Patents
Literature
38results about How to "Large output voltage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
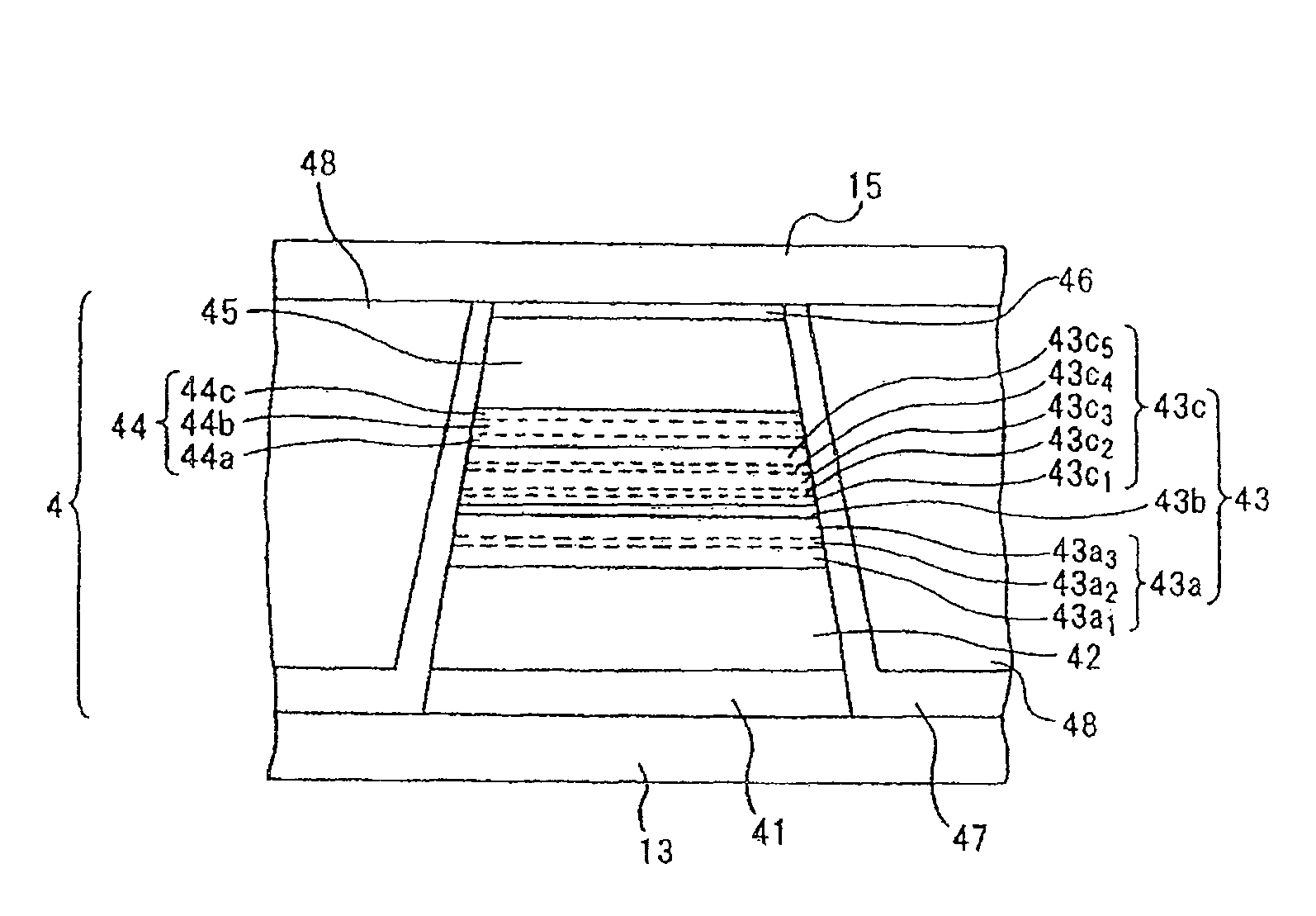
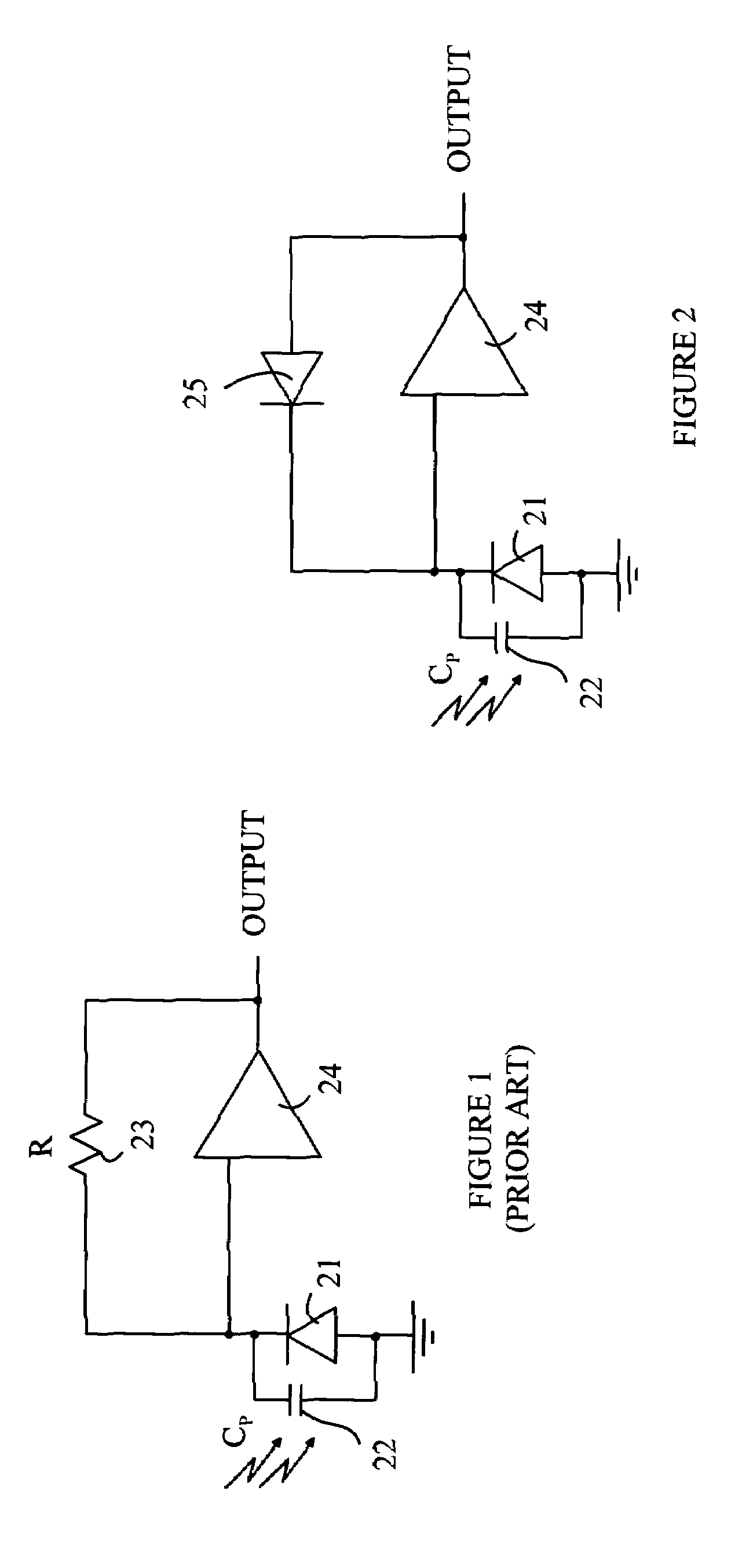
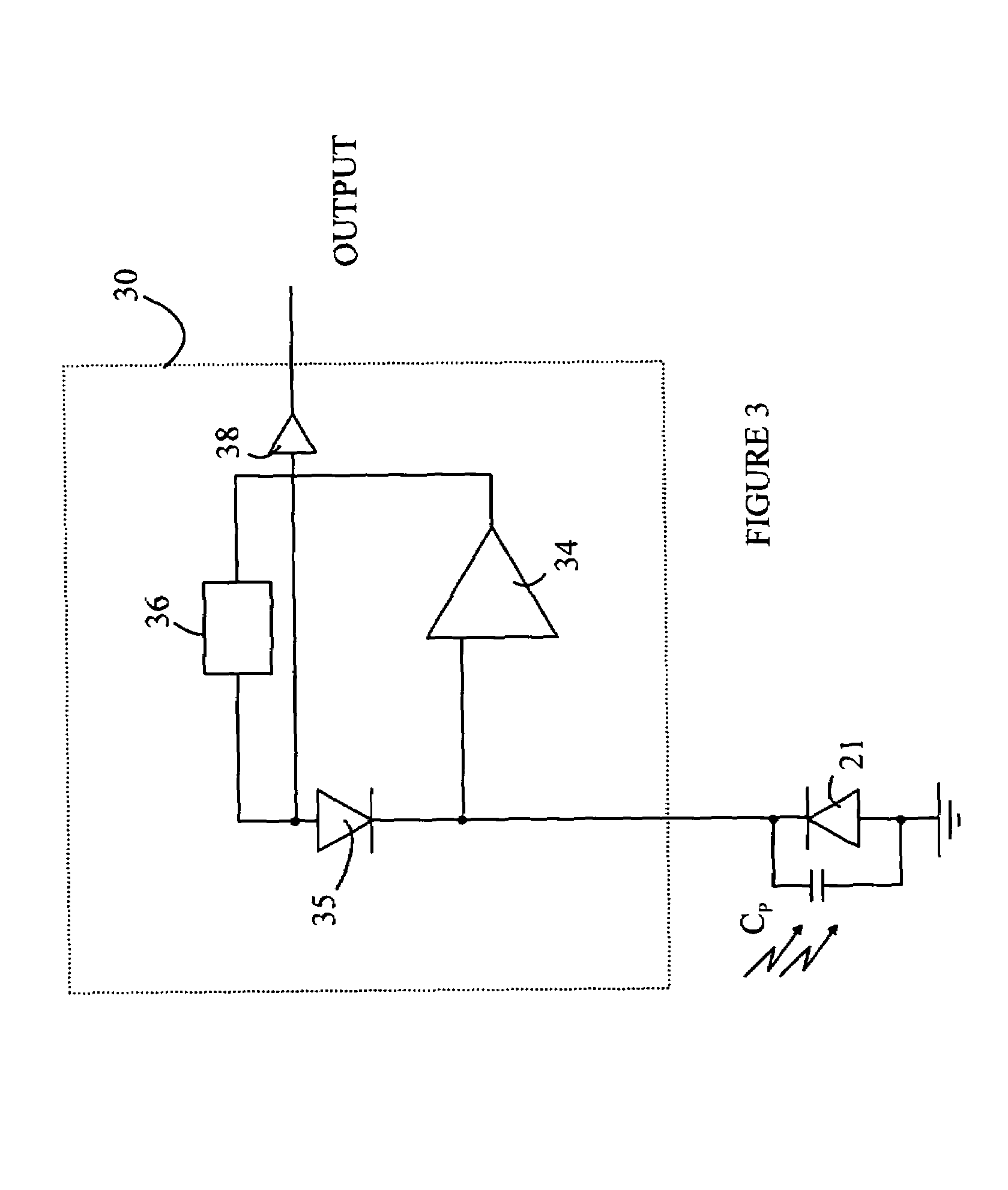
Transimpedance amplifier
InactiveUS7135932B2Minimise currentWide bandwidthAmplifier combinationsAmplifiers controlled by lightAudio power amplifierEngineering
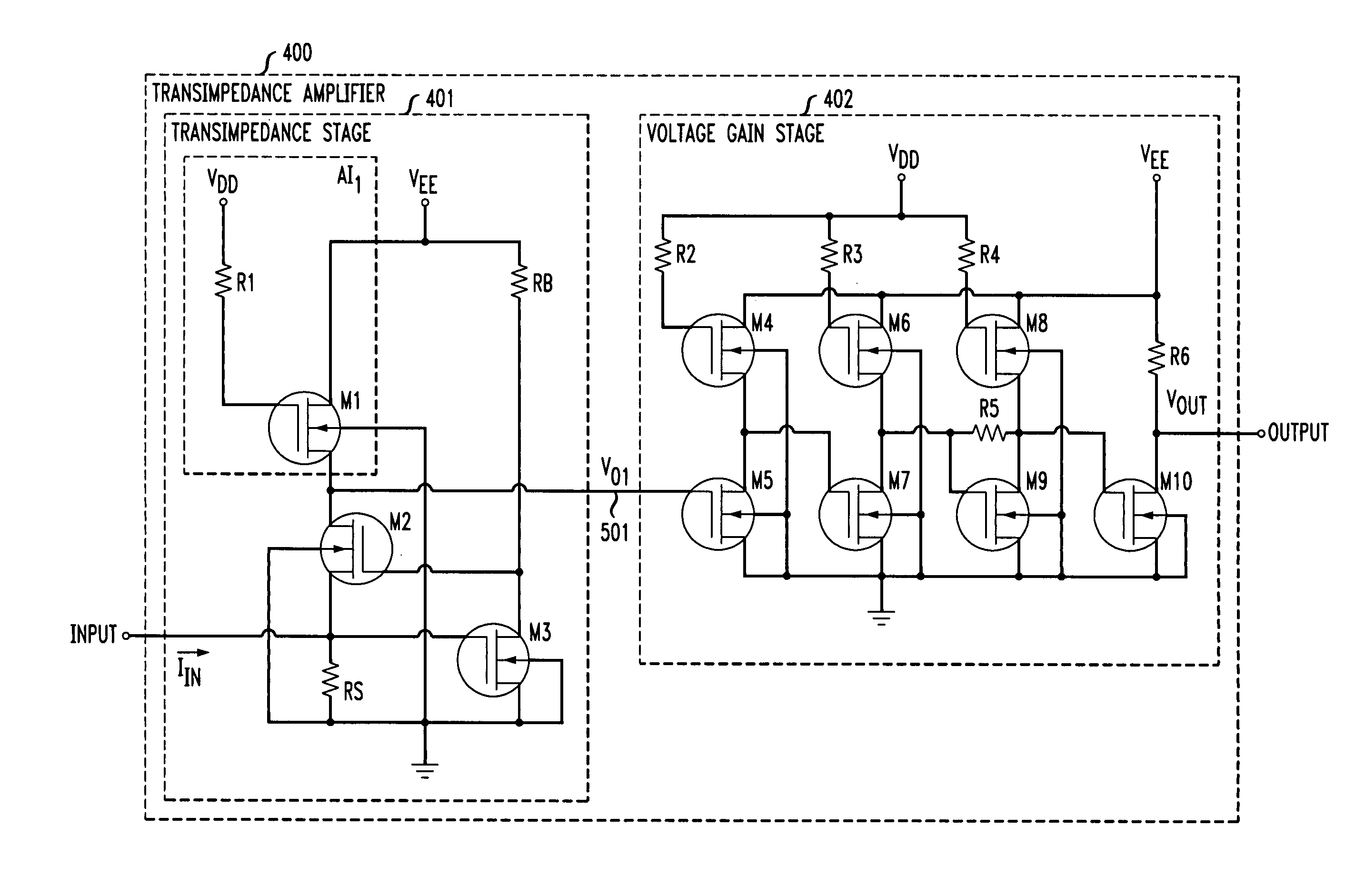
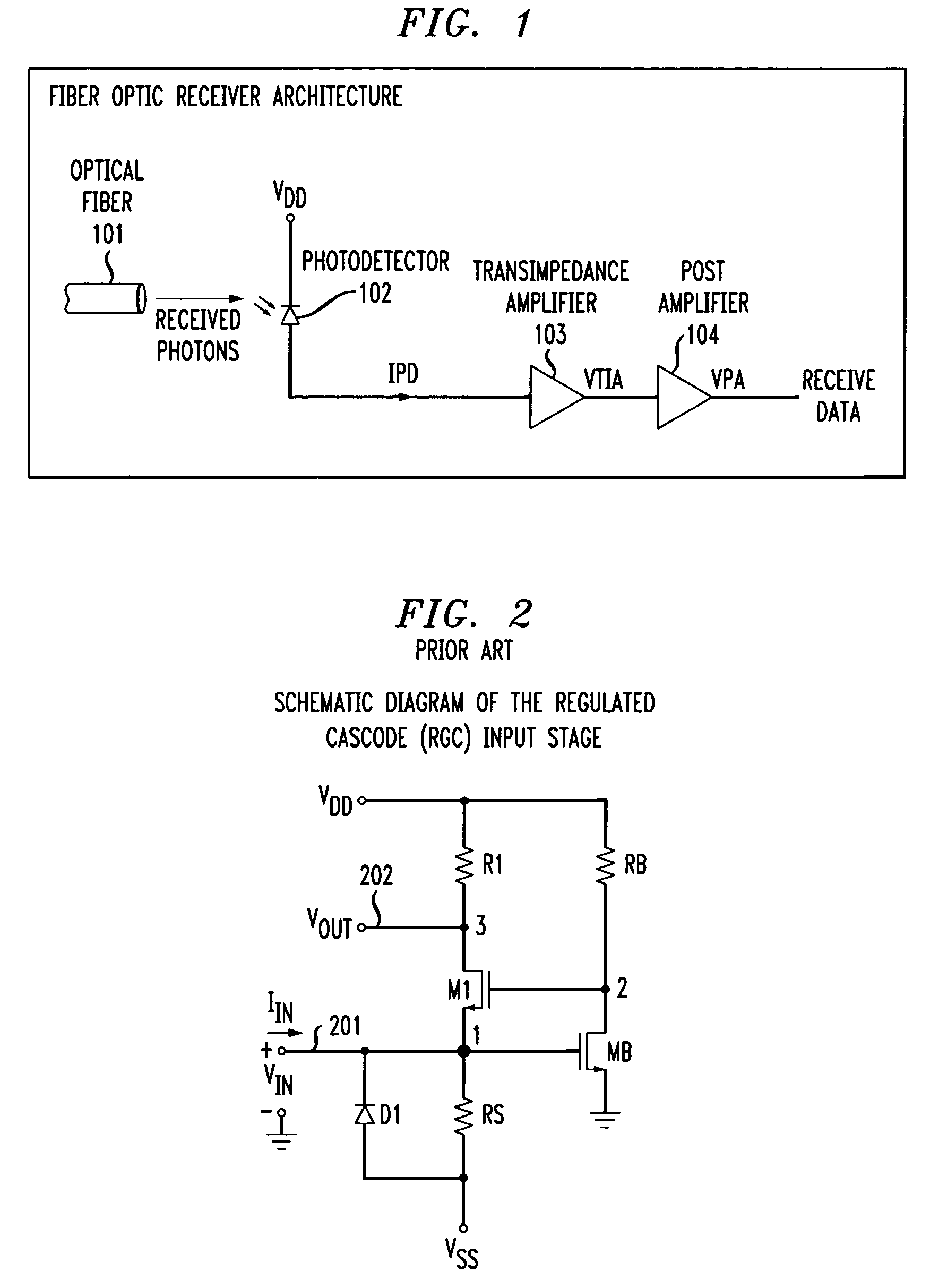
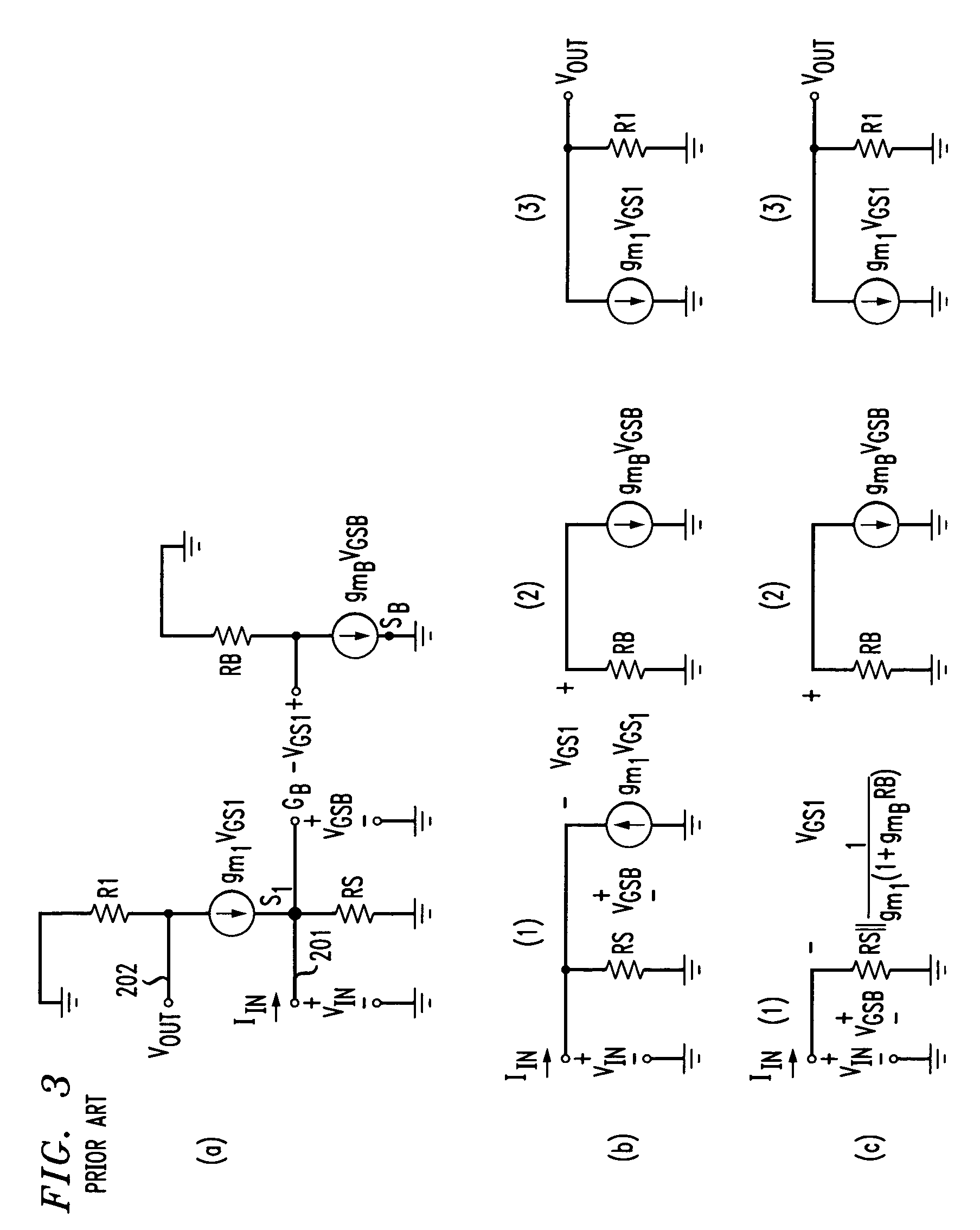
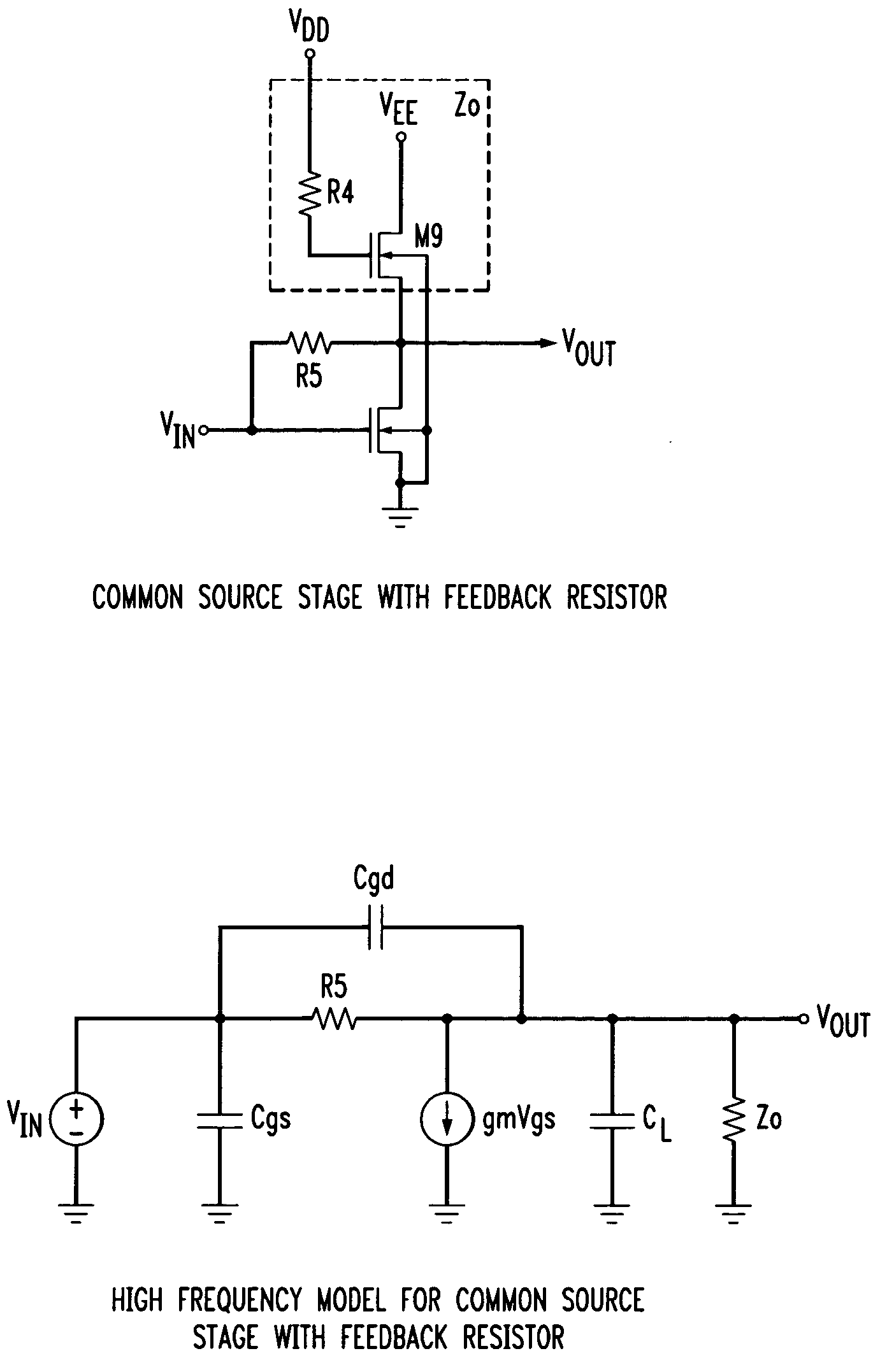
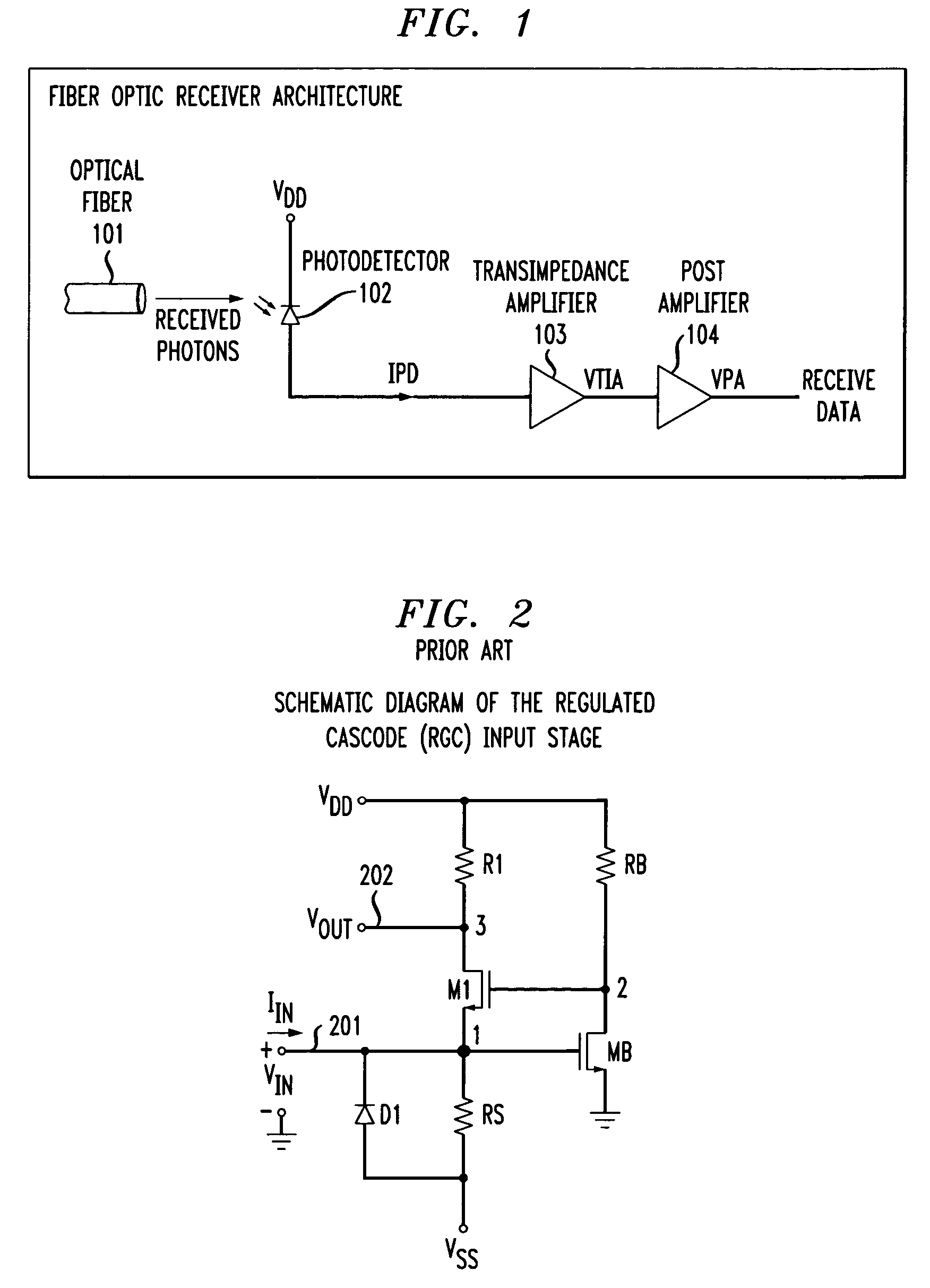
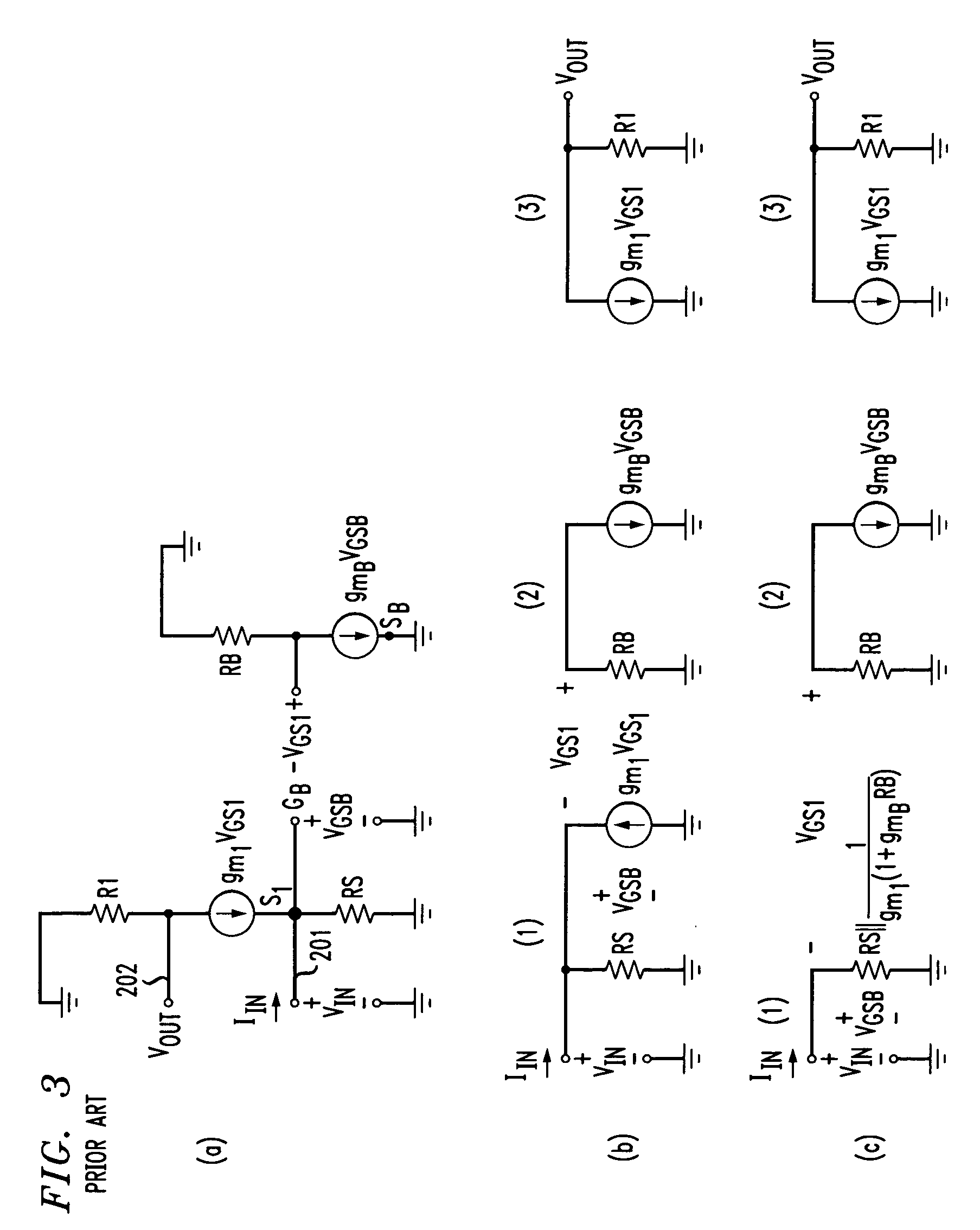
A transimpedance amplifier, which is useful as an optical fiber preamplifier, is disclosed. The illustrative embodiment exhibits four characteristics. First, it minimizes the equivalent input noise current. Second, it has a wide bandwidth. Third, it has a reasonably large output voltage, and fourth, it is stable over wide temperature and voltage ranges. The illustrative embodiment comprises a transimpedance stage and a gain stage. Both stages employ a pure NMOS design which contributes to the above four advantages. Bandwidth is further increased over the prior art by the use of inductive loads. The inductive loads of the illustrative embodiment are not physical inductors, but transistor-based “active” inductors: the combination of a resistor connected in series with the gate of an NMOS transistor.
Owner:SIRES LABS
Super-wide output voltage range charger based on LLC topology and control method
ActiveCN104467443AAchieve zero voltage turn-onReduce turn-on lossDc-dc conversionMobile unit charging stationsMOSFETNew energy
The invention discloses a super-wide output voltage range charger based on LLC topology and a control method. The super-wide output voltage range charger comprises an LLC resonant converter and a control circuit. The LLC resonant converter comprises a switch network composed of an MOSFET full-bridge conversion circuit, the input end of the switch network is connected with the input end of a power source, the output end of the switch network is