Patents
Literature
100 results about "Metal semiconductor field effect transistors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
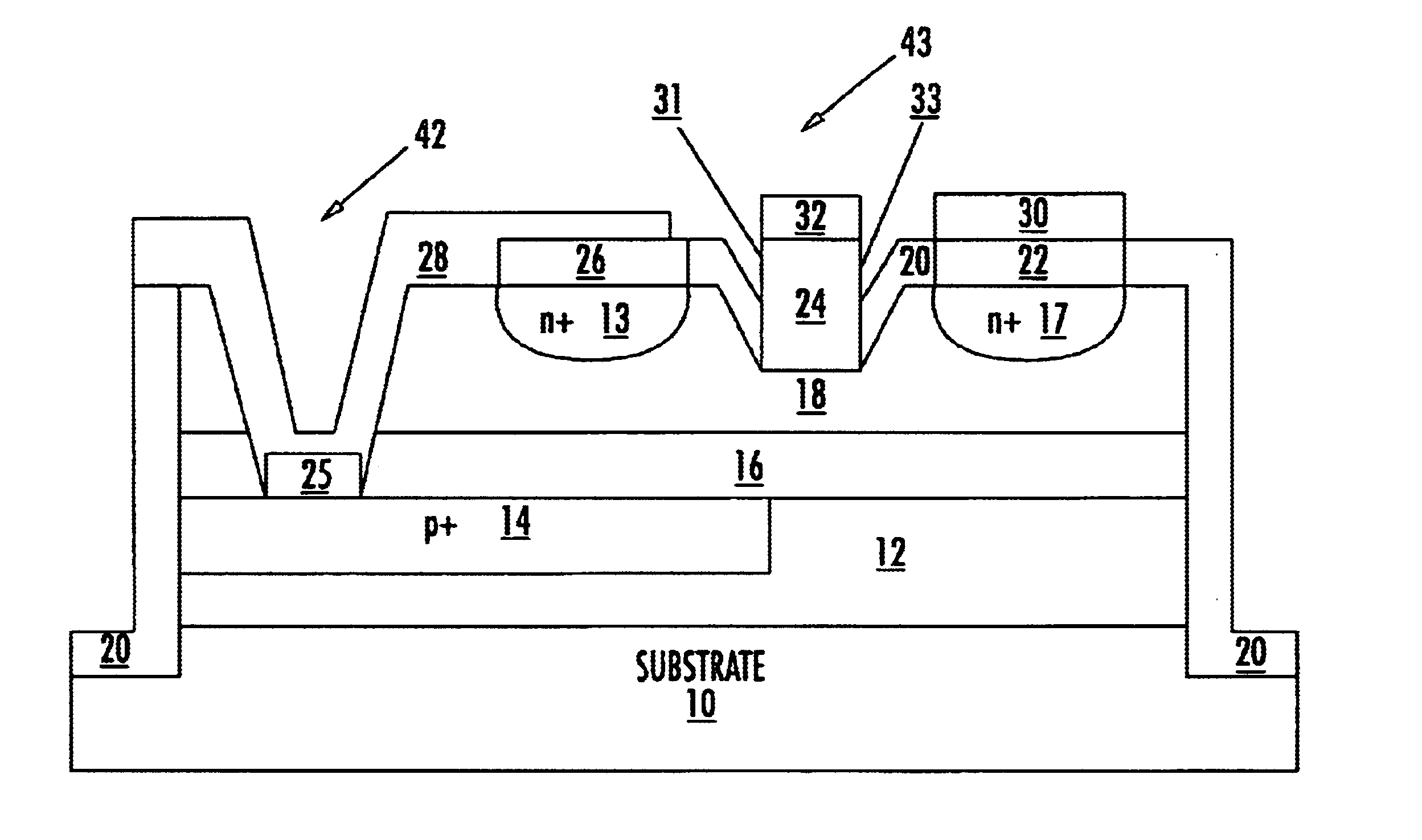
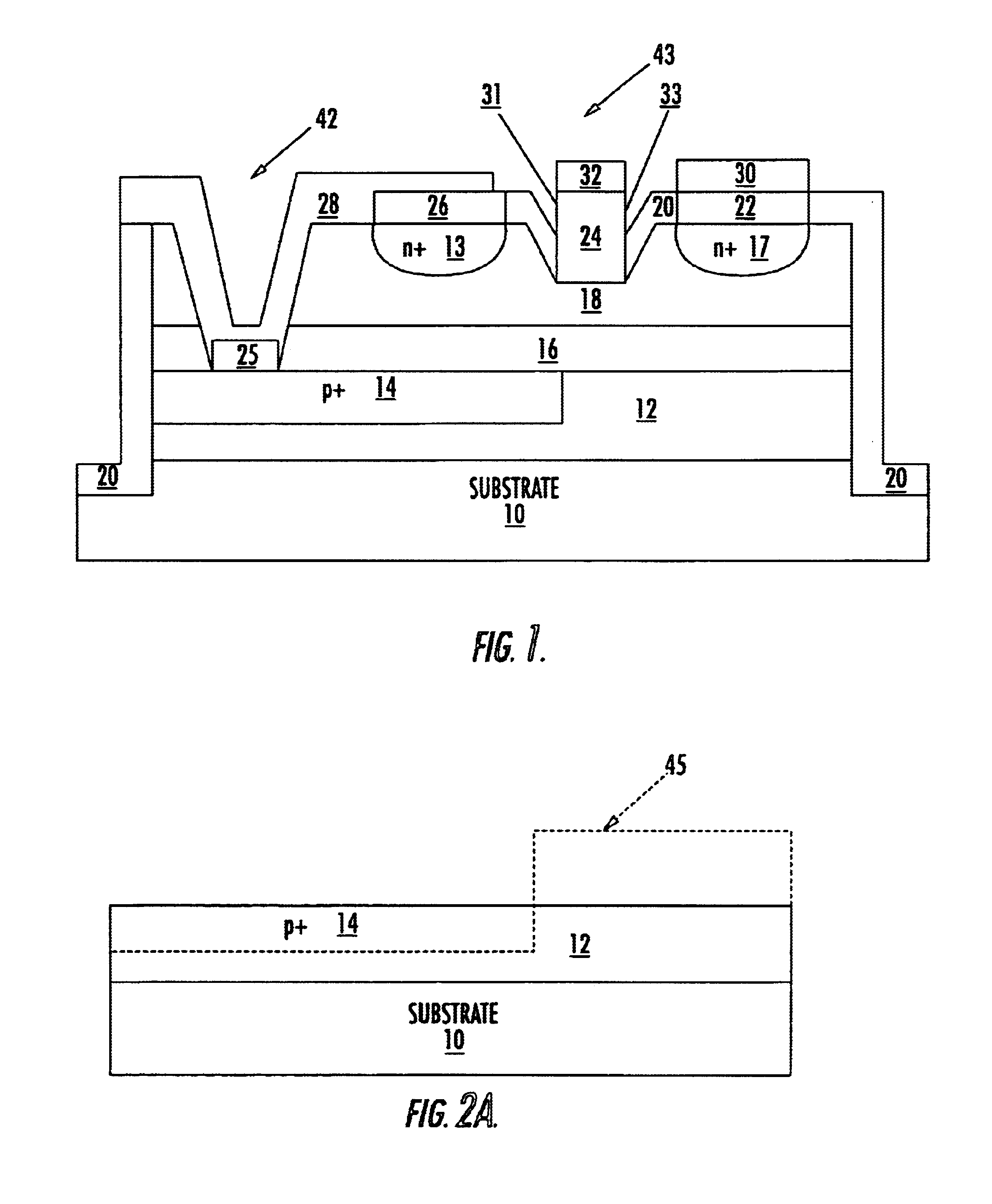
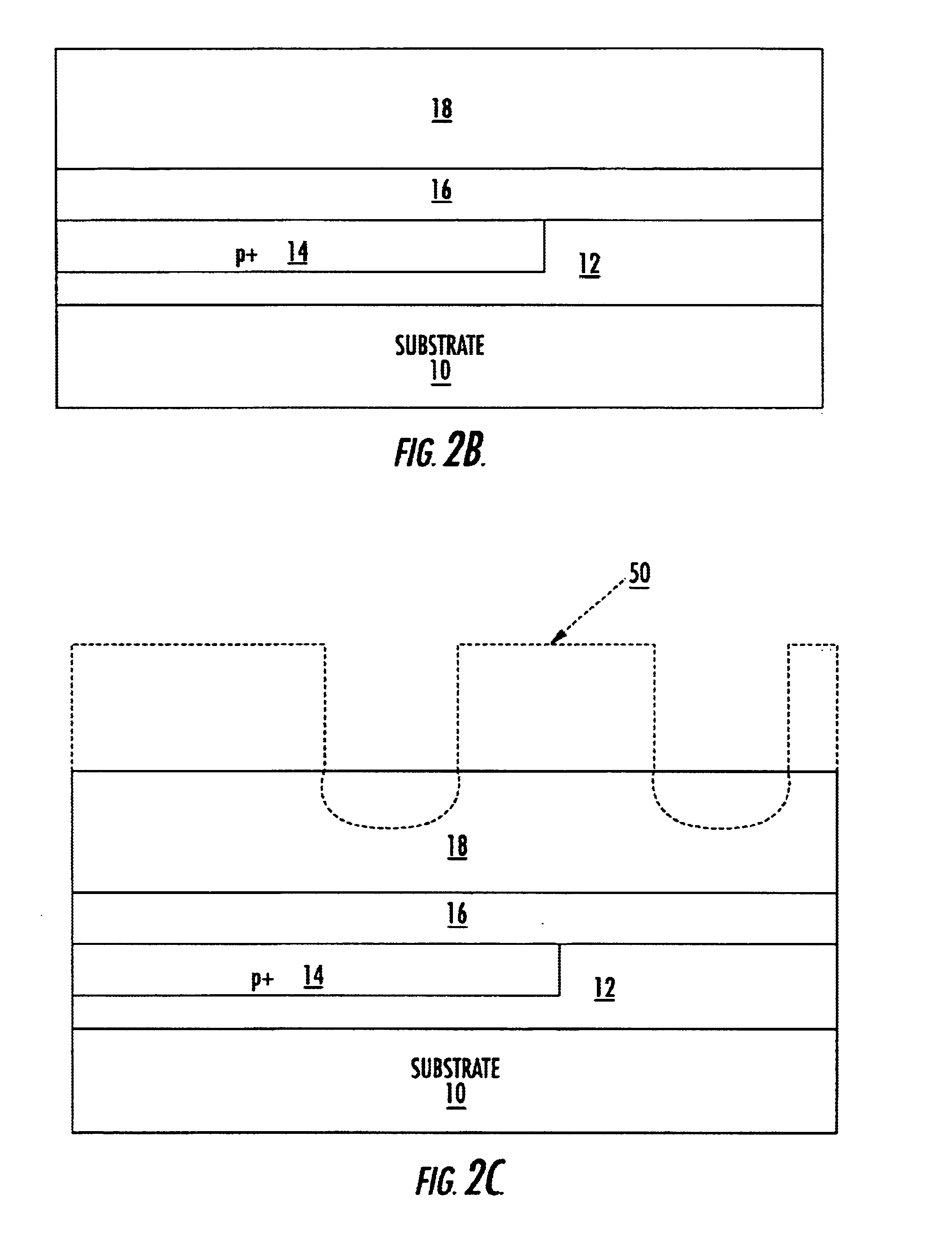
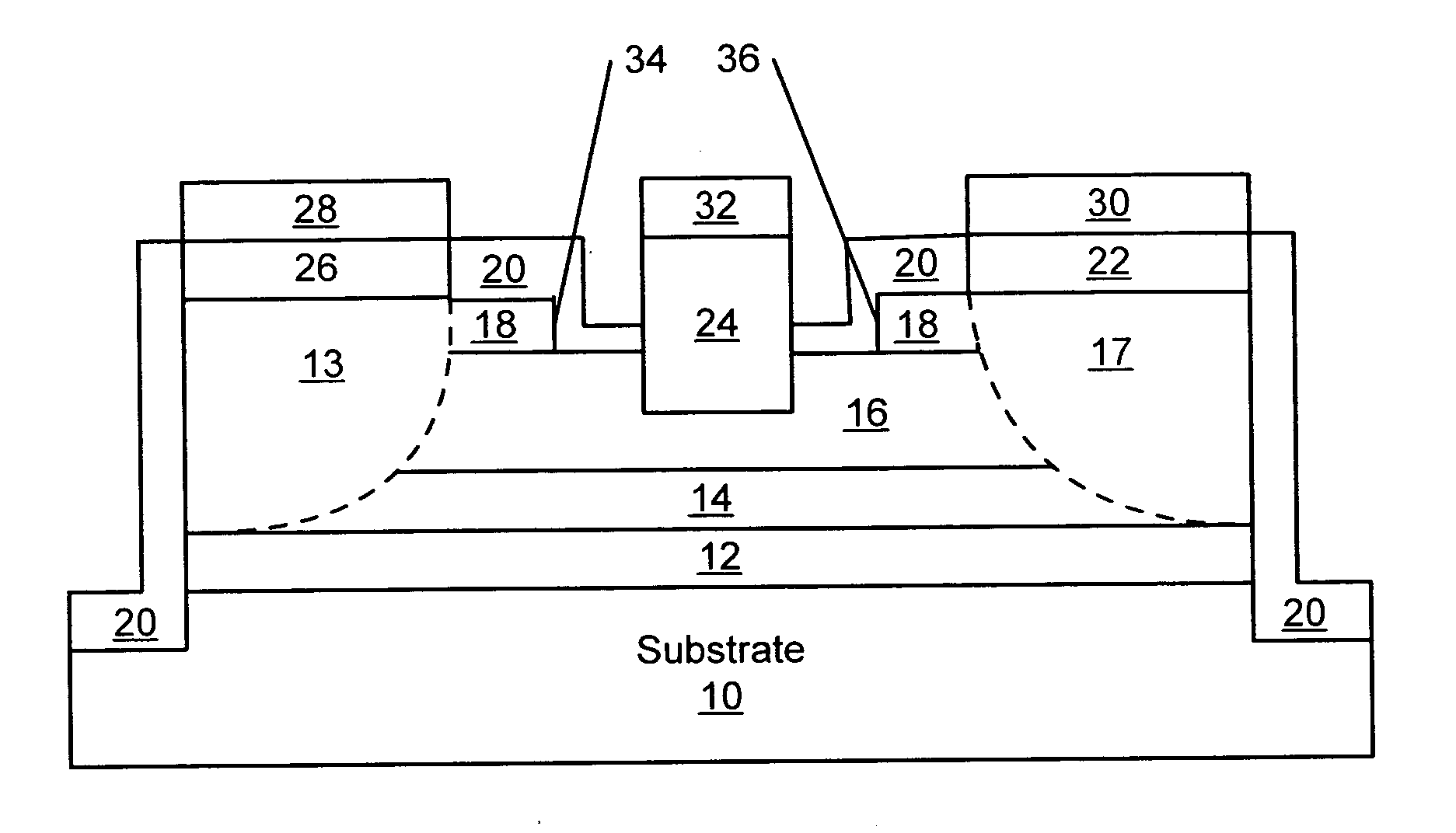
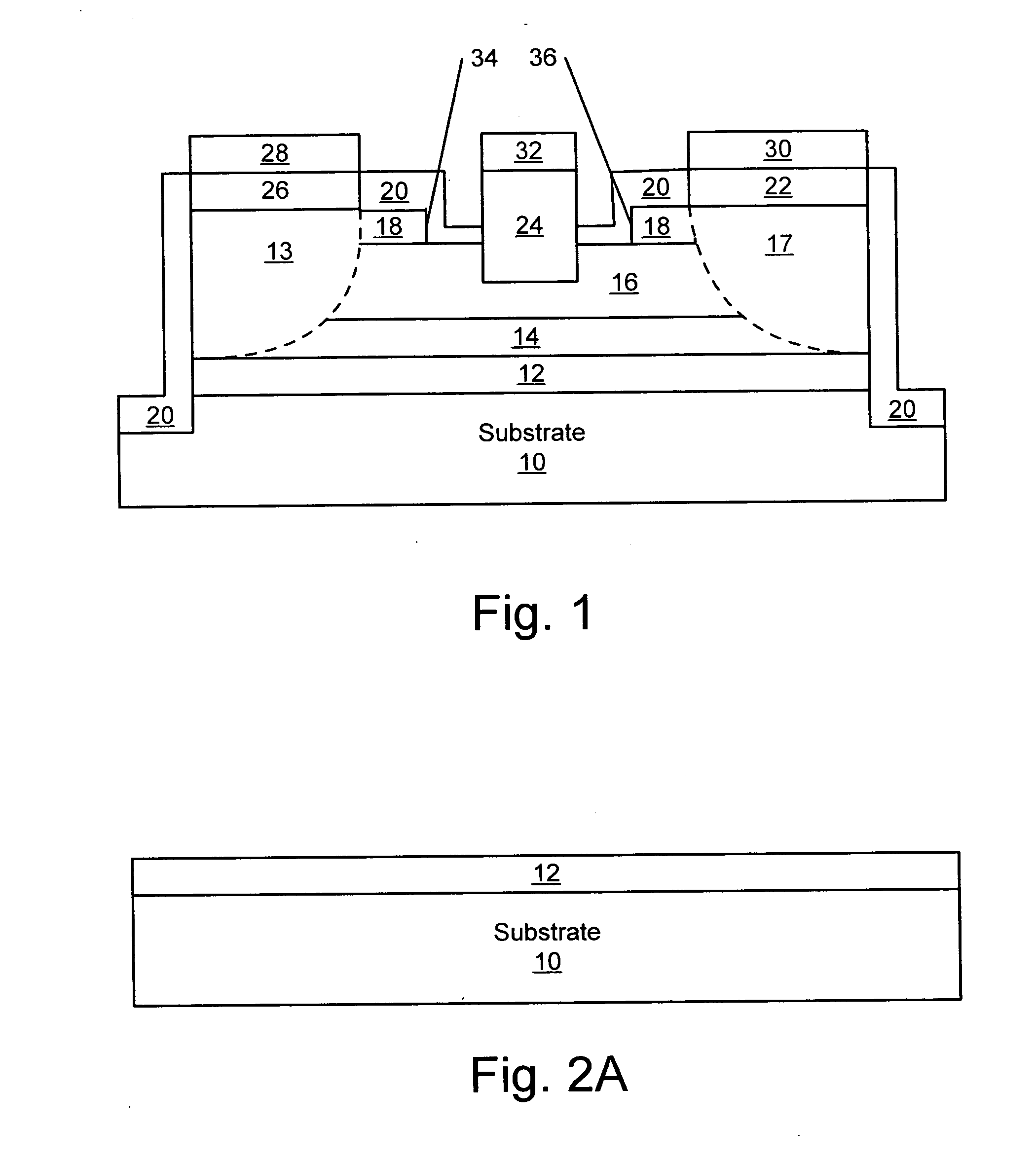
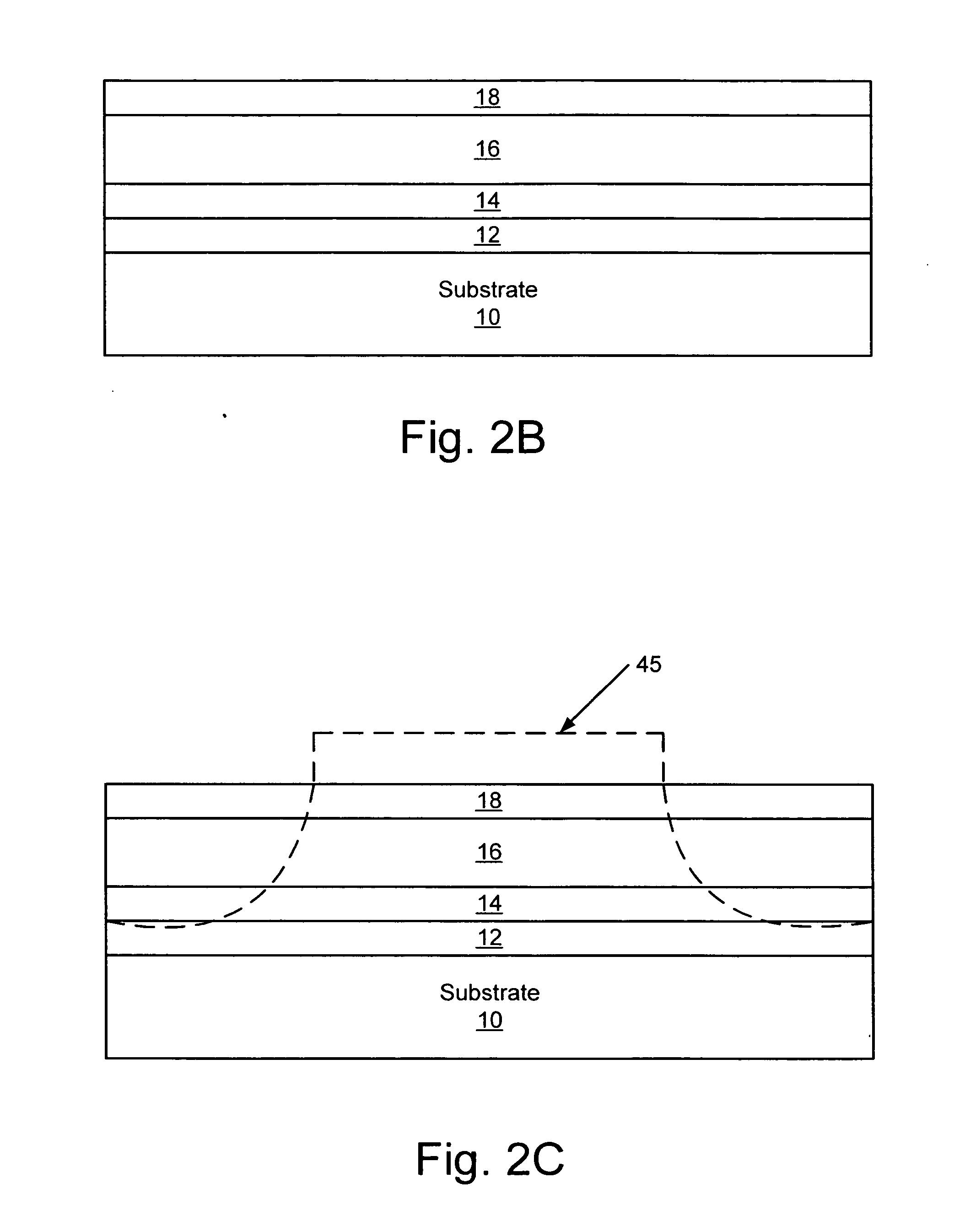
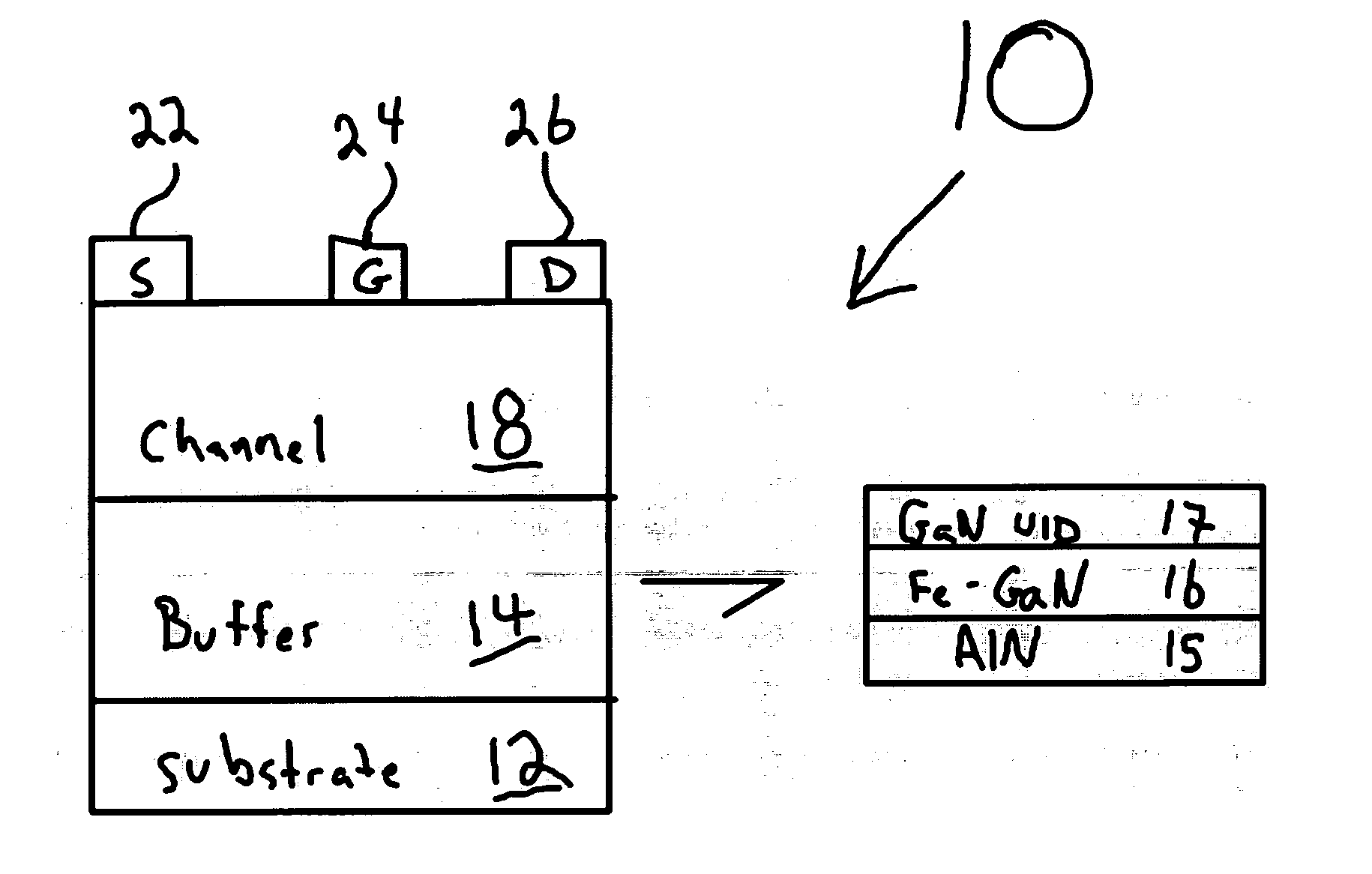
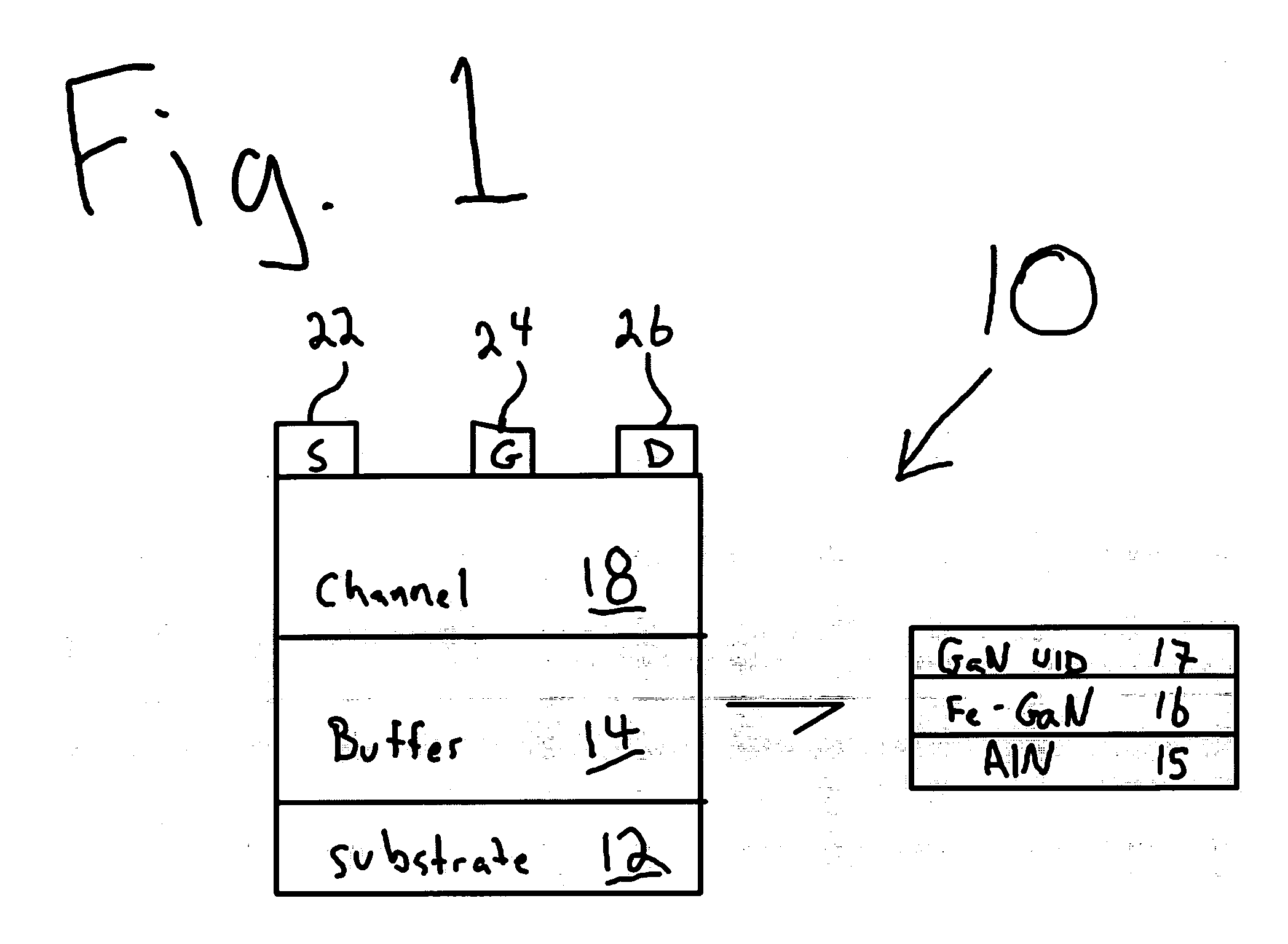
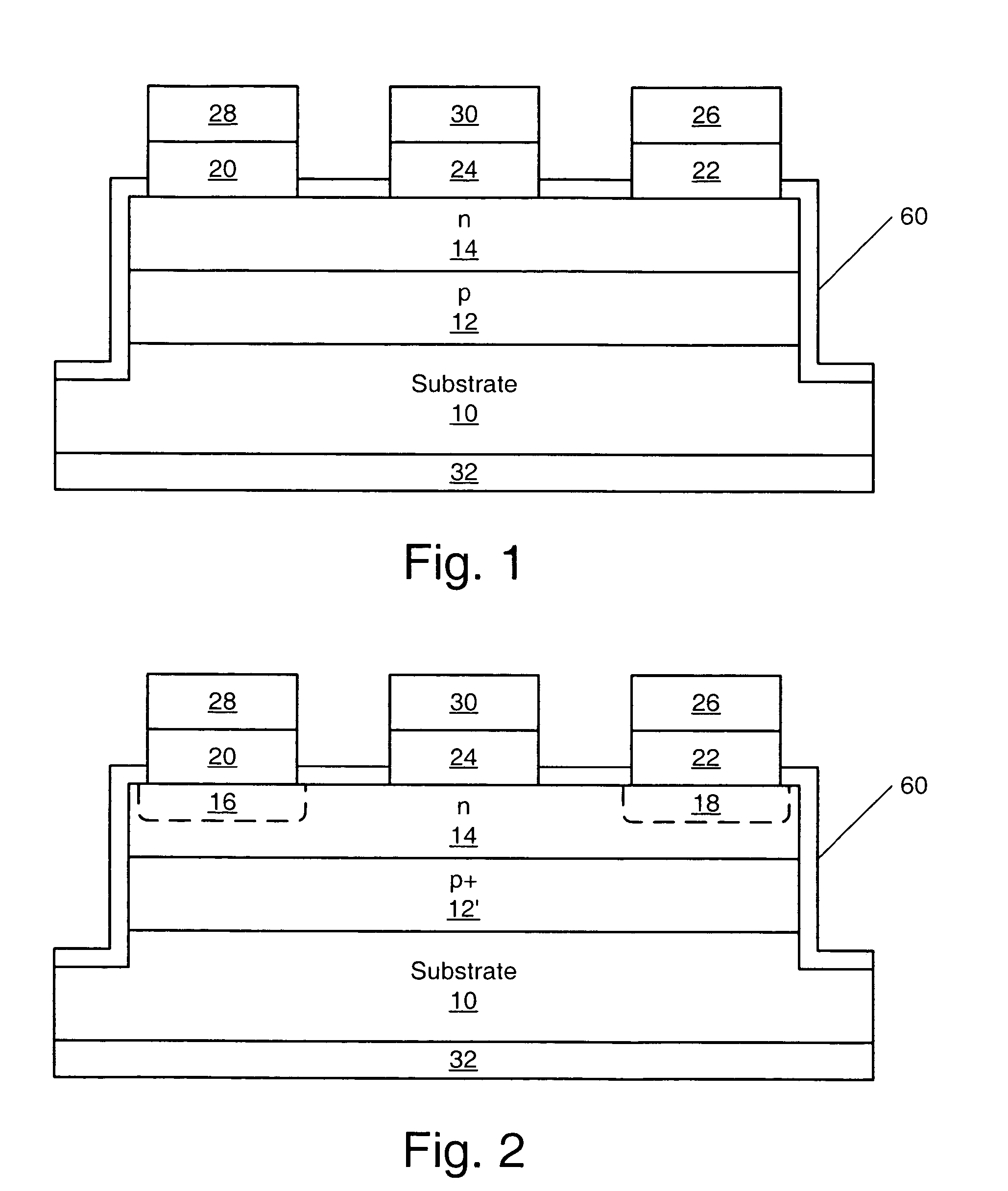
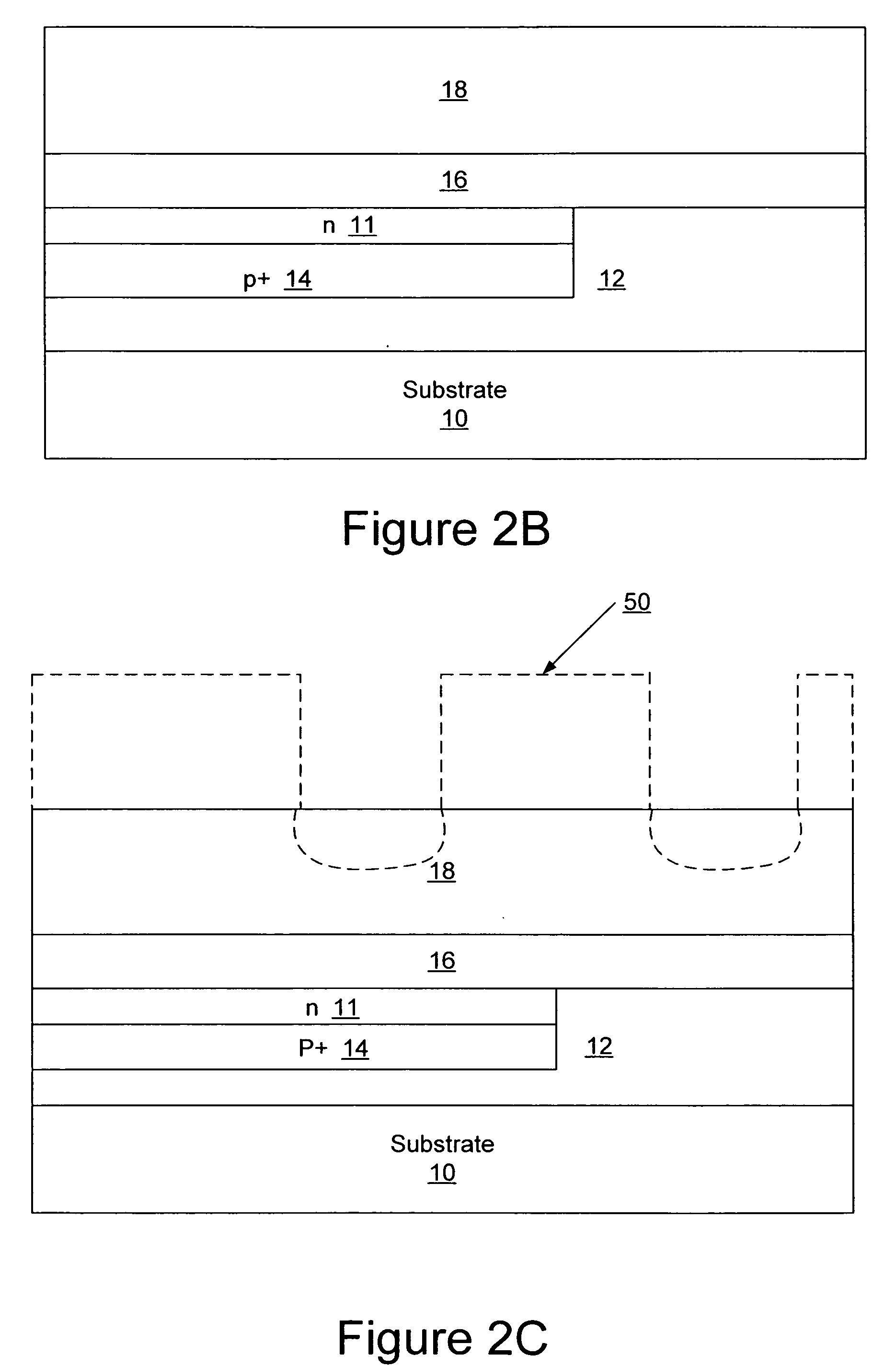
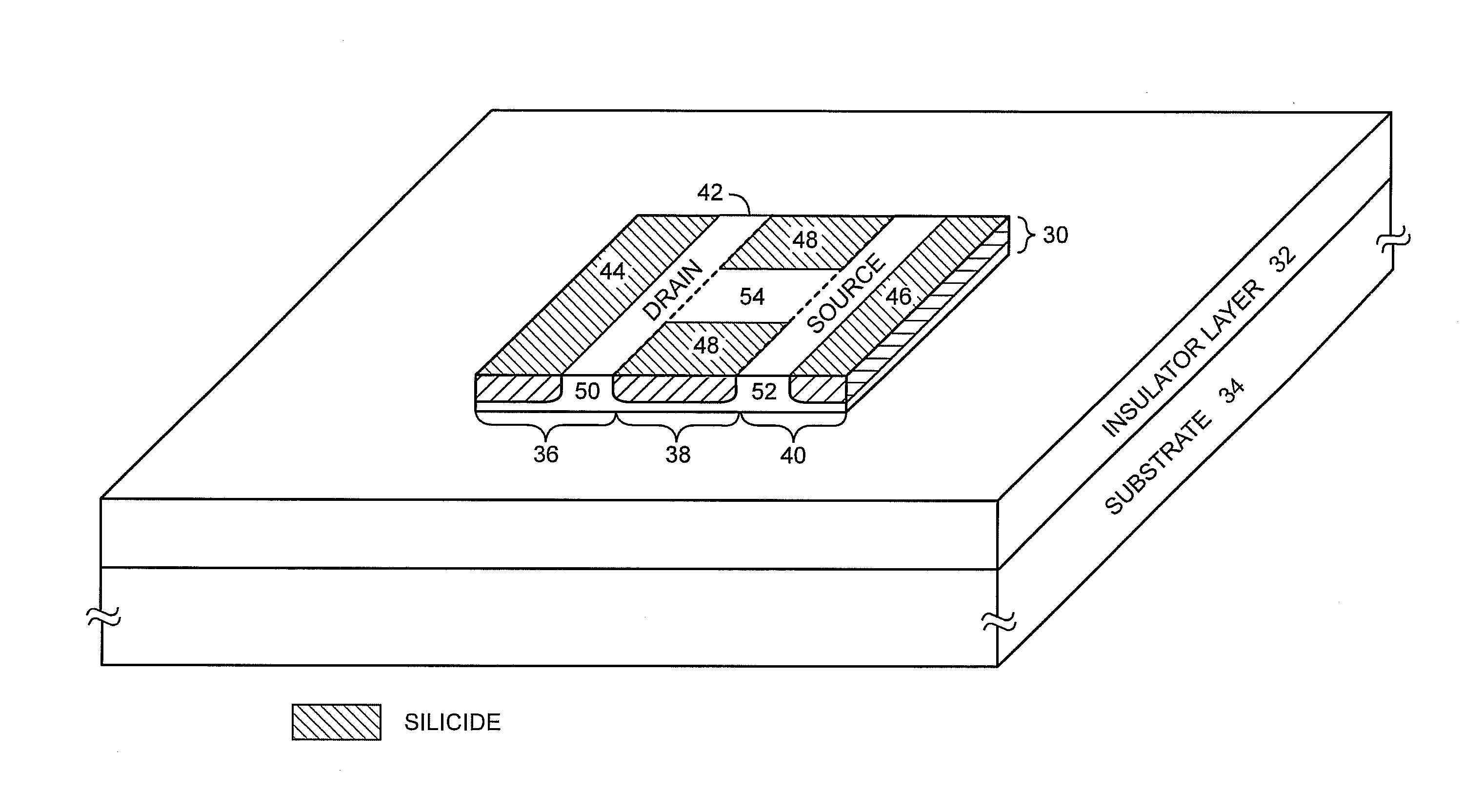
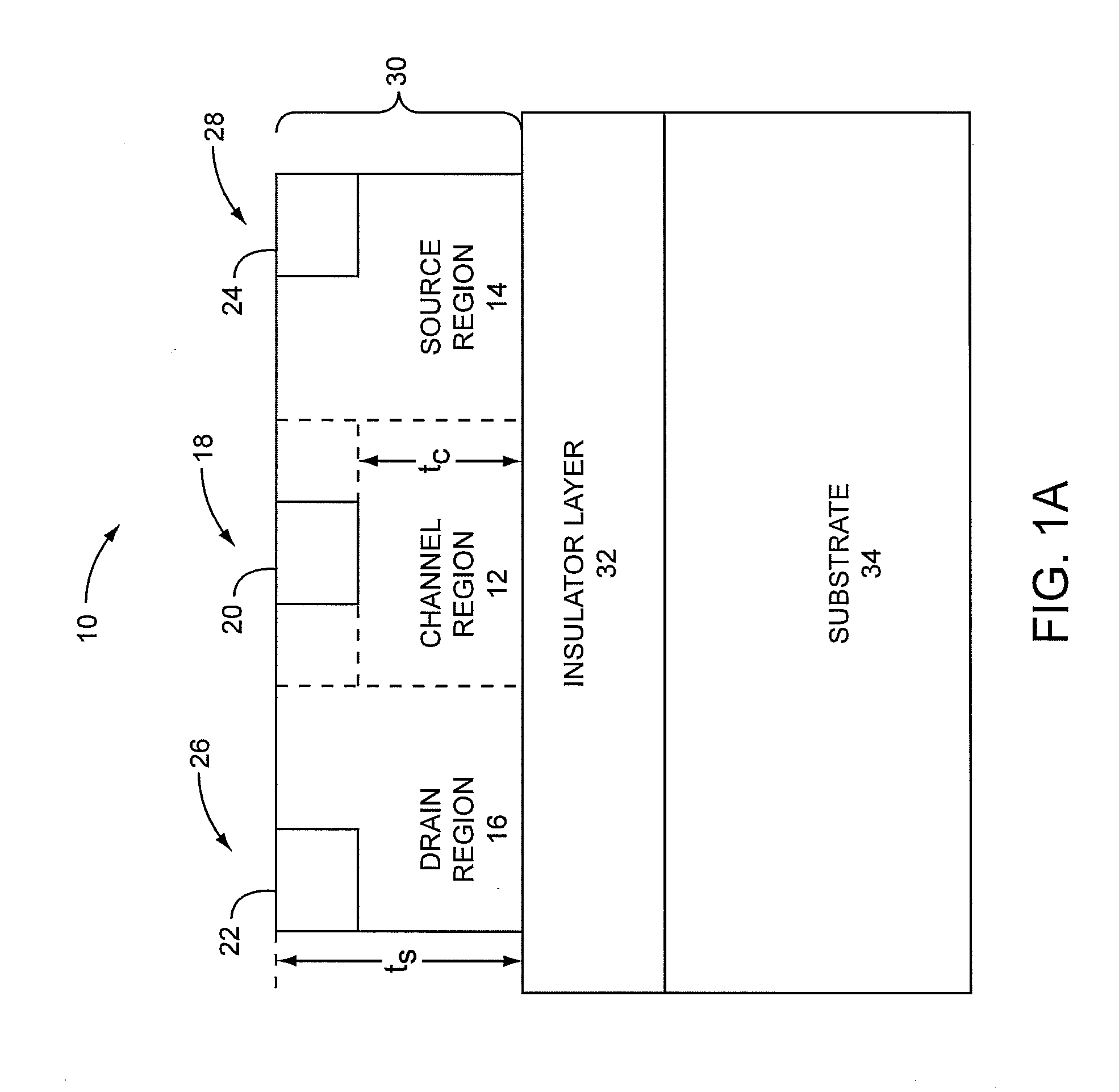
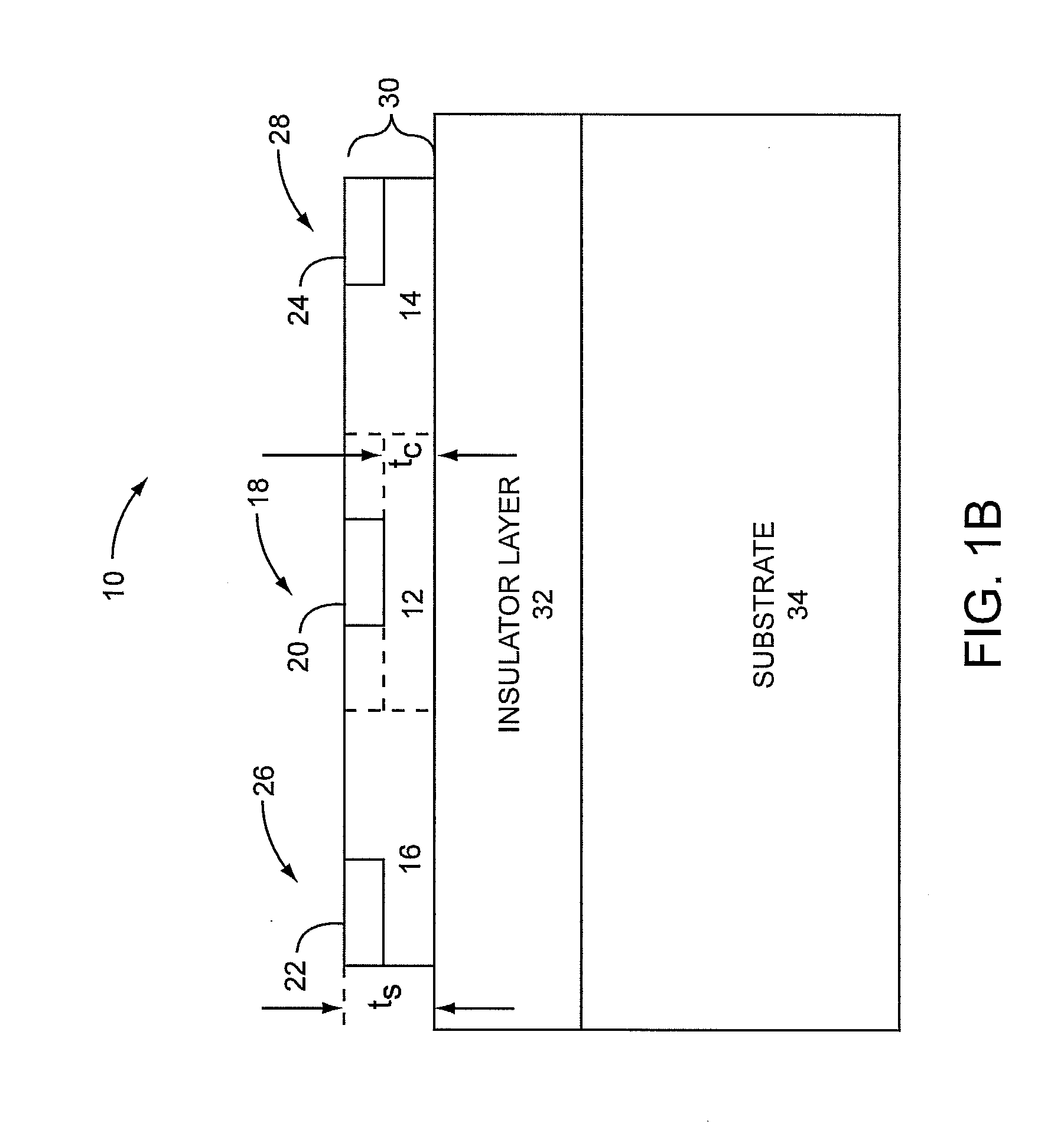
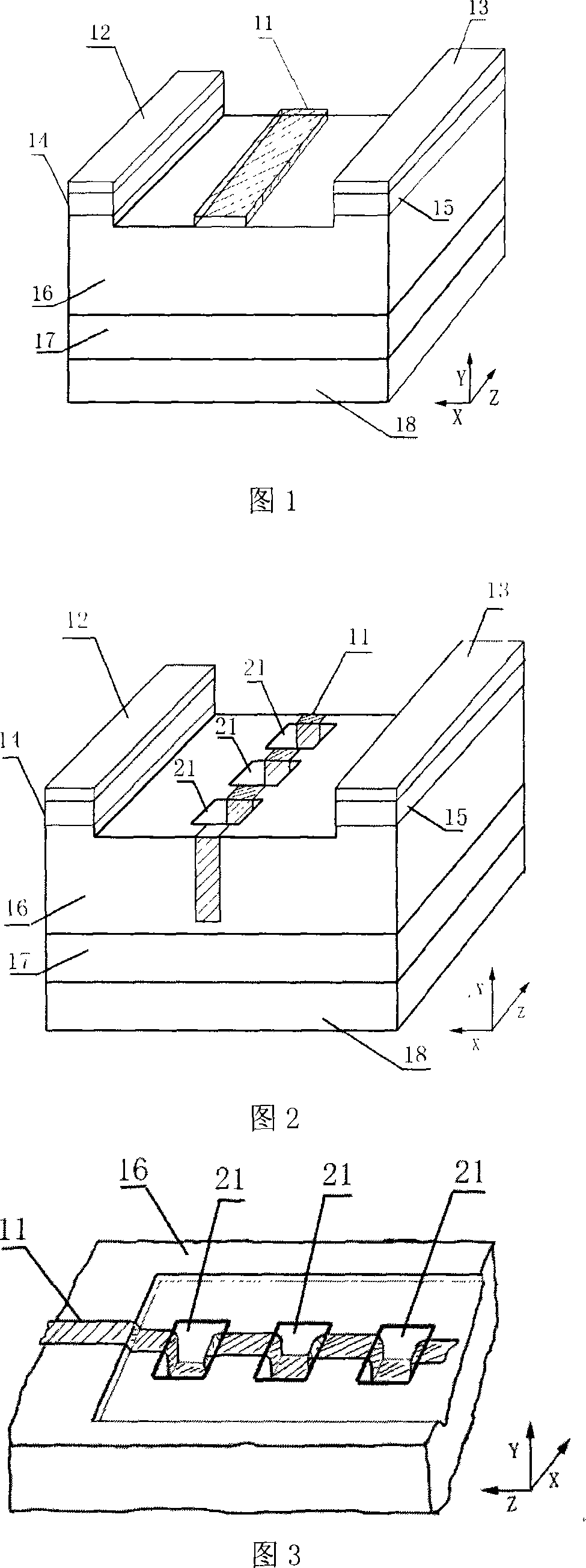
