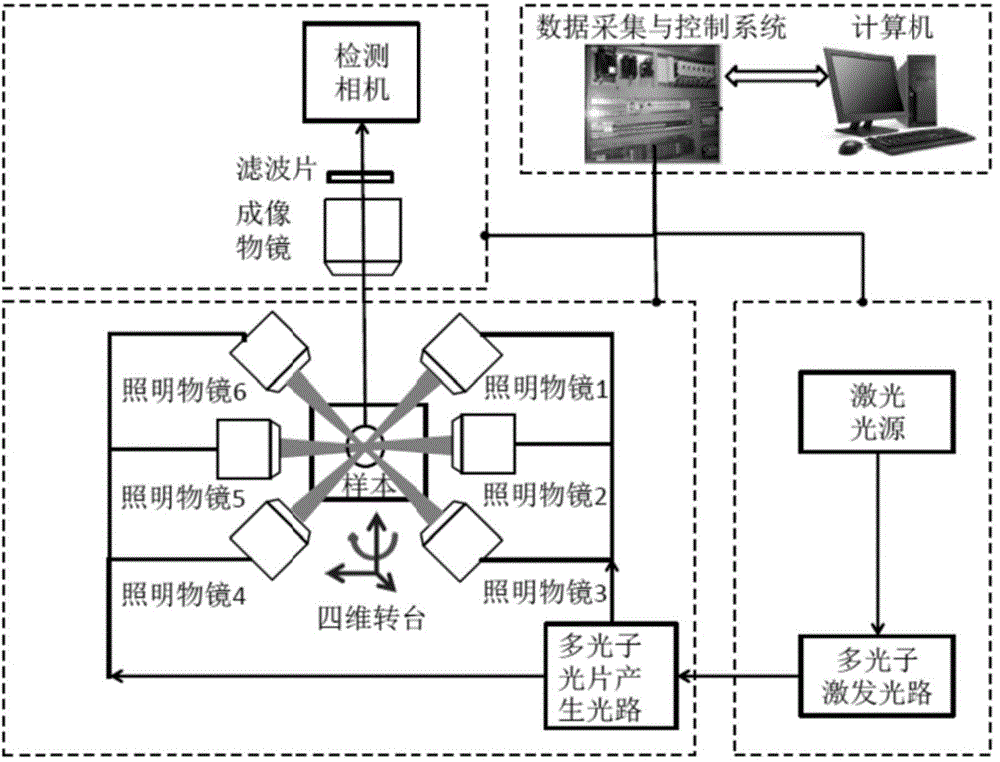
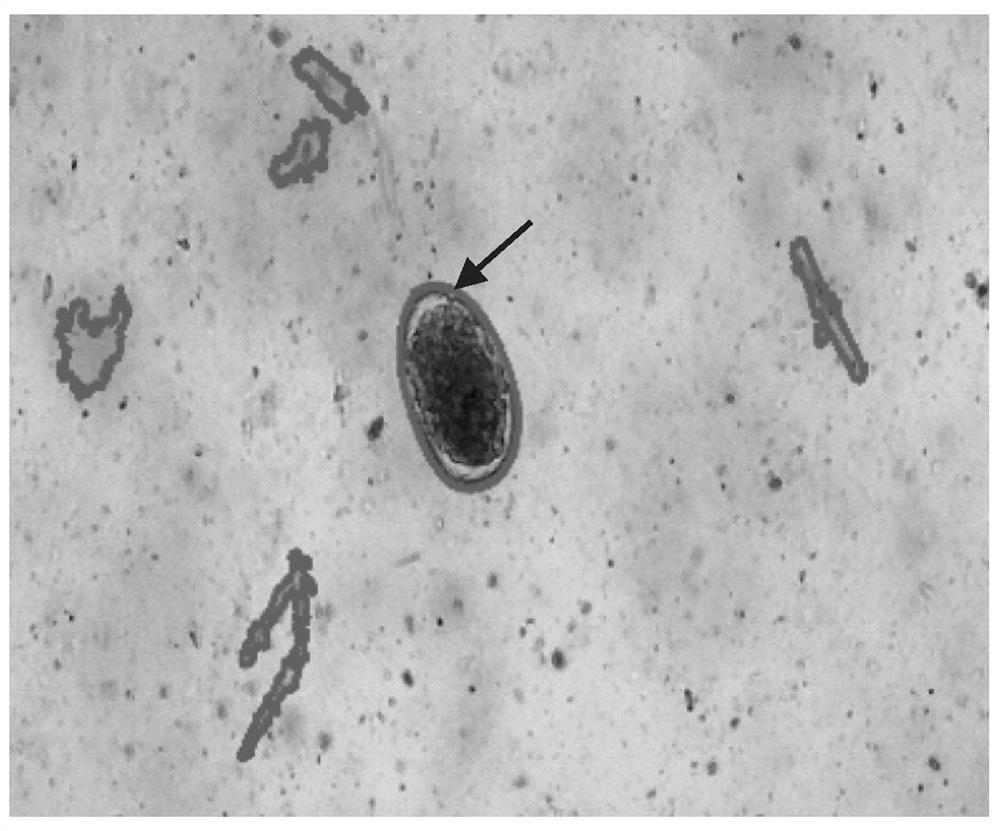
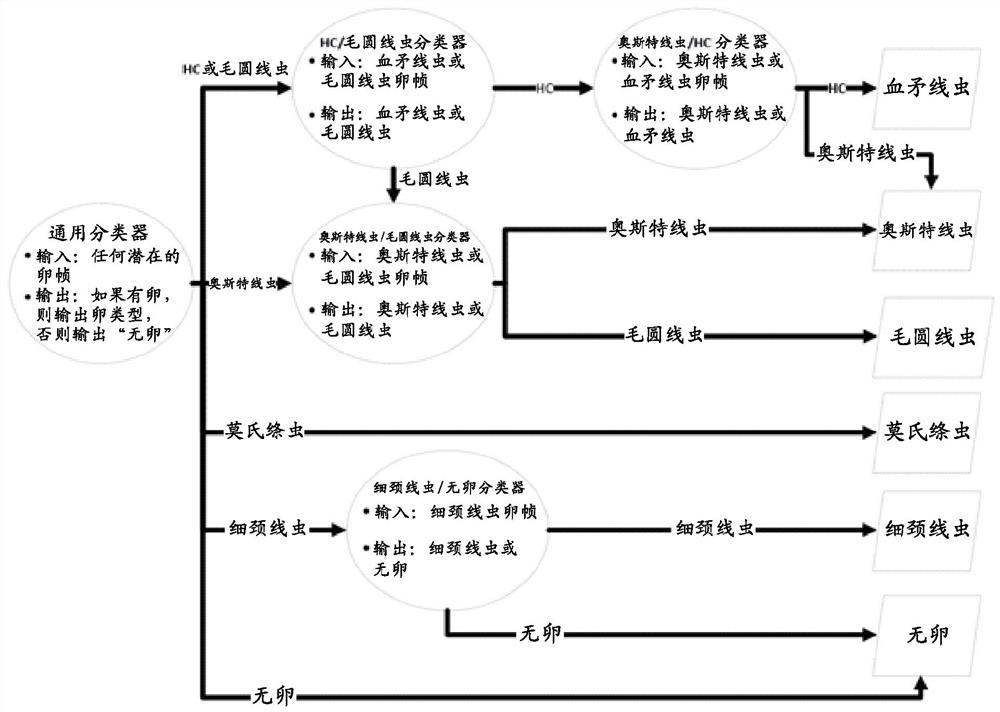
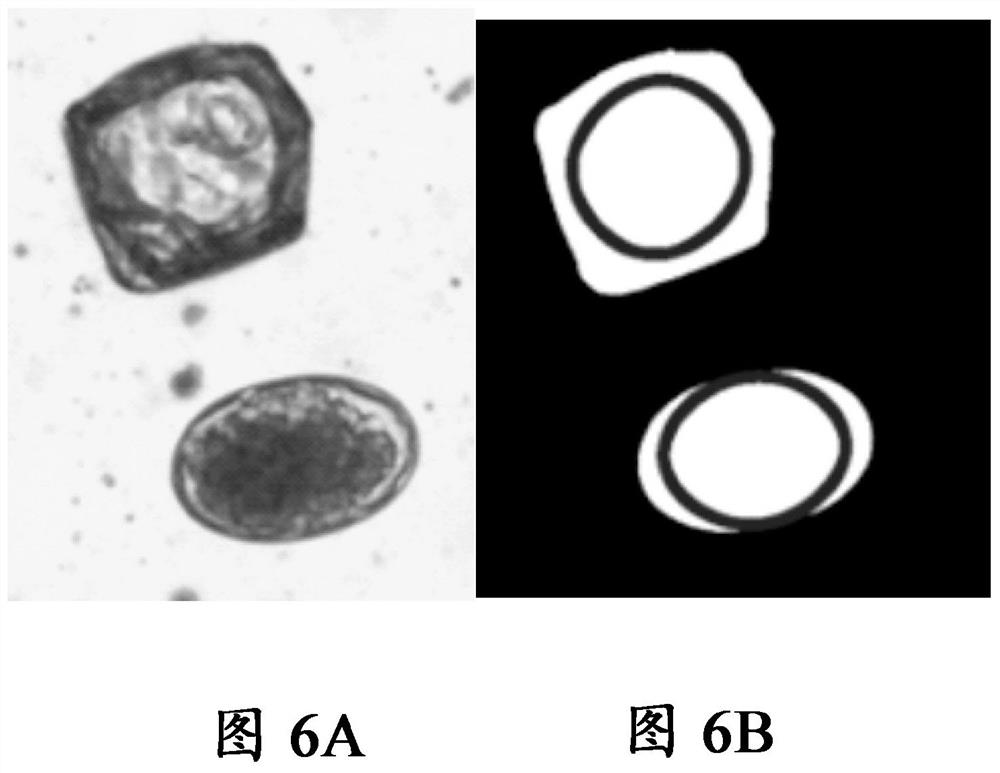
Patents
Literature
65 results about "Light microscopy technique" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bright field microscopy is the simplest of all the light microscopy techniques. Sample illumination is via transmitted white light, i.e. illuminated from below and observed from above. Limitations include low contrast of most biological samples and low apparent resolution due to the blur of out-of-focus material.
Automated macromolecular crystal detection system and method
InactiveUS7227983B1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionBase function
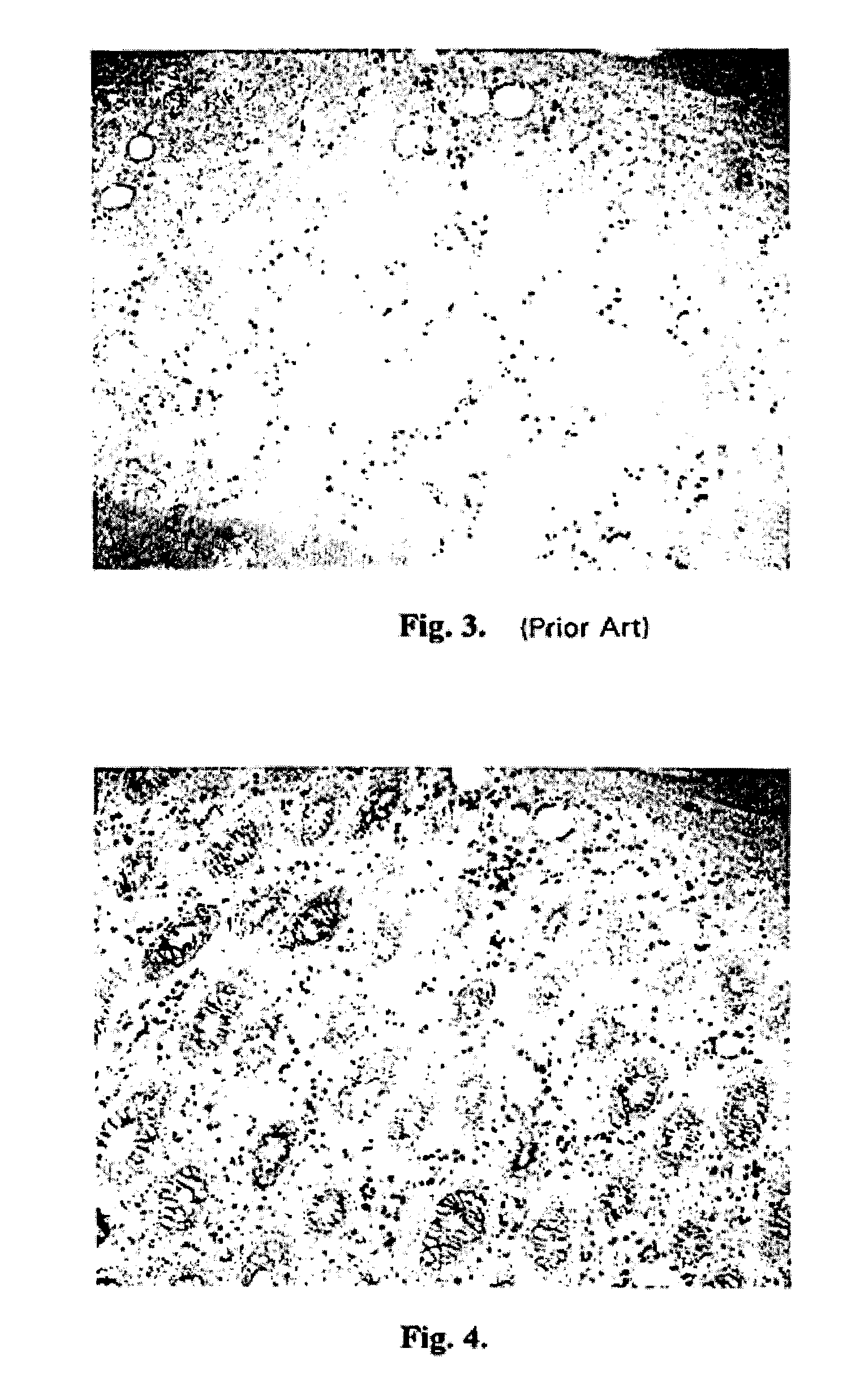
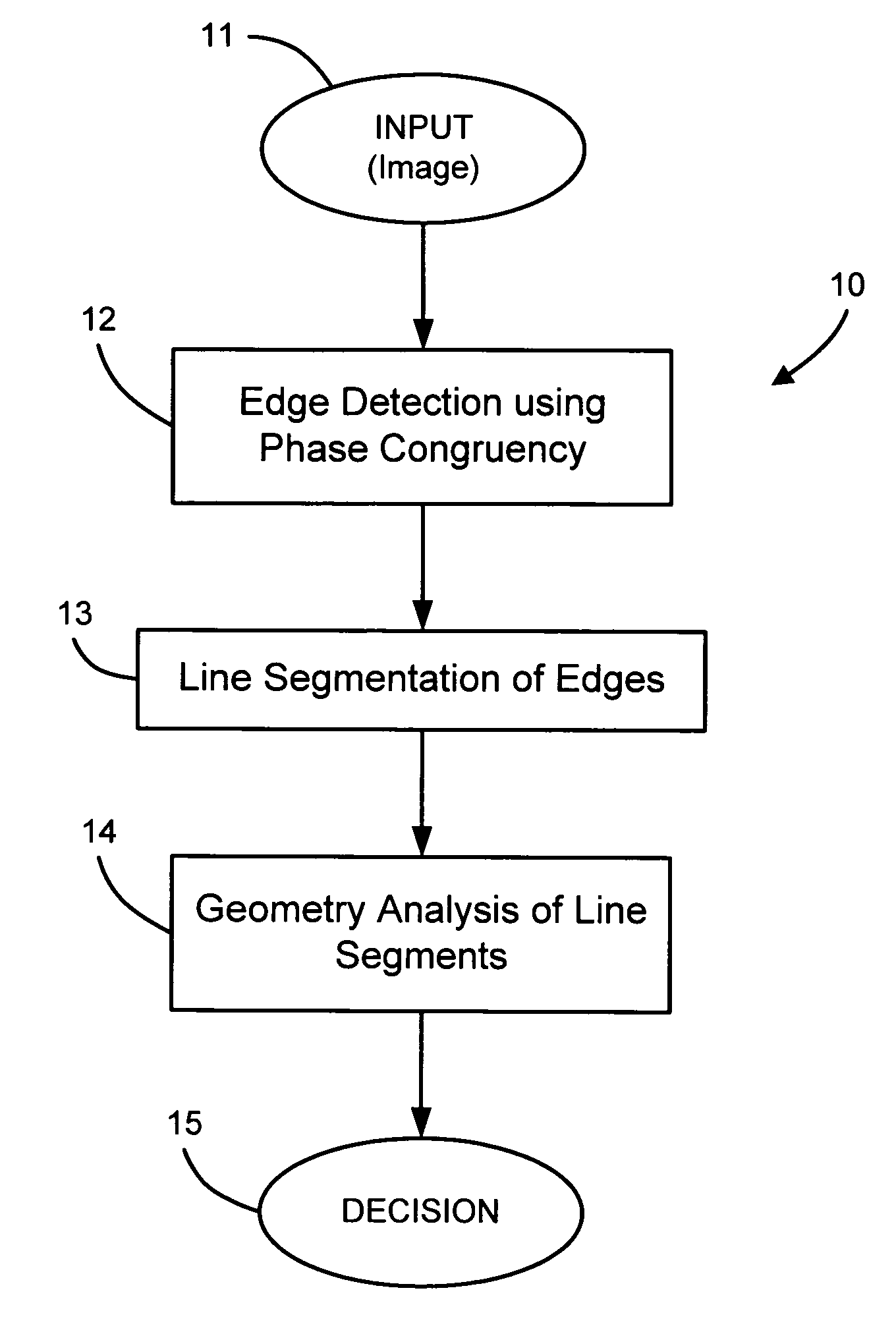
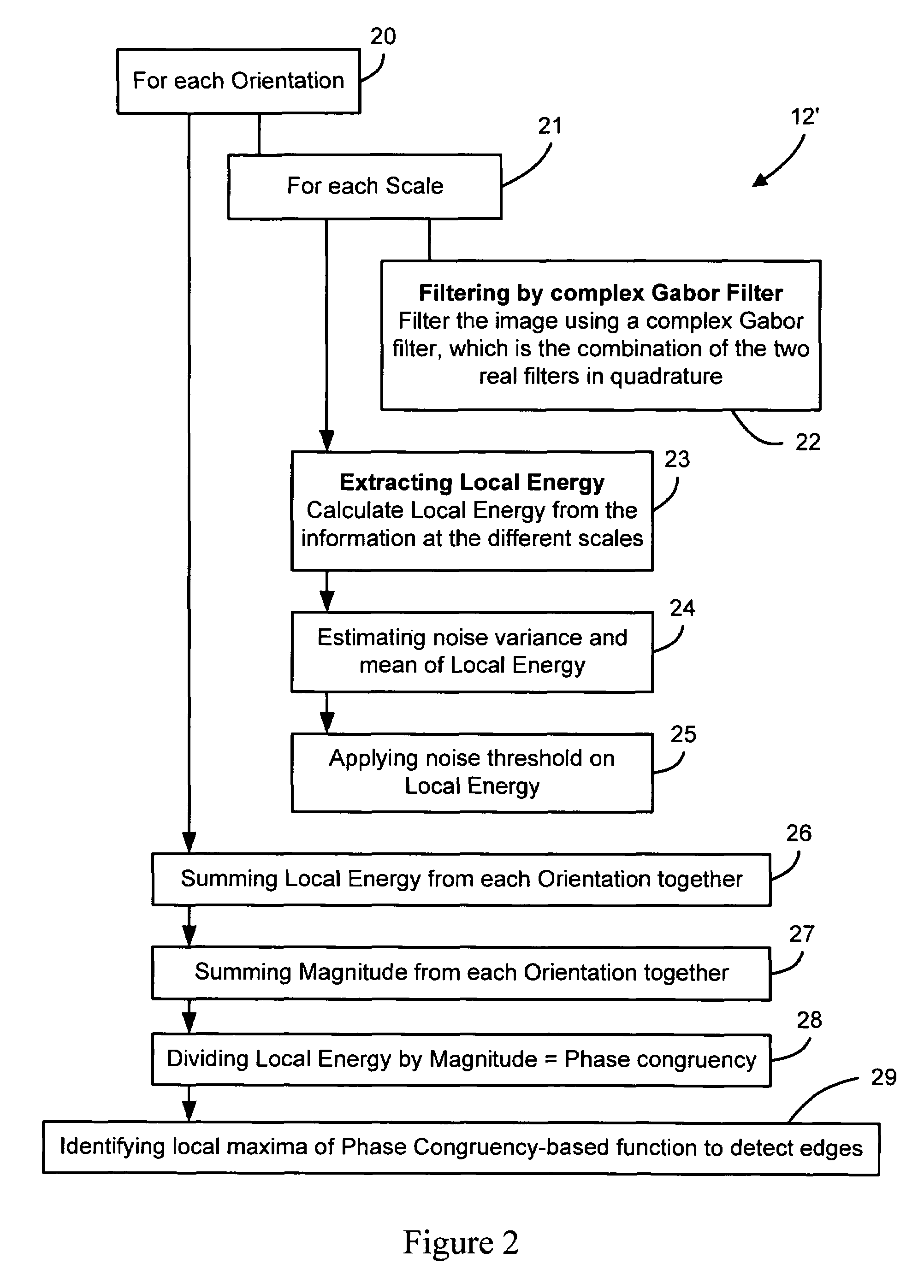
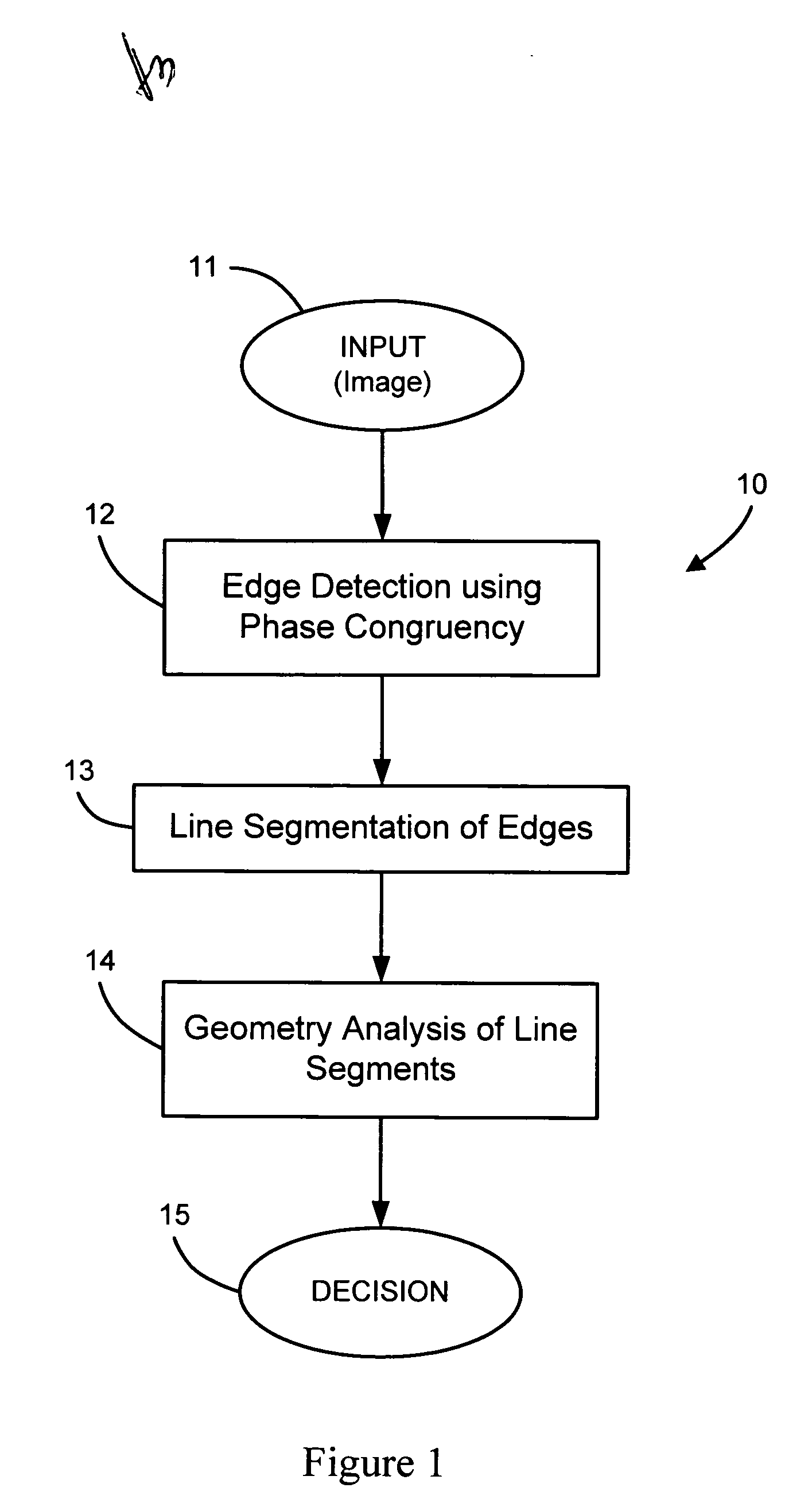
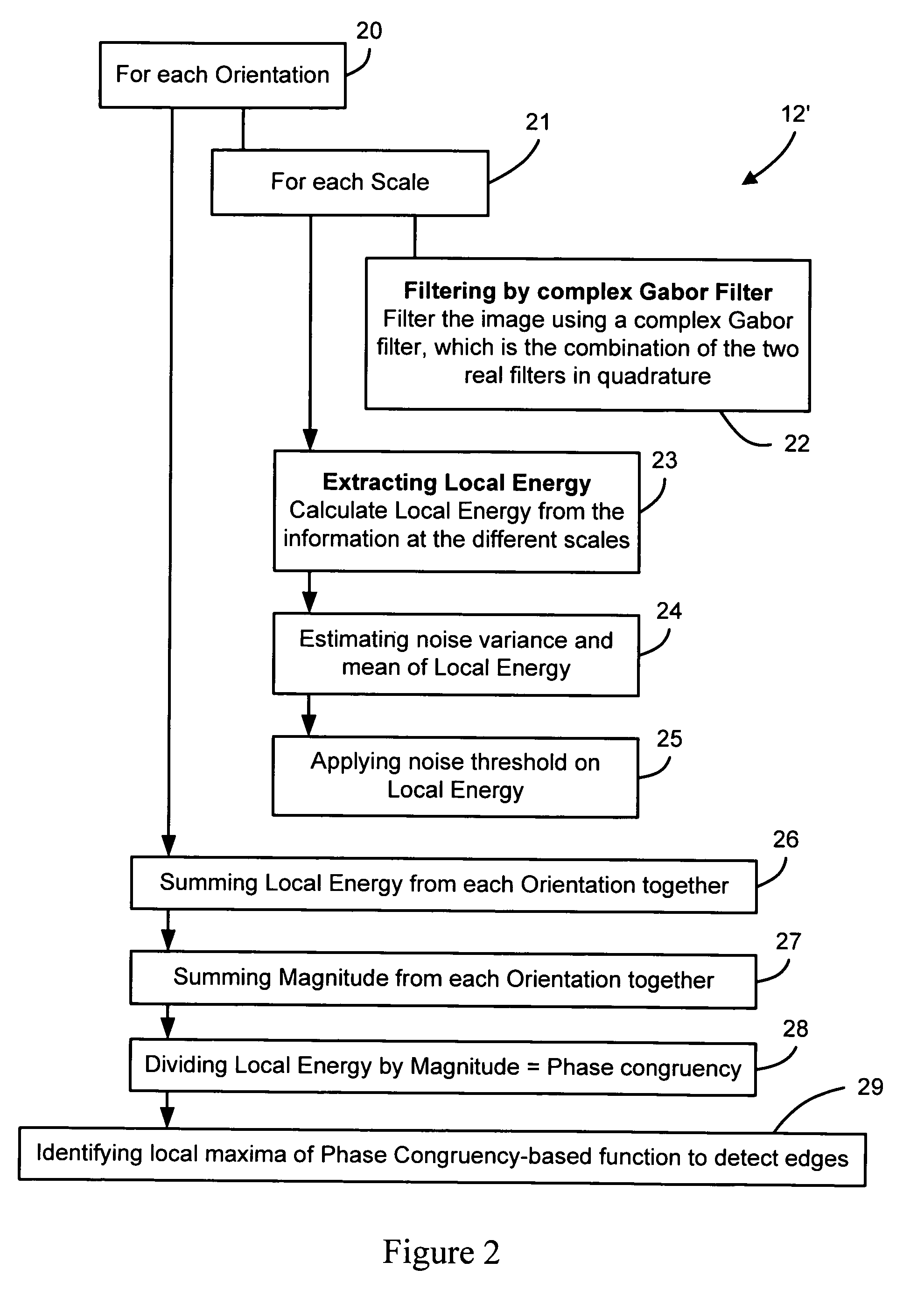
An automated macromolecular method and system for detecting crystals in two-dimensional images, such as light microscopy images obtained from an array of crystallization screens. Edges are detected from the images by identifying local maxima of a phase congruency-based function associated with each image. The detected edges are segmented into discrete line segments, which are subsequently geometrically evaluated with respect to each other to identify any crystal-like qualities such as, for example, parallel lines, facing each other, similarity in length, and relative proximity. And from the evaluation a determination is made as to whether crystals are present in each image.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Automated macromolecular crystal detection system and method
An automated macromolecular method and system for detecting crystals in two-dimensional images, such as light microscopy images obtained from an array of crystallization screens. Edges are detected from the images by identifying local maxima of a phase congruency-based function associated with each image. The detected edges are segmented into discrete line segments, which are subsequently geometrically evaluated with respect to each other to identify any crystal-like qualities such as, for example, parallel lines, facing each other, similarity in length, and relative proximity. And from the evaluation a determination is made as to whether crystals are present in each image.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Damman wave zone plate
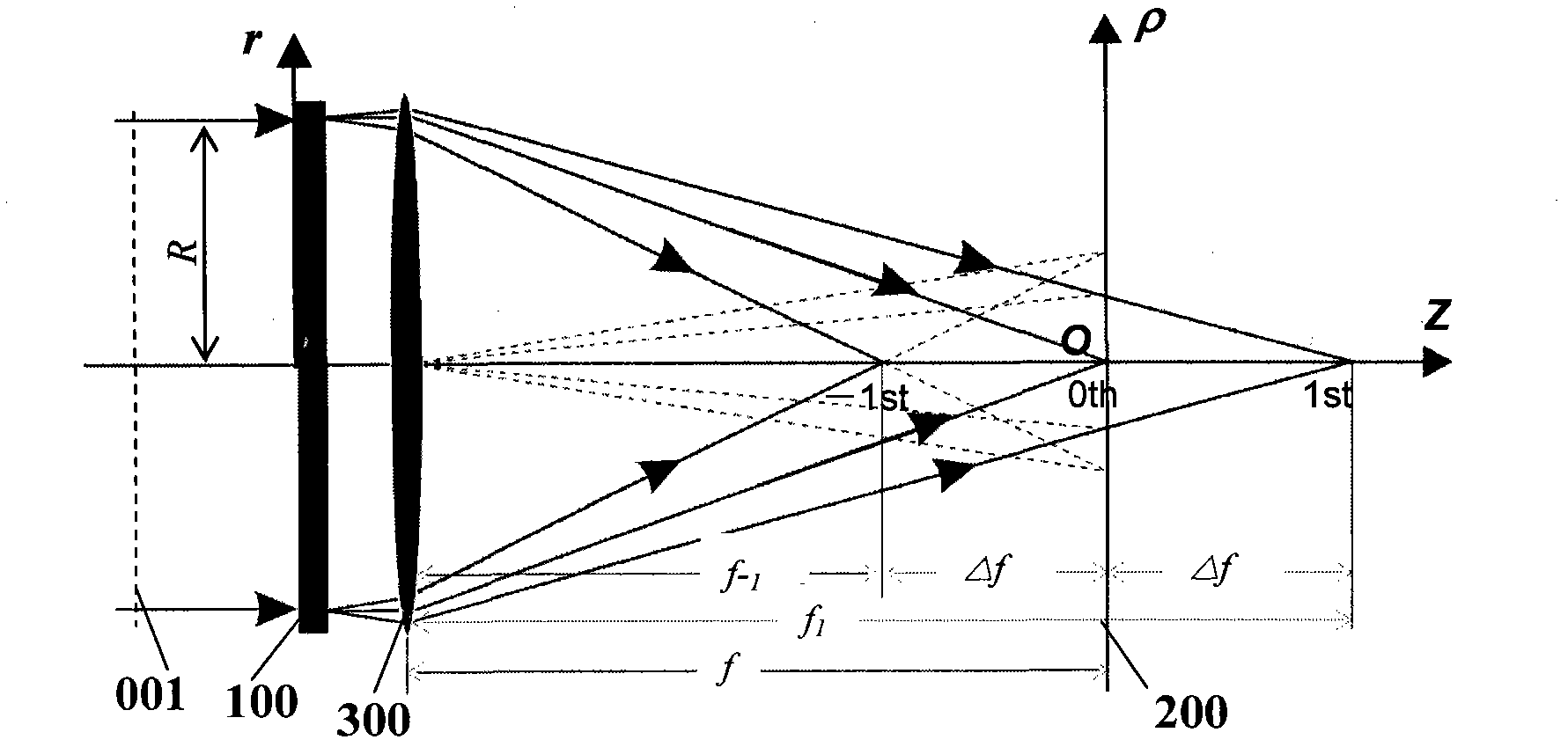
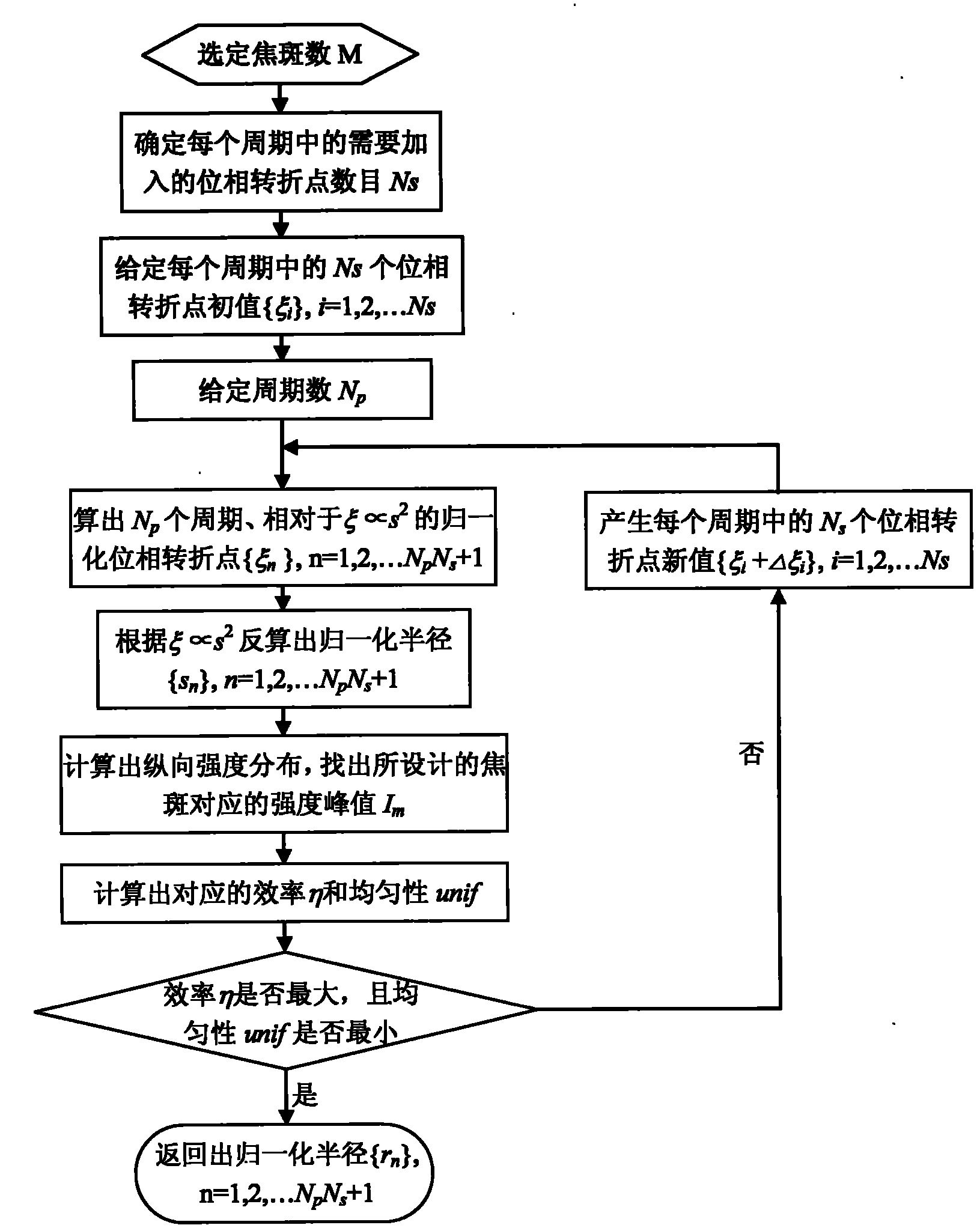
The invention relates to a damman wave zone plate which is characterized in that a phase modulation detail is added in each period of the traditional binary phase-only type (0, pi) zone wave plate structure relative to the square of the radial coordinate so as to generate axial constant-strength distribution of focal spots with any numbers within a certain range. The distribution of a plurality of constant-strength focal spots along the optical axis direction can be widely applied to imaging systems (optical microscopes), optical tweezers, implantable contact lens, and the like with large depth of field-. Besides, the damman wave zone plate in binary phase-only distribution is a series of concentric circle structures intuitively and is easy to process and duplicate. Therefore, the damman wave zone plate has important application prospect in the fields of optical imaging systems and biomedicine.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optical microscope and spectrum measuring method
ActiveUS20100128263A1Reduce the number of timesReduced measurement timeRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationOptical axisLaser light
