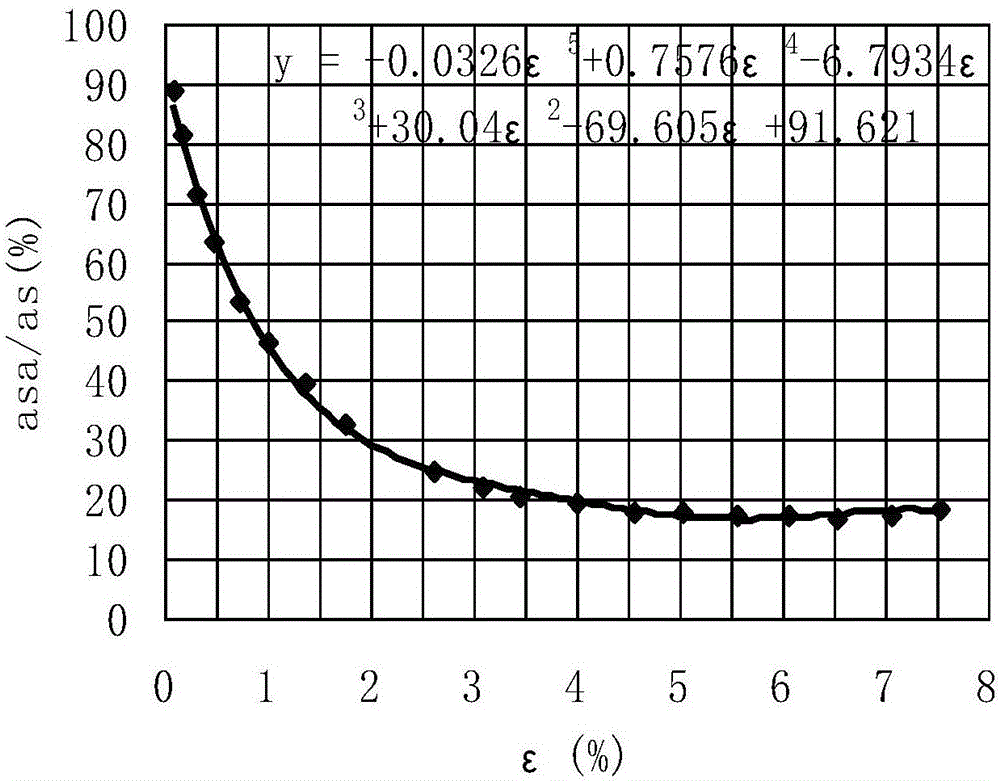
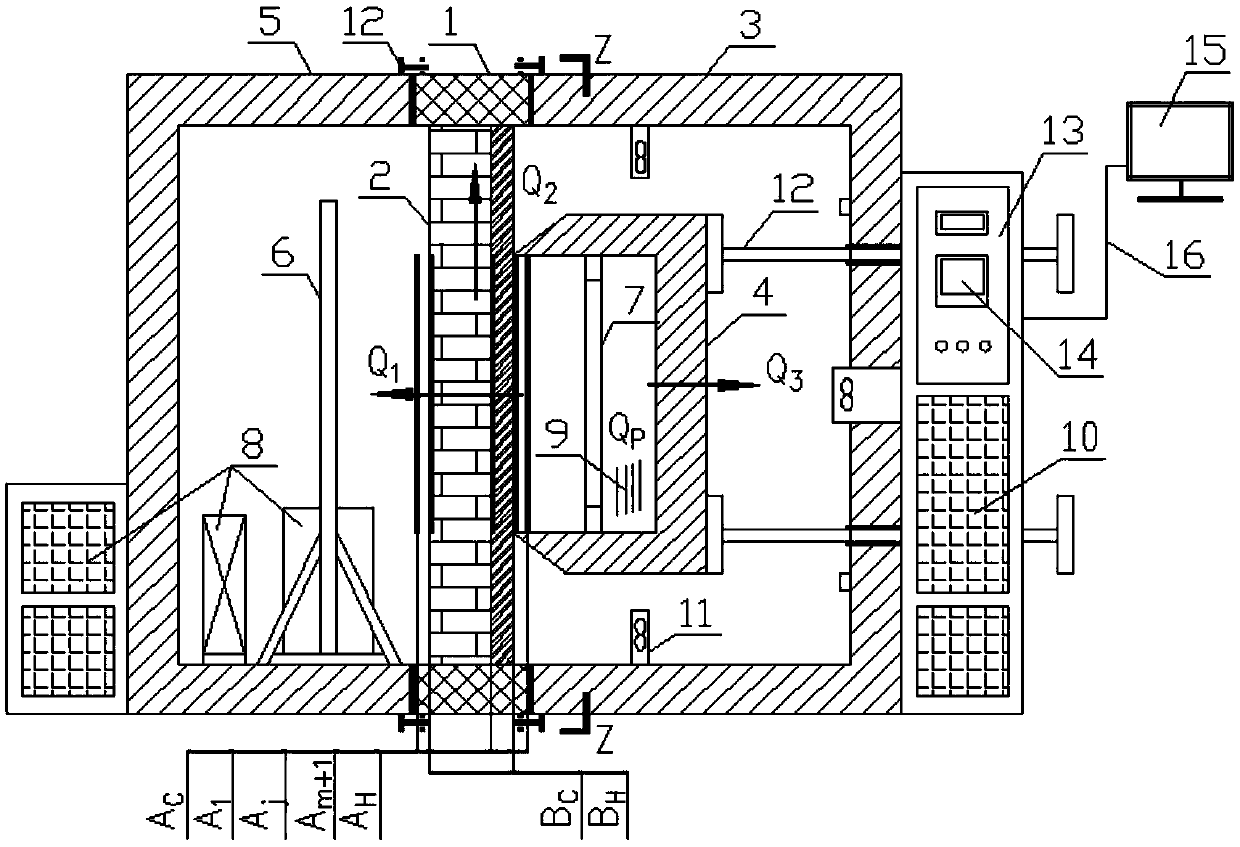
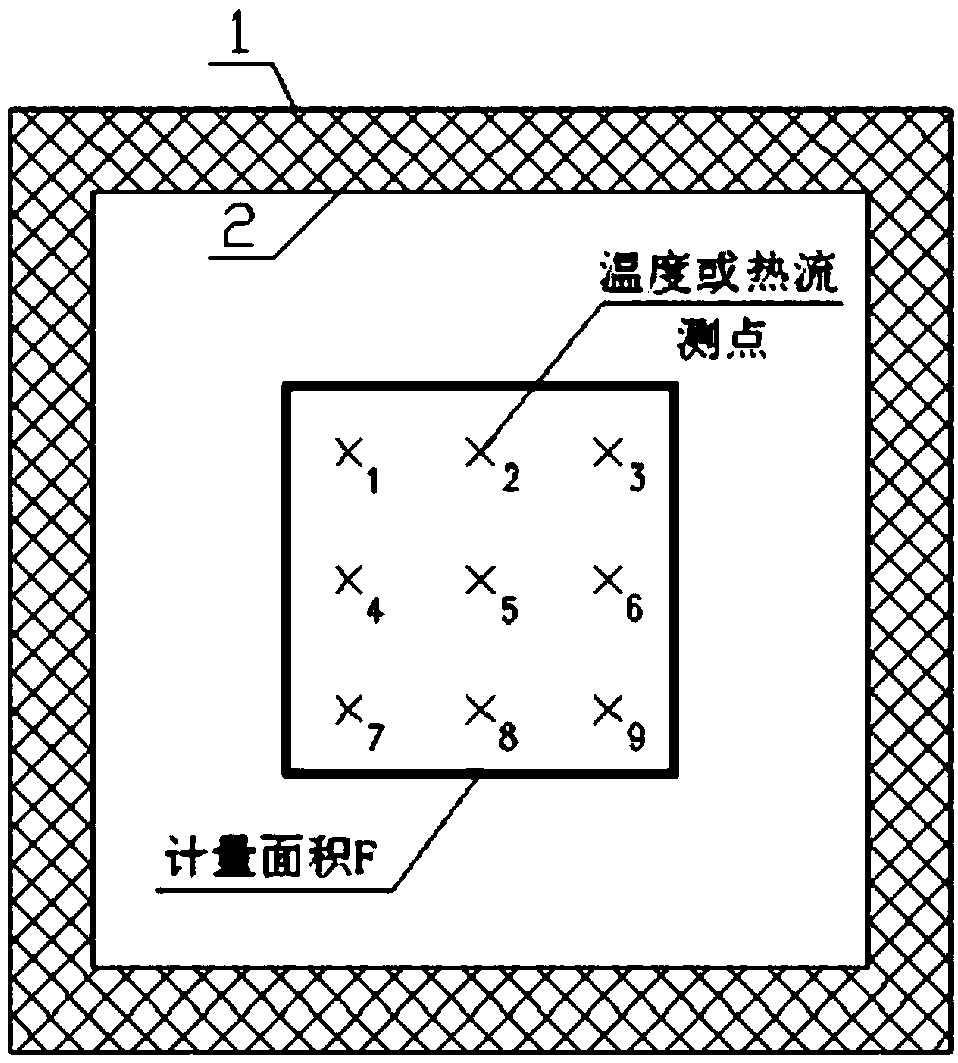
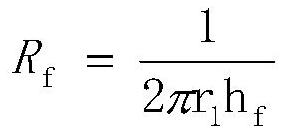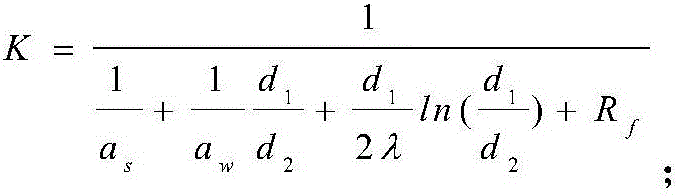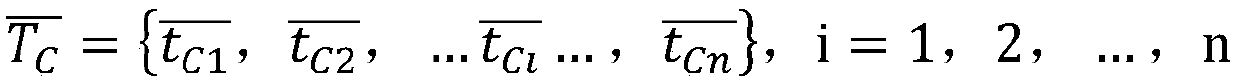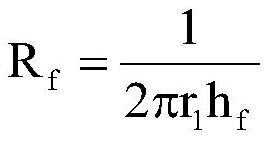Patents
Literature
32 results about "Steady state heat transfer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Steady-state Heat Transfer. A steady-state heat transfer analysis is used to determine the steady-state temperature distribution and heat flow. This type of analysis can be performed when the temperature at every point within the model, including the surfaces, is independent of time.
A method for measuring high temperature thermal conductivity
ActiveCN102288641AEasy to testEasy to adjustMaterial heat developmentHeat flowTemperature difference
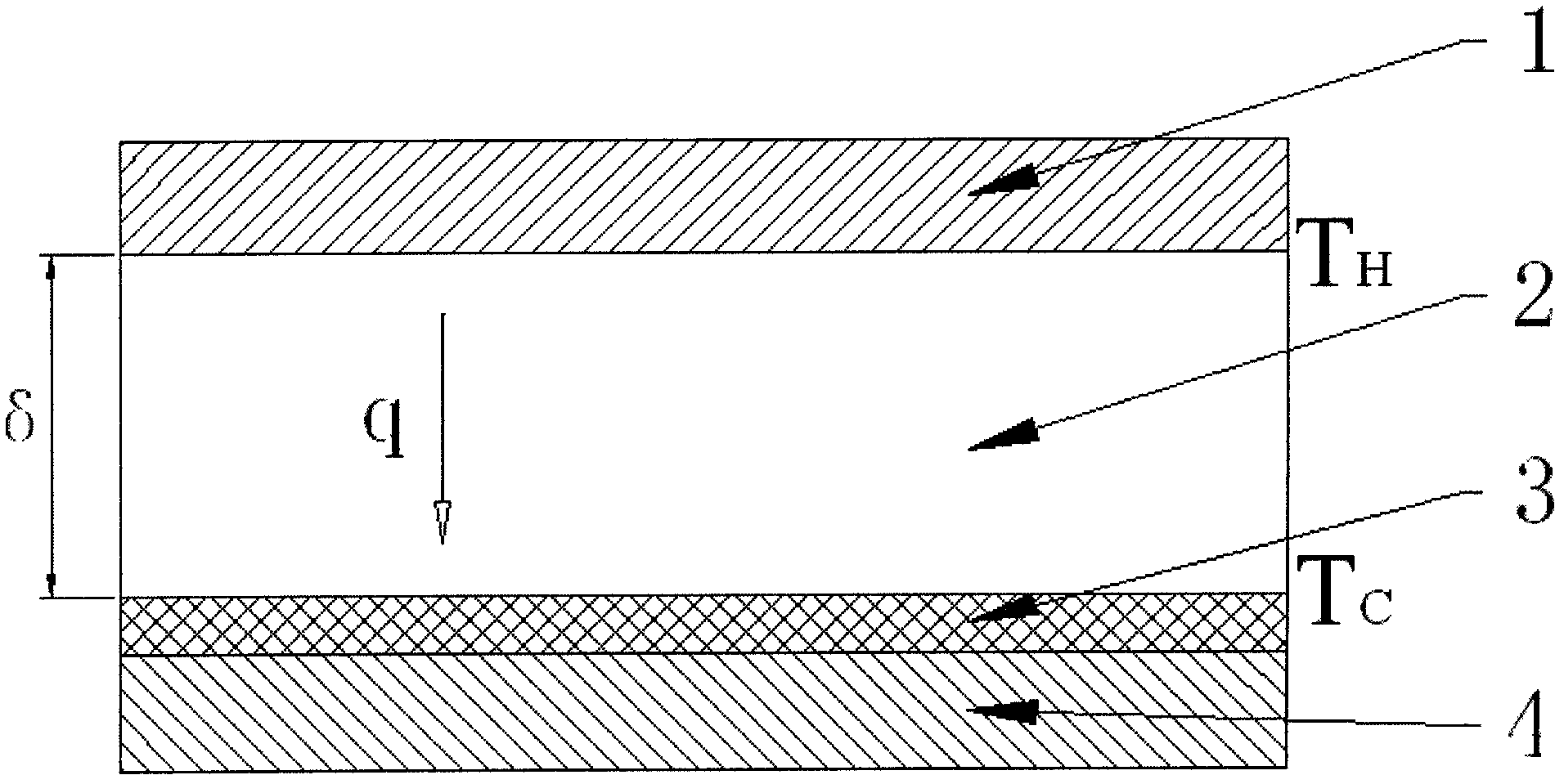
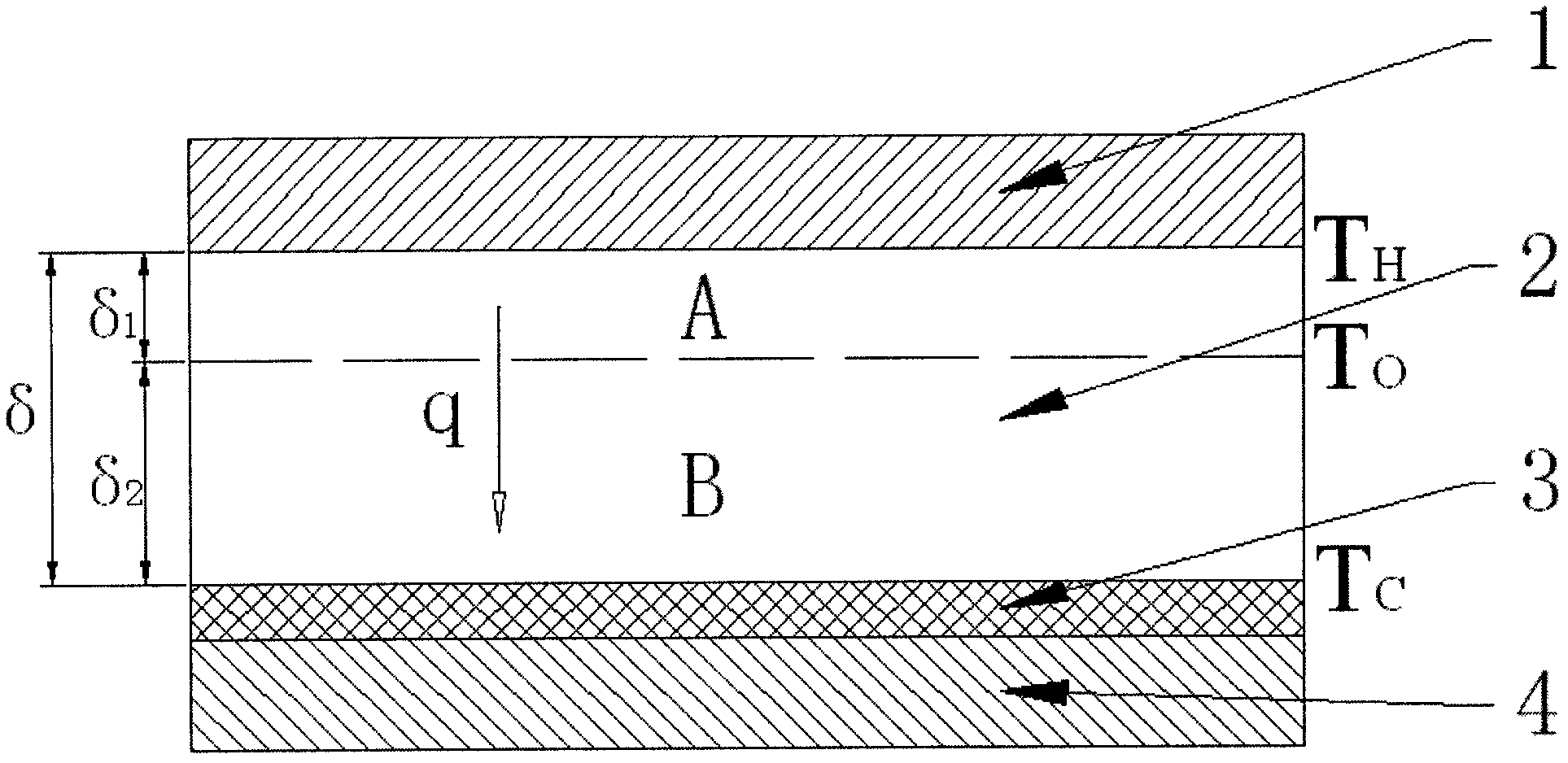
The invention relates to the field of thermal conductivity coefficient of a material, in particular to a method for measuring high temperature thermal conductivity coefficient. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: firstly testing steady state thermal transfer thermal current density q of the material sample with the thickness Theta under the conditions that 'temperature difference is TH-TC and average temperature is (TH+TC) / 2'; then testing steady state thermal transfer thermal current density q1 of the sample in the first step under the conditions that 'the temperature difference is To-TC and the average temperature is (To+TC) / 2', wherein To can be in accordance with engineering requirements and is set to be a value close to TH in the first step, and To value is required to be less than TH value; and determining the thermal conductivity coefficient under the conditions that 'the temperature difference is TH-To and the average temperature is (TH+To) / 2' by combining a formula (1) and utilizing the thermal current density data acquired by the steps. In the invention, a T0 temperature layer in the material sample is selected, measurement accuracy can be relatively conveniently adjusted, measurement on the thermal conductivity coefficients of different temperature regions is realized, accurate measurement of the thermal conductivity coefficient at high temperature can be realized especially when T0 is close to the temperature of a hot plate, and the method provided by the invention is simple and convenient to operate and has greater practical application value.
