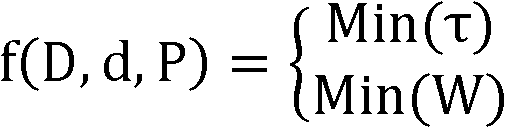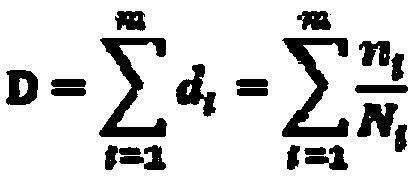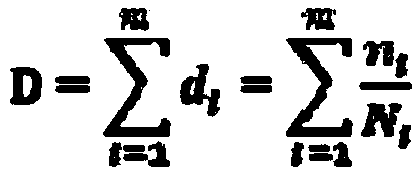Patents
Literature
53 results about "Stress resultants" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
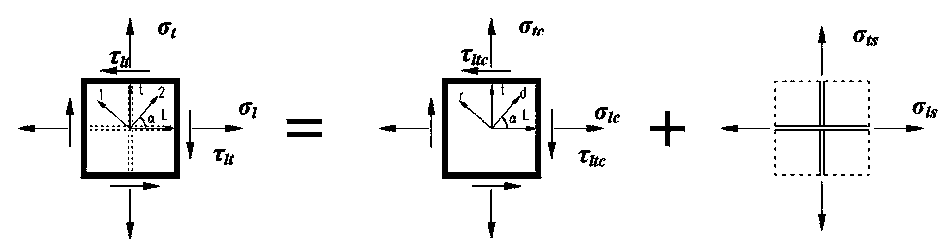
Stress resultants are simplified representations of the stress state in structural elements such as beams, plates, or shells. The geometry of typical structural elements allows the internal stress state to be simplified because of the existence of a "thickness'" direction in which the size of the element is much smaller than in other directions. As a consequence the three traction components that vary from point to point in a cross-section can be replaced with a set of resultant forces and resultant moments. These are the stress resultants (also called membrane forces, shear forces, and bending moment) that may be used to determine the detailed stress state in the structural element. A three-dimensional problem can then be reduced to a one-dimensional problem (for beams) or a two-dimensional problem (for plates and shells).
Fatigue analysis method and fatigue analysis device of structural member in wind generating set
ActiveCN104573172AStress calculation results are accurateReflect changes in stress stateSpecial data processing applicationsFatigue damageElement model
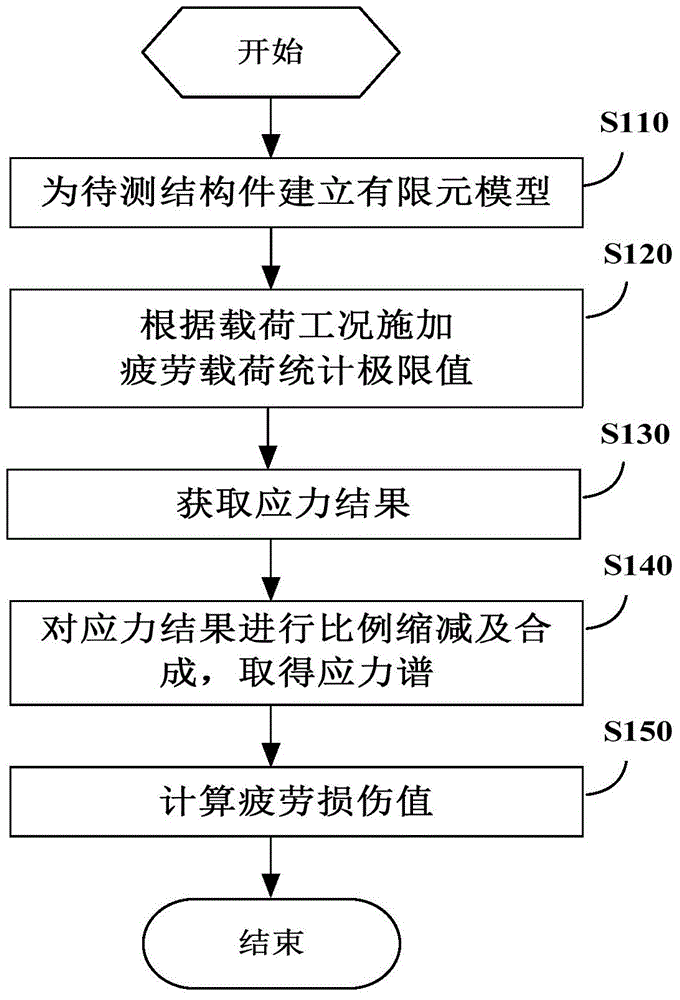
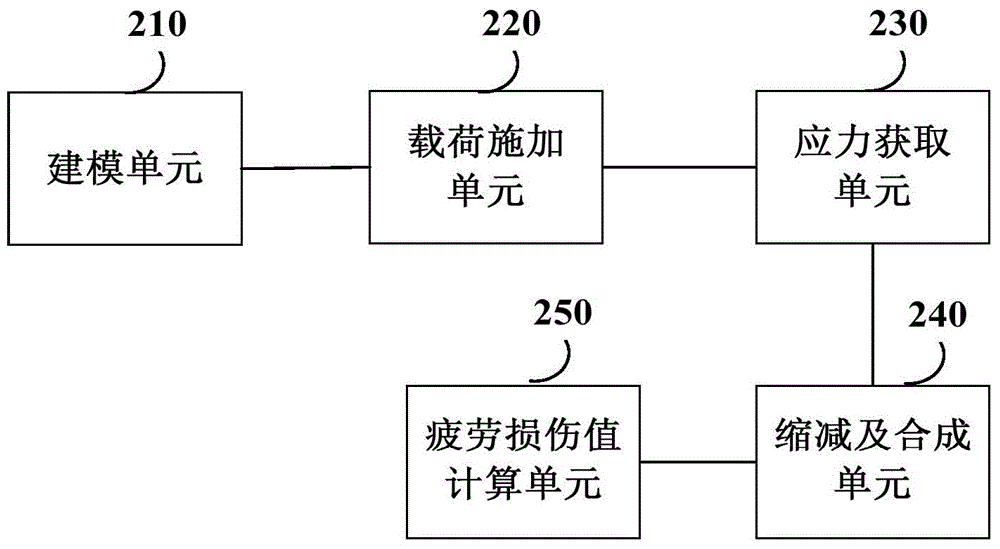
The invention provides a fatigue analysis method and a fatigue analysis device of a structural member in a wind generating set. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a finite element model for a to-be-measured structural member involving bearing connection and related structural members thereof; applying load to the finite element model according to various preset load working conditions respectively; acquiring each node stress result of the to-be-measured structural member under each load working condition through finite element analysis; scaling down the acquired stress results by taking a fatigue load sequence which is pretreated through regularization as a coefficient; synthesizing the stress results under the different load components after scaling down to obtain a stress spectrum of each node of the finite element model of the to-be-measured structural member; calculating a fatigue damage value of the to-be-measured structural member according to the stress spectrum of each node and the stress-life curve of the to-be-measured structural member. By applying the method and the device, the fatigue analysis result of the structural member in the wind generating set is more accurate.
Owner:XINJIANG GOLDWIND SCI & TECH
Abnormal formation pressure calculation method
ActiveCN104698492AHigh precisionEliminate the effects ofSeismic signal processingMedicineYoung's modulus
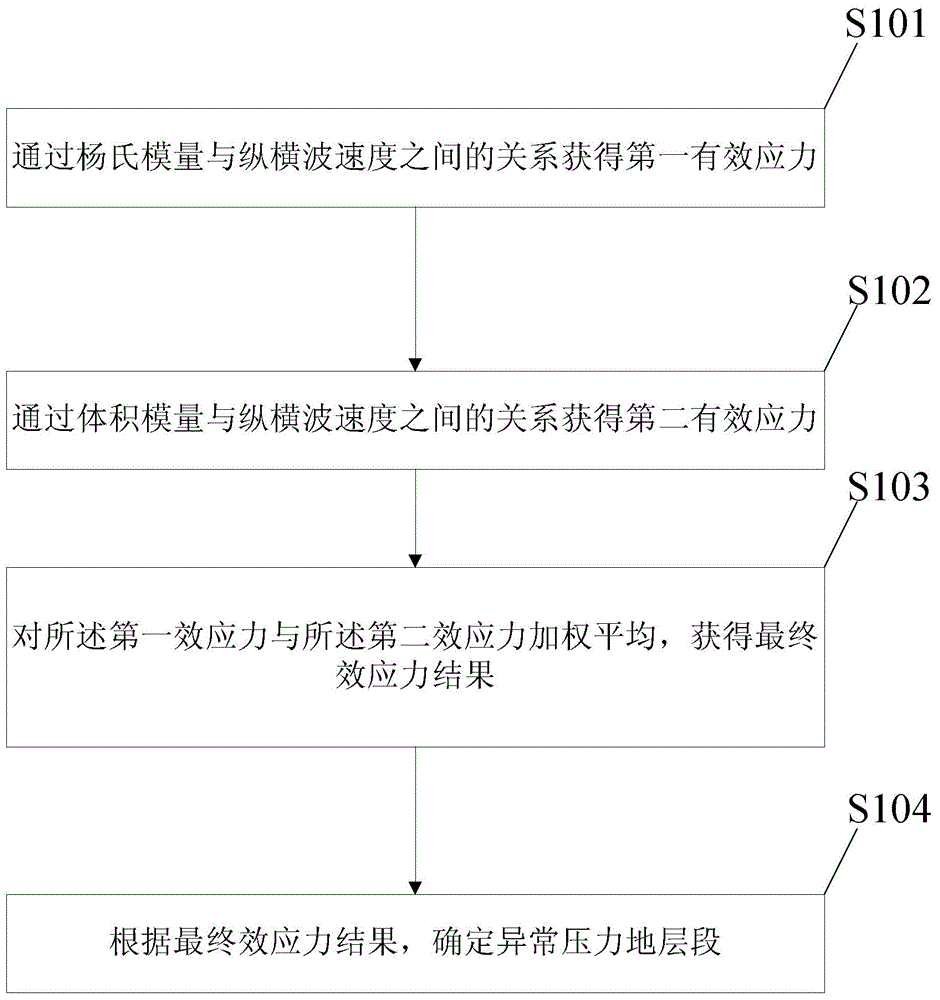
The invention discloses an abnormal formation pressure calculation method. The method includes: acquiring first effective stress through the relation between Young modulus and longitudinal and transverse wave velocity; acquiring second effective stress through the relation between bulk modulus and the longitudinal and transverse velocity; subjecting the first effective stress and the second effective stress to weighted average to acquire a final effective stress result; according to the final effective stress result, determining abnormal formation pressure sections by the aid of the effective stress theory. With the method, precision in predicting formation pressure is improved, influence of containing gas in the formation on formation velocity is eliminated, a high-precision model is established between the formation velocity and the effective stress, and an elastic modulus weighing method is developed to have the formation pressure predicated.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Vibration stress numerical analysis method for turbomachinery blades
ActiveCN106528932AImprove calculation accuracyCalculation speedDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSolid regionEngineering
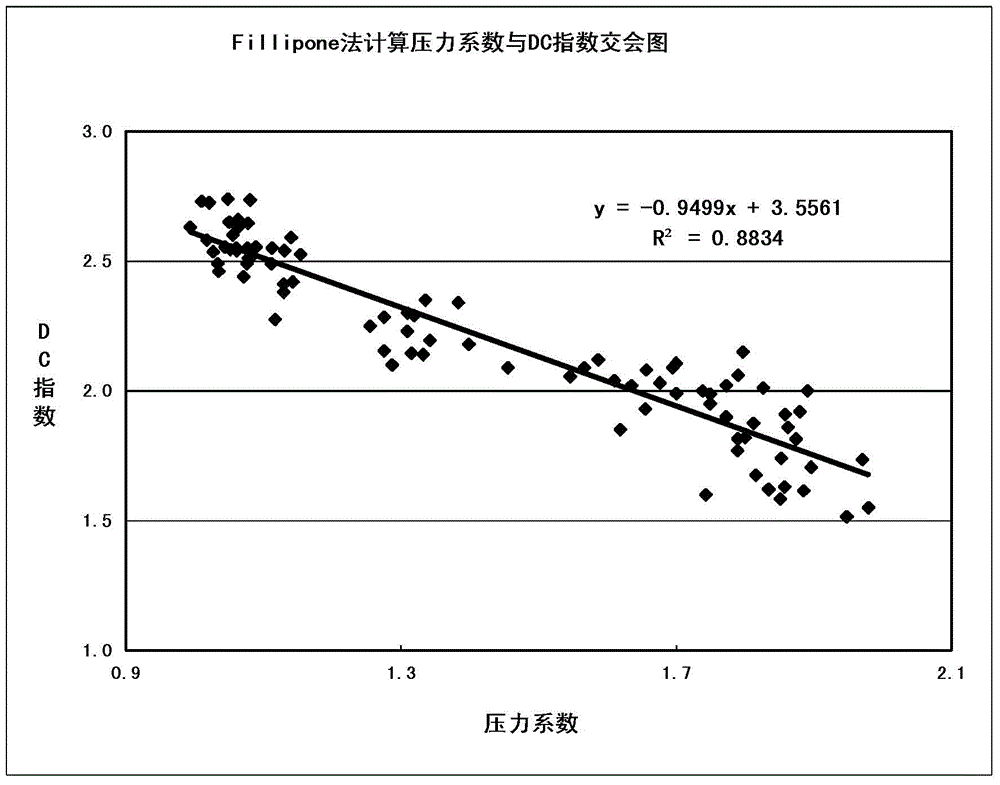
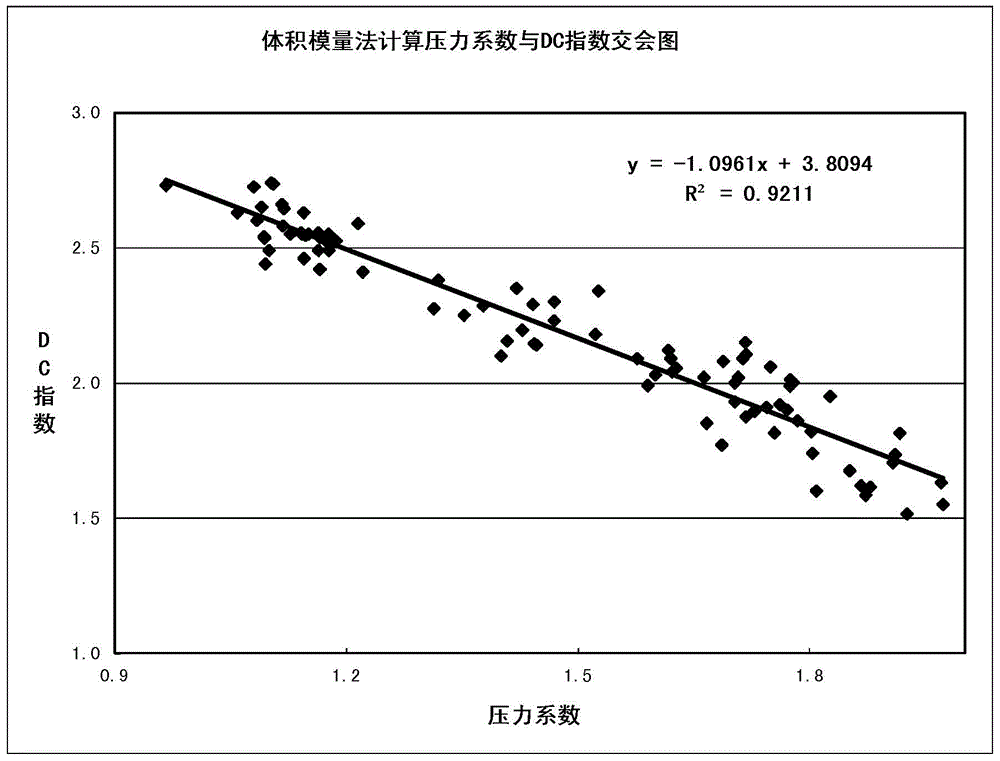
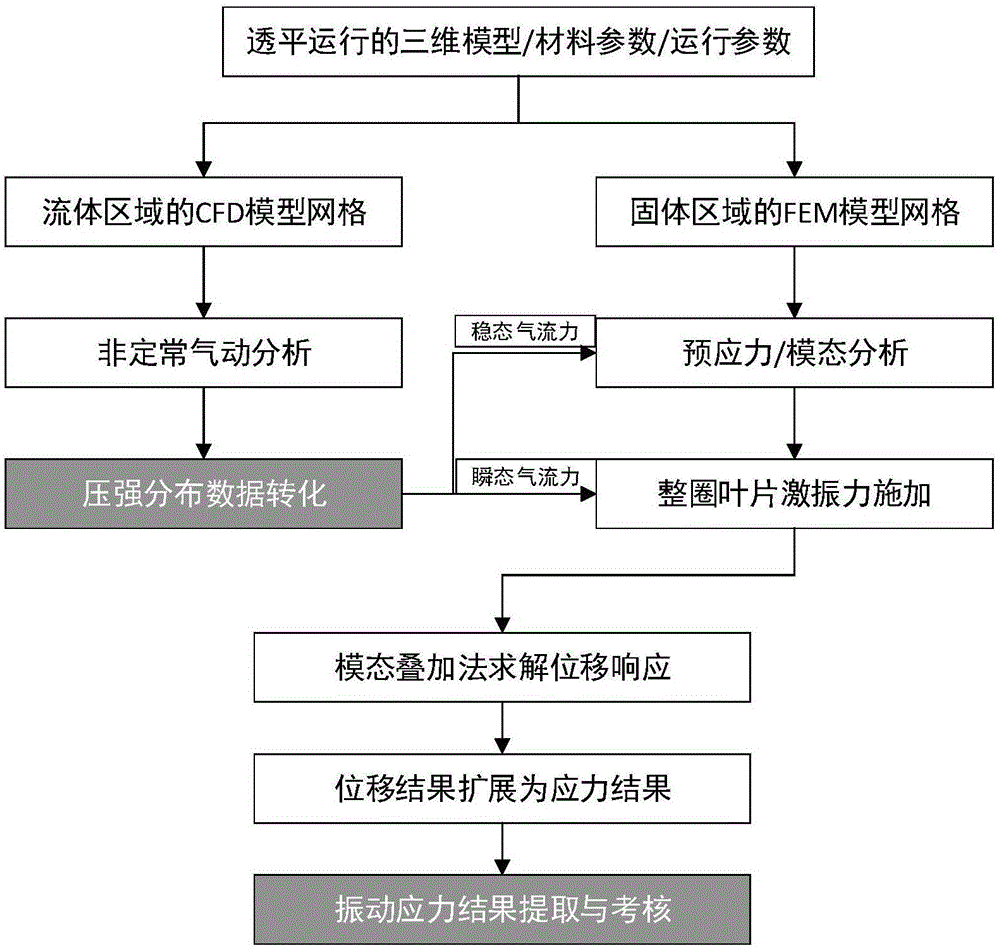
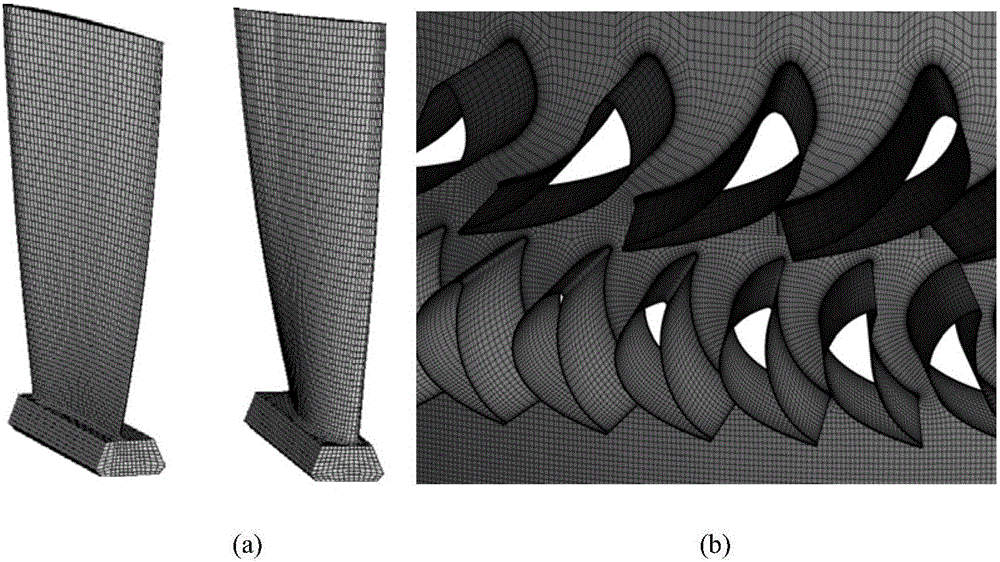
The invention discloses a vibration stress numerical analysis method for turbomachinery blades. The method comprises the steps of 1, building an FEM model of a solid region of an entire circle of the blades and CFD models of periodically symmetric fluid regions; 2, obtaining steady-state pressure intensity field distribution of meshes of the fluid regions of the blades and instant pressure intensity field distribution of each time step in a pneumatic period; 3, converting pressure intensity field distribution data; 4, performing finite element mode analysis of the entire circle of the blades; 5, obtaining node force load vectors of blade surfaces of all time steps; 6, solving a vibration displacement response by a mode superposition method; 7, expanding a displacement response result into a stress result; and 8, performing vibration stress result extraction and check. According to the method, the pressure intensity distribution of the blade surfaces is obtained by adopting a non-steady computing method, and an accurate air exciting-vibration force load is obtained by interpolation from the meshes of the fluid regions of the blades to the pressure intensity of the meshes of the solid region, so that the computing precision is improved; and each sector adopts a CPU+GPU heterogeneous parallel computing mode, so that the computing speed is greatly increased.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Bolt strength analysis method for directly-driven wind-driven generator
ActiveCN103020377AAccurate analysisTrue descriptionSpecial data processing applicationsWind drivenPrincipal stress
The invention discloses a bolt strength analysis method for a directly-driven wind-driven generator. The bolt strength analysis method comprises the following steps of: (1) performing finite element modeling on a directly-driven wind-driven generator structure; (2) applying an external load to the directly-driven wind-driven generator structure; (3) computing and extracting a bolt stress result under the action of the external load; (4) performing post-processing on the extracted bolt stress result; and (5) computing the fatigue strength and ultimate strength of the bolt according to a post-processing result, wherein in the step (3), the bolt stress result comprises a result of axial stress on the same section of the bolt and two vertical bending stresses; and correspondingly, in the step (4), a post-processing process comprises the following steps of: performing superimposing computation on the axial stress and the two vertical bending stresses; and synthesizing resultant stress according to a maximum principal stress method. The analysis method disclosed by the invention can be used for analyzing bolt strength more accurately, and plays a more important role in guiding practical design of a bolt structure.
