Patents
Literature
32results about How to "Minimize application" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
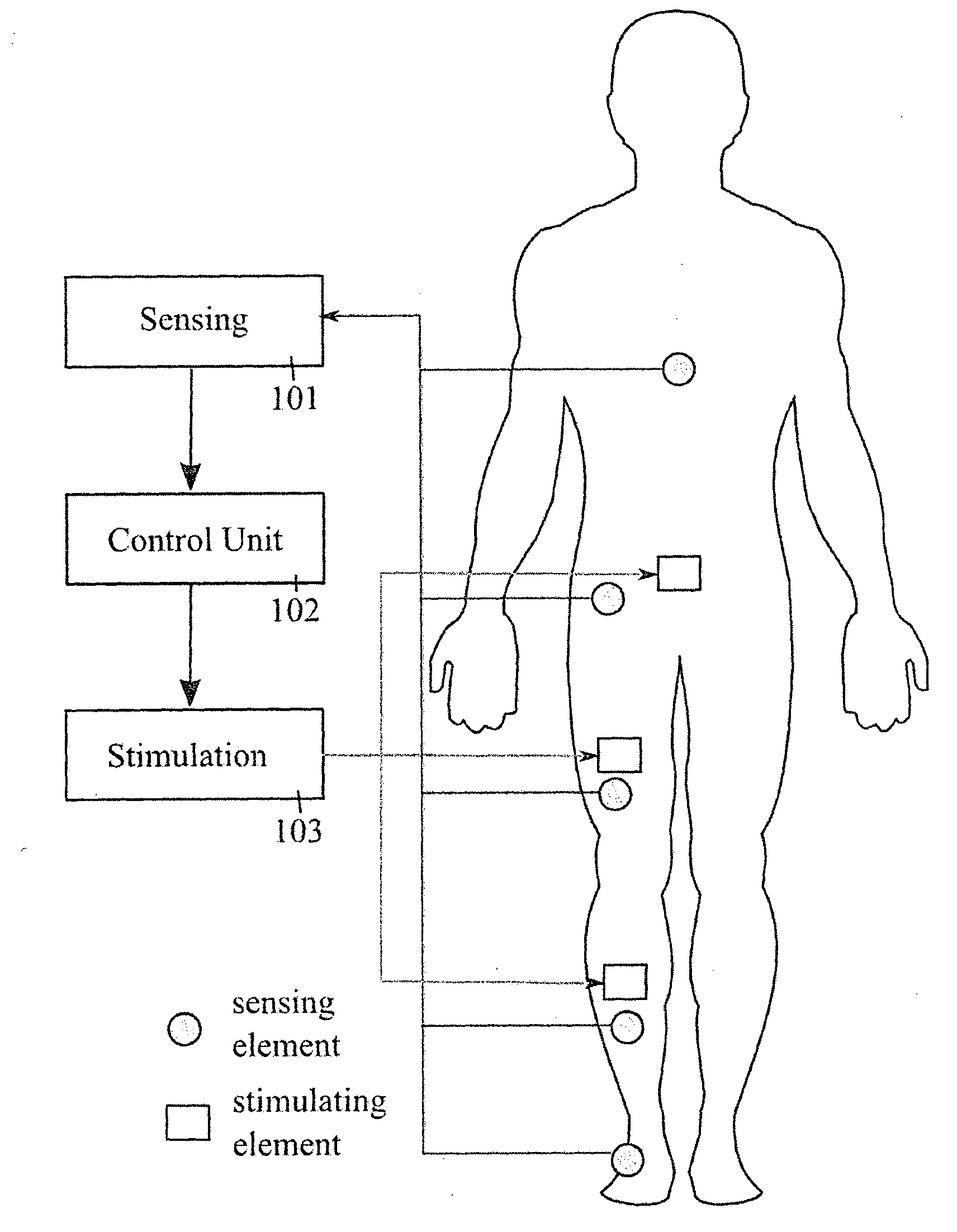
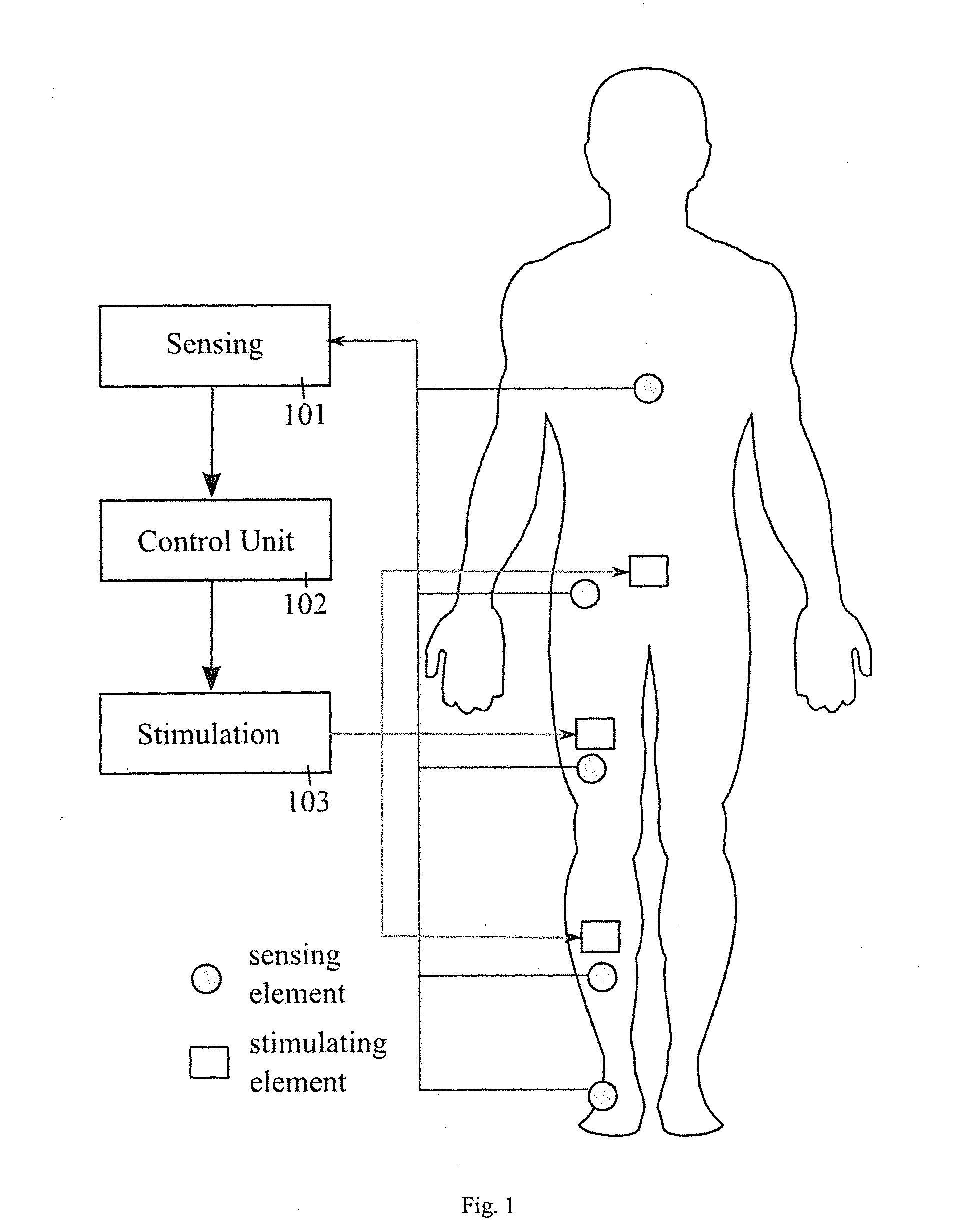
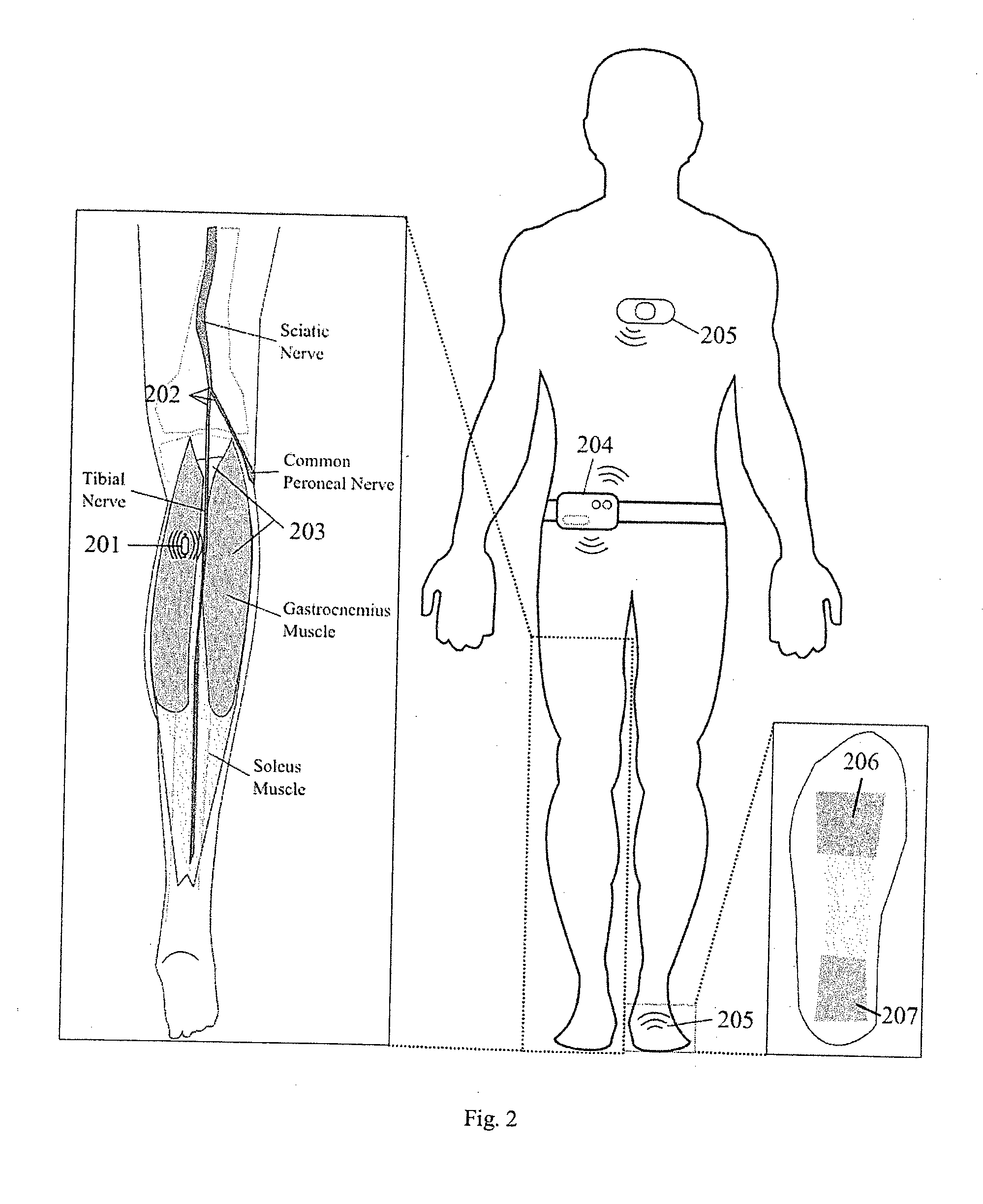
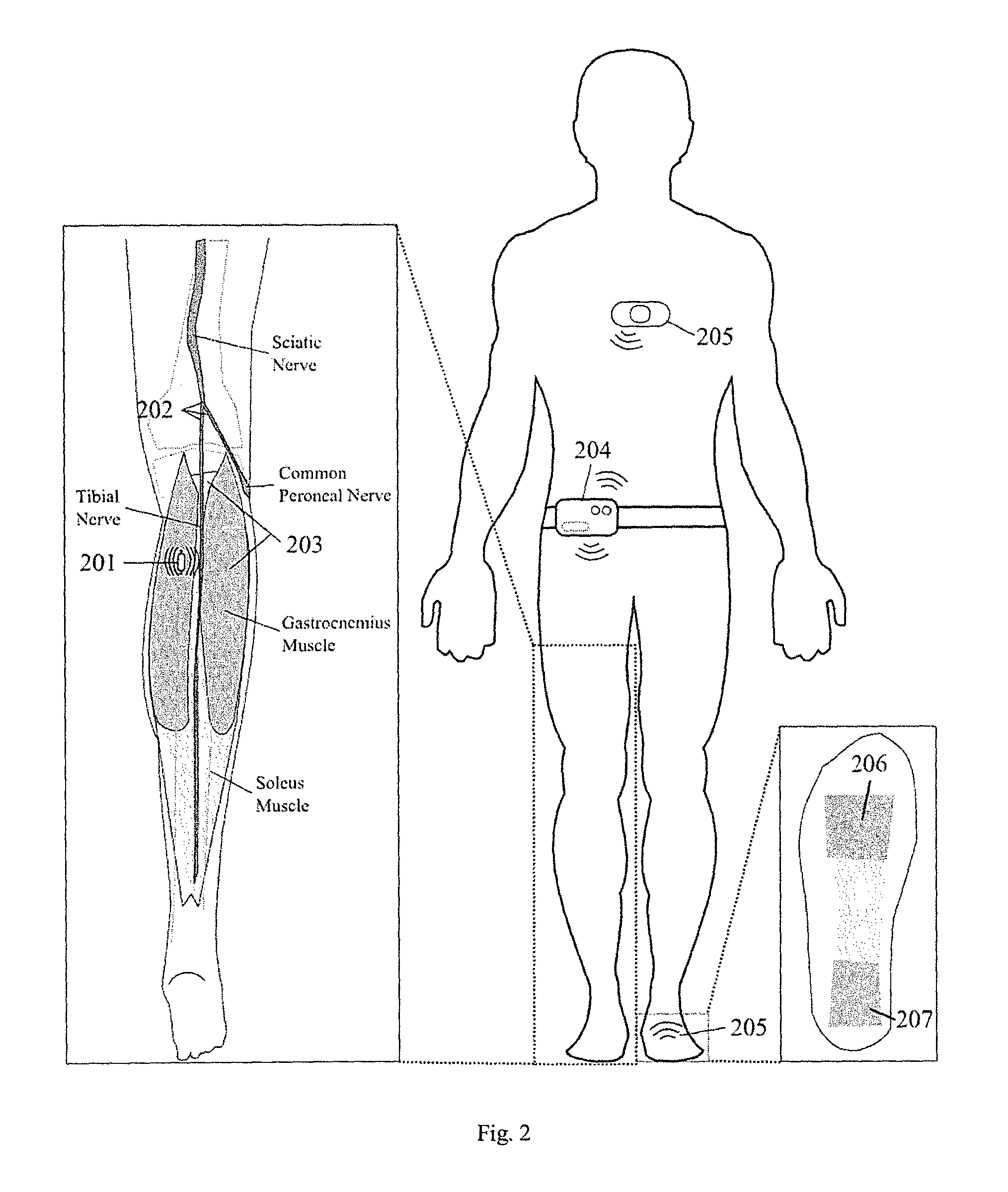
Apparatus and methods for prevention of syncope
ActiveUS20140358193A1Easy to installRemove changeSpinal electrodesElectrocardiographyMonitoring systemFinite-state machine
A monitoring system has biomechanical sensors, physiological sensors and a controller which receive sensory inputs from the sensors to provide output signals for the output device, and it detects from the sensory inputs risk of a syncopal event The bio-mechanical sensors include sensors arranged to allow the processor to detect a user postures and posture transitions. The processor operates a finite state machine, in which there is a state corresponding to each of a plurality of user physical postures and to each of a plurality of transitions between said postures, and the processor determines a relevant state depending on the sensory inputs. A device output may be muscle stimulation to prevent syncope, and there are stimulation permissions associated with the finite state machine states.
