Patents
Literature
40results about How to "Increased elongation at room temperature" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
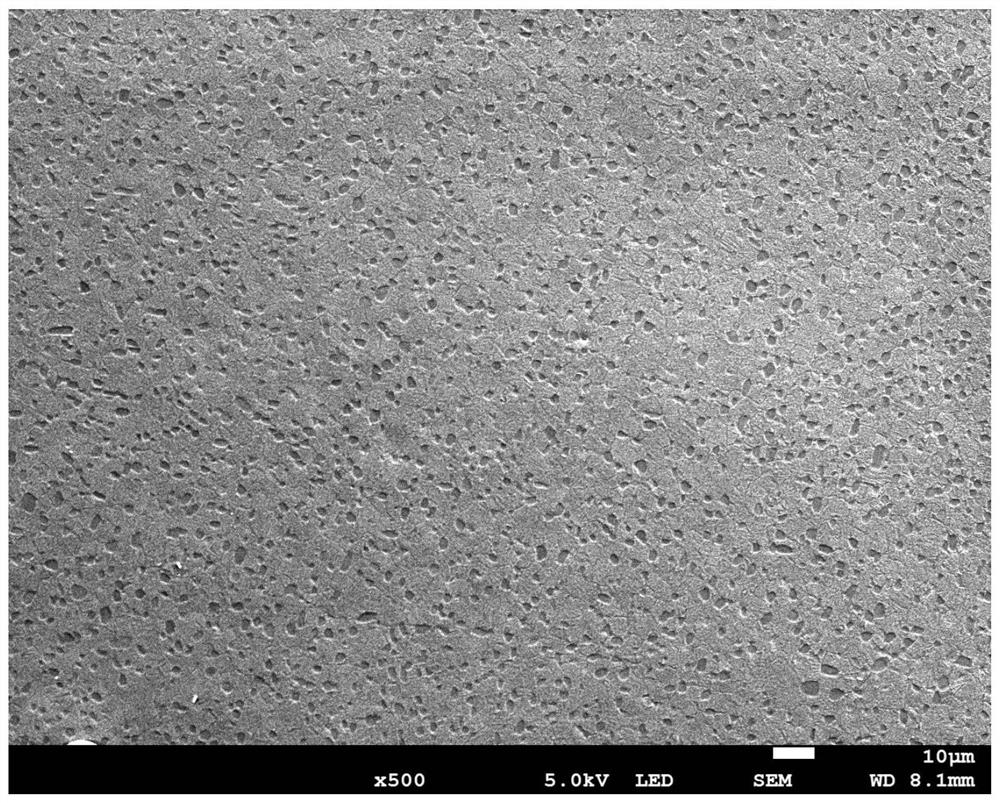
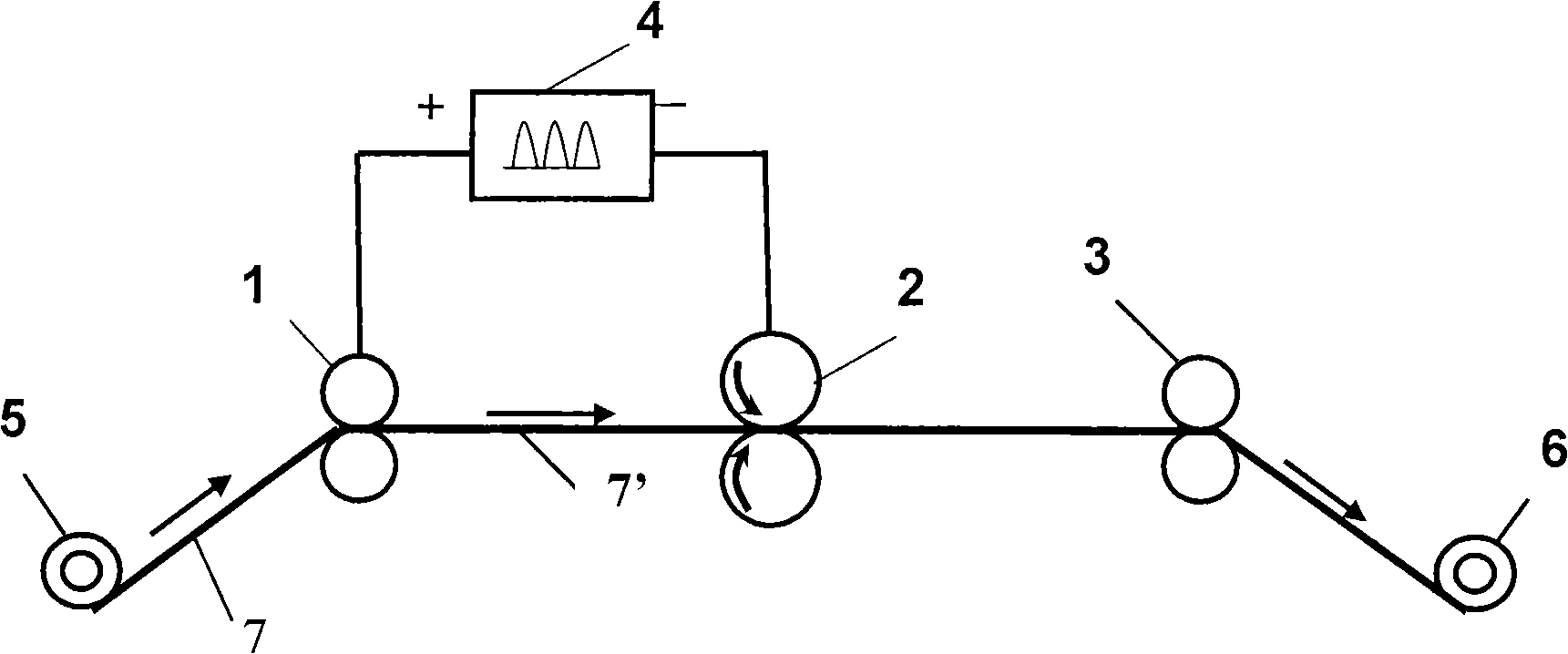
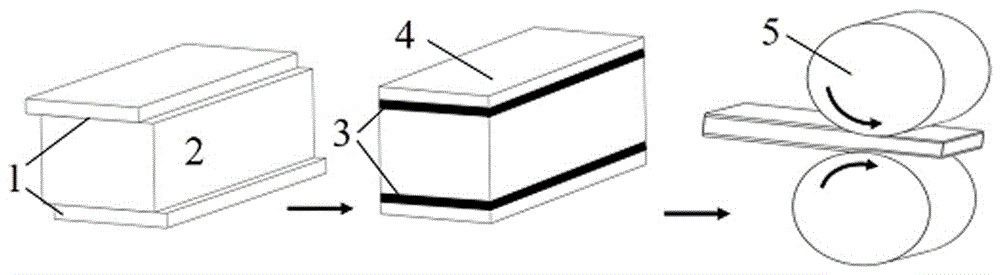
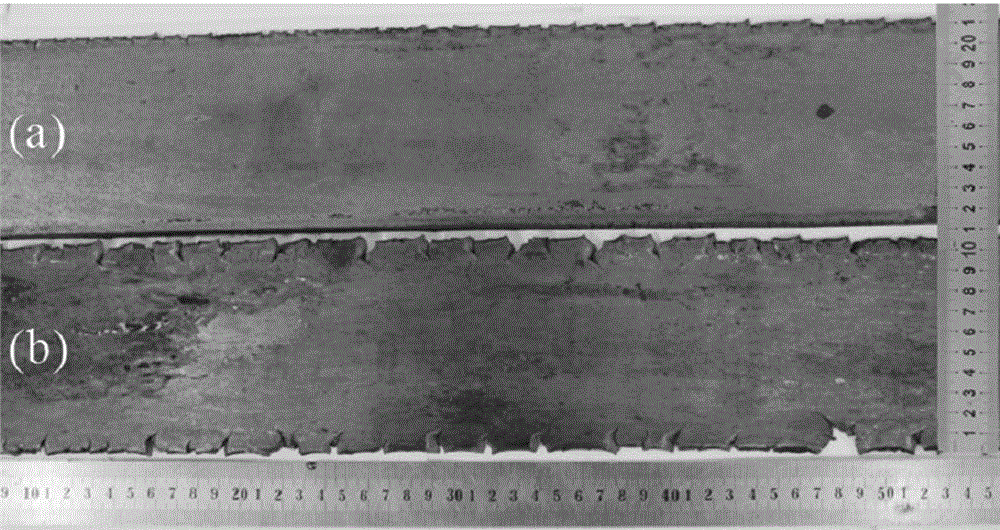
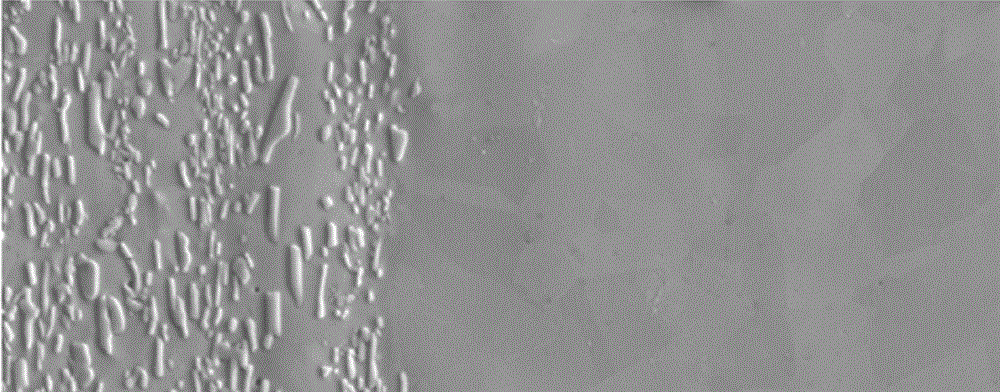
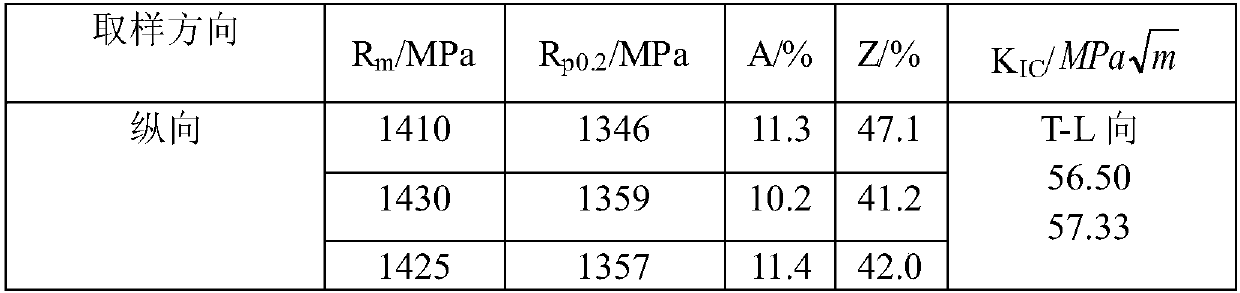
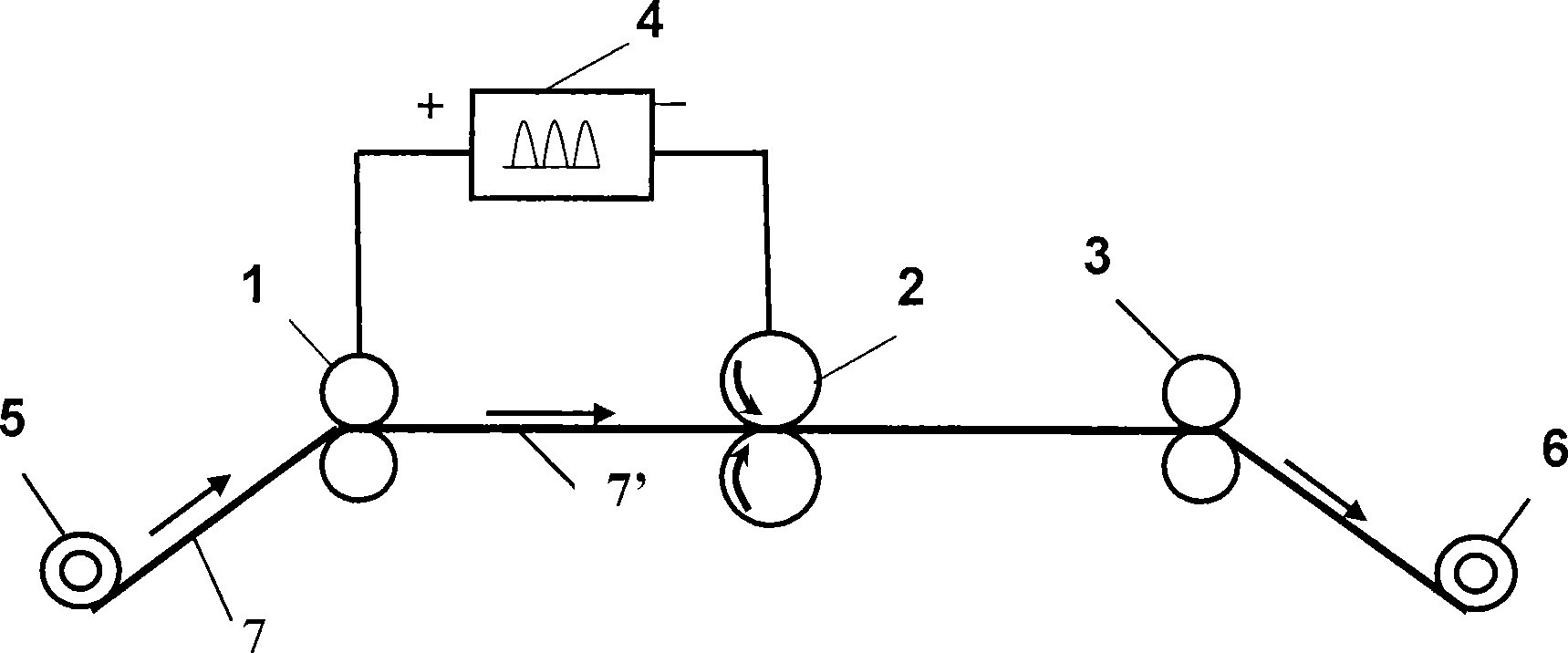
High-strength high-toughness AZ91 magnesium alloy strip eletrotoughening process method and system
InactiveCN101298653AOxidation does not occurToughening treatment is widely applicableHigh energyRoom temperature
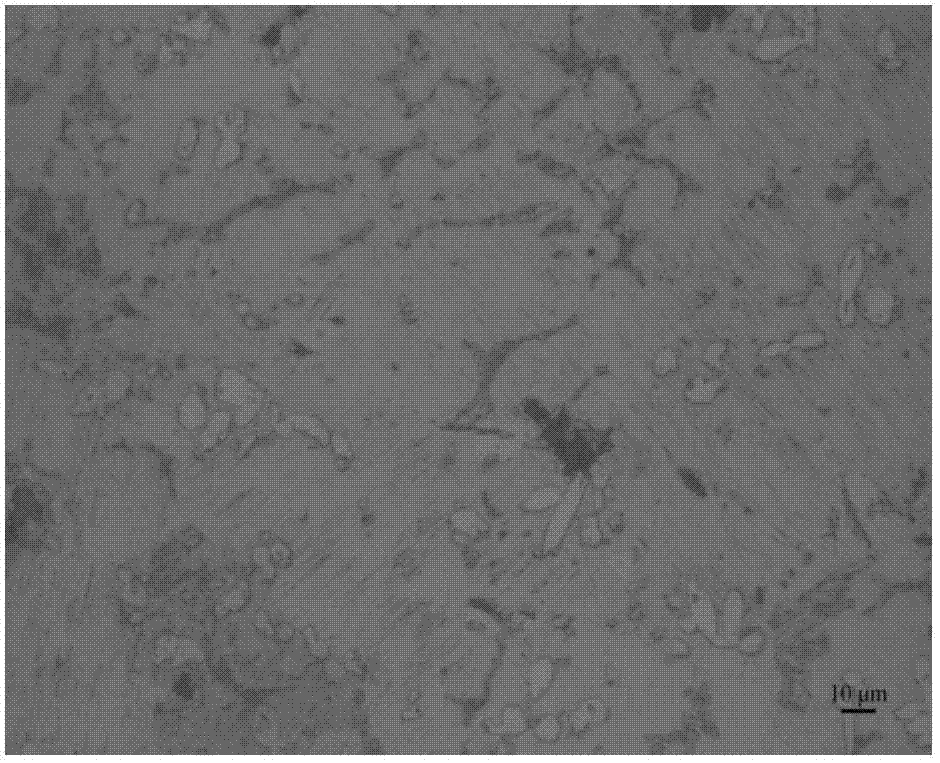
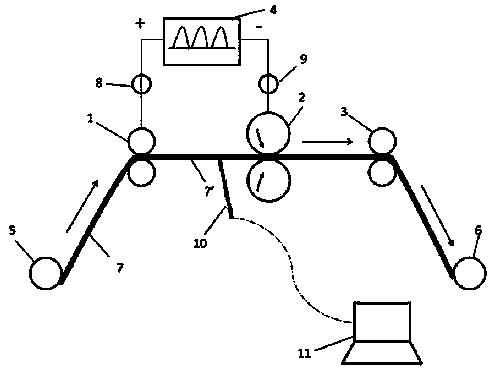
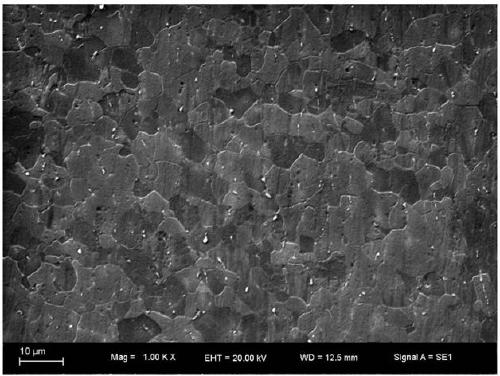
The invention discloses an electro-strengthening and toughening processing method of a belt material of AZ91 magnesium alloy and a system thereof. The electro-strengthening and toughening processing method comprises following steps: when the belt material of magnesium alloy is transmitted at a certain speed which is driven by a roller on an electro plastic rolling machine, high-energy impulse current that is output by an impulse power source through an electrode is input into an electriferous region section of the moving belt material of magnesium alloy, and the Joule heating effect and the non-heating effect are generated in the electriferous region section, thus causing the phase transition of internal microscopic constitution from bulky lath-shaped Beta-Mg17Al12 that are gathering and agglomerating in an initial state to Beta-Mg17Al12 particles that are evenly distributed and approximately sphere-shaped, or causing the solid solution effect that leads Beta-Mg17Al12 to be dissolved in a substrate; the processed belt material can be naturally air cooled at room temperature. The electro-strengthening and toughening processing method of the belt material of AZ91 magnesium alloy has short processing time and high production efficiency, and simultaneously avoids the high-temperature oxidation of the magnesium alloy. After the electro-strengthening and toughening processing, the microscopic constitution of the belt material of magnesium alloy can be remarkably improved, the unit extension of the microscopic constitution is increased from 11.8 percent in the initial aging state to over 20 percent, and the tensile strength of the microscopic constitution is not dramatically lowered.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
High-plasticity and low-anisotropism deformed magnesium alloy plate and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108796327AImprove mechanical propertiesEasy rolling deformationAnisotropic deformationMetallic materials
The invention relates to the technical field of light metal materials, in particular to a high-plasticity and low-anisotropism deformed magnesium alloy plate and a preparation method thereof. The high-plasticity and low-anisotropism deformed magnesium alloy plate is composed of the following components of, by mass, 3.0-5.0% of Al, 0.3-0.6% of Mn, 0.1-0.9% of Y, 0.1-0.8% of Ca, 0.1-0.5% of Zn, andthe balance Mg and unavoidable impurities, wherein the content of the impurities is smaller than or equal to 0.3%. The prepared magnesium alloy plate has the high plasticity and low anisotropism at the room temperature, the basal texture strength is obviously weakened, and the comprehensive mechanical property is good.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Repeated solid solution aging thermal treatment process of titanium alloy
