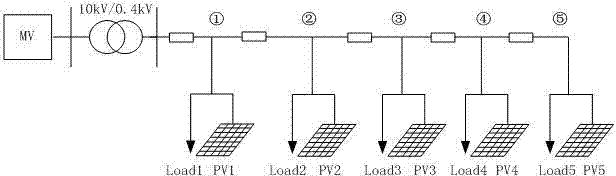
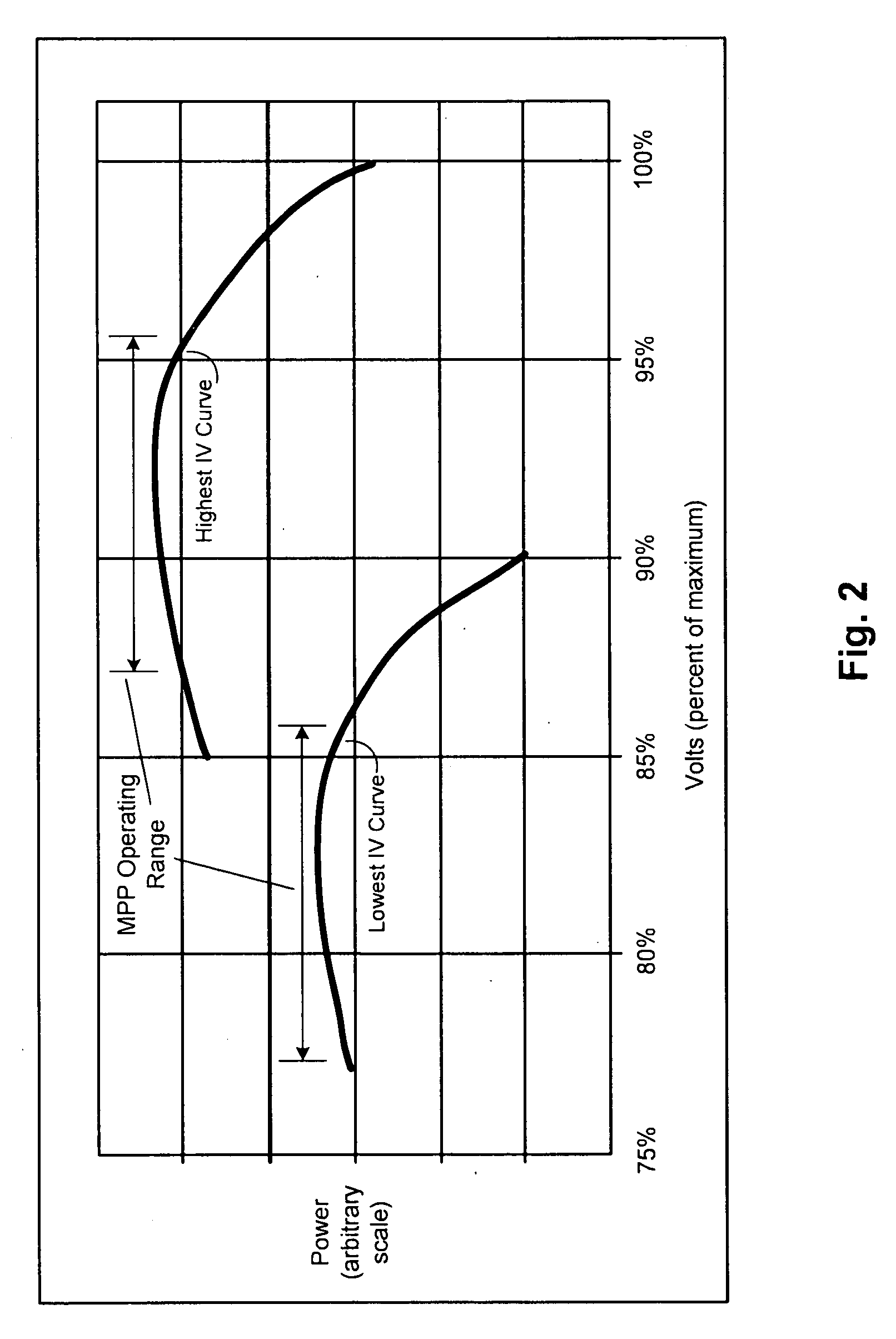
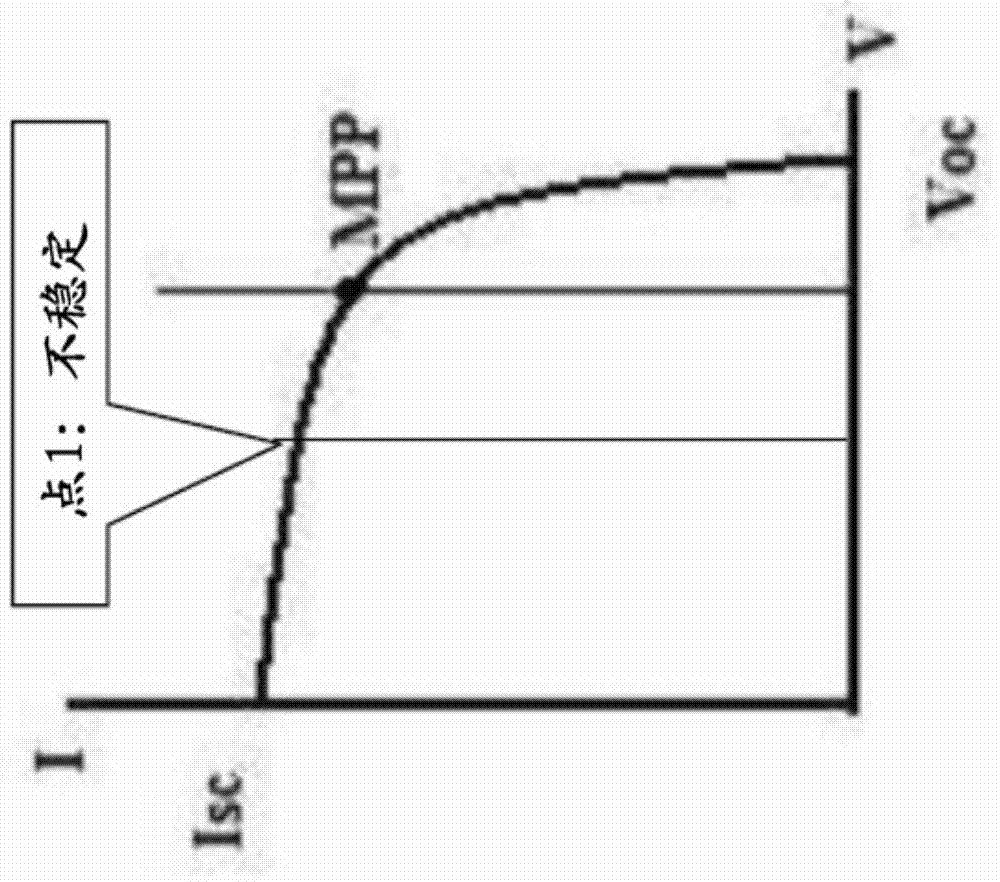
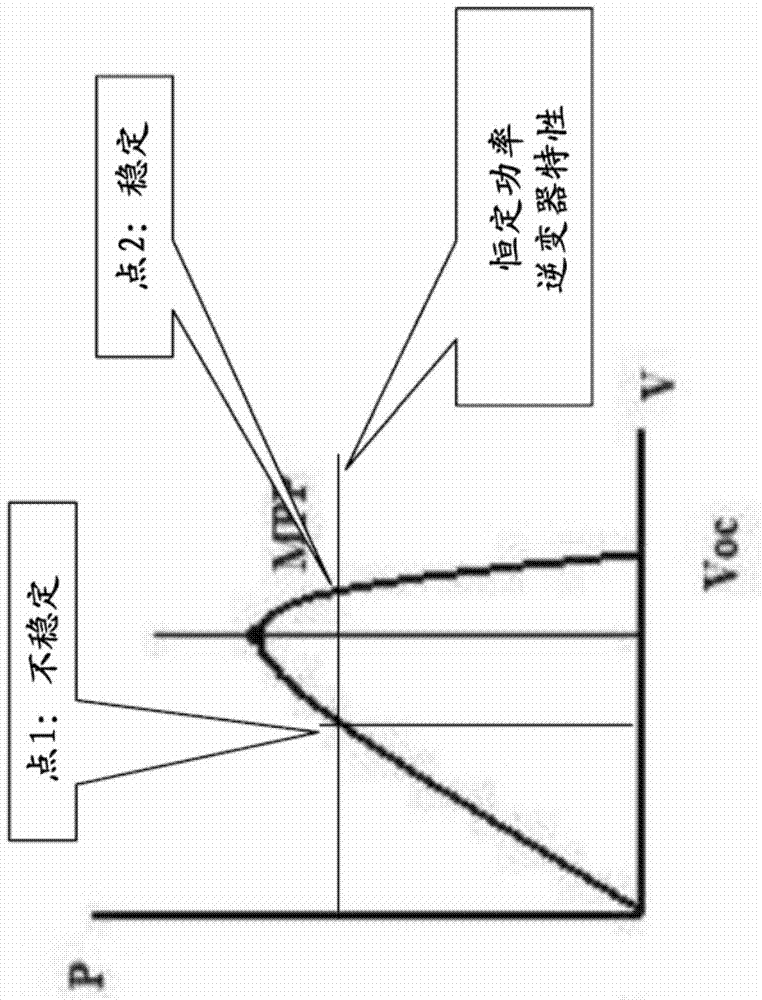
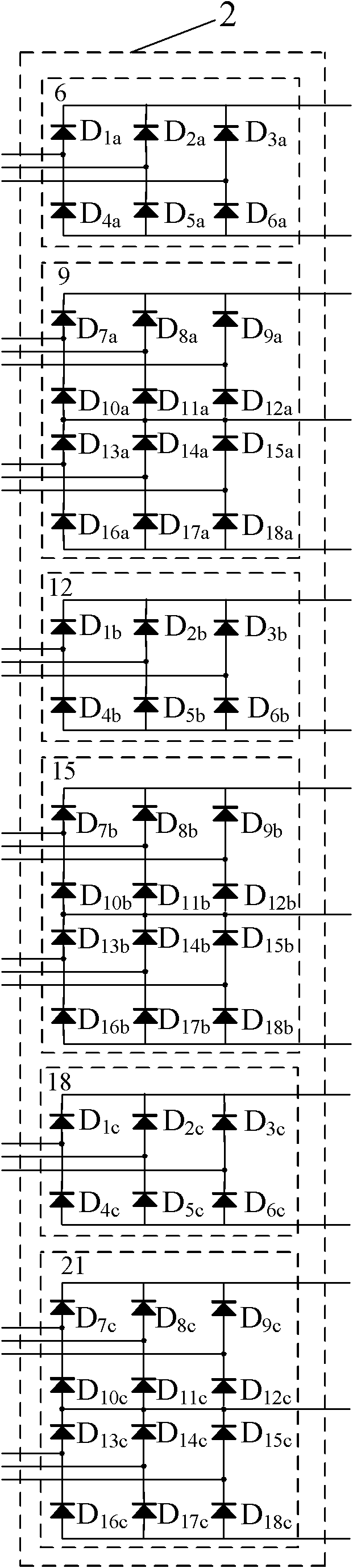
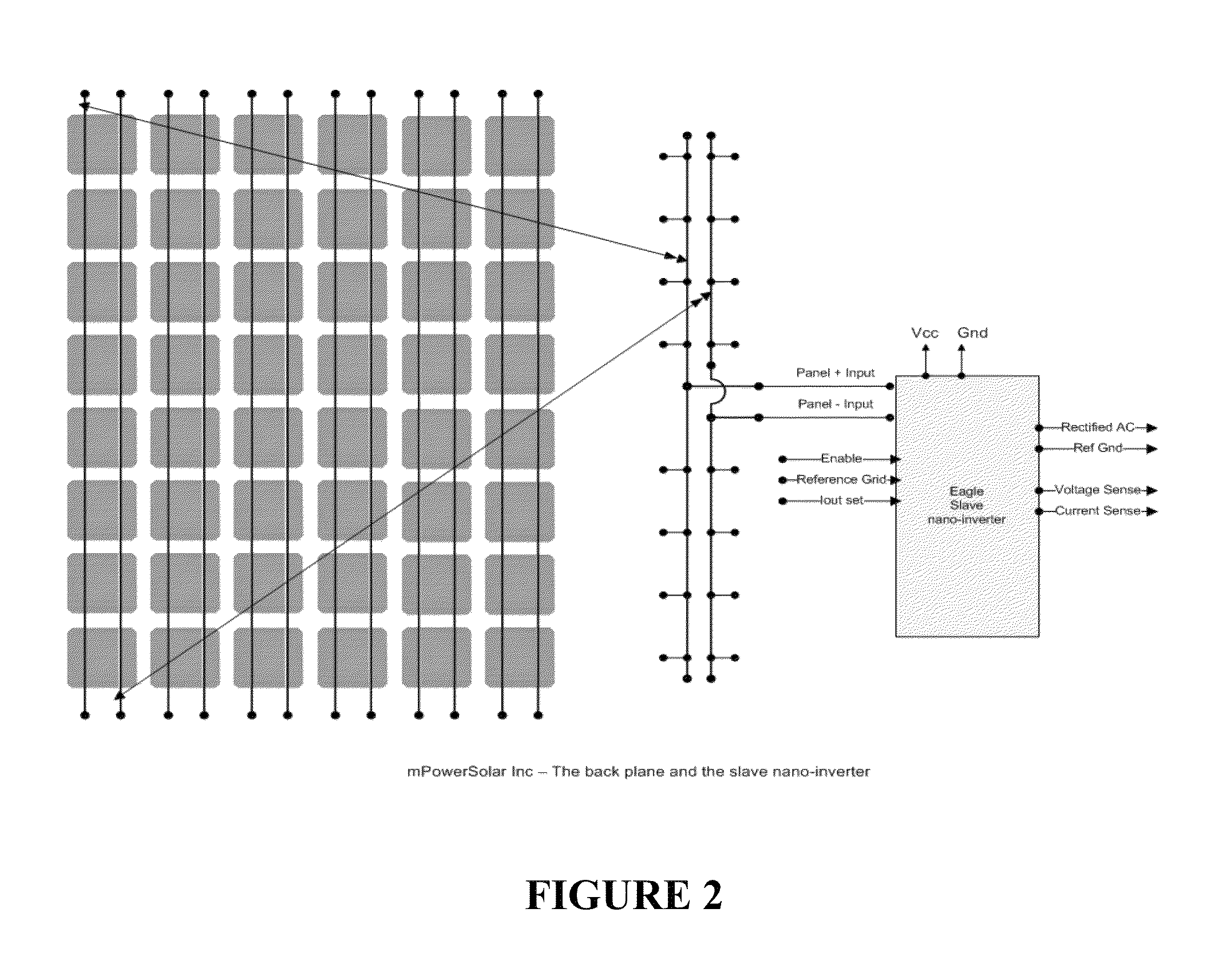
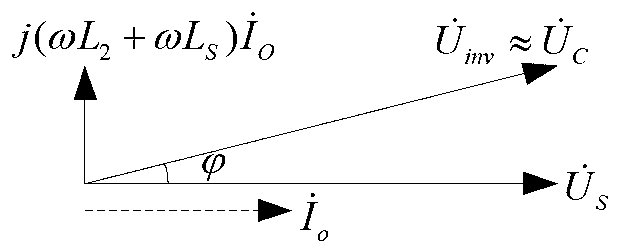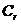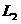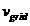Patents
Literature
311 results about "Solar inverter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
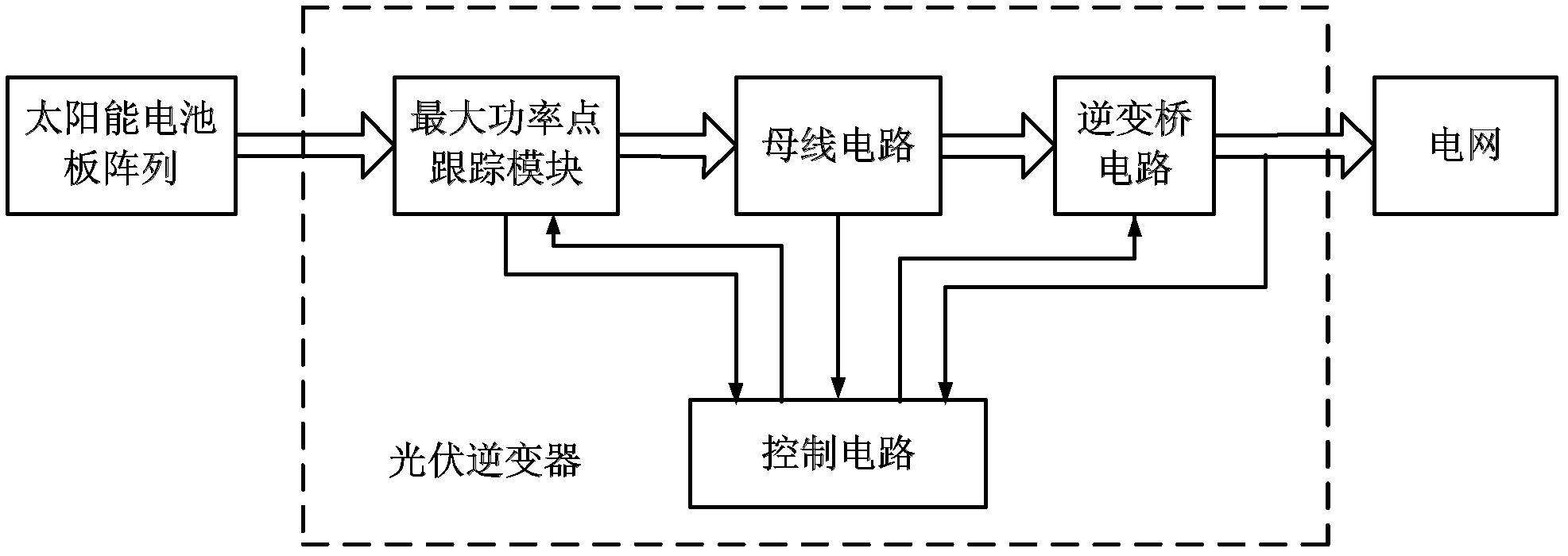
A solar inverter or PV inverter, is a type of electrical converter which converts the variable direct current (DC) output of a photovoltaic (PV) solar panel into a utility frequency alternating current (AC) that can be fed into a commercial electrical grid or used by a local, off-grid electrical network. It is a critical balance of system (BOS)–component in a photovoltaic system, allowing the use of ordinary AC-powered equipment. Solar power inverters have special functions adapted for use with photovoltaic arrays, including maximum power point tracking and anti-islanding protection.
Solar inverter and control method
ActiveUS8184460B2Conversion with intermediate conversion to dcDc-dc conversionControl signalEngineering
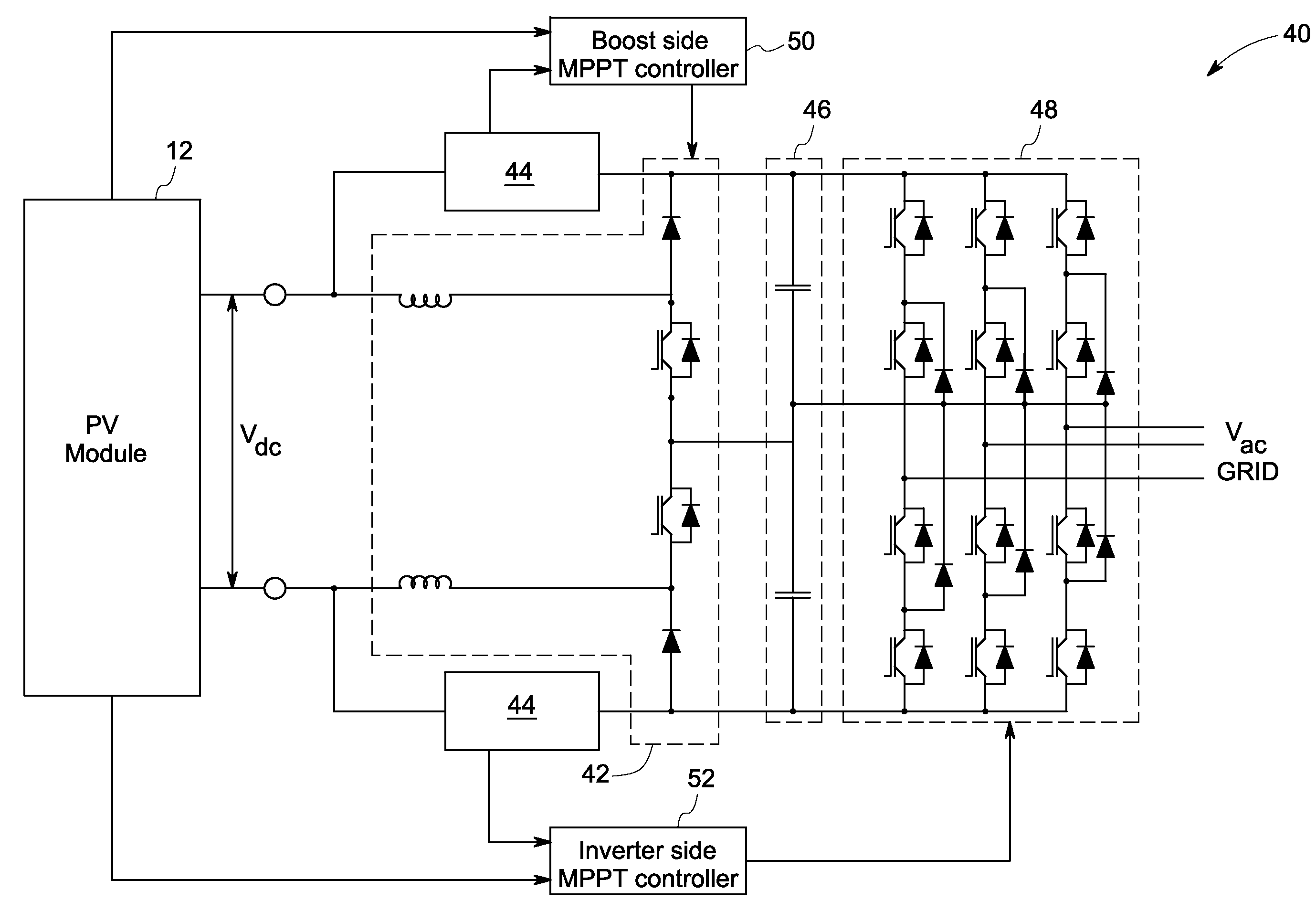
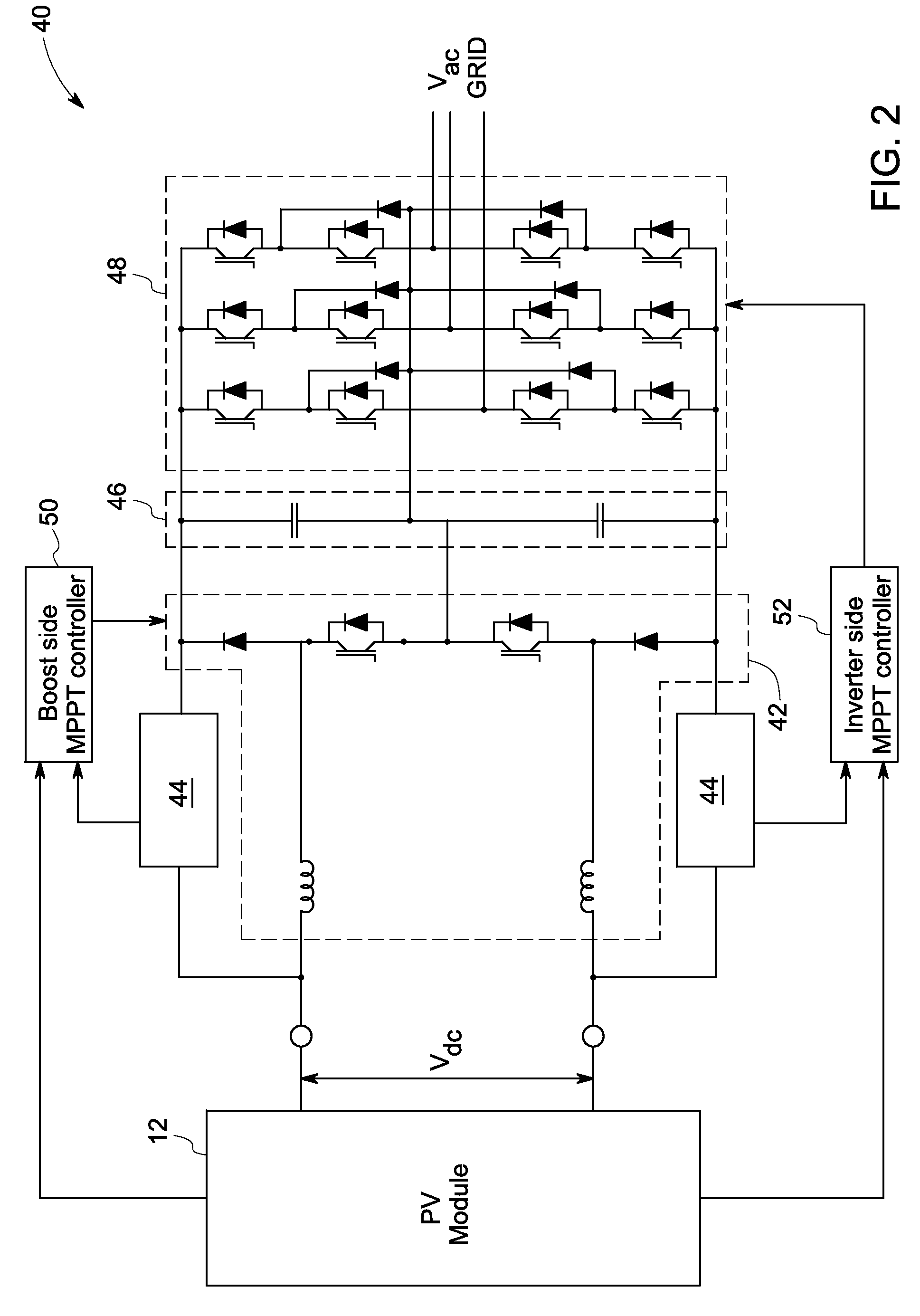
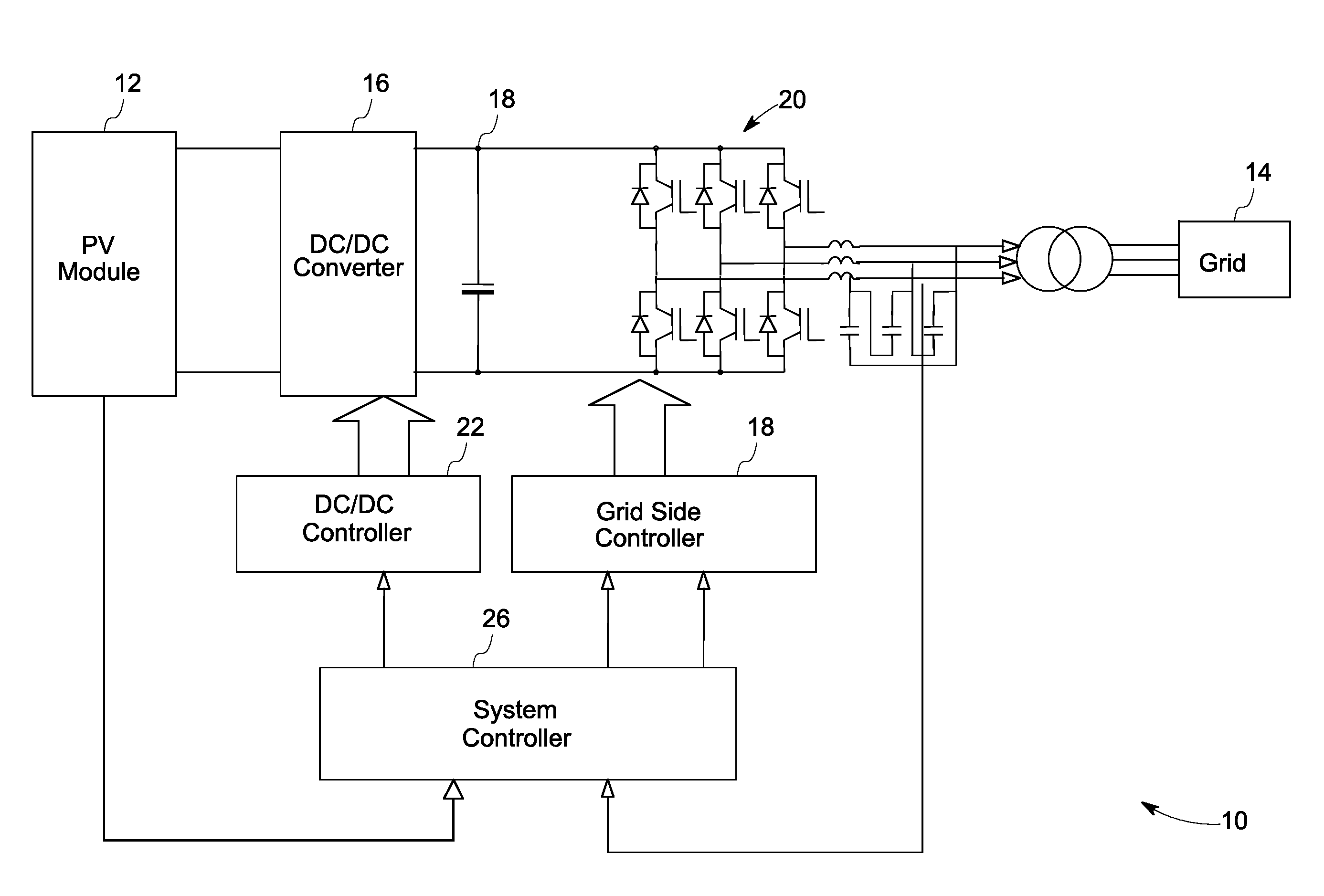
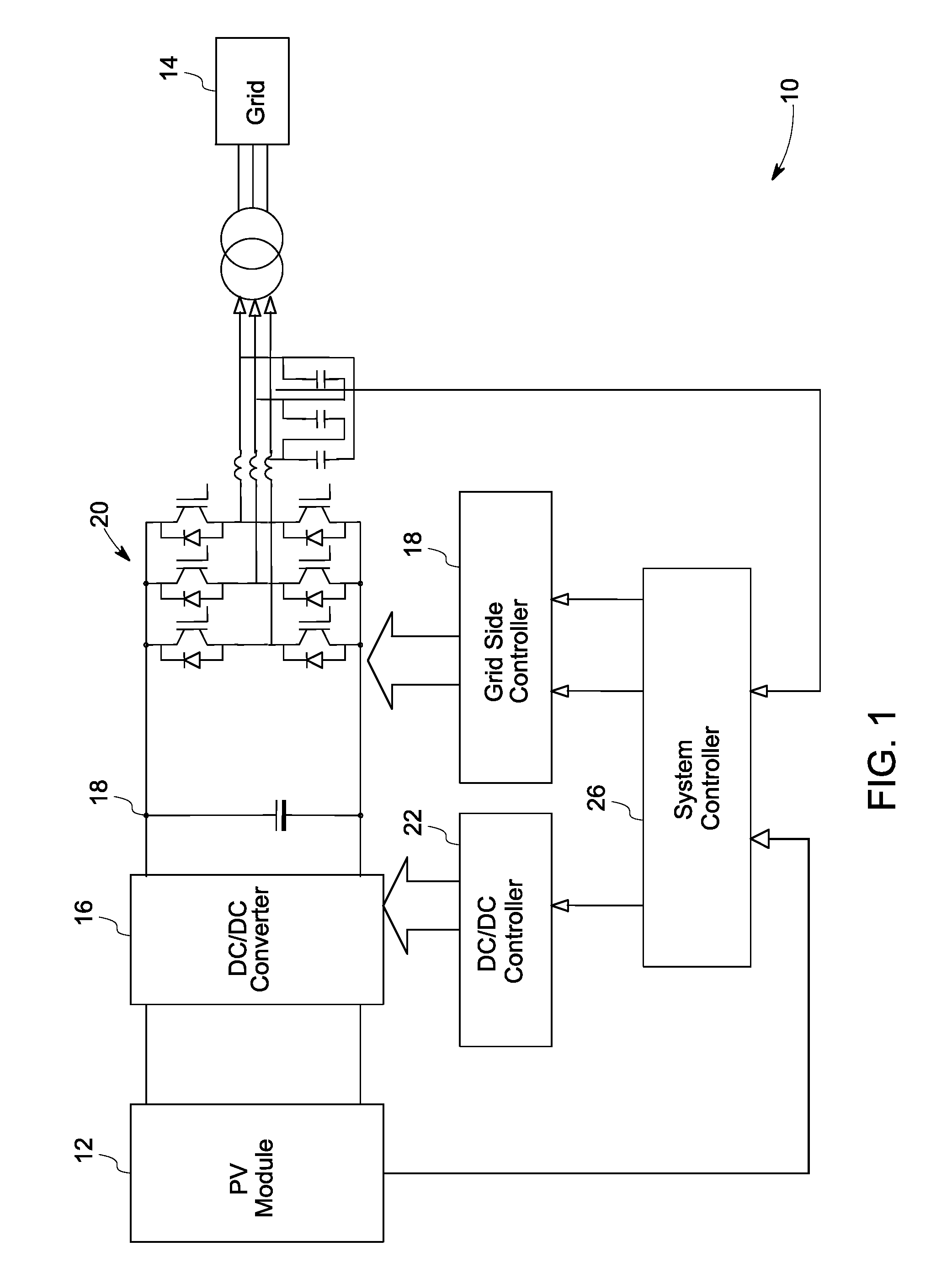
A power generation system including a photovoltaic (PV) module to generate direct current (DC) power is provided. The system includes a controller to determine a maximum power point for the power generation system and a boost converter for receiving control signals from the controller to boost the power from the PV module to a threshold voltage required to inject sinusoidal currents into the grid. A DC to alternating current (AC) multilevel inverter is provided in the system to supply the power from the PV module to a power grid. The system also includes a bypass circuit to bypass the boost converter when an input voltage of the DC to AC multilevel inverter is higher than or equal to the threshold voltage.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Solar Inverter and Photovoltaic Installation Comprising Several Solar Inverters
InactiveUS20070252716A1Compact implementationBatteries circuit arrangementsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsElectric power systemComputer module
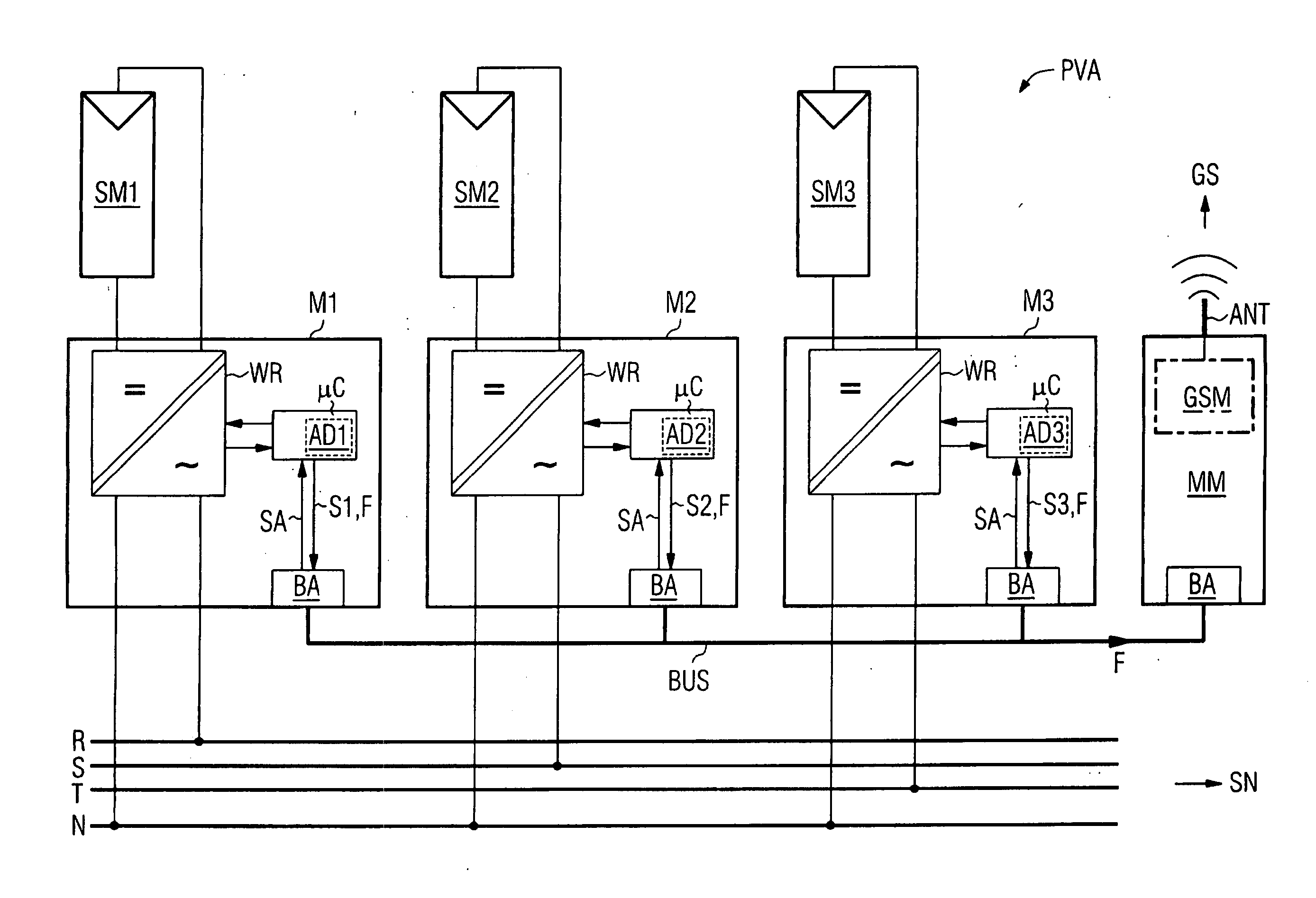
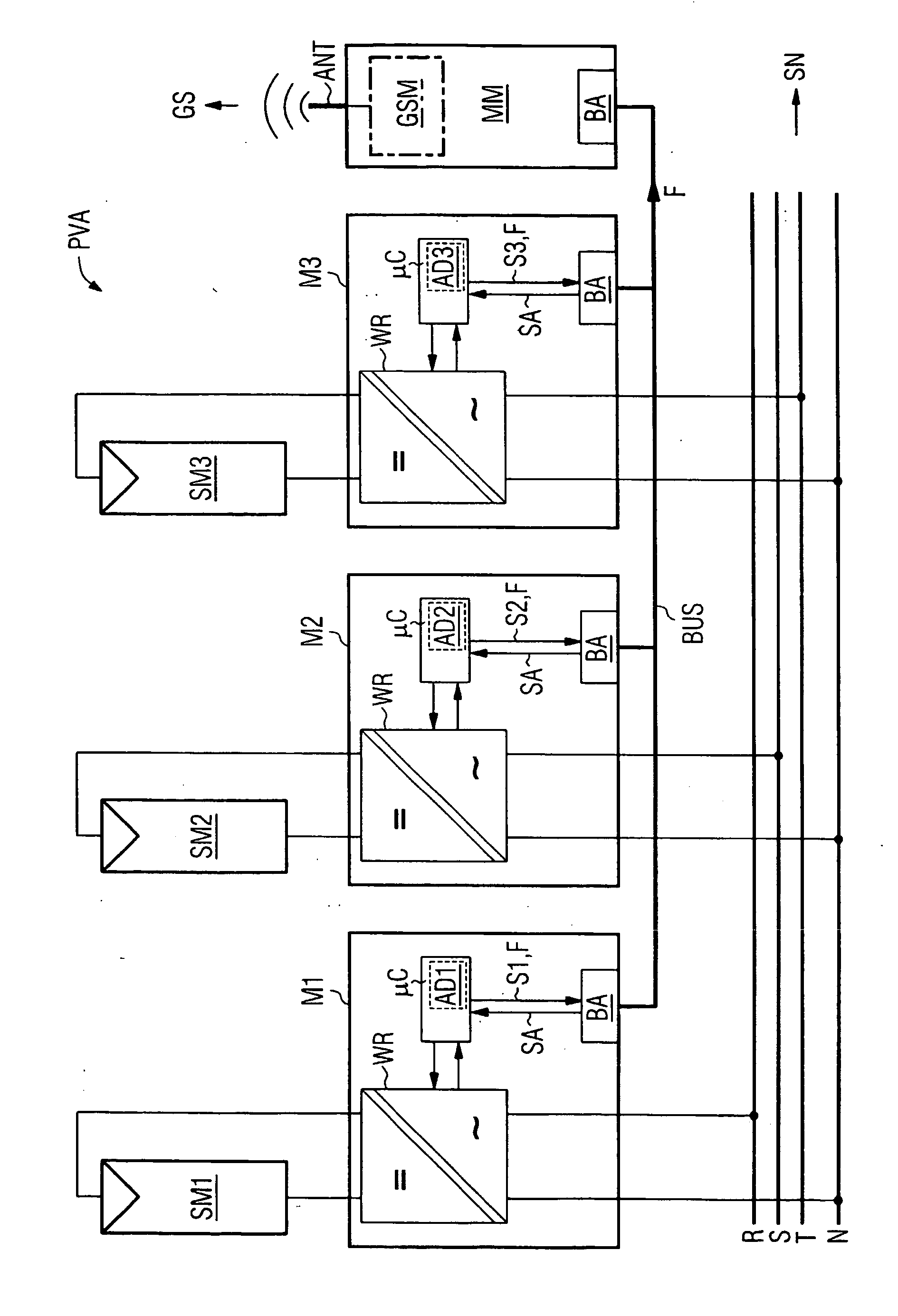
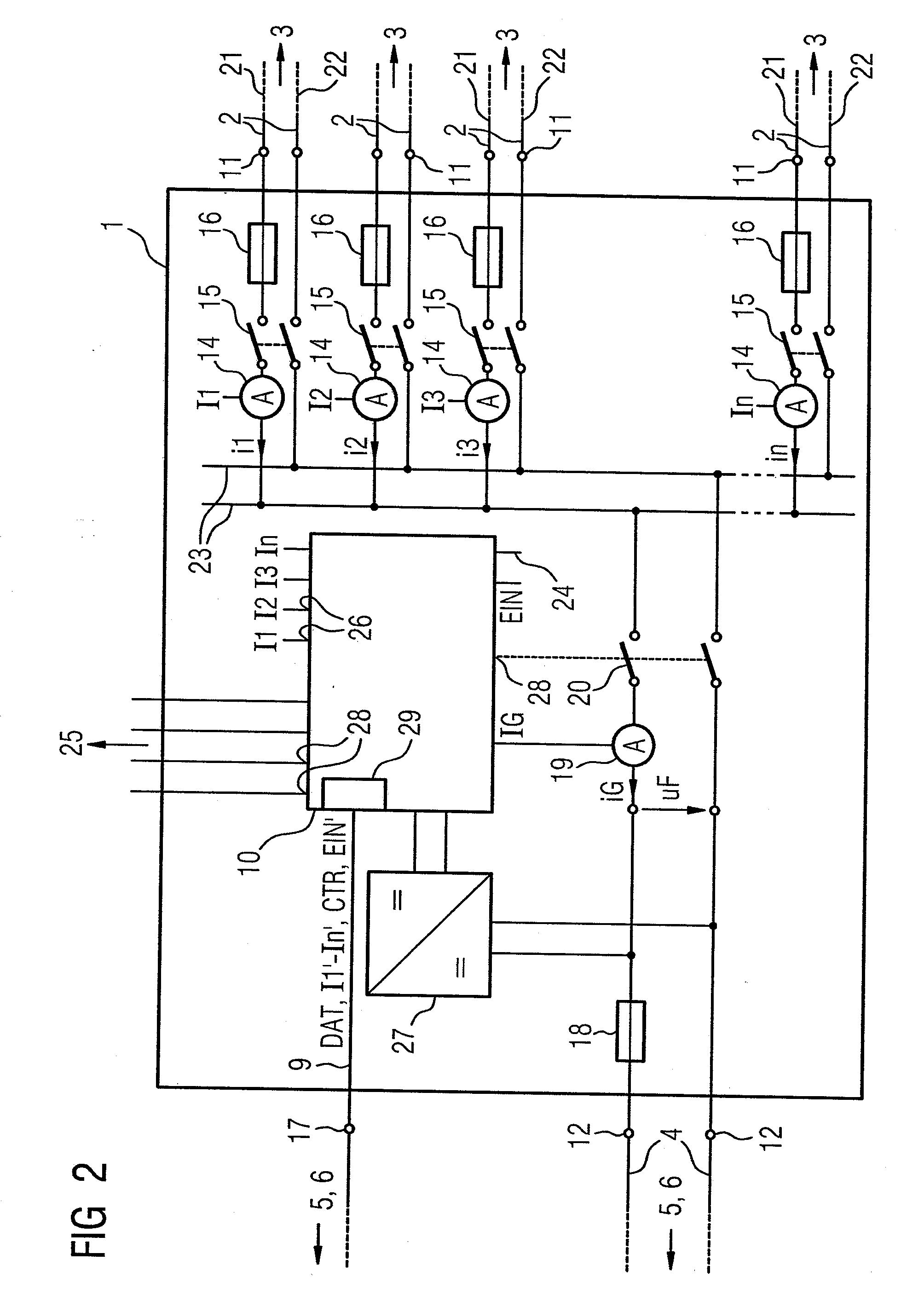
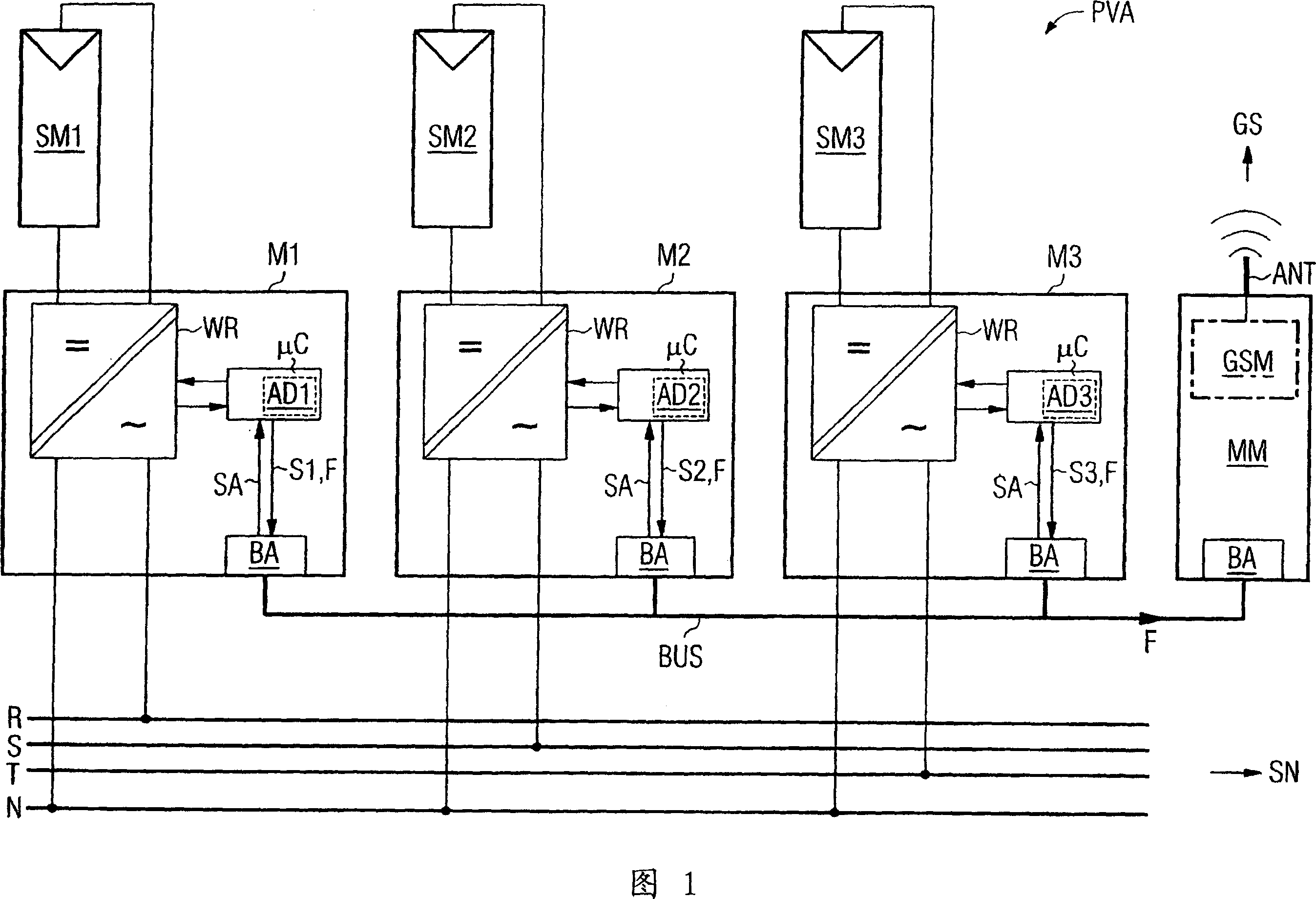
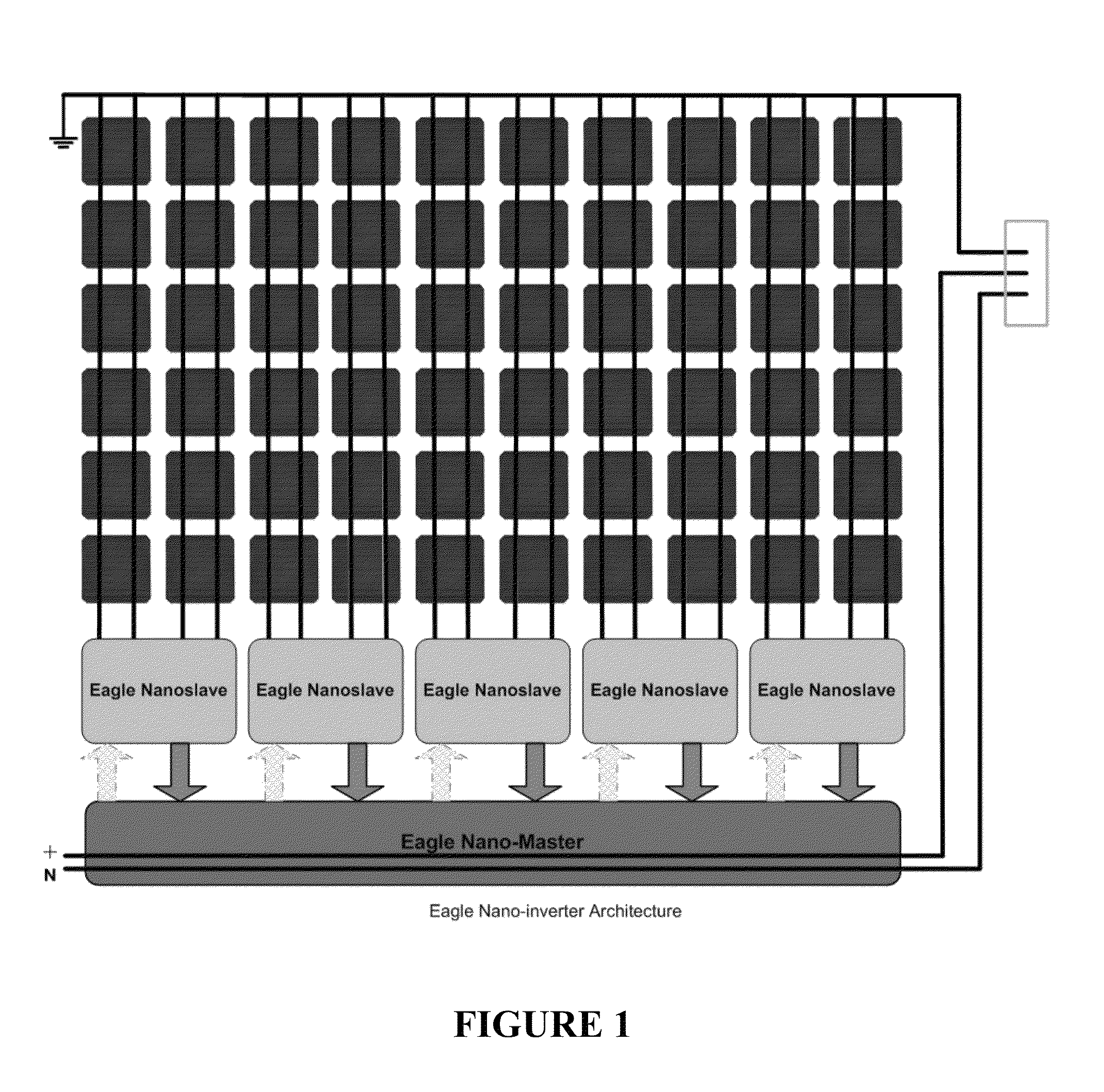
In one aspect, a solar inverter which can be connected to at least one photovoltaic generator at the input end and to a power system at the output end is provided. The solar inverter includes an inverter module, an electronic control unit at least for diagnosing an inverter module, and a bus interface for technically connecting the electronic control unit to a communication bus. The electronic control unit cyclically outputs a piece of status information of the solar inverter on the communication bus, and outputs an error message on the communication bus, cyclically reads status information of other solar inverters that are connected to the communication bus, and outputs an error message on the communication bus in case at least one expected additional piece of status information fails to be output. Whereby, the need for a separate monitoring unit is eliminated.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Solar inverter and plant for converting solar energy into electrical energy
InactiveUS8148849B2Dc network circuit arrangementsPhotovoltaic monitoringPhotovoltaic generatorEngineering
Owner:ELETTRONICA SANTERNO
