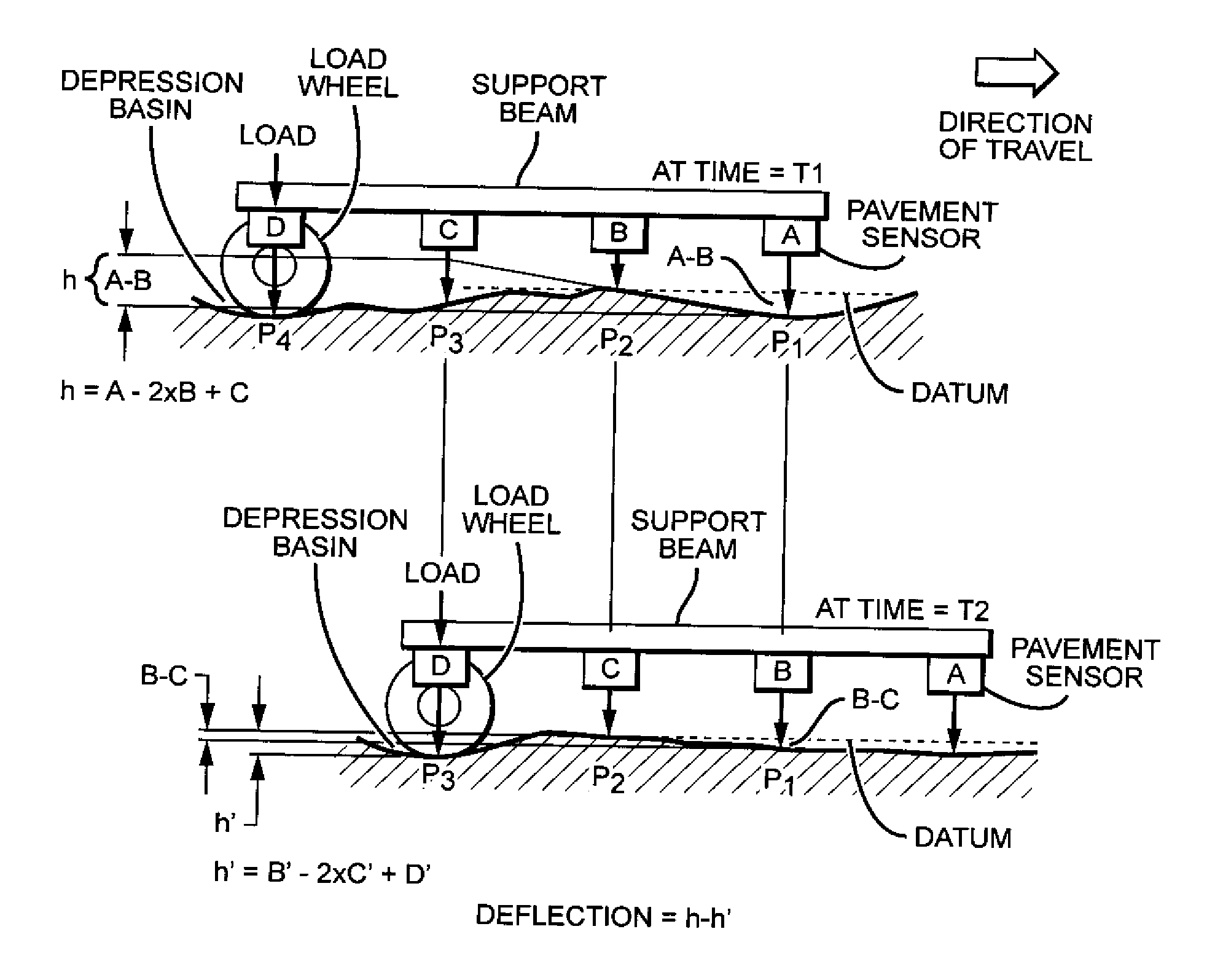
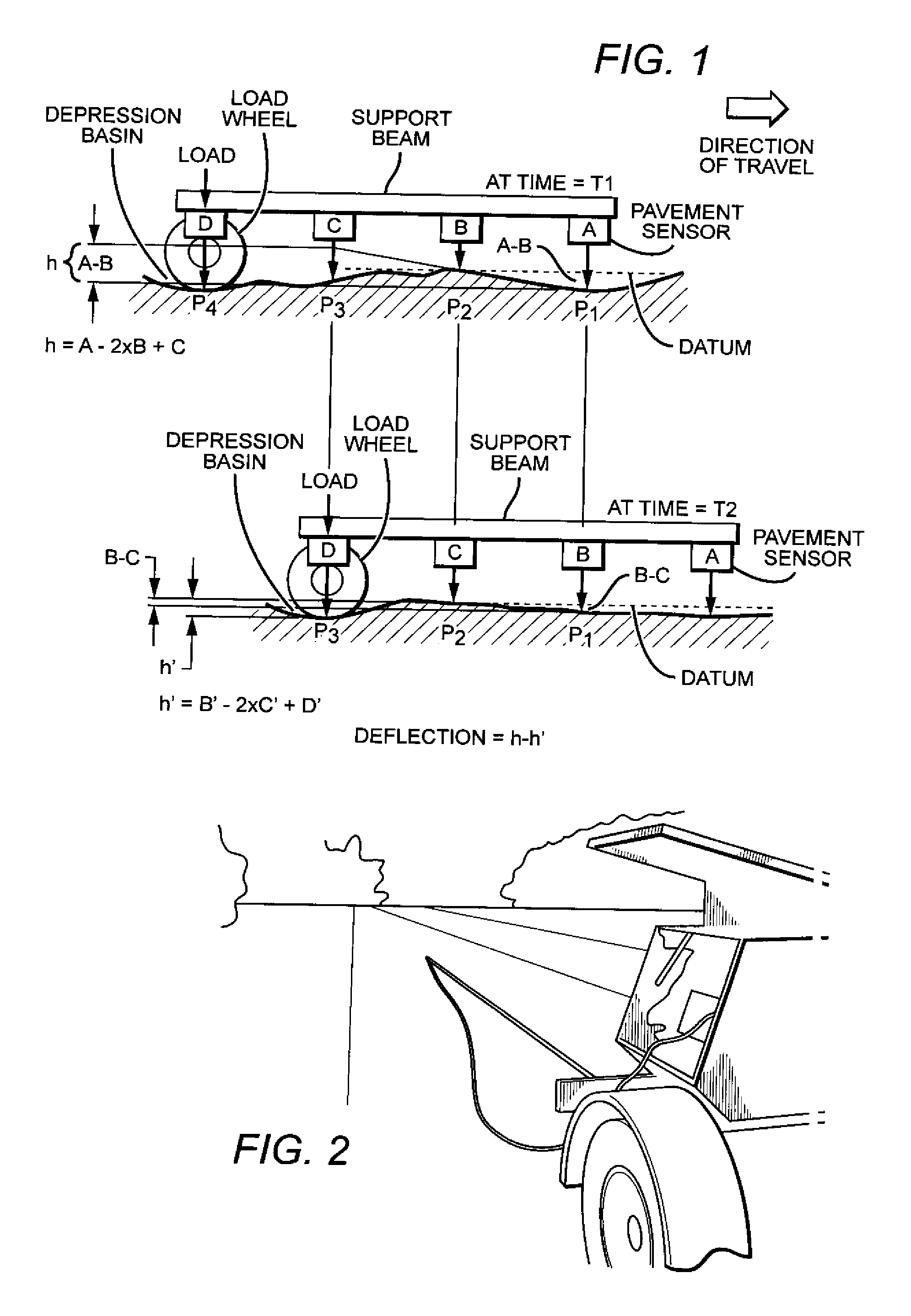
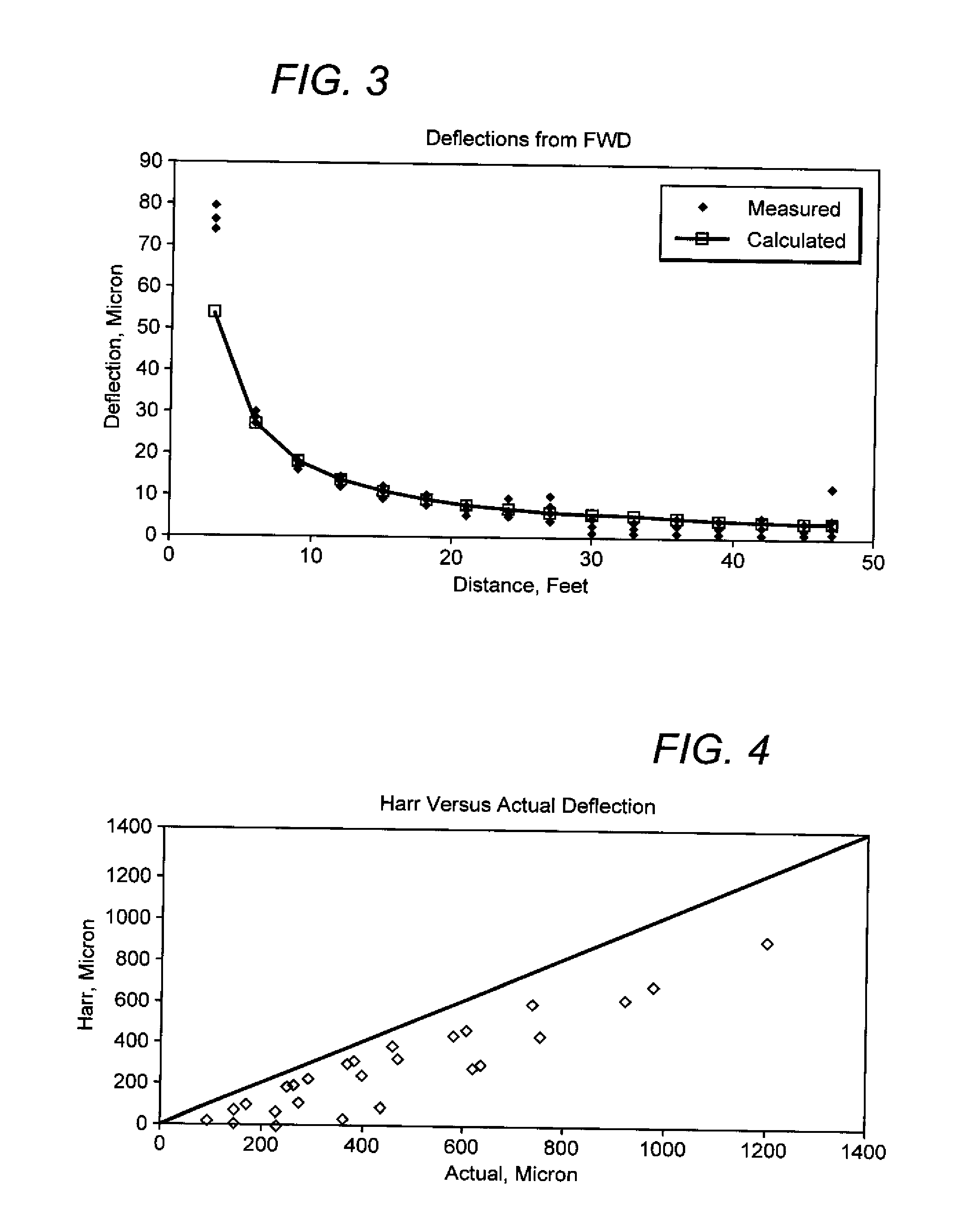
Patents
Literature
144 results about "Load deflection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
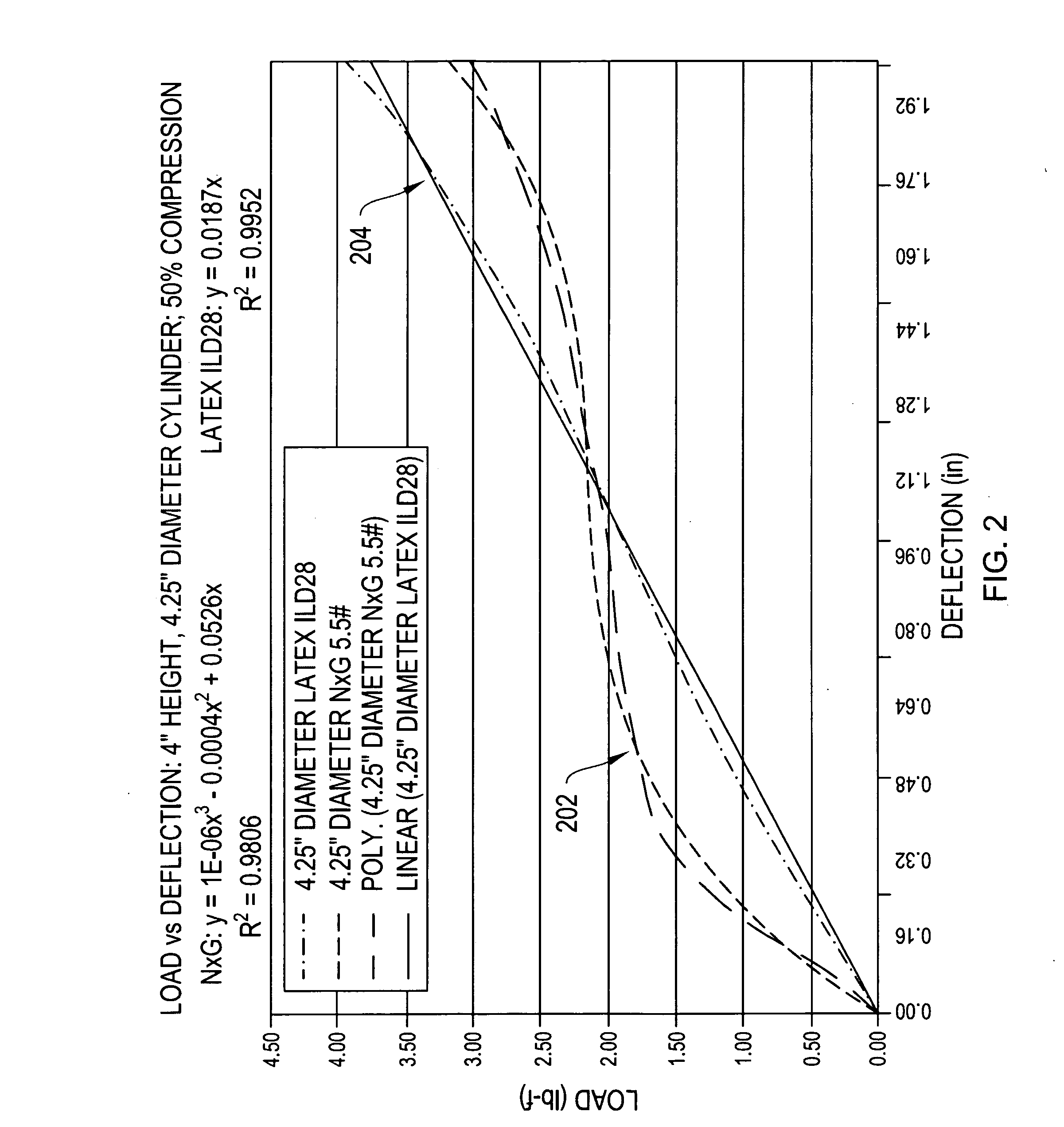
Load deflection. [′lōd di‚flek·shən] (mechanical engineering) The change in position of a body when a load is applied to it.
