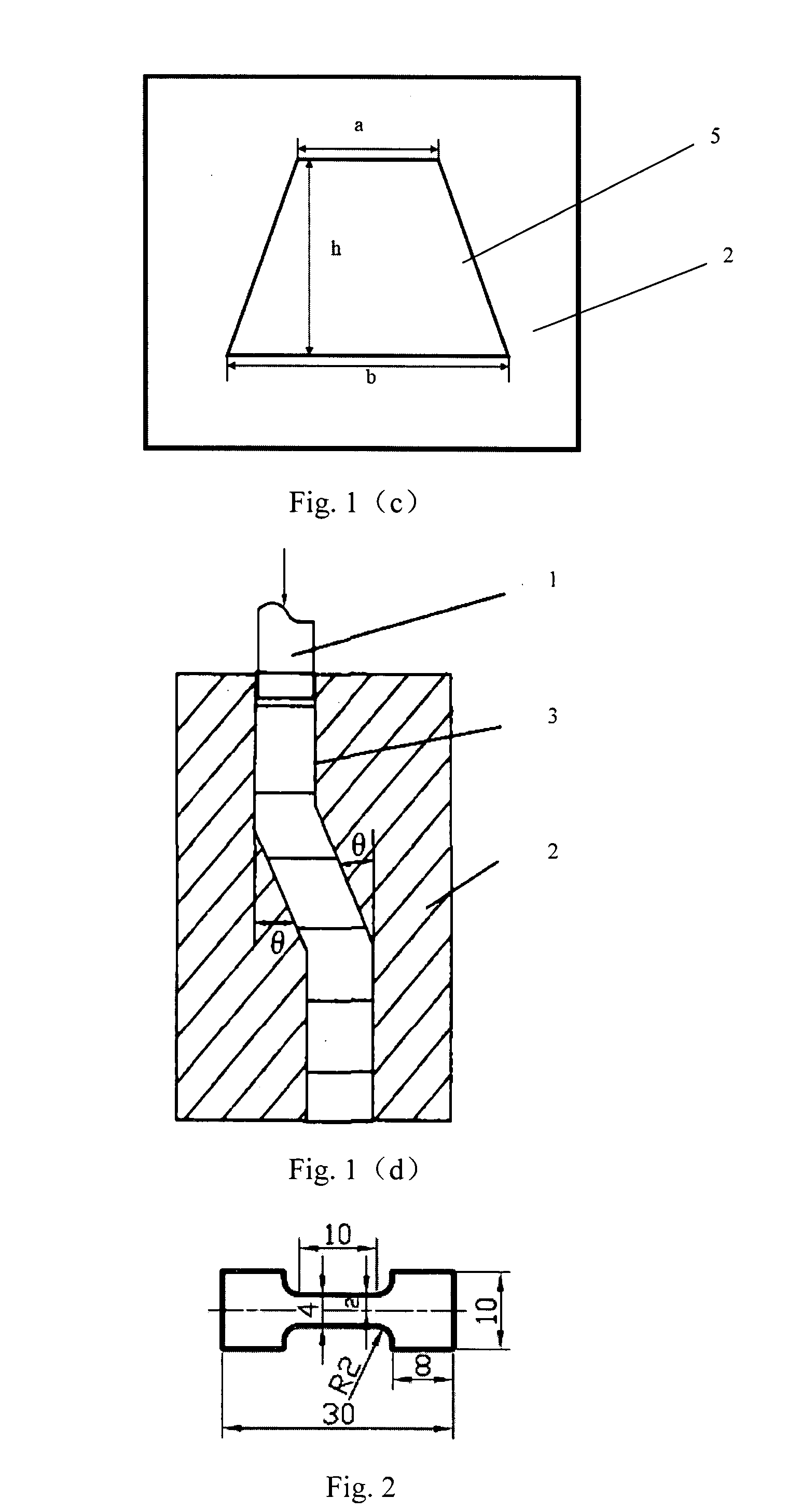
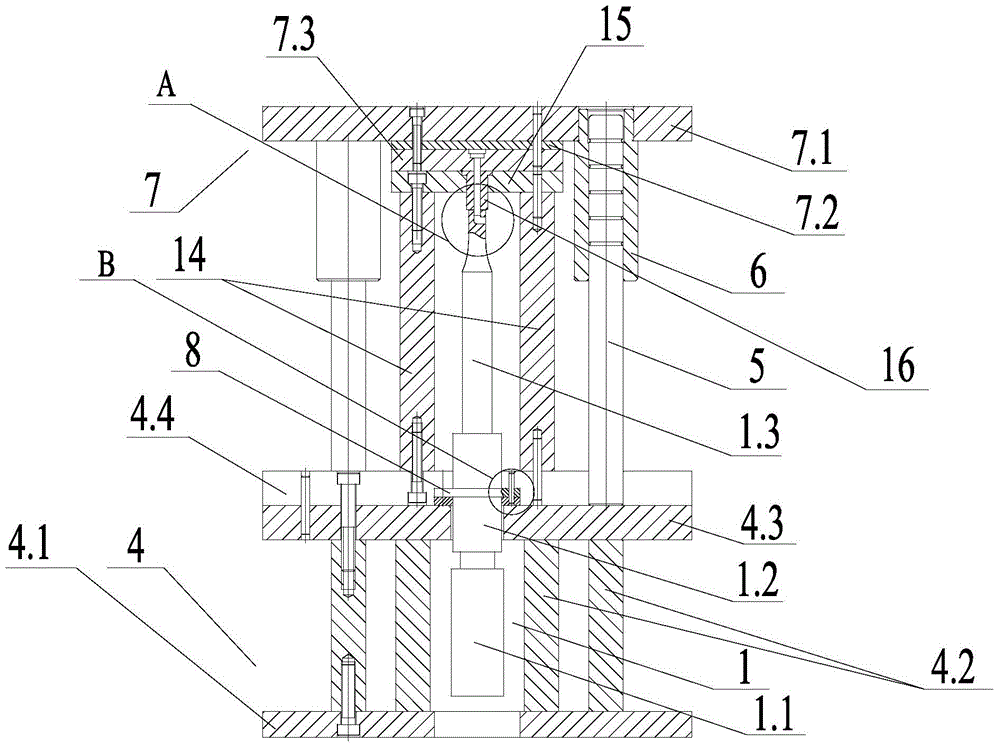
Patents
Literature
138 results about "Equal channel angular extrusion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
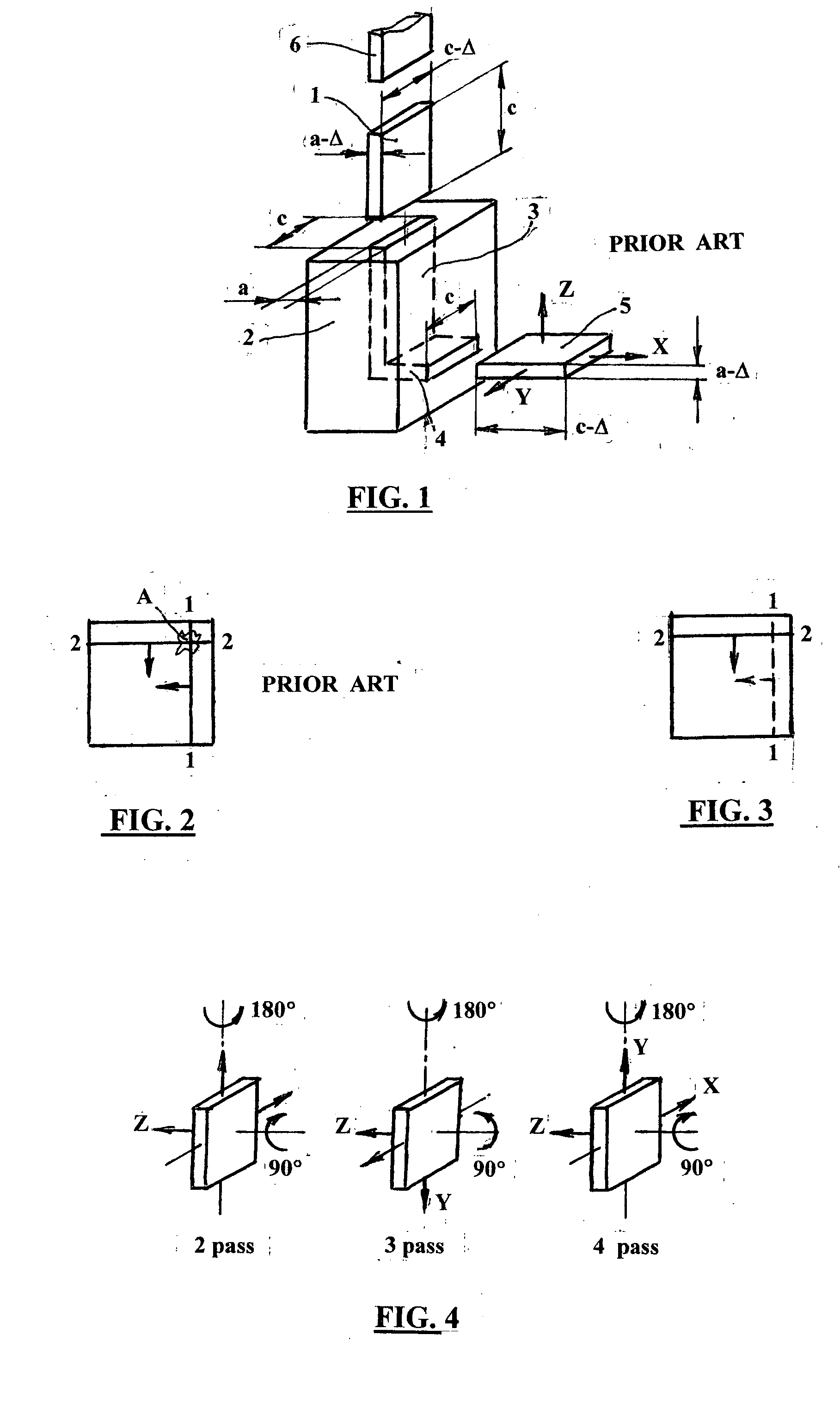
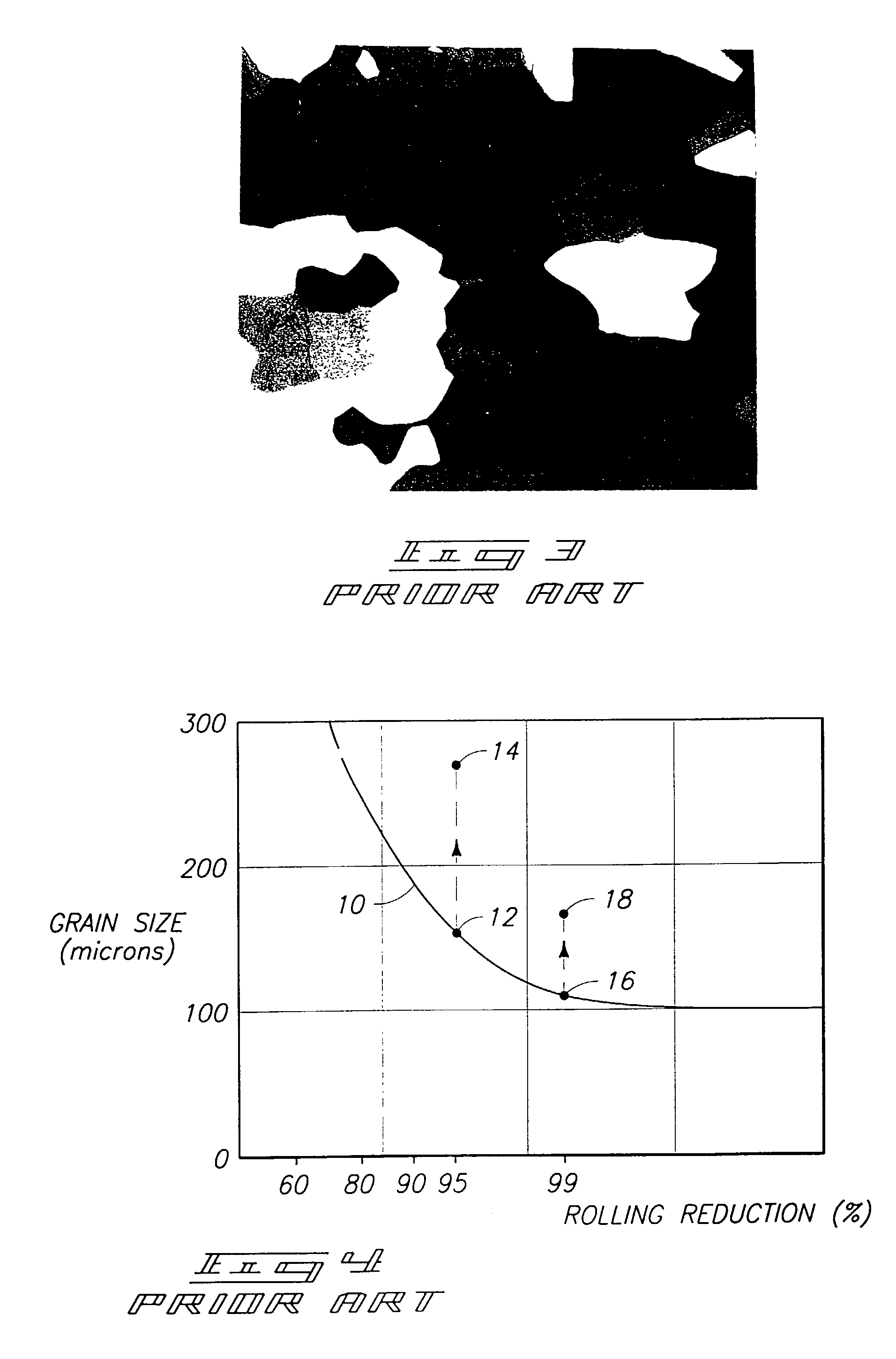
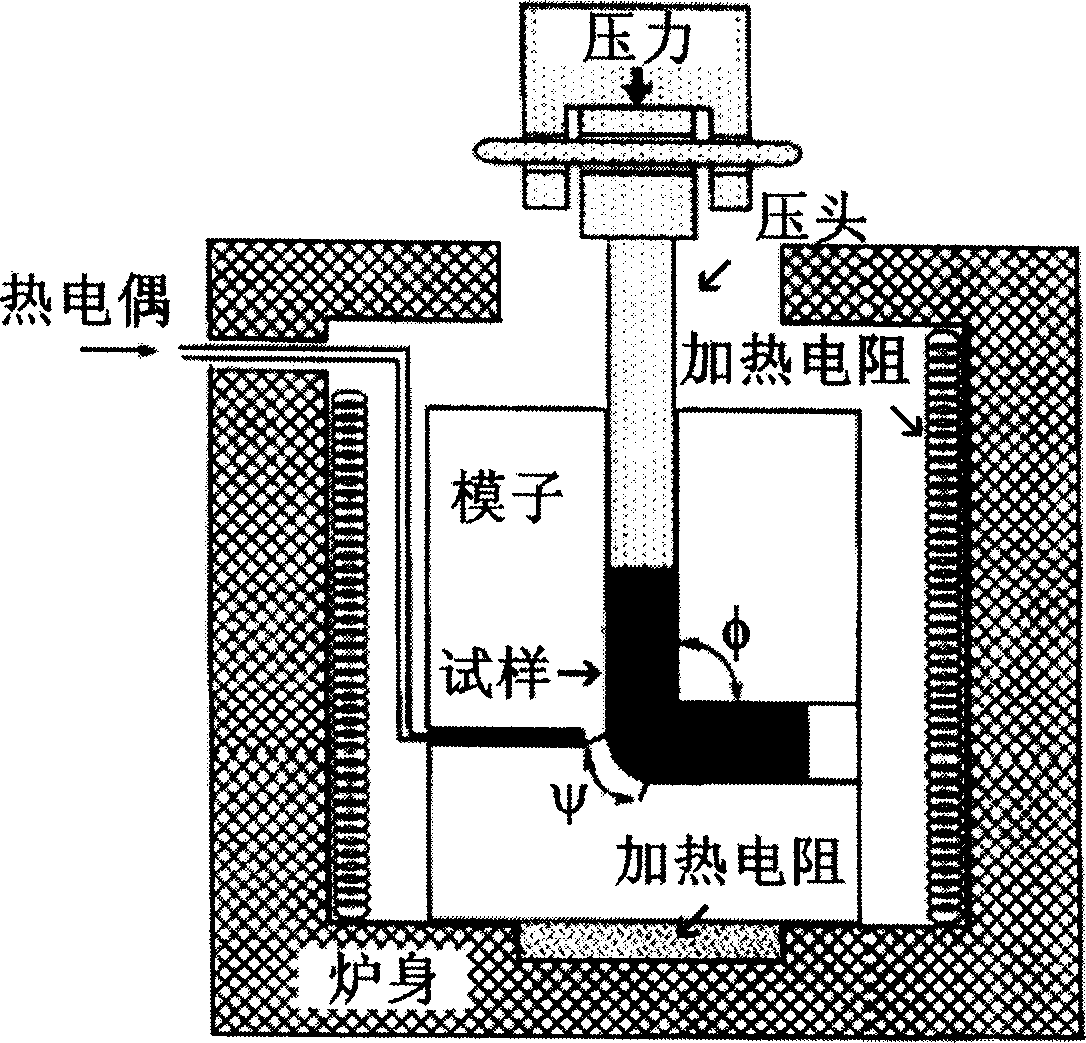
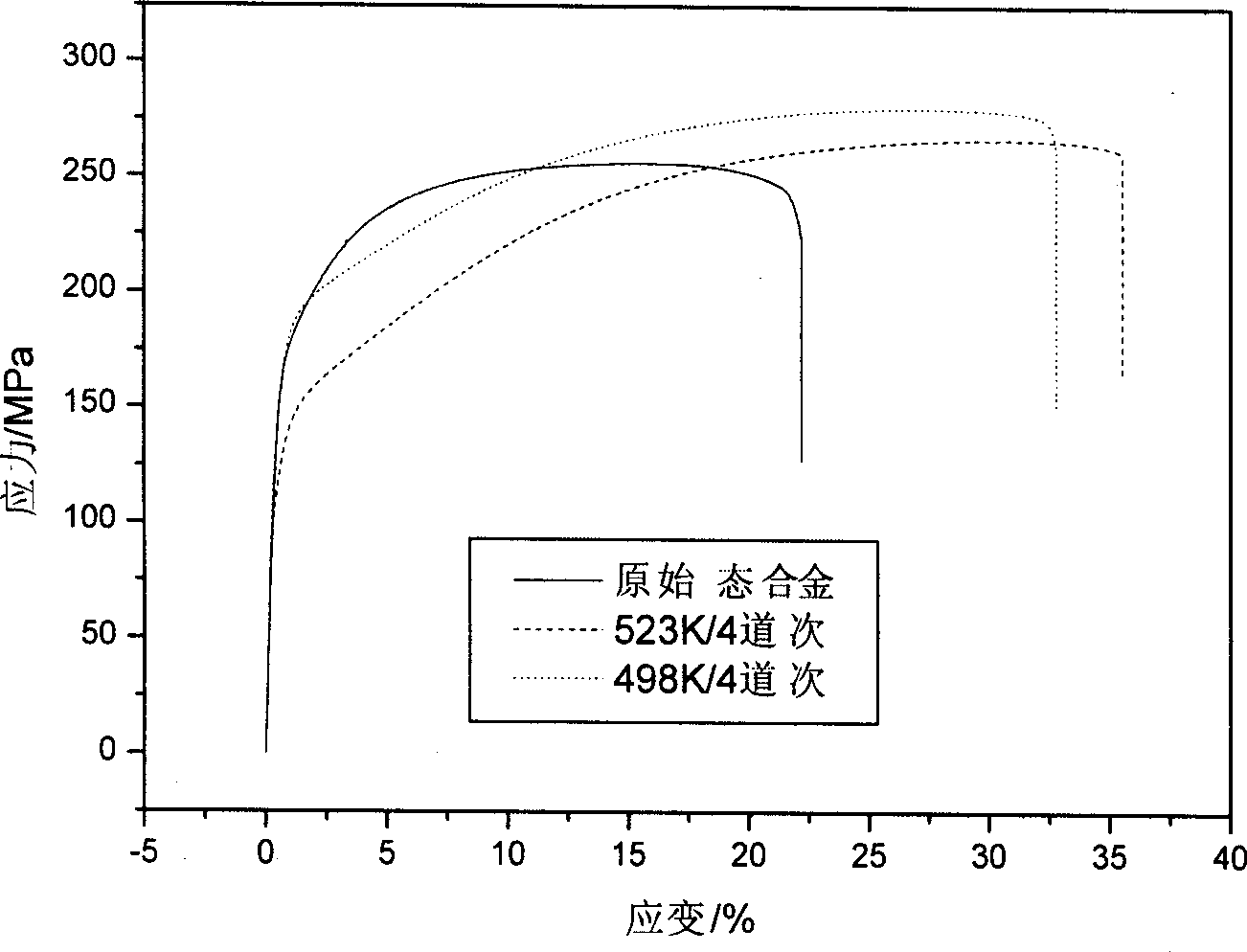
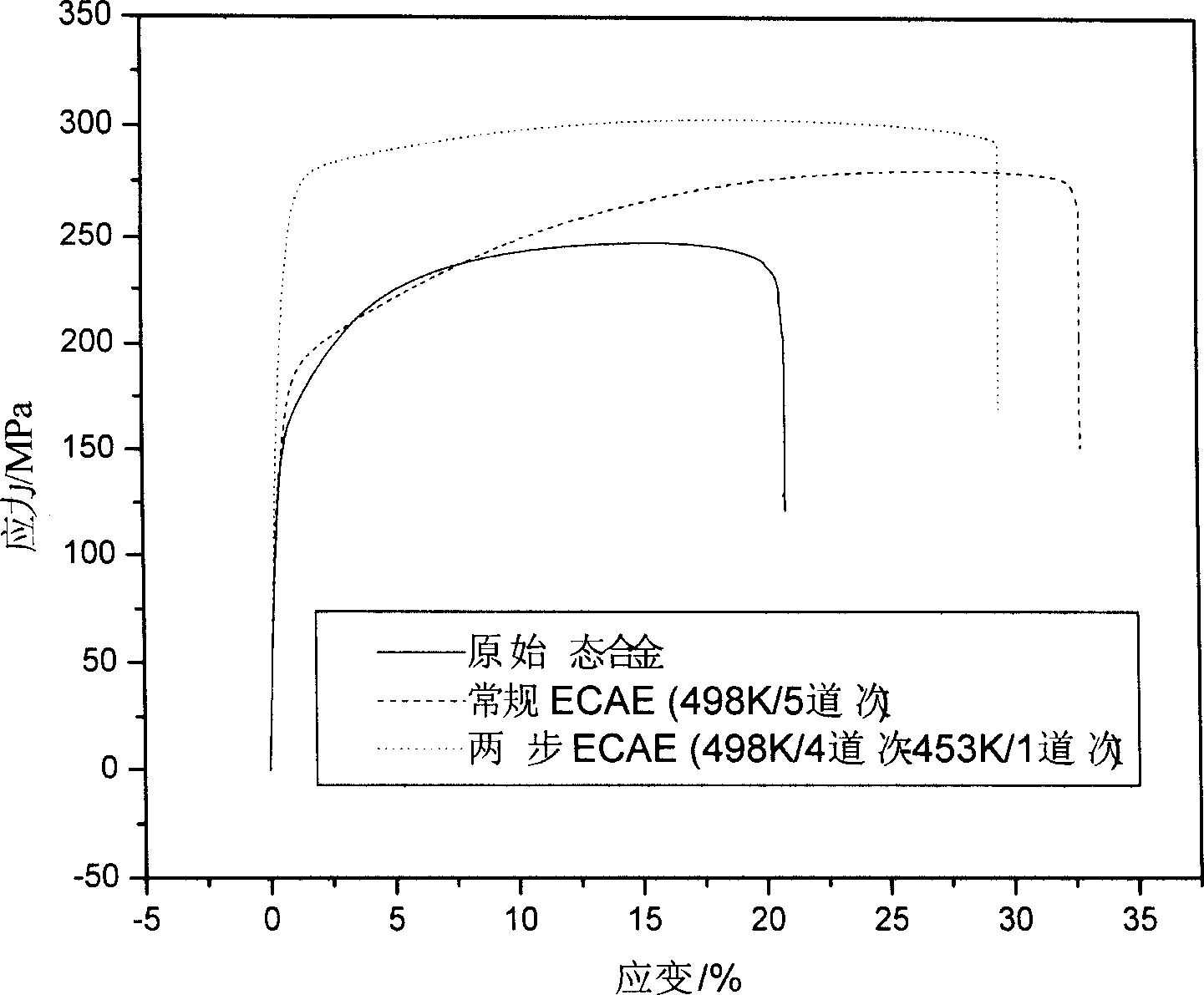
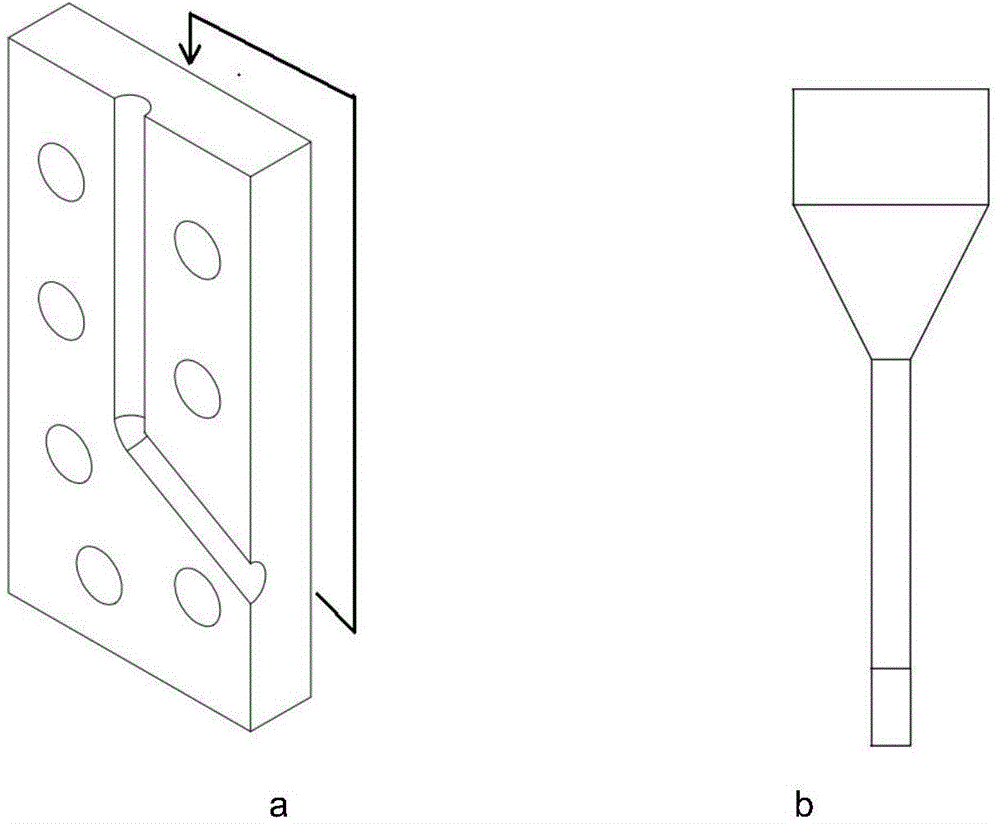
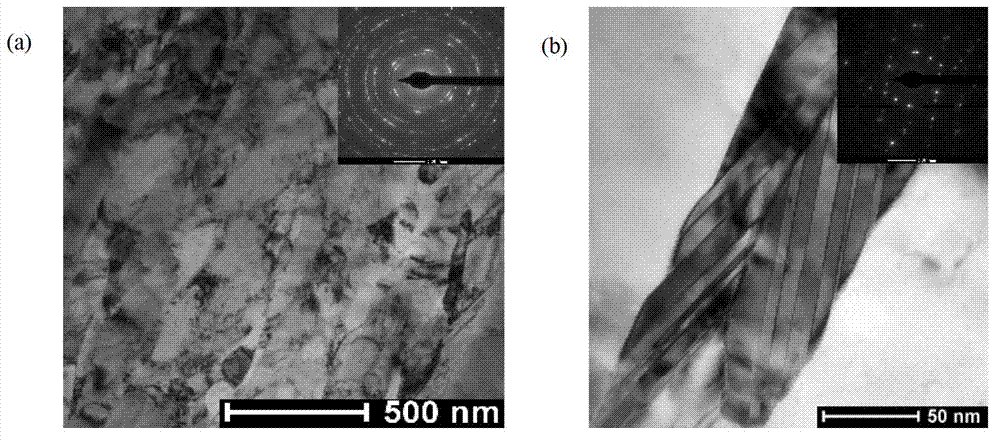
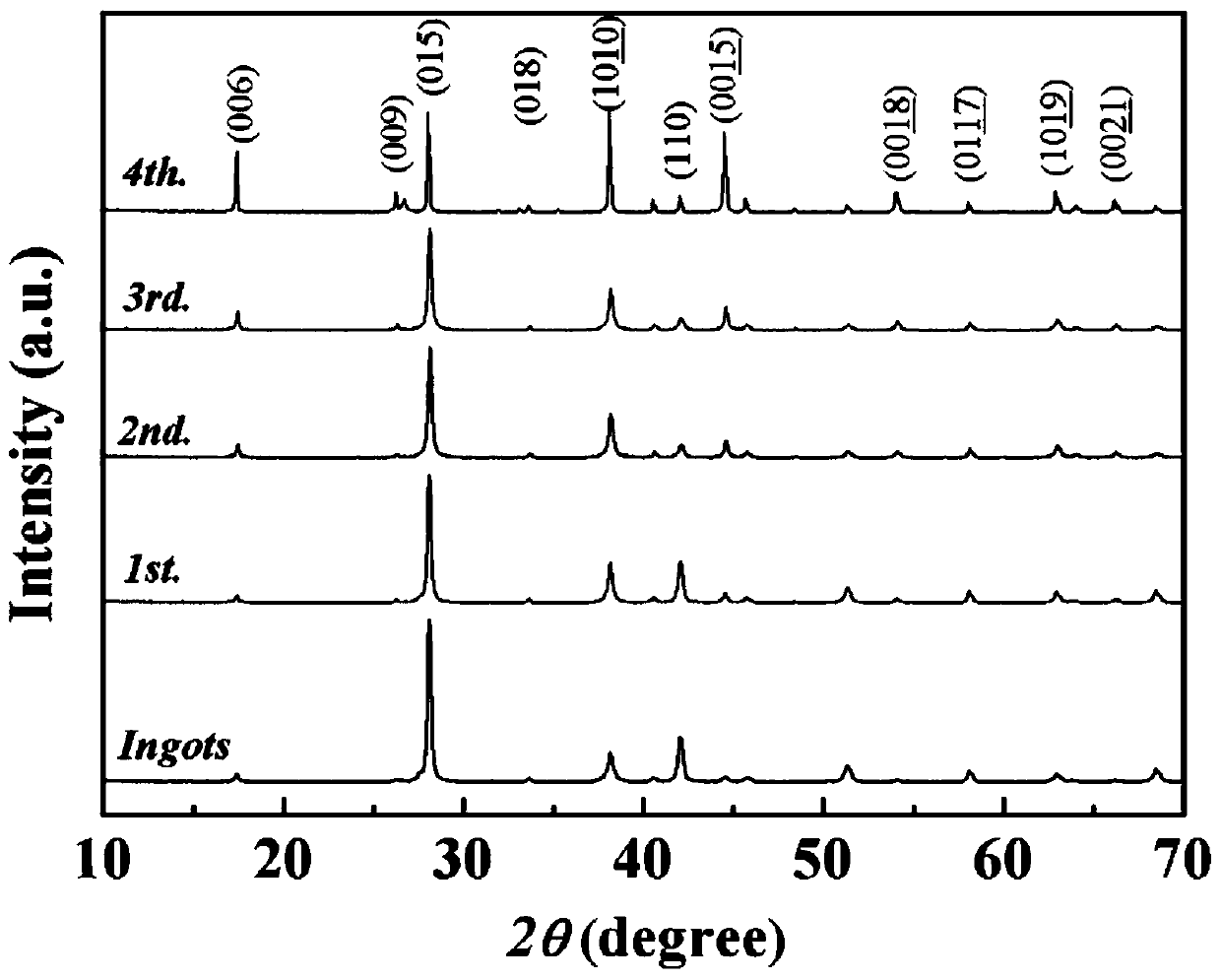
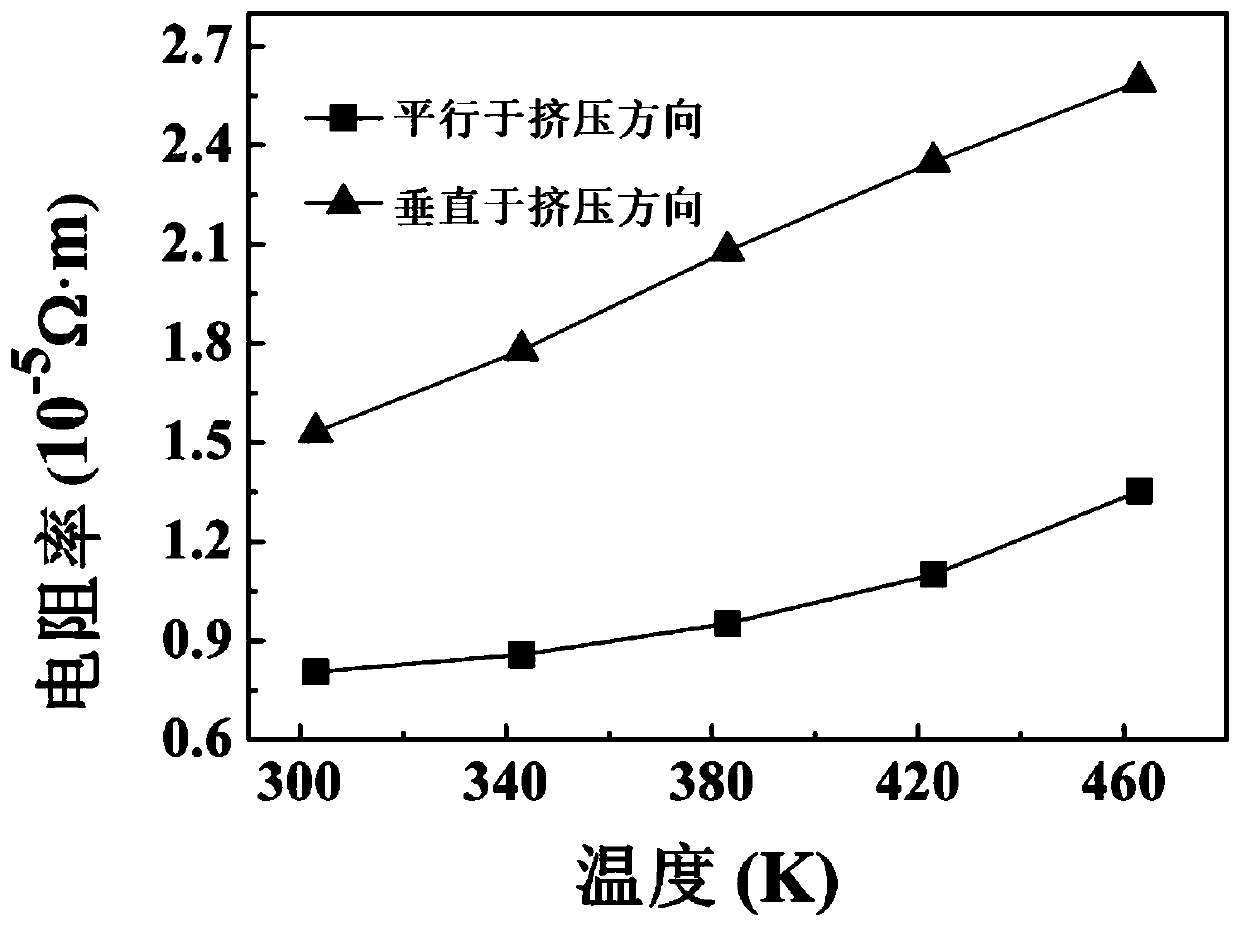