Solar inverter and control method
ActiveUS20100302819A1High strengthConversion with intermediate conversion to dcDc-dc conversionControl signalPower grid
A power generation system including a photovoltaic (PV) module to generate direct current (DC) power is provided. The system includes a controller to determine a maximum power point for the power generation system and a boost converter for receiving control signals from the controller to boost the power from the PV module to a threshold voltage required to inject sinusoidal currents into the grid. A DC to alternating current (AC) multilevel inverter is provided in the system to supply the power from the PV module to a power grid. The system also includes a bypass circuit to bypass the boost converter when an input voltage of the DC to AC multilevel inverter is higher than or equal to the threshold voltage.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
PV Sub-Generator Junction Box, PV Generator Junction Box, and PV Inverter for a PV System, and PV System
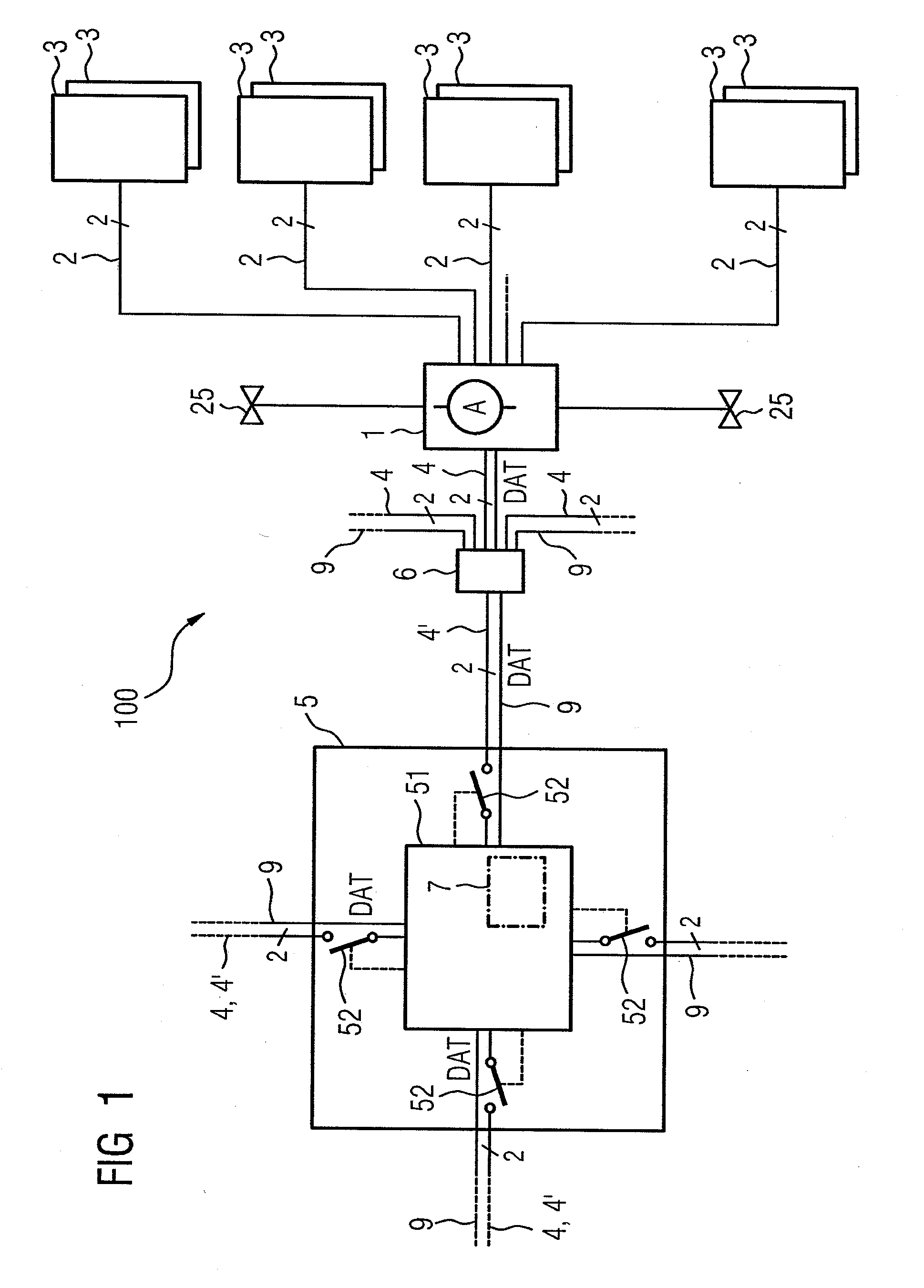
ActiveUS20110031814A1Reduce spendingData transmission securityDc network circuit arrangementsTransmission/receiving by adding signal to waveModem deviceEngineering
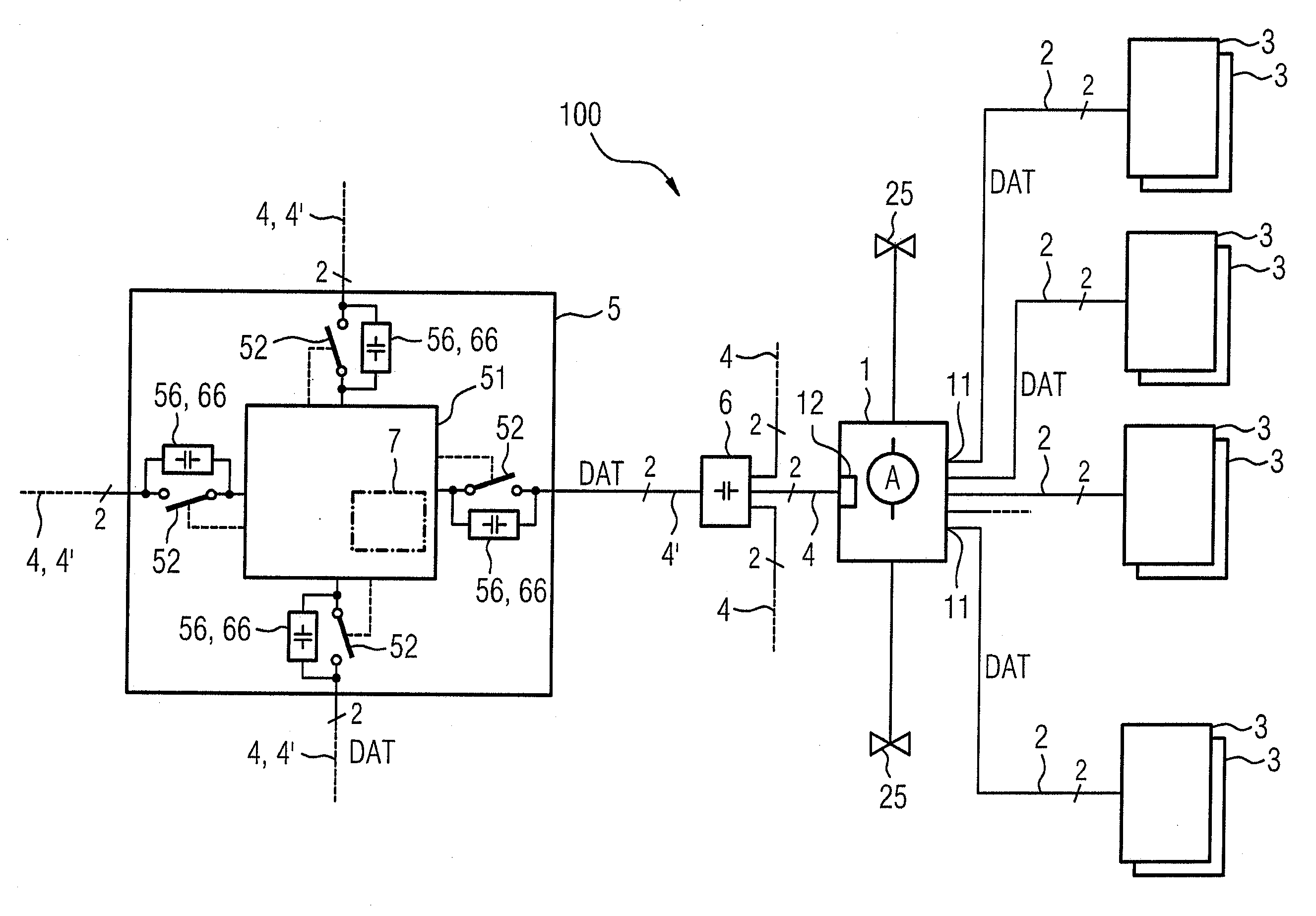
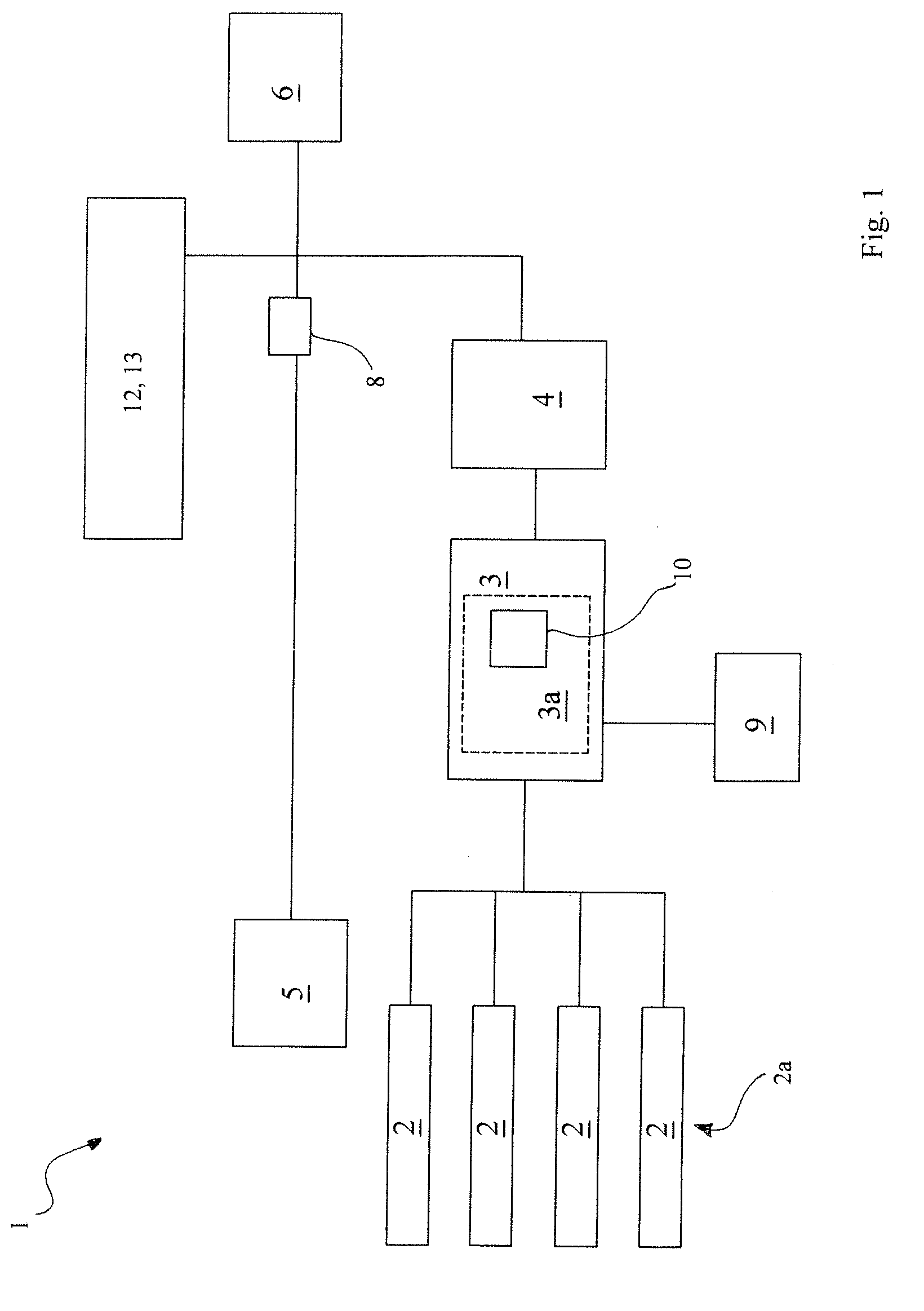
A photovoltaic (PV) sub-generator junction box (1) for a PV system (100) comprises a plurality of electric terminals (11) for optionally connecting one respective PV string (2) of one or more serially connected PV modules (3). Said PV sub-generator junction box (1) further comprises a sub-generator line terminal (12) for connecting a PV sub-generator line (4) of a remote central PV inverter (5) or connecting a PV sub-generator line (4) of an inserted PV generator junction box (6). The PV sub-generator junction box (1) also comprises an electronic control unit (10) that is connected to a central control unit (7) of the PV inverter (5) in order to exchange data (DAT). According to the invention, the PV sub-generator junction box (1) comprises a power line modem (8) for feeding and retrieving the data (DAT) via the PV sub-generator line (4).
Owner:SMA SOLAR TECH AG
Air conditioning system with integrated solar inverter
Methods and systems are provided for air conditioning, capturing combustion contaminants, desalination, and other processes using liquid desiccants.
Owner:7AC TECH
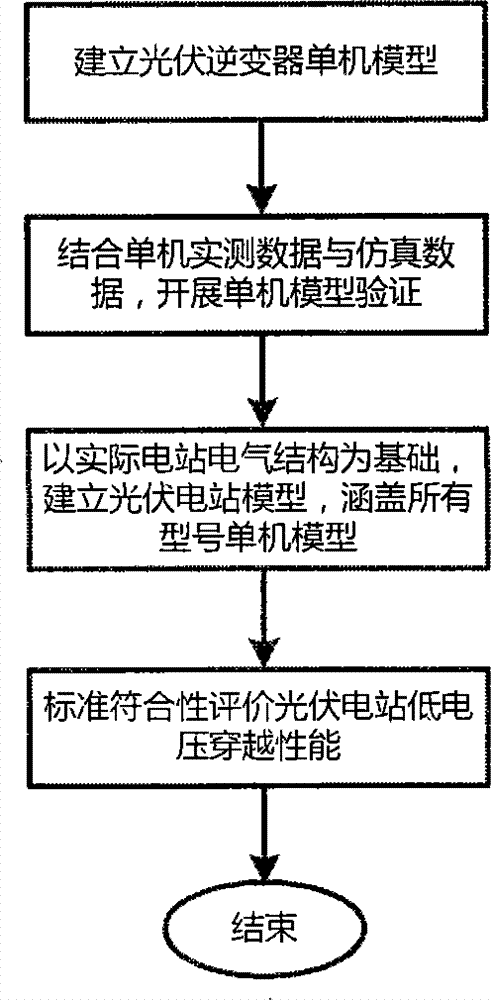
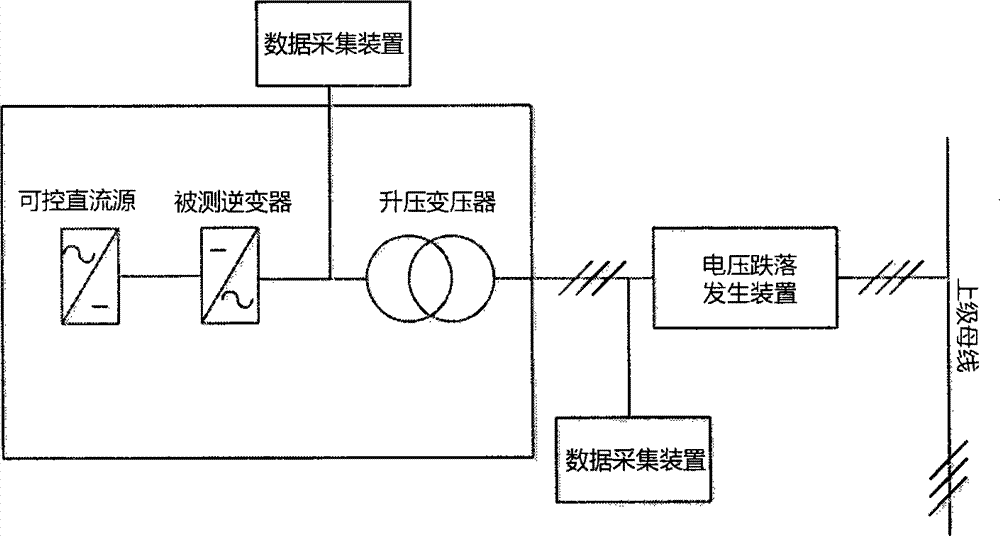
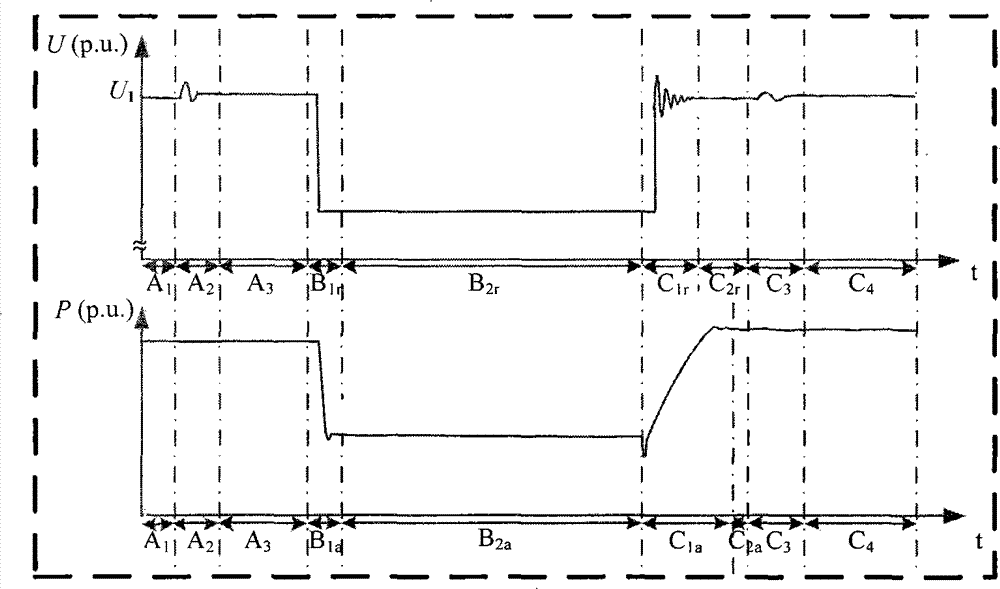
Photovoltaic-power-station low-voltage penetrating performance evaluation method based on inverter model test
ActiveCN103944507AAccurately reflect the transient processCircumvention of Field TestsPhotovoltaic monitoringPhotovoltaic energy generationLow voltageModel test
The invention provides a photovoltaic-power-station low-voltage penetrating performance evaluation method based on an inverter model test. The method includes the following steps: step1: carrying out a low-voltage penetrating model test on a photovoltaic inverter single-machine model; performing fault simulation on a grid-connection photovoltaic inverter model according to test parameters of the model test and verifying the low-voltage penetrating performance of the photovoltaic inverter single-machine model; step2: constructing a photovoltaic power station model; step3: performing steady-state power flow calculation on the photovoltaic power station model and analyzing the steady-state performance of the photovoltaic power station model; step4: according to a low-voltage penetrating performance standard of the photovoltaic power station, verifying the low-voltage penetrating performance of the photovoltaic power station model. Compared with the prior art, the photovoltaic-power-station low-voltage penetrating performance evaluation method based on the inverter model test is capable of meeting evaluation demands of power grids on low-voltage penetrating technical requirements of a large-size photovoltaic power station under conditions that a low-voltage penetrating test on the whole of a photovoltaic power station cannot be carried out and a test on a photovoltaic power generation unit cannot be carried out effectively.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
