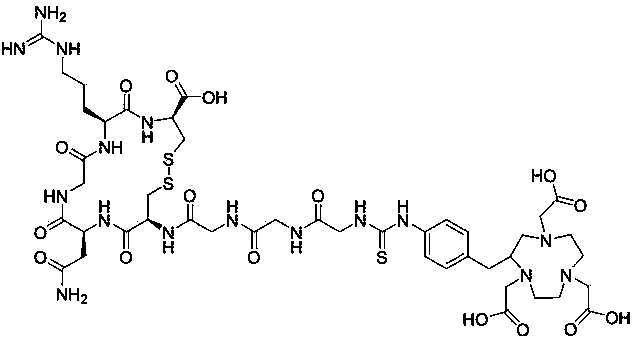
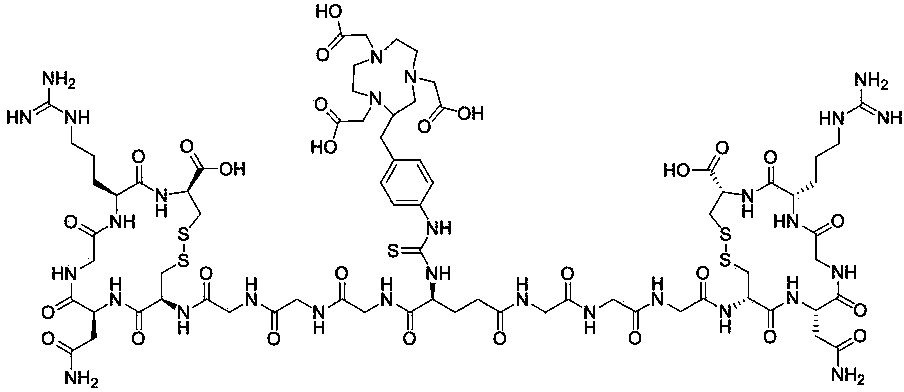
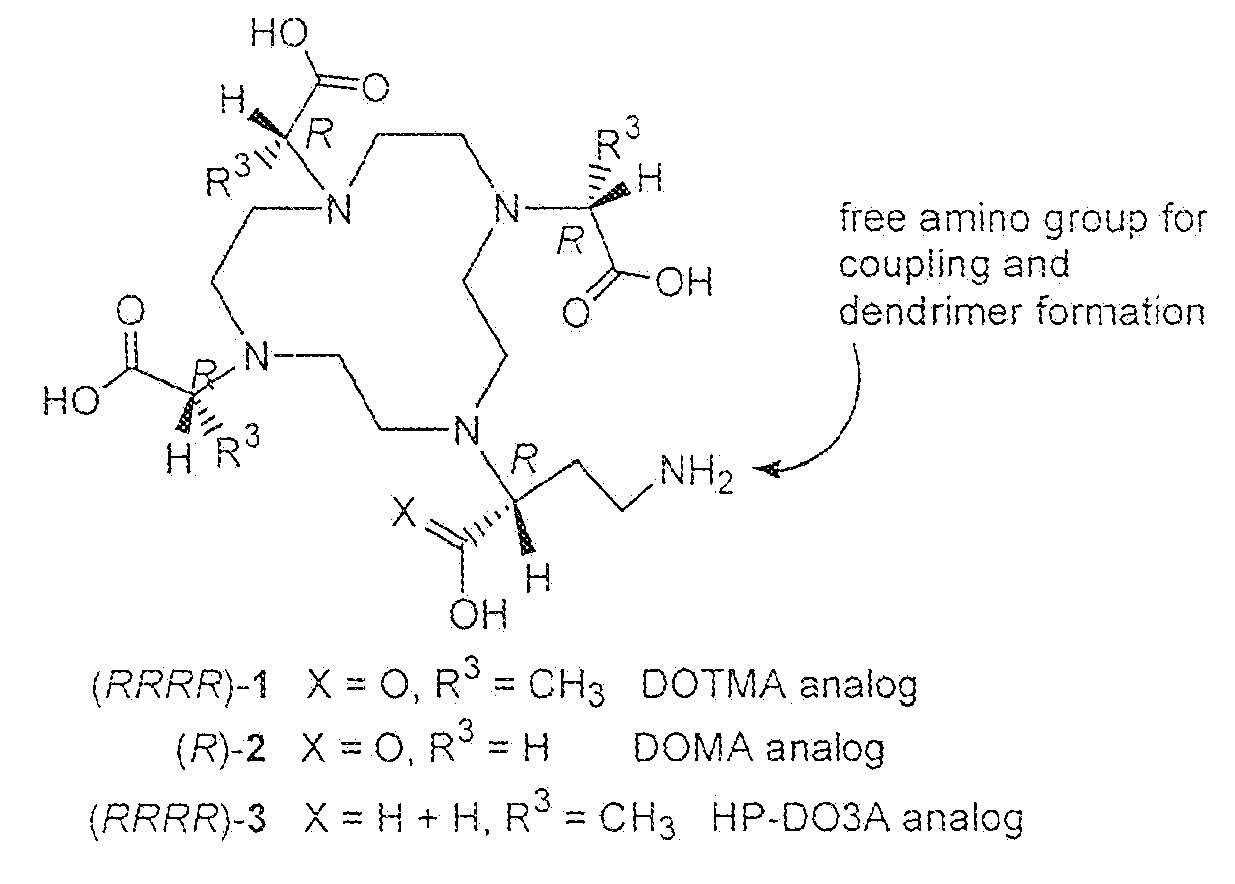
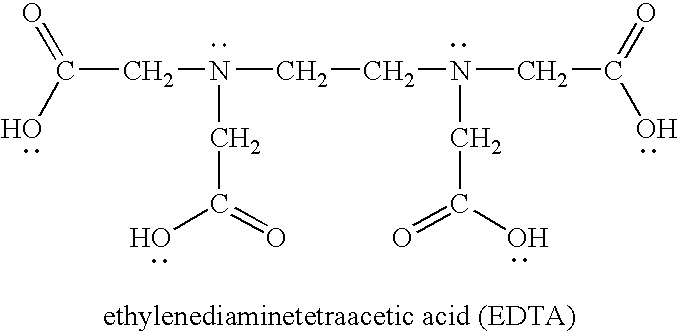
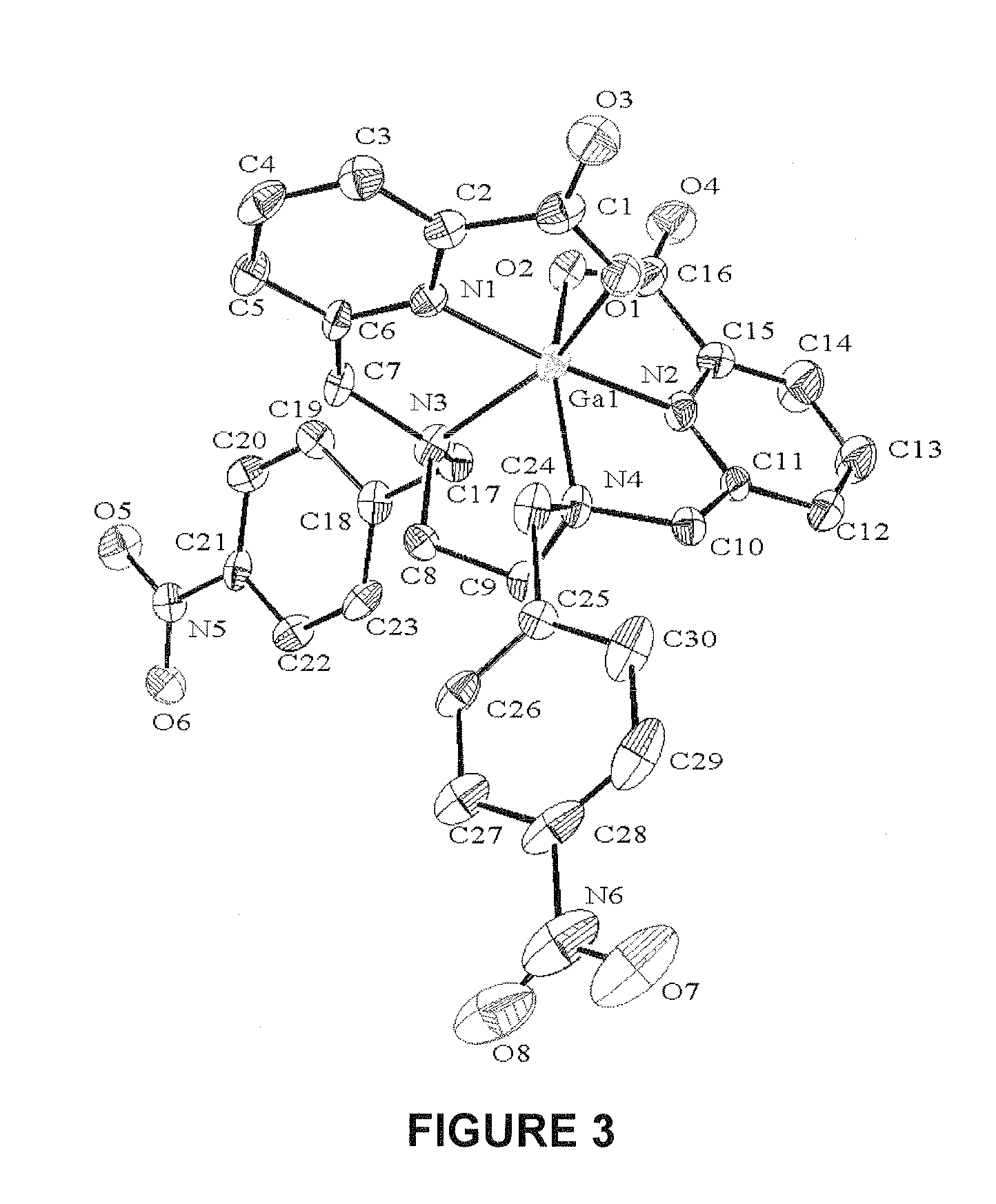
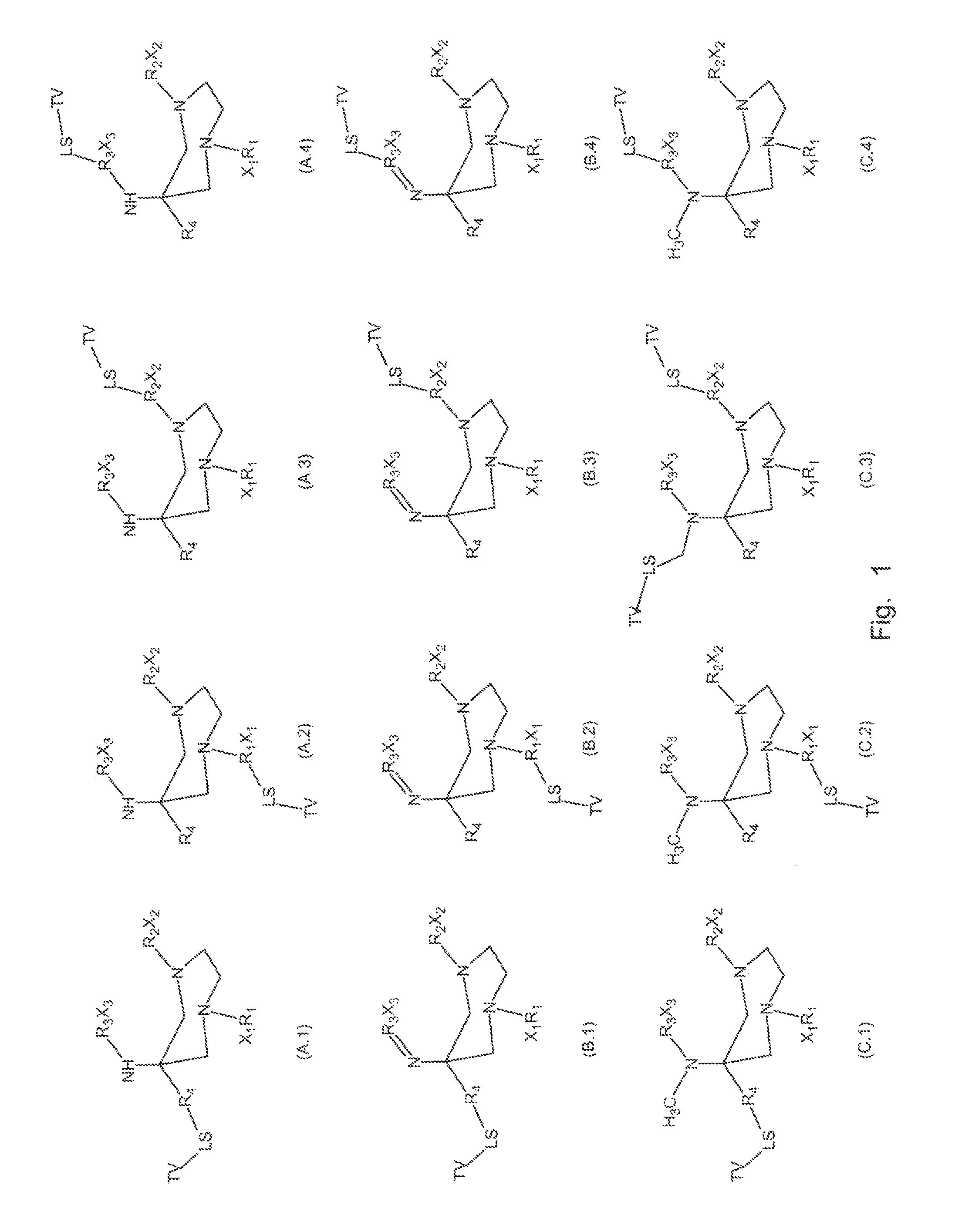Patents
Literature
79 results about "Bifunctional chelator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
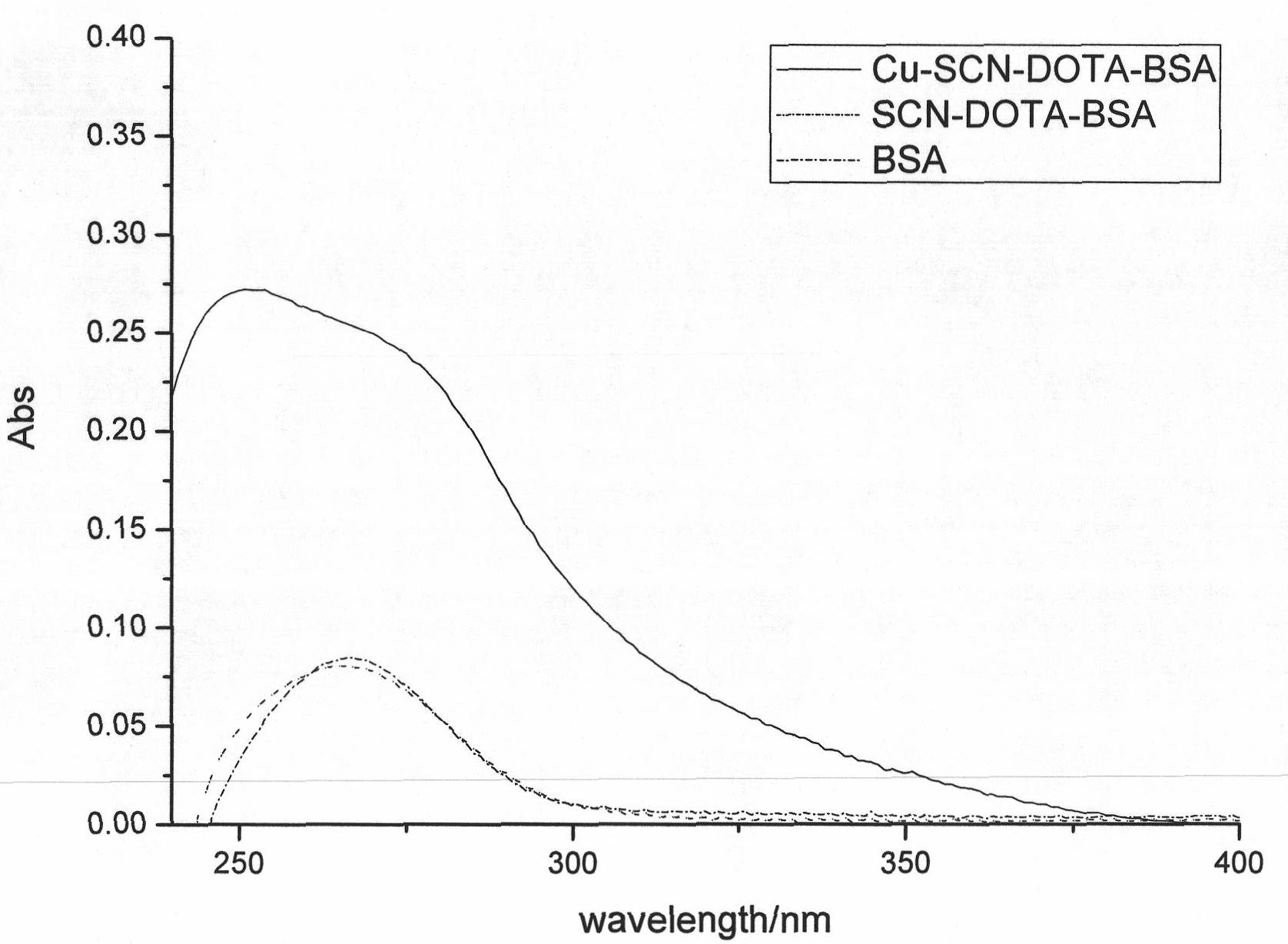
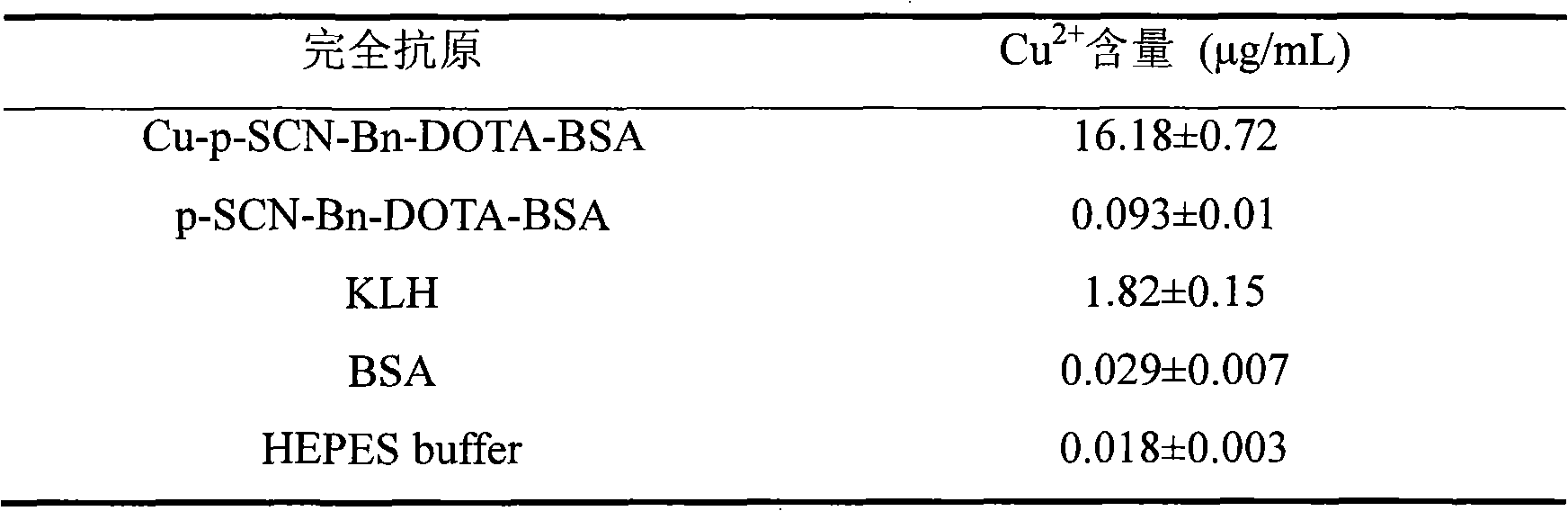
Heavy metal Cu<2+> complete antigen and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101775074ASolve the technical difficulties of preparationSolve technical difficultiesOvalbuminSerum albuminSorbentMonoclonal antibody
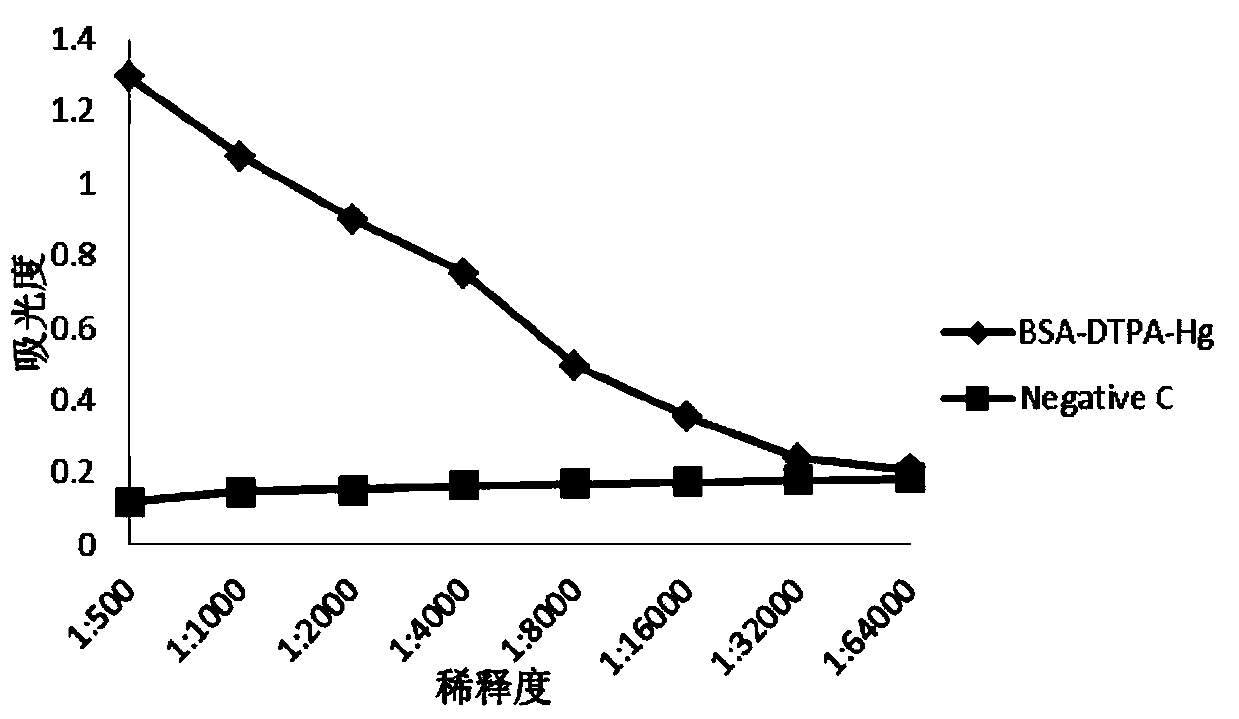
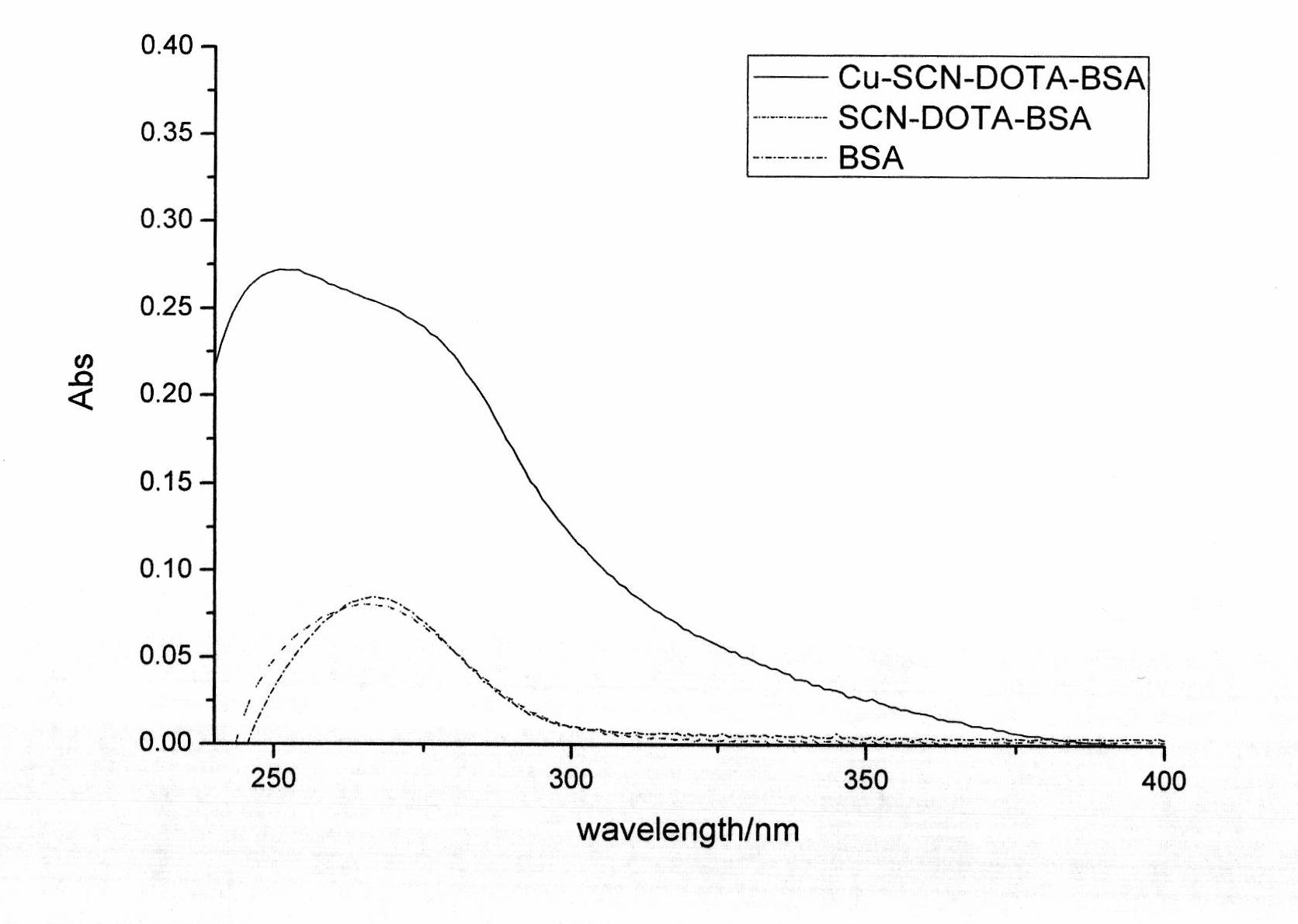
The invention discloses a heavy metal Cu<2+> complete antigen and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: Cu<2+> is reacted with a bifunctional chelating agent to form a hapten; and a Cu<2+>-chelating agent hapten is reacted with a carrier protein to form a Cu<2+>-chelating agent-carrier protein complete antigen. The antigen has better immunogenicity; and an immune mice with the antigen can be used for preparing a Cu<2+> specific monoclonal antibody and further preparing a rapid Cu<2+> detection ELISA (enzyme-linked immuno sorbent assay) kit of various heavy metals and colloidal gold immunochromatography assay test paper.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Macrocyclic chelants for metallopharmaceuticals
InactiveUS6916460B2High binding affinityGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsRadioactive preparation carriersMetal chelateHeteroatom
This invention relates to macrocyclic chelants comprised of one or two heteroatom-containing bridges, compositions containing them and their use in medicine, particularly in diagnostic imaging and radiotherapy. This invention relates especially to the use of metal chelates of the macrocyclic chelants as metallopharmaceuticals