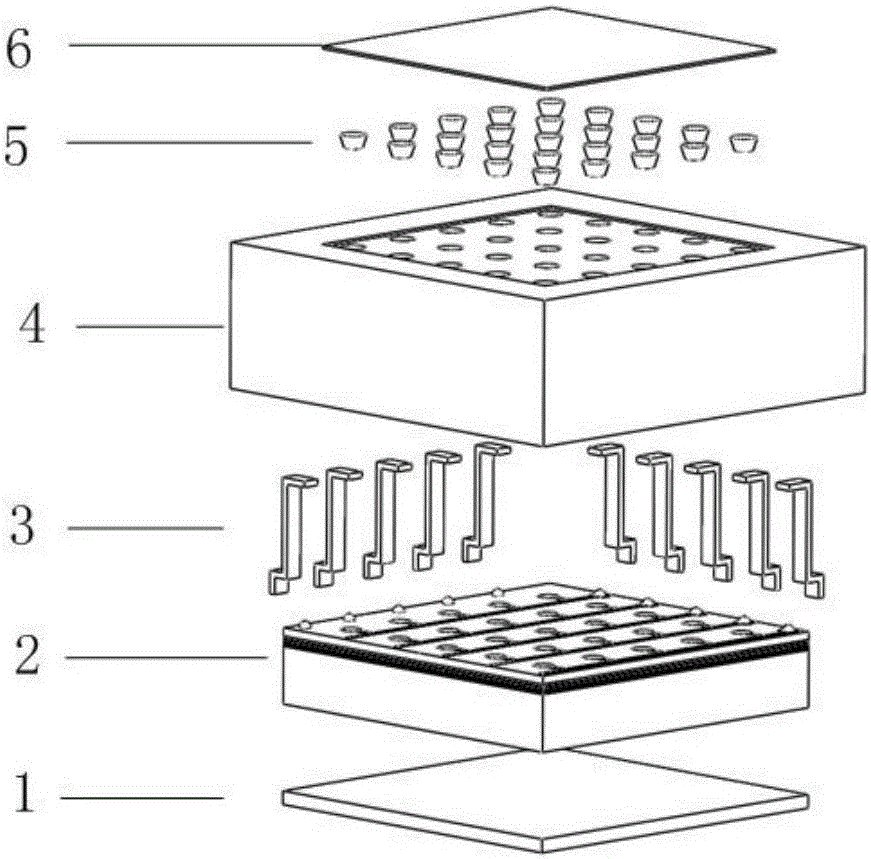
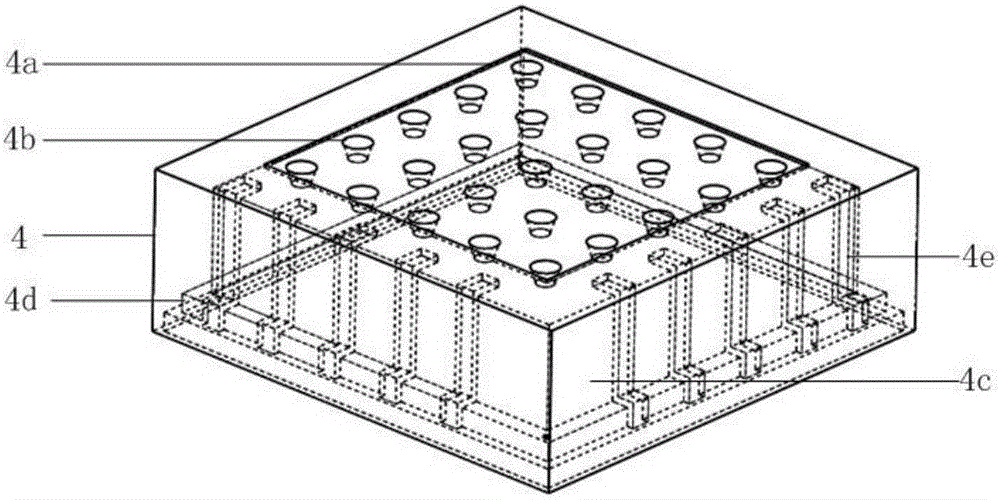
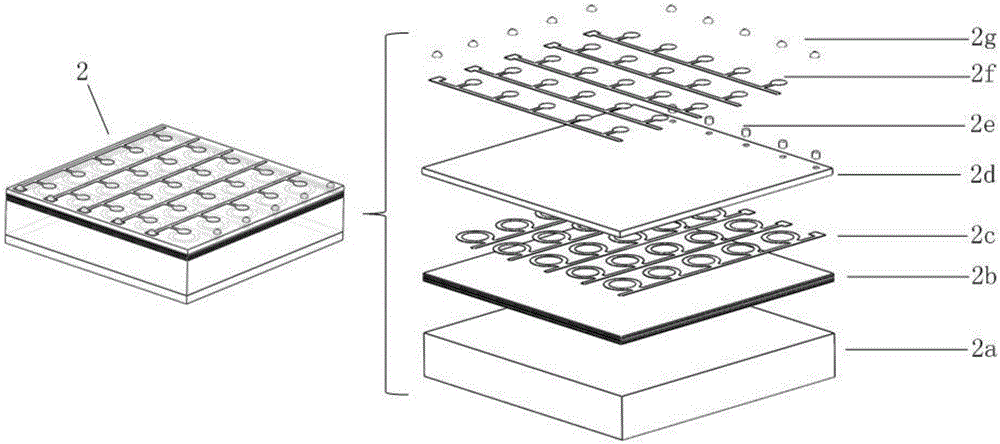
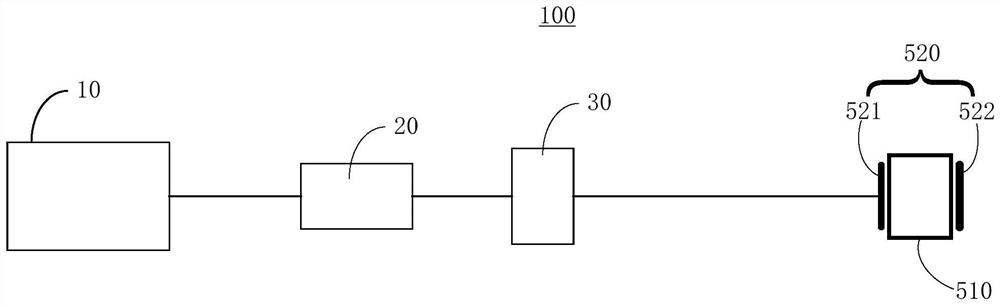
Patents
Literature
30 results about "Magnetic field imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
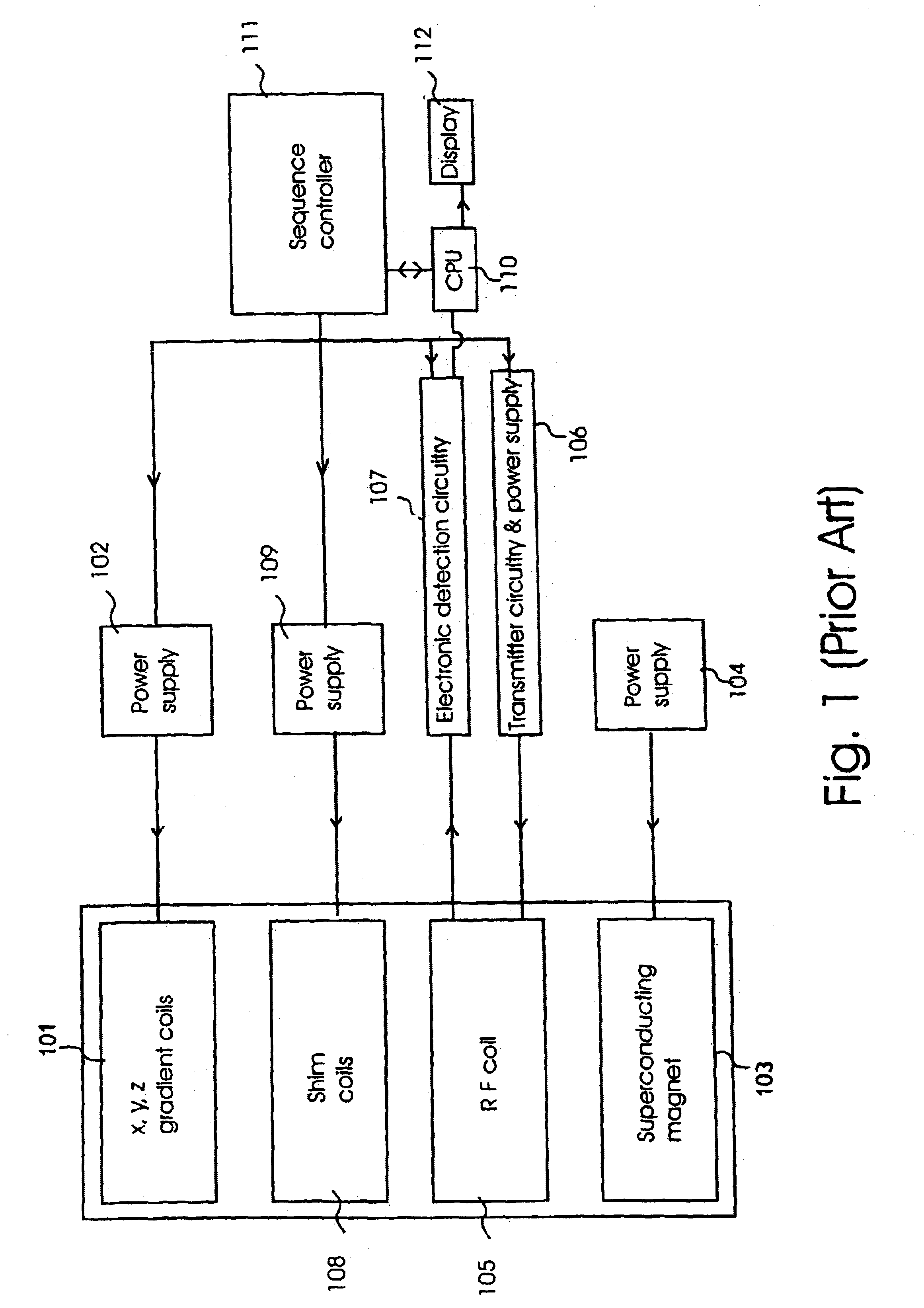
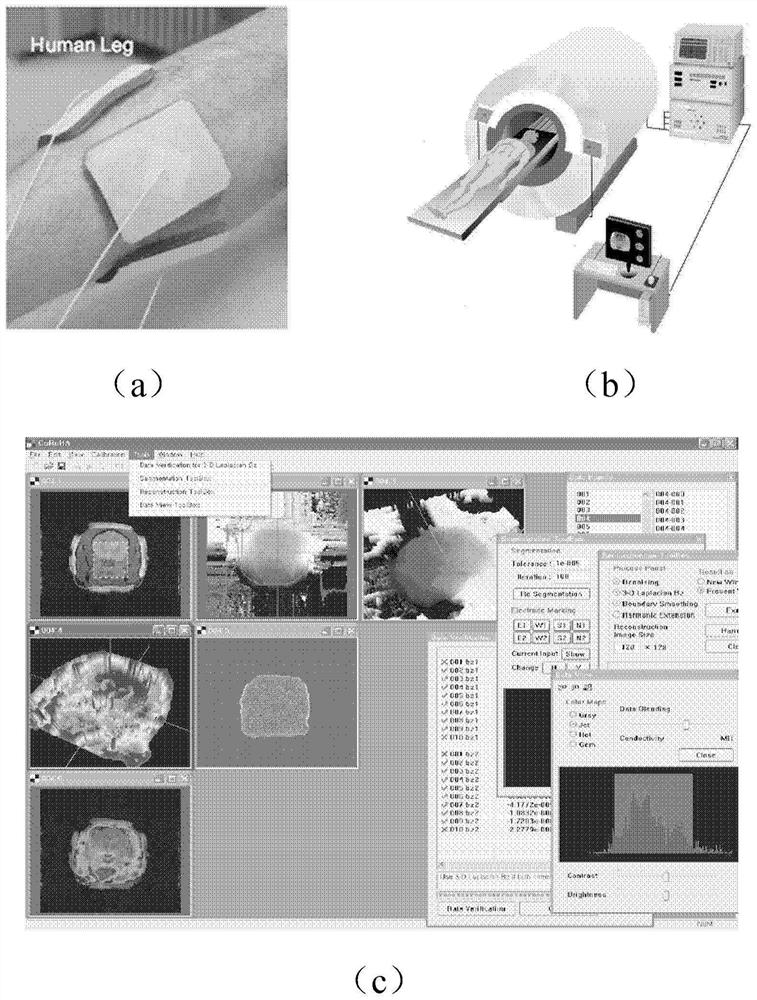
Magnetic Field Imaging (MFI) is a non-invasive and side-effect-free cardiac diagnostic method. In more recent technology, magnetocardiography (MCG) has become the clinically predominant application for recording the heart's magnetic signals. that detects and records the electromagnetic signals that are associated with the heartbeat using a multi-channel magnetic sensor array. The electric signals are known from the ECG. In the 1990s and beyond, more recent technology has supplanted the MFI, particularly MCG (xref. Cardiomag Imaging, Inc.). Through clinical research in Europe, Asia, and the U.S. (see publications in footnotes), MCG has been proven to have practical application for diagnosis of cardiac disease, and has become the clinically predominant application for recording the heart's magnetic signals. In comparison to MCG, MFI, among others, records the whole relevant area above the chest of the person.
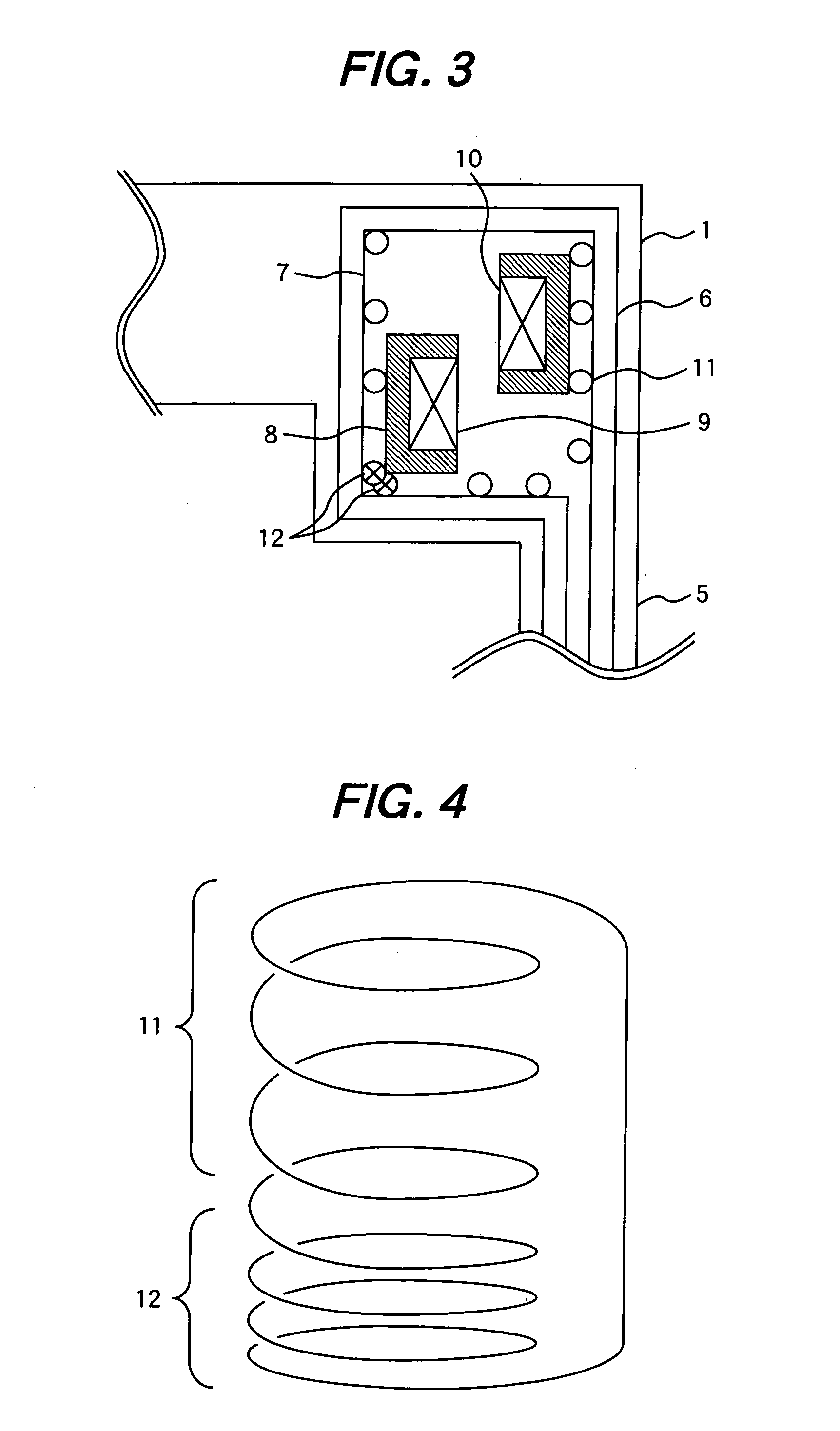
Multi-modality marking material and method
InactiveUS20050033157A1Enhance multi-modality imaging characteristicSurgeryDiagnostic markersDiagnostic Radiology ModalityImaging modalities
The present invention provides markers and methods of using markers to identify or treat anatomical sites in a variety of medical processes, procedures and treatments. The markers of embodiments of the present invention are permanently implantable, and are detectable in and compatible with images formed by at least two imaging modalities, wherein one of the imaging modalities is a magnetic field imaging modality. Images of anatomical sites marked according to embodiments of the present invention may be formed using various imaging modalities to provide information about the anatomical sites.
