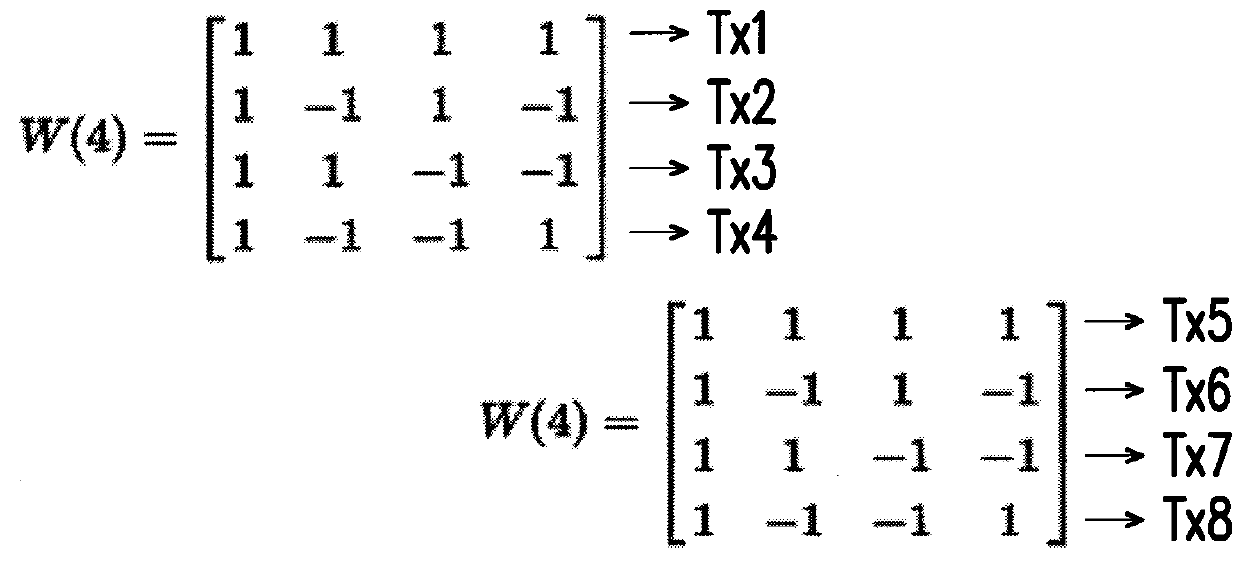Patents
Literature
34results about How to "Noise and interference" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
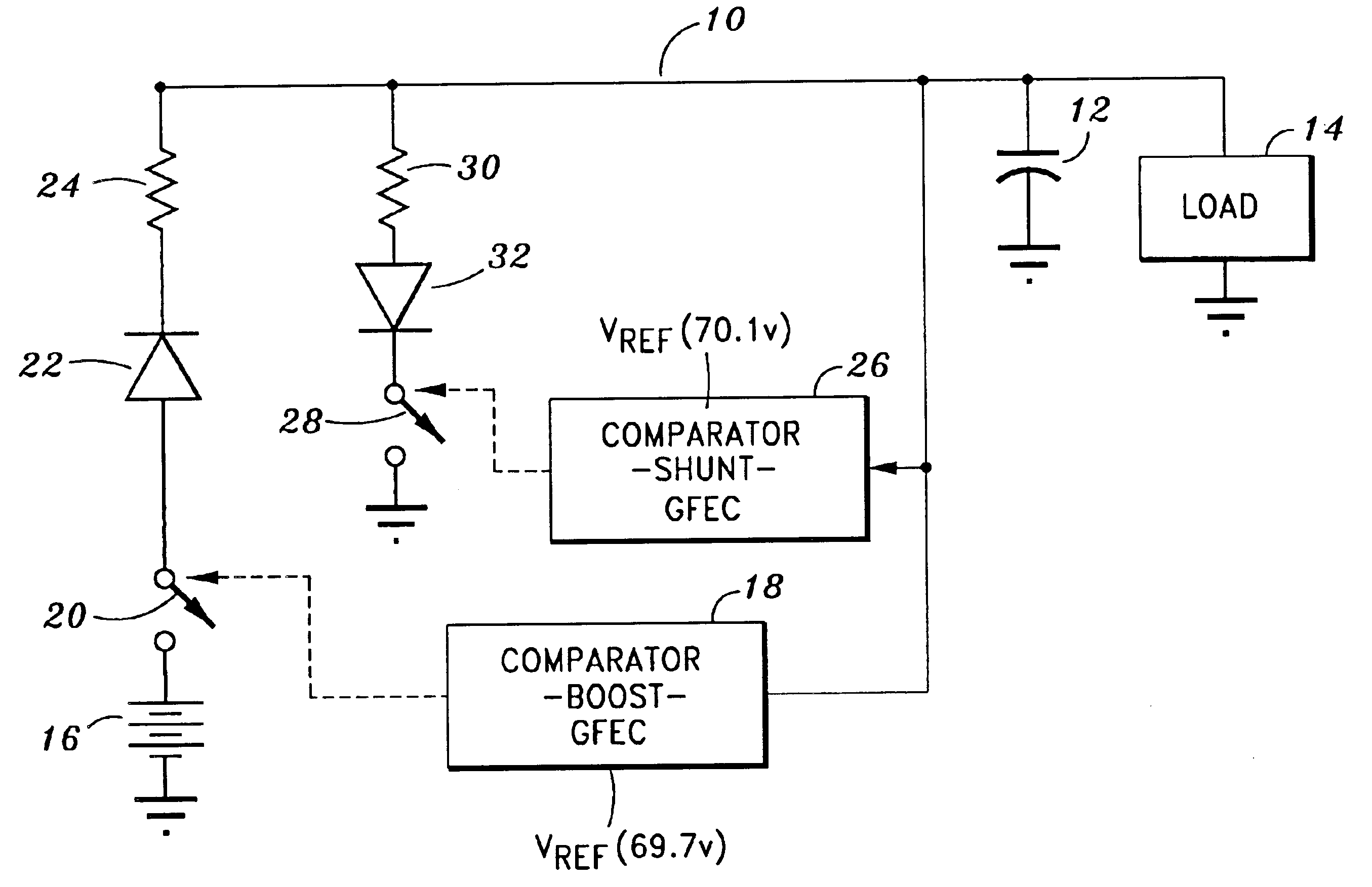
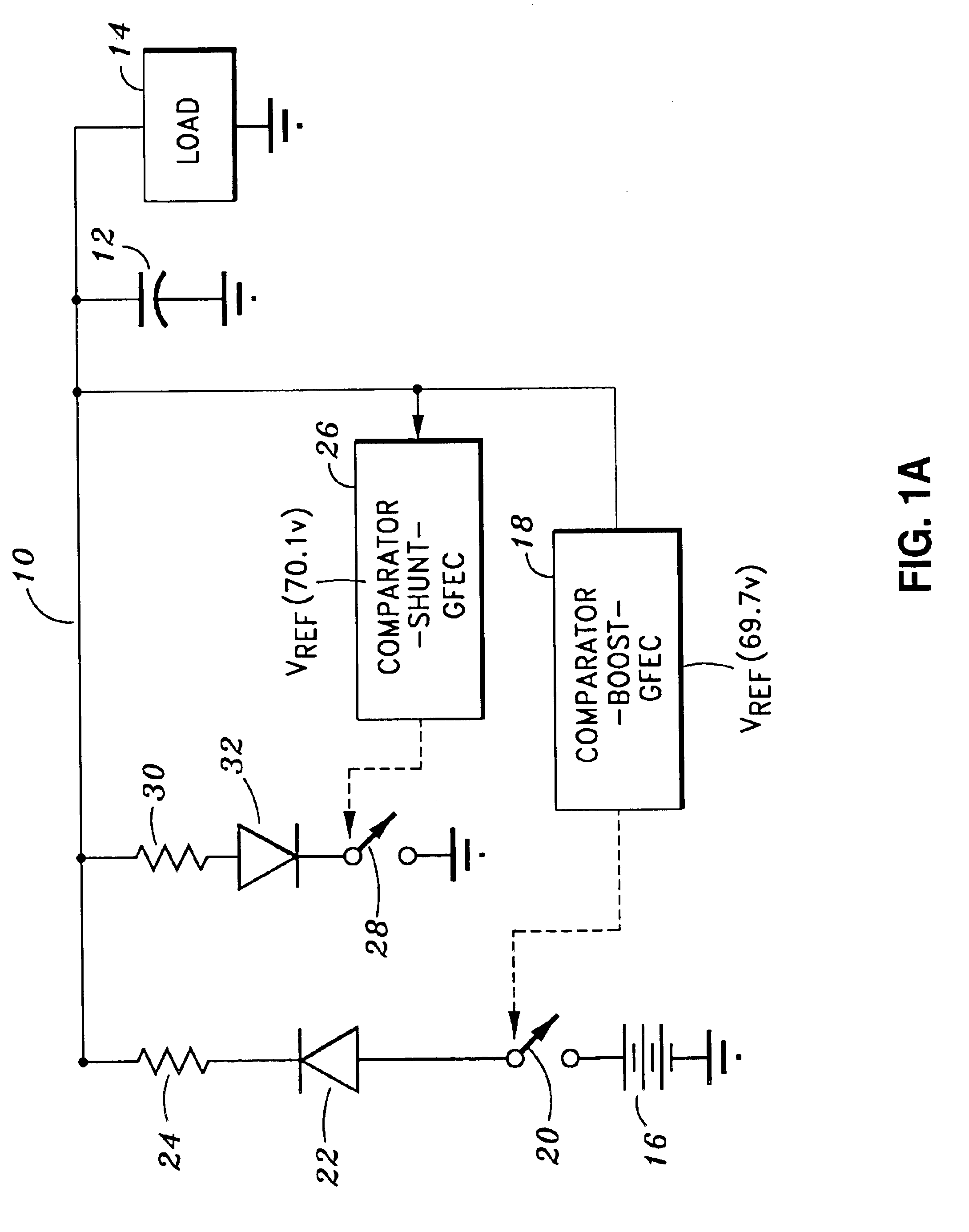
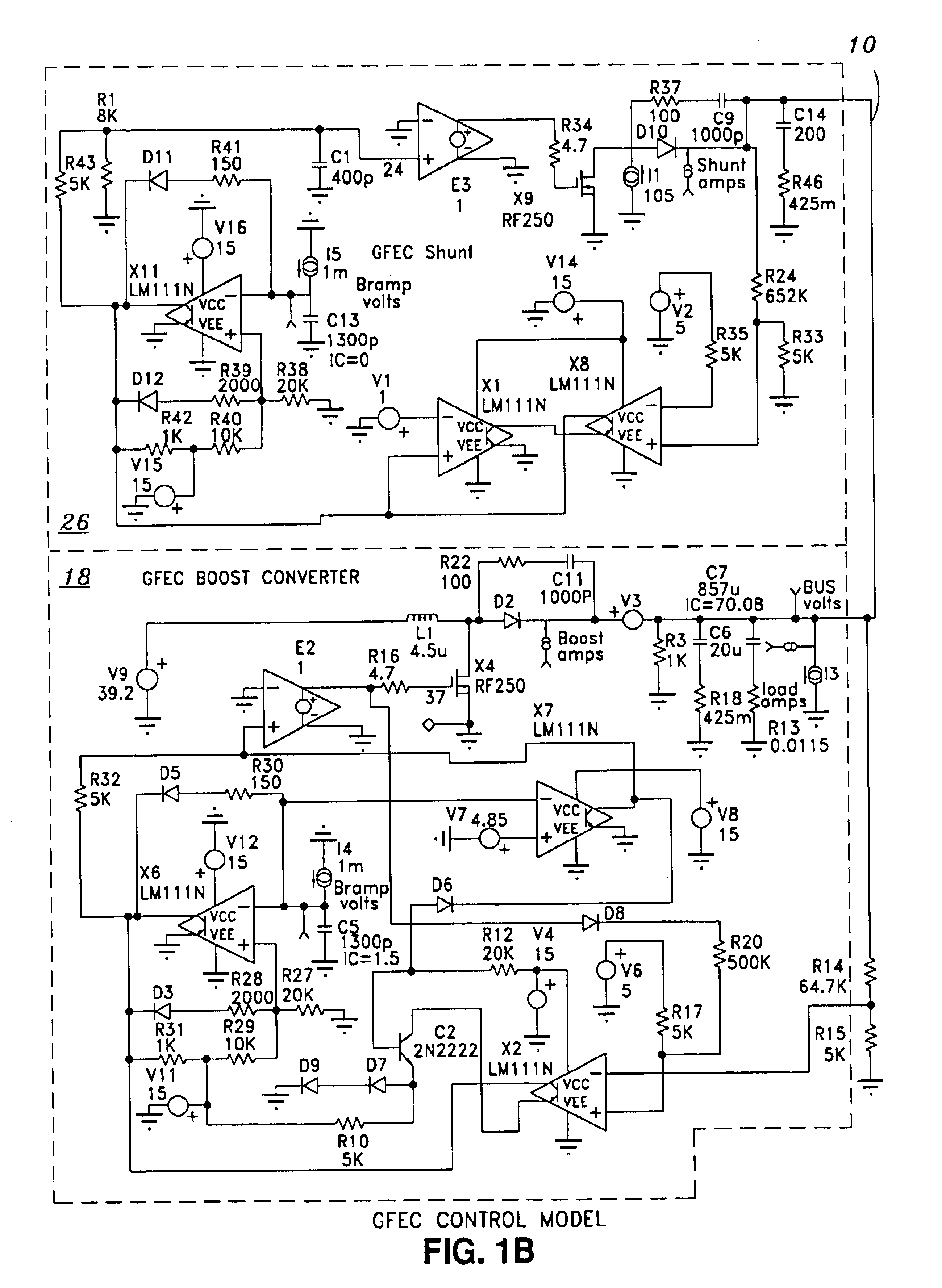
Bus voltage control using gated fixed energy pulses
InactiveUS6888339B1Noise and interferenceEasy to useBatteries circuit arrangementsDc-dc conversionOff timePulse voltage
Voltage on a DC power bus is controlled using gated fixed energy pulses. The power bus includes a bus capacitor for storing charge and can have a varying load. A battery is provided for providing electrical power to the bus through a power boost circuit including a boost switch for selectively applying a pulse of a fixed amount of energy to the bus in response to comparison of the bus voltage and a first reference voltage. The power boost circuit can include a choke coil and a timer for establishing an on time and an off time for each pulse, the on time establishing the amount of energy to be delivered to the bus, and the off time allowing the energy to be delivered to the load. A shunt path including a shunt switch can be provided for shunting energy from the bus when the bus voltage reaches a second reference voltage higher than the first reference voltage. In a preferred embodiment, the shunt path shunts energy to the battery for recharging the battery.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
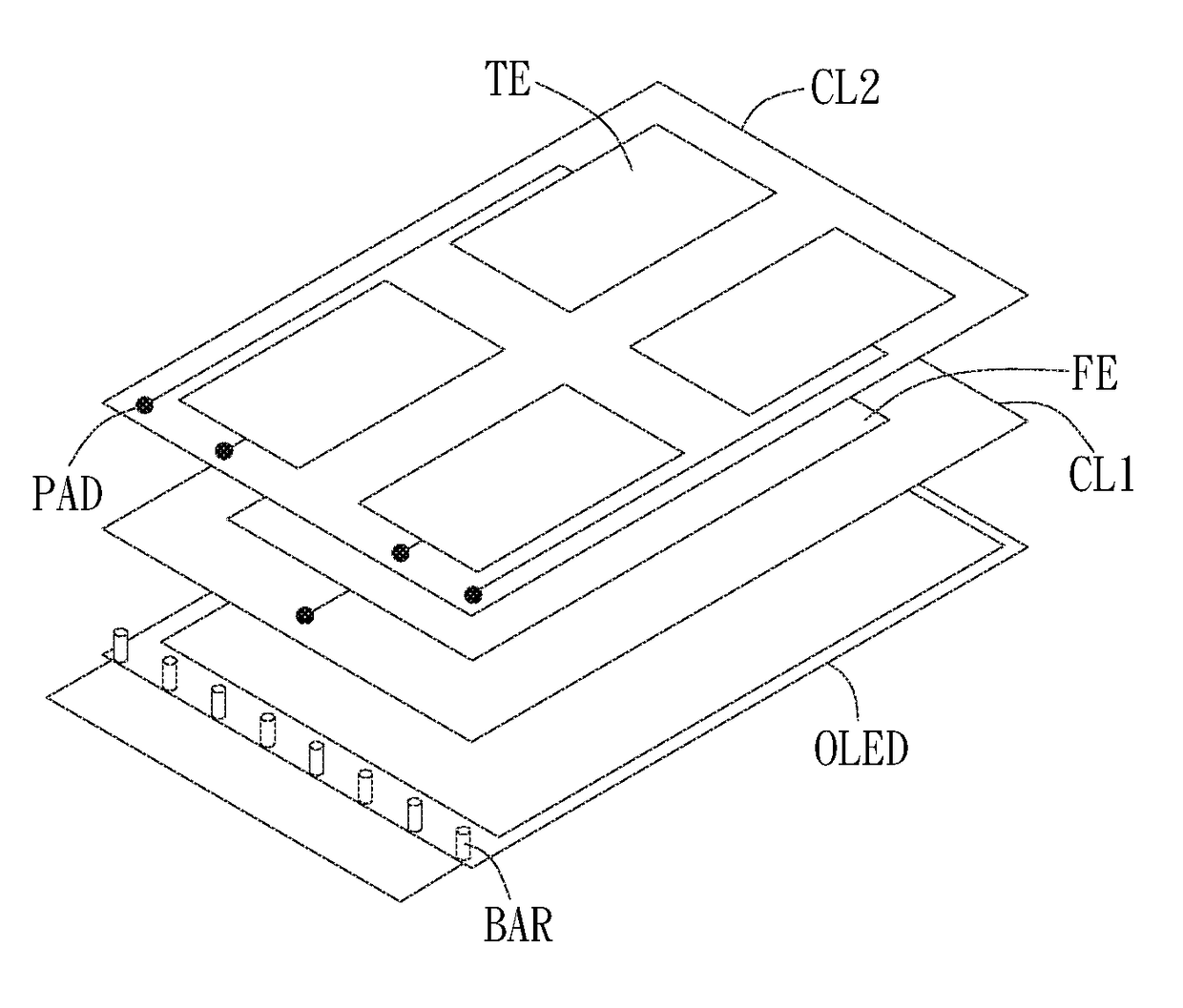
Capacitive force sensing touch panel
InactiveUS20170075493A1Noise and interferenceIncreasing original entire thicknessSolid-state devicesInput/output processes for data processingTouch SensesOptoelectronics
A capacitive force sensing touch panel is disclosed. The capacitive force sensing touch panel includes pixels. A laminated structure of each pixel includes a first substrate, an anode layer, an OLED layer, a cathode layer, a second substrate, a first conductive layer and a second conductive layer. The anode layer is disposed above the first substrate. The OLED layer is disposed above the anode layer. The cathode layer is disposed above the OLED layer. The second substrate is disposed above the cathode layer. The first conductive layer and the second conductive layer are disposed on a first plane and a second plane above the OLED layer respectively and selectively driven to be a touch sensing electrode or force sensing electrode.
Owner:RAYDIUM SEMICON
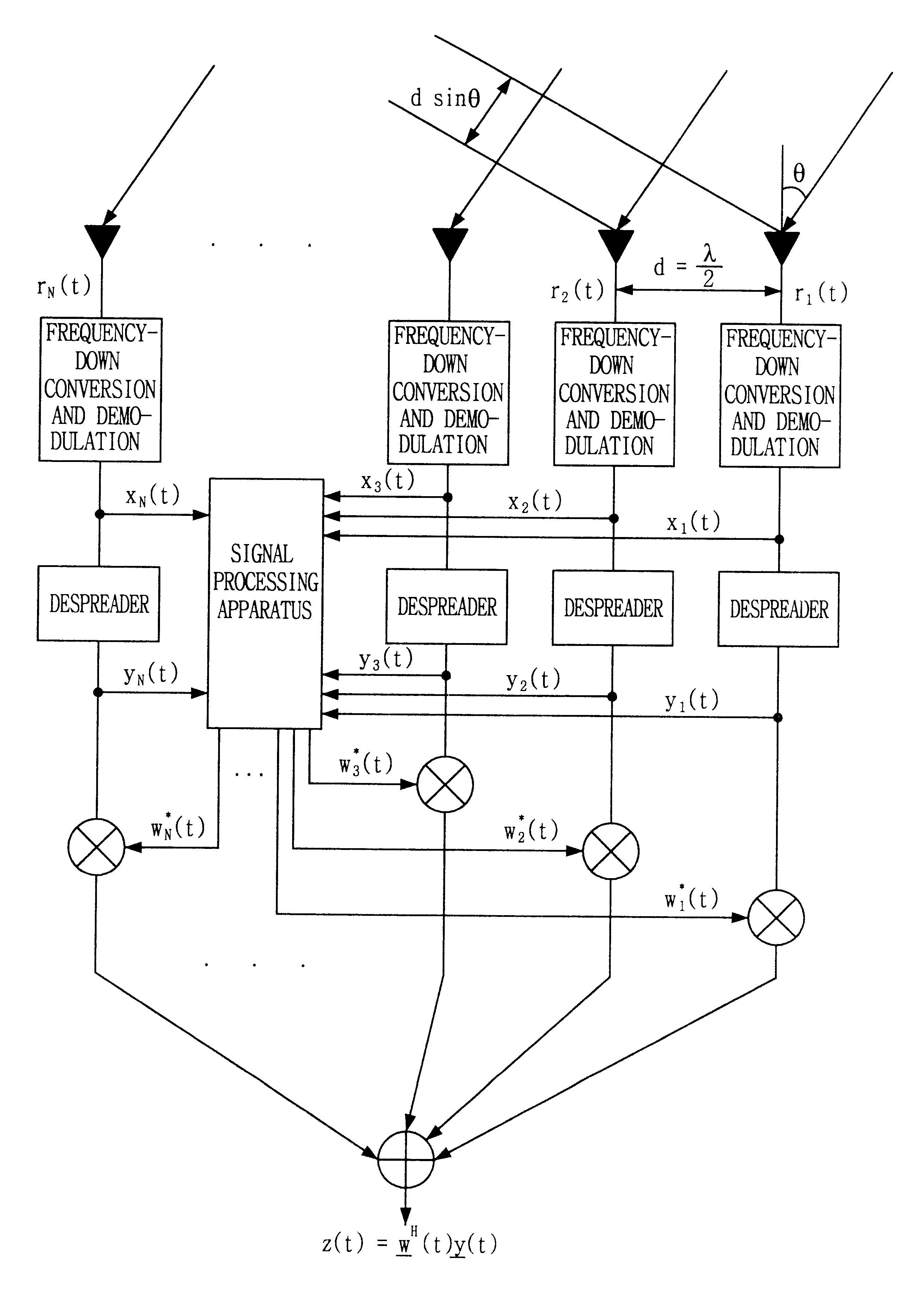
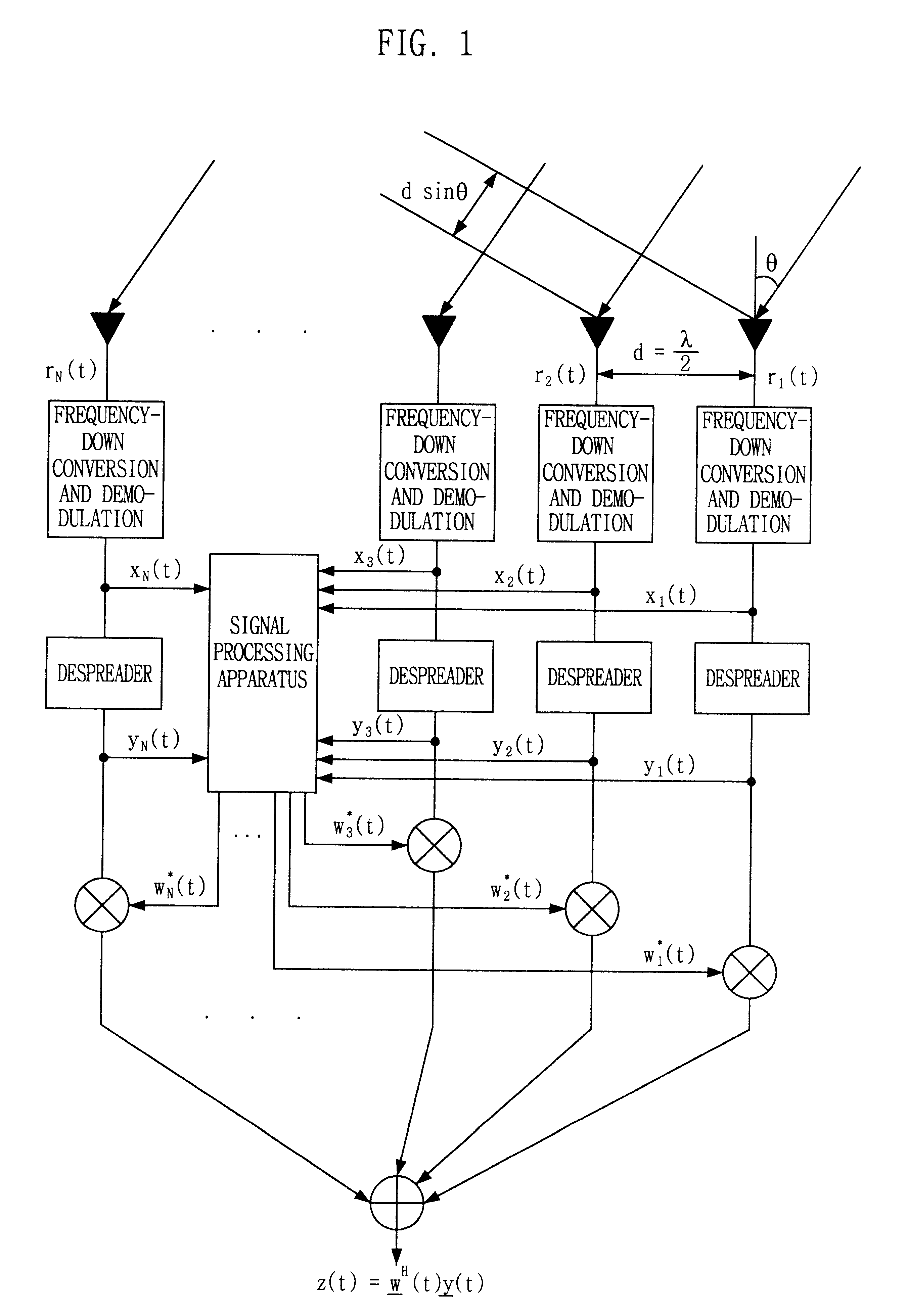
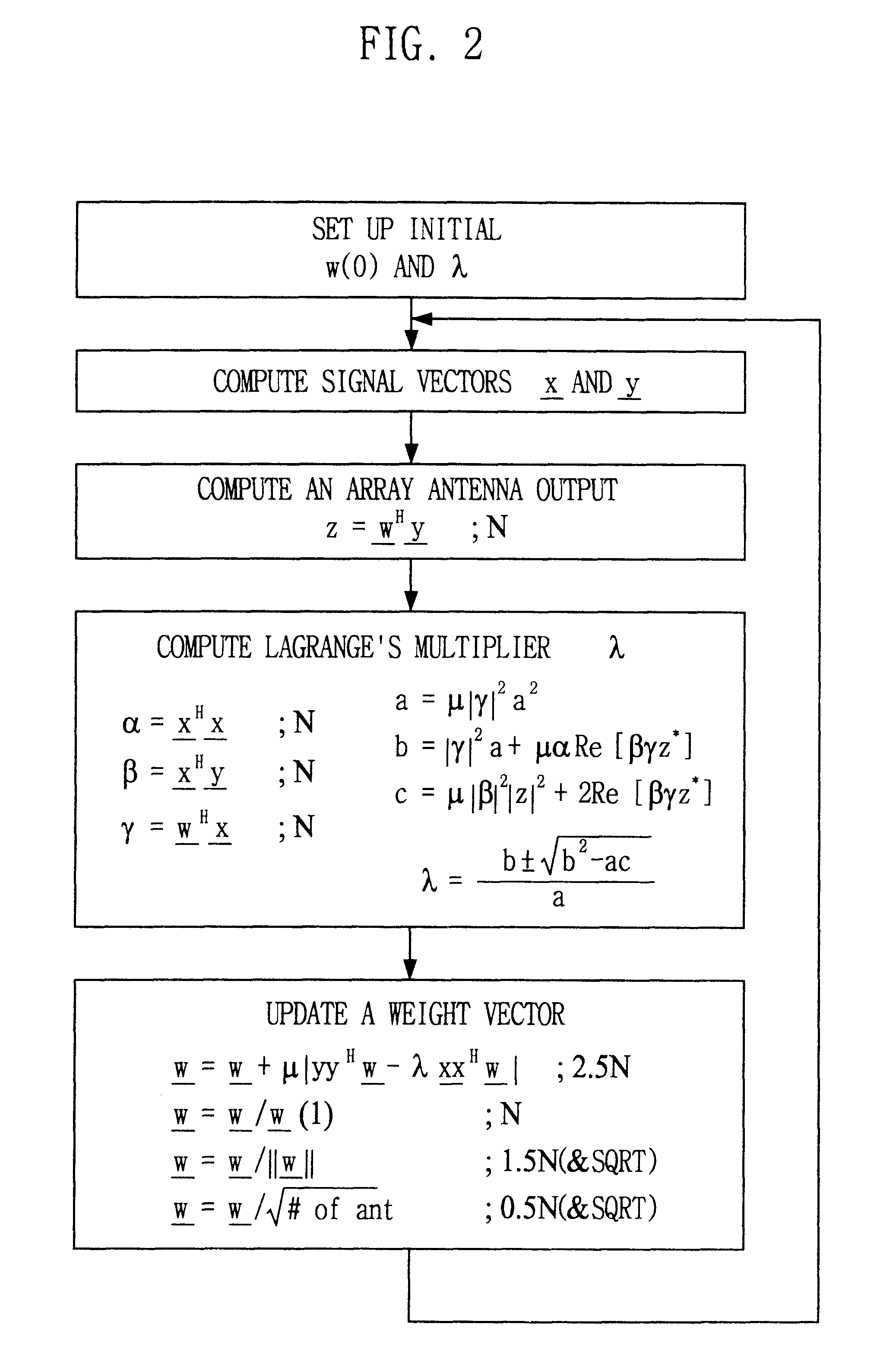
Signal processing method and apparatus for computing an optimal weight vector of an adaptive antenna array system
InactiveUS6462709B1Simple and accurate wayMaximizes the signal to interference plus noise ratioSpatial transmit diversityRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsOff the shelfTarget signal
This invention relates to a signal processing method and apparatus for an adaptive array antenna. The objective is to suggest an adaptive procedure of computing the suboptimal weight vector for an array antenna system that provides a beampattern having its maximum gain along the direction of the mobile target signal source in a blind signal environment, where the transmitted data are not known (or not to be estimated) at the receiver. It is the ultimate goal of this invention to suggest a practical way of enhancing both the communication quality and communication capacity through the optimal weight vector of the array system that maximizes SINR(Signal to Interference+Noise Ratio). In order to achieve this goal, the method of Lagrange multiplier is modified in such a way that the suboptimal weight vector is produced with the computational load of about O(8N), which has been found to be small enough for the real-time processing of signals in most land mobile communications with the digital signal processor (DSP) off the shelf, where N denotes the number of antenna elements of the array.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL DISCOVERY CO LTD