in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and radiopharmaceuticals. This invention also relates to macrocyclic chelants as bifunctional chelating agents (BFC's) for the labeling of biologically active targeting molecules such as proteins, peptides, peptidomimetics, and non-peptide receptor ligands, with metal ions and radioisotopes.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB PHARMA CO
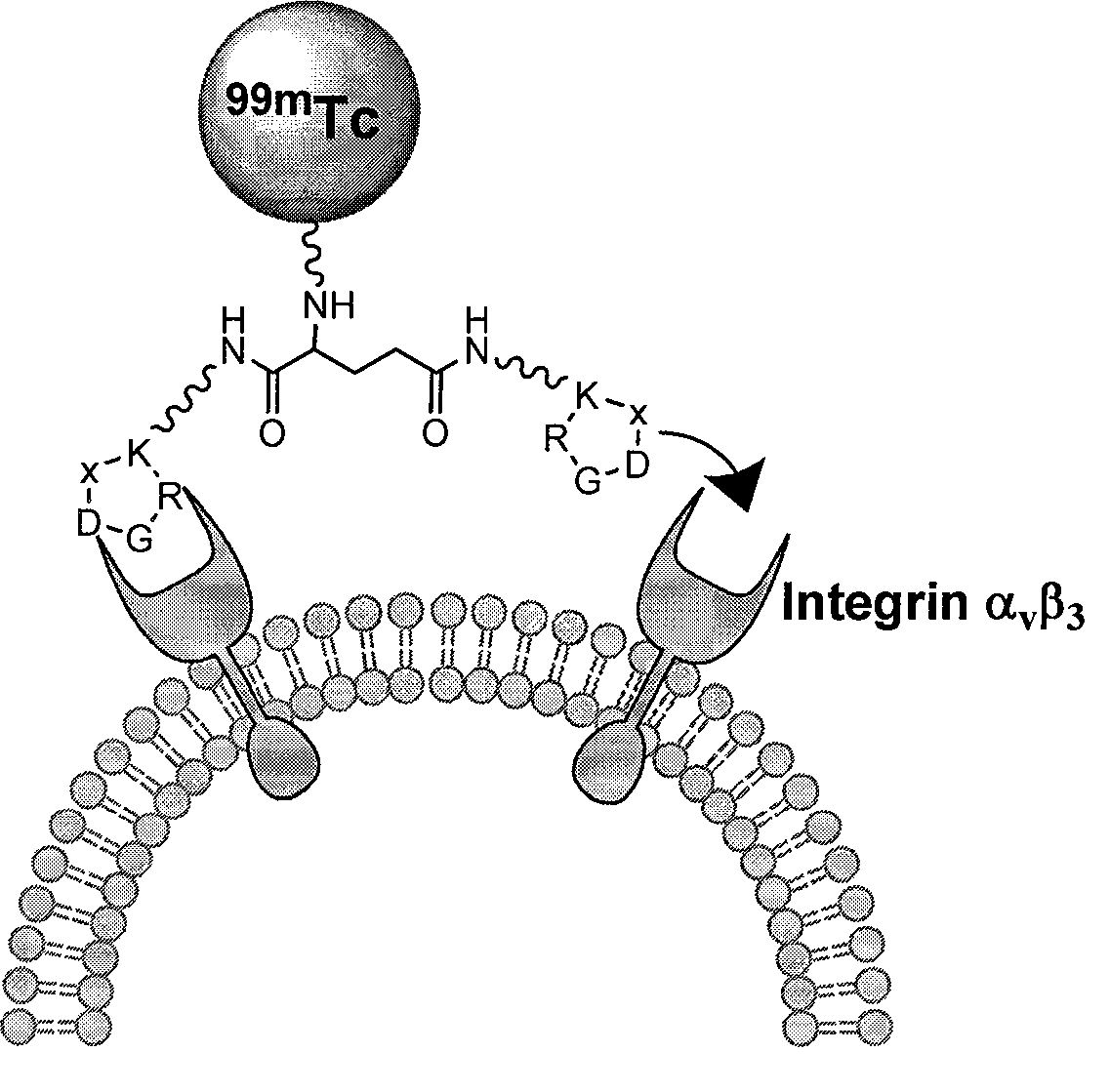
RGD polypeptide radiopharmaceuticals and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101428148AIncrease intakeHigh binding affinityIn-vivo radioactive preparationsAntineoplastic agentsDimerCyclic peptide
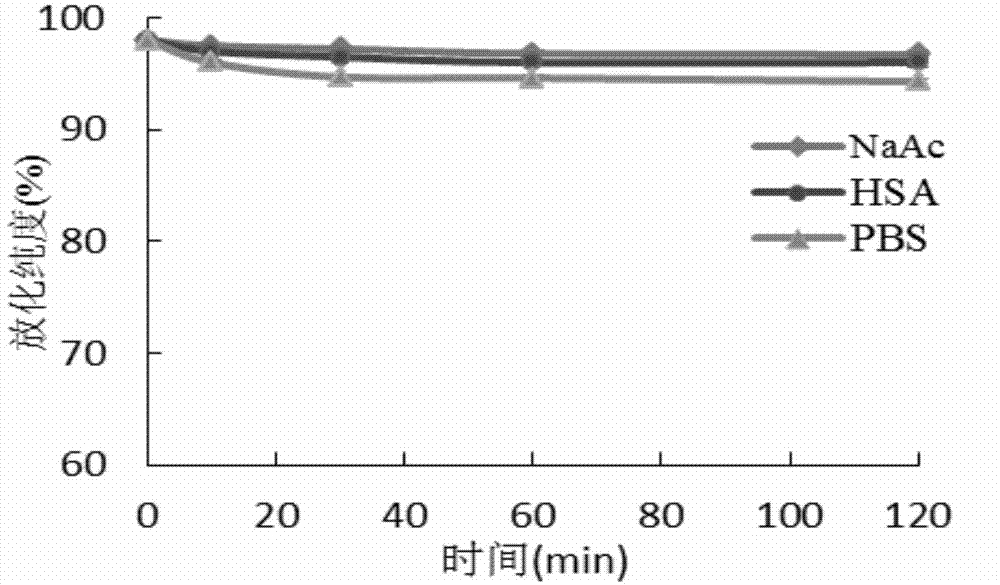
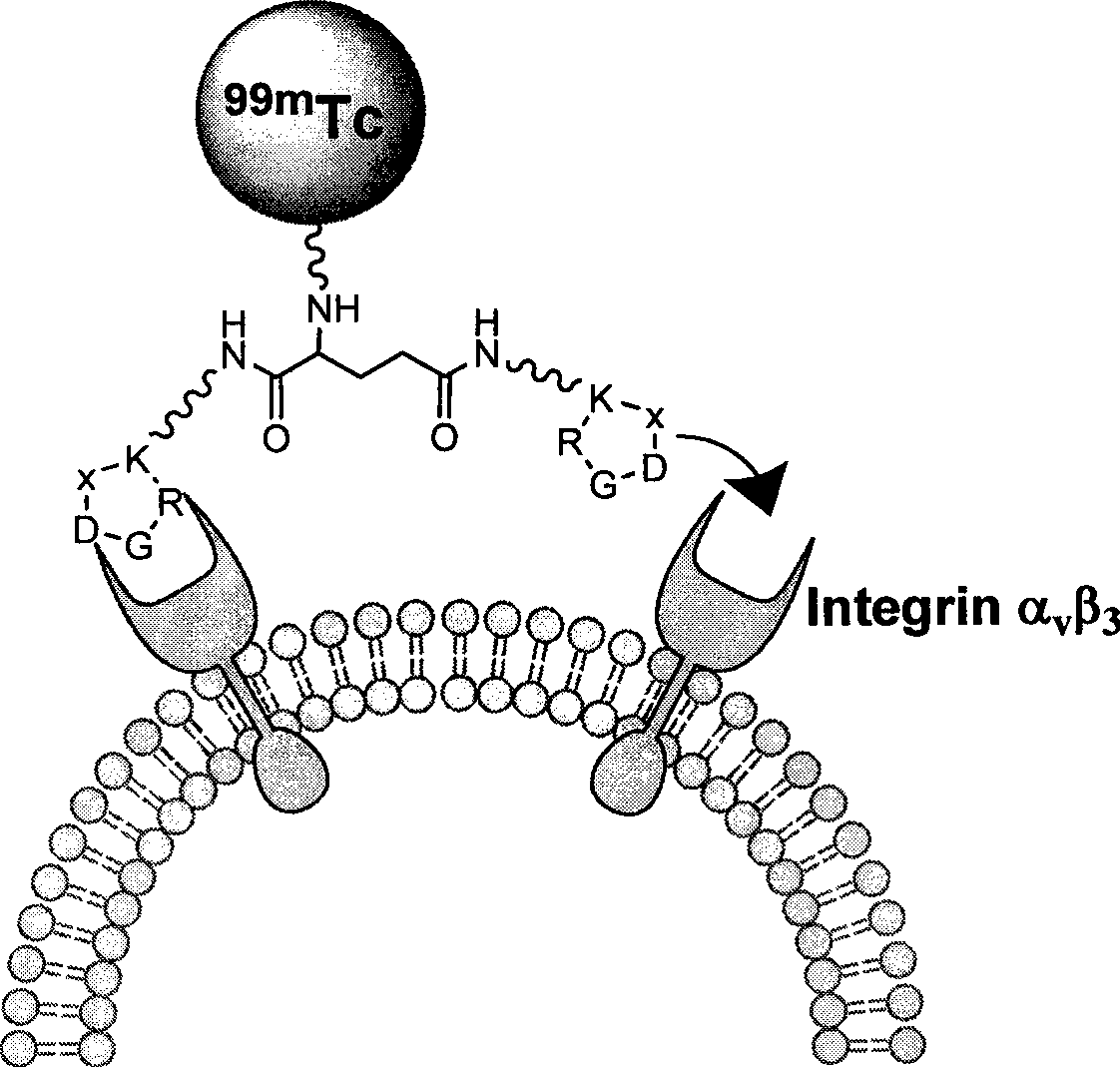
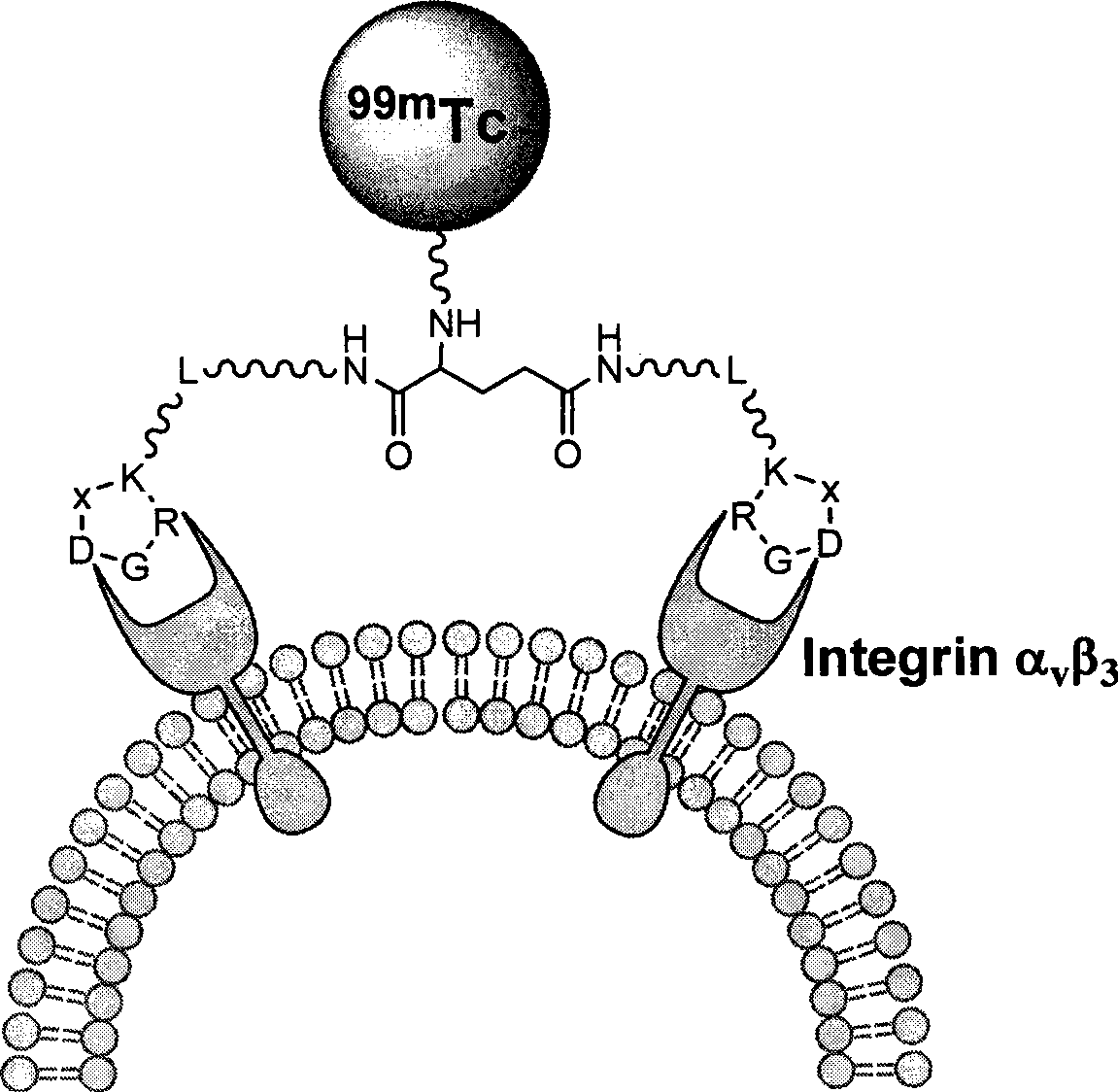
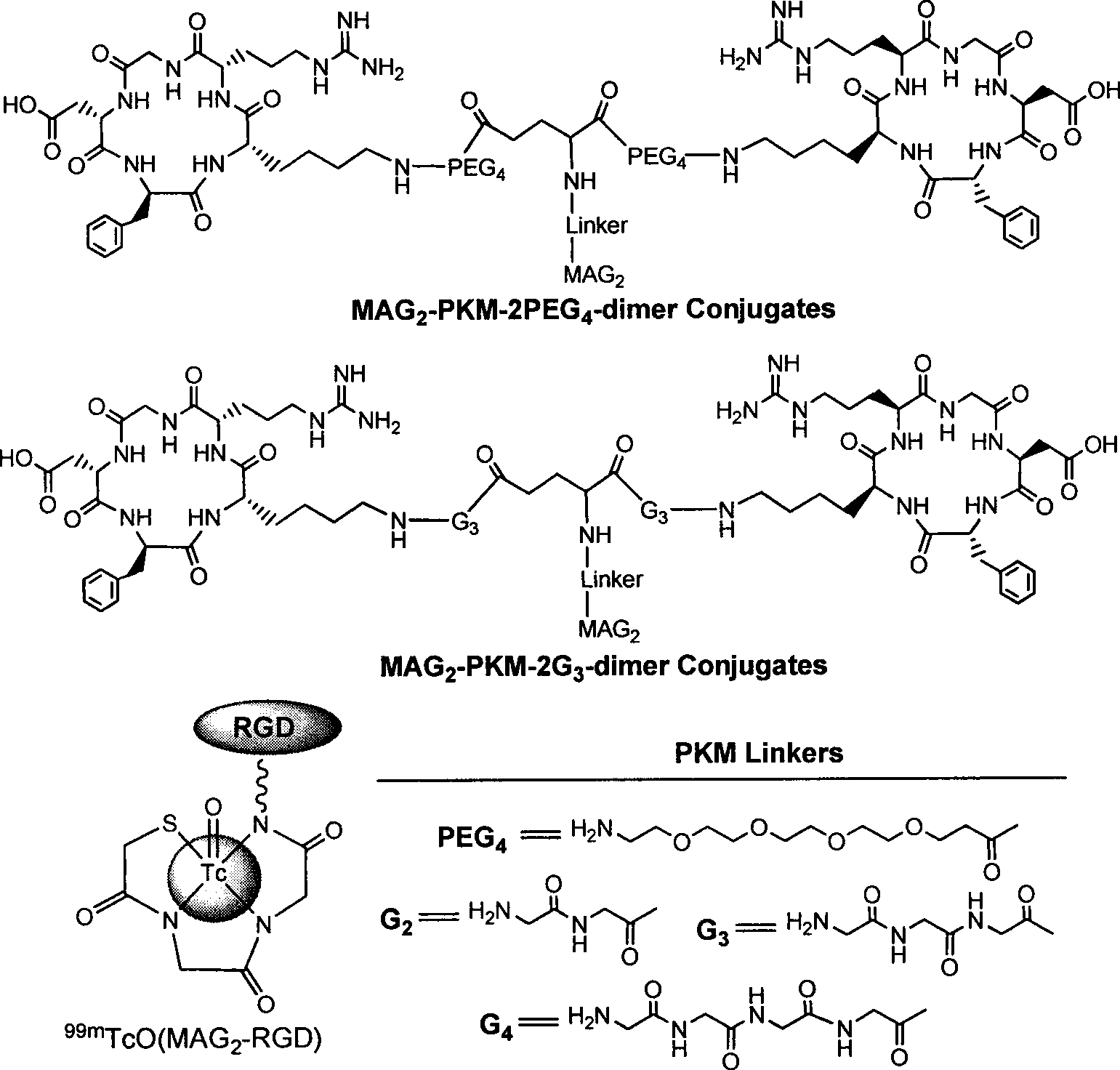
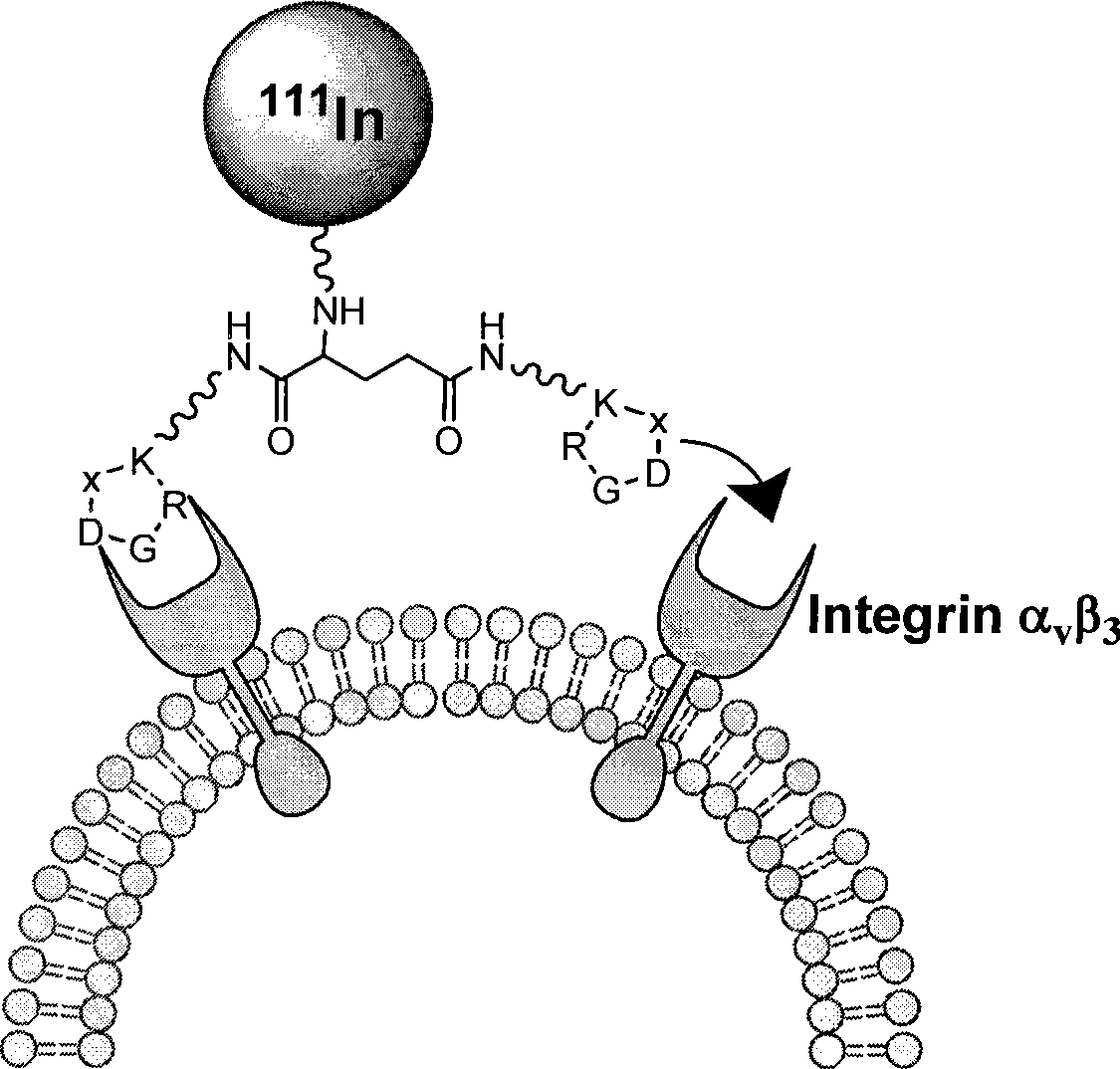
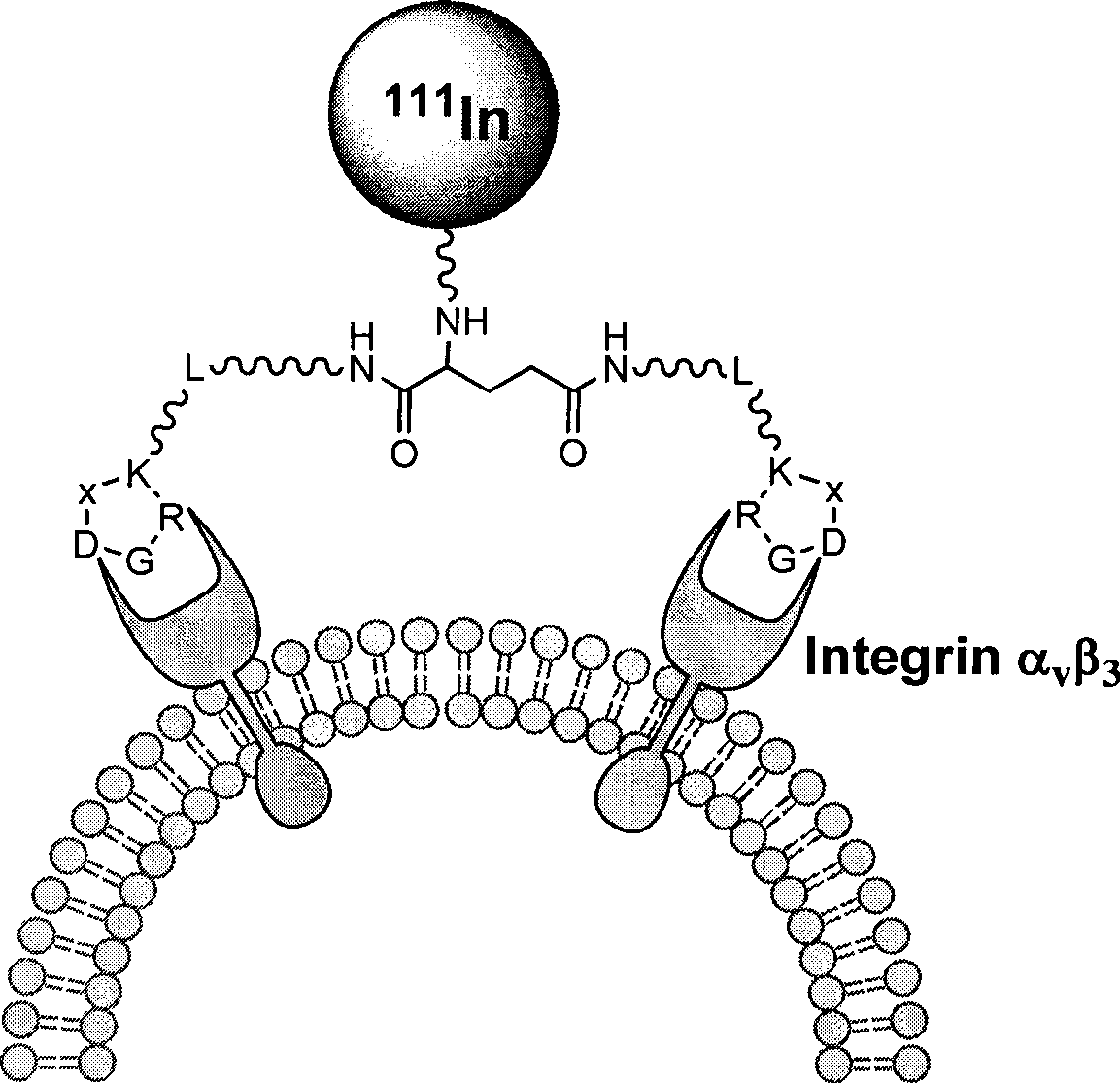
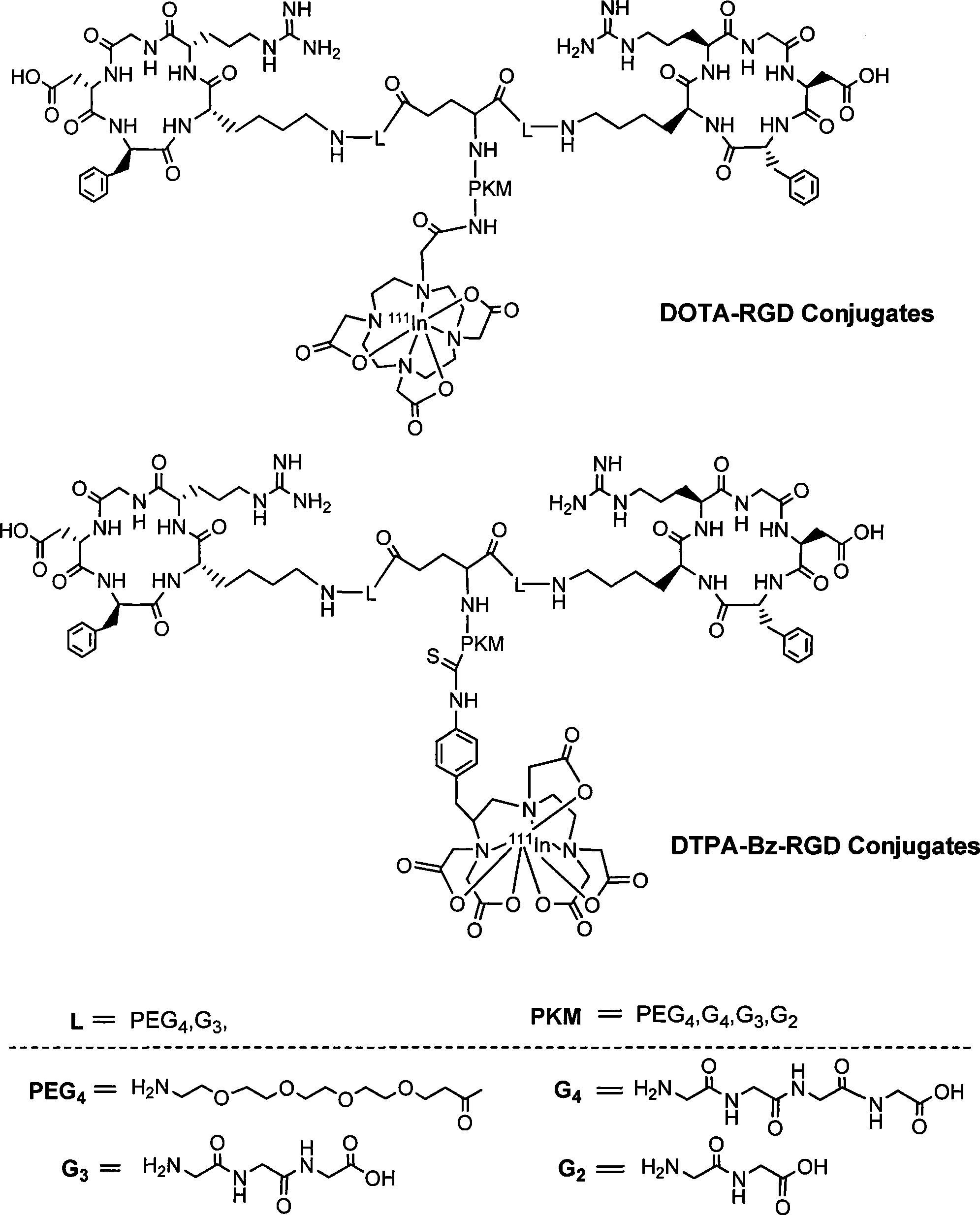
The invention relates to an RGD polypeptide radiopharmaceutical and a preparation method thereof. The RGD polypeptide radiopharmaceutical includes an RGD polypeptide and a radionuclide<99m>Tc, wherein, the RGD polypeptide radiopharmaceutical is an RGD cyclopeptide dimmer, that is, E(L-cRGDxK)2 which is synthesized by dimerizing two RGD polypeptide monomers connected with coupling agent L. The radionuclide<99m>Tc serves to mark the RGD cyclopeptide dimmer through a bifunctional chelating agent HYNIC. A pharmacokinetics modified molecule PKM is further connected between the RGD cyclopeptide dimmer and the bifunctional chelating agent. The RGD polypeptide radiopharmaceutical is <99m>Tc-HYNIC-PKM-E(L-cRGDxK)2. The RGD polypeptide radiopharmaceutical is colorless and transparent liquid injection. The RGD polypeptide radiopharmaceutical provided by the invention has the advantages of further reinforcing the binding affinity and the ingestion of drugs by tumor, and achieving better diagnosis effect.