Owner:CHINA AIRPLANT STRENGTH RES INST
Temperature variation sensing and index calculating method of textiles
InactiveCN104316557ASatisfy productivityMeet activityMaterial heat developmentSpecial data processing applicationsFiberTest sample
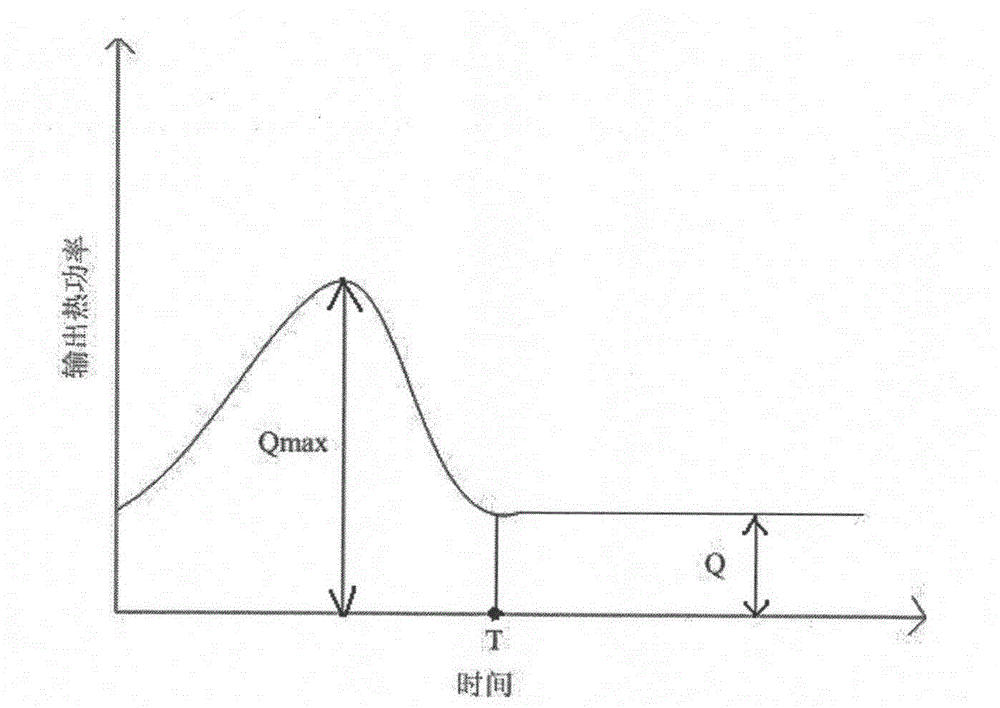
The invention relates to a temperature variation sensing and index calculating method of textiles. The method comprises the steps of testing a to-be-tested test sample in a required temperature and humidity environment after balancing; preheating a preheating test sample covered with an instrument hot plate, replacing the preheated test sample by utilizing the to-be-tested test sample, starting the test and recording a thermal power curve; defining a cold sensing time T as a peak of an initial section of the thermal power curve, i.e. a period of cold feeling time; defining the total heat loss W1 in the cold feeling time as the total heat loss of a unit area of the test sample in the cold feeling time T; defining the pure cold feeling heat loss W2 as the heat transferred from the human body to the textile due to the temperature difference at the beginning of the contact between the textile and the skin of a human body, wherein the pure cold feeling heat loss W2 is calculated in a way of subtracting the heat transferred by a unit area of test sample under the steady-state heat transfer condition within the period of time T from the total heat loss in the cold feeling time. The method is used for evaluating the temperature variation characteristic of a planar or curved fiber aggregation.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV +1
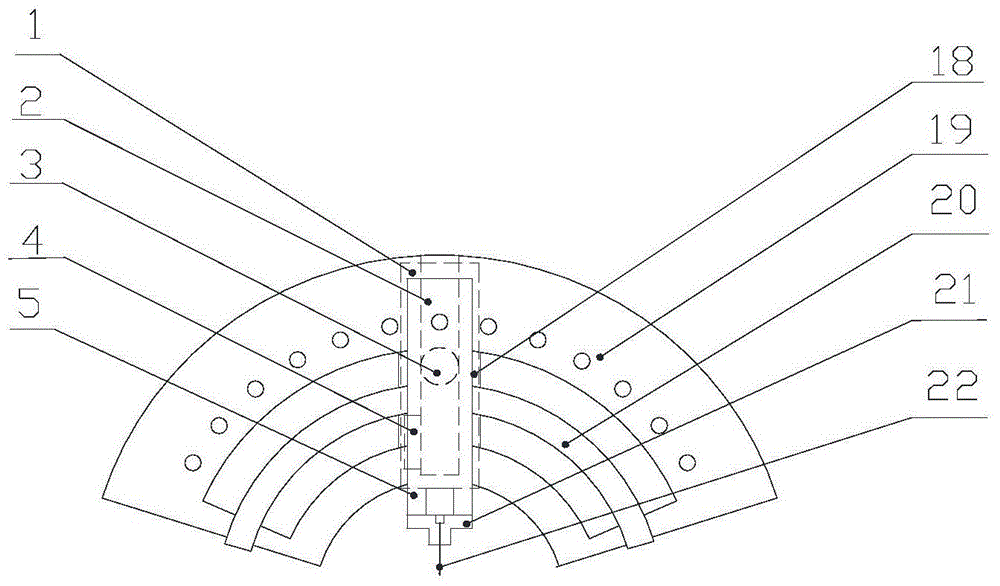
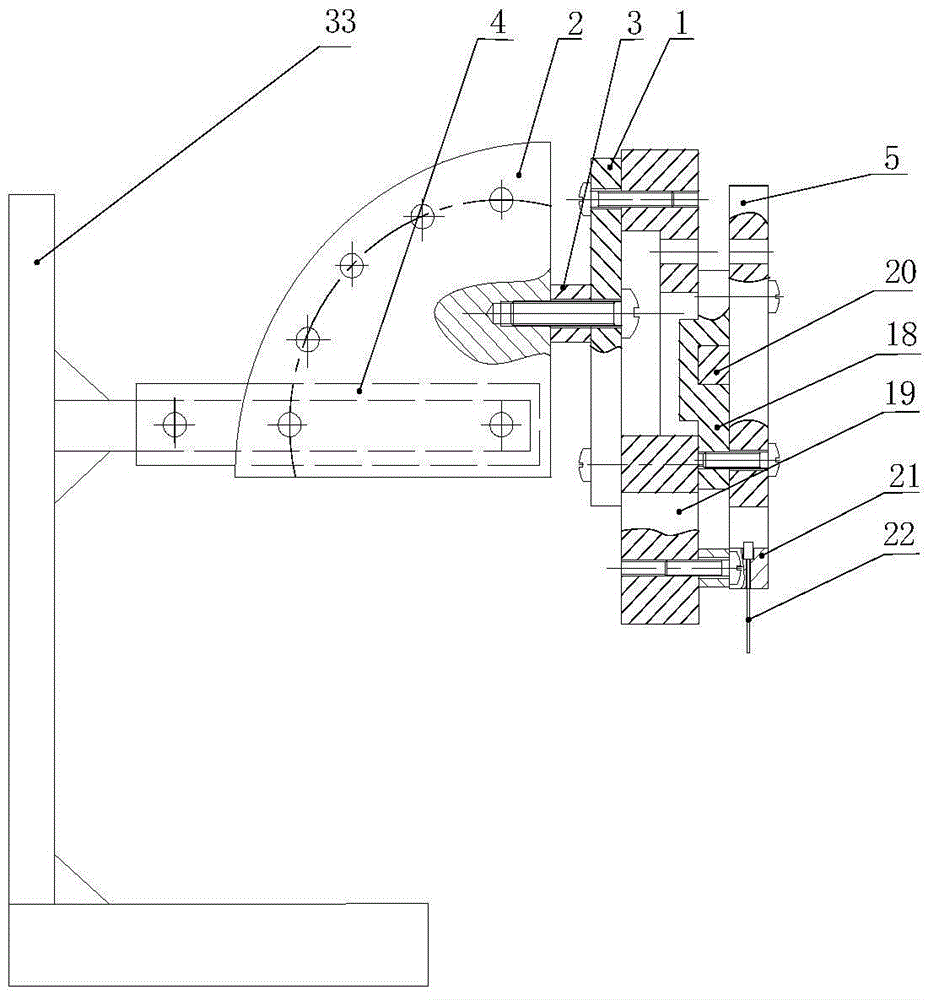
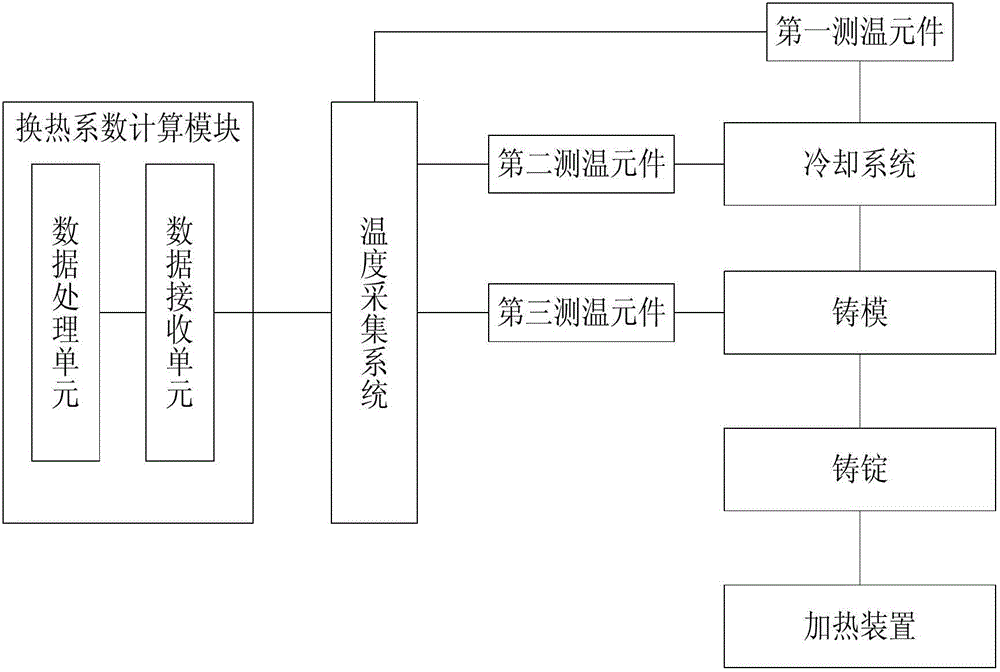
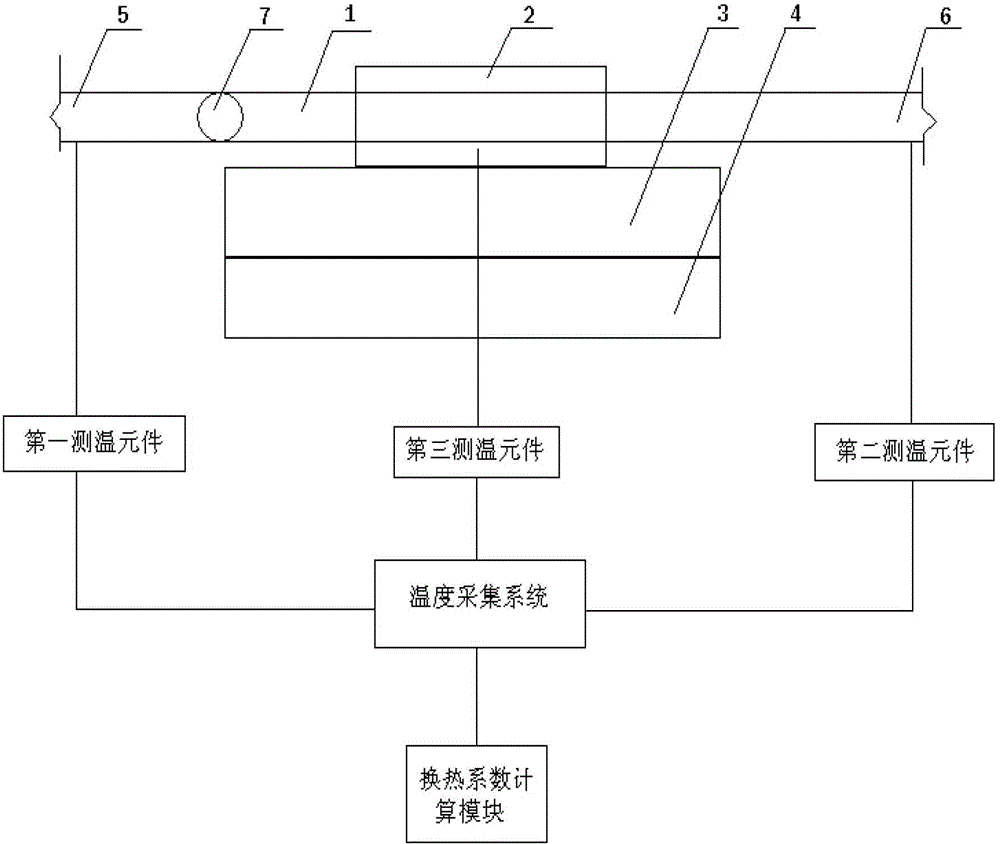
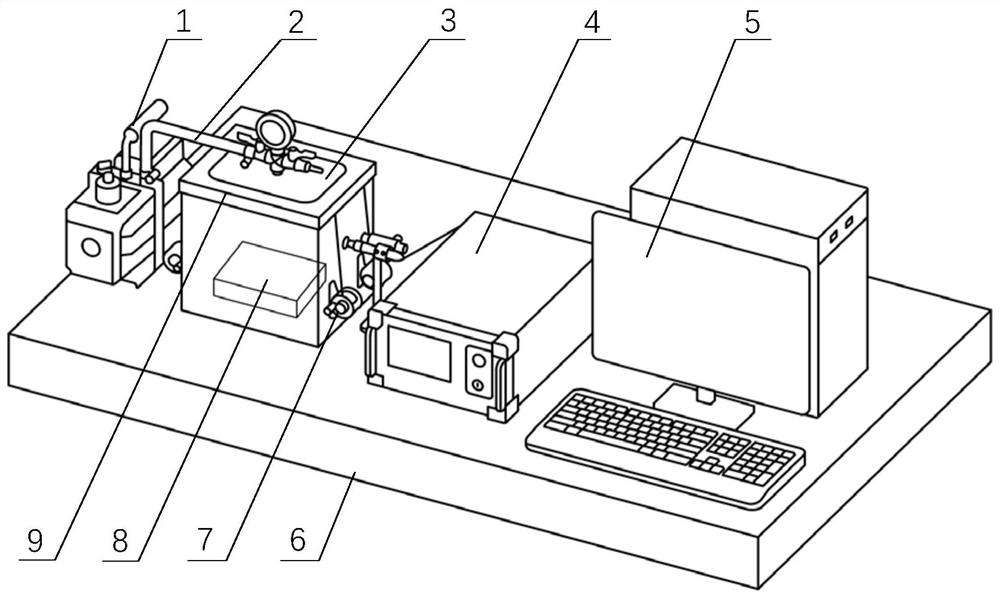
Experiment device for detecting heat exchange coefficient of water cooling mould
ActiveCN102928461ASimple structureEasy to operateMaterial thermal conductivityMaterial heat developmentStable stateHeat transmission
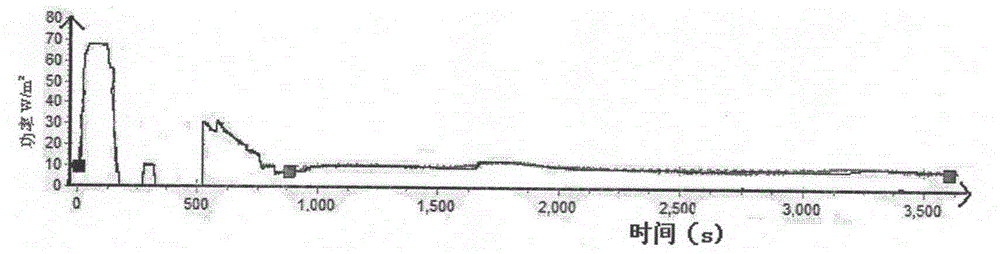
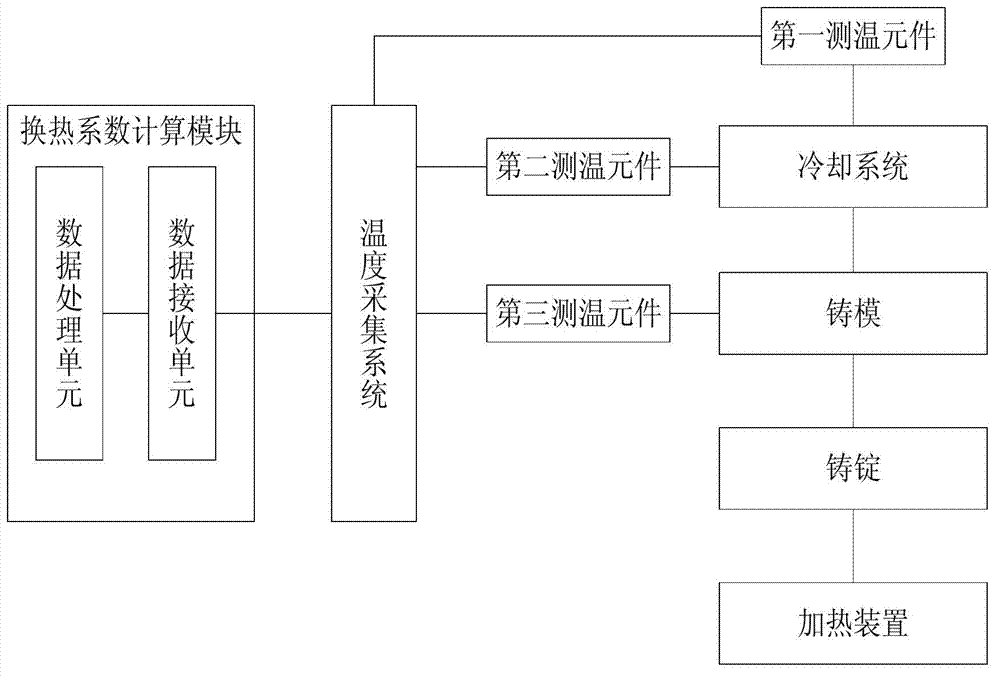
The invention discloses an experiment device for detecting a heat exchange coefficient of a water cooling mould. The experiment device comprises a mould, a cast ingot, a cooling system, a temperature collecting system, a heating device and a heat exchange coefficient calculation module. The experiment device provided by the invention is characterized in that an input end of the temperature collecting system is connected with the cooling system, the mould and the cast ingot respectively, and an output end of the temperature collecting system is connected with the heat exchange coefficient calculation module; the cast ingot and the mould are in contact; and the cast ingot and the heating device are in mutual contact; meanwhile, a flow meter is arranged in the cooling system and is used for controlling cooling strength in the device, and the temperatures of the cooling system, the mould and the cast ingot at the different positions can be collected in real time by using the temperature collecting system; and heat exchange coefficients of the different positions under different flow velocities can be calculated according to the fact that the heat entering the mould in a stable-state heat transmission process is equal to the heat brought away by cooling water. The experiment device has the advantages of simple structure, convenience in operation and high accuracy.
