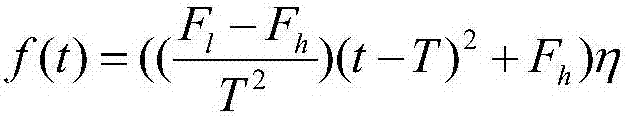Patents
Literature
115 results about "B mode ultrasound" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
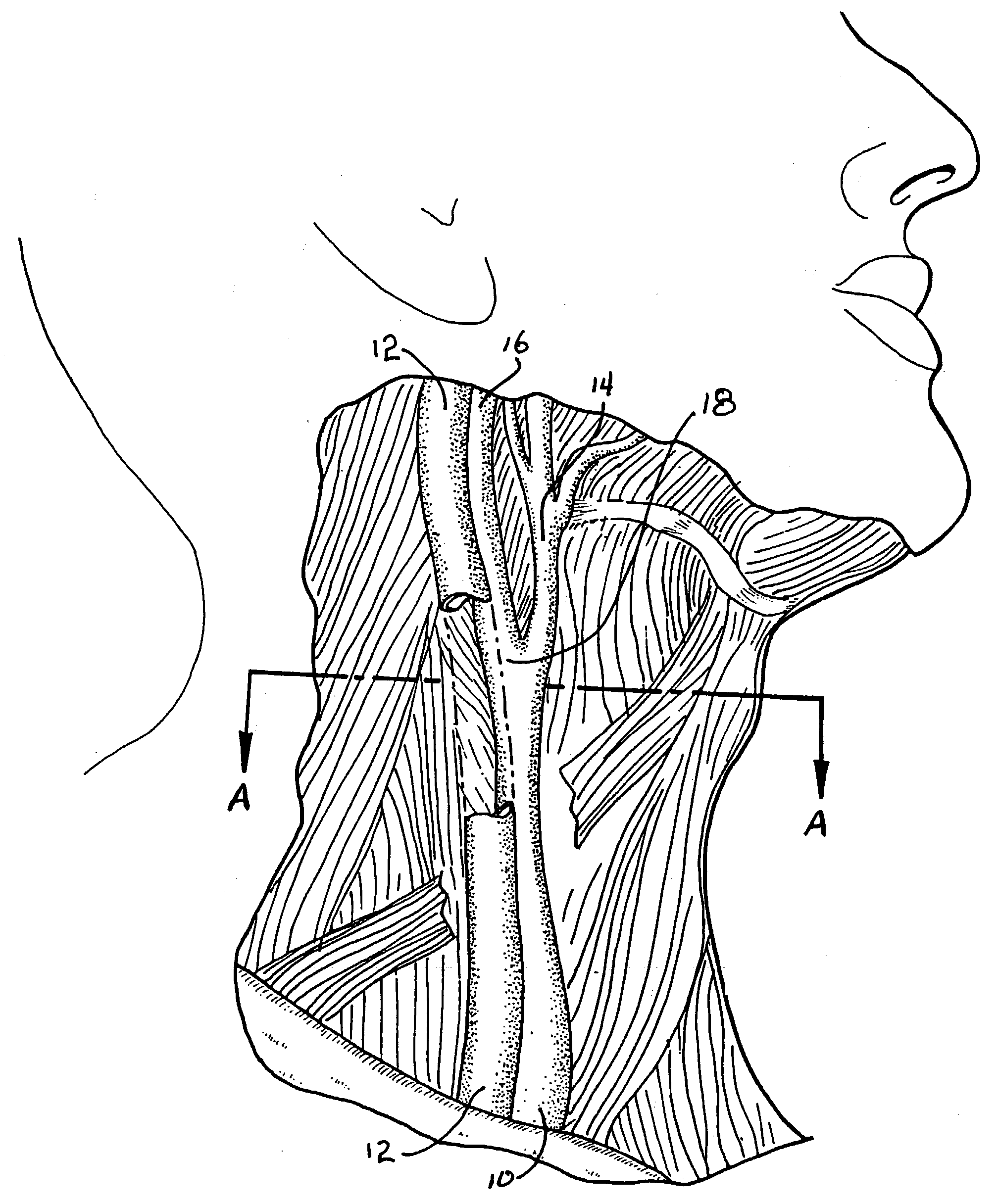
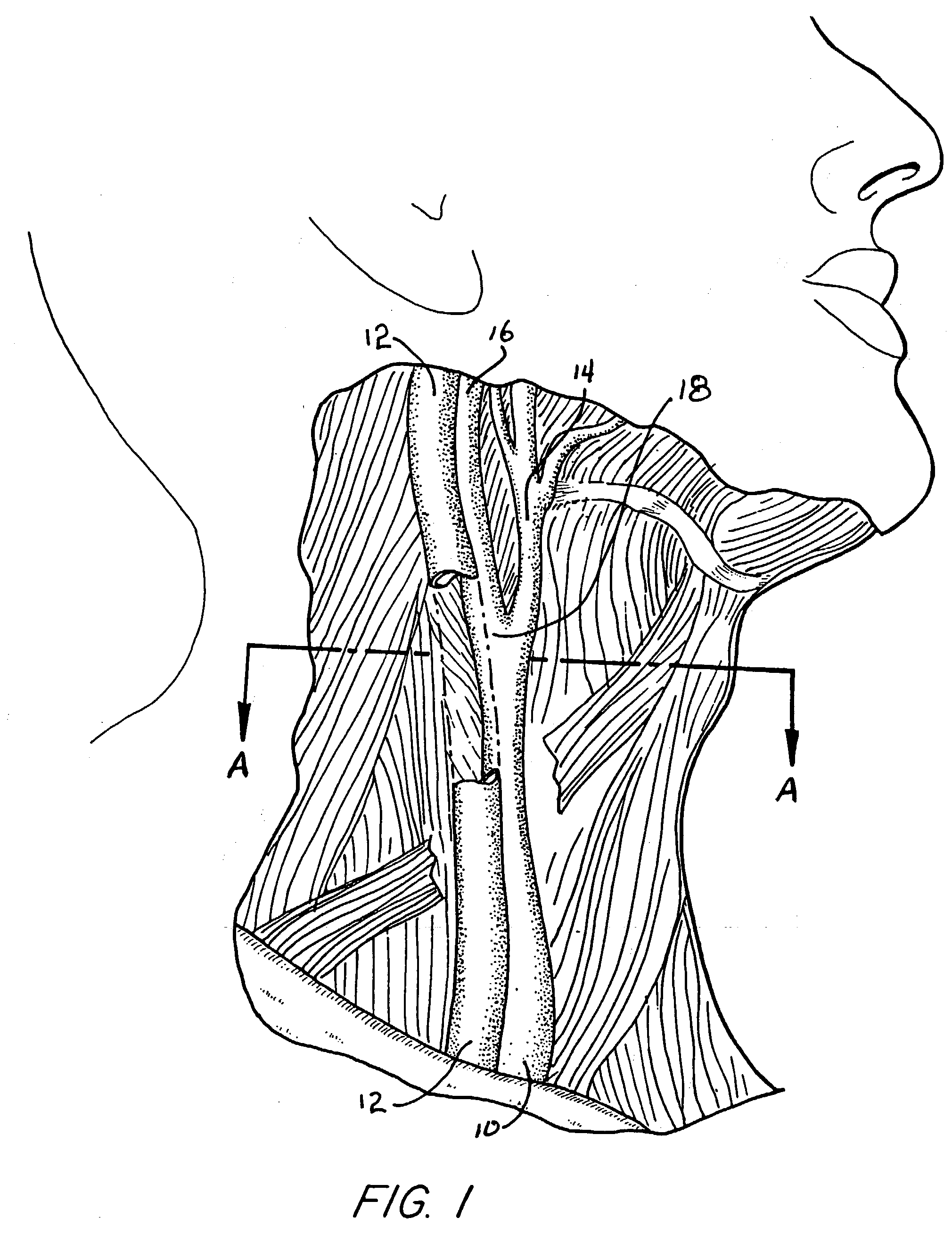
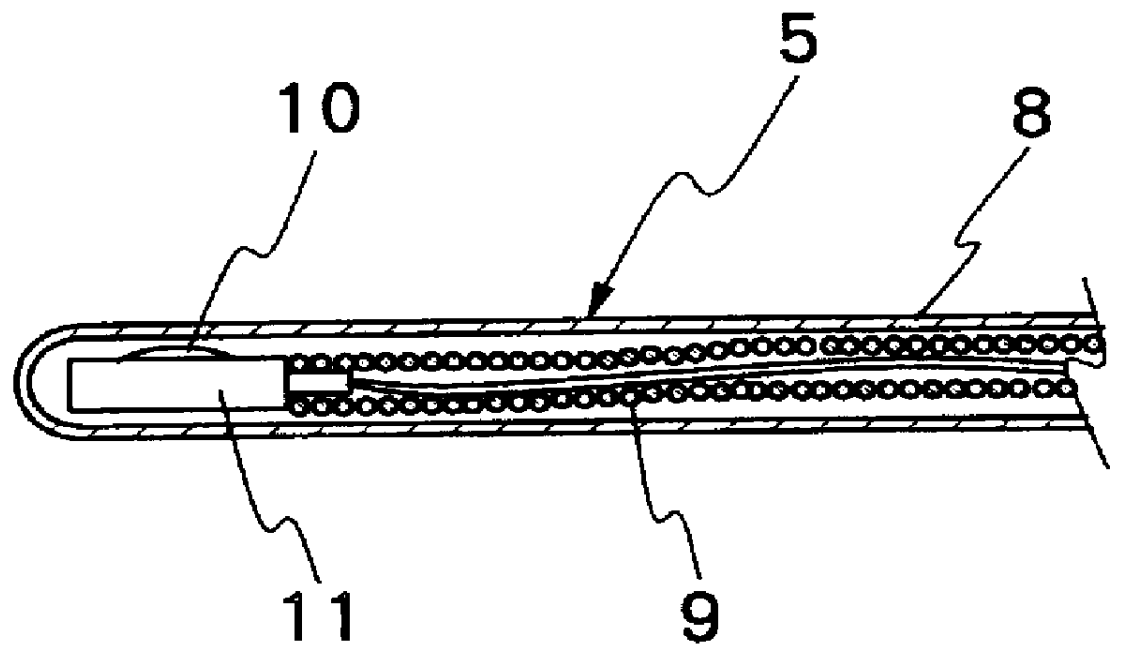
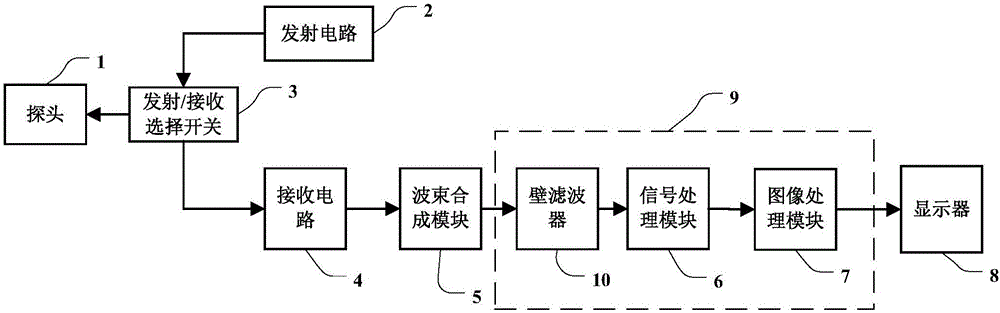
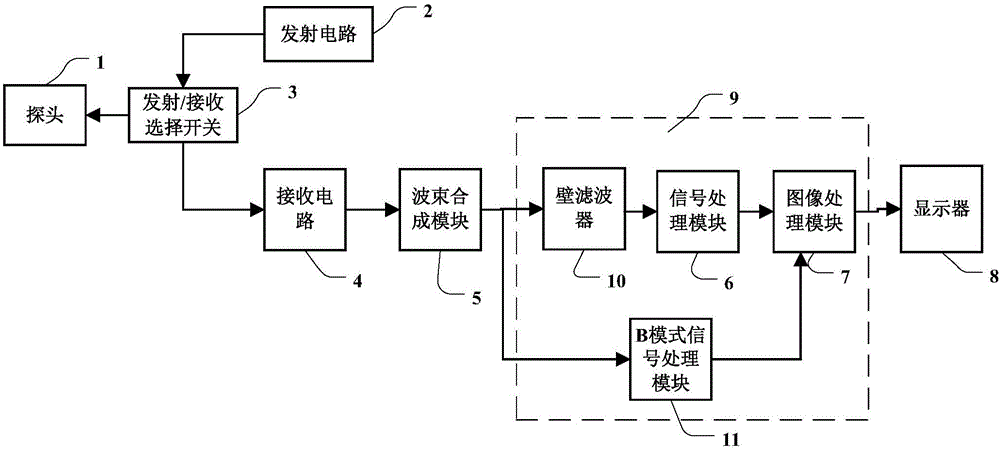
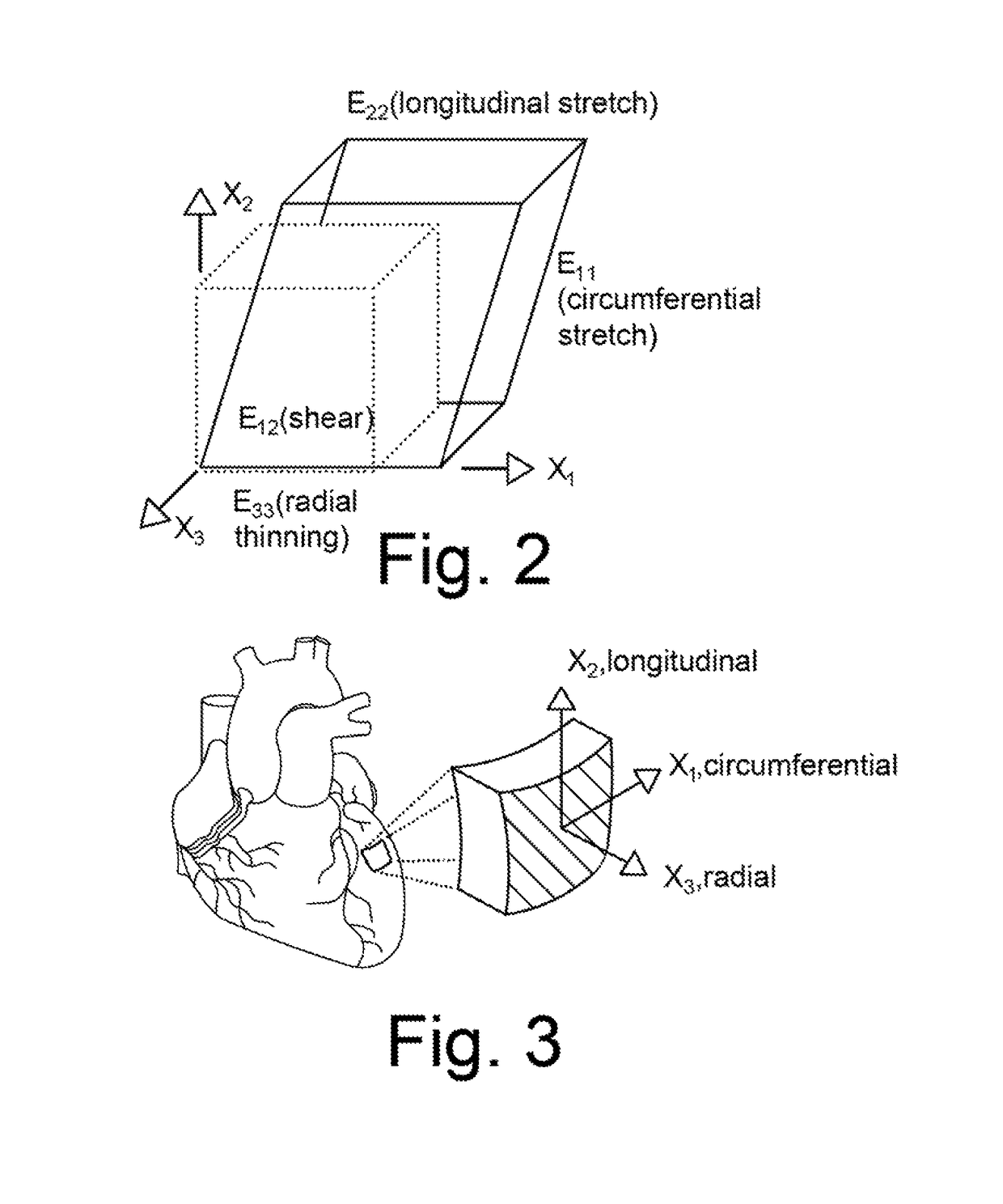
B-Mode is a two-dimensional ultrasound image display composed of bright dots representing the ultrasound echoes. The brightness of each dot is determined by the amplitude of the returned echo signal.
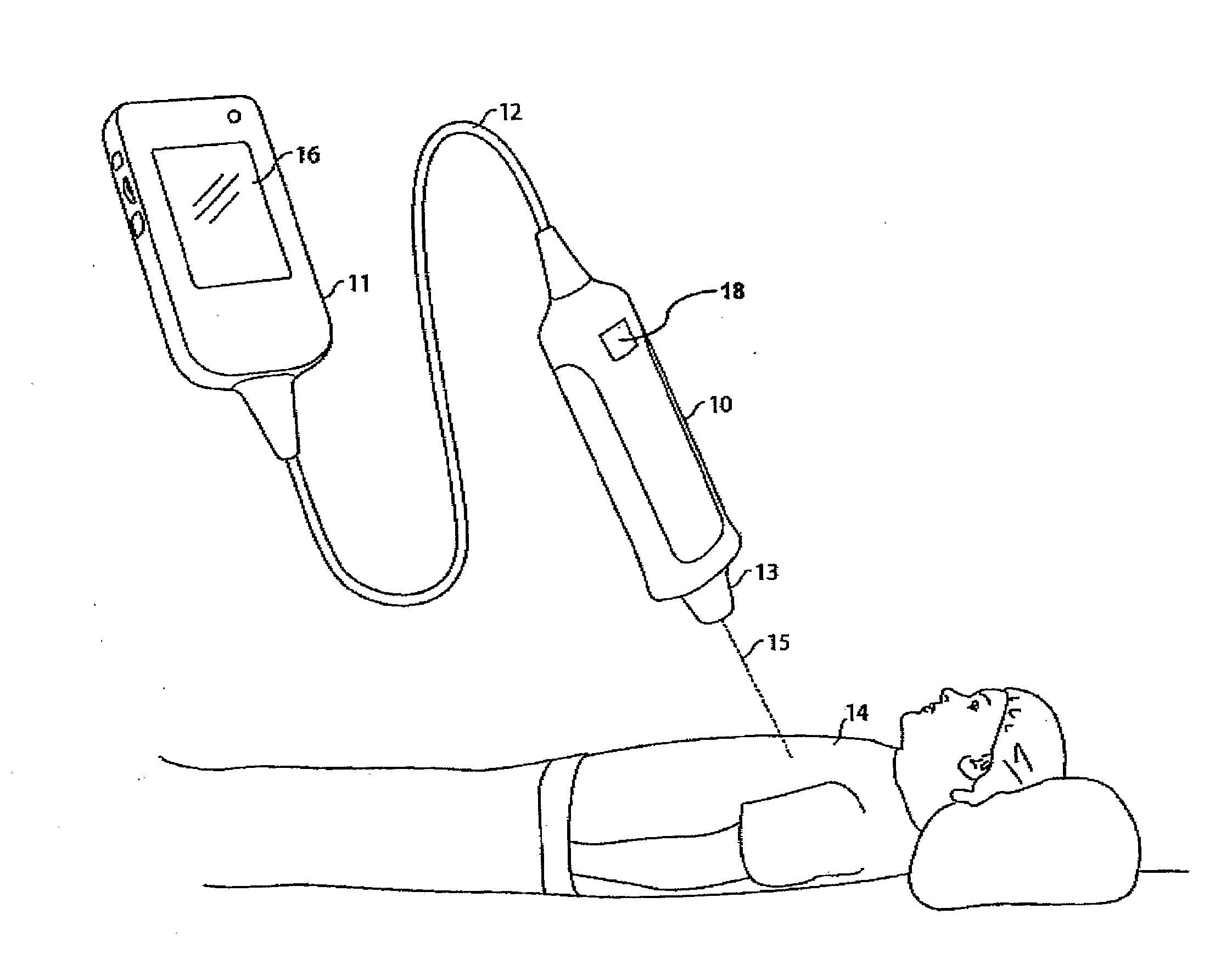
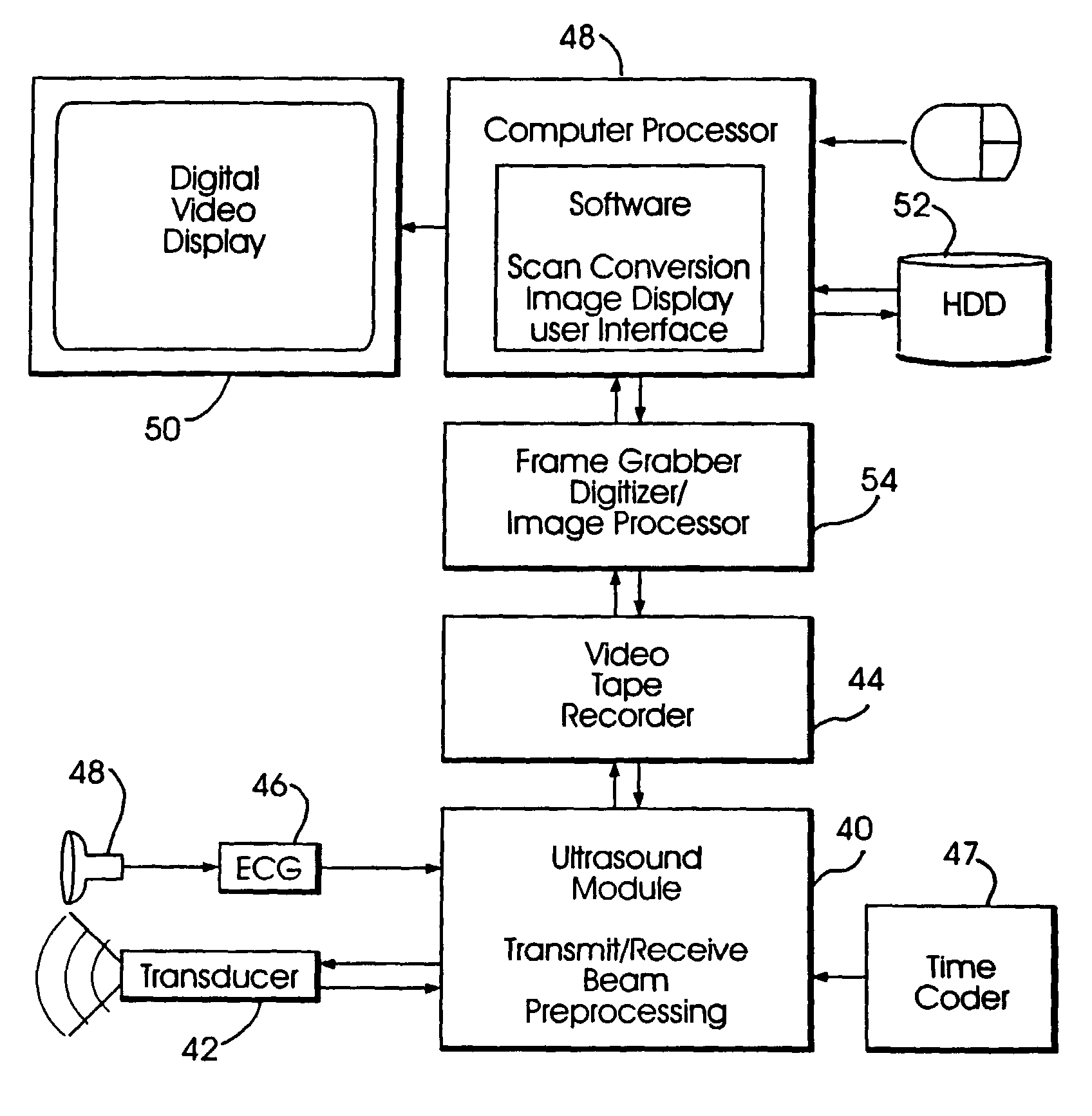
System and method for improving ultrasound image acquisition and replication for repeatable measurements of vascular structures
InactiveUS20040116812A1ElectrocardiographyOrgan movement/changes detectionAnatomical landmarkUltrasonic sensor
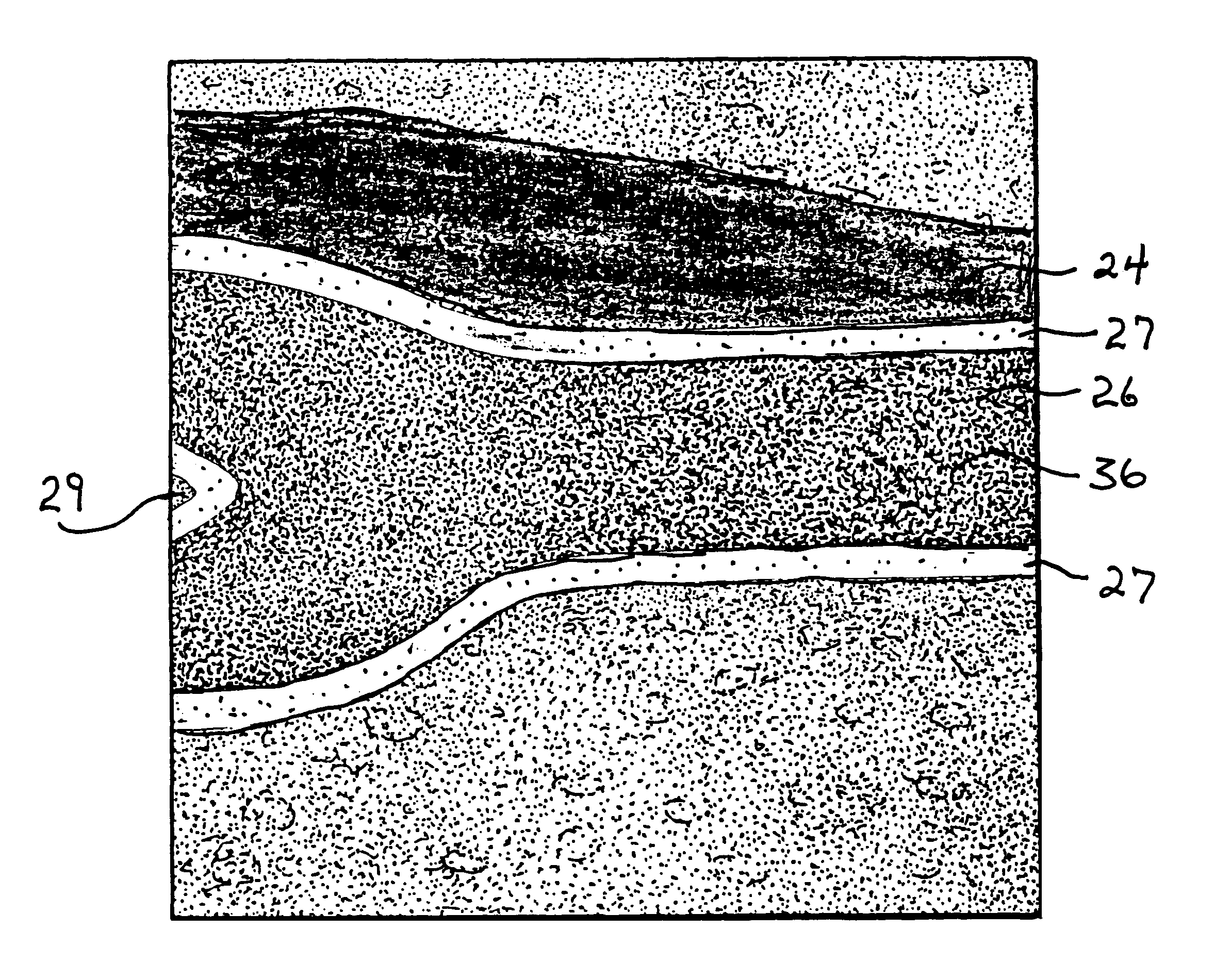
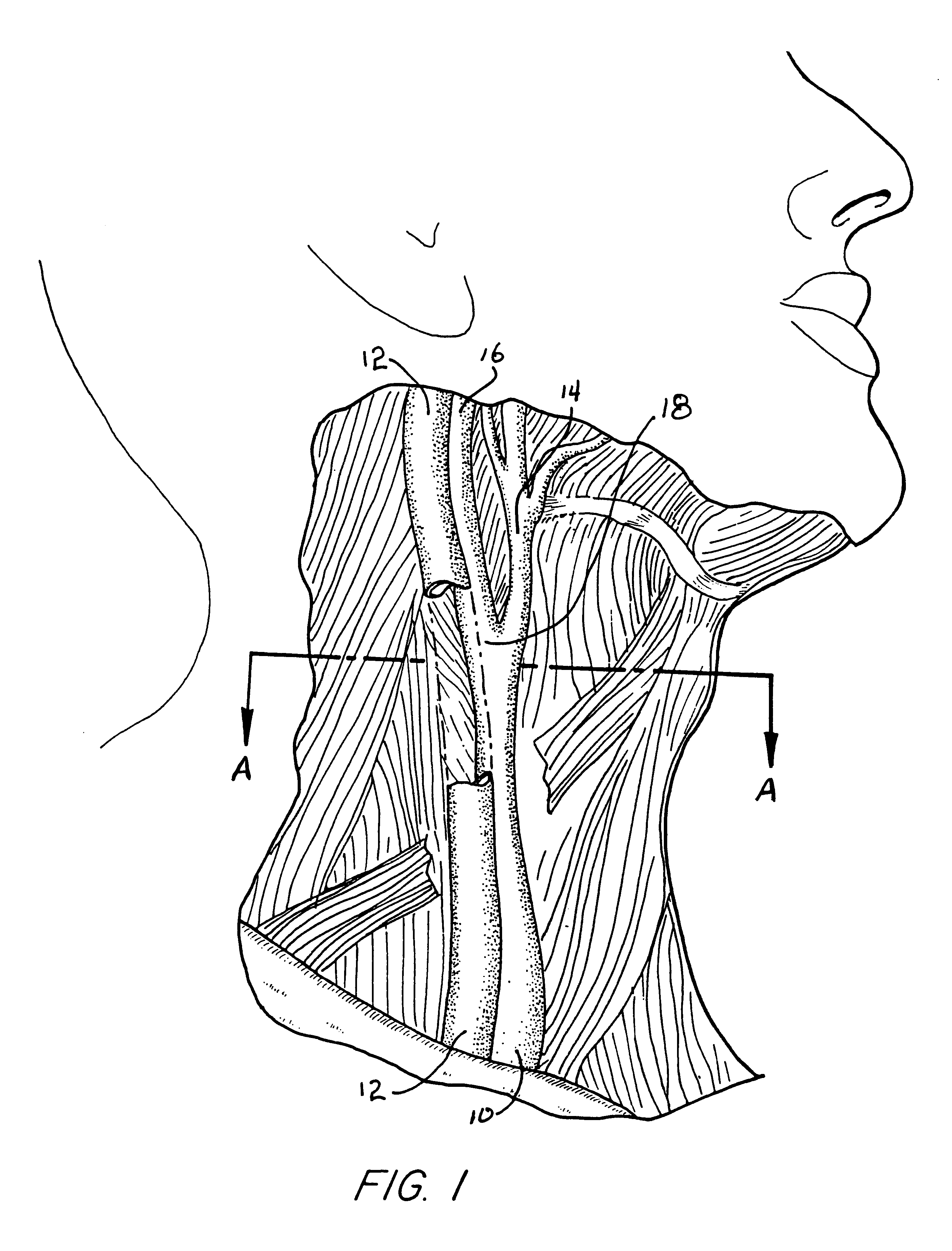
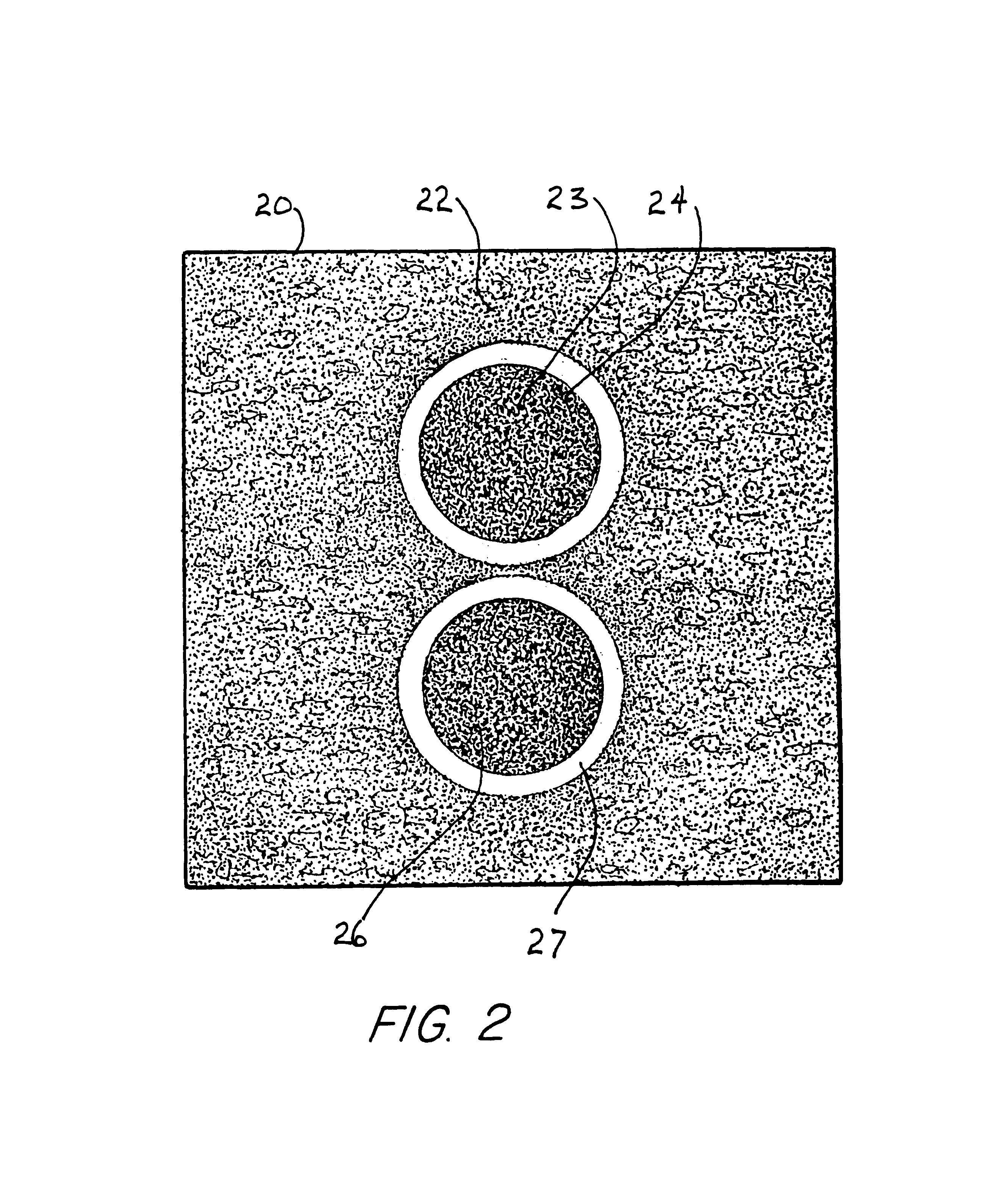
High resolution B-mode ultrasound images of the common carotid artery are obtained with an ultrasound transducer using a standardized methodology. Subjects are supine with the head counter-rotated 45 degrees using a head pillow. The jugular vein and carotid artery are located and positioned in a vertical stacked orientation. The transducer is rotated 90 degrees around the centerline of the transverse image of the stacked structure to obtain a longitudinal image while maintaining the vessels in a stacked position. A computerized methodology assists operators to accurately replicate images obtained over several spaced-apart examinations. The methodology utilizes a split-screen display in which the arterial ultrasound image from an earlier examination is displayed on one side of the screen while a real-time "live" ultrasound image from a current examination is displayed next to the earlier image on the opposite side of the screen. By viewing both images, whether simultaneously or alternately, while manually adjusting the ultrasound transducer, an operator is able to bring into view the real-time image that best matches a selected image from the earlier ultrasound examination. Utilizing this methodology, measurement of vascular dimensions such as carotid arterial IMT and diameter, the coefficient of variation is substantially reduced to values approximating from about 1.0% to about 1.25%. All images contain anatomical landmarks for reproducing probe angulation, including visualization of the carotid bulb, stacking of the jugular vein above the carotid artery, and initial instrumentation settings, used at a baseline measurement are maintained during all follow-up examinations.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
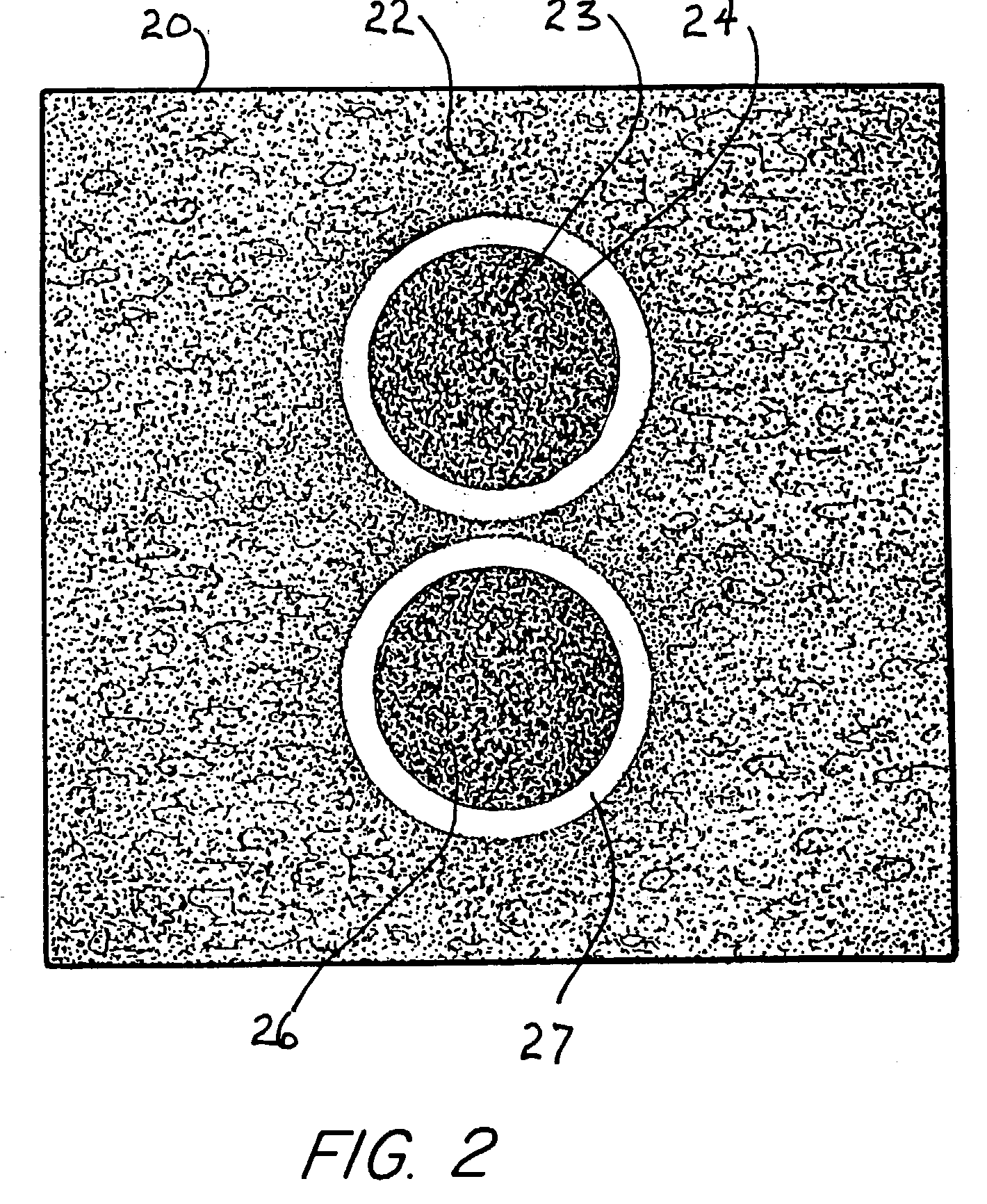
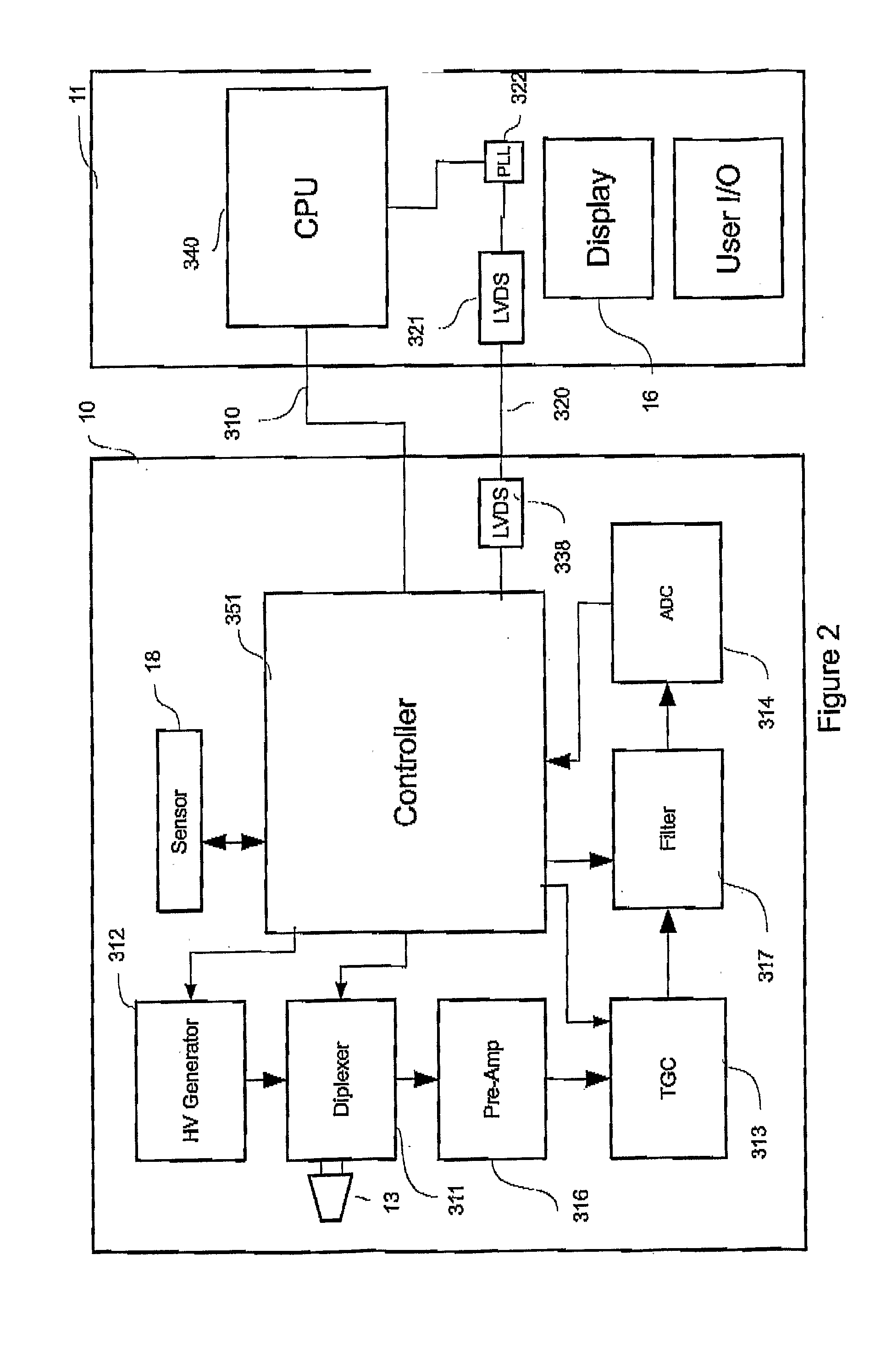
Ultrasound image processing system
InactiveUS6108439AEasy to operateSimplify and accelerate signal processing operationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUltrasonic sensorImaging processing
An ultrasound image processing system, having an ultrasound image capture device such as a B-mode ultrasound probe capable of making 2D scans over a predetermined range, and a drive for moving an ultrasound transducer in a direction different from the direction of 2D scans by the transducer to capture 2D ultrasound images sequentially in a predetermined pitch in the direction of movement of the ultrasound transducer. The ultrasound image processing system is provided with a marker for inserting a marker sign on field images selected from a large number of 2D ultrasound images sequentially captured by the image capture device, for use in three-dimensional image processing in a subsequent stage.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
Focused Ultrasound Therapy System