connected with the input end of a resonant network, the output end of the resonant network is connected with a leakage inductor of a transformer, and a secondary side coil of the transformer is connected with a rectifying and filtering network; the control circuit comprises a control unit, the control unit controls MOS tubes of the MOSFET full-bridge conversion circuit to be connected or disconnected according to received signals at the input end and the output end of the LLC resonant converter, and therefore the LLC resonant converter can achieve no-voltage connection of a primary side switch tube and no-current disconnection of a secondary side rectifying diode within a full voltage range. The super-wide output voltage range charger is wide in output voltage, free of limitation of the input voltage range of a charged object and capable of charging various new energy electric vehicles.
Owner:SHANDONG LUNENG SOFTWARE TECH
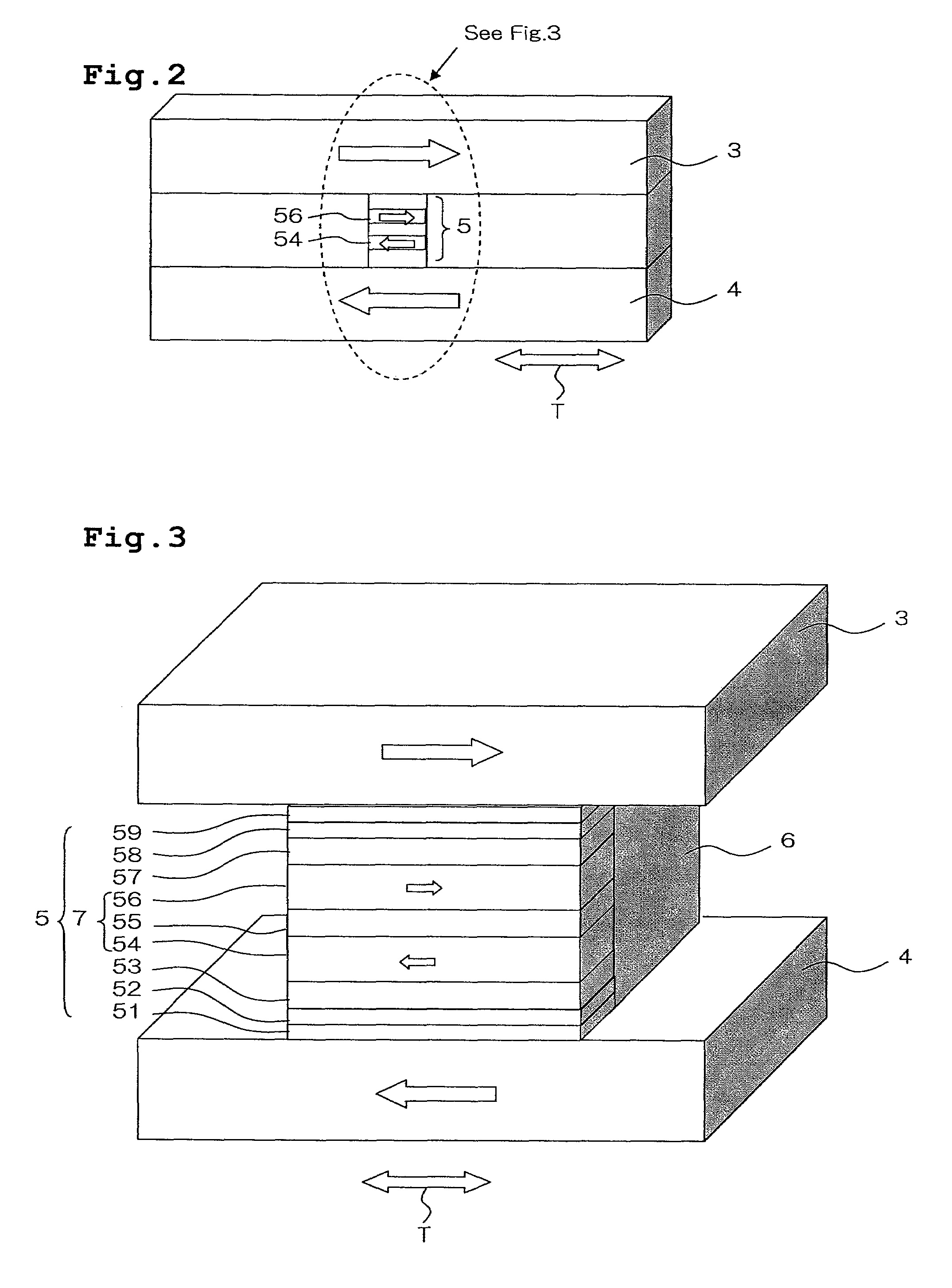
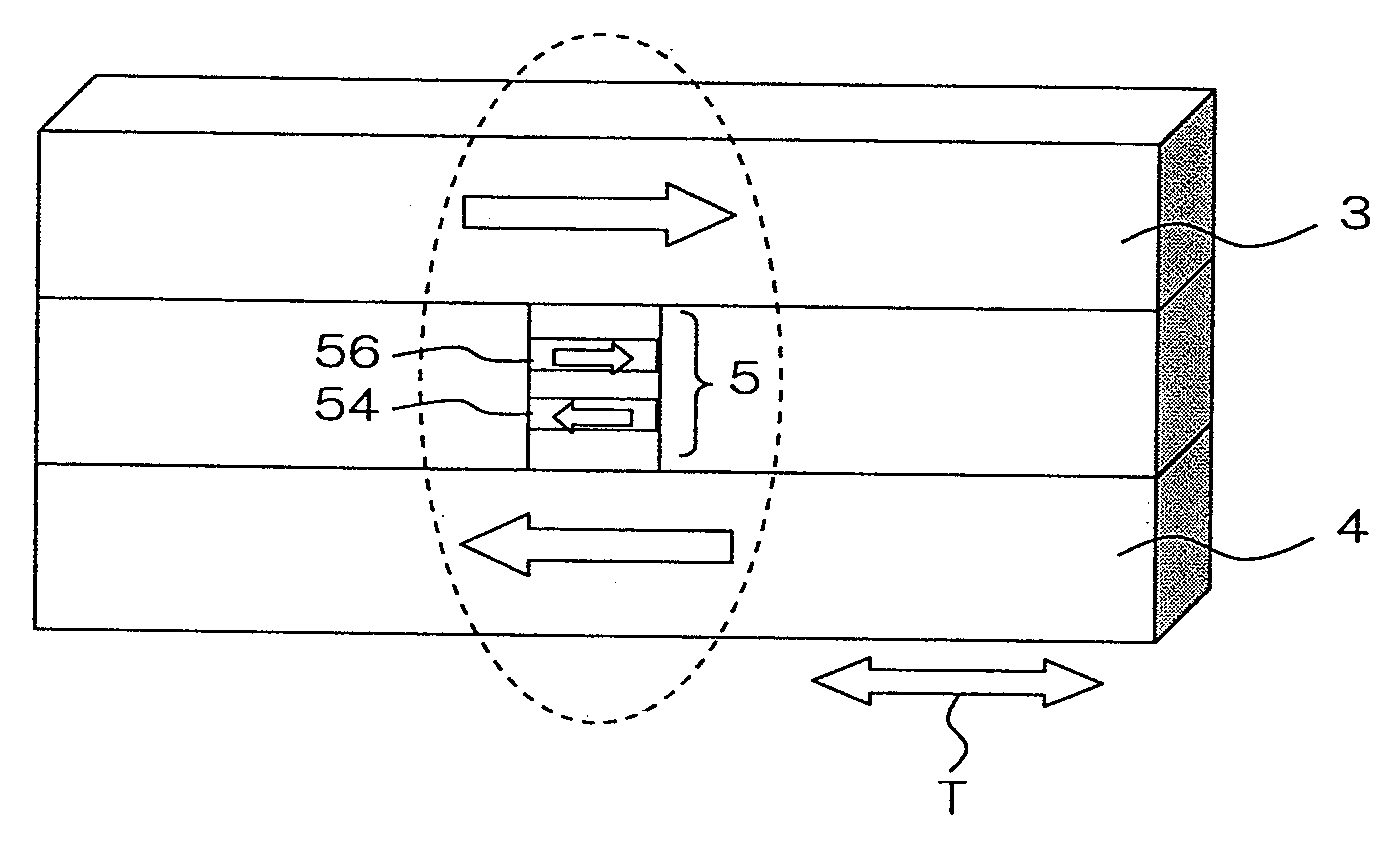
Synchronized primary winding current shunting technique for controlling electro-stimulus level
An electronic apparatus (1) for training an animal is supported against the animal's skin, and includes stimulus electrodes (5) for electrically contacting the skin. A controller including output terminals producing aversive stimulus control signals, a first switch (Q4) coupled to a winding to produce therein a burst of first current pulses in response to a first signal produced by the controller (33) and a second switch (Q2) coupled to the first switch (Q4) operative to synchronously shunt predetermined trailing portions of the first current pulses away from the winding in response to a second signal produced by the controller to reduce the amount of energy delivered to the winding by the switching transistor (Q4) without substantially changing a peak value of a flyback voltage across the winding. The controller sets various values of time intervals during which portions of the first current pulses are shunted away from the winding in order to set various corresponding intensities of aversive stimulus.