Owner:WISDRI ENG & RES INC LTD
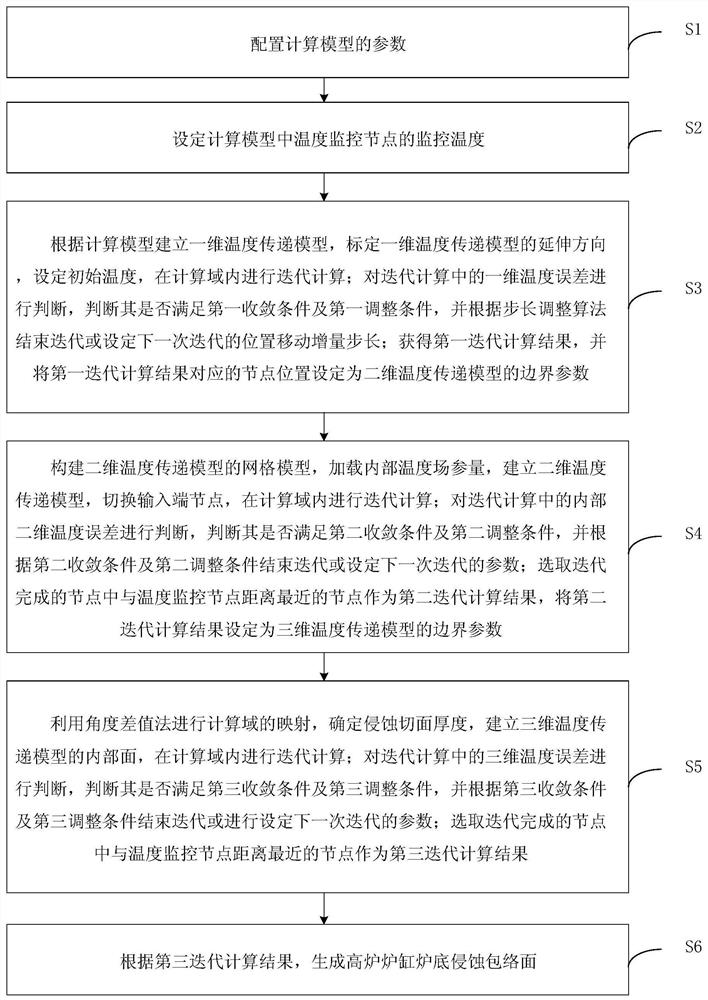
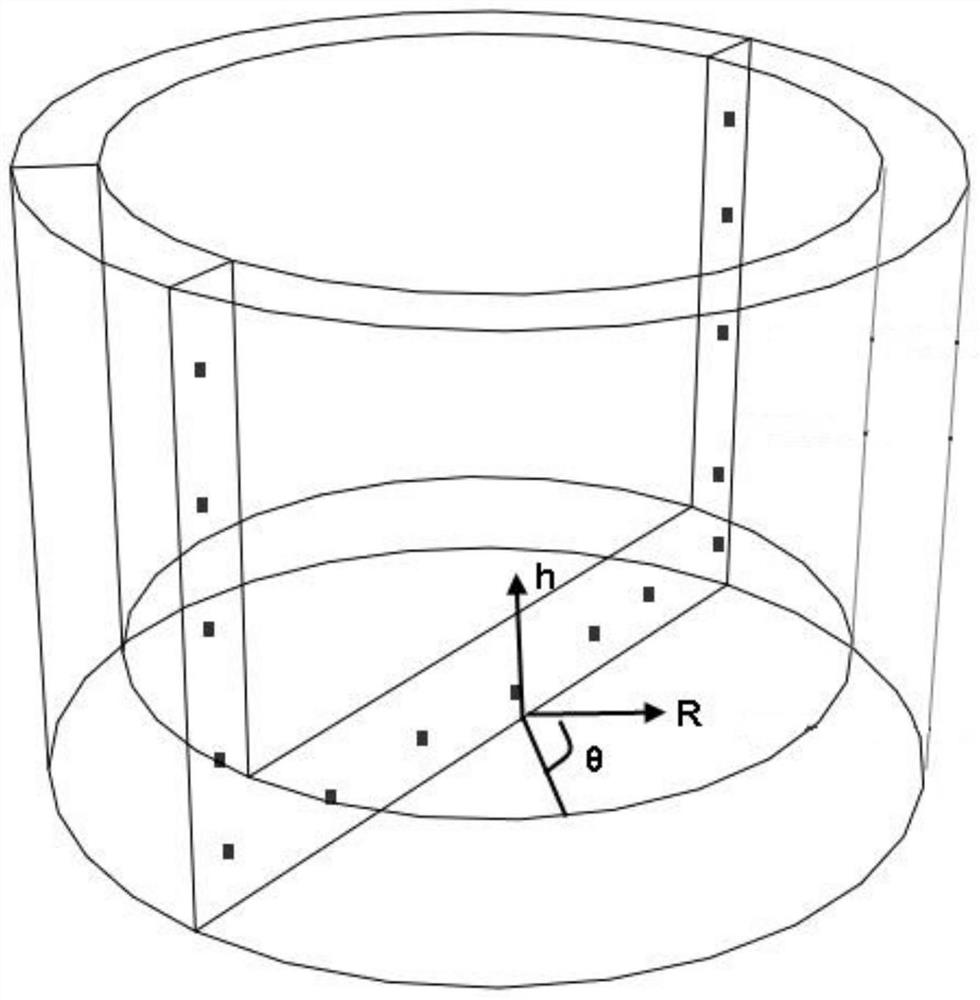
Method for determining blast-furnace hearth bottom erosion envelope surface
ActiveCN108090293AHigh precisionImprove accuracySteel manufacturing process aspectsDesign optimisation/simulationAccuracy improvementHypothesis
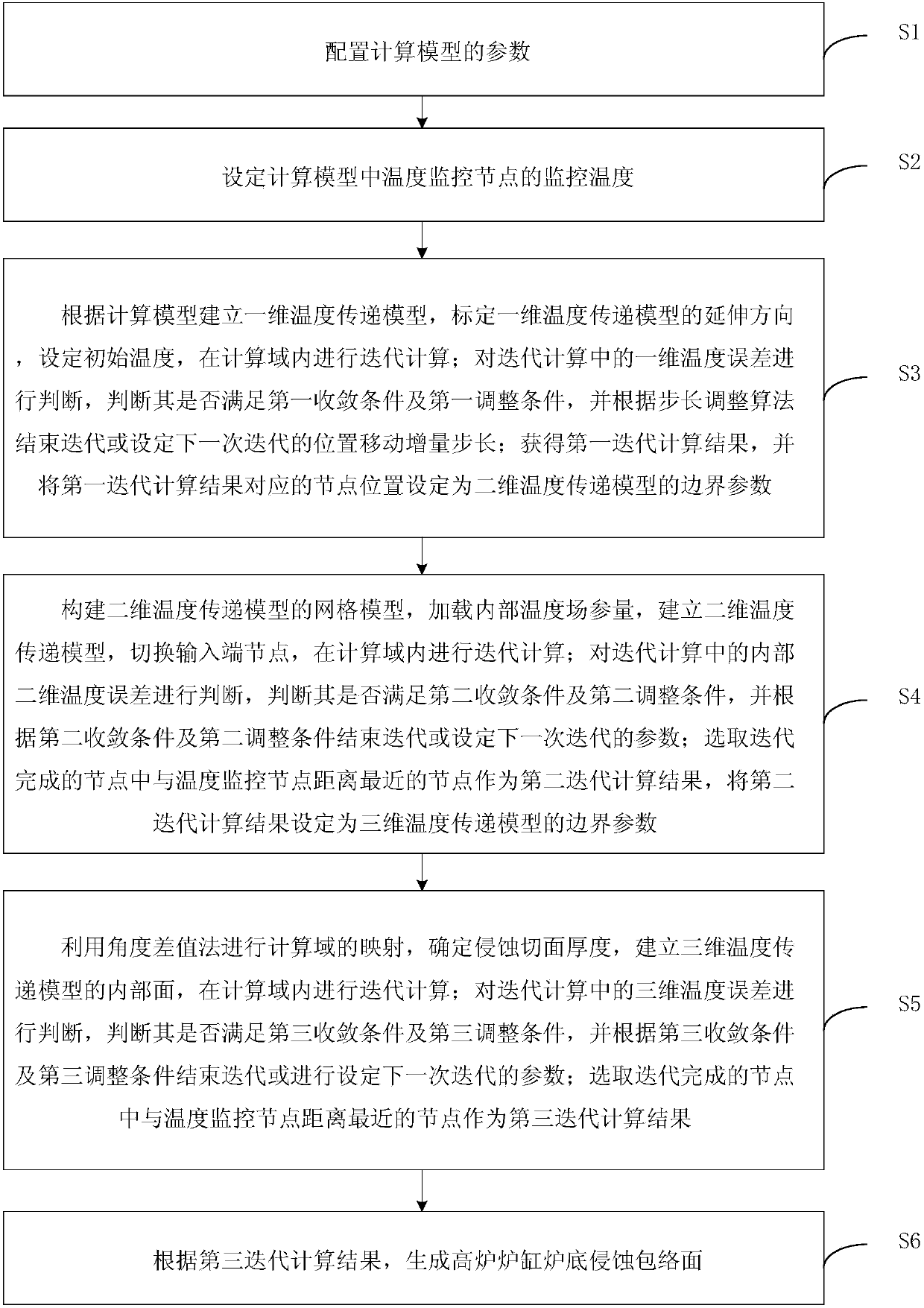
The invention provides a method for determining a blast-furnace hearth bottom erosion envelope surface and relates to the technical field of blast-furnace hearth bottom erosion detection. The method has the advantages that a method based on unchanged grids and a dimensionality approaching method is used, different-dimensionality feature simplification is performed on blast-furnace hearth bottom models according to the rule hypothesis of steady-state heat transfer in blast-furnace simulation models, the needs of precision are considered, and the different-dimensionality simulation models are calculated; the highest temperature of detecting points is acquired according to hearth thermocouple monitoring data of different periods; precision increasing is converted into dimensionality expansionby using obtained hearth bottom inner boundary as the initial condition of high dimensionality; unit dimension differences are ignored during envelope surface regulation, the solving of the accurateposition of an erosion surface is not needed, an overall solution for solving a blast-furnace envelope surface is formed, the accuracy of blast-furnace erosion calculation measuring results is increased, calculation quantity is reduced at the same time, and the problems that erosion detection results are large in errors, and erosion detection is high in calculation quantity in the prior art are alleviated.
Owner:国家超级计算天津中心
Fluid velocity measurement method and device based on convective heat transfer
InactiveCN110058046ANo blockageNo breaking problemFluid speed measurement using thermal variablesSteady state heat transferCooling fluid
The invention discloses a fluid velocity measurement method and device based on convective heat transfer. The method comprises the steps of: S1, selecting a measurement probe, and enabling the interior of the selected measurement probe to have a flow channel for a medium to flow in and out; S2, conveying constant-temperature cooling fluid into the flow channel, and putting the measurement probe inthe measured fluid; S3, when heat transfer between the measurement probe and the measured fluid is steady heat transfer, obtaining the temperature T<k> of the measured fluid, the surface temperatureT<w> of the measurement probe and the temperature T<2> of the cooling fluid at the outlet end of the flow channel; and S4, obtaining the velocity u of the measured fluid by calculation based on the T<k>, the T<w>, the T<2> and a pre-set formula. The device comprises the measurement probe, a pumping mechanism, a flowmeter, a first temperature meter, a second temperature meter, a third temperature meter and a controller. The method and device in the invention are not interfered by the fluid; blocking of a measurement hole of a Pitot tube and breakage of the hot wire of a hot-wire anemometer do not exist; and measurement is accurate.
Owner:CHINA DATANG CORP SCI & TECH RES INST CO LTD EAST CHINA BRANCH +2
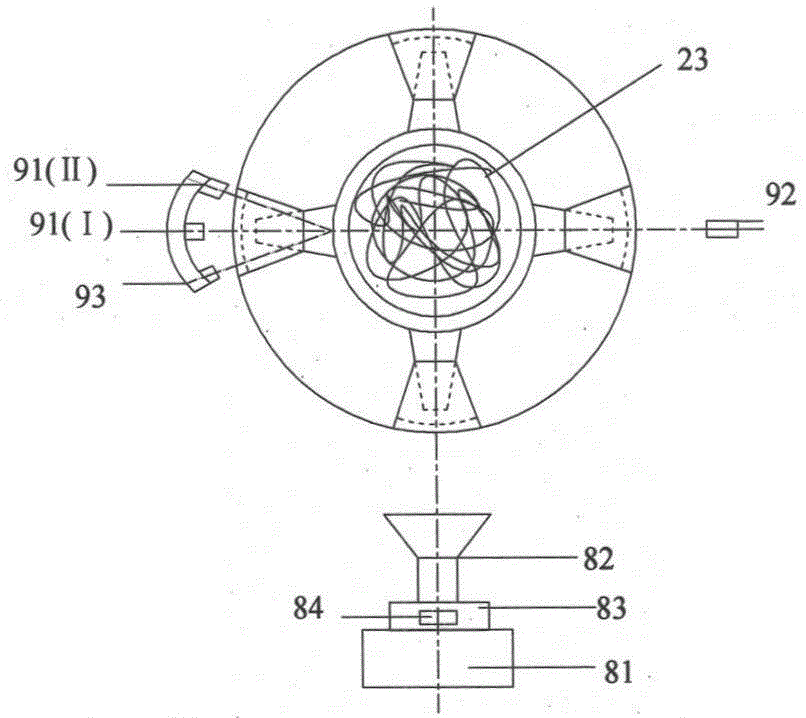
Electrostatic atomizing and cooling capacity evaluation device with adjustable nozzle space angle
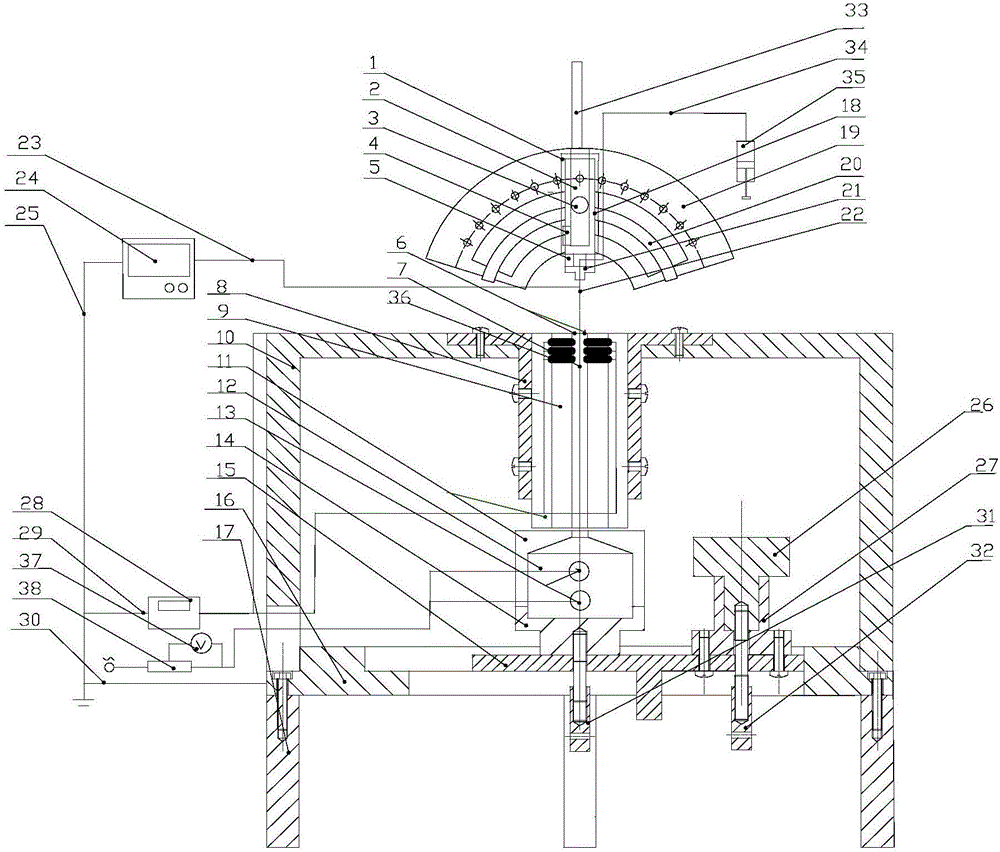
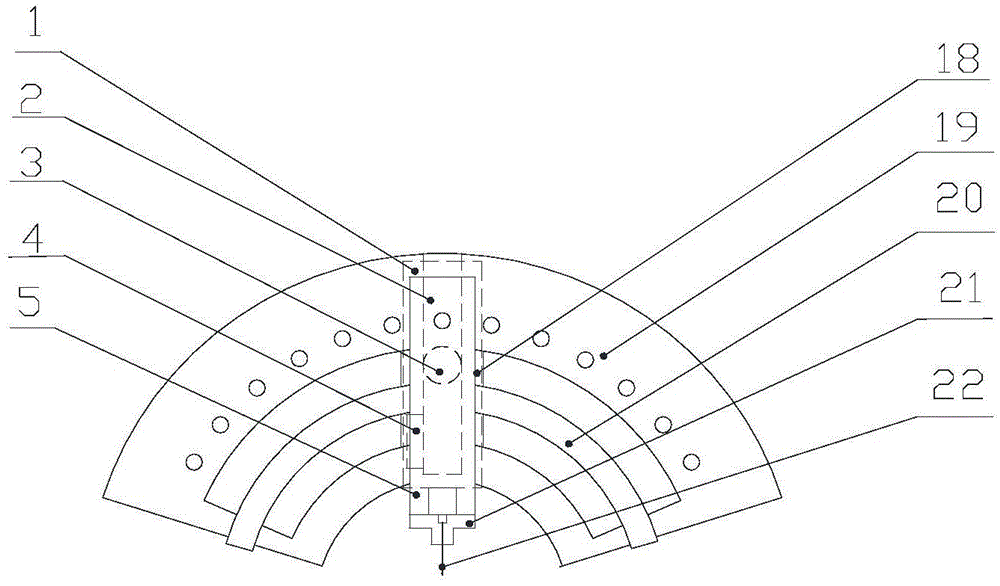
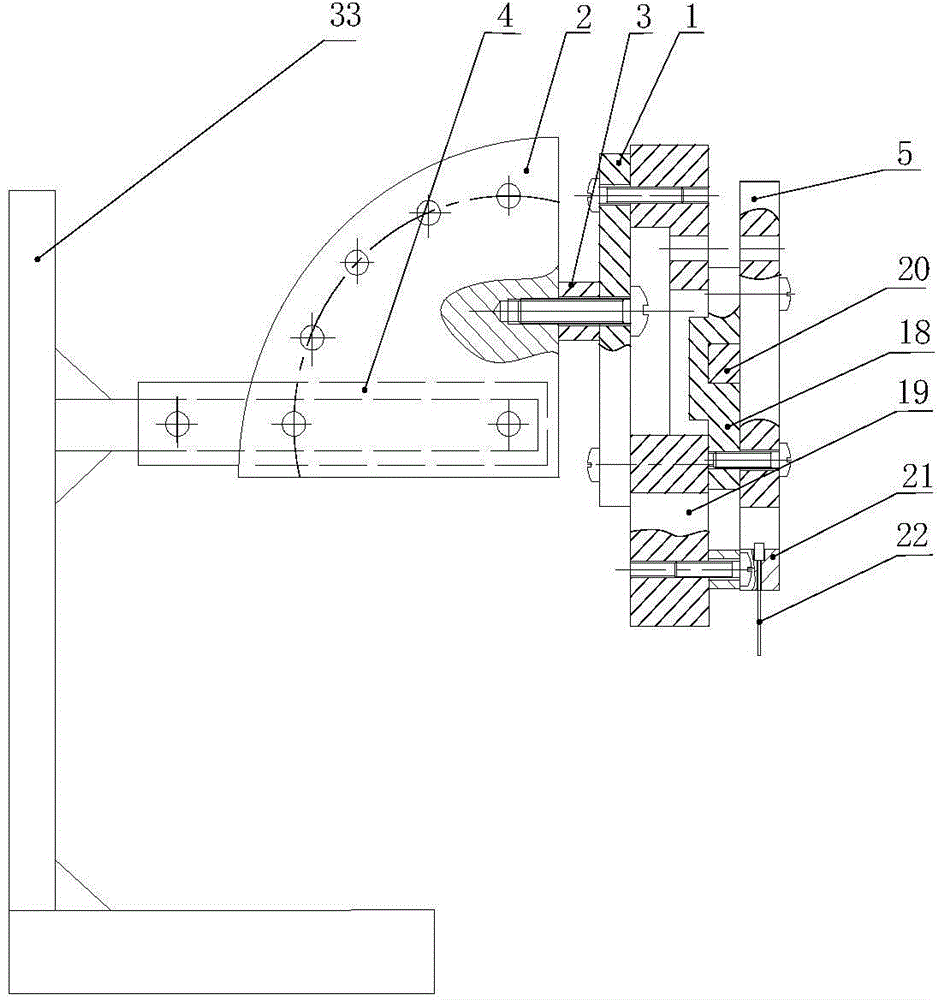
The invention discloses an electrostatic atomizing and cooling capacity evaluation device with an adjustable nozzle space angle, belonging to the technical fields of heat exchange and cooling. The electrostatic atomizing and cooling capacity evaluation device comprises an electrostatic atomizing and cooling system and a critical heat flux and heat transfer coefficient measurement system, wherein the electrostatic atomizing and cooling system comprises a big fan-shaped disc, a small fan-shaped disc, an adjustable handle, a guide rail, a first sliding block, an injection pump, a silicone rubber tube and a bracket; the critical heat flux and heat transfer coefficient measurement system comprises a purple copper bar, a K-shaped thermocouple wire, a heat insulation sleeve, a box cover, a purple copper block, an electric heating bar, a graphite felt heat insulation tray, a second sliding block, a base, a supporting block, a graphite felt heat insulation supporting block, a guide block, a voltage meter, a variable resistor and a K-shaped thermocouple. According to the electrostatic atomizing and cooling capacity evaluation device, electrostatic atomization transient-state and steady-state heat transfer experiments can be carried out on the same device at different nozzle space angles, in different target distances and with different output voltages, heating powers and cooling medium fluxes of a high voltage static generator, and the critical heat flux and the heat transfer coefficient can be measured.
