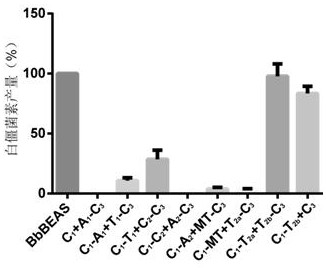
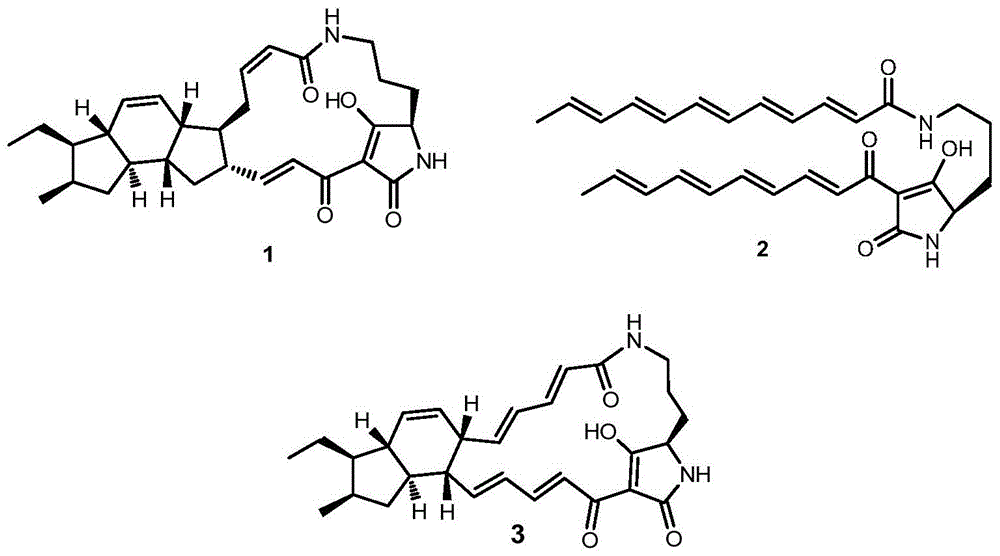
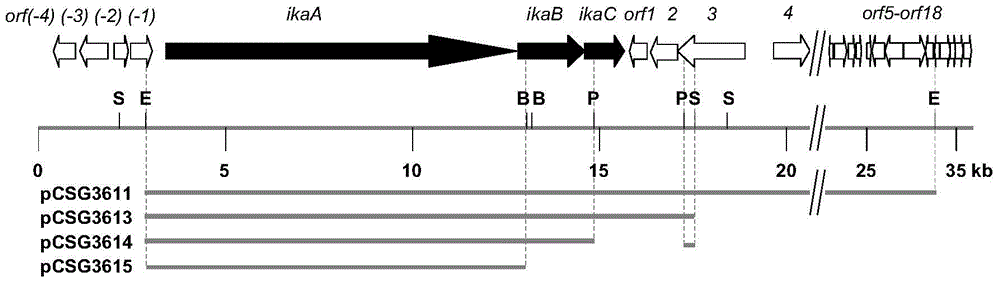
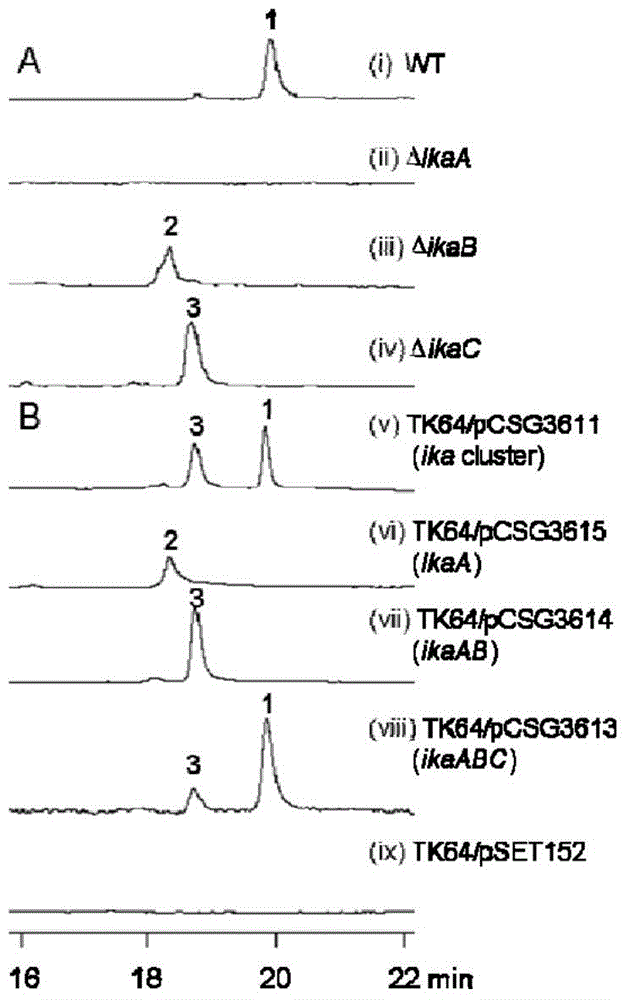
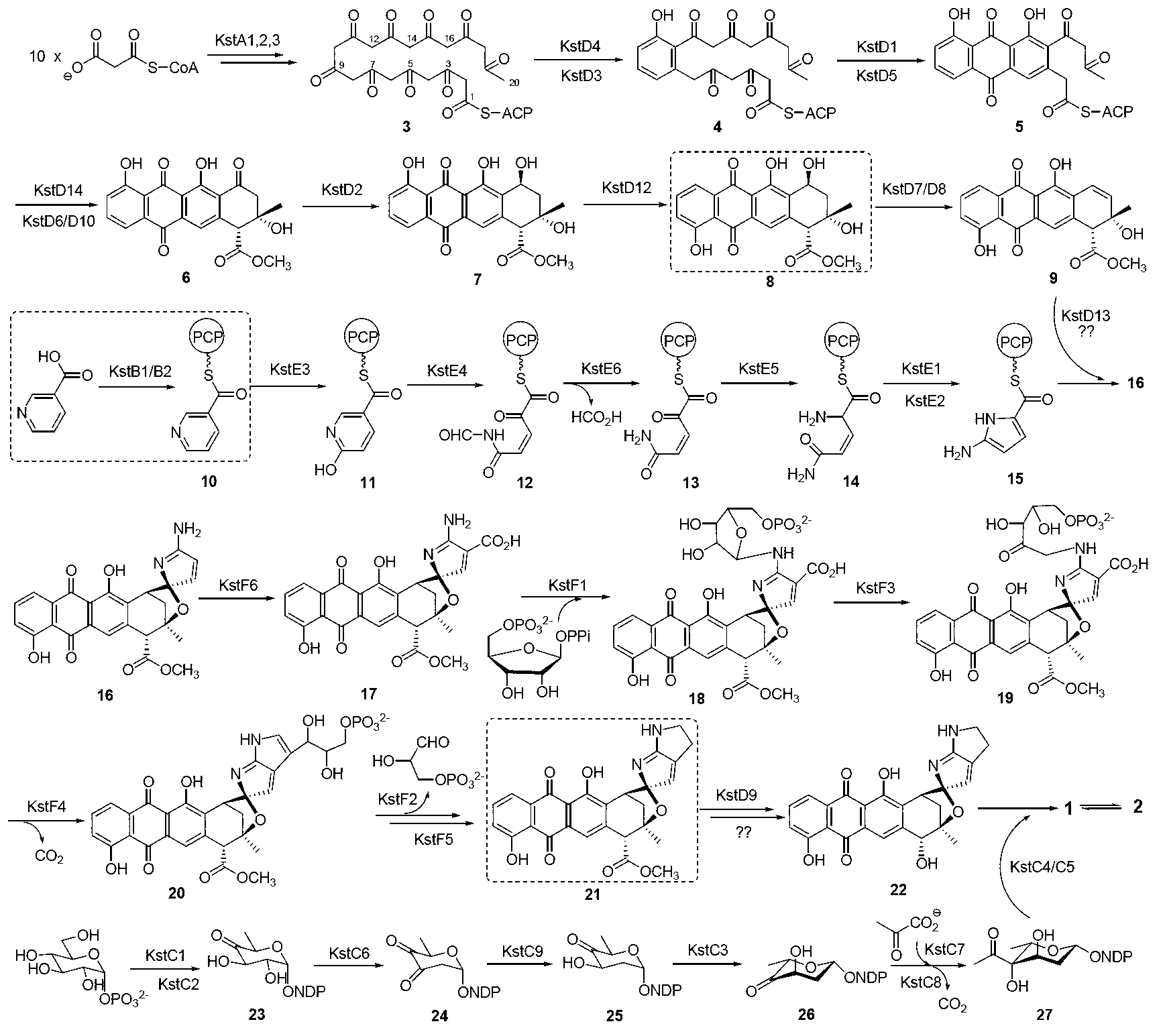Patents
Literature
31 results about "Peptide Synthetases" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Biosynthetic gene cluster of FR901464
ActiveCN101818158AUnderstanding Biosynthetic MechanismsDepsipeptidesFermentationBiosynthetic genesGenetic engineering
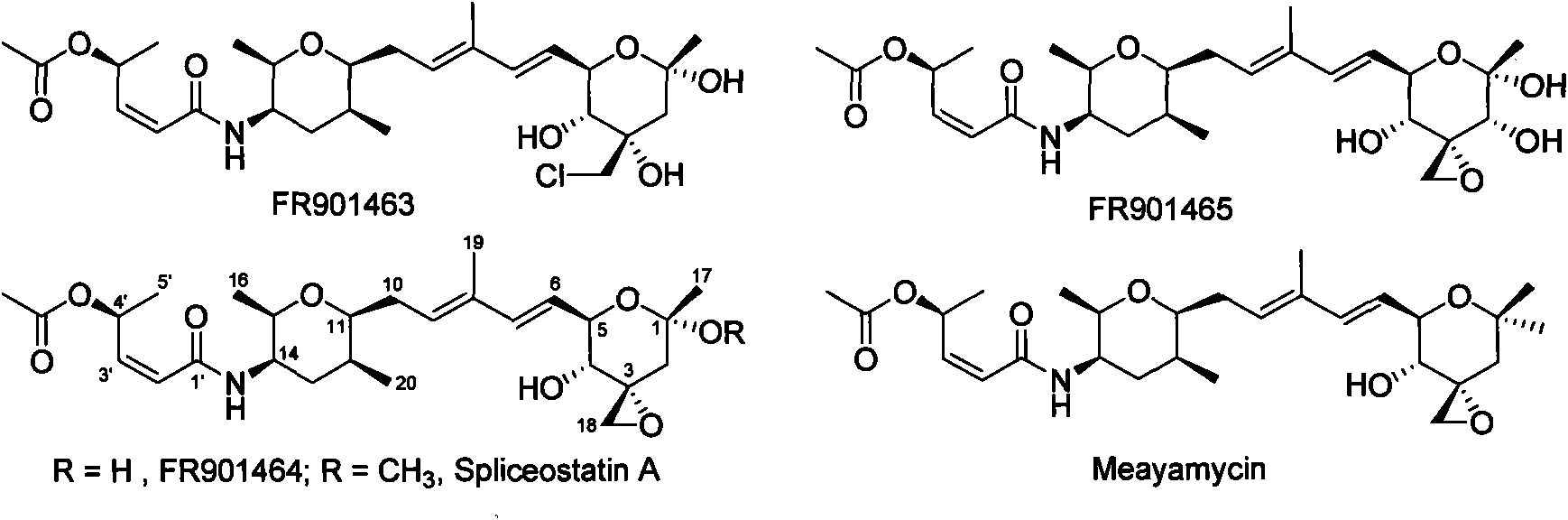
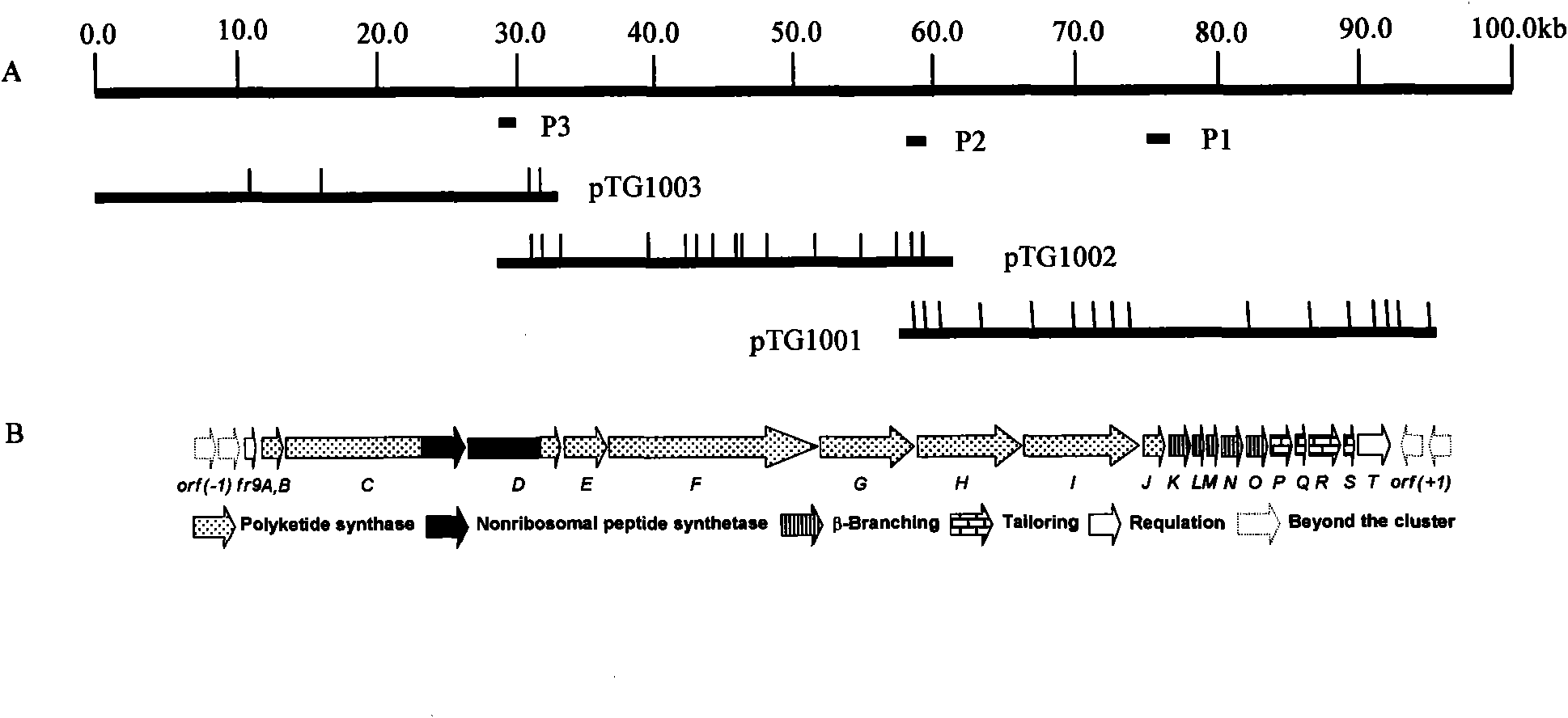
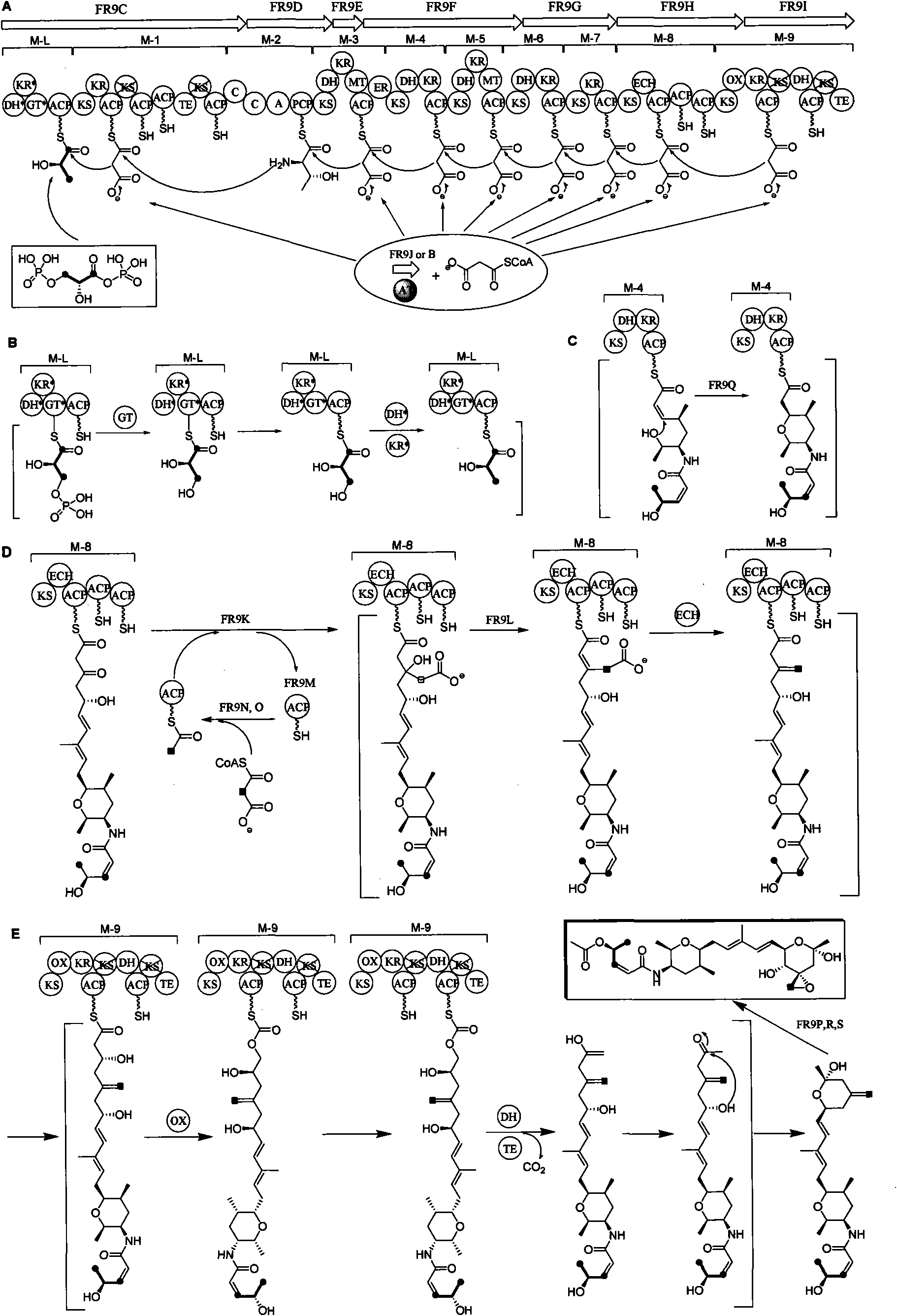
The invention relates to cloning, sequencing, analysis and functional study of a biosynthetic gene cluster of a natural product FR901464 which has anti-tumor activity and is generated from pseudomonas as well as the application thereof. The whole gene cluster contains 20 genes: five polyketide synthase genes, one hybrid polyketide / non-ribosomal polypeptide synthase gene, one non-ribosomal polypeptide synthase gene, three independent acyltransferase genes, four genes related to polyketide backbone alkylation, four post-modification genes and two control-related genes. The genetic operation of the biosynthetic gene can block the biosynthesis of FR901464. The provided gene and protein thereof can be used for genetic engineering, protein expression, enzyme catalysis reaction, and the like of the compound and can also be used for searching and discovering compounds that can be used in medicines, industry or agriculture or genes and proteins thereof.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
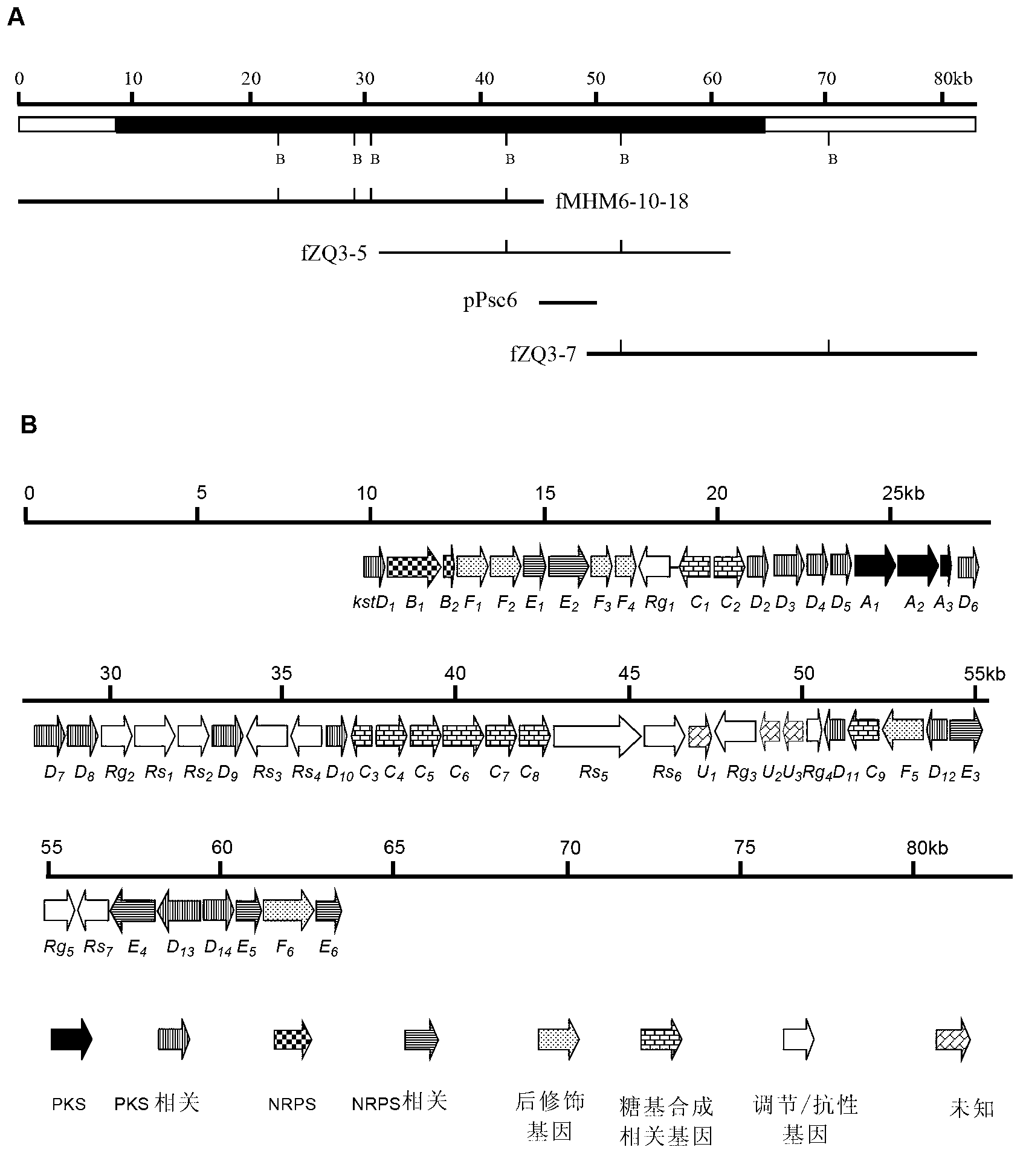
Biosynthesis gene cluster of kosinostatin and application thereof
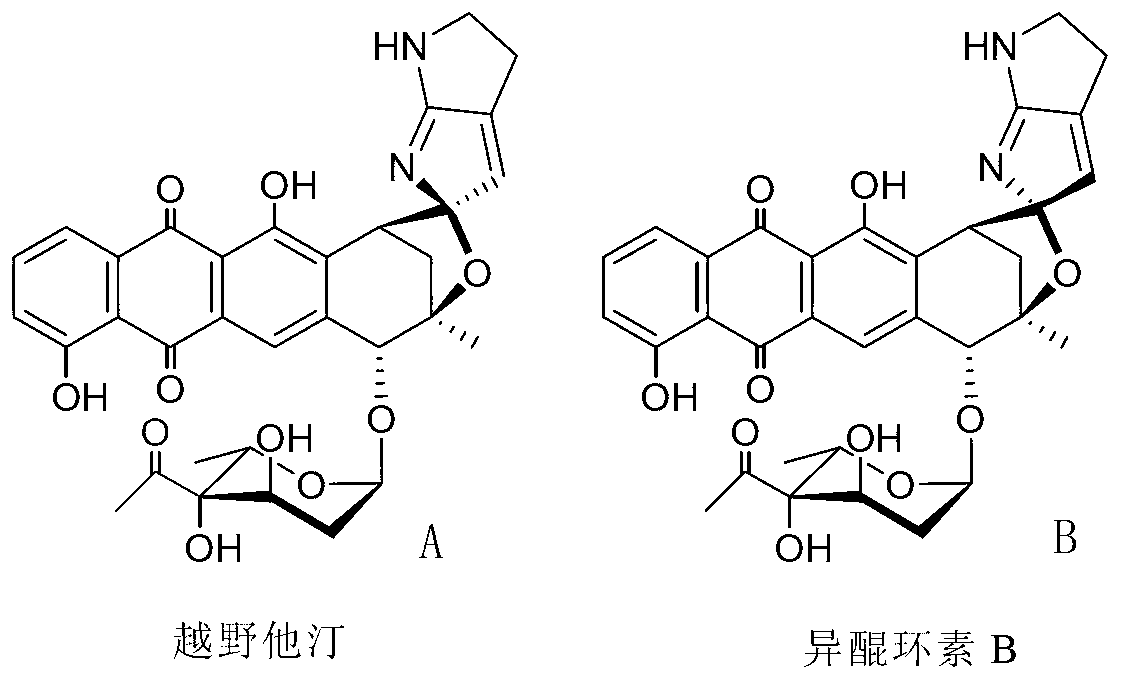
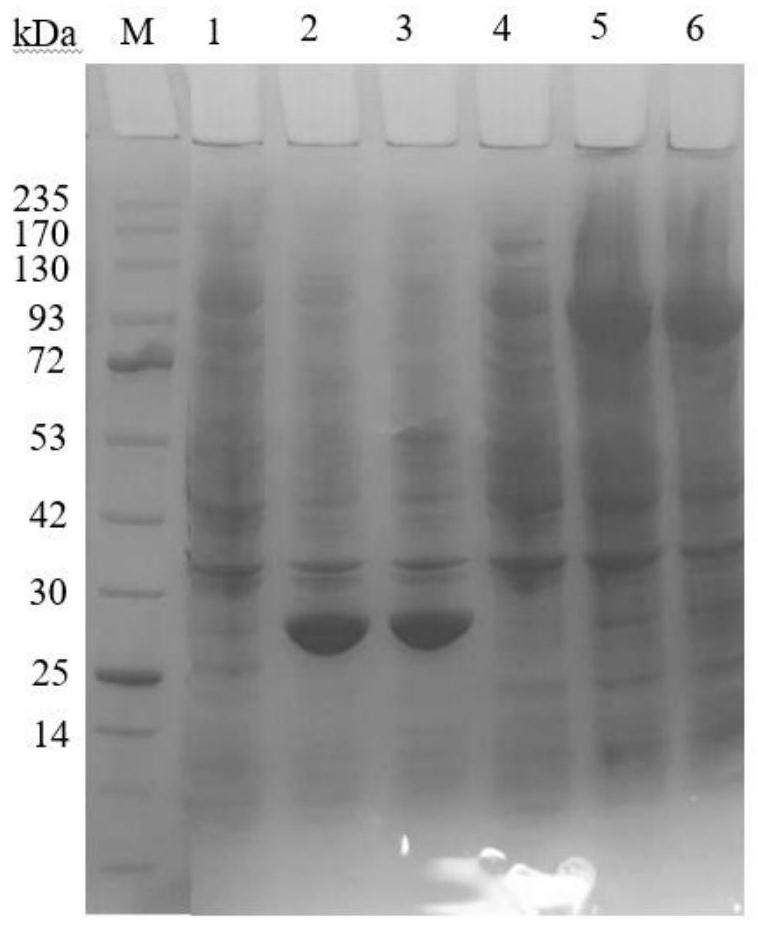
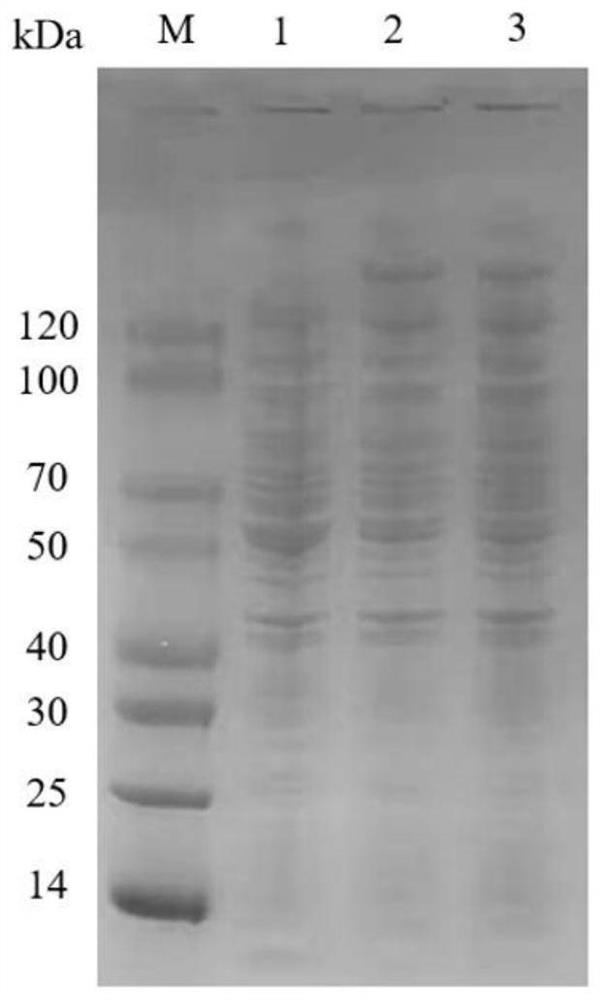
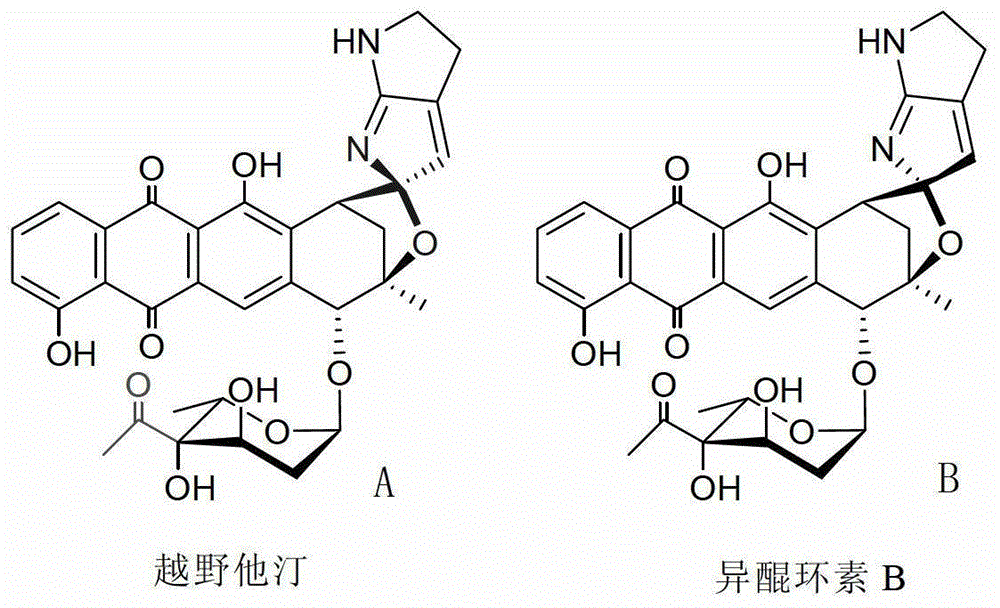
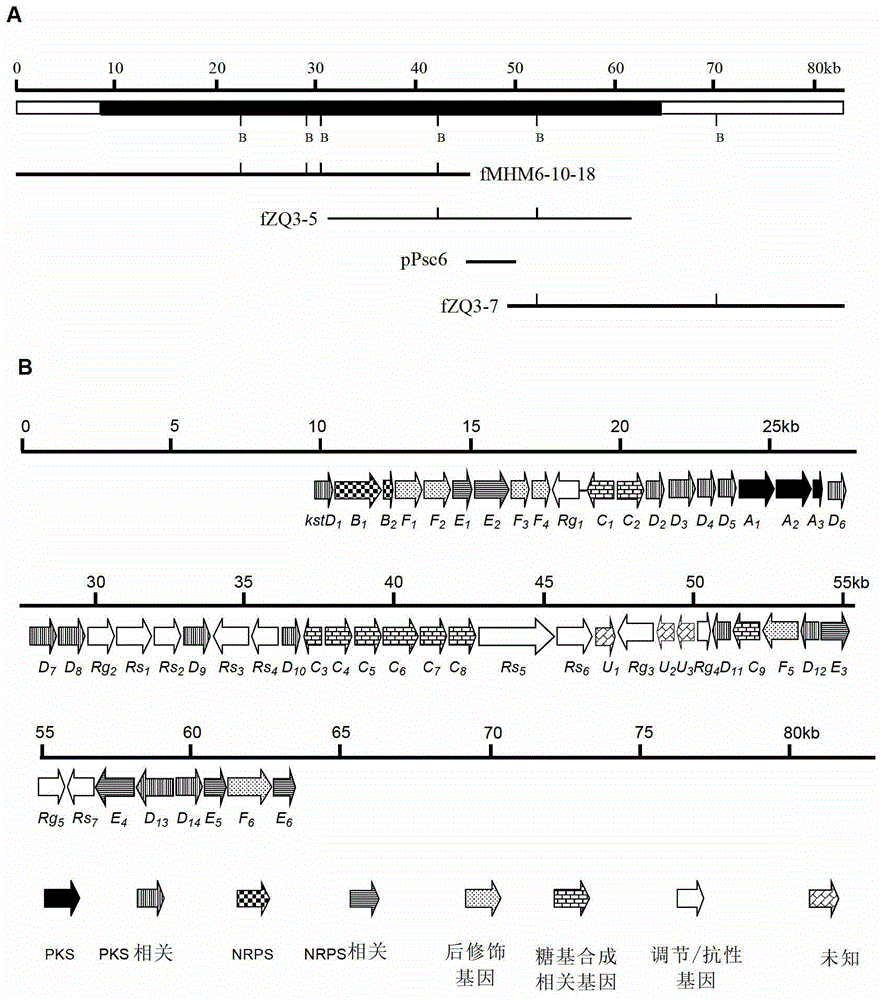
