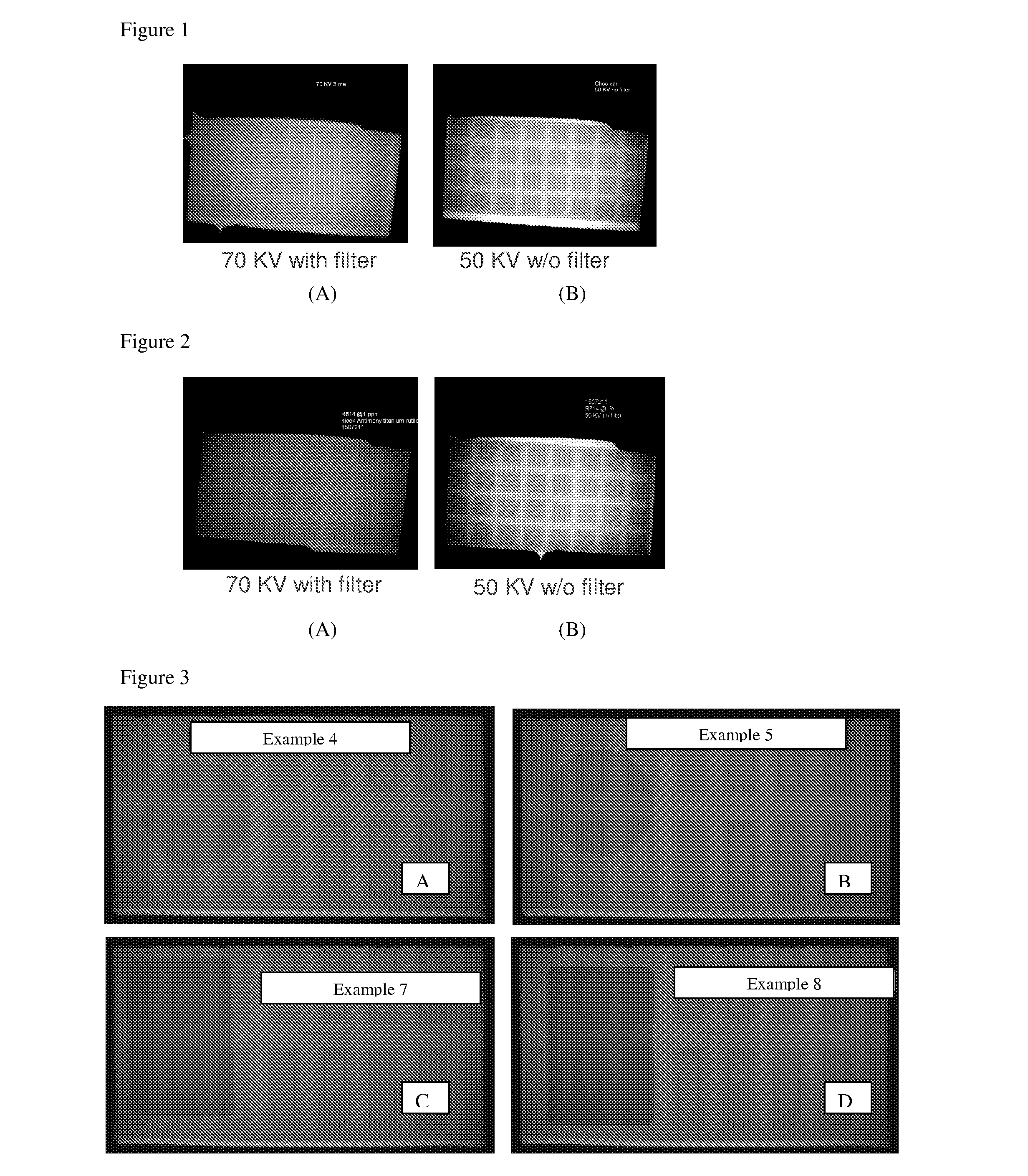
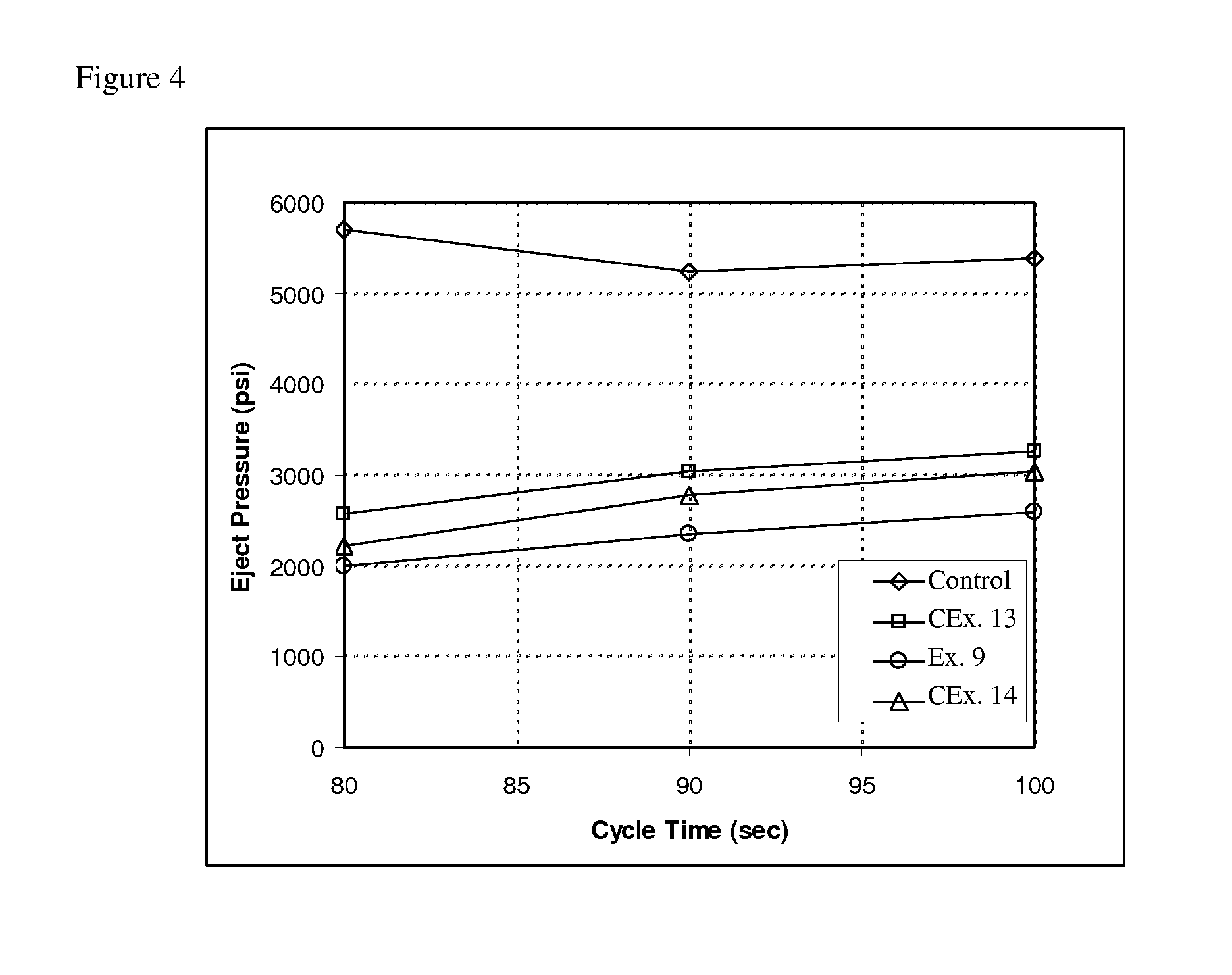
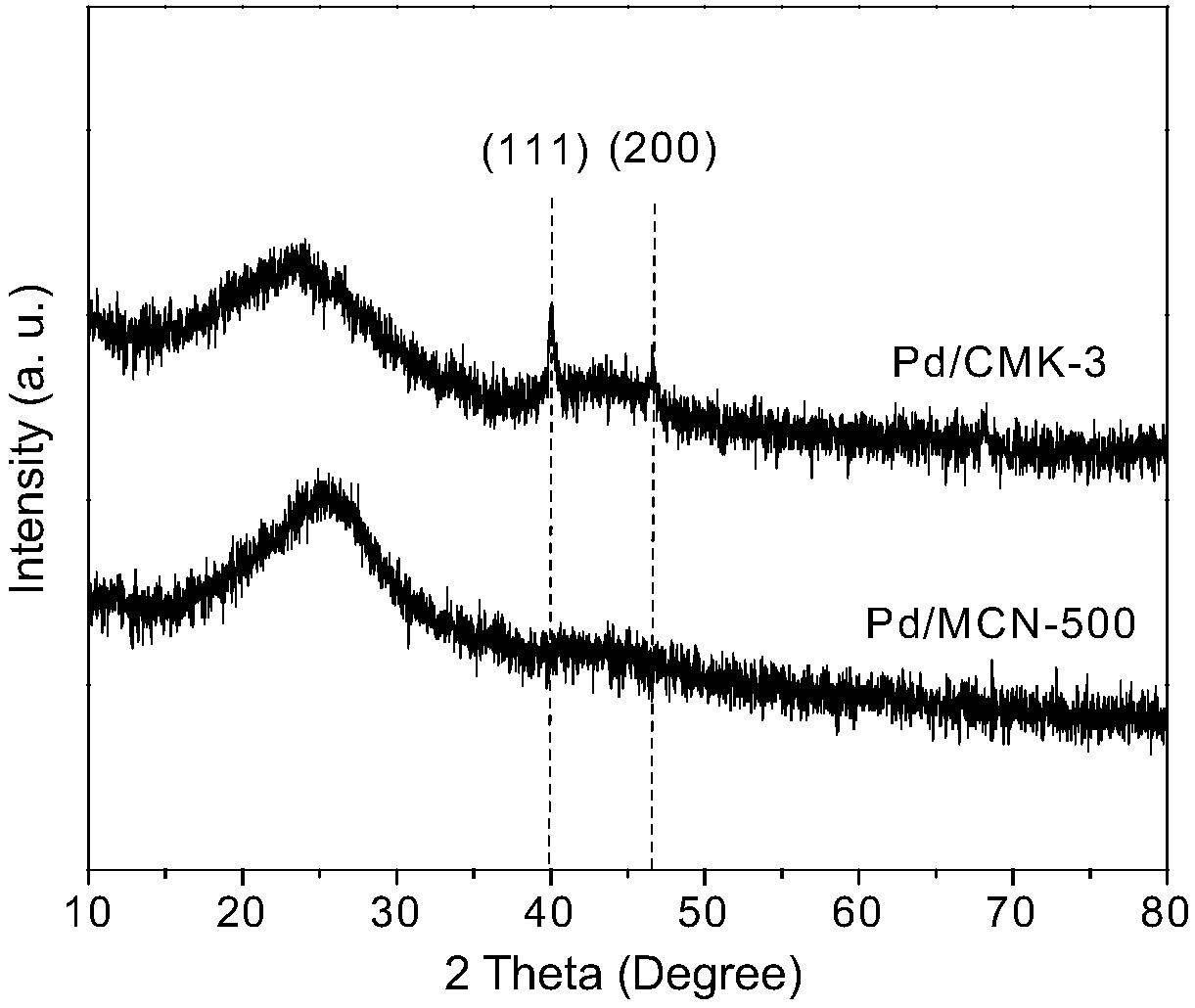
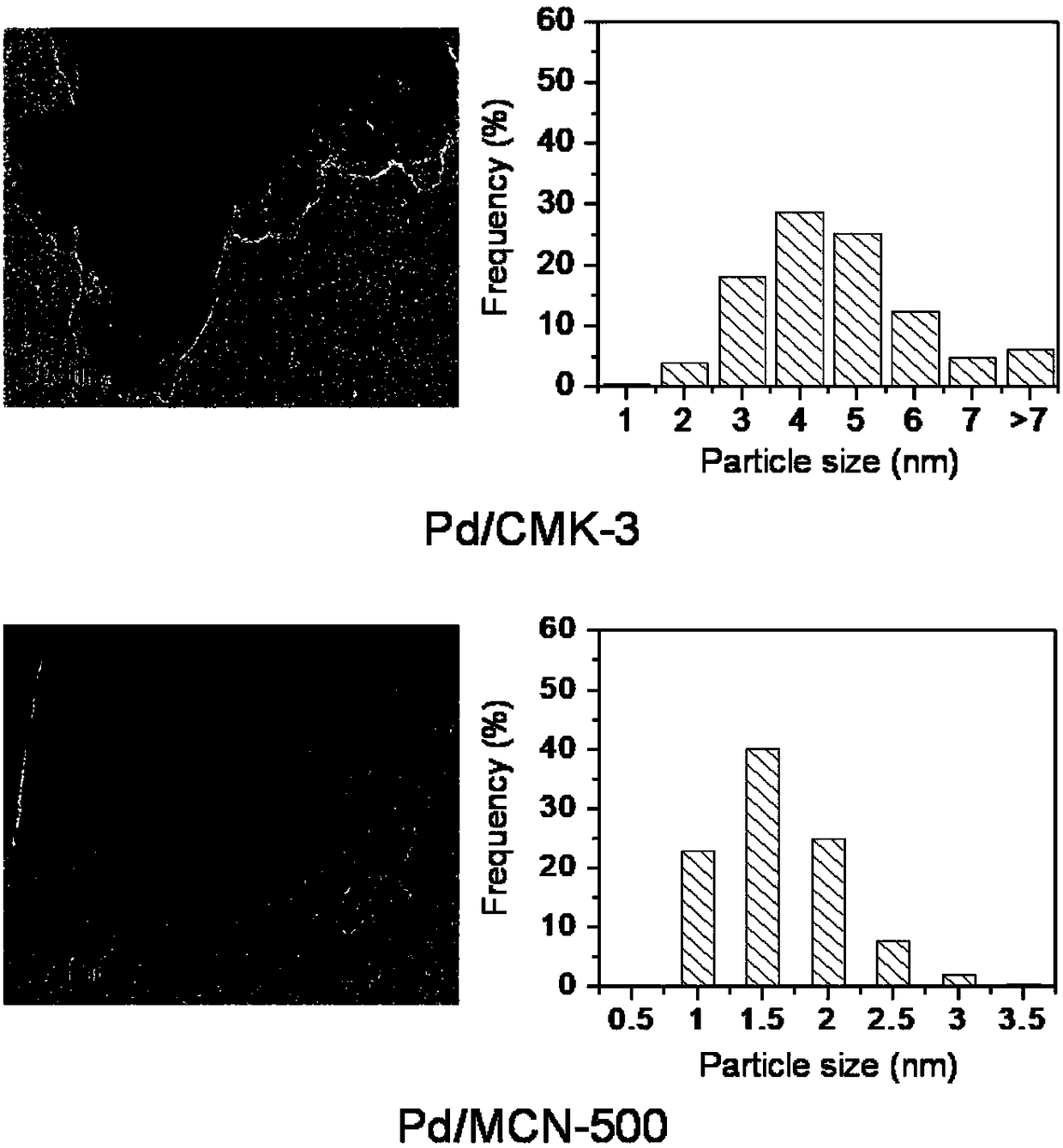
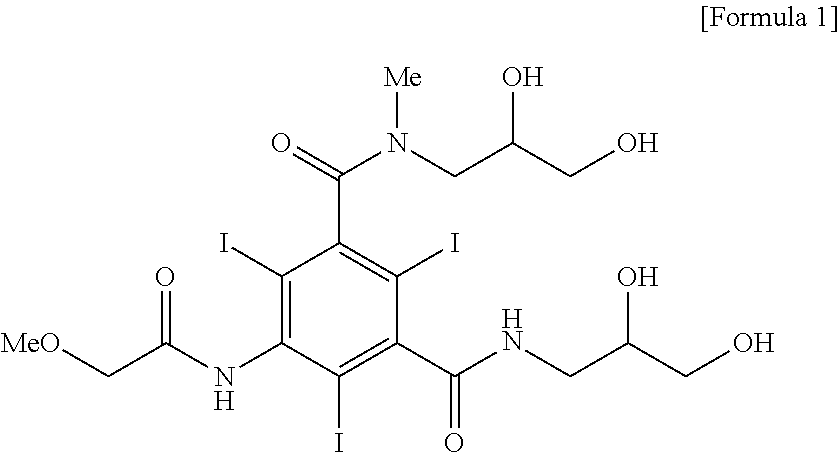
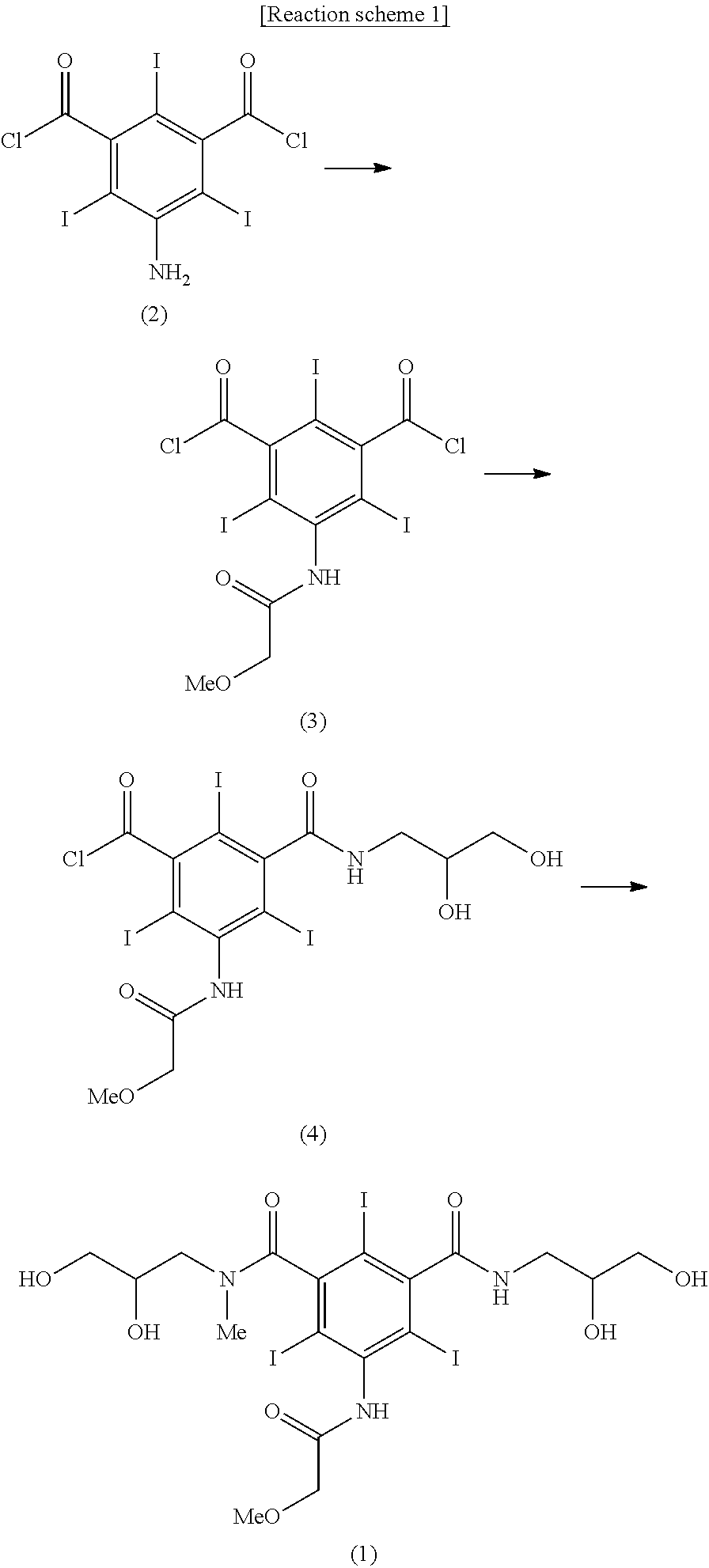
Patents
Literature
84 results about "X-ray contrast media" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
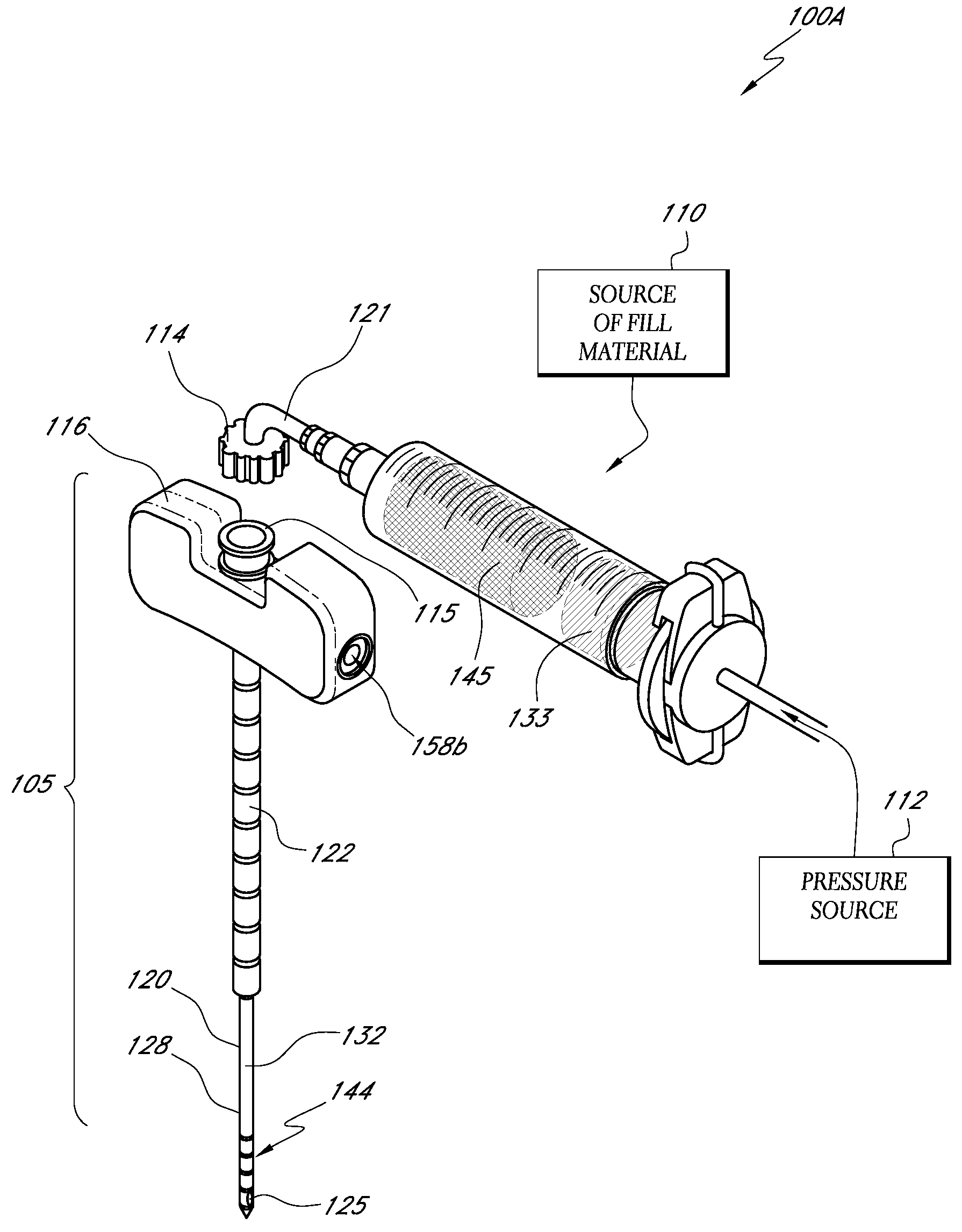
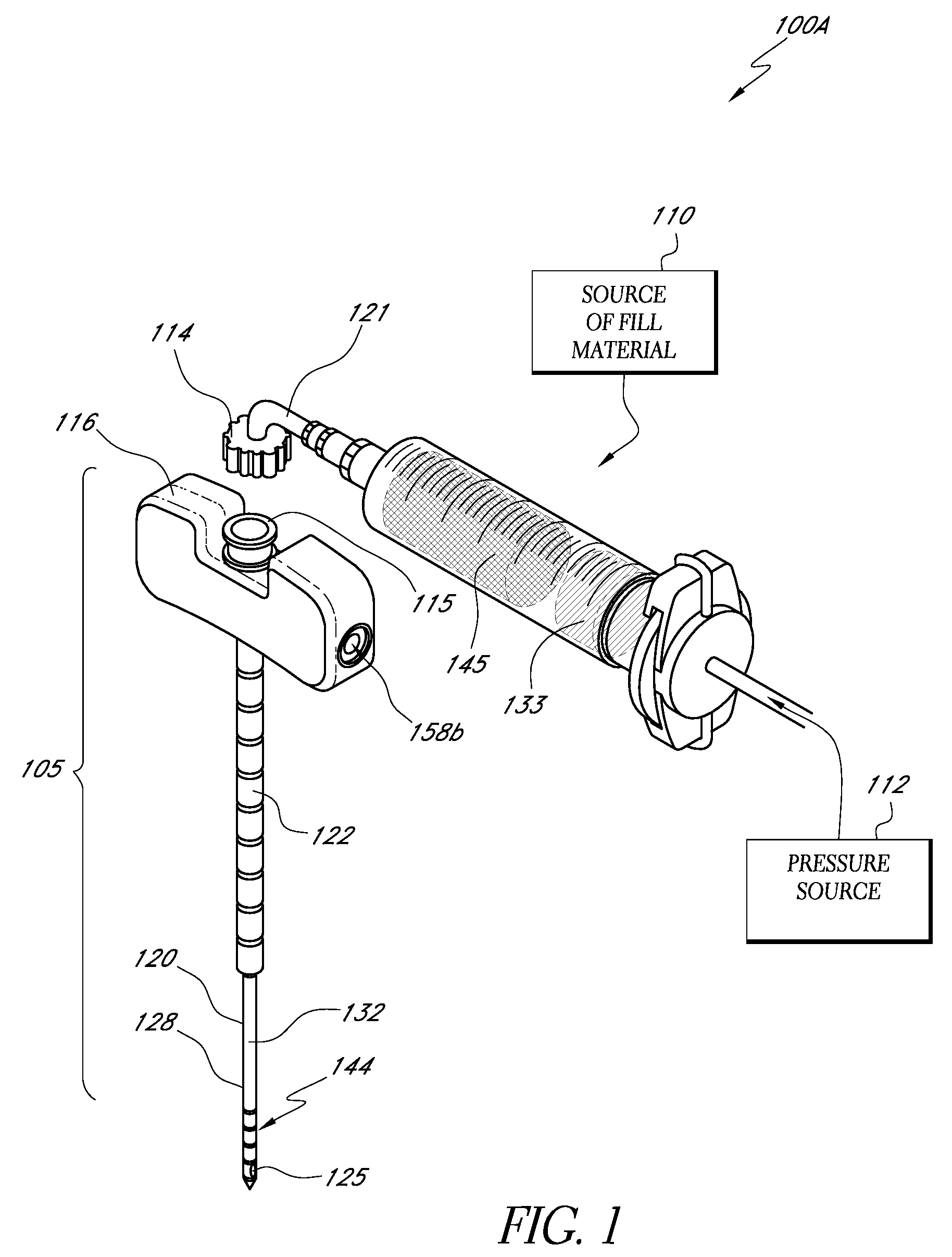
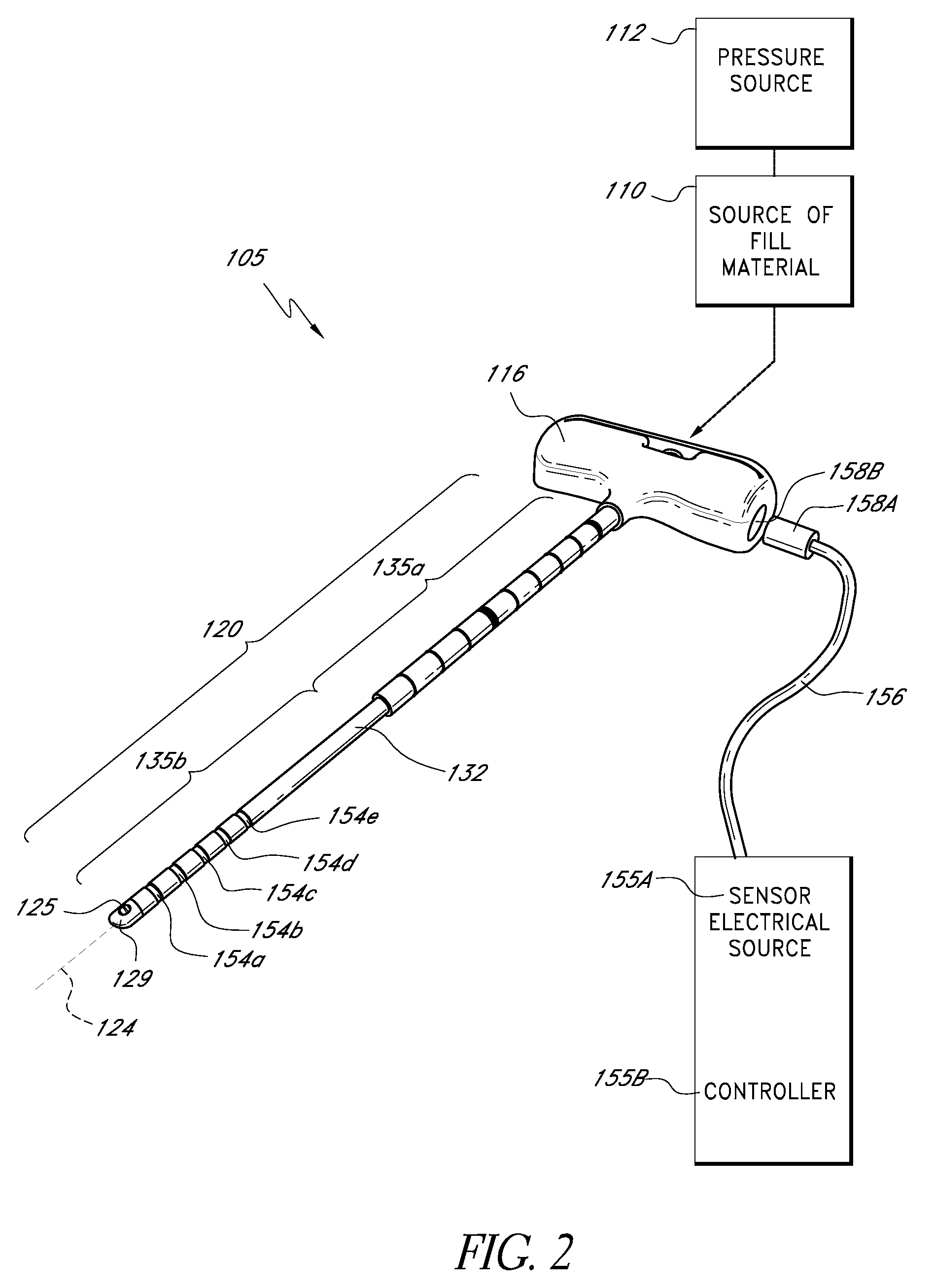
Bone treatment systems and methods
InactiveUS20080188858A1High viscosityImprove setting timeSurgical adhesivesTissue regenerationBone cementMaterials science
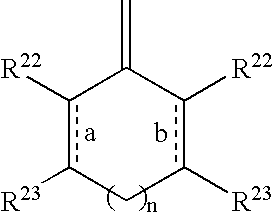
Bone cement formulations are provided that have an extended working time for use in vertebroplasty procedures and other osteoplasty procedures. In one embodiment, a settable bone cement includes a polymerizable composition with a powder component comprising an X-Ray contrast medium and a liquid component, wherein the setting time of the cement is at least about 25 minutes, at least about 30 minutes, at least about 35 minutes, and at least about 40 minutes.
Owner:DFINE INC
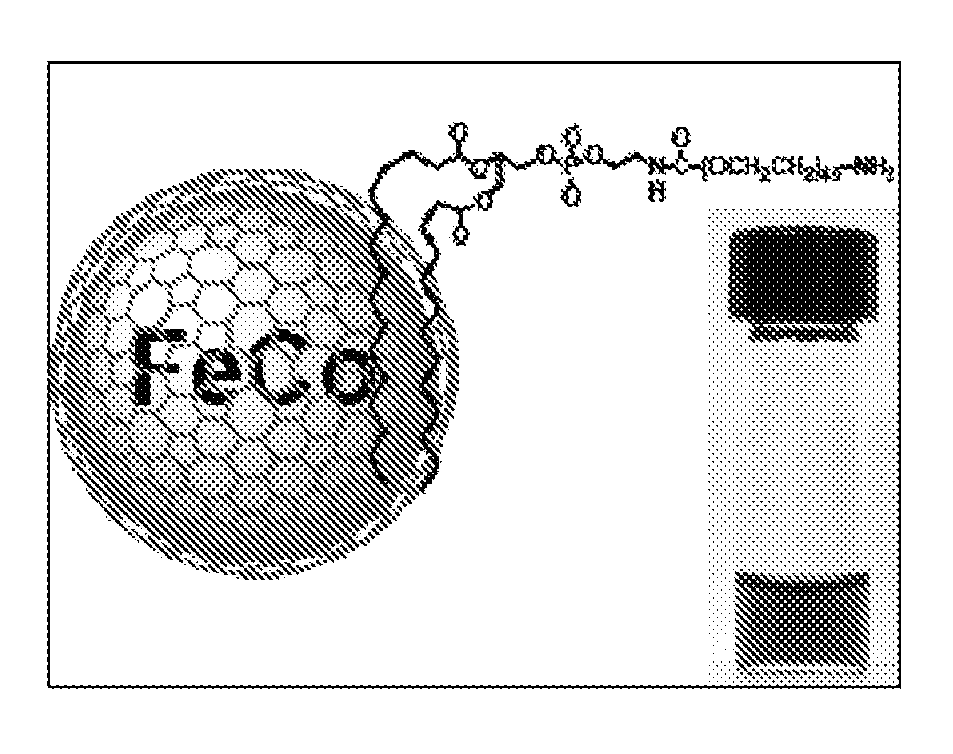
Multifunctional metal-graphite nanocrystals
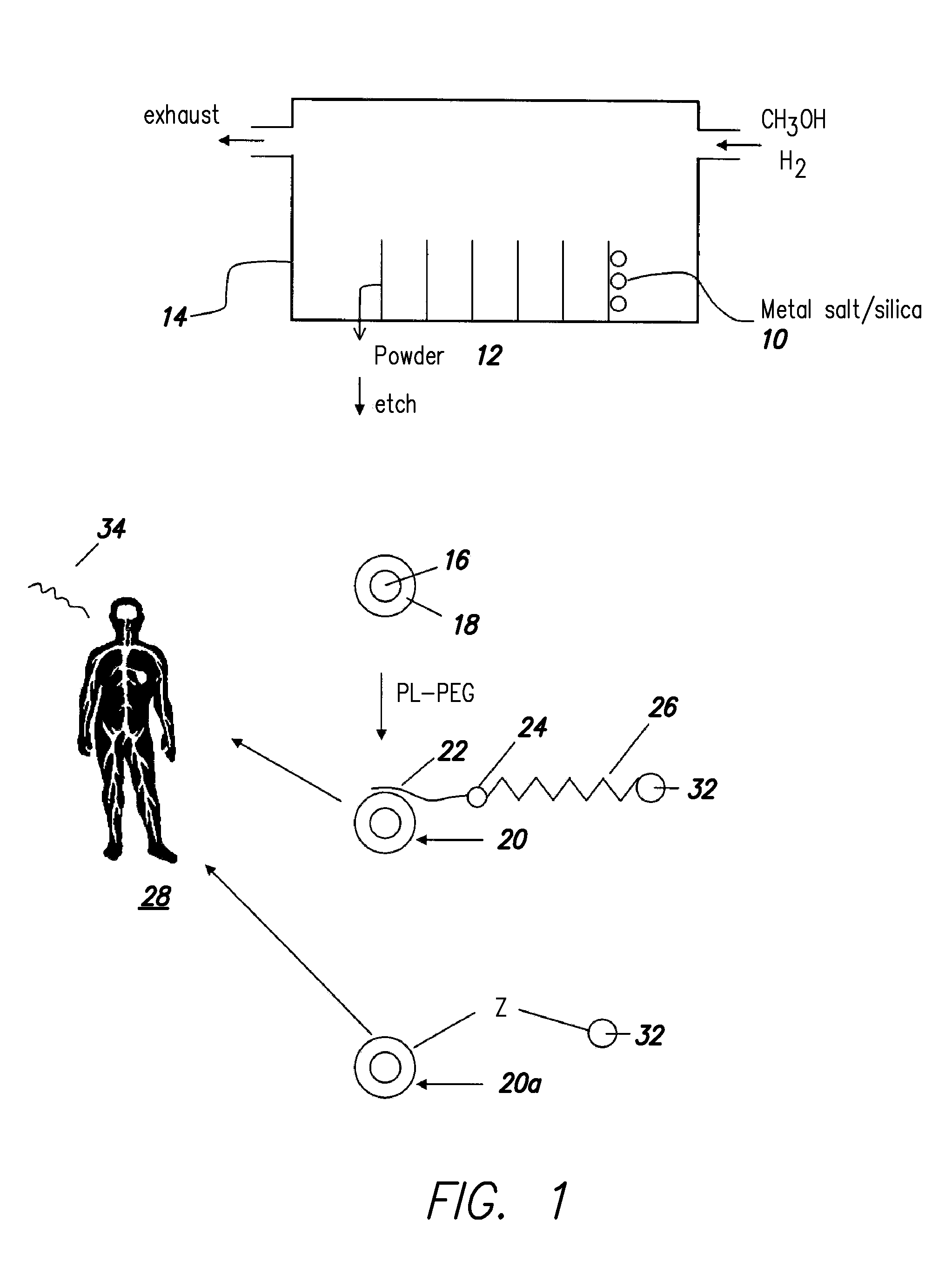
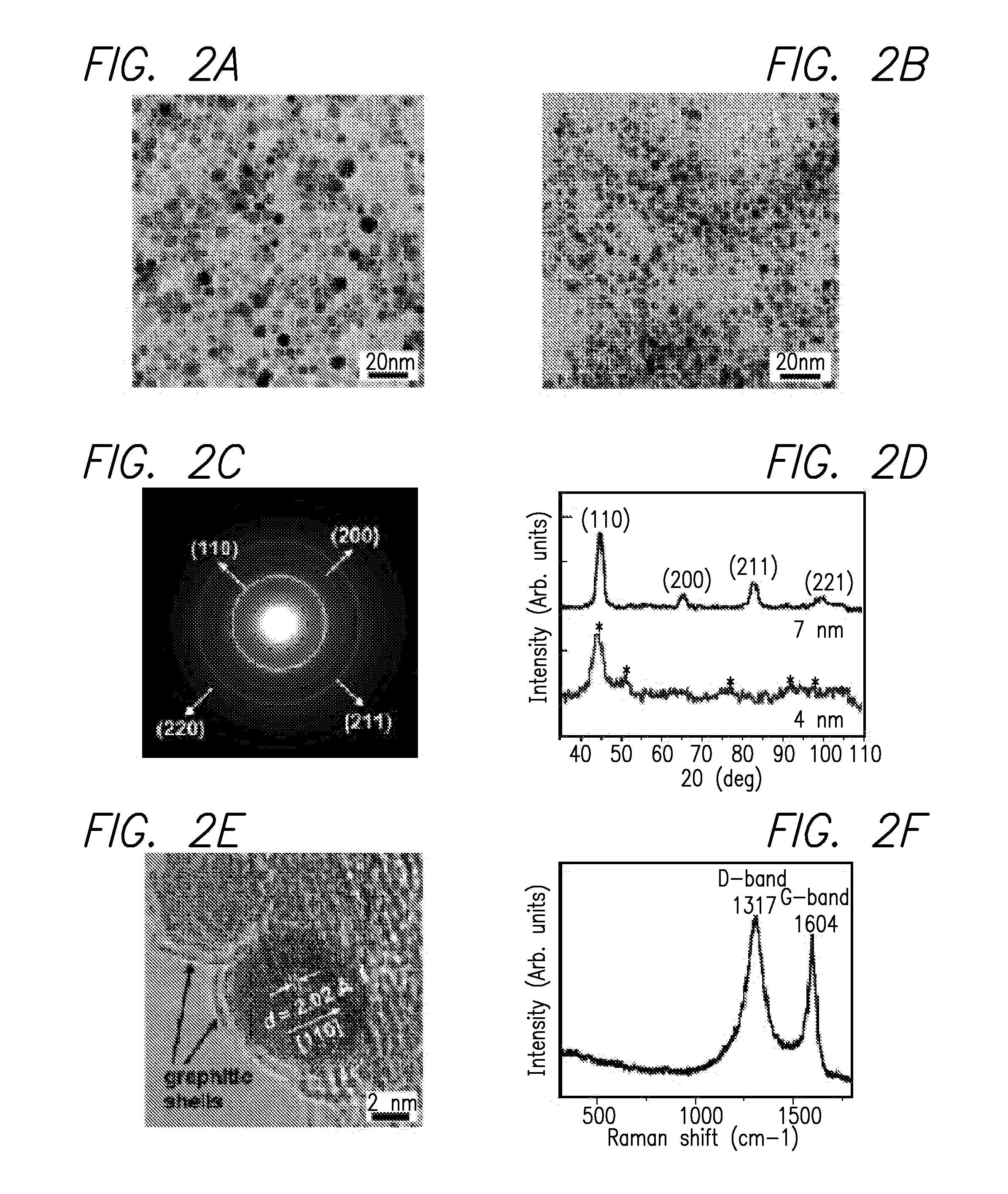
InactiveUS20080213189A1High resolutionShrink tumorPowder deliveryInorganic active ingredientsMRI contrast agentPolyethylene glycol
Disclosed are nanocrystals comprising metals and metal alloys, which are formed by a process that results in a layer of graphite in direct contact with the metallic core. The nanocrystals may be used in vivo as MRI contrast agents, X-ray contrast agents, near IR (NIR) heating agents, drug delivery, protein separation, catalysis etc. The nanocrystals may be further functionalized with a hydrophilic coating, e.g., phospholipid-polyethylene glycol, which improves in vivo stability. The process comprises chemical vapor deposition of metals adsorbed onto silica as a fine powder, in conjunction with a carbon containing gas, which coats the metal particles. The silica is then etched away. Preferred metals include iron, gold, cobalt, platinum, ruthenium and mixtures thereof, e.g., FeCo and AuFe. The process permits control of the alloy compositions, size, and other characteristics.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method and system for X-ray diagnosis of object in which X-ray contrast agent is injected
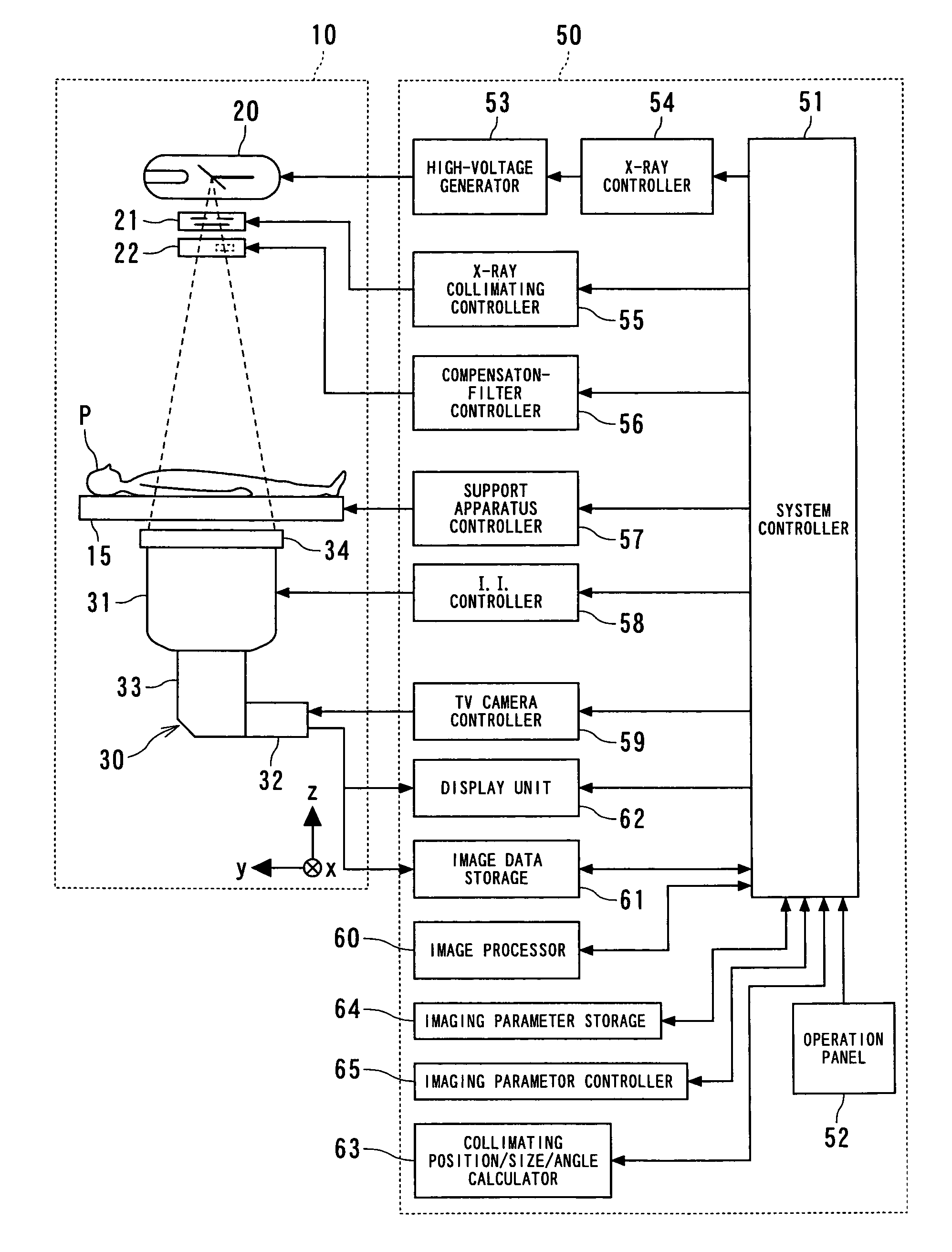
InactiveUS7634308B2Reduce operational burdenAdjustable openingDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSoft x rayBody axis
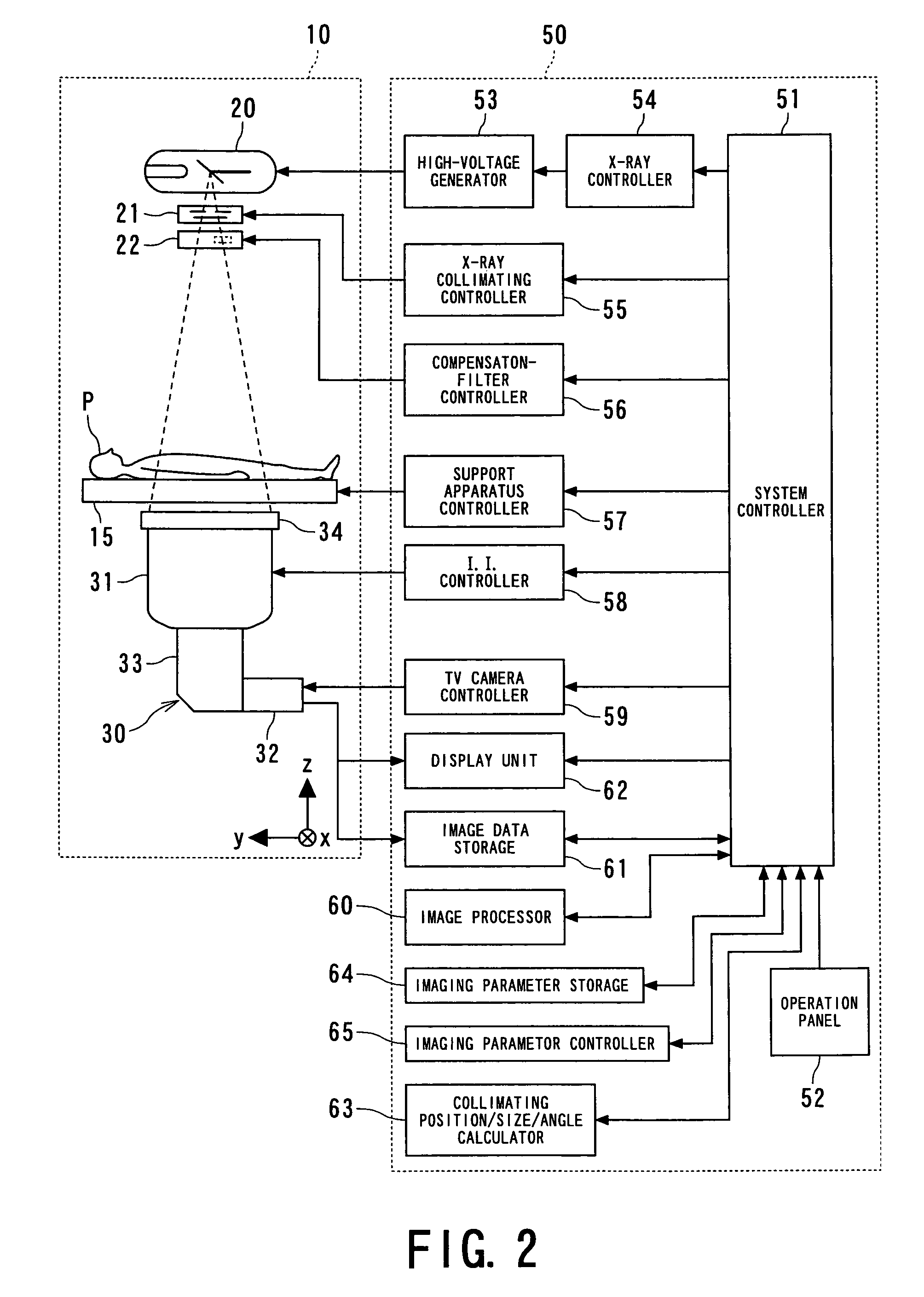
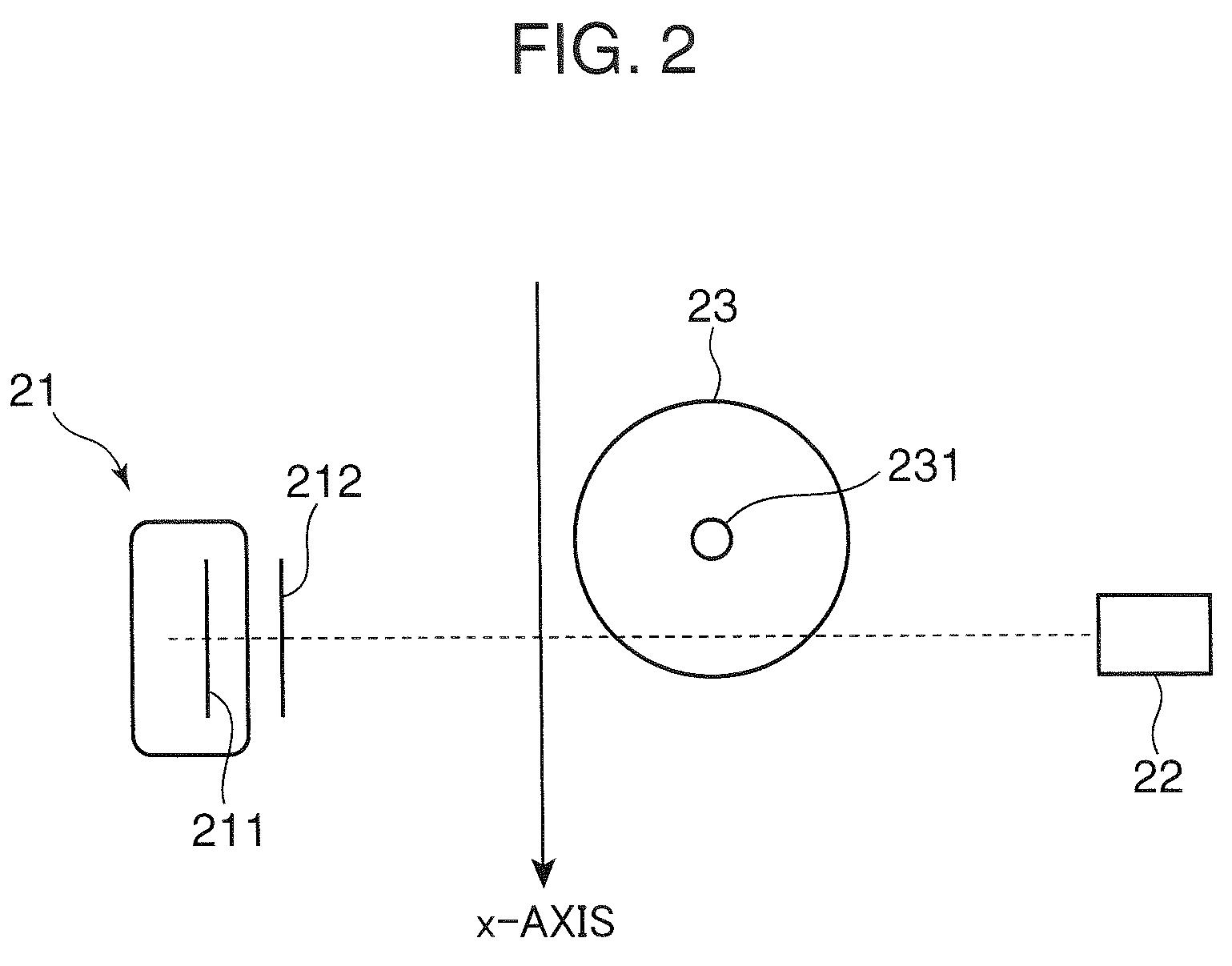