Owner:THE NAT UNIV OF IRELAND GALWAY +2
Fiber optic imaging catheter
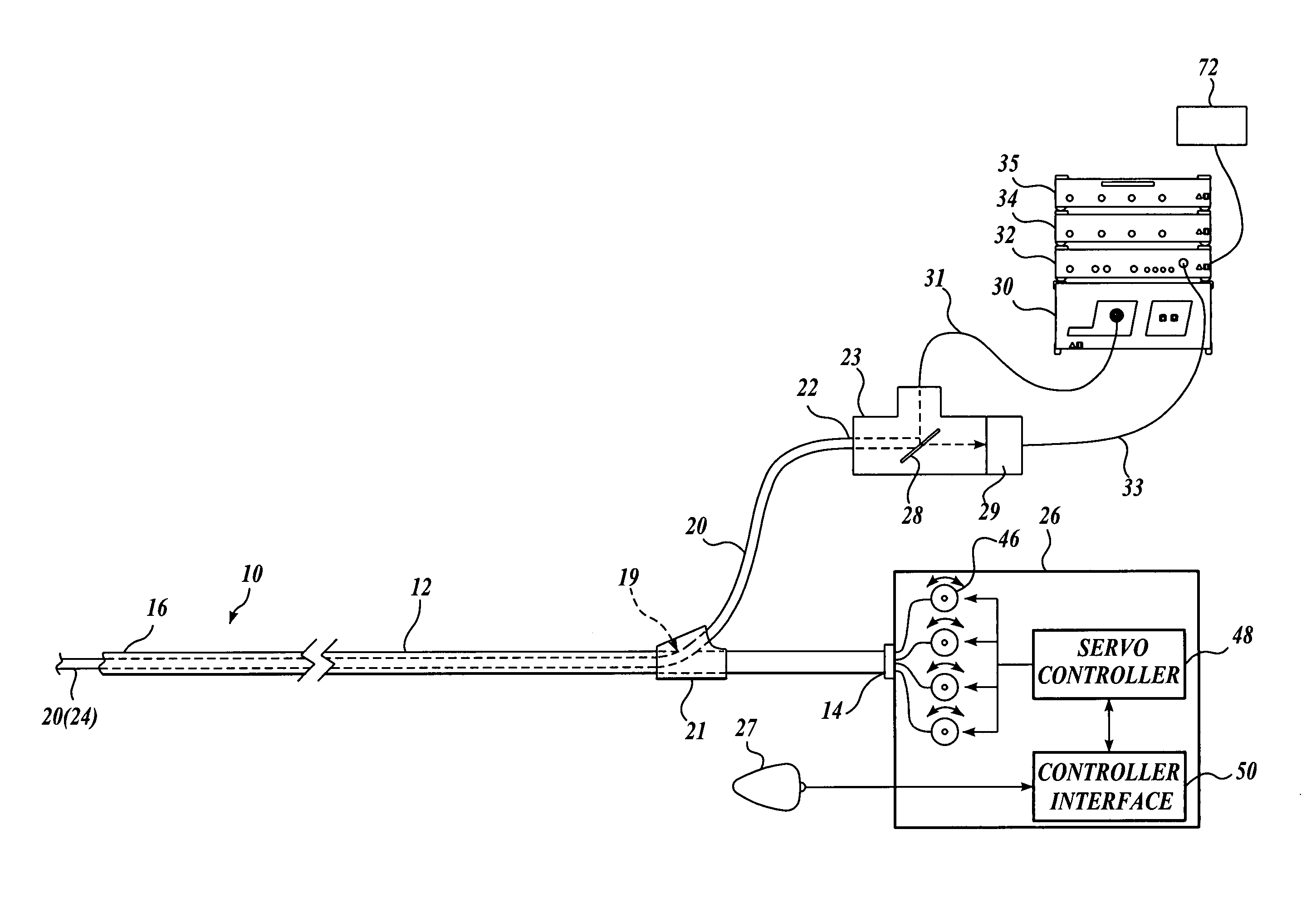
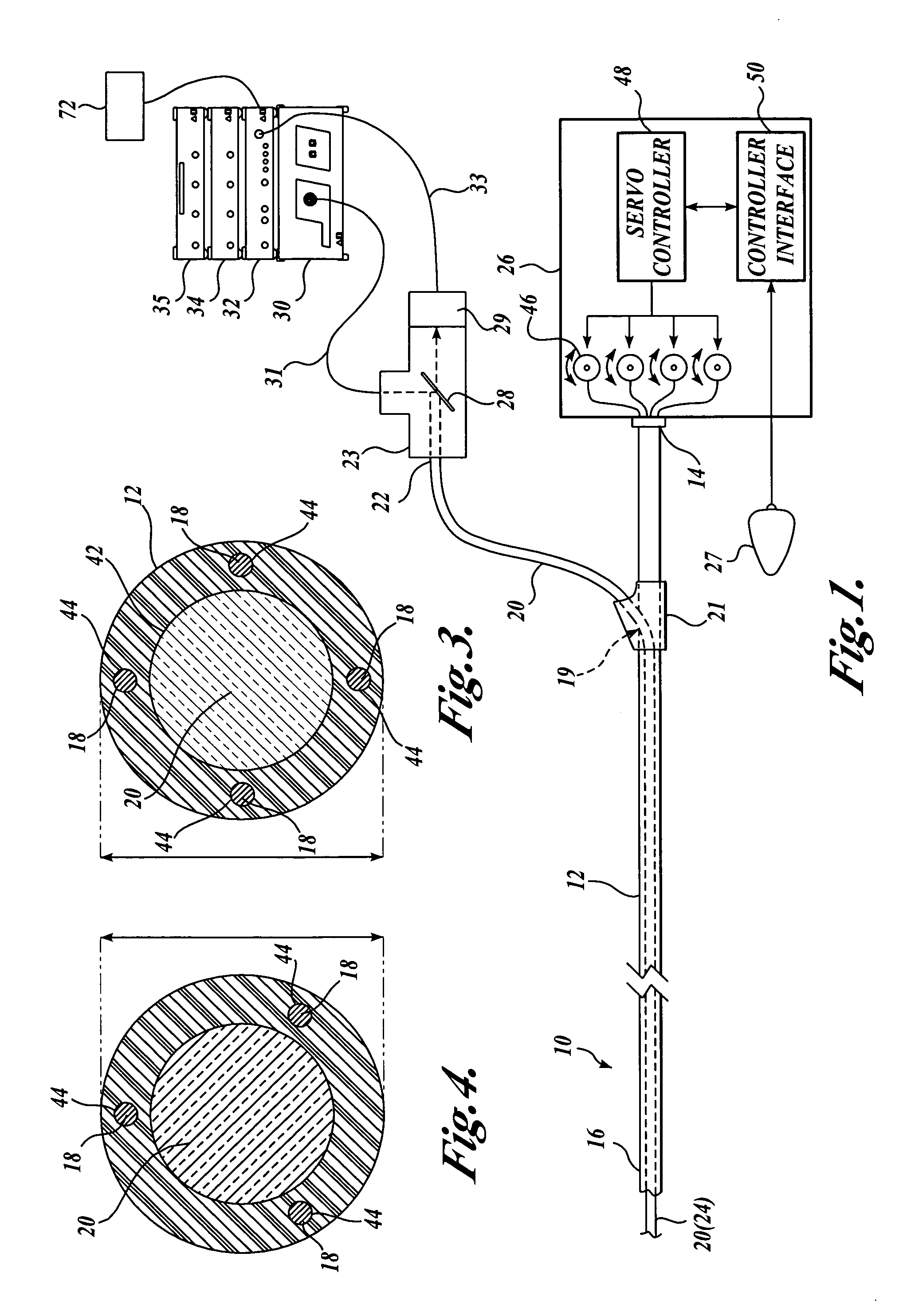
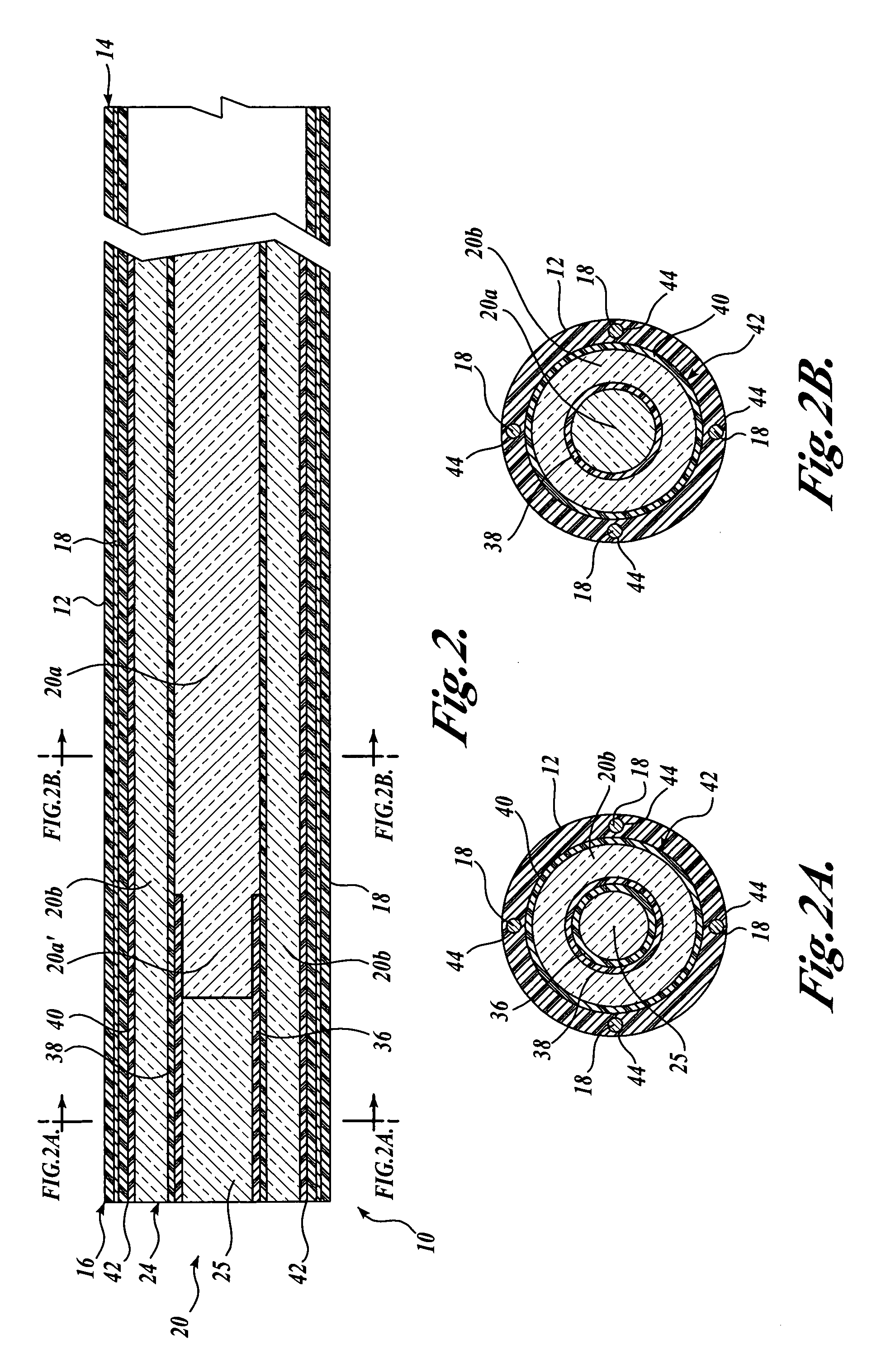
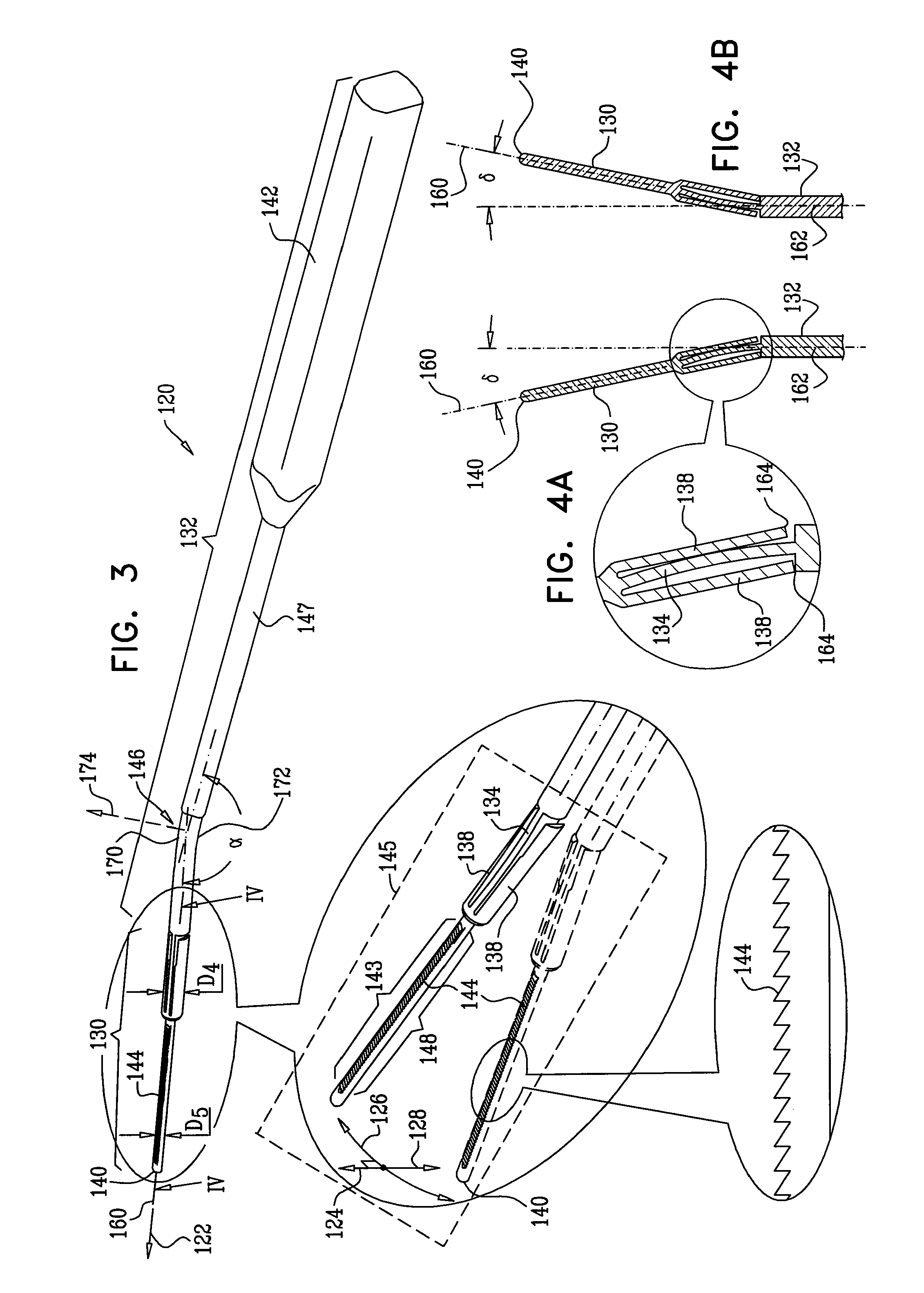
InactiveUS20060030753A1Minimize applicationMinimizes unduly twisting and damagingSurgeryEndoscopesFiberOptical fiber cable
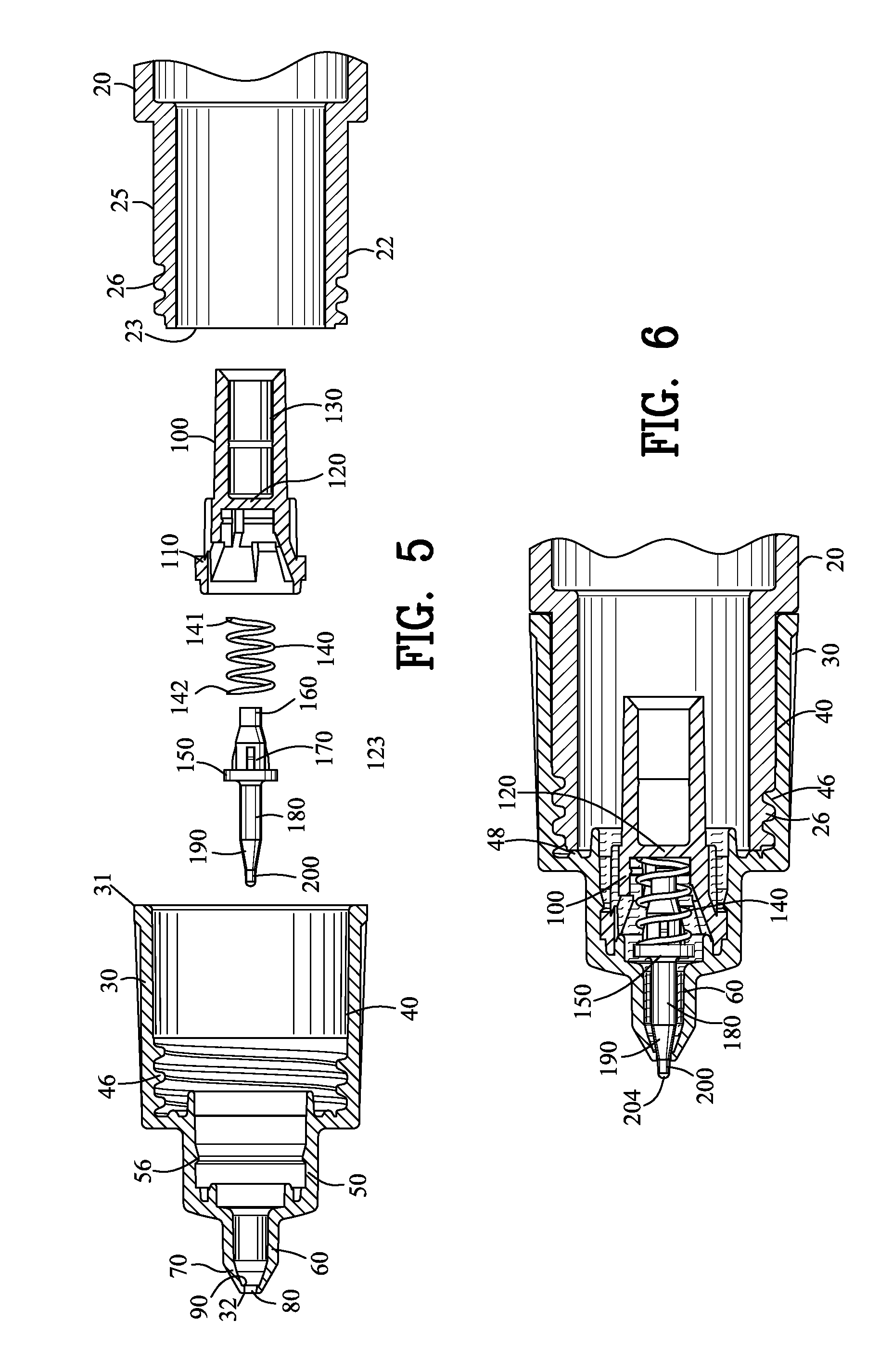
A steerable imaging catheter is provided, including an elongated catheter tube, at least one steering cable extending along the catheter tube to control the movement of the distal end thereof, and a fiber optic cable extending along the catheter tube. The fiber optic cable transmits illumination light from its proximal end to its distal end and transmits an image from its distal end to its proximal end. In one embodiment, two or more steering cables are used, and the catheter tube is configured to have greater flexibility near its distal end than its proximal end so as to concentrate the movement (flexing) of the catheter tube at its distal end. The use of two or more steering cables, together with the catheter tube having varying flexibility, permit better control of the distal end of the catheter tube while reducing undue twisting of the remainder of the catheter tube.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Flexible tools for preparing bony canals
Apparatus is provided that includes a surgical tool, which includes a proximal shaft, a distal rod, and a target sight. A proximal end of the distal rod is coupled to a distal end of the proximal shaft such that the distal rod articulates with the proximal shaft. The target sight includes an aiming element, which is coupled to the distal rod and extends toward the proximal shaft, and which is indicative of an alignment of the distal rod with respect to the proximal shaft. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:BRAINSGATE LTD
Fiber optic imaging catheter
InactiveUS7922654B2Minimize applicationMinimizes unduly twisting and damagingSurgeryEndoscopesFiberWell control
A steerable imaging catheter is provided, including an elongated catheter tube, at least one steering cable extending along the catheter tube to control the movement of the distal end thereof, and a fiber optic cable extending along the catheter tube. The fiber optic cable transmits illumination light from its proximal end to its distal end and transmits an image from its distal end to its proximal end. In one embodiment, two or more steering cables are used, and the catheter tube is configured to have greater flexibility near its distal end than its proximal end so as to concentrate the movement (flexing) of the catheter tube at its distal end. The use of two or more steering cables, together with the catheter tube having varying flexibility, permit better control of the distal end of the catheter tube while reducing undue twisting of the remainder of the catheter tube.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
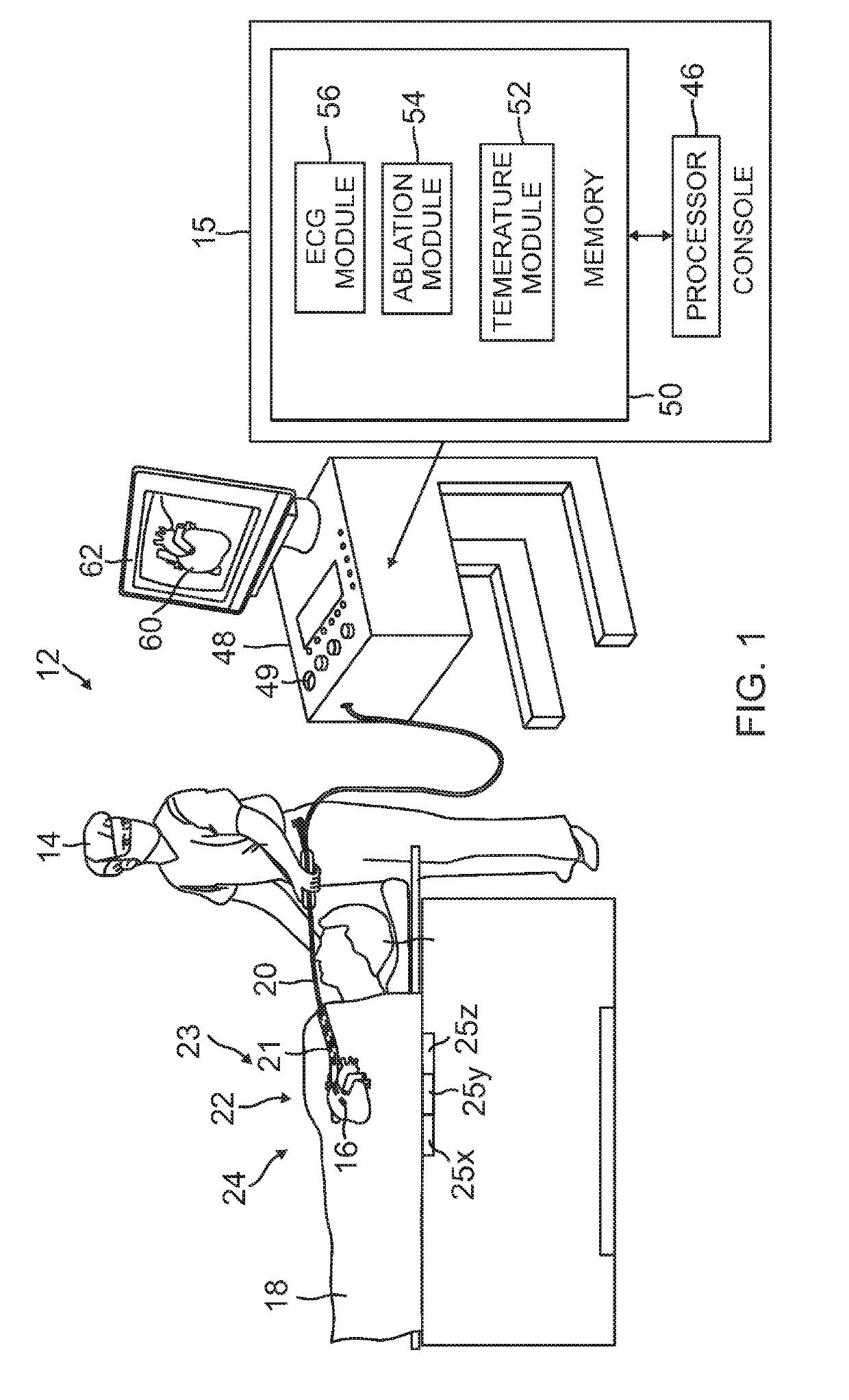
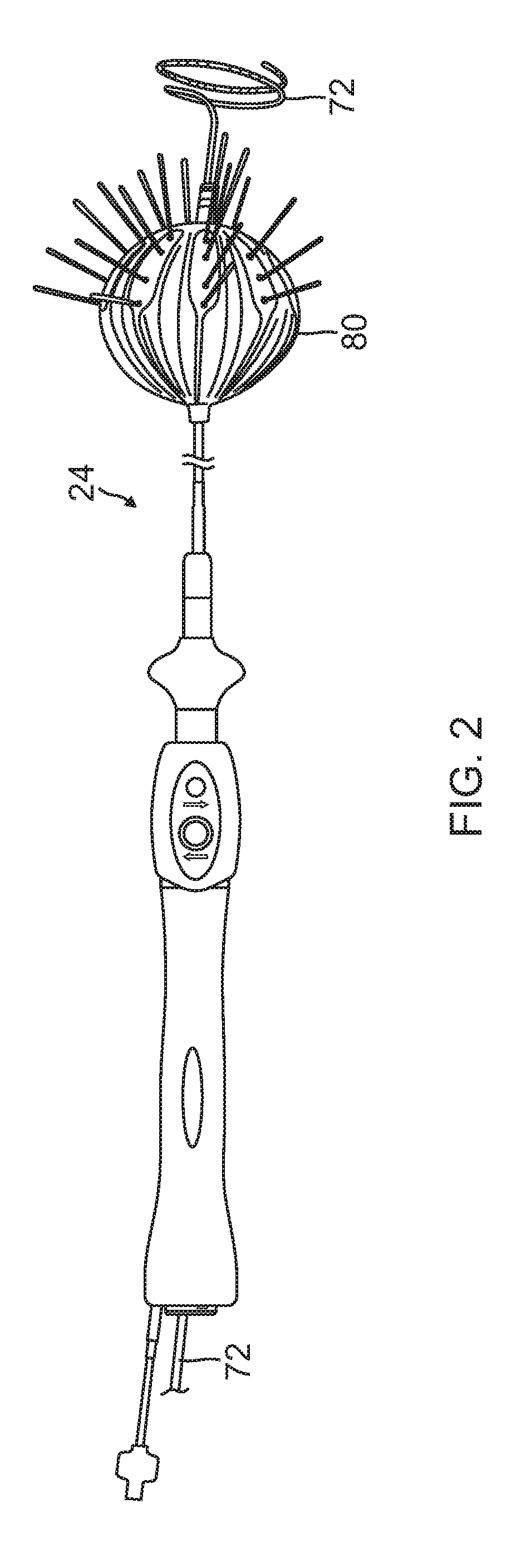
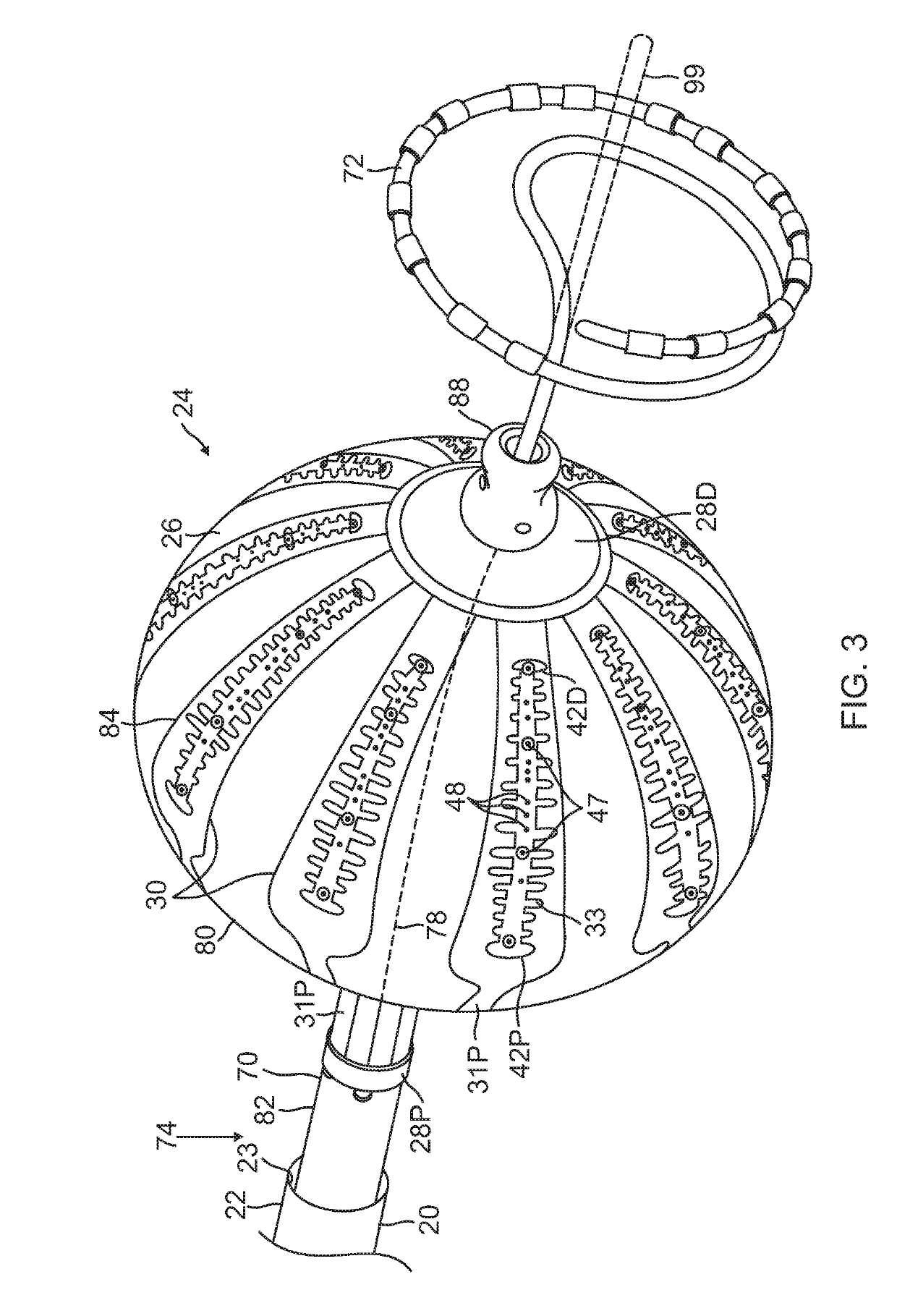
Irrigated electrophysiology catheter with distinguishable electrodes for multi-electrode identification and orientation under 2-d visualization
InactiveUS20190298441A1Little and effectSimpler to useEndoscopesSurgical instruments for heatingElectrophysiologyPosterior wall
An electrophysiology catheter is disclosed having a balloon with a membrane. Electrodes may be disposed on the membrane. Each electrode may include a radiopaque marker. The markers may have different forms, e.g., alphanumeric or polygonal, to facilitate visualization of the electrodes using a bi-stable image and allow for selection of the appropriate electrodes to be energized during ablation of tissue. The inventive subject matter allows for proper orientation of electrodes on the balloon under a two-dimensional imaging system. This allows the operator or physician to determine if certain electrodes are adjacent or contiguous to the posterior surface of the left atrium and ablate such posterior surface for shorter duration or at a lower power to create an effective transmural lesion on the posterior wall of the left atrium while reducing the chances of damaging the adjacent anatomical structures.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
