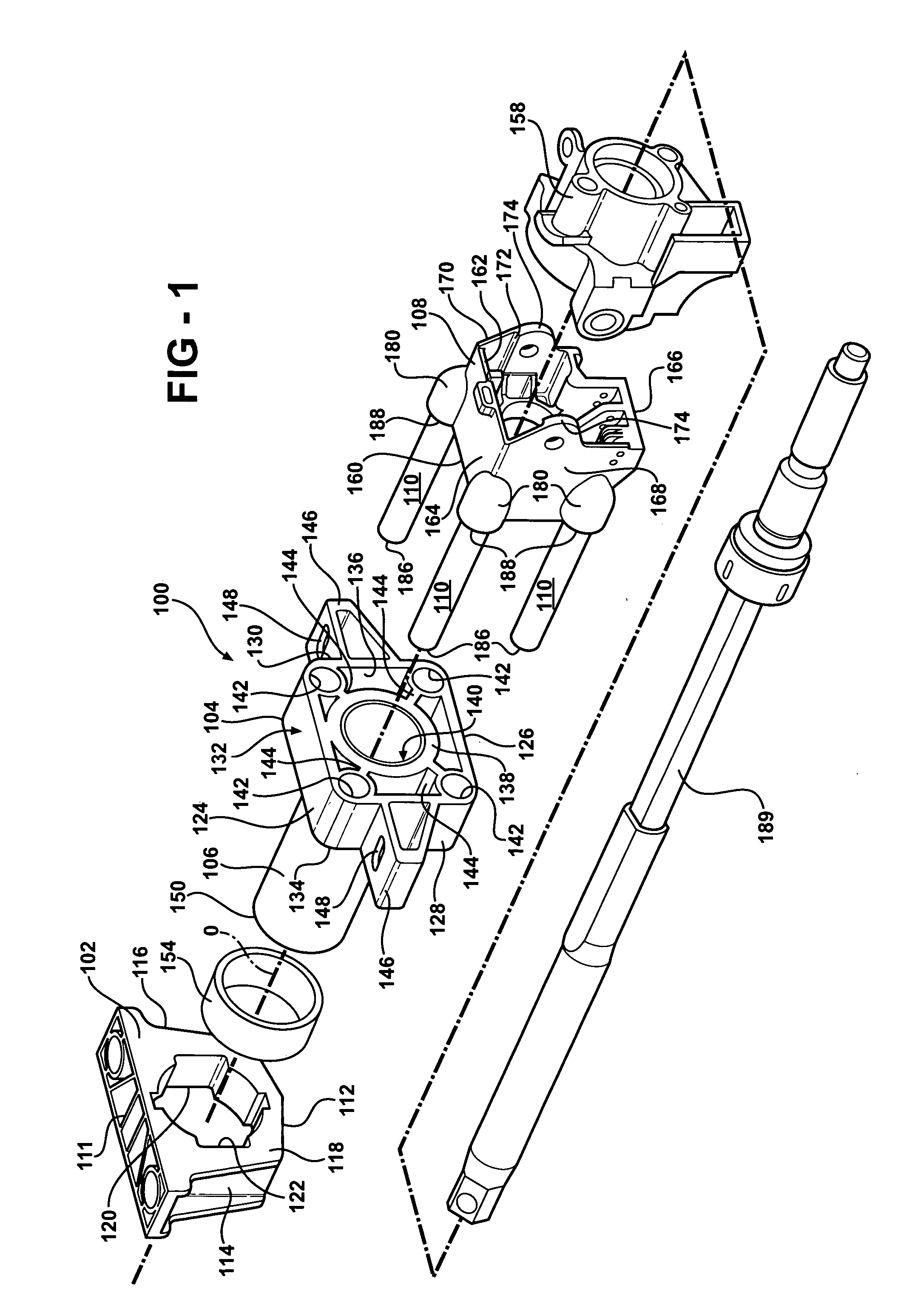
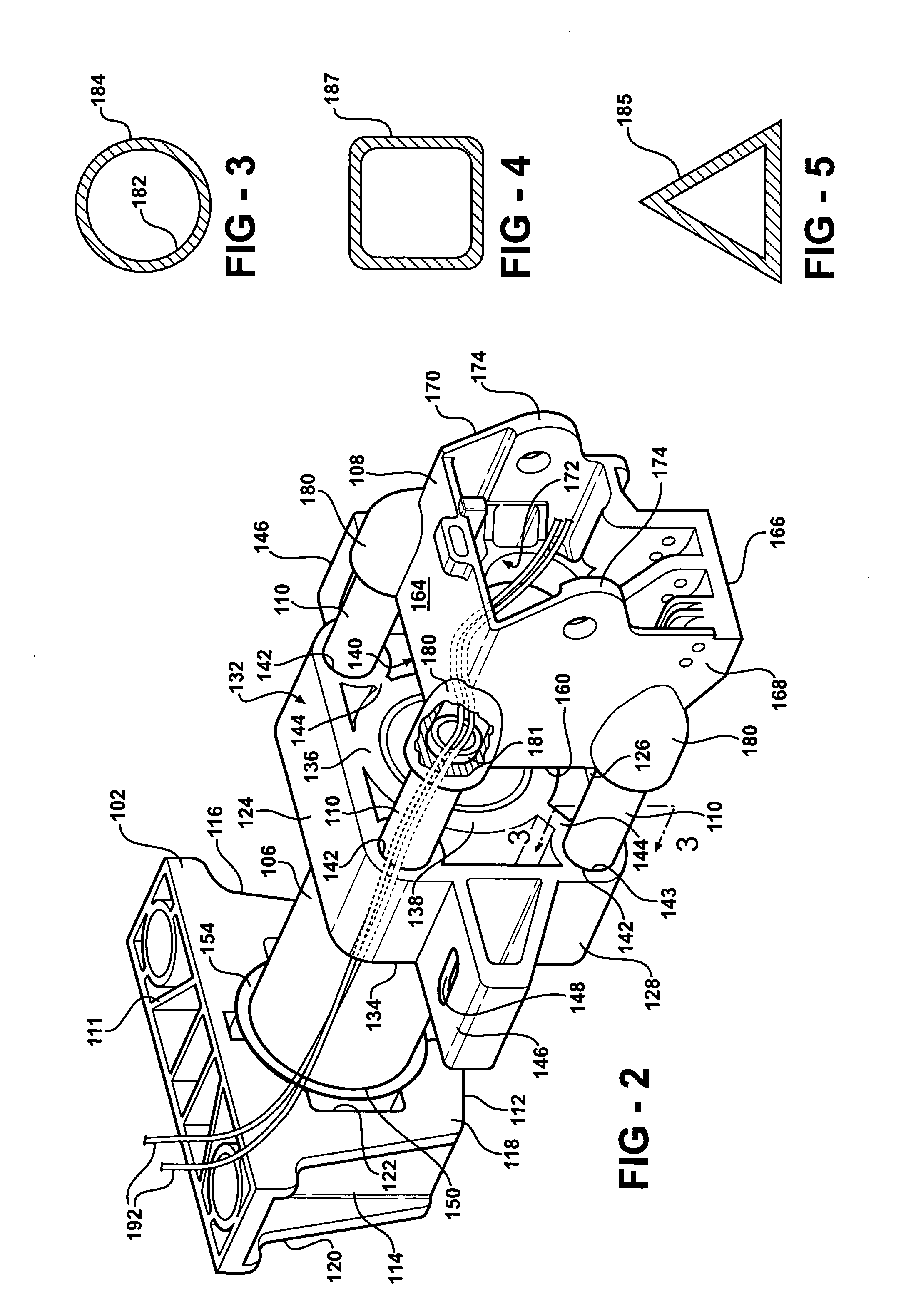
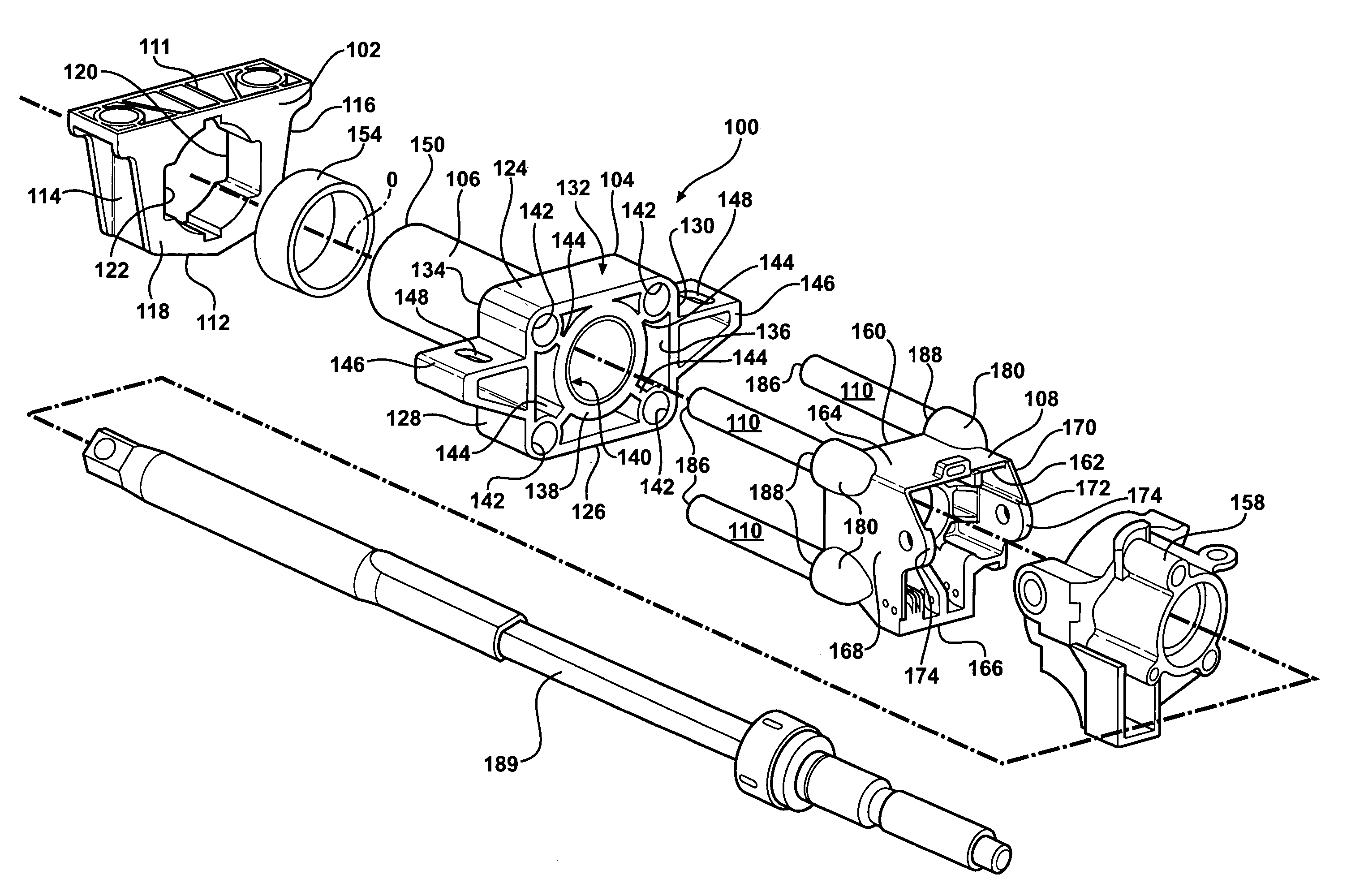
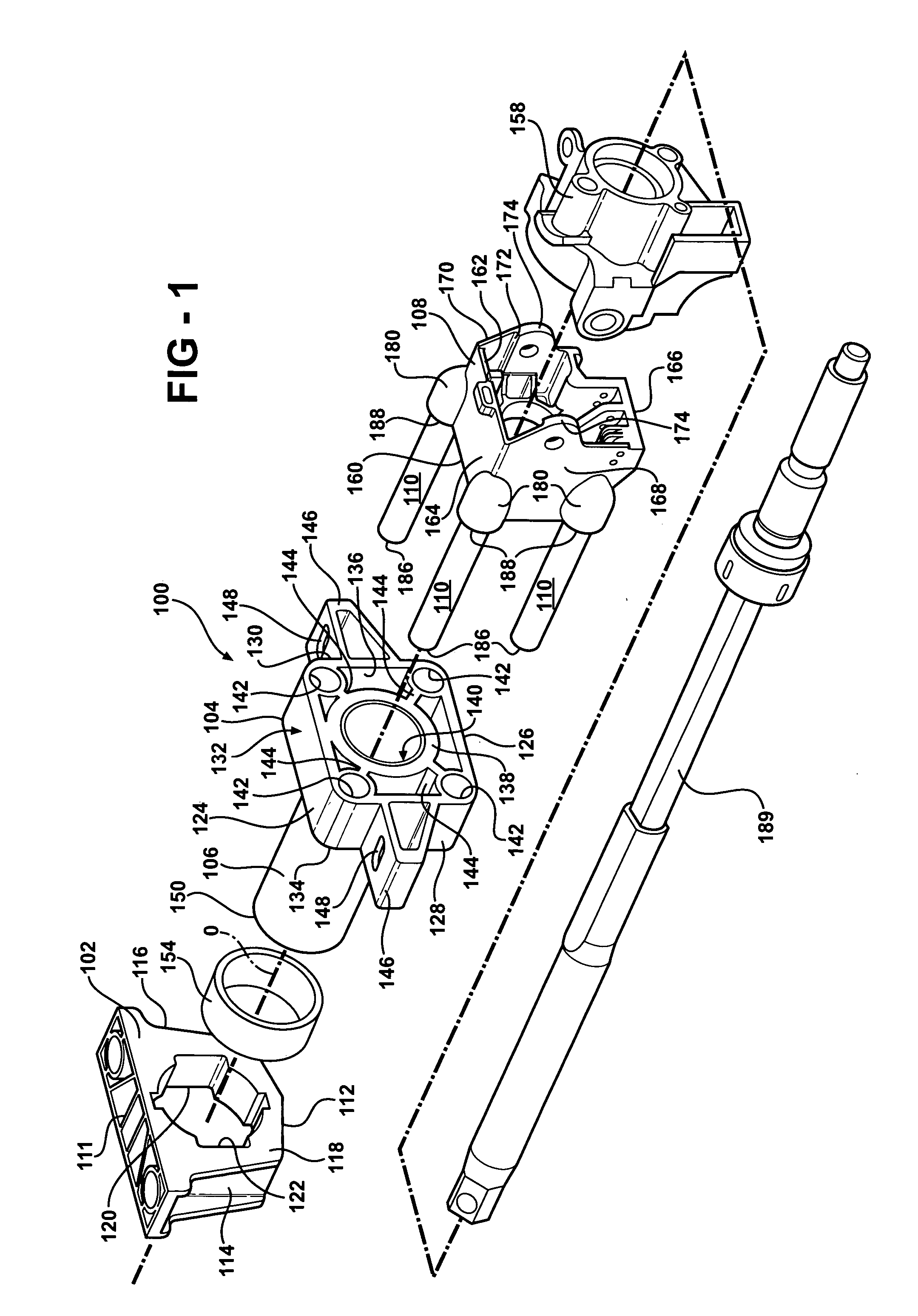
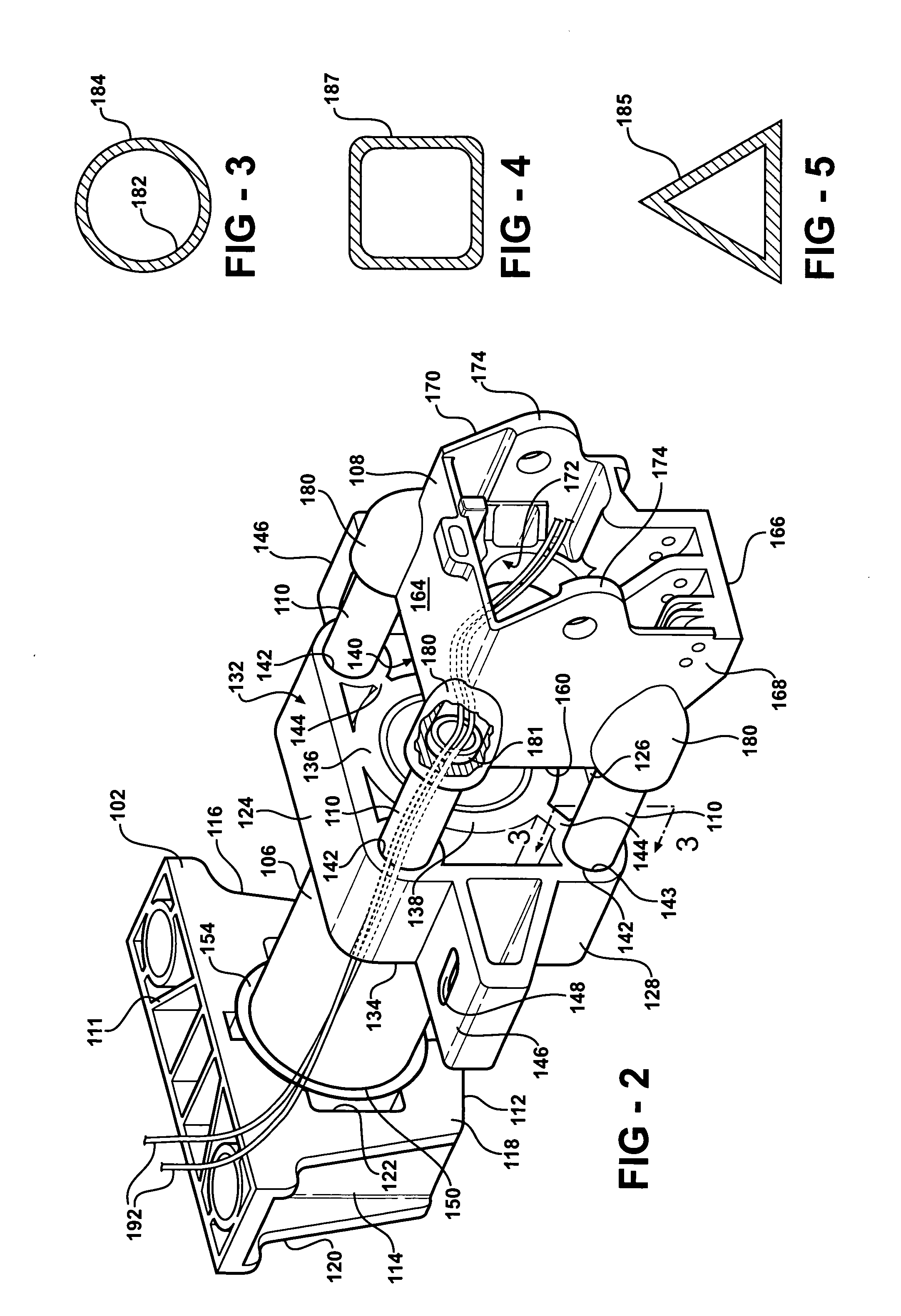
Steering column assembly and method of fabricating the same
InactiveUS20050189756A1High section modulusImproved and predetermined stiffness characteristicSteering columnsSteering columnEngineering
A steering column assembly of the present invention includes a lower support bracket, an upper support bracket, and a jacket disposed within and extending along a longitudinal axis through the lower support bracket and the upper support bracket. The steering column assembly includes a yoke support housing and a plurality of tubes spaced from one another circumferentially about the longitudinal axis and interconnecting the yoke support housing and the upper support bracket. The invention includes a method of fabricating the assembly. An advantage of the present invention is to provide the