Owner:广东瑞迪奥科技有限公司
Methods and Compositions for Improved F-18 Labeling of Proteins, Peptides and Other Molecules
The present application discloses compositions and methods of synthesis and use of 18F or 19F-labeled molecules of use in PET, SPECT and / or MR imaging. Preferably, the 18F or 19F is conjugated to a targeting molecule by formation of a complex with a group IIIA metal and binding of the complex to a bifunctional chelating agent, which may be directly or indirectly attached to the targeting molecule. In other embodiments, the 18F or 19F labeled moiety may comprise a targetable construct used in combination with a bispecific antibody to target a disease-associated antigen. The disclosed methods and compositions allow the simple and reproducible labeling of molecules at very high efficiency and specific activity in 30 minutes or less. In preferred embodiments, the labeled molecule may be used for imaging in a subject without purification after labeling.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
Novel radionuclide labelled somatostatin analogue molecular probe and application thereof
InactiveCN104491890AMaximize labeling efficiencyHigh affinityRadioactive preparation carriersDiseaseSSTR Positive
The invention provides a novel radionuclide labelled somatostatin analogue molecular probe and its application and belongs to the field of radiopharmaceuticals labelling and nuclear medicine technologies. A bifunctional chelator couples cyclic polypeptide Pasireotide, and then radionuclide is used for labelling so as to obtain a radionuclide labelled neuroendocrine neoplasm specific somatostatin analogue radioactive molecular probe. The molecular probe can be combined with a tumor expression somatostatin receptor (SSTR), and SSTR positive tumor tissue can be accurately positioned by means of nuclear medicine. Thus, the purpose of disease target molecular imaging diagnosis and treatment is achieved. The synthesized molecular probe has higher affinity and functional activity for SSTR and is expected to become a somatostatin analogue developer and tumor therapeutic agent with a good prospect.
Owner:BEIJING CANCER HOSPITAL PEKING UNIV CANCER HOSPITAL
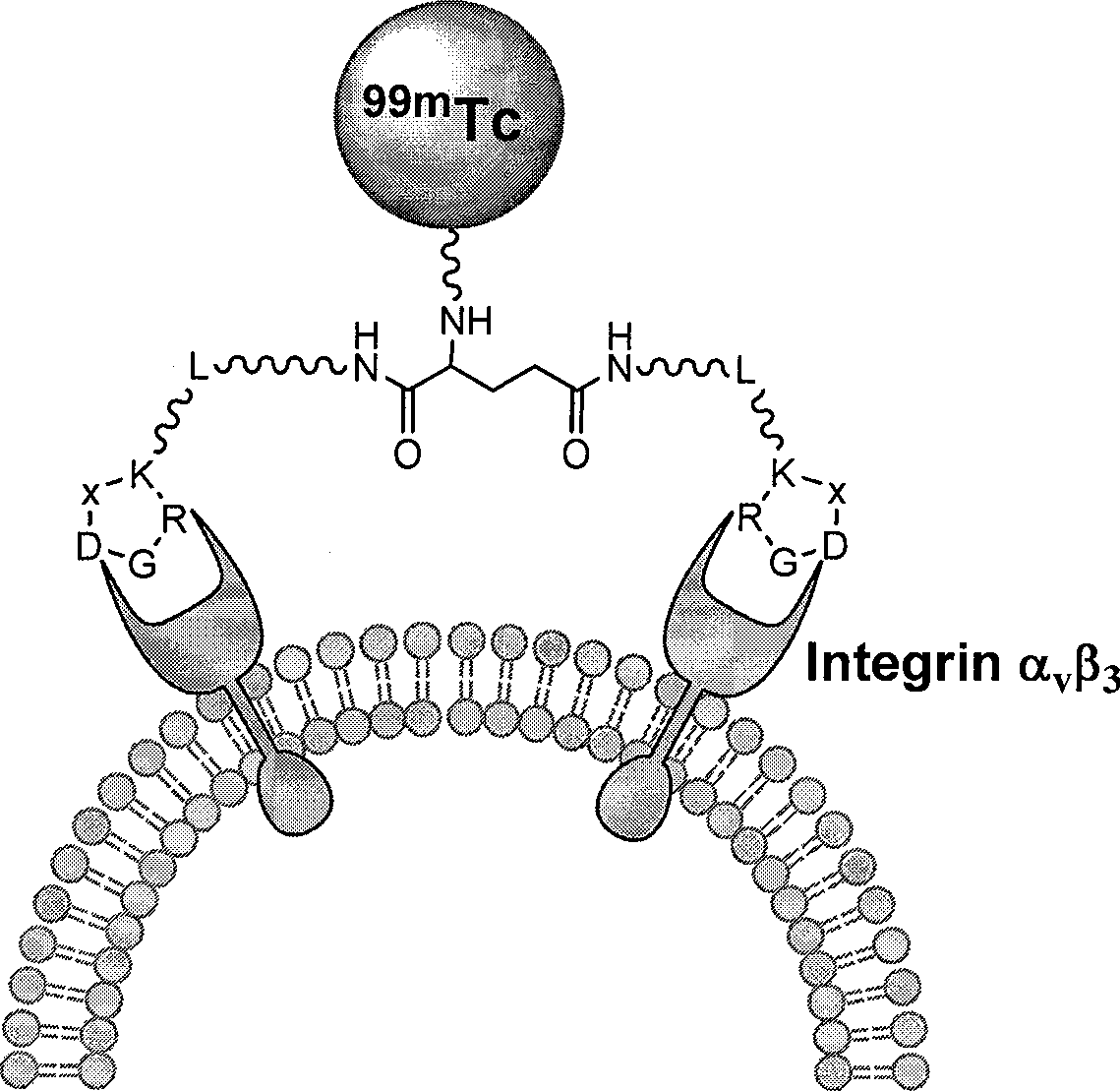
Radioactive nuclide marked RGD polypeptide medicament and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101485891AIncrease intakeHigh binding affinityPharmaceutical delivery mechanismRadioactive preparation carriersCyclic peptideIntegrin
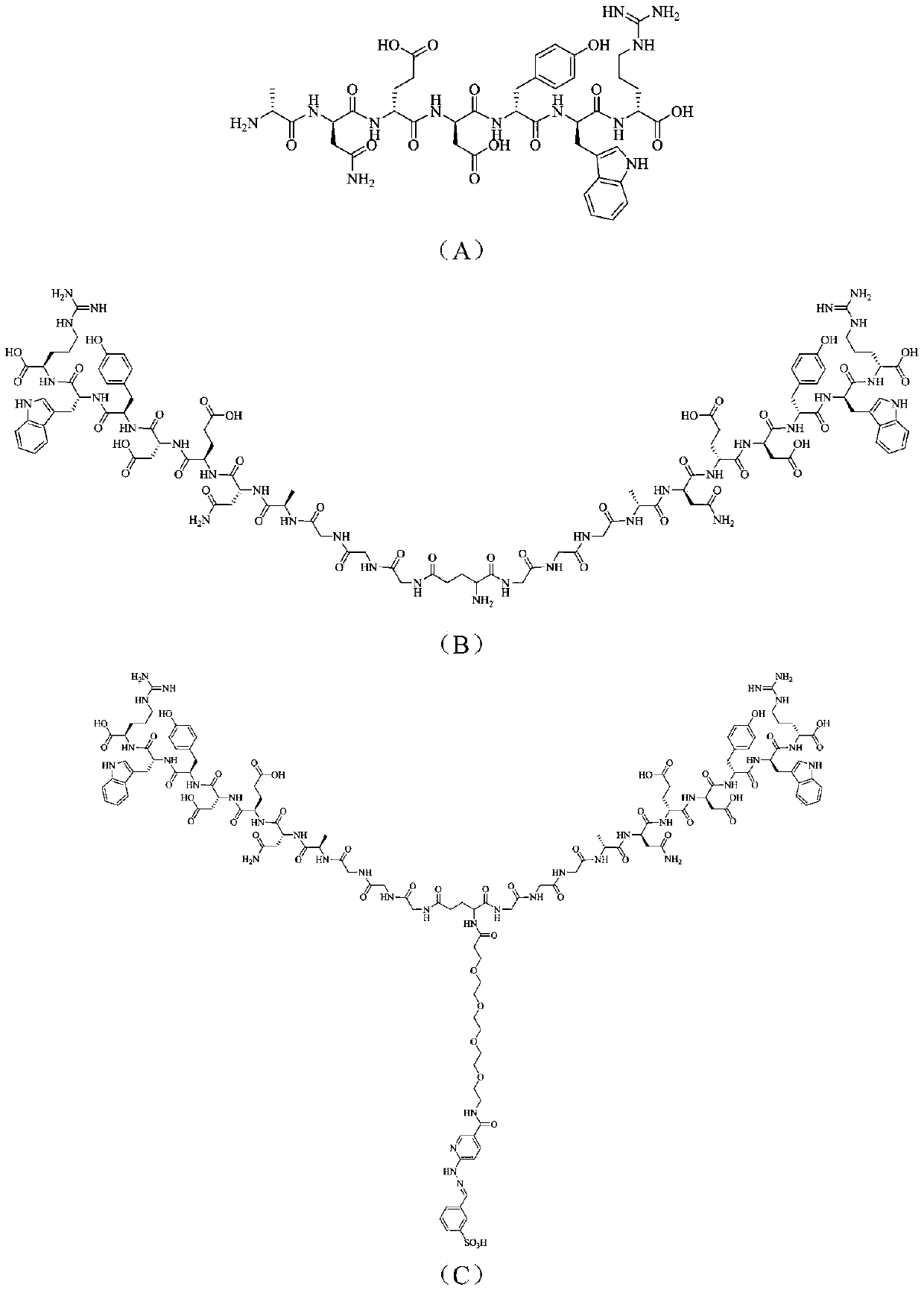
The invention relates to a radionuclide-marked RGD polypeptide medicine and a preparation method thereof. The medicine comprises RGD polypeptide, a bifunctional Chelator and radioactive Nuclide, wherein the RGD polypeptide is RGD cyclic peptide dimer, namely E(L-c(RGDxK))2, which is synthesized by connecting a connecting agent L and an RGD polypeptide monomer and dimerizing two RGD polypeptide monomers connected with the connecting agent L; the radioactive Nuclide marks the RGD cyclic peptide dimer through the bifunctional Chelator; and a pharmacokinetic modified molecule PKM is also connected between the RGD cyclic peptide dimer and the bifunctional Chelator. The radionuclide-marked RGD polypeptide medicine is Nuclide-Chelator-PKM-E(L-c(RGDxK))2, and is a colorless and transparent liquid injection solution. The radionuclide-marked RGD polypeptide medicine is used for diagnosing and treating integrin alpha v beta 3 positive tumor.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Cage-Like Bifunctional Chelators, Copper-64 Radiopharmaceuticals and PET Imaging Using the Same
ActiveUS20100196271A1Stable in vivoStable complexPeptide sourcesTripeptide ingredientsImaging agentCarboxylic acid
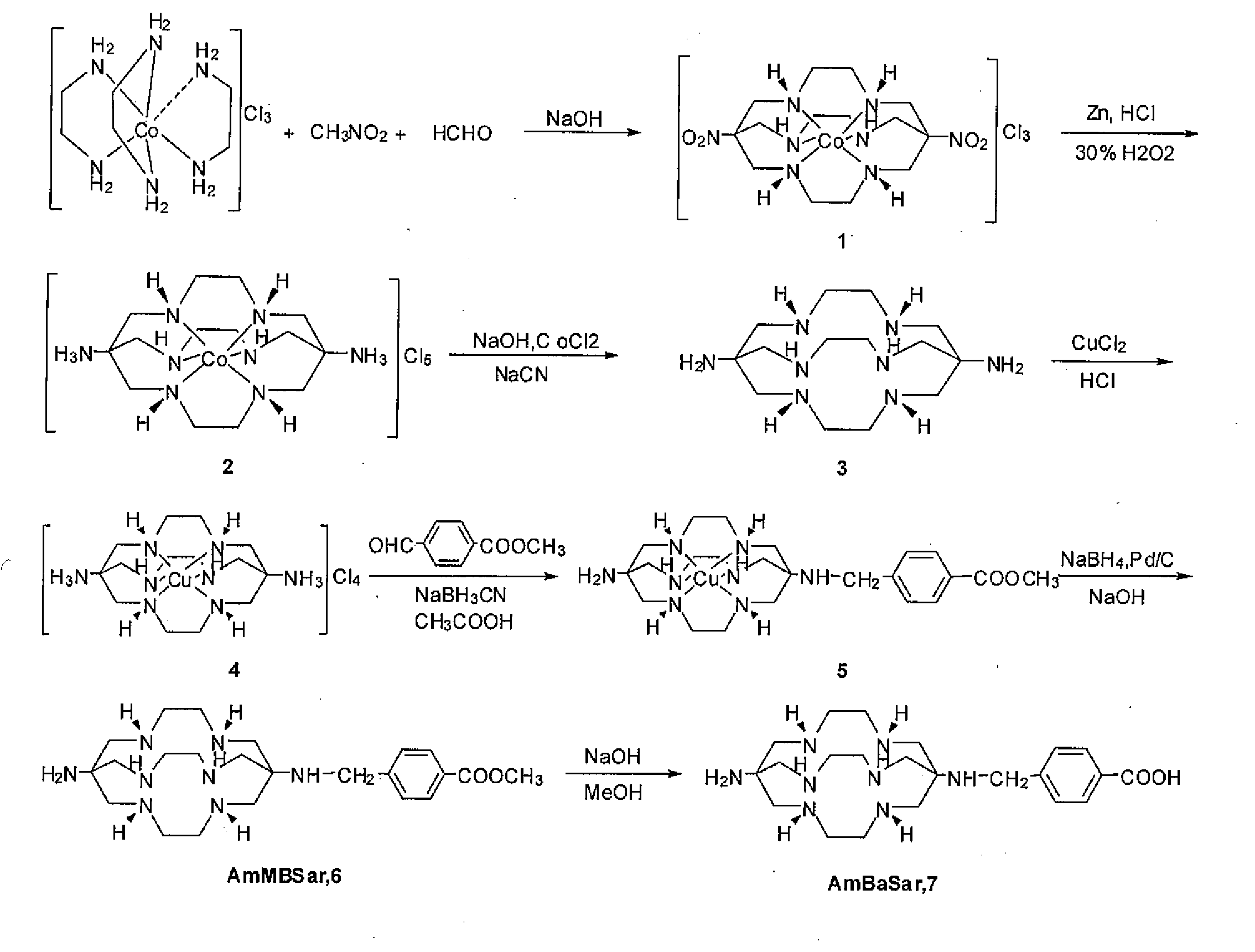
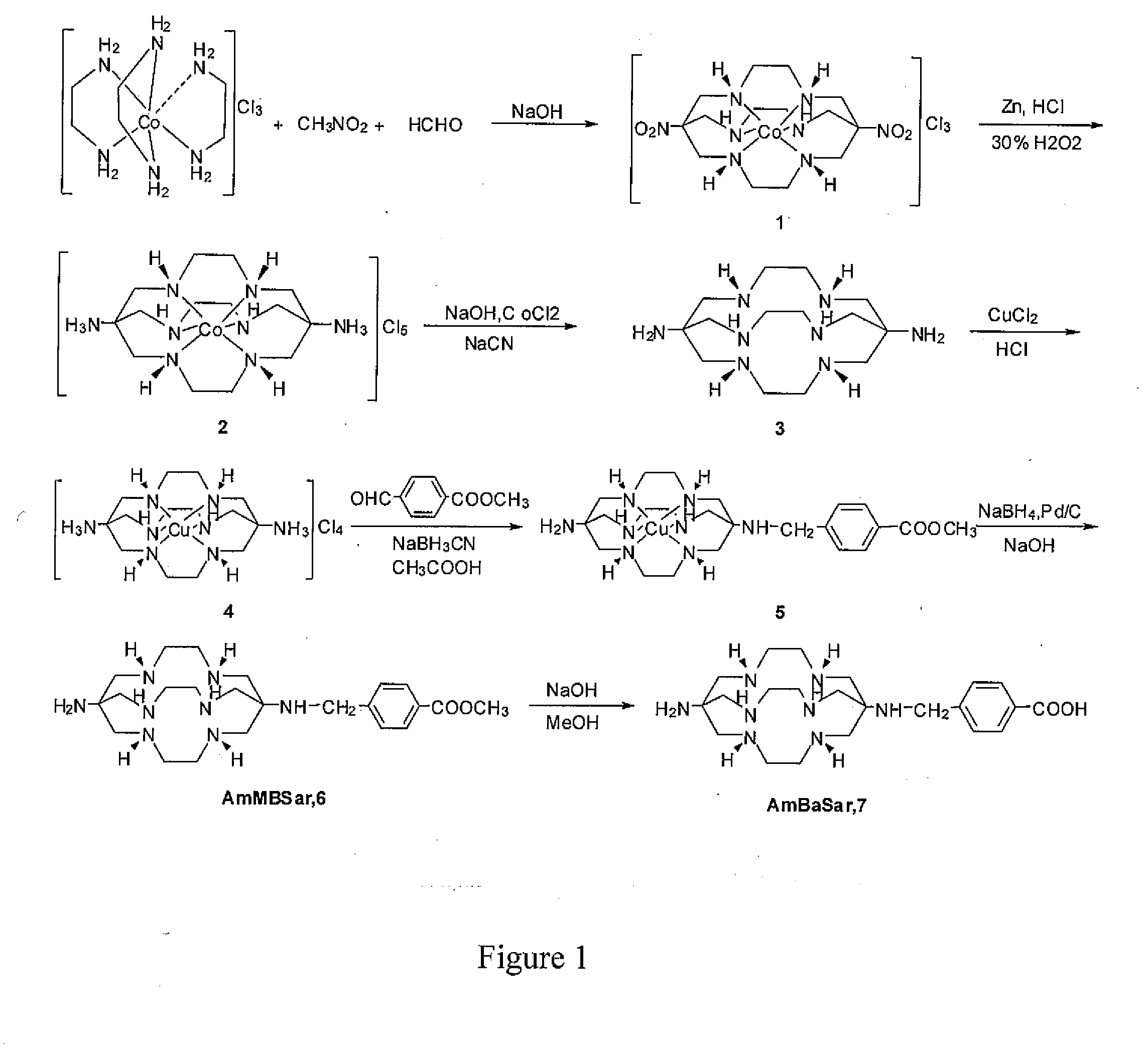
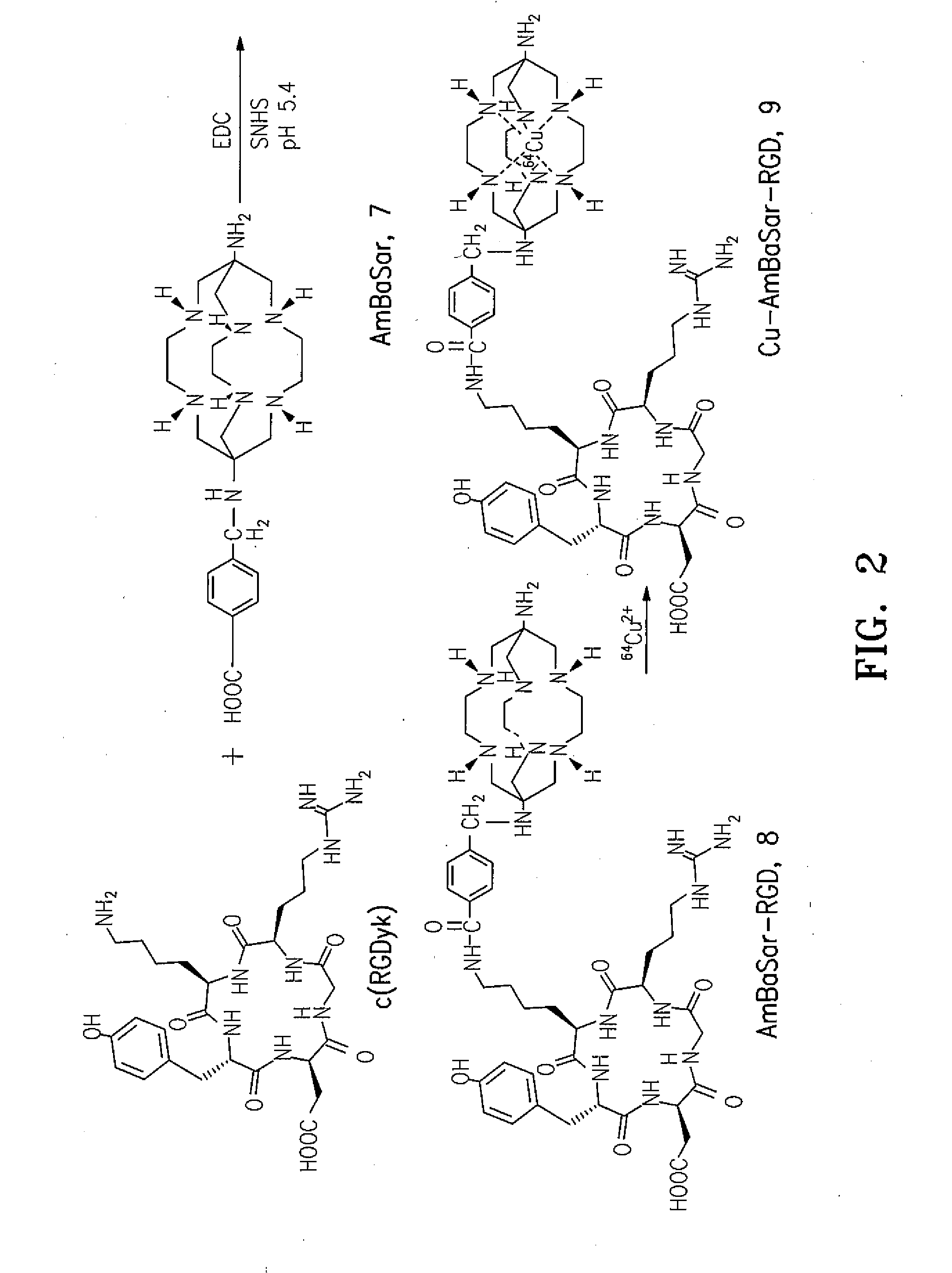
Disclosed is a class of versatile Sarcophagine based bifunctional chelators (BFCs) containing a hexa-aza cage for labeling with metals having either imaging, therapeutic or contrast applications radiolabeling and one or more linkers (A) and (B). The compounds have the general formulawhere A is a functional group selected from group consisting of an amine, a carboxylic acid, an ester, a carbonyl, a thiol, an azide and an alkene, and B is a functional group selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, an amine, a carboxylic acid, and ester, a carbonyl, a thiol, an azide and an alkene. Also disclosed are conjugate of the BFC and a targeting moiety, which may be a peptide or antibody. Also disclosed are metal complexes of the BFC / targeting moiety conjugates that are useful as radiopharmaceuticals, imaging agents or contrast agents.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
RGD polypeptide radiopharmaceutical for integrin alphav beta3 positive tumor and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101474415AIncrease intakeHigh binding affinityIn-vivo radioactive preparationsAntineoplastic agentsCyclic peptideCombinatorial chemistry
The invention relates to a RGD polypeptide radiopharmaceutical used for integrin alphavbeta3 positive tumor. The RGD polypeptide radiopharmaceutical comprises RGD polypeptide, difunctional Chelator and radioactive Nuclide. The RGD polypeptide is RGD cyclic peptide dimer which is RGD cyclic peptide dimer E(L-c(RGDxK))2 which is synthesized by connecting the coupling agent L with RGD polypeptide monomer c(RGDfK) and dimerizing two RGD polypeptide monomer L-c(RGDfK) which are connected with the coupling agent L. The radioactive nuclide marks the RGD cyclic peptide dimer by one difunctional Chelator, and pharmacokinetic modifying molecule PKM is connected between the RGD cyclic peptide dimer and the difunctional chelator. The RGD polypeptide radiopharmaceutical is Nuclide-Chelator-PKM-E(L-c(RGDxK))2, and the RGD polypeptide radiopharmaceutical is colorless transparent liquid injection.