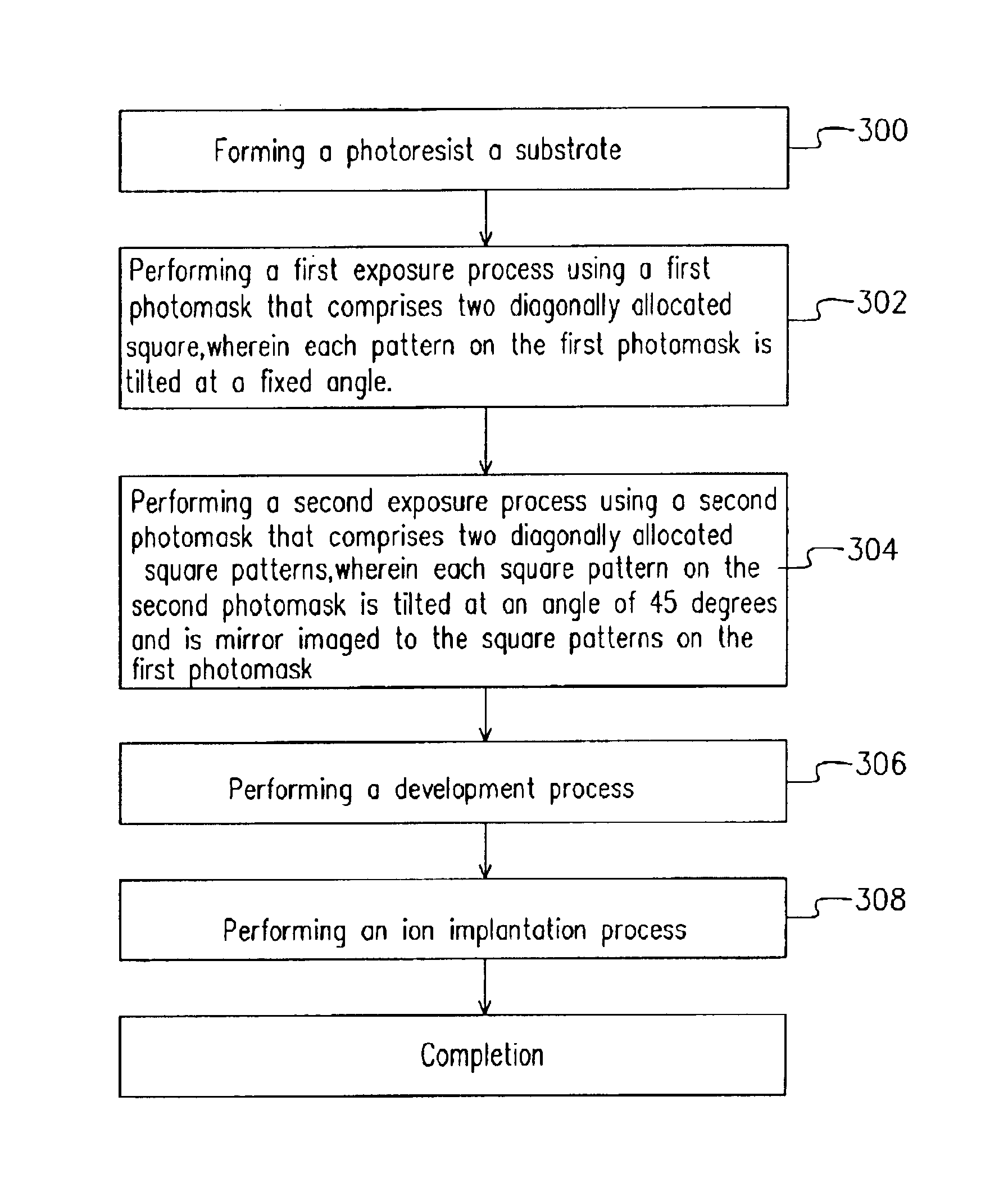
Fabrication method for semiconductor hole
InactiveUS6852453B2Prevent peelingImprove image contrastPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistSingle exposure
A fabrication method for a semiconductor hole is described. The method provides a circular or a elliptical hole pattern. A first exposure is performed with a first photomask that comprises a plurality of diagonally allocated square patterns wherein the square patterns on the first photomask are tilted at an angle of 45 degrees. Thereafter, a second exposure is performed using a second photomask, wherein patterns on the second photomask are mirror images to those on the second photomask to prevent the peeling of the photoresist at between the diagonally allocated hole patterns.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Apparatus and methods for prevention of syncope
ActiveUS20160331974A1Easy to installRemove changeSpinal electrodesInertial sensorsMonitoring systemFinite-state machine
A monitoring system has biomechanical sensors, physiological sensors and a controller which receive sensory inputs from the sensors to provide output signals for the output device, and it detects from the sensory inputs risk of a syncopal event The bio-mechanical sensors include sensors arranged to allow the processor to detect a user postures and posture transitions. The processor operates a finite state machine, in which there is a state corresponding to each of a plurality of user physical postures and to each of a plurality of transitions between said postures, and the processor determines a relevant state depending on the sensory inputs. A device output may be muscle stimulation to prevent syncope, and there are stimulation permissions associated with the finite state machine states.
Owner:NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF IRELAND +2
Apparatus and methods for prevention of syncope
ActiveUS9403000B2Easy to installRemove changeSpinal electrodesElectrocardiographyMonitoring systemFinite-state machine
A monitoring system has biomechanical sensors, physiological sensors and a controller which receive sensory inputs from the sensors to provide output signals for the output device, and it detects from the sensory inputs risk of a syncopal event The bio-mechanical sensors include sensors arranged to allow the processor to detect a user postures and posture transitions. The processor operates a finite state machine, in which there is a state corresponding to each of a plurality of user physical postures and to each of a plurality of transitions between said postures, and the processor determines a relevant state depending on the sensory inputs. A device output may be muscle stimulation to prevent syncope, and there are stimulation permissions associated with the finite state machine states.
Owner:THE NAT UNIV OF IRELAND GALWAY +2
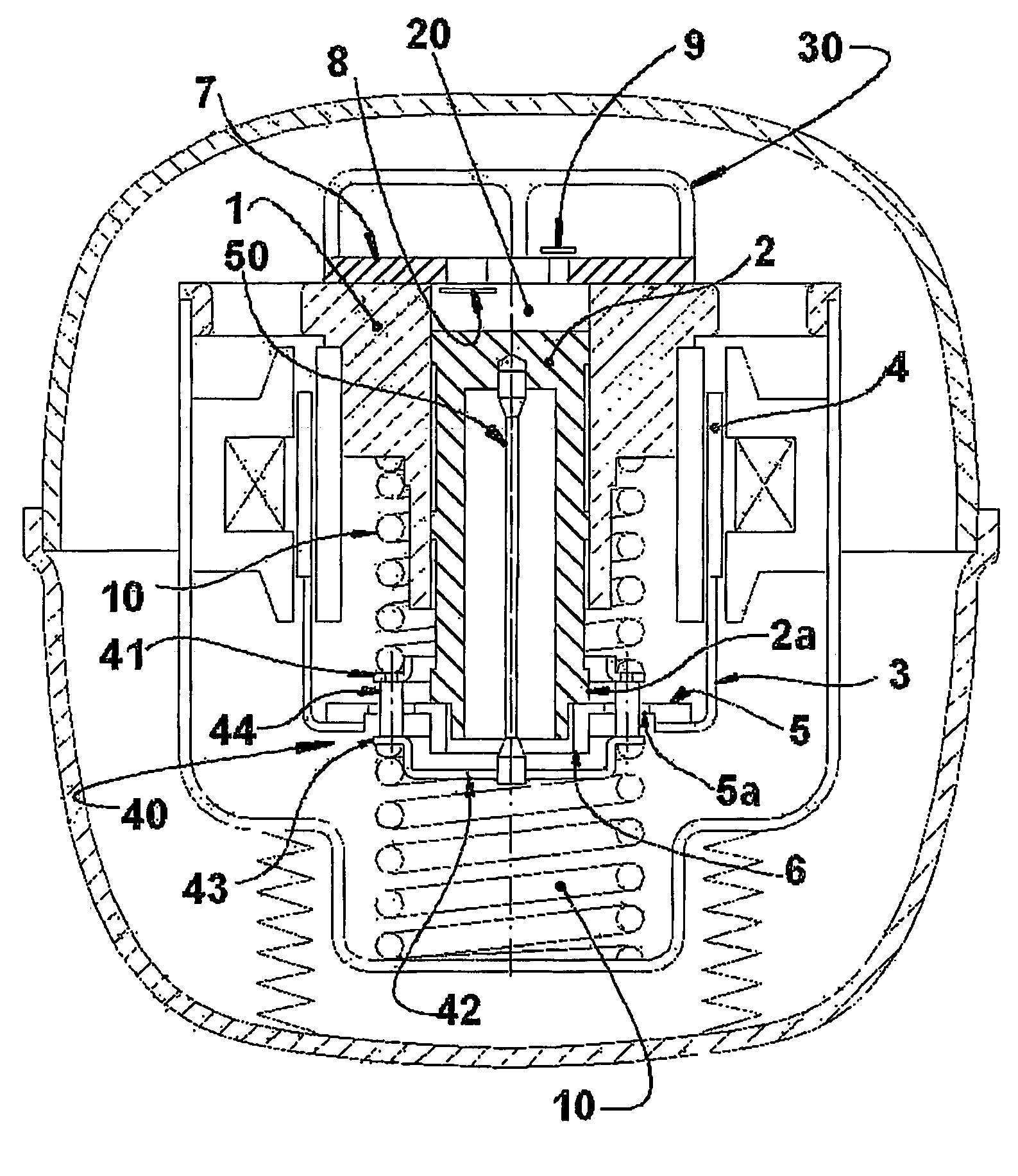
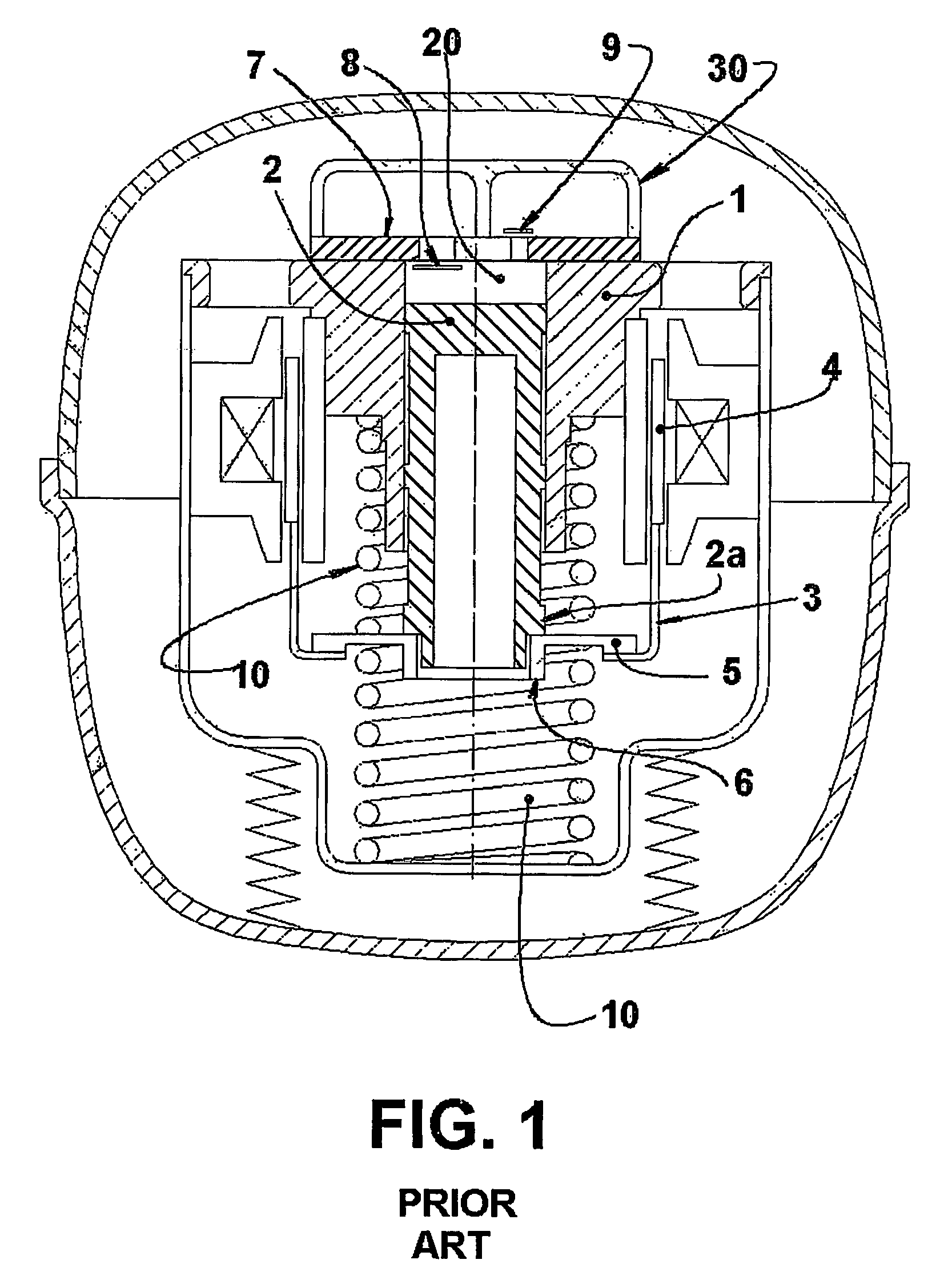
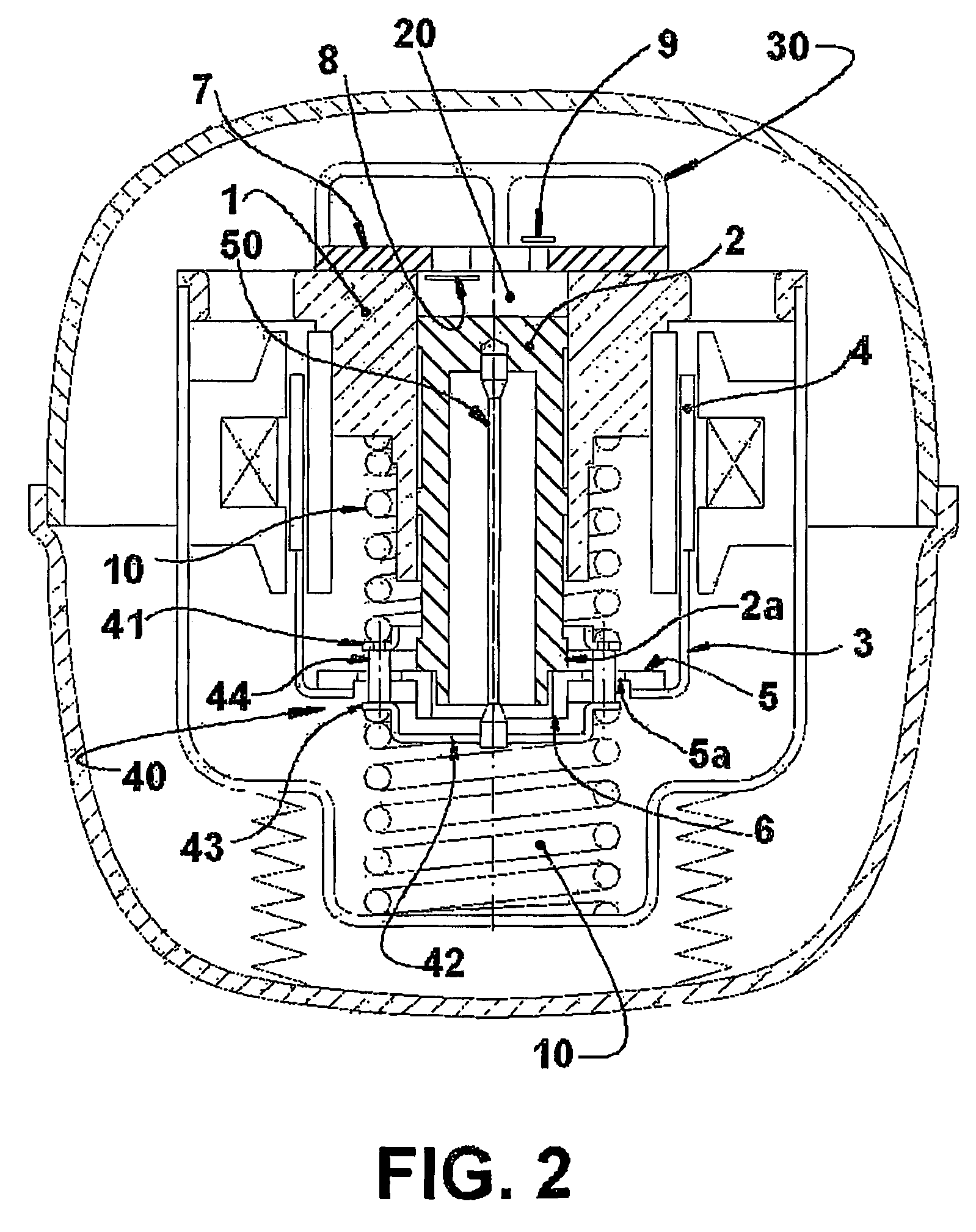
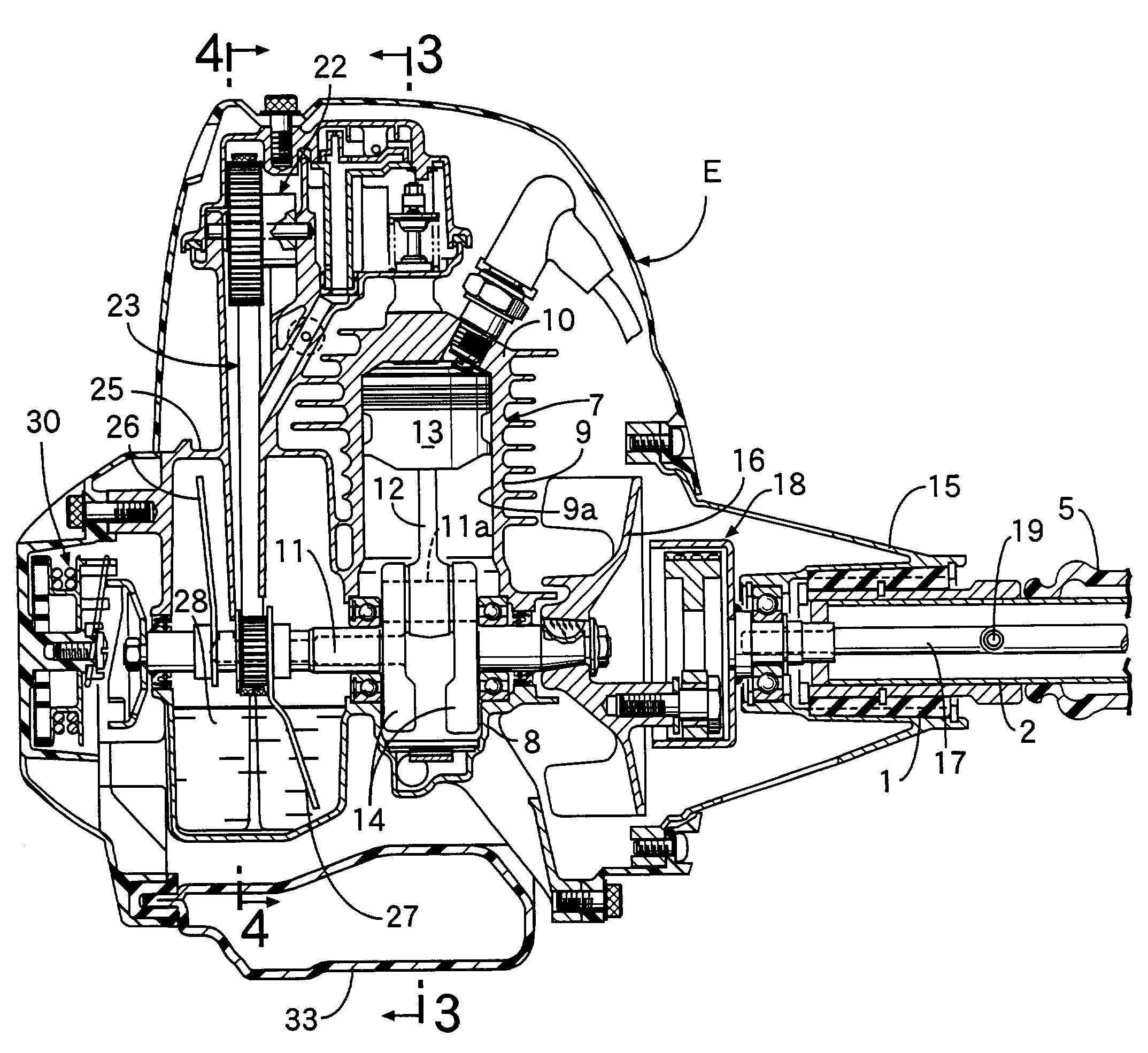
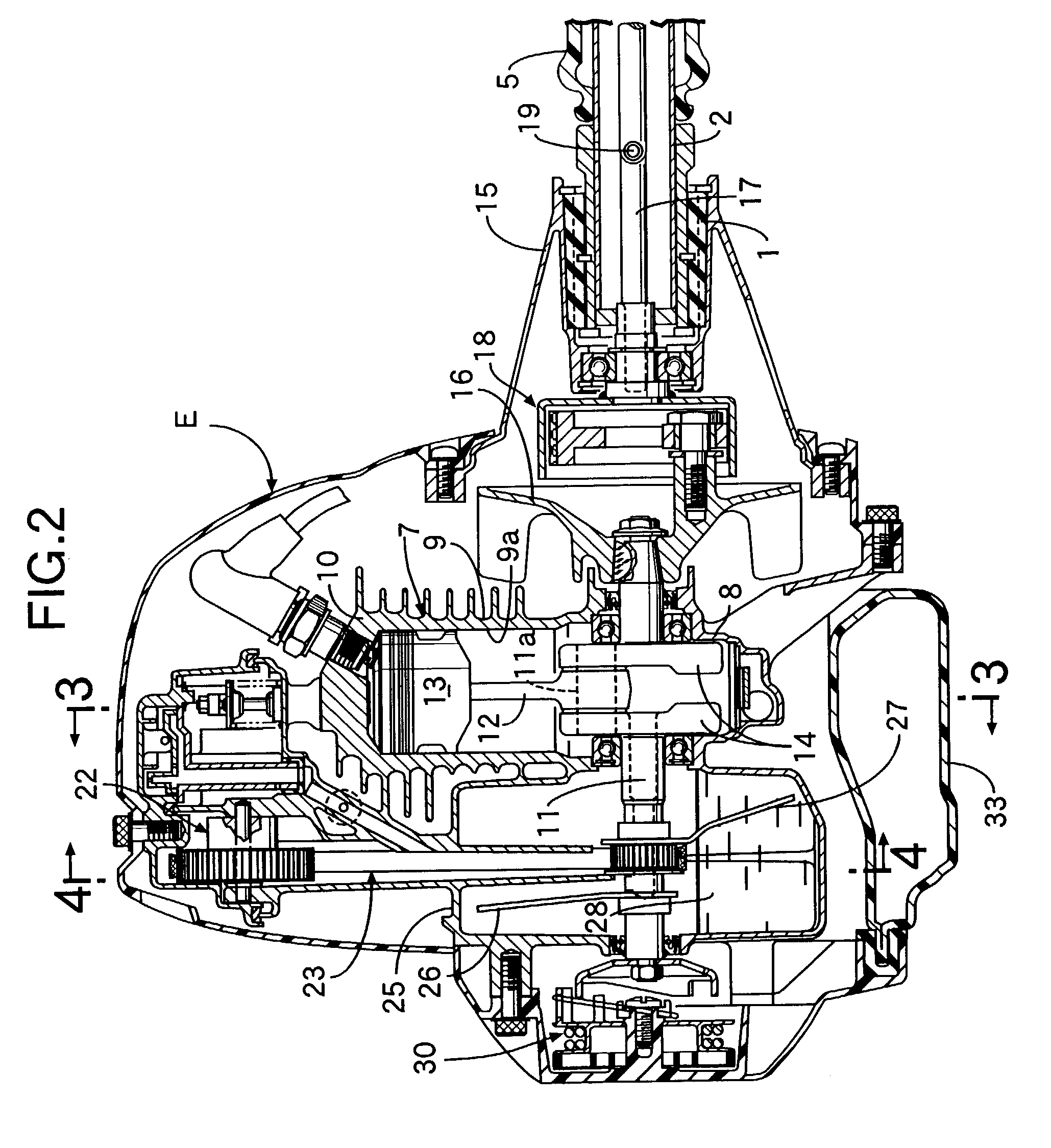
Reciprocating compressor driven by a linear motor
InactiveUS7316547B2Minimizes lateral forceEasy constructionPositive displacement pump componentsPiston pumpsCouplingReciprocating motion
A reciprocating compressor driven by a linear motor, comprising a shell, within which are mounted: a reference assembly formed by a motor and a cylinder (1); a resonant assembly formed by a piston (2) reciprocating inside the cylinder (1), and by an actuating means (3) operatively coupling the piston (2) to the motor; two spring means (10) mounted to the resonant assembly and to the reference assembly and which are elastically and axially deformed in the displacement direction of the piston (2); a mounting element (40) coupling an end of one spring means (10) to an end of the other spring means (10); and a coupling element (50) mounted to the piston (2) and to the mounting element (40), which is axially displaced together with the piston (2) and displaced freely and transversally to the displacement direction of the piston (2), said coupling element (50) transmitting the axial forces between the piston (2) and the mounting element (40) and minimizing the application of radial forces to the piston (2).