InactiveUS20090054772A1Accurately find out target areaLow costUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapySonificationAcoustic energy
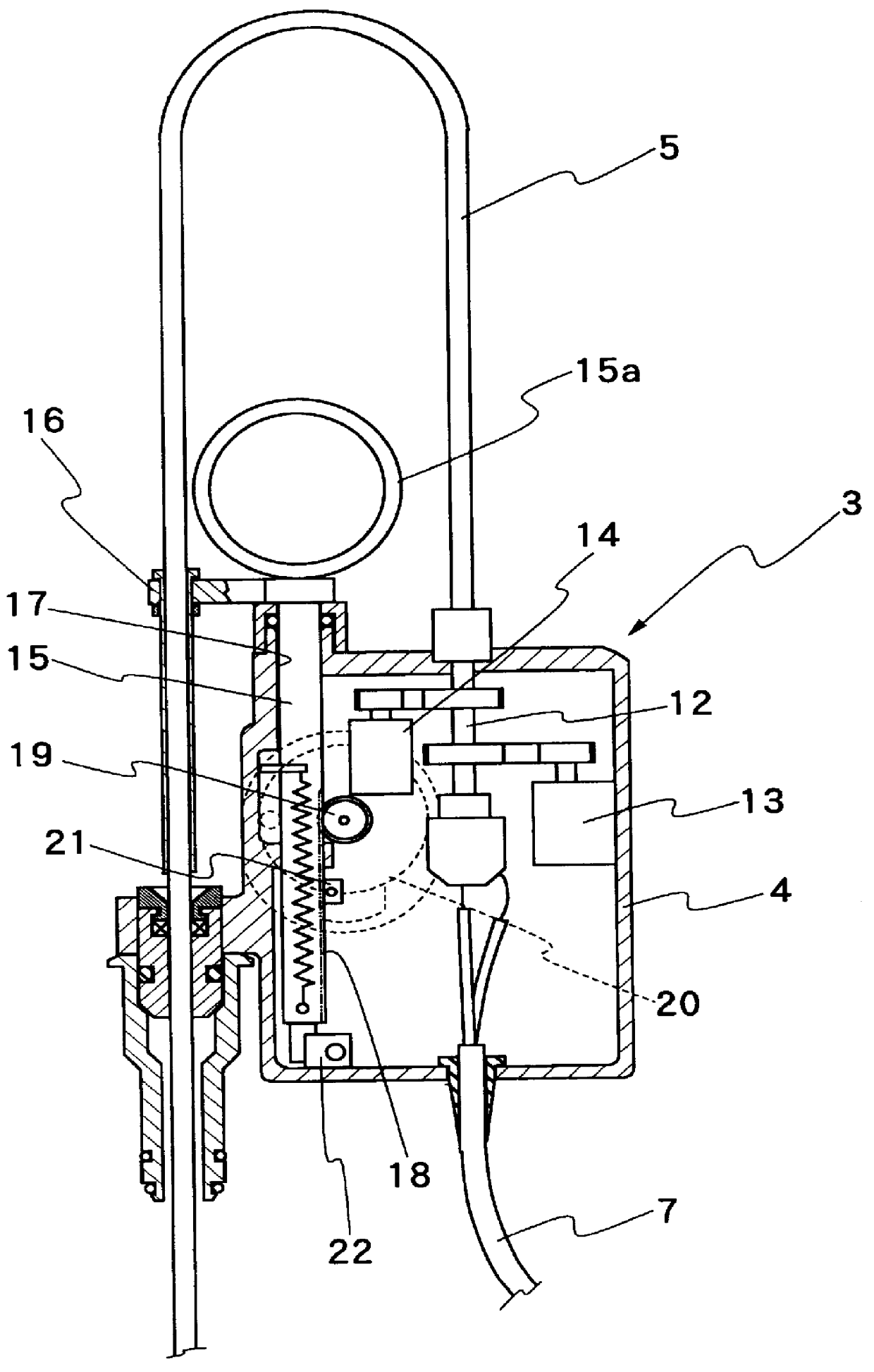
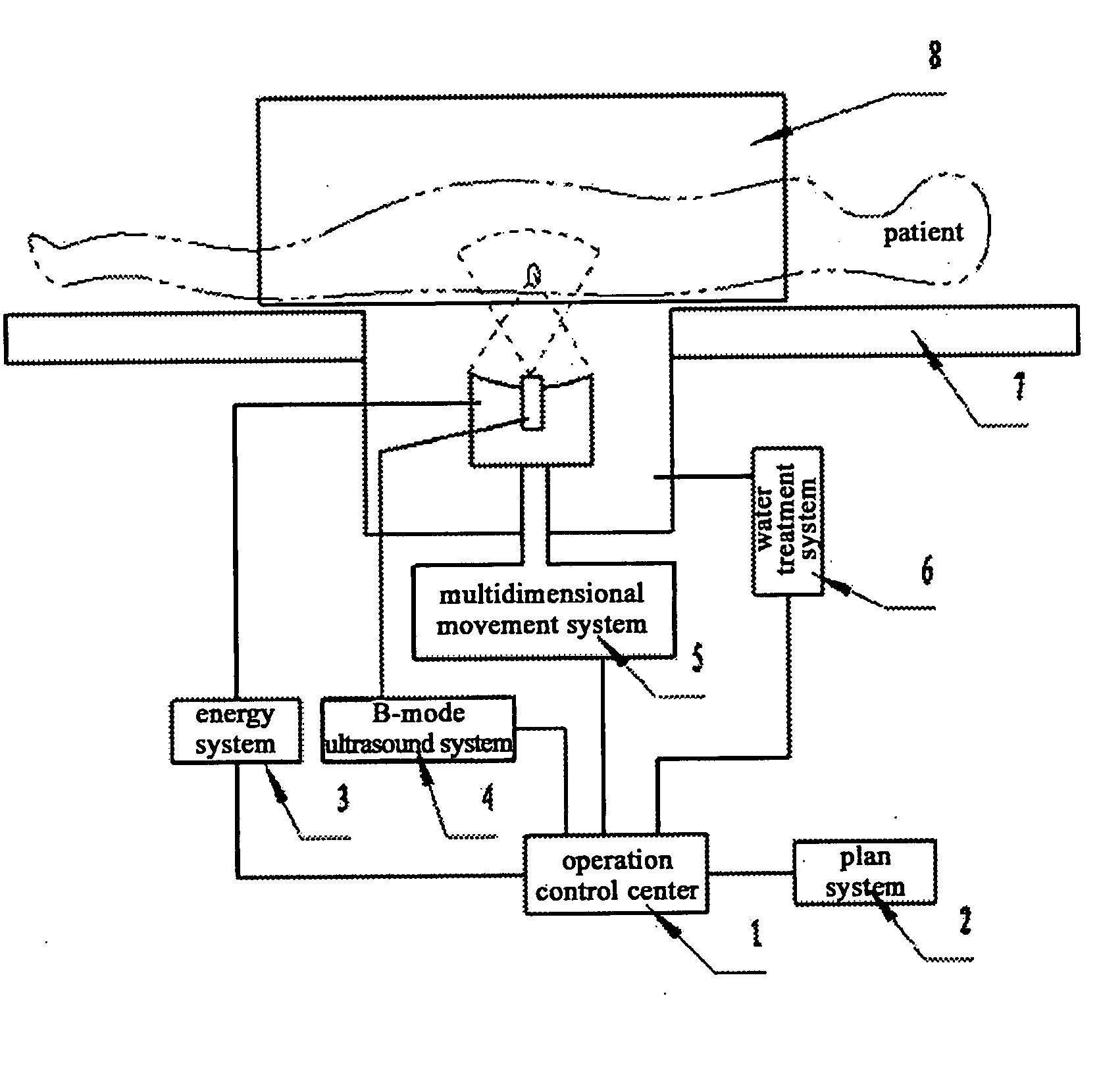
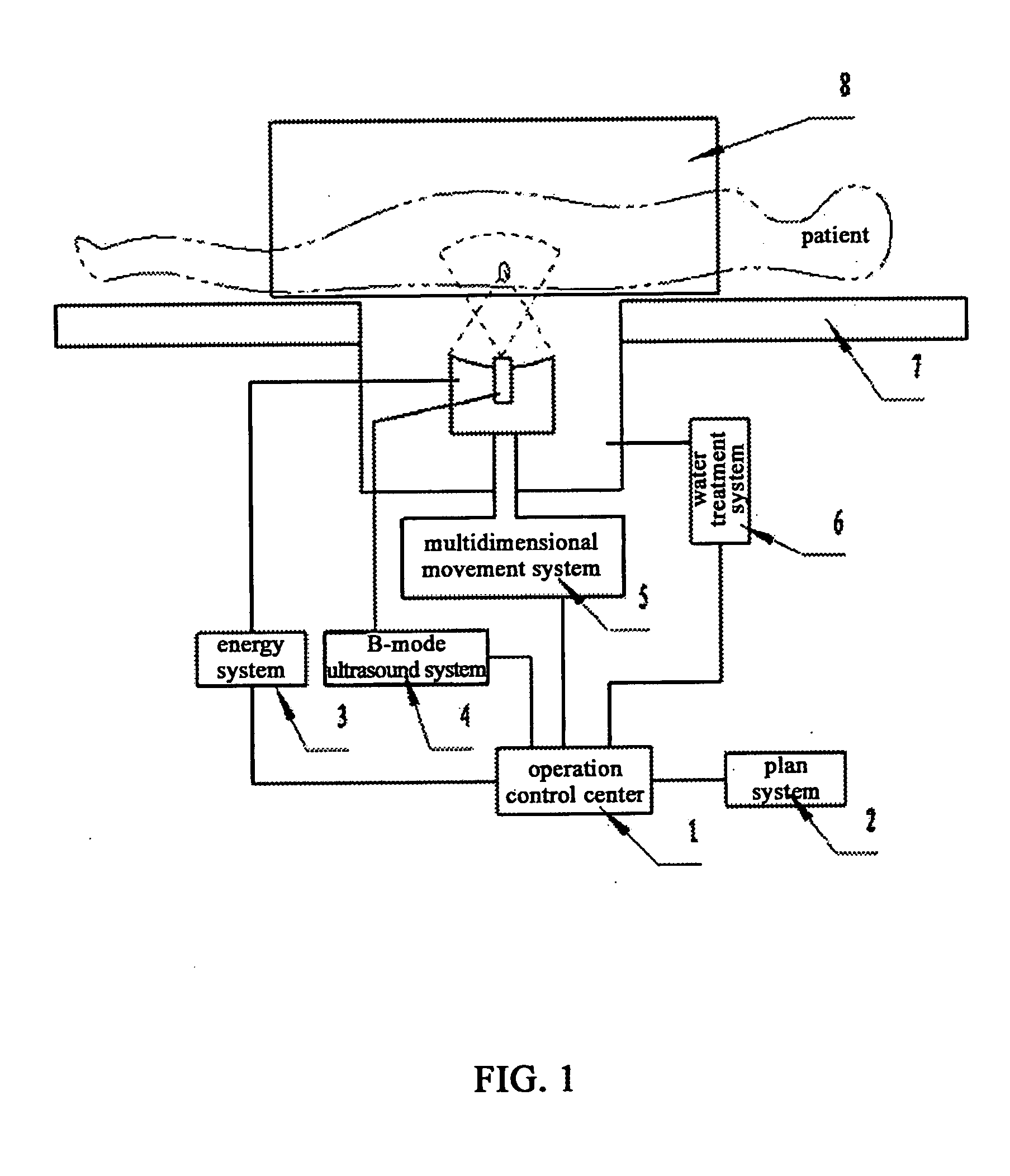
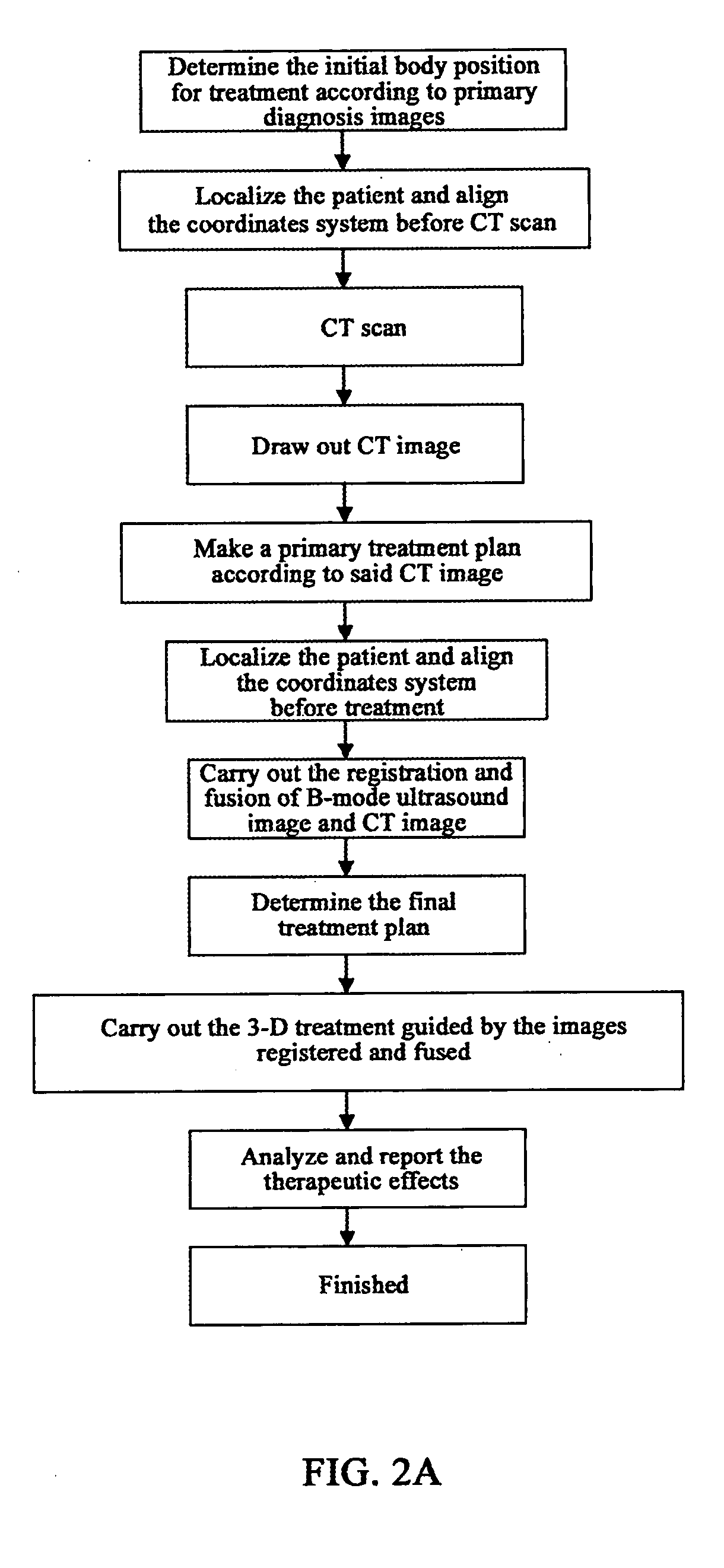
The present invention pertains to an ultrasound therapy system and more specifically, to a high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) therapy apparatus guided by image registration and fusion method. The therapy system of the present invention comprises a central control means; an acoustic energy applicator; a mechanical driving and locating means of said acoustic energy applicator; a real-time B-mode ultrasound image guiding device. Further the therapy system of the present invention comprises an immobilization means for body position. By the help of this immobilization means for body position, real-time B-mode ultrasound images can be registered with diagnosis images, and then on the basis of registration, said B-mode ultrasound images are fused with said diagnosis images for guiding said therapy. Comparing to the existed technical solutions in this field, the present invention has effectively solved the difficult problems in high-intensity focused ultrasound therapy and particularly for tumor treatment with a low cost. And it provides a very practical technical solution, which can be easily applied to clinical treatment of tumors.
Owner:CHONGQING HAIFU MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
System and method for improving ultrasound image acquisition and replication for repeatable measurements of vascular structures
InactiveUS7074187B2ElectrocardiographyOrgan movement/changes detectionAnatomical landmarkUltrasonic sensor
High resolution B-mode ultrasound images of the common carotid artery are obtained with an ultrasound transducer using a standardized methodology. Subjects are supine with the head counter-rotated 45 degrees using a head pillow. The jugular vein and carotid artery are located and positioned in a vertical stacked orientation. The transducer is rotated 90 degrees around the centerline of the transverse image of the stacked structure to obtain a longitudinal image while maintaining the vessels in a stacked position. A computerized methodology assists operators to accurately replicate images obtained over several spaced-apart examinations. The methodology utilizes a split-screen display in which the arterial ultrasound image from an earlier examination is displayed on one side of the screen while a real-time “live” ultrasound image from a current examination is displayed next to the earlier image on the opposite side of the screen. By viewing both images, whether simultaneously or alternately, while manually adjusting the ultrasound transducer, an operator is able to bring into view the real-time image that best matches a selected image from the earlier ultrasound examination. Utilizing this methodology, measurement of vascular dimensions such as carotid arterial IMT and diameter, the coefficient of variation is substantially reduced to values approximating from about 1.0% to about 1.25%. All images contain anatomical landmarks for reproducing probe angulation, including visualization of the carotid bulb, stacking of the jugular vein above the carotid artery, and initial instrumentation settings, used at a baseline measurement are maintained during all follow-up examinations.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
Split-screen display system and standardized methods for ultrasound image acquisition and processing for improved measurements of vascular structures
InactiveUS6979294B1Accurately and cost-effectively screenOrgan movement/changes detectionHeart/pulse rate measurement devicesSub-pixel resolutionSonification