An optical microscope applies laser light to a sample through the an objective lens, detects reflected light reflected by the sample through the objective lens, changes a focal position of the laser light in an optical axis direction, extracts a focal position for spectrum measurement based on a detection result of the reflected light when the focal position of the laser light is changed, adjusts the focal position to coincide with the extracted focal position, separates outgoing light exiting from the sample by application of the laser light with the adjusted focal position from the laser light, and measures a spectrum of the outgoing light separated from the laser light with a spectroscope.
Owner:NANOPHOTON
Optical microscopy and its use in the study of cells
InactiveUS6929934B1Minimize damageExposure of light can be limitedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsIon currentLive cell imaging
The present invention pertains to an apparatus for imaging an object, comprising a probe via which an assay component may be delivered; a sensor to detect ion current; and means for controlling the position of the probe relative to the object in response to the ion current. Such apparatus can be used to image live cells, without affecting them, in solution, e.g., using light, wherein the distance between probe and cell is less than the wavelength of light.
Owner:IONSCOPE
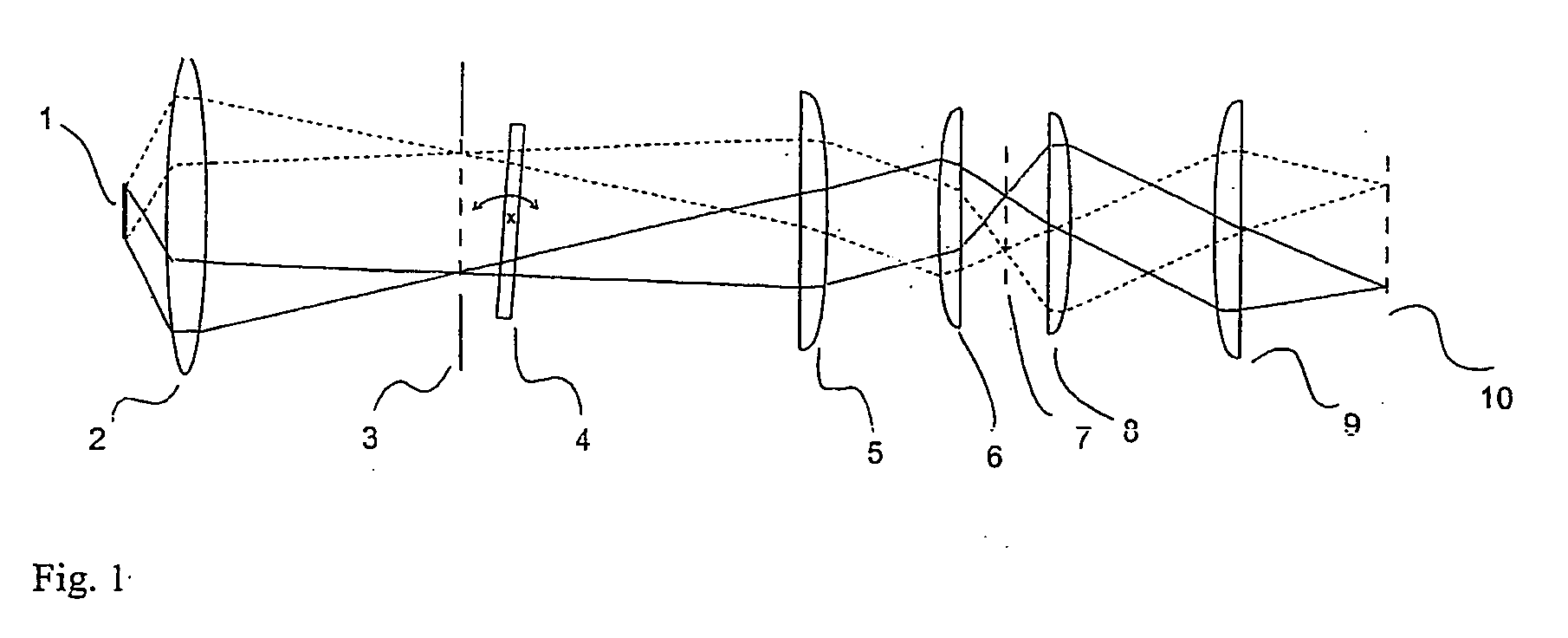
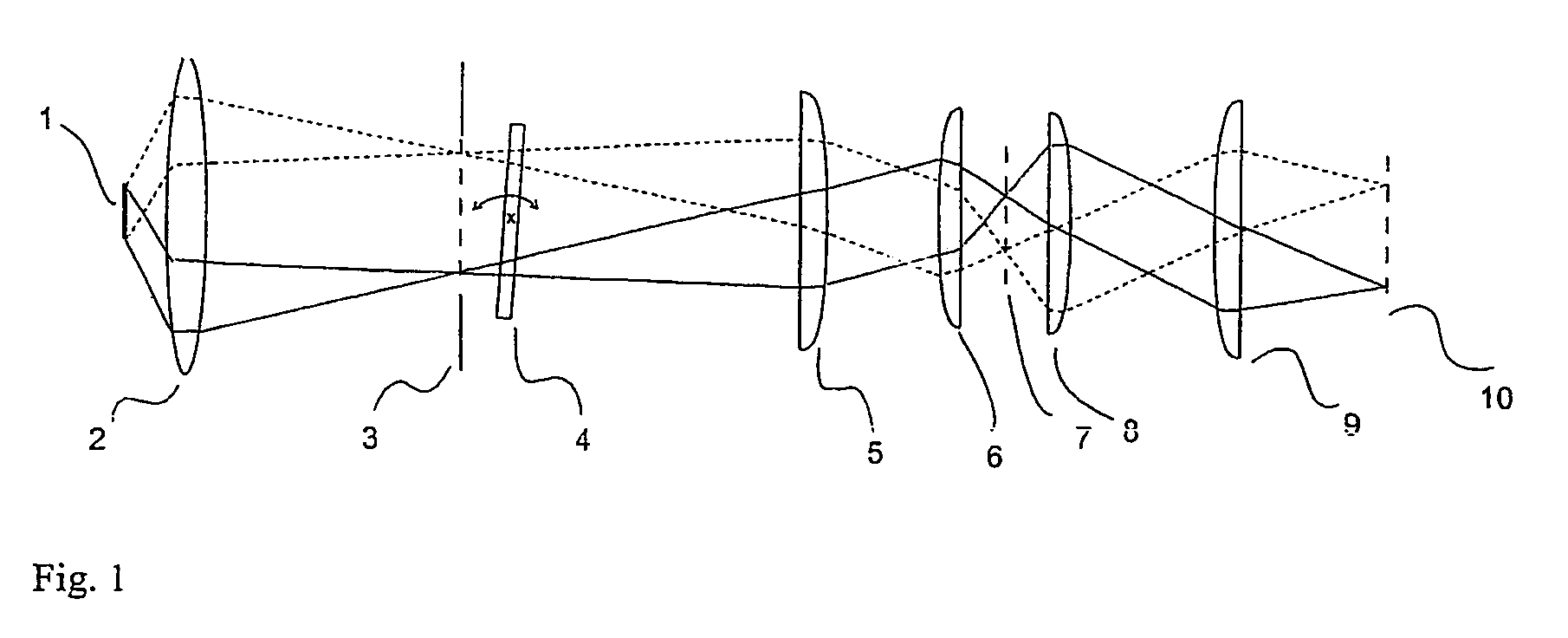
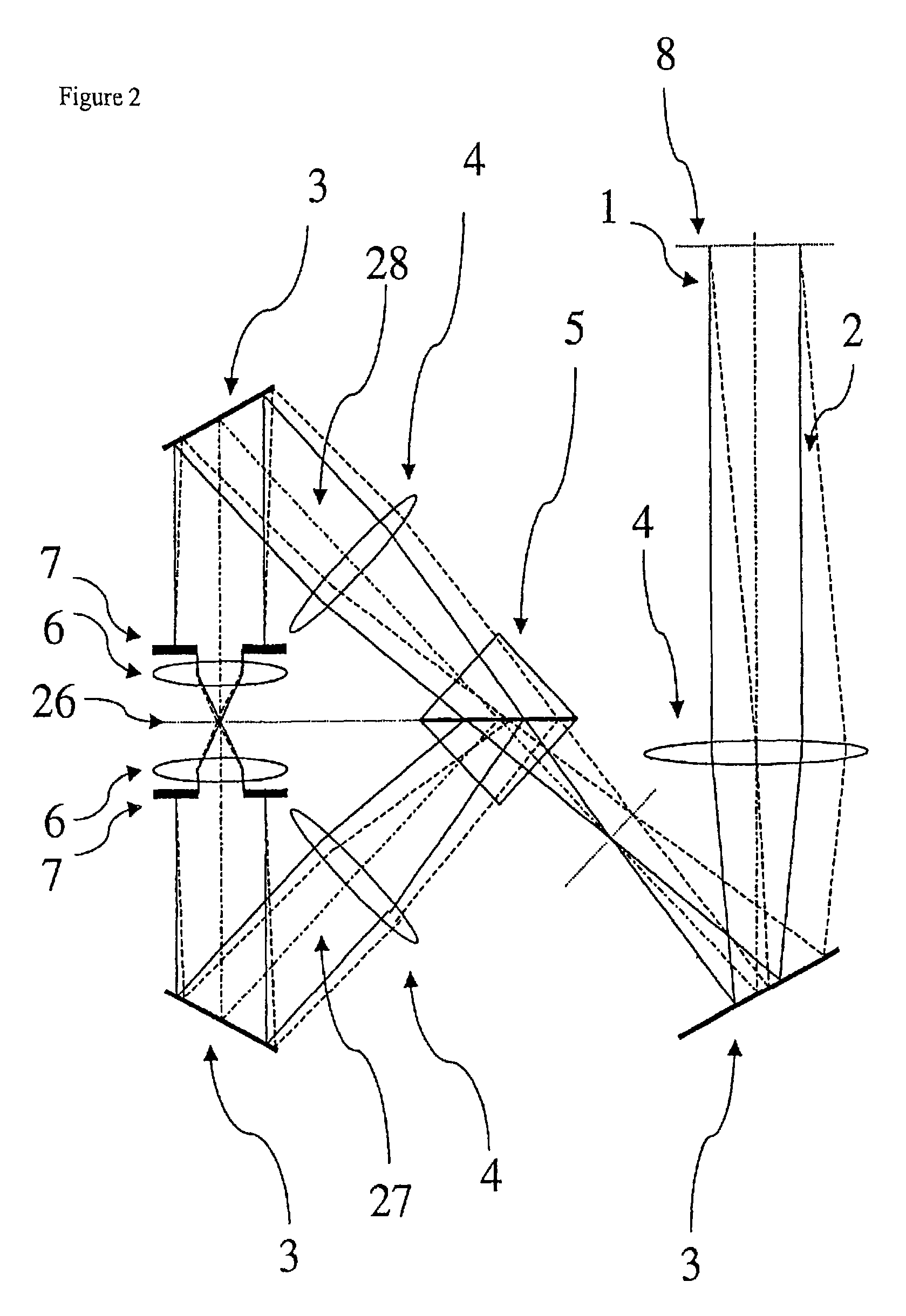
Method for improving depth discrimination in optical reproduction systems
ActiveUS20060186311A1Improving depth discriminationOvercome disadvantagesProjectorsMaterial analysis by optical meansImaging qualityFluorescence
The invention is directed to a method for improving the depth discrimination in optically imaging systems. It is applicable in particular in light microscopy for improving image quality when examining three-dimensionally extending objects. It is applicable in the method of structured illumination as described in WO 97 / 6509. For this purpose, influences due to variations in the brightness of the light source, positioning of the imaged periodic structure and bleaching of the object in fluorescence illumination are determined and taken into account in the calculation of the object structure.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
Method for improving depth discrimination in optical reproduction systems
The invention is directed to a method for improving the depth discrimination in optically imaging systems. It is applicable in particular in light microscopy for improving image quality when examining three-dimensionally extending objects. It is applicable in the method of structured illumination as described in WO 97 / 6509. For this purpose, influences due to variations in the brightness of the light source, positioning of the imaged periodic structure and bleaching of the object in fluorescence illumination are determined and taken into account in the calculation of the object structure.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
Darkfield illumination system
Owner:CARL ZEISS JENA GMBH
Method for detecting a target using enzyme directed deposition of elemental metal
InactiveUS7888060B2High sensitivityFacilitates chromogenic detection of signalImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsChromogenicEnzyme
Disclosed embodiments concern site-specific, enzymatic-directed deposition of elemental metal for in-situ analysis. Enzyme substrates are contacted with metal ions and subsequently direct the deposition of elemental metals. Sensitive and selective detection of target molecules, such as biomarkers in various biological samples, can be obtained using various methods, such as in-situ chromogenic immunohistochemical (IHC) detection with bright field light microscopy.