An X-ray diagnostic system is provided, which uses X-rays to image the lower limb of an object under conditions suitable for a flow of an X-ray contrast agent injected into the object. In the system, a C-shaped arm supports both an X-ray tube and an X-ray detector so that an object-laid tabletop is located between both the tube and the detector. For instance, one of the tabletop and the C-shaped arm is relatively moved with respect to the other so that the object is imaged along a body-axis direction thereof. The apparatus is able to perform a fluoroscopic scan to obtain a body-axis directional fluoroscopic image of the agent-injected object and to set imaging parameters, region by region in the body-axis direction, necessary for an imaging scan using the fluoroscopic image. The imaging parameters are used for the imaging scan of the agent-injected object.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Bone cement mixture and x-ray contrast medium as well as method for their preparation
A bone cement mixture comprised of a polymer component containing an x-ray contrast medium and a monomer component, wherein the x-ray contrast medium is a polymer or copolymer having compounds of radio-opaque elements bonded thereto, or is in the form of substantially spherical polymer or copolymer particles with radio-opaque inorganic nano-particles dispersed therein.
Owner:HERAEUS KULZER
Intra body capsule motion sensing and position determination systems and methods
A system for detecting clinically-relevant features of a gastrointestinal (GI) tract of a subject. The system comprises an external magnetic field generator adapted to be affixed to a patient for generating at predetermined time intervals a magnetic field with respect to the subject. The magnetic field has a predetermined polarity and flux density, thereby establishing a patient coordinate system based upon the magnetic field. The system includes a capsule adapted to be swallowed by a subject. The system further includes at least one radiation source emitting X-ray or gamma radiation and at least one radiation detector. The radiation detector is configured to detect in a first energy window collimated X-ray fluorescence radiation from the X-ray contrast agent composition excited by the emitted radiation, and to detect a second energy window Compton-backscattered radiation from the X-ray contrast agent and the wall of the GI tract produced in response to the emitted radiation. The system includes a magnetic field detector configured to generate a first output responsive to a detected polarity and detected levels of flux density during exposure to the externally generated magnetic field. A processor generates a second output based upon relative changes in the first output, the first output varying as a function of relative changes in physical location or angular orientation of the capsule associated with movement of the capsule within the GI tract. A control unit configured to selectively enable or disable X-ray or gamma ray emissions from the capsule produced by the at least one radiation source based upon the second output, such that the GI tract is selectively irradiated upon detected movement of the capsule.
Owner:CHECK CAP
X-ray contrast medium and method for protecting against harmful effects thereof
InactiveUS6149891ASufficient amountGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsX-ray constrast preparationsX-rayNuclear medicine