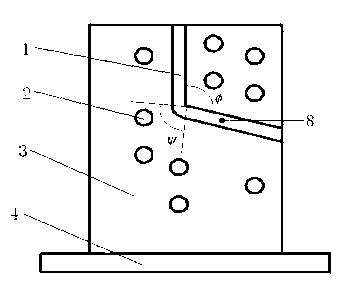
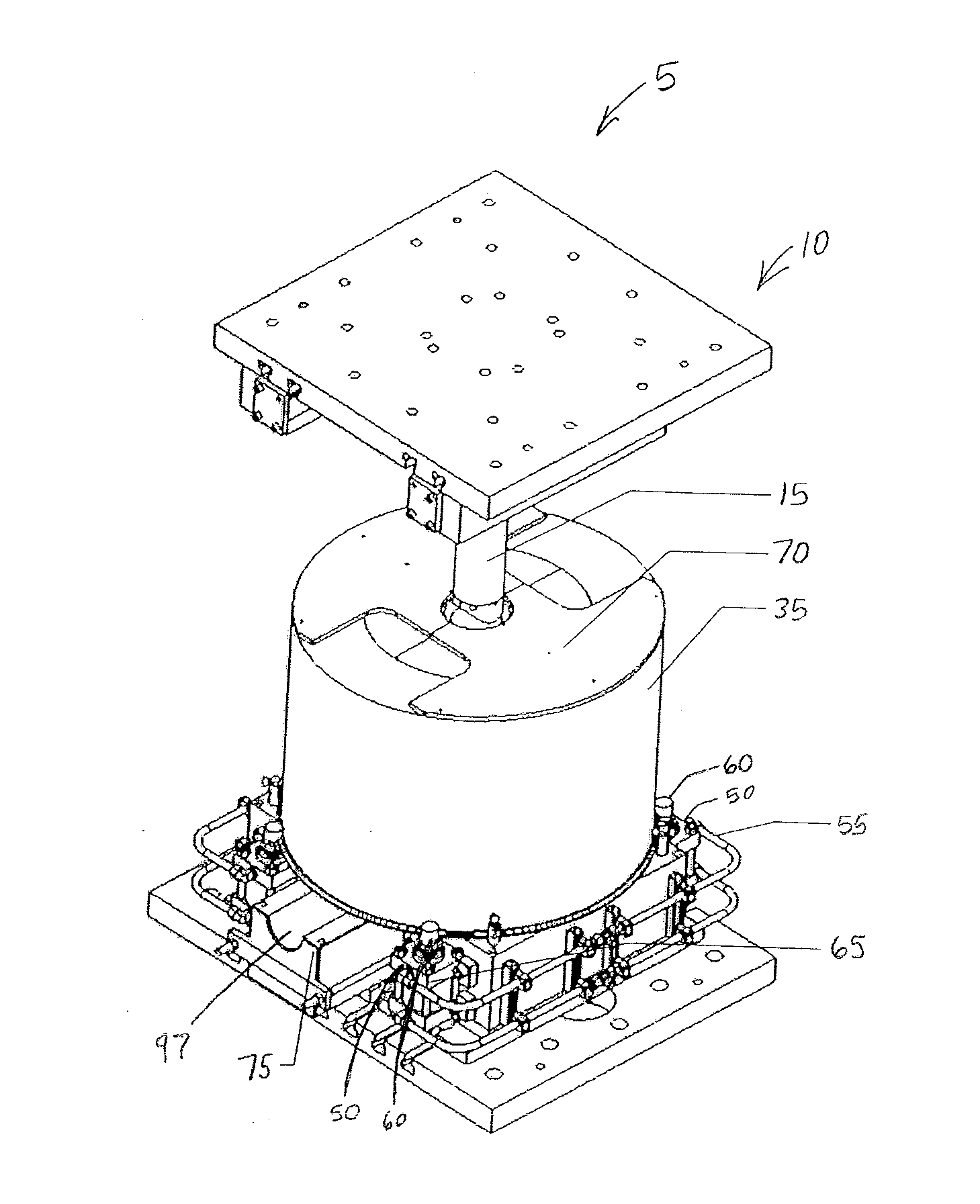
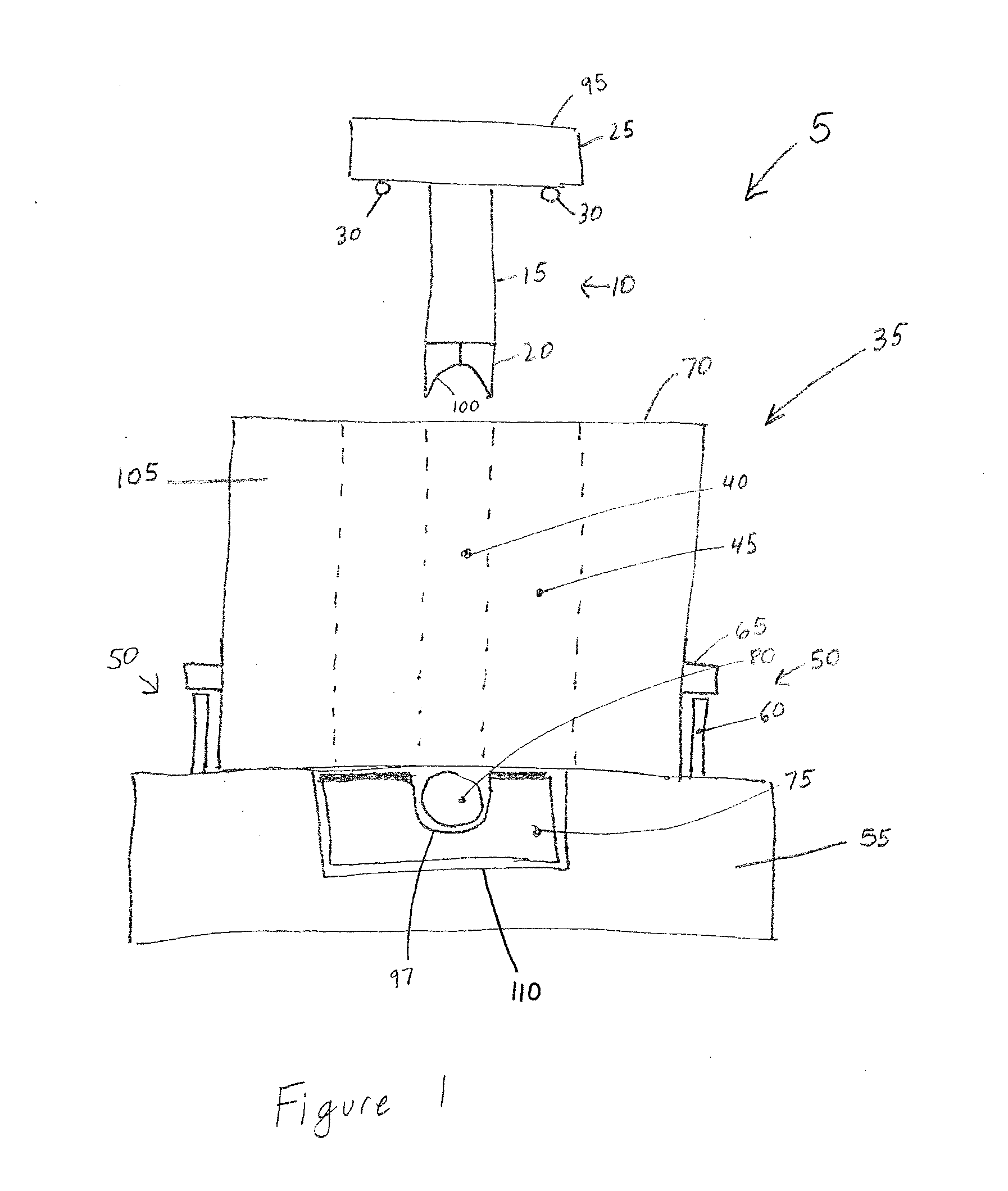
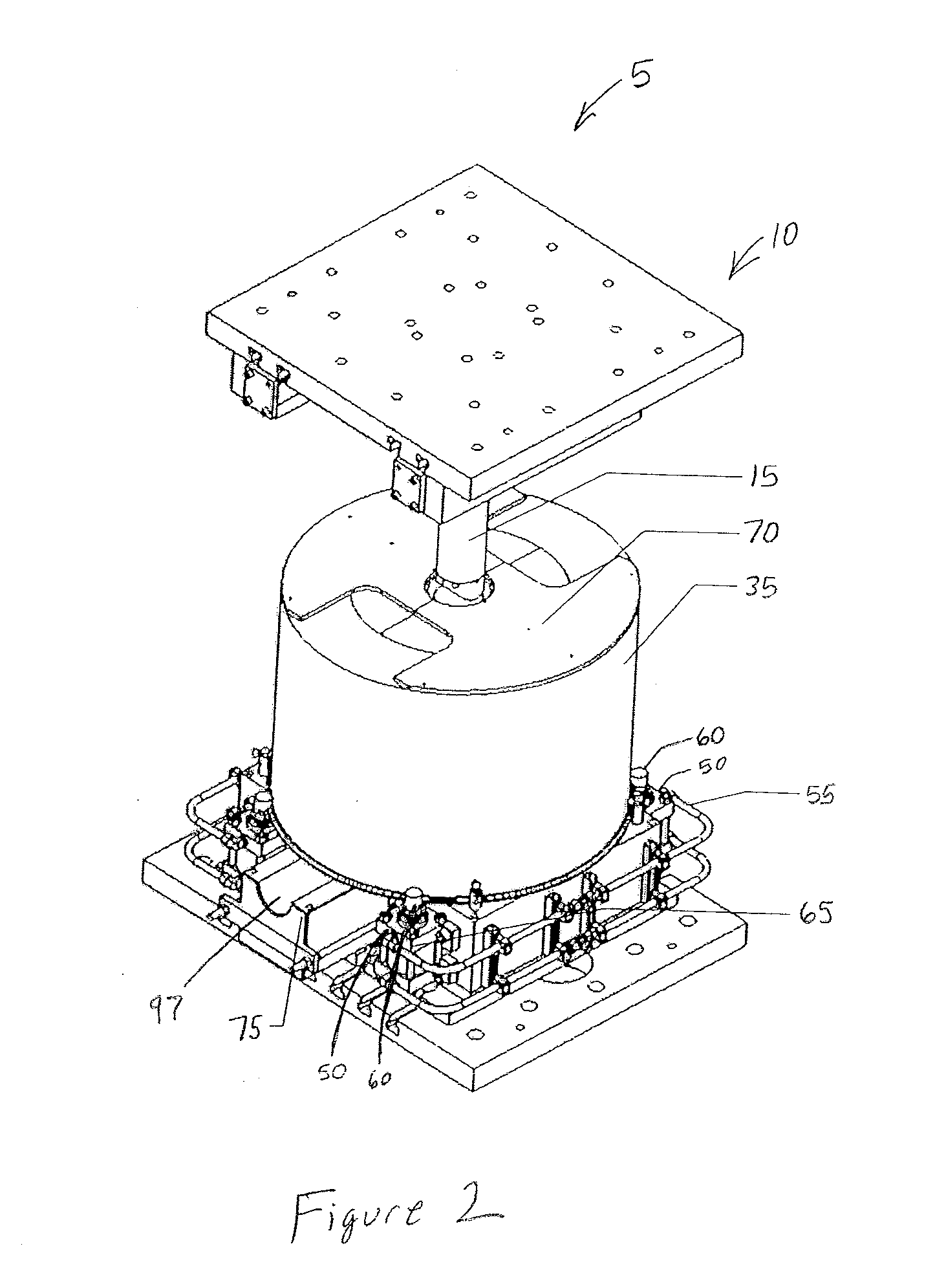
Equal channel angular extrusion (ECAE) is one technique from the Severe Plastic Deformation (SPD) group, aimed at producing Ultra Fine Grained (UFG) material. Developed in the Soviet Union in 1973. However, the dates are not always consistent. In industrial metalworking, it is an extrusion process, The technique is able to refine the microstructure of metals and alloys, thereby improving their strength according to the Hall-Petch relationship.