Owner:广东瑞迪奥科技有限公司
Rapid detection method and kit for mercury poisoning based on magnetic separation and quantum dot marking
InactiveCN103698526AImprove disposal capacityImprove the level of public health managementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceBovine serum albumin
The invention provides a rapid detection method for mercury in a liquid biological sample based on magnetic separation and quantum dots (QDs) marking. The method comprises the steps: (1) preparing mercury-resistant monoclonal antibodies; (2) coupling the mercury-resistant monoclonal antibodies with magnetic nanobeads through covalent bonds to prepare mercury-resistant immunomagnetic nanobeadd; and (3) adding a difunctional chelating agent, bovine serum albumin (BSA) and triethylamine (TEA) into the liquid biological sample to incubate, then, adding the mercury-resistant immunomagnetic nanobeads to sufficiently mix, next, carrying out magnetic separation, and adding biotinylated BSA antibodies and streptavidinylated QDs into a sediment, and carrying out fluorescence detection by using a fluorescence microplate, wherein the sediment is obtained through magnetic separation. The invention also provides a rapid detection kit for mercury in a liquid biological sample.
Owner:CAPITAL UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
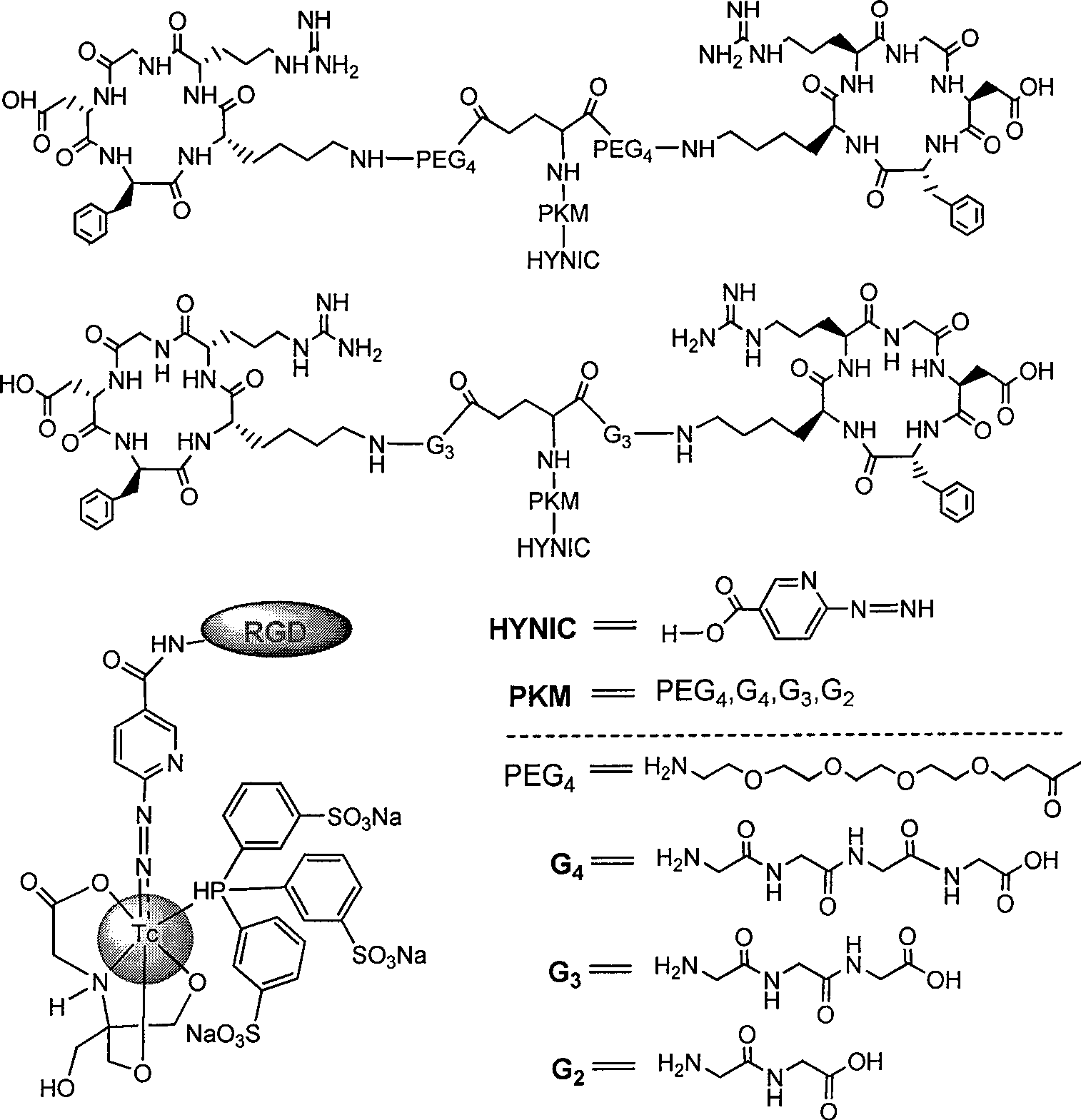
99mtc-labeled RGD (arginine-glycine-aspartic acid) polypeptide tumor diagnosis medicament and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102552949AImprove image qualityIdeal metabolic rateRadioactive preparation carriersGlycineArginine
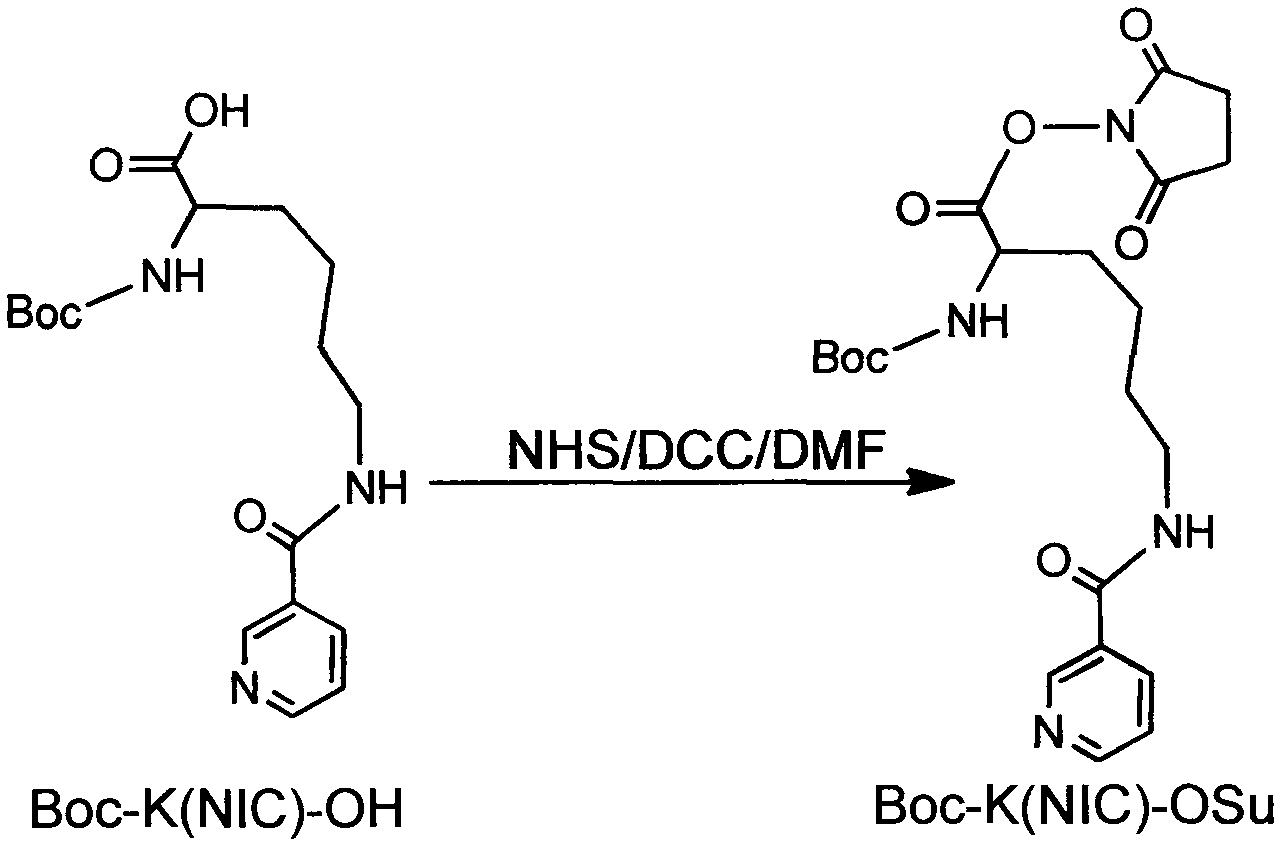
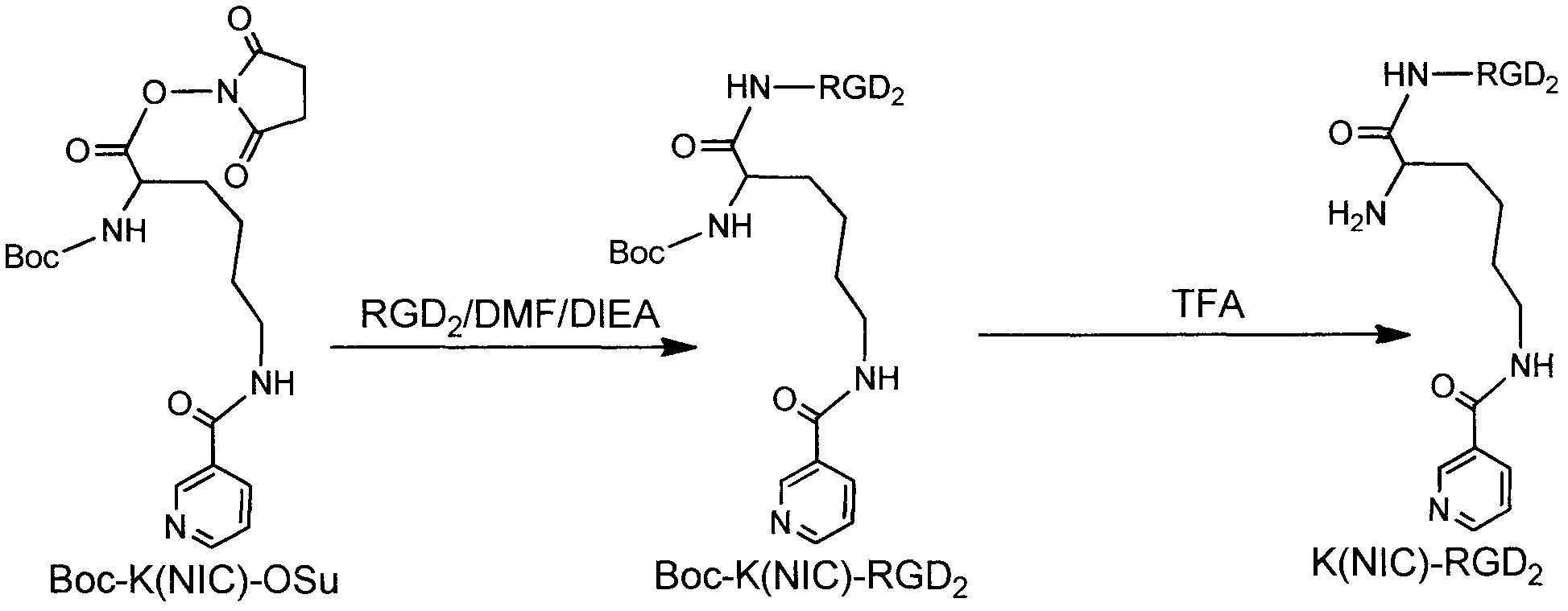
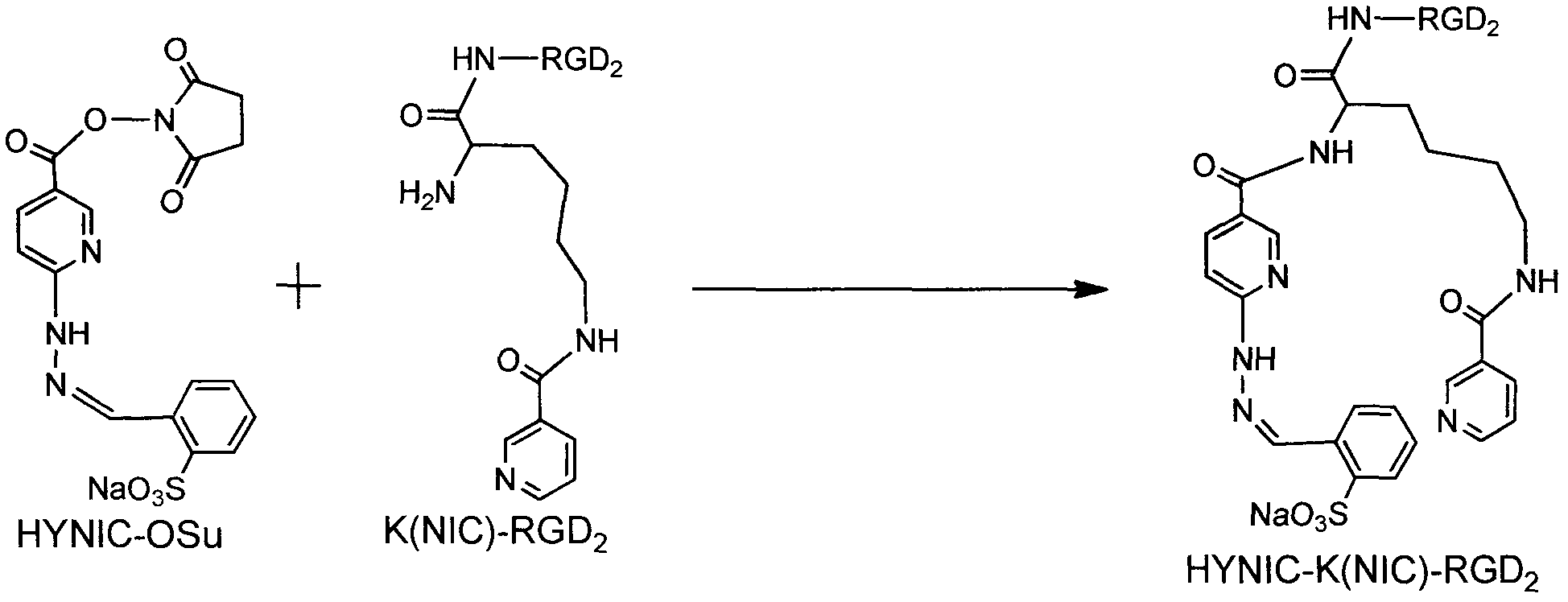
The invention relates to three RGD (Arginine-Glycine-Aspartic acid) polypeptide radioactive medicaments for positive tumor diagnosis of an intergrinalphavbeta3 receptor and preparation methods thereof. The three RGD polypeptide radioactive medicaments are structurally RGD annular dipolymers, and radioactive nuclein 99mTc labeling is performed through a dual-functional chelating agent. The medicaments are mainly characterized in that: a [K(NIC)] structure which is connected with RGD is used for replacing the conventional 99mTc-labeled synergistic ligand, i.e., trisodium salt of tri(m-sulfonphenyl) phosphine (TPPTS), so that the molecular weight of a medicament structure is reduced, and the metabolism velocity of a radioactive medicament in a non-target organ is increased. The three radioactive medicaments include 99mTc-HYNIC-K(NIC)-RGD2, 99mTc-HYNIC-K(NIC)-3G-RGD2 and 99mTc-HYNIC-K(NIC)-3P-RGD2, and are colorless and transparent liquid injections.