Owner:HUAWEI TEHCHNOLOGIES CO LTD
Method for numerical solution of fuzzy steady state heat conduction problem based on full grid point collocation theory
InactiveCN105677995AImprove approximation accuracyQuickly identify extreme pointsDesign optimisation/simulationFuzzy logic based systemsTemperature responseCommercial software
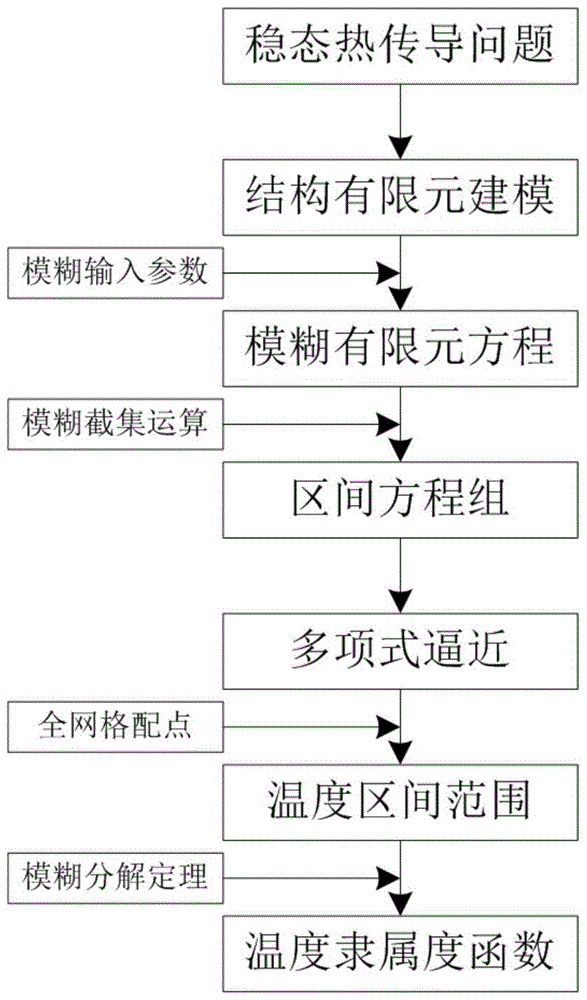
The invention discloses a method for numerical solution of a fuzzy steady state heat conduction problem based on a full grid point collocation theory. The method comprises the first step of carrying out finite element modeling of a steady state heat conduction structure; the second step of utilizing fuzzy variables to represent uncertain input parameters and then obtaining a fuzzy finite element equation of the heat conduction problem; the third step of utilizing cut set operation to rewrite the fuzzy finite element equation to be a group of interval finite element equations; the fourth step of performing approximate representation on temperature response functions in the interval finite element equations based on a polynomial theory; the fifth step of quickly solving the interval variation range of a temperature response approximate functions according to the full grid point collocation theory; the sixth step of utilizing a fuzzy resolution theory to recombine temperature response intervals under all cut set levels, and finally obtaining a membership function of the fuzzy temperature response. According to the method, the prediction of structure heat conduction temperature field containing fuzzy uncertain parameters can be achieved systematically, and the calculation accuracy can be effectively improved on the premise of guaranteeing that the calculation efficiency meets the engineering requirements, which cannot be achieved through common commercial software.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
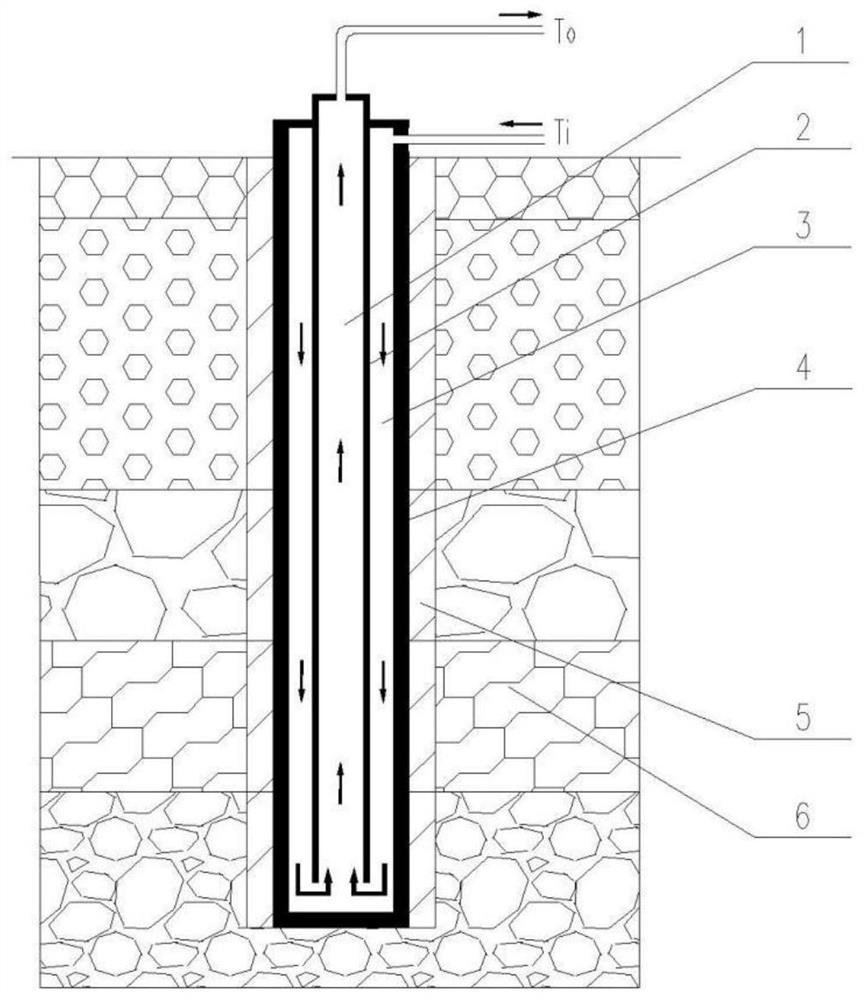
Seasonal heat storage system for exchanging heat by utilizing buried pipe
ActiveCN102692150AIncrease the temperature difference between inlet and outletAchieve deep coolingHeat storage plantsEnergy storageThermal energyCooling tower
The invention discloses a seasonal heat storage system taking rock soil as heat storage media and taking a buried pipe buried in rock soil as a heat exchange means as well as a heat transfer model thereof. Compared with other heat storage modes, the heat storage system has the characteristics of high heat storage quantity, long heat storage cycle, less heat loss, low cost per unit of heat storage quantity and high adaptability. The heat storage system also can be used by combining with a heat pump, and also the heat storage quantity and heat storage temperature difference can be enlarged further. During the operation of the heat storage working conditions, the system can partially replace the traditional cooling tower, and the water utilization conservation of a cooling tower is achieved. The seasonal heat storage technology for exchanging heat by utilizing the buried pipe provides economic and reasonable technique means for utilizing low-grade heat energy of industrial residue heat, solar energy and the like in a staggered seasonal mode. The invention also discloses a quasi-stable-state heat transfer model of heat transfer analysis by utilizing the seasonal heat transfer system for exchanging heat by the buried pipe, and the theory basis for the design and calculation is provided.
Owner:山东中瑞新能源科技有限公司
Device and method for in situ measuring steady-state heat transfer character of variable density fibrous
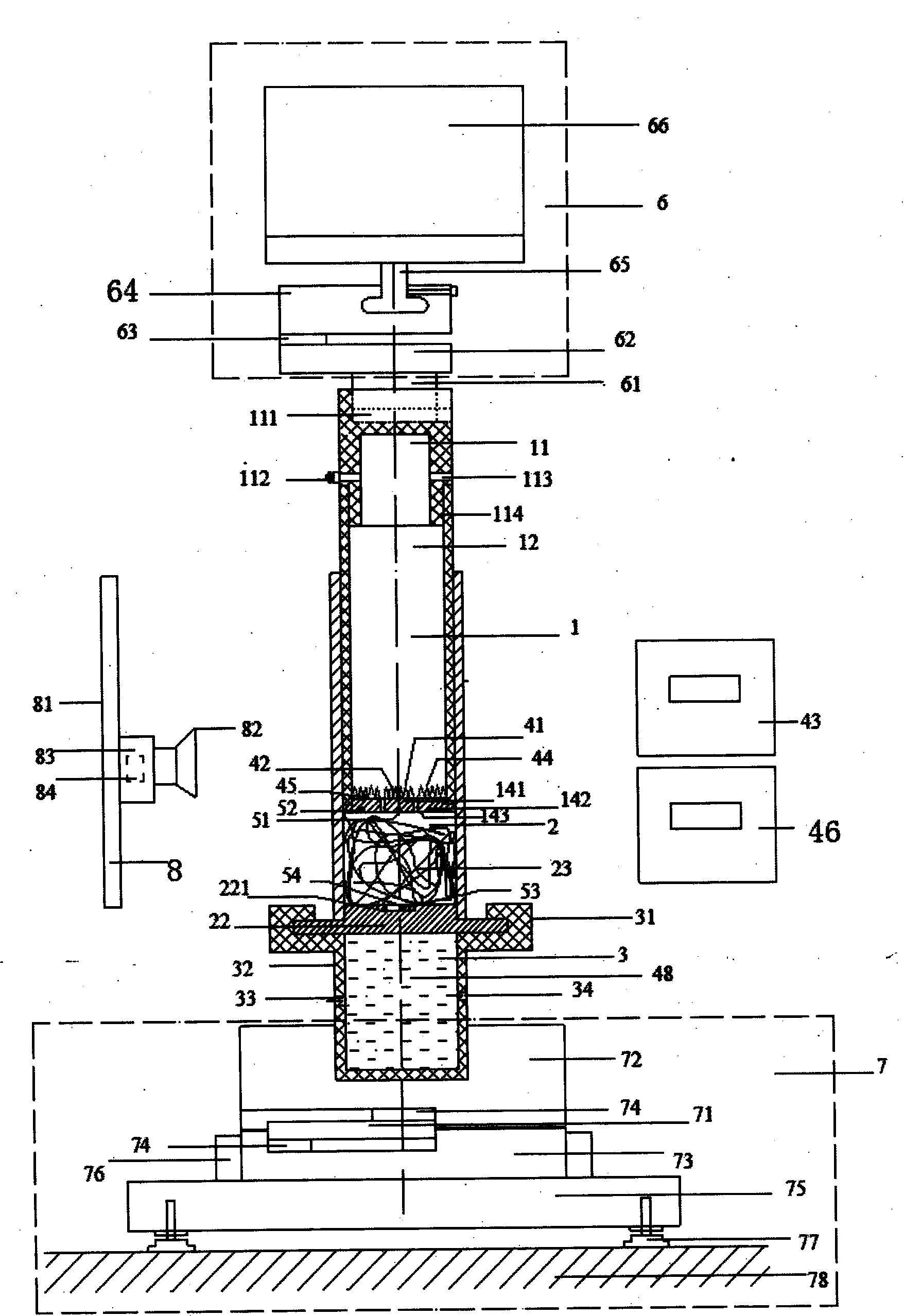
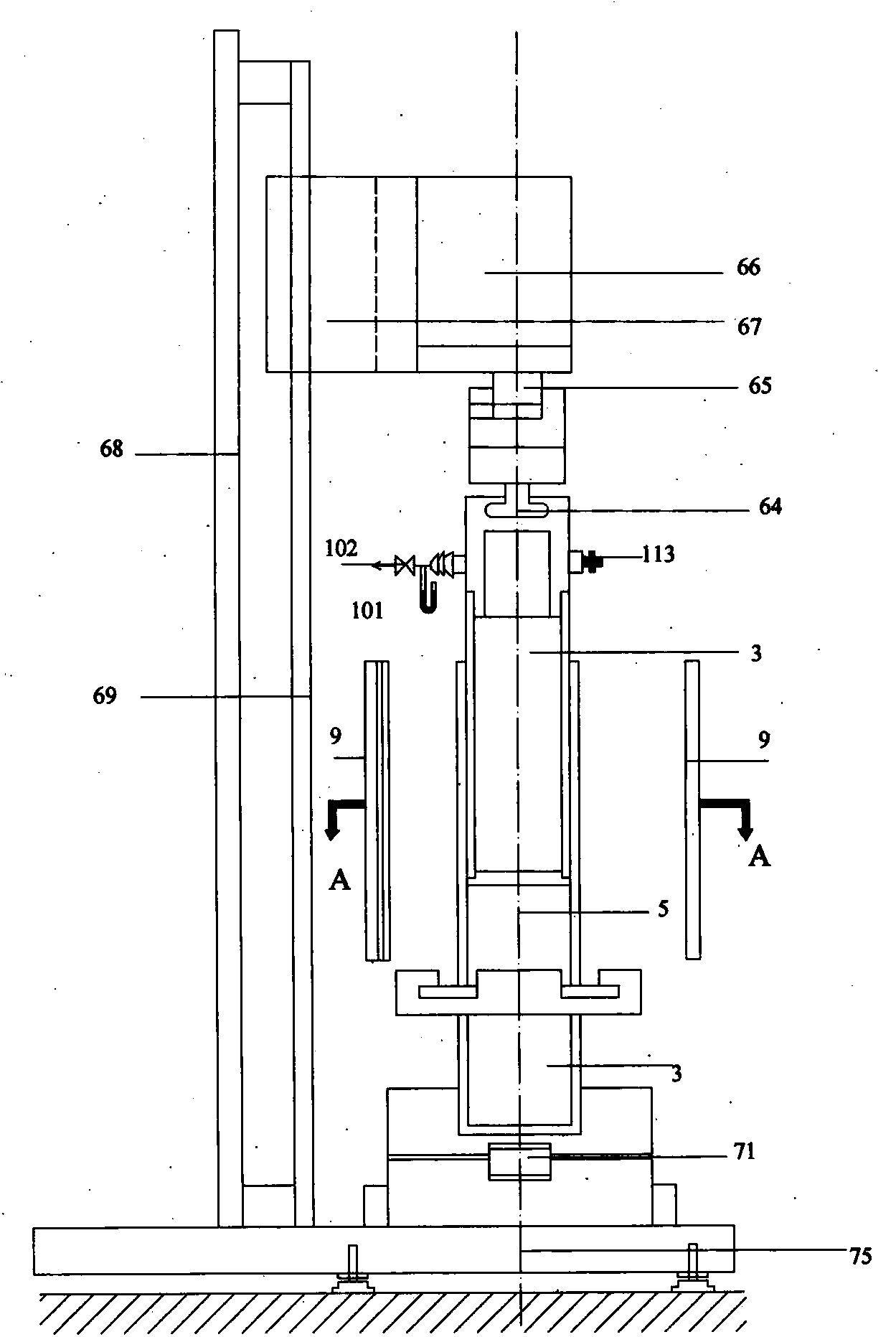
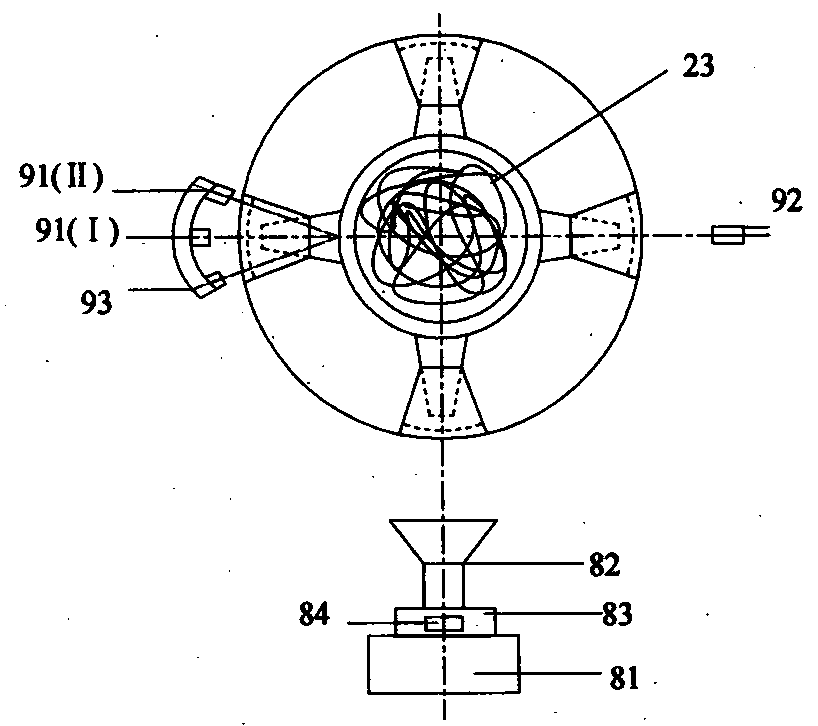
ActiveCN103454305AIn line with the actual use statusEasy accessMaterial heat developmentFiberHeat flux
The invention relates to a device and method for in situ measuring steady-state heat transfer character of variable density fibrous. The device comprises a main force application device, a load-bearing positioning device, a digital camera device, a light measurement device, an intra-cavity pressure measurement device, a data acquiring card, a driving and control circuit, a data acquiring treatment and interface control module and a computer in the original patent, and further comprises improved components such as a push barrel measurement cavity, a fiber plug barrel, a lower measurement cavity, a heating control device, a heat testing device, a data acquiring card and a data acquiring processing module, wherein the data acquiring card and the data acquiring processing module are connected with the push barrel measurement cavity, the fiber plug barrel, the lower measurement cavity, the heating control device and the heat testing device. The testing method of the device comprises the steps of playing the effect of the force on the fibrous to change the density and the density distribution, playing the heating effect on the fibrous to generate a certain temperature difference between two ends of the fibrous, testing the temperature difference and heat fluxes at the two ends of the fibrous to obtain a heat conductivity coefficient and the heat resistance of the fibrous. The method and the device disclosed by the invention are high in measurement precision, convenient for sample preparation, short in testing time, wide in applicable range, and suitable for the in-situ measurement on the steady-state heat transfer character under a fibrous variable density condition.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
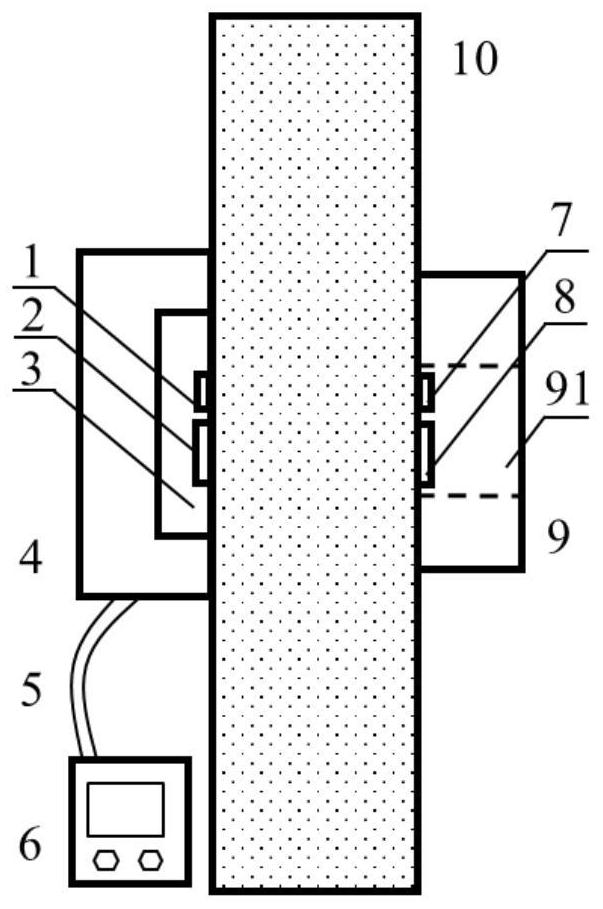
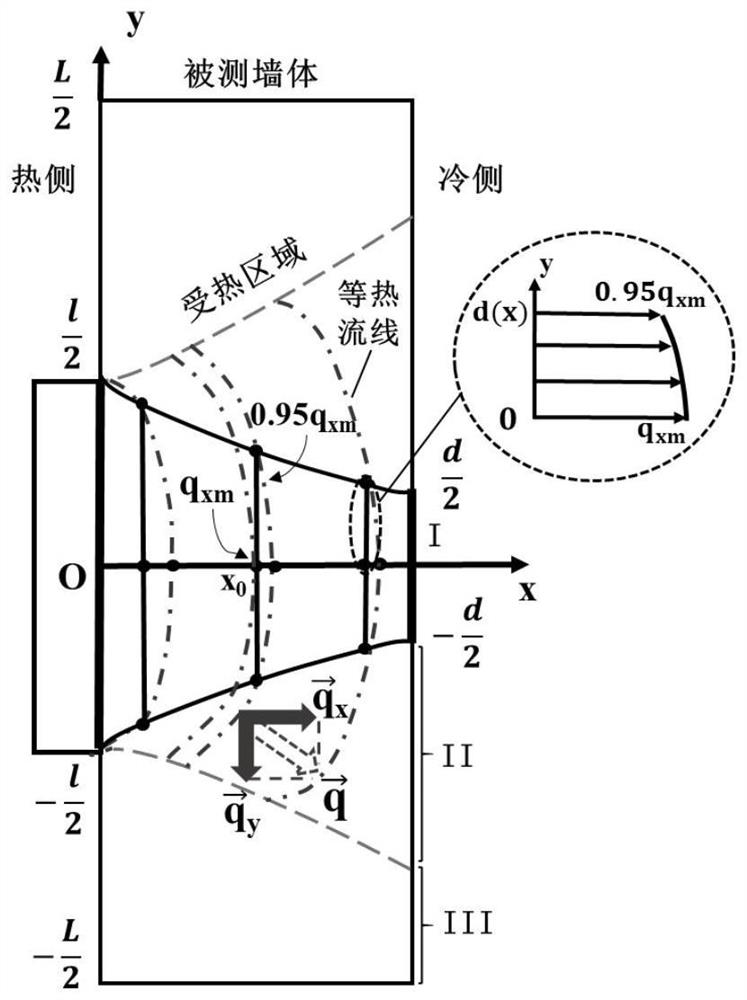
Building wall thermal resistance field test device and method
PendingCN112229869AHigh accuracy of resultsSimple calculationMaterial heat developmentTemperature controlCold side