Physical vapor deposition targets, and methods of fabricating metallic materials
InactiveUS6946039B1High strengthMaintain grain sizeCellsElectric discharge tubesGas phaseMetallic materials
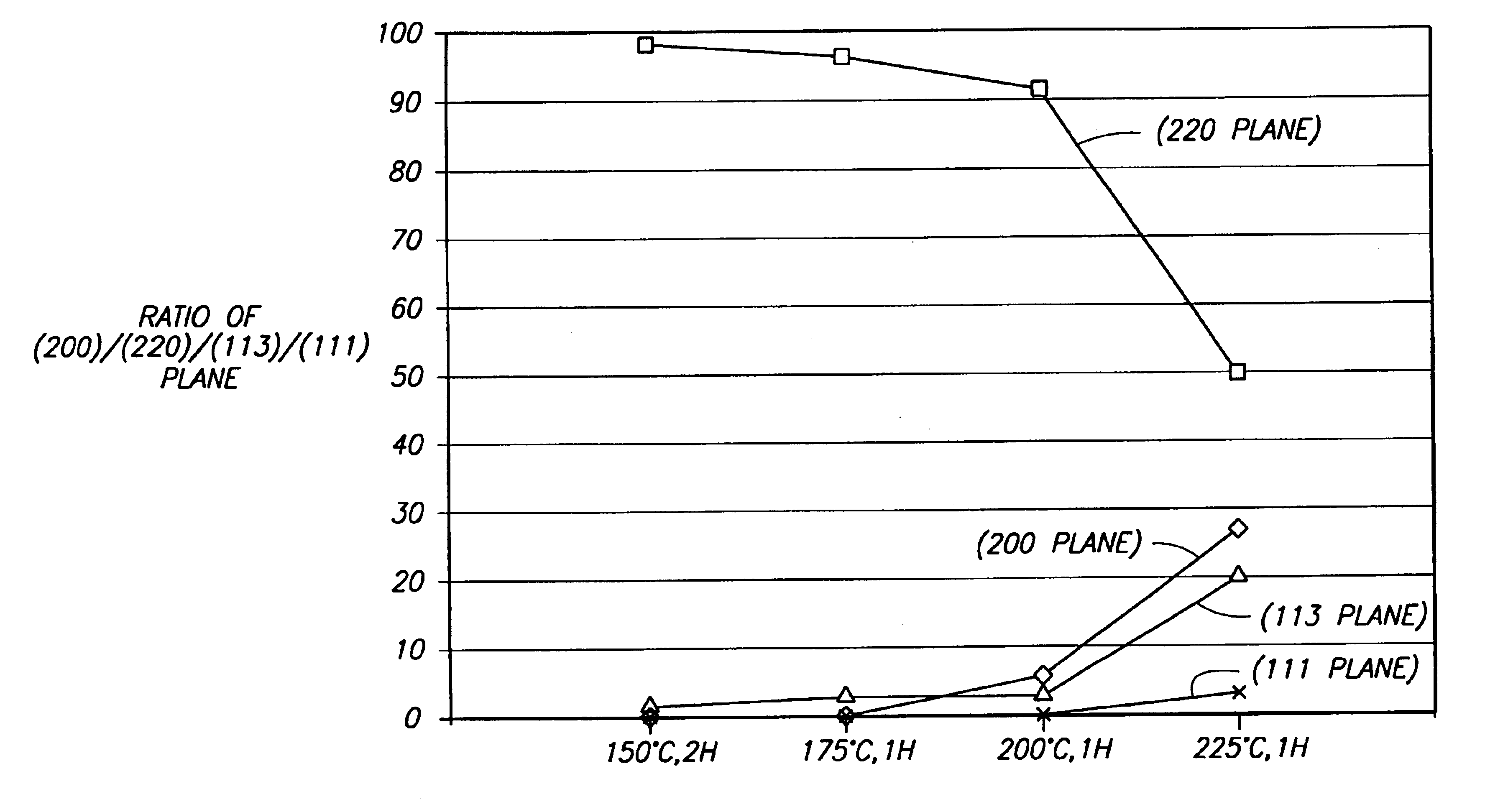
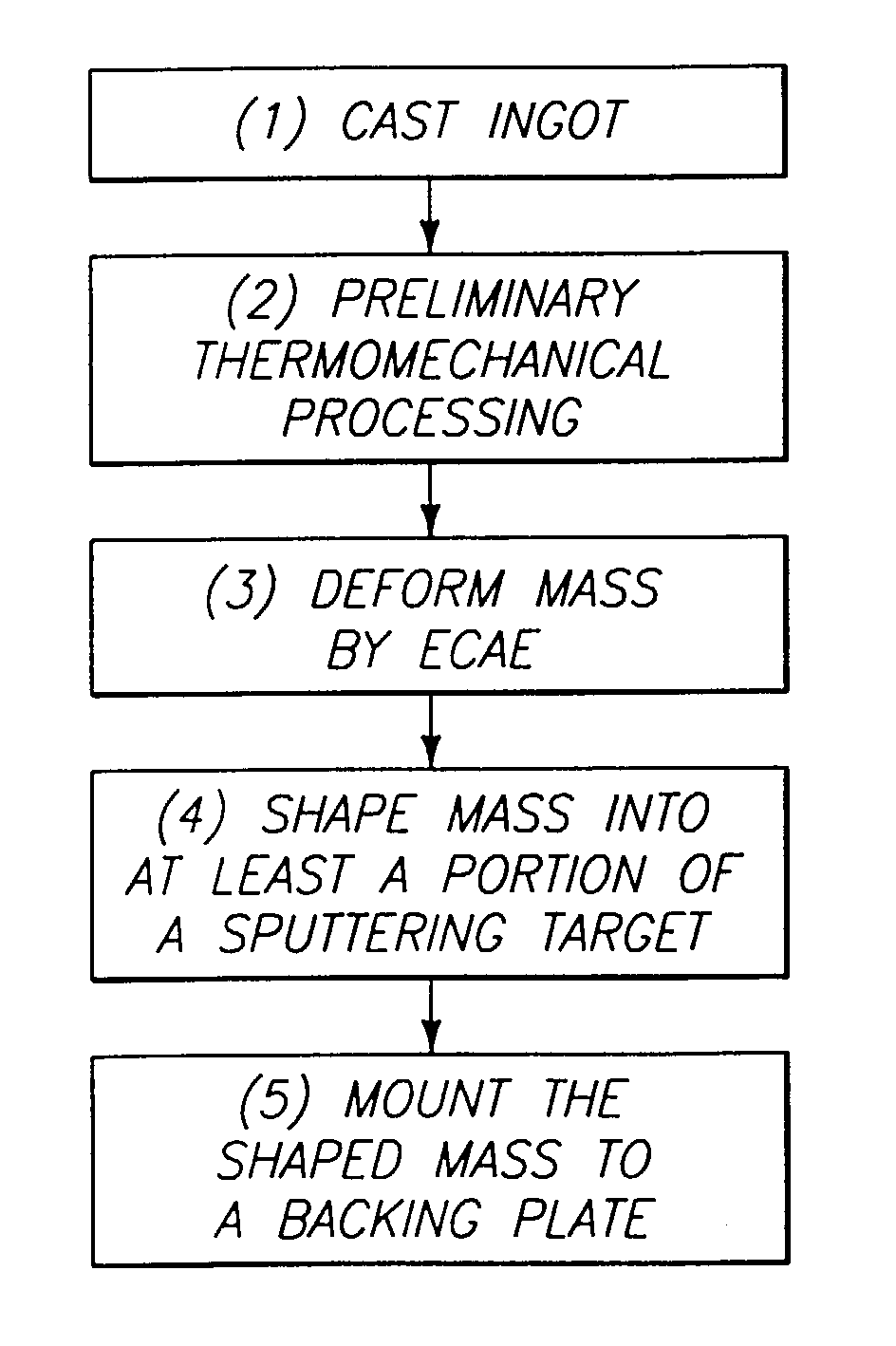
The invention includes a physical vapor deposition target composed of a face centered cubic unit cell metal or alloy and having a uniform grain size less than 30 microns, preferably less than 1 micron; and a uniform axial or planar <220> texture. Also described is a method for making sputtering targets. The method can comprise billet preparation; equal channel angular extrusion with a prescribed route and number of passes; and cross-rolling or forging subsequent to the equal channel angular extrusion.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Method of forming phsical gas phase deposition target contg. aluminium, sputtering film and component of target
InactiveCN1432070AVacuum evaporation coatingMetal-working apparatusGas phaseEqual channel angular extrusion
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Equal channel angular extrusion method
InactiveUS6883359B1Quantity minimizationMinimized volumeExtrusion containersClassical mechanicsEqual channel angular extrusion
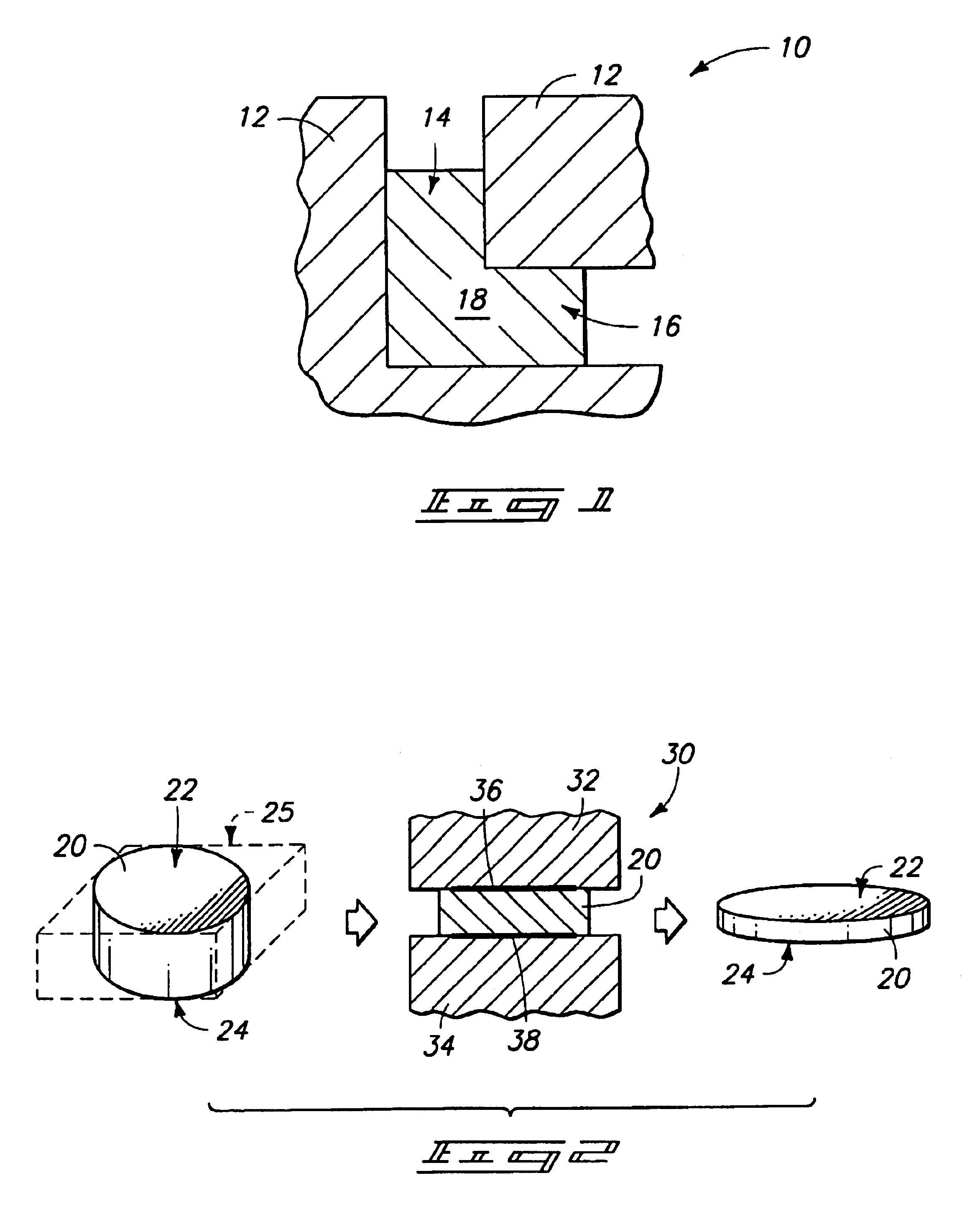
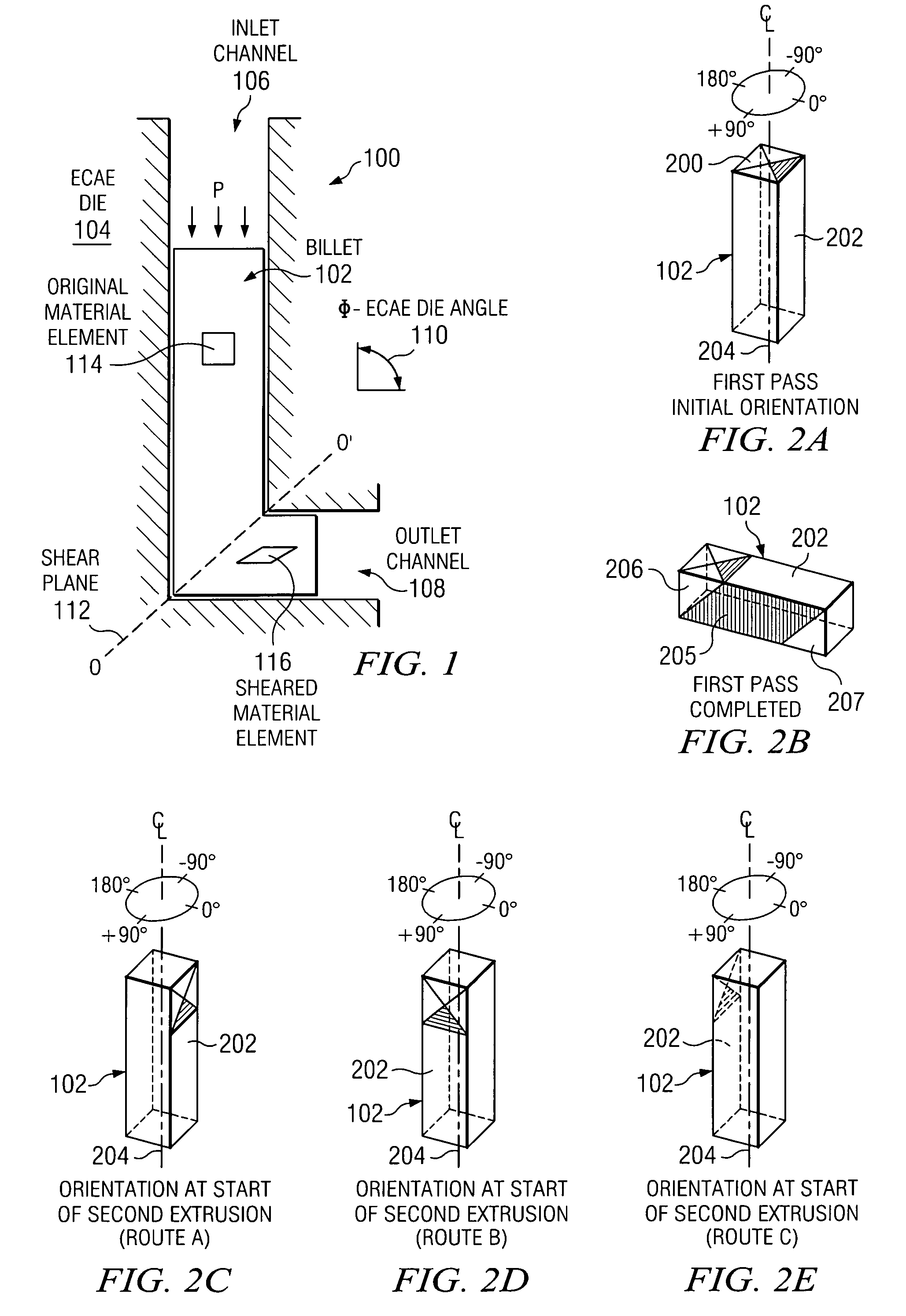
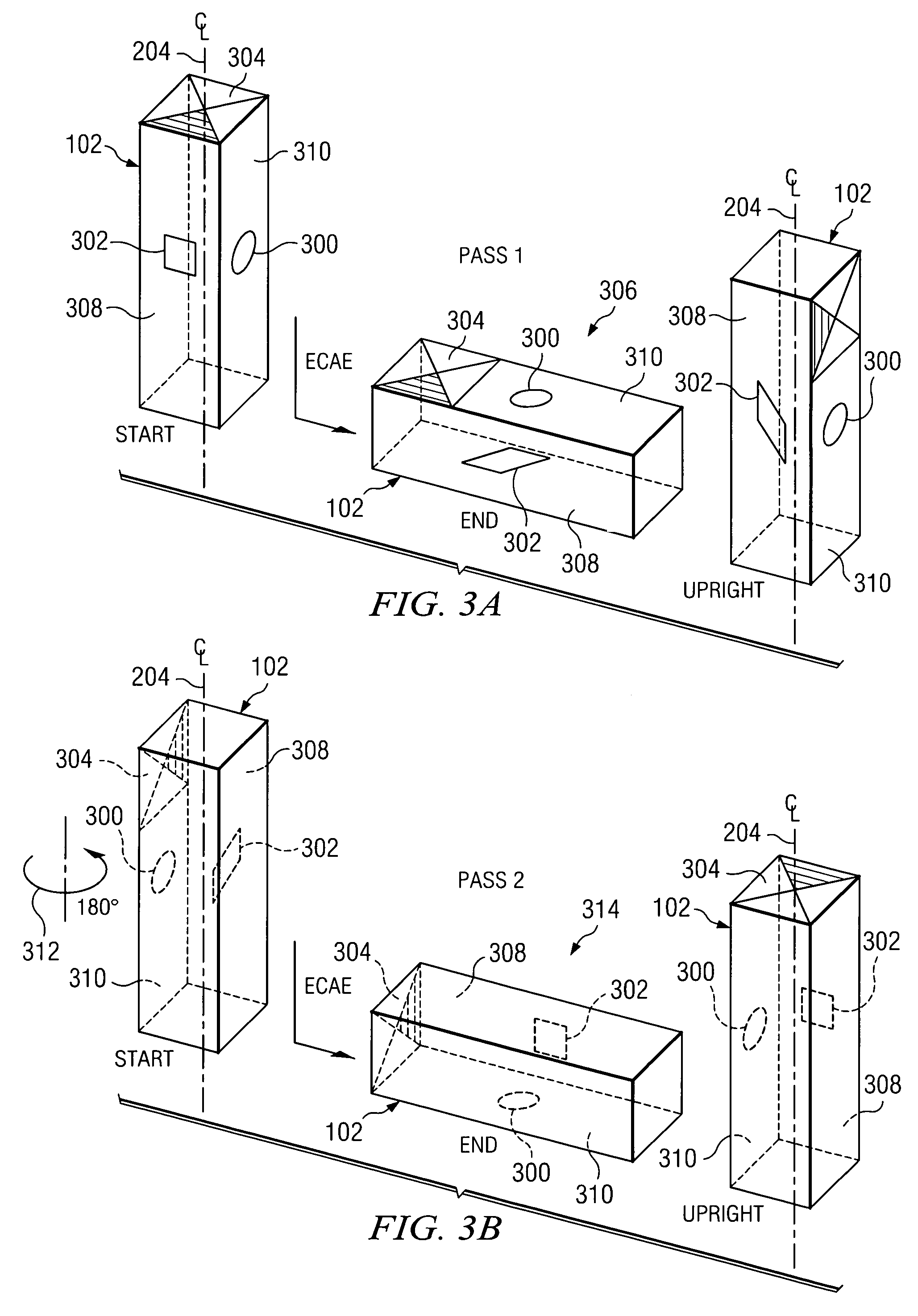
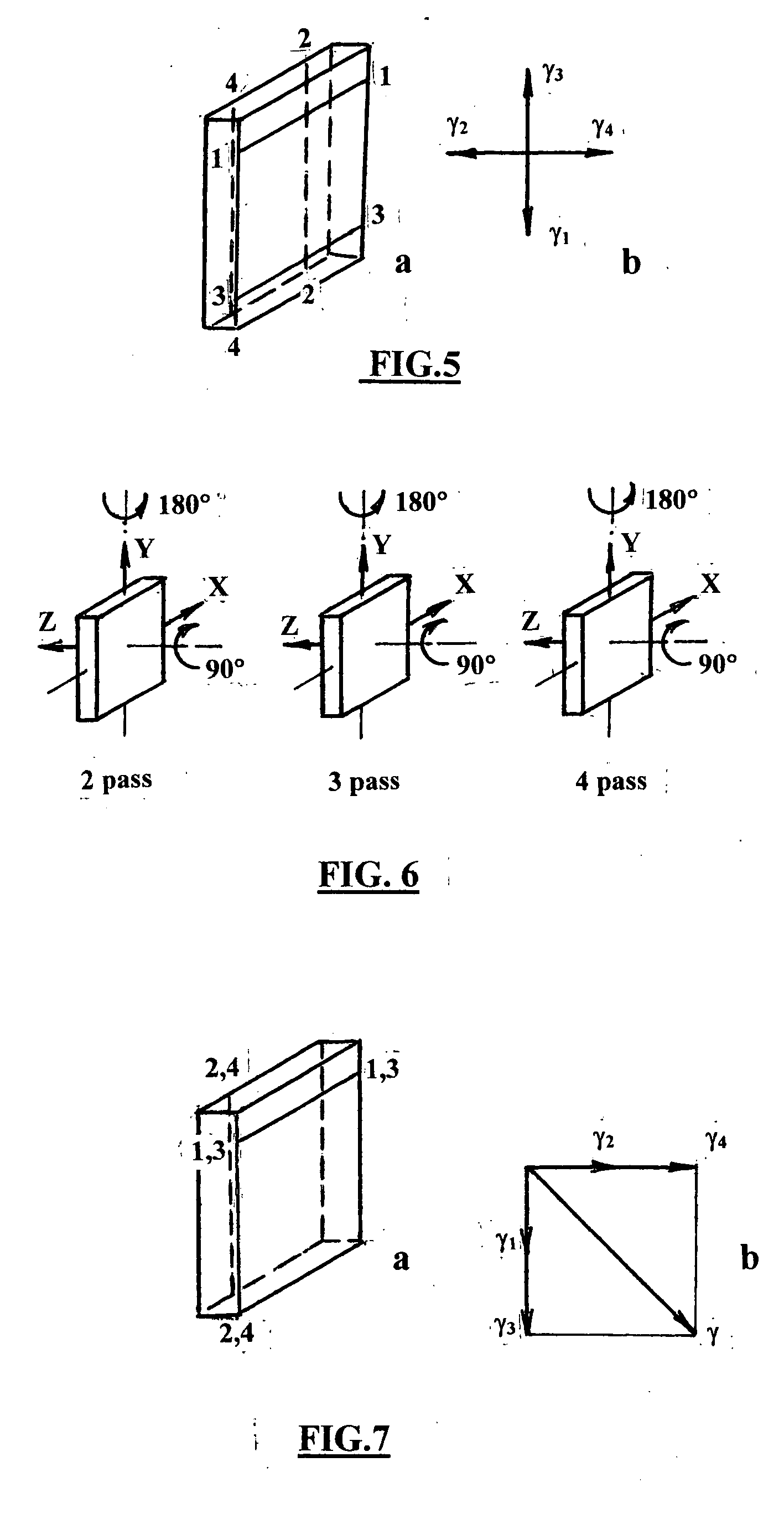
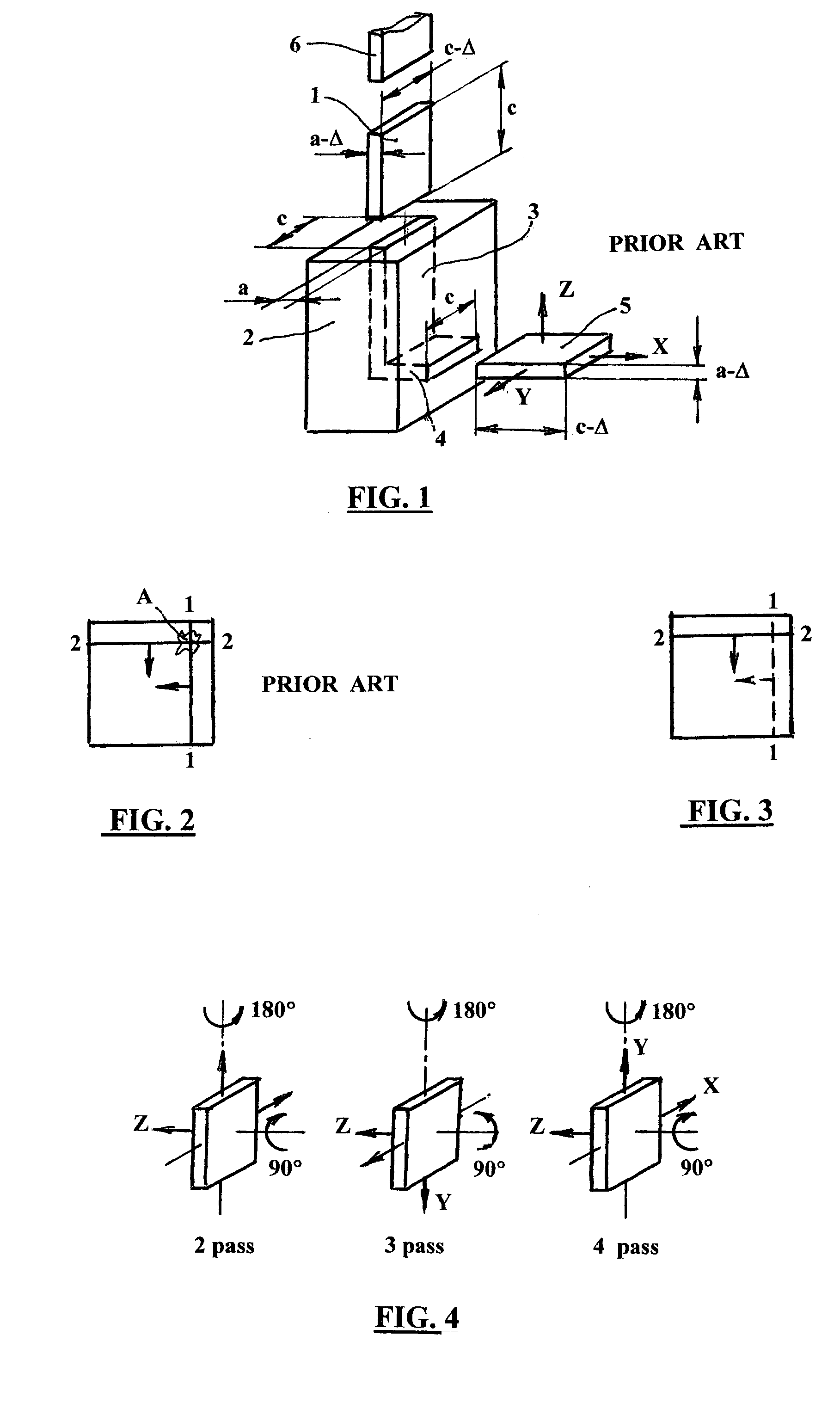
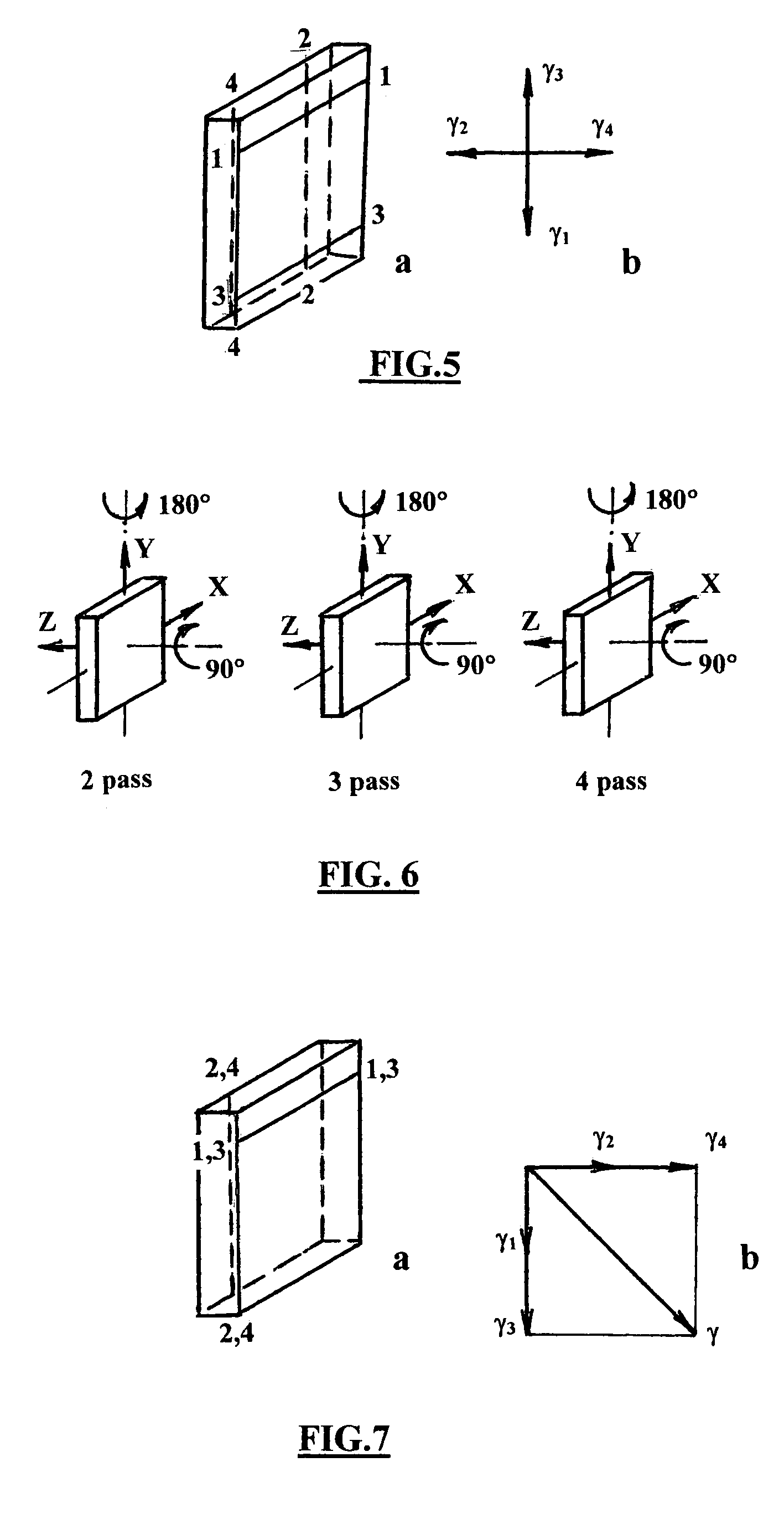
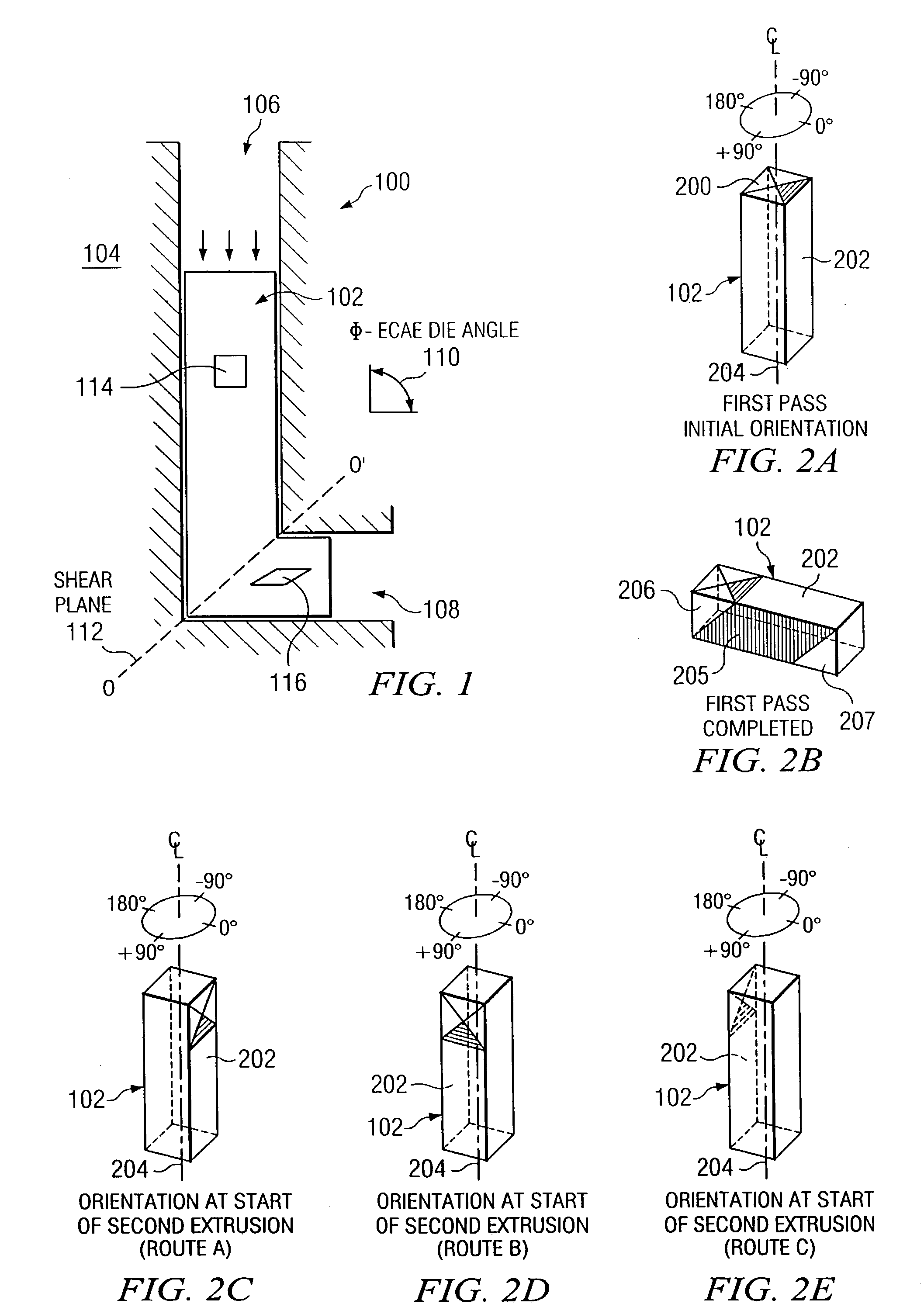
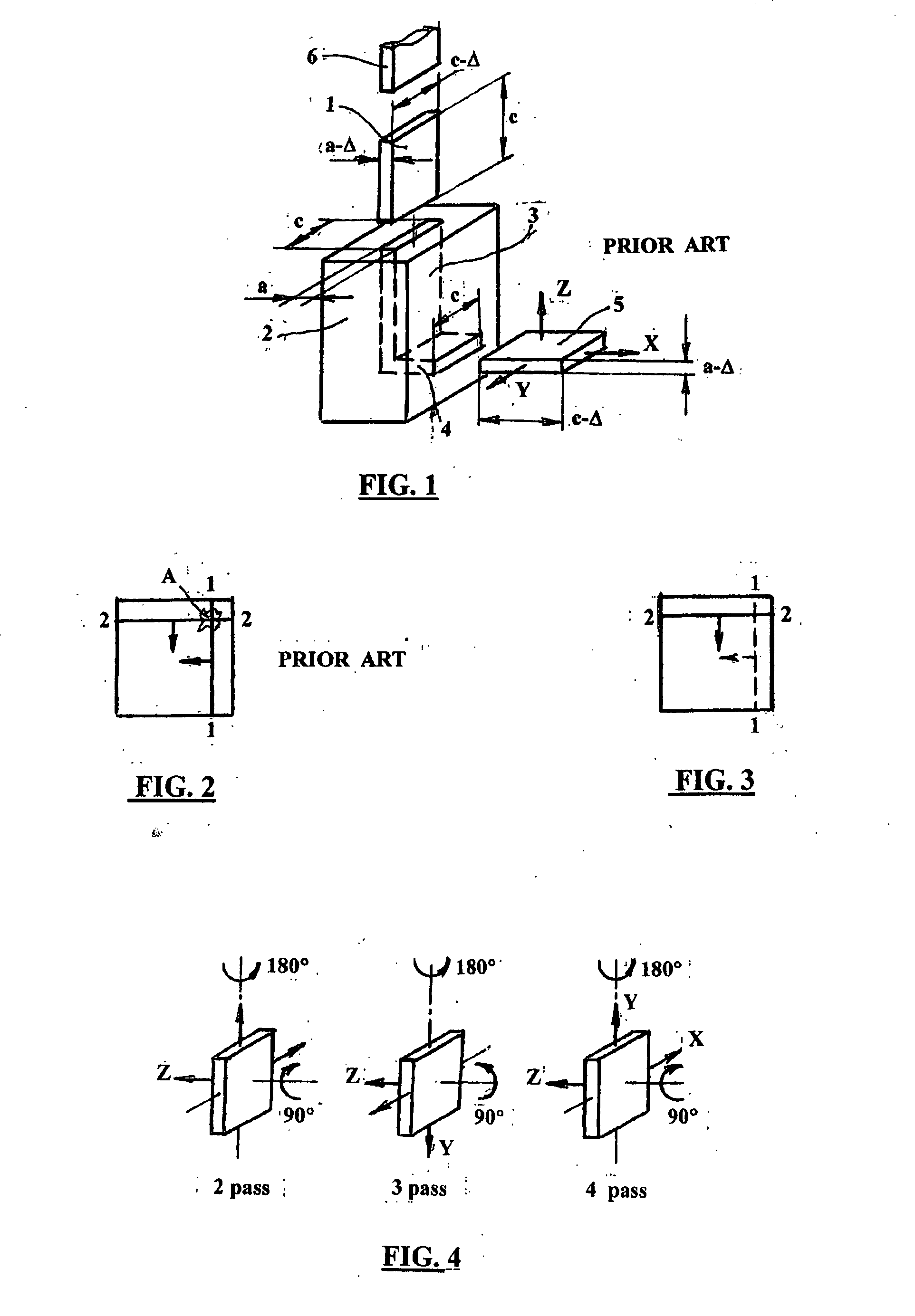
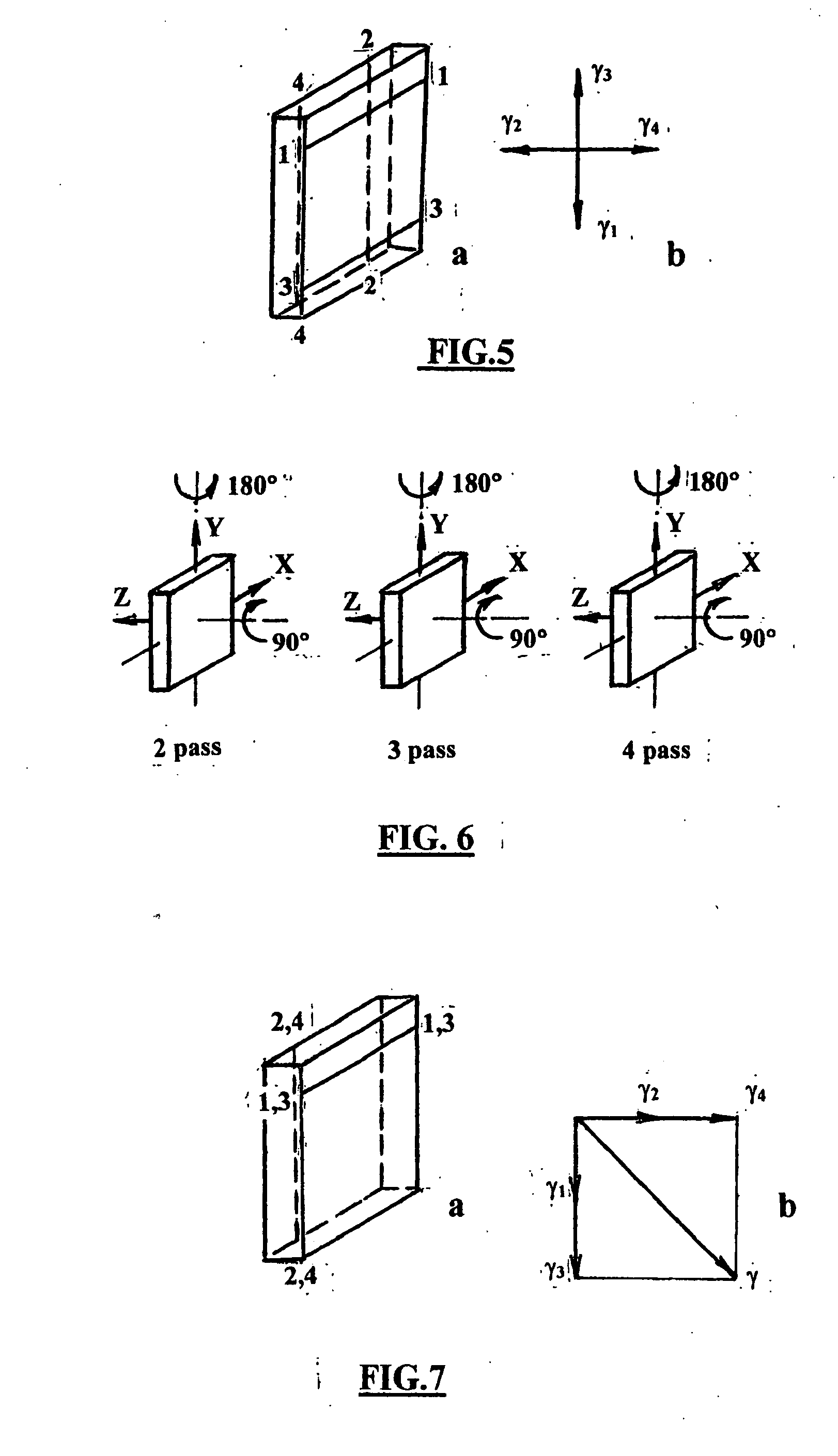
According to one embodiment of the present invention, an equal channel angular extrusion (ECAE) method includes extruding a billet of material along a first axis in a first orientation through an ECAE die, extruding the billet along the first axis in a second orientation through the ECAE die, the second orientation oriented approximately 180° from the first direction, extruding the billet along the first axis in a third orientation through the ECAE die, the third orientation oriented approximately 90° from the second orientation, and extruding the billet along the first axis in a fourth orientation through the ECAE die, the fourth orientation oriented approximately 180° from the third orientation.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
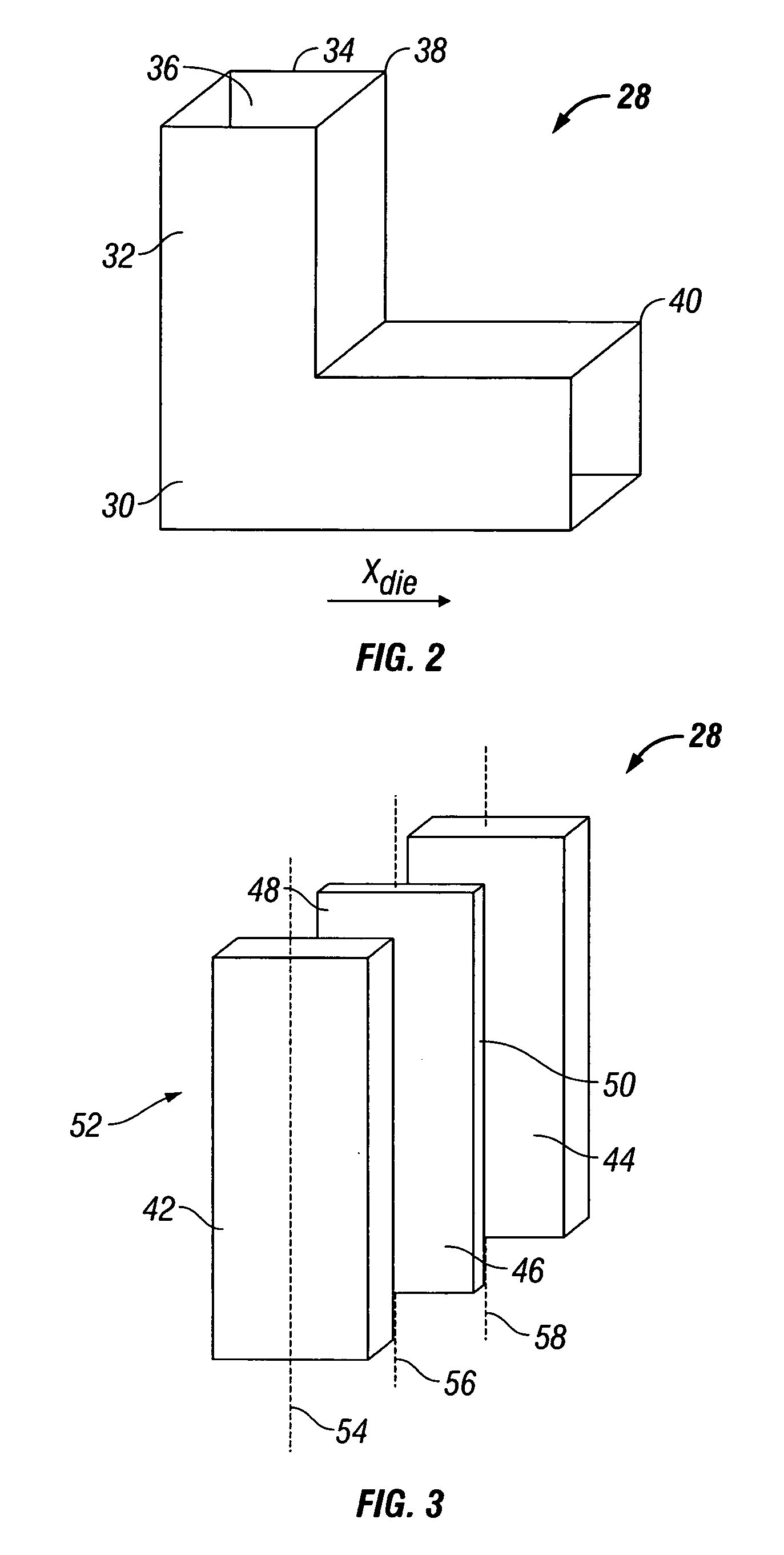
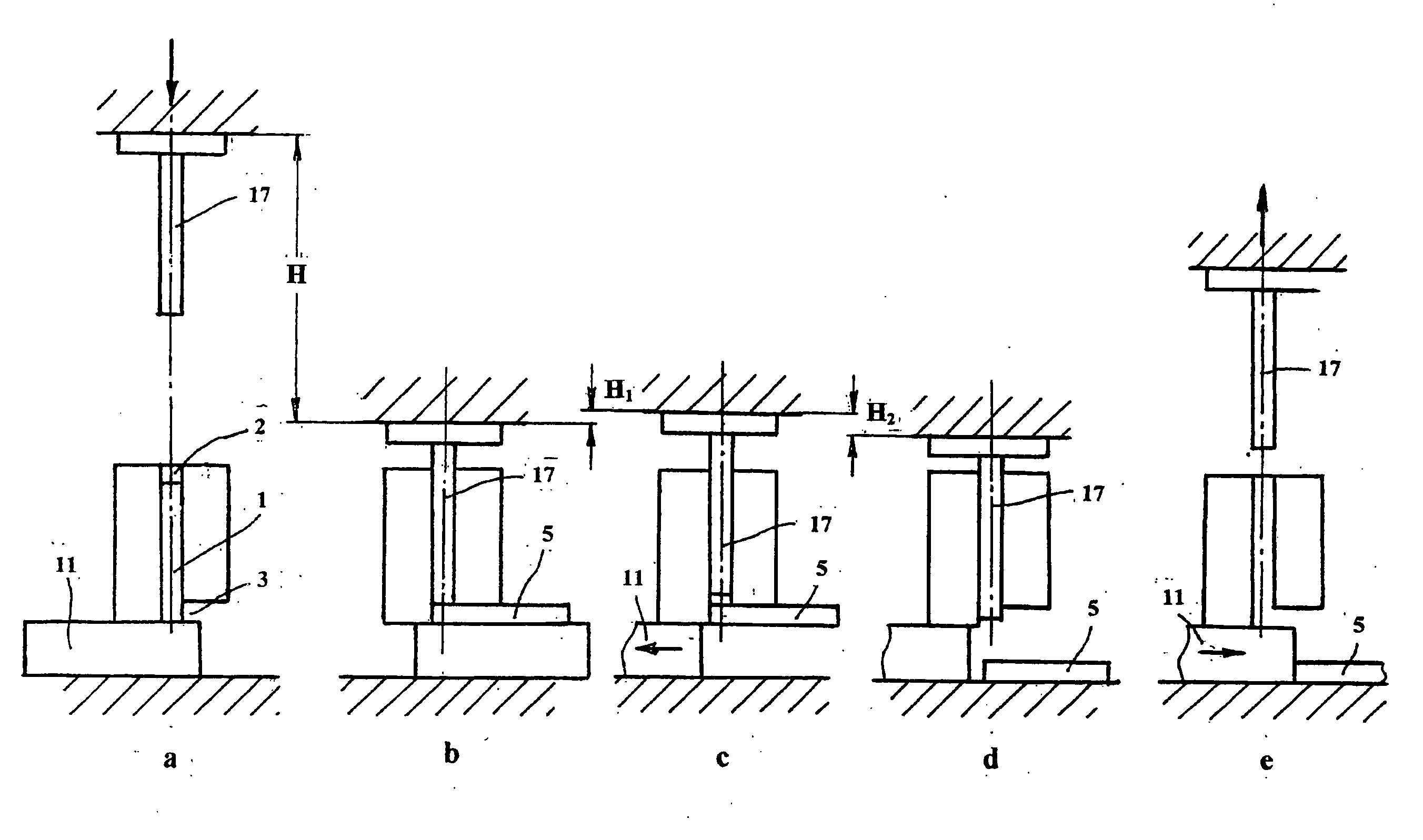