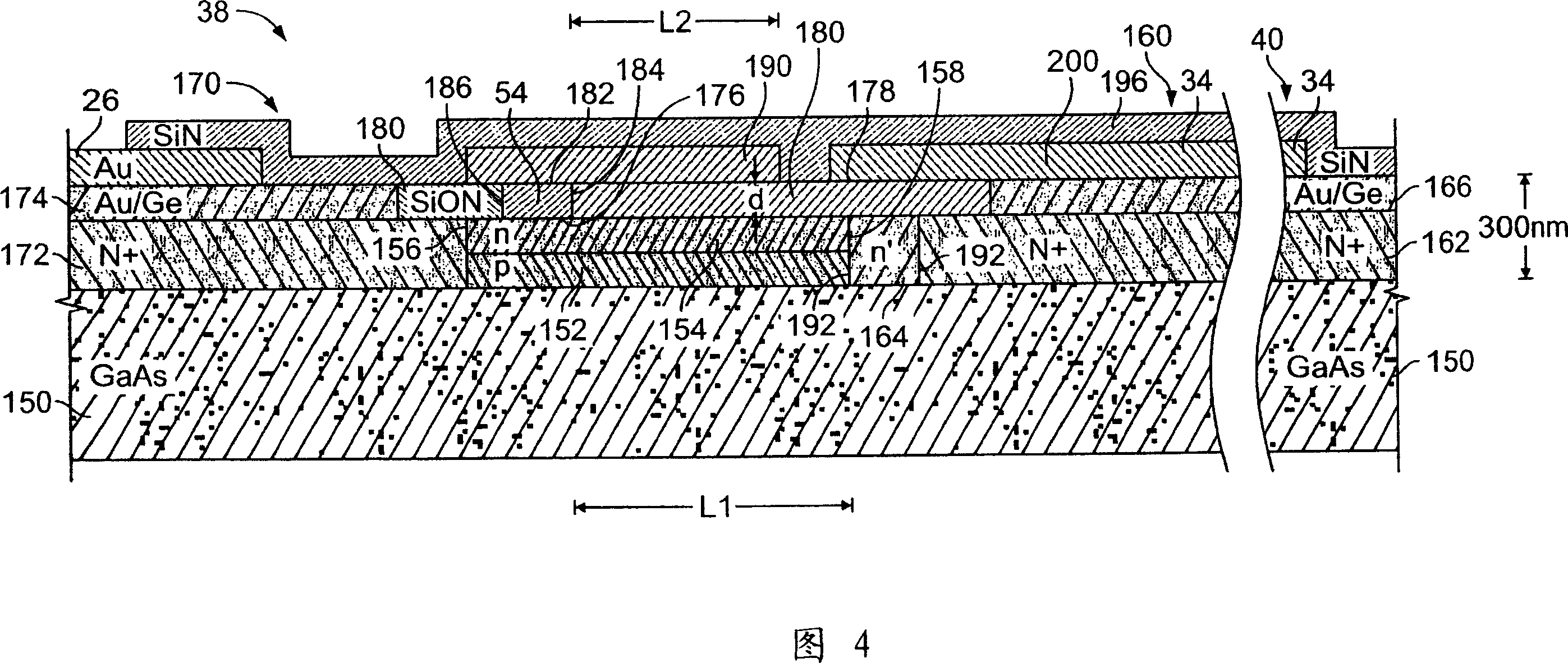
Metal-semiconductor field effect transistors (MESFETs) having drains coupled to the substrate and methods of fabricating the same
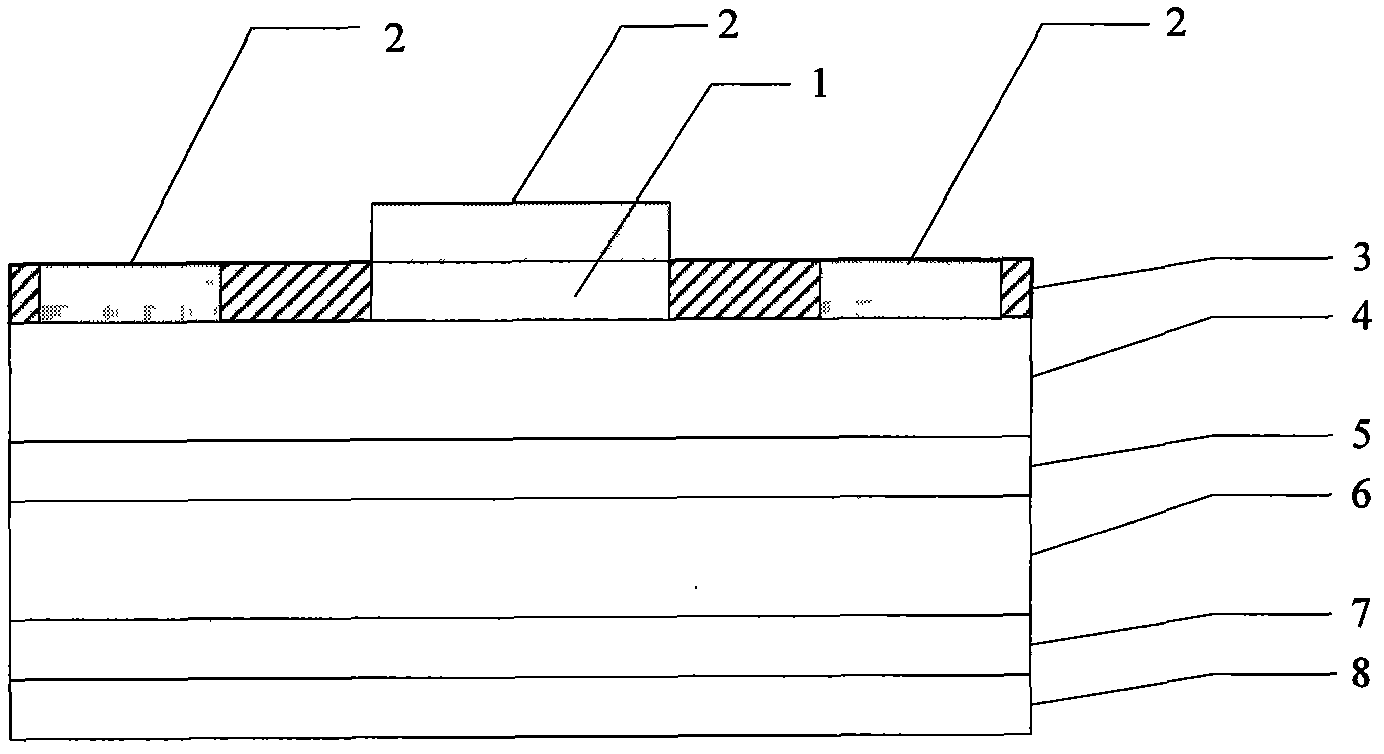
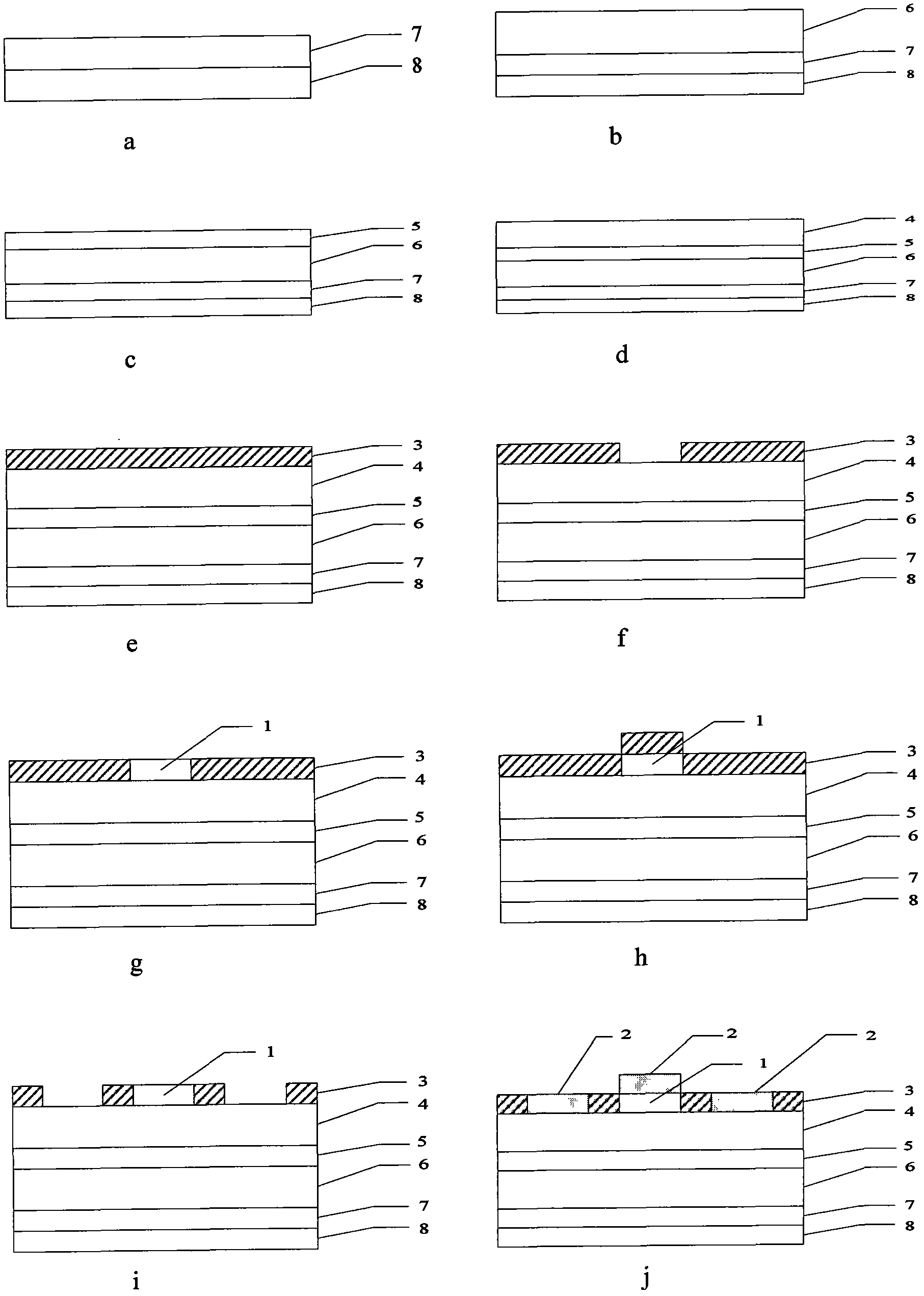
The present invention provides a unit cell of a metal-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MESFET). The unit cell of the MESFET includes a MESFET having a source region, a drain region and a gate contact. The gate contact is disposed between the source region and the drain region. The drain region is electrically coupled to the substrate through a contact via hole to the substrate. Related methods of fabricating MESFETs are also provided herein.
