Patents
Literature
68 results about "Programmable load" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A programmable load is a type of test equipment or instrument which emulates DC or AC resistance loads normally required to perform functional tests of batteries, power supplies or solar cells. By virtue of being programmable, tests like load regulation, battery discharge curve measurement and transient tests can be fully automated and load changes for these tests can be made without introducing switching transient that might change the measurement or operation of the power source under test.
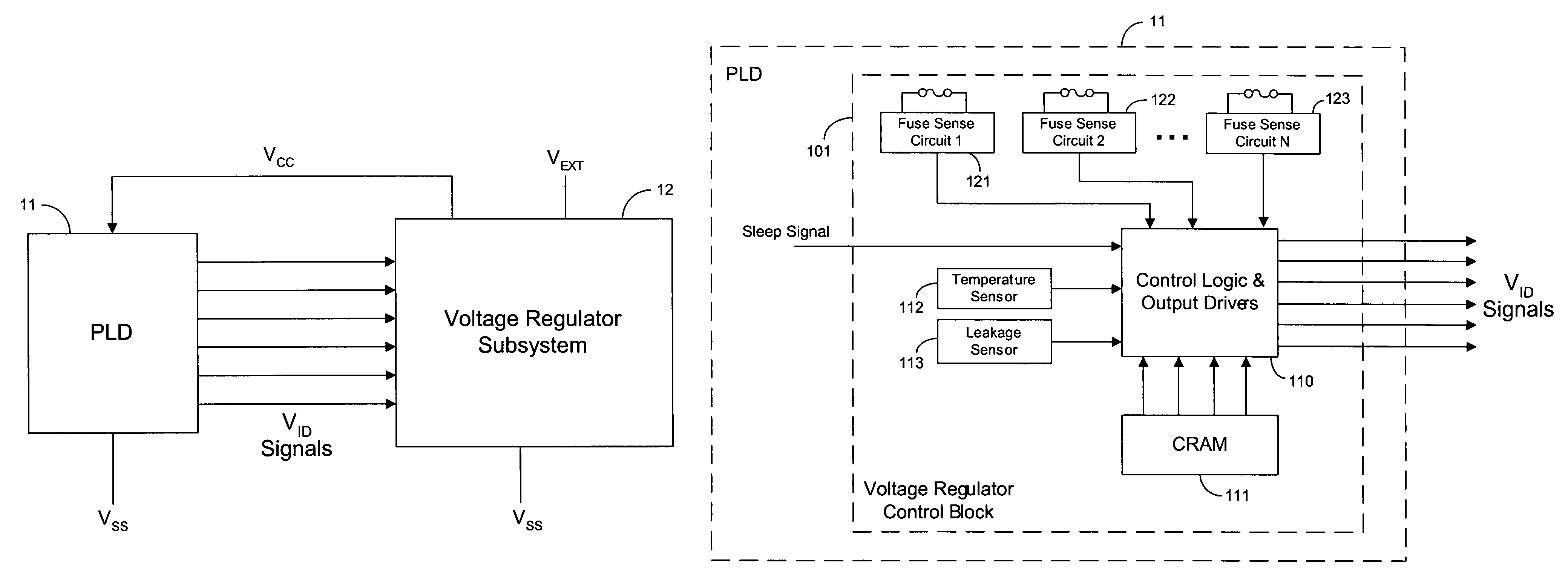
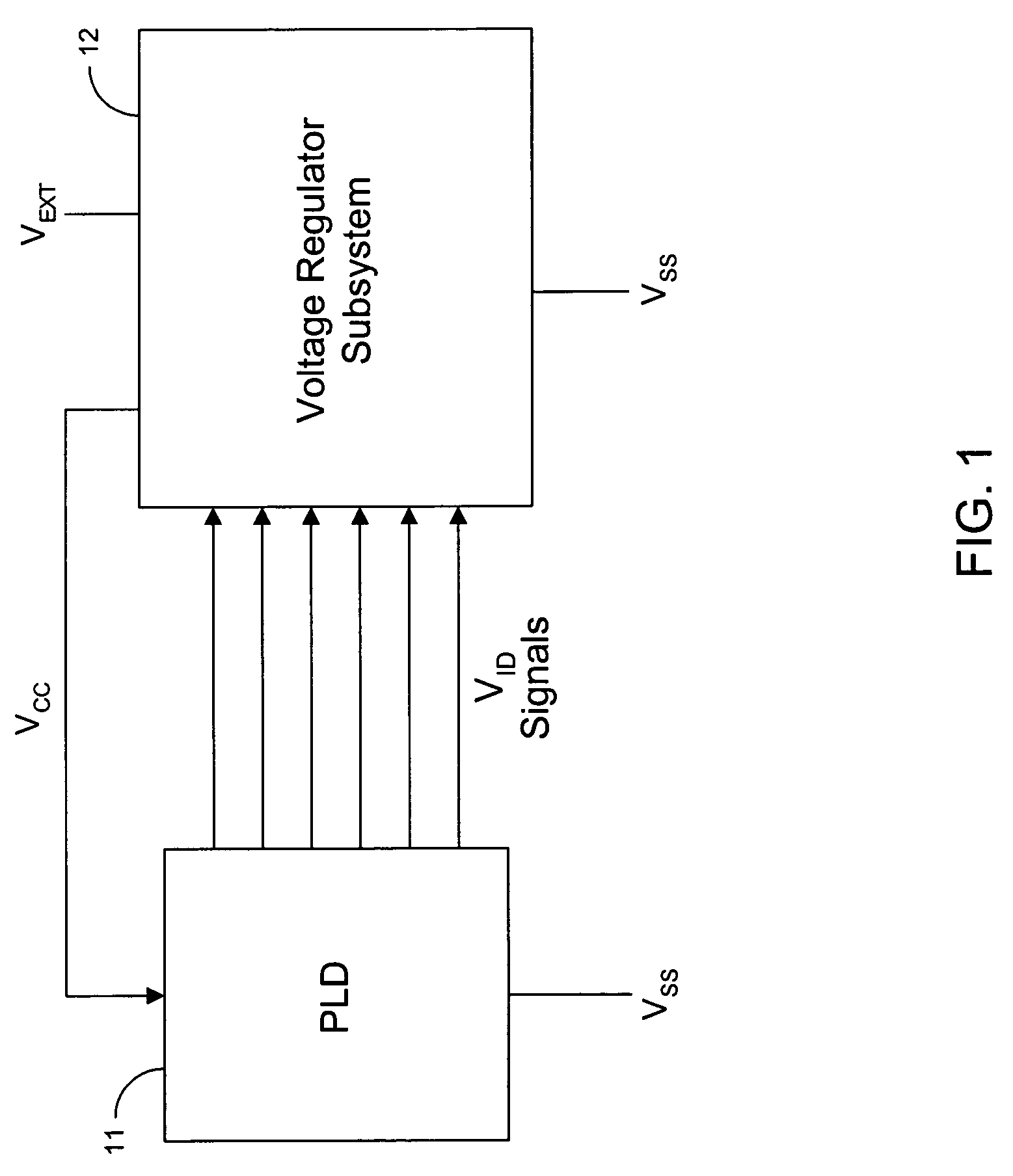
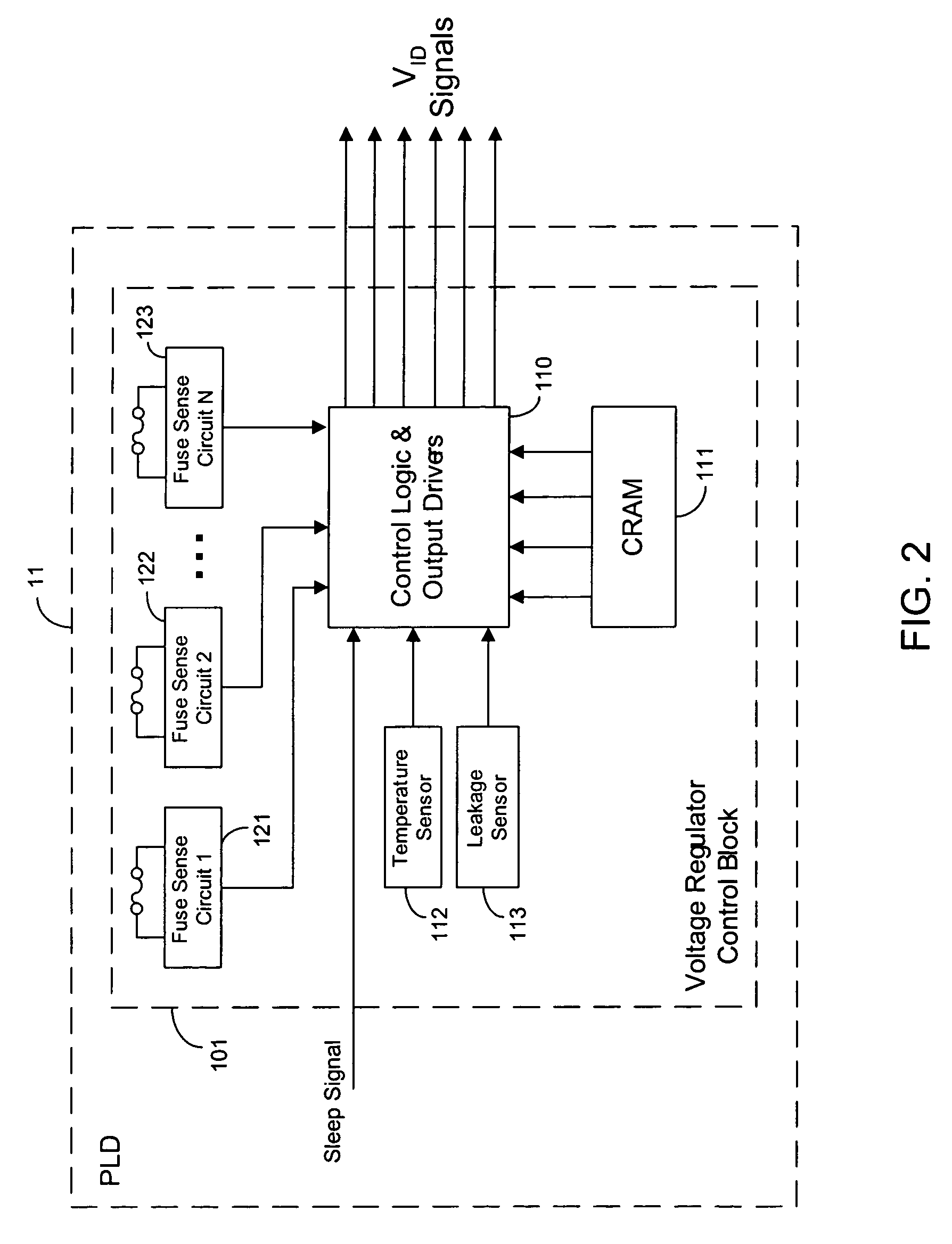
Adaptive power supply voltage regulation for programmable logic
ActiveUS7142009B1Reduce power consumptionPower consumption reductionVolume/mass flow measurementVoltage regulator moduleProgrammable logic device
Adaptive regulated power supply voltages are applied to programmable logic integrated circuits. Control circuitry in a programmable logic IC generates control signals that are transmitted to an external voltage regulator. The voltage regulator generates one or more power supply voltages in response to the control signals. The values of control signals determine the target values of the supply voltages. The control circuitry can adapt the power supply voltages to compensate for temperature and process variations on the IC. The power supply voltages can be programmed by a manufacturer or by a user to achieve desired target values. The control circuitry can also put a programmable logic IC into a sleep mode by dropping the high supply voltage to a low value to reduce power consumption during periods of low usage.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
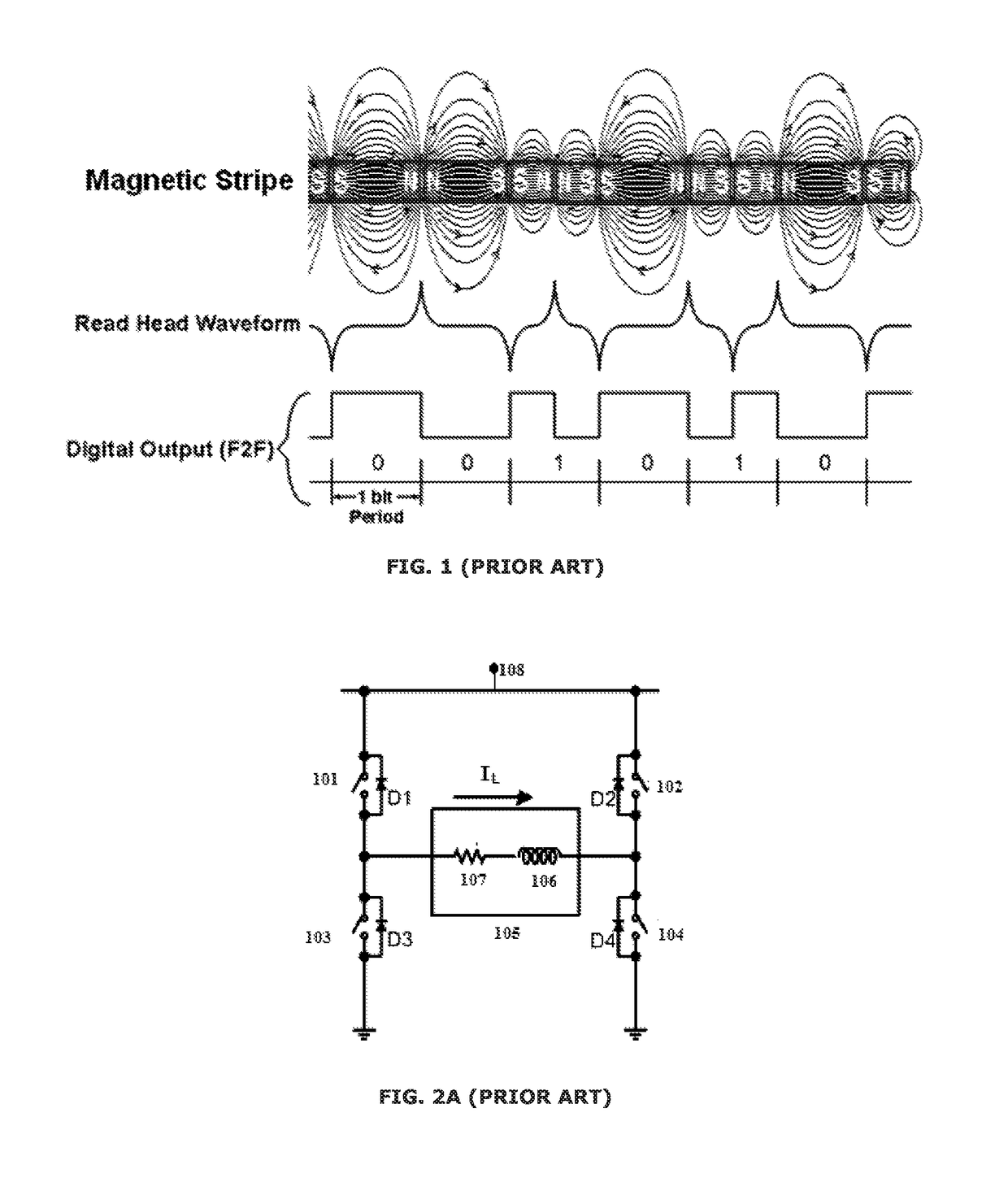
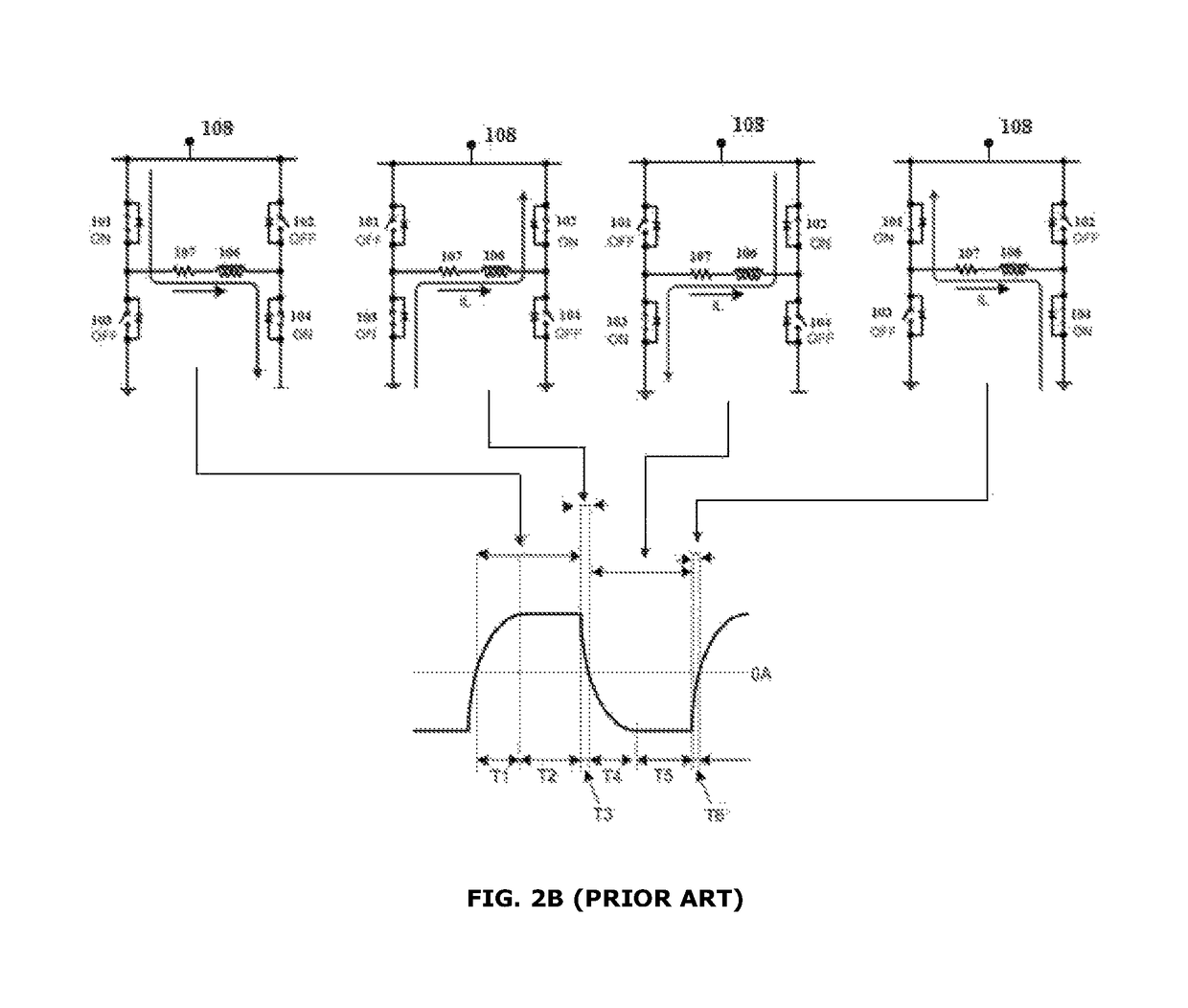
Magnetic stripe data transmission system and method for reliable data transmission and low power consumption
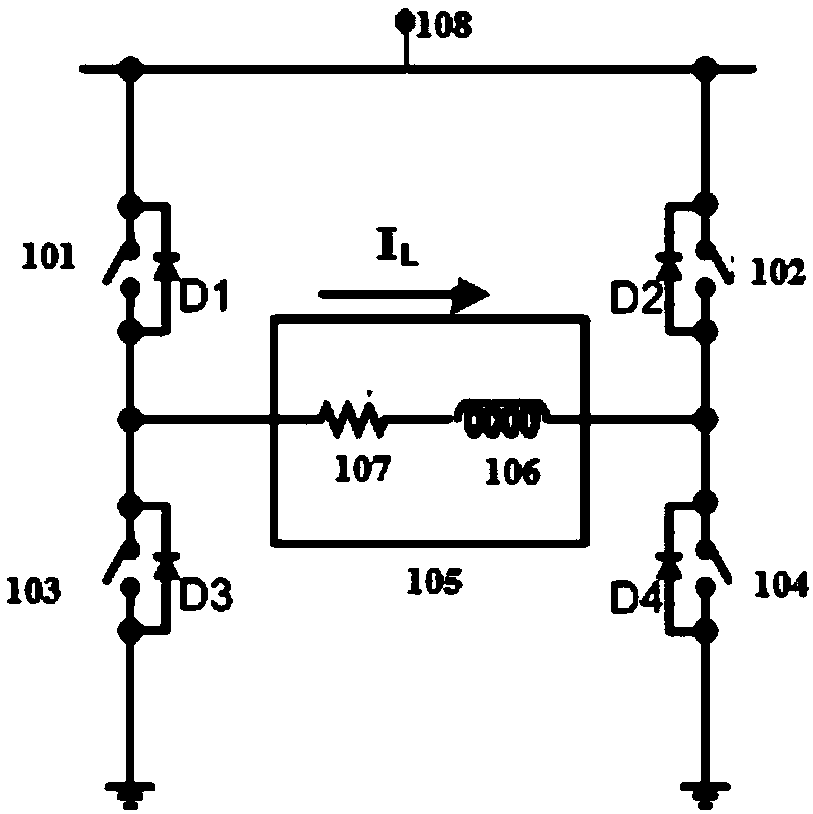
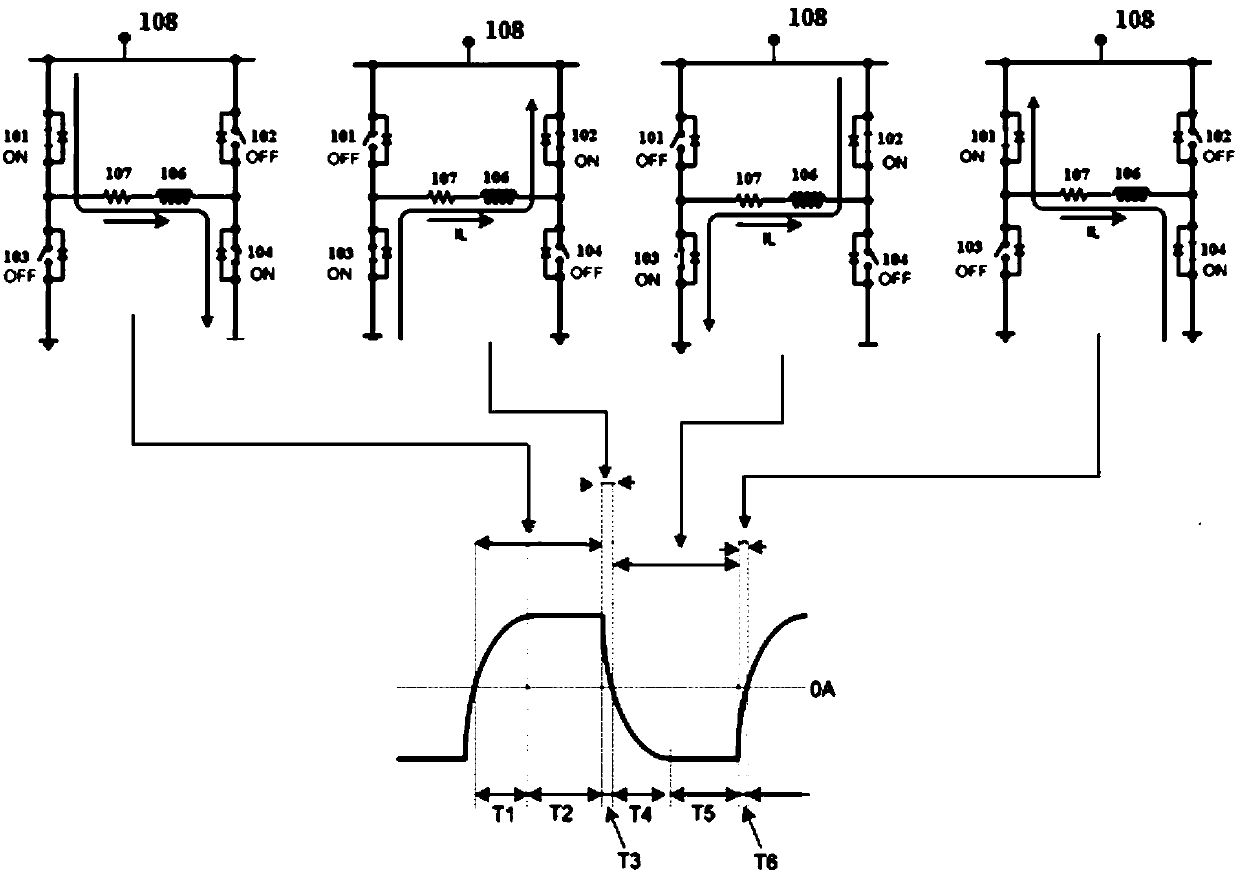
ActiveUS9697450B1Reduce power consumptionReliable transmissionNear-field transmissionPayment architectureFull bridgeProgrammable load
A magnetic stripe data transmission (MST) driver and a method for driving the MST are disclosed. The MST driver is configured to transmit magnetic strip data comprising of streams of pulses. The MST driver comprises a pair of high side switches and a pair of low side switches. The pair of high side switches comprises a first switch and a second switch. The pair of low side switches comprises a third switch and a fourth switch. The first, second, third and fourth switches are arranged in a full bridge type configuration connected across a voltage source and a ground. An inductive coil is connected across outputs of the full bridge type configuration of the switches. The MST driver includes a switch driver configured to drive the pair of low side switches and the pair of high side switches under current slope control using pulse width modulation. The driven load current has a rising portion and a falling portion through the inductive coil in a forward direction or in a reverse direction with programmable load current rising and falling slopes to induce a recognizable back electromagnetic force at a receiver emulating the magnetic strip data during the load current rising and falling portions and to reduce power loss during time periods without signal transmission.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON INC
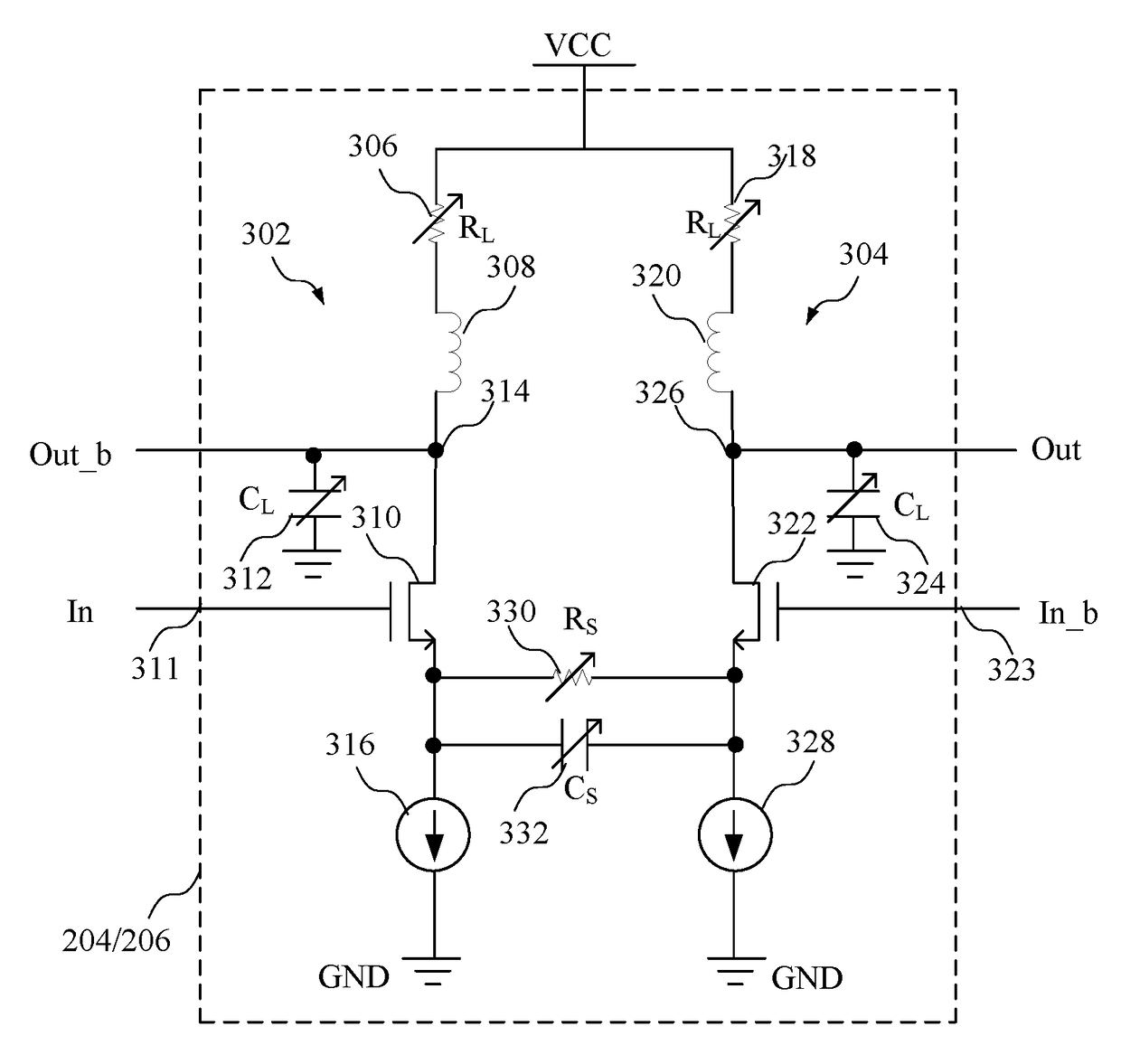
Circuit for and method of receiving an input signal
ActiveUS9806915B1High-frequency gainGain controlTransmitter/receiver shaping networksProgrammable loadCapacitor
A continuous time linear equalizer comprises an input of a first equalizer path configured to receive a first differential input signal; an input of a second equalizer path configured to receive a second differential input signal; a first programmable load capacitor coupled to an output of the first equalizer path; a second programmable load capacitor coupled to an output of the second equalizer path; and a programmable source capacitor coupled between the first equalizer path and the second equalizer path.