Owner:EMPRESA BRASILEIRA DE COMPRESSORES SA (EMBRACO)
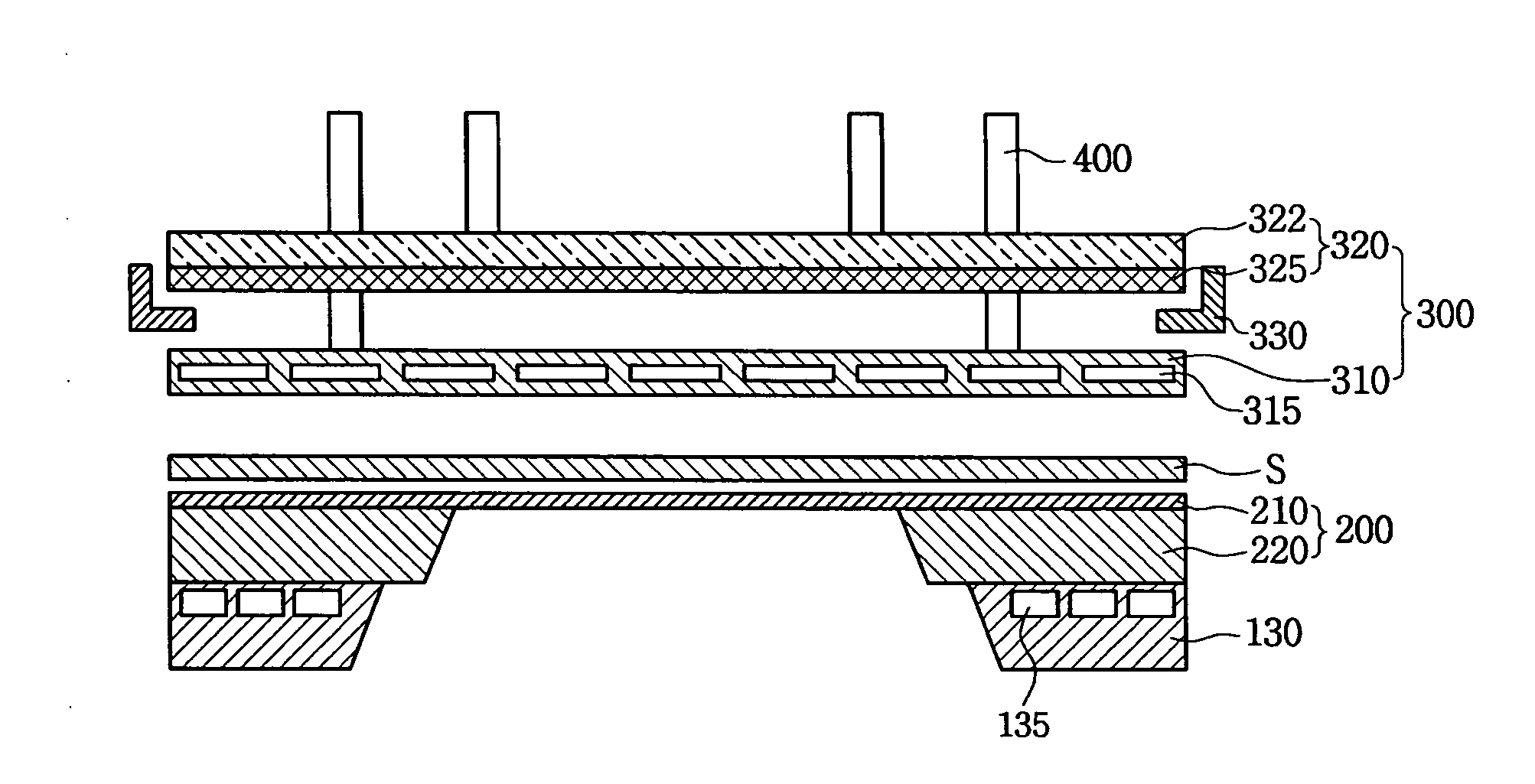
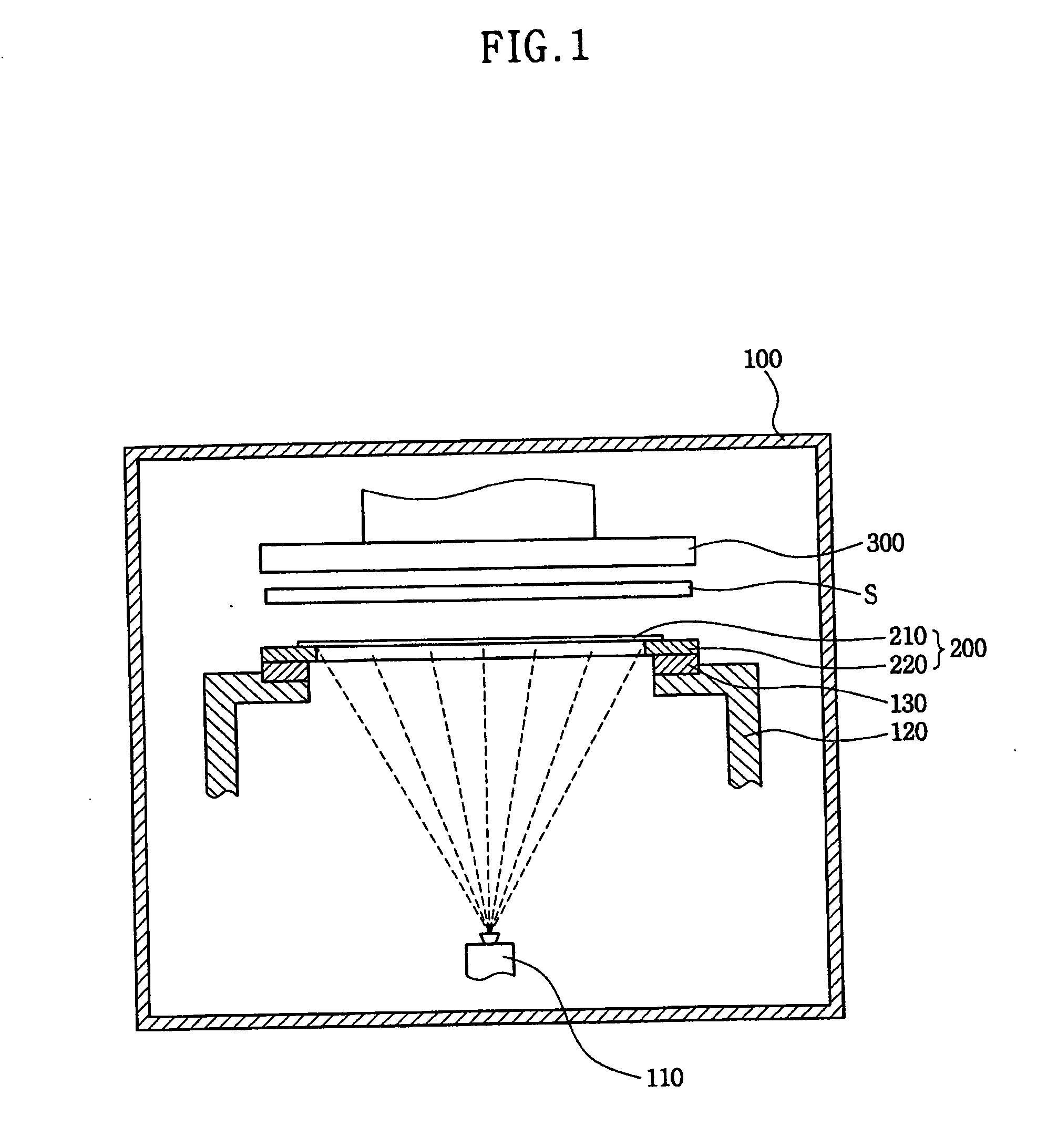
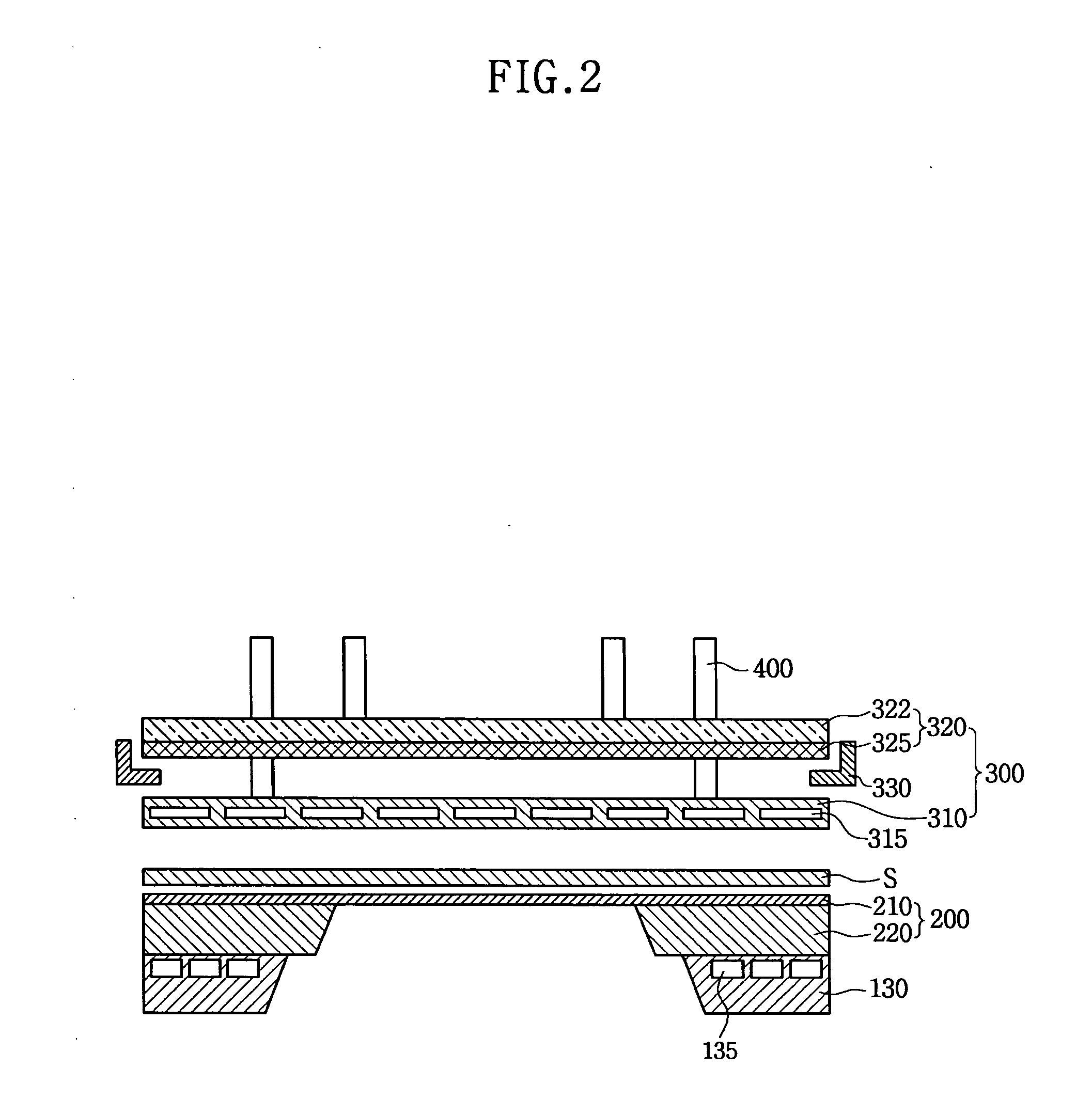
Mask adhesion unit and deposition apparatus using the same
InactiveUS20100206222A1Minimize applicationAvoid deformationLiquid surface applicatorsElectroluminescent light sourcesElectrical and Electronics engineeringControl unit
A mask adhesion unit for a deposition apparatus includes a magnetic assembly, a cap plate spaced apart from the magnetic assembly, and a magnetic control unit between edges of the magnetic assembly, and the cap plate. A deposition apparatus using the same is capable of adhering a substrate and a mask assembly together using the mask adhesion unit to improve deposition precision, while preventing deformation of a slit of the mask assembly.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
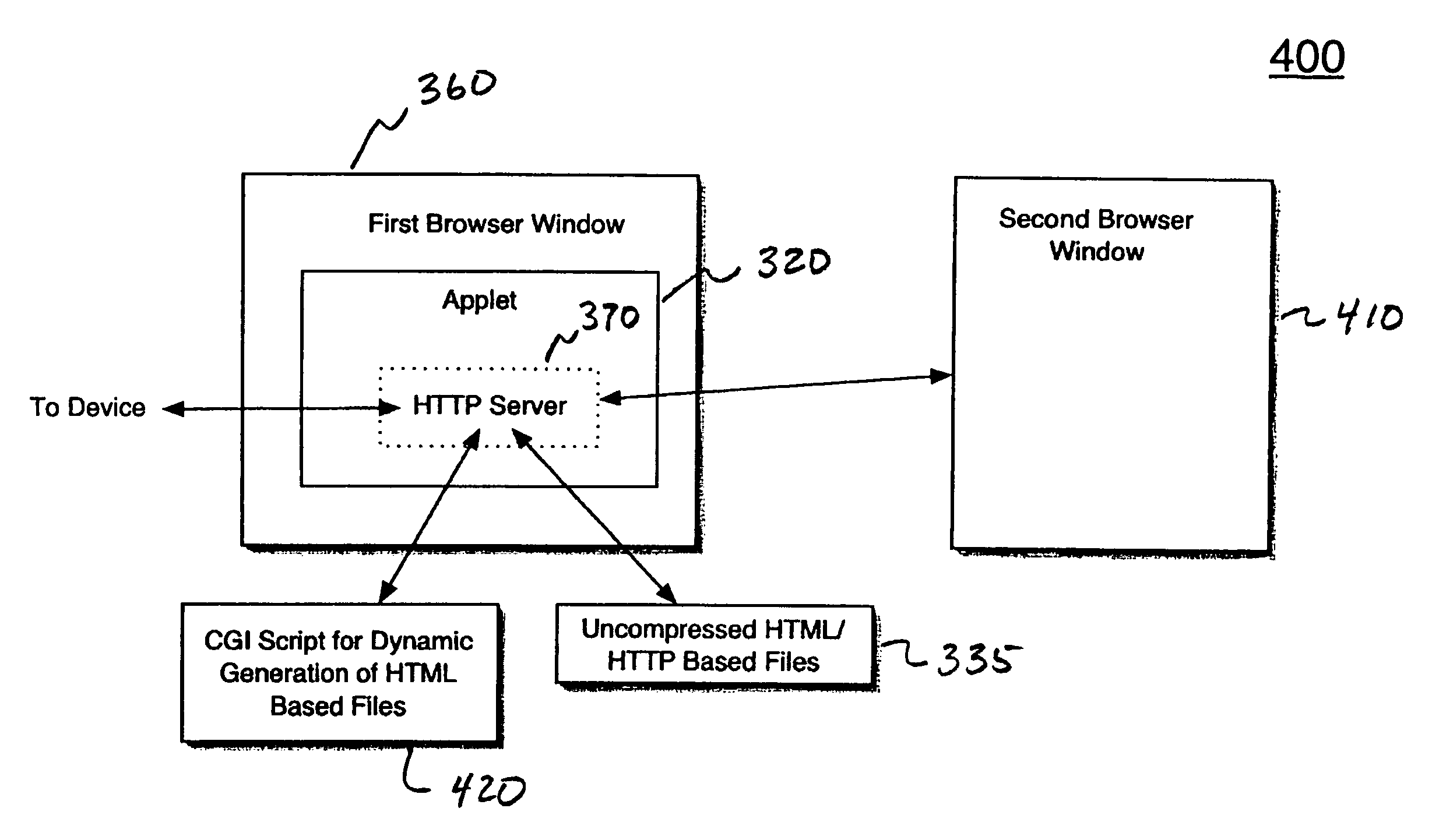
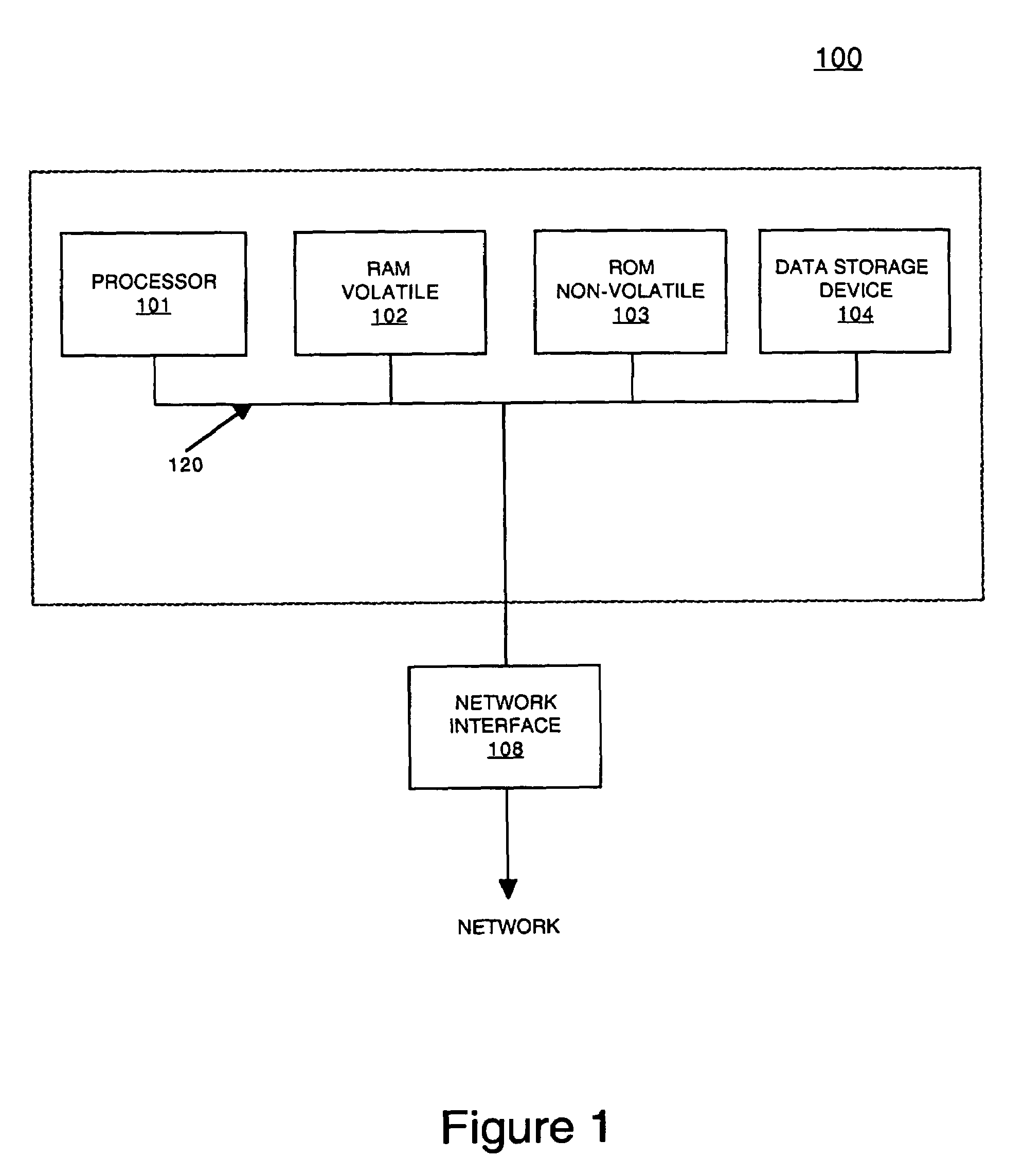
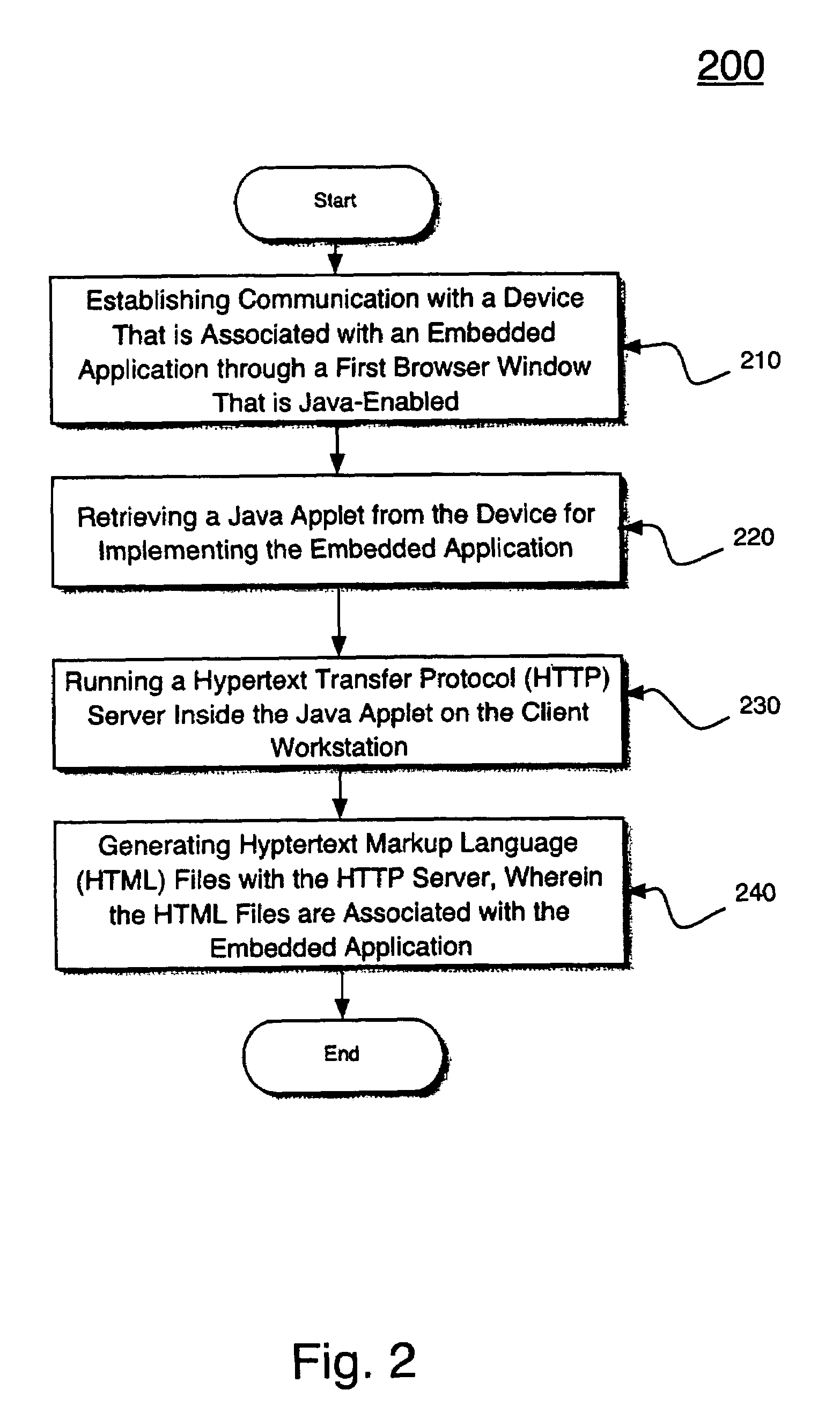
Method and system for footprint minimized, HTML/HTTP-based systems for Java-based embedded device management applications
InactiveUS7580990B1Increasing effectively available amount of memoryMinimize applicationMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlEmbedded applicationsNetwork management application
A method and system for accessing HTML / HTTP based information for Java-based embedded applications. Specifically, in one embodiment, a method is disclosed for accessing HTTP / HTML based information from a client workstation. The embodiment of the method begins by establishing communication with a device that is associated with an embedded application through a first browser window that is Java-enabled. The method then continues by retrieving a Java applet from the device for implementing the embedded application. Then, the embodiment continues by running a hypertext transfer protocol (HTTP) server inside the Java applet on the client workstation. Thereafter, the embodiment continues by generating hypertext markup language / hypertext transfer protocol (HTML / HTTP) based files with the HTTP server, wherein the HTML / HTTP based files are associated with the embedded application.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
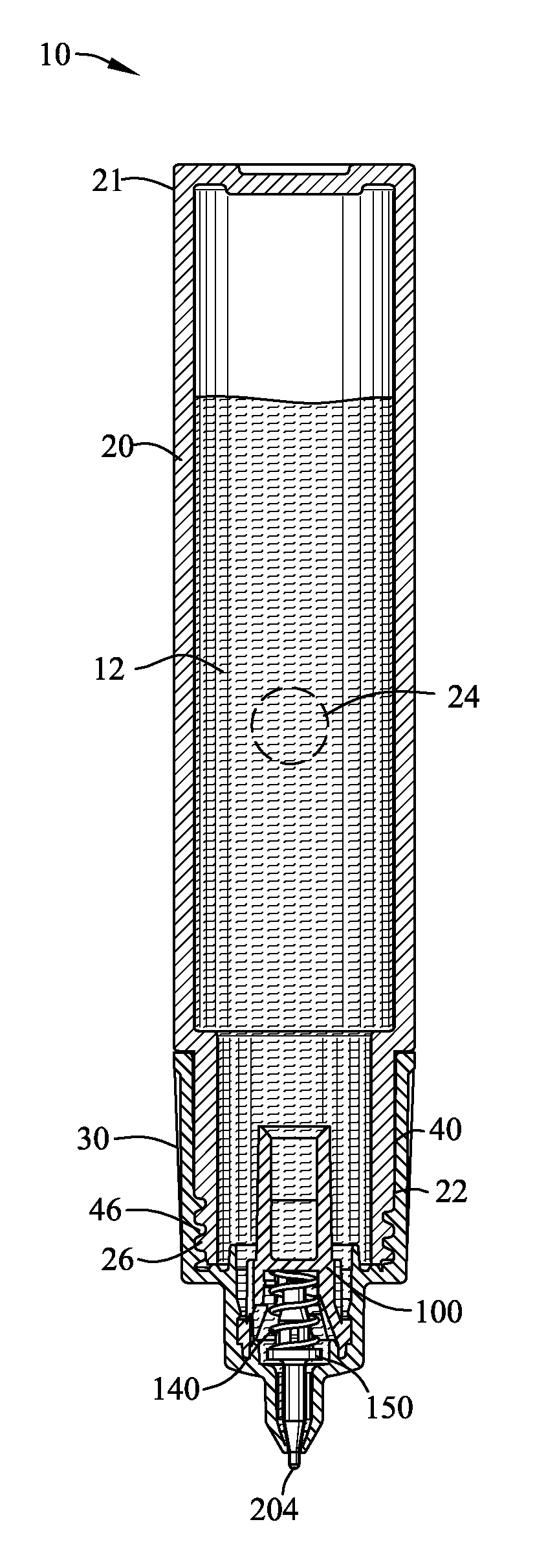
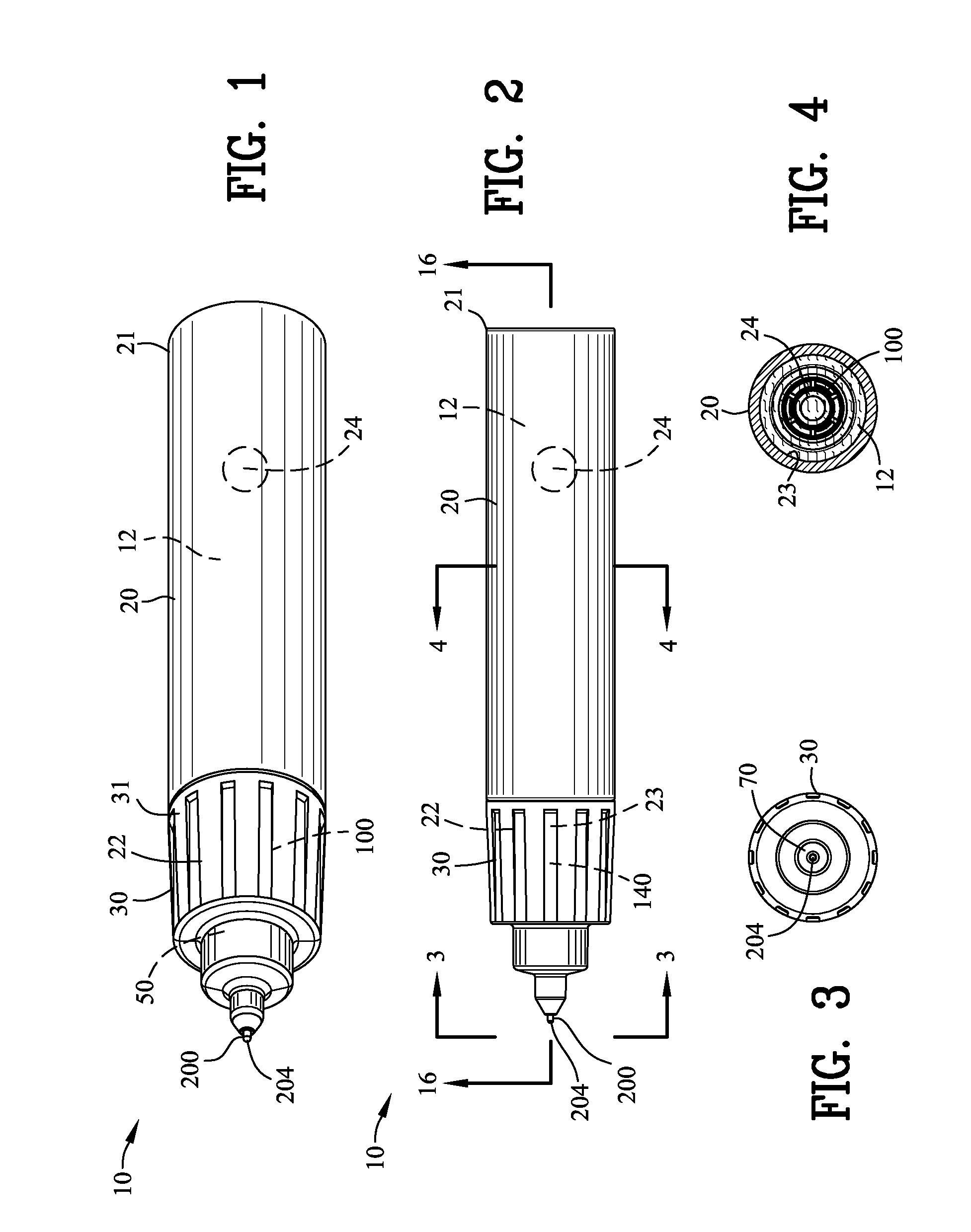
Precision Liquid Applicator
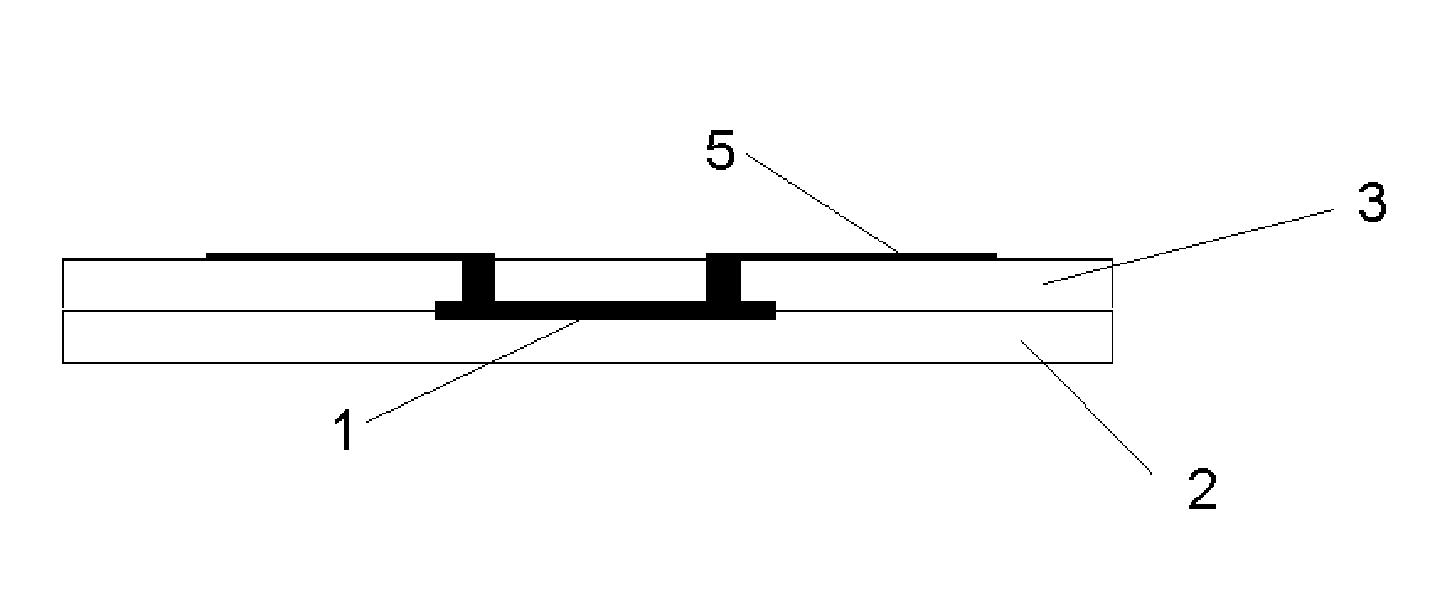
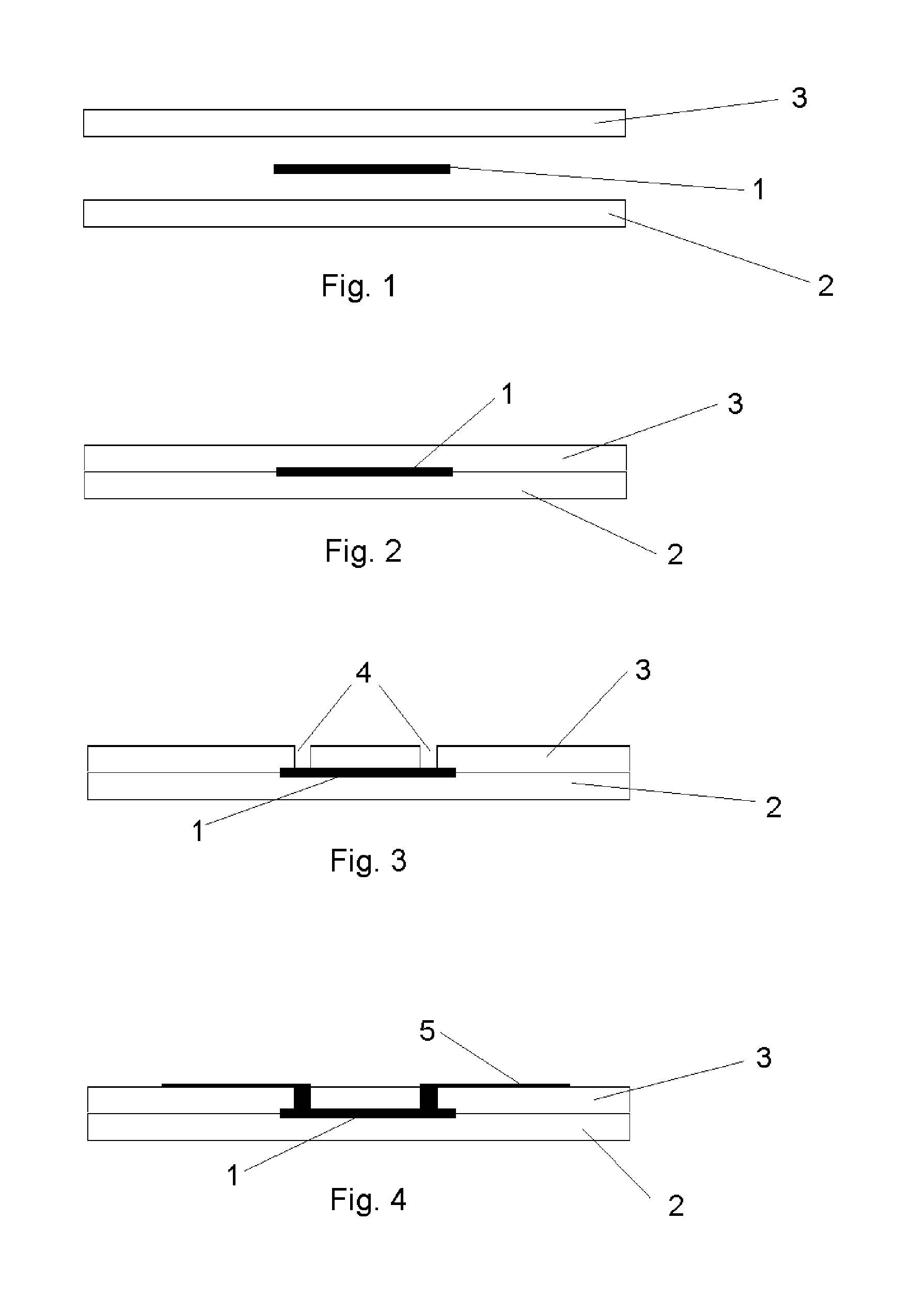
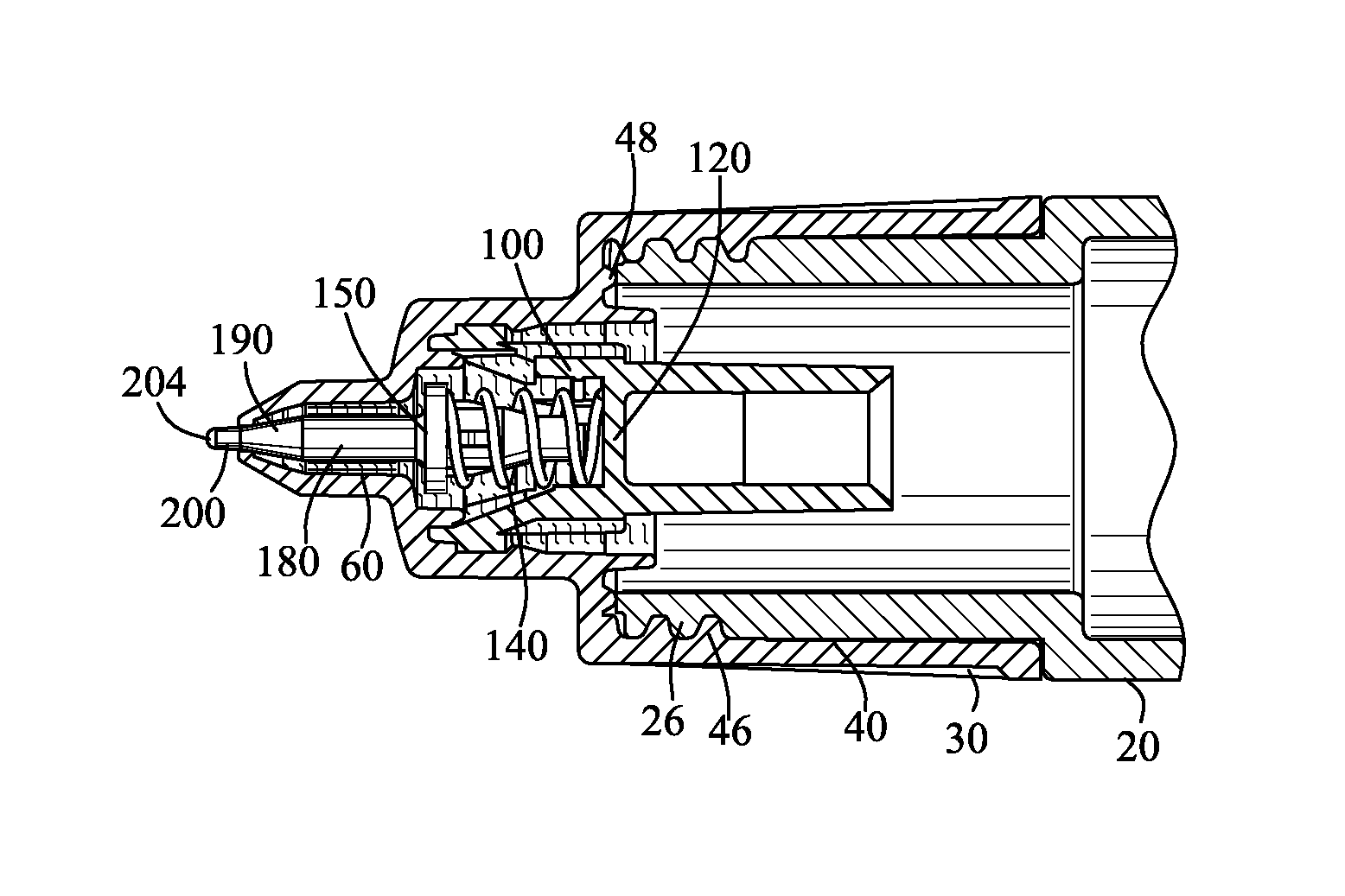
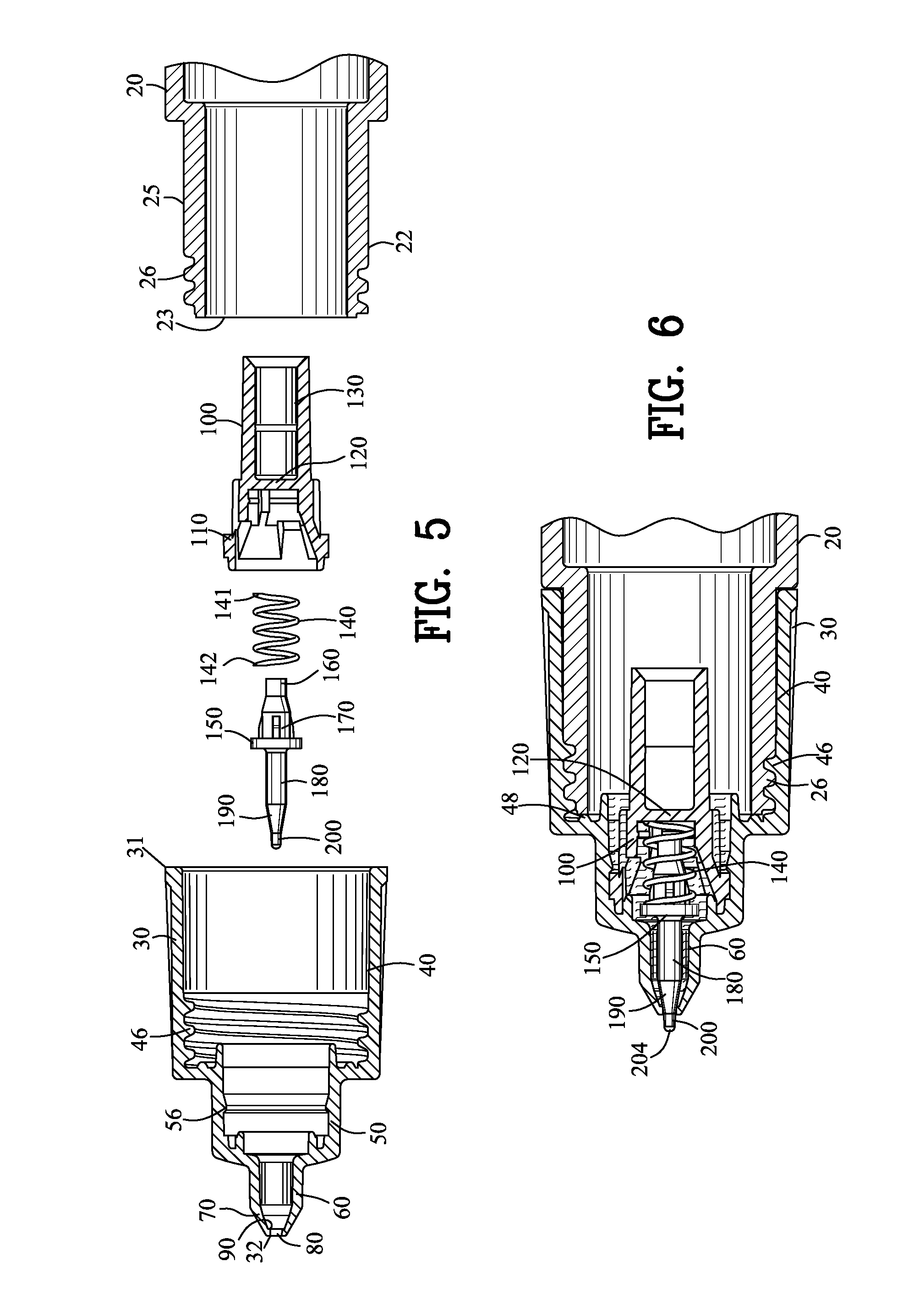
ActiveUS20130243514A1Minimize applicationAvoid flowPackaging toiletriesBall-point pensBiomedical engineeringValve seat