Owner:CREE INC
Thin film semiconductor device and method of manufacturing a thin film semiconductor device
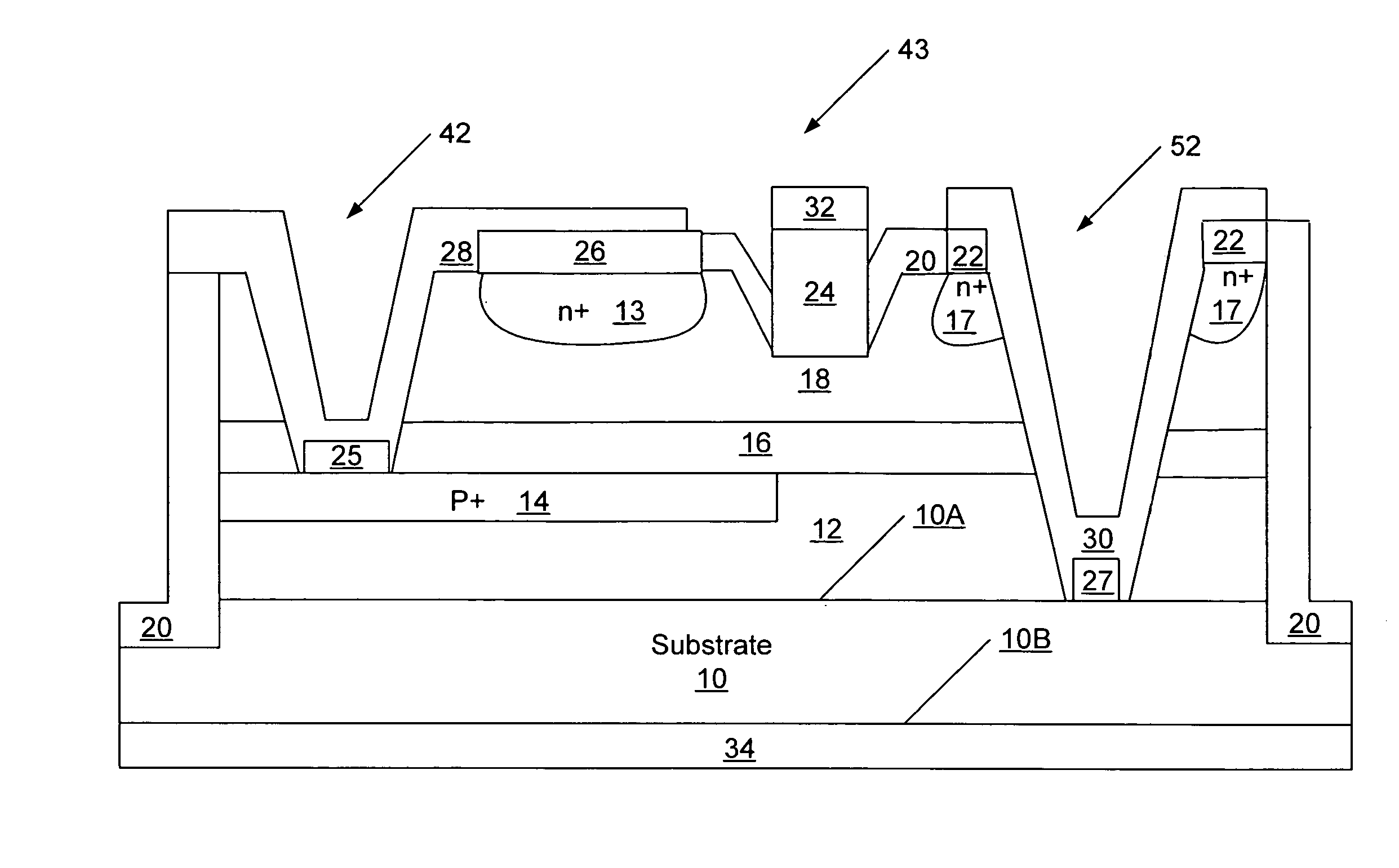
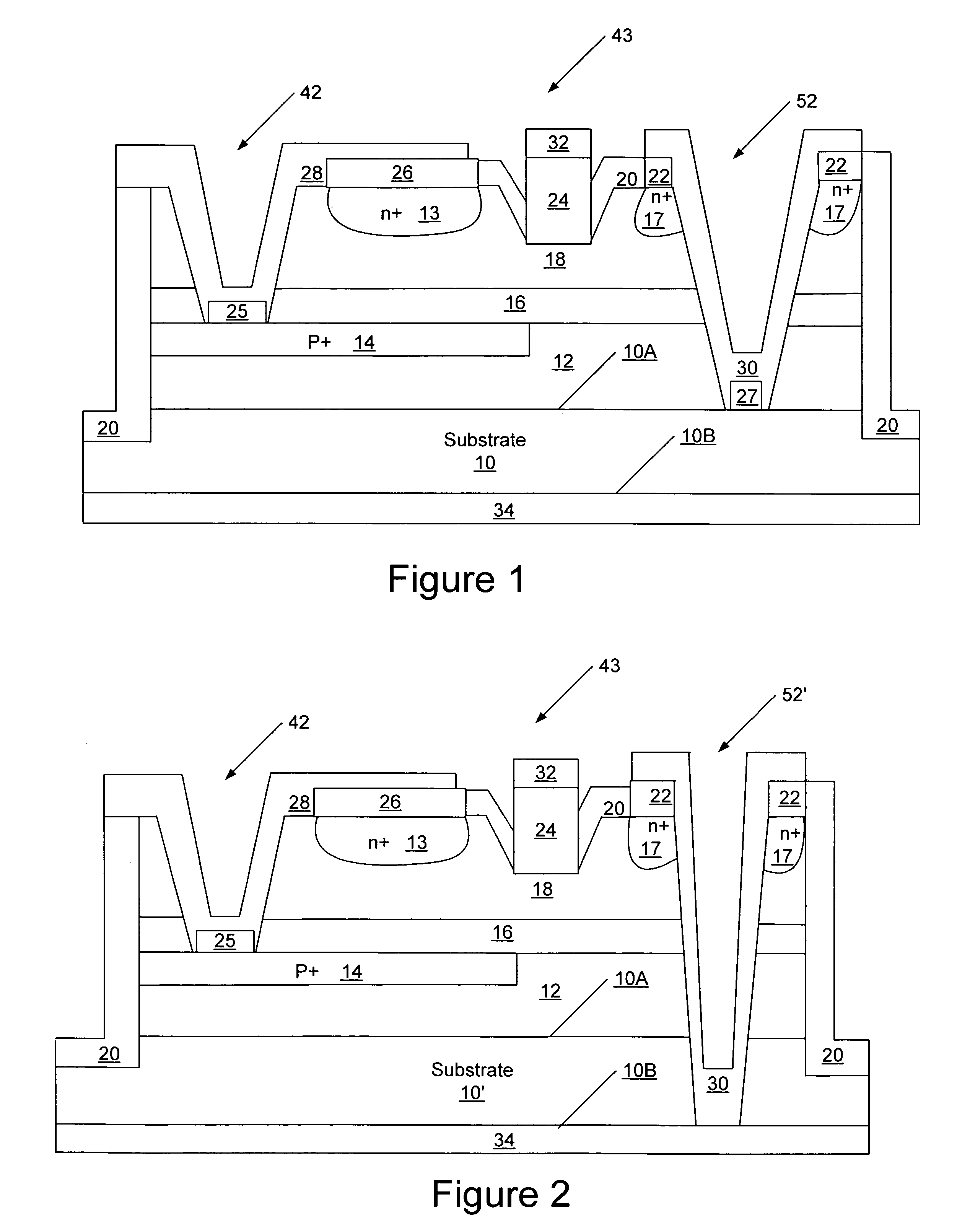
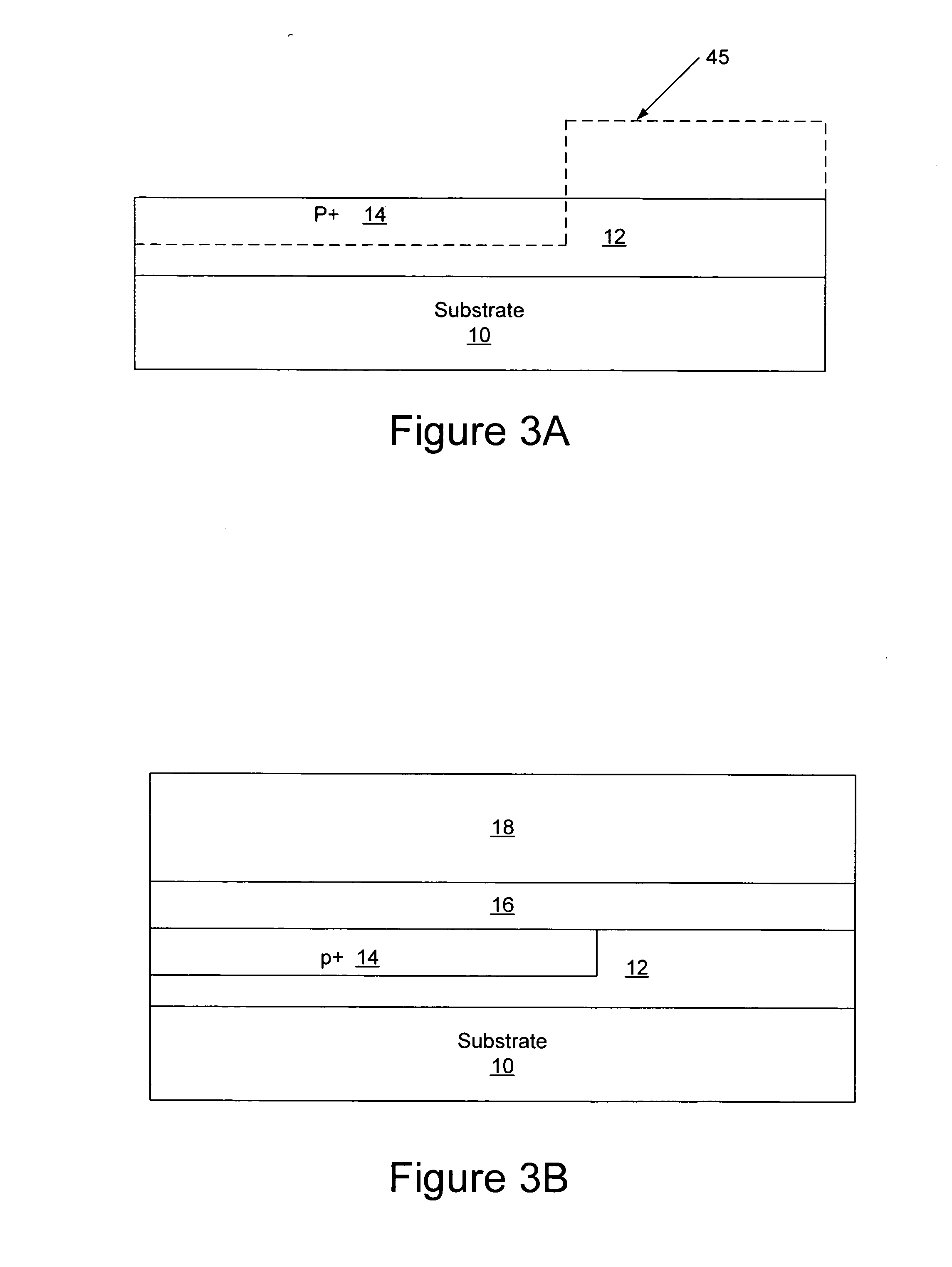
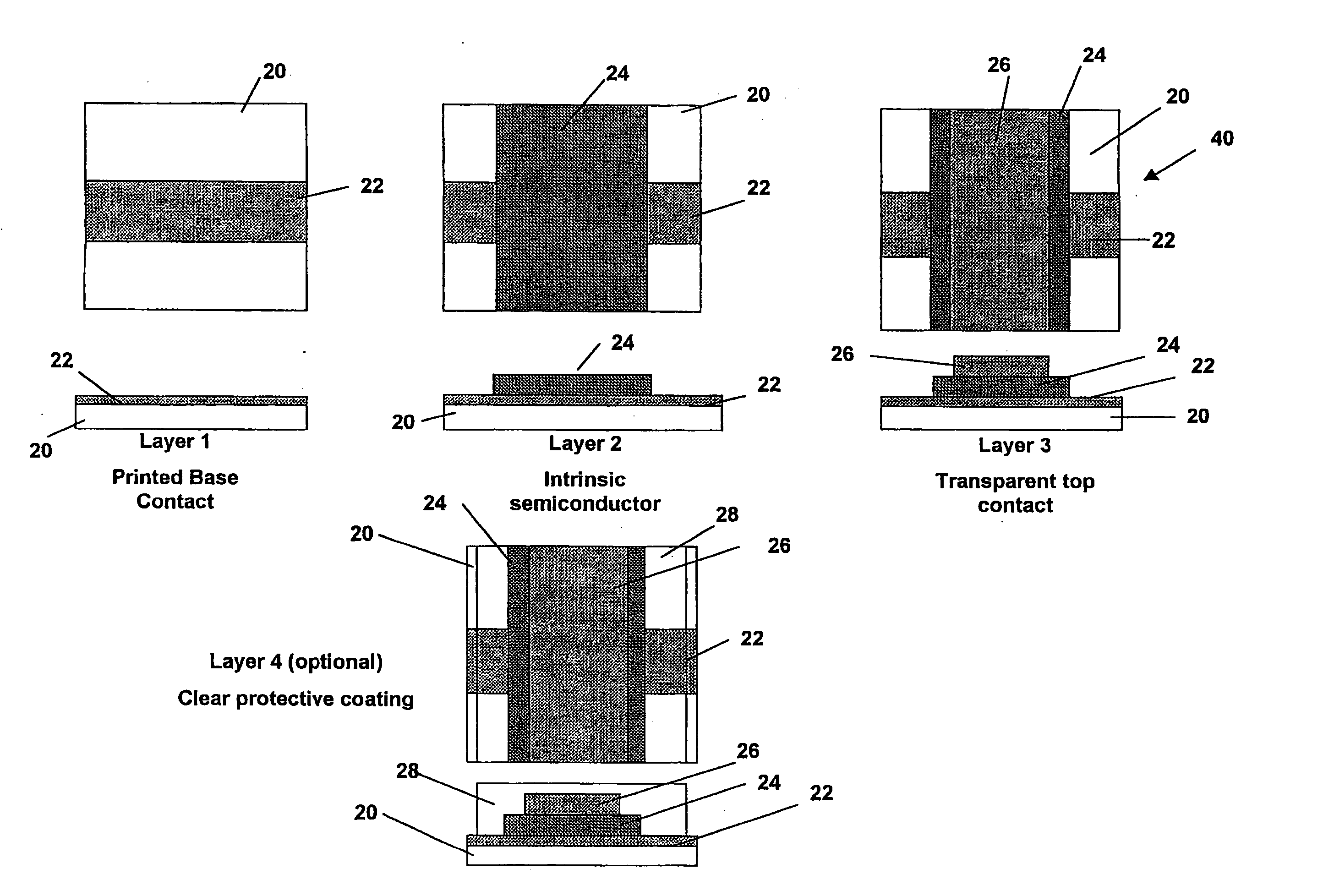
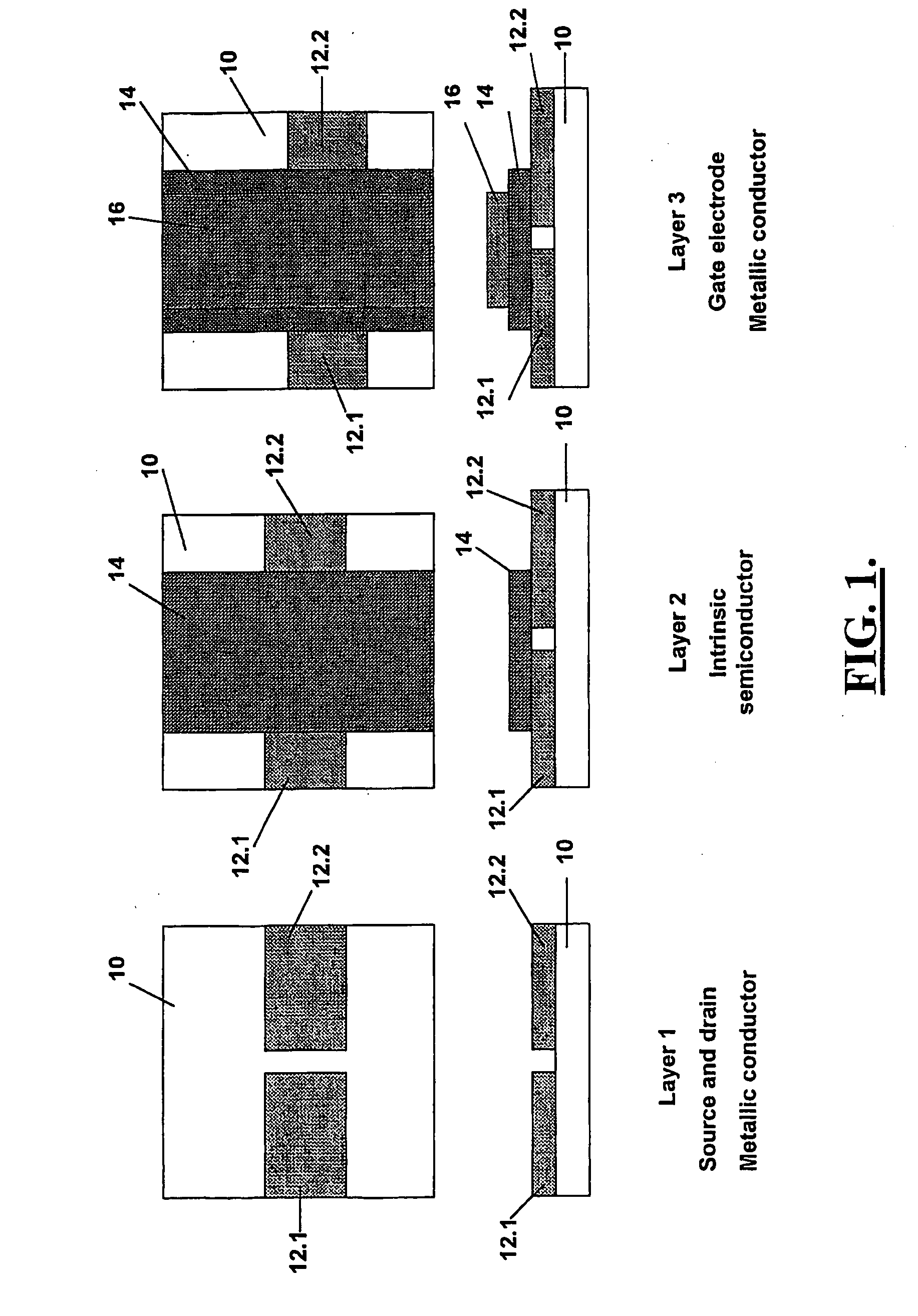
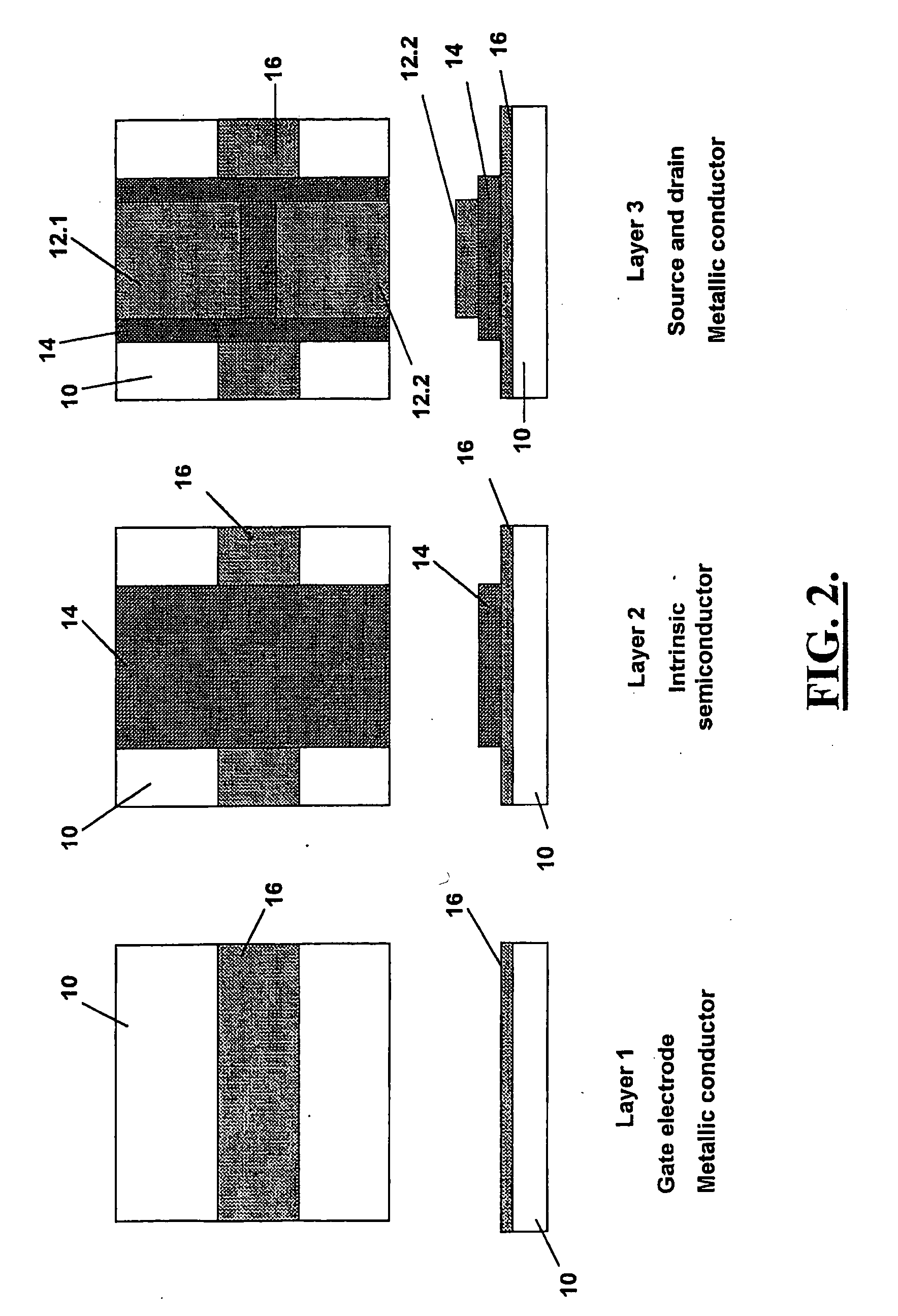
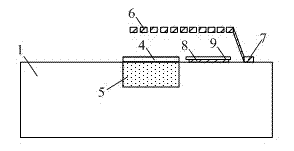
A thin film semiconductor in the form of a metal semiconductor field effect transistor, includes a substrate 10 of paper sheet material and a number of thin film active inorganic layers that are deposited in layers on the substrate. The active layers are printed using an offset lithography printing process. A first active layer comprises source 12.1 and drain 12.2 conductors of colloidal silver ink, that are printed directly onto the paper substrate. A second active layer is an intrinsic semiconductor layer 14 of colloidal nanocrystalline silicon ink which is printed onto the first layer. A third active layer comprises a metallic conductor 16 of colloidal silver which is printed onto the second layer to form a gate electrode. This invention extends to other thin film semiconductors such as photovoltaic cells and to a method of manufacturing semiconductors.