Owner:GARMIN
Tandem rotary electric machine
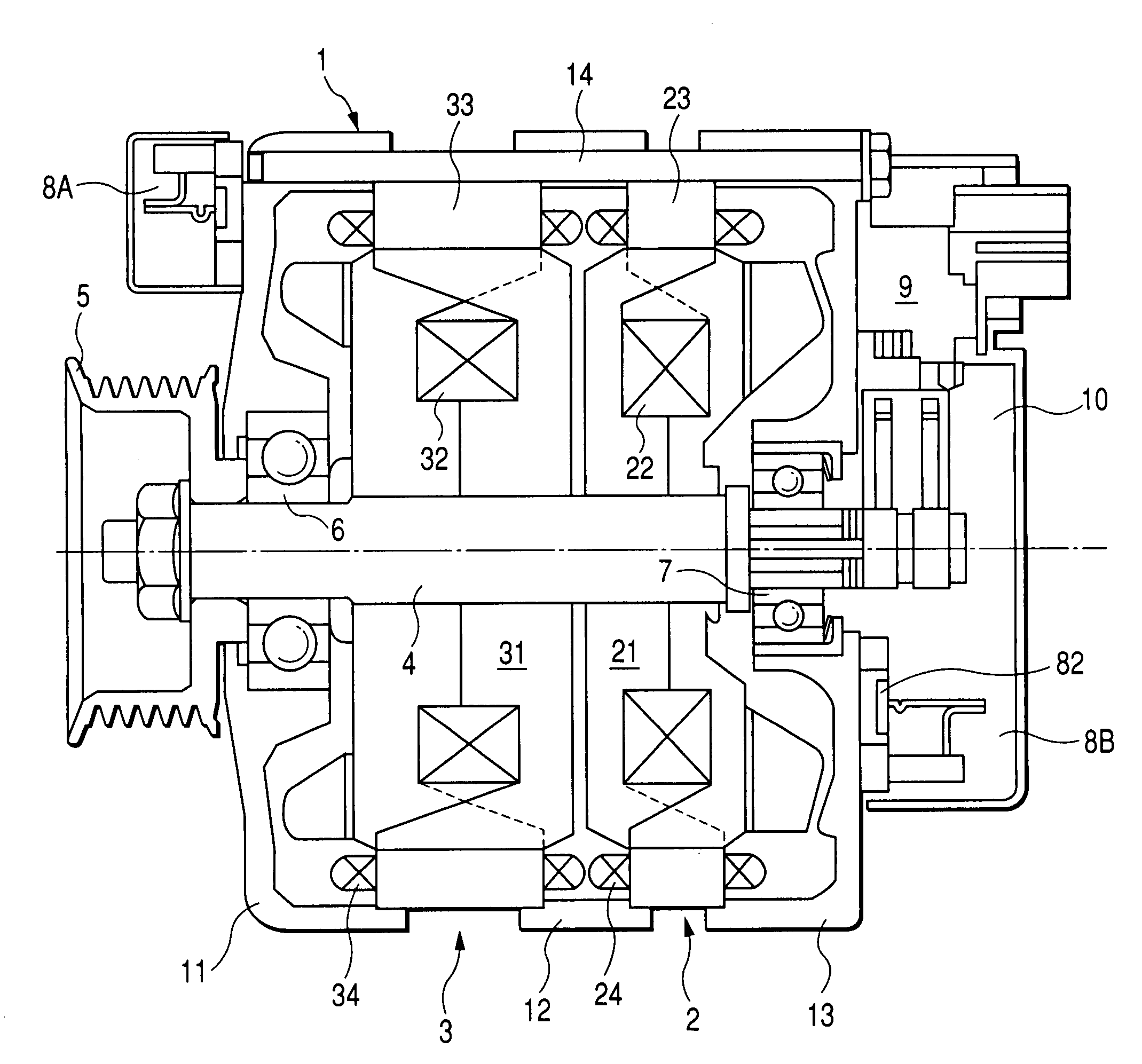
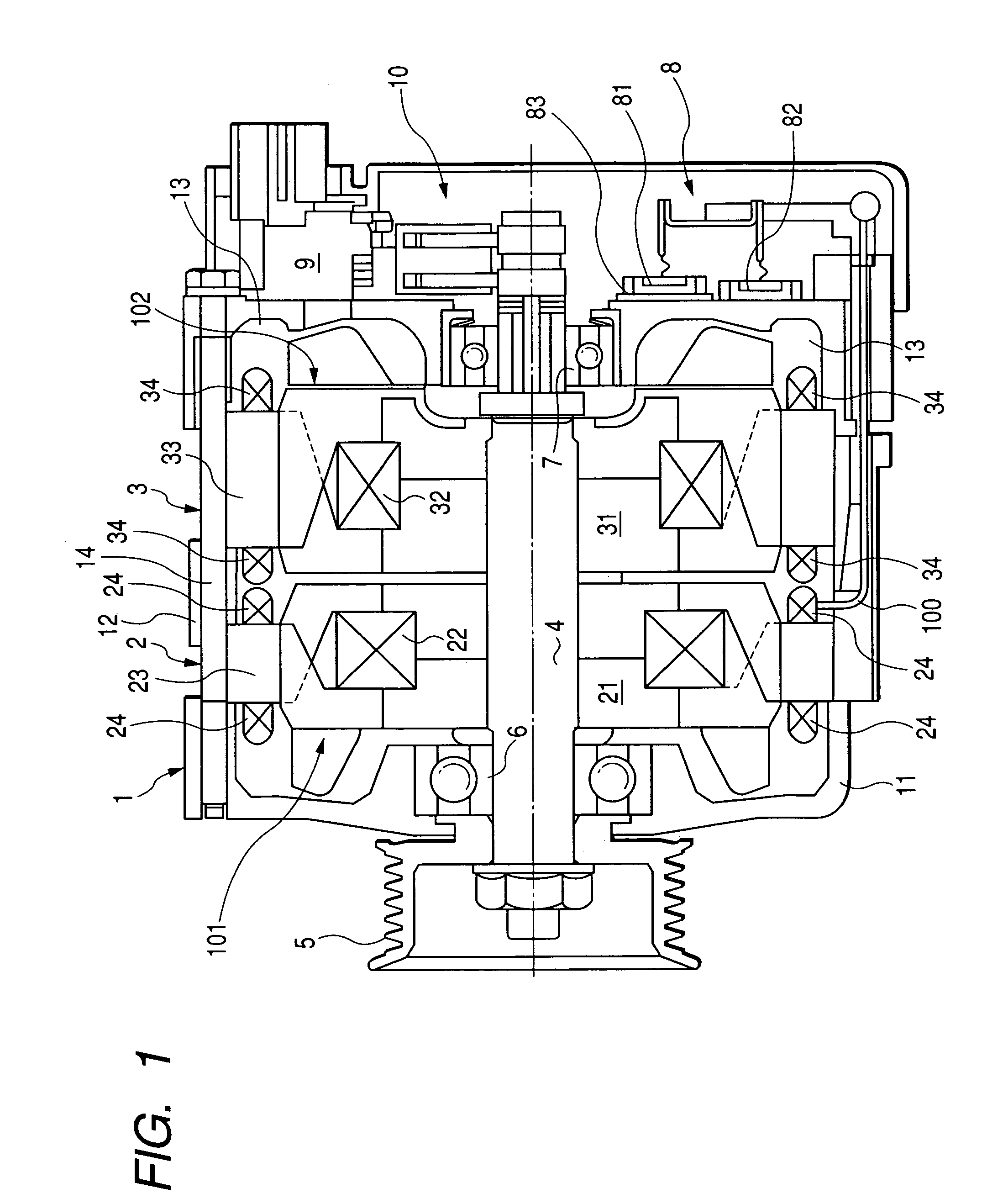
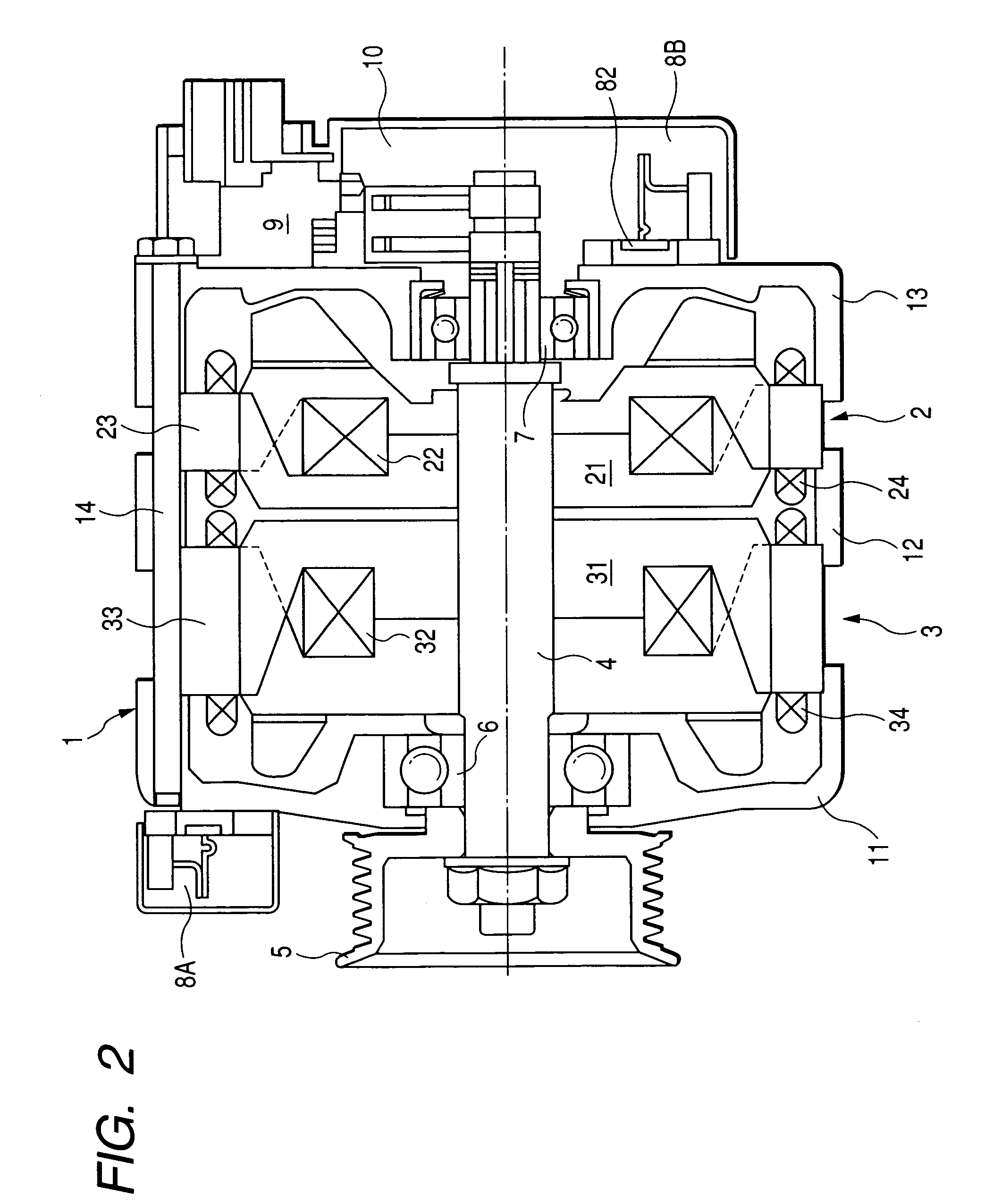
InactiveUS7397157B2Increasing total size and volume and weightImprove cooling effectSynchronous generatorsMagnetic circuit rotating partsElectric machineEngineering
A tandem rotary electric machine, to be applicable to various types of mobile bodies such as vehicles, is equipped with a primary rotary electric machine and a secondary rotary electric machine arranged in tandem mechanism. In the tandem rotary electric machine, heat energy generated by positive diodes and negative diodes forming one or more rectifier devices is dissipated to a stator core of the secondary rotary electric machine. The stator core of the secondary rotary electric machine acts as a heat sink through the housing. The stator core of the secondary rotary electric machine has a less frequency use, and a large size and a large weight than those of the primary rotary electric machine of high frequent and normal is used as a heat sink in order to prevent the temperature rise of the positive diode and the negative diode of the rectifier devices.
Owner:DENSO CORP
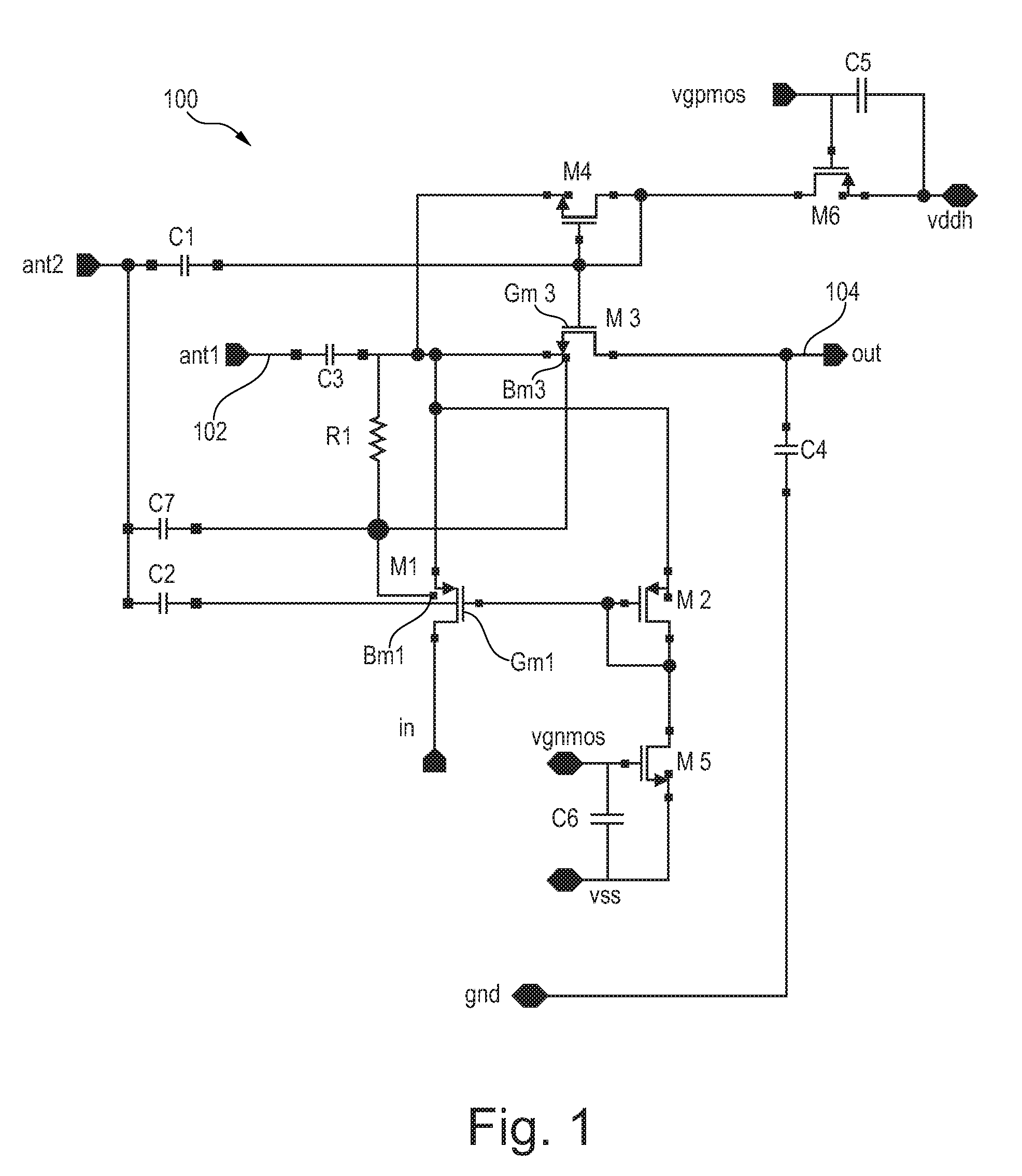
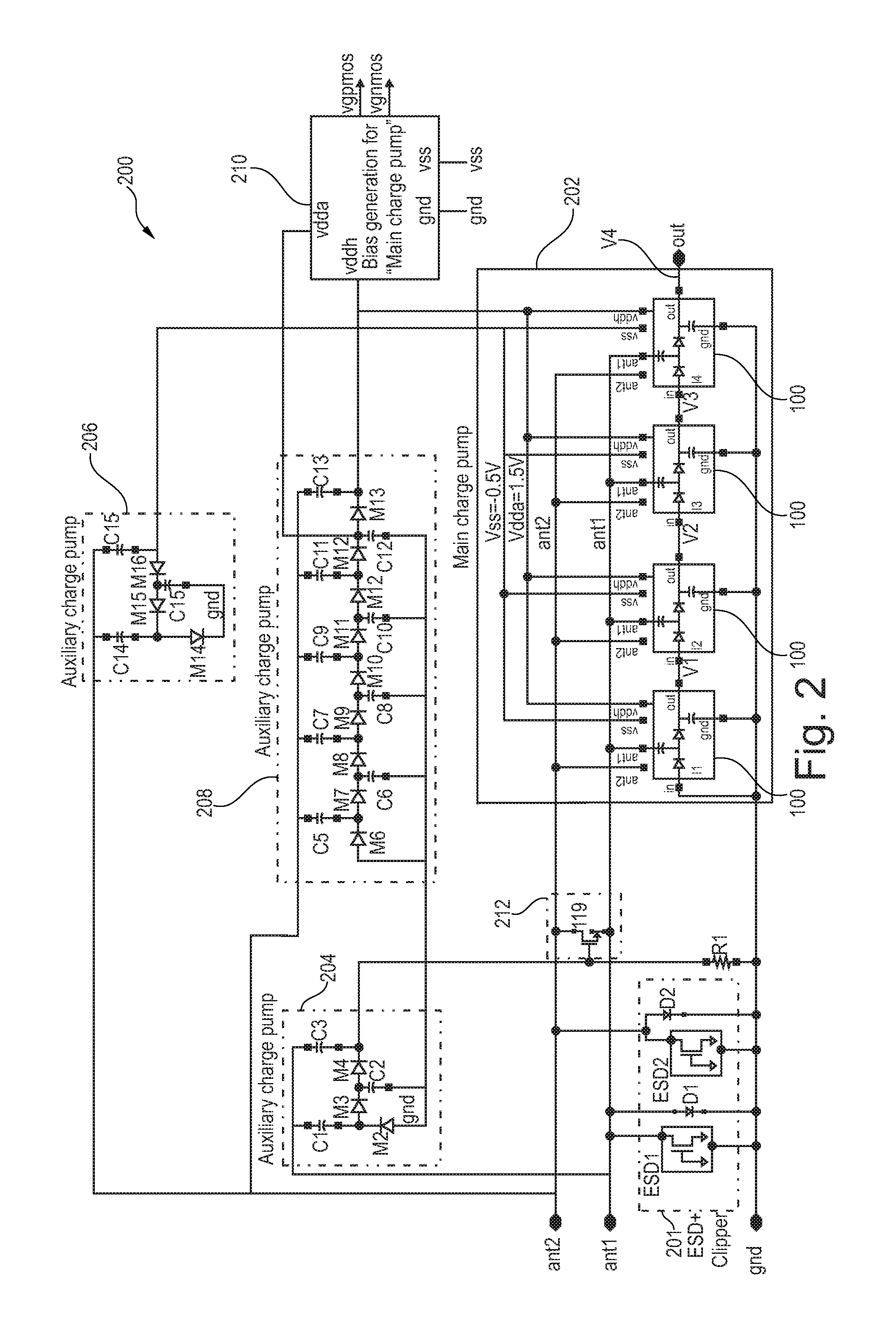
Charge pump circuit
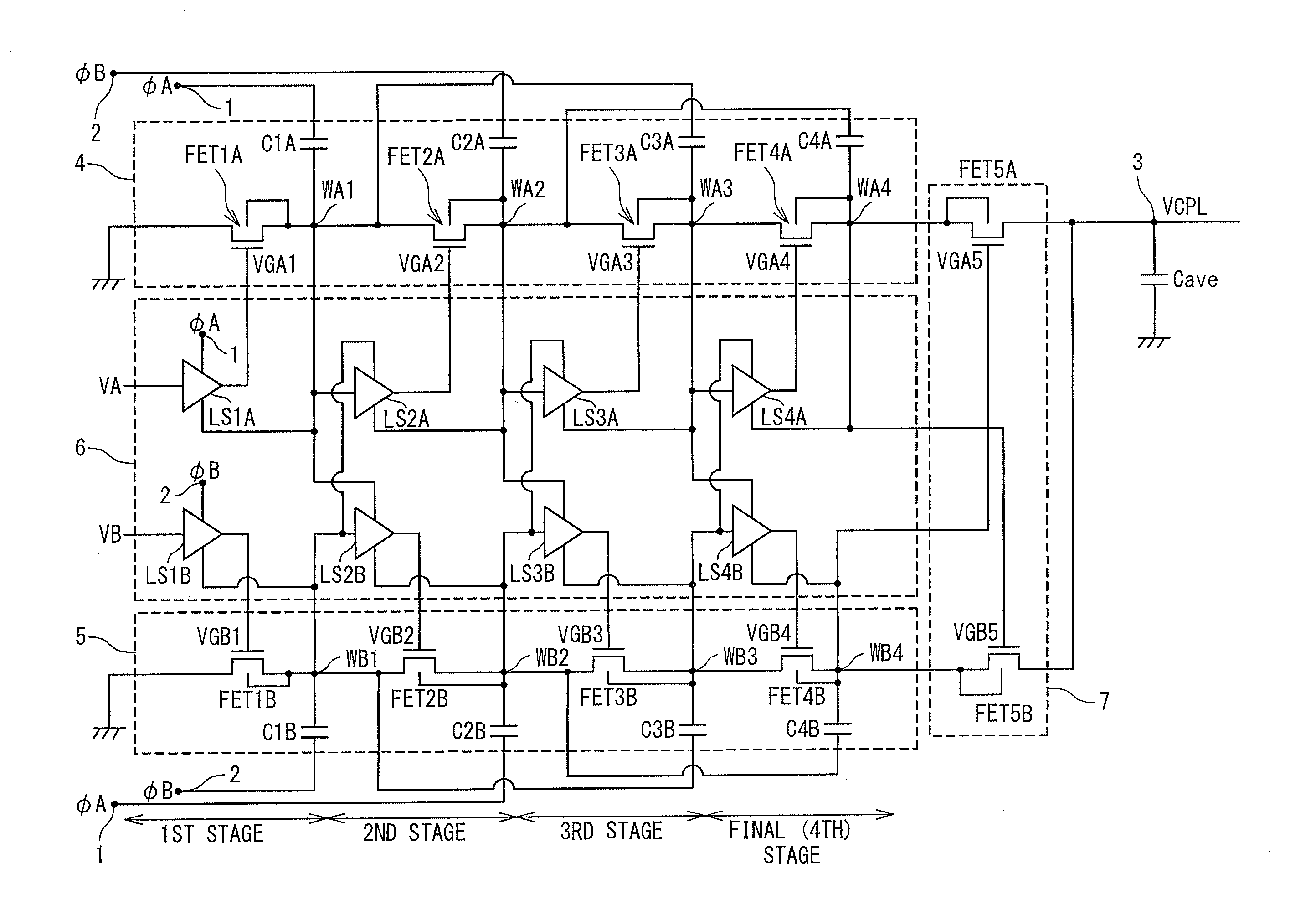
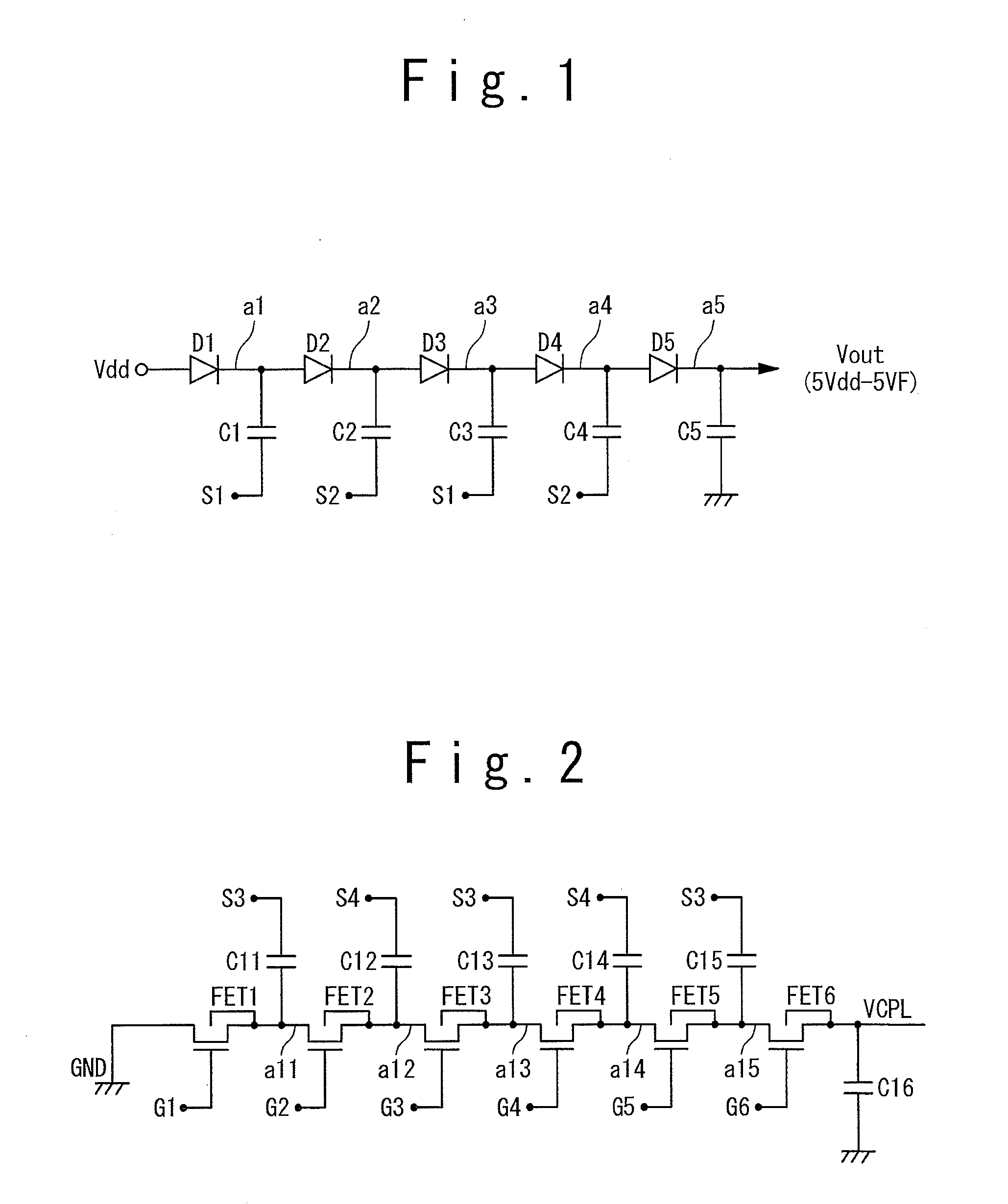
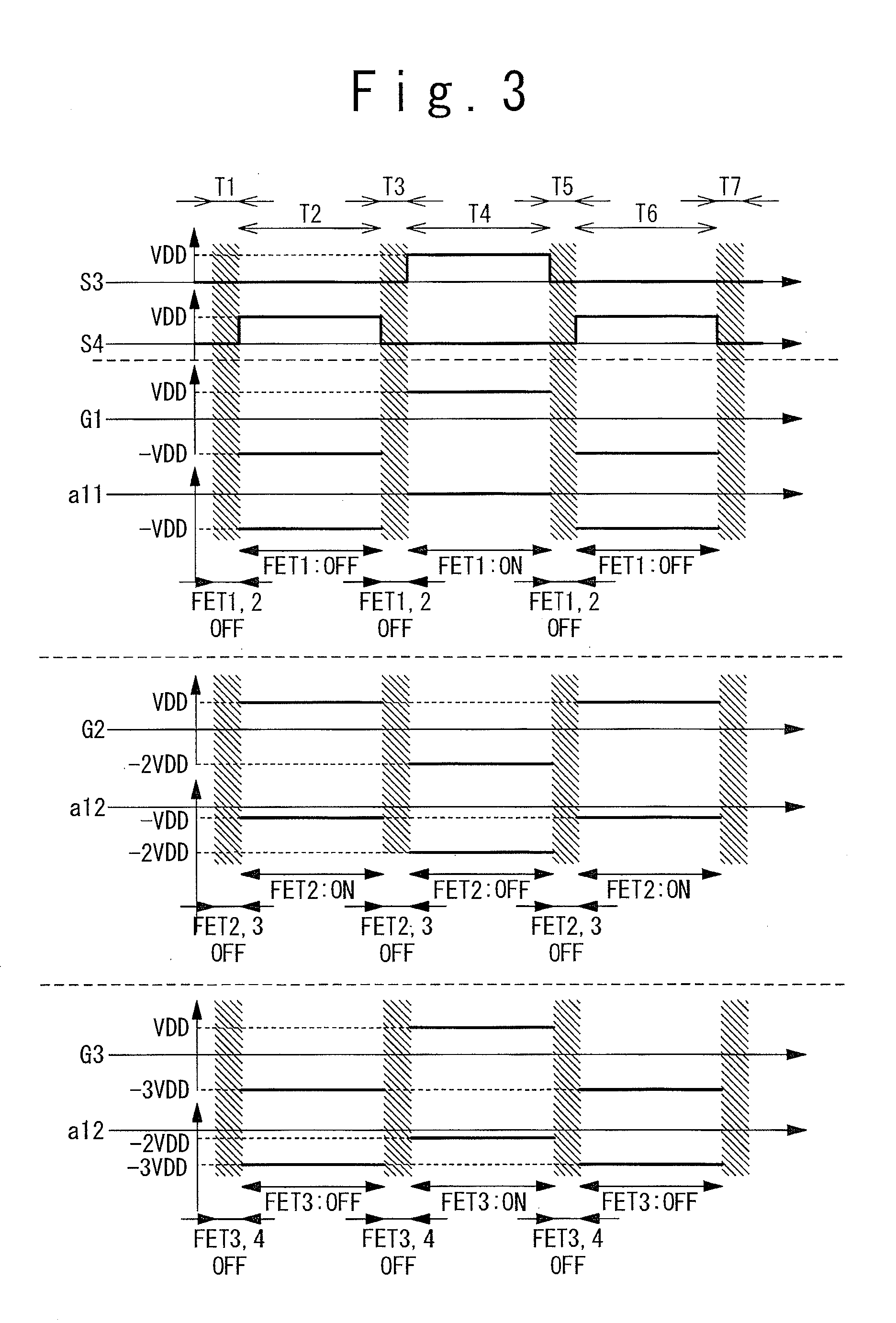
InactiveUS20110133821A1Large output voltageElement breakdown voltage of be reduceDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationPower inverterControl circuit
A charge pump circuit has: first and second charge pump circuits alternately performing boosting operations; and a control circuit. The first (second) charge pump circuit has: plural stages of first (second) switch transistors connected in series; plural stages of first (second) connection nodes respectively connected to sources of the first (second) switch transistors; and plural stages of first (second) capacitors respectively connected to the first (second) connection nodes. The control circuit has: plural stages of first inverters and plural stages of second inverters. The n-th-stage first (second) inverter is supplied with a positive-side power supply voltage from the (n−1)-th-stage second (first) connection node, is supplied with a negative-side power supply voltage from the n-th-stage first (second) connection node, is supplied with an input voltage from the (n−1)-th-stage first (second) connection node, and outputs an output voltage to a gate of the n-th-stage first (second) switch transistor.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Synchronized primary winding current shunting technique for controlling electro-stimulus level
ActiveUS20050145199A1Easy to adjustSmall sizeAlarmsTaming and training devicesControl signalPeak value
An electronic apparatus (1) for training an animal is supported against the animal's skin, and includes stimulus electrodes (5) for electrically contacting the skin. A controller including output terminals producing aversive stimulus control signals, a first switch (Q4) coupled to a winding to produce therein a burst of first current pulses in response to a first signal produced by the controller (33) and a second switch (Q2) coupled to the first switch (Q4) operative to synchronously shunt predetermined trailing portions of the first current pulses away from the winding in response to a second signal produced by the controller to reduce the amount of energy delivered to the winding by the switching transistor (Q4) without substantially changing a peak value of a flyback voltage across the winding. The controller sets various values of time intervals during which portions of the first current pulses are shunted away from the winding in order to set various corresponding intensities of aversive stimulus.