A standardized acquisition methodology assists operators to accurately replicate high resolution B-mode ultrasound images obtained over several spaced-apart examinations. The methodology utilizes a split-screen display in which the arterial ultrasound image from an earlier examination is displayed on one side of the screen while a real-time “live” ultrasound image from a current examination is displayed next to the earlier image on the opposite side of the screen. A computerized echo edge recognition and tracking methodology automatically identifies ultrasound echo boundaries of the intima-media complex and automatically extracts IMT and arterial dimension measurements, without introducing human measurement error. Measurement accuracy is enhanced by use of sub-pixel resolution for echo edge boundary definition. Utilizing this methodology, measurement of vascular dimensions, such as carotid arterial IMT and diameter, the coefficient of variation is substantially reduced to values approximating from about 1.0% to about 1.25%. Dynamic material properties of arterial structures are measured in a standardized region in accordance with a standardized methodology in order to promote measurement repeatability.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
Ultrasound gray-scale imaging system and method
ActiveCN106102588AImprove time resolutionResolve distortionBlood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsDisplay deviceB mode ultrasound
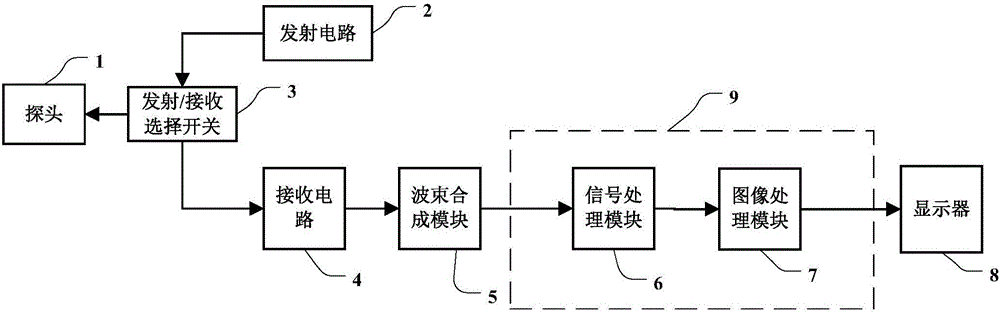
An ultrasound gray-scale imaging system and method. The system comprises a probe (1); a transmission circuit (2) for exciting the probe (1) to transmit non-focused ultrasound beams to fluid; a receiving circuit (4) and a beam-forming module (5) for receiving echoes of the non-focused ultrasound beams and obtaining non-focused ultrasound echo signals; a signal processing module (6) for obtaining fluid display data after performing signal detection and enhancement process on the multi-group of non-focused ultrasound echo signals; an image processing module (7) for performing data conversion on the fluid display data and obtaining a B mode ultrasound image sequence; and a display (8) for displaying the B mode ultrasound image sequence to present the visual effect of fluid dynamic flow. A plurality of scanning lines even the whole image can be obtained for one time by utilization of non-focused wave or plane wave emission, time resolution of the ultrasound image can be largely improved, and the distortion problem when high-speed blood flow is displayed by traditional gray-scale blood flow imaging is solved.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
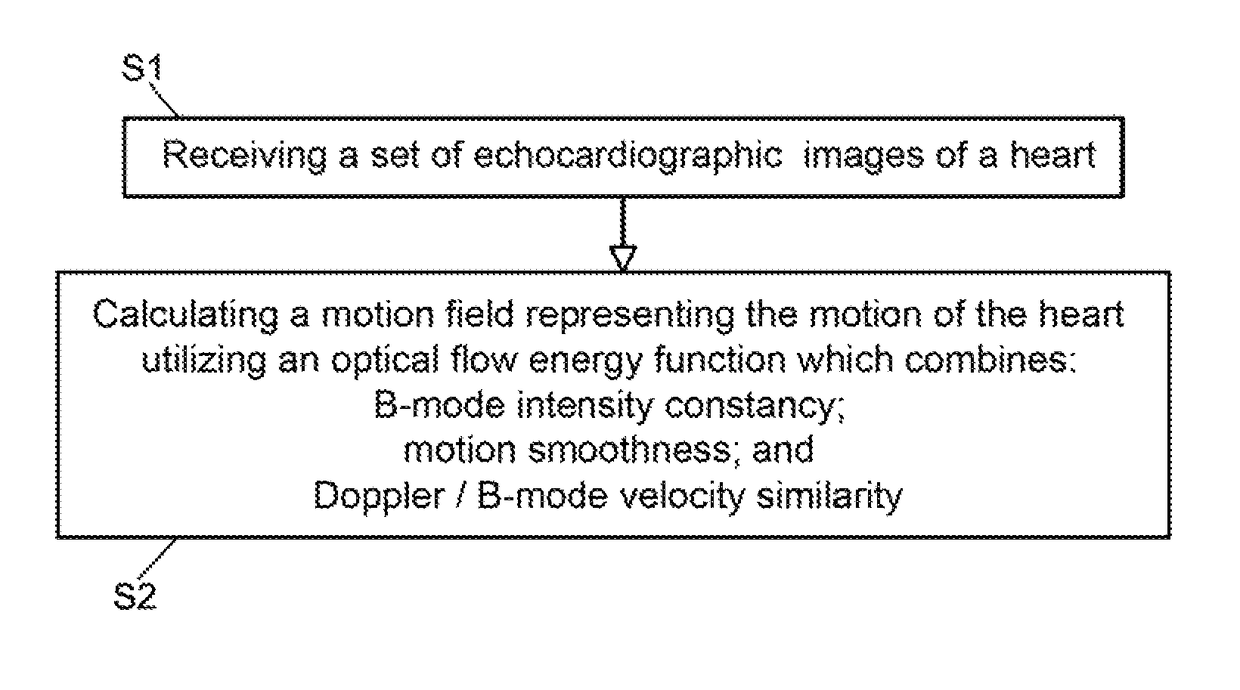
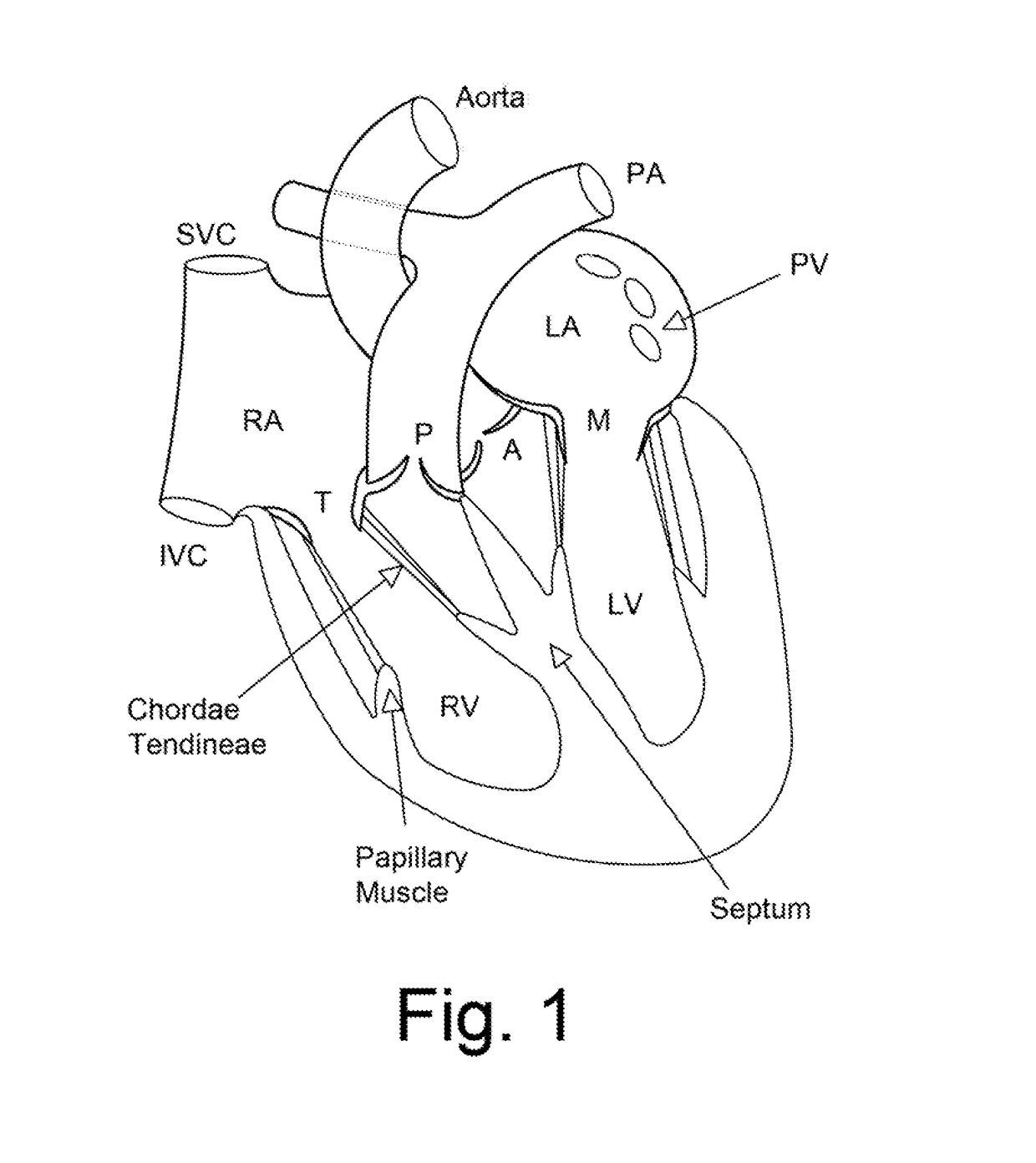
Combined B-mode / tissue doppler approach for improved cardiac motion estimation in echocardiographic images
ActiveUS9629615B1Promote resultsImprove smoothnessImage enhancementImage analysisSonificationMotion field
A method for cardiac motion estimation includes: receiving a set of echocardiographic images of a heart, the echocardiographic images including B-mode ultrasonic images and Tissue Doppler Imaging (TDI) images; and calculating, by the image processing machine, a motion field representing the motion of the heart using the B-mode ultrasonic images and applying a velocity constraint from the TDI images. A system for cardiac motion estimation, includes: an imaging device configured to acquire a set of echocardiographic images of a heart, the echocardiographic images including B-mode ultrasonic images and TDI images; a data storage device in communication with the imaging device and configured to store the set of echocardiographic images; an image processing machine in communication with the data storage device and configured to calculate a motion field representing the motion of the heart using the B-mode ultrasonic images and applying a velocity constraint from the TDI images.