Owner:XILINX INC
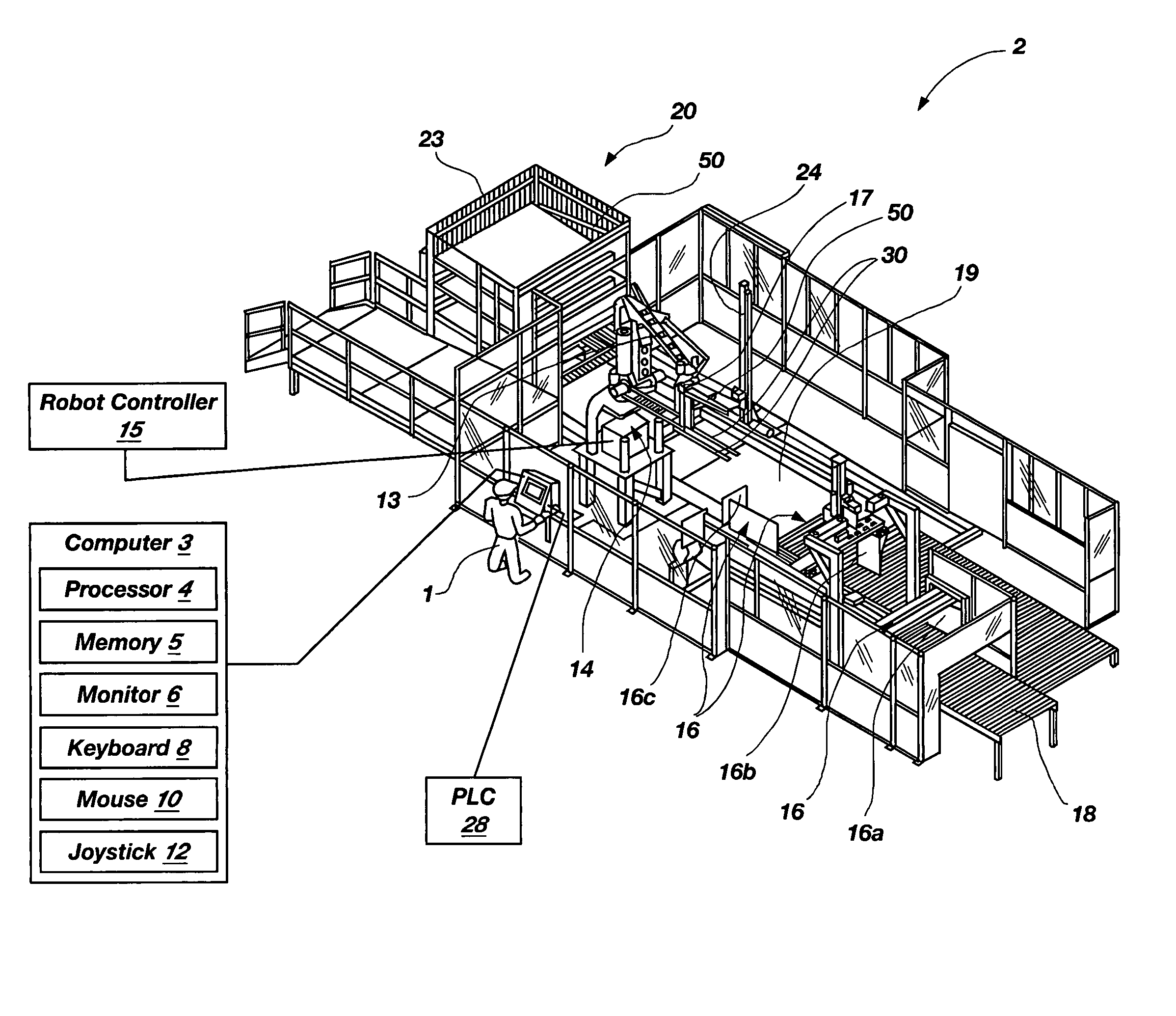
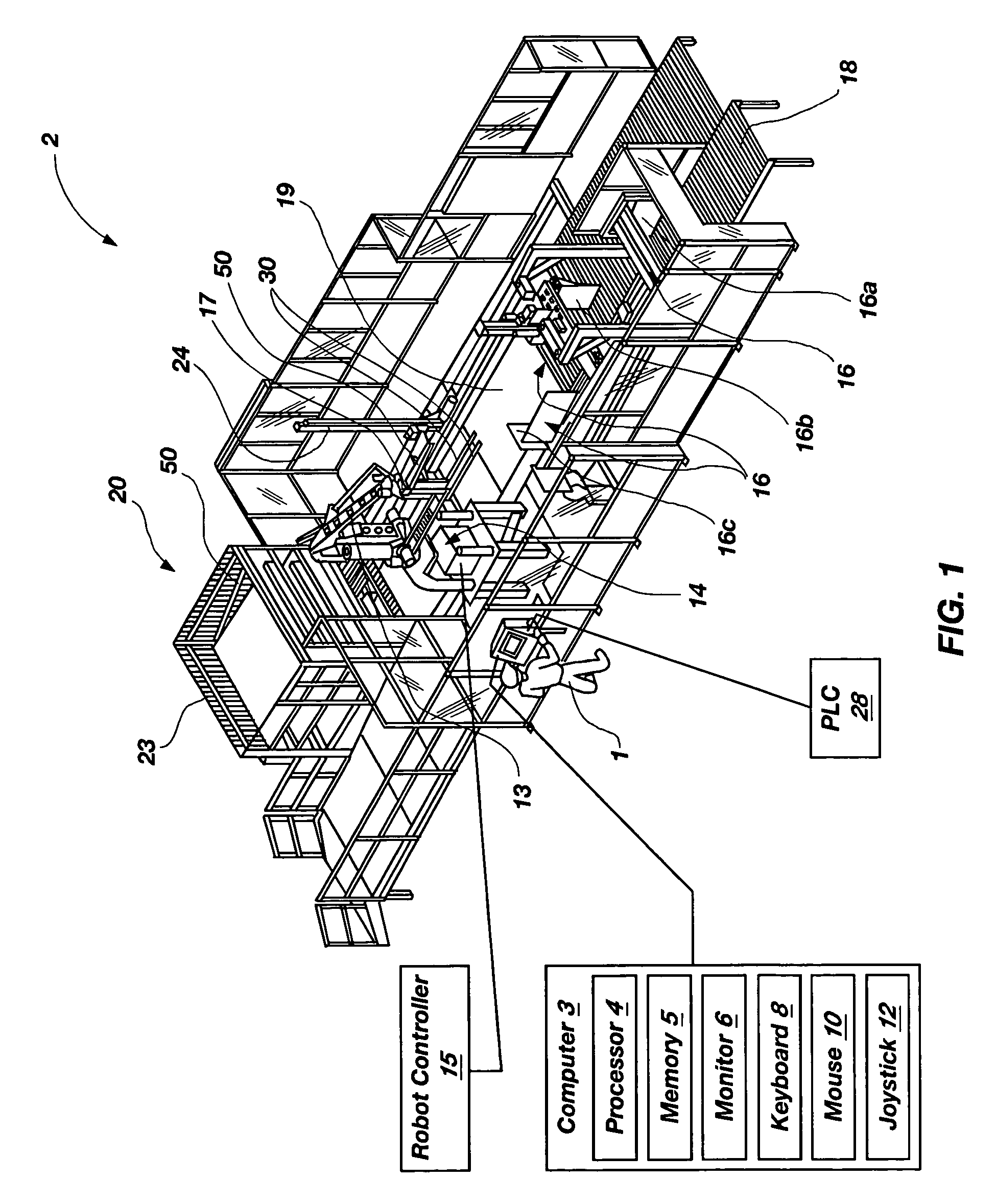
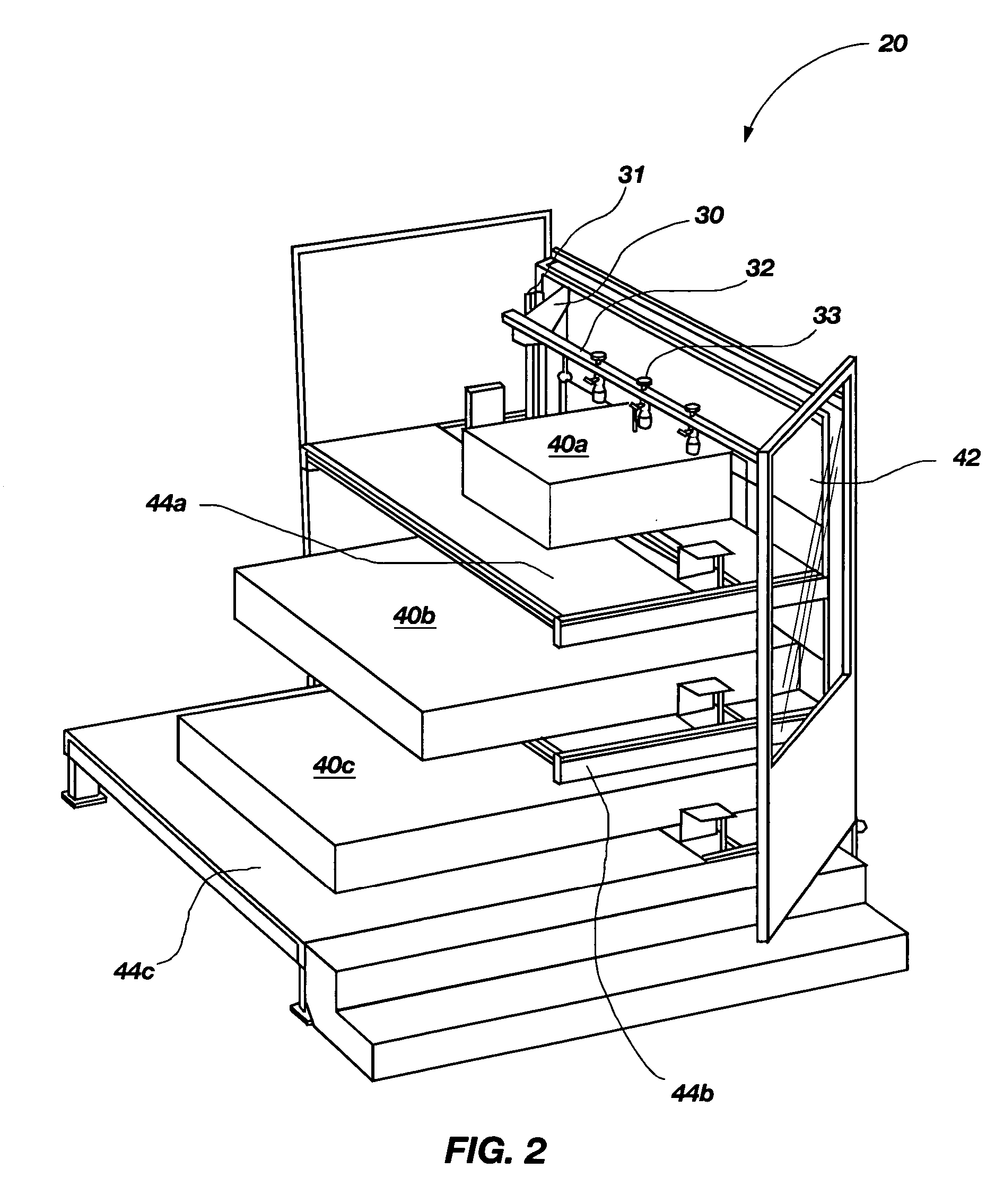
Programmable load forming system, components thereof, and methods of use
InactiveUS20060106487A1Easy to changeImprove processing throughputDigital data processing detailsArc welding apparatusProgrammable loadSimulation
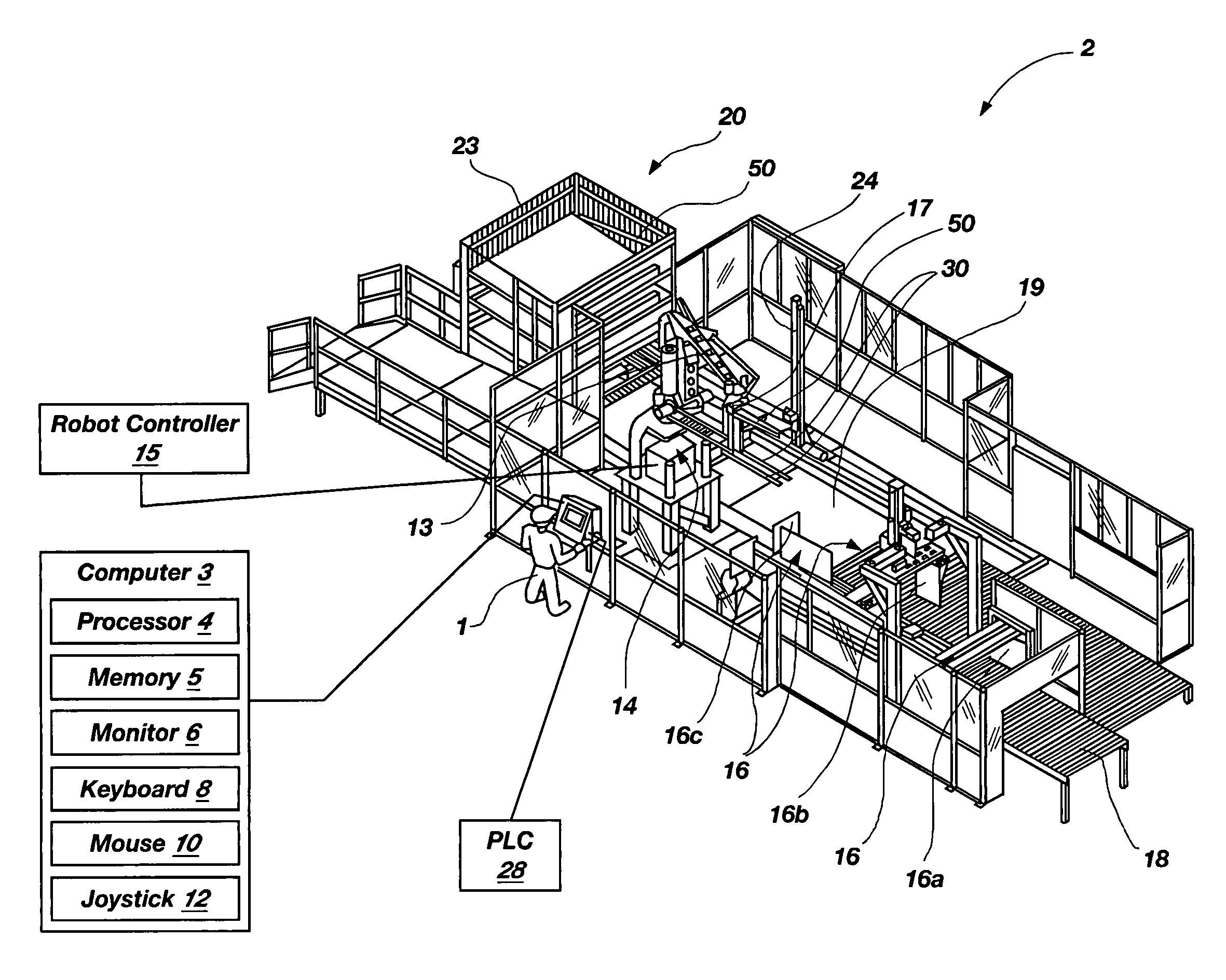
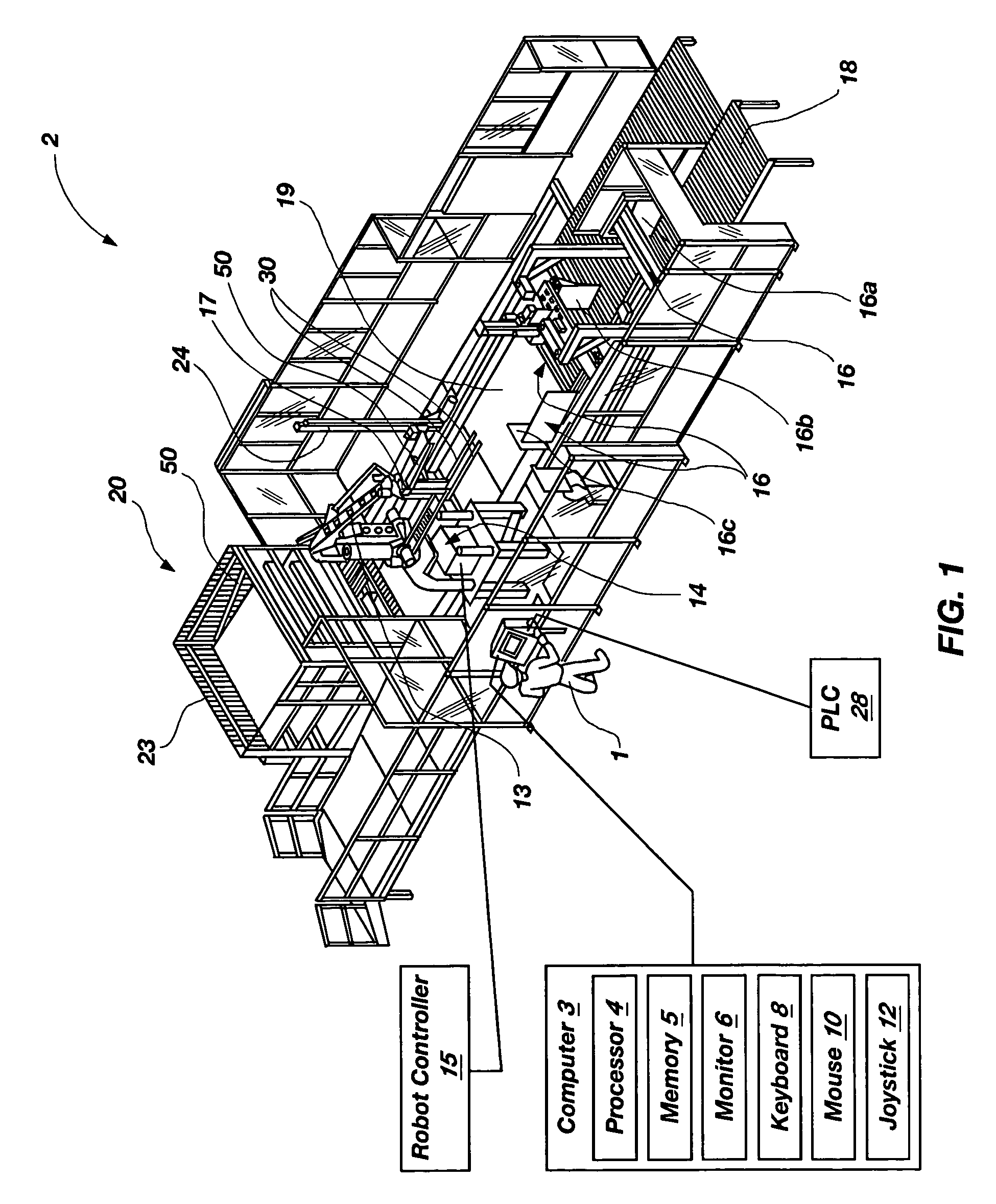
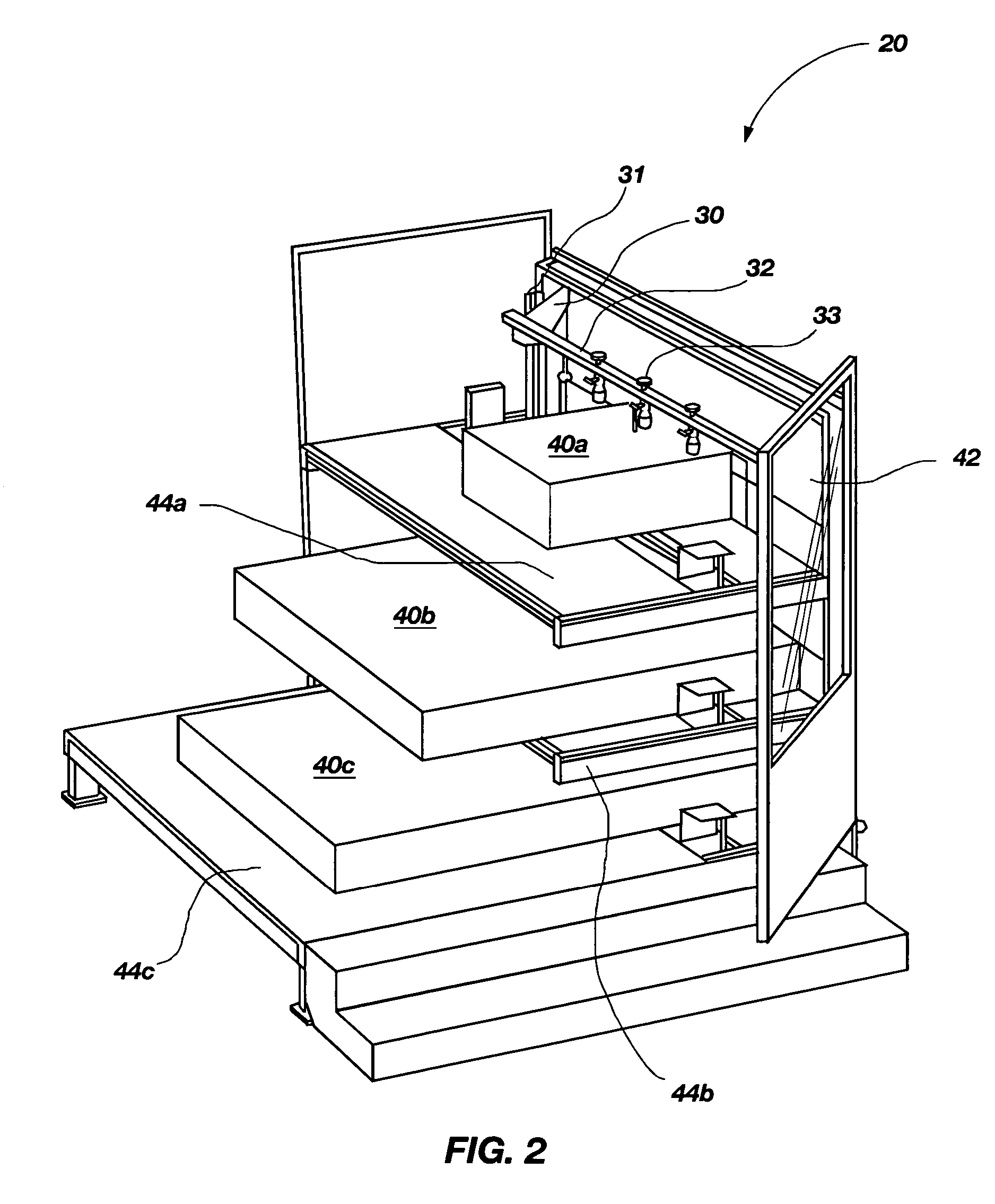
Programmable load forming systems, components thereof, and methods of use are disclosed. In one aspect, a programmable load forming system is programmed to perform the method of downloading a calculated path from the computer to the robot controller, moving one or more bundles along the calculated path to position the one or more bundles in a predetermined stacking position of a stacking pattern using the robot, and determining if the robot has completed moving along the calculated path. The calculated path is defined, in part, by the stacking pattern and other parameters such as, for example, bundle geometry, bundle levelness, bundle compressibility, among other parameters. In another aspect, the system is programmed to perform a method of sensing the top of a bundle and controllably placing a bundle. Additional aspects are directed to systems and methods of safely operating the robot and an inventive hopper design for holding bottom / tie sheets.
Owner:ALLIANCE MACHINE SYST INTENAT
Programmable load forming system, components thereof, and methods of use
InactiveUS8000837B2Easy to changeImprove processing throughputDigital data processing detailsArc welding apparatusProgrammable loadSimulation
In one aspect, a programmable load forming system is programmed to perform the method of downloading a calculated path from the computer to the robot controller, moving one or more bundles along the calculated path to position the one or more bundles in a predetermined stacking position of a stacking pattern using the robot, and determining if the robot has completed moving along the calculated path. The calculated path is defined, in part, by the stacking pattern and other parameters such as, for example, bundle geometry, bundle levelness, bundle compressibility, among other parameters. In another aspect, the system is programmed to perform a method of sensing the top of a bundle and controllably placing a bundle. Additional aspects are directed to systems and methods of safely operating the robot and an inventive hopper design for holding bottom / tie sheets.