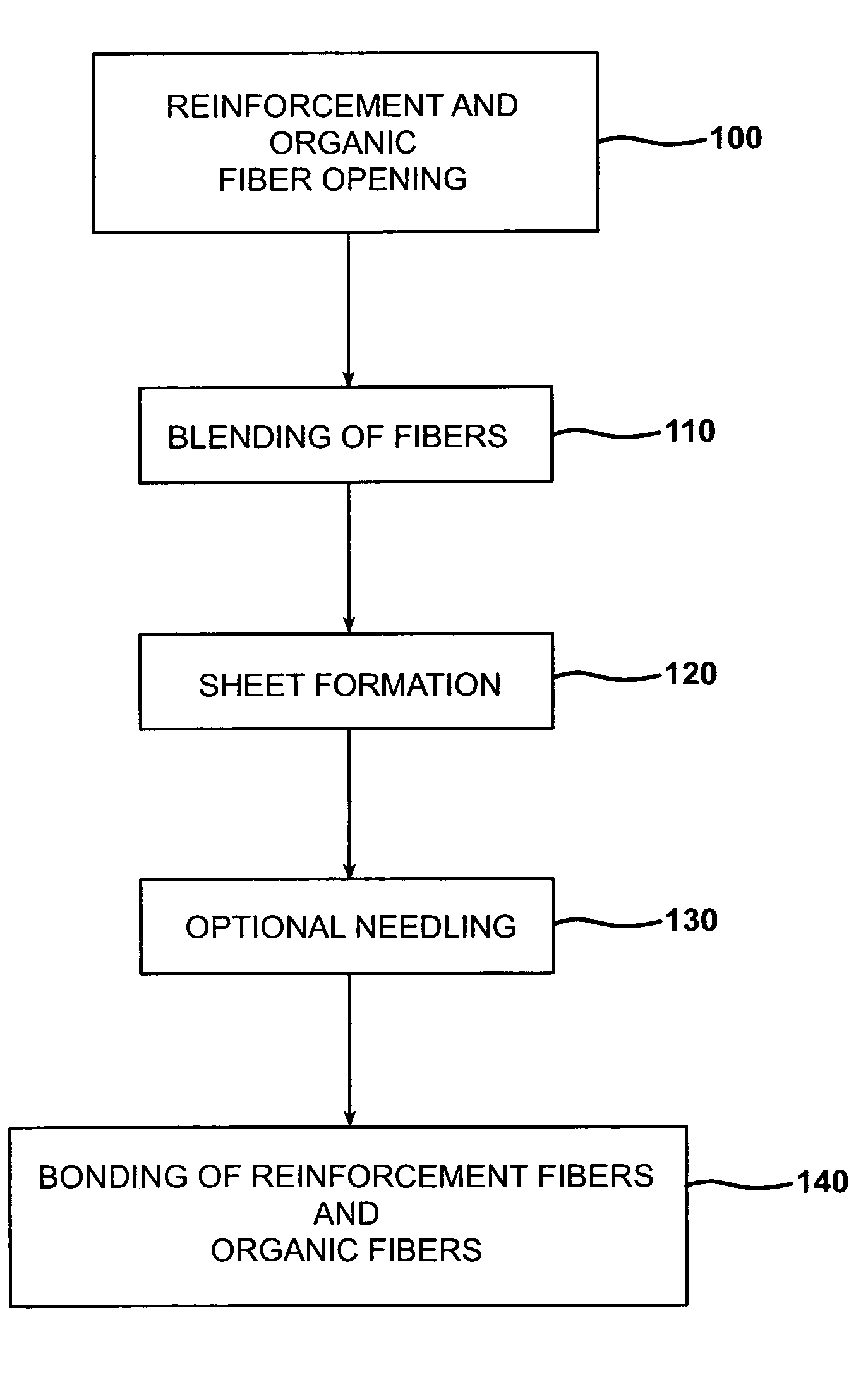
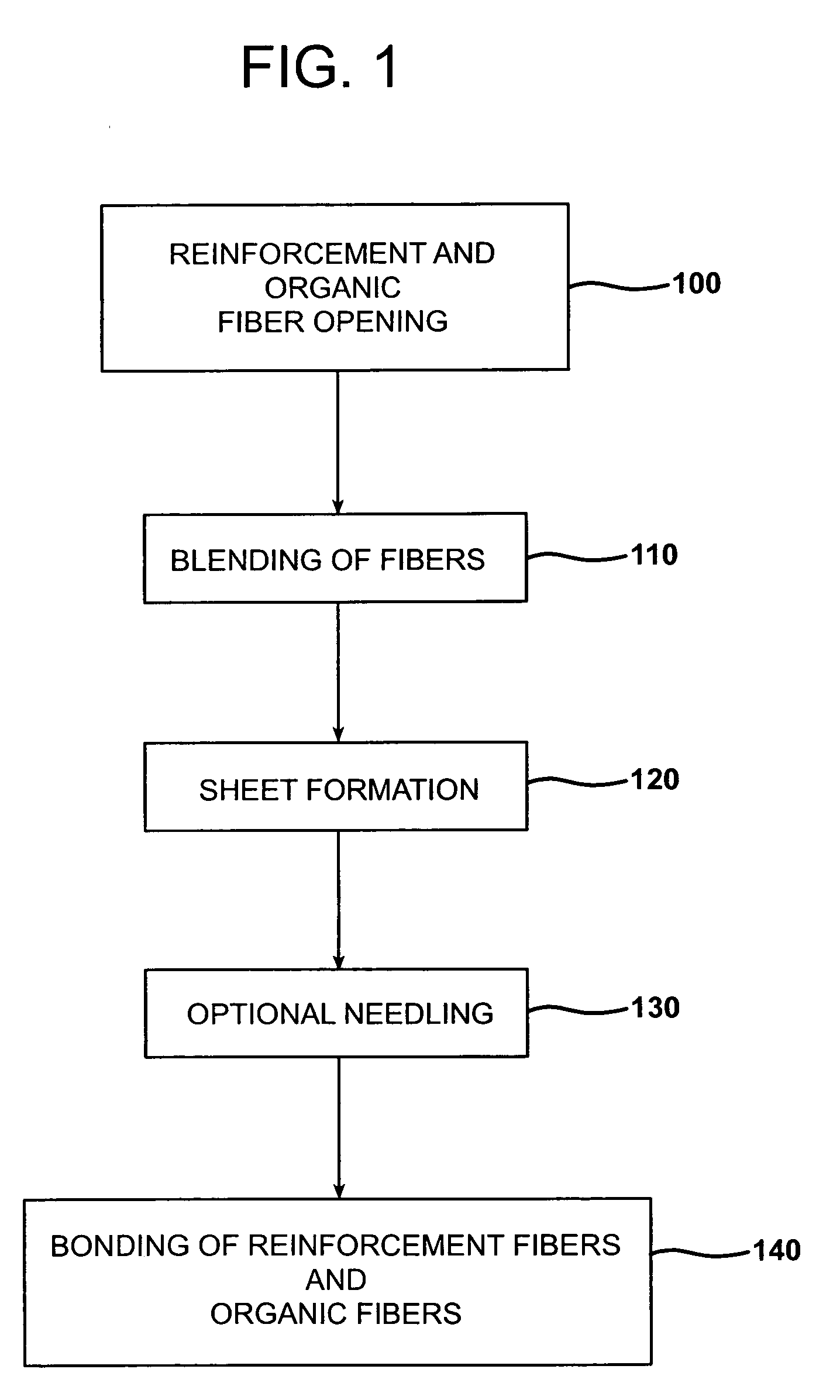
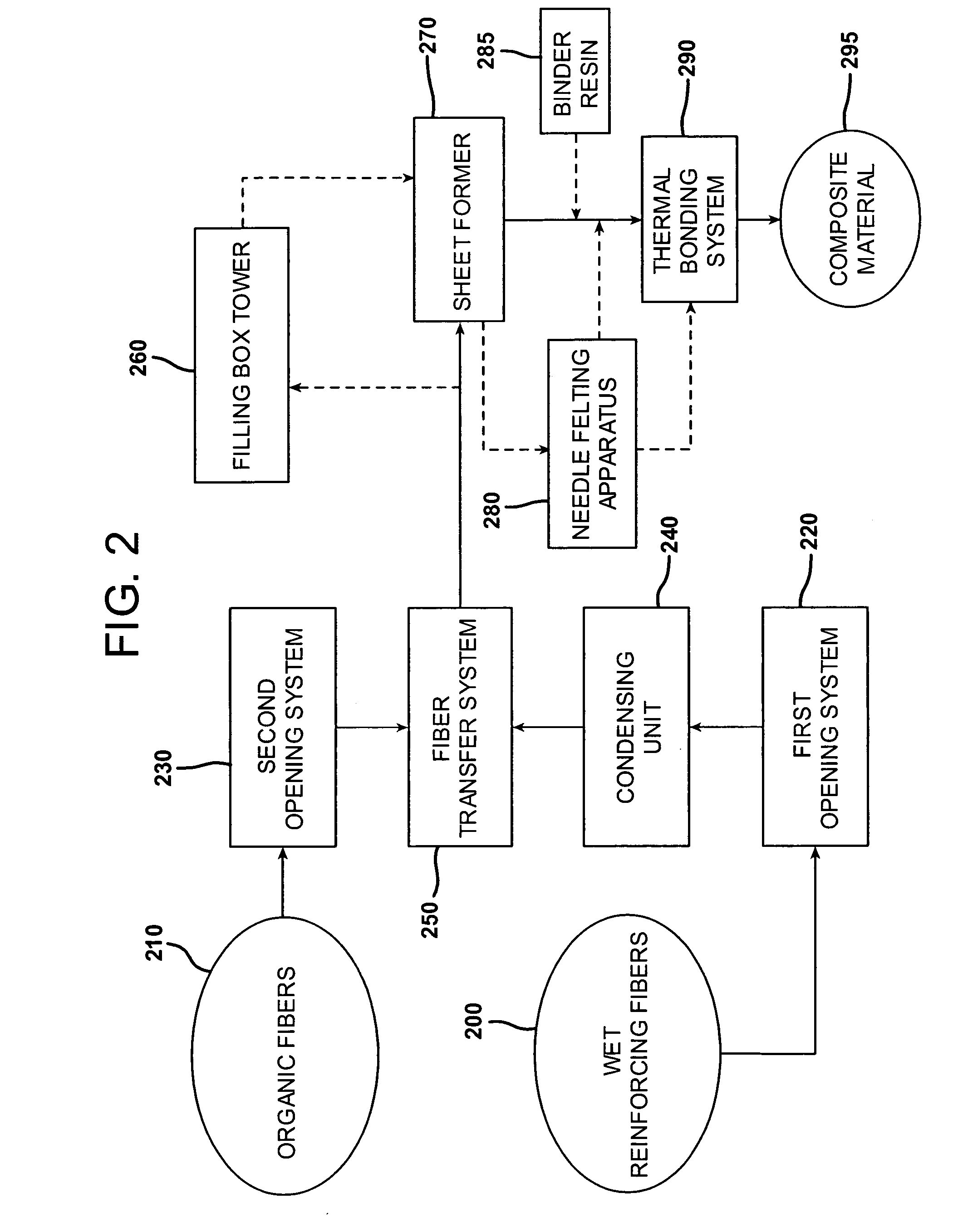
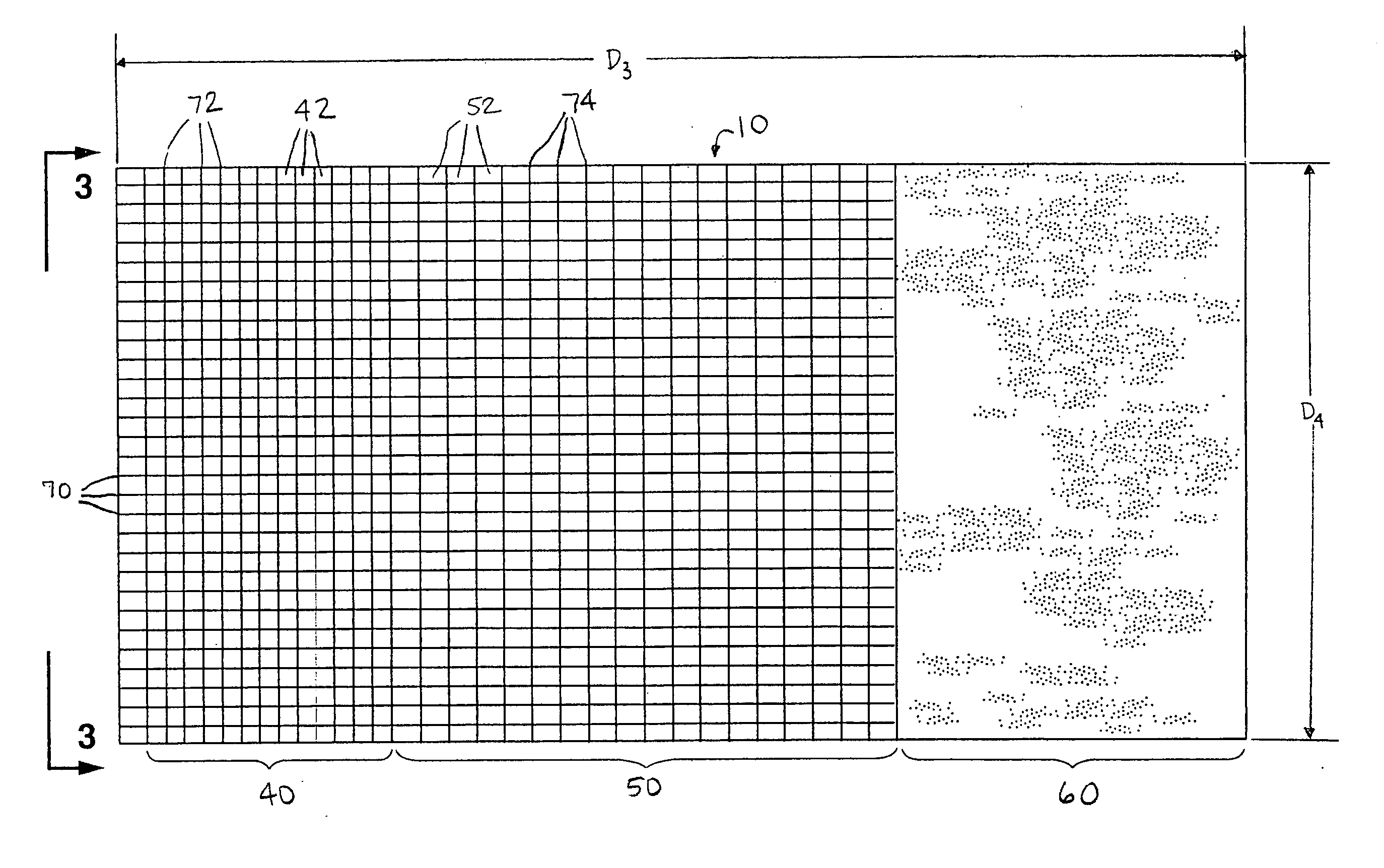
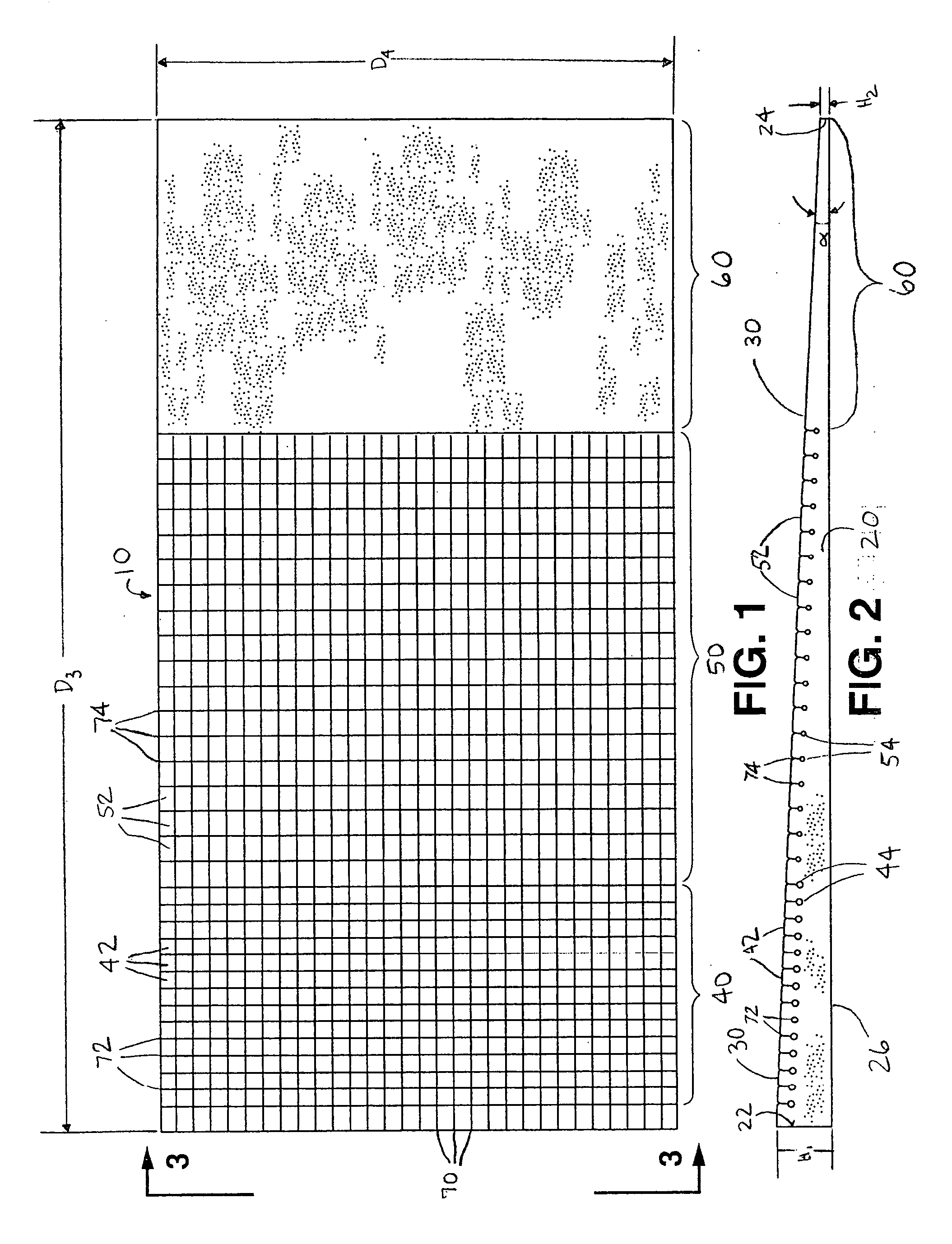
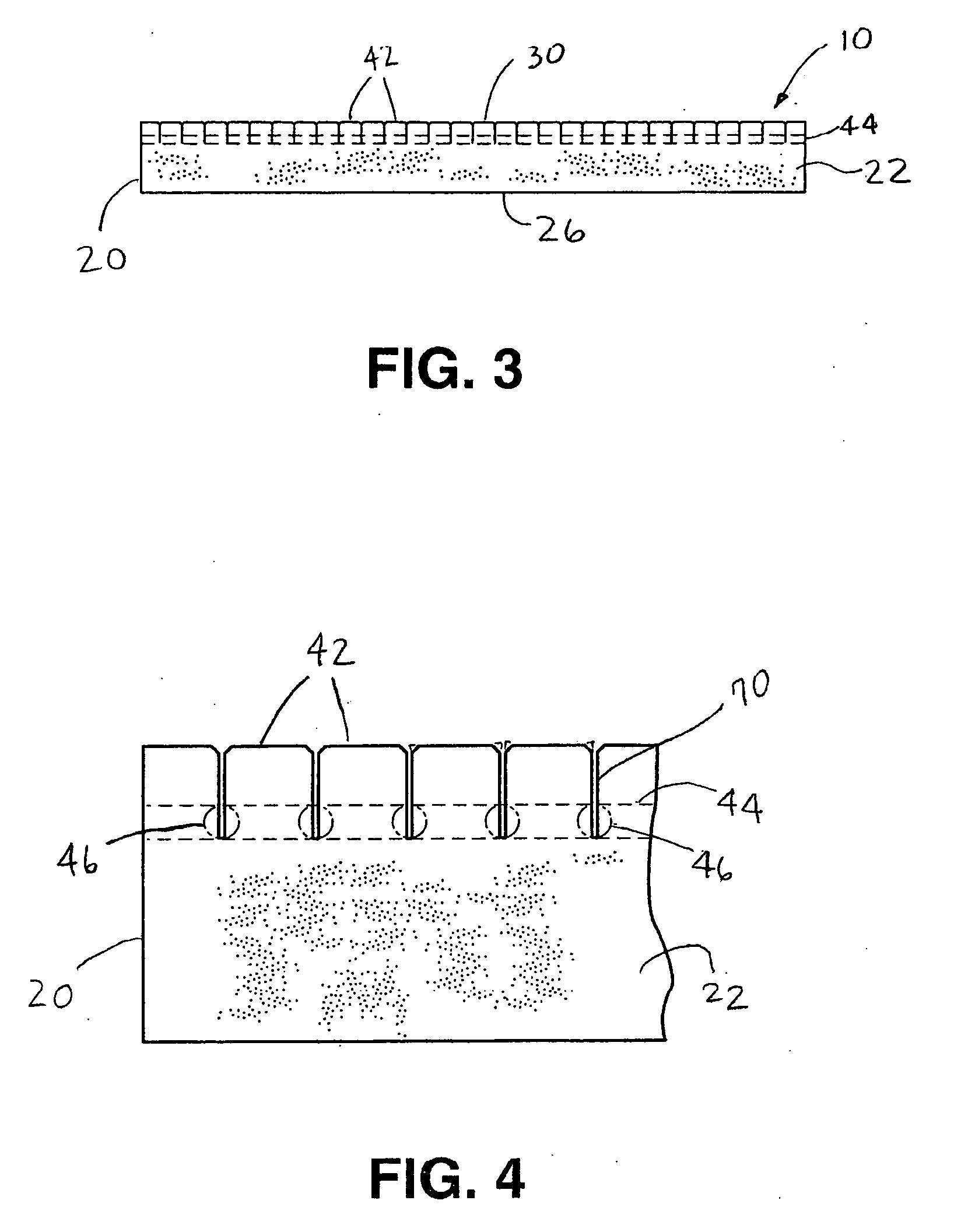
Sandwich composite material using an air-laid process and wet glass
InactiveUS20060141260A1Increase deflectionMeet growth requirementsWood working apparatusFurniture partsGlass fiberFiber
A sandwich composite material formed of a core layer positioned between first and second skin layers is provided. Either the core layer or the first and second skin layers are formed of a composite material that includes reinforcement fibers and organic fibers. Preferably, the reinforcing fibers are wet use chopped strand glass fibers. The composite material may be formed by opening the reinforcement fibers, blending the reinforcement and organic fibers, forming the reinforcement and organic fibers into a sheet, and bonding the sheet. The core layer and first and second skin layers may be attached by adhesives or resin tie layers. The sandwich composite material may include a facing layer affixed to an exposed major surface of one or both of the first and second skin layers. The strength, stiffness, and load deflection of the sandwich composite material may be modified by changing the amount and / or type of fibers present.