Method and apparatus for equal channel angular extrusion of flat billets
InactiveUS20050016243A1Reliable billet ejectionReduce pressureWork treatment devicesMetal rolling arrangementsCost effectivenessControl system
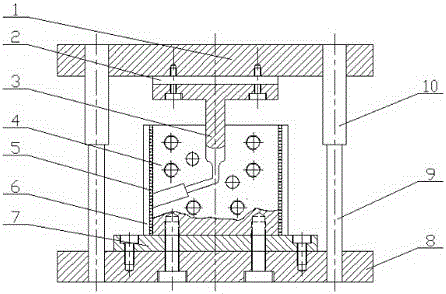
The invention comprises a method and apparatus for equal channel angular extrusion (ECAE) of flat billets to control material structure and properties. The improvements of the method include the special systems of billet orientations, billet lubrication, billet ejection from dies, and a press / die control system those eliminate surface cracks, flashes and billet reshaping or deburring between passes. Therefore, multi-pass ECAE becomes a cost-effective industrial operation and may be applied to large billets.
Owner:ENGINEERED PERFORMANCE MATERIALS
High-strength mechanical and structural components, and methods of making high-strength components
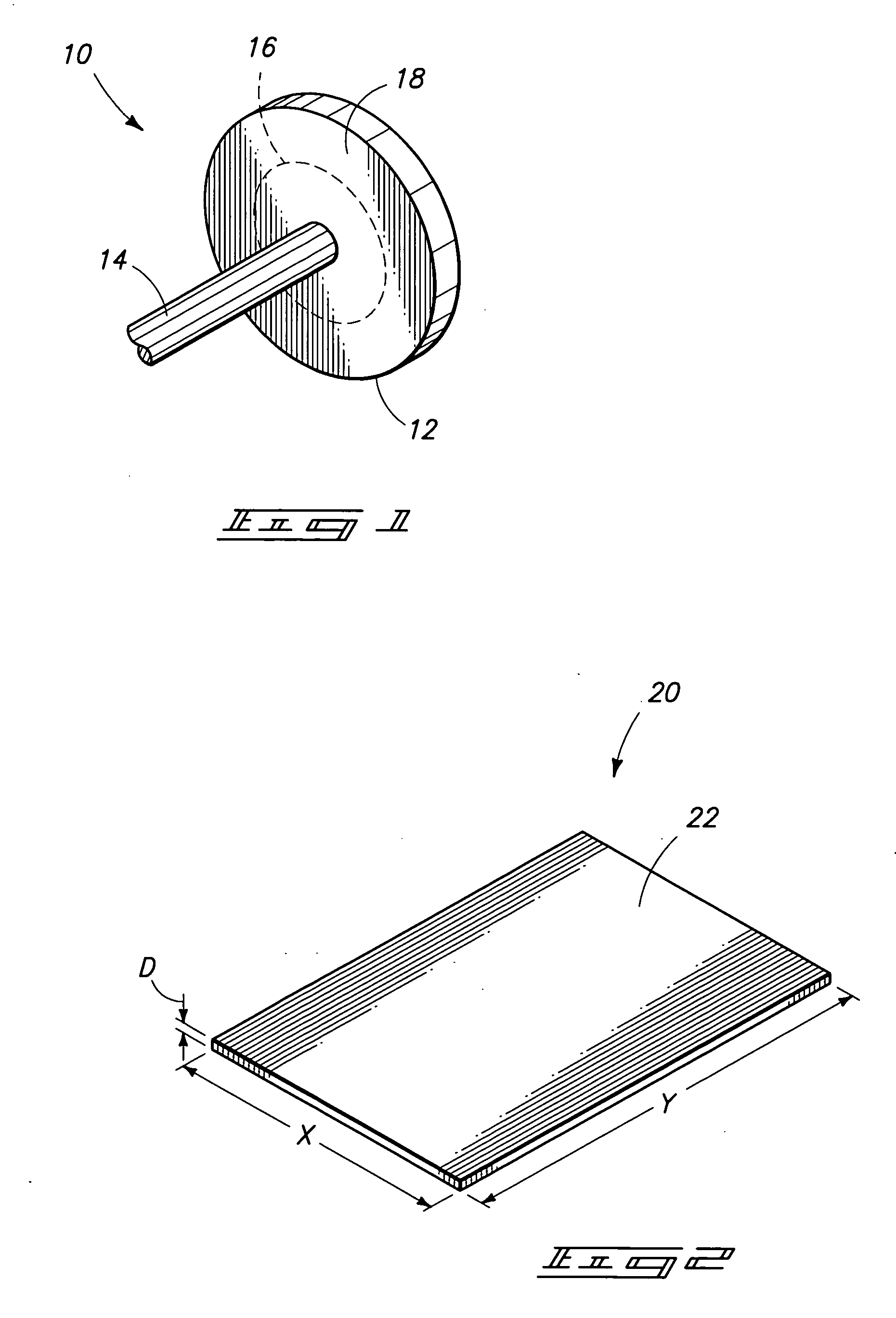
The invention includes components comprising an alloy containing a base metal and less than or equal to 30% alloying elements. The material has a grain size of less than or equal to about 30 microns and an absence of voids and inclusions of a size greater than 1 micron. The components have a yield strength at least 50% greater than the identical alloy composition in the 0 temper condition. Where the material is heat treatable, the yield strength is at least 10% greater than the identical composition in the T6 temper condition. The invention includes a method of producing components by casting and initial treatment to form a billet. The billet is subjected to equal channel angular extrusion and subsequent annealing at a temperature of less than or equal to 0.85 times the minimum temperature for inducing growth of submicron grains to over 1 micron.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Copper-containing pvd targets and methods for their manufacture
InactiveUS20070039817A1CellsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsGas phaseEqual channel angular extrusion
The invention includes a physical vapor deposition target containing copper and at least two additional elements selected from Ag, Al, As, Au, B, Be, Ca, Cd, Co, Cr, Fe, Ga, Ge, Hf, Hg, In, Ir, Li, Mg, Mn, Nb, Ni, Pb, Pd, Pt, Sb, Sc, Si, Sn, Ta, Te, Ti, V, W, Zn and Zr, a total amount of the at least two additional elements being from 100 ppm to 10 atomic %. The invention additionally includes thin