The invention provides a building wall thermal resistance field test device and method. The test device comprises two heating plates, two temperature controllers, two temperature sensors, two heat flow sensors and two insulation plates. The first temperature sensor, the first heat flow sensor, the heating plate and the first heat preservation plate are all attached to the hot side of a measured wall, the second temperature sensor, the second heat flow sensor and the second heat preservation plate are all attached to the cold side of the measured wall, and a through hole serving as a heat flowone-dimensional channel is formed in the middle of the second heat preservation plate. The second temperature sensor and the second heat flow sensor are positioned in the through hole. The testing method comprises the following steps: quantitatively determining the size of the one-dimensional heat transfer area on the cold side and the hot side of the wall, measuring and recording the surface temperature of the one-dimensional heat transfer area on the cold side and the hot side of the wall and the density of heat flow passing through the one-dimensional heat transfer area, and calculating theequivalent thermal resistance of the wall. By arranging the one-dimensional channel facilitating centralized passing of heat flow and adopting a two-stage heating method, steady-state heat transfer can be rapidly established, and the test time is effectively shortened.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
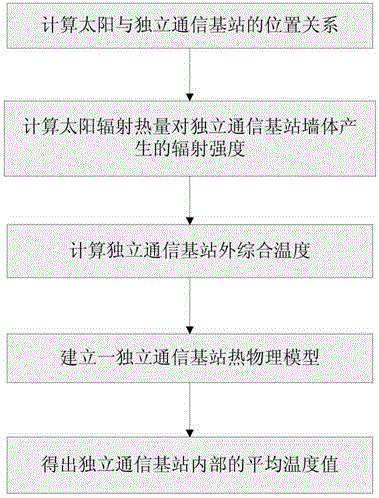
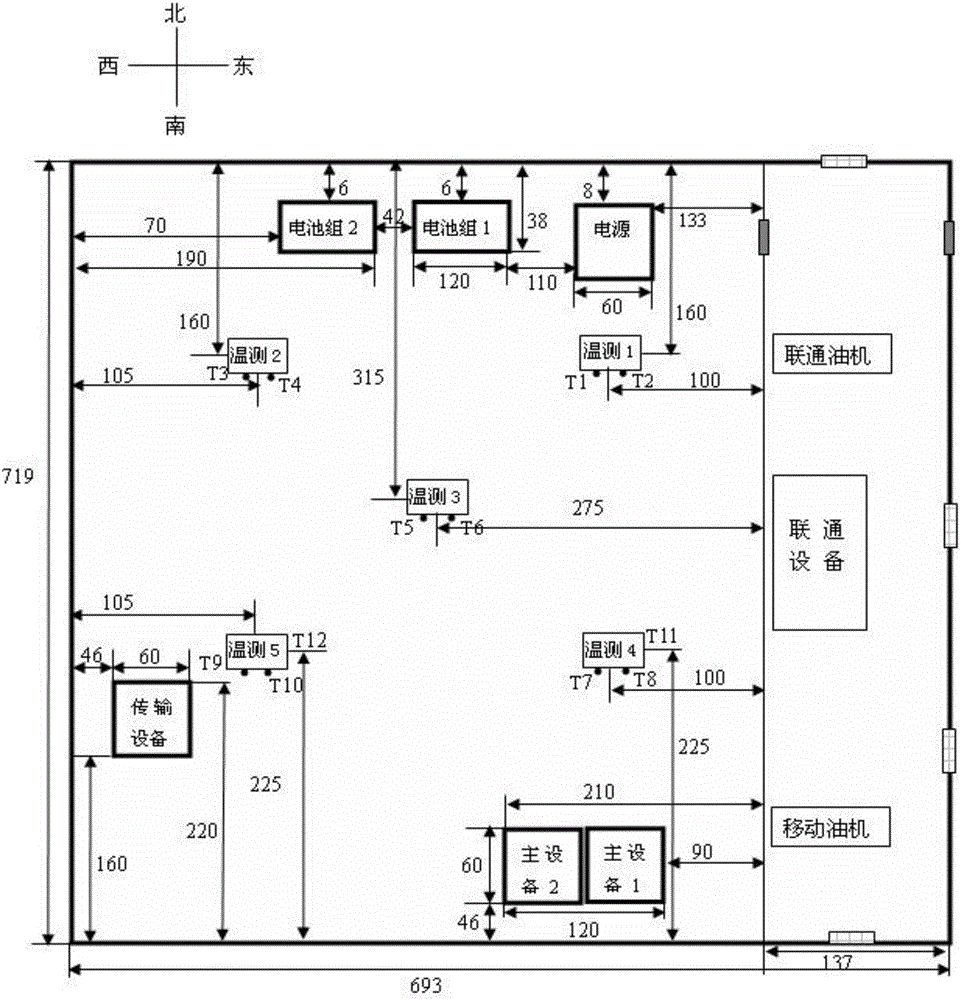
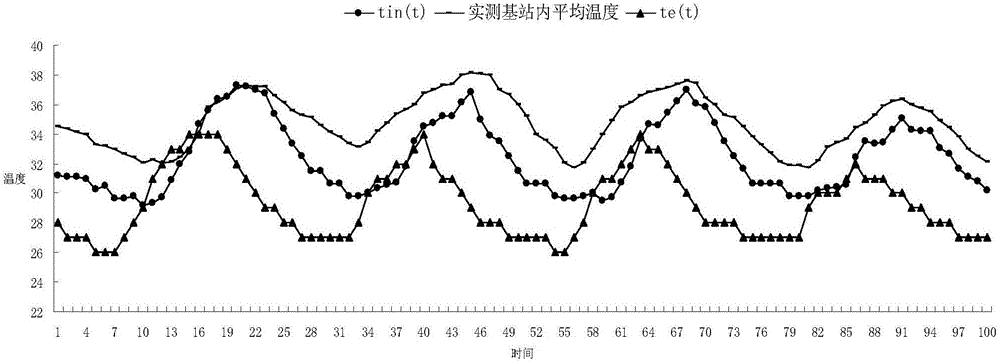
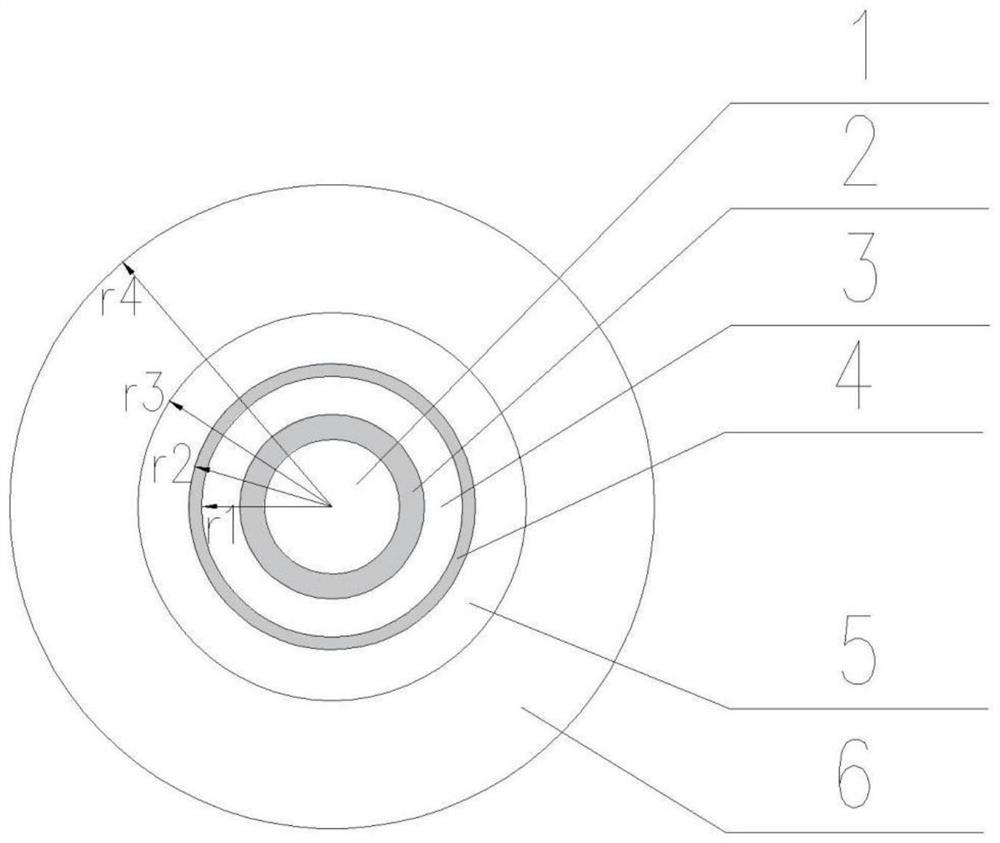
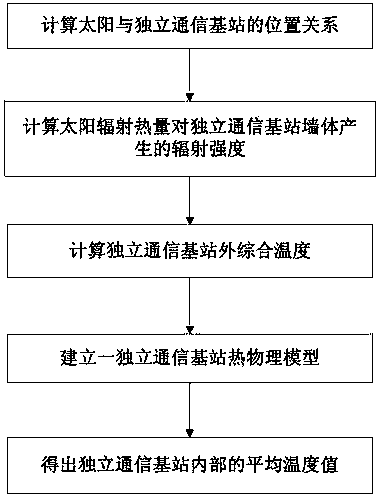
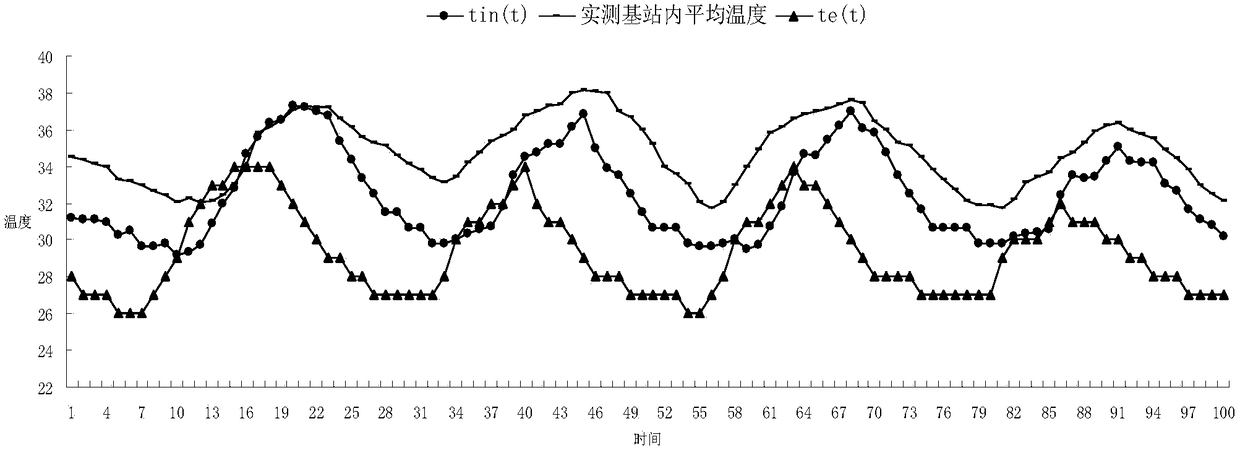
Method for predicting internal temperature of independent communication base station
InactiveCN105760686AInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsSteady state heat transferInternal temperature
The invention discloses a method for predicting the internal temperature of an independent communication base station. The method comprises the steps of establishing a thermophysical model of an independent communication base station according to positional relation between the sun and the independent communication base station, radiation intensity of solar radiation heat to a wall body of the independent communication base station as well as a comprehensive temperature outside the independent communication base station, and calculating to obtain an average temperature value in the independent communication base station. According to the method, the thermophysical model of the independent communication base station is established based on a steady-state heat transfer theory, and the average temperature value in the independent communication base station can be calculated, thereby facilitating the research of optimal design, simulation prediction, performance evaluation and base station assisting energy-efficient equipment of space enclosing structures of the independent communication base station.
Owner:GUANGDONG IND TECHN COLLEGE
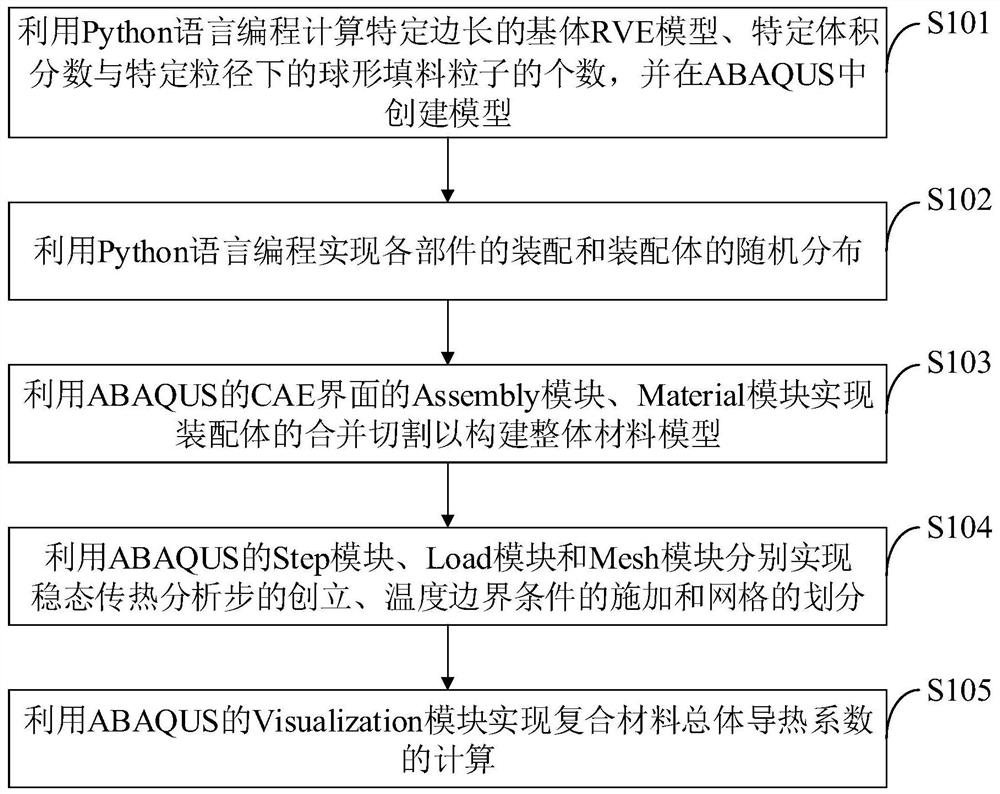
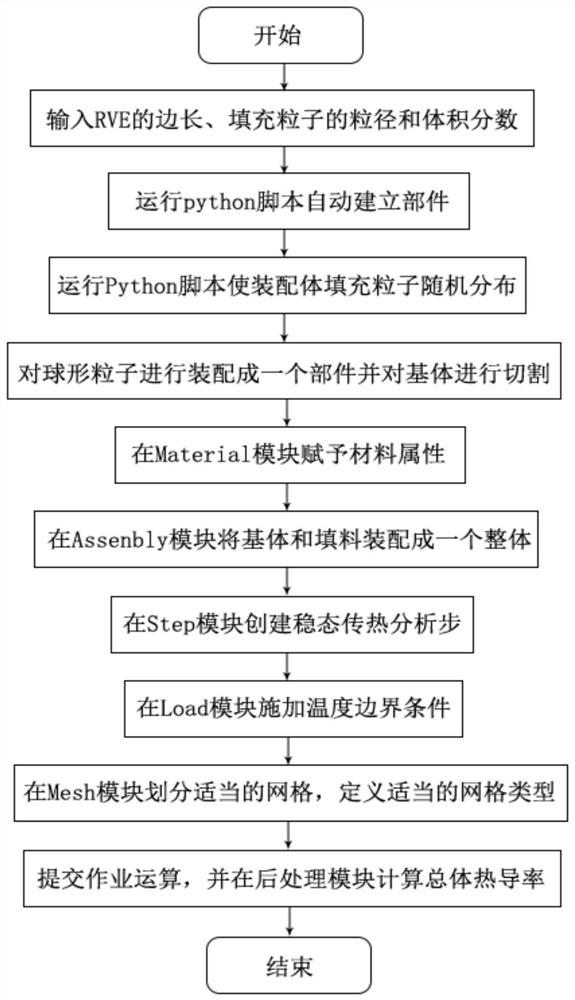
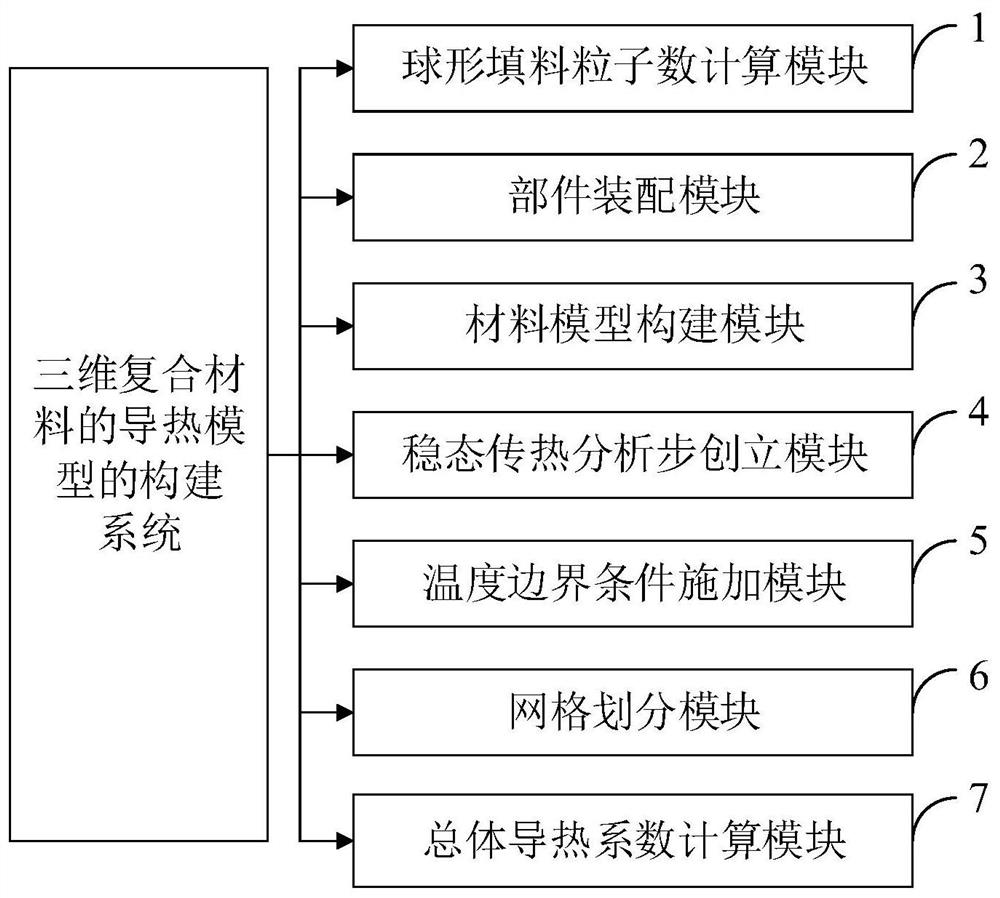
Construction method and system of heat conduction model of three-dimensional composite material, terminal and medium
ActiveCN113361147AConvenient researchSolving Modeling DifficultiesDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsThermal coefficientMechanical engineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of analysis and calculation of heat conduction performance of a composite material with a spherical particle filling matrix, and discloses a construction method and system of a heat conduction model of a three-dimensional composite material, a terminal and a medium. The construction method of the heat conduction model of the three-dimensional composite material comprises the following steps of: calculating the number of spherical filler particles under a matrix RVE model with a specific side length, a specific volume fraction and a specific particle size, and creating a model; assembling all components and randomly distributing assembly bodies; combining and cutting the assembly bodies to construct an integral material model; establishing a steady-state heat transfer analysis step, applying a temperature boundary condition and dividing grids; calculating the overall heat conductivity coefficient of the composite material. The ABAQUS software is used in the whole process of calculating the heat conductivity coefficient of the composite material, the final result can be calculated without other software tools, and the method is simple and efficient. The calculated heat conductivity coefficient of the composite material is highly matched with an actual result, and a processing result can be predicted and guided.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
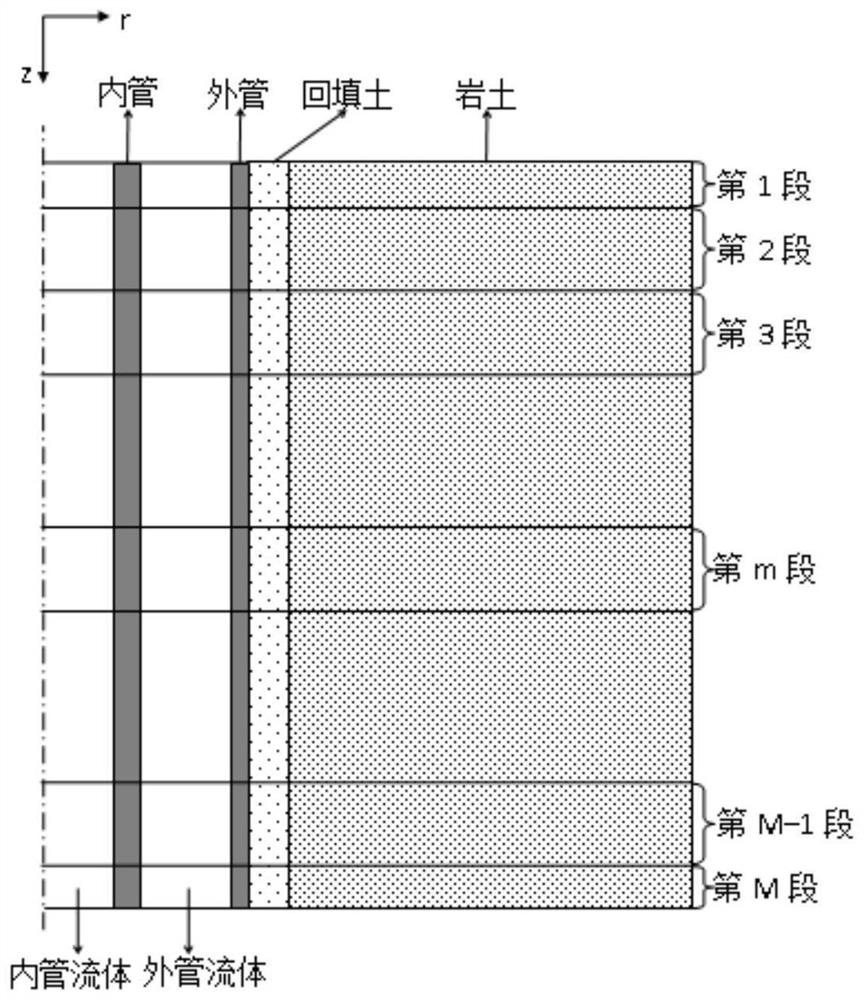
Medium-deep layer buried pipe fluid temperature field analysis method considering underground water seepage
PendingCN113468743AHigh precisionSmall amount of calculationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsHeat flowField analysis
The invention provides a medium-deep layer buried pipe fluid temperature field analysis method considering underground water seepage, which is used for calculating temperature fields of inner pipe fluid and outer pipe fluid of a medium-deep layer buried pipe changing along with depth and time. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, assuming that heat transfer in a drill hole is steady-state heat transfer and the drill hole is approximated to a moving linear heat source, then establishing a steady-state heat transfer equation of an inner pipe fluid and an outer pipe fluid, and establishing an equation of a drill hole wall surface temperature and a heat flow transferred to rock soil from the drill hole by adopting a moving linear heat source model and a variable heat flow superposition principle; and secondly, axially dividing the drill hole of the middle-deep layer buried pipe and rock soil outside the drill hole into a plurality of sections, setting a time step length, discretizing the equation, and solving the equation by adopting an iteration method, so as to obtain temperature fields of the inner pipe fluid and the outer pipe fluid of the middle-deep layer buried pipe. According to the method, the influence of underground water seepage on the middle-deep layer buried pipe is considered, the precision is high enough, and the calculated amount is small.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