Owner:OWENS CORNING FIBERGLAS TECH INC
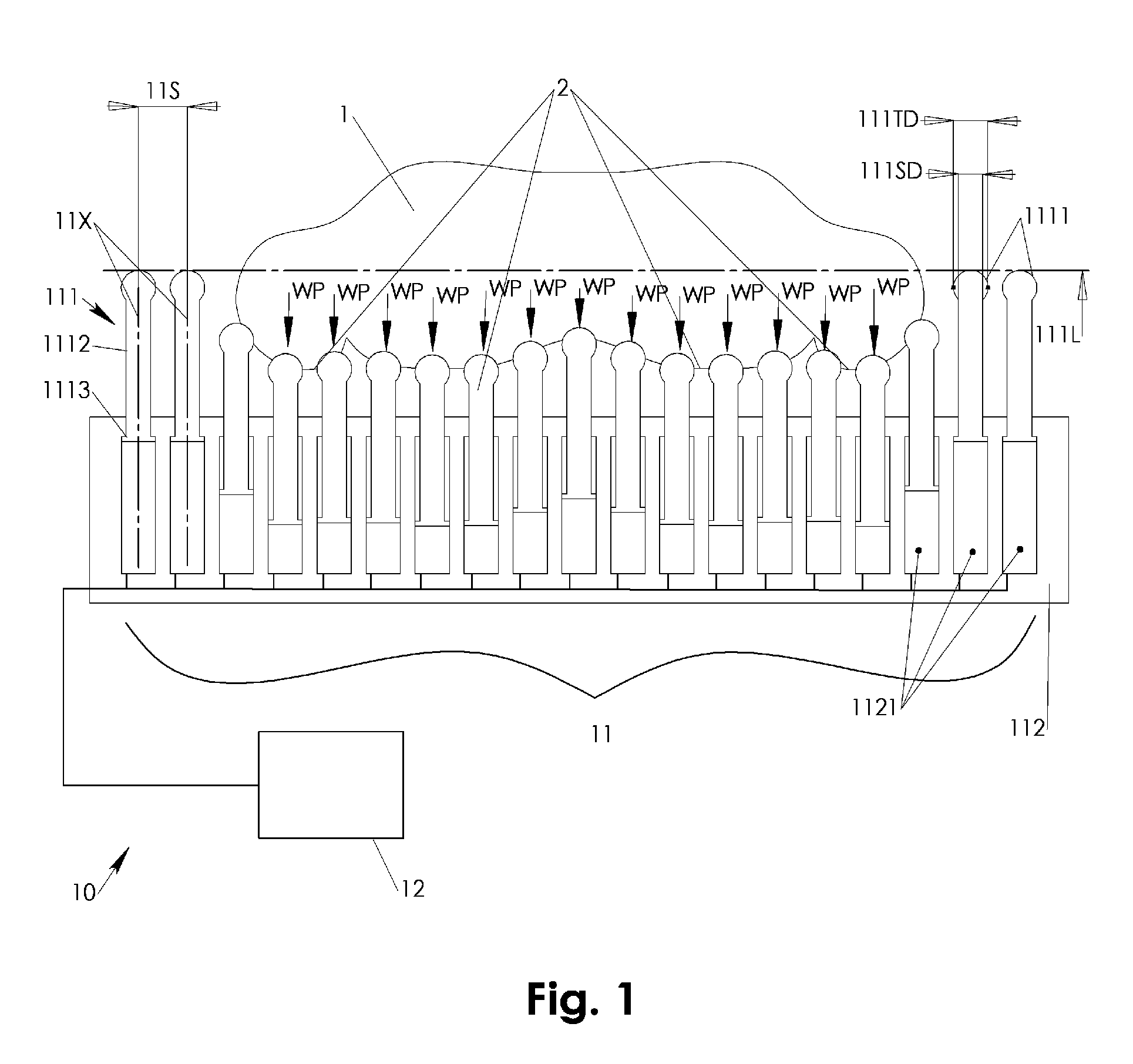
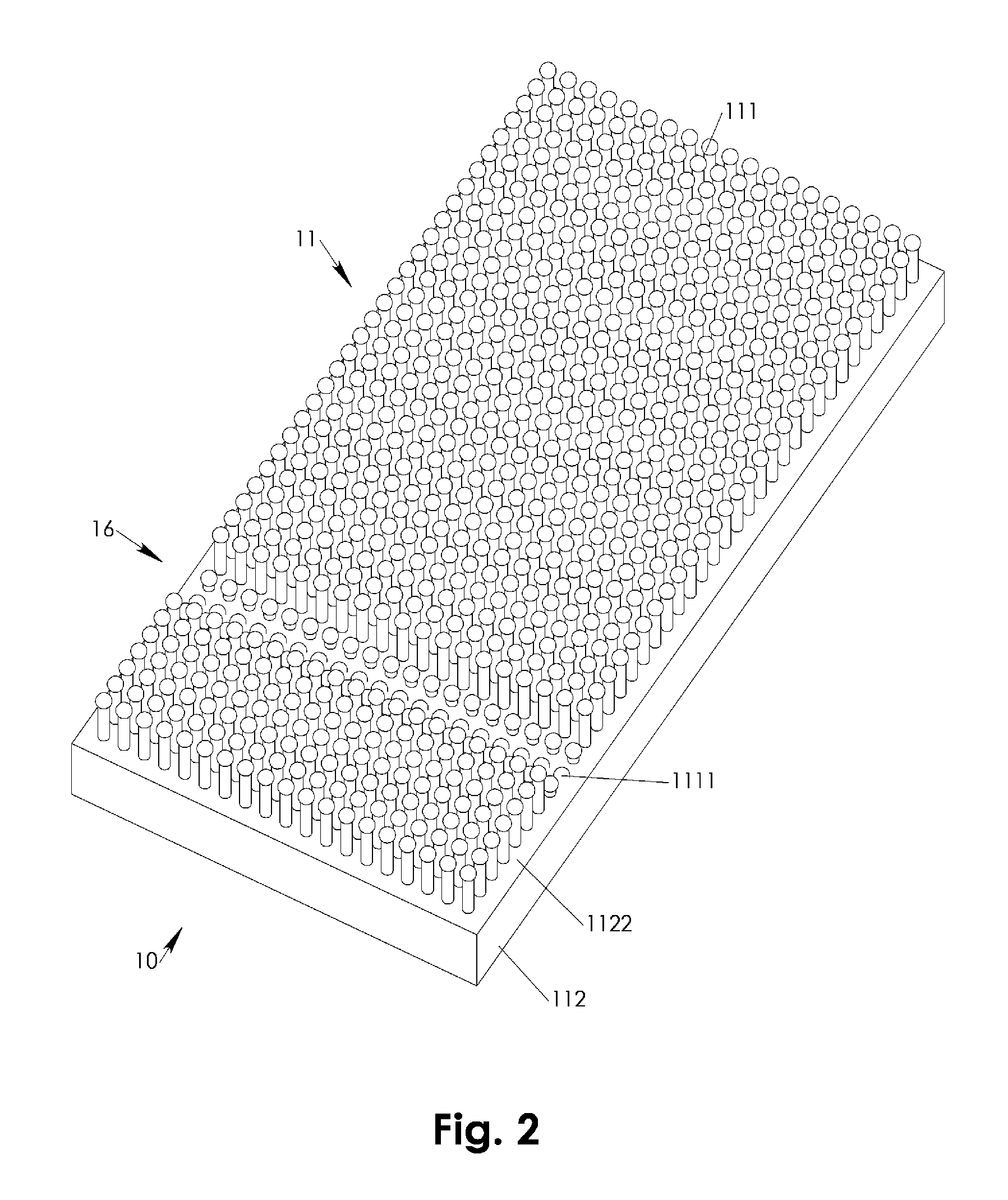
Patient bedding system with dense matrix or individually suspended directly body supporting pins
InactiveUS7520011B1Eliminated pressure peakReduce weighing pressureSpring mattressesSofasContact pressureControl system
A support pin matrix features a number of support pins densely two dimensionally arrayed and individually springily suspended such that a patient's body or body portions may be bedded directly on the support pins. The pins are preferably pressurized by a fluid pressure system for highly balanced contact pressure irrespective the individual pins' load deflection. A control system may provide a pin retraction wave of the support pins. A body resting surface accessing device may be moved across the support pin matrix and beneath a bedded patient in conjunction with the pin retraction wave. The resting surface accessing device may be configured for cleaning, drying, inspecting, irradiating, and / or massaging the body resting surface and / or for maintaining the body support pin matrix. A body carrying net may be retracted and raised in between the body support pins to lift the patient off the support pin matrix.
Owner:LIBERKOWSKI JANUSZ
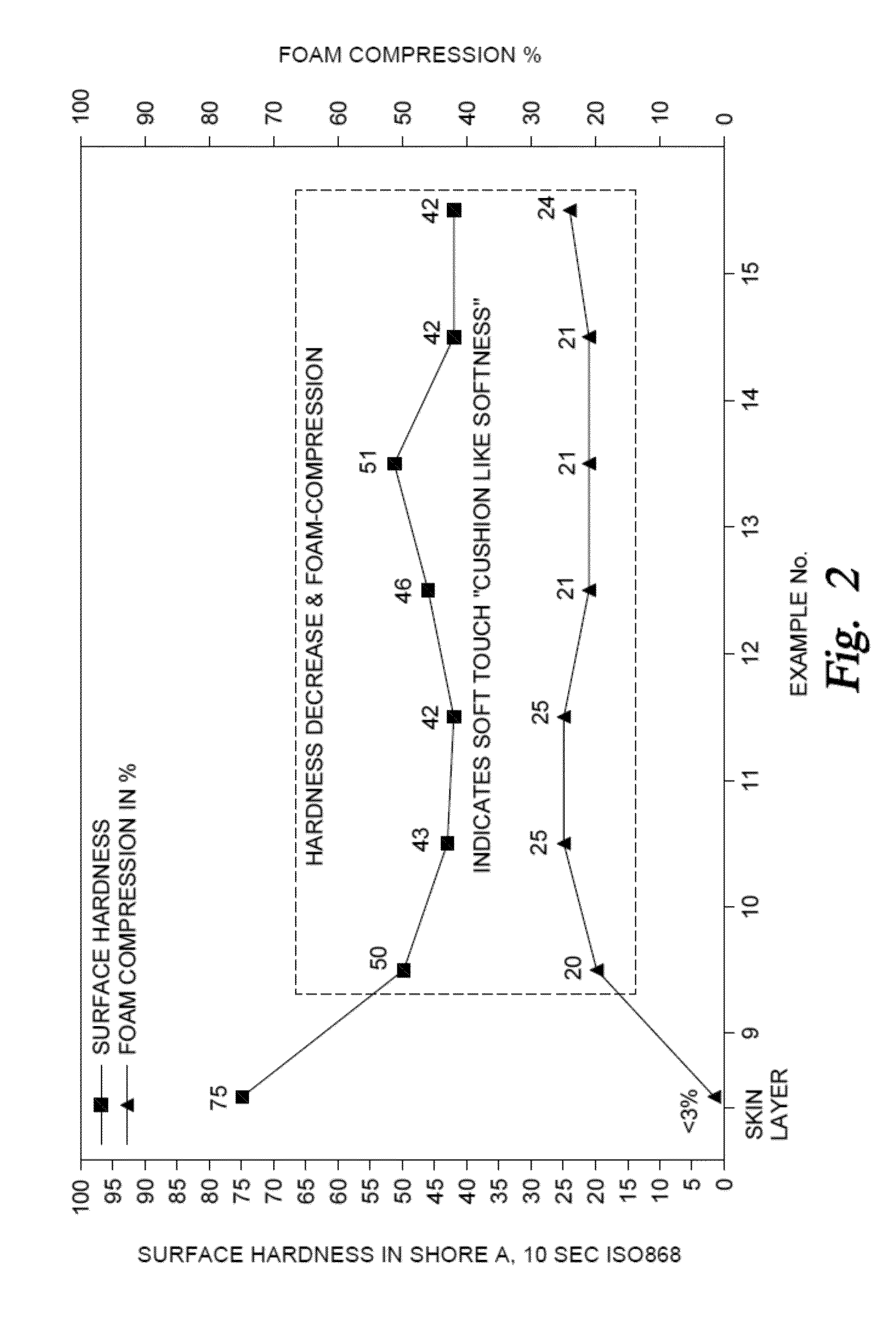
Composition, Foam and Article Made Therefrom
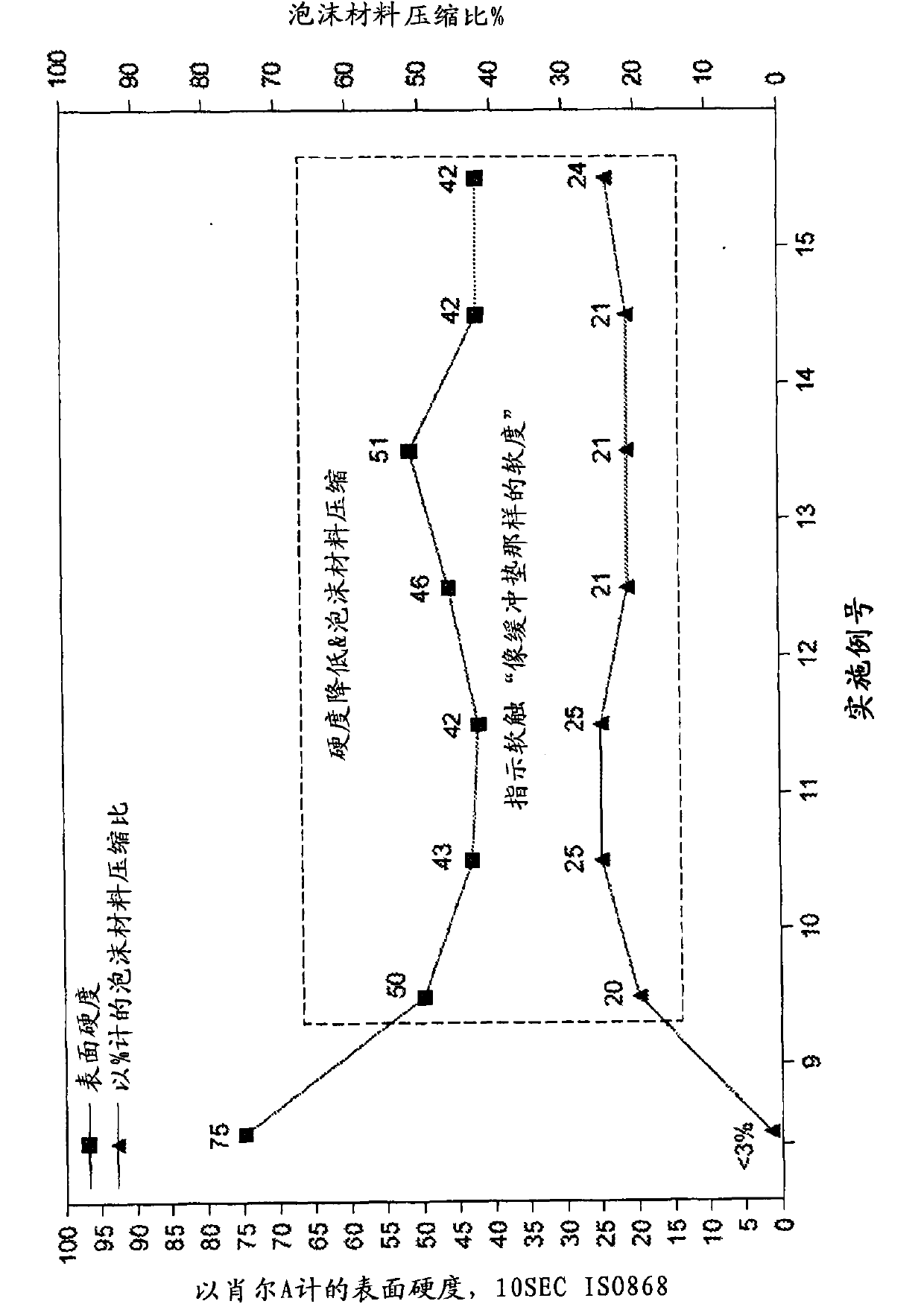
InactiveUS20130101826A1Balanced load deflectionBalanced elasticitySynthetic resin layered productsThin material handlingPolymer scienceLoad deflection
The present invention discloses a composition comprising a) a thermoplastic vulcanizate and b) a thermo-expandable microsphere comprising a polymer shell and a propellant encapsulated in said polymer shell based on the total weight of the composition. The composition is suitable for making foam with balanced load deflection and elasticity, including soft touch, reduced to low deflection, improved relaxation performance and low water absorption, replacing either soft paint or assembled constructions with foam sheets and meeting requirements in soft touch applications.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Inclined mattress pad
InactiveUS20060179580A1Precise positioningReduce morbidityStuffed mattressesSpring mattressesEngineeringLoad deflection
A full length mattress pad is provides improved patient support for all parts of the user's body through provision of a support surface supplement for use with existing support surfaces, such as for use on top of a conventional mattress or hospital bed. The pad has a body of resilient material having a relatively flat, planar lower surface for being received on top of the existing support surface, and has a length at least generally the same as that of the mattress, or at least long enough to support the full length of a user. An inclined upper surface is defined by the body of resilient material, and has a plurality of different longitudinal sections. The plurality of different longitudinal sections collectively define a predetermined angle of inclination for the inclined upper surface which is relatively constant along the entire length of the body of resilient material relative to its planar lower surface. At least one of the plurality of different longitudinal sections has a relatively flat surface inclined at the predetermined angle of inclination, while at least one other of the plurality of different longitudinal sections has a surface formed with respective or different projections therein, so that improved patient support is provided through a combination of the inclined upper surface and the plurality of different longitudinal sections. Preferably, the predetermined angle of inclination is no more than about 10°. Characteristics of the plurality of longitudinal sections are selected based upon one or more of the type of resilient material used, the thickness of such material, the change in thickness of such material due to the predetermined angle of inclination, the material density, and the indention load deflection characteristics of such material, with such selection and combination of characteristics determined so as to optimize the inclined pad for support for the user's body which is engineered on the basis of the intended end use of said mattress pad. The longitudinal sections are also formed by one or both of longitudinal and lateral cuts within a selected portion of the inclined upper surface, also preselected to address the relieving of support pressure points to decrease the chance of decubitus ulcers in users of the mattress pad. At least one of the depths, widths, and lengths of such cuts, forming cross-sectional shapes of the different or respective projections, are preselected on the basis of the intended end use of said mattress pad. A plurality of channels may be formed between adjacent of the respective projections, for dissipating heat and moisture from a user who is supported on the inclined upper surface, to increase the health and comfort of such user.