Owner:NANOPROBES
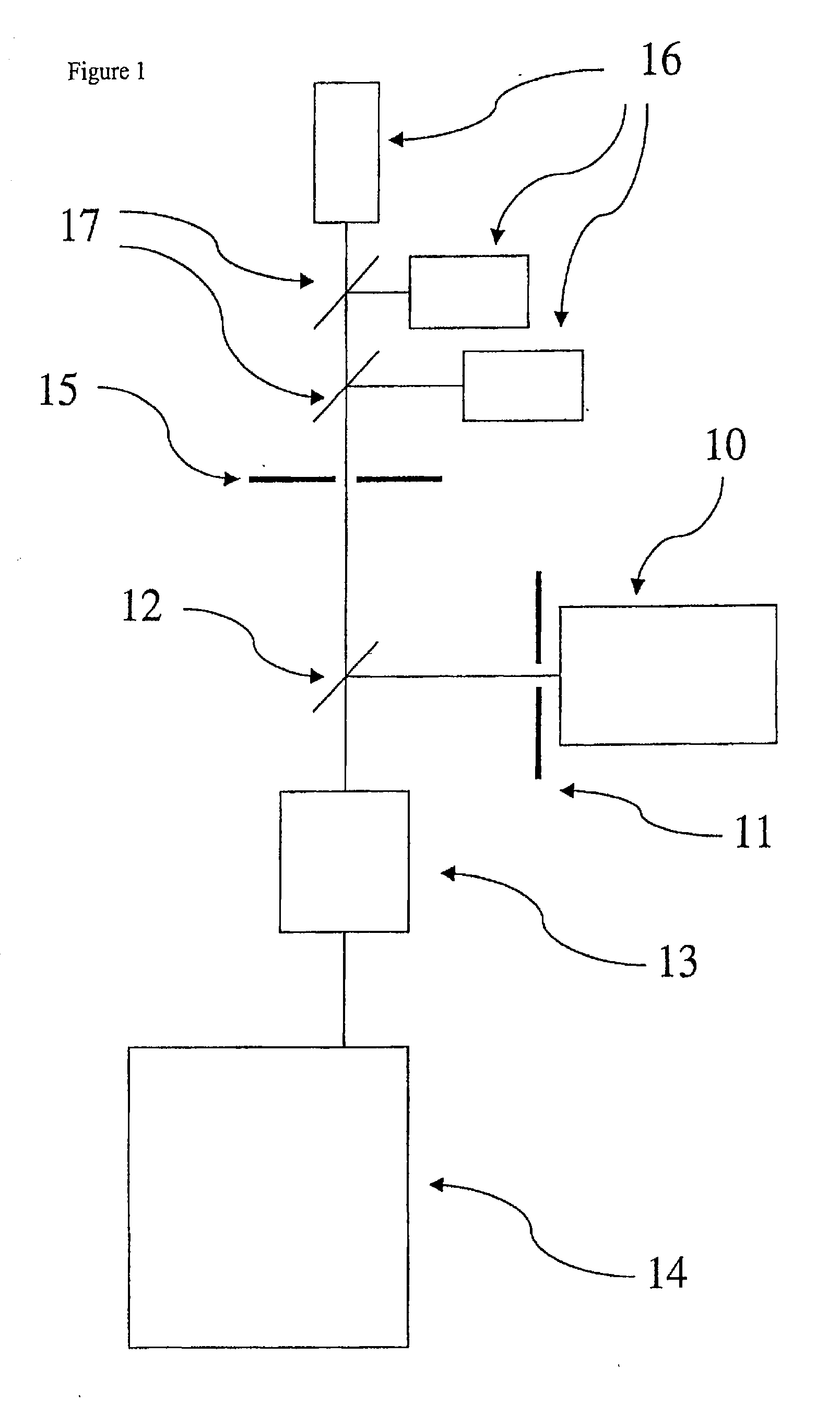
Interference microscope, and method for operating an interference microscope
The present invention concerns an interference microscope and a method for operating an interference microscope, in particular a 4π microscope, standing wave field microscope, or I2M, I3M, or I5M microscope, at least one specimen support unit associated with the specimen being provided. For determination of the phase position of the interfering light in the specimen region, on the basis of which the interference microscope can be aligned, the interference microscope is characterized in that for determination of the illumination state in the specimen region of the interference microscope, at least one planar area of the specimen support unit is configured to be detectable by light microscopy.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
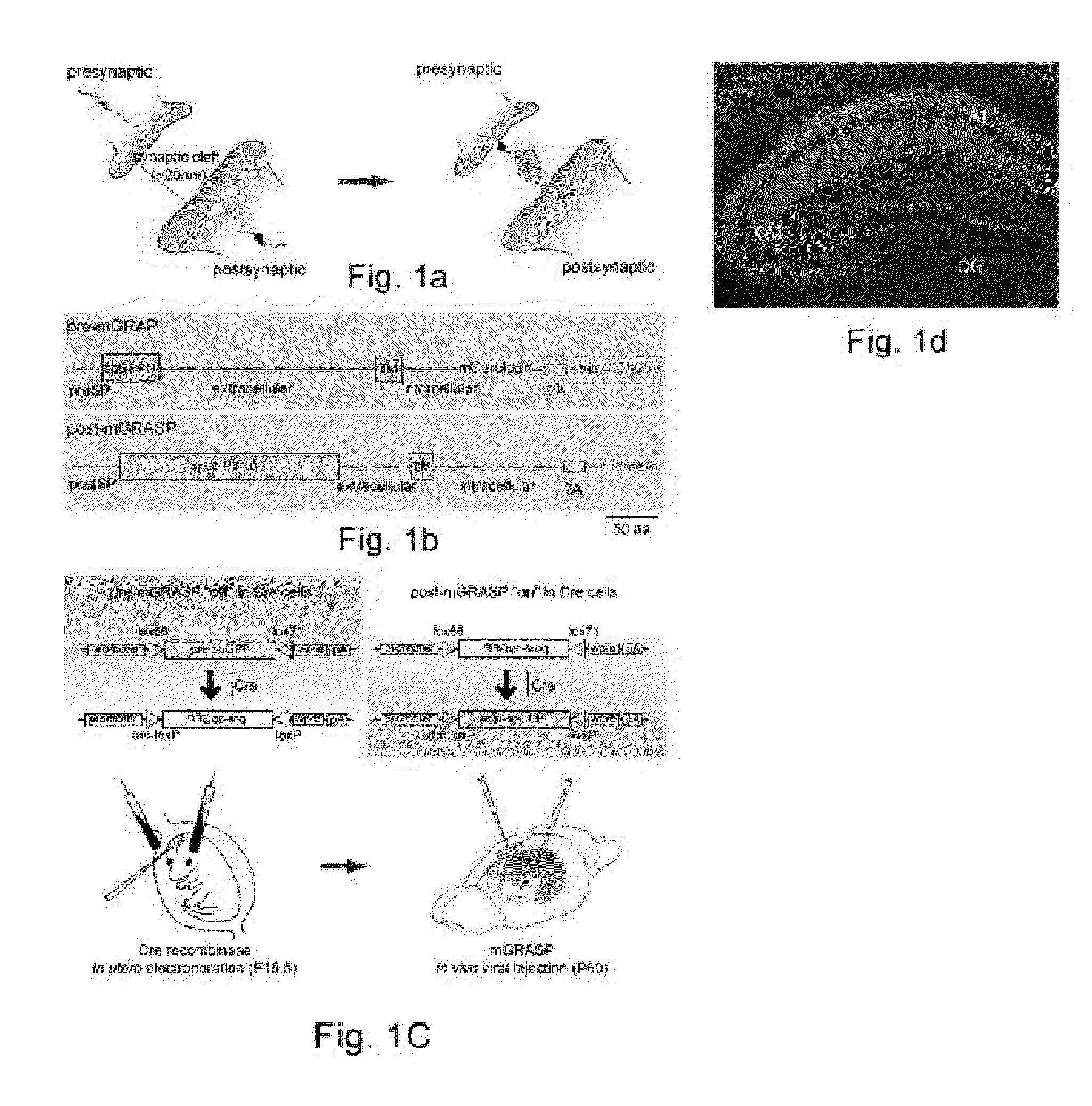
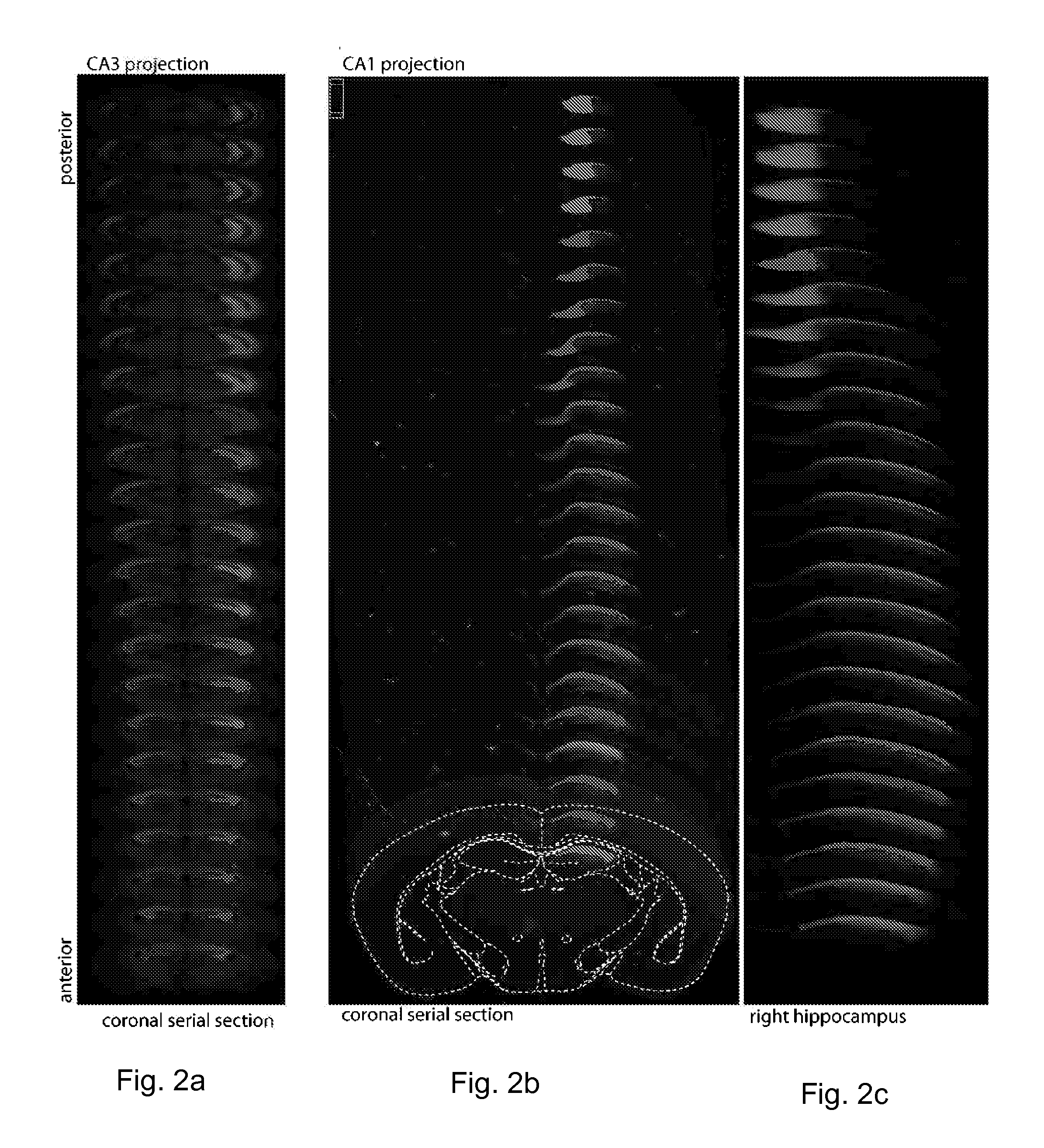
Method and system for mapping synaptic connectivity using light microscopy
InactiveUS20130058871A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsOrganic active ingredientsSynapseGreen fluorescent protein
A mammalian Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) Reconstruction Across Synaptic Partners (mGRASP) method and system is provided by optimizing synaptic transmelectron microscopicbrane carriers for mammalian synapses. The method and system in one form integrates molecular and cellular approaches with a novel computational strategy to reliably reconstruct neurons in 3D. The method and system allows mGRASP to be applied to both long-range and local microcircuits, analysis of synaptic distribution at the level of single neurons and dendritic compartments within neural cells.