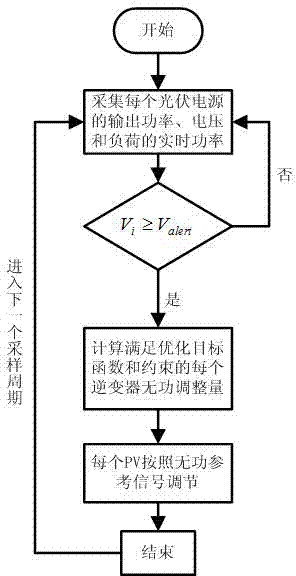
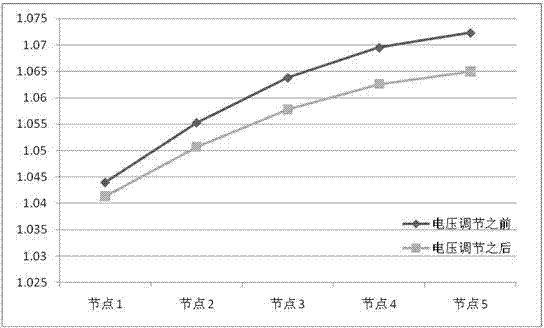
Voltage regulation method based on inverter power coordination control
ActiveCN104767221AAvoid power lossActive power avoidanceSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsAc network voltage adjustmentMathematical modelVoltage regulation
The invention discloses a voltage regulation method based on inverter power coordination control. The method comprises the steps that during one sampling period, a constrained and optimized mathematical model is used for conducting power coordination control over photovoltaic inverters; the objective function (shown in the specification) of the constrained and optimized mathematical model is the minimum of the sum of reactive power output by all photovoltaic power sources, and the constraint conditions include the inverter capacity constraint, the node flow constraint, the node voltage constraint and the inverter power adjustment weight constraint; on the condition of meeting all the proposed constraint conditions, a set of reactive power adjustment quantities of the minimum sum of the reactive power output by all the photovoltaic power sources are solved through an optimization algorithm and serve as reactive power reference values for coordination control over all the photovoltaic inverters, and voltage adjustment of grid-connection points in an area is achieved. By means of the method, on the premise of not reducing the photovoltaic output active power, the voltage adjustment capacity of each inverter can be fully utilized, and the situation that unnecessary lien power losses are caused by output of excessive reactive power can be avoided.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +3
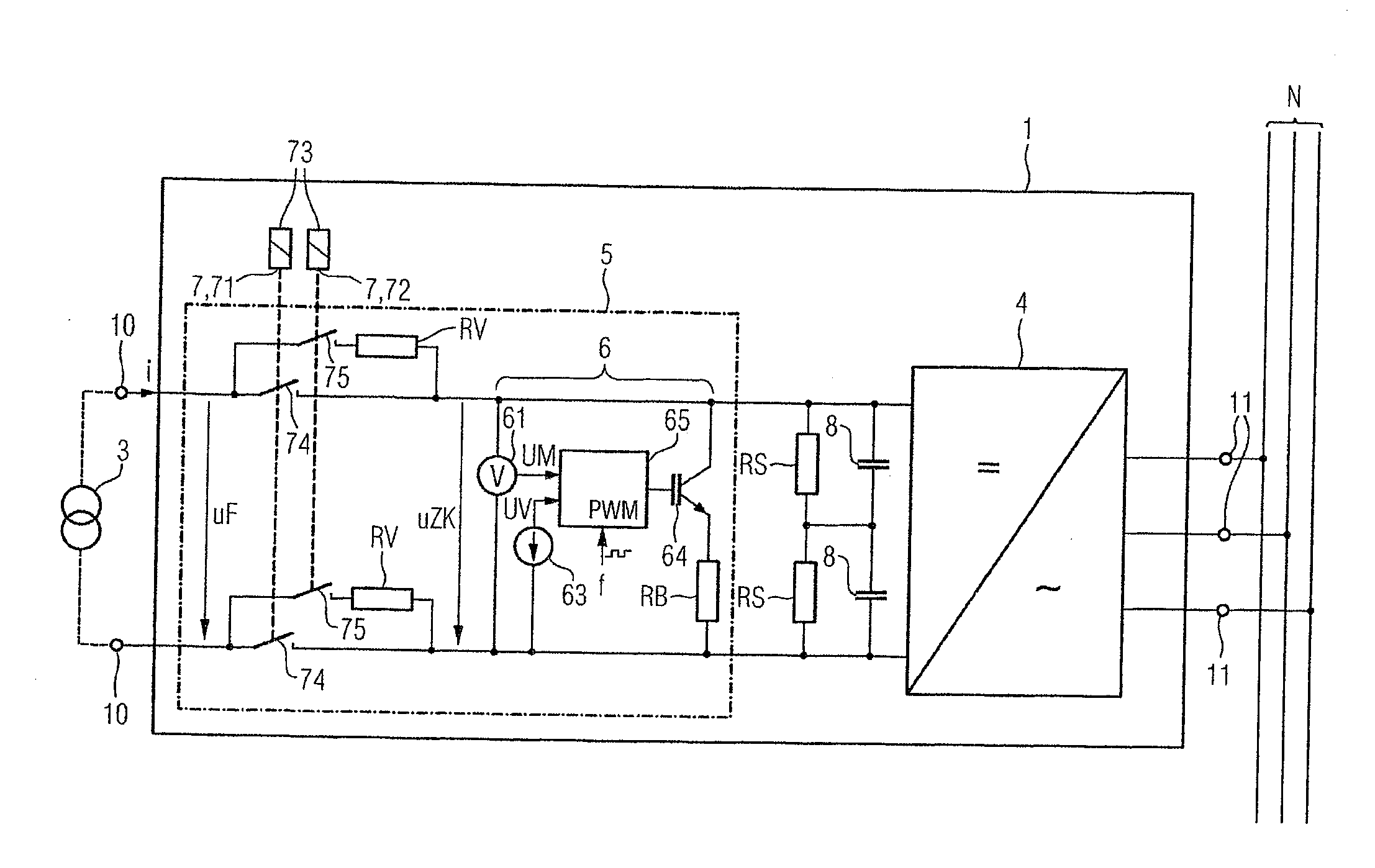
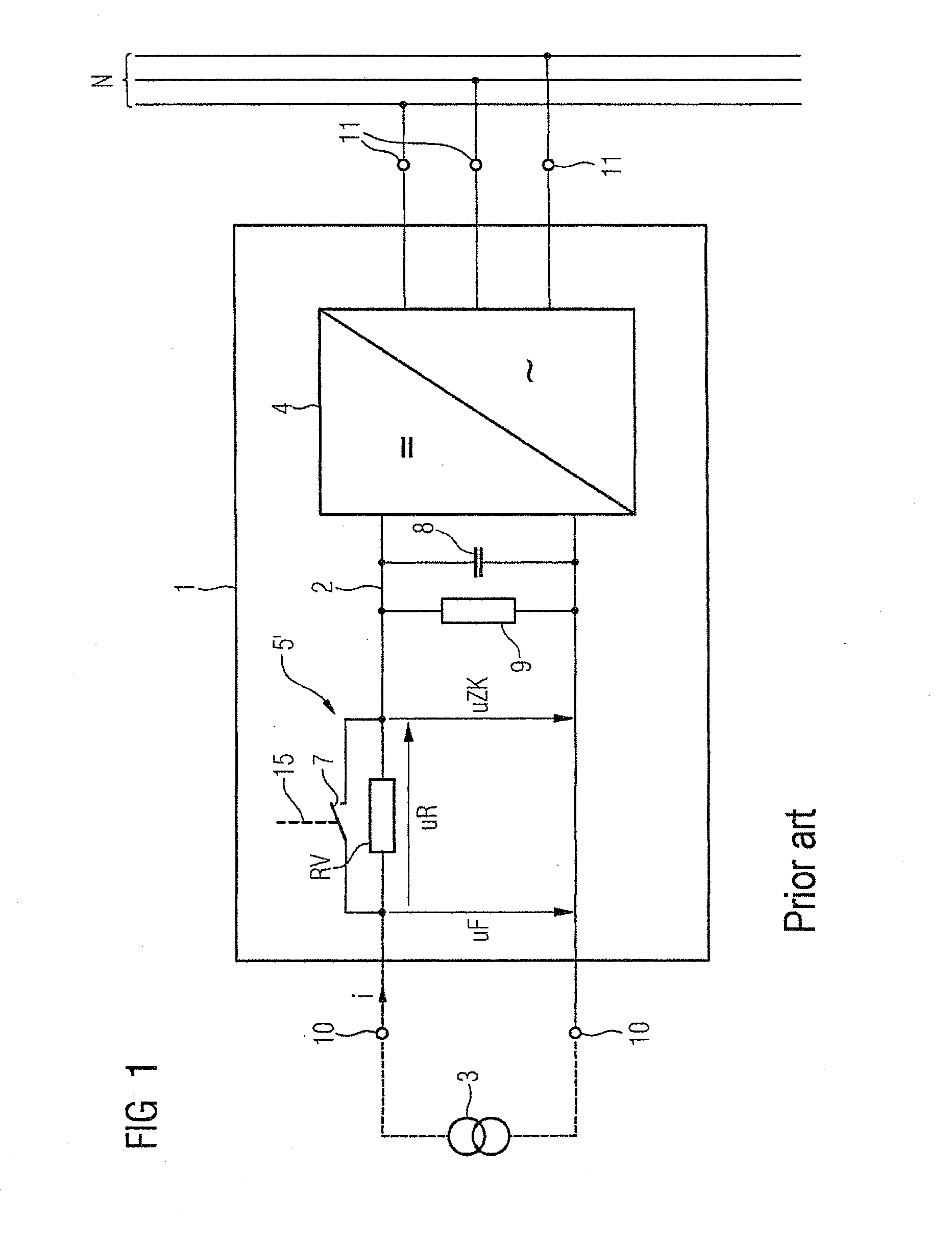
Protection Circuit for Protecting an Intermediate Circuit of a Solar Inverter Against Overvoltages
InactiveUS20110194216A1Little power lossSimple circuit designEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentPower conversion systemsPower inverterOvervoltage
An input-side protective circuit for protecting an intermediate circuit of an inverter against overvoltages, wherein the input-side protective circuit includes an upstream element for limiting the voltage of the intermediate circuit connected upstream of the intermediate circuit and which is bridgeable by a mechanical switching device that is controllable such that it opens in a feed-in operation of the inverter when an intermediate circuit voltage is greater than a specified voltage limit. The protective circuit also includes an electronic voltage limiter connected downstream of the upstream element and connected in parallel to the intermediate circuit.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
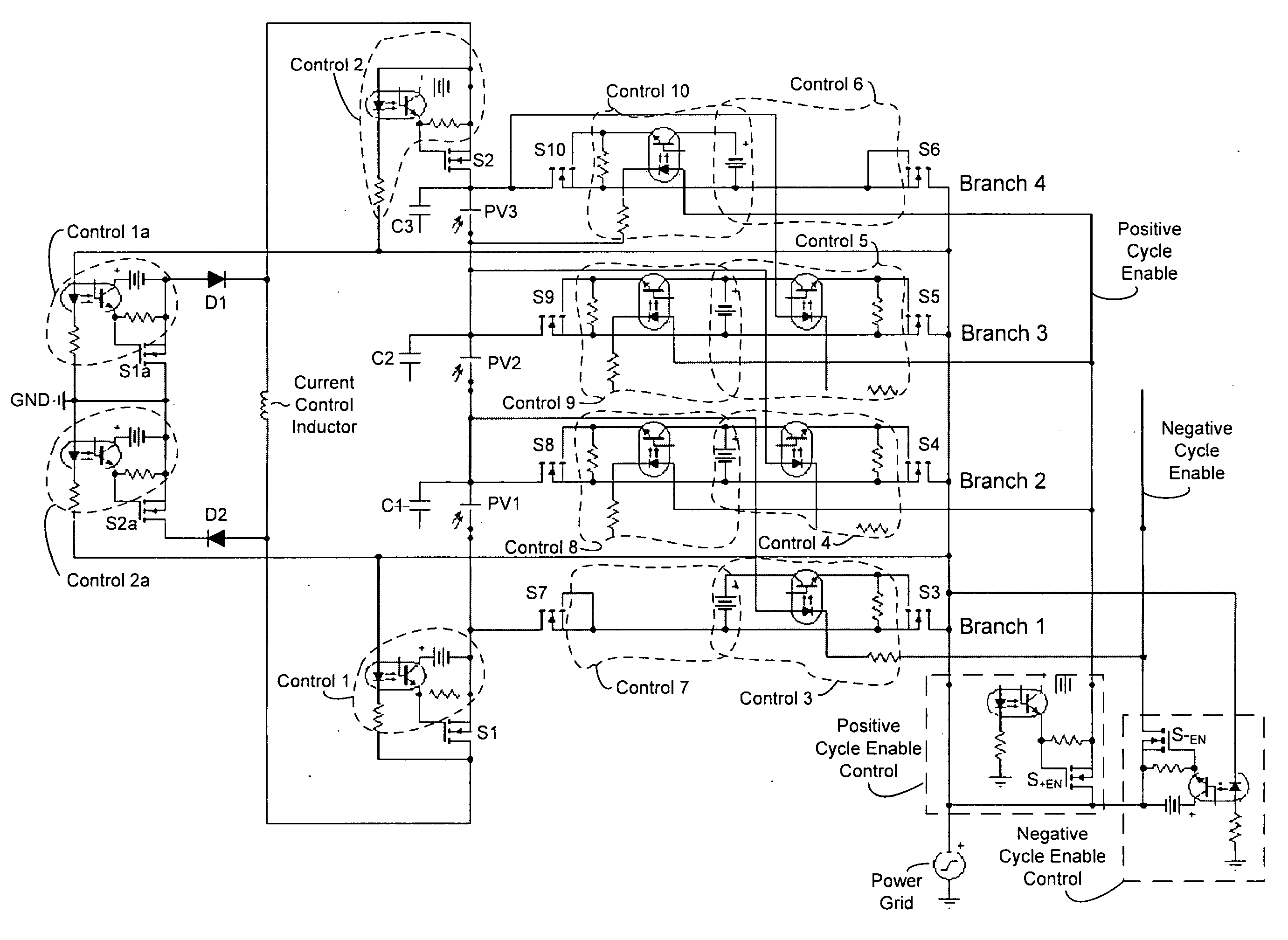
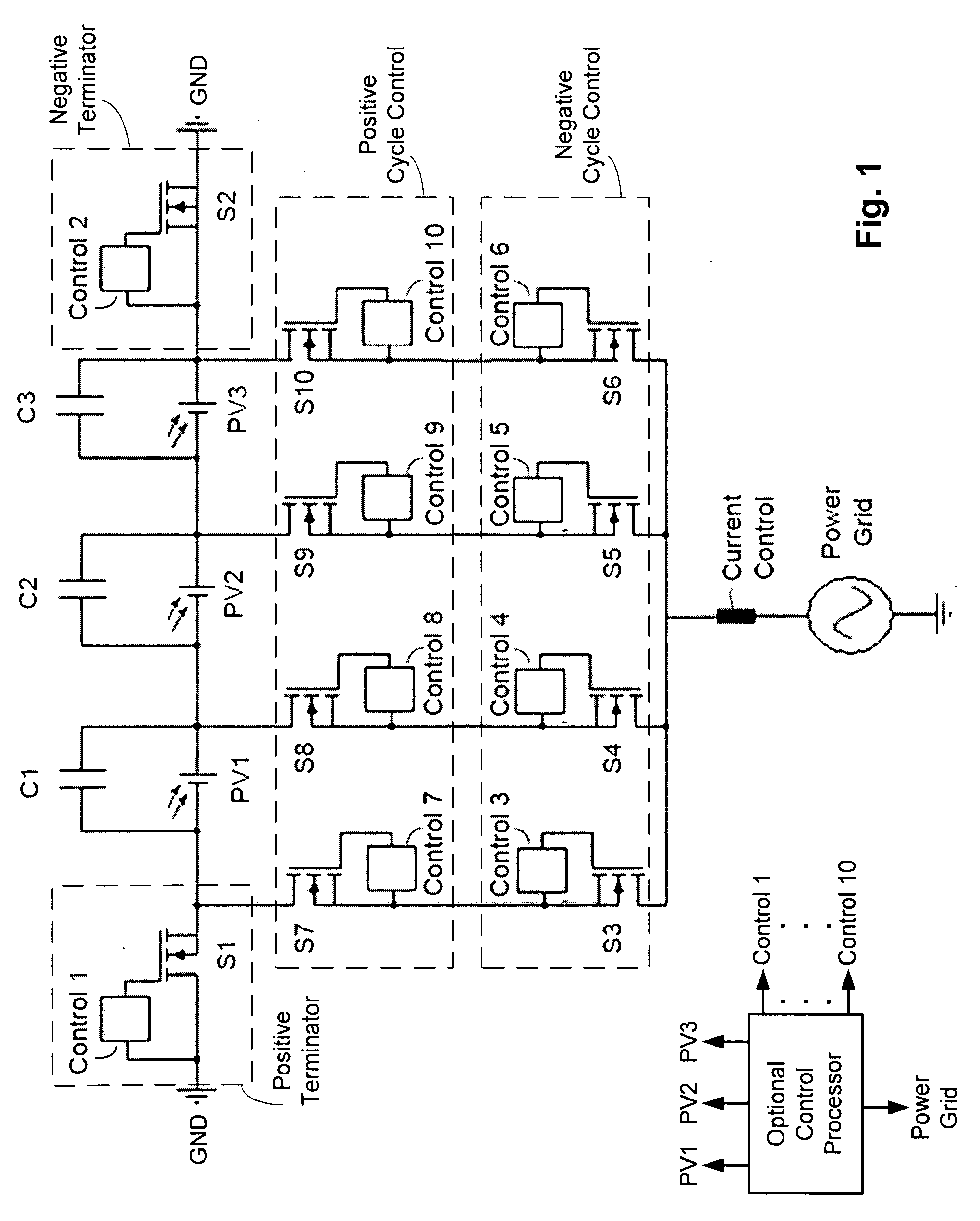
Photovoltaic ladder inverter
InactiveUS20090212629A1Batteries circuit arrangementsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPower gridEngineering
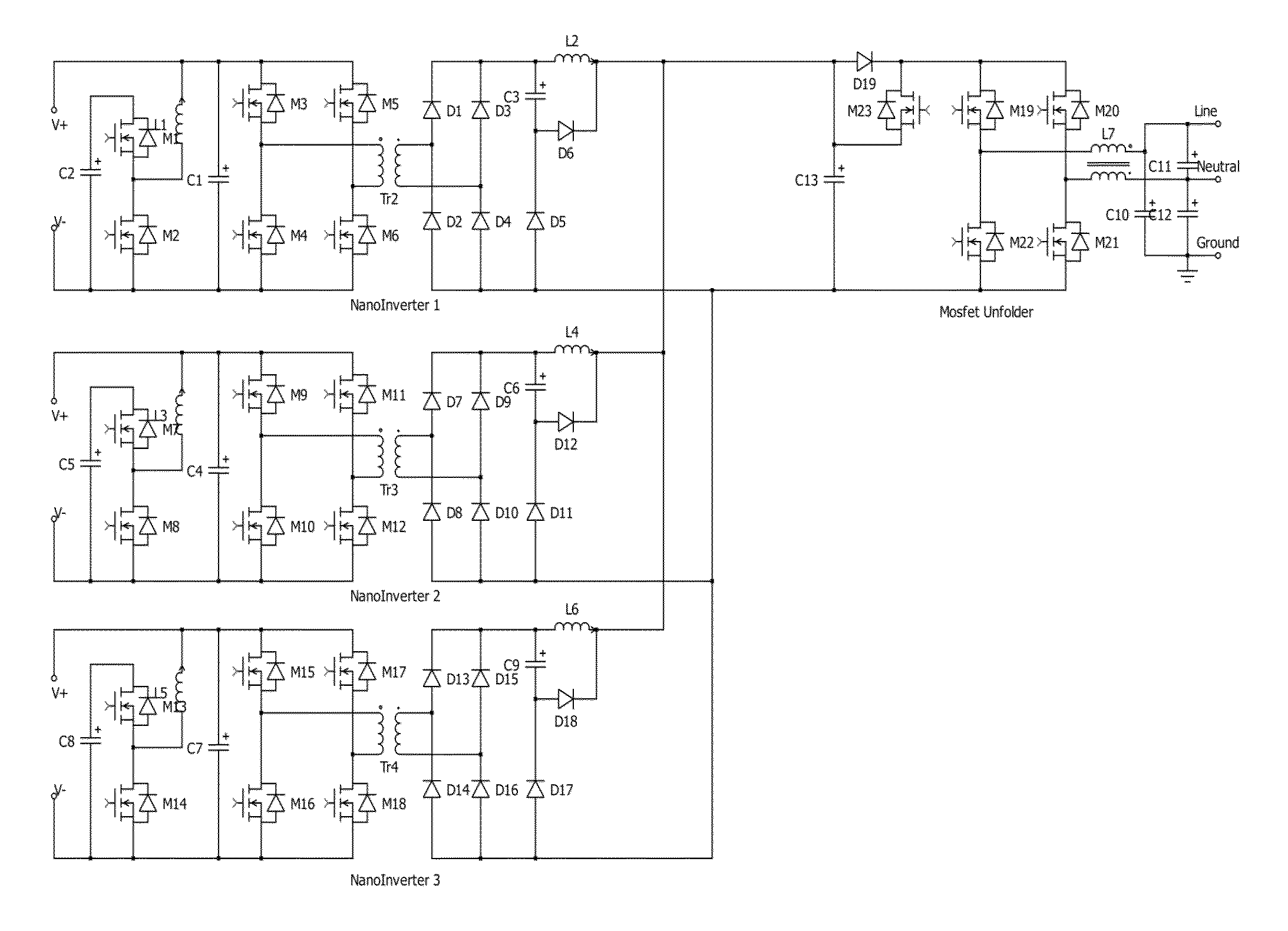