Owner:SPAN-AMERICA MEDICAL SYSTEMS
Supportive upper body constraint device
A supportive upper body constraint device comprising a base comprising a foam material with a preselected impression load deflection (ILD) ratio for a desired resiliency, and a smooth-surface cover on the base comprising an elastomeric foam material with an ILD ratio less than the base. The device comprises opposing support members on the base, the cover supportingly disposed by the base and support members in a concave contour defining a cavity.
Owner:TEMPLE MARK
Systems and methods for manufacturing springs with foam characteristics
ActiveUS20110041252A1Non-linear characteristicUpholstery manufactureStuffed mattressesProcess engineeringEngineering
Systems and methods include a spring-coil assembly having non-linear load-deflection characteristics that are substantially similar to foam. In particular, the systems and methods described herein include a first set of encased springs that are in a partially compressed state and a second set of shorter springs. These two sets of springs may be arranged in alternating rows such that the resulting spring-coil assembly displays non-linear load-deflection characteristics similar to foam.
Owner:DREAMWELL
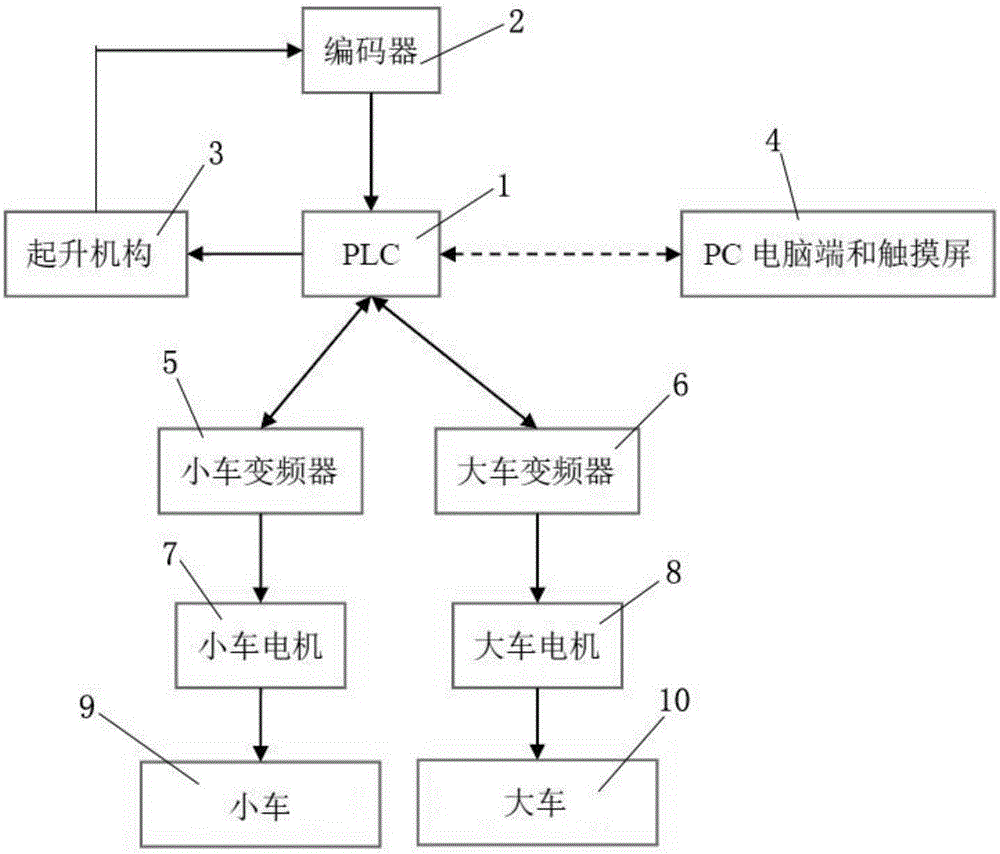
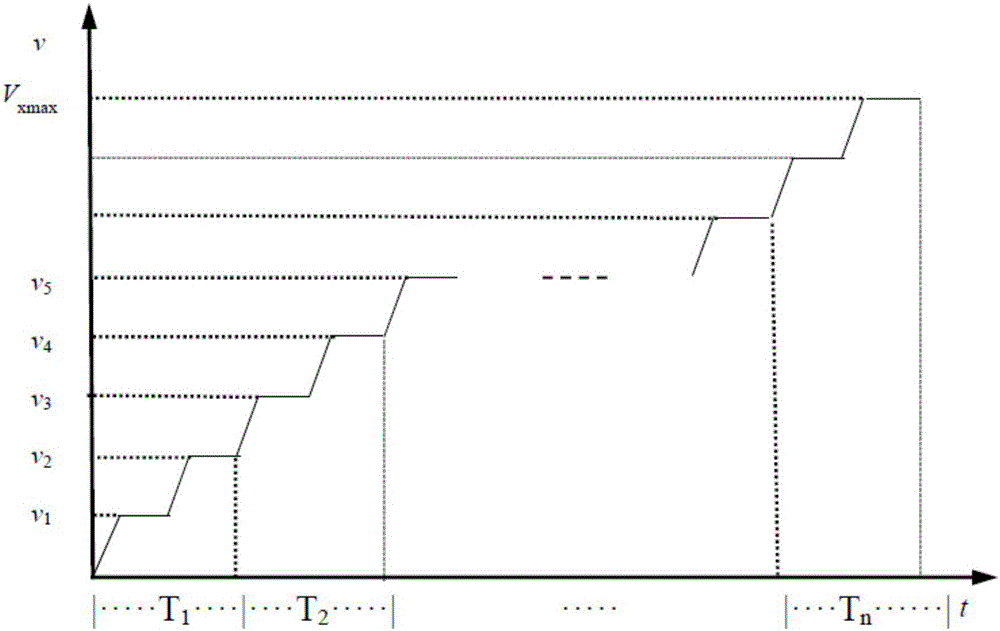
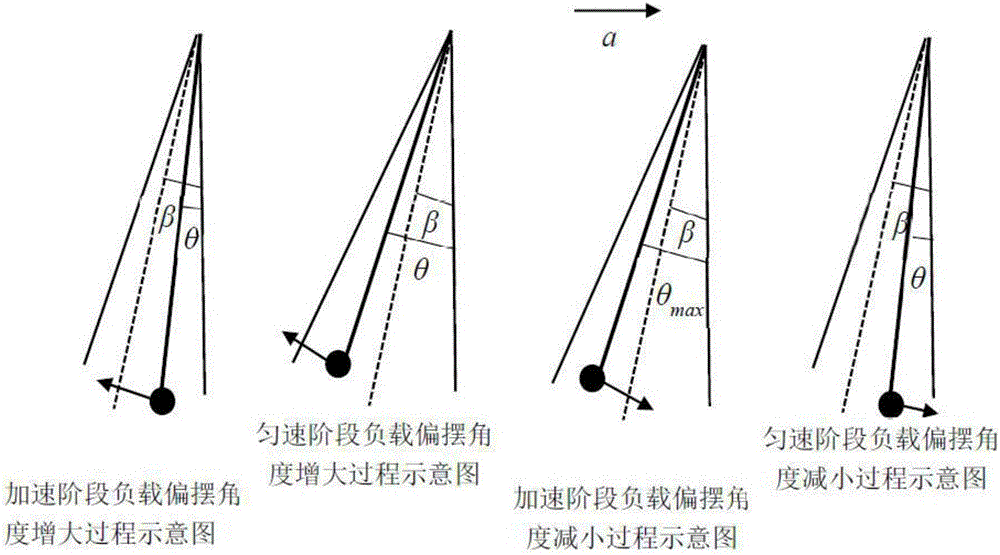
Intelligent anti-swing control method for multi-section uniformly-variable-speed crane
ActiveCN105883615AFully consider the use of securityImprove horizontal accuracyLoad-engaging elementsEngineeringLoad deflection
The invention discloses an intelligent anti-swing control method for a multi-section uniformly-variable-speed crane. The acceleration process of a running mechanism is divided into multiple sections of the uniform acceleration processes or the deceleration process of the running mechanism is divided into multiple sections of the uniform deceleration processes by taking the preset maximum allowable load swing amplitude and the lifting rope length as input variables on the basis of the system dynamics analysis rule of the crane through the input shaping principle of a two-order oscillation system according to the load deflection cycle, and load deflection is finally inhibited by controlling running of the running mechanism; meanwhile, multiple sections of the uniformly variable speed processes are optimized through an interpolation method. According to the method, by taking the maximum allowable load swing amplitude as the input variable, the safety of the crane in the running process is fully taken into account, the precision is controlled, and the safety and the working efficiency of the crane are significantly improved.
Owner:SHANDONG ZHONGYANG MACHINERY CO LTD +1
Load-deflection resistant loading system for free hydraulic forging press
ActiveCN101837416AHigh dimensional accuracyImprove forging qualityForging press drivesEngineeringCopper
The invention discloses a load-deflection resistance loading system for a free forging hydraulic press, and relates to the forging hydraulic press. The invention solves the problem that in the conventional loading system for the free forging hydraulic press, as a plunger and a movable cross beam are in rigid connection, the movable cross beam is subjected to eccentric load in the eccentric forging process to accelerate abrasion of a guide copper sleeve and a seal to cause earlier failure and leakage of seal of a main working cylinder so as to cause poor eccentric forging resistance of the loading system. The loading system for transmitting forging pressure of the free forging hydraulic press is characterized in that the combination movable cross beam with an overlong guide structure, fully enclosed wedge-shaped plane guide devices which can adjust gaps of the peripheries of upright posts, a double concave ball hinged short cylindrical rocker shaft device of which the main plunger is connected with the movable cross beam, and a levelness sensor monitoring device of the movable cross beam are adopted on the free forging hydraulic press. The load-deflection resistant loading system not only can be applied to various free forging hydraulic presses, but also can be popularized and applied to other vertical hydraulic presses suitable for the process.
Owner:TAIYUAN HEAVY IND
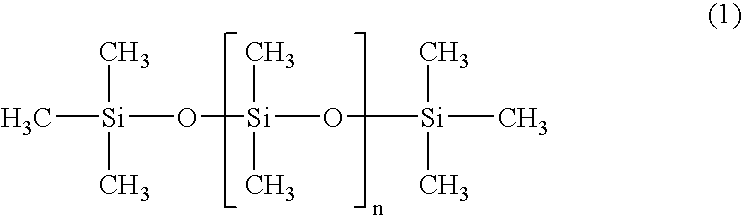
Flexible polyurethane foam, process for its production, and seat for automobile
InactiveUS20070219284A1Improve featuresLittle bottom-hitting feelingStuffed mattressesSpring mattressesPolyolLoad deflection
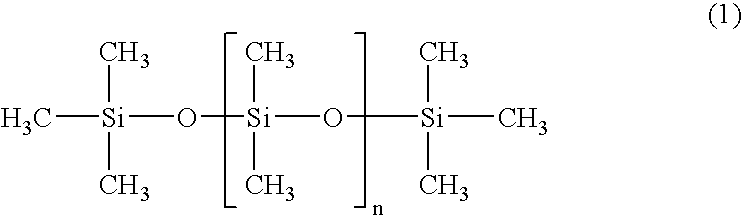
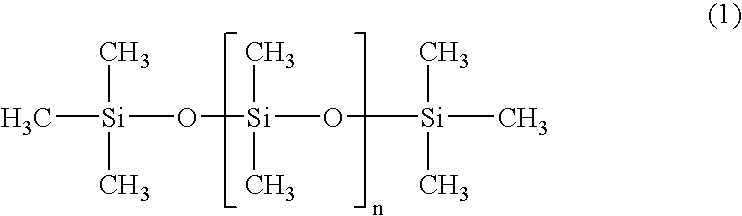
A flexible polyurethane foam excellent in the vibration characteristics and the load-deflection characteristics, a process for producing the flexible polyurethane foam stably and inexpensively, and a seat for an automobile excellent in posture-stability performance and supported feeling with little bottom-hitting feeling, are provided. When a polyoxyalkylene polyol and a polyisocyanate compound are reacted in the presence of a urethane-forming catalyst, a blowing agent and a foam stabilizer, a predetermined amount of a compound of the following formula (1) is used: wherein the average of n is from 13 to 2,100.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Multi-Canted Coils, Tubes, and Structures
Coil, tube, and other structures configured with a plurality of individual coils, internal structures, legs or extensions with each having multiple cants per coil, internal structure, leg or extension, and wherein the cants formed therein allow for a load-deflection force when each is compressed. In addition, any horizontal or moment forces are substantially reduced and / or eliminated when a downward vertical force is applied, as minimal or no torsion is created in the individual coils, legs or extensions.