Owner:安徽筑梦生物科技有限公司
NGR polypeptide radiopharmaceutical as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103483422AAffect coordinationReduce intakeRadioactive preparation carriersPeptide preparation methodsDimerCyclic peptide
The invention relates to an NGR (asparagine-glycine-arginine) polypeptide radiopharmaceutical as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The currently reported radionuclide-labeled NGR-containing sequence has a higher liver uptake rate. The NGR polypeptide radiopharmaceutical is formed with the preparation method comprising the steps as follows: monomers and dimmers of an NGR cyclopeptide are connected with a chelating agent NOTA to form a coordination compound, and the coordination compound finally forms the radiopharmaceutical through chelation of the NOTA (disodium edta) and radionuclides; the targeting action of the NGR polypeptide enables the radiopharmaceutical to be concentrated to a tumor part, and the nuclear medicine positron emission computerized tomography technology is utilized to image the CD13 positive tumor, so as to achieve the purpose of specific diagnosis. According to the invention, since the NOTA is used as a bifunctional chelator to be chelated with the radionuclides, and the p-SCN-Bn is used as a coupling agent to enable the NGR to be directly connected to a carbon skeleton of the NOTA, the situation that the coordination of the carboxyl oxygen atoms and the radionuclides is influenced by connection of the coupling agent and the NOTA carboxyl is avoided; seen from the metabolism in vivo, the radiopharmaceutical can be quickly metabolized through the kidney after being injected into the body, and the liver uptake rate is lower.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
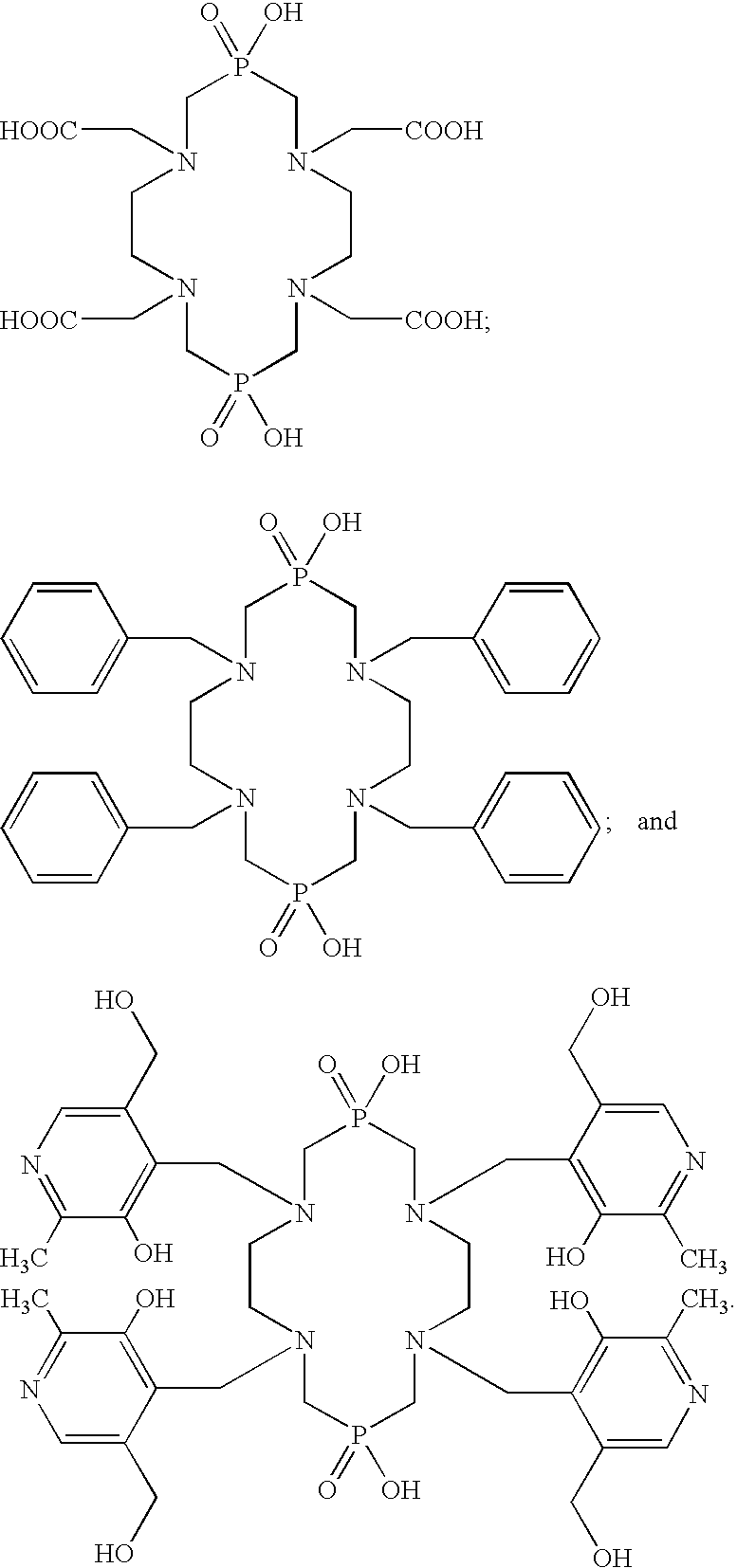
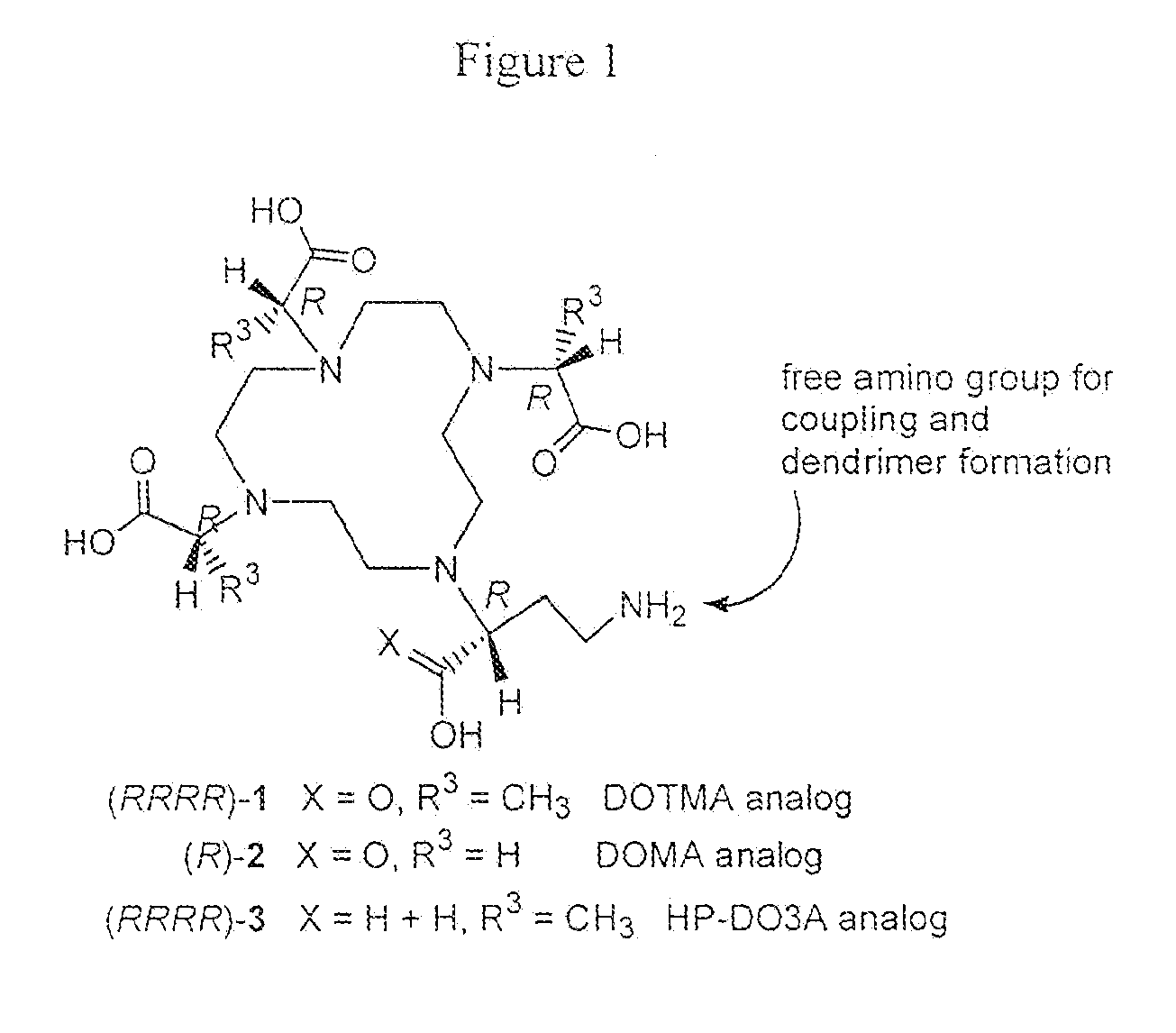
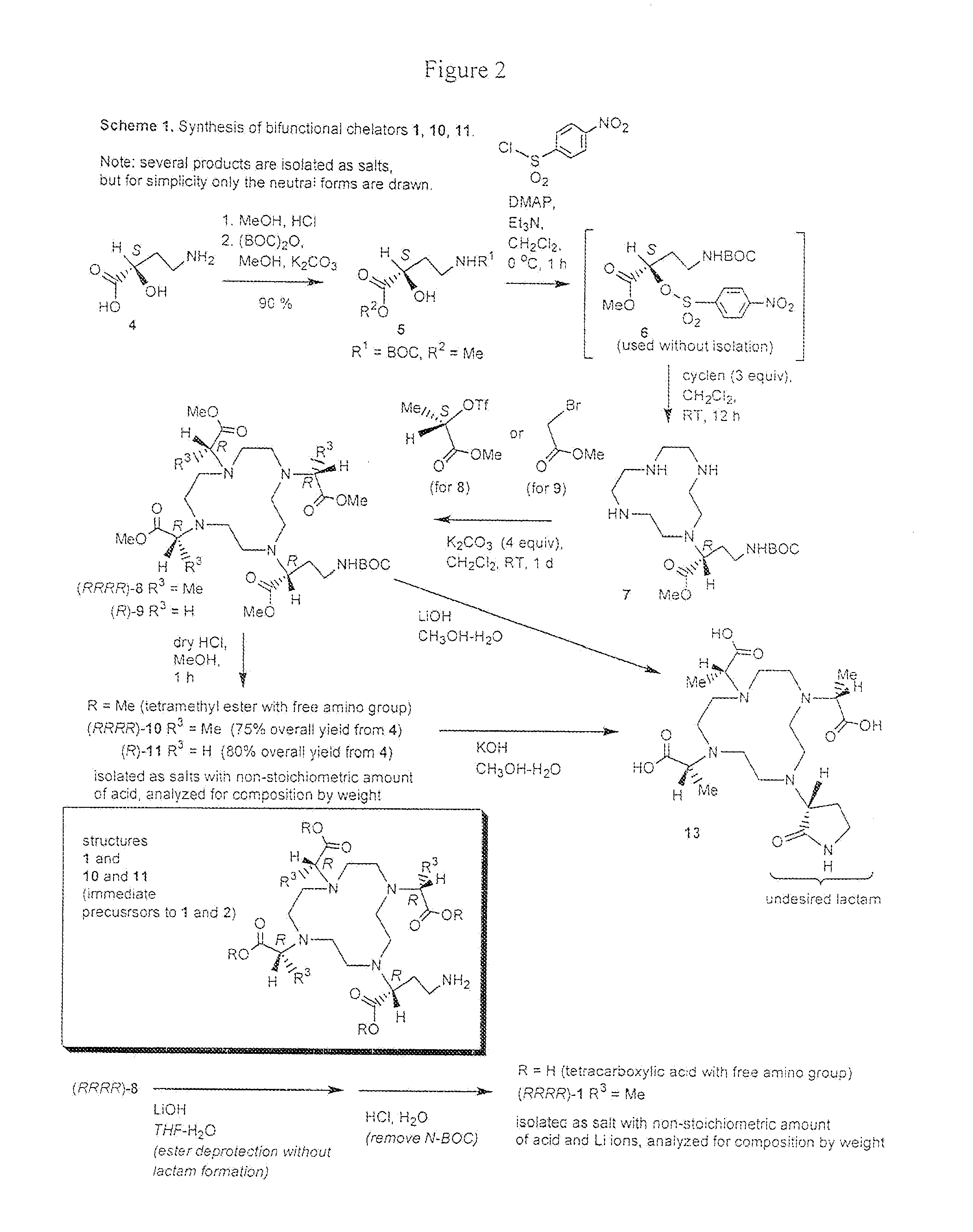
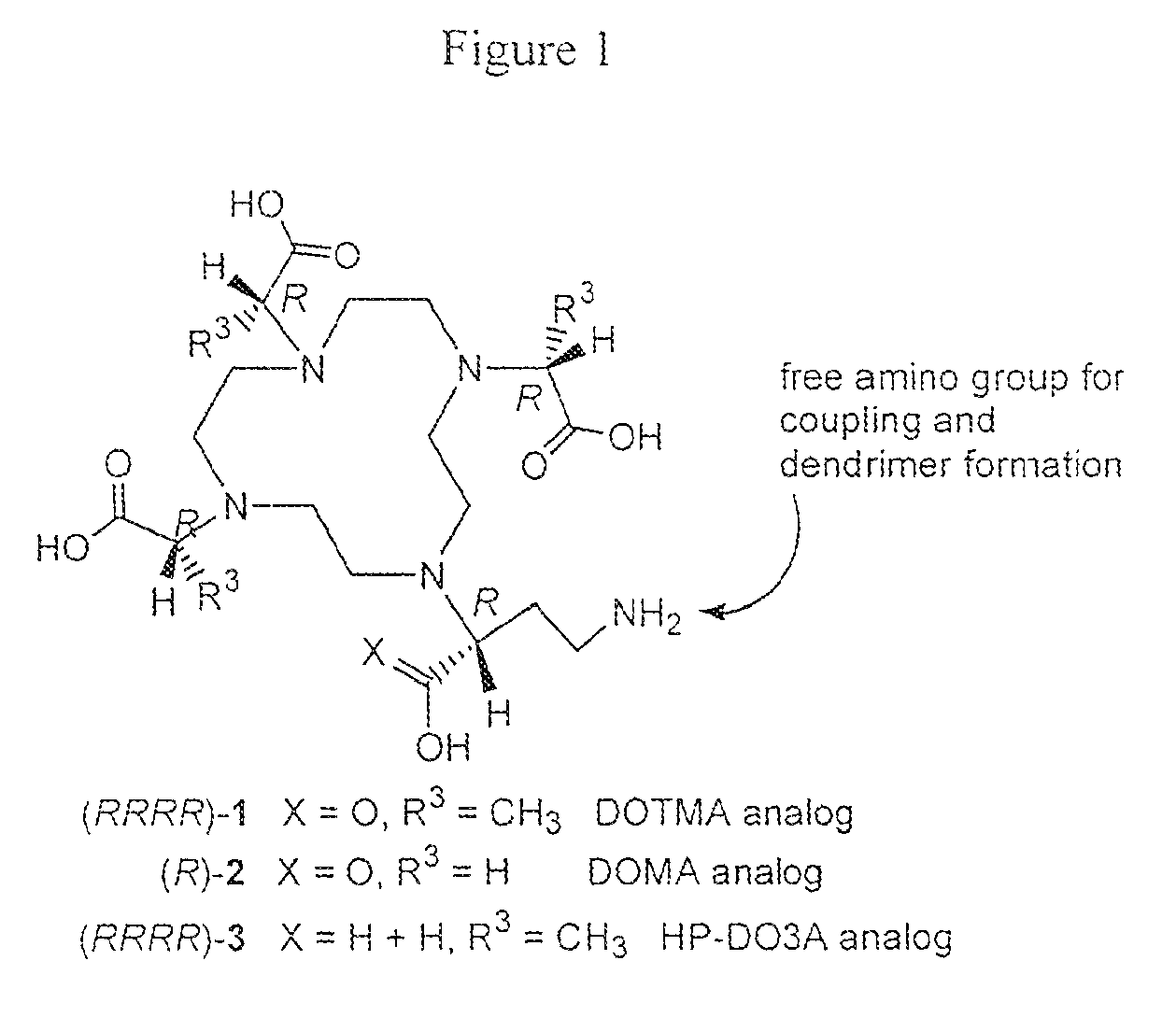
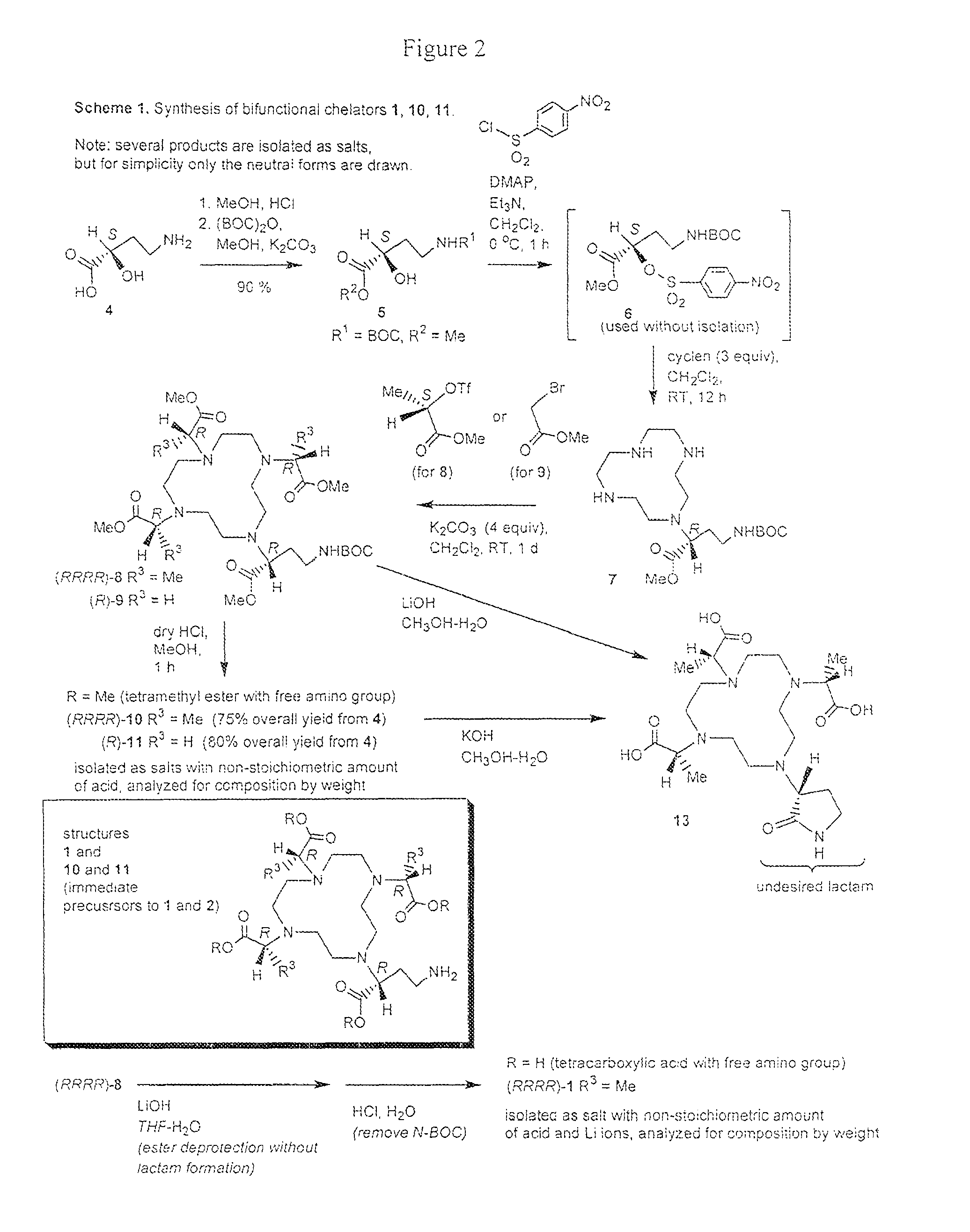
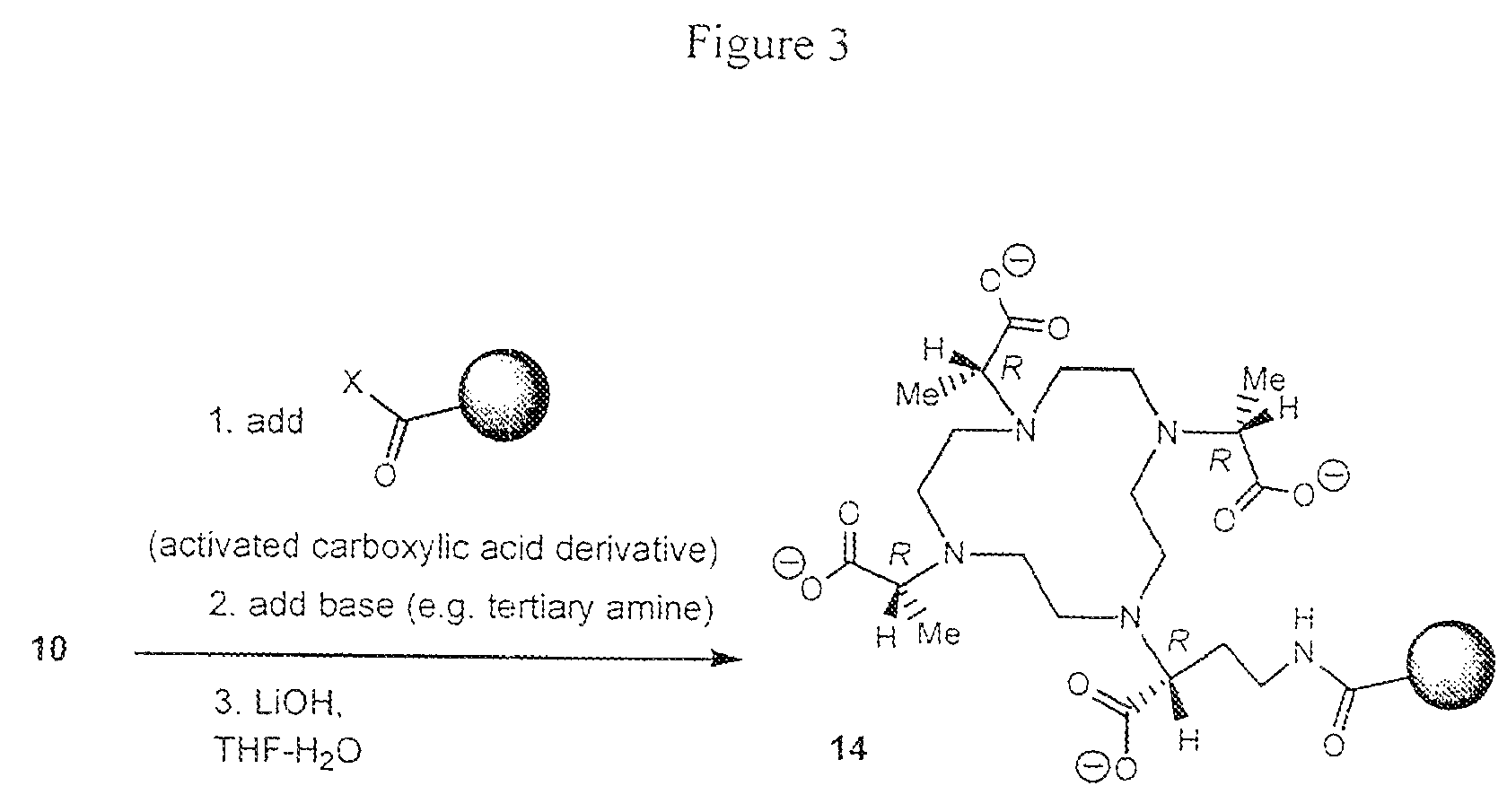
Bifunctional chelators for sequestering lanthanides
ActiveUS20080107606A1Minimizes streakingSynthetic is simpleOrganic chemistryGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsLanthanideTetra
The present invention relates to a method for preparing a bifunctional chelator for lanthanide. The method comprises the steps of providing a starting material which has an amino and carboxyl group; protecting the amino with an amino protecting group and the carboxyl with a carboxyl protecting group to produce a protected compound; reacting the protected compound with cyclen to generate a monoalkylated cyclen; reacting the monoalkylated cyclone with an activated compound to generated tetra-alkylated cyclone; removing the amino protecting group with a first protecting group removal reagent; and removing the carboxyl protecting groups with a second protecting group removal reagent to yield a bifunctional chelator having three more carboxyl groups and one or more amino groups.
