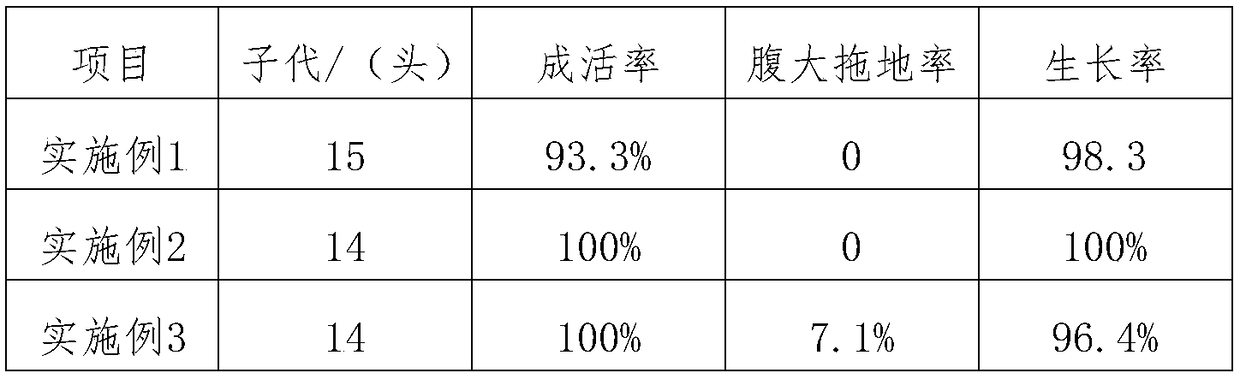
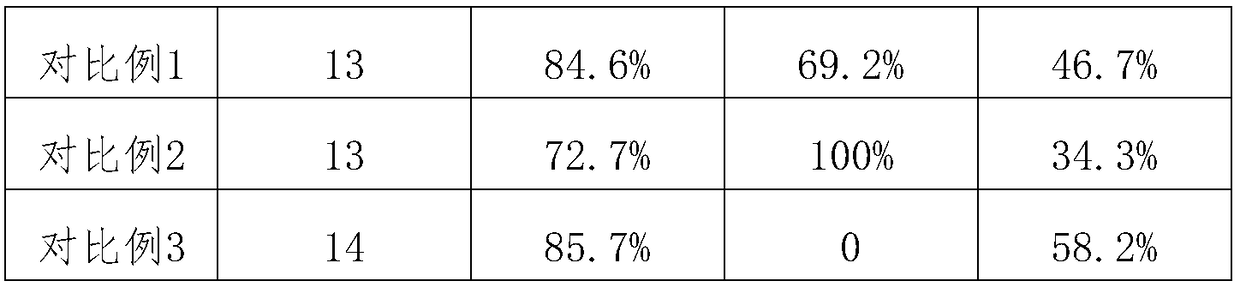
Patents
Literature
30 results about "Small ears" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Seedless cultivation technology of ruby rose grapes
InactiveCN104067871AFully cater to the requirementsEarly maturityCultivating equipmentsHorticulture methodsEconomic benefitsFresh food
The invention relates to a seedless treatment method of ruby rose grapes. The seedless treatment method is suitable for the seedless treatment of the ruby rose grapes. The seedless treatment method comprises dispersing flower ears before 14 days of the full-bloom stage, leaving small ears with the 4 to 5 cm length of ear tips, and performing flower ear treatment through a gibberellin solution which is 12.5 to 15 mg every L; trimming the flower ears during the full-bloom stage to enable about 25 small ears of e every ear tip to be left, enabling the flower ears to be soaked in the gibberellin solution which is 12.5 to 15 mg every L for 5 seconds, and performing routine management after the treatment; performing treatment on the flower ears through a mixed solution of the gibberellin which is 25 mg every L and the forchlorfenuron which is 5 mg every L after 11 days of the full-bloom stage. According to the seedless cultivation technology of the ruby rose grapes, the seedless rate of the cultivated ruby rose grapes reaches 100%, the single fruit weight is improved by 155%, the market prospects of the produced large seedless fresh food grapes are great due to the seedless treatment on the ruby rose grapes through the gibberellin and the forchlorfenuron, and the considerable economic benefits can be obtained.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
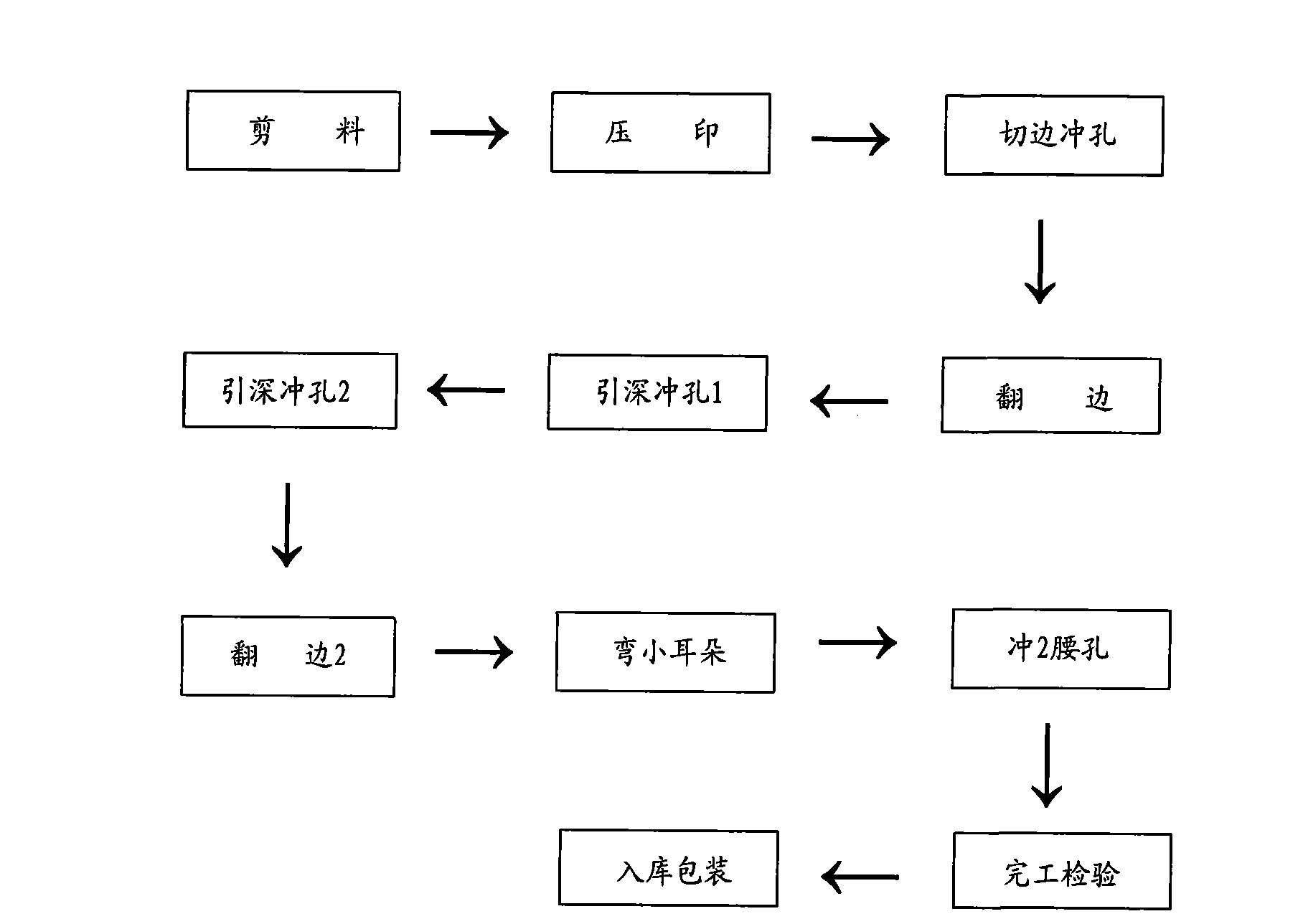
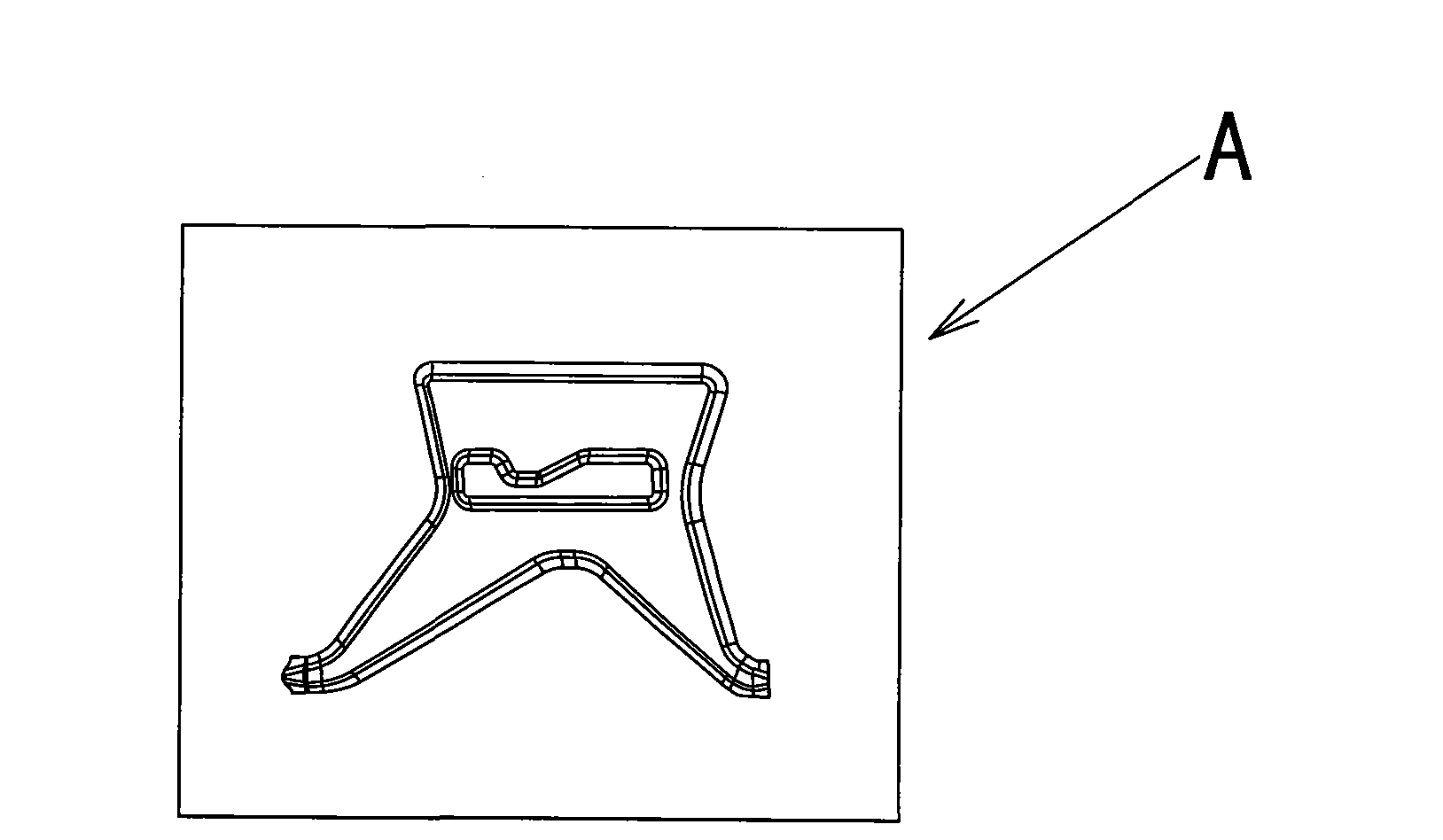
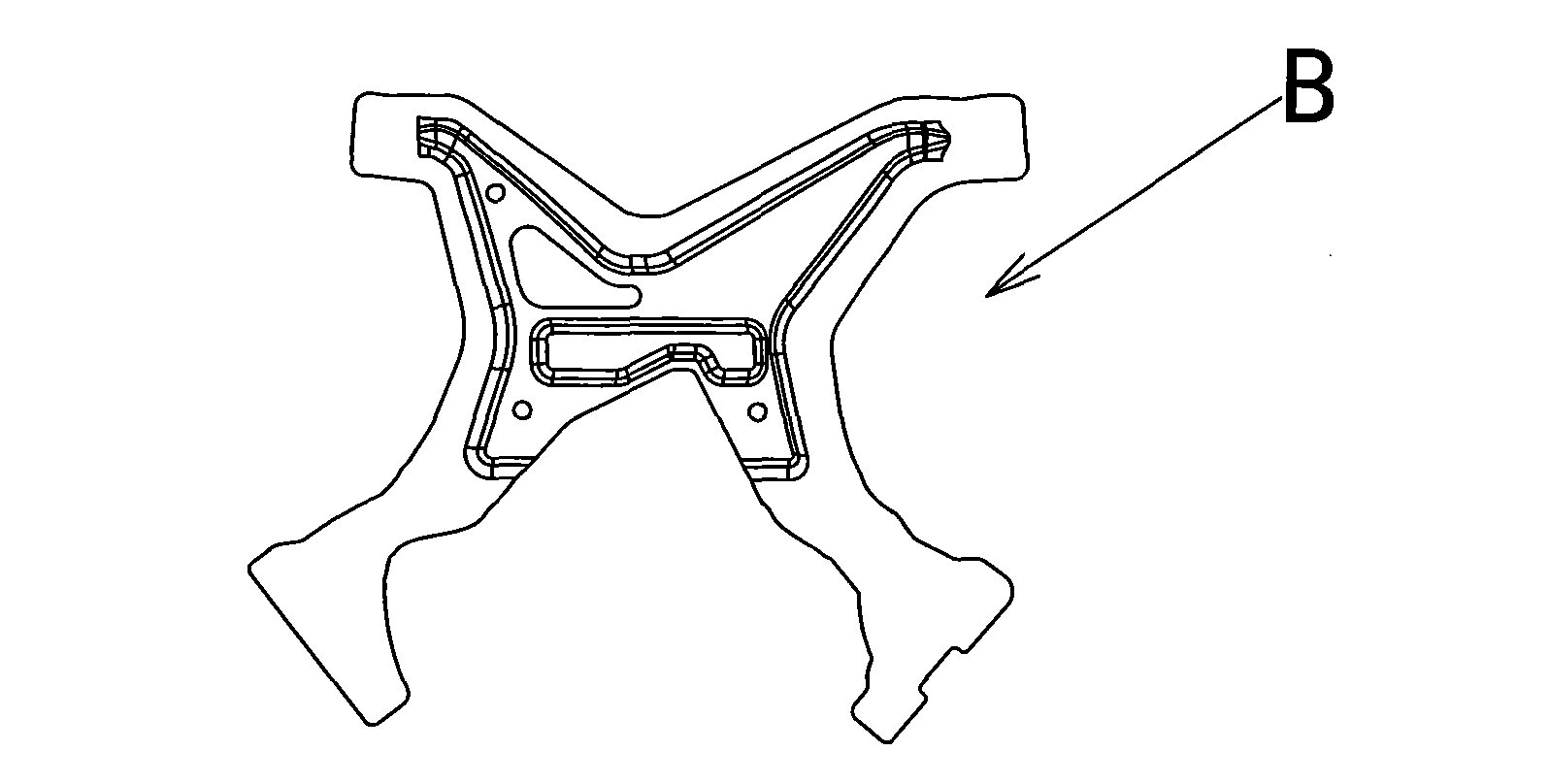
Machining method for fixed angle plate of automobile instrument skeleton beam
InactiveCN102039355ASimple processProcess arrangement is reasonableVehicle componentsPunch pressSmall ears