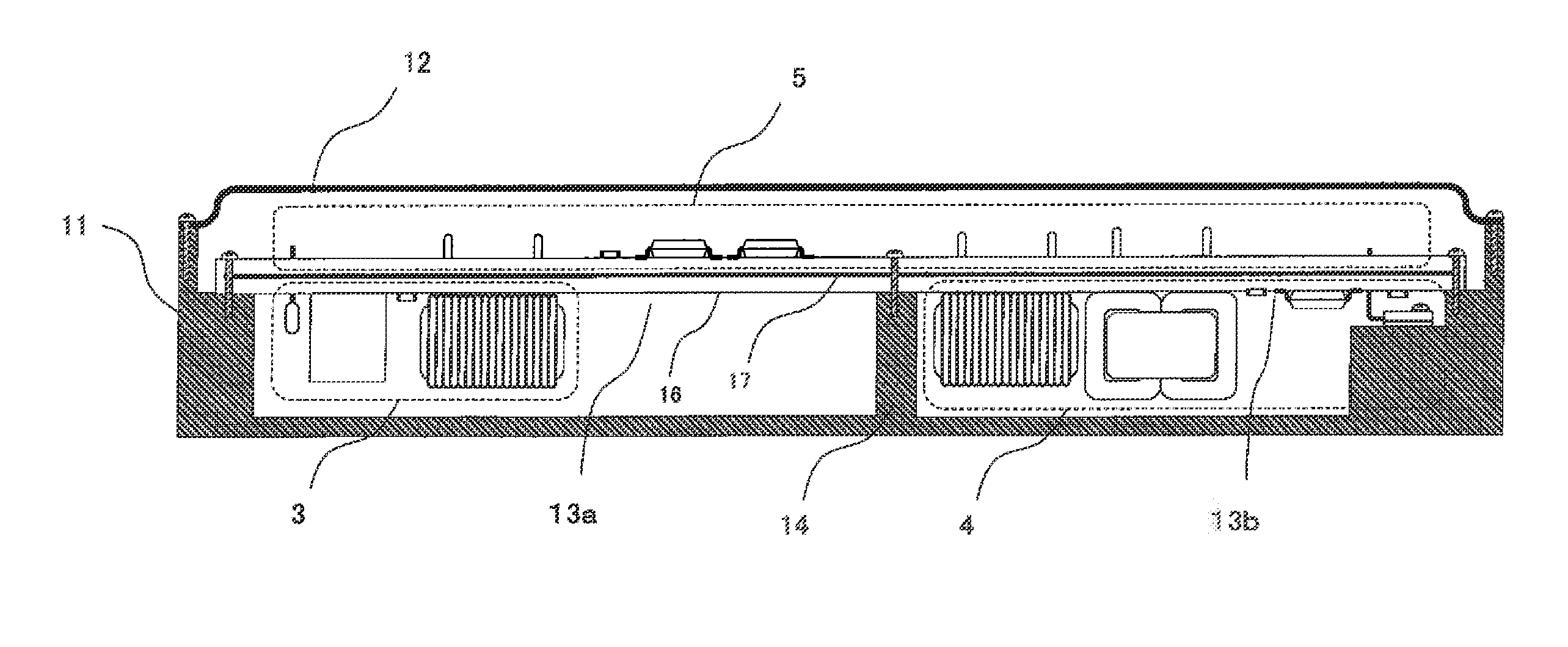
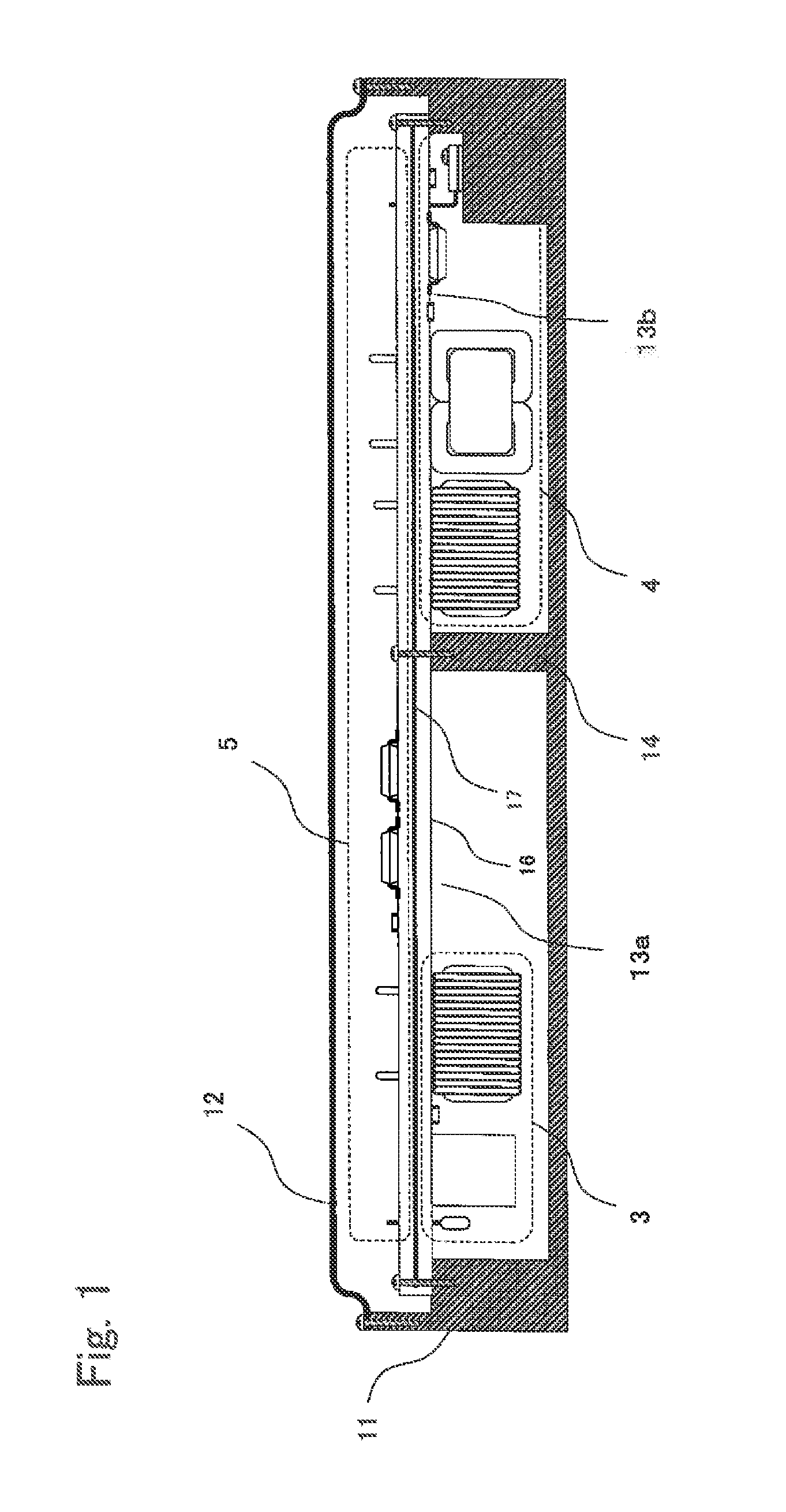
In-vehicle power conversion system
ActiveUS20150048675A1Low costSmall sizeMagnetic/electric field screeningConversion constructional detailsElectricityIn vehicle
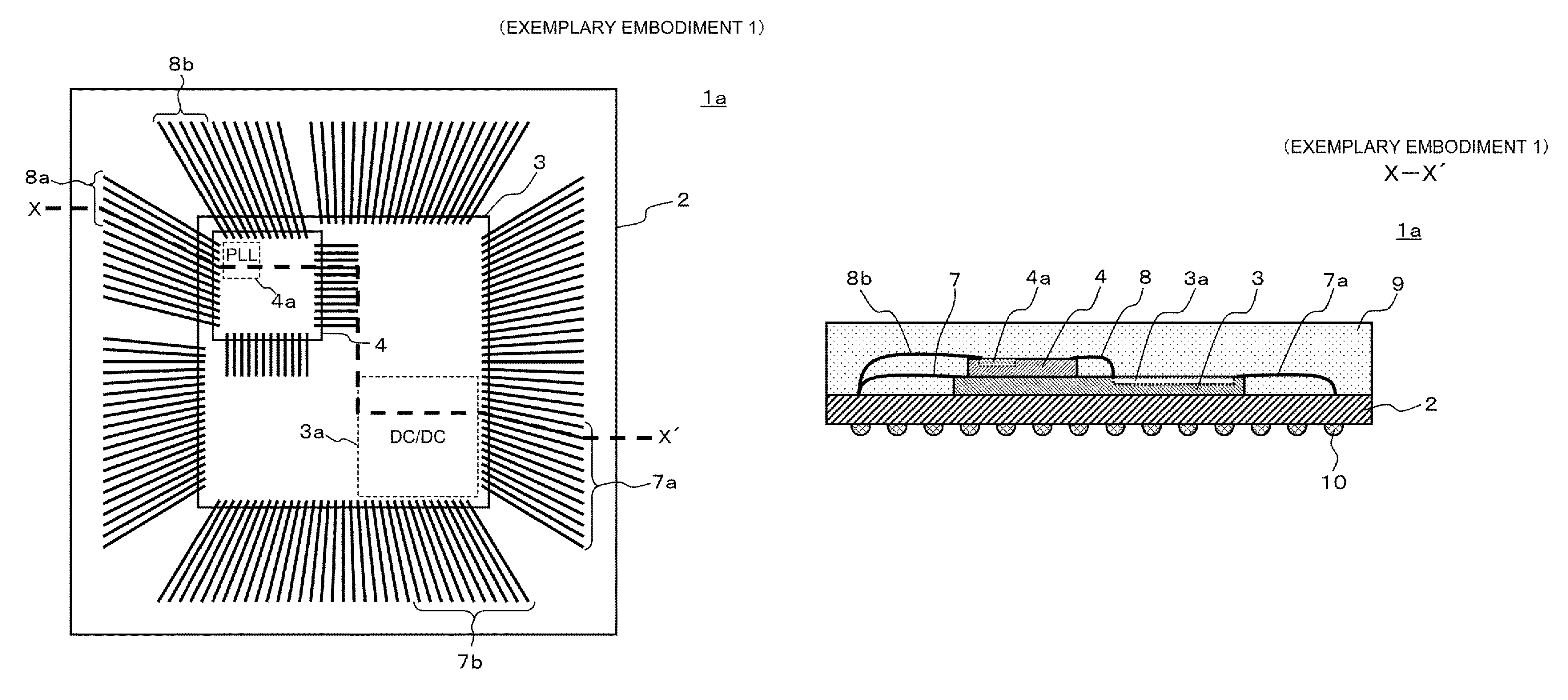
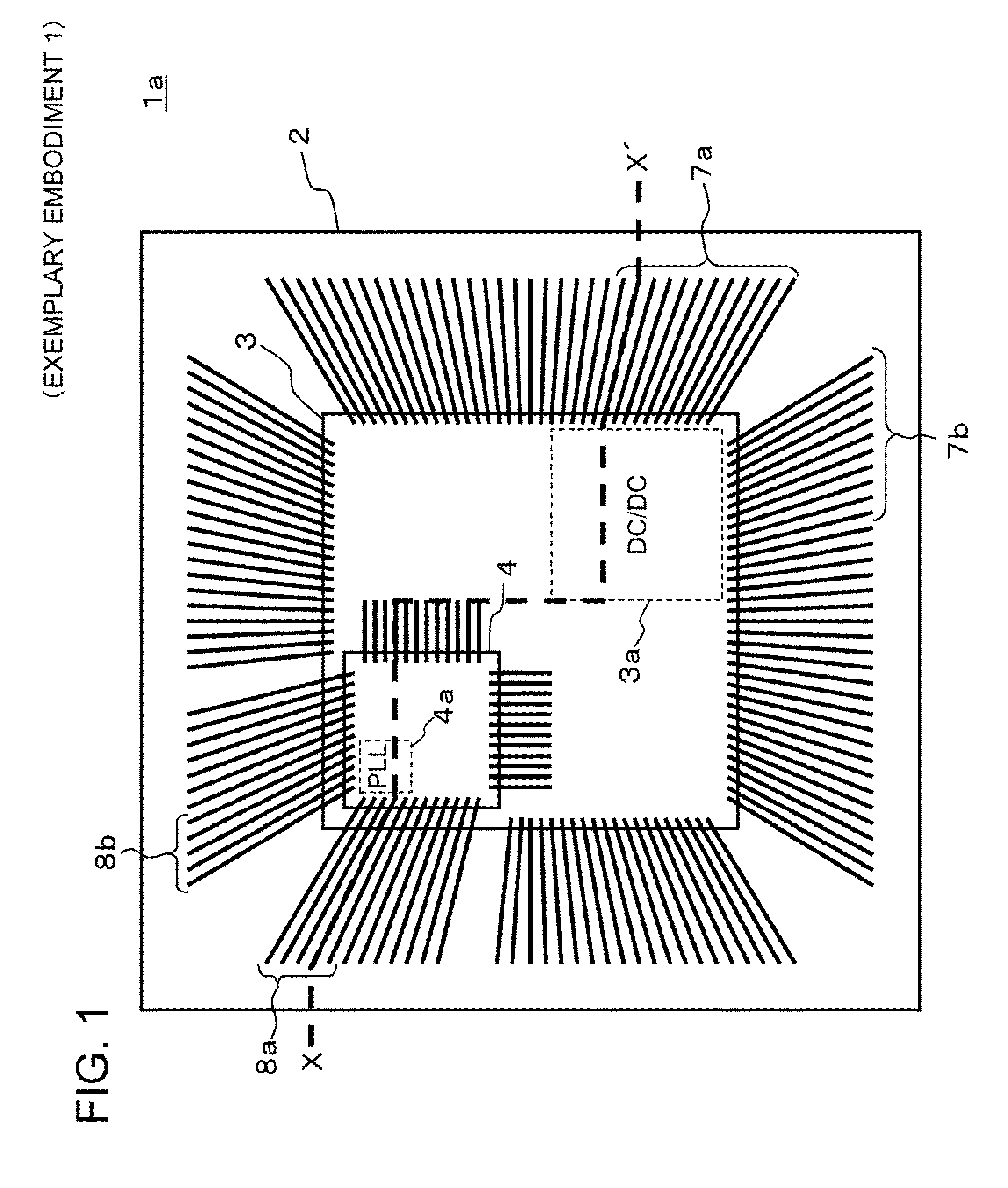
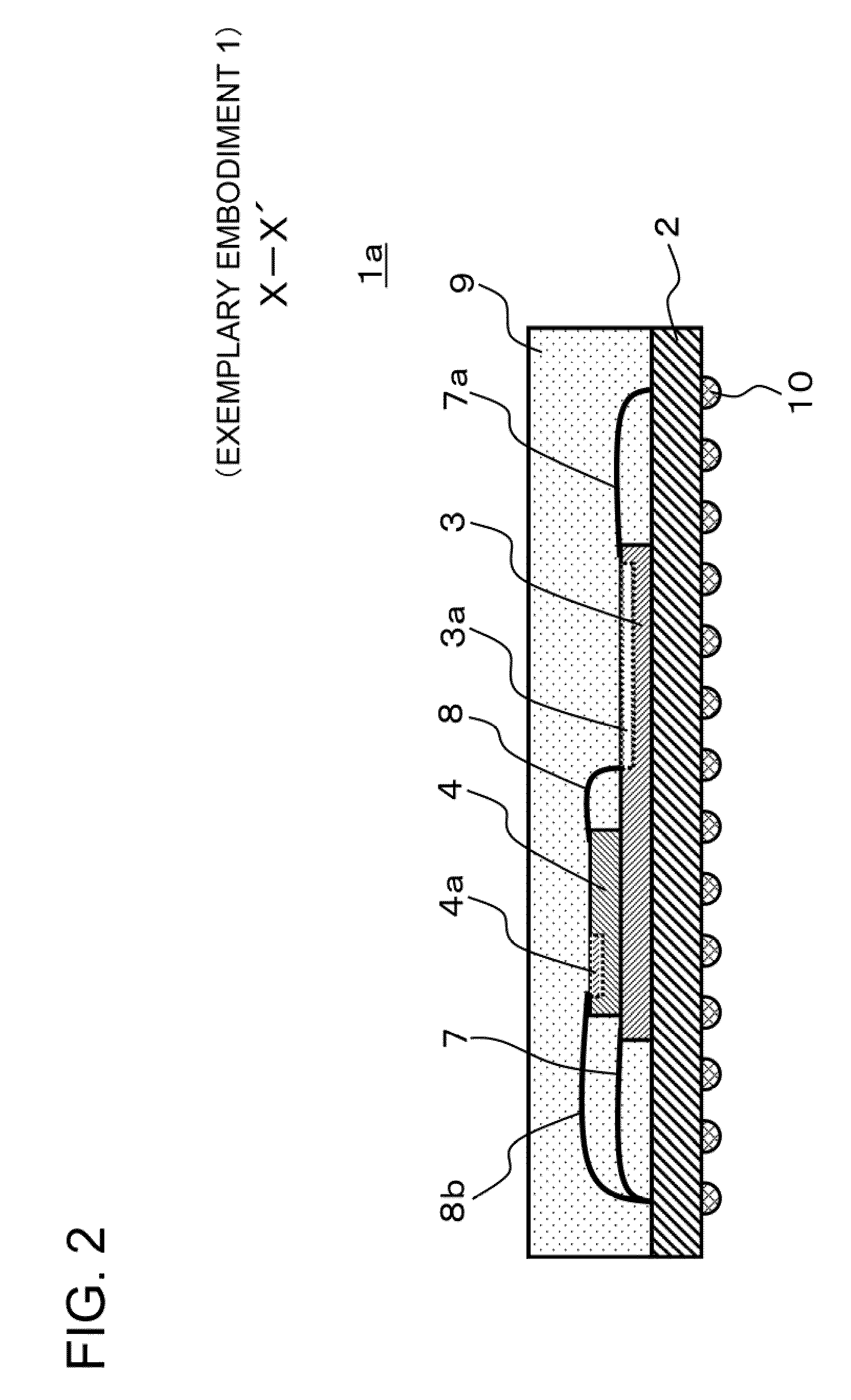
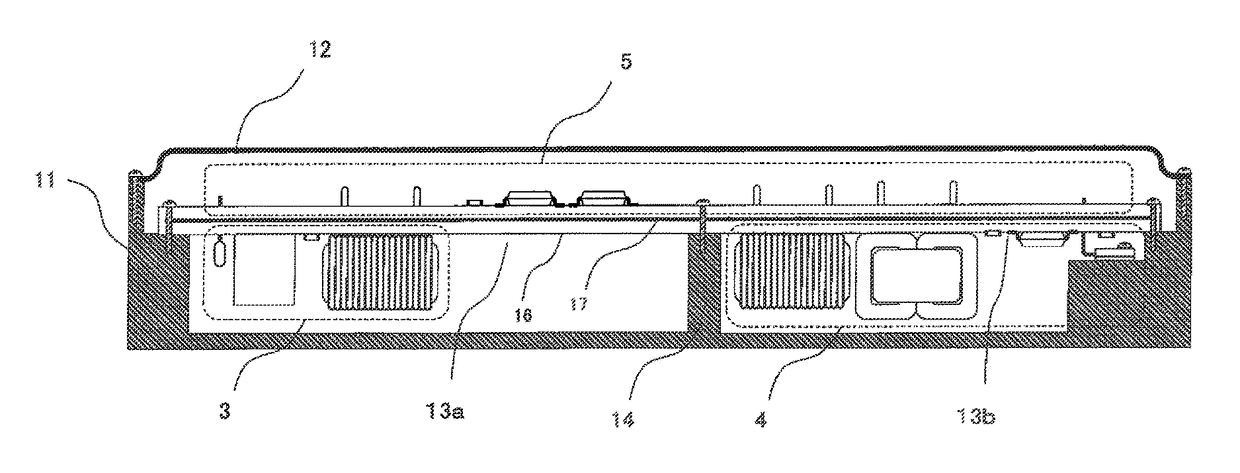
An in-vehicle power conversion system, which can shield a circuit unit without using a particular shield member and can achieve reduction in cost and size, is obtained. Included are: a conductive housing having an opening; and a multilayer printed wiring board in which circuit units are mounted and one layer is a GND plane. The multilayer printed wiring board is assembled to an opening surface of an opening of the conductive housing to form a closed space; and the GND plane of the multilayer printed wiring board is electrically connected to the conductive housing to shield the circuit units stored in the closed space surrounded by the conductive housing and the multilayer printed wiring board.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
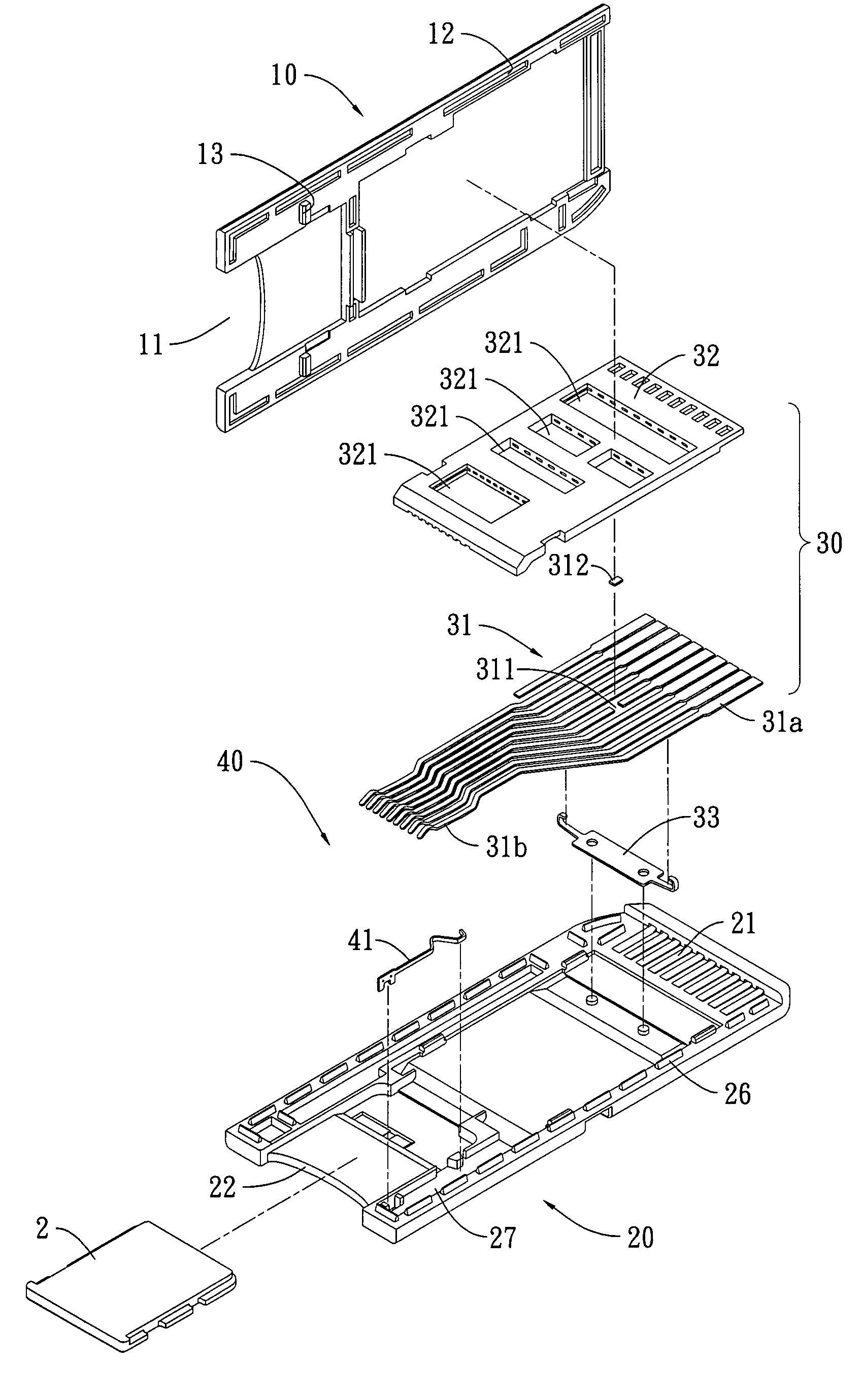
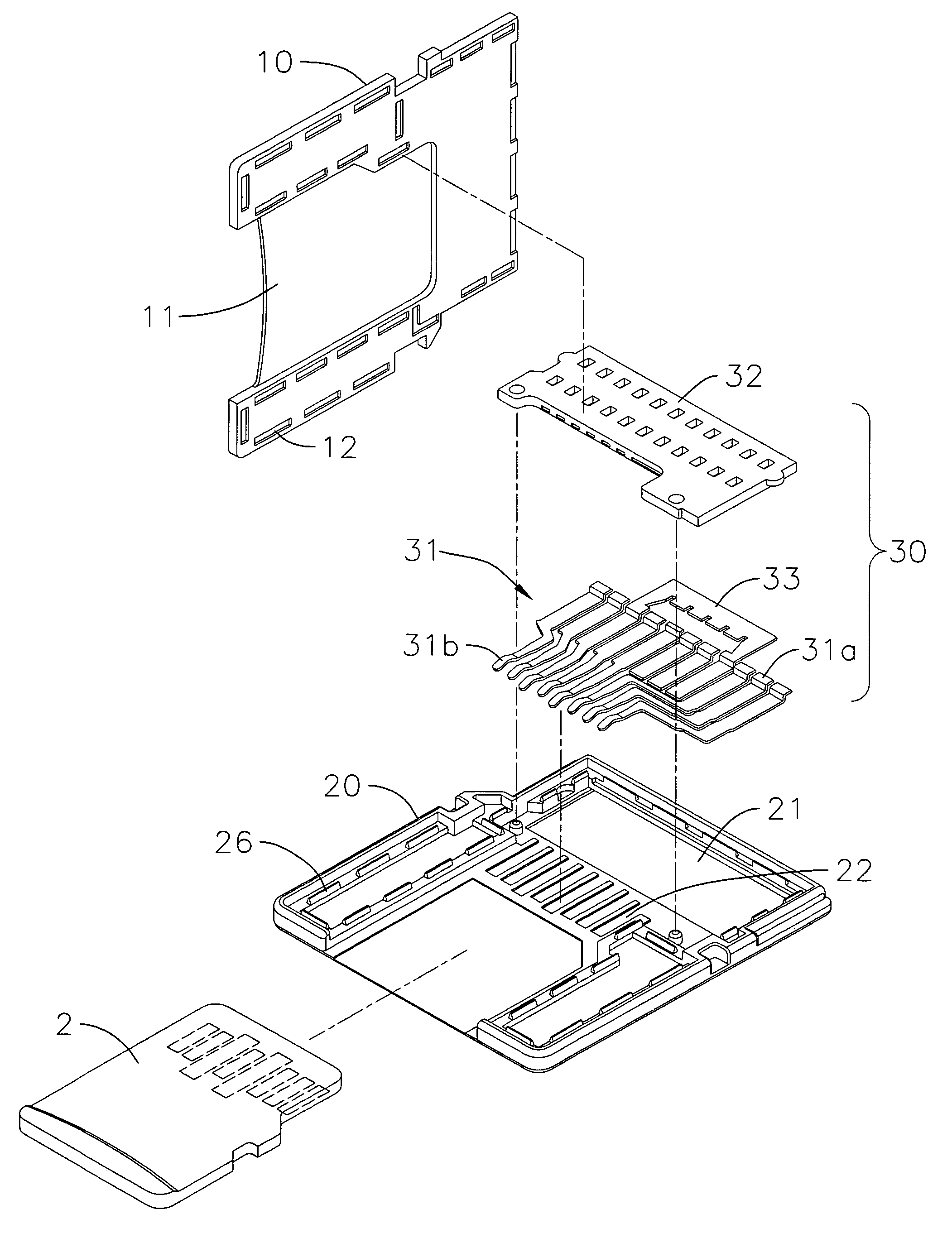
Card adapter structure
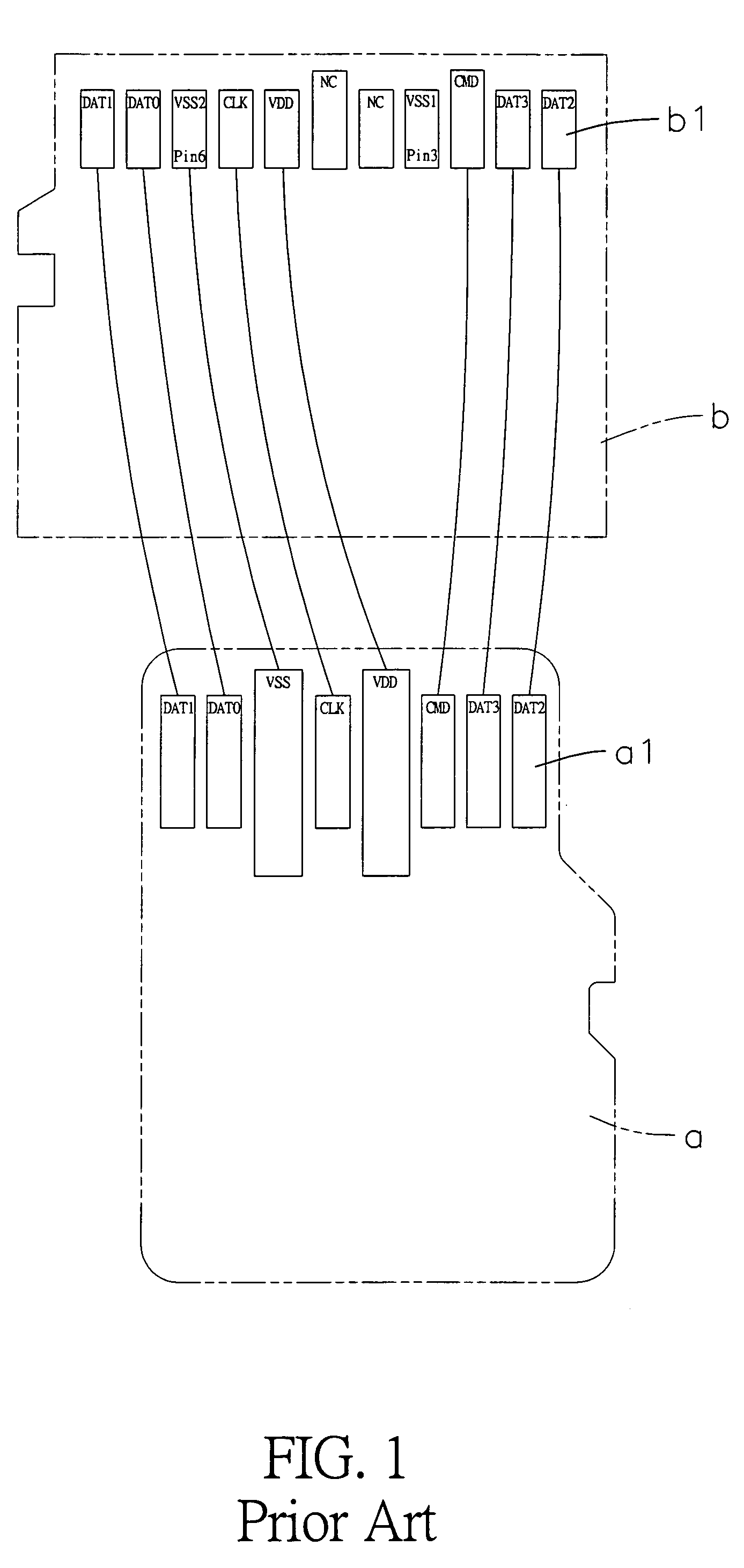
InactiveUS7326086B1Increasing practicability and convenienceSimple structureTwo-part coupling devicesRecord carriers used with machinesElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
The present invention provides an improved card adapter structure that includes an upper cover, a lower cover, a converter terminal set and a positioning elastic strip set. The upper cover has a structure designed to conform to short memory card (MS) specifications, wherein an insertion slot is defined at the rear of the upper cover corresponding to the shape of a micro memory card (M2). The lower cover has a fixing portions and a positioning structure corresponding to those of the upper cover. Moreover, at least one terminal of the No. four, six, seven and eight terminals of the converter terminal set is configured with a gap that is joined to an electric resistance. The positioning elastic strip set is correspondingly located between both covers. Accordingly, the present invention is able to convert a micro memory card into a short memory card of relatively larger size.
Owner:LEE YUN HSIU
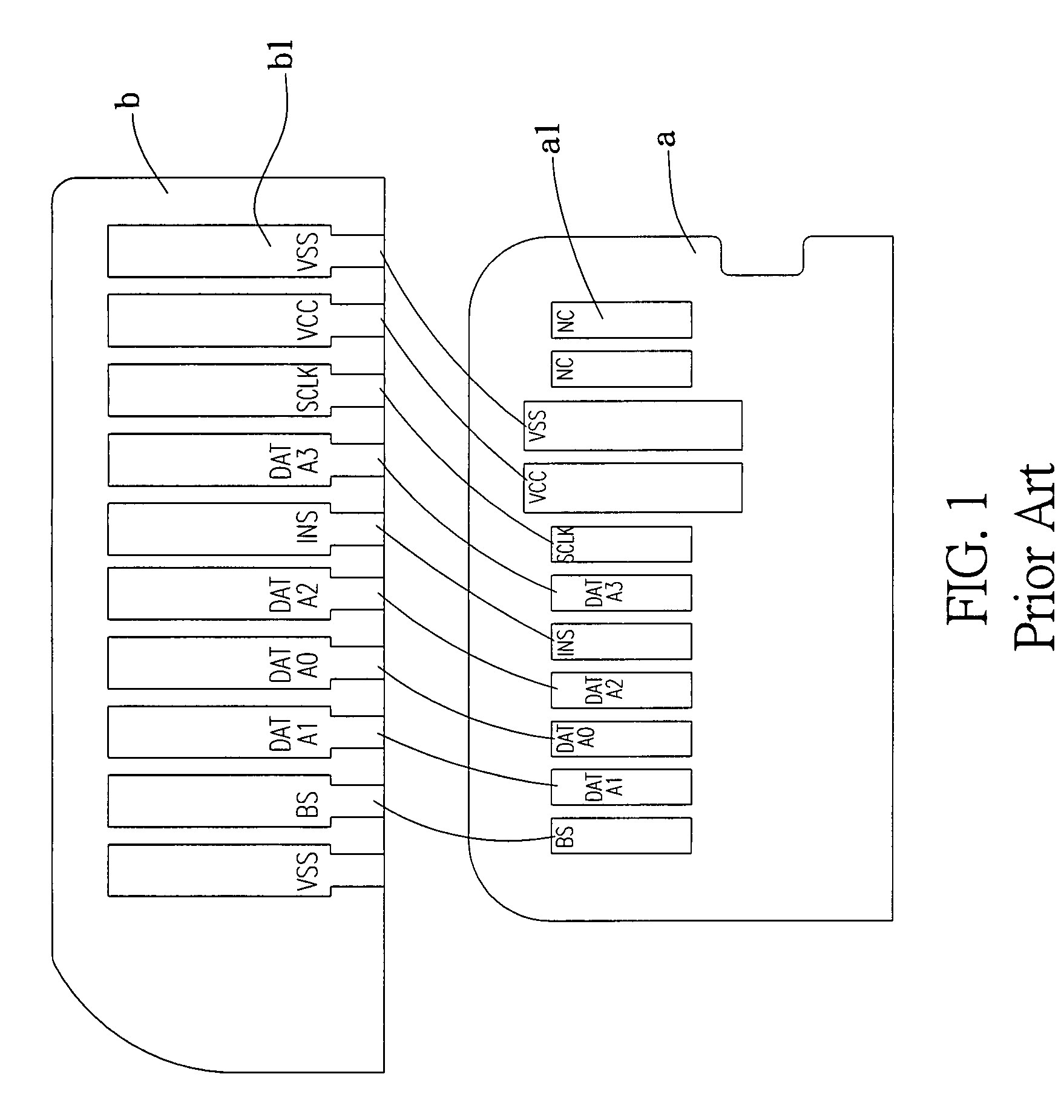
Card adapter structure
InactiveUS7371119B1Large and stable grounding areaAvoid signalingTwo-part coupling devicesSensing record carriersEngineeringMemory cards
The present invention provides an improved card adapter structure which includes an upper cover, a lower cover and a converter terminal set. The upper cover is designed to conform to short memory card specifications, wherein an insertion slot is defined at the rear of the upper cover corresponding to the shape of a micro memory card. A port is configured in a central portion of the lower cover to accommodate a micro memory card. The converter terminal set is configured with eleven terminals, wherein an injection molded fixing mount fixedly covers each pin of the converter terminal set, and eleven pins extend outward towards a short memory card opening. Pin three and pin six are jointly configured with a large grounding area, and eight pins extend outward towards the micro memory card port. Accordingly, the adapter structure conveniently converts a micro memory card into a short memory card.