PCT No. PCT / US96 / 07666 Sec. 371 Date Nov. 25, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Nov. 25, 1997 PCT Filed May 24, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 38183 PCT Pub. Date Dec. 5, 1996Contrast medium injectable into the blood circulation comprising an effective amount of a contrast agent useful in X-ray imaging and a protecting agent, wherein the protecting agent is active in protecting against possible damaging effects of the contrast medium.
Owner:ISRAEL HUMANITARIAN FOUND LTD - 40 INTEREST +4
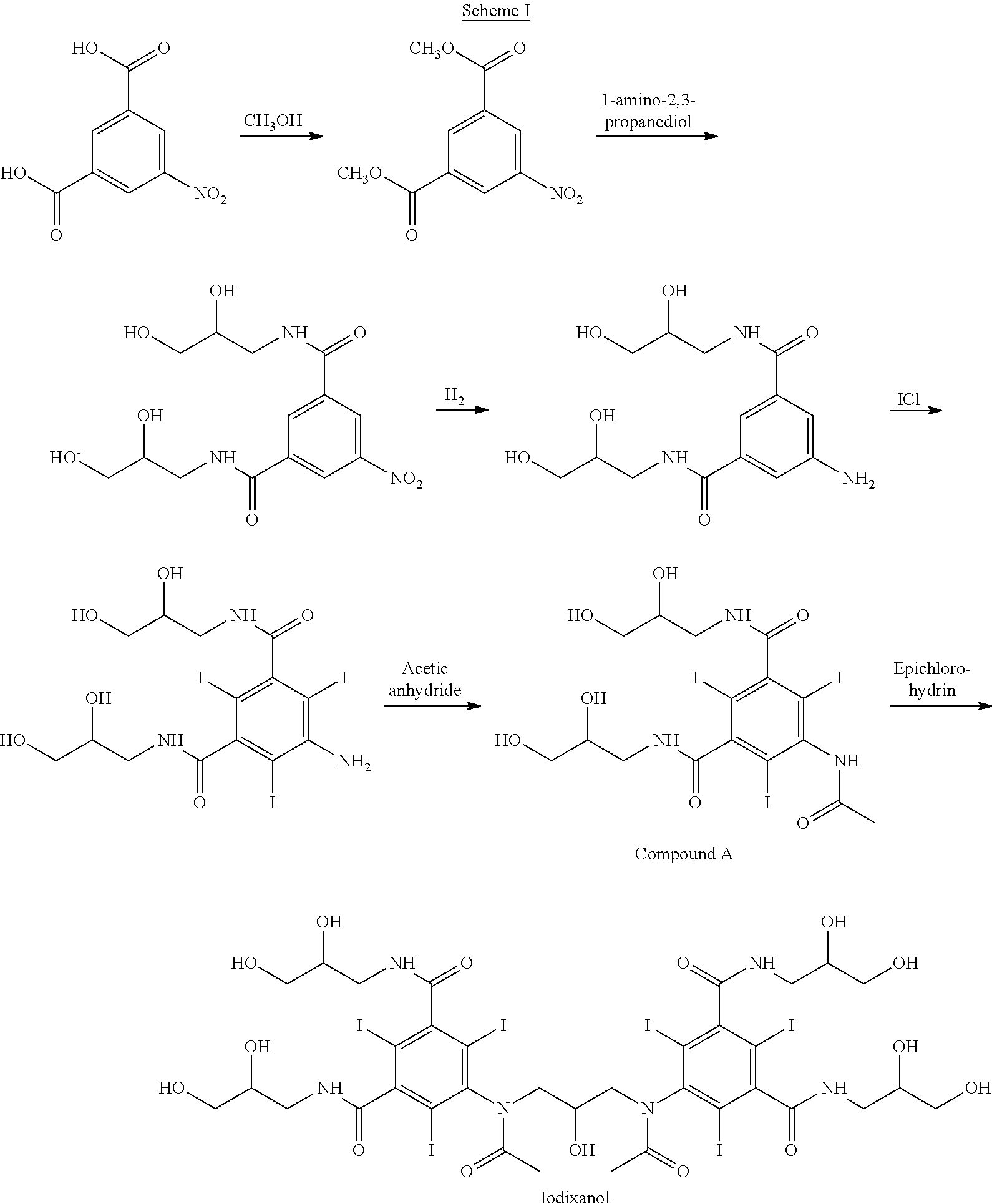
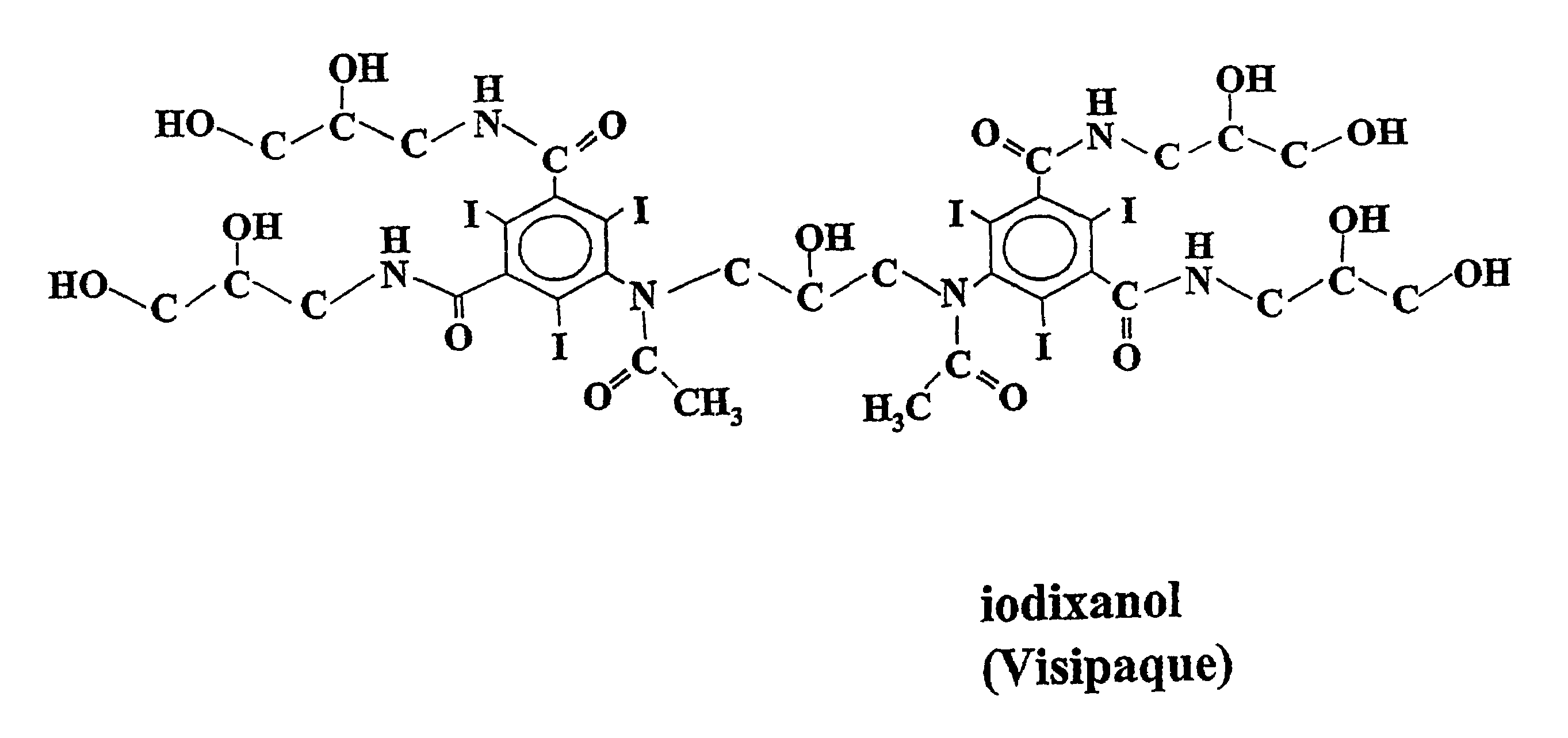
Processing crude iodixanol mixture by nanofiltration
This invention relates generally to industrial preparation of iodixanol (1,3-bis(acetamido)-N,N′-bis[3,5-bis(2,3-dihydroxypropylaminocarbonyl)-2,4,6-triiodophenyl]-2-hydroxypropane), a non-ionic X-ray contrasting agent. It further relates to a method for preparing a crude mixture of the dimerisation reaction from 5-acetamido-N,N-bis(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-2,4,6-triiodoisophthalamide (“Compound A”) to iodixanol for the crystallization of iodixanol. In particular, it relates to an industrial procedure of simultaneously reducing the salt content and the alcoholic dimerisation solvent using a nanofiltration system prior to the crystallization of iodixanol.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE AS
Cerium oxide nanoparticle-based device for the detection of reactive oxygen species and monitoring of chronic inflammation
ActiveUS8795731B1Prevent adverse side effectsEffect andPowder deliveryDiagnostic recording/measuringRos scavengingFluorescence
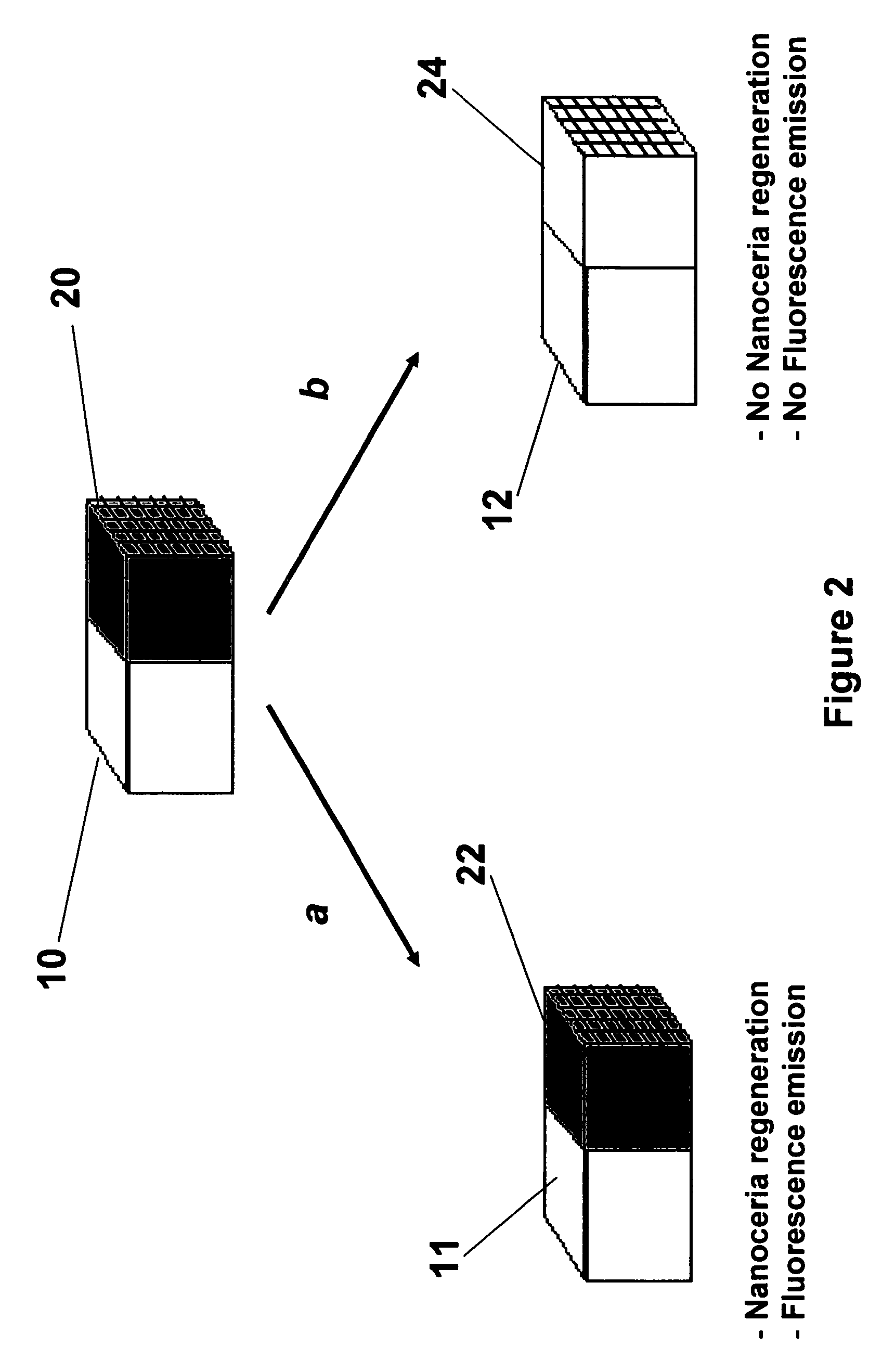
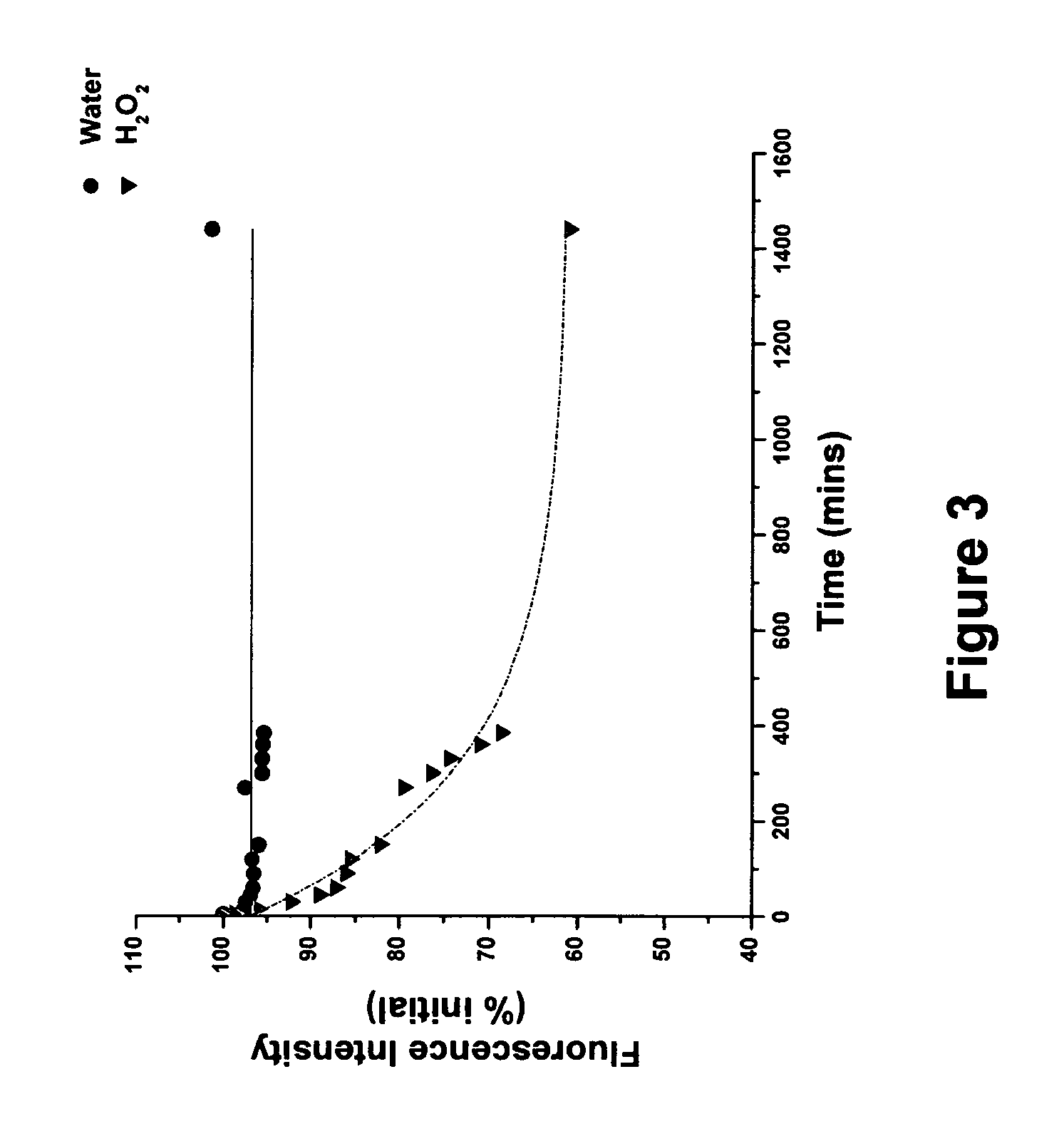
A polymer-coated cerium oxide based device and system is disclosed for detecting reactive oxygen species and monitoring chronic inflammation. The device and system encapsulate free therapeutic nanoparticle elements not present in a living body in a prosthetic or implantable unit. Embodiment one is a two-chamber structure with a reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenging component on one end and at the opposite end is an imaging agent consisting of at least one of a fluorophore capable of fluorescence emission, a chemiluminescent agent, a magnetic relaxation agent and an X-ray contrast agent. Embodiment two is a single chamber device consisting of a multifunctional nanocomposite with a ROS-scavenging nanoparticle constituent (nanoceria) and a multimodal reporting nanoparticle component (i.e. Dex-IO-DiR). The device and system are utilized in treatment of diseases with a pro-inflammatory component, including, but not limited to, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, inflammatory bowel disease, cystic fibrosis, arthritis, and cancer chemotherapy.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Barium Sulfate Product
This invention generally relates to a barium sulfate product particularly useful as an X-ray contrast agent in preparations administered for examination of the gastrointestinal tract and to processes for making the product from naturally occurring barite ore containing barium sulfate crystals and gangue materials. The process includes treating or contacting the barium sulfate-containing particles obtained from barite ore with a fluidizing agent in a liquid medium to remove gangue materials present therein.