The invention relates to a processing method for a fixed angle plate of an automobile instrument skeleton beam, comprising the following steps of: firstly, coining: stamping raw materials with a coining mould and a press machine, to get a workpiece A; secondly, edge scraping and punching: carrying out edge scraping and punching on the workpiece A with a trimming and punching mould and the press machine, to get a workpiece B; thirdly, first turnuping: turning up the side of the workpiece B with a first turnuping mould and a punching machine, to get a workpiece C; fourthly, first lead deep punching: punching the workpiece C with a first lead deep punching mould and the punching machine, to get a workpiece D; fifthly, secondary lead deep punching: punching the workpiece D with a second lead deep punching mould and the punching machine, to get a workpiece E; sixth, secondary turnuping: turning up the workpiece E with the second turnuping mould and the punching machine, to get a workpiece F; seventhly, small ear bending: punching the workpiece F with a small ear bending mould and the punching machine, to get a workpiece G; and eighthly, waist hole punching: punching the workpiece G with a waist hole punching mould and the punching machine, to get a workpiece H.
Owner:上海德真工贸有限公司
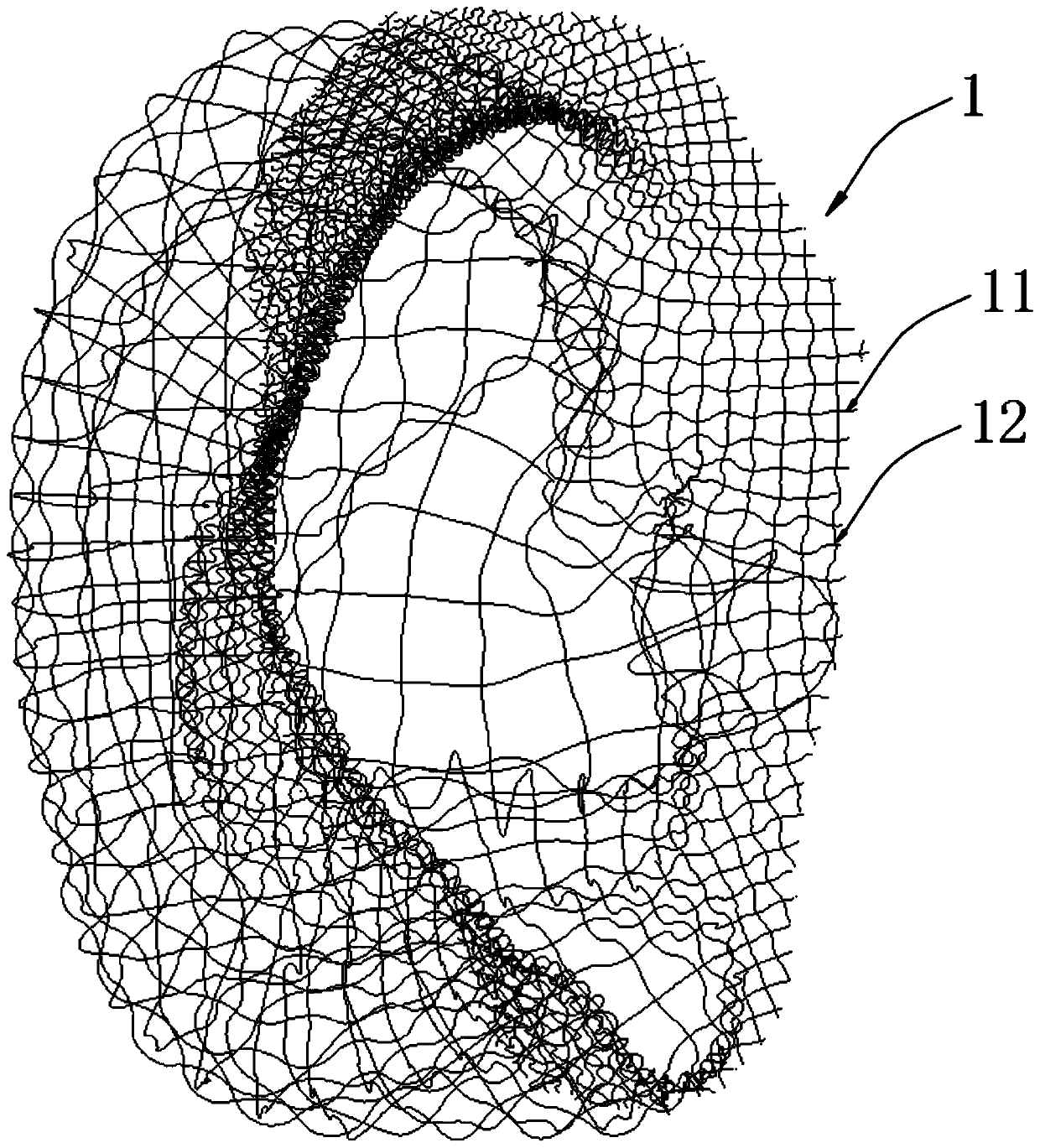
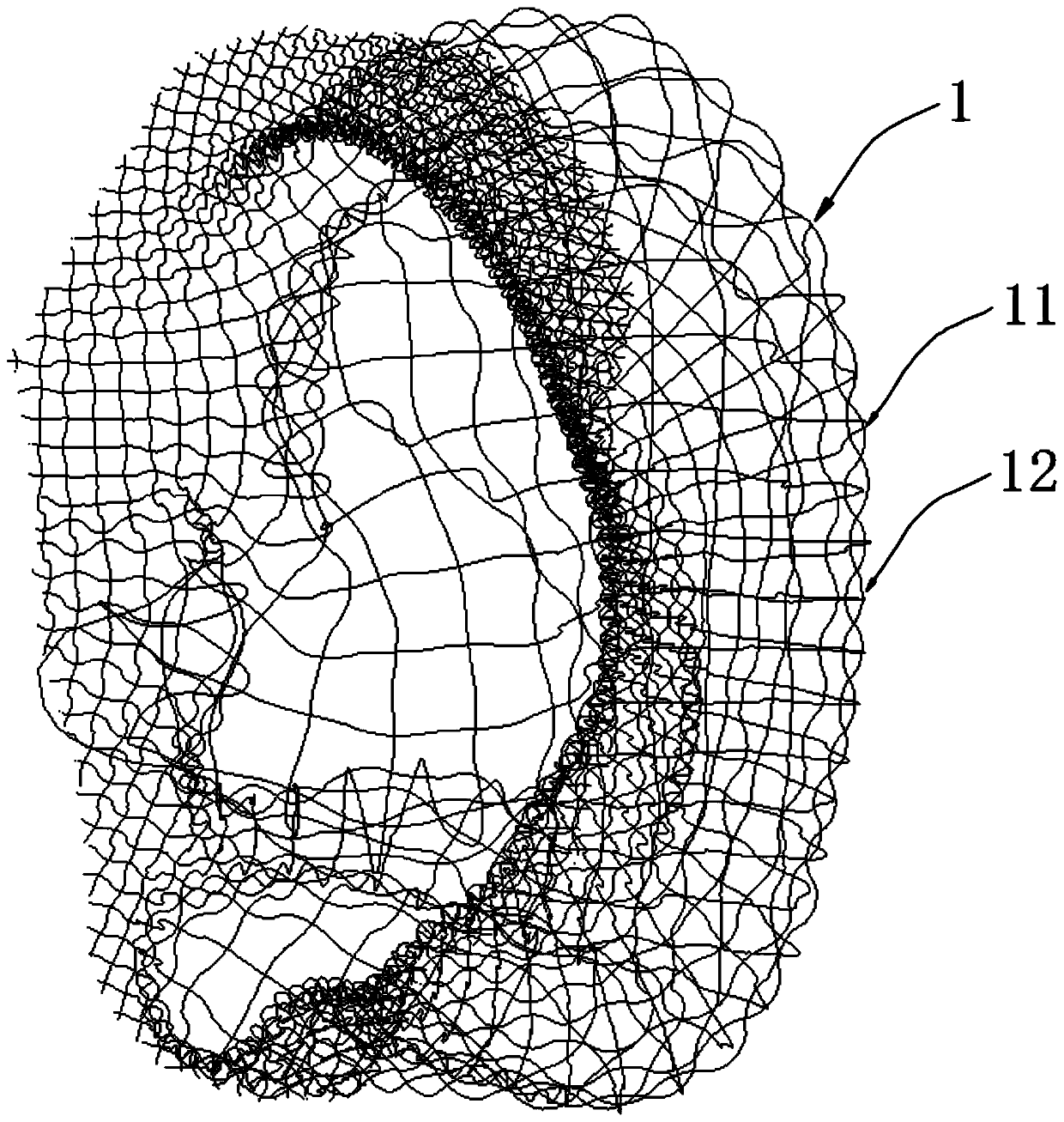
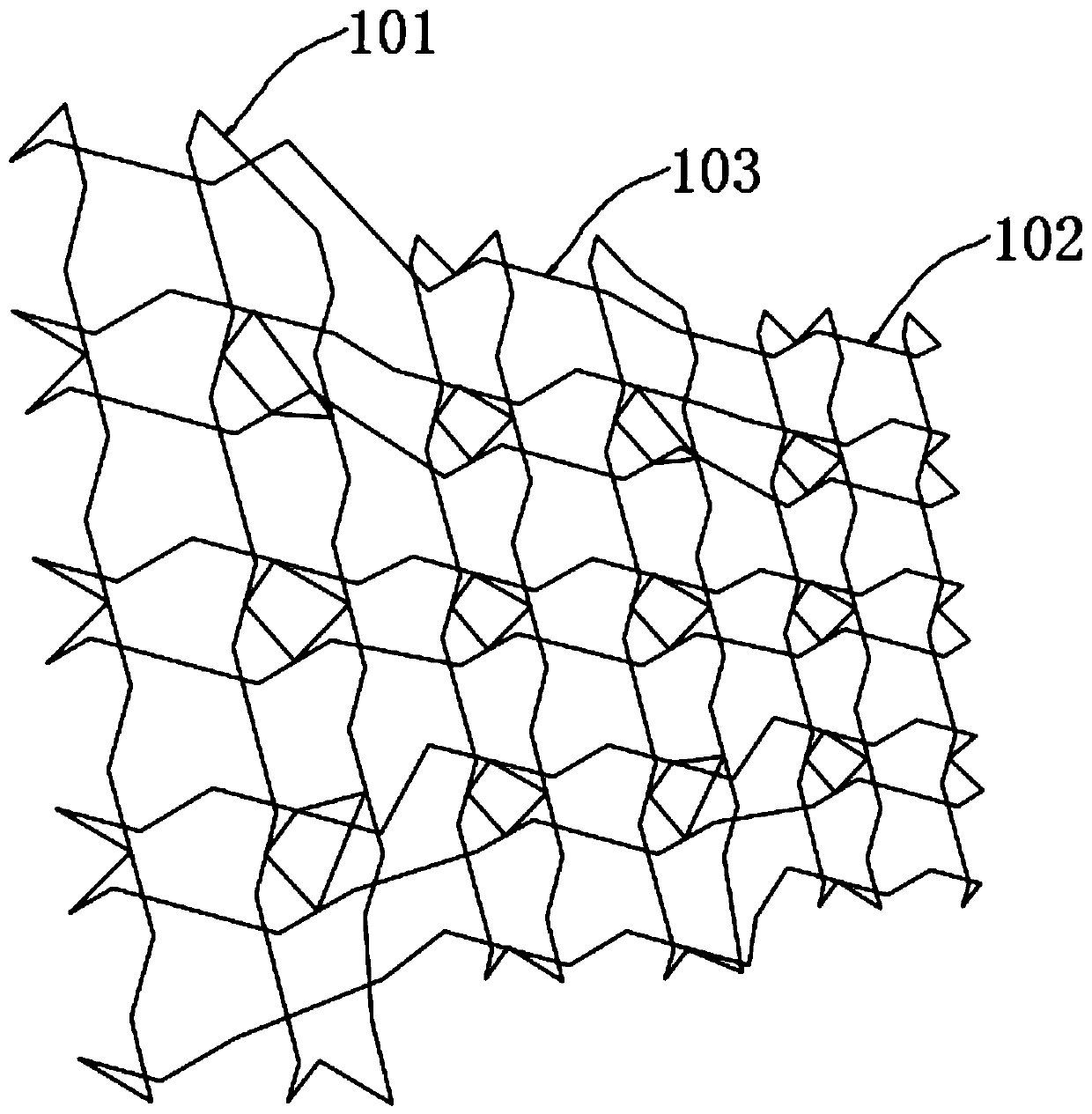
Tissue engineering bracket with partitions
ActiveCN109893305ARelieve painSimplify tedious stepsAdditive manufacturing apparatusEar treatmentEngineeringSmall ears
The invention relates to the technical field of human bioengineering, in particular to a tissue engineering bracket with partitions, the tissue engineering bracket comprises a bracket body, wherein the bracket body is composed of a plurality of groups of parallel net strips with different directions between each group, and reinforcing edges for interweaving and connecting the net strips are arranged between the net strips. A sparse structure area and a compact structure area are regularly arranged on the bracket body, and a transition structure area is arranged between the sparse structure area and the compact structure area. According to the tissue engineering bracket with partitions, a plurality of groups of parallel net strips with different directions between each group are connected to form a model with a specific