A precision liquid applicator is disclosed for dispensing an applicator liquid from a container onto a surface. The precision liquid applicator comprises a closure defining a terminal orifice and a valve seat. A valve comprises a precision applicator tip extending through the terminal orifice and comprises a valve seal for sealing with the valve seat. A depression of the precision applicator tip onto the surface displaces the valve seal from the sealing surface for providing an annular passageway between the precision applicator tip and the terminal orifice to enable the flow of the applicator liquid onto the surface. A valve stop cooperates with a stop wall for limiting movement of the valve to control a cross-sectional area of the passageway between the precision applicator tip and the terminal orifice and for ensuring the precision applicator tip extends beyond the second end of the closure. The precision liquid applicator is suitable for applying paint into a scratch within a painted surface without excessive application of paint outside of the scratch.
Owner:FLOCON
Method for adding a fusible material to a container wall
ActiveUS20100239877A1Additional costProcess be complicateFurnaces without endless corePig casting plantsInduction heaterMetal
A method for adhering a shaped fusible material (6) to a portion of a metallic container wall (2) comprising applying the shaped material to said wall portion in a contacting relationship, heating said wall portion with an induction heater to melt the contacting surface of the shaped fusible material, and cooling the assembly to re-solidify the melted surface of the fusible material; and products of the foregoing method.
Owner:TEMPRA TECH
Tool for removing dents from sheet metal
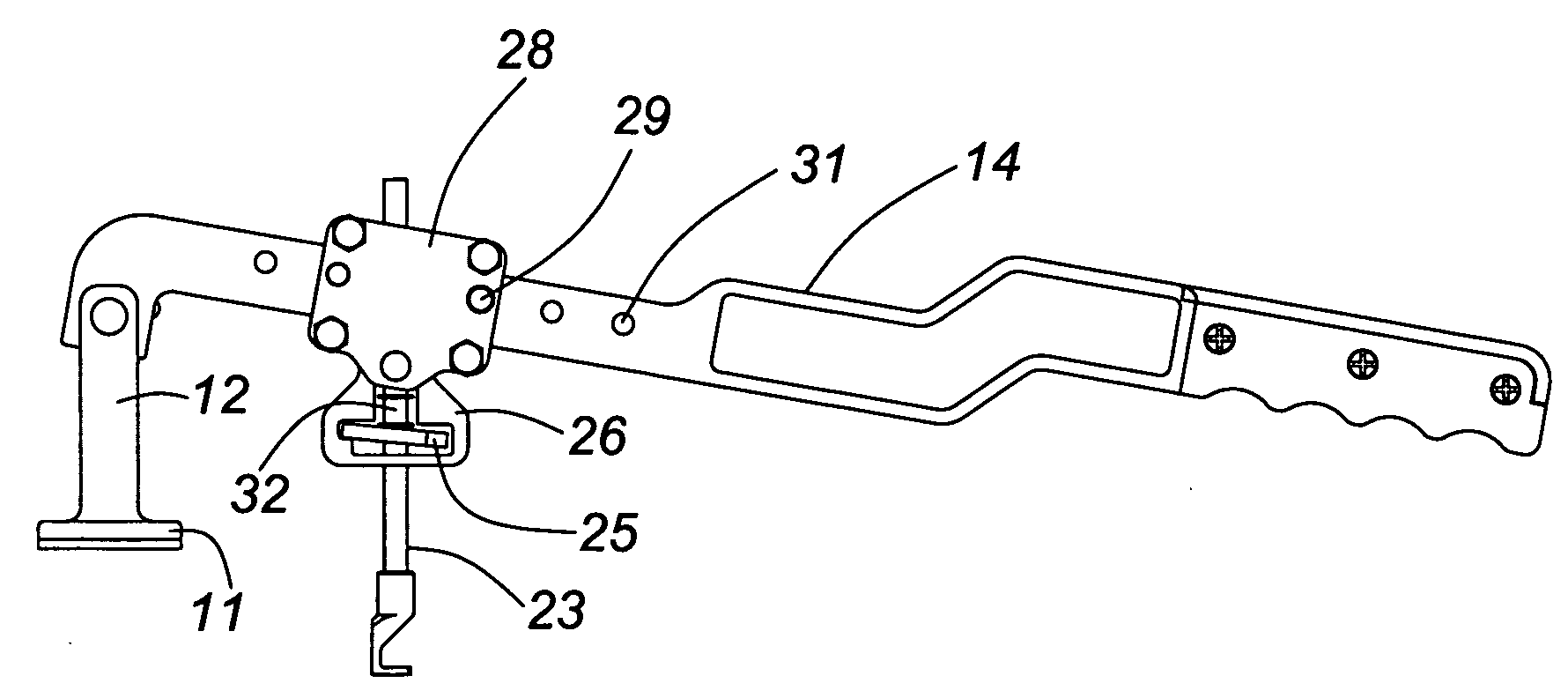
A tool for pulling a dent out of a sheet metal surface has a support post with a foot shaped to rest against a portion of the sheet metal surface adjacent the dent. The tool includes a hinged lever arm which is pivotally connected to this support post at a lever arm pivot point which is elevated above the foot and adjacent sheet metal region. The tool also includes a pulling rod for coupling, through a fastener or connecting means, to the dented portion of the surface which is to be drawn-out, the pulling rod being connected to the hinged lever arm through a pivoting joint. The pivoting joint of the pulling rod and the lever arm pivoting point are positionable through actuation of the lever arm able to lie in a common plane which is substantially parallel to the sheet metal surface into which the dent is to be drawn into alignment. The pulling rod is adjustable in its engagement with the lever arm to permit the lever arm to swing through a limited angular range. Coupling between the pulling rod and lever arm is either discrete or continuous. Fasting means connecting the tool to the sheet metal include a self-tapping, self-drilling screw or a bolt provided with a magnetic washer or magnetic head.
Owner:KNOWLES STEVEN MICHAEL
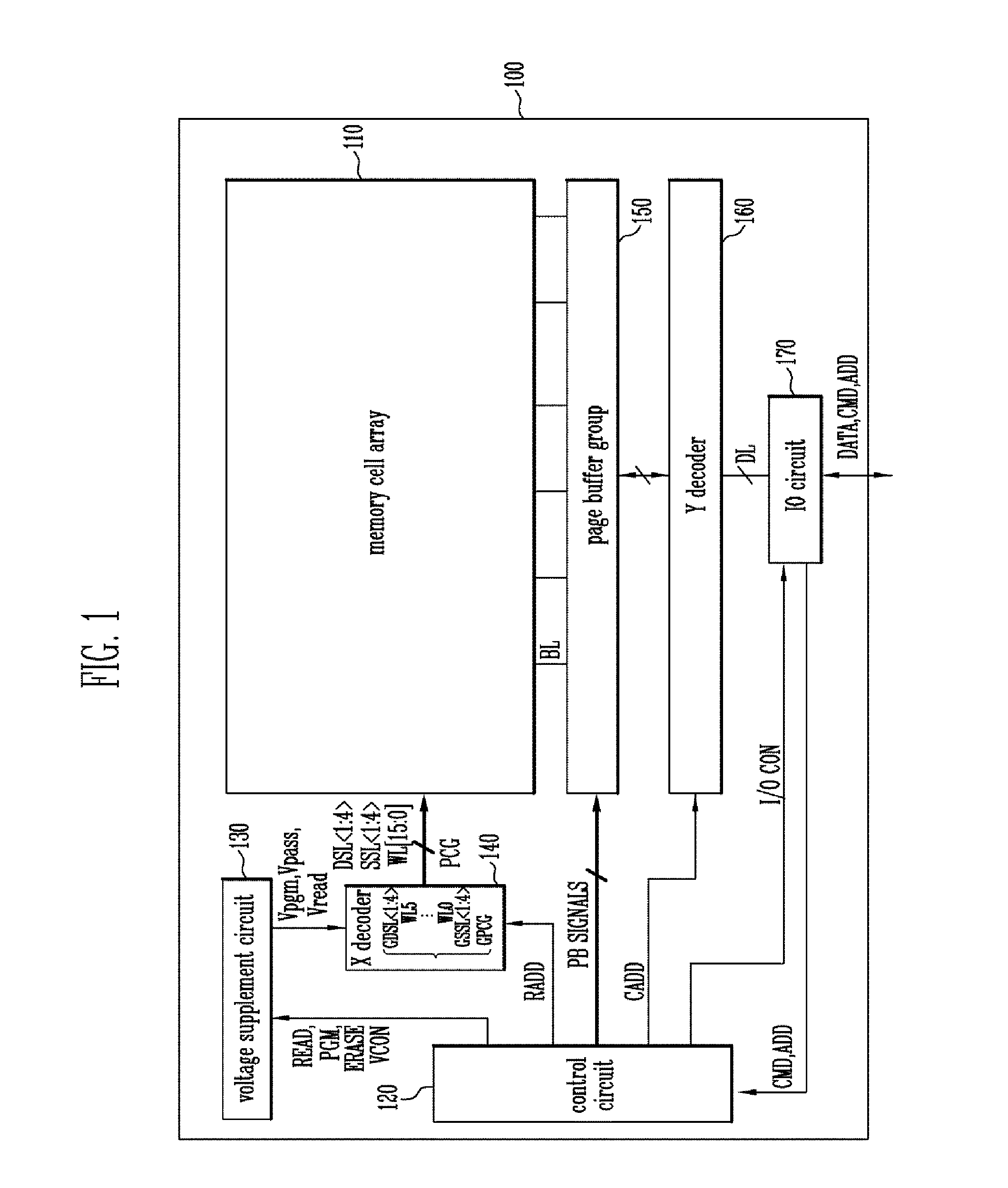
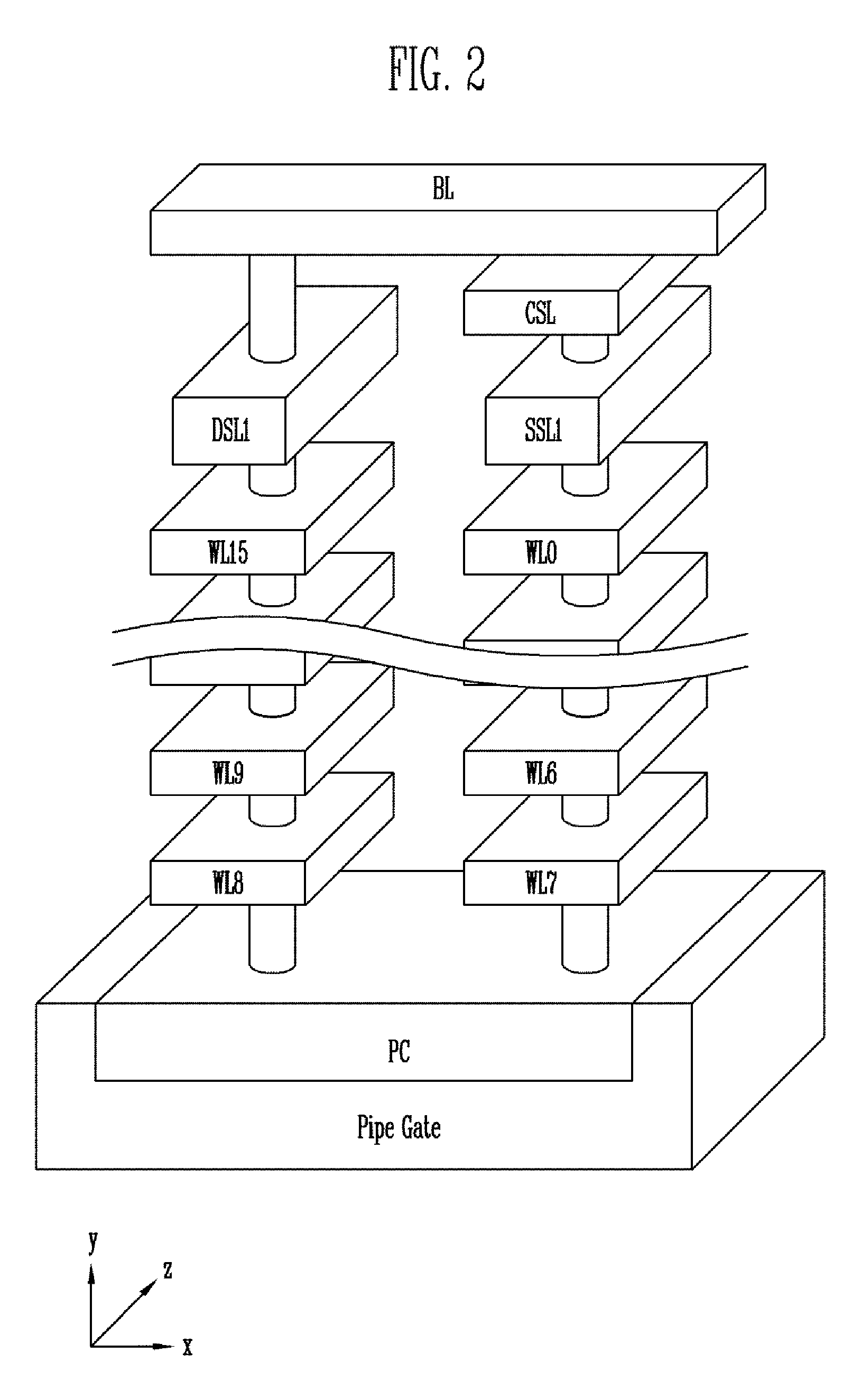
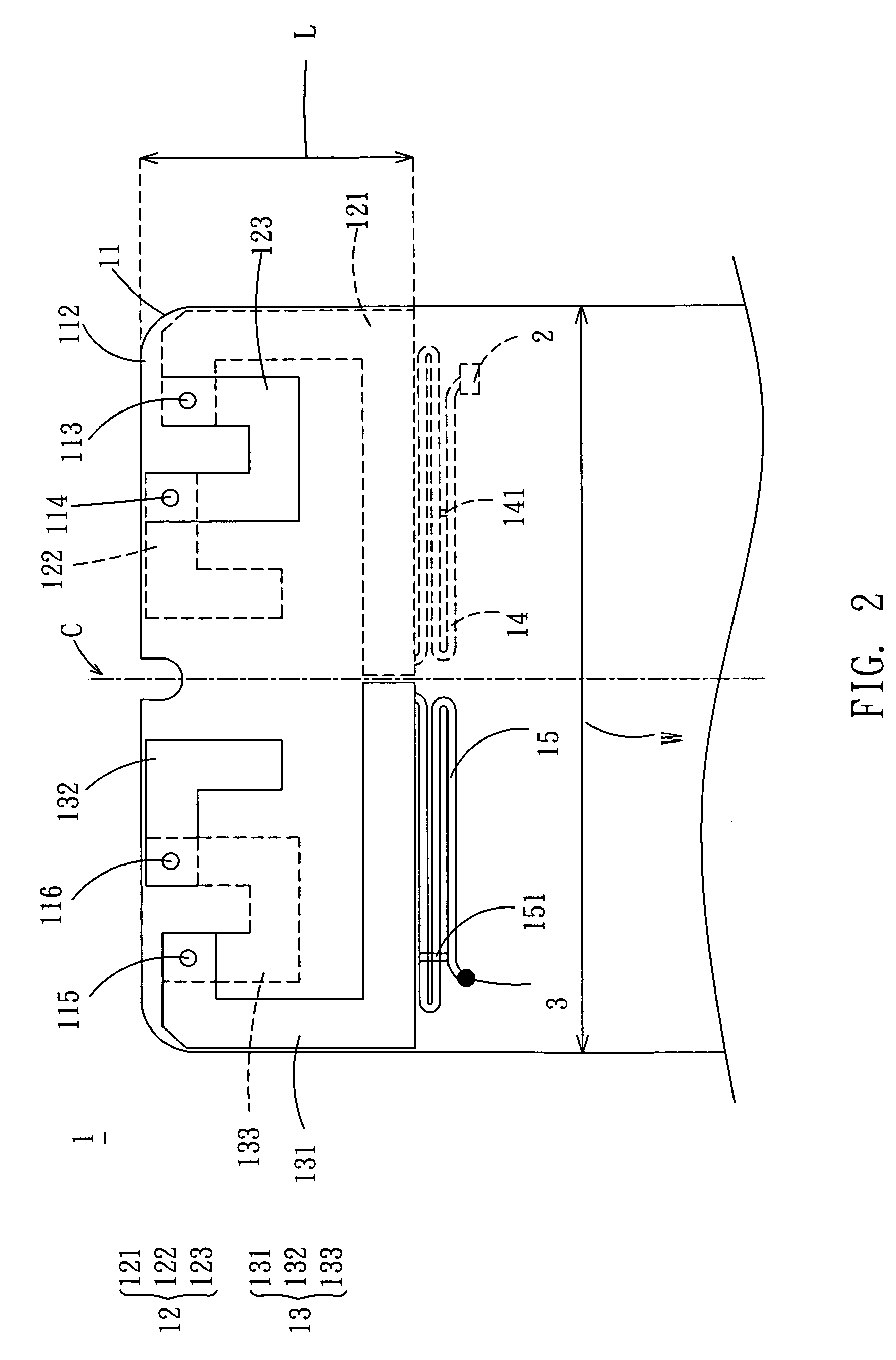
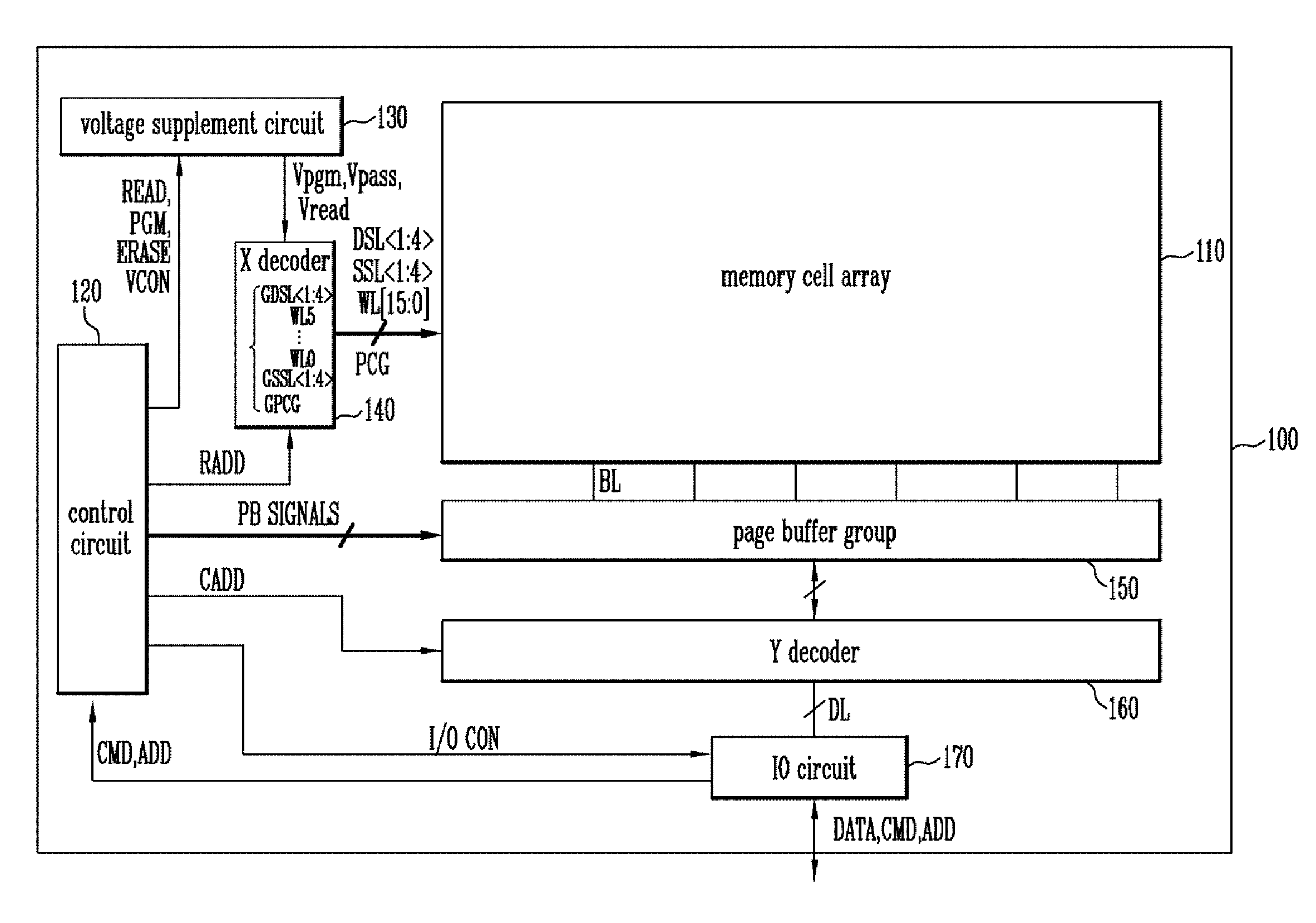
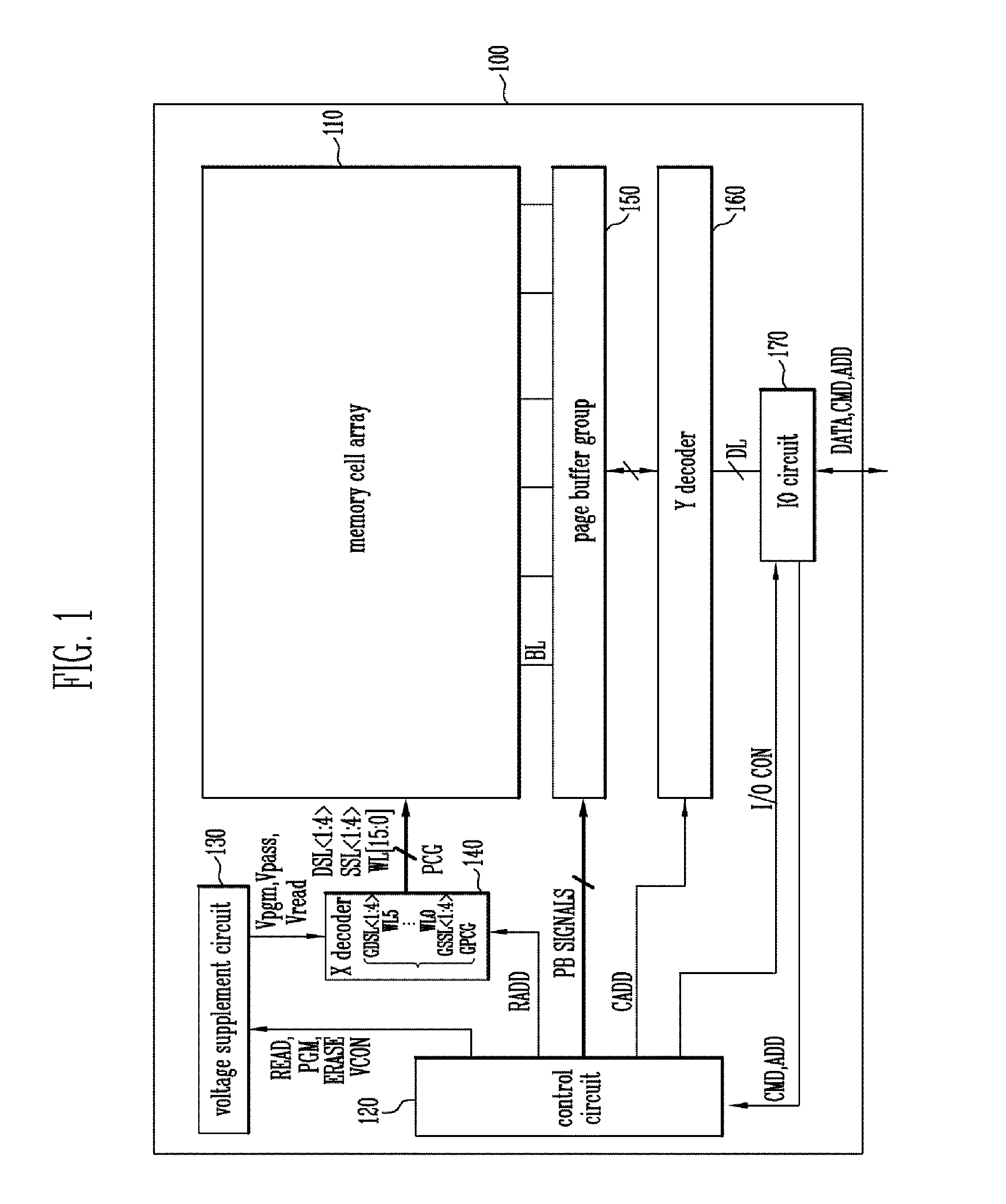
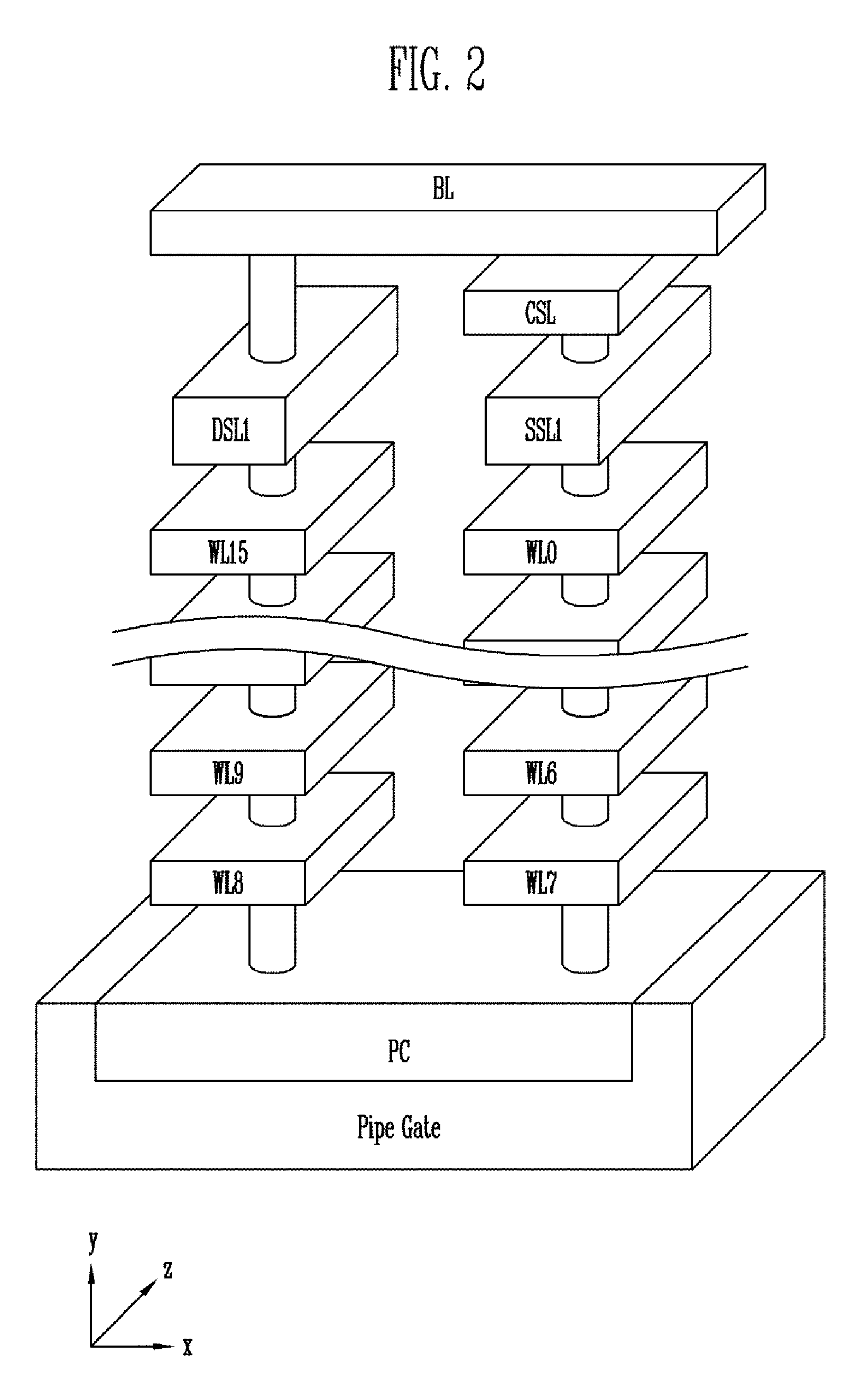
Semiconductor memory device and method of operating the same