Owner:LEE YUN HSIU
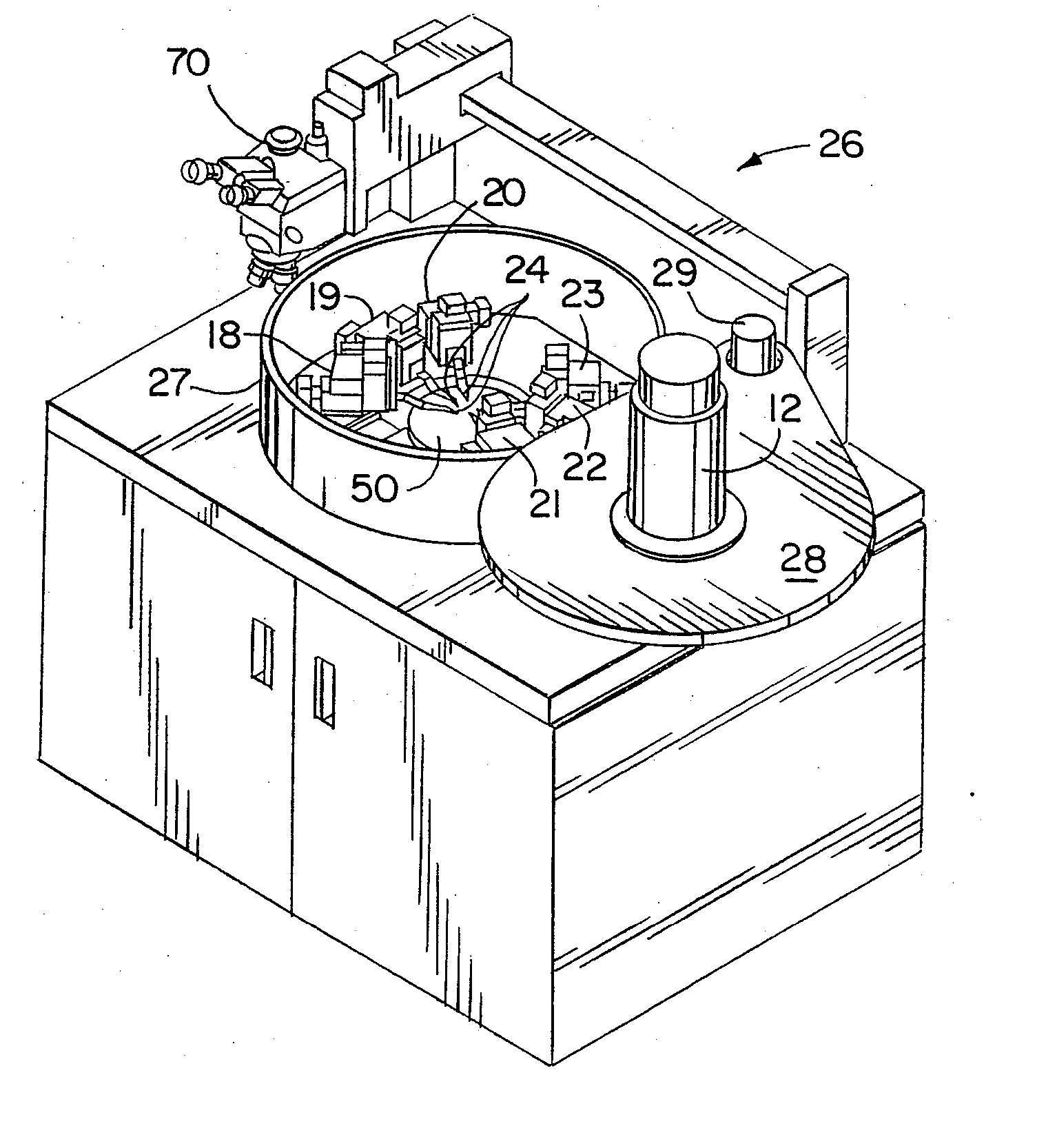
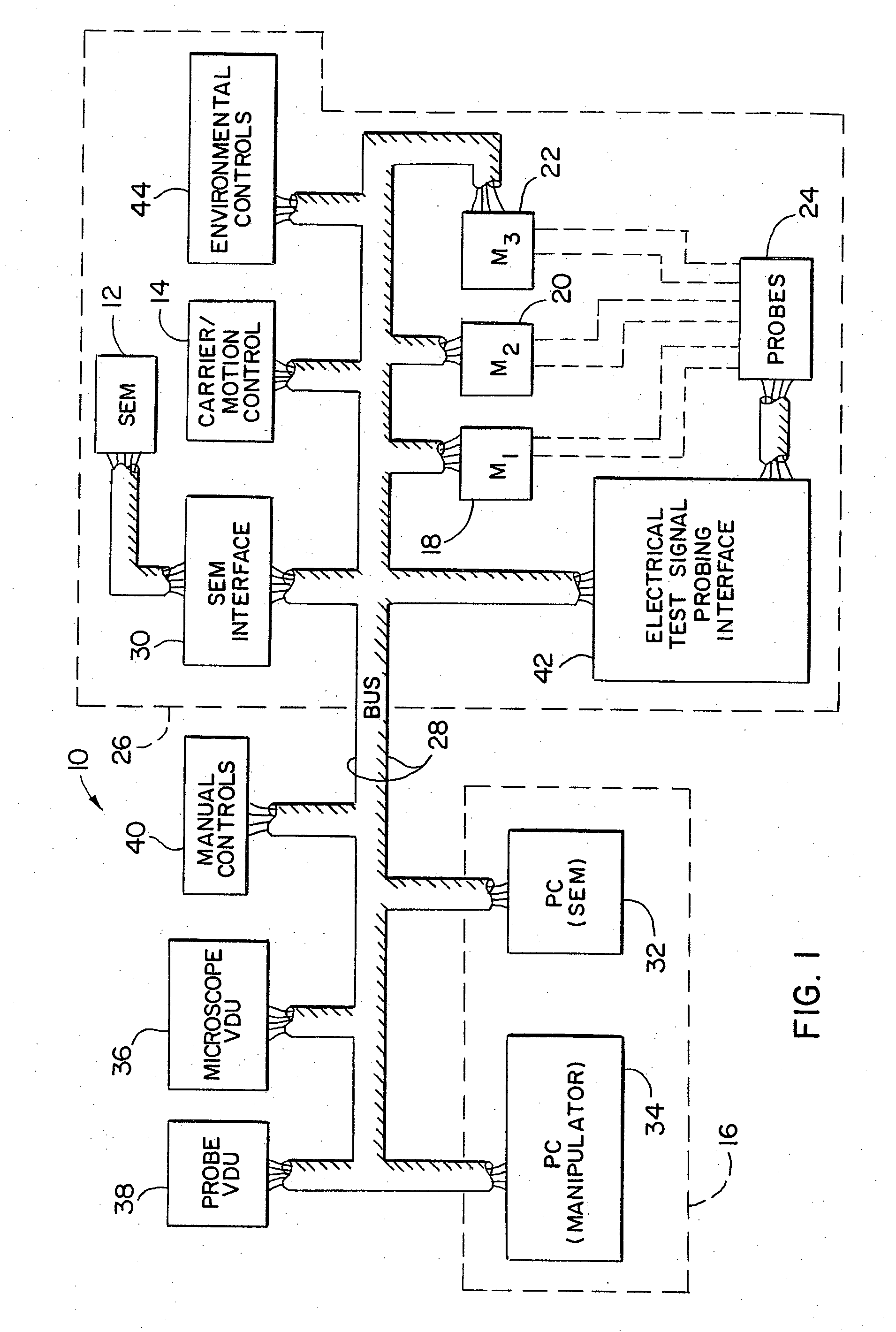
High Resolution Analytical Probe Station
InactiveUS20070290703A1Precise positioningReduce riskSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectric discharge tubesElectricitySignal on
A method and system for probing with electrical test signals on an integrated circuit specimen using a high resolution microscope positioned for observing a surface of the specimen exposing electrically conductive terminals thereon. A housing is provided with a carrier therein for supporting the specimen in relation to the microscope and a probe assembly is positionable on the surface of the specimen for conveying and acquiring electrical test signals to and from the specimen. A drive system is provided for shifting at least one of the probe and the carrier to a predetermined test position. In one form the system has a heat shield for protecting one of the probe assembly and the carrier from heat energy generated upon operation of the drive system, and in another form, the system has an environmental control for maintaining a desired temperature within the housing so that accurate measurements may be taken from the specimen.
Owner:MICROMANIPULATOR
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20090315167A1Easy to generate noiseImprove noiseSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor chipEngineering
A semiconductor device in which a plurality of semiconductor chips is stacked. A first semiconductor chip is stacked in a region, on a second semiconductor chip, in which a circuit that generates noise is not disposed within said second semiconductor chip, and a wire of a circuit that easily receives noise within said first semiconductor chip is disposed so as not to extend over said circuit that generates noise.
Owner:GK BRIDGE 1
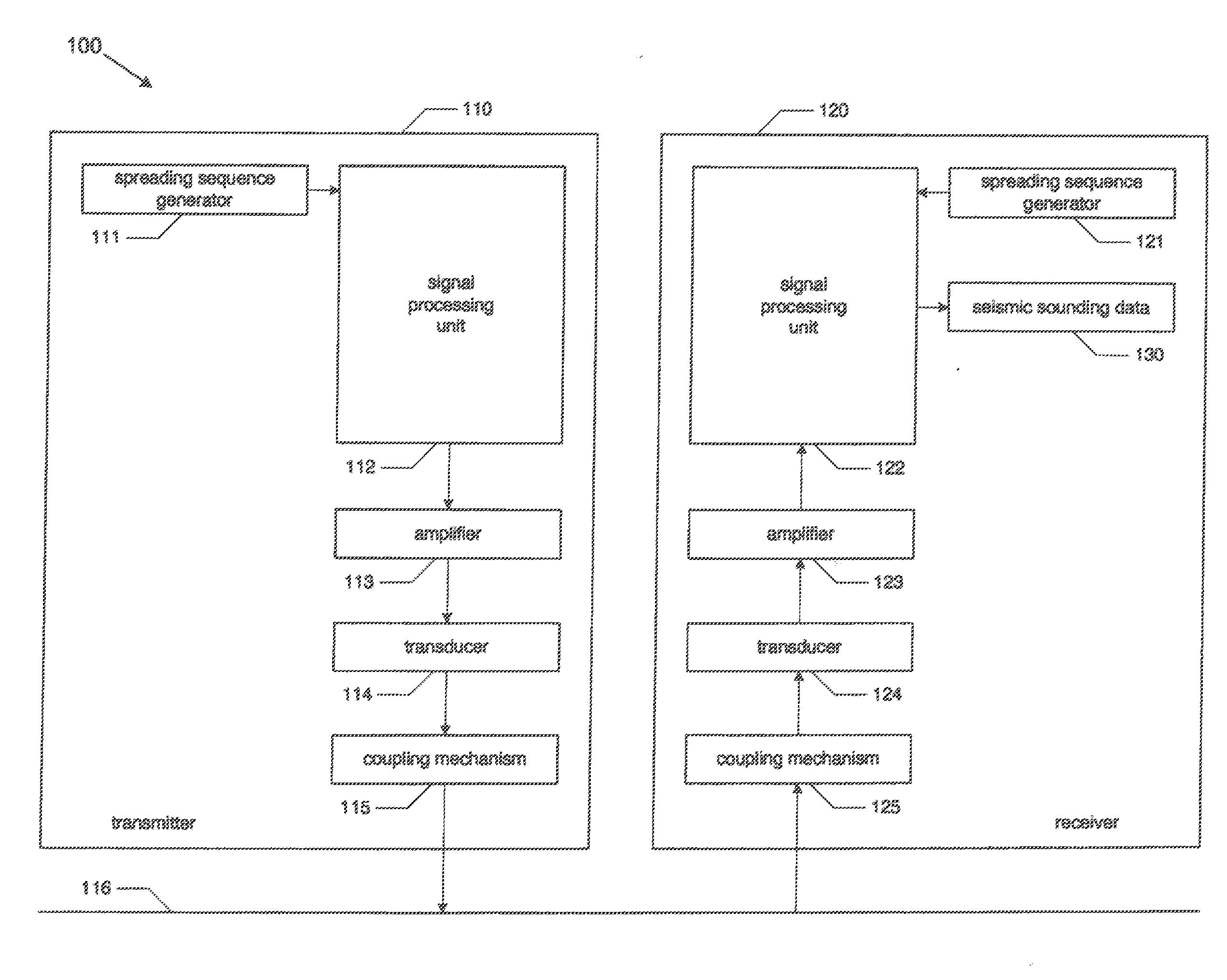
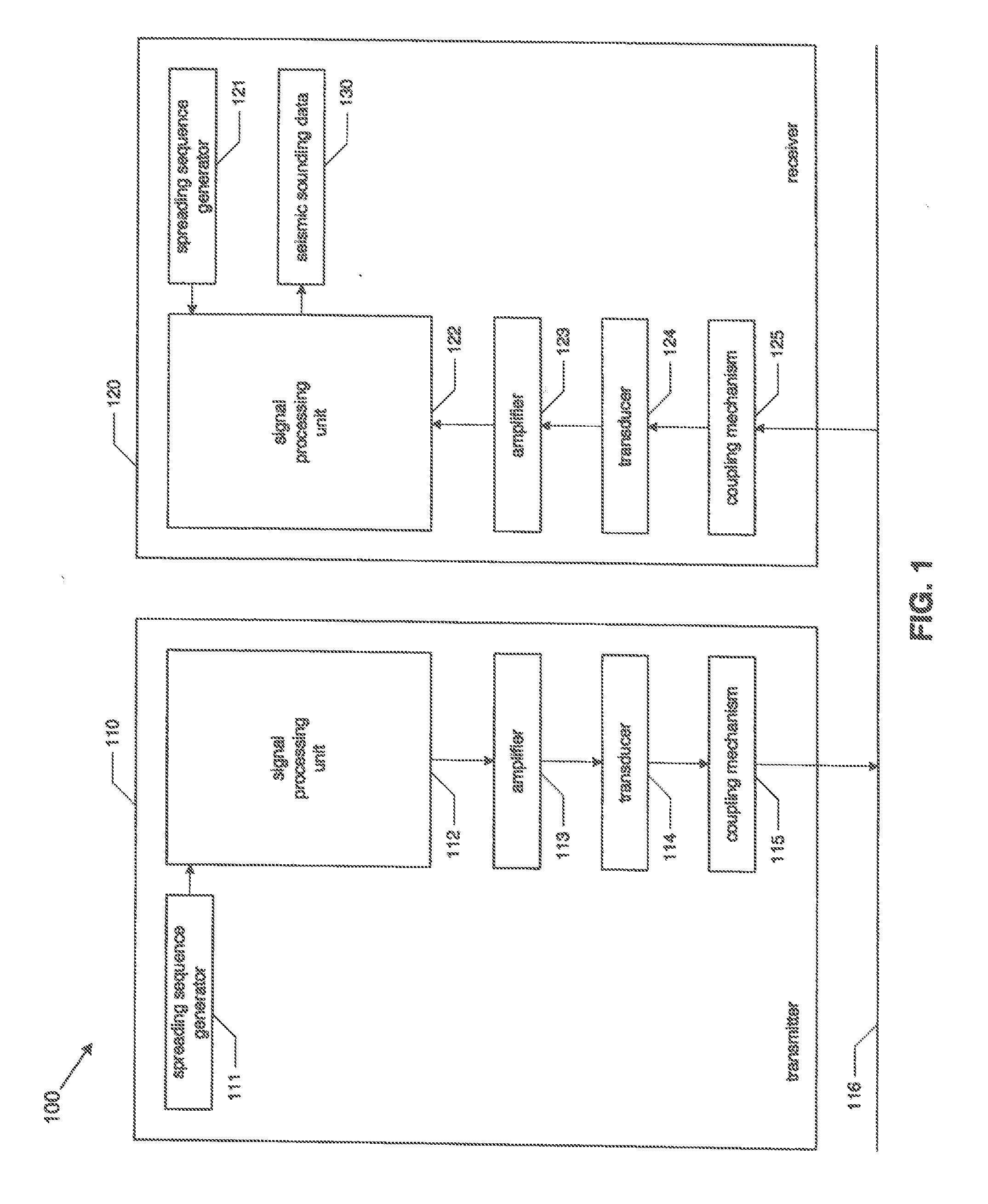
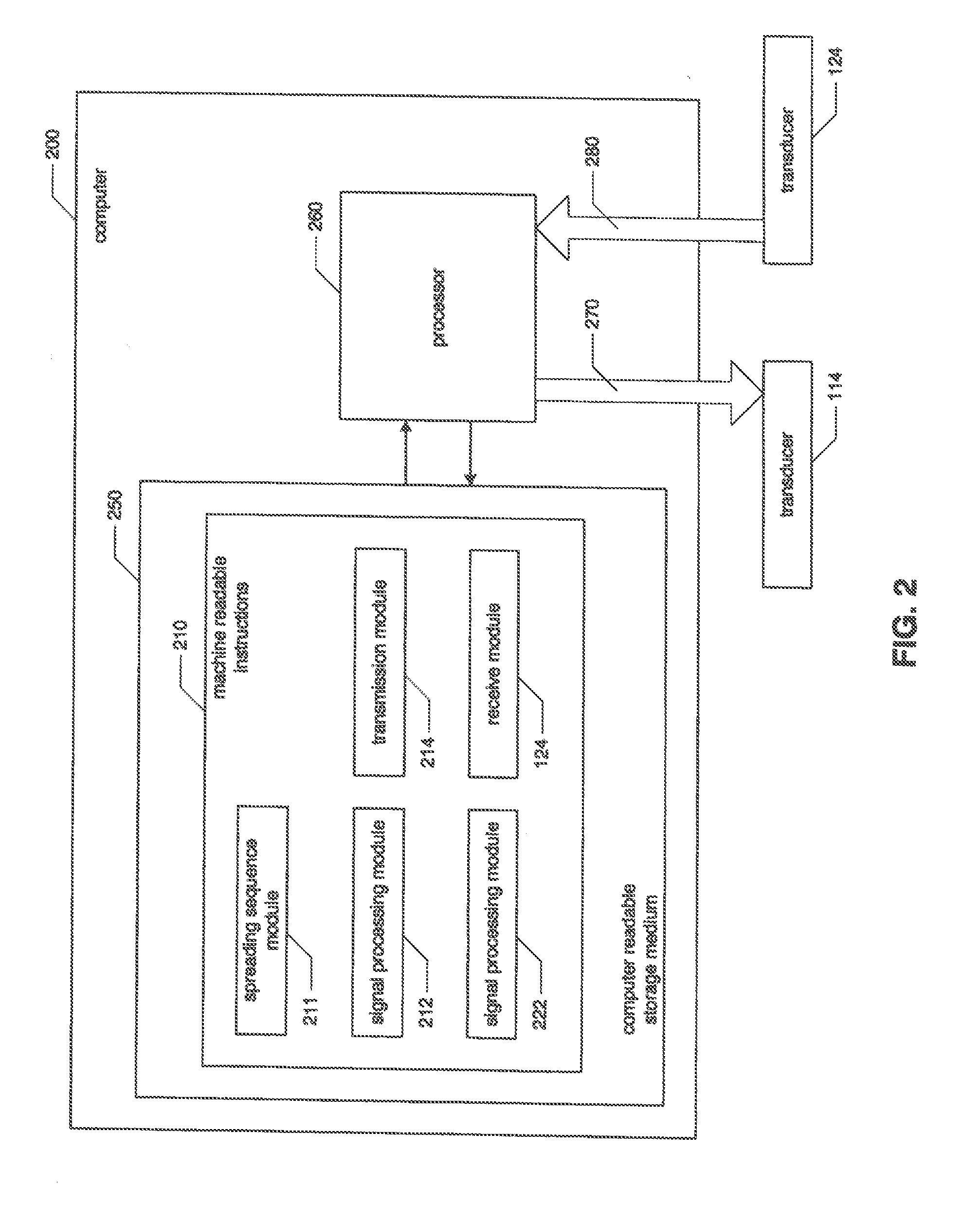
System and method for seismological sounding
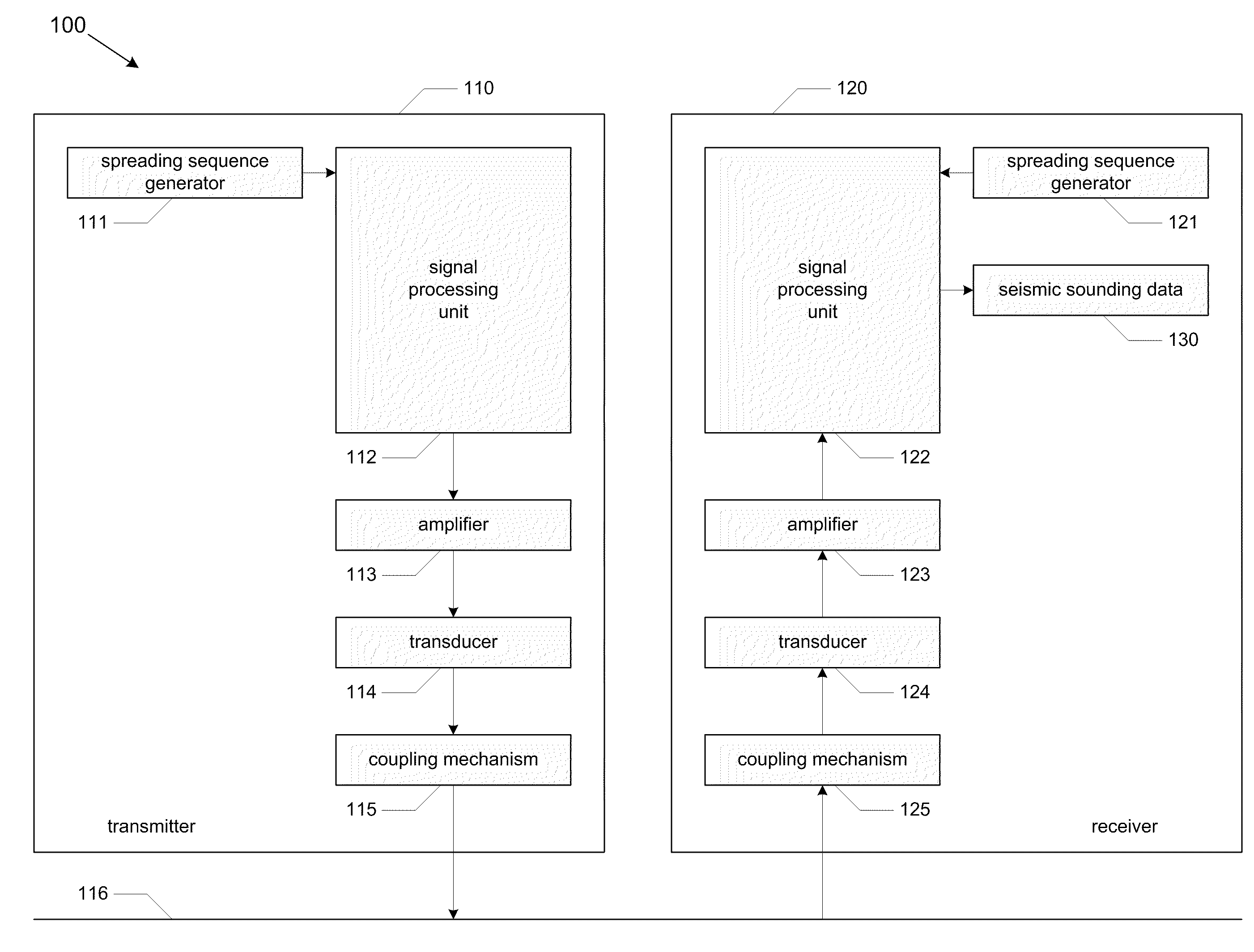
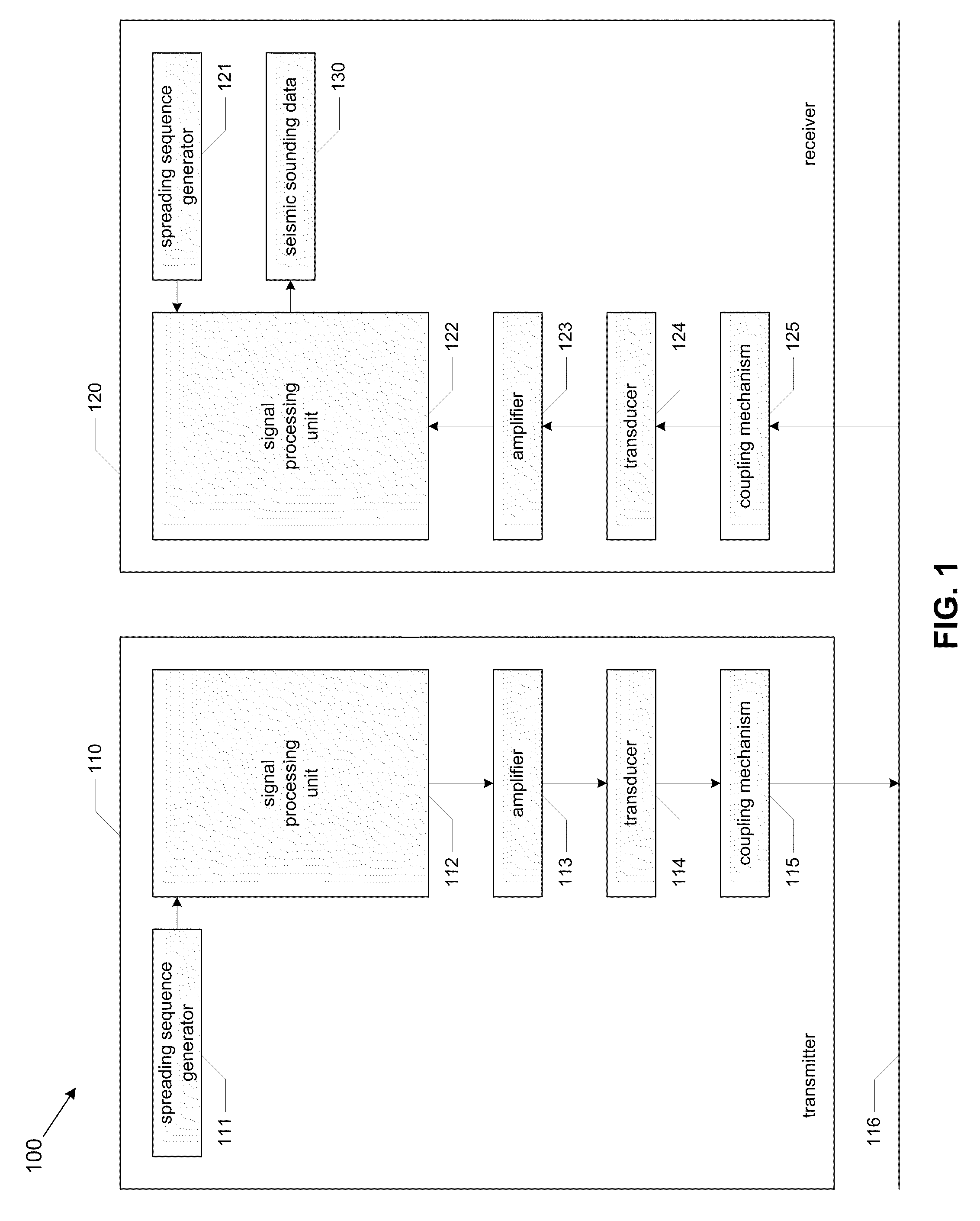
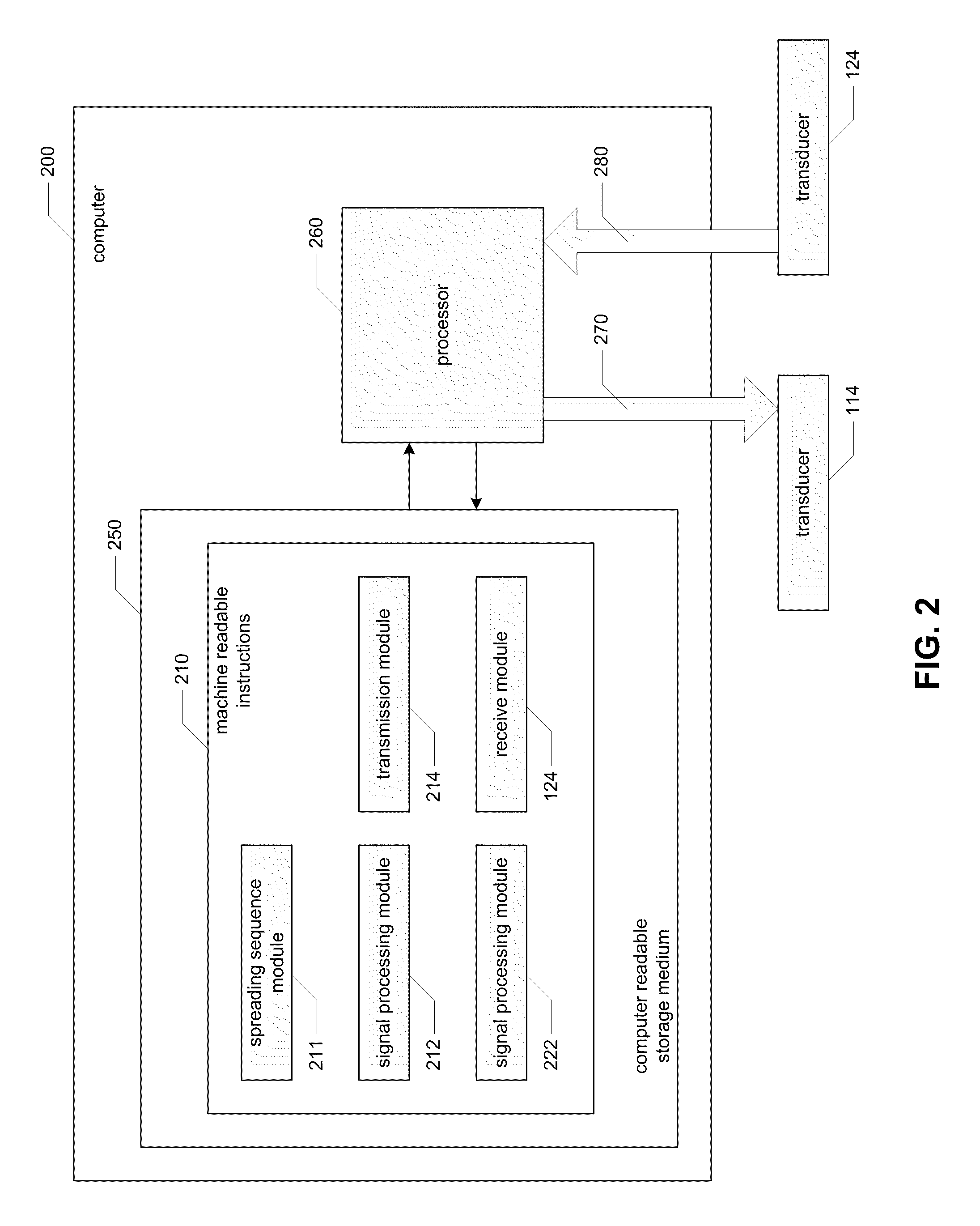
InactiveUS20110069741A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioReduce energy densitySeismic data acquisitionSeismic signal processingAcoustic waveSpread spectrum
Systems and methods for seismological sounding with acoustic signals and, more particularly, systems and methods for performing geophysical surveys using spread spectrum acoustic waves generated by non-impulsive sources. A spread spectrum signal is generated and coupled to a medium that is to be sounded for propagation of an acoustic wave through the medium. One or more return signals are received from the medium that are generated by interaction between the acoustic wave and the medium. The return signals are possessed to obtain seismic sounding data describing the structural features of the medium.