steering column assembly that achieves a high section modulus, improved and predetermined stiffness characteristics, and improved packaging characteristics to hold various components such as ECL mechanisms, steering tube position sensors, BSTI switches, wires and the like.
Owner:STEERING SOLUTIONS IP HLDG +1
Opening method and device thereof
ActiveUS20150121985A1Controlled plastic deformationMetal-working feeding devicesFilament handlingYoung's modulusMetal sheet
An opening radial dimension is set as a radial direction permissible dimension K of the metal coil as expressed by the following equation or lower.K=Yp×Z2EIR2(Θ-sinΘcosΘ)Wherein: K is a radial direction permissible dimension at the load action point position in mm; Yp is a yield stress of the metal sheet, in kgf / mm2; Z is a section modulus of the metal sheet, in mm3; R=(a metal coil radius r)−½(the plate thickness t of the metal sheet), in mm; E is a Young's modulus of the metal sheet, in kgf / mm2; I is a second moment of area of the metal sheet in mm4; and Θ is an angle in radians about the axis of the metal coil from the load action point to the nearest restraining roll along a rewind direction of the metal coil.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Spark plug with increased durability
A spark plug is provided which is designed to be compact without sacrificing a mechanical strength of a porcelain insulator. The spark plug includes a metal shell having a base end and a top end. The porcelain insulator is made of a hollow cylinder which includes a body and an insulator head. The body is retained within the metal shell. The insulator head extends from the base end of the metal shell in a lengthwise direction of the porcelain insulator and has a length made up of a major body leading to the body of the porcelain insulator and an end portion lying far away from the body. The major body has an outer diameter D 1 , an inner diameter D 2 , and a section modulus Z at a smallest-outer diameter portion thereof which meet relations of 7.1 mm<=D 1 <=8.8 mm, D 2 >=2.8 mm, and Z>=33 mm<3>.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Equipment for bending, forming and tempering automobile glass
This invention relates to a device for bending, molding and steeling of car glasses, in which, the bending unit includes corresponding up and down bending units and rollers, and each of the bending units includes a side bending unit, and each side bending unit includes a spring steel board, a link frame, an elevator, a bearing base, and two ends of the steel board are hinged with the elevator fixedly, the spring steel blard is hinged with the link frame, a fixed pin is set in the middle of the hemline of the link frame and multiple bearing bases are installed on the board characterizing that it is integral bending when a solid frame composed of the spring steel board and the link frame is bent, and its section modulus is much greater than that of a single spring steel board.