Owner:ALLIANCE MACHINE SYST INTENAT
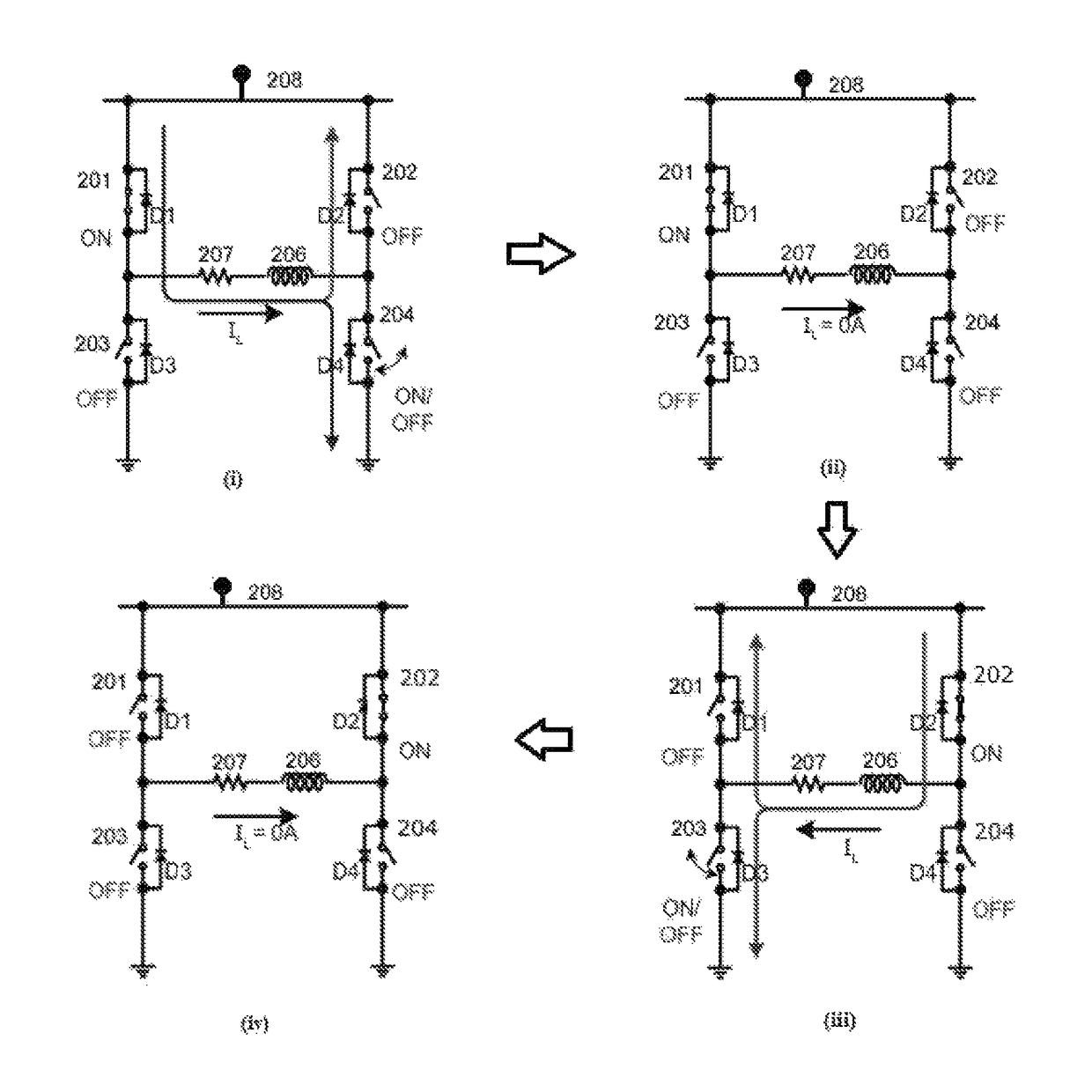
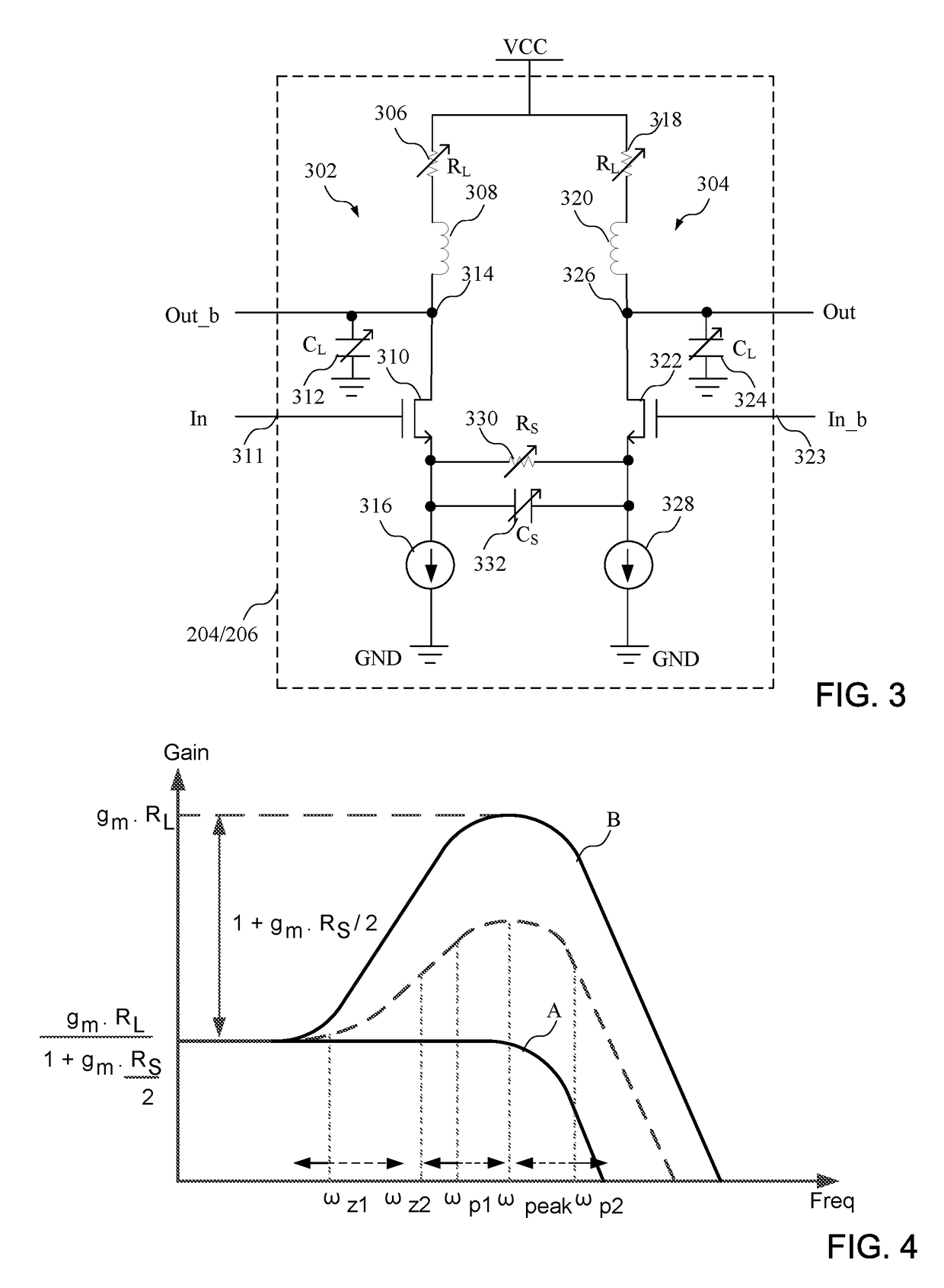
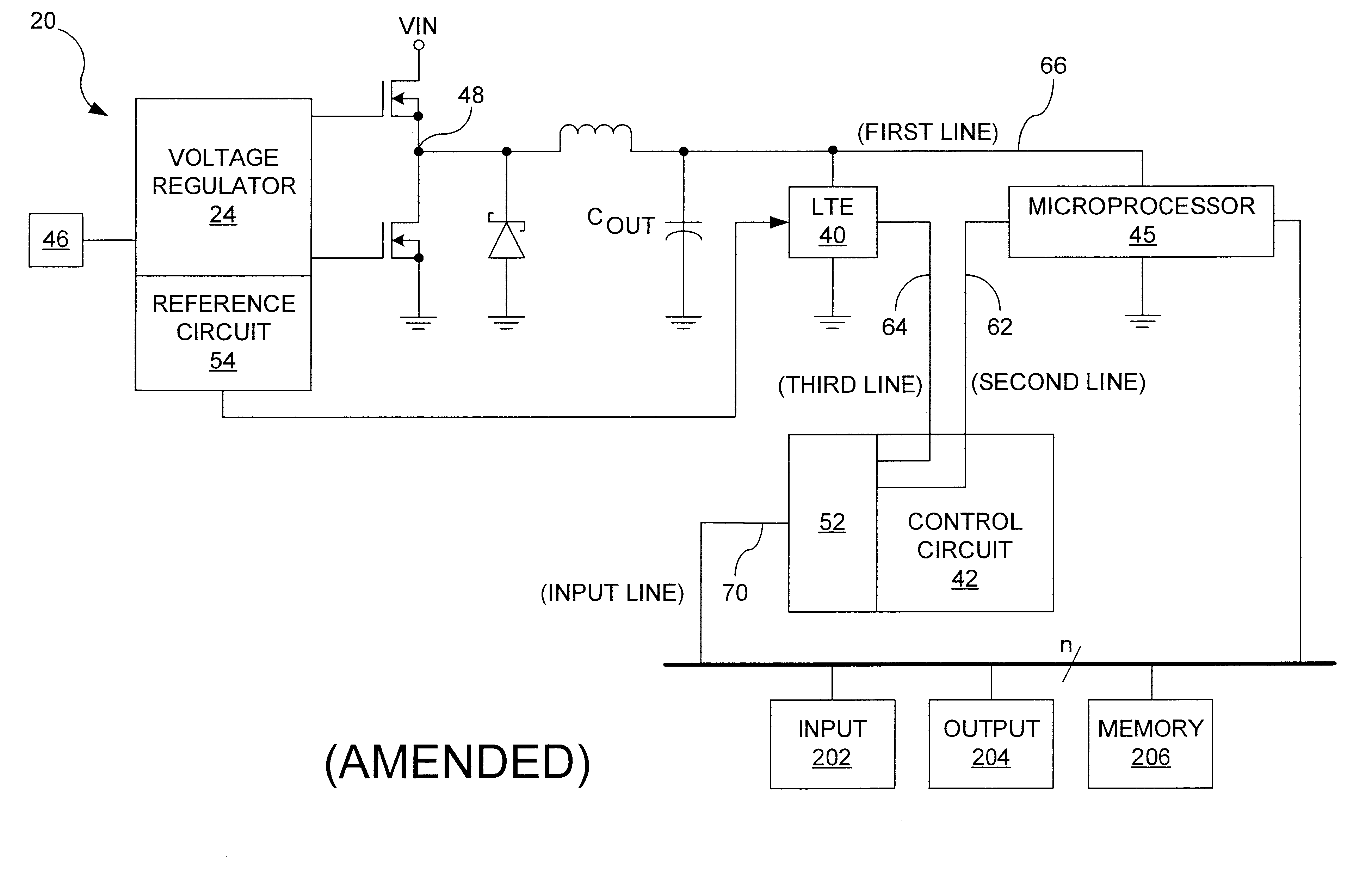
Programmable load transient compensator for reducing the transient response time to a load capable of operating at multiple power consumption levels
InactiveUSRE38891E1Decrease in transient response timeShorten the timeDc network circuit arrangementsVolume/mass flow measurementProgrammable loadEngineering
A load transient compensator and method of operating the load transient compensator for reducing the transient response time to a load capable of operating at either of several consumption levels when the load changes its power consumption level . The load transient compensator has a comparator having an output connected to an input of an upper driver and of a lower driver with the output of each of the driver being connected to a gate of a power transistor. When the load is in sleep mode and is about to start being accessed, the upper driver is turned on to turn on its associated transistor to supply additional current to the load, regulated by the comparison circuit. When the load is in the power up mode and it is about to stop being accessed, the lower driver is turned on to turn on its associated transistor to drain current supplied to the load by a supply, regulated by the comparison circuit. This allows a quicker response to the large changes in current required by the load when the load is changing its level of power consumption without greatly increasing the cost of the system containing the load and without compromising the stability of the system.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Capacitive high-side switch driver for a power converter
InactiveCN1846345AStrong anti-interference abilityAvoid disadvantagesTransistorElectronic switchingProgrammable loadElectric power
Owner:SYST GEN
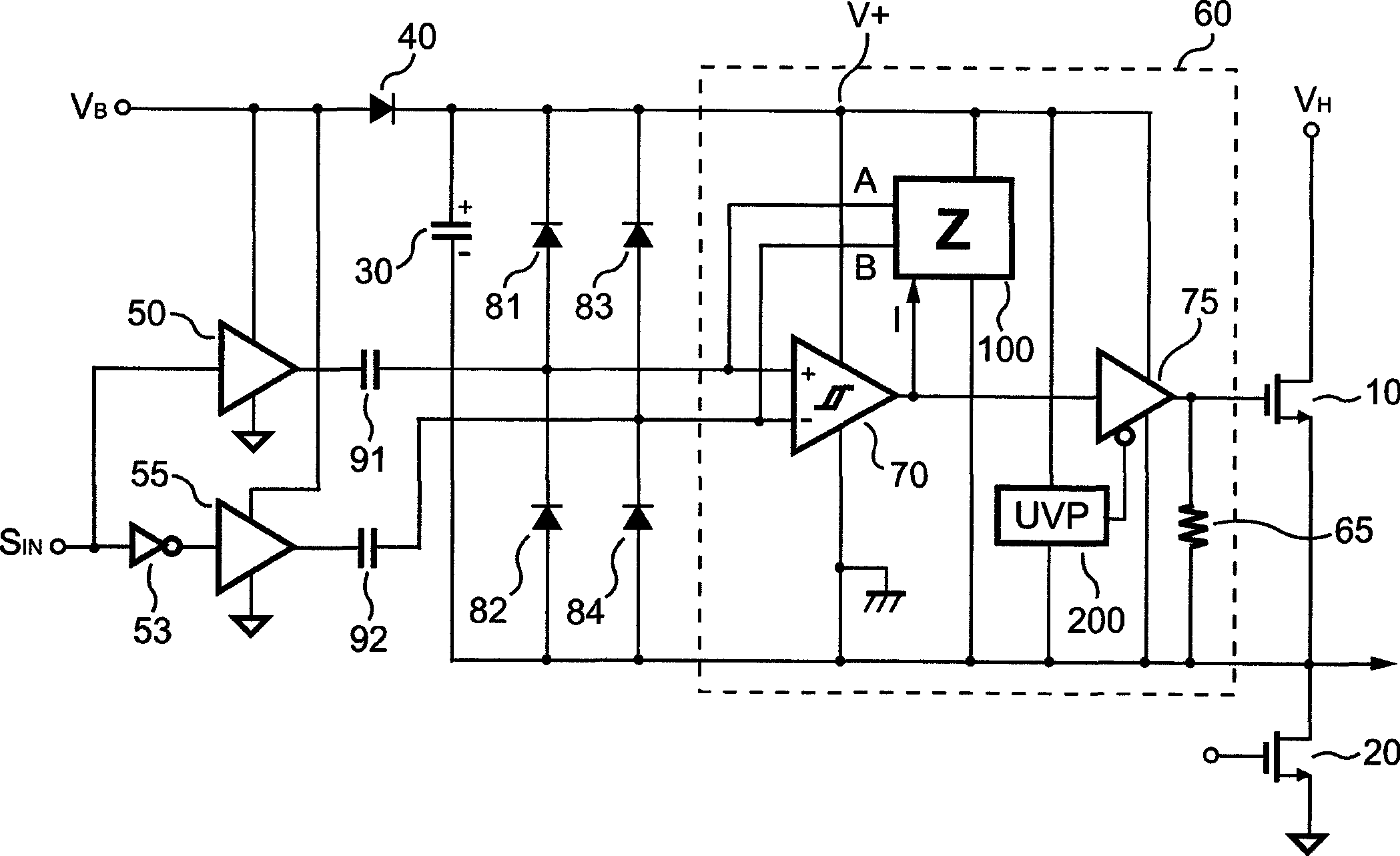
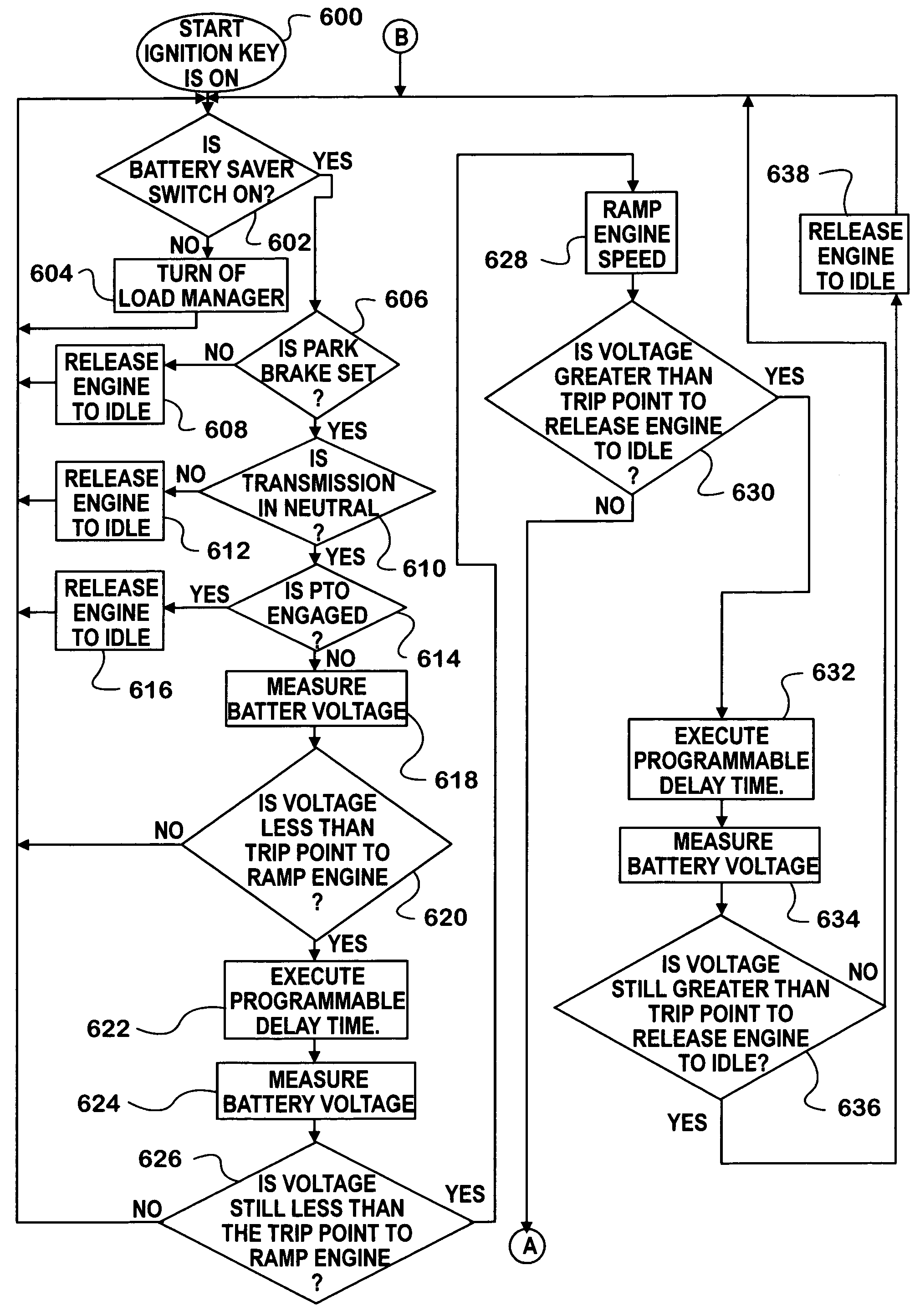
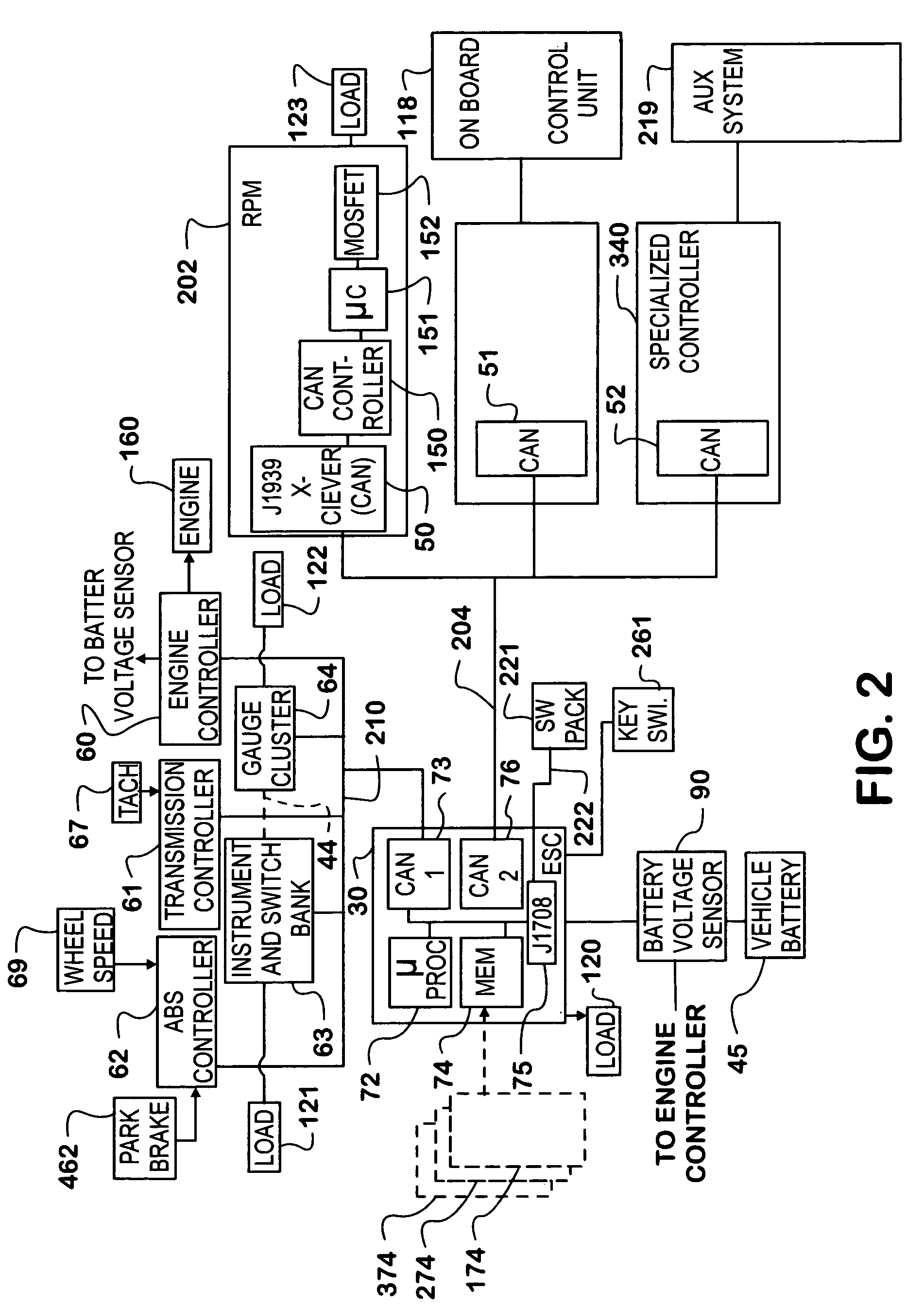
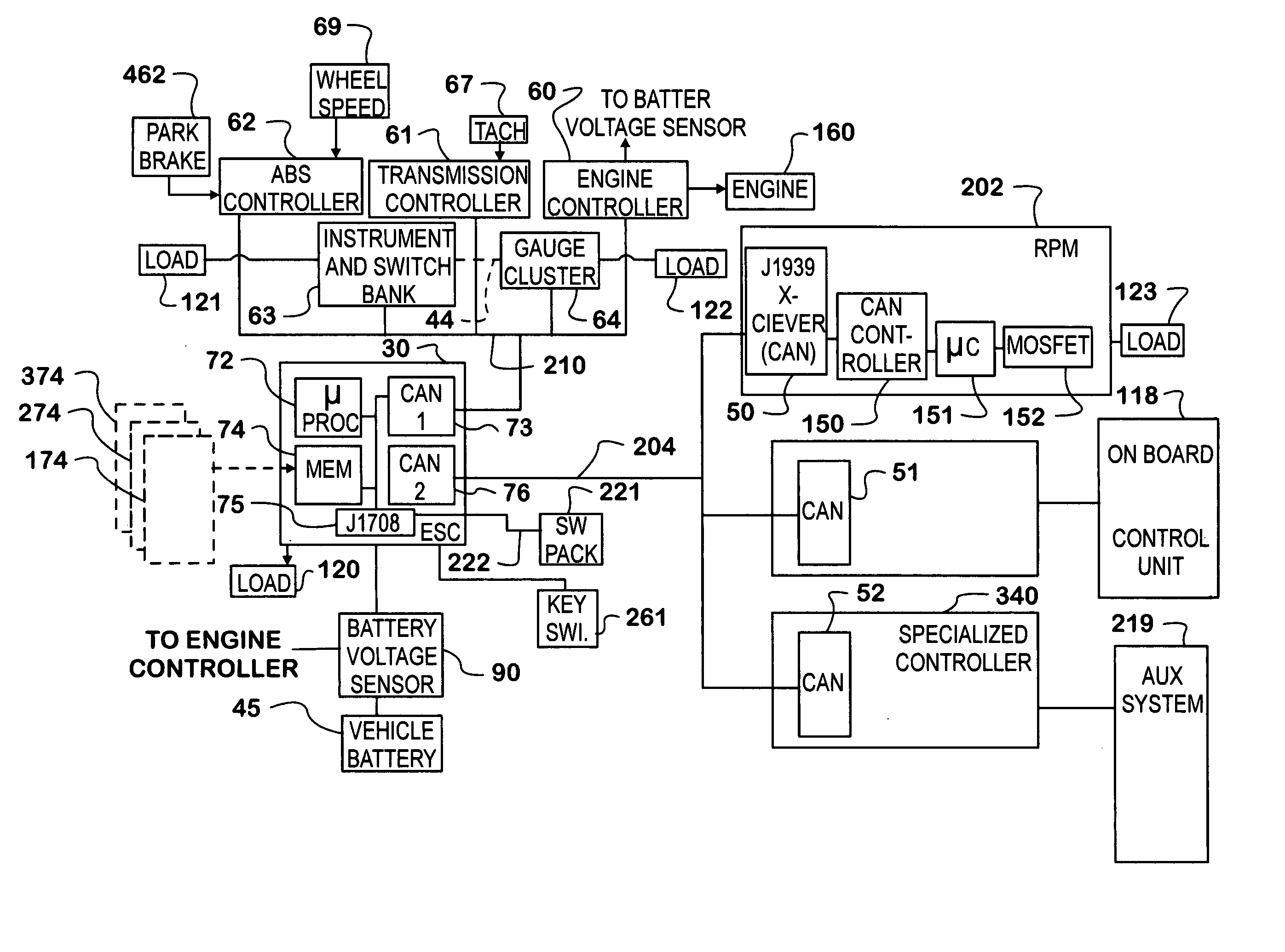
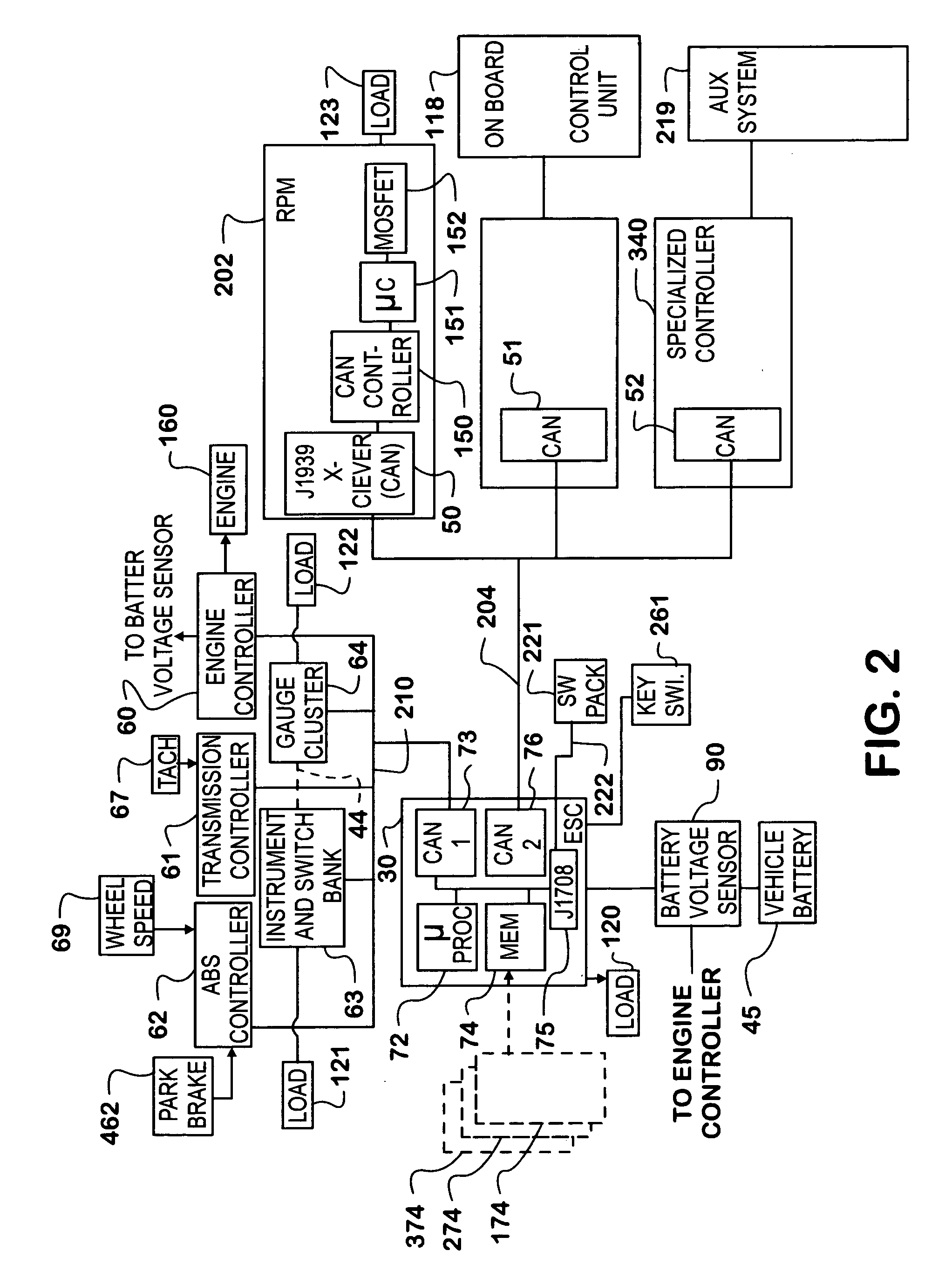
Automated vehicle battery protection with programmable load shedding and engine speed control
ActiveUS7421323B2Analogue computers for vehiclesDC motor speed/torque controlArea networkElectrical battery
Automated motor vehicle battery voltage protection is provided by setting voltage trip points for increasing engine speed and for shedding selected electrical loads. The system is effected by programming a vehicle body computer which communicates with, and exerts control over, various vehicle system controllers over one or more controller area networks. The body computer is programmed to monitor battery voltage and initiates an increase in engine speed first, and if that fails to restore a minimum battery voltage level, begins shedding loads in a predetermined order.