Owner:ERICKSON ALAN
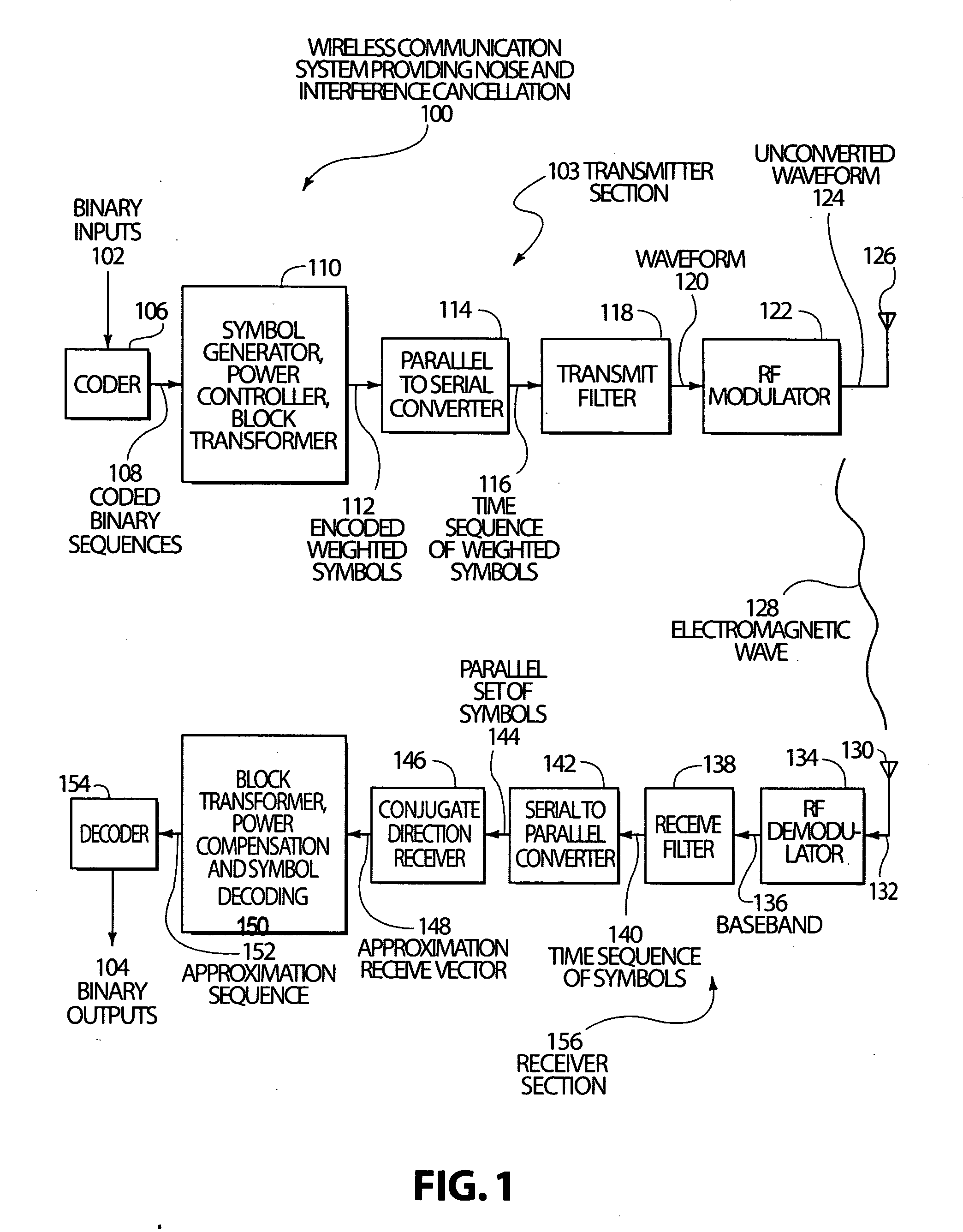
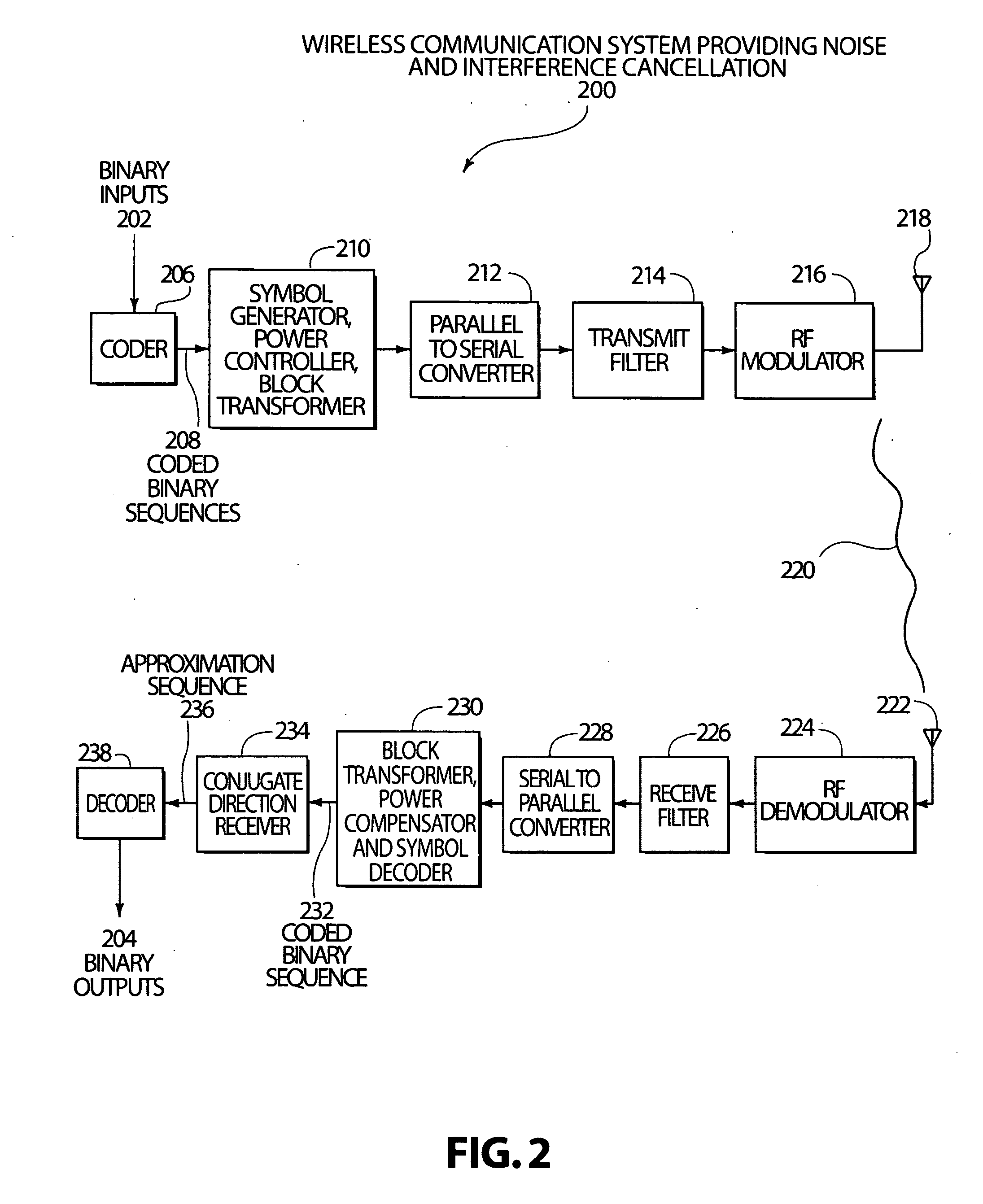
Code, signal and conjugate direction design for rapidly-adaptive communication receivers and electromagnetic, acoustic and nuclear array processors
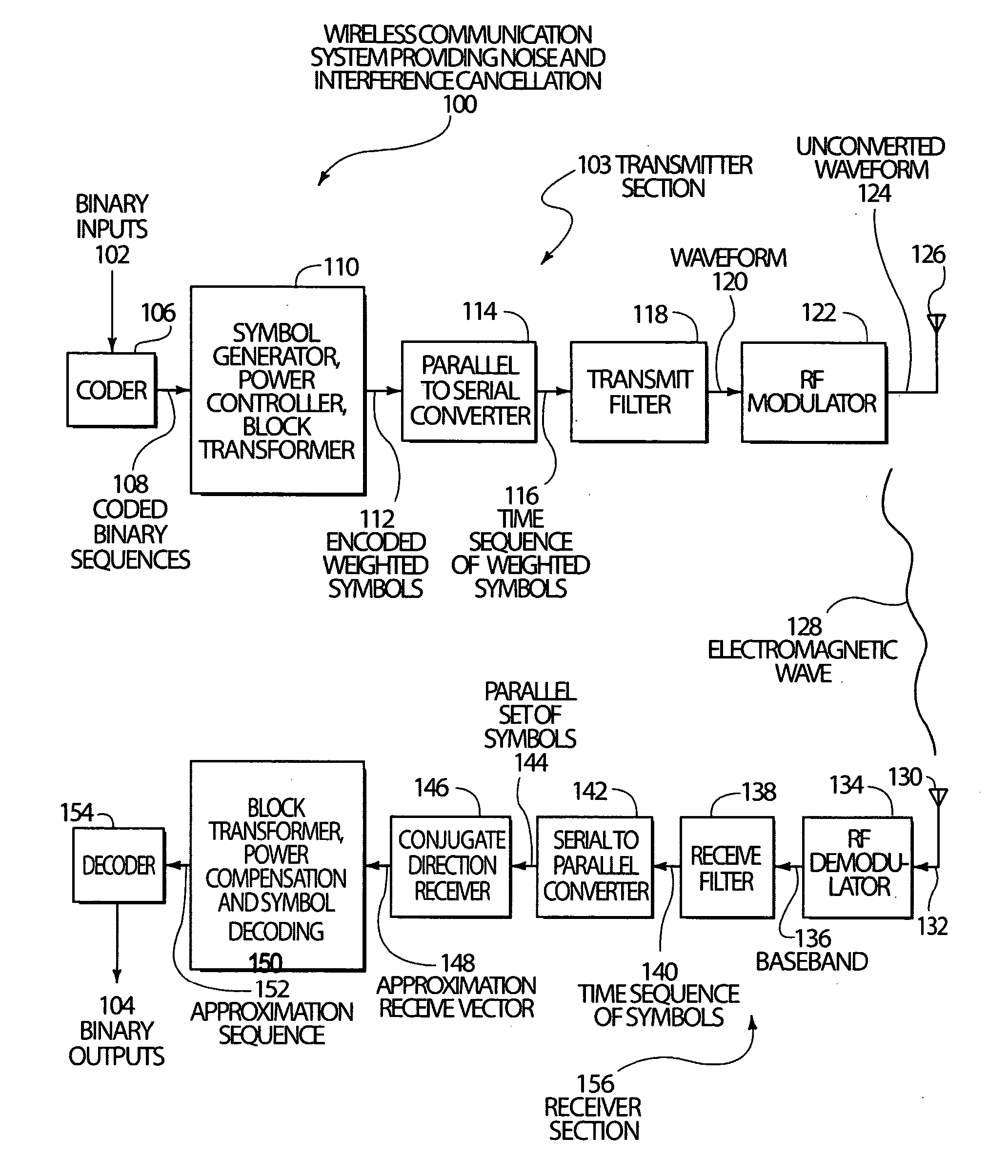
A system and method are disclosed that substantially reduce the complexity of receivers in digitally modulated wireless communication systems such as systems that use CDMA and similar multi-access coding. Transmitted signals are designed to use orthogonal or non-orthogonal codes with specific amplitudes that reduce the number of distinct eigenvalues in a code correlation matrix or in a code-plus-interference-plus-noise correlation matrix, so that a few steps of a conjugate direction calculation will compute a reduced rank Wiener filter that can be used to provide approximate de-correlation type receivers in a substantially reduced number of steps when compared to inverse correlation matrix calculations, or when compared to conjugate direction computations run on correlation matrices with un-shaped eigenvalues. These techniques can also be applied to active or passive imaging systems such as sonar, ultrasound and radar imaging systems and phased array systems that use beam forming. Cancellation of interference and noise can also be accomplished by exploiting eigenvalue shape or by designing the codes and amplitudes of the transmitted signal and using the reduced rank Wiener filter to filter interference and noise from the receive signal. The techniques enable the use of code design and power control for the control of system complexity and bandwidth.
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
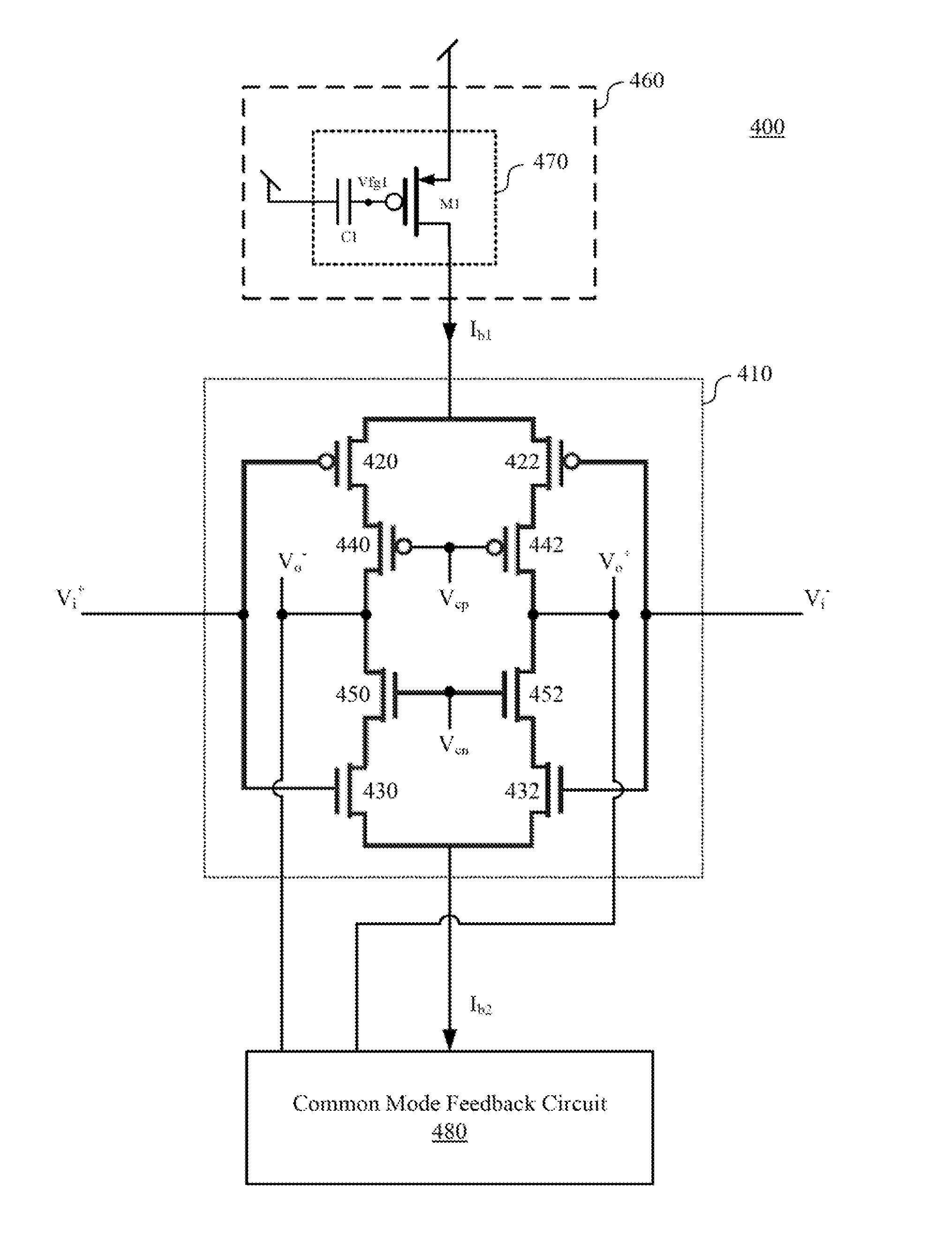
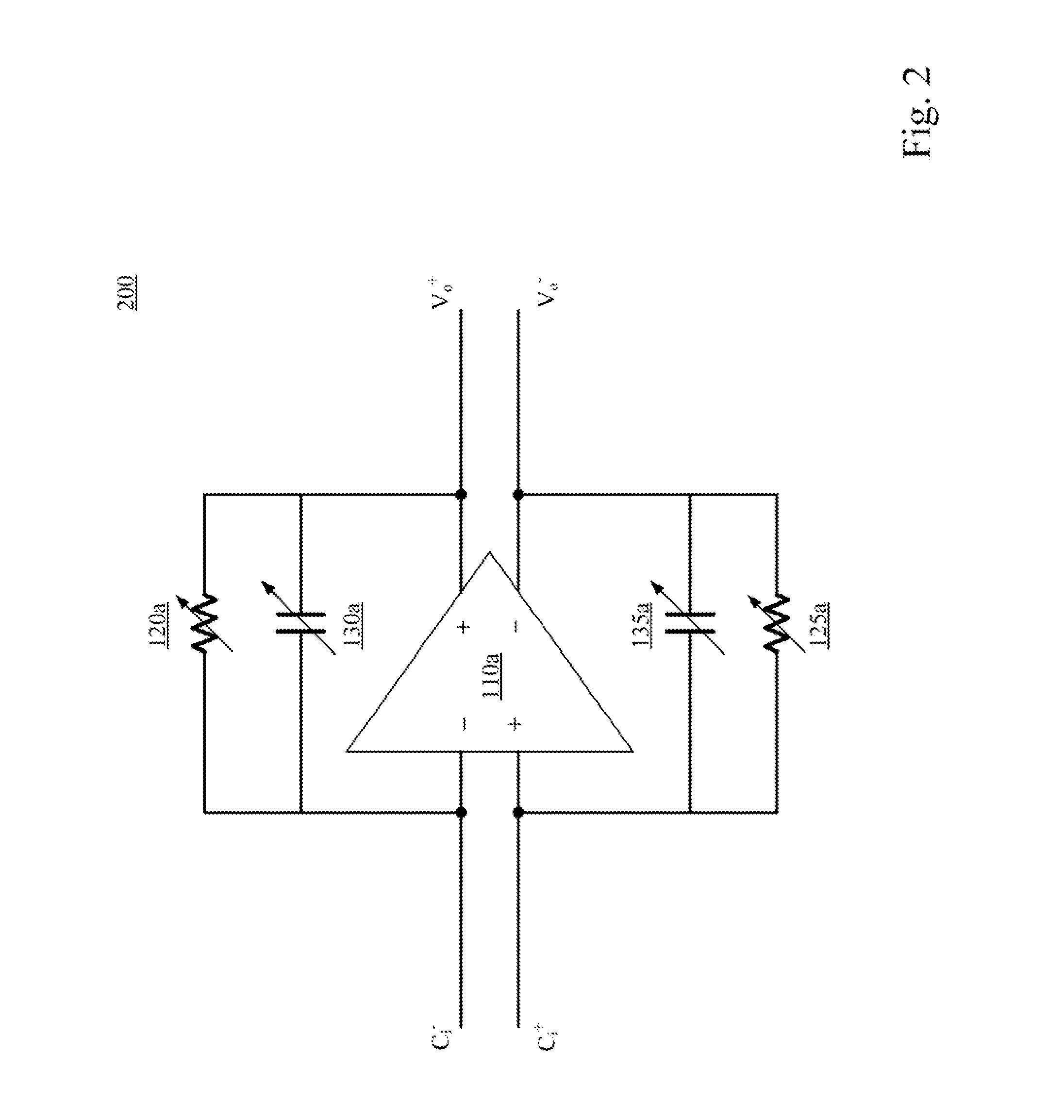
Operational transconductance amplifier, reconfigurable fully differential voltage sensing amplifier and reconfigurable fully differential capacitive sensing amplifier
ActiveUS20150200635A1Reduce stepsPrecise bias driving circuitDifferential amplifiersAmplifier detailsPower flowAudio power amplifier
An operational transconductance amplifier includes a cascode differential-pair amplifying circuit, a bias driving circuit, and a common mode feedback circuit. The cascode differential-pair amplifying circuit is configured for receiving a differential input voltage and for providing a differential output voltage. The bias driving circuit is configured for providing a first bias current to drive the cascode differential-pair amplifying circuit and for adjusting the transconductance of the transconductance amplifier. The bias driving circuit includes a first floating-gate transistor. The first floating-gate transistor is configured for adjusting the first bias current. The common mode feedback circuit is configured for adjusting a second bias current of the cascode differential-pair amplifying circuit according to the differential output voltage so that the differential output voltage is stabilized. A reconfigurable fully differential voltage sensing amplifier and a reconfigurable fully differential capacitive sensing amplifier are disclosed herein as well.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
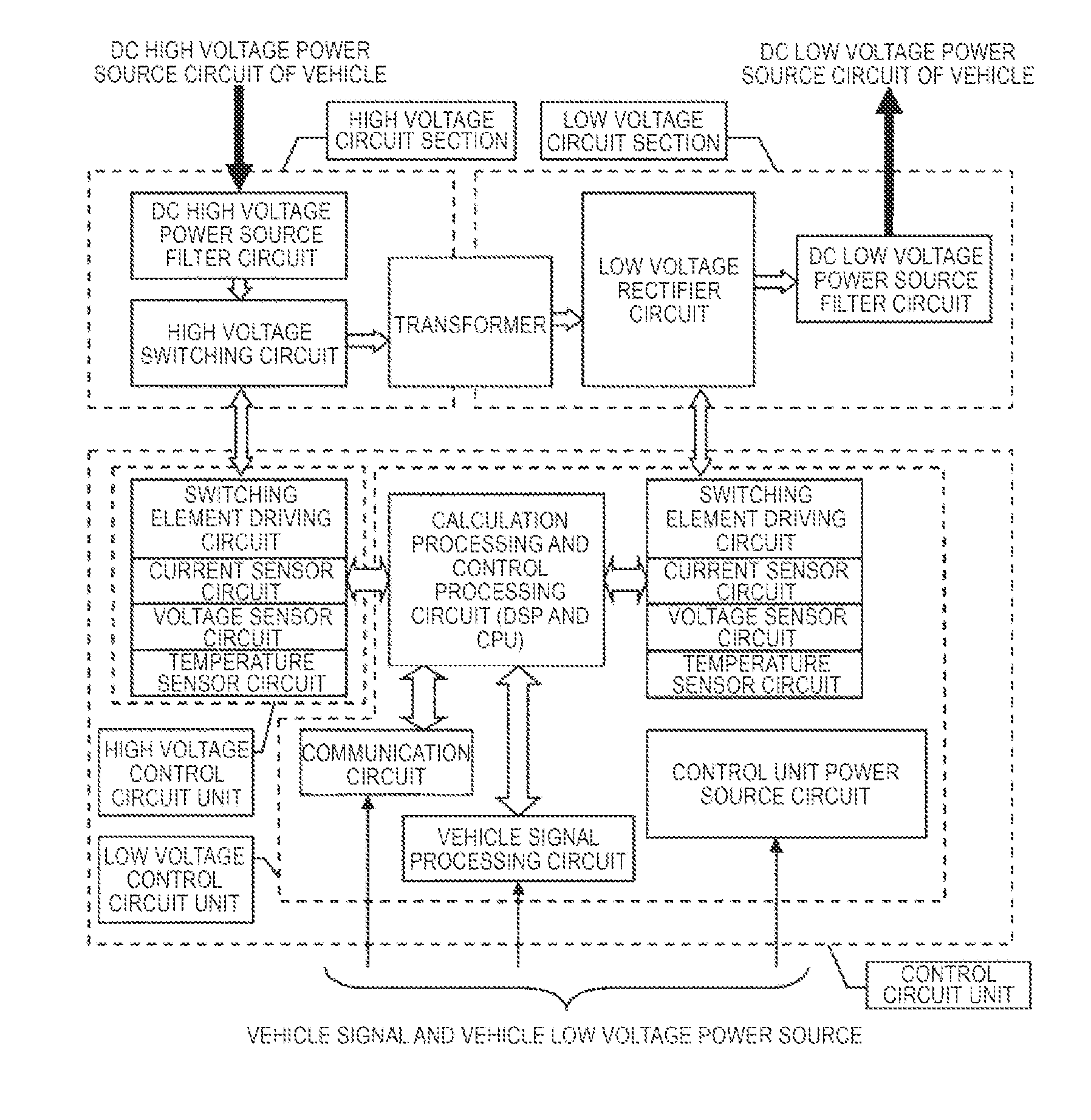
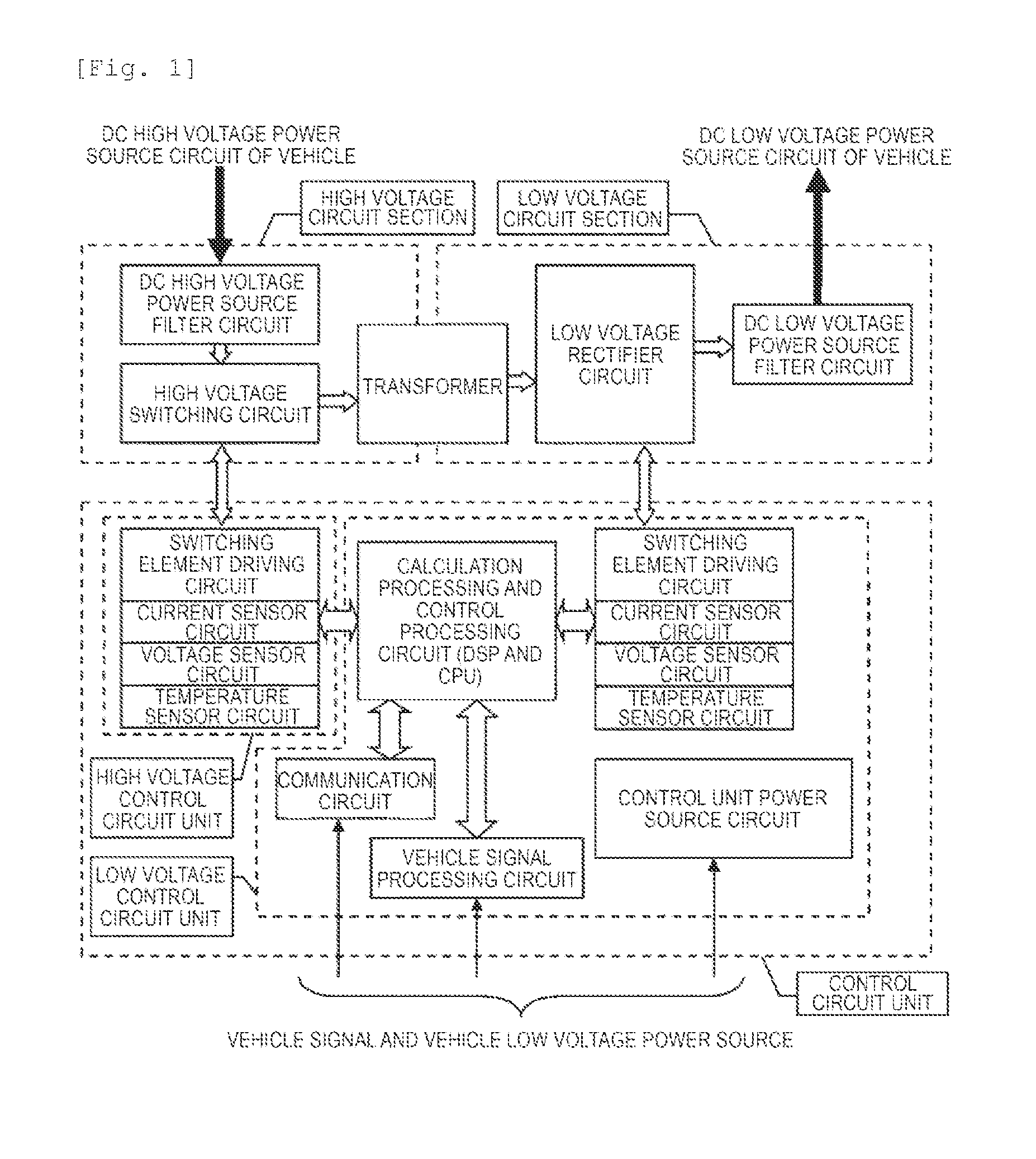
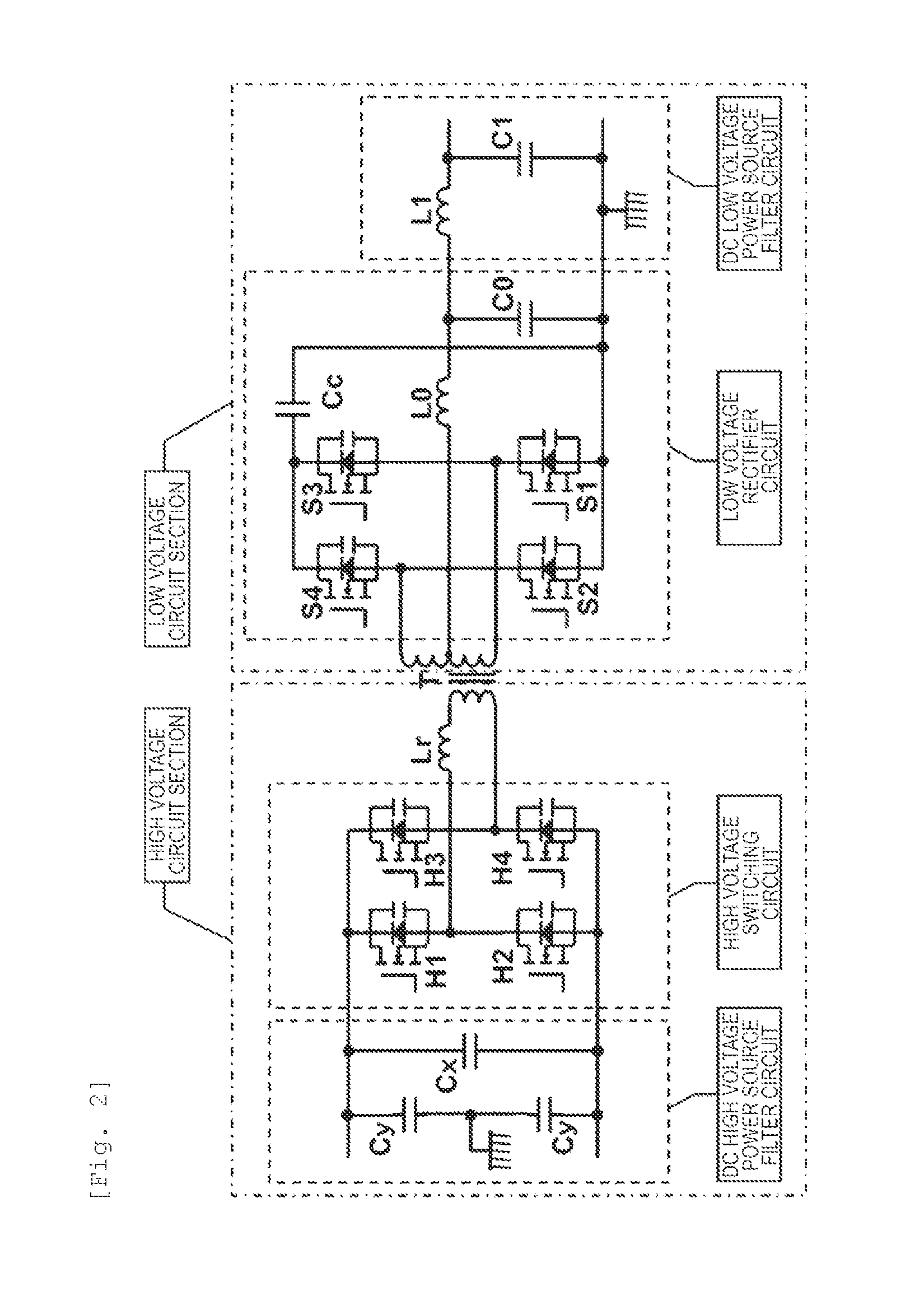
DC-DC Converter
ActiveUS20150306960A1Reduce noiseMinimal numberElectric devicesConversion constructional detailsElectricityLow voltage circuits
As an object of reducing a noise resulted from the mutual influences between circuit-configuring components, a DC-DC converter includes a high voltage circuit section that is electrically connected to a transformer, a low voltage circuit section that is electrically connected to the transformer, a housing in which the high voltage circuit section and the low voltage circuit section are accommodated, a control circuit board that controls the driving of the low voltage circuit section, and a frame that supports the control circuit board. The frame is arranged on a position facing a bottom surface of the housing while crossing the low voltage circuit section. The housing includes a first wall that separates a first space in which the high voltage circuit section is accommodated and a second space in which circuit components configuring the low voltage circuit section are accommodated. The frame forms a second wall that protrudes toward a direction approaching a leading end of the first wall.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Dynamoelectric machine
InactiveUS7605519B2Improve reliabilityNoise and interferenceMagnetic circuit rotating partsCooling/ventillation arrangementMagnetic polesField coil