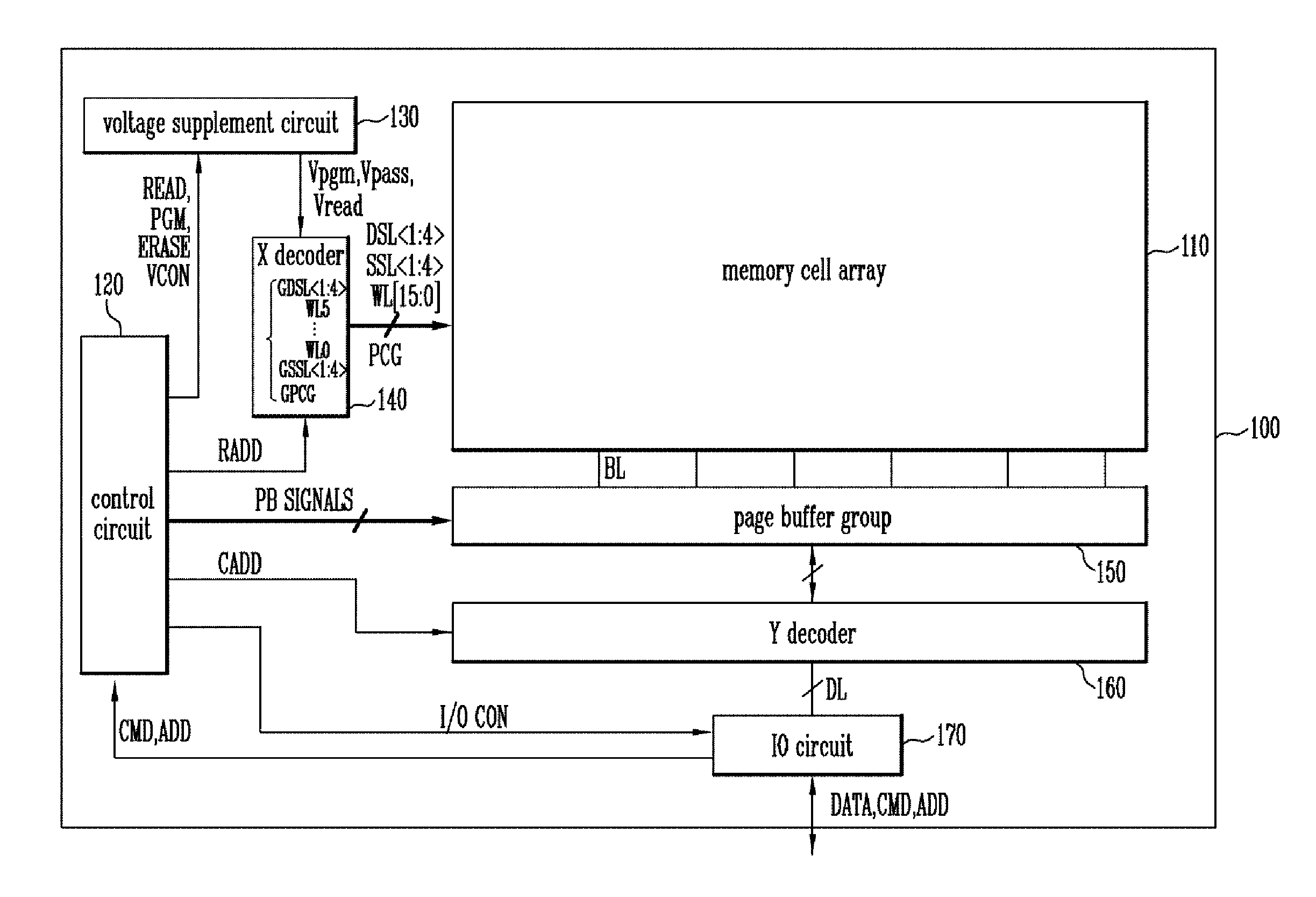
ActiveUS20130301366A1Reduce distractionsReduce voltageRead-only memoriesDigital storageVertical channelControl circuit
A semiconductor memory device of the present invention includes a memory cell array with cell strings having word lines stacked on a substrate and a vertical channel layer formed through the word lines, a peripheral circuit configured to select one of the word lines and perform a program operation on the selected word line, and a control circuit configured to control the peripheral circuit to perform the program operation by applying a program voltage to a word line selected for the program operation, applying a ground voltage to a word line of which a program operation has been completed and applying a pass voltage to the other word lines.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Dipole antenna
InactiveUS7212171B2Reduced dimensionProduct can be minimizedSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsDipole antennaPhysics
A dipole antenna includes a substrate, a first radiating member and a second radiating member. The substrate has a first surface and a second surface opposite to the first surface. The first radiating member and the second radiating member are symmetrically disposed on the first surface and the second surface of the substrate, and electrically connected to a grounding point and a feeding point, respectively. The first radiating member has a first radiating part, a second radiating part and a third radiating part, which are respectively disposed on the first surface and the second surface of the substrate and electrically connected to one another. The second radiating member has a fourth radiating part, a fifth radiating part and a sixth radiating part, which are respectively disposed on the first surface and the second surface of the substrate and are electrically connected to one another.
Owner:ARCADYAN
Alkaline hydrolysis of organic waste including specified risk materials and effluent disposal by mixing with manure slurry
InactiveUS20150107319A1Shorten the timeShort timeBio-organic fraction processingProductsSpecified risk materialFeces
A method for sterilization of pathogenic waste includes steps of introducing animal tissues, carcasses or parts, pathogenic waste, or by-products of slaughter or processing into an unpressurized vessel, adding NaOH and KOH in a ratio of about 2.2 to 2.3:1, adding water sufficient to create a 1.5 to 1.6 Molar solution, such that the tissue to water ratio is about 1:1.5, heating the vessel indirectly to near but below the boiling point of the solution, holding the temperature for about 16-20 hours, while continuously agitating the contents of the vessel, displacing the solution volume in the reaction vessel about every 2-3 minutes. Optimally, the tissue is introduced into the vessel first, then dry NaOH and KOH, and finally water. The end product is a homogenous, aqueous solution that is sterile, pathogen-free and suitable for land application or mixing directly into manure retention vessels, prior to land application of the mixture.