Owner:GUODIAN UNITED POWER TECH
Method for calculating load of wing integral fuel tank
ActiveCN105205267AAccurately reflectSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelAerodynamic load
The invention discloses a method for calculating a load of a wing integral fuel tank. The method comprises the steps of first calculating loads which fuel is subjected to in the X-direction, Y-direction and Z-direction by utilizing the principle that the loads can be overlaid linearly in the structure on-line elastic range; respectively calculating pressure distribution of each end face of the inner wall of the fuel tank under unidirectional overloads; finally overlaying pressure generated by each unidirectional overload, and obtaining pressure distribution of the wing fuel tank; establishing a wing fuel tank local detail finite element model in a full-aircraft overall finite element model, adding the pressure load of each end face of the fuel tank to the finite element model, applying corresponding working condition aerodynamic loads, and performing finite element stress analysis to obtain finite element stress result under each working condition. Under the conditions that the aircraft wing integral fuel tank is not pressurized and an inertial load of the fuel to the fuel tank exists, the method for calculating the load of the fuel tank is used for intensity assessment, and the load which the fuel tank is subjected to can be reflected genuinely.
Owner:JIANGXI HONGDU AVIATION IND GRP
A method for determining a mixed dimensional model interface constraint equation coefficient
ActiveCN106021644AEasy to writeConsistent changeDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelEngineering
The invention provides a method for determining a mixed dimensional model interface constraint equation coefficient. The method comprises the steps of cutting beam parts on the two sides of a cantilever beam connecting face to establish a static force analysis model, the model boundary constraint conditions being the same as those of an original model; deducing required stress distribution according to a multipoint constraint equation and performing relevant static force analysis; exporting a stress result of a finite element model node at the section of the connecting face through finite element software. The method is a fine dynamic response calculation method giving consideration to total dynamic features and local structures, and can establish a unified solving procedure of a multipoint constraint equation and complete the solving of the multipoint constraint equation rapidly, thus facilitating the application of a mixed dimensional model in engineering. The method forms a unified solving step for a stress coordination multipoint constraint equation, facilitates unified programming, and thus facilitates promotion in engineering application; the first 10-order modal frequency error of the finite element model established by using the method and a real model is within 1%, and an obtained frequency response curve and the frequency response curve of the real model show consistent changes.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
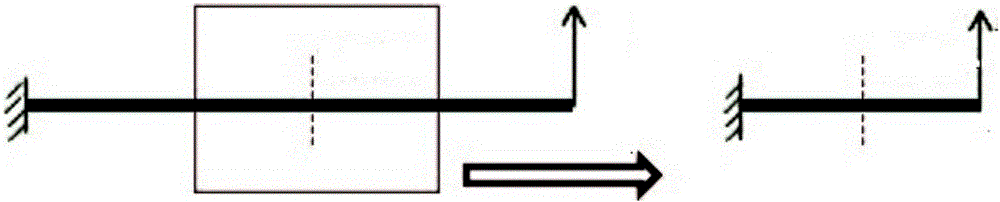
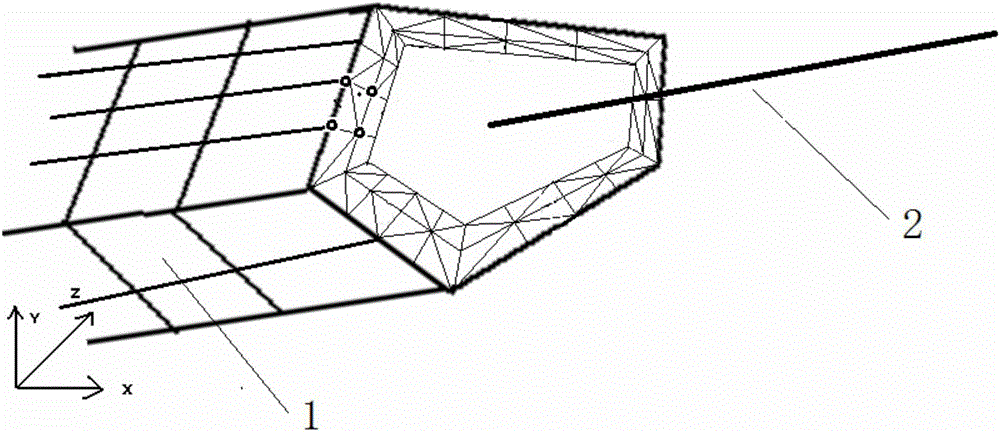
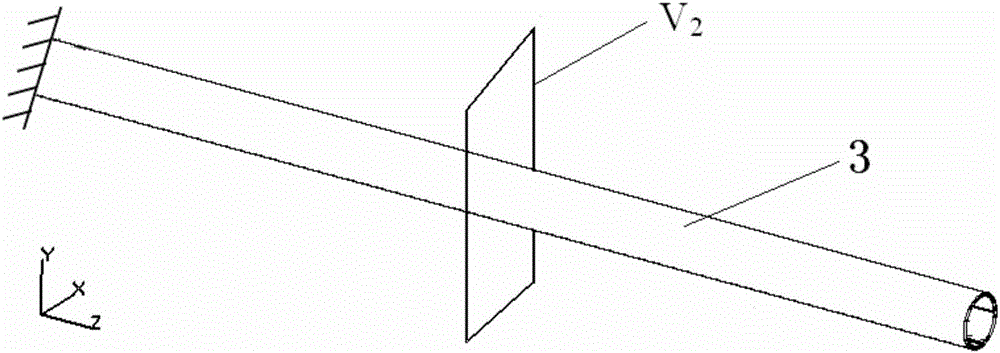
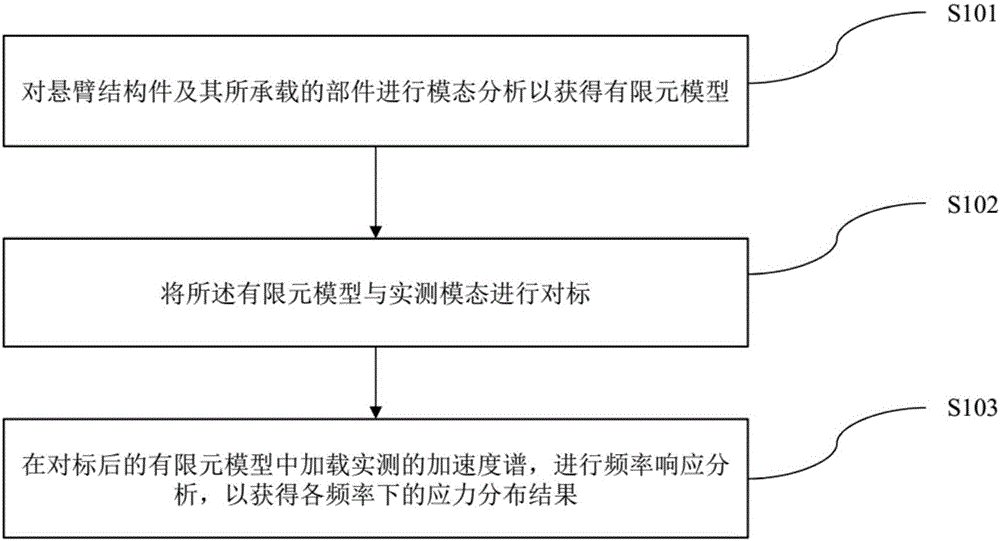
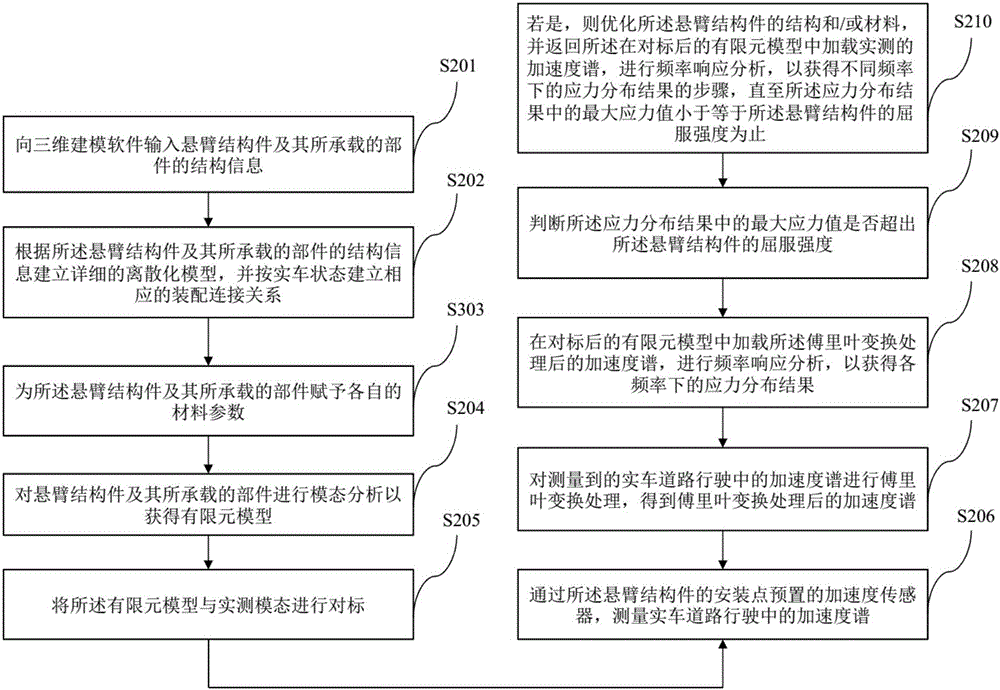
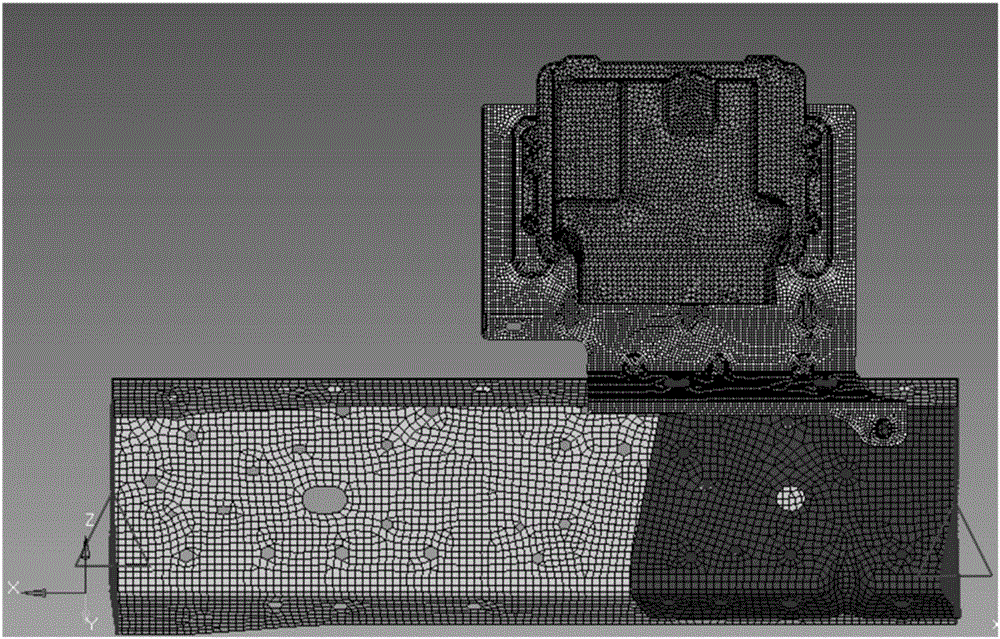
Strength analysis method of automotive cantilever structural part
InactiveCN106777478AConforms to the state of stress distributionSupport developmentDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelField tests
The invention discloses a strength analysis method of an automotive cantilever structural part. The strength analysis method comprises the following steps: a finite element model is obtained by performing modal analysis on the cantilever structural part and a part borne by the cantilever structural part; the finite element model and actually measured modal are subjected to benchmarking; an actually measured acceleration spectrum is loaded to the finite element model after benchmarking for frequency response analysis, and results of stress distribution at different frequencies are obtained. According to the method, the finite element model subjected to benchmarking with the actually measured modal is taken as the base model, the actually measured acceleration spectrum is loaded for frequency response analysis, the results of stress at different frequencies are output, the vibration factor can be mainly considered, the stress distribution state of the cantilever structural part better meeting a field test state is obtained finally, and the analysis precision is higher.