A magnet seat is disposed on a second yoke portion and projects into respective spaces between circumferentially-adjacent pairs of second claw-shaped magnetic pole portions, and permanent magnets are disposed only near the second yoke portion so as to be held by the magnet seat so as to face an inner circumferential surface near a tip end of each of a plurality of first claw-shaped magnetic pole portions. Each of the permanent magnets is magnetically oriented in a reverse direction to an orientation of a magnetic field that a field coil produces.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
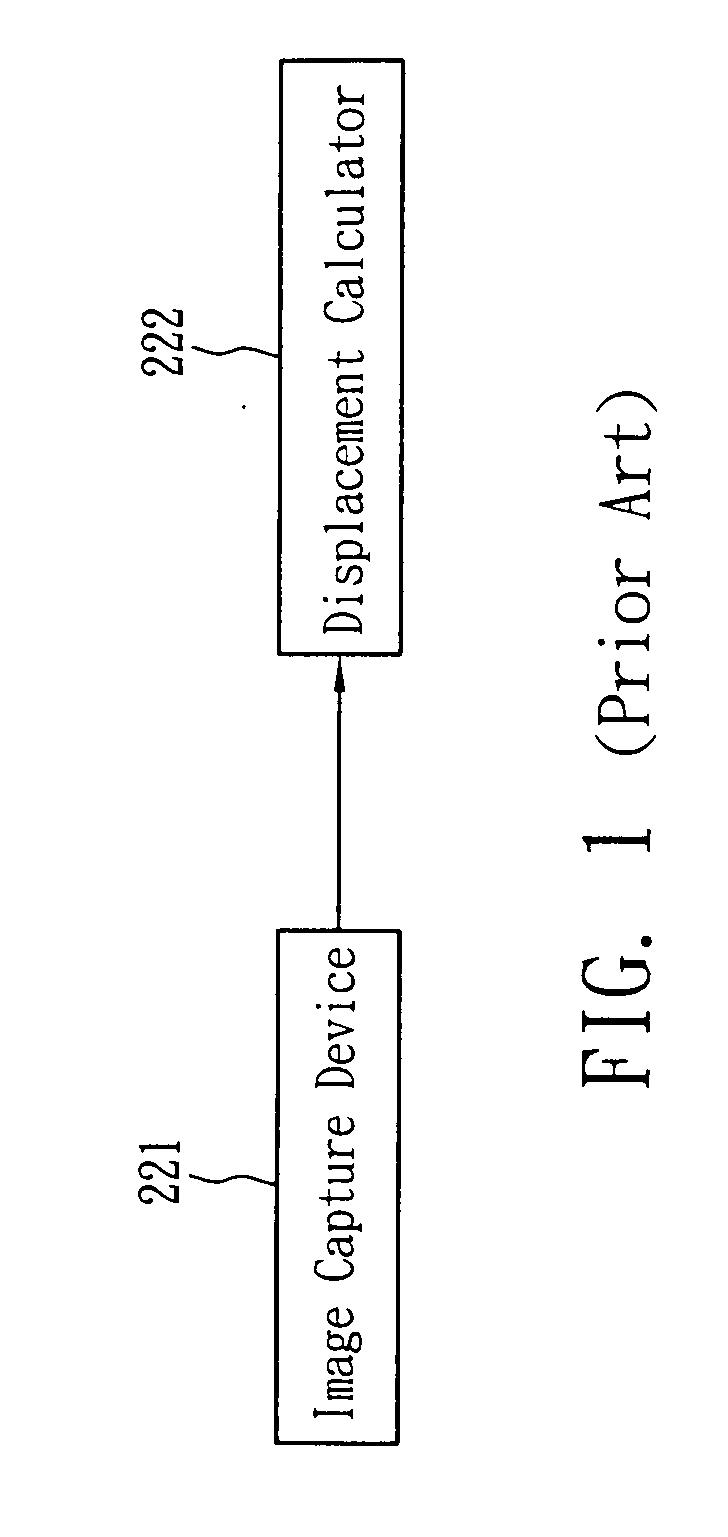
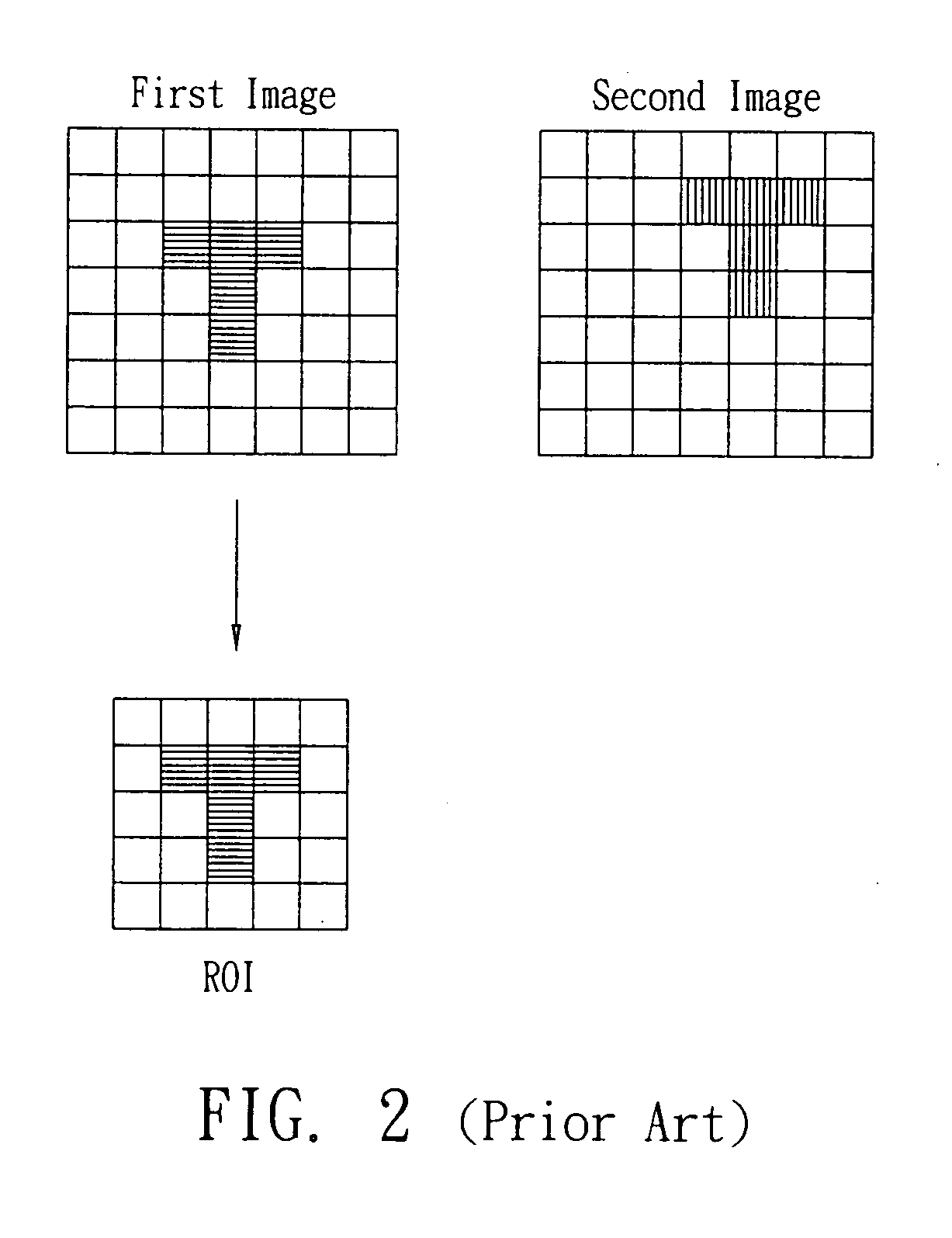
Displacement estimation device and method for the same
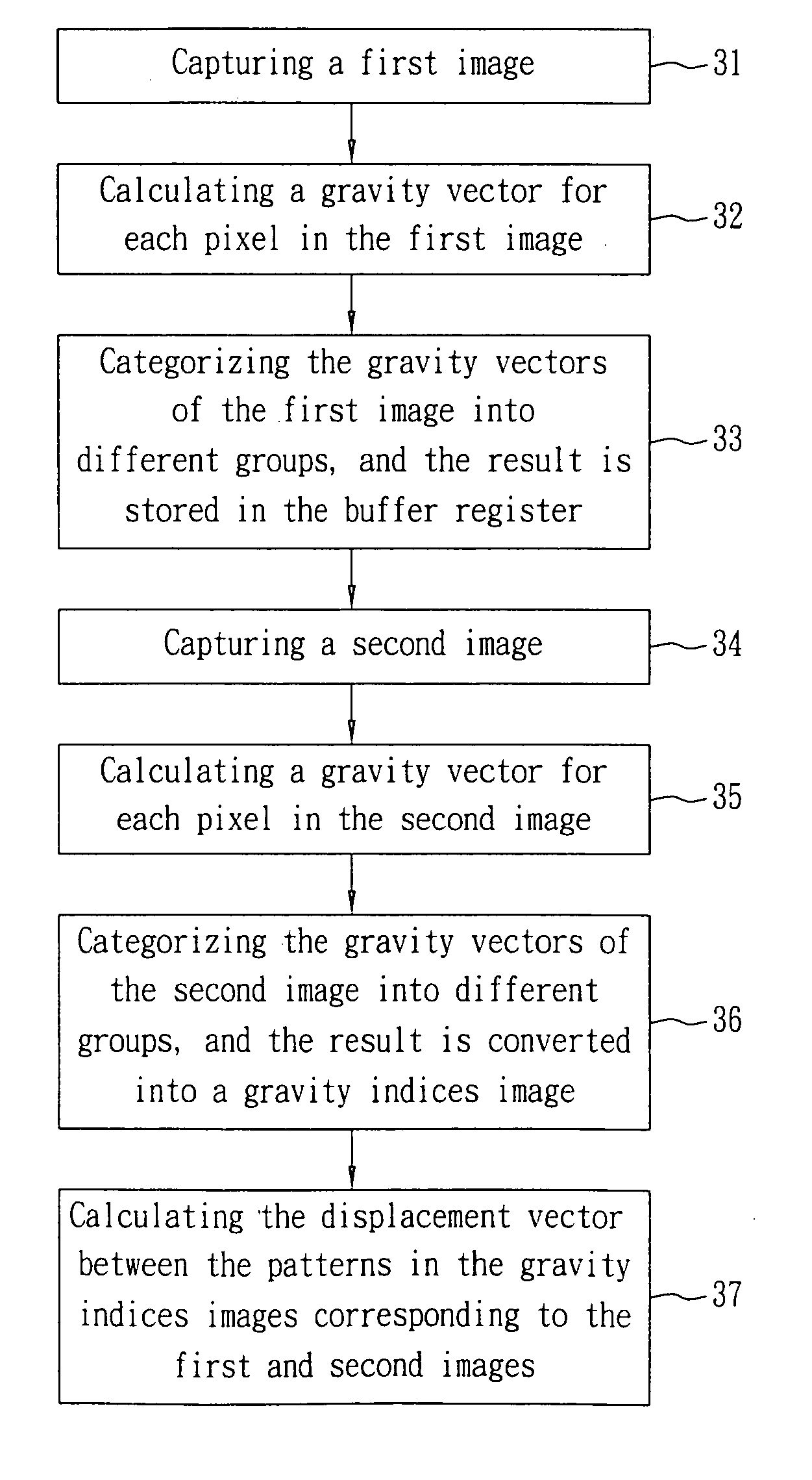
ActiveUS20070154069A1Less sensitiveLess sensitive to pattern distortion and light shadingTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionRegion of interestImage based
A displacement estimation device includes a vector calculator and a displacement calculator, for use in estimating a displacement vector from a pattern in a first original image to a pattern in a second original image. The vector calculator calculates a parameter for each pixel in the first original image and the second original image. The parameter of a pixel integrates the information of the intensities of all the pixels in a region of interest (ROI) surrounding the pixel, and the relative distances from all the pixels in the ROI to the pixel. The displacement calculator calculates the displacement vector from a pattern in the first original image to a pattern in the second original image based on the parameters calculated by the vector calculator for the first original image and the second original image.
Owner:PIXART IMAGING INC
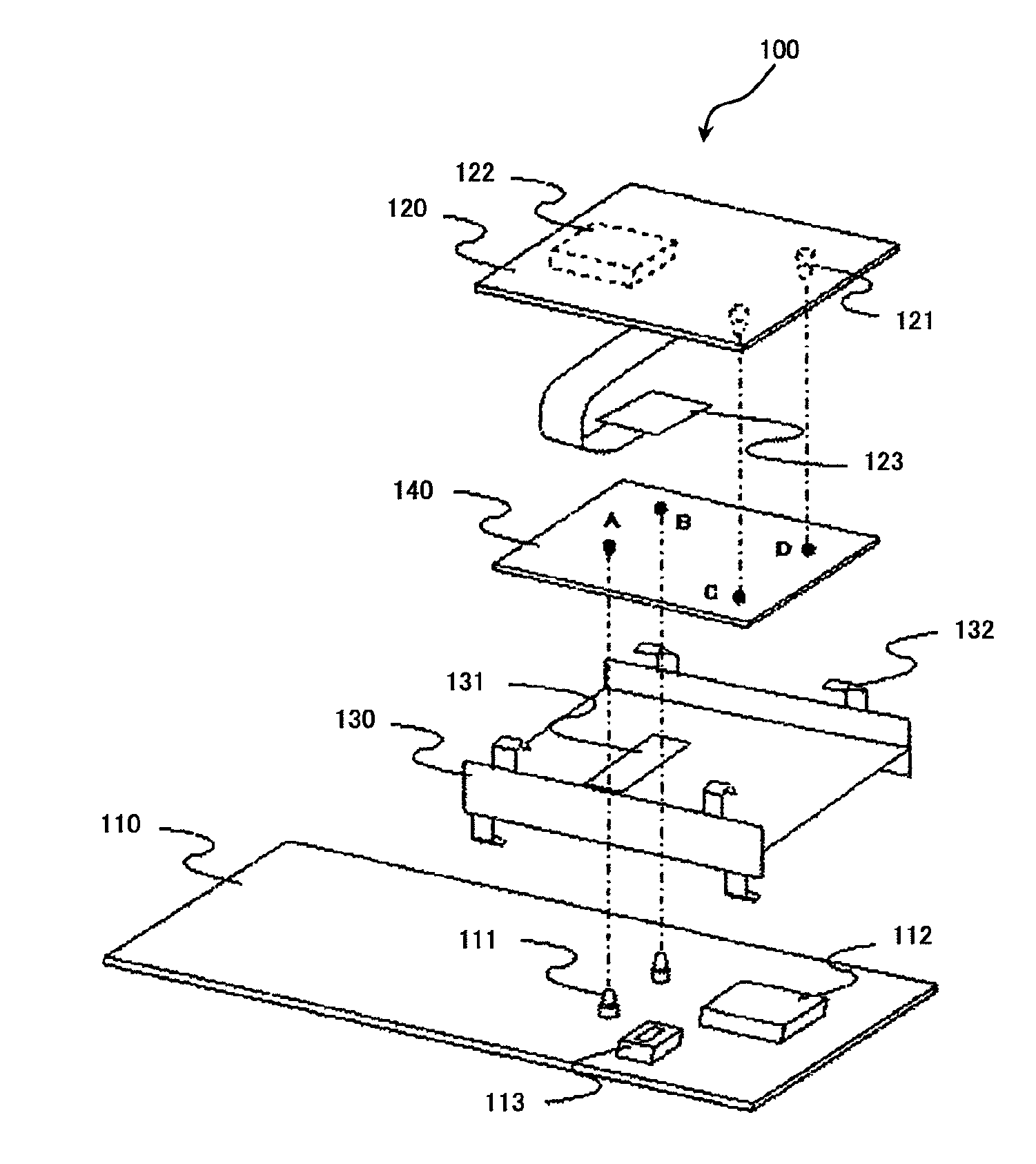
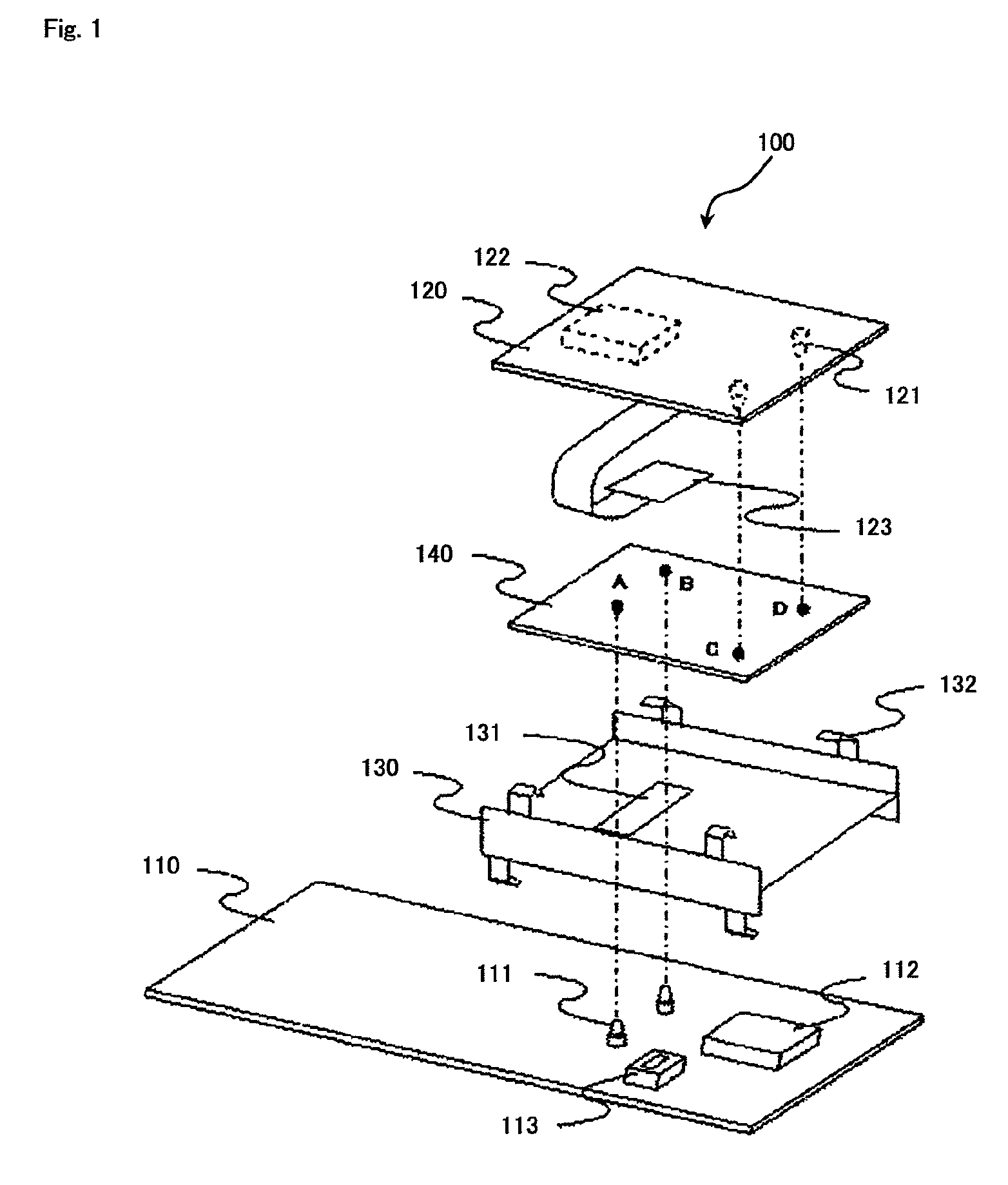
Circuit board device, electronic device provided with the same, and GND connecting method
InactiveUS8116099B2Easy to useLow costSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsElectricityDegrees of freedom
Provided is a circuit board device, wherein degrees of freedom are provided for a GND connecting position among plural printed boards, and noise shield and / or heat sink effects are provided. An electronic device provided with the circuit board device and a GND connecting method are also provided. Circuit board device (100) includes a pair of printed boards (110, 120), noise generating component (112) and / or heat generating component (122), and metal plate (140). Printed boards (110, 120) include mounting surfaces and GND connecting terminals (111, 121) arranged on the respective mounting surfaces, and the mounting surfaces are arranged to face each other. Noise generating component (112) and / or heat generating component (122) is mounted on the mounting surface of at least one of a pair of printed boards (110, 120). Metal plate (140) is arranged between the mounting surfaces of the pair of printed boards (110, 120), and is located at a distance from at least one of noise generating component (112) and heat generating component (122) so as to overlap with the noise generating component and / or the heat generating component. Furthermore, metal plate (140) is in contact with each of GND connecting terminals (111, 121) so that GND connecting terminals (111, 121) are electrically connected to each other.
Owner:LENOVO INNOVATIONS LTD HONG KONG
Driving device and driving method
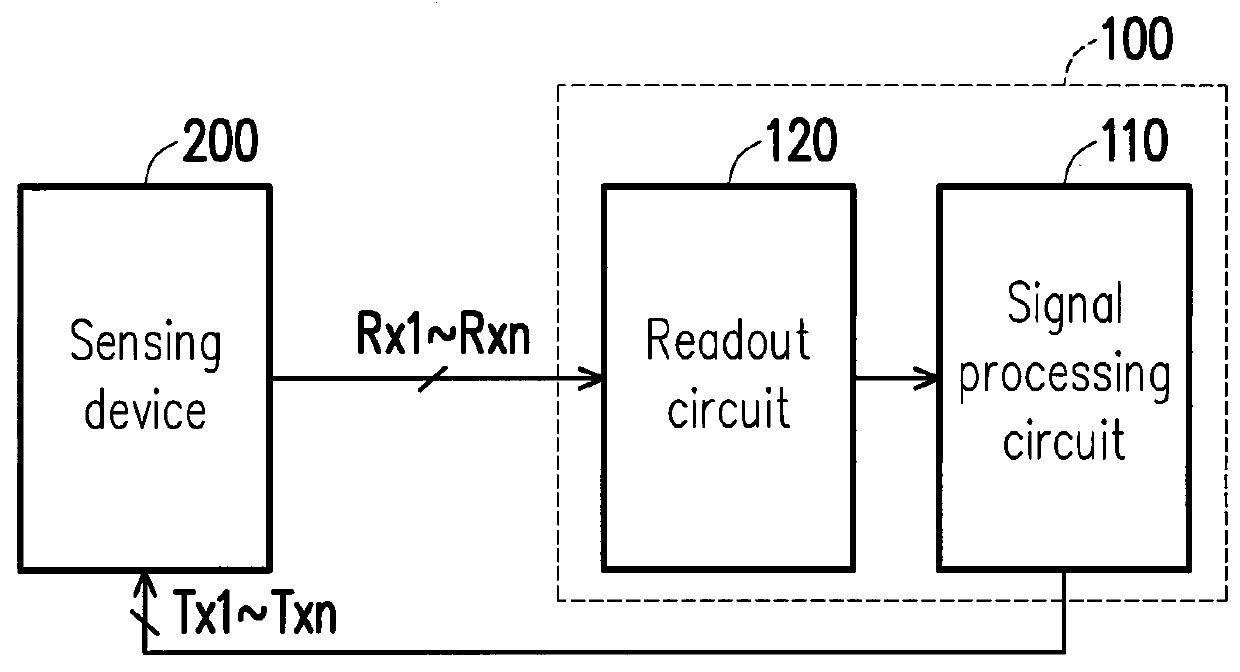
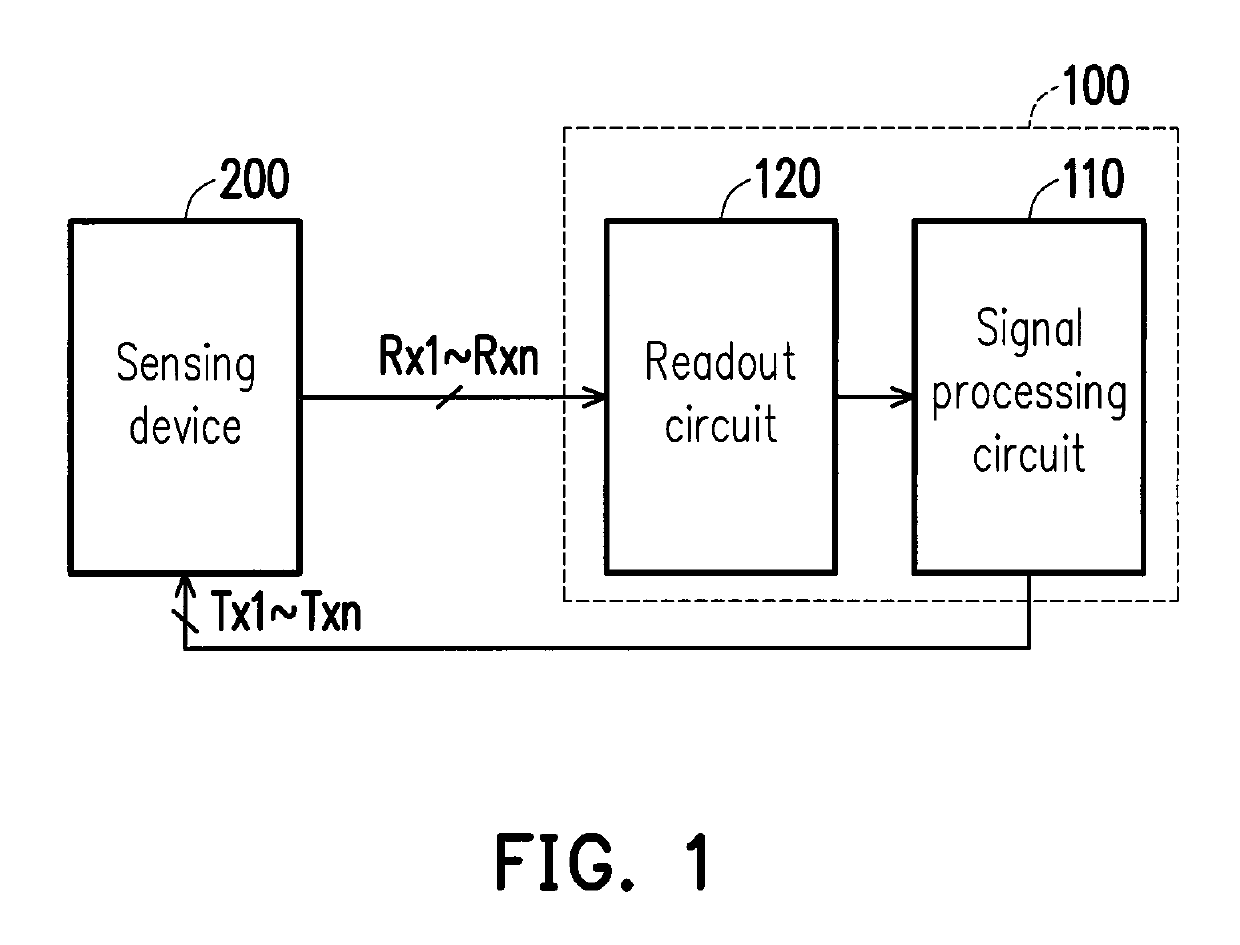
ActiveUS20180181258A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioNoise and interferenceSolid-state devicesInput/output processes for data processingElectricitySignal processing circuits
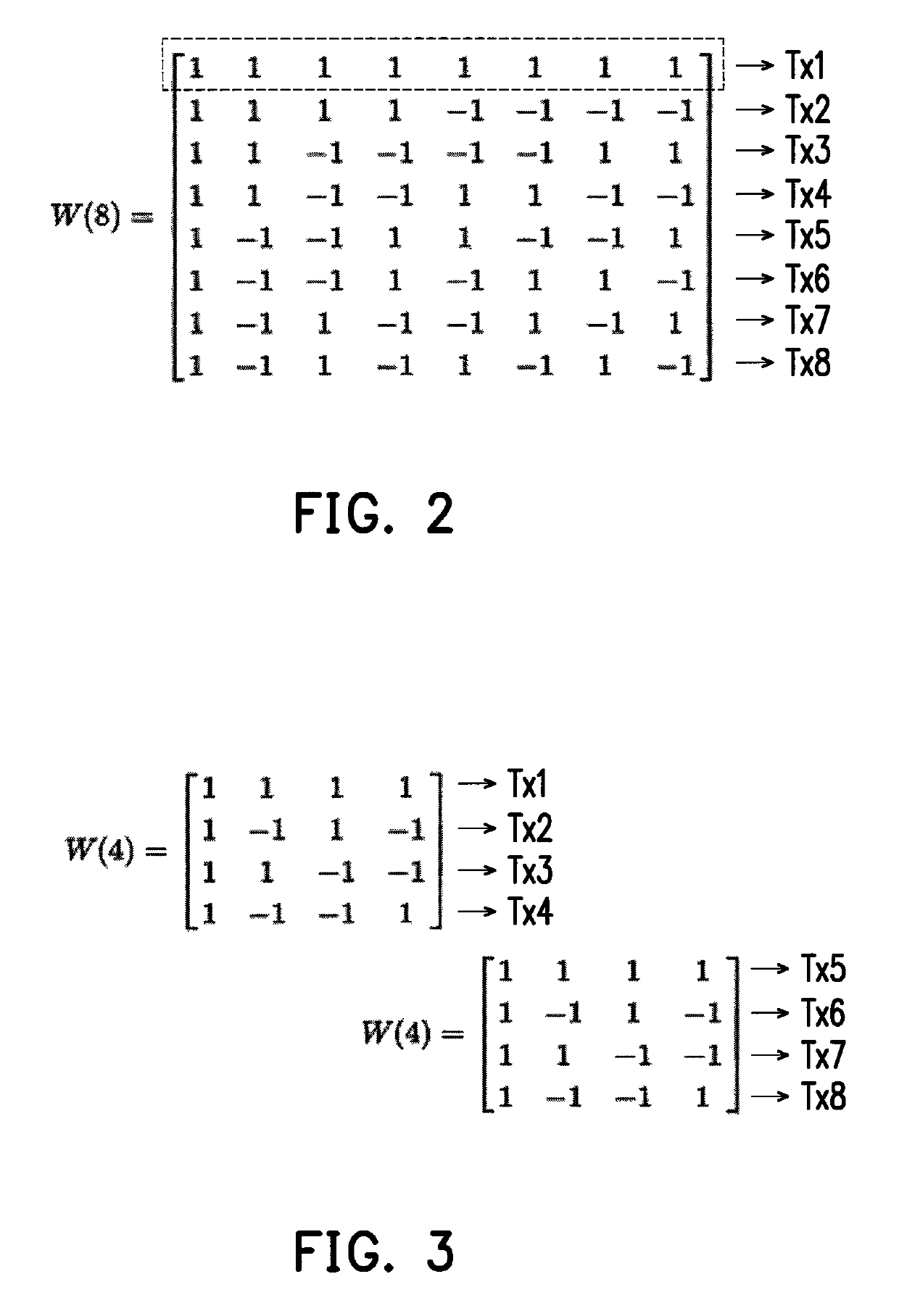
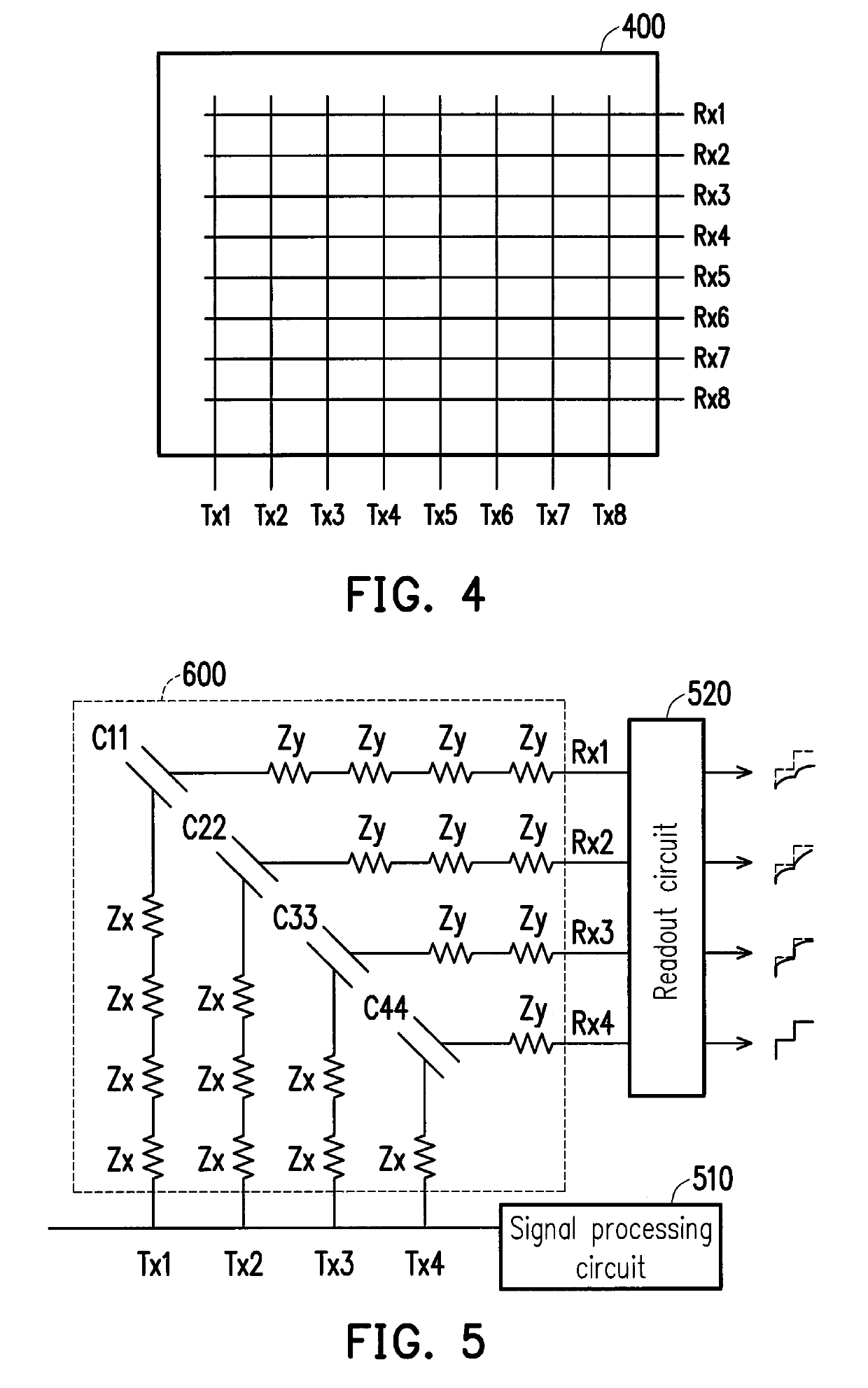
The present disclosure provides a driving device for driving a sensing device having a plurality of driving electrodes and a plurality of sensing electrodes. The driving device includes a signal processing circuit and a readout circuit. The signal processing circuit is electrically connected to the plurality of driving electrodes of the sensing device. The signal processing circuit is configured to generate a plurality of driving signal to drive the sensing device. The signal processing circuit selects a plurality of Walsh codes from a plurality of rows or columns of a Walsh matrix to serve as a plurality of driving signals. The readout circuit readouts the sensing device to generate a plurality of sensing signals and provides the plurality of sensing signals to the signal processing circuit, so that the signal processing circuit demodulates the plurality of sensing signals. In addition, a driving method is also provided.