The invention relates to a repeated solid solution aging thermal treatment process of titanium alloy. The process includes the steps that a titanium alloy forge is subjected to heat preservation at the temperature T for t minutes, wherein T is larger than or equal to Tbeta-15 DEG C but smaller than or equal to Tbeta+15 DEG C, t is equal to eta*delta max, delta max is the maximum section thickness of the forge and is shown in millimeters, and eta is the heating coefficient and ranges from 0.2 min / mm to 0.8 min / mm; then the forge is discharged out of a furnace to be air-cooled or wind-cooled or water-cooled to be at the room temperature, then the cooled forge is subjected to heat preservation at the temperature of T for t minutes, wherein T is larger than or equal to Tbeta-25 DEG C but smaller than or equal to Tbeta-50 DEG C, the computational formula of t is as above, namely t=eta*delta max, and the heating coefficient eta ranges from 0.3 min / mm to 1.2 min / mm; then the forge is discharged out of the furnace to be air-cooled or wind-cooled or water-cooled to be at the room temperature, the cooled forge is subjected to heat preservation at the temperature T ranging from 540 DEG C to 600 DEG C, and the heat preservation time t ranges from 0.5 hour to 2 hours; the forge is discharged out of the furnace to be air-cooled to be at the room temperature, the cooled forge is subjected to heat preservation at the temperature T ranging from 400 DEG C to 540 DEG C, and the heat preservation time t ranges from 4 hour to 24 hours; and then the forge is discharged out of the furnace to be air-cooled to be at the room temperature. The repeated solid solution aging thermal treatment process of the titanium alloy is suitable for thermal treatment of near-beta type, metastable beta type and steady beta type ultrahigh-toughness titanium alloy so as to obtain required microscopic structures with high overall performance and multi-scale precipitated phases mixed.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS
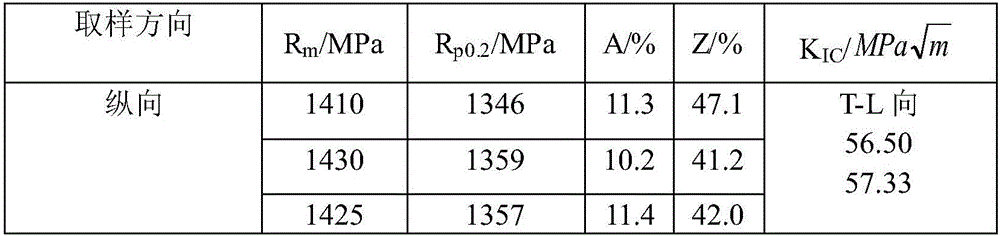
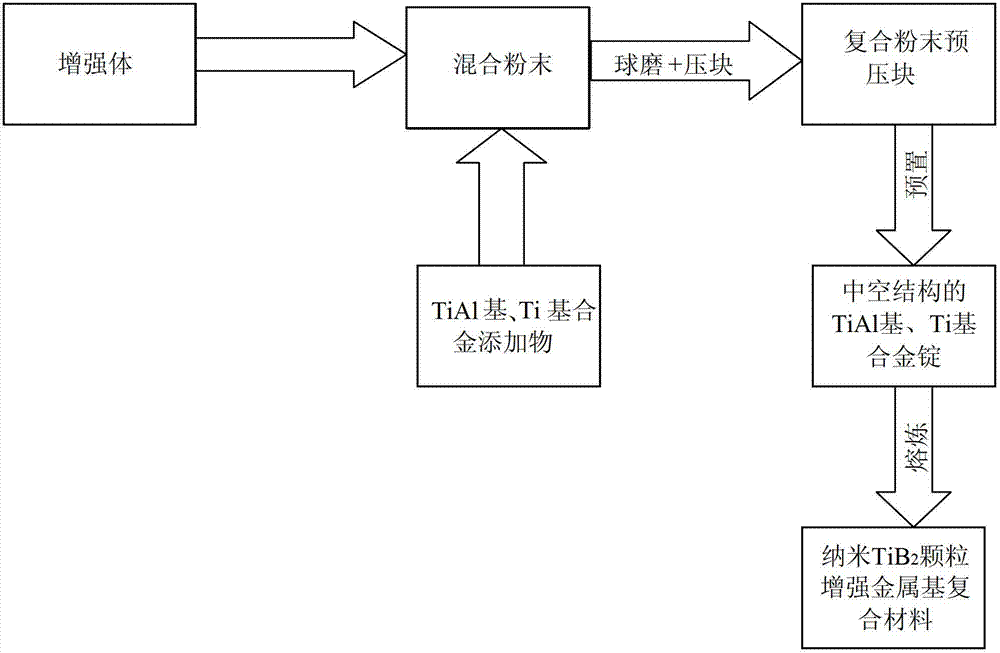
Nano TiB2 particle reinforced metal-base composite material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a nano TiB2 particle reinforced metal-base composite material and a preparation method thereof. The composite material reinforcer nano TiB2 particle accounts for 1-30 vol% of the composite material, the particle size is 20-500nm, and the matrix alloy is TiAl or Ti-base alloy. The preparation method comprises the following steps: mixing the reinforcer particle and metal additive, and carrying out composite ball milling to form composite powder; precompacting the composite powder to obtain a precompacted block; and finally, putting the precompacted block in a hollow matrix alloy ingot, and carrying out vacuum smelting to obtain the nano TiB2 particle reinforced metal-base composite material. The invention overcomes the defect of uncontrollable particle size of the reinforcer in the in-situ synthesis method, and avoids the problem of aggregation due to direct addition of ultrafine particles, so that the material can have favorable reinforced effect, thereby improving the room-temperature and high-temperature strength and elongation percentage of the material.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for promoting phase change strengthening and toughening of two-phase titanium alloy strip by using pulse current and strip