shape through a plurality of reinforcing edges which are interval distributed and are generally connected with each other to form a rhombic shape, and the model is emphatically partitioned to enable different parts of the model to have different densities and strengths; an auricle bracket is manufactured by adopting a 3D printing titanium alloy method, so that the artificial auricle bracket is closer to the structure of a real auricle; the preparation is made for improving the conventional small-ear deformity auricle reconstruction operation, rib cartilage does not need to be intercepted through thoracic operation, and the pain of patients is relieved.
Owner:SIR RUN RUN HOSPITAL NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Forging die for large hinge beam and production process of large hinge beam
ActiveCN107414003ASolve the strength problemSolve the problem of longevityForging/hammering/pressing machinesSmall earsEngineering
The invention discloses a forging die for a large hinge beam and a production process of the large hinge beam. The forging die is composed of a forging die lower die body and an upper die assembly. The forging die lower die body is composed of a bottom die assembly and a lower die assembly located on the bottom die assembly. The bottom die assembly is composed of a die pad, a bottom die, a big / small ear insert and a lower die insert. The lower die assembly is composed of a die body and an upper die insert. The upper die insert is arranged above the lower die insert and is fixed to the die body. The upper die assembly is composed of an upper flat die, an outer punch and an inner punch. A cutter is movably arranged on the side face of the big / small ear insert in a penetrating manner. The cutter comprises big ear cutter bodies and small ear cutter bodies, wherein the big ear cutter bodies are perpendicular to the small ear cutter bodies. By the adoption of the forging die for the large hinge beam and the production process of the large hinge beam, the situation of machining a hinge beam workblank by means of a traditional casting manner is changed thoroughly, and thus the problems that the hinge beam is poor in strength and short in service life are solved.