Owner:HOWARD HUGHES MEDICAL INST
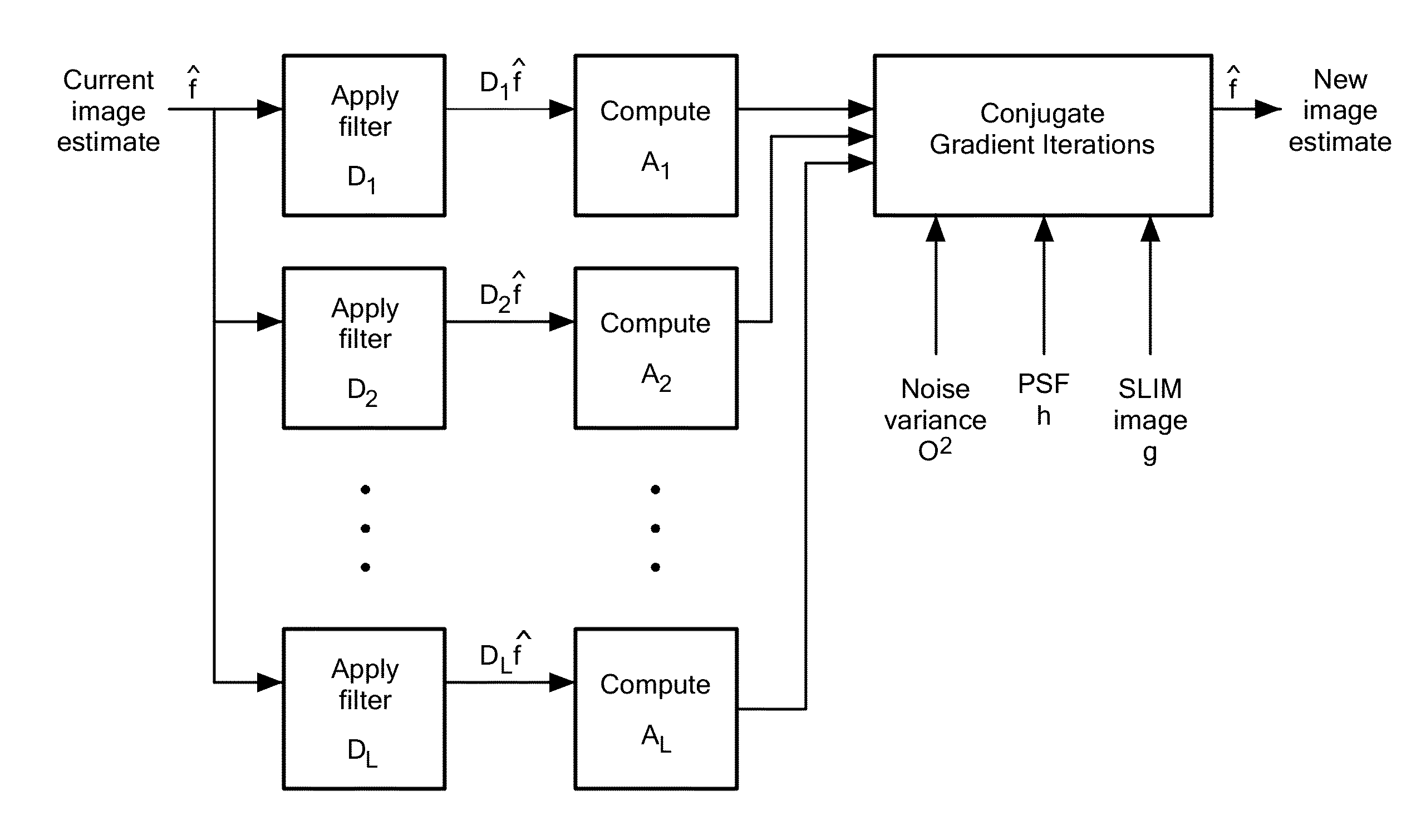
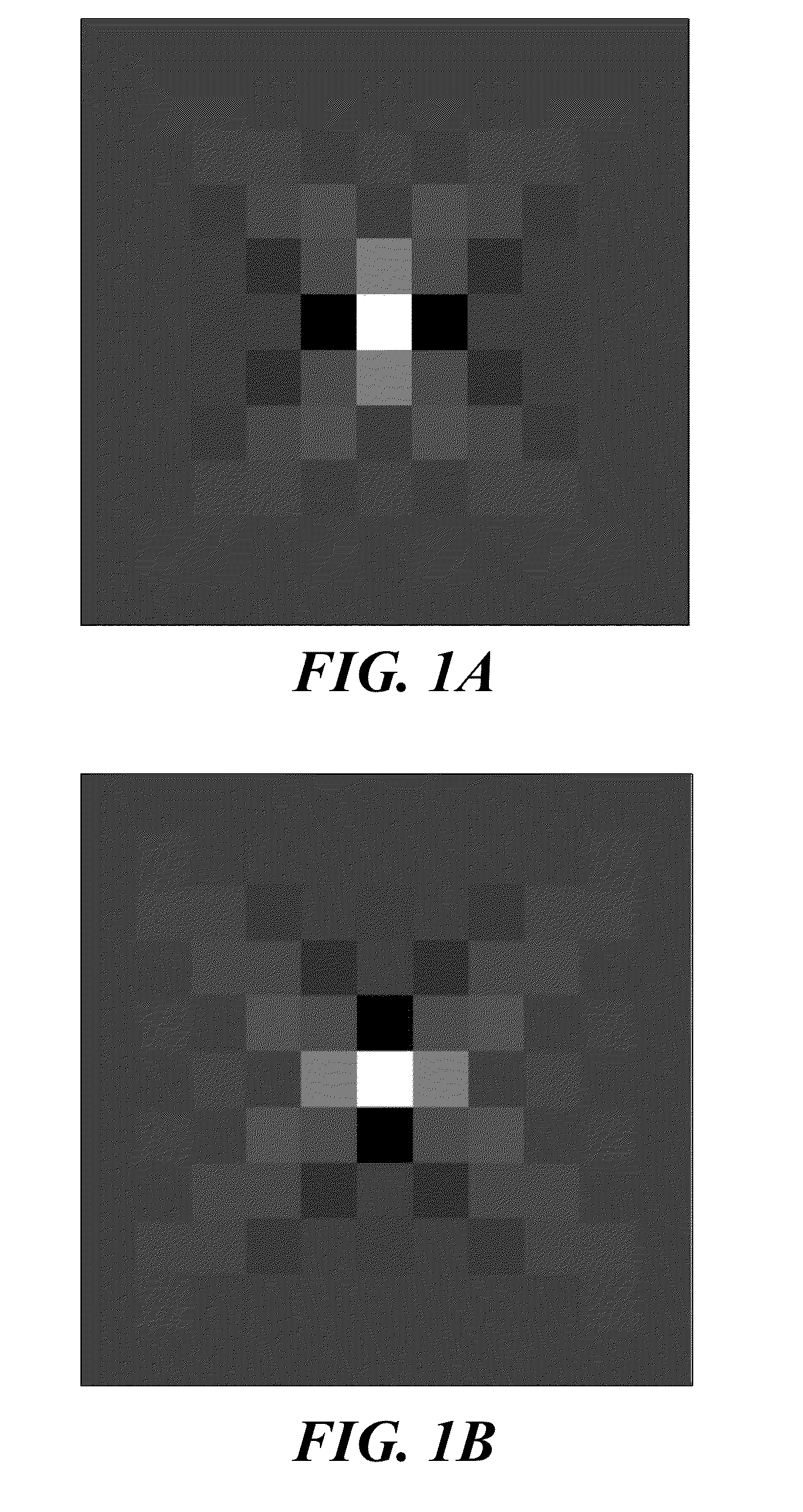
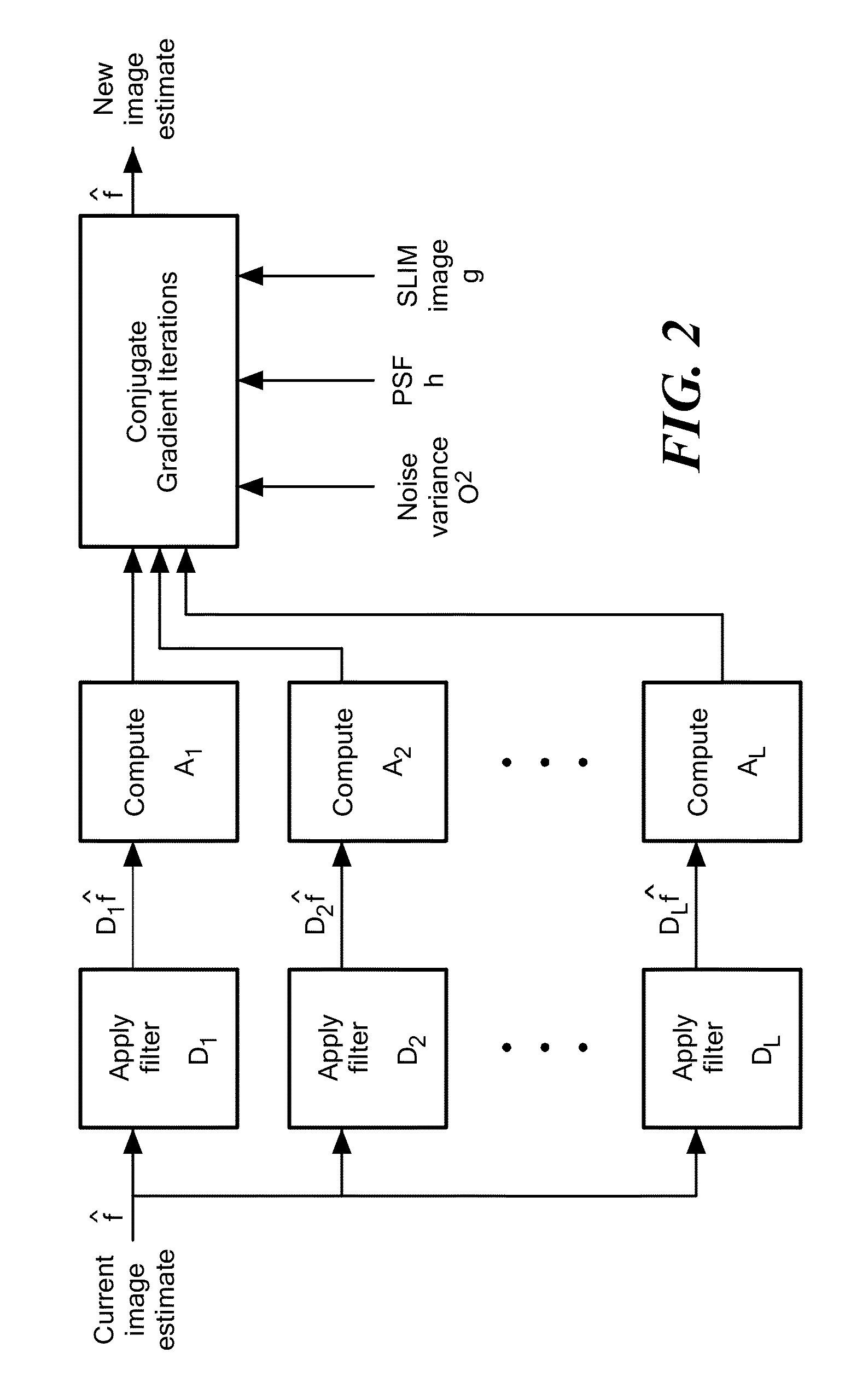
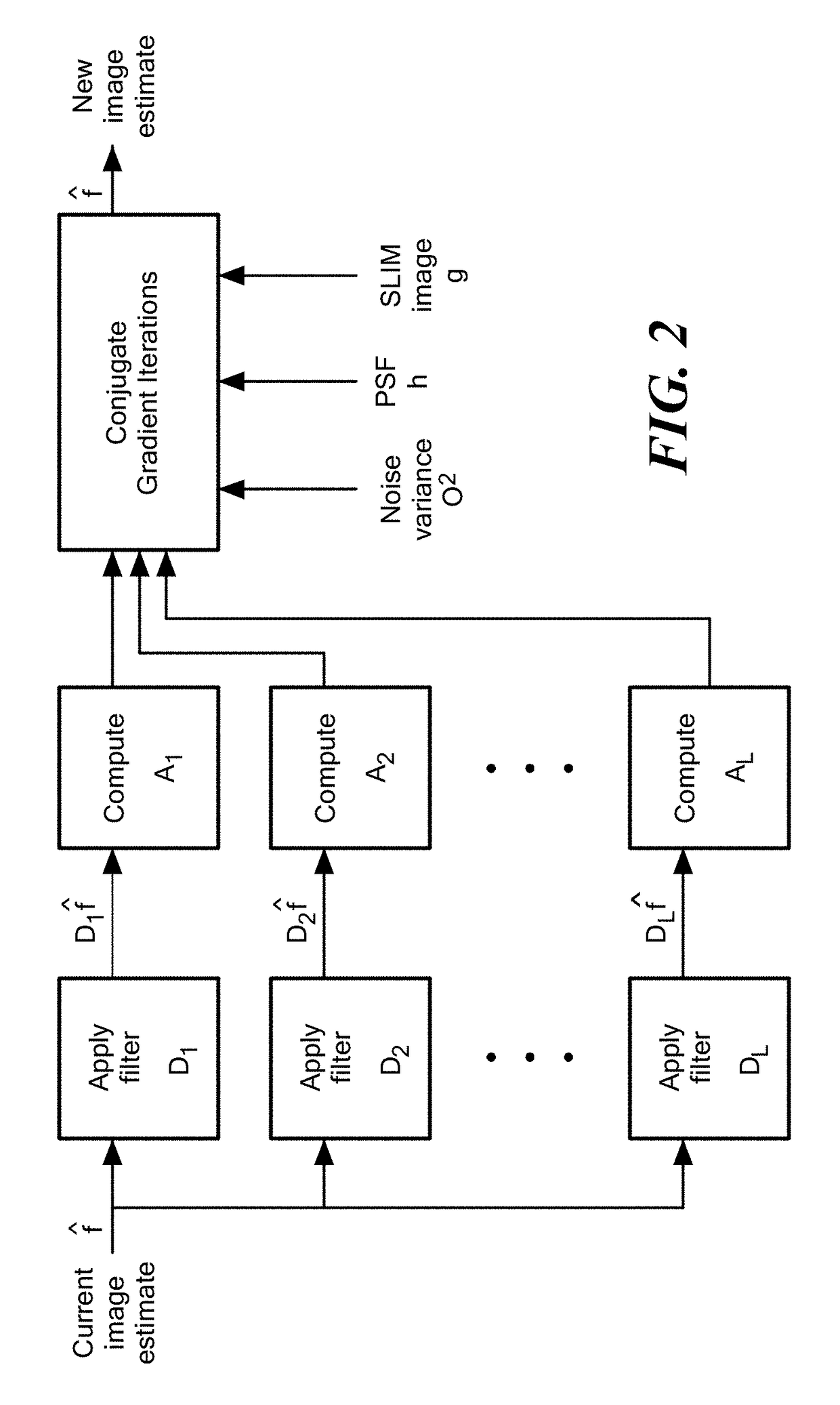
Sparse Deconvolution Spatial Light Microscopy in Two and Three Dimensions
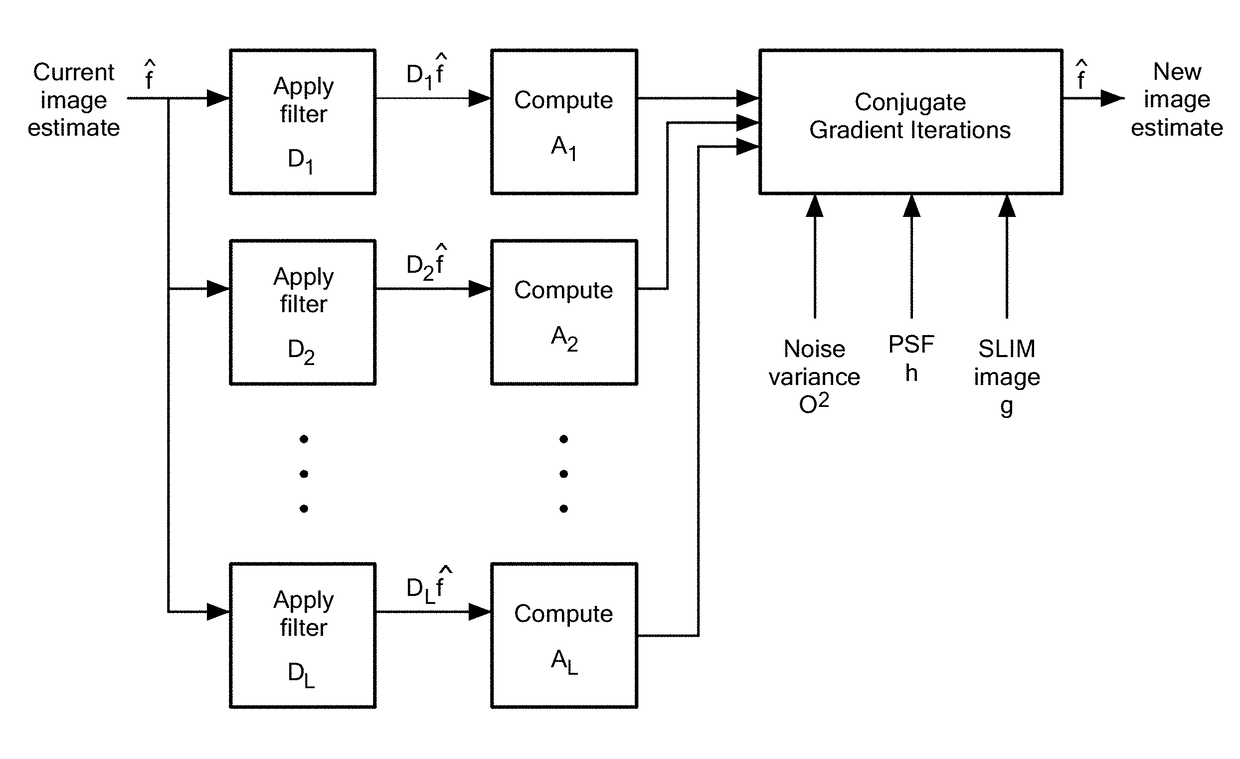
Methods and a computer program product for applying deconvolution to spatial light interference microscopy for resolution enhancement with respect to the diffraction limit in two and three dimensions. By exploiting the sparsity properties of the phase images, which is prominent in many biological imaging applications, and modeling of the image formation via complex fields, the very fine structures can be recovered which were blurred by the optics. The resolution improvement leads to higher accuracy in monitoring dynamic activity over time. Experiments with primary brain cells, i.e. neurons and glial cells, reveal new subdiffraction structures and motions. This new information can be used for studying vesicle transport in neurons, which may shed light on dynamic cell functioning. Finally, the method may flexibly incorporate a wide range of image models for different applications and can be utilized for all imaging modalities acquiring complex field images.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Noninvasive sperm form and ultrastructure analysis method
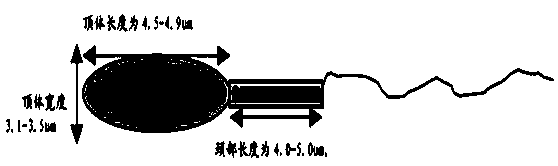
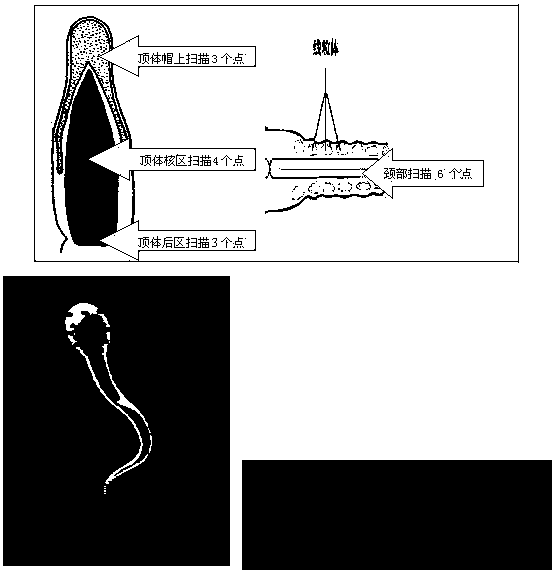
The invention relates to a noninvasive sperm form and ultrastructure analysis method. The method comprises the following steps: analyzing by using a dispersion type confocal Raman spectrometer, selecting an excitation Raman spectrum, placing sperm cells under a reflected light microscopy, and acquiring the chemical group spectrum of the sperm cells through a certain excitation power and a certain exposure time; respectively dividing the acrosome, the neck and the tail of a sperm into scanning areas, scanning three times to obtain a Raman data spectrum peak, and analyzing the waveform change and the displacement of the spectrum peak; and retrieving the acquired sperm form Raman spectrums in an RRUFF Raman database to obtain the Raman spectra of all areas of the sperm form. The laser Raman spectrum adopted in the invention is a noninvasive technology, so the characteristics of the ultrastructures of different individuals and the scattering substances of different components of each sperm can be reflected without any dye or fixation, and a new assessment method is provided for the sperm morphology analysis.