Owner:VELOCE LABS
Zoned foam mattress with alternating lateral regions of HD foam and memory foam
A zoned foam mattress includes an upper foam layer and a zoned foam layer. The lower side of the upper foam layer is adjacent to the upper side of the zoned foam layer. The zoned foam layer has first, second and third lateral regions with the second region being disposed between the first region and the third region. The first lateral region is disposed at the head end of the mattress. The first and third lateral regions are formed from high-density polyurethane foam (HD foam), whereas the second lateral region is formed from visco-elastic polyurethane foam (memory foam). A person's shoulder can sink farther into the second lateral region than into the first or third lateral regions even if all of the lateral regions have the same indentation load deflection (ILD). By allowing a person's shoulders and hips to sink into memory foam regions, the person's spine is kept straight.
Owner:ZINUS
Calibration method for indention load-depth curve of micro-bridge of micro-electro-mechanical system
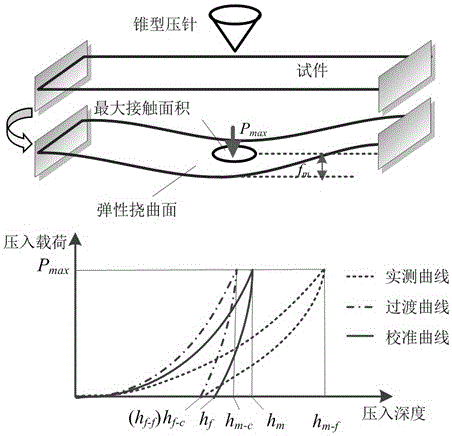
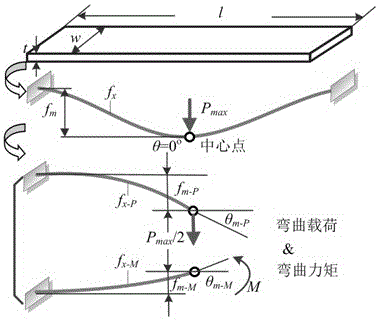
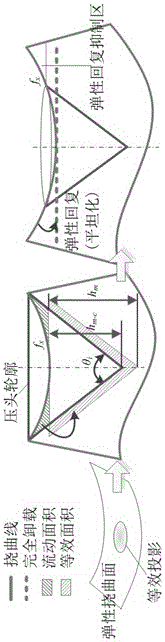
ActiveCN106501111AExact bending strengthExact yield strengthInvestigating material hardnessMaximum depthYoung's modulus
The invention relates to a calibration method for the indention load-depth curve of a micro-bridge of a micro-electro-mechanical system, belonging to the field of testing of the mechanical properties of materials. The bending load-deflection curve and the indention load-depth curve of a micro-bridge structure are synchronously acquired through a nanoindentation test on the micro-bridge structure, wherein the characteristic size of the micro-bridge structure is of a micron order, and two ends of the micro-bridge structure are fixed; and quantitative testing is carried out on the rigidity, Young modulus, hardness, yield stress and breaking strength of a bridge structure of a micro-electro-mechanical system device. Through analysis of a statically indeterminate structure of the micro-bridge, the actual maximum displacement of the tip end of an indenter is accurately parsed to be a sum of the maximum flexural deflection of the micro-bridge and the maximum indention depth of the indenter embedded into the surface of the micro-bridge; and a method for estimating a load-depth curve under the condition of elastic semi-infinite half-space by using the actually-measured indention load-depth curve is established on the basis of both the actual maximum displacement of the indenter and theoretical analysis of maximum depth of indentation by an elastic deflection surface and elastic deflection at the edge of an indentation micro-area; so a novel measuring method is provided for research on the mechanical behaviors of the micro-electro-mechanical system device under stress induction.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
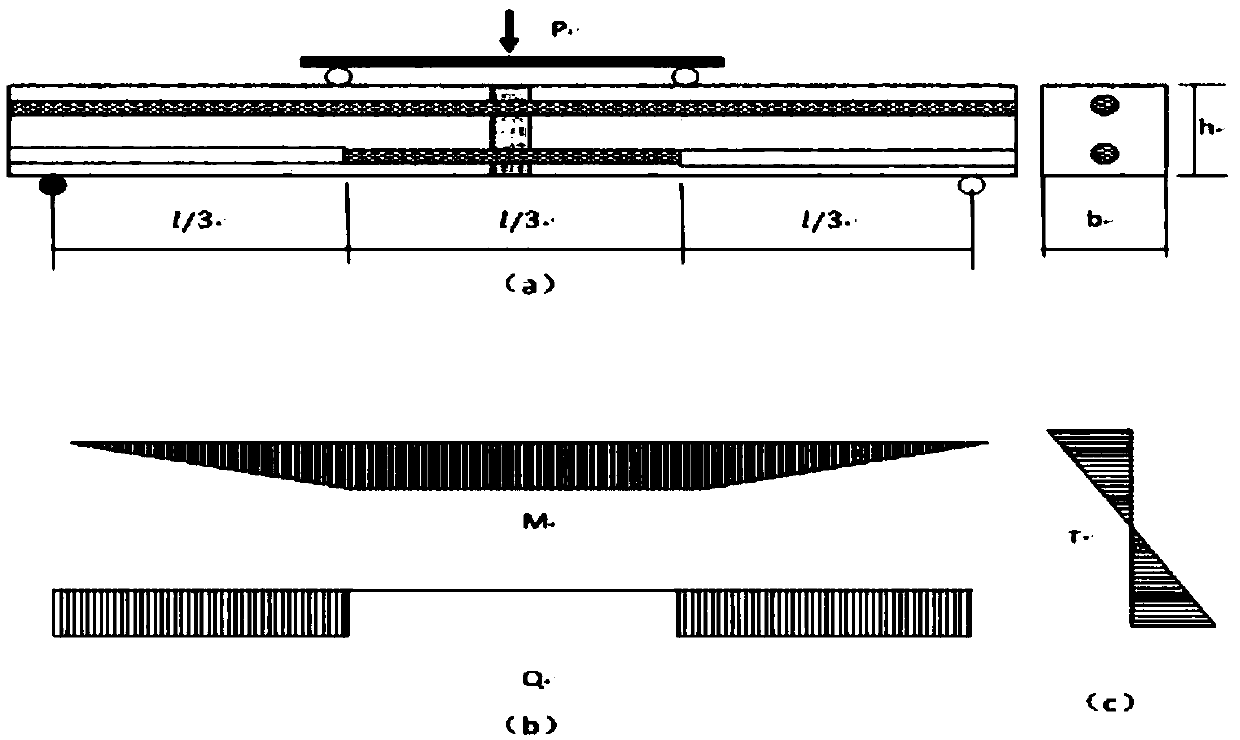
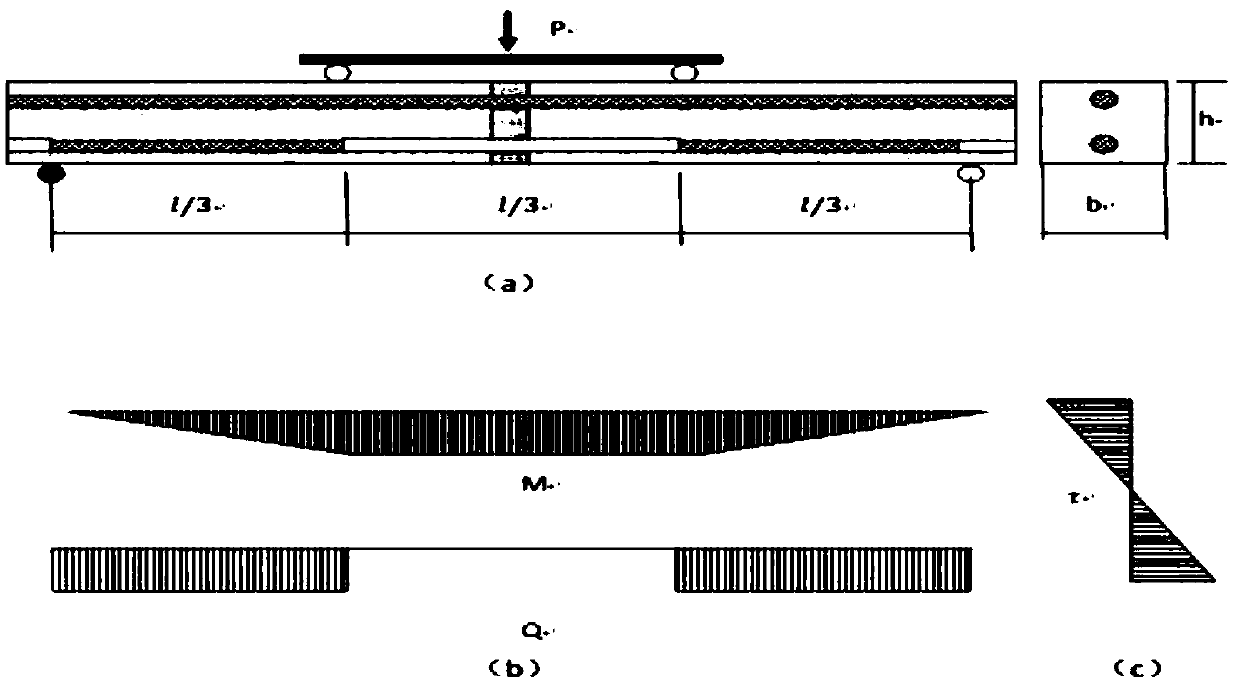
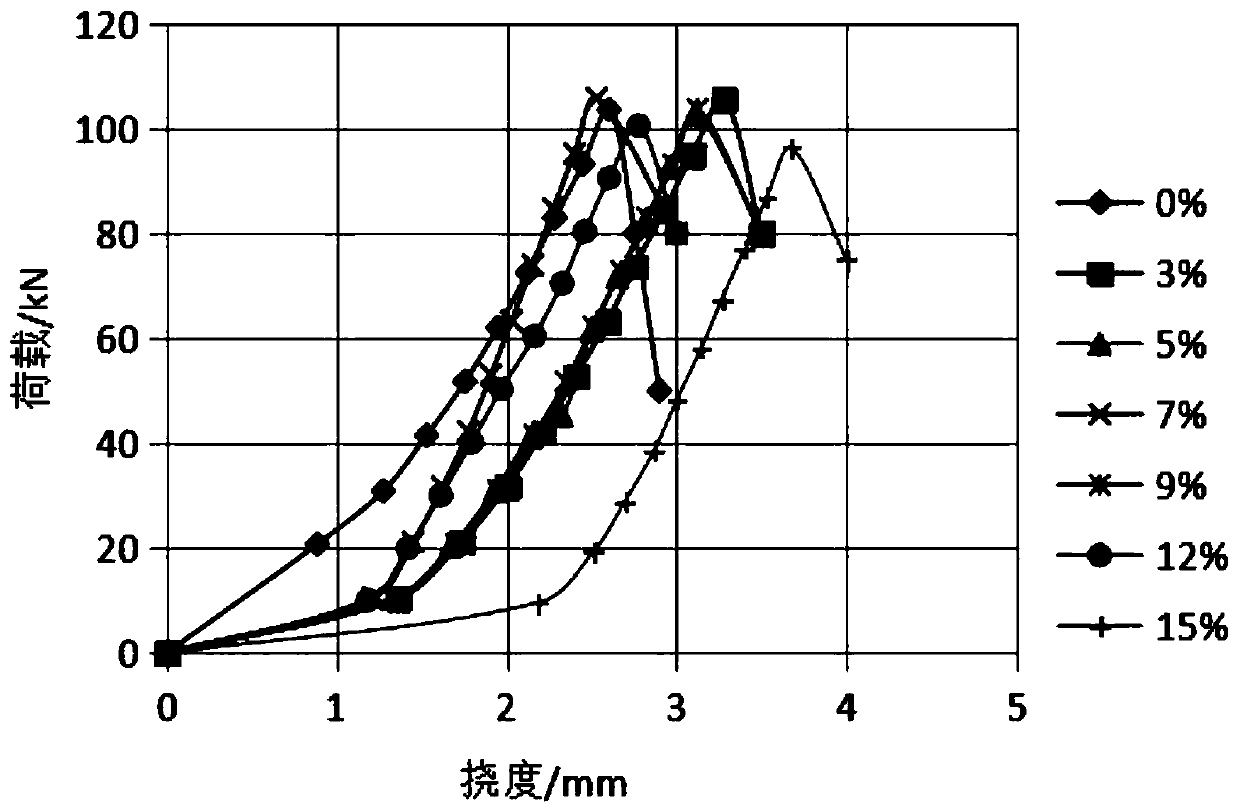
Testing method for testing steel bar-concrete bonding and slipping performance
The invention discloses a testing method for testing steel bar-concrete bonding and slipping performance. The testing method comprises the following steps: carrying out a testing design according to astress moment theory; determining a loading method, a section size of a test piece and a production method of the test piece; determining a load-deflection curve and calculating steel bar slipping strain, bonding stress, maximum slipping amount and bonding strength; then identifying a damage mode and processing a testing result. According to the testing method, measured bonding-slipping characteristic parameters eliminate influences, caused by various factors of the testing method, on the testing result; the bonding strength is close to the tensile strength of concrete; the testing method hasgood repeatability and stability. The testing method can be used for researching the bonding and slipping performance of concrete with different types and different strengths, and steel bar-concretewith different types; the testing cost is low and the testing precision is high; abundant results are obtained, and the testing method has a remarkable effect on structure analysis, design and new finding of steel reinforced concrete.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Multi-canted coils, tubes, and structures
InactiveUS9010740B2Reduce and eliminate horizontal forceRing springsShock absorbersEngineeringLoad deflection
Coil, tube, and other structures configured with a plurality of individual coils, internal structures, legs or extensions with each having multiple cants per coil, internal structure, leg or extension, and wherein the cants formed therein allow for a load-deflection force when each is compressed. In addition, any horizontal or moment forces are substantially reduced and / or eliminated when a downward vertical force is applied, as minimal or no torsion is created in the individual coils, legs or extensions.
Owner:VELOCE LABS
Triangulation of pavement deflections using more than four sensors
InactiveUS20110259114A1Improve accuracyHigh accuracy pavement deflection measurementForce measurementEarth material testingNon destructiveTriangulation
Systems and methods are disclosed that provide improved non-destructive testing of pavements and in particular non-destructive testing of pavements using rolling wheel deflectometer systems having more than four sensors. The additional sensors more accurately detect pavement deflections under load by compensating for the influence the load deflection basin can have on sensors beyond those at the wheel load. The sensors should be spaced with equal distances from the rolling weight and can have a distance between adjacent sensors that is greater than the equivalent thickness of the pavement being measured.