Owner:INT TRUCK INTPROP LLC
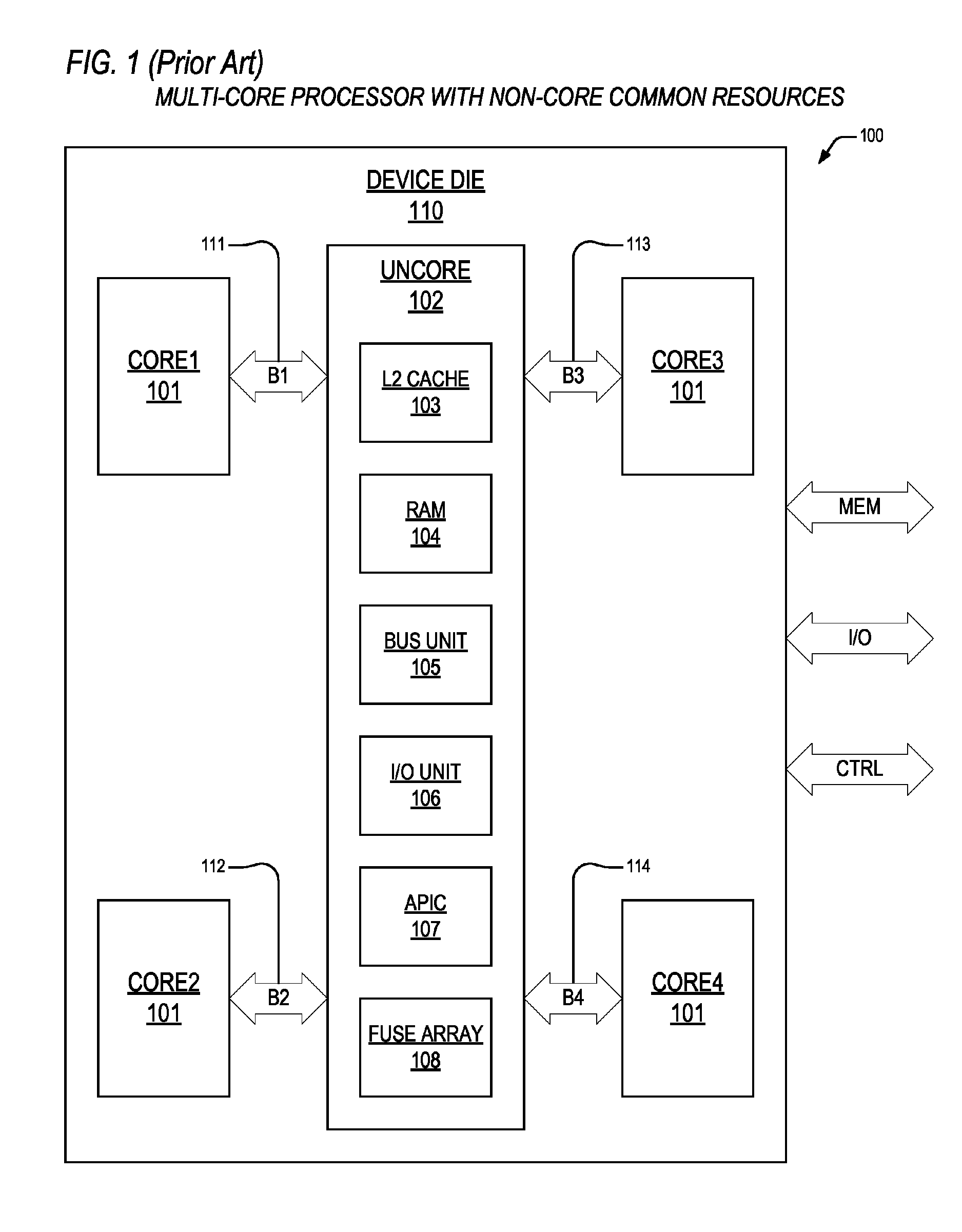
Parallel computer having a hierarchy structure
InactiveUS20060020771A1Single instruction multiple data multiprocessorsResource allocationInstruction memoryMulti processor
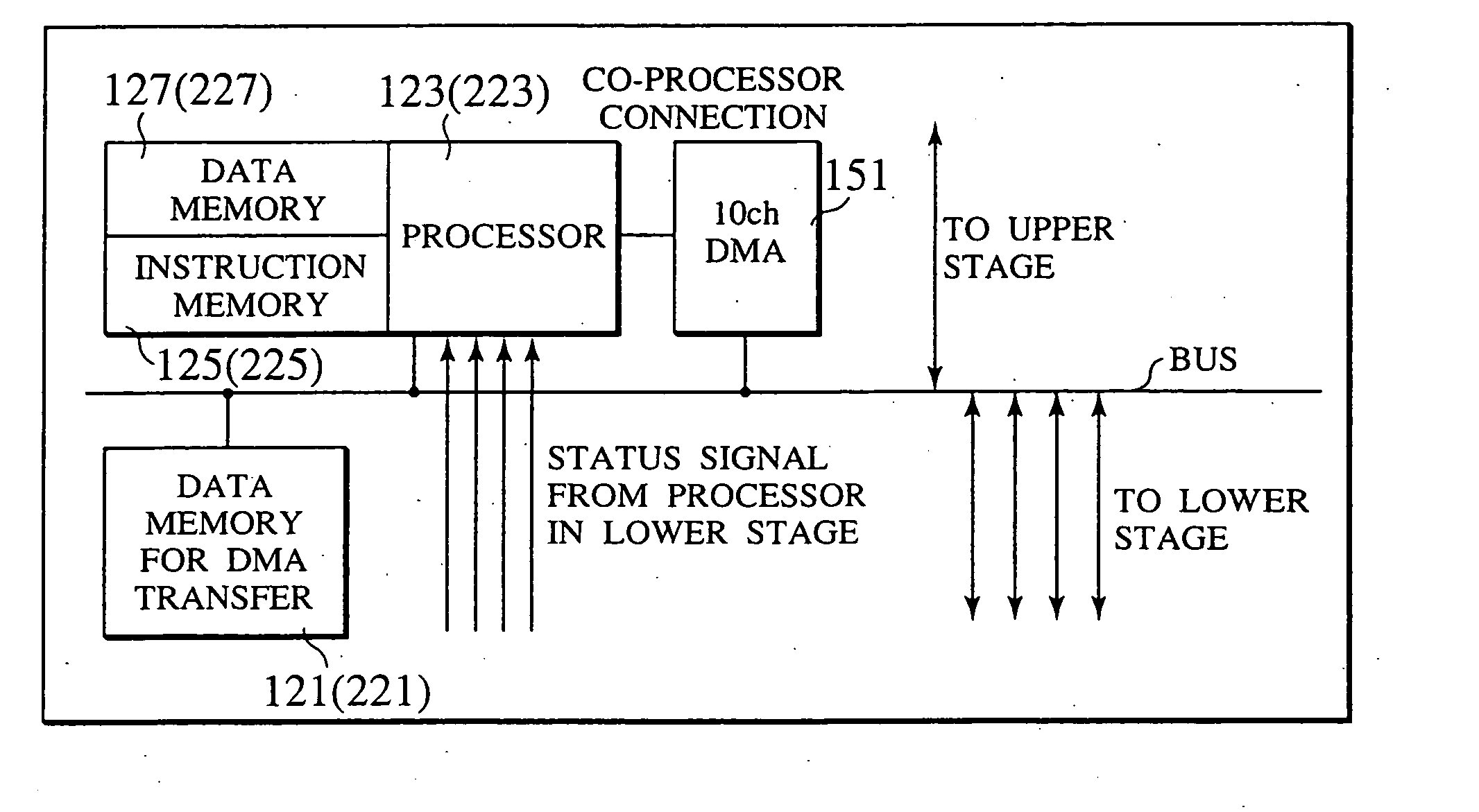
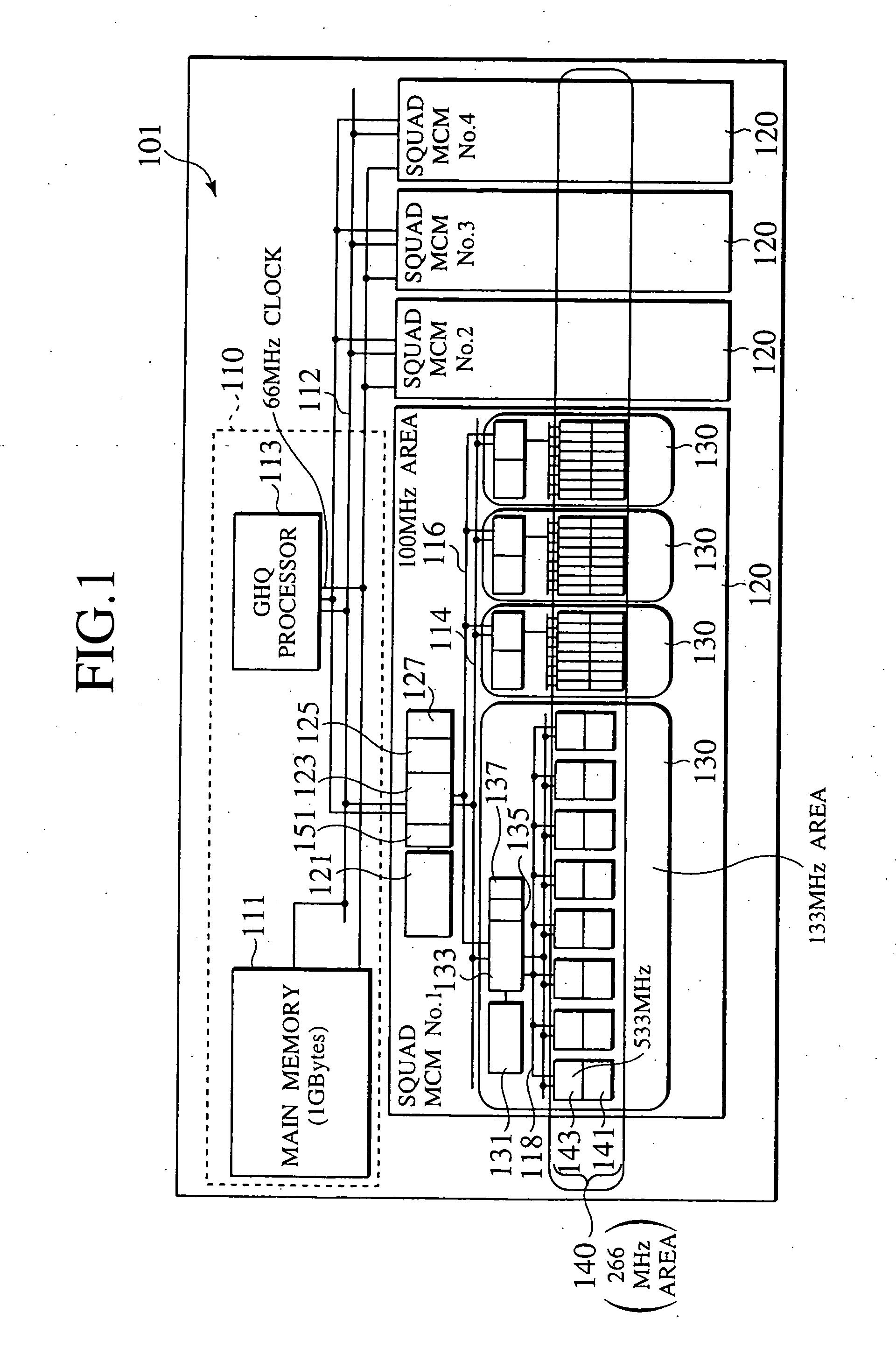
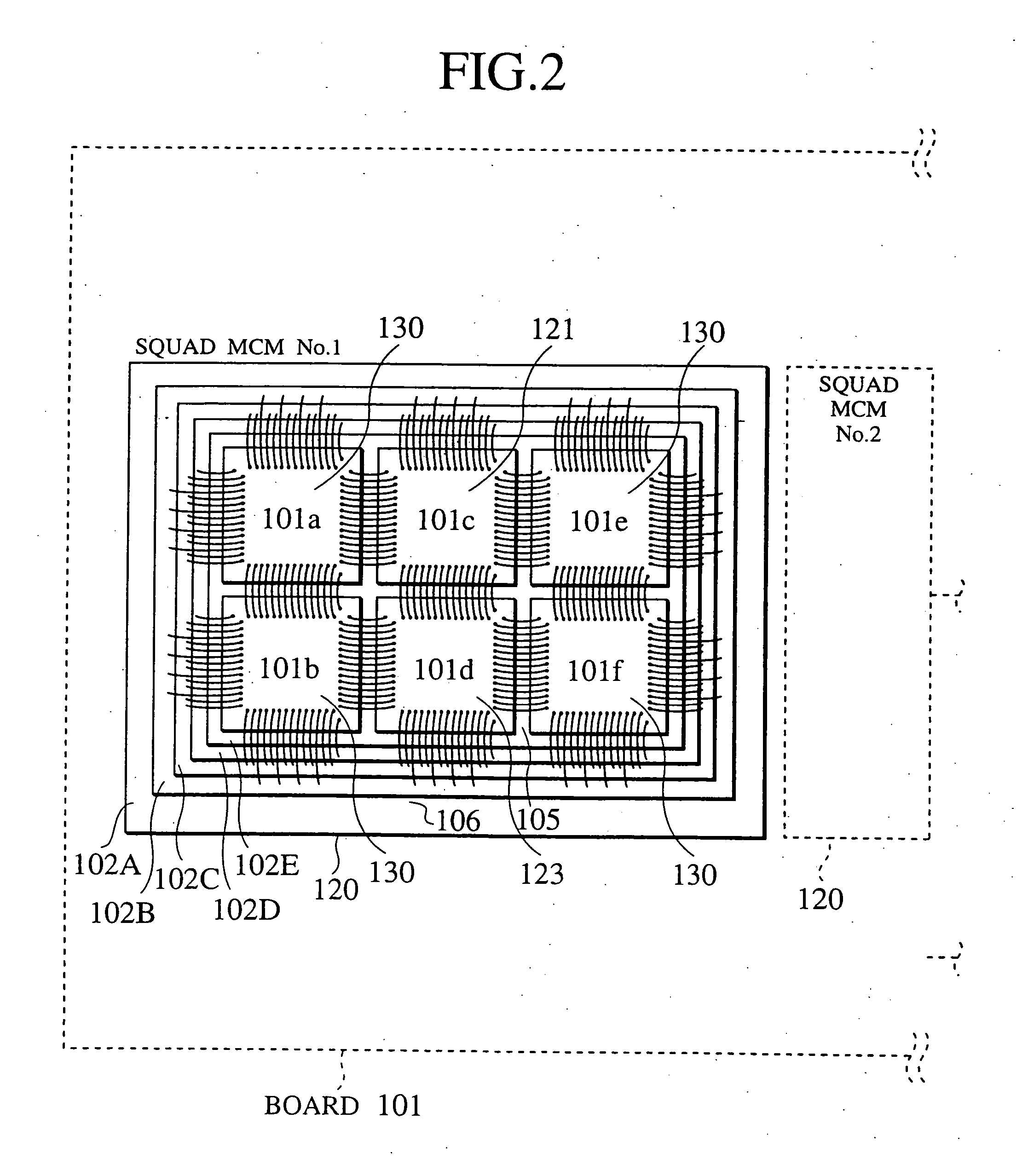
In a multiprocessor system of a hierarchy configuration as a parallel computer of a common-bus structure, a processing unit (120) in an intermediate stage has a processor (123) having a programmable function that is equal to a normal processor, an instruction memory (125), and a data memory (127). The processing unit (120) receives a status signal from a lower processor (143), and a DMA controller (151) having a memory for the transfer of large sized data performs compression, decompression, programmable load dispersion, and load dispersion according to the state of operation of each lower processor.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
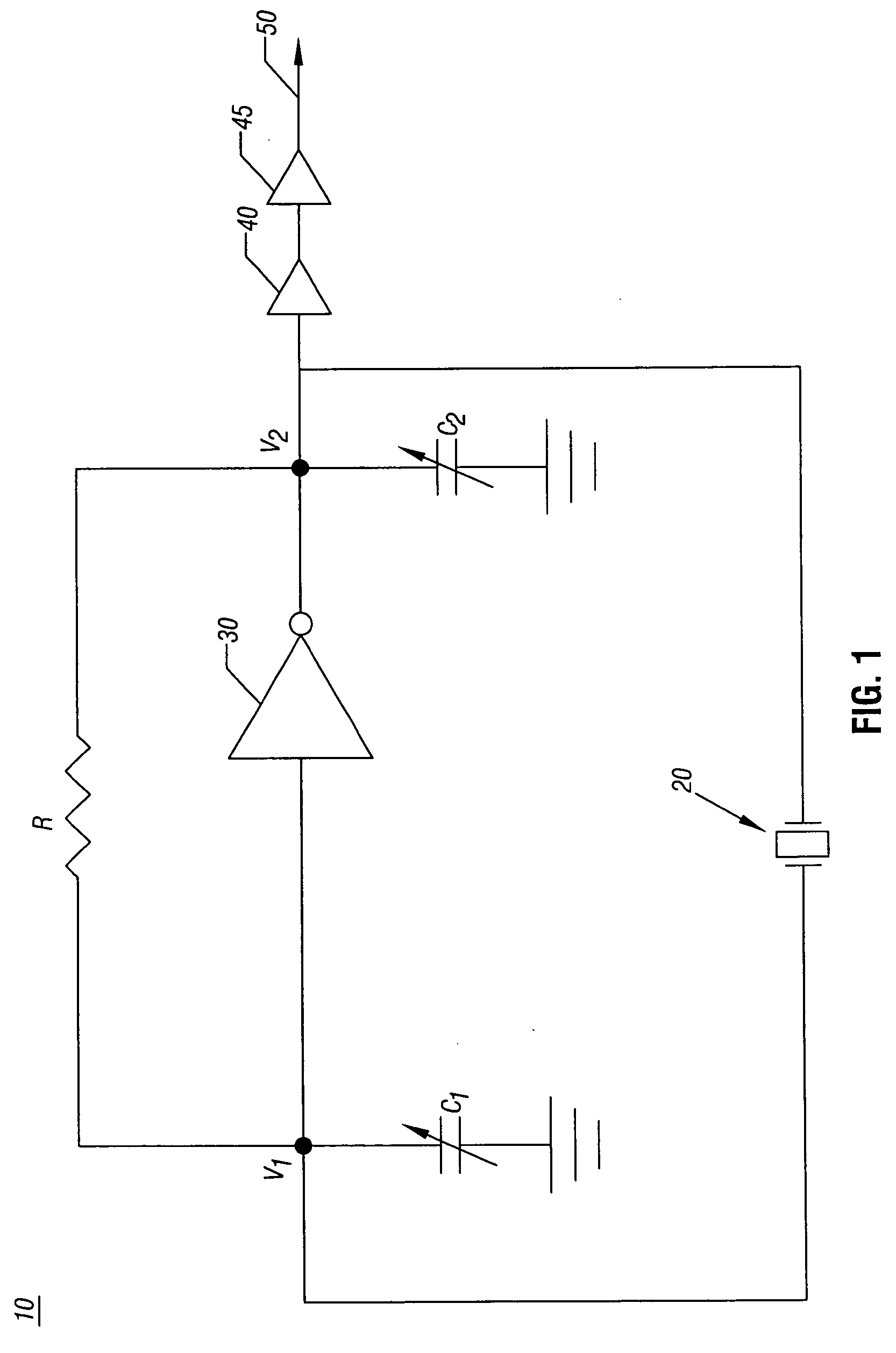
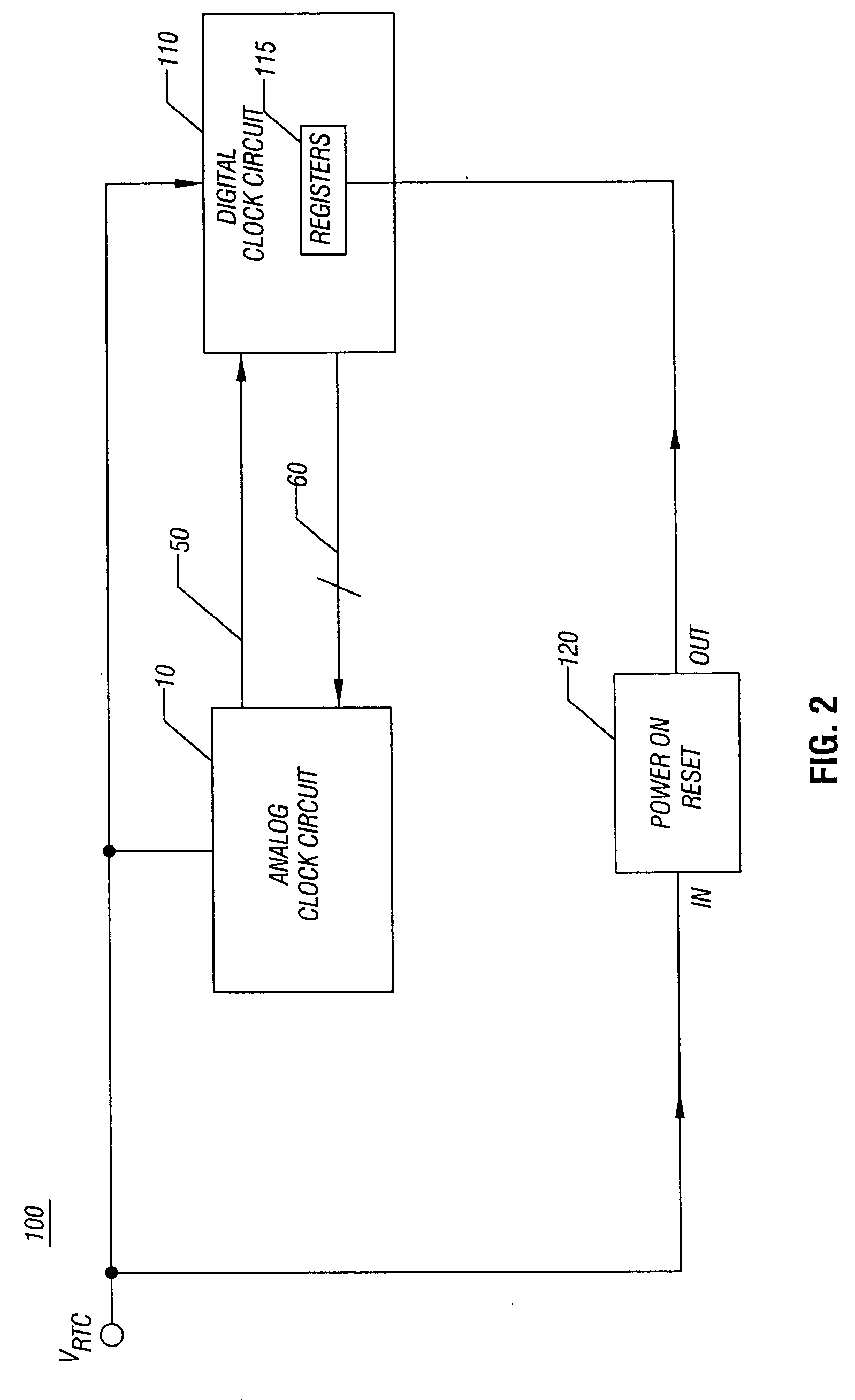
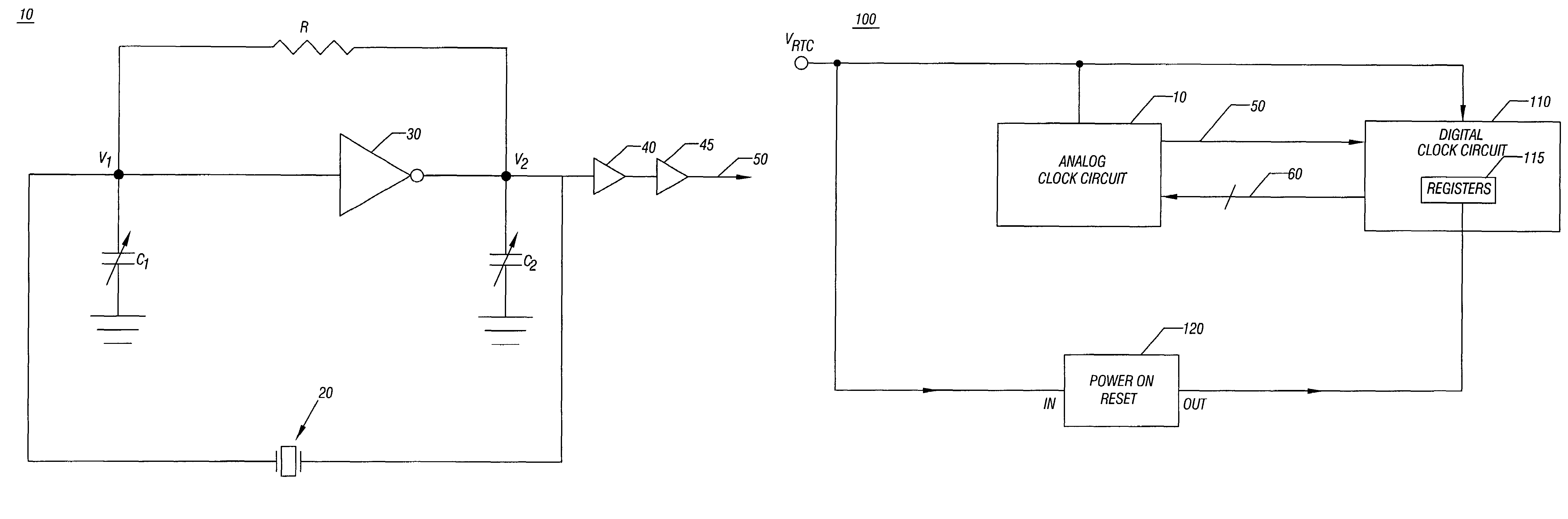
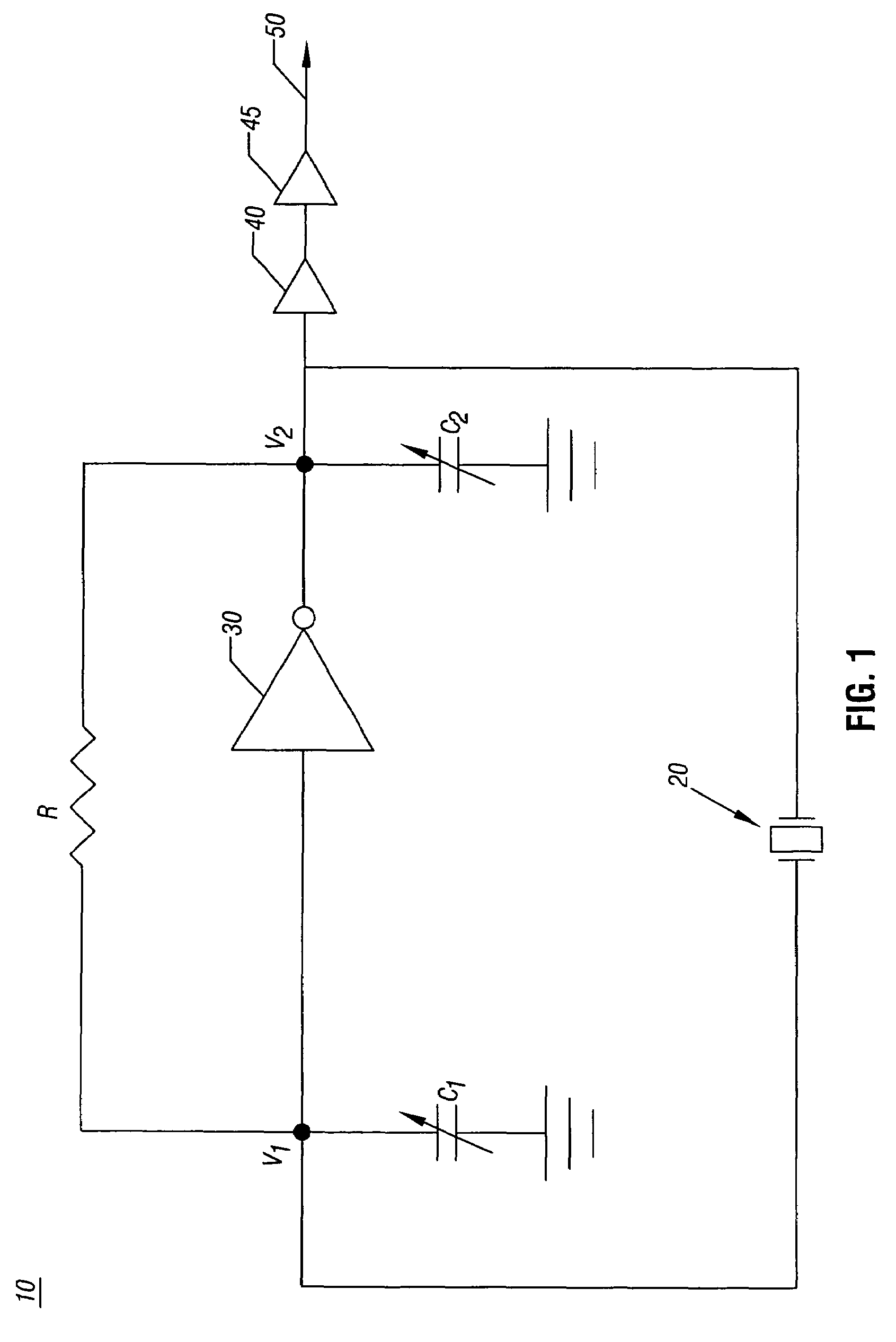
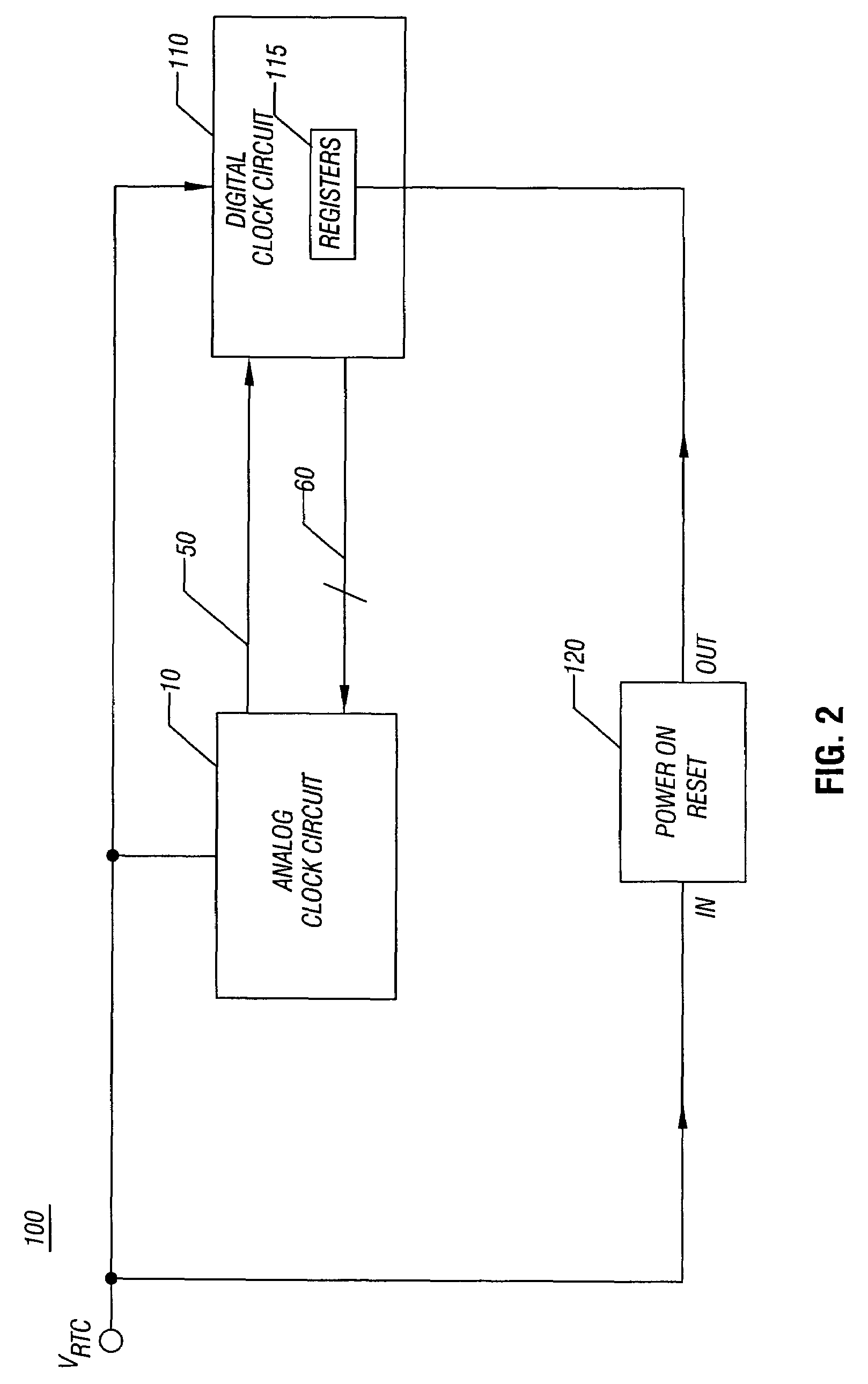
Clock circuit with programmable load capacitors
InactiveUS20060214738A1Reduce component countReduce board sizePulse automatic controlAngle modulation detailsReal-time clockProgrammable load
In one embodiment, the present invention includes methods and apparatus for providing initial control values to programmable load capacitors of an oscillator, such as that of a real time clock circuit. Using the initial values, the real time clock circuit may begin operation, enabling additional circuitry within an integrated circuit to begin operation. This additional circuitry may cause operating values to program the load capacitors to provide a desired reference clock based on a given system's requirements.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
Automated vehicle battery protection with programmable load shedding and engine speed control
ActiveUS20060253237A1Reduce electricity loadAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlArea networkElectrical battery
Automated motor vehicle battery voltage protection is provided by setting voltage trip points for increasing engine speed and for shedding selected electrical loads. The system is effected by programming a vehicle body computer which communicates with, and exerts control over, various vehicle system controllers over one or more controller area networks. The body computer is programmed to monitor battery voltage and initiates an increase in engine speed first, and if that fails to restore a minimum battery voltage level, begins shedding loads in a predetermined order.