Owner:PST SENSORS
Extremely high-speed switchmode DC-DC converters
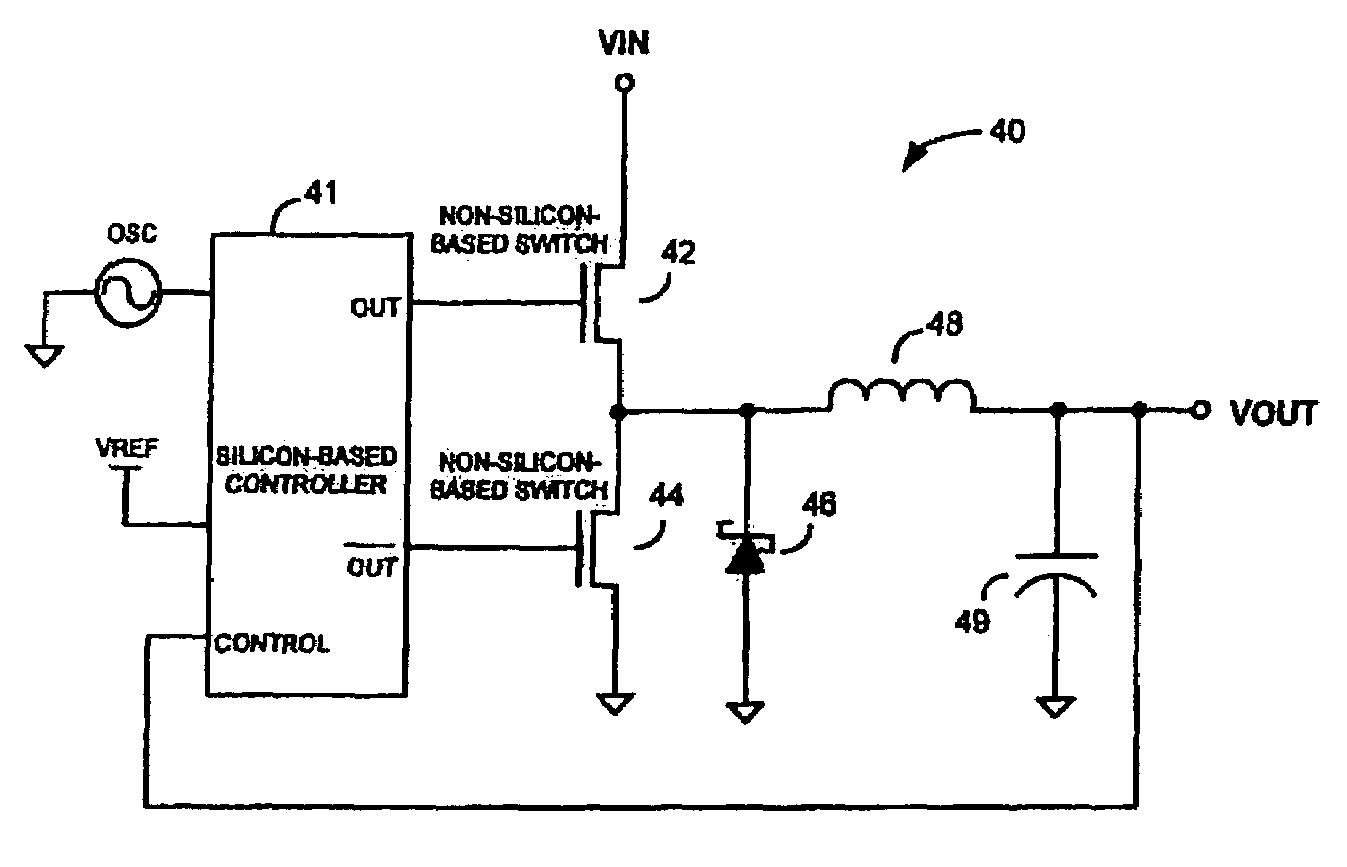
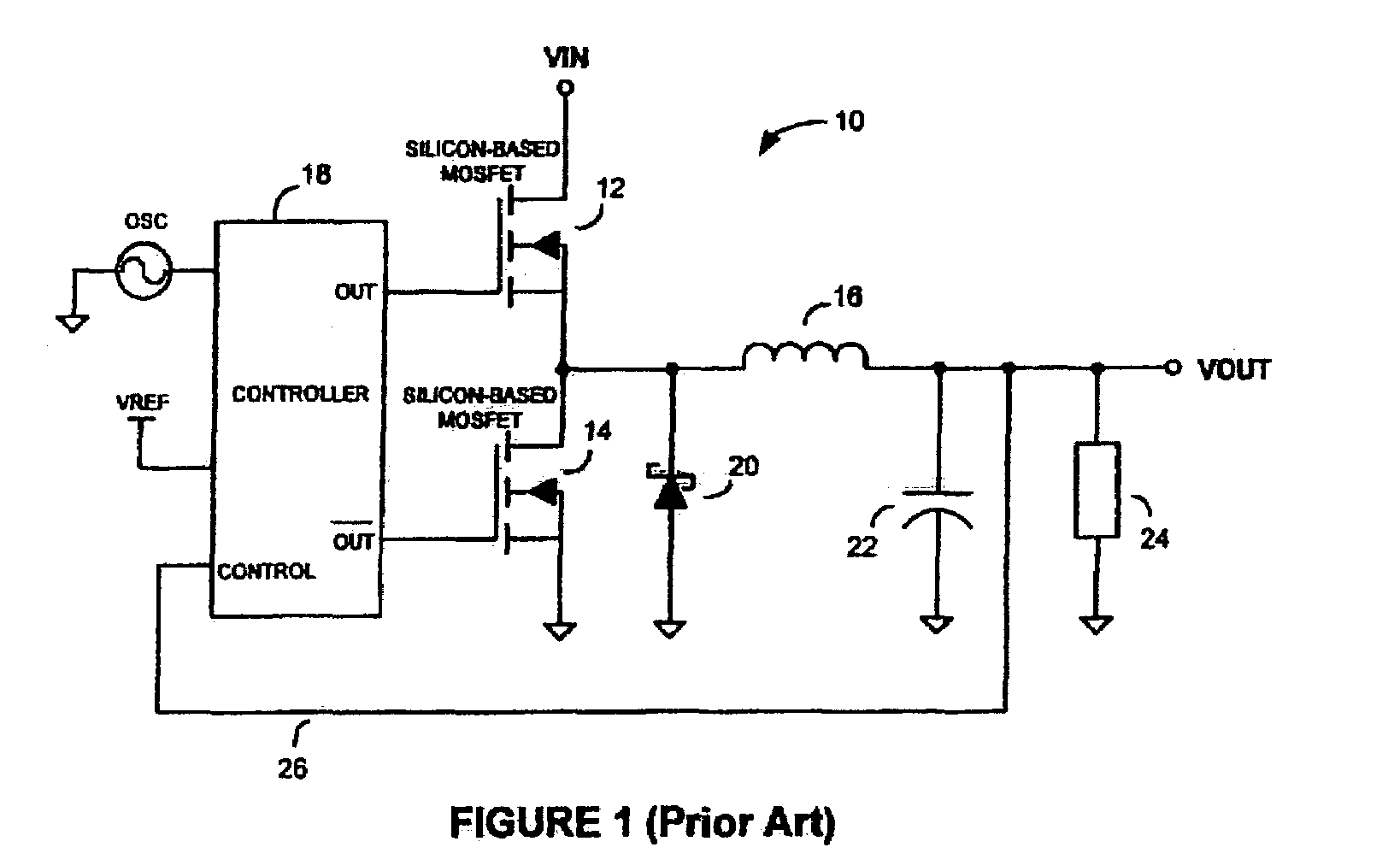
InactiveUS7026797B2Improve efficiencyImproving efficiency and battery savingResonant long antennasEfficient power electronics conversionFigure of meritCMOS
Switchmode DC—DC power converters using one or more non-Silicon-based switching transistors and a Silicon-based (e.g. CMOS) controller are disclosed. The non-Silicon-based switching transistors may comprise, but are not necessarily limited to, III-V compound semiconductor devices such as gallium arsenide (GaAs) metal-semiconductor field effect transistors (MESFETS) or heterostructure FETs such as high electron mobility transistors (HEMTs). According to an embodiment of the invention, the low figure of merit (FoM), τFET, of the non-Silicon-based switching transistors allows the converters of the present invention to be employed in envelope tracking amplifier circuits of wireless devices designed for high-bandwidth technologies such as, for example, EDGE and UMTS, thereby improving the efficiency and battery saving capabilities of the wireless devices.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD +1
Metal-semiconductor field effect transistors (MESFETs) having drains coupled to the substrate and methods of fabricating the same
The present invention provides a unit cell of a metal-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MESFET). The unit cell of the MESFET includes a MESFET having a source region, a drain region and a gate contact. The gate contact is disposed between the source region and the drain region. The drain region is electrically coupled to the substrate through a contact via hole to the substrate. Related methods of fabricating MESFETs are also provided herein.
Owner:CREE INC
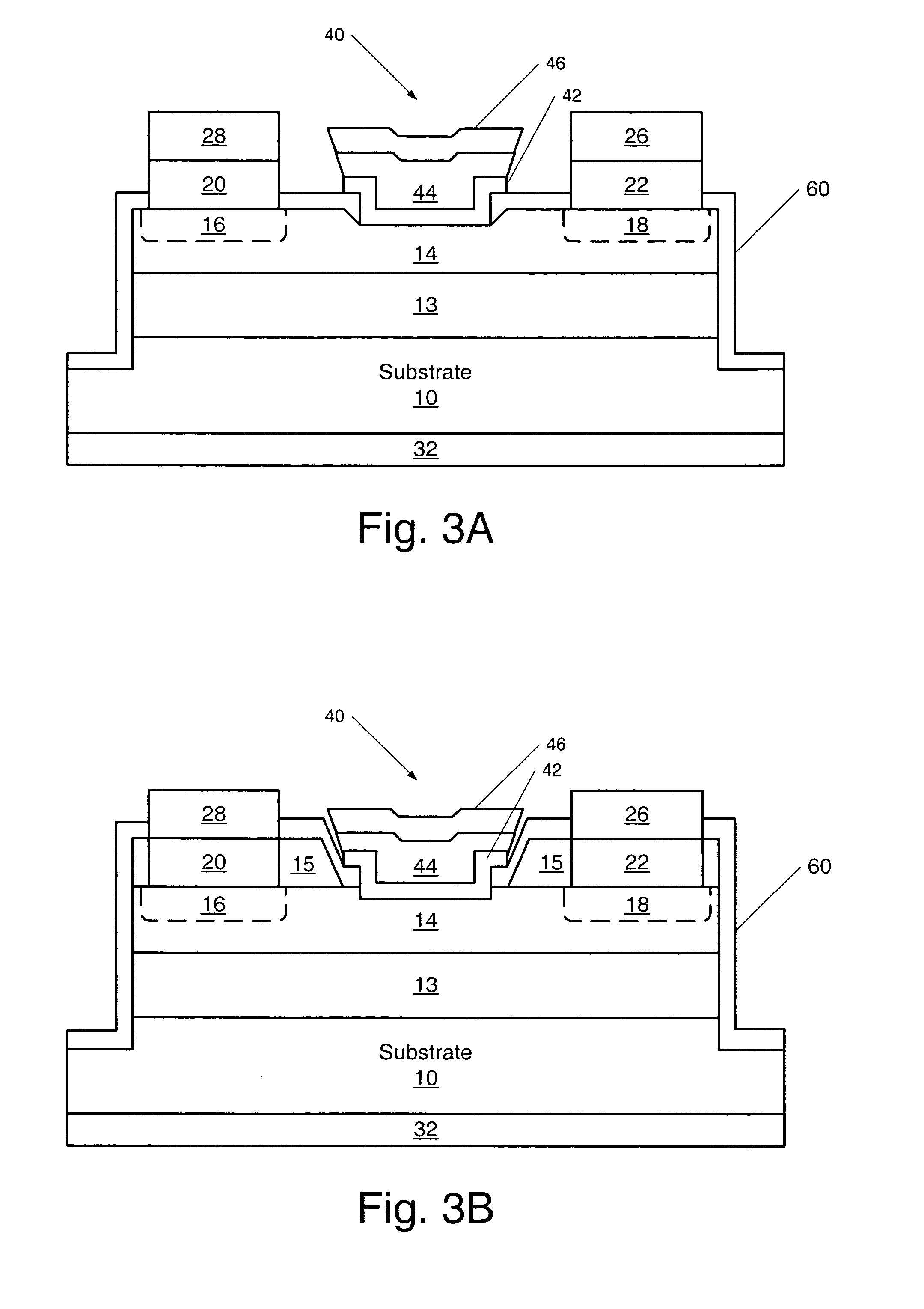
Transistors having buried p-type layers beneath the source region
InactiveUS6956239B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMESFETEngineering
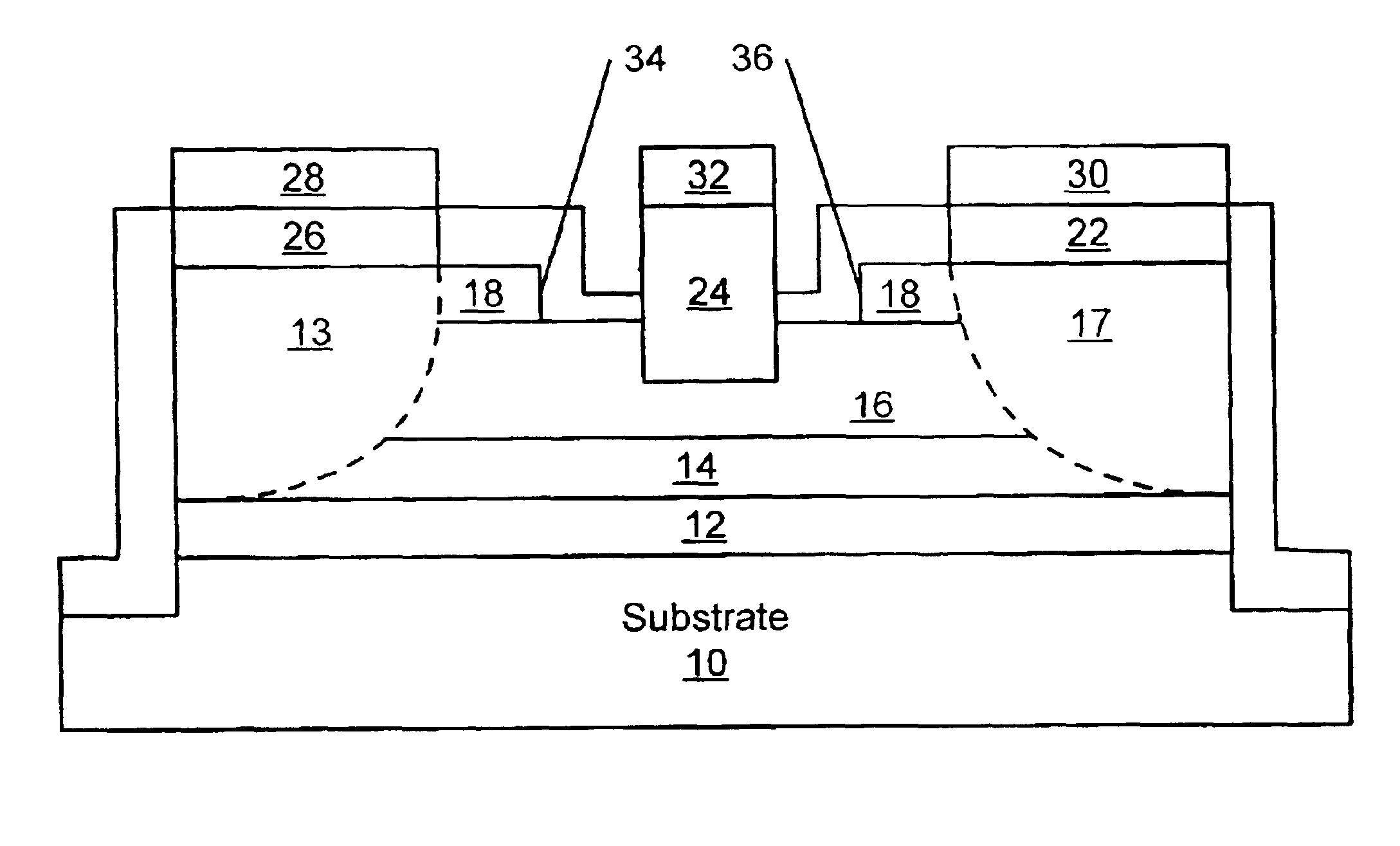
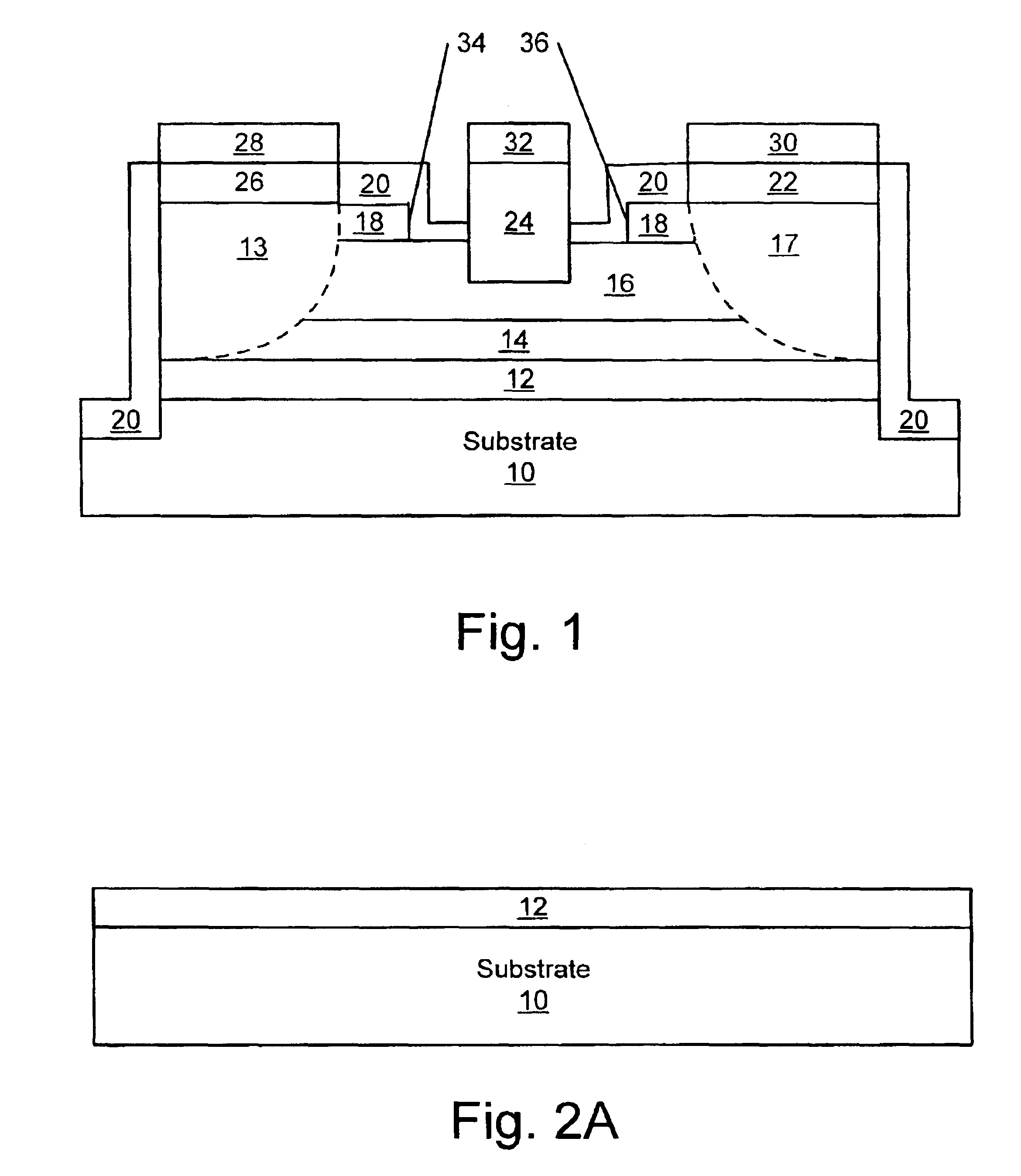
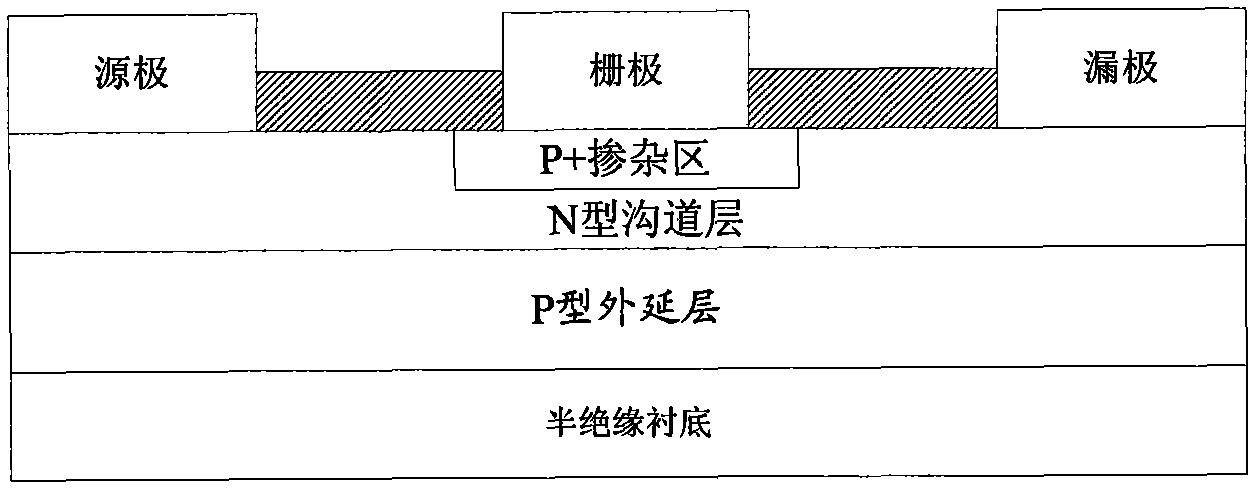
The present invention provides a unit cell of a metal-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MESFET). The unit cell of the MESFET includes a source, a drain and a gate. The gate is disposed between the source and the drain and on an n-type conductivity channel layer. A p-type conductivity region is provided beneath the source and has an end that extends towards the drain. The p-type conductivity region is spaced apart from the n-type conductivity channel region and is electrically coupled to the source.
Owner:CREE INC
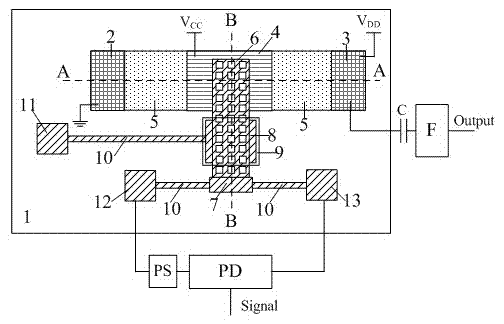
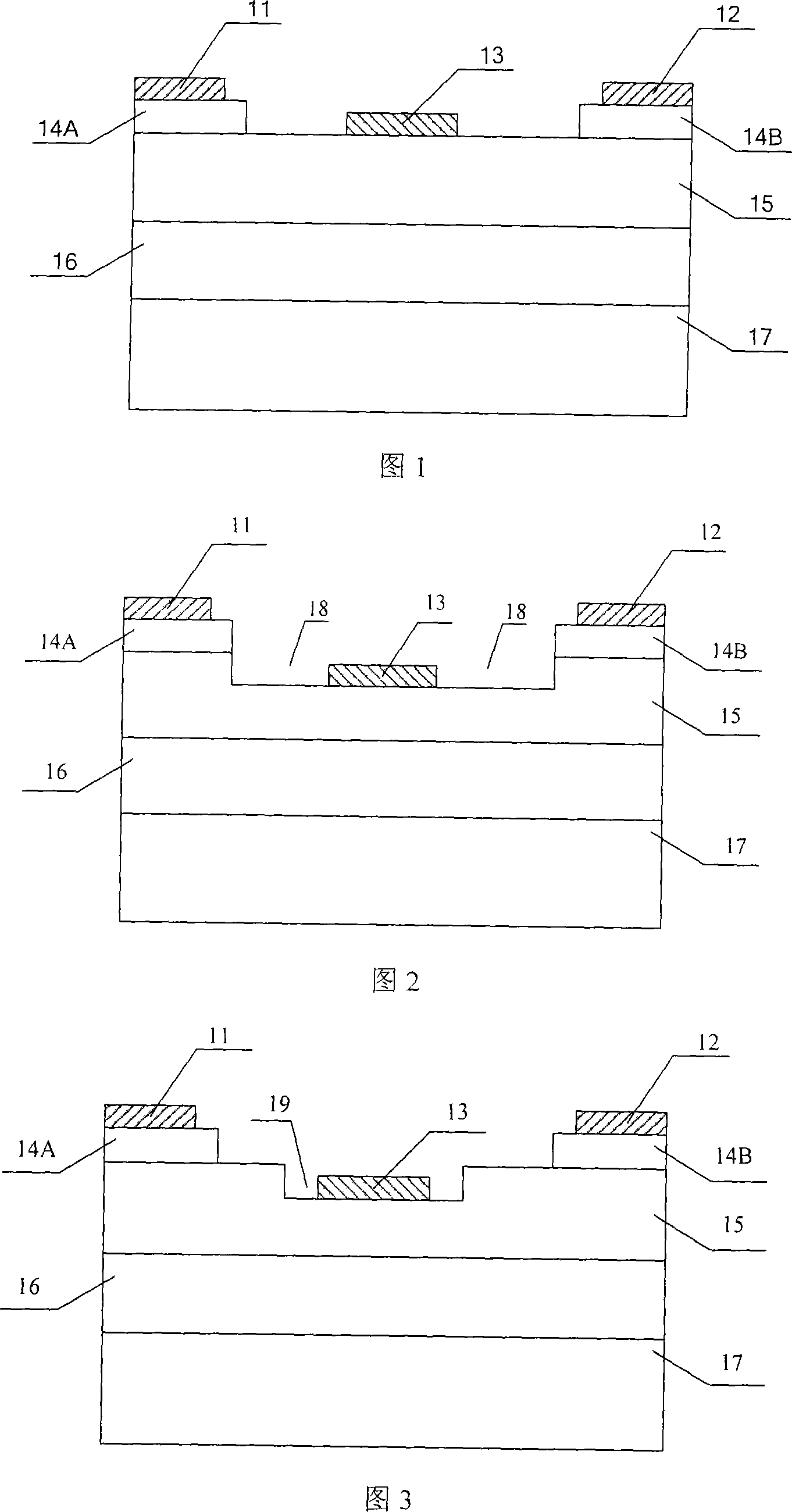
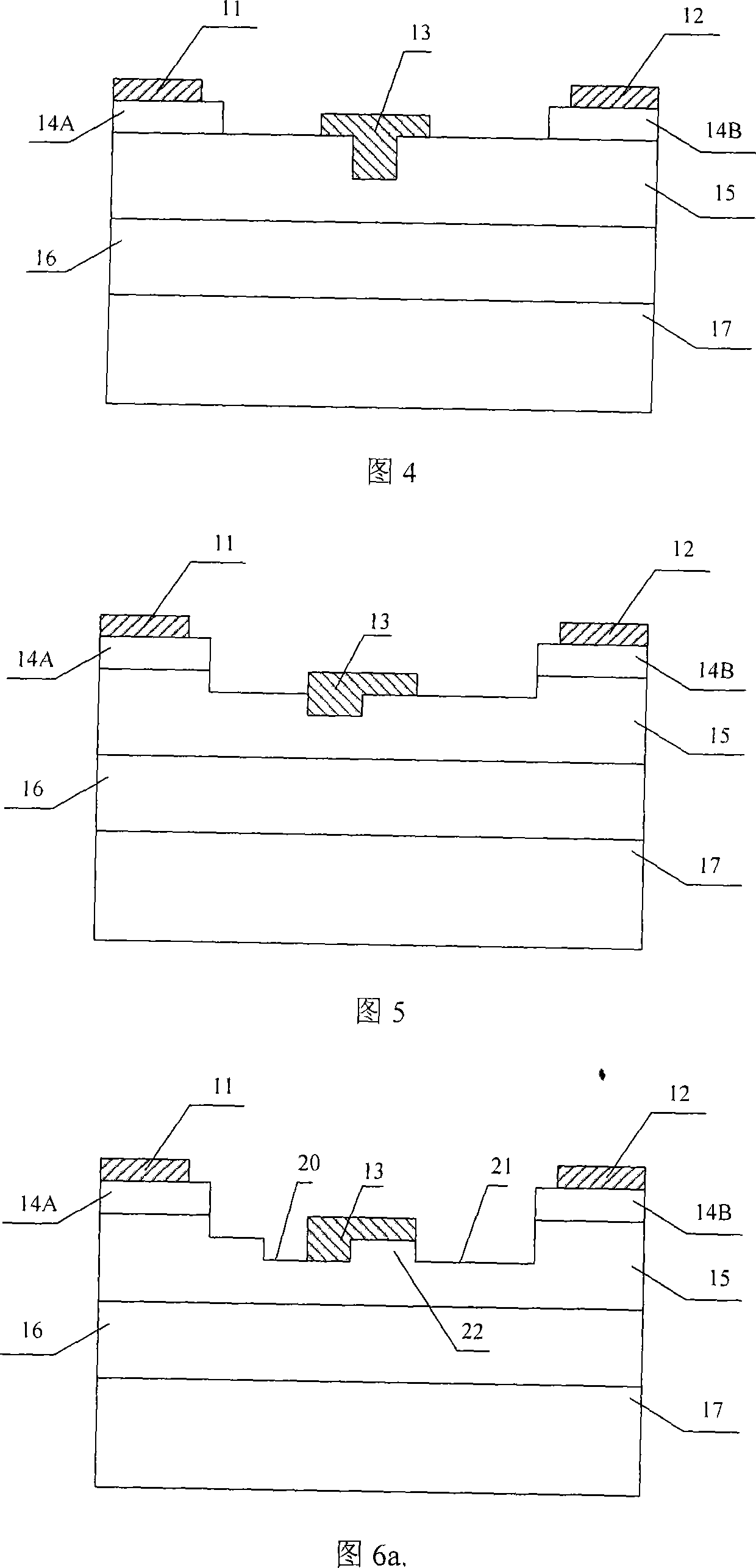
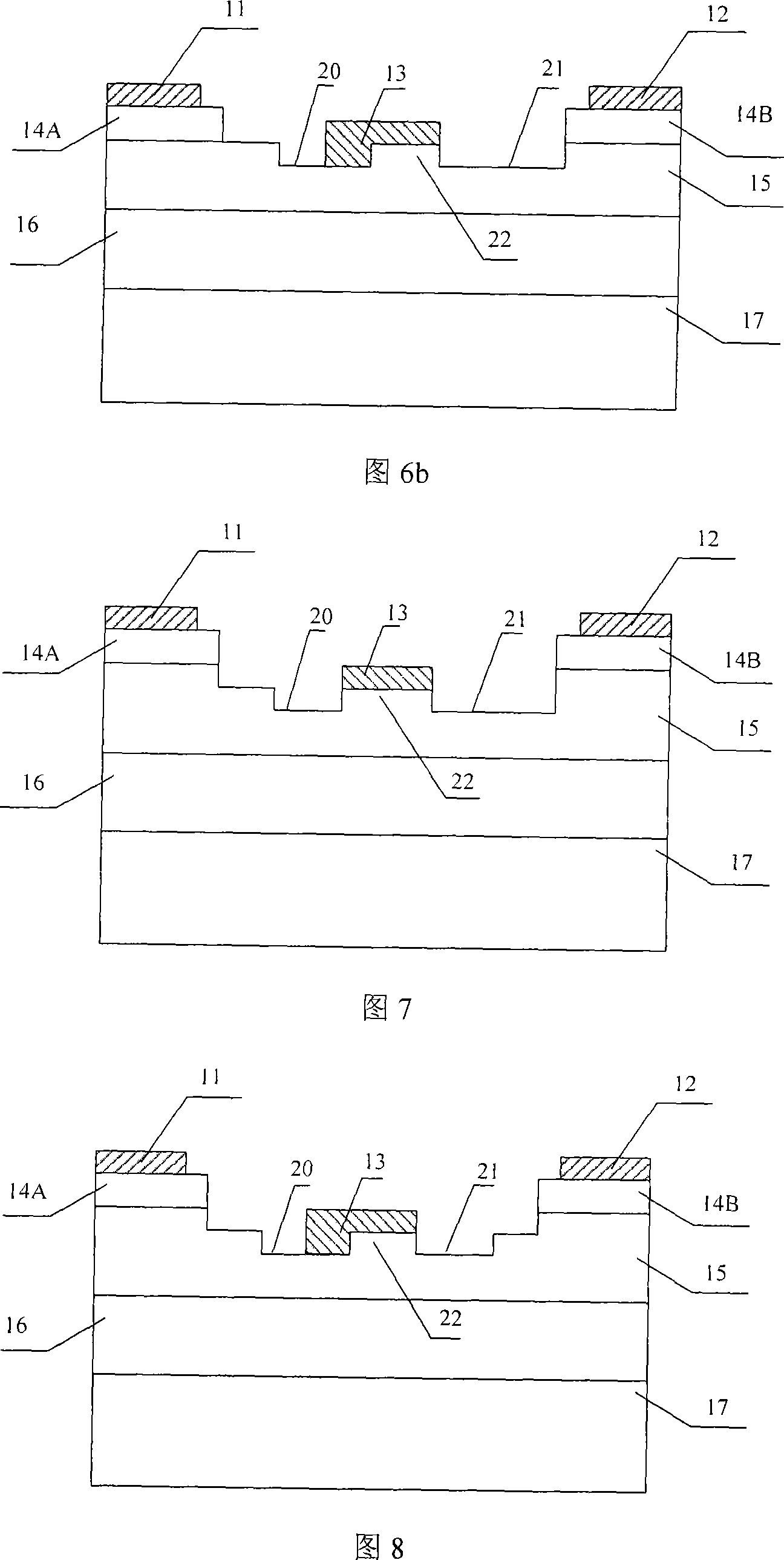
Methods of fabricating delta doped silicon carbide metal-semiconductor field effect transistors having a gate disposed in a double recess structure
InactiveUS20050023535A1Improve breakdown voltageReduce resistanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDelta dopingMESFET
The present invention provides a unit cell of a metal-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MESFET). The unit cell of the MESFET includes a delta doped silicon carbide MESFET having a source, a drain and a gate. The gate is situated between the source and the drain and extends into a doped channel layer of a first conductivity type. Regions of silicon carbide adjacent to the source and the drain extend between the source and the gate and the drain and the gate, respectively. The regions of silicon carbide have carrier concentrations that are greater than a carrier concentration of the doped channel layer and are spaced apart from the gate.