Owner:DYNATEST INT AS
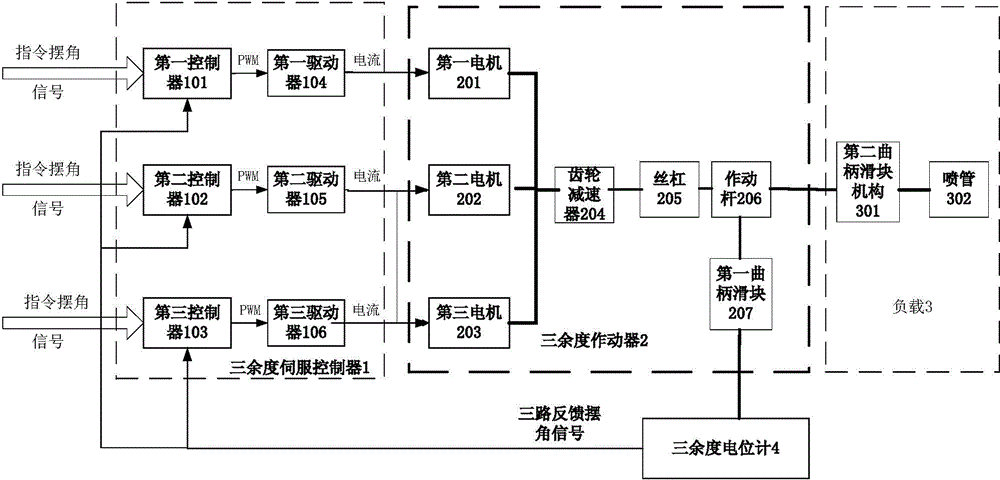
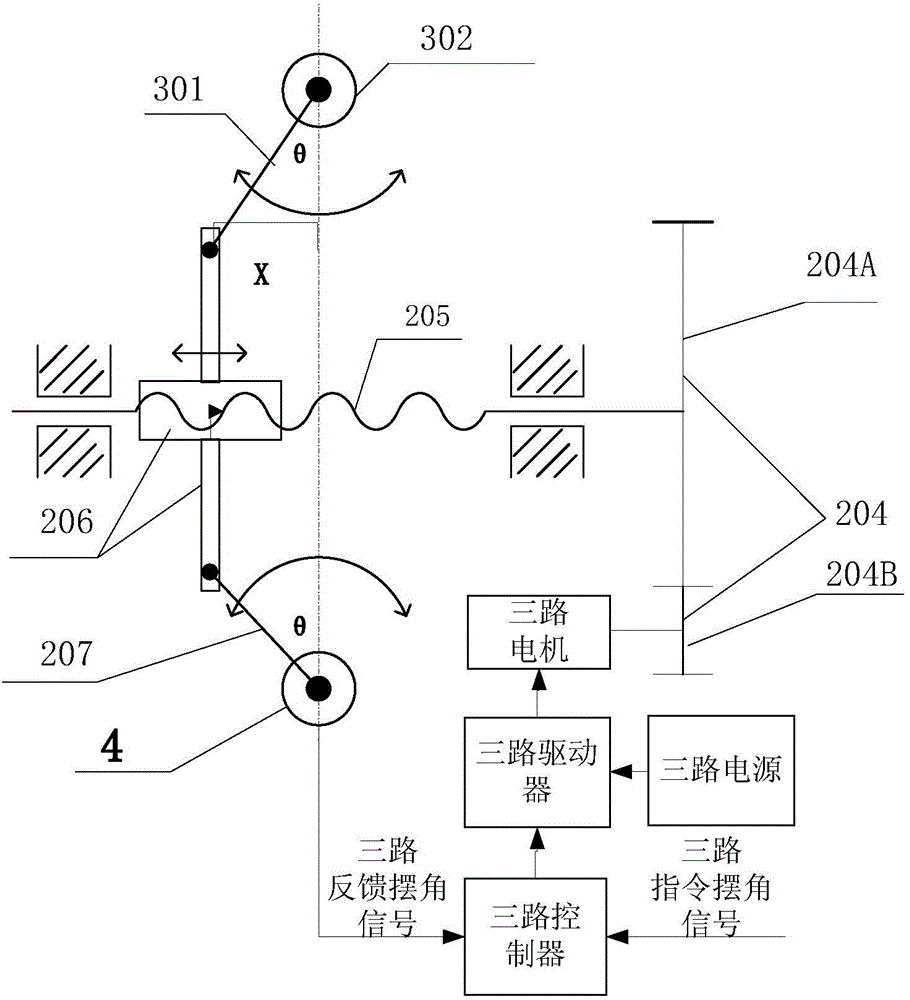
High-redundancy integrated tri-redundancy electromechanical servo mechanism
InactiveCN104579027AAvoid misuseAchieve deep redundancyMultiple dc dynamo-electric motors controlMotor driveControl signal
The invention belongs to electromechanical servo mechanisms, and particularly discloses a high-redundancy integrated tri-redundancy electromechanical servo mechanism which comprises a tri-redundancy servo controller, a tri-redundancy actuator, a load and a tri-redundancy potentiometer, wherein the signal input end of the tri-redundancy servo controller is communicated with the input end of the tri-redundancy actuator; one output end of the tri-redundancy actuator is communicated with the input end of the load; the other output end of the tri-redundancy actuator is communicated with the input end of the tri-redundancy potentiometer; the feedback output end of the tri-redundancy potentiometer is communicated with the feedback input end of the tri-redundancy servo controller; being output to the tri-redundancy servo controller, the control signal is converted into a motor three-phase current signal through the tri-redundancy servo controller; a motor drives the tri-redundancy actuator to work; the tri-redundancy actuator drives the load to deflect; the tri-redundancy potentiometer acquires a load deflection signal, and feeds back the load deflection signal to the tri-redundancy servo controller. Through the adoption of the high-redundancy integrated tri-redundancy electromechanical servo mechanism, the maintenance performance and the reliability of a secondary servo mechanism of an aircraft can be obviously improved.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF PRECISE MECHATRONICS CONTROLS +1
Simplified calculation method for mechanical property of FRP-rebar-reinforced concrete beam
InactiveCN107742019ACalculation of flexural mechanical propertiesSmall amount of calculationGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationConcrete beamsRectangular coordinates
The invention provides a simplified calculation method for the mechanical property of an FRP-rebar-reinforced concrete beam. The method comprises the steps that a space rectangular coordinate system is built, a material stress-strain expression of the FRP-rebar-reinforced concrete beam is analyzed and calculated, a motion control equation of the FRP-rebar-reinforced concrete beam and the force boundary conditions of the FRP-rebar-reinforced concrete beam are built, and a final calculation model of the FRP-rebar-reinforced concrete beam is solved. By means of the method, the overall bending-resistant mechanical property (a load-deflection curve) of the concrete beam, the FRP-rebar strain, the concrete strain, the depth of the neutral axis of the concrete beam and other local mechanical properties can be accurately calculated, the calculated amount is greatly reduced, and the calculation efficiency is improved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
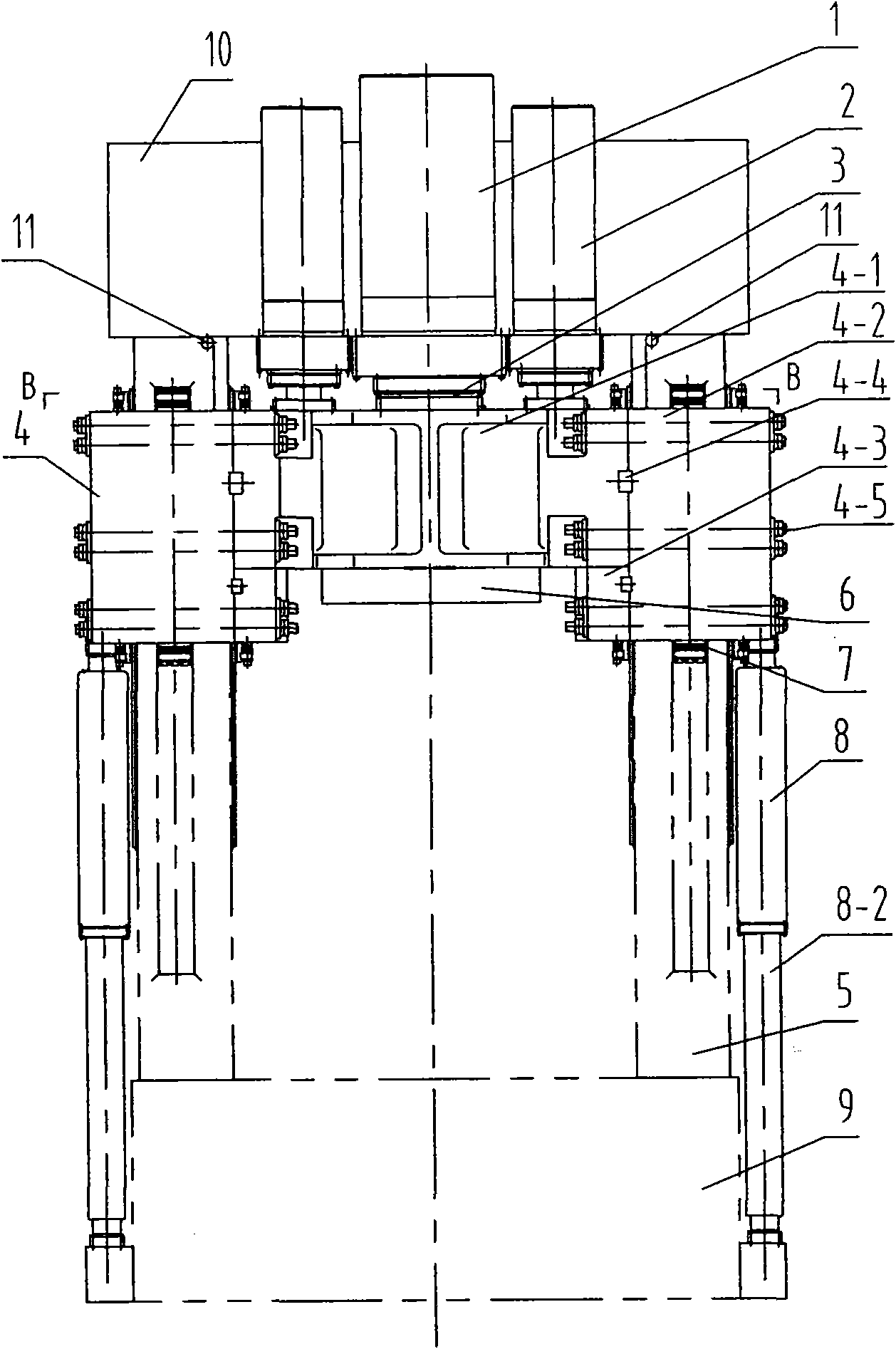
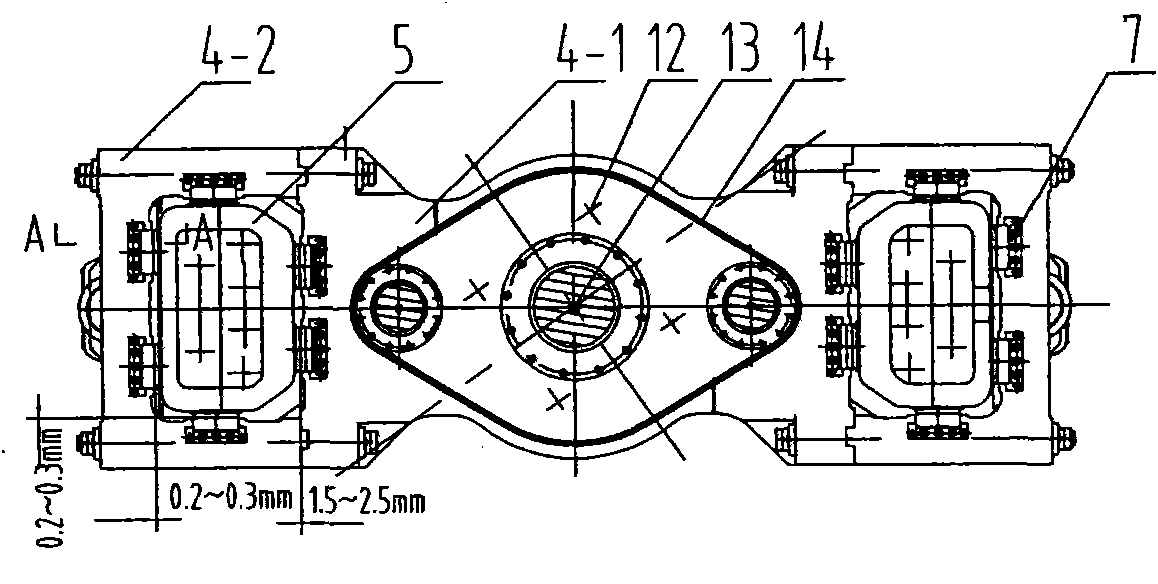
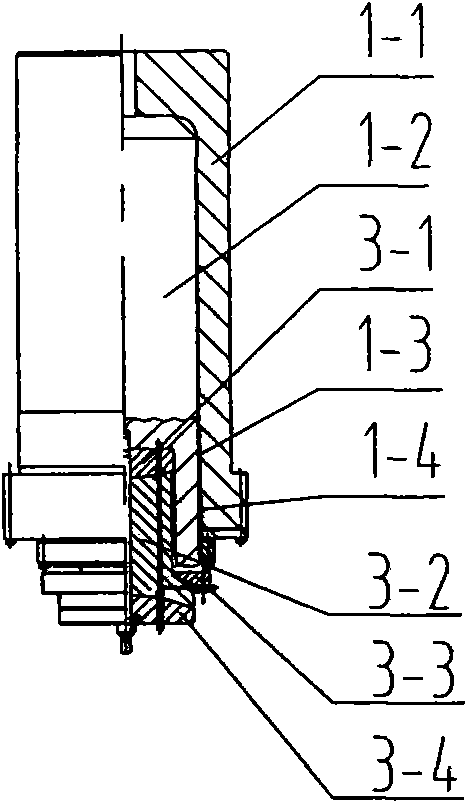
Low-internal-leakage load-deflection resistance hydraulic cylinder system
The invention relates to a low-internal-leakage load-deflection resistance hydraulic cylinder system. The system comprises a cylinder body, a piston arranged in a piston chamber of the cylinder body,and a piston rod, wherein the piston rod is connected with the piston and extends out of the cylinder body through a piston rod channel in the cylinder body. The piston chamber is divided into a leftpart and a right part by the piston. The system further comprises a static pressure supporting bearing and an oil control device, wherein the static pressure supporting bearing is fixedly arranged inthe piston rod channel and is arranged outside the piston rod in a sleeving manner, and the oil control device is connected with an oil communication hole in the cylinder body. Compared with the priorart, the low-internal-leakage load-deflection resistance hydraulic cylinder system has the advantages of being lower in internal leakage, effectively resistant to load deflection, and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
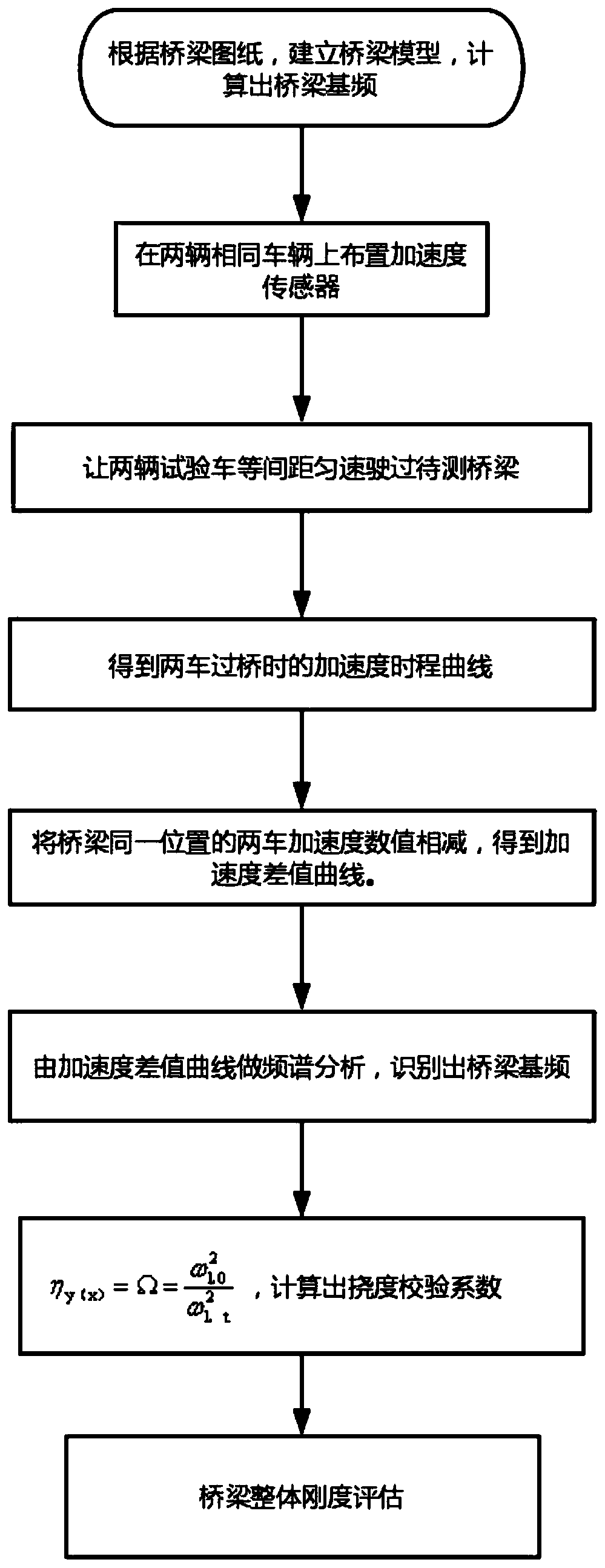
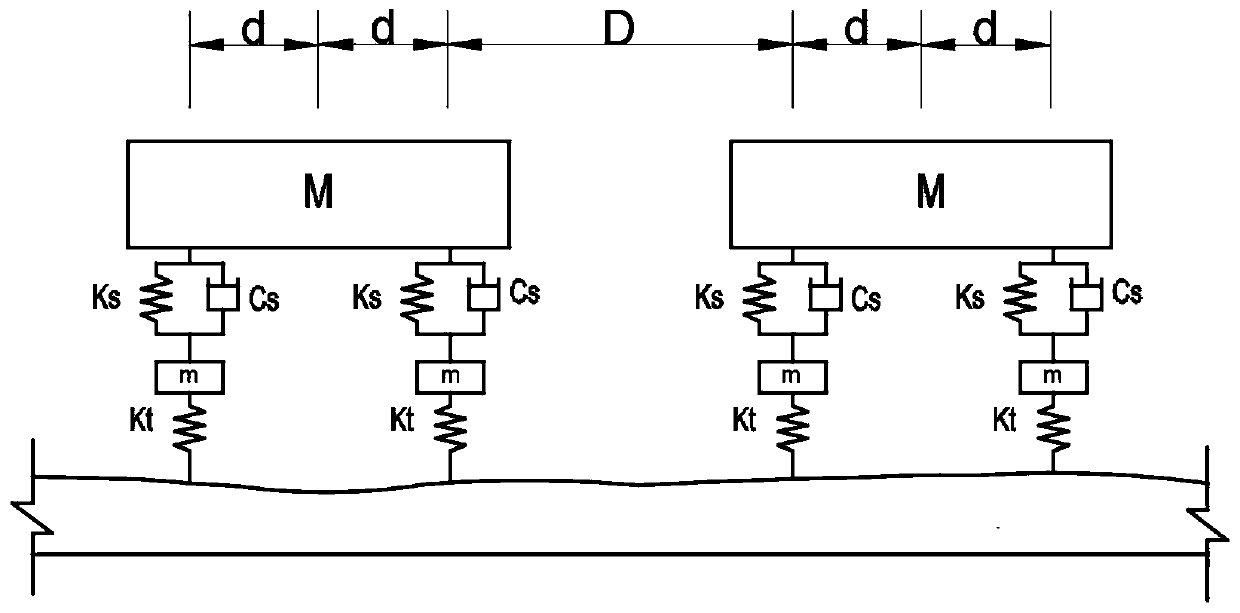
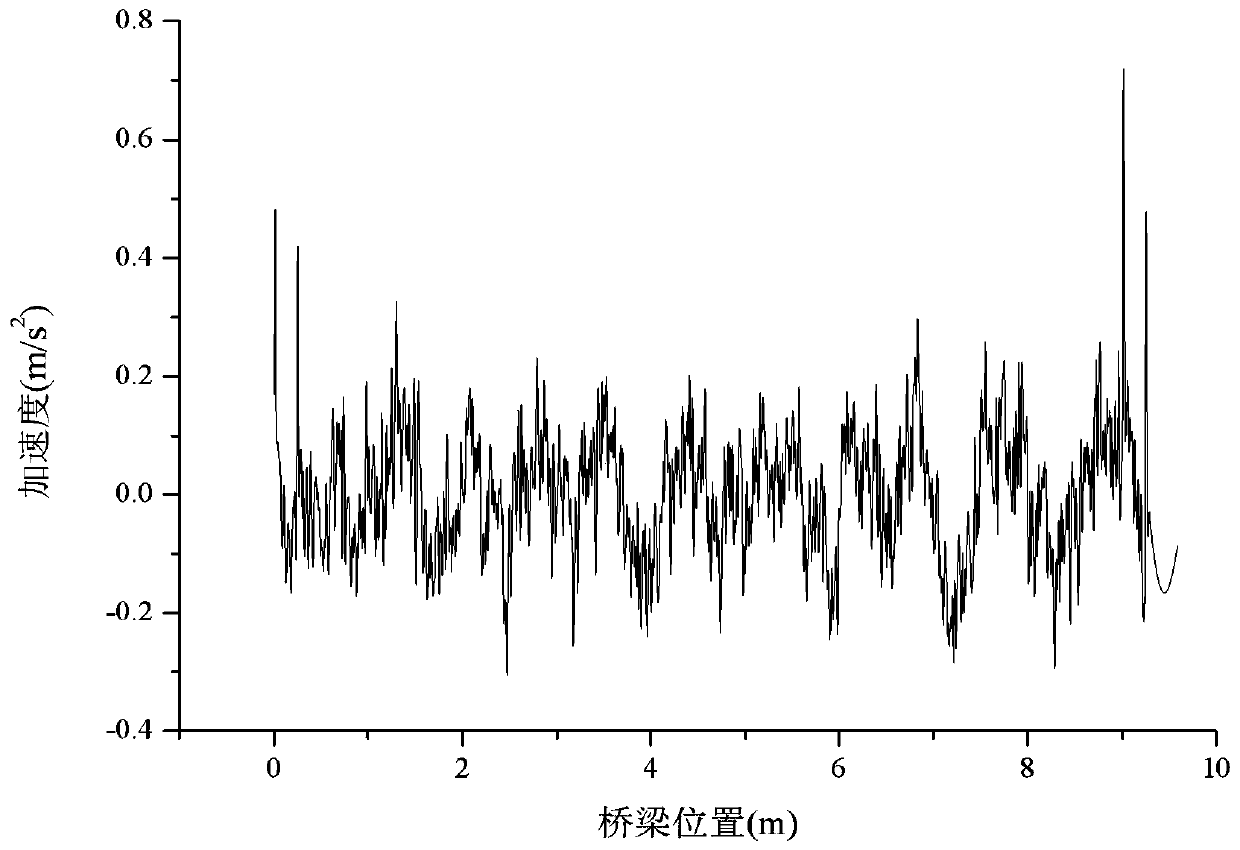
Beam bridge integral rigidity evaluation method based on vehicle vibration
InactiveCN110553808AAvoid complicationsOvercoming the difficulty of interrupting traffic for detectionComplex mathematical operationsElasticity measurementVertical vibrationFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a beam bridge integral rigidity evaluation method based on vehicle vibration. According to the technical scheme, acceleration sensors are erected on two same vehicles, the twovehicles pass through a bridge to be measured at equal intervals at a constant speed, vertical vibration acceleration information of vehicle bodies of the vehicles in the running process is measured,and an acceleration time travel curve when the two vehicles pass through the bridge is obtained; the vehicle body vertical acceleration values of the two vehicles at the same position of the bridge are subtracted to obtain an acceleration difference time-history curve, then spectrum transformation on the vehicle vertical acceleration difference time-history curve is carried out, and a bridge fundamental frequency measured value in a spectrogram is identified; and the actually measured fundamental frequency is compared with the theoretical fundamental frequency of the bridge to obtain an approximate value of the static load deflection check coefficient of the bridge so as to evaluate the integral rigidity of the bridge. According to the invention, erection of the sensors on the bridge can be avoided, traffic interruption is not needed in the measurement process, the purpose of detecting the bridge without getting off the vehicle can be realized, the test time can be greatly shortened, and the test cost is reduced.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