Techniques for DC-to-AC conversion are disclosed, and may be embodied in a solar inverter device that can operatively couple to a power grid. The device includes a photovoltaic (PV) stack including series-connected PV modules. Each PV module is associated with a capacitor for storing output of that PV module. A positive terminator circuit switches a negative end of the PV stack to ground during positive half of grid cycle, and a negative terminator switches a positive end of the PV stack to ground during negative half of grid cycle. A connecting branch couples each PV module output to a common bus, each branch including control circuitry configured to selectively couple the corresponding PV module output to bus. During a first half of grid cycle, some of the capacitors discharge to the grid while a balance of the capacitors charge in preparation for discharge during a second half of grid cycle.
Owner:STELLARIS
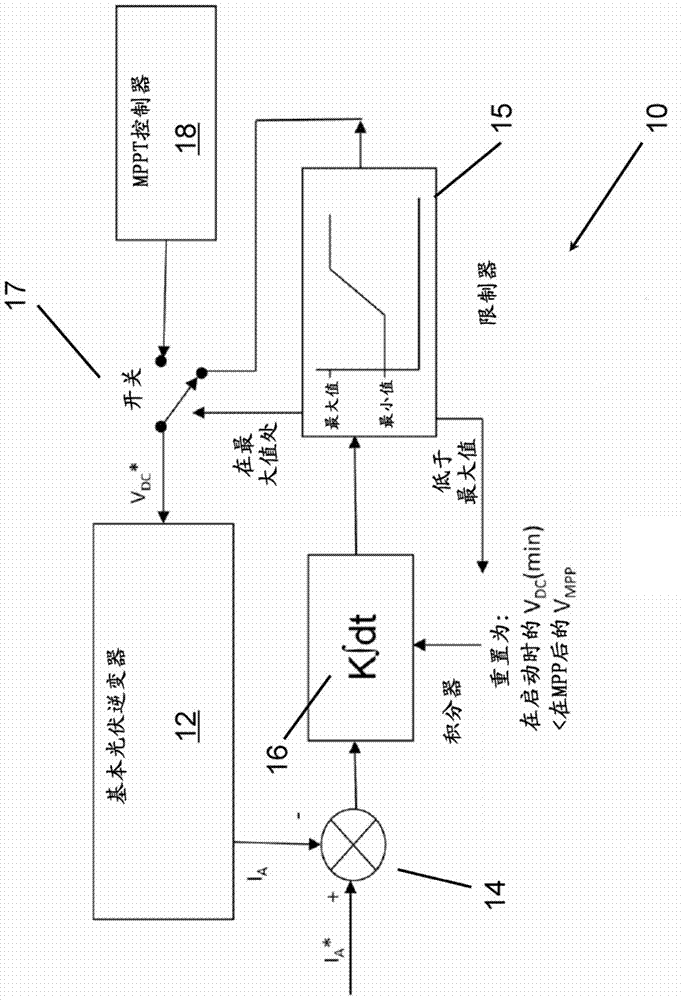
Method and system for controlling power output of an inverter
InactiveCN104779636AAvoid problems with voltage rising above the level at which the inverter can operateLow costPhotovoltaicsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsControl powerPower flow
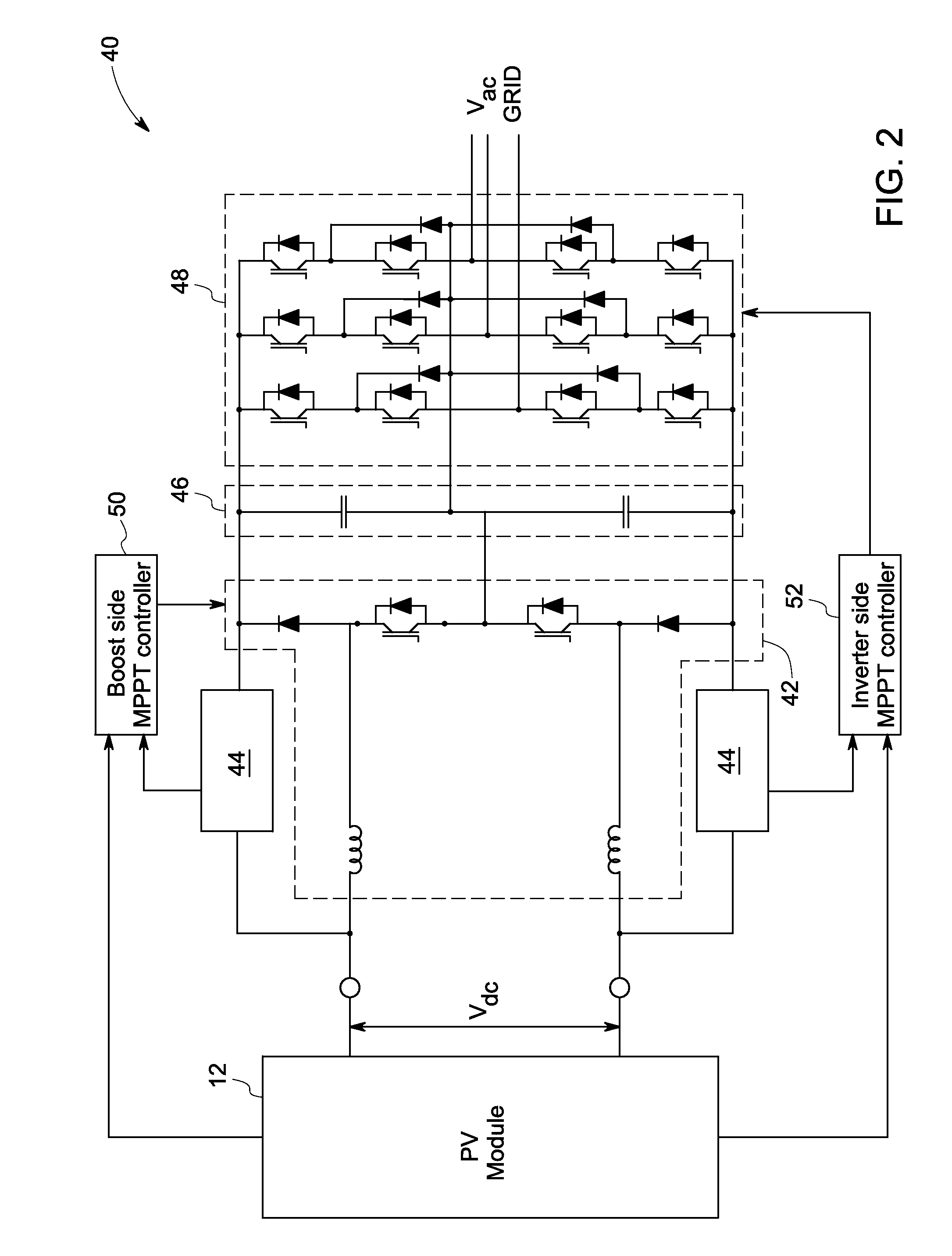
According to a first aspect of the invention, there is provided a method of controlling a power output of an inverter (12). The method comprises measuring an output current (I A ) of the inverter (12), determining a difference between the output current (I A ) and a reference current (I A *), and controlling a reference input voltage (V DC *) of the inverter (12) as a function of the determined difference. In a second aspect of the invention, there is described a system (10) for controlling a power output of an inverter (12). The system comprises an inverter (12) arranged to output a current (I A ) as a function of a reference input voltage (V DC *). The system (10) further comprises a controller (14, 16) arranged to determine a difference between the output current (I A ) and a reference current (I A *). The controller (14, 16) is further arranged to control the reference input voltage (V DC *) as a function of the determined difference. The method may allow for control of a photovoltaic inverter at a power less than its maximum capability for a given solar irradiation, which may avoid the problem of the photovoltaic array voltage rising above a level where the inverter can run.
Owner:NIDEC CONTROL TECHN LTD
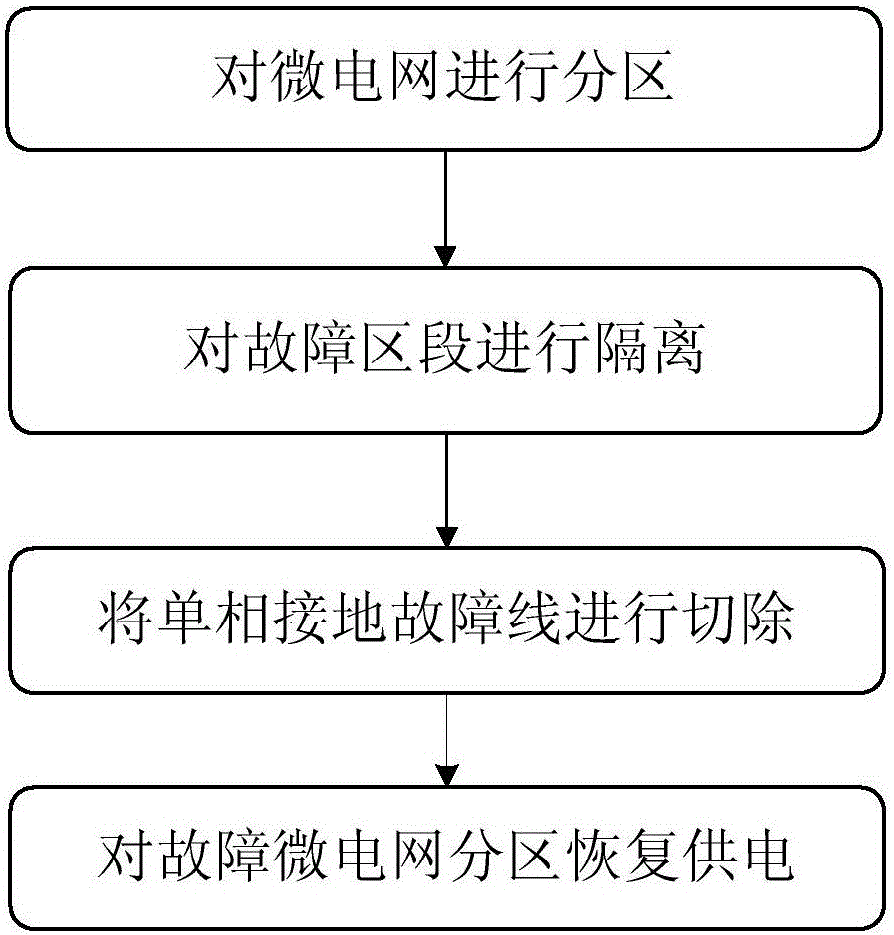
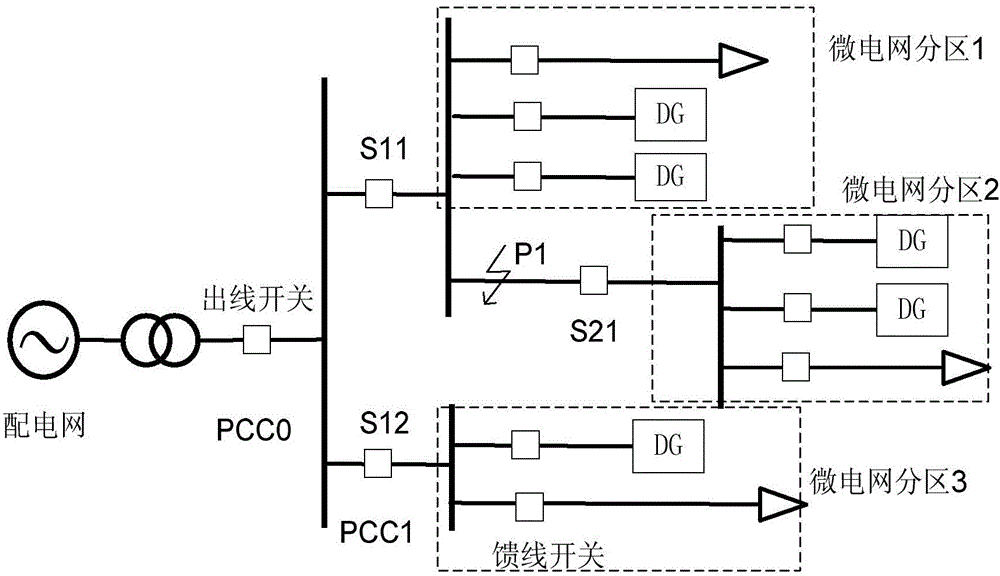
Photovoltaic microgrid fault isolation method based on fault state
ActiveCN105119255ASolve the problem of unreliable relay protectionReduce the scope of outagesEmergency protective circuit arrangementsFault locationMicrogridIslanding
For the single-phase grounding fault and instant fault of a power distribution network including a photovoltaic microgrid, the invention discloses a photovoltaic microgrid fault isolation method based on a fault state. The method includes the following steps of (1) partitioning the microgrid; (2) isolating the fault sections; (3) cutting off a single-phase grounding fault wire; and (4) recovering the power supply of fault microgrid partitions. The microgrid is reasonably partitioned, the fault sections are isolated through a boundary switch, and the power-off range is reduced. By the full use of the anti-islanding protection function of a photovoltaic inverter, a fault line is selected through S transform after the photovoltaic power supply and the power grid are isolated, so that the reliability of relay protection and the accuracy of line selection are improved, and the problem that the power distribution network including the photovoltaic power supply is unreliable in relay protection due to the bidirectional flow of power is solved. The photovoltaic microgrid fault isolation method has better protection effects on the single-phase grounding fault and other instant faults in the power distribution network.