Owner:CREE INC
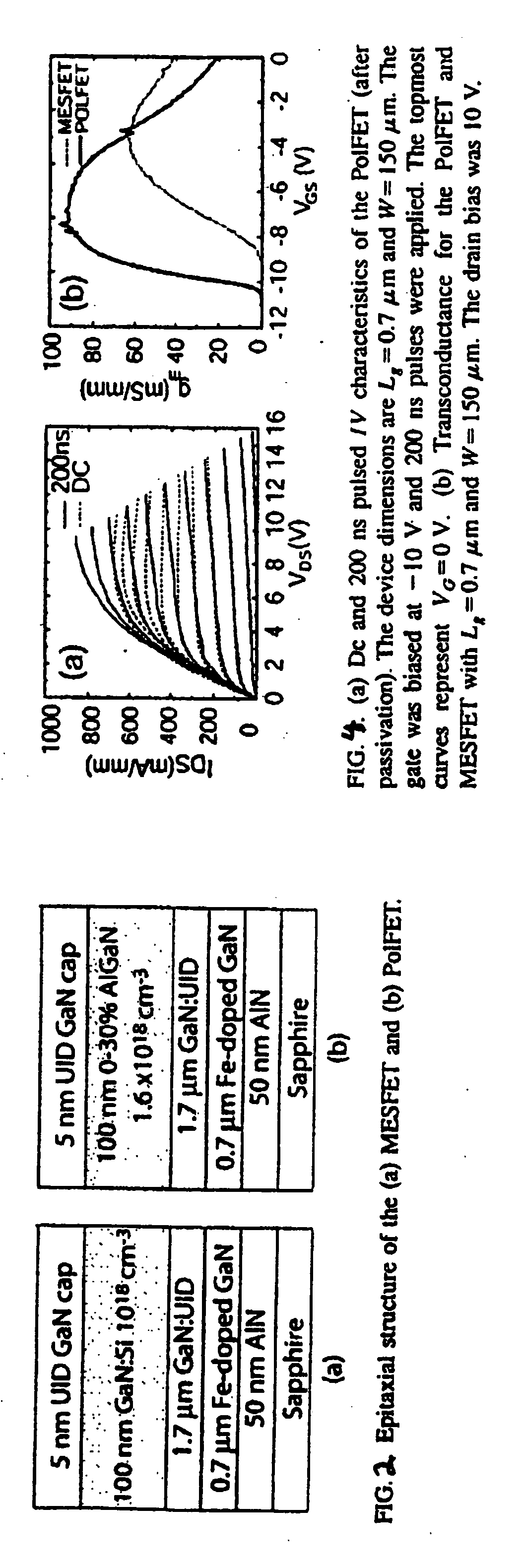
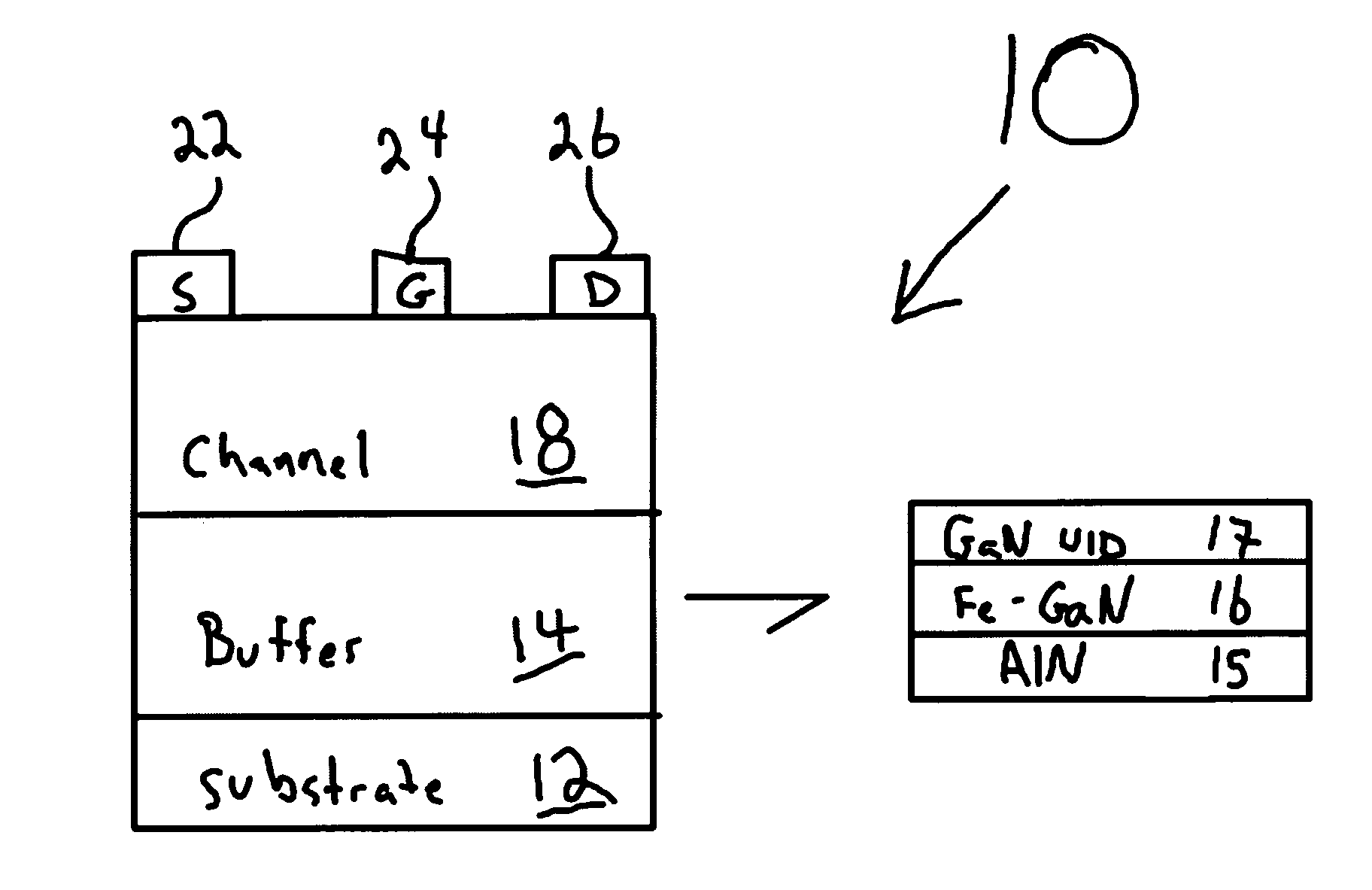
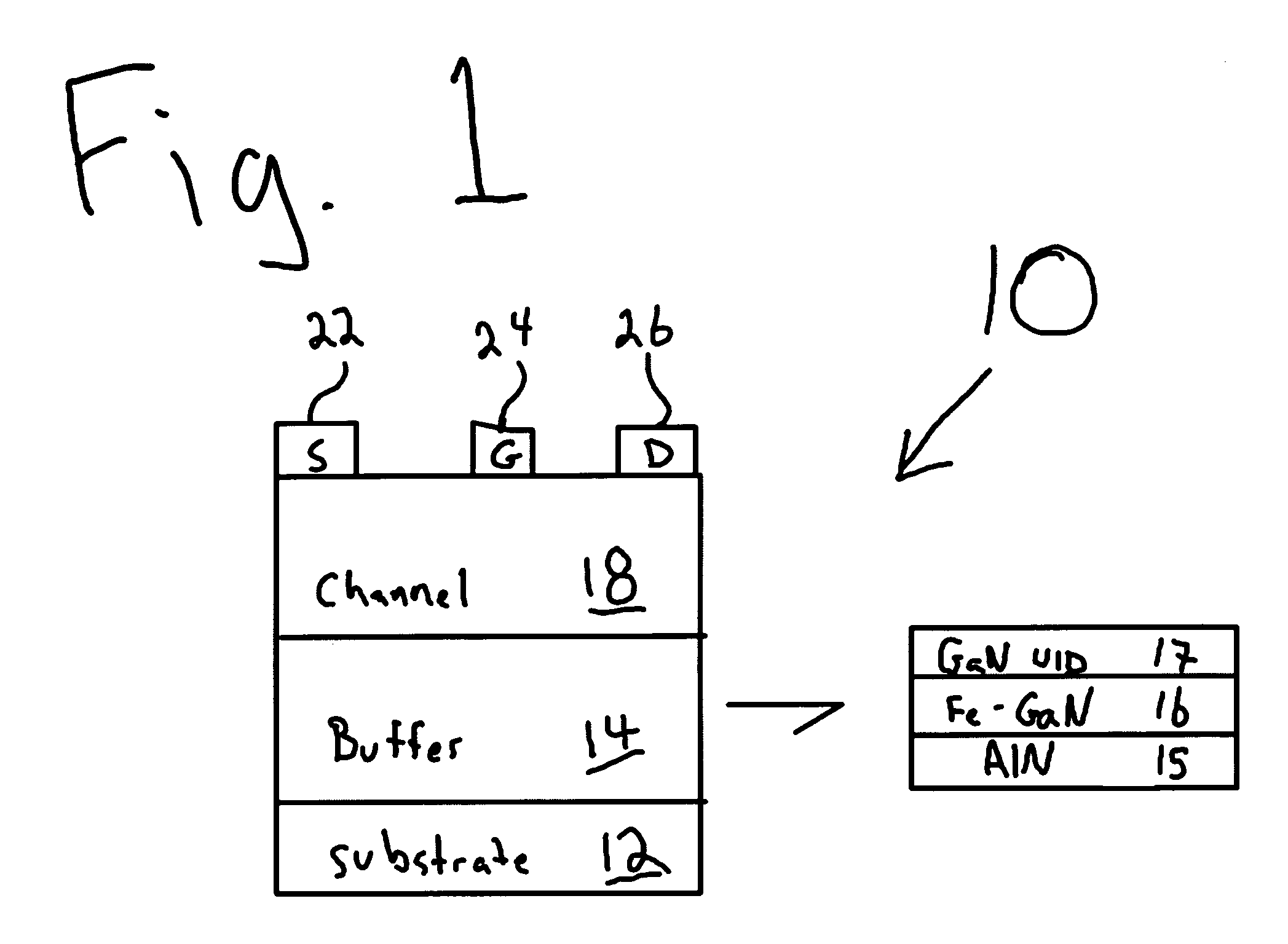
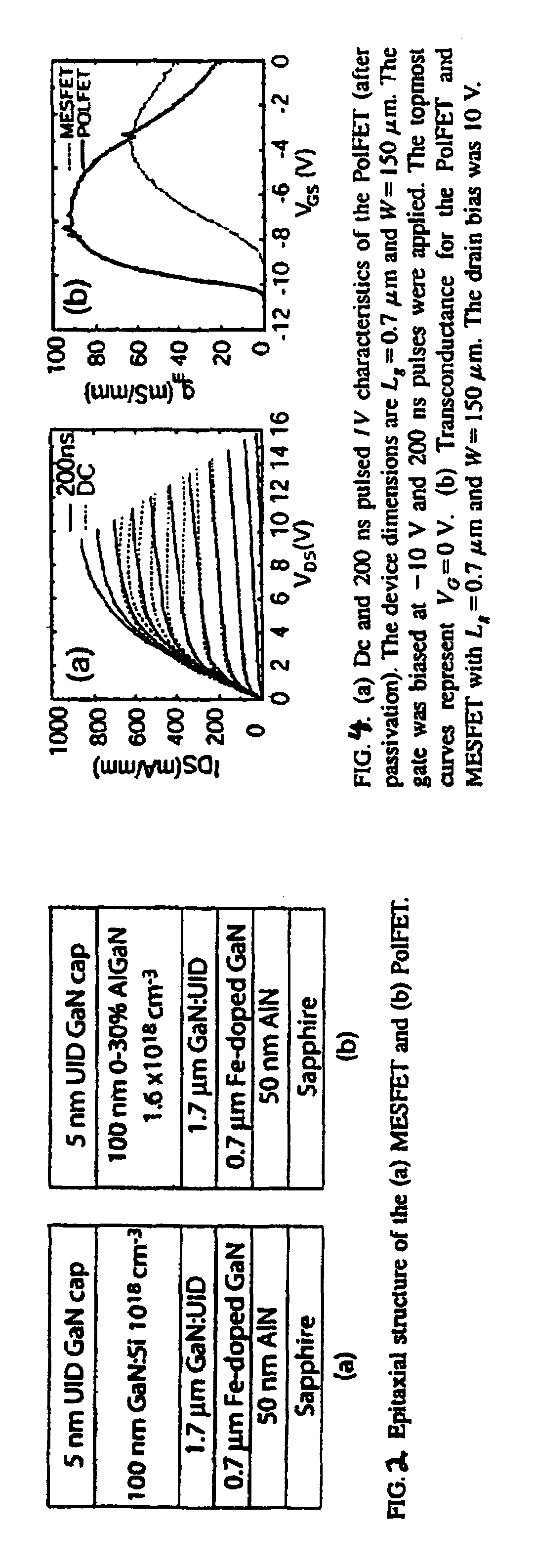
Polarization-doped field effect transistors (POLFETS) and materials and methods for making the same
Novel GaN / AlGaN metal-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MESFET) structures grown without any impurity doping in the channel. A high-mobility polarization-induced bulk channel charge is created by grading the channel region linearly from GaN to Al0.3Ga0.7N over a distance, e.g., 1000 Å. A polarization-doped field effect transistor (PolFET) was fabricated and tested under DC and RF conditions. A current density of 850 mA / mm and transconductance of 93 mS / mm was observed under DC conditions. Small-signal characterization of 0.7 μm gate length devices had a cutoff frequency, ƒτ=19 GHz, and a maximum oscillation of ƒmax=46 GHz. The PolFETs perform better than comparable MESFETs with impurity-doped channels, and are suitable for high microwave power applications. An important advantage of these devices over AlGaN / GaN HEMTs is that the transconductance vs. gate voltage profile can be tailored by compositional grading for better large-signal linearity.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
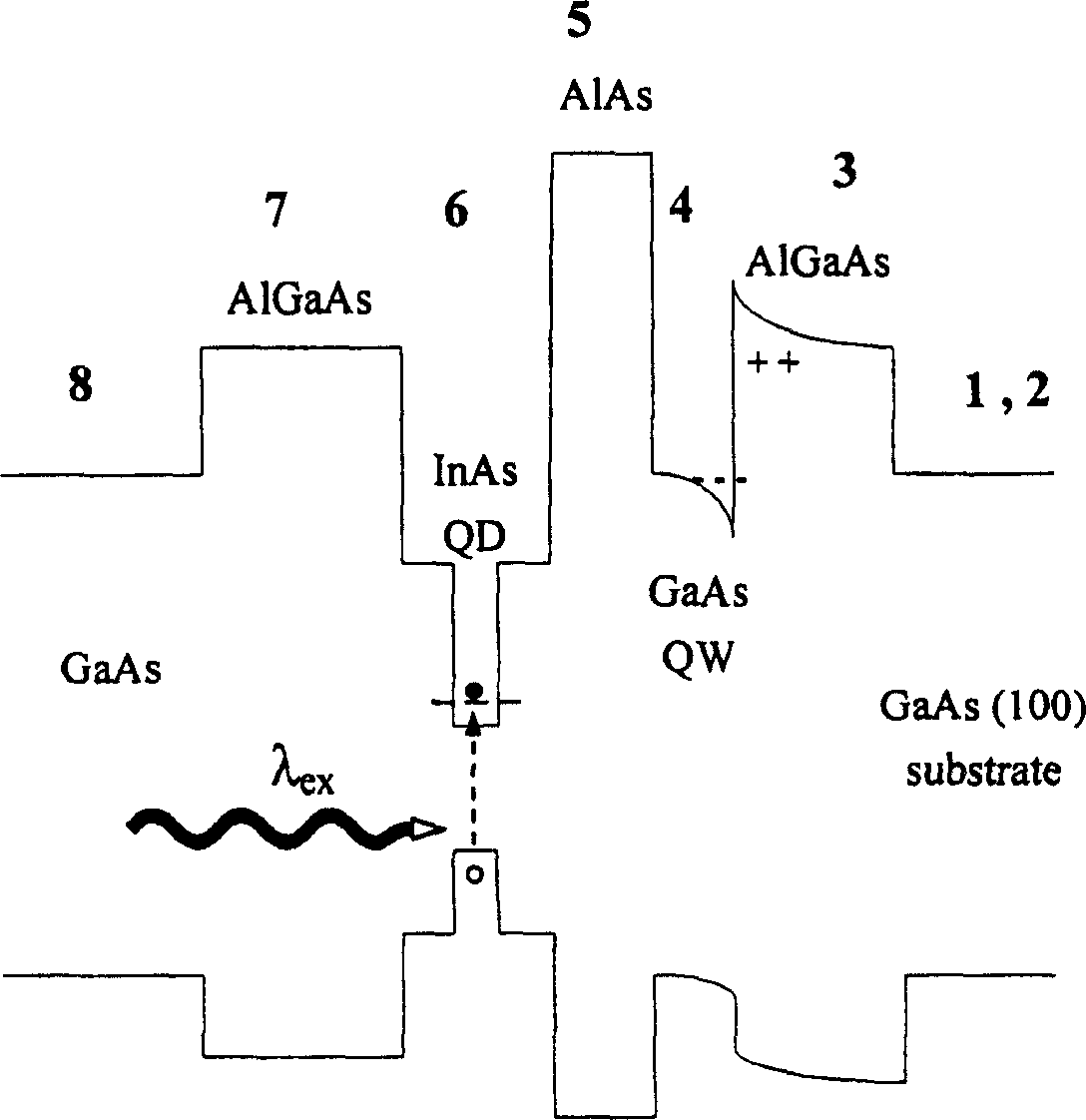
Optical detection field effect transistor containing quantum point and manufacturing method
InactiveCN1832208AImprove response efficiencySimple structureFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesGratingIndium arsenide
This invention relates to an optical detection field effect transistor containing quantum points and its manufacturing method characterizing: 1, longitudinally integrating a compound semiconductor optical detector and a metal-semiconductor field effect transistor to grow on a same substrate material, 2, separating the active region mesa of InAs quantum points under the grating and the source / drain region to connect the modulated conduction channel under the quantum points with the source / drain to constitute a conducting loop to realize the effective integration of optical devices and electric appliances.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
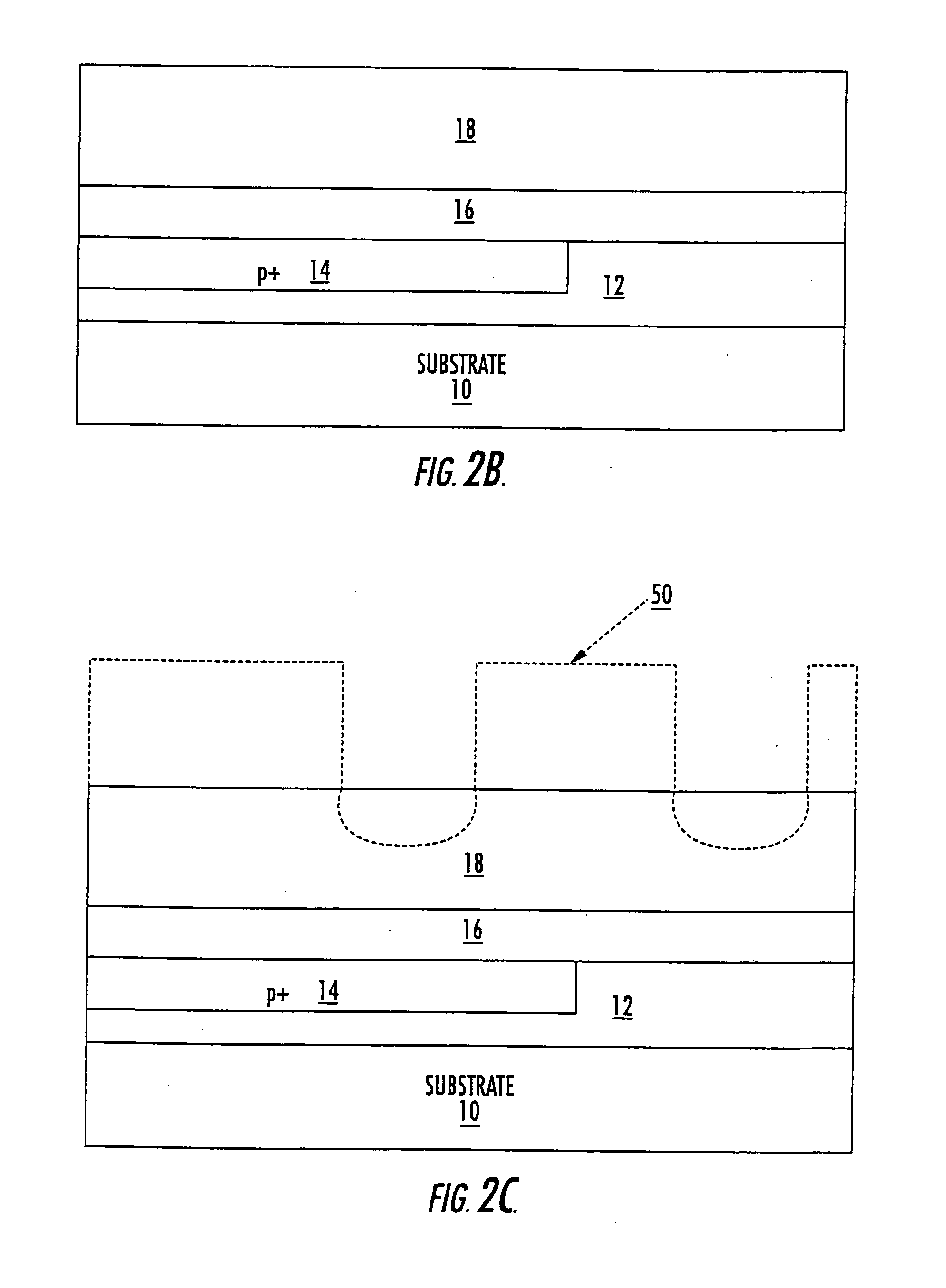
Methods of fabricating silicon carbide metal-semiconductor field effect transistors
InactiveUS7067361B2Improve performanceReduce the impactSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate effectDeep level
SiC MESFETs are disclosed which utilize a semi-insulating SiC substrate which substantially free of deep-level dopants. Utilization of the semi-insulating substrate may reduce back-gating effects in the MESFETs. Also provided are SiC MESFETs with a two recess gate structure. MESFETS with a selectively doped p-type buffer layer are also provided. Utilization of such a buffer layer may reduce output conductance by a factor of 3 and produce a 3 db increase in power gain over SiC MESFETs with conventional p-type buffer layers. A ground contact may also be provided to the p-type buffer layer and the p-type buffer layer may be made of two p-type layers with the layer formed on the substrate having a higher dopant concentration. SiC MESFETs according to embodiments of the present invention may also utilize chromium as a Schottky gate material. Furthermore, an oxide-nitride-oxide (ONO) passivation layer may be utilized to reduce surface effects in SiC MESFETs. Also, source and drain ohmic contacts may be formed directly on the n-type channel layer, thus, the n+ regions need not be fabricated and the steps associated with such fabrication may be eliminated from the fabrication process. Methods of fabricating such SiC MESFETs and gate structures for SiC FETs as well as passivation layers are also disclosed.
Owner:CREE INC
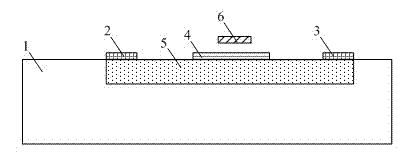
Cantilever beam frequency detector and detection method based on micromechanical gallium arsenide
InactiveCN102735928ASmall sizeNovel structureFrequency to amplitude conversionCapacitanceLow-pass filter
The invention discloses a cantilever beam frequency detector and a cantilever beam frequency detection method based on micromechanical gallium arsenide. The frequency detector comprises a power divider (PD), a phase shifter (PS), a low pass filter (F) and a gallium arsenide metal semiconductor field effect transistor (MESFET), wherein the PD is used for receiving a microwave signal to be detected and dividing the microwave signal to be detected into two branch signals with the same amplitude and phase. The detection method comprises the following steps that: when a pull-down electrode (8) is loaded with direct current (DC) offset and a cantilever beam (6) is pulled down and contacted with a gate (4), the gate (4) is loaded with the two paths of microwave signals simultaneously, so that the magnitude of saturation current between a source (2) and a drain (3) is changed; and through a capacitor and a filter, the frequency is measured by detecting the magnitude of the saturation current between the source (2) and the drain (3). By the detector and the method, DC power consumption is low, and the frequency is easy to measure.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Methods of fabricating delta doped silicon carbide metal-semiconductor field effect transistors having a gate disposed in a double recess structure
InactiveUS6902964B2Improve breakdown voltageReduce resistanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDelta dopingCharge carrier
The present invention provides a unit cell of a metal-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MESFET). The unit cell of the MESFET includes a delta doped silicon carbide MESFET having a source, a drain and a gate. The gate is situated between the source and the drain and extends into a doped channel layer of a first conductivity type. Regions of silicon carbide adjacent to the source and the drain extend between the source and the gate and the drain and the gate, respectively. The regions of silicon carbide have carrier concentrations that are greater than a carrier concentration of the doped channel layer and are spaced apart from the gate.