Owner:GARMIN
Transistor drive circuit of power converter operating in a wide voltage range
ActiveUS7471121B2Wide voltage rangeLarge output voltageTransistorDc-dc conversionDriver circuitVoltage clamp
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Transimpedance amplifier
InactiveUS20050007199A1Minimise currentWide bandwidthAmplifier combinationsAmplifiers controlled by lightEngineeringTransimpedance amplifier
A transimpedance amplifier, which is useful as an optical fiber preamplifier, is disclosed. The illustrative embodiment exhibits four characteristics. First, it minimizes the equivalent input noise current. Second, it has a wide bandwidth. Third, it has a reasonably large output voltage, and fourth, it is stable over wide temperature and voltage ranges. The illustrative embodiment comprises a transimpedance stage and a gain stage. Both stages employ a pure NMOS design which contributes to the above four advantages. Bandwidth is further increased over the prior art by the use of inductive loads. The inductive loads of the illustrative embodiment are not physical inductors, but transistor-based “active” inductors: the combination of a resistor connected in series with the gate of an NMOS transistor.
Owner:SIRES LABS
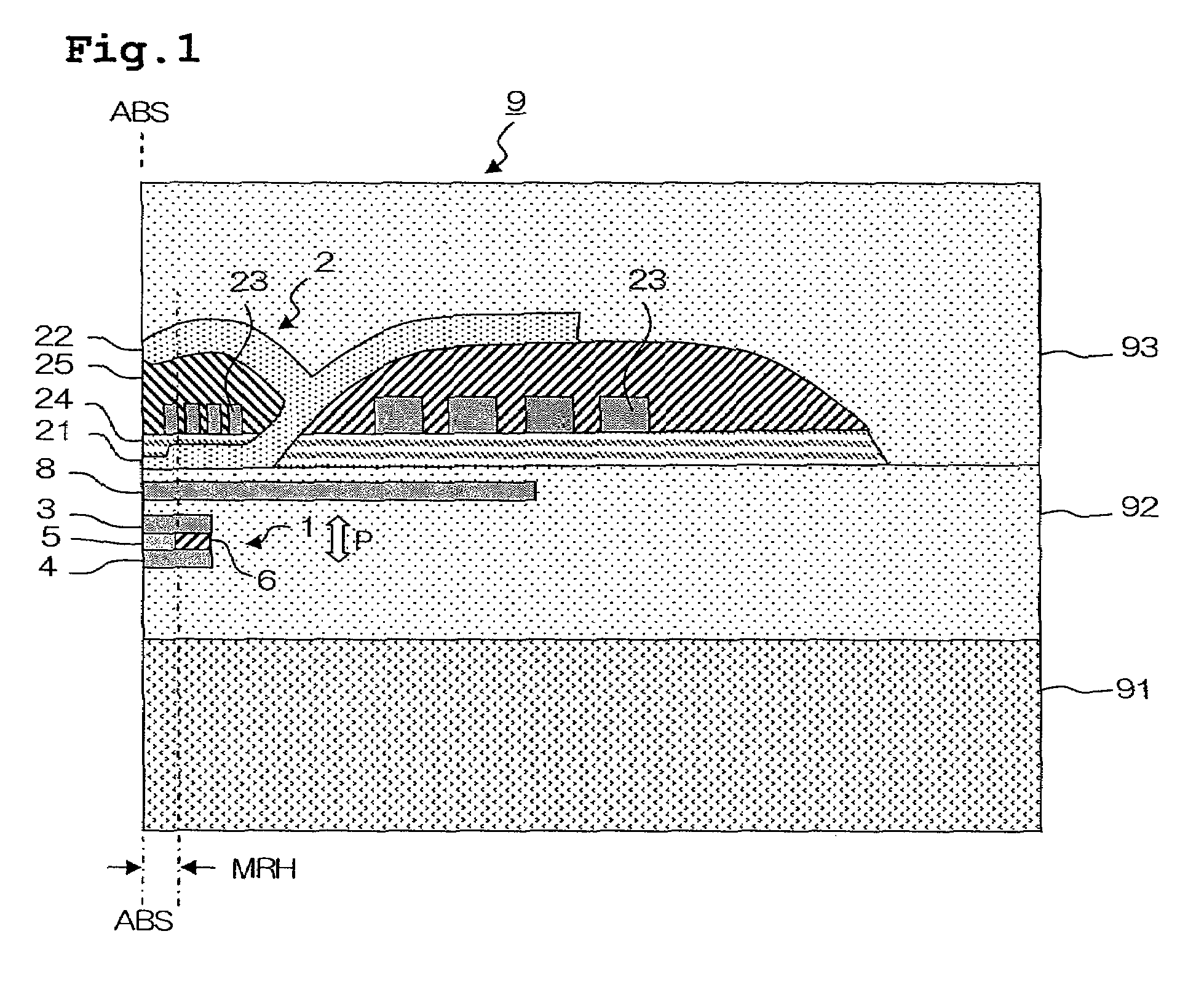
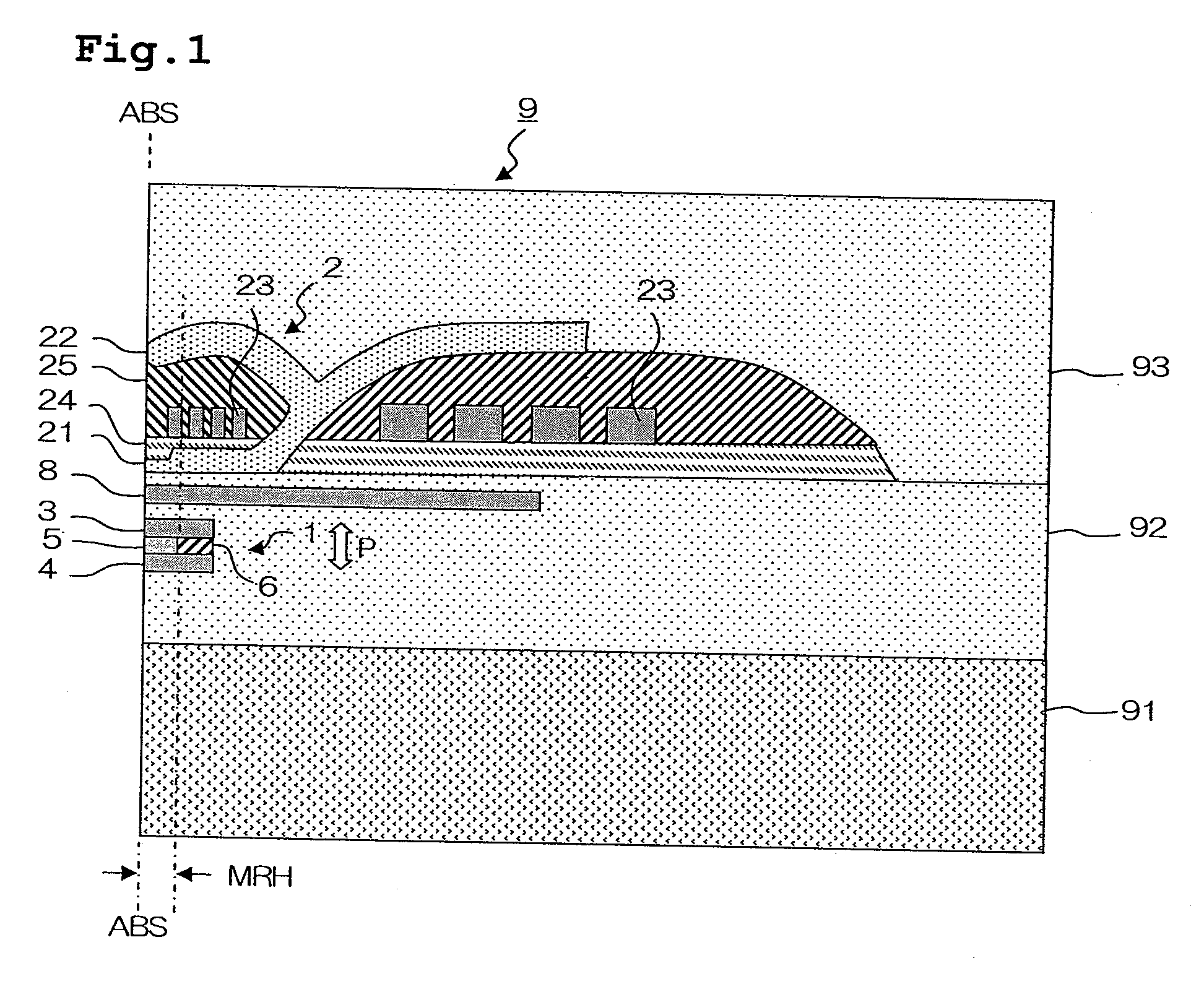
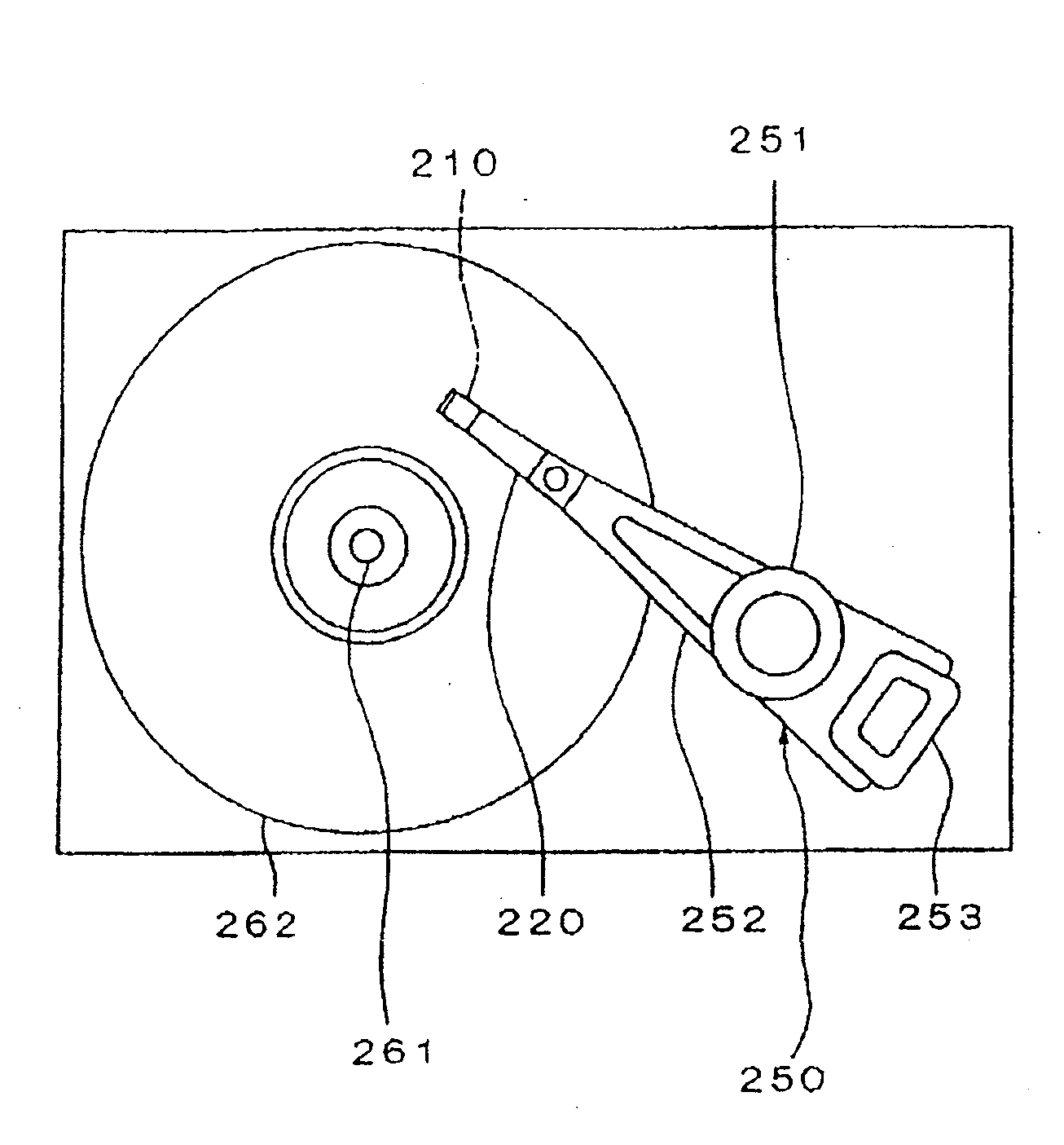
Method for inspecting magnetic characteristics of a plurality of thin magnetic heads by means of local application of magnetic field
InactiveUS7683610B2Sufficiently simulating a high-frequency alternating magnetic fieldPromote generationMagnetic property measurementsMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsEngineeringMagnetic characteristic
A method for inspecting magnetic characteristics of a thin film magnetic head that is arranged in a row bar includes: a step of preparing a row bar having sliders including a thin film magnetic head formed therein and lapping guides having magnetoresistance effect; a step of preparing a magnetic field applying row bar having first and second magnetic field applying elements; a first positioning step in which said magnetic field applying row bar is arranged opposite to said row bar; a second positioning step in which a relative movement between said magnetic field applying row bar and said row bar is made so that at least one of said lapping guides exhibits a largest output voltage; and a measurement step in which a relationship between the intensity of the magnetic field and an output voltage of a magnetic field sensor is obtained.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Method for inspecting magnetic characteristics of a plurality of thin magnetic heads by means of local application of magnetic field
InactiveUS20090219018A1Sufficiently simulating a high-frequency alternating magnetic fieldPromote generationMagnetic property measurementsMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsRelative motionEngineering
A method for inspecting magnetic characteristics of a thin film magnetic head that is arranged in a row bar includes: a step of preparing a row bar having sliders including a thin film magnetic head formed therein and lapping guides having magnetoresistance effect; a step of preparing a magnetic field applying row bar having first and second magnetic field applying elements; a first positioning step in which said magnetic field applying row bar is arranged opposite to said row bar; a second positioning step in which a relative movement between said magnetic field applying row bar and said row bar is made so that at least one of said lapping guides exhibits a largest output voltage; and a measurement step in which a relationship between the intensity of the magnetic field and an output voltage of a magnetic field sensor is obtained.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