The invention relates to a biosynthesis gene cluster of kosinostatin, and in particular relates to cloning, sequencing, analysis, functional study and application of the biosynthesis gene cluster of the kosinostatin, which is an antharcycline antibiotic with antitumor activity and generated from micromonospora sp.TP-A0468. The whole gene cluster comprises 55 genes in all, that is, 17 II-type polyketone synthetase (PKS) related genes, 8 non-ribosome polypeptide synthetase (NRPS) related genes, 9 glycosyl synthetic related genes, 6 special post-modifying genes, 7 antibiotic genes, 5 conditioning genes and 3 genes without definite functions. Through the genetic manipulation of the biosynthesis genes, the biosynthesis of kosinostatin can be blocked, the output is changed, or novel compounds are produced. The gene cluster can be applied to gene engineering, protein expression, enzymatic catalytic reaction and the like of antharcycline compounds, and can also be used for finding and discovering compounds, genes or proteins for medicines, industry or agriculture.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods of Identifying and Characterizing Natural Product Gene Clusters
InactiveUS20130260436A1Rapid and reproducible assessmentHigh detection sensitivityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionSecondary metabolite biosynthesisADAMTS Proteins
The invention relates to methods and compositions for identifying a candidate nucleic acid (CNA) comprising a polynucleotide sequence encoding at least a part of a natural product gene cluster (NPGC), a secondary metabolite biosynthesis cluster (SMBC), a non ribosomal peptide (NRP), a polyketide (PK) biosynthesis cluster, a protein involved in NRP and / or PK biosynthesis, a protein involved in other secondary metabolite biosynthesis, and / or a phosphopantetheinyl transferase (PPTase), by expressing the candidate nucleic acid (CNA) to form at least one PPTase, incubating the PPTase with a non ribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS), and detecting activation of the NRPS, wherein activation indicates that said CNA comprises a polynucleotide sequence encoding at least one of the above.