films and interconnects which contain the mixture of copper and at least two added elements. The invention also includes forming a copper-containing target. A mixture of copper and two or more elements is formed. The mixture is cast by melting and is subsequently cooled to form a billet which is worked utilizing one or both of equal channel angular extrusion and thermomechanical processing to form a target.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Method and apparatus for equal channel angular extrusion of flat billets
InactiveUS7191630B2Eliminate surface cracksGood material uniformityWork treatment devicesMetal rolling arrangementsCost effectivenessControl system
The invention comprises a method and apparatus for equal channel angular extrusion (ECAE) of flat billets to control material structure and properties. The improvements of the method include the special systems of billet orientations, billet lubrication, billet ejection from dies, and a press / die control system those eliminate surface cracks, flashes and billet reshaping or deburring between passes. Therefore, multi-pass ECAE becomes a cost-effective industrial operation and may be applied to large billets.
Owner:ENGINEERED PERFORMANCE MATERIALS
Nanostructured commercially pure titanium for biomedicine and a method for producing a rod therefrom
ActiveUS20110179848A1Improve failureImprove propertiesNanostructure manufactureMetal-working apparatusEqual channel angular extrusionCommercially pure titanium
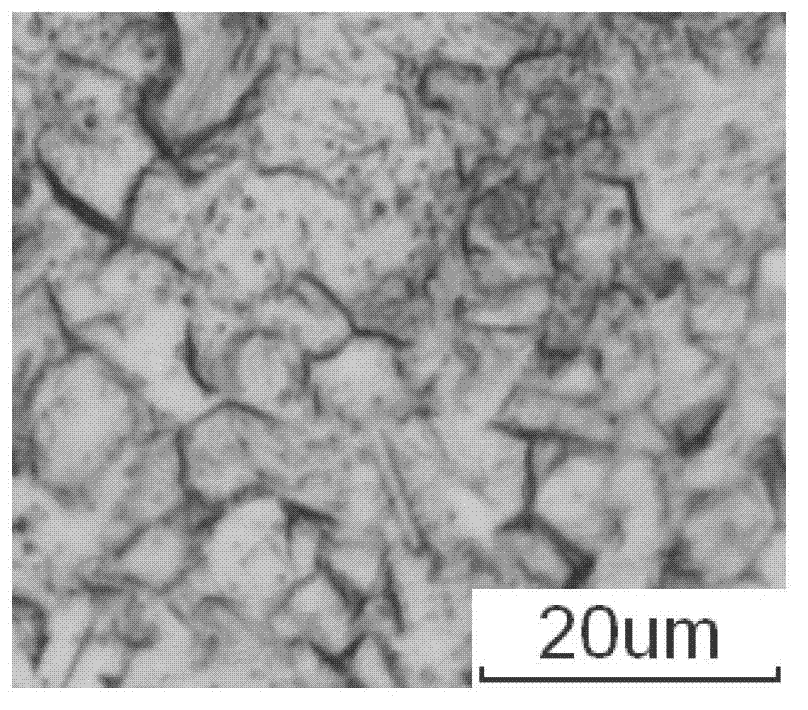
Commercially pure titanium having UFG structure and enhanced mechanical and biomedical characteristics has nanocrystalline alpha-phase grains with a hexagonal close-packed lattice, in which the share of grains with a size of 0.1 . . . 0.5 μm and a grain shape coefficient of no more than 2 in the mutually perpendicular planes makes no less than 90%, over 60% of the grains having high-angle boundaries disoriented in relation to the adjacent grains by the angles from 15 to 90°.The method for making a rod of the material provides for equal-channel angular pressing of a billet at T≦450° C. with the total accumulated true strain e≧4 to effect severe plastic deformation of the billet and subsequent thermomechanical treatment with a gradual decrease of the temperature in the range of 450 . . . 350° C. and the strain rate of 10−2 . . . 10−4 s−1 with the strain degree from 40 to 80% to effect additional plastic deformation.