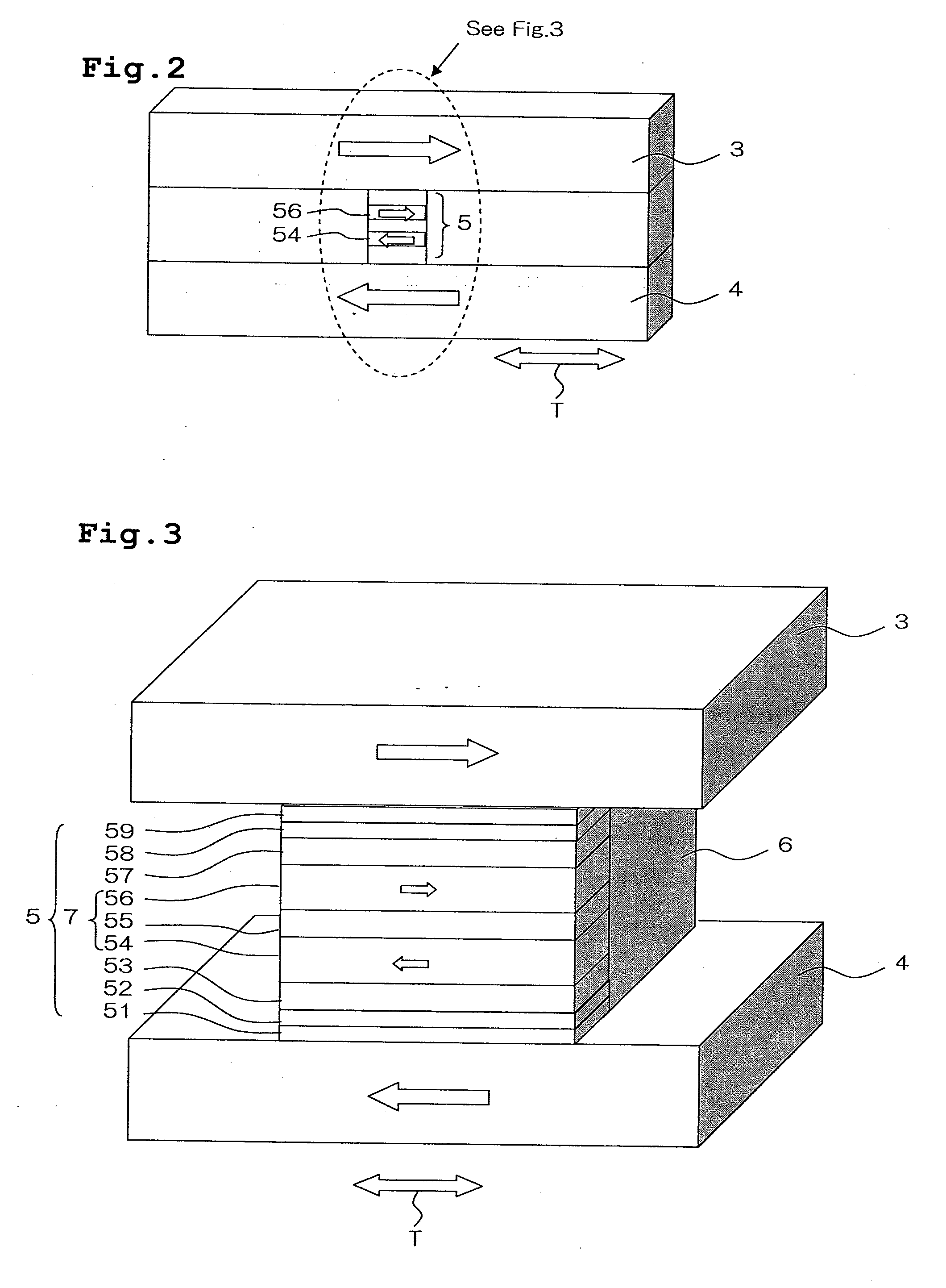
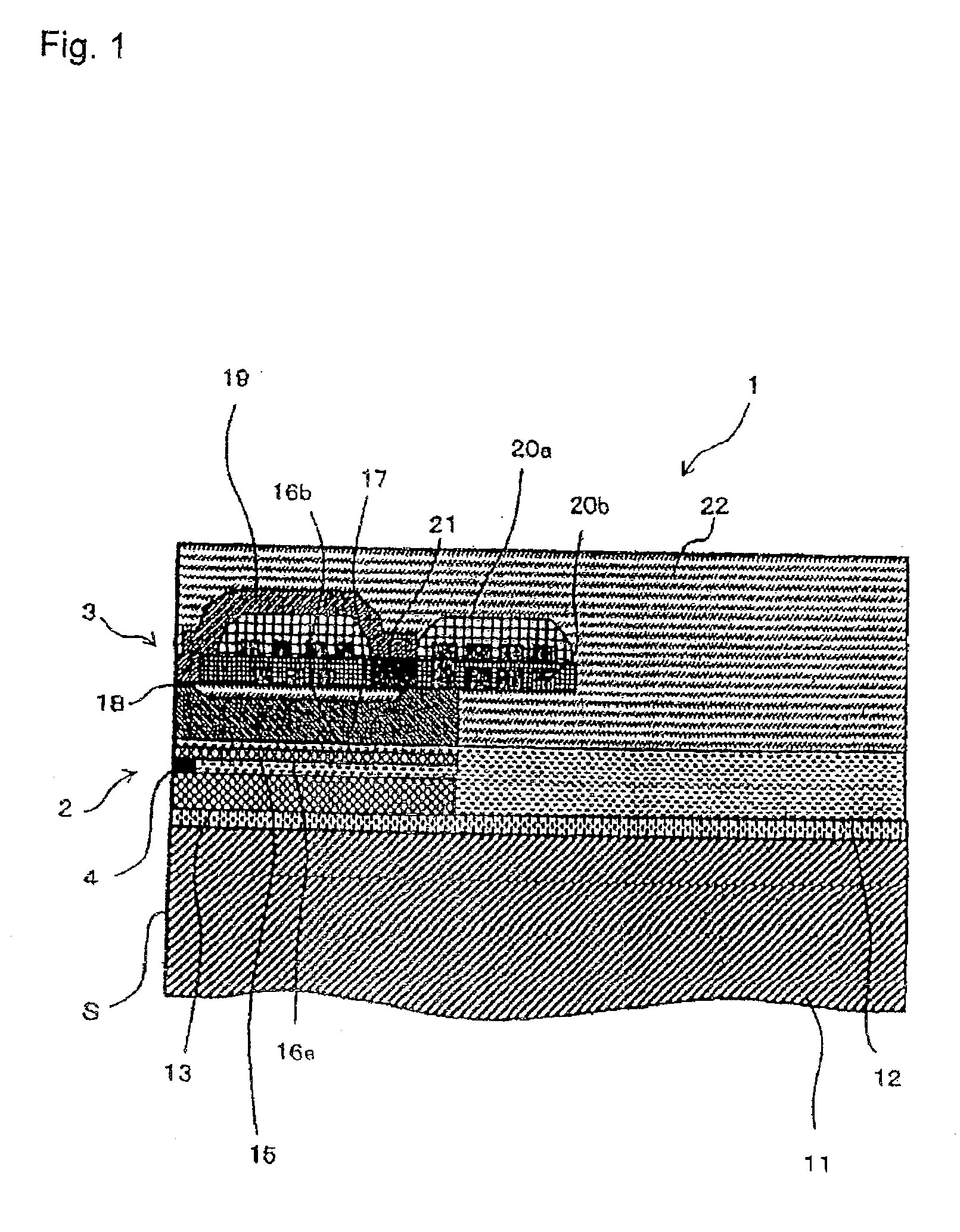
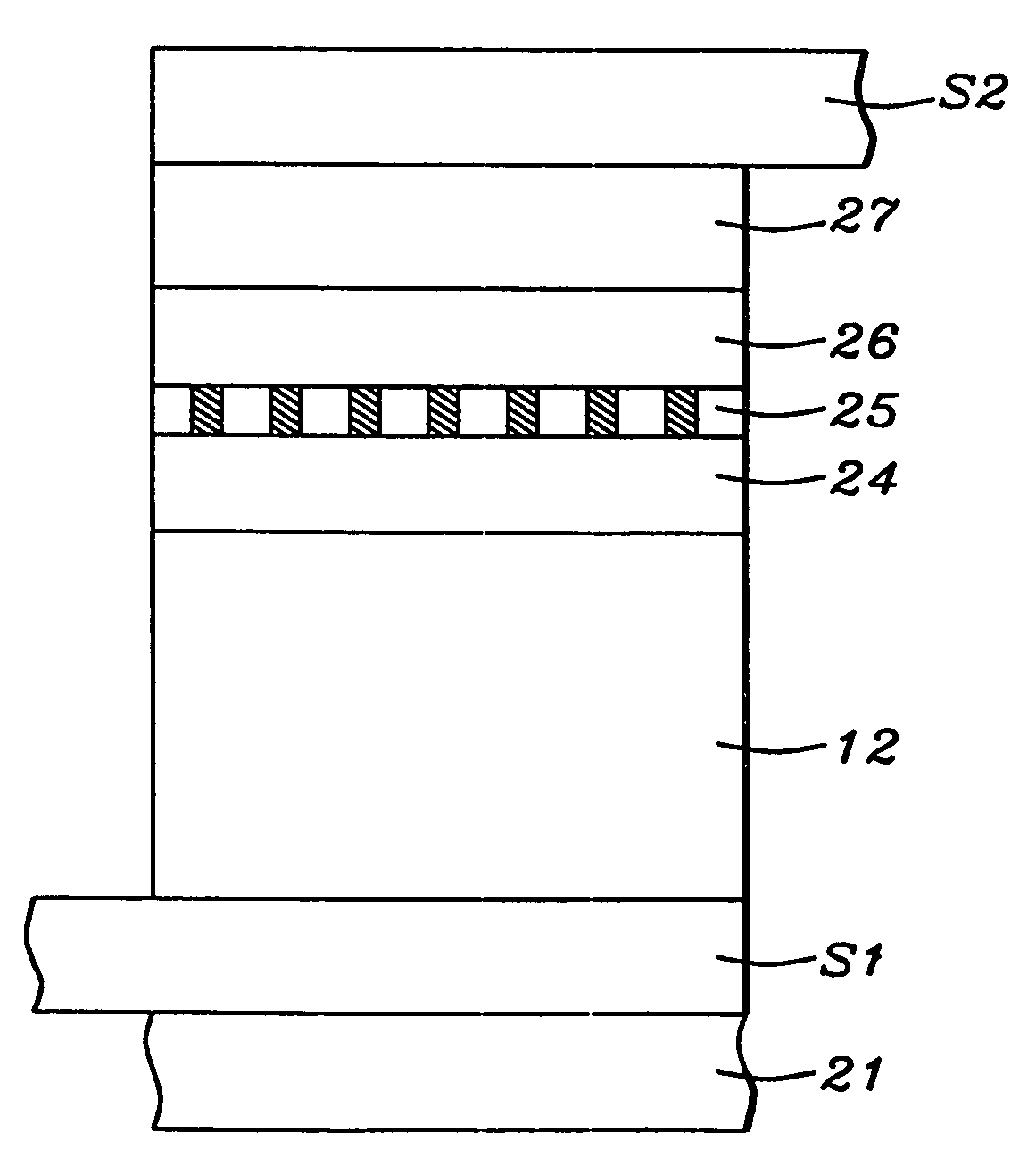
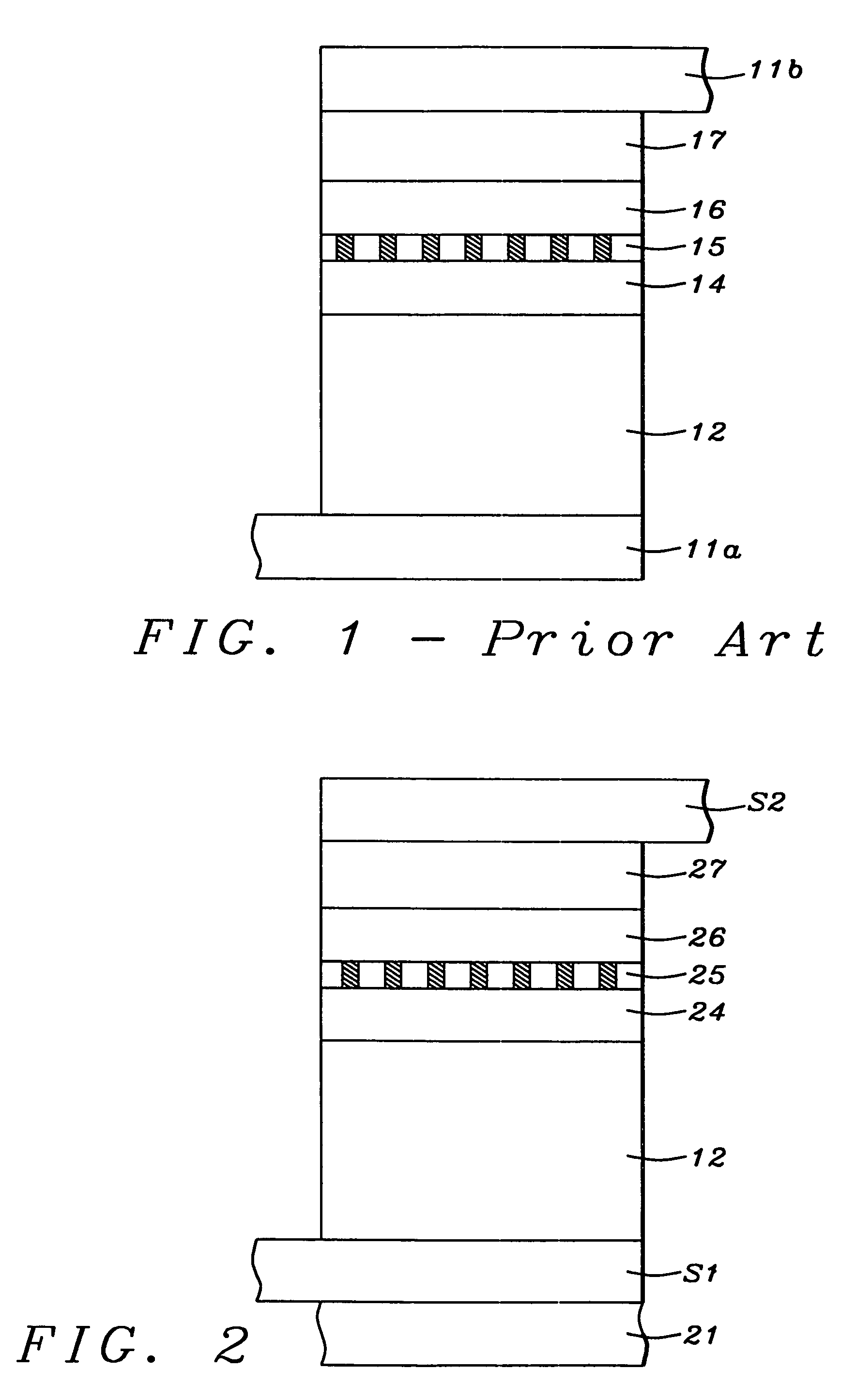
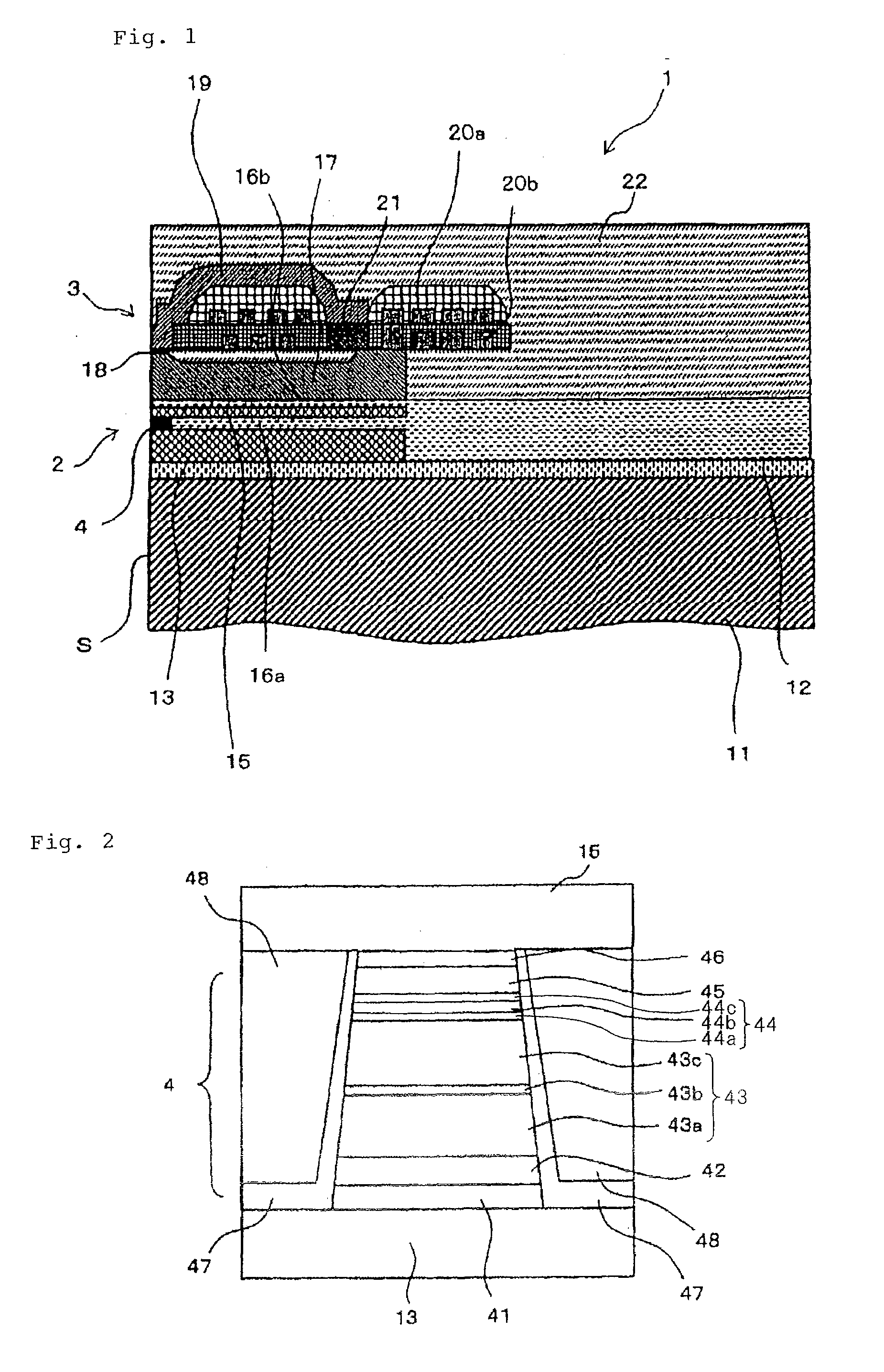
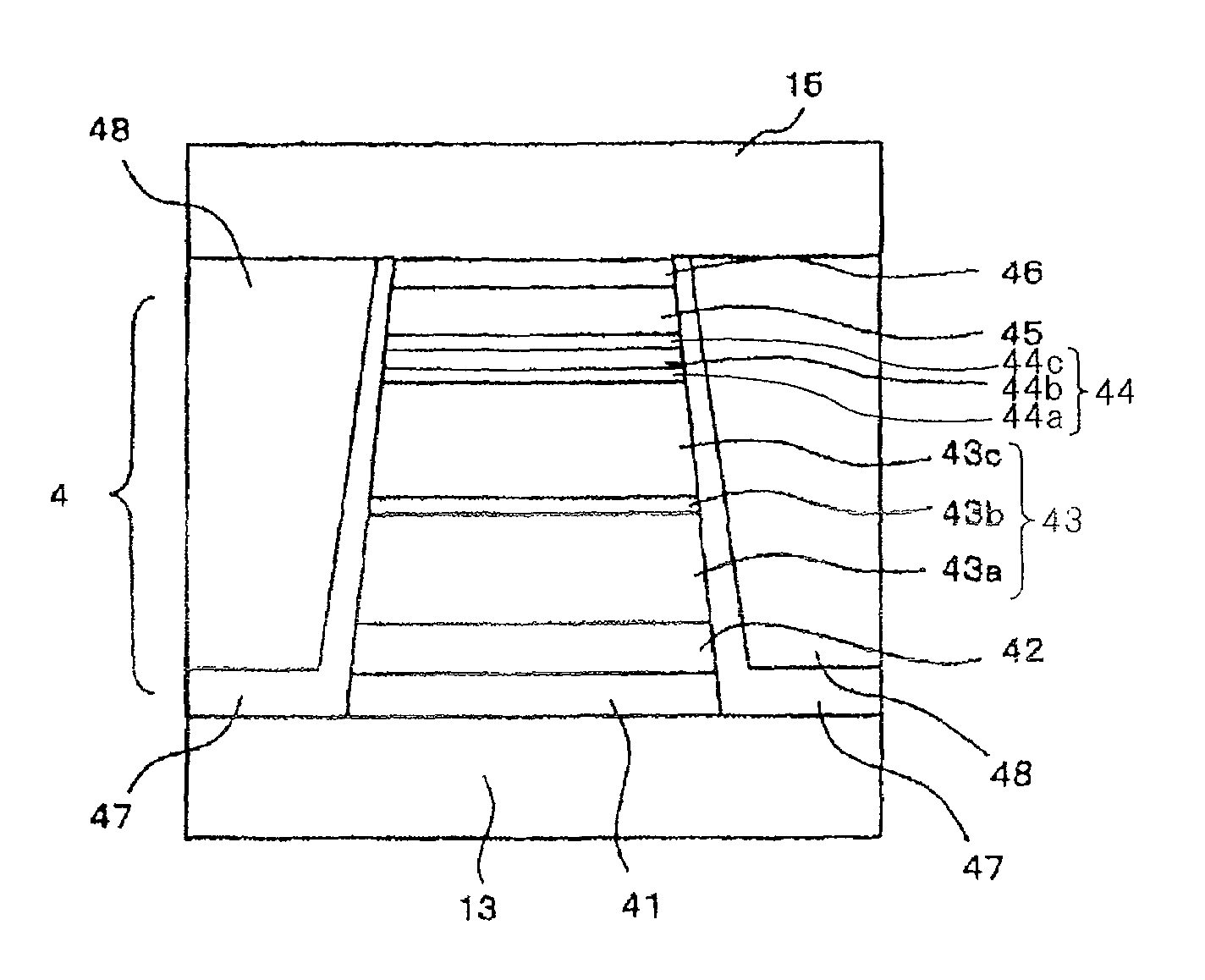
Magneto-resistance effect element having diffusion blocking layer and thin-film magnetic head
InactiveUS20080226948A1High MR ratioGood element characteristicNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsDiffusionMagnetization
A magnetoresistance effect element (MR element) for use in a thin-film magnetic head has a buffer layer, an antiferromagnetic layer, a pinned layer, a spacer layer, a free layer, and a cap layer that are successively stacked. A sense current flows in a direction perpendicular to layer surfaces via a lower shield layer and an upper shield layer. The pinned layer comprises an outer layer having a fixed magnetization direction, a nonmagnetic intermediate layer, and an inner layer in the form of a ferromagnetic layer. The spacer layer comprises a first nonmagnetic metal layer, a semiconductor layer made of ZnO, and a second nonmagnetic metal layer. The inner layer or the outer layer includes a diffusion blocking layer made of an oxide of an element whose electronegativity is equal to or smaller than Zn, e.g., ZnO, TaO, ZrO, MgO, TiO, or HfO, or made of RuO.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
High-fidelity piezoelectric contact-type microphone structure
InactiveUS20060291677A1Simple structureAvoid distortionSingle transducer incorporationPiezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesUltrasound attenuationResonance
A piezoelectric contact-type microphone structure is provided. With this structure, the piezoelectric element directly touches the speaker's skin without the intervening sponge or spring to fully pick up the skin vibration and to avoid high-frequency attenuation. The structure also provides an ample room for the piezoelectric element to undergo full structural change. The structure avoids the low-frequency distortion resulted from a resonance structure formed by the piezoelectric element, the sponge or spring, and the casing of the microphone. A microphone using this structure has a flat frequency response and a superior performance both for high- and low-frequency voice signals.
Owner:AIRDIGIT
Rectifier and high efficiency charge pump for RFID
ActiveUS8687395B2High bandwidthImprove conversion efficiencyAc-dc conversionElectronic switchingMOSFETEngineering
It is described a high efficiency rectification stage using dynamic threshold MOSFET. The idea is to use the input signal to reduce the threshold voltage when the transistor has to be on, and to increase the threshold when the transistor has to be off. This allows reducing both the resistive losses and the leakage current. A matching network allows the generation of a second higher voltage signal to drive the control gates and the bulk, i.e. the wells, of the transistors. Further, a self-tuned front-end is provided to extend the bandwidth of the high-Q charge pump.