Owner:VICTORIA LINK LTD
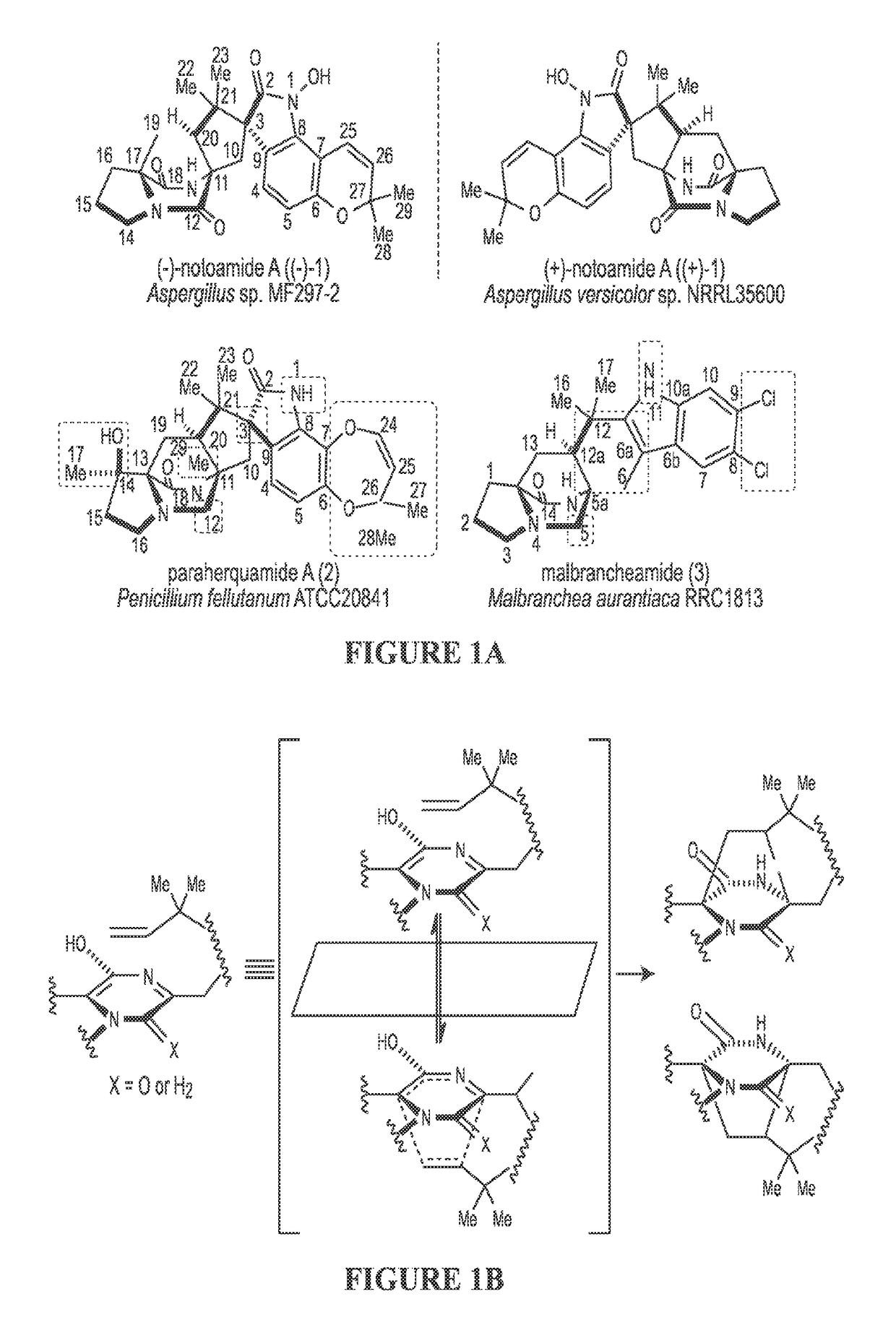
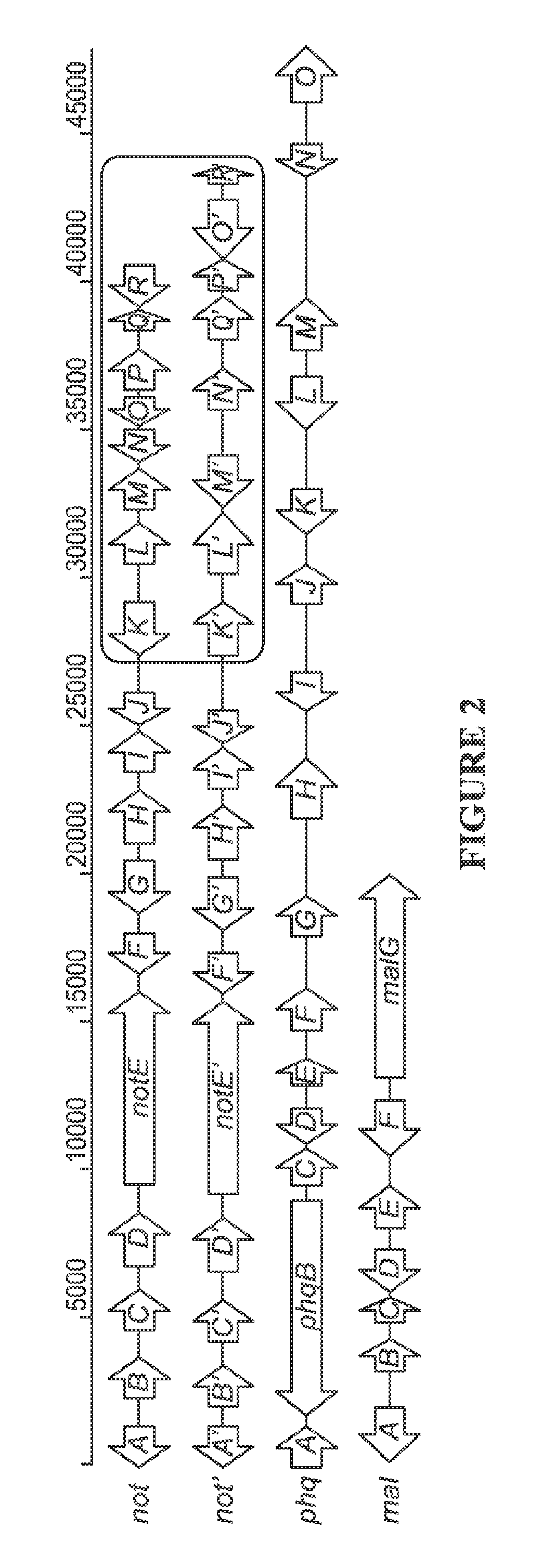
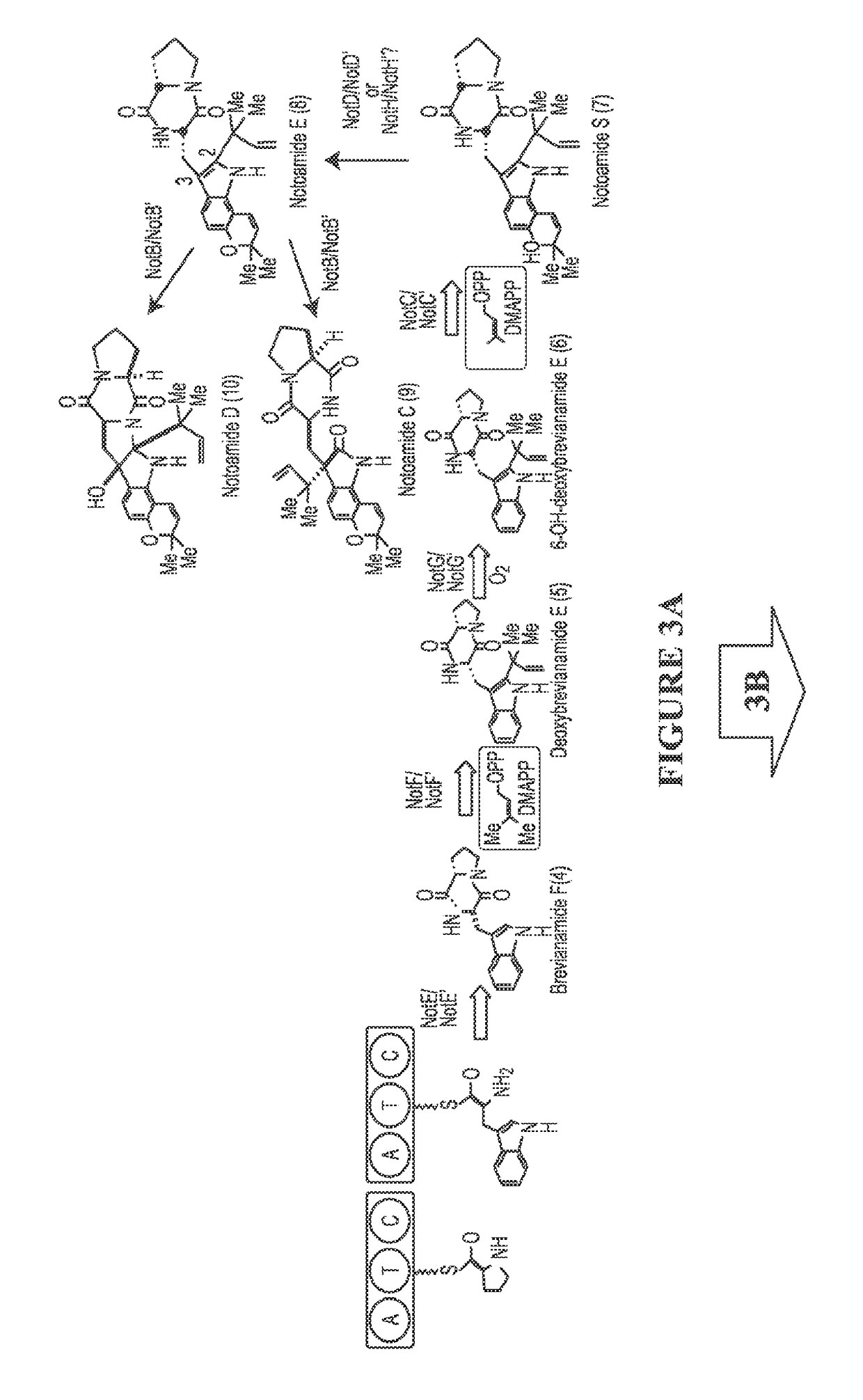
Biosynthetic Systems Producing Fungal Indole Alkaloids
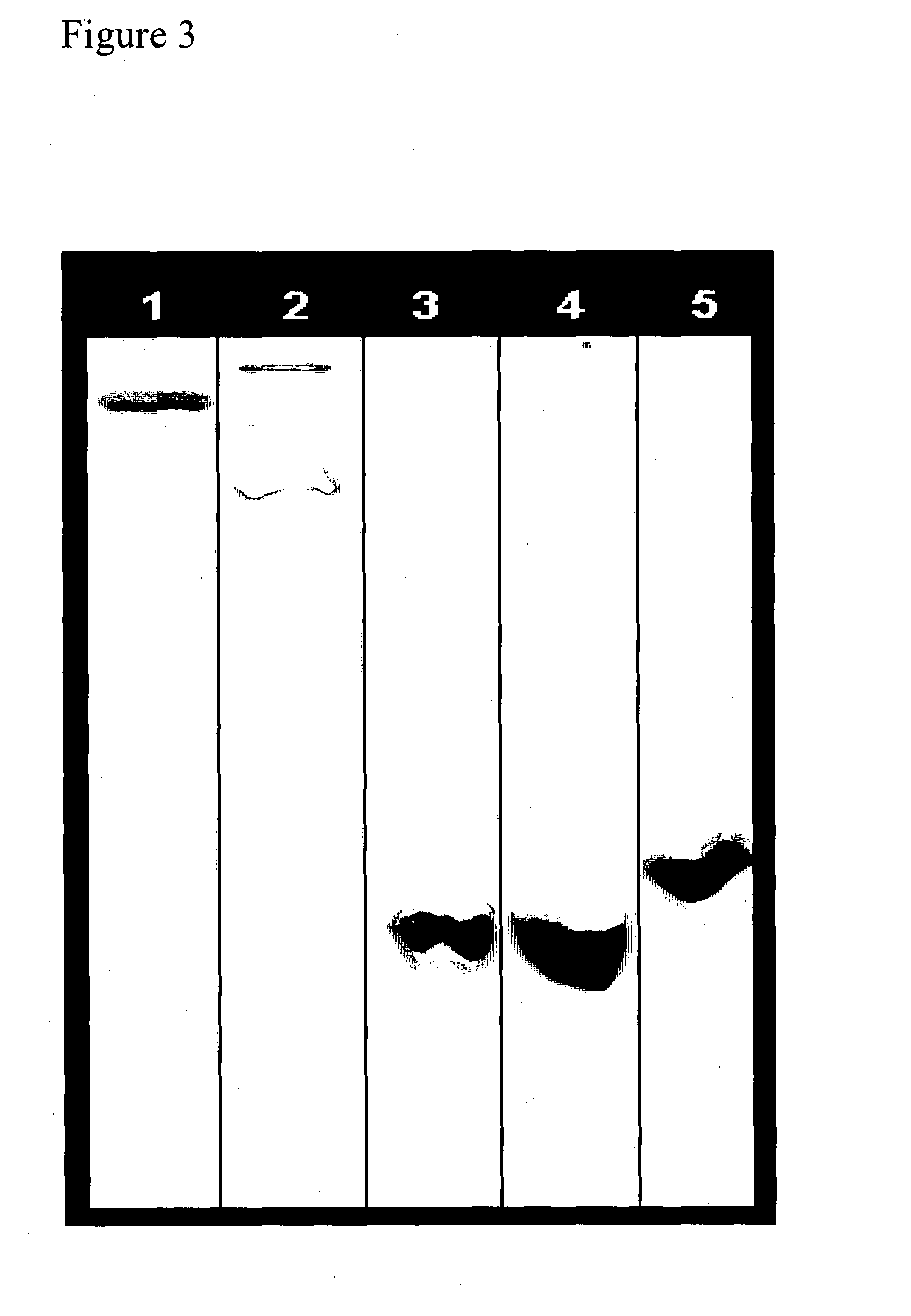
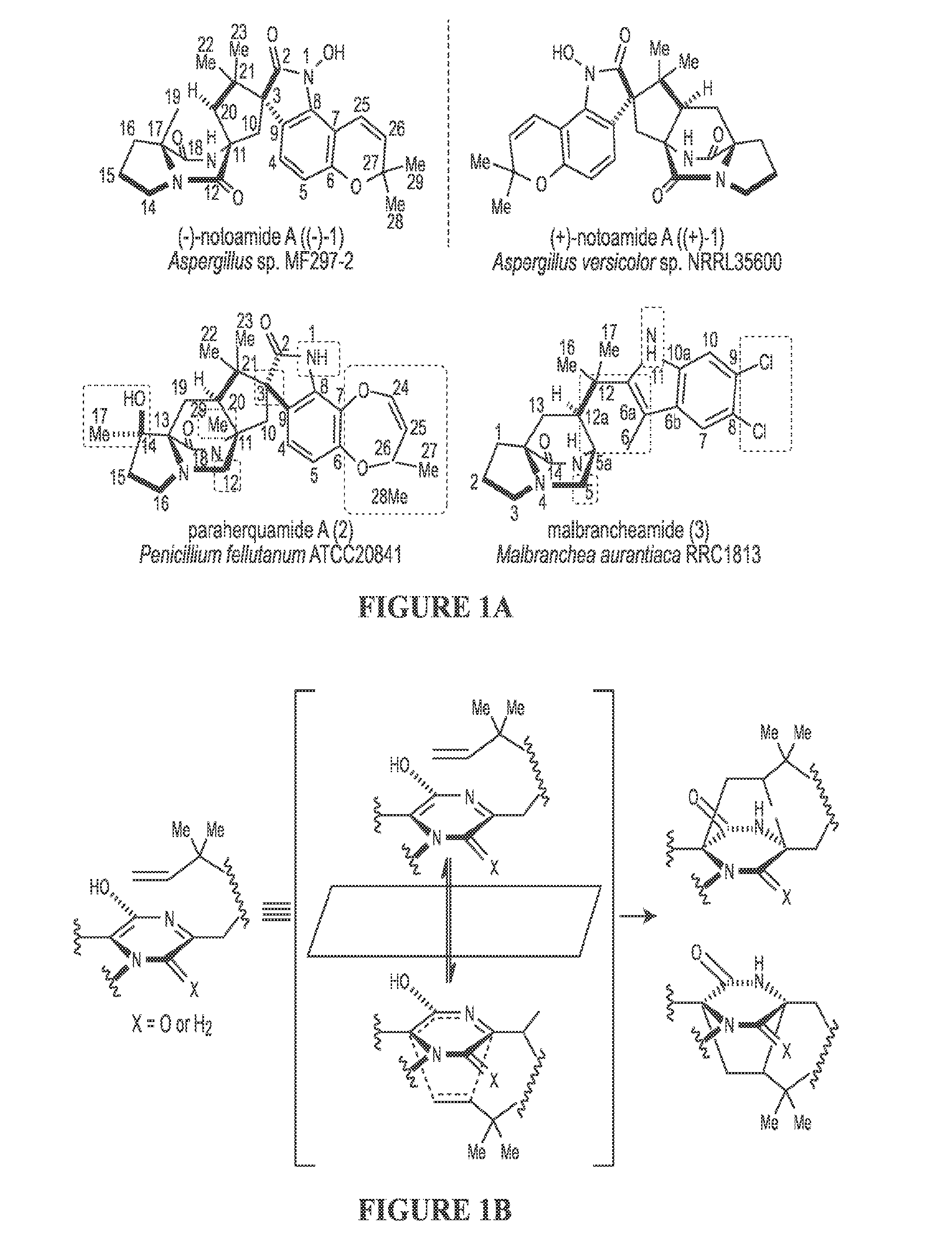
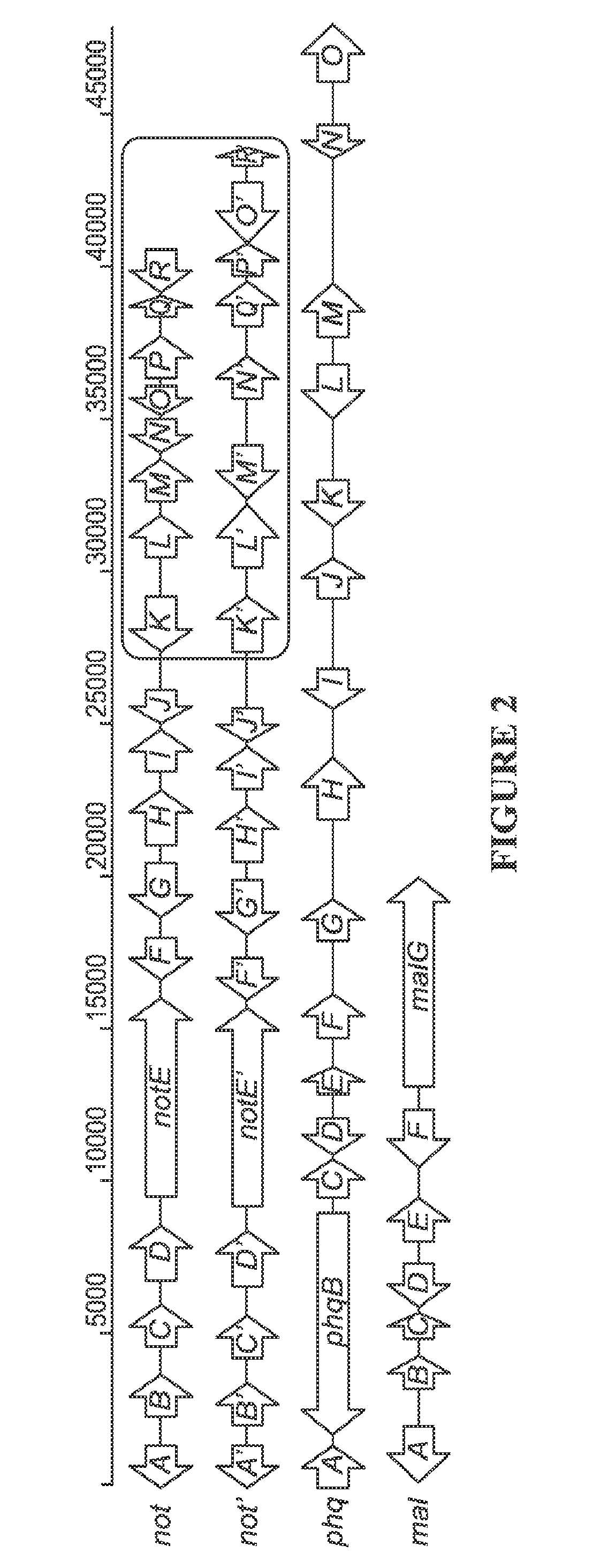
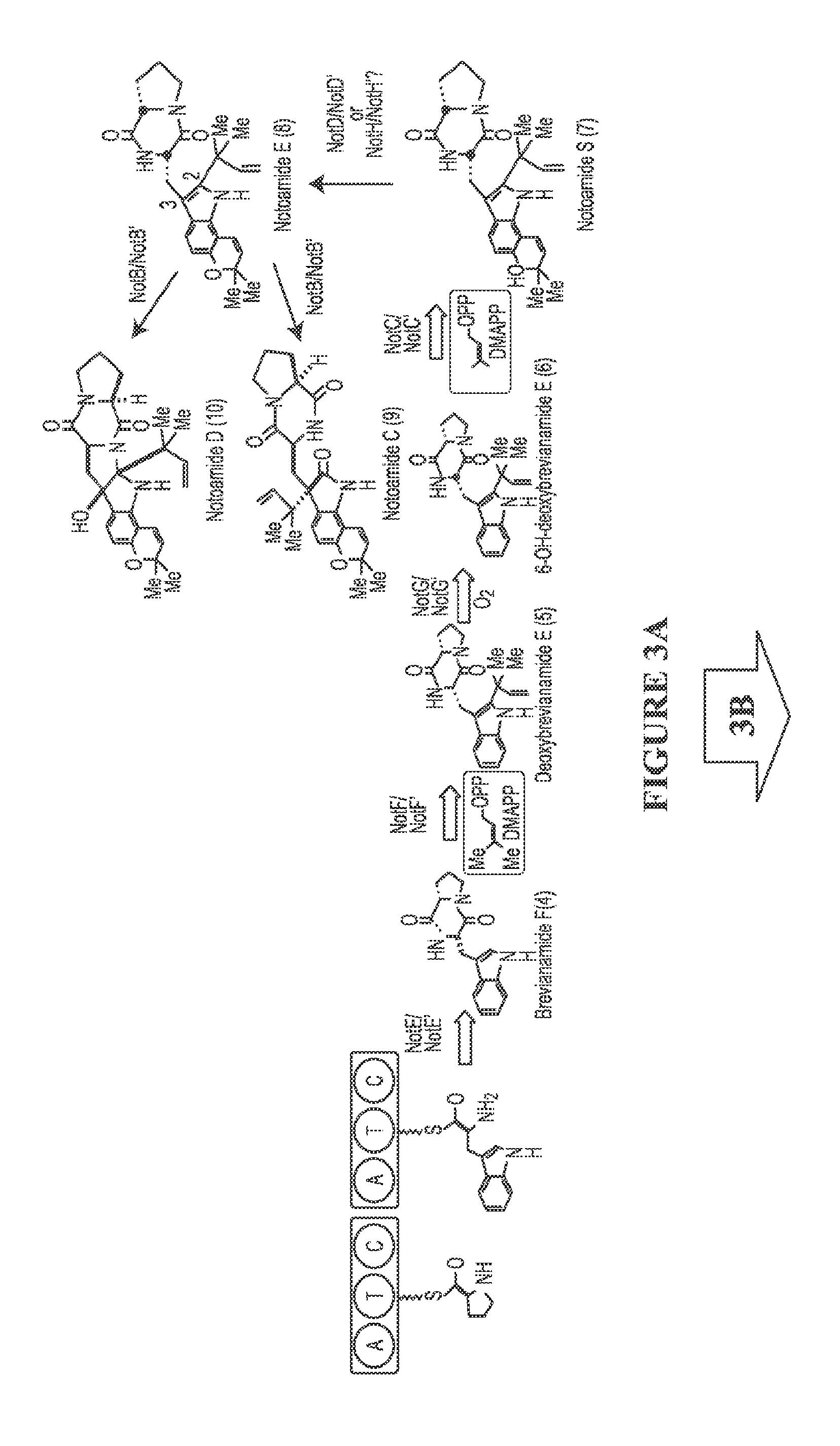
The biosynthesis of fungal bicyclo[2.2.2]diazaoctane indole alkaloids with a wide spectrum of biological activities have attracted increasing interest. Their intriguing mode of assembly has long been proposed to feature a non-ribosomal peptide synthetase, a presumed intramolecular Diels-Alderase, a variant number of prenyltransferases, and a series of oxidases responsible for the diverse tailoring modifications of their cyclodipeptide-based structural core. Until recently, the details of these biosynthetic pathways have remained largely unknown due to lack of information on the fungal derived biosynthetic gene clusters. Herein, we report a comparative analysis of four natural product metabolic systems of a select group of bicyclo[2.2.2]diazaoctane indole alkaloids including (+) / (−)-notoamide, paraherquamide and malbrancheamide, in which we propose an enzyme for each step in the biosynthetic pathway based on deep annotation and on-going biochemical studies.