The invention discloses a method for promoting phase change strengthening and toughening of a two-phase titanium alloy strip by using pulse current. The method comprises the following steps: tensioning a TC4 titanium alloy strip through a decoiling device, a winding device, a roller and a support roller of a rolling mill, so that the strip is in tightly elastic contact with the roller; driving the strip to transmit at the speed of 150-800mm / min through friction force by virtue of the roller; inputting the pulse current into a power-up area section of the strip through the roller, the support roller and the like, wherein the pulse current generates a joule heating effect and a non-thermal effect in the power-up area section of the strip within 12-18 seconds, so that the internal microstructure of the strip turns into a two-phase long-axis structure or a two-phase dual-state structure from an original quasi-single phase thick equiaxed structure; and then cooling by natural air at room temperature. Through adjustment of parameters of the pulse current, the TC4 strip with the two-phase long-axis structure and the two-phase dual-state structure can be quickly obtained, thus the ductility is increased; the treatment temperature is far lower than 960 DEG C of a traditional thermal treatment process; the processing process of the titanium alloy strip can be finished without a short period of time at relatively low temperature without an oxidation phenomenon; and therefore, the method is energy-saving, environmentally friendly, safe and efficient.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Multi-component small-amount high-strength plasticity magnesium alloy and large-rolling-reduction short-process preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a multi-component small-amount high-strength plasticity magnesium alloy and a large-rolling-reduction short-process preparation method thereof. The multi-component small-amounthigh-strength plasticity magnesium alloy is prepared from the chemical components in percentage by mass: 0.8-1.5% of zinc, 0.8-1.5% of tin, 0.08-0.4% of calcium, 0.08-0.8% of yttrium and the balanceof magnesium and an adding element. The adding element is one or more of zirconium, gadolinium and manganese, and the adding element is prepared from the components in percentage by mass: 0.05-0.2% ofzirconium, 0.05-0.2% of gadolinium and 0.05-0.3% of manganese. The large-rolling-reduction short-process preparation method of the alloy comprises three steps of sub-rapid solidification, rolling andannealing. A high solid solution casting-rolling blank is directly obtained, the single-pass or less-pass large press quantity deformation can be realized, solid solution processing and multi-pass rolling complex process before rolling of a conventional magnesium alloy are eliminated, the preparation process of a magnesium rolled plate is greatly shortened, the tensile strength of the obtained multi-component small-amount magnesium alloy rolled plate after annealing is greater than 250 MPa, the elongation is greater than 25%, the room-temperature mechanical property is excellent, no obvious edge cracking is caused, and the yield is high.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