Owner:湖南巨峰科技实业有限公司
Fresh corn positioning and spike cutting device
ActiveCN110271044AAvoid cutting ears too largeAvoid the problem of being too smallMetal working apparatusEngineeringSmall ears
The invention relates to the technical field of fresh corn spike cutting, and discloses a fresh corn positioning spike cutting device. A visual detection mechanism and a controller are arranged, the visual detection mechanism can identify the size and the positions of corns with spikes to be cut and can classify the corns according to the size, and the controller can automatically adjust the diameter and size of a positioning mechanism according to the identification and the size classification of the corns by the visual detection mechanism, so that the problem of over-large or over-small ear cutting when corns with different sizes are subjected to spike cutting positioning can be avoided, the problem of waste caused by over-large corn cutting can be reduced as much as possible, and meanwhile, automatic conveying, automatic material pushing and cutting can be realized; according to the device, a spike cutting device is arranged, under the driving of a motor, the spike cutting device can drive slices to carry out up-and-down cutting movement, so that corn spikes can be cut off, the traditional manual ear cutting process is replaced, and the labor intensity of workers is reduced.
Owner:ANHUI SCI & TECH UNIV
Groove-type embedded part
The invention relates to a groove-type embedded part, which comprises a C-shaped groove and two side wings. The C-shaped groove comprises a base and two side walls. The two side walls extend from the two sides of the base. Extension arms extend from the front ends of the side walls. The two side walls, the extension arms and the base are integral. By adopting the technical scheme and by adopting integral design and a plate bending and punching technology to realize the production of the embedded part, the groove-type embedded part has the beneficial effects that: 1. plate machining can be used during mass production and the material wastage is reduced by optimizing plate setting; 2. the groove-type embedded part is flexible to produce and manufacture; 3. the machining strength of steel plates is higher than the strength of plates which are produced by adopting the existing techniques such as casting; and 4. the punched holes or small ear plates can increase the area of contact with concrete and the pulling strength is improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG KIN LONG HARDWARE PROD CO LTD
Folded fitness device suitable for waist and abdomen training and folding method
InactiveCN107485824AEnhance the ability to exert force from multiple anglesForce fitGymnastic exercisingSpace saving gamesMuscle trainingSmall ears
The invention relates to a folded fitness device suitable for waist and abdomen muscle training and a folding method. According to the method for training the waist and abdomen muscle, the self-motion can be used for training, a user lies on the ground and makes the right motion to stimulate the muscle of parts which need training, and meanwhile through assistance of waist and abdomen muscle training instruments, the strength of the waist and abdomen muscle is improved. The device comprises a ground supporting rack (1), a rotation rack (2) and a length telescopic rack (3), a pair of large ear plates (4) and a set of angle adjustment hook plates (5) are vertically welded to the upper portion of a beam (101) of the ground supporting rack, and the large ear plates are connected with the rotation rack through rotation shafts; the length telescopic rack is inserted into the rotation rack, a pair of first small ear plates (6) are vertically welded to one side of the rotation rack, a pair of second small ear plates (7) are welded to the other side of the rotation rack, and hook foot stands (8) are connected onto the first small ear plates through rotation shafts. The folded fitness device suitable for waist and abdomen muscle training is applied to the field of physical fitness.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV
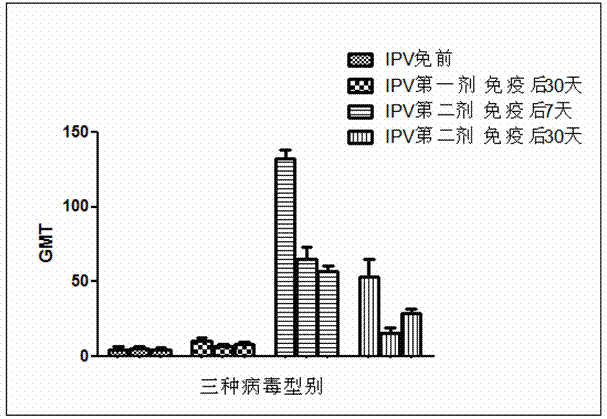
Establishment method of animal model for evaluating IPV (inactivated poliovirus vaccine) intradermal immunization effectiveness
ActiveCN103877596ASimple methodImprove standardizationIn-vivo testing preparationsTesting medicinal preparationsCytopathic effectTISSUE CULTURE INFECTIOUS DOSE 50%
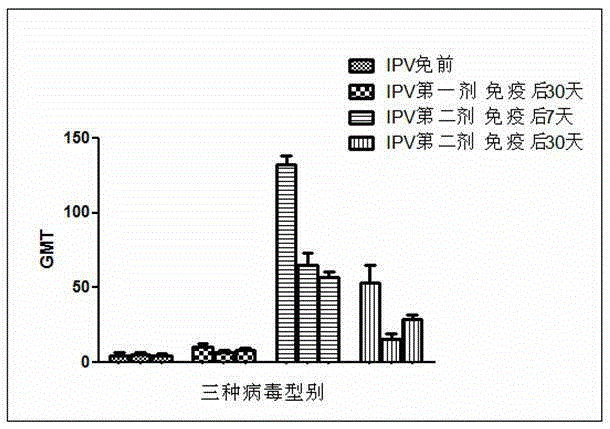
The invention provides an establishment method of an animal model for evaluating IPV (inactivated poliovirus vaccine) intradermal immunization effectiveness. The establishment method includes the following steps: selecting Yunnan Xishuangbanna small ear pigs belonging to Southern China pigs, with pig ages of 3-5 months and weights of 10-20kg, randomly grouping the pigs, respectively injecting an IPV vaccine through needleless intradermal injection for the first time, sampling blood after immunity for 30 days, separating serum, respectively injecting the IPV vaccine through needleless intradermal injection for the second time, sampling blood after immunity for 7 days and 30 days, separating the serum, respectively injecting the IPV vaccine through needleless intradermal injection for the third time, sampling blood after immunity for 1 month, 6 months, 12 months, 18 months and 24 months, separating the serum, inactivating the serums for 30 minutes at 56 DEG C, conventionally diluting the serums, neutralizing the serums by using Sabin strain I type and II type and Pfizer III type viruses, wherein the dosage of the viruses is 30-300 TCID50 (tissue culture infectious dose 50), naturalizing for 3 hours at 35-37 DEG C, adding cells, culturing at 35-36 DEG C for 7 days, and judging a result according to CPE (Cytopathic Effect), thus establishing the animal model for evaluating IPV intradermal immunization effectiveness. By adopting the establishment method provided by the invention, a rational animal model is provided for an intradermal immunization research on vaccines, and a reliable measure is provided for reducing the dosage of vaccine antigen in the intradermal immunization research.
Owner:INST OF MEDICAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Breeding method of small-ear pigs
InactiveCN106614382AImprove developmentFast growthFood processingAnimal feeding stuffTerrainHuman body
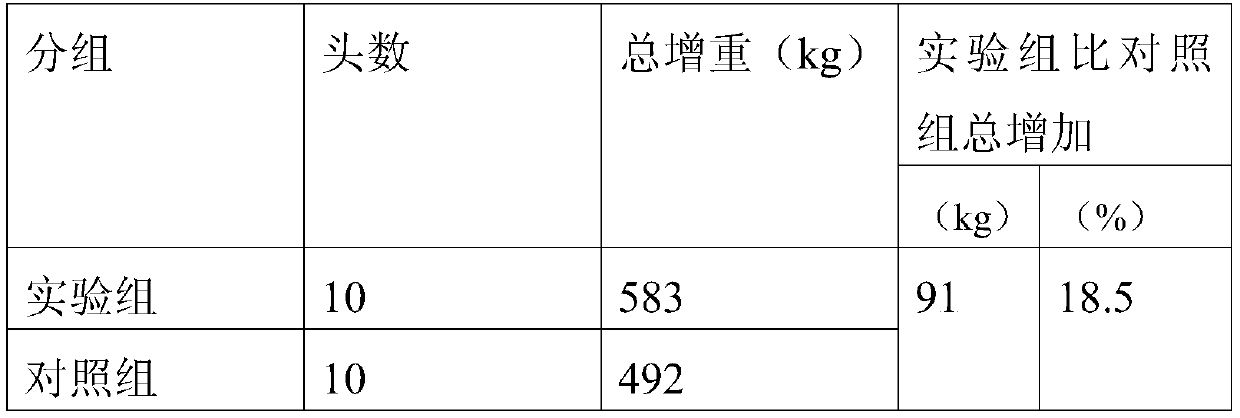
The invention discloses a breeding method of small-ear pigs. The breeding method comprises the following steps: (1) selecting a breeding farm: selecting a region which is leeward and exposed to the sun and has fresh air as the breeding farm; (2) constructing a pig house and an activity space: building wall by bricks at the periphery of the breeding farm, constructing the pig house at a position with a relatively high terrain and constructing the activity space on a land outside the pig house; (3) introducing piglets: selecting healthy 40-day-old to 60-day-old piglets with good varieties and feeding; and carrying out vaccine inoculation; (4) carrying out feeding management: carrying out the feeding management with different manners at two phases including a young stage and an adult stage; and (5) slaughtering: slaughtering after feeding the piglets for 8-10 months. The small-ear pigs bred by the method have good development, high resistance, rapid growth speed and short breeding period, and the lean meat percentage reaches 50% or more; the meat is tender and delicious, has high protein and low energy and abundant nutrients, and meets healthy requirements of human bodies; and the breeding effect of the small-ear pigs is improved by the method and the economic benefits of breeding are increased.
Owner:红河县九冲畜牧业发展有限公司
Double-ring iris expander for intraocular surgery
InactiveCN110547907AReduce Aspiration and InjuryImproved prognosisEye surgeryIntraocular pressureCataract surgery
The invention relates to a double-ring iris expander for an intraocular surgery. The double-ring iris expander consists of an upper ring, a lower ring and an elastic macromolecule film which is connected with the upper ring and the lower ring, wherein the diameter of the upper ring is smaller than that of the lower ring; a plurality of annular small ears which are distributed in an equal distanceare arranged on the inner side of the macromolecule film which is connected with the upper ring and the lower ring; the upper ring and the lower ring can be folded to be placed in the same plane; a groove of which the concave surface faces the center of a ring is formed through the plane and the elastic macromolecule film; and the diameter difference between the upper ring and the lower ring can enable the upper ring to be embedded in the lower ring. According to the double-ring iris expander disclosed by the invention, under the situation that a conventional cataract surgery incision is not increased or extended, a pupil of a patient suffering from a cataract surgery or a vitreous body surgery can be sufficiently, quickly, softly and minimally invasively extended, the surgery field can besufficiently exposed, the possibility of accidentally sucking and accidentally injuring the iris is reduced, the surgery time is shortened, postoperative reactions and complications are alleviated, and prognosis of the patient subjected to the cataract surgery and the patient subjected to the vitreous body surgery is improved.