Owner:INT TRUCK INTPROP LLC
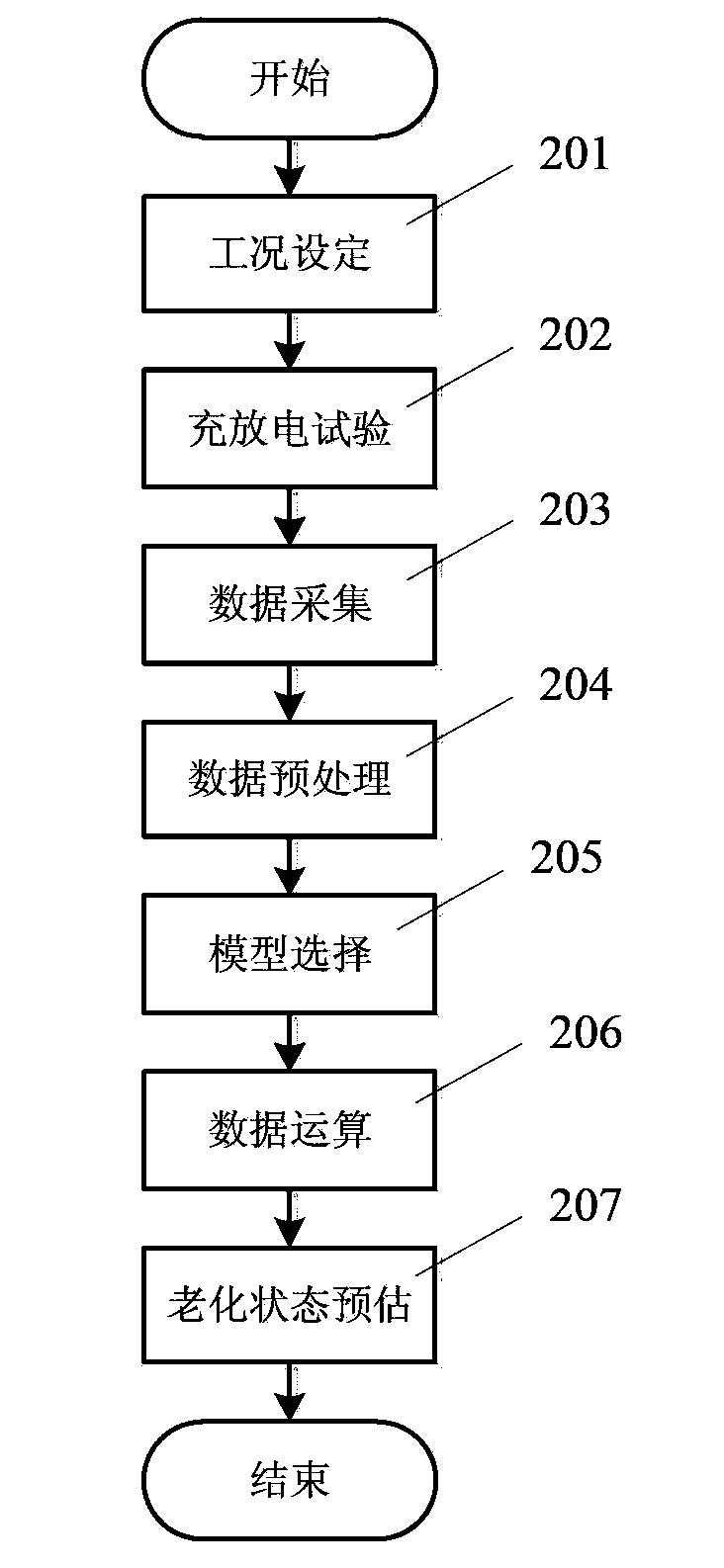
Super capacitor-based aging state estimation detection system and method
ActiveCN104297577AIncrease energy densityStrong targetingElectrical testingCommunication unitProgrammable load
The invention relates to a super capacitor-based aging state estimation detection system and method. The super capacitor-based aging state estimation detection system includes a programmable power source, a tested super capacitor, a programmable load, a data storage unit, a data acquisition communication unit, a data operating processing unit and an aging state estimation unit. The detection method includes the following steps that: a required condition is set, and test data are acquired and are subjected to frequency division and noise reduction pre-processing; model parameters are identified according to the model of the super capacitor, and characteristic parameters are calculated; and then, aging state evaluation is performed. Compared with the prior art, the super capacitor-based aging state estimation detection system and method of the invention can detect the aging state of the super capacitor in different stages, and has the advantages of high application universality, high condition targeted performance, accurate aging state judgment, short consumed time of aging detection, high reliability of results and the like.
Owner:智车上海实业有限公司
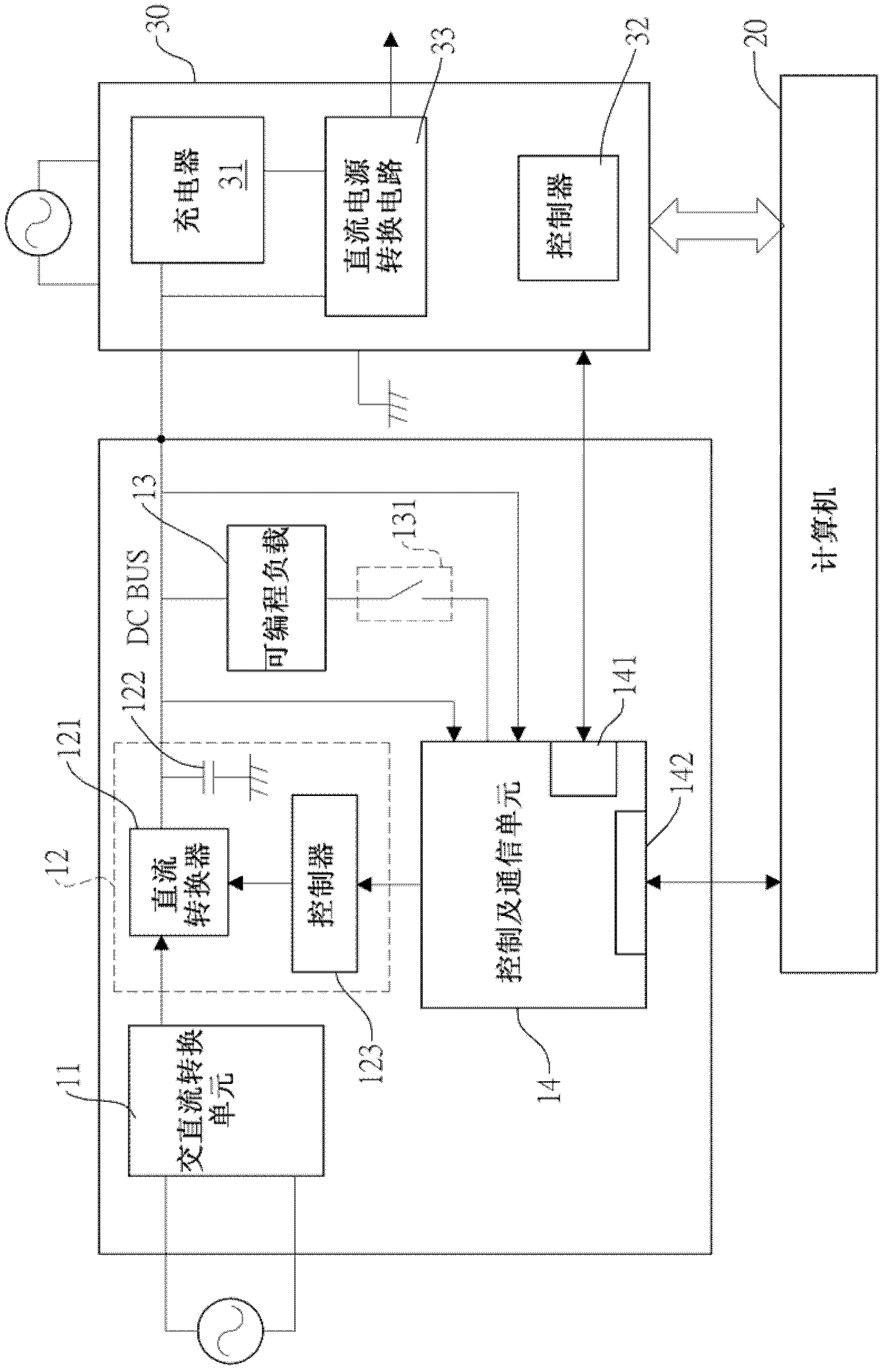
Battery stimulation device
InactiveCN102841317ASimple structureReduced structureElectrical testingCommunication interfaceElectricity
The invention provides a battery stimulation device comprising an AC-DC conversion unit, an adjustable type DC conversion unit, a programmable load, and a control and communication unit. The control and communication unit is electrically connected with a pulse width nodulation input end of a controller of the adjustable type DC conversion unit, and is connected with an external computer by a computer communication interface. Therefore when a user selects the corresponding battery charging and discharging stimulation modes according to the rechargeable battery of the power supplier of the machine to be detected, the control and communication unit is automatically used to control the adjustable-type AC-DC conversion unit and the programmable load mode battery charging and discharging states, then the external power can carry out the machine detection program. In addition, the power of the DC conversion unit is provided by the AC-DC conversion unit, therefore no other battery used for the power supply is required, and the integral structure can be effectively reduced.
Owner:ACBEL POLYTECH INC
Defect monitor for semiconductor manufacturing capable of performing analog resistance measurements
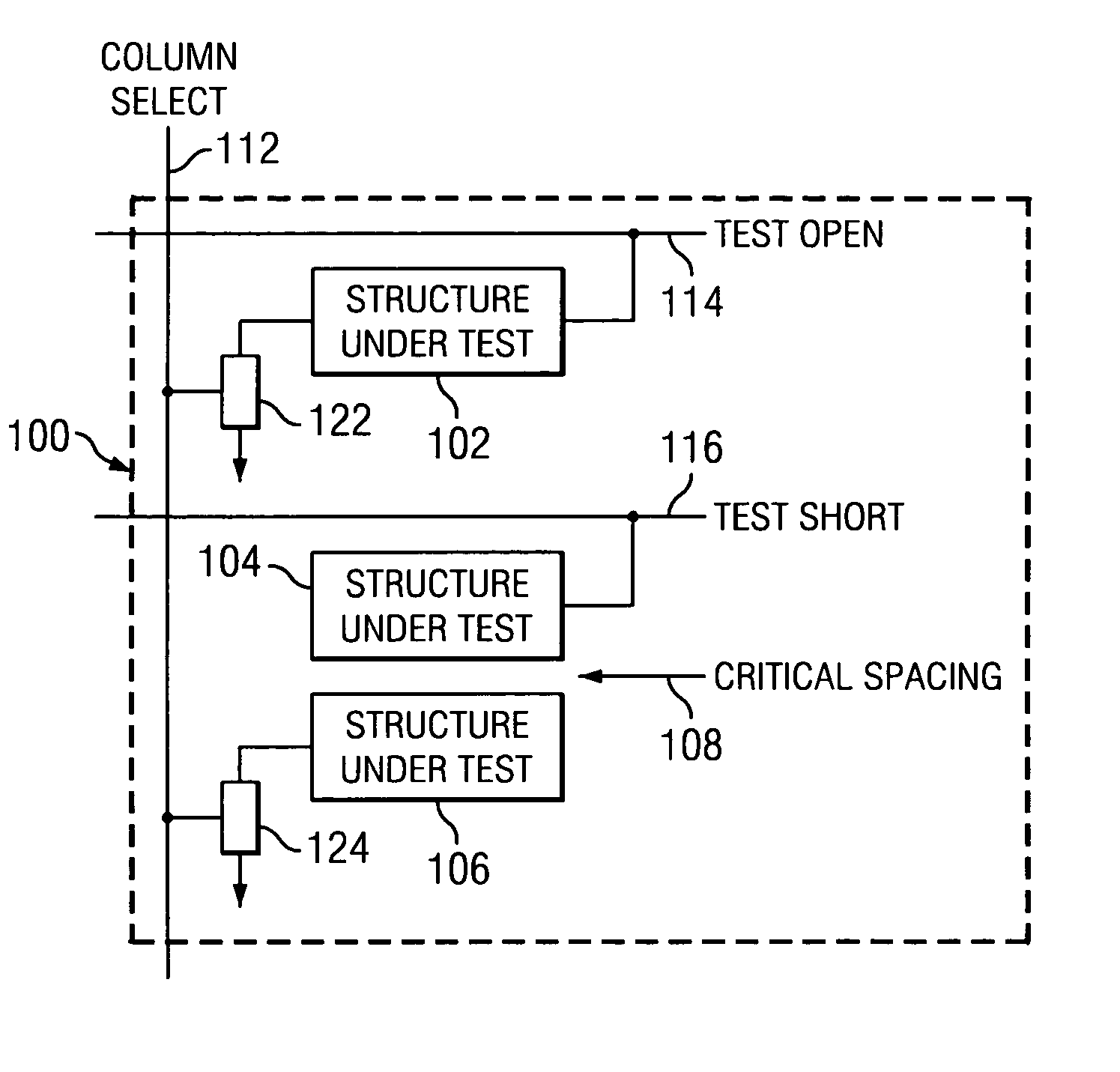
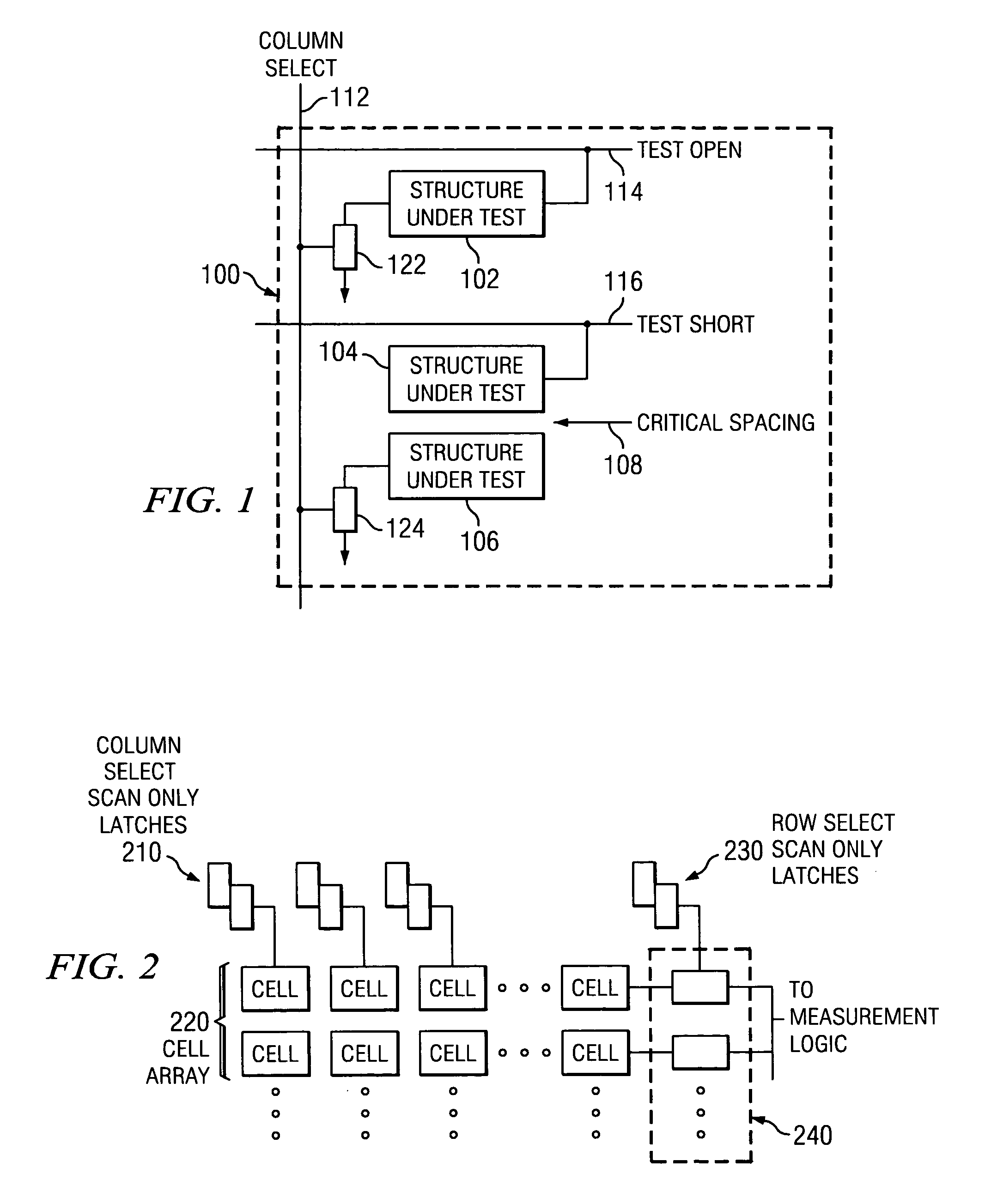
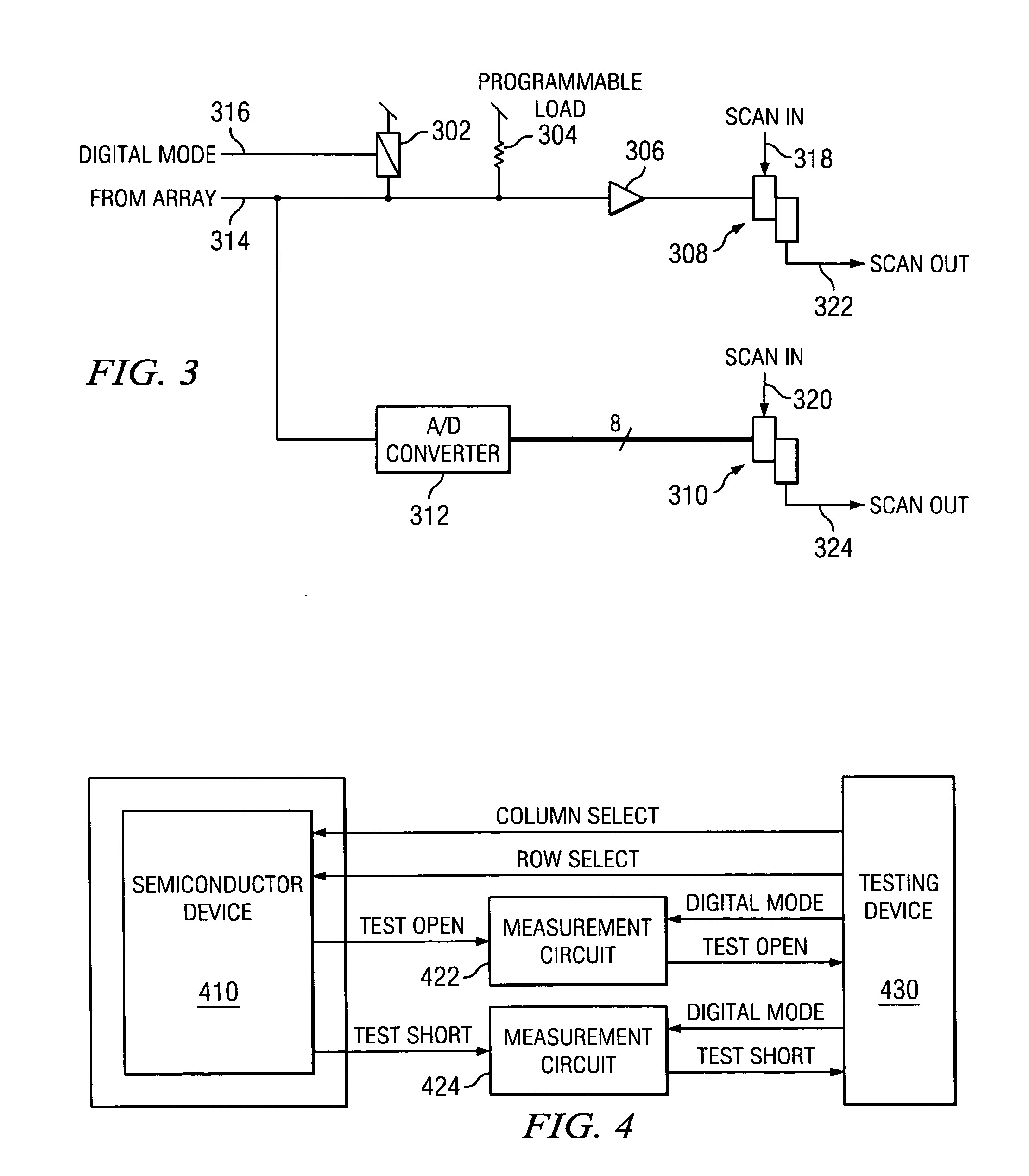
InactiveUS20060022695A1Individual semiconductor device testingElectrical resistance and conductanceSignal on
A mechanism is provided to address a structure under test and to identify a point of failure. A test open line carries a signal that indicates whether a structure under test is open or closed. A test short line carries a signal that indicates whether a structure under test is shorted. A test structure may include an array of cells, where each cell includes a circuit including structures to test. The cells may be scanned using scan only latches and signals on the test open and / or test short lines may be recorded. A test circuit may include a digital mode and an analog mode. The digital mode provides an open or closed value. The analog mode includes a programmable load. The output of the analog mode provides a resistance value that is relative to the programmable load.