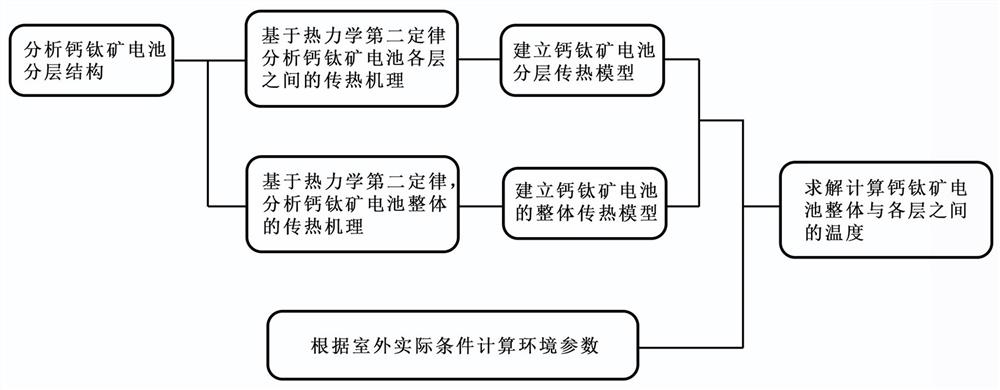
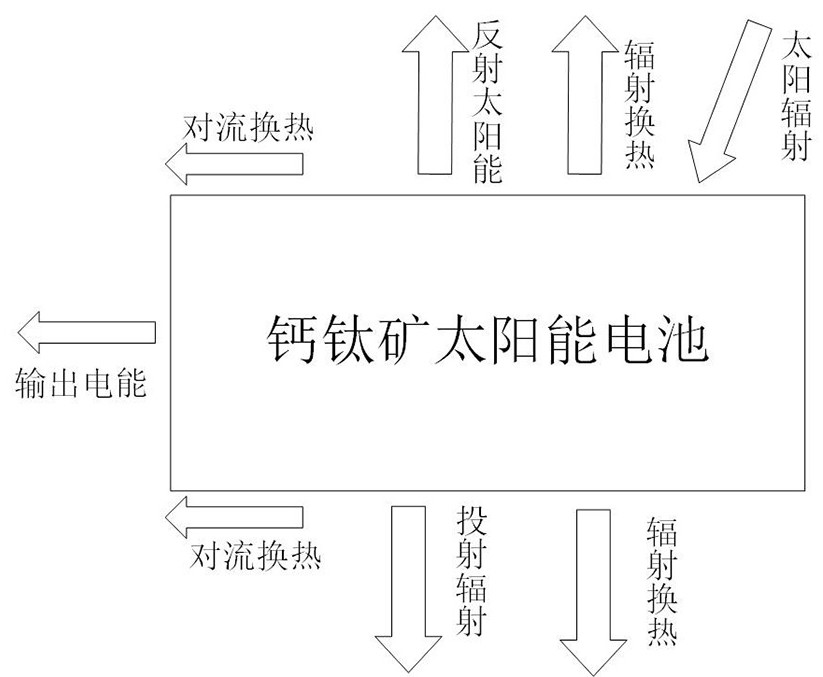
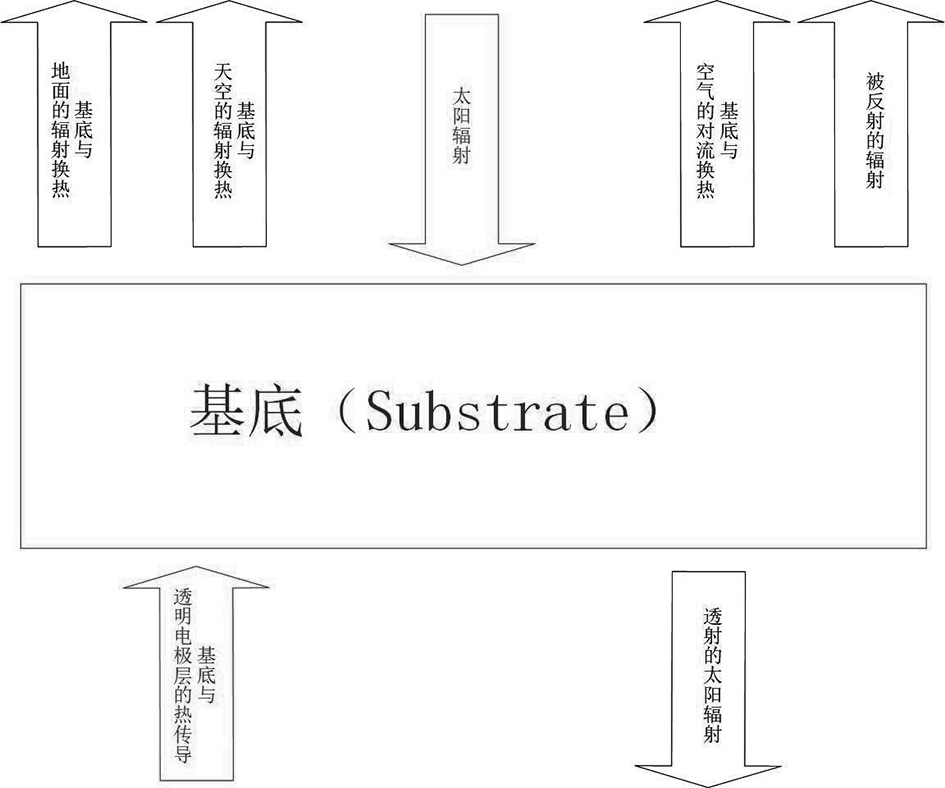
Perovskite battery heat transfer model based on steady-state heat transfer
PendingCN112395739AAccurately predict temperatureForecast temperatureDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSteady state heat transferBattery cell
The invention relates to the field of thermal simulation of perovskite batteries, in particular to a perovskite battery heat transfer model based on steady-state heat transfer. According to the technical scheme, compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that on the basis of the second law of thermodynamics, the overall structure and the structure and material characteristics of each layer of the perovskite cell are combined, an overall heat transfer model and a layered heat transfer mode of the perovskite cell are analyzed and considered, and the perovskite cell is optimized on the premise that environmental factors are known. The overall temperature and the temperature of each layer of the perovskite cell are accurately predicted in a numerical simulation mode, so that the temperature of the perovskite cell is accurately predicted, and the non-negligible influence on the economical efficiency of component power generation is achieved.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
Motor controller using phase change material to absorb heat
PendingCN114340322AFast conductionSolve the problem of rapid temperature riseSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectric machineEngineering
The invention discloses a motor controller utilizing a phase change material to absorb heat, which comprises a conductive mechanism, a gasket positioned below the conductive mechanism and a heat absorption mechanism positioned below the gasket and used for absorbing heat generated by the conductive mechanism, and is characterized in that the heat absorption mechanism comprises a shell mechanism and the phase change material positioned in the shell mechanism; the phase-change material generates phase change to absorb a large amount of heat, the arrangement of the phase-change material can absorb a large amount of heat, the problem of rapid temperature rise caused by large amount of heating of the MOS tube in a short time is solved, and the arrangement of the division bars can be used for heat conduction and transient heat absorption, and facilitates steady-state heat transfer at the same time.
Owner:河南嘉晨智能控制股份有限公司
Simplified calculation method for sleeve type ground heat exchanger
PendingCN114491949ACalculation method is simpleSimple calculationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention relates to the technical field of geothermal resource development and utilization, and discloses a simplified calculation method of a sleeve type ground heat exchanger, which comprises the following steps: 1) the thermophysical properties of a backfill material and surrounding rock soil are uniform and consistent, the thermophysical parameters of the backfill material and surrounding rock soil do not change along with the change of radial and vertical sizes, and the influence of groundwater seepage and soil moisture transfer is neglected; and 2) no heat conduction phenomenon exists in the vertical direction, that is, the heat transfer process is a two-dimensional heat transfer problem along the radial direction of the buried pipe. According to the simplified calculation method of the sleeve type buried pipe heat exchanger, by adopting the calculation method, grid division in the heat transfer calculation process of the sleeve type buried pipe heat exchanger can be reduced, and meanwhile, the complex three-dimensional unsteady-state heat transfer problem is simplified into the two-dimensional unsteady-state heat transfer problem; therefore, simplified calculation can be carried out on the sleeve type ground heat exchanger under different conditions, calculation efficiency is improved, and the method has certain actual use value and popularization value.
Owner:HENAN WANJIANG NEW ENERGY DEV CO LTD
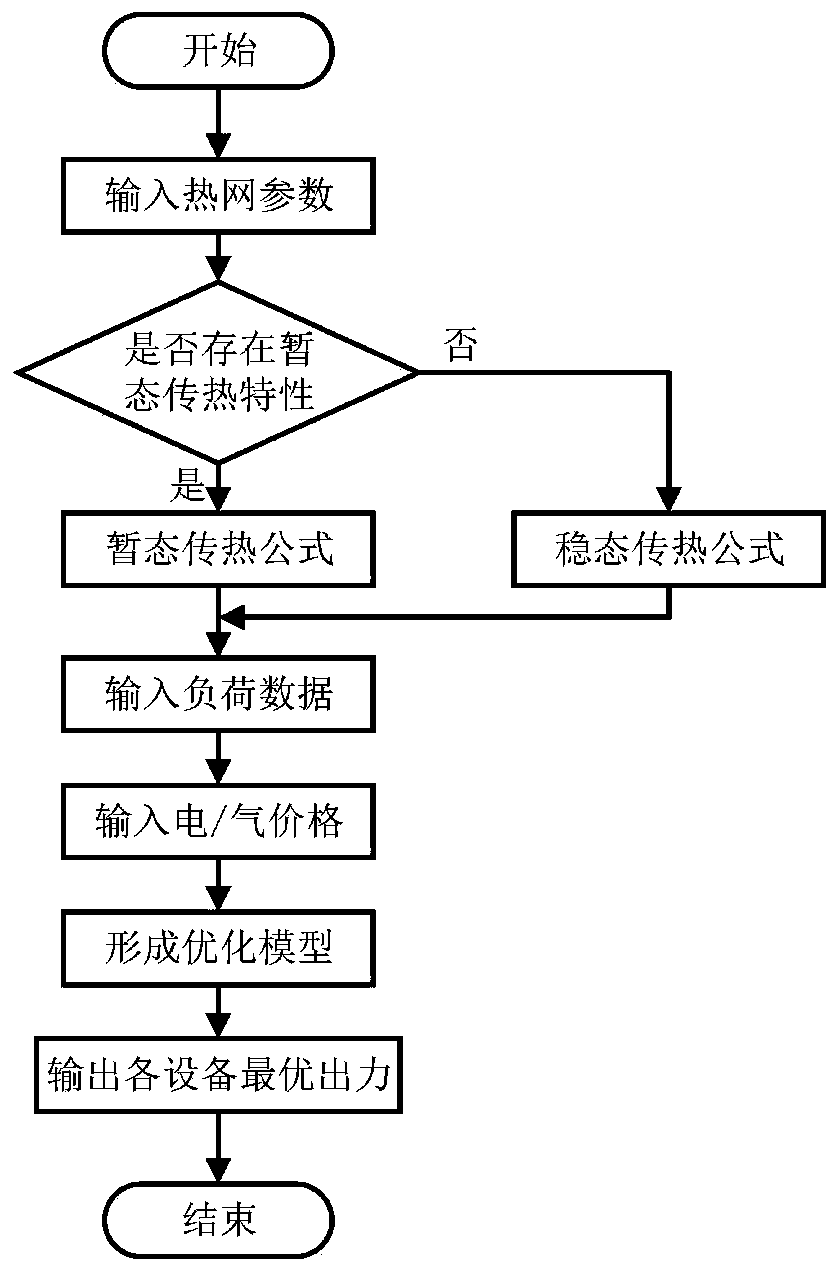
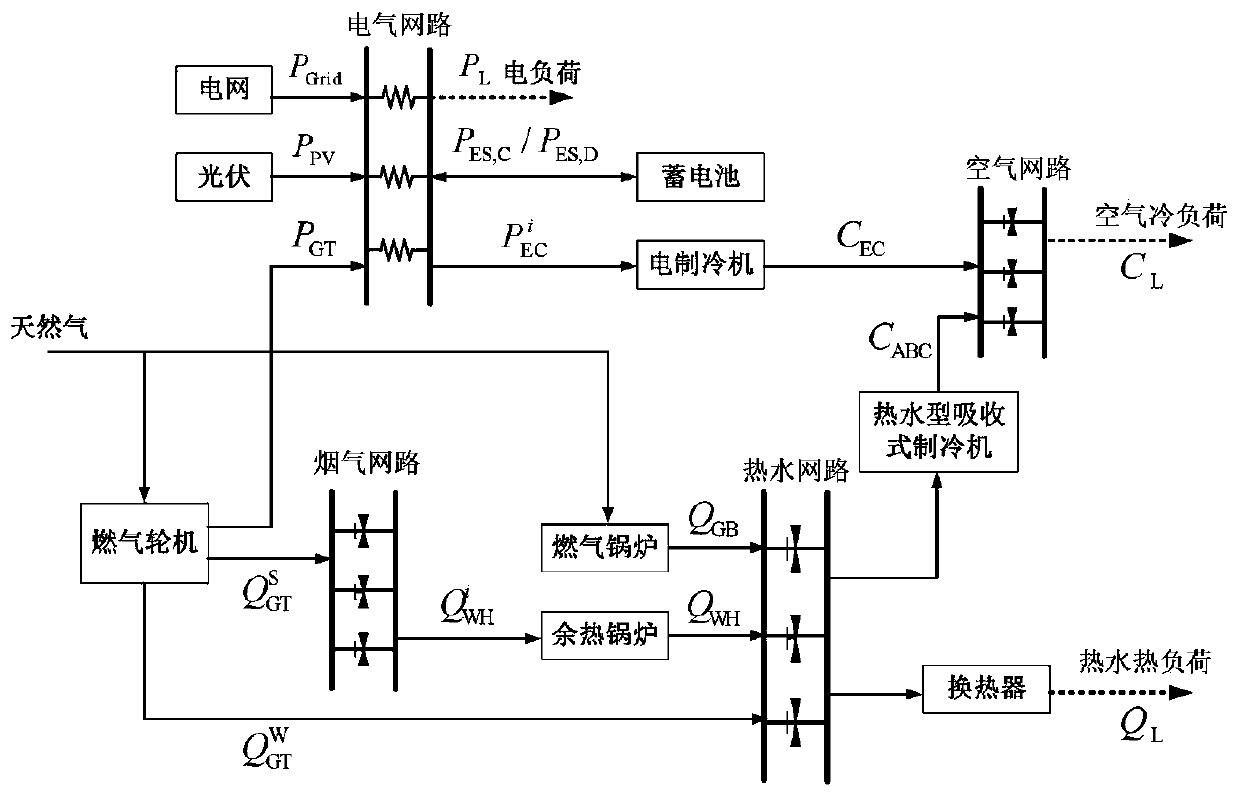
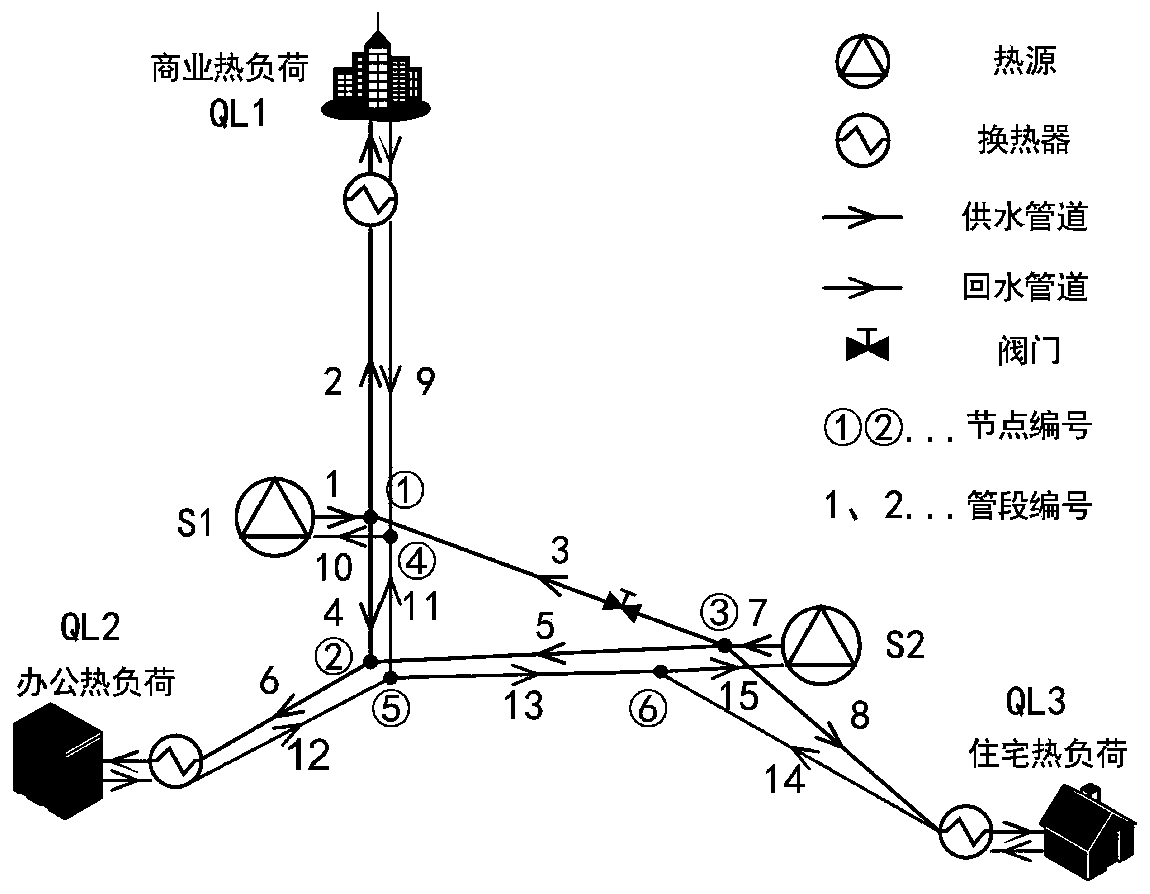
Optimal operation method of multi-energy flow system considering transient heat transfer characteristics of district heating network
ActiveCN108599137BReduce complexityEasy to solveLoad forecast in ac networkSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsTransient stateGraph theoretic
The invention discloses a multi-energy flow system optimization operation method considering the transient heat transfer characteristics of a regional heat network. The method includes the following steps that: step 1) a regional heat network transient heat transfer characteristic model considering a water return pipe network topological structure, a pipe section temperature change dynamic processand a pipe section transmission delay is established based on a graph theory, wherein the model mainly comprises six aspects, namely, a heat source characteristic a heat load characteristic, node flow balance, a node power fusion characteristic, a pipe section heat transfer characteristic and a pipe section transient / steady heat transfer characteristic; and step 2) a multi-energy flow system operation optimization model is established, with the lowest total operating cost of a system in the next 4 hours adopted as an objective function, on the basis of operational constraints that the systemshould meet, the real-time output of each device in the multi-energy flow system, the real-time supply and return water temperature of each heat source of the heat network, and the like, are realized,and the scheduling and optimized operation of the system can be realized. According to the method of the invention, the transient heat transfer characteristics of the regional heat network are considered, so that the optimal operating state of the multi-energy flow system is more consistent with the actual operating state of the system.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