Composition, foam, and article made therefrom
InactiveCN103874726ASynthetic resin layered productsThin material handlingPolymer scienceLoad deflection
The present invention discloses a composition comprising a) a thermoplastic vulcanizate and b) a thermo-expandable microsphere comprising a polymer shell and a propellant encapsulated in said polymer shell based on the total weight of the composition. The composition is suitable for making foam with balanced load deflection and elasticity, including soft touch, reduced to low deflection, improved relaxation performance and low water absorption, replacing either soft paint or assembled constructions with foam sheets and meeting requirements in soft touch applications.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Concrete beam nonlinear model correction method based on response surface method
ActiveCN110489924AVerify application valueSpecial data processing applicationsTest designNonlinear model
The invention discloses a concrete beam nonlinear model correction method based on a response surface method. The concrete beam nonlinear model correction method comprises the following steps: obtaining a deflection curve under a certain-stage load of a beam or a load-deflection curve at a certain position of the beam through a static test; selecting a proper material constitutive equation; preliminarily screening parameters influencing the constitutive equation of the material as initial to-be-corrected parameters; determining a reasonable parameter value interval of the material constitutiveequation; performing test design on parameters of the material constitutive equation to obtain a sample space of the parameters, and calculating response values corresponding to the sample points through a nonlinear program; determining a response surface model, screening the parameters of the material constitutive equation through variance analysis, and reserving the parameters having significant influence on deflection to fit the response surface equation; performing precision inspection on the fitted response surface equation; and obtaining a correction value of the parameter by using an optimization algorithm to complete nonlinear model correction. The method can be applied to reference model establishment of the nonlinear material beam and beam structure state evaluation.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Lower pull rod type bogie braking fulcrum device
The invention relates to railway goods transporters, in particular to a bogie for a rail wagon. A lower pull rod type bogie braking fulcrum device comprises a braking beam, a lever and a lower pull rod. A fulcrum seat is installed on a swing bolster of the bogie. The lower pull rod type bogie braking fulcrum device is characterized in that the fulcrum seat comprises a mounting plate and a connecting plate connected with the mounting plate; a strip hole is formed in the connecting plate; a braking fulcrum comprises an ear plate and a clamping plate connected with the ear plate, wherein the mounting plate is installed on the swing bolster of the bogie, the ear plate is connected with the connecting plate through the strip hole, and the clamping plate is connected with the lever. The lower pull rod type bogie braking fulcrum device has the advantages that the strip hole is formed in the connecting plate of the fulcrum seat, the ear plate of the braking fulcrum penetrates through the strip hole through a pull rivet pin, as a result, the fulcrum seat and the braking fulcrum are flexibly connected, the braking fulcrum has the self-adaption property, the device can adapt to differences in empty and load deflection of the rail wagon, influence on a barding device by the differences in empty and load deflection of the rail wagon is reasonably eliminated, the misalignment phenomenon between braking devices of the bogie for the rail wagon can be remarkably reduced, and the problem that brake release of the rail wagon is poor is effectively solved.
Owner:CRRC MEISHAN
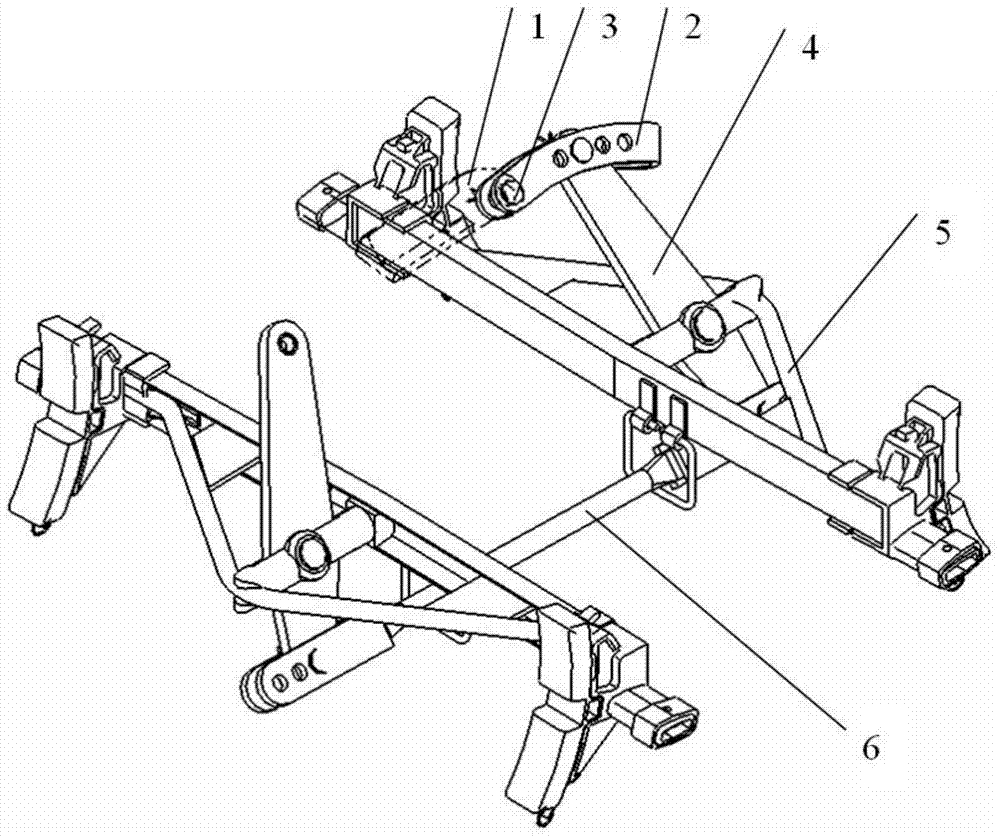
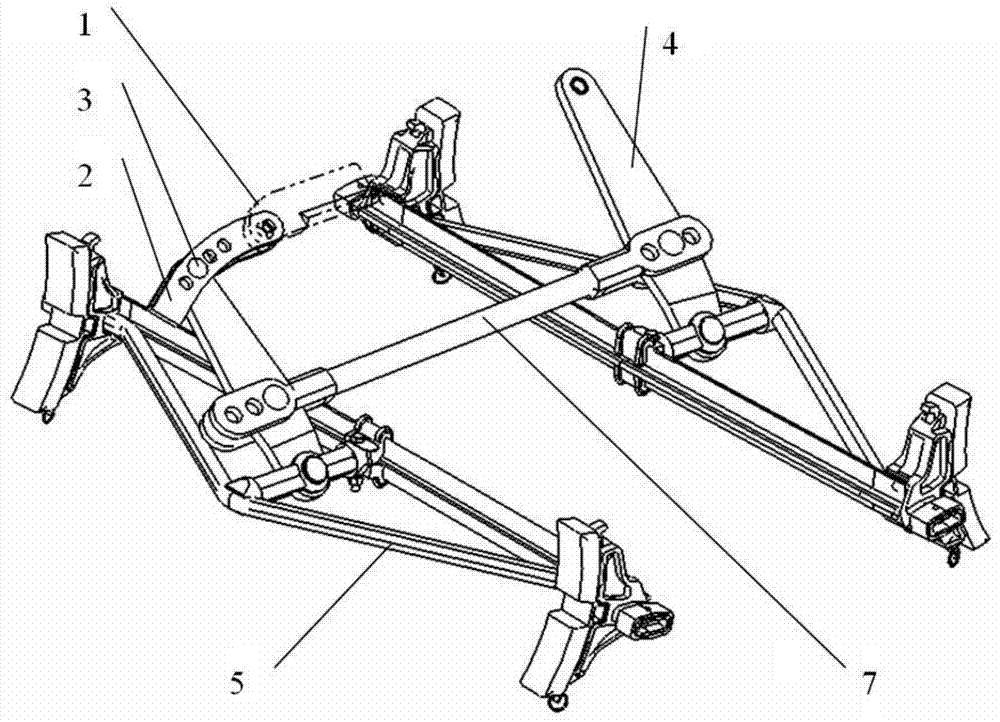
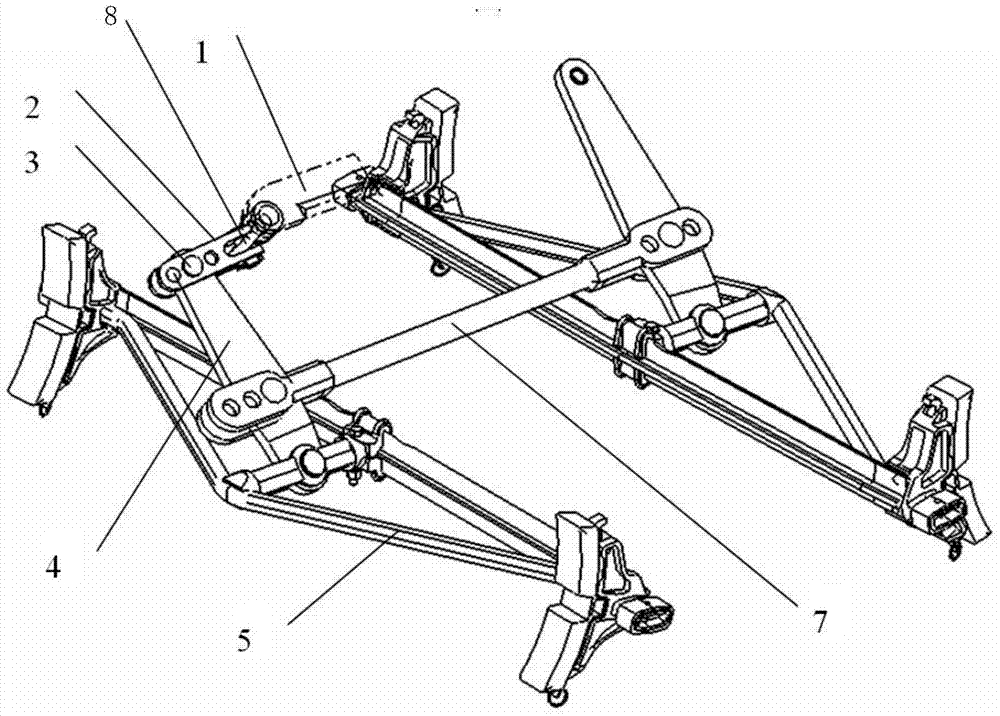
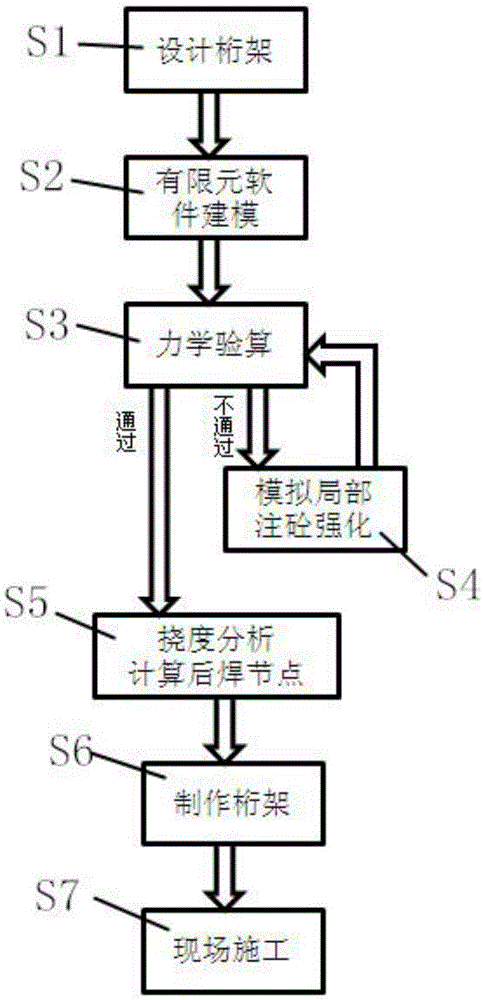
Construction method of rear welded joints of a truss
The invention discloses a construction method of rear welded joints of a truss. The method comprises the following steps that building construction requirements are collected; a truss structure is designed; a structural model of the truss and a substructure and a superstructure which are connected with the truss is built through finite element software; mechanics checking calculation is conducted on the model, a high stress section of the truss is calculated, and local cement pouring reinforcement is conducted; deflection analysis is conducted on the model through the finite element software, after the truss is loaded, downward displacement of lower chord members is calculated, notches are formed in the connection positions of the two ends of the lower chord members which move downwards and uprights, and the notches serve as the rear welded joints; the truss is manufactured, wherein rear welded junctions are formed in the positions, corresponding to the rear welded joints, of the uprights; site construction is conducted. By means of detailed design, the finite element software is utilized to calculate the local cement pouring points and analyze load deflection of the truss, the rear welded joint positions are set, the rear welded junctions are reserved, and the problem that oblique pulling force is produced to the uprights by the chord members due to the fact that the chord members are deformed under stress is effectively solved by conducting repair welding on the rear welded junctions during construction in later stage.