Owner:COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY +1
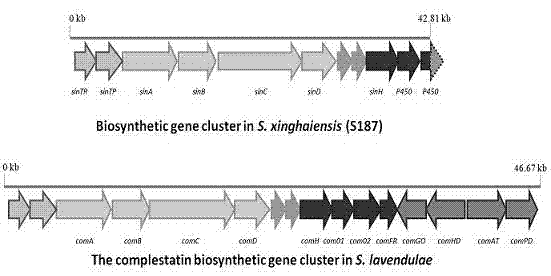
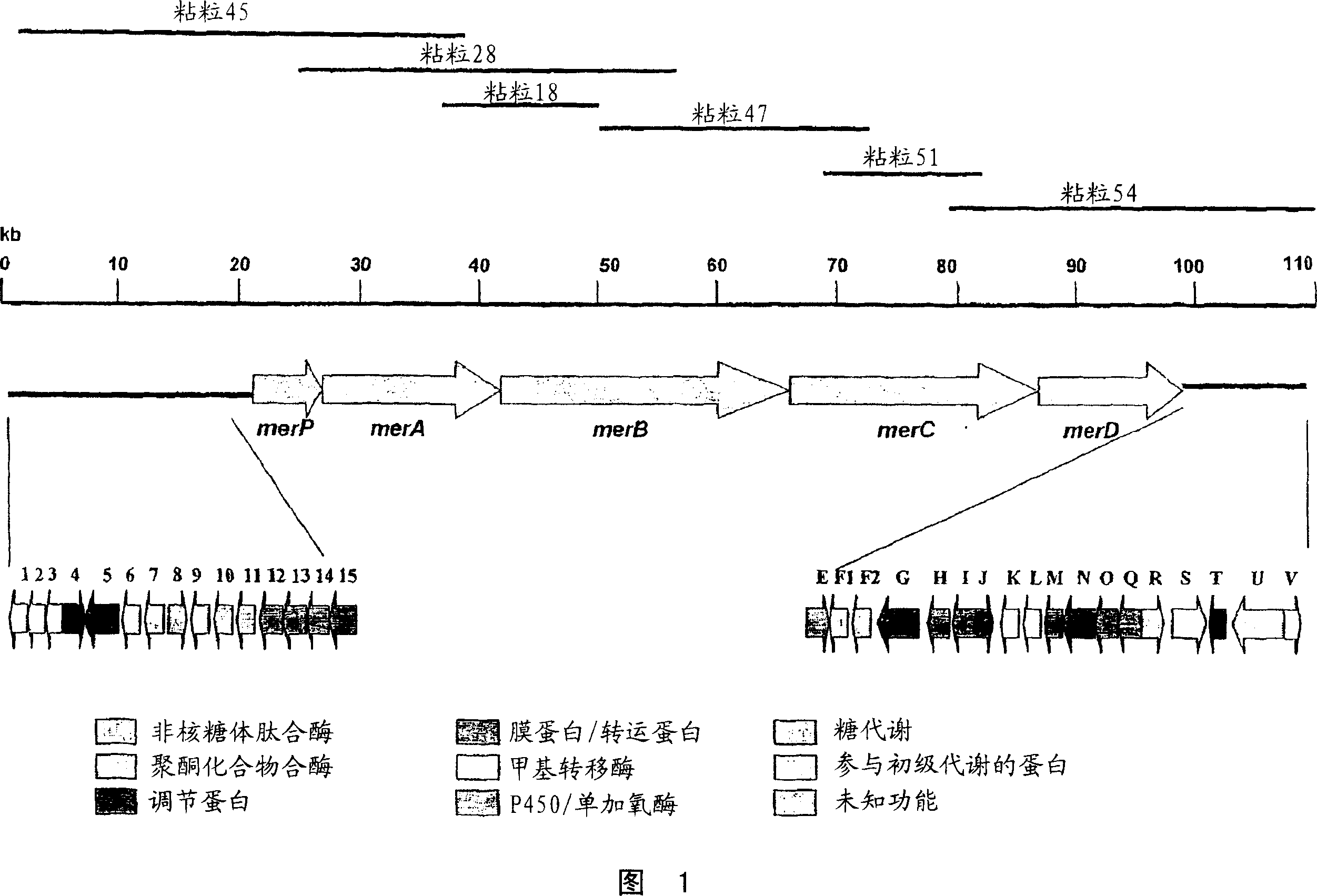
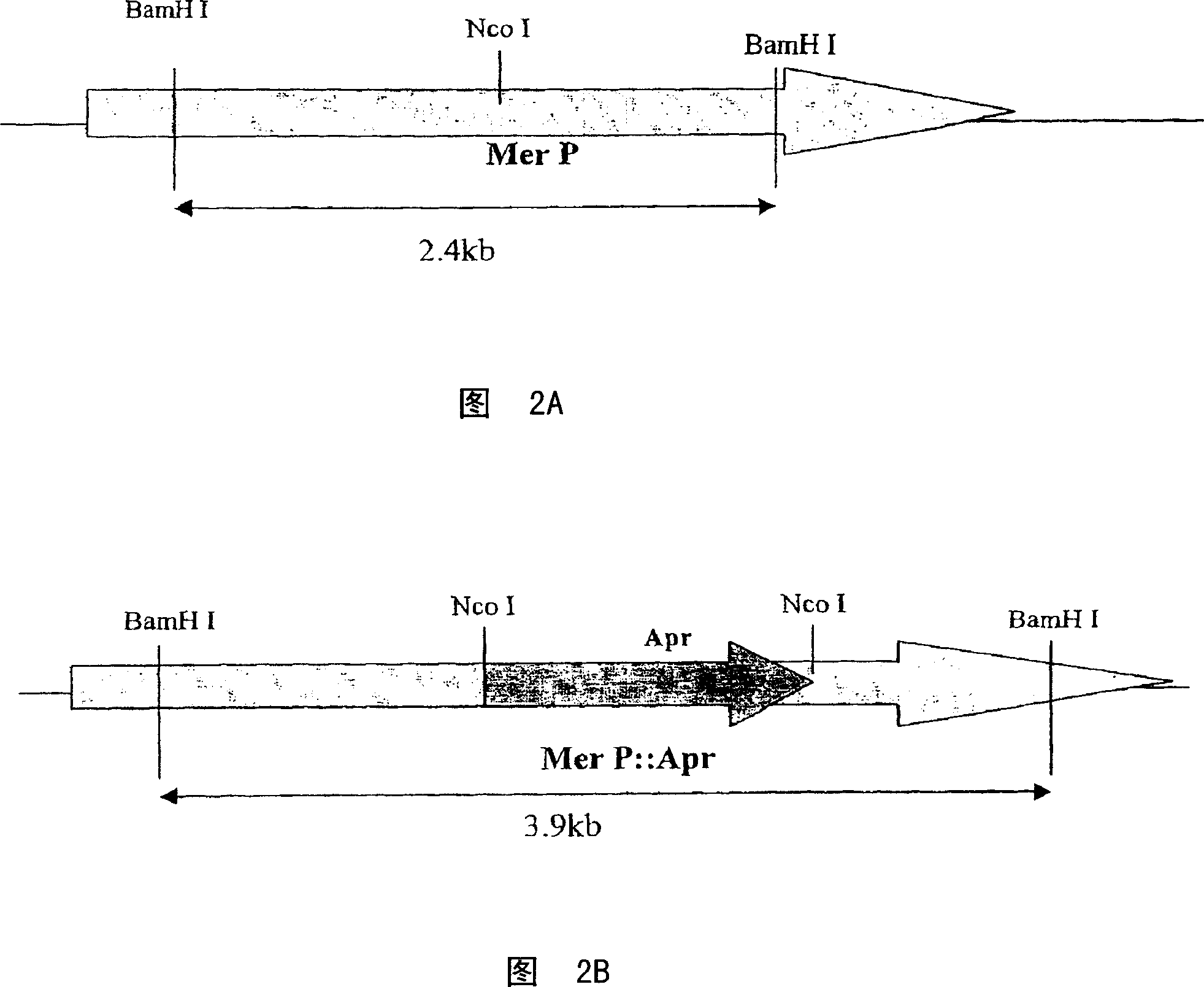
Halogenase gene of streptomyces xinghaiensis and product thereof, biosynthesis cluster of product modified by halogenase gene
InactiveCN102533800AAvoid preferenceReduce the number of copiesMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzymesEnzyme GeneBiosynthetic genes
The invention relates to the field of genetic engineering, and discloses a nucleotide sequence of halogenase gene of marine streptomyce. The nucleotide sequence is characterized by comprising nucleic acid in a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.1, an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.2, and nucleic acid which has 75 percent of sequence sameness with the nucleic acid in SEQ ID NO.1 and maintains functions of halogenase. A method for establishing a Fosmid genome library is adopted, the library is subjected to polymerase chain reaction (PCR) screening by a conserved probe for the halogenase gene, and new halogenase gene is obtained. Compared with the traditional SuperCos vector, the invention has the advantages that: restriction enzyme cutting is not adopted when the Fosmid library is constructed, the preference of restriction enzyme cutting sites is avoided, and the copy number is small, so the stability is higher. The Fosmid library is quickly screened through PCR, the overall length of the halogenase gene and a cluster where the halogenase gene is located are obtained successfully. The cluster comprises 11 protein synthesis genes, and the sequences of the genes have high homology with non-ribosomal peptide synthetase gene, regulator gene, transfer protein gene and the like.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
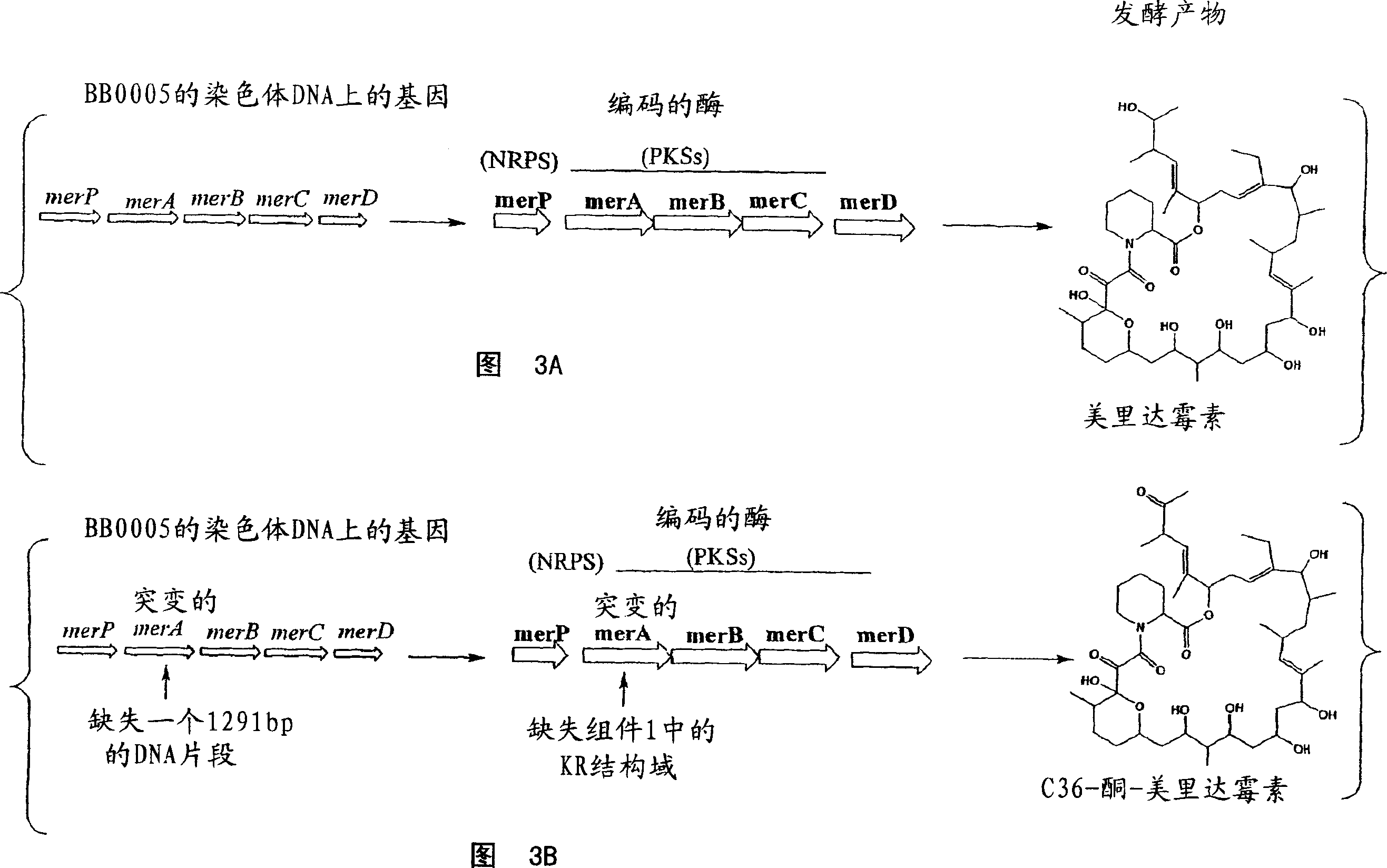
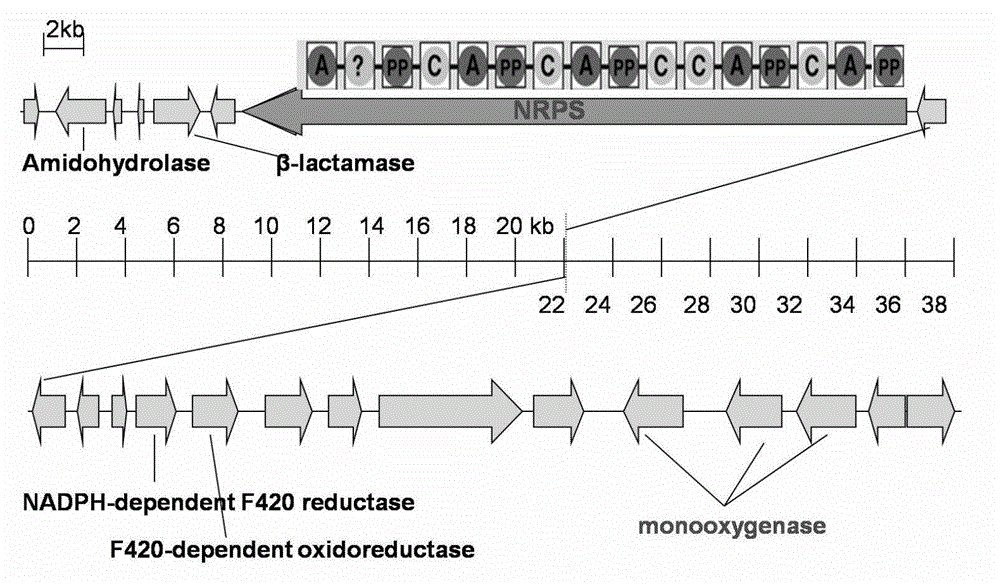
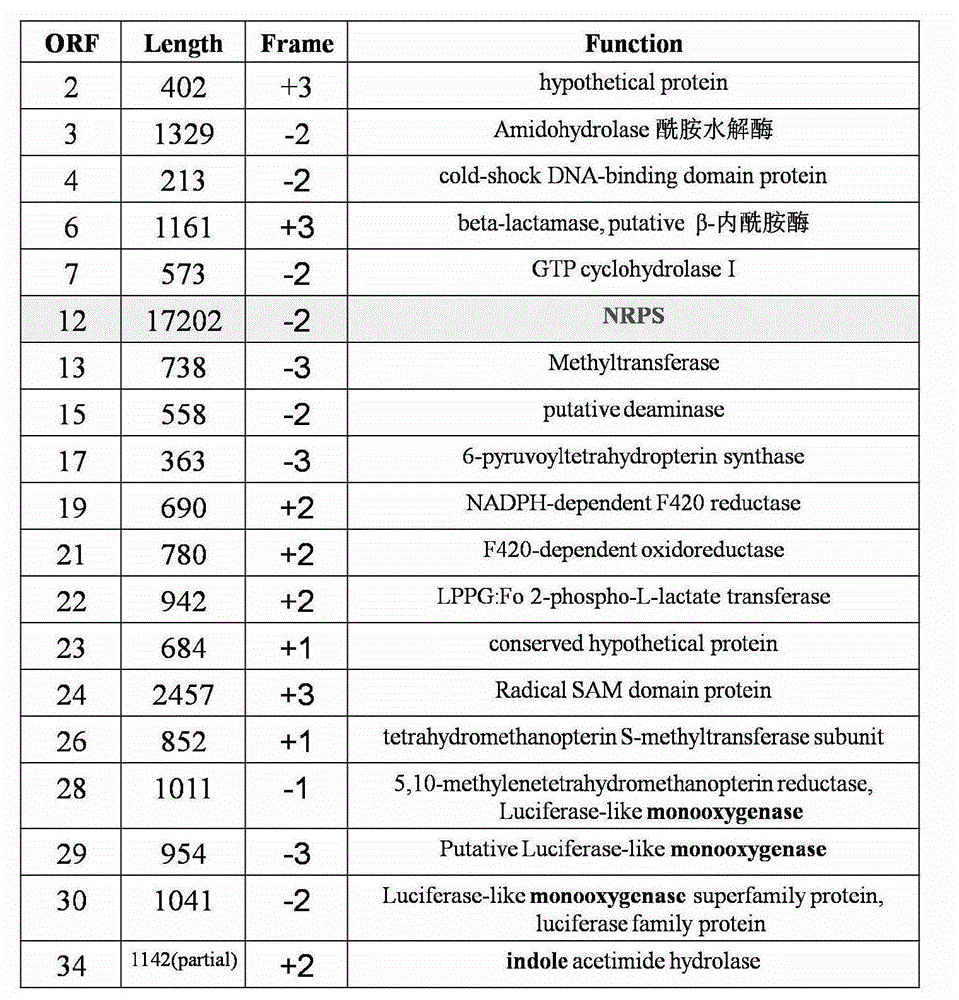
Biosynthetic gene cluster for the production of a complex polyketide
A polyketide synthase complex composed of polyketide synthase with 15 total modules, a non-ribosomal peptide synthetase with I module, and a cytochrome P450 hydroxylase is described. Also provided are novel Streptomyces species and methods of modified Streptomyces species. Further described are novel compounds, 36-ketomeridamycin, C9-deoxomeridamycin, and C9-deoxoprolylmeridamcyin and uses thereof.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Novel non-ribosomal peptide synthetase gene and cloning and expression of adenylylation structural domains thereof
The invention discloses a novel non-ribosomal peptide synthetase gene named NRPS114. The nucleotide sequence of the non-ribosomal peptide synthetase gene is shown in SEQ ID NO 1. Besides, the invention further discloses a preparation method of the non-ribosomal peptide synthetase gene, a plasmid pCC1FOS<TM> Fosmid-NRPS114 containing the non-ribosomal peptide synthetase gene and an expression vector of a recombinant plasmid pET28a-A-2his of five adenylylation structural domains in the non-ribosomal peptide synthetase gene. Additionally, the invention further discloses the five adenylylation structural domains and a preparation method thereof. Recombinant adenylylation structural domains are obtained by means of over-expression of the adenylylation structural domains A1, A2, A3, A4 and A5 in an escherichia coli prokaryotic expression system, and the non-ribosomal peptide synthetase gene has high activity enabling amino acid to undergo adenylylation, provides more genetic manipulation materials for study of combinatorial biology and has a huge application prospect in research and development of new drugs.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
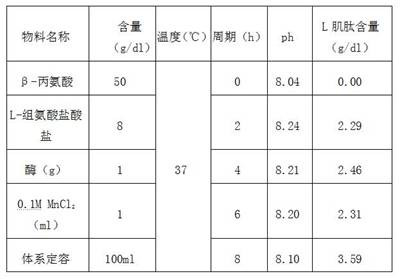
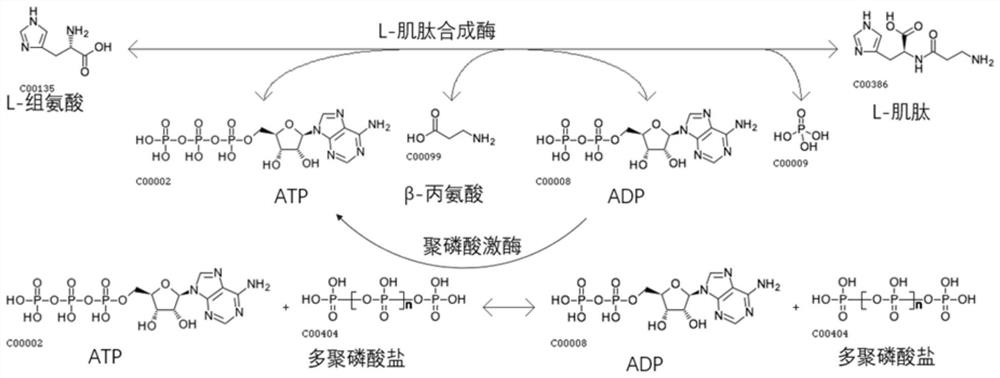
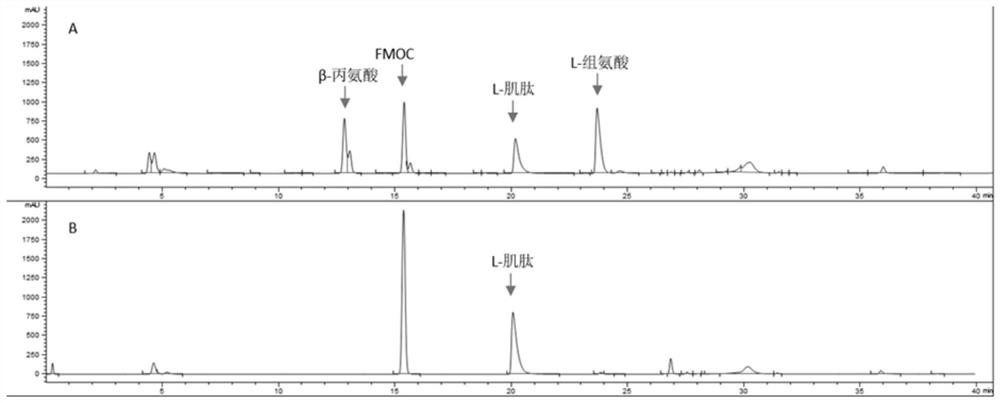
Preparation process of L-carnosine synthetase
PendingCN112592942AImprove efficiencyHigh product concentrationFermentationHydrolysisEnzyme catalyzed
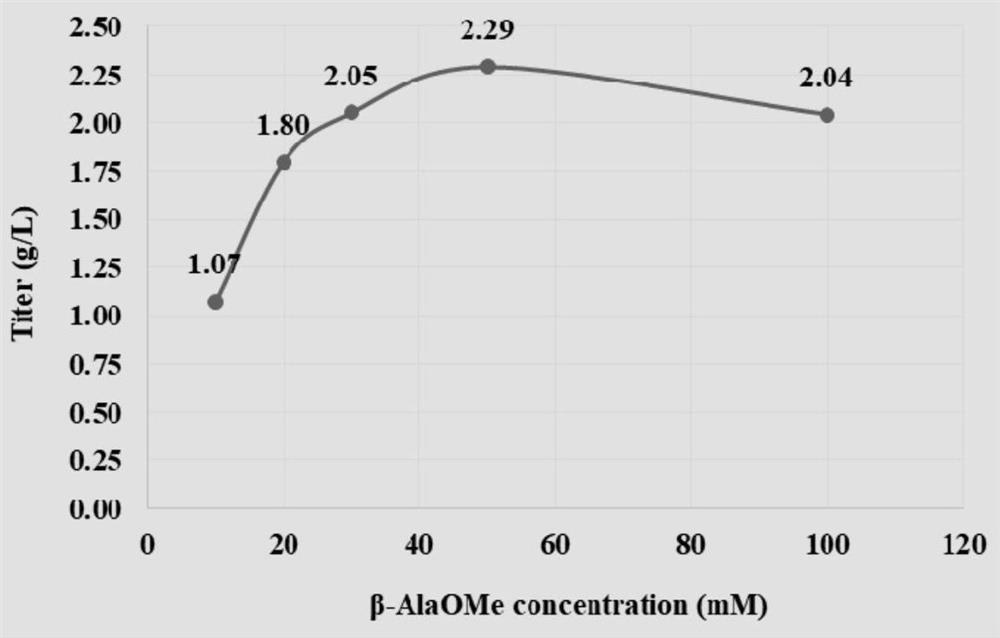
The invention discloses a preparation process of L-carnosine synthetase. The preparation process comprises the following steps: by using beta-alanine and L-histidine hydrochloride as raw materials andMnCl2 as a catalyst, adding L-carnosine hydrolase, and performing enzymatic reaction catalysis at 35-40 DEG C under the pH value of 8.0-8.5 to synthesize L-carnosine. Aiming at the defects of the prior art in the enzymatic reverse hydrolysis synthesis of the L-carnosine catalyzed by the carnosine hydrolase, the conversion process conditions are optimized, the efficiency and the product concentration of the peptide hydrolase for synthesizing the L-carnosine are improved, and the preparation process has the advantages of low raw material price, short enzymatic conversion time, simplicity and convenience in operation, high product concentration, high conversion efficiency, low production cost, and the like.