Owner:IBM CORP
Delay test circuitry
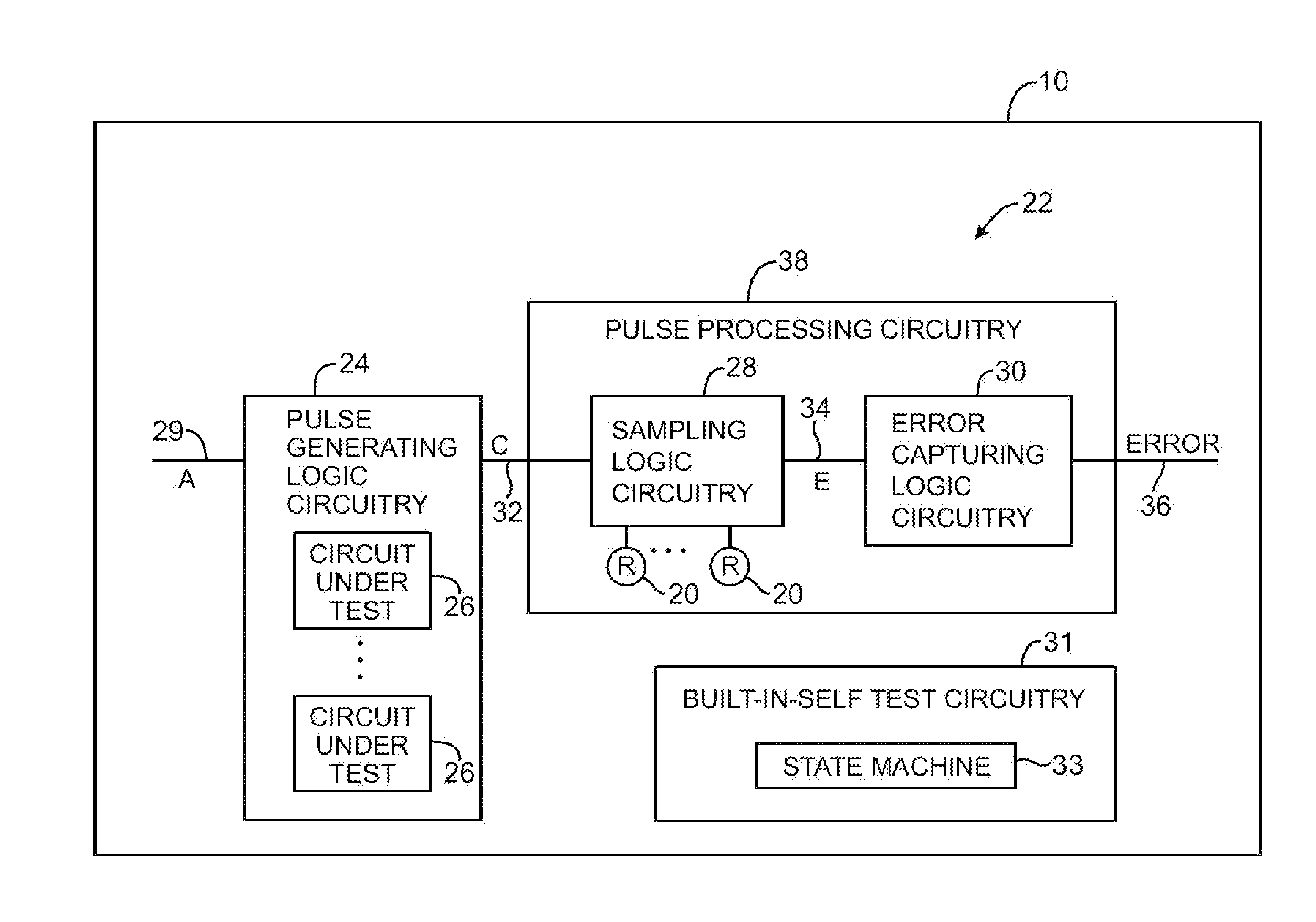
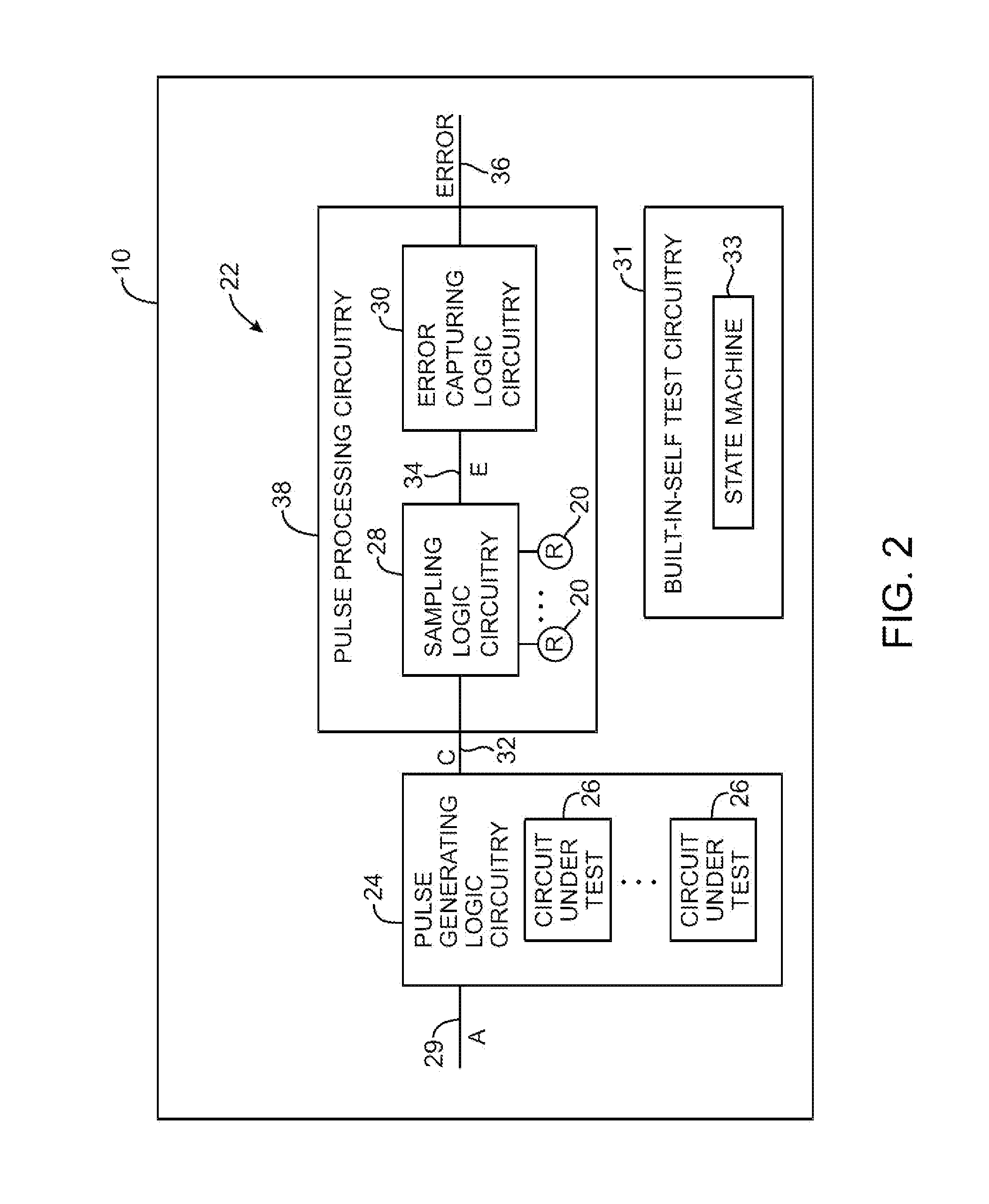
InactiveUS8531196B1Electronic circuit testingIndividual semiconductor device testingProgrammable loadCircuit under test
Programmable delay test circuitry is provided for testing a circuit under test on an integrated circuit. Delay test circuitry may use logic circuitry to output an error signal when a delay time provided by the circuit under test is greater than a characteristic time that may be programmed into the programmable delay test circuitry. Programmable delay test circuitry may use a logic gate to provide a pulse that has a pulse width equal to the delay of the delay circuitry. Programmable delay test circuitry may contain a programmable load that may be programmed to have a characteristic time. Programmable delay test circuitry may assert an error signal when the delay time is greater than the characteristic time of the test circuitry.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
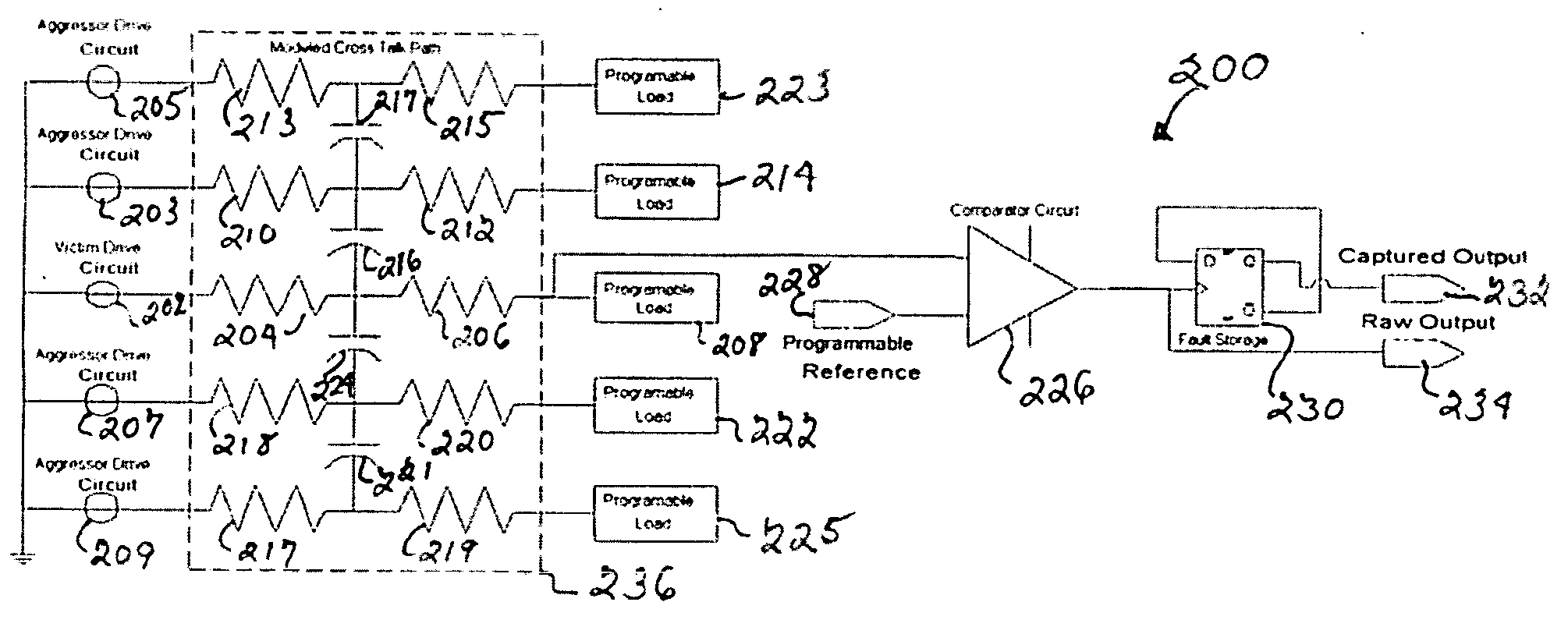
System and method for signal integrity testing of electronic circuits
InactiveUS20060190872A1Accurate identificationExcessive levelDetecting faulty computer hardwareElectrical testingExternal referenceProgrammable load
A system and method are disclosed for measuring signal crosstalk in an electronic circuit device or Integrated Circuit (IC) device, correlating the results with modeled information, and accurately identifying one or more levels of coupling noise in the device. For example, a system is disclosed that provides data on levels of crosstalk between conductive lines in a device. The system uses programmable victim and aggressor lines, programmable drive capability, and programmable loading through one or more known crosstalk structures to compare an output signal with a reference signal and accurately identify one or more levels of coupling noise in the device. An external reference signal can be used to detect upsets or crosstalk in the device. As such, using such programmability features of the system, numerous combinations of coupling in a device can be measured at a time. For example, one or more lines in the device can be programmed to represent victim lines, while other lines in the device can be programmed to represent aggressor lines. An output signal of the system can be compared to a known signal. For example, a DC offset voltage can be used to determine an exact level of upset or crosstalk that exists in the device. Alternatively, an AC clocking signal can be used to measure timing push-out or edge degradation in the device.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
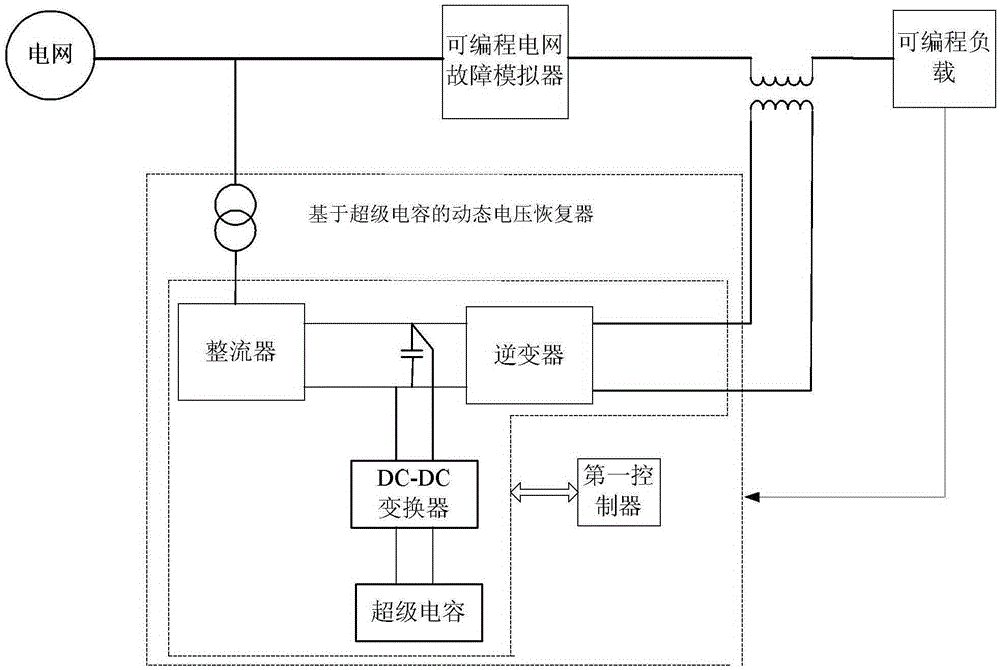
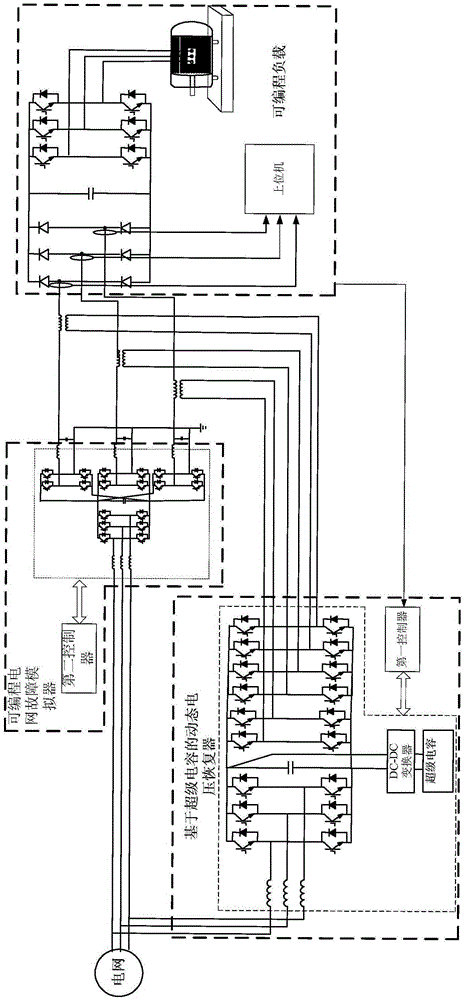
Voltage support experiment testing platform and method with super-capacitor-based dynamic voltage restorer
The invention, which belongs to the technical field of the voltage support of the power grid, provides a voltage support experiment testing platform and method with a super-capacitor-based dynamic voltage restorer. In order to solve a problem of lack of accurate theoretical data of the super-capacitor-based dynamic voltage restorer in practical application, the testing platform comprises a programmable grid fault simulator, a programmable load and, and a super-capacitor-based dynamic voltage restorer. The programmable grid fault simulator is used for simulating a voltage drop of a simulated grid and inputting a working voltage for a programmable load; the super-capacitor-based dynamic voltage restorer is used for collecting the voltage outputted by the programmable grid fault simulator, determining a drop situation according to the voltage, and carrying out compensation on the working voltage of the programmable load based on the drop; and the programmable load is used for setting loads with different low-voltage protection threshold values. According to the invention, the provided testing platform is used for providing data for scientific researches. And according to the testing method, the testing platform is realized by using software programs to carry out a simulated experiment.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Automatic measurement of fuel cell resistance
InactiveUS7270900B2Electrolysis componentsPhotography auxillary processesLoad circuitInstrumentation amplifier
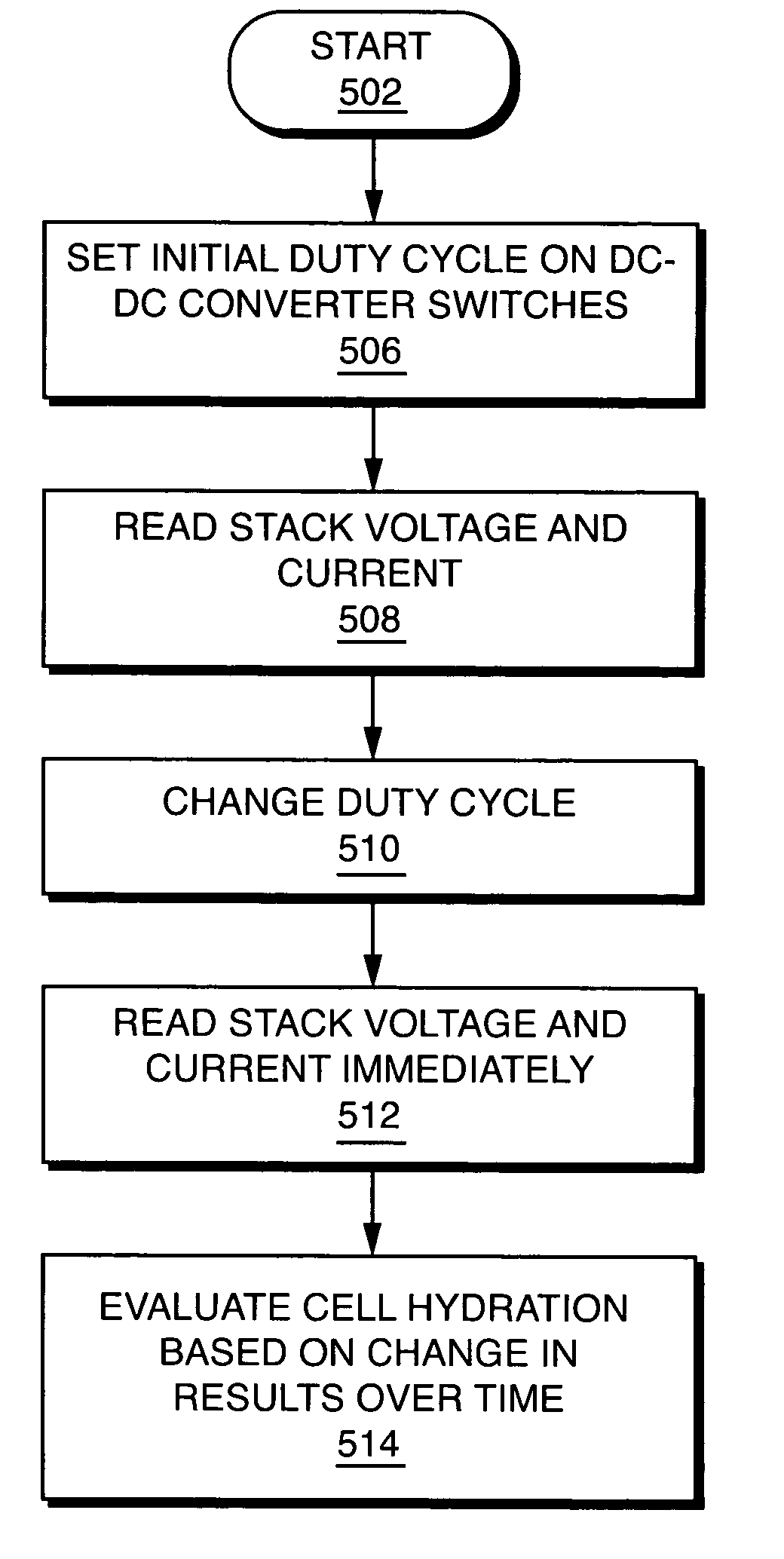
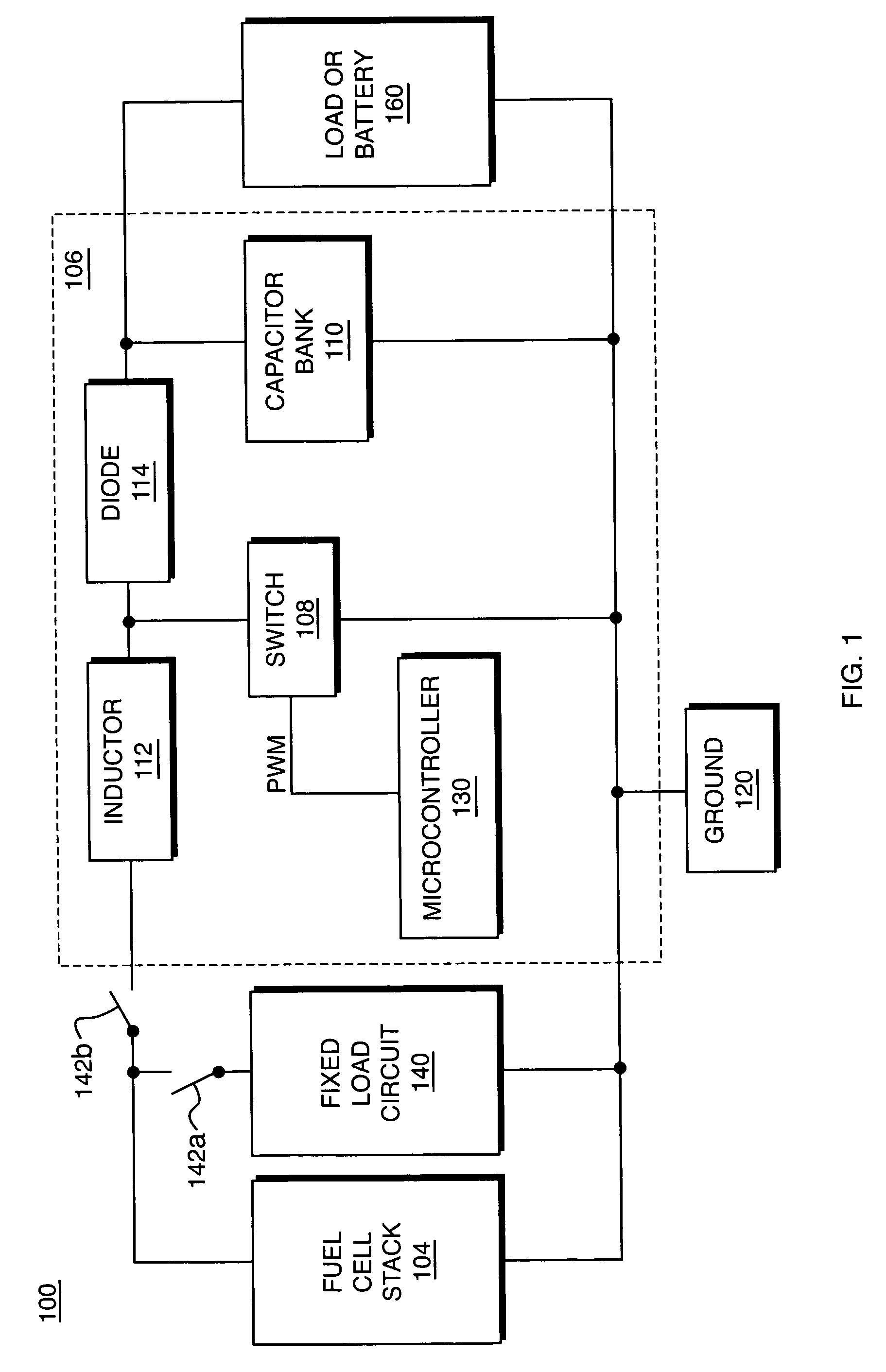
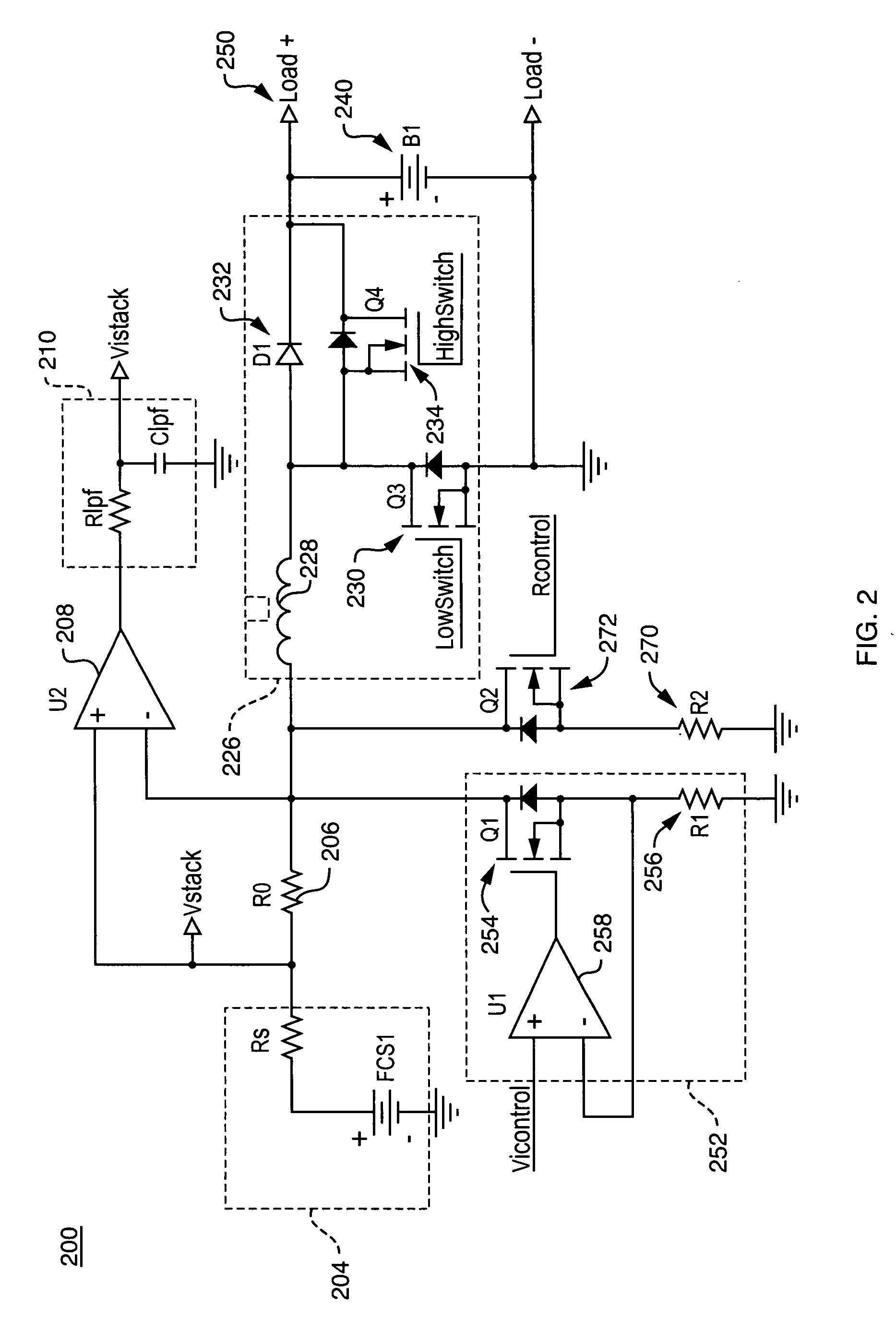
This invention presents a method and apparatus for measuring the resistance across a fuel cell stack, a fuel cell array, or an individual fuel cell. The invention employs a fixed load circuit to switch a fixed resistance or to connect a fixed load current to the stack or array. When the load is turned on, the stack voltage is read, then the load is turned off and the stack voltage is read again to determine the voltage jump. A change in resistance is calculated that is related to cell hydration. In accordance with another aspect of the invention, the stack includes a programmable DC-DC switch under PWM microprocessor control. The DC-DC converter is used to switch the load on and off and the voltage jump is read using a sample and hold methodology with an optional instrumentation amplifier and a Kalman filter to determine accurate results for resistance with no additional hardware. The resistance measurements are used to identify and evaluate cell hydration.