Owner:THE SECOND XIANGYA HOSPITAL OF CENT SOUTH UNIV
Breeding method for high-quality Luchuan pigs
InactiveCN109042510AImprove the slaughter rateImprove conversion rateFodderFeed conversion ratioLean meat
The invention belongs to the technical field of cross breeding, and particularly relates to a breeding method for high-quality Luchuan pigs. South Yunnan small-ear boars and local Luchuan pigs are selected to be mated so that F1 generation breeding boars can be generated, large white sows and local Luchuan pigs are selected to be mated so that F1 generation breeding sows can be generated, the F1 generation breeding boars and the F1 generation breeding sows are matched, and produced and bred F2 generation piglets are the high-quality Luchuan pigs. The bred high-quality Luchuan pigs overcome thedefects that the local Luchuan pigs are short and small in body, excessively concaved in back and waist, slow in growth speed, low in dressing percentage, lean meat percentage, feed conversion ratioand number of broods of piglets produced by the sows and the like; the high-quality Luchuan pigs are resistant to temperature and more suitable for being bred in the Guangxi region; specially-made feedstuff is used for breeding the F1 generation breeding boars, the F1 generation breeding sows and the F2 generation piglets, can supply sufficient nutrient substances for the F1 generation breeding boars, the F1 generation breeding sows and the F2 generation piglets, and can also increase the survival rate of the piglets.
Owner:NANNING UNIV
Method for breeding new pig variety by hybridizing wild boar with domestic pig
Disclosed is a method for breeding a new pig variety by hybridizing a wild boar with a domestic pig. The method comprises the steps that the first filial generation of wild pigs is obtained by the hybridization and improvement of purebred wild boars and small-ear sows from southern Yunnan, then, sows from the first filial generation of wild pigs and boars from Duroc pigs are hybridized, and the new pig variety is obtained. Pigs of the new variety integrate the advantages of purebred wild boars and domestic pigs, and are strong in disease resistance, high in farrowing rate, good in pork quality, strong in flavor, and high in market value.
Owner:绿春县绿原生态野猪繁殖专业合作社
Ear lifting system of stalk and ear harvesting type corn harvester
InactiveCN113498673AQuick liftImprove harvesting efficiencyHeadersAgricultural engineeringSmall ears
The invention discloses an ear lifting system of a stalk and ear harvesting type corn harvester, which comprises a small elevator and an upper header auger which are arranged on an ear harvesting header, and the small elevator is arranged at the front end of the upper header auger; the front end of a large elevator is communicated with the upper header auger, and the rear end of the large elevator is communicated with the husker; a main shaft power output belt wheel and a husker transmission chain wheel are arranged on a main shaft; the main shaft power output belt wheel is in transmission connection with the small elevator and the upper header auger; and the husker transmission chain wheel is in transmission connection with the large elevator. The chain scraper conveyor type small elevator is adopted to replace a traditional seedling pulling chain to lift ears, the lifting speed is not limited by the seedling pulling speed and can be reasonably adjusted, the ears can be quickly lifted to an inlet of the large elevator, the lifting efficiency is high, the limitation of the sizes of the ears is avoided, the small ears can be lifted to the large elevator as well, and the lifting quality is high.
Owner:河北英虎农业机械股份有限公司
Ticket clip
The invention relates to a bill fold containing multilayer folders for conveniently storing the bills in a bill arranging fold according to categories. The bill fold consists of a single-side ear clamping piece a, a single-side ear clamping piece b, a double-side ear clamping piece, a small shaft a, a spring a, a small shaft b, and a spring b. The bill fold is characterized in that the double-side ear clamping piece is arranged between the single-side ear clamping piece a and the single-side ear clamping piece b; the spring a is arranged in the small shaft a, and the small shaft a is inserted into small holes on small ears of the single-side ear clamping pieces and the double-side ear clamping piece; the spring b is arranged in the small shaft b, and the small shaft b is inserted into the small holes on the small ears of the single-side ear clamping pieces and the double-side ear clamping piece. The multilayer bill fold can achieve the purpose of sorting, arranging and storing the bills.
Owner:NANTONG YIXUE STATIONERY
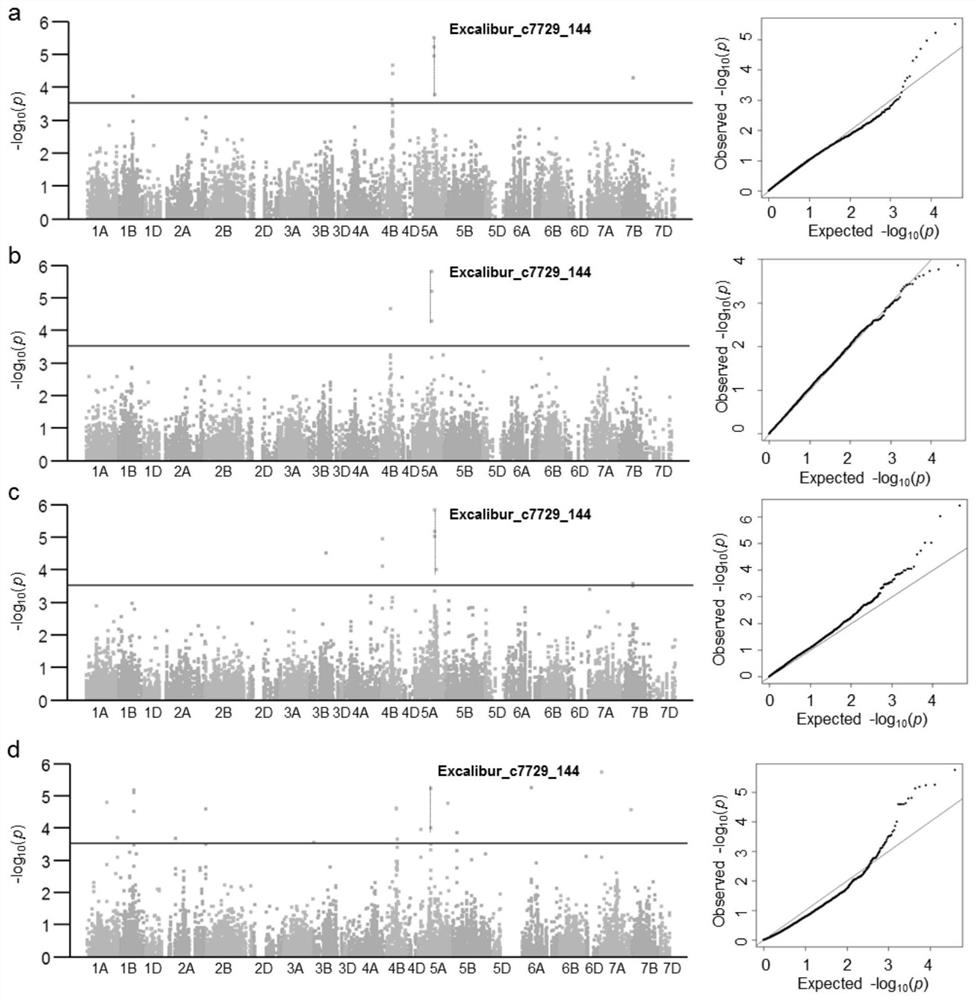
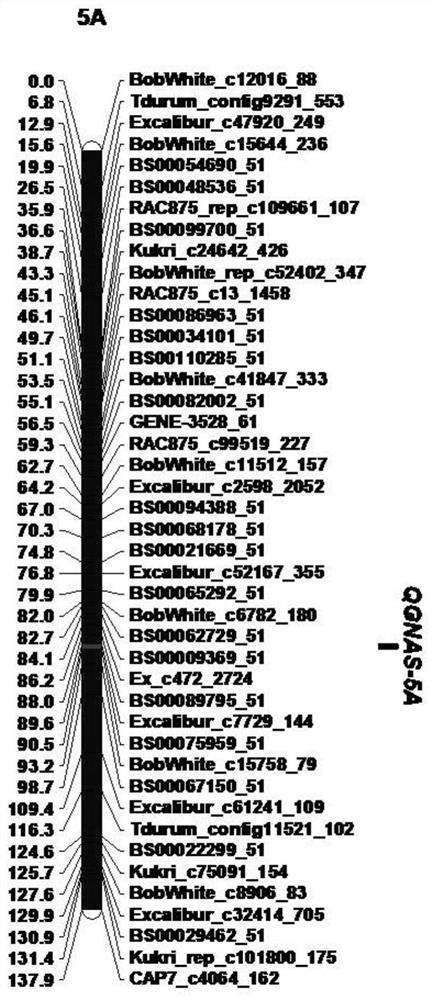
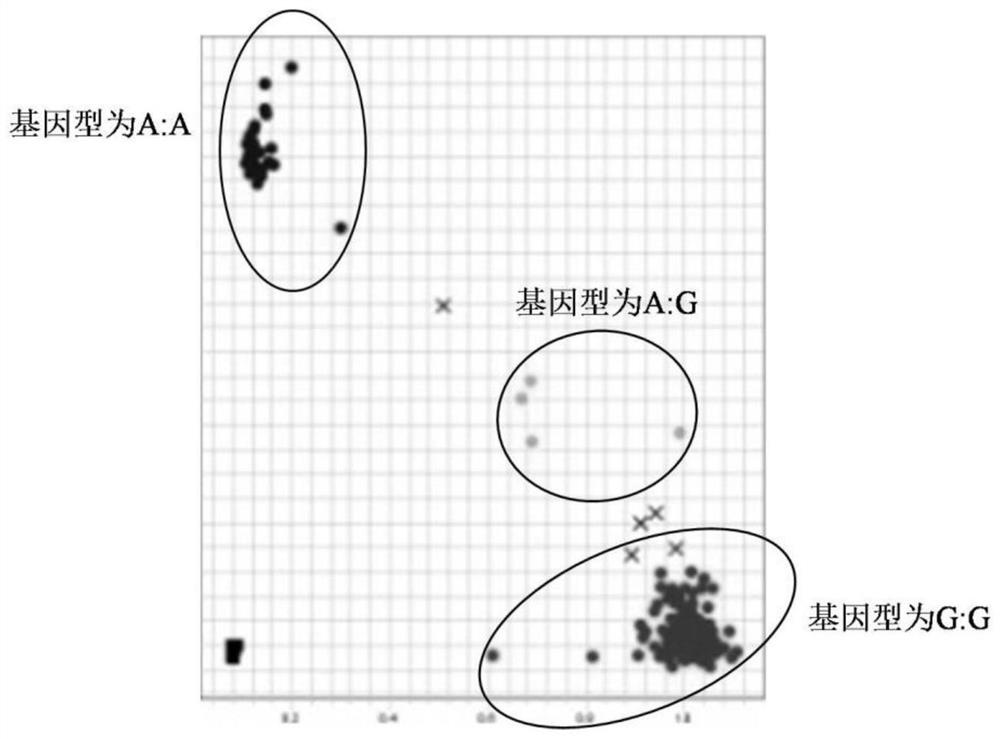
KASP Molecular Marker and Its Application of the Main Qtl for Spikelet Fruity at the Top of Wheat Spike
ActiveCN111118191BImprove firmnessImprove detection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMolecular breedingSmall ears
This case involves a KASP molecular marker and its application of the major QTL for spikelet fruitiness at the top of the wheat ear. Primers were designed according to the target SNP site, and the corresponding SNP was typed by using the specific matching of the bases at the end of the primer. The present invention is developed by excavating the closely linked markers of the main effect QTL of spikelet number at the top of wheat spikelets. The designed KASP molecular marker has a large and stable genetic effect and is closely linked with the target QTL, which is important for improving the spikelet fruiting at the top of wheat spikelets. Practical significance, providing excellent genetic resources and selection tools for molecular breeding of wheat yield traits, greatly improving the selection efficiency.