Owner:JIANGLING MOTORS
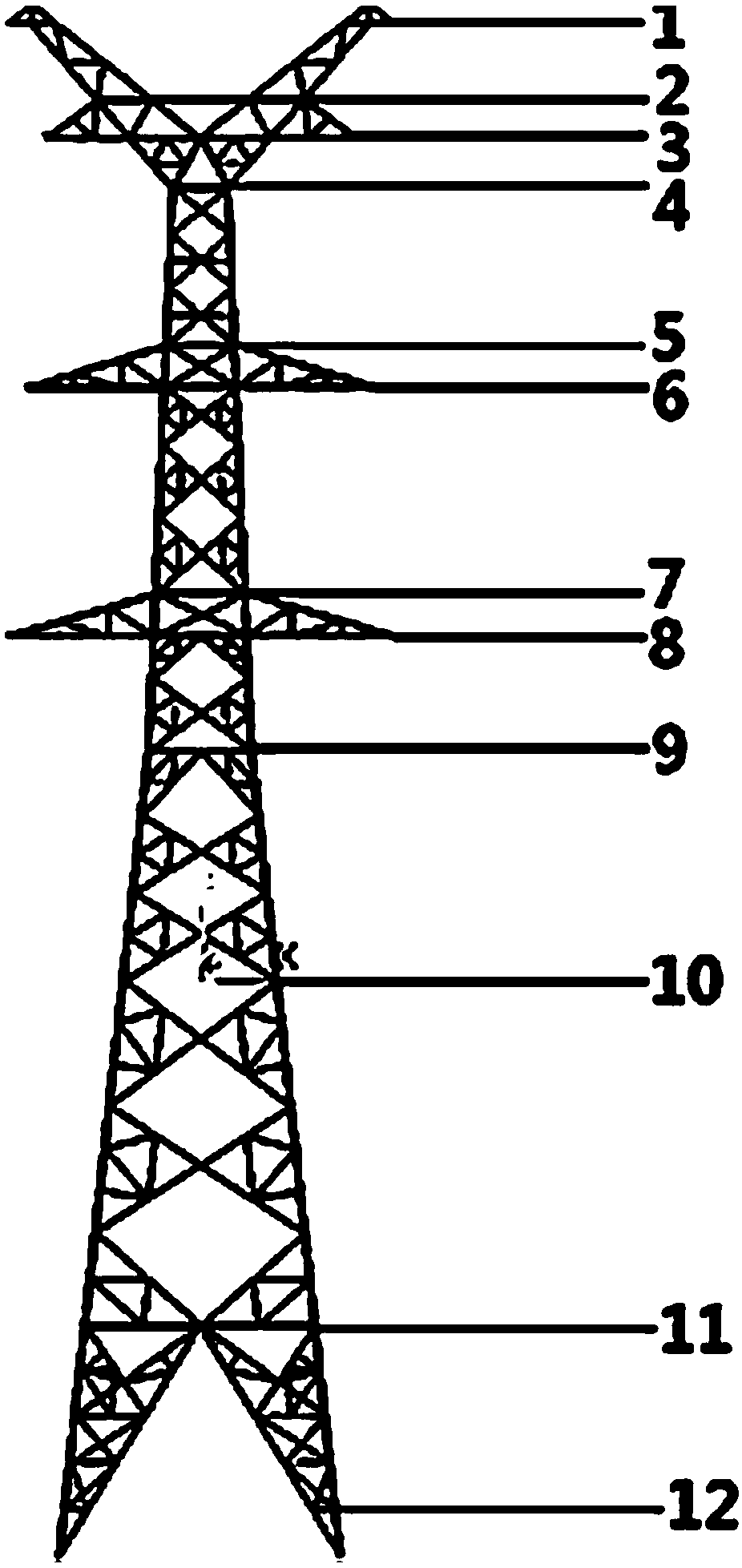
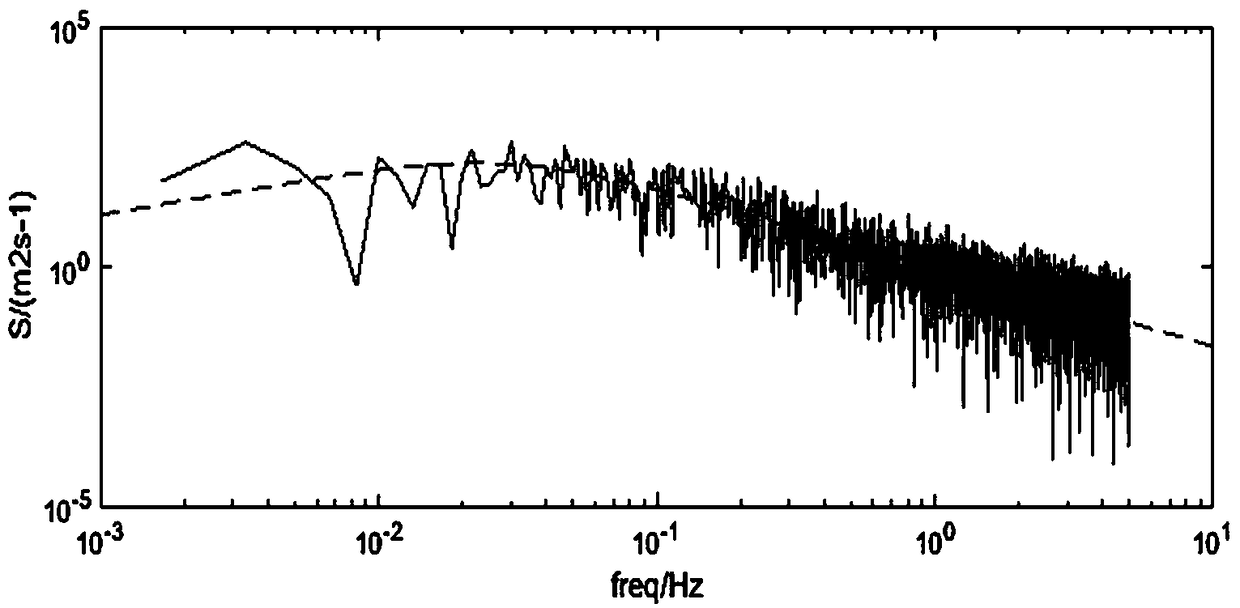
A transmission linewind speed field simulation method considering the spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of wind loads is presented
ActiveCN109359359AHarm reductionData processing applicationsDesign optimisation/simulationElement modelEngineering
The invention relates to a transmission line wind speed field simulation method considering the space-time distribution characteristics of wind load, comprising the following steps: 1) the average wind speed field simulation and the fluctuating wind speed field simulation are carried out to obtain the time series of the average wind speed value and the fluctuating wind speed of each point; 2) thatfluctuating wind speed time series is superimposed on the average wind speed value of each point to obtain the actual wind speed time series; 3) cyclic shift transformation is performed on the fluctuating wind speed time series obtained in the step 1) to obtain a set of wind speed time series considering the space-time distribution characteristics; 4) The wind speed time series considering the spatial and temporal distribution characteristics is transformed into the wind load data, which is applied to the finite element model of transmission line in the form of segmentation, and the transientsolution is performed and displacement is extracted, and the wind vibration calculation of transmission line is completed by the stress result. The present invention provides a basis for further wind-induced vibration response analysis of transmission lines considering the temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of wind loads, and then reduces the harm of wind loads to high-voltage transmission lines.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Ergonomic weight-distributing vest
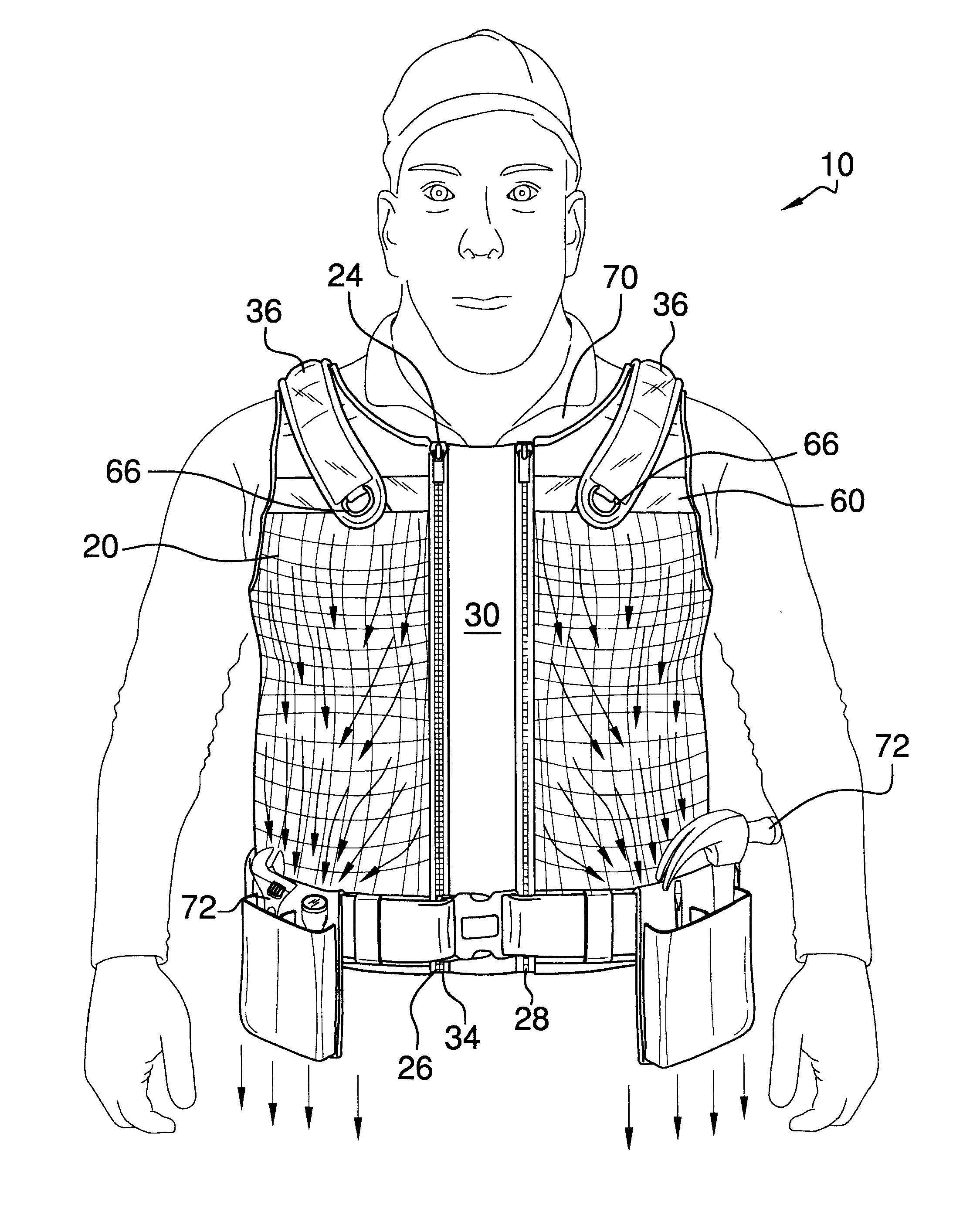
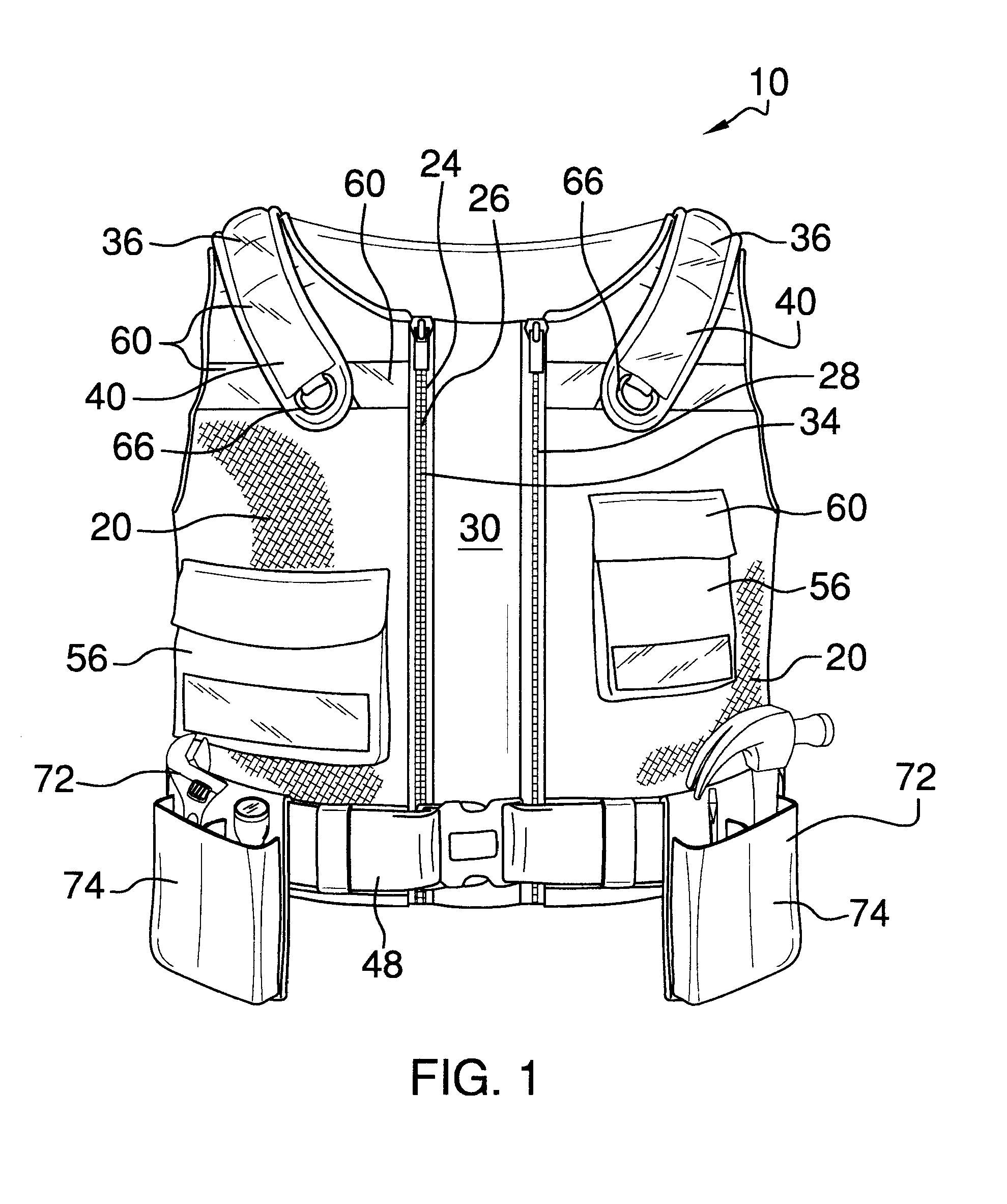
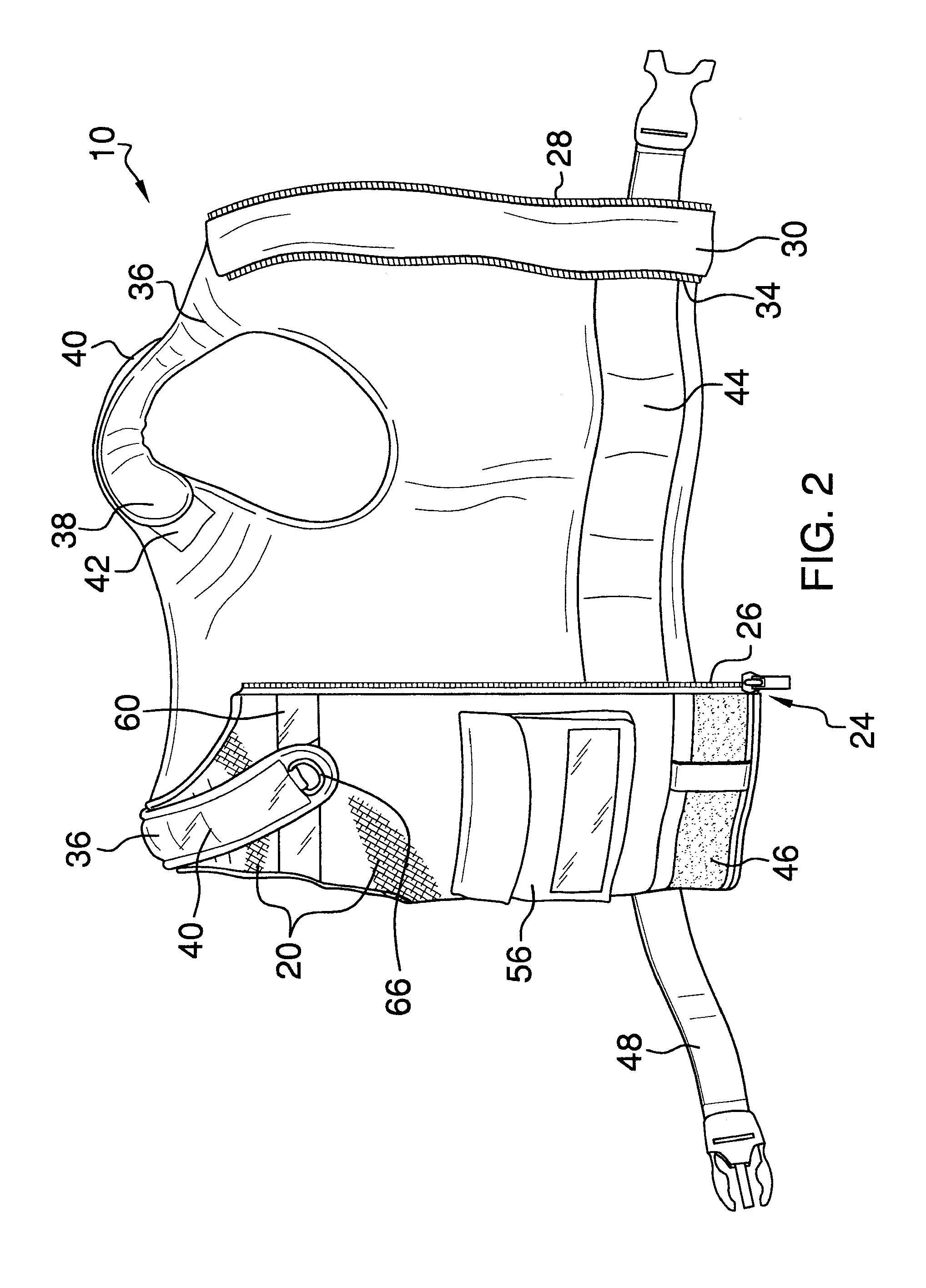
InactiveUS20150374043A1Prevent and alleviate stress injuries wreakedCreating damageProtective garmentBiomedical engineeringTorso
An ergonomic weight distributing vest that includes a non-stretch mesh fabric that enables multiple anatomical contact points of said fabric across the torso of a wearer, each of said contact points conforming the vest to the contours of the torso of the wearer, wherein the weight of extant articles suspended from the vest and attached thereto, is distributed evenly throughout the mesh fabric over said multiple anatomical contact points across the contours of a wearer's torso, whereby said weight is more evenly distributed across a wearer's body and load bearing is thereby ergonomically configured to lessen local stresses resultant from carrying said articles at specific positions upon the body over extended periods of time.