Owner:STATE GRID SHANDONG ELECTRIC POWER +1
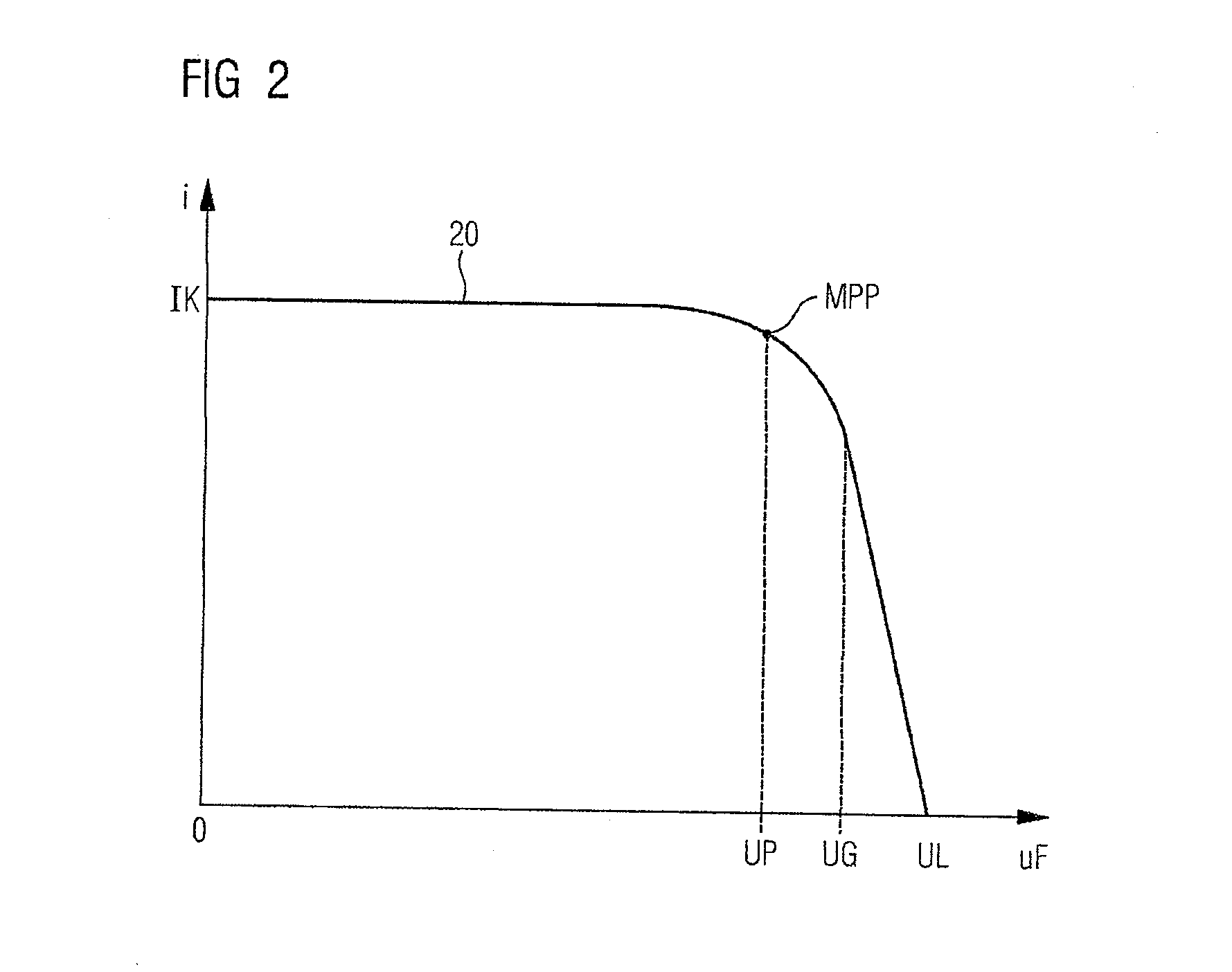
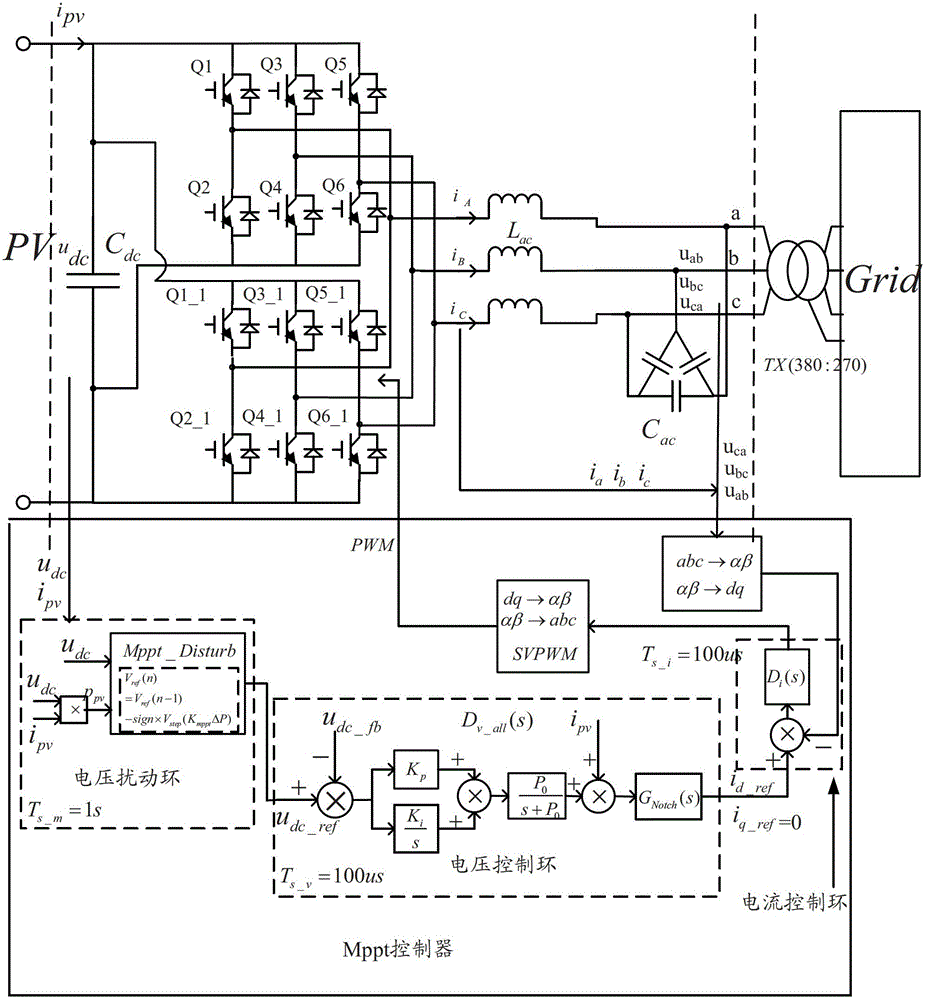
Stable MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) control system and method of single-stage photovoltaic inverter
ActiveCN102723740AGood dynamic responseImprove steady state performanceSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPhotovoltaic energy generationPower flowSingle stage
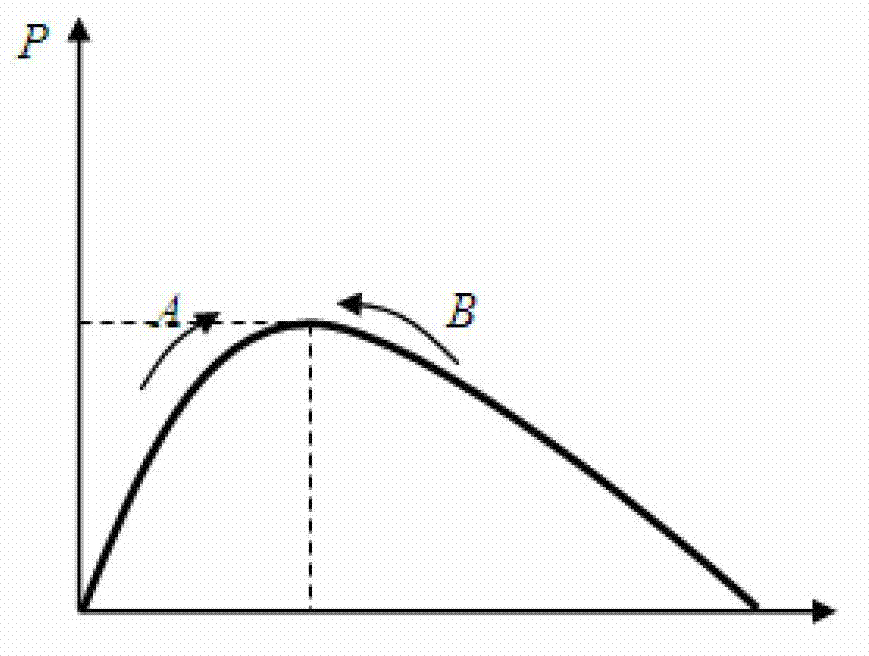
The invention provides a stable MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) control system and method of a single-stage photovoltaic inverter. The stable MPPT control system comprises a solar panel, a photovoltaic inverter, a power grid and an MPPT controller, wherein the solar panel, the photovoltaic inverter and the power grid are sequentially connected with one another; and the MPPT controller is respectively connected with the solar panel and the photovoltaic inverter. According to the stable MPPT control method, a novel voltage ring controller is adopted and comprises a proportional integral (PI) control module, a pole compensation module and a notching filter module, and the voltage ring controller and a current ring controller adopt a same control period, thus ensuring the operation stability of a single-stage inversion system and guaranteeing the single-stage inversion system to output electric energy with good quality; and an MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) variable-step voltage disturbance method is adopted, a proportional coefficient is regulated to guarantee better dynamic response and steady-state performance of MPPT, and thus the use efficiency of the solar panel is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG EIFESUN ENERGY TECH
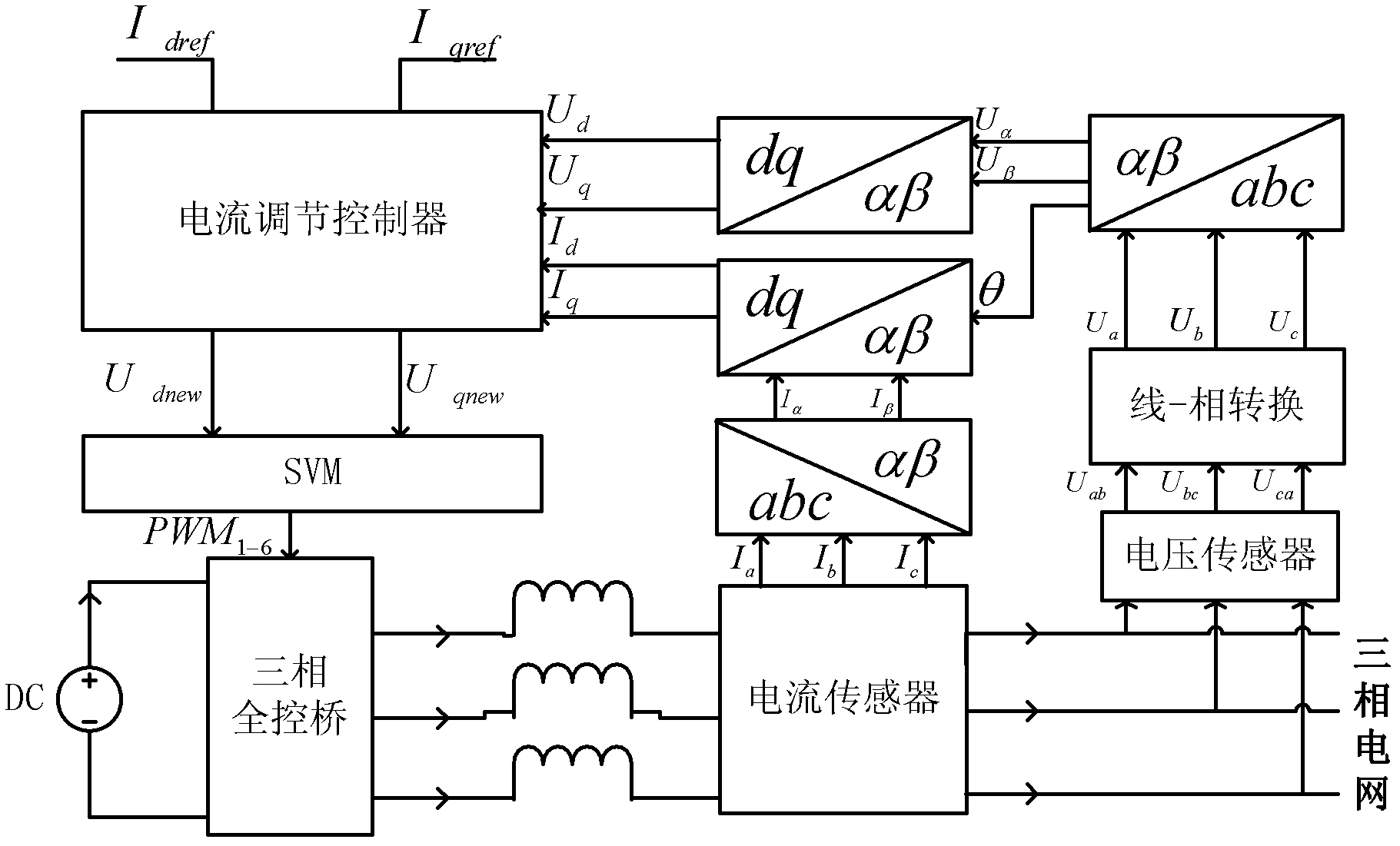
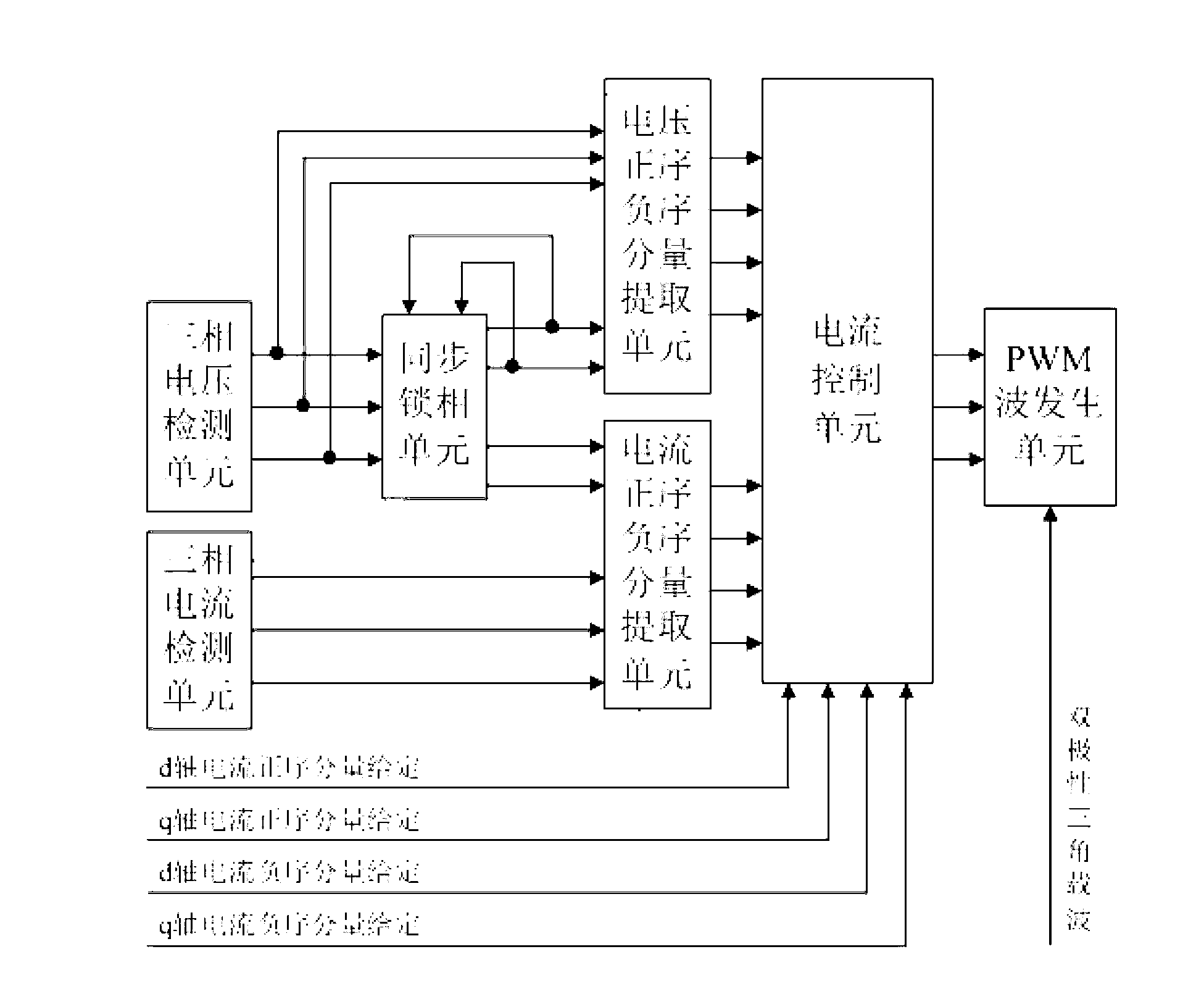
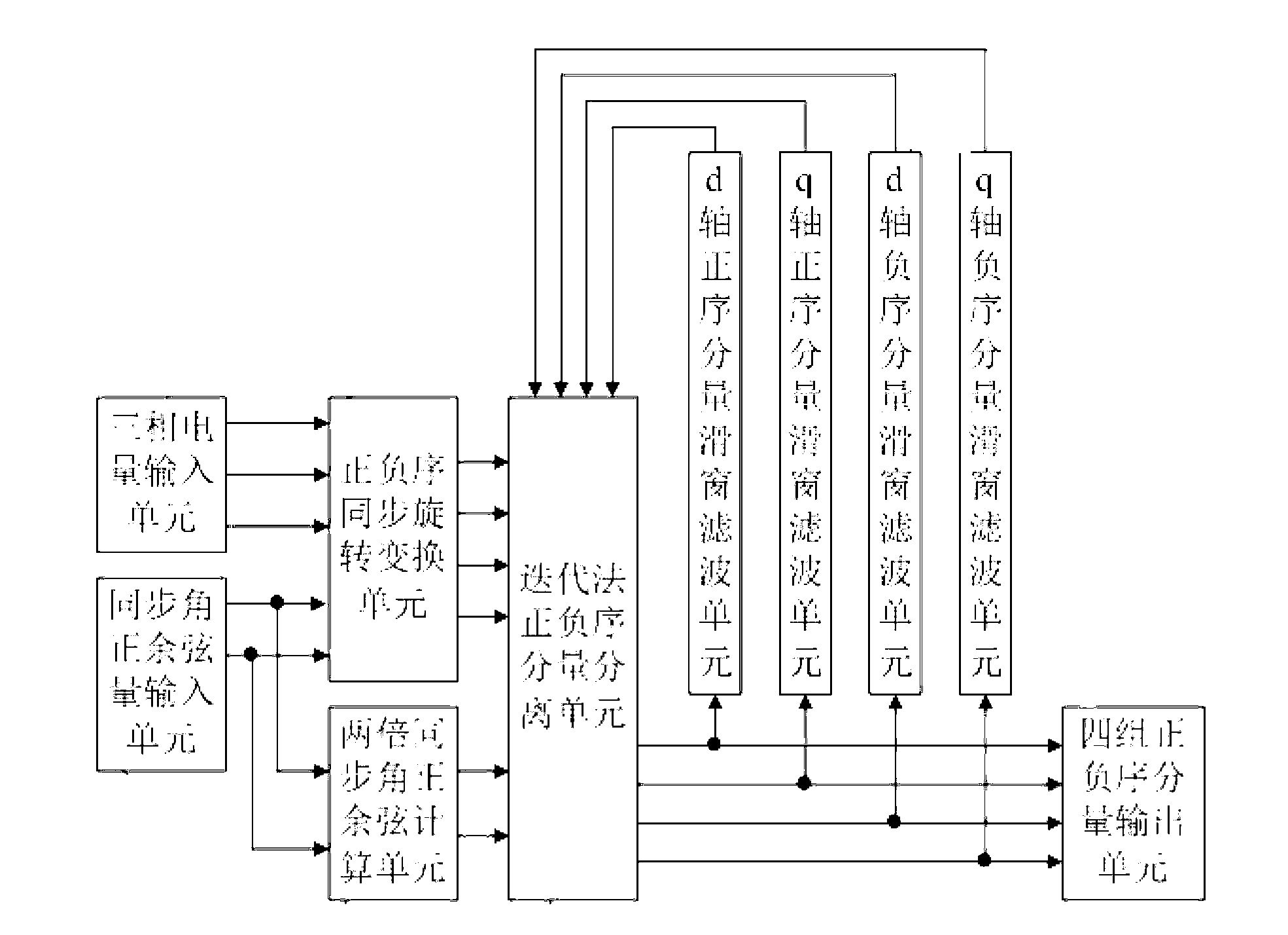
Photovoltaic grid-connected inverter current control method based on positive and negative sequence component separation
InactiveCN102629768AStable controlIdeal grid-connected current waveformSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPhotovoltaic energy generationVoltage vectorEngineering
The invention provides a photovoltaic grid-connected inverter current control method based on positive and negative sequence component separation aiming at the problem that in the first step abc-alpha beta of the prior SVPWM (Space Vector Pulse Width Modulation) coordinate transformation, the sum of default three-phase voltage vectors is zero constantly, so that when the three-phase unbalanced grid voltage is subjected to SVPWM transformation, the information distortion is caused, so that a voltage waveform can not be accurately reduced in the SVPWM inverse transformation. The photovoltaic grid-connected inverter current control method has the beneficial effects that through decomposing the unbalanced grid voltage into respective balanced standard positive sequence components U+d and U+q and respective balanced standard negative sequence components U-d and U-q, due to the respective balance of the positive and negative sequence grid voltage components, the voltage waveform inverted by utilizing a component space vector method can be better simulated, so that a more ideal grid-connected current waveform is obtained under the unbalanced power grid voltage.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA +1
Voltage frequency adjustment method considering photovoltaic maximum power tracking for active power distribution network
ActiveCN105262096ASimplified impedance relationshipGuaranteed maximum power outputSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsAc network voltage adjustmentVoltage amplitudeEngineering
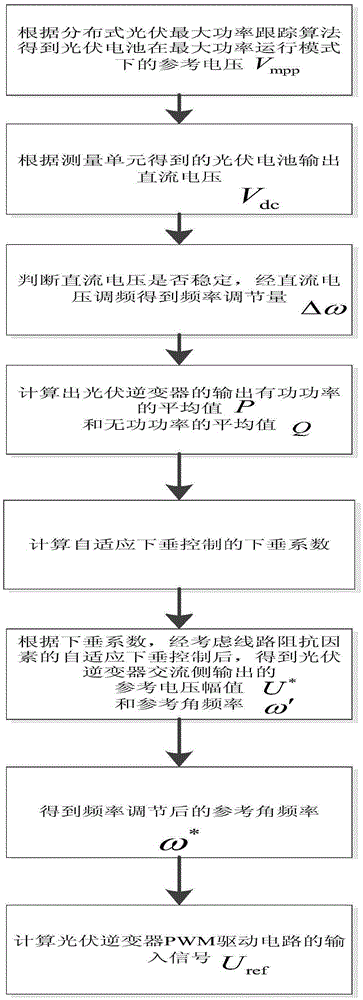
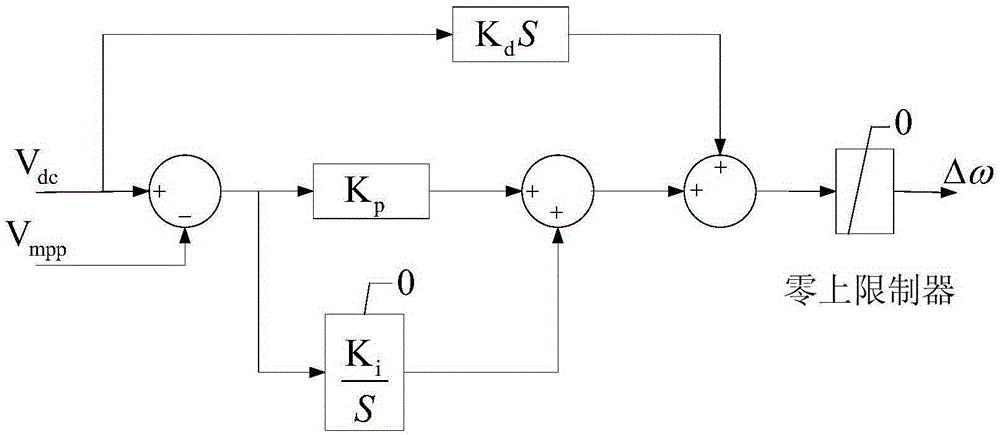
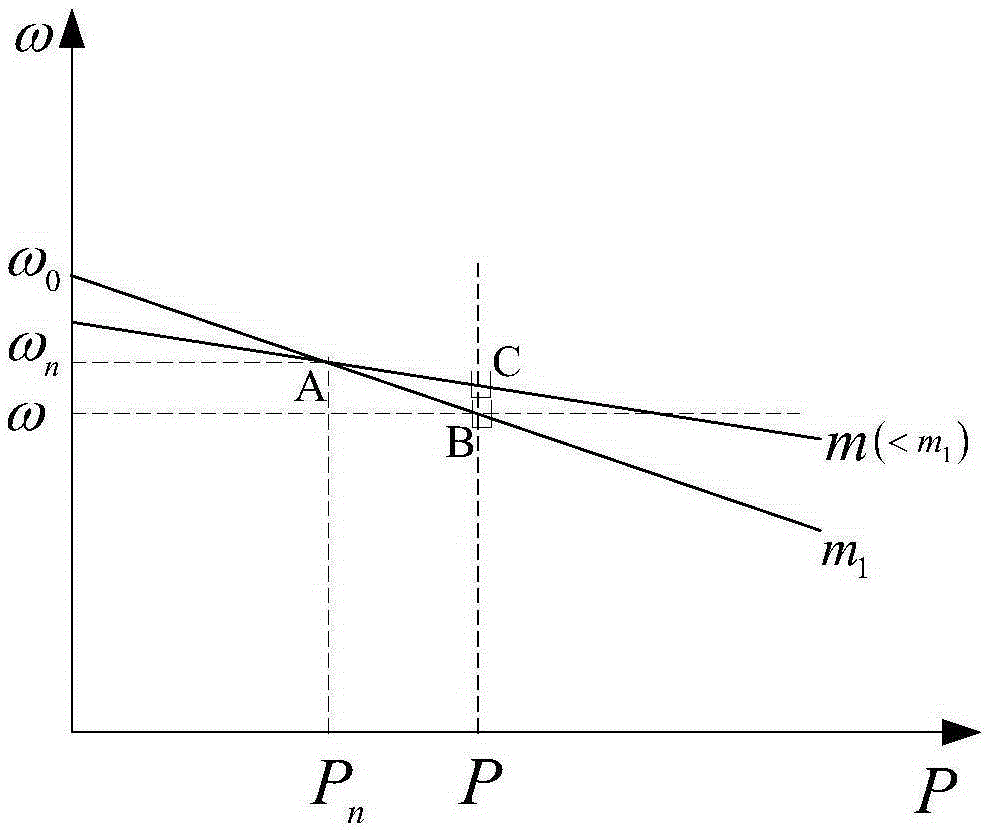
The invention discloses a voltage frequency adjustment method considering photovoltaic maximum power tracking for an active power distribution network. The voltage frequency adjustment method comprises the following steps of acquiring a reference voltage V<mpp> of a photovoltaic cell in a maximum power running mode; acquiring a DC voltage V<dc> output from the photovoltaic cell; carrying out frequency adjustment on the DC voltage V<dc> to obtain a frequency adjustment quantity Delta Omega; calculating an average value P of active power and an average value Q of reactive power output from a photovoltaic inverter; calculating a droop coefficient of a self-adaptive droop control; obtaining a reference voltage amplitude U<*> and a reference angular frequency Omega' output from an AC side of the photovoltaic inverter after considering the self-adaptive droop control of a circuit impedance factor; obtaining a reference angular frequency Omega' after frequency adjustment; and calculating an input signal U<ref> of a pulse width modulation (PWM) driving circuit of the photovoltaic inverter. By the voltage frequency adjustment method, distributed photovoltaic maximum power can be ensured to be output, and meanwhile, the influence of the circuit impedance is considered; and when a load or an environment changes, active power and reactive power can be accurately allocated to the photovoltaic inverter, and the purpose of improving the reliability of distributed photovoltaic power supply is achieved.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +3
System and method for determining potential power of inverters during curtailment mode
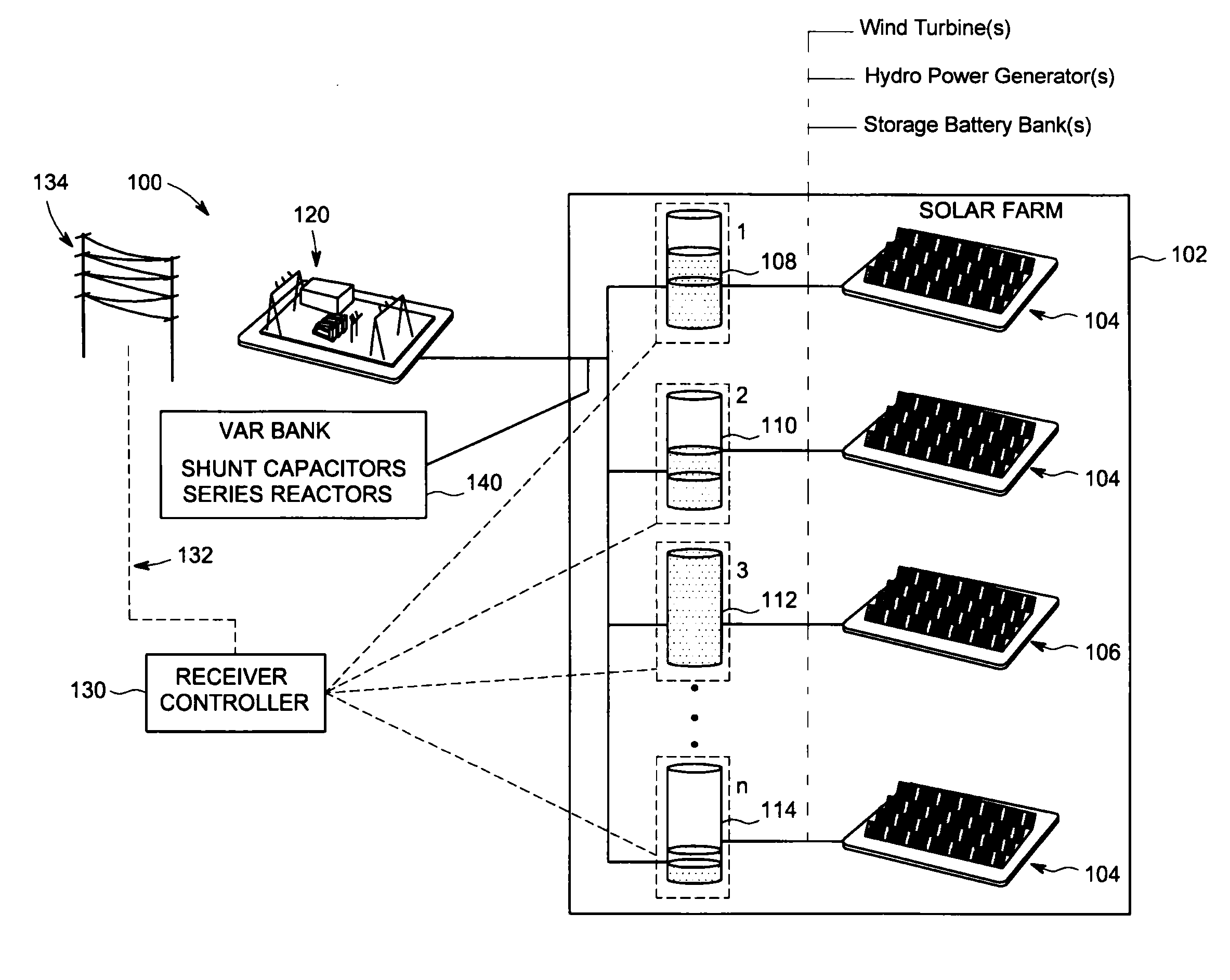
ActiveUS20130131884A1Efficient use ofMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlPower utilityPower inverter
A power inverter system includes a plurality of power inverters such as solar inverters receiving power from at least one energy source. Each power inverter includes algorithmic maximum peak power tracking (MPPT) software or integrated MPPT firmware to calculate its own potential real power. A controller is in electrical communication with selected power inverters that are operating in curtailed modes of operation and commands each selected power inverter to shift its power production duties and to perform MPPT sweeps. Each selected power inverter then calculates its own potential real power capability in response to corresponding MPPT sweep data. The potential real power capability information is received by the controller that transmits the information to a power utility allowing the power utility to more efficiently utilize real and reactive power available by the plurality of power inverters