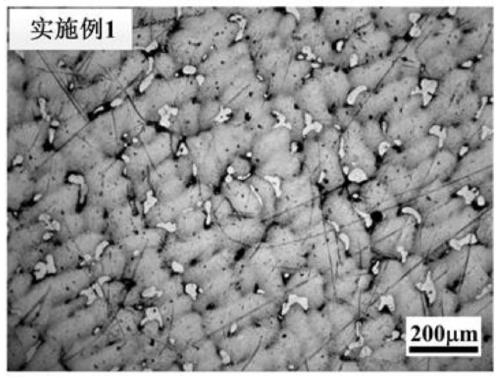
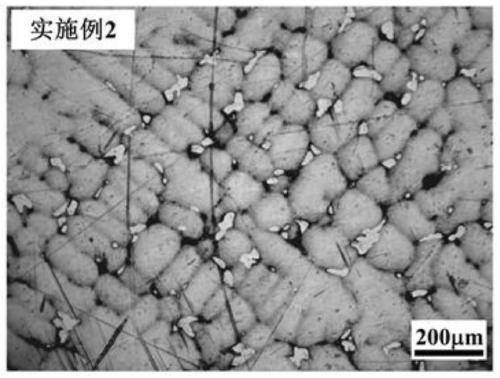
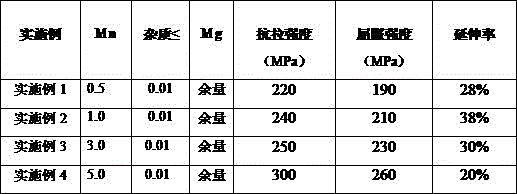
Mg-Mn wrought magnesium alloy and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a Mg-Mn wrought magnesium alloy and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the field of magnesium alloy design. The Mg-Mn wrought magnesium alloy comprises the following raw material components in percentage by mass: 0.2-5.0% of industrial pure manganese and the balance of industrial pure magnesium and inevitable impurities. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly melting magnesium, then adding magnesium-manganese intermediate alloy, stirring and refining and then pouring into an ingot, subsequently carrying out homogenizing heat treatment on the ingot, and extruding, so that corresponding extruded section is obtained. According to the invention, cheap magnesium manganese intermediate alloy is utilized, novel wrought magnesium alloy with good strength and toughness is prepared, compared with the currently widely used commercial magnesium alloy, the wrought magnesium alloy section is low in cost (compared with AZ31 magnesium alloy, cost can be greatly saved in a Mg-Mn (calculated according to Mn content in 1.0wt%) binary wrought magnesium alloy), heat distortion temperature of the alloy is low, the novel wrought magnesium alloy has excellent moulding and processing performances, and strength and toughness of the novel wrought magnesium alloy are obviously better than those of the traditional commercial AZ31 magnesium alloy.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Precipitation strengthened heat resistant steel and preparation process thereof
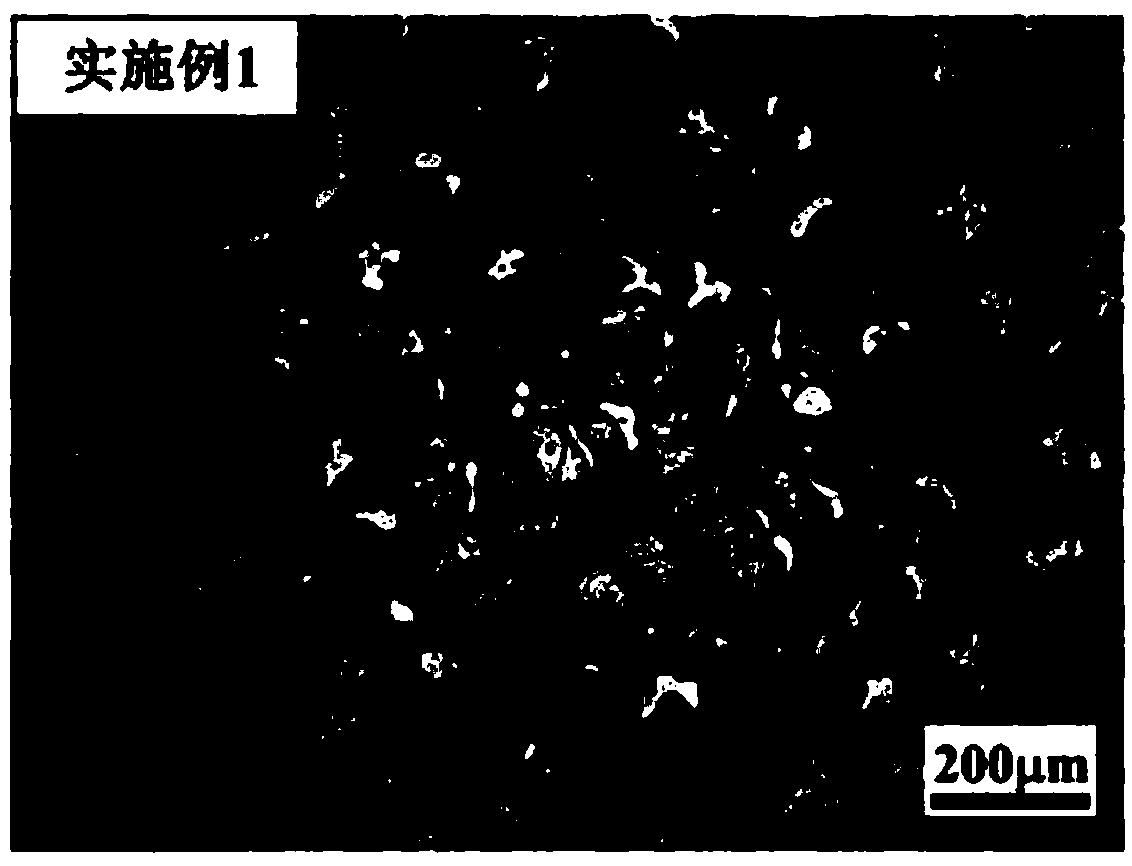
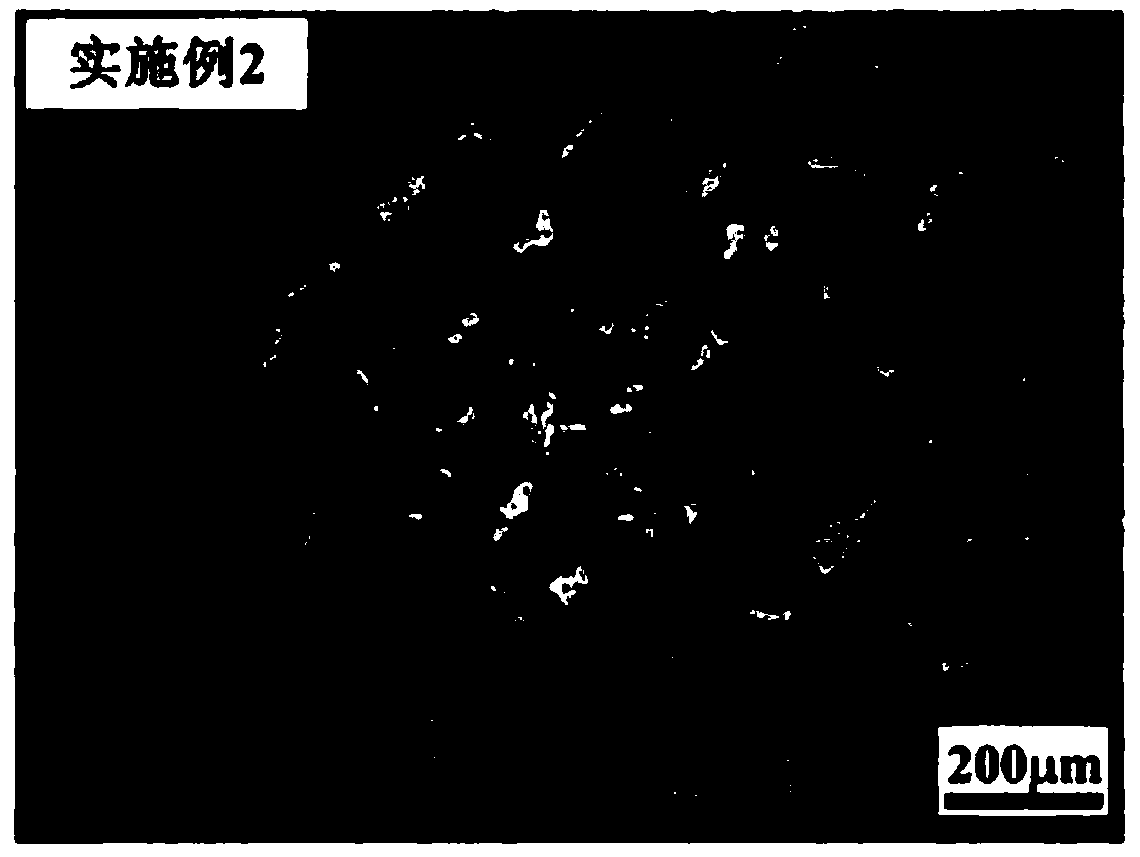
ActiveCN107587080AReduce the ductile-brittle transition temperaturePromote precipitationRoom temperatureIngot
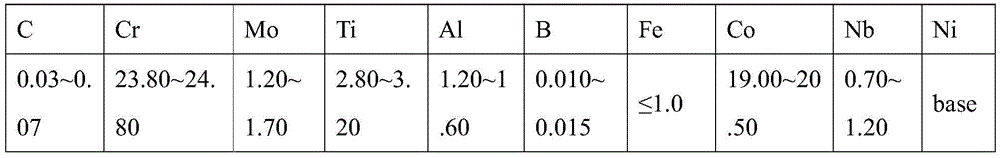
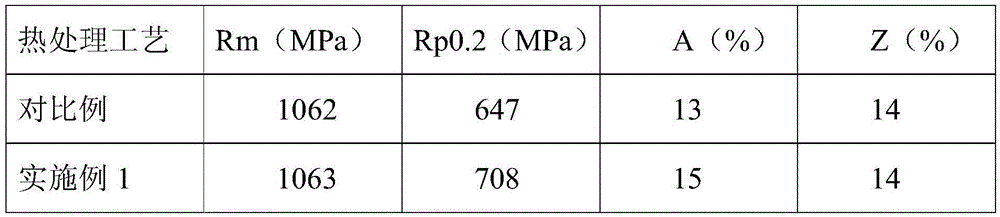
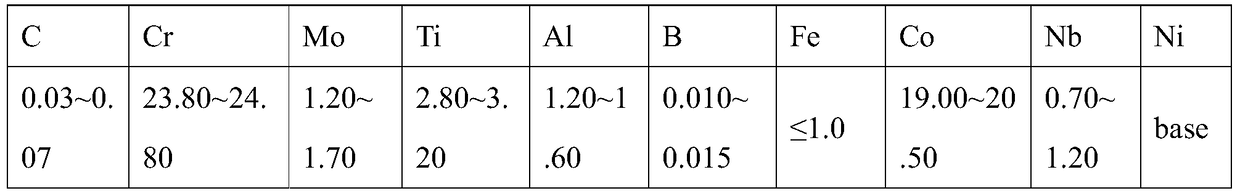
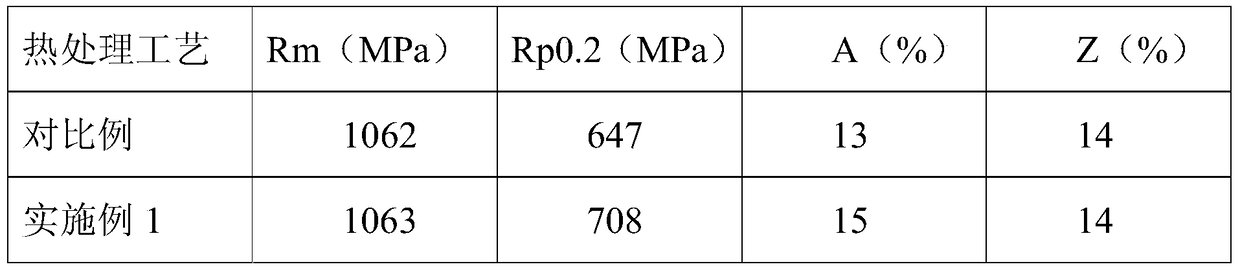
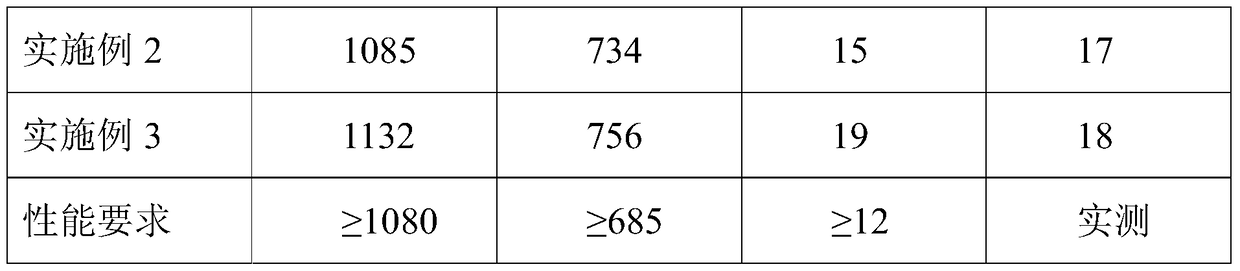
The invention relates to precipitation strengthened heat resistant steel and a preparation process of the precipitation strengthened heat resistant steel. The components of an alloy meet the followingrange requirements by mass percent: 003-0.06% of C, 6-10% of Ni, 8-13% of Cr, 1.5-2.4% of Al, less than or equal to 3% of Co, less than or equal to 0.1% of Nb, less than or equal to 0.1% of Zr, and the balance of Fe; the prepared alloy is smelted into an alloy mother liquid and is finally prepared into an alloy ingot; the alloy ingot is rolled into a sheet at the temperature range of 850-1100 DEGC; and the rolled sheet is subjected to solid solution treatment and aging treatment to obtain the precipitation strengthened heat resistant steel. The heat resistant steel is excellent in room temperature toughness and has an excellent strength property at the same time. The room temperature tensile strength of the alloy is not lower than 1000 MPa, the yield strength exceeds 900 MPa, the room temperature elongation percentage is higher than 12%, and the reduction of area is higher than 50%.