Owner:FUYAO GLASS IND GROUP CO LTD
Fuel supply device
ActiveUS20190017474A1Reduce the cross-sectional areaResistant to breakageElectrical controlFuel injection apparatusStress concentrationCoupling
A fuel supply device configured to supply fuel from an inside of a fuel tank to an internal combustion engine includes: a cover body that is installed to an upper wall of the fuel tank; a pump unit that is placed on a bottom wall of the fuel tank and is configured to discharge the fuel from the inside of the fuel tank toward the internal combustion engine; and a coupling stay that couples between the cover body and the pump unit. The coupling stay includes: an upper stay that extends on a lower side of the cover body; and a lower stay that is installed to the pump unit and is slidably fitted to the upper stay in a top-to-bottom direction. A stress concentrating portion, which reduces a section modulus to concentrate a stress around the stress concentrating portion, is formed at a specific location of the lower stay.
Owner:AISAN IND CO LTD
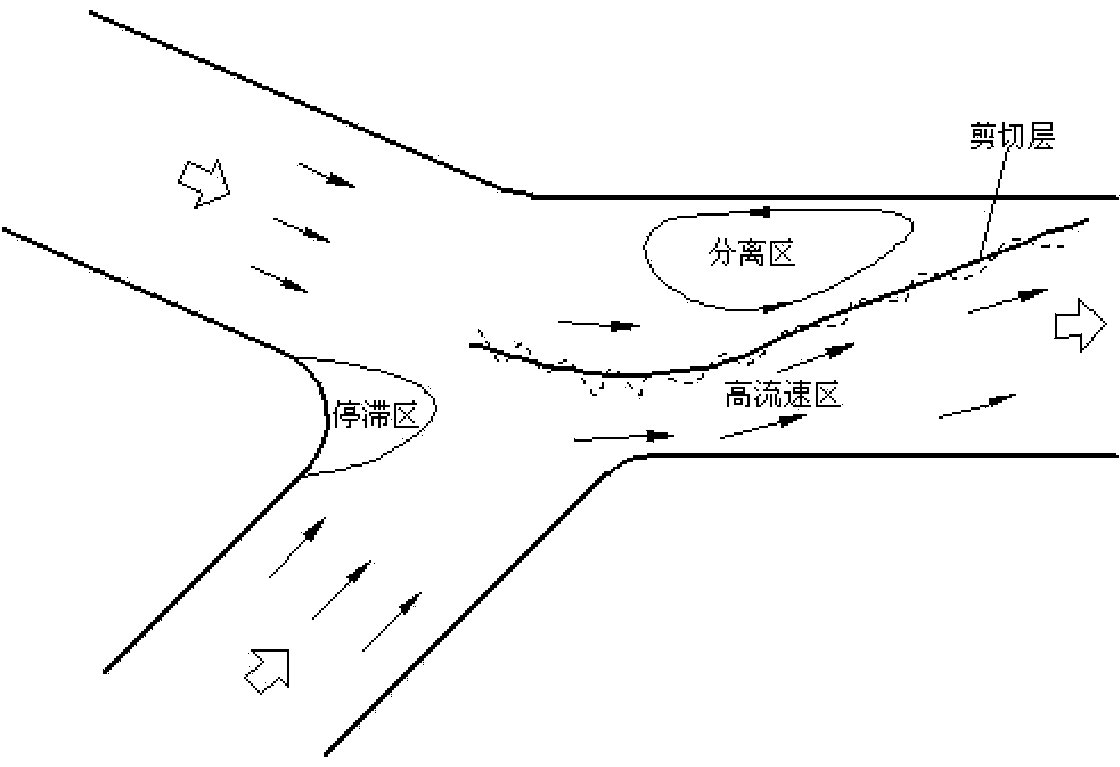
Riverway intersection water flow stagnant area wedge cone and building method and application thereof
InactiveCN104195979AIncrease flow rateAvoid siltingStream regulationStructure of the EarthWater flow
The invention discloses a riverway intersection water flow stagnant area wedge cone. According to a building method of the cone, under the main and branch water flow incoming representative flow condition, SMS numerical value simulation software is utilized for calculating a two-dimensional flow velocity field of a main and branch water flow intersection area under the natural terrain condition, flow velocity contour maps at the different water level elevation positions are extracted, contour lines equal to the sediment incipient motion critical flow velocity Uc in the different water level elevation flow velocity contour lines are determined through the sediment incipient motion critical flow velocity Uc, and the contour lines are overlapped to form a wedge cone structure; a connection line of flow velocity contour line intersection points with the main and branch water flow velocity equal to the Uc in the lowest water level process and shoreline intersection points is defined as a y axis, section subdivision is carried out on the stagnant area along the y axis, water levels of the contour lines on the section are extracted to be fitted, the section water levels meet a parabolic equation that z is equal to a ax<2>+bx+c, section modulus a, b and c build a relation with the y axis, and the structural terrain elevation of the wedge cone is obtained. The wedge cone can effectively reduce the jacking effect of the intersection area, the water flow in the intersection area is uniform, and the wedge cone is suitable for the flow rectification engineering of the intersected riverway water flow stagnant area
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Process for casting piston-ring blanks
ActiveCN102407292AImprove product qualityMeet performance indicatorsPiston ringsFoundry mouldsPiston ringSection modulus
The invention discloses a process for casting piston-ring blanks. The process mainly comprises the steps of template manufacturing, sand mulling, modeling, smelting, casting, sand shakeout, blank sorting, cleaning and blank finishing; and a template used in the step of modeling is of a lantern ring structure, and a gas-ring model loop and an oil-ring model loop (the section modulus of a blank of the gas-ring model loop is close to that of the oil-ring model loop) are selected and bonded in one baseplate to carry out casting, therefore, on the basis of ensuring the stable product quality, the product yield and working efficiency of the casting process for piston-ring blanks can be significantly improved, and the production cost can be reduced.