Owner:CREE INC
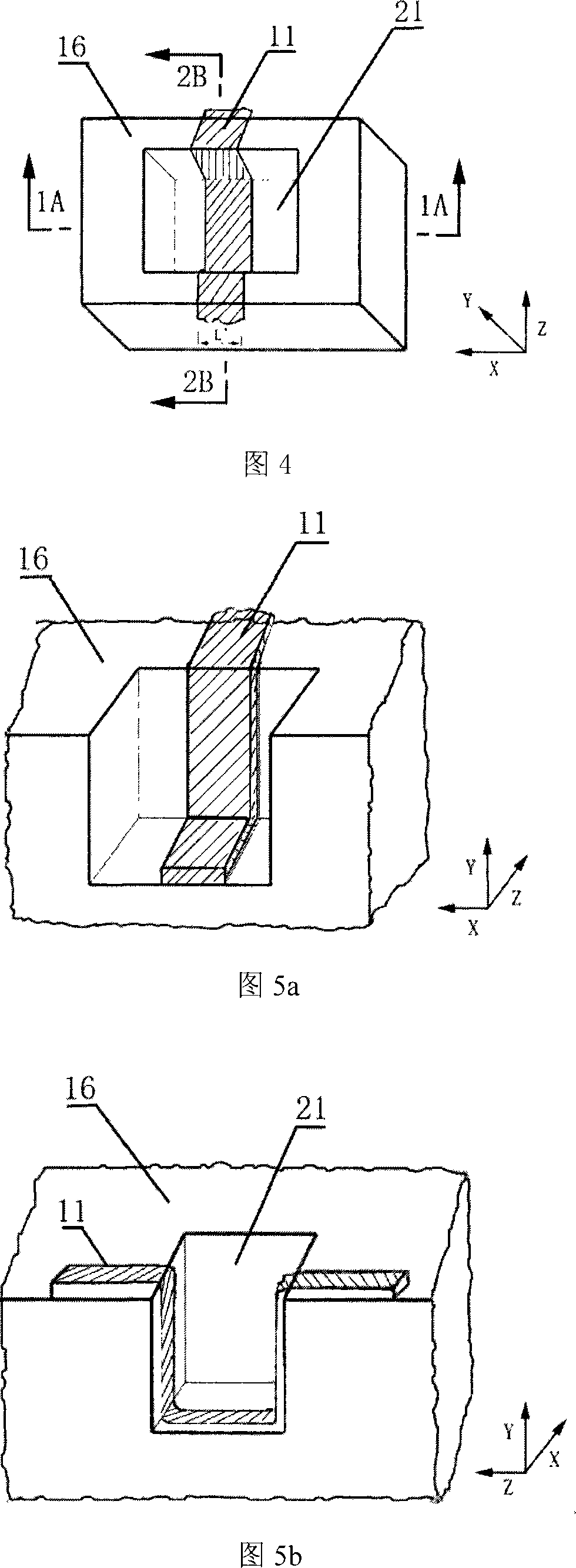
Metal-semiconductor field effect transistor with source-drain double-concave structure
InactiveCN101022129AImprove frequency characteristicsImprove output power densitySemiconductor devicesCapacitanceEngineering
This invention puts forward a MESFFT structure used in HF and large power field, namely, a biconcave structure of MESFET, in which, two independent grooves are formed on the active layer between a gate source and a drain by etching and a projected platform is formed between the two grooves, the gate electrode can deposit on the platform totally or the groove between the platform and the gate source to form a step structure, and the groove between the gate source and the drain stops the exhaust layer under the gate electrode to expand to the source and drain shift region so as to reduce the source and drain capacitance to increase the frequency property of the devices, and the groove can reduce thickness of channels of the shift region and modulate the field distribution of the shift region.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Apparatus and methods for transient overstress protection in compound semiconductor circuit applications
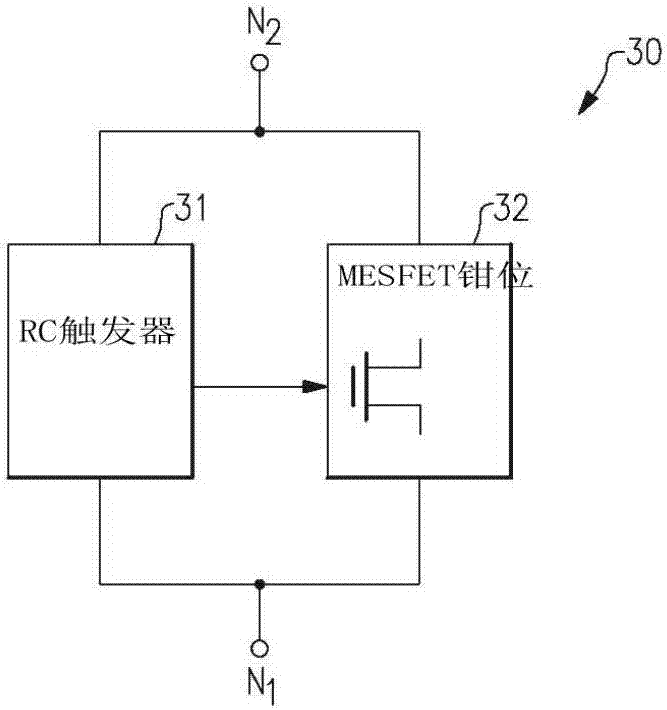
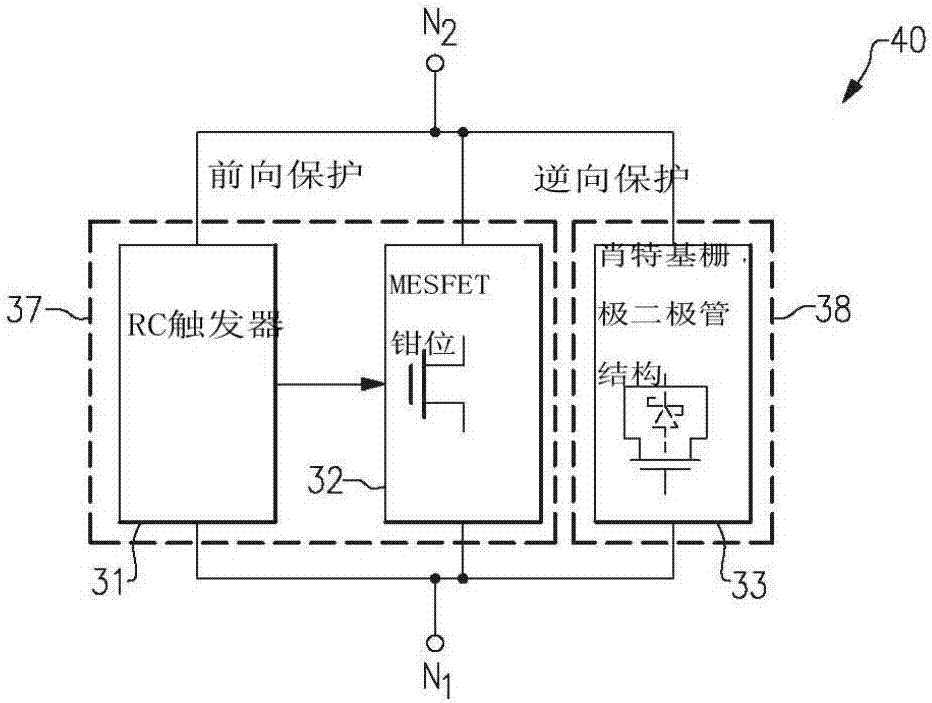
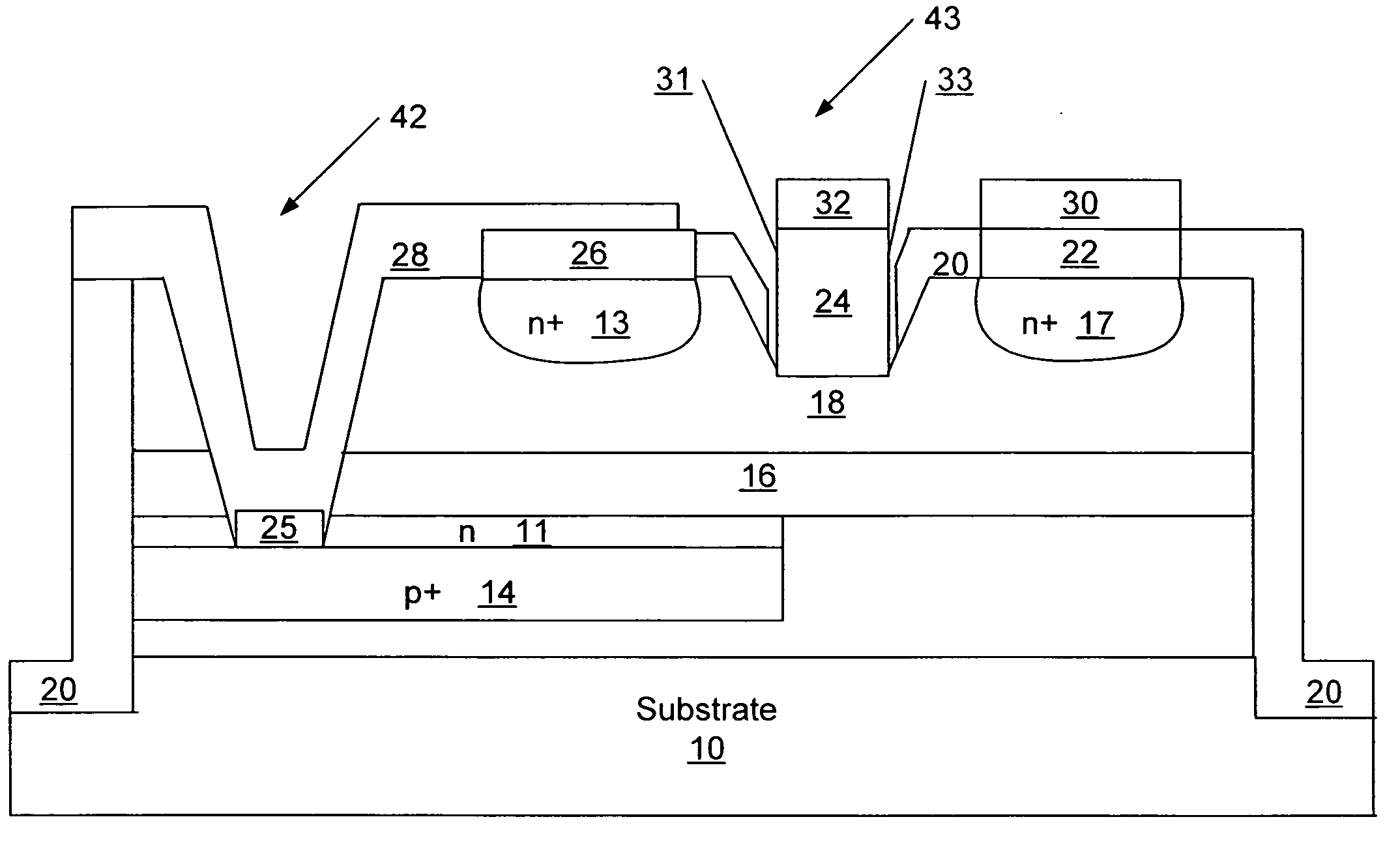
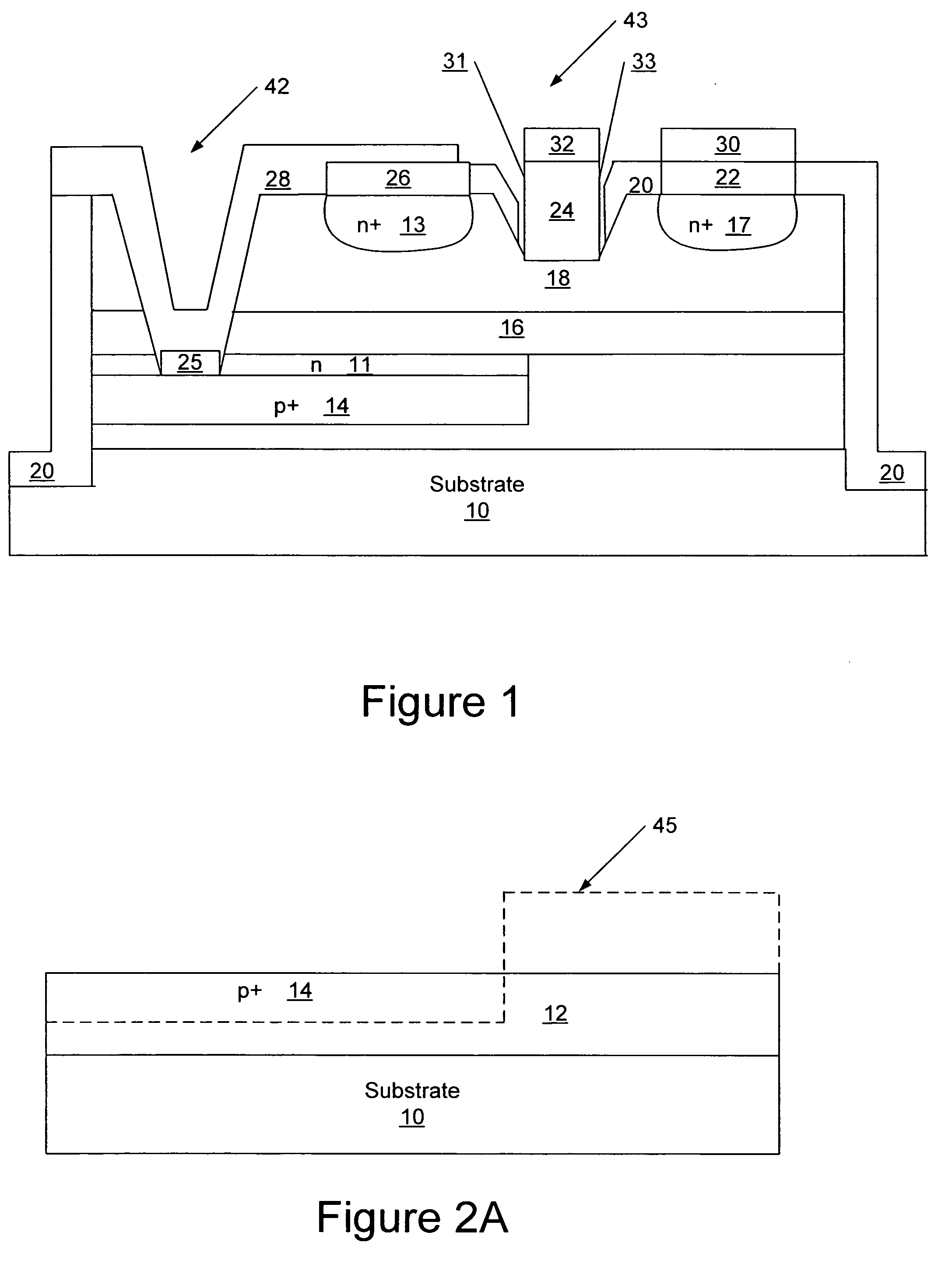
Disclosed are an apparatus and method for transient overstress protection in compound semiconductor circuit applications. An apparatus and methods for compound semiconductor protection clamps are provided herein. In certain configurations, a compound semiconductor protection clamp includes a resistor-capacitor (RC) trigger network and a metal-semiconductor field effect transistor (MESFET) clamp. The RC trigger network detects when an ESD / EOS event is present between a first node and a second node, and activates the MESFET clamp in response to detecting the ESD / EOS event. When the MESFET clamp is activated, the MESFET clamp provides a low impedance path between the first and second nodes, thereby providing ESD / EOS protection. When deactivated, the MESFET clamp provides high impedance between the first and second nodes, and thus operates with low leakage current and small static power dissipation.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
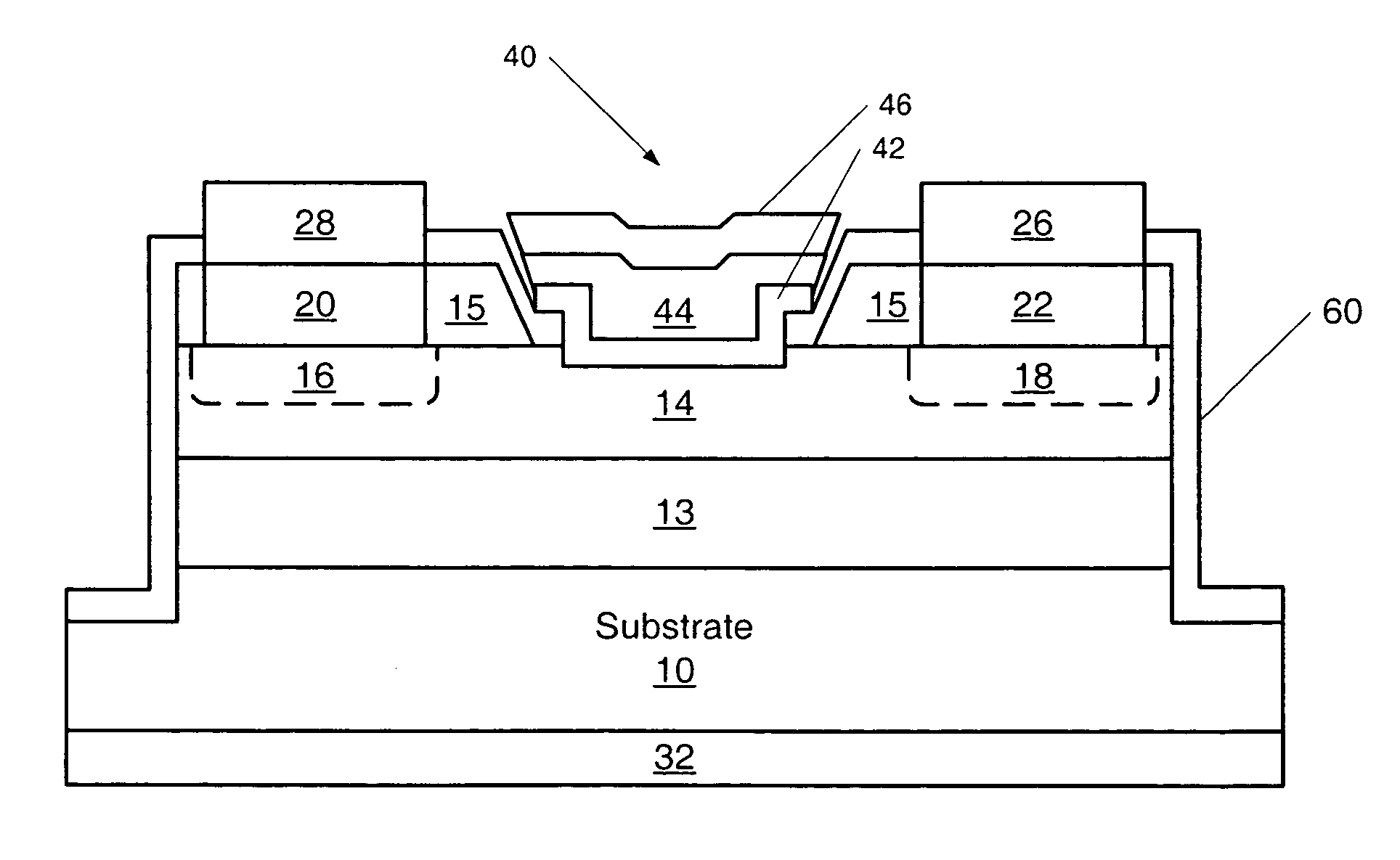
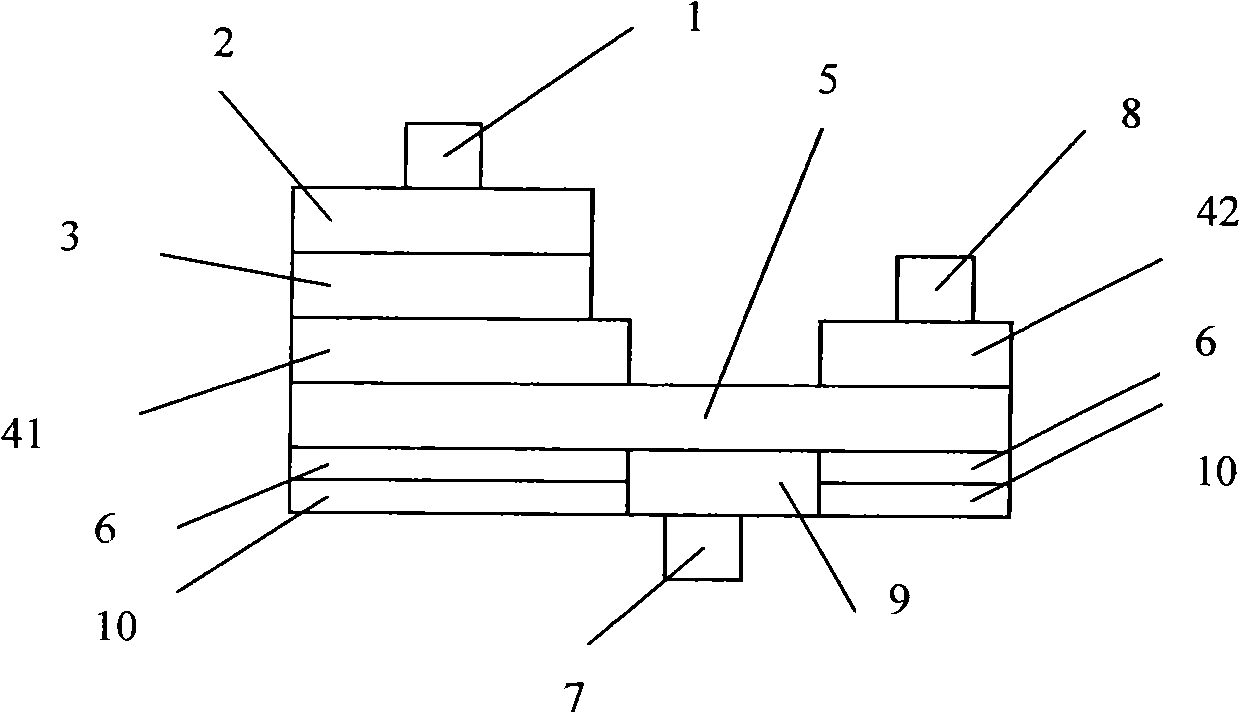
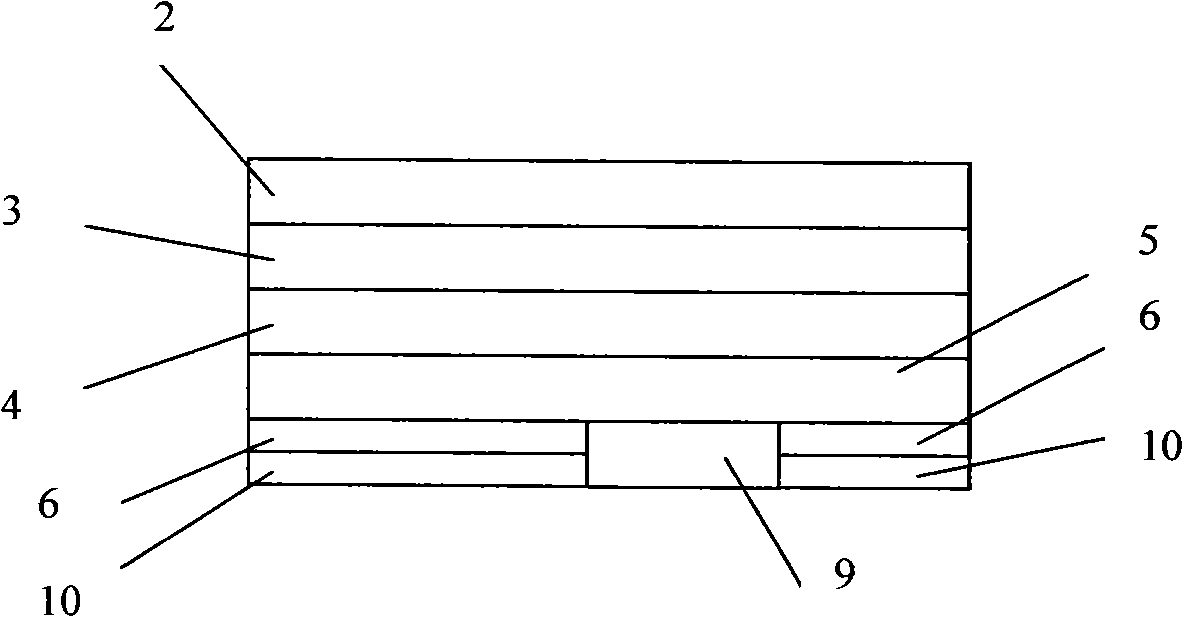
Transistors having buried N-type and P-type regions beneath the source region and methods of fabricating the same
ActiveUS20060125001A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectronic switchingMESFETEngineering
The present invention provides a unit cell of a metal-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MESFET). The unit cell of the MESFET includes a source, a drain and a gate. The gate is disposed between the source and the drain and on an n-type conductivity channel layer. A p-type conductivity region is provided beneath the source and has an end that extends towards the drain. The p-type conductivity region is spaced apart from the n-type conductivity channel region and is electrically coupled to the source. An n-type conductivity region is provided on the p-type conductivity region beneath the source region and extending toward the drain region without extending beyond the end of the p-type conductivity region. Related methods of fabricating MESFETS are also provided.
Owner:CREE INC
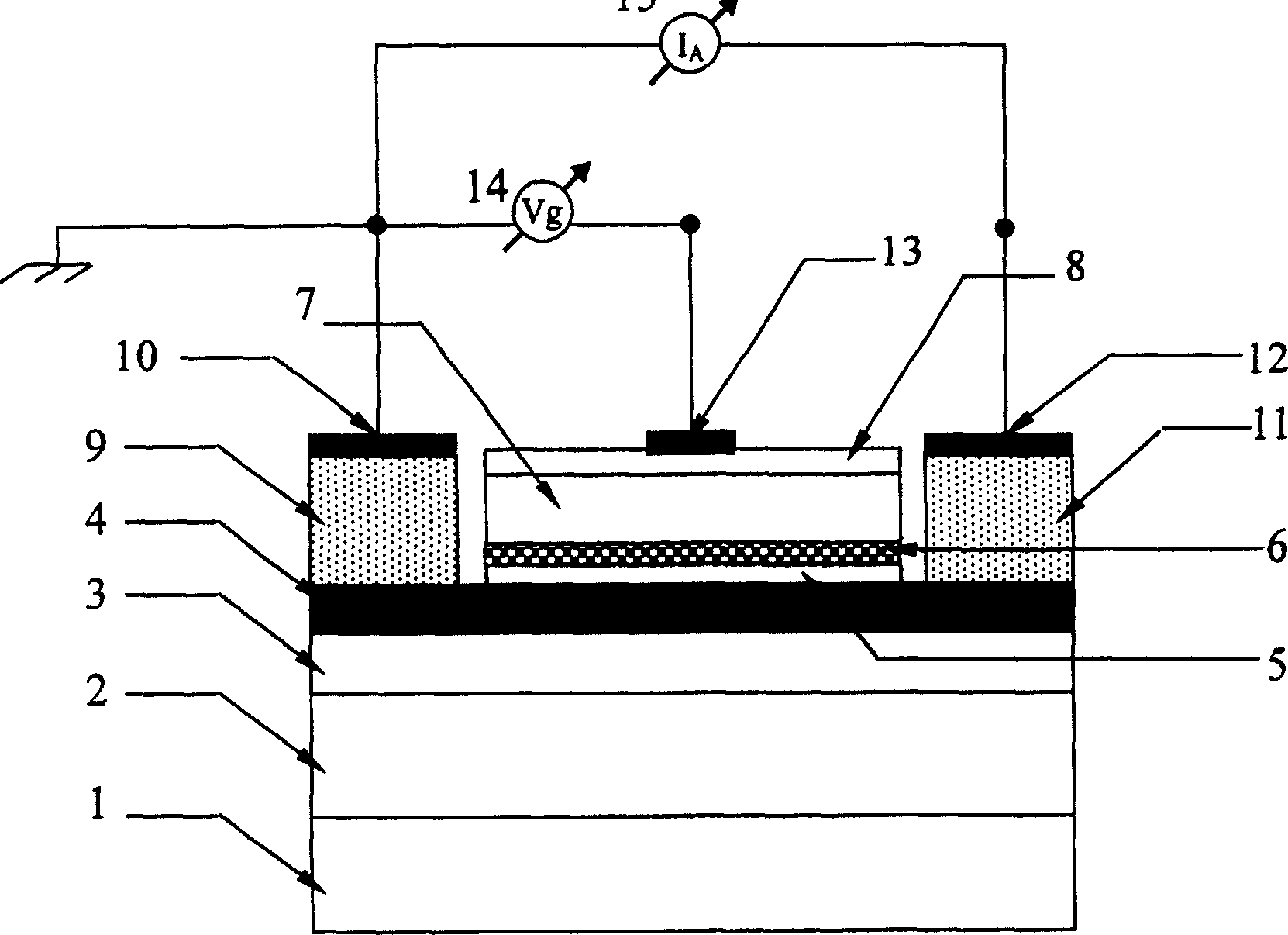
Horizontally depleted metal semiconductor field effect transistor
InactiveUS20100320508A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesContact formationDepletion region
The present invention provides a horizontally depleted Metal Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MESPET). A drain region, a source region, and a channel region are formed in the device layer such that the drain region and the source region are spaced apart from one another and the channel region extends between the drain region and the source region. First and second gate contacts are formed in the device layer on either side of the channel region, and as such, the first and second gate contacts will also reside between opposing portions of the source and drain regions. With this configuration, voltages applied to the first and second gate contacts effectively control vertical depletion regions, which form on either side of the channel region.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Beta irradiation detector based on silicon carbide junction field-effect transistor (JFET)
ActiveCN102074611AImprove performanceWeaken or eliminate surface trapping effectsFinal product manufactureRadiation intensity measurementHigh energyOhmic contact
The invention discloses a beta ray irradiation detector based on a silicon carbide metal-semiconductor field effect transistor structure, which is used for mainly solving the problems of poor irradiation resistance and low energy conversion efficiency of an existing beta irradiation detector. The detector comprises an n-type substrate (8), a p-type buffer layer (7), an n-type channel (6) with the concentration of 3.5*10<17>cm<-3> to 4*10<17>cm<-3>, an n-type buffer layer (5) and an ohmic contact layer (4) from top to bottom, wherein a source and a drain (2) are deposited on the ohmic contact layer; a semitransparent Schottky contact layer (1) is deposited on the n-type buffer layer; the Schottky contact layer is formed by high barrier Schottky metals of Au, Ti and Pt, and is embedded in the n-type buffer layer (5) with the depth of 0.06-0.08 mu m; and a surface area except a grid electrode as well as the source and drain is covered with a SiO2 passivation layer (3). The beta ray irradiation detector has the characteristics of strong resistance to radiation, high energy conversion efficiency and high detection efficiency, and can be applied to detecting beta rays in nuclear energy.