Owner:DAHL JON S
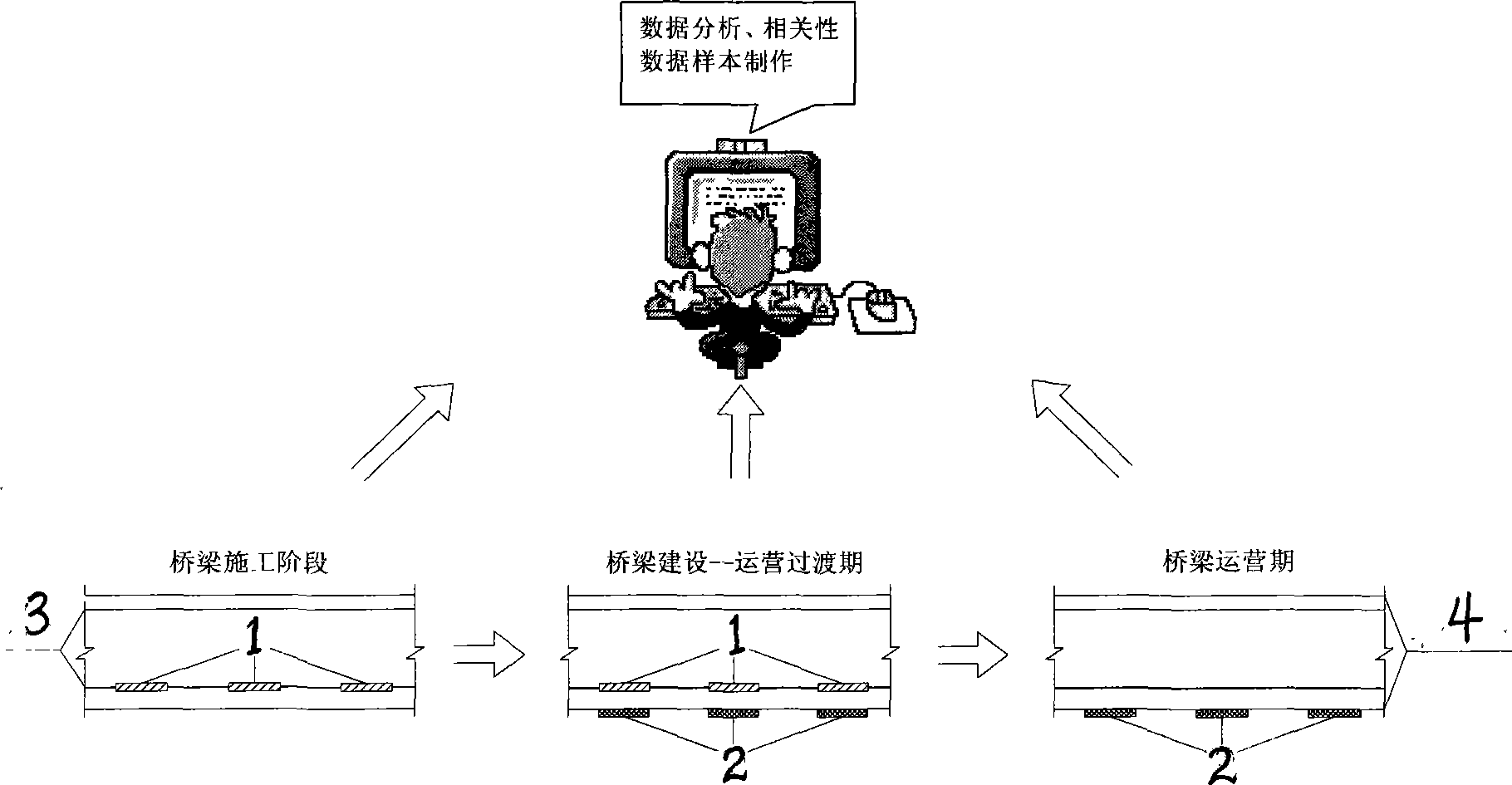
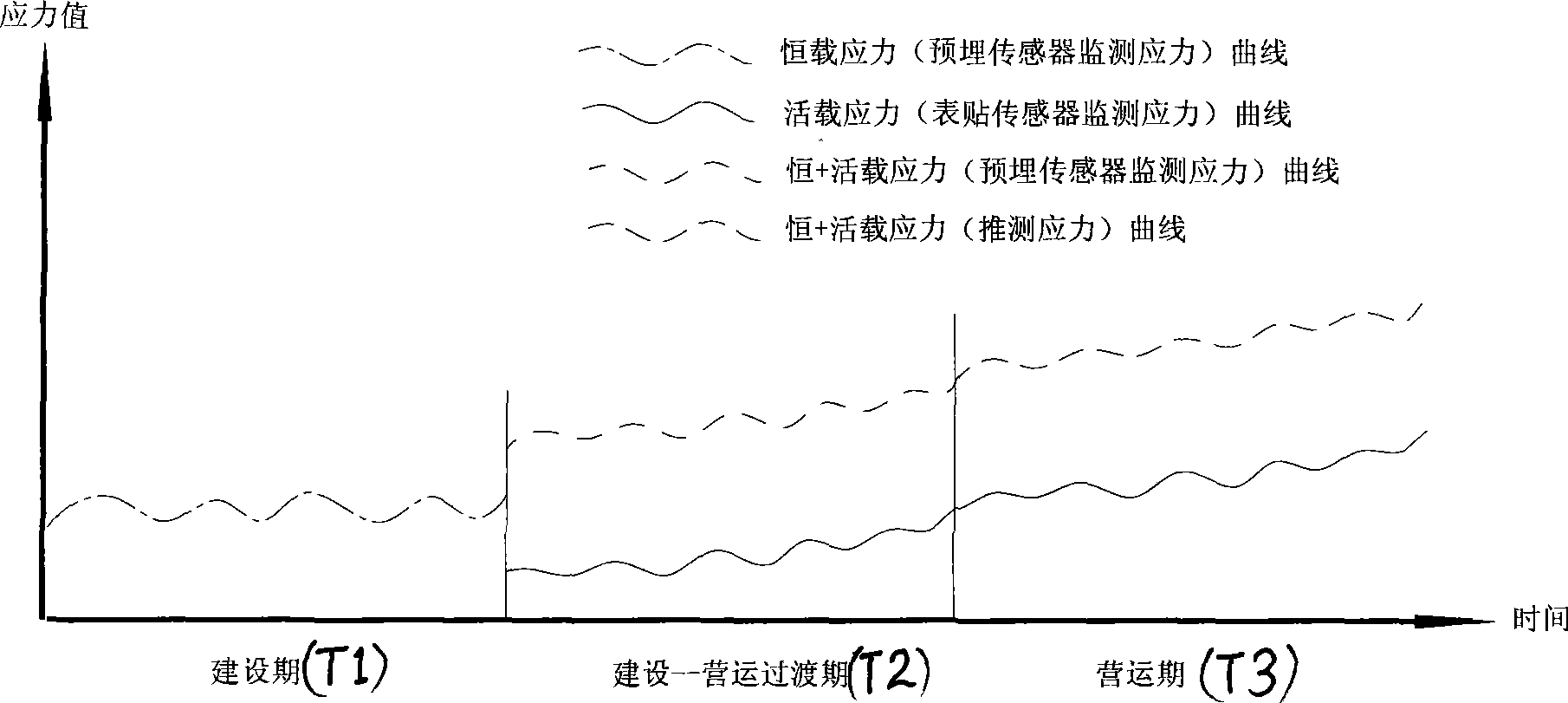
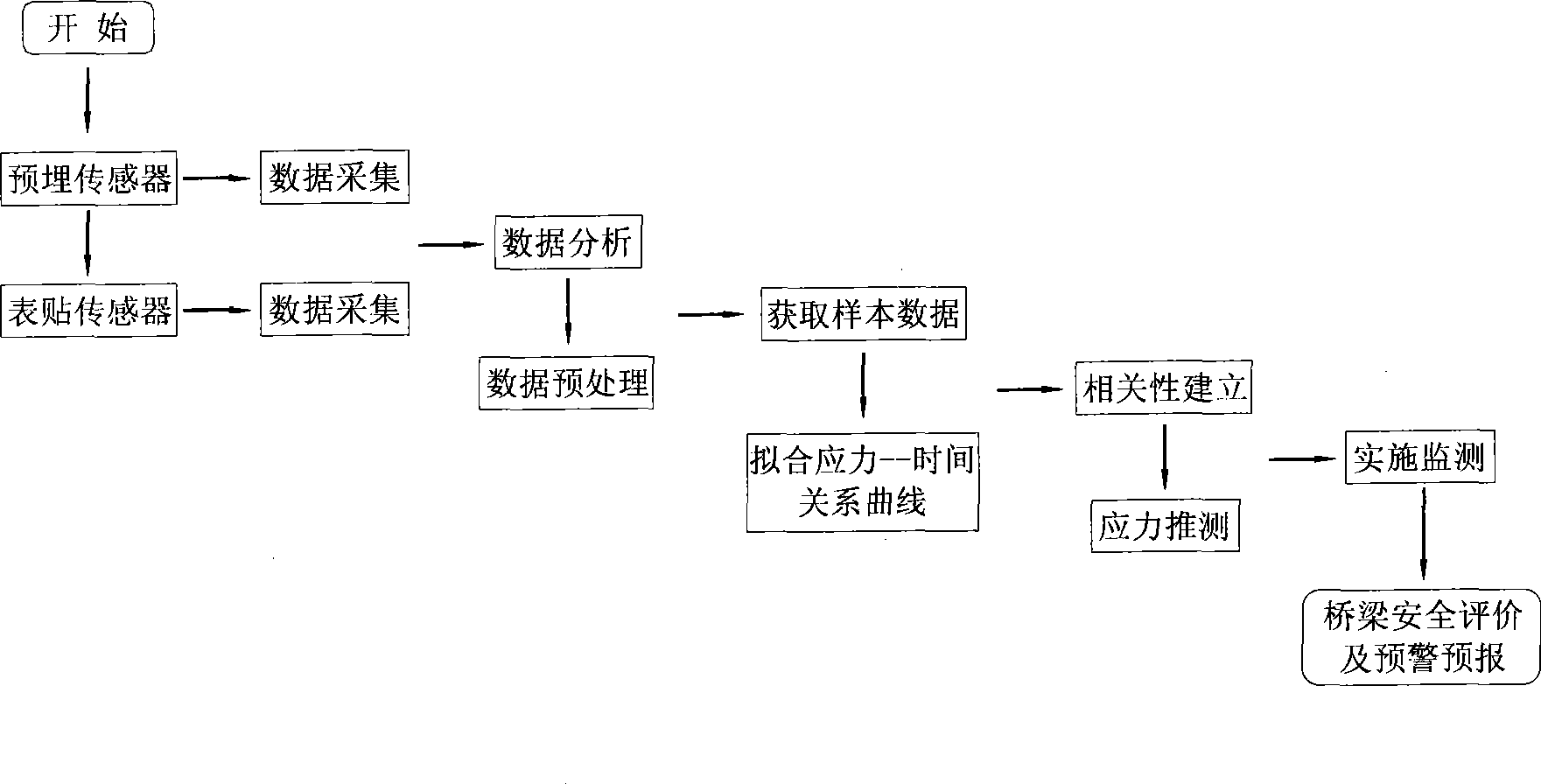
Long term monitoring methods for structure stress of bridge
InactiveCN101363760ARealize long-term security monitoringRealize complementary advantagesForce measurementSurface mountingLong term monitoring
The invention discloses a long-term monitoring method for bridge structural stress. The method comprises the steps: monitoring the structural stress of a bridge through a pre-embedded sensor and a surface mounting sensor; respectively building stress-time curve of the pre-embedded sensor and the surface mounting sensor to seek a correlated parameterization function of two stress-time curve; and reversely educing the stress of the bridge structure under the action of dead load and live load by combining the stress result of the surface mounting sensor and the correlated function, after the pre-embedded sensor is ineffective. The invention has the advantages that the method analyzes and induces the correlation obtained by two stress monitoring means of the pre-embedded sensor and the surface mounting sensor, realizes the complementary advantages of the two stress monitoring means, and realizes long-term safety monitoring for the bridges in operation period.
Owner:CHONGQING JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY +1
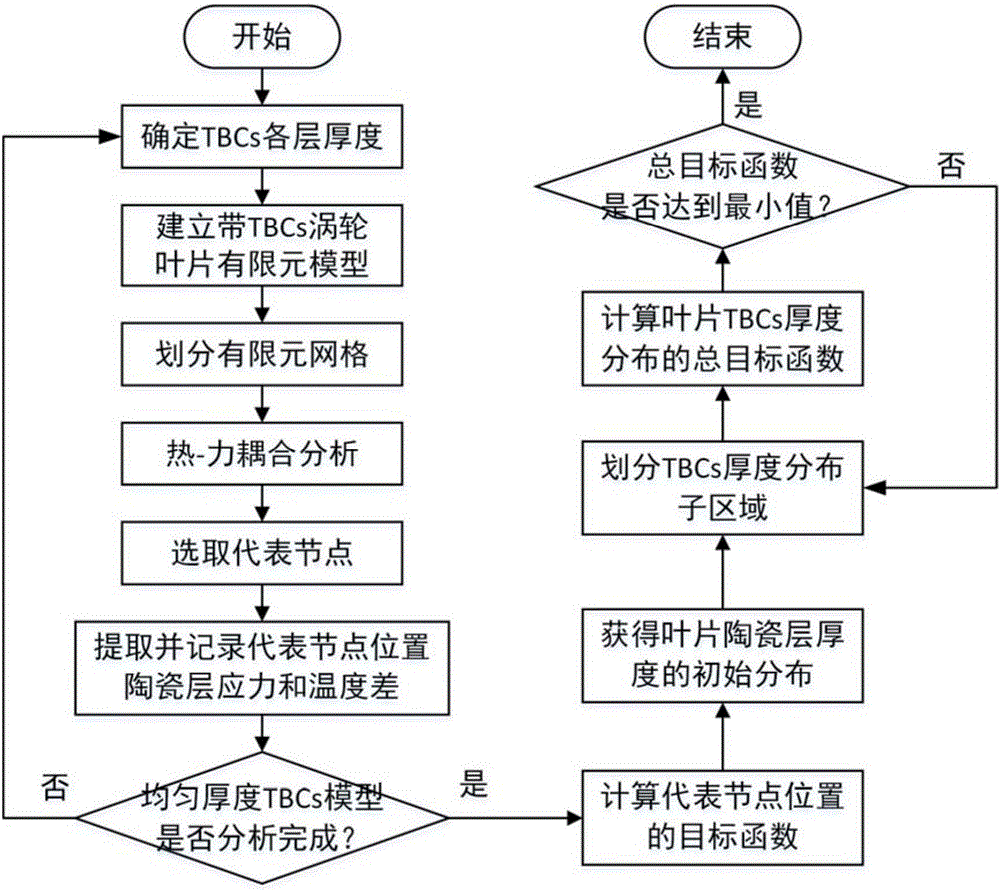
Thickness optimization design method for thermal barrier coatings of turbine blade
ActiveCN106649934AEnsure service safetyImprove efficiencyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationMulti objective optimization algorithmTurbine blade
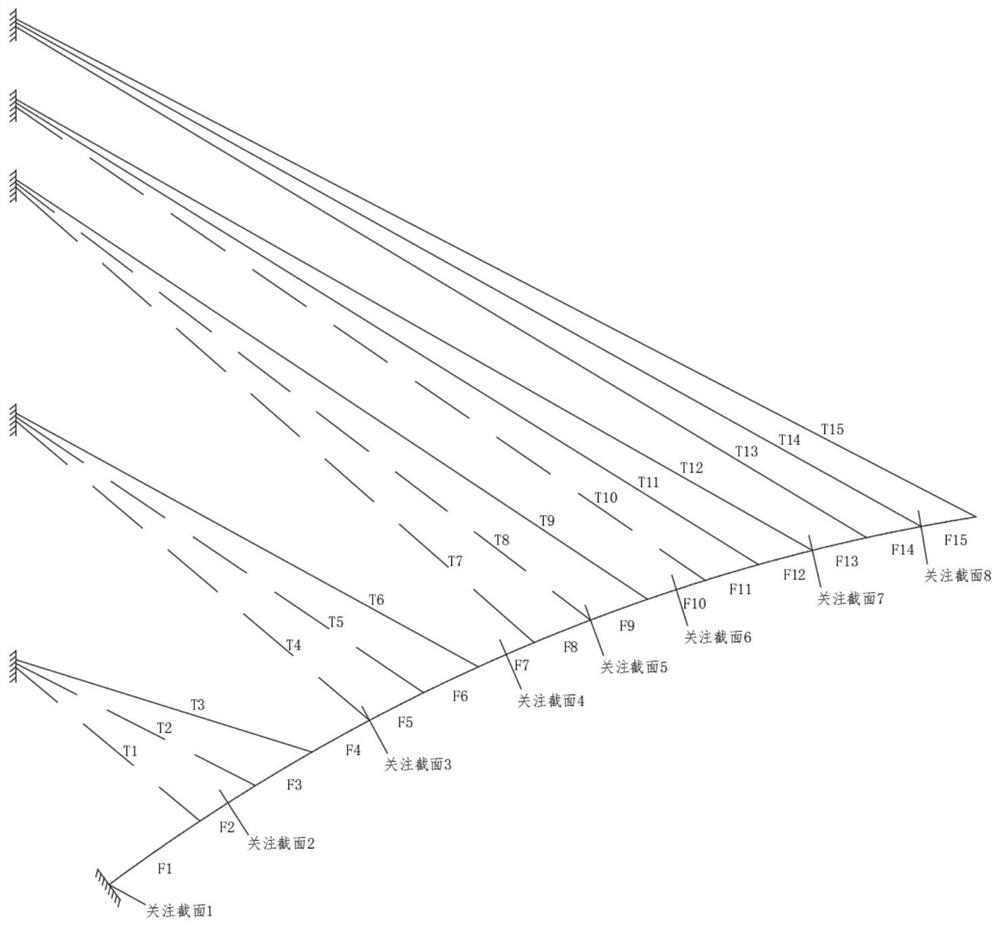
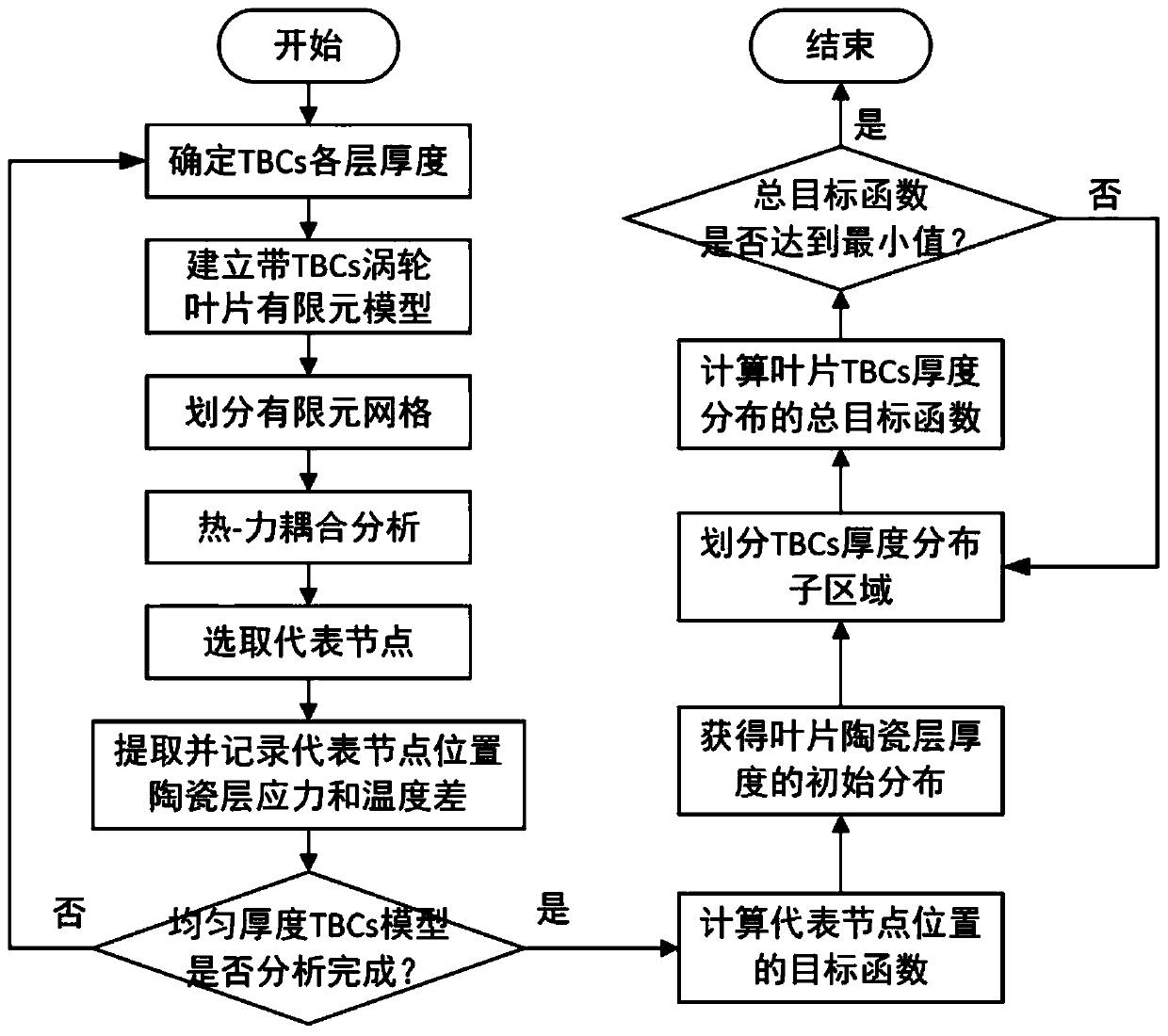
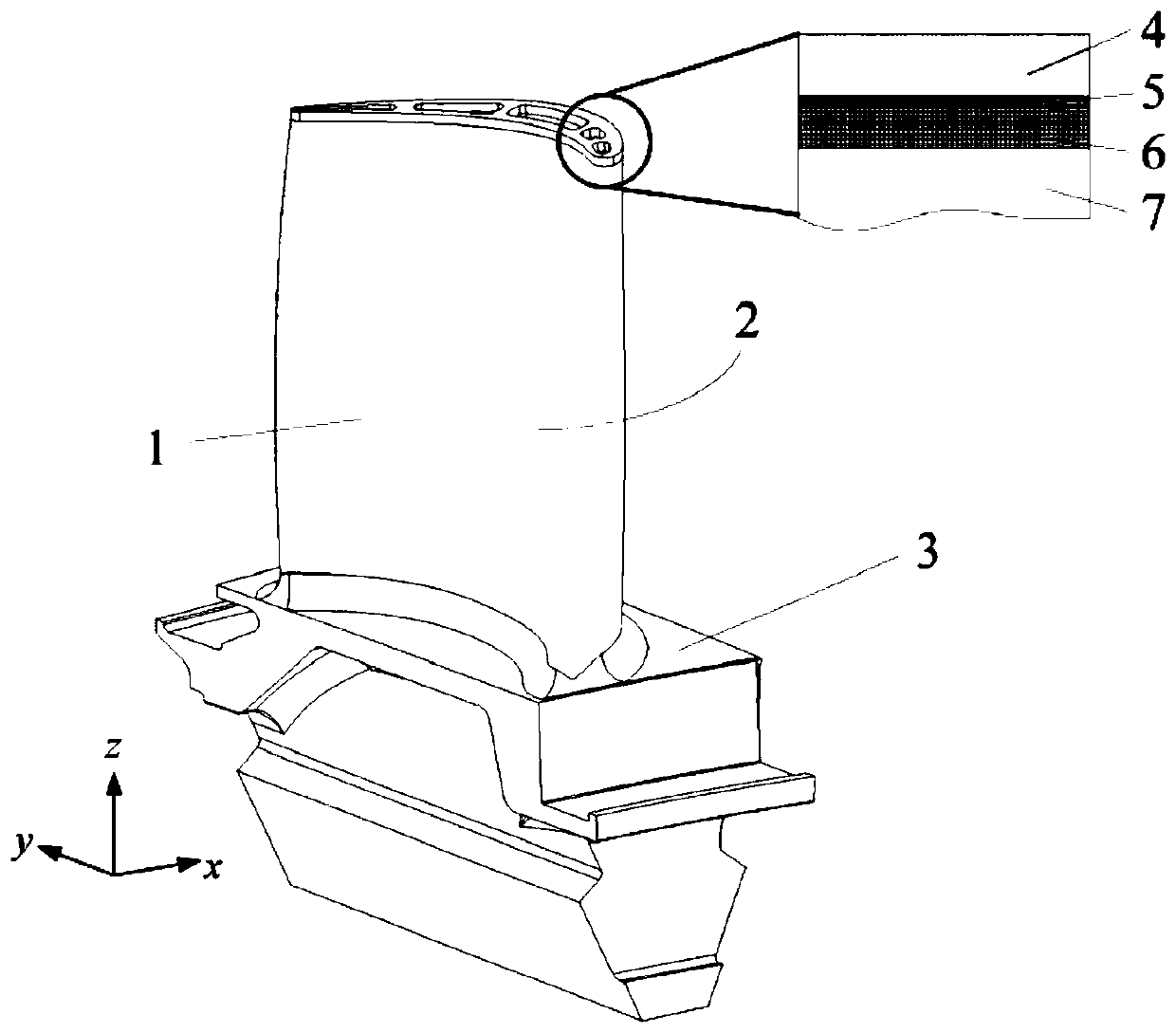
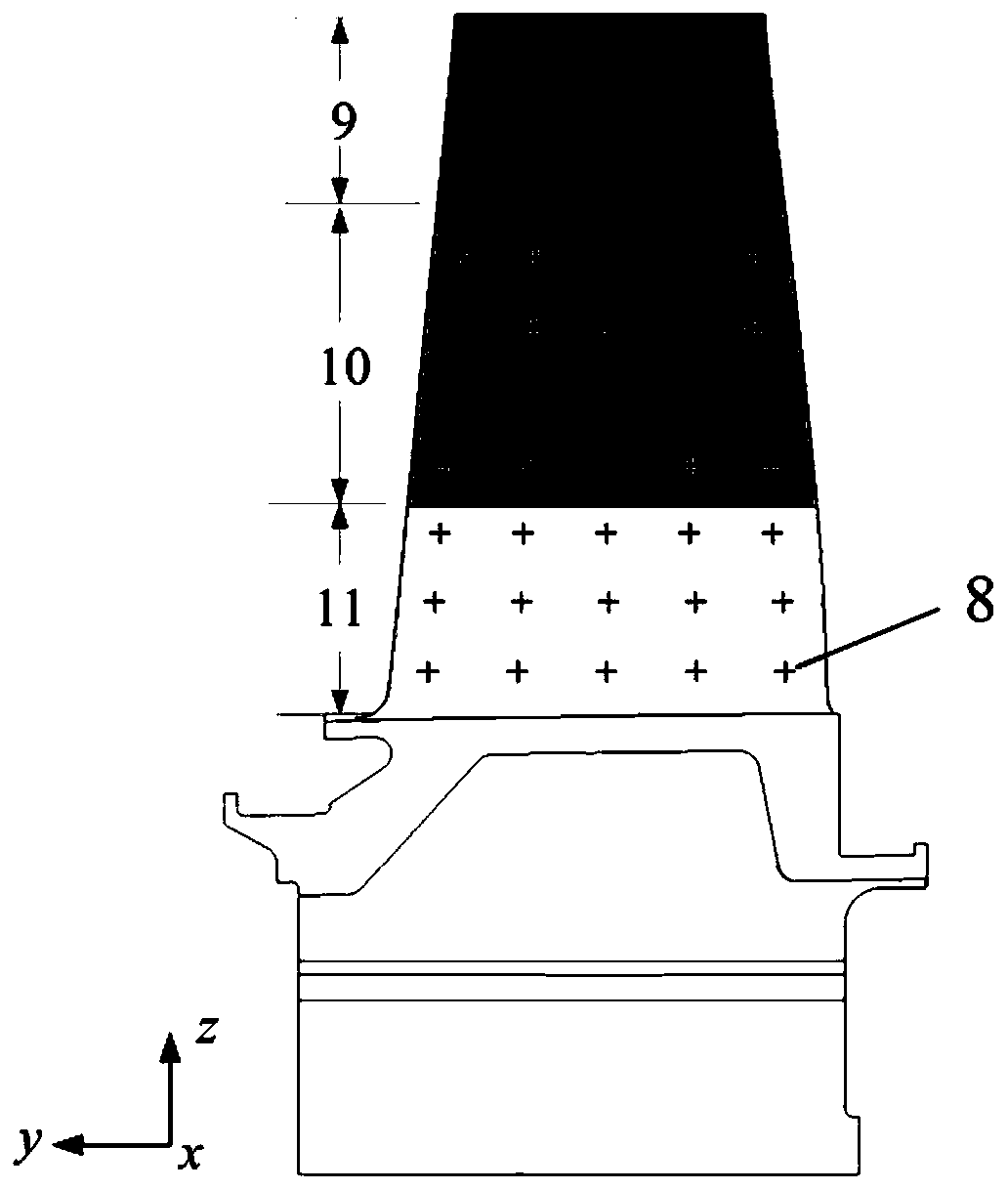
The invention discloses a thickness optimization design method for thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) of a turbine blade, and belongs to the technical field of surface coating protection. Representative nodes uniformly distributed on the turbine blade are selected, the states of local regions are reflected by temperatures and stress results of representative node positions, and TBCs thickness analysis of a complex blade is equivalent to thickness optimization design of a finite number of representative node positions, so that the analysis calculation amount is reduced; a mathematic formula is established for reflecting design objectives of high heat insulation performance, low stress level and low preparation cost, calculation is performed by introducing a multi-objective optimization algorithm to obtain optimal ceramic layer thickness of each representative node position, and a total objective function value is taken as a TBCs thickness optimization design and evaluation parameter of the blade, so that the advantages and disadvantages of a TBCs thickness distribution scheme can be quantitatively evaluated and the shortcoming that an existing method only can perform qualitative evaluation is overcome; and the method can ensure the service safety of the coatings and improve the usage efficiency of the coatings.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