Owner:RENJI HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
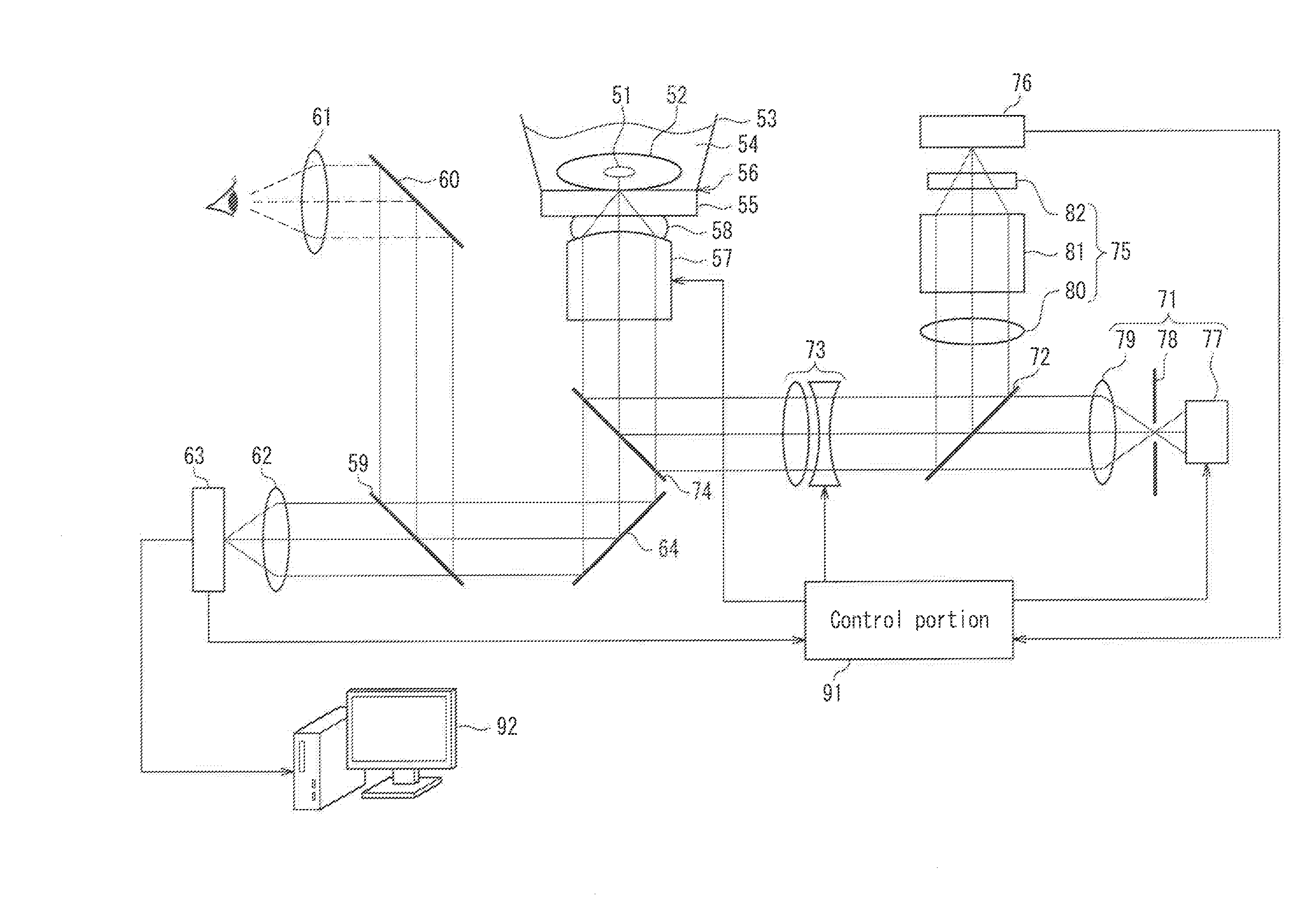
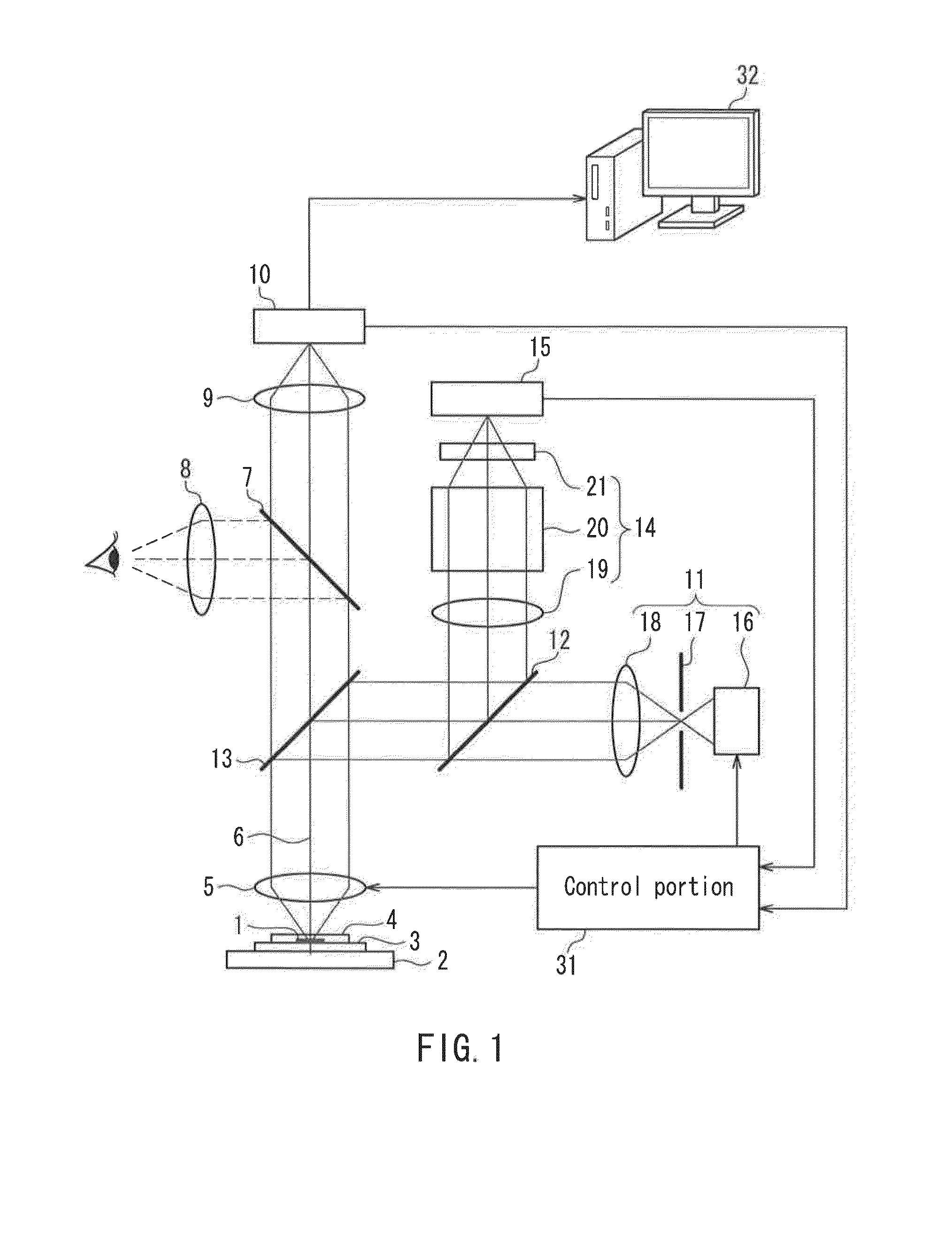
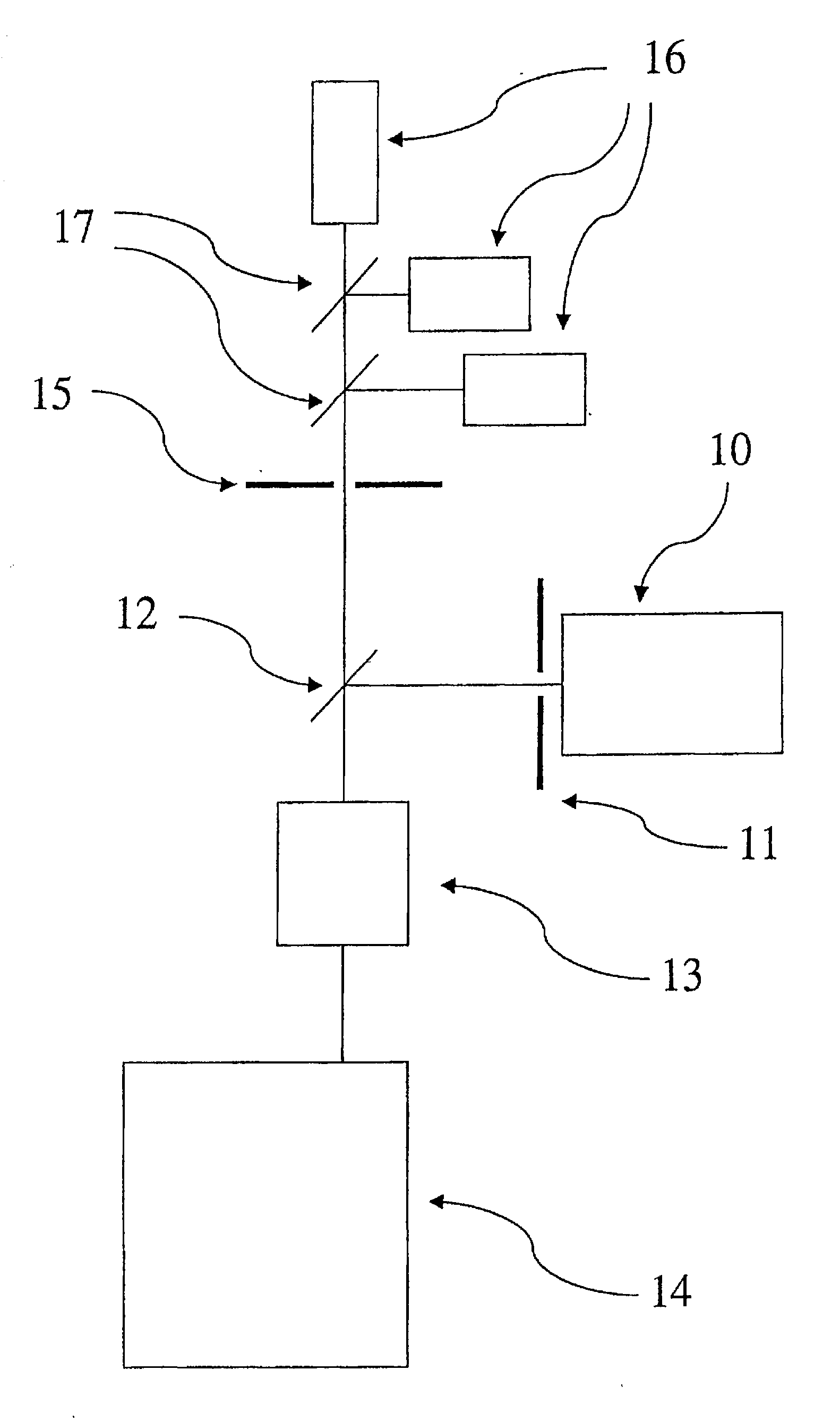
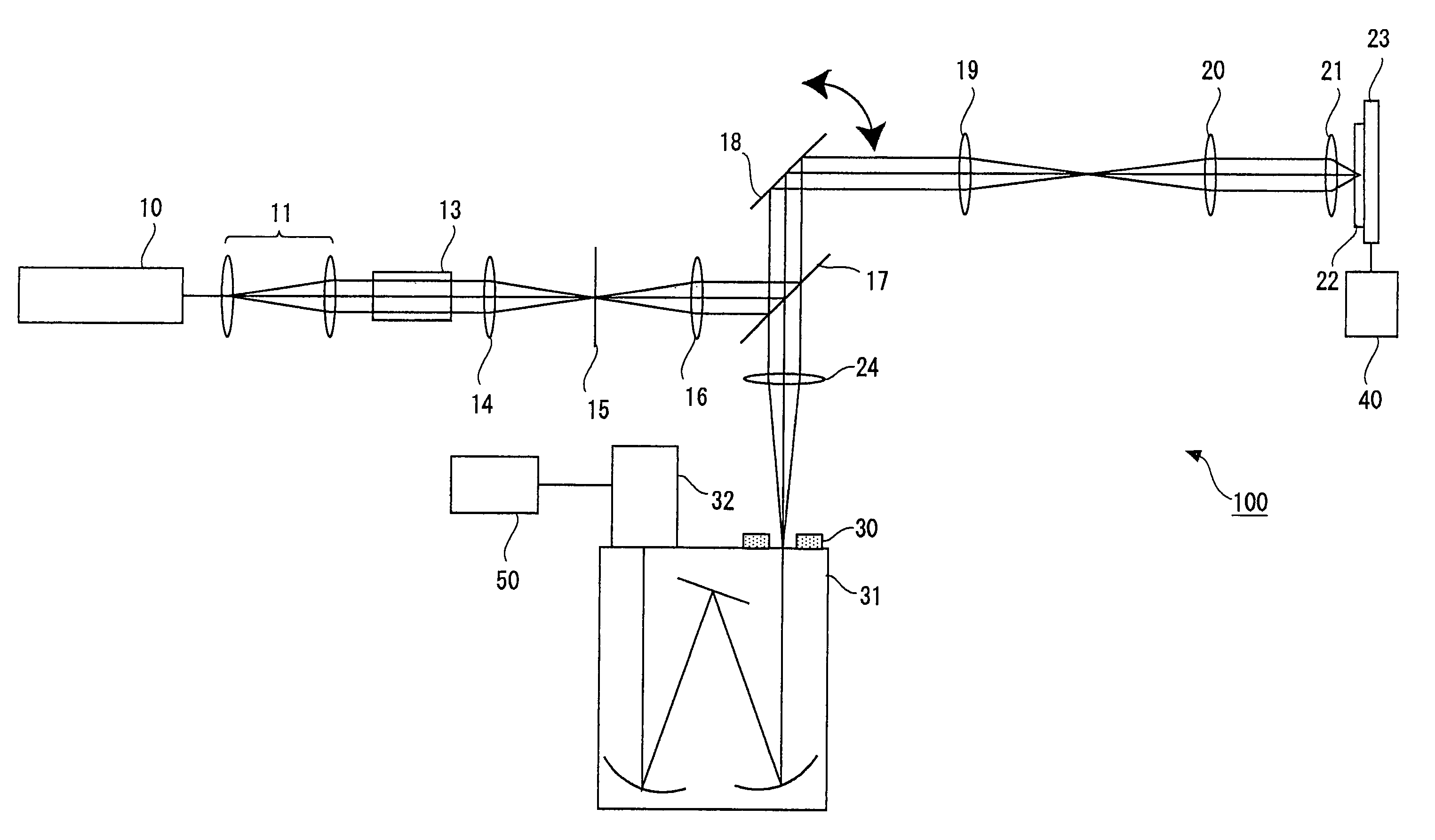
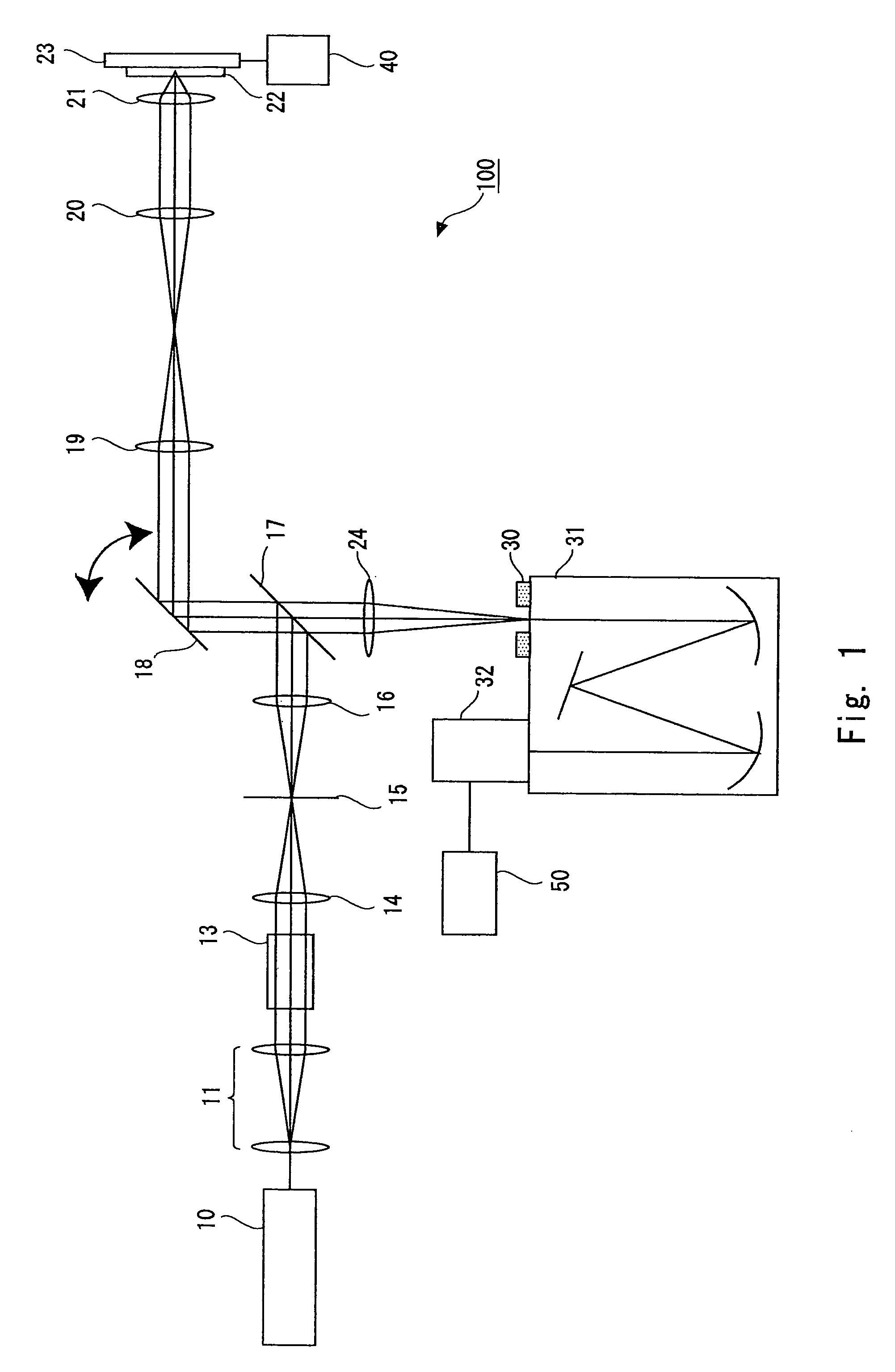
Optical microscope, and autofocus device for optical microscope
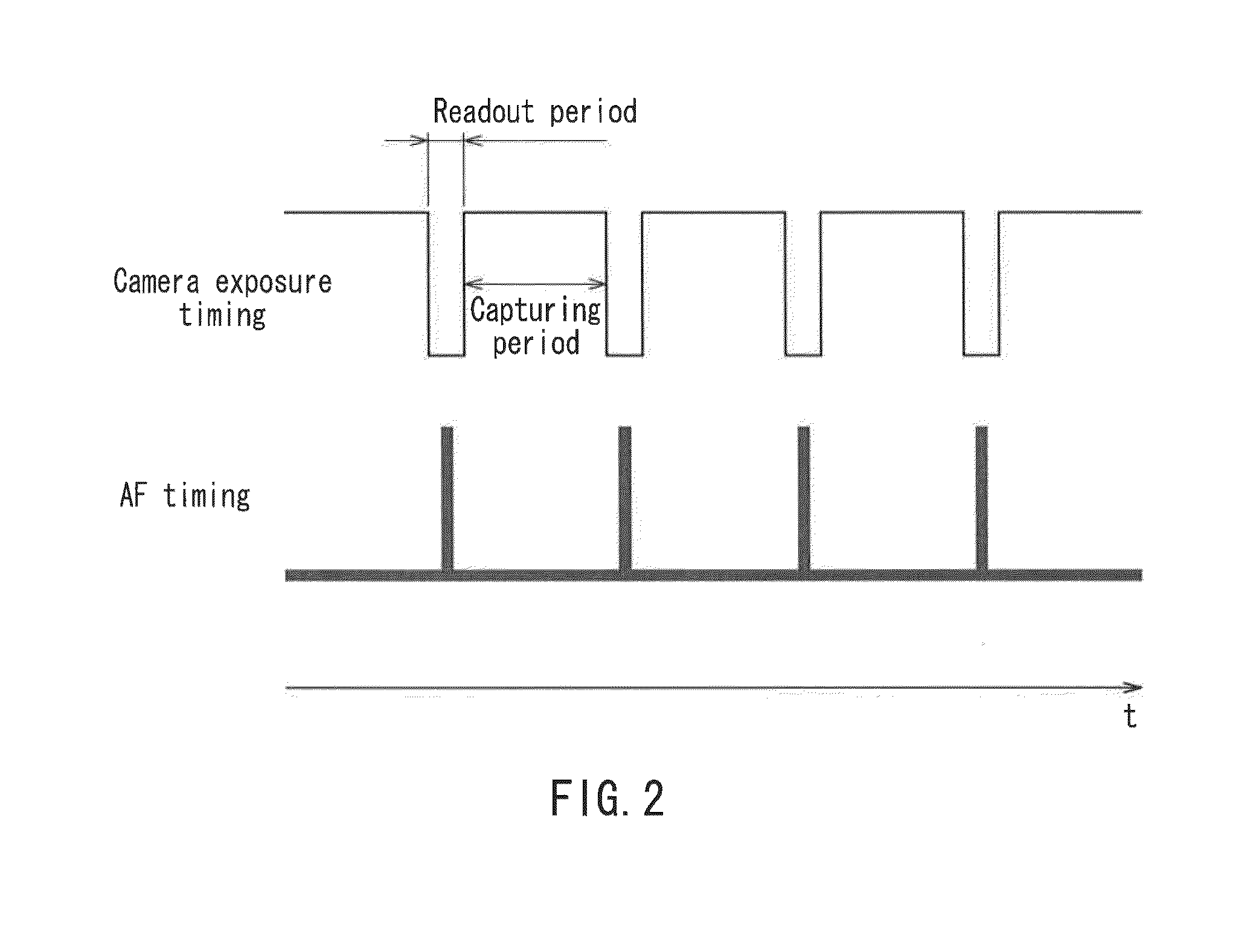
Provided is an optical microscope capable of maintaining an objective lens in a focus state without adversely affecting a captured image even when a substance with a weak emission is used as an observation target object. The optical microscope includes an observation optical system capable of capturing, with an image pickup device (10), an optical image of an observation target object (1) that has been obtained with an objective lens (5), and sending out the optical image as an image signal; and an autofocus device that adjusts a focal position of the objective lens based on autofocus light emitted from a focusing light source (11) so as to focus on the observation target object, wherein the autofocus light is emitted from the focusing light source during a non-capturing period during which the image pickup device is not capturing an image of the observation target object.
Owner:OSAKA UNIV
Interference microscope, and method for operating an interference microscope
The present invention concerns an interference microscope and a method for operating an interference microscope, in particular a 4π microscope, standing wave field microscope, or I2M, I3M, or I5M microscope, at least one specimen support unit associated with the specimen being provided. For determination of the phase position of the interfering light in the specimen region, on the basis of which the interference microscope can be aligned, the interference microscope is characterized in that for determination of the illumination state in the specimen region of the interference microscope, at least one planar area of the specimen support unit is configured to be detectable by light microscopy.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Optical microscope and spectrum measuring method
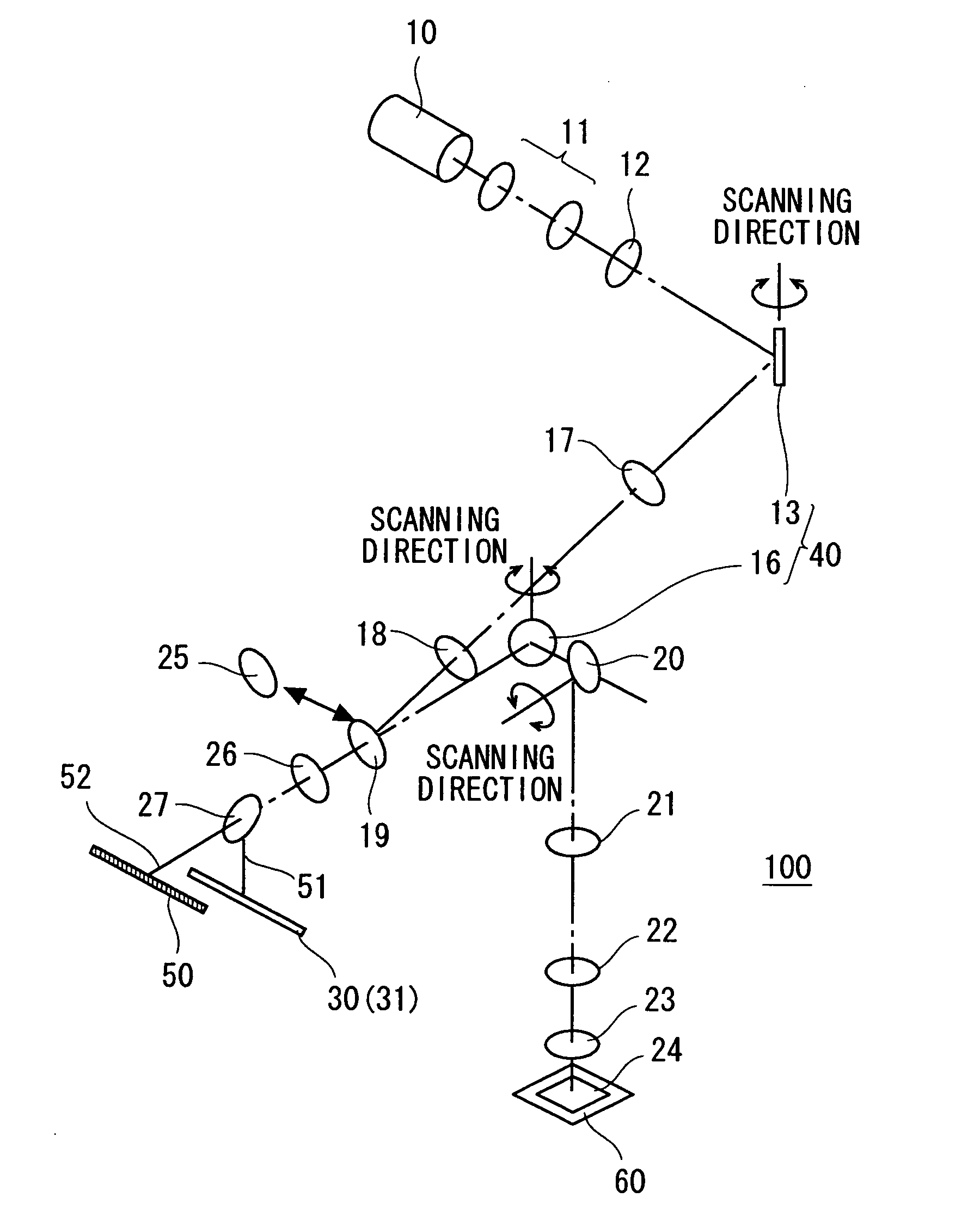
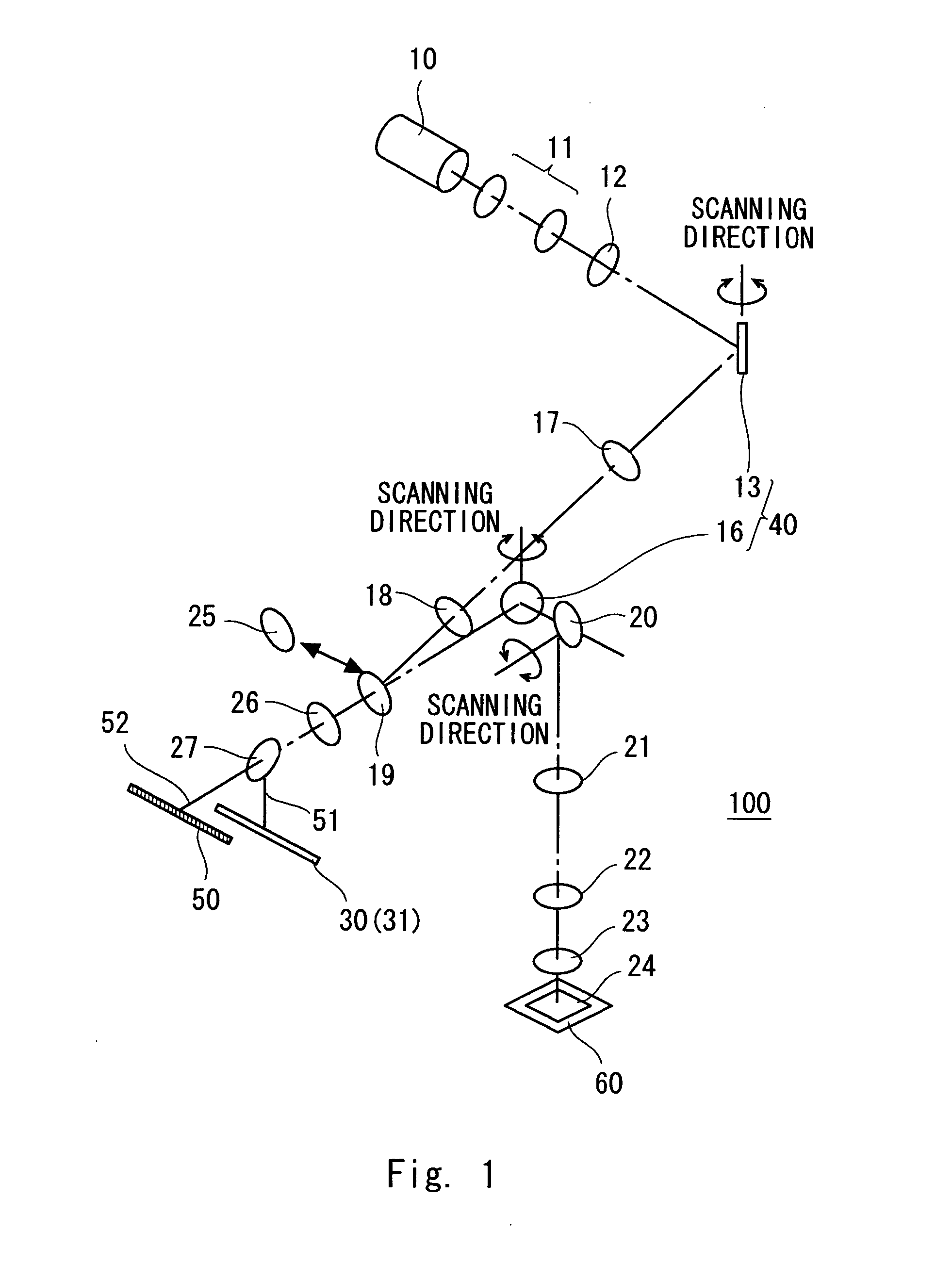
ActiveUS7561265B2High precision measurementUniform scanning speedRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationBeam splitterLight beam
An optical microscope according to a first embodiment of the present invention includes: a laser light source; a Y-directional scanning unit moving the light beam in a Y direction; an objective lens; a X-directional scanning unit moving the light beam in a X direction; a beam splitter provided in an optical path from the Y-directional scanning unit to the sample, and separating outgoing light out of the light beam incident on the sample, which exits from the sample toward the objective lens from the light beam incident on the sample from the laser light source; a spectroscope having an entrance slit extending along the Y direction and spatially dispersing the outgoing light passed through the entrance slit in accordance with a wavelength of the light; and a detector detecting the outgoing light dispersed by the spectroscope.