Owner:CARBON MEDICAL TECH
Methods & apparatus for magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS6980001B2Shorten Image Acquisition TimeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMagnetizationPhysical entity
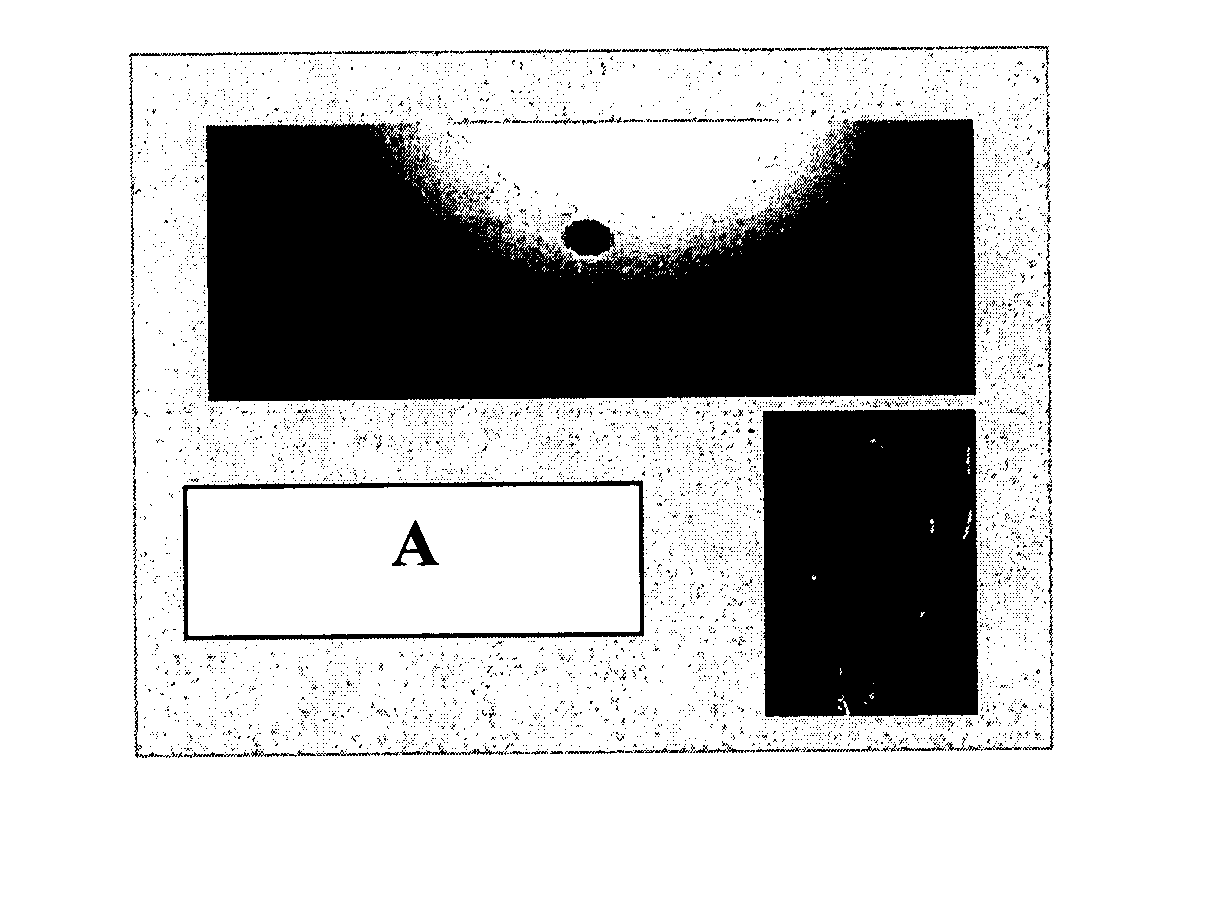
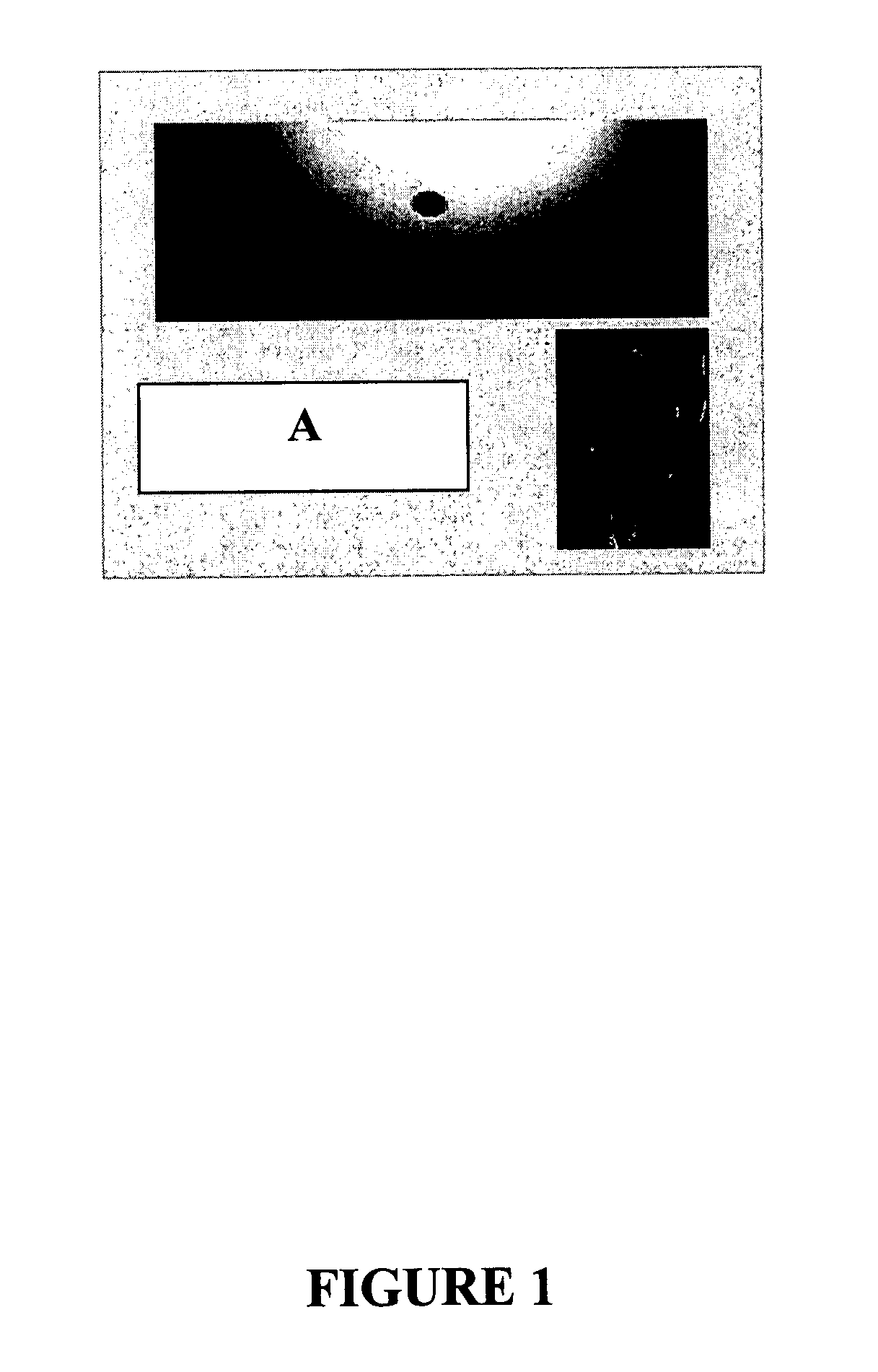
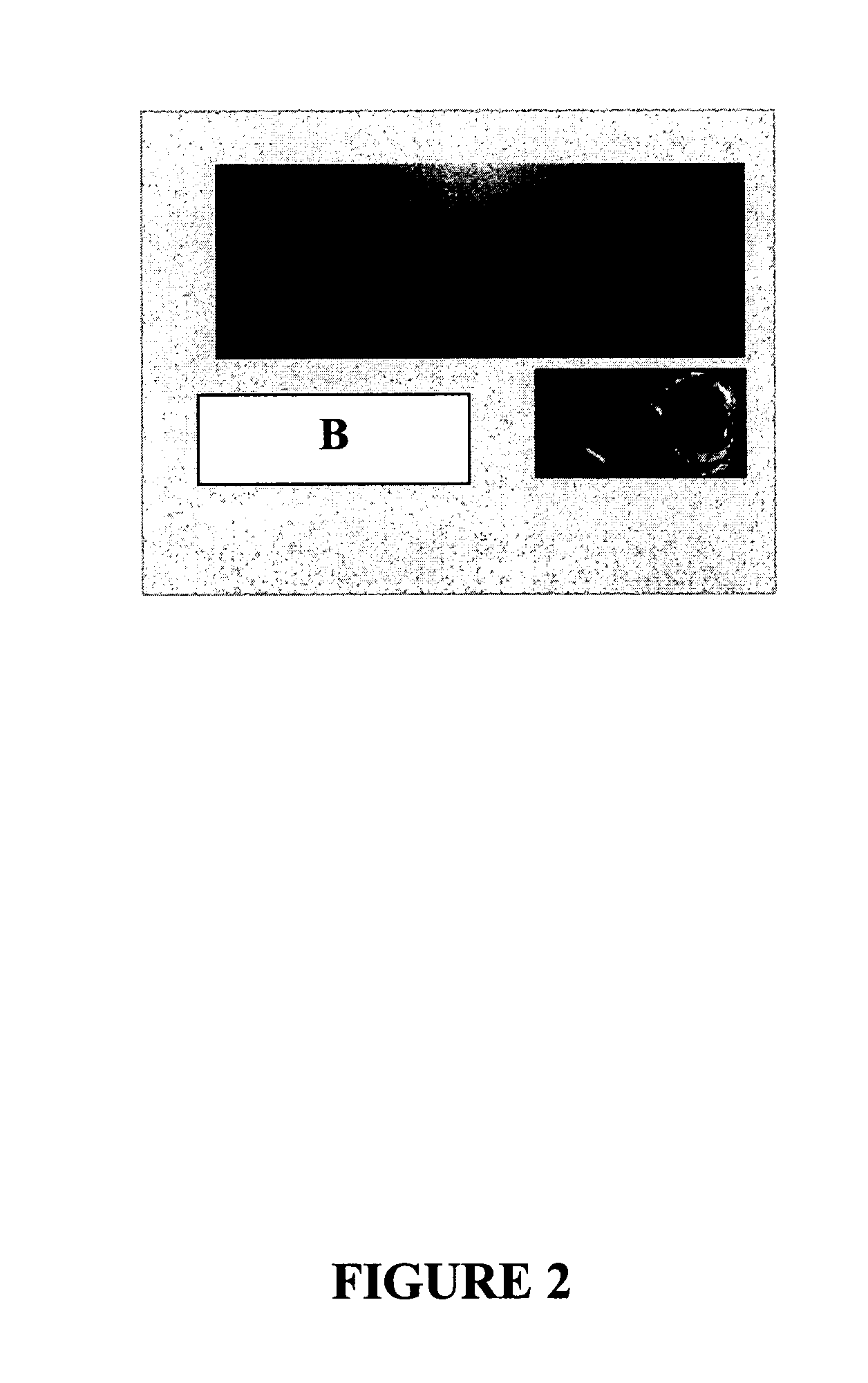
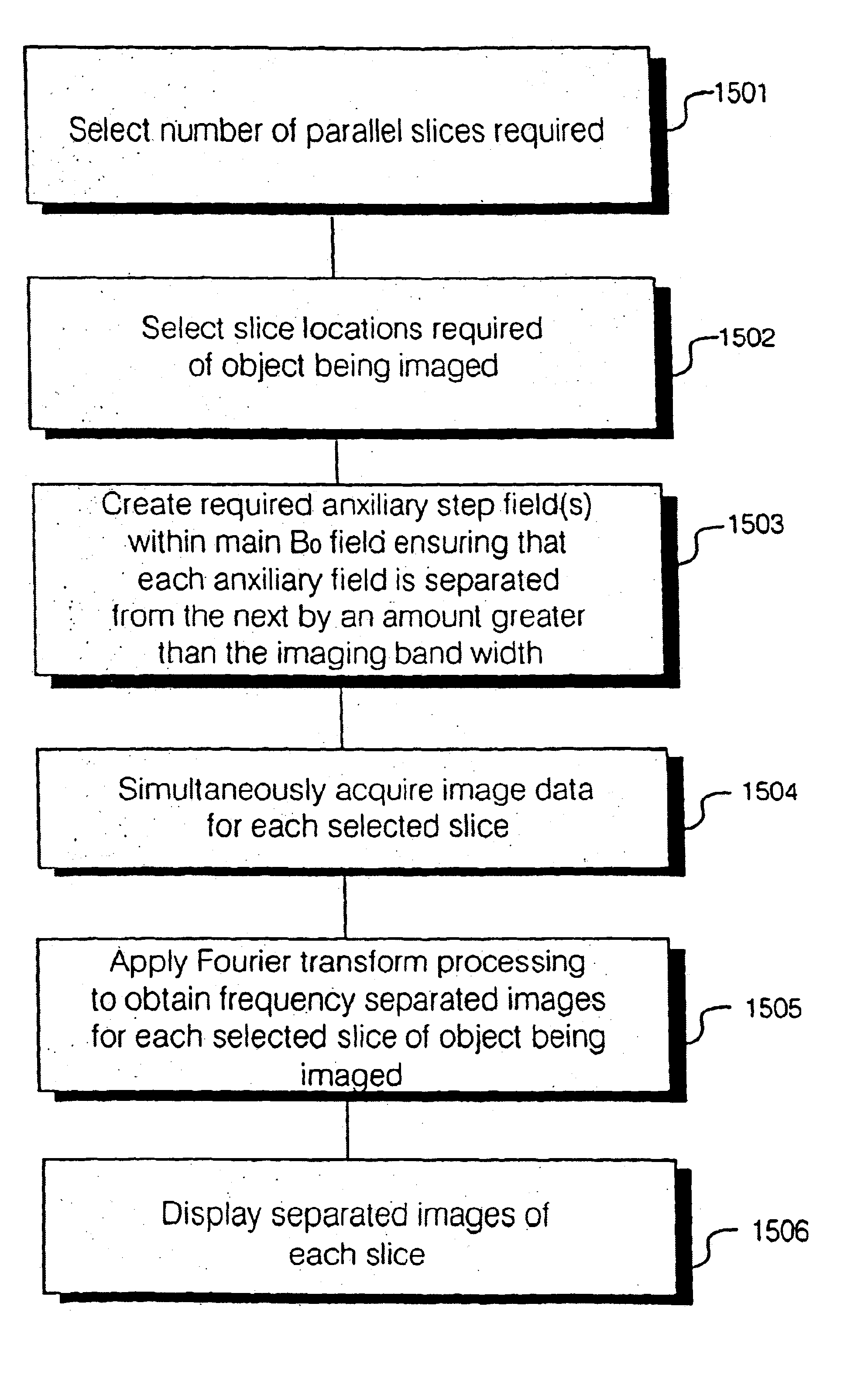
A parallel magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) apparatus configurable to image a physical entity comprises:a main magnetic flux source for providing a uniform fixed magnetic field, B0;an RF array system comprising a plurality of RF coils and receivers, said RF system configured for:generating rotating RF excitation magnetic fields B1; andreceiving RF signals due to precessing nuclear magnetization on multiple spatially distinct radio frequency coils and associated receiver channels, said RF system being configured to operate in accordance with a B1 sensitivity encoding technique;a control processor for controlling imaging functionality, collecting image data and effecting data processing of the captured image data the control processor being configured with post processing capability for the B1 sensitivity encoding technique;an image display means for displaying processed image data as resultant images; andan auxiliary magnetic field means capable of producing at least one auxiliary uniform B0 step magnetic field imaging region within the main B0 magnetic field;wherein:the auxiliary magnetic field, means is configured to operate in combination with the RF coil system and the B1 sensitivity encoding technique, the imaging apparatus thereby providing faster image acquisition than that attributed to the speed up factor provided solely by the B1 sensitivity encoding technique.The invention also includes a method of imaging using this apparatus.Furthermore, the invention also includes a method and apparatus for three-dimensional MR imaging using a 1D Multiple Acquisition Micro B0 array coupled with a 2D Multiple Acquisition Micro B0 array.
Owner:UNIV OF SHEFFIELD AT WESTERN BANK THE
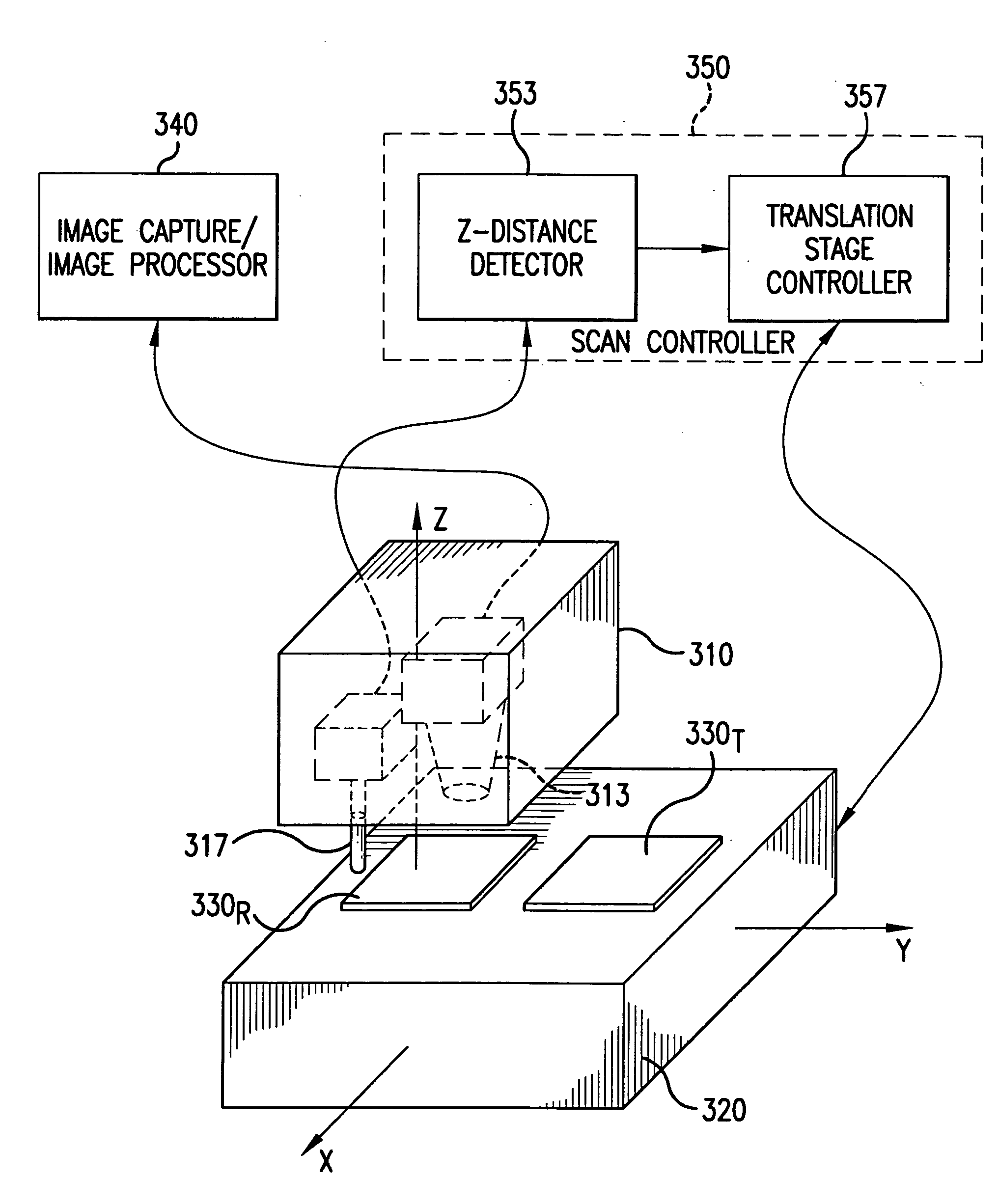
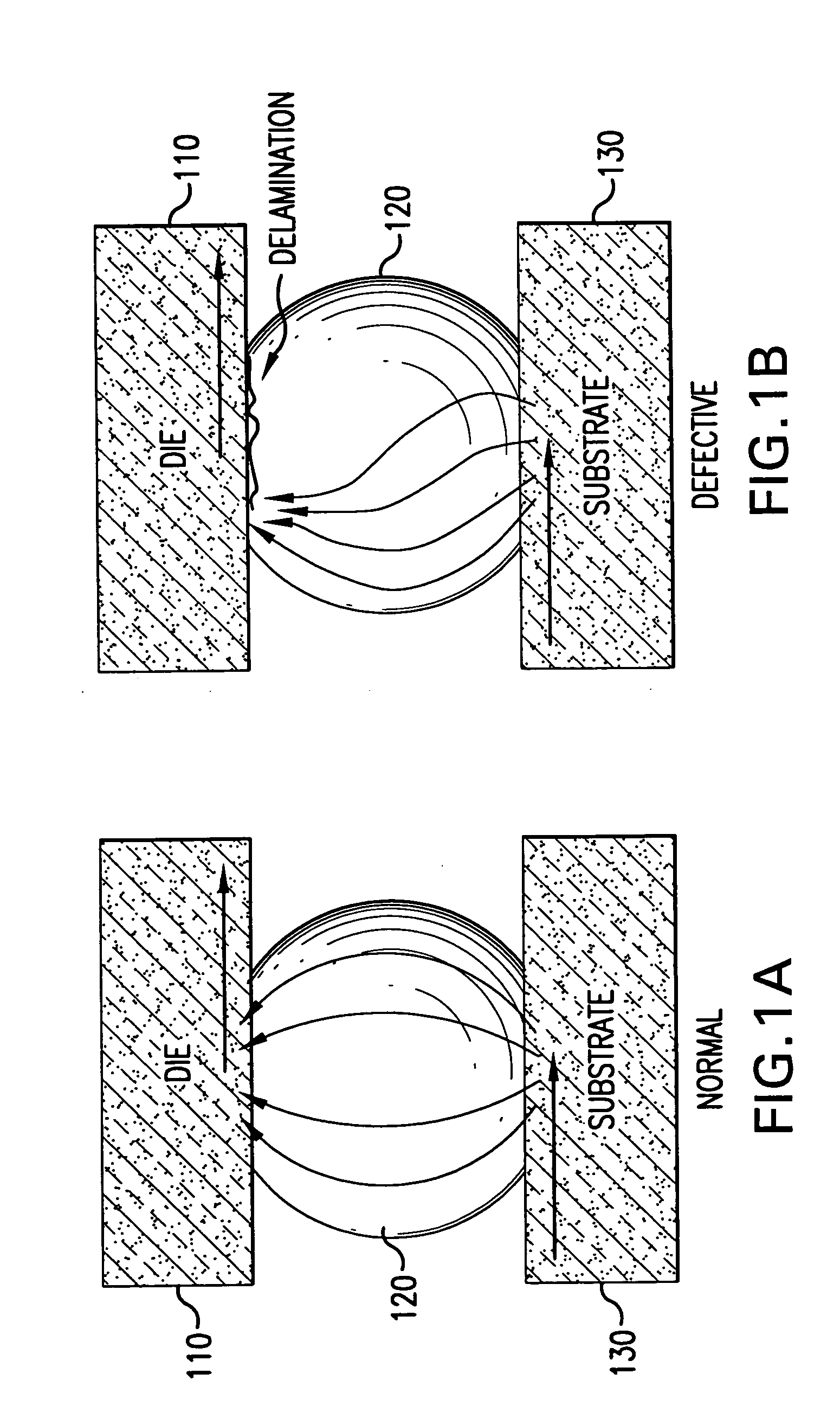
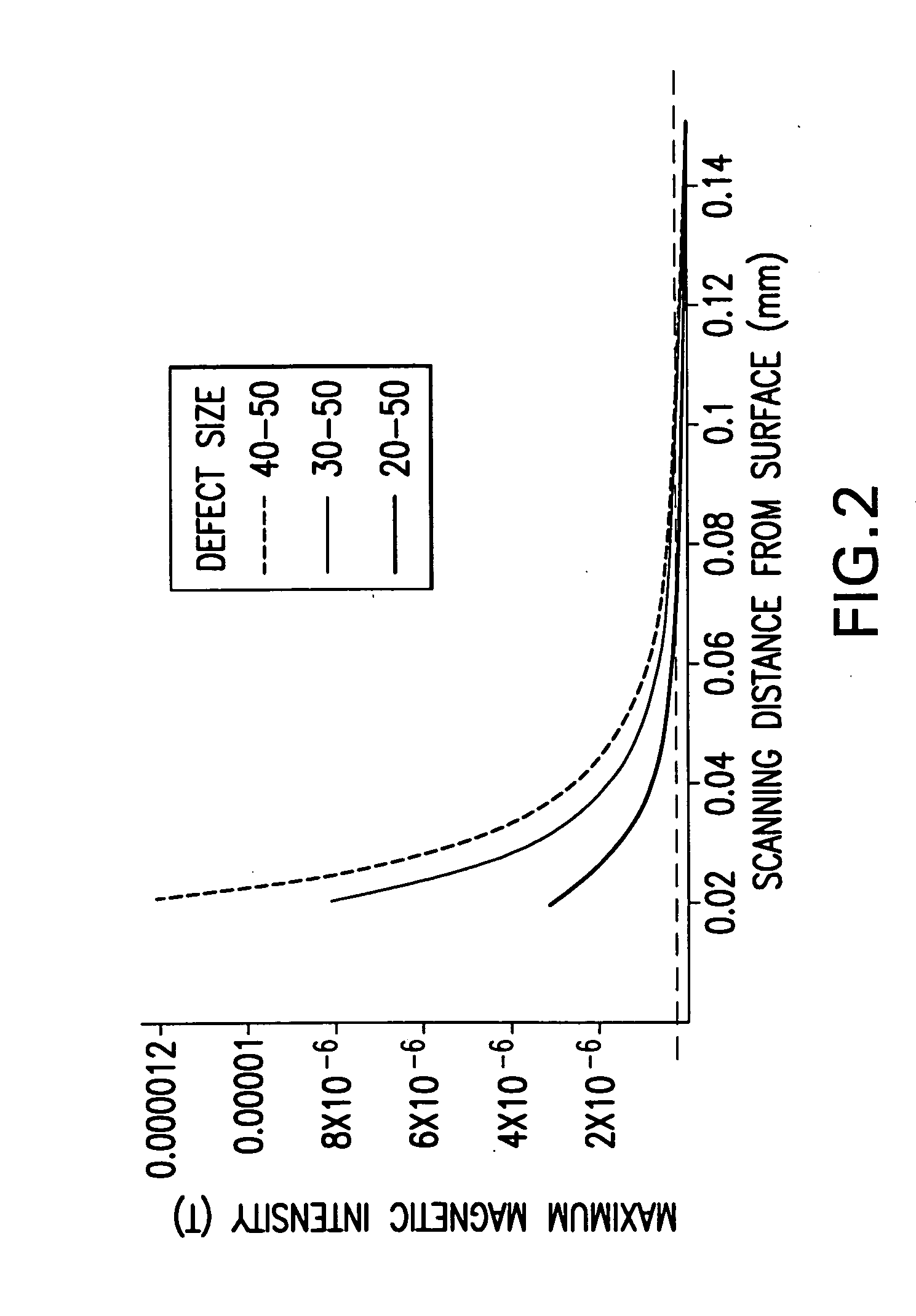
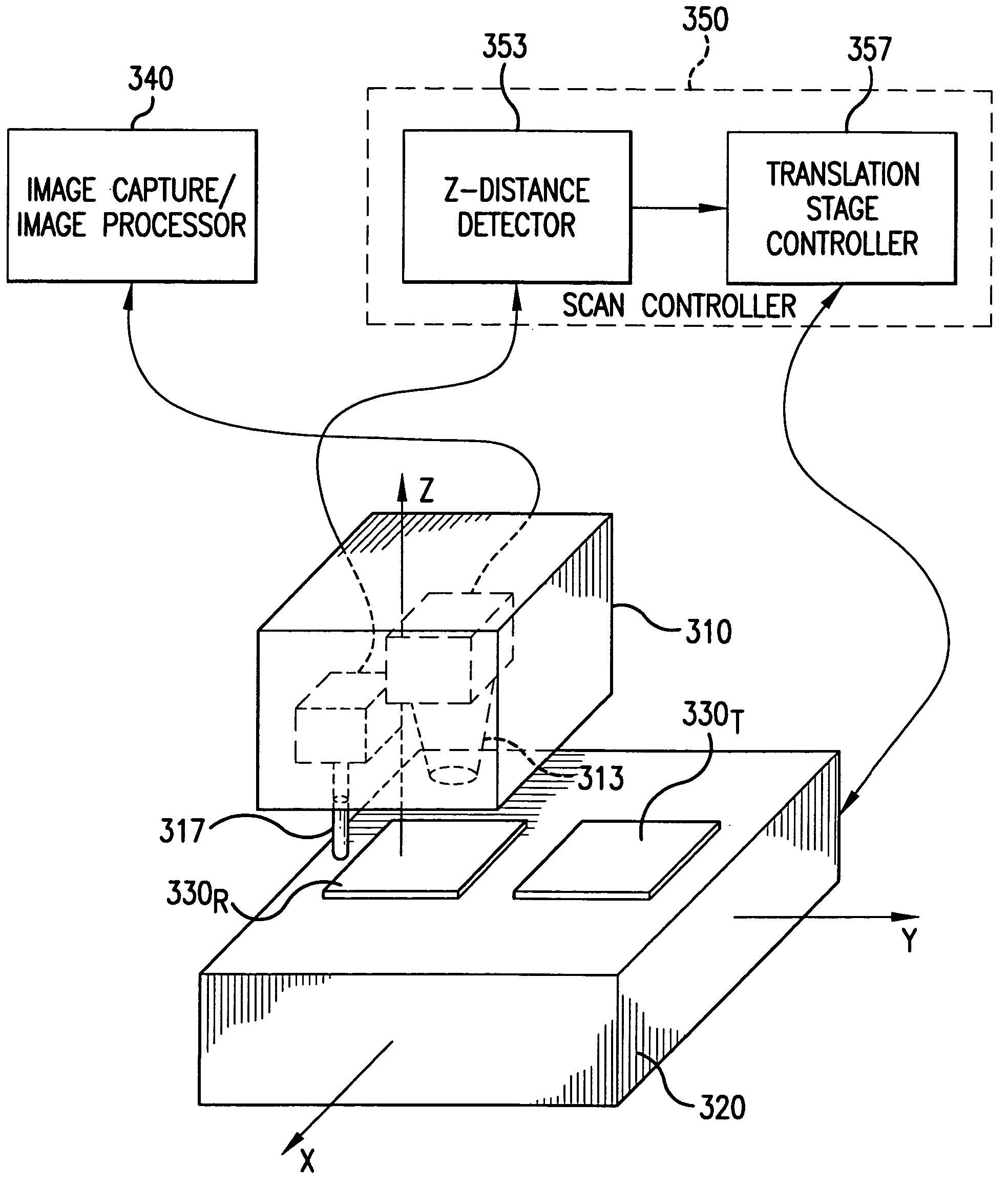
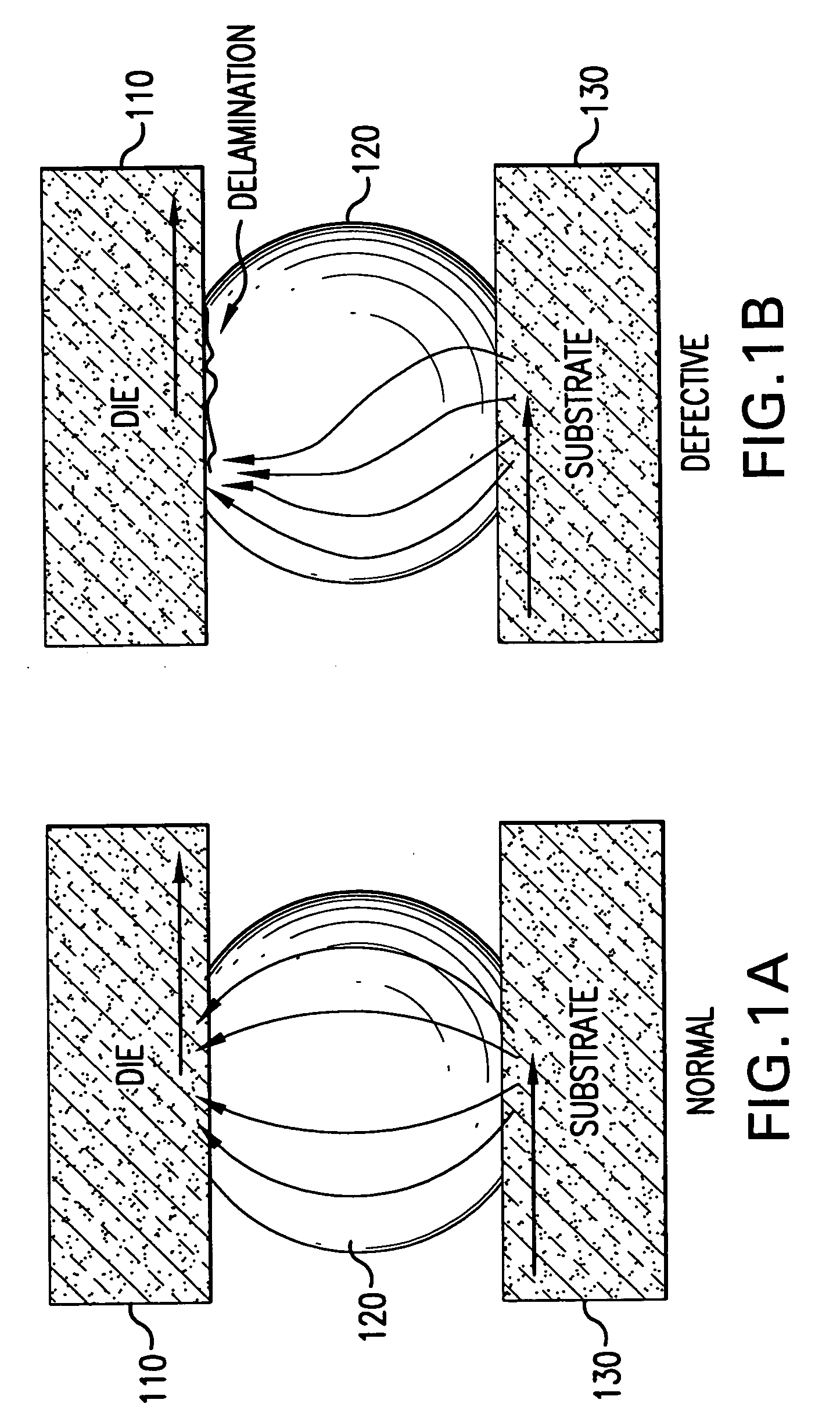
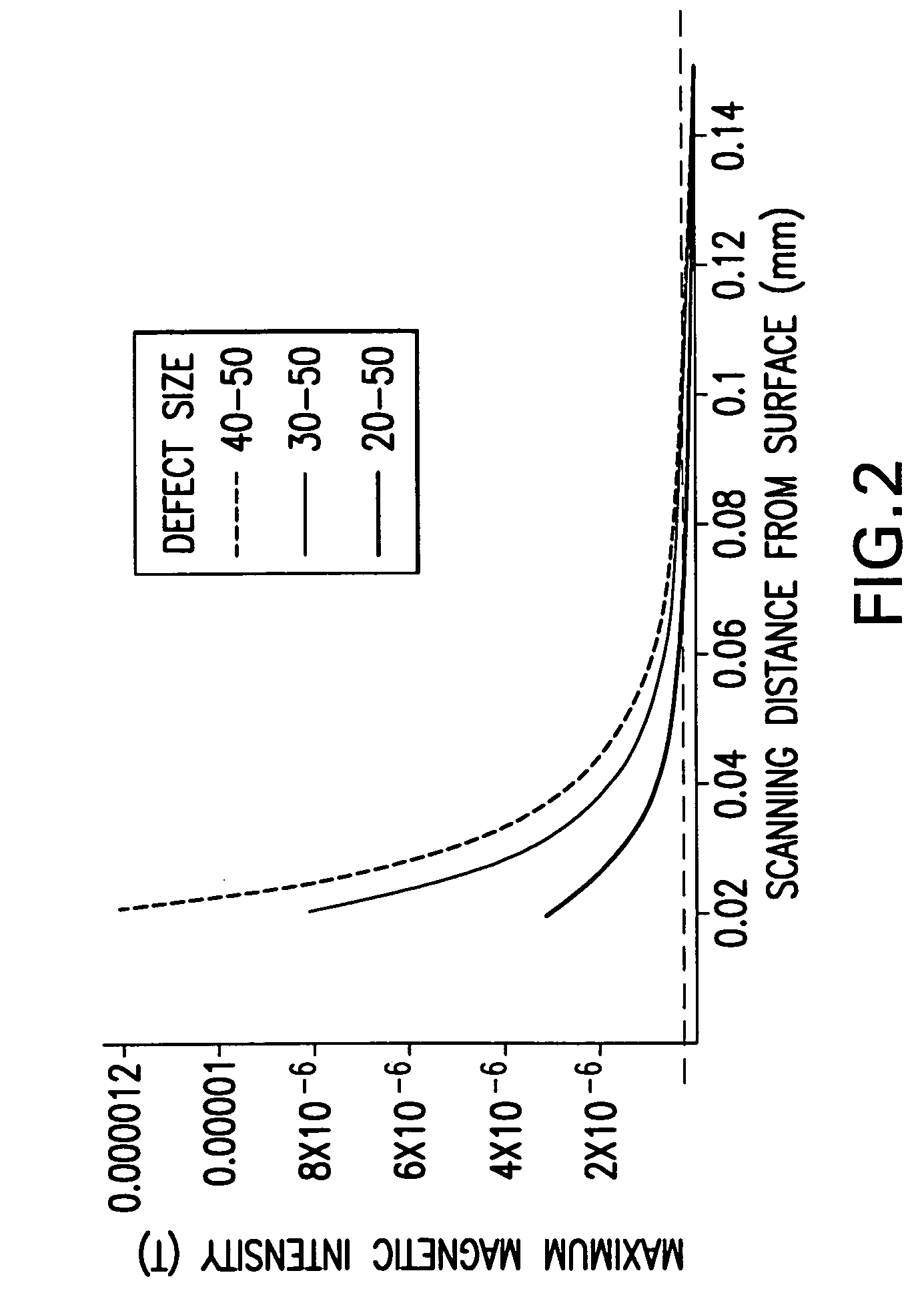
Fault isolation of circuit defects using comparative magnetic field imaging
ActiveUS20050057246A1Magnetic property measurementsElectrographic process apparatusHigh resistanceAmpere
Circuit flaws in microelectronic circuitry present regions of high resistance in which a current distribution deviates from that of a defect-free circuit. The altered current distribution emits a correspondingly altered magnetic field in accordance with Ampere's Law. When compared with the magnetic field of a defect-free circuit, the anomaly in the magnetic field of the defective device is detected and the location of the circuit flaw may be determined therefrom. As the anomaly in the magnetic field is very small in magnitude, a sensitive magnetic microscope is utilized to obtain images of the magnetic fields of a defect-free reference device and a device-under-test. The distance between the magnetic sensor and the devices being scanned is precisely controlled to minimize influences of scanning distance on the difference in measured magnetic field strength. Comparative image analysis reveals the location of the circuit flaw. Maximal image registration through image interpolation, displacement and resampling optimizes the comparative image analysis.
Owner:NEOCERA