Owner:NXP BV
Cantilever beam oscillating ferroelectric generator
InactiveCN101572506AIncrease the output voltageLarge output voltageElectrical storage systemPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesCantilevered beamElectricity
The invention relates to a cantilever beam oscillating ferroelectric generator. The current piezoelectric generator has low generating efficiency. And the invention comprises a metal cantilever beam, a mass block, a base, a ferroelectric film and an accumulator circuit. The base can oscillate up and down, one end of the strip metal cantilever beam is fixedly connected with the base and the other end thereof is fixedly connected with the mass block. The upper surface and the lower surface of the metal cantilever beam are respectively provided with the ferroelectric films in array, the top and the bottom of each ferroelectric film are provided with electricity collecting points in matrix, all collecting points on the top thereof are connected with top electrode wires by conductors, and all collecting points on the bottom thereof are connected with bottom electrode wires by the conductors. The top electrode wires are connected with one end input by the accumulator circuit, the bottom electrode wires are connected with the other end input by the accumulator circuit. Because the invention adopts the ferroelectric material as an electromechanical converter of the generator, susceptiveness is largely improved and larger output voltage and generation efficiency can be obtained.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Device with thermoelectric cooling
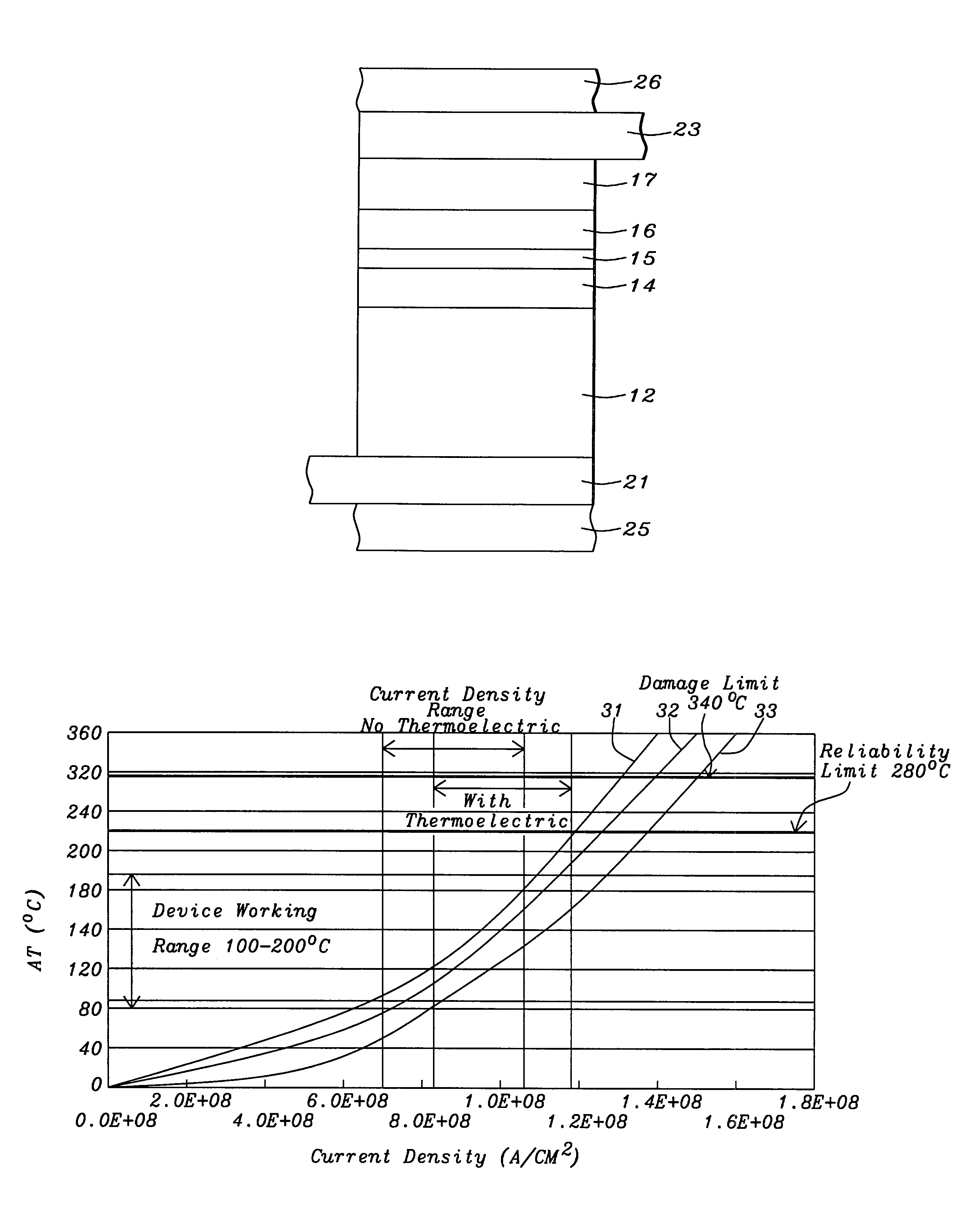
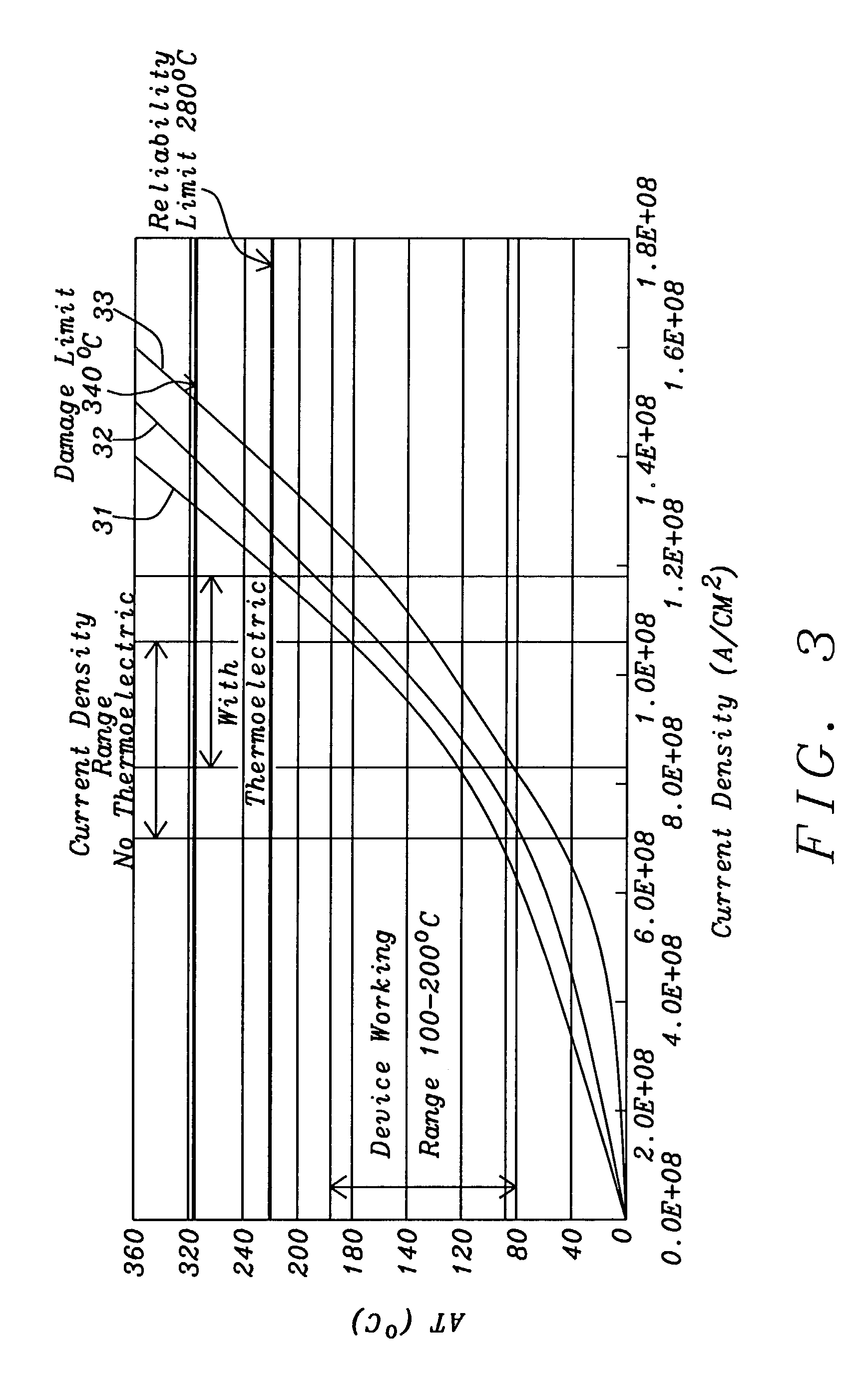
ActiveUS6987650B2Increase powerLarge output voltageNanomagnetismDomestic cooling apparatusThermoelectric coolingEngineering
Increasing the output signal from CPP GMR devices by increasing the read current has not previously been considered an option because it would make the device run too hot. This problem has been overcome by using, for the upper and lower leads, materials that differ significantly in their thermoelectric powers. Thus, when DC is passed through the device, from − to + TEP leads, hot and cold junctions are formed and heat is transferred from the micro-device into the leads, resulting in a net local cooling of the device which enables it to operate at higher power. For a GMR device, this translates to a larger output voltage, making it easier, more sensitive, and more reliable to use.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Method to increase CCP-CPP GMR output by thermoelectric cooling
InactiveUS7382584B2Improve carrying capacityNo loss in reliabilityThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectDomestic cooling apparatusThermoelectric coolingEngineering
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Tandem rotary electric machine
InactiveUS20070007847A1Large massSmall heat resistanceSynchronous generatorsMagnetic circuit rotating partsFrequency of useHeating energy
A tandem rotary electric machine, to be applicable to various types of mobile bodies such as vehicles, is equipped with a primary rotary electric machine and a secondary rotary electric machine arranged in tandem mechanism. In the tandem rotary electric machine, heat energy generated by positive diodes and negative diodes forming one or more rectifier devices is dissipated to a stator core of the secondary rotary electric machine. The stator core of the secondary rotary electric machine acts as a heat sink through the housing. The stator core of the secondary rotary electric machine has a less frequency use, and a large size and a large weight than those of the primary rotary electric machine of high frequent and normal is used as a heat sink in order to prevent the temperature rise of the positive diode and the negative diode of the rectifier devices.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Dc-dc buck circuit
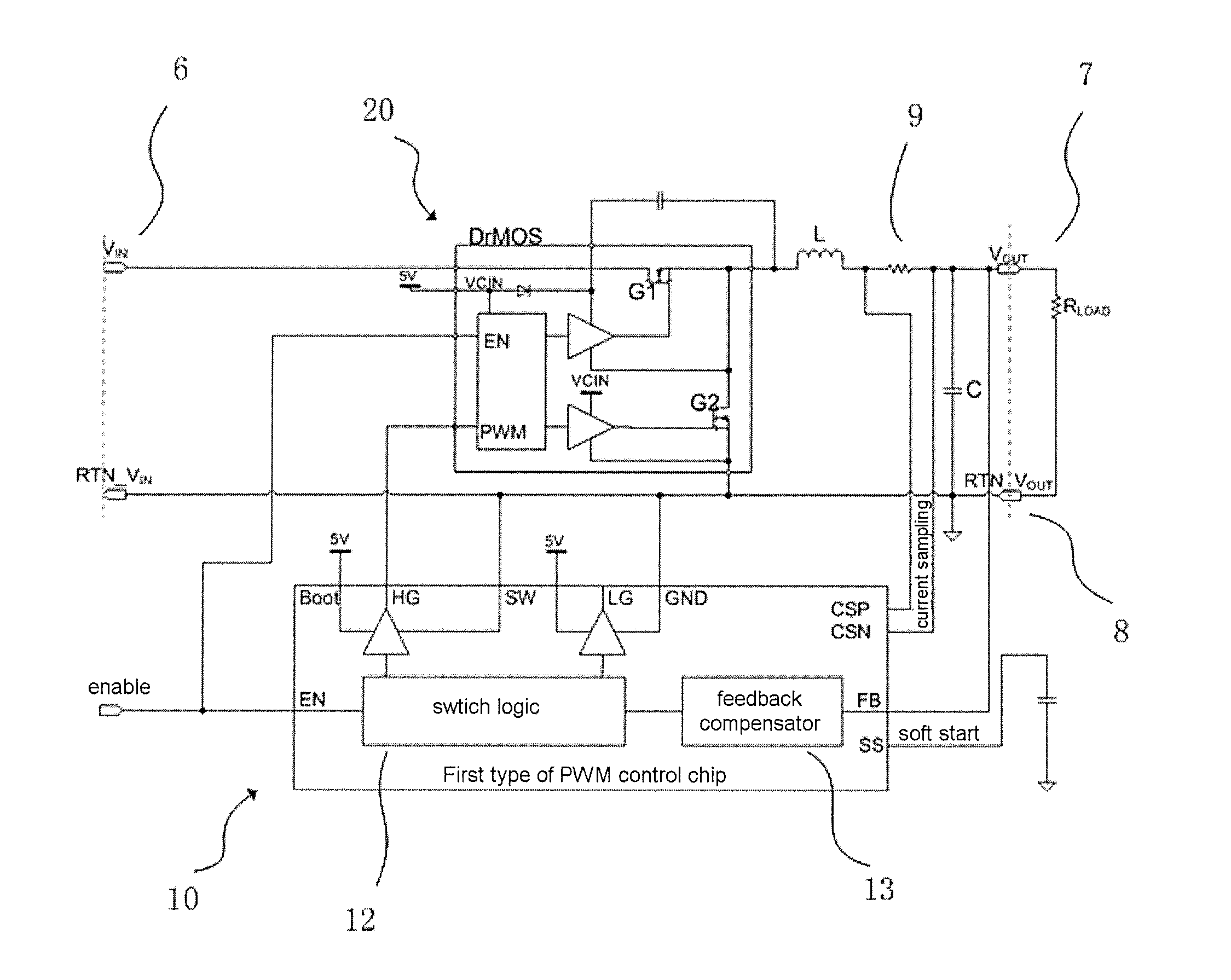
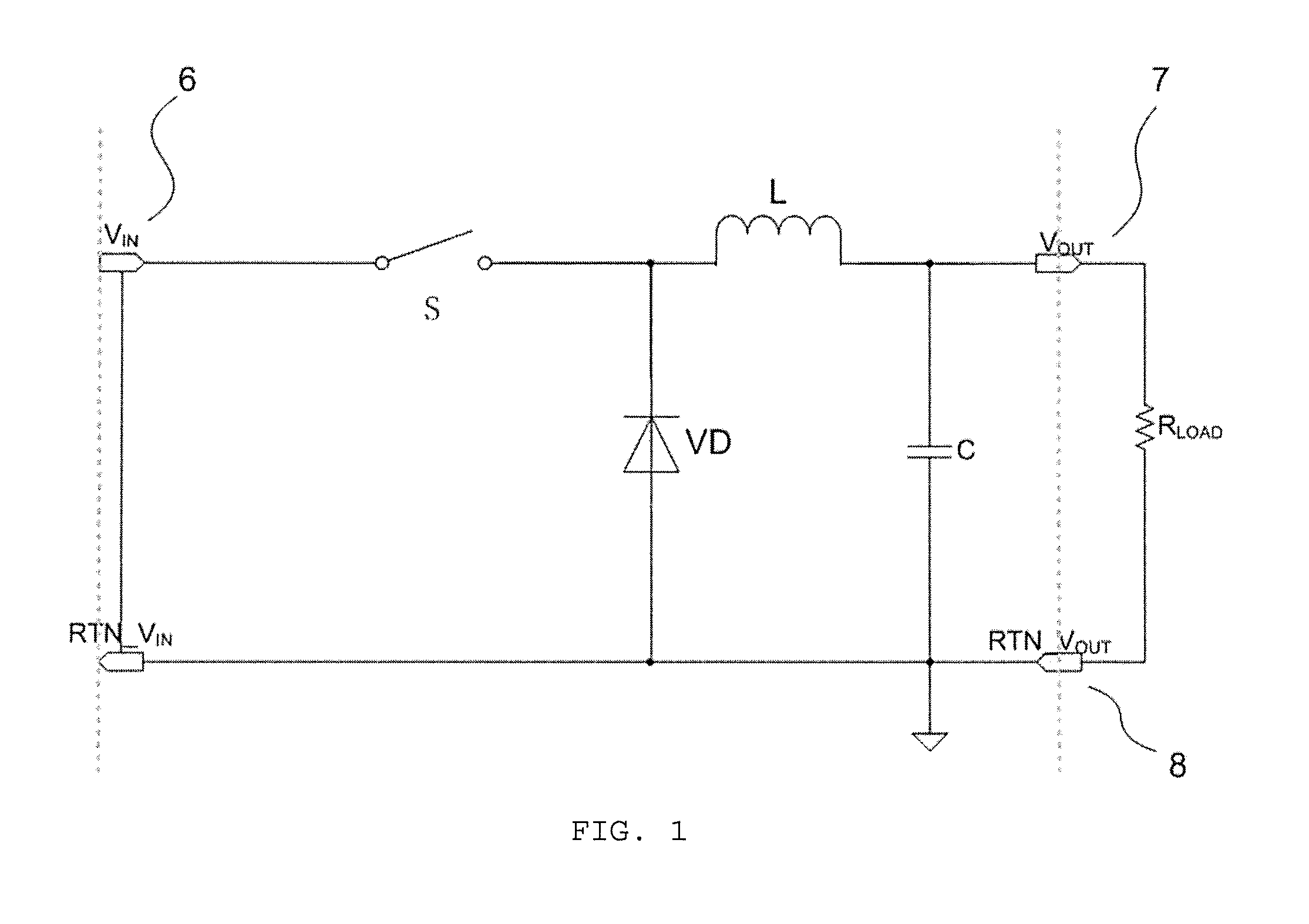
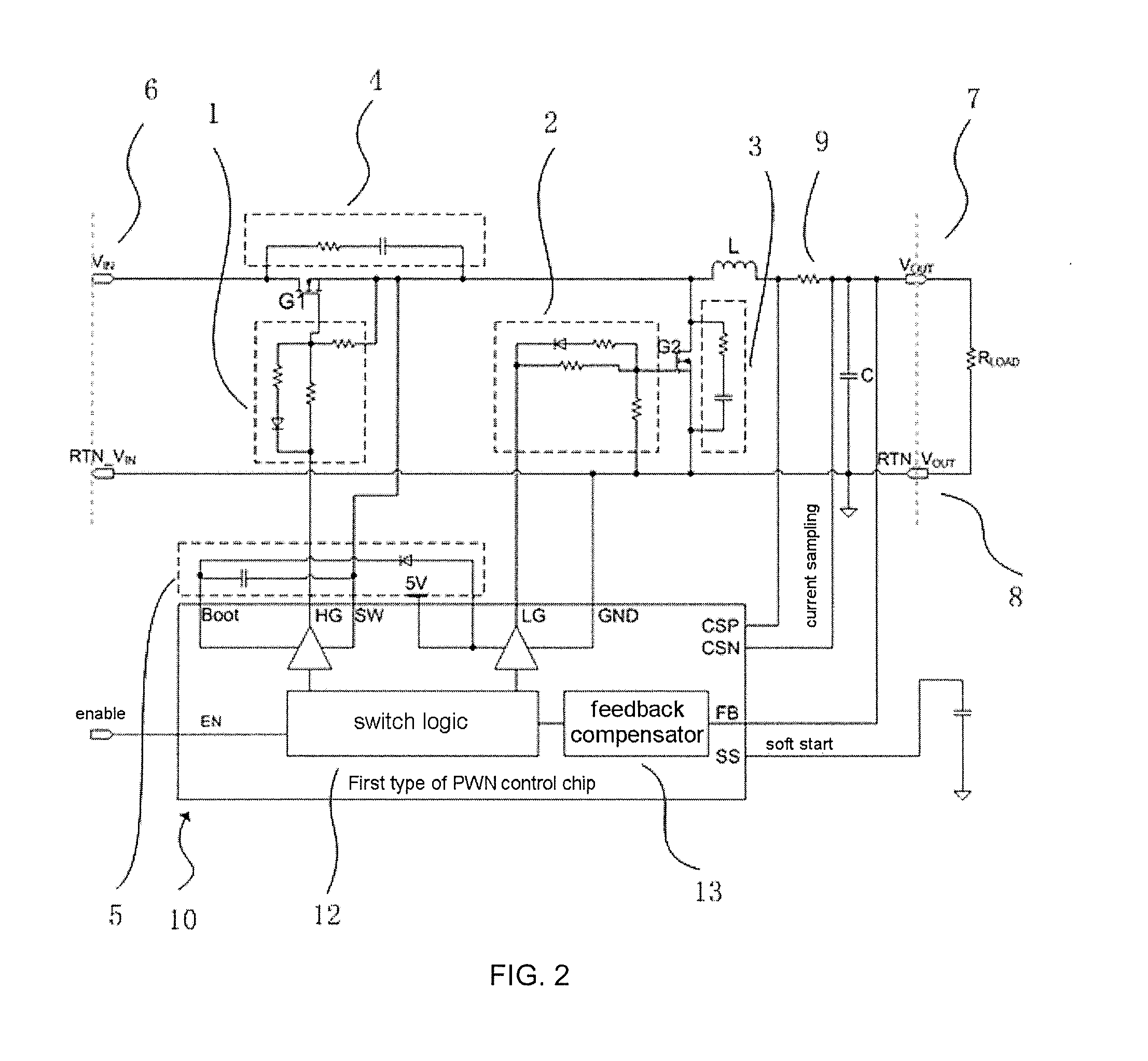
InactiveUS20140210443A1Large output voltageCompact and effective circuit designEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionInductorInductance
A DC-DC Buck circuit has a DC input terminal, a DC output terminal, a ground terminal, an inductor, a capacitor, a sampling resistor, a PWM control chip and a DrMOS chip. The output of the driver pin of the PWM control chip is unrelated to the voltage between the inductor and the sampling resistor. The DC-DC Buck circuit can produce a larger output voltage while also being compatible with a DrMOS chip.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
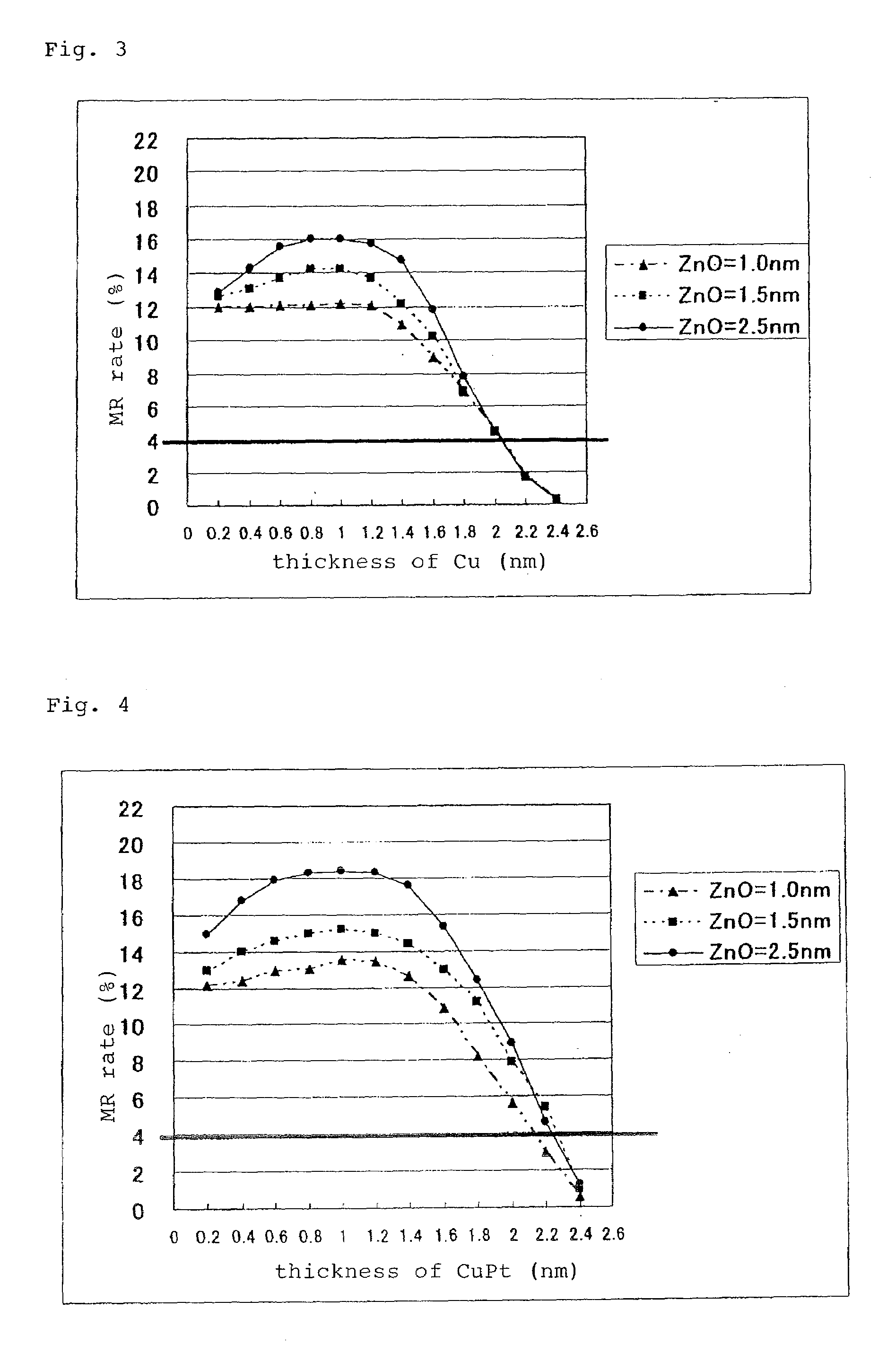
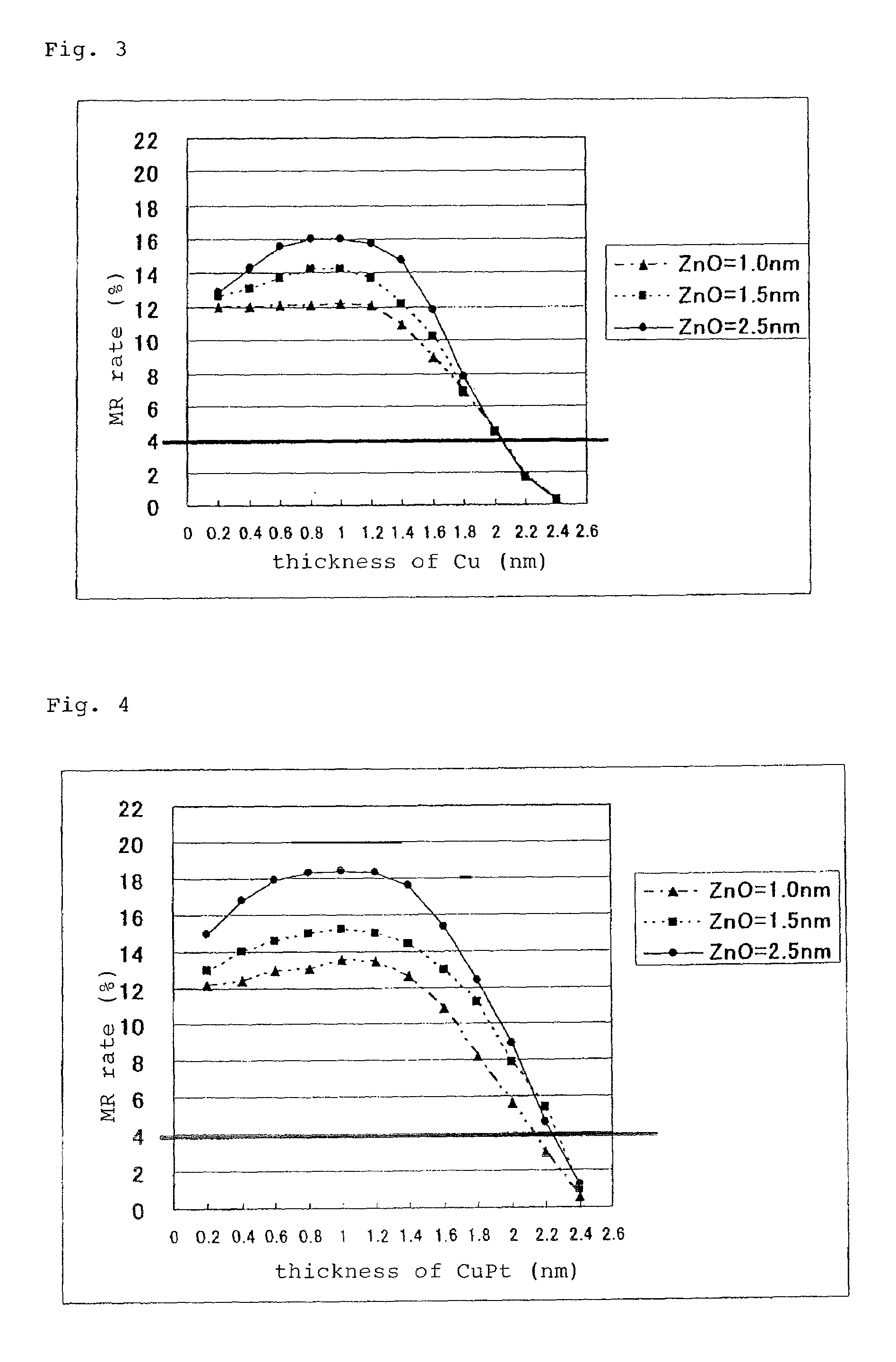
Magneto-resistance effect element and thin-film magnetic head
InactiveUS20080218907A1High MR ratioResistance can be madeRecord information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsMagnetizationEngineering
A magneto-resistance effect element (MR element) used for a thin film magnetic head is configured by a buffer layer, an anti-ferromagnetic layer, a pinned layer, a spacer layer, a free layer, and a cap layer, which are laminated in this order, and a sense current flows through the element in a direction orthogonal to the layer surface, via a lower shield layer and a upper shield layer. The pinned layer comprises an outer layer in which a magnetization direction is fixed, a non-magnetic intermediate layer, and an inner layer which is a ferromagnetic layer. The spacer layer comprises a first non-magnetic metal layer, a semiconductor layer, and a second non-magnetic metal layer. The first non-magnetic metal layer and the second non-magnetic metal layer comprise CuPt films having a thickness ranging from a minimum of 0.2 nm to a maximum of 2.0 nm, and the Pt content ranges from a minimum of 5 at % to a maximum of 25 at %. The semiconductor layer comprises a ZnO film, ZnS film, or GaN film having a thickness ranging from a minimum of 1.0 nm to a maximum of 2.5 nm.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
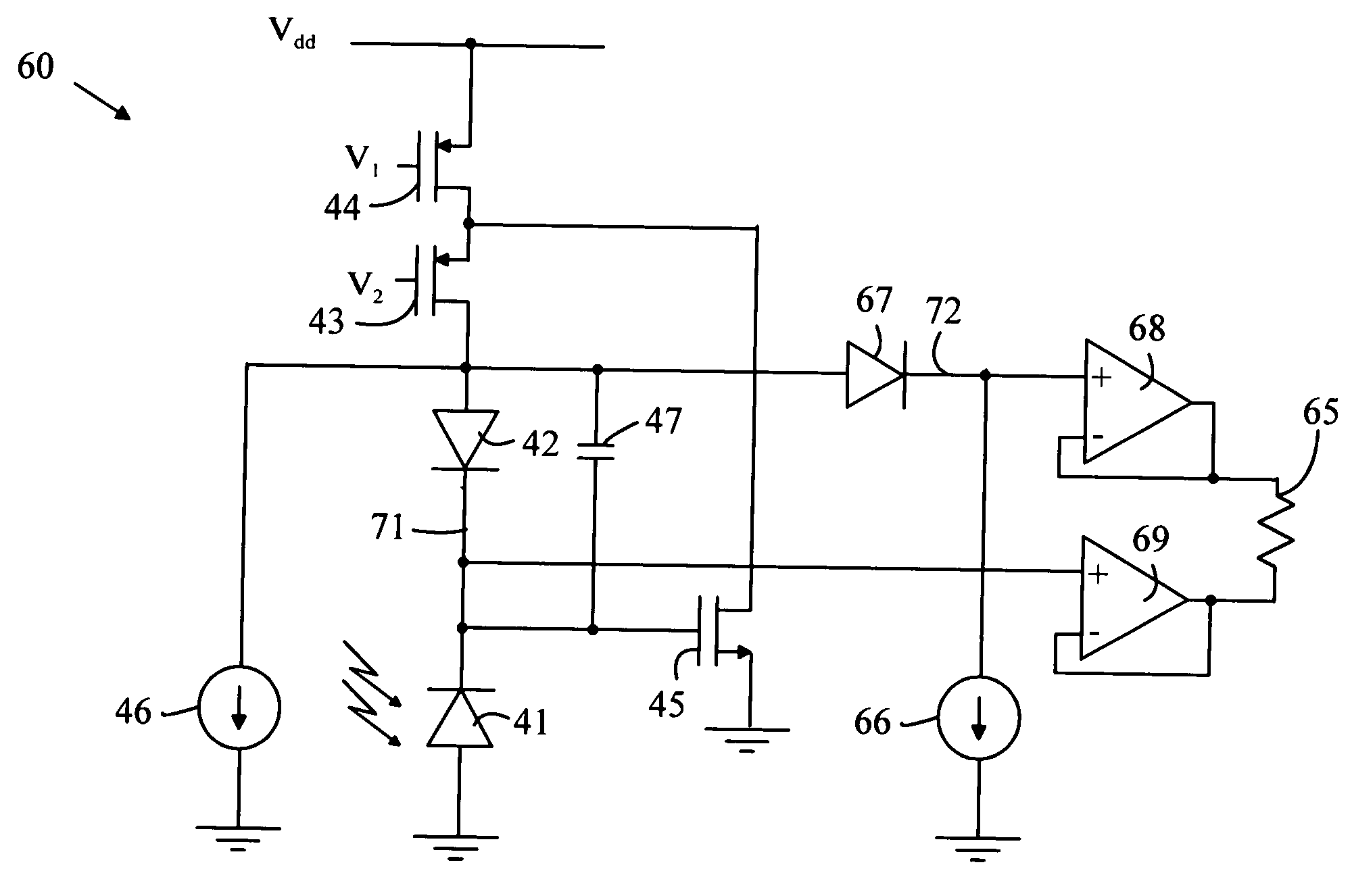
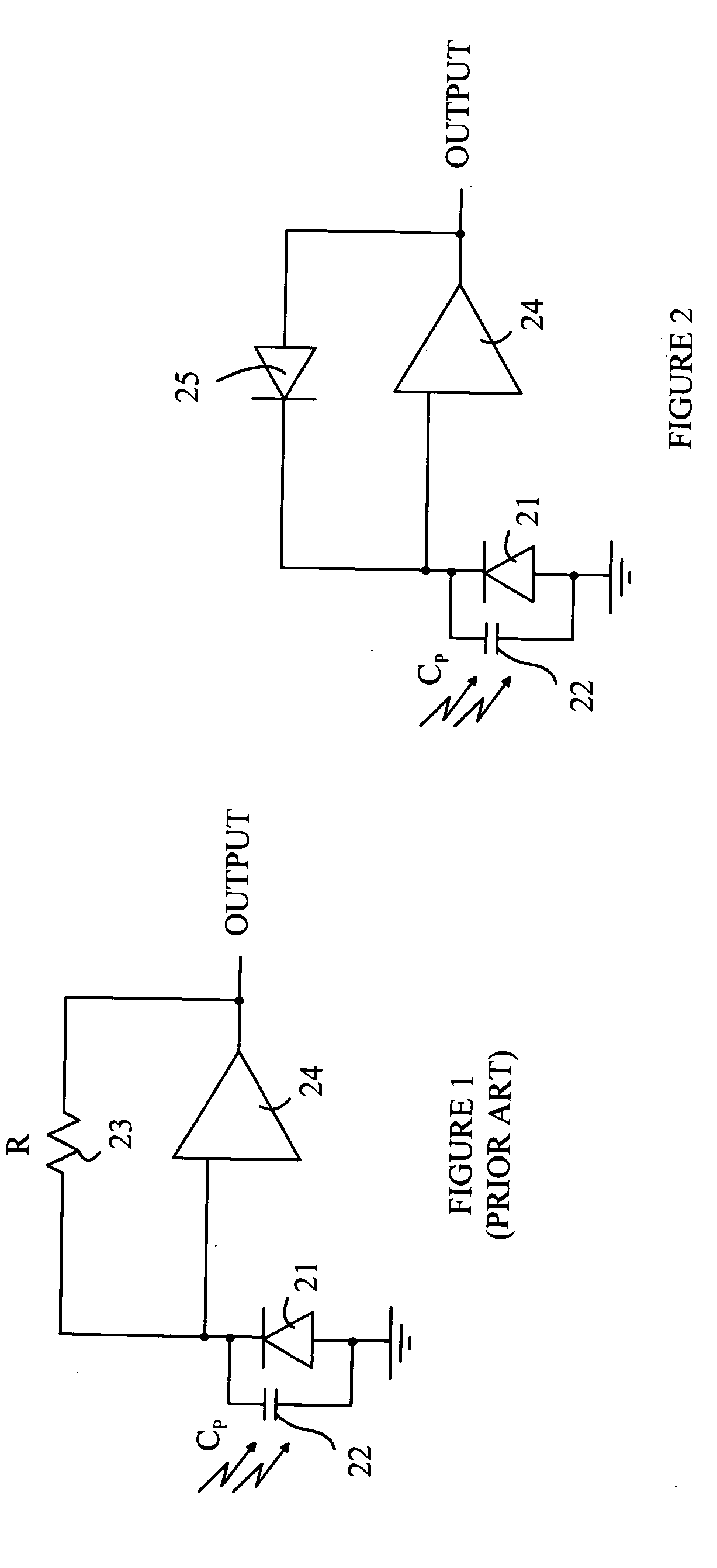
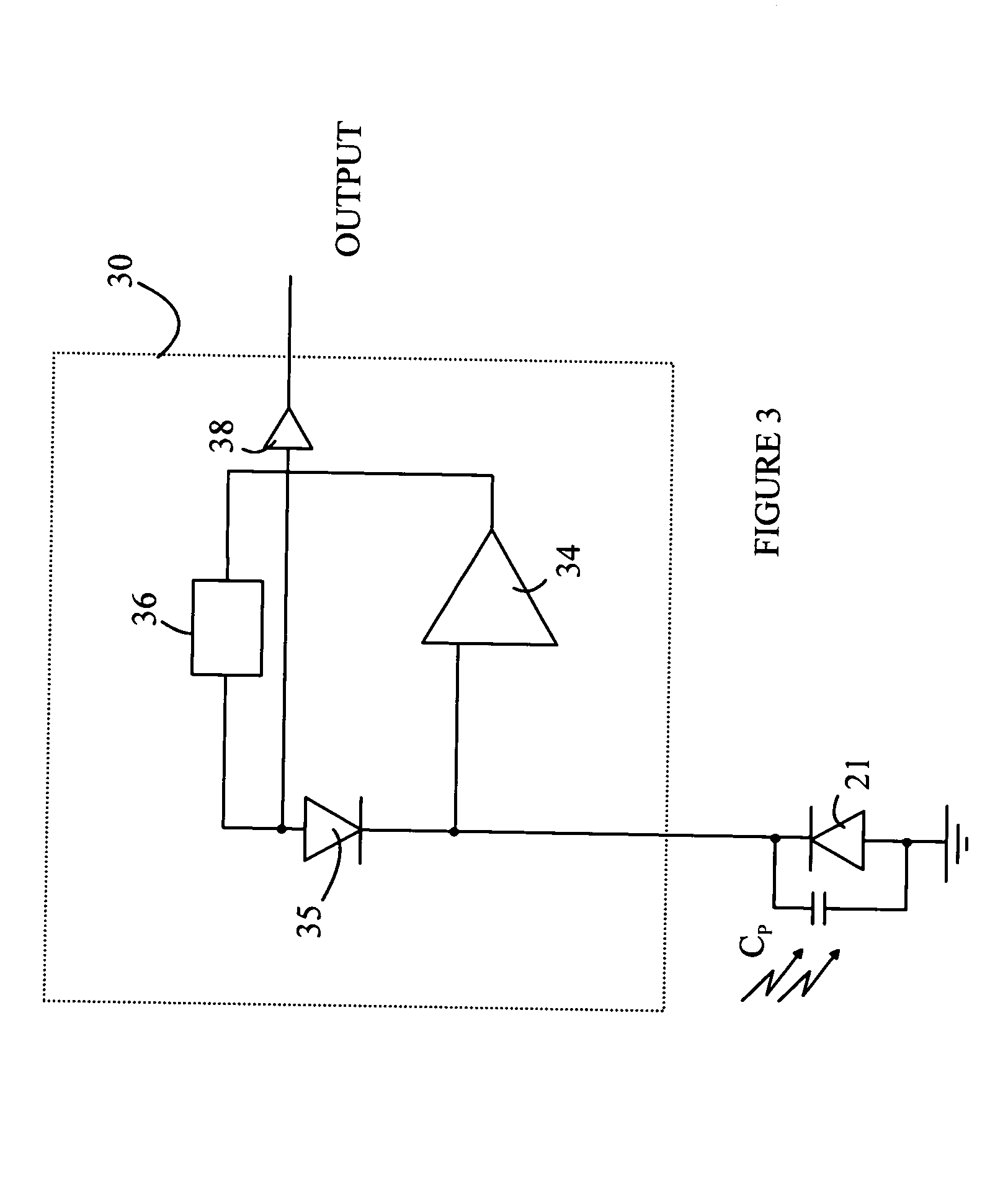
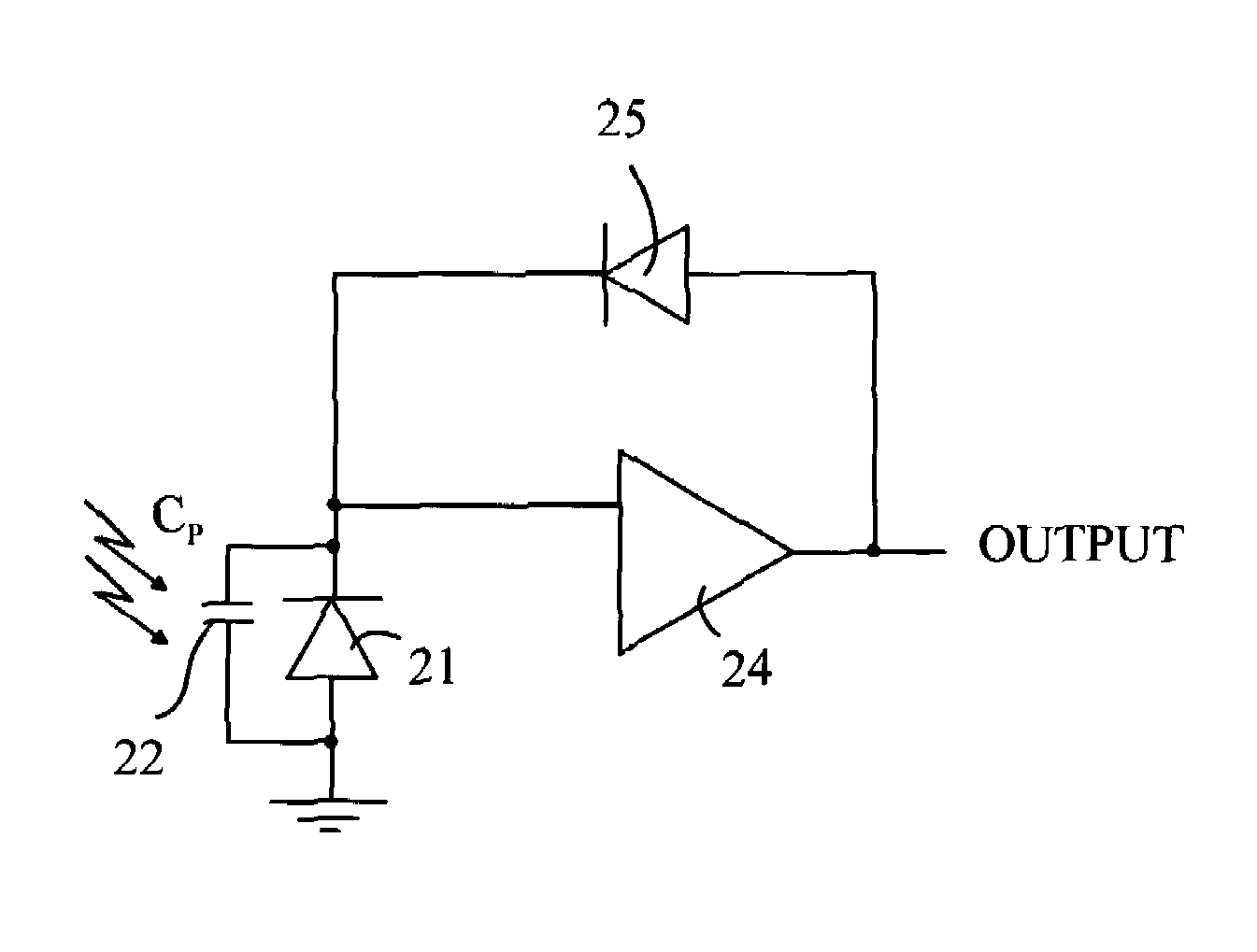
High dynamic range optical receiver
ActiveUS20080101803A1Easy to understandReduce sensitivityNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsGain controlPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
An optical receiver having a photodetector, amplifier, feedback loop, and output circuit is disclosed. The photodetector generates a current between first and second nodes in response to being illuminated with light. The amplifier has an input connected to the first node and an output connected to a third node. The feedback path connects the third node to the first node, and includes a diode in series with a circuit element having an impedance greater than a predetermined value, the diode is connected between the first and fourth nodes. The output circuit is connected to the fourth node and provides an output signal to an external circuit. The output circuit can be configured to provide an output signal that is proportional to the logarithm of the intensity of the light that illuminates the photodetector.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
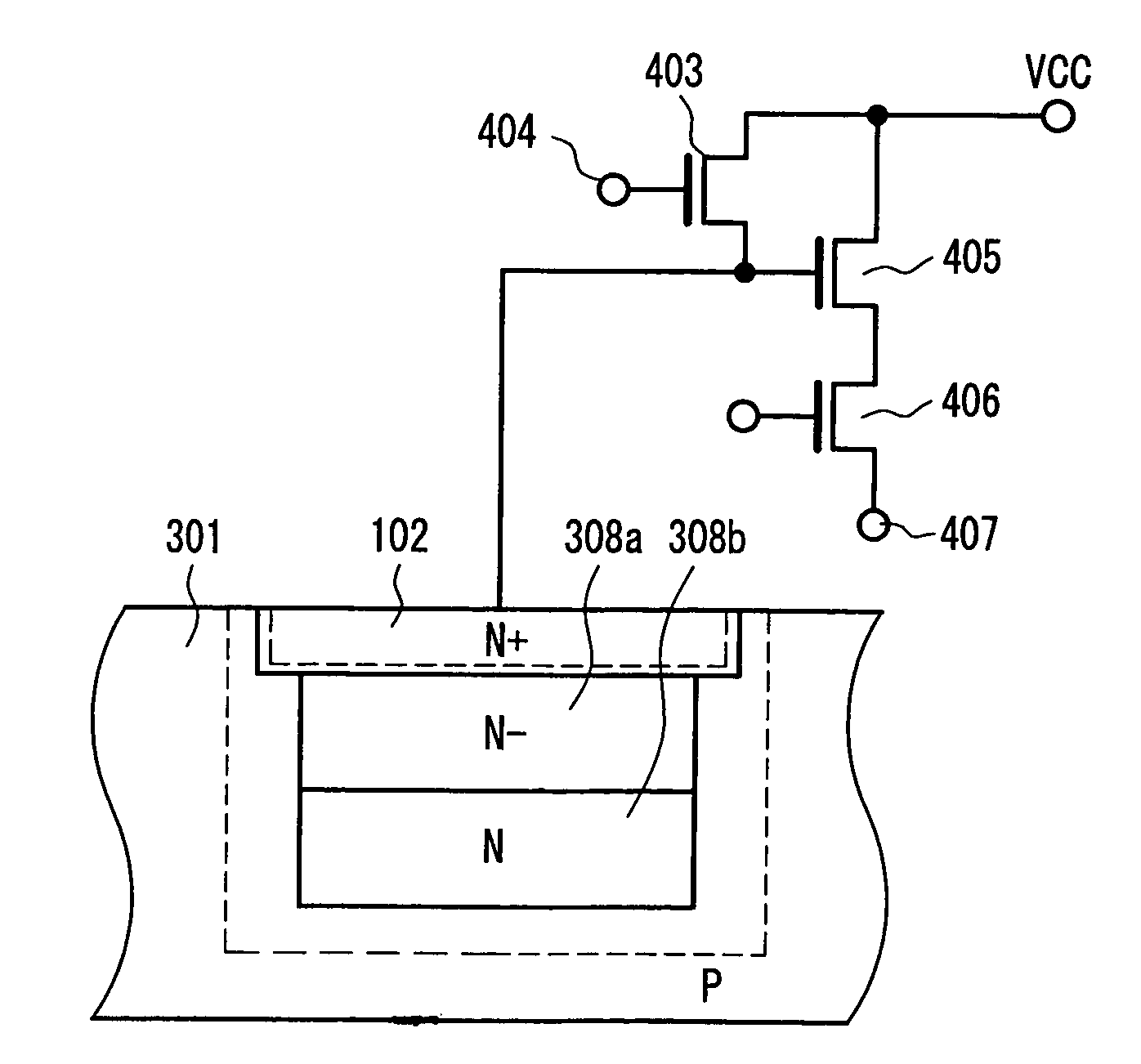
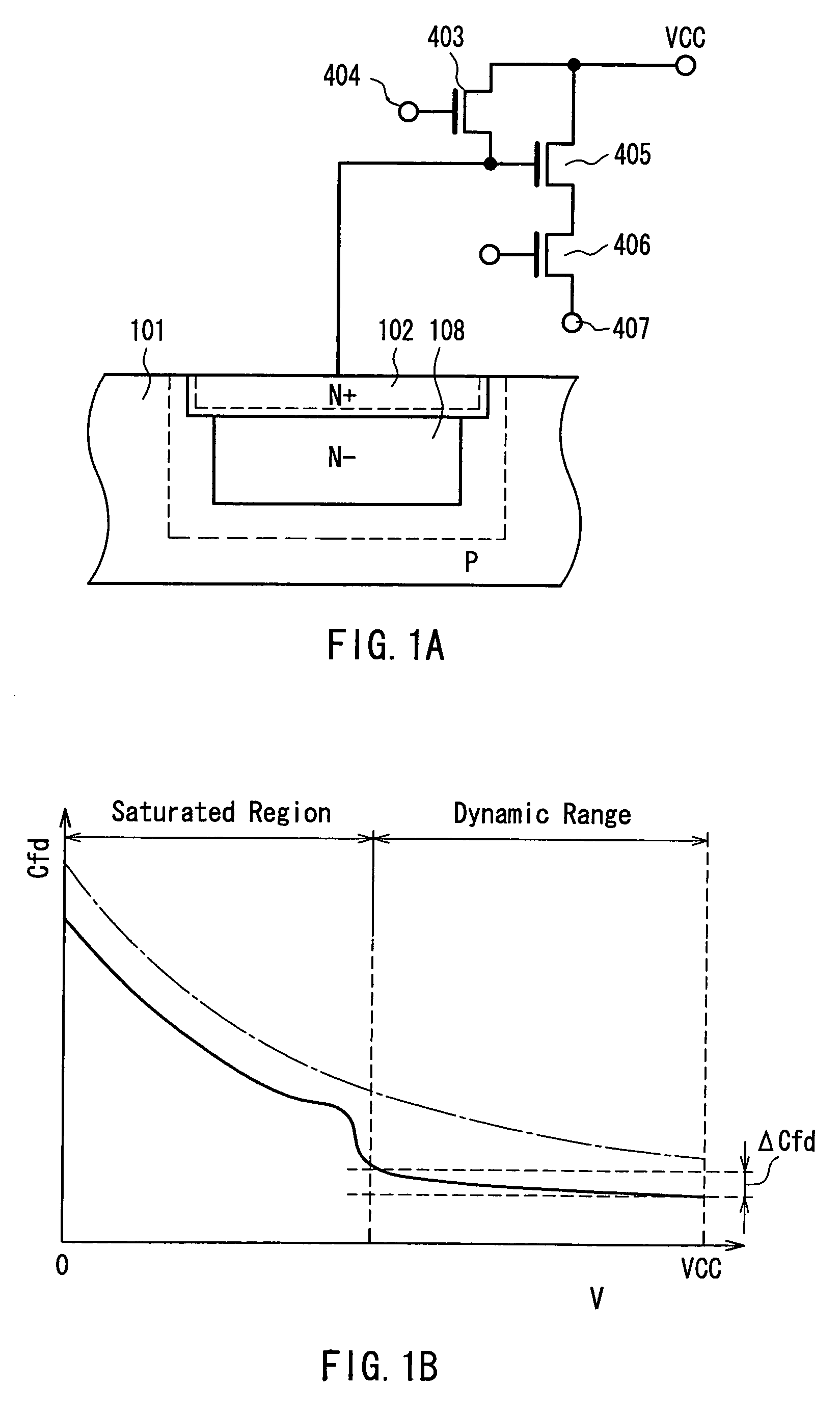
Charge detecting device
InactiveUS7034347B2Large dynamic rangeSatisfactory linearityTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesHigh concentrationLow voltage
There is provided a charge detecting device that can convert an accumulated charge to a voltage at a low voltage and a high efficiency, and has a large dynamic range of an output voltage and satisfactory linearity of a conversion efficiency. The charge detecting device includes a charge accumulating portion including a low concentration N-type (N−) layer 108 formed in a P-type well 101 and a high concentration N-type (N+) layer formed between the N− layer and a principal surface. The N+ layer is connected to an input terminal of an amplifying transistor of an output circuit, and after a reverse bias is applied to the N+ layer during discharging of the accumulated charge, the entire N− layer is depleted at least until a saturated charge is accumulated.