Owner:BARNYARD TECH
Semiconductor memory device and method of operating the same
ActiveUS8913427B2Reduce distractionsReduce voltageRead-only memoriesDigital storageHemt circuitsVertical channel
A semiconductor memory device of the present invention includes a memory cell array with cell strings having word lines stacked on a substrate and a vertical channel layer formed through the word lines, a peripheral circuit configured to select one of the word lines and perform a program operation on the selected word line, and a control circuit configured to control the peripheral circuit to perform the program operation by applying a program voltage to a word line selected for the program operation, applying a ground voltage to a word line of which a program operation has been completed and applying a pass voltage to the other word lines.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Method for manufacturing an electronic device
ActiveUS20110189824A1Cost-effectiveFacilitate handlingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesIntegrated circuitElectronic equipment
In a method for manufacturing an electronic device an integrated circuit (1) is arranged between two layers (2, 3) of a substrate, said integrated circuit (1) having at least one contacting surface, a hole (4) is formed in at least one substrate layer (3) above said at least one contacting surface, a conductive structure (5) is formed on a surface of said at least one substrate layer (3) facing away from the integrated circuit (1) and said conductive structure (5) is connected to said contacting surface by means of said hole (4).
Owner:NXP BV
Precision liquid applicator
ActiveUS9346072B2Minimize applicationAvoid flowBall-point pensPackaging toiletriesBiomedical engineeringValve seat
A precision liquid applicator is disclosed for dispensing an applicator liquid from a container onto a surface. The precision liquid applicator comprises a closure defining a terminal orifice and a valve seat. A valve comprises a precision applicator tip extending through the terminal orifice and comprises a valve seal for sealing with the valve seat. A depression of the precision applicator tip onto the surface displaces the valve seal from the sealing surface for providing an annular passageway between the precision applicator tip and the terminal orifice to enable the flow of the applicator liquid onto the surface. A valve stop cooperates with a stop wall for limiting movement of the valve to control a cross-sectional area of the passageway between the precision applicator tip and the terminal orifice and for ensuring the precision applicator tip extends beyond the second end of the closure. The precision liquid applicator is suitable for applying paint into a scratch within a painted surface without excessive application of paint outside of the scratch.