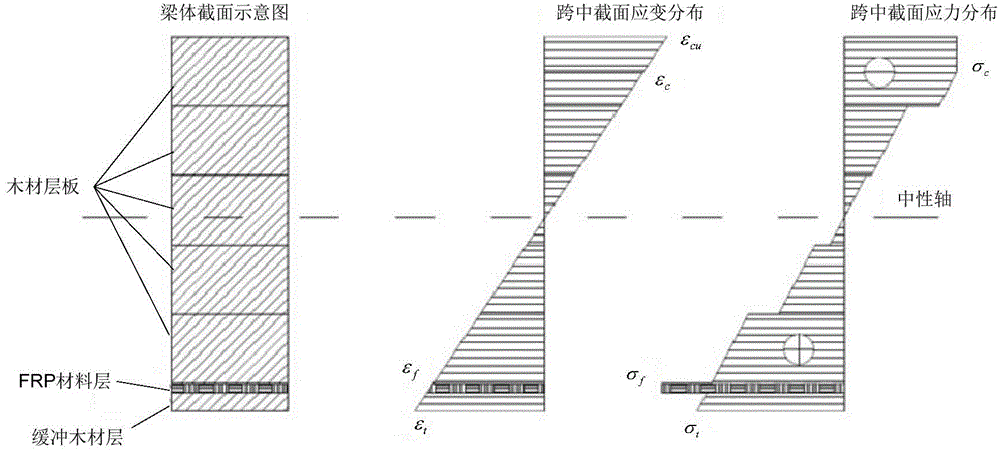
Method for efficiently and accurately predicting laminated wood beam ultimate bending moment used for FRP (Fiber Reinforced Plastic) enhancement structure
InactiveCN104915572AQuick measurementAccurate measurementSpecial data processing applicationsFiberMaterial resources
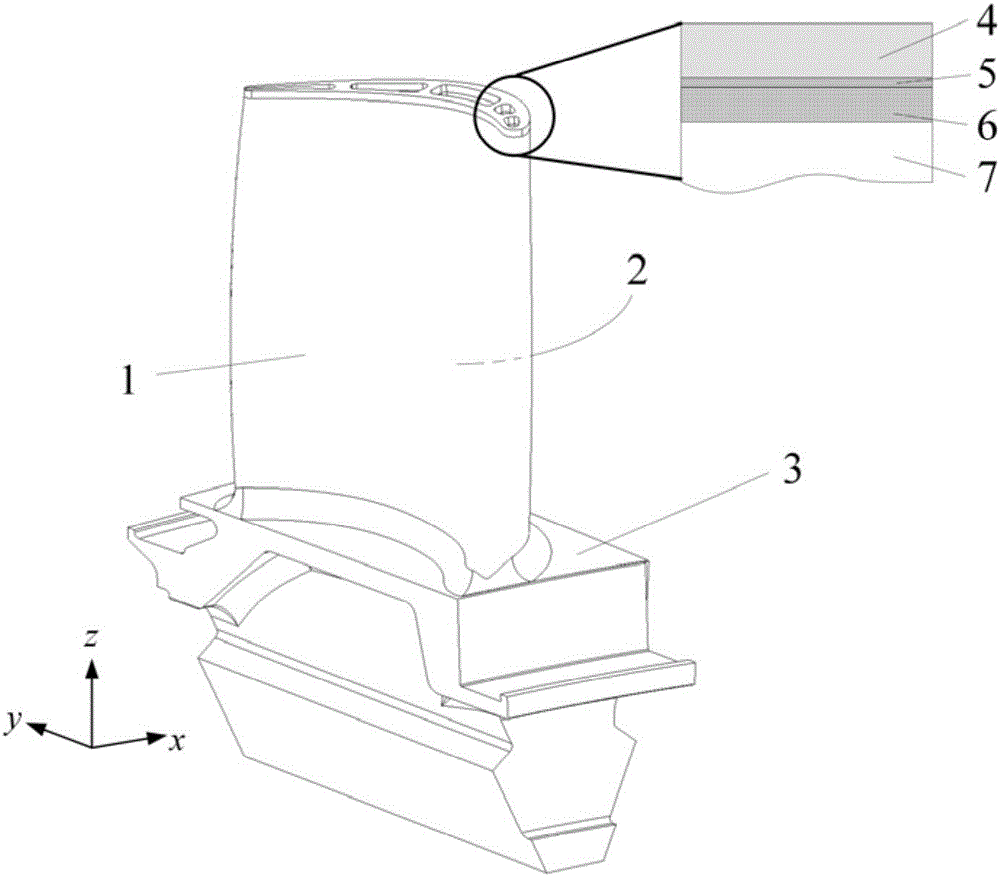
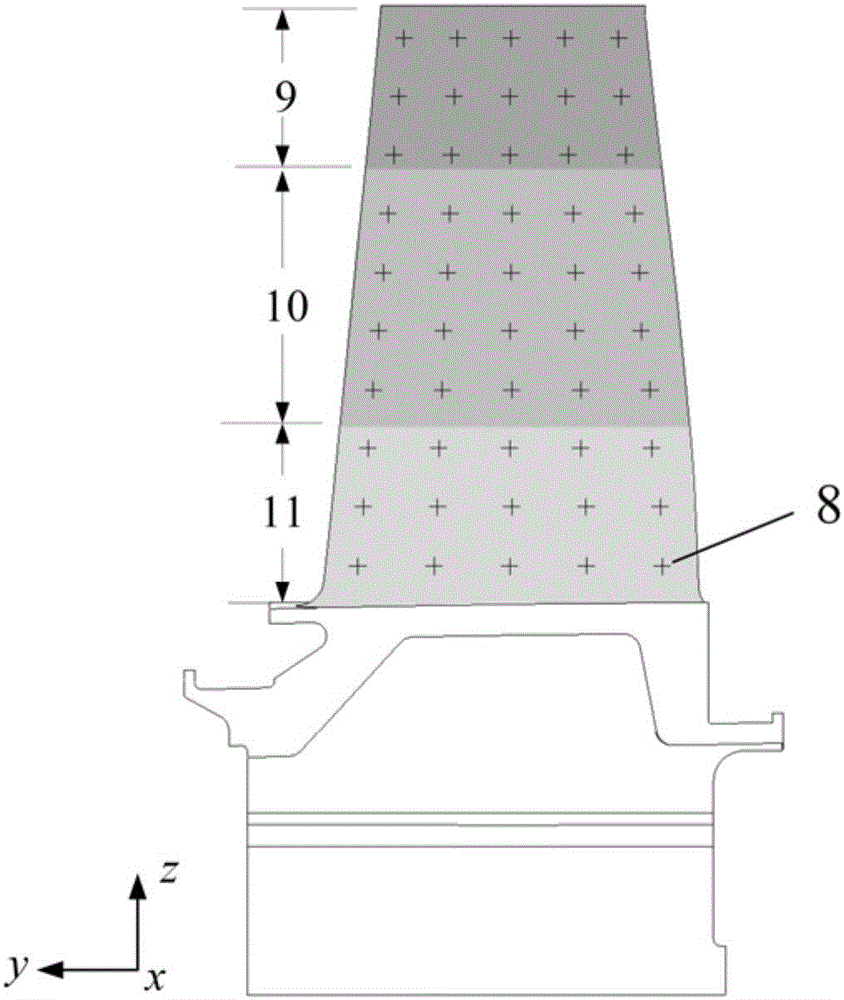
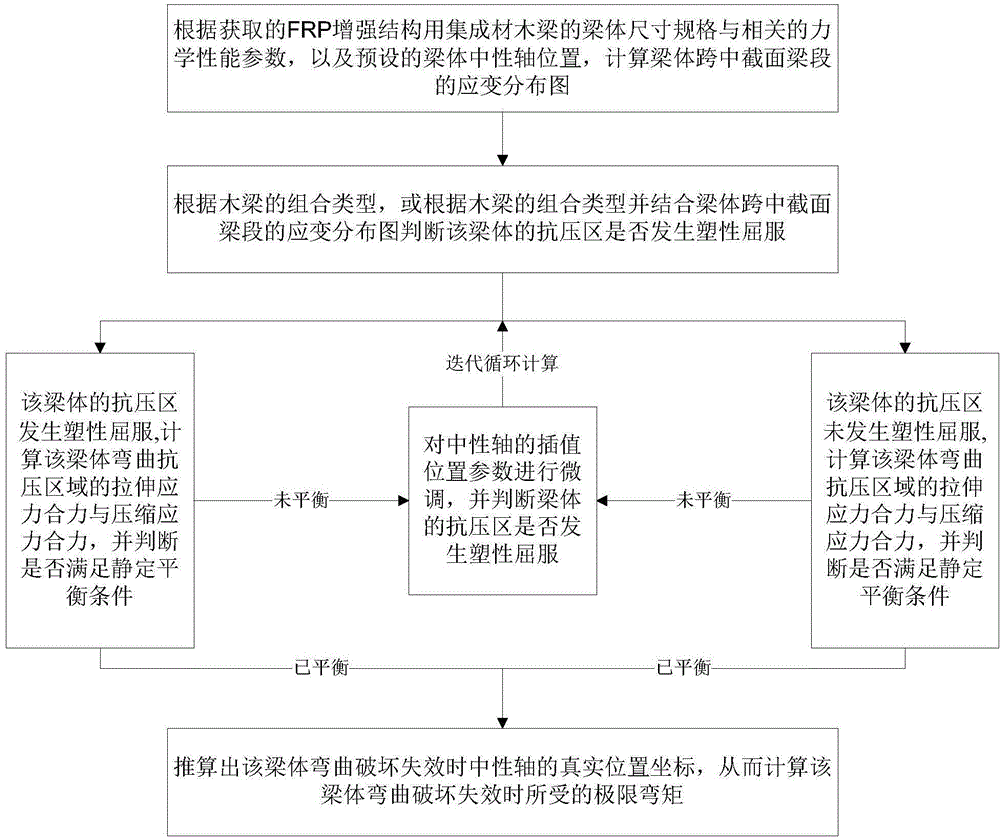
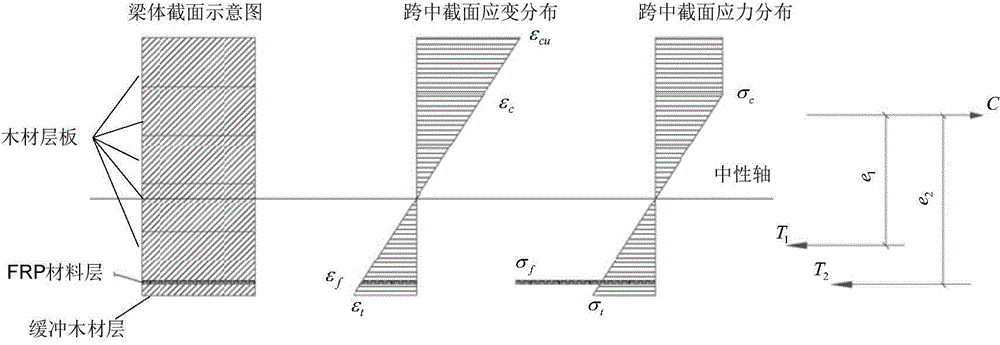
The invention discloses a method for efficiently and accurately predicting a laminated wood beam ultimate bending moment used for an FRP (Fiber Reinforced Plastic) enhancement structure. The method can judge whether a compression resistance area of a beam body is subjected to plastic yield or not through a strain distribution or stress distribution diagram of the section of the beam body and also can carry out the fine tuning of an interpolation position of a neutral axis through judging whether the tensile stress resultant force and the compression stress resultant force of the bending compression resistance area of the beam body meet a static determinacy balance condition so as to calculate the ultimate bending moment borne on the beam body during bending damage failure according to a real position coordinate of the central axis. On one hand, manpower and material resource consumption in an actual measurement process of a traditional method can be saved, and errors generated in a measurement process are eliminated; and on the other hand, a complex calculation process of the traditional method can be saved so as to realize the quick and accurate measurement of the laminated wood beam ultimate bending moment used for the FRP enhancement structure.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
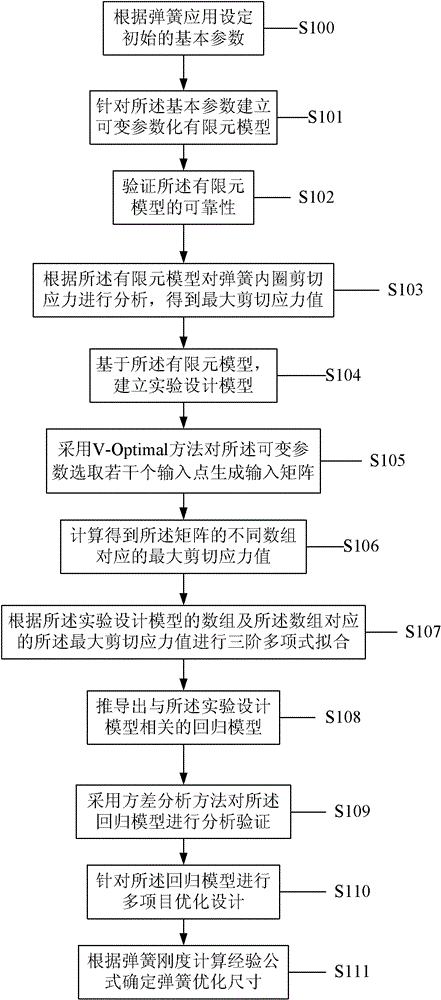
Spring optimizing design method
InactiveCN102799696ASmall sizeChange the value rangeSpecial data processing applicationsShear stressArray data structure
The invention discloses a spring optimizing design method. The method comprises the steps of (1) setting initial basic parameters according to the application of a spring and establishing a variable parameterization finite element model based on the basic parameters; (2) analyzing the shear stress of the spring inner ring according to the finite element model to obtain a maximum shear stress value and comparing the maximum shear stress value with a theoretical calculated stress value result to verify the setting accuracy of the finite element model (3) establishing an experimental design model based on the finite element model and generating an input matrix by selecting a plurality of input points of the variable parameter by using a V-optimal method so as to acquire a maximum shear stress value; (4) performing third-order polynomial fitting according to the array of the experimental design model and the maximum shear stress value and deriving a regression model related to the experimental design model; (5) performing multi-project optimization designs according to the regression model and determining the optimized size of the spring. The method provided in the utility model has high accuracy and can be applied for obtaining optimized spring sizes.