Owner:CHINA HUANENG GRP CO LTD +1
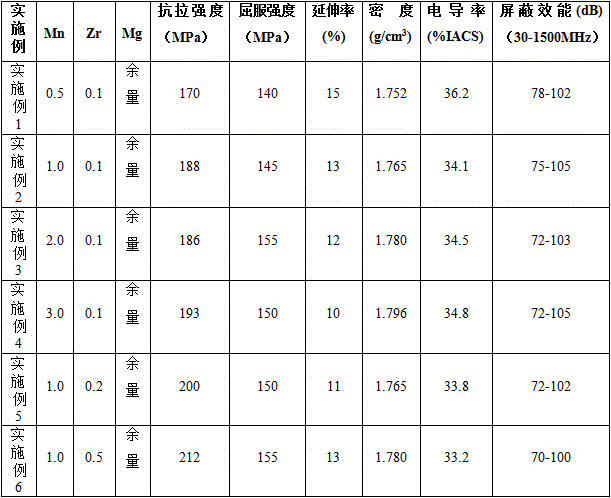
High-conductivity and high-shielding-effectiveness magnesium alloy and preparation method thereof
The invention provides high-conductivity and high-shielding-effectiveness magnesium alloy and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of design of materials. The high-conductivity and high-shielding-effectiveness magnesium alloy is prepared from the following raw material components in percentage by mass: 0.5wt% to 3wt% of manganese, 0.1wt% to 0.5wt% of zirconium and the balance of pure magnesium and inevitable impurities. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly melting magnesium; adding magnesium-manganese intermediate alloy and magnesium-zirconium intermediate alloy; stirring, standing and then casting into a cast ingot; subsequently thermally homogenizing the cast ingot and rolling to obtain a corresponding plate. According to the preparation method disclosed by the invention, low-content magnesium-manganese intermediate alloy and magnesium-zirconium intermediate alloy are used for preparing novel high-conductivity and high-shielding-effectiveness wrought magnesium alloy; in comparison with an existing widely-used shielding material, the shielding material is low in cost, high in specific strength, higher than a traditional metal shielding material and a composite shielding material in specific shielding effectiveness, excellent in molding processability and applicable to the field of weight-sensitive electromagnetic protection.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Method for improving hot-working performance and room-temperature plasticity of high-boron stainless steel
ActiveCN106702287AGood plasticity at room temperatureIncreased elongation at room temperatureSS - Stainless steelQuenching
A method for improving the hot-working performance and the room-temperature plasticity of high-boron stainless steel is carried out through the following steps that firstly, molten steel is smelted, and a high-boron stainless steel cast ingot is obtained in a die casting manner, wherein the high-boron stainless steel cast ingot comprises 17.0%-19.5% of Cr, 12.0%-15.0% of Ni, 1.5%-2.0% of Mn, 1.75%-2.25% of B, smaller than 0.08% of C and the balance Fe; secondly, cutting and surface finishing are carried out on the high-boron stainless steel cast ingot; thirdly, cutting and surface finishing are carried out on austenitic stainless steel plates; fourthly, surface washing is carried out; fifthly, the austenitic stainless steel plates are arranged on the upper face and the lower face of the square high-boron stainless steel billet, the austenitic stainless steel plates and the square high-boron stainless steel billet are aligned, and welding is carried out on the vacuum condition; sixthly, hot rolling is carried out; and seventhly, water quenching is carried out after solution treatment is completed. By means of the method, the production procedures are short, the production cost is low, only slight edge cracking occurs to the high-boron stainless steel in the hot rolling process, and the finally obtained high-boron stainless steel clad plate has relatively excellent room temperature plasticity.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Nano TiC particle toughened Fe-Ni base cast high-temperature alloy for manufacturing vehicular turbosupercharger and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108842082AGuaranteed StrengthImprove plastic toughnessMachines/enginesEngine componentsSuperalloyToughness
The invention discloses a nano TiC particle toughened Fe-Ni base cast superalloy for manufacturing a vehicular turbosupercharger. The nano TiC particle toughened Fe-Ni base cast superalloy comprises the following chemical components of, by mass percent, less than or equal to 0.10% of C, 11.00-16.00% of Cr, 34.00-45.00% of Ni, 4.00-8.00% of W, 1.80-2.40% of Al, 3.00-5.00% of Ti, 0.01-0.30% of TiC and the balance Fe. According to the nano TiC particle toughened Fe-Ni base cast superalloy for manufacturing the vehicular turbosupercharger, a nano TiC particle modificator is endogenously added to the nano TiC particle toughened Fe-Ni base cast superalloy for toughening a Fe-Ni base cast superalloy. The invention further provides a preparation method of the nano TiC particle toughened Fe-Ni basecast superalloy for manufacturing the vehicular turbosupercharger. A nano TiC iron base intermediate alloy is added to a Fe-Ni base superalloy melt, so that the endogenous nano TiC ceramic particle modificator toughened Fe-Ni base superalloy is obtained, and the plasticity and toughness of the Fe-Ni base cast superalloy are improved on the premise of ensuring the strength of the Fe-Ni base cast superalloy.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Heat treatment method for Nimonic101 nickel-based alloy
ActiveCN105543748AIncreased room temperature tensile strength and yield strengthIncreased room temperature elongation and reduction of areaDuctility% area reduction
The invention provides a heat treatment method for Nimonic101 nickel-based alloy. The heat treatment method for the Nimonic101 nickel-based alloy comprises the following steps that (1) solid solution heat treatment is conducted on a Nimonic101 nickel-based alloy forged piece, and the Nimonic101 nickel-based alloy forged piece is discharged out of a furnace and air cooled; (2) intermediate heat treatment is conducted on the air-cooled Nimonic101 nickel-based alloy forged piece at the temperature of 1020-1080 DEG C, heat preservation is conducted for 8-16 hours, and then the Nimonic101 nickel-based alloy forged piece is discharged out of the furnace and air cooled; and (3) aging heat treatment is conducted on the air-cooled Nimonic101 nickel-based alloy forged piece, and then the Nimonic101 nickel-based alloy forged piece is discharged out of the furnace and air cooled, so that the Nimonic101 nickel-based alloy is prepared. Compared with heat treatment methods which are frequently used at present, the heat treatment method can remarkably improve the indoor-temperature tensile strength and indoor-temperature yield strength and can also slightly improve the indoor-temperature ductility and indoor-temperature percentage of area reduction.
Owner:WUXI TURBINE BLADE
High-room-temperature-elongation wrought magnesium alloy and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105296831AHigh room temperatureHigh room temperature ductilityChemical compositionRoom temperature
The invention belongs to the field of non-ferrous metallurgy, specifically relates to wrought magnesium alloy and a preparation method thereof, discloses high-room-temperature-elongation wrought magnesium alloy and a preparation method thereof and provides high-room-temperature-elongation wrought magnesium system alloy. The high-room-temperature-elongation wrought magnesium alloy is prepared from not larger than 2% of Al, not larger than 0.2% of Mn, not larger than 0.4% of Ca and the balance magnesium, the room temperature elongation can reach 24%, and rolling, extruding, stamping and other plastic deforming can be easily completed on the basis. Meanwhile the method for preparing the alloy is provided, in other words, Al, Mn, Ca and other elements are added in pure magnesium ingots and are smelted into magnesium and aluminum alloy, and the wrought magnesium alloy prepared through the method is small and uniform in crystal particle and excellent in performance and can be used for the industries of aviation, aerospace, electronics, automobiles and the like.