Owner:MTI MICROFUEL CELLS
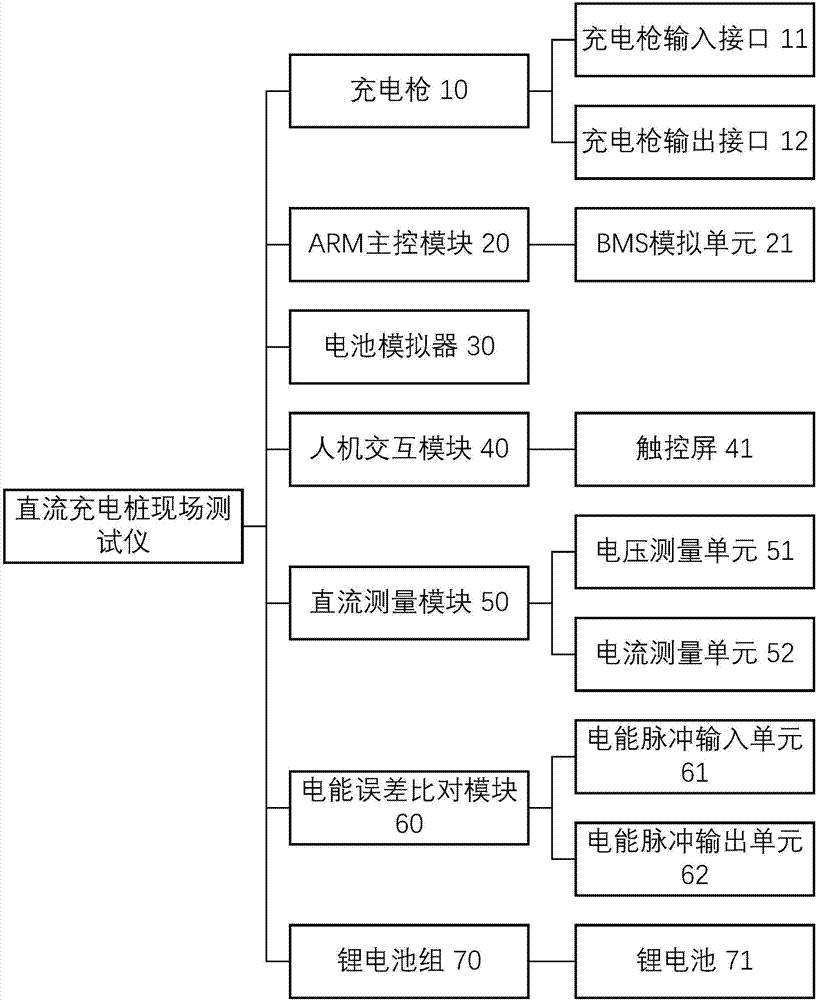
DC charging pile field tester
PendingCN107367635AAchieve meteringAchieve testCurrent/voltage measurementElectricityInternal resistance
The invention discloses a DC charging pile field tester. A charging gun comprises a charging gun input interface and a charging gun output interface, the charging gun input interface is connected with the output interface of a charging pile to be tested, the charging gun output interface is externally connected with the input interface of the charging pile to be tested through a programmable load box. An ARM main control module is provided with a BMS simulation unit, and the BMS simulation unit is electrically connected to a battery simulator for generating and outputting a BMS simulation parameter signal. The battery simulator acquires the BMS simulation parameter signal and generates and outputs a simulation test power pulse based on the BMS simulation parameter signal. The DC charging pile field tester can simulate a full-process charging process such as BSM protocol and internal resistance change of an electric vehicle, monitor the charging status and calculate the power output, so as to realize the measurement and verification of the DC charging pile.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HARNPU POWER TECH
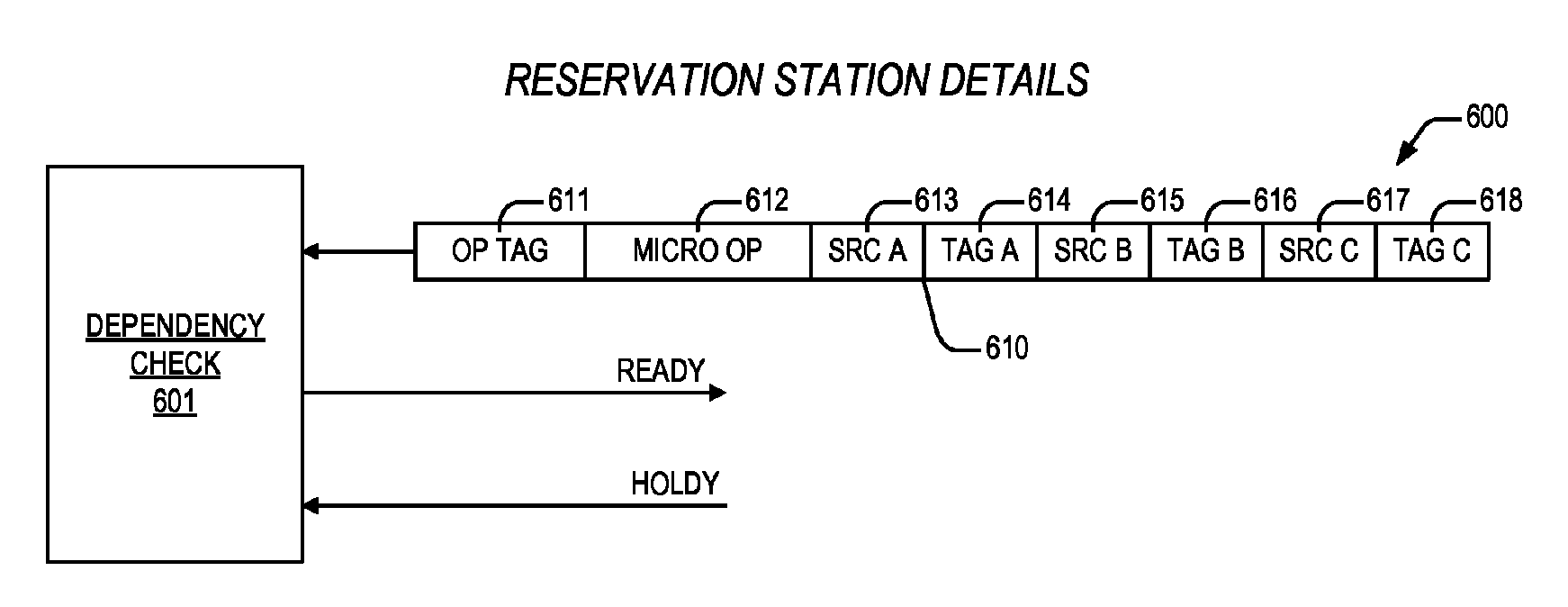
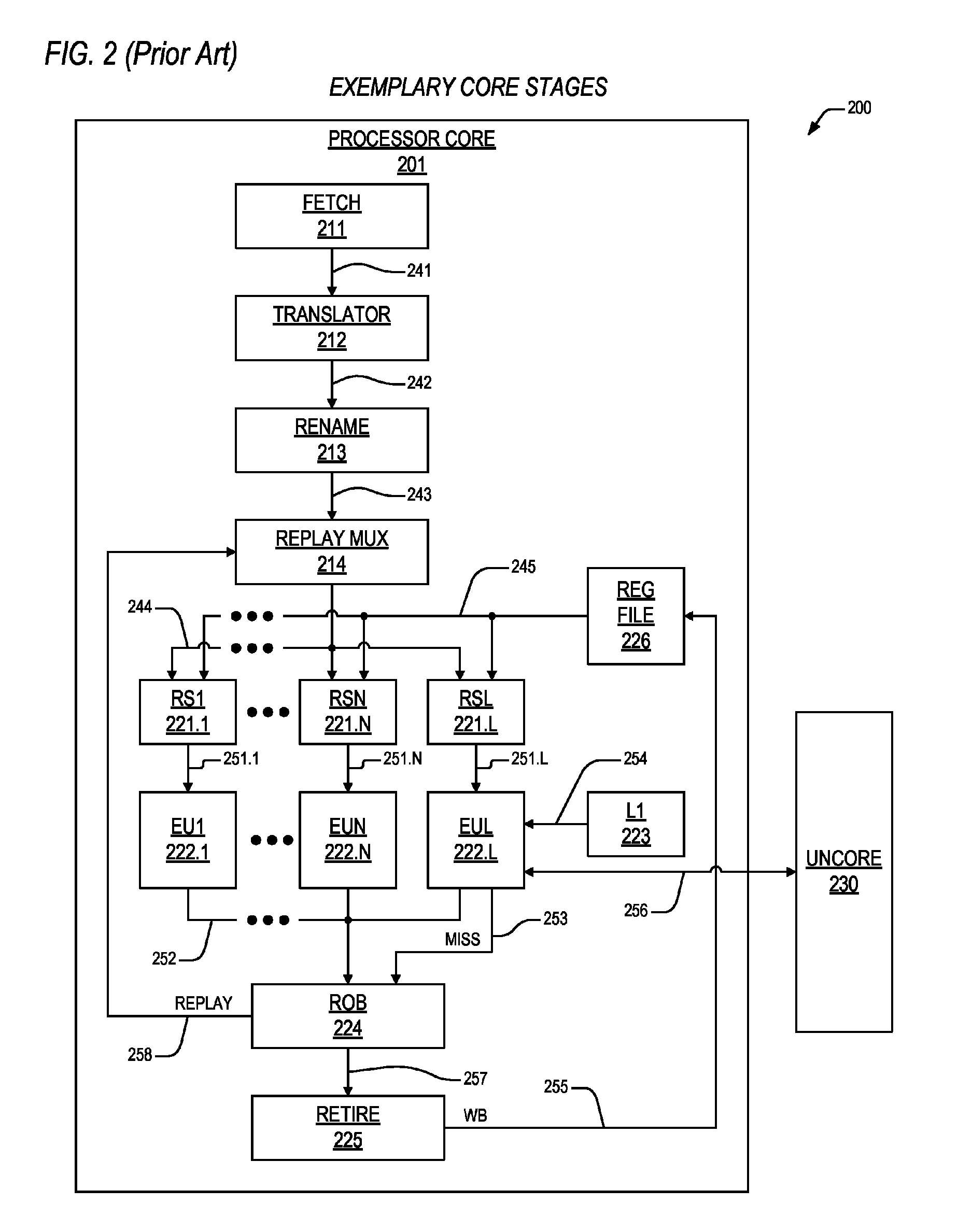
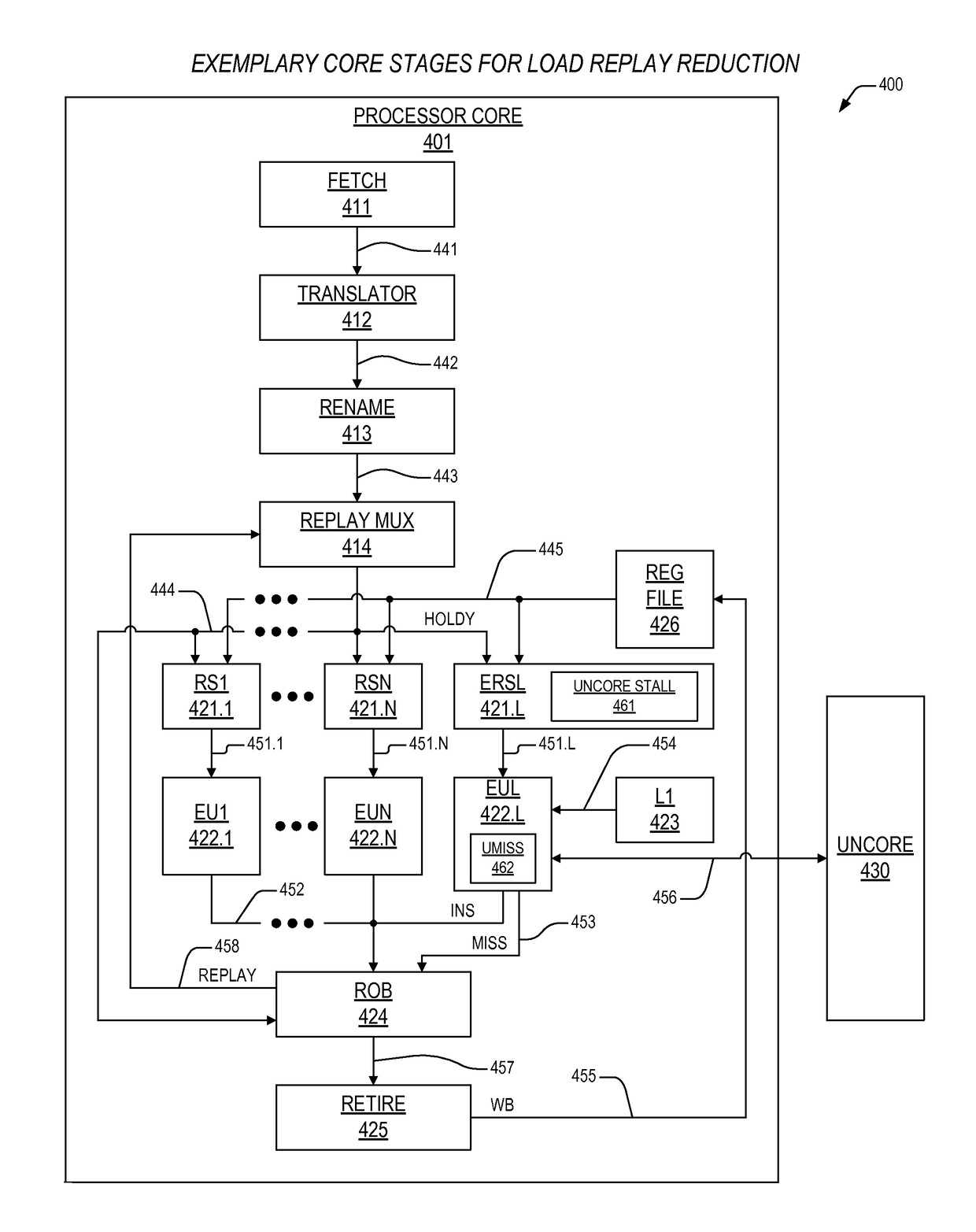
Apparatus and method for programmable load replay preclusion
ActiveUS20160350123A1Reducing replayConcurrent instruction executionLoad instructionReservation station
An apparatus including first and second reservation stations. The first reservation station dispatches a load micro instruction, and indicates on a hold bus if the load micro instruction is a specified load micro instruction directed to retrieve an operand from a prescribed resource other than on-core cache memory. The second reservation station is coupled to the hold bus, and dispatches one or more younger micro instructions therein that depend on the load micro instruction for execution after a number of clock cycles following dispatch of the first load micro instruction, and if it is indicated on the hold bus that the load micro instruction is the specified load micro instruction, the second reservation station is configured to stall dispatch of the one or more younger micro instructions until the load micro instruction has retrieved the operand. The plurality of non-core resources includes a random access memory, programmed via a Joint Test Action Group interface with the plurality of specified load instructions corresponding to the out-of-order processor which, upon initialization, accesses the random access memory to determine said plurality of specified load instructions.
Owner:VIA ALLIANCE SEMICON CO LTD
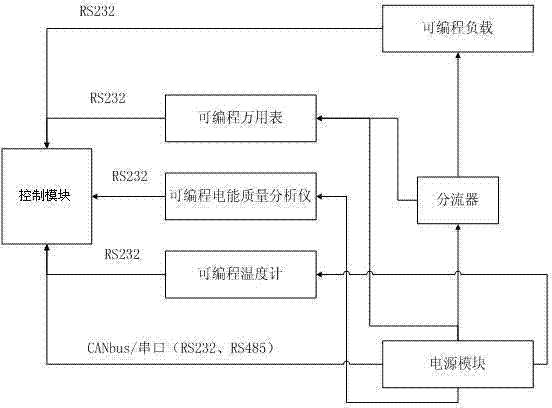
Automatic calibration device for power module and calibration method
InactiveCN103760498AReduce manual errorsImprove efficiencyPower supply testingPower qualityProgrammable load
The invention discloses an automatic calibration device for a power module and a calibration method. The automatic calibration device comprises the power module, a control module, a programmable universal meter, a programmable power quality analyzer, a programmable thermometer, a programmable load and a shunt, wherein the control module is connected with the power module. An output end of the power module is connected with an input end of the programmable load and an input end of the programmable universal meter through the shunt respectively. The output end of the power module is further connected with the input end of the programmable universal meter, an input end of the programmable power quality analyzer and an input end of the programmable thermometer. An output end of the programmable load, an output end of the programmable universal meter, an output end of the programmable power quality analyzer and an output end of the programmable thermometer are connected with the control module. Compared with traditional manual calibration, the automatic calibration device for the power module reduces manual operation errors and greatly improves efficiency and accuracy.
Owner:JIANGSU JIAYU NEW POWER TECH
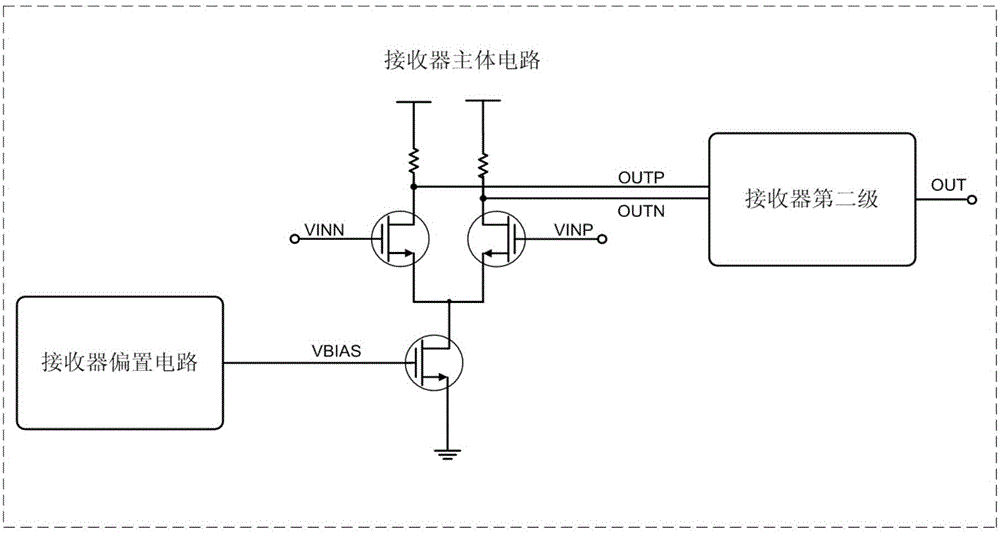
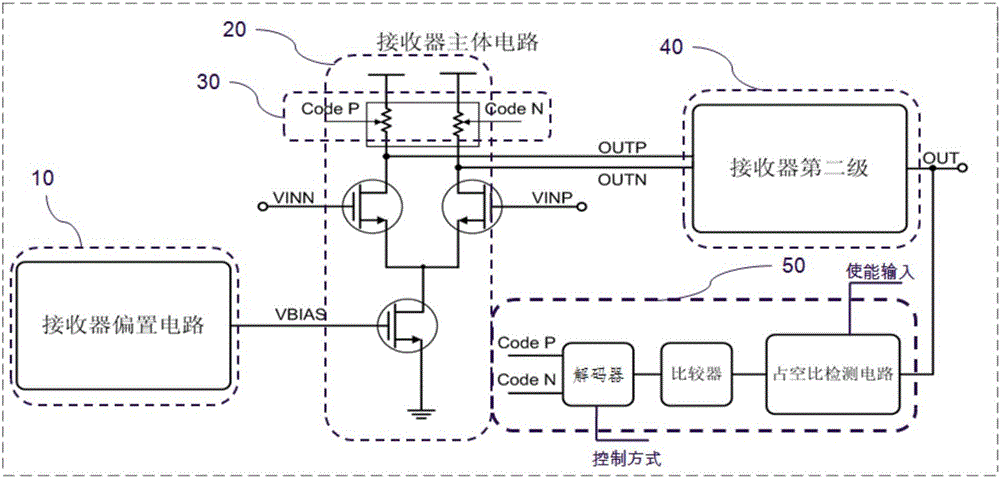
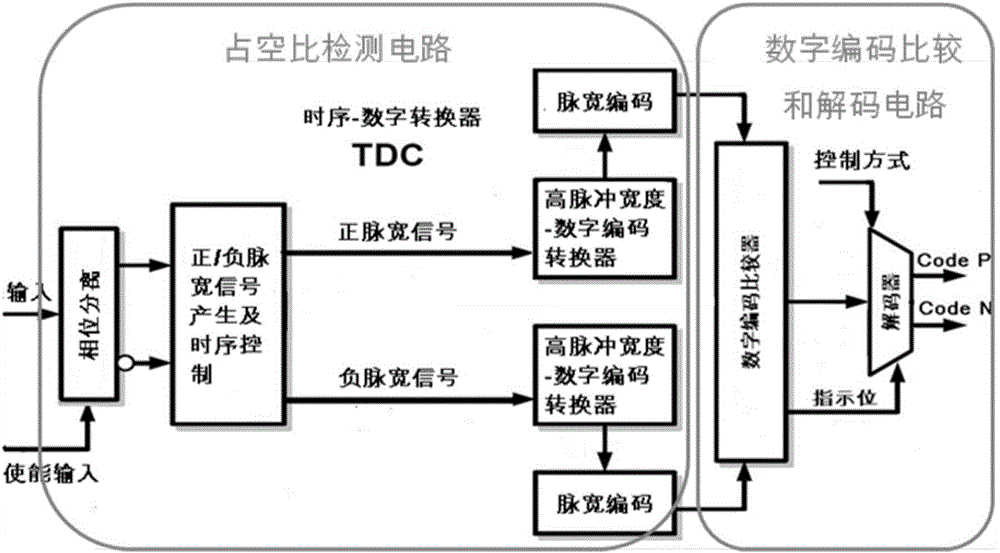
Self-adaptive duty cycle detection and adjustment receiver and control method thereof
ActiveCN106026979AMeet the design requirementsStability is not affectedElectric pulse generatorLoad resistanceProgrammable load
The invention discloses a self-adaptive duty cycle detection and adjustment receiver and a control method thereof. The duty cycle problem of output signals of the receiver can be eliminated. The receiver comprises a bias circuit, a first stage amplifier circuit, a second stage amplifier circuit and a duty cycle dynamic detection circuit which are connected in sequence. The first stage amplifier circuit comprises a bias transistor, input geminate transistors and a load resistor array which are connected in sequence. The gate of the bias transistor is connected with the bias circuit. The load resistor array comprises a master load resistor which is always connected with the drain ends of the input geminate transistors, and a programmable resistor array which is selectively connected with the drain ends of the input geminate transistors. The duty cycle dynamic detection circuit comprises a duty cycle detection circuit, a digital encoding comparer and a decoder which are connected in sequence. Two output ways of the decoder are connected with the programmable resistor array through adoption of forward encoding and reverse encoding control codes. The forward encoding and reverse encoding control codes control access or short circuit of the programmable load resistor array on the two drain ends of the input geminate transistors.
Owner:XI AN UNIIC SEMICON CO LTD
Variable load detection method in electricity meter channeling detection
PendingCN105911418ASolve technical problems with high cost and low efficiencyImprove detection efficiencyElectrical testingElectricity marketProgrammable load
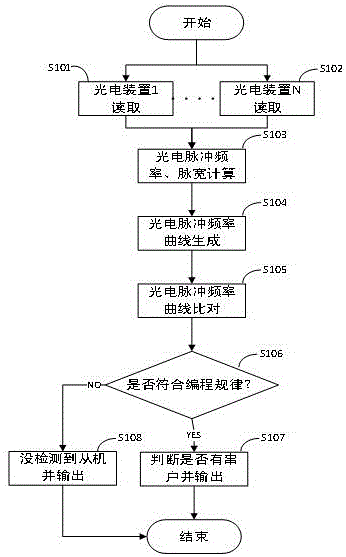
The invention discloses a variable load detection method in electricity meter channeling detection. The method comprises the following steps of: step 1, downloading a detection task by virtue of a detection host, and checking whether user electricity meter numbers needing to be detected are consistent with task requirements; step 2, mounting a photoelectric metering pulse reading device of the detection host on a user electricity meter with channeling suspicion; step 3, connecting the detection slave to a socket on the user side, allowing the detection slave to start working, and changing the load of the socket according to programmable load equipment; and step 4, detecting photoelectric metering pulse generated by different electricity meters by the detection host, and comparing the detection result of the detection host and load change of variable load equipment on the user side. Therefore, the technical effects of improving the electricity meter channeling detection efficiency and electricity meter channeling judgment accuracy and alleviating the labor intensity are achieved.
Owner:STATE GRID SICHUAN ELECTRIC POWER CORP ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +2
Radiation effect measurement and control system of DC-DC (Direct Current-Direct Current) power module
InactiveCN104345284AAvoid wastingOvercome the disadvantage of not being able to accurately record the moment when radiation effects occurPower supply testingControl systemData acquisition
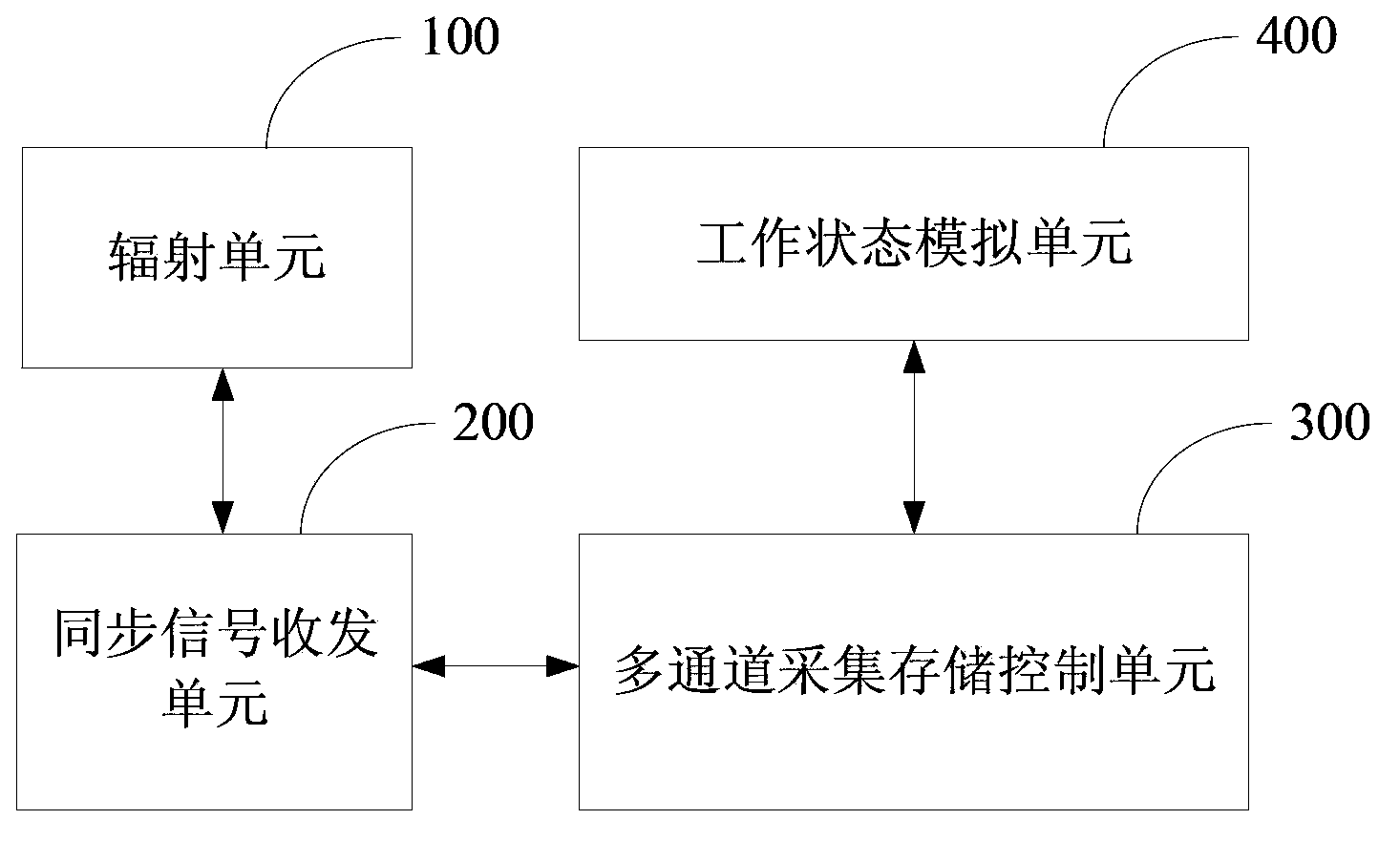
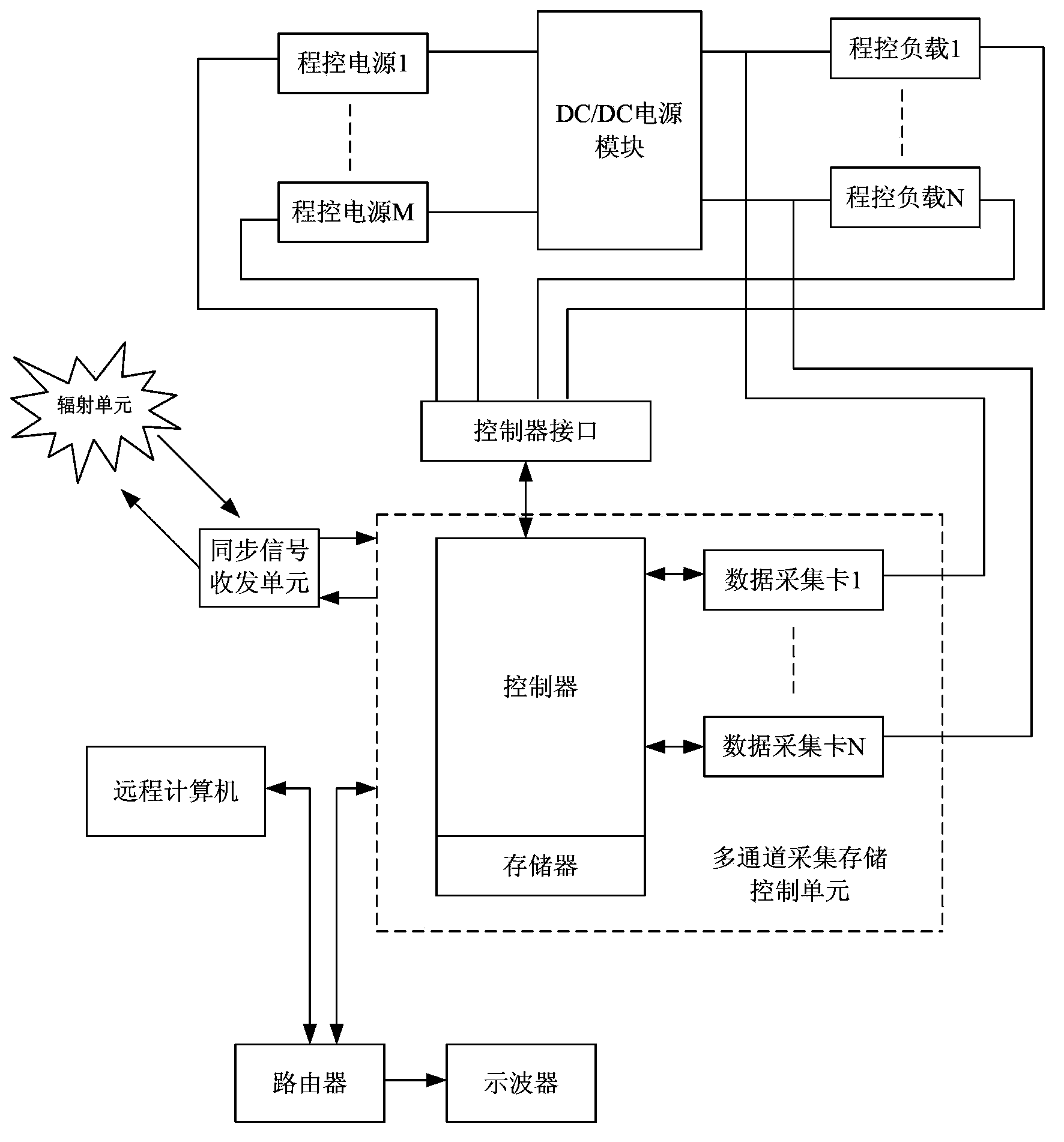
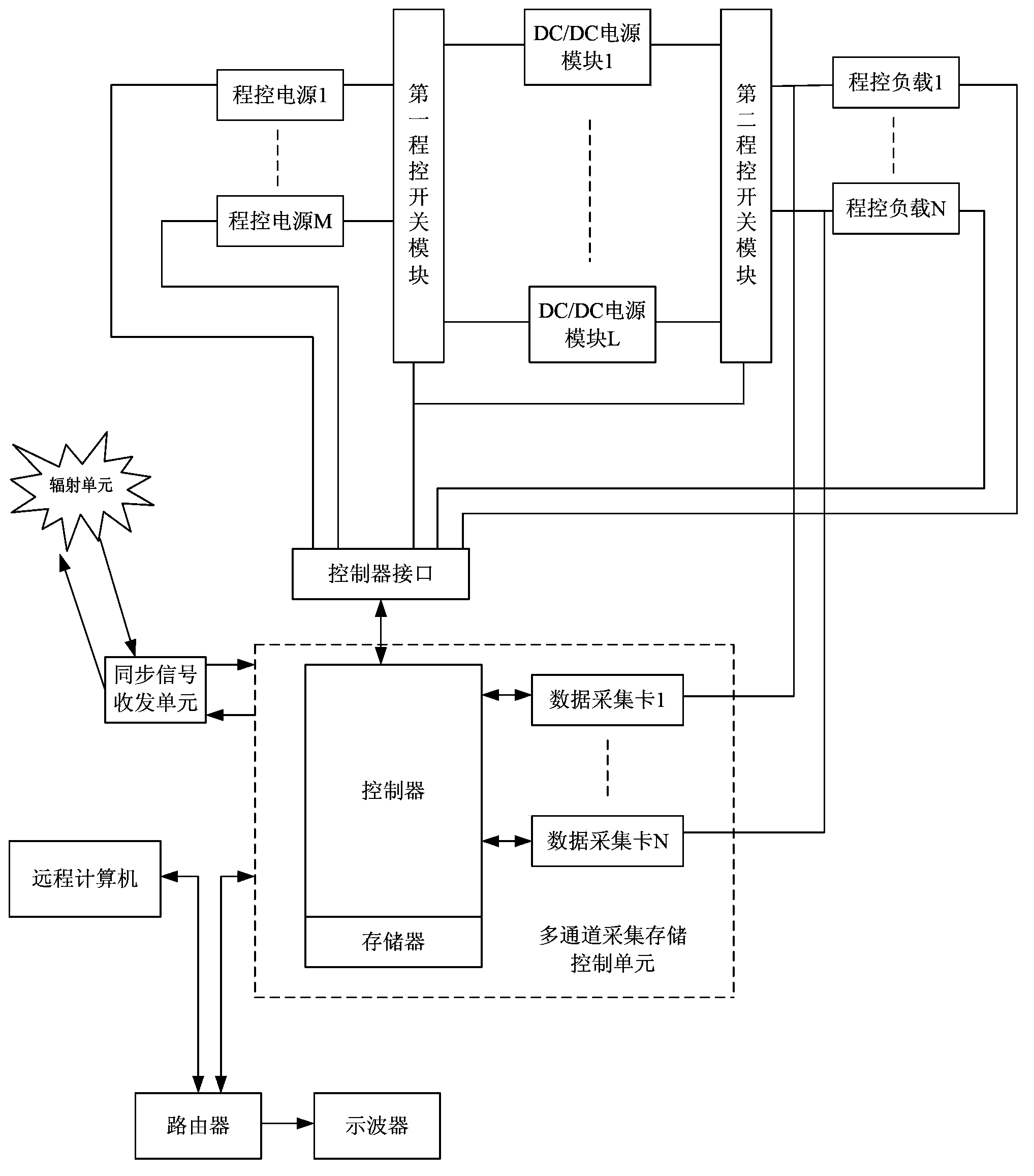
The invention discloses a radiation effect measurement and control system of a DC-DC (Direct Current-Direct Current) power module. In the system, a synchronizing signal receiving and transmitting unit is connected between a radiation unit and a multi-channel acquisition and storage control unit; a working state simulation unit comprises a programmable power module and a programmable load module; the multi-channel acquisition and storage control unit is connected with a control port of the programmable power module and a control port of the programmable load module; the DC-DC power module is placed in a test region of the radiation unit; an input end of the DC-DC power module is connected with the programmable power module, and an output end of the DC-DC power module is connected with the programmable load module; each data acquisition port of the multi-channel acquisition and storage control unit is connected with input and output ports needing to be monitored of the DC-DC power module. According to the system, high-speed parallel acquisition and storage of a plurality of parameters can be realized, transient pulse can also be completely captured, and switch access testing of a plurality of DC-DC power modules is realized.