Owner:FORT VALE ENG SHANGHAI LTD
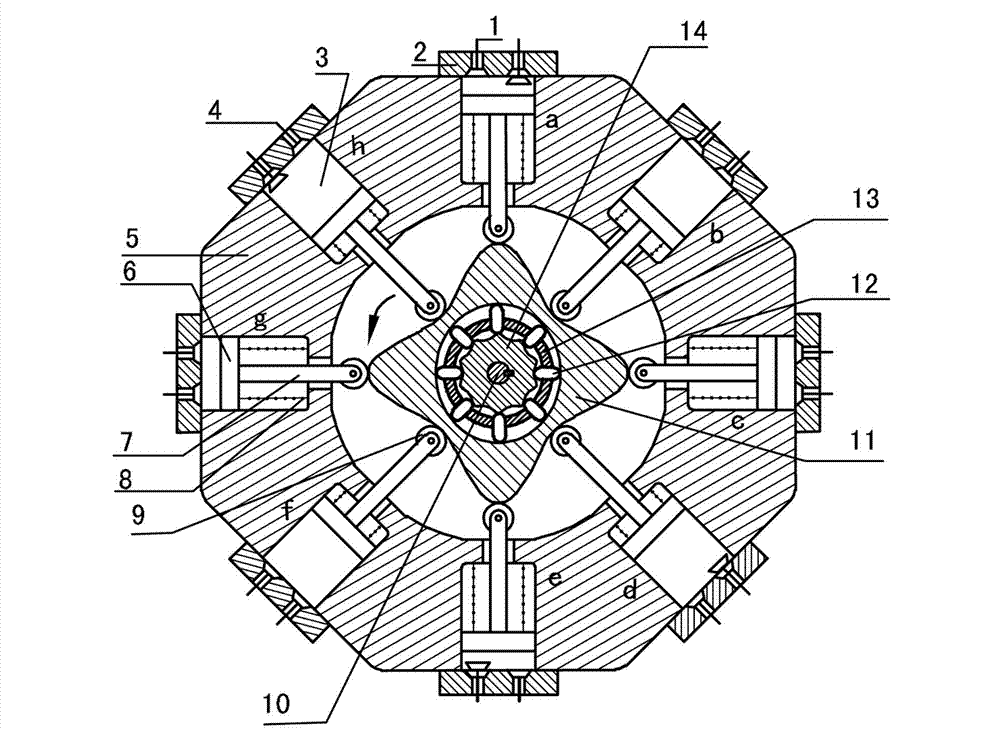
Internal-combustion engine with two-phase inner cam shock wave shifting for transmission
InactiveCN102926863AReduce axial sizeCompact structureValve drivesMachines/enginesShock waveLow speed
The invention relates to an internal-combustion engine with two-phase inner cam shock wave shifting for transmission, relates to the field of gas power, and belongs to a multi-cylinder internal-combustion engine. The invention provides a novel internal-combustion engine, wherein eight air cylinders are symmetrically uniformly distributed on the periphery of a two-phase inner cam in an annular manner, the stressed resultant force of a convex inner two-phase inner cam is zero, an air cylinder piston is directly acted on the convex inner two-phase inner cam through a push rod, and power is passed on an output shaft connected with a center wheel key through two-phase inner cam shock wave moving teeth of the convex inner two-phase inner cam. In the internal-combustion engine, a connecting rod and a crank shaft of the traditional internal-combustion engine are omitted, and a convex inner two-phase inner cam shock wave shifting transmission mechanism has no eccentric quality, has inertia force and service load self balancing; and the rotation speed of the output shaft depends on the transmission ratio of the living teeth transmission, if a living teeth frame is fixed, a center wheel outputs at a low speed in a large torque, and the internal-combustion engine is broadly used to project machines, armored cars and the like which need high power. The internal-combustion engine provided by the invention has the advantages that the structure is simple and compact, the axial size is small, the stressing is self-balanced, and the operation is stable.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Terahertz time-domain spectroscopy system-based stress measurement method
InactiveCN104568249AConvenient researchRich measurement methodsForce measurement by measuring optical property variationStress measurementPhase difference
The invention discloses a terahertz time-domain spectroscopy system-based stress measurement method. The method comprises the following steps: placing an experimental piece and loading equipment into a constructed terahertz spectroscopy system together; generating a terahertz pulse by utilizing a femtosecond laser, and receiving a signal by utilizing a terahertz detecting device; acquiring phase frequency curves under an unloaded working condition and a loaded working condition; performing subtraction on the two phase frequency curves to obtain a terahertz wave phase difference value caused by external stress; reversely deducing a stress component of an loaded experimental piece by utilizing the change of a terahertz wave phase; optimizing the stress component of the experimental piece through a target function, and acquiring a final stress result. A transparent material can be measured by the method, and a non-transparent material can also be measured by the method without manufacturing an experimental model. According to the method, an improved terahertz time-domain spectroscopy system is utilized; the internal stress information of a loaded piece is obtained by analyzing the phase change of a terahertz wave; a new experiment means is provided for detecting the internal stress of an object.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Beam unit counting method with thickness
InactiveCN1912267AGuaranteed Numerical AccuracySimple designBuilding constructionsEngineeringGeneralized degrees of freedom
A method for calculating beam unit with certain thickness includes utilizing generalized node finite-element to calculate structure displacement and stress result, treating each node as a point with arbitrarily many freedom to obtain displacement function expression of said finite element, deriving out unit stress according to said displacement function then converting stress calculation result of entity unit to be bending moment and axle force as well as shear force in engineering as per rod and beam unit theory.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
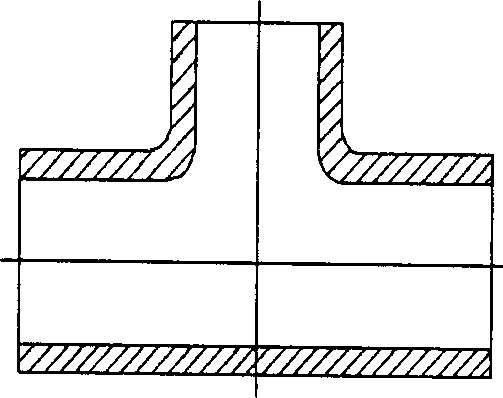
Tee joint shape optimization design method
A method for optimizing the shape design of three-way includes such steps as calculating stress, and modifying boundary shape to obtain a low-stress three-way. It is characterized by the trade-off between the structure modification and stress decreasion.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Mesh layout method for simulating deformation of free surfaces of rubber spherical hinge
InactiveCN102750409AMeet the setup requirementsPredicted Stress ResultsSpecial data processing applicationsMarking outEngineering
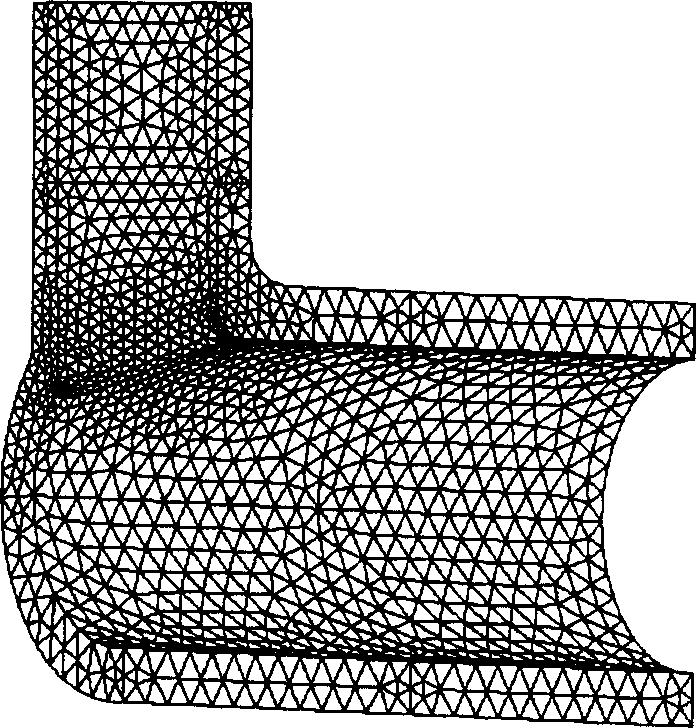
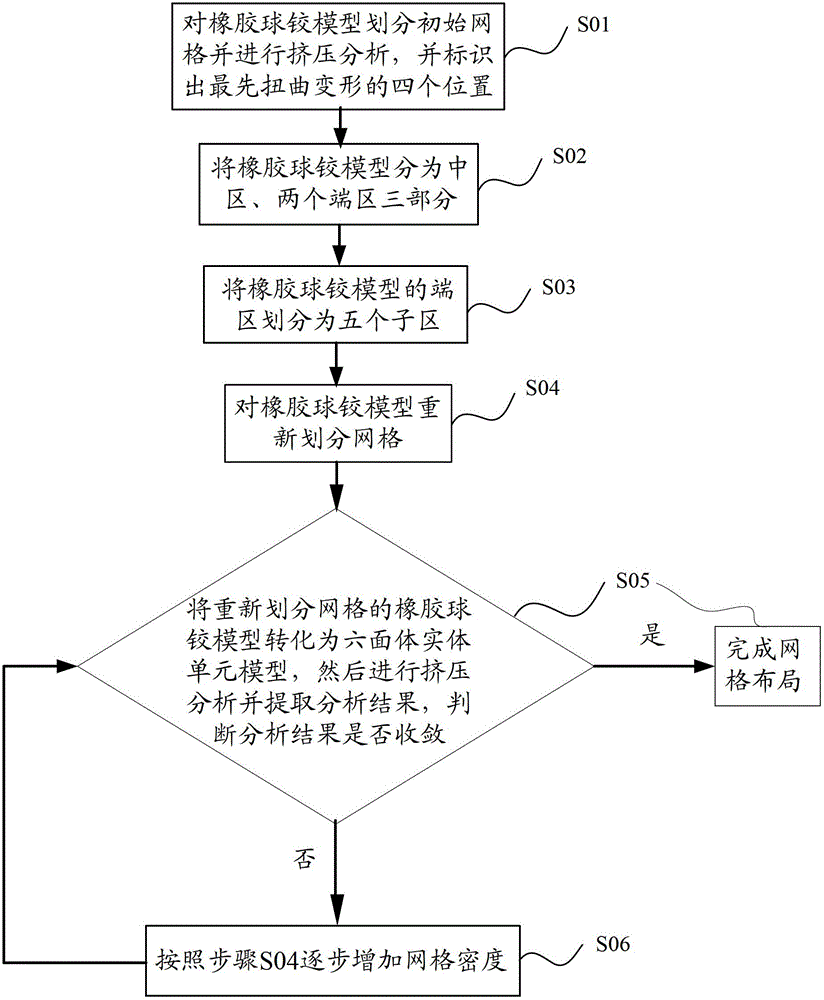
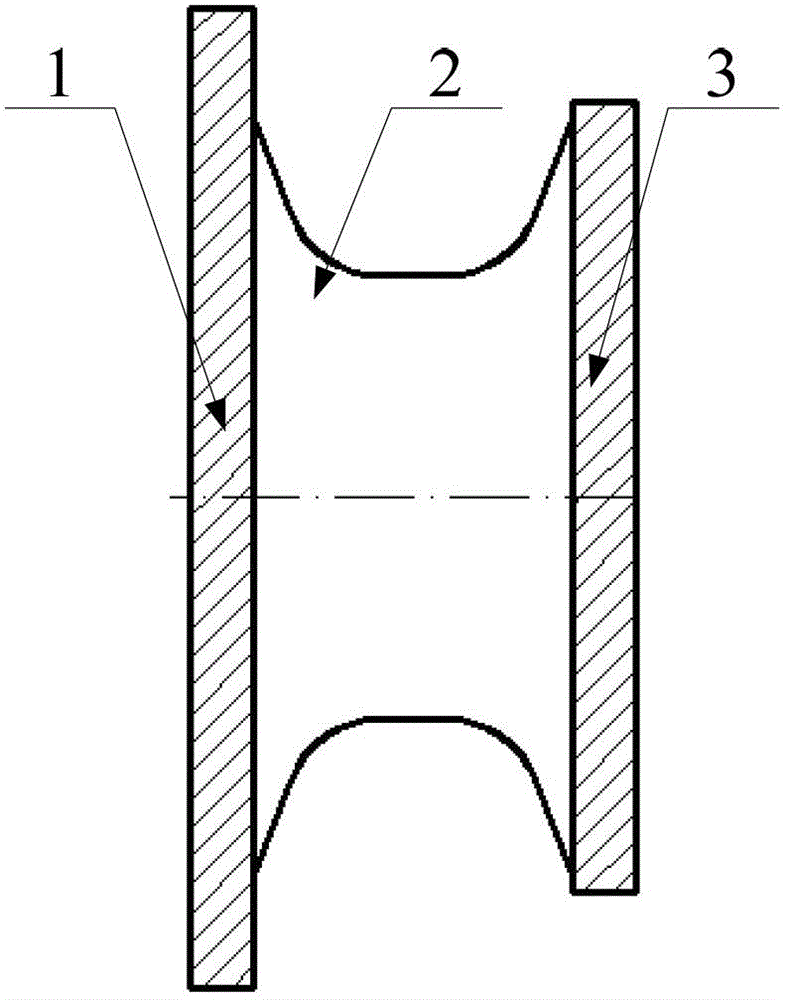
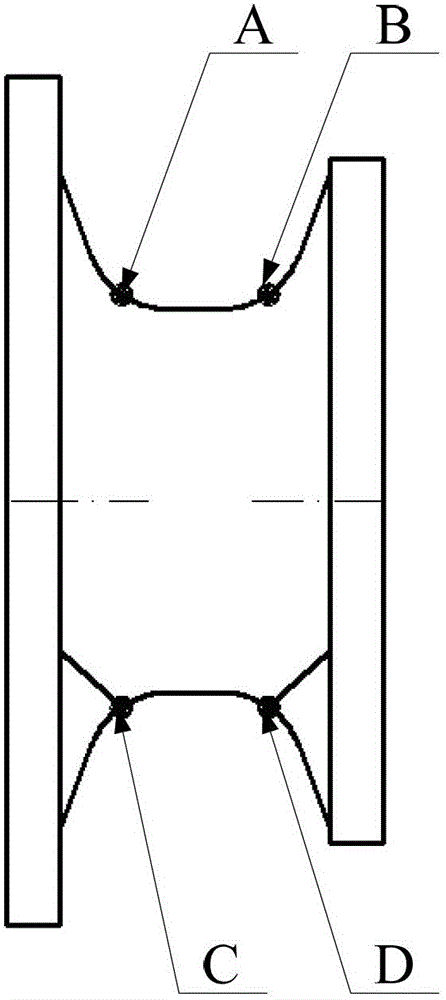
The invention provides a mesh layout method for simulating deformation of free surfaces of a rubber spherical hinge. The method includes marking out a position where distortion emerges first through initial mesh division and extrusion analysis and performing vertical subdivision at the position so as to guide further emerging distortion; dividing a rubber spherical hinge model into a central area and an end area through a main subdivision line and dividing the end area into five sections through a main depth subdivision line and an auxiliary depth subdivision line; and performing meshing on request at last, performing parameterization configuration on the meshes along with surface depth, laying out meshes in a suitable quantity on each free surface, and finishing the mesh layout through regulation of the mesh density. According to the mesh layout method, shape features and loading characteristics of the free surfaces of the rubber spherical hinge are reflected by the divided meshes, therefore mesh setting requirements in a high distortion area can be satisfied, stress results of the high distortion area is predicted accurately, and a premise is provided for finishing the deformation simulation of the free surfaces of the rubber spherical hinge.