Owner:陕西半导体先导技术中心有限公司
Metal-semiconductor field effect transistor
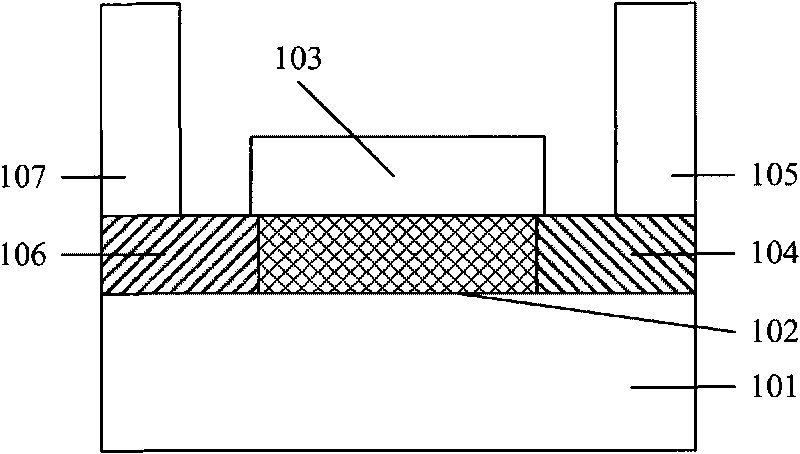
The invention relates to a metal-semiconductor field effect transistor, which comprises a grid electrode formed by metal, and a trench area which is made of a semiconductor material and is in Schottky contact with the grid electrode; the grid electrode is provided with a through hole inside; and at least part of the trench area is positioned in the through hole. Compared with the prior art, the meal grid electrode completely enclosing a trench area is formed in the metal-semiconductor field effect transistor so as to fully prevent the generation of leakage current.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
Transistors having buried p-type layers beneath the source region and methods of fabricating the same
ActiveUS20050224809A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMESFETEngineering
The present invention provides a unit cell of a metal-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MESFET). The unit cell of the MESFET includes a source, a drain and a gate. The gate is disposed between the source and the drain and on an n-type conductivity channel layer. A p-type conductivity region is provided beneath the source and has an end that extends towards the drain. The p-type conductivity region is spaced apart from the n-type conductivity channel region and is electrically coupled to the source.
Owner:CREE INC
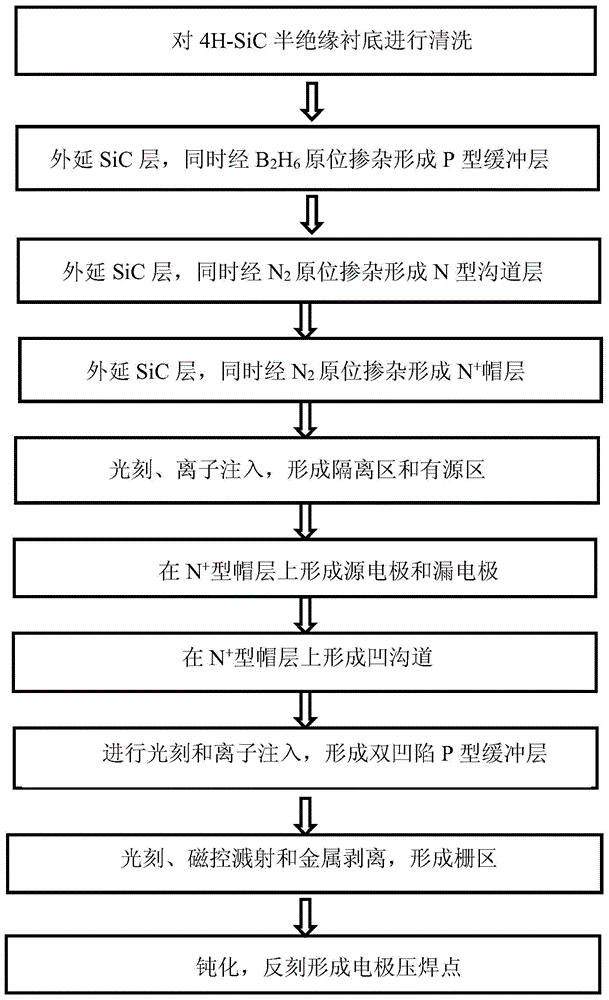
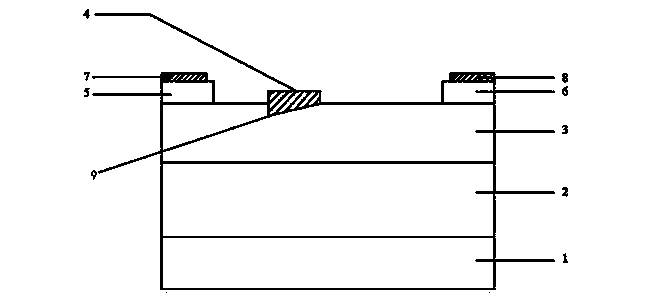
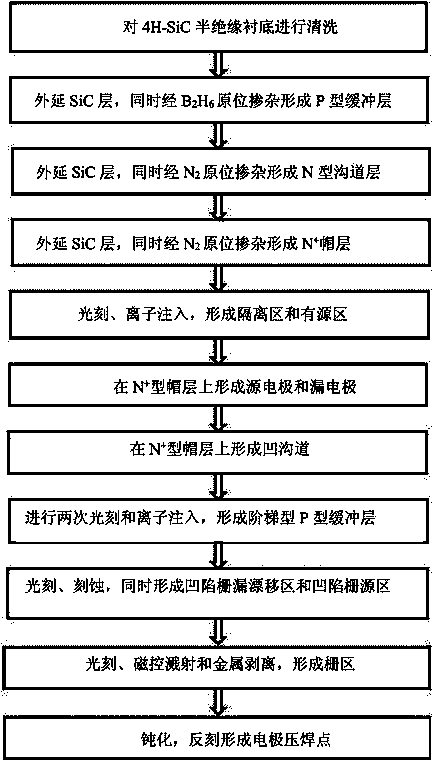
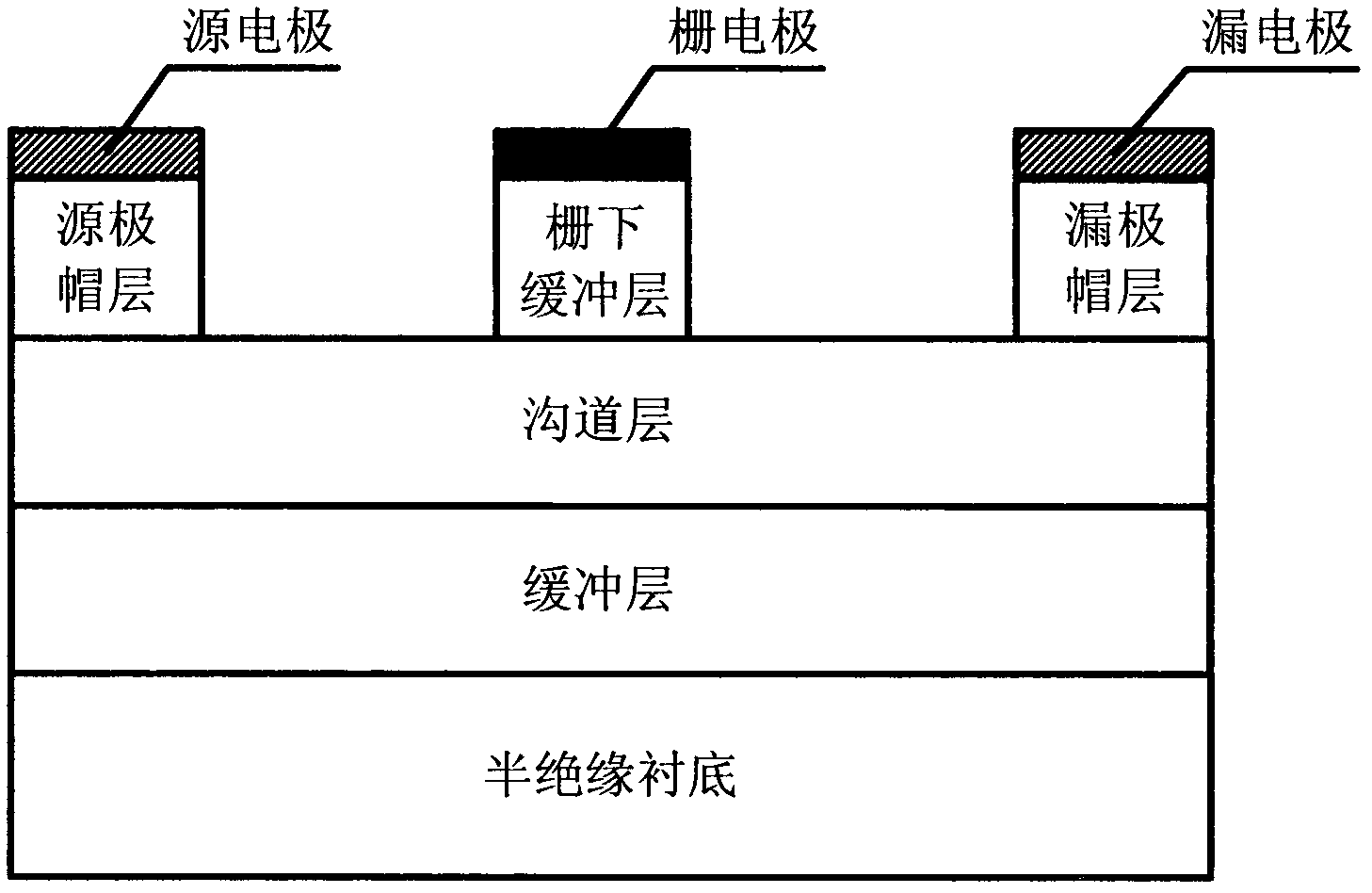
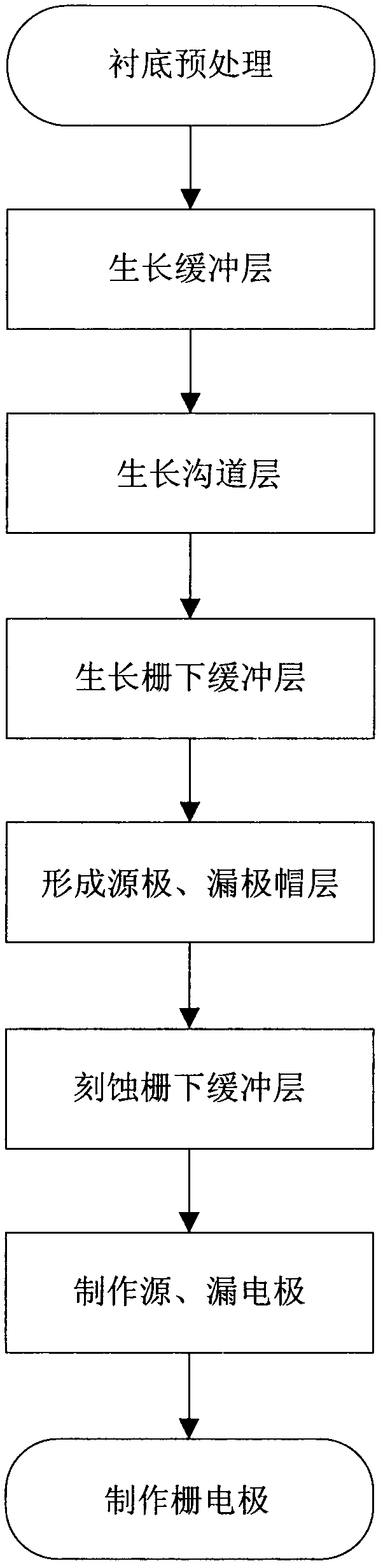
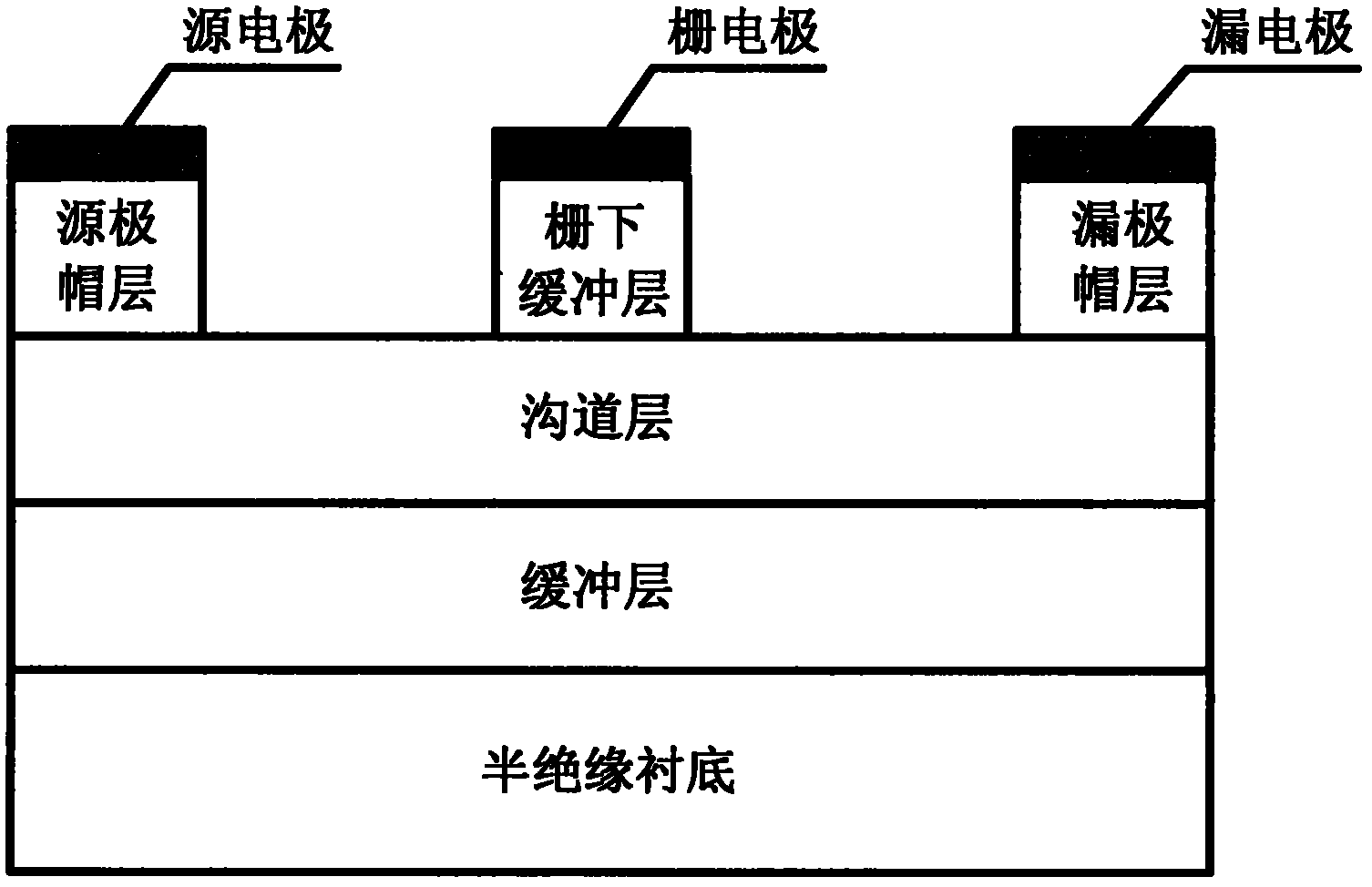
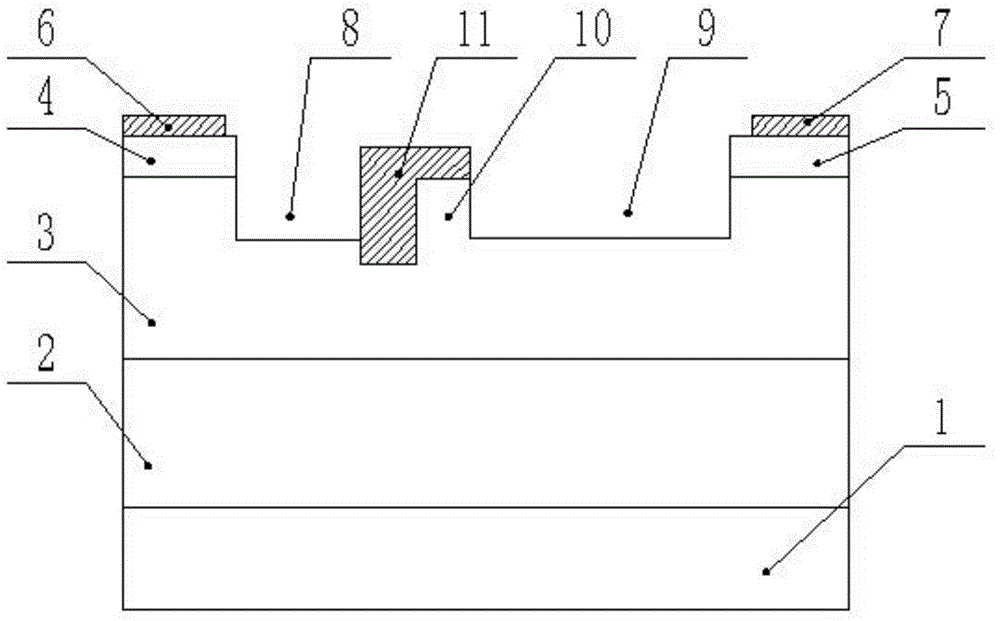
4H-SiC metal-semiconductor field effect transistor with double-sunken buffer layer
ActiveCN104681618ADrain current increasesLarge channel thicknessSemiconductor devicesPower flowSemi insulating
The invention discloses a 4H-SiC metal-semiconductor field effect transistor with a double-sunken buffer layer. The 4H-SiC metal-semiconductor field effect transistor comprises a 4H-SiC semi-insulating substrate, a P type buffer layer and an N type channel layer from bottom to top, wherein a source electrode cap layer and a drain electrode cap layer are respectively arranged on two sides of the N type channel layer; a source electrode and a drain electrode are respectively arranged on the surfaces of the source electrode cap layer and the drain electrode cap layer; a gate electrode is formed on one side, close to the source electrode cap layer, above a channel; grooves are arranged on the upper end face of the P type buffer layer and under a gate source and a gate leakage. The 4H-SiC metal-semiconductor field effect transistor has the advantages that the output drain electrode current is obviously improved, and the breakdown voltage is stable.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
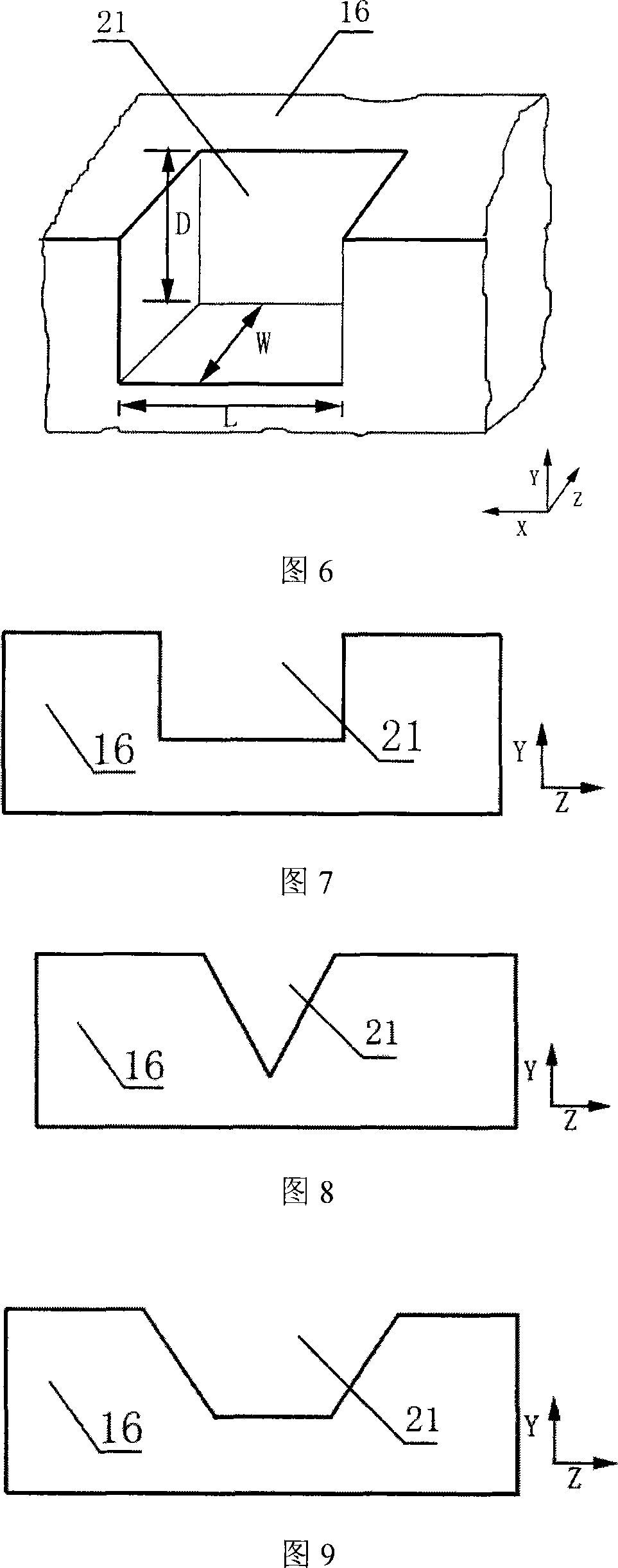
Three-dimensional slot grid metal semiconductor field effect transistor
InactiveCN101022127AImprove breakdown voltageIncrease saturation currentSemiconductor devicesGratingMESFET
This invention puts forward a kind of 3-D groove grating metal semiconductor field effect transistor structure, which opens one or many grooves in an active layer between the source and drain regions in the shape of a square, V, trapezia or a ladder designed according to the actual needs and the grating electrode is covered in the grooves continuously, which greatly increases grating width in the same surface areas of devices due to the existence of the grating grooves compared with the traditional MESFET structure.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
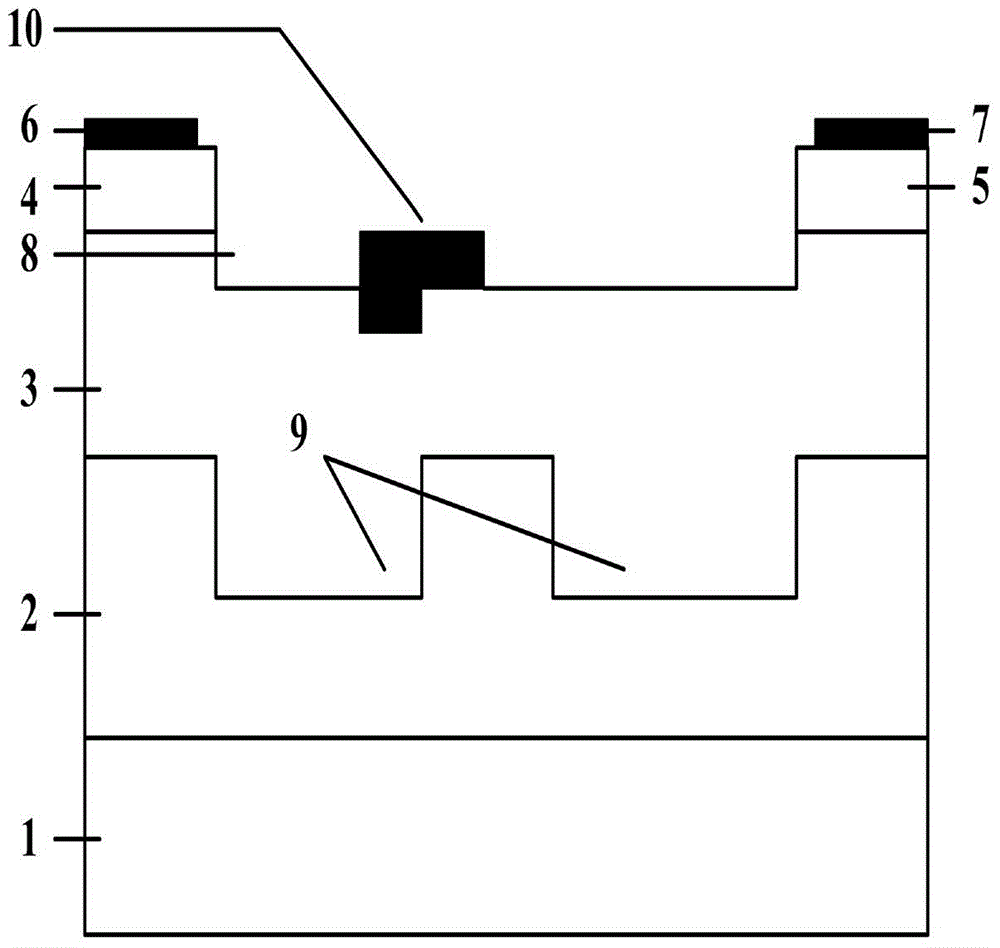
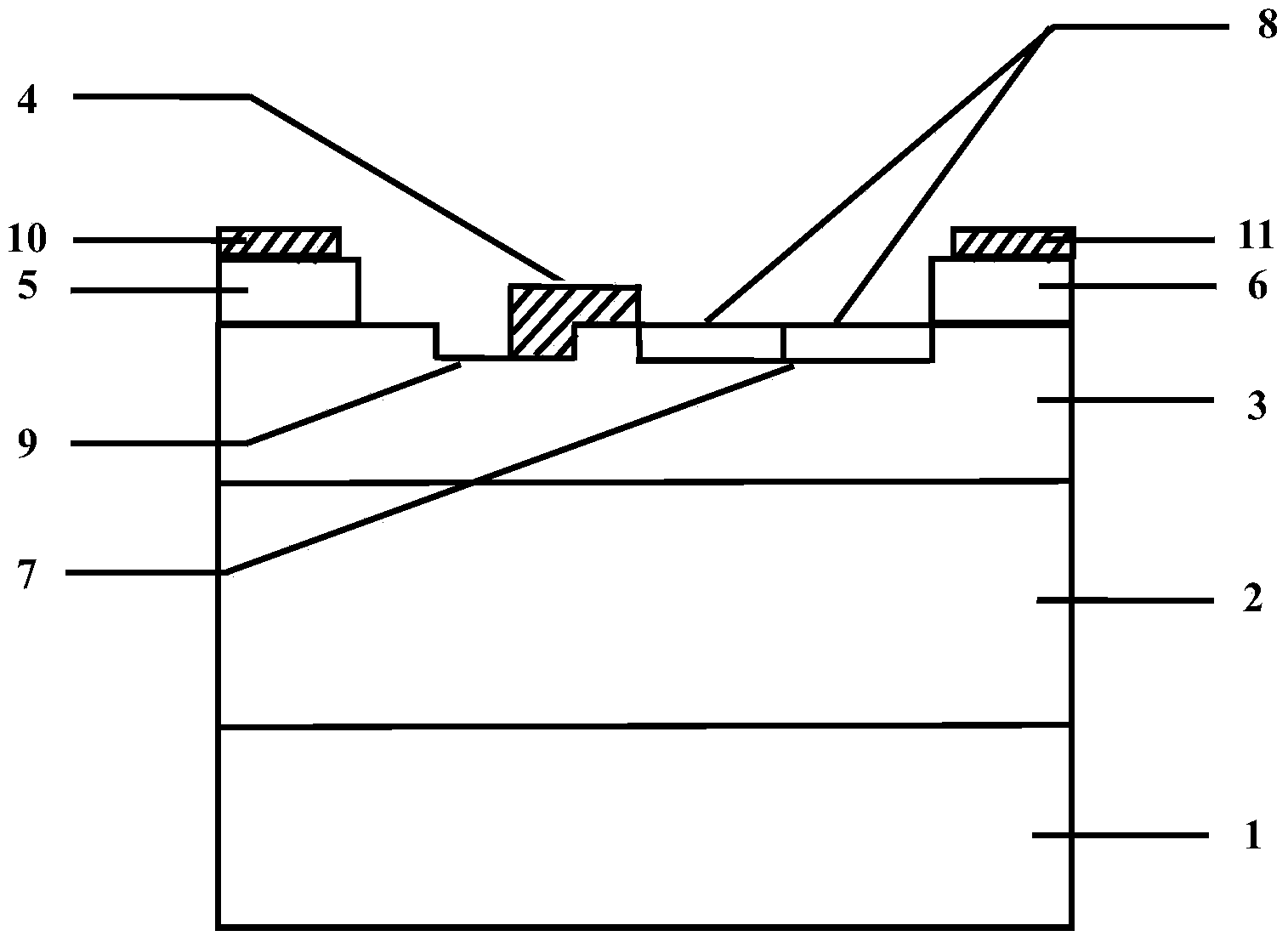
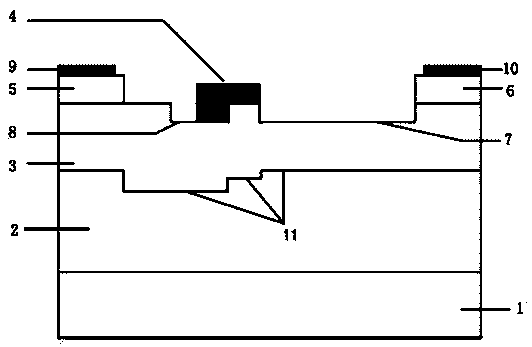
4H-SiC metal semiconductor field-effect transistor
InactiveCN103928529APrevent degradationAvoid damageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSemi insulatingBreakdown voltage
The invention discloses a 4H-SiC metal semiconductor field-effect transistor. The 4H-SiC metal semiconductor field-effect transistor mainly solves the problems that in the prior art, output current of a drain electrode is unstable, and breakdown voltage is low. The 4H-SiC metal semiconductor field-effect transistor structurally comprises a 4H-SiC semi-insulating substrate (1), a P-type buffer layer (2) and an N-type channel layer (3) from bottom to top, wherein a source electrode cap layer (5) and a drain electrode cap layer (6) are arranged on the surface of the N-type channel layer (3), a source electrode (10) and a drain electrode (11) are arranged on the surface of the source electrode cap layer (5) and the surface of the drain electrode cap layer (6) respectively, a gate electrode (4) is formed on one side of the portion, close to the source electrode cap layer (5), of the top of the N-type channel layer (3), a sunken gate source drift region (9) is formed between the gate electrode (4) and the source electrode cap layer (5), a sunken gate drain drift region (7) is formed between the gate electrode (4) and the drain electrode cap layer (6), and transverse PN junctions (8) are arranged on the surface of the sunken gate drain drift region (7). The 4H-SiC metal semiconductor field-effect transistor has the advantages that the breakdown voltage is high, and the output current of the drain electrode is stable.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Polarization-doped field effect transistors (POLFETS) and materials and methods for making the same
Novel GaN / AlGaN metal-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MESFET) structures grown without any impurity doping in the channel. A high-mobility polarization-induced bulk channel charge is created by grading the channel region linearly from GaN to Al0.3Ga0.7N over a distance, e.g., 1000 Å. A polarization-doped field effect transistor (PolFET) was fabricated and tested under DC and RF conditions. A current density of 850 mA / mm and transconductance of 93 mS / mm was observed under DC conditions. Small-signal characterization of 0.7 μm gate length devices had a cutoff frequency, fτ=19 GHz, and a maximum oscillation of fmax=46 GHz. The PolFETs perform better than comparable MESFETs with impurity-doped channels, and are suitable for high microwave power applications. An important advantage of these devices over AlGaN / GaN HEMTs is that the transconductance vs. gate voltage profile can be tailored by compositional grading for better large-signal linearity.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
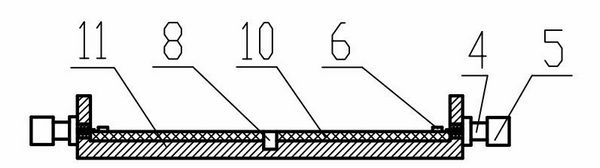
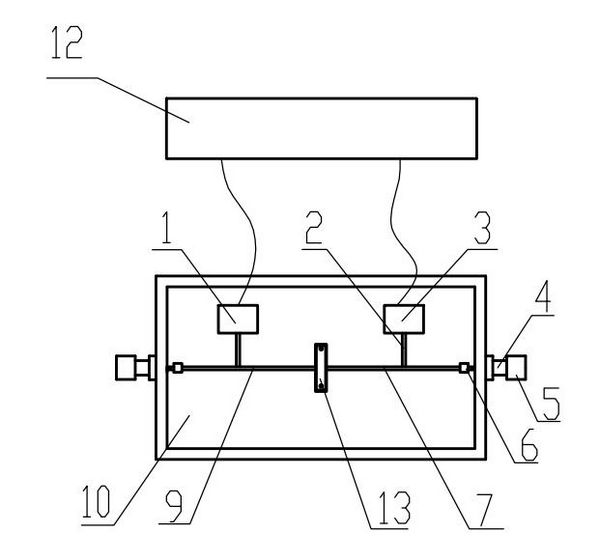
Clamp used for SiC MESFET (Metal Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor) direct current test
ActiveCN102023238AElimination of self-excitationImprove test efficiencyMeasurement instrument housingIndividual semiconductor device testingTest efficiencyComputer module
The invention discloses a clamp used for a SiC MESFET (Metal Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor) direct current test, belonging to the field of field effect transistor tests. The clamp comprises a PCB (Printed Circuit Board) distributed with a filter circuit and a metal board carrying the PCB, wherein the metal board is provided with a groove for fixing a SiC MESFET device to be tested, the PCB is provided with a through hole corresponding to the groove, the filter circuit includes a grid filter circuit and a drain filter circuit, the output ends of the grid filter circuit and the grain filter circuit are respectively connected with a grid transmission wire and a drain transmission wire through offset lines, one ends of the grid transmission wire and the drain transmission wire are respectively provided with a contact respectively connected with a grid electrode and a drain electrode of the SiC MESFET device to be tested, and the other ends of the grid transmission wire and the drain transmission wire are respectively provided with a self-excitation prevention module. The clamp can eliminate self-excitation of the device by the self-excitation prevention modules, improve device test efficiency and accumulate valuable data for the representation of device characteristics.