Owner:FSBFEI HPE USATU 50 +1
High-plasticity two-phase yttrium-containing magnesium-lithium-aluminum alloy and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses high-plasticity two-phase yttrium-containing magnesium-lithium-aluminum alloy and a preparation method thereof. The alloy comprises the following specific components in percentage by weight: 9.50-10.80% of Li, 3.00-5.00% of Al, 0.50-0.70% of Y, 0.10-0.30% of Zr and the balance of Mg; the alloy has the structural characteristics that an alpha phase, a beta phase and a precipitated phase exist at the same time, wherein the alpha phase is a Mg-based solid solution and is in a close-packed hexagonal structure, the beta phase is a Li-based solid solution and is in a body-centered cubic structure, and the precipitated phase is a rare earth compound Al2Y; and the alloy has the characteristics of low density, high plasticity and higher strength. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is a normal-temperature plastic deformation method which combines casting with equal channel angular extrusion or traditional extrusion deformation process; and compared with the traditional high-temperature deformation process, the preparation method has good practicality and is simpler and more convenient to operate, and can be used for effectively lowering the production cost, thus the preparation method has good industrial production prospects.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Methods of forming aluminum-comprising physical vapor deposition targets; sputtered films; and target constructions
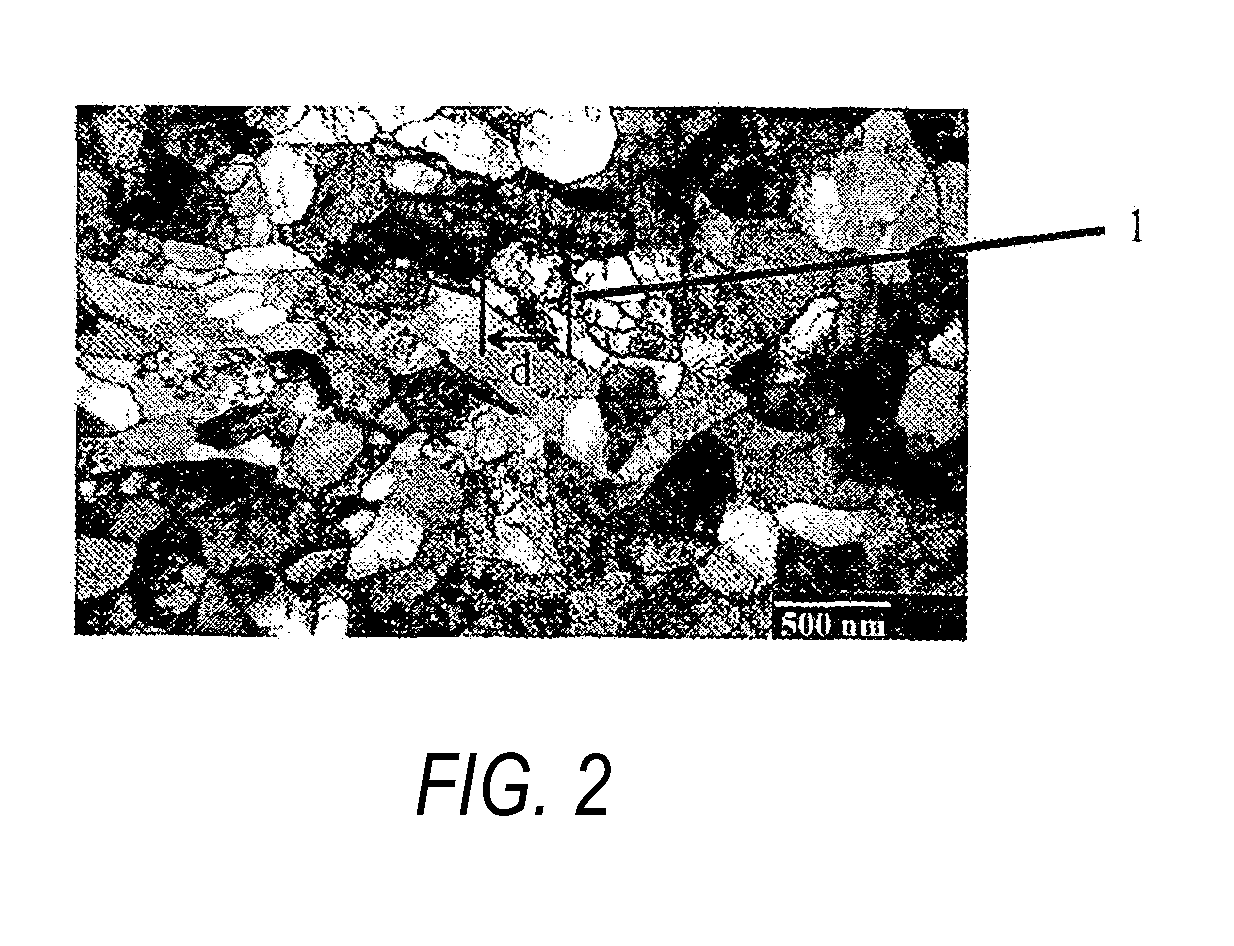
The invention includes a method of forming an aluminum-comprising physical vapor deposition target. An aluminum-comprising mass is deformed by equal channel angular extrusion. The mass is at least 99.99% aluminum and further comprises less than or equal to about 1,000 ppm of one or more dopant materials comprising elements selected from the group consisting of Ac, Ag, As, B, Ba, Be, Bi, C, Ca, Cd, Ce, Co, Cr, Cu, Dy, Er, Eu, Fe, Ga, Gd, Ge, Hf, Ho, In, Ir, La, Lu, Mg, Mn, Mo, N, Nb, Nd, Ni, O, Os, P, Pb, Pd, Pm, Po, Pr, Pt, Pu, Ra, Rf, Rh, Ru, S, Sb, Sc, Se, Si, Sm, Sn, Sr, Ta, Tb, Te, Ti, Tl, Tm, V, W, Y, Yb, Zn and Zr. After the aluminum-comprising mass is deformed, the mass is shaped into at least a portion of a sputtering target. The invention also encompasses a physical vapor deposition target consisting essentially of aluminum and less than or equal to 1,000 ppm of one or more dopant materials comprising elements selected from the group consisting of Ac, Ag, As, B, Ba, Be, Bi, C, Ca, Cd, Ce, Co, Cr, Cu, Dy, Er, Eu, Fe, Ga, Gd, Ge, Hf, Ho, In, Ir, La, Lu, Mg, Mn, Mo, N, Nb, Nd, Ni, O, Os, P, Pb, Pd, Pm, Po, Pr, Pt, Pu, Ra, Rf, Rh, Ru, S, Sb, Sc, Se, Si, Sm, Sn, Sr, Ta, Tb, Te, Ti, Tl, Tm, V, W, Y, Yb, Zn and Zr. Additionally, the invention encompasses thin films.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Developing the texture of a material
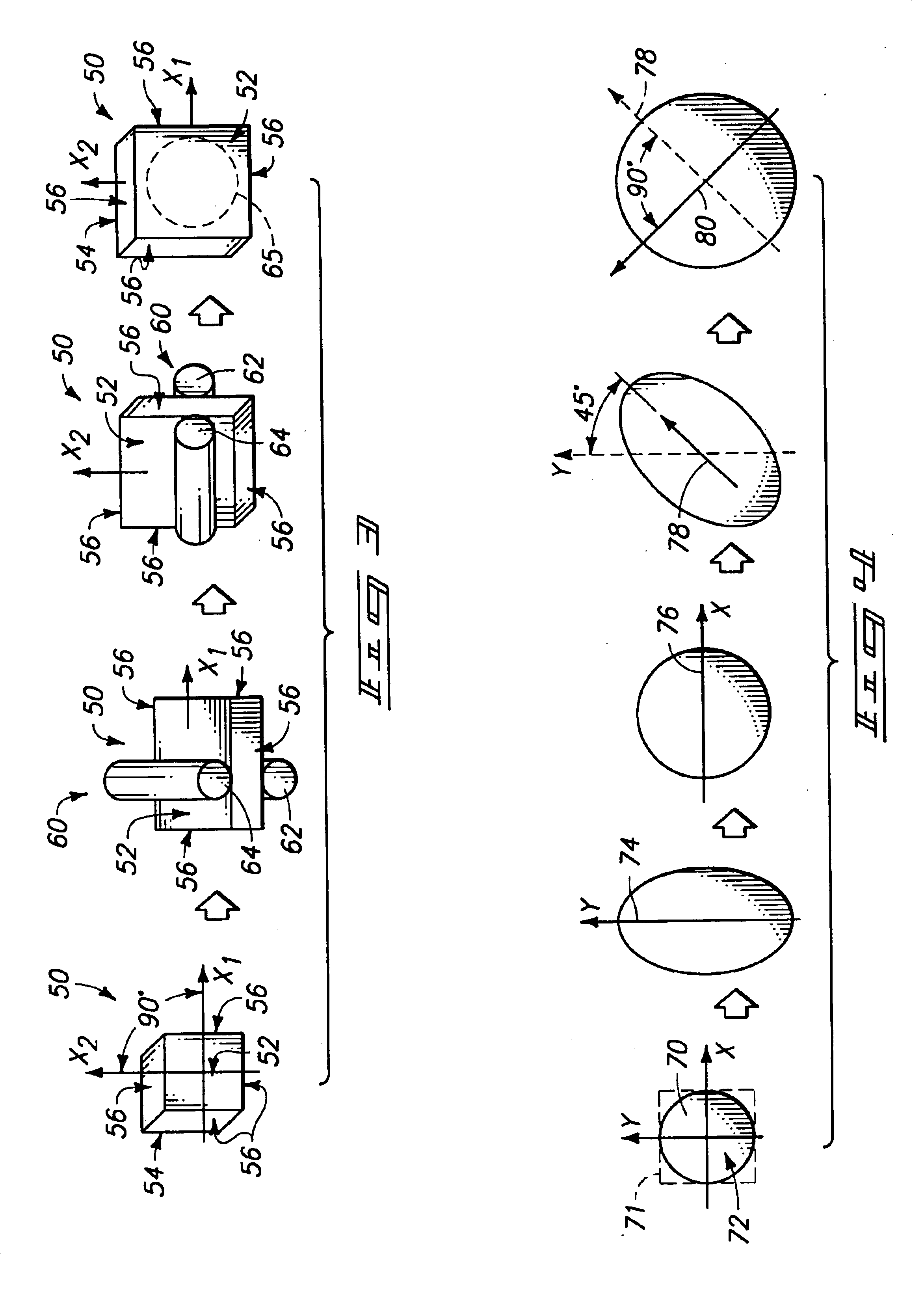
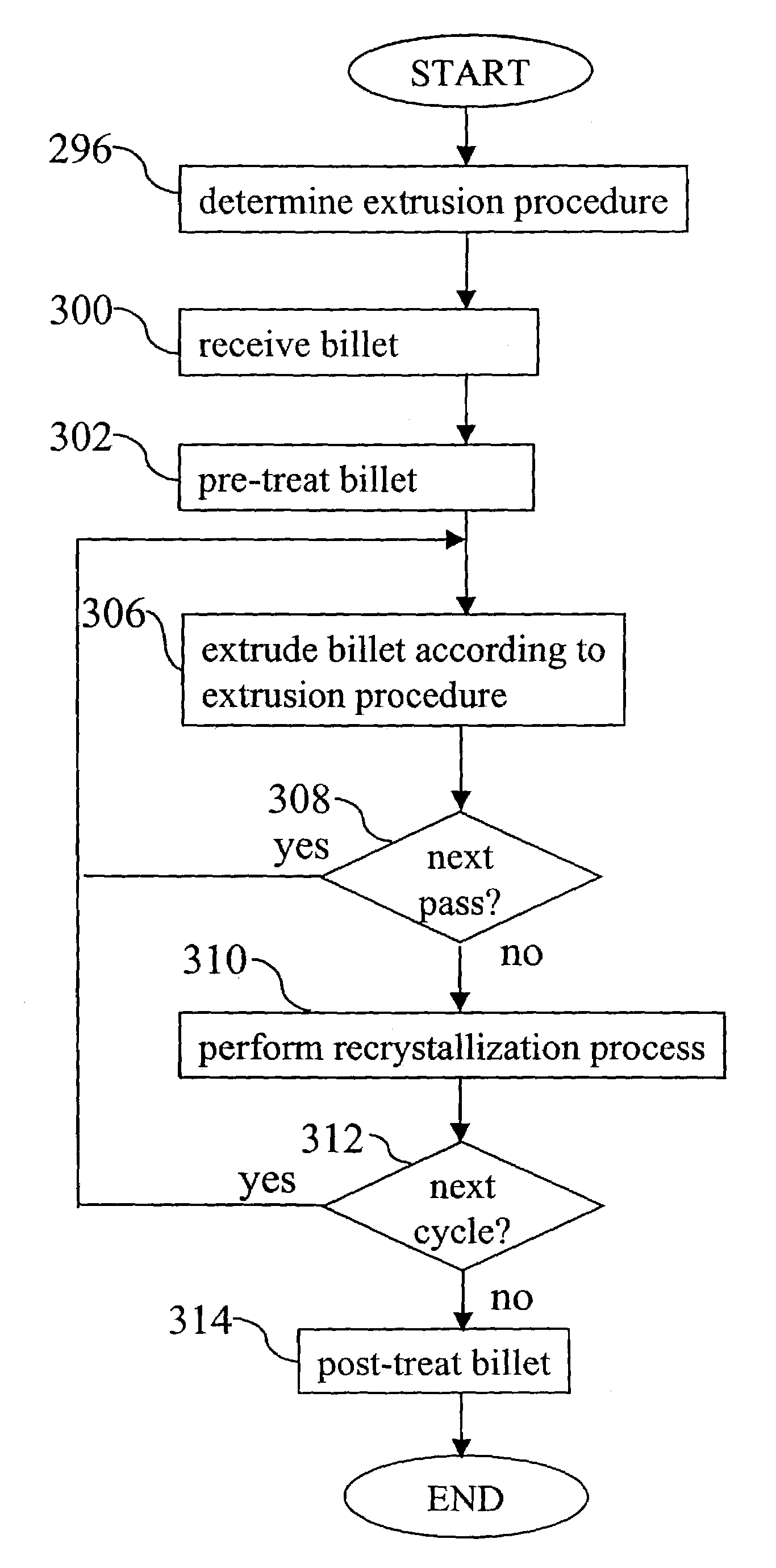
InactiveUS6976380B1Uniform textureUniform microstructureShaping toolsInlet channelEqual channel angular extrusion
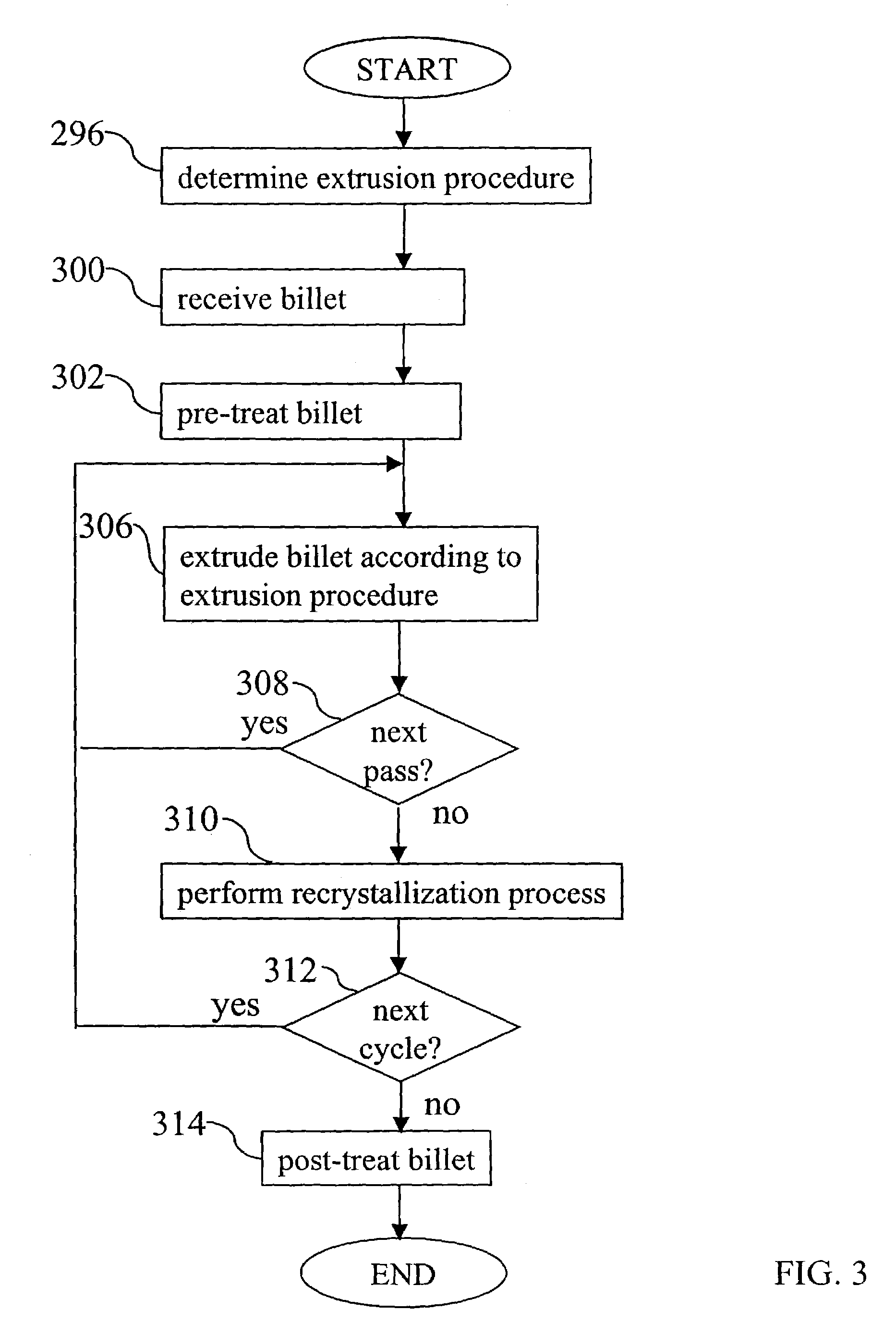
Developing a texture of a material includes receiving a billet of material having an initial texture. The billet is associated with an extrusion procedure having extrusion routes executed as passes. The following is repeated for each pass to transform the initial texture to a developed texture: the billet is extruded through an inlet channel of an equal channel angular extrusion die according to the routes, and the billet is extruded through an outlet channel of the equal channel angular extrusion die according to the extrusion routes.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
Method for extrusion two-step equal channel angle of magnesium alloy
InactiveCN1792487AGrain refinementImprove organizational structureExtrusion control devicesEqual channel angular extrusionMaterials processing
A two-step squeeze method with equal channel angle for Mg-alloy includes such steps as designing equi-channel squeezing die set, regulating deformation speed and temp to find out the lowest temp for non-crack deformation, equichannel squeezing by 2-4 passes, lowering the deformation temp, and squeezing by 4-8 passes. Its advantage is high strength and toughness.
Owner:FENGYANG L S NET FORMING CO LTD
Nanostructured commercially pure titanium for biomedicine and a method for producing a rod therefrom
ActiveUS8919168B2Improve failureImprove propertiesNanostructure manufacturePig casting plantsEqual channel angular extrusionCommercially pure titanium
Commercially pure titanium having UFG structure and enhanced mechanical and biomedical characteristics has nanocrystalline alpha-phase grains with a hexagonal close-packed lattice, in which the share of grains with a size of 0.1 . . . 0.5 μm and a grain shape coefficient of no more than 2 in the mutually perpendicular planes makes no less than 90%, over 60% of the grains having high-angle boundaries disoriented in relation to the adjacent grains by the angles from 15 to 90°.The method for making a rod of the material provides for equal-channel angular pressing of a billet at T≦450° C. with the total accumulated true strain e≧4 to effect severe plastic deformation of the billet and subsequent thermomechanical treatment with a gradual decrease of the temperature in the range of 450 . . . 350° C. and the strain rate of 10−2 . . . 10−4 s−1 with the strain degree from 40 to 80% to effect additional plastic deformation.