Owner:SHANXI AGRI UNIV
A device for positioning and cutting spikes of fresh corn
ActiveCN110271044BReduce wasteImplement automatic transferMetal working apparatusAgricultural scienceAgricultural engineering
The invention relates to the technical field of fresh corn spike cutting, and discloses a fresh corn positioning spike cutting device. A visual detection mechanism and a controller are arranged, the visual detection mechanism can identify the size and the positions of corns with spikes to be cut and can classify the corns according to the size, and the controller can automatically adjust the diameter and size of a positioning mechanism according to the identification and the size classification of the corns by the visual detection mechanism, so that the problem of over-large or over-small ear cutting when corns with different sizes are subjected to spike cutting positioning can be avoided, the problem of waste caused by over-large corn cutting can be reduced as much as possible, and meanwhile, automatic conveying, automatic material pushing and cutting can be realized; according to the device, a spike cutting device is arranged, under the driving of a motor, the spike cutting device can drive slices to carry out up-and-down cutting movement, so that corn spikes can be cut off, the traditional manual ear cutting process is replaced, and the labor intensity of workers is reduced.
Owner:ANHUI SCI & TECH UNIV
Wattmeter
InactiveCN107389999AEasy to replaceReduce labor costsSpecial tariff metersEngineeringFire prevention
The invention discloses an electric meter, which comprises a main body of the electric meter. The main body of the electric meter is composed of two parts: an electric meter box and an anti-theft base. Protruding small ears are arranged on the left and right sides of the electric meter box, and fire extinguishing devices are arranged inside the small ears. The electric meter box There is an anti-theft panel on the front, a digital display window on the anti-theft panel, a buzzer under the digital display window, and a remote monitoring power device in the meter box on one side of the digital display window; the anti-theft base is a closed box with a front opening, The left and right sides of the anti-theft base are provided with sunken big ears, and the big ears are provided with small ear slots. The beneficial effects of the present invention are: reasonable structure, simple design, convenient and practical, with alarm function, and can remotely monitor the power consumption, greatly It reduces the trouble of manual meter reading, reduces the labor cost of the power department, and also increases the functions of anti-theft, fire prevention, and remote monitoring.
Owner:DEZHOU LINGCHENG POWER SUPPLY CO OF STATE GRID SHANDONG ELECTRIC POWER CO +1
Shoes with fixed shoelaces
InactiveCN103126171ASimple structureShoe lace fasteningsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationShoe laces
A hollow 'small ear' is added to each side of an original shoe so as to effectively improve the functions of shoes and achieve convenience and comfort in walking, tied shoelaces can be plugged into the small ears, and the problem that the shoelaces are easy to drop is solved.
Owner:CHONGQING BEIBEI DISTRICT WANGPU MIDDLE SCHOOL
Ecological breeding method of small-eared pigs
InactiveCN106614329BImprove stocking viabilityPromote sportsFood processingAnimal feeding stuffPig farmsAnimal science
The invention discloses an ecological breeding method of small-ear pigs. The method comprises the following steps: (1) selecting a land and distributing for a cultivating farm; (2) disinfecting a pig farm; (3) performing raising management of piglets; (4) performing raising management of middle pigs; (5) performing raising management of middle and big pigs; (6) performing raising management of growing and fattening pigs; and (7) preventing diseases. Pigs bred by adopting the ecological breeding method of small-ear pigs is strong in self resistance, low in morbidity, delicious in meat, rich in nutrients, and fast to grow; and the bred small ears meet the requirement of green food.
Owner:红河县九冲畜牧业发展有限公司
Establishment method of animal model for ipv intradermal immunity evaluation
ActiveCN103877596BSimple methodImprove standardizationIn-vivo testing preparationsTesting medicinal preparationsCytopathic effectVaccine antigen
The invention provides an establishment method of an animal model for evaluating IPV (inactivated poliovirus vaccine) intradermal immunization effectiveness. The establishment method includes the following steps: selecting Yunnan Xishuangbanna small ear pigs belonging to Southern China pigs, with pig ages of 3-5 months and weights of 10-20kg, randomly grouping the pigs, respectively injecting an IPV vaccine through needleless intradermal injection for the first time, sampling blood after immunity for 30 days, separating serum, respectively injecting the IPV vaccine through needleless intradermal injection for the second time, sampling blood after immunity for 7 days and 30 days, separating the serum, respectively injecting the IPV vaccine through needleless intradermal injection for the third time, sampling blood after immunity for 1 month, 6 months, 12 months, 18 months and 24 months, separating the serum, inactivating the serums for 30 minutes at 56 DEG C, conventionally diluting the serums, neutralizing the serums by using Sabin strain I type and II type and Pfizer III type viruses, wherein the dosage of the viruses is 30-300 TCID50 (tissue culture infectious dose 50), naturalizing for 3 hours at 35-37 DEG C, adding cells, culturing at 35-36 DEG C for 7 days, and judging a result according to CPE (Cytopathic Effect), thus establishing the animal model for evaluating IPV intradermal immunization effectiveness. By adopting the establishment method provided by the invention, a rational animal model is provided for an intradermal immunization research on vaccines, and a reliable measure is provided for reducing the dosage of vaccine antigen in the intradermal immunization research.
Owner:INST OF MEDICAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
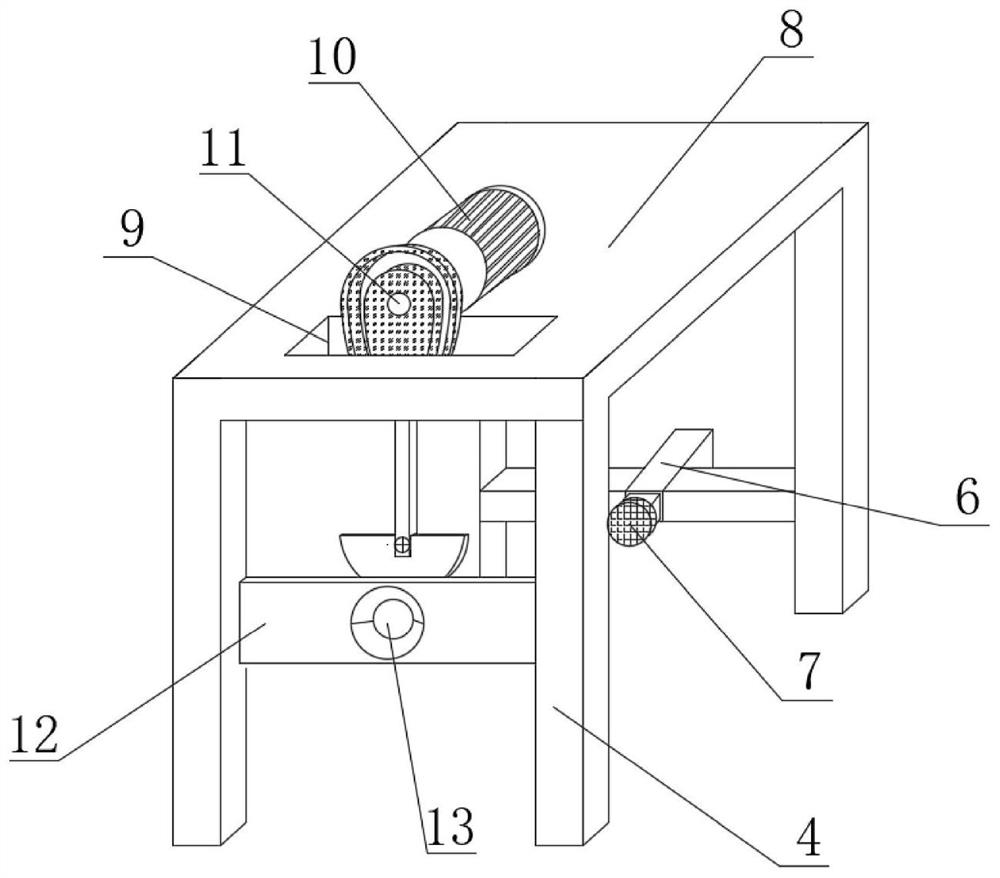
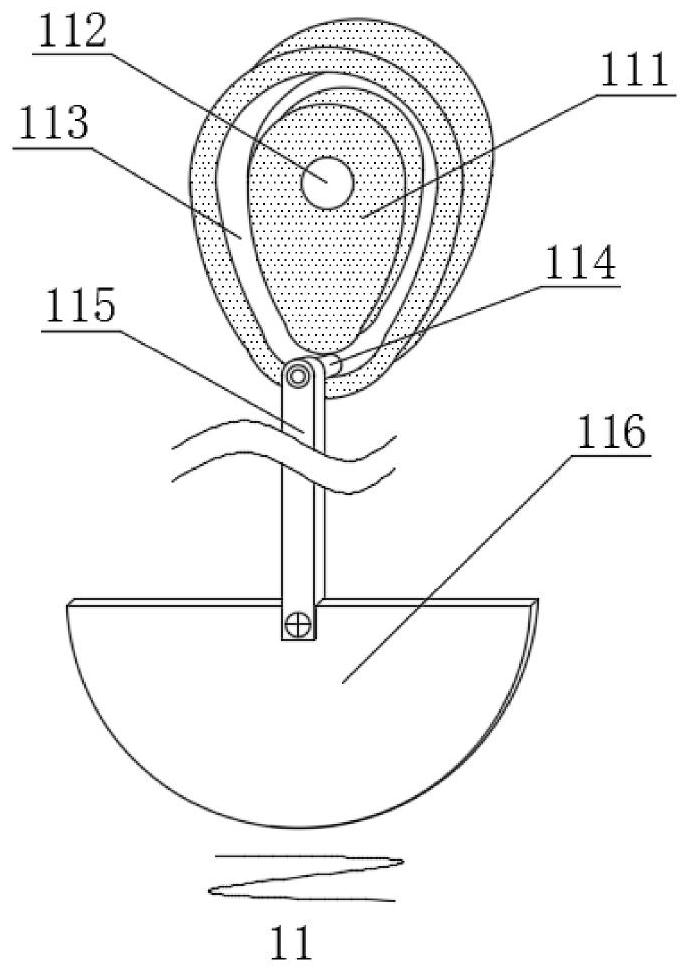
Manufacturing method of auricle corrector for ear boat shaping
The manufacturing method comprises the following steps: (1) selecting a bendable outer tube with an opening at the top end and a closed bottom end, and inserting a metal wire into the outer tube from the opening at the top end of the outer tube; 2) sealing the top end of the outer tube by using a tube plug; and 3) bending the outer tube and the metal wire to a preset curvature to obtain the auricle corrector. An adhesive layer is arranged on the outer side face of the outer pipe. Compared with the prior art, the outer tube, the metal wire and the tube plug are combined together in a detachable assembly mode, processing and manufacturing are easy, and the manufactured auricle corrector has the advantages of self-adhesion, self-elasticity, stability, reliability and flexibility in use, and has a good application prospect on auricles, cup-shaped auricles, elf auricles and auricular deformity (including most auricular deformity types). Especially, the device plays an important role in correction of big and small ears on two sides.