Owner:MALLINCKRODT INC
Gel formulations for guiding radiotherapy
ActiveUS20160089454A1Improve solubilityIncrease contrastPowder deliveryIn-vivo radioactive preparationsInjection pointX-ray
The present invention describes an X-ray contrast composition for local administration, wherein the X-ray contrast composition exhibits contrast properties and wherein at least 60% of an administrated amount of said X-ray contrast composition remains more than 24 hours within 10 cm from an injection point when the X-ray contrast composition is administrated to a human or animal body.
Owner:NANOVI RADIOTHERAPY APS +1
Liposome containing hydrophobic iodine compound
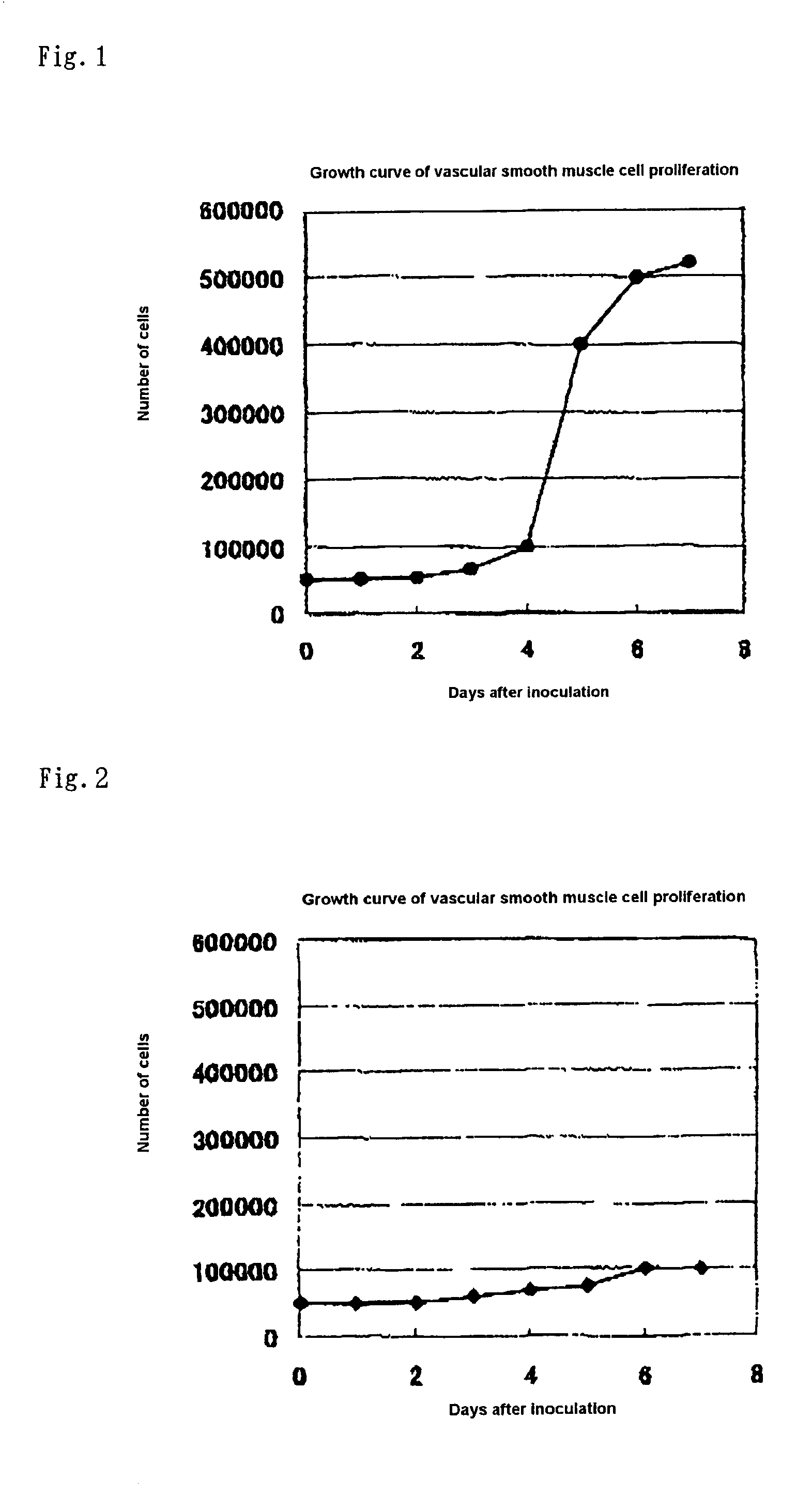
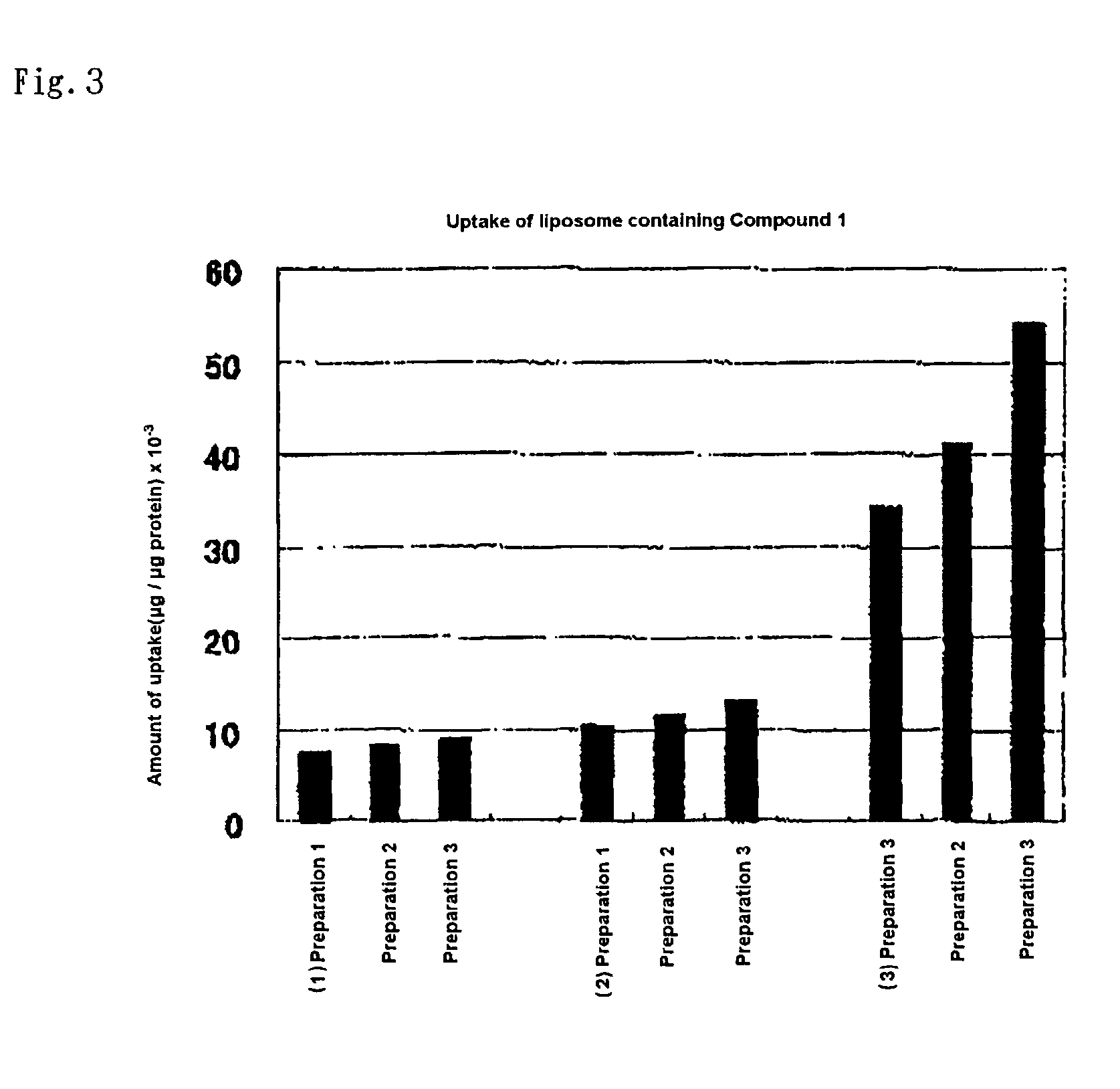
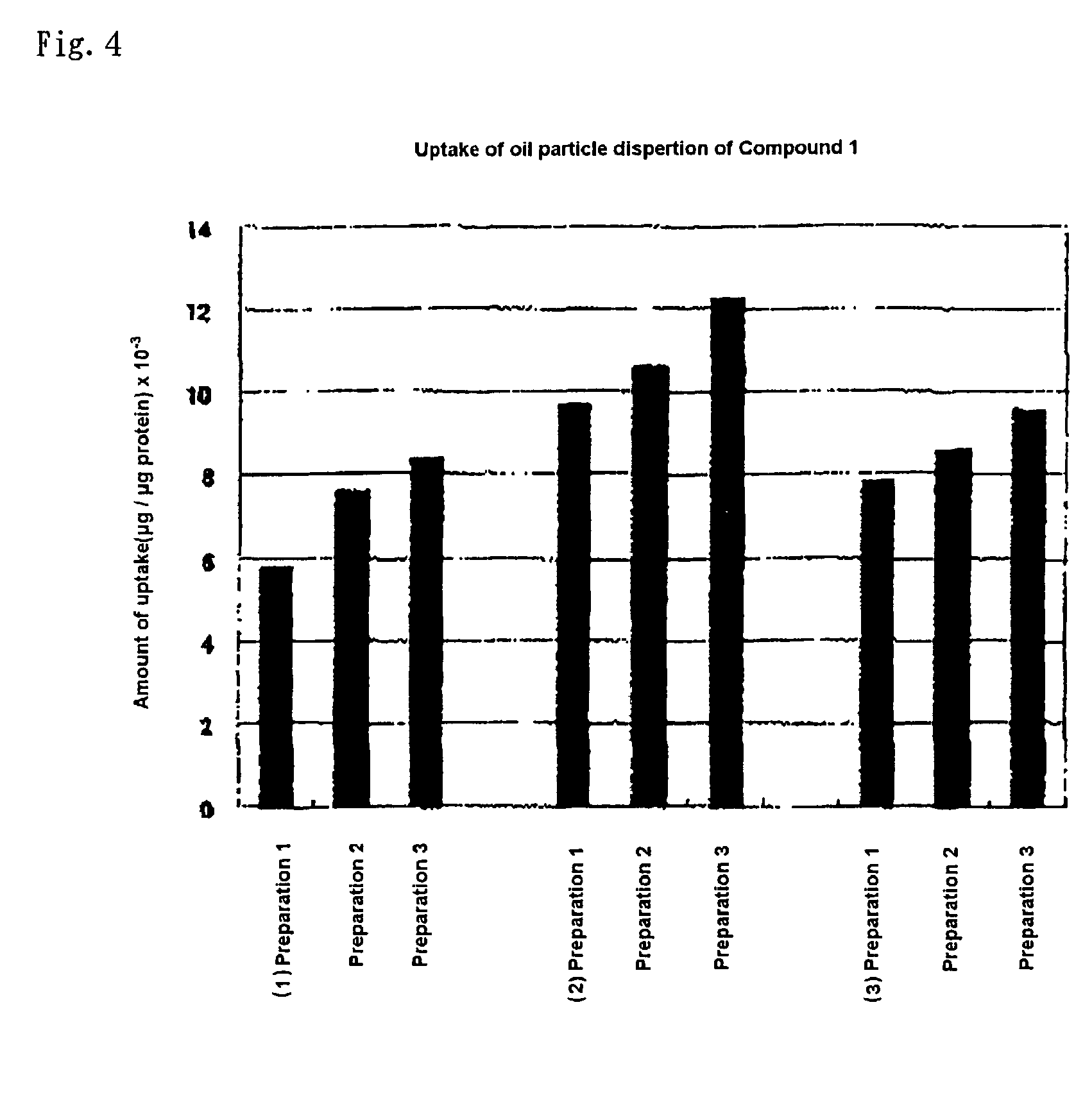
A liposome containing a hydrophobic iodine compound such as a 1,3,5-triiodobenzene derivative having at least one substituent containing 18 or more carbon atoms as a membrane component, and an X-ray contrast medium containing the liposome for use in radiography of a vascular disease and the like.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
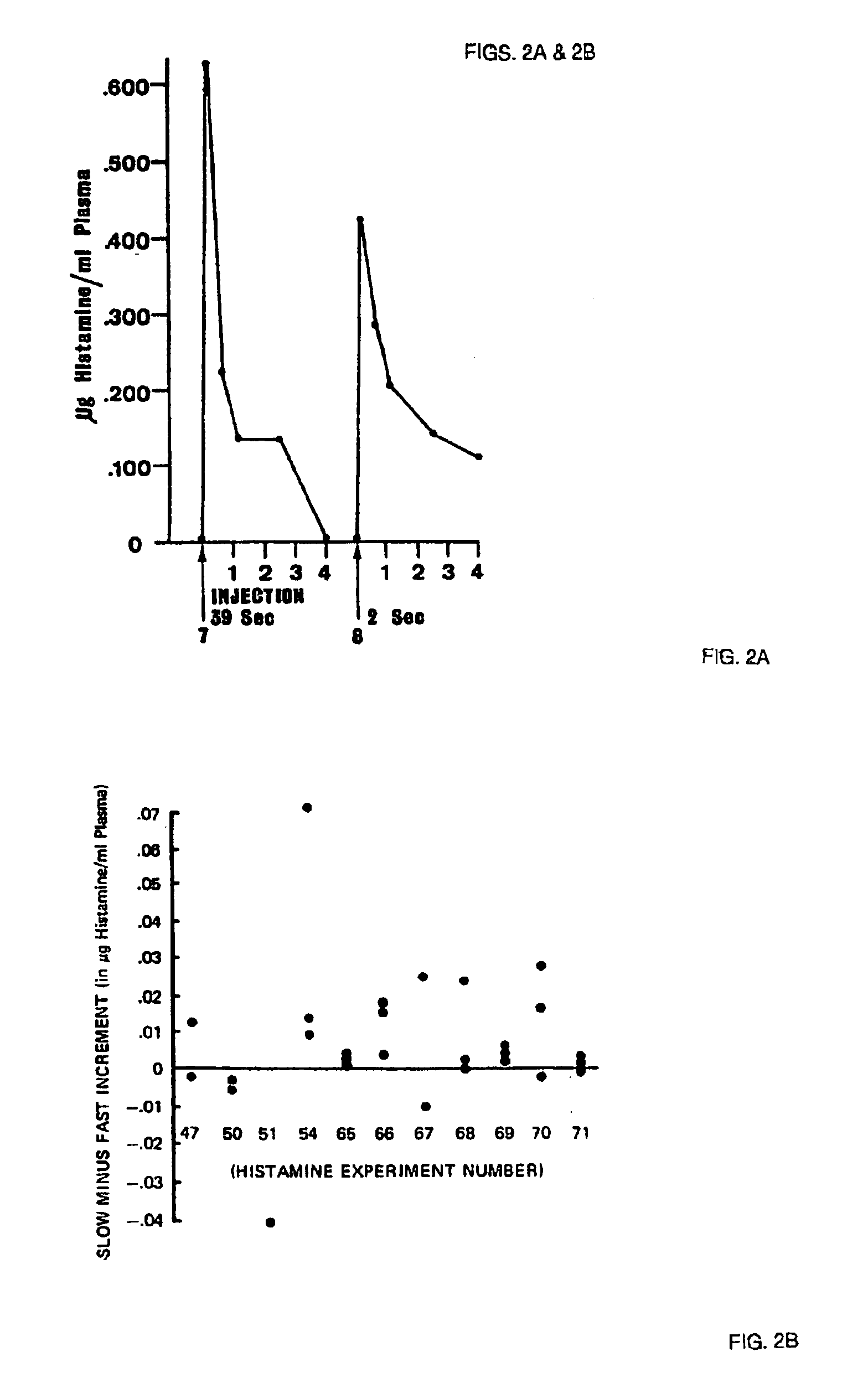
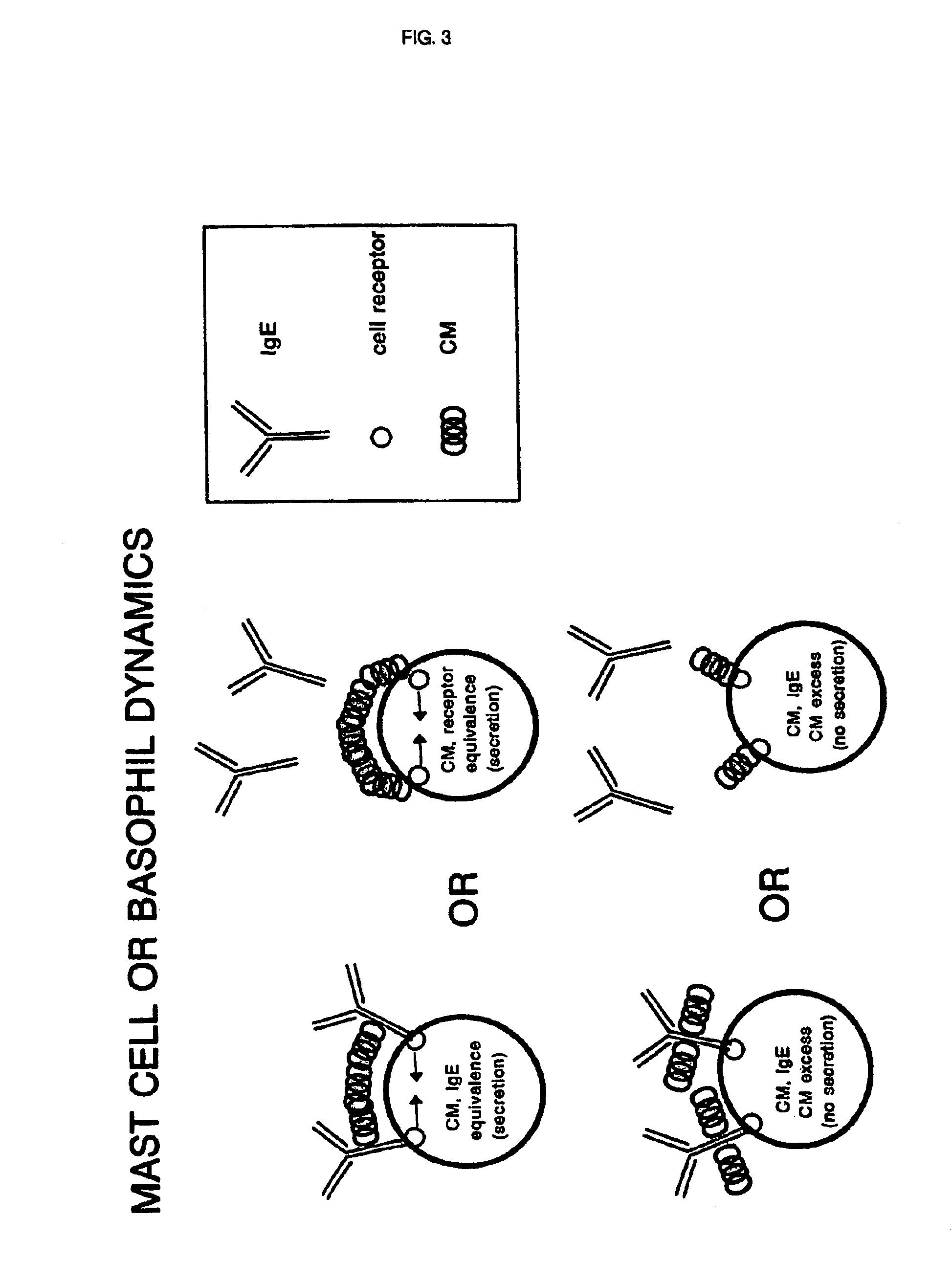
Compositions and methods for the treatment of inflammatory conditions
Embodiments of the invention relate to methods and compositions for treating symptoms related to inflammatory conditions and to methods and compositions for treating inflammatory components of common cold, utilizing various method of administration of X-ray contrast media (CM).