Owner:NANOPHOTON
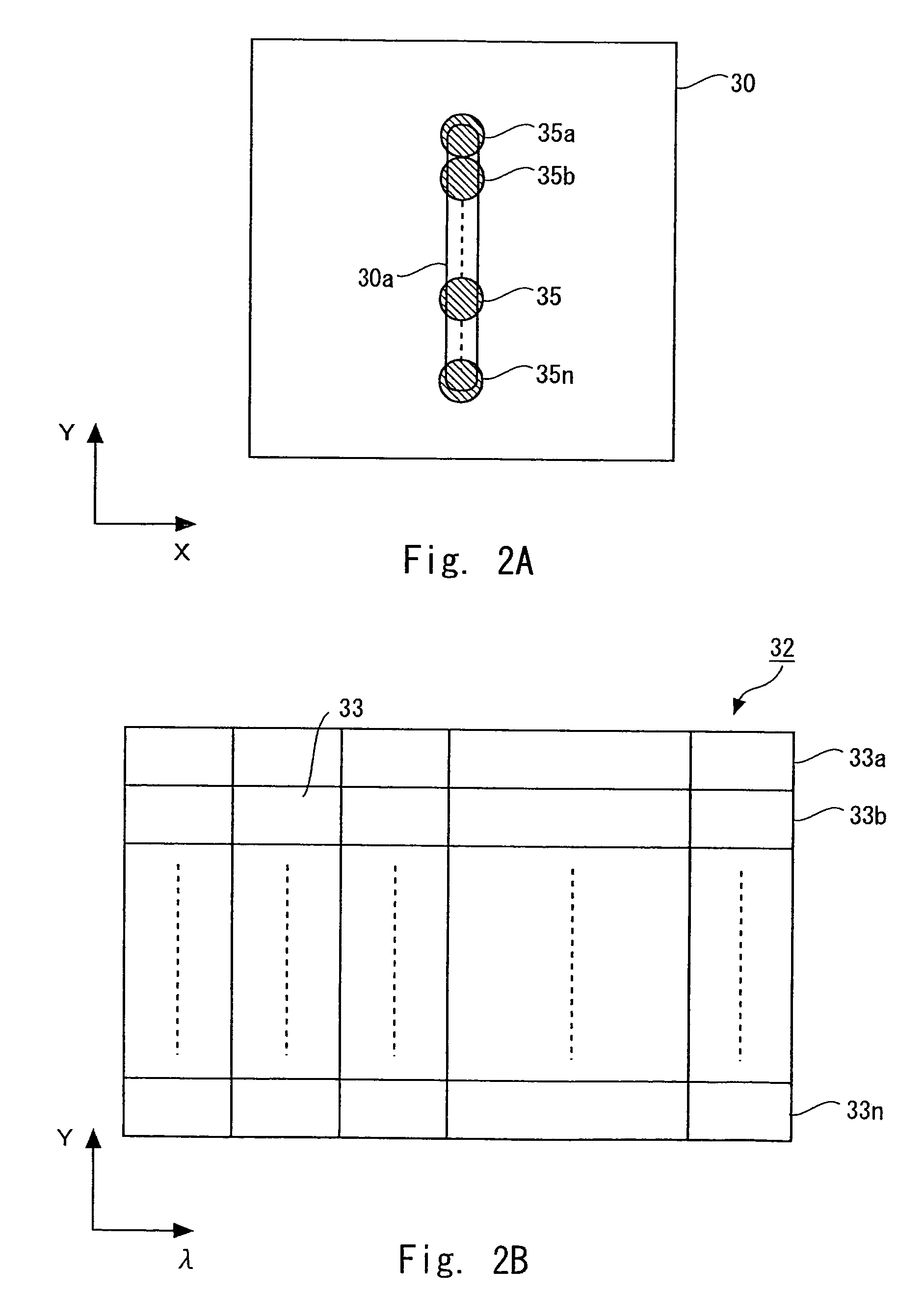
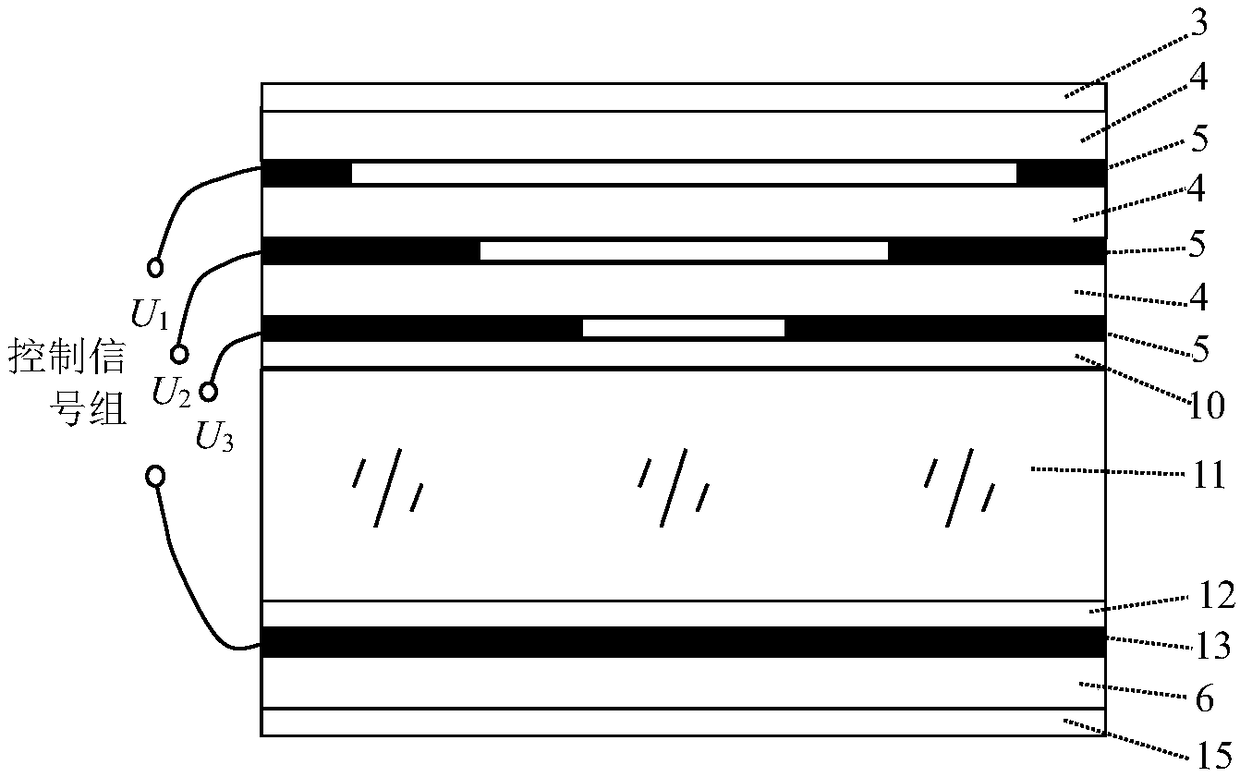
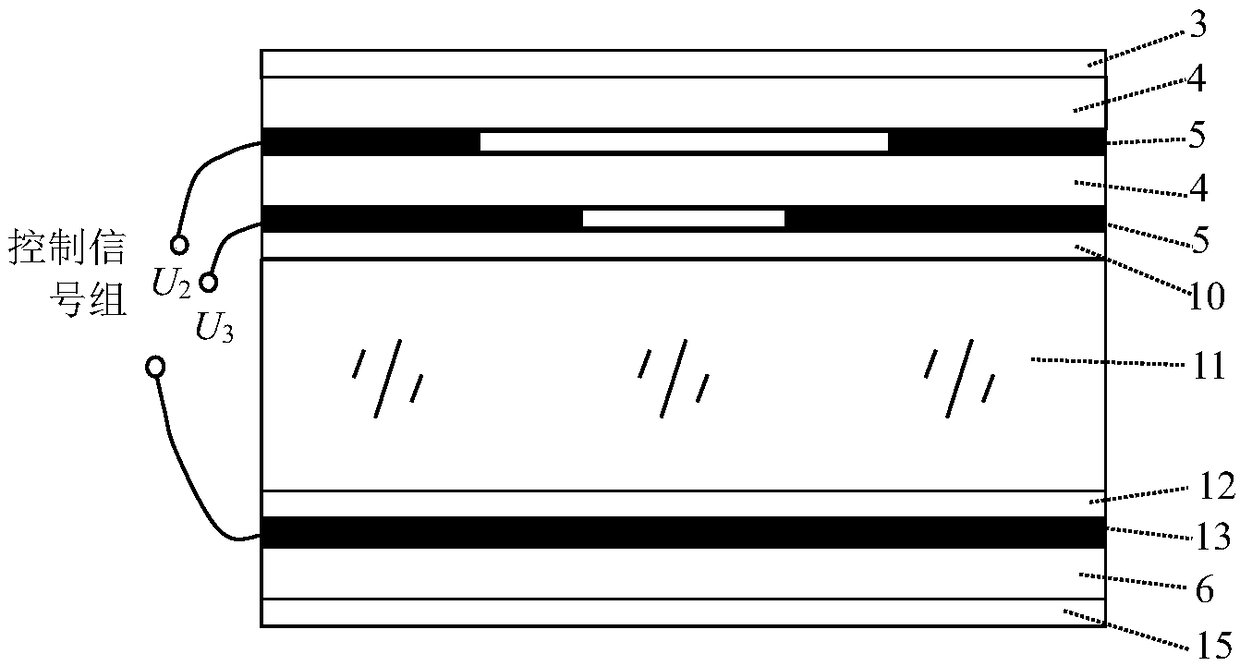
Electric-control liquid crystal objective and ten-thousand-level amplification factor optical microscope utilizing same
ActiveCN108803163AImprove Microscopic Imaging ObservationHigh precision measurementMicroscopesNon-linear opticsElectric controlNanostructure
The invention discloses an electric-control liquid crystal objective and a ten-thousand-level amplification factor optical microscope utilizing the same. The electric-control liquid crystal objectivecomprises a first antireflection film, at least two annular pattern electrodes, at least one first substrate, a first PI orientation layer, a liquid crystal layer, a second PI orientation layer, a public electrode, a second substrate and a second antireflection film which are arranged in parallel, wherein the centers of the annular pattern electrodes are overlapped in the vertical direction, the outer diameters of all the annular pattern electrodes are the same, and the inner diameters of the annular pattern electrodes gradually decrease from top to bottom; the first substrate is arranged between two adjacent annular pattern electrodes; the first PI orientation layer is arranged at the lower part of the lower annular pattern electrode; and the public electrode is arranged between the second PI orientation layer and the second substrate, and the center of the public electrode is overlapped with the centers of the annular pattern electrodes in the vertical direction. According to the electric-control liquid crystal objective, the technical problem that an existing optical microscope has poor microimaging and observing capacities to samples with submicron even nanometer structures oractive biological tissues with strong scattering feature is solved.
Owner:NANJING OPY ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Super-resolution fluorescence fluctuation microscopy imaging method and device and storage medium
InactiveCN108318464AHigh-resolutionReduce the number of probesFluorescence/phosphorescenceImage resolutionComputer science
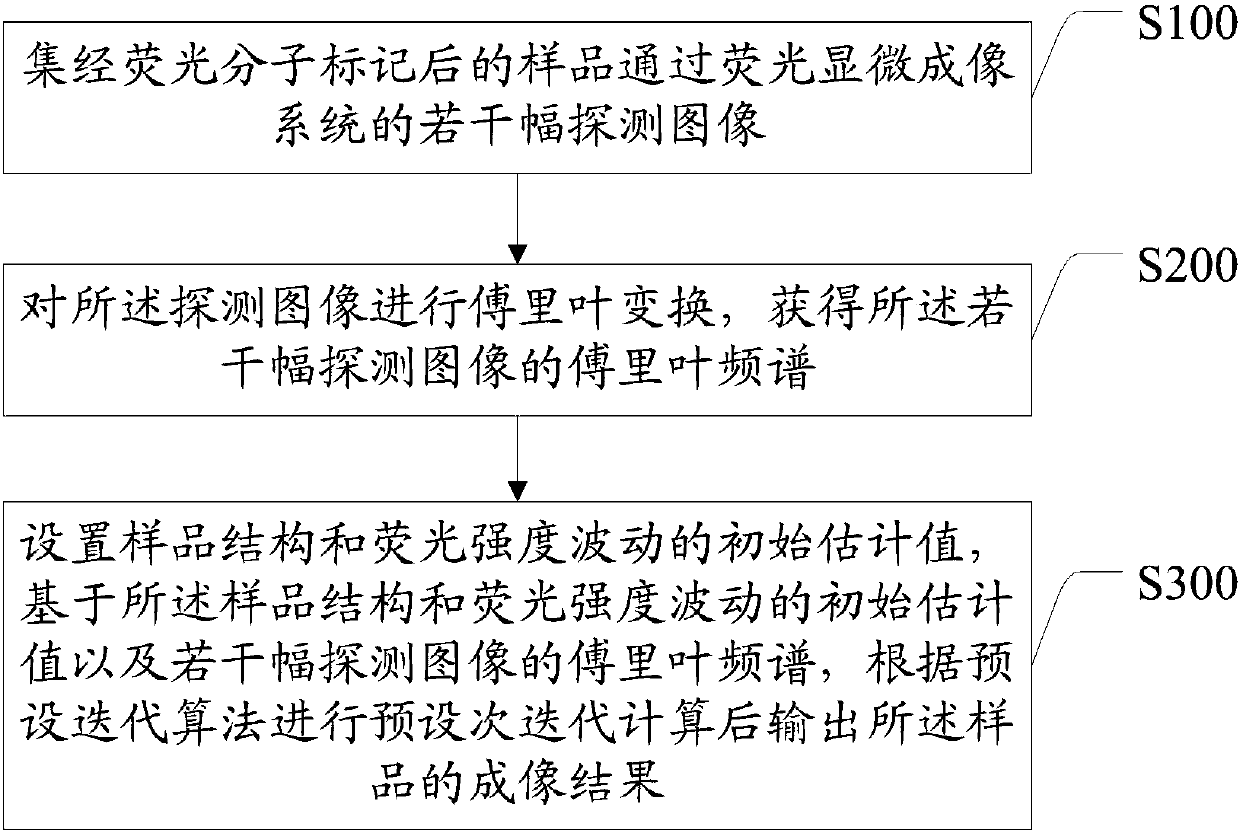
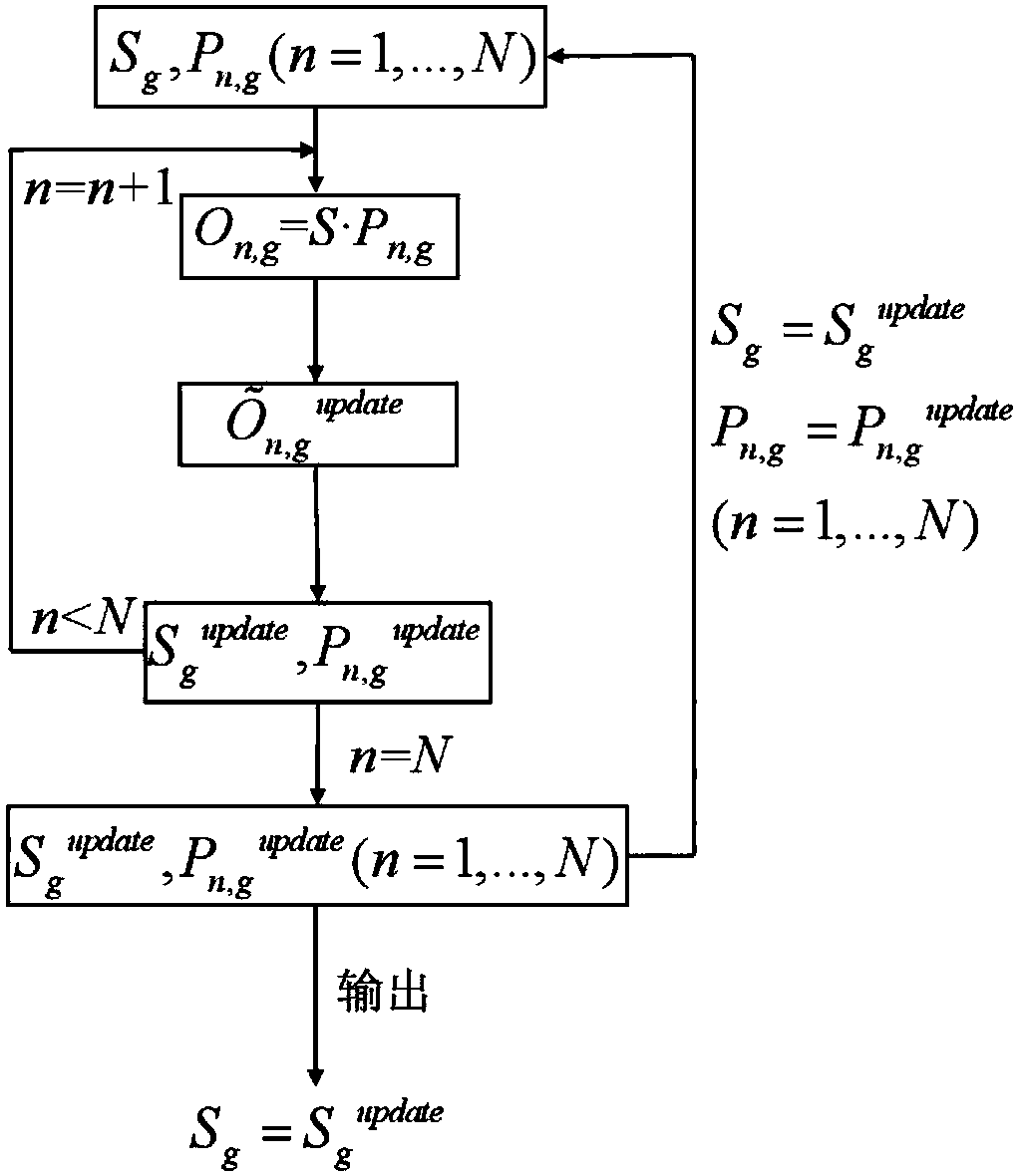
The invention discloses a super-resolution fluorescence fluctuation microscopy imaging method and device and a storage medium. The super-resolution fluorescence fluctuation microscopy imaging method comprises the following steps: acquiring a plurality of detection images of fluorescent molecule labeled samples by virtue of a fluorescence microscopy imaging system; performing Fourier transform on the detection images to obtain Fourier spectrums of the plurality of detection images; setting initial estimated values of sample structures and fluorescence intensity fluctuations, performing iterative computations for preset times according to a preset iterative algorithm based on the initial estimated values of sample structures and fluorescence intensity fluctuations and the plurality of detection images, and outputting imaging results of the samples. Fluorescence blinking intensity changes serve as random speckles needed in ordinary structured light imaging, and the super-resolution imagesare acquired by virtue of the iterative algorithm, so that the structured light does not need to be introduced by an extra experimental device, the resolution ratio of structured light lighting microscopy imaging can be improved under a low detection frequency, and a balance between the resolution ratio and the imaging cost is realized.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Microscope having a reference specimen
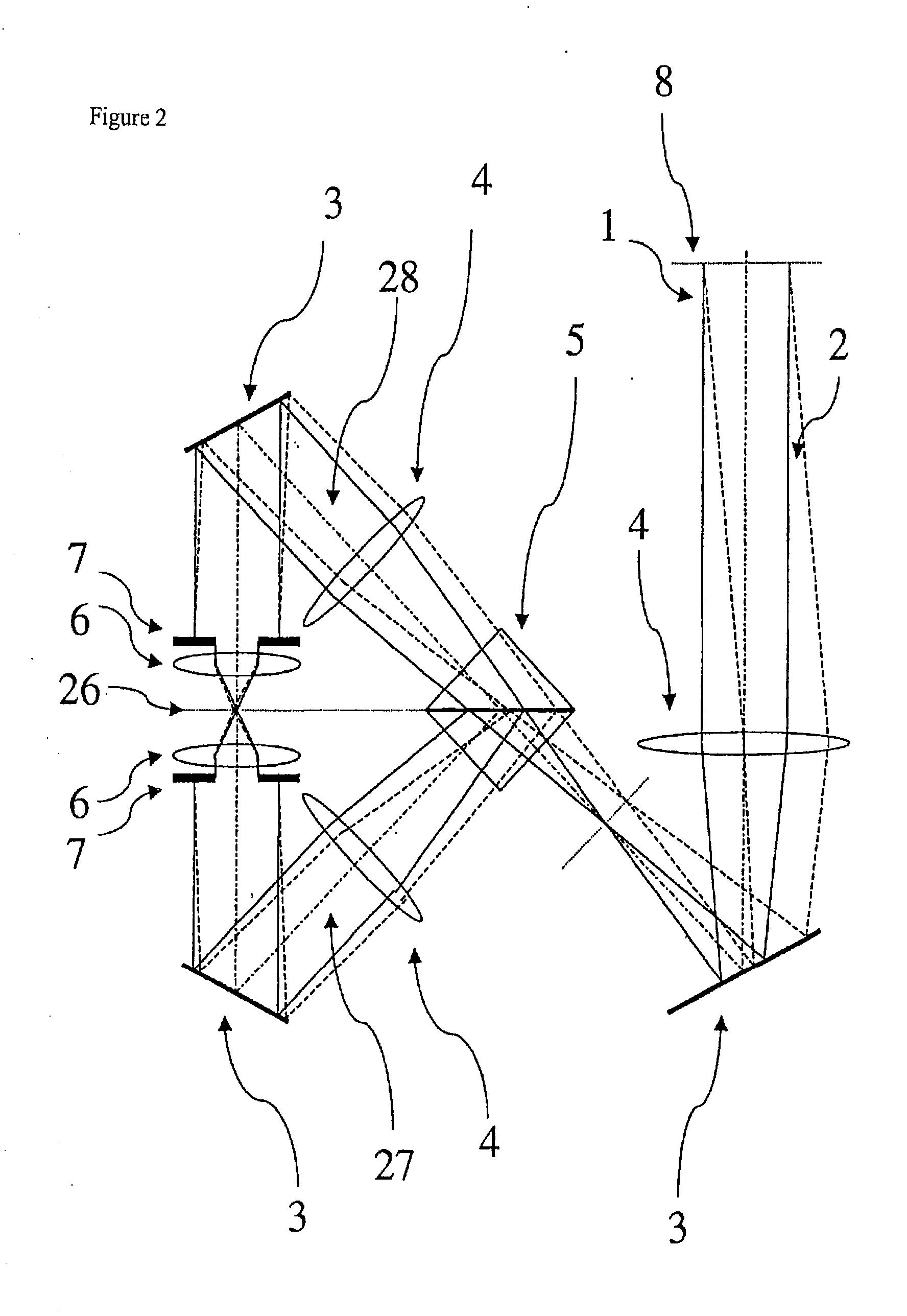
InactiveUS20050078361A1Easily and reliably focusedMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopesConfocal scanning microscopyMicroscope
The present invention concerns a microscope, in particular a confocal or double confocal scanning microscope, as well as a method for operating a microscope, at least one specimen support unit associated with the specimen being provided, at least one reference specimen of known configuration being provided, and the reference specimen being detectable by light microscopy for calibration, alignment or adjustment of the microscope. With the microscope according to the present invention and the method according to the invention for operating a microscope, drift-related changes can be detected and compensated for. Auxiliary means with which a specimen can easily and reliably be focused are also provided.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Optical microscope with modifiable lighting and operating process of such a microscope
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
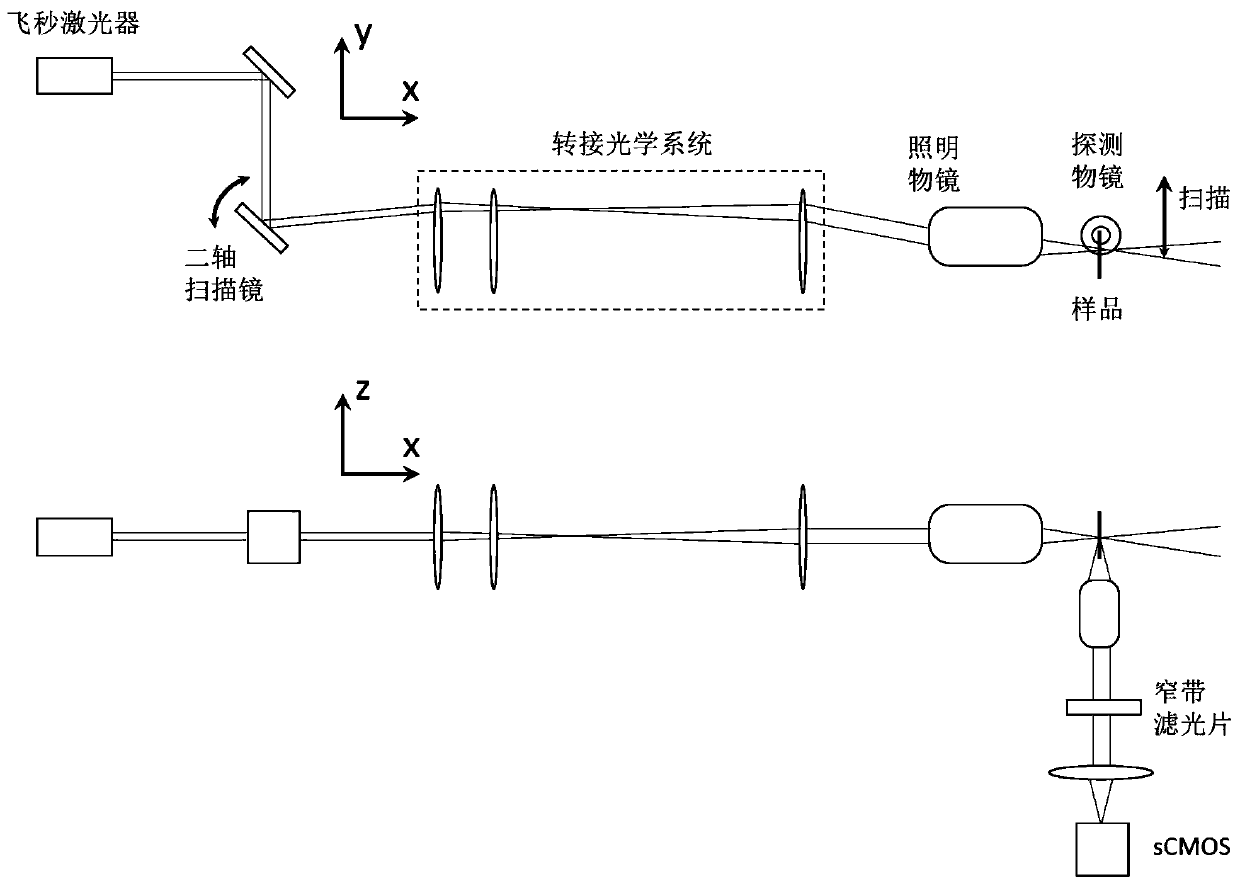
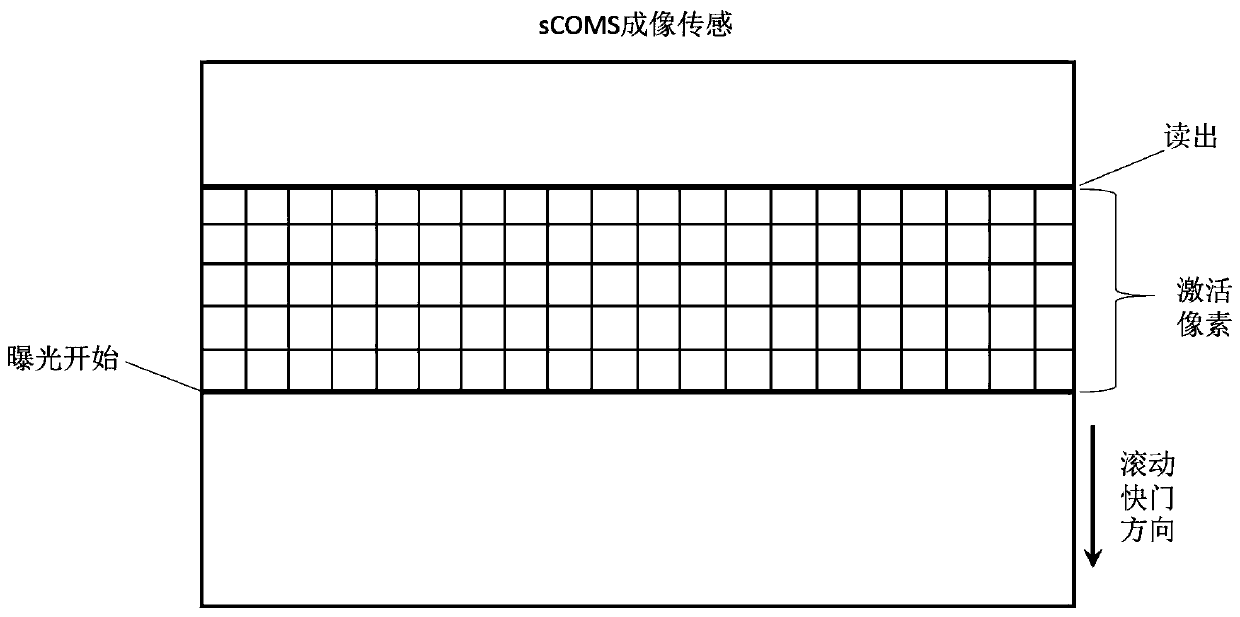
Harmonic microscopic measurement method based on sheet-light microscopy and confocal slit detection
ActiveCN109884053AIncrease speedIncrease contrastMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopic imageHigh frame rate