Owner:NANYANG NORMAL UNIV
Ti2AlNb particle plasticized TiAl-based composite material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112981156AImprove stabilityImprove room temperature plasticityAdditive manufacturing apparatusNew materialsAdditive layer manufacturing
The invention belongs to the technical field of new material design and additive manufacturing. The invention provides a Ti2AlNb particle plasticized TiAl-based composite material and a preparation method thereof. The composite material is composed of, by volume, 1.0%-10.0% of Ti2AlNb and 90.0%-99.0% of TiAl alloy, wherein the TiAl alloy is composed of, by atomic percent, 45%-48.5% of Ti, 45%-48.5% of Al and 3%-5% of other alloy elements, the alloy elements are the combination of 2-4 elements of Cr, Nb, V, Mn, Mo and C, and the atomic percent of C in the TiAl alloy is smaller than or equal to 0.15%. The preparation method comprises the following steps of carrying out high-temperature heating treatment on a substrate before forming; and preparing by adopting a synchronous high-temperature heating and electromagnetic stirring assisted laser direct deposition method; According to the TiAl-based composite material and the preparation method, grain refinement of the material is achieved, the room-temperature plasticity is greatly improved, and the TiAl-based composite material and the preparation method have important significance in promoting development and application of the TiAl-based material in engine parts.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS
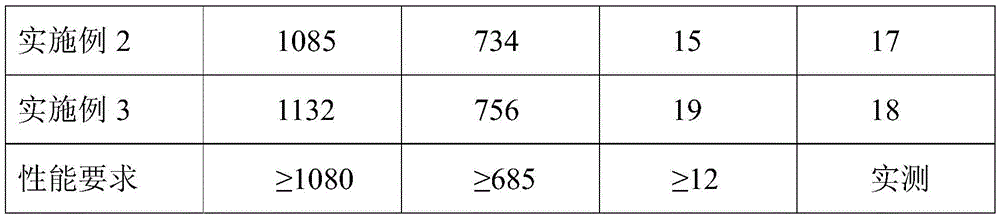
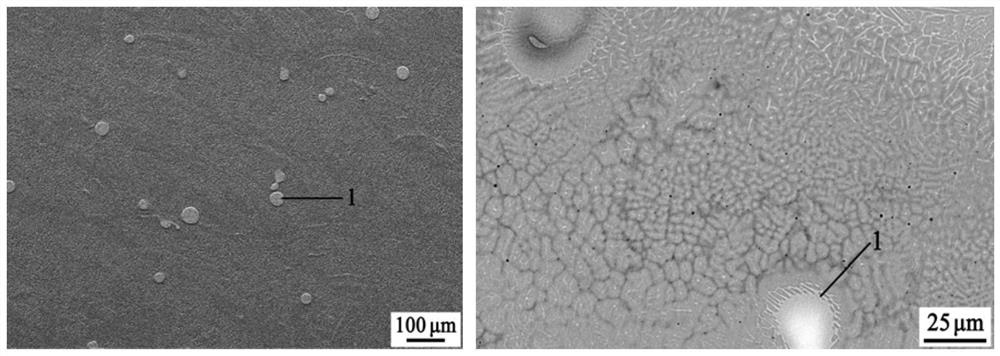
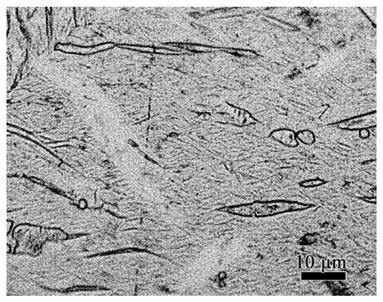
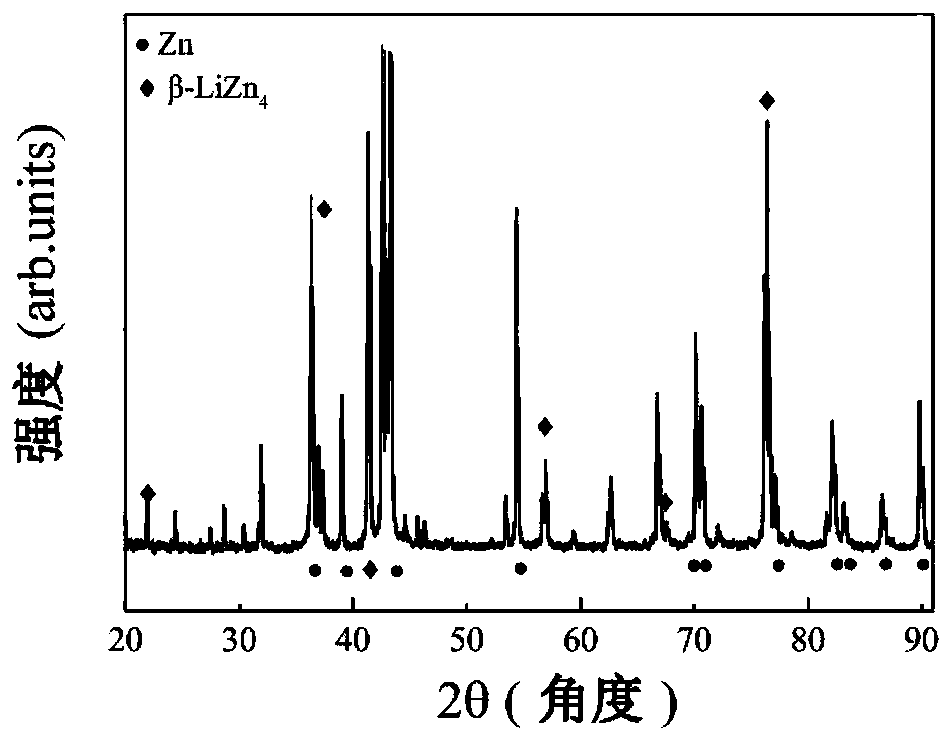
High-plasticity degradable LiZn4-X intermetallic compound and preparing method thereof
The invention discloses a high-plasticity degradable LiZn4-X intermetallic compound and a preparing method thereof. An X element is one or multiple of Cu, Mg, Ca, Sr, Mn, Fe, Ag, Co, Cr, Ti, Sn, Si, Se or Ge, and the balance is a beta-LiZn4 phase. Through a series of machining processes of vacuum melting preparing, heat treatment, plastic deforming and low-temperature aging, the intermetallic compound is modified, an alloy is subjected to high-temperature heat treatment, and is formed by a polycrystal and transgranular Zn+beta-LiZn4 lamellar structure multi-stage structure, the intermetallic compound is uniform in structure, the room-temperature tensile yield strength of the obtained intermetallic compound is 200 to 500 MPa, the tensile strength is 450 to 800 MPa, the ductility is 18 to 40%, the room-temperature compression yield strength is 500 to 800 MPa, the compressive strength is 1000 to 2000 MPa, the ductility is 15 to 45%, in simulated body fluid, degrading is uniform, the degrading rate is 0.008 to 0.5mm / y, contained elements are biosafety elements, poisonousness of L929 osteogenesis fiber cells and MG63 cells is lower than 2 levels, and use needs of multiple human implantable device materials can be met. The LiZn4-X intermetallic compound is excellent in property, uniform in degrading and good in biocompatibility.
Owner:北京尚宁科智医疗器械有限公司
Shielded cable and preparation method of magnesium alloy foil material in shielding layer of shielded cable
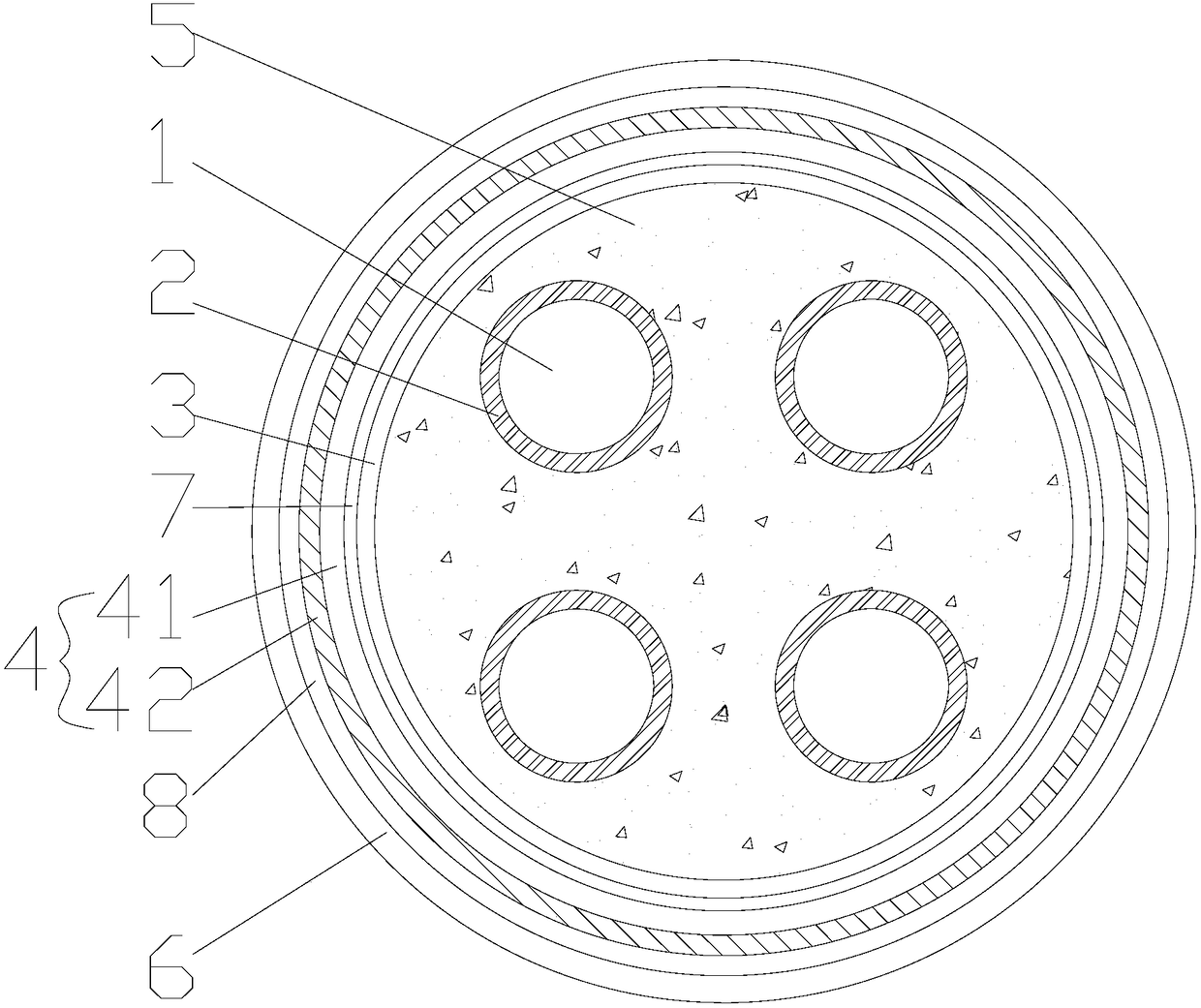
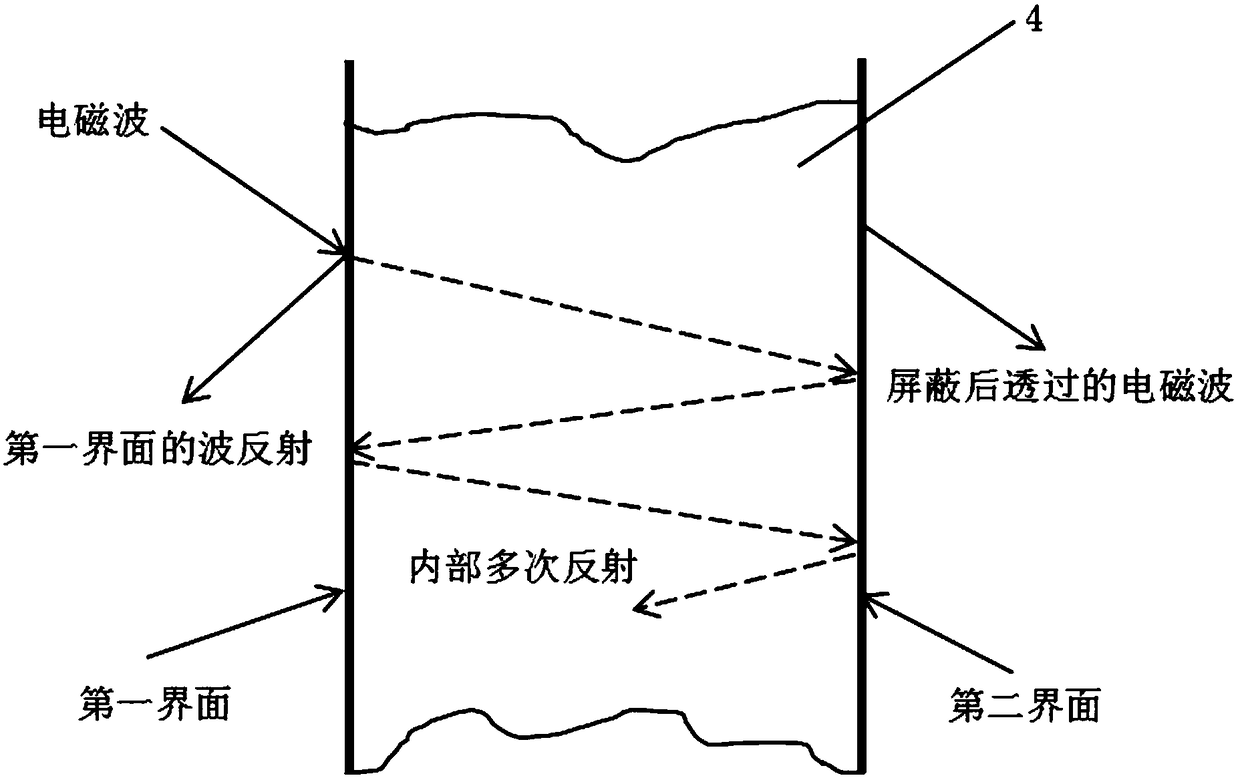
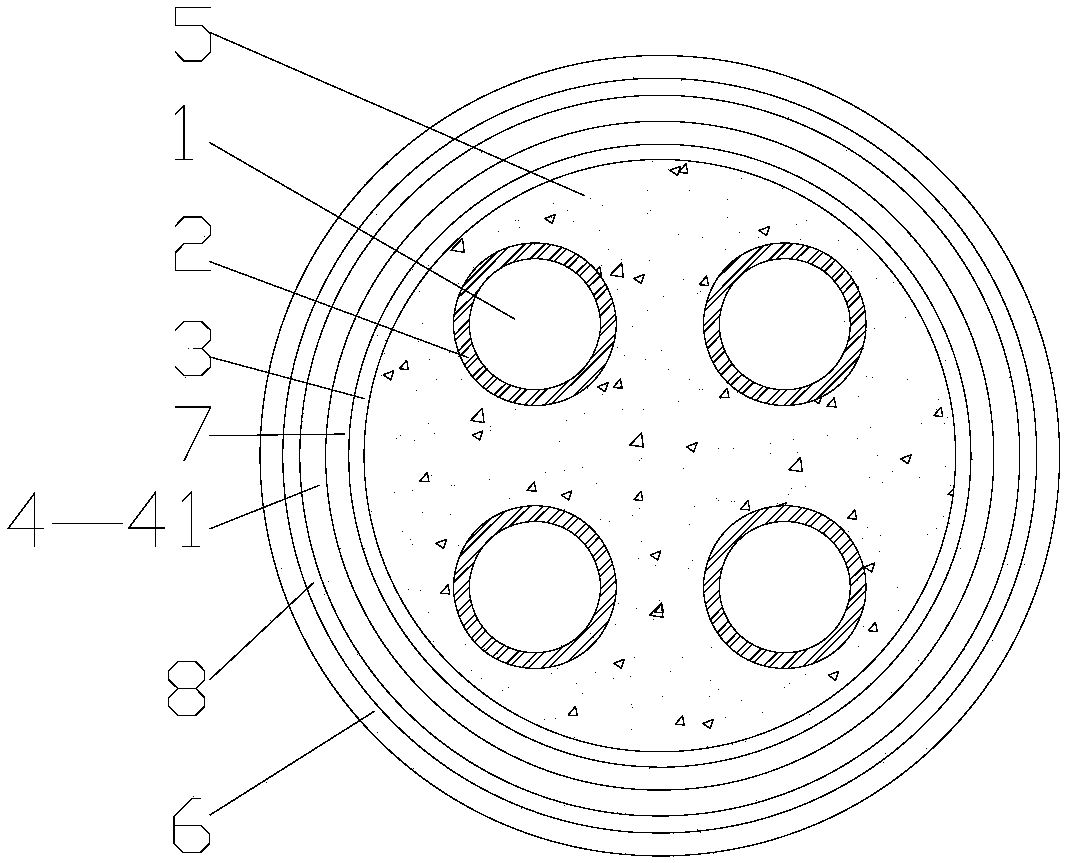
PendingCN108281227AReduce weightEasy constructionClimate change adaptationInsulated cablesShielded cableMetallurgy
The invention discloses shielded cables and particularly relates to a shielded cable and a preparation method of a magnesium alloy foil material in the shielding layer of the shielded cable. The shielded cable comprises at least one wire, wrapping layers, an inner protecting jacket, a shielding layer, an outer protecting jacket and a waterproof layer and is characterized in that one wrapping layerwraps each wire, the inner protecting jacket wraps the wrapping layers, the shielding layer wraps the inner protecting jacket, and the outer protecting jacket wraps the shielding layer; the shieldinglayer of a magnesium alloy shielding layer, and the waterproof layer is arranged between the inner protecting jacket and the shielding layer. The prepared shielded cable has the advantages that the shielded cable is simple in structure, lightweight, good in shielding effect, high in tensile strength, durable, resistant to corrosion and long in service life; the shielding layer is low in density,and the preparation process is simple, mature, and high in yield.
Owner:鞍山至镁科技有限公司
Ti2AlNb-based alloy bar and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN114262852AImprove tissue uniformityHigh strengthFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesIngotHeat conservation
The invention relates to the technical field of Ti2AlNb-based alloys, in particular to a Ti2AlNb-based alloy bar as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (A) carrying out homogenizing heat treatment on a Ti2AlNb-based alloy cast ingot at 1160-1200 DEG C to obtain a cast ingot blank; (B) carrying out heat preservation treatment at 1130-1170 DEG C, and then extruding and drawing out to obtain a primary bar blank; (C) carrying out heat preservation treatment on the primary bar billet at 1020-1060 DEG C, then cooling the primary bar billet to 500 DEG C or below along with the furnace, and discharging the primary bar billet; (D) carrying out heat preservation treatment at 960-980 DEG C, and then extruding and drawing out to obtain a secondary bar blank; and (E) the secondary bar blank is subjected to solid solution heat treatment and aging heat treatment, and the Ti2AlNb-based alloy bar is obtained. According to the method, the tensile strength, the ductility and the structure uniformity of the Ti2AlNb-based alloy bar are improved.