Owner:LASSER FAMILY PARTNERSHIP
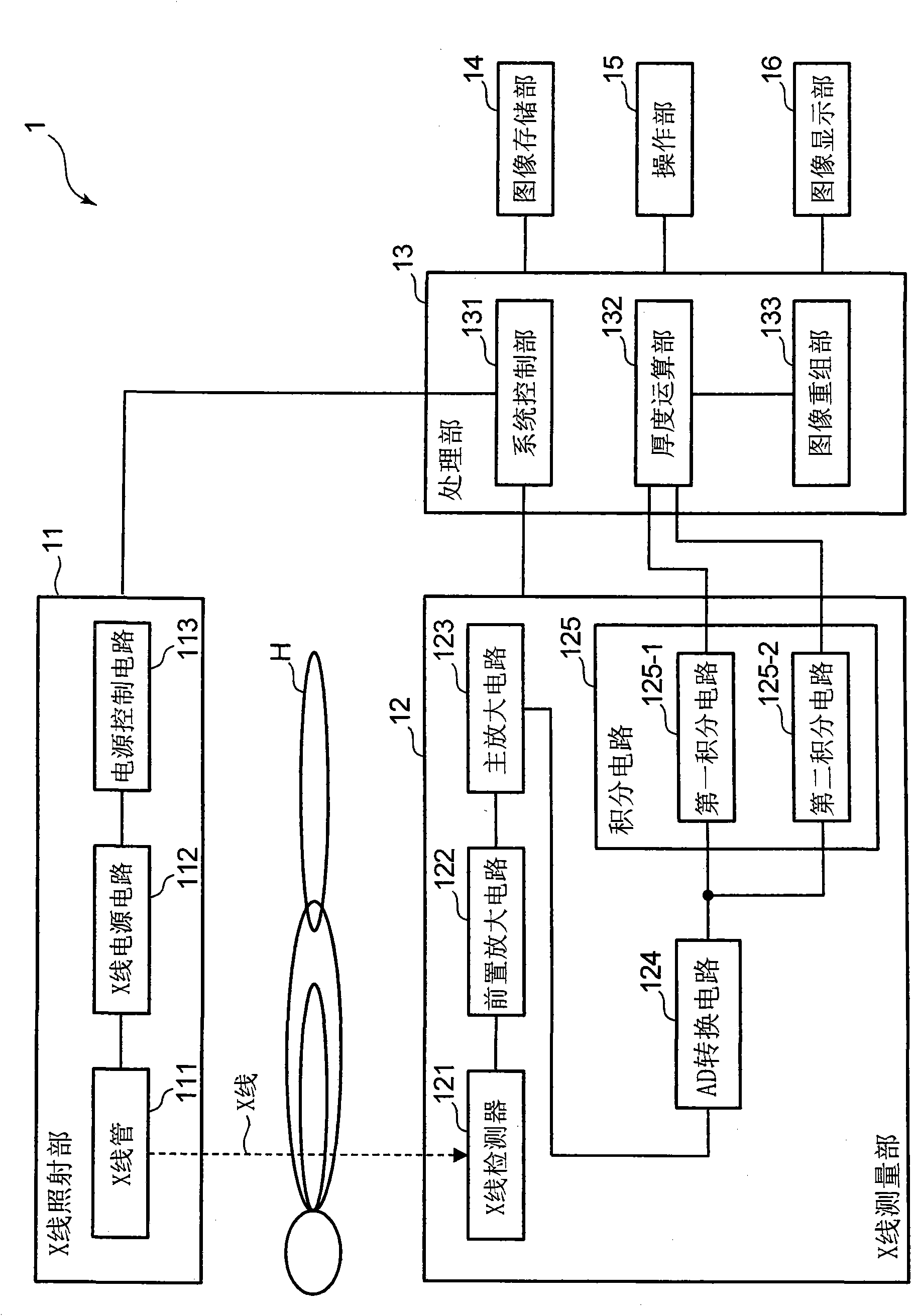
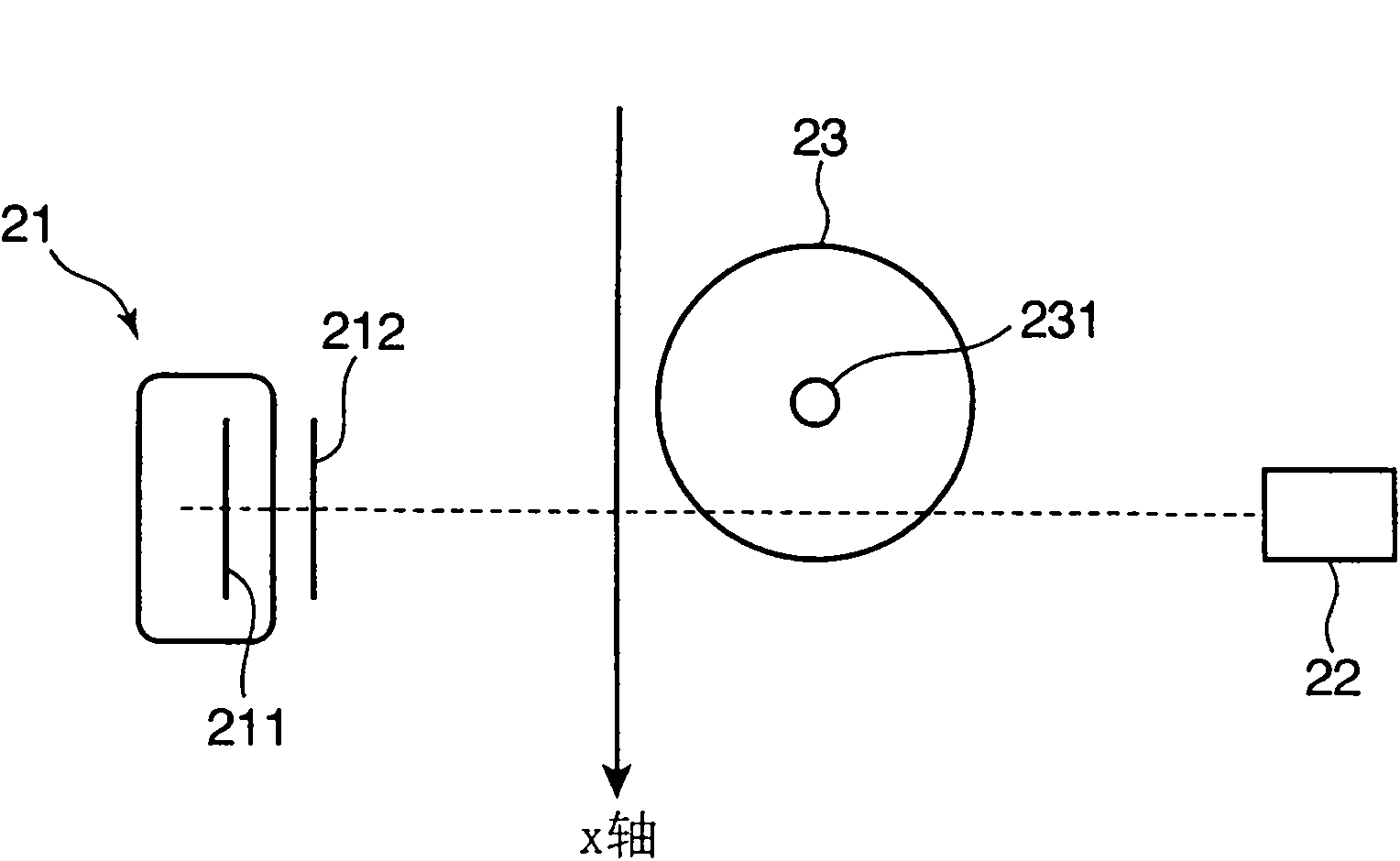
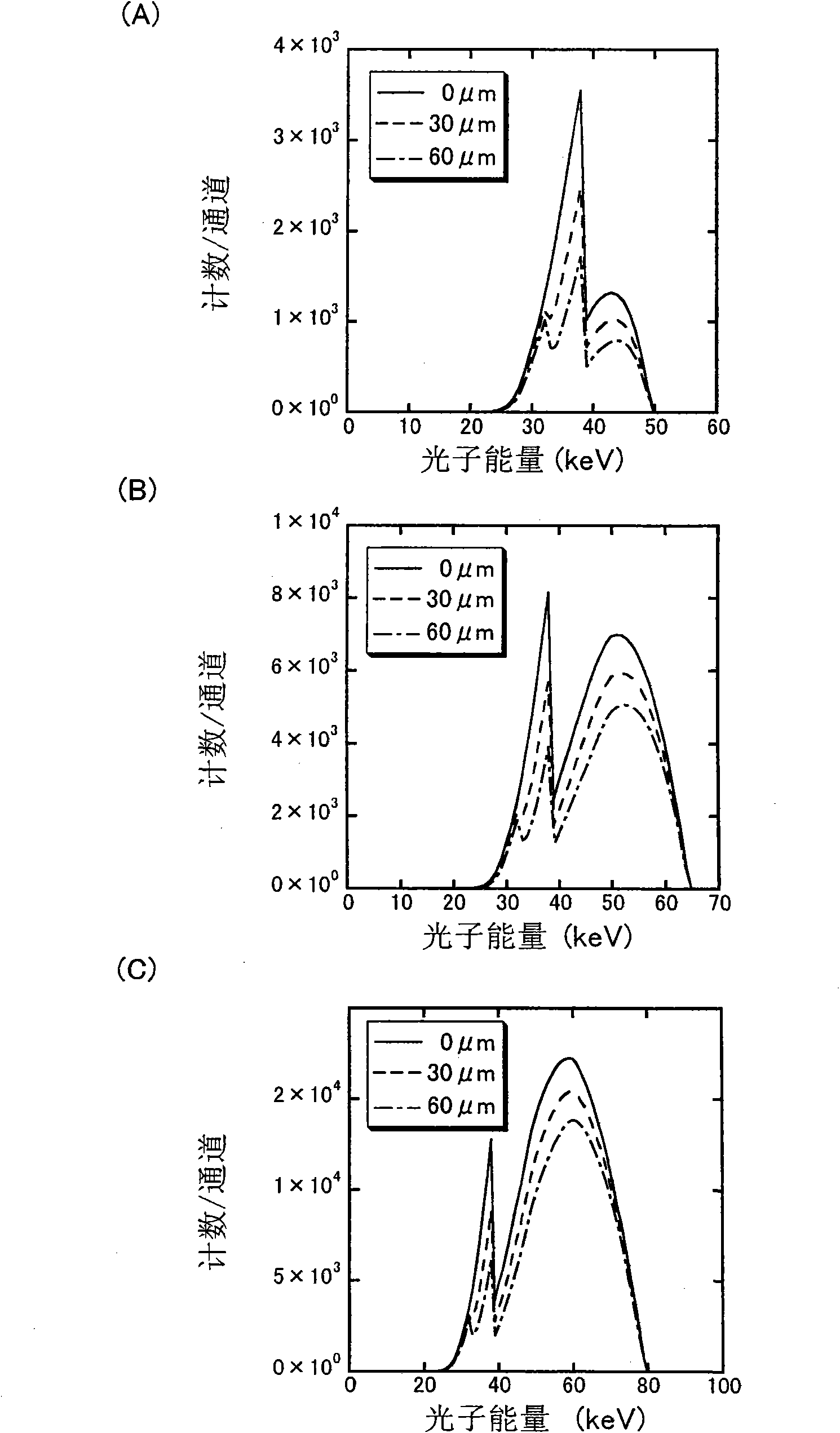
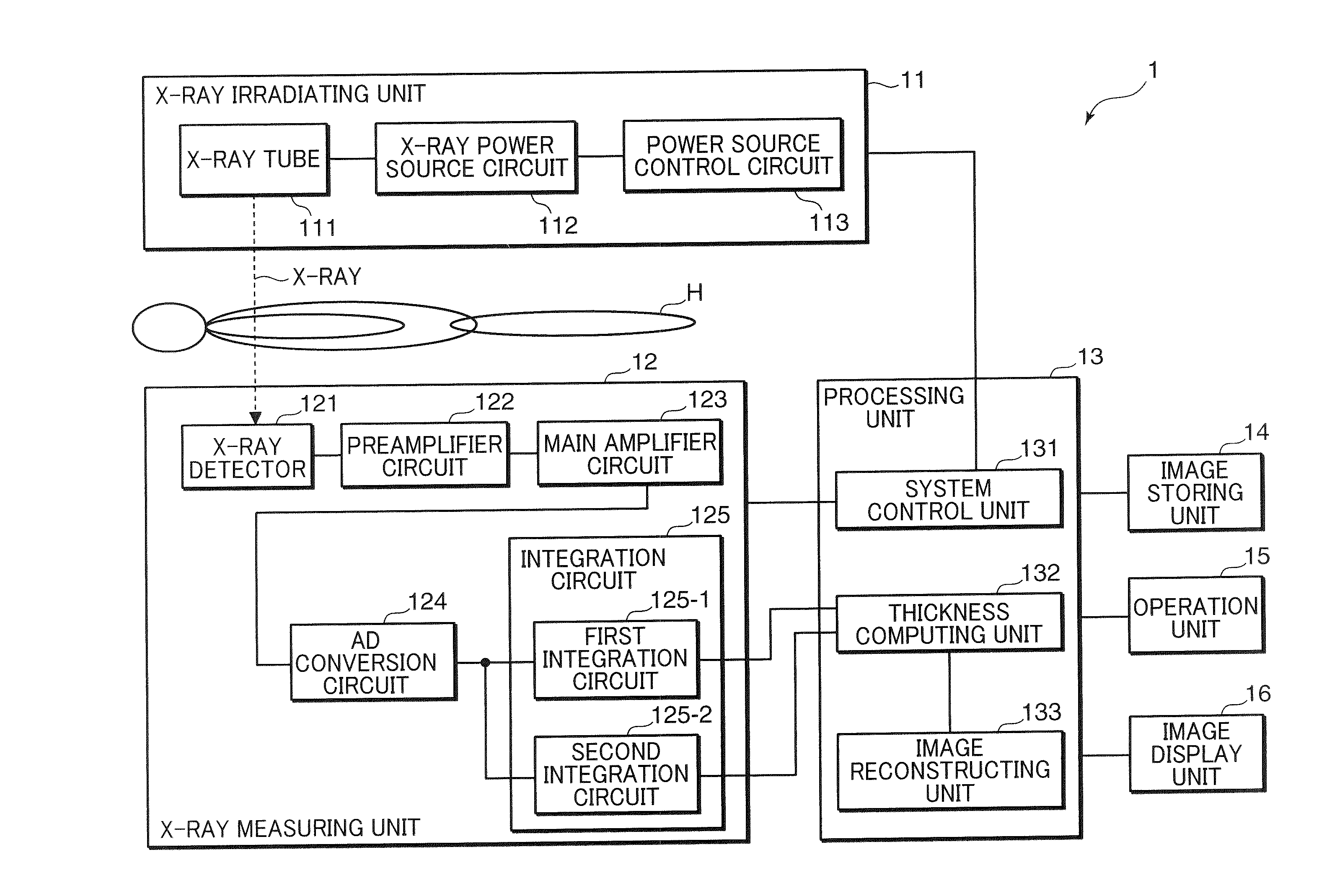
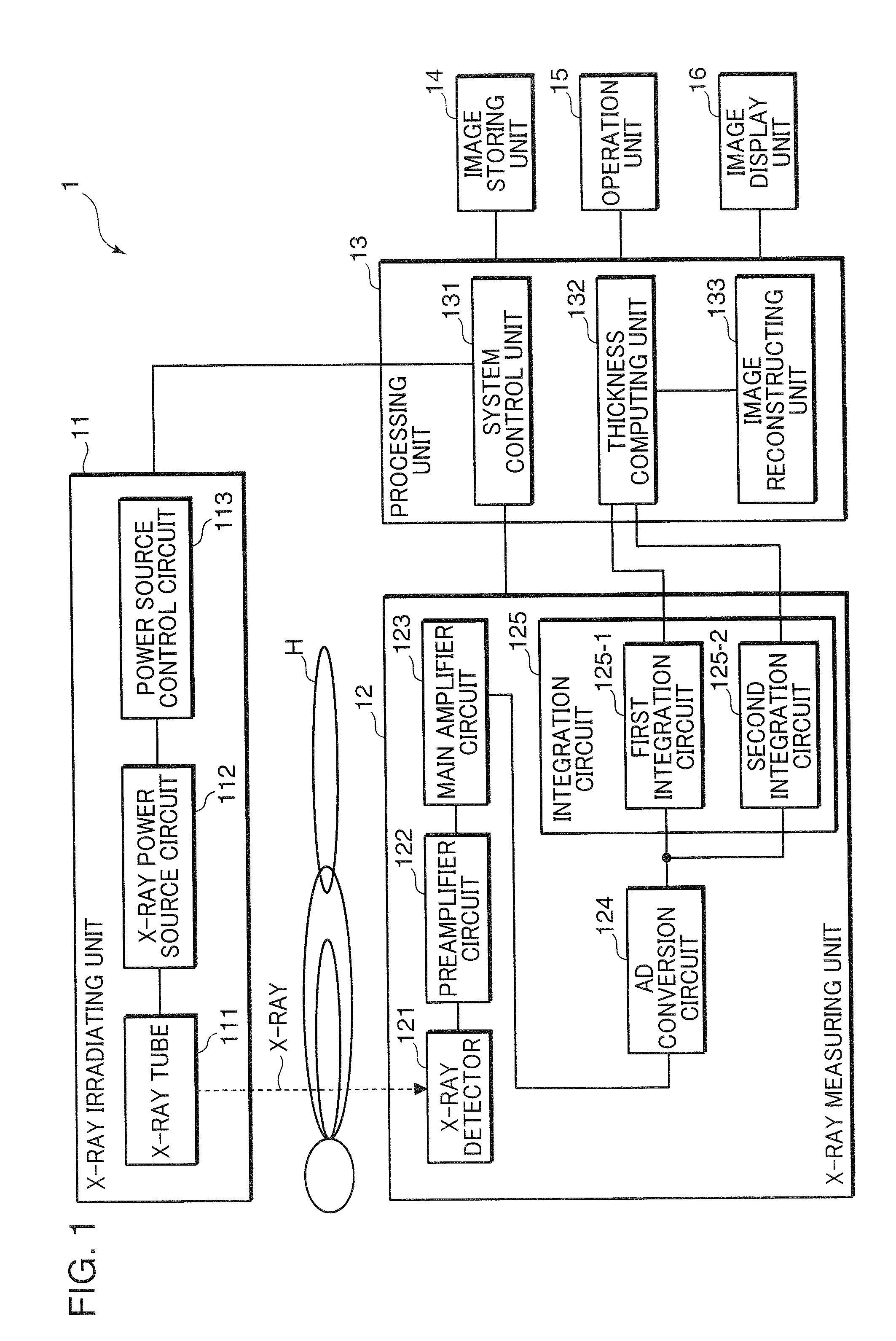
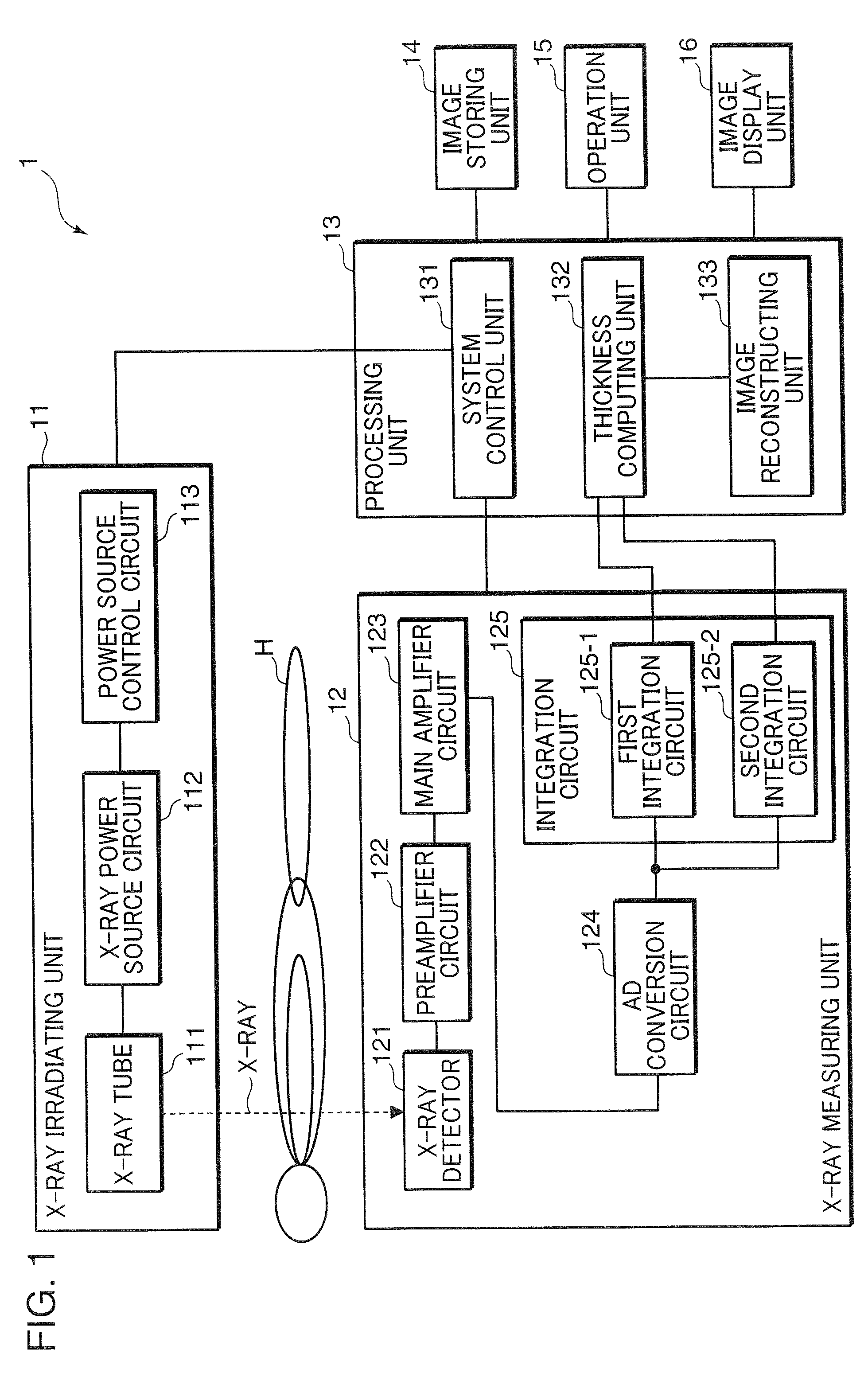
X-ray ct apparatus, and its method
ActiveCN102215754AStable generationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationComputerised tomographsX-rayVoltage
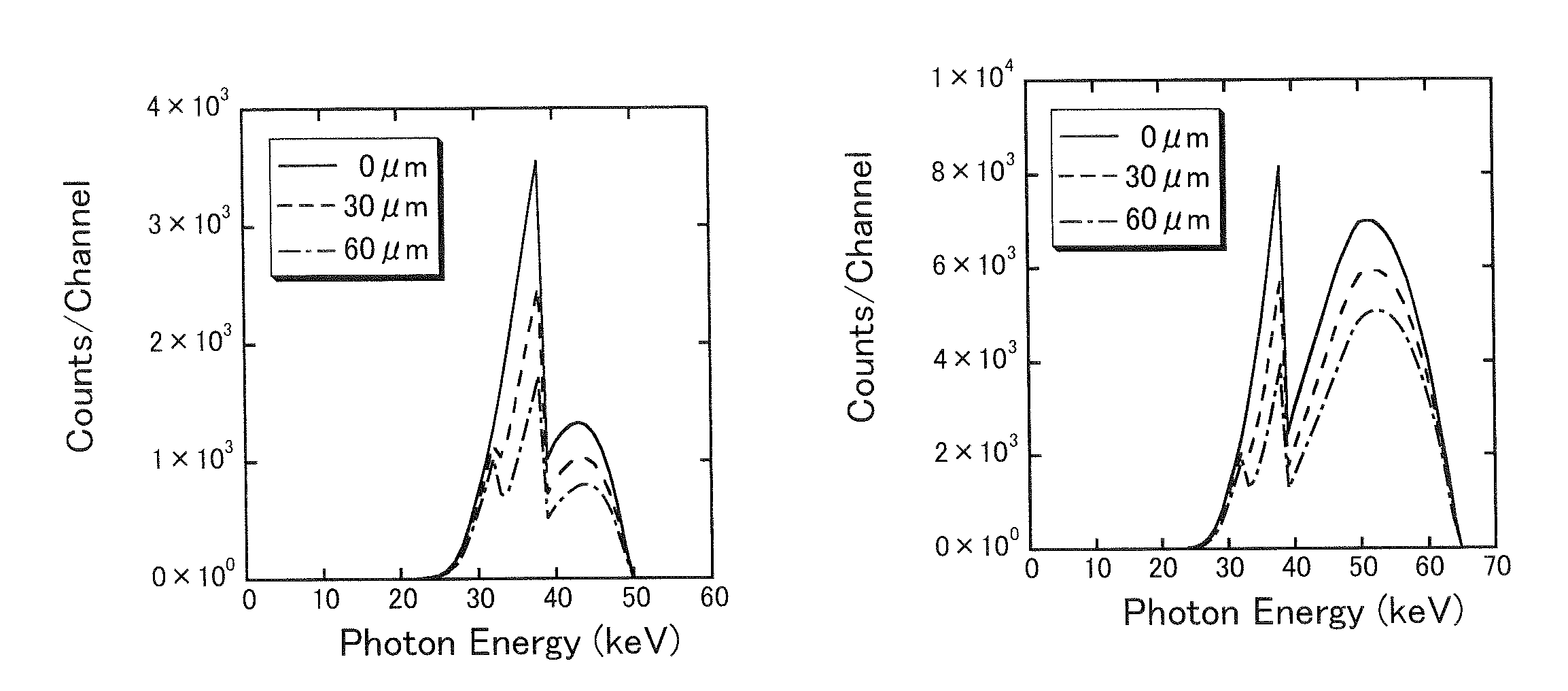
In an X-ray CT apparatus (1) and an X-ray CT method, the thickness of an inspection object is computed on the basis of the number of transmission X-rays in a specific energy range set by the upper and lower K-absorption ends of an X-ray contrast media acting as the inspection object, and a CT image is reconstituted on the basis of the computed thickness of the inspection object. These X-ray CT apparatus (1) and X-ray CT method can create the X-ray CT image stably independently of the magnitude of the inspection object and the X-ray tube voltage (or the energy distribution of the X-ray).