The invention discloses a harmonic microscopic measurement method based on sheet-light microscopy and confocal slit detection, and belongs to the field of non-linear optical measurement. In the harmonic microscopy measurement, the detection direction of a harmonic signal is perpendicular to the illumination direction of a sample, so that sheet-light measurement in harmonic microscopy is achieved.Confocal slit detection is achieved by using sCMOS as a detector and a rolling shutter working mode. A femtosecond laser pulse is reflected by a scanning galvanometer, then enters a switching opticalsystem for spherical aberration compensation, and is converged in the sample by a microscopic objective to form an excitation focusing light -spot needed by harmonic signal generation. The harmonic signal excited by the sample is collected by a detecting objective perpendicular to the illumination direction, and then passes through a spike filter to filter stray light, and is received for detection by the sCMOS working in a rolling shutter mode. The scanning process and rolling shutter docking are synchronic, and harmonic images with different position pixels are compounded by algorithms. According to the harmonic microscopic measurement method, the contrast ratio and the signal-to-noise ratio of harmonic microscopic imaging can be effectively increased, and harmonic microscopic imaging with the high frame rate is achieved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
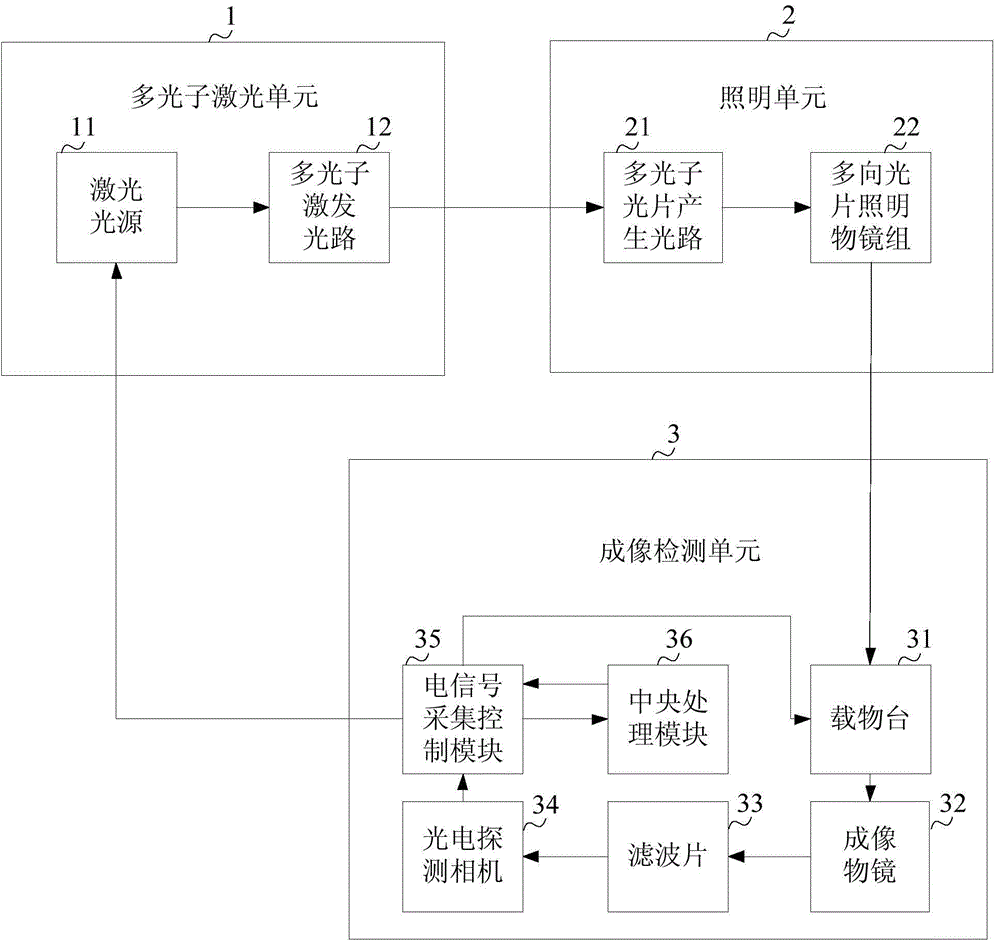
Multi-photon excited multidirectional lighting microscopy imaging system
InactiveCN104677872ARealize dynamic imagingFast imagingFluorescence/phosphorescenceRapid imagingFluorescence
The invention discloses a multi-photon excited multidirectional lighting microscopy imaging system. From front to back, the microscopy imaging system comprises a multi-photon laser unit, a lighting unit and an imaging detection unit which are sequentially arranged on a fluorescent light path of the imaging system, wherein the multi-photon laser unit is used for generating and modulating laser and for transmitting the modulated laser to the lighting unit; the lighting unit is used for receiving the modulated laser, generating multidirectional light sheet illumination and exciting a to-be-detected sample to generate fluorescent light; and the imaging detection unit is used for detecting the fluorescent light generated from the to-be-detected sample and converting the fluorescent light into a digital image. The multi-photon excited multidirectional lighting microscopy imaging system disclosed by the invention can image rapidly, so as to image for the dynamic development of living organisms or record neuronal activities.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods for identifying biological material by microscopy
The present invention relates generally to the field of computer-based image recognition. More particularly, the invention relates to methods and systems for the identification, and optionally the quantitation of, discrete objects of biological origin such as cells, cytoplasmic structures, parasites, parasite ova, and the like which are typically the subject of microscopic analysis. The inventionmay be embodied in the form of a method for training a computer to identify a target biological material in a sample. The method may include accessing a plurality of training images, the training images being obtained by light microscopy of one or more samples containing a target biological material and optionally a non-target biological material. The training images are cropped by a human or a computer to produce cropped images, each of which shows predominantly the target biological material. A human then identifies the target biological material in each of the cropped images where identification is possible, and associating an identification label with each of the cropped images where identification was possible. A computer-implemented feature extraction method is then applied to each labelled cropped image. A computer-implemented learning method is then applied to each labelled cropped image to associate extracted features of a biological material with a target biological material.
Owner:ヴァーディクトホールディングスプロプライエタリーリミテッド
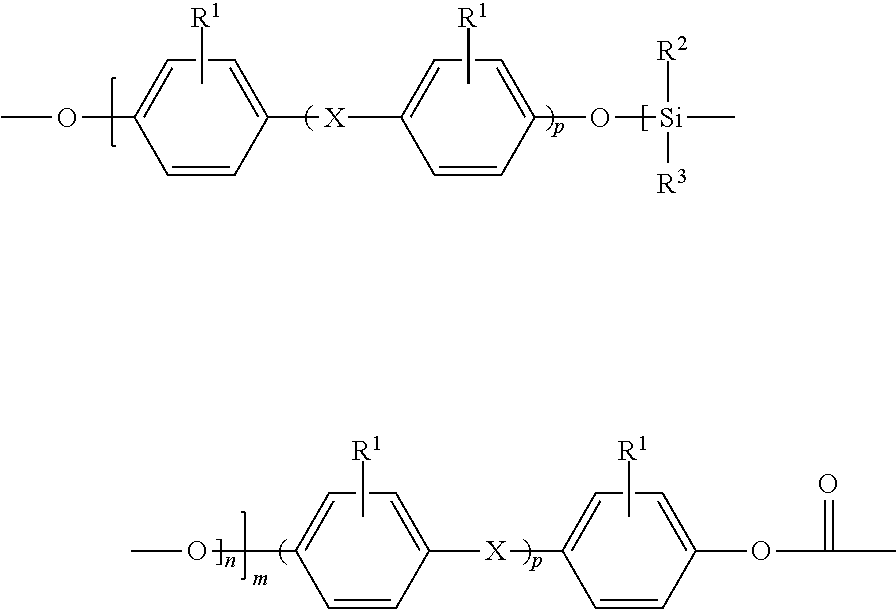
Polysiloxane-polycarbonate block cocondensates with improved rheological properties
The present invention relates to polysiloxane-polycarbonate block cocondensates derived from a continuous melt transesterification process comprising polysiloxane blocks of the formula (1)and polycarbonate blocks having recurring units of the formula (2)having improved rheological properties and good mechanical properties as well as to mouldings and extrudates made from these polysiloxane-polycarbonate block cocondensates and wherein the polysiloxane-polycarbonate block cocondensate has a siloxane domain distribution (diameter of siloxane domains) from 200 nm to 1 μm measured by atomic force microscopy and light microscopy which is in the range of 0.01%-2.5%, based on the total number of siloxane domains.