Owner:SAN DIEGO STATE UNIVERSITY +1
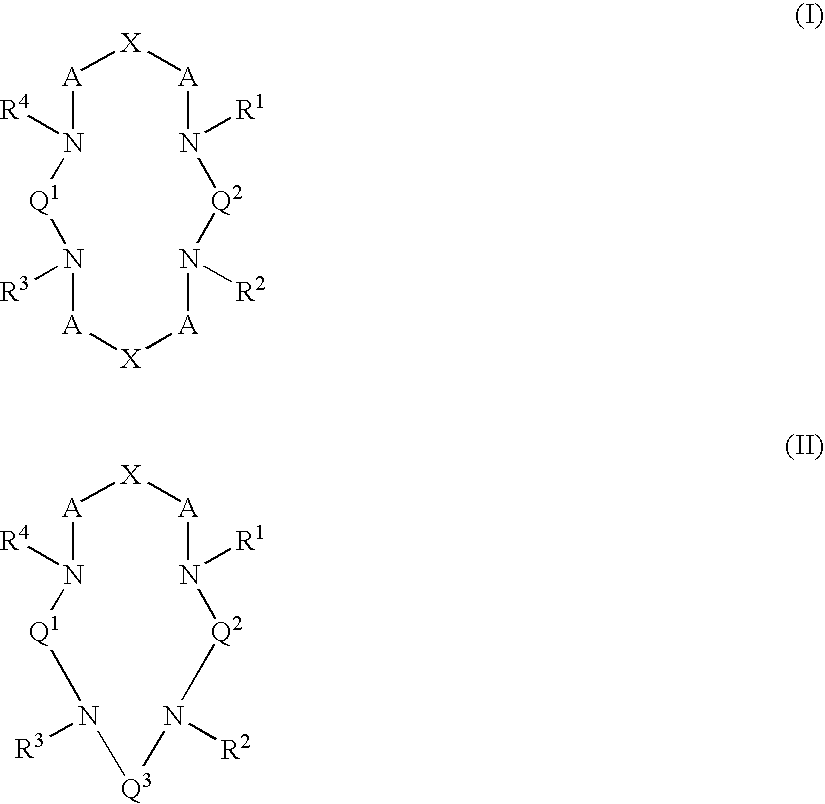
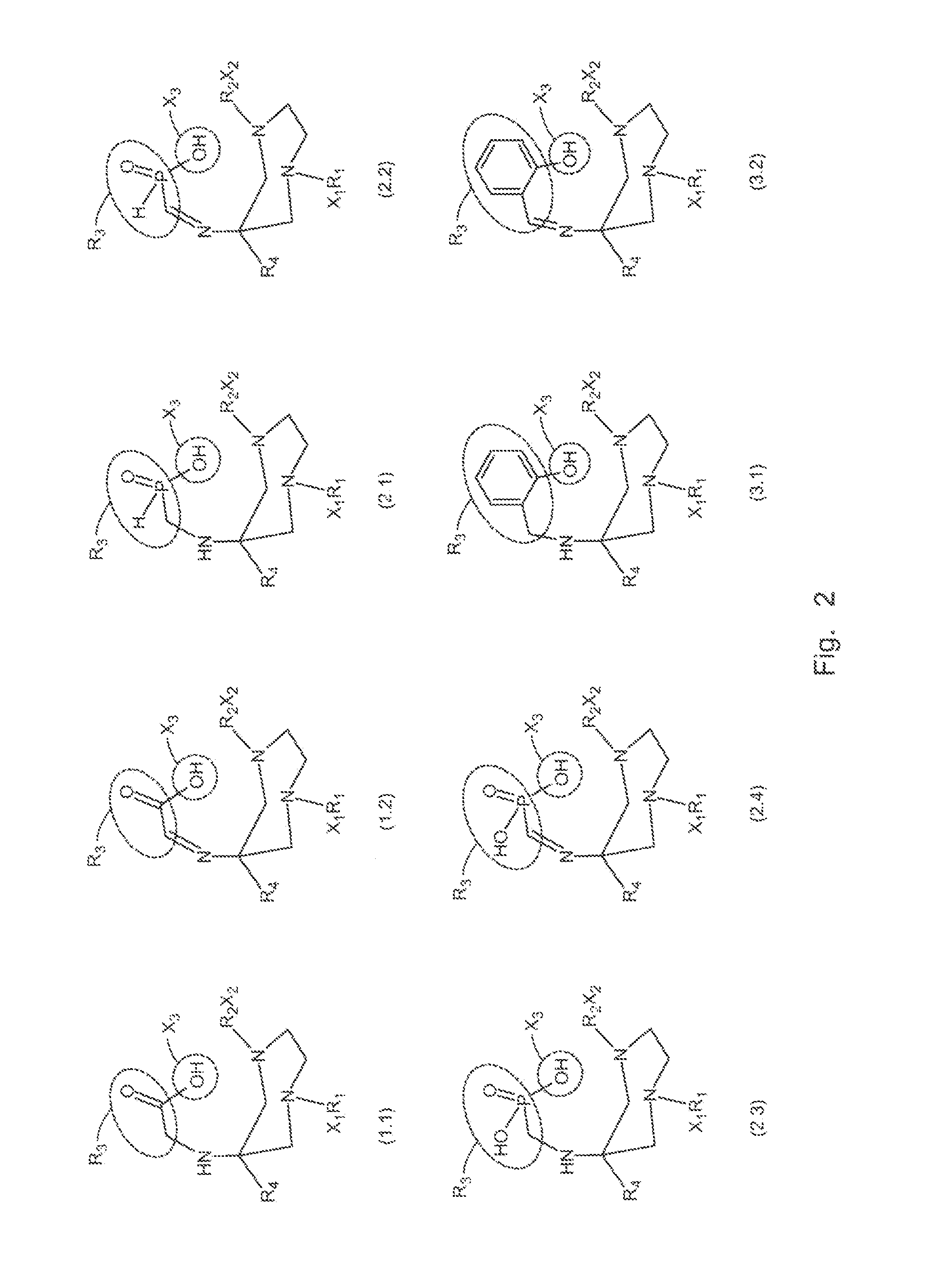
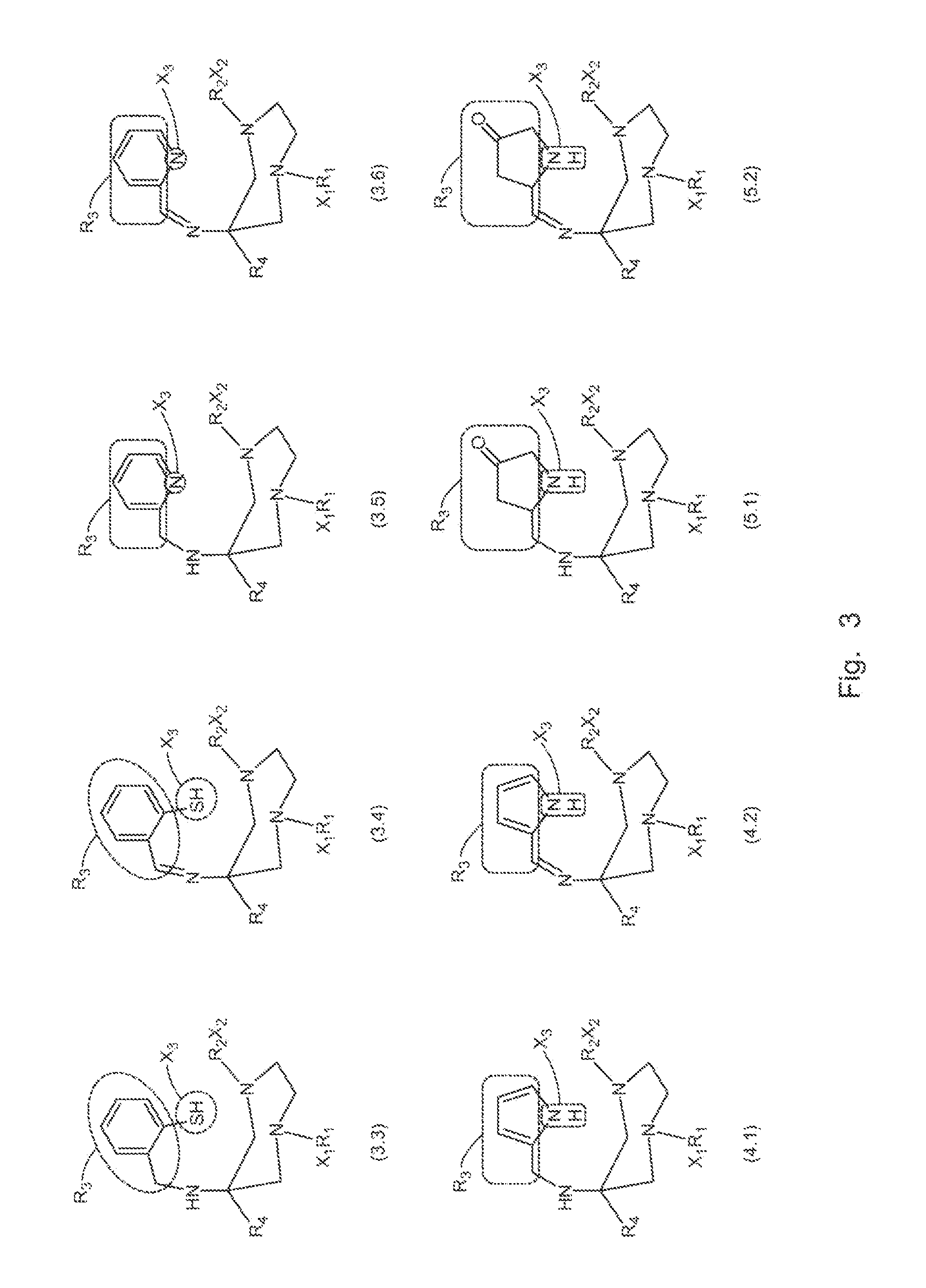
Bifunctional chelating agents based on the 1,4-diazepine scaffold (DAZA) for non-invasive molecular imaging
ActiveUS20160136309A1Minimize interferenceGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsRadioactive preparation carriersDiazepineMolecular imaging
A compound fur radio metal complexation includes a chelator and one or more biological targeting vectors TV conjugated to said chelator, wherein the chelator has structure (A) or (B)or (C).based on 1,4-diazepine with groups R1, R2, R3, R4, X1, X2, X3. The compound is particularly suited for complexation of radio-isotopic metals, such as 66Ga(III), 67Ga(III) and 68Ga(III).
Owner:SPECIALCHEMICALS VERTRIEB GMBH
Radioactive complex targeting HER2 and preparation method and application of radioactive complex
ActiveCN110251695AEfficient targetingReduce radioactive concentrationPowder deliveryRadioactive preparation carriersHER2 Positive Breast CancerStructural formula
The invention provides a polypeptide compound with a HER2 targeting function. The polypeptide compound with the HER2 targeting function is formed by connecting a HER2 affinity with a bifunctional chelating agent through a polypeptide sequence; the polypeptide sequence is Met-Val-Lys; the general structural formula of the polypeptide compound is shown in formula (I) as shown in specification, wherein R is a HER2 affinity molecule and X is a bifunctional chelator group. The invention also provides a radiolabelled complex targeting HER2 by taking the polypeptide compound as a ligand. The radiolabeled complex provided by the invention can be used as a radioactive diagnostic probe for evaluating the HER2 receptor of breast cancer, and the probe can reduce the concentration of the kidney under the condition of keeping the uptake of the tumor unchanged, so that the target-to-non-target ratio of the tumor is improved, and the radiation dose to the kidney is reduced. The invention also provides a preparation method of the polypeptide compound and the radiolabelled complex, and application of the polypeptide compound and the radiolabelled complex in preparation of a HER2 positive breast cancer radioactive diagnosis and treatment probe for humans or animals.
Owner:SHANGHAI THERANOSTICS BIOTECH CO LTD
Bifunctional chelating agent for the design and development of site specific radiopharmaceuticals and biomolecule conjugation strategy
InactiveUS6635235B1General/multifunctional contrast agentsRadioactive preparation carriersDiagnostic agentMetal
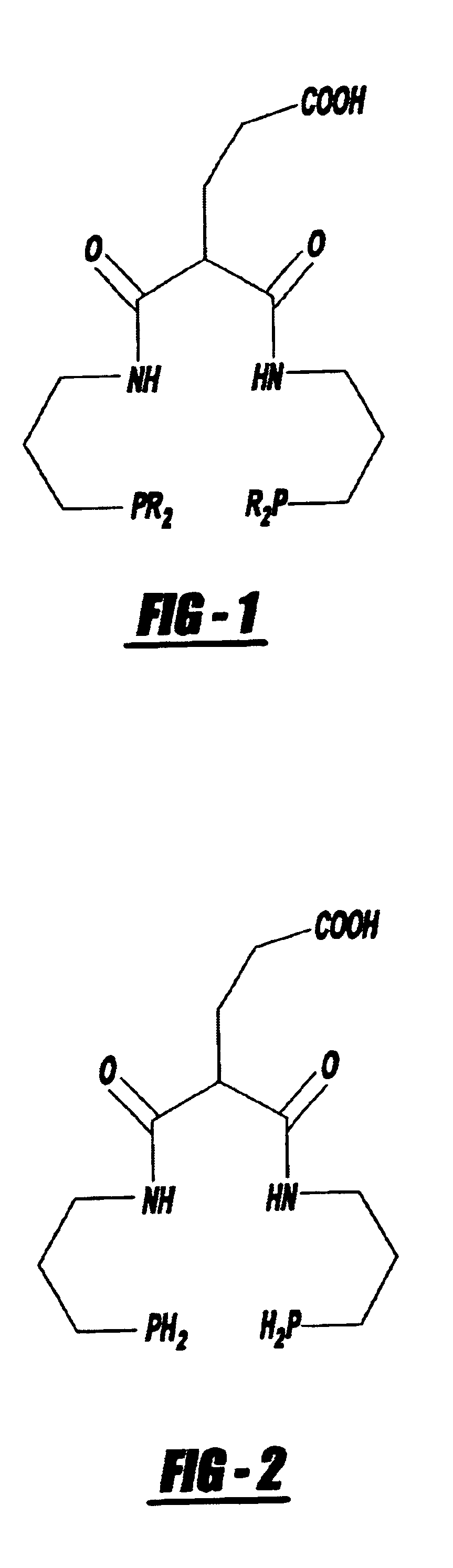
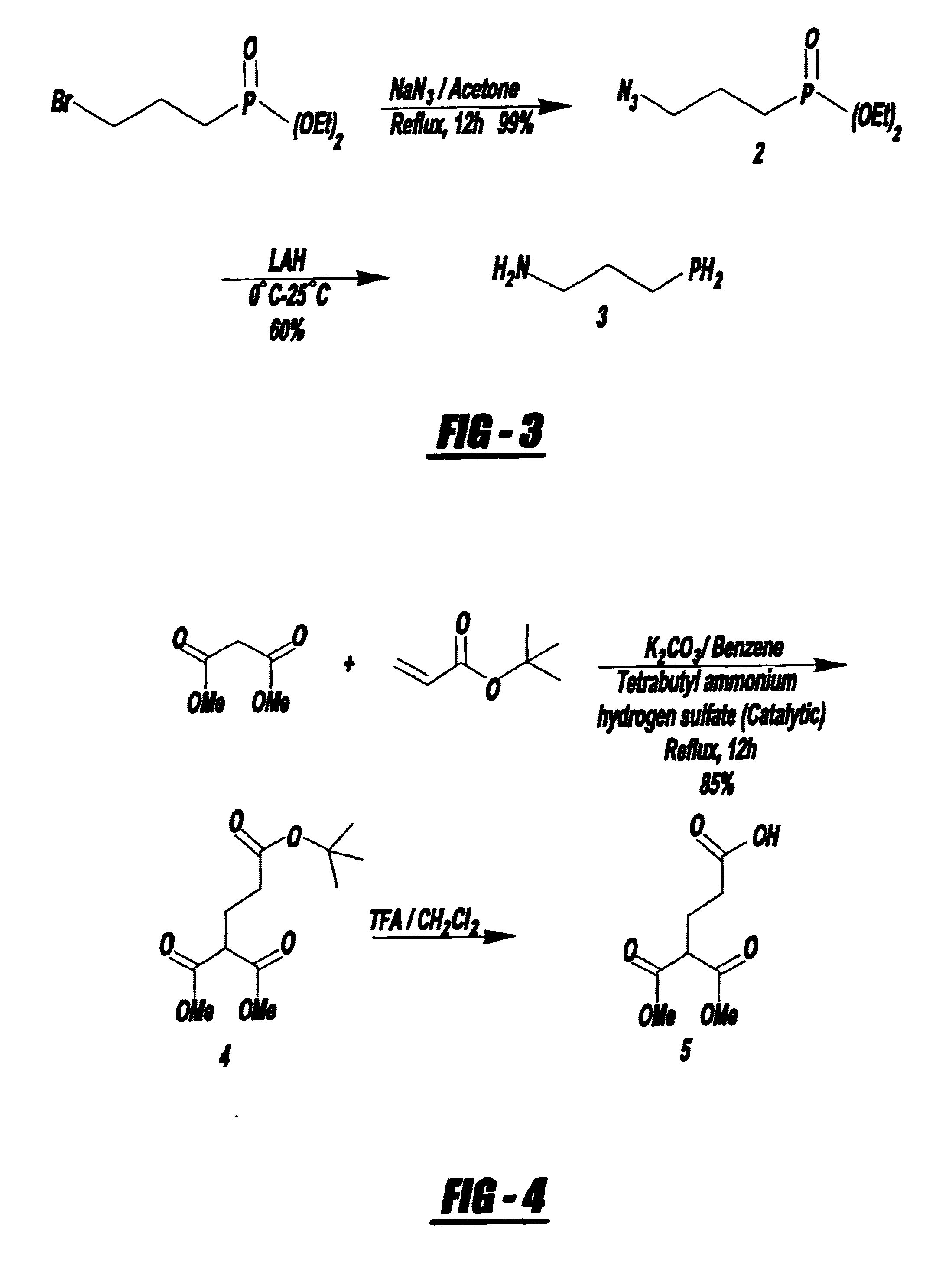
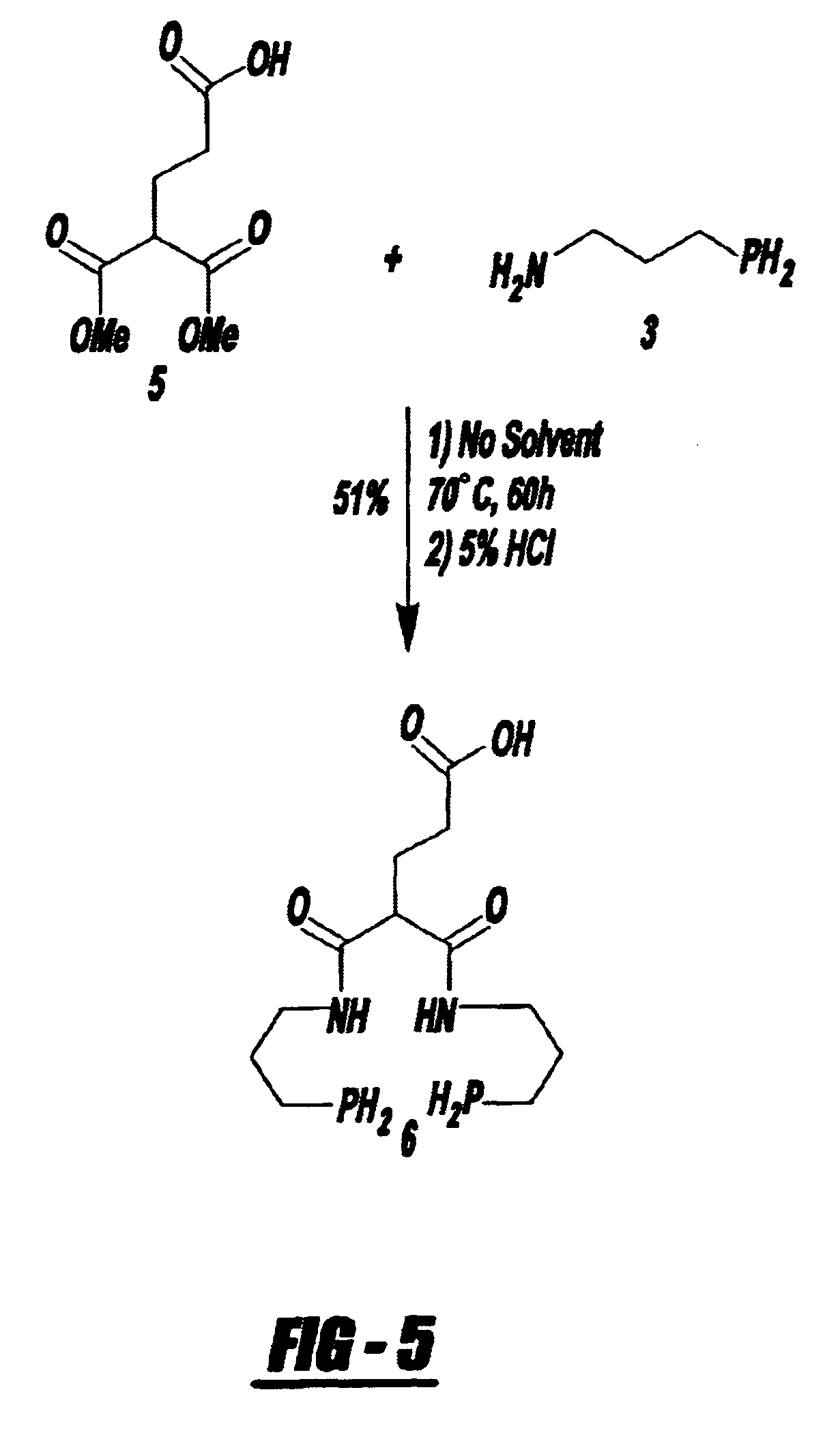
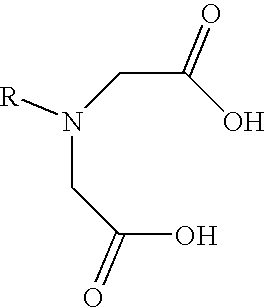
There is provided a method of labeling a biomolecule with a transition metal or radiometal in a site specific manner to produce a diagnostic or therapeutic pharmaceutical compound by synthesizing a P.sub.2 N.sub.2 -bifunctional chelating agent intermediate, complexing the intermediate with a radio metal or a transition metal, and covalently linking the resulting metal-complexed bifunctional chelating agent with a biomolecule in a site specific manner. Also provided is a method of synthesizing the --PR.sub.2 containing biomolecules by synthesizing a P.sub.2 N.sub.2 -bifunctional chelating agent intermediate, complexing the intermediate with a radiometal or a transition metal, and covalently linking the resulting radio metal-complexed bifunctional chelating agent with a biomolecule in a site specific manner. There is provided a therapeutic or diagnostic agent comprising a --PR.sub.2 containing biomolecule.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Method for reducing odor using metal-modified particles
A method for reducing odor is provided. In one embodiment, the method comprises forming a coordination complex between particles having a positive zeta potential and a transition metal. The method further comprises contacting the coordination complex with an odorous compound, the transition metal providing one or more active sites for capturing the odorous compound. For example, in one embodiment, the particles are formed from alumina-coated silica. In addition, the coordination complex may be formed using a bifunctional chelating agent.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
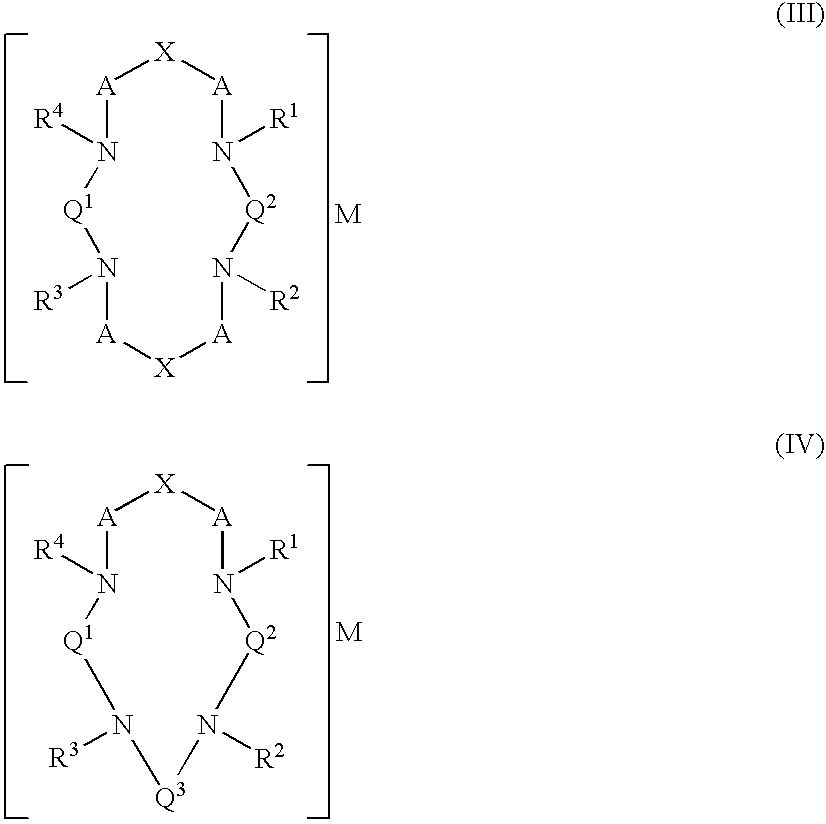
Bifunctional chelating agents
ActiveUS20110313130A1Hormone peptidesRadioactive preparation carriersCombinatorial chemistryPharmaceutical Substances
A bifunctional chelating agent of the formula (I):wherein the variables R1, R1′, Q1, Q2 and M are as defined in the description of the present application. Also described is a complex of the above chelating agent to an ion of a stable or radioactive metal; a conjugate of the complex covalently attached to a biological carrier; and a pharmaceutical composition containing the conjugate.