Owner:EYE & ENT HOSPITAL SHANGHAI MEDICAL SCHOOL FUDAN UNIV
Buckle small ear device for glove packaging machine
ActiveCN113306762BReduce labor intensityImprove packaging efficiencyPackagingElectric machinerySmall ears
The invention discloses a small ear buckle device for a glove packaging machine, comprising: a fixing frame, a conveyor is fixedly installed at the bottom of the inner wall of the fixing frame; and a buckle ear mechanism includes a fixing plate, a moving plate and a first screw motor and a mechanical claw, a fixing plate is fixedly installed at the bottom of the fixing frame and located on one side of the conveyor, and a first screw motor is fixedly installed at the top of one side of the fixing plate through a bracket. A moving plate is fixedly installed at the output end, and a mechanical claw is fixedly installed on one side of the bottom of the moving plate; a pressing mechanism includes a mounting plate, a second screw motor, a placing plate, a pressing plate, and a third screw The motor, the connecting plate, and the support frame effectively solve the problem that in order to ensure the protective ability of the packaging box, the small ears on both sides of the packaging box need to be engaged with each other. When the existing packaging machine is buckled, there are low efficiency, The problem of high packaging error rate and the problem of not meeting the needs of use.
Owner:淄博卓正机械有限公司
Lean meat type pig breeding method
The invention relates to a pig breeding method, in particular to a lean meat type pig breeding method. The lean meat type pig breeding method comprises the following steps: hybridizing Southern Yunnan small-ear pigs with Jinhua pigs to produce first generation of hybrid lean meat type pigs; hybridizing the first generation of hybrid lean meat type pigs with Bama miniature pigs to produce second generation of hybrid lean meat type pigs, hybridizing the second generation of hybrid lean meat type pigs with Southern Yunnan small-ear pigs to produce third generation of hybrid lean meat type pigs, hybridizing the third generation of hybrid lean meat type pigs with Jinhua pigs to produce fourth generation of hybrid lean meat type pigs, mutually hybridizing the fourth generation of hybrid lean meat type pigs as first generation of commercial pigs, mutually hybridizing the first generation of commercial pigs as second generation of commercial pigs, performing population reproduction on the second generation of commercial pigs and taking produced lean meat type pigs as commercial lean meat type pigs for feeding; the commercial lean meat type pigs bred through the steps are gray black in whole body hair, straight in nose, straight in back and waist, longer in trunk, full in hindquarter, robust in limb, strong in physique and mild in temperament, have the excellent characteristics of being strong in disease resistance, quick in growth, high in piglet productivity, high in lean meat percentage, good in meat quality, resistant to cold and heat and the like.
Owner:合肥申仁养殖有限公司
Fast labor-saving iron shovel
The invention provides a fast labor-saving iron shovel. The iron shovel comprises an iron shovel rod and a handle; and the bottom end of the iron shovel rod is fixed on an iron shovel handle, pedal handles are fixed under the iron shovel handle, supports are separately fixed under two sides of the pedal handles, an iron shovel head is fixed under the pedal handles and the supports, and curved blades are separately fixed on two sides of the bottom of the iron shovel head. According to the fast labor-saving iron shovel provided by the invention, two curved blades similar to small ears are fixedon two sides of the bottom of the iron shovel head, so that when ditching is performed, a whole mud block can be dug up when shovelling is performed once; knife edges of the two curved blades similarto the small ears are not flat and can be arc-shaped, so that resistance is reduced; and in addition, in order to solve the problem of insufficient force, two pedal handles and supports are added on two sides of the iron shovel, force is increased by using feet, so that the iron shovel is very fast and labor-saving, and has a very good effect.
Owner:KUNSHAN CITY YUSHAN TOWN SHILONG DESIGN STUDIO
File clip
InactiveCN101439630ASimple structureEasy to useFiling appliancesSheet bindingSmall earsComputer science
The invention relates to a file folder having multiplayer clamping pieces capable of respectively clamping files in a hierarchical and assorted way. The file folder consists of a file folder back board, a clamp back board, a rivet, a clamping piece a, a clamping piece b, a small shaft a, a spring a, a small shaft b and a spring b. The file folder is characterized in that small ears on two sides of the clamping piece a are corresponding to the small ears on the clamp back board; the small shaft a passes through small holes on the small ears on the two sides of the clamping piece a and the small holes on the small ears on the clamp back board, and the spring a is sheathed on the middle of the small shaft a; the small ears on the two sides of the clamping piece b are corresponding to the small ears on the clamp back board; the small shaft b passes through the small holes on the small ears on the two sides of the clamping piece b and the small holes on the small ears on the clamp back board; and the spring b is sheathed on the middle of the small shaft b. The file folder can respectively clamp the files in different clamping layers according to categories of the files, and achieve the purpose of respectively clamping the files in the hierarchical and assorted way.