Methods & apparatus for magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS20040044280A1Diagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsData displayMagnetization
A parallel magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) apparatus configurable to image a physical entity comprises: a main magnetic flux source for providing a uniform fixed magnetic field, Balpha; an RF array system comprising a plurality of RF coils and receivers, said RF system configured for: generating rotating RF excitation magnetic fields B1; and receiving RF signals due to precessing nuclear magnetization on multiple spatially distinct radio frequency coils and associated receiver channels, said RF system being configured to operate in accordance with a B1 sensitivity encoding technique; a control processor for controlling imaging functionality, collecting image data and effecting data processing of the captured image data the control processor being configured with post processing capability for the B1 sensitivity encoding technique; an image display means for displaying processed image data as resultant images; and an auxiliary magnetic field means capable of producing at least one auxiliary uniform Bo step magnetic field imaging region within the main B0 magnetic field; wherein: the auxiliary magnetic field, means is configured to operate in combination with the RF coil system and the B1 sensitivity encoding technique, the imaging apparatus thereby providing faster image acquisition than that attributed to the speed up factor provided solely by the B1 sensitivity encoding technique. The invention also includes a method of imaging using this apparatus. Furthermore, the invention also includes a method and apparatus for three-dimensional MR imaging using a 1D Multiple Acquisition Micro Bo array coupled with a 2D Multiple Acquisition Micro Bo array.
Owner:UNIV OF SHEFFIELD AT WESTERN BANK THE
Optimization of RF transmit and gradient magnetic field imaging using radio frequency and gradient coils
InactiveUS20110118587A1Improving MR image qualityIncrease amplitudeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsControl systemRadio frequency
The invention provides various systems, machine readable programs and methods for performing imaging using a MR scanner. The MR scanner includes at least one local radio-frequency transmit coil and at least one local gradient coil. The local radio-frequency transmit coil(s) and local gradient coil(s) cooperate to define an imaging volume. The MR scanner further includes a control system for performing an imaging operation on a patient's anatomy disposed within the imaging volume. The control system permits a selective simultaneous increase of the gradient magnetic field strength and peak B1 field strength by substantially the same factor, f.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
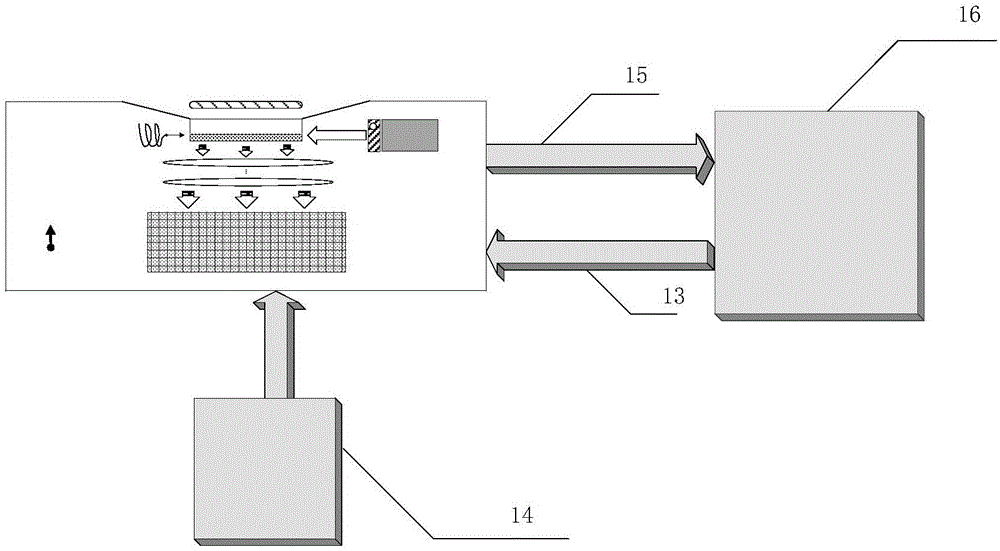
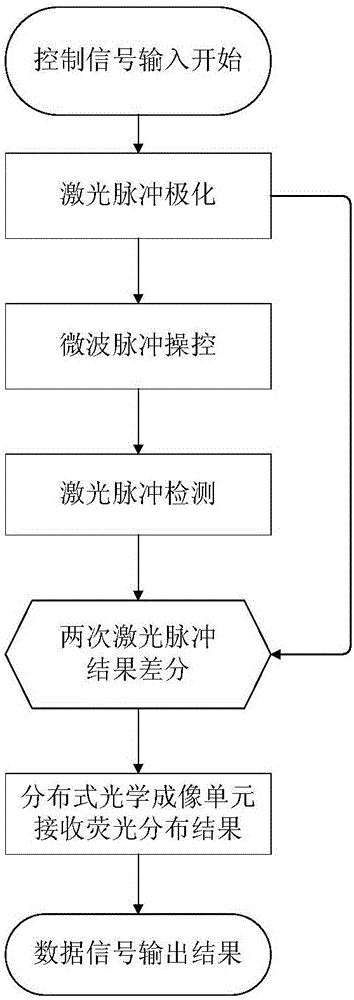
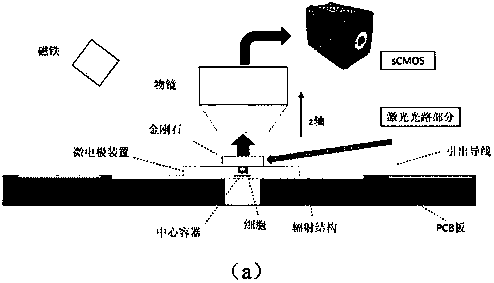
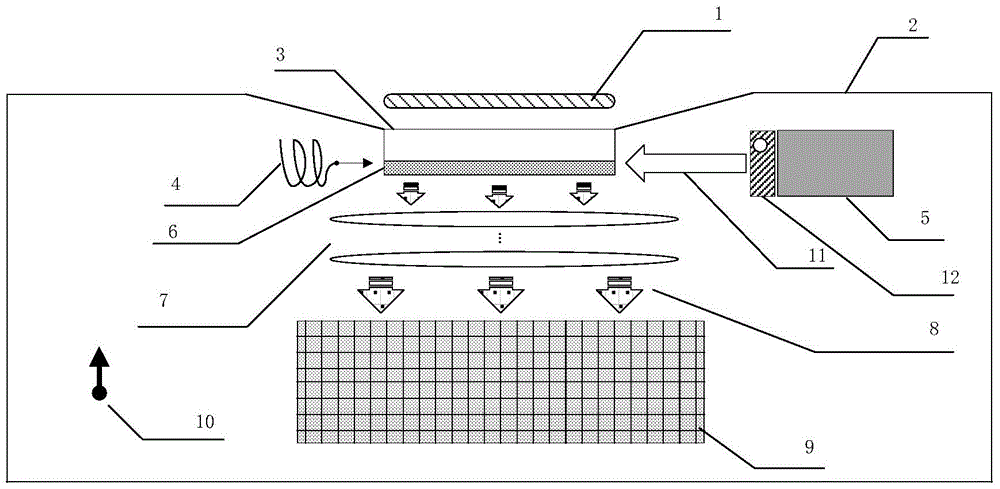
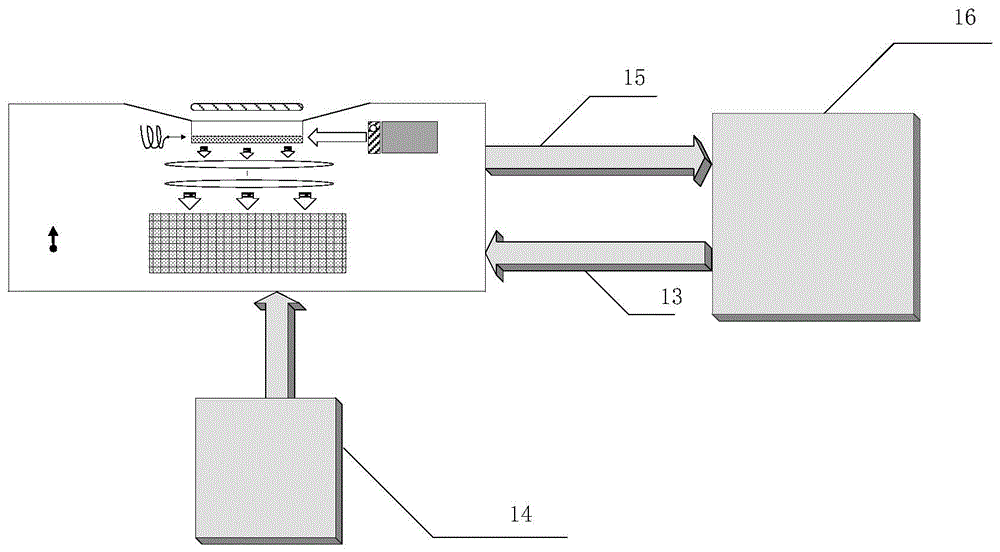
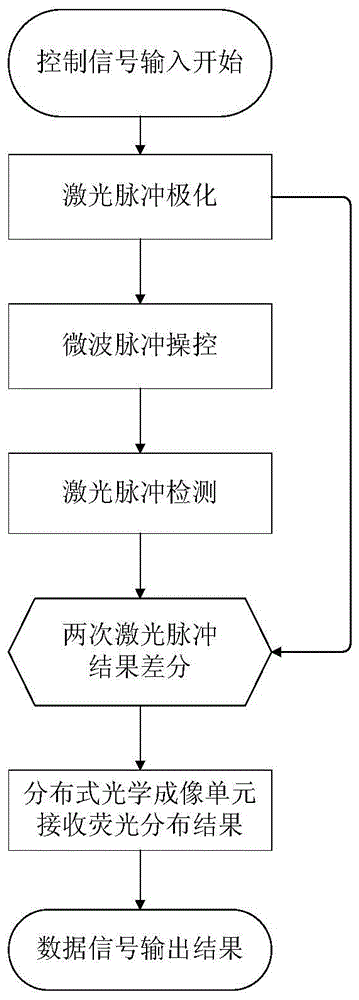
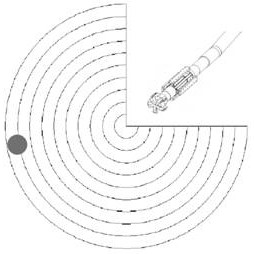
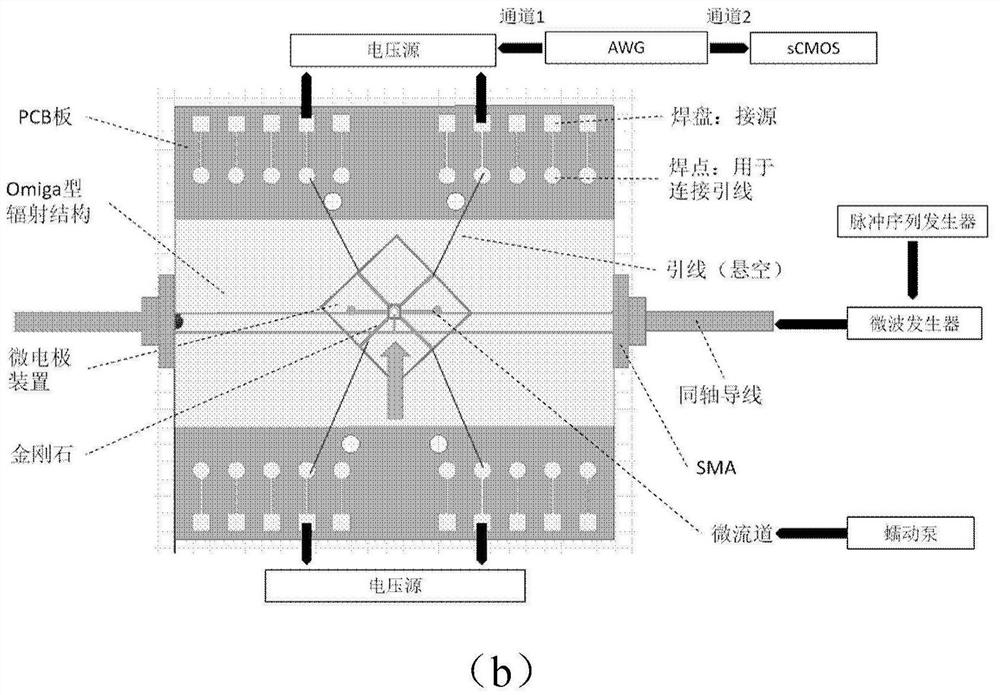
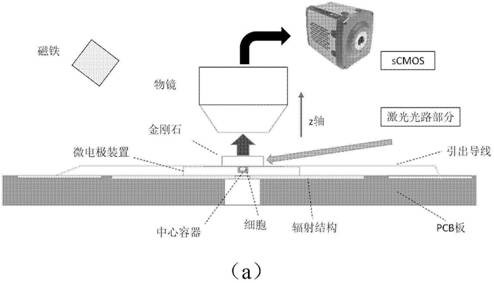
Chip-level diamond NV-color center magnetic imaging device and method
ActiveCN105137371AReduce volumeQuick responseMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringMedical diagnosisElectromagnetic shielding