Owner:COLLABO INNOVATIONS INC
Input converter for a hearing aid and signal conversion method
ActiveUS20120007760A1Large output voltageReduce magnificationPower saving provisionsElectric signal transmission systemsIntegratorCurrent consumption
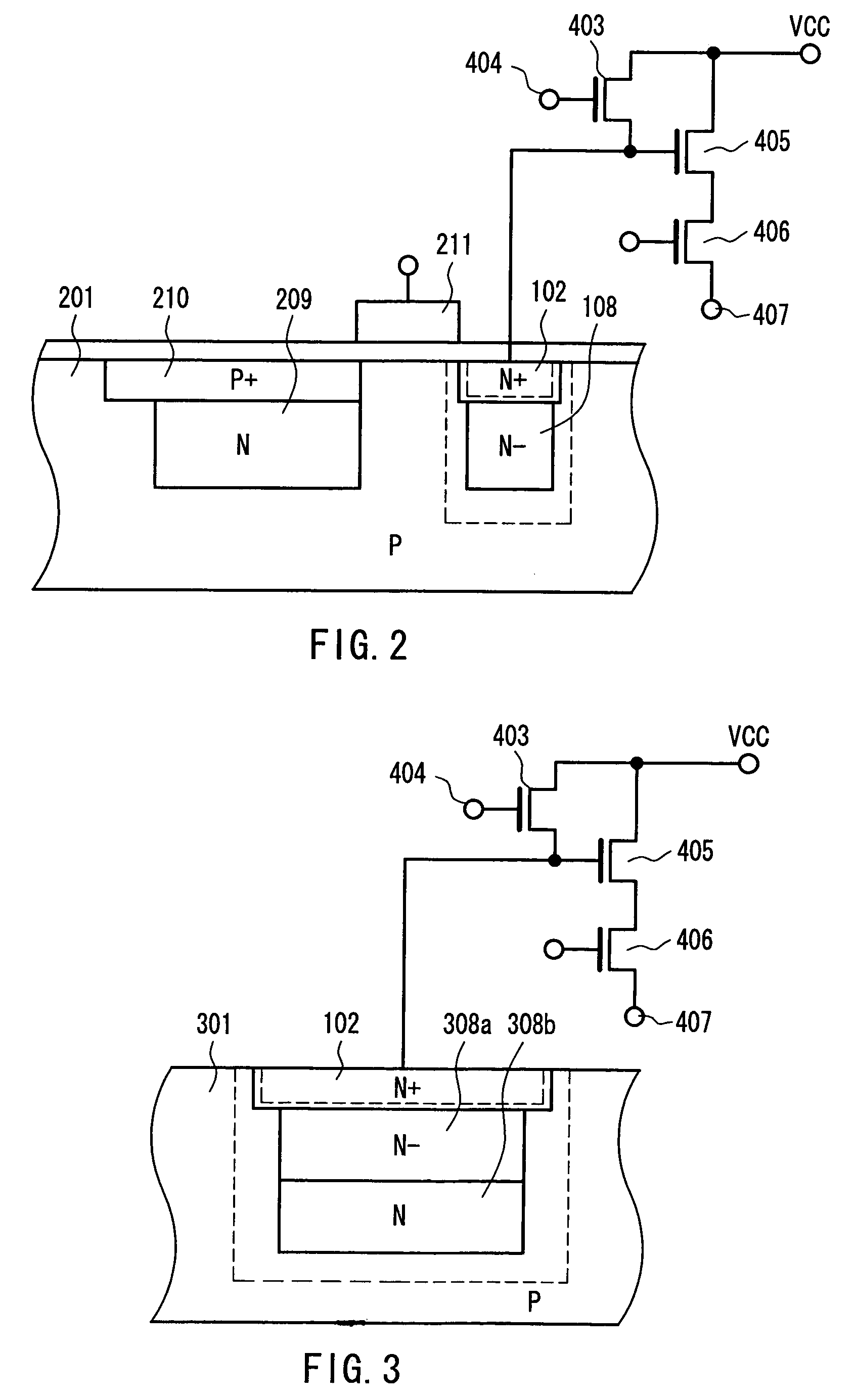
In order to minimize noise and current consumption in a hearing aid, an input converter comprising a first voltage transformer and an analog-to-digital converter of the delta-sigma type for a hearing aid is devised. The analog-to-digital converter of the input converter has an input stage, an output stage, and a feedback loop, and the input stage comprises an amplifier (QA) and an integrator (RLF). The first voltage transformer (IT) has a transformation ratio such that it provides an output voltage larger than the input voltage and is placed in the input converter upstream of the input stage. A second voltage transformer (OT) having a transformation ratio such that it provides an output voltage larger than the input voltage, is optionally placed in the feedback loop of the converter. The voltage transformers (IT, OT) are switched-capacitor voltage transformers, each transformer (IT, OT) having at least two capacitors (Ca, Cb, Cc, Cd). The invention further provides a method of converting an analog signal.
Owner:WIDEX AS
Magneto-resistance effect element and thin-film magnetic head having non-magnetic spacer layer composed of one semiconductor layer and two metal layers
InactiveUS7764470B2Resistance can be madeLow densityRecord information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsMagnetizationEngineering
A magneto-resistance effect element used for a thin film magnetic head is configured by a buffer layer, an anti-ferromagnetic layer, a pinned layer, a spacer layer, a free layer, and a cap layer, which are laminated in this order, and a sense current flows through the element in a direction orthogonal to the layer surface, via a lower shield layer and a upper shield layer. The pinned layer comprises an outer layer in which a magnetization direction is fixed, a non-magnetic intermediate layer, and an inner layer which is a ferromagnetic layer. The spacer layer comprises a first and second non-magnetic metal layer, and a semiconductor layer. The first and second non-magnetic metal layer and comprise CuPt films having a thickness of more than 0 nm but no more than 2.0 nm, and the Pt content ranges from a minimum of 5 to a maximum of 25 at %.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Power supply apparatus and image forming apparatus
ActiveUS20180335747A1Large output voltageSimple configurationAc-dc conversion without reversalApparatus without intermediate ac conversionInductorVoltage boosting
The power supply apparatus includes an inductor; a switching element connected to another end of the inductor, the switching element configured to drive the inductor by being turned on or turned off in accordance with an input pulse signal; a boost converter circuit connected to both ends of the inductor and including a plurality of rectification units, the boost converter circuit configured to amplify a voltage generated in the inductor, each of the plurality of rectification units including a diode and a capacitor; and a voltage boosting element configured to supply a voltage obtained by boosting an input voltage to the inductor.
Owner:CANON KK
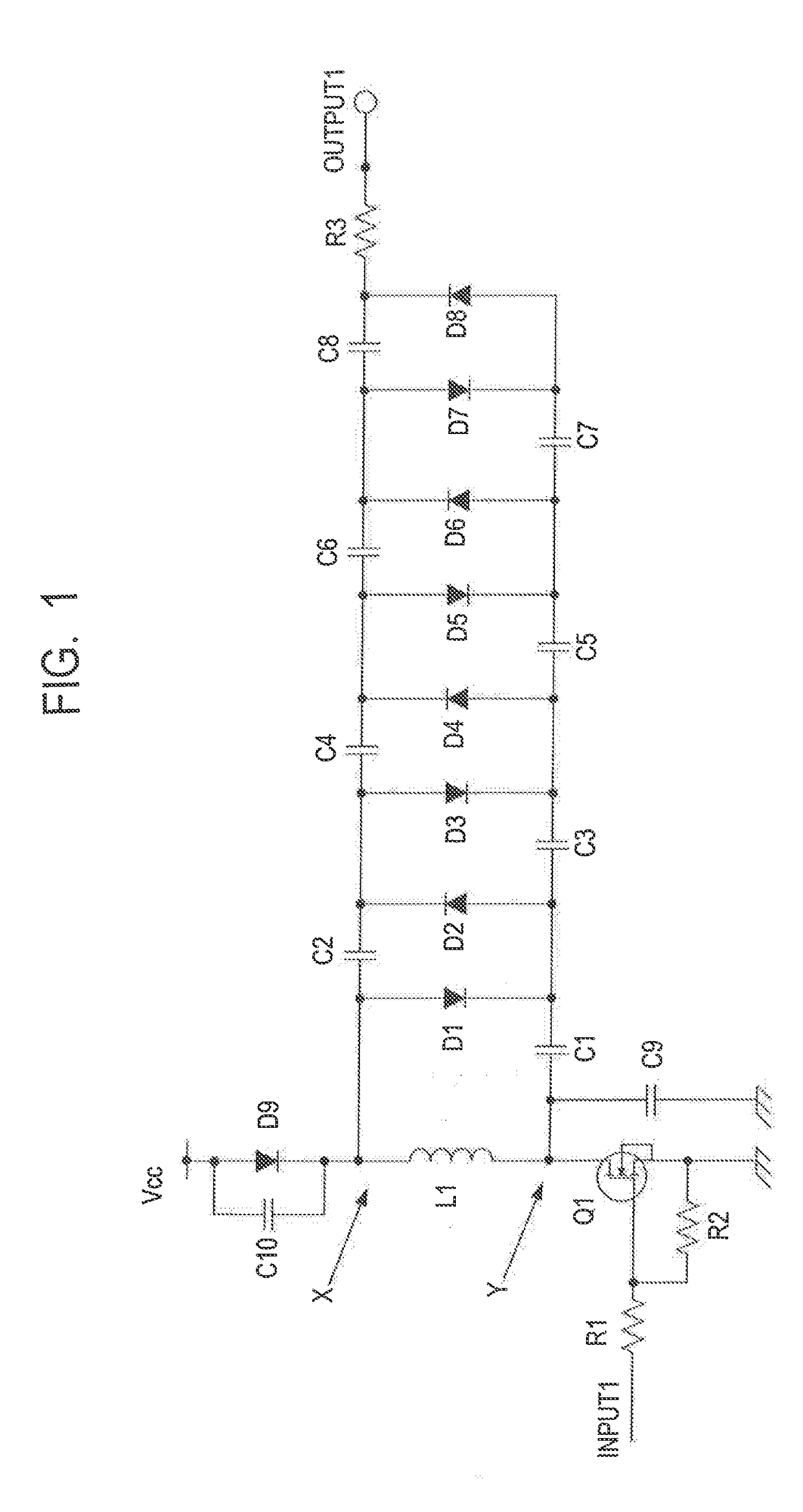
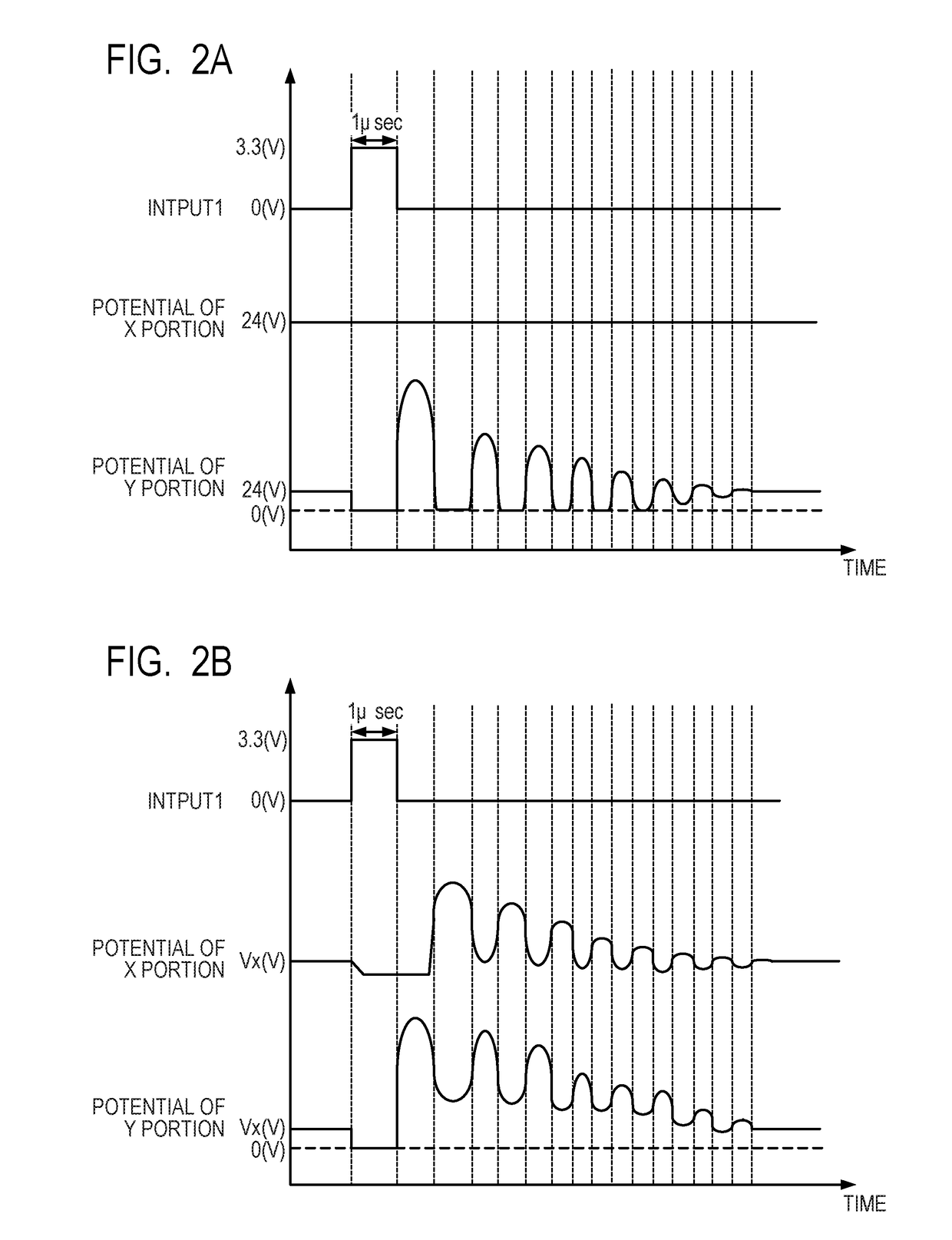
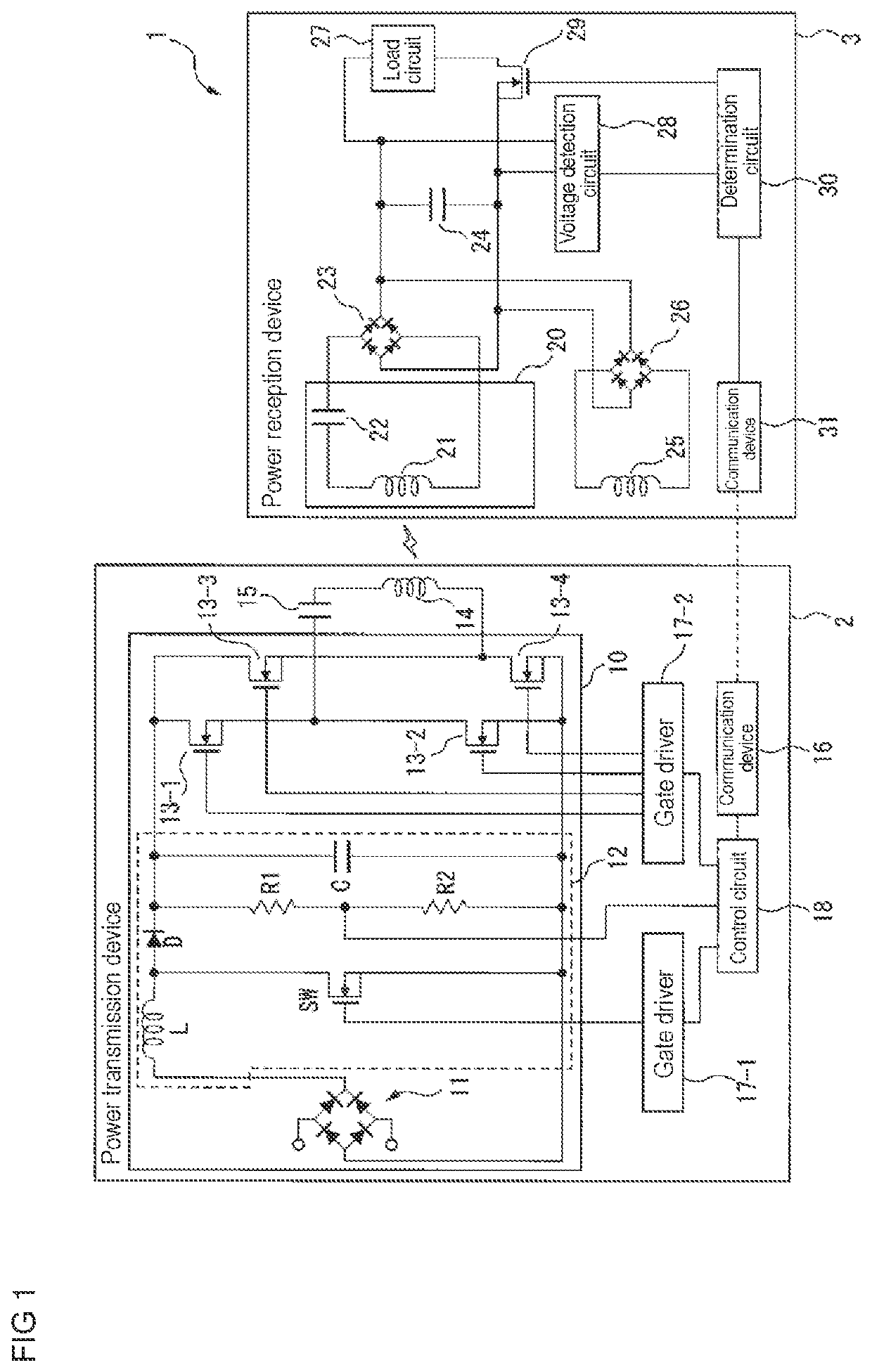
Non-contact power feeding device
ActiveUS20210344229A1Reduce power factorImprove efficiencyCircuit arrangementsCapacitanceElectric power transmission
A power reception device of a non-contact power feeding device has: a resonant circuit having a reception coil configured to receive electric power from a power transmission device and a resonant capacitor connected in series with the reception coil; a first rectifier circuit configured to rectify electric power received via the resonant circuit; a smoothing capacitor connected to the first rectifier circuit and configured to smooth a voltage outputted from the first rectifier circuit; a sub-coil arranged to be capable of being electromagnetically coupled to the reception coil; and a second rectifier circuit connected between the sub-coil and the smoothing capacitor, and configured to output electric power according to a voltage generated in the sub-coil to the smoothing capacitor in response to a voltage obtained by rectifying a voltage generated in the sub-coil being higher than a voltage between both terminals of the smoothing capacitor.
Owner:ORMON CORP
Multi-stage synchronous generator
ActiveUS20200266742A1Reduce weightConsequence of failure can be mitigatedSynchronous generatorsPower installationsExcitation currentControl engineering
The disclosed embodiments aim to improve upon existing multi stage generators for providing power to a load. In particular, embodiments of the invention include a regulator situated between the output of a pilot exciter and the main exciter of a multi stage generator system, the regulator arranged to limit the voltage available to a field current control element which sets the field current supplied to the main exciter.
Owner:LABINAL POWER SYST
Magneto-resistance effect element having diffusion blocking layer and thin-film magnetic head
InactiveUS7764471B2High MR ratioGood element characteristicNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsDiffusionMagnetization
A magnetoresistance effect element (MR element) for use in a thin-film magnetic head has a buffer layer, an antiferromagnetic layer, a pinned layer, a spacer layer, a free layer, and a cap layer that are successively stacked. A sense current flows in a direction perpendicular to layer surfaces via a lower shield layer and an upper shield layer. The pinned layer comprises an outer layer having a fixed magnetization direction, a nonmagnetic intermediate layer, and an inner layer in the form of a ferromagnetic layer. The spacer layer comprises a first nonmagnetic metal layer, a semiconductor layer made of ZnO, and a second nonmagnetic metal layer. The inner layer or the outer layer includes a diffusion blocking layer made of an oxide of an element whose electronegativity is equal to or smaller than Zn, e.g., ZnO, TaO, ZrO, MgO, TiO, or HfO, or made of RuO.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
High dynamic range optical receiver
ActiveUS7474978B2Easy to understandReduce sensitivityNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsGain controlPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
An optical receiver having a photodetector, amplifier, feedback loop, and output circuit is disclosed. The photodetector generates a current between first and second nodes in response to being illuminated with light. The amplifier has an input connected to the first node and an output connected to a third node. The feedback path connects the third node to the first node, and includes a diode in series with a circuit element having an impedance greater than a predetermined value, the diode is connected between the first and fourth nodes. The output circuit is connected to the fourth node and provides an output signal to an external circuit. The output circuit can be configured to provide an output signal that is proportional to the logarithm of the intensity of the light that illuminates the photodetector.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
GaN DRIVER USING ACTIVE PRE-DRIVER WITH FEEDBACK
ActiveUS20200076426A1High power supply voltageLarge output voltageTransistorElectronic switchingPhysicsGate driver
An enhancement mode GaN FET based gate driver circuit including an active pre-driver to drive a high-slew rate, high current output stage GaN FET. Due to the active driver current from the pre-driver, the output stage pull-up FET can turn on faster as compared to a pre-driver that utilizes a passive pull-up load. The active pre-driver must provide a voltage to drive the gate of the output stage pull-up FET which is higher than the normal supply voltage to enable the maximum output level of the driver FET to approach the normal supply voltage. A feedback circuit is included in the active pre-driver to avoid the need for two supply voltages.
Owner:EFFICIENT POWER CONVERSION CORP
Power supply apparatus and image forming apparatus
ActiveUS10541613B2Large output voltageSimple configurationAc-dc conversion without reversalApparatus without intermediate ac conversionConvertersSoftware engineering
The power supply apparatus includes an inductor; a switching element connected to another end of the inductor, the switching element configured to drive the inductor by being turned on or turned off in accordance with an input pulse signal; a boost converter circuit connected to both ends of the inductor and including a plurality of rectification units, the boost converter circuit configured to amplify a voltage generated in the inductor, each of the plurality of rectification units including a diode and a capacitor; and a voltage boosting element configured to supply a voltage obtained by boosting an input voltage to the inductor.
Owner:CANON KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com