Owner:工业和信息化部电子工业标准化研究院
Series type fault arc test platform based on deep learning and test method thereof
ActiveCN109738771AImprove accuracyMake up for the gap in the marketTesting dielectric strengthTest powerData acquisition
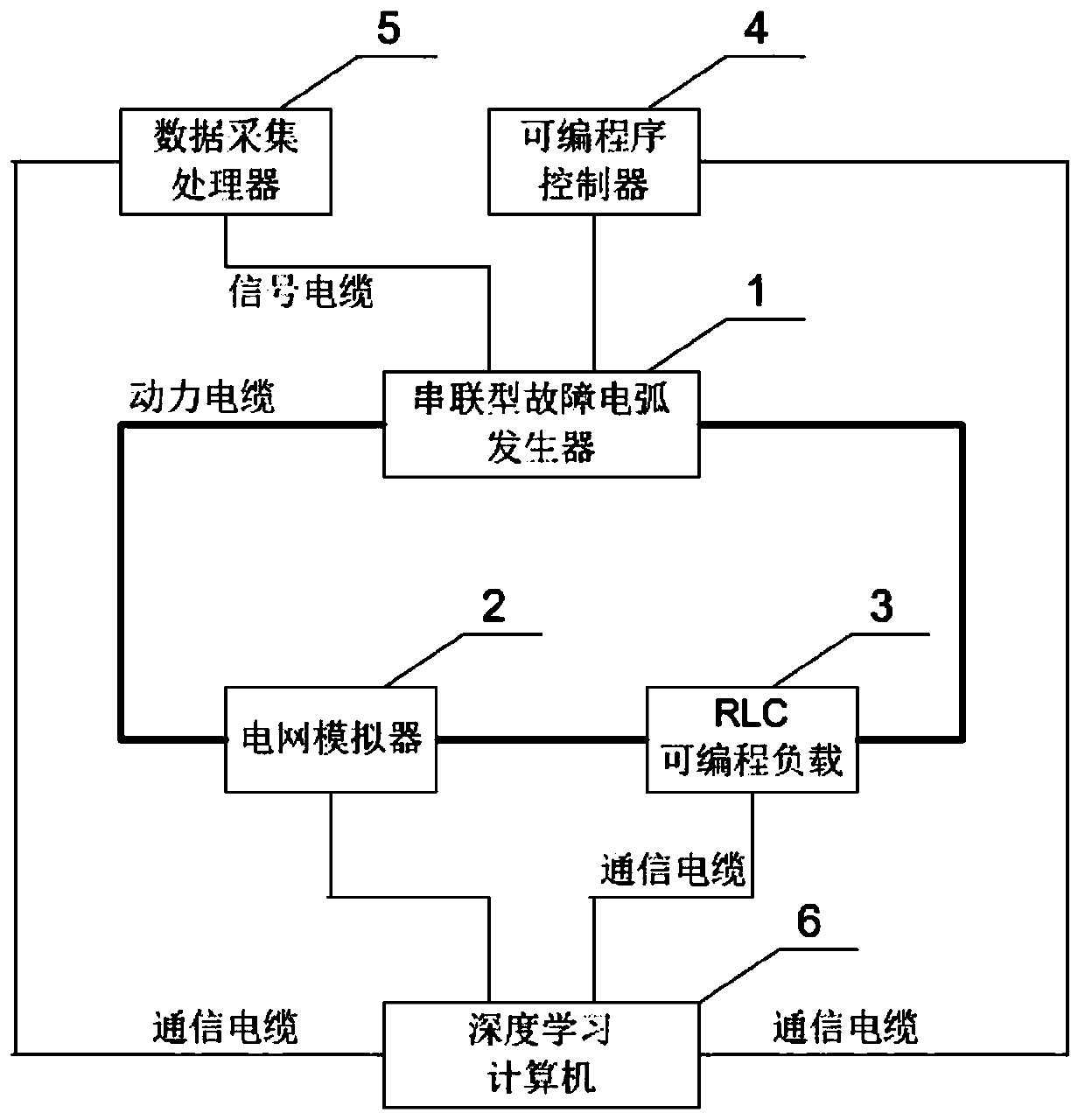
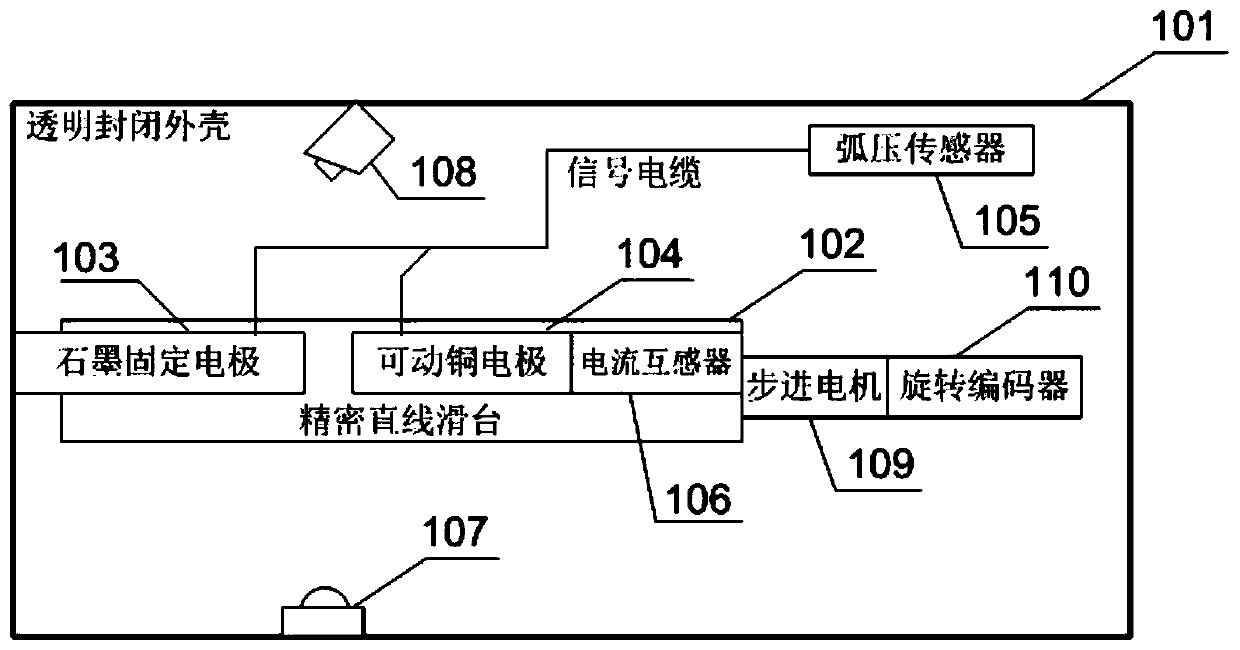
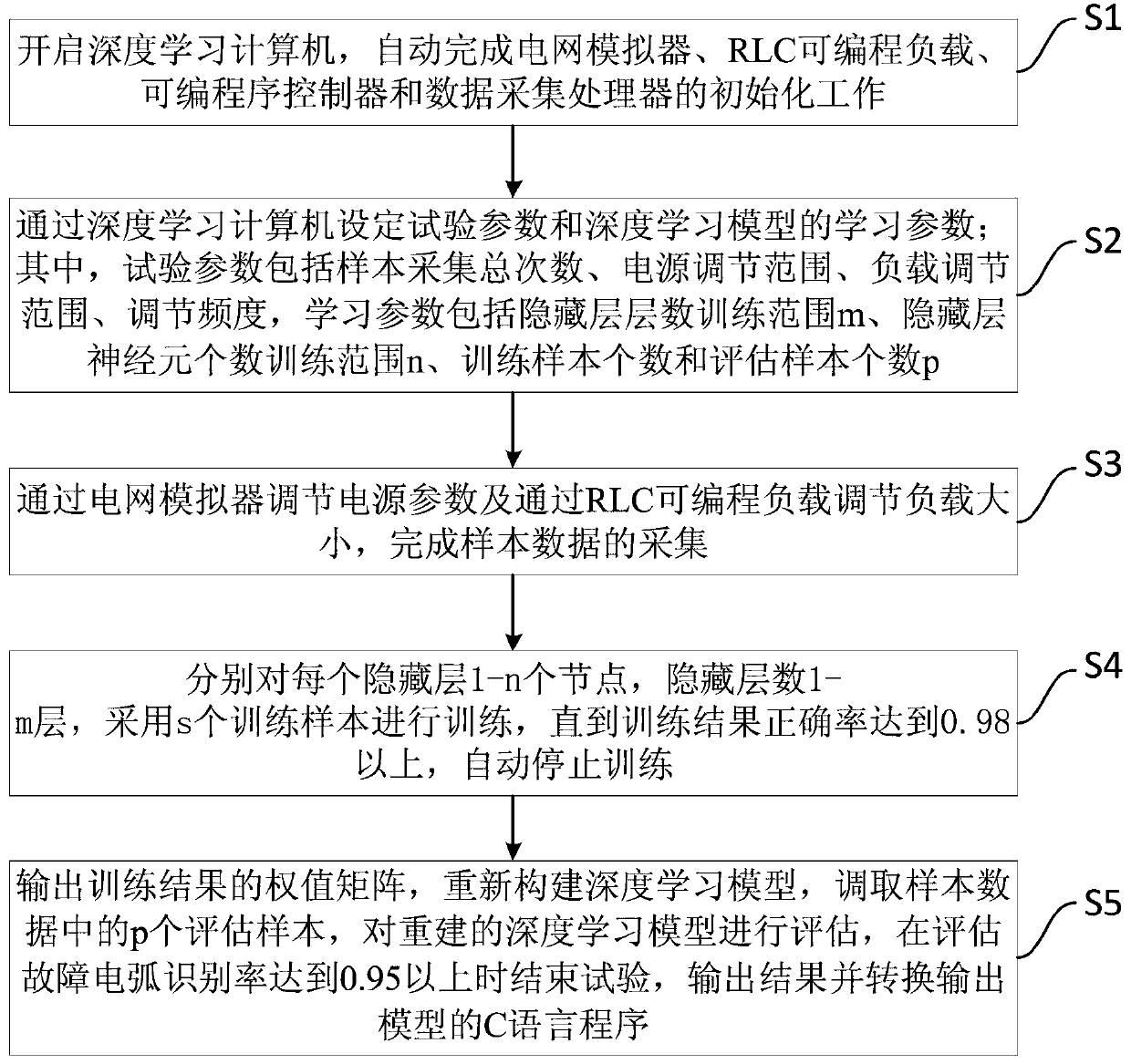
The invention relates to a series type fault arc test platform based on deep learning and a test method thereof, and belongs to the field of electrical fire-protection application. The test platform comprises a series type fault arc generator, a grid simulator, an RLC programmable load, a programmable program controller, a data collection processor and a deep learning computer; the series type fault arc generator is serially connected between the grid simulator and the RLC programmable load via a cable to form a test power supply and load regulation loop; the grid simulator, the RLC programmable load, the programmable program controller and the data collection processor are respectively connected with the deep learning computer; the data collection processor is connected with an arc pressure sensor, a current transformer and an arc light sensor inside the series type fault arc generator; and the programmable controller is connected with a step motor and a rotary encoder inside the series type fault arc generator. According to the series type fault arc test platform based on the deep learning and the test method thereof provided by the invention, the accuracy for series type fault arc detection and identification is improved, and the market blank for such a type of product is remedied.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF TECH
Telescopic material conveyer apparatus
ActiveUS20170305672A1Reduce load pressureLower height requirementConveyorsPackagingHydraulic motorProgrammable load
A telescopic material conveyer apparatus has a main boom assembly reinforced by a steel saddle frame connected to a turn table and a lift mechanism, an extension boom assembly adapted by two or more roller assemblies and connecting hardware to travel mechanically within the main boom assembly and to extend therefrom, one or more connected drive motors, a conveyer belt supported by frame architecture and a pulley and drive chain system, at least one hydraulic motor having operative connection to the turntable, lift mechanism and to a belt drive drum, at least one hydraulic valve connected inline in the hydraulic line controlling the belt drive motor, the valve electronically operable via input received from a load sensor integrated within or to the lift mechanism, a programmable load threshold determining open and close operation states of the valve and directing run and stop state operations of the conveyer belt.
Owner:CLEASBY LLC
Clock circuit with programmable load capacitors
InactiveUS7400206B2Reduce countSmall sizePulse automatic controlAngle modulation detailsReal-time clockProgrammable load
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
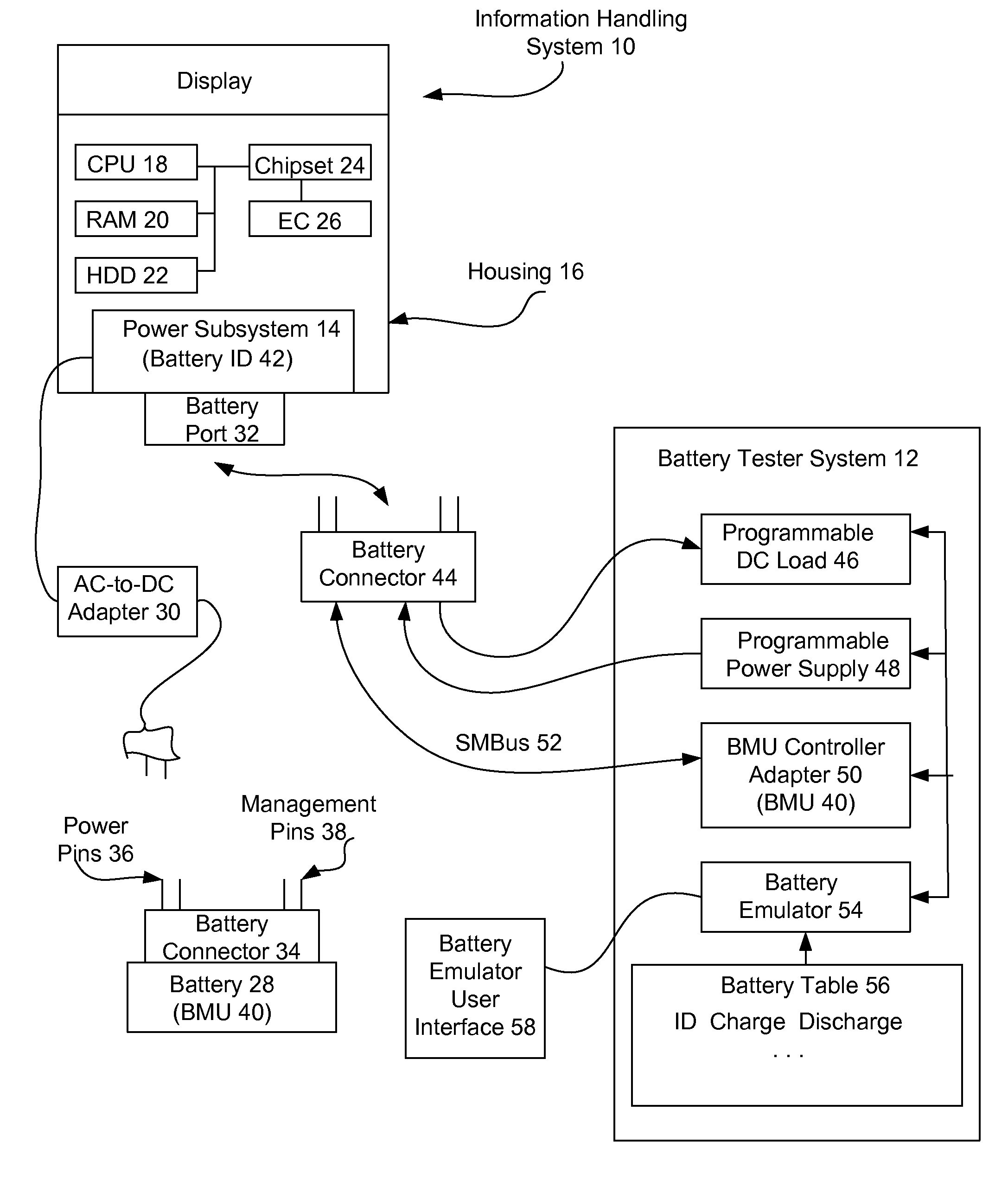
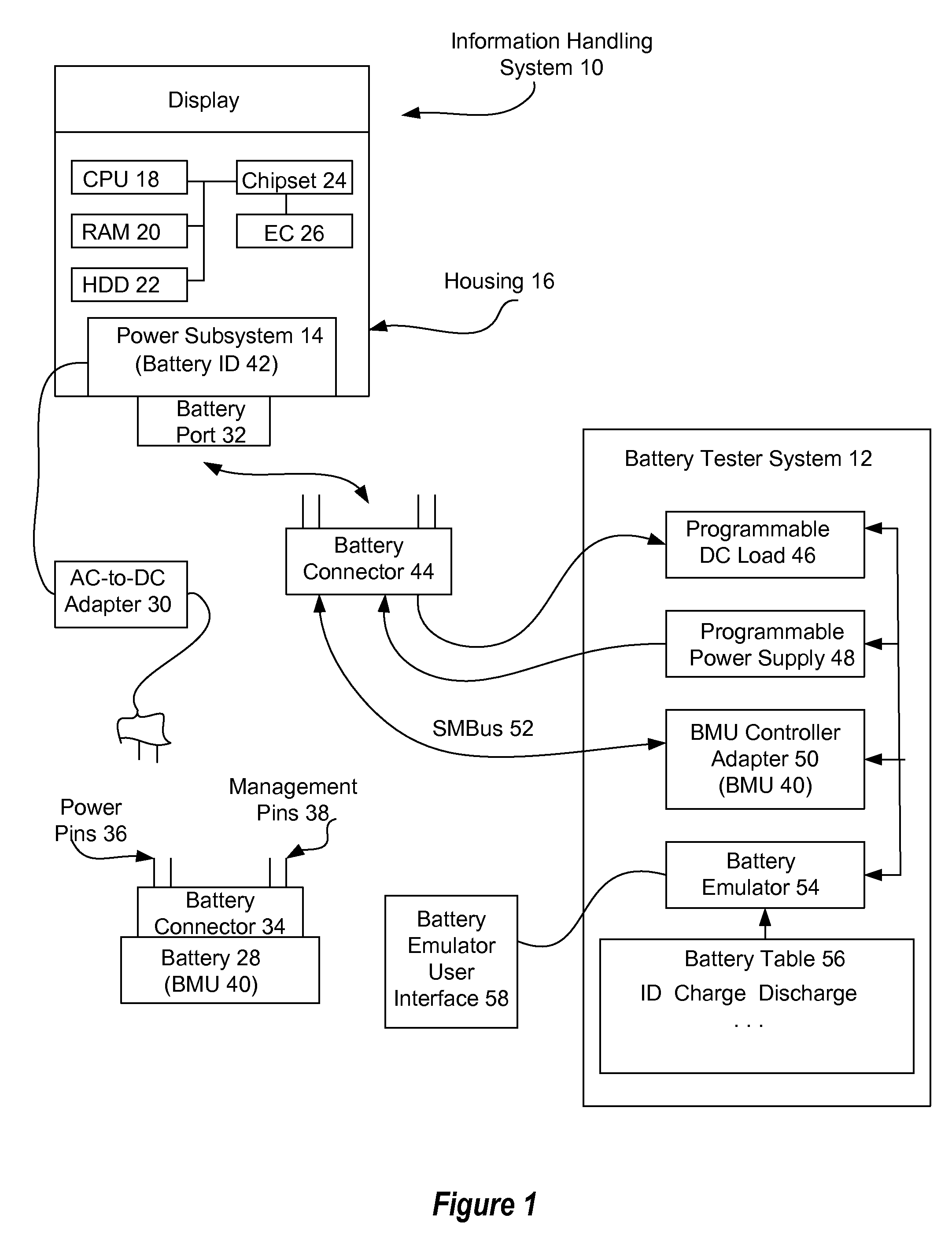
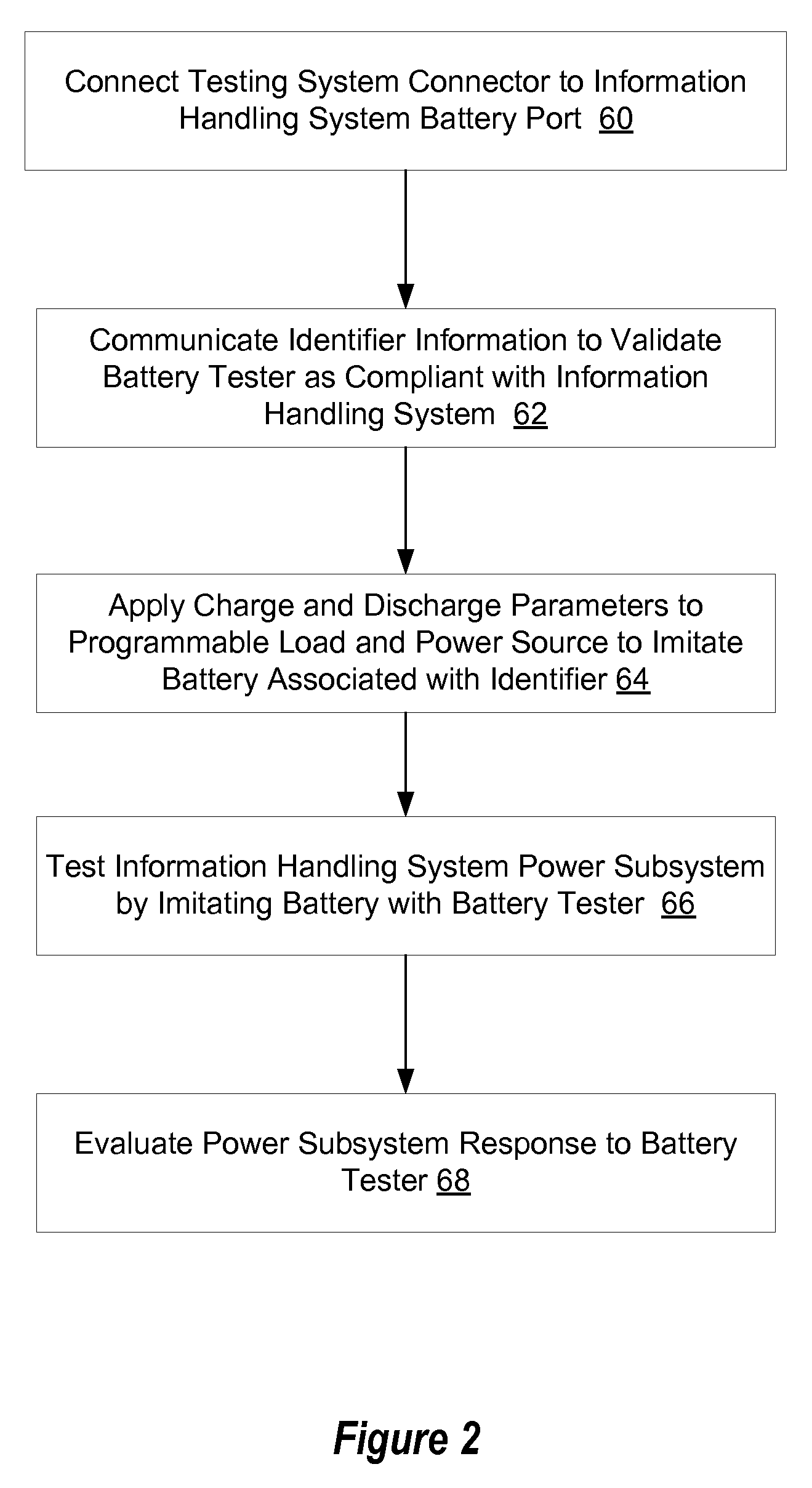
Information handling system battery emulation testing system and method
ActiveUS8405398B2Reduce disadvantagesReduce problemsBatteries circuit arrangementsAnalogue computers for electric apparatusManagement unitElectrical battery
Owner:DELL PROD LP
Programmable load replay precluding mechanism
ActiveUS10114794B2Reducing replayDigital data processing detailsConcurrent instruction executionReservation stationProgrammable load
Owner:VIA ALLIANCE SEMICON CO LTD
Magnetic stripe data transmission system and method for reliable data transmission and low power consumption
ActiveCN107665319AReliable transmissionReduce power consumptionNear-field transmissionPayment architectureFull bridgeEngineering
A magnetic stripe data transmission (MST) driver and a method for driving the MST are disclosed. The MST driver is configured to transmit magnetic strip data comprising of streams of pulses. The MST driver comprises a pair of high side switches and a pair of low side switches. The pair of high side switches comprises a first switch and a second switch. The pair of low side switches comprises a third switch and a fourth switch. The first, second, third and fourth switches are arranged in a full bridge type configuration connected across a voltage source and a ground. An inductive coil is connected across outputs of the full bridge type configuration of the switches. The MST driver includes a switch driver configured to drive the pair of low side switches and the pair of high side switches under current slope control using pulse width modulation. The driven load current has a rising portion and a falling portion through the inductive coil in a forward direction or in a reverse directionwith programmable load current rising and falling slopes to induce a recognizable back electromagnetic force at a receiver emulating the magnetic strip data during the load current rising and fallingportions and to reduce power loss during time periods without signal transmission.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON INT LP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com