Owner:BEIJING CISRI GAONA TECH
Rapid extrusion aluminum alloy section with low rare earth content and preparation process thereof
The invention discloses a rapid extrusion aluminum alloy profile with low rare earth content and a preparation process thereof, and belongs to the technical field of metal materials. The aluminum alloy comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 0.8 to 1.2 percent of Mg, 0.7 to 1.2 percent of Si, 0.5 to 0.6 percent of Cu, 0.2 to 0.8 percent of Sc, 0.2 to 0.5 percent of Zr and the balance of aluminum. A trace or a small amount of rare earth element (Sc) is added into the aluminum alloy, so that the alloy cost is effectively reduced. The extrusion speed is higher than 5m / min, the extrusion production efficiency is high, the cost of the extrusion material is reduced, the surface of the obtained extrusion material is smooth and free of surface cracks, and the yield of the extrusion material is guaranteed; meanwhile, the obtained extruded material also possibly has a weak basal texture or a weak non-basal texture; and the room-temperature elongation of the extruded material can be greater than or equal to 8% through optimized components. Therefore, the method has good application and popularization prospects and can be applied to the low-cost civil fields such as electric buses and rail transit.
Owner:SHANDONG NANSHAN ALUMINUM
A kind of magnesium alloy with high electrical conductivity and high shielding effectiveness and preparation method thereof
The invention provides high-conductivity and high-shielding-effectiveness magnesium alloy and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of design of materials. The high-conductivity and high-shielding-effectiveness magnesium alloy is prepared from the following raw material components in percentage by mass: 0.5wt% to 3wt% of manganese, 0.1wt% to 0.5wt% of zirconium and the balance of pure magnesium and inevitable impurities. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly melting magnesium; adding magnesium-manganese intermediate alloy and magnesium-zirconium intermediate alloy; stirring, standing and then casting into a cast ingot; subsequently thermally homogenizing the cast ingot and rolling to obtain a corresponding plate. According to the preparation method disclosed by the invention, low-content magnesium-manganese intermediate alloy and magnesium-zirconium intermediate alloy are used for preparing novel high-conductivity and high-shielding-effectiveness wrought magnesium alloy; in comparison with an existing widely-used shielding material, the shielding material is low in cost, high in specific strength, higher than a traditional metal shielding material and a composite shielding material in specific shielding effectiveness, excellent in molding processability and applicable to the field of weight-sensitive electromagnetic protection.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Magnesium-aluminium-zinc alloy containing rare earth and its preparing method
The invention relates to metal plastic forming technology, in particular to a rare earth-containing magnesium-aluminum-zinc alloy and a corresponding preparation method thereof. The components and mass percentage of the material are: 2.0-6.0% aluminum, 0.3-1.5% zinc, 0.3-0.6% manganese, 0.1-0.5% rare earth, and the rest are magnesium and unavoidable trace impurities. The invention combines the alloying of rare earth elements and the plastic deformation process of equal channel angular extrusion, and has remarkable effects on the refinement of the microstructure of the magnesium alloy and the improvement of the strength and toughness of the material. The room temperature tensile strength of the magnesium alloy obtained by the preparation method is above 260MPa, and the normal temperature elongation is above 45%. The material prepared by the present invention has the characteristics of high strength and high plasticity, not only overcomes the shortcomings of low strength and low elongation of cast magnesium alloys, but also has a large plasticity compared with magnesium alloys prepared by conventional hot extrusion technology. improve. In addition, compared with the conventional hot extrusion process, the extrusion force required for forming by the preparation method is very low, thereby reducing the requirements for forming equipment.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Low-bursting-rate pure titanium seamless pipe for metal corrugated pipe and production process of low-bursting-rate pure titanium seamless pipe
PendingCN112044979AIncreased elongation at room temperatureUniform tissueRoll mill control devicesFurnace typesTitaniumPipe
The invention relates to a low-bursting-rate pure titanium seamless pipe for a metal corrugated pipe and a production process of the low-bursting-rate pure titanium seamless pipe The seamless pipe ischaracterized in that the seamless pipe has the grain size of 6-7 levels, the tensile strength Rm is larger than or equal to 300 MPa and smaller than or equal to 400 MPa, the yield strength Rp0.2 is larger than or equal to 180 MPa and smaller than or equal to 310 MPa, the ductility is larger than or equal to 50%, the wall thickness is uniform and is + / -5%t, the limit flaring rate is larger than orequal to 60%, and the bursting rate is smaller than or equal to 3%. According to the pure titanium seamless pipe prepared through the method, the grain size reaches the 6-7 levels, the room-temperature ductility reaches 50% or above, the wall thickness deviation is controlled to be + / -5%t, the limit flaring rate reaches 60% or above, and the bursting rate in subsequent corrugated pipe preparationcan be 3% or below.