Owner:FLOCON
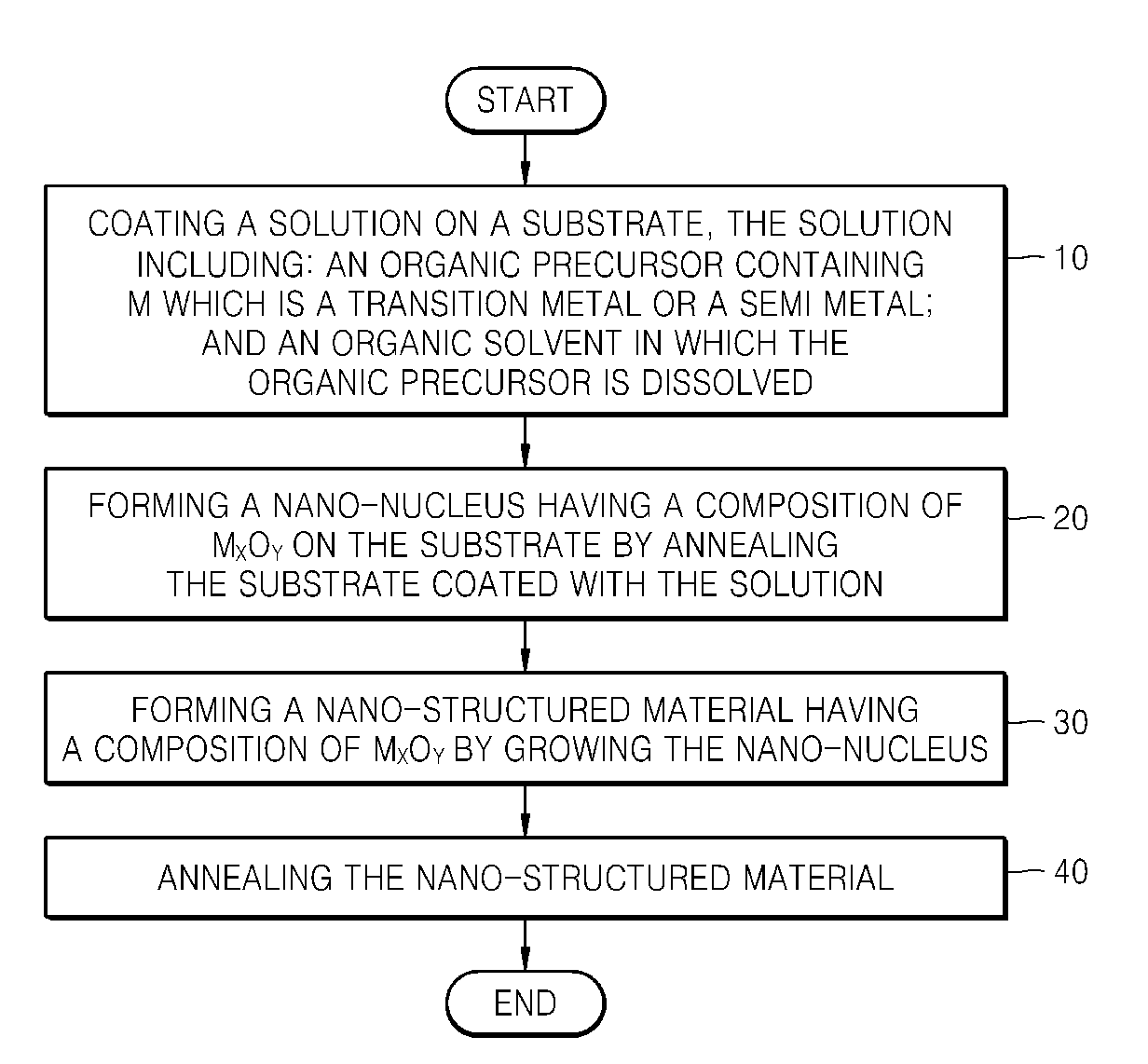
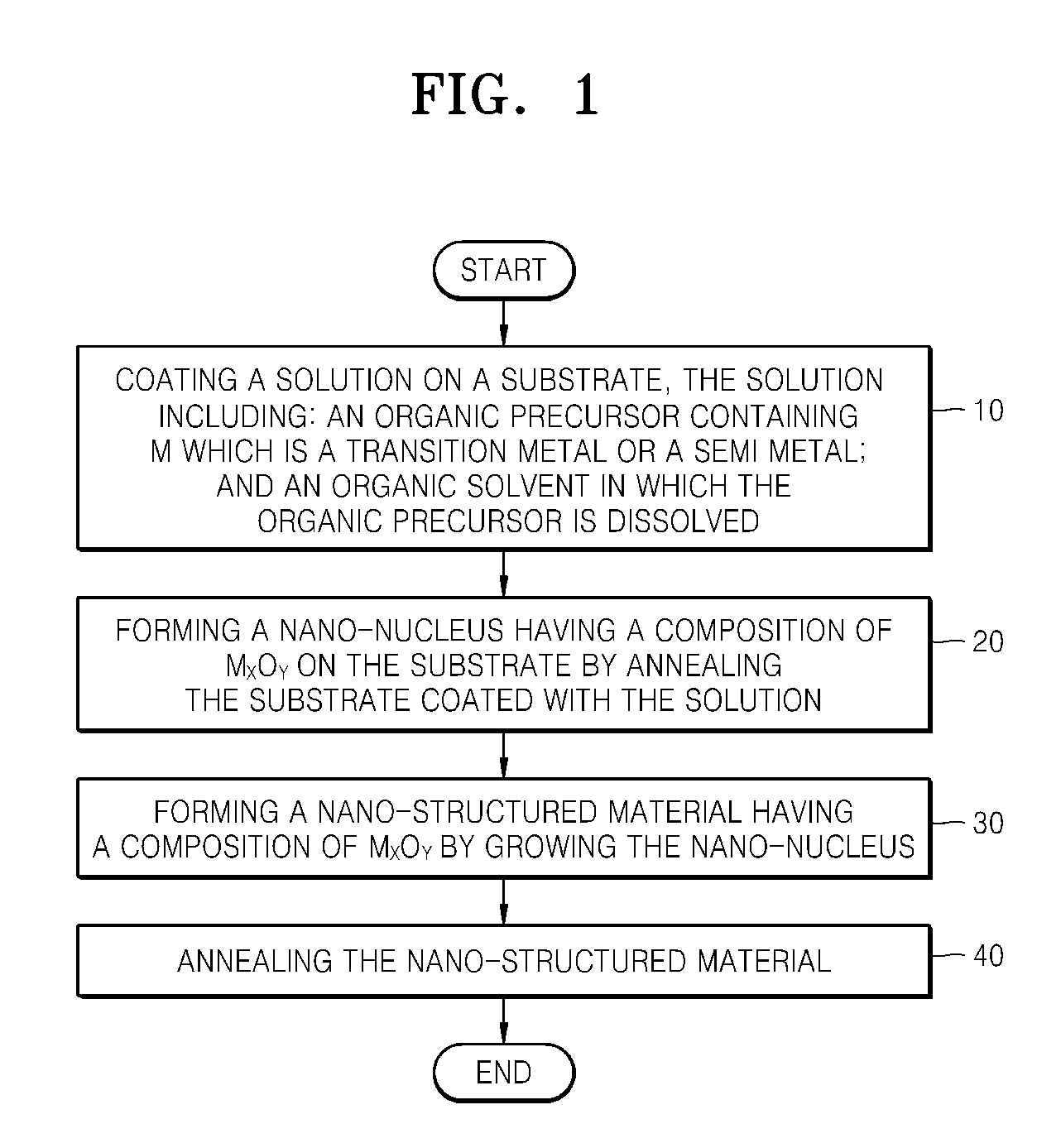
Method of forming oxide-based nano-structured material
InactiveUS20080268656A1High crystallinityReduce manufacturing costMaterial nanotechnologyArsenites/arsenatesOrganic solventPhysical chemistry
Provided is a method of forming an oxide-based nano-structured material including growing a nano-structured material using a nano-nucleus having the same composition as the desired oxide-based nano-structured material. A solution is coated on a substrate, the solution including: an organic precursor containing M which is a transition metal or a semi metal; and an organic solvent in which the organic precursor is dissolved. A nano-nucleus having a composition of MxOy is formed on the substrate by annealing the substrate. A nano-structured material having a composition of MxOy is formed by growing the nano-nucleus while supplying a reaction precursor containing M into the nano-nucleus, and the nano-structured material is annealed.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
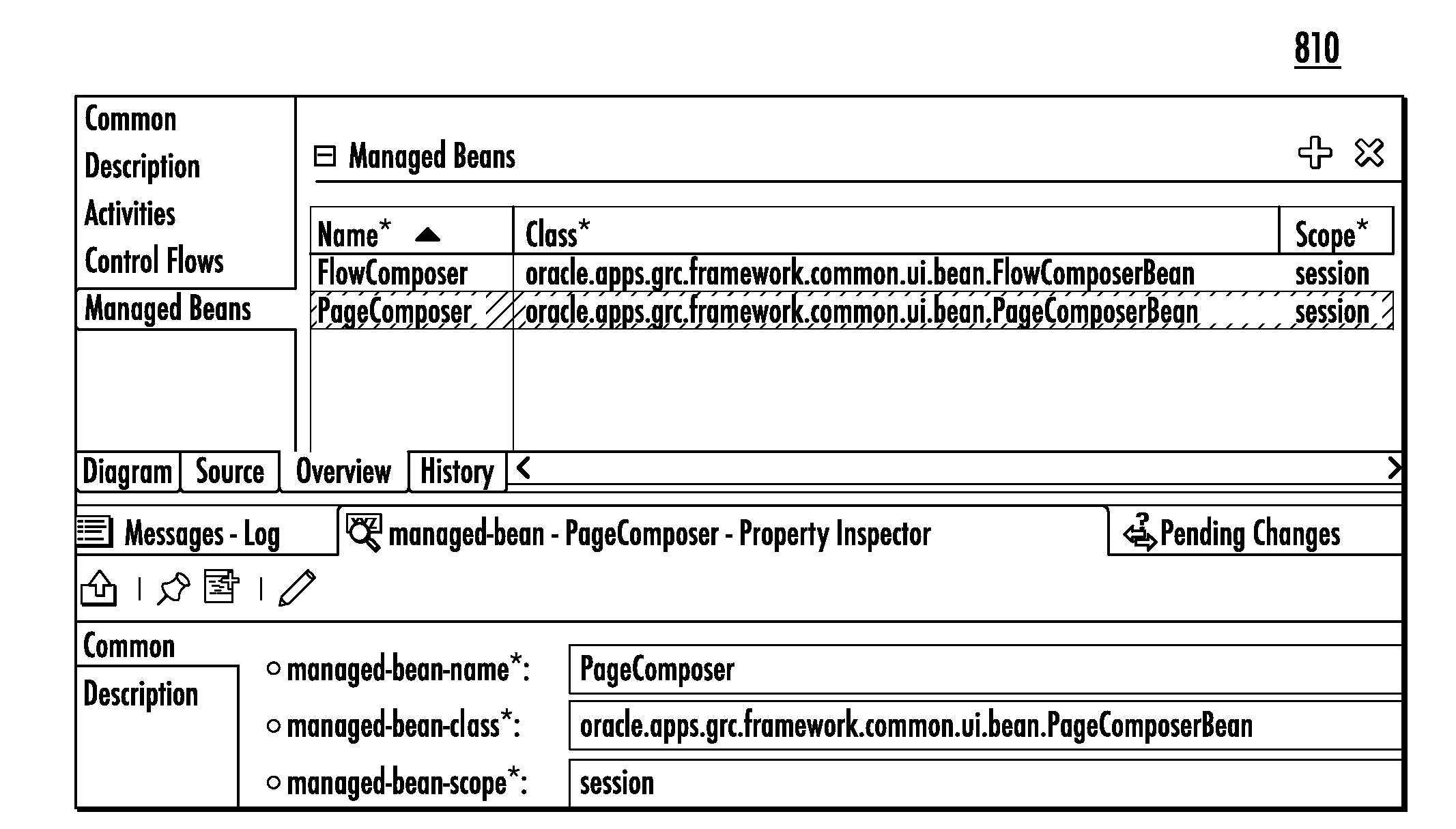
Real-Time Page and Flow Compositions
ActiveUS20100242049A1Minimize applicationAvoid shutdownMultiprogramming arrangementsOffice automationApplication softwareUser interface
Task flows are utilized for real-time page compositions, real-time flow compositions, or both. At design time, a plurality of task flows are provided as a database or library. A manager, or other type of user, can associate task flows with dynamic regions in an application page being designed. The application page can include one or more dynamic regions that act as a container for task flows. Metadata is generated from the customization of input parameters. At runtime, application pages are generated on-the-fly for display in a user interface. The application pages are composed according to the task flows embedded therein. The application pages are presented to the user according to an application flow. Through a user interface, the user can enter and retrieve information related to governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) activities, or other types of activities.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
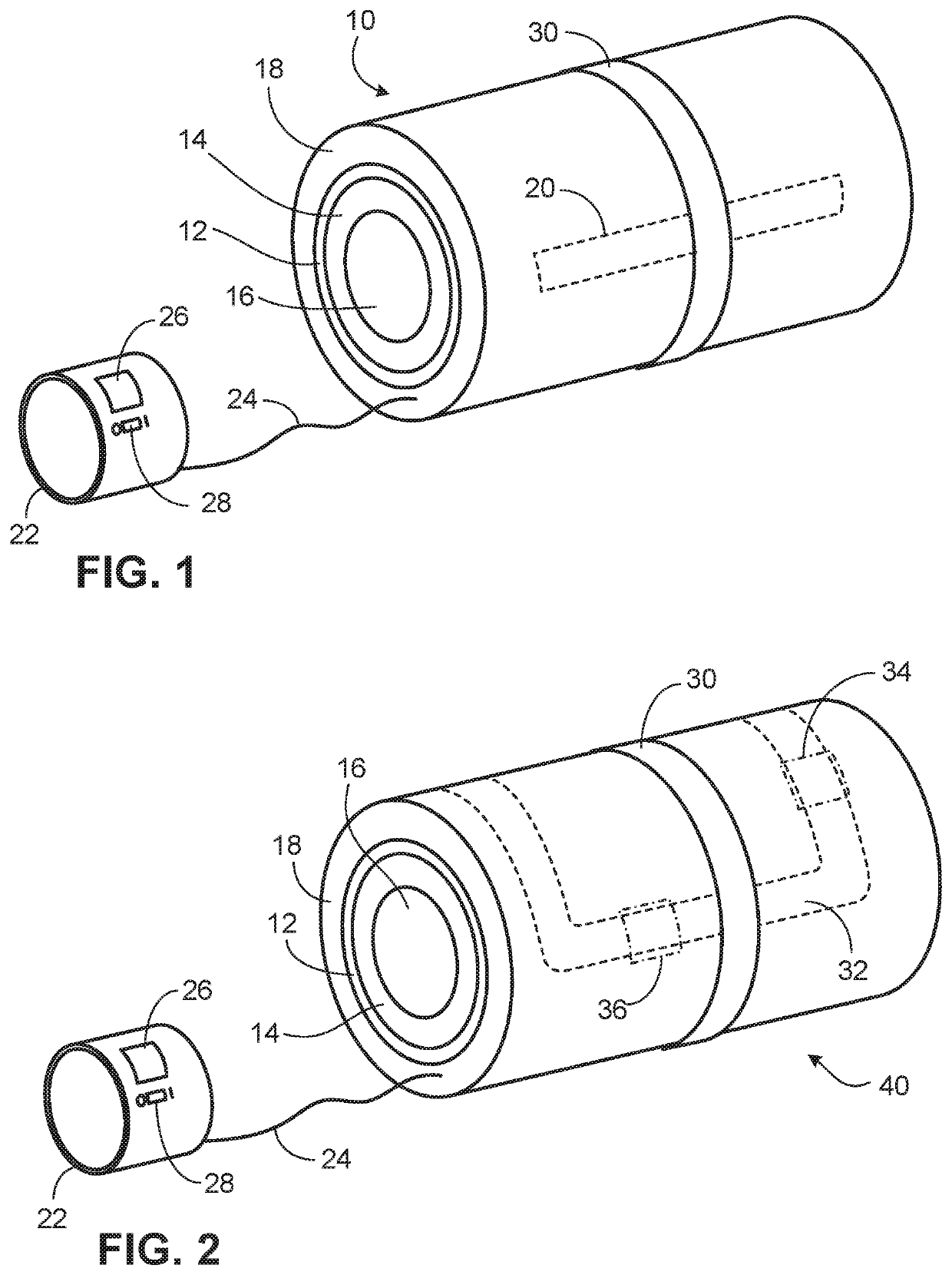
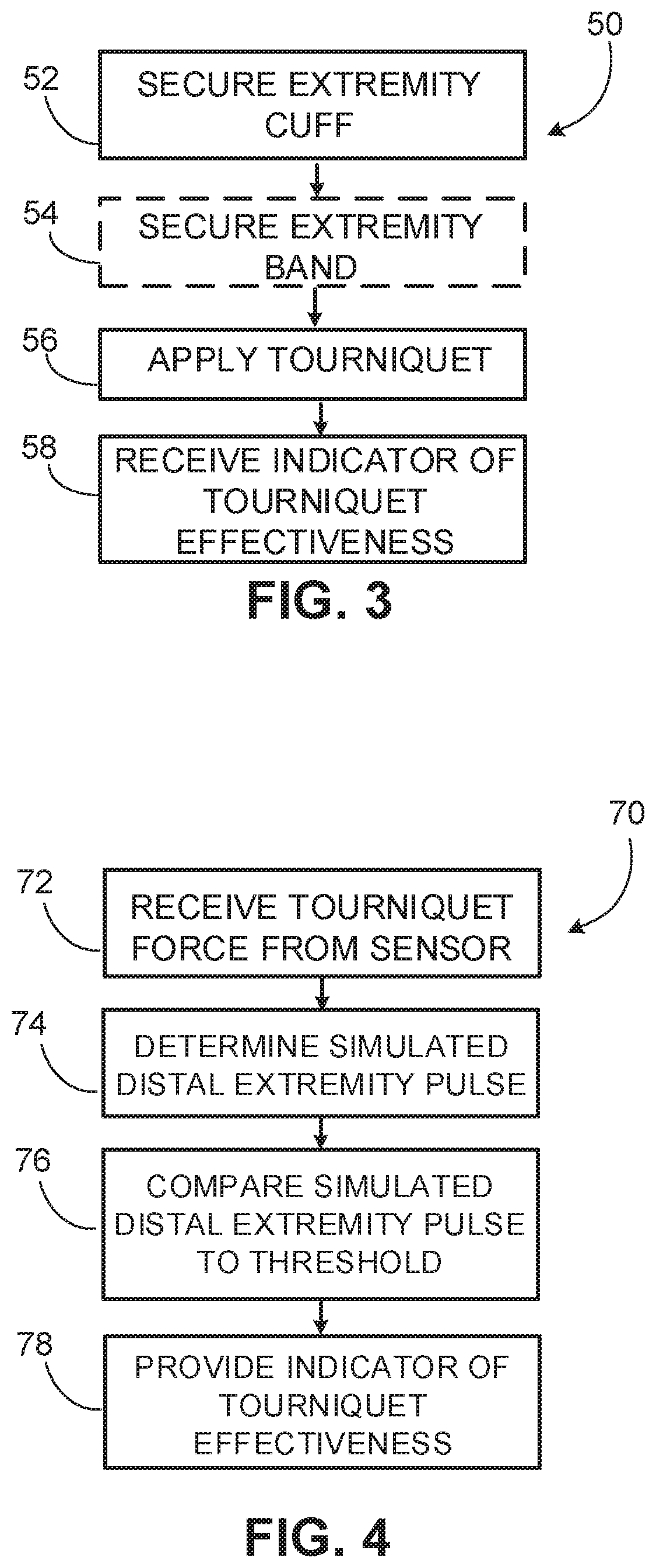
Tourniquet training device
ActiveUS20200170649A1Easy to useIncrease practice timeDiagnostics using pressureSensorsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationPhysical therapy
This document provides methods and materials for improving the training on the use of tourniquets. For example, methods and devices for confirming the proper pressure of a tourniquet using a tourniquet training device are provided.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Engine operated machine system
ActiveUS7036478B2Avoid complicationsIncrease structural weightValve arrangementsInertia force compensationGravity centerEngineering
In an engine operated machine system including a hollow support rod connected at one end to an engine through a vibration insulator, an auxiliary weight is mounted at the other end of a crankshaft for generating a centrifugal force in the same direction as an inertia force of a piston, when the piston reaches top and bottom dead centers. Thus, it is possible to bring a center of gravity of the engine closer to the position of the vibration insulator, thereby suppressing the application of the vibration from the engine to the support rod to the utmost.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Heat generating device
InactiveUS20150122799A1Reduce the total massMinimize applicationOhmic-resistance heating detailsPrinted circuit manufactureEngineeringResistor
To provide a heat generating device which is capable of minimizing the application of a large amount of heat through a contact with the heat generating device. The heat generating device includes an insulating base which contains a thermoplastic resin and has a front surface and a reverse surface and in which a plurality of via holes are formed to extend through a thickness, and heating resistors which are disposed in the via holes and generated heat when energized. Some of the heating resistors are connected in parallel.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Air purification device
ActiveUS20200171925A1Sufficient support rigidityHinders thermal conductionAir-treating devicesGas treatmentAir cleaningEnvironmental engineering
An air purification device includes an adsorption block, a housing, an introduction port for indoor air, an introduction port for heated air, a return port for indoor air, and a discharge port for used regeneration air. The adsorption block adsorbs purification target substances in indoor air, and is regenerated by dispersing the adsorbed purification target substances by circulating heated air. The housing accommodates the adsorption block therein. The introduction port for indoor air and the introduction port for heated air are provided on one end side of the housing. The return port for indoor air and the discharge port for used regeneration air are provided on the other end side of the housing. An insulating layer is provided between the housing and an outer surface of the adsorption block.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Dipole antenna
InactiveUS20070052611A1Reduced dimensionMinimize applicationSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsDipole antennaPhysics
A dipole antenna includes a substrate, a first radiating member and a second radiating member. The substrate has a first surface and a second surface opposite to the first surface. The first radiating member and the second radiating member are symmetrically disposed on the first surface and the second surface of the substrate, and electrically connected to a grounding point and a feeding point, respectively. The first radiating member has a first radiating part, a second radiating part and a third radiating part, which are respectively disposed on the first surface and the second surface of the substrate and electrically connected to one another. The second radiating member has a fourth radiating part, a fifth radiating part and a sixth radiating part, which are respectively disposed on the first surface and the second surface of the substrate and are electrically connected to one another.
Owner:ARCADYAN
Method for manufacturing an electronic device
ActiveUS8695207B2Minimize applicationSmall designSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesIntegrated circuitElectronic equipment
In a method for manufacturing an electronic device an integrated circuit (1) is arranged between two layers (2, 3) of a substrate, said integrated circuit (1) having at least one contacting surface, a hole (4) is formed in at least one substrate layer (3) above said at least one contacting surface, a conductive structure (5) is formed on a surface of said at least one substrate layer (3) facing away from the integrated circuit (1) and said conductive structure (5) is connected to said contacting surface by means of said hole (4).
Owner:NXP BV
Driving simulation device for executing a simulating game
InactiveUS20090286602A1Minimize applicationHigh strengthVideo gamesSpecial data processing applicationsCouplingEngineering
A driving simulation device for executing a simulating game includes a mounting frame and a seat body. The seat body has a coupling portion and a seating portion located above the coupling portion. The seat body further includes first and second connecting rods having at least two fixing parts journaled to the mounting frame, two swinging parts journaled to the coupling portion of the seat body and two coupling parts interconnecting the fixing parts and the swinging parts and transversely crossing each other. Once a rider is seated on the seating portion and swings the seat body so as to simulate a driving action, the seating portion and the coupling portion swing respectively in two directions opposite to each other, and thereby a swinging center of the seat body can fall between the coupling portion and the seating portion.
Owner:INTERNATIONAL GAMES SYSTEM
Real-time page and flow compositions
ActiveUS9691050B2Minimize applicationAvoid shutdownMultiprogramming arrangementsOffice automationComputer scienceUser interface
Task flows are utilized for real-time page compositions, real-time flow compositions, or both. At design time, a plurality of task flows are provided as a database or library. A manager, or other type of user, can associate task flows with dynamic regions in an application page being designed. The application page can include one or more dynamic regions that act as a container for task flows. Metadata is generated from the customization of input parameters. At runtime, application pages are generated on-the-fly for display in a user interface. The application pages are composed according to the task flows embedded therein. The application pages are presented to the user according to an application flow. Through a user interface, the user can enter and retrieve information related to governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) activities, or other types of activities.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com