Owner:KYOTO UNIV +1
Liposome containing hydrophobic iodine compound and X-ray contrast medium for radiograph comprising the liposome
InactiveUS7008614B2Clear imagingDispersion deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsVascular diseaseLiposome
A liposome containing a hydrophobic iodine compound represented by the following general formula (I) as a membrane component:R1—CO2—R2wherein R1 represents a substituted or unsubstituted 2,3,5-triiodophenyl group or a substituted or unsubstituted 3,4,5-triiodophenyl group; and R2 represents a hydrocarbon group having 10 or more carbon atoms, and an X-ray contrast medium, which comprises said liposome which is used for radiography of a vascular disease.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Cerium-oxide nanoparticle based device for the detection of reactive oxygen species and monitoring of chronic inflammation
ActiveUS8795733B1Prevent adverse side effectsEffect andCompounds screening/testingPowder deliveryRos scavengingFluorescence
A polymer-coated cerium oxide based device and system is disclosed for detecting reactive oxygen species and monitoring chronic inflammation. The device and system encapsulate free therapeutic nanoparticle elements not present in a living body in a prosthetic or implantable unit. Embodiment one is a two-chamber structure with a reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenging component on one end and at the opposite end is an imaging agent consisting of at least one of a fluorophore capable of fluorescence emission, a chemiluminescent agent, a magnetic relaxation agent and an X-ray contrast agent. Embodiment two is a single chamber device consisting of a multifunctional nanocomposite with a ROS-scavenging nanoparticle constituent (nanoceria) and a multimodal reporting nanoparticle component (i.e. Dex-IO-DiR). The device and system are utilized in treatment of diseases with a pro-inflammatory component, including, but not limited to, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, inflammatory bowel disease, cystic fibrosis, arthritis, and cancer chemotherapy.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Pharmaceuticals for the imaging of angiogenic disorders
InactiveUS7052673B2Improve stabilityGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsCyclic peptide ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthUltrasound contrast media
The present invention describes novel compounds of the formula:(Q)d—Ln—Ch,useful for the diagnosis and treatment of cancer, methods of imaging tumors in a patient, and methods of treating cancer in a patient. The present invention also provides novel compounds useful for monitoring therapeutic angiogenesis treatment and destruction of new angiogenic vasculature. The pharmaceuticals are comprised of a targeting moiety that binds to a receptor that is upregulated during angiogenesis, an optional linking group, and a therapeutically effective radioisotope or diagnostically effective imageable moiety. The imageable moiety is a gamma ray or positron emitting radioisotope, a magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent, an X-ray contrast agent, or an ultrasound contrast agent.
Owner:LANTHEUS MEDICAL IMAGING INC
X-ray CT apparatus and method thereof
ActiveUS20110194668A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayRadiographic Contrast Agent
In an X-ray CT apparatus 1 and an X-ray CT method, the thickness of an object to be inspected is computed on the basis of the number of transmitted X-rays in a specific energy range set above and below the K-absorption edge of an X-ray contrast medium serving as the object to be inspected, and a CT image is reconstructed on the basis of the computed thickness of the object to be inspected. Such X-ray CT apparatus 1 and X-ray CT method can generate an X-ray CT image stably and independently of the size of the object to be inspected and of X-ray tube voltage (X-ray energy distribution).
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Method for removing iodo-X-ray contrast medium in water
InactiveCN109293103AControl concentrationHigh removal rateWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater contaminantsFiltrationUltraviolet
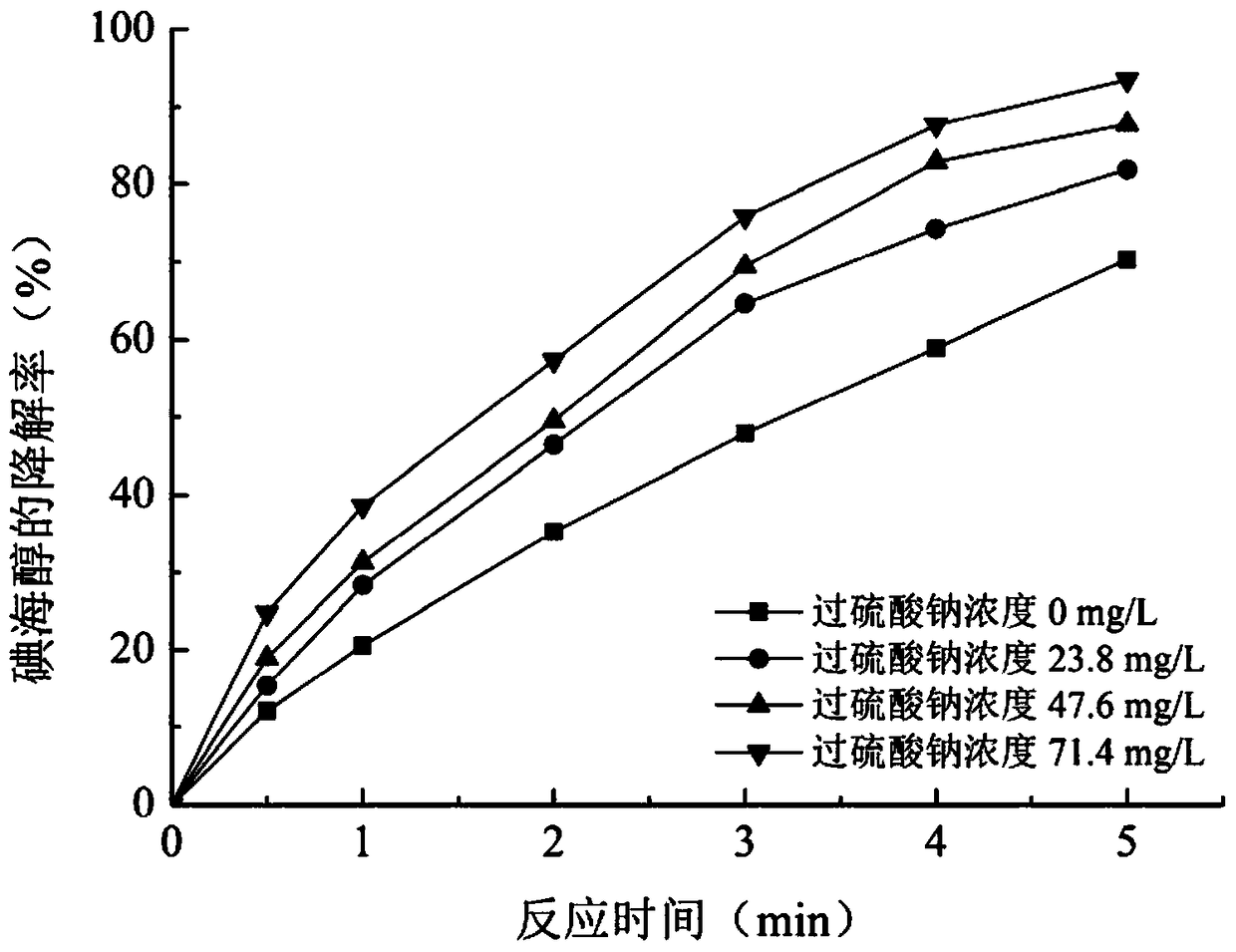
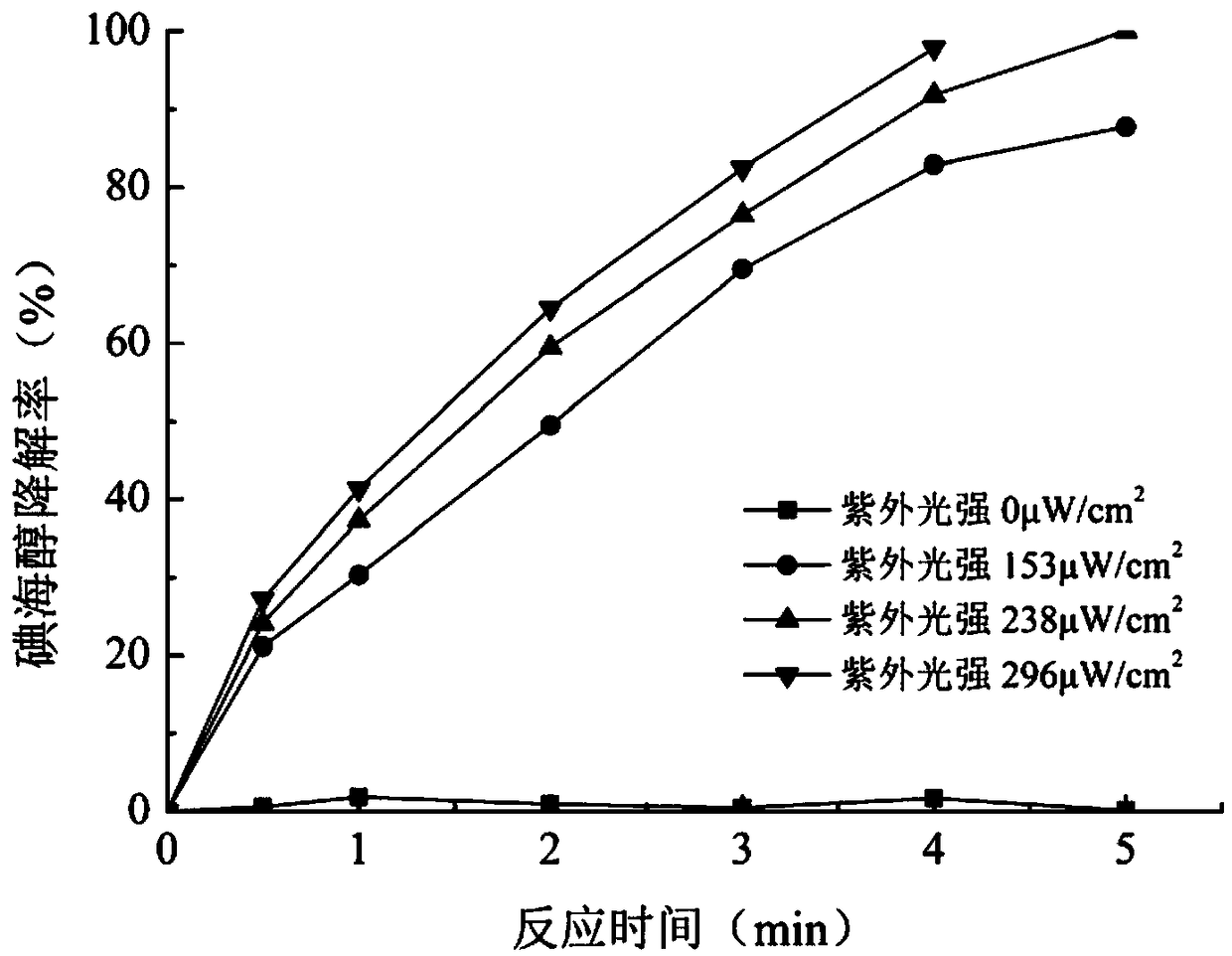
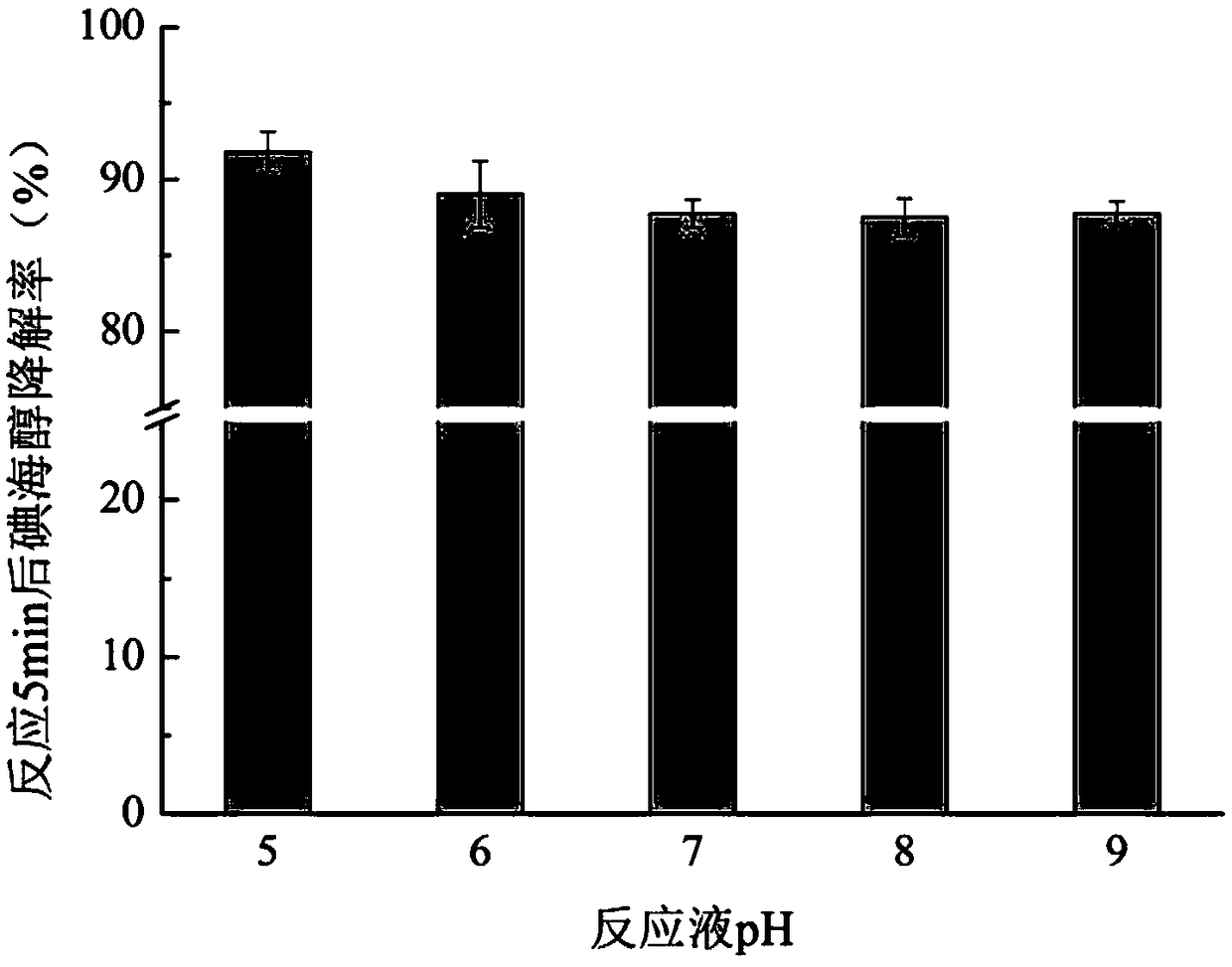
The invention relates to a method for removing an iodo-X-ray contrast medium in water. The method includes the steps: oxidant feeding, to be more specific, adding sodium persulfate into to-be-treatedwater until the concentration of sodium persulfate in the water reaches 23.8-71.4mg / L; ultraviolet irradiation, to be more specific, subjecting the to-be-treated water to ultraviolet irradiation for 5-10 minutes after oxidant feeding. Compared with the prior art, the method has advantages that high degradation efficiency is achieved, the concentration of the ICM (iodo-X-ray contrast medium) in thewater can be decreased by 87% or more, the method is slightly affected by pH (potential of hydrogen) changes, and reaction products are mainly sulfate ions and iodate ions and can be removed by simple coagulation, precipitation or membrane filtration, so that the method is a safe and stable drinking water treatment method.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
Concentrated X-ray contrast media can act as universal antigens and can inhibit or prevent allergic reactions
InactiveUS6951641B2Avoid allergic reactionsBiocideSenses disorderAntibody antigen reactionsNuclear medicine
The present application is directed to the use of X-ray contrast media that act as universal antigens that are labeled herein as “pseudoantigens.” X-ray contrast media have the potential to exist in an aggregated state that is greater in increased concentrations. In this aggregated state, contrast media assume the role of multivalent antigens and can successfully compete with any other antigens involved in antibody-antigen reactions that lead to anaphylaxis. In this competition, the large quantity of contrast media serves to inhibit the adverse effects of antibody-antigen reactions without the contrast media itself creating antibodies or creating toxicity problems.