The invention discloses a chip-level diamond NV-color center magnetic imaging device and method, and the method achieves the hyperfine magnetic field imaging of the two-dimensional surface of an object, such as a magnetic image of a biological cell. The method comprises the steps: carrying out the polarization of a laser pulse and a microwave pulse; generating fluorescent light generated at the NV-color center of a diamond in an external magnetic field; employing the laser pulse to generate fluorescent light again, wherein the difference result of fluorescent light of two times can reflect the magnetic field intensity of the NV-color center, thereby achieving the conversion of magnetic field information to optical information; and employing a nano-level convex lens group and a distributed optical imaging unit to convert an optical signal into an electric signal. The invention also relates to a packaging method for enabling a whole system to be packaged in a manner of chip level, and the method comprises temperature control and electromagnetic shielding. The method is great in value in the fields of biomedical research and medical diagnosis.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +1
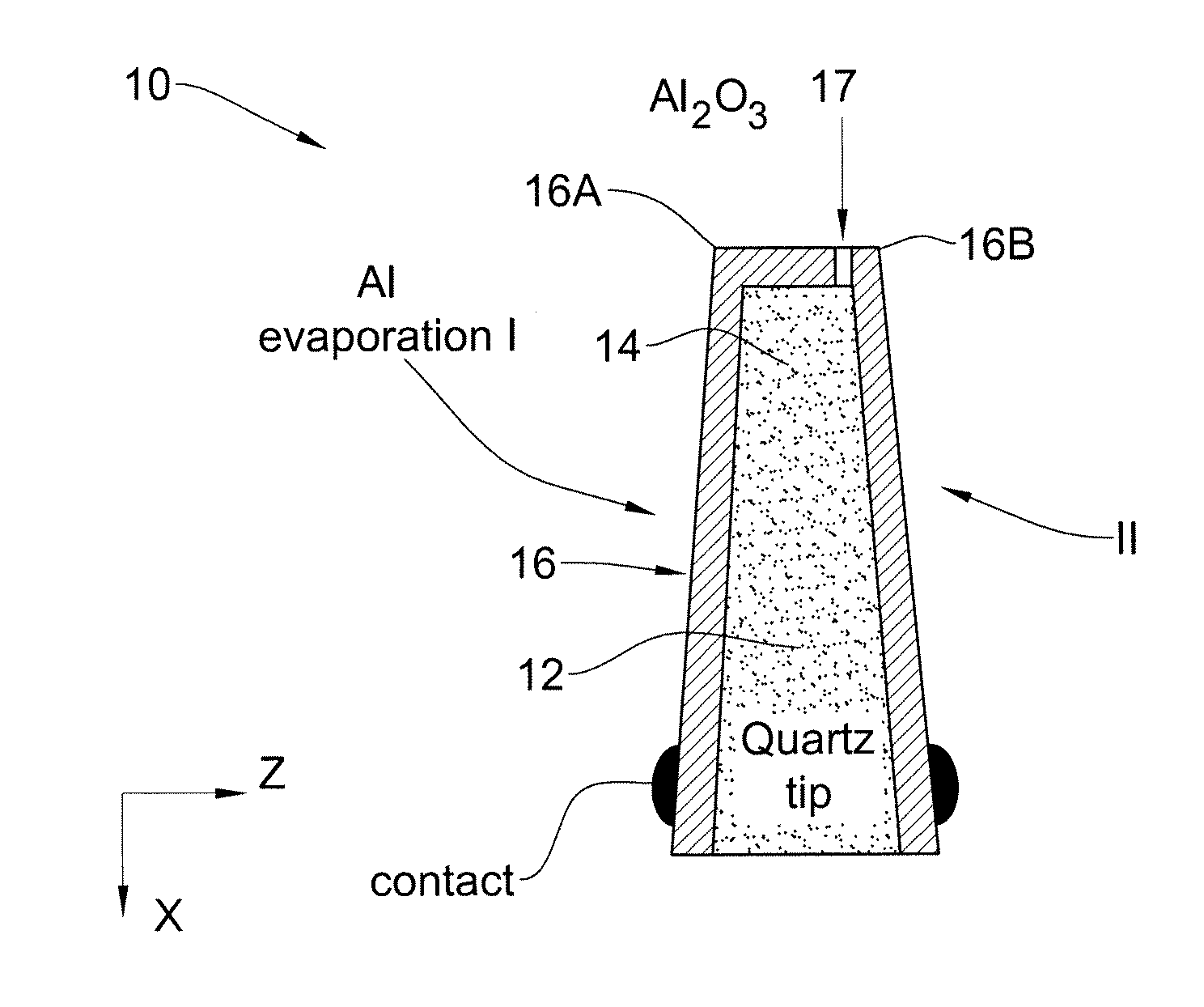
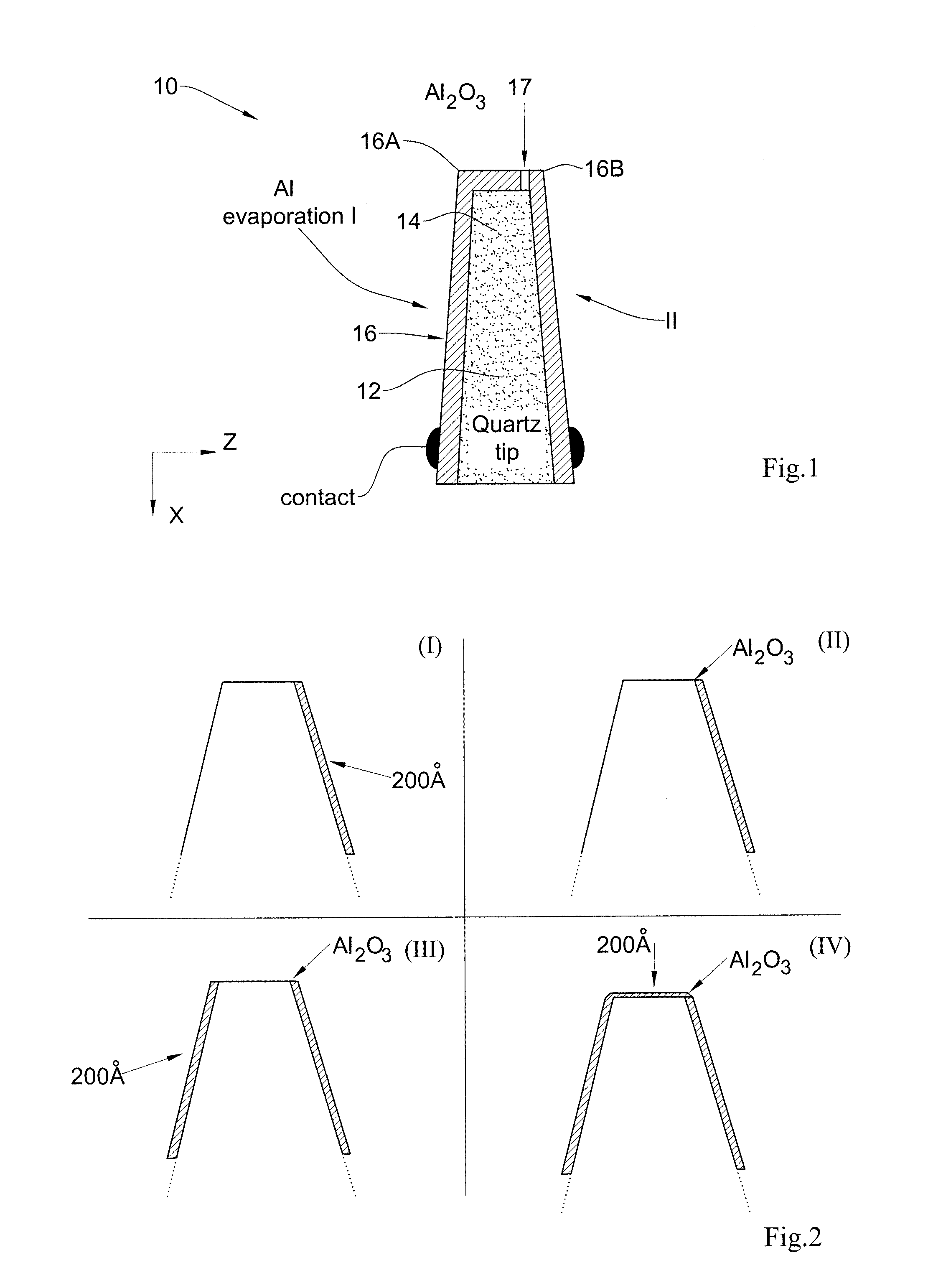
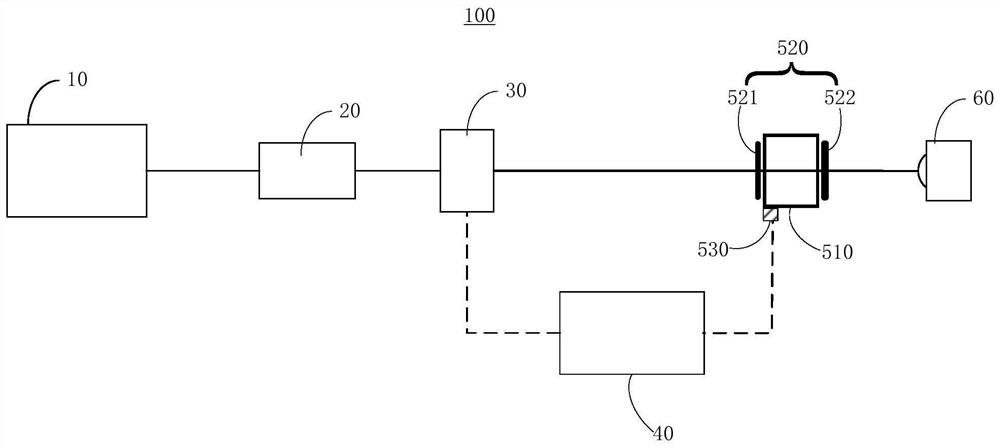
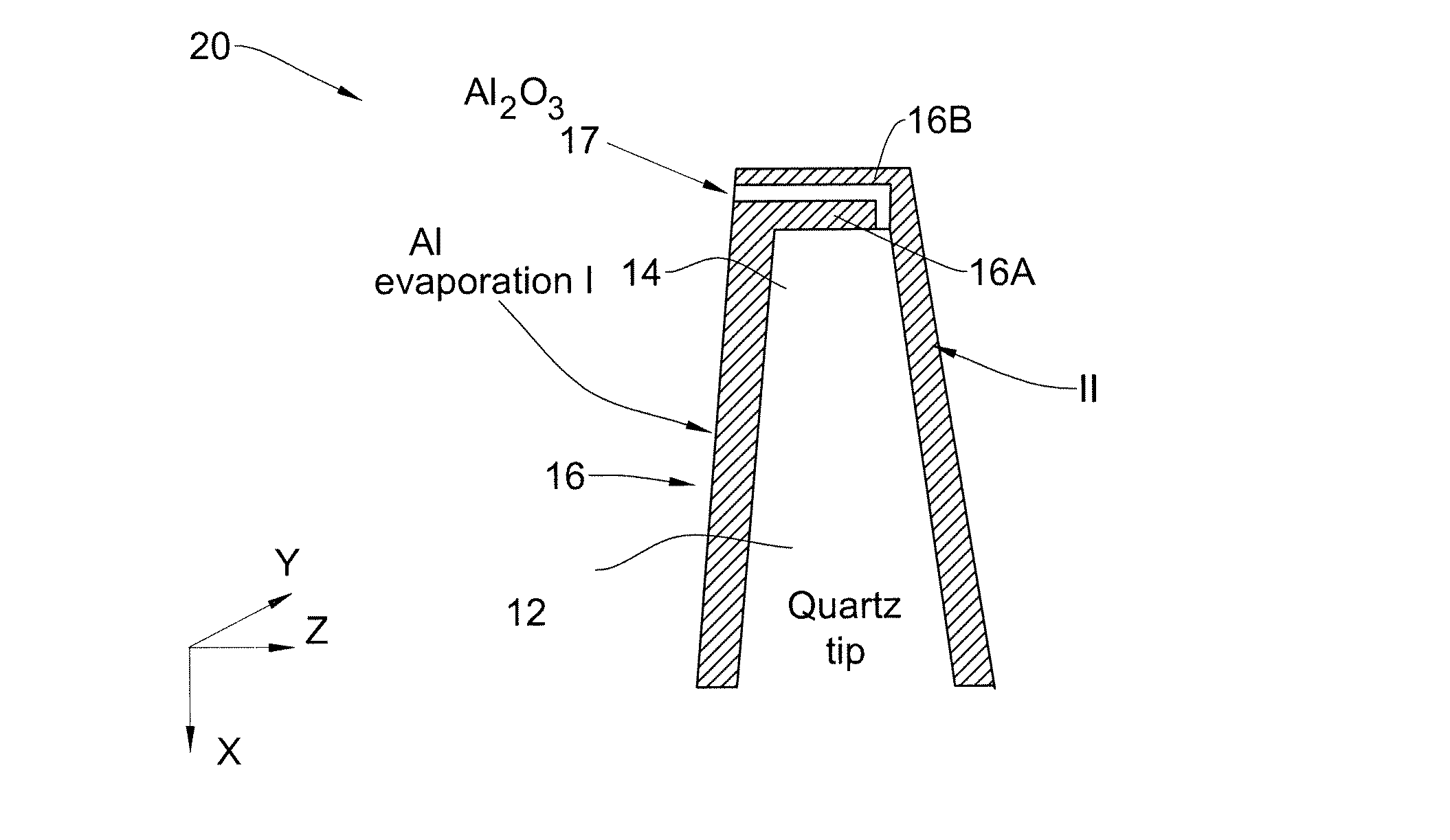
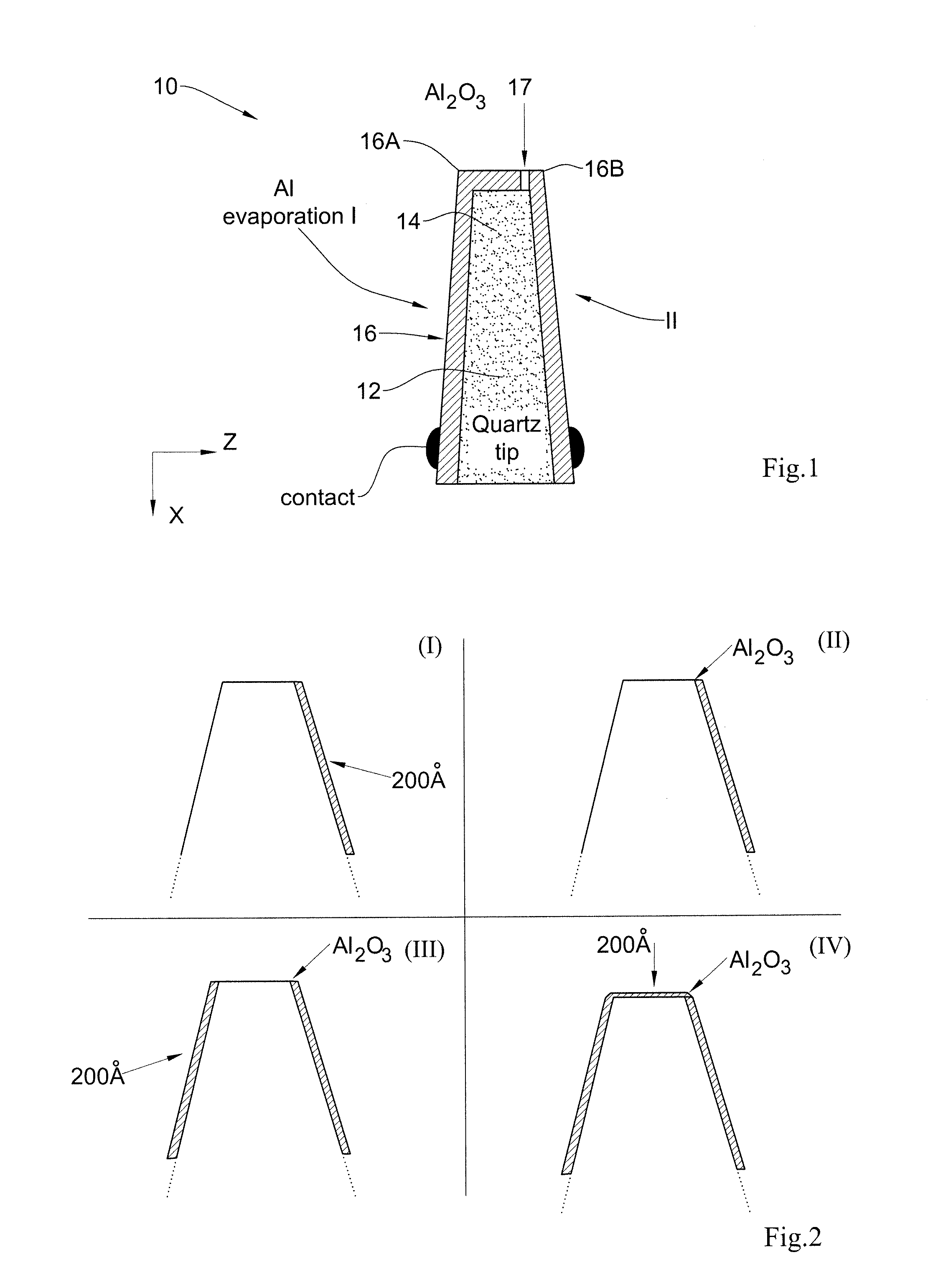
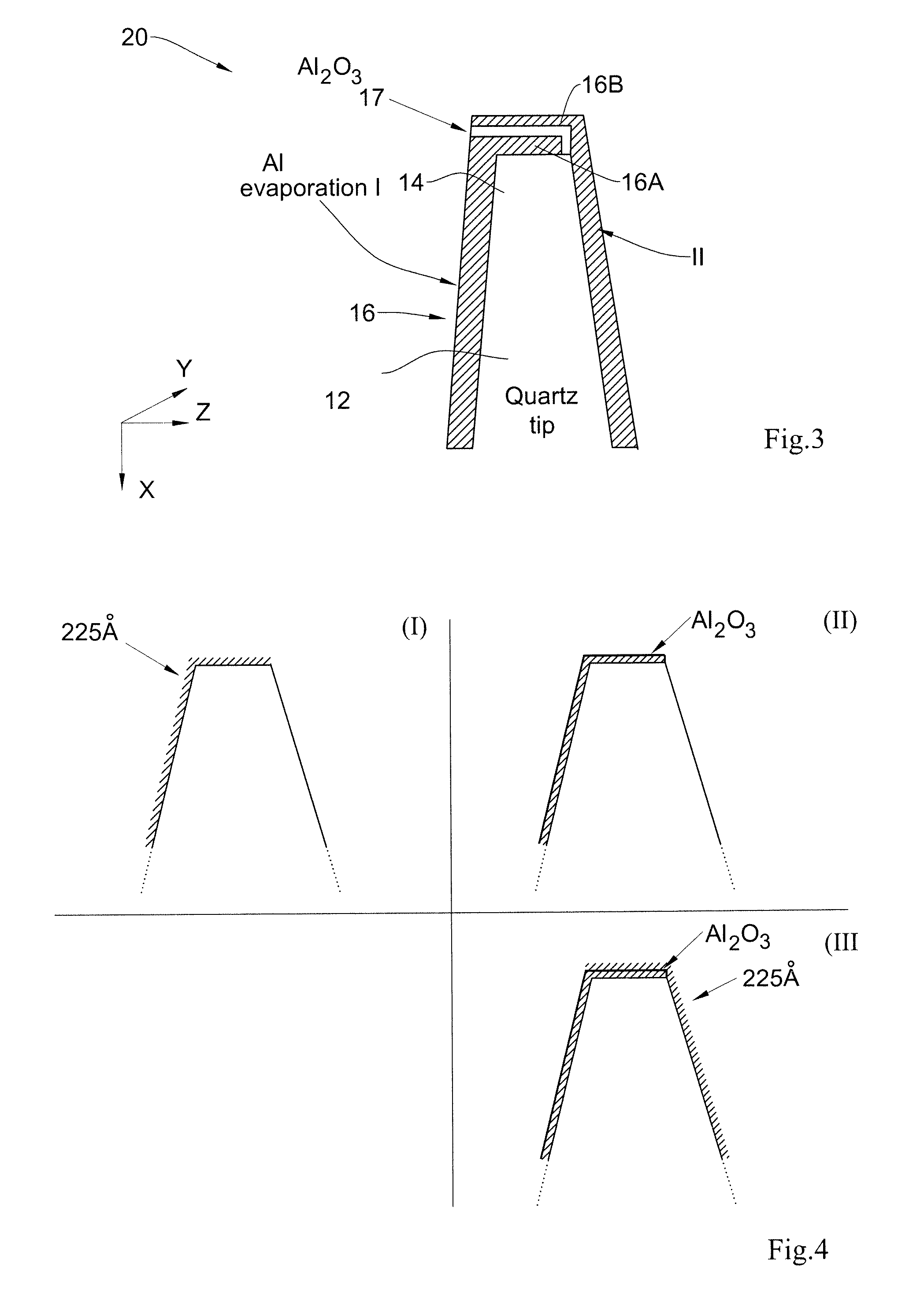
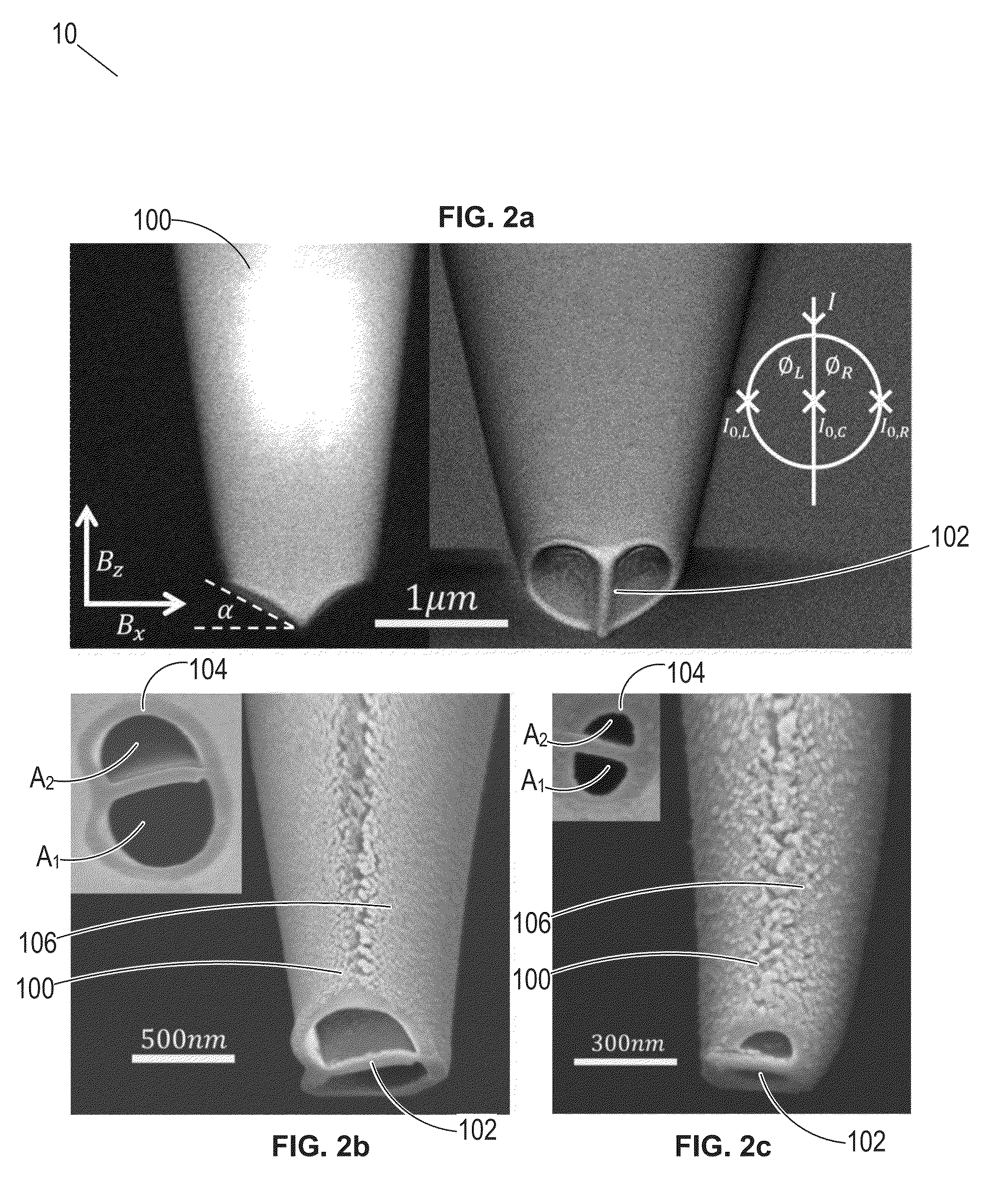
Magnetic field sensor device for direct magnetic field imaging and method of fabrication thereof
ActiveUS20100207622A1NanomagnetismMagnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesElectronCondensed matter physics
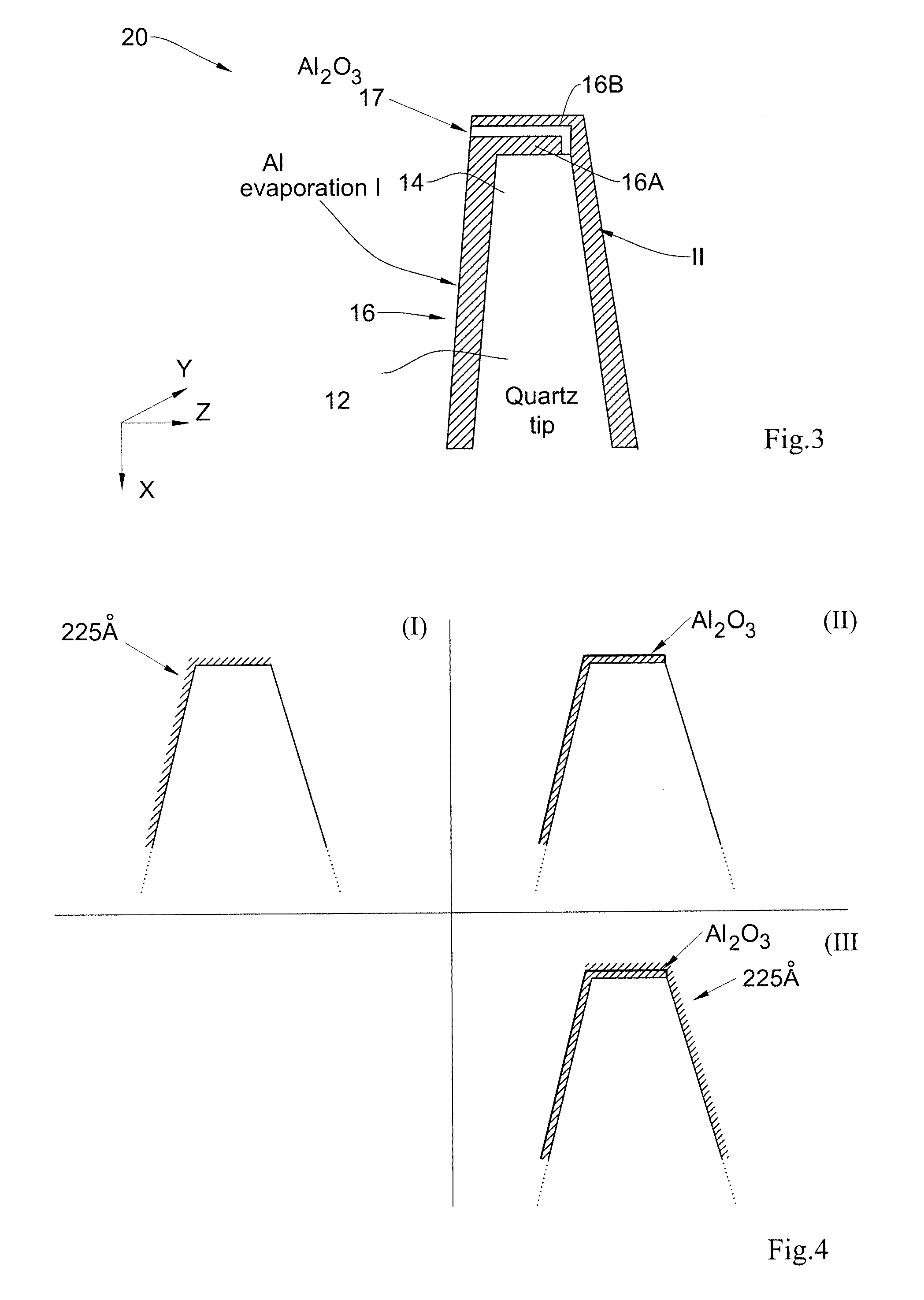
The present invention discloses a novel magnetic sensor device performing direct magnetic field imaging, comprising a probe having a conical tip portion which is configured as a sensor having two superconductors separated by a thin non-superconducting layer (such as a Josephson junction based sensor), where the non-superconducting layer is located at the apex portion of said conical tip, thereby defining electron tunneling region(s) at said apex portion. The technique of the present invention enables the sensor device to be very small and to be brought very close to the sample surface.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Medical magnetic resonance imager monohedral magnet device
InactiveCN101598775ABuild accuratelyLow costDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsResonanceMagnetic poles
The invention relates to a medical magnetic resonance imager monohedral magnet device, belonging to the technical field of medical instruments. The invention comprises a main monohedral magnet, a first gradient coil, a second gradient coil, an imaging zone and a bracket, wherein, the main monohedral magnet comprises a first main magnetic pole, a second main magnetic pole, a first adjusting magnetic pole, a second adjusting magnetic pole, a first pole surface, a second pole surface and a base. The invention has the following advantages: the main monohedral magnet forms an even lamelliform magnetic field imaging zone on the outer side of the magnet; a first monoplane gradient coil and a second monoplane gradient coil provide a gradient magnetic field with favourable degree of linearity in the imaging zone so as to realize phase encoding and frequency encoding of images; by revising the incline angle of a polar surface and adjusting magnetic pole interval, an even amelliform magnetic field can be precisely built. Compared with the traditional magnetic resonance imager magnet device, the device of the invention has the advantages of small volume, light weight and good openness, and greatly lowers the cost of the magnetic resonance imager.