Owner:BWXT ITG CANADA INC
Radiopharmaceutical targeting galectin-1 and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110743017AIncrease contrastQuick clearRadioactive preparation carriersPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsRadioactive drugTherapeutic effect
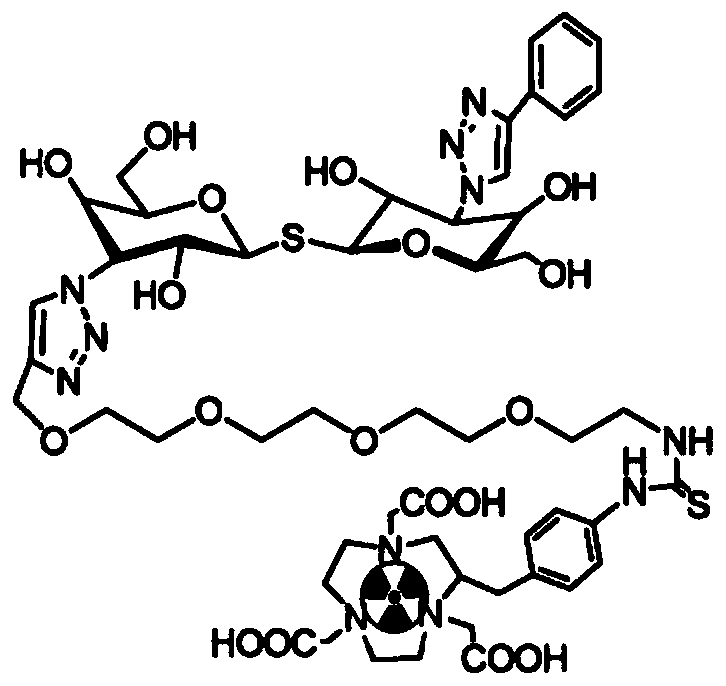
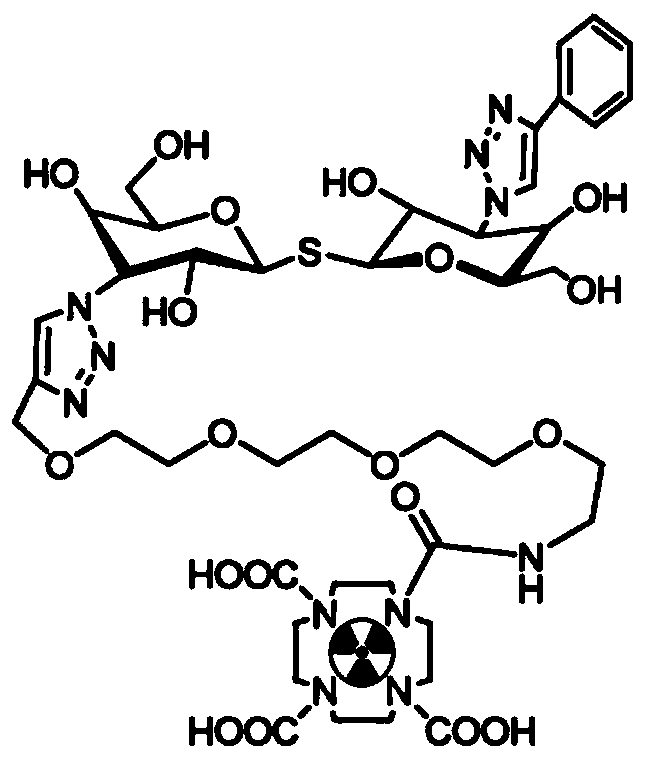
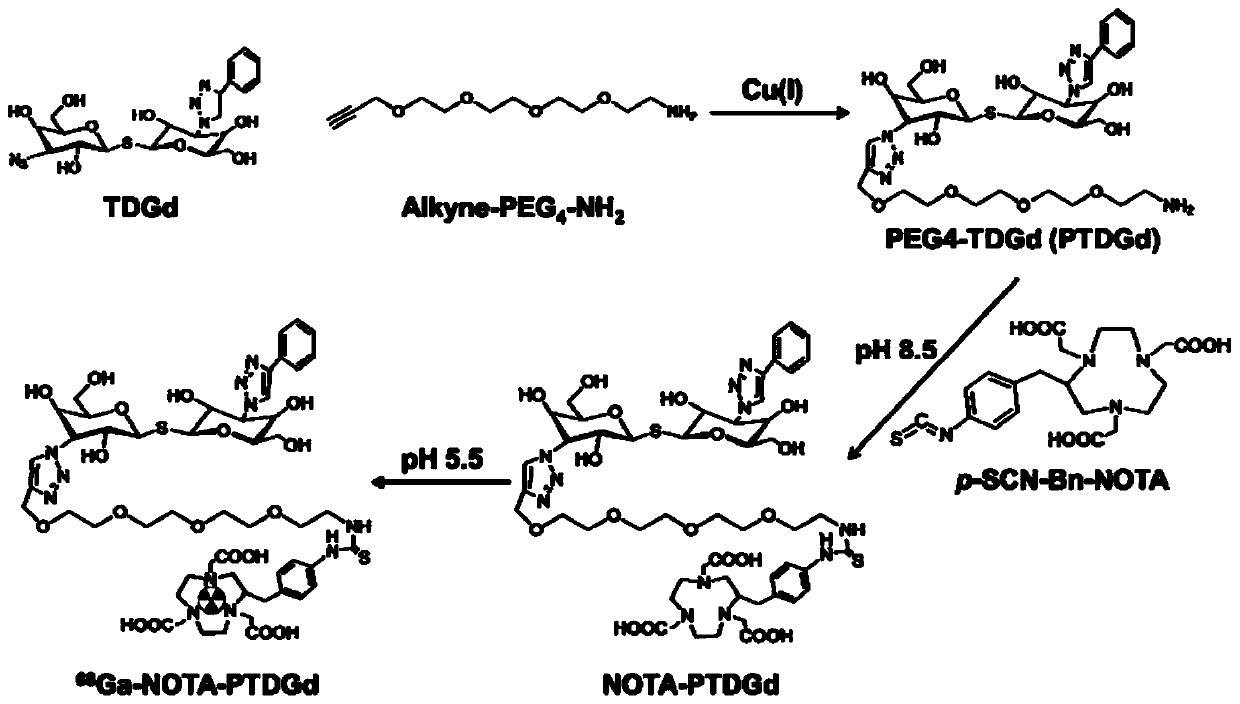
The invention discloses the radiopharmaceutical targeting galectin-1 and a preparation method thereof. The radiopharmaceutical is the conjugate of radionuclide, a difunctional chelating agent and PEG4-TDGd. The PEG4-TDGd is marked by the radionuclide through the difunctional chelating agent. According to the radiopharmaceutical targeting galectin-1, in vivo, because of specific recognition of TDGdto galectin-1 and modification of PEG4 according to pharmacokinetics, radionuclide is delivered to the surfaces of tumor cells with galectin-1 highly expressed or the hypoxia parts of a tumor with galectin-1 highly expressed, nuclear medicine positron emission computed tomography on the specificity of the tumor and the hypoxia areas of the tumor can be implemented, and monitoring on the therapeutic effect by adopting interventional treatment means such as radiotherapy on the tumor can be implemented.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Cu2<+> specific monoclonal antibody and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101845096AThe detection process is fastHigh sensitivityOvalbuminSerum albuminAnimal productCarrier protein
The invention relates to a Cu2<+> specific monoclonal antibody and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: reacting Cu2<+> with a difunctional chelating agent to form a half hapten; reacting Cu2<+>-chelating agent with carrier protein to form a complete antigen; immuning a BALB (Binaural Alternate Loudness Balance) / c mouse by using the complete antigen; and fusing a splenocyte of the mouse with an SP2 / 0 cell to prepare a hybridoma cell and obtaining a Cu2<+>-resisting monoclonal antibody. The monoclonal antibody has the specificity on the Cu2<+>, high titer and strong specificity. The invention also provides a preparation method of the Cu2<+>-resisting monoclonal antibody. The antibody and a detection technology are used for detecting residual Cu2<+> in agricultural and animal products and have the advantages of high detection speed, high sensitivity, strong selectivity and low detection cost.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
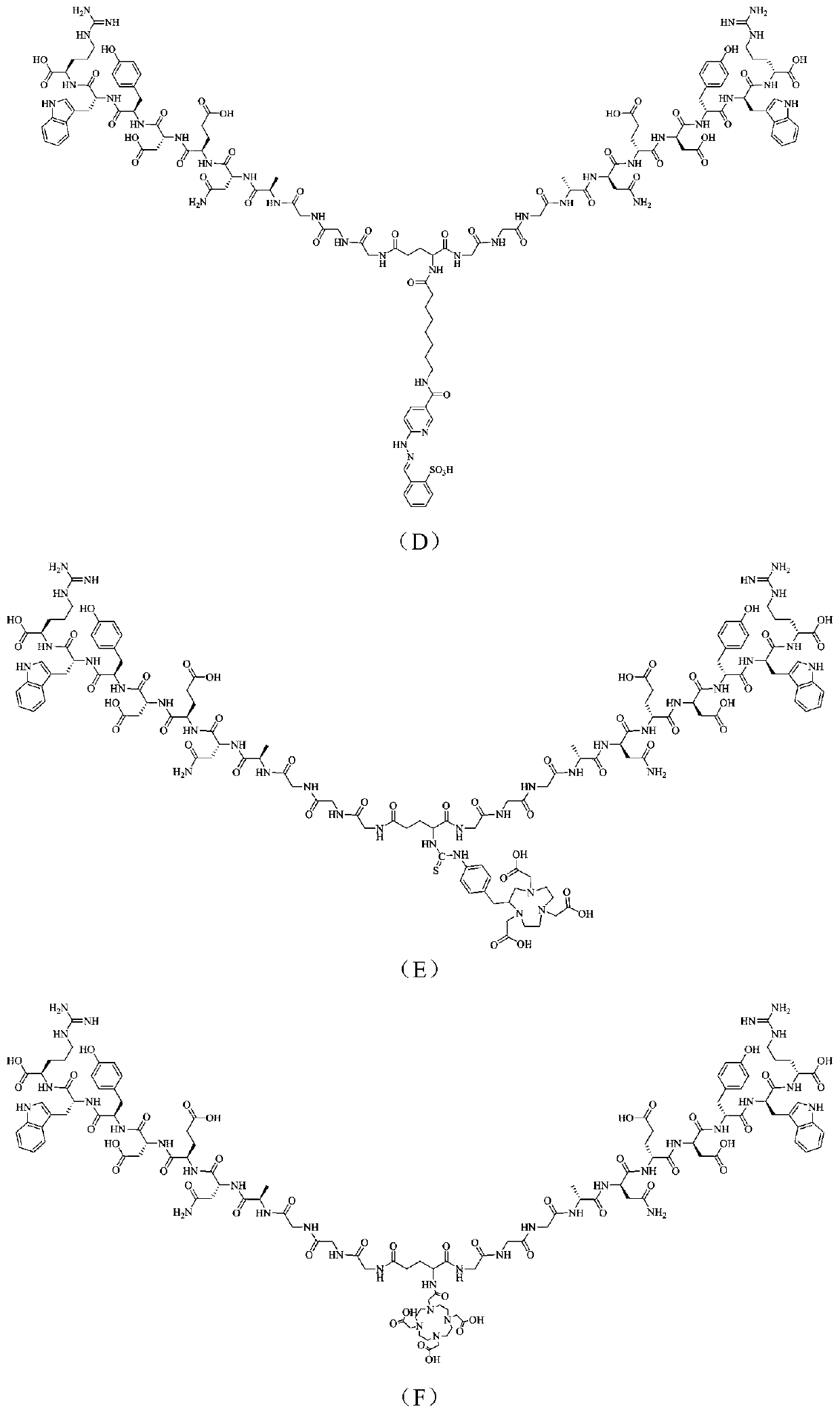
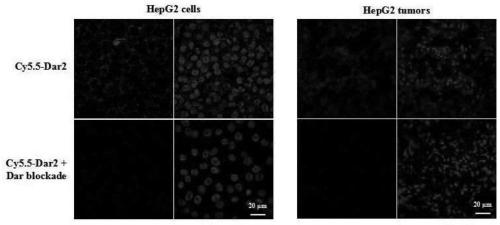
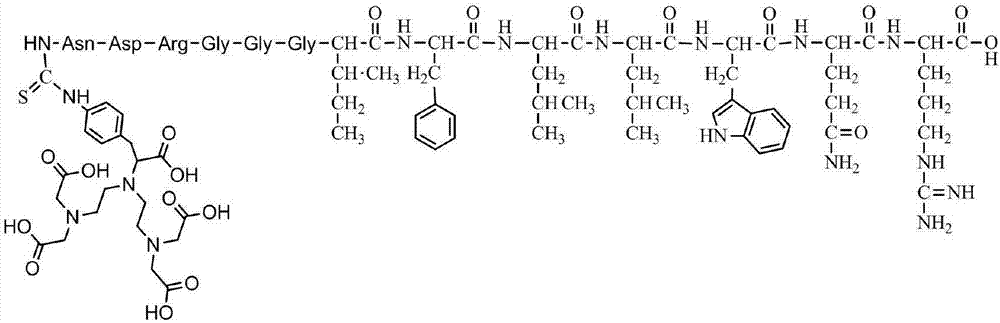
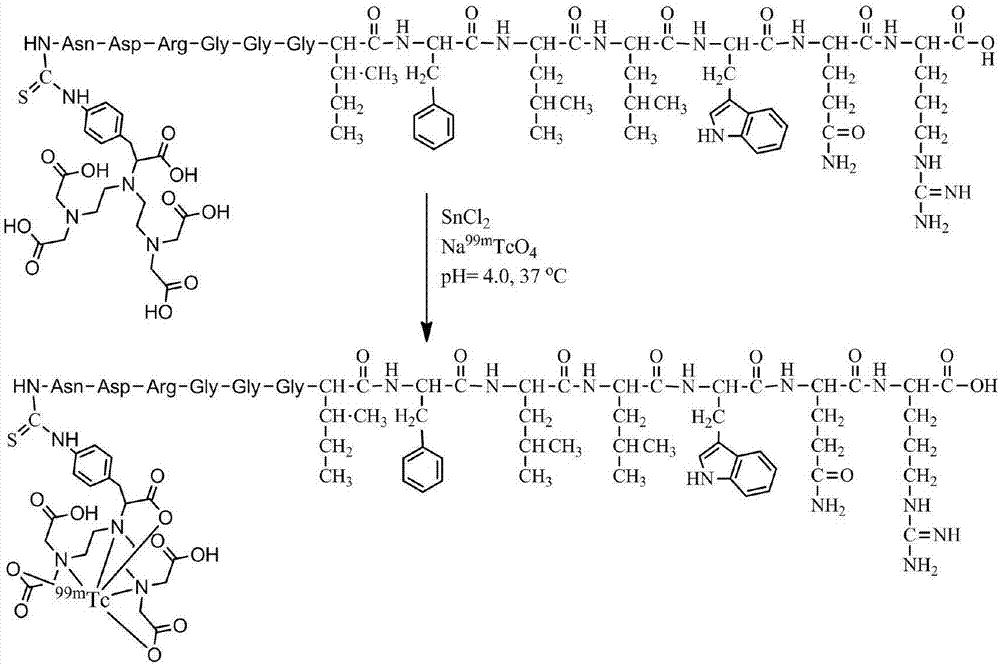
Dar2 polypeptide radioactive drug and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111228521AIncrease intakeImprove metabolic stability in vivoRadioactive preparation carriersDimerPhoton emission
The invention discloses a Dar2 polypeptide radioactive drug and a preparation method thereof. The drug comprises a Dar polypeptide dimer and a radioactive nuclide, wherein the radioactive nuclide canmark the Dar polypeptide dimer through a bifunctional chelating agent; the Dar polypeptide dimer is a polypeptide dimer which is synthesized through the steps of enabling GGG to be connected with twoDar polypeptide monomers and performing dimerization on the two Dar polypeptide monomers connected to the GGG; and each Dar polypeptide monomer is D type amino acid linear heptatomic polypeptide, andthe sequence is anedywr. According to the drug disclosed by the invention, the radioactive nuclide is marked on Dar polypeptide dimer molecules through the bifunctional chelating agent, the in vivo marked drug is concentrated to tumor positions through the targeting effects of Dar polypeptide, and through a single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) technique or a positron emission computed tomography (PET) technique of nuclear medicine, tomography diagnosis is performed on integrin alpha 6 positive tumor.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES +1
Chelants and macrocyclic metal complex radiopharmaceuticals thereof
InactiveUS20050010038A1Group 5/15 element organic compoundsRadioactive preparation carriersImaging agentEnzyme inhibitor
Chelants and macrocyclic metal complexes thereof, methods of preparing the chelants and macrocyclic metal complexes, and radiopharmaceutical compositions comprising the macrocyclic metal complexes are disclosed. Methods of using the macrocyclic metal complexes as radiopharmaceuticals for the diagnosis of cardiovascular disorders, infectious diseases and cancer are also disclosed. Chelants as bifunctional chelators (BFCs) for the radiolabeling of target-specific biomolecules, such as proteins, peptides, peptidomimetics, non-peptide receptor ligands, enzyme inhibitors, and enzyme substrates are disclosed. Methods of using macrocyclic metal complexes containing the chelant-biomolecule conjugates as target-specific diagnostic radiopharmaceuticals that selectively localize at sites of disease and allow an image to be obtained of the loci using gamma scintigraphy are disclosed. Methods of use of the radiopharmaceuticals as imaging agents for the diagnosis of cardiovascular disorders, such as thromboembolic disease or atherosclerosis, infectious disease and cancer are further disclosed.
Owner:LANTHEUS MEDICAL IMAGING INC
Polypeptide with tumor vessel targeting, molecular probe and preparation method and application of polypeptide and molecular probe
ActiveCN107308466AOvercome Metabolism ProblemsMaintain biological activityRadioactive preparation carriersFluorescenceImaging agent
The invention provides a polypeptide with tumor vessel targeting, a molecular probe and a preparation method and application of the polypeptide and the molecular probe, and belongs to the technical field of diagnostic imaging agents. The polypeptide has an amino acid sequence as shown in a sequence table Seq ID No. 1. The single-photon or positive-electron molecular probe has a structure as shown in X-N-G, wherein X is a single-photon developing nuclide or a positive-electron developing nuclide; N is a dual-functional chelating agent; and G is the polypeptide. The fluorescent molecular probe has a structure as shown in X-G, wherein X is fluorescent nuclide; and G is the polypeptide. By the modified polypeptide, the abdomen background can be reduced obviously, and the picture contrast is improved. The obtained molecular probe is simple to prepare, low in price and high in target-to-nontarget ratio.
Owner:WUXI PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Method for preparing heavy metal holoantigen with high coupling rate and high activity
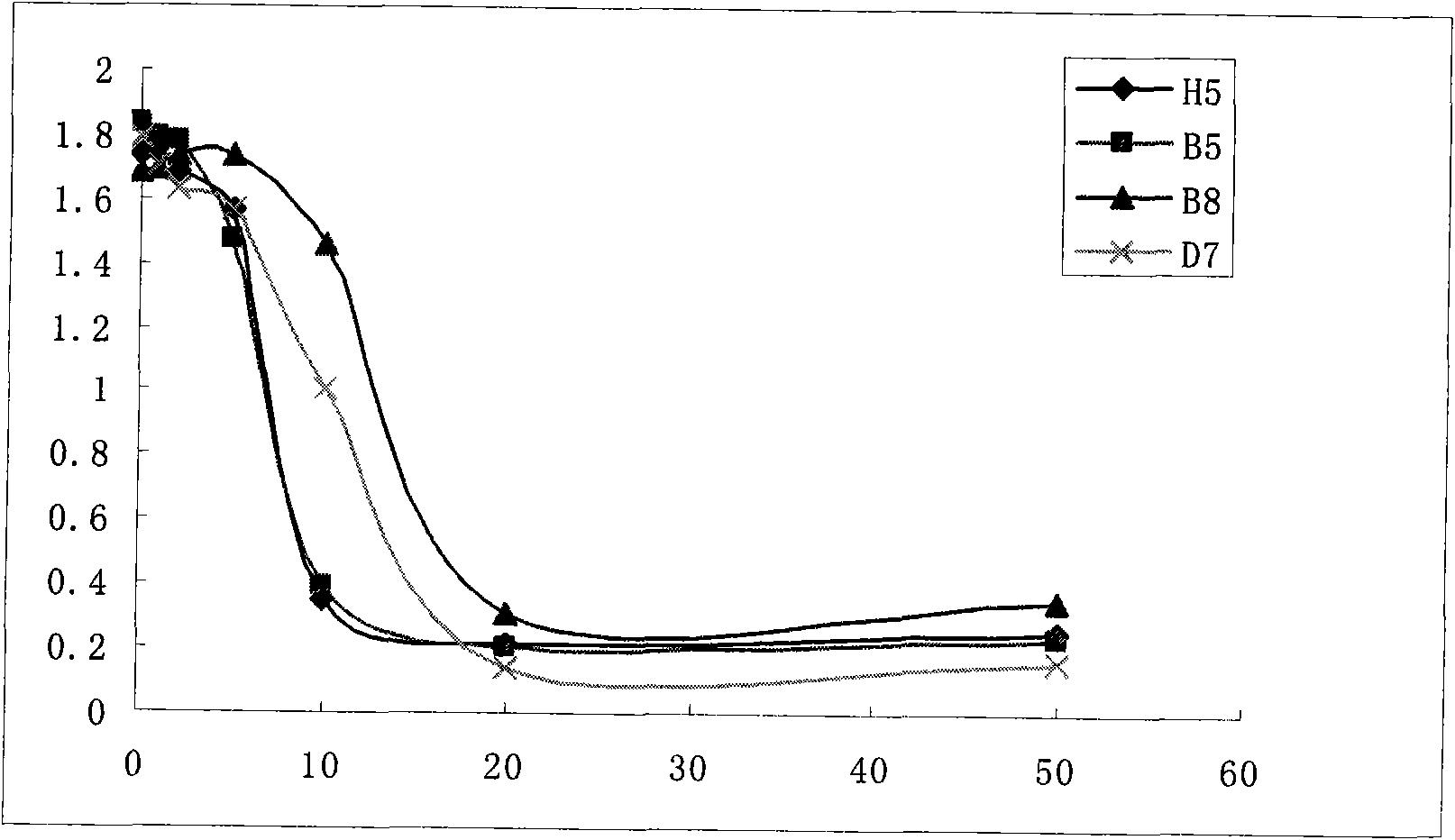
InactiveCN102875668AReduce damageHigh coupling rateOvalbuminSerum albuminPhysical chemistryCarrier protein
The invention discloses a method for preparing heavy metal holoantigen with high coupling rate and high activity. The method is implemented by improving the synthetic sequence of the heavy metal holoantigen and comprises the following steps of: reacting superfluous heavy metal ion with bifunctional chelator completely, regulating the pH value by using a NaOH solution; performing centrifugal precipitation; removing the superfluous heavy metal ion to obtain a metal ion and chelator compound, so that the metal ion and chelator compound cannot be well reacted with a biomacromolecule; coupling the metal ion and chelator compound with carrier protein, so that the activity of protein in the prepared holoantigen is guaranteed; and thus obtaining the holoantigen with high coupling rate and high activity. Immune tests in mice prove that the prepared holoantigen has high immunogenicity and is simple and practicable, and the preparation method has high repeatability.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Targeted tumor PD-L1 PET imaging agent as well as labeled precursor, preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN113583089ADesign scienceIngenious ideaRadioactive preparation carriersPeptide preparation methodsCyclic peptideRadioactive drug
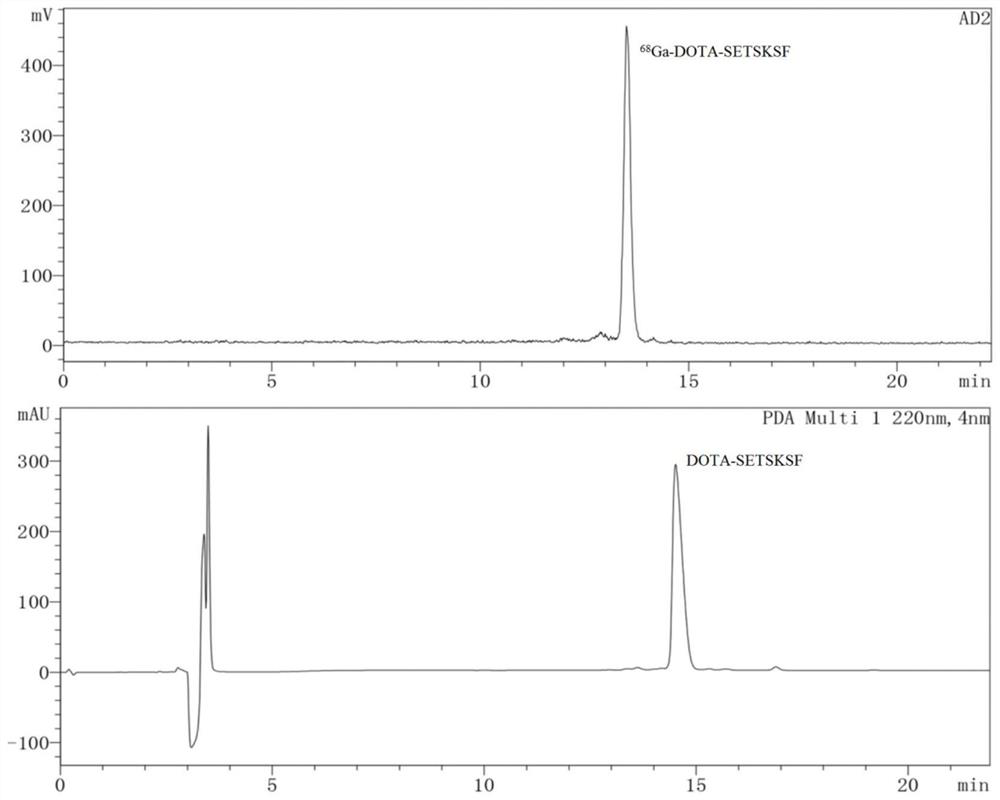
The invention discloses a tumor PD-L1 targeting PET imaging agent as well as a labeled precursor, a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of radiopharmaceutical chemistry. The structure of a labeled precursor of the tumor PD-L1 targeting PET developer is shown as a formula I, and the structure of the tumor PD-L1 targeting PET developer is shown as a formula II. According to the invention, a bifunctional chelating agent DOTA and a cyclic peptide inhibitor SETSKSF are creatively connected together, and a labeled precursor of a PET imaging agent of a targeted tumor PD-L1 as shown in a formula I is synthesized. After the precursor compound is marked with Ga-68, a compound shown in a formula II can be obtained, and the compound has good stability, excellent pharmacokinetics, good binding specificity with tumor PD-L1 and easy synthesis.
Owner:THE AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SOUTHWEST MEDICAL UNIV
Cadmium ion detection kit and application thereof
The invention provides a cadmium ion detection kit as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. Complete antigen of a cadmium ion is a complex of the cadmium ion, a chelating agent andcarrier protein, wherein the chelating agent comprises any one of or a combination of any two of EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid), DTPA (diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid), a derivative of DTPA, DOTA (1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-N,N,N,N-tetraacetic acid) and DOTA-NHS (1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid-N-hydroxysuccinimide eater). The heavy metal cadmium ion is coupled with the carrier protein through a bifunctional chelating agent, the complete antigen of the cadmium ion is obtained, a cadmium ion monoclonal antibody with high immunogenicity and high valence for the cadmium ion is prepared, and the formed kit has high specificity and sensitivity and can be used for detecting the cadmium ion.