Owner:石家庄金刚内燃机零部件集团有限公司
Calculating method for bending strength of dust-collector-box standing column under transverse-load effect
ActiveCN108021775AAccurate Force Transmission MechanismImprove accuracyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationEngineeringSection modulus
The invention discloses a calculating method for the bending strength of a dust-collector-box standing column under the transverse-load effect. Engineering designers can conveniently and accurately calculate the maximum section bending moment of the internal force of the middle standing column when box wall plates suffer from the transverse-load effect according to the formula and related calculation coefficient tables; synergistic work of the wall plates and the standing column are considered, the wall plates in the effective width on the two sides of the standing column serve as extending parts of standing-column flanges to form a compound section, and the compound section and the standing column jointly bear the bending moment; in this way, the standing-column section modulus is multiplied by a correction coefficient gamma, and calculation and analysis of finite elements of multiple embodiments show that the gamma can be valued as 1.06 based on the safety, and therefore checking calculation of the bending strength of the section of the standing column is carried out.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Column-beam connection structure
InactiveCN102209818AReduce weightEasy to processArc welding apparatusBuilding constructionsEngineeringHot working
Bending moment applied to a beam causes out-of-plane deformation to a panel when the panel zone is hollow, and thereby a load bearing by a web cannot be expected in an elastic region. Since the section modulus of a beam end which is used in the structure calculation of a building structure is limited to the section modulus of only the flange not including the web, the beam end has a low strength. Therefore, a beam larger in size must be used and an extra beam depth is required, thus causing an increase in the weight of a steel beam. As the result of various studies, it has been found that various problems could be resolved by significantly increasing the plate thickness of a diaphragm in the direction of the web, and imparting prestress by hot working or overlaying the underside surface of the beam.
Owner:ARCREATE
High-pressure sealing