Owner:SHENYANG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Magnetic sensor array integrated structure and making method thereof
ActiveCN106405446ASmall attenuationIncreased sensitivityMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsSensor arrayGlass cover
The invention discloses a magnetic sensor array integrated structure and a making method thereof. The magnetic sensor array is composed of a bias magnet, a bulk acoustic resonator array chip, chip pins, a ceramic package base, a magnetic fluid, and a glass cover sheet. The bulk acoustic resonator array chip comprises a silicon substrate, a Prague acoustic reflection layer, a bottom electrode, a piezoelectric film layer, a top electrode, via filler, and electrode pads. According to the magnetic sensor array provided by the invention, the magnetic measurement mechanism of detection of the rheological response of the magnetic fluid to an external magnetic field under a saturated bias field by use of high-frequency shear wave is put forward for the first time, wide response range of the magnetic fluid and high resolution and high degree of integration of a thickness shear wave type bulk acoustic resonator are fully utilized, a high-precision and wide-range novel magnetic sensor array is realized, and the technical requirements of weak magnetic field imaging for the magnetic sensor array can be met effectively.
Owner:NO 719 RES INST CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND
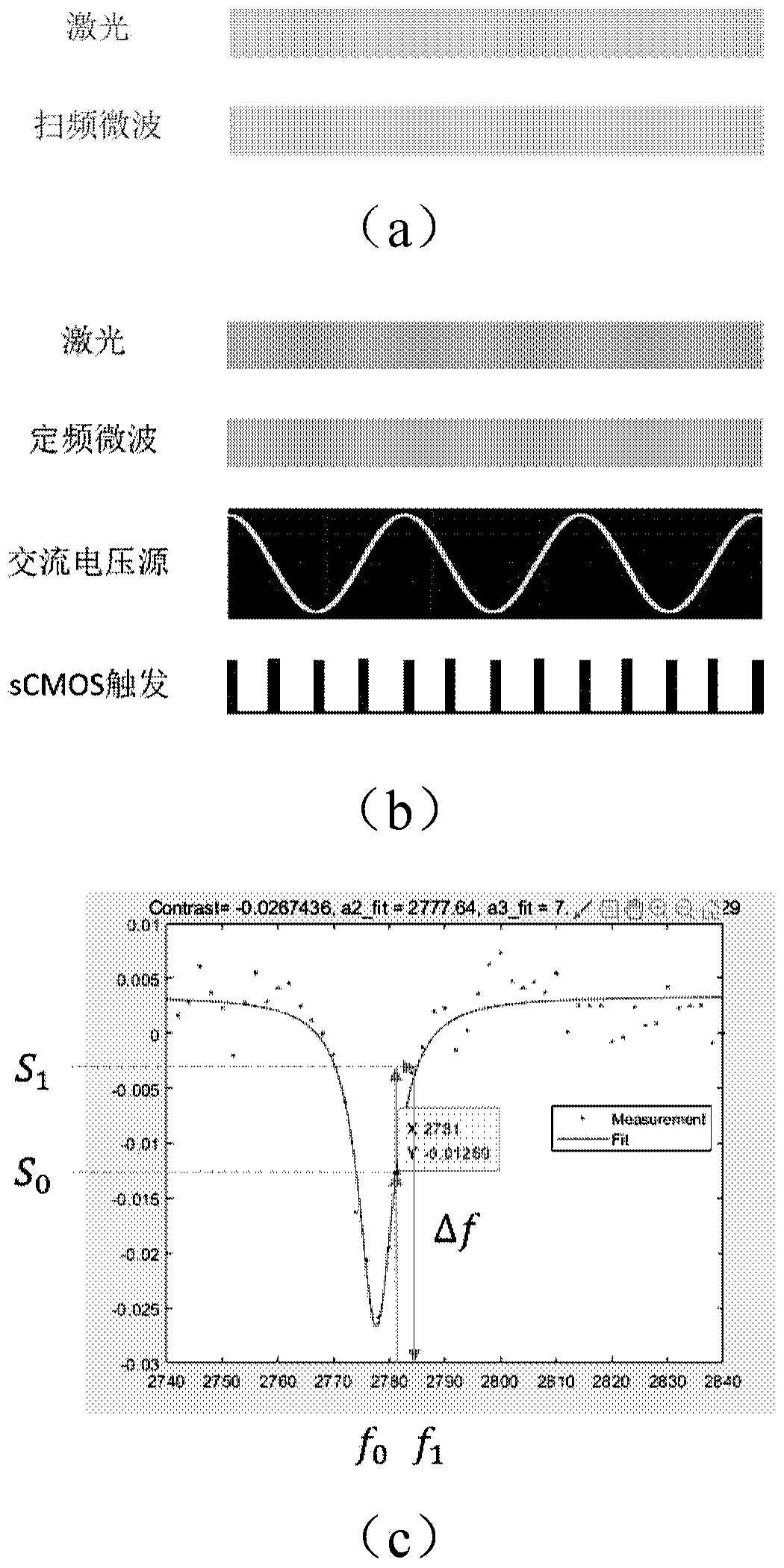
Atom magnetometer and magnetic field imaging system
ActiveCN111983526ASimple structureAvoid introducingMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesMagnetic heatingTemperature control
The invention relates to an atom magnetometer and a magnetic field imaging system. First wavelength laser and second wavelength laser are formed through a laser light source and a frequency doubling module. The optical power of the first wavelength laser is adjusted through an optical attenuation module, non-magneto-optical heating of an atomic gas chamber is achieved, and the attenuation amount is adjusted for temperature control. And the second wavelength laser enters the atomic gas chamber to realize magnetic field detection. Therefore, an atom magnetometer can realize non-magnetic heatingand atom pumping detection without coupling of heating laser and pumping laser, and the complexity of an optical path is reduced. And one laser light source in a magnetic field imaging system is connected with a plurality of atom magnetometer probes. Through the position information of the plurality of atom magnetometer probes and the detected magnetic field information, accurate positioning of the magnetic field position can be realized so as to realize multidimensional magnetic field space reconstruction.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Magnetic field sensor device for direct magnetic field imaging and method of fabrication thereof
ActiveUS8723514B2NanomagnetismMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsElectronCondensed matter physics
The present invention discloses a novel magnetic sensor device performing direct magnetic field imaging, comprising a probe having a conical tip portion which is configured as a sensor having two superconductors separated by a thin non-superconducting layer (such as a Josephson junction based sensor), where the non-superconducting layer is located at the apex portion of said conical tip, thereby defining electron tunneling region(s) at said apex portion. The technique of the present invention enables the sensor device to be very small and to be brought very close to the sample surface.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Microcosmic electrical impedance imaging device and method based on diamond NV color center
ActiveCN111504884AImprove spatial resolutionIndividual particle analysisMetallic electrodeDiamond color
A microcosmic electrical impedance imaging device based on a diamond NV color center comprises a magnetic field imaging module adopting a diamond ensemble NV as a weak magnetic field detector; a microwave radiation structure module which adopts an omega-shaped radiation structure as a microwave antenna to radiate a microwave magnetic field to the diamond NV color center; a microelectrode module which is used for injecting alternating current into the buffer solution by adopting a cross-shaped iridium-iridium oxide metal electrode with two pairs of electrode arms. According to the invention, the spatial resolution of the existing magnetic resonance electrical impedance imaging is expanded, and the spatial resolution of the electrical impedance imaging is improved to a micron scale to a submicron scale, so an electrical impedance imaging method on a microcosmic scale is realized, and the method is suitable for conductivity imaging of a cell biological sample.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Fault isolation of circuit defects using comparative magnetic field imaging
ActiveUS7019521B2Magnetic property measurementsElectrographic process apparatusHigh resistanceAmpere
Circuit flaws in microelectronic circuitry present regions of high resistance in which a current distribution deviates from that of a defect-free circuit. The altered current distribution emits a correspondingly altered magnetic field in accordance with Ampere's Law. When compared with the magnetic field of a defect-free circuit, the anomaly in the magnetic field of the defective device is detected and the location of the circuit flaw may be determined therefrom. As the anomaly in the magnetic field is very small in magnitude, a sensitive magnetic microscope is utilized to obtain images of the magnetic fields of a defect-free reference device and a device-under-test. The distance between the magnetic sensor and the devices being scanned is precisely controlled to minimize influences of scanning distance on the difference in measured magnetic field strength. Comparative image analysis reveals the location of the circuit flaw. Maximal image registration through image interpolation, displacement and resampling optimizes the comparative image analysis.
Owner:NEOCERA
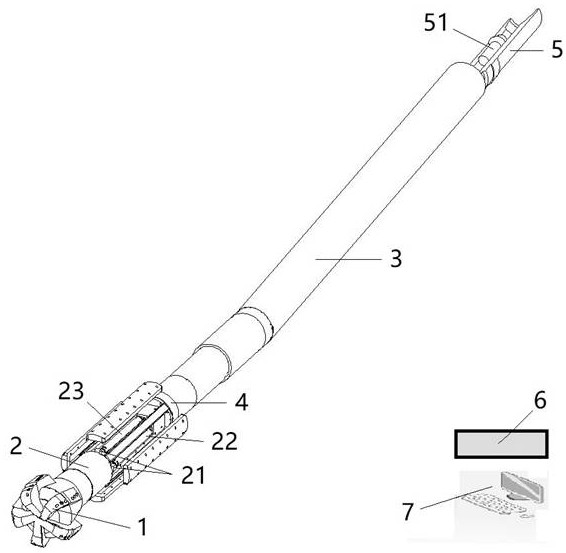
Near-bit magnetic field imaging positioning measuring instrument and working method
ActiveCN111734397AAccurate measurementSurveyConstructionsMeasuring instrumentThree-dimensional space