Owner:3E THERAPEUTICS
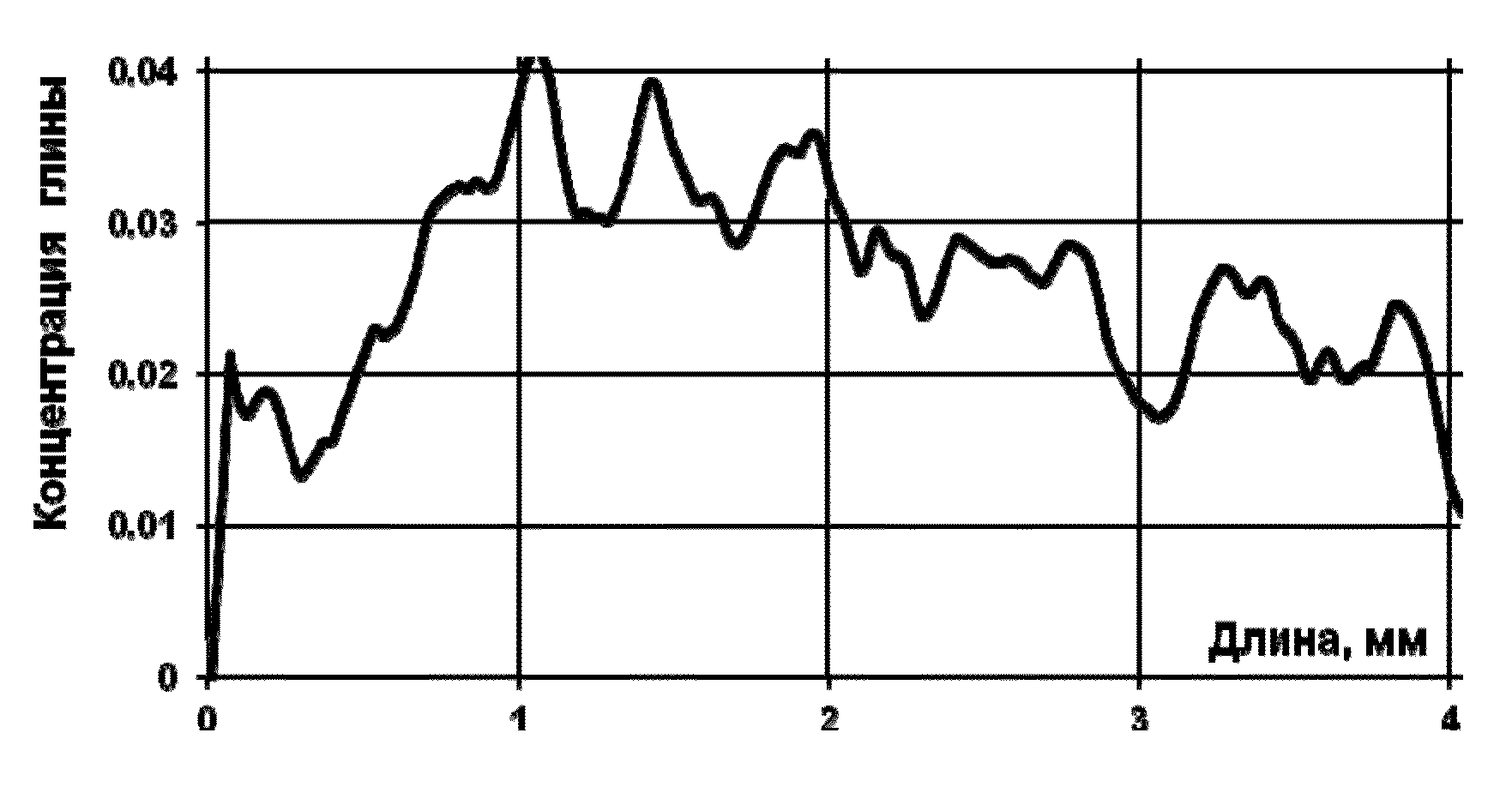
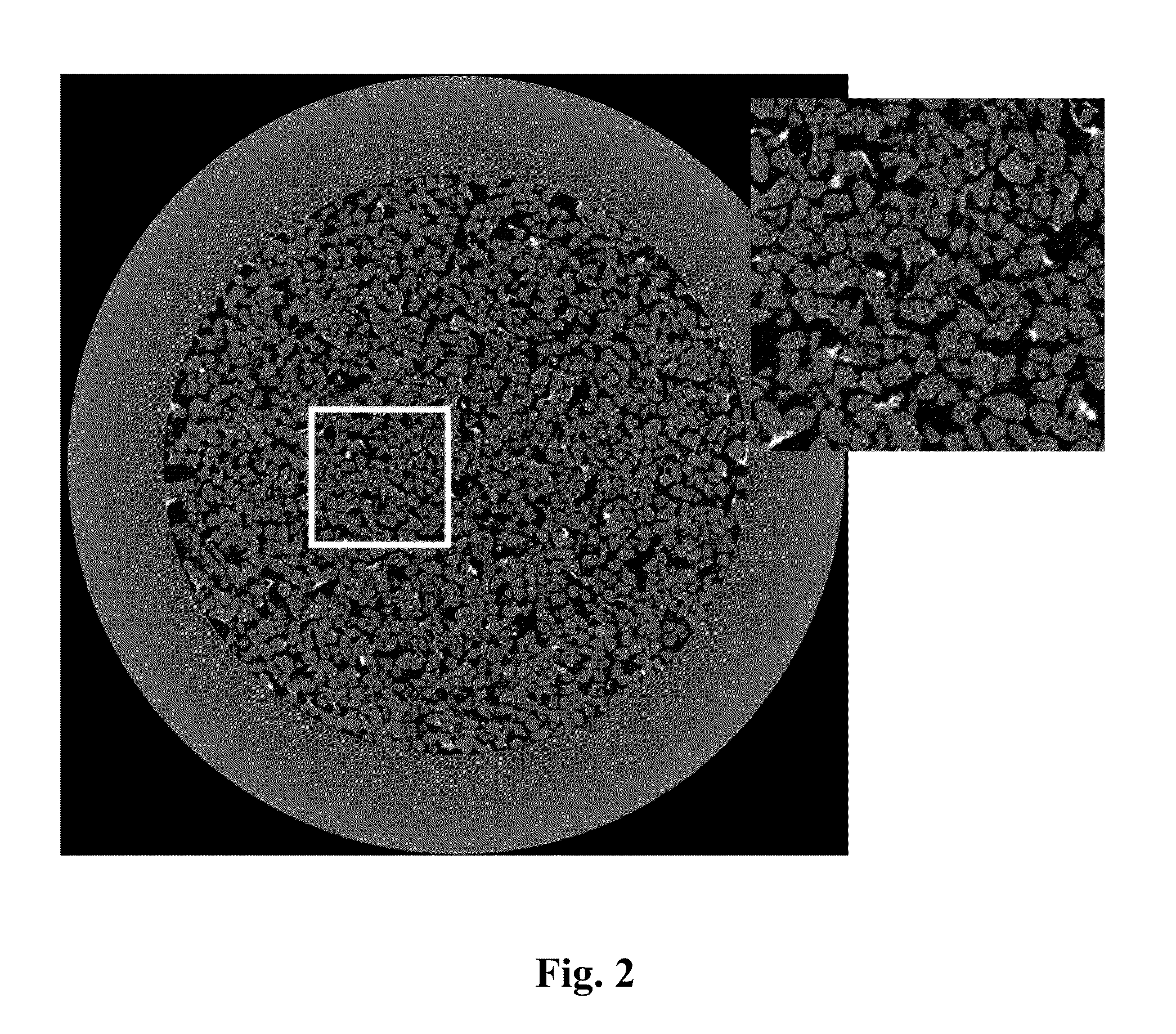
Method for determining spatial distribution and concentration of clay in a core sample
InactiveUS20130010919A1High measurement accuracyIncrease contrastX-ray spectral distribution measurementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSolubilityX-ray
A water-soluble salt of a metal with a high atomic weight is selected as an X-ray contrast substance providing a selective ion-exchange reaction with a clay. The salt has a general formula R+M−, where R− is selected from a group consisting of Ba2+; Sr2+; Tl+; Rb+ . . . , and M− is selected from a group consisting of Cln; NOn; OHn; CH3COO, SO4; . . . in accordance with a standard table of inorganic substances' water solubility. The X-ray contrast substance is injected into a core sample. Upon completion of the selective ion exchange reaction a non-contrast displacing agent is injected into the sample. The sample is scanned by computer X-ray microtomography and an image of the sample is obtained. An area of interest and a reference cross-section are selected at the obtained computer tomography image. Grayscale histograms in cross-sections of the sample are obtained. Spatial distribution and concentration of the clay is estimated by means of histograms analysis starting from the reference cross-section histogram.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
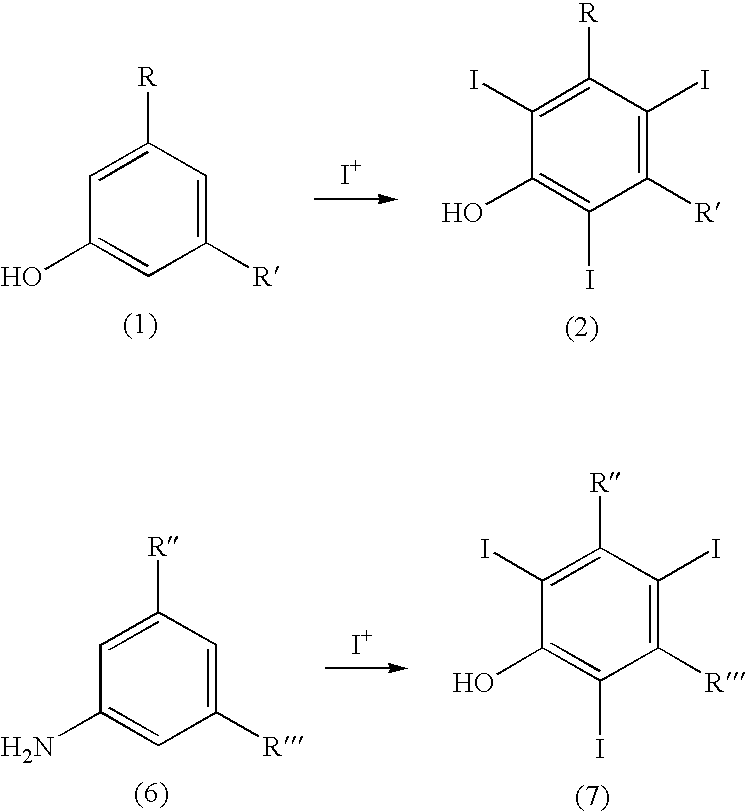
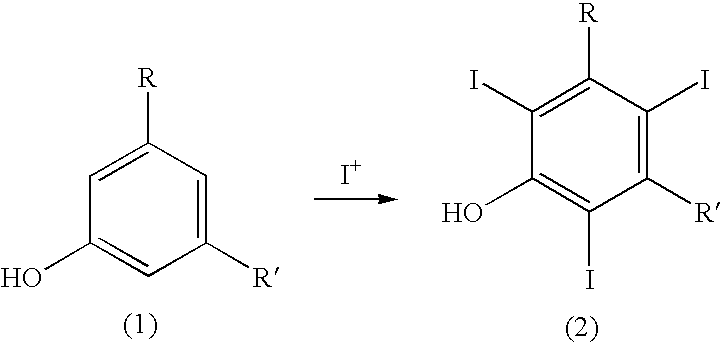
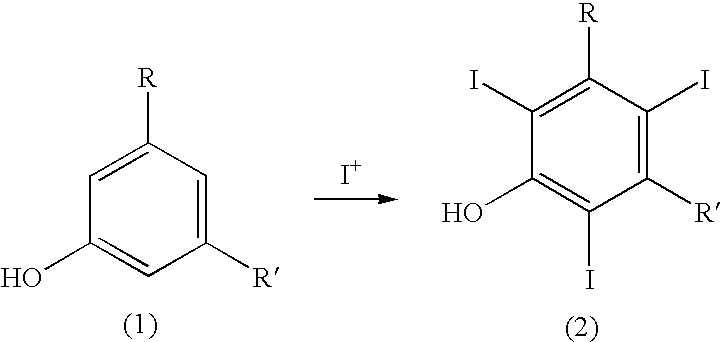
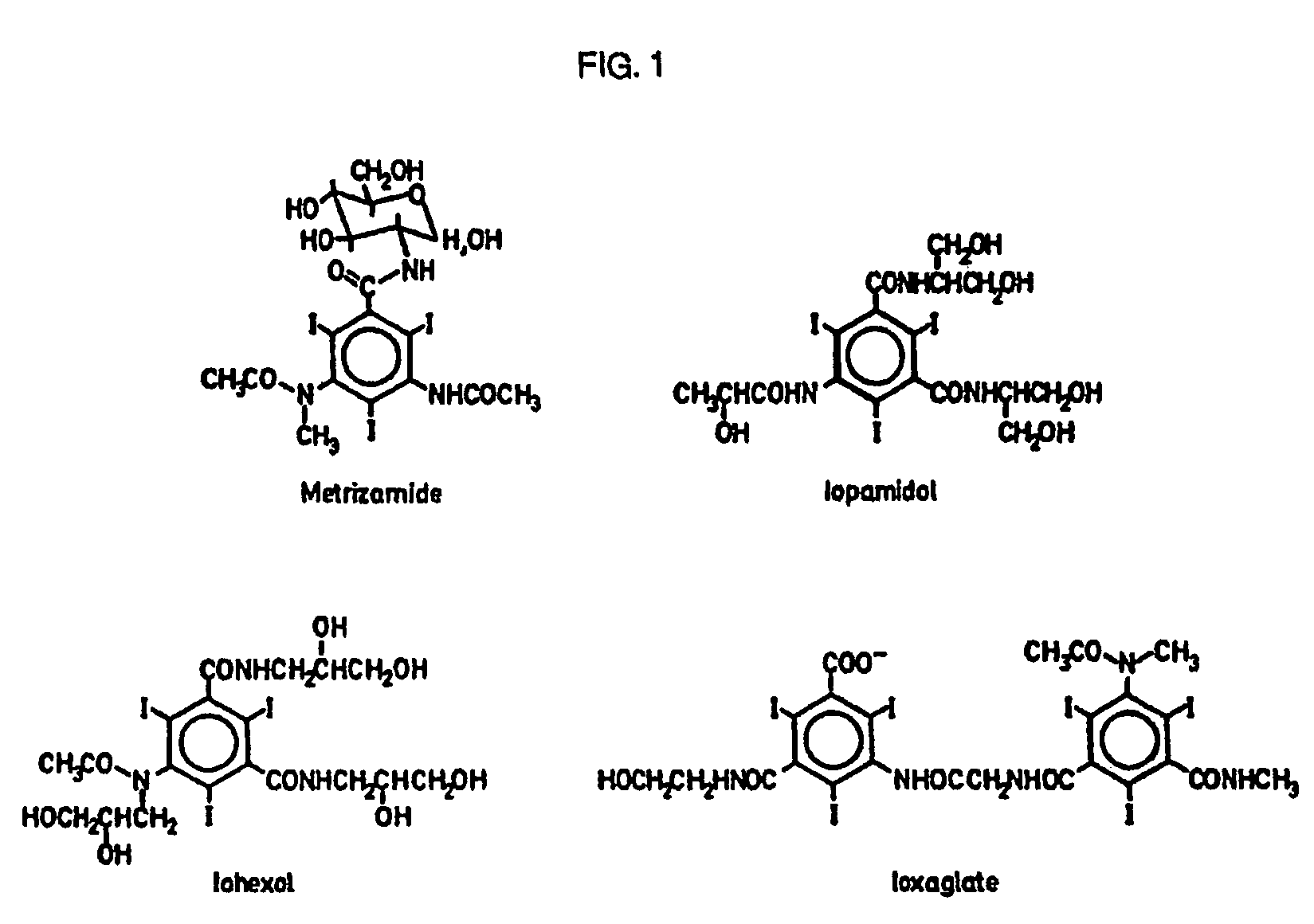
Process for the iodination of aromatic compounds
ActiveUS20100331567A1High purityHigh yieldElectrolysis componentsOrganic compound preparationAnilinePhenol
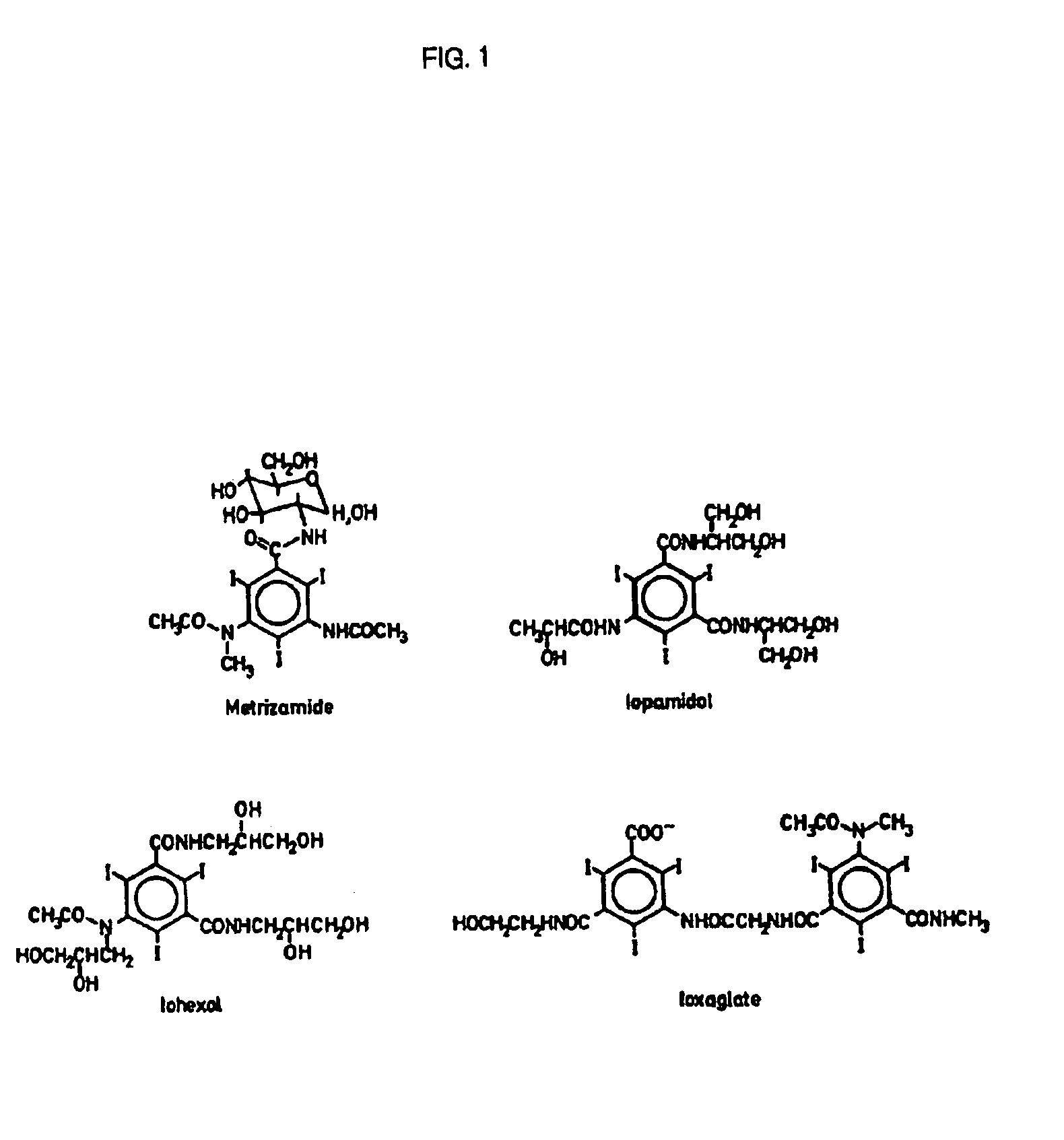
The present invention relates to a process for the preparation of iodinated phenols, —in particular, it relates to a process including the electrochemical iodination of 3,5-disubstituted phenols of formula (1) to the corresponding 3,5-disubstituted-2,4,6-triiodophenols of formula (2), which are useful intermediates for the synthesis of x-ray contrast media, and to the preparation of the contrast media themselves. Furthermore, the present invention includes the electrochemical iodination of 3,5-disubstituted anilines of formula (6) to the corresponding 3,5-disubstituted-2,4,6-triiodoanilins of formula (7).