Owner:NANTONG ZILANG BIOPHARMA TECH CO LTD
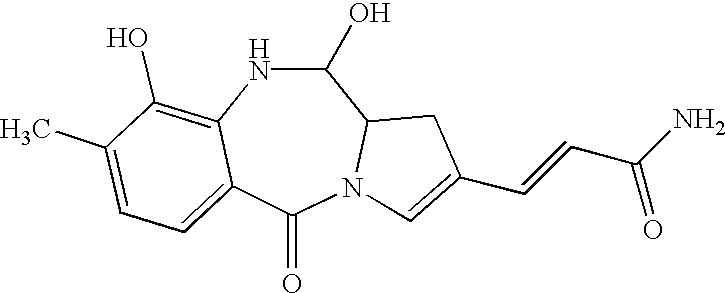
Nucleic acid fragment encoding an NRPS for the biosynthesis of anthramycin
InactiveUS7108998B2Improve the level ofSugar derivativesBacteriaPeptide SynthetasesStreptomyces refuineus
Genes and proteins involved in the biosynthesis of benzodiazepines by microorganisms, including the genes and proteins forming the biosynthetic loci for the benzodiazepine anthramycin from Streptomyces refuineus subsp. thermotolerans including non-ribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPS). The genes and proteins allow direct manipulation of benzodiazepines and related chemical structures via chemical engineering of the enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of anthramycin.
Owner:THALLION PHARMA
Recombinant cell screening system and building method thereof
The invention relates to a recombinant cell screening system and a building method thereof. The recombinant cell screening system comprises the receptor cells of constitutive expression non-ribosomal peptide synthetase encoding genes and plasmids containing phosphopantetheine transferase encoding genes. The recombinant cell screening system has the advantages that exogenous substrate needs not to be added, special detecting equipment is not needed, and a screening process can be completed fast, simply, economically and efficiently. The application example, namely clone screening of gene segments, of the system is specifically elaborated in the embodiment of the invention, and the application example proves that the system can be effectively used for screening recombinant cells.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Production of beta-lactam antibiotics
ActiveUS20100009404A1High specific activitySimple reaction conditionsSugar derivativesBacteriaBeta lactam antibioticSide chain
The present invention describes a process for the production of an N-α-amino-hydroxyphenylacetyl or an N-α-aminophenylacetyl β-lactam antibiotic comprising an IPNS-catalysed conversion of a precursor tripeptide hydroxyphenylglycyl-cysteinyl-valine (HpgCV) or phenylglycyl-cysteinyl-valine (PgCV), respectively, to the N-hydroxyphenylglycyl or the N-phenylglycyl β-lactam antibiotic, respectively. The tripeptide HpgCV or the tripeptide PgCV may further be prepared by contacting the amino acids hydroxyphenylglycine (Hpg) or phenylglycine (Pg), cystein (C) and valine (V) with a non-ribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS) to effect formation of the tripeptide HpgCV or the tripeptide PgCV, the NRPS comprising a first module M1 specific for Hpg or Pg, a second module M2 specific for C and a third module M3 specific for V An IPNS is further provided having an improved activity in this conversion, as well as an NRPS catalysing the formation of the tripeptides. Also a host cell is provided capable of fermentatively producing β-lactam antibiotics with N-α-amino-hydroxyphenylacetyl or an N-α-aminophenylacetyl side chains.
Owner:DSM SINOCHEM PHARMA NETHERLANDS
Chaperone-assisted protein expression and methods of use
InactiveUS20110086388A1Increase success rateWide applicabilityDepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsBiotechnologyBiosynthetic genes
The present disclosure provides methods of utilizing chaperone proteins for the production of active protein such as those encoded by the genes of natural biosynthetic clusters. The methods provided herein have applicability for a wide variety of genes ranging from small fatty acid biosynthetic genes to large non-ribosomal peptide synthetase genes.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Method for isolation of biosynthesis genes for bioactive molecules
Degenerate primers which hybridize with various classes of antibiotic biosynthesis genes were used to amplify fragments of DNA from soil and lichen extracts. Cloning and sequencing of the amplified products showed that these products included a variety of novel and previously uncharacterized antibiotic biosynthesis gene sequences, the products of which have the potential to be active as antibiotics, immunosuppressors, antitumor agents, etc. Thus, antibiotic biosynthesis genes can be recovered from soil or lichens by a combining a sample with a pair of amplification primers under conditions suitable for polymerase chain reaction amplification, wherein the primer set is a degenerate primer set selected to hybridize with conserved regions of known antibiotic biosynthetic pathway genes, for example Type I and Type II polyketide synthase genes, isopenicillin N synthase genes, and peptide synthetase genes; cycling the combined sample through a plurality of amplification cycles to amplify DNA complementary to the primer set; and isolating the amplified DNA.