Owner:HANNSTAR DISPLAY CORPORATION
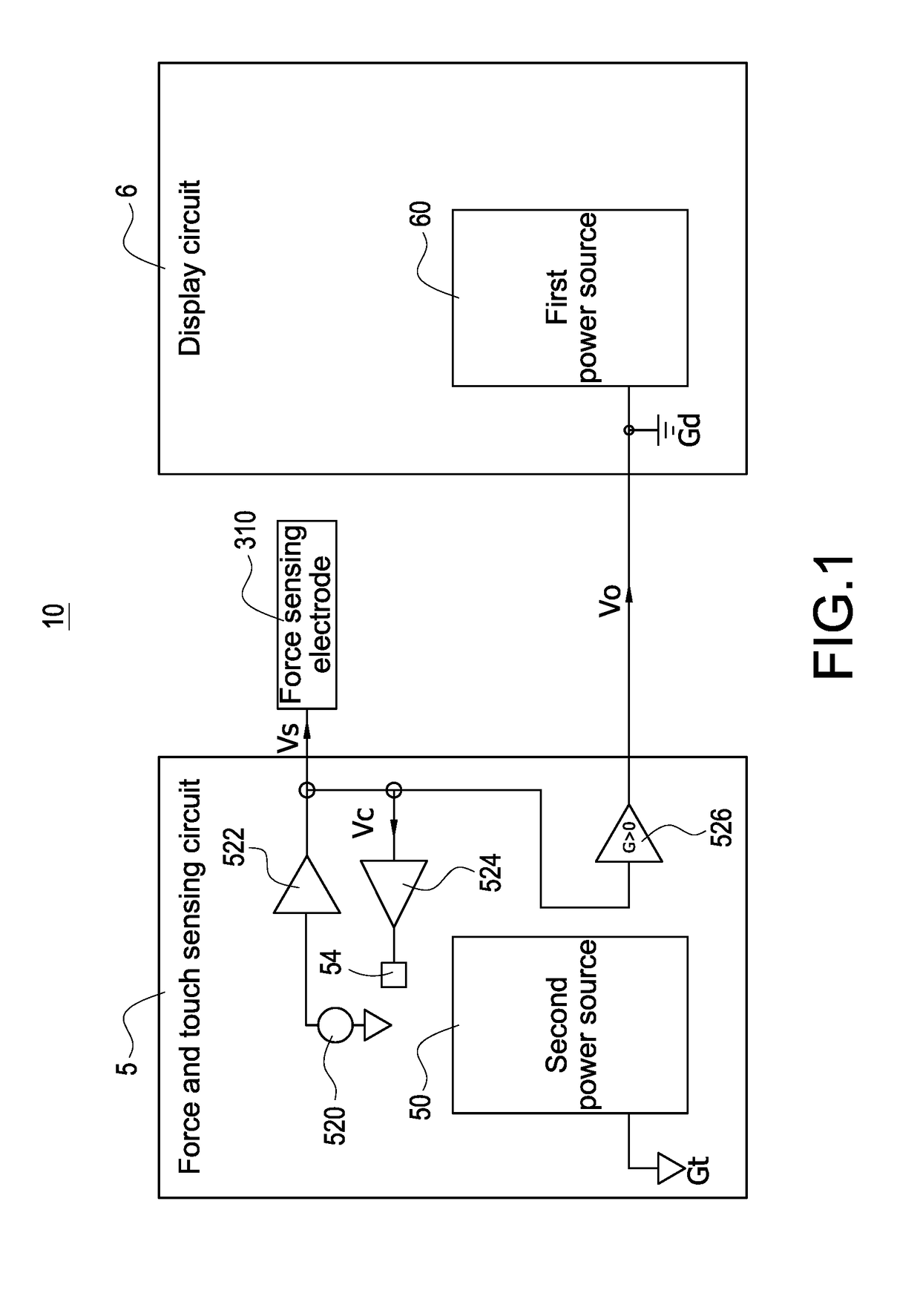
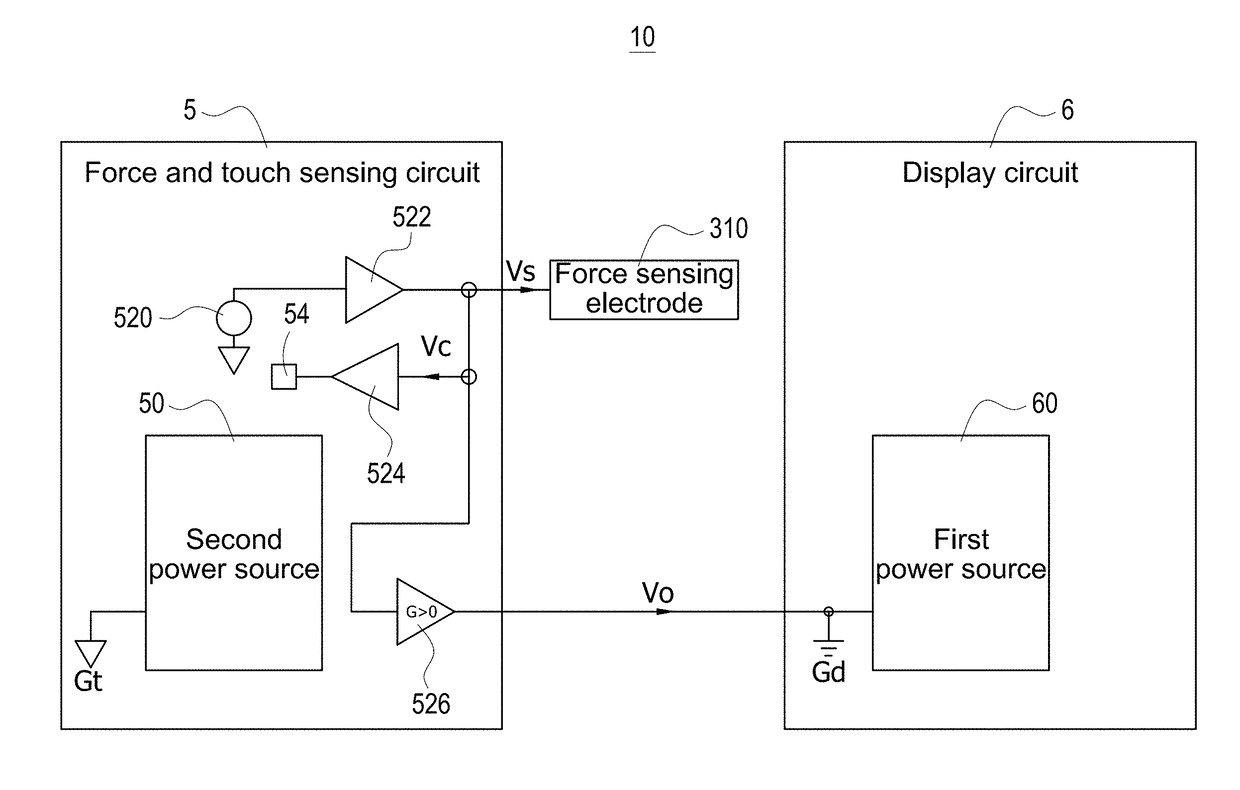
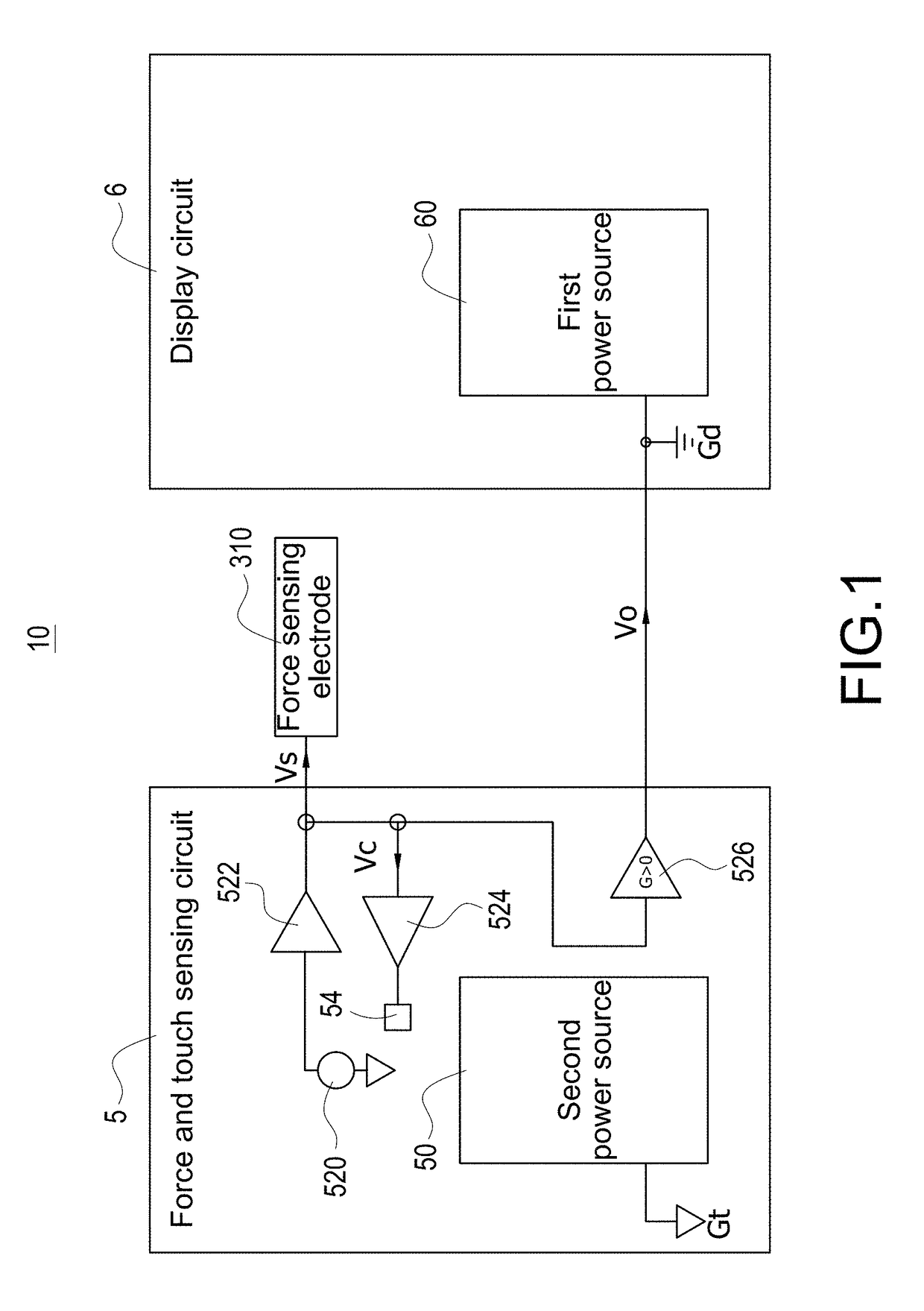
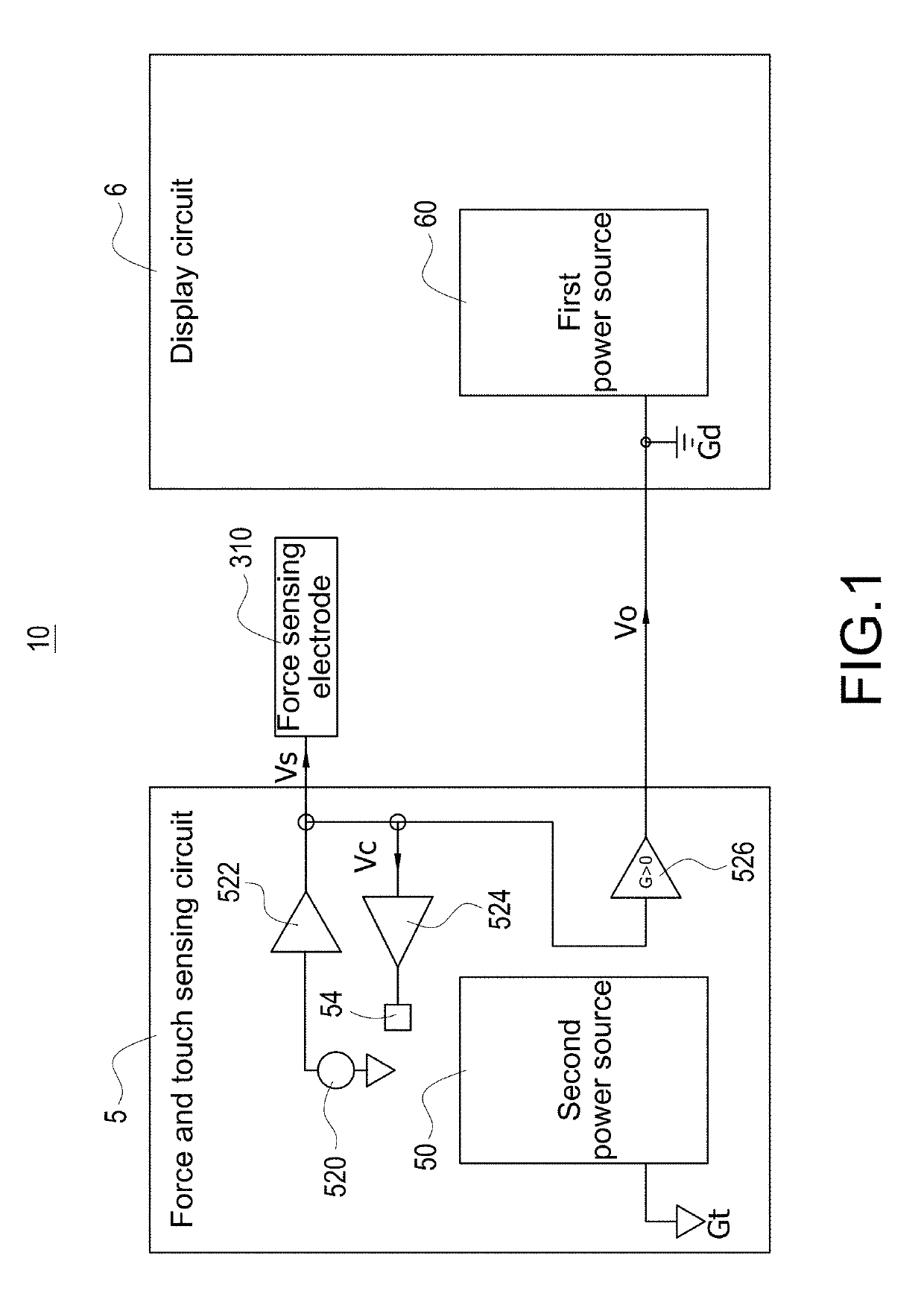
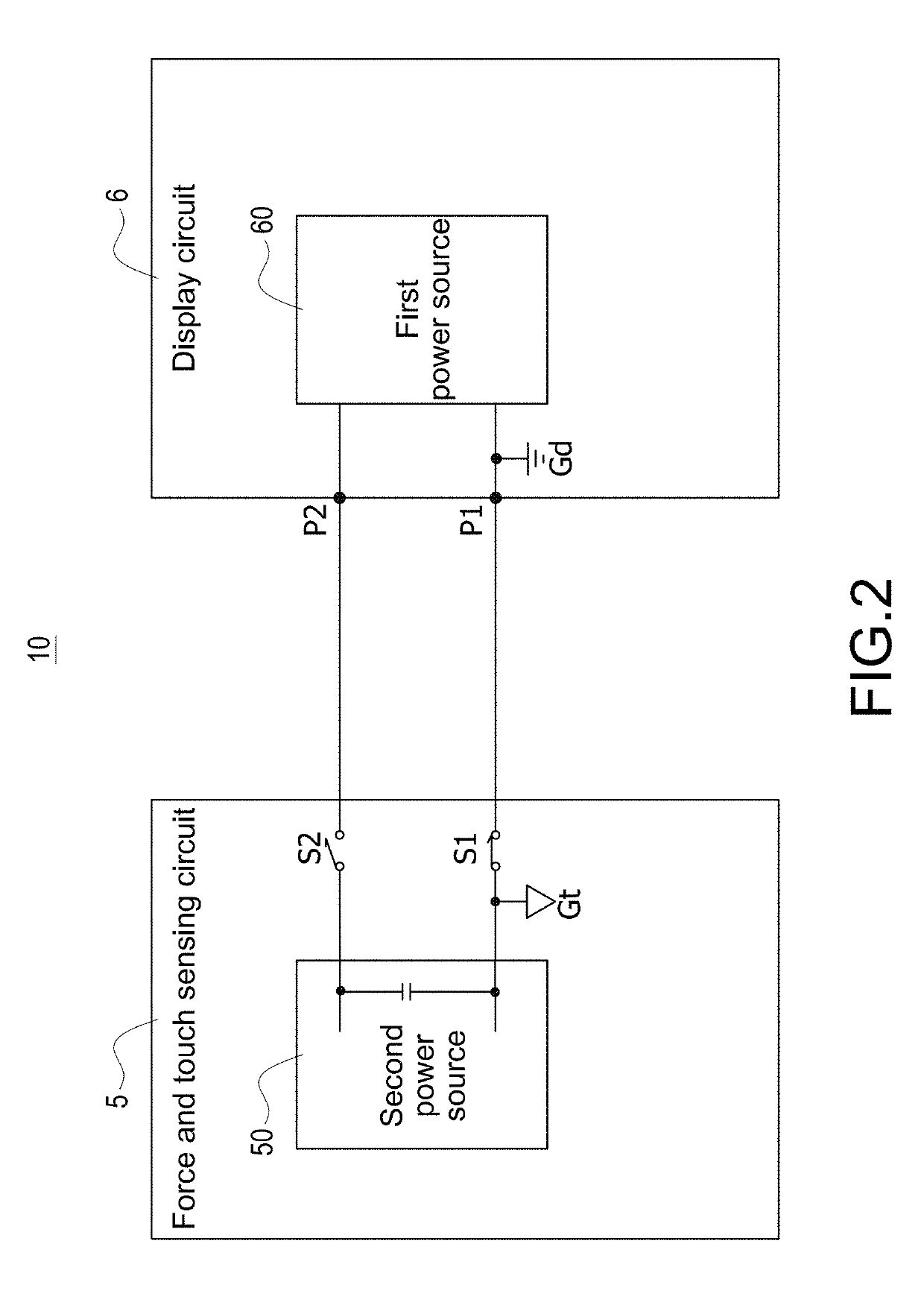
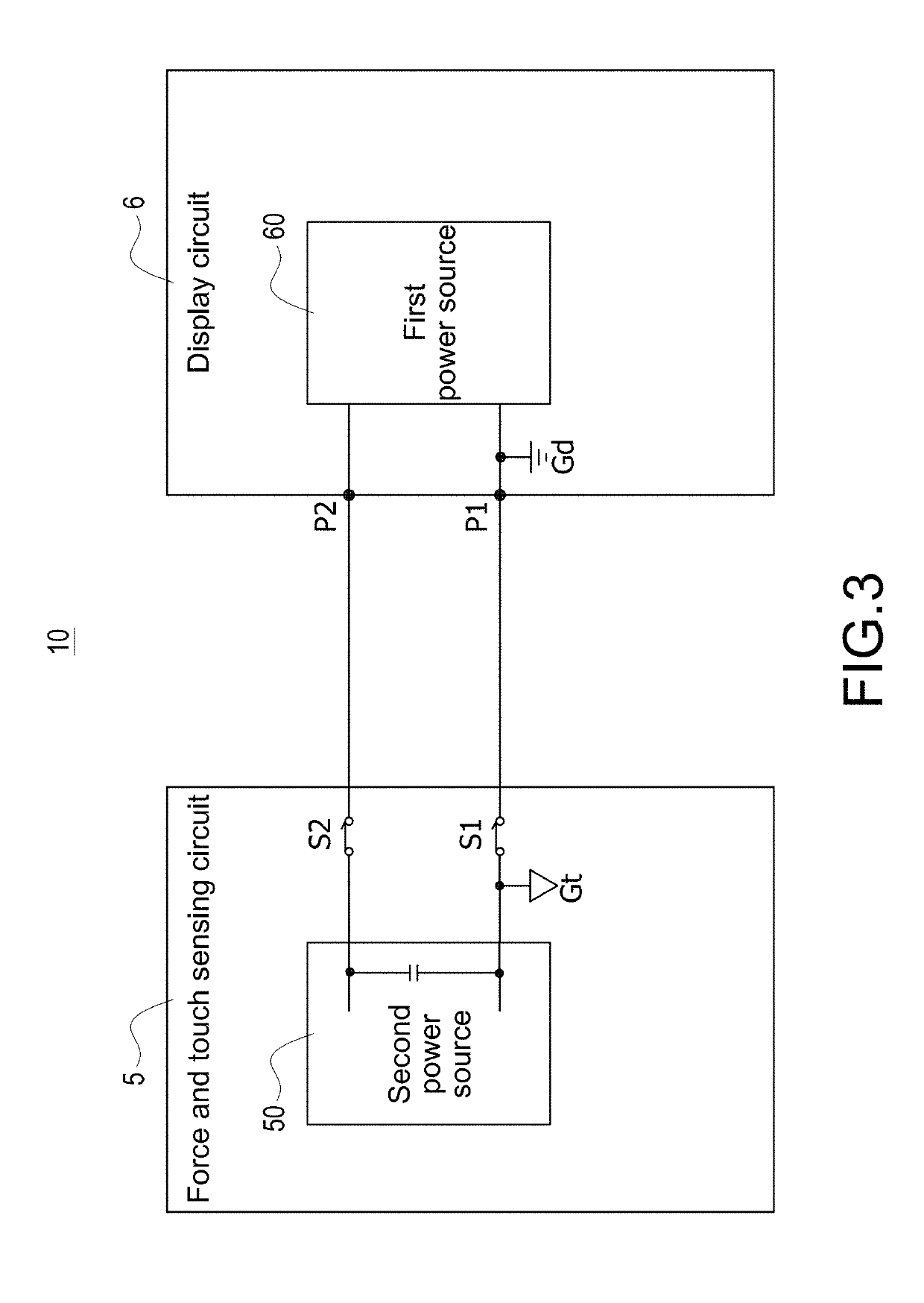
Electronic apparatus with independent power sources
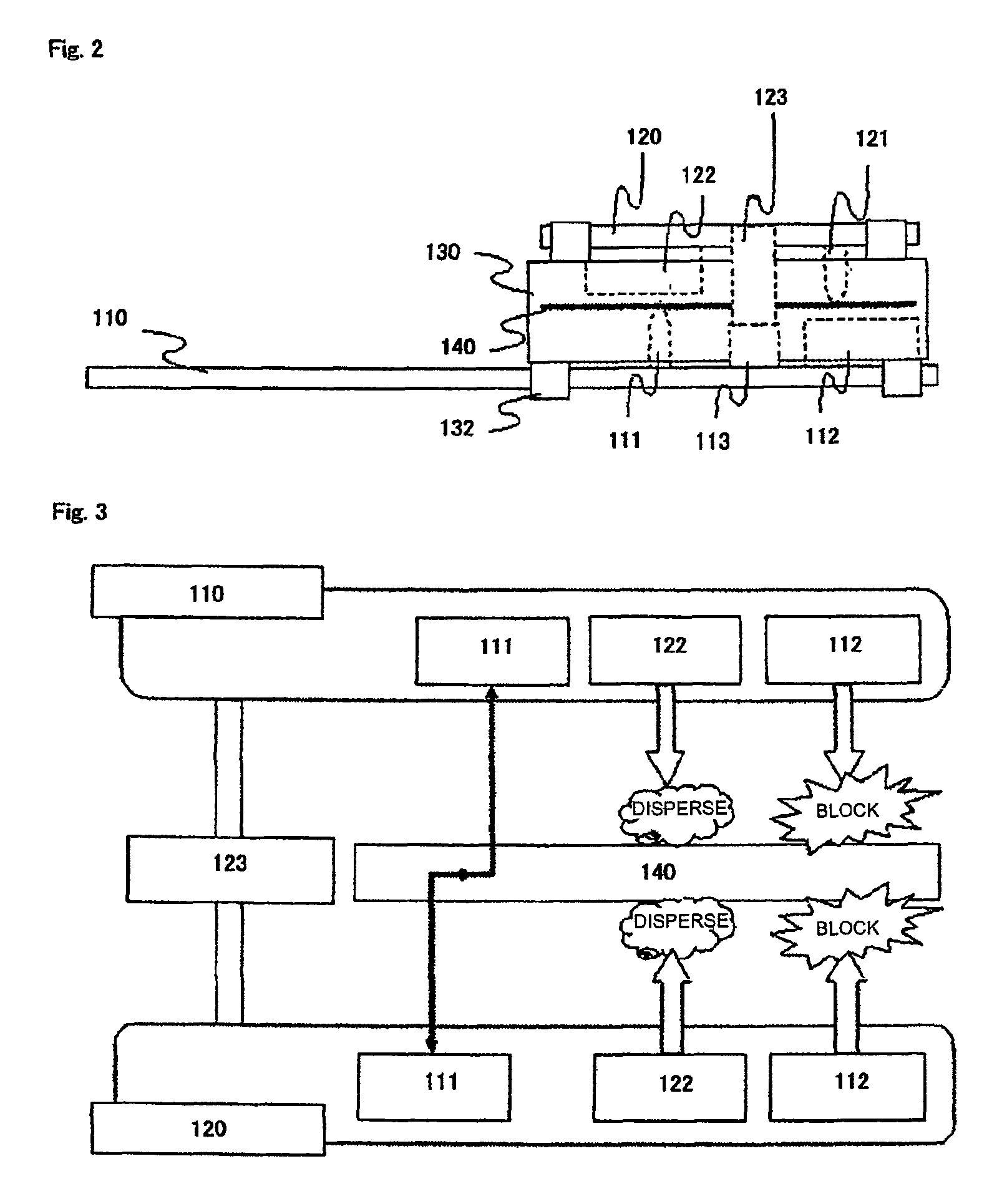
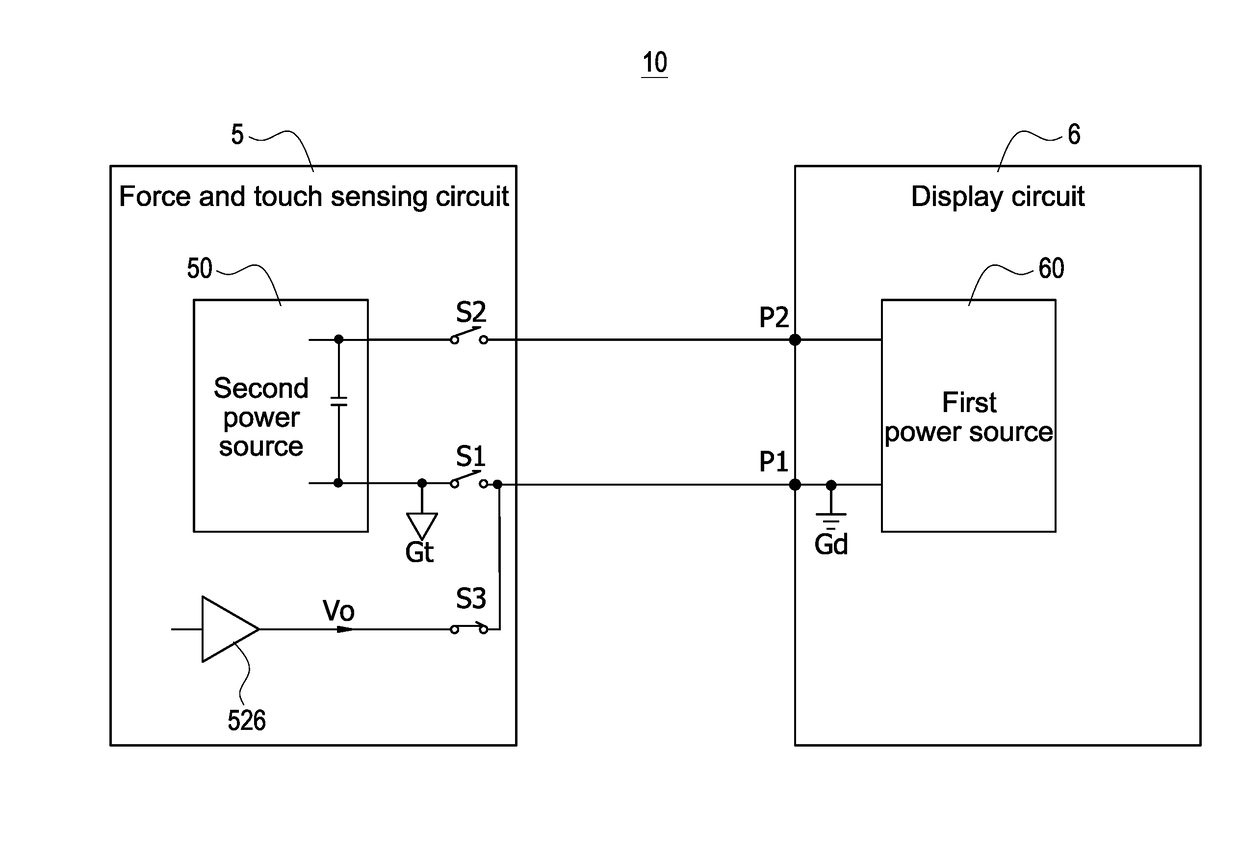
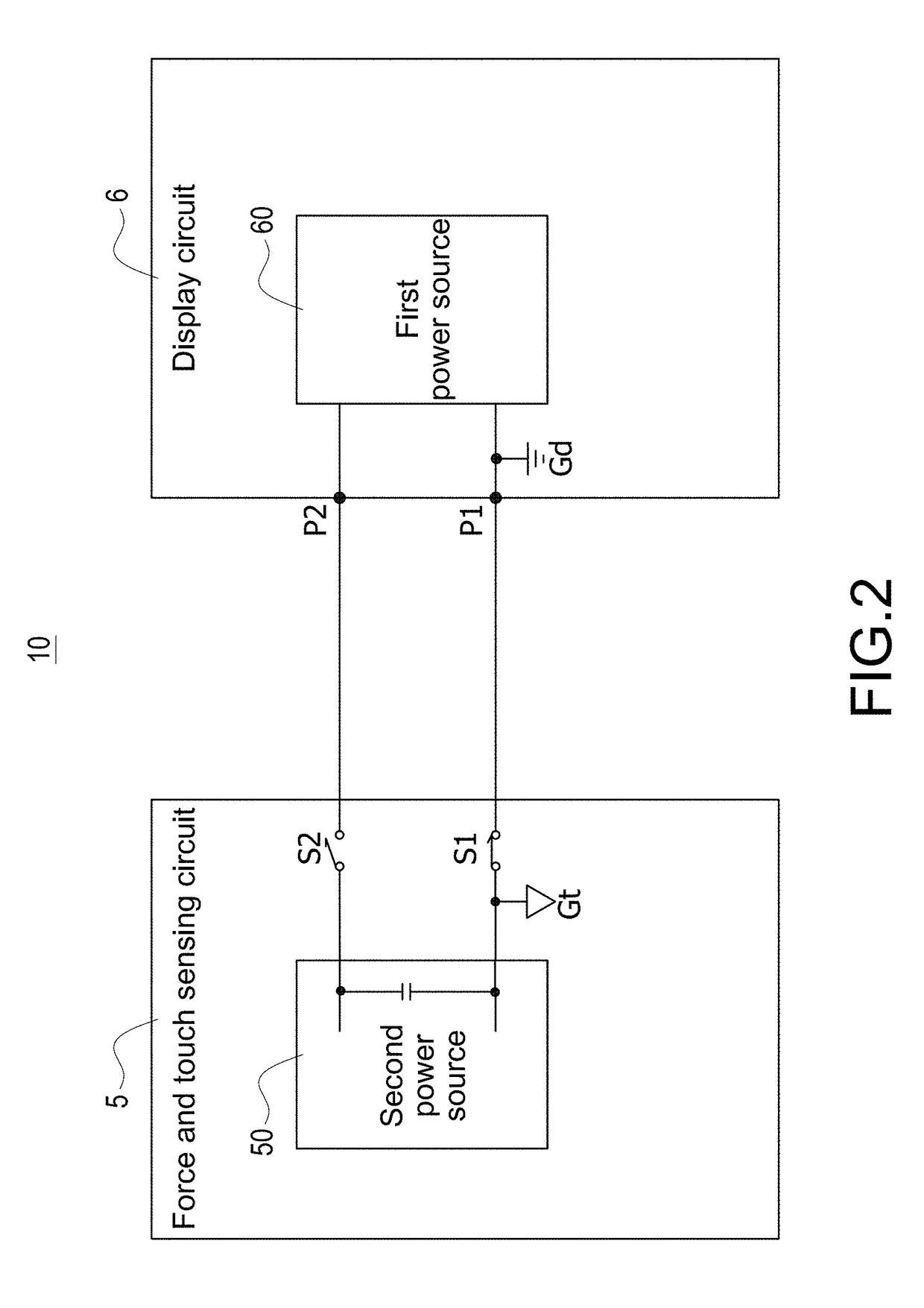
ActiveUS20170357366A1Noise and interferenceEliminate noise distractionsPower supply for data processingInput/output processes for data processingElectricityTouch Senses
An electronic apparatus with independent power sources includes a functional circuit, a plurality of touch sensing electrodes, at least one force sensing electrode and a force and touch sensing circuit, wherein the functional circuit and the force and touch sensing circuit are powered by a first power source and a second power source different with the first power source, respectively. The force and touch sensing circuit is electrically connected with the touch sensing electrodes and the force sensing electrode to sense external touch and touching force by driving the touch sensing electrodes and the force sensing electrode. The first power source and the second power source have no common current loop therebetween during touch or force sensing operation.