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Large-scale photovoltaic power station and distribution grid harmonic wave cross-impact analysis model building method
The invention discloses a large-scale photovoltaic power station and distribution grid harmonic wave cross-impact analysis model building method and belongs to the technical field of new energy power generation and transmission. The large-scale photovoltaic power station and distribution grid harmonic wave cross-impact analysis model building method is mainly used for analyzing harmonic wave interaction influence of a large-scale photovoltaic power station and a distribution grid. The large-scale photovoltaic power station adopts a power electronic device as a grid-connection interface and can fill a large amount of harmonic wave into a power grid inevitably, and by means of specificity of a photovoltaic inverter, the generated harmonic wave has the advantages of being wide in broadband, high in frequency and capable of generating series-parallel connection resonance with distributed capacitors of the power grid. A large-scale photovoltaic power station and distribution grid harmonic wave cross-impact analysis model is formed by a photovoltaic harmonic analysis model and a distribution grid equivalent circuit, the photovoltaic harmonic analysis model is used for analyzing power station harmonic wave output characteristics, and the distribution grid equivalent circuit is used for representing the distribution grid which the power grid is connected in. The large-scale photovoltaic power station and distribution grid harmonic wave cross-impact analysis model can provide a theoretical basis for issues of photovoltaic power station and distribution grid planning, harmonic wave estimation, estimation of photovoltaic power station accepting capability of the distribution grid, photovoltaic grid connection regulation formulation and the like.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
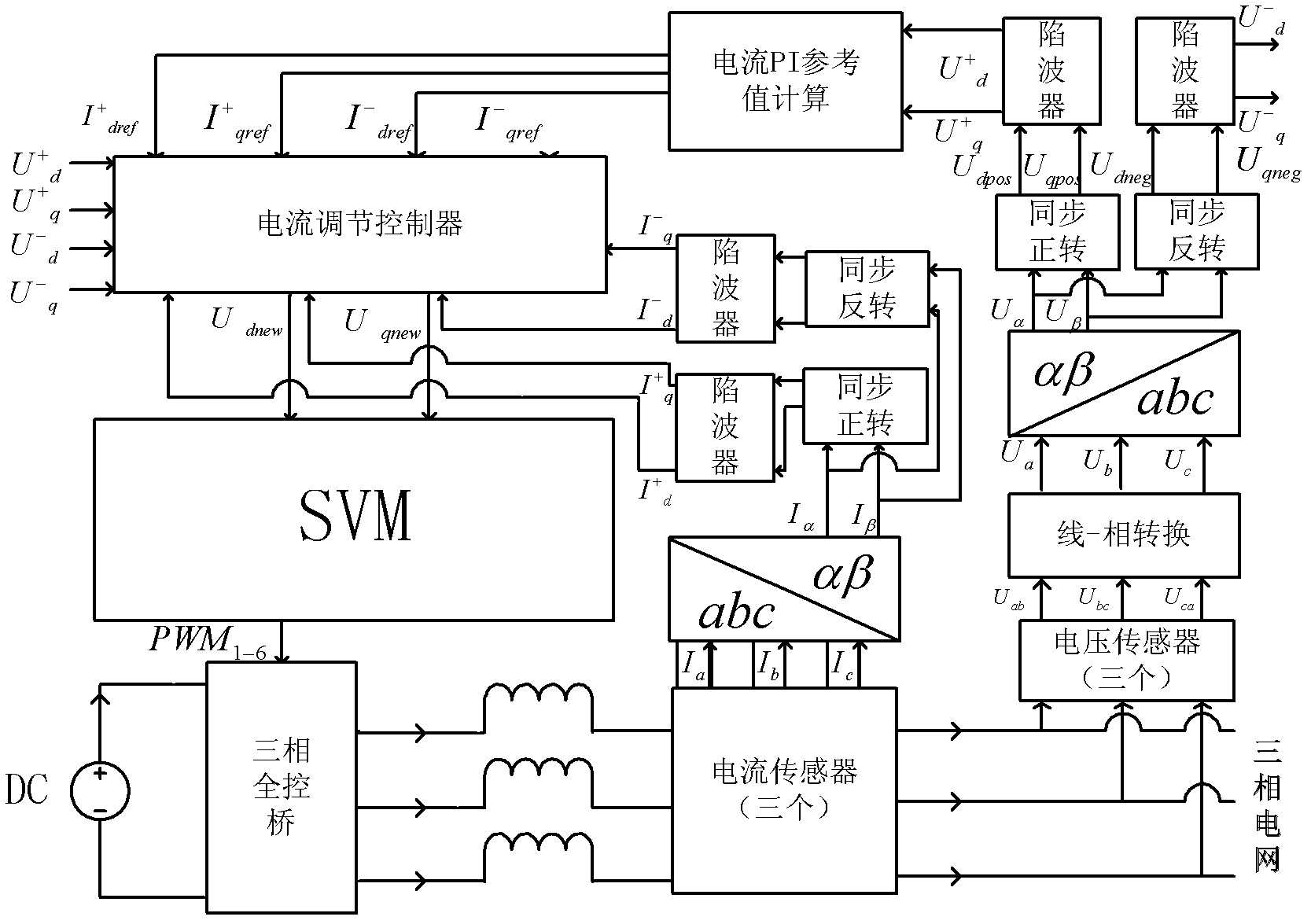
Positive and negative sequence component separation method of low-voltage ride-through control of photovoltaic grid-connected inverter
InactiveCN103269086ARealize low voltage ride through controlThe method is simple and reliableSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPhotovoltaic energy generationCarrier signalVoltage reference
The invention discloses a positive and negative sequence component separation method of low-voltage ride-through control of a photovoltaic grid-connected inverter. The positive and negative sequence component separation method of the low-voltage ride-through control of the photovoltaic grid-connected inverter is characterized by comprising the following steps of obtaining three-phase voltage instantaneous values and three-phase current instantaneous values through detection of voltage and current of a power gird, obtaining output signals which are a voltage synchronous phase angle sine value and a voltage synchronous phase angle cosine value of the power grid, and output signals which are a current synchronous phase angle sine value and a current synchronous phase angle cosine value of the power grid through processing of a synchronous phase locking unit, obtaining three-phase reference voltages of the photovoltaic grid-connected inverter according to four obtained voltage positive and negative sequence components, four obtained current positive and negative sequence components and four current positive and negative sequence component set values which are set according to output power of a photovoltaic cell panel through a current control unit, and obtaining a PWM switching signal corresponding to the three-phase inverter according to the three-phase reference voltages and bipolar triangle carrier signals through a PWM wave generating unit to achieve the low-voltage ride-through control of the photovoltaic grid-connected inverter. The positive and negative sequence component separation method of the low-voltage ride-through control of the photovoltaic grid-connected inverter is simple and reliable in method and good in practicability.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Solar inverter and photovoltaic installation comprising several solar inverters
InactiveCN1954484ABatteries circuit arrangementsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPower gridComputer module
Owner:SIEMENS AG
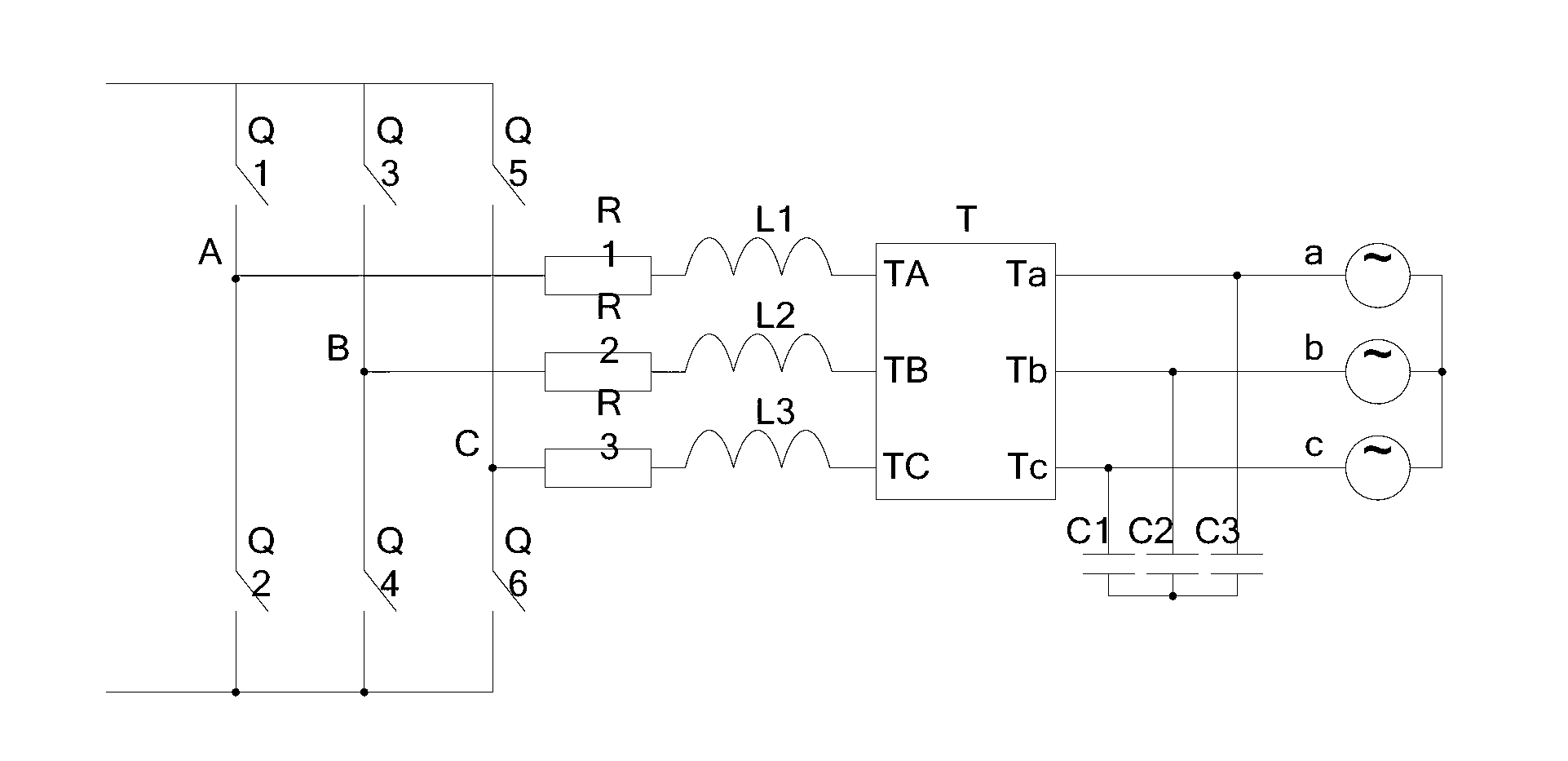
Quasi-Z-source inverter based single-phase photovoltaic off-grid inverter and soft switch control method thereof
InactiveCN104796030AReduce lossImprove system efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionZ-source inverterSquare waveform
The invention discloses a quasi-Z-source inverter based single-phase photovoltaic off-grid inverter and a soft switch control method thereof. A preceding quasi-Z-source inverter generates direct-current bus voltages with no-voltage slots, provides square-wave voltages with no-voltage slots for a succeeding single-phase full-bridge inversion circuit, and is synchronized with SPWM (sinusoidal pulse width modulation) signals, with low switching frequency, generated according to a rule sampling method to control on-off of a power switch of the single-phase full-bridge inversion circuit, rising edges and falling edges of the SPWM signals, acting on the single-phase full-bridge inversion circuit, of each switching cycle are within the no-voltage slot ranges of the square-wave voltages with the no-voltage slots, and no-voltage on-off of the succeeding single-phase full-bridge inversion circuit is achieved, so that switching loss is reduced and system efficiency is improved.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Single-phase photovoltaic grid-connected inverter
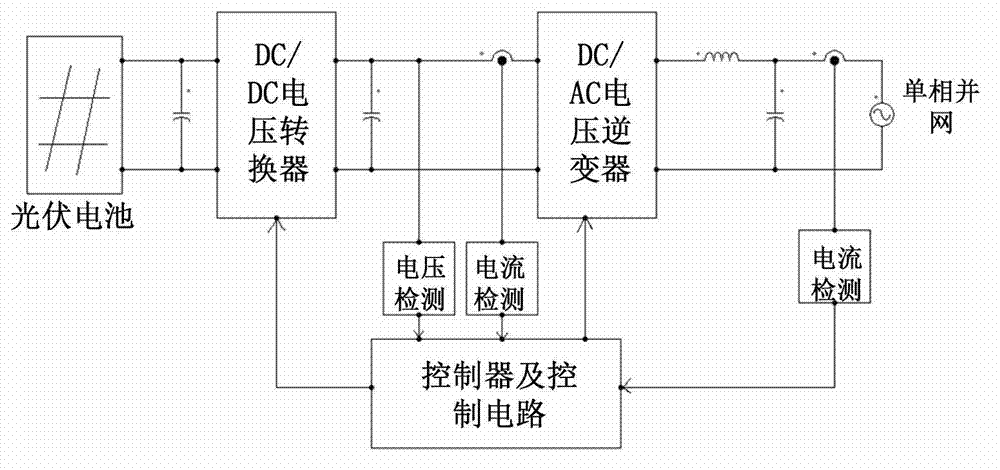
InactiveCN103208937AImprove energy utilizationSimple designDc-ac conversion without reversalCapacitanceClosed loop