Owner:UNIV OF LOUISVILLE RES FOUND INC
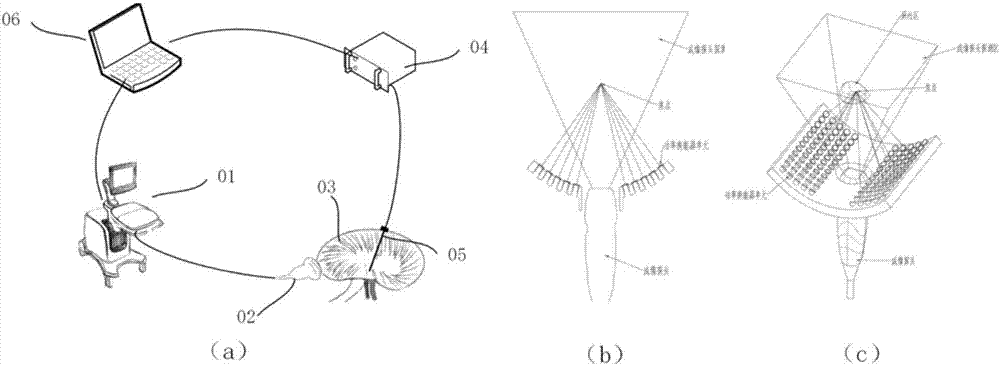
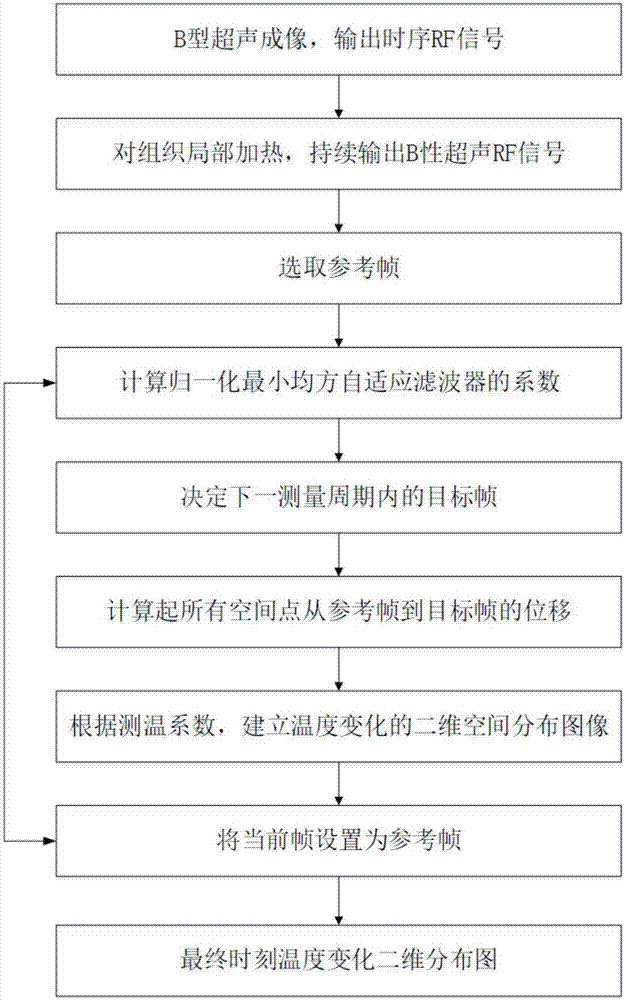
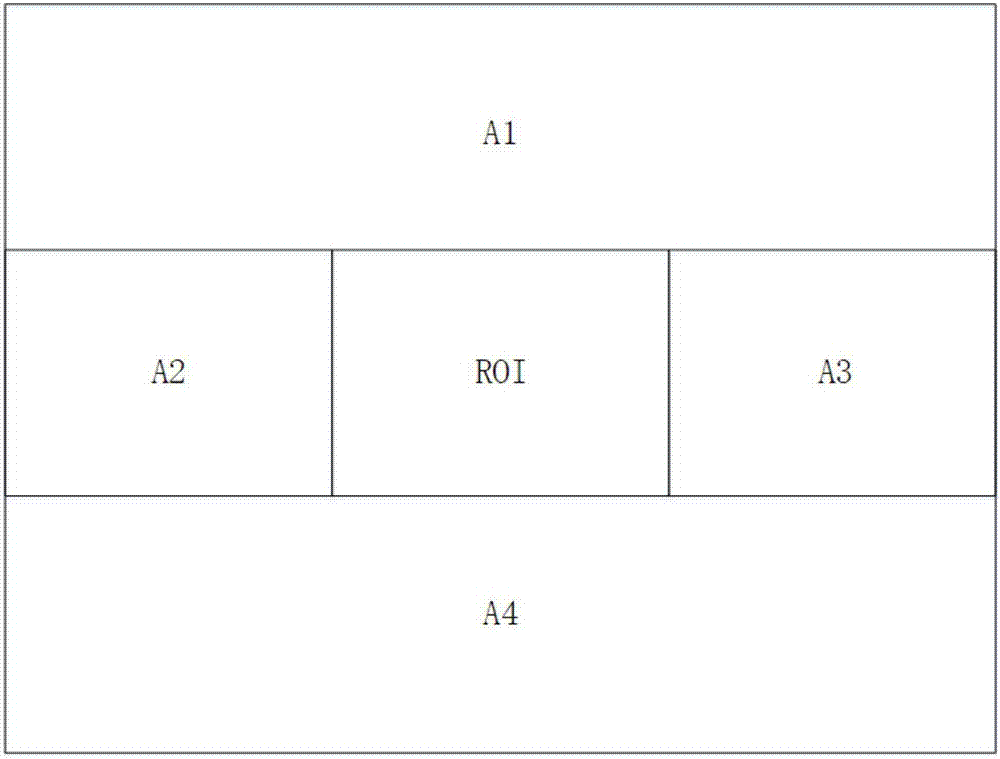
Ultrasonic method for measuring temperature change of biological tissue based on thermal expansion and gating algorithm
ActiveCN107569256ALow costEasy to deploy at scaleOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsDiseaseTissue heating
The invention discloses an ultrasonic method for measuring temperature change of biological tissue based on thermal expansion and gating algorithm. Aiming at the problem that temperature increment ofa target area cannot be effectively monitored in methods for treating diseases based on various current body tissue heating modes, a method for evaluating the temperature change of the biological tissue by using B-mode ultrasound RF signals is established. According to the method, methods such as focused ultrasound, radio frequency and microwave are used for locally heating the biological tissue,B-mode ultrasound is used for imaging the target area and collecting the RF signals of the target area, a target frame is selected based on B-mode ultrasound timing sequence images, time delay imagesthat ultrasound passes through the tissue are calculated, and accordingly temperature change images are obtained; according to images outside a heating area, the coefficient of a self-adaption filteris calculated, and the obtained temperature change images are subjected to noise suppression. According to the ultrasonic method, the error in the temperature increment range of 18 DEG C is smaller than or equal to 2 DEG C, the temperature increment monitoring technology of B-mode ultrasound is promoted to be applied to thermal therapy, and the safety and effectiveness of the thermal therapy can be remarkably improved.
Owner:NANJING GUANGCI MEDICAL TECH
Method and apparatus for detecting a gas pocket using ultrasound
ActiveUS20160345931A1Easy to useIncrease contrastWave based measurement systemsOrgan movement/changes detectionSonificationVisual observation
Existing gas pocket detection approaches are based on visual observations of B-mode ultrasound images showing comparisons between normal soft tissue and gas pockets, which are time-consuming and dependent on operator experience. The present invention proposes an ultrasound system and a method of detecting a gas pocket. The ultrasound system comprises: an ultrasound probe (110) for transmitting an ultrasound signal toward the ROI and acquiring an ultrasound echo signal reflected from the ROI along a plurality of scanning lines; an obtaining unit (130) for obtaining a second harmonic component of the ultrasound echo signal for each depth of a plurality of depths along each scanning line of the plurality of scanning lines; and a deriving unit (140) for deriving a change in a center frequency of the second harmonic component along with the depth.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Method and apparatus for ultrasound imaging and elasticity measurement
ActiveUS8147410B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCharacter and pattern recognitionUltrasound imagingHigh frame rate
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
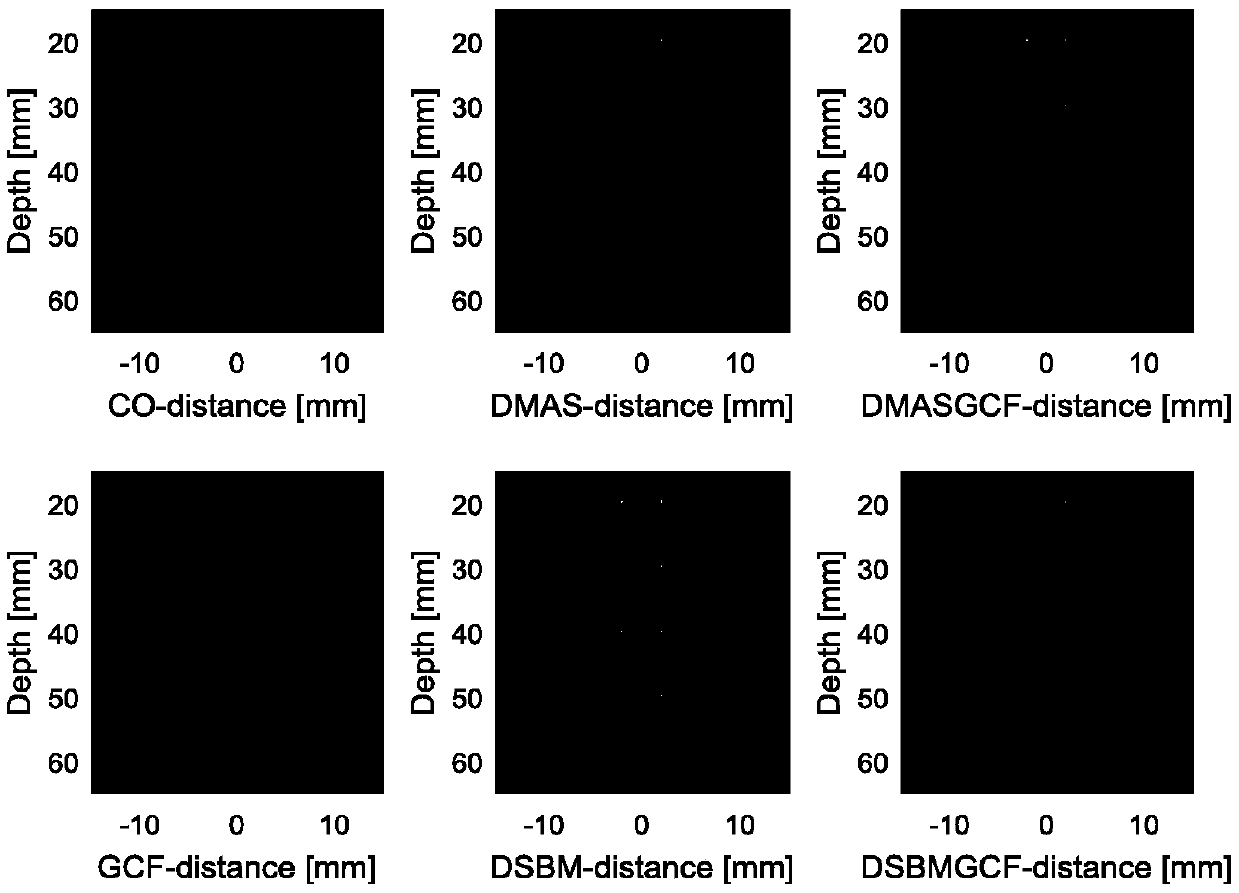
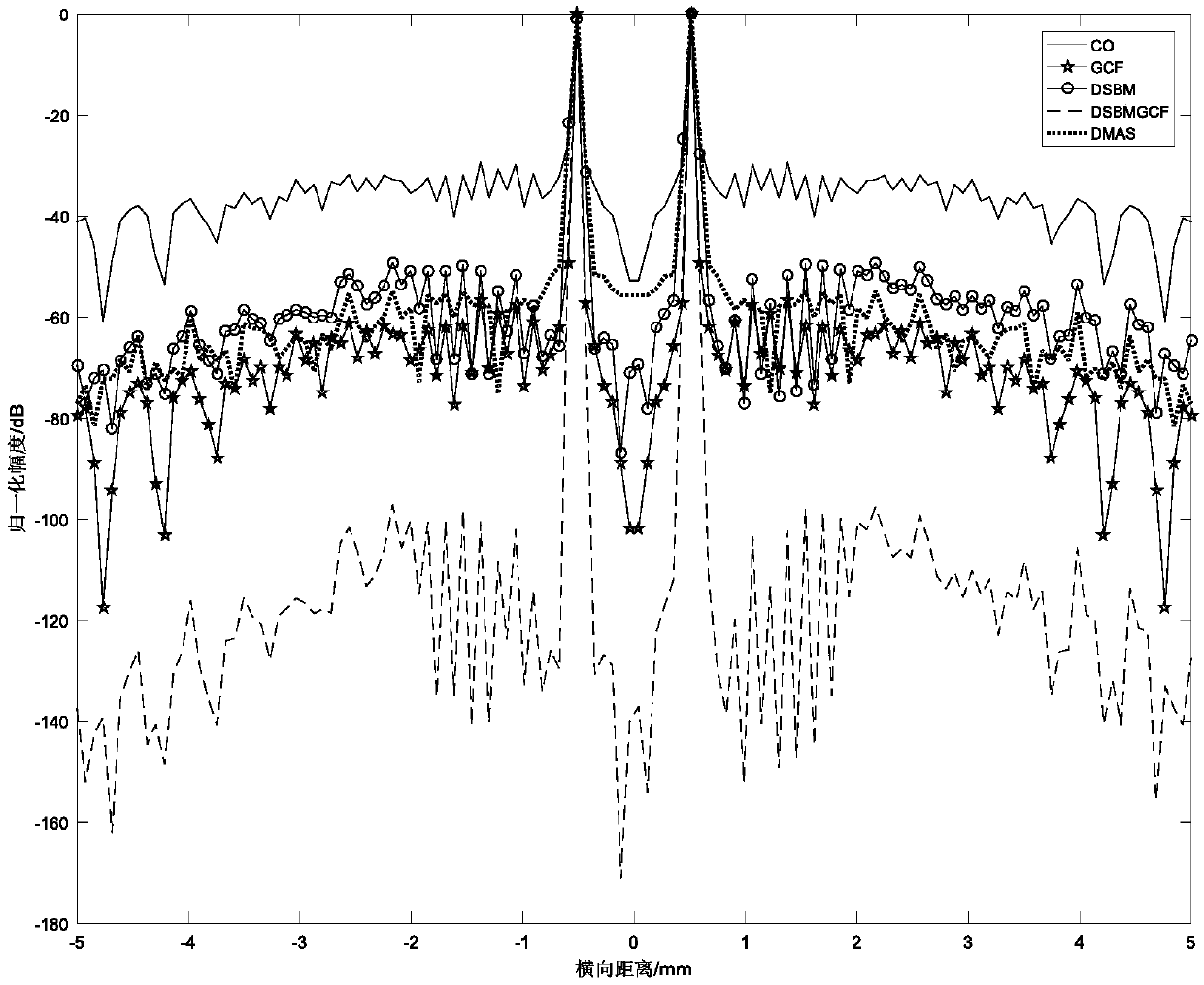
Ultrasonic plane wave imaging method based on modified DMAS (delay-multiplication accumulative beamforming synthesis) algorithm
InactiveCN108670304AReduce complexitySolve incompatibility problemsOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsCorrelation coefficientSonification
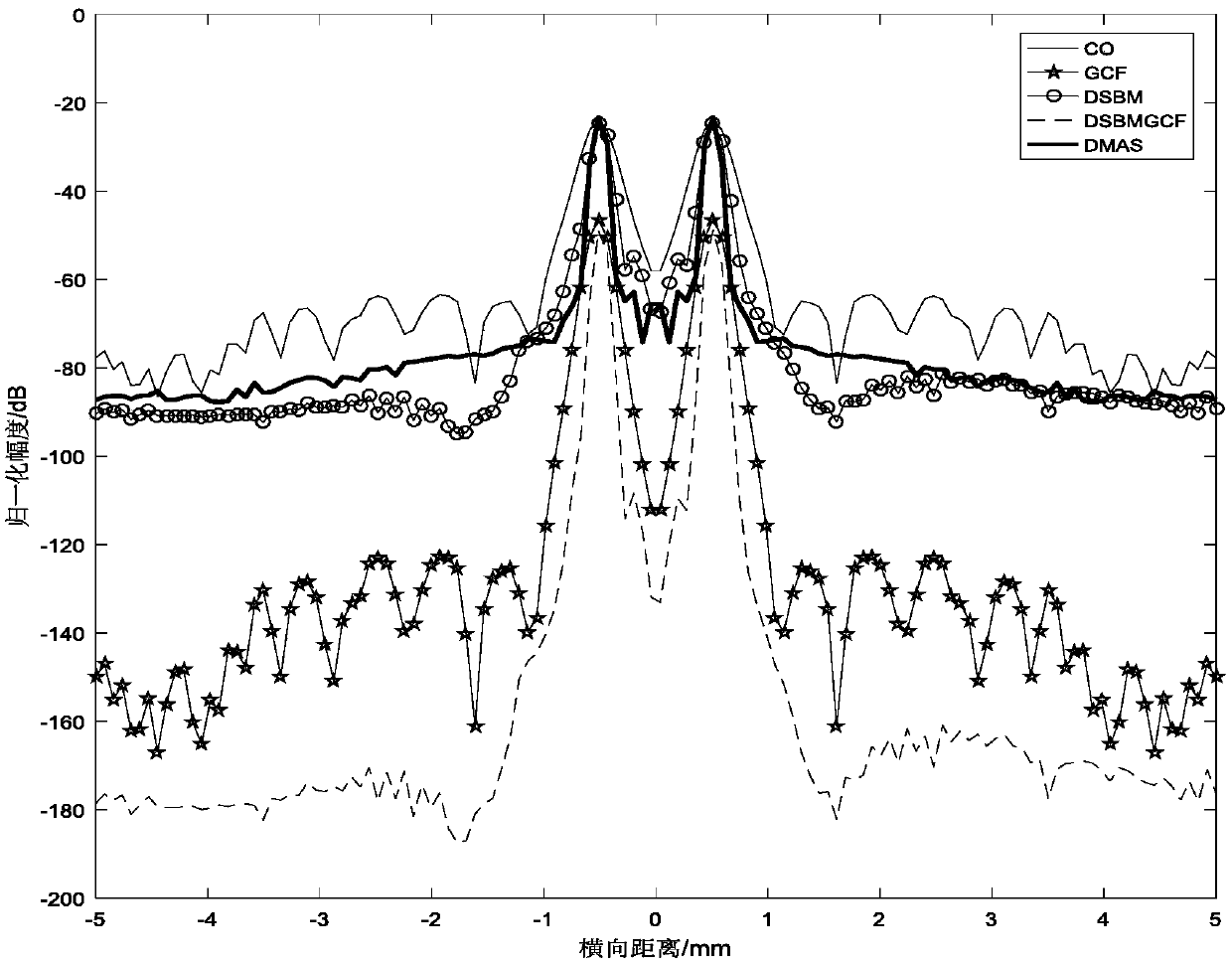
The invention belongs to the field of ultrasonic plane wave imaging and particularly relates to an ultrasonic plane wave imaging method based on a modified DMAS (delay-multiplication accumulative beamforming synthesis) algorithm, comprising the steps of 1) transmitting, by a FieldII-simulated B-mode ultrasound apparatus to emit a plane wave ultrasonic signal of certain composite angle; 2) calculating echo data square root of the plane wave ultrasonic signal and it's a cumulative sum item; 3) modifying the DMAS algorithm to obtain a DSBM (delay-accumulation multiplication beamforming) algorithm; 4) repeating the steps 2 to 3 to obtain data of each frame image; 5) acquiring a DSBMGCF (delay-accumulation multiplication beamforming generalized correlation coefficient) algorithm in conjunctionwith generalized correlation coefficient, and acquiring corrected imaging results according to the DSBMGCF algorithm. The advantages of the delay-multiplication accumulation beamforming synthesis algorithm and those of the generalized correlation coefficient are integrated; the problem that good plane wave spatial combination image quality and high imaging frame frequency cannot be attained at thesame time is solved at the premise of ensuring high imaging frame frequency, and fewer memory resources are utilized.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Medical scanning apparatus and method
InactiveUS20100262007A1Low castSmooth changeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationEcho intensity
A system and method of ultrasound scanning to achieve apparent real-time display of a sector ultrasound scan Including a single scanline ultrasound scanning apparatus with a sensor adapted to sense the position and / or orientation of the transducer and to output this as data and a screen to display a B-mode ultrasound scan image formed from a series of scanlines, each scanline being a dataset having a series of echo intensity values and a direction captured by reciprocating a transducer probe against a surface of a subject to be scanned such that a planar sector or series of planar sectors of the subject are swept by an ultrasound beam producing a series of scanlines and continuously processing and displaying said scanlines to produce an image that changes in real time In accordance with the features of the subject in the sector being scanned.