Owner:ZHUZHOU TIMES NEW MATERIALS TECH
Analysis and judgment method for fatigue life of fusion reactor divertor
ActiveCN106653099AEvaluation results are objectiveNuclear energy generationThermonuclear fusion reactorFatigue damageTemporal change
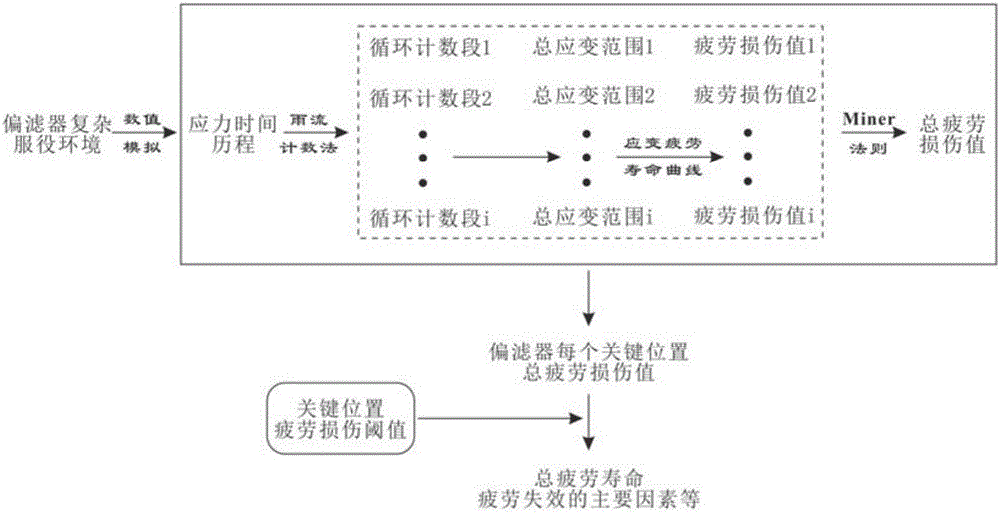
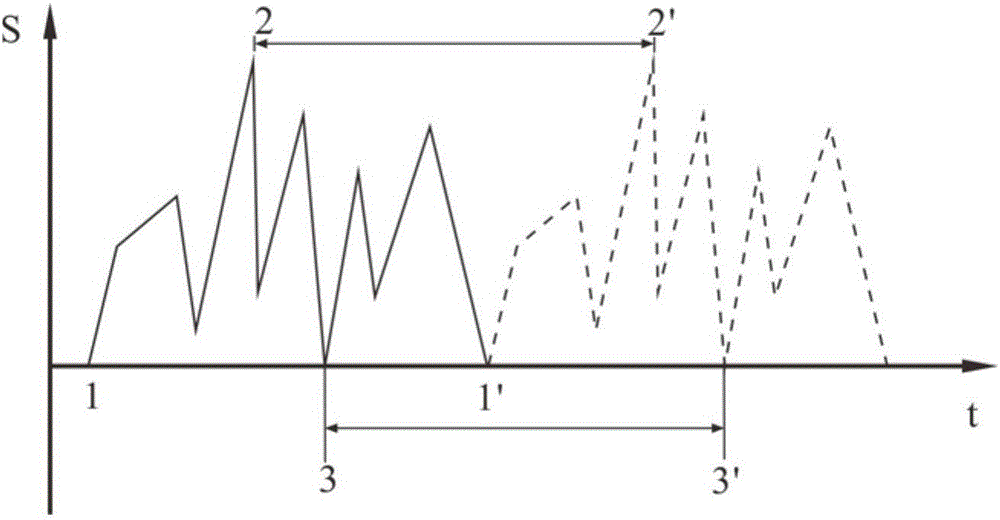
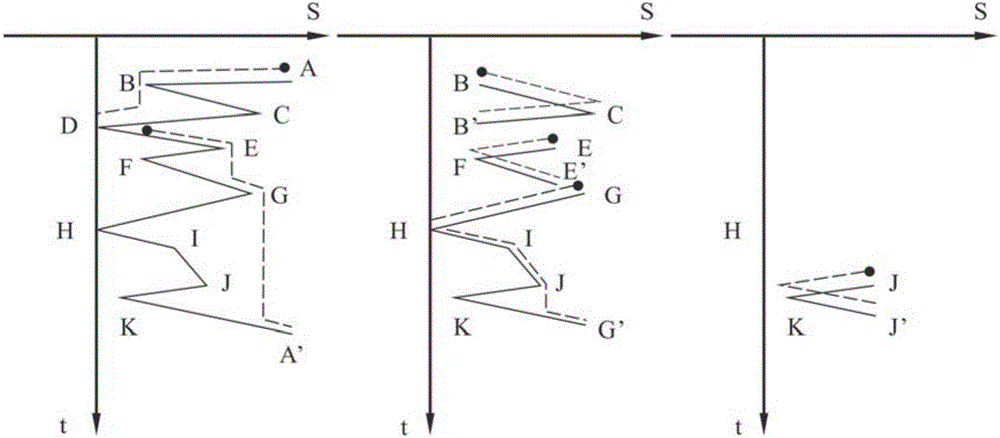
The present invention discloses an analysis and judgment method for the fatigue life of a fusion reactor divertor. According to the method, firstly, a complex load applied onto a divertor in a service environment is converted into a temperature and stress-time changing course. Secondly, a series of cycle counting sections during an irregular stress course are subjected to the rain-flow counting treatment. Thirdly, for each counting section, an elastic stress range thereof is obtained according to a numerical analysis result. Fourthly, based on a stress-strain analysis formula, the stress result of the finite element elasticity analysis is converted into the total cycle strain range of the above counting section. Fifthly, according to the cycle strain fatigue life curve of materials, different stress levels are subjected to the quantization of the fatigue damage. Sixthly, a fatigue damage value corresponding to each cycle of each counting section during the stress course can be obtained. According to the technical scheme of the invention, a given service environment is subjected to result evaluation. Therefore, related protective measures and maintenance recommendations are provided, or improvement opinions are provided for the design of the divertor. As a result, an obtained evaluation result is more objective and more real for engineering practices.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A method for calculating fatigue strength of a wind turbine cabin structure
PendingCN109726411AImprove securityImprove reliabilitySpecial data processing applicationsFatigue damageNacelle
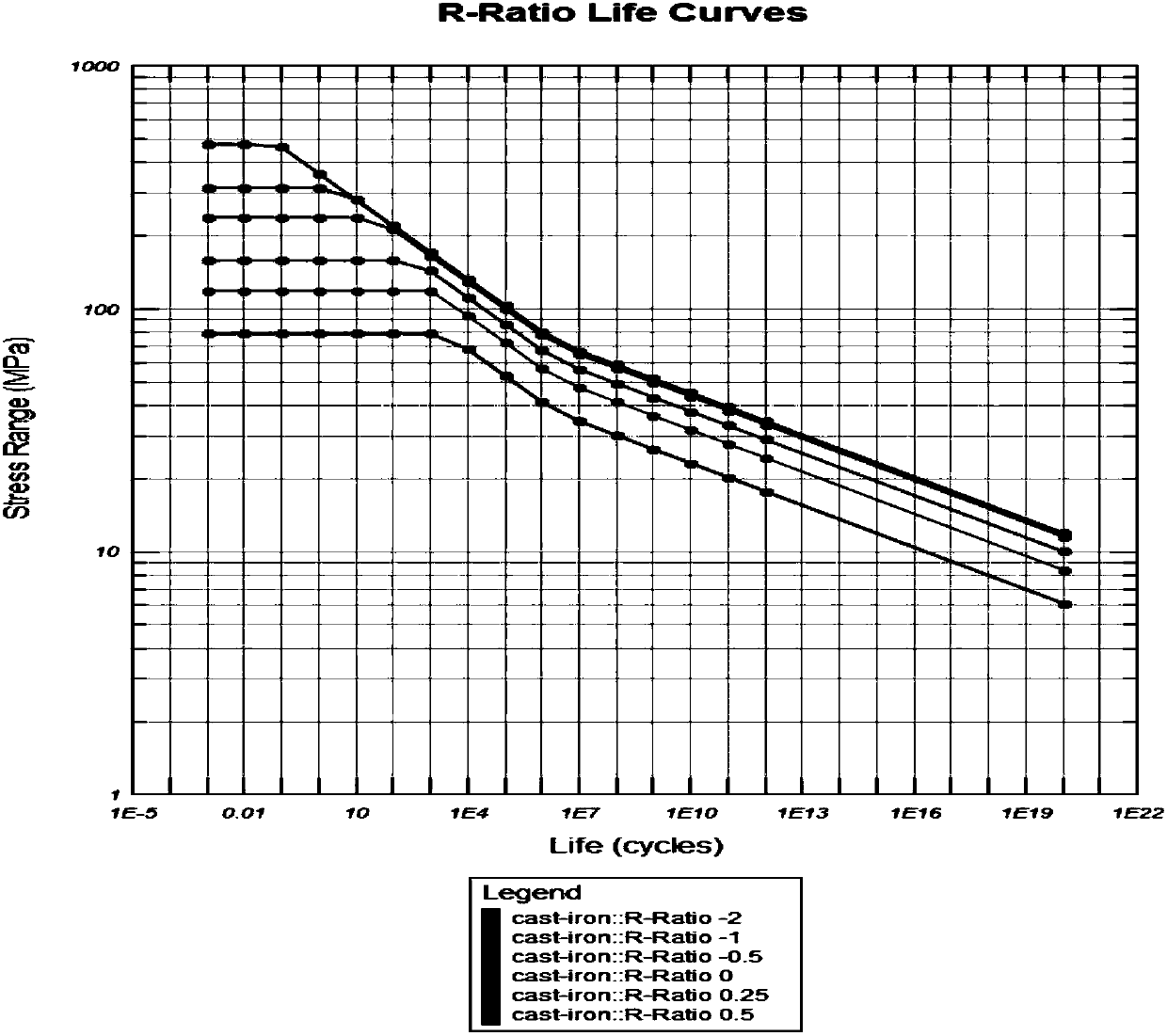
The invention belongs to the technical field of wind turbine cabin structure fatigue strength calculation, and particularly relates to a method for calculating fatigue strength of a wind turbine cabinstructure. The objective of the invention is to make wind turbine cabin structure fatigue checking more accurate and reliable, overcome incomplete consideration of fatigue strength influence factorsin a previous calculation process, and inaccuracy of fatigue damage calculation. A unit load component and a generator gravity working condition stress result are obtained through a finite element analysis method, a stress time sequence is obtained in combination with a fatigue time sequence, a stress spectrum is obtained through a rain flow counting method, and then S-N curve cluster of the material under different stress ratios is established. And finally, the final damage is calculated by adopting a Miner linear cumulative damage theory. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: determining a stress spectrum; Calculating S-under different stress ratios of material An N-curve family; checking the Cabin structure fatigue strength. The method is more accurate and moresuitable for actual load working conditions, fatigue damage of the cabin structure of the wind turbine can be more accurately analyzed, and the operation safety and reliability of wind turbine generator equipment are improved.
Owner:BEIJING WANYUAN IND
Vertical air-control balance stop valve
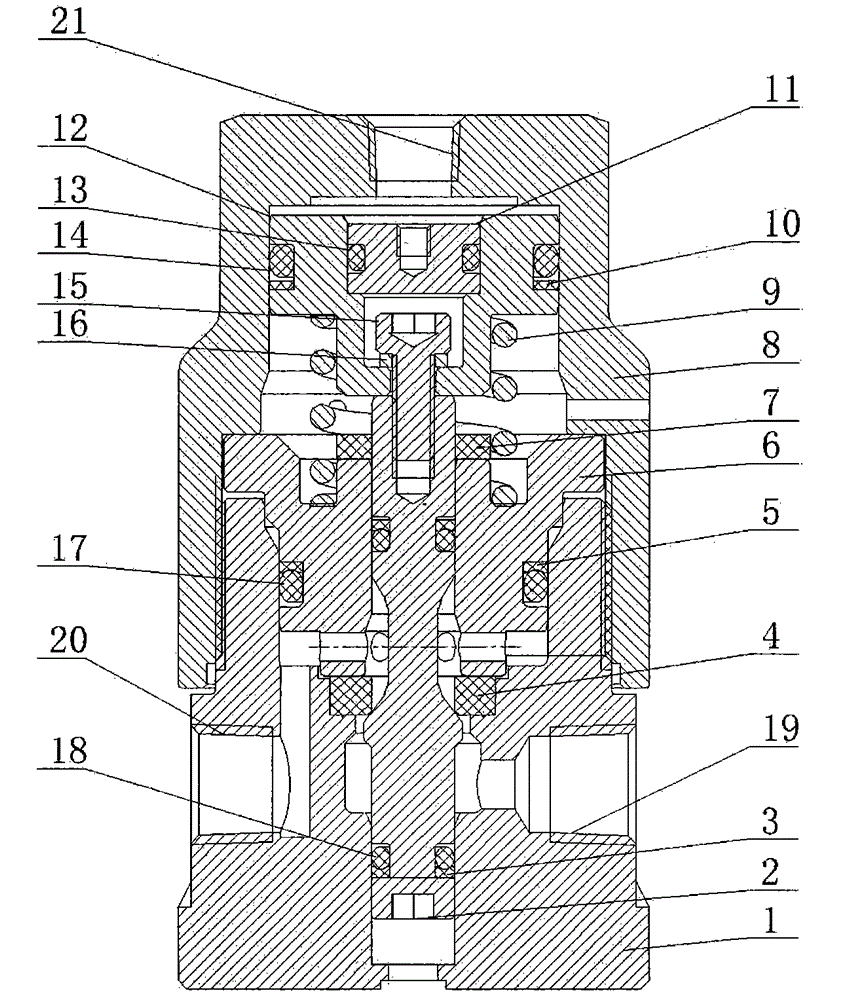
ActiveCN105889580AIncrease the bearing areaImprove pressure bearing capacityEqualizing valvesSafety valvesHigh pressurePiston
The invention discloses a vertical air-control balance stop valve which comprises a valve body. A C-shaped control port is formed in the upper portion of the valve body. A piston is mounted on the inner side of the valve body and located on the lower portion of the C-shaped control port. A plug is mounted on the upper side of the middle portion of the piston. A socket head cap screw is mounted on the lower side of the middle portion of the piston. A valve element is mounted at the end of the screw rod of the socket head cap screw. The vertical air-control balance stop valve has the advantages that the valve element is located in high-pressure media, the overall axial stress resultant force is zero, piston control stress area is not increased, overall size of the valve is not increased, and the service life, reliability and economy of the valve are unaffected; due to the fact that pressure at a valve element sealing part is high, a first retaining ring with one arc-shaped face is used, and the pressure bearing capacity of a fourth C-shaped ring is increased; the valve element is integrally connected with the valve body, so that the valve is compact in structure and small in size.