The invention discloses a single-phase photovoltaic grid-connected inverter which mainly comprises a direct current / direct current (DC / DC) voltage converter, a direct current / alternating current (DC / AC) voltage converter, a current and voltage detecting circuit, a controller and a control circuit. The DC / DC part adopts a logic link control (LLC) resonance half bridge to finish conversion of direct current voltage, and a closed loop control circuit for outputting voltage is added, so that the DC / DC no longer outputs constant direct current voltage but the voltage with the steam-bread-shaped waveform and having the same frequency and phase with a power grid, and a resonance inductor and a resonance capacitor in the circuit are designed to effectively reduce switch loss and switch noises. In the DC / AC part, the voltage with the steamed-bread-shaped waveform serves as the input voltage to be connected with a direct current side of the inverter, so that effective inversion of the voltage is achieved, simultaneously voltage difference between two ends of a filter inductor in the inversion circuit is effectively reduced, the output current is smooth, and the harmonic content is reduced. The single-phase photovoltaic grid-connected inverter is small in size, high in efficiency, stable in performance, and easy to implement, and the harmonic content after the inversion is less, and the size of a harmonic suppression circuit is small.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Solar inverter and plant for converting solar energy into electrical energy
InactiveUS20100007212A1Meet the requirementsDc network circuit arrangementsPhotovoltaic monitoringPhotovoltaic generatorElectrical impulse
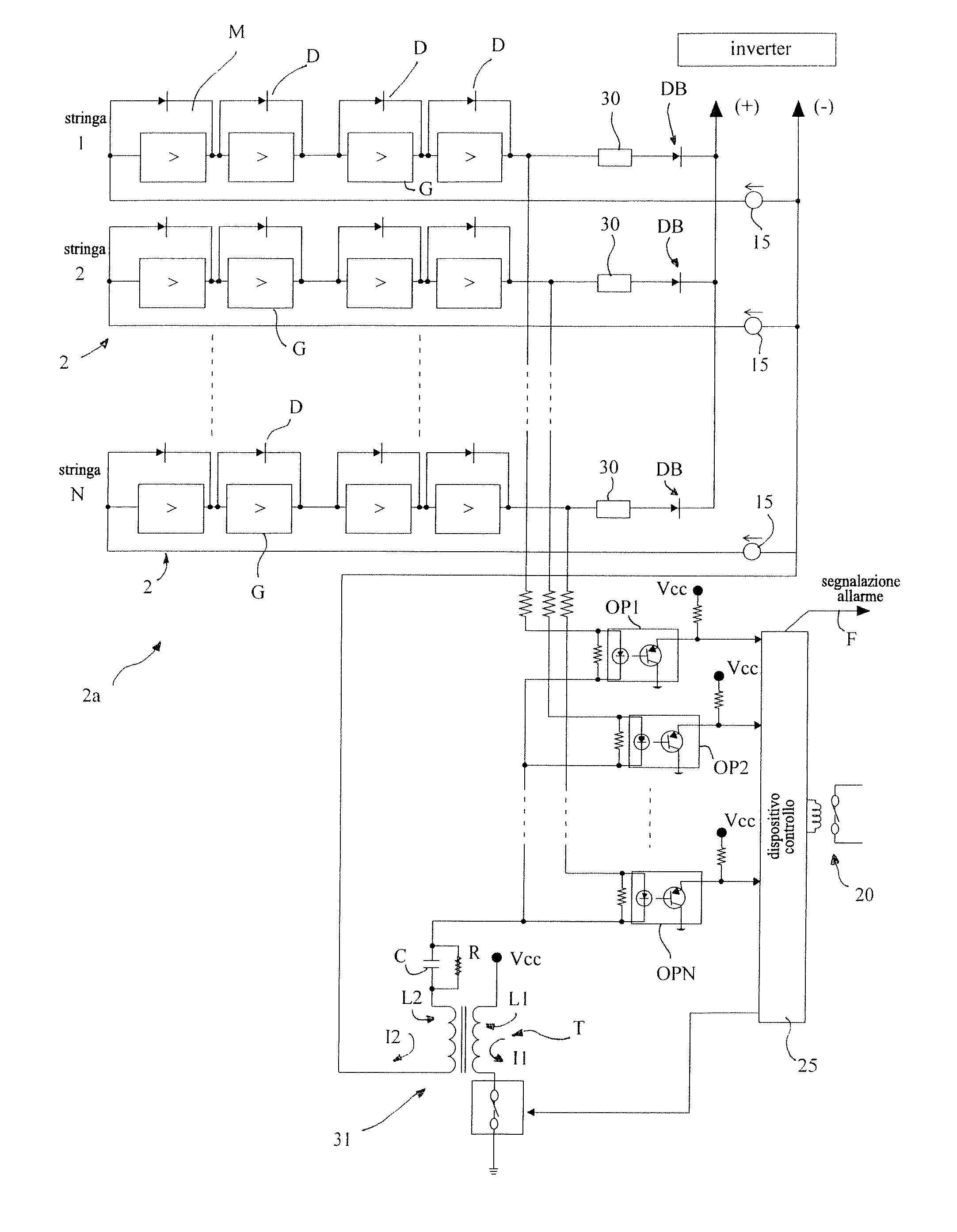
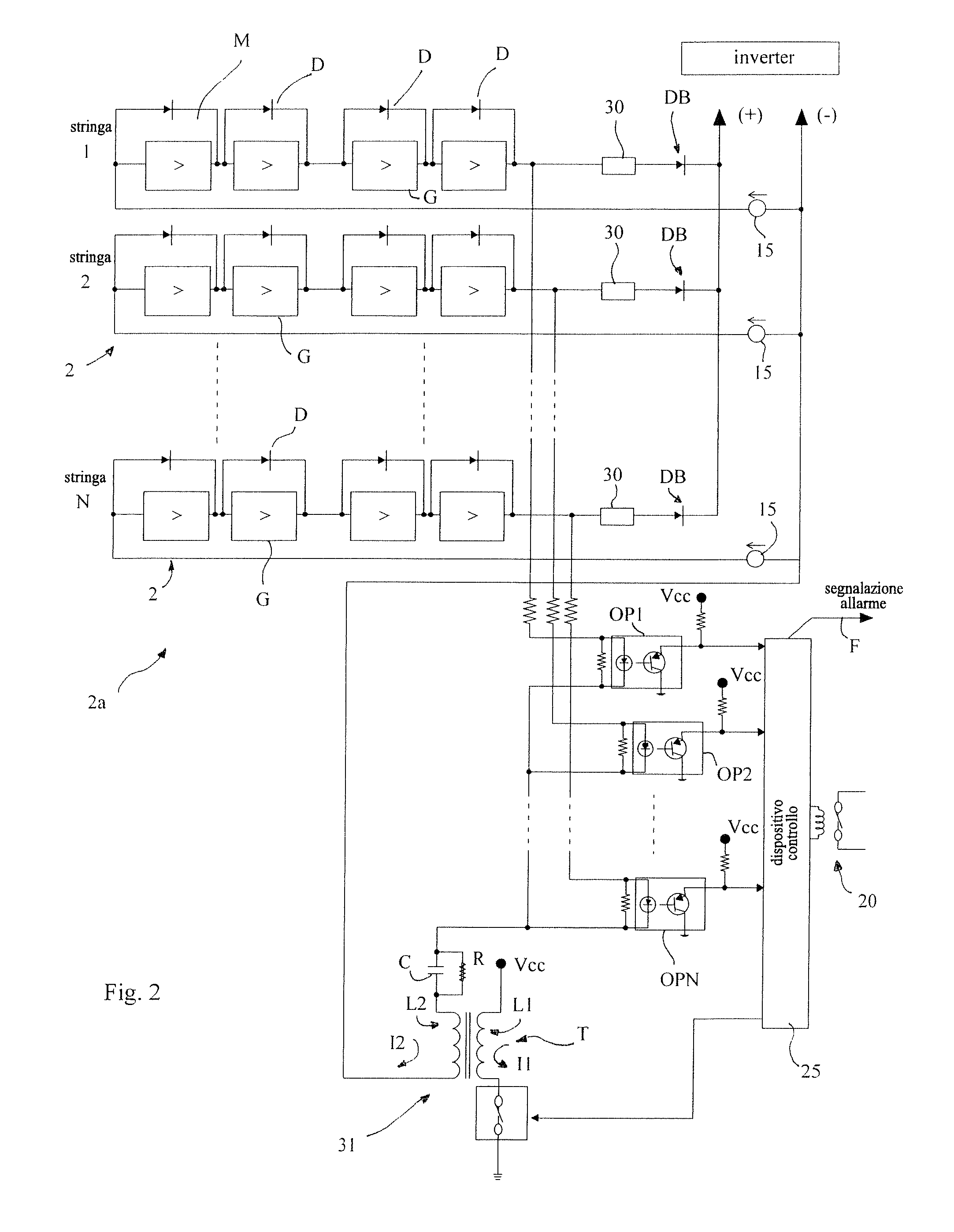
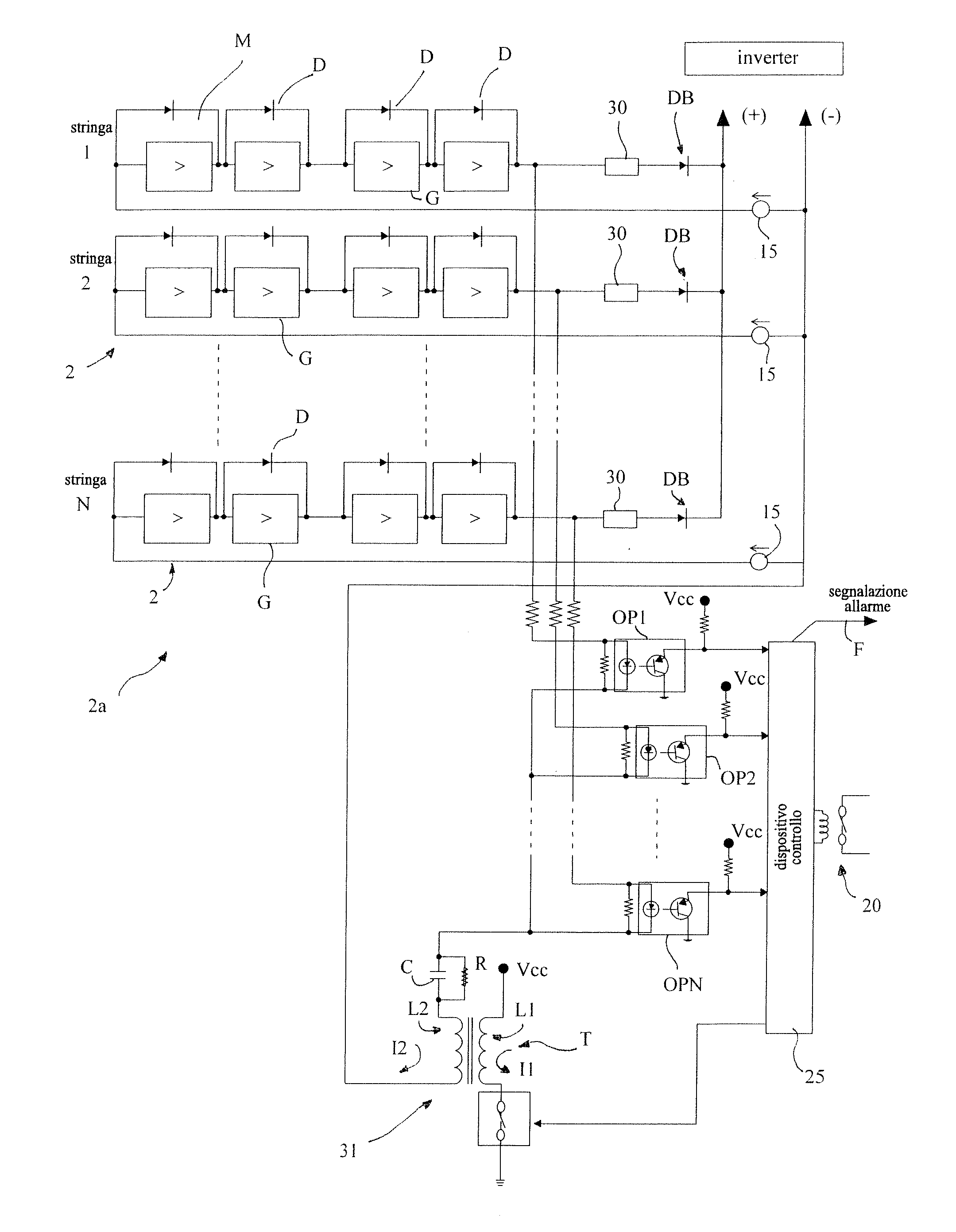
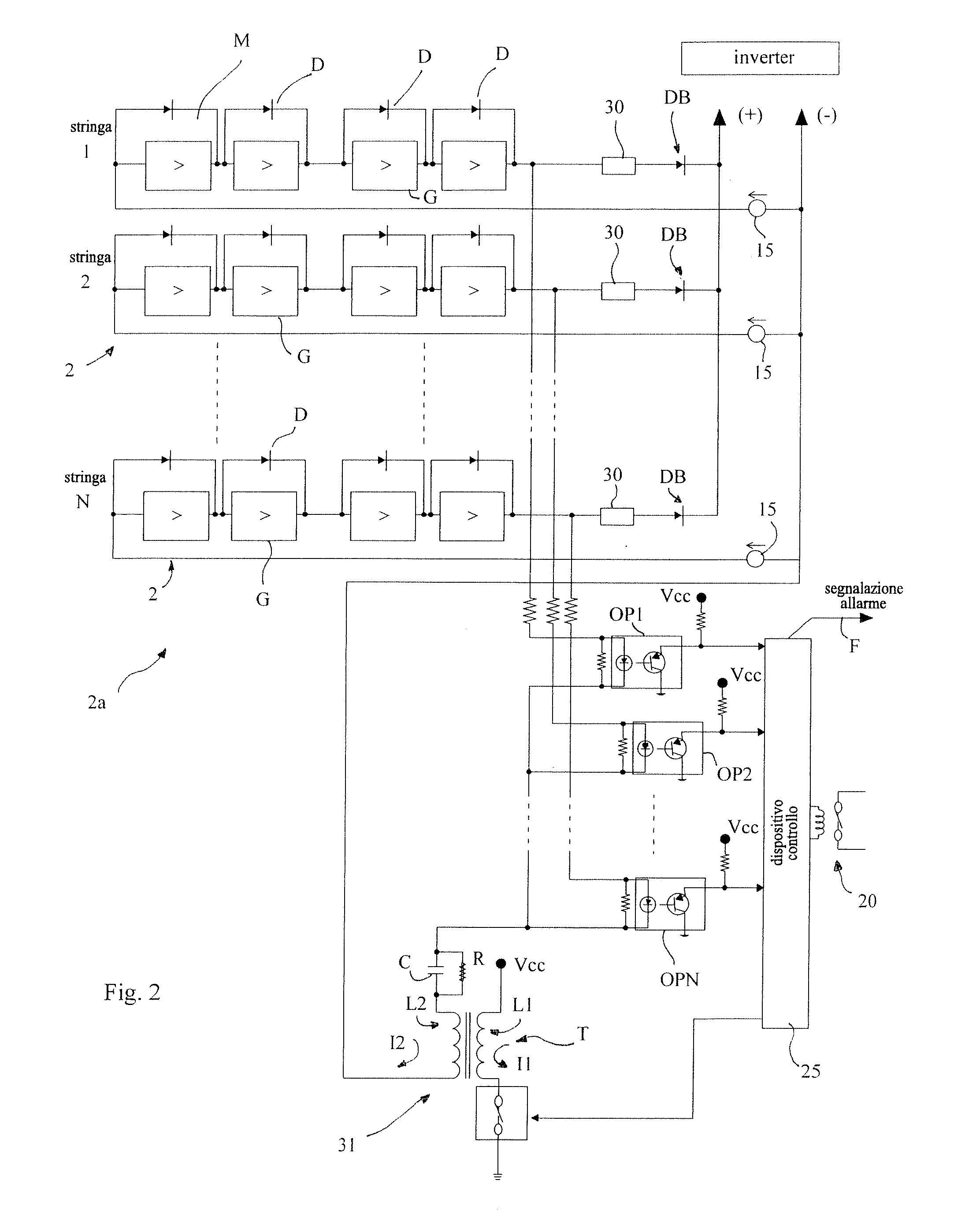
There is described a plant (1) for converting solar energy into electrical energy, comprising a photovoltaic generator (2a) including at least one string (2) of photovoltaic modules (M), a pulse generator (31) able to send electrical pulses to the input of the string (2), a signal detector (OP) arranged at the output of the string (2) and able to detect, at the output of the string (2), the presence of a signal which is a function of the electrical pulses at the input, and alarm means connected to the signal detector (OP) and able to generate an alarm in the event that there is no signal at the output of the string (2).
Owner:ELETTRONICA SANTERNO
Integrated gate-commutated thyristor (IGCT)-based hybrid cascaded H-bridge multi-level high-voltage inverter
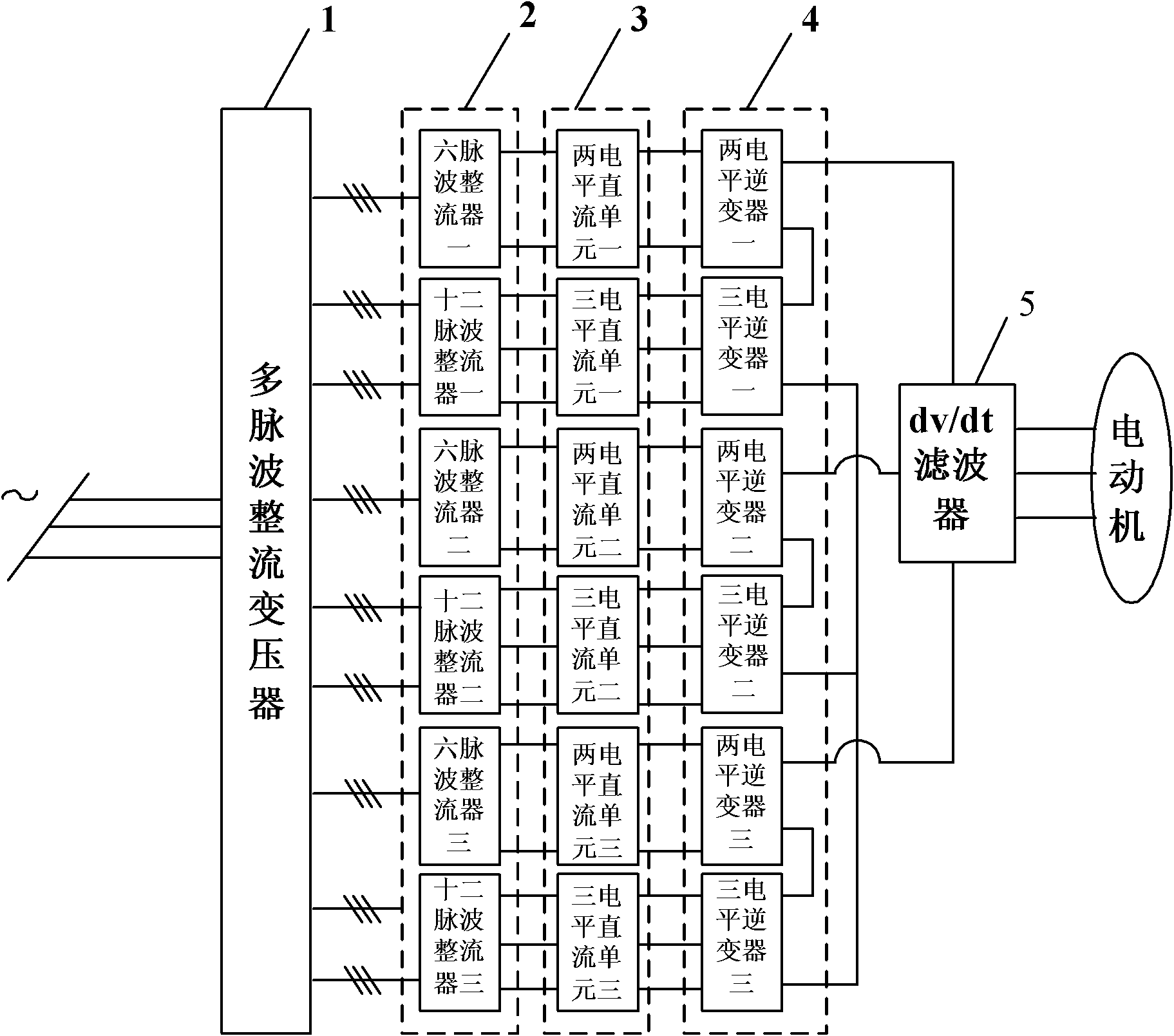
ActiveCN102035402AReduce harmonic interferenceGuaranteed Harmonic Distortion RateAC motor controlAc-dc conversionFrequency changerIntegrated gate-commutated thyristor
The invention relates to an integrated gate-commutated thyristor (IGCT)-based hybrid cascaded H-bridge multi-level high-voltage inverter, which belongs to the technical field of electric drive. The inverter comprises a rectification unit, a DC unit, an inversion unit and a dv / dt filter, wherein the secondary side of a multi-winding rectifier transformer is connected with the input of the rectification unit; the output of the rectification unit is connected with the input of the DC unit; the output of the DC unit is connected with the inversion unit; and the output of the inversion unit is connected with the dv / dt filter. The inverter solves the problem that 10 kV high-voltage high-capacity output is obtained without realizing direct series connection by IGCT devices, less impacts a power grid in a working process, increases the sine degree of output voltages, has relatively lower difficulties in control and enhanced reliability, improves the working stability of a system, effectively inhibits current harmonics on a power grid side, and makes the distortion rate of line current on an input side meet standard requirements.
Owner:武汉长海电力推进和化学电源有限公司
High boost circuit, solar inverter and solar cell system
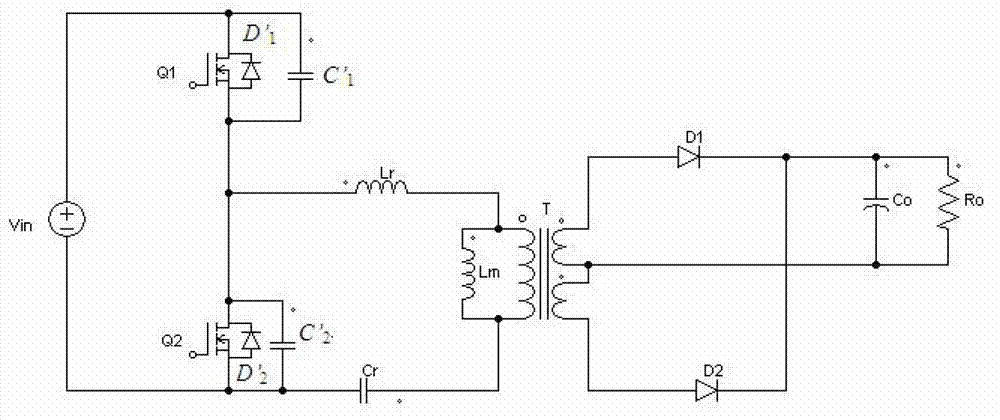
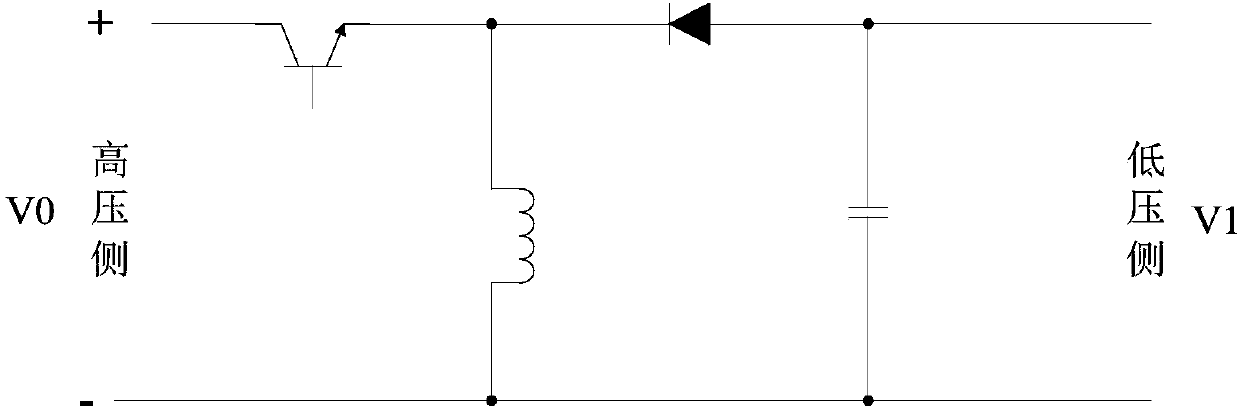
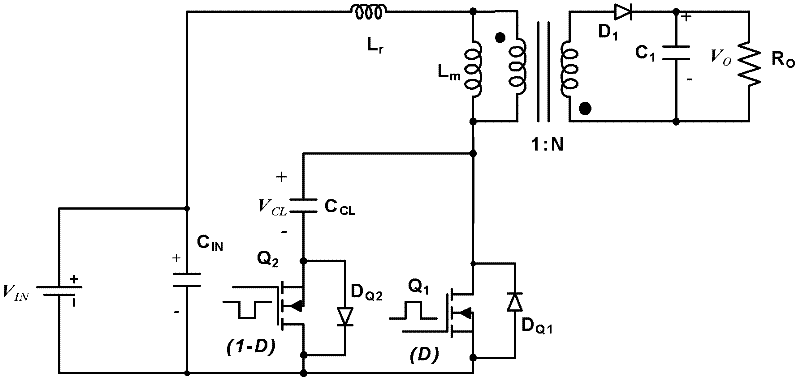
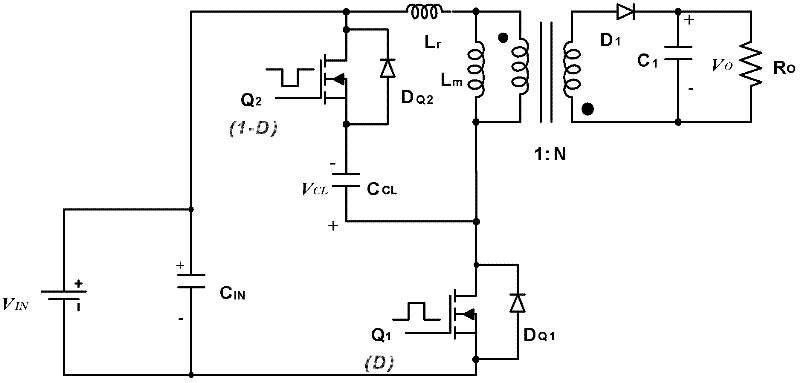
InactiveCN102638164ALow costReduce lossDc-dc conversionConversion without intermediate conversion to dcElectrical batteryHigh energy
The invention discloses a high boost circuit, a solar inverter and a solar cell system. The high boost circuit comprises a direct current input voltage Vin, a converter unit and a transformer unit, wherein the converter unit is connected with the direct current input voltage Vin and is used for outputting a direct current output voltage V0; and the transformer unit is connected between the primary side and secondary side of the converter unit in a matched manner and is used for separating the primary side and secondary side of the converter unit and / or is used for performing boosting process on the output voltage of the secondary side of the converter unit on the basis of the input voltage of the primary side of the converter unit. The high boost circuit, the solar inverter and the solar cell system can be used for overcoming the defects in the prior art of high cost, large extra loss, low energy conversion efficiency, poor environment friendliness and the like, and has the advantages of low cost, small extra loss, high energy conversion efficiency, good environmental friendliness and the like.
Owner:LEADSOLAR ENERGY
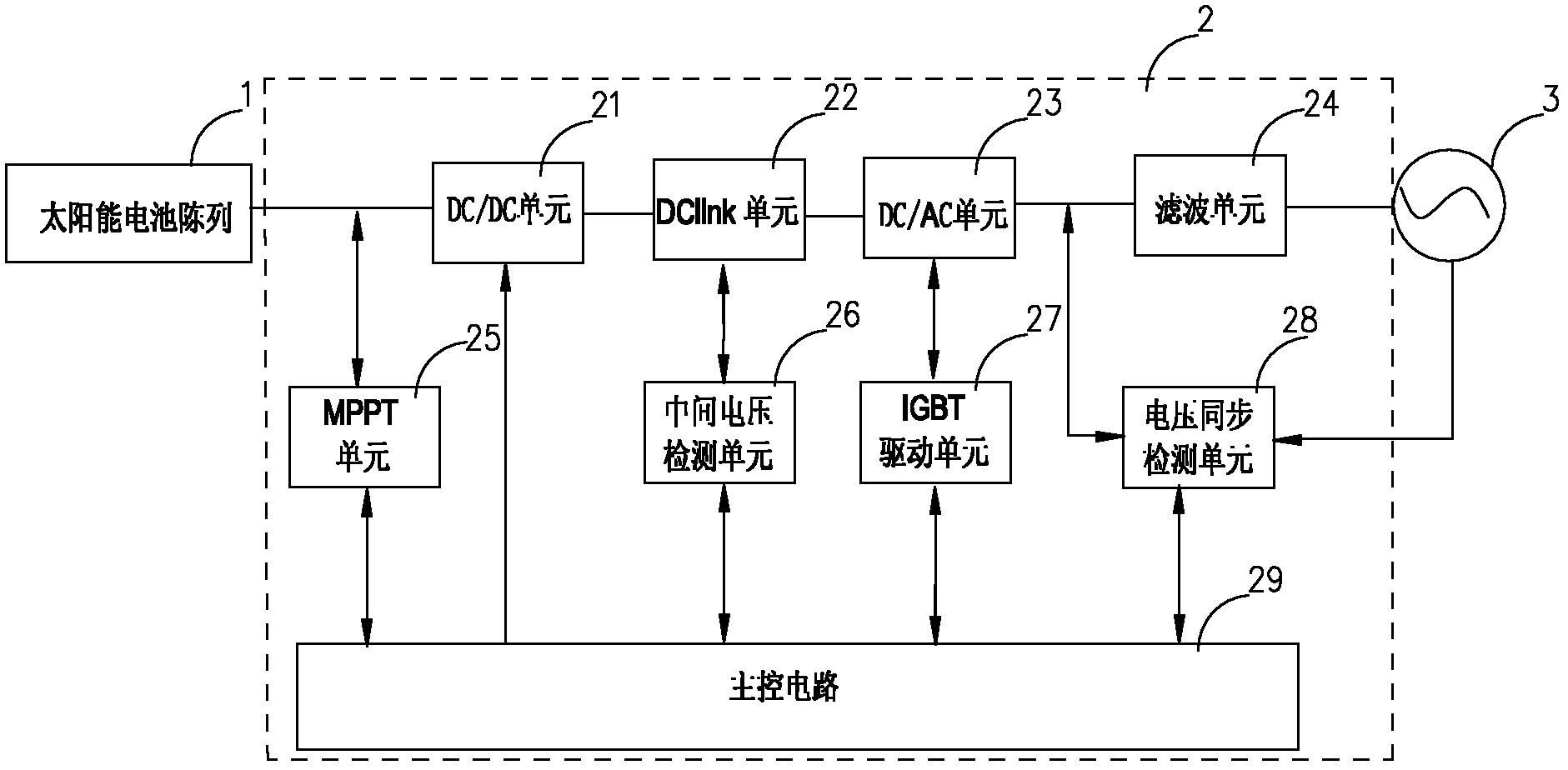
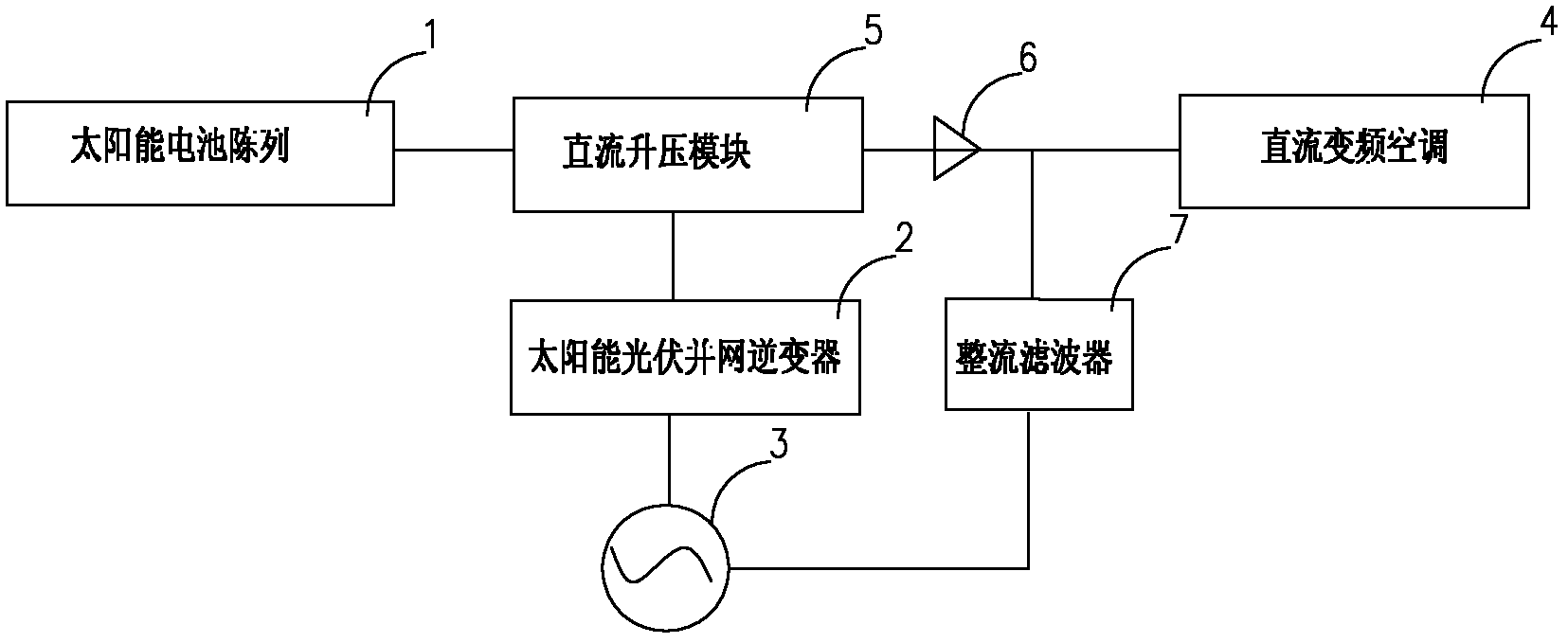
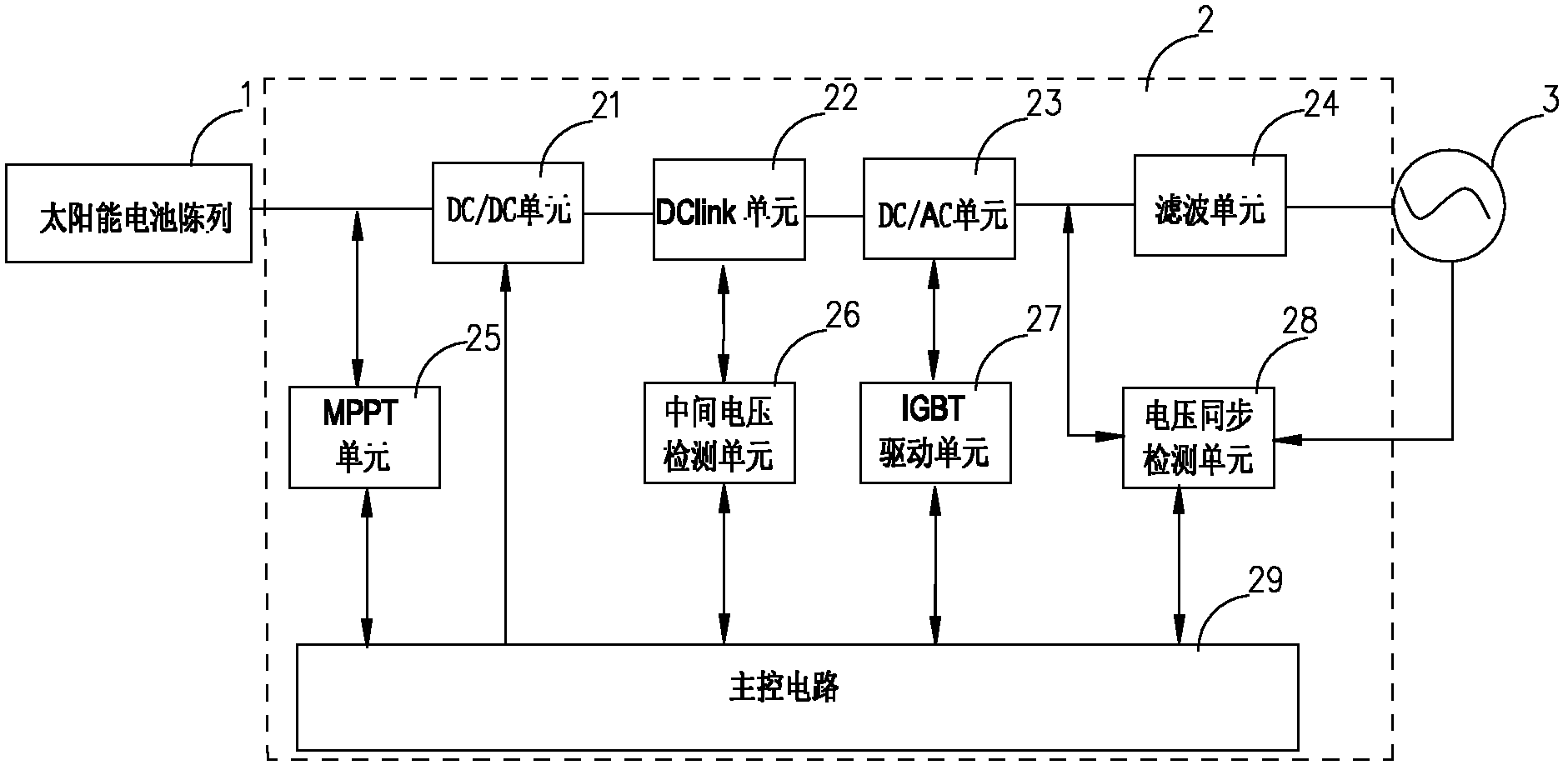
Solar photovoltaic grid-connected inverter and solar inverter air conditioning system
InactiveCN102291026AImprove protectionReduce manufacturing costSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPhotovoltaic energy generationOperating pointGrid connected inverter
The invention discloses a solar photovoltaic grid-connected inverter, which includes a power circuit and a control circuit. The power circuit includes a DC / DC unit, a DC / AC unit, and a filter unit; Collect digital and / or analog signals in the system, control the power devices in the power circuit after completing the corresponding operations, and dynamically track the maximum power point of the solar cell array to adjust the working point of the solar cell array. The invention also discloses a solar inverter air conditioner system, which includes a solar cell array, a DC boost module, a solar photovoltaic grid-connected inverter, and a DC inverter air conditioner. The grid-connected inverter is connected between the DC step-up module and the utility grid. The invention realizes that the air conditioner is jointly driven by the solar energy and the mains power, and when the air conditioner is idle or the solar energy is surplus, the electric energy can be fed back to the city network.