Owner:SIGNOSTICS LTD
Split-screen display system and standardized methods for ultrasound image acquisition and multi-frame data processing
InactiveUS7927278B2Accurately and cost-effectively screenOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationUltrasonic sensor
A standardized acquisition methodology assists operators to accurately replicate high resolution B-mode ultrasound images obtained over several spaced-apart examinations utilizing a split-screen display in which the arterial ultrasound image from an earlier examination is displayed on one side of the screen while a real-time “live” ultrasound image from a current examination is displayed next to the earlier image on the opposite side of the screen. By viewing both images, whether simultaneously or alternately, while manually adjusting the ultrasound transducer, an operator is able to bring into view the real-time image that best matches a selected image from the earlier ultrasound examination. Utilizing this methodology, dynamic material properties of arterial structures, such as IMT and diameter, are measured in a standard region over successive image frames. Each frame of the sequence has its echo edge boundaries automatically determined by using the immediately prior frame's true echo edge coordinates as initial boundary conditions. Computerized echo edge recognition and tracking over multiple successive image frames enhances measurement of arterial diameter and IMT and allows for improved vascular dimension measurements, including vascular stiffness and IMT determinations.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
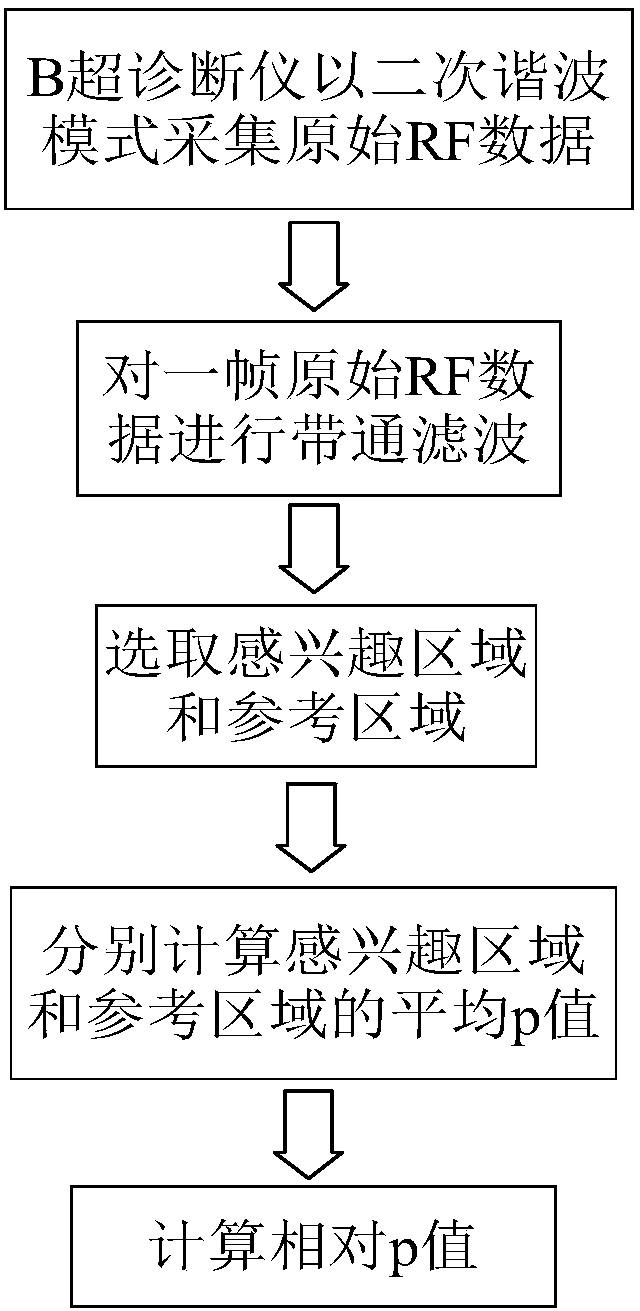
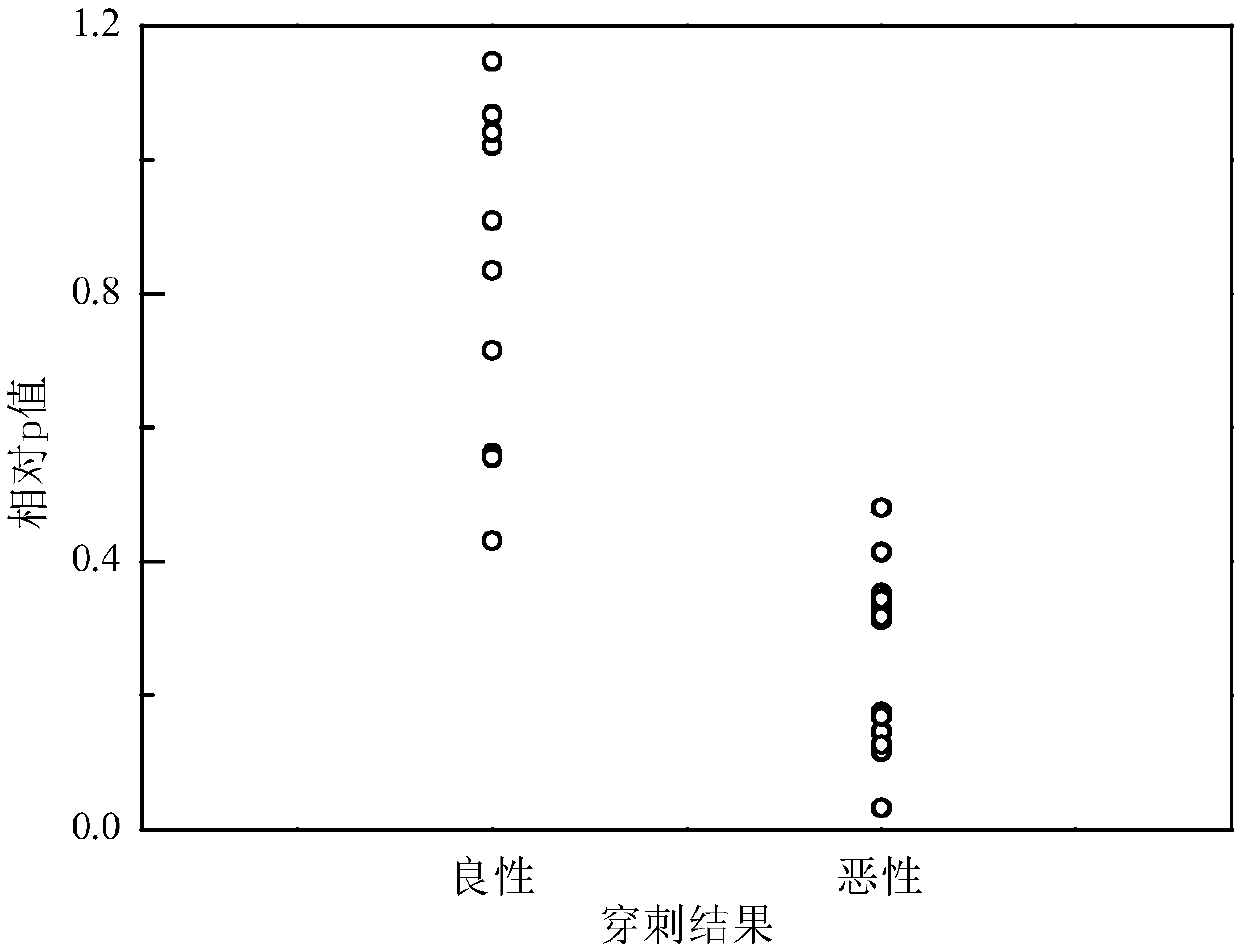
Parameter for reflecting biological tissue abnormity and measuring method thereof
InactiveCN106983524ASimple calculationImprove versatilityOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsHypothesisHarmonic
The invention discloses a parameter for reflecting biological tissue abnormity and a measuring method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of hypothesis testing in B-mode ultrasound diagnosis and statistics. The method comprises the steps of firstly setting a B-mode ultrasound diagnosis apparatus into a second harmonic scanning mode to scan and store original RF data of tissue; secondly conducting band-pass filtering on one frame of the RF data to select interested and reference areas in the frame of the RF data; then calculating the root-mean-square value of second harmonics in each cycle or several cycles on each scanning line in the interested area and reference area; then conducting Kolmogorov-Smirnov testing to conduct comparison on the root-mean-square value and the reference value of the each scanning line in each area, and calculating a corresponding p value; finally using the arithmetic mean p value of the interest area to divide the arithmetic mean p value of the reference value to obtain the corresponding p value. According to the parameter for reflecting biological tissue abnormity and the measuring method thereof, the problems that subjectivity is strong in identification of complex biological tissue abnormity in current B-mode ultrasound diagnosis and rich clinical experiences are needed in the current B-mode ultrasound diagnosis are solved, and measurement is accurate, and implementation is conducted easily.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Multifunctional gynecological and obstetrical clinical prenatal diagnosing therapeutic equipment
InactiveCN109498347ASimple structureImprove efficiencyOrgan movement/changes detectionOperating tablesPrenatal diagnosisObstetrics gynaecology
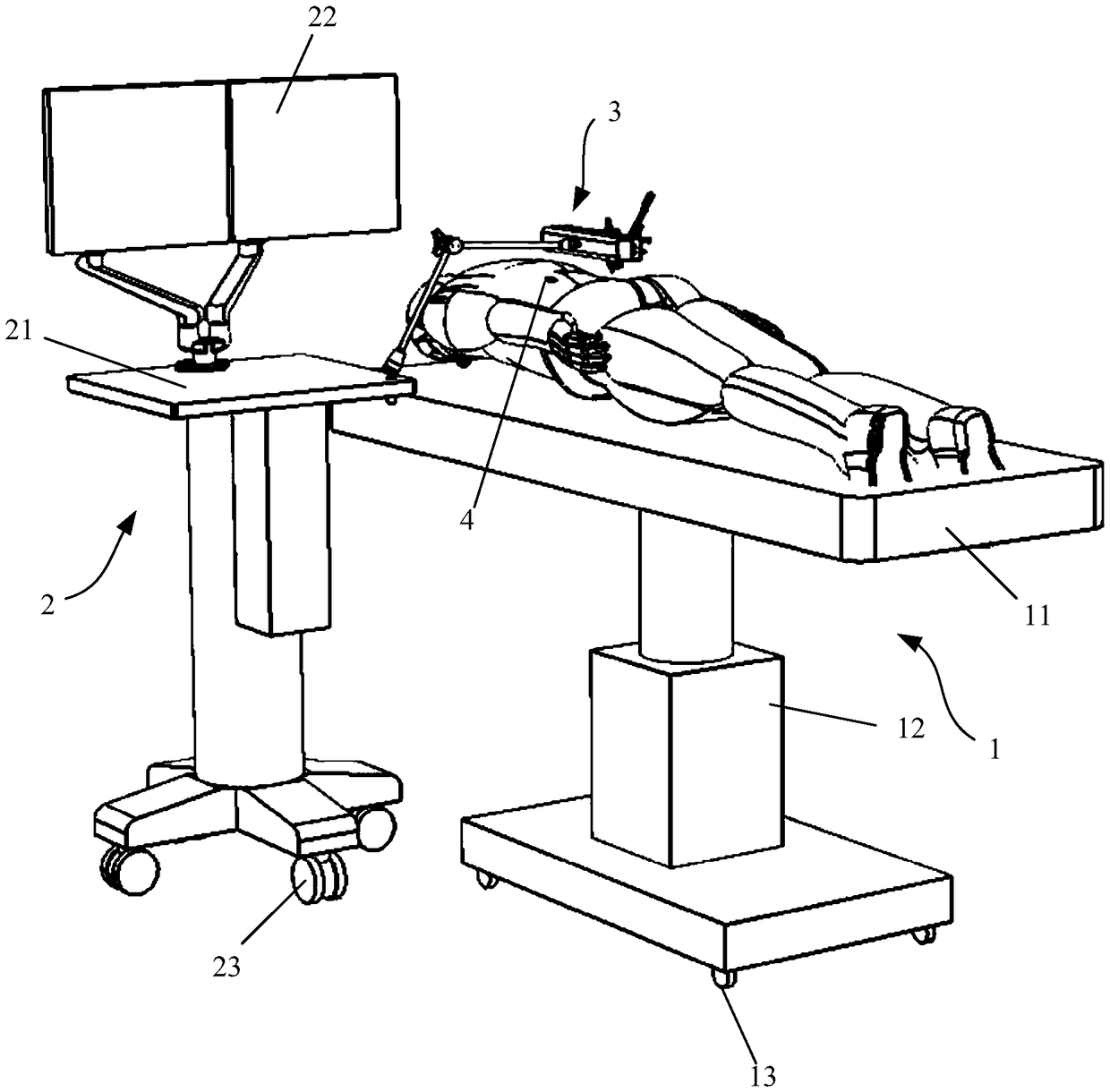
The invention discloses multifunctional gynecological and obstetrical clinical prenatal diagnosing therapeutic equipment. The multifunctional gynecological and obstetrical clinical prenatal diagnosingtherapeutic equipment comprises a bottom plate, a lifting device is arranged at the upper end of the bottom plate, a top end of a lifting column of the lifting device is fixedly connected with a center of an underside of a lying plate, a breathable rubber mat is arranged at the upper end of the laying plate, a lying pillow is arranged on a rear side of an upper end of the breathable rubber mat, and a first adjusting device is arranged in a middle portion of a right side of the lying plate. The multifunctional gynecological and obstetrical clinical prenatal diagnosing therapeutic equipment issimple in structure and convenient to operate and use, great convenience in use is brought to medical workers, a reasonably diagnosing position of a probe can be adjusted by the first adjusting deviceand a second adjusting device according to needs, overmuch movement of a pregnant woman is avoided, B-mode ultrasound image developing, blood glucose and blood pressure monitoring, fundal height andabdominal girth measuring and weight detecting can be implemented for the pregnant woman, multiple antenatal physical sign detections can be provided for the pregnant woman, health of the pregnant woman and the infant can be guaranteed, and utilization efficiency of prenatal diagnosing therapeutic equipment is improved.
Owner:吴永玲
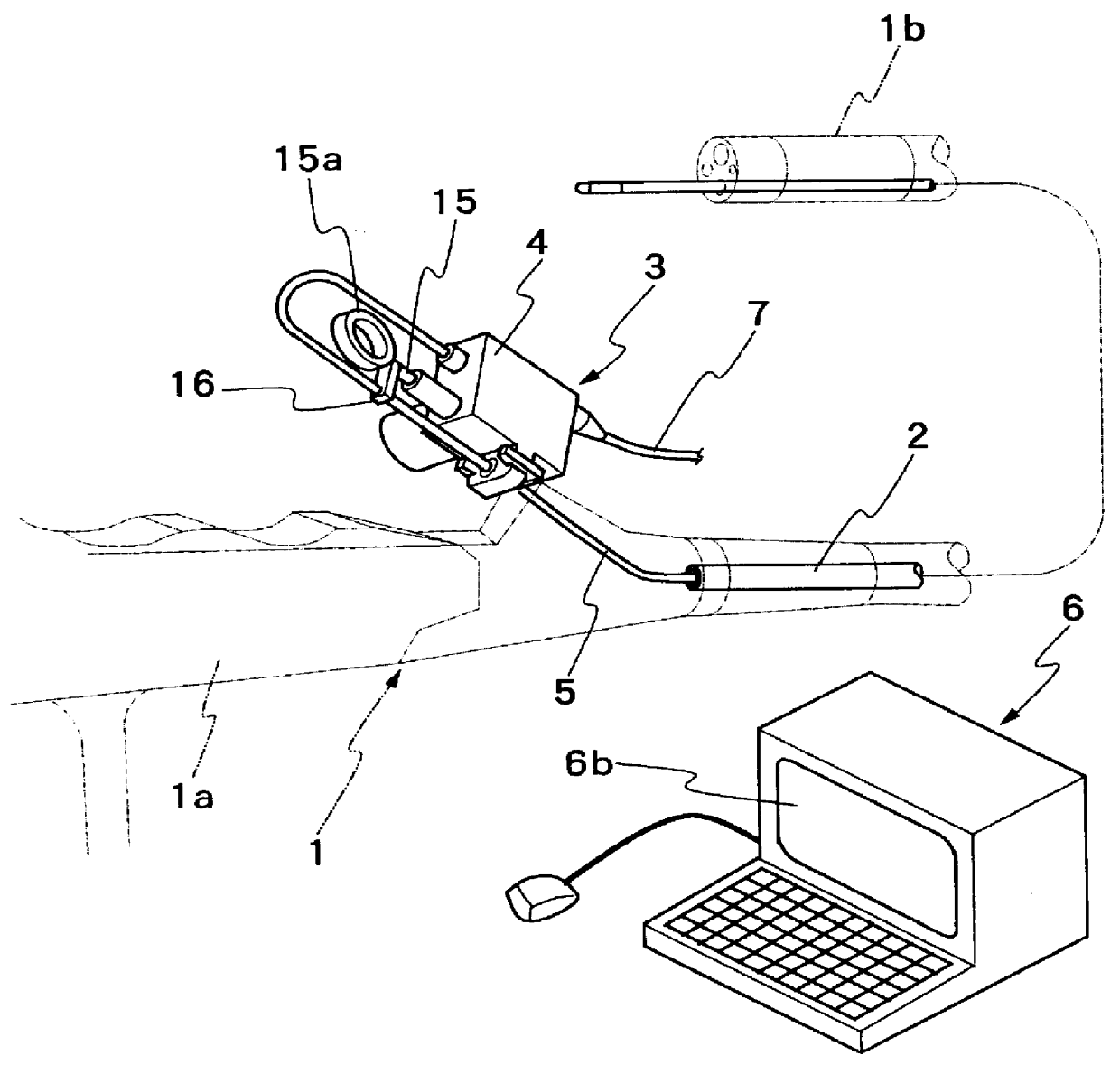
Puncture surgery system
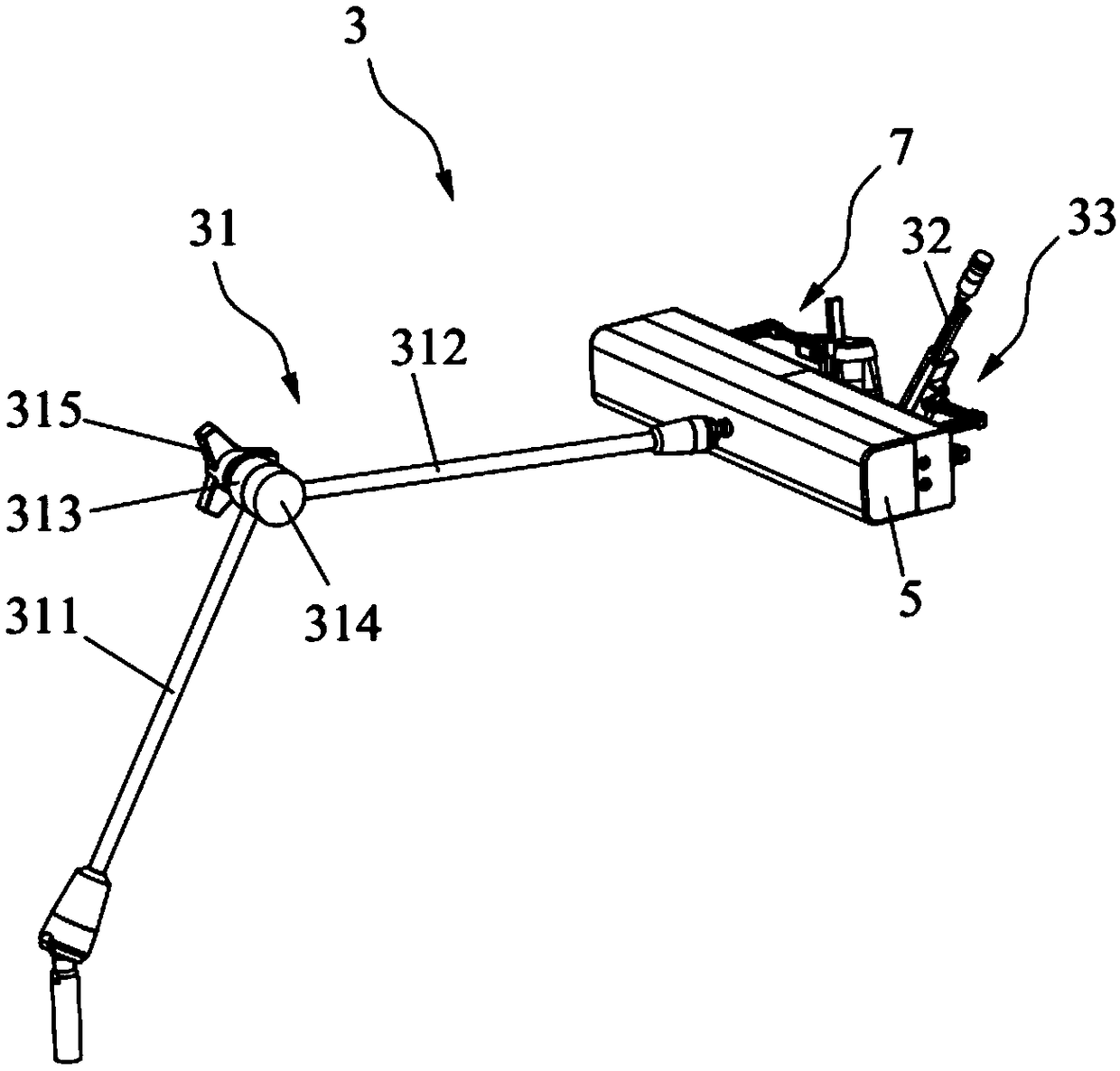
PendingCN108852473AGuaranteed accuracyReal-time monitoring of puncture pathSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsCt scannersSurgical site
The invention discloses a puncture surgery system and relates to the technical field of puncture surgery. The puncture surgery system includes a lying bed, an imaging device, a puncture mechanism, a target object, a CT scanning instrument, a camera and a B-mode ultrasound probe. The target object is fixed to a surgical part of a patient; the CT scanning instrument is used for scanning the target object and the tissue of the surgical part before puncture to obtain images of the target object and the tissue of the surgical part; the camera is used for taking pictures of the target object and theskin of the surgical part before puncture to obtain images of the target object and the skin of the surgical part; a puncture needle is arranged on the puncture mechanism, and the position and angleof the puncture needle can be adjusted; the B-mode ultrasound probe is used for monitoring the tissue around a puncture point and a puncture path during puncture in order to obtain images of the periphery of the puncture point; the imaging device is used for displaying the images obtained by the B-mode ultrasound probe. The puncture surgery system can achieve real-time adjustment of the position and angle of the puncture needle and ensure the accuracy of puncture.
Owner:ULTRASOUND ASSISTED MEDTECH PTE LTD
Medical image recognition system and method based on multi-modal fusion
ActiveCN109858540AOvercome the difficulty of combiningComprehensive and Effective FeaturesCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesImage detectionVideo sequence
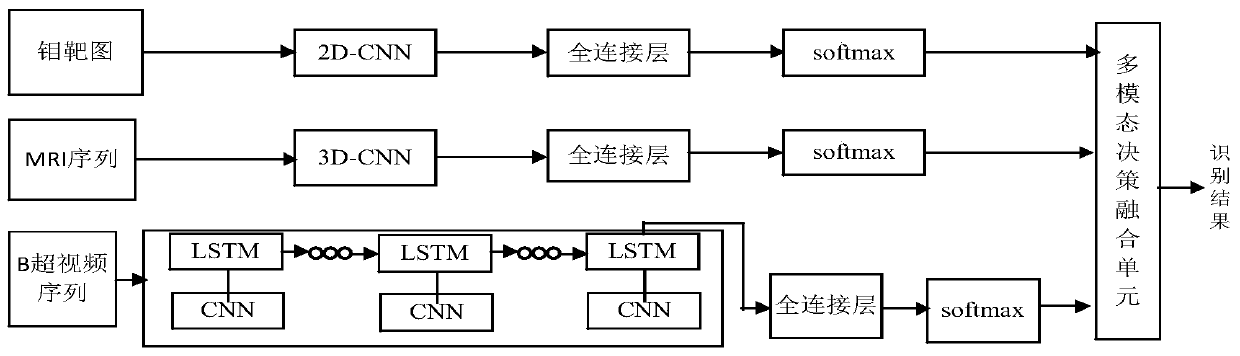
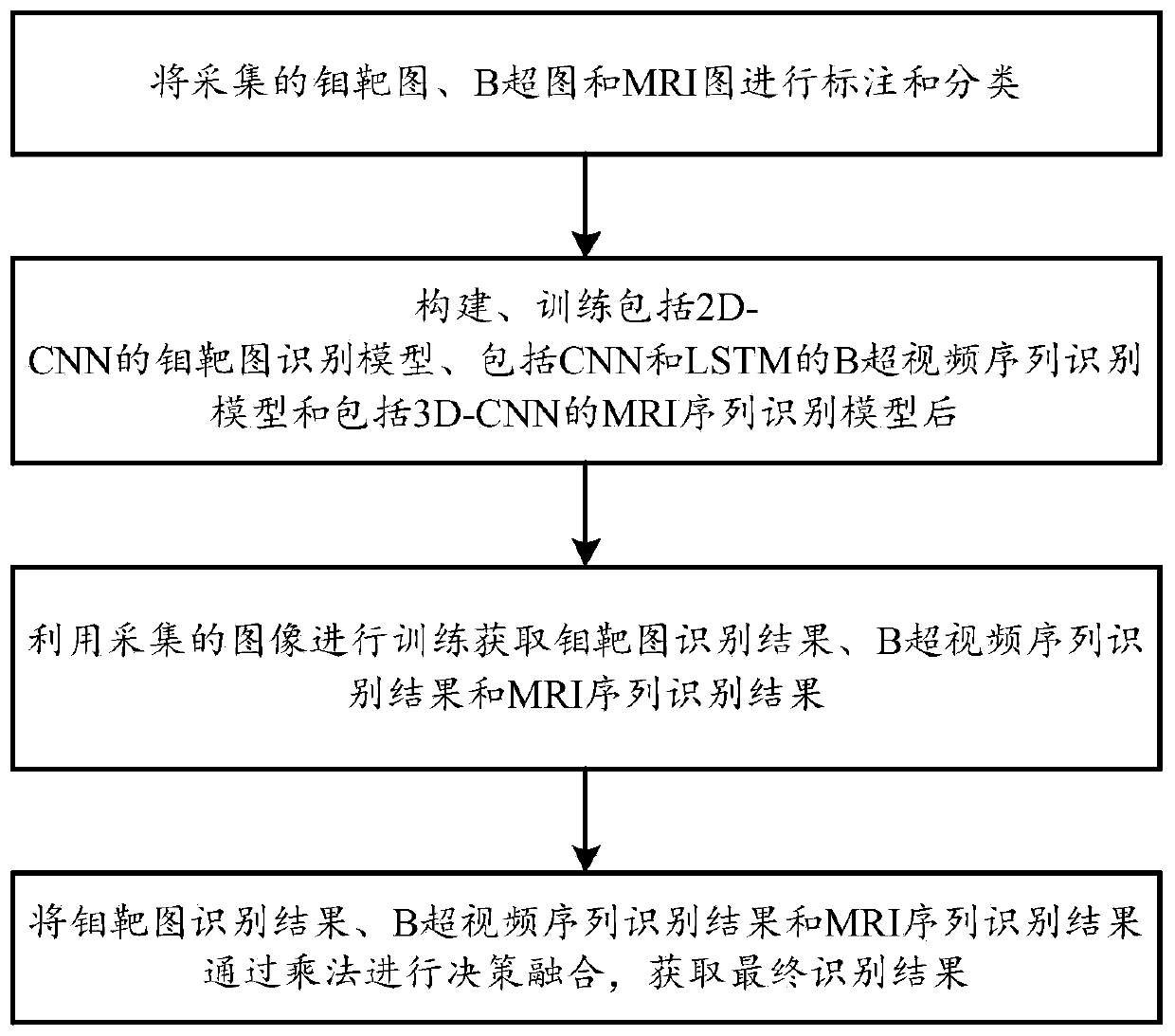
The invention discloses a medical image recognition system and method based on multi-modal fusion, and relates to the field of medical image detection. The system comprises a molybdenum target image recognition model which is used for constructing a 2D-CNN structure to obtain molybdenum target image characteristics to complete molybdenum target image recognition, a B-mode ultrasound video sequencerecognition model which is used for constructing a CNN and LSTM structure to obtain B-mode ultrasound sequence characteristics to complete B-mode ultrasound video sequence recognition, and an MRI sequence recognition model which is used for constructing a 3D-CNN to obtain MRI sequence characteristics to complete MRI sequence recognition, and a multi-modal decision fusion unit which is used for carrying out decision fusion on molybdenum target image recognition result, B-mode ultrasound video sequence recognition result and MRI sequence recognition result through multiplication to obtain finalrecognition result. According to the method, different structures are designed for training according to the characteristics of the molybdenum target, the B-ultrasonic image and the MRI image, the difficulty of combining the images with completely inconsistent characteristics is overcome, decision fusion is performed on multi-dimensional recognition results through multiplication, more comprehensive and effective characteristics are obtained, and the recognition accuracy is improved.