Owner:SUPERC TOUCH CORP
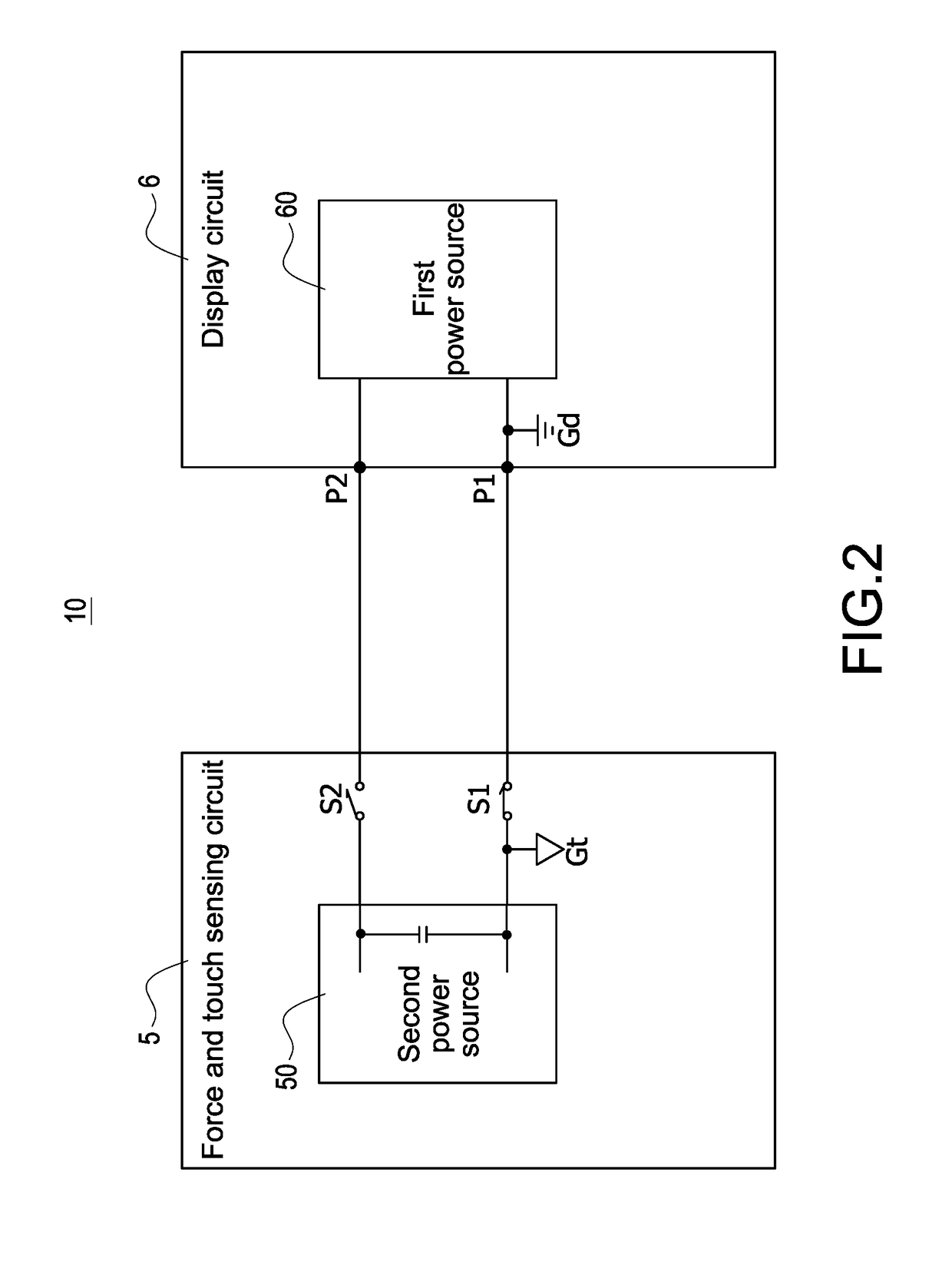
Method for operating electronic apparatus with independent power sources
ActiveUS20170357364A1Noise and interferenceEliminate noise distractionsDigital data processing detailsInput/output processes for data processingCapacitanceTouch Senses
A method for operating electronic apparatus with independent power sources and having a functional circuit and a force and touch sensing circuit, the functional circuit and the force and touch sensing circuit are respectively powered by a first power source and a second power source different with the first power source. The method comprises (a) connecting the first power source and the second power source to different grounds; (b) the force and touch sensing circuit applying a capacitive sensing excitation signal to a force sensing electrode or a touch sensing electrode; and (c) the force and touch sensing circuit detecting a sensing signal from the force sensing electrode or the touch sensing electrode. In above step (b) or (c), the first power source and the second power source have no common current loop therebetween.
Owner:SUPERC TOUCH CORP
Optical network and optical signal modulation method thereof
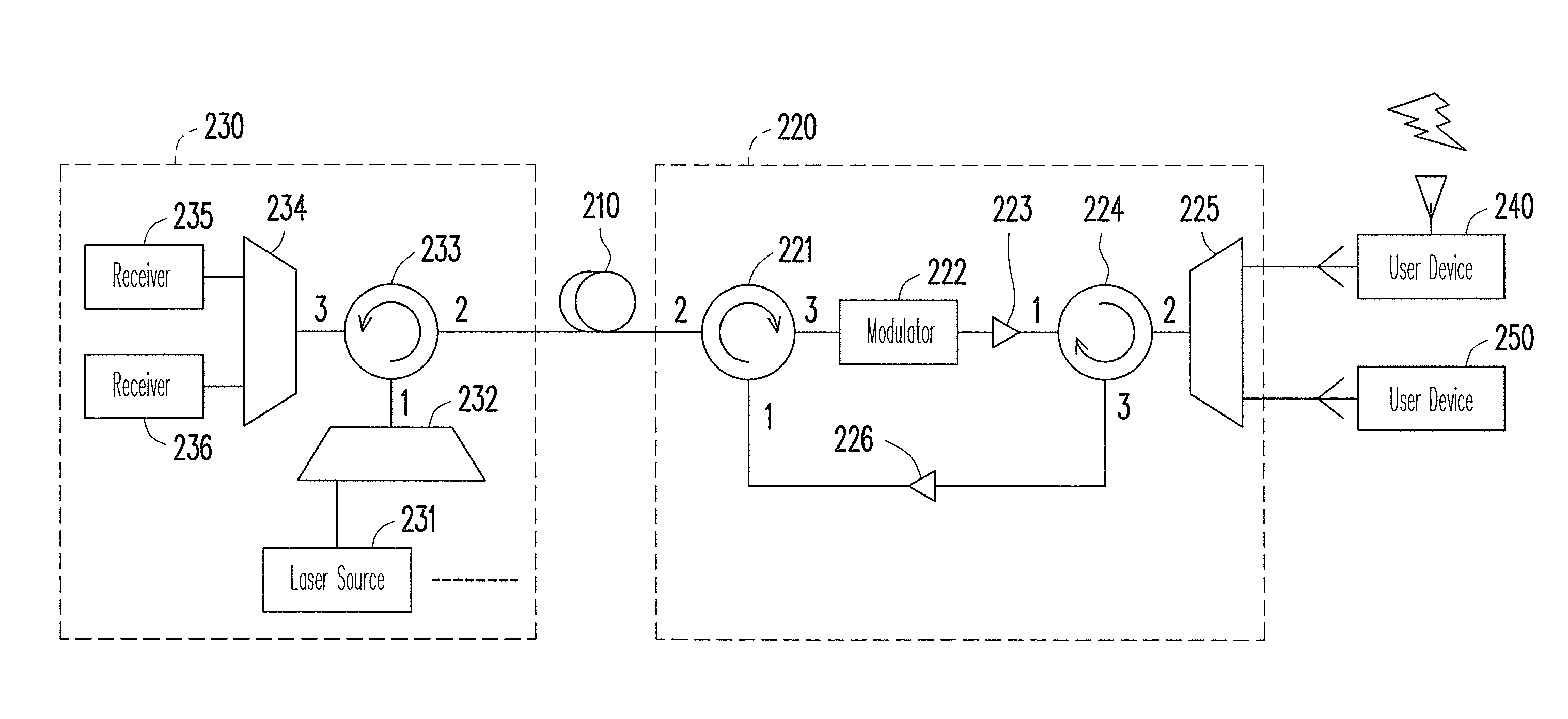
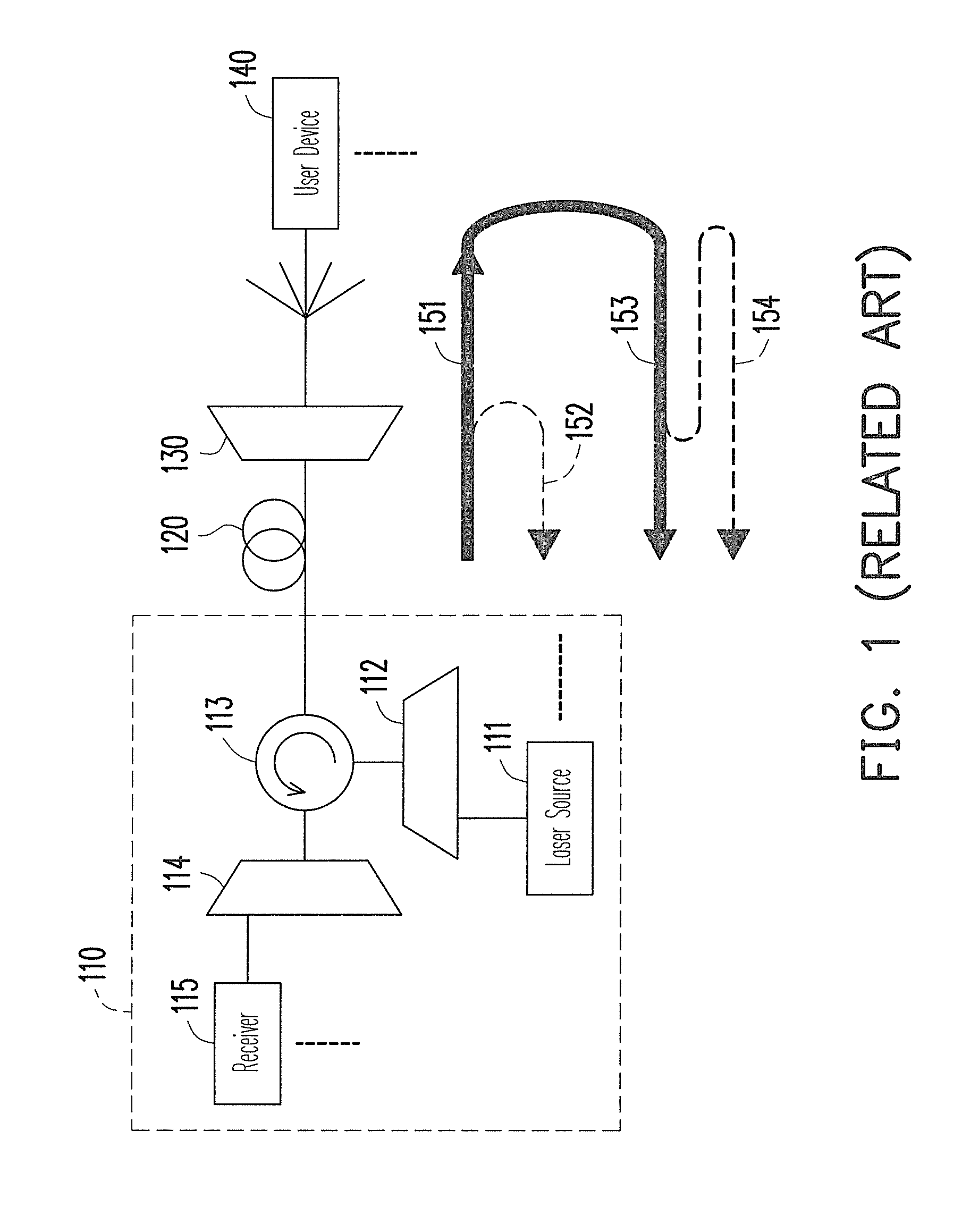
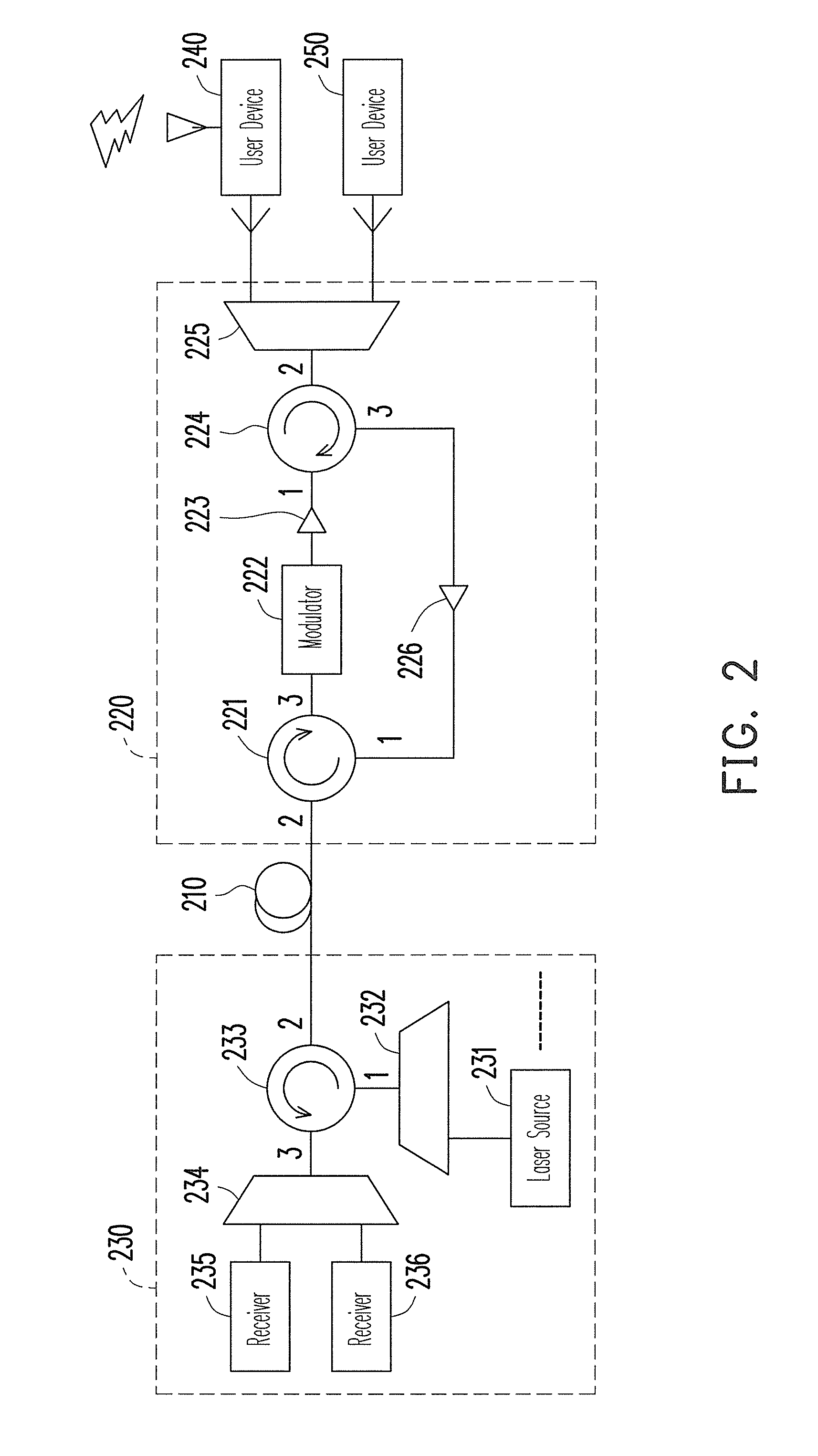
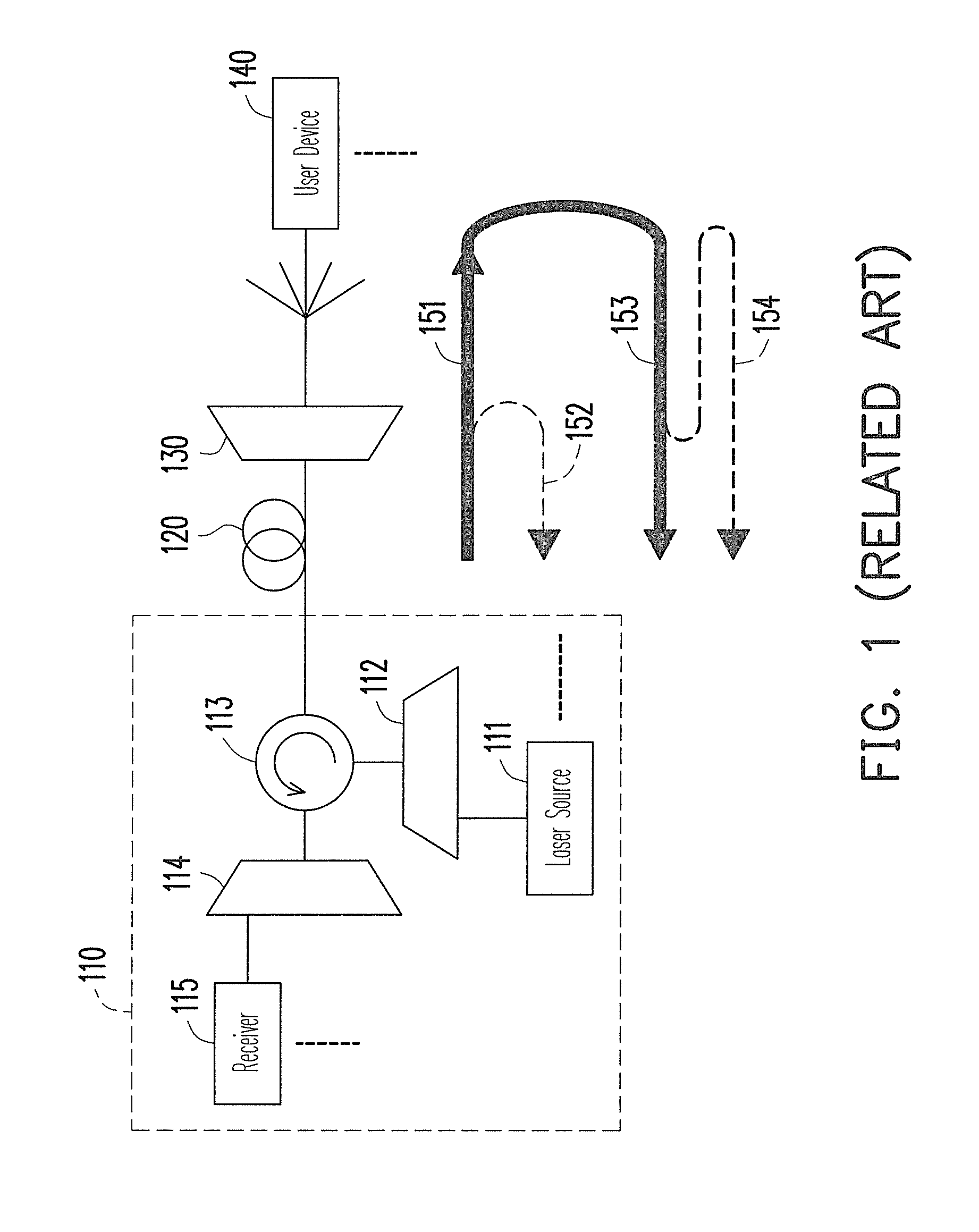
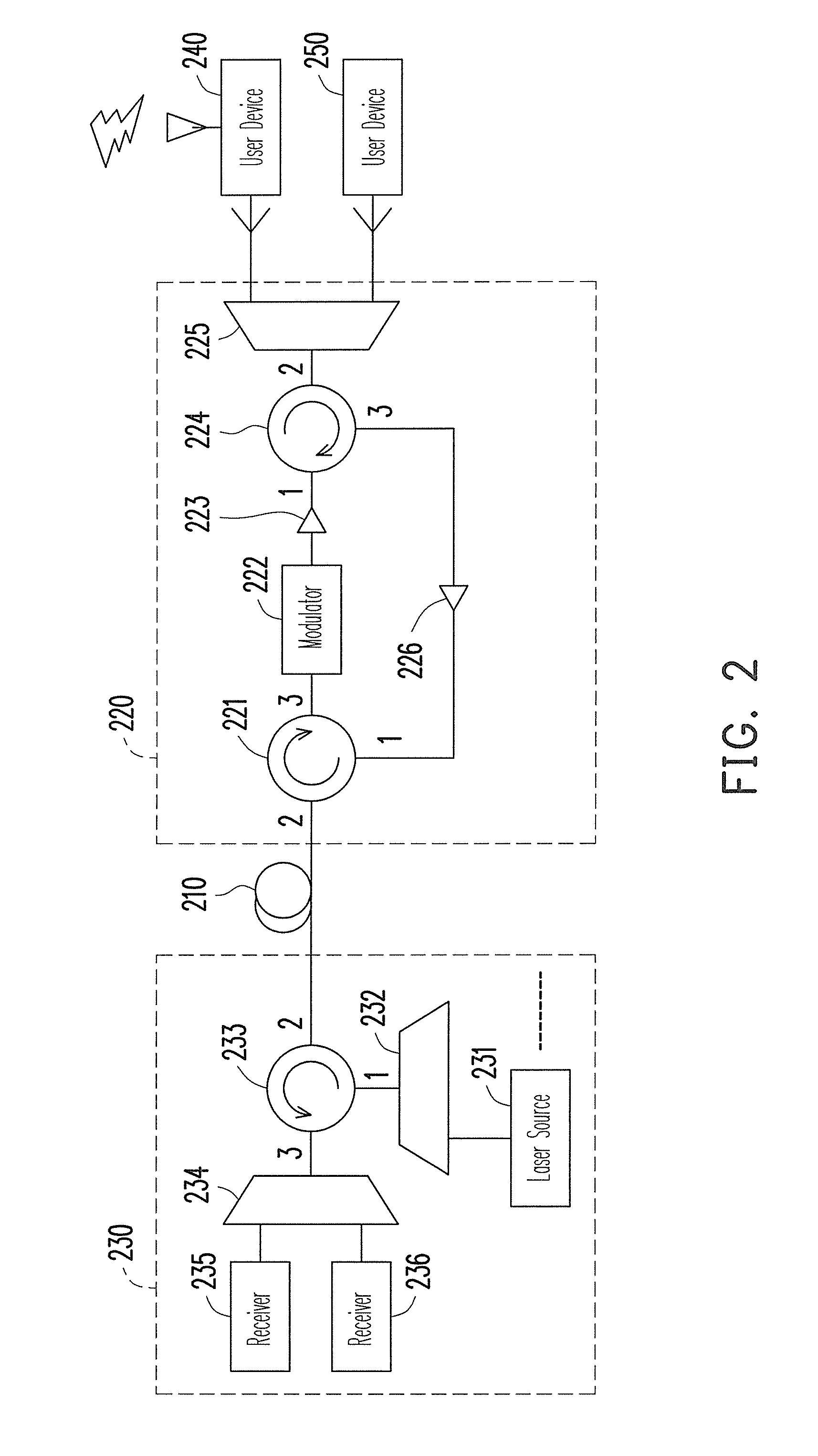
ActiveUS8364039B2Reduce distractionsNoise and interferenceWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultiple station single light sourceUser deviceCarrier signal
An optical network and an optical signal modulation method thereof are provided. The optical network includes an optical fiber and a remote node (RN). The RN receives a continuous carrier wave from the optical fiber and modulates the continuous carrier wave to generate a first frequency offset carrier wave The frequency of the first frequency offset carrier wave is different from that of the continuous carrier wave. A first user device re-modulates and loads data to the first frequency offset carrier wave to generate a first upstream signal. The frequency of the first upstream signal is the same as that of the first frequency offset carrier wave. The RN inputs the first upstream signal into the optical fiber.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Hv converter with reduced EMI
ActiveUS20190304924A1Improve cooling effectNoise and interferenceEfficient power electronics conversionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectromagnetic interferenceCopper
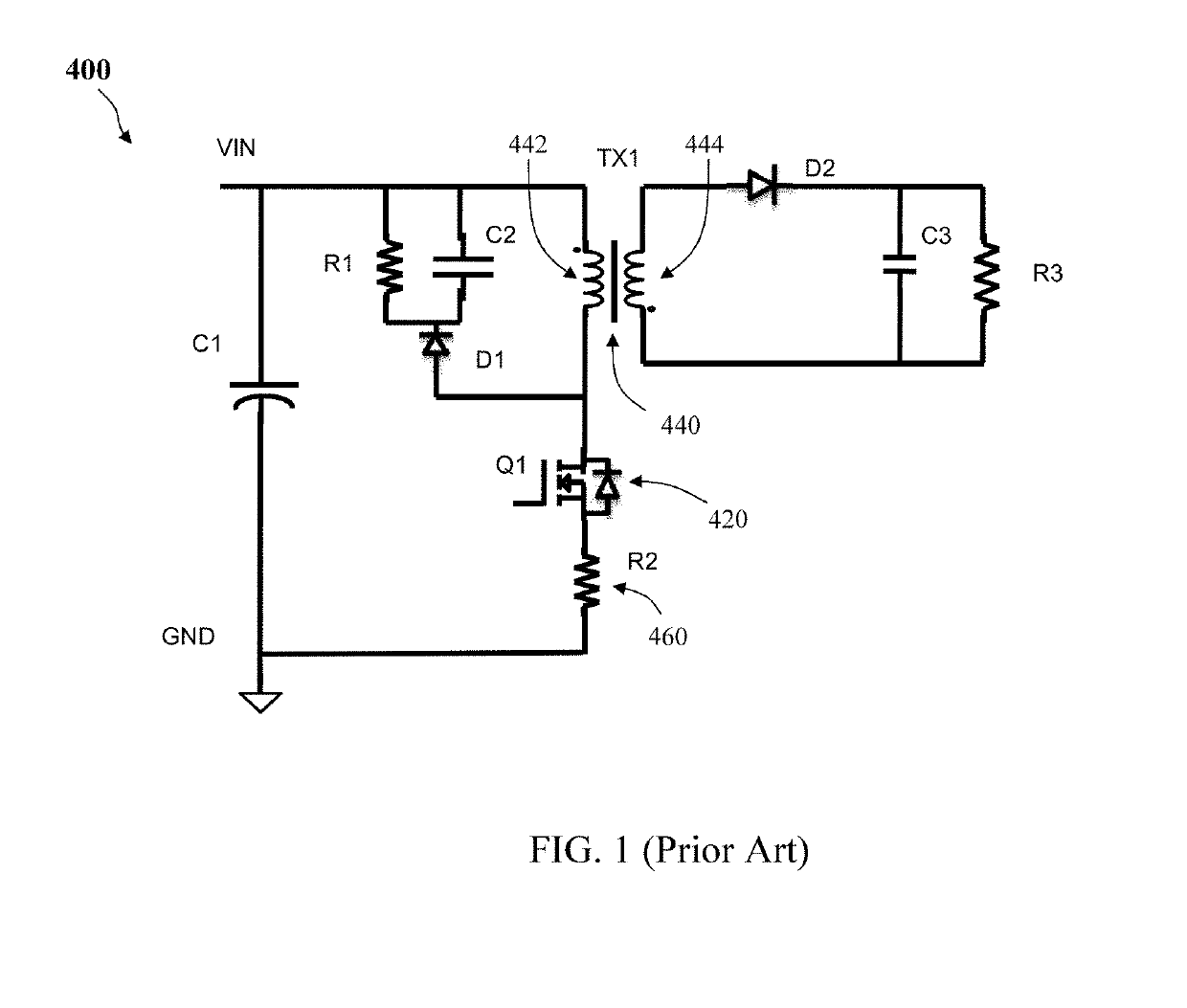
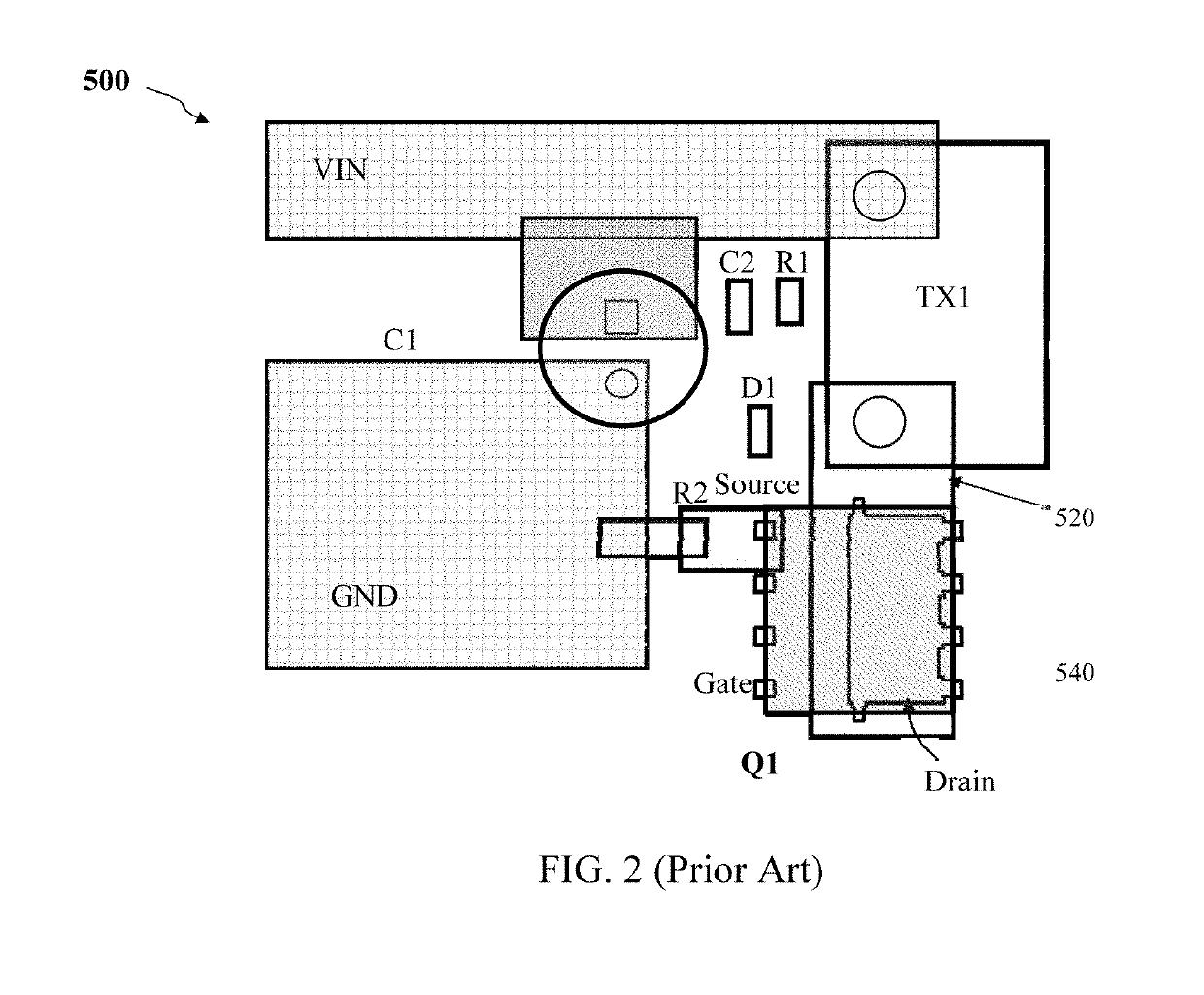
A high voltage (HV) converter implemented on a printed circuit board (PCB) includes a double diffused metal oxide semiconductor (DMOS) package comprising a lead frame and a main DMOS chip. The lead frame includes a gate section electrically connected to a gate electrode of the main DMOS chip, a source section electrically connected to a source electrode of the main DMOS chip and a drain section electrically connected to a drain electrode of the main DMOS chip. The PCB layout includes a large area source copper pad attached to and overlapping the source section of the DMOS package to facilitate cooling and a small area drain copper pad attached to and overlapping the drain section of the DMOS package to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) noise.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON CAYMAN
Driving device and device method
ActiveUS10474291B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioNoise and interferenceInput/output processes for data processingElectricitySignal processing circuits
The present disclosure provides a driving device for driving a sensing device having a plurality of driving electrodes and a plurality of sensing electrodes. The driving device includes a signal processing circuit and a readout circuit. The signal processing circuit is electrically connected to the plurality of driving electrodes of the sensing device. The signal processing circuit is configured to generate a plurality of driving signal to drive the sensing device. The signal processing circuit selects a plurality of Walsh codes from a plurality of rows or columns of a Walsh matrix to serve as a plurality of driving signals. The readout circuit readouts the sensing device to generate a plurality of sensing signals and provides the plurality of sensing signals to the signal processing circuit, so that the signal processing circuit demodulates the plurality of sensing signals. In addition, a driving method is also provided.