In a high-pressure cylinder with an axial plunger, a seal assembly for scaling the gap between the cylinder wall and the plunger. The assembly is disposed in an annual recess in the wall having an open end and a bottom opposite thereto, and comprises a plunger-sealing ring, a cylinder-sealing ring, a resilient low-pressure ring, and an annual seal holder. The seal holder urges the plunger-sealing ring against the cylinder-sealing ring and the low-pressure ring, and urges the latter two rings against the recess bottom and against each other. The plunger-sealing ring and the cylinder-sealing ring are metallic, their mutual contact surfaces are fitted to each other, and the plunger-sealing ring has sufficient section modulus to ensure that under high pressure the contact and bending deformations at the mutual contact surfaces will be sufficiently small as to keep a tight fit therebetween.
Owner:MLC EXTRUSION SYST
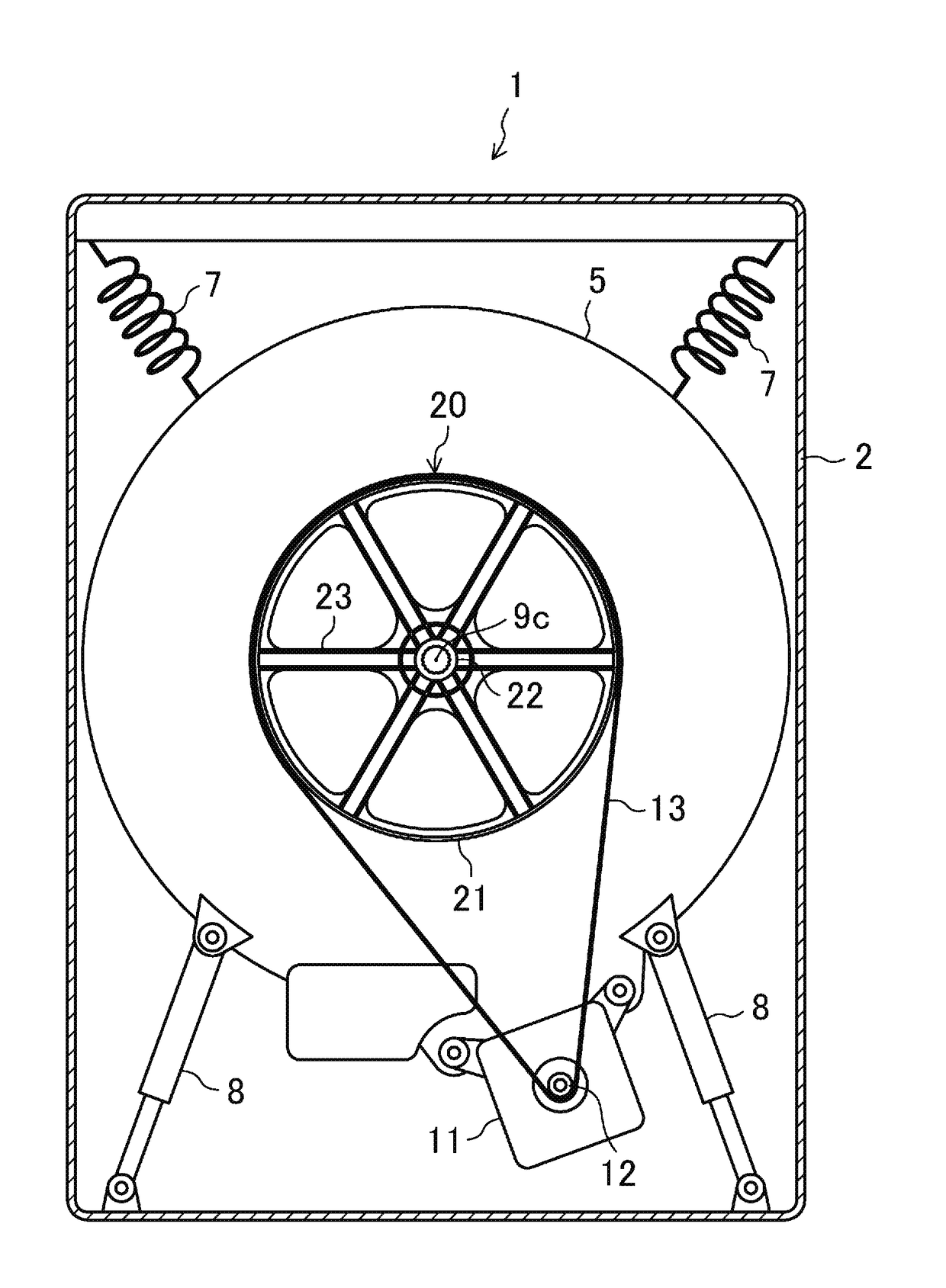
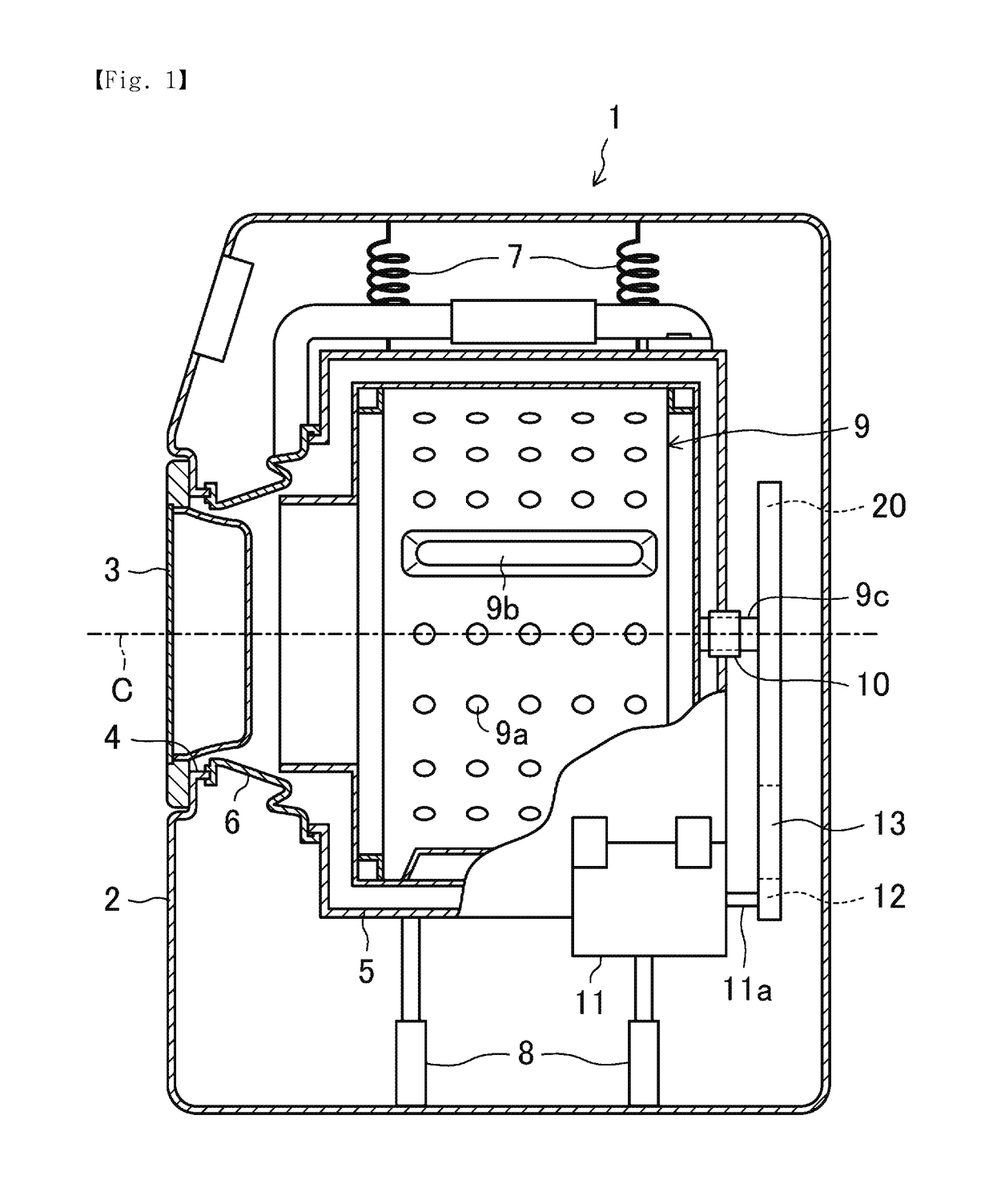
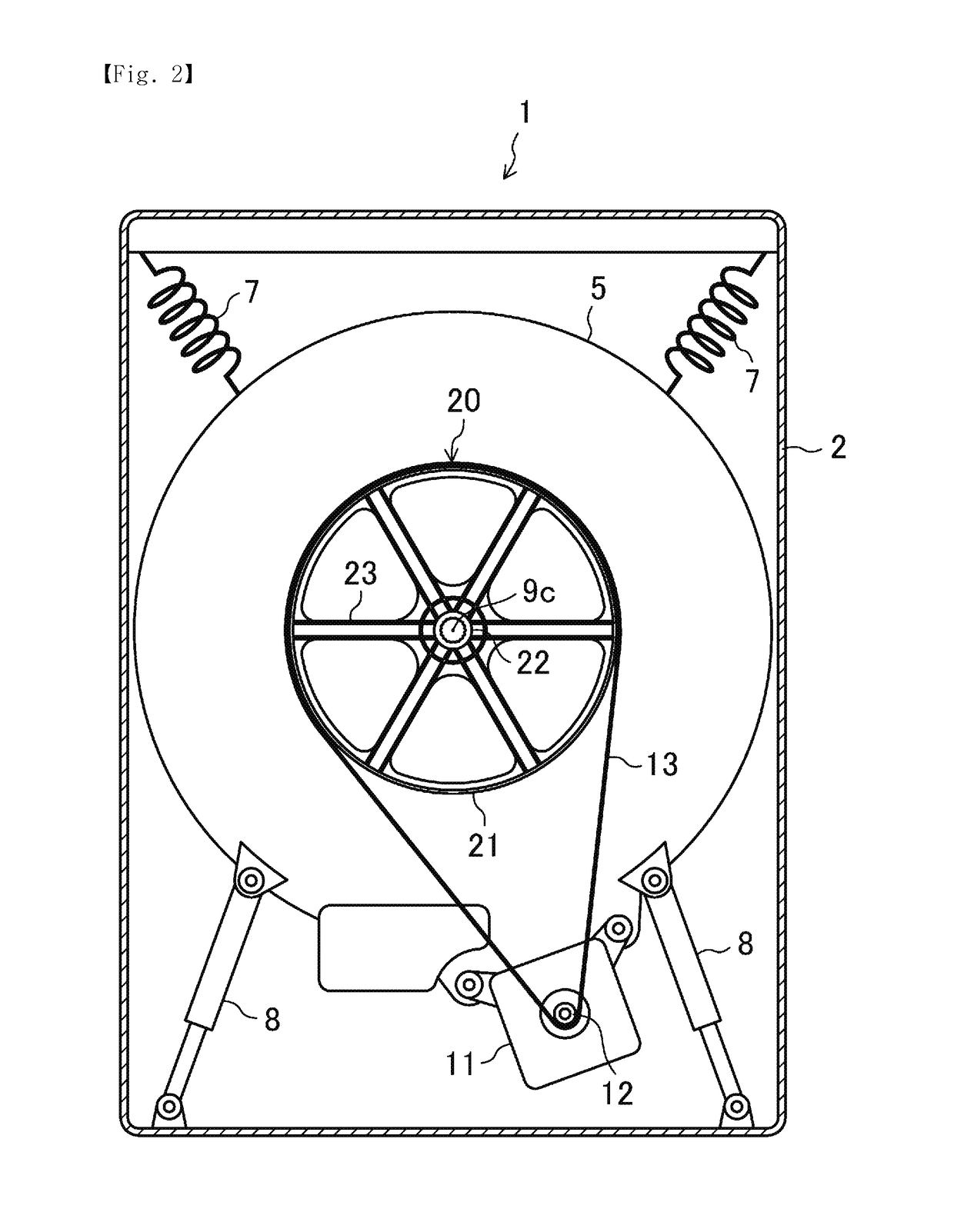
Washing machine and pulley for washing machine
By improving the rigidity of a pulley while suppressing a weight of the pulley from increasing, excessive noises due to resonance can be reduced. A washing machine 1 includes a drum 9 rotatably disposed in the water tub 5. The washing machine 1 has a motor to rotationally drive a pulley 20, which is fixed to the drum 9, via an endless belt 13. The pulley 20 has a plurality of arms 23 radially extend from the boss 22 to support an outer wheel 21. The arm 23 has a variable cross-sectional portion 24 in which a section modulus against bending in an axial direction gradually decreases from the boss 22 to the outer wheel 21.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Steering column assembly and method of fabricating the same
A steering column assembly of the present invention includes a lower support bracket, an upper support bracket, and a jacket disposed within and extending along a longitudinal axis through the lower support bracket and the upper support bracket. The steering column assembly includes a yoke support housing and a plurality of tubes spaced from one another circumferentially about the longitudinal axis and interconnecting the yoke support housing and the upper support bracket. The invention includes a method of fabricating the assembly. An advantage of the present invention is to provide the steering column assembly that achieves a high section modulus, improved and predetermined stiffness characteristics, and improved packaging characteristics to hold various components such as ECL mechanisms, steering tube position sensors, BSTI switches, wires and the like.