Owner:CUBIST PHARMA INC
Isolated polypeptide, nucleic acid and application thereof
The invention provides a separated polypeptide. Compared with a wild carnosine synthetase SEQ ID NO: 1, the polypeptide has 310 amino acid mutations. The polypeptide provided by the invention can be used for efficiently preparing carnosine, is green and environment-friendly, and is suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Artificial non-ribosomal peptide synthetases
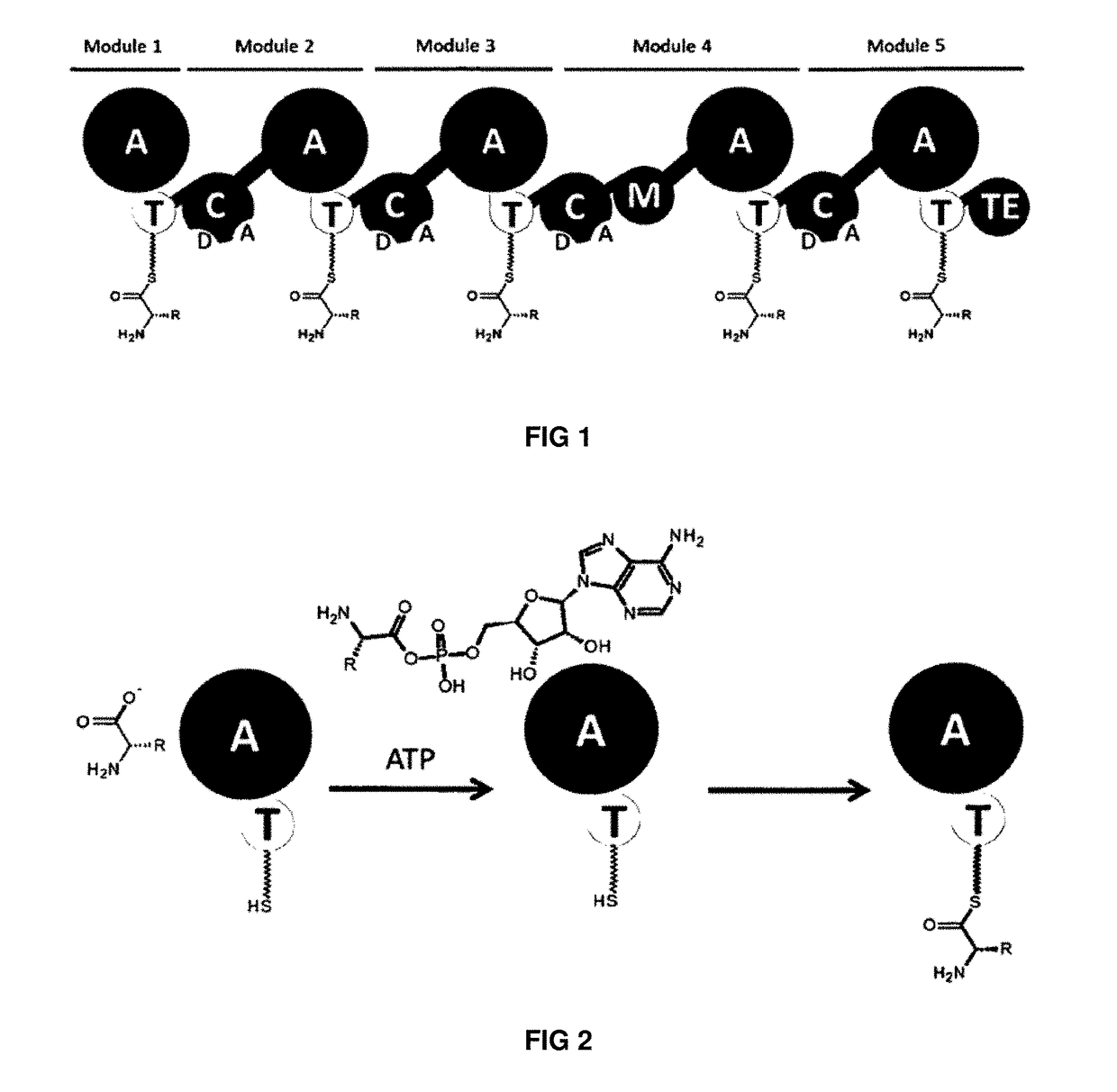
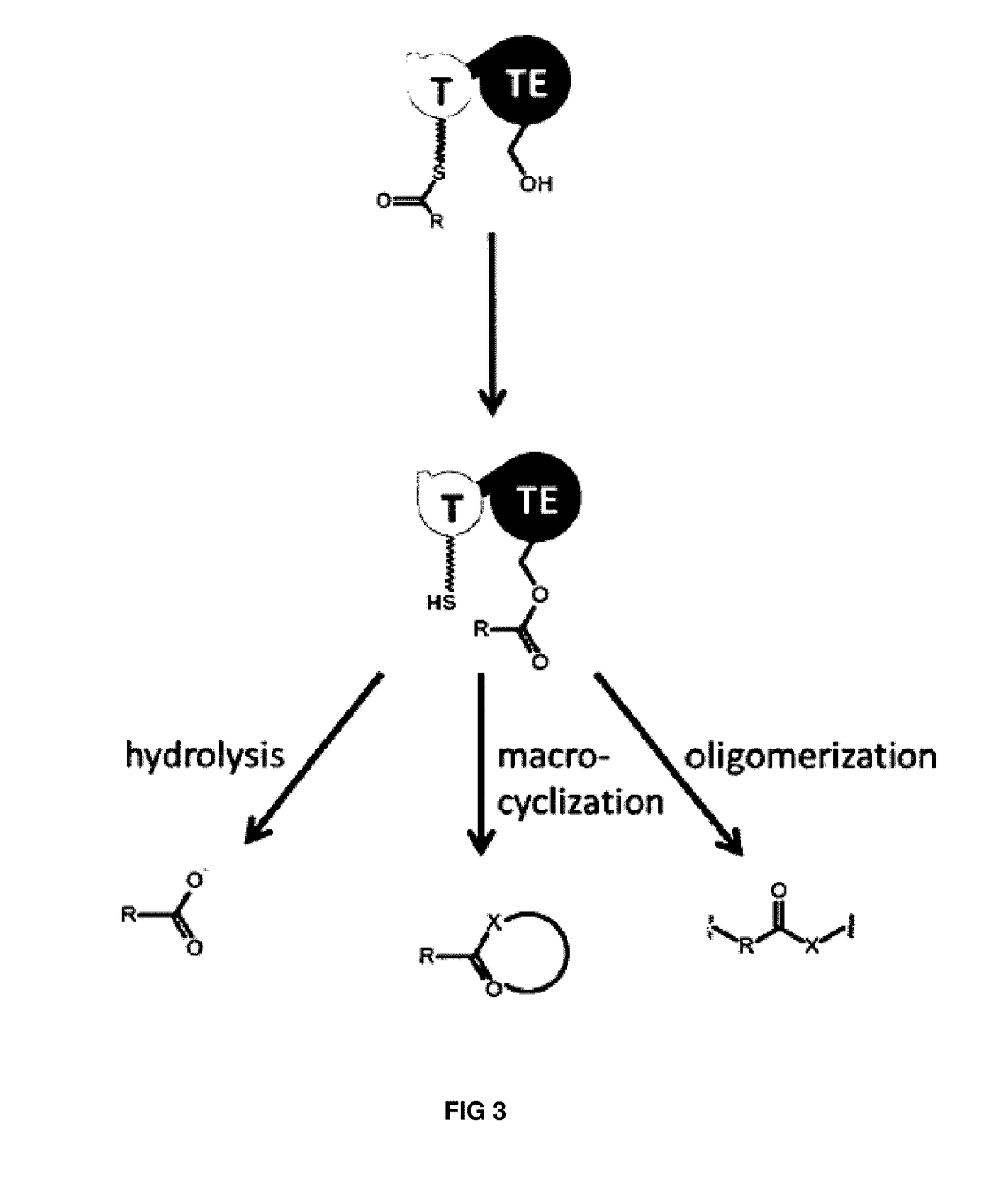
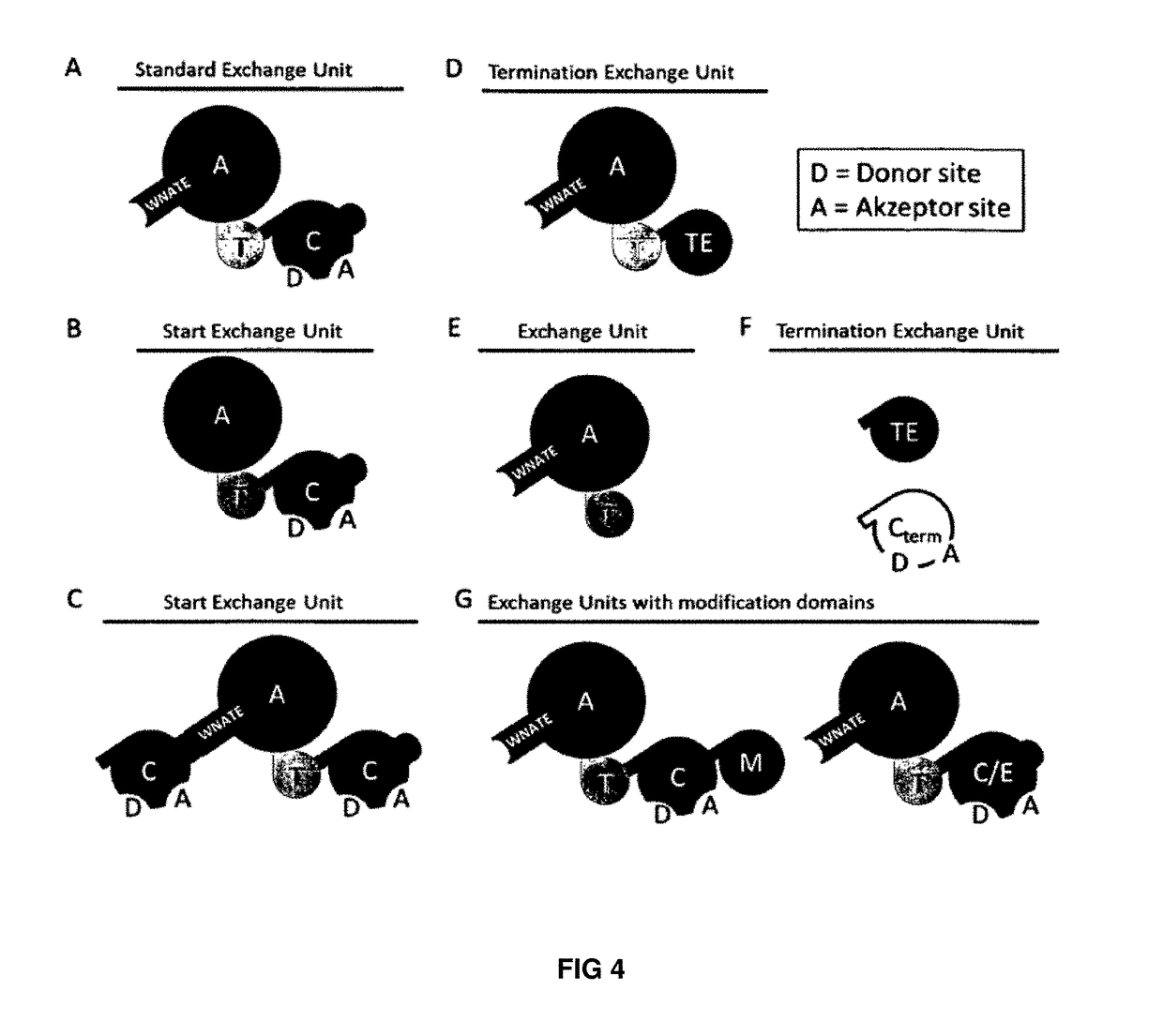
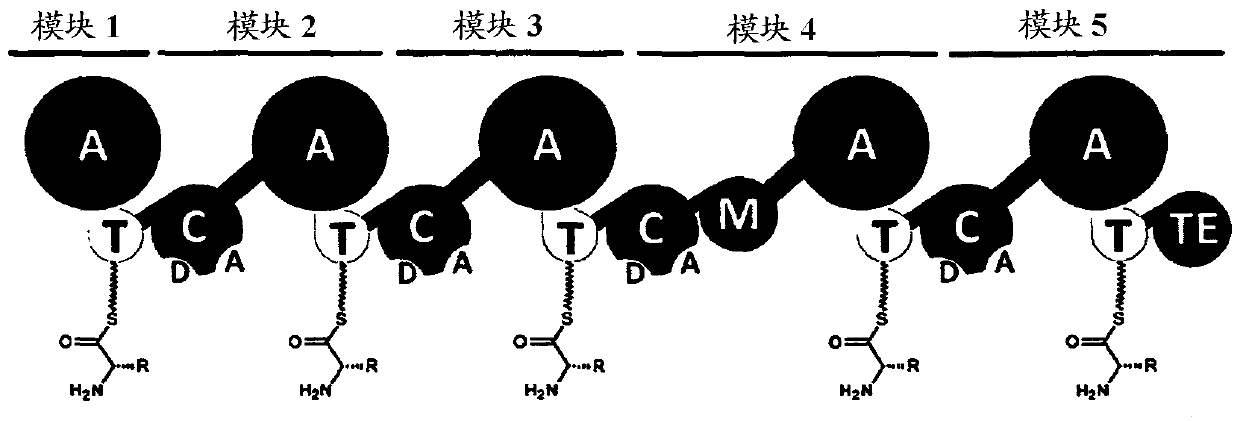
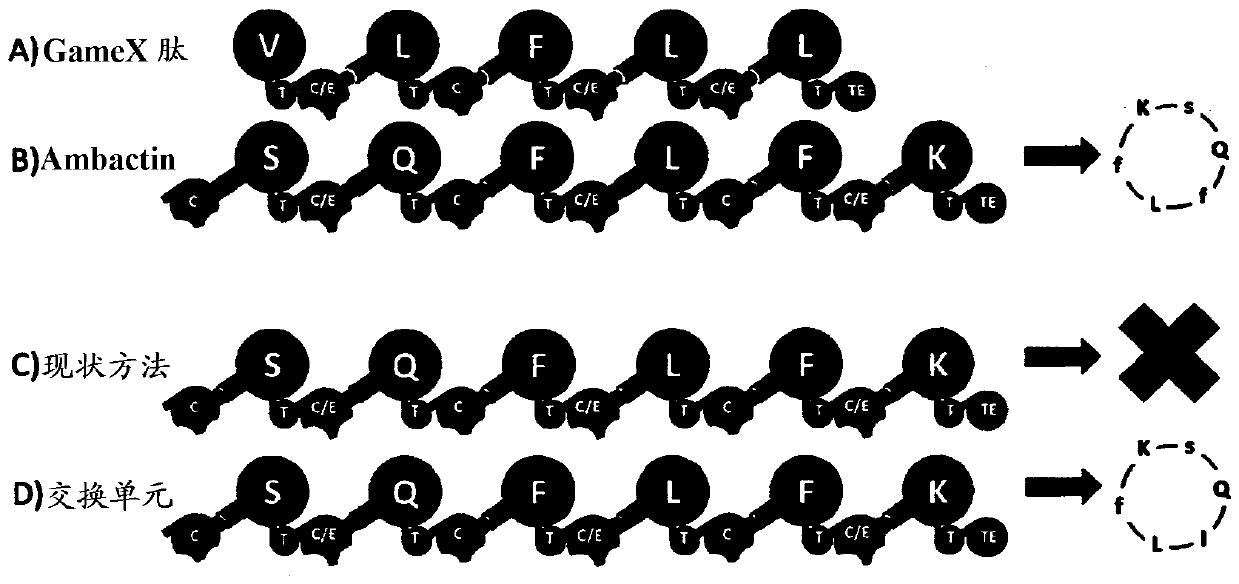
The present invention concerns a novel method for the modification and / or custom-made design of artificial non-ribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs) from naturally available NRPSs. The artificial NRPSs are of predetermined length and amino acid composition and sequence. Via fusion of well-defined NRPS units (so-called “exchange units”) in a certain manner, using a specific sequence motif in the linker areas it is possible to construct artificial and / or modified NRPS assembly lines, which have the ability of synthesizing peptides of a desired structure.
Owner:JOHANN WOLFGANG GOETHE UNIV FRANKFURT AM MAIN
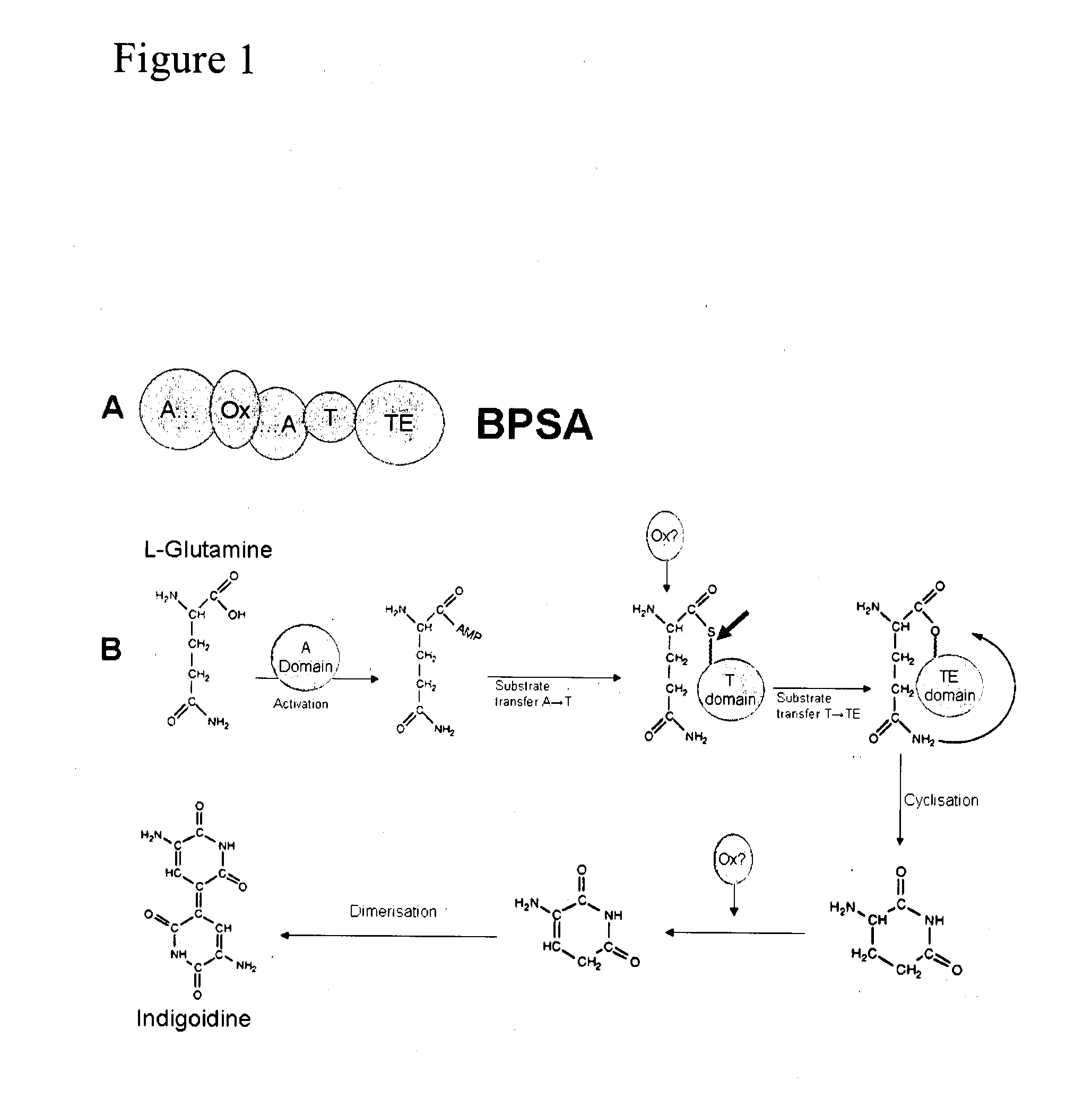
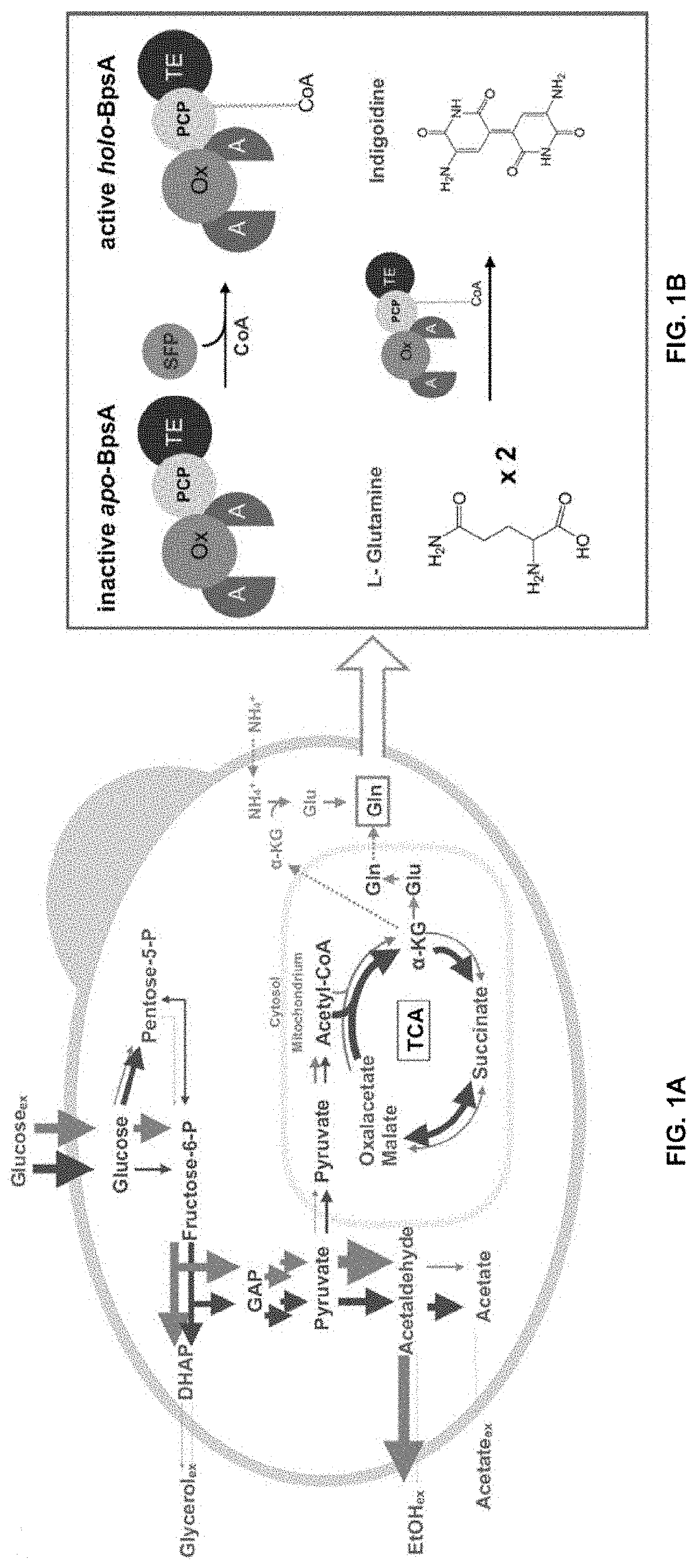
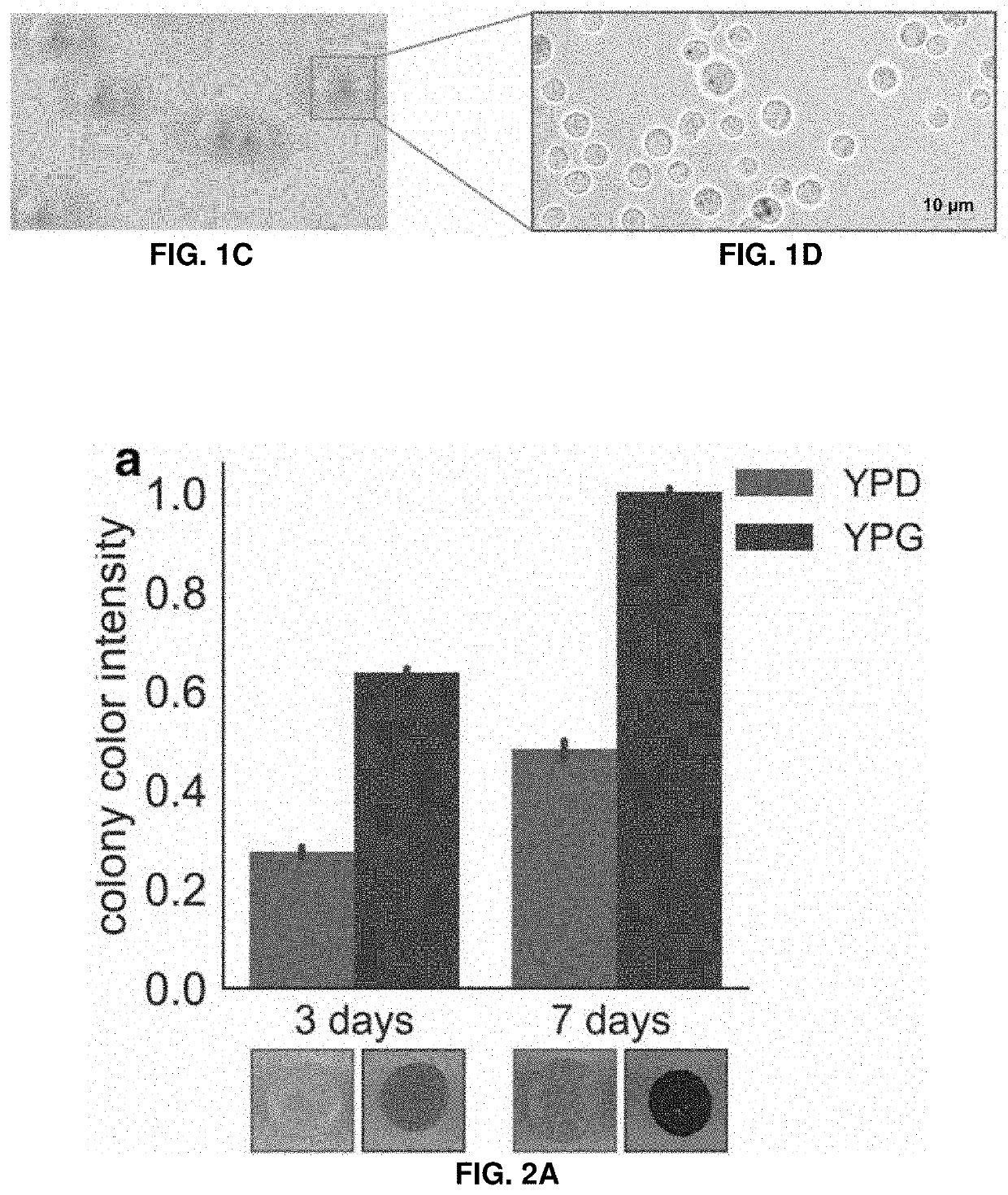
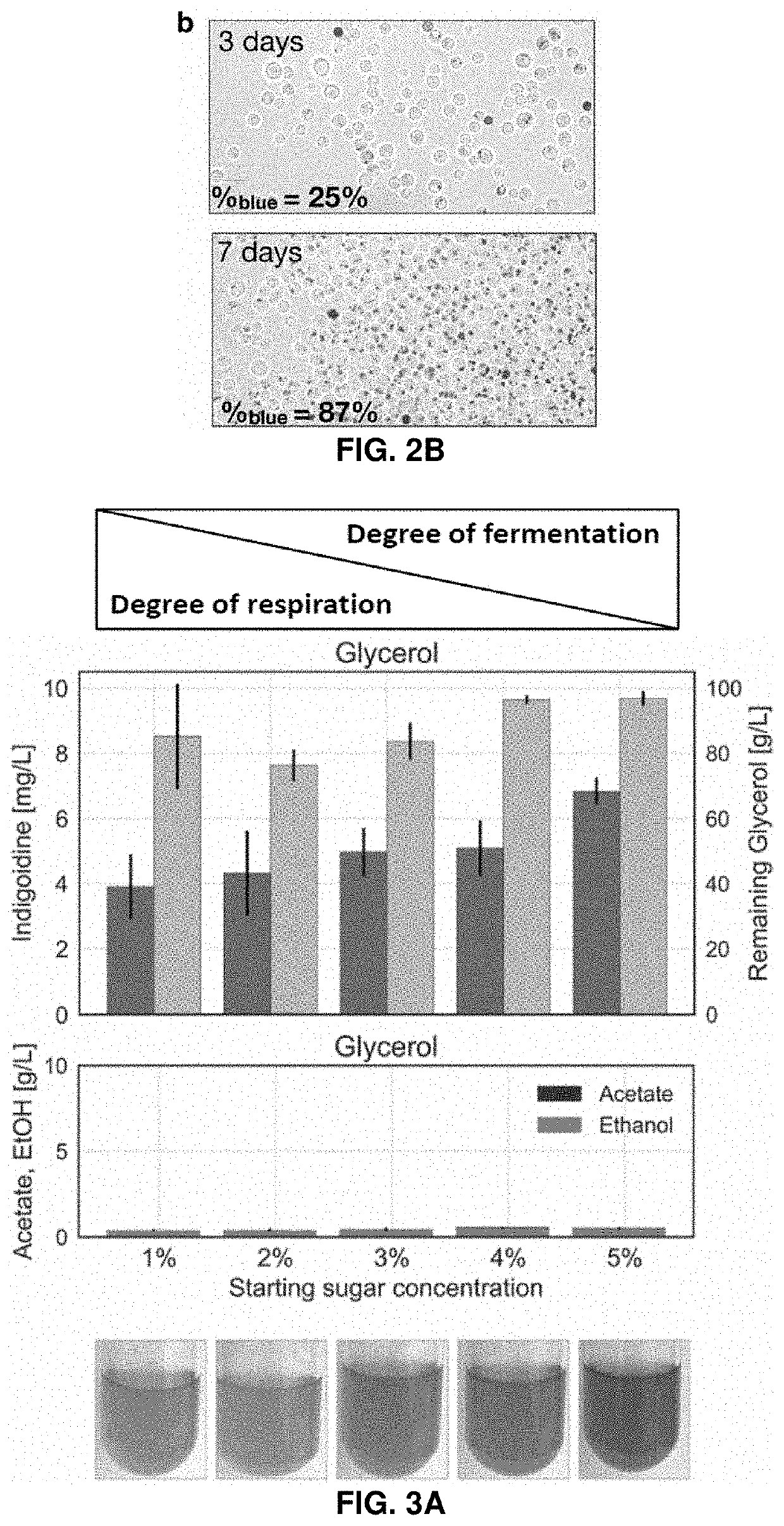
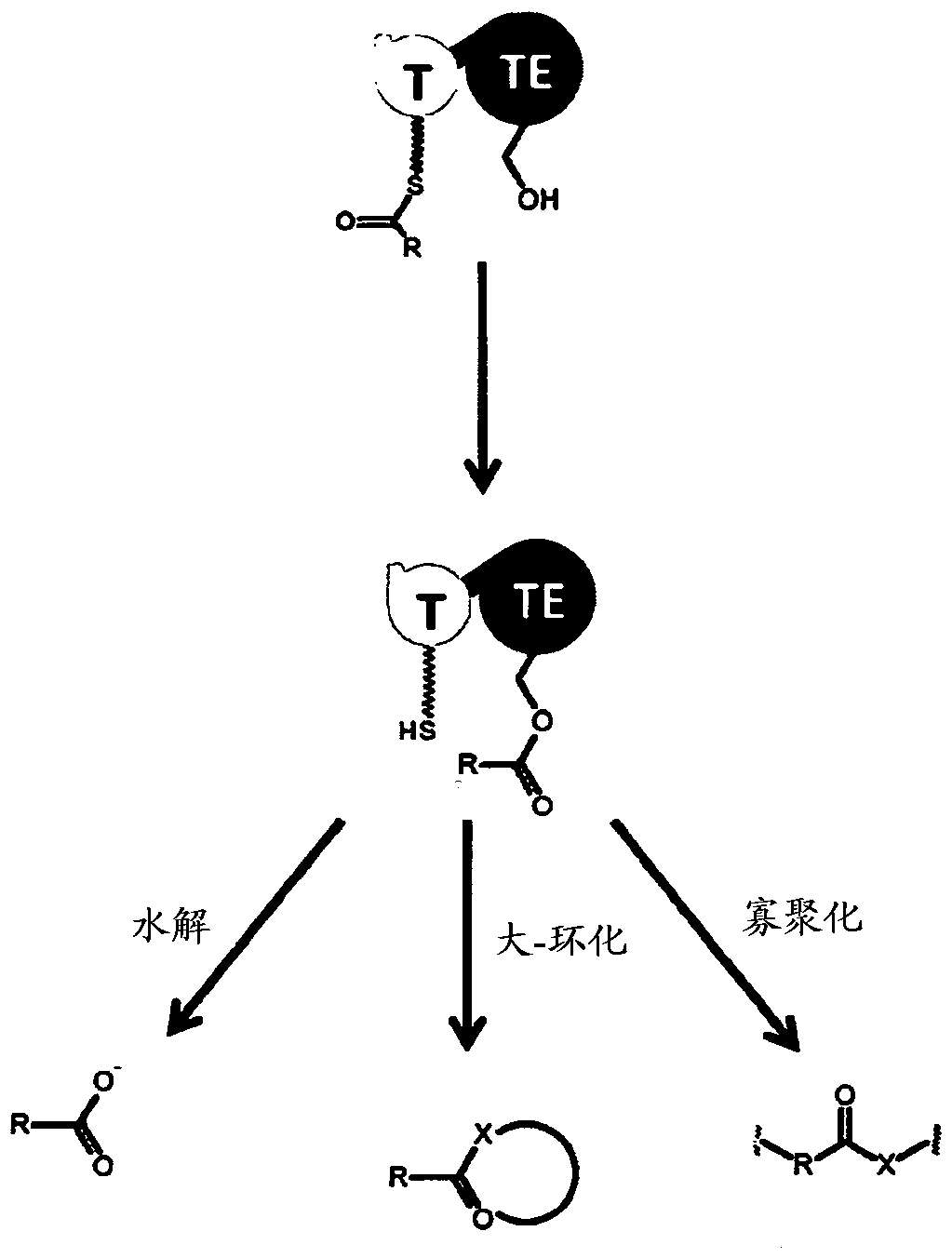
Host yeast cells and methods useful for producing indigoidine
PendingUS20220112531A1High titer productionHigh productMicroorganism based processesLigasesYeastIndigoidine
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Artificial non-ribosomal peptide synthetases