Owner:青岛中科智康医疗科技有限公司
Real-time image generation method for super-resolution B ultrasonic image
ActiveCN110136067ASimple preparation processImprove signal-to-noise ratioImage enhancementImage analysisAlgorithmB mode ultrasound
The invention discloses a real-time image generation method for a super-resolution B-mode ultrasound image, and aims to solve the problem that the definition in a B-mode ultrasound real-time image generation process needs to be improved. The method comprises the following steps: establishing an MSE-based loss function; preparing two losses for different stages: using cross entropy loss to performbinary classification on the gray level of the black and white image, initializing network internal characteristics and attention parameters, and using MSE as a loss function of a later stage refiningresult; constructing the neural network according to the core block of the deep convolutional neural network; using a block structure to perform stacking to obtain a deep convolutional network, and generating a static graph; using an Adam optimizer to initialize the cross entropy loss in the step b, stopping training when the loss rate is reduced to be nearly flat, changing the loss into MSE loss, and performing refining to generate enough reasoning results to improve the PSNR; and exporting the weight, and integrating and operating the weight in the medical equipment by using the static graph. According to the invention, single-frame input and single-frame output can be realized, and a result superior to a manual design image enhancement algorithm is obtained.
Owner:SHANGQIU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Remote-controlled B-mode ultrasound detection device with coupling-agent automatic addition function
PendingCN110101412AImprove Sensitive AccuracyRealize remote controlMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesInfrasonic diagnosticsRemote controlB mode ultrasound
A remote-controlled B-mode ultrasound detection device with a coupling-agent automatic addition function includes a five-axis linkage remote-controlled intelligent manipulator, a remote control terminal, a B-mode ultrasonic detection main unit capable of transmitting and receiving data over a network, and a coupling-agent supplying device capable of automatically adding a coupling agent. The tailend of the intelligent manipulator is provided with a detection probe of the B-mode ultrasonic detection main unit, an agent outlet of the coupling-agent supplying device is formed near the probe, thetail end of the intelligent manipulator is provided with at least three distance sensors and one pressure sensor, the pressure sensor can detect pressure the probe suffers from, the distance sensorsare uniformly distributed on the periphery of the probe, and the remote control terminal can control the manipulator to move to do various motions.
Owner:THE SECOND HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO WENZHOU MEDICAL COLLEGE
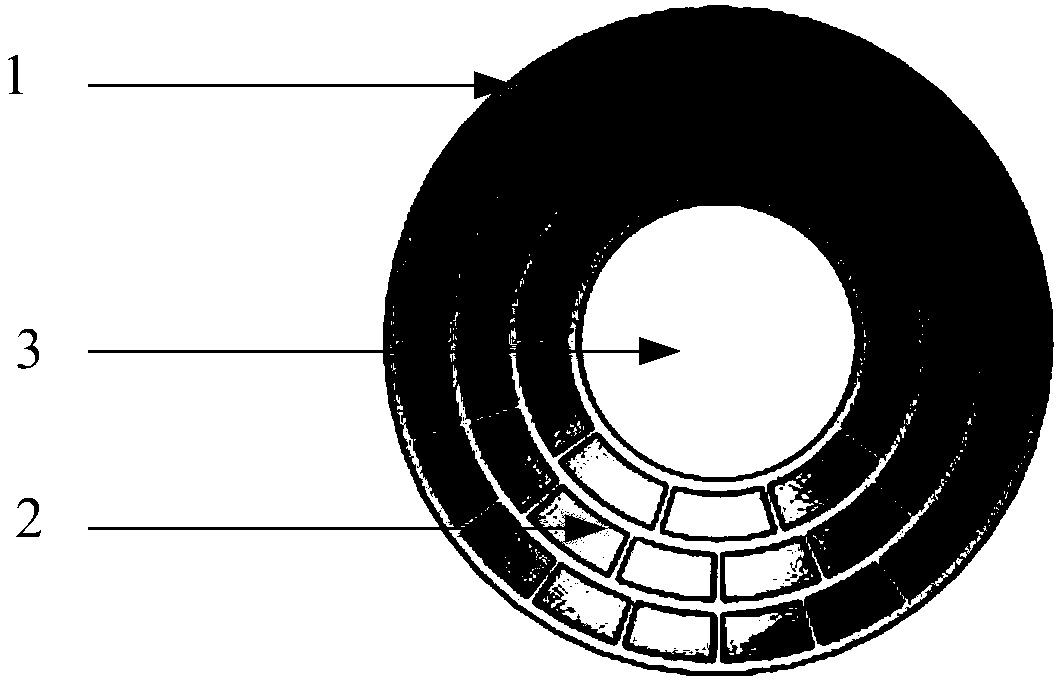
Annular self-focusing ultrasonic phased array energy converter
PendingCN107661853AIndependent control assuranceAvoid damageUltrasound therapyMechanical vibrations separationB mode ultrasoundPhased array
The invention discloses an annular self-focusing ultrasonic phased array energy converter. The energy converter comprises a crown-shaped spherical shell and a plurality of annular-sector piezoelectricceramic wafers, wherein a round hole is formed in the center of the crown-shaped spherical shell to bring convenience to installing a B-mode ultrasound probe, the plurality of the annular-sector piezoelectric ceramic wafers are bonded on the concave spherical surface of the crown-shaped spherical shell to be spliced into a ring shape, the plurality of the annular-sector piezoelectric ceramic wafers can form a group of concentric rings, the central lines of the concentric rings coincide with the central line of the crown-shaped spherical shell, and each annular-sector piezoelectric ceramic wafer is connected with an independent control end. Therefore, independent control on each annular-sector piezoelectric ceramic wafer is ensured; furthermore, the annular self-focusing ultrasonic phasedarray energy converter has the advantages of changeable focal length, single-point focusing mode, multi-point focusing mode and the like. In medical treatment, the phased array energy converter can effectively avoid bones on an ultrasound channel, prevents the bones from absorbing ultrasonic energy and tissues from being damaged and reduces patient pain.
Owner:SHENZHEN PRO HIFU MEDICAL TECH
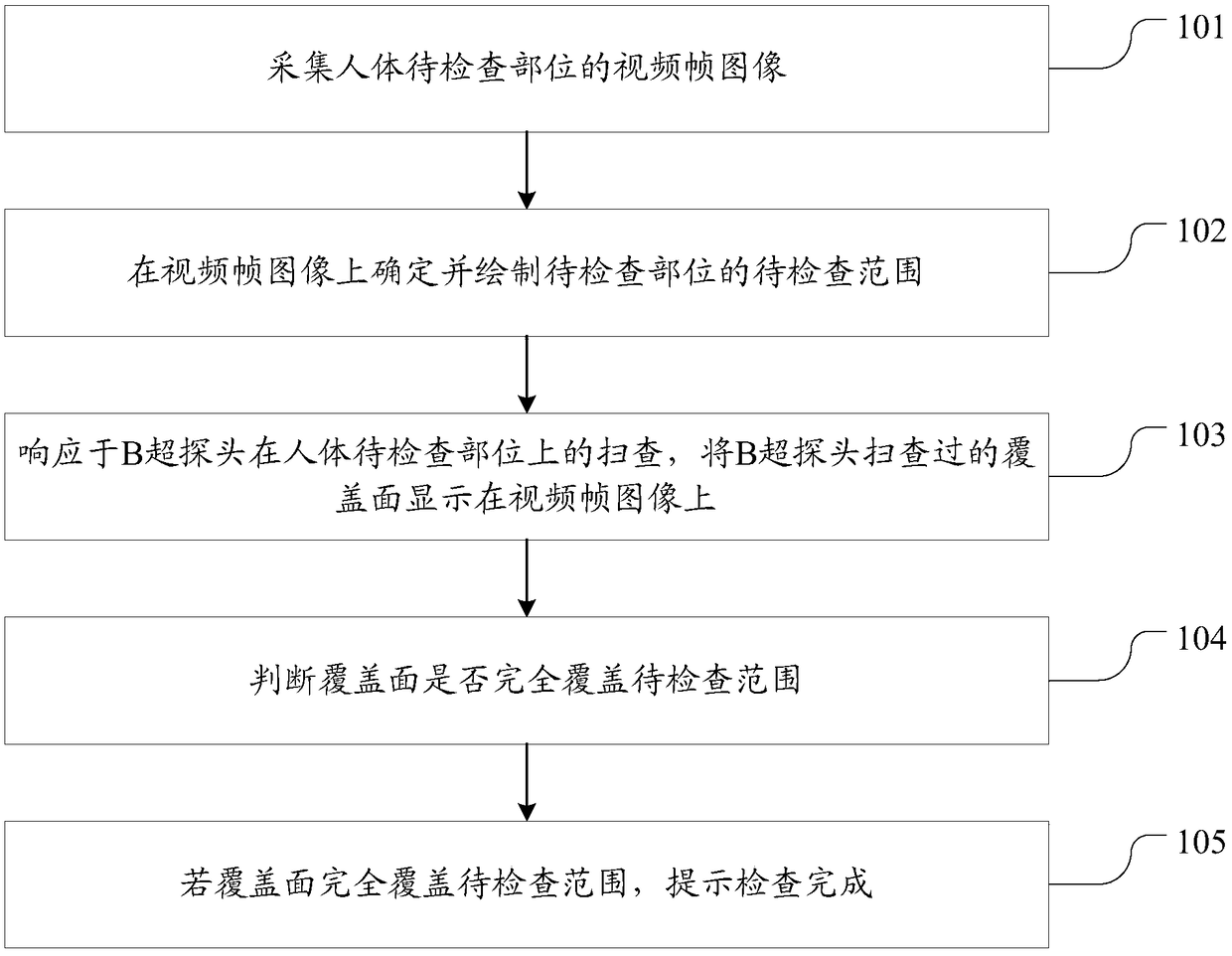
Method and system for B-mode ultrasound probe scanning without blind areas
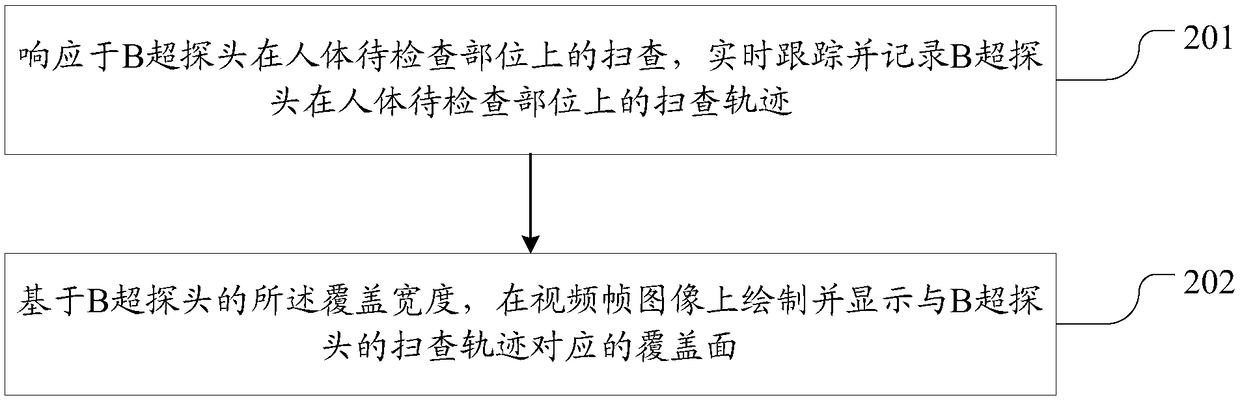
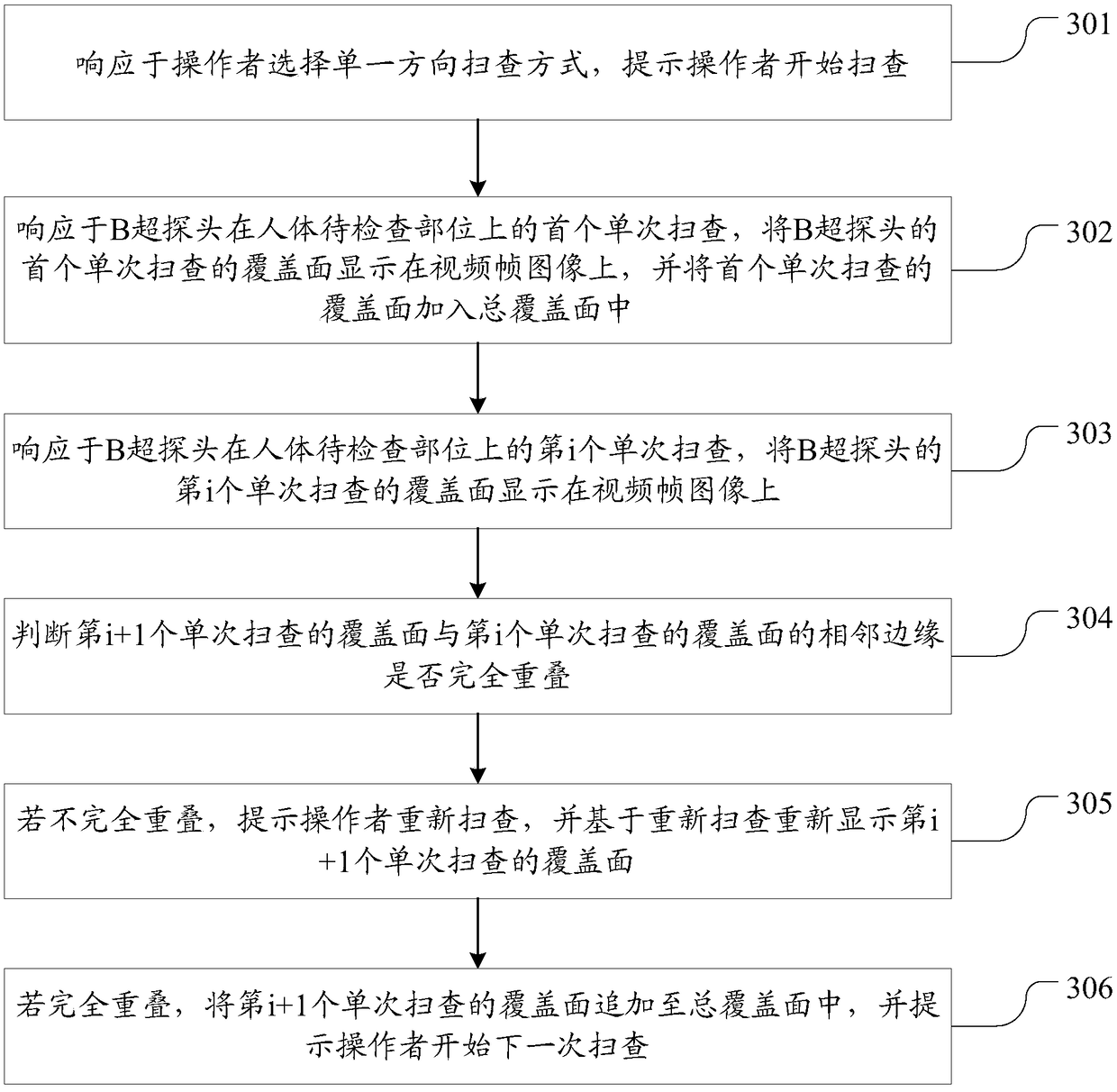
InactiveCN108634985AAvoid missed diagnosisUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsB mode ultrasoundComputer science
The invention discloses a method and a system for a B-mode ultrasound probe scanning without blind areas. The method comprises the following steps that video frame images of a part to be inspected ofa human body are acquired; a range to be checked of the part to be checked is determined and drawn on the video frame images; in response to the scanning of the B-mode ultrasound probe on the part ofthe human body to be examined, the coverage scanned by the B-mode ultrasound probe is displayed on the video frame images; whether the coverage completely covers the range to be inspected or not is judged; and if the coverage completely covers the range to be inspected, the completion of the inspection is prompted. According to the method and the system, a method for assisting an operator to carryout B-mode ultrasound scanning is provided, by tracking and recording a scanning track of the B-mode ultrasound probe in real time, the operator can see the scanned coverage more intuitively, and thescanning omission is effectively prevented.
Owner:广州尚医网信息技术有限公司
B-mode ultrasound coupling agent and its prepn
InactiveCN1374133ASmall sound attenuation coefficientGood biocompatibilityEchographic/ultrasound-imaging preparationsGlycerolMethyl cellulose
The coupling agent for B-mode ultrasound diagnostic instrument consists of povidone-iodine 0.5-5 %, glycerin 1-7 %, sodium carboxy methyl cellulose 3-6 %, ethanol 10-15 % and pure water 67-85.5 %. During its preparation, povidone-iodine is first dissolved in water, sodium carboxyl methyl cellulose and ethanol are mixed homogeneously through stirring, the povidone-iodine solution is then mixed with mixed sodium carboxy methyl cellulose and ethanol solution through stirring, and the mixed solution is 80-120 mesh filtered to obtain the coupling agent. The coupling agent is used in supersonic test in hospital and can kill bacteria and virus and prevent crossed infection.
Owner:黎国梓
Ultrasonic therapy tissue temperature change display equipment using digital grey scale processing
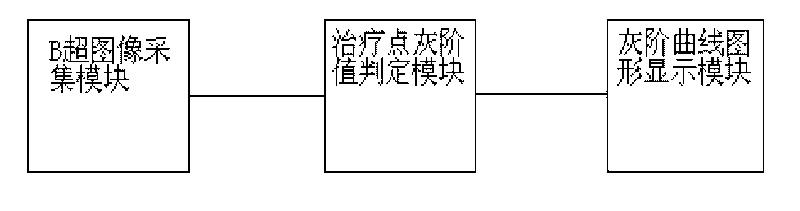
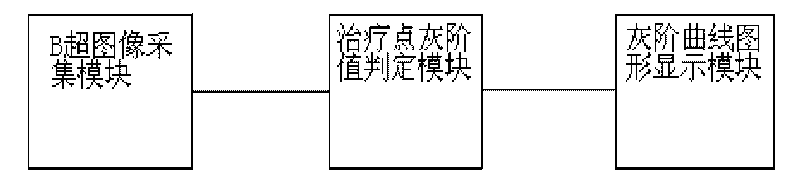
InactiveCN101690842AReal-time and accurate monitoring of temperature changesAccurately monitor temperature changesUltrasound therapyDiagnostic recording/measuringDigital signal processingTreatment effect
In ultrasonic therapy, the change of the grey scale of a B-mode ultrasound image of a treated point and the change of tissue temperature have a known relationship, so temperature change conditions corresponding to the treated point can be obtained by observing the change of the grey scale of the B-mode ultrasound image of the treated point so as to get an idea of treatment effect. The ultrasonic therapy tissue temperature change display equipment using digital grey scale processing of the invention comprises a B-mode ultrasound image acquisition module, a treated point grey scale determination module and a grey scale curvilinear graph display module which are sequentially connected. In the ultrasonic therapy, the digital grey scale processing of the B-mode image of the treated point is performed, the tissue temperature change conditions are monitored accurately in real time and a curve of the change in tissue temperature of the same treated point before and after treatment is directly displayed in a graphical mode, the anesthesia time of a patient in a treatment process is reduced, and the treatment efficiency is improved and the treatment is finished more safely and effectively.