The invention discloses a near-bit magnetic field imaging positioning measuring instrument and a working method, and belongs to the technical field of oil drilling measurement. The near-bit magnetic field imaging positioning measuring instrument comprises a drill bit, a near-bit magnetic field imaging positioning short section, a power drilling tool, a wireless short pass transmitting assembly, awireless short pass receiving assembly, a ground receiving device and a processing computer. A non-magnetic drill bit and a non-magnetic near-bit magnetic field imaging positioning short section are adopted to form a stable magnetic anomaly detection environment nearby the drill bit, a magnetic field acquisition sensor can perform three-dimensional detection on a three-dimensional space nearby thedrill bit during rotation, the positions of anomalous fields can be accurately measured, and range information is given; and a ground computer visually displays the anomalous fields in front of the drill bit in real time on a screen according to the measured information, the interaction position of nearby sleeves and the drill bit can further be identified, and collision early warning and suggestions on pile wrapping are made.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
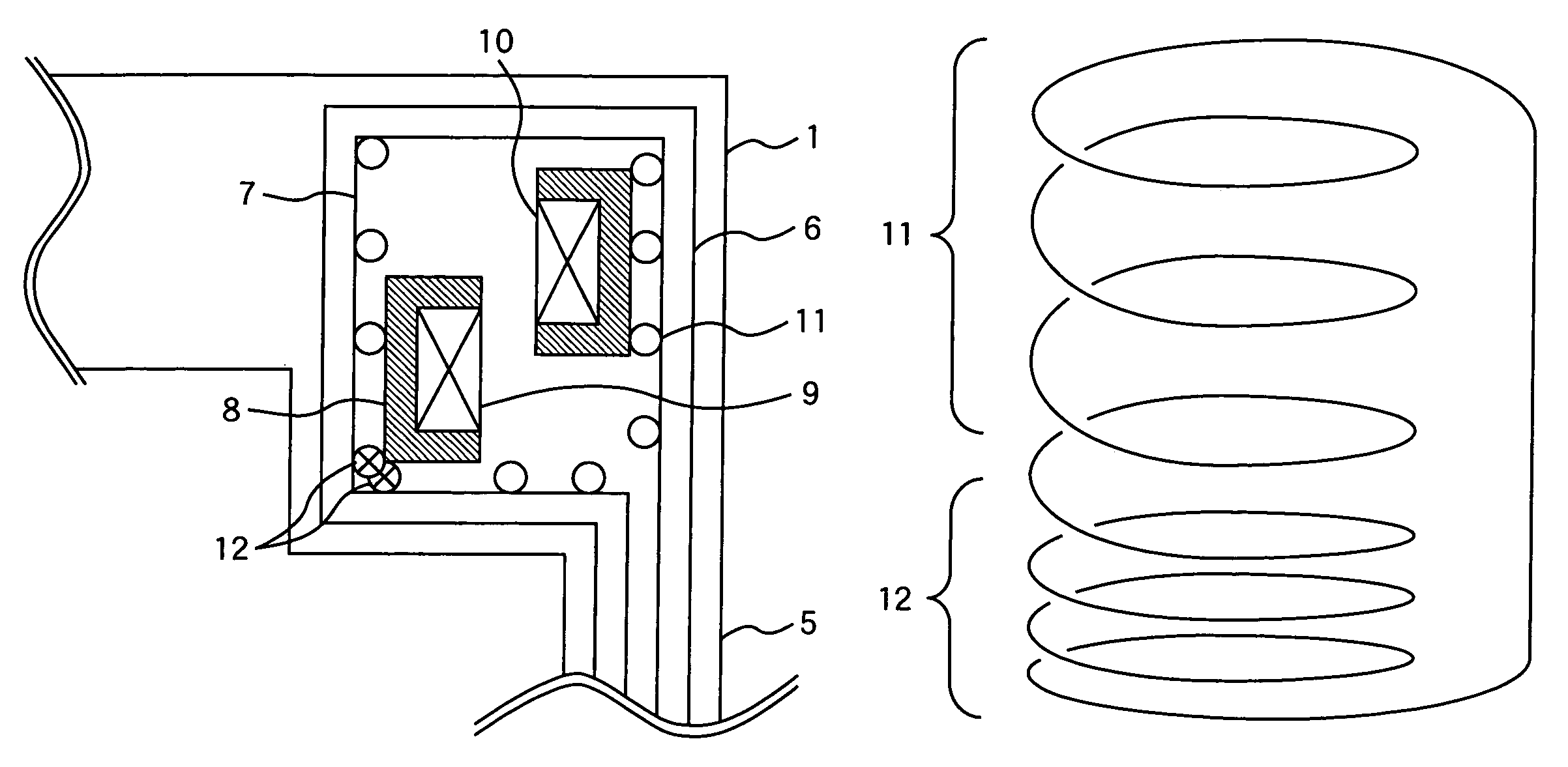
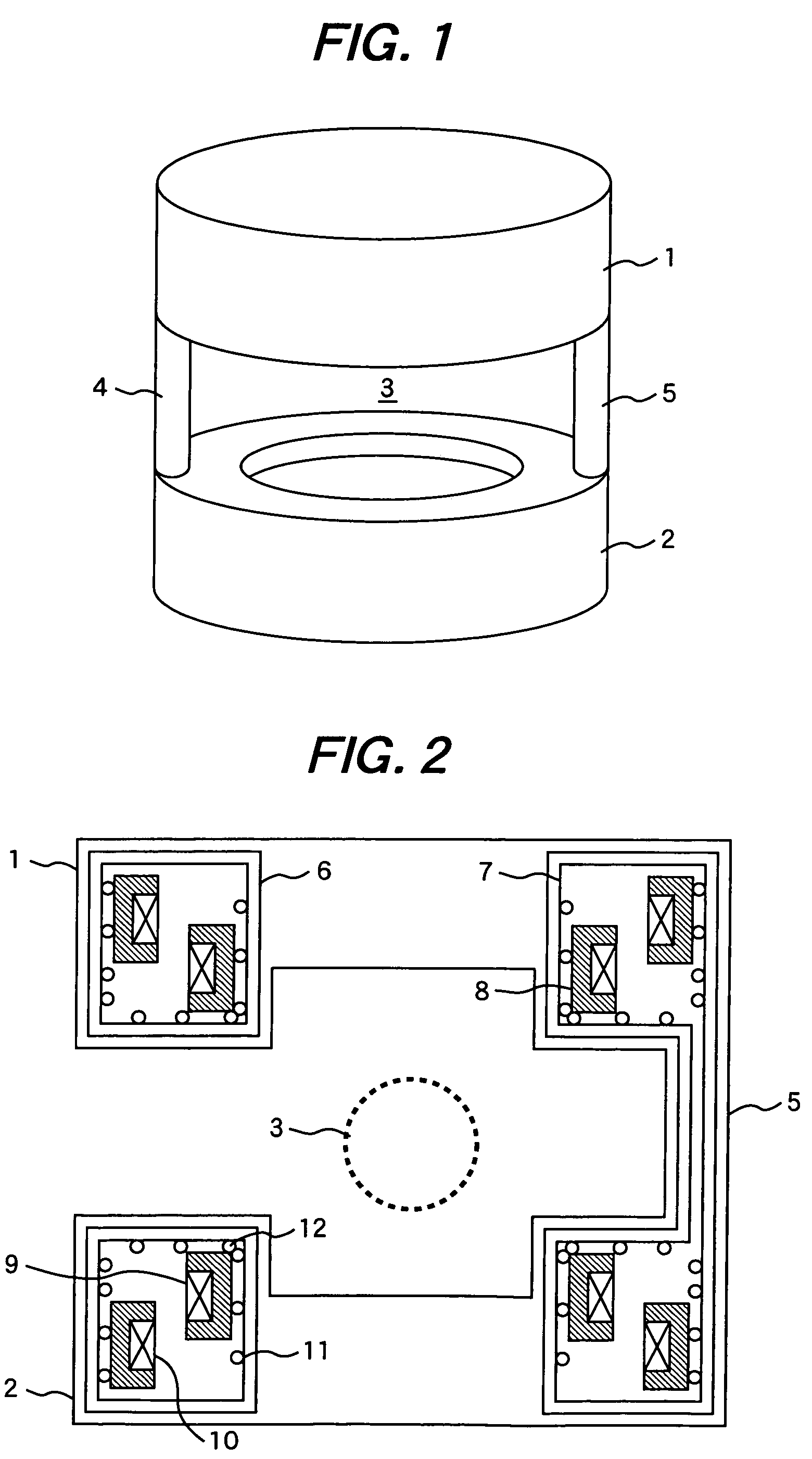
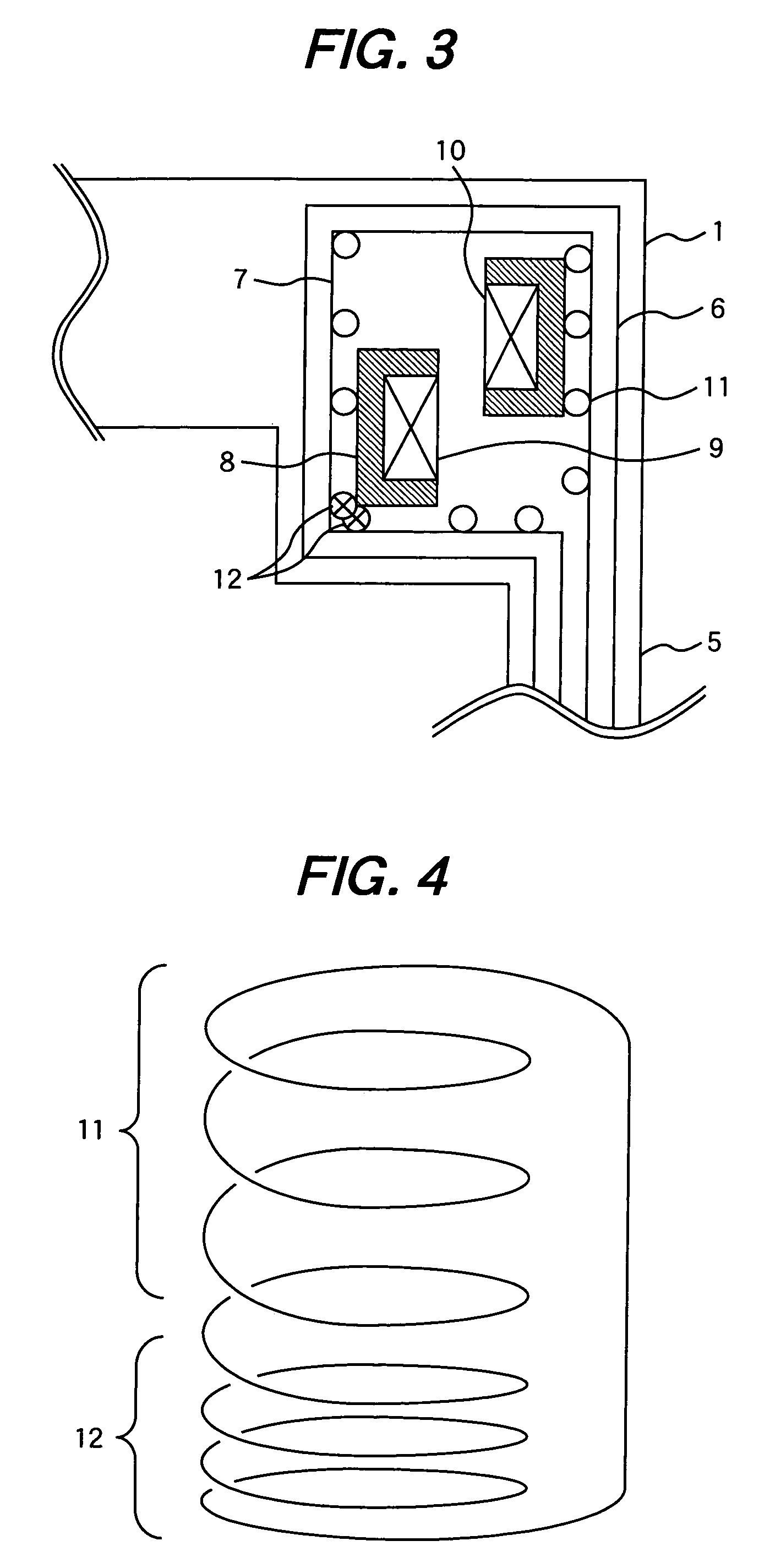
Magnet device
InactiveUS20070057667A1Reduce performanceRise in the inductance of the coilsMagnetsMagnetic property measurementsCouplingMagnetic flux
A magnet device has main coils in a pair positioned facing each other to form a static magnetic field space in between and external magnetic flux shielding coils placed coaxially to the main coils. The external magnetic flux shielding coils have a first coil group having a small coefficient of coil coupling and a second coil group having a coefficient of coil coupling greater than that of the first coil group. The first coil group is connected in series to the second coil group. External magnetic flux entering the magnetic field imaging space formed by main coils in a pair positioned facing each other is effectively warded off.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
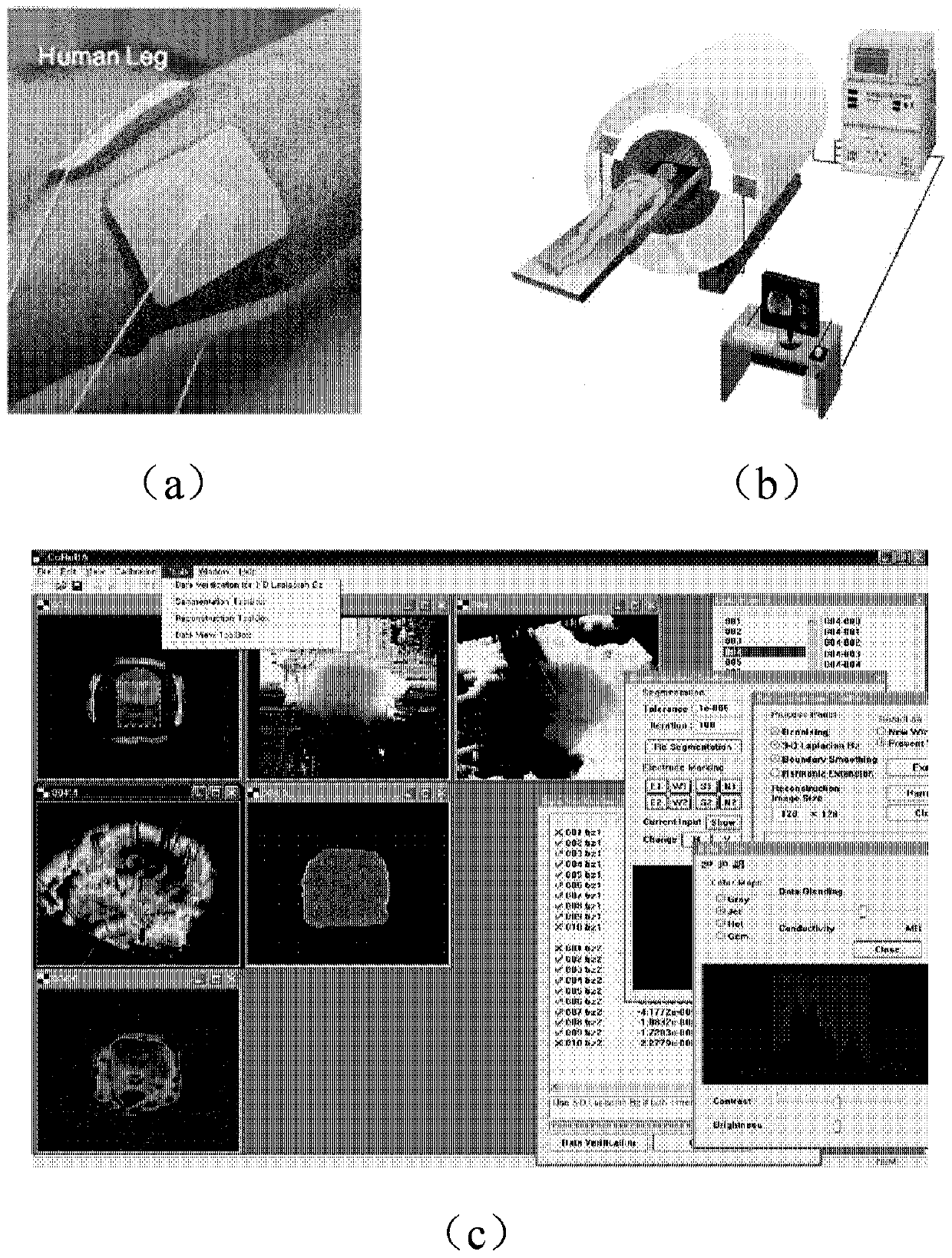
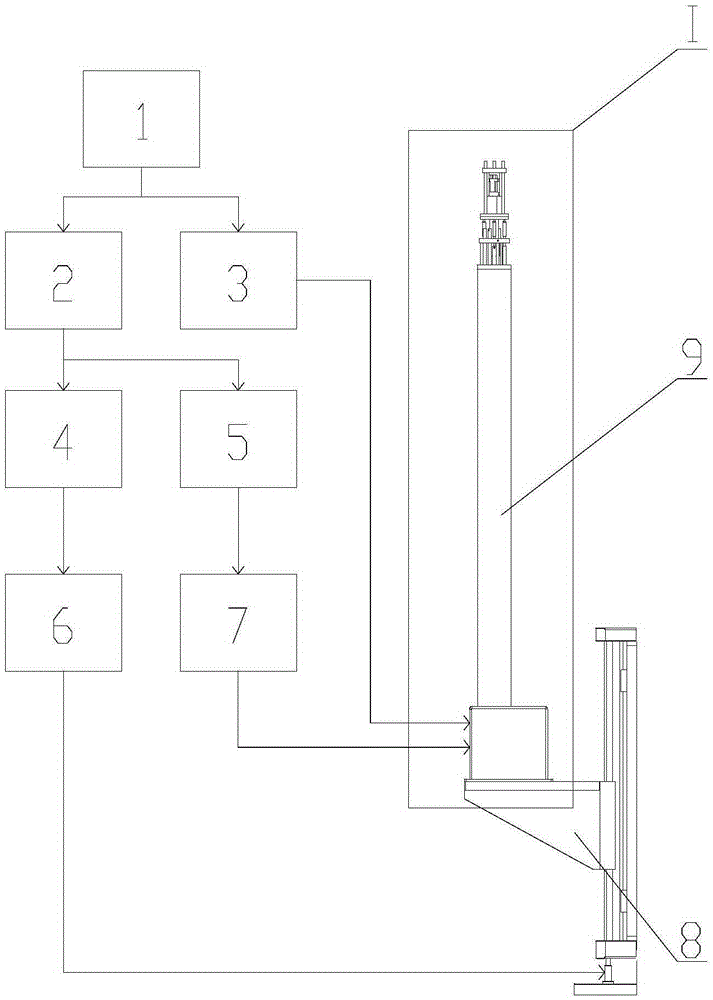
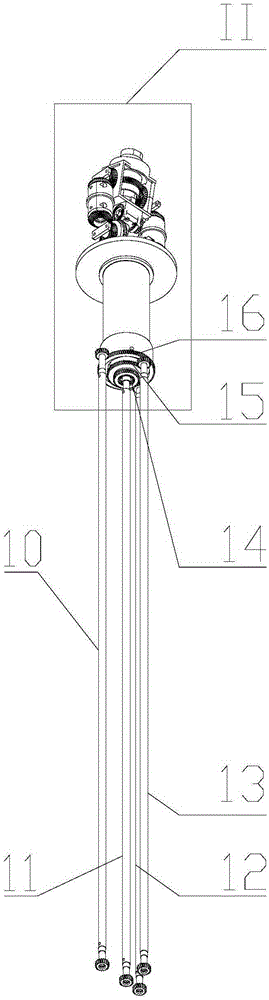
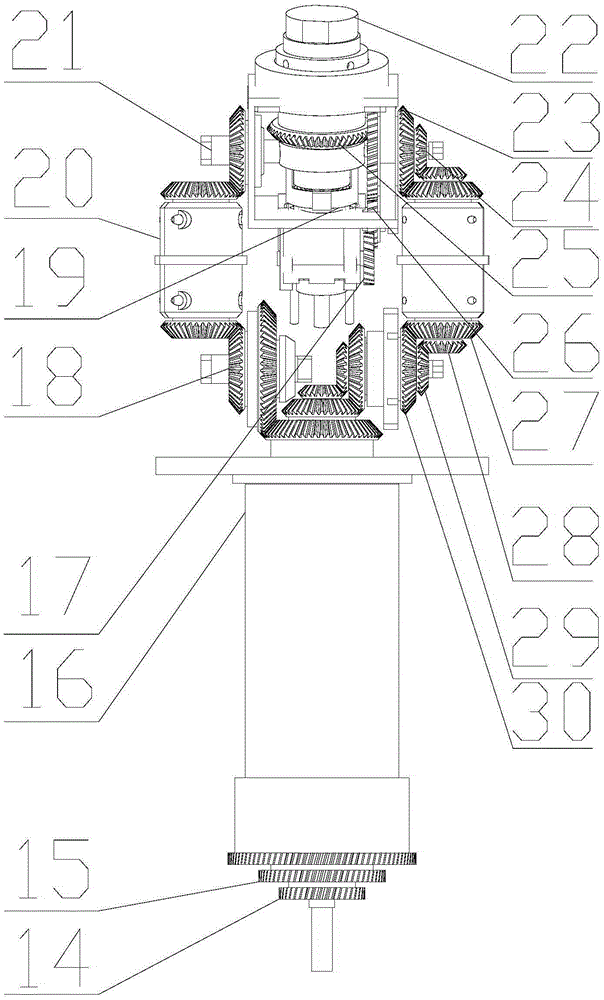
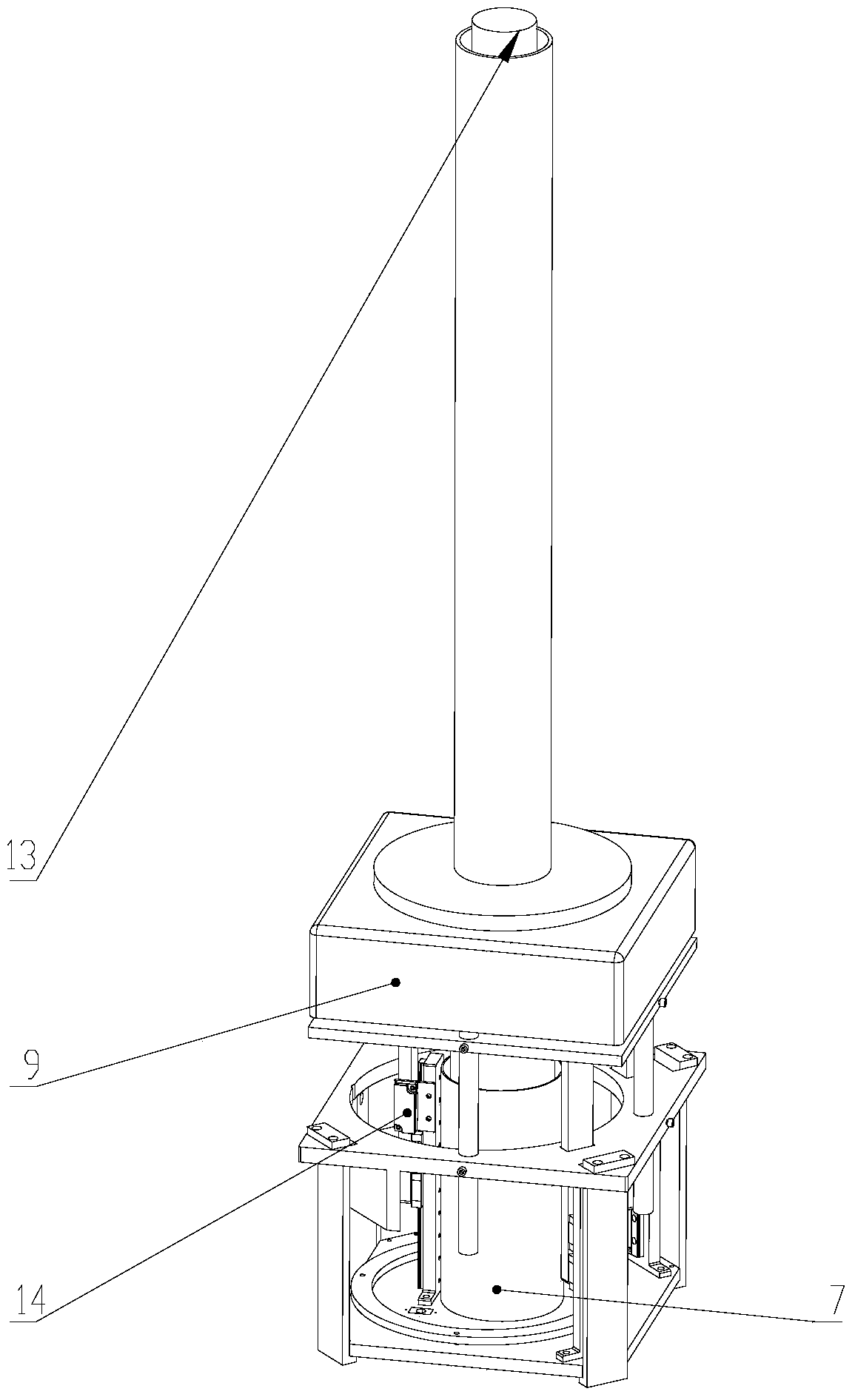
Multi-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance fringe magnetic field imaging experimental device
ActiveCN105259199ATo overcome the shortcomings of relatively single means of useAvoid poor rotational stabilityMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceRelative motionSample image
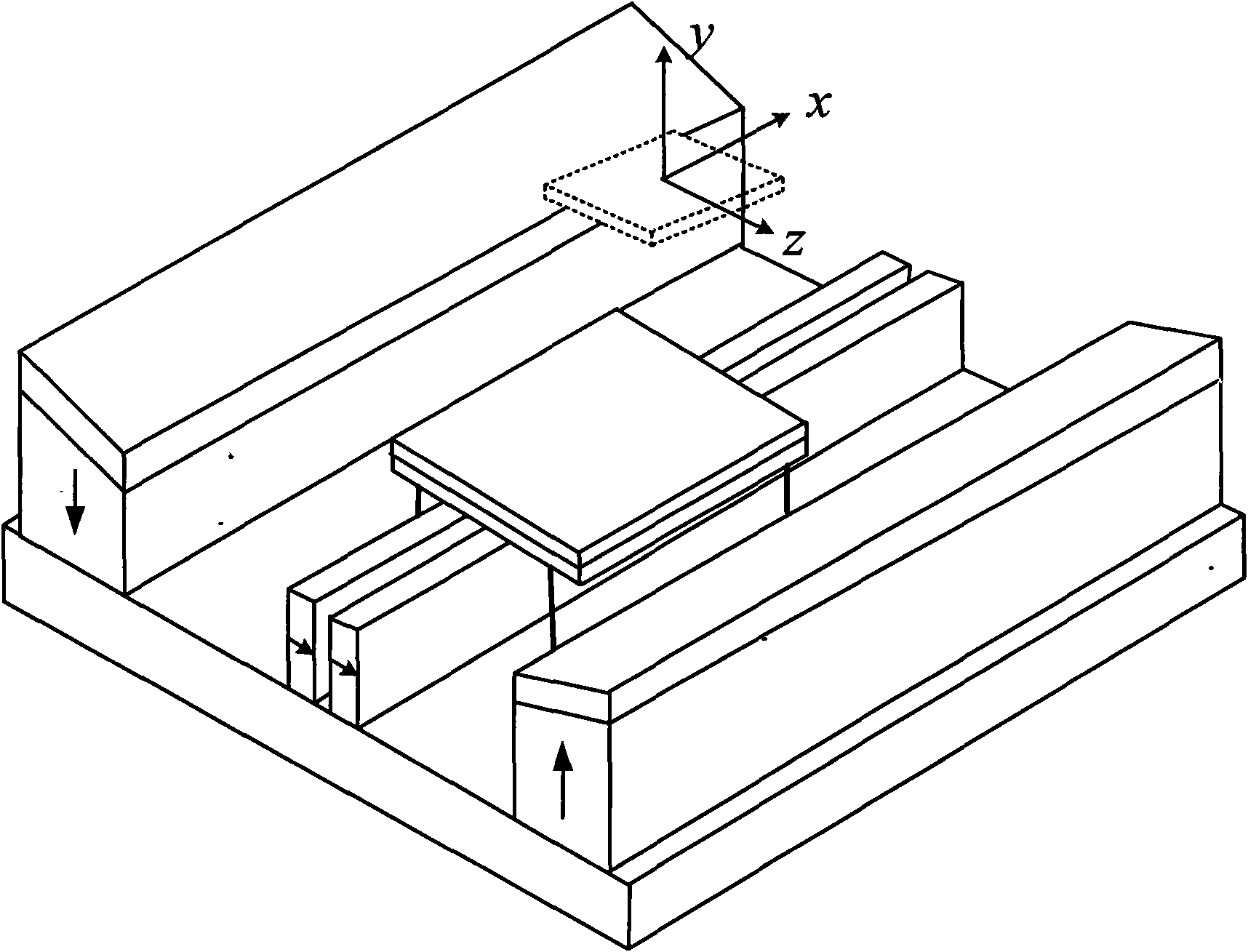
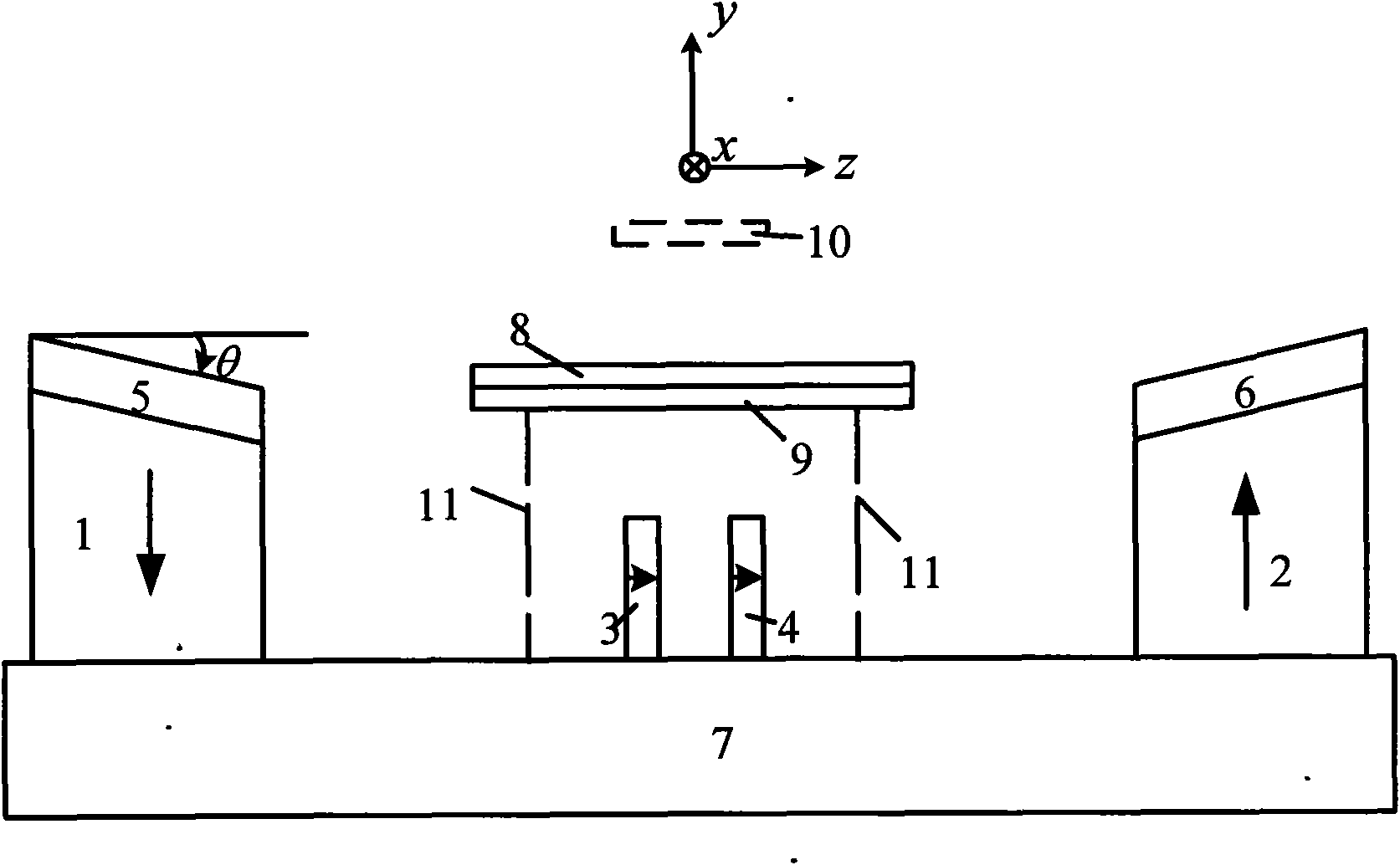
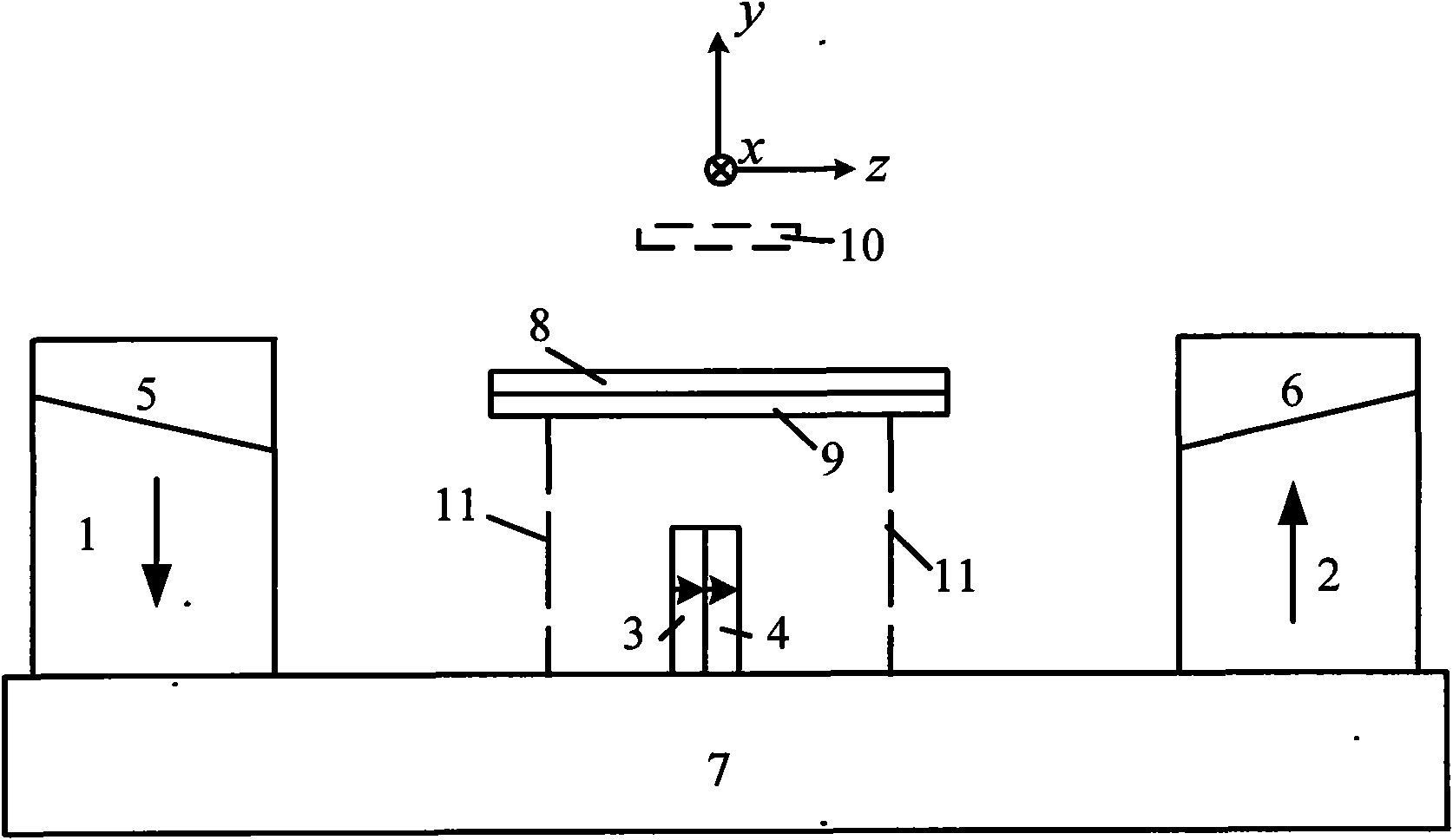
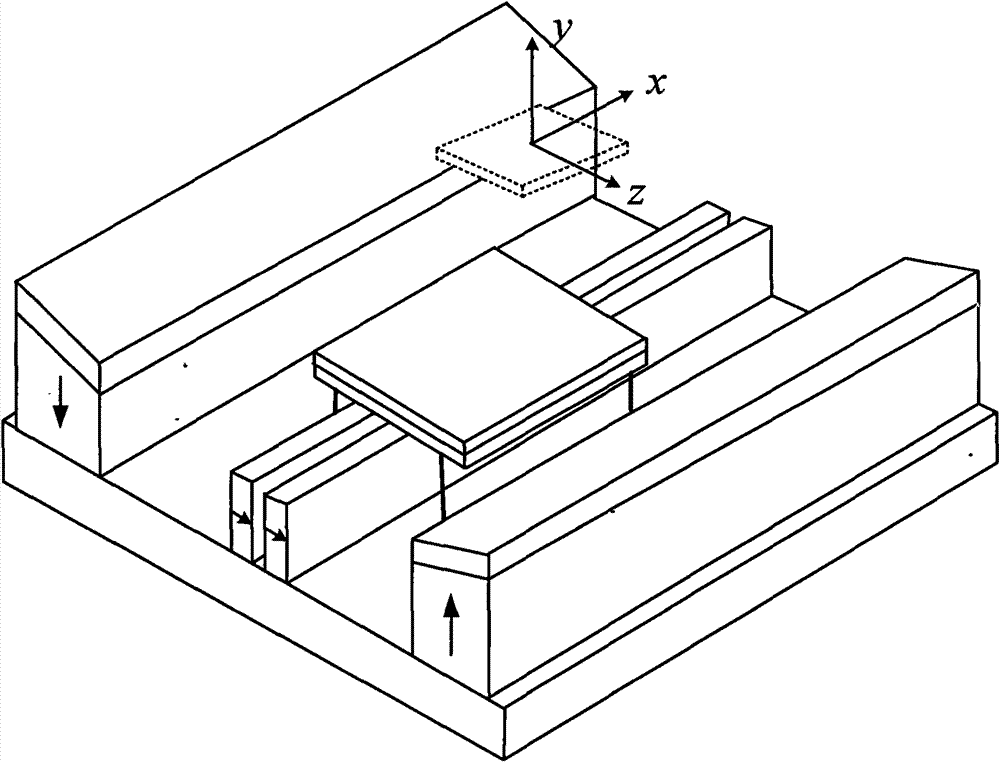
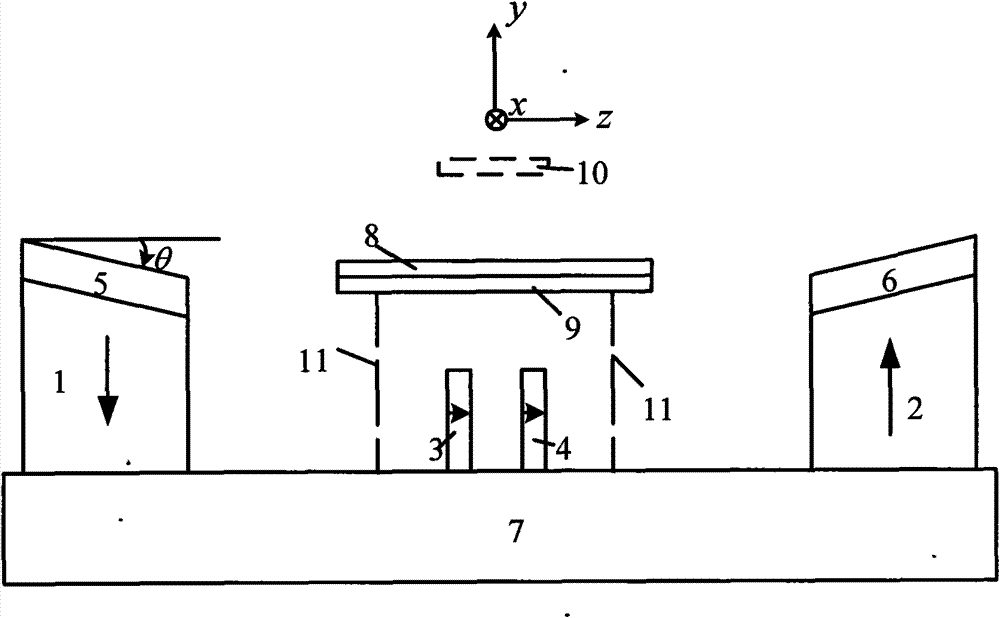
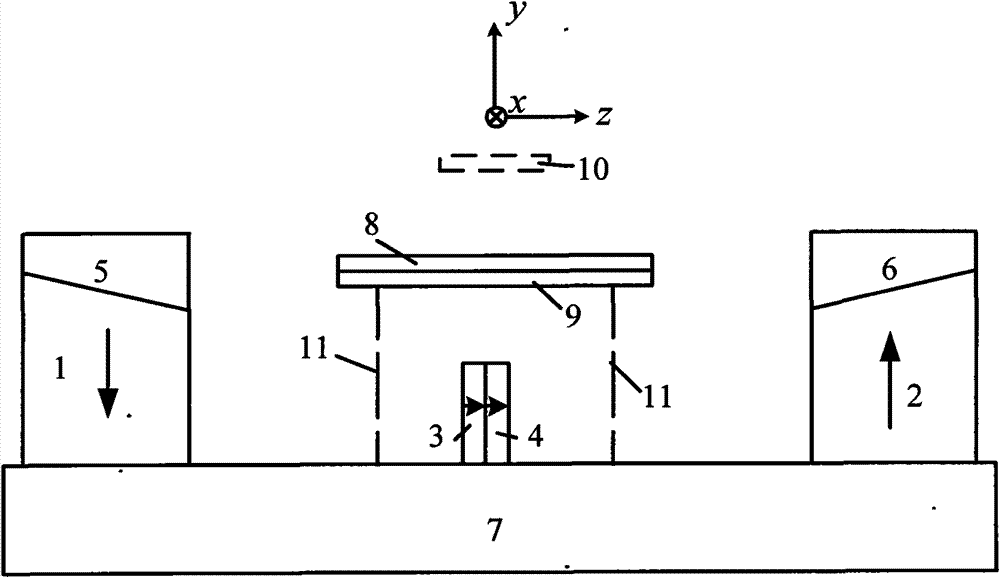
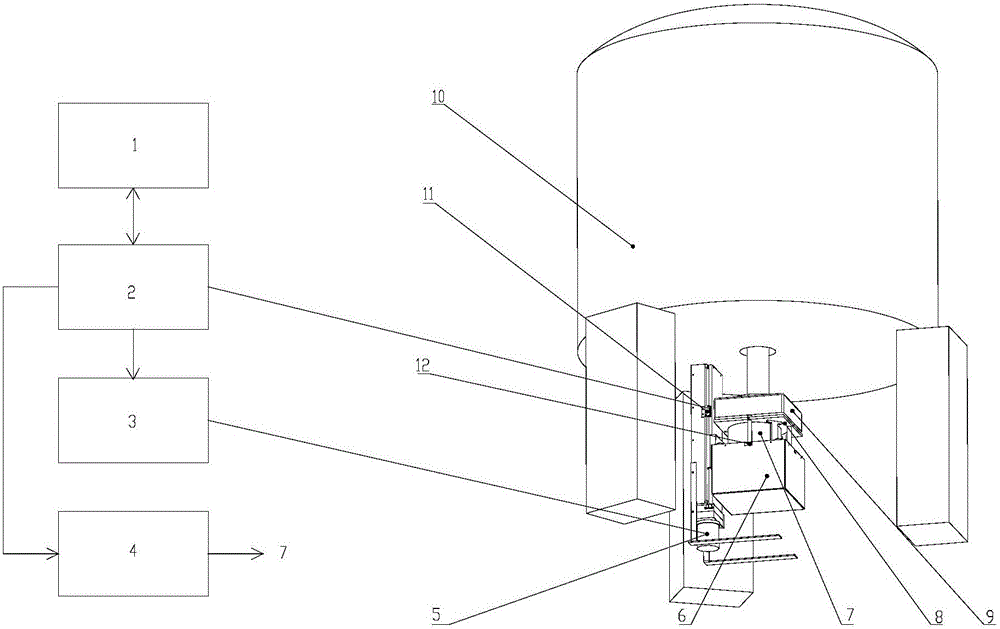
Relating to nuclear magnetic resonance imaging, the invention provides a multi-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance fringe magnetic field imaging experimental device. The experimental device is equipped with a host computer, a PMAC controller, a spectrometer, an AC servo motor driver, four DC servo motor drivers, an AC servo motor, four DC servo motors, a fringe magnetic field imaging plane lifting platform, an imaging probe, two sample chamber Y axis motion system power transmission lines, five sample chamber rotation motion system power transmission lines, seven sample chamber up-and-down motion system power transmission lines, four sample chamber X axis motion system power transmission lines, a probe coil, and a sample chamber up-and-down motion system worm. The experimental device can realize arbitrary angle adjustment of the sample chamber, stable mechanical discontinuous rotation and relative motion of the sample chamber and the probe coil. Through combination of positioning algorithm and a precise mechanical structure, the experimental device realizes movement of the sample chamber relative to the coil, and solves the problem that existing multi-dimensional fringe magnetic field imaging probe experimental devices in the world cannot realize large size sample imaging under an ultrastrong gradient field.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Lithium battery pack consistency detection method and device based on in-situ magnetic field imaging
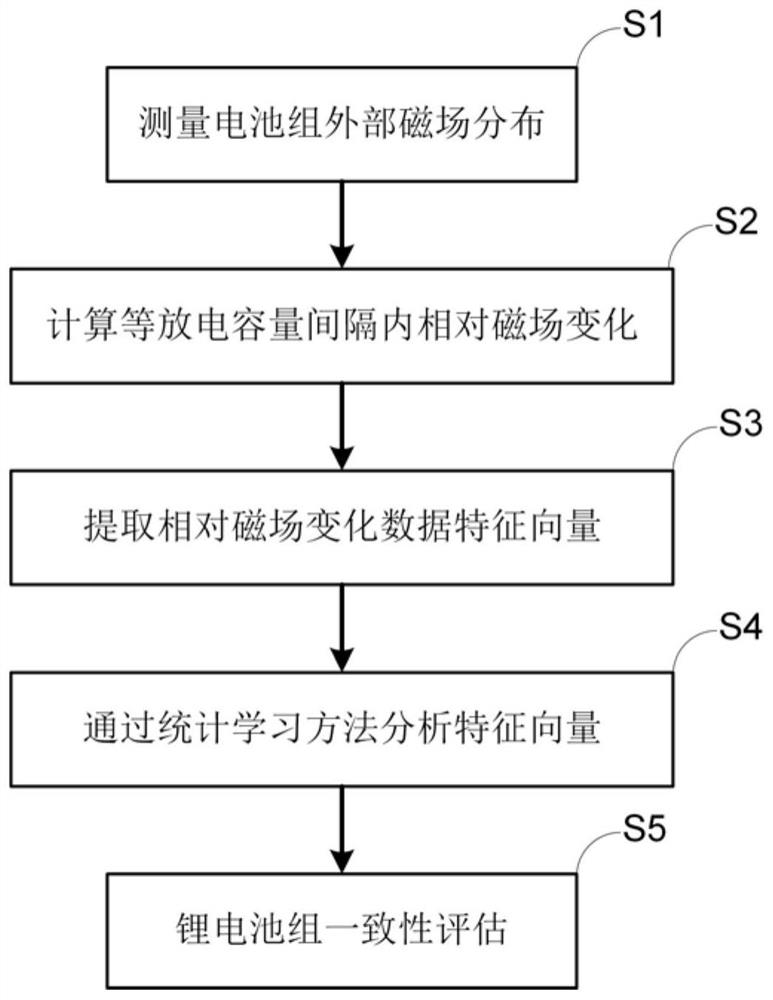
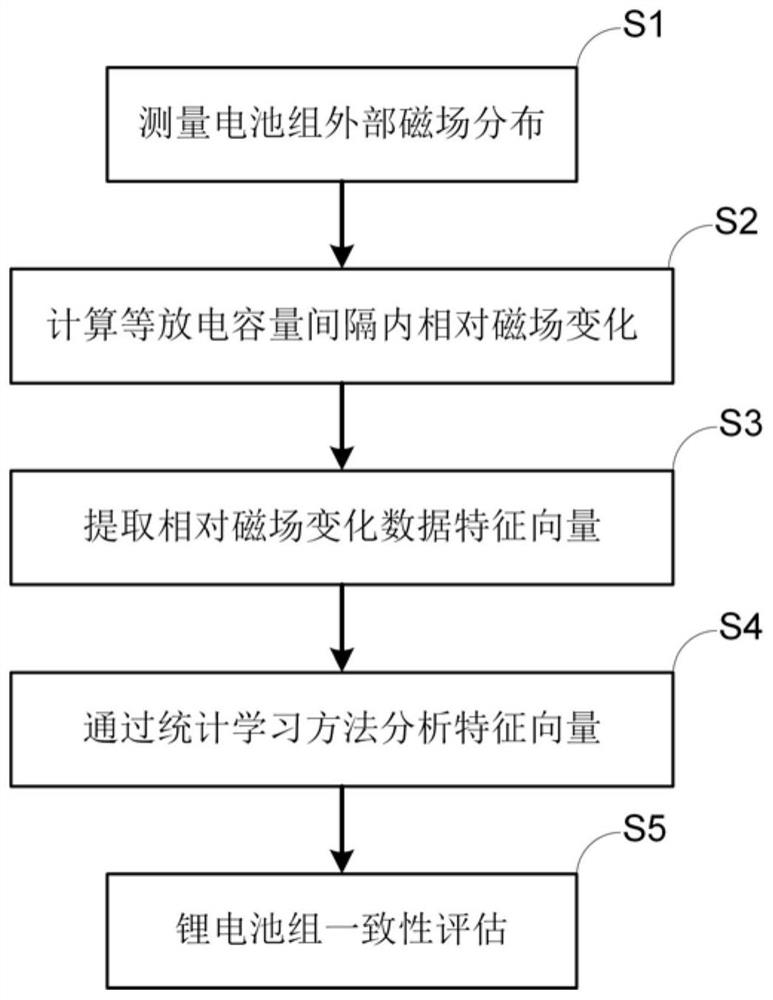
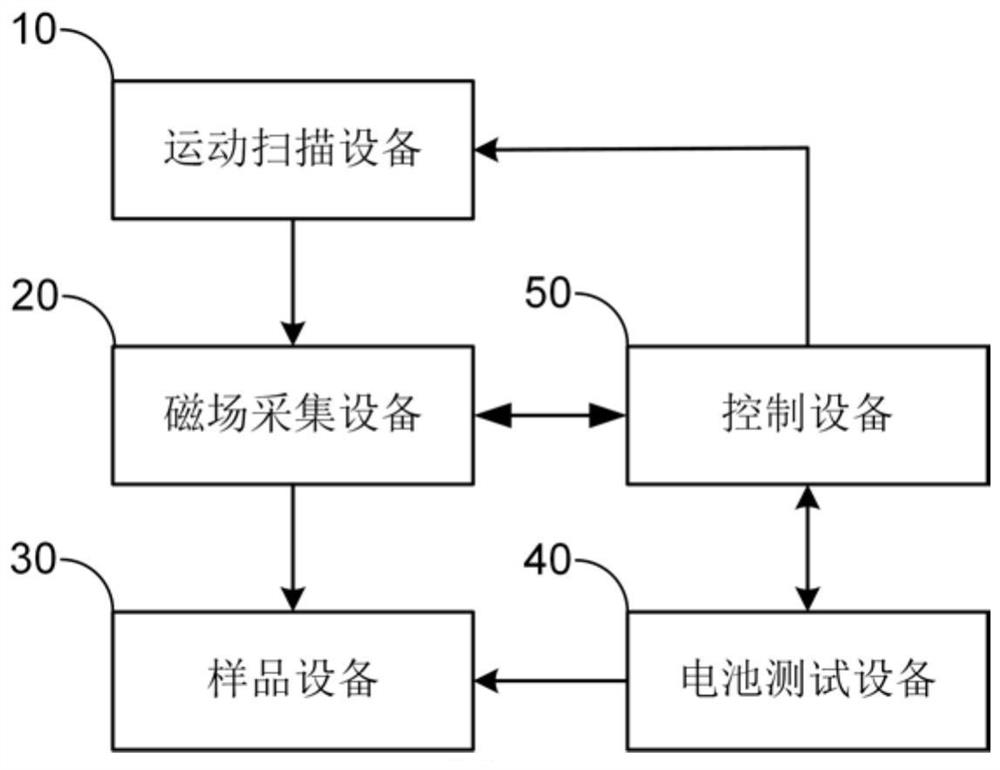
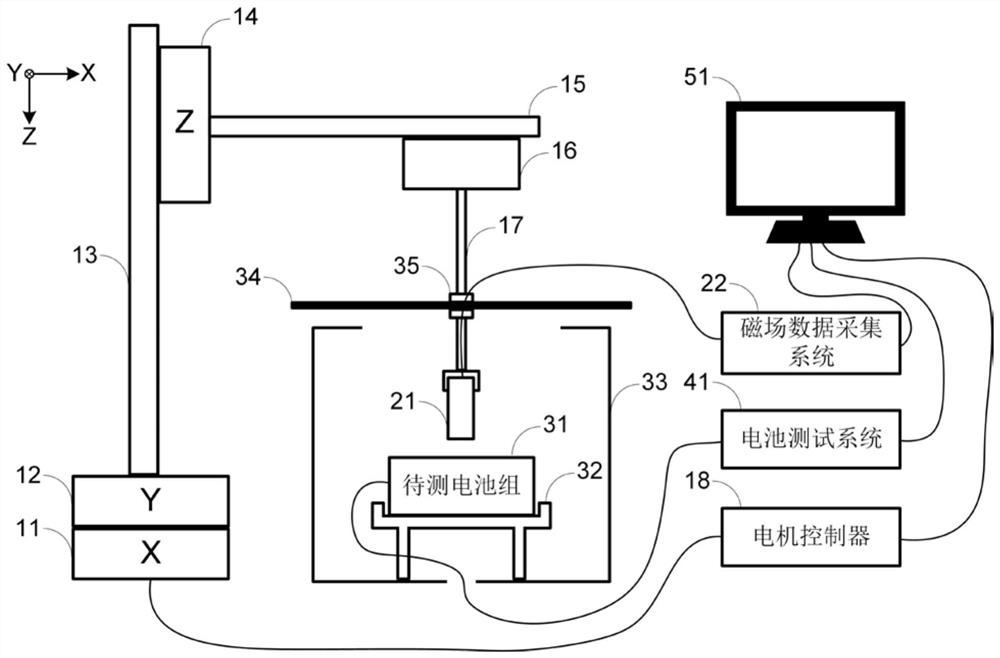
ActiveCN113296012APrecise positioningNo contactElectrical testingThree-component magnetometersElectrical batteryStatistical analysis
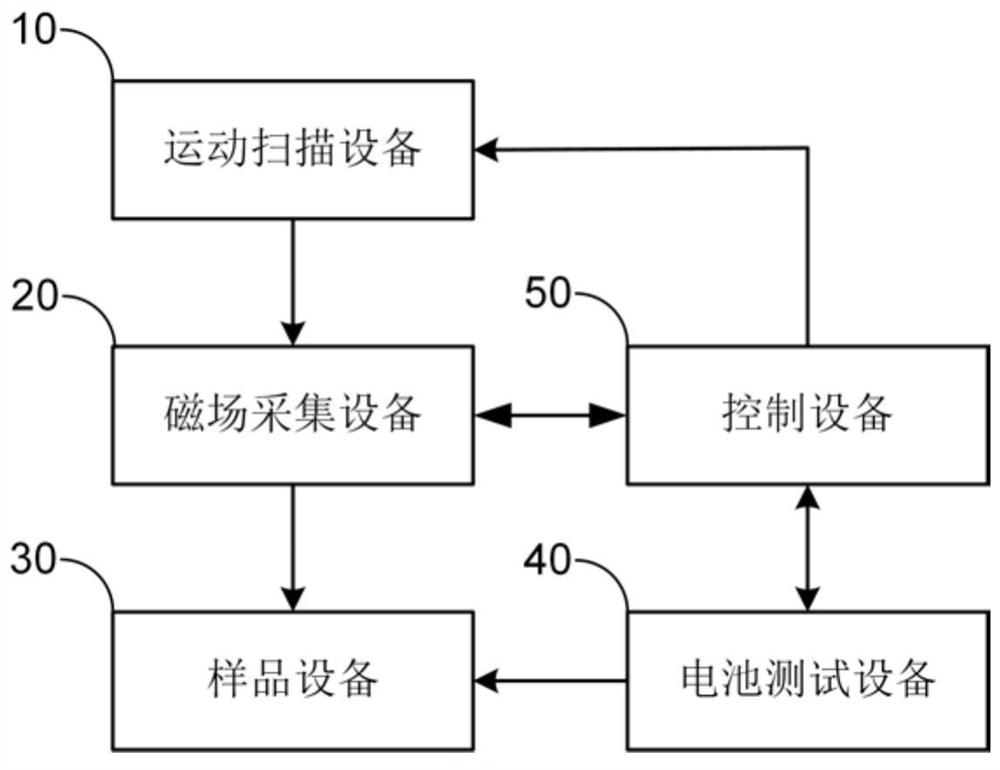
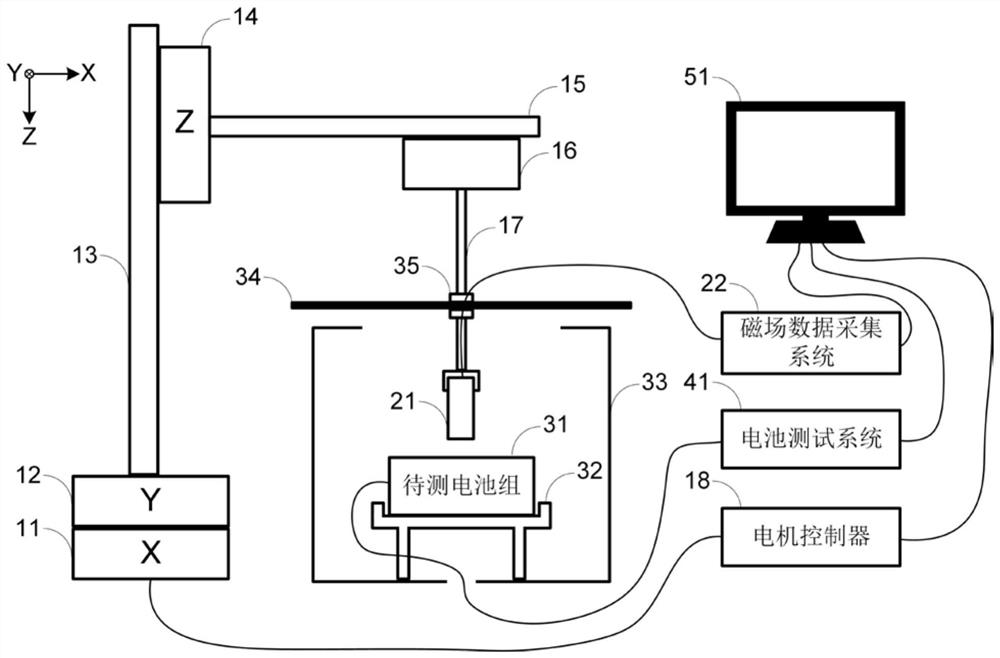
The invention discloses a lithium battery pack consistency detection method and device based on in-situ magnetic field imaging. The method comprises the following steps: measuring external magnetic field distribution of a lithium battery pack at equal discharge capacity intervals in a constant-current discharge process of the lithium battery pack to be measured; calculating the relative change of the external magnetic field distribution of the lithium battery pack in the equal capacity interval; adopting a statistical analysis method to extract statistical feature vectors relative to magnetic field changes; and analyzing the statistical feature vectors by adopting a statistical learning method, and detecting and evaluating the consistency of the battery pack and positioning the batteries with abnormal performance according to an analysis result. The device comprises a motion scanning device, a magnetic field acquisition device, a control device, a battery test device and a sample device. The method has the advantages of no damage, no contact, high efficiency and the like, solves the problem that an existing lithium battery pack consistency detection method cannot monitor all single batteries in the battery pack in a service state on line, and provides technical support for scenes of life prediction, maintenance, safety evaluation and the like of the lithium battery pack.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Sensor device for direct magnetic field imaging
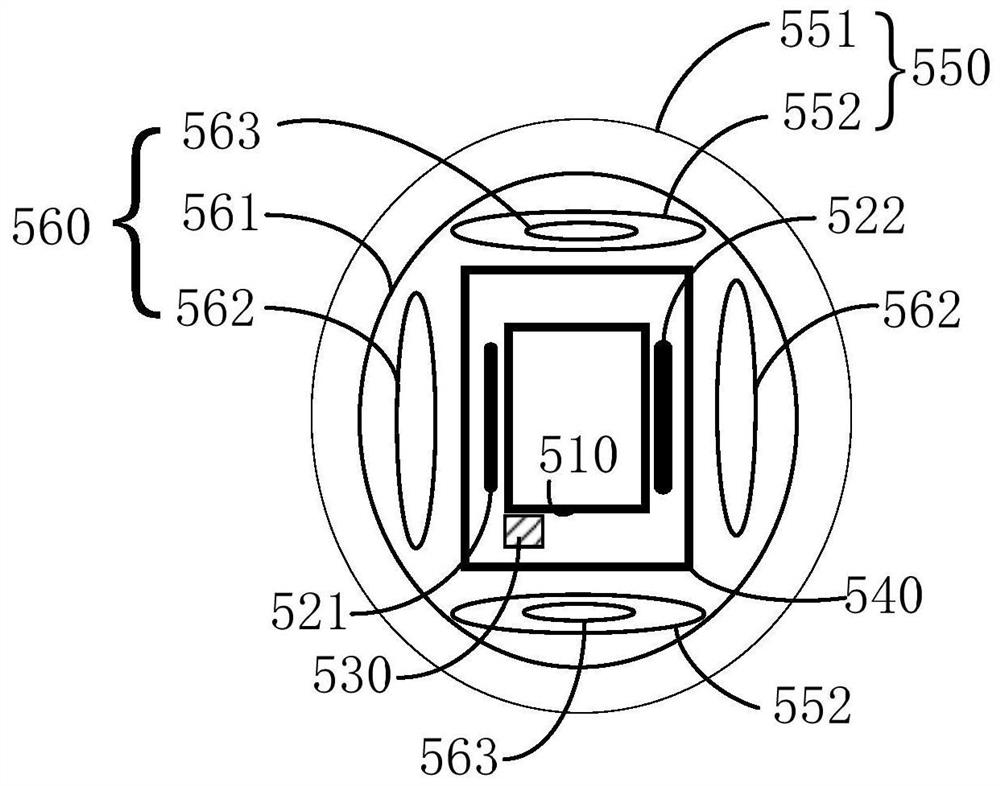
InactiveUS20160103192A1Improve spatial resolutionDistanceMagnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesSingle device manufacturingIn planeClosed loop
The present invention discloses a sensor device comprising a probe carrying a three-dimensional magnetic field sensor. The probe has a conical tip portion with an edge being configured as the three-dimensional magnetic field sensor. The sensor at the edge of the tip comprises at least three Josephson junctions, each junction being formed of a superconducting layer interrupted by a barrier. The barrier comprises a non-superconducting layer or a geometrical constriction. The conical tip portion of the probe forms a tapered three-dimensional structure having at least one arc-like part crossing the opening of the tip portion such that the apex has a closed-loop basis and a plurality of complimentary spaced-apart facets defined by the at least one arc, thereby enabling measurement of both in-plane and out-of-plane magnetic fields separately.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