Owner:FSBFEI HPE USATU 50 +1
ECAE (equal channel angular extrusion) based preparation method of ultrafine crystal NiTi shape memory alloy tube
The invention provides an ECAE (equal channel angular extrusion) based preparation method of an ultrafine crystal NiTi shape memory alloy tube. A metal core is inserted into a NiTi shape memory alloy tube blank to be shaped, then the NiTi shape memory alloy tube blank is enclosed in a metal covering, and the metal covering, the NiTi shape memory alloy tube blank and the metal core are simultaneously extruded to generate shear plastic deformation in an ECAE production tool consisting of male die and a female die, so as to realize grain refinement of the NiTi shape memory alloy tube blank. Based on the fundamental of the ECAE method, a preparation method of an ultrafine crystal NiTi shape memory alloy tube is provided by the invention, so that high quality ultrafine crystal NiTi shape memory alloy tube can be produced, and production costs of the ultrafine crystal NiTi shape memory alloy tube can be reduced substantially.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Large plastometric set method for producing ultra-fine crystal material
InactiveCN101294238AOvercome deficienciesExtended service lifeProcess efficiency improvementEqual channel angular extrusionUltra fine
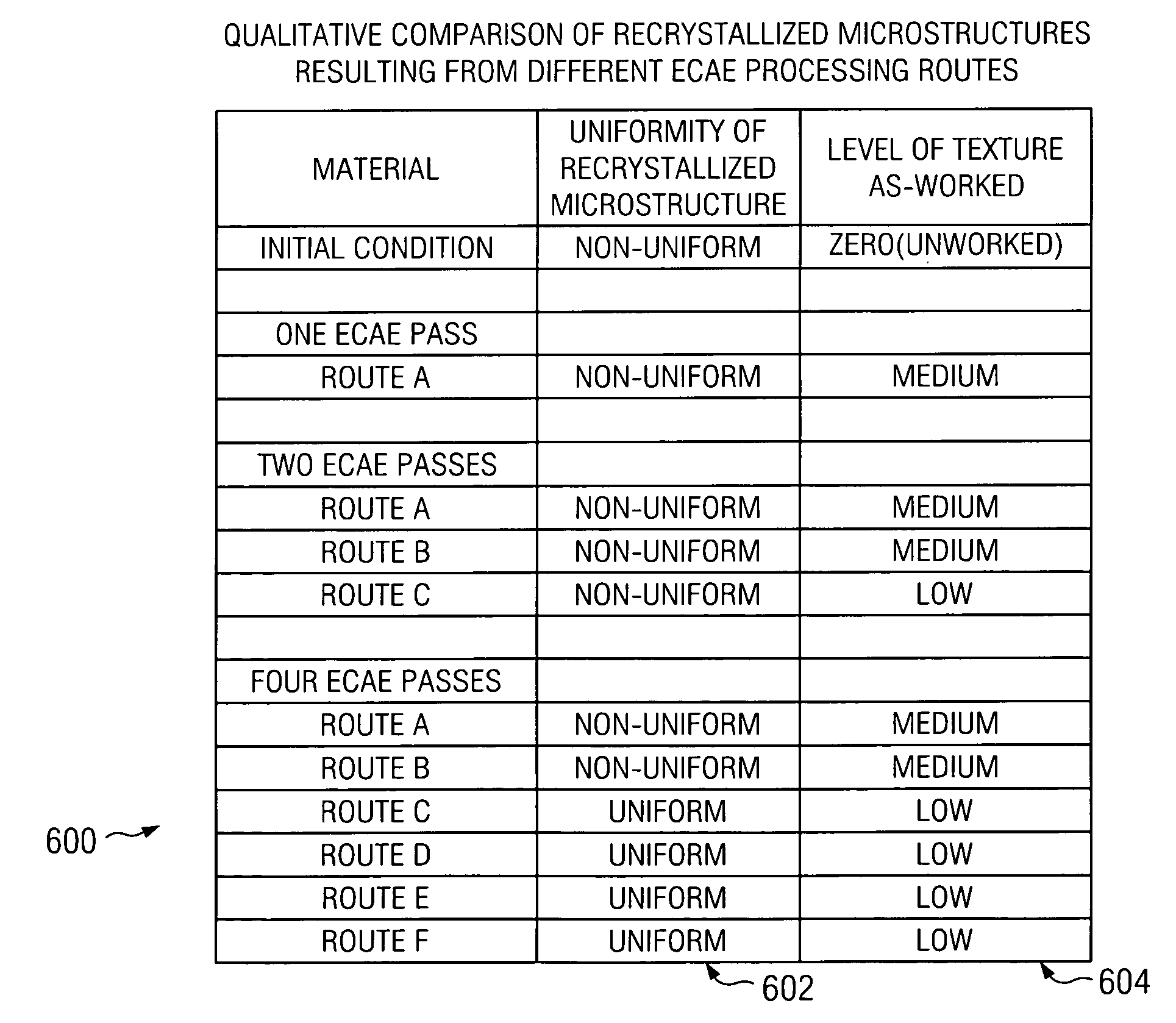
The invention provides a severe plastic deformation method for manufacturing ultra-fine grain material, which comprises an equal-channel angular extrusion step. The method is characterized in that the severe plastic deformation method has the following processing steps, namely the preparation of raw material, homogenizing annealing, compression extrusion deformation, equal-channel angular extrusion deformation, repeated upsetting-extrusion deformation, and annealing treatment. The shapes and sizes of the material before and after the extrusion deformation are the same so as to realize the multi-pass accumulated deformation; combining the other technologies, the disadvantages during the manufacture process of the ultra-fine grain material are effectively avoided because of absorbing the advantages of a equal-channel angular extrusion method, thereby realizing that the uniform ultra-fine grain microstructure material can be obtained after less-pass upsetting-extrusion deformation; therefore, the uniform and stable ultra-fine grain bulk material is obtained, in addition, the productivity effect is increased obviously, the service life of an extrusion die is prolonged, the manufacturing cost is lowered, and the severe plastic deformation method is favorable for realizing large-scale industrial production at the same time.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation method for ultra-fine grain pure titanium through equal channel angular pressing
The invention provides a preparation method for ultra-fine grain pure titanium through equal channel angular pressing. According to the invention, test conditions are improved on the basis of the prior art, a to-be-extruded sample is designed to be a copper-wrapped titanium rod, so frictional force generated during contact between the sample and a channel is reduced during extruding; extruding force is decreased to no more than 150 KN, so experimental operability is improved, and refining of industrial pure titanium can be finished at room temperature under small extruding force through equal channel angular pressing. At room temperature, the phenomena of restoring and recrystallization softening of crystal grains during refining hardly occur, so a substantial crystal grain refining effect is obtained and a high-strength industrial pure titanium block can be obtained through few times of extruding. According to results of testing of mechanical properties of the prepared ultra-fine grain pure titanium, the ultra-fine grain pure titanium has substantially improved comprehensive mechanical properties, block ultra-fine grain pure titanium can be used in practice, and the application scope of the ultra-fine grain pure titanium is broadened.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Processing method of high-obdurability and high-conductivity copper magnesium alloy
The invention relates to a processing method of a high-obdurability and high-conductivity copper magnesium alloy, which comprises the following steps of: 1) with cathode copper and pure magnesium as raw materials, preparing the copper magnesium alloy with the magnesium content of 0.1-0.4 percent, and adopting an up-drawing continuous casting technology and continuous hot extrusion processing to obtain a copper magnesium alloy feedstock with the average particle size of 5-10 microns; and 2) carrying out continuous equal channel angular extrusion processing on the copper magnesium alloy feedstock obtained in the step 1) to finally obtain the copper magnesium alloy, wherein the extrusion temperature is 273-573K, an equal channel angle in a die is 90-120 degrees, the average particle size of the copper magnesium alloy is smaller than 500nm, the tensile strength is no less than 560MPa, the elongation is no less than 20 percent, the electrical conductivity is no less than 80 percent IACS, and the copper magnesium alloy can be used for a contact line material of a high-speed railway. With the adoption of the processing method, copper magnesium alloy crystal particles can be remarkably refined, the obdurability of the copper magnesium alloy is greatly improved, the processing process is also simple, and subsequent processing is not needed.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV +1
Preparation method of preferentially oriented n-type bismuth telluride-based polycrystalline bulk thermoelectric material
ActiveCN110002412AImprove performanceGood repeatabilityMetal selenides/telluridesBismuth tellurideHearth
The invention provides a preparation method of a preferentially oriented n-type bismuth telluride-based polycrystalline bulk thermoelectric material, comprising the following steps: using Bi, Te and Se elemental powders as raw materials, weighing the ingredients according to Bi2Te3-xSex stoichiometric ratio, placing the above raw materials into a quartz glass tube or a high borosilicate glass tubeand vacuum-sealing, putting the sealed quartz glass tube or the high borosilicate glass tube into a rocking furnace and fully smelting, rotating a hearth of the rocking furnace to a vertical positionafter the smelting, and cooling to prepare an n-type bismuth telluride-based alloy ingot; cutting the prepared n-type bismuth telluride-based alloy ingot into blocks, and placing the blocks into an equal channel angular extrusion die and sintering and extruding in a hot-pressed sintering furnace so as to obtain the preferentially oriented n-type bismuth telluride-based polycrystalline bulk thermoelectric material. The prepared n-type bismuth telluride-based polycrystalline bulk thermoelectric material has low resistivity, high Seebeck coefficient, low thermal conductivity and high dimensionless thermoelectric figure of merit.
Owner:湖北赛格瑞新能源科技有限公司
Mould of pure titanium equal channel angular extrusion and process method
InactiveCN103252377AIncrease squeezeSqueeze to meetExtrusion diesTitaniumEqual channel angular extrusion
The invention provides a mould of pure titanium equal channel angular extrusion and a process method. An integral concave mould design is adopted. A concave mould comprises a concave mould main body, a concave mould base and a concave mould cover plate; the mould of the pure titanium equal channel angular extrusion comprises an equal angular channel; the concave mould main body comprises the equal angular channel; the concave mould cover plate comprises a side face of the equal angular channel; and the concave mould main body and the concave mould cover plate are fastened by a bolt and a nut. The mould of the pure titanium equal channel angular extrusion disclosed by the invention adopts a novel mould structure of the integrated concave mould so that the extrusion force capable of being borne by the mould is increased; with the adoption of an isothermal extrusion technology, the extrusion of pure titanium with a close-packed hexagonal structure, higher rigidity and lower plasticity and the equal angular channel of an alloy thereof can be met; the mould is relatively simple in structure, and lubrication and fault treatment of the channel are convenient to carry out; and the service life of the mould can be prolonged to a certain extent.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Method of forming a structural component having a NANO sized/sub-micron homogeneous grain structure
A method of making nano / sub-micron sized grains in a work piece material having a lateral side has the steps of providing a die. The die has an entrance channel with a longitudinal axis and an exit channel. The entrance channel and the exit channel are connected to one another to form an angle. The method has the step of providing a first sacrificial material with a complementary size to the work piece and placing the sacrificial first material and the work piece in an entrance channel. The first sacrificial material and the work piece are aligned with the longitudinal axis. The method has the step of extruding the combination of the first sacrificial material, and the work piece through the intersection of the entrance and the exit channels. The resulting shear deformation forms the nano / sub-micron sized grains in the work piece. This configuration reduces frictional effects thereby producing homogenous nano grain structure. This configuration reduces applied load and enables equal channel angular extrusion of thin sheets.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Equal channel angular twist extrusion preparation process for porous copper-based shape memory alloy
The invention discloses an equal channel angular twist extrusion preparation process for a porous copper-based shape memory alloy. The process is characterized by comprising the following steps: pressing and sintering the mixed Cu-Zn-Al powder by virtue of a simple pressing mold; performing multi-pass equal channel angular twist extrusion (ECAP-T) formation on the sintered blank, so that the grains of the powder sintered body are crushed, sub-grains and lots of nucleation are generated, and the grains are refined; performing quenching heat treatment on the porous sintered copper-based blank subjected to multi-pass equal channel angular twist extrusion, finally obtaining solution treatment, thereby obtaining the copper-based shape memory alloy material with good preparation performance. Compared with the prior art, the process disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the formation processes such as powder smelting, casting, repeated hot forging and repeated rolling needed in the preparation of the traditional porous copper-based shape memory alloy are omitted in the whole preparation process, the preparation cost is greatly reduced, the production process is simple, the process route is short, and the green and environment-friendly effects are intensified. From the characteristics of the whole preparation process, the process method has the characteristics of the conventional preparation process of the porous copper-based shape memory alloy, such as a hot isostatic pressing method, a conventional powder sintering method, a sintering evaporation method and the like.
Owner:JIUJIANG UNIVERSITY
Method and apparatus for equal channel angular extrusion of flat billets
InactiveUS20070131013A1Eliminate surface cracksGood material uniformityCost effectivenessControl system
Owner:ENGINEERED PERFORMANCE MATERIALS
Preparation method of magnesium alloy microtubule and special-purpose die
Owner:常州市申鑫新材料科技有限公司
Low-temperature high-strength and high-toughness wear-resistant aluminum and bronze alloy and preparing method thereof
The invention discloses low-temperature high-strength and high-toughness wear-resistant aluminum and bronze alloy and a preparing method thereof. The aluminum and bronze alloy comprises the following components in a percent by weight: 6.5-12.0% of aluminum, 2.0-5.5% of iron, 2.5-6.0% of nickel, 0.5-3.0% of manganese, 0.2-0.3% of titanium and the balance of bronze. The aluminum and bronze alloy is prepared by carrying out a casting and hot-forging technology and an equal-channel angular extrusion technology on metal raw materials corresponding to each component. The aluminum and bronze alloy has better impact toughness at the low temperature of -196 DEG C than at room temperature, and the comprehensive mechanical properties of the aluminum and bronze alloy are obviously improved. The aluminum and bronze alloy is particularly suitable for manufacturing wear-resistant parts used in low-temperature environments in the fields of aviation, aerospace and the like and has great meaning in reducing production cost, improving product quality and prolonging the service life of equipment.
Owner:GENERAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE FOR NONFERROUS METALS BEIJNG
Preparation method of fine-grain/ultra-fine-grain metal stratified material
InactiveCN103394537AImprove impact resistanceImprove bending abilityExtrusion diesUltra fineShearing deformation
The invention discloses a preparation method of a fine-grain / ultra-fine-grain metal stratified material. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: (1) selecting n metal material samples, and preprocessing laminated faces of the metal material samples, wherein n is more than or equal to 2; and (2) laminating the metal material samples to form a combined sample, putting the combined sample into a non-equal channel angular extrusion-rolling mold, carrying out composite extrusion-rolling: applying an extrusion force to enable the combined sample to pass through a corner of the mold so that the combined sample generates shear deformation and compression deformation at the same time so as to form the fine-grain / ultra-fine-grain metal stratified material, wherein the composite extrusion-rolling is single-pass composite extrusion-rolling or multi-pass composite extrusion-rolling. By utilizing the method disclosed by the invention, the fine-grain or ultra-fine-grain metal stratified material can be prepared, and the high interface bonding strength can be achieved. The method has the characteristics of simple process, high efficiency, low device requirement and the like; and meanwhile, the material prepared by utilizing the method has good mechanical properties.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of laminated composite materials of different alloys
ActiveUS20080276681A1Low costImprove reliabilityExtrusion control devicesMetal layered productsBond interfaceShearing deformation
The invention relates to a new preparation technique of composites, in details, i.e. a method of producing laminated composite materials of different alloys. In the preparation method, the bi-layer or multi-layer composites are prepared by means of the equal channel angular extrusion / pressure (ECAE / ECAP). Firstly, the appropriate alloys pairs or groups are selected, and the rational arrangements are carried out after pre-treating surfaces; then, the clad process is performed by extrusion and shear deformation in ECAE die; finally, the composite material is produced after one single pass or multiple passes clad extrusion. The annealing treatment can be performed subsequently to enhance the interfacial bonding strength by diffusion after the clad extrusion, and the heat treatment parameters consist of annealing temperature and holding time, which are chosen carefully to meet the demands of the refining microstructures and good properties for both the interfaces and individual component metals. Consequently, the layer-metal composite is produced with the firmly bonding interface, good microstructures and excellent properties. In the invention, the selection and assembling manners of the materials are very free, such as composites with bi-layer or interval multi-layer manners, and the method is suitable for most of the metal materials. The invention is a new method of fabricating composites and the preparation cost is low enough to meet the demand of large-scale industrial production.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Ultrasonic wave vibration equal channel angular extrusion combined mold
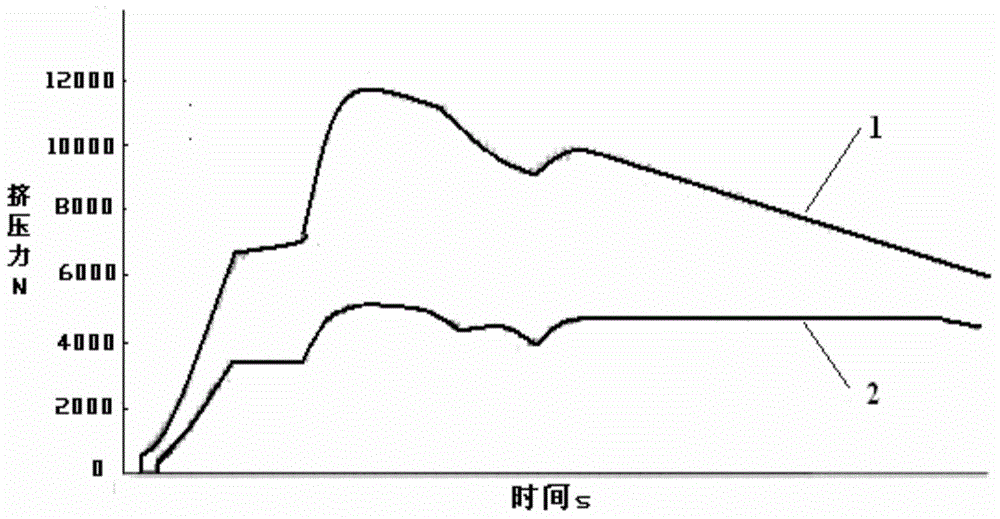
ActiveCN104307910ALower yield stressHigh fillingExtrusion diesMechanical vibrations separationFlow stressEqual channel angular extrusion
The invention discloses an ultrasonic wave vibration equal channel angular extrusion combined mold. An ultrasonic wave vibration system is fixed on a mold base in the vertical direction; an L-shaped concave mold hole is formed in the output end of the ultrasonic wave vibration system; the feeding direction of the concave mold hole is parallel to the ultrasonic wave vibration direction; the discharge direction of the concave mold hole is perpendicular to the ultrasonic wave vibration direction; guide columns are uniformly arranged on the mold base; guide sleeves which relatively move in match with the guide columns are arranged on the guide columns; the guide sleeves are fixed on a top base of the mold; a convex mold is also fixed on the top base of the mold; a plurality of material guide sleeve support rods are uniformly fixed on the mold base; material guide sleeve fixing plates are fixed on the tops of the material guide sleeve support rods; material guide sleeves in match with the convex mold are fixed on the material guide fixing plates; the material guide sleeves are positioned above the convex mold hole; gaps are formed between the material guide sleeves and the concave mold hole. The ultrasonic wave vibration system and an equal channel angular extrusion mold are reasonably combined to form the ultrasonic wave vibration equal channel angular extrusion combined mold, so that both the yield stress and the flowing stress of a material are reduced, and crystal grains of the material are refined, and the comprehensive mechanical property of the material is improved.