Owner:绵阳索尼克电子有限责任公司
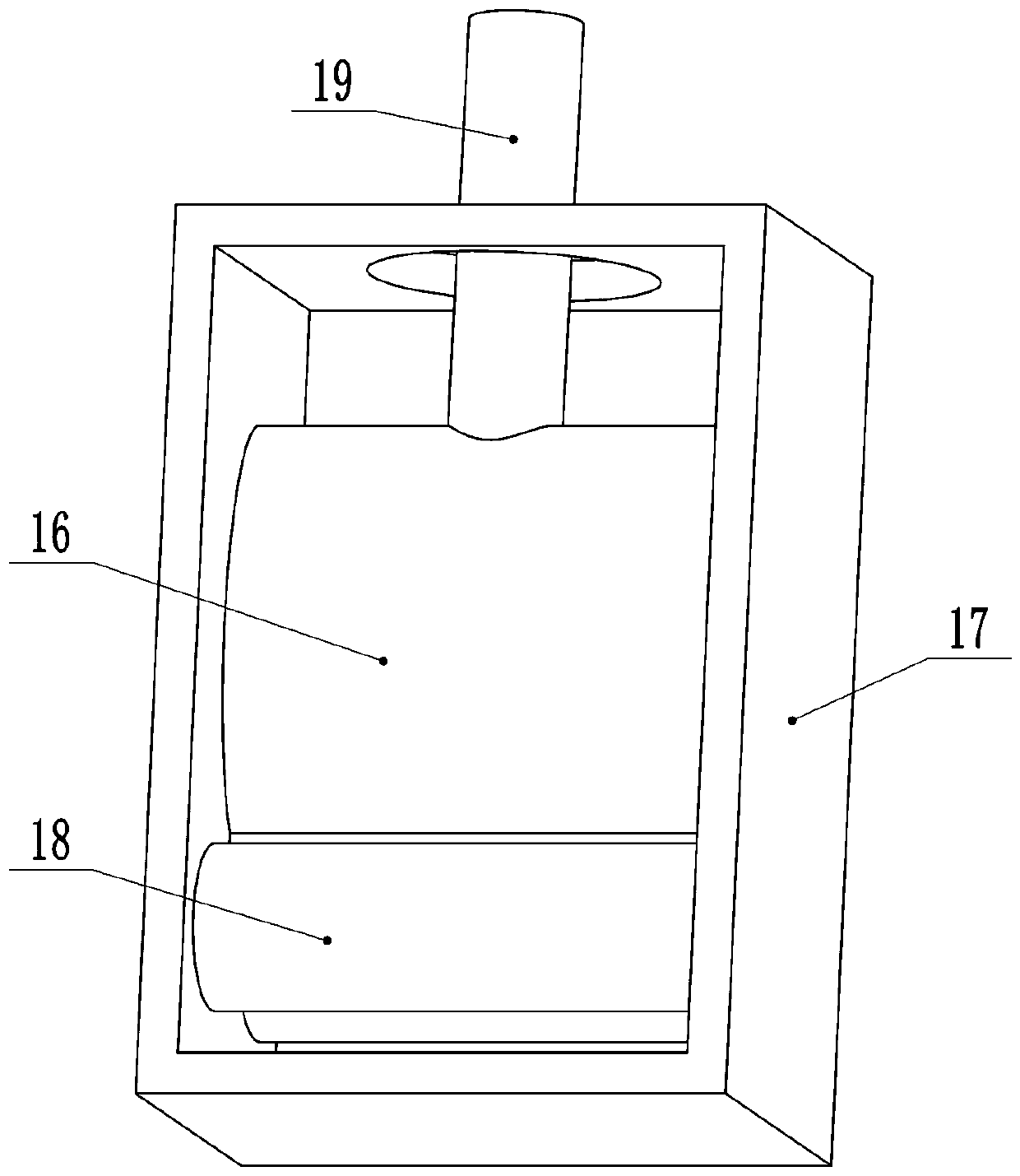
Multifunctional prenatal diagnosis and treatment instrument for clinical use in gynecology and obstetrics
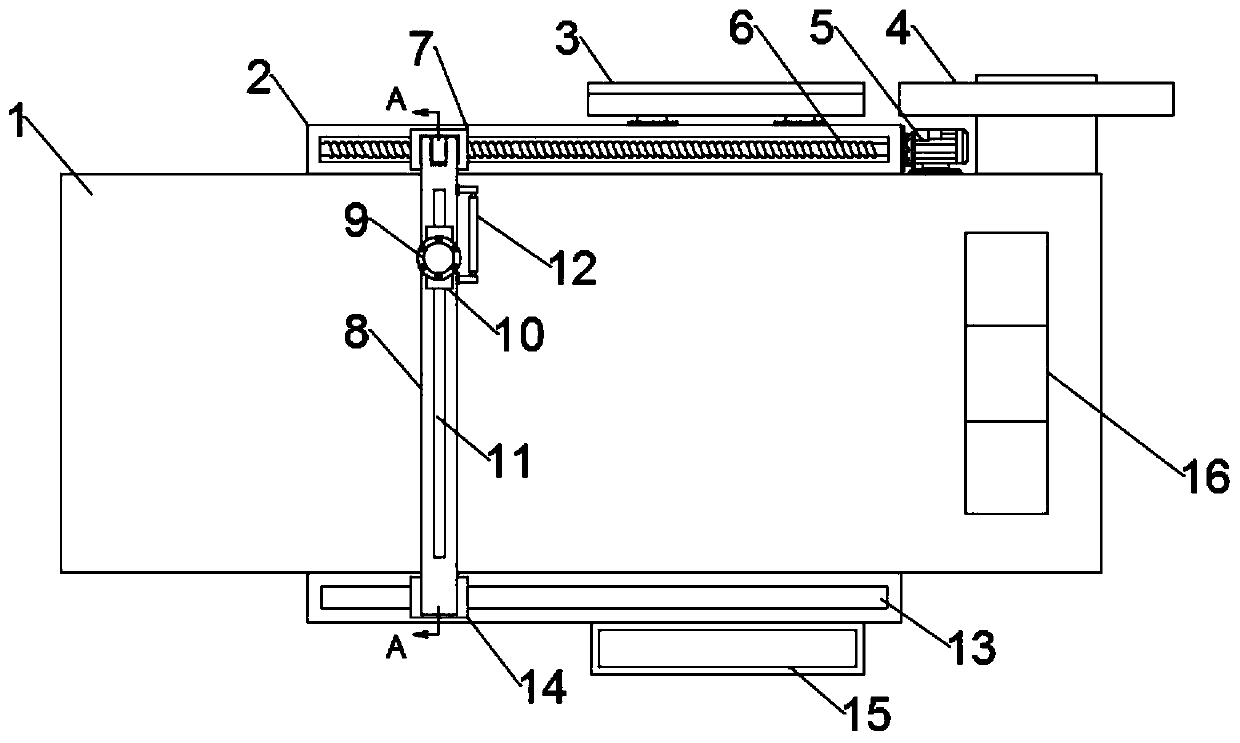
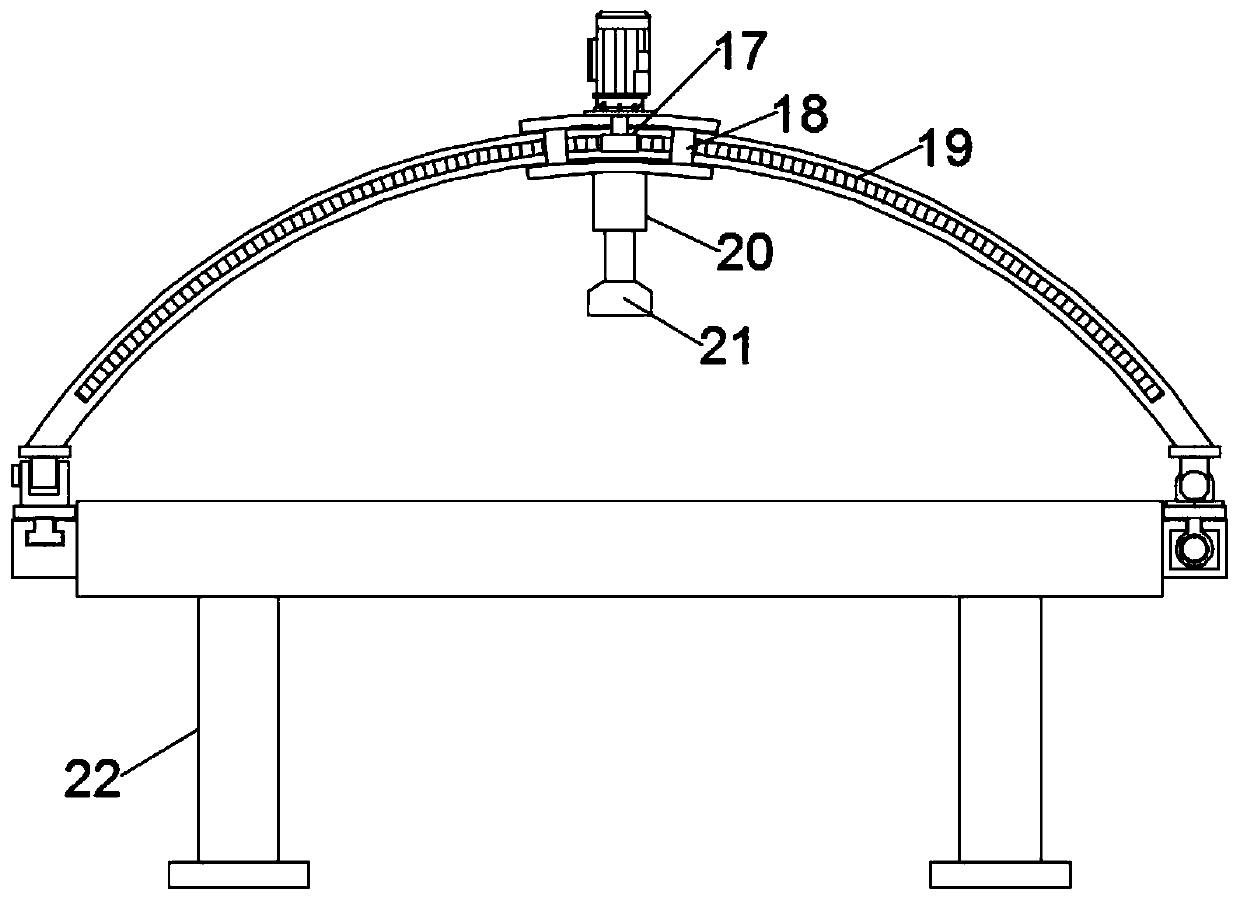
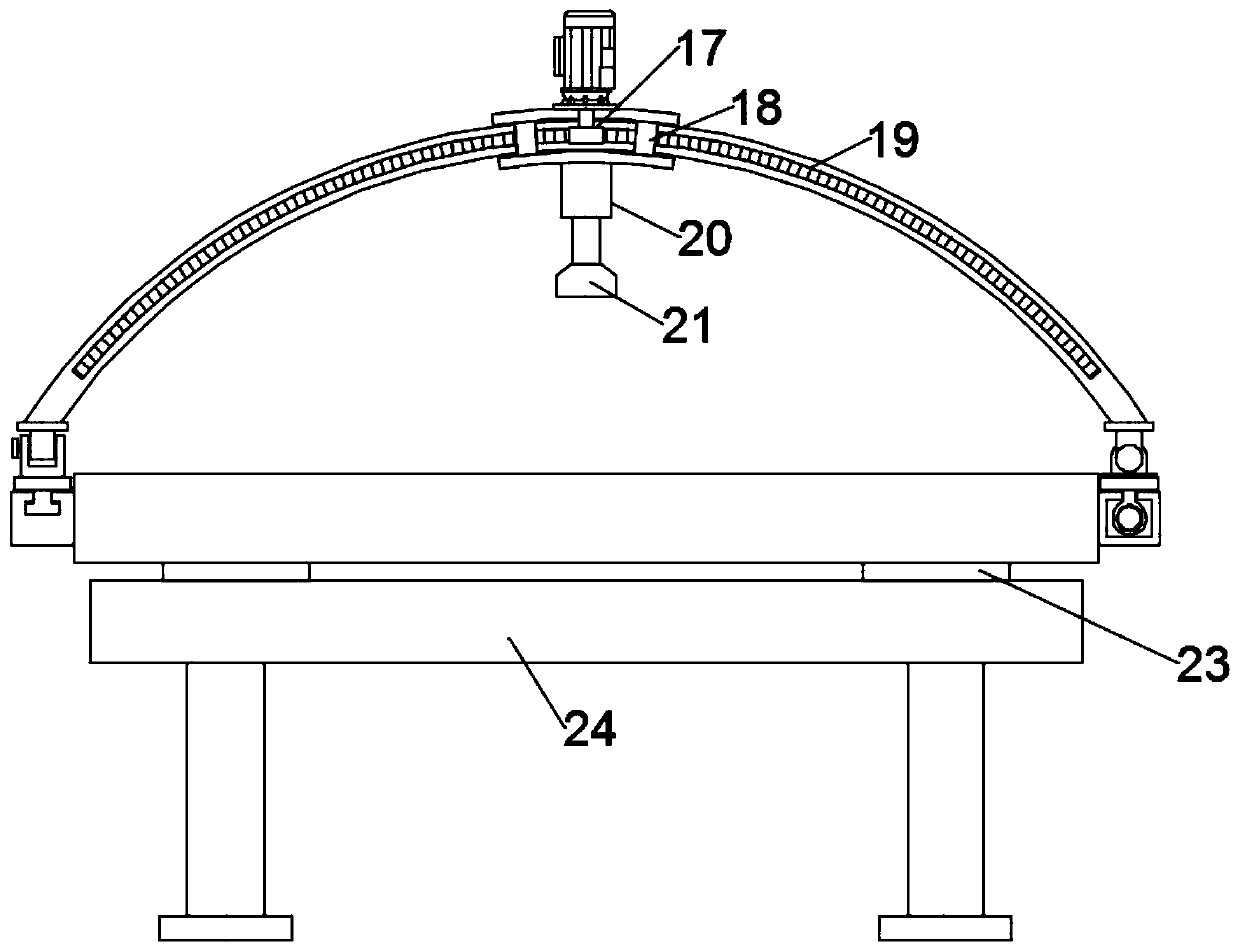
InactiveCN110464378AAchieve comprehensivenessQuick checkInfrasonic diagnosticsSonic diagnosticsClamp connectionPrenatal diagnosis
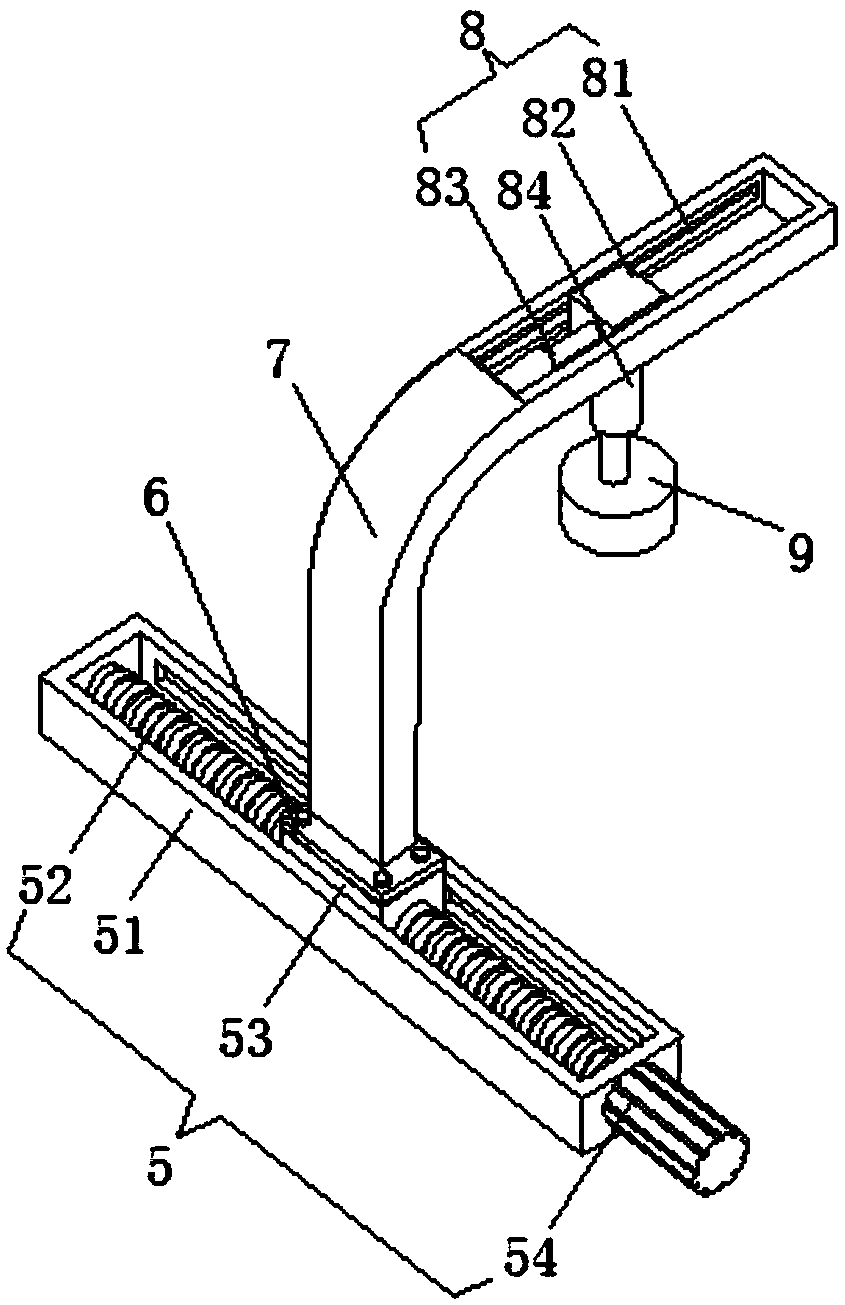
The invention relates to the technical field of medical devices, and concretely relates to a multifunctional prenatal diagnosis and treatment instrument for clinical use in gynecology and obstetrics.The instrument includes a bed plate; and extension cavities are symmetrically arranged at both sides of the bed plate, and the extension cavities are provided with a moving block and a sliding block which can slide along the corresponding extension cavities respectively, wherein the moving block is connected with a driving assembly arranged in one of the extension cavities, the driving assembly drives the moving block to move, the sliding block is slidingly mounted in a sliding slot arranged in the remaining extension cavity, an arc-shaped bracket is arranged on the bed plate, one end of the arc-shaped bracket is hinged to the moving block, the other end of the arc-shaped bracket is in clamping connection with the sliding block, the arc-shaped bracket is provided with an adjustment assembly capable of movably adjusting along the arc-shaped bracket, and the adjustment assembly provided with an B-mode ultrasound probe. The instrument has the advantages of novel design, realization of thecomplete inspection of pregnant women through adjusting the position of the B-mode ultrasound by the arc-shaped bracket and the adjustment assembly, no manual operation, fastness in inspection, and effective reduction of the labor intensity of the medical staff.
Owner:姚海凤
Method and system for processing ultrasonic imaging data
InactiveCN104470443AUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasonic imagingB mode ultrasound
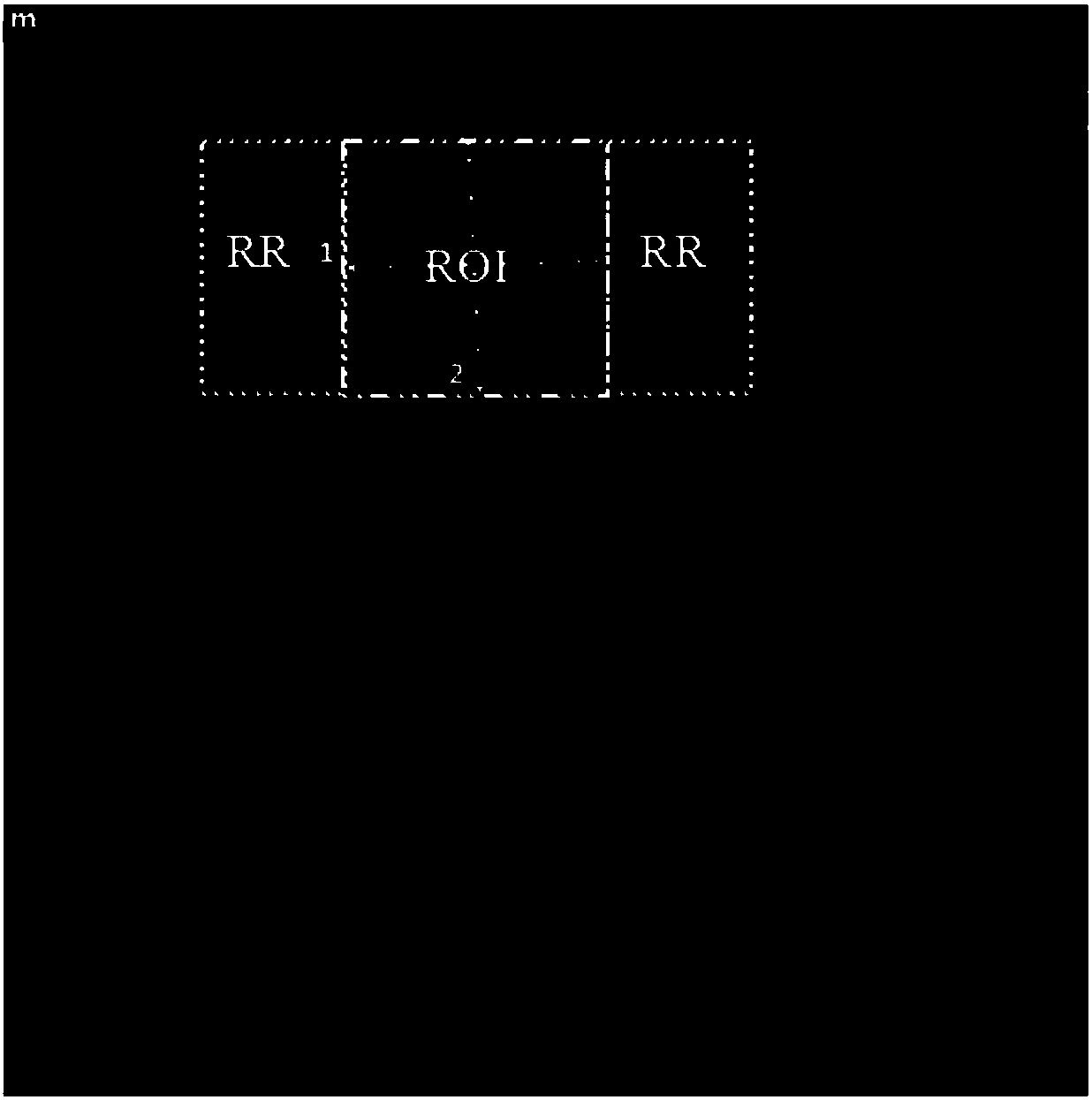
The present invention provides a method and a system for processing ultrasonic data. The method comprises: obtaining (210) a B-mode ultrasonic image; setting (220) a first ROI on the ultrasonic image according to a first input received from a user; measuring (230) elasticity-related data for the first ROI by using a shear wave ultrasonic imaging technique; generating (240) a second ROI on the ultrasonic image on the basis of the first ROI; and extracting image features for the second ROI from the ultrasonic image.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Method and system for processing ultrasonic imaging data
ActiveUS20150190120A1Efficient and reliableOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasonic imagingImaging Feature
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Self-adaptive control device for mammary gland minimally invasive operation
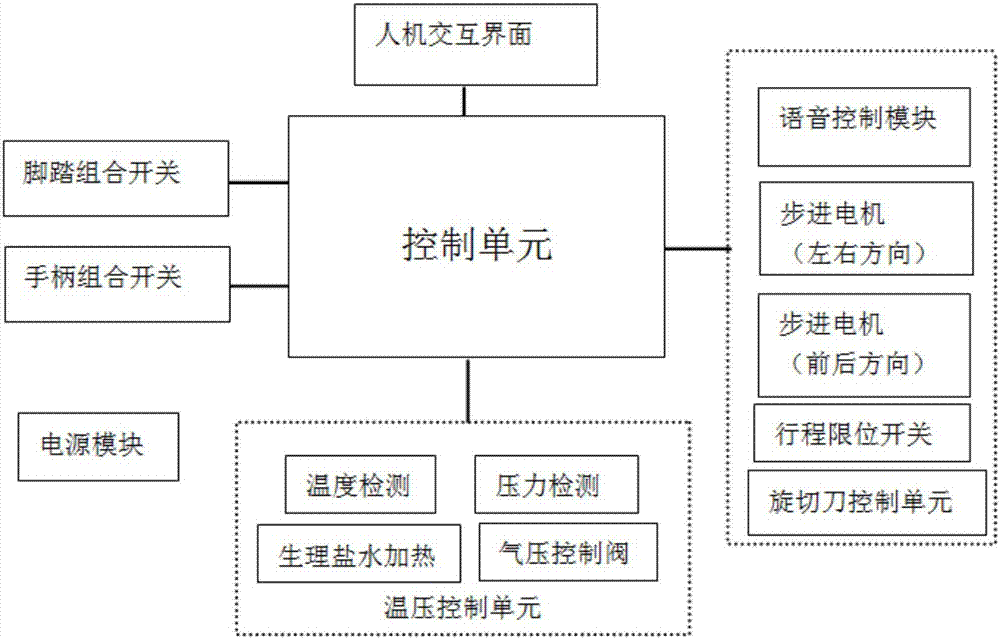
ActiveCN106880379ASupport customized voice recordingSuction parameter adjustmentEnemata/irrigatorsSurgical needlesTissue densityOperation mode
The invention discloses a self-adaptive control device for a mammary gland minimally invasive operation. The device includes a control unit, a man-machine interface, a voice control module, a pedal combination switch, a handle combination switch, a temperature and pressure control unit, a power supply module and the like; the temperature and pressure control unit includes a pressure sensor and a temperature sensor; the pressure sensor detects air pressure in a puncture channel, and the temperature sensor detects the temperature in the puncture channel; according to temperature and pressure data collected by the pressure sensor and the temperature sensor respectively and tissue density data obtained through B-mode ultrasound image analysis, the control unit performs automatic adjustment, drives a corresponding motor to operate, and automatically completes tissue rotary cutting, cut tissue vacuum suction and physiological saline injection for cleaning. The device achieves the integration of B-mode ultrasound, a vacuum pump and a rotary cutting device; multiple operation modes are supported, customized voice recording is supported, and anti-misoperation is supported; the mechanical structure and circuit of the device are simple and reliable, and batch production is easily achieved.