Owner:GUANGDONG CHIGO AIR CONDITIONING
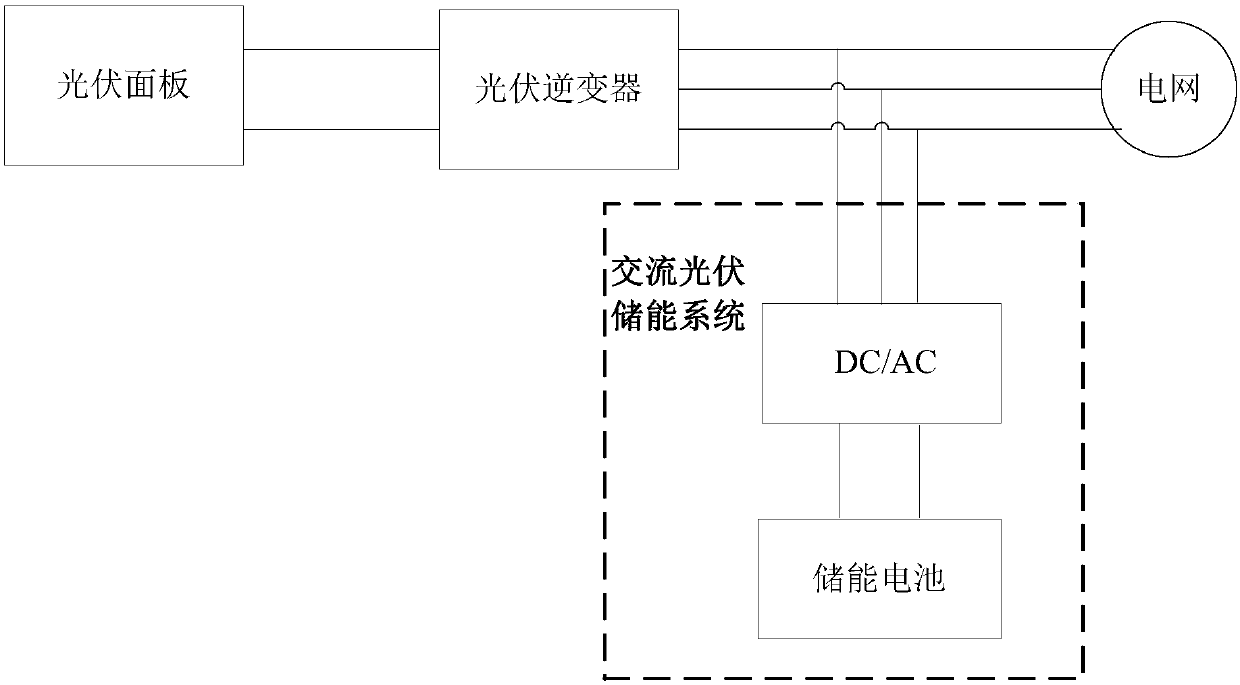
Photovoltaic microgrid system and control method thereof
InactiveCN107872070ASimple structureGood autonomySingle network parallel feeding arrangementsEnergy storageMicrogridCurrent sensor
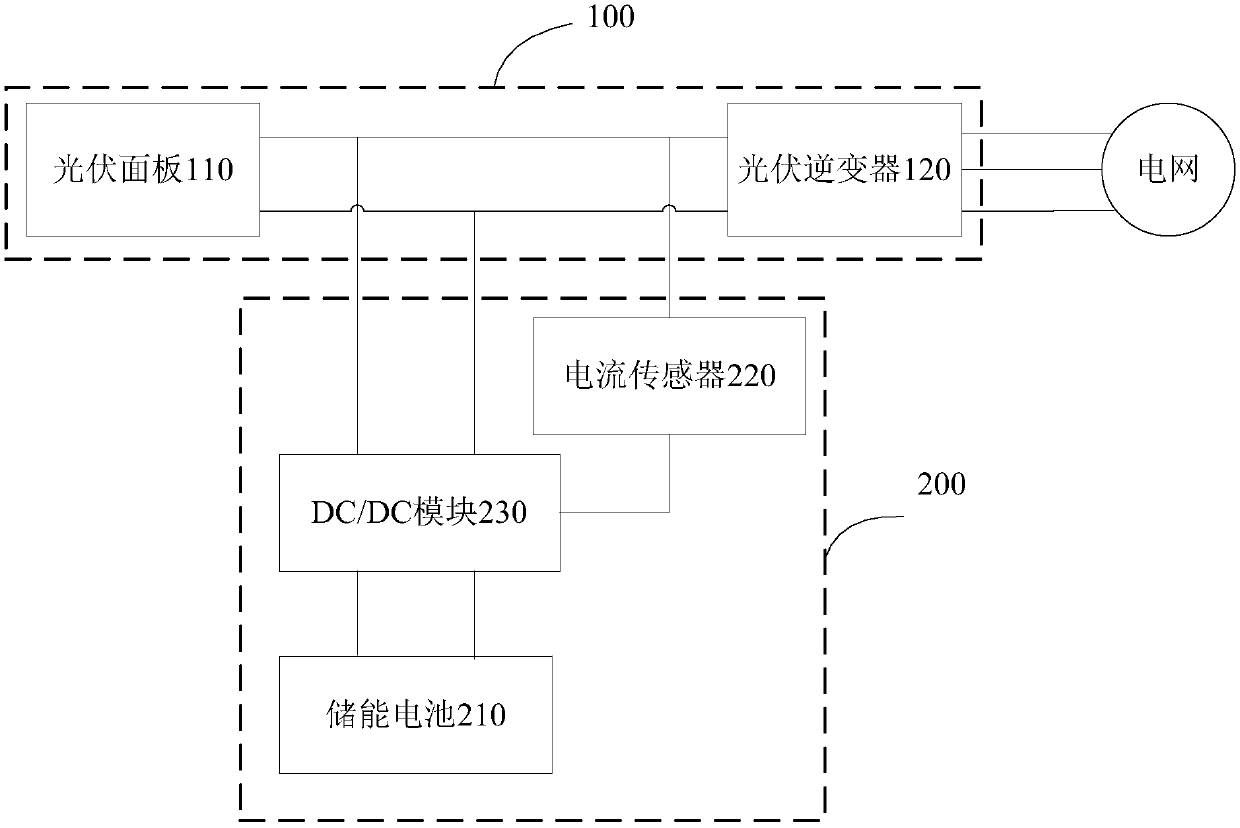
The invention discloses a photovoltaic microgrid system and a control method thereof. The photovoltaic microgrid system comprises a photovoltaic power generation system, and a photovoltaic energy storage system. The photovoltaic power generation system comprises a photovoltaic panel and a photovoltaic inverter. The photovoltaic energy storage system comprises an energy storage battery, a current sensor and a DC / DC module. The first end of the DC / DC module is connected with the output end of the photovoltaic panel. The second end of the DC / DC module is connected with the energy storage battery.The third end of the DC / DC module is connected with the direct-current side of the photovoltaic inverter through the current sensor. The DC / DC module is used for calculating the output power of the photovoltaic inverter according to the output voltage of the photovoltaic panel and the current of the direct-current side of the photovoltaic inverter, and adjusting the working state of the photovoltaic energy storage system according to the output power of the photovoltaic inverter, the output voltage of the photovoltaic panel and the SOC of the energy storage battery. The system is simple in structure and good in autonomy. The alternating current harmonic of the power grid and the photovoltaic inverter is not influenced at all, and the energy utilization rate of the photovoltaic panel is high.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
Solar inverter
ActiveUS9270201B1Dc-dc conversionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsFull bridgeEnergy recovery
An inverter device has an active ripple cancellation boost circuit being configured to a DC source from a plurality of solar cells and configured to filter an AC current ripple back to the DC source and boost the DC voltage to an intermediary 12-15 voltage range. The device has a wave shaper circuit comprising a phase shift zero voltage switching full bridge circuit and a rectifier energy recovery circuit, the phase shift zero voltage switching full bridge circuit configured to shape the DC source to a half wave rectified 120V to 240V waveform. The device has an analog mixed signal controller module configured to generate a PWM waveform and synchronize the rectified waveform to a grid voltage.
Owner:SUNEDISON MICROINVERTER PROD
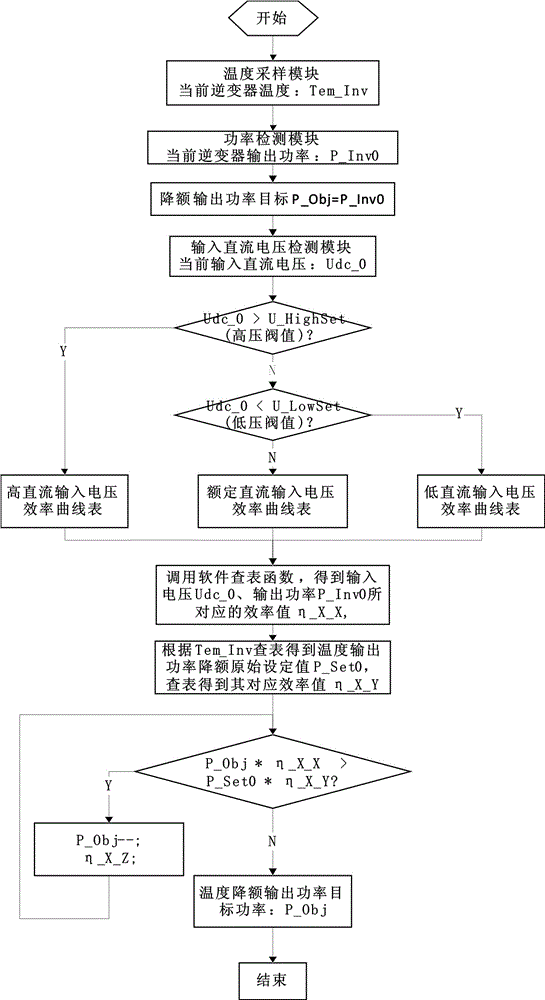
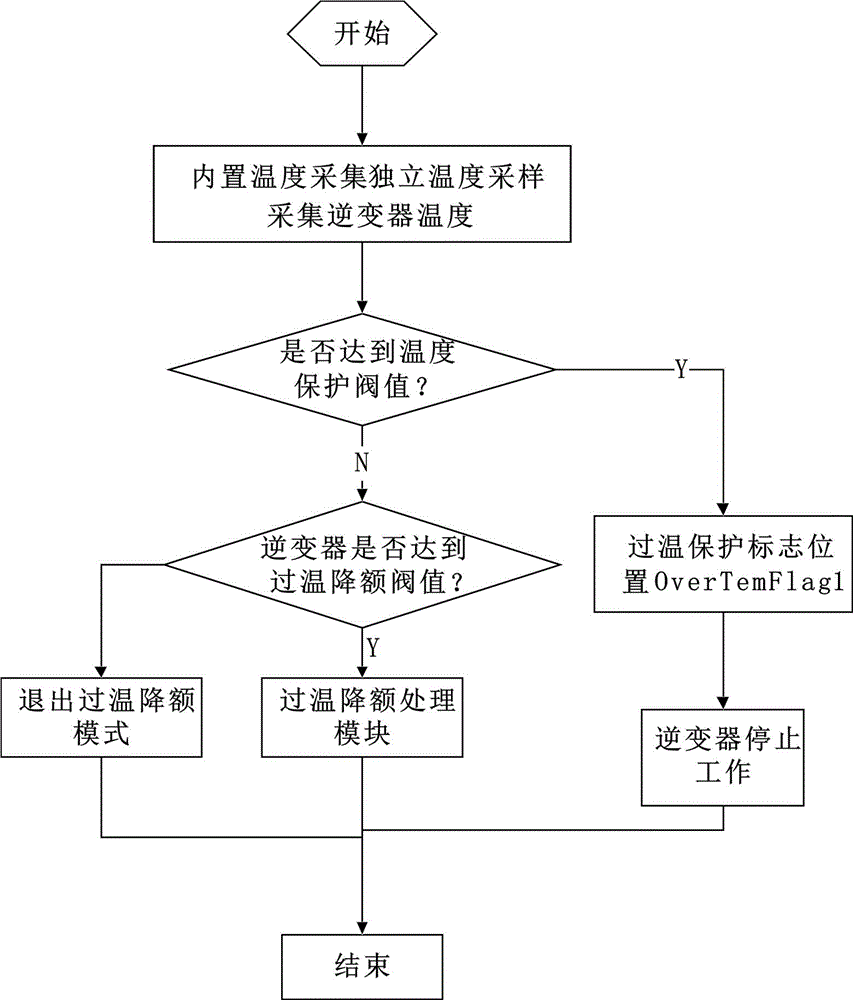
Software control method for derating output power of photovoltaic inverter in case of over-temperature
ActiveCN103825251AIncrease charging powerEasy dischargeEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringProduct value
The invention discloses a software control method for derating output power of a photovoltaic inverter in case of over-temperature. The method comprises the following steps: data storage, i.e., setting a power curve and an efficiency-power curve for temperature-derating and storing the curves in the form of a corresponding table; current temperature detection; current power detection; current DC voltage detection; efficiency-power curve selection; current efficiency determination; derating set power and efficiency determination; and derating target power calculation and determination, i.e., comparing the product value of the initial power value and the current efficiency of derating target power to the product value of the derating set power and efficiency, and if the product value of the initial power value and the current efficiency of the derating target power is greater than or equal to the product value of the derating set power and the efficiency, continuing diminishing the power value of the derating target power until the product value of the initial power value and the current efficiency of the derating target power is smaller than the product value of the derating set power and the efficiency. By using such a method, it is ensured that the photovoltaic inverter can maintain quite high power charge and discharge in case of over-temperature power derating.
Owner:HUIZHOU TEN SOURCES SOLAR ELECTRICITY
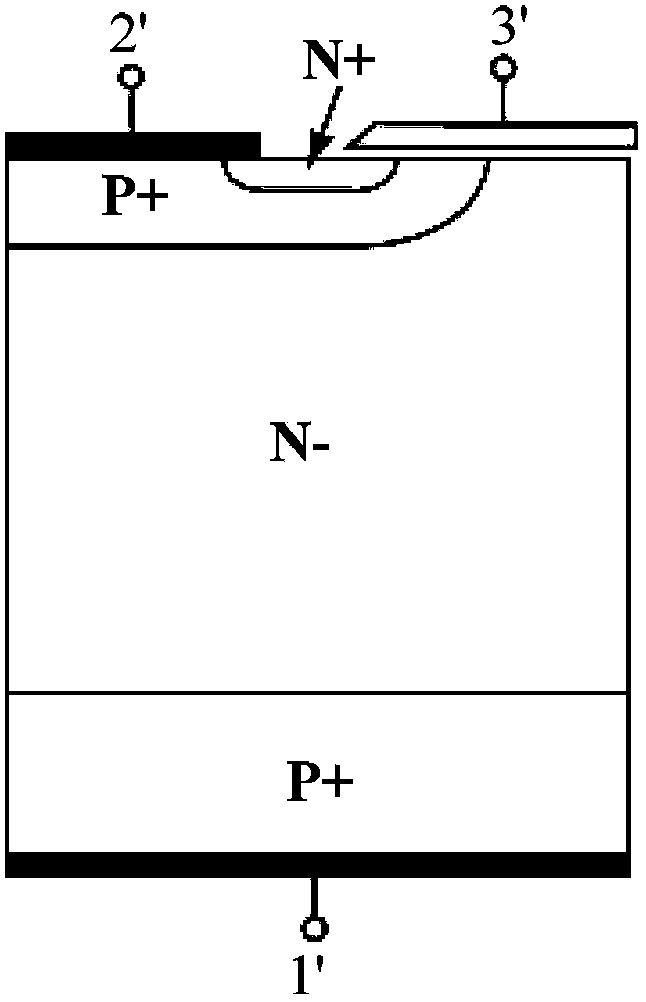
Semiconductor power device
InactiveCN103579230AFast switching speedReduce sizeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesElectrical resistance and conductancePower flow
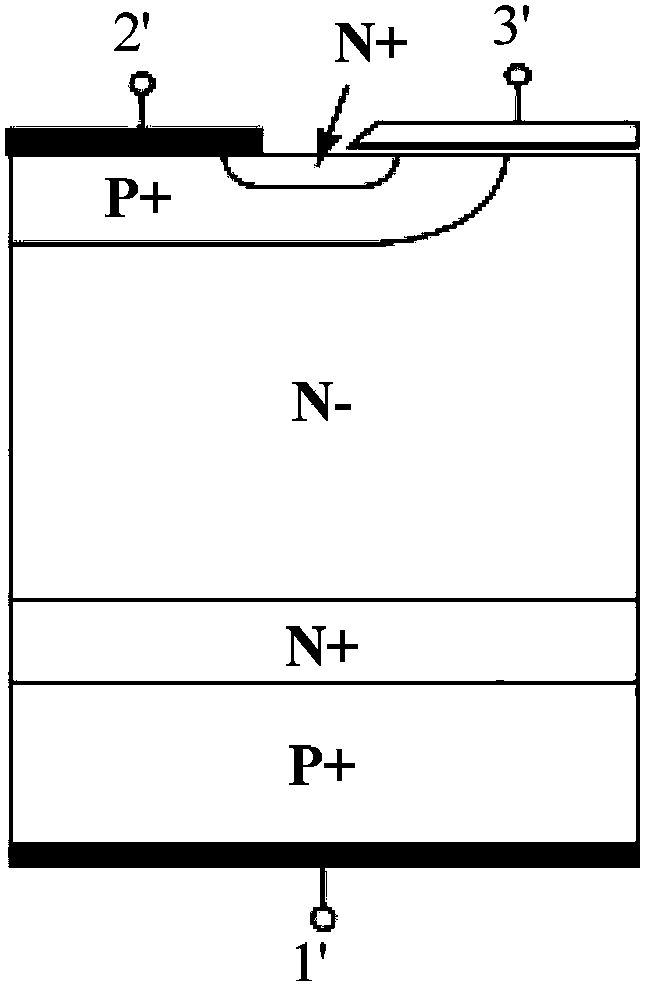
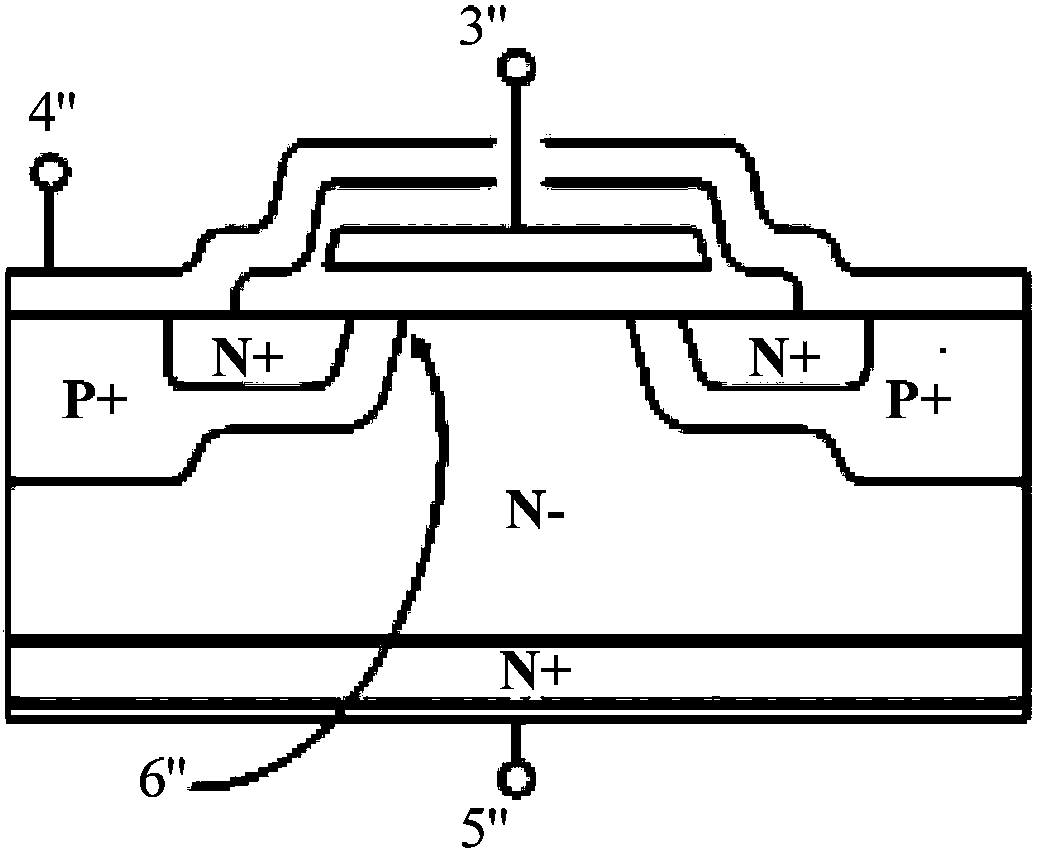
The invention provides a semiconductor power device. A traditional IGBT and a traditional VDMOS are ingeniously combined to form the novel semiconductor power device provided with a common part and consisting of a basic transverse IGBT and a basic VDMOS. The doping concentration of a re-doped second electric conduction type region is adjusted or a service life controlling method is adopted to decrease first forward breakover current produced by the basic transverse IGBT and meanwhile increase second forward breakover current produced by the basic VDMOS, and the first forward breakover current is smaller than the second forward breakover current. Compared with the traditional IGBT and the traditional VDMOS, the switching speed of the device is improved while the reduction of the breakover resistance loss and the breakover power loss of the device is ensured. By improving a structure of a drifting region, a forward breakover negative resistance region is eliminated, and the performance of the semiconductor power device is improved. The semiconductor power device is applied to the fields of power supplies, solar inverters, motor driving and other fields needing high-voltage and high-frequency switching.
Owner:WUXI VERSINE SEMICON CORP
Transformer with high set-up ratio, solar inverter and solar battery system
InactiveCN102447396AHigh boost ratioImprove conversion efficiencyBatteries circuit arrangementsAc-dc conversionHigh energyElectrical battery
The invention discloses a transformer with a high set-up ratio, a solar inverter and a solar battery system. According to the invention, the low output voltages of power sources are converted to high output voltages through the transformer with the high set-up ratio; and according to the specific application and different control methods, the outputs of the transformer with the high set-up ratio from a first technical scheme to a fourth technical scheme can be standard direct current voltages or controlled and modulated specific voltage wave forms. By using the transformer with the high set-up ratio, the solar inverter and the solar battery system, the defects of small set-up ratio, long transmission path, large additional loss, low energy conversion efficiency and the like in the prior art can be overcome, so as to realize the advantages of large set-up ratio, short transmission path, small additional loss and high energy conversion efficiency.
Owner:LEADSOLAR ENERGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com