Owner:THE 13TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP CORP
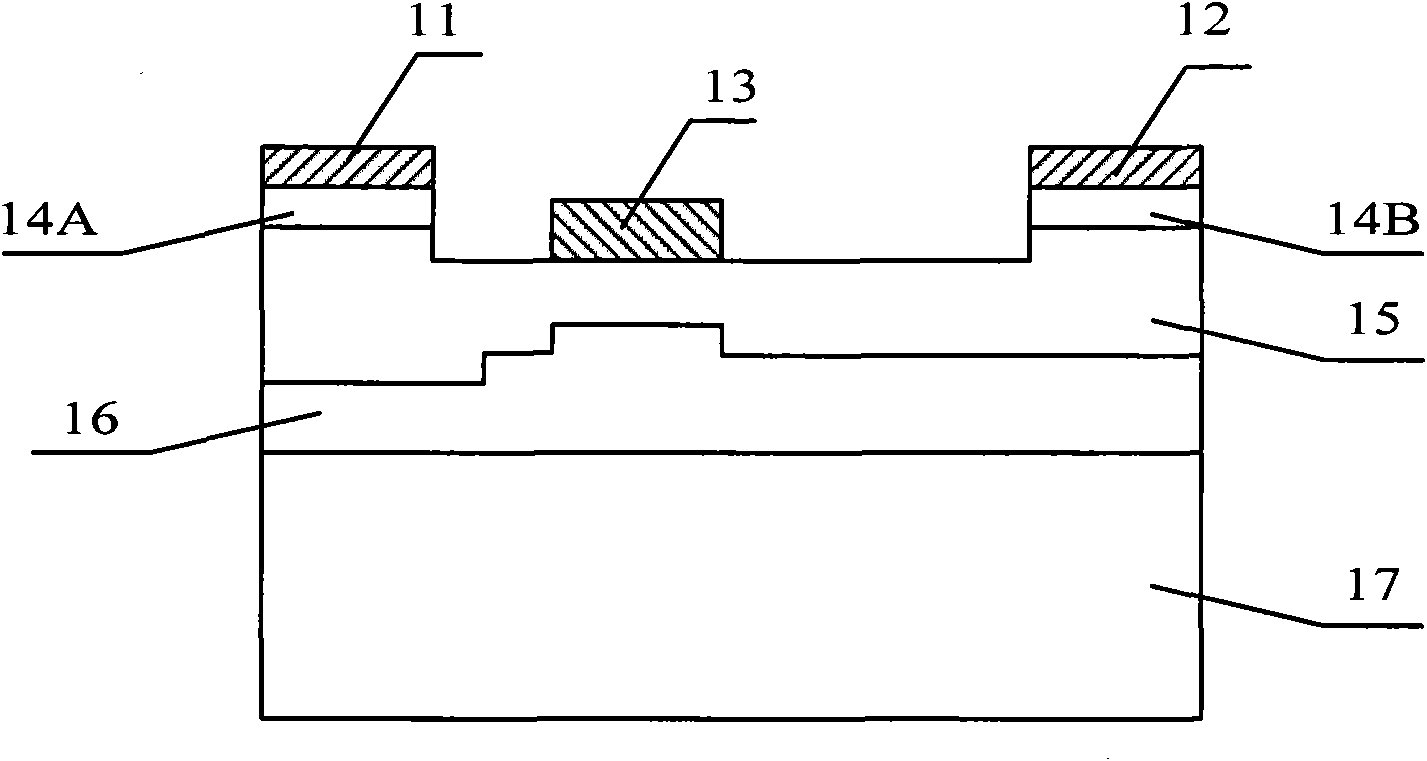
Metal-semiconductor field effect transistor with stepped buffer layer structure
InactiveCN101964363AImprove DC characteristicsImprove high-frequency small-signal characteristicsSemiconductor devicesPower semiconductor deviceMESFET
The invention relates to a MESFET (Metal-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor) with a stepped buffer layer structure, belonging to the technical field of power semiconductor devices. The buffer layer becomes stepped by etching an epitaxial buffer layer of the device, so that an active layer epitaxially growing on the buffer layer has varying channel thickness. The thickest part of the buffer layer is right below a gate electrode, and the thickness of the buffer layer below both sides of the gate electrode is small. The active layer is reversely stepped, the thinnest part of the active layer is right below the gate electrode, and the thickness of the active layer below both sides of the gate electrode is large. The MESFET with the stepped buffer layer structure has the advantages of good DC characteristic, frequency characteristic and output power density, and is applicable to microwave and high power fields.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
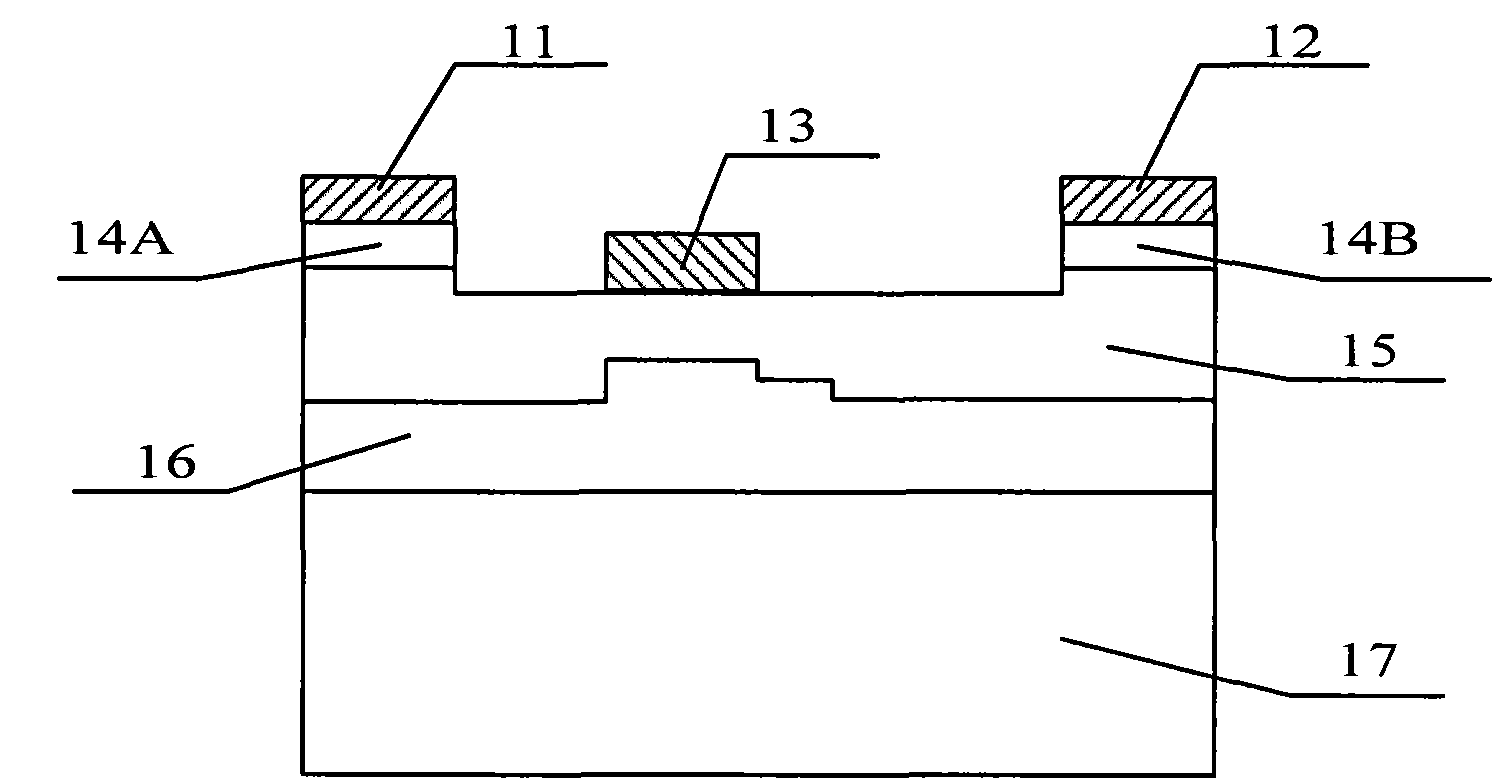
4H-SiC metal semiconductor field effect transistor with slope-shaped grid and manufacturing method
ActiveCN104282764ADrain current increasesLower channel resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPower flowMetal
The invention discloses a 4H-SiC metal semiconductor field effect transistor with a slope-shaped grid. The 4H-SiC metal semiconductor field effect transistor comprises a 4H-SiC semi-insulating substrate, a P-type buffer layer and an N-type channel layer from bottom to top, a source electrode cap layer and a drain electrode cap layer are arranged on the surface of the N-type channel layer, a source electrode and a drain electrode are arranged on the surface of the source electrode cap layer and the surface of the drain electrode cap layer respectively, a slope-shaped groove inclined towards one side of the source electrode cap layer is formed in the upper end face of the N-type channel layer, the slope-shaped grid is arranged is arranged in the slope-shaped groove, the lower end face of the slope-shaped grid is matched with the slope-shaped groove, the upper end face of the slope-shaped grid is parallel to the upper end face of the N-type channel layer, and the distance between the slope-shaped grid and the source electrode cap layer is smaller than that between the slope-shaped grid and the drain electrode cap layer. The field effect transistor has the advantages of being high in drain electrode output current and excellent in frequency property.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
4H-SiC metal semiconductor field effect transistor with step buffer layer structure
ActiveCN104393047AIncrease saturation currentLower breakdown voltageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSemi insulatingBreakdown voltage
The invention discloses a 4H-SiC metal semiconductor field effect transistor with a step buffer layer structure. The 4H-SiC metal semiconductor field effect transistor comprises a 4H-SiC semi-insulating substrate, a P-type buffer layer and an N-type channel layer from the bottom to the top. The two sides of the N-type channel layer are respectively provided with a source electrode cap layer and a drain electrode cap layer. The surface of the source electrode cap layer and the drain electrode cap layer is respectively provided with a source electrode and a drain electrode. A gate electrode is formed on one side which is arranged above the N-type channel layer and close to the source electrode cap layer. A concave gate source drift region is formed between the gate electrode and the source electrode cap layer. A concave gate drain drift region is formed between the gate electrode and the drain electrode cap layer. The position, which is arranged on the upper end surface of the P-type buffer layer and close to the source electrode cap layer, is provided with a groove. One side, which is arranged in the groove and close to the drain electrode cap layer, is provided with two steps. The 4H-SiC metal semiconductor field effect transistor with the step buffer layer structure has advantages of being stable in breakdown voltage and high in output drain electrode current.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
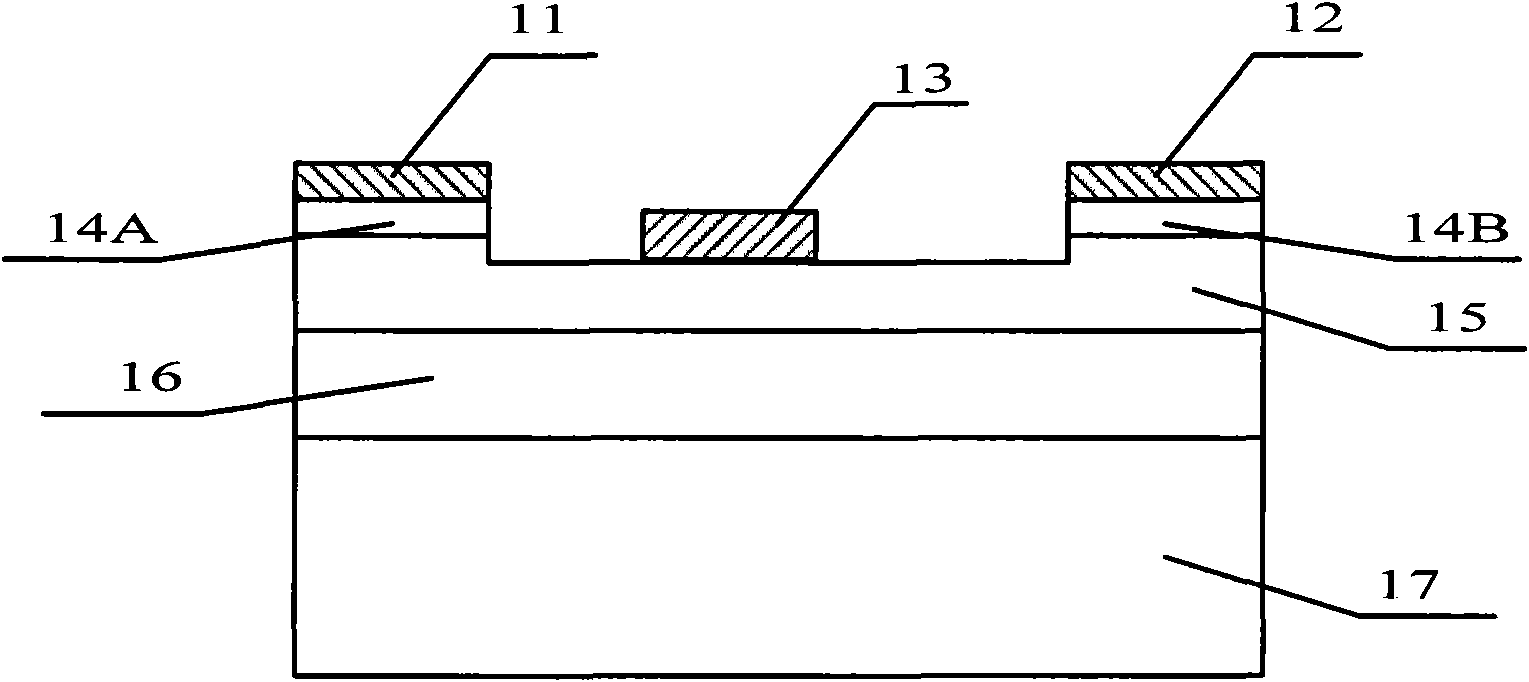
Metal-semiconductor field-effect transistor with gate lower buffer layer structure and manufacturing method
InactiveCN102290434AIncrease output currentReduce the depletion layerSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHigh concentrationIon implantation
The invention relates to a metal-semiconductor field effect transistor with an under-grid buffer layer structure and a manufacturing method; the transistor comprises a semi-insulating substrate, a buffer layer, a channel layer, an under-grid buffer layer, a source electrode cap layer, a drain electrode cap layer, a source electrode, a drain electrode and a grid electrode, wherein the under-grid buffer layer, the source electrode cap layer and the drain electrode cap layer are sequentially formed on the channel layer; the under-grid buffer layer forms a raised platform on the channel layer; and the grid electrode is formed on the raised platform. The manufacturing method of the transistor comprises the following steps of: sequentially growing a P type buffer layer, an N type channel layer and an N type under-grid buffer layer on the semi-insulating substrate; carrying out high concentration N type ion implantation on regions of both ends of the under-grid buffer layer corresponding to the source electrode and the drain electrode to form a source electrode cap layer and a drain electrode cap layer; etching a part of the under-grid buffer layer which is positioned between a grid source and a grid drain; and manufacturing the source electrode and the drain electrode on the source electrode cap layer and the drain electrode cap layer, and manufacturing the grid electrode on the under-grid buffer layer. The transistor of the invention can increase the power density and frequency response of a microwave power amplifier circuit and a microwave power amplifier system; and the manufacturing process is simple.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
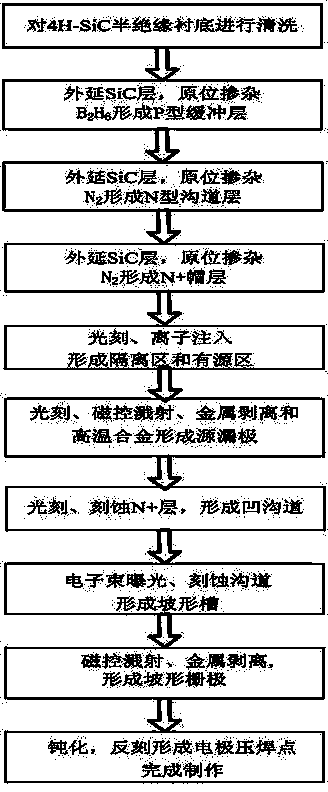
Preparation method for metal semiconductor field effect transistor with wide channel and deep recesses
InactiveCN104867835AGood barrierSimple processSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLithographic artistPower flow
The invention belongs to the technical field of field effect transistors, and particularly discloses a preparation method for a metal semiconductor field effect transistor with wide channels and deep recesses. The preparation method for the metal semiconductor field effect transistor with the wide channels and deep recesses settles the problems in prior art and has advantages of realizing simple manufacture process, enlarging an output current and a breakdown voltage, and improving frequency characteristic. The preparation method comprises the steps of cleaning a semi-insulating substrate; realizing epitaxial growth of a P-type buffer layer; realizing epitaxial growth of an N-type channel layer on the P-type buffer layer; realizing epitaxial growth of an N<+> cap layer on the N-type channel layer; preparing an isolation region and an active region; preparing a source electrode and a drain electrode; performing lithography and etching on the N<+> between the source electrode and the drain electrode, thereby forming a high-gate area; manufacturing a gate electrode; and manufacturing an electrode pads, thereby finishing device preparation.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
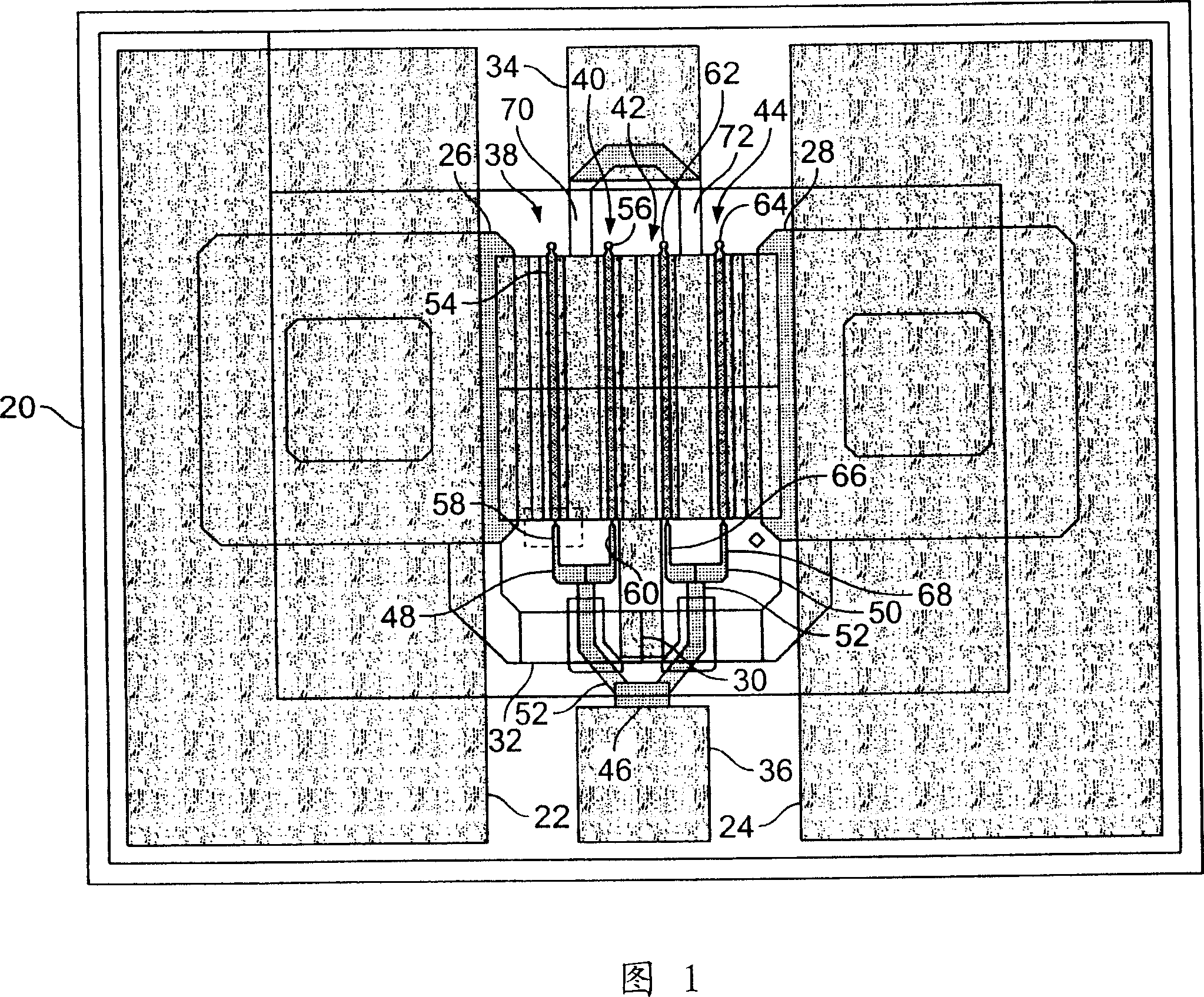
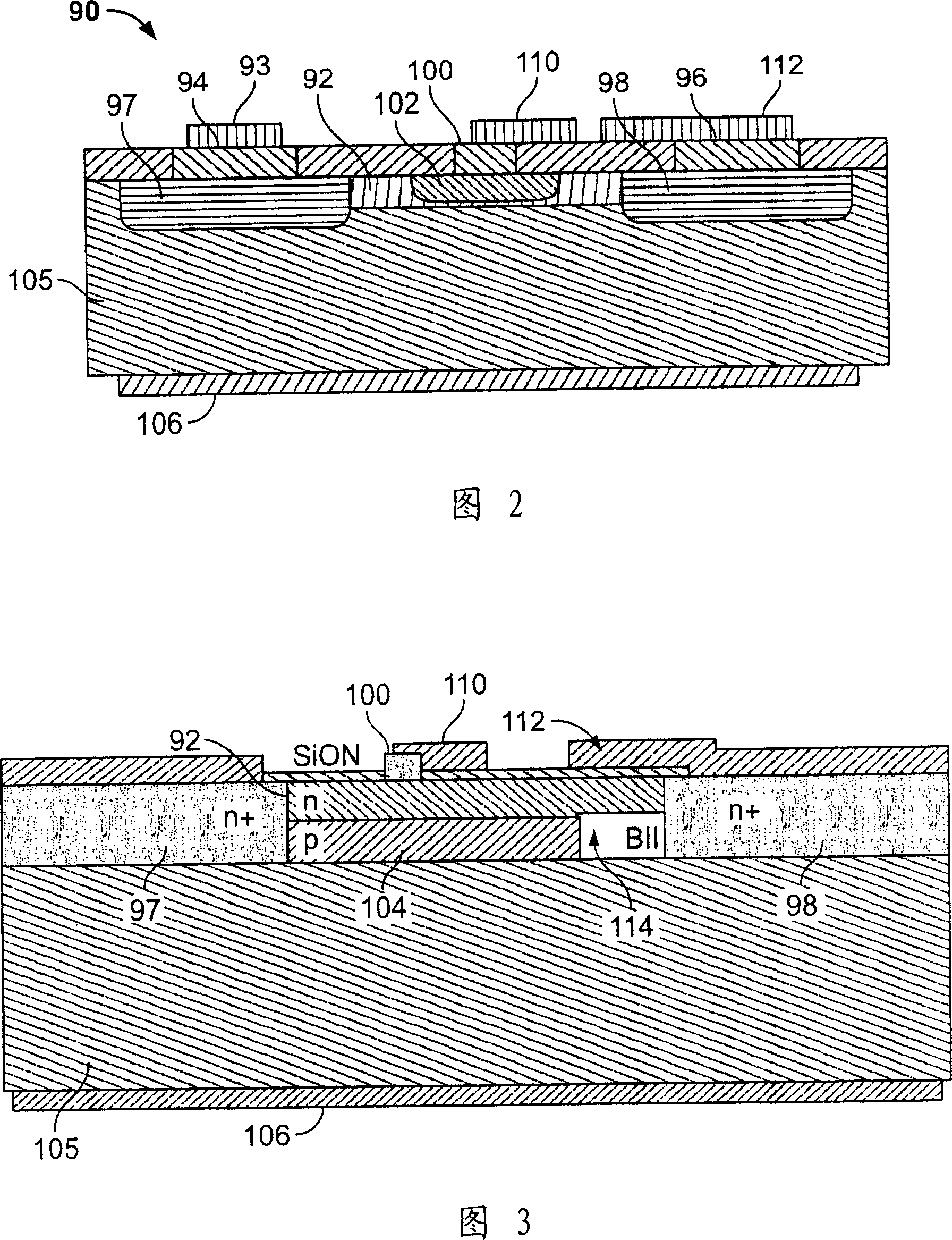
Dual field plate mesfet and its forming method
InactiveCN101005096ASemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesField effectMESFET
A dual field plate MESFET (90) and method of forming a MESFET. The MESFET (90) includes a gate electrode (100) and a drain electrode (96), with the gate electrode (100) and drain electrode (96) formed on a substrate (105). The MESFET further includes a gate side field plate (110) at the gate electrode (100) and a drain side field plate (112) in proximity to the drain electrode (96) and extending over a burnout improvement region in the substrate (105).
Owner:COBHAM DEFENSE ELECTRONICS SYST CORP
Metal semiconductor field effect light emitting transistor and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN101308895AImprove performanceReduce etch damageSemiconductor devicesQuantum wellOhmic contact
The invention discloses a metal semiconductor field effect transistor and the fabrication method thereof. The metal semiconductor field effect transistor comprises a substrate, a buffer layer which is arranged on the substrate, a first n type heavily doped layer above the buffer layer, a multi-quantum well layer and a p type layer which are sequentially arranged on the n type layer, a second n type heavily doped layer above the buffer layer, a source electrode which is in Ohmic contact with the second n type heavily doped layer, and a drain electrode which is in Ohmic contact with the p type layer. The first n type heavily doped layer is not connected with the second n type heavily doped layer. The metal semiconductor field effect transistor is characterized in that a slightly doped n type layer is arranged between the buffer layer and first and second n type heavily doped layers, and a SiO2 layer connected with the slightly doped n type layer is embedded between the substrate and the buffer layer. The metal semiconductor field effect transistor further comprises a gate electrode which is in Schottky contact with the SiO2 layer. The metal semiconductor field effect transistor reduces etching damages, thus improving the performance of the components.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com