Owner:COVESTRO DEUTSCHLAND AG
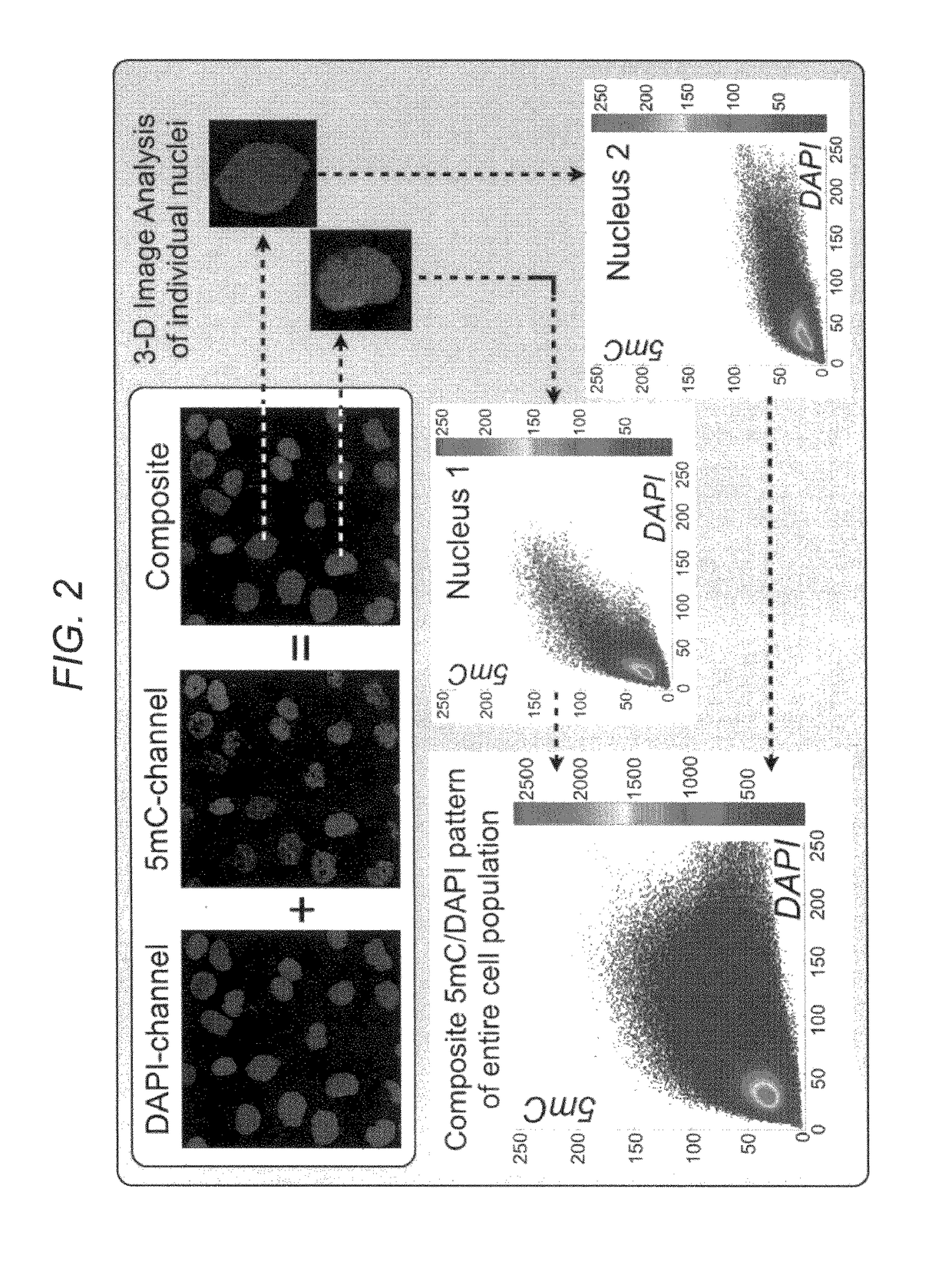
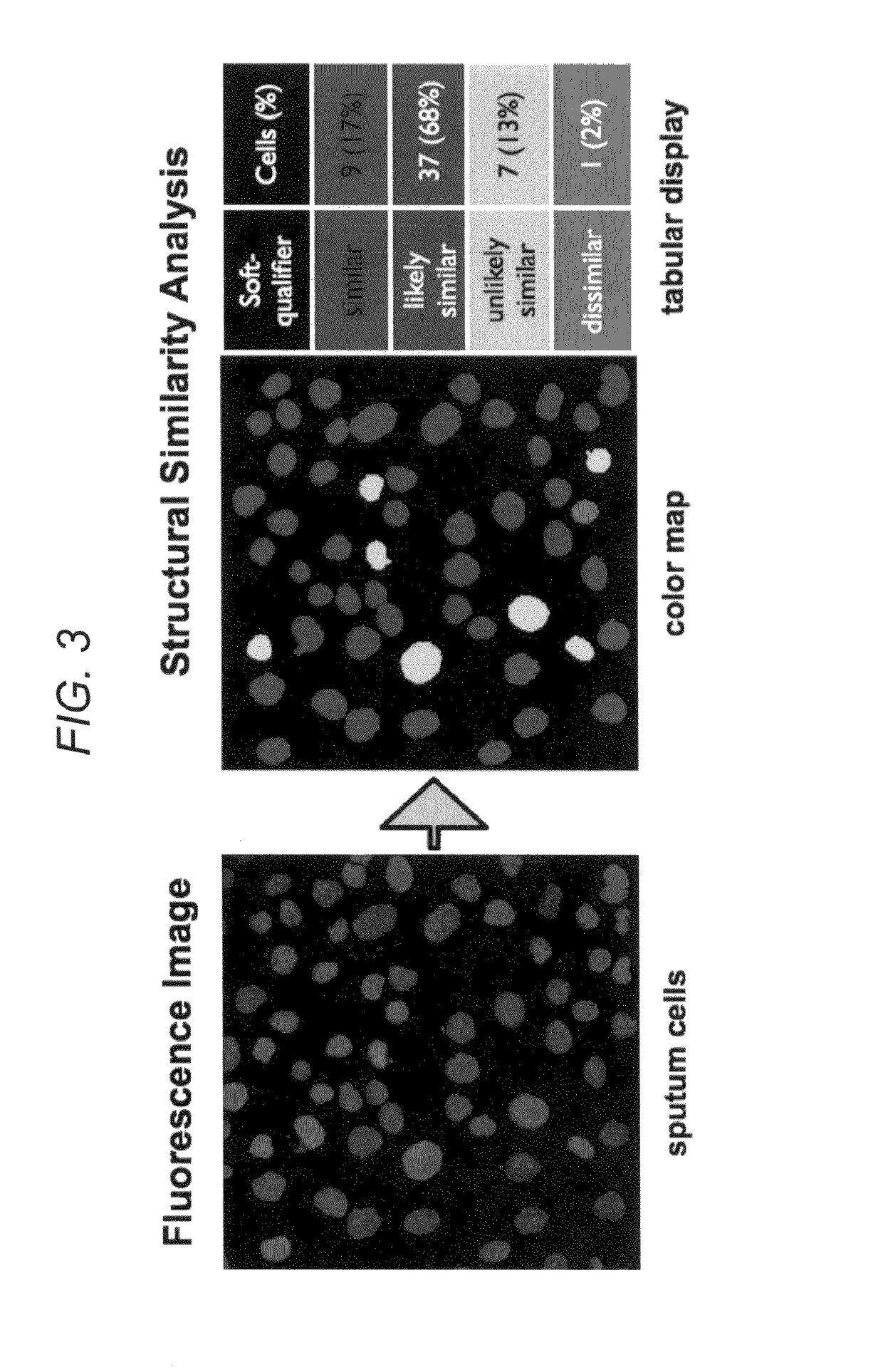
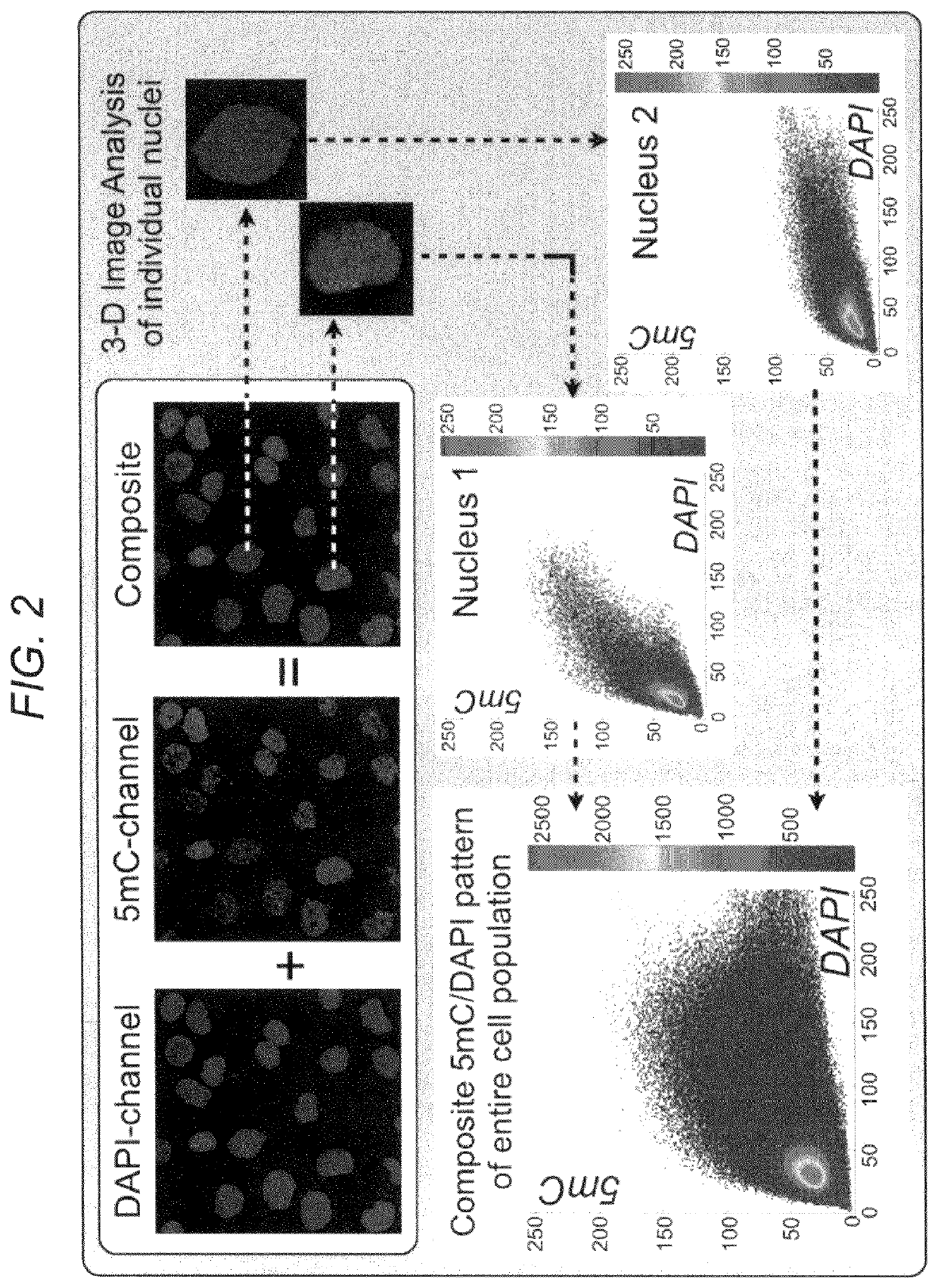
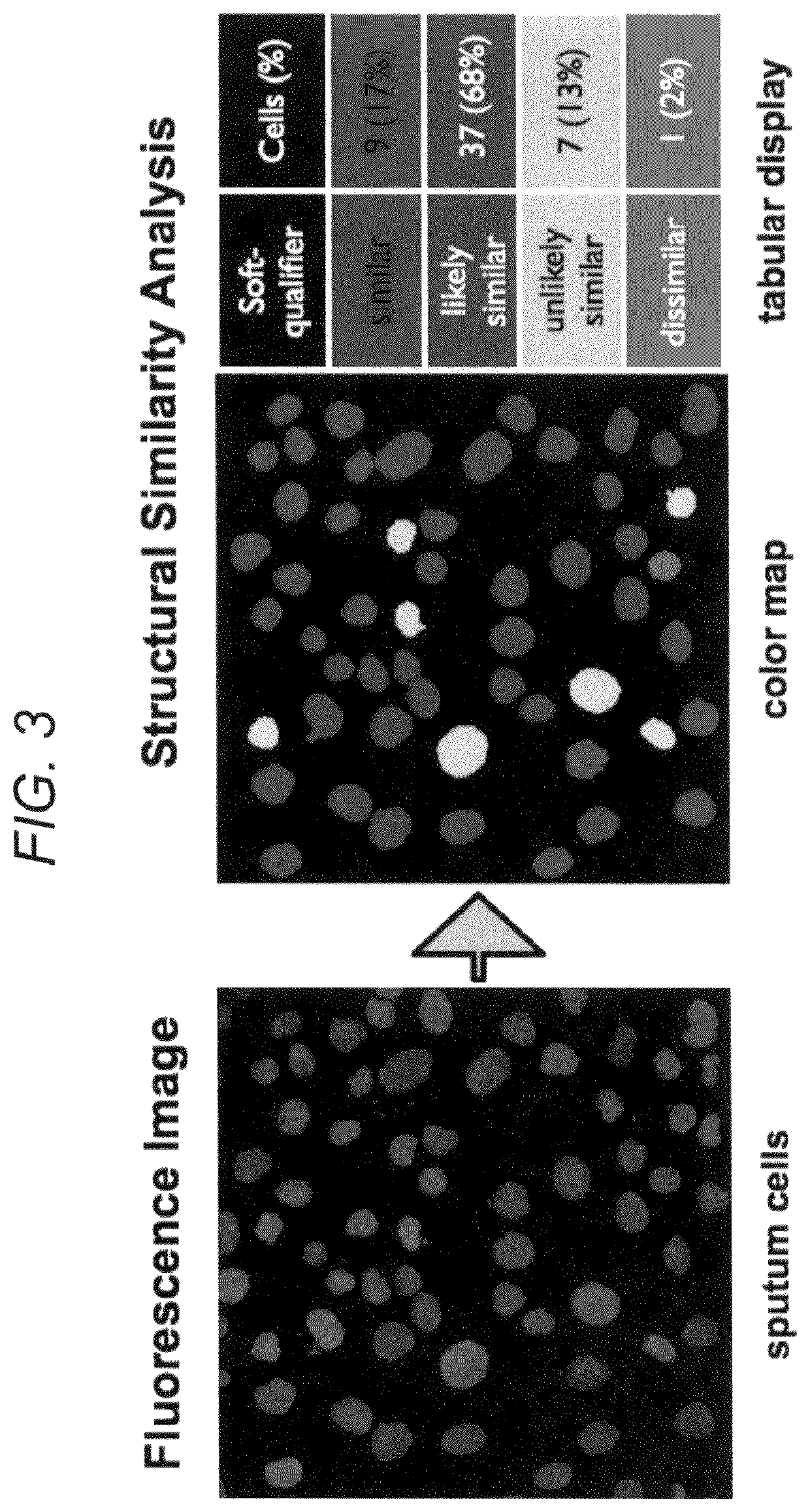
Early lung cancer detection by DNA methylation phenotyping of sputum-derived cells
ActiveUS20170283881A1Reduced feature requirementsMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationDNA methylationStaining
In certain embodiments, this application discloses methods for detecting lung cancer. The method includes characterization of cells extracted from human sputum, which is a valuable tissue surrogate and source of upper respiratory cells that become cancerous early in 5 the process of lung cancer development. The method includes the staining of extracted cells with fluorescent reporters that produce a specific pattern in the nuclei of labeled cells, which can be made visible by light microscopy. The pattern is relevant to a type of epigenetic coding of DNA known as DNA methylation, which changes in specific cells of the lung during cancer development, in comparison to normal respiratory cells.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT +2
Early lung cancer detection by DNA methylation phenotyping of sputum-derived cells
ActiveUS10961587B2Reduced feature requirementsMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationStainingEpigenetic Profile
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT +2
Free floating cryostat sections for use in light and electron microscopy and method
InactiveUS6555334B2Bridging the gapEase of progressive processingPreparing sample for investigationDead animal preservationTissue sampleElectron microscope
A method is described of viewing a single tissue sample with a light microscope and an electron microscope. A tissue sample is cryopreserved, cryo sectioned and then floated in a cryoprotectant solution on a surface of a glass slide or in a well and is viewed by light microscopy. The step of floating the tissue sample does not destroy said tissue sample for subsequent electron microscope viewing. The same tissue sample is then prepared by conventional ultrastructural processing for viewing by electron microscopy. The data from the light microscope and electron microscope images of selected sites of the same tissue sample can be compared and analyzed.
Owner:GOVERNMENT OF THE U S AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY U S MEDICAL RES & MATERIEL COMMAND THE
Sparse deconvolution spatial light microscopy in two and three dimensions
Methods and a computer program product for applying deconvolution to spatial light interference microscopy for resolution enhancement with respect to the diffraction limit in two and three dimensions. By exploiting the sparsity properties of the phase images, which is prominent in many biological imaging applications, and modeling of the image formation via complex fields, the very fine structures can be recovered which were blurred by the optics. The resolution improvement leads to higher accuracy in monitoring dynamic activity over time. Experiments with primary brain cells, i.e. neurons and glial cells, reveal new subdiffraction structures and motions. This new information can be used for studying vesicle transport in neurons, which may shed light on dynamic cell functioning. Finally, the method may flexibly incorporate a wide range of image models for different applications and can be utilized for all imaging modalities acquiring complex field images.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Light microscope with novel digital method to achieve super-resolution
Owner:WAVEFRONT ANALYSIS
Marker for fenestrae
InactiveUS20070141637A1Less ambiguousMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingMoesinBiology
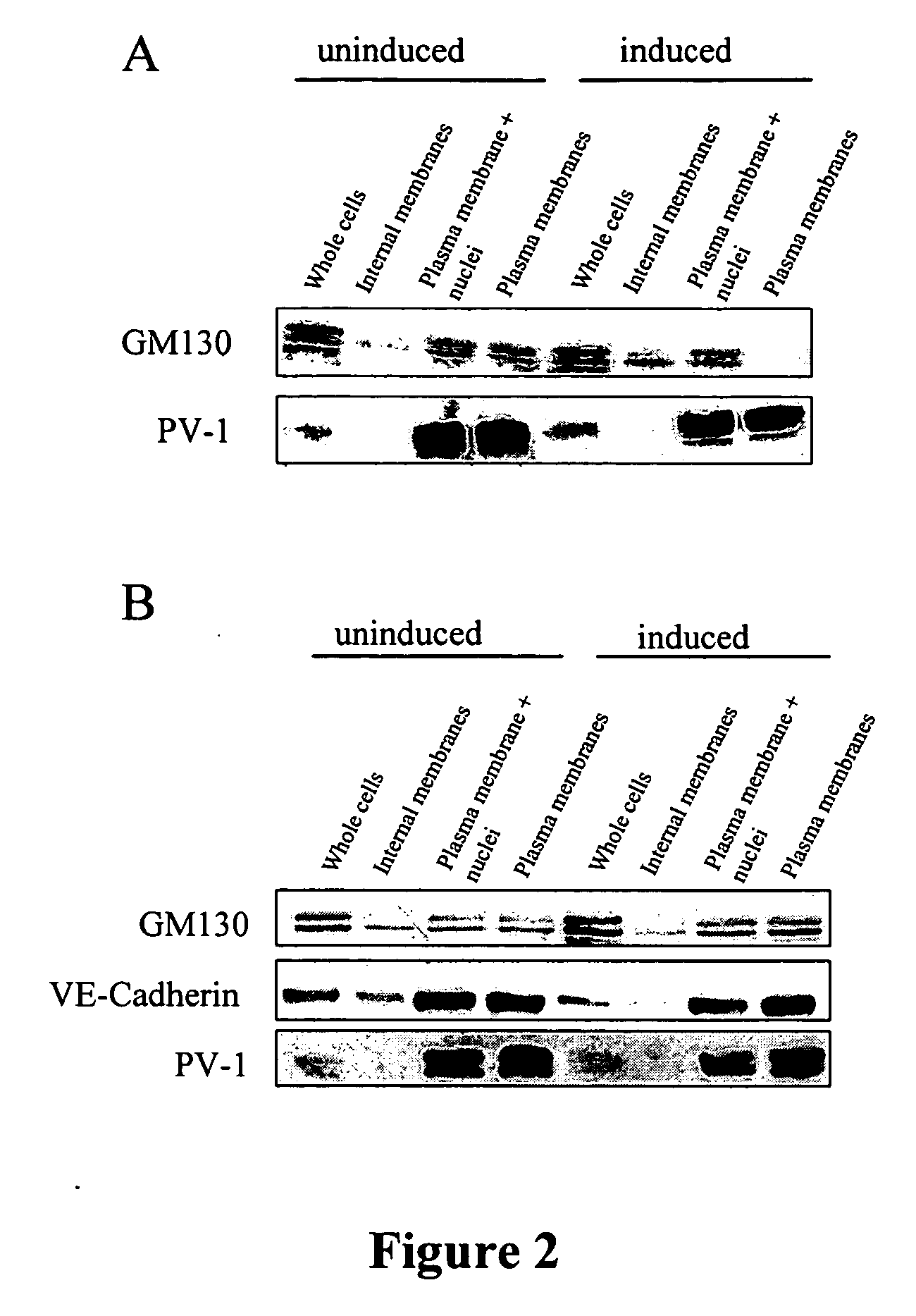
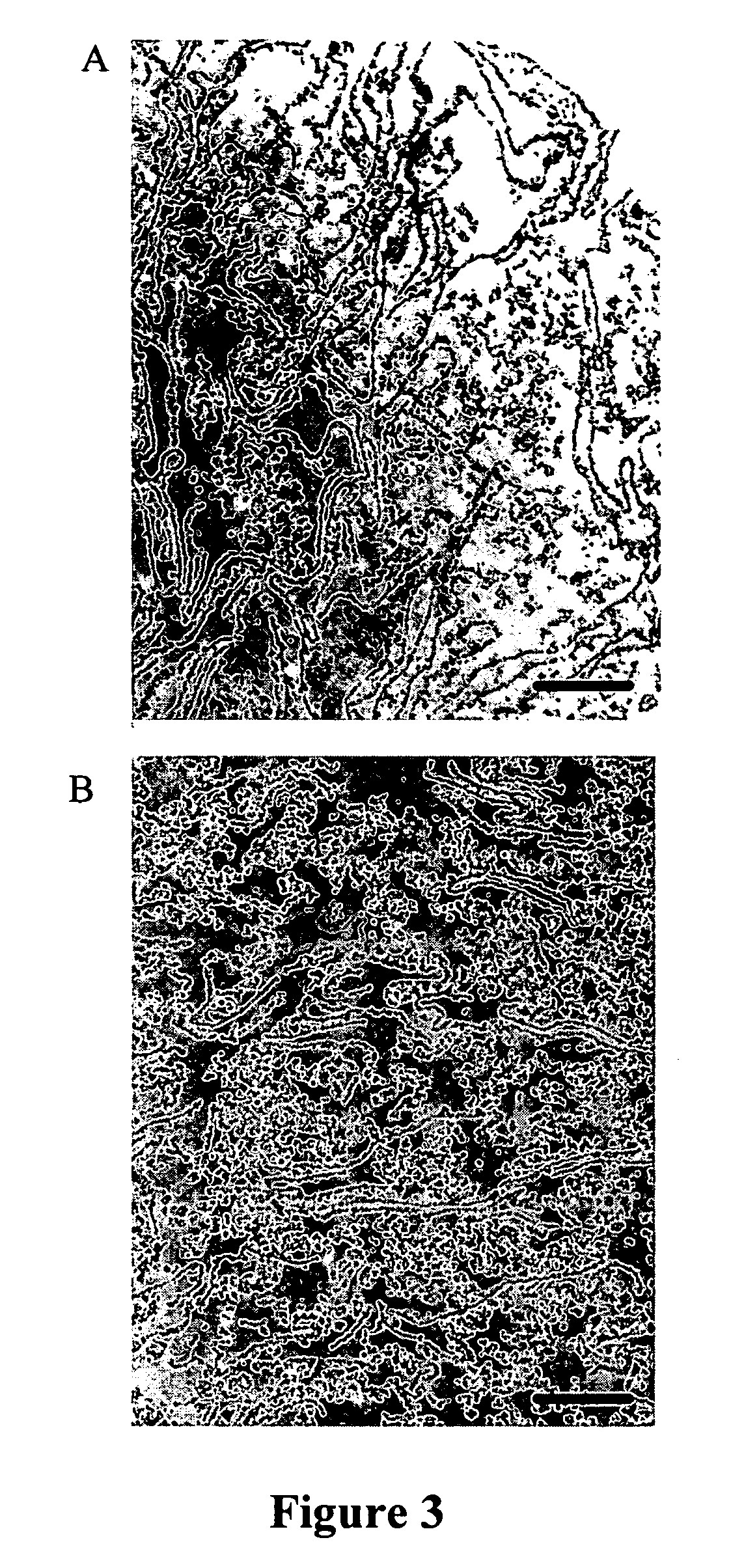
The invention relates to a plasma membrane marker for identifying fenestrae. The invention also relates to a method of visualizing fenestrae utilizing a plasma membrane marker and light microscopy. The invention also relates to a method of identifying a plasma membrane marker for fenestrae. In particular, the invention relates to the characterization of moesin as a component of fenestrae sieve plates. More particularly, the invention relates to the use of moesin as a plasma membrane marker. Moesin may be used as a plasma membrane marker for the identification of fenestrae or permeability of endothelial cells.
Owner:(OSI) EYETECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com