Owner:苏州仁端生物医药科技有限公司
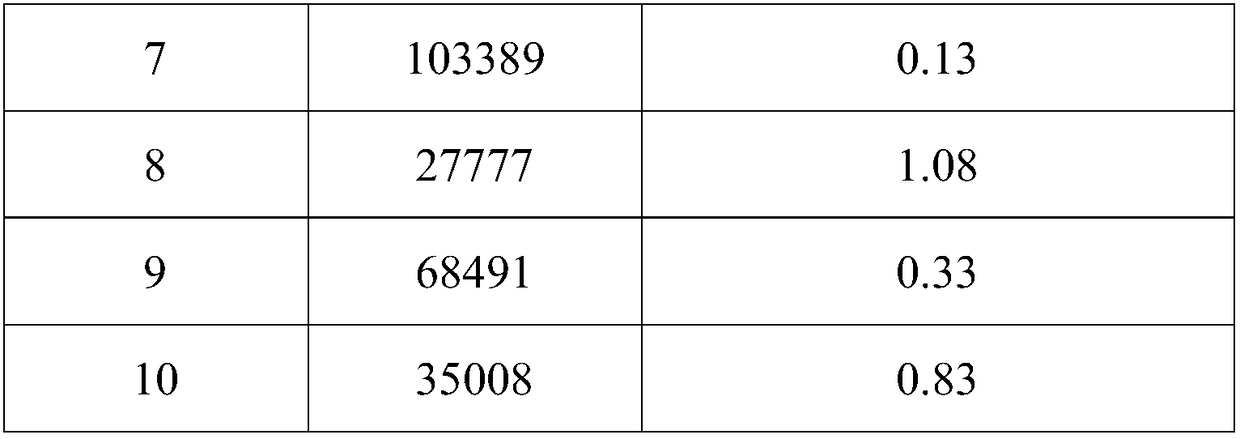
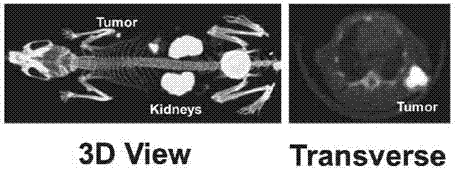
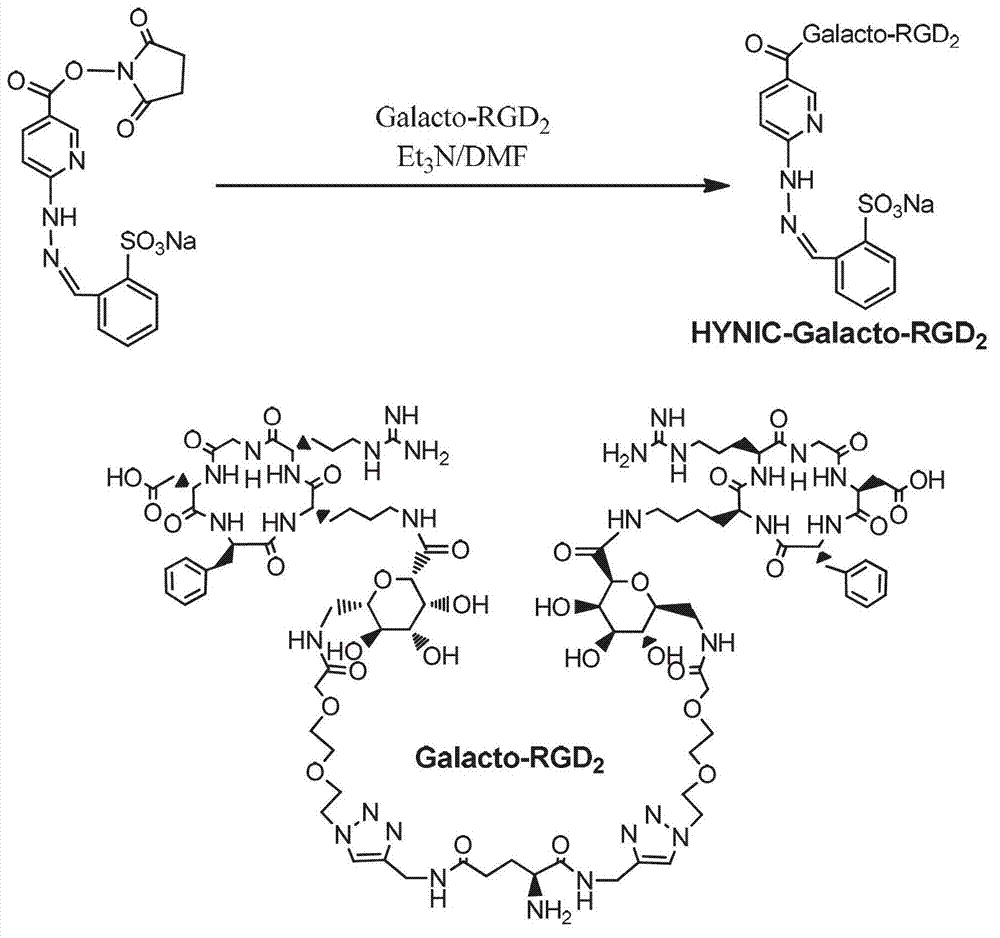
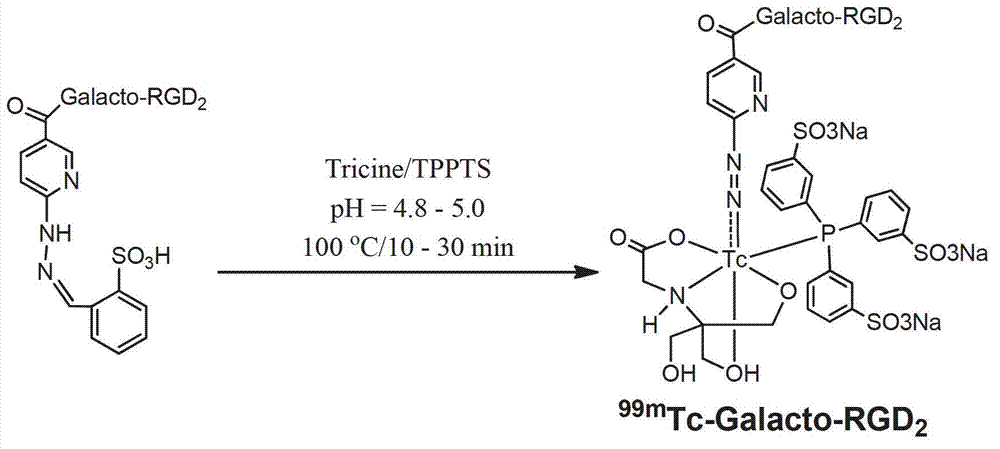
99mTc labeling galactosed arginyl-glycyl-aspartic acid (RGD) tumor diagnosis medicine and preparation method
InactiveCN102861347AReduce intakeImprove image qualityRadioactive preparation carriersDimerRadioactive drug
The invention relates to an arginyl-glycyl-aspartic acid (RGD) polypeptide radioactive medicine and preparation method thereof for intergrin alpha-v-beta3 receptor positive tumor diagnosis. The medicine is a galactosed RGD cyclic dimer in structure, and the medicine is subjected to a radionuclide 99mTc labeling through a bifunctional chelator hydrazino nicotinamide (HYNIC). The medicine is characterized in that two galactoses are used as a joining chain of the RGD, the uptaking of the medicine in non-target organs of intestinal canal, lungs and the like is reduced, and thereby the image quality of tumor imaging is improved. The radioactive medicine is 99mTc-Galacto-RGD2 and is a colorless transparent liquid injection.
Owner:安徽筑梦生物科技有限公司
Novel VQ polypeptide radioactive medicine and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103330951AInflammation clearly visualizedRadioactive preparation carriersPeptide preparation methodsImage diagnosisRadioactive drug
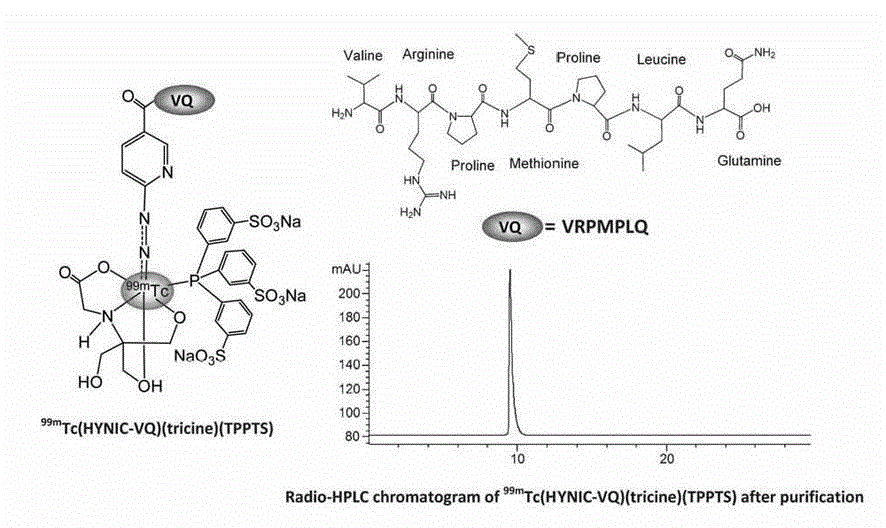
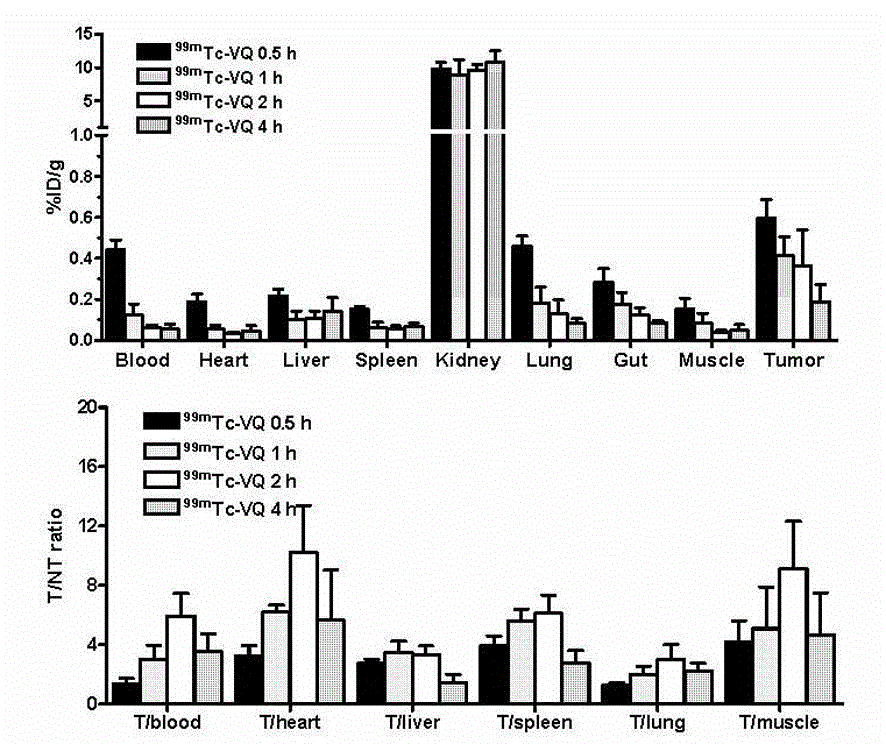
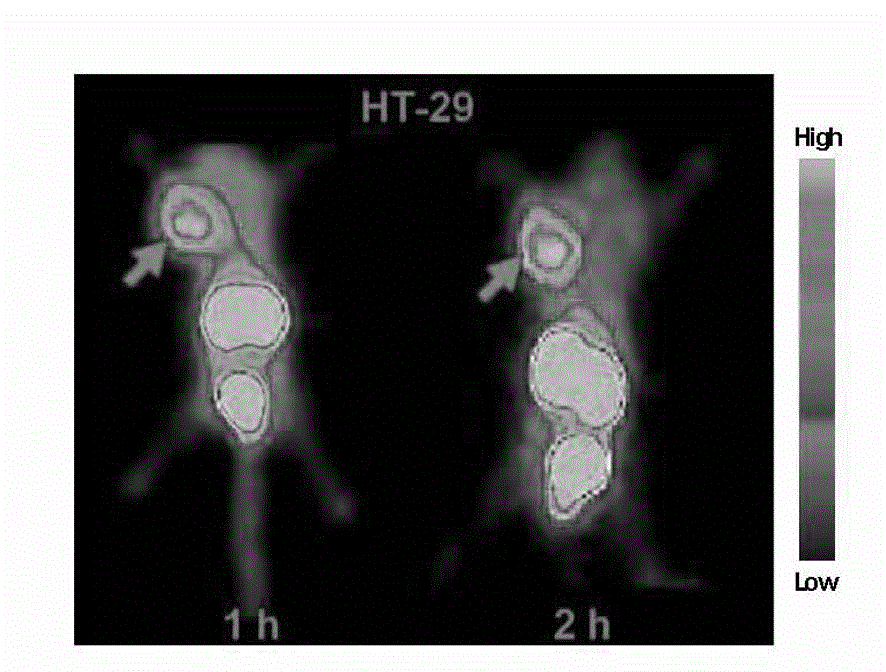
The invention relates to a VQ polypeptide radioactive medicine which comprises VQ polypeptide, a difunctional chelator and a radioactive nuclide, wherein the VQ polypeptide is linear heptad of which the sequence is VRPMPLQ (Val-Arg-Pro-Met-Pro-Leu-Gln, VQ), the radioactive nuclide marks the VQ linear heptad through the difunctional chelator, the VQ polypeptide radioactive medicine is Nuclide-Chelator-VQ, and the VQ polypeptide radioactive medicine is colorless and transparent liquid injection. The VQ polypeptide radioactive medicine can be used for early diagnosis of various tumors, the medicine enables the radioactive nuclide 99 mTc to be marked on the VQ polypeptide molecule through the difunctional chelator, marked medicine in body is concentrated to a tumor part through the targeting effect of the VQ polypeptide, and by using nuclear medicine single photon emission tomograph, imaging diagnosis is performed on various tumors.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
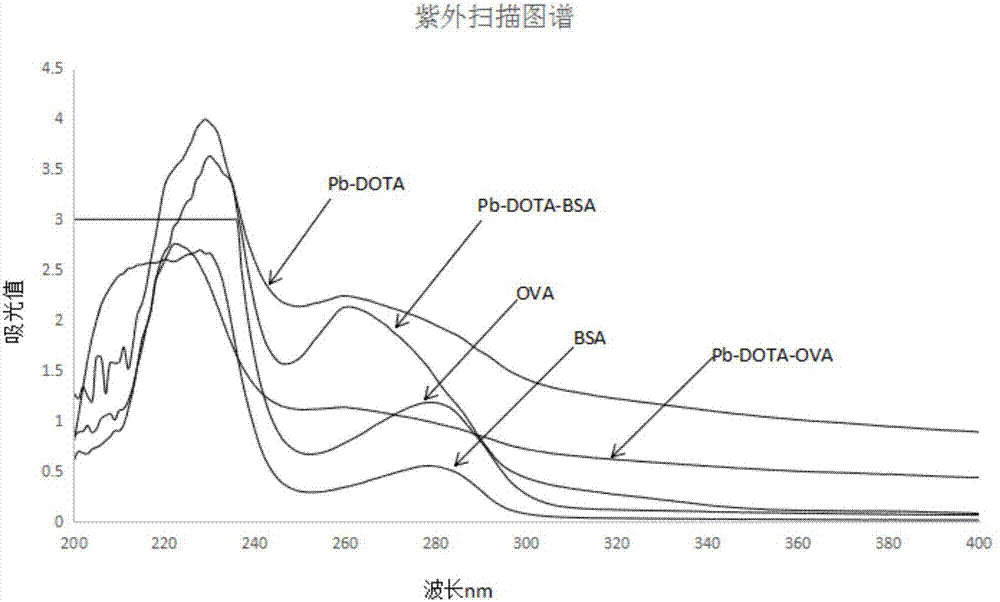
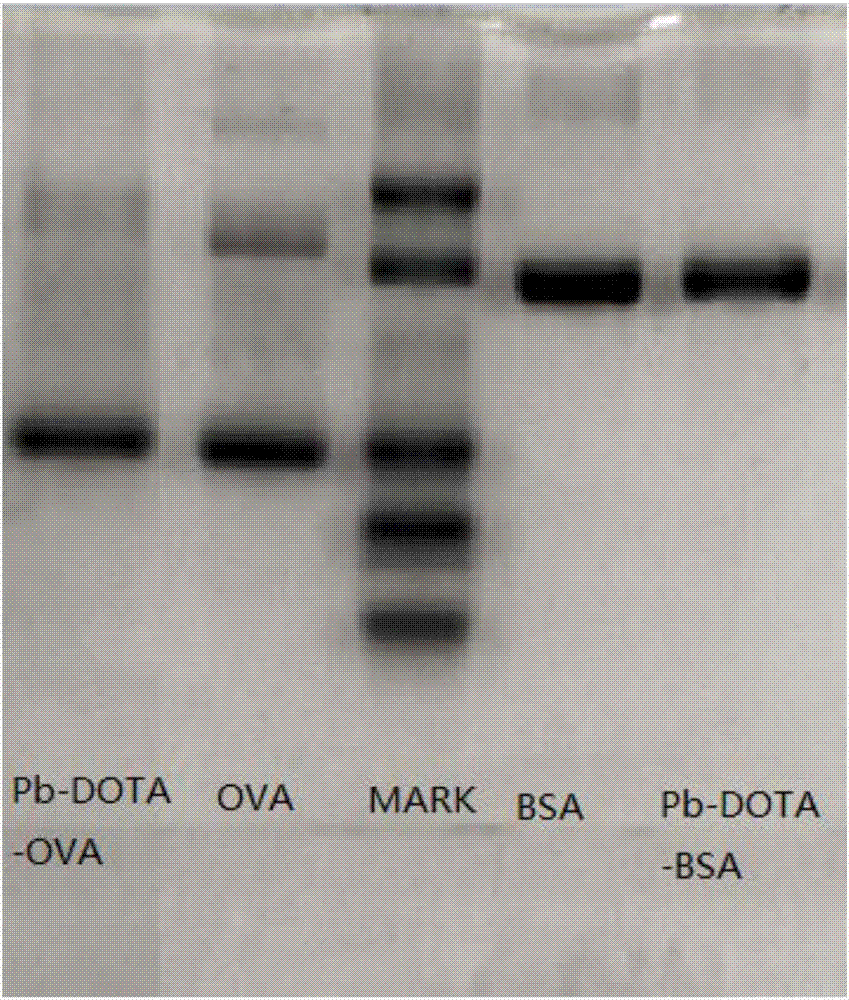
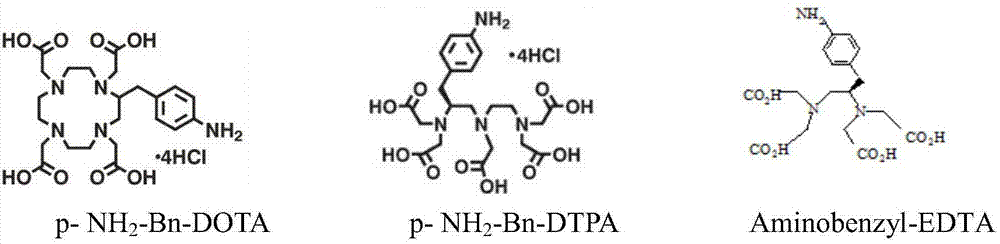
Improved synthesis method of heavy metal lead artificial antigen and application of DOTA (2-S-(4-amino-benzene)-1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclononane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid) to preparation of heavy metal lead artificial antigen reagent
The invention provides a synthesis method for preparing a heavy metal lead artificial antigen based on a novel difunctional chelating agent DOTA (2-S-(4-amino-benzene)-1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclononane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid). According to the preparation method, DOTA is taken as the chelating agent, a lead ion chelating agent compound is coupled with BSA (bovine serum albumin) as carrier protein orKHL (human serum albumin), and the artificial antigen is prepared. According to the method, the step of sodium borohydride reduction is added on the original traditional basis, so that the coupling efficiency is improved. The invention further provides an application of DOTA to preparation of the heavy metal lead artificial antigen.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GONGSHANG UNIVERSITY
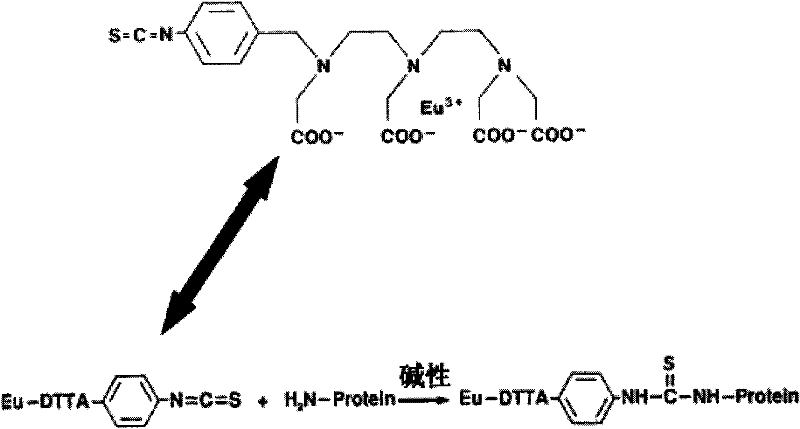
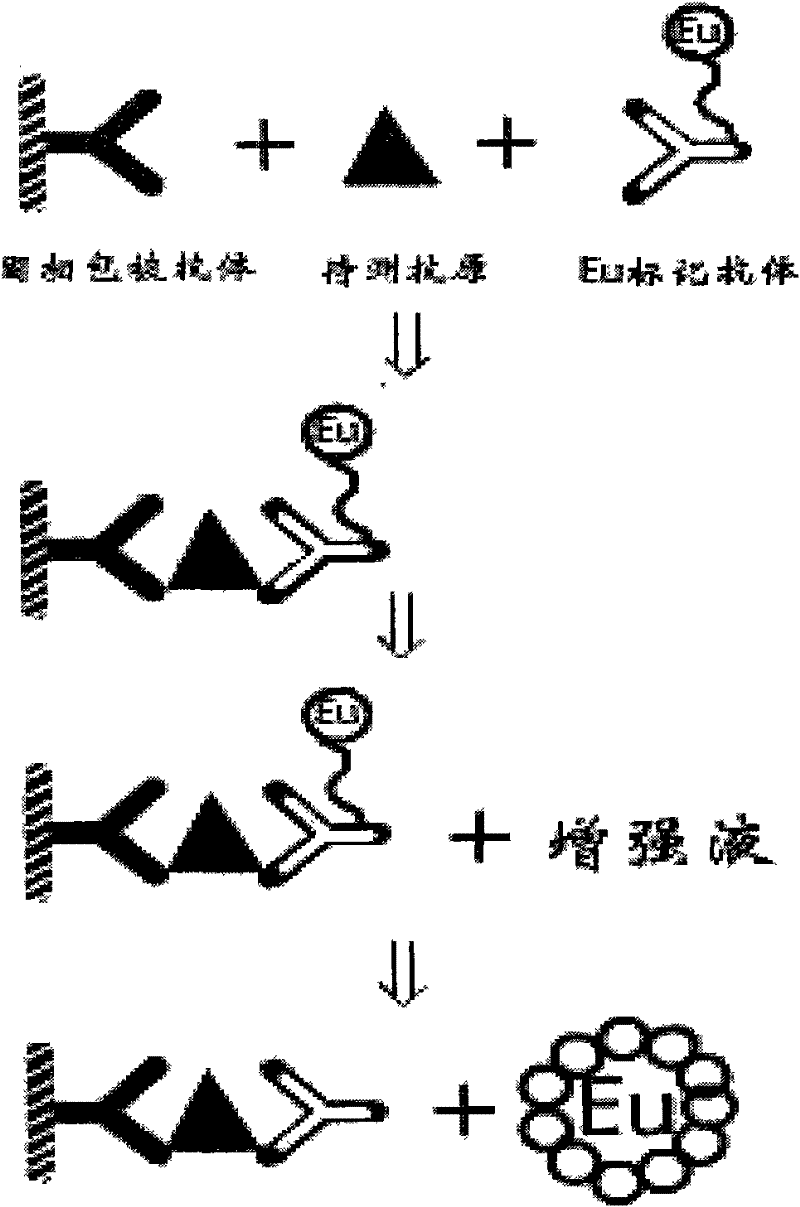
Preparation method of TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone) quantitative detection kit based on time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay
The invention provides a TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone) quantitative detection kit based on time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay, applicable to clinical screening of neonatal hypothyroidism. The preparation method of the kit is characterized by comprising the following steps of: 1, separating an antibody conjugate (Eu-Anti-TSH) from free rare earth ions (Eu<3+>) by using a specific chromatograph column; (2) using a bifunctional chelator (DTTA) for marking, wherein one end of the bifunctional chelator is chelated with rare earth ions (Eu) and the other end of the bifunctional chelator is connected with -NH2 of protein; adding beta-NTA to reinforcing liquid and regulating the concentration so that the fluorescence intensity of a finally obtained reagent is improved; and (4) adding a substitute Proclin300 for sodium azide to an analysis buffer system. Based on the characteristics of the steps in the preparation method, the TSH quantitative detection kit based on time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay can be produced and other in vitro diagnosis detection reagents can be developed.
Owner:北京协和洛克生物技术有限责任公司
Bifunctional chelators for sequestering lanthanides
ActiveUS7777029B2Minimizes streakingSynthetic is simpleOrganic chemistryGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsLanthanideProtecting group
Owner:SAN DIEGO STATE UNIVERSITY +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com