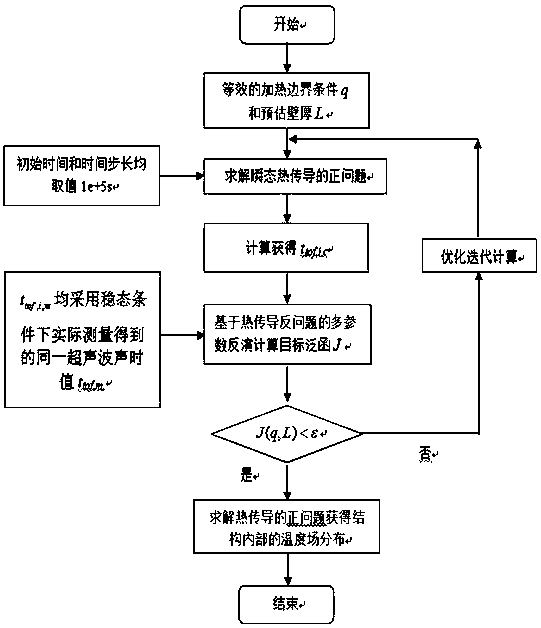
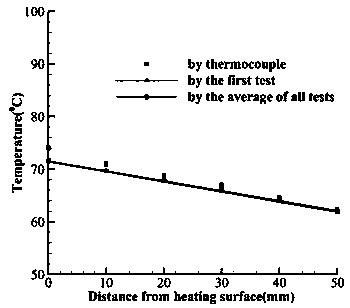
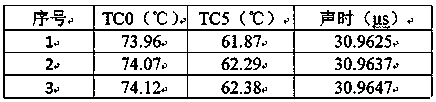
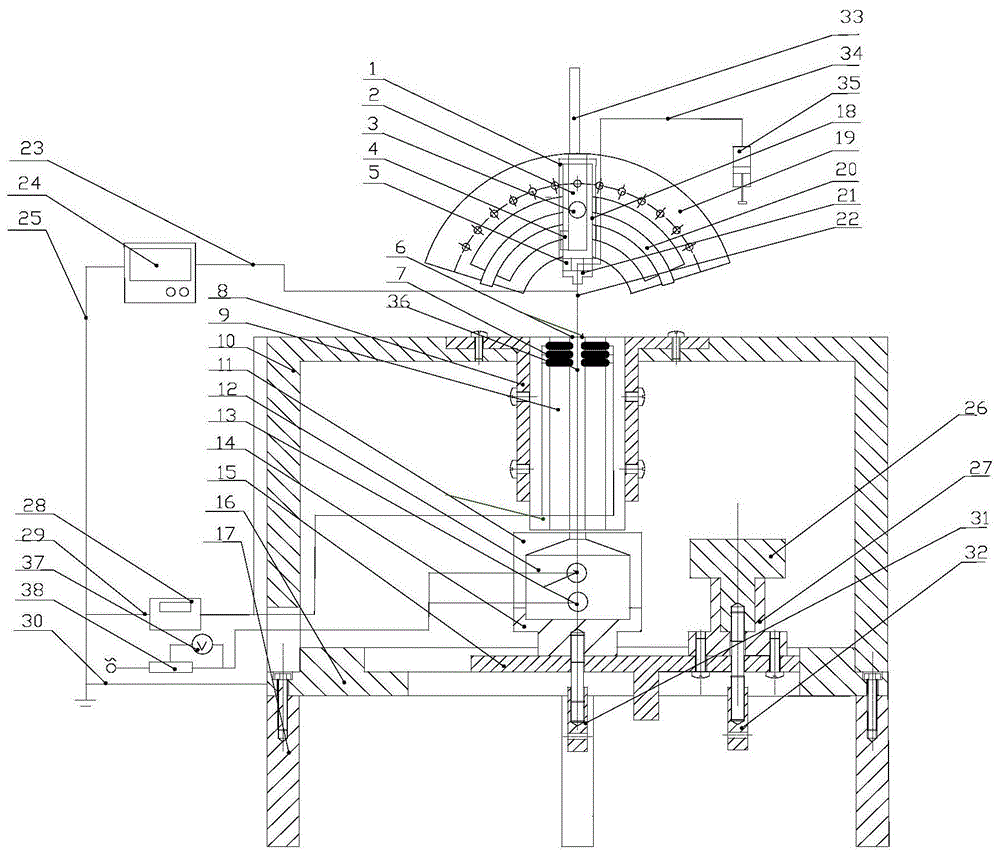
Method for simultaneously measuring internal temperatures and wall thicknesses of high-temperature structures under steady-state conditions
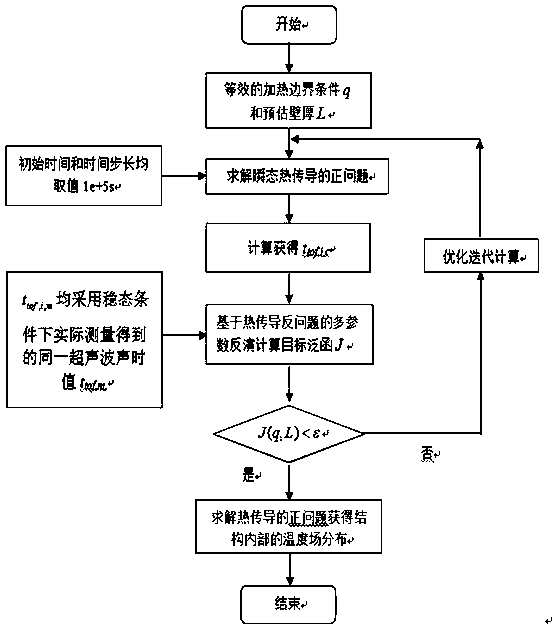
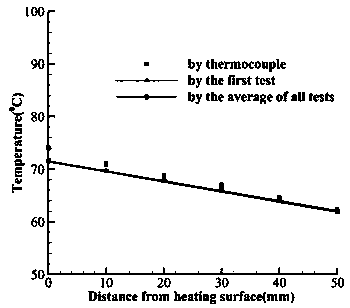
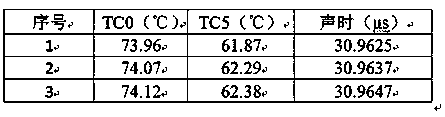
ActiveCN109506807ASolve the matrix singularity problem caused by insufficientUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansThermometers using physical/chemical changesEngineeringActive measurement
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously measuring internal temperatures and wall thicknesses of high-temperature structures under steady-state conditions. The method has the advantages that the problem of incapability of simultaneously measuring internal temperatures and wall thicknesses of existing high-temperature structures under existing steady-state conditions can be solved by theaid of the method; the method is based on ultrasonic detection signals, and structure thickness and internal temperature simultaneous measurement is transformed into heat boundary conditions of heatconduction problems and multi-parameter identification problems for structure thicknesses; the initial time and time steps are prolonged, transiently solved internal non-uniform temperature field andsteady-state results of the structures keep consistent, a valid measurement datum under steady-state heat transfer conditions is transformed into a plurality of valid measurement data under transientconditions, and accordingly the problem of matrix singularity due to insufficient input information during multi-parameter identification can be effectively solved by the aid of the method; the inverse heat conduction problems can be solved, and accordingly the internal temperatures and the thicknesses of the related structures under the steady-state heat transfer conditions can be quickly and nondestructively measured in a non-contact manner by the aid of the method.
Owner:CALCULATION AERODYNAMICS INST CHINA AERODYNAMICS RES & DEV CENT
A Calculation Method of Critical Air Leakage Amount Caused by Condenser Vacuum Deterioration
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF STATE GRID SHANDONG ELECTRIC POWER COMPANY +2
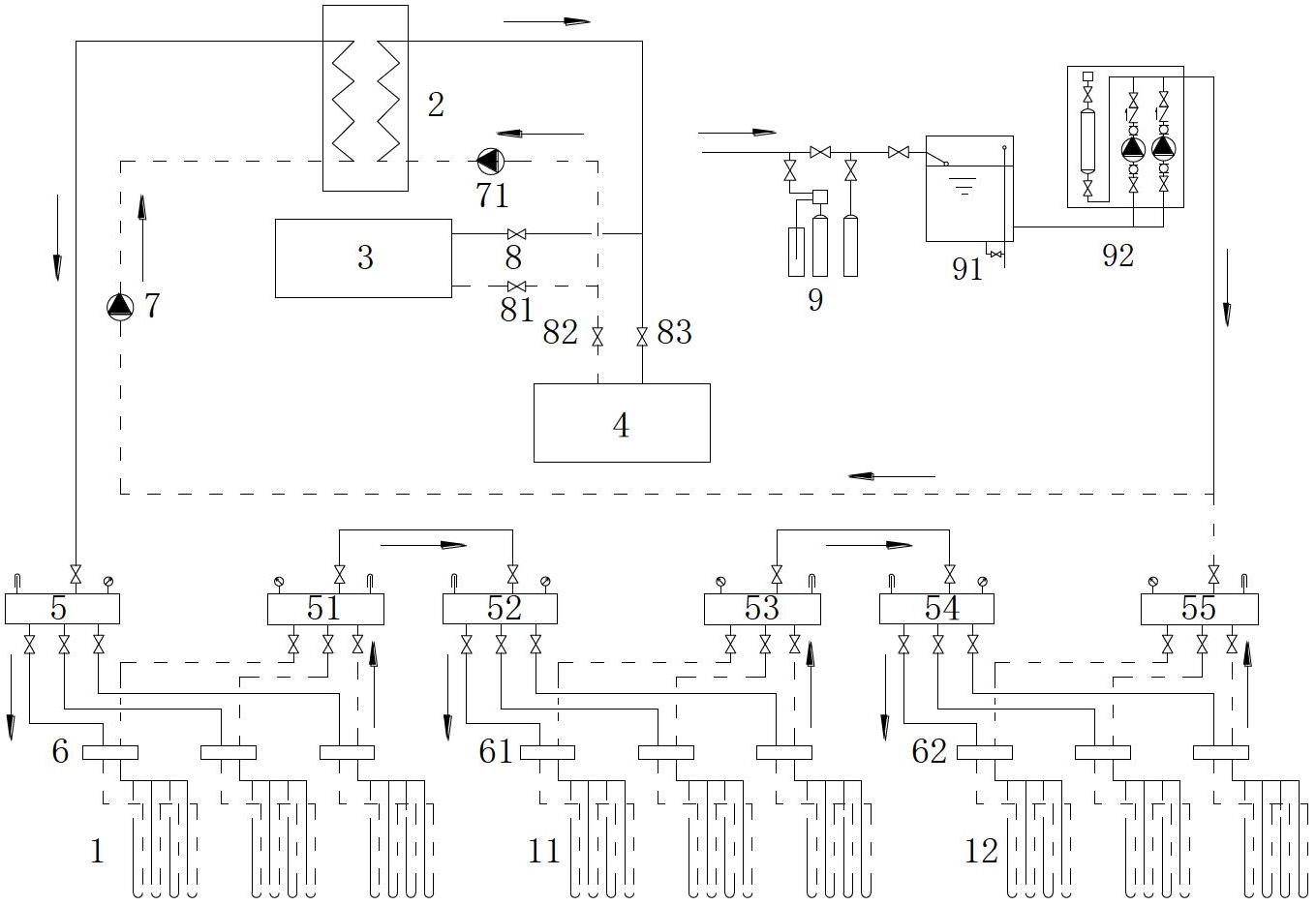
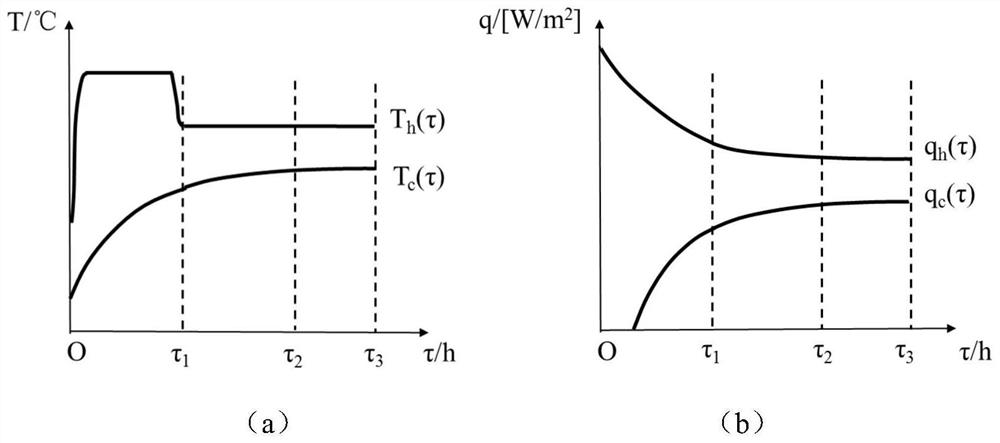
A method for testing the dynamic heat transfer process of building walls
The invention discloses a device and method for testing the dynamic heat transfer process of a building wall. The device comprises a box system, a computer and an instrument monitoring system. The box system is used for testing the dynamic and steady-state heat transfer process of the wall according to test working conditions input by users; the computer and the instrument monitoring system are used for testing the setting of the working conditions, achieving control over the wall heat transfer process, collecting data such as temperature, heat flow and electric heating power in the heat transfer process in real time, intelligently analyzing the wall heat transfer process and thermal performances according to preset calculation rules, and automatically generating a heat transfer process analysis table. Not only can a function of detecting a wall heat transfer coefficient in the steady-state heat transfer process be achieved, but also the dynamic wall heat transfer process in different cities and building environments of different types can be simulated and tested, the wall thermal performance and the heat transfer process thereof are analyzed intelligently, different wall structures are provided for different indoor environment regulating demand, and the theoretical basis is provided for formulating relevant standards.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
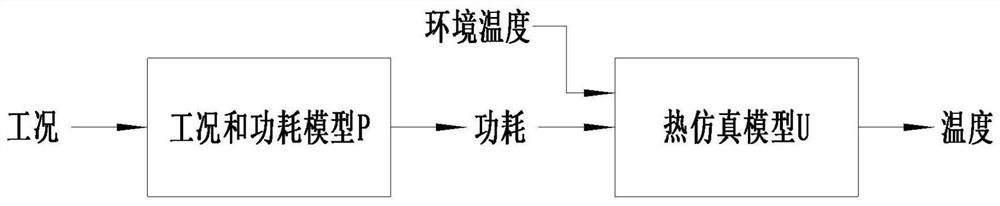
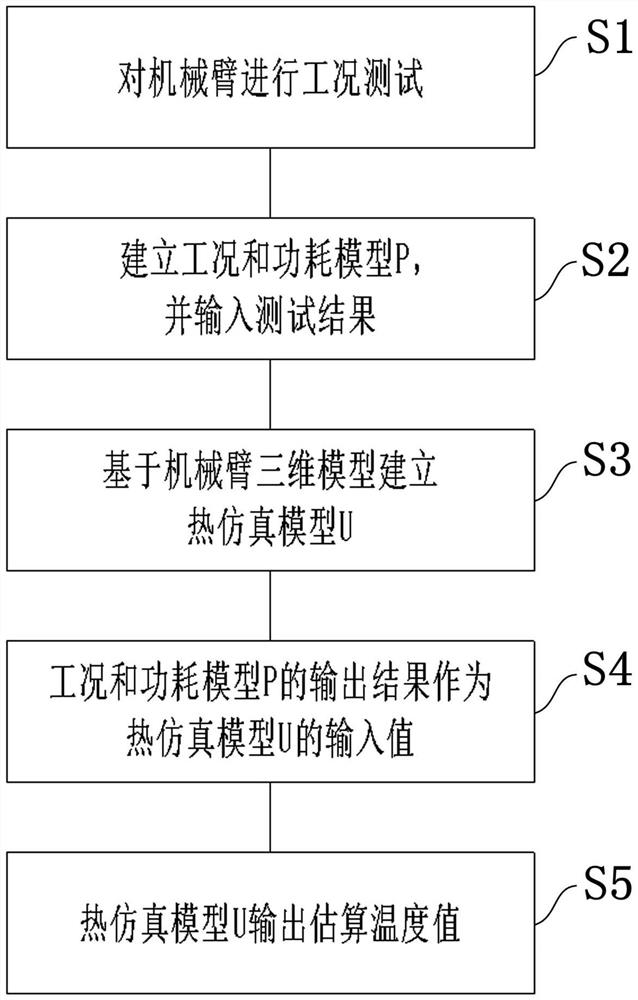
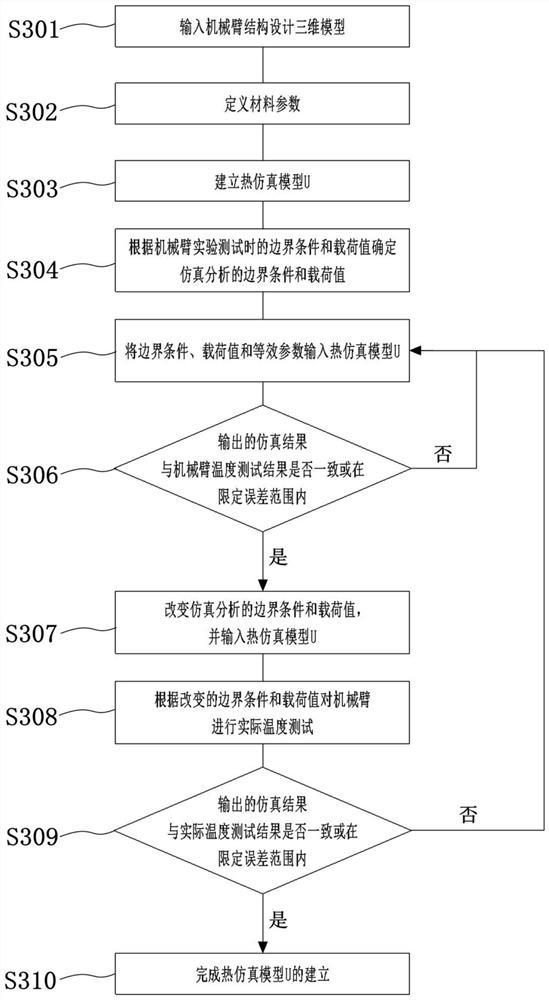
Temperature estimation method based on mechanical arm steady-state heat transfer model
PendingCN113591349AEasy to set upLow costGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationThermodynamicsTester device
The invention provides a temperature estimation method based on a mechanical arm steady-state heat transfer model. The temperature estimation method comprises: carrying out working condition testing on a mechanical arm; establishing a working condition and power consumption model P, and inputting a test result; establishing a thermal simulation model U based on the mechanical arm three-dimensional model; taking the output result of the working condition and power consumption model P as the input value of the thermal simulation model U; and outputting an estimated temperature value by the thermal simulation model U. According to the temperature estimation method provided by the invention, the actually required working condition test data of the mechanical arm is less, and excessive test instruments are not needed, so that the temperature estimation cost is greatly reduced. In addition, the model of the temperature estimation method is established quickly, model parameters can be quickly converted for different mechanical arms, the temperature estimation speed is high, the accuracy is high, and the personnel cost can be greatly reduced.