The present invention concerns a novel method for the modification and / or custom-made design of artificial non-ribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs) from naturally available NRPSs. The artificial NRPSs are of predetermined length and amino acid composition and sequence. Via fusion of well-defined NRPS units (so-called "exchange units") in a certain manner, using a specific sequence motif in the linker areas it is possible to construct artificial and / or modified NRPS assembly lines, which have the ability of synthesizing peptides of a desired structure.
Owner:JOHANN WOLFGANG GOETHE UNIV FRANKFURT AM MAIN
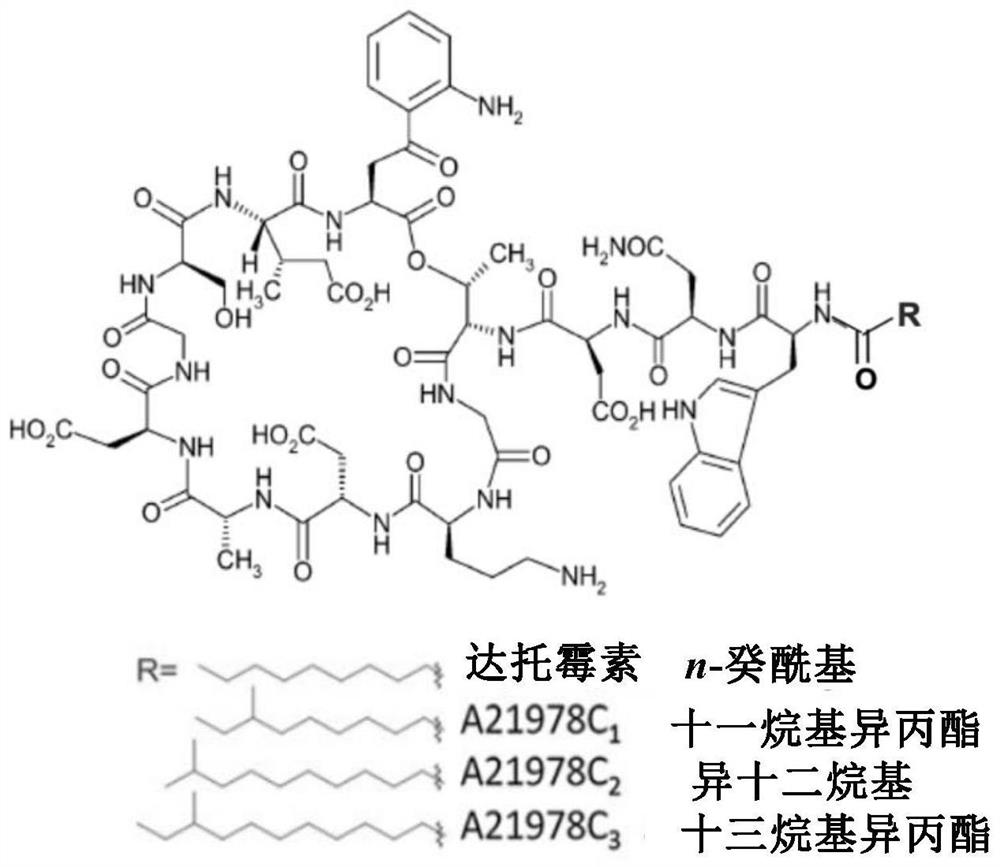
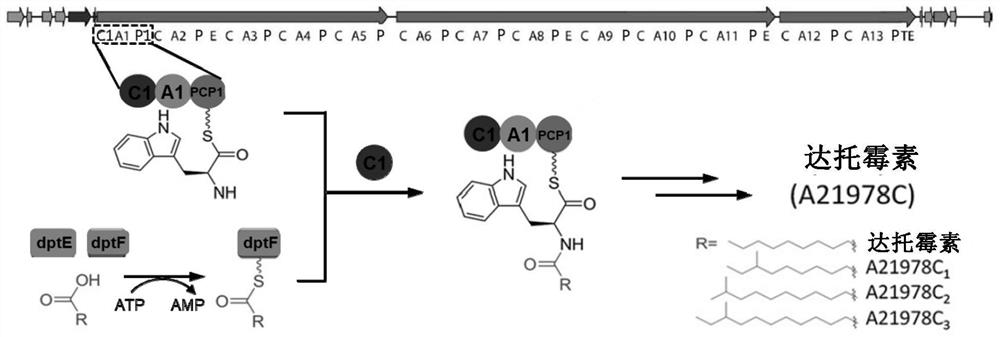
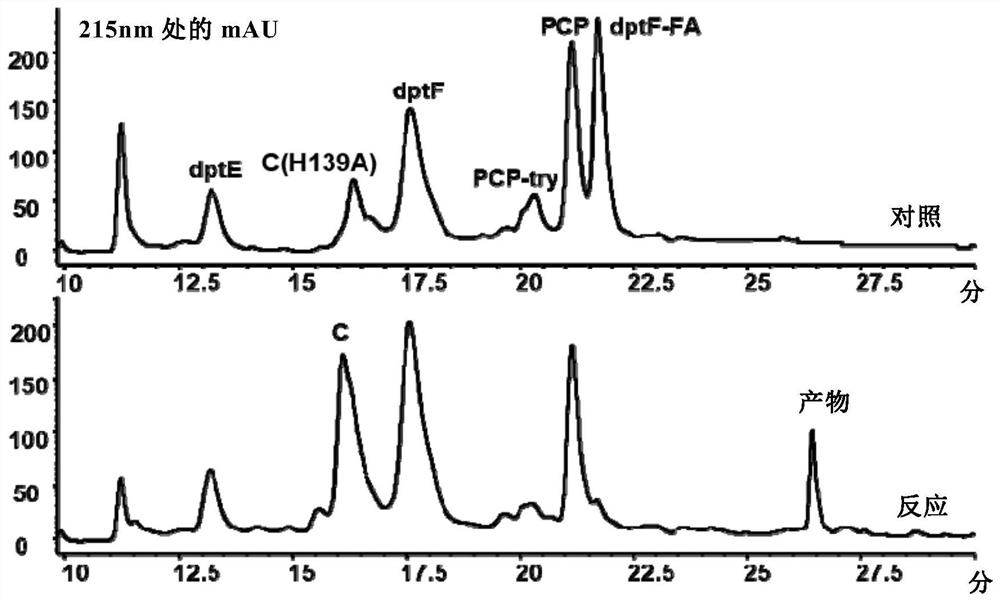
Construction of a dptc1 mutant for daptomycin biosynthesis
ActiveCN111575251BMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisMutated proteinArginine
The invention provides the construction of a dptC1 mutant used for the biosynthesis of daptomycin. Specifically, the present invention provides a dptC1 mutein, which is based on the first C domain of the wild-type non-ribosomal peptide synthetase NRPS (dptC1 protein) shown in SEQ ID NO: 2, selected One or more amino acid positions are mutated from the following group: glutamine at position 15 (Q), tyrosine at position 145 (Y), arginine at position 247 (R), threonine at position 314 (T) and the 355th valine (V); and, the dptC1 mutant protein has the activity of catalyzing the reaction of the decanoyl substrate into N-decanoyl compounds. The inventive dptC1 mutant protein of the present invention can improve the catalytic efficiency of decanoyl substrate, and realize high and high yield of daptomycin.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV
Mbth-like proteins in the production of semi synthetic antibiotics
The present invention relates to the preparation of β-lactam antibiotics comprising contacting 4-hydroxyphenylglycine or phenylglycine, cysteine and valine with a non-ribosomal peptide synthetase and subsequent cyclization using an isopenicillin N synthase in the presence of an MbtH-like protein and to a host cell equipped to perform such preparation.