Owner:JIANGHAN UNIVERSITY
Apparatus for Deformation of Solid Sections
ActiveUS20130276501A1Extrusion profiling toolsAuxillary shaping apparatusInlet channelEqual channel angular extrusion
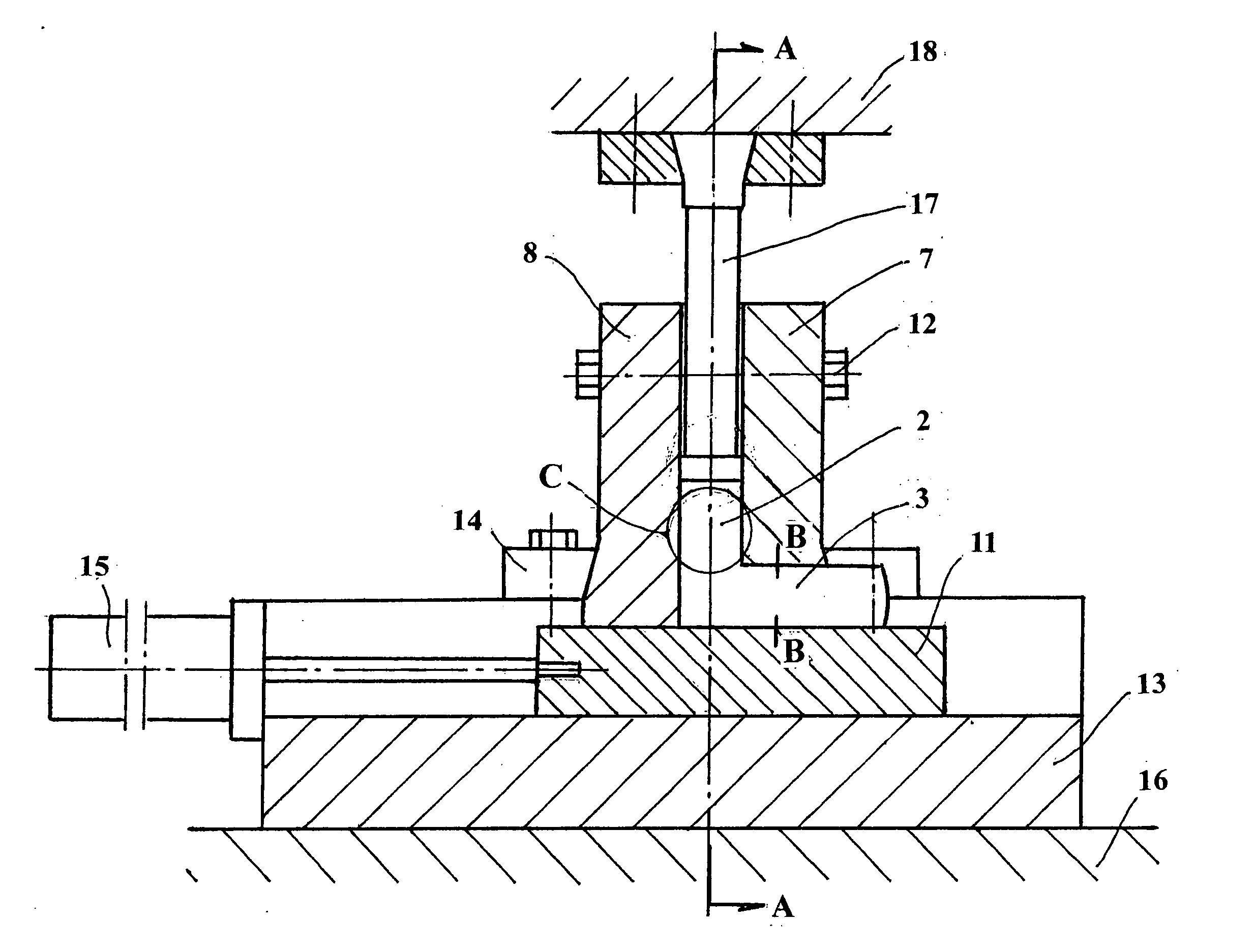
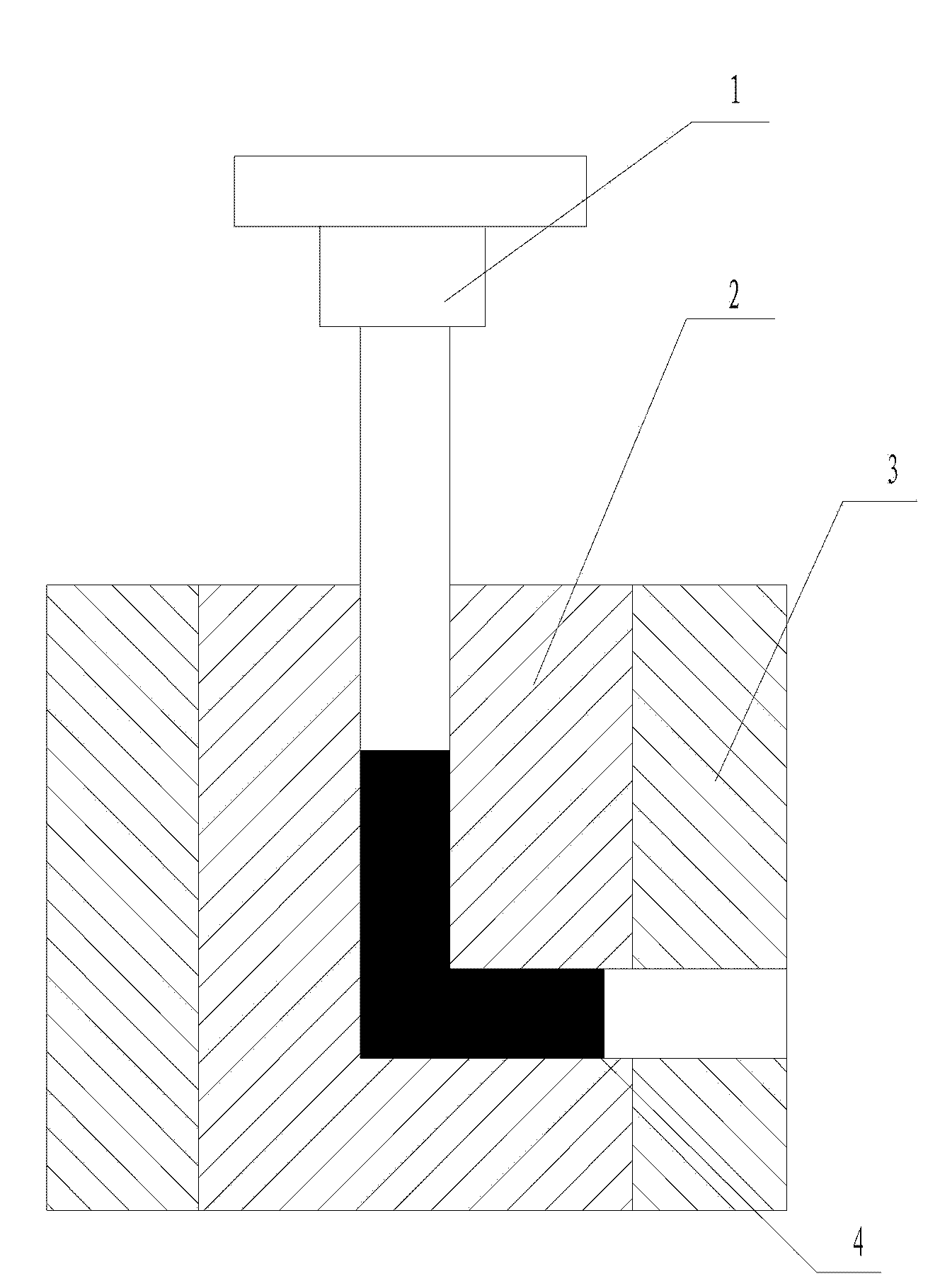
An equal channel angular extrusion tool comprising a punch assembly, a die set assembly, a base assembly, and a bottom slider assembly. The punch assembly comprises a punch, a punch nose, and a punch trolley. The die set assembly comprises an inlet channel and a removable core. The base assembly comprises a lifting mechanism which further comprises a die lift cylinder and a hold down ram. The bottom slider assembly comprises an ejection ram. The tool also includes a billet. The billet may be disposed in the bottom slider assembly. Severe plastic deformation is applied to the billet in the bottom slider assembly.
Owner:SHEAR FORM
Device capable of realizing accurate control of equal-channel angular extrusion processing route
InactiveCN101856678APrevent rotationAchieving sample rotationExtrusion diesExtrusion control devicesInlet channelEngineering
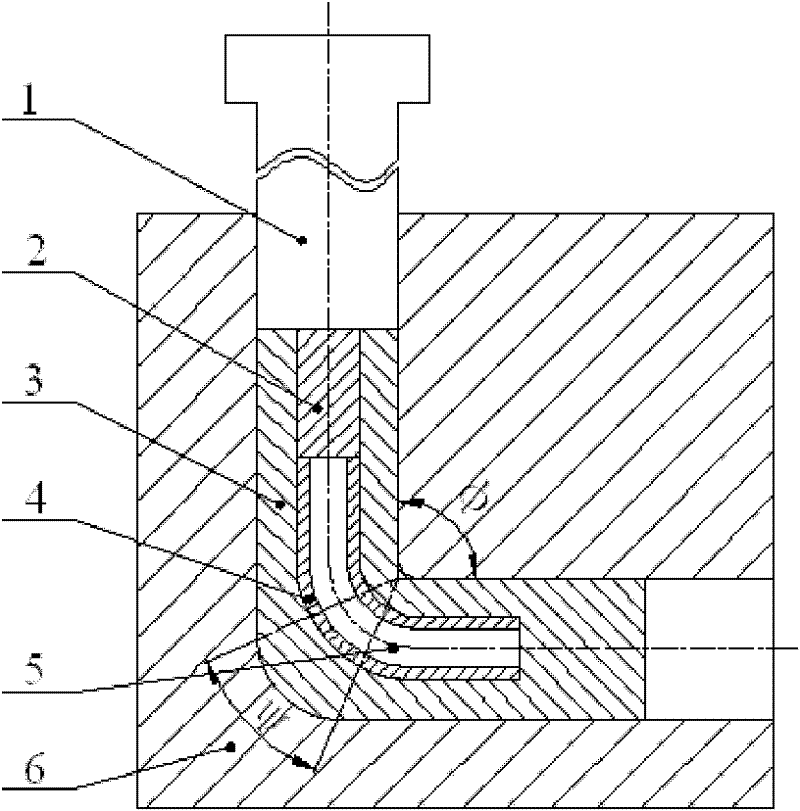
The invention discloses a device capable of realizing accurate control of an equal-channel angular extrusion processing route, which comprises an extrusion stem (1) and an extrusion female die (2); the extrusion female die (2) is divided into two half female dies which are connected through a plurality of bolts, a fixing ring (3) is sleeved at the periphery of the extrusion female die (2), the transverse cross-section of a female die channel (5) for the extrusion female die (2) takes a shape of regular polygon (N>=4), a section of extrusion channel (6) with slightly small sectional dimension is arranged at the position where an outlet channel of the female die channel (5) is adjacent to the corner, and the rest part of the outlet channel of the female die channel (5) is the same as the dimension of an inlet channel; and scales (7) at equal intervals are arranged on the surface at the inlet of the female die channel (5). The device is an equal-channel angular pressing device, which has the advantages of simple structure and reliable performance and can realize the wide-range of processing route and accurately control the rotational angle.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
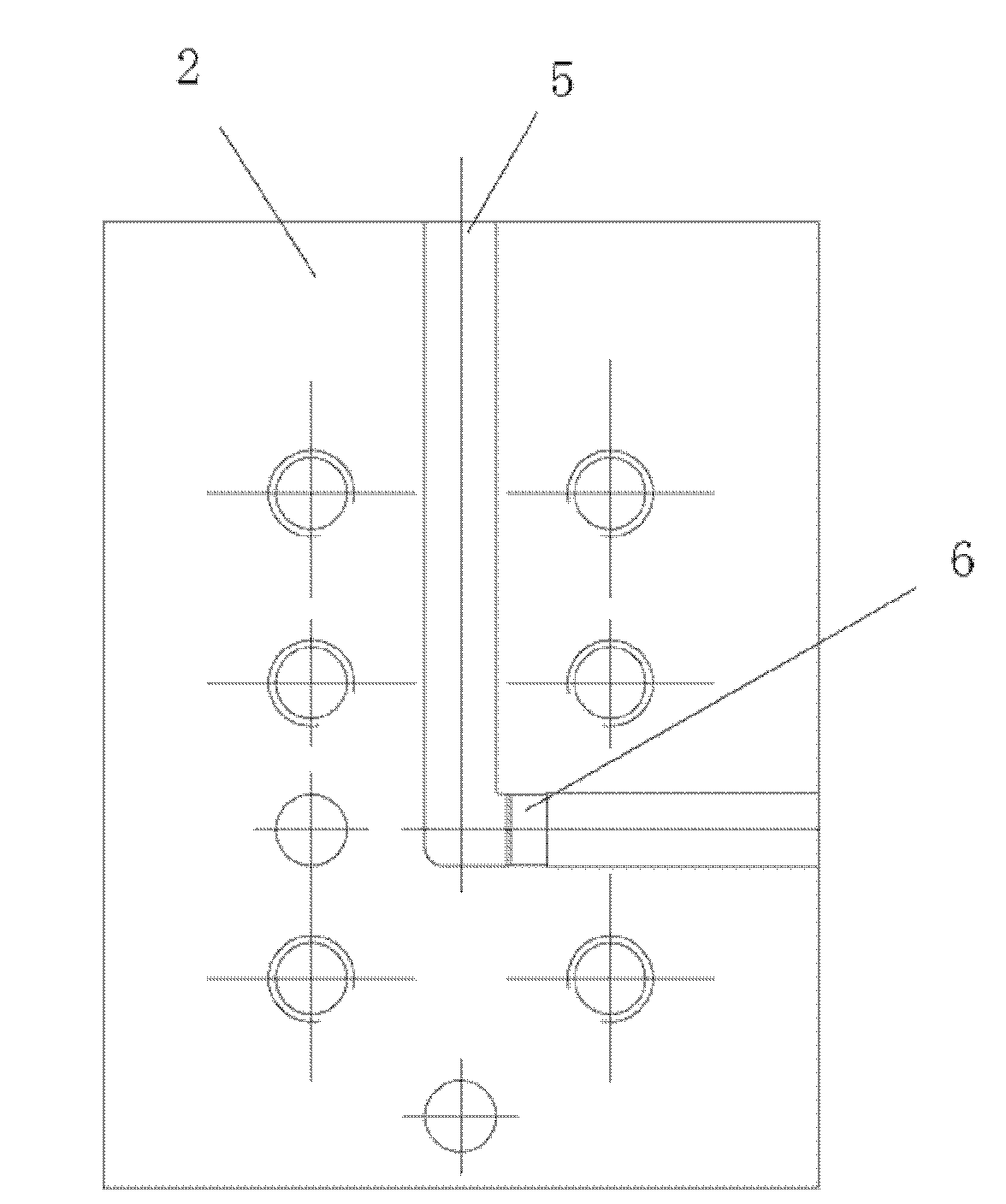
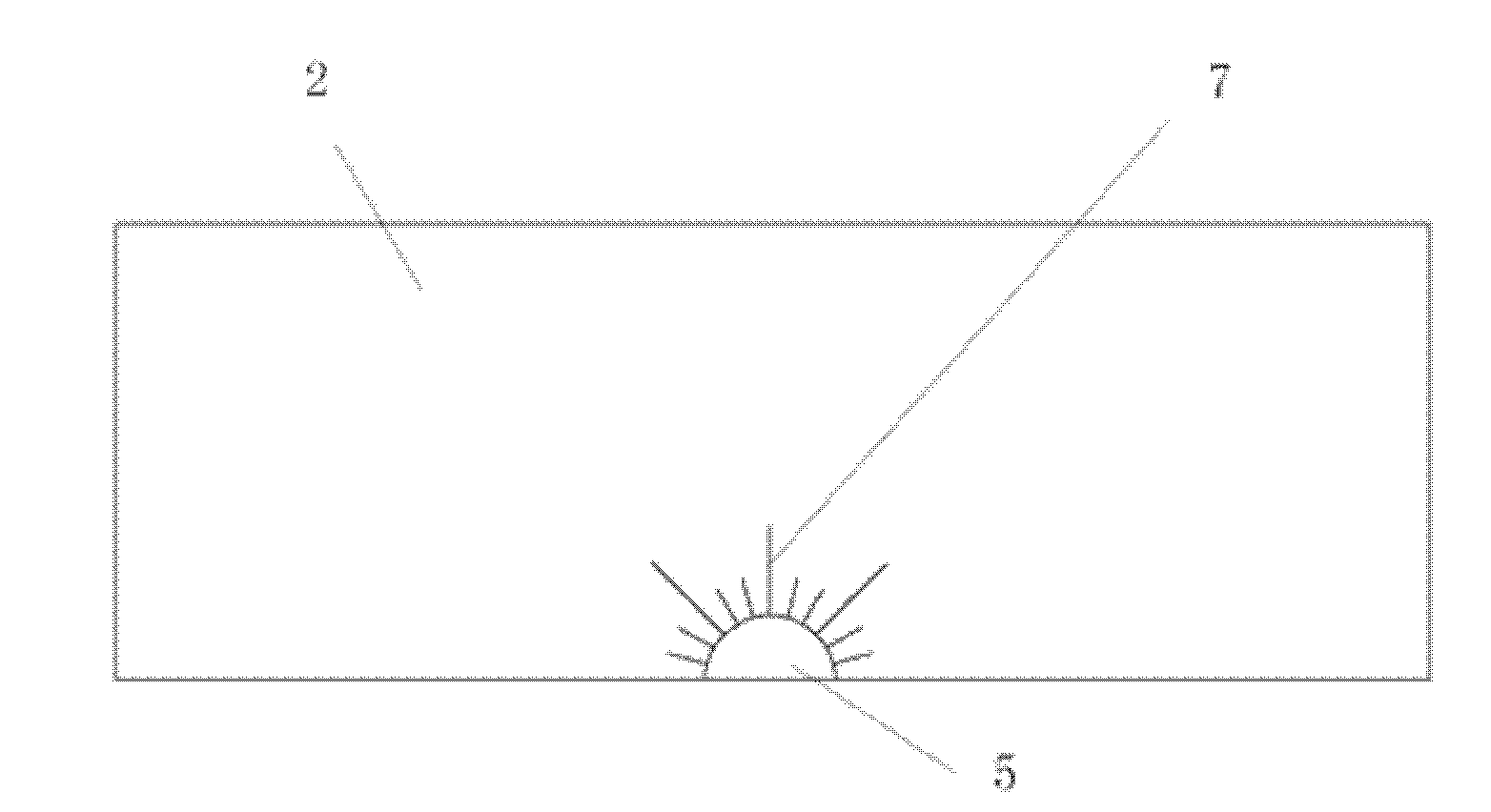
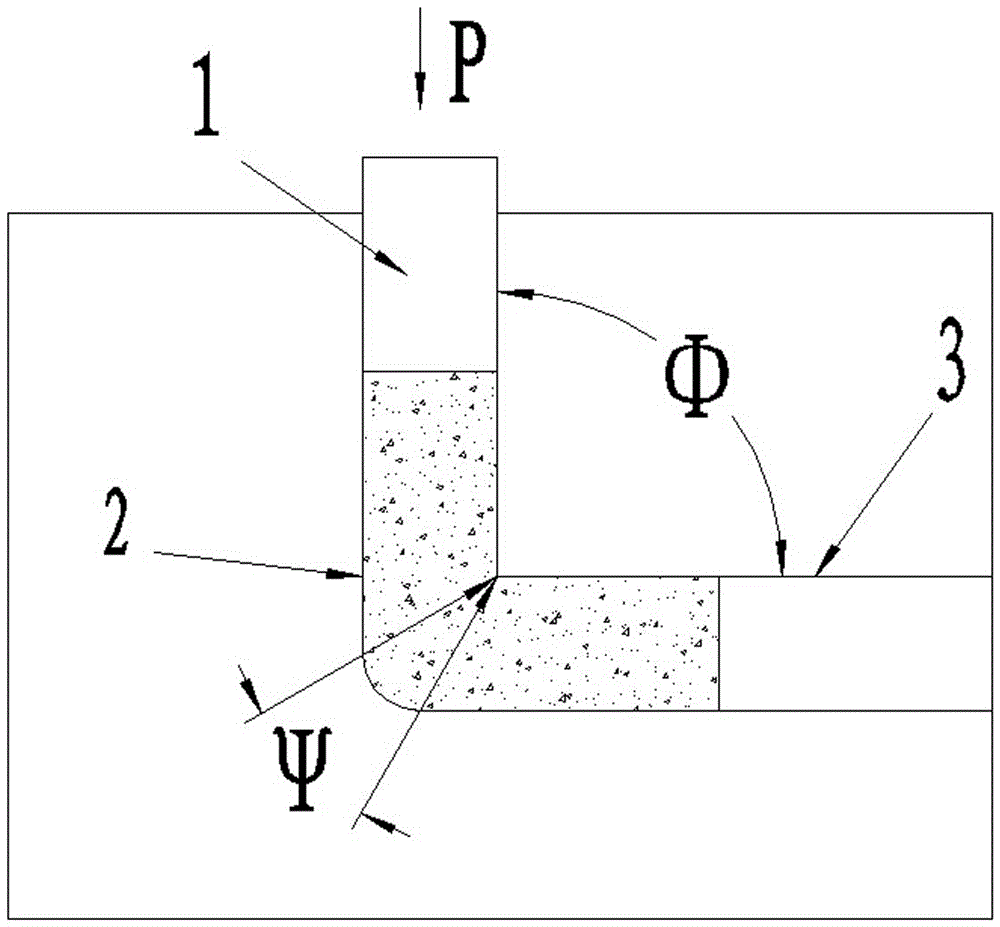
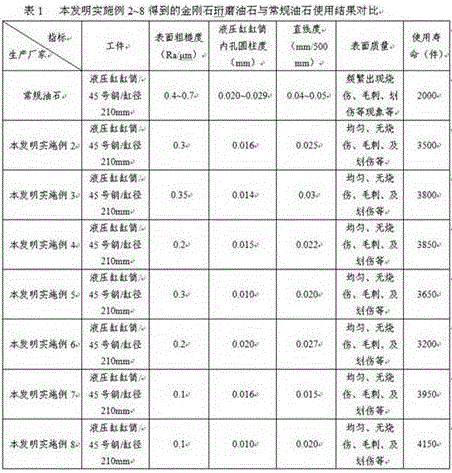
Diamond honing oilstone and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106217273AImprove cooling effectImprove plasticityAbrasion apparatusGrinding devicesHydraulic cylinderGranularity
The invention provides a diamond honing oilstone and a preparation method thereof. The diamond honing oilstone is prepared from, by weight percent, 5%-10% of diamond micro-powder with the granularity ranging from 400 meshes to 1000 meshes and 90%-95% of a metal bond. The metal bond is composed of 45%-55% of copper-tin pre-alloyed powder, 12%-20% of silver powder, 30%-33% of magnesium powder and 2%-5% of talcum powder with the granularity ranging from 200 meshes to 800 meshes. The specific preparation method includes the steps that an oilstone blank is prepared through the procedures such as material mixing, mold forming, sintering and equal channel angular extrusion; and finally, machining is conducted on the oilstone blank, and a finished product with the qualified size precision is obtained. The oilstone manufactured through the method solves the problems that at present, a hydraulic cylinder barrel honing oilstone machining hydraulic cylinder barrel is low in cylindricity and poor in straightness accuracy, the surface roughness does not reach the standard, and burns, burrs and hydraulic cylinder barrel inner hole surface scratches exist, meanwhile, hardness of the oilstone is improved, the shape retention is improved, and the service life is prolonged.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU RES INST FOR ABRASIVES & GRINDING CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com