Owner:HANNSTAR DISPLAY CORPORATION
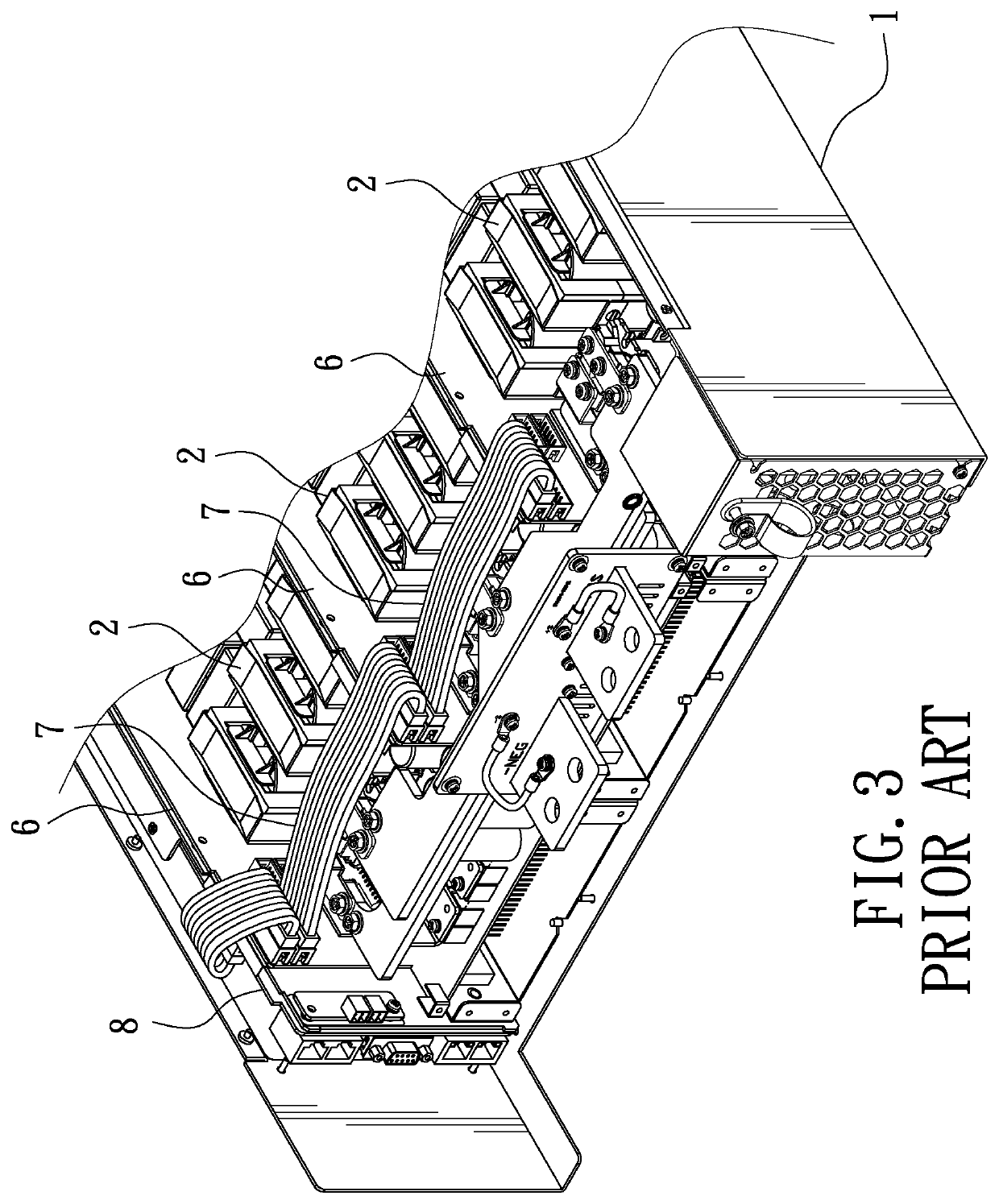
Adapter board structure for power module of DC power supply
ActiveUS10609846B1Easy wiringImprove cooling effectLocalised screeningCross-talk/noise/interference reductionElectrical connectionElectromagnetic interference
An adapter board structure for a power module of a DC power supply is disclosed. The DC power supply includes a casing. A main circuit control board and at least one power module are disposed in the casing. One side of the power module is provided with a secondary circuit control board. The secondary circuit control board has an input port and an output port for connection of a control wire. Another side of the power module is provided with an adapter board. The adapter board also has an input port and an output port for connection of the control wire. The power module can be electrically connected through the adapter board, and the adapter board has the functions of shielding and wind guiding, thereby isolating noise and electromagnetic interference and improving heat dissipation.
Owner:CHYNG HONG ELECTRONICS
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS8148816B2Noise and interferenceEasily deterioratedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceSemiconductor chip
Owner:GK BRIDGE 1
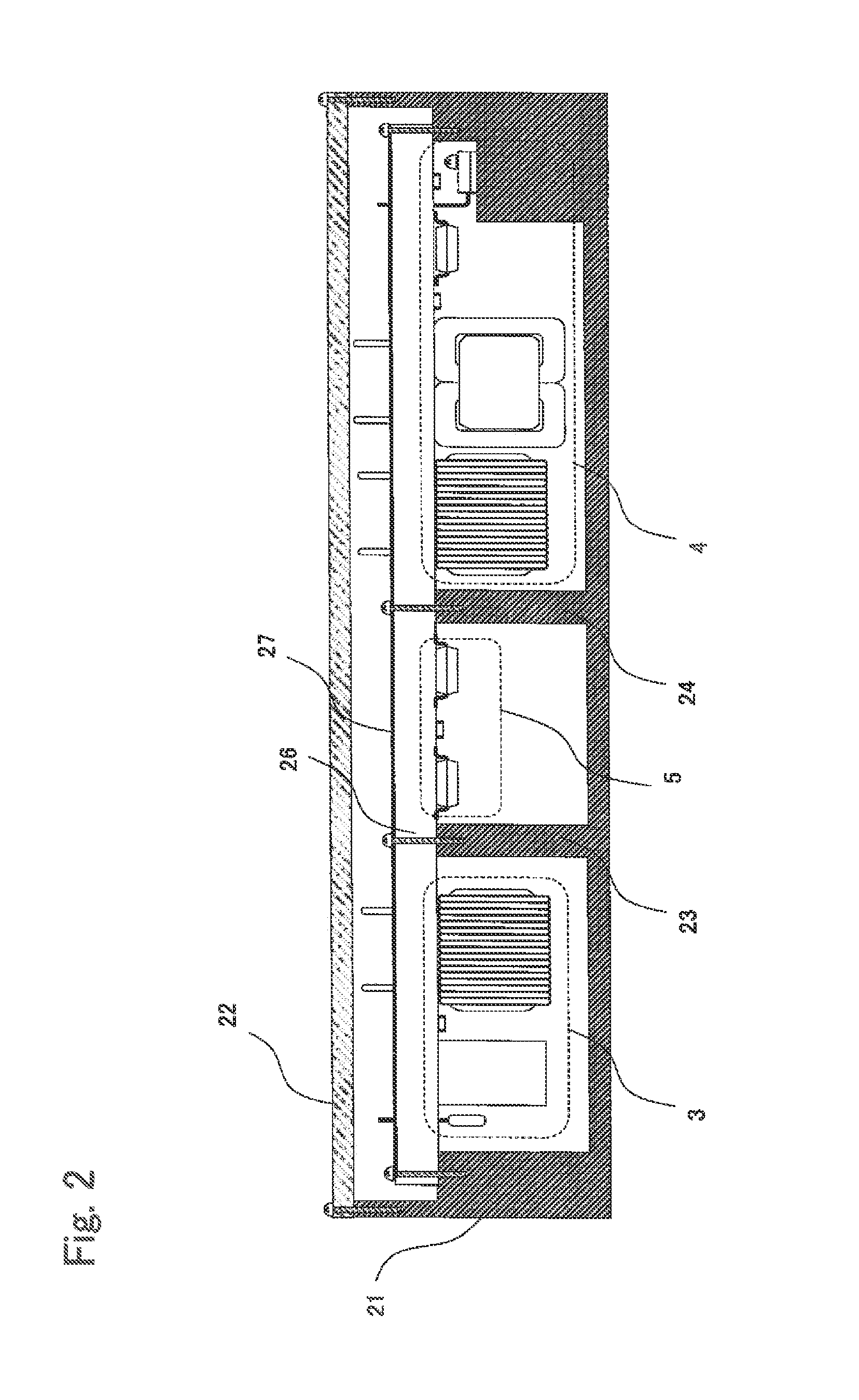
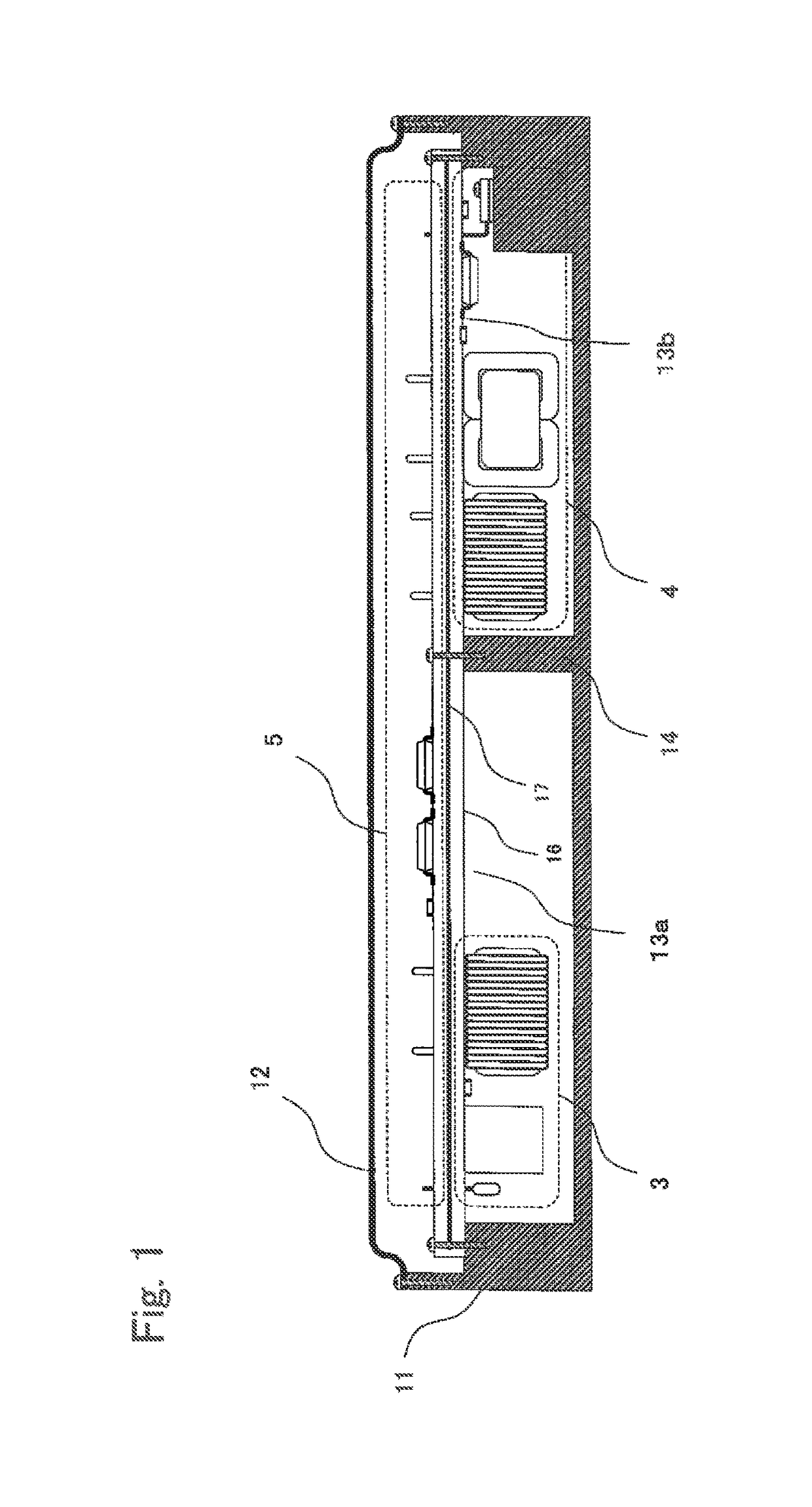
In-vehicle power conversion system
ActiveUS9712039B2Low costSmall sizeMagnetic/electric field screeningConversion constructional detailsElectricityIn vehicle
An in-vehicle power conversion system, which can shield a circuit unit without using a particular shield member and can achieve reduction in cost and size, is obtained. Included are: a conductive housing having an opening; and a multilayer printed wiring board in which circuit units are mounted and one layer is a GND plane. The multilayer printed wiring board is assembled to an opening surface of an opening of the conductive housing to form a closed space; and the GND plane of the multilayer printed wiring board is electrically connected to the conductive housing to shield the circuit units stored in the closed space surrounded by the conductive housing and the multilayer printed wiring board.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Optical network and optical signal modulation method thereof
ActiveUS20110110667A1Noise and interferenceReduce interferenceWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultiple station single light sourceCarrier signalSignal modulation
An optical network and an optical signal modulation method thereof are provided. The optical network includes an optical fiber and a remote node (RN). The RN receives a continuous carrier wave from the optical fiber and modulates the continuous carrier wave to generate a first frequency offset carrier wave The frequency of the first frequency offset carrier wave is different from that of the continuous carrier wave. A first user device re-modulates and loads data to the first frequency offset carrier wave to generate a first upstream signal. The frequency of the first upstream signal is the same as that of the first frequency offset carrier wave. The RN inputs the first upstream signal into the optical fiber.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Reducing Effects of Rig Noise on Telemetry
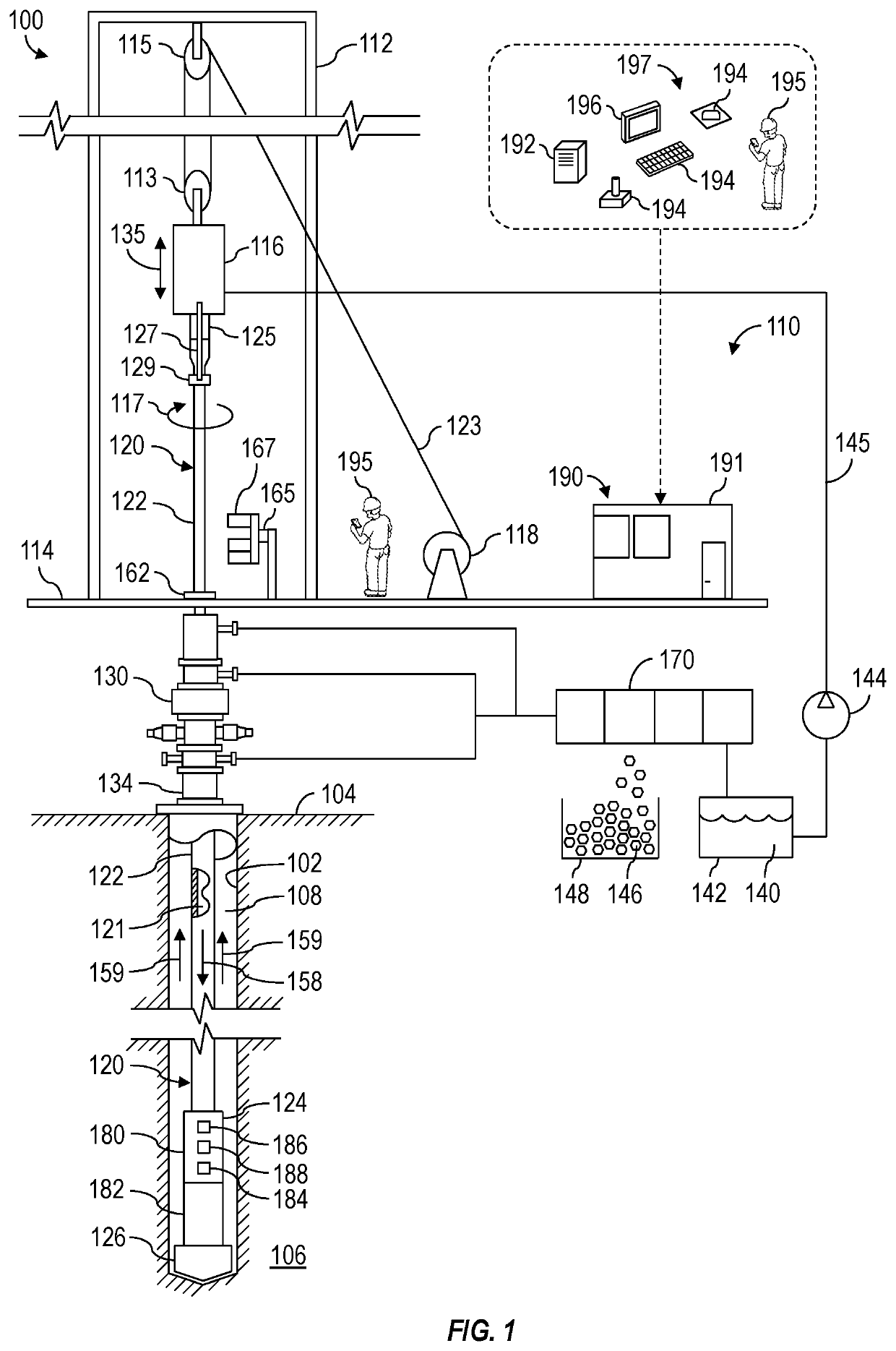
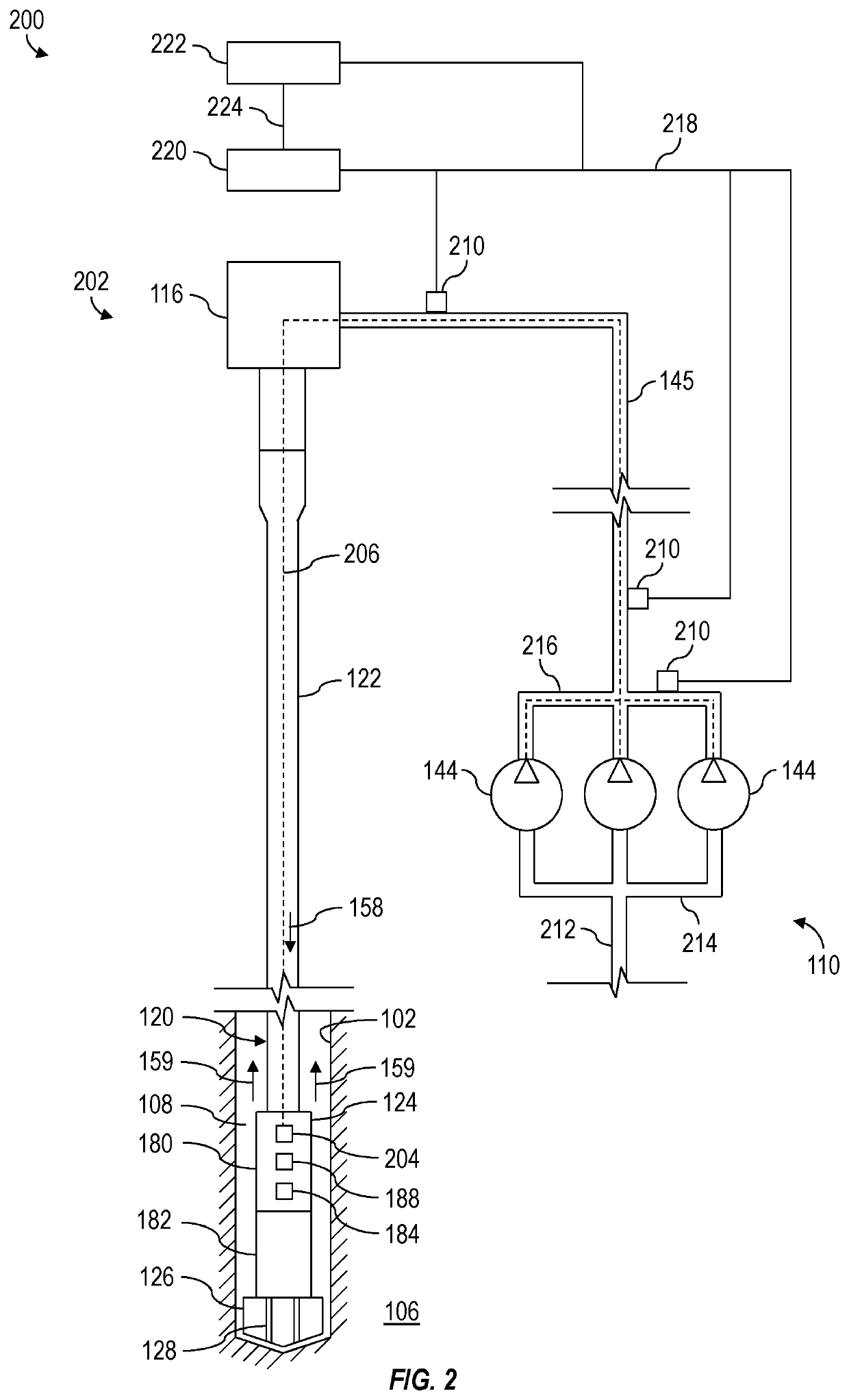
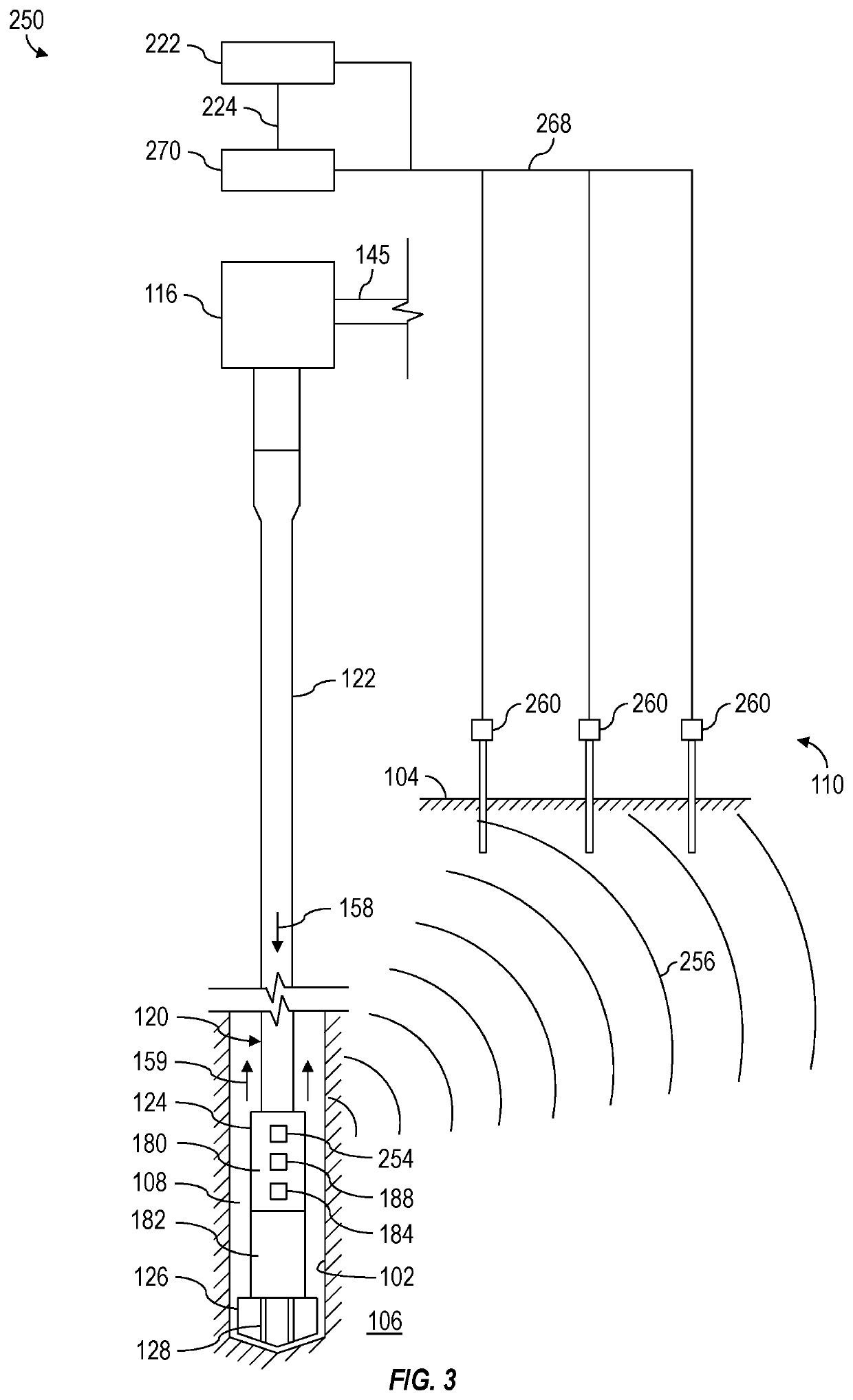
InactiveUS20210189869A1Reduce distractionsNoise and interferenceSurveyConstructionsControl engineeringControl theory
Apparatus and methods for reducing effects of rig noise on telemetry. A method may include commencing operation of a telemetry system of a drilling rig and commencing operation of an equipment controller of the drilling rig. Commencing operation of the equipment controller may cause the equipment controller to automatically output control commands to automatically change operational parameters of the telemetry system and / or rig equipment of the drilling rig to reduce interference by rig noise with a telemetry signal.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Operational transconductance amplifier, reconfigurable fully differential voltage sensing amplifier and reconfigurable fully differential capacitive sensing amplifier
ActiveUS9337779B2Reduce stepsPrecise bias driving circuitAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAmplifier modifications to reduce detrimental impedencePower flowAudio power amplifier
An operational transconductance amplifier includes a cascode differential-pair amplifying circuit, a bias driving circuit, and a common mode feedback circuit. The cascode differential-pair amplifying circuit is configured for receiving a differential input voltage and for providing a differential output voltage. The bias driving circuit is configured for providing a first bias current to drive the cascode differential-pair amplifying circuit and for adjusting the transconductance of the transconductance amplifier. The bias driving circuit includes a first floating-gate transistor. The first floating-gate transistor is configured for adjusting the first bias current. The common mode feedback circuit is configured for adjusting a second bias current of the cascode differential-pair amplifying circuit according to the differential output voltage so that the differential output voltage is stabilized. A reconfigurable fully differential voltage sensing amplifier and a reconfigurable fully differential capacitive sensing amplifier are disclosed herein as well.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
System and method for seismological sounding
InactiveUS20130094326A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioReduce energy densitySeismic data acquisitionSeismic signal processingAcoustic waveGeophysical survey
Systems and methods for seismological sounding with acoustic signals and, more particularly, systems and methods for performing geophysical surveys using spread spectrum acoustic waves generated by non-impulsive sources. A spread spectrum signal is generated and coupled to a medium that is to be sounded for propagation of an acoustic wave through the medium. One or more return signals are received from the medium that are generated by interaction between the acoustic wave and the medium. The return signals are possessed to obtain seismic sounding data describing the structural features of the medium.
Owner:ERICKSON ALAN
Method for operating electronic apparatus with independent power sources
ActiveUS10289240B2Noise and interferenceEliminate noise distractionsVolume/mass flow measurementPower supply for data processingCapacitanceTouch Senses
A method for operating electronic apparatus with independent power sources and having a functional circuit and a force and touch sensing circuit, the functional circuit and the force and touch sensing circuit are respectively powered by a first power source and a second power source different with the first power source. The method comprises (a) connecting the first power source and the second power source to different grounds; (b) the force and touch sensing circuit applying a capacitive sensing excitation signal to a force sensing electrode or a touch sensing electrode; and (c) the force and touch sensing circuit detecting a sensing signal from the force sensing electrode or the touch sensing electrode. In above step (b) or (c), the first power source and the second power source have no common current loop therebetween.
Owner:SUPERC TOUCH CORP
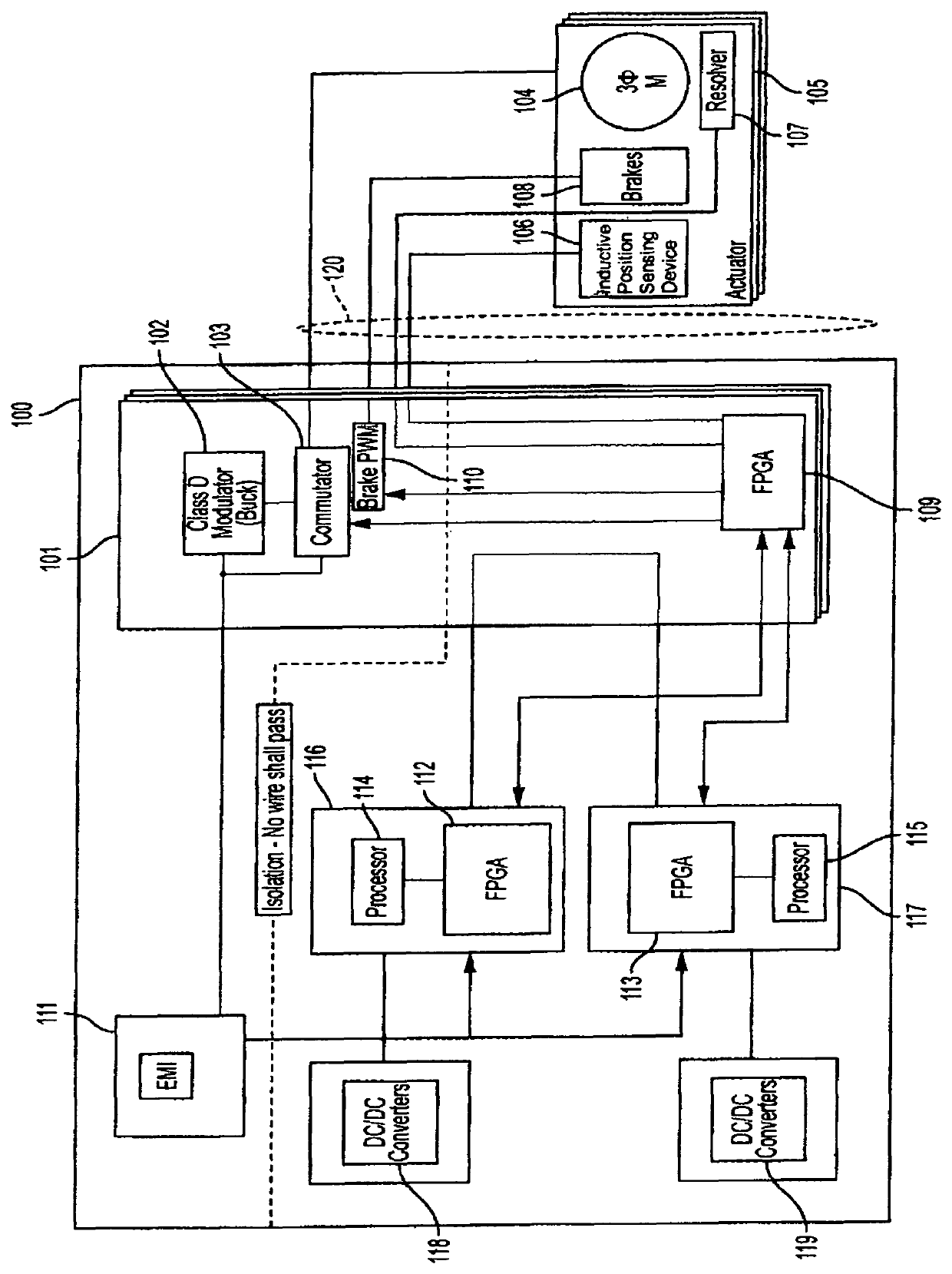
Robot electronics unit (REU) motor controller board (MCB)
ActiveUS10715073B1Reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) noiseUtilize power moreProgramme-controlled manipulatorAssociation with control/drive circuitsConvertersRobotic arm
The present invention relates to a Robot Electronics Unit (REU) motor controller board (MCB) with a trapezoid wave design, which can utilize power efficiently and reduce electromagnetic interference. The MCB uses a modulator or Buck Converter to regulate the voltage before it is passed to the motors used in robotic arms in space applications. The REU MCB includes: a commutator disposed on the MCB and connected to a three-phase induction motor; and a modulator disposed on the MCB and which precedes the commutator, the modulator which utilizes pulse width modulation (PWM) to regulate a voltage to the commutator and provide a predetermined current to the commutator. The modulator regulates the voltage by stepping it down from a 100V power input signal before the voltage is passed to the motor. The output of the modulator includes a trapezoid waveform design which controls the motor and reduces electromagnetic interference.
Owner:NASA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com