Owner:宁夏中色金航钛业有限公司
Asphalt modifier and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108102281AHigh surface friction coefficientImprove low temperature performanceBuilding insulationsWeather resistanceCrack resistance
The invention belongs to the technical field of pavement composite materials, and provides an asphalt modifier and a preparation method thereof. The asphalt modifier comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 90-110 parts of a styrene-butadiene-styrene triblock copolymer (SBS), 8-15 parts of dimethicone, 12-30 parts of carbon black and 2-8 parts of silicon dioxide. The modifier cangreatly improve the weather resistance and the crack resistance of asphalt. The preparation method of the asphalt modifier comprises the following steps: (1), mixing the SBS, the dimethicone, the carbon black and the silicon dioxide, and then stirring to obtain a mixture; and (2), extruding the mixture at 160-190 DEG C according to a rotating speed of 20-120 r / min to obtain a cylindrical strip, then cooling, and then cutting into granules to obtain the asphalt modifier. The preparation method is simple, and can be widely applied to the field of asphalt roads, building waterproofing and the like.
Owner:中昊黑元化工研究设计院有限公司
Preparation method and application of a zinc-copper supersaturated solid solution vascular stent material
ActiveCN111154992BHas antibacterial propertiesAvoid infectionExtrusion control devicesProsthesisSolution treatmentCapillary Tubing
The invention discloses a preparation method of a supersaturated solid solution zinc-copper alloy and its application in the preparation of vascular stents, which belong to the field of metal material technology and biomedical materials. The invention obtains accurate The mass fraction is melted according to a certain mass fraction ratio, stirred or high-energy ultrasonic, cast into an alloy ingot, the alloy ingot is subjected to large plastic deformation, and finally the zinc-copper alloy after severe plastic deformation is subjected to solid solution treatment, and then taken out The microstructure of single-phase supersaturated solid solution can be obtained by rapid quenching and cooling in the medium, and finally the capillary tube made by drawing has fine grains and obvious reduction of the second phase.
Owner:SHANDONG RIENTECH MEDICAL TECH
A kind of high plasticity, low anisotropic deformation magnesium alloy plate and its preparation method
ActiveCN108796327BImprove mechanical propertiesEasy rolling deformationAnisotropic deformationUltimate tensile strength
The invention relates to the technical field of light metal materials, in particular to a high-plasticity and low-anisotropism deformed magnesium alloy plate and a preparation method thereof. The high-plasticity and low-anisotropism deformed magnesium alloy plate is composed of the following components of, by mass, 3.0-5.0% of Al, 0.3-0.6% of Mn, 0.1-0.9% of Y, 0.1-0.8% of Ca, 0.1-0.5% of Zn, andthe balance Mg and unavoidable impurities, wherein the content of the impurities is smaller than or equal to 0.3%. The prepared magnesium alloy plate has the high plasticity and low anisotropism at the room temperature, the basal texture strength is obviously weakened, and the comprehensive mechanical property is good.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
A kind of heat treatment method of nimonic101 nickel base alloy
The invention provides a heat treatment method for Nimonic101 nickel-based alloy. The heat treatment method for the Nimonic101 nickel-based alloy comprises the following steps that (1) solid solution heat treatment is conducted on a Nimonic101 nickel-based alloy forged piece, and the Nimonic101 nickel-based alloy forged piece is discharged out of a furnace and air cooled; (2) intermediate heat treatment is conducted on the air-cooled Nimonic101 nickel-based alloy forged piece at the temperature of 1020-1080 DEG C, heat preservation is conducted for 8-16 hours, and then the Nimonic101 nickel-based alloy forged piece is discharged out of the furnace and air cooled; and (3) aging heat treatment is conducted on the air-cooled Nimonic101 nickel-based alloy forged piece, and then the Nimonic101 nickel-based alloy forged piece is discharged out of the furnace and air cooled, so that the Nimonic101 nickel-based alloy is prepared. Compared with heat treatment methods which are frequently used at present, the heat treatment method can remarkably improve the indoor-temperature tensile strength and indoor-temperature yield strength and can also slightly improve the indoor-temperature ductility and indoor-temperature percentage of area reduction.
Owner:WUXI TURBINE BLADE
A small amount of multi-component high-strength plastic magnesium alloy and its preparation method with a large reduction and a short process
ActiveCN109504884BIncreased elongation at room temperatureEliminate solution treatment processFurnace typesRollsSolution treatmentManganese
The invention discloses a multi-component small-amount high-strength plasticity magnesium alloy and a large-rolling-reduction short-process preparation method thereof. The multi-component small-amounthigh-strength plasticity magnesium alloy is prepared from the chemical components in percentage by mass: 0.8-1.5% of zinc, 0.8-1.5% of tin, 0.08-0.4% of calcium, 0.08-0.8% of yttrium and the balanceof magnesium and an adding element. The adding element is one or more of zirconium, gadolinium and manganese, and the adding element is prepared from the components in percentage by mass: 0.05-0.2% ofzirconium, 0.05-0.2% of gadolinium and 0.05-0.3% of manganese. The large-rolling-reduction short-process preparation method of the alloy comprises three steps of sub-rapid solidification, rolling andannealing. A high solid solution casting-rolling blank is directly obtained, the single-pass or less-pass large press quantity deformation can be realized, solid solution processing and multi-pass rolling complex process before rolling of a conventional magnesium alloy are eliminated, the preparation process of a magnesium rolled plate is greatly shortened, the tensile strength of the obtained multi-component small-amount magnesium alloy rolled plate after annealing is greater than 250 MPa, the elongation is greater than 25%, the room-temperature mechanical property is excellent, no obvious edge cracking is caused, and the yield is high.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
A kind of Fe-Ni based casting superalloy and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108842082BGuaranteed StrengthImprove plastic toughnessMachines/enginesEngine componentsSuperalloyToughness
The invention discloses a nano TiC particle toughened Fe-Ni base cast superalloy for manufacturing a vehicular turbosupercharger. The nano TiC particle toughened Fe-Ni base cast superalloy comprises the following chemical components of, by mass percent, less than or equal to 0.10% of C, 11.00-16.00% of Cr, 34.00-45.00% of Ni, 4.00-8.00% of W, 1.80-2.40% of Al, 3.00-5.00% of Ti, 0.01-0.30% of TiC and the balance Fe. According to the nano TiC particle toughened Fe-Ni base cast superalloy for manufacturing the vehicular turbosupercharger, a nano TiC particle modificator is endogenously added to the nano TiC particle toughened Fe-Ni base cast superalloy for toughening a Fe-Ni base cast superalloy. The invention further provides a preparation method of the nano TiC particle toughened Fe-Ni basecast superalloy for manufacturing the vehicular turbosupercharger. A nano TiC iron base intermediate alloy is added to a Fe-Ni base superalloy melt, so that the endogenous nano TiC ceramic particle modificator toughened Fe-Ni base superalloy is obtained, and the plasticity and toughness of the Fe-Ni base cast superalloy are improved on the premise of ensuring the strength of the Fe-Ni base cast superalloy.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
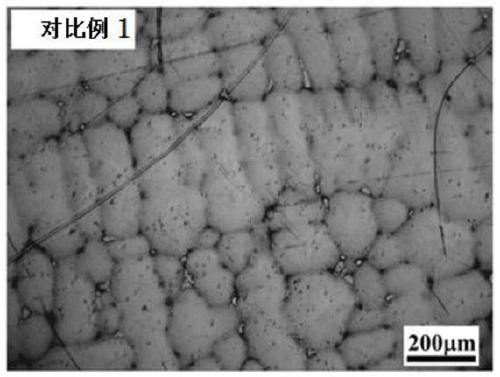
A kind of mg-mn deformed magnesium alloy and its preparation method
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
A kind of titanium alloy multiple solid solution aging heat treatment process
The invention relates to a repeated solid solution aging thermal treatment process of titanium alloy. The process includes the steps that a titanium alloy forge is subjected to heat preservation at the temperature T for t minutes, wherein T is larger than or equal to Tbeta-15 DEG C but smaller than or equal to Tbeta+15 DEG C, t is equal to eta*delta max, delta max is the maximum section thickness of the forge and is shown in millimeters, and eta is the heating coefficient and ranges from 0.2 min / mm to 0.8 min / mm; then the forge is discharged out of a furnace to be air-cooled or wind-cooled or water-cooled to be at the room temperature, then the cooled forge is subjected to heat preservation at the temperature of T for t minutes, wherein T is larger than or equal to Tbeta-25 DEG C but smaller than or equal to Tbeta-50 DEG C, the computational formula of t is as above, namely t=eta*delta max, and the heating coefficient eta ranges from 0.3 min / mm to 1.2 min / mm; then the forge is discharged out of the furnace to be air-cooled or wind-cooled or water-cooled to be at the room temperature, the cooled forge is subjected to heat preservation at the temperature T ranging from 540 DEG C to 600 DEG C, and the heat preservation time t ranges from 0.5 hour to 2 hours; the forge is discharged out of the furnace to be air-cooled to be at the room temperature, the cooled forge is subjected to heat preservation at the temperature T ranging from 400 DEG C to 540 DEG C, and the heat preservation time t ranges from 4 hour to 24 hours; and then the forge is discharged out of the furnace to be air-cooled to be at the room temperature. The repeated solid solution aging thermal treatment process of the titanium alloy is suitable for thermal treatment of near-beta type, metastable beta type and steady beta type ultrahigh-toughness titanium alloy so as to obtain required microscopic structures with high overall performance and multi-scale precipitated phases mixed.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS
High-strength high-toughness AZ91 magnesium alloy strip eletrotoughening process method and system
The invention discloses an electro-strengthening and toughening processing method of a belt material of AZ91 magnesium alloy and a system thereof. The electro-strengthening and toughening processing method comprises following steps: when the belt material of magnesium alloy is transmitted at a certain speed which is driven by a roller on an electro plastic rolling machine, high-energy impulse current that is output by an impulse power source through an electrode is input into an electriferous region section of the moving belt material of magnesium alloy, and the Joule heating effect and the non-heating effect are generated in the electriferous region section, thus causing the phase transition of internal microscopic constitution from bulky lath-shaped Beta-Mg17Al12 that are gathering and agglomerating in an initial state to Beta-Mg17Al12 particles that are evenly distributed and approximately sphere-shaped, or causing the solid solution effect that leads Beta-Mg17Al12 to be dissolved in a substrate; the processed belt material can be naturally air cooled at room temperature. The electro-strengthening and toughening processing method of the belt material of AZ91 magnesium alloy hasshort processing time and high production efficiency, and simultaneously avoids the high-temperature oxidation of the magnesium alloy. After the electro-strengthening and toughening processing, the microscopic constitution of the belt material of magnesium alloy can be remarkably improved, the unit extension of the microscopic constitution is increased from 11.8 percent in the initial aging stateto over 20 percent, and the tensile strength of the microscopic constitution is not dramatically lowered.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com