Owner:DSM SINOCHEM PHARMA NETHERLANDS
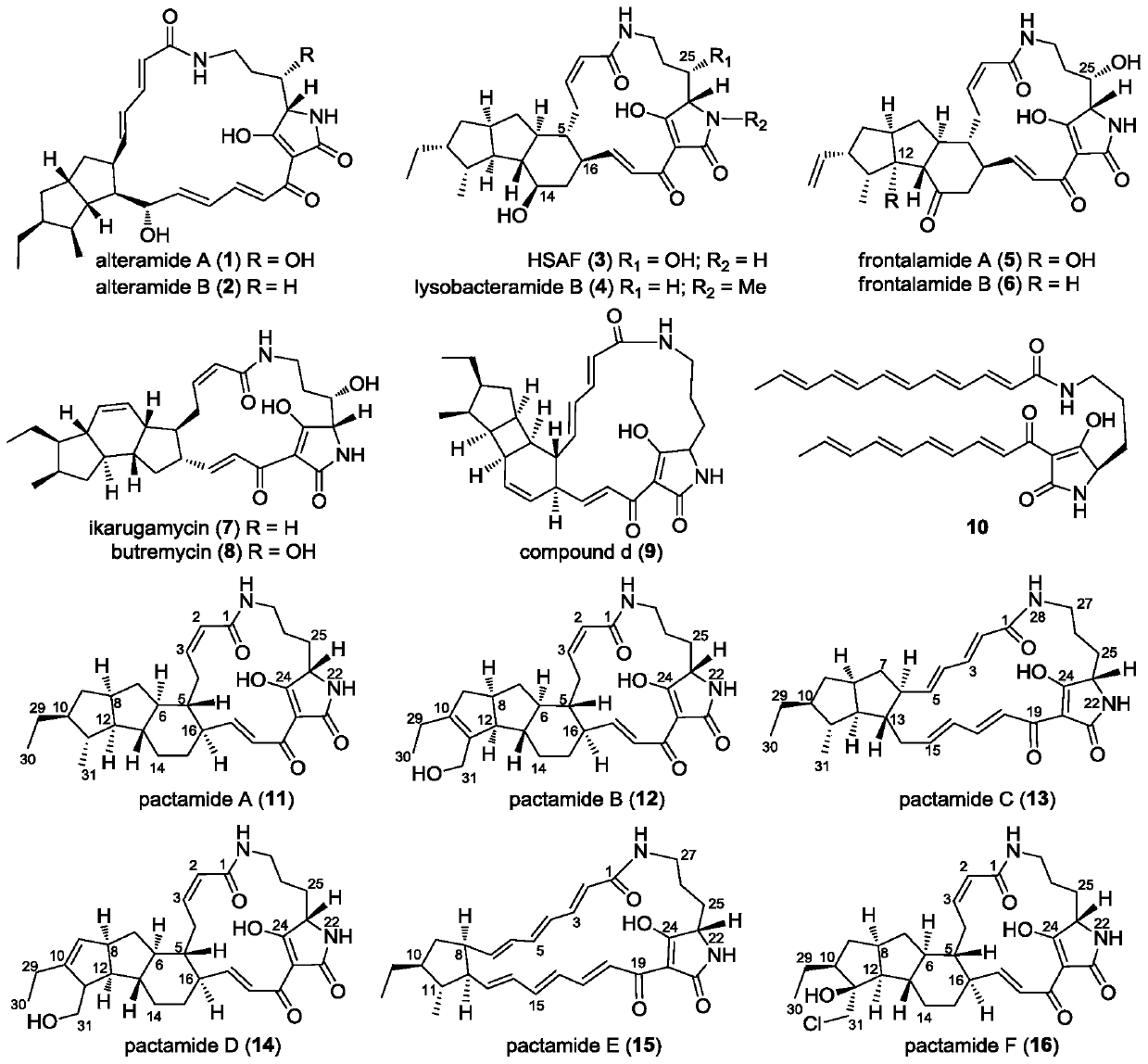
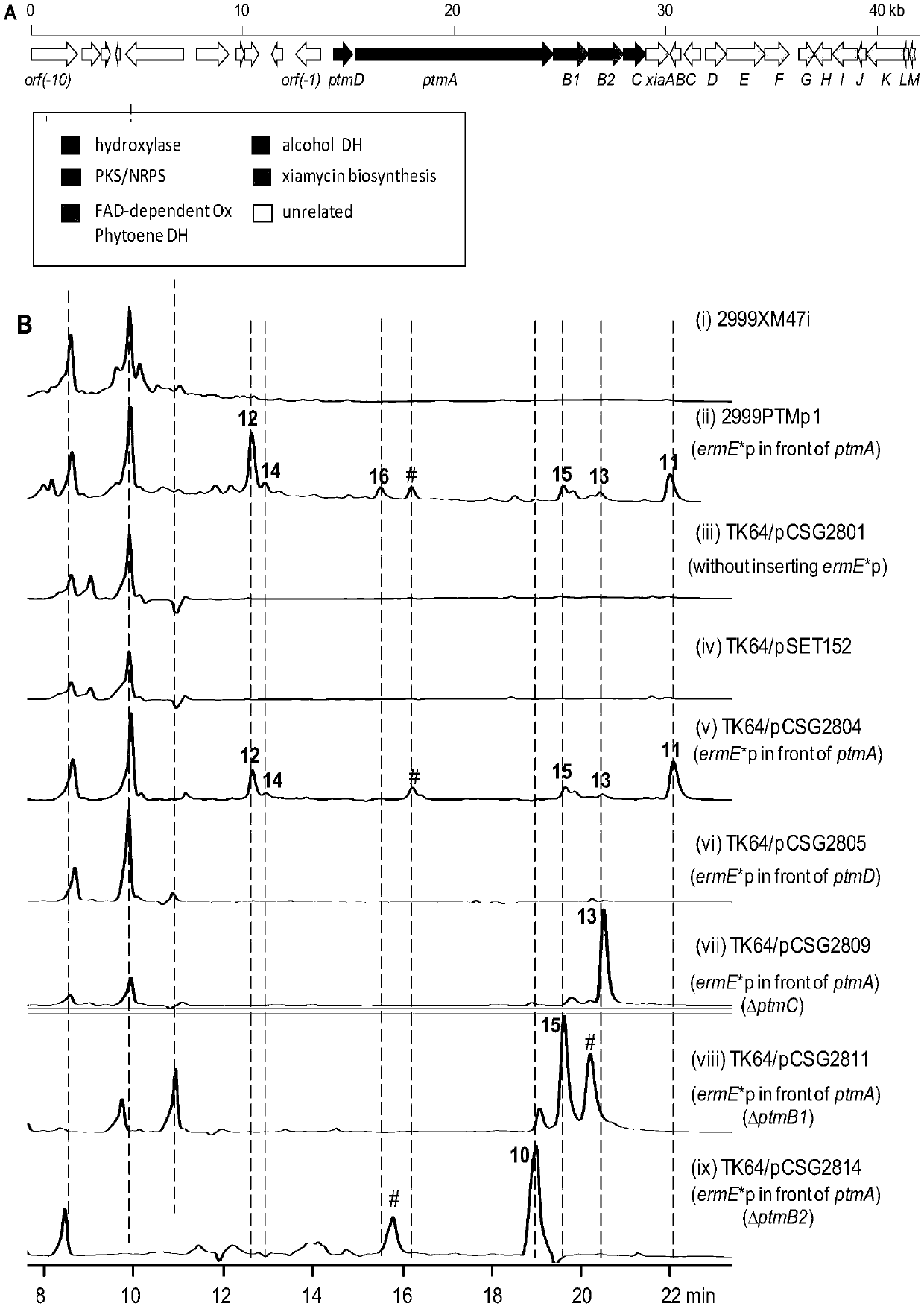
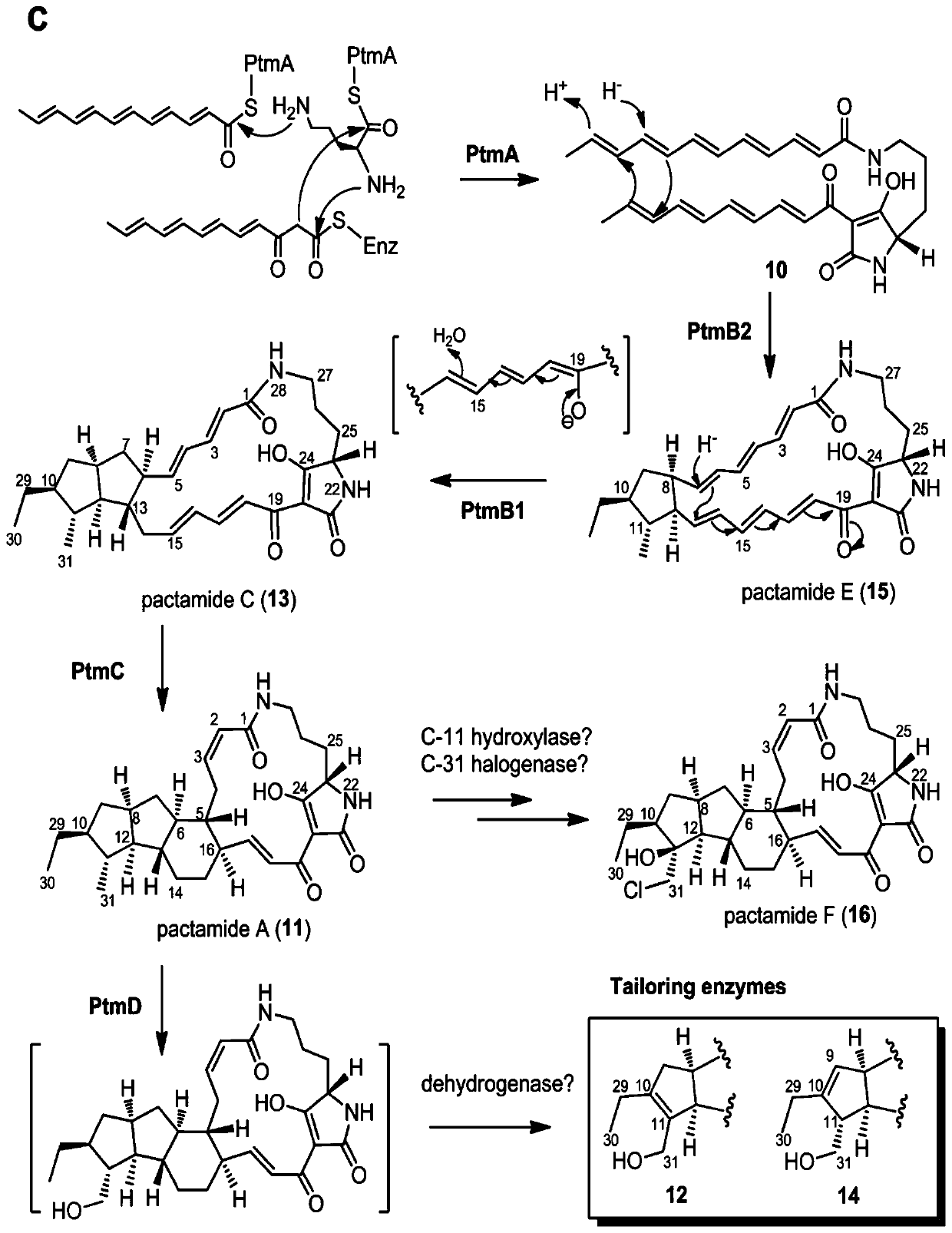
A biosynthetic gene cluster of pactamide and its application
The invention discloses a biosynthetic gene cluster of paquete amide and an application thereof. The biosynthetic gene cluster of paquete amide comes from (Streptomyces pactum)SCSIO 02999, and the cluster comprises five genes including heterozygous polyketone / nonribosomal peptide synthetases genes ptmA, FAD dependent redox enzyme genes ptmB1, phytoene dehydrogenase genes ptmB2, cyclase genes ptmC and hydroxylase genes ptmD. According to the biosynthetic gene cluster of paquete amide and the application thereof, information in genes and proteins related to biosynthesis of the paquete amide provides theoretical foundations and materials for conducting genetic modification on the biosynthesis of multi-ring tetramate macrocylic lactam family. By conducting genetic modifications on the biological synthetic genes, 6 new structures antineoplastic paquete amide compounds pactamide A-F are obtained, and thus effective compound entities are provided for research and development of antineoplastic drugs.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Production of β-Lactam antibiotics
The present invention describes a process for the production of an N-α-amino-hydroxyphenylacetyl or an N-α-aminophenylacetyl β-lactam antibiotic comprising an IPNS-catalysed conversion of a precursor tripeptide hydroxyphenylglycyl-cysteinyl-valine (HpgCV) or phenylglycyl-cysteinyl-valine (PgCV), respectively, to the N-hydroxyphenylglycyl or the N-phenylglycyl β-lactam antibiotic, respectively. The tripeptide HpgCV or the tripeptide PgCV may further be prepared by contacting the amino acids hydroxyphenylglycine (Hpg) or phenylglycine (Pg), cystein (C) and valine (V) with a non-ribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS) to effect formation of the tripeptide HpgCV or the tripeptide PgCV, the NRPS comprising a first module M1 specific for Hpg or Pg, a second module M2 specific for C and a third module M3 specific for V An IPNS is further provided having an improved activity in this conversion, as well as an NRPS catalysing the formation of the tripeptides. Also a host cell is provided capable of fermentatively producing β-lactam antibiotics with N-α-amino-hydroxyphenylacetyl or an N-α-aminophenylacetyl side chains.
Owner:DSM SINOCHEM PHARMA NETHERLANDS
Cell for expressing phosphotransferase and non-ribosomal peptide synthetase and application thereof
The invention provides a cell for expressing phosphotransferase and non-ribosomal peptide synthetase and application thereof. The cell for expressing phosphotransferase and non-ribosomal peptide synthetase is obtained by transferring an expression plasmid containing a phosphotransferase gene and an expression plasmid containing a non-ribosomal peptide synthetase gene into a host cell. The decarboxylated carnosine is prepared by constructing the recombinant genetically engineered bacteria and using a biological enzyme catalysis method, and the method is more environment-friendly than an existing chemical synthesis method. The method for preparing the decarboxylated carnosine through a whole-cell catalysis method is reported for the first time for preparing the decarboxylated carnosine through a biological method.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Glutathione synthetase culture process
The invention discloses a glutathione synthetase culture process. The glutathione synthetase culture process comprises the following steps: A, a fermentation section: preparing materials, culturing seeds, performing pretreating, performing fermenting and performing centrifuging; and B, a curing section: performing pulping, performing homogenizing and breaking walls, performing centrifuging, performing heat treatment, performing nanofiltration, performing loading, performing mixing and dewatering, and performing airing at low temperature, and airing mixed and dewatered loaded polyester foam sheets in an airing chamber at low temperature of 20 DEG C to obtain the finished product of a glutathione synthetase preparation. Through the mode, the glutathione synthetase culture process particularly limits raw materials, performs high-temperature sterilization on a test tube, a shake flask, a fermentation tank and a culture medium, and particularly limits the sterilization temperature and time of the fermentation tank and the culture medium, so that the problem of infectious microbe infection is reduced, and increasing the yield is facilitated; and airing at low temperature is adopted, so that the production difficulty and cost are reduced.
Owner:常熟盈赛生物科技有限公司
Polyamino acid synthetase and gene encoding the same
The present invention provides an enzyme which catalyzes amino acid polymerization in the form of a non-ribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS) and a gene encoding the same.
Owner:JNC CORP
Biosynthetic gene clusters of off-road statins and their applications
The invention relates to a biosynthesis gene cluster of kosinostatin, and in particular relates to cloning, sequencing, analysis, functional study and application of the biosynthesis gene cluster of the kosinostatin, which is an antharcycline antibiotic with antitumor activity and generated from micromonospora sp.TP-A0468. The whole gene cluster comprises 55 genes in all, that is, 17 II-type polyketone synthetase (PKS) related genes, 8 non-ribosome polypeptide synthetase (NRPS) related genes, 9 glycosyl synthetic related genes, 6 special post-modifying genes, 7 antibiotic genes, 5 conditioning genes and 3 genes without definite functions. Through the genetic manipulation of the biosynthesis genes, the biosynthesis of kosinostatin can be blocked, the output is changed, or novel compounds are produced. The gene cluster can be applied to gene engineering, protein expression, enzymatic catalytic reaction and the like of antharcycline compounds, and can also be used for finding and discovering compounds, genes or proteins for medicines, industry or agriculture.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Mbth-like proteins in the production of semi synthetic antibiotics
The present invention relates to the preparation of β-lactam antibodies comprising contacting 4-hydroxyphenylglycine of phenylglycine, cysteine and valine with a non-ribosomal peptide synthetase and subsequent cyclization using an isopenicillin N synthase in the presence of an MbtH-like protein and to a host cell equipped to perform such preparation.
Owner:CENTRIENT PHARMA NETHERLANDS BV
A kind of one-step synthesis method of L-carnosine and truncated L-carnosine synthetase
ActiveCN109851658BAchieve recyclingWide variety of sourcesPeptidesEnzymesPhosphorylationCarnosine synthetase
The invention discloses a method for synthetizing L-carnosine by a one-step method and truncated L-carnosine synthetase. According to the method, beta-alanine, L-histidine, ATP and polyphosphate are used as raw materials, MgCl2 is used as an activator, L-carnosine synthetase and polyphosphate kinase are added, and through an enzymatic reaction under the condition of pH being 6.5-8.5 and the temperature being 30-45 DEG C, the carnosine is coupled, catalyzed and synthetized. According to the method disclosed by the invention, escherichia coli is used for respectively expressing the truncated L-carnosine synthetase (of which the amino acid sequence is as shown in SEQID No.3) and the polyphosphate kinase, through purification, mixing is performed, a dual-enzyme coupling system is formed, and the L-carnosine synthetase in truncated expression can catalyze the L-carnosine synthetized from beta-alanine and L-histidine; besides, accompanied with ATP dephosphorylation, ADP is formed, the polyphosphate kinase catalyzes polyphosphate transphosphorylation groups, and ATP is formed for the ADP, so that circulation and regeneration of the ATP can be realized; and through the dual-enzyme couplingsystem, a reaction is performed under the appropriate reaction condition, so that carnosine is obtained. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the raw materials are low in cost, the enzymatic conversion time is short, the operation is simple and convenient, and the production cost is low.
Owner:苏州百因诺生物科技有限公司
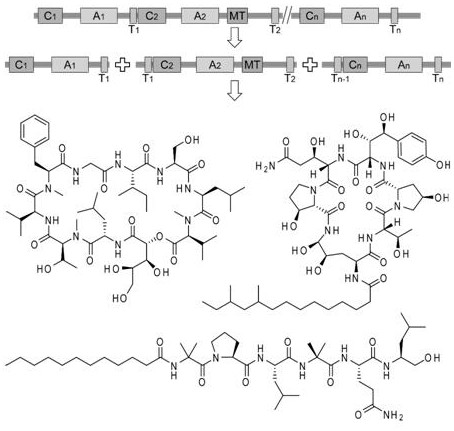
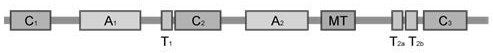
Novel non-ribosome polypeptide synthetase resolution expression method
PendingCN114657155AIncrease productionFungiMicroorganism based processesHeterologousCombinatorial synthesis
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, and discloses a non-ribosome polypeptide synthetase resolution expression method, which is characterized in that according to the prediction of an NRPS structural domain and a three-dimensional structure, NRPS is subjected to resolution expression at a special resolution site by taking Tn-1-Cn-An-Tn as a unit, so that the expression of an NRPS gene is converted into multi-gene co-expression by taking a resolution unit as an independent gene, and the non-ribosome polypeptide synthetase is obtained. The corresponding non-ribosome polypeptide product is efficiently obtained. The method not only can be used for heterologous expression of the giant NRPS in fungi and increase the yield of the non-ribosome polypeptide, but also provides a theoretical basis and way for synthesizing novel non-ribosome polypeptide by performing inter-module combination through a combinatorial biosynthesis method. The method has relatively high practical application value in the aspects of excavation of natural non-ribosome polypeptides by utilizing synthetic biology, yield improvement, creation of non-natural non-ribosome polypeptides and the like.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
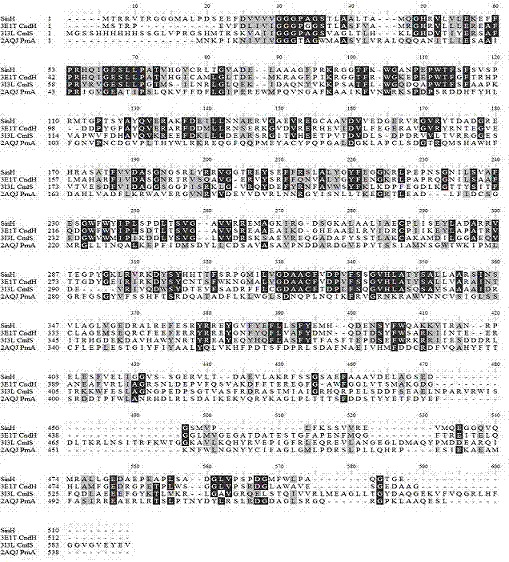
A kind of dovemycin biosynthetic gene cluster and its application
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Biosynthetic systems producing fungal indole alkaloids
Owner:COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com