Owner:SIASUN CO LTD
A Method for Determining the Erosion Envelope Surface of Blast Furnace Hearth Bottom
ActiveCN108090293BHigh precisionImprove accuracySteel manufacturing process aspectsDesign optimisation/simulationHearthThermocouple
The invention provides a method for determining the enveloping surface of blast furnace hearth bottom erosion, which relates to the technical field of blast furnace hearth bottom erosion detection. By adopting the method based on the invariant grid and the dimension approach method, according to the steady state of the blast furnace simulation model Based on the law assumption of state heat transfer, the characteristics of different dimensions of the blast furnace hearth and bottom model are simplified, and the simulation model of different dimensions is calculated considering the need for accuracy improvement. According to the hearth thermocouple monitoring data in different periods, the maximum temperature of the detection point is obtained. The obtained inner boundary of hearth and bottom is used as the initial condition of high dimension, so that the improvement of accuracy is transformed into the expansion of dimension. The difference in unit scale is ignored when the envelope surface is adjusted, and there is no need to solve the exact position of the erosion surface, forming a set of overall solutions for solving the envelope surface of the blast furnace, which improves the accuracy of the measurement results of the blast furnace erosion calculation and reduces the amount of calculation, thereby alleviating the The existing technology has the problems of large error in erosion detection results and large amount of calculation.
Owner:国家超级计算天津中心
Simplified calculation method for sleeve type ground heat exchanger
PendingCN114117691ASimple calculationReduce meshingGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationSoil characteristicsEngineering
The invention relates to a simplified calculation method for a casing pipe type ground heat exchanger, which comprises the following steps: step 1, simplifying the casing pipe type ground heat exchanger into five layers according to geological rock-soil characteristics, and calculating each layer as a two-dimensional unsteady heat transfer process, and step 2, assuming calculation conditions, and calculating the two-dimensional unsteady heat transfer process according to the assumed calculation conditions. The influence condition is simulated according to the actual situation; and 3, single-segment solution is carried out on the single layer under the assumed condition. According to the simplified calculation method of the sleeve type buried pipe heat exchanger, by adopting the calculation method, grid division in the heat transfer calculation process of the sleeve type buried pipe heat exchanger can be reduced, and meanwhile, a complex three-dimensional unsteady-state heat transfer problem is simplified into a two-dimensional unsteady-state heat transfer problem; therefore, simplified calculation can be carried out on the sleeve type buried pipe heat exchanger under different conditions, the calculation efficiency is improved, certain actual use value and popularization value are achieved, and the problems that in the prior art, the heat transfer calculation process of the sleeve type buried pipe heat exchanger is complex, and the calculation efficiency is low are solved.
Owner:HENAN WANJIANG NEW ENERGY DEV CO LTD
A method for predicting the internal temperature of an independent communication base station
InactiveCN105760686BSpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsInternal temperatureSteady state heat transfer
The invention discloses a method for predicting the internal temperature of an independent communication base station. The method comprises the steps of establishing a thermophysical model of an independent communication base station according to positional relation between the sun and the independent communication base station, radiation intensity of solar radiation heat to a wall body of the independent communication base station as well as a comprehensive temperature outside the independent communication base station, and calculating to obtain an average temperature value in the independent communication base station. According to the method, the thermophysical model of the independent communication base station is established based on a steady-state heat transfer theory, and the average temperature value in the independent communication base station can be calculated, thereby facilitating the research of optimal design, simulation prediction, performance evaluation and base station assisting energy-efficient equipment of space enclosing structures of the independent communication base station.
Owner:GUANGDONG IND TECHN COLLEGE
A Simultaneous Measurement Method of Internal Temperature and Wall Thickness of High-temperature Structures under Steady-state Conditions
ActiveCN109506807BSolve the matrix singularity problem caused by insufficientUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansThermometers using physical/chemical changesUltrasonic testingMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously measuring internal temperatures and wall thicknesses of high-temperature structures under steady-state conditions. The method has the advantages that the problem of incapability of simultaneously measuring internal temperatures and wall thicknesses of existing high-temperature structures under existing steady-state conditions can be solved by theaid of the method; the method is based on ultrasonic detection signals, and structure thickness and internal temperature simultaneous measurement is transformed into heat boundary conditions of heatconduction problems and multi-parameter identification problems for structure thicknesses; the initial time and time steps are prolonged, transiently solved internal non-uniform temperature field andsteady-state results of the structures keep consistent, a valid measurement datum under steady-state heat transfer conditions is transformed into a plurality of valid measurement data under transientconditions, and accordingly the problem of matrix singularity due to insufficient input information during multi-parameter identification can be effectively solved by the aid of the method; the inverse heat conduction problems can be solved, and accordingly the internal temperatures and the thicknesses of the related structures under the steady-state heat transfer conditions can be quickly and nondestructively measured in a non-contact manner by the aid of the method.
Owner:CALCULATION AERODYNAMICS INST CHINA AERODYNAMICS RES & DEV CENT
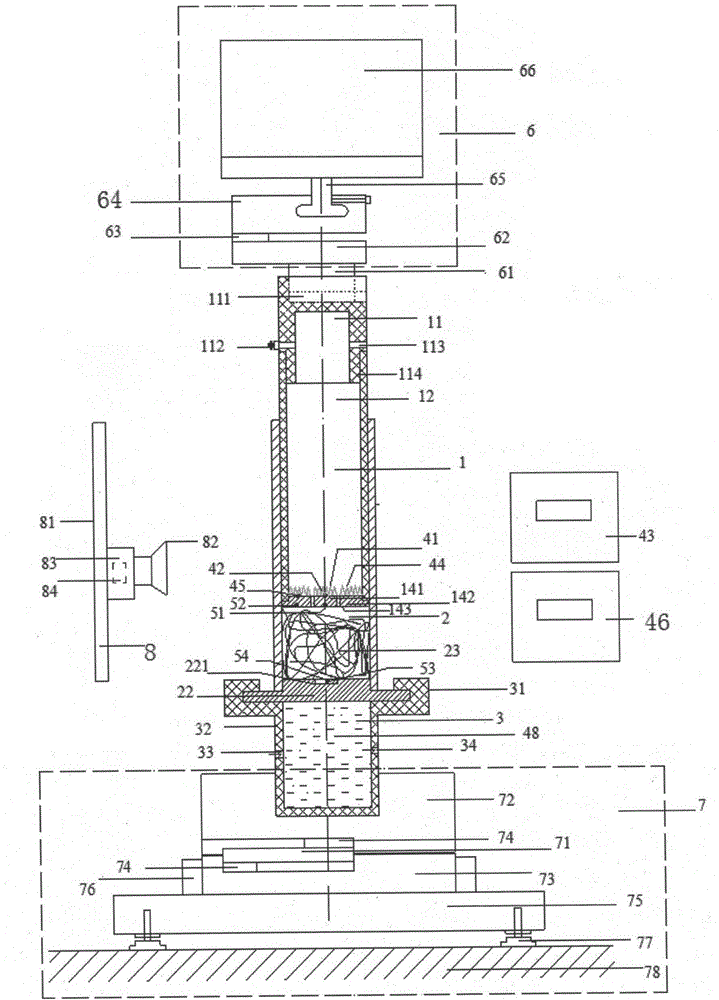
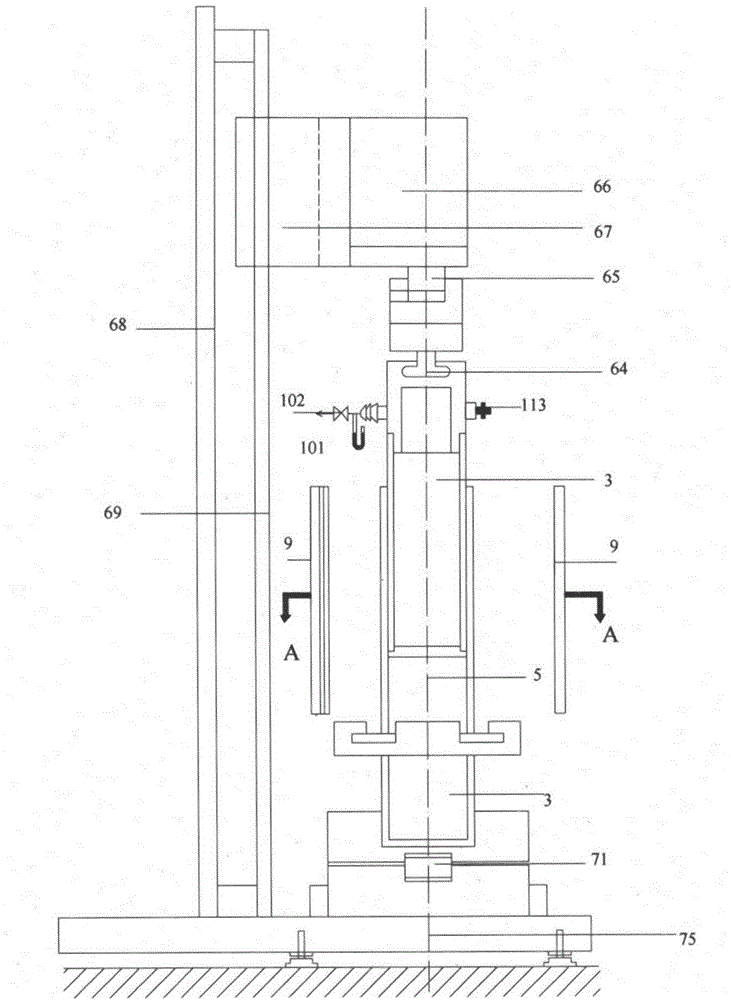
A device and method for in-situ measurement of steady-state heat transfer properties of variable-density fibers
ActiveCN103454305BIn line with the actual use statusEasy accessMaterial heat developmentFiberHeat flux
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
An electrostatic atomization cooling capacity evaluation device with adjustable nozzle space angle
Owner:HUAWEI TEHCHNOLOGIES CO LTD
Experimental device for determining the heat transfer coefficient of water-cooled casting molds
ActiveCN102928461BSimple structureEasy to operateMaterial thermal conductivityMaterial heat developmentStable stateHeat transmission
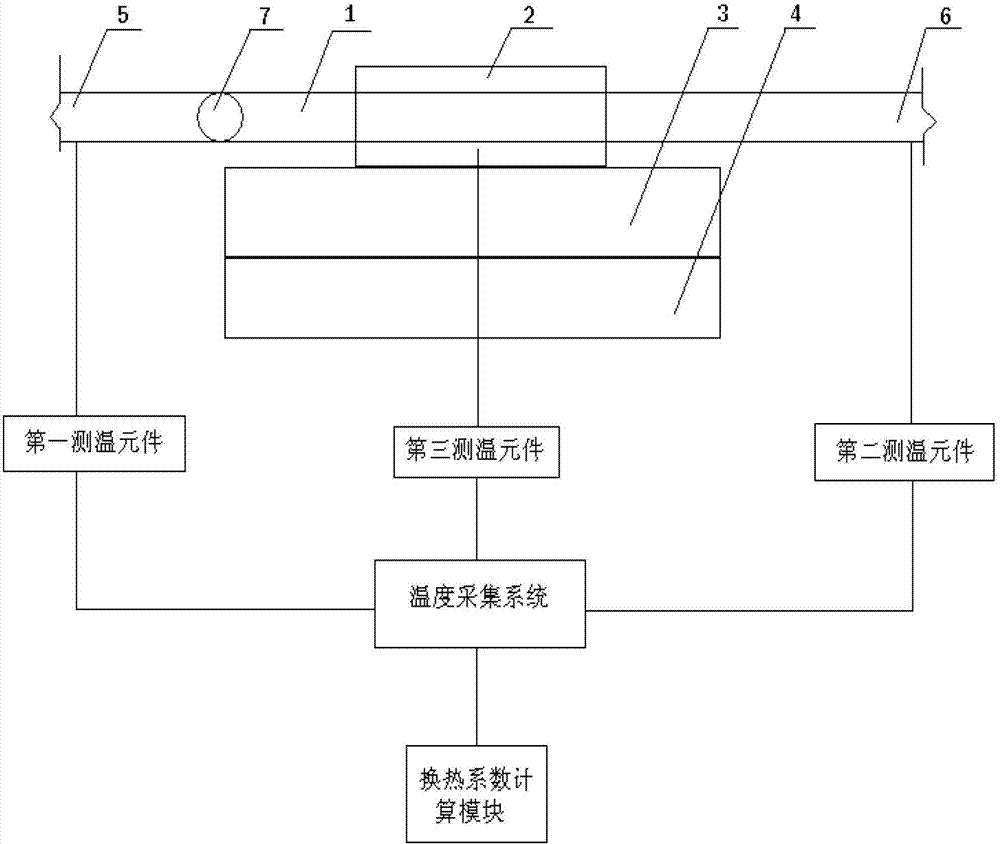
The invention discloses an experiment device for detecting a heat exchange coefficient of a water cooling mould. The experiment device comprises a mould, a cast ingot, a cooling system, a temperature collecting system, a heating device and a heat exchange coefficient calculation module. The experiment device provided by the invention is characterized in that an input end of the temperature collecting system is connected with the cooling system, the mould and the cast ingot respectively, and an output end of the temperature collecting system is connected with the heat exchange coefficient calculation module; the cast ingot and the mould are in contact; and the cast ingot and the heating device are in mutual contact; meanwhile, a flow meter is arranged in the cooling system and is used for controlling cooling strength in the device, and the temperatures of the cooling system, the mould and the cast ingot at the different positions can be collected in real time by using the temperature collecting system; and heat exchange coefficients of the different positions under different flow velocities can be calculated according to the fact that the heat entering the mould in a stable-state heat transmission process is equal to the heat brought away by cooling water. The experiment device has the advantages of simple structure, convenience in operation and high accuracy.
Owner:WISDRI ENG & RES INC LTD
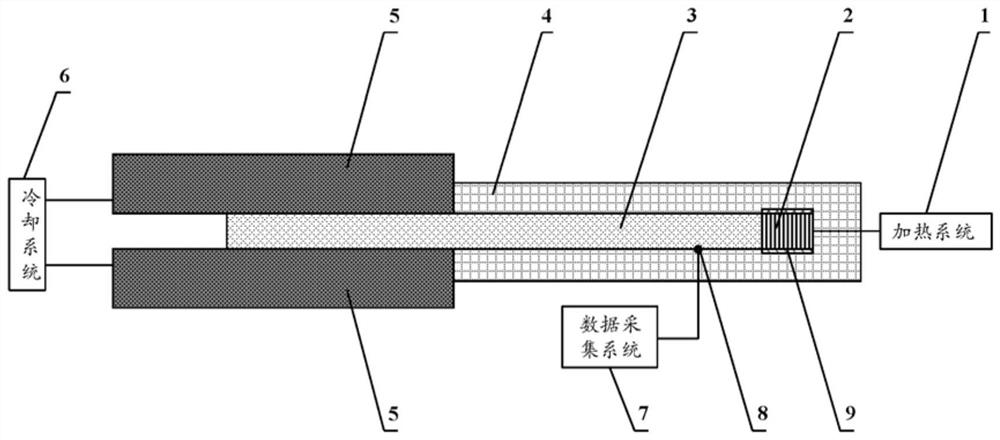
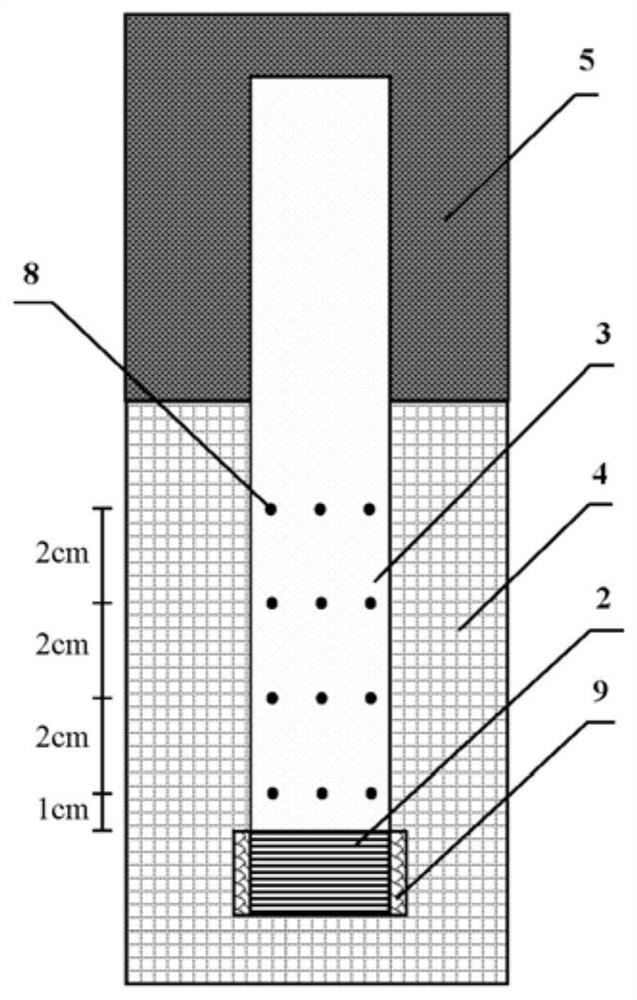
A Simple Steady State Test System for Thermal Conductivity of High Thermal Conductivity Materials
ActiveCN109781780BConvenient and flexible heating methodIncrease flexibilityMaterial heat developmentConstant powerThermal insulation
The invention discloses a simple and simple steady-state testing system for thermal conductivity of high thermal conductivity materials. During the test, the heating section is heated with constant power through the connection of the heating system and the electric heating film, the cooling system is connected with the cooling chamber to cool the cooling section at a constant temperature, and the data acquisition and processing system is connected with the thermocouple to complete the process of the tested high thermal conductivity material. Real-time acquisition and output of temperature. In addition, heat insulation materials are used to insulate the heating section and the insulation section of the tested high thermal conductivity material during the test, so that the heat is transferred along the length direction of the tested high thermal conductivity material, forming a one-dimensional stability of the tested high thermal conductivity material along the length direction. State-to-state heat transfer can realize a large temperature difference along the surface of the tested high thermal conductivity material under a small heating power, ensuring a certain test accuracy. The invention can solve the problems in the prior art that when testing the thermal conductivity of high thermal conductivity materials, the sample size is large, the heating power is large, it is difficult to implement, the test accuracy is low, and the thermal conductivity of the material cannot be obtained through a one-time test.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Point heat source solid material thermophysical parameter testing experimental device
PendingCN112179944AAnti-shedding functionMinimize the effect of acquisition temperatureMaterial heat developmentLaser transmitterEngineering
The invention relates to the technical field of material thermophysical parameter testing, in particular to a point heat source solid material thermophysical parameter testing experimental device which comprises a laser point heat source unit, a sample experimental unit and a signal acquisition unit. The experimental device for measuring the thermophysical parameters of the solid material by usingthe laser point heat source unsteady state heat transfer model is developed by means of forming a point heat source on a sample by utilizing spots emitted by a laser emitter. A tested sample is in avacuum environment so that the influence of an external environment on the acquisition temperature of a test point in an experiment process is reduced. Meanwhile, the experimental device avoids unevenheating of the surface of the sample caused by uneven surface of the sample, and effectively improves the parameter testing precision.
Owner:ANHUI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com