Owner:NANTONG YIXUE STATIONERY
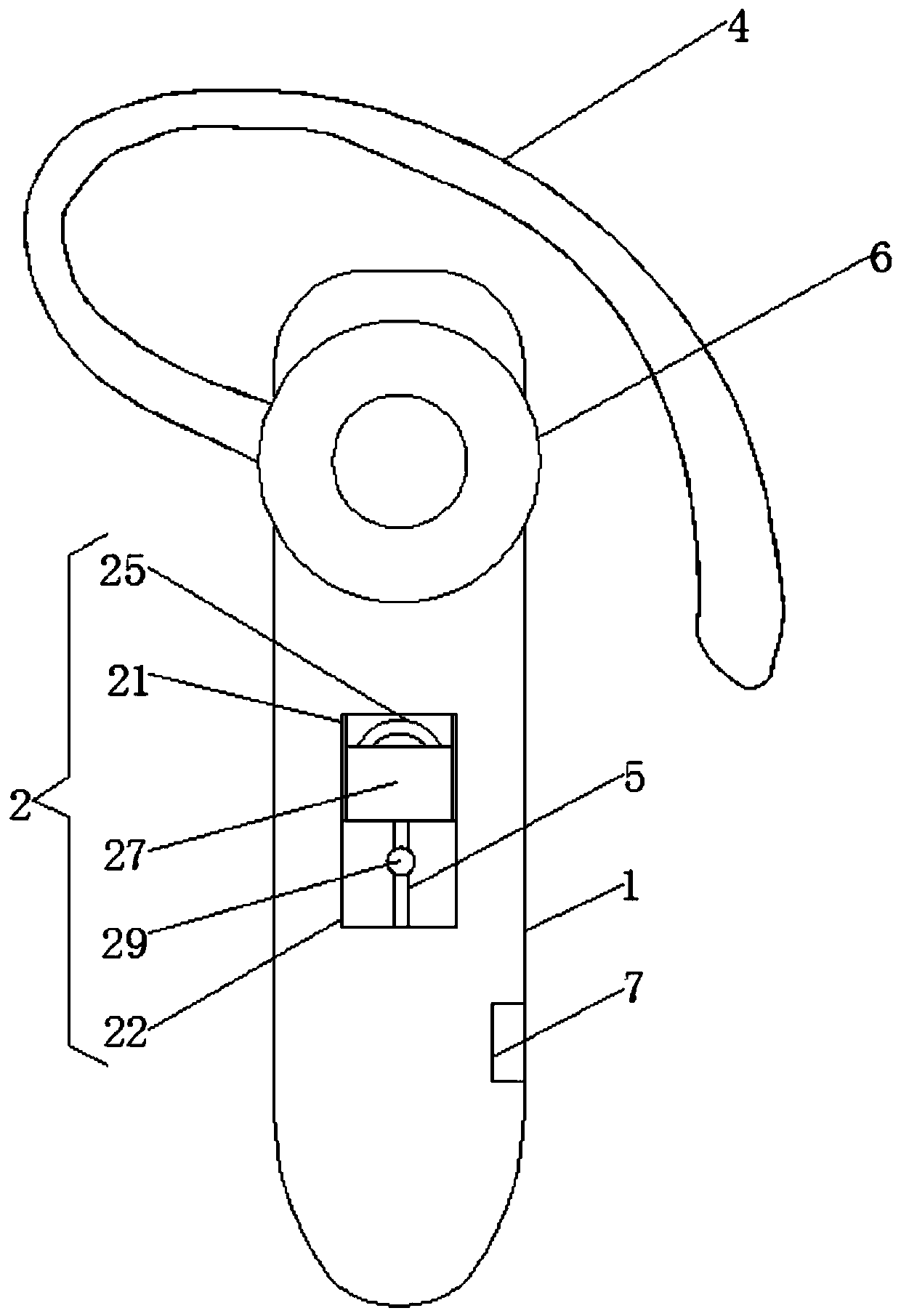
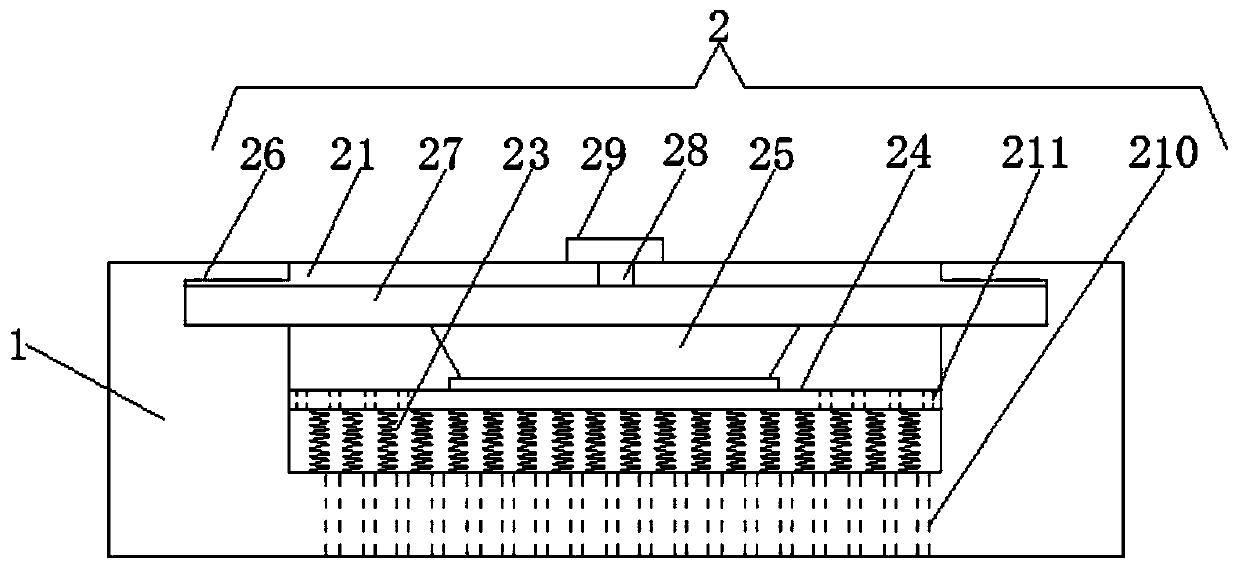
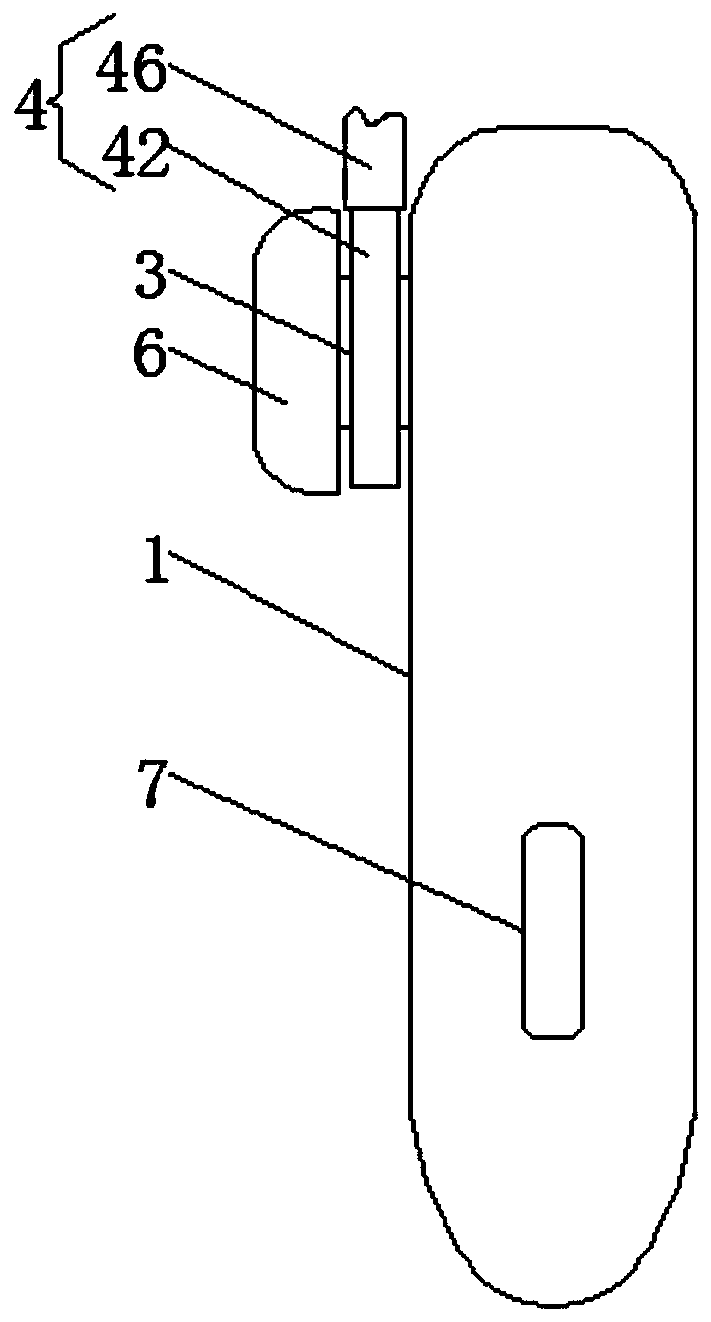
A bluetooth earphone with double wearing effect
Owner:广州市轻聆电子科技有限公司
Cross breeding method for Caoguo pigs
InactiveCN113796350AStrong disease resistanceImprove litter rateAnimal husbandryDomestic pigSmall ears
The invention relates to the technical field of variety pig hybridization, in particular to a cross breeding method of Caoguo pigs. The cross breeding method of the Caoguo pigs comprises the following steps: S1, taking a sow of a Jinghong small-ear pig as a female parent and a Bama minipig as a male parent for hybridization to breed a first-filial generation wild pig; S2, taking a sow in the first-filial generation wild pig as a female parent and taking a second-generation Gaoligong mountain wild boar as a male parent for hybridization to obtain a second-filial generation wild pig; S3, taking a boar in the hybridized second-generation wild pig as a male parent and a sow in the hybridized second-generation wild boar as a female parents for cross-breeding to obtain a cross-bred progeny wild pig; and S4, carrying out 4-6 generations of breeding on the cross-bred progeny wild pig to finally obtain the Caoguo pig variety. Aiming at the defects in the prior art, the invention provides the cross breeding method for the Caoguo pigs, and provides a method for breeding new-variety pigs by hybridizing wild pigs and domestic pigs, so that the bred new-variety pigs integrate the advantages of purebred wild pigs and domestic pigs, and are high in disease resistance, high in farrowing rate and good in meat quality.
Owner:云县兴旺牧业专业合作社
Method for obtaining transgenic wheat by impregnating young ears through agrobacterium tumefaciens
InactiveCN102559746BNormal growthEasy to operateGenetic engineeringFermentationTriticeaeTransformation efficiency
The invention relates to the field of plant transgenic engineering, in particular to a method for obtaining transgenic wheat by impregnating young ears through agrobacterium tumefaciens. The method for obtaining the transgenic wheat by impregnating the young ears through the agrobacterium tumefaciens comprises the following steps of: 1) culturing agrobacterium tumefaciens strains containing expression vectors which carry target genes, and suspending the strains by using an impregnating culture medium; and 2) selecting the wheat at a heading stage for transformation, removing underdeveloped small ears at the top ends and the tail ends of the young ears, shearing about 1 / 3 of the top ends of the wheat, and soaking the young ears of the wheat into the impregnating culture medium containing the agrobacterium tumefaciens. The method is easy and convenient to operate, saves manpower and material resources, and is high in transformation rate which can reach 26.3 to 82.3 percent; and the impregnated plants can normally grow and fruit, so the method has significance for theoretical research and genetic breeding practice on the aspect of wheat gene engineering.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
Process of attaching small ear film on glass cover-plate of mobile phone
The invention relates to the technical field of glass cover-plate production, in particular to a process of attaching a small ear film on a glass cover-plate of a mobile phone. The process comprises the following steps: step one, cutting a protective film; step two, attaching the protective film; and step three, attaching the small ear film. Firstly, according to the position of the small ear holeof the glass cover-plate, a gap consistent with the ear hole in shape is cut on the protective film, then the protective film cut with the gap is attached on the glass cover-plate, so that the smallear hole is free from being covered by the protective film, and then the small ear film can be directly attached on the small ear hole, therefore when the protective film is glued up by an adhesive glue stick, the dust is glued on the glass cover-plate or the protective film in the prior art can be avoided, then the quality of the glass cover-plate can be improved.
Owner:DONGGUAN JINGBO PHOTOELECTRIC BIT CO
Method for obtaining transgenic wheat by impregnating young ears through agrobacterium tumefaciens
InactiveCN102559746ANormal growthEasy to operateGenetic engineeringFermentationTriticeaeTransformation efficiency
The invention relates to the field of plant transgenic engineering, in particular to a method for obtaining transgenic wheat by impregnating young ears through agrobacterium tumefaciens. The method for obtaining the transgenic wheat by impregnating the young ears through the agrobacterium tumefaciens comprises the following steps of: 1) culturing agrobacterium tumefaciens strains containing expression vectors which carry target genes, and suspending the strains by using an impregnating culture medium; and 2) selecting the wheat at a heading stage for transformation, removing underdeveloped small ears at the top ends and the tail ends of the young ears, shearing about 1 / 3 of the top ends of the wheat, and soaking the young ears of the wheat into the impregnating culture medium containing the agrobacterium tumefaciens. The method is easy and convenient to operate, saves manpower and material resources, and is high in transformation rate which can reach 26.3 to 82.3 percent; and the impregnated plants can normally grow and fruit, so the method has significance for theoretical research and genetic breeding practice on the aspect of wheat gene engineering.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com