NMR fringe magnetic field imaging experimental device
InactiveCN104991208BAccurate displacementAvoid inaccuraciesDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsFine structureGrating
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
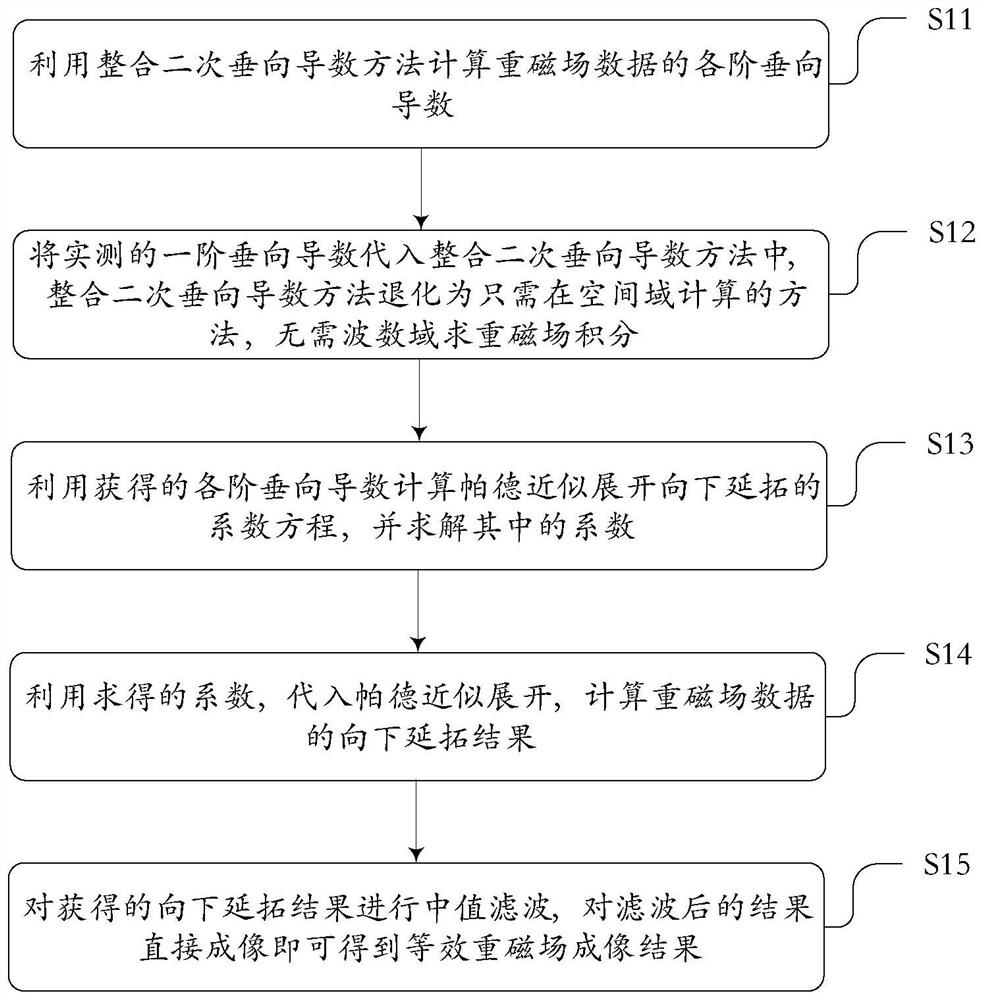
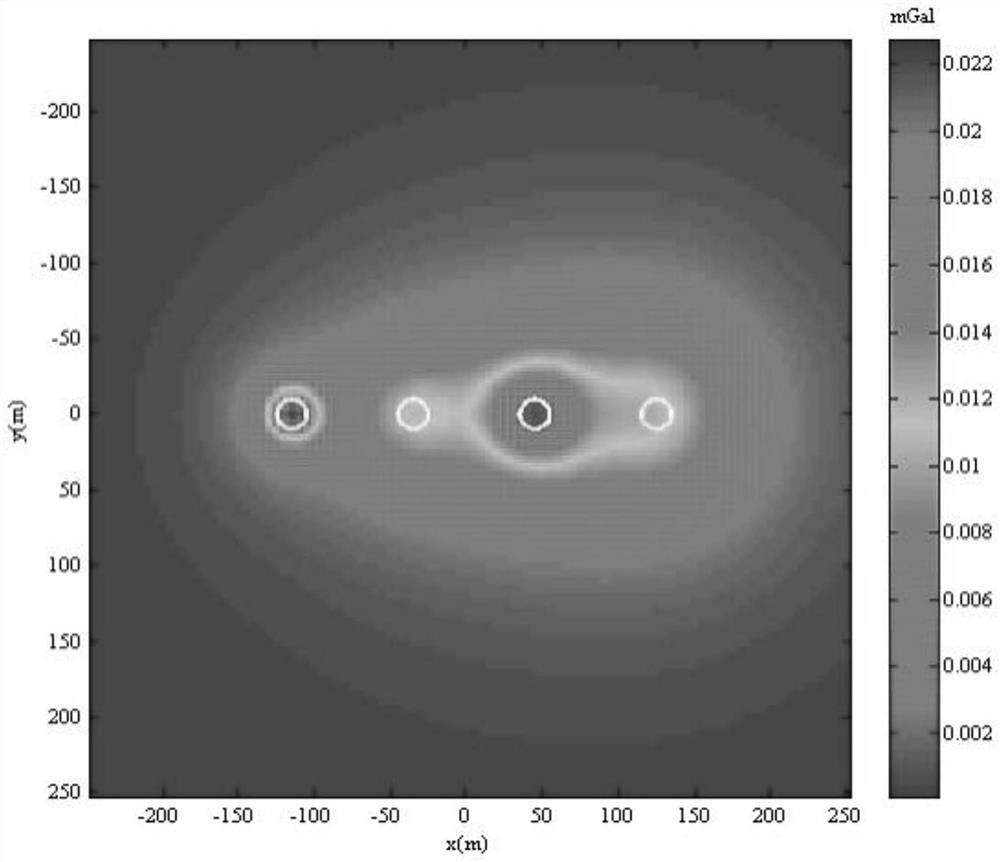
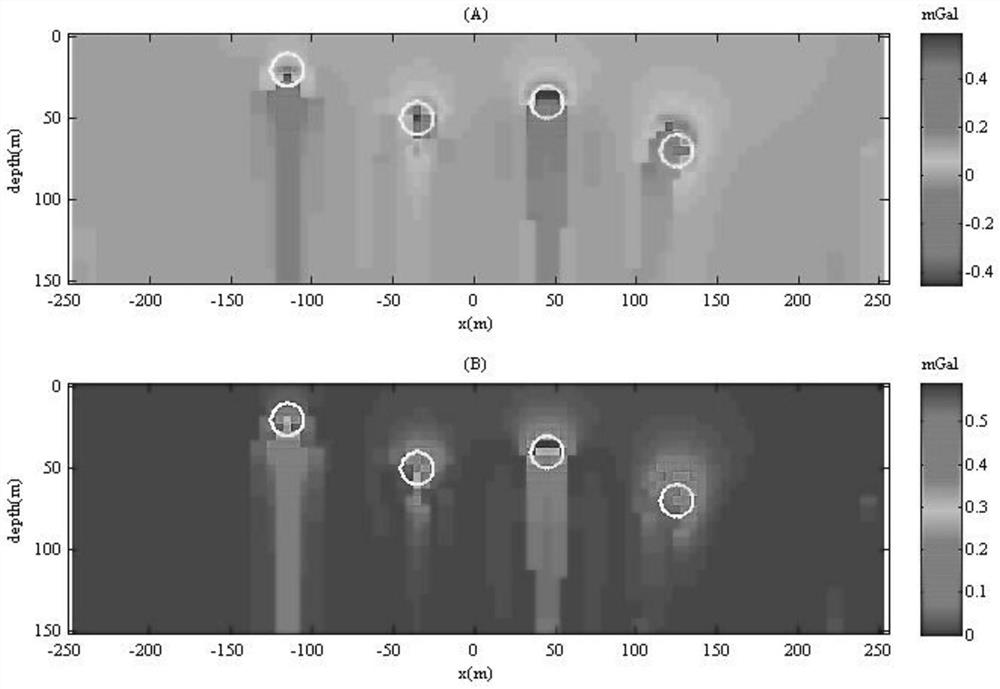
Gravity magnetic field imaging method and system
PendingCN114779357AGuaranteed stabilityGuaranteed finenessElectric/magnetic detectionComplex mathematical operationsComputational physicsVertical derivative
The invention provides a gravity magnetic field imaging method and system. The method comprises the following steps: calculating all orders of vertical guide numbers {Tn} of gravitational magnetic field data by utilizing an integrated quadratic vertical guide number method; substituting the actually measured first-order vertical derivative into the method for integrating the second-order vertical derivative, and degrading the method for integrating the second-order vertical derivative into a method which only needs to calculate in a spatial domain without solving a heavy magnetic field integral in a wavenumber domain; calculating a coefficient equation of Pade approximate expansion downward continuation by utilizing the obtained vertical guide number {Tn} of each order, and solving coefficients in the coefficient equation; substituting the obtained coefficient into Pade approximate expansion, and calculating a downward continuation result of the gravity magnetic field data; and performing median filtering on the obtained downward continuation result, and directly imaging the filtered result to obtain an equivalent gravity magnetic field imaging result. The gravity magnetic field imaging method and system provided by the invention can be used for improving the accuracy and reducing the dependence on depth weighting on the premise of ensuring the stability.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF GEOLOGICAL SCI
A lithium battery pack consistency detection method and device based on in-situ magnetic field imaging
ActiveCN113296012BPrecise positioningNo contactElectrical testingThree-component magnetometersElectrical batteryStatistical analysis
The invention discloses a lithium battery pack consistency detection method and device based on in-situ magnetic field imaging. The method includes: during the constant current discharge process of the lithium battery pack to be tested, measuring the external magnetic field distribution of the lithium battery pack at equal discharge capacity intervals; calculating the relative change of the external magnetic field distribution of the lithium battery pack within the equal capacity interval; using a statistical analysis method to extract Statistical eigenvectors of relative magnetic field changes; Statistical learning methods are used to analyze the aforementioned statistical eigenvectors, and based on the analysis results, battery pack consistency detection and evaluation and abnormal performance battery location are realized. The device includes motion scanning equipment, magnetic field acquisition equipment, control equipment, battery testing equipment and sample equipment. The method has the advantages of non-destructive, non-contact, high efficiency, etc., and solves the problem of online monitoring of all single cells in the battery pack under the service state of the existing lithium battery pack consistency detection method. Security assessment and other scenarios provide technical support.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Experimental device for multi-dimensional NMR fringe magnetic field imaging
ActiveCN105259199BTo overcome the shortcomings of relatively single means of useAvoid poor rotational stabilityMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceMotor drive
The invention relates to a multi-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance edge magnetic field imaging experimental device, which relates to nuclear magnetic resonance imaging. Equipped with upper computer, PMAC controller, spectrometer, AC servo motor driver, four DC servo motor drivers, AC servo motor, four DC servo motors, edge magnetic field imaging plane lifting platform, imaging probe, two sample chambers Y-axis movement System power transmission lines, five sample chamber rotary motion system power transmission lines, seven sample chamber up and down motion system power transmission lines, four sample chamber X-axis motion system power transmission lines, probe coils, sample chamber up and down motion system worm. It can realize arbitrary angle adjustment of the sample cavity, stable mechanical discontinuous rotation and relative movement between the sample cavity and the probe coil. Through the combination of positioning algorithm and precision mechanical structure, the movement of the sample cavity relative to the coil is realized, which solves the problem that the current international multi-dimensional edge magnetic field imaging probe experimental device cannot realize the imaging of large-scale samples under a super-strong gradient field.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
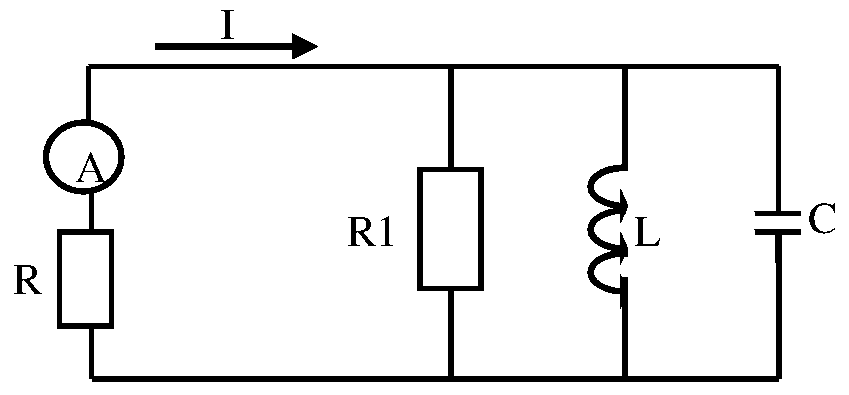
High current, low power magnetic field signal differential acquisition device
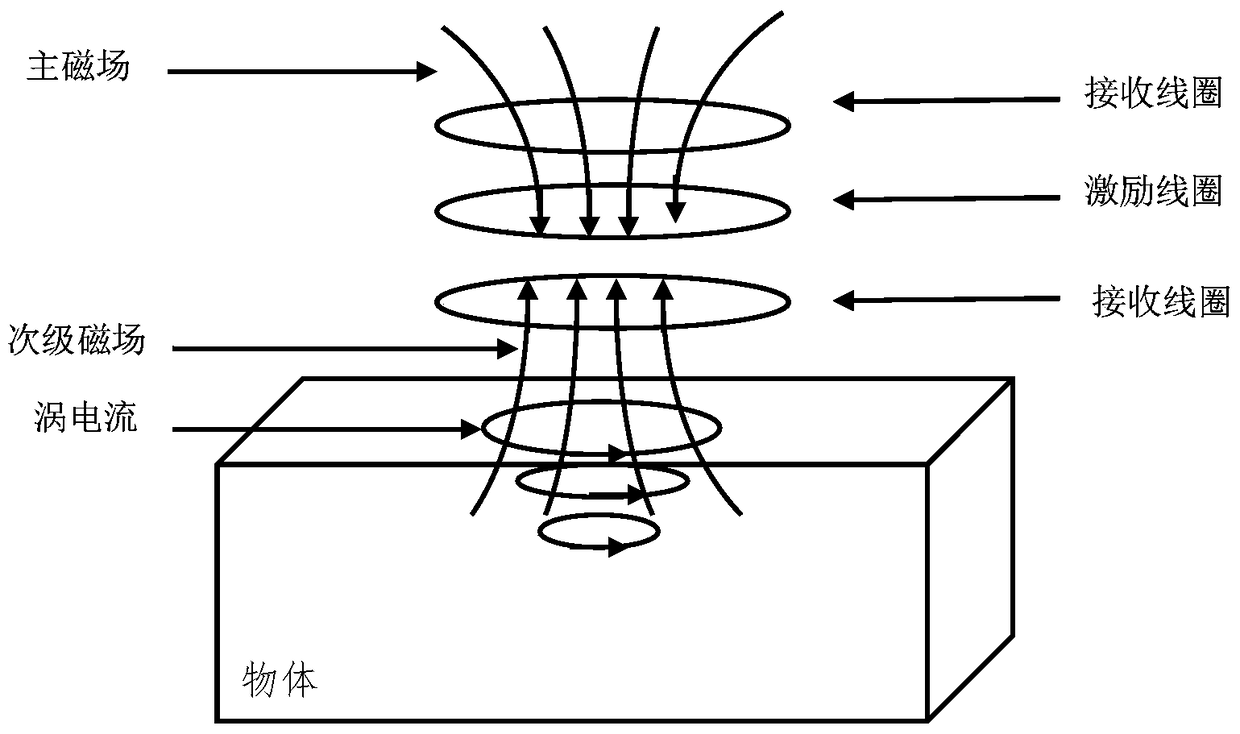
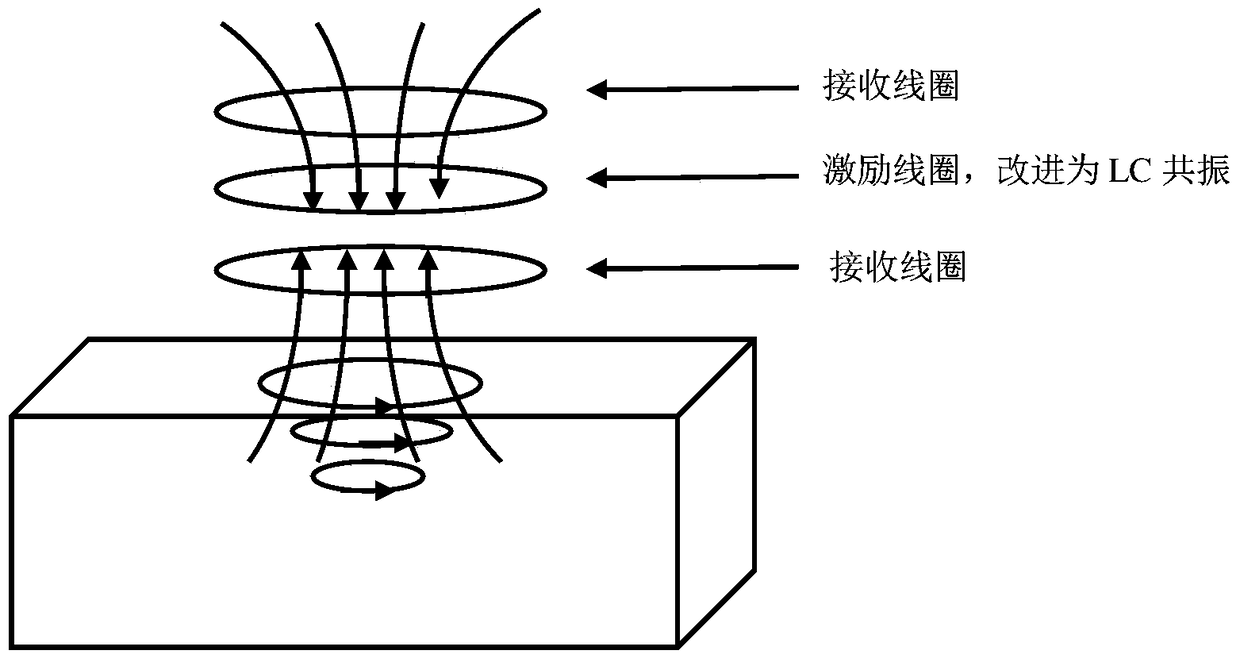
InactiveCN105182256BReduce energy consumptionIncrease the magnetic fieldMagnetic field measurement using flux-gate principleMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesCapacitanceAcquisition apparatus
The invention, which relates to the technical field of the magnetic field imaging, provides a heavy-current low-power magnetic field signal difference acquisition apparatus. On the basis of improvement of a traditional gradiometer, a secondary magnetic field can be measured easily; and the apparatus has the great research values and practical application value. According to the technical scheme, the apparatus is formed by an excitation unit clamped between two receiving units; and the excitation unit is a low-power heavy-current LC oscillating circuit and is formed by parallel connection of inductive capacitors. The apparatus is mainly applied to the design and manufacturing of magnetic field imaging equipment.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
A chip-scale diamond nv ‑ Color center magnetic imaging device and imaging method
ActiveCN105137371BReduce volumeQuick responseMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringMedical diagnosisElectromagnetic shielding
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +1
Medical magnetic resonance imager monohedral magnet device
InactiveCN101598775BBuild accuratelyLow costDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsResonanceMagnetic poles