Owner:BRACCO IMAGINIG SPA
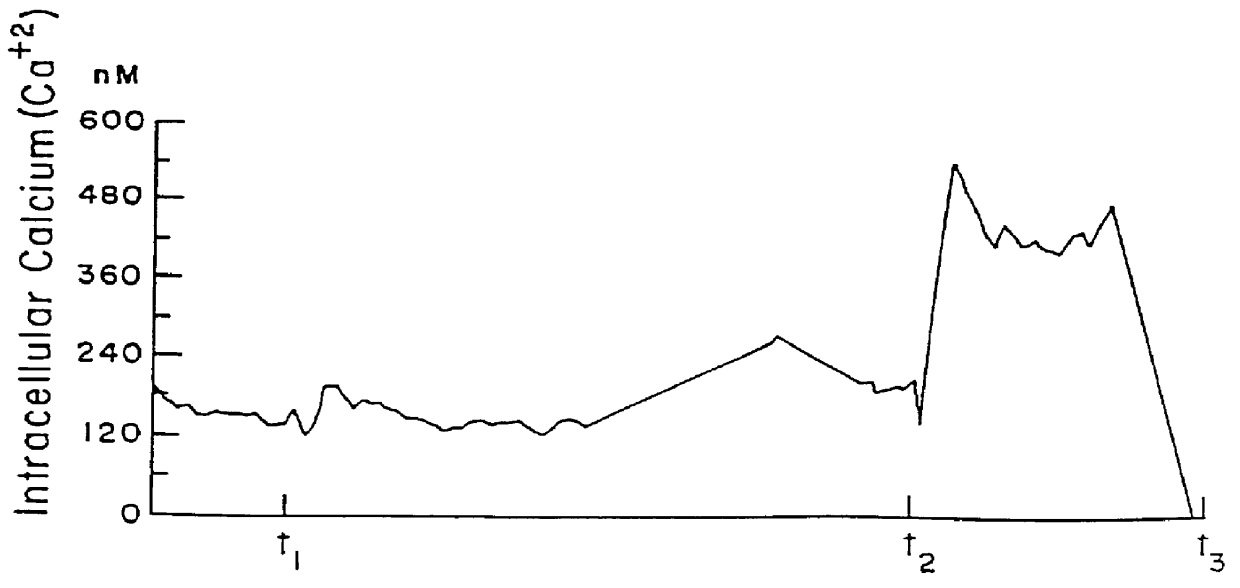
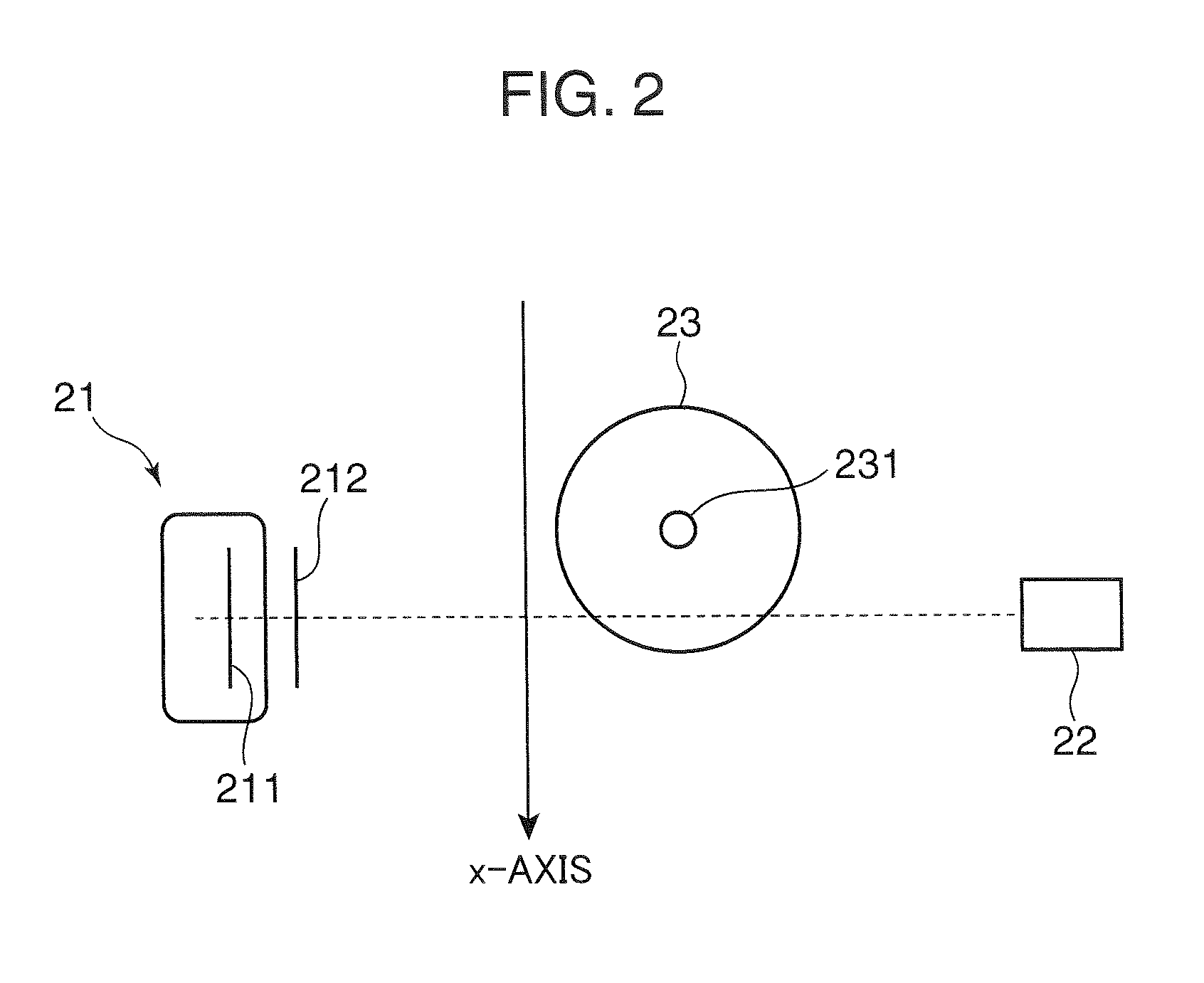
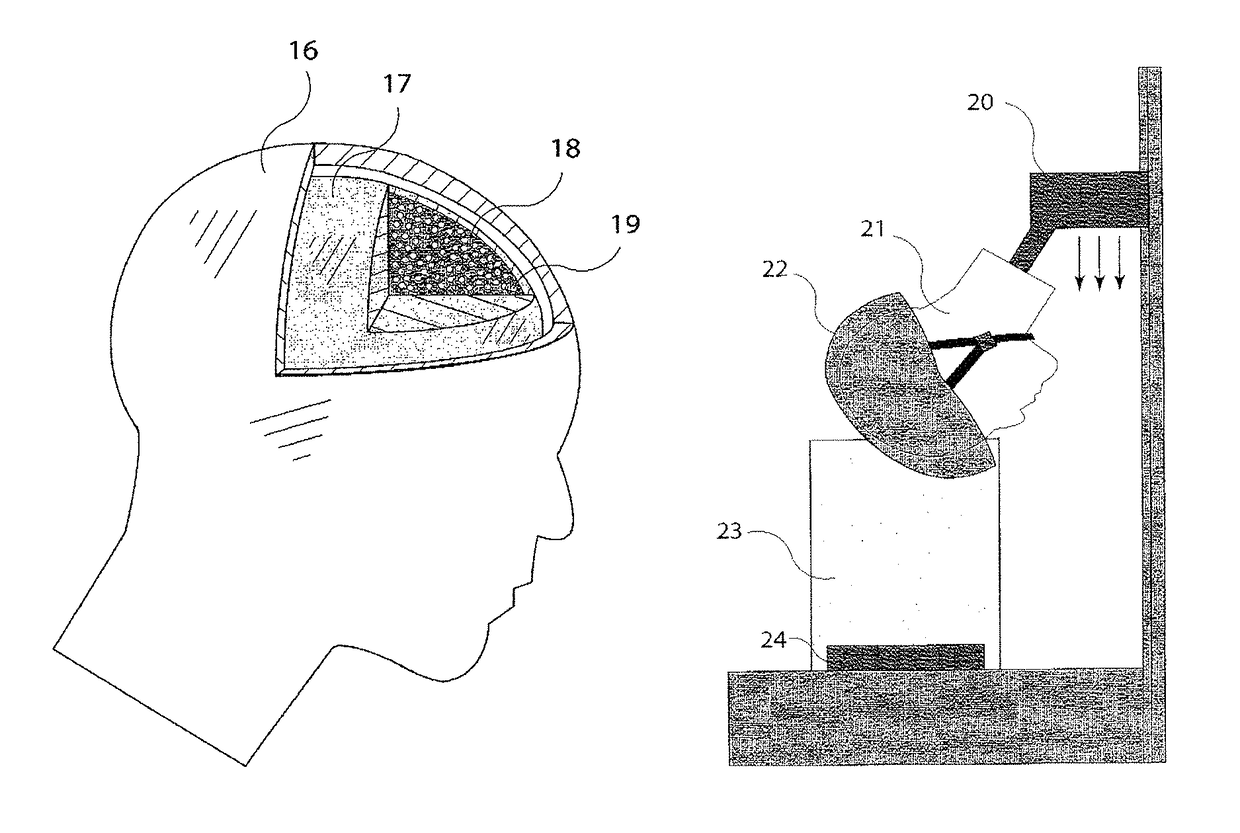
Diagnostic for in situ deformation and strain measurements applicable to traumatic internal injury investigation and prevention
ActiveUS9826954B2Improve reliabilityImprove certification standardMedical imagingDiagnostic recording/measuringBiomechanicsX-ray
A diagnostic gage (12) that can be implemented into a tissue-simulating headform (17) or other anthropomorphic surrogate test device (11) as a means of determining the internal strain within the test surrogate. One embodiment of the gage consists of a matrix or substrate embedded with x-ray contrast agents (14) and a series of holes within the substrate (15) that provide contrasting markers in an x-ray image and a means of closely coupling the gage to the test specimen. The relative motion of these contrasting markers can be monitored using x-ray fluoroscopy equipment (e.g., source (10) and detector (13)). This gage provides a means of determining the internal strain within a headform surrogate model for the purpose of evaluating the performance of helmets in terms of reducing the occurrence of concussion among other biomechanical injuries from trauma.
Owner:PETEL OREN E
X-ray CT apparatus and method thereof
ActiveUS8180016B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayVoltage
In an X-ray CT apparatus 1 and an X-ray CT method, the thickness of an object to be inspected is computed on the basis of the number of transmitted X-rays in a specific energy range set above and below the K-absorption edge of an X-ray contrast medium serving as the object to be inspected, and a CT image is reconstructed on the basis of the computed thickness of the object to be inspected. Such X-ray CT apparatus 1 and X-ray CT method can generate an X-ray CT image stably and independently of the size of the object to be inspected and of X-ray tube voltage (X-ray energy distribution).
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Iopromide preparation method
ActiveCN105001113AHigh purityAchieve separationOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid amides preparationX-rayIopromide
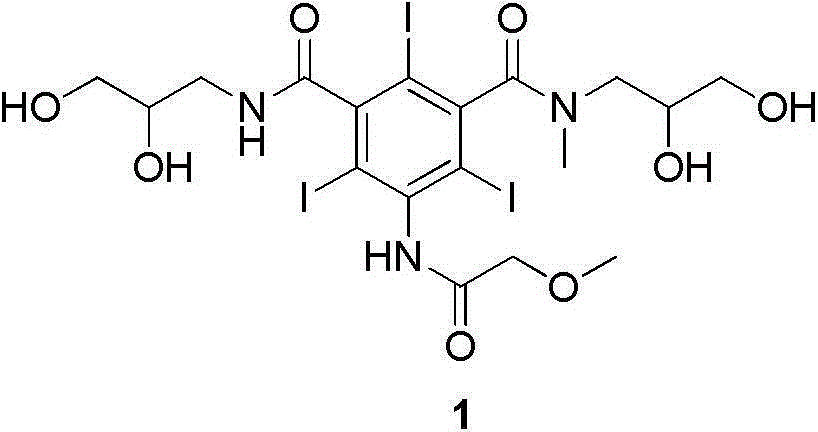
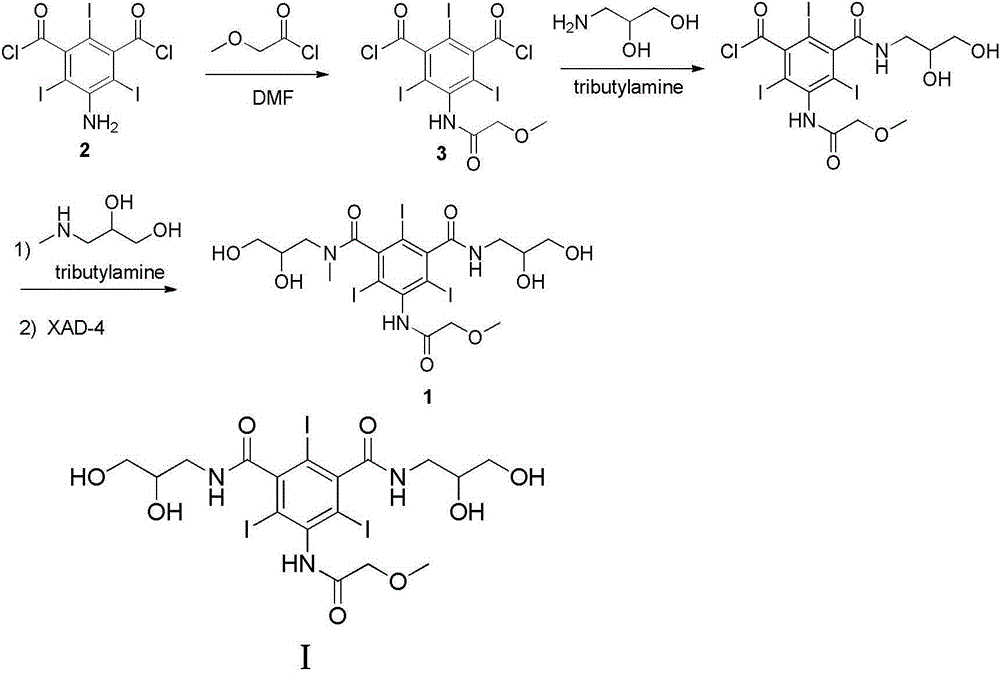
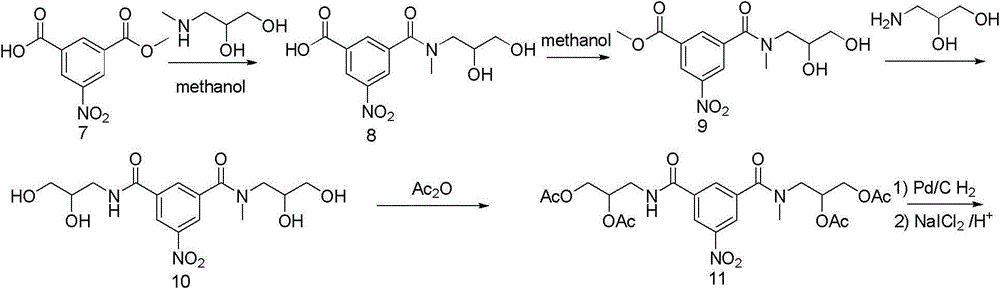
The present invention relates to an X-ray contrast agent iopromide preparation method. According to the method, 3-methoxy acetyl-5-(2,3-dihydroxy-N-methyl-n-propyl-carbamoyl)-2,4,6-triiodobenzoic acid (4) is introduced as an intermediate, the used raw material is cheap and easy to obtain, the experiment operation is relatively simple, the reaction condition is mild, and the product purity is qualified.
Owner:白银京宇新药业有限公司
Concentrated X-ray contrast media can act as universal antigens and can inhibit or prevent allergic reactions
InactiveUS7151117B2Avoid allergic reactionsBiocideSenses disorderAntibody antigen reactionsNuclear medicine
The present application is directed to the use of X-ray contrast media that act as universal antigens that are labeled herein as “pseudoantigens.” X-ray contrast media have the potential to exist in an aggregated state that is greater in increased concentrations. In this aggregated state, contrast media assume the role of multivalent antigens and can successfully compete with any other antigens involved in antibody-antigen reactions that lead to anaphylaxis. In this competition, the large quantity of contrast media serves to inhibit the adverse effects of antibody-antigen reactions without the contrast media itself creating antibodies or creating toxicity problems.
Owner:3E THERAPEUTICS
Thermoplastic composition having improved x-ray contrast, method of making, and articles prepared therefrom
ActiveUS20100080972A1Mitigate such drawbackIncreasing x-ray contrastSynthetic resin layered productsFerroso-ferric oxidesX-rayPolycarbonate
Disclosed herein is an article and thermoplastic composition comprising a polysiloxane-polycarbonate, optionally, a polycarbonate, and an X-ray contrast agent comprising X-ray scattering atoms having an atomic number of greater than or equal to 22, wherein an article molded from the thermoplastic composition and having a thickness of 3.2 mm has a notched Izod impact (NII) strength of greater than or equal to about 620 J / m, when measured at a temperature of 0° C. according to ASTM D256-04, or a notched Izod impact strength of greater than or equal to about 409 J / m, when measured at a temperature of −30° C. according to ASTM D256-04, wherein an article molded from the thermoplastic composition and having a thickness of 3.2 mm has an Equivalent Al Thickness of greater than 0.51 mm, when irradiated with 50 kV X-ray radiation, and wherein for melt volume rates of the thermoplastic composition determined under a load of 1.2 kg at a temperature of 300° C. according to ASTM D1238-04, a melt volume rate measured at a dwell time of 18 minutes increases relative to a melt volume rate measured at a dwell time of 6 minutes by less than or equal to 31%. A method of improving X-ray contrast in a polycarbonate composition, and specific articles are also disclosed.
Owner:SHPP GLOBAL TECH BV
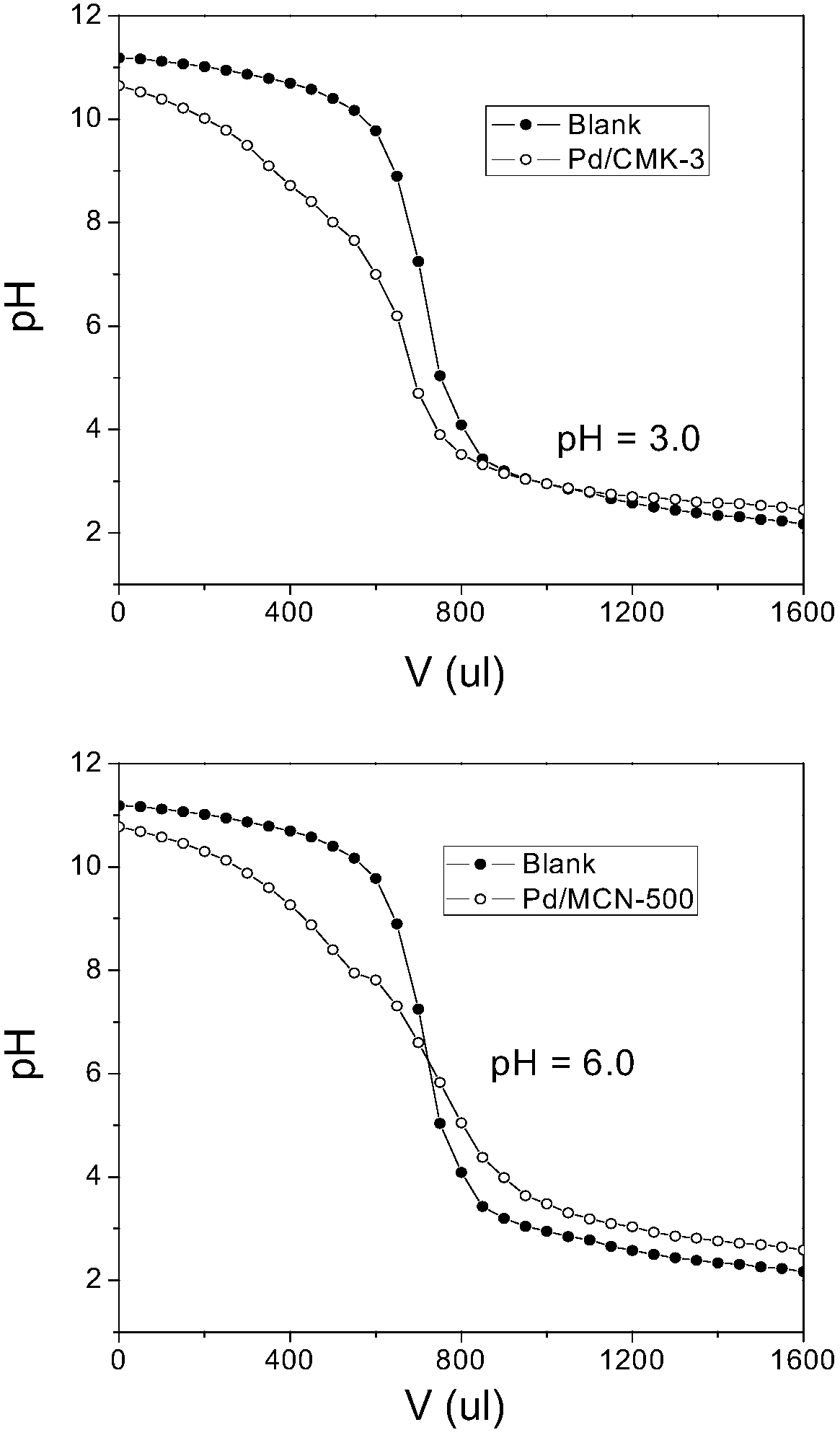
Method for liquid phase catalytic hydrogenation deiodination of iodination X-ray contrast medium
InactiveCN108465190ARemove or reduce toxicityImprove degradation efficiencyPhysical/chemical process catalystsHydrogenPorous carbon
The invention discloses a method for the liquid phase catalytic hydrogenation deiodination reaction of an iodination X-ray contrast medium. The method comprises the steps that a catalyst in the methoduses the porous carbon MCN in the mixed nitrogen as a carrier, the noble metal Pd or Pt is loaded through a precipitation deposition method, and a noble metal catalyst with the MCN loaded is obtained; and the noble metal catalyst with the MCN loaded is added into an aqueous solution containing the iodination X-ray contrast medium, and after nitrogen balancing is carried out, the hydrogen is introduced into the solution for the liquid phase catalytic hydrogenation deiodination reaction. According to the method, the catalyst is used for liquid phase catalytic hydrogenation deiodination of the iodination X-ray contrast medium so that relatively high reaction activity can be realized, the toxicity of the ICM can be effectively removed or reduced, the degradation efficiency is high, and the reaction speed is high.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
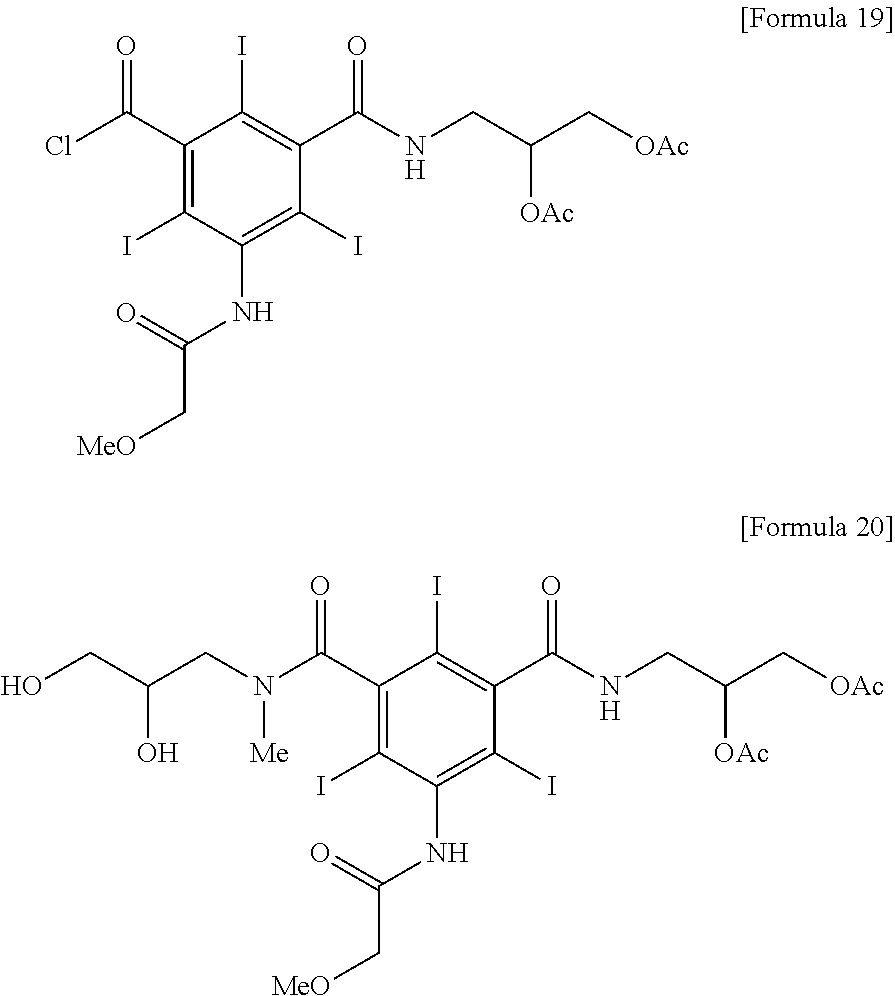
Novel process for preparation of iopromide
InactiveUS20110034730A1Efficient removalHigh purityOrganic compound preparationX-ray constrast preparationsX-rayIopromide
The present invention relates to a novel process for preparing iopromide which is used as a contrast agent for X-ray, wherein 5-methoxyacetylamino-2,4,6-triiodoisophthalic acid (2,3-diacetoxypropyl)amide chloride of formula (19) and 5-methoxyacetylamino-2,4,6-triiodoisophthalic acid [(2,3-dihydroxy-N-methylpropyl)-(2,3-diacetoxypropyl)]diamide of formula (20) are introduced as intermediates, by which a bismer by-product generated during the preparation process can be removed even without an additional removal procedure and thus iopromide with high purity can be prepared in high yield.
Owner:LG LIFE SCI
Method for determining spatial distribution and concentration of clay in a core sample
InactiveUS8761334B2High measurement accuracyIncrease contrastRadiation/particle handlingEarth material testingIon exchangeX-ray
A water-soluble salt of a metal with a high atomic weight is selected as an X-ray contrast substance providing a selective ion-exchange reaction with a clay. The salt has a general formula R+M−, where R+ is selected from a group consisting of Ba2+; Sr2+; Tl+; Rb+ . . . , and M− is selected from a group consisting of Cln; NOn; OHn; CH3COO, SO4; . . . . The X-ray contrast substance is injected into a core sample. Upon completion of the selective ion exchange reaction a non-contrast displacing agent is injected into the sample. The sample is scanned by computer X-ray microtomography. An area of interest and a reference cross-section are selected at the obtained computer tomography image. Grayscale histograms in cross-sections of the sample are obtained. Spatial distribution and concentration of the clay is estimated by means of histograms analysis starting from the reference cross-section histogram.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com