Owner:GUANGZHOU JISHI CONSTR GRP
Non-linear hourglass type auxiliary spring
InactiveCN104976262AAdd Compression NonlinearitySolve the overload problemRubber-like material springsEngineeringInverted t
The invention belongs to the technical field of damping devices and relates to a non-linear hourglass type auxiliary spring. The load rigidity of the spring can be increased instantly, and the difference between heavy-load deflection and no-load deflection can be lowered. The non-linear hourglass type auxiliary spring comprises a support, rubber and a bottom plate. The support is of an inverted-T structure. The bottom surface of the support is provided with a downward supporting column. The bottom surface of the support is an inward concave surface. A concave hole matched with the supporting column is formed in the center of the rubber. The whole supporting column is wrapped by the rubber through the concave hole. The edge of the rubber is of an oblique ellipsoid structure. The top of the rubber makes contact with the inward concave surface of the support. The compression non-linearity of the auxiliary spring is remarkably improved, and the problem that the difference between heavy-load deflection and no-load deflection of a traditional auxiliary spring is too large is solved. The non-linear hourglass type auxiliary spring is simple in structure and low in cost.
Owner:CRRC QINGDAO SIFANG ROLLING STOCK RES INST
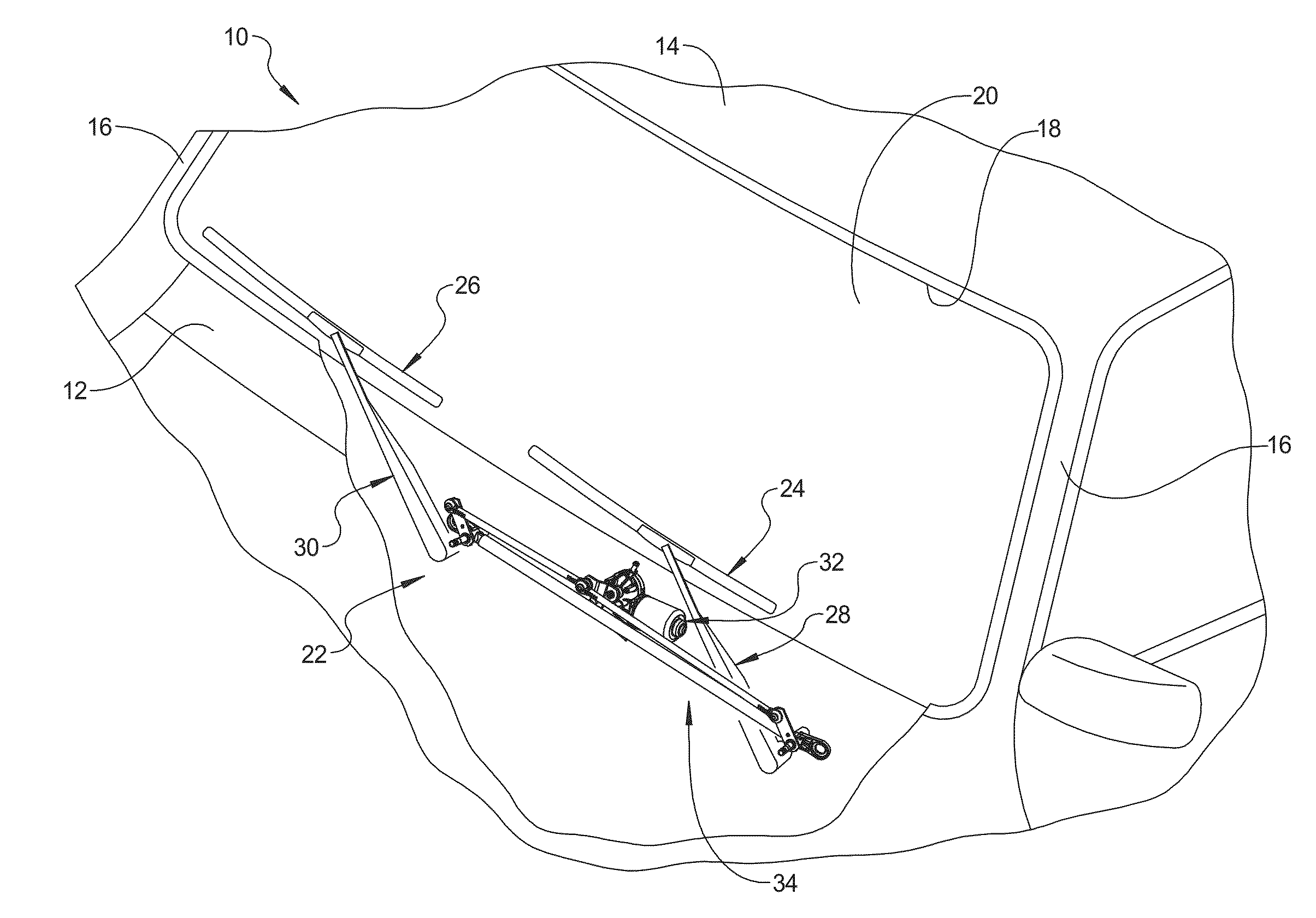
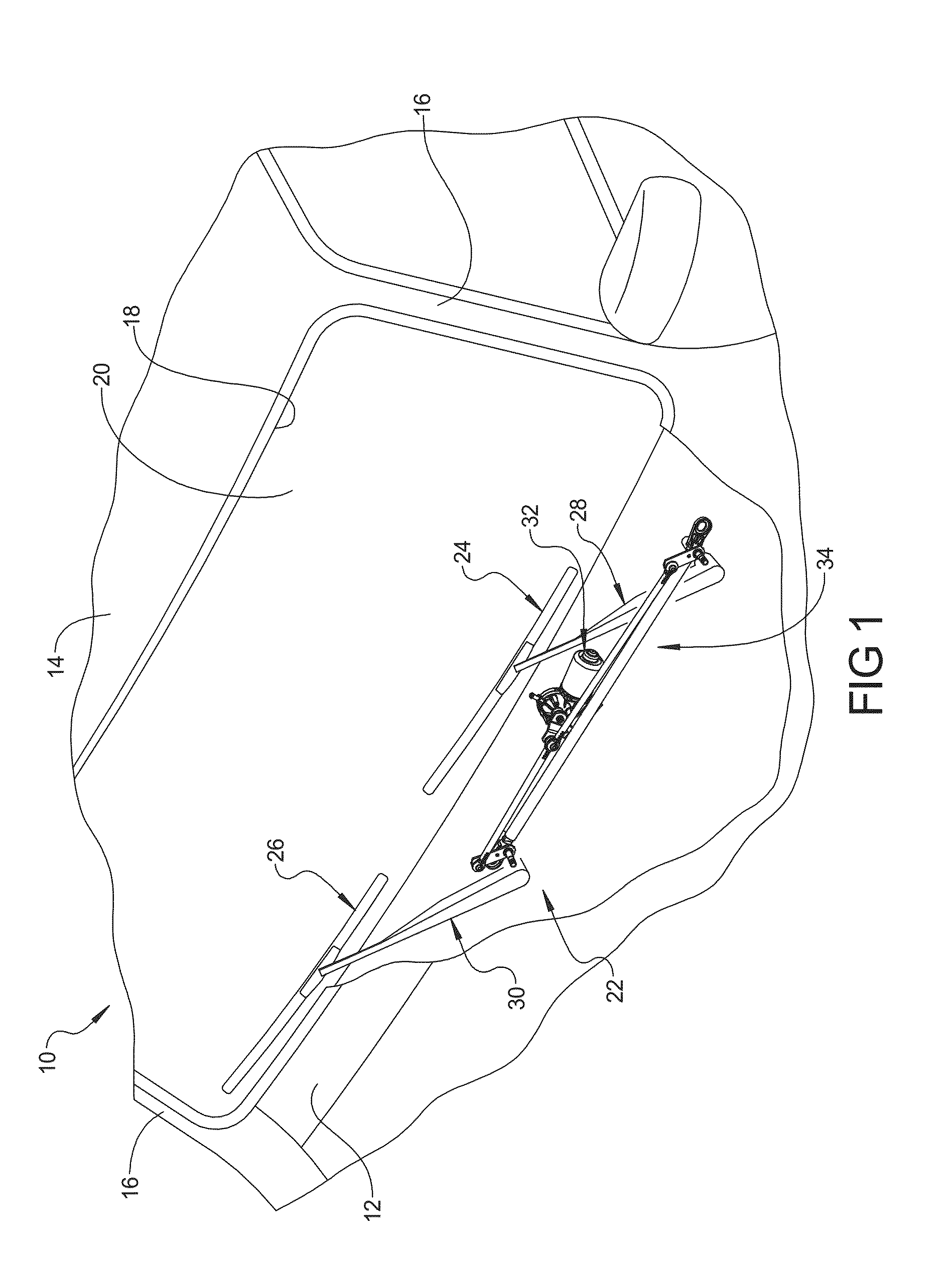
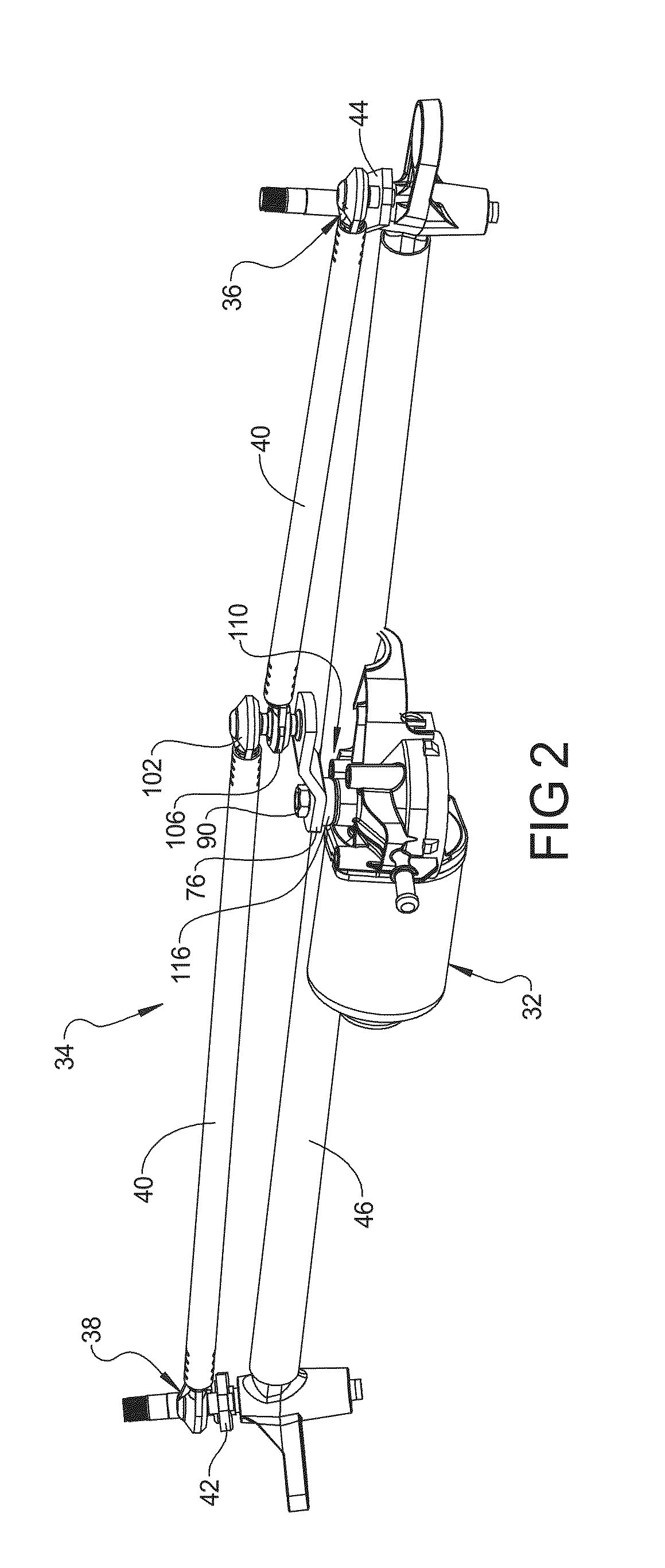
Wiper System Having Resilient Interface Assembly For Worm-Driven Reduction Gear Motor
A wiper system includes at least one wiper assembly, a linkage assembly connected to the at least one wiper assembly, and at least one worm-driven reduction gear motor having a housing, an output shaft rotatably supported by the housing, and a motor arm connected to the output shaft and the linkage assembly to drive the at least one wiper assembly in repeated wiping motion across a surface to be wiped. The wiper system also includes a resilient interface assembly disposed between the housing and the motor arm to provide resistance to loading deflection and damp axial and cross-axial movement of the output shaft of the motor.
Owner:TRICO PROD CORP
Particles for display media and information display panel using the particles
InactiveCN101071247AImprove heat resistanceEnsure pigment contentNon-linear opticsHeat resistanceEngineering
The invention provides particles for display media: which are manufactured using a thermoplastic resin which has high thermal resistance and is easily pulverized; whose Izod impact strength is less than a predetermined strength value and a load-deflection temperature is not less than a predetermined temperature; and whose thermal resistance is high and content of pigment is secured. Particles for display media constitute the display media used for an information display panel, in which the display media are sealed between two substrates 1, 2, at least one substrate being transparent, and, in which the display media to which an electrostatic field is applied, are made to move so as to display information such as an image. One of the particles is produced by crushing resin blocks and classifying them, and the Izod impact strength of the resin constituting the particles for display media (based on ASTM D256) is less than 4 (kgf * cm / cm) and the load-deflection temperature of the resin constituting the particles for display media (base on ASTM D648) exceeds 100[deg.]C. The particles for display media having high thermal resistance and secured content of pigment are obtained by using above particles.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Multi-parallel girder weighing sensor
PendingCN106918379AHigh precisionHigh measurement accuracyWeighing apparatus using elastically-deformable membersElastomerSteel ball
A multi-parallel girder weighing sensor comprises an elastomer and a strain gage arranged on the elastomer. The multi-parallel girder weighing sensor is characterized in that: the elastomer comprises a pedestal, a plurality of support columns are uniformly and vertically upwards arranged at intervals at the position, close to the edge of the pedestal, on the pedestal, the internal sides of the support columns are extended inwards to form a plurality of horizontal strain beams, a plurality of the strain beams are mutually connected to form girder structure of central ray distribution, a bearing head is protruded at the center intersection of a plurality of strain beams, a strain beam area is formed between the bottom of the bearing head and the pedestal, and strain gages are arranged at the lower surface of a plurality of strain beams. The elastomer is integrated girder structure of central ray distribution, and is high in precision and high in load-deflection resistance capability, the support portion and the strain portion are arranged on the pedestal, the external portion is welded and sealed with the pedestal through a sleeve, and the middle bearing portion employs steel ball loading or pressure head loading mode. The multi-parallel girder weighing sensor is reasonable in structure, high in measurement precision and high in load-deflection resistance capability, and can be applied to the electronic weighing instrument field such as an electronic truck scale.
Owner:KELI SENSING TECH NINGBO CO LTD
Device for measuring load and deflection of materials
A system for measuring normal load and deflection of a material that includes a portable load deflection device and a method of using the same is disclosed. The system includes a support arm having a first end and a second end opposite said first end. The first end can be attached to a base surface. The support arm can provides at least three degrees of freedom of movement and includes at least one sensor for determining a position of the second end. A uniaxial load cell can be operably attached to the second end. The system can also include a processing system operable to receive position data and corresponding force data when the support arm is used to apply a non-normal compression force to the test surface. The data can be used to calculate normal force versus deflection data for the test surface.
Owner:OLD DOMINION UNIVERSITY RESEARCH FOUNDATION
Load-deflection-resisting static pressure bearing sealing hydraulic cylinder
InactiveCN108194453AReduce frictionGood for resisting side loadsFluid-pressure actuatorsHydraulic cylinderEngineering
The invention discloses a load-deflection-resisting static pressure bearing sealing hydraulic cylinder which comprises a static pressure piston, a static pressure guide sleeve, a static pressure connection body, a piston rod, upper and lower cylinder bodies, upper and lower cylinder covers and a sealing ring. Static pressure bearing oil films are produced between the piston and the inner wall of ahydraulic cylinder barrel and produced between the piston rod and the guide sleeve according to the liquid static pressure bearing sealing principle through a gap between the piston and the inner wall of the hydraulic cylinder barrel and a gap between the piston rod and the guide sleeve, and the piston or the piston rod is suspended in hydraulic oil. Leakage of hydraulic oil can be effectively prevented through the reasonable gaps, friction force produced through sealing of a sealing ring adopted by a traditional hydraulic cylinder is greatly reduced, the hydraulic cylinder can resist lateralload, deviation correction of the piston is facilitated, the vibration frequency and positioning precision of the hydraulic cylinder can be improved, and movement stability and dynamic responsivenessof movement components are improved.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Seat cushion pad for vehicle, seat back pad for vehicle, and seat for vehicle
A seat cushion pad for a vehicle and a seat back pad for a vehicle producing no discomfort between seat comfort of an under-hip section and a backrest section and that of the other sections. The seat cushion pad for a vehicle, in which a part of or entire seating surface except the under-hip section is composed of a material b having a density lower than the density of a material a, or the seat back pad has any one of features described in the following items (i) to (iii). (i) Load-deflection lines of the material a and the material b are allowed to substantially agree with each other. (ii) Amounts of depression or static spring constants of the material a and the material b by a specific reaction force (for example, 50 N or 100 N) based on a JASO-B408 testing method are allowed to substantially agree with each other. (iii) Reaction forces at a specific amount of deflection of the material a and the material b based on a push-pull gage measuring method are allowed to substantially agree with each other.
Owner:ARCHEM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com