Owner:戴凌虹
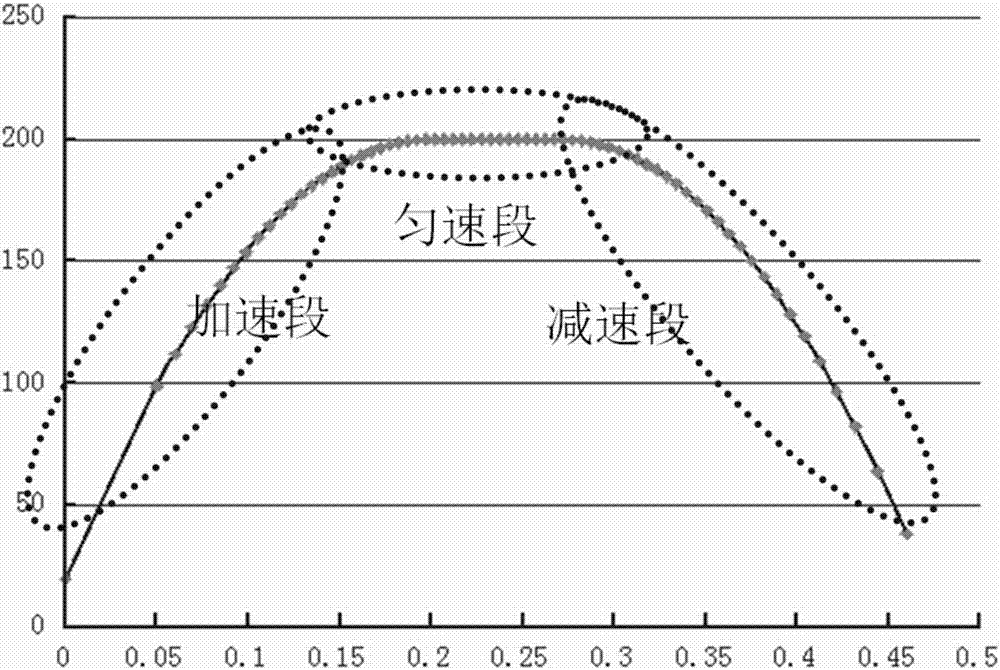
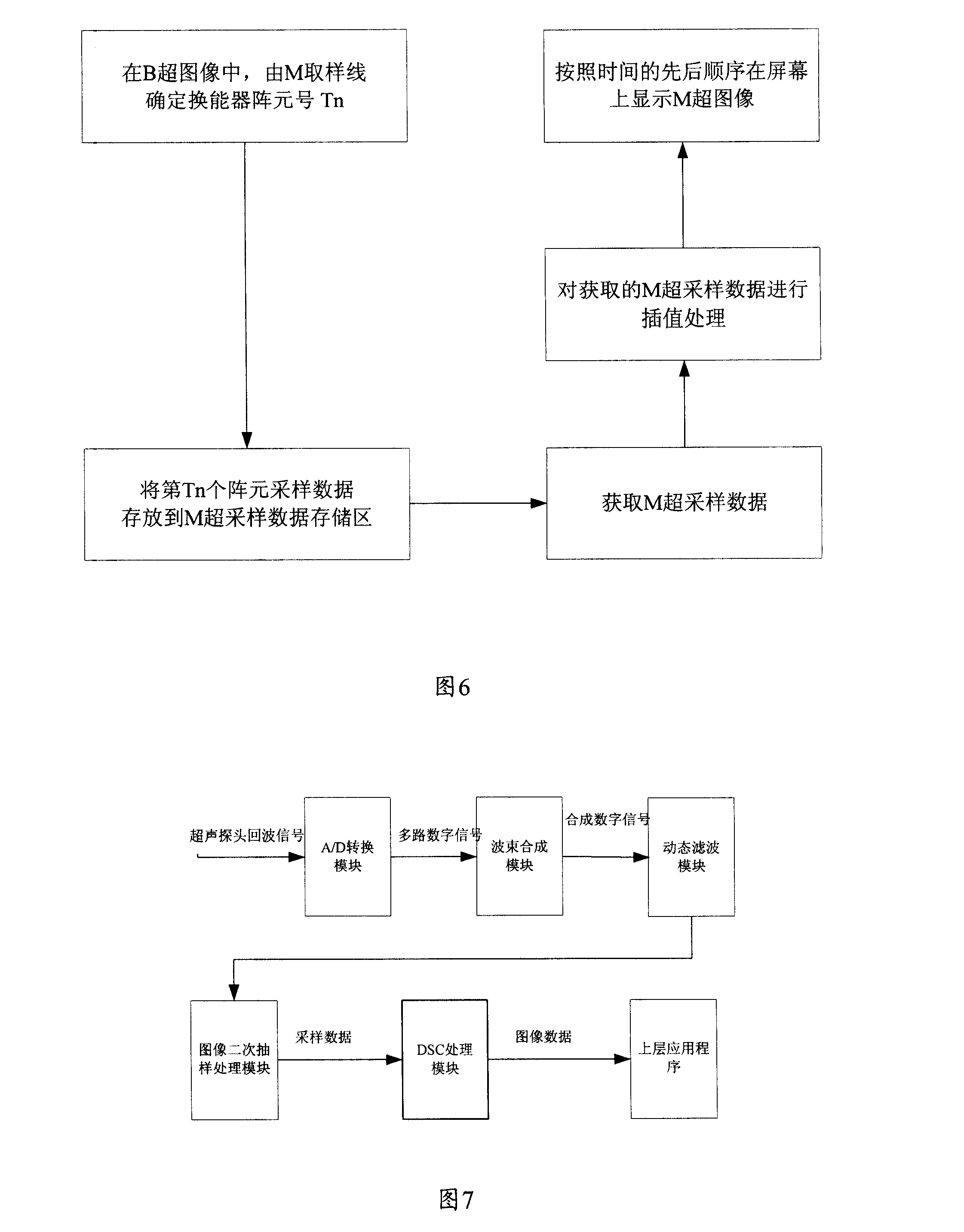
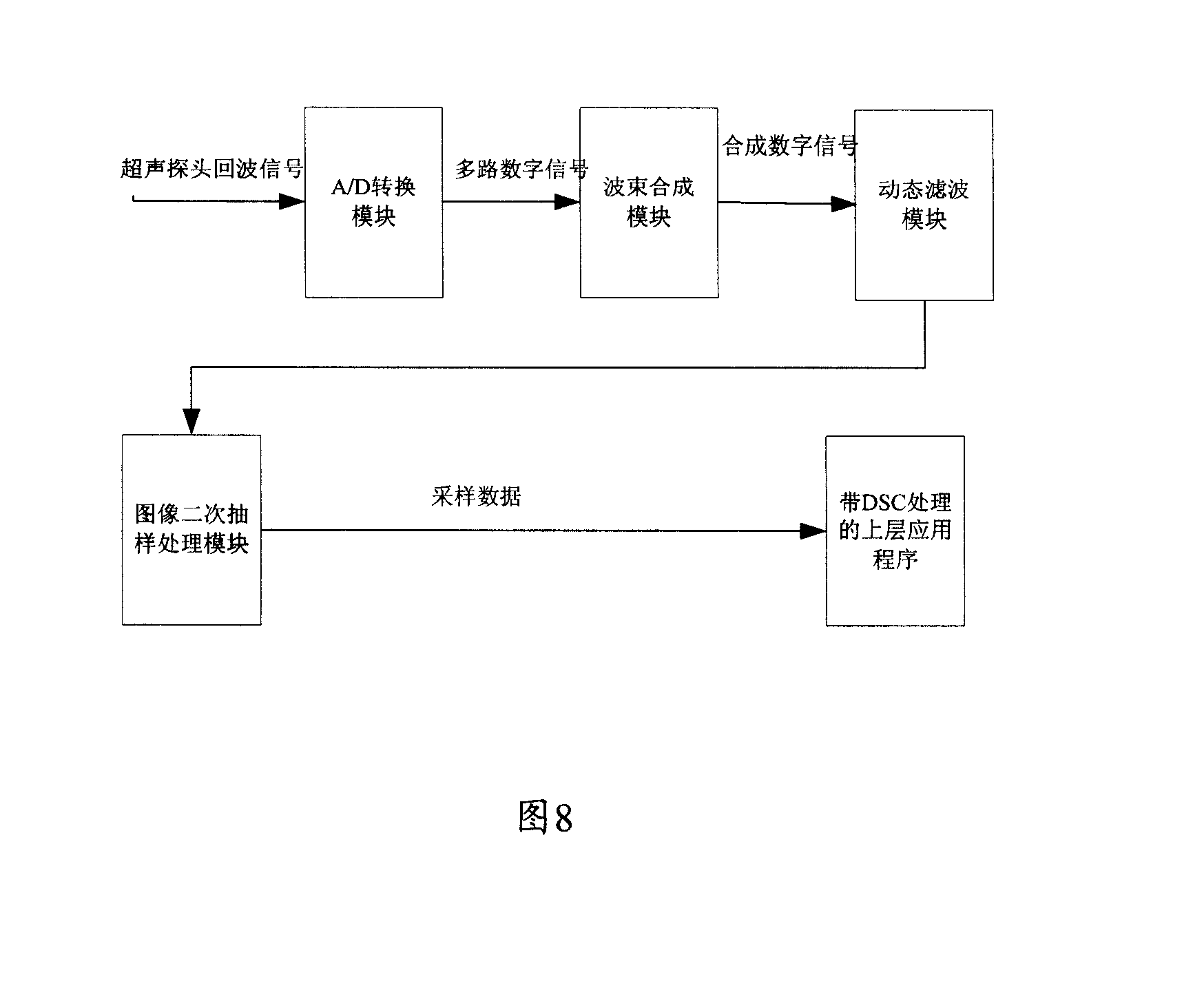
A display method of B/M mode ultrason image
The invention relates to a B / M mode ultrasonic image display method which comprises the following procedure: A1,the arrangement directions and the display scales of a B model ultrasonic image and an M model ultrasonic image on a screen are determined; A2, a software module is utilized to display the B model ultrasonic image on the screen; A3, an M sampling line is selected on the B model ultrasonic image; A4, the software module is utilized to display the B model ultrasonic image corresponding to the M sampling line on the screen. The invention uses software to perform the DSC treatment and to perform the display of the B / M model ultrasonic image, a hardware processing module of DSC is omitted, the hardware cost is saved, the hardware volume is reduced, and the great convenience is provided for the post-treatment of the image.
Owner:SHENZHEN LANDWIND IND
Apparatus and method for measuring an amount of urine in a bladder
InactiveUS20160192904A1Organ movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsTransducerB mode ultrasound
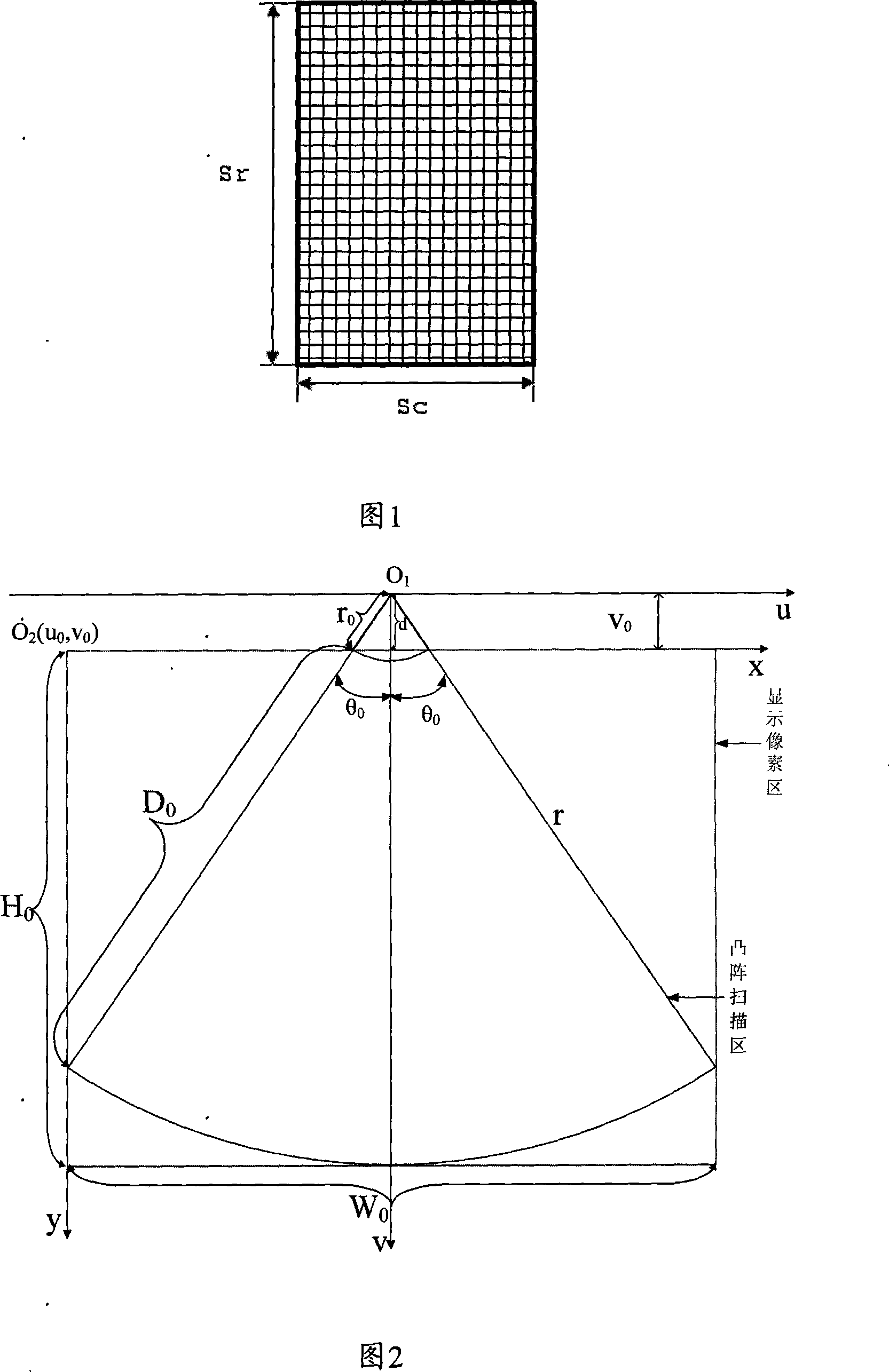
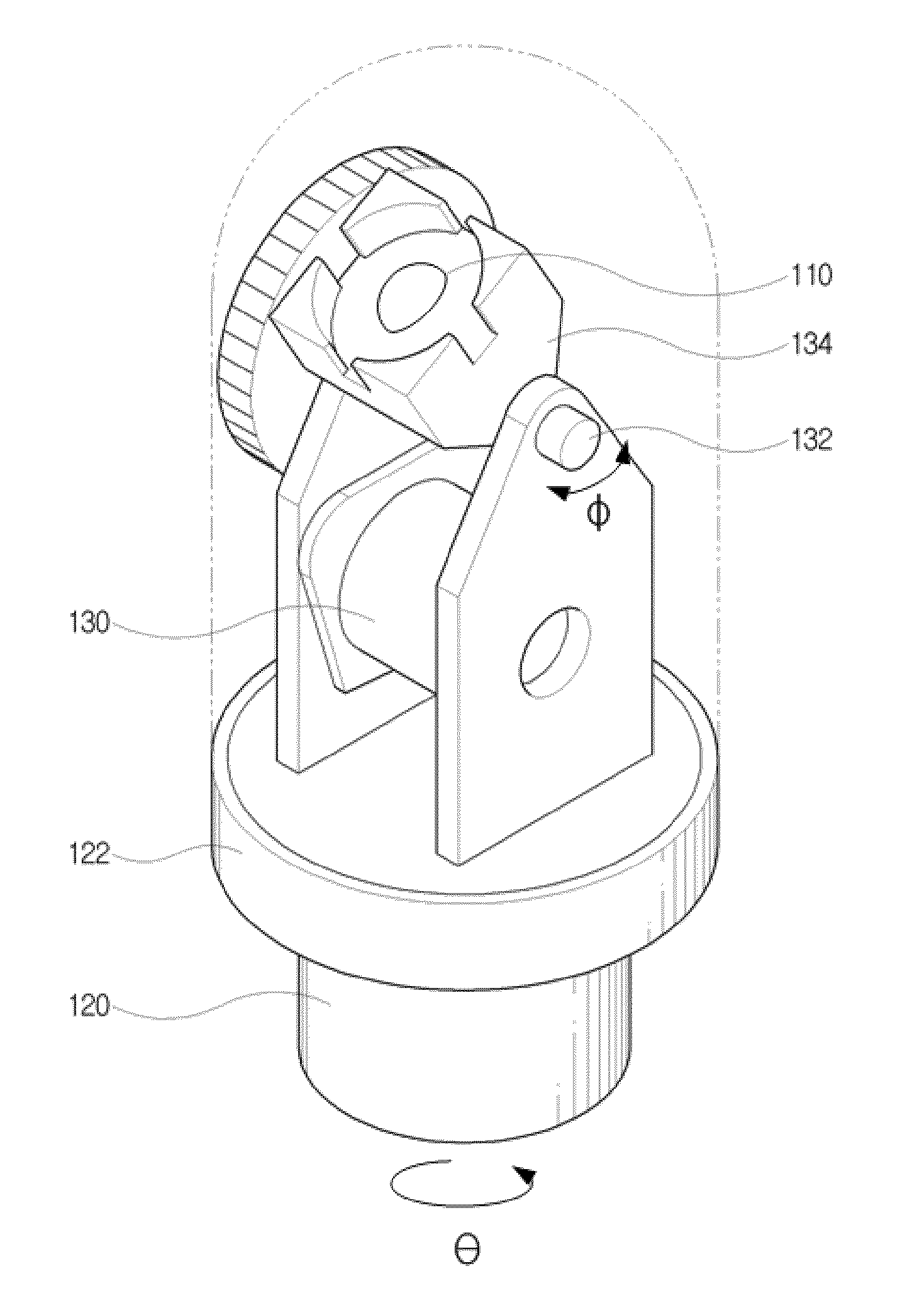
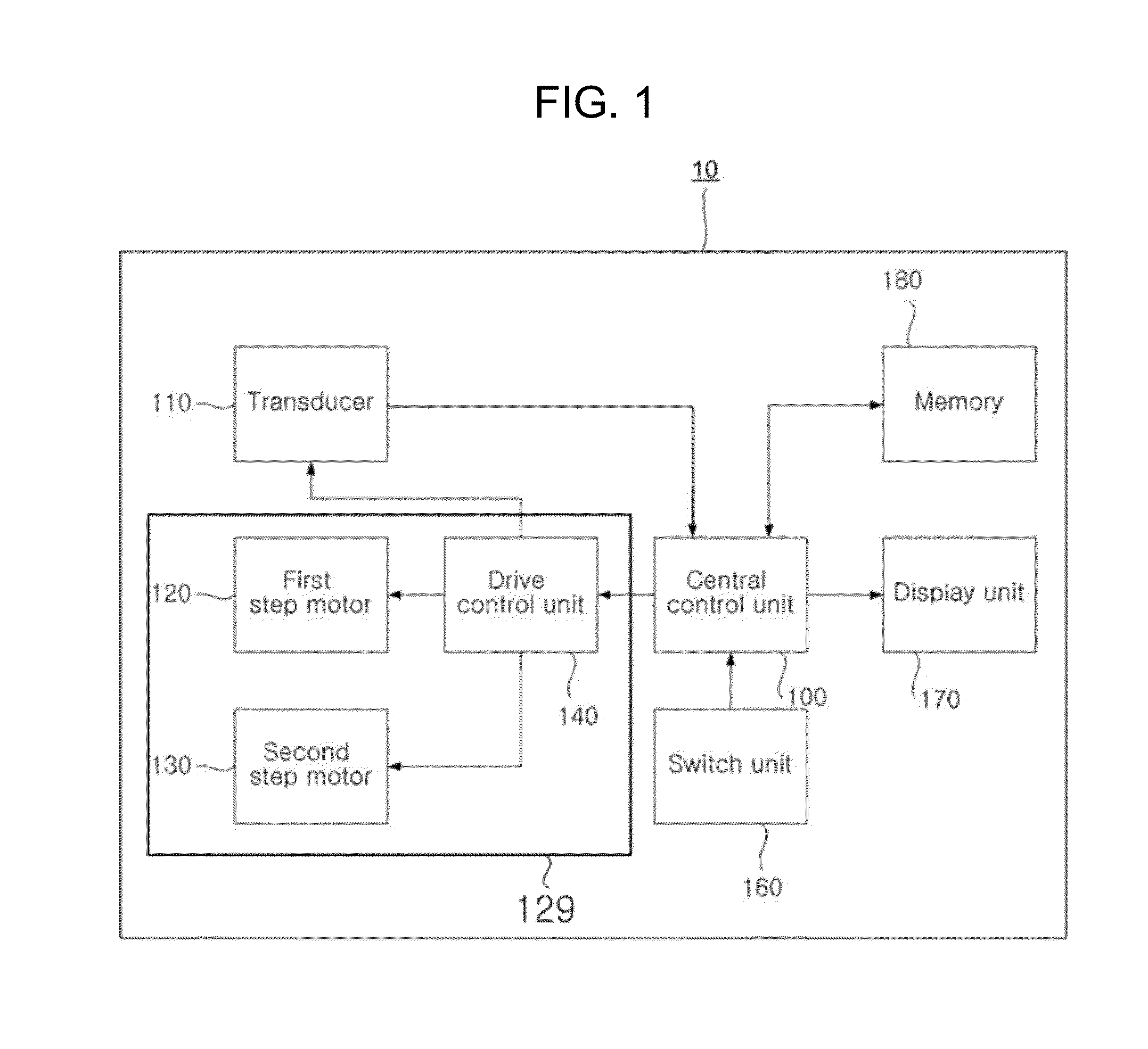
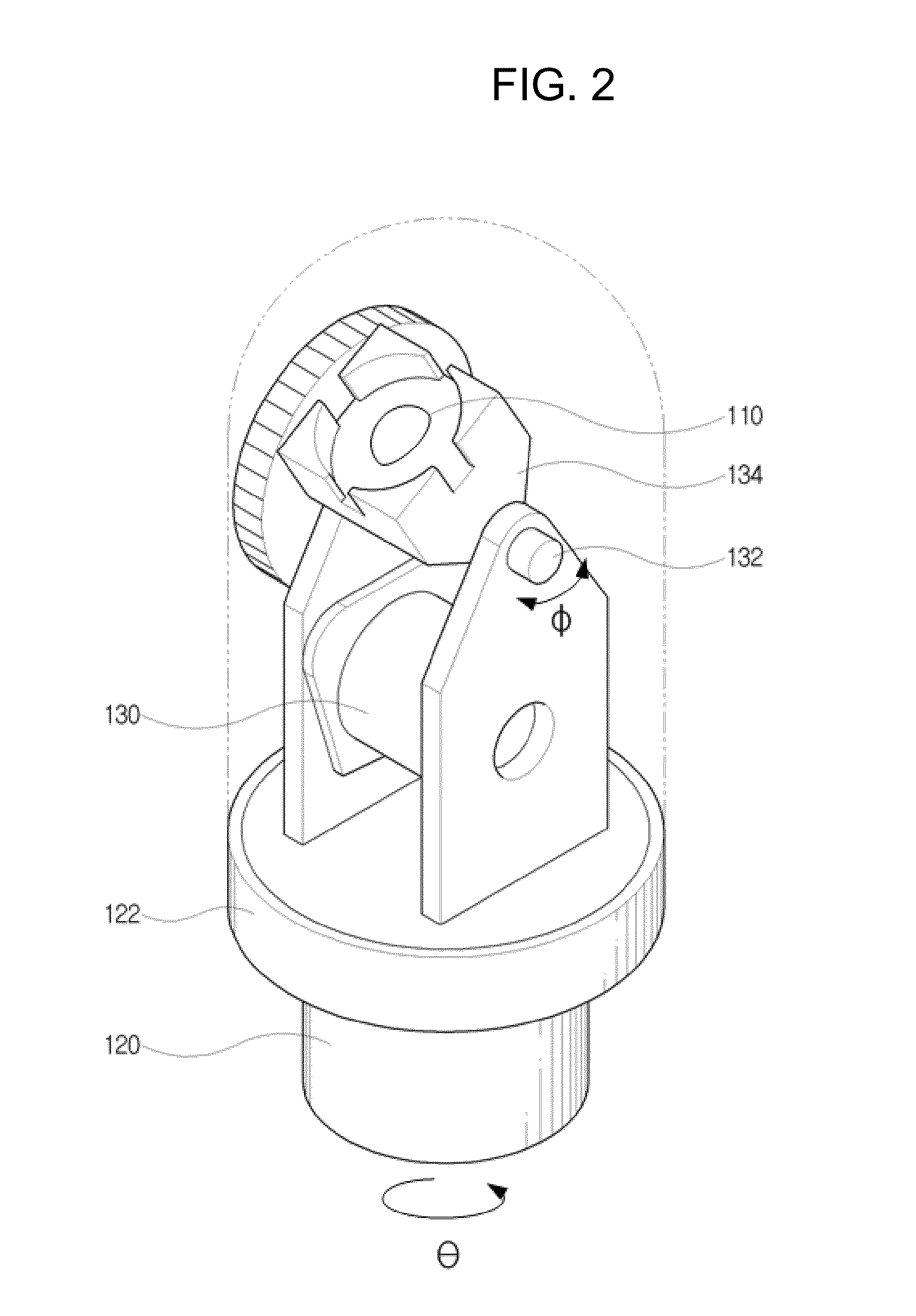
An apparatus for measuring an amount of urine in a bladder using ultrasonic signals includes: a transducer; a switch for selecting one of operational modes, which include a preliminary scan mode and a scan mode; a transducer drive unit for driving the transducer; and a central control unit for operating according to the operational mode to provide an amount of urine in the bladder. The central control unit in the preliminary scan mode performs a preliminary scan to obtain ultrasonic signals for a single scan plane from the transducer, generates a 2-D B-mode ultrasonic image using the ultrasonic signals obtained in the preliminary scan, trace an outline of a bladder on the 2-D B-mode ultrasonic image, generates an aiming image, estimate a volume of the bladder, and displays the 2-D B-mode ultrasonic image represented the traced outline, the aiming image and the estimated value to the display unit.
Owner:MCUBETECH
Medical wireless WIFI transmission B-mode ultrasound equipment
InactiveCN105147323AAccurate diagnosisImprove transmission efficiencyBlood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsChannel dataImaging processing
The invention relates to medical wireless WIFI transmission B-mode ultrasound equipment. The medical wireless WIFI transmission B-mode ultrasound equipment comprises a shell, a probe, a WIFI module, a built-in antenna, an antenna terminal, an FPGA chip, a receiving chip, a transmitting chip, an upper cover and a host. Due to the fact that only the transmitting chip, the receiving chip and the FPGA chip are included for simple signal processing and beam forming, the part with the large information handling capacity is transplanted to the host, more image processing is conducted through the powerful function of the host, excellent images are obtained, and then correct diagnosis of clinicians is guaranteed. Due to the fact that the data volume transmitted through WIFI is limited, signal transmission is completed through eight-channel data transmission, the patch antenna is arranged, and the transmission efficiency of the wireless WIFI is improved.
Owner:苏州斯科特医学影像科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com