Owner:STEERING SOLUTIONS IP HLDG +1
Self-propelled traction ship model control and measurement method
PendingCN110082065ATimely processingSimple and fast operationHydrodynamic testingMeasurement deviceDrive motor
The invention relates to a self-propelled traction ship model control and measurement method, which is characterized by setting navigation acceleration, speed and stroke and the like of a ship model by utilizing a computer editing instruction; then, transmitting the information to a driving motor on a ship model tractor through lines to control the ship model tractor to drag the ship model to operate and monitoring the ship attitude through a measurement device; and determining various technical indexes, such as ship rinsing and sinking amount, water surface fluctuation, ship safety surplus, section modulus, channel surface fluctuation and ship speed in and out of a ship compartment in the prototype. The method has simple operation, and stable operation; and the measured data has the advantages of high real-time performance, high precision and good fitting effect with the prototype.
Owner:NANJING HYDRAULIC RES INST
Spark plug with increased durability
InactiveUS7234429B2Simple structureSmall sizeSparking plugsGenerator generated ignition energyEndurabilityEngineering
A spark plug is provided which is designed to be compact without sacrificing a mechanical strength of a porcelain insulator. The spark plug includes a metal shell having a base end and a top end. The porcelain insulator is made of a hollow cylinder which includes a body and an insulator head. The body is retained within the metal shell. The insulator head extends from the base end of the metal shell in a lengthwise direction of the porcelain insulator and has a length made up of a major body leading to the body of the porcelain insulator and an end portion lying far away from the body. The major body has an outer diameter D1, an inner diameter D2, and a section modulus Z at a smallest-outer diameter portion thereof which meet relations of 7.1 mm≦D1≦8.8 mm, D2≧2.8 mm, and Z≧33 mm3.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com