Owner:HENAN AEROSPACE HYDRAULIC & PNEUMATIC TECH
Combined environmental stress simulation method
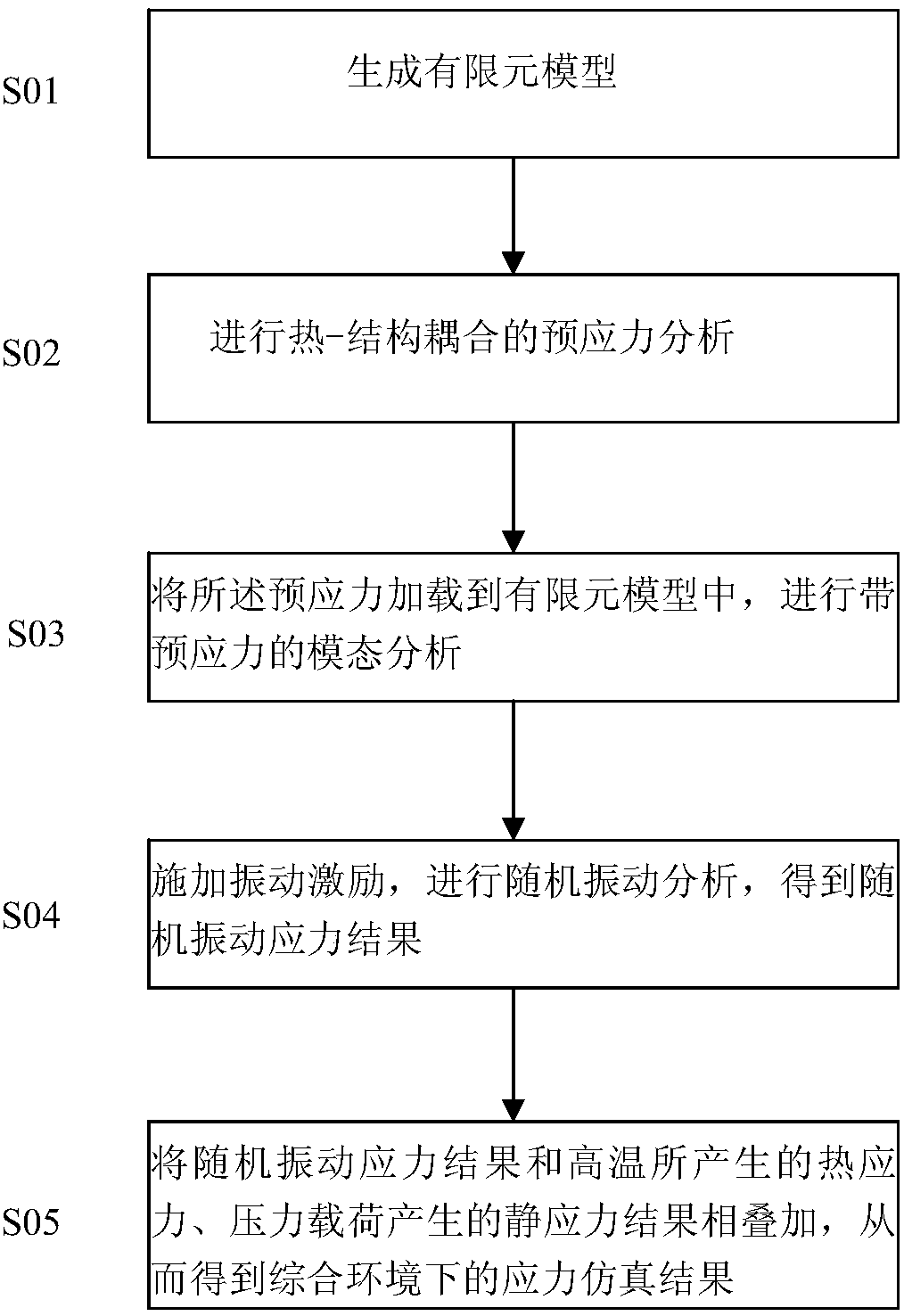
InactiveCN107563071AThe simulation results conform toSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelStructural coupling
The invention relates to a finite element simulation technology, and discloses a combined environmental stress simulation method which can analyze the stress distribution of a simulation model under acombined environment and make simulation results better conform to actual situations. The method comprises the steps that a, a geometric model is created, material parameters at different temperatures are defined, the model is segmented, and a grid is divided, and a finite element model is generated; b, heat-structural coupling prestress analysis conducted, wherein the temperature and the pressure load are applied to obtain comprehensive stress of thermal stress generated by high temperature and a static stress generated by a pressure load, and the comprehensive stress serves as prestress forsubsequent random vibration analysis; c, the prestress is loaded into the finite element model for modal analysis with prestress; d, vibration excitation is applied, random vibration analysis is carried out, and a random vibration stress result is obtained; e, a random vibration stress result, the thermal stress generated by the high temperature and a static stress result generated by the pressure load are superposed. The method is suitable for combined environmental stress simulation analysis.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method and system for predicting residual stress of aluminum alloy large component
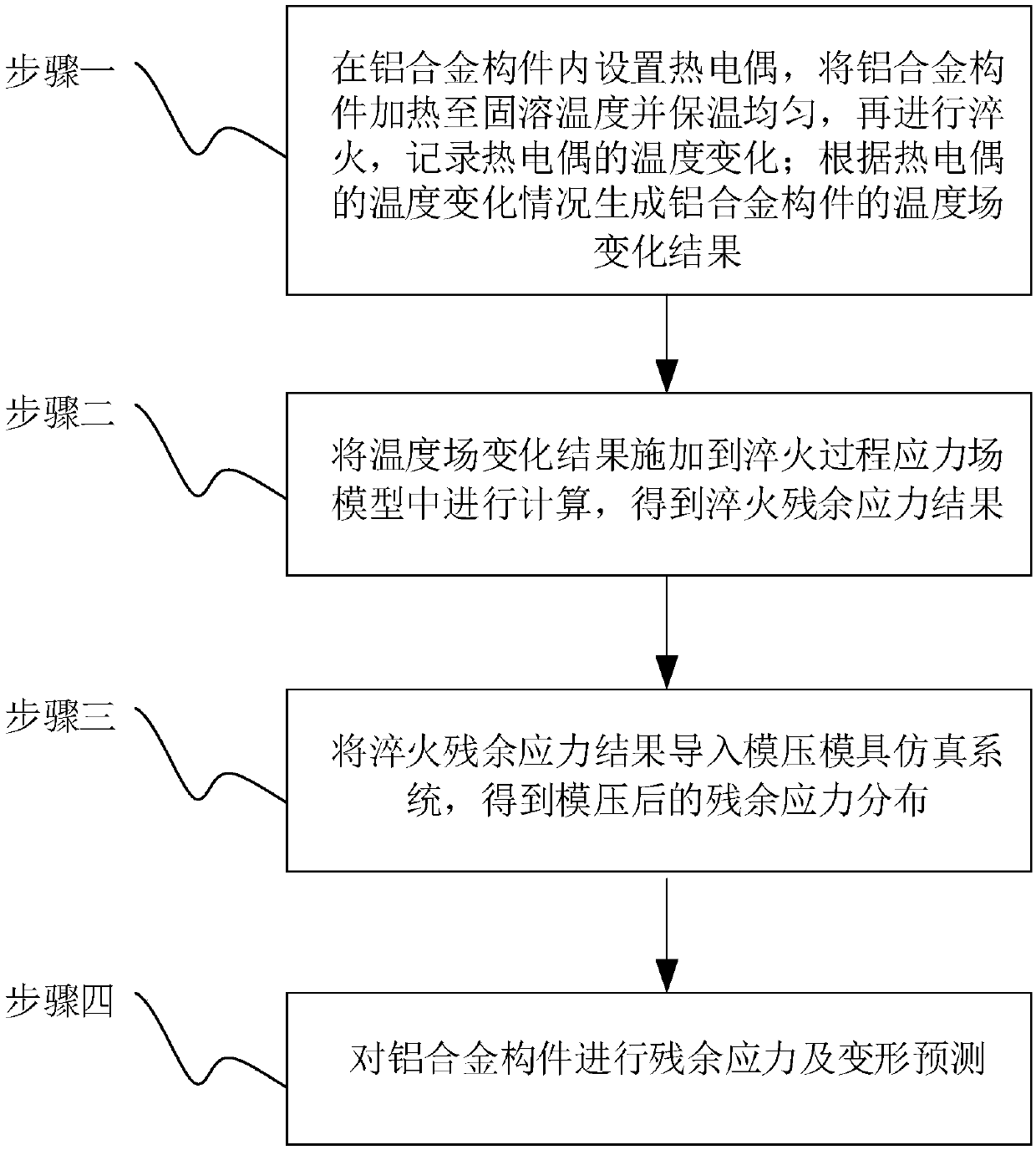
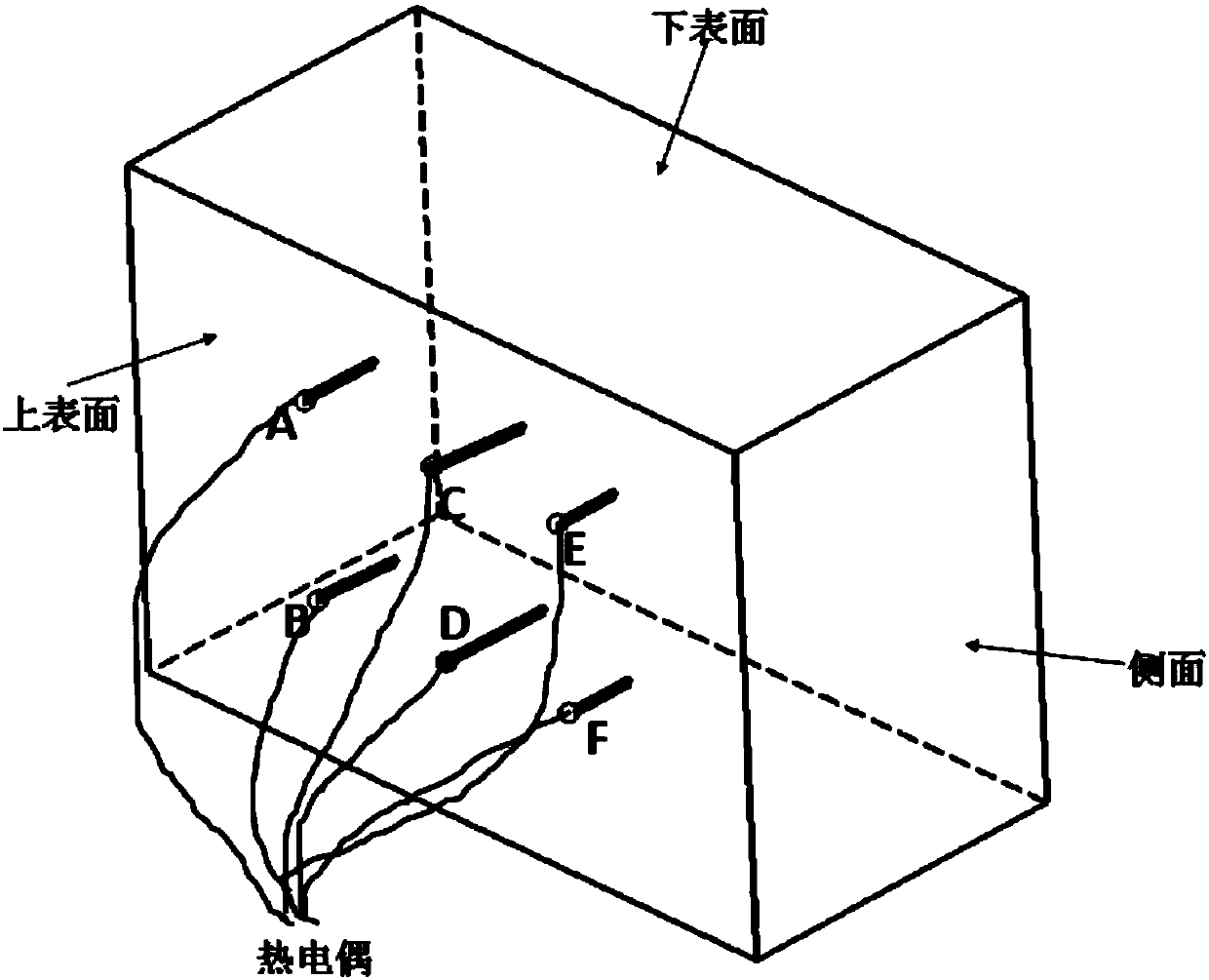
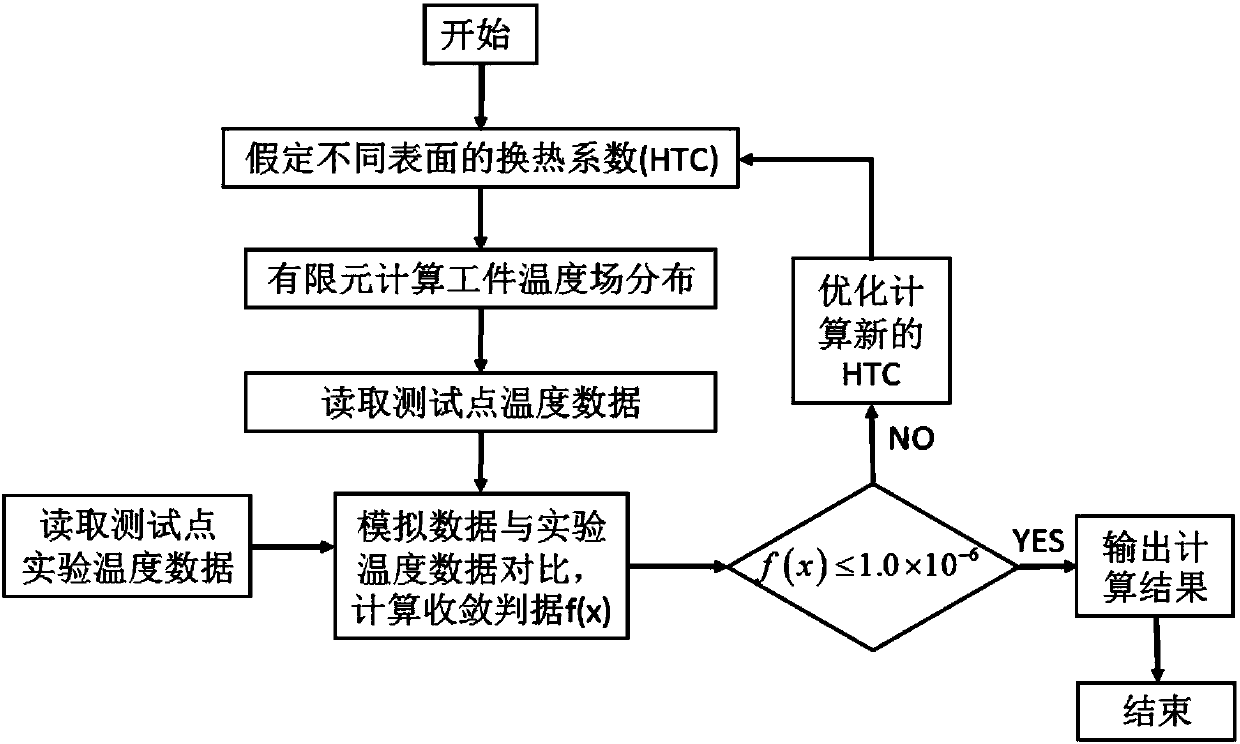
PendingCN108595895ARealize optimal control of residual stressContinuous descriptionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSolution treatmentPrediction system
The invention relates to a method and a system for predicting a residual stress of an aluminum alloy large component, and belongs to the field of heat treatment and machining. The method and the system are pushed forward with an objective to solve the shortage that the existing system cannot accurately predict a complex changing residual stress. The method comprises the steps of arranging a thermocouple in the aluminum alloy component, heating the aluminum alloy component to a solution treatment temperature and keeping a temperature to be uniform, then performing quenching and recording a temperature change of the thermocouple; generating a temperature field change result of the aluminum alloy component according to a temperature change condition of the thermocouple; applying the temperature field change result to a stress field model of a quenching process to calculate to obtain a quenching residual stress result; importing the quenching residual stress result to a die-pressing mouldsimulation system to obtain a residual stress distribution after the die pressing; and performing residual stress and deformation prediction on the aluminum alloy component. The method and the systemare applied to a residual stress control and prediction system in a whole manufacturing process of the aluminum alloy large component.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for checking calculation of arc wall and inclined wall reinforcing bars
ActiveCN103971013AChange the design status quoWallsSpecial data processing applicationsShear stressRebar
The invention provides a method for checking calculation of arc wall and inclined wall reinforcing bars. It is assumed that walls are provided with section steel bars according to a stress result, the steel bars in the walls only bear uniaxial stress, concrete tensile strength is omitted, and the steel bars in the walls are in a yielding critical point; it is assumed that tensile stress in sections is completely borne by the steel bars arranged in the direction and the steel bars yield just now, stress borne by concrete is shearing stress of the walls and normal stress in which steel bar tension is removed, and if the stress can be borne, it shows that the wall reinforcing bars can meet the bearing force requirements; if not, the sections or the reinforcing bars need to be adjusted, and calculation is conducted again until the wall reinforcing bars meet the bearing force requirements. Whether the arc wall and inclined wall section reinforcing bars can meet the section bearing force requirements or not can be rechecked according to the practical engineering situation. The design status mainly depending on an estimation means in the prior art is changed, the arc wall and inclined wall reinforcing bars are quantified and rechecked, and the structure construction and design of practical engineering can be directly guided.
Owner:香港华艺设计顾问(深圳)有限公司
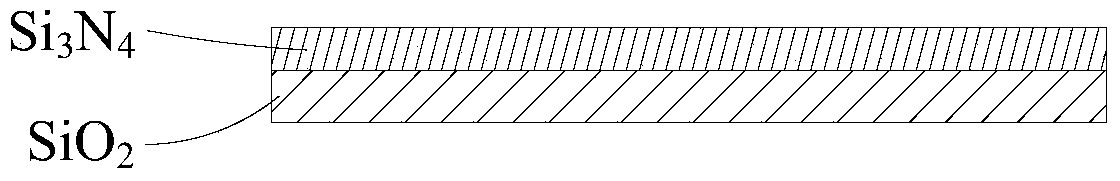
Vibrating plate, liquid jetting device and printing device
ActiveCN103963467ANot easy to warp and deformThe amount of displacement change is reducedPrintingLiquid jetSilicon dioxide
The embodiment of the invention provides a vibrating plate, a liquid jetting device and a printing device. The vibrating plate comprises a silicon dioxide layer and a silicon nitride layer, wherein the silicon nitride layer is arranged on the silicon dioxide layer, the stress of the silicon dioxide layer and the stress of the silicon nitride layer are counteracted so that the stress resultant of the vibrating plate can be zero, the vibrating plate is not prone to being cocked and deformed, and meanwhile the displacement variation of a piezoelectric element in the process that the piezoelectric element is repeatedly driven can be prevented from being reduced.
Owner:ZHUHAI SAILNER 3D TECH CO LTD
Method for judging rupture risk of reconstructed ear scaffold
The invention discloses a method for judging the rupture risk of a reconstructed ear scaffold. The method comprises the following steps that: S1: scanning the ear scaffold, and obtaining the outline data of the ear scaffold; S2: importing an entity model into geomagic FreeFrom&touch X software to carry out hook face repairing; S3: generating a Nurbs hook surface; S4: importing the IGES (The Initial Graphics Exchange Specification) format of S3 into HyperMesh14.0 software to establish a finite element model; S5: importing a three-dimensional finite element ear model which is obtained in S4 andcontains cartilages and different skin thicknesses into finite element specialty analysis software Abaqus to carry out finite element analysis; and S6: obtaining a stress-strain analysis result of cartilages, skin, cartilage deformation and skin deformation, and judging the rupture risk of the ear scaffold according to the finite element stress result. By use of the method, a situation that the rupture may happen when the ear scaffold is used can be evaluated in advance, and a rupture possibility is lowered.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Method for the manufacture of filter plate
A method is disclosed for making a substantially flat filter plate comprising a substantially flat polymer, preferably thermoplastic, frame and substantially flat filter material seated fixedly therein. The method is characterized by its reduced exposure of the filter material to adverse mechanical stresses resultant of polymeric frame formation and curing. Toward such end, the substantially flat polymeric frame is formed in at least two separate steps, in the course of which said substantially flat filter material is incorporated. The portion formed first serves as a mechanical restraint, insulating the later incorporated filter material from any propensity of the second ''embedding'' portion to shrink or otherwise warp during its formation.
Owner:MILLIPORE CORP
Large-span arch bridge temporary inhaul cable force calculation method based on influence matrix method
ActiveCN113688455AAccurate calculationEasy to operateGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationFinite element softwareLong span
The invention discloses a large-span arch bridge temporary inhaul cable force calculation method based on an influence matrix method, and relates to an arch bridge cable force calculation method. The method comprises steps of determining control conditions of structural states, and determining the number and positions of concerned sections in the arch rib and allowable values of internal force or stress of the concerned sections; extracting four types of influence matrixes through finite element software; calculating cable force change in a specific state, considering four conditions according to control conditions in each construction stage, performing trial calculation on the cable force change, and selecting the specific state; calculating a structural state to obtain an internal force or stress result of the concerned section; judging the structure state, comparing the trial value with the allowable value, if the requirement is met, calculating the next construction stage, and if the requirement is not met, adjusting the structure state until the requirement is met. By considering the influence of each variable load and each fixed load on the inhaul cable, the corresponding influence matrix is obtained, the factors are comprehensively considered, and the cable force of the inhaul cable can be quickly and accurately calculated.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
A Thickness Optimization Design Method of Turbine Blade Thermal Barrier Coating
ActiveCN106649934BEnsure service safetyImprove efficiencyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationMulti objective optimization algorithmTurbine blade
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
A Finite Element Mesh Size Determination Method for Concentrated Load Metal Joints
ActiveCN106777650BHigh solution accuracyImprove numerical solution accuracyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationIntegration pointFinite element solution
The invention relates to a method for determining the size of a finite element grid of a concentrated load-transfer type metal joint. The method is applicable to concentrated load-transfer type metal joints with complex geometric structures. The method comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out secondary unit grid division on the metal joint; (2) selecting a solver for solving; (3) checking a stress result, and determining a high-stress region of a structure; and (4) inquiring a unit integration point stress numerical value and a unit node numerical value of the high-stress region, if the two numerical values are the same, indicating that the size of the grid is reasonable, and if the two numerical values are quite different, further refining the grid and repeatedly carrying out the steps (2) to (4) until the two numerical values are the same. By virtue of the method for determining the size of the finite element grid of the concentrated load-transfer type metal joint, a structural numerical value solution can be accurately obtained, the finite element solution precision is improved, the defects caused by the depending of an ''experience'' method in the prior art are overcome, the number of iterations is decreased, and the solution precision of the numerical values is improved, so that the research cycle is shortened, and the research cost is lowered.
Owner:XIAN AIRCRAFT DESIGN INST OF AVIATION IND OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com