The invention relates to a medical magnetic resonance imager monohedral magnet device, belonging to the technical field of medical instruments. The invention comprises a main monohedral magnet, a first gradient coil, a second gradient coil, an imaging zone and a bracket, wherein, the main monohedral magnet comprises a first main magnetic pole, a second main magnetic pole, a first adjusting magnetic pole, a second adjusting magnetic pole, a first pole surface, a second pole surface and a base. The invention has the following advantages: the main monohedral magnet forms an even lamelliform magnetic field imaging zone on the outer side of the magnet; a first monoplane gradient coil and a second monoplane gradient coil provide a gradient magnetic field with favourable degree of linearity in the imaging zone so as to realize phase encoding and frequency encoding of images; by revising the incline angle of a polar surface and adjusting magnetic pole interval, an even amelliform magnetic field can be precisely built. Compared with the traditional magnetic resonance imager magnet device, the device of the invention has the advantages of small volume, light weight and good openness, and greatly lowers the cost of the magnetic resonance imager.
Owner:SHENYANG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Nuclear magnetic resonance fringe magnetic field imaging experimental device
InactiveCN104991208AAccurate displacementAvoid inaccuraciesDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsGratingClosed loop
A nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) fringe magnetic field imaging experimental device relates to NMR imaging. The device comprises a servo motor, a voice coil motor, a coarse adjustment non-magnetic lifting platform, a fine adjustment non-magnetic lifting platform, a NMR fringe magnetic field imaging probe, a sample chamber, a probe coil and sample relative-mobile / static conversion pin, a coarse adjustment and fine adjustment non-magnetic lifting platform grating ruler, and a control system. The control system is composed of a principal computer, a PMAC controller, a servo motor driver, and a voice coil motor controller. A coarse adjustment and fine adjustment two-stage lifting high-precision mechanical structure and an advanced closed-loop control algorithm are combined to realize high-precision sample movement with the highest precision of 1micron and complete high-precision and high-resolution NMR fringe magnetic field imaging. Two experimental methods, namely, probe coil and sample relative-mobile imaging and probe coil and sample relative-static imaging, can be completed on one experimental device without the need for any secondary transformation, and that a strong magnetic environment is not affected is guaranteed to the maximum. Closed-loop control makes sample displacement more precise and the result more accurate.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
A near-drill magnetic field imaging positioning measuring instrument and working method
ActiveCN111734397BAccurate measurementSurveyConstructionsMeasuring instrumentThree-dimensional space
The invention discloses a near-bit magnetic field imaging positioning measuring instrument and a working method, and belongs to the technical field of oil drilling measurement. The near-bit magnetic field imaging positioning measuring instrument comprises a drill bit, a near-bit magnetic field imaging positioning short section, a power drilling tool, a wireless short pass transmitting assembly, awireless short pass receiving assembly, a ground receiving device and a processing computer. A non-magnetic drill bit and a non-magnetic near-bit magnetic field imaging positioning short section are adopted to form a stable magnetic anomaly detection environment nearby the drill bit, a magnetic field acquisition sensor can perform three-dimensional detection on a three-dimensional space nearby thedrill bit during rotation, the positions of anomalous fields can be accurately measured, and range information is given; and a ground computer visually displays the anomalous fields in front of the drill bit in real time on a screen according to the measured information, the interaction position of nearby sleeves and the drill bit can further be identified, and collision early warning and suggestions on pile wrapping are made.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Microscopic electrical impedance imaging device and method based on diamond nv color center
ActiveCN111504884BImprove spatial resolutionIndividual particle analysisMetallic electrodeDiamond color
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Magnet device
InactiveUS7436179B2Reduce performanceRise in the inductance of the coilsMagnetsMagnetic property measurementsCouplingMagnetic flux
A magnet device has main coils in a pair positioned facing each other to form a static magnetic field space in between and external magnetic flux shielding coils placed coaxially to the main coils. The external magnetic flux shielding coils have a first coil group having a small coefficient of coil coupling and a second coil group having a coefficient of coil coupling greater than that of the first coil group. The first coil group is connected in series to the second coil group. External magnetic flux entering the magnetic field imaging space formed by main coils in a pair positioned facing each other is effectively warded off.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Atomic Magnetometer and Magnetic Field Imaging System
ActiveCN111983526BSimple structureAvoid introducingMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesMagnetic heatingTemperature control
The present application relates to an atomic magnetometer and a magnetic field imaging system. The first wavelength laser and the second wavelength laser are formed by a laser light source and a frequency doubling module. The optical power of the first-wavelength laser is adjusted through the optical attenuation module to realize the non-magnetic optical heating of the atomic gas chamber, and the attenuation is adjusted to control the temperature. The laser light of the second wavelength enters the atomic gas chamber to realize the magnetic field detection. Therefore, the atomic magnetometer does not need to couple the heating laser and the pumping laser, and can realize non-magnetic heating and atomic pumping detection, which reduces the complexity of the optical path. In the magnetic field imaging system, a laser light source is connected with multiple atomic magnetometer probes. Through the position information of multiple atomic magnetometer probes and the detected magnetic field information, the accurate positioning of the magnetic field position can be realized, so as to realize the